Wireless localization method based on an efficient multilateration algorithm over a wireless sensor network and a recording medium in which a program for the method is recorded
a wireless sensor network and multilateration algorithm technology, applied in direction finders using radio waves, instruments, special services for subscribers, etc., can solve the problems of high cost, inconvenient indoor channel environment of gps, inability to achieve precise localization, etc., to reduce the error in estimated distance, improve the accuracy of estimated location of blind nodes, and the effect of reducing the error
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0034]Referring to the figures, embodiments of the present invention are described in detail below.
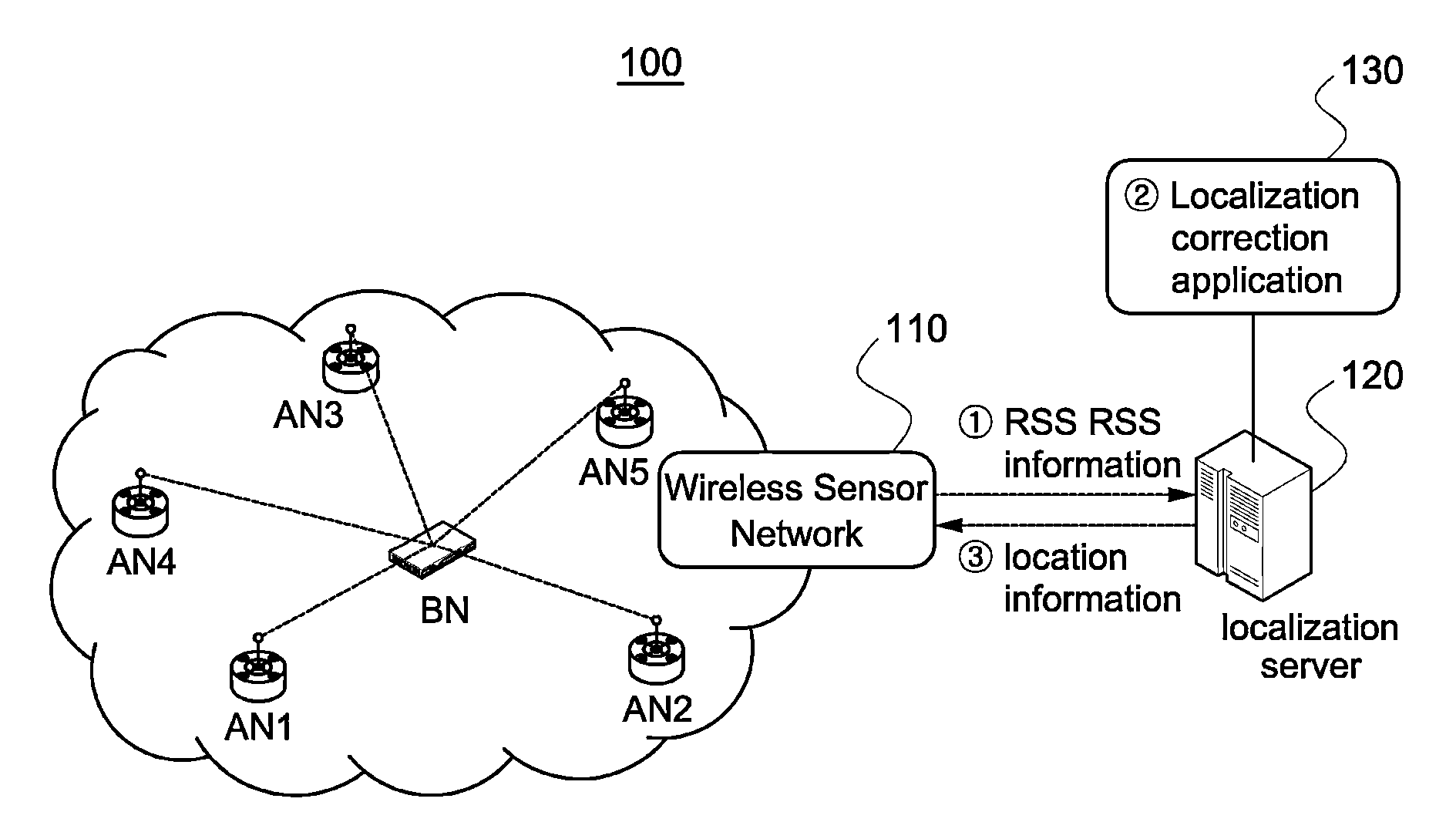
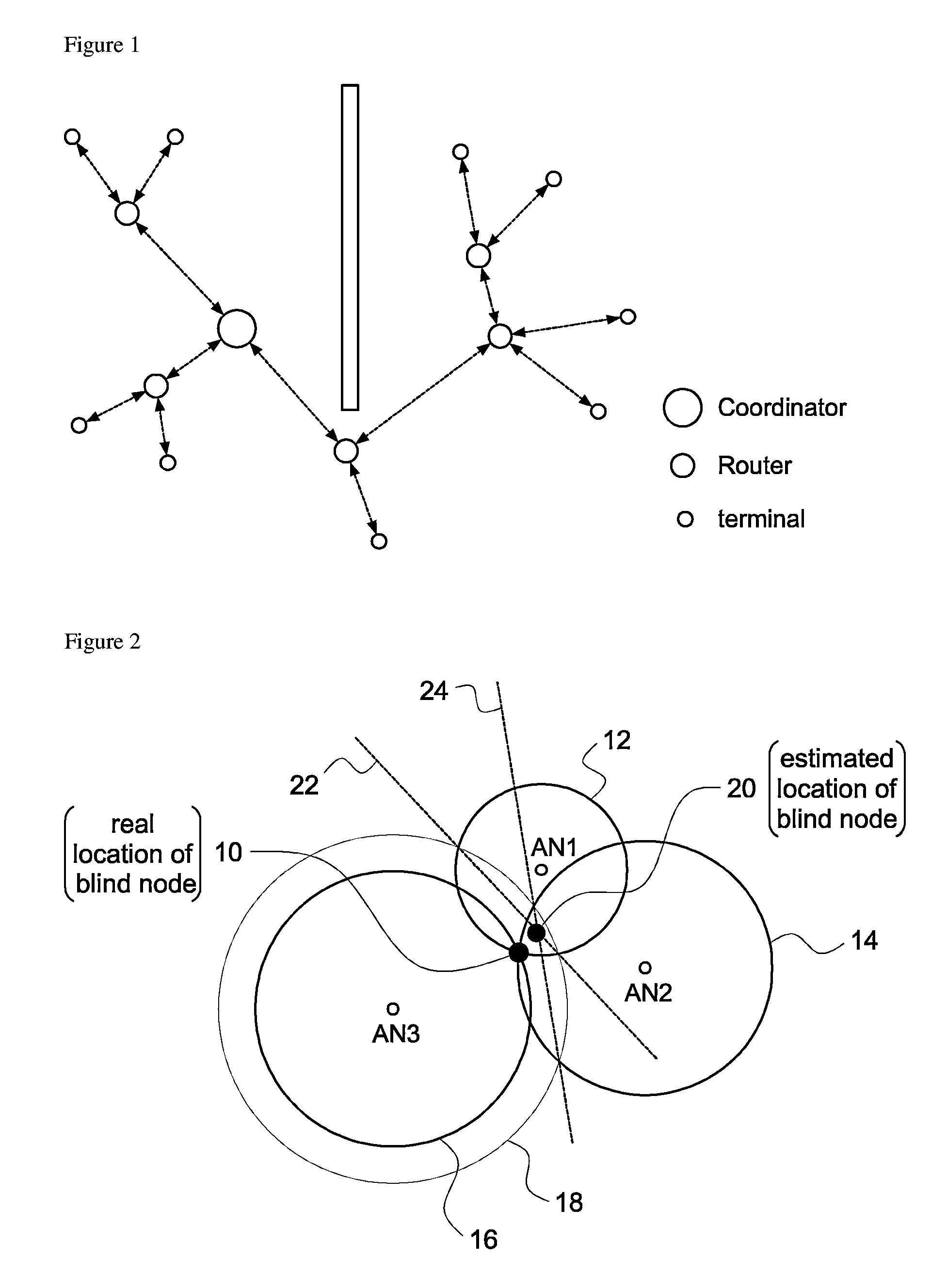
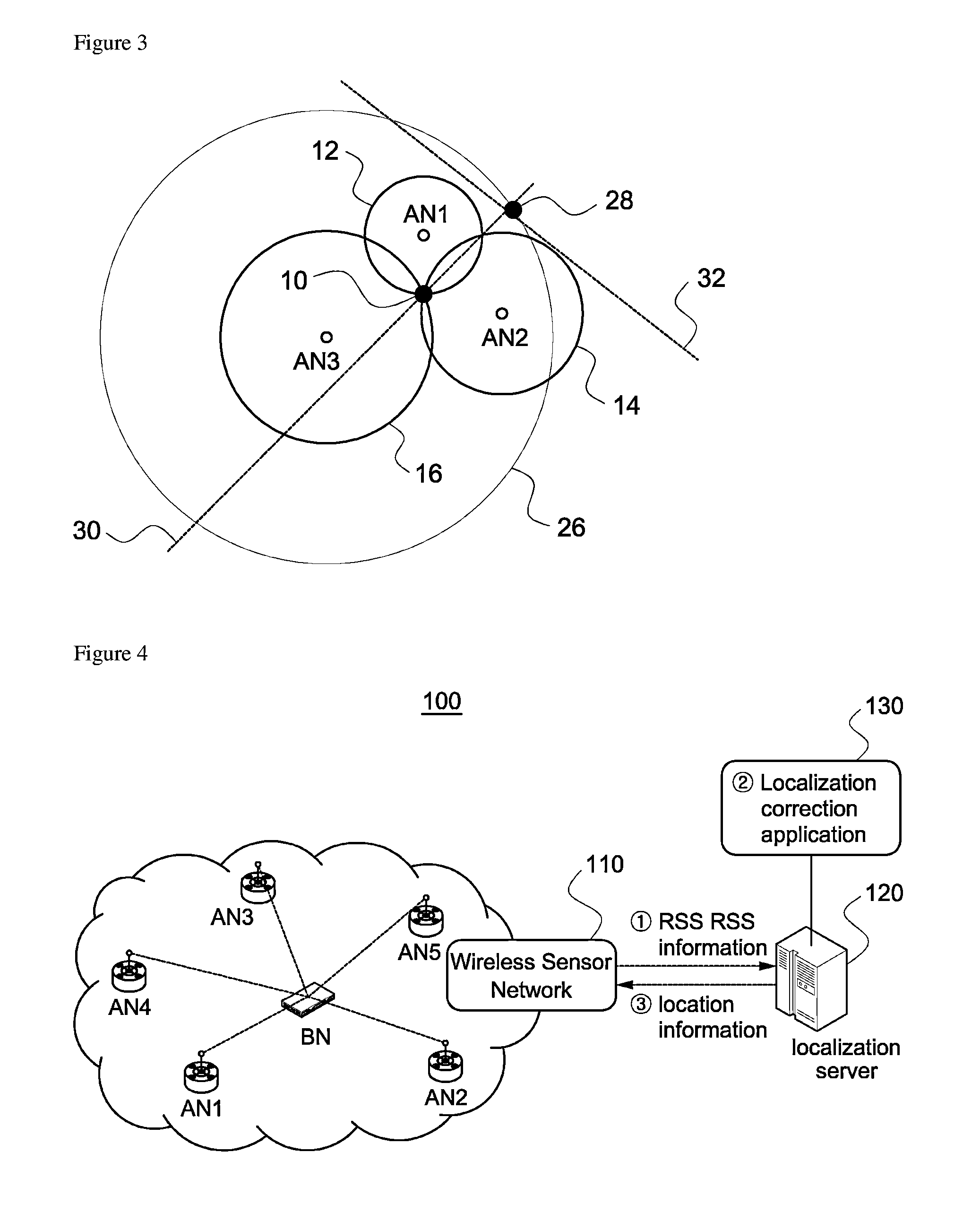
[0035]The wireless localization method according to the present invention measures distances from blind node to each reference node using RSS, and estimates the location of the blind node through trilateration using the estimated distance values.
[0036](1) Indoor Path-Loss Model
[0037]RSS can be measured with respect to each of packets which the reference nodes received from the blind node. It is well known that the strength of the transmitted signal decreases proportional to the distance between the transmitting side and the receiving side. Due to the random property of shadowing, it has a specific average value and follows a Gaussian distribution with the average value as a center (when the distance between the transmitting side and the receiving side is constant). When using Gaussian model, the strength Pij (average value of RSS ensemble) of signal which the i-th reference node (recei...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com