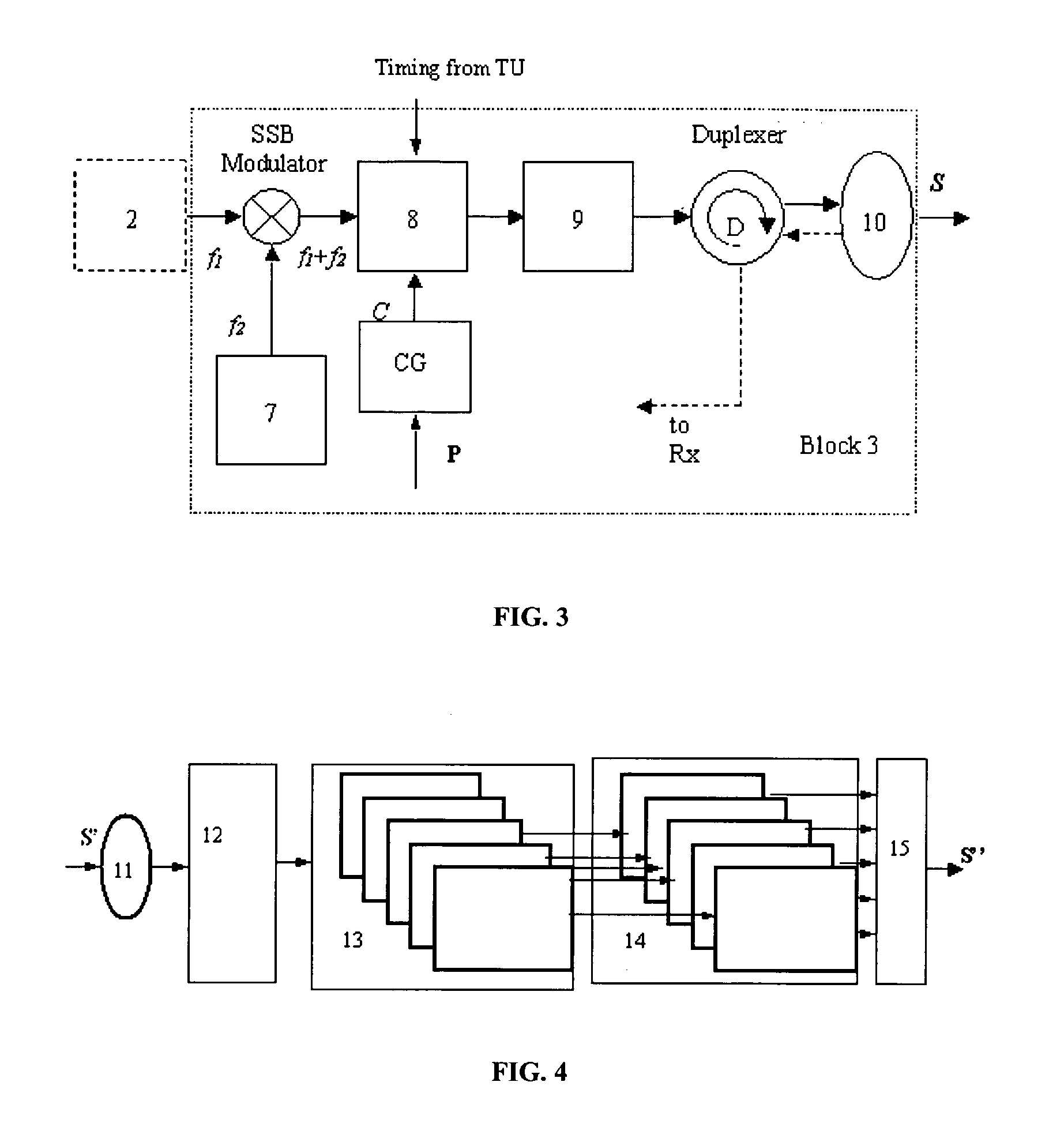
Patents
Literature
119 results about "Automatic dependent surveillance-broadcast" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
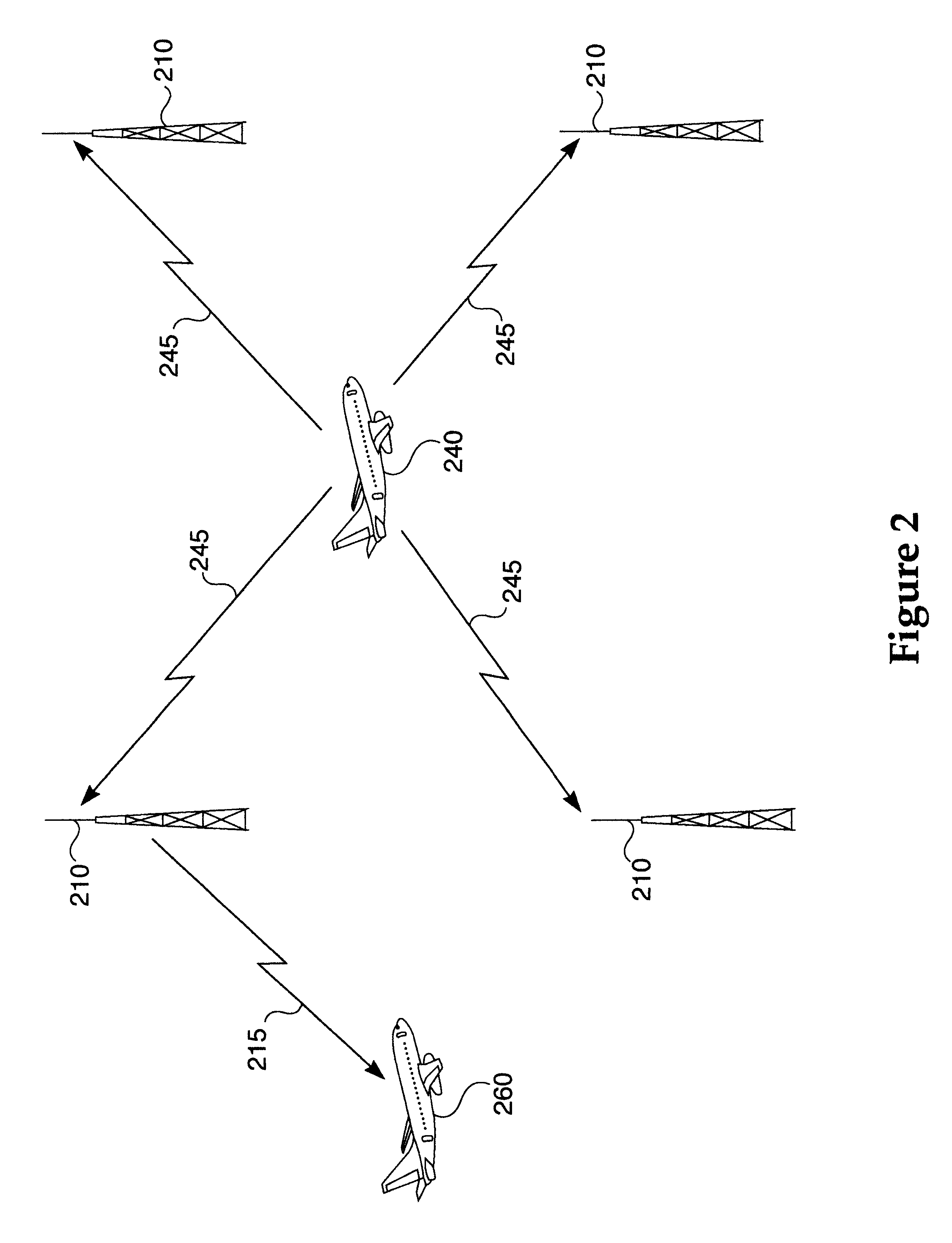
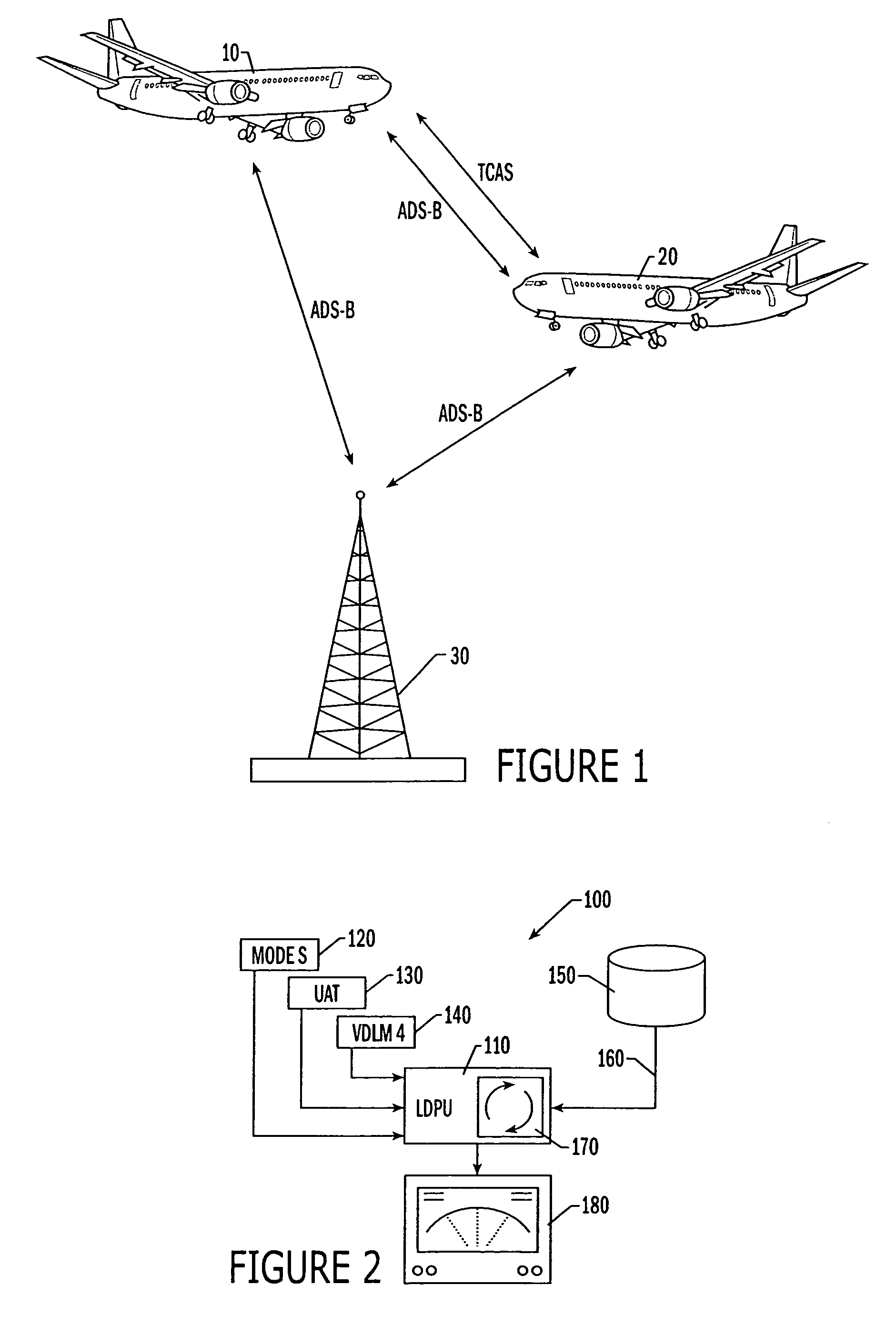
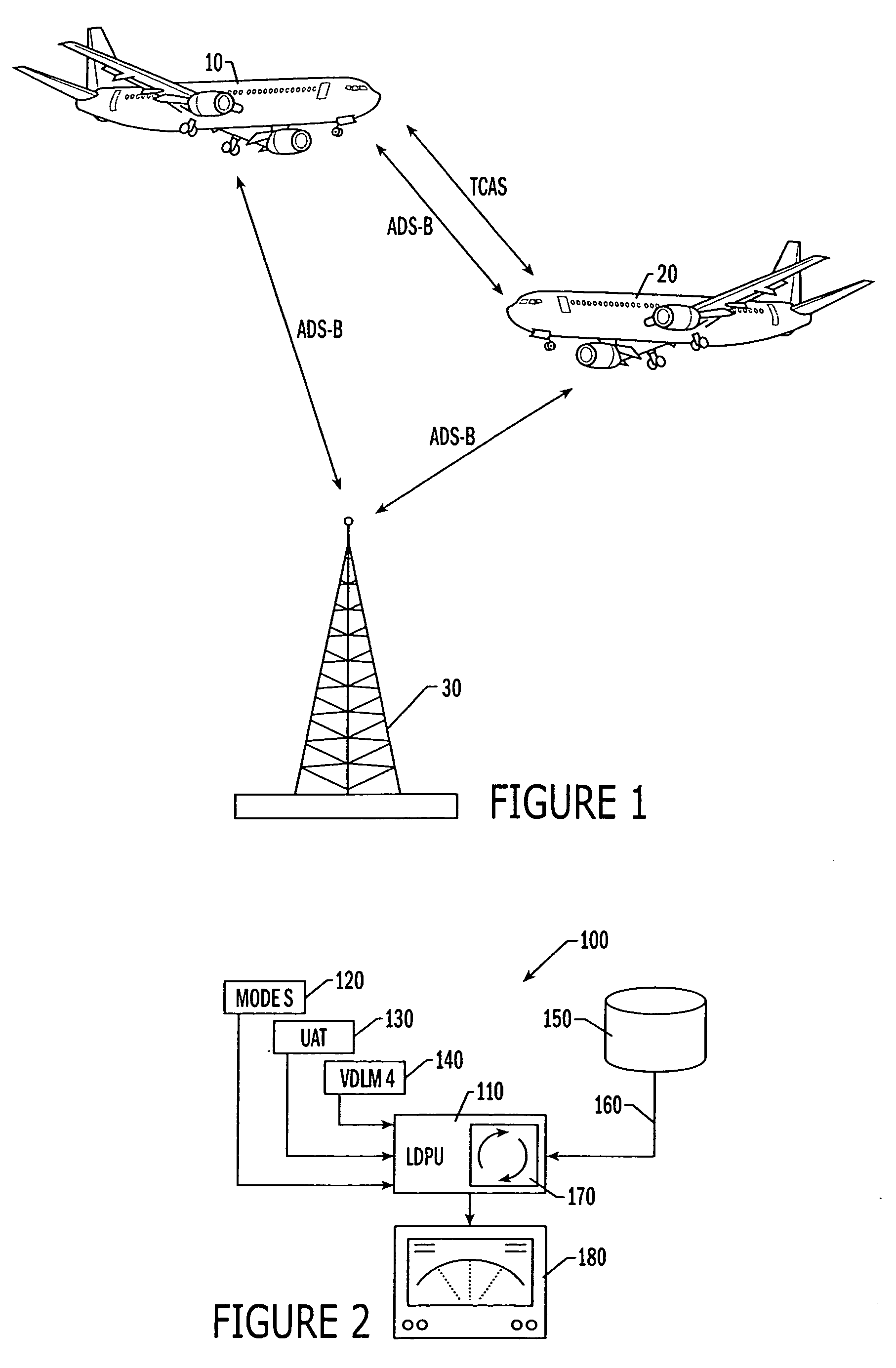
Automatic dependent surveillance—broadcast (ADS–B) is a surveillance technology in which an aircraft determines its position via satellite navigation and periodically broadcasts it, enabling it to be tracked. The information can be received by air traffic control ground stations as a replacement for secondary surveillance radar, as no interrogation signal is needed from the ground. It can also be received by other aircraft to provide situational awareness and allow self-separation.
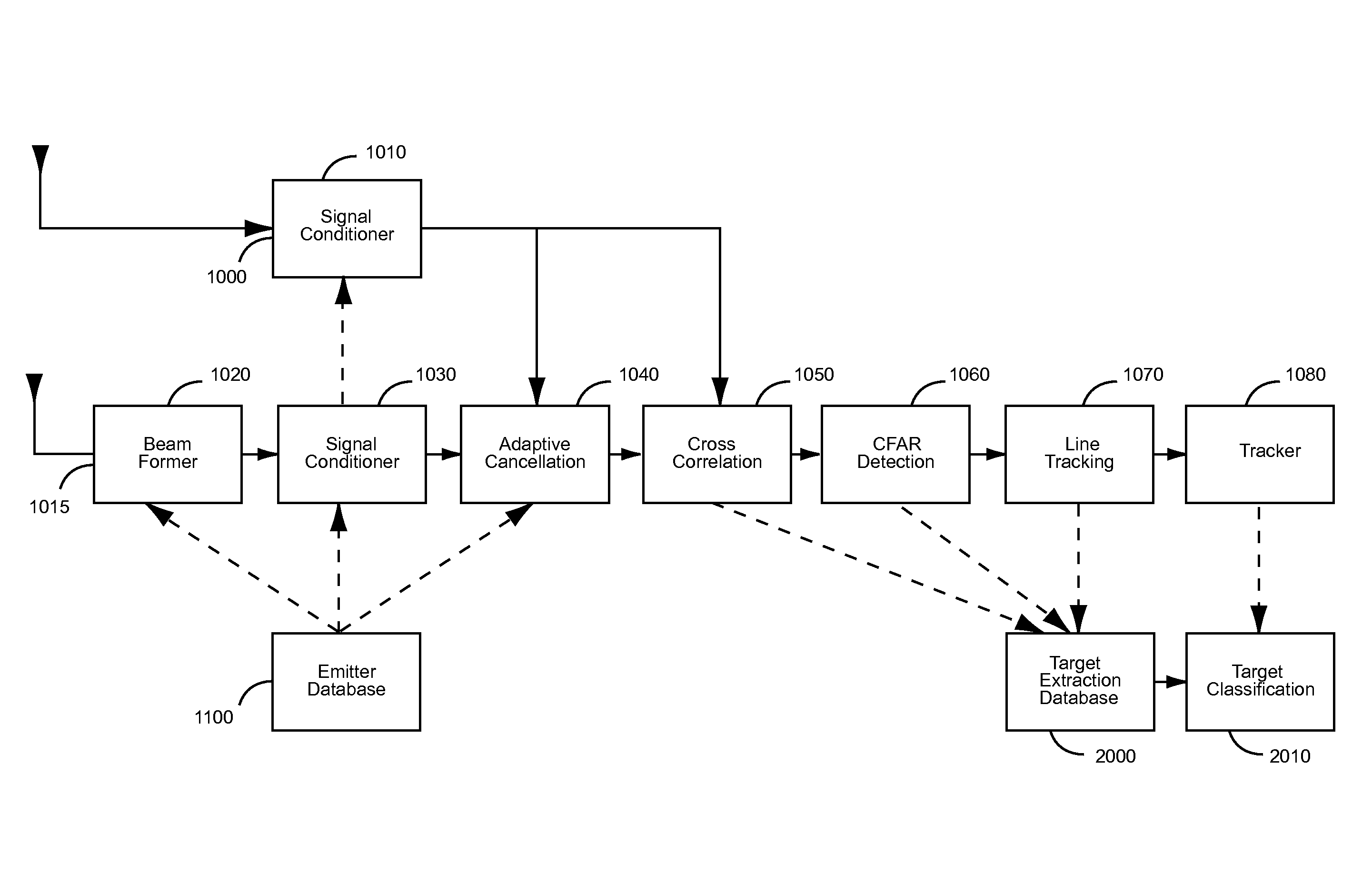
Enhanced Passive Coherent Location Techniques to Track and Identify UAVs, UCAVs, MAVs, and Other Objects
InactiveUS20080088508A1ConfidenceDirection finders using radio wavesPosition fixationMicro air vehicleRadar
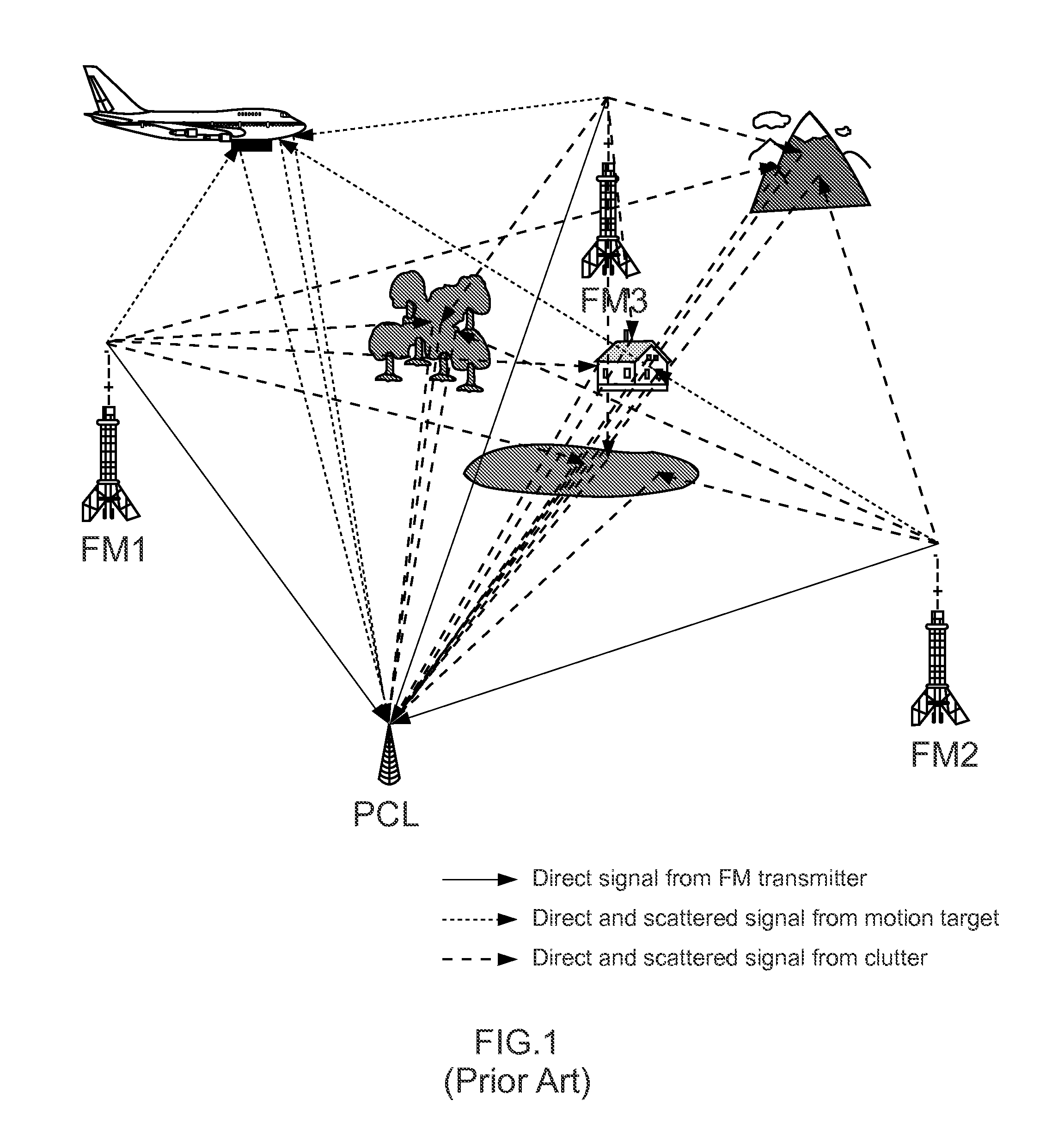
A system and technique is described which has the capability to track and identify, in real time, various aircraft and objects including Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs), Unmanned Combat Aerial Vehicles (UCAVs), and Micro Aerial Vehicles (MAVs). The system uses a combination of techniques including conventional automatic dependent surveillance broadcast (ADS-B), transponder multilateration, broadband emitter multilateration, primary and secondary radar, and passive coherent location. A series of enhancement to conventional passive coherent location are described.
Owner:ERA AS
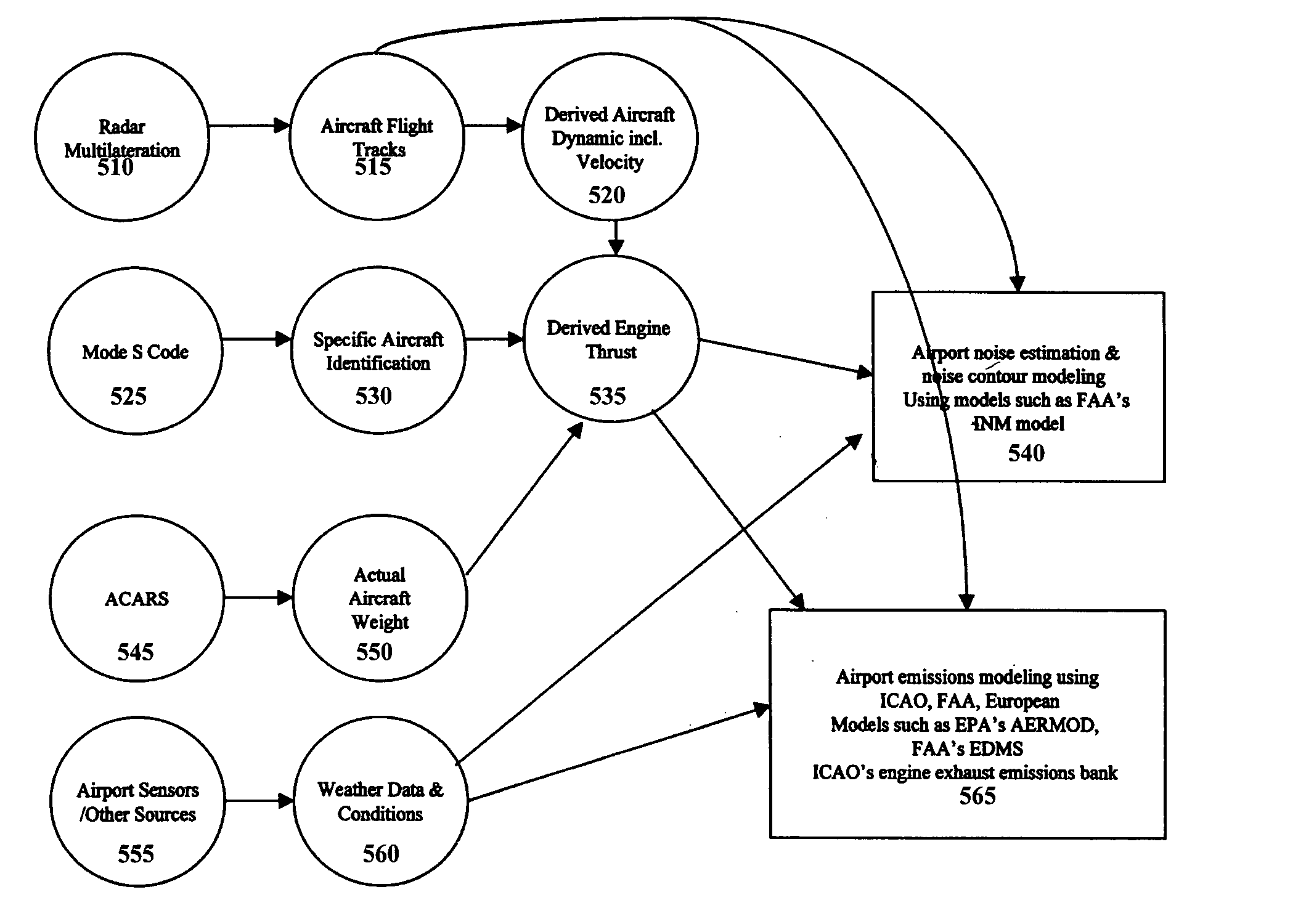
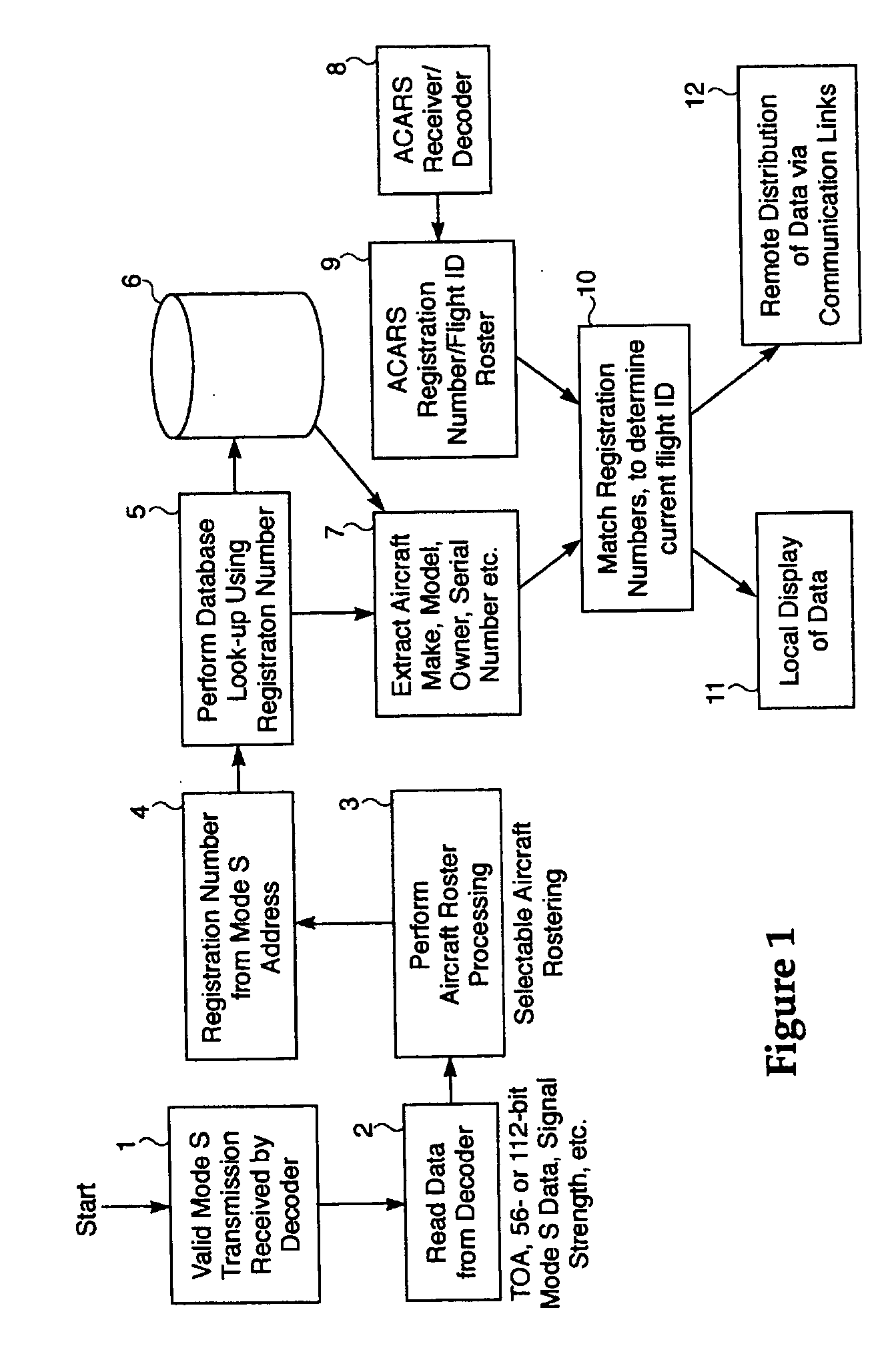
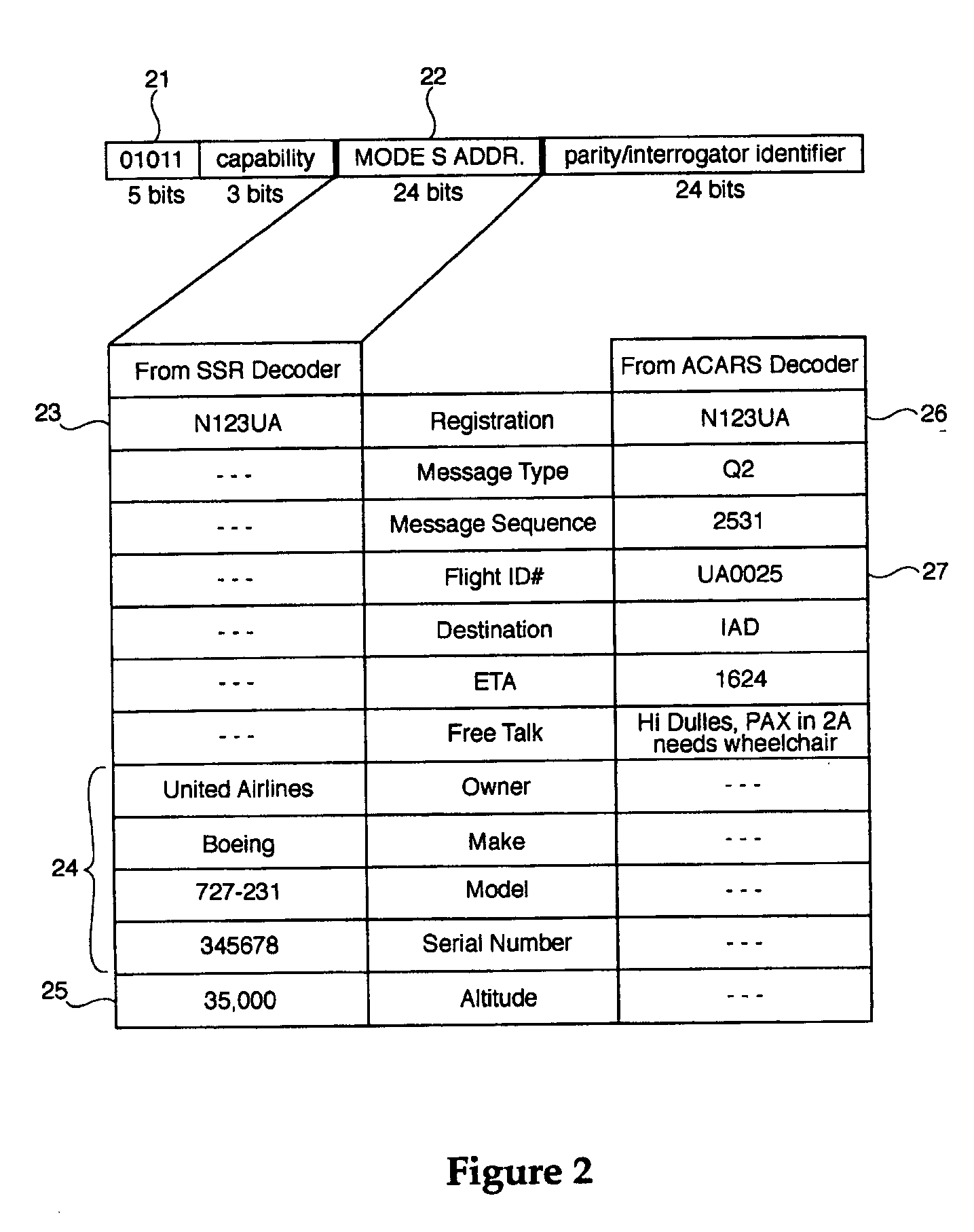
Correlation of flight track data with other data sources
InactiveUS20050007272A1Accurately determineAccurate calculationDirection finders using radio wavesPosition fixationMonitoring systemData source
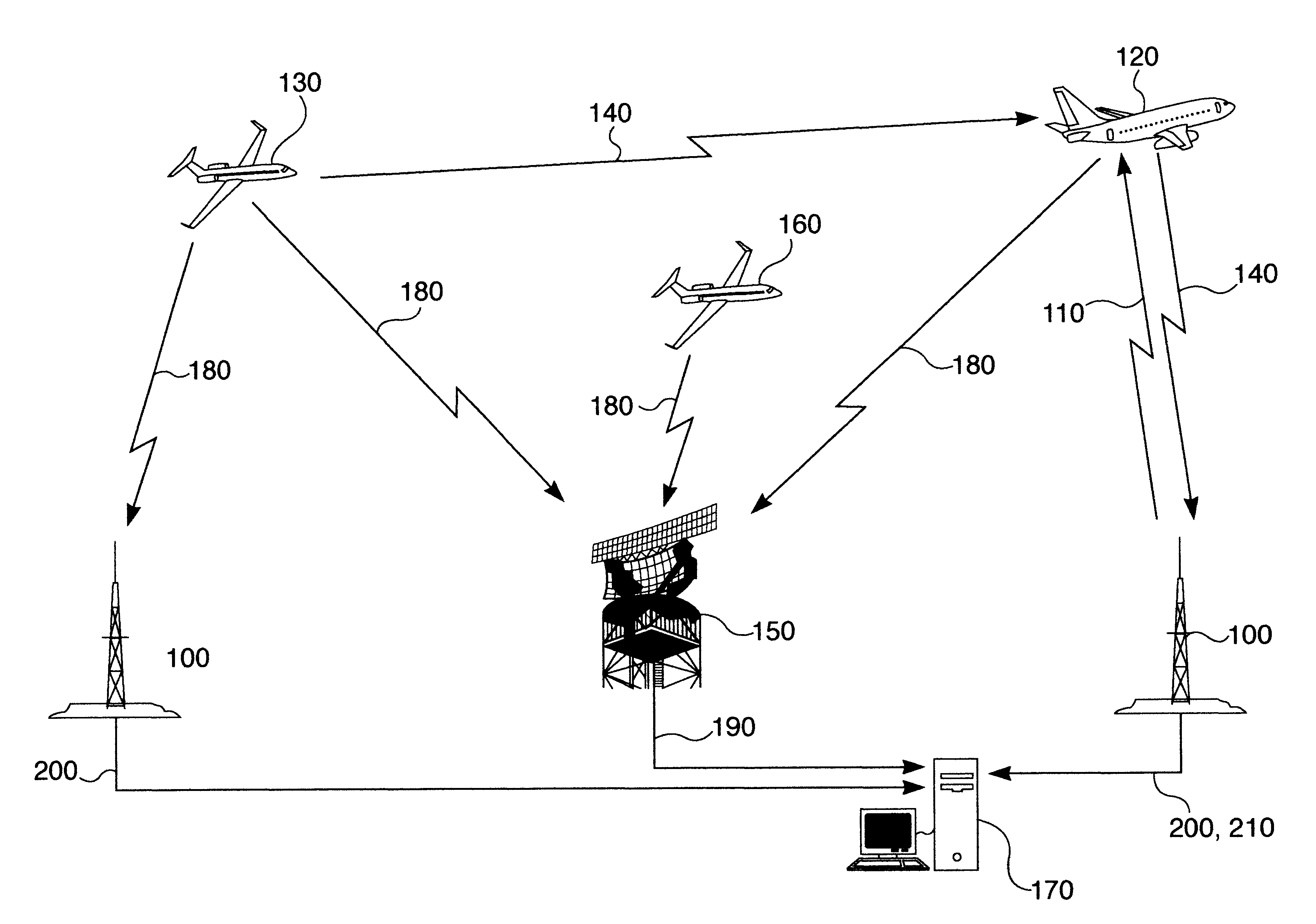
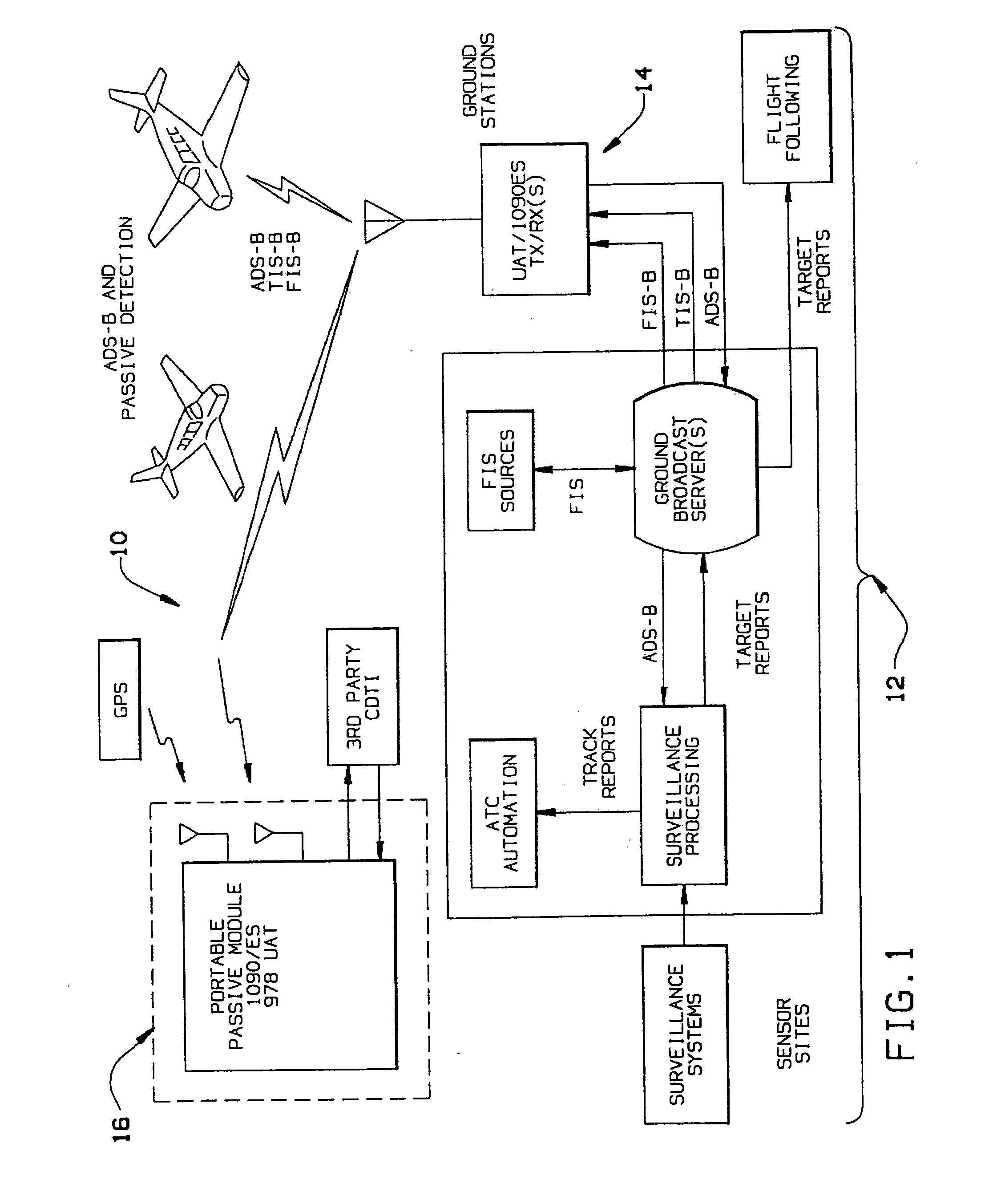
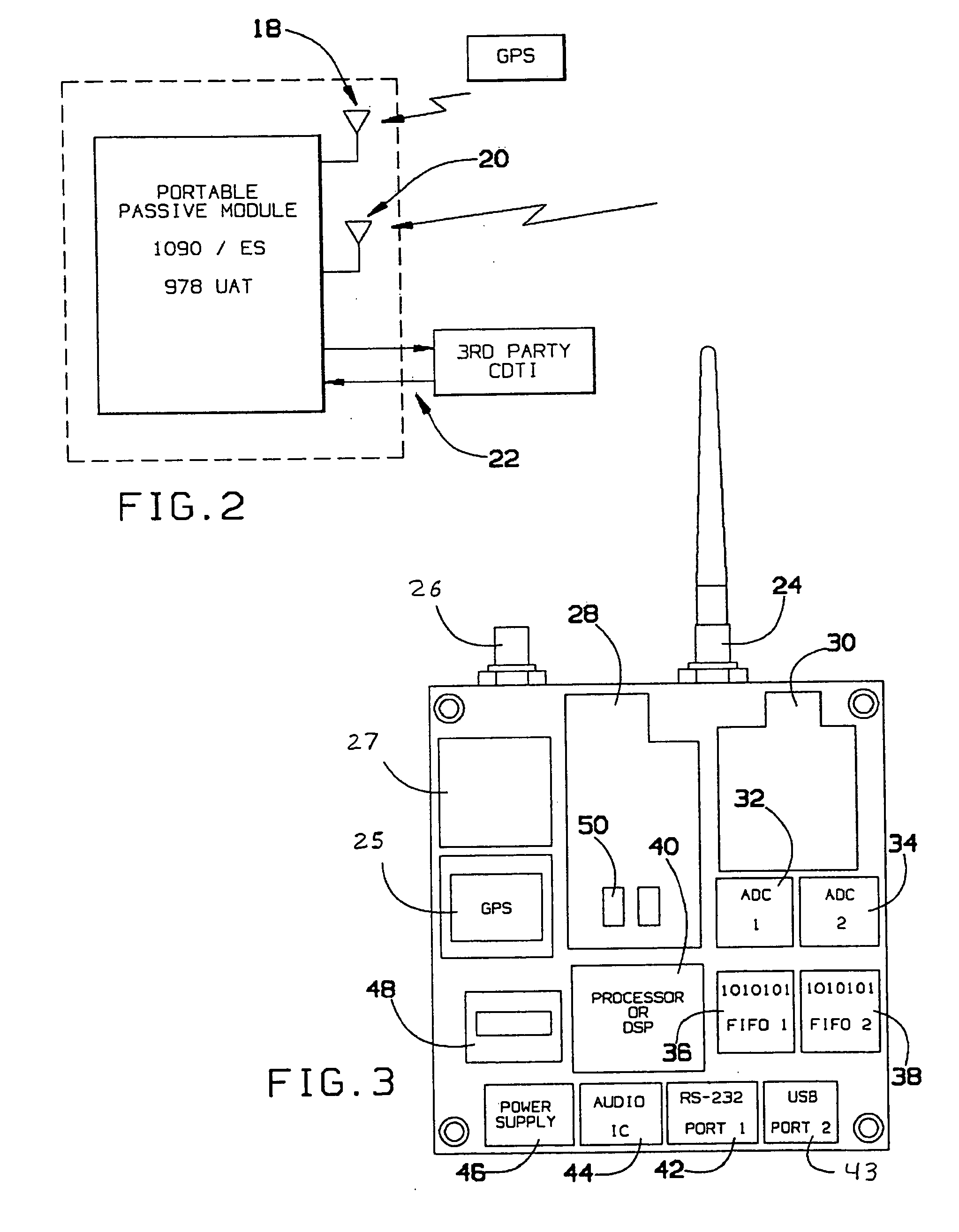
The surveillance system provides a means to augment Automatic Dependent Surveillance-Broadcast (ADS-B) with “look alike ADS-B” or “pseudo ADS-B” surveillance transmissions for aircraft which may not be ADS-B equipped. The system uses ground based surveillance to determine the position of aircraft not equipped with ADS-B, then broadcasts the identification / positional information over the ADS-B data link. ADS-B equipped aircraft broadcast their own position over the ADS-B data link. The system enables aircraft equipped with ADS-B and Cockpit Display of Traffic Information (CDTI) to obtain surveillance information on all aircraft whether or not the proximate aircraft are equipped with ADS-B.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
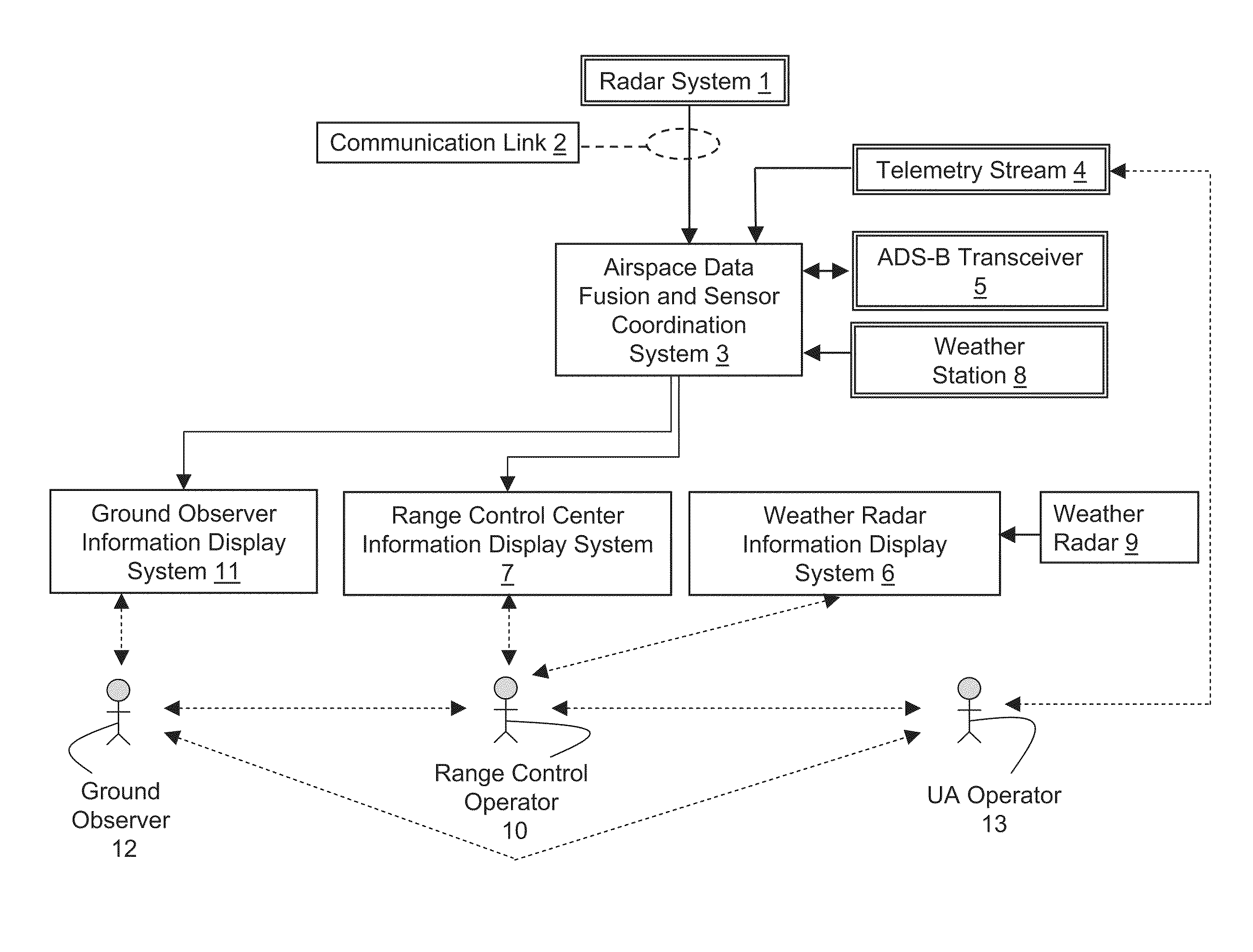
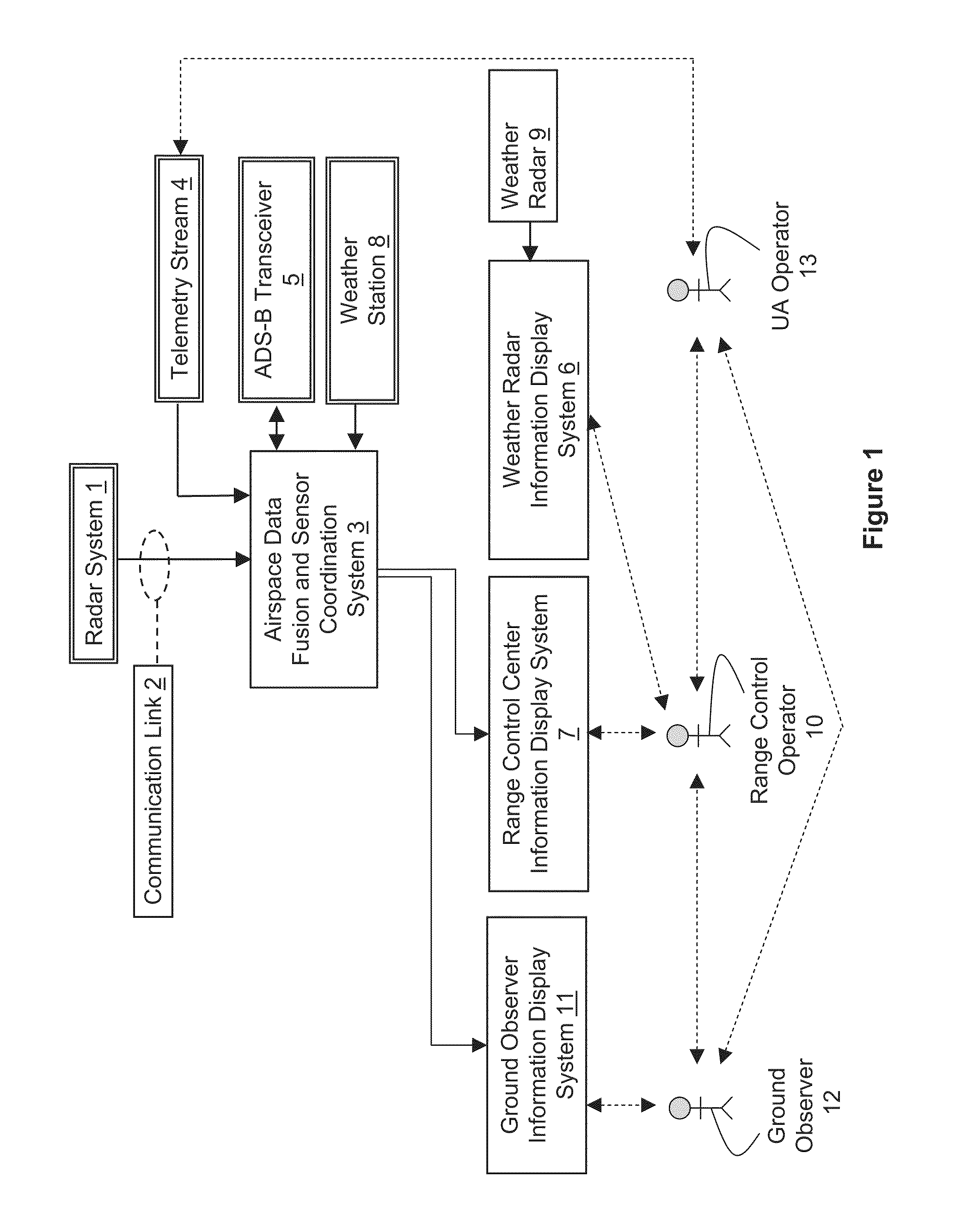
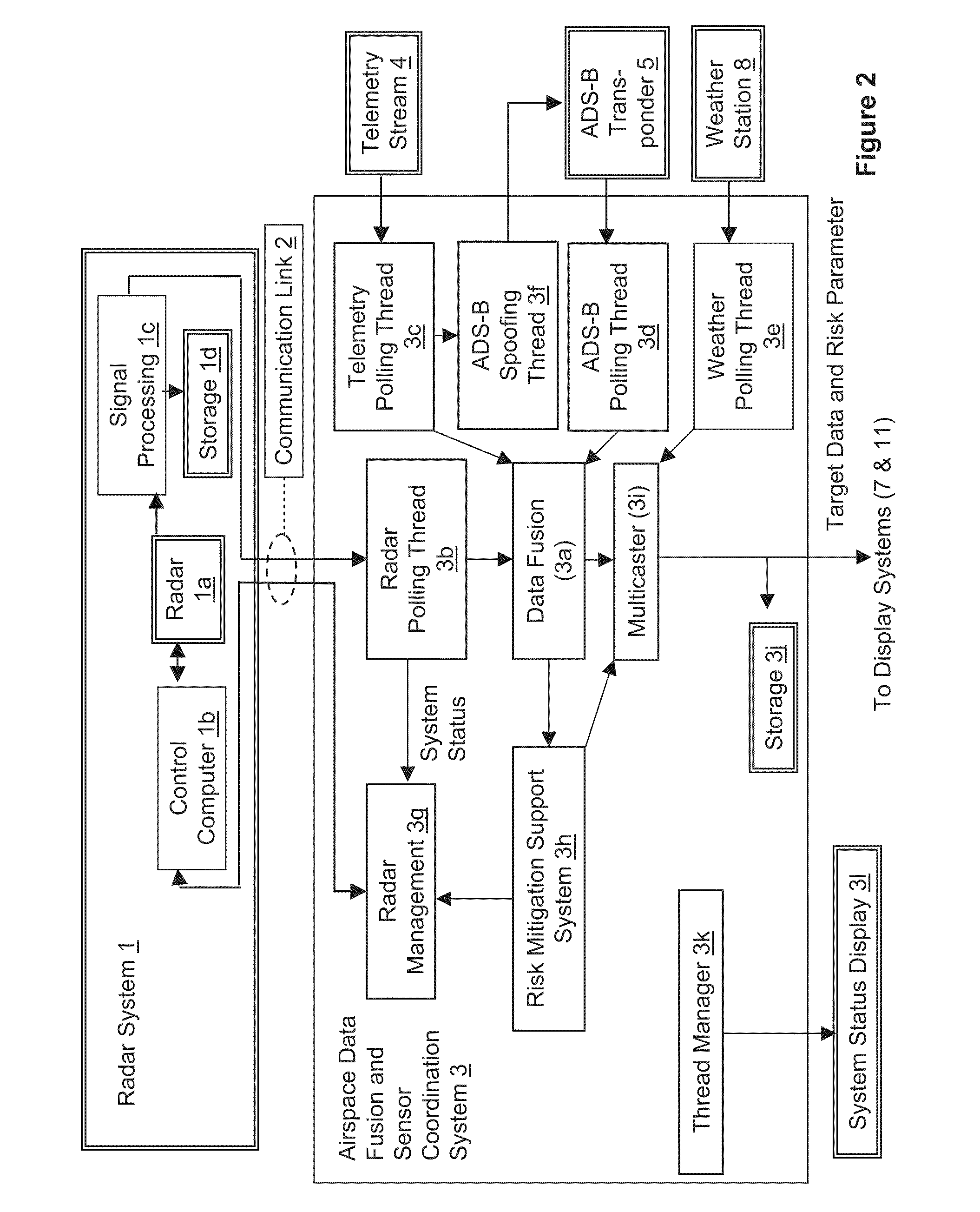
Airspace risk mitigation system
ActiveUS20100315281A1Efficient and effectiveEffective decision-makingComputation using non-denominational number representationComplex mathematical operationsSupporting systemTelecommunications link
An airspace risk mitigation system includes a plurality of airspace input sources, an airspace data fusion and sensor coordination system, a communications link, and a risk mitigation support system. The airspace input sources includes a radar for generating radar data for an airspace, and an Automatic Dependent Surveillance-Broadcast (ADS-B) receiver for generating additional data for the airspace. The airspace data fusion and sensor coordination system is configured to receive airspace data from the plurality of airspace input sources, correlating airspace data with new or known objects in the airspace, fusing airspace data into a common airspace data set, and generating target and system status information. The risk mitigation support system is configured to calculate a risk associated with aircraft operation in the airspace as a function of the target and system status information.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF NORTH DAKOTA
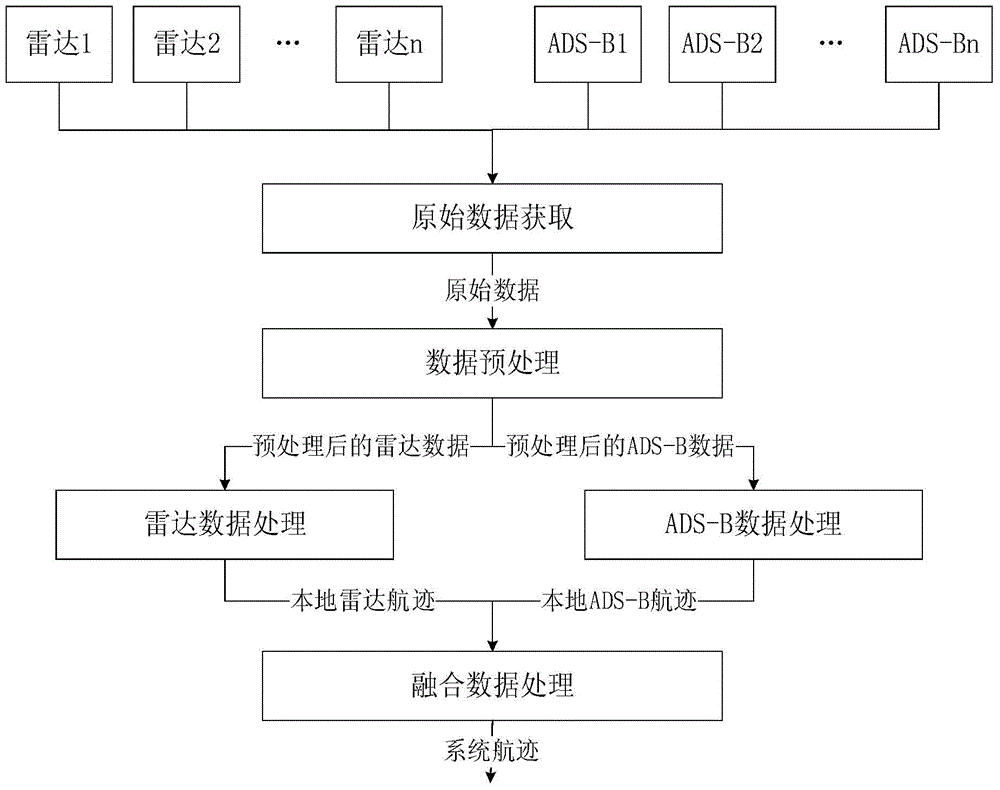
Multi-surveillance-source flying target parallel track processing method
ActiveCN104808197AMeet the requirements of real-time processingControl quantityRadio wave reradiation/reflectionData processing systemHigh availability
The invention discloses a multi-surveillance-source flying target parallel track processing method. The method includes the steps: multi-surveillance-source data receiving; multi-surveillance-source data analysis; radar data processing; ADS-B (automatic dependent surveillance-broadcast) data processing; multi-surveillance-source data fusion. Surveillance of quality of data accessing to radar is realized by monitoring and analyzing quality of radar signals. In addition, real-time receive processing of the radar data is realized by means of multithreading, high safety, high reliability and high usability of a data processing system can be further guaranteed, and accuracy and quickness in track processing of flying targets in different data types from different surveillance sources can be realized.
Owner:四川九洲空管科技有限责任公司
Employing local, opportunistic automatic dependent surveillance-broadcast (ADS-B) information processed by an unmanned aerial vehicle ground control station to augment other source “knowledge” of local aircraft position information for improving situational awareness
ActiveUS9274521B1Enhanced Situational AwarenessEnhance local situational awareness displayCharacter and pattern recognitionRemote controlled aircraftUncrewed vehicleCivil aviation
A system and method are provided for employing local, opportunistic Automatic Dependent Surveillance-Broadcast (ADS-B) information to augment other source “knowledge” of local aircraft position information for improving situational awareness in areas lacking ADS-B coverage provided by other aircraft control agencies including the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA), other Civil Aviation Authorities (CAAs), and / or other Air Traffic Control (ATC) entities. Locally-received, e.g., in a vicinity of a UAV or sUAS, ADS-B positional information is received by a UAV, sUAS or associated ground control station and integrated on a display component of the ground control station, e.g., a pilot display, for the UAV or sUAS. Received positional information is forwarded to other interested users / systems, including those associated with agencies or entities in overall tactical, operational or surveillance control of a particular area of operations, as appropriate as an integrated situational awareness map display picture.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
Enhanced passive coherent location techniques to track and identify UAVs, UCAVs, MAVs, and other objects
InactiveUS7782256B2ConfidenceDirection finders using radio wavesPosition fixationMicro air vehicleRadar
Owner:ERA AS
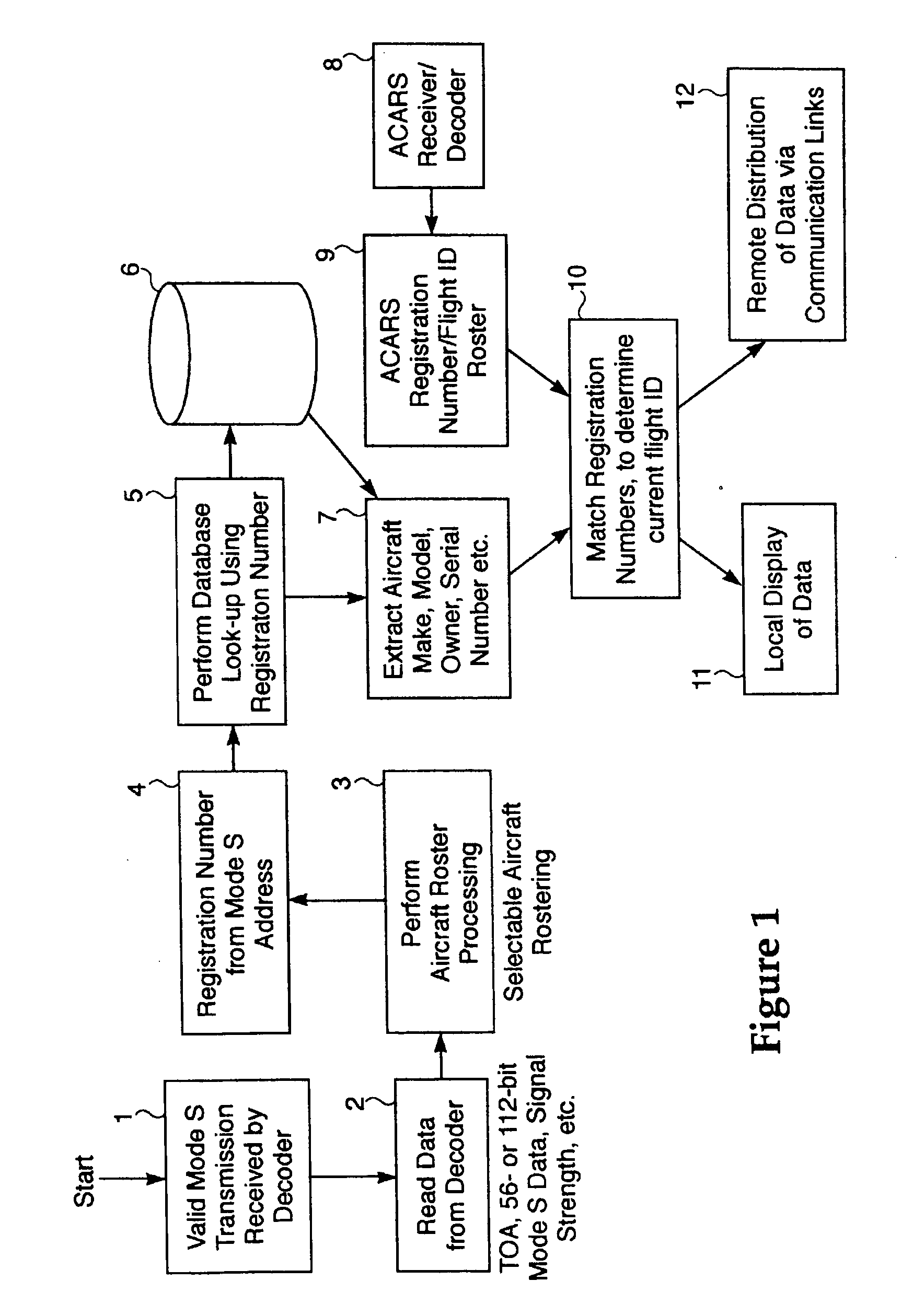
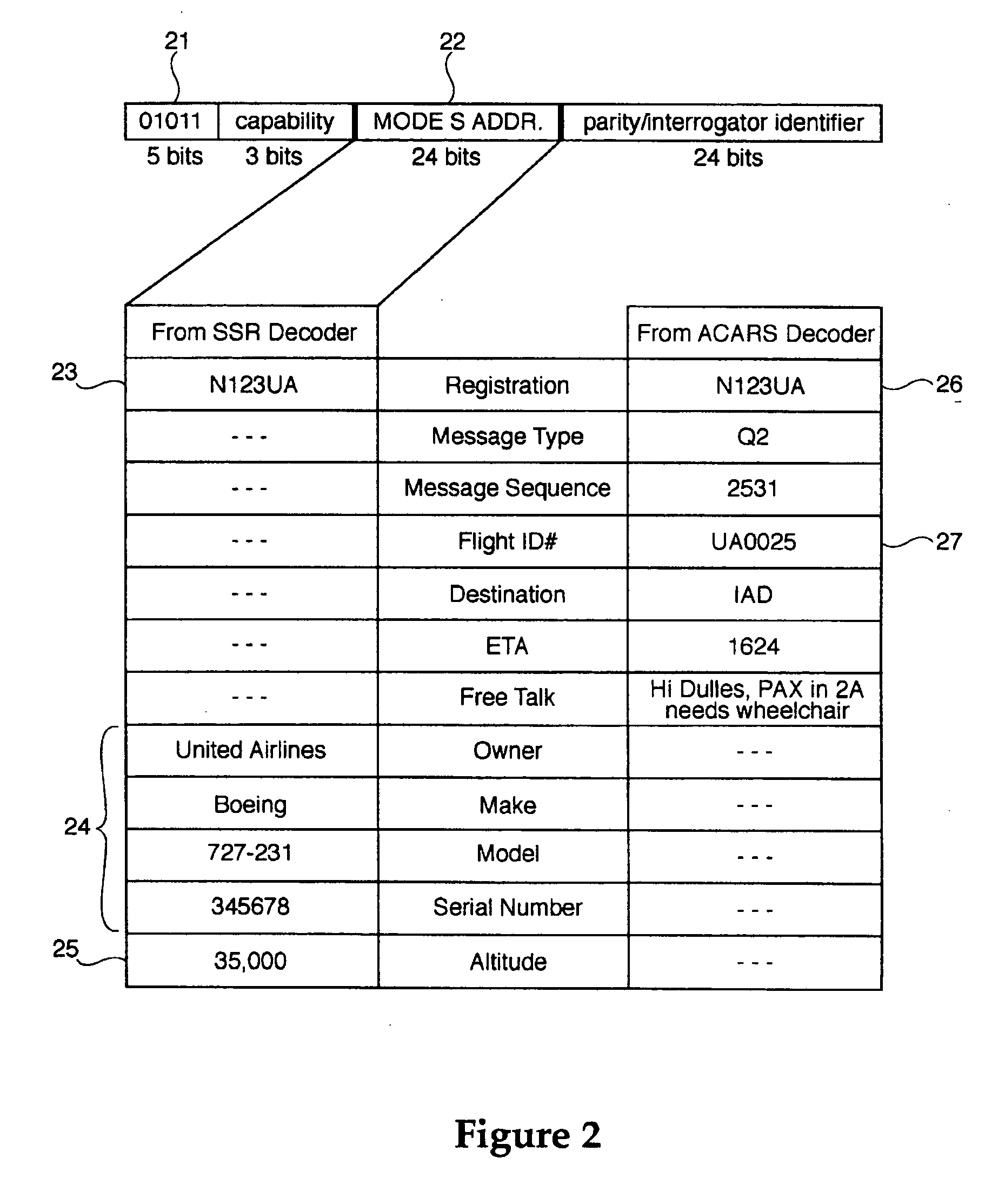
Method and apparatus for improving utility of automatic dependent surveillance
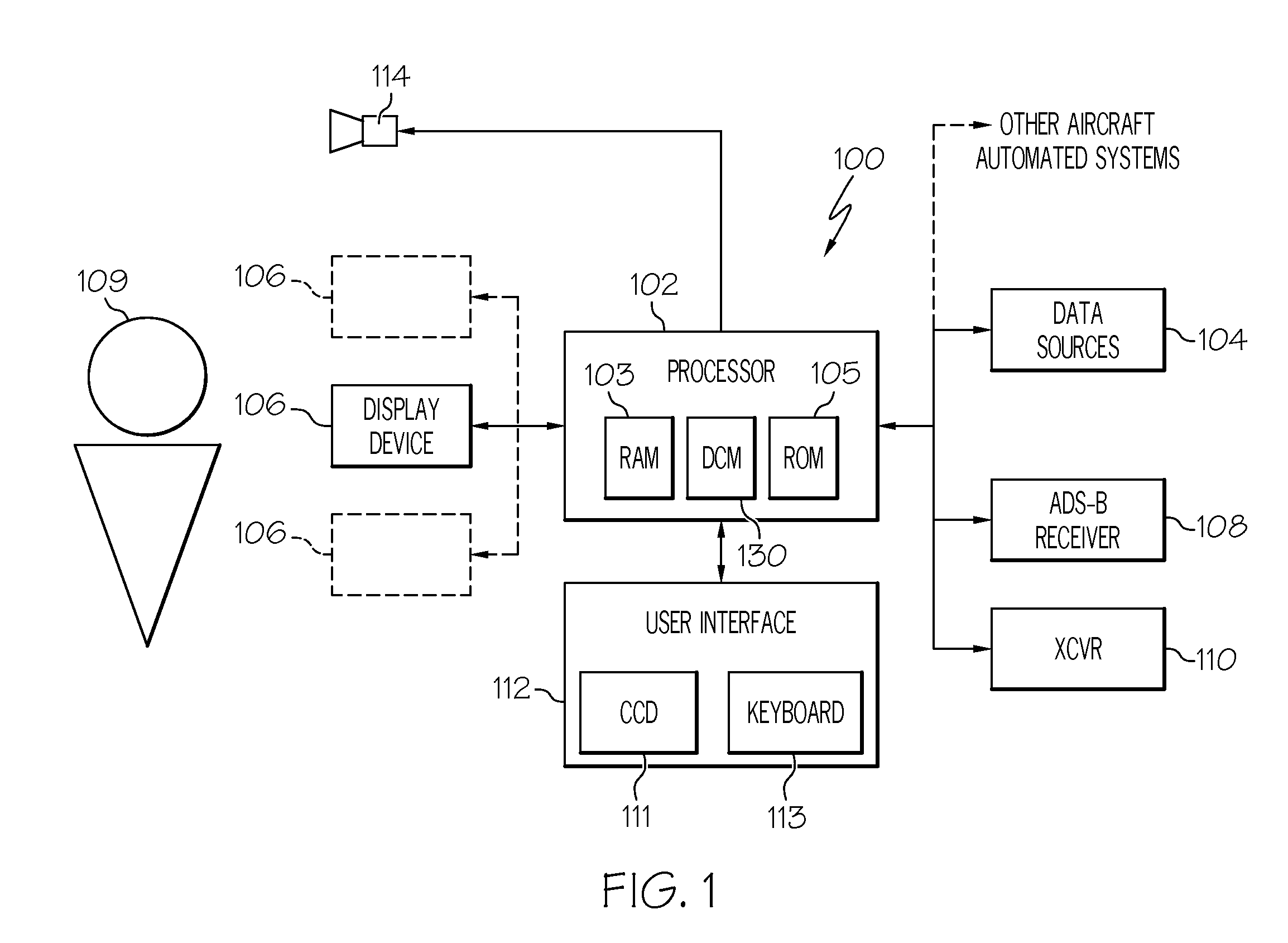
InactiveUS6567043B2Spread the wordDirection finders using radio wavesAircraft ground controlDisplay deviceMonitoring system
The surveillance system provides a means to augment Automatic Dependent Surveillance--Broadcast (ADS-B) with "look alike ADS-B" or "pseudo ADS-B" surveillance transmissions for aircraft which may not be ADS-B equipped. The system uses ground based surveillance to determine the position of aircraft not equipped with ADS-B, then broadcasts the identification / positional information over the ADS-B data link. ADS-B equipped aircraft broadcast their own position over the ADS-B data link. The system enables aircraft equipped with ADS-B and Cockpit Display of Traffic Information (CDTI) to obtain surveillance information on all aircraft whether or not the proximate aircraft are equipped with ADS-B.
Owner:OMNIPOL
Communication navigation monitoring system based on multi-mode data link
ActiveCN103873133AEasy to install on-boardEasy to modifyRadio transmissionGround stationData pre-processing
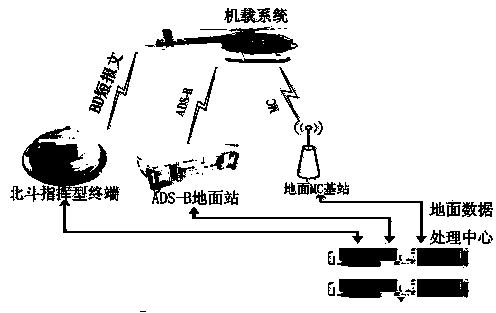
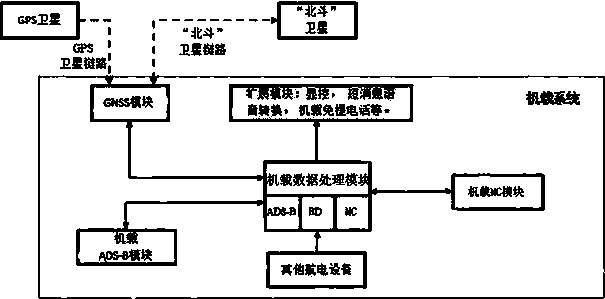
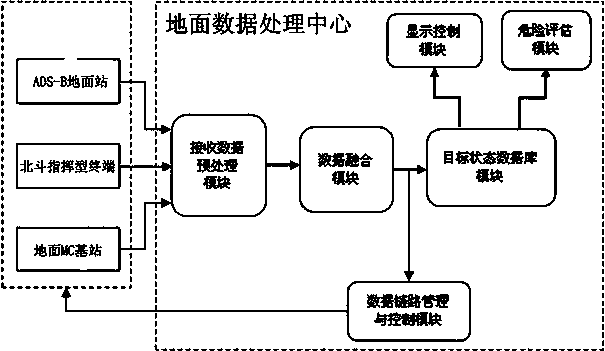
The invention discloses a communication navigation monitoring system based on a multi-mode data link. The communication navigation monitoring system based on the multi-mode data link comprises an airborne system, a Beidou commanding terminal, an ADS-B (automatic dependent surveillance-broadcast) ground station, a ground MC (mobile communication) base station and a ground data processing center, wherein a GNSS (global navigation satellite system) module is used for collecting positioning information in the airborne system, and data interaction is carried out between the GNSS module and a ground Beidou sending and receiving terminal via a satellite link; an airborne ADS-B module is used for sending and receiving ADS-B information; an MC data link is established by an airborne MC module; an airborne data processing module is used for carrying out link judgment and switching; in the ground data processing center, a data link management and control module is in charge of link selection; the link information is firstly pre-processed by a receiving data pre-processing module and is then processed by a data fusion module to be stored into a target state database module. According to the communication navigation monitoring system based on the multi-mode data link, which is disclosed by the invention, the modular design is adopted, the communication navigation monitoring system has the expandability, data link judgment and switching can be carried out in real time, and therefore operation cost is reduced.
Owner:THE SECOND RES INST OF CIVIL AVIATION ADMINISTRATION OF CHINA
Systems and methods for correlation in an air traffic control system of interrogation-based target positional data and GPS-based intruder positional data
InactiveUS6967616B2Minimizes and eliminates displayOvercome in accuracyAnalogue computers for vehiclesAnalogue computers for trafficControl systemComputer science
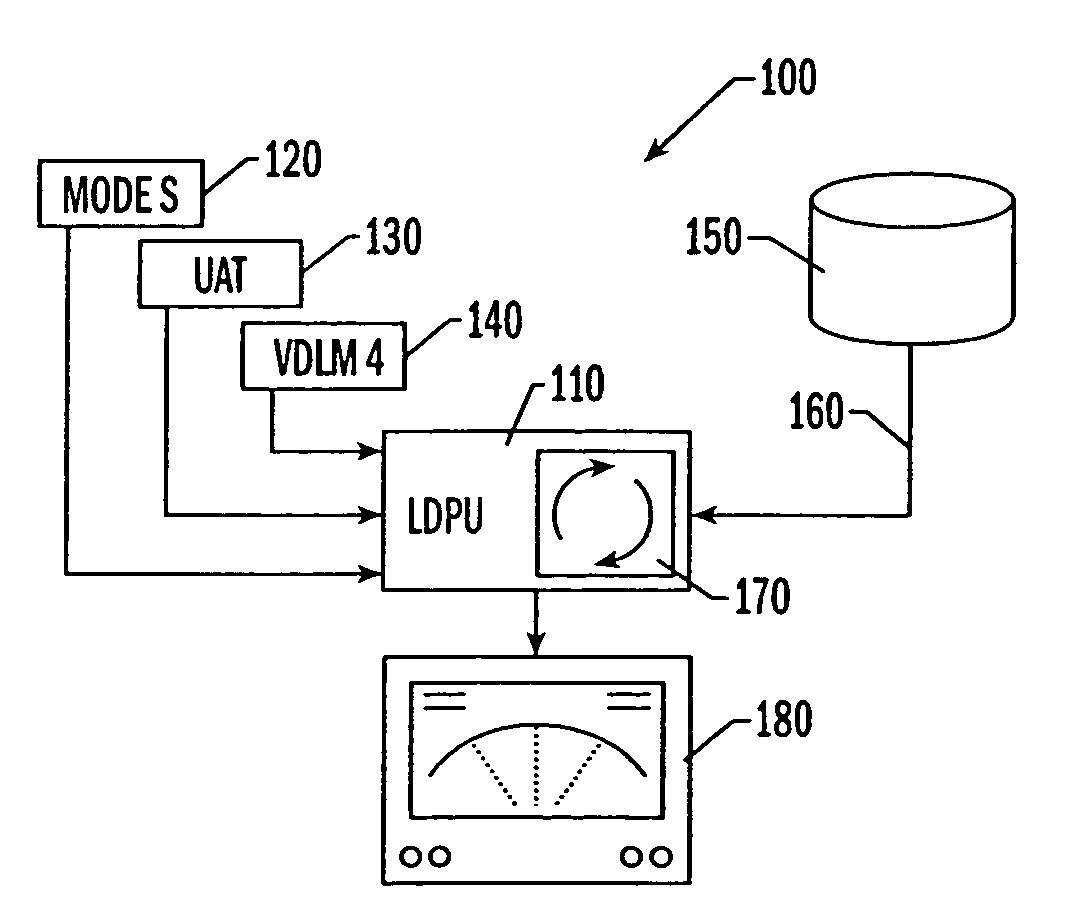
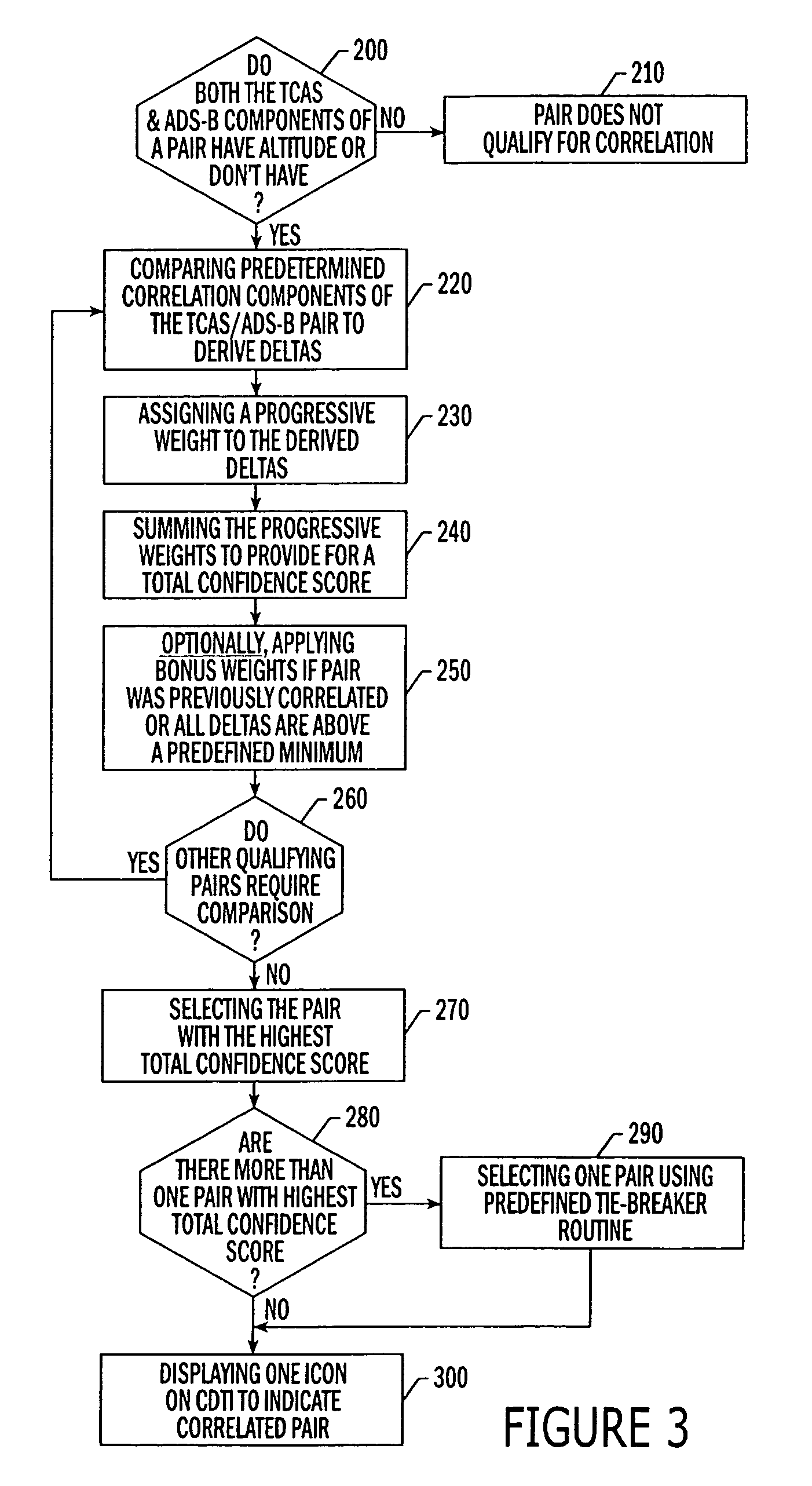
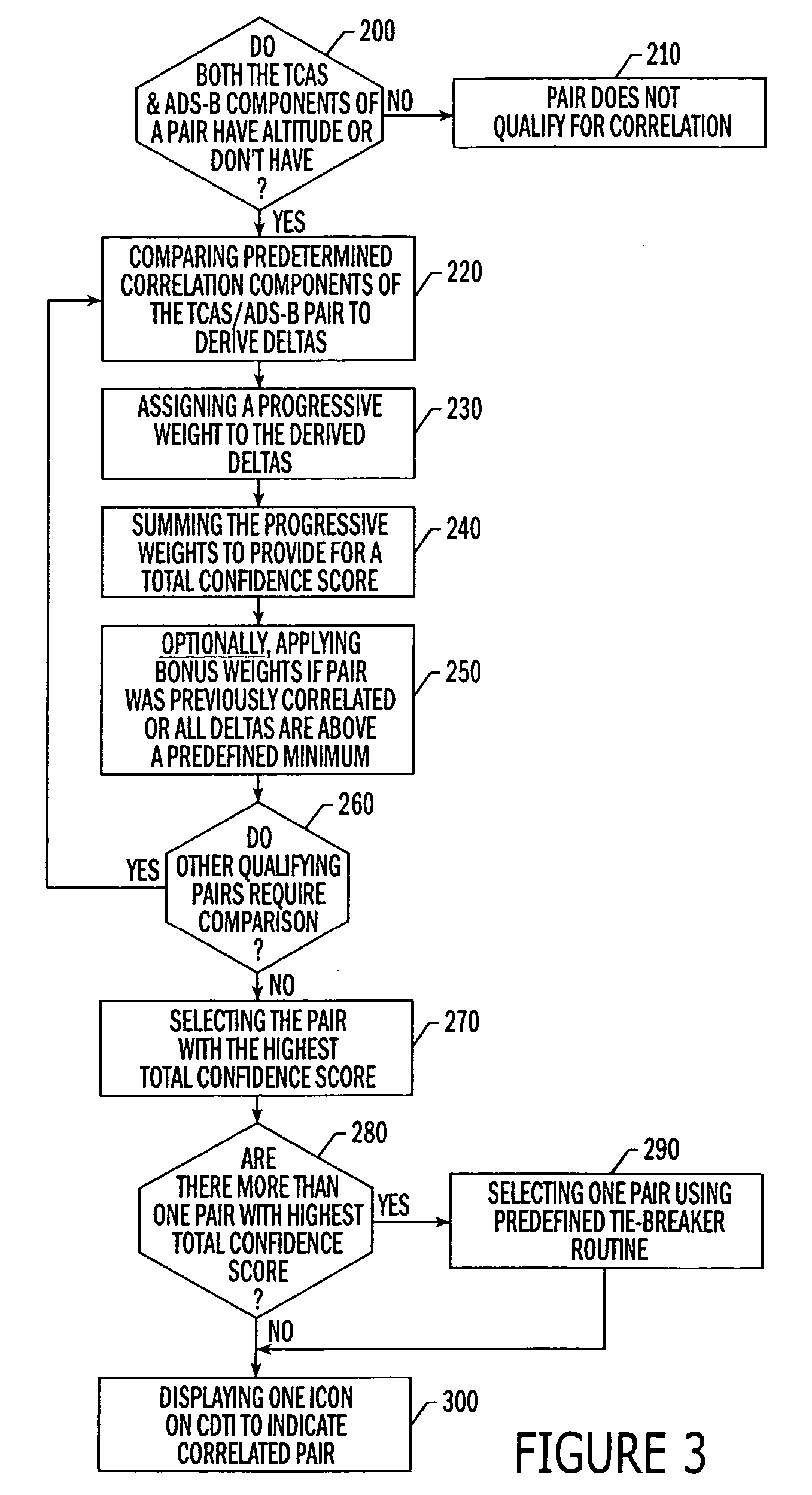
An improved system and methods for correlating an interrogation-based air traffic surveillance intruder, such as an Traffic alert and Collision Avoidance System (TCAS) intruder, and a GPS-based air traffic surveillance target, such as an Automatic Dependent Surveillance Broadcast (ADS-B) target to minimize or eliminate the display of two symbols for the same intruder / target on the CDTI of an aircraft. The method comprises the steps of receiving ADS-B data at a processing unit and calculating select component deltas for the ADS-B data versus an entry in a TCAS intruder file. Progressive weights are assigned to the deltas and the progressive weights are summed, resulting in a total confidence score. Total confidence scores of ADS-B target and TCAS intruder pairs are compared to determine correlation between the ADS-B target and the TCAS intruders.
Owner:GARMIN AT
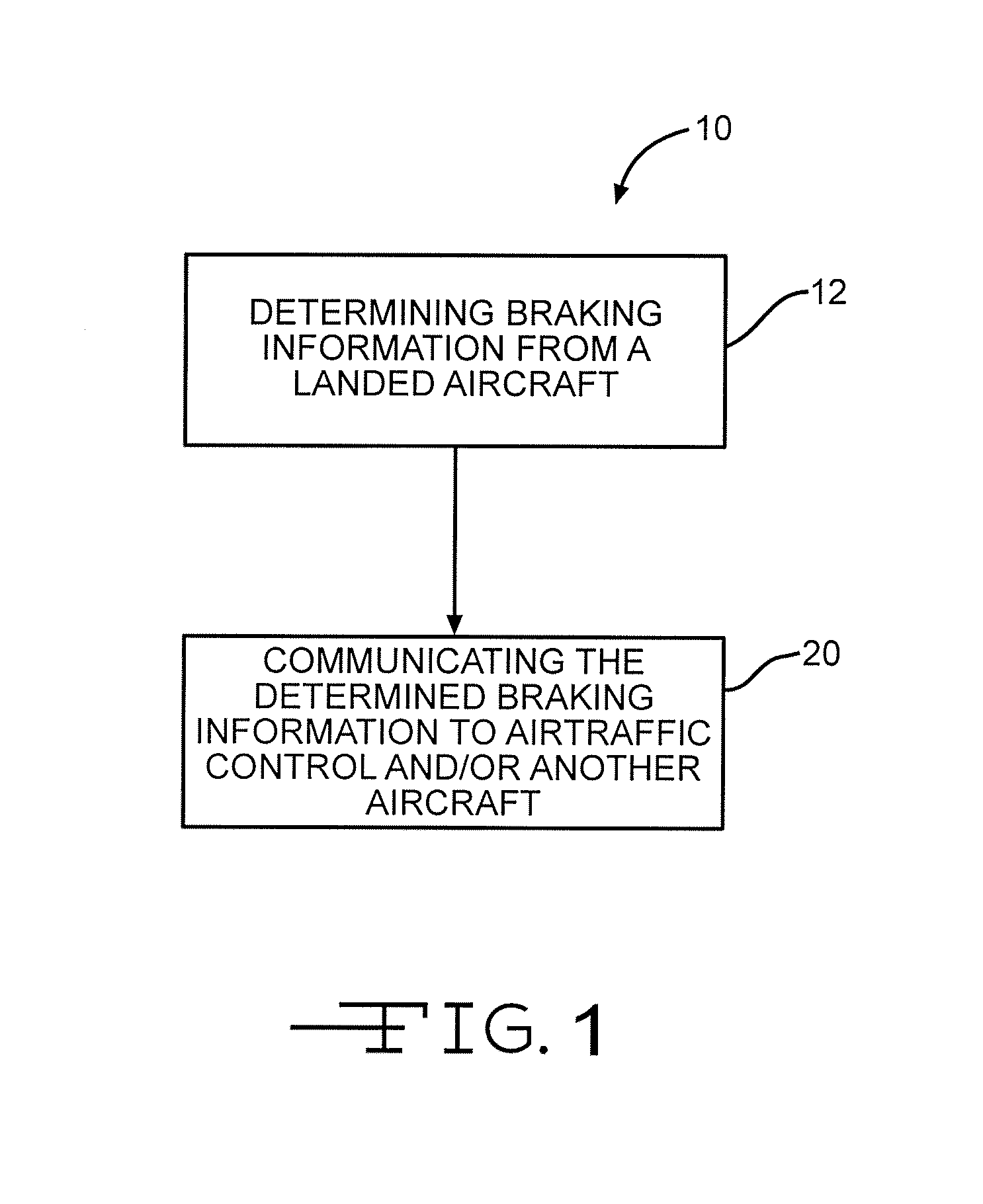
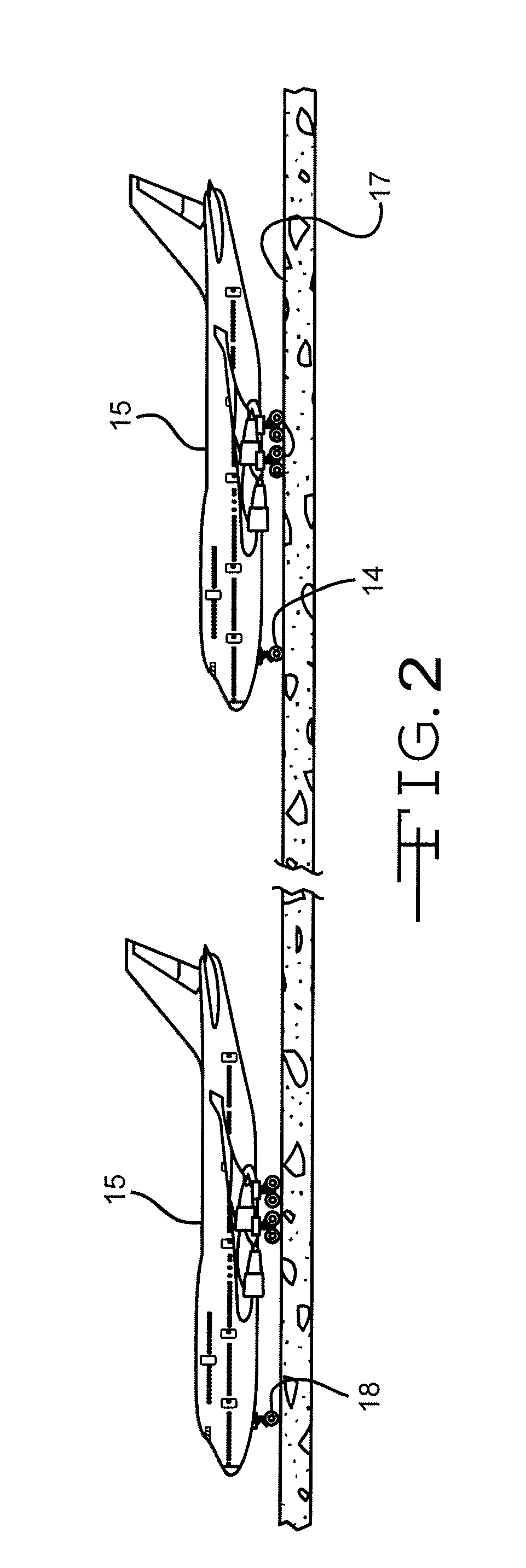
Communication of landing conditions
ActiveUS7626513B2Road vehicles traffic controlNavigation instrumentsRoad traffic controlFlight vehicle
The invention discloses differing embodiments of methods, aircraft, and apparatus for communicating the braking conditions of a runway. In one embodiment, braking information may be determined from a first aircraft which has landed on the runway. The braking information may be communicated to air traffic control and / or a second aircraft. Communication of the braking information may take place utilizing an Automatic Dependent Surveillance Broadcast system (ADS-B) and / or other type of automatic networking system.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Systems and methods for space-time determinations with reduced network traffic
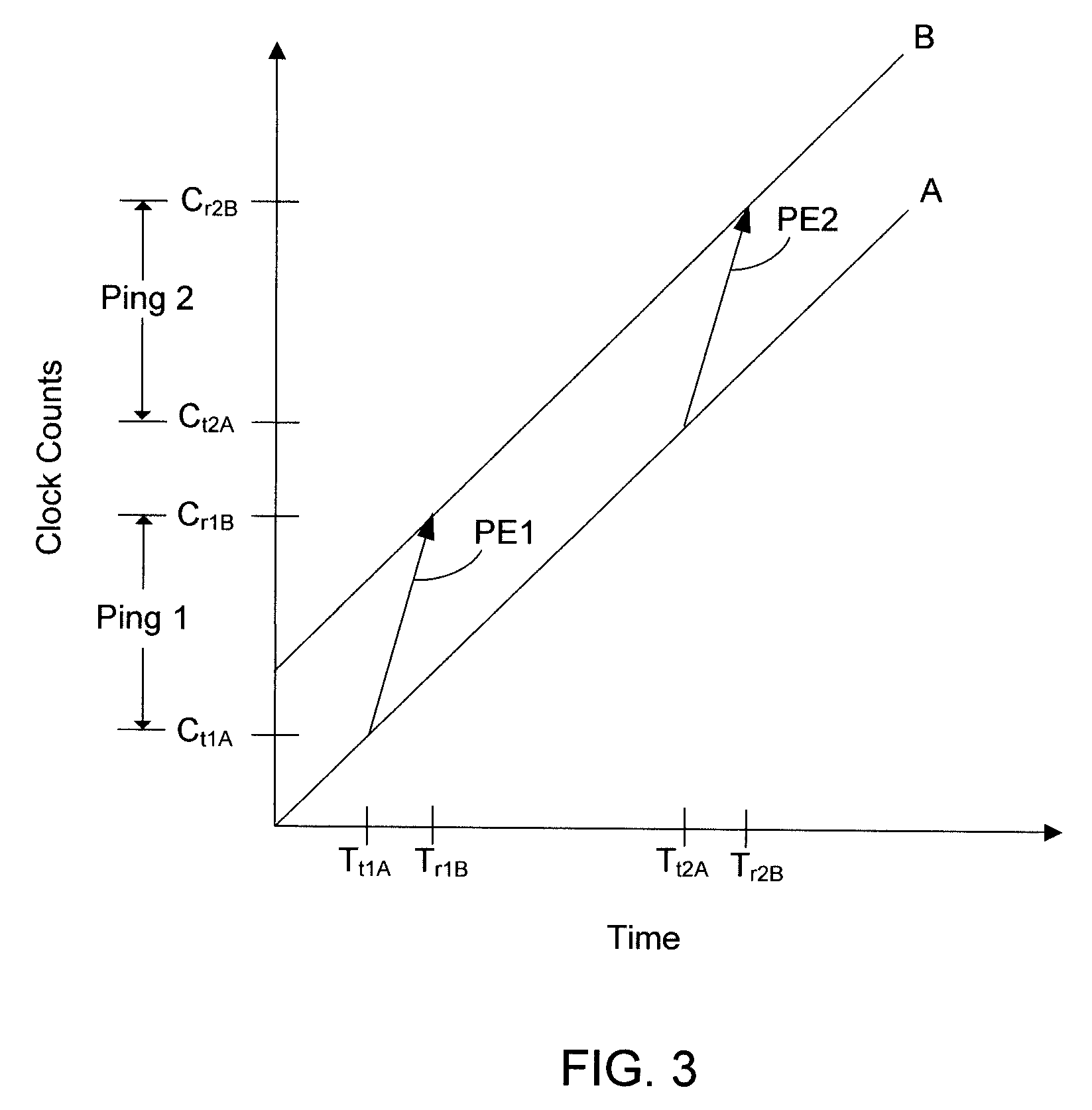
InactiveUS20100202300A1Direction finders using radio wavesError preventionSystem timeNavigation system
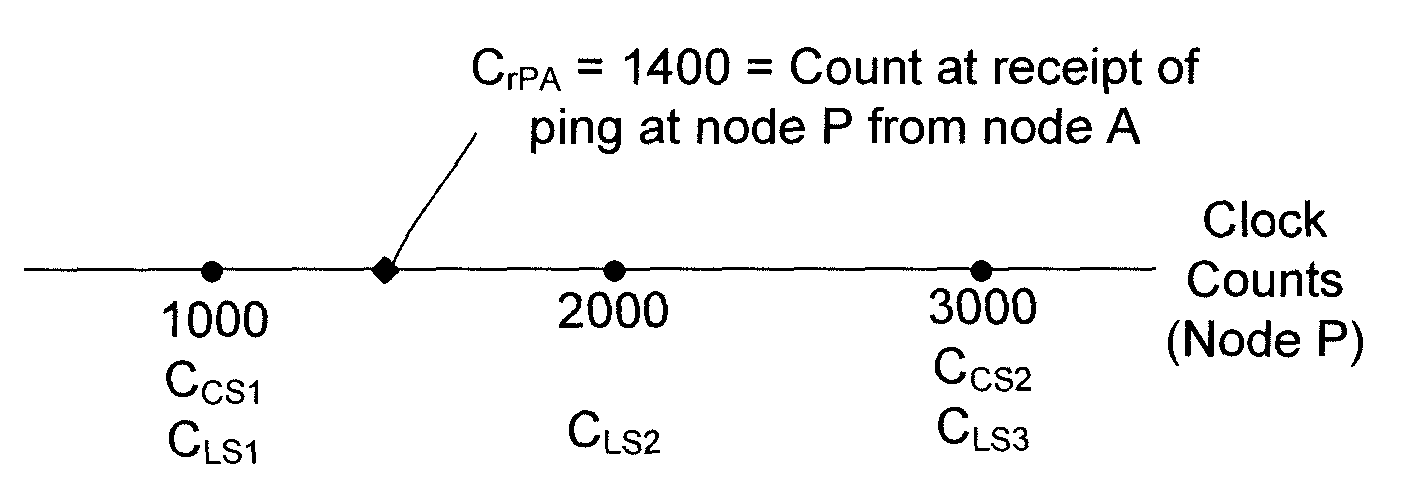
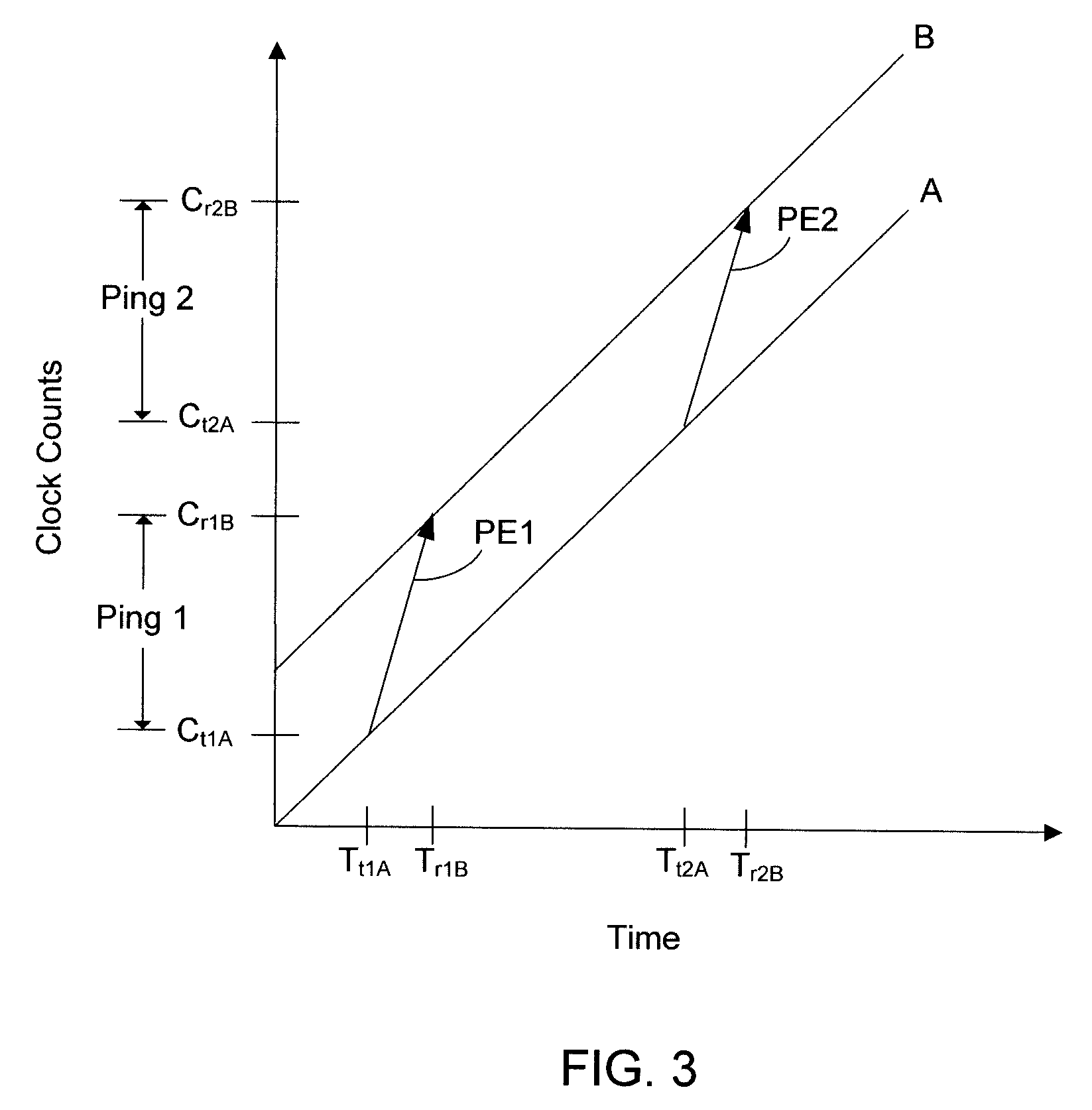
Space-time solutions are determined by exchanging pings among nodes in a network. Each ping includes a current space-time state of the transmitting node, which includes the transmitting node's currently estimated location and corrected time (as a count stamp). A particular node in the network receives pings from the other nodes in the network and uses the data in the received pings to estimate its own current position and to correct its own free-running clock relative to a common system time. As a service to the network, the particular node then transmits its corrected time (as a count stamp) and estimated position to the other nodes. In some embodiments, the space-time solutions discussed herein are used as backup to other navigation systems, such as the Automatic Dependent Surveillance-Broadcast (ADS-B) system.
Owner:DIGIMARC CORP
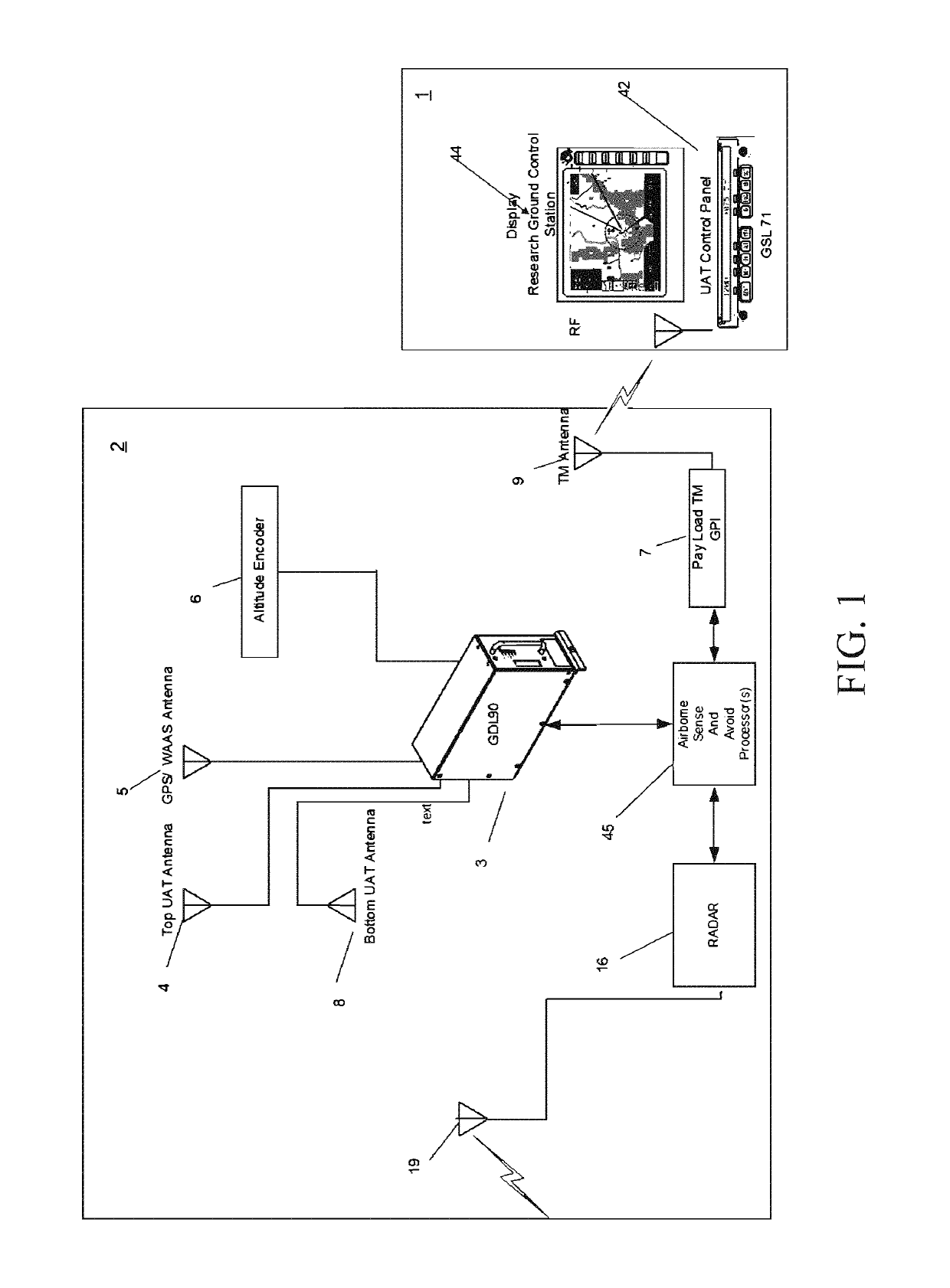
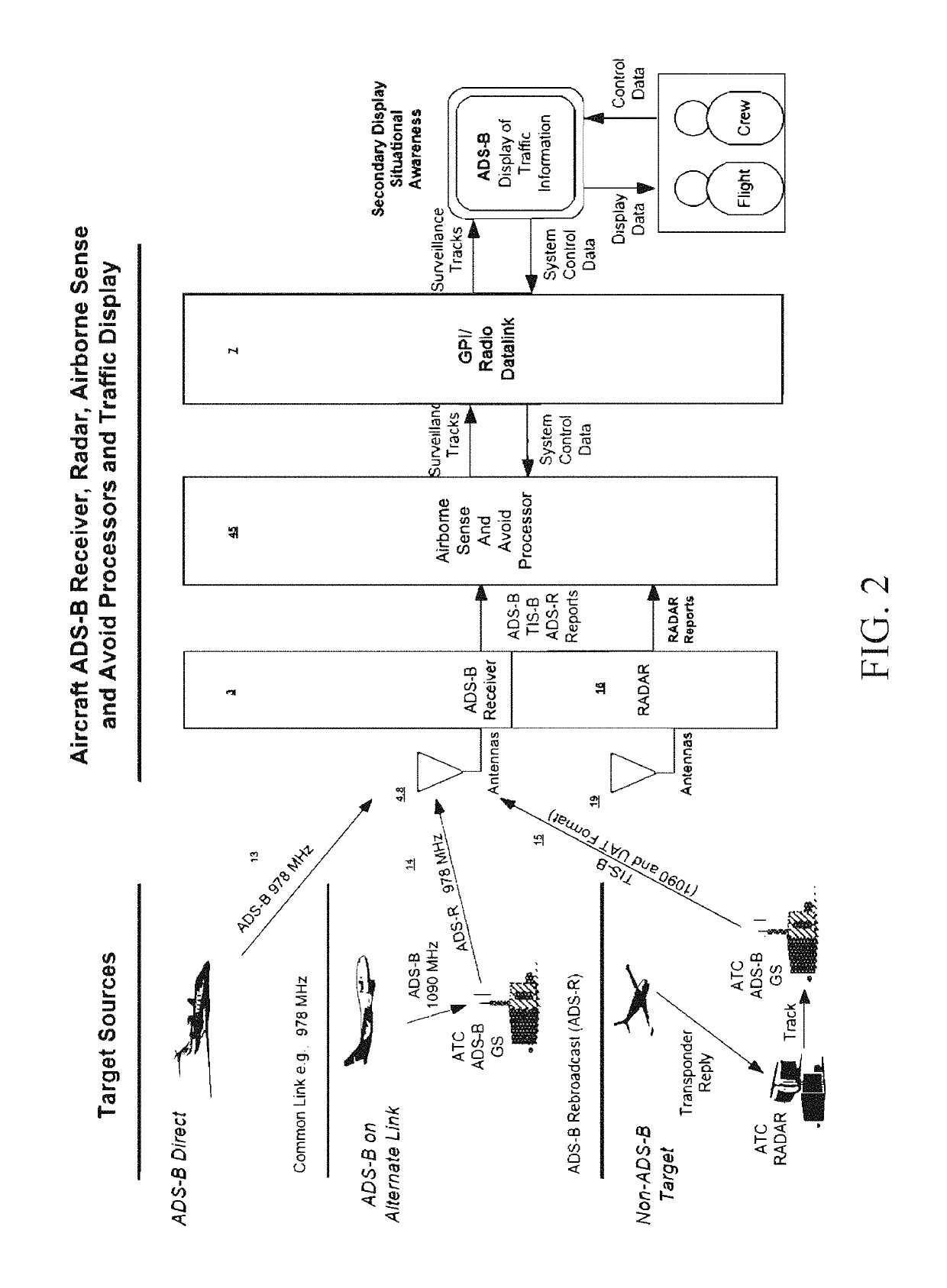
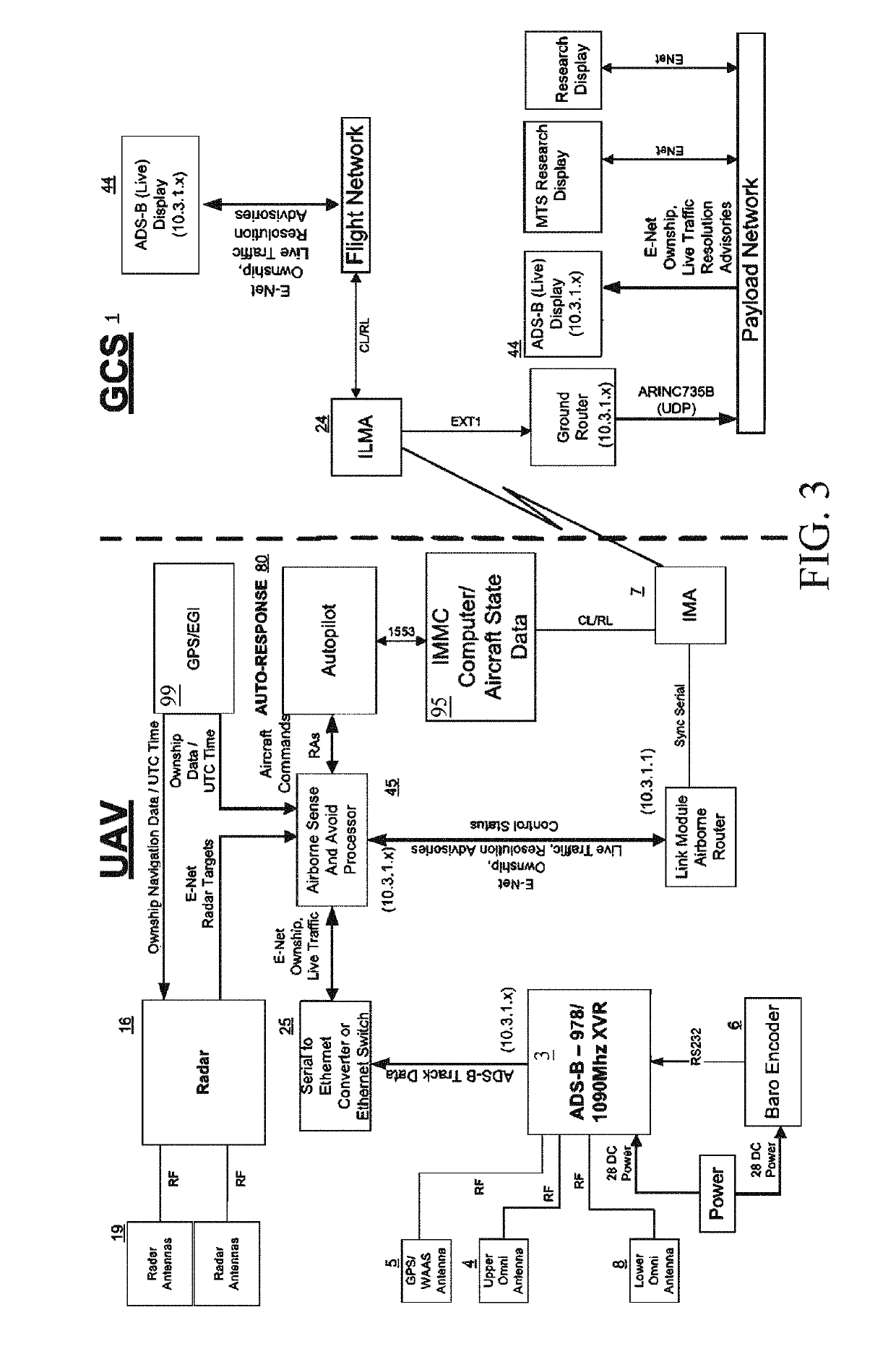
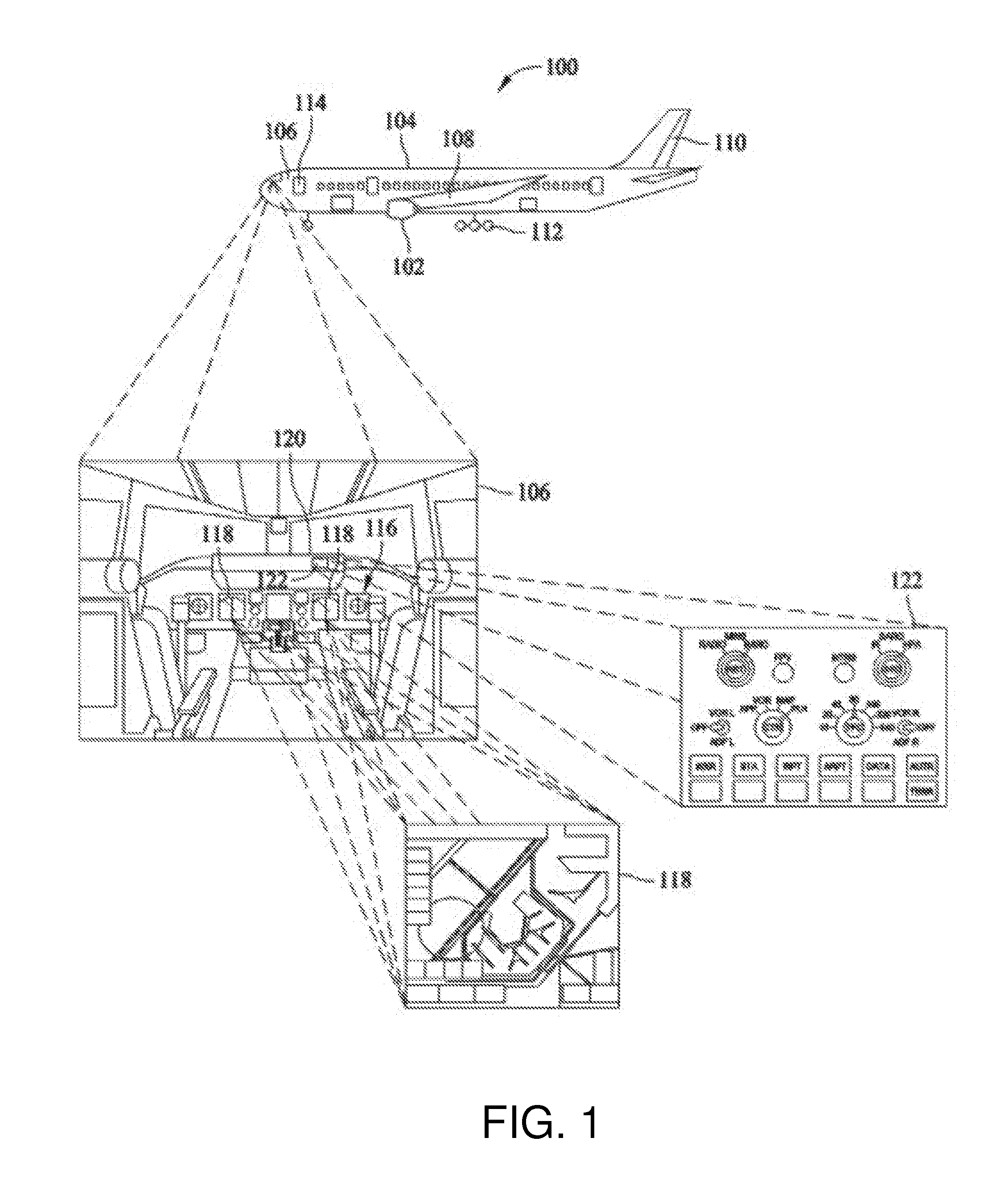
Automatic dependent surveillance broadcast (ADS-B) system with radar for ownship and traffic situational awareness
ActiveUS10302759B1Enhanced ownship situational awarenessEnhanced Situational AwarenessSatellite radio beaconingRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadarVisual perception
The present invention proposes an automatic dependent surveillance broadcast (ADS-B) architecture and process, in which priority aircraft and ADS-B IN and radar traffic information are included in the transmission of data through the telemetry communications to a remote ground control station. The present invention further proposes methods for displaying general aviation traffic information in three and / or four dimension trajectories using an industry standard Earth browser for increased situation awareness and enhanced visual acquisition of traffic for conflict detection. The present invention enable the applications of enhanced visual acquisition of traffic, traffic alerts, and en-route and terminal surveillance used to augment pilot situational awareness through ADS-B IN display and information in three or four dimensions for self-separation awareness.
Owner:UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE ADMINISTATOR OF NASA
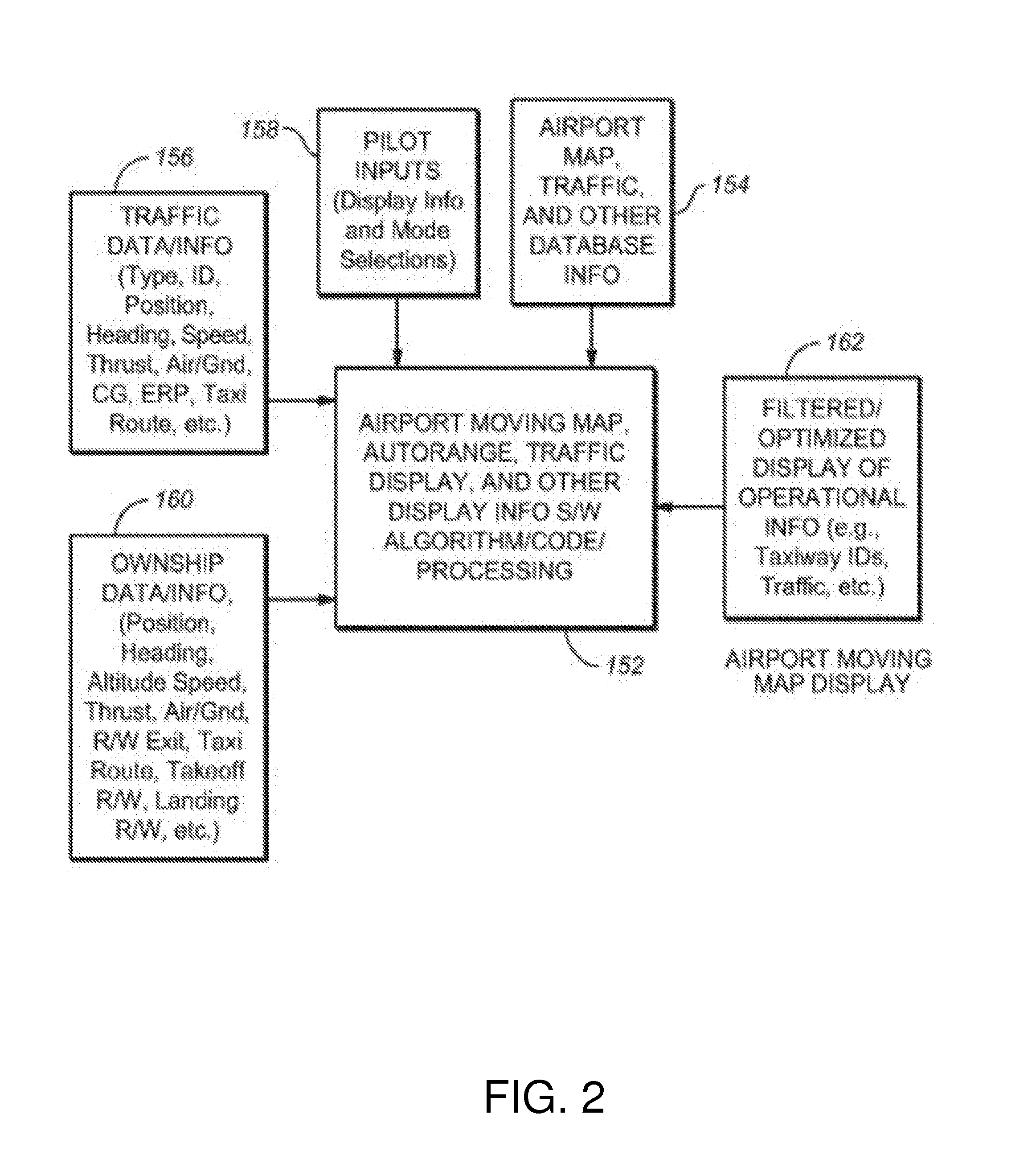
Methods and Systems for Filtering Traffic Information for Display
ActiveUS20120130624A1Analogue computers for vehiclesAnalogue computers for trafficSymbolic SystemsTraffic capacity
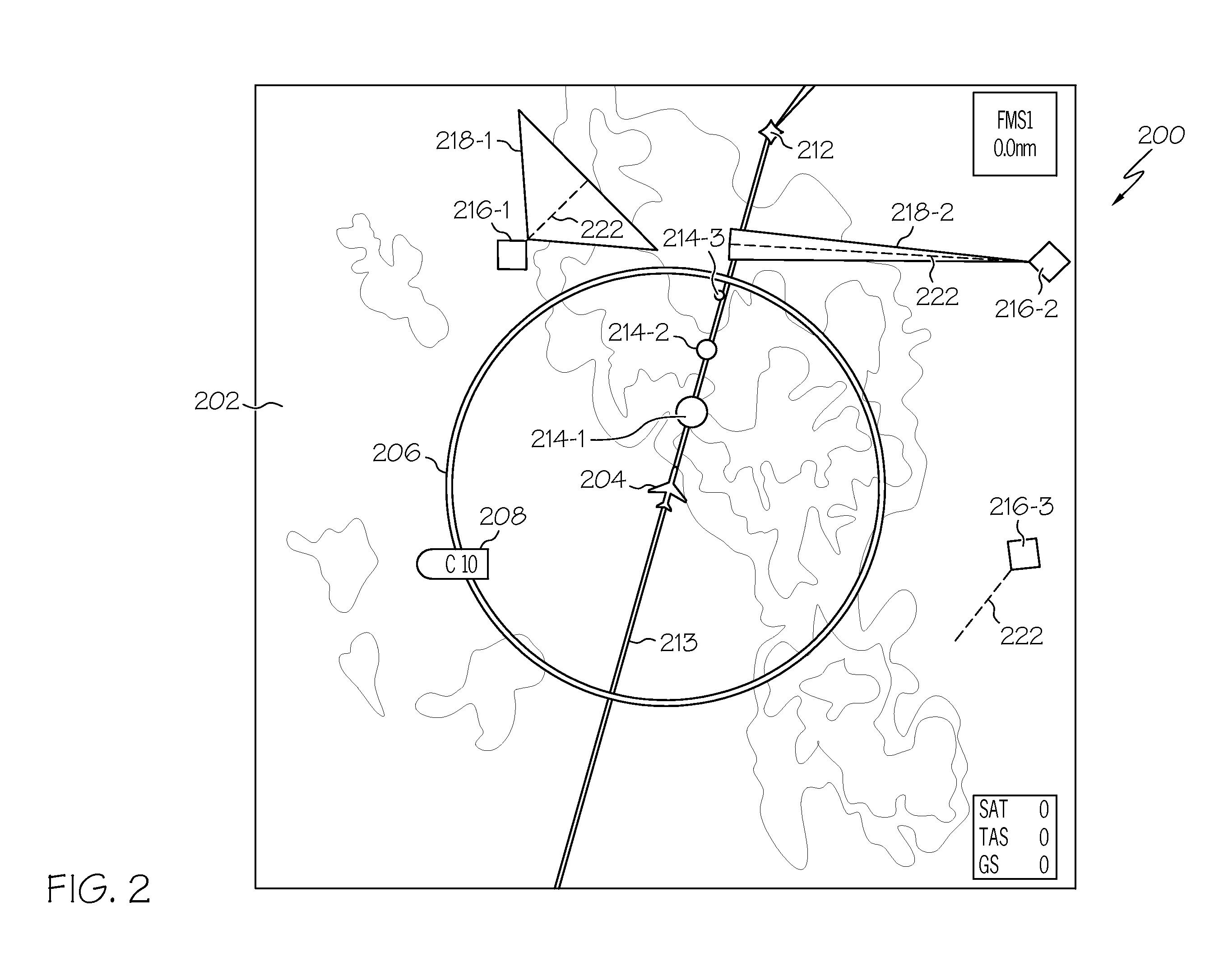
A method and a system for displaying an airport or runway moving map with traffic information on a display screen in the cockpit or flight deck of an aircraft. Symbology representing surface and near-surface aircraft and surface vehicle traffic and associated traffic data are filtered to prevent or limit clutter on the display screen. Traffic symbology is automatically and manually filtered to display only relevant traffic. Traffic data is selectively displayed and displayed as / when relevant or needed. The displayed traffic information may be derived from automatic dependent surveillance-broadcast, traffic information system-broadcast, automatic dependent surveillance-rebroadcast, traffic collision avoidance system or other source.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
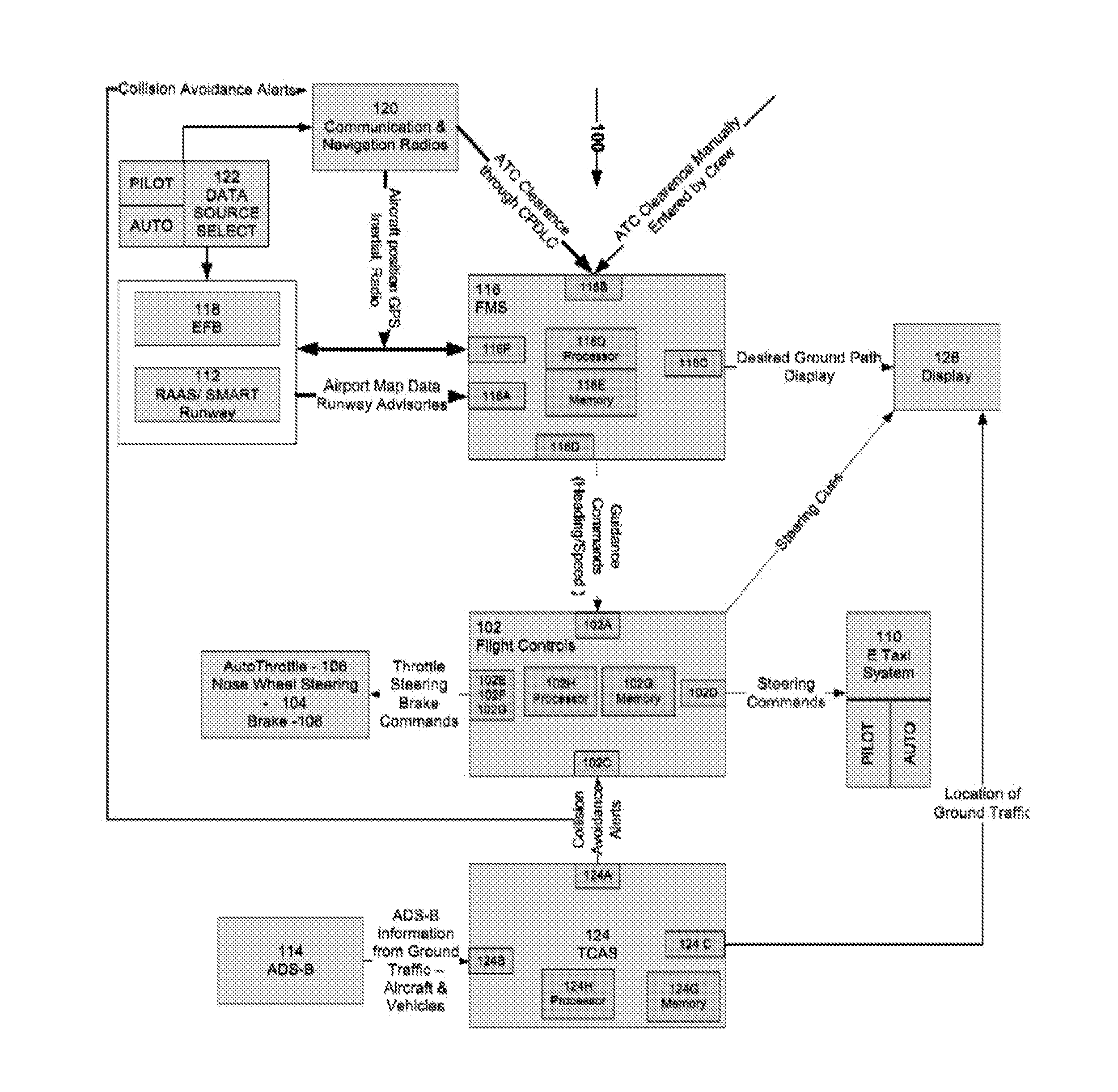
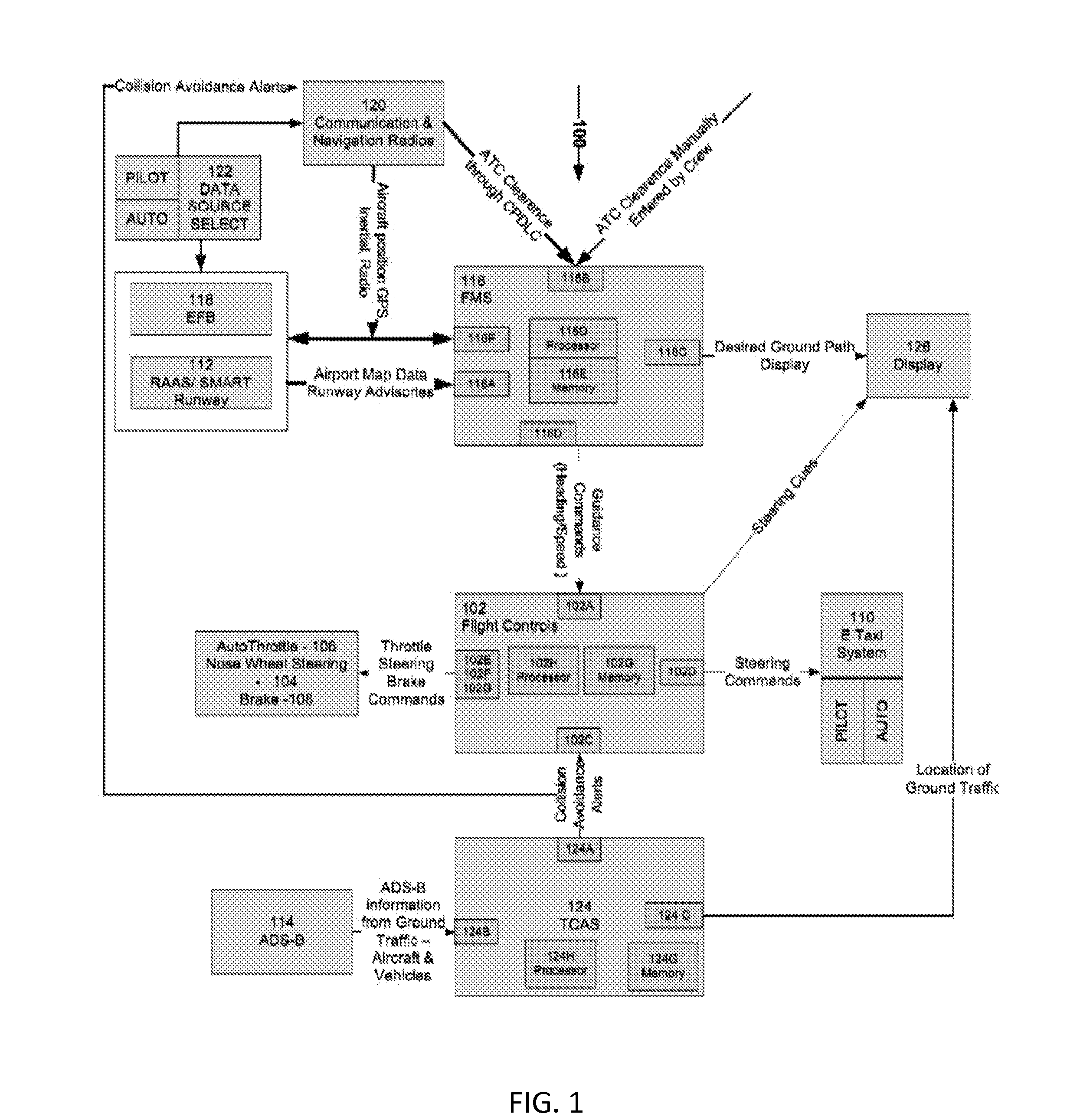
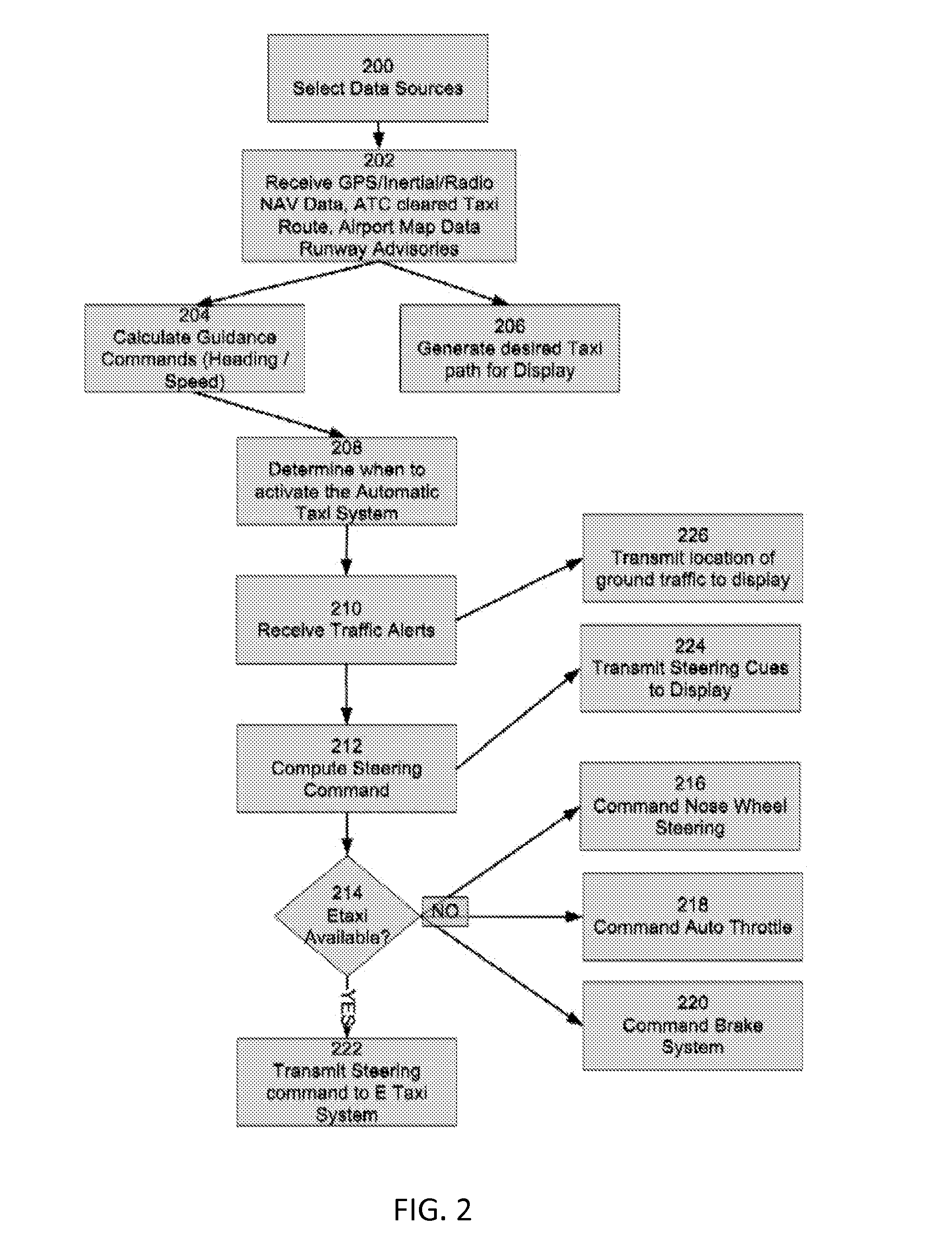
Aircraft taxiing system
InactiveUS20140278037A1Safely taxiAvoid collisionAnalogue computers for vehiclesAnalogue computers for trafficFlight management systemAutomatic dependent surveillance-broadcast
An aircraft taxiing system is provided, comprising a flight control system, an electric taxi system having controls, a flight management system (FMS), at least one data input source coupled to the FMS, and a traffic collision avoidance system (TCAS). The FMS is programmed with instructions to calculate guidance speed and heading commands, augment the guidance commands to avoid runway incursions, and transmit the guidance commands to the flight control system. The TCAS is programmed with instructions to receive Automatic Dependent Surveillance-Broadcast (ADS-B) data from ground traffic, generate collision avoidance alerts; and transmit the collision avoidance alerts to the flight control system. The flight control system is programmed with instructions to receive guidance commands from the FMS, receive the traffic collision avoidance alerts from the TCAS, and compute the steering commands, and transmit the commands to the electric taxi system to taxi the aircraft along a calculated taxi route.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
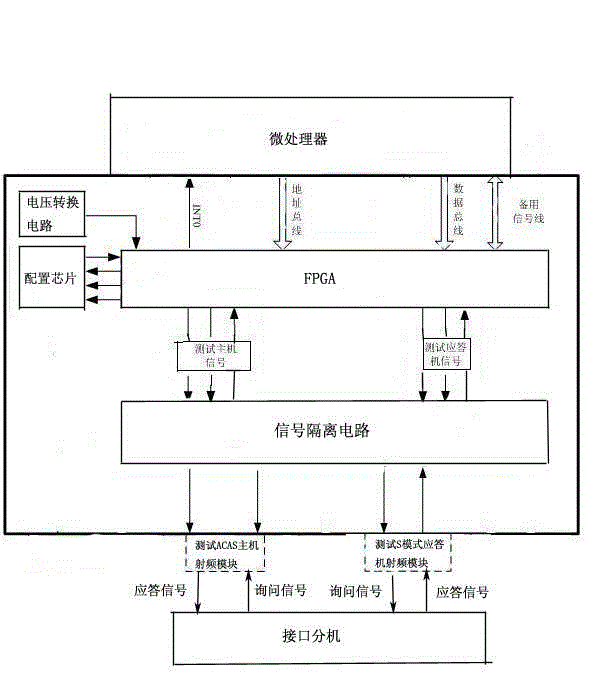
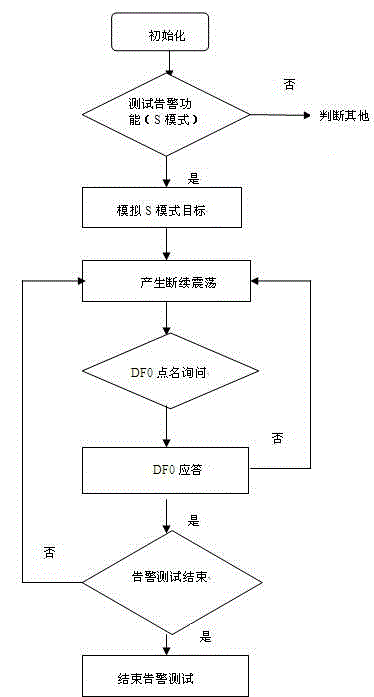
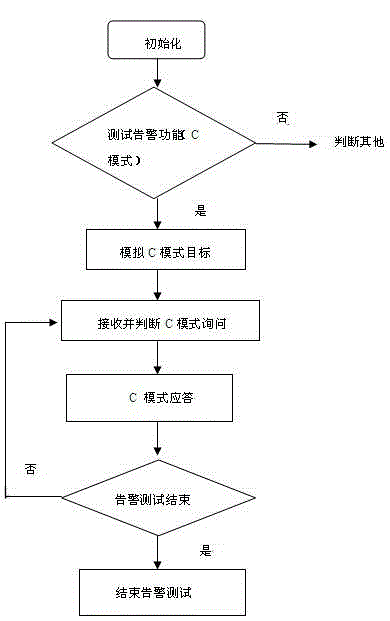
Airborne collision avoidance system tester and testing method
The invention discloses an airborne collision avoidance system (ACAS) tester and a testing method. The tester comprises a signal processing module, a testing ACAS host radio frequency module, a testing S-mode responder radio frequency module and an interface extension, wherein the signal processing module comprises a microprocessor, an FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array), a signal driving and isolating circuit, a configuration chip and a voltage conversion circuit. The signal processing module accomplishes coding of a transmitting-receiving host inquiry signal of an ACAS, analyzes an S-mode protocol, judges an inquiry format, codes according to an inquiry mode, generates a responding signal, generates an A / C / S-mode inquiry signal for an S-mode responder of the ACAS, codes the responding signal, analyzes the S-mode protocol, and obtains the height and identity data (an S-mode address) of the S-mode responder, and requirements on functions such as blank pipe response, air traffic alarm, ADS-B OUT (Automatic Dependent Surveillance Broadcast Out) of the ACAS tester are met.
Owner:四川九洲空管科技有限责任公司
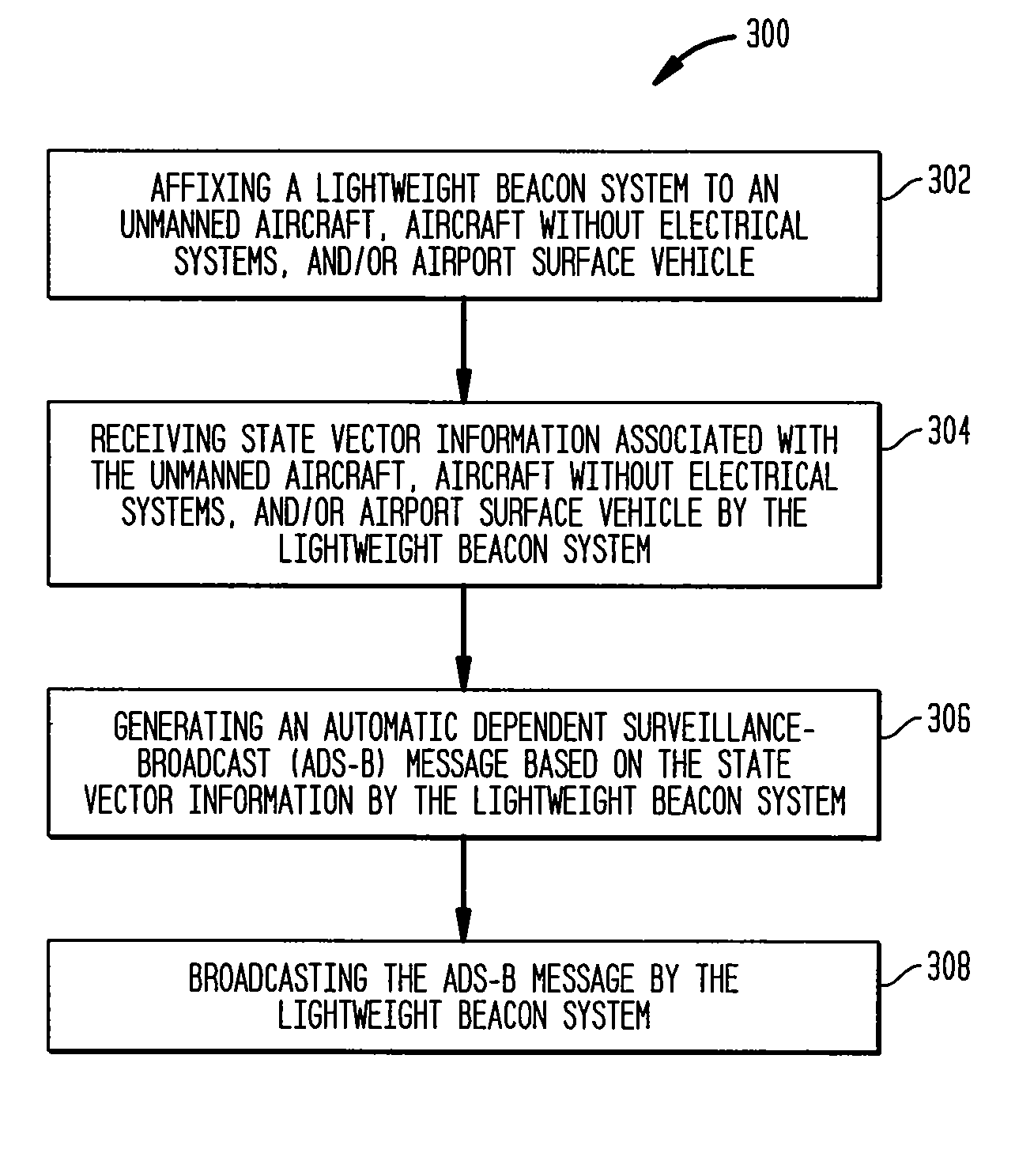
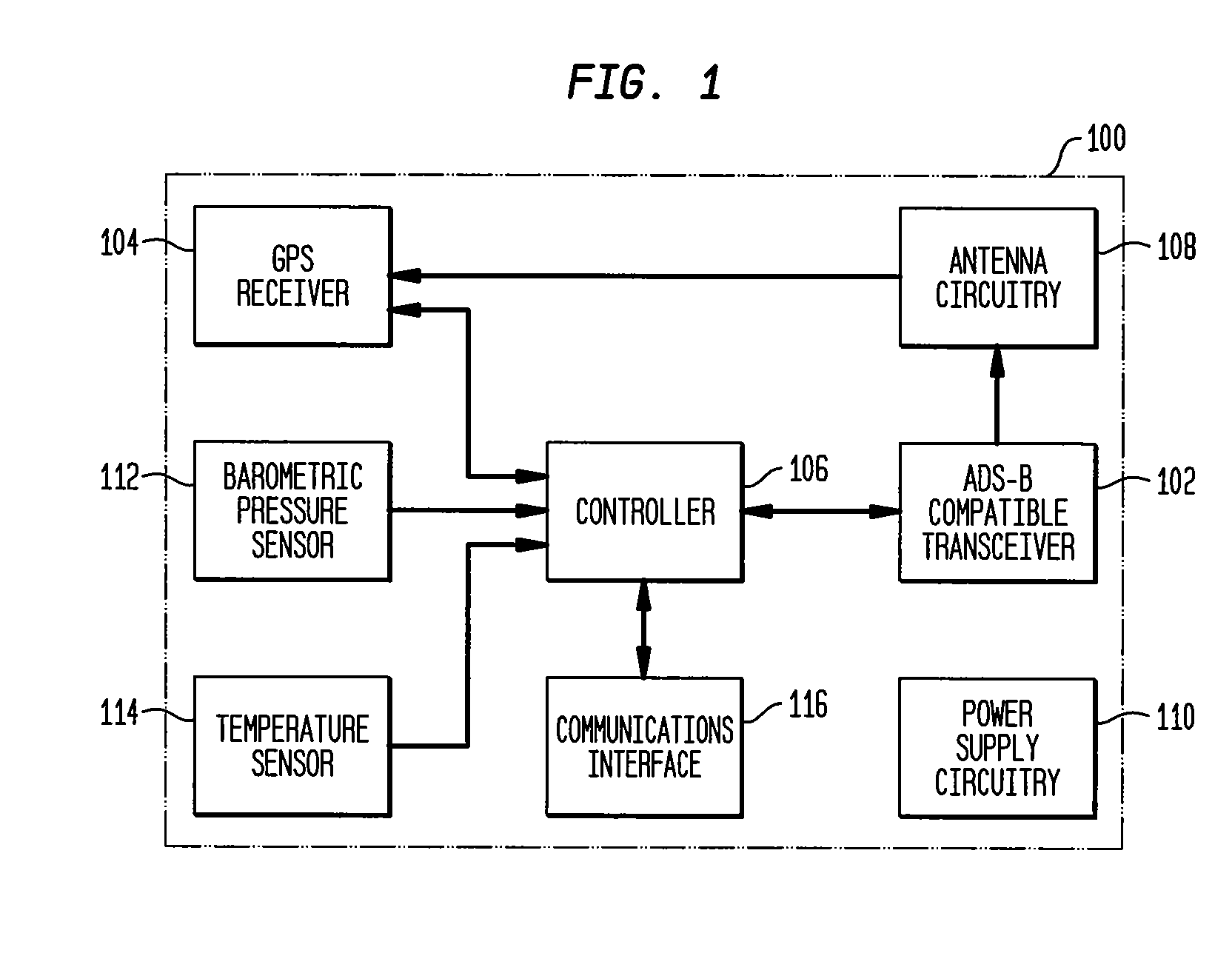
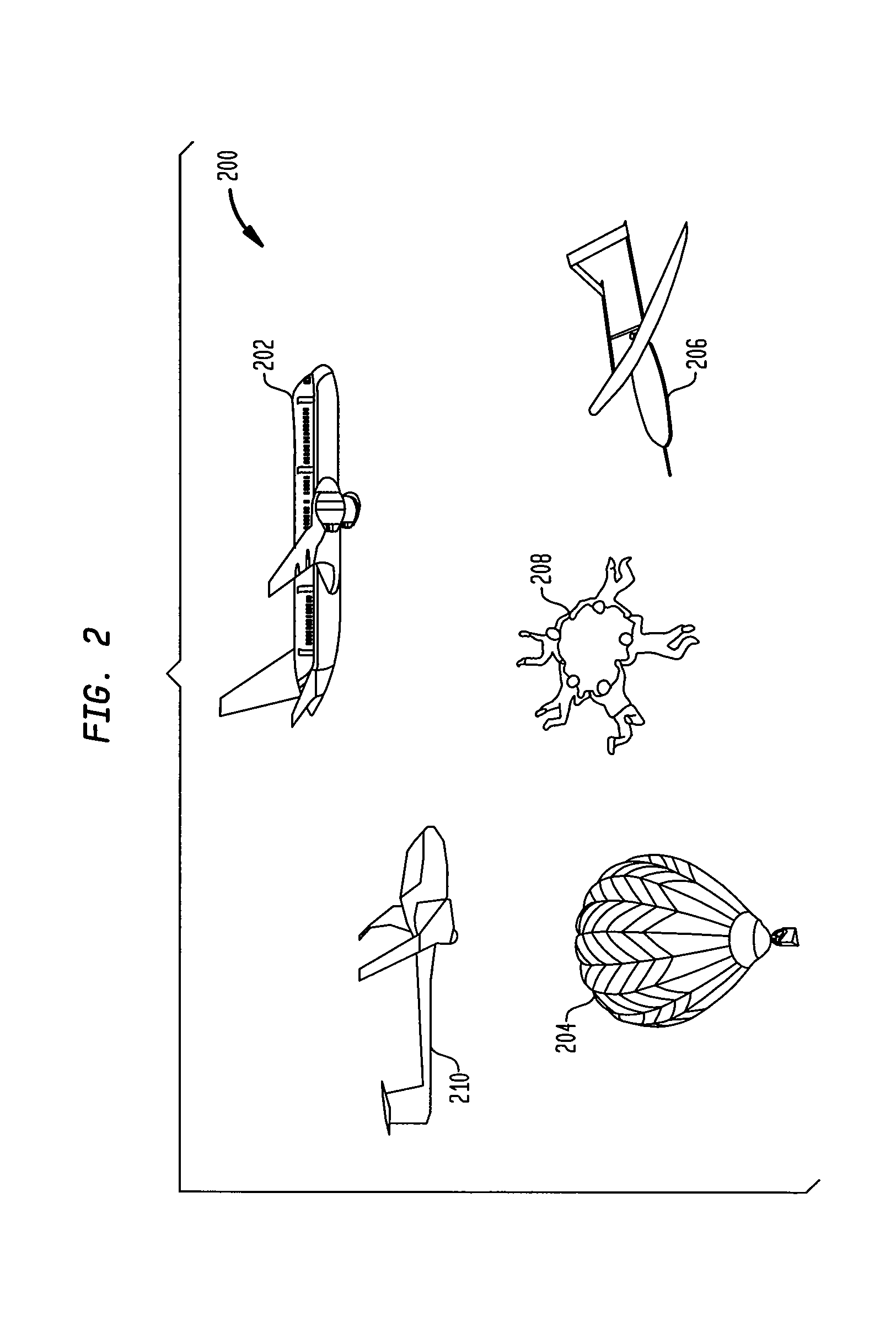
Observability of unmanned aircraft and aircraft without electrical systems
InactiveUS20100283661A1Improve ObservabilitySimplify identification and trackingPosition fixationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionGround vehiclesObservability
The present invention relates to a lightweight beacon system, affixable, for example, to UAS, aircraft without electrical systems, airport surface vehicles, skydivers, gliders, and / or balloons. The lightweight beacon system uses a small, low-powered, portable radio beacon to broadcast the location of the aircraft, vehicle, or person to which the beacon system is attached. The lightweight beacon system is compatible with the FAA's Automatic Dependent Surveillance-Broadcast (ADS-B) service, thereby providing a means for unmanned aircraft systems (UAS), aircraft without electrical systems, airport surface vehicles, or persons to be observable to other general aviation aircraft operating in their proximity.
Owner:MITRE SPORTS INT LTD
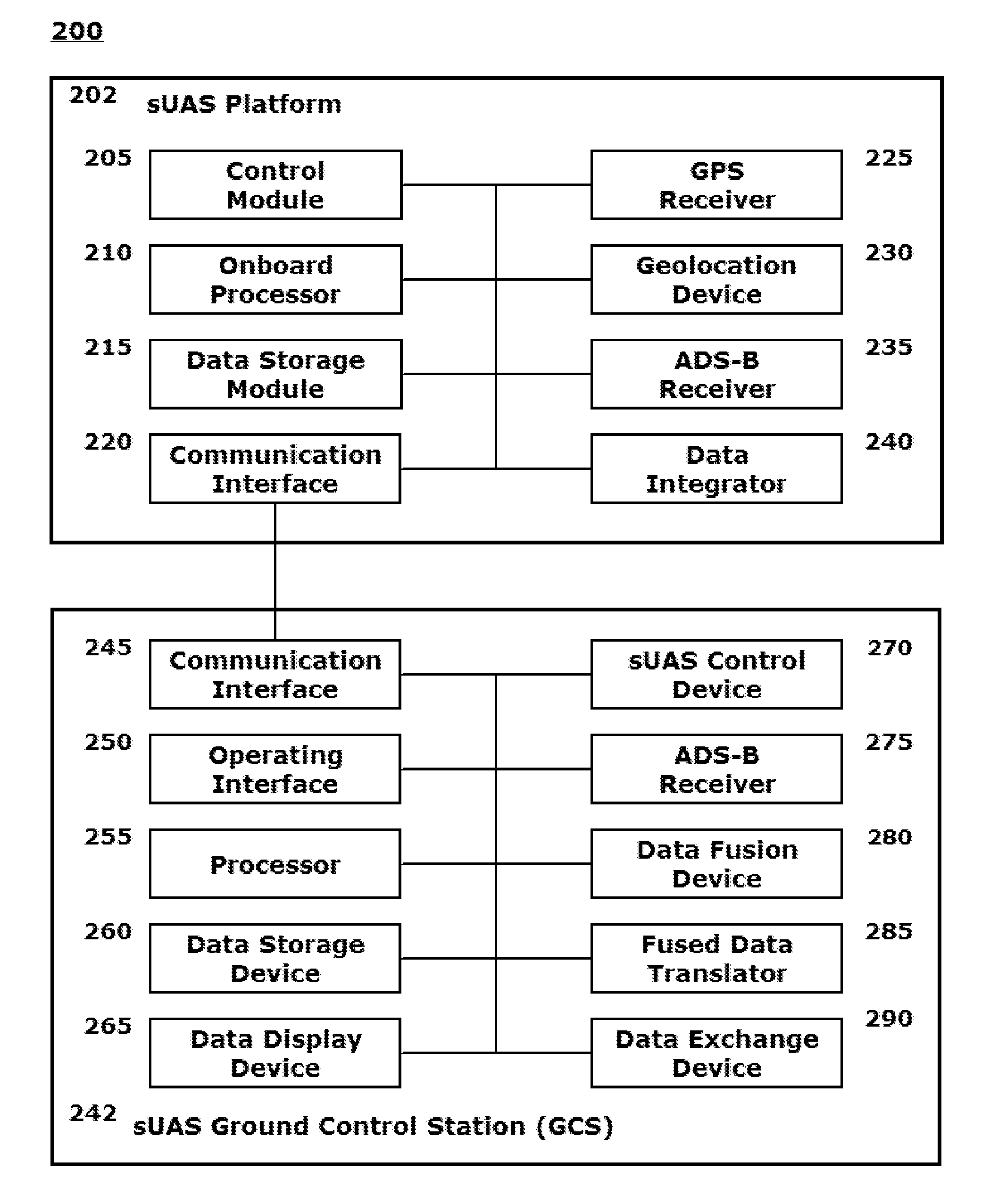
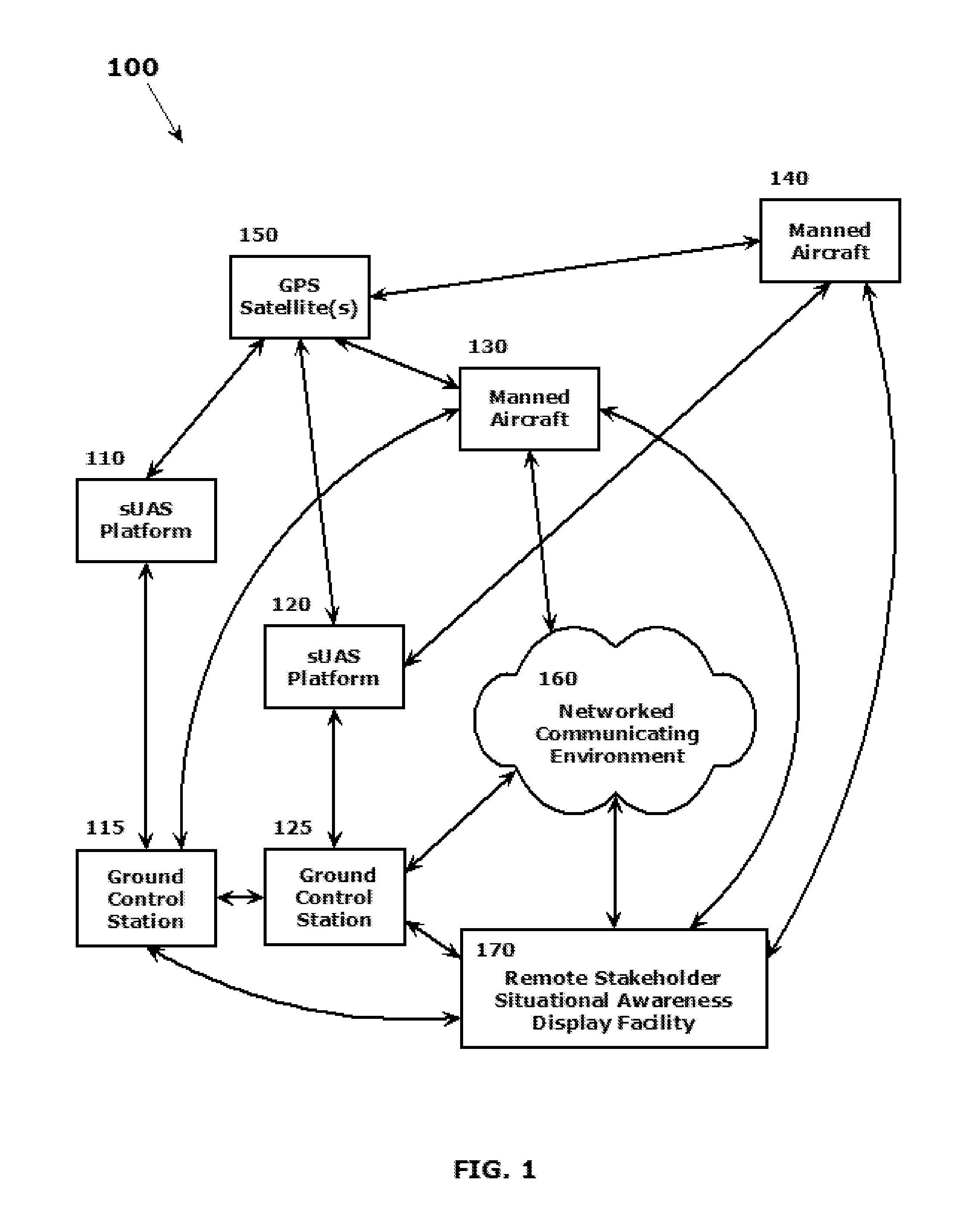
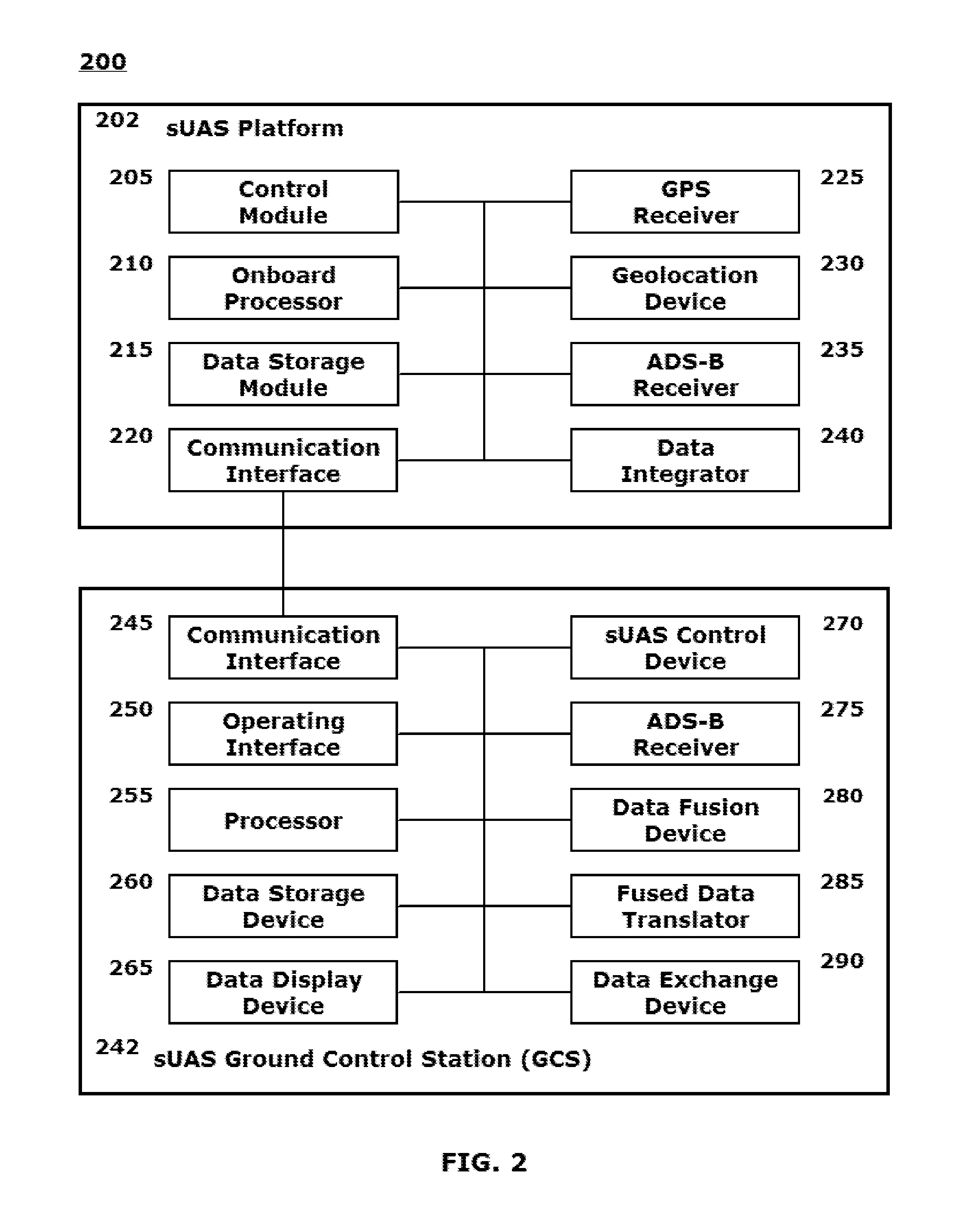
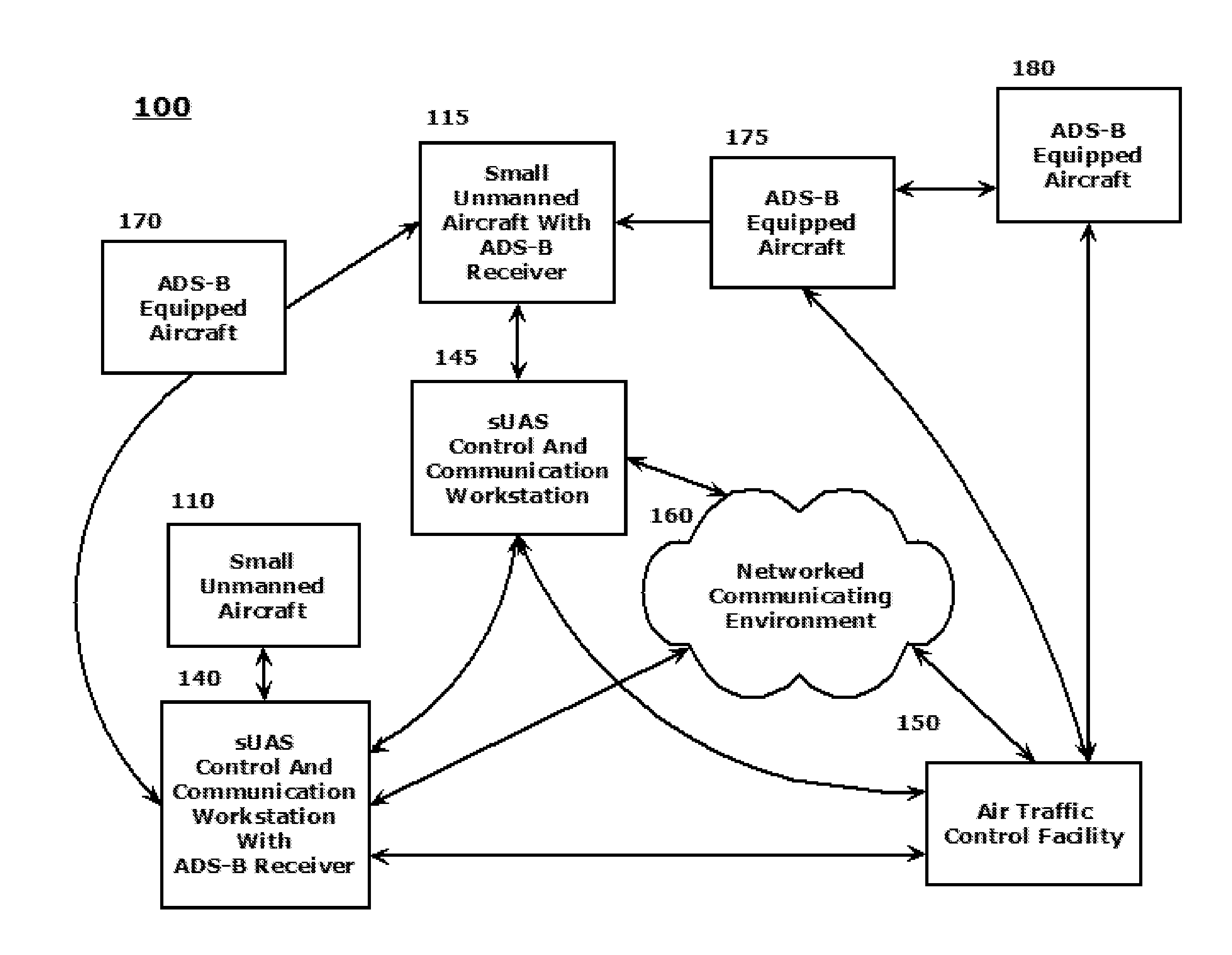
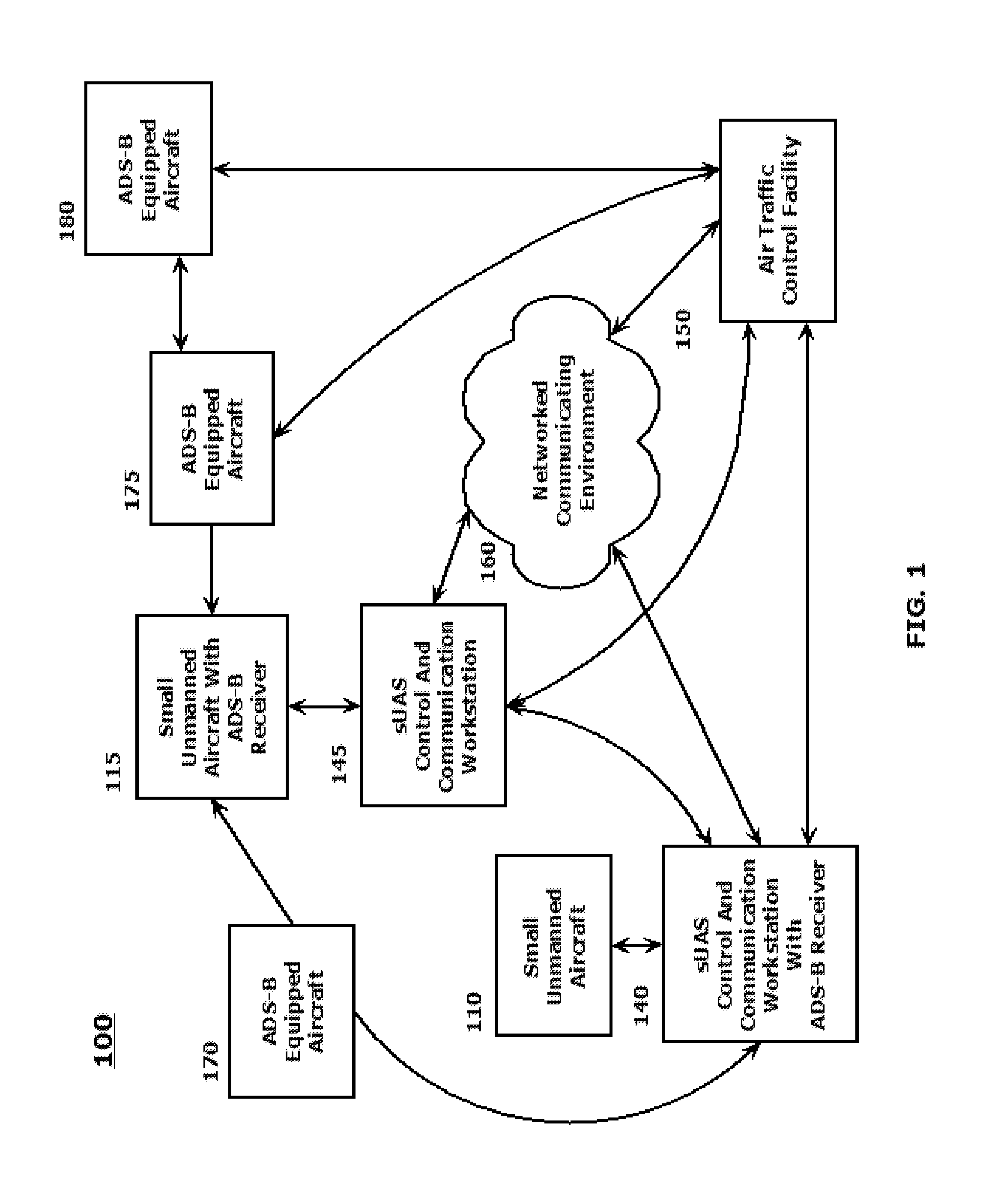
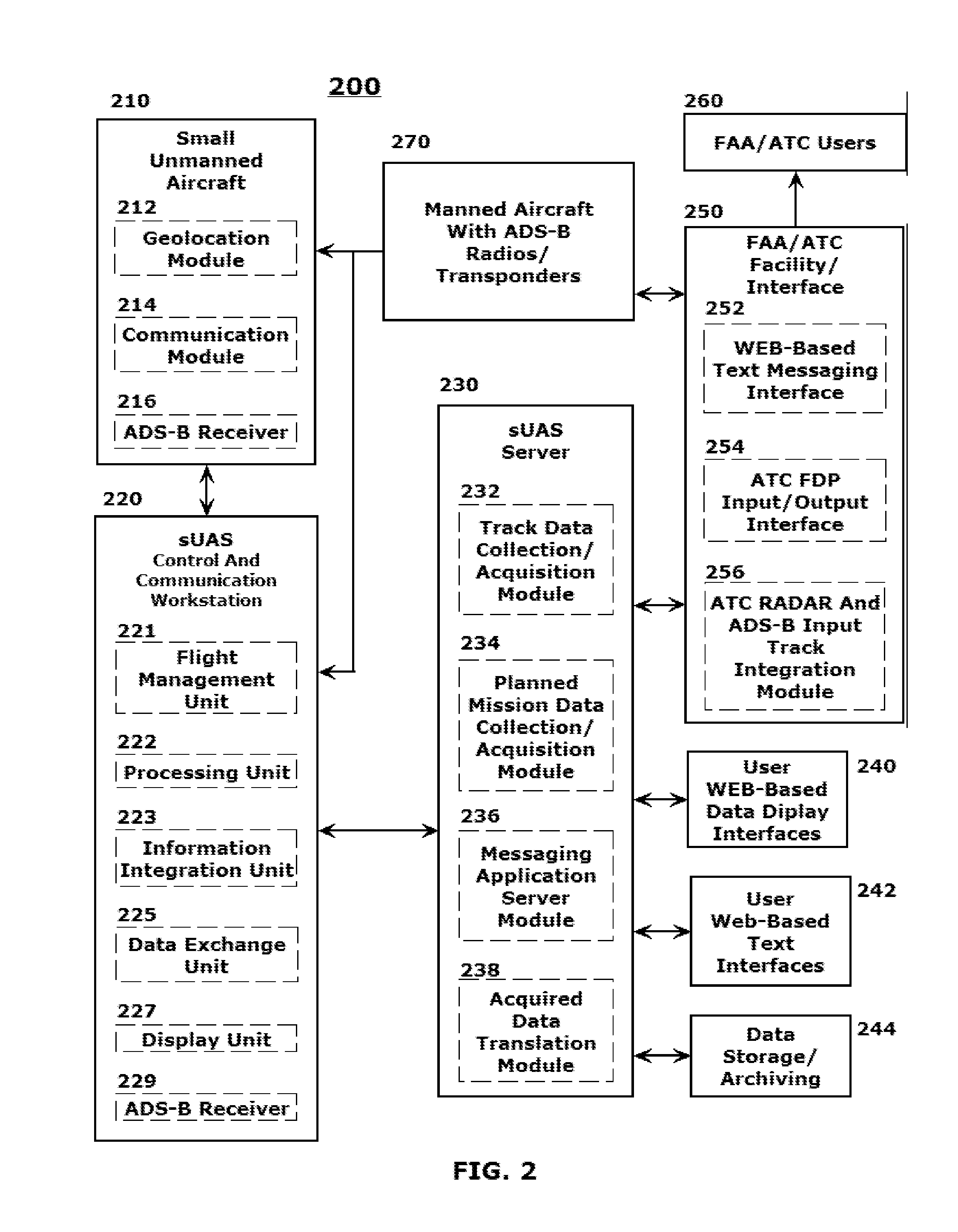
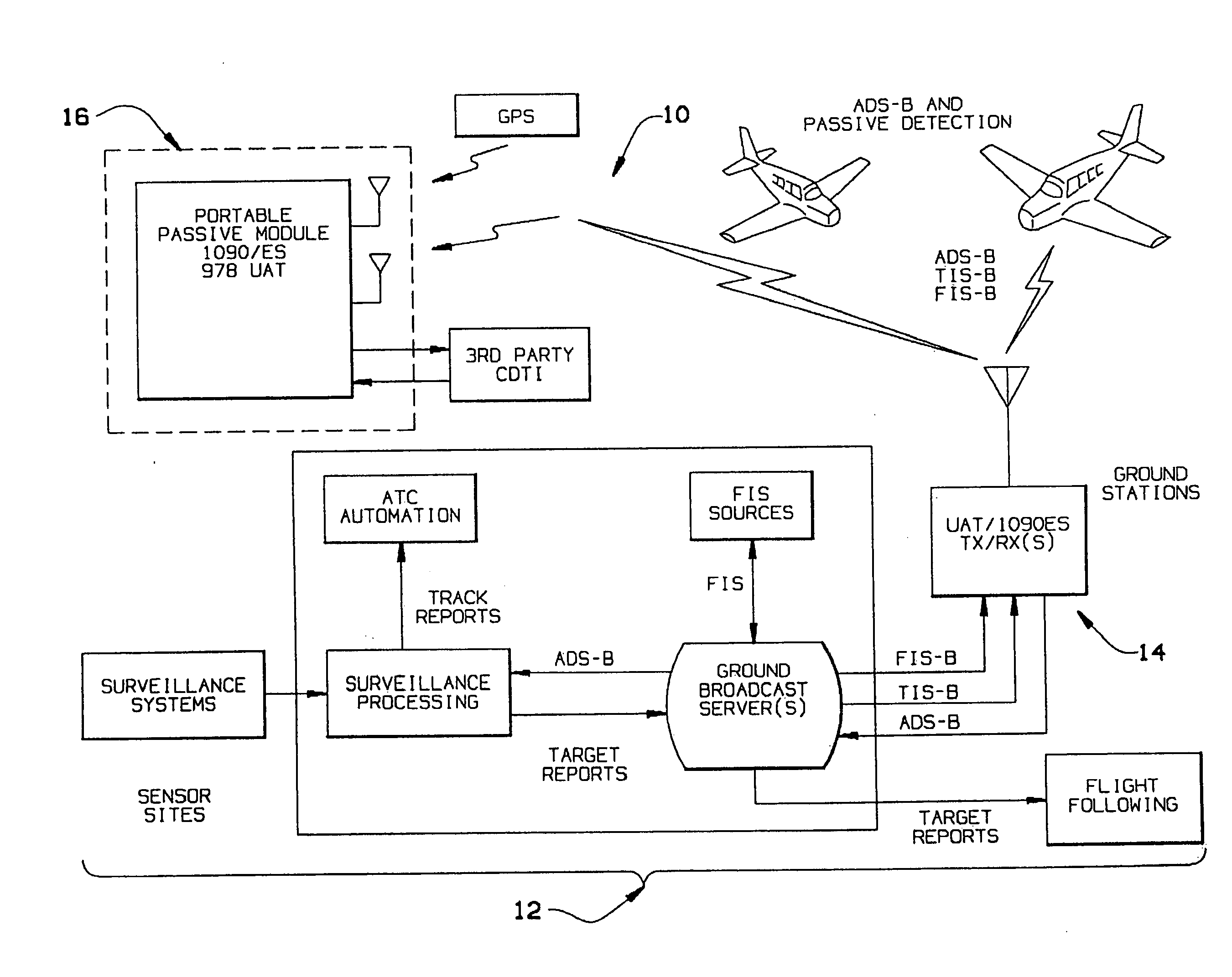
SYSTEMS AND METHODS FOR INTEGRATING AUTOMATIC DEPENDENT SURVEILLANCE-BROADCAST CAPABILITIES IN SMALL UNMANNED AIRCRAFT SYSTEM (sUAS) OPERATIONS
ActiveUS20160101855A1Easy to integrateEnhance overall local situational awarenessUnmanned aerial vehiclesDigital data processing detailsFlight vehicleUncrewed vehicle
A system and method are provided to support accommodating safe integration of small unmanned aircraft systems (sUASs) into the National Airspace Structure in the United States and to augment previously untracked aircraft positions by opportunistically acquiring their position information and forwarding this information to other systems for display. The disclosed schemes integrate automatic dependent surveillance-broadcast (ADS-B) capabilities in sUASs by providing an ADS-B receiver on the small unmanned aircraft or in association with a ground-based sUAS control and communication workstation. Processing of the ADS-B information is integrated with processing of acquired information on sUAS aerial platform operations. Processed integrated information is displayed locally on the workstation and transmitted to other facilities to be remotely displayed. Acquired position information for the sUAS aerial platform and manned aerial vehicles in a vicinity of the sUAS aerial platform are converted to formats commonly used by air traffic control systems.
Owner:ARINC
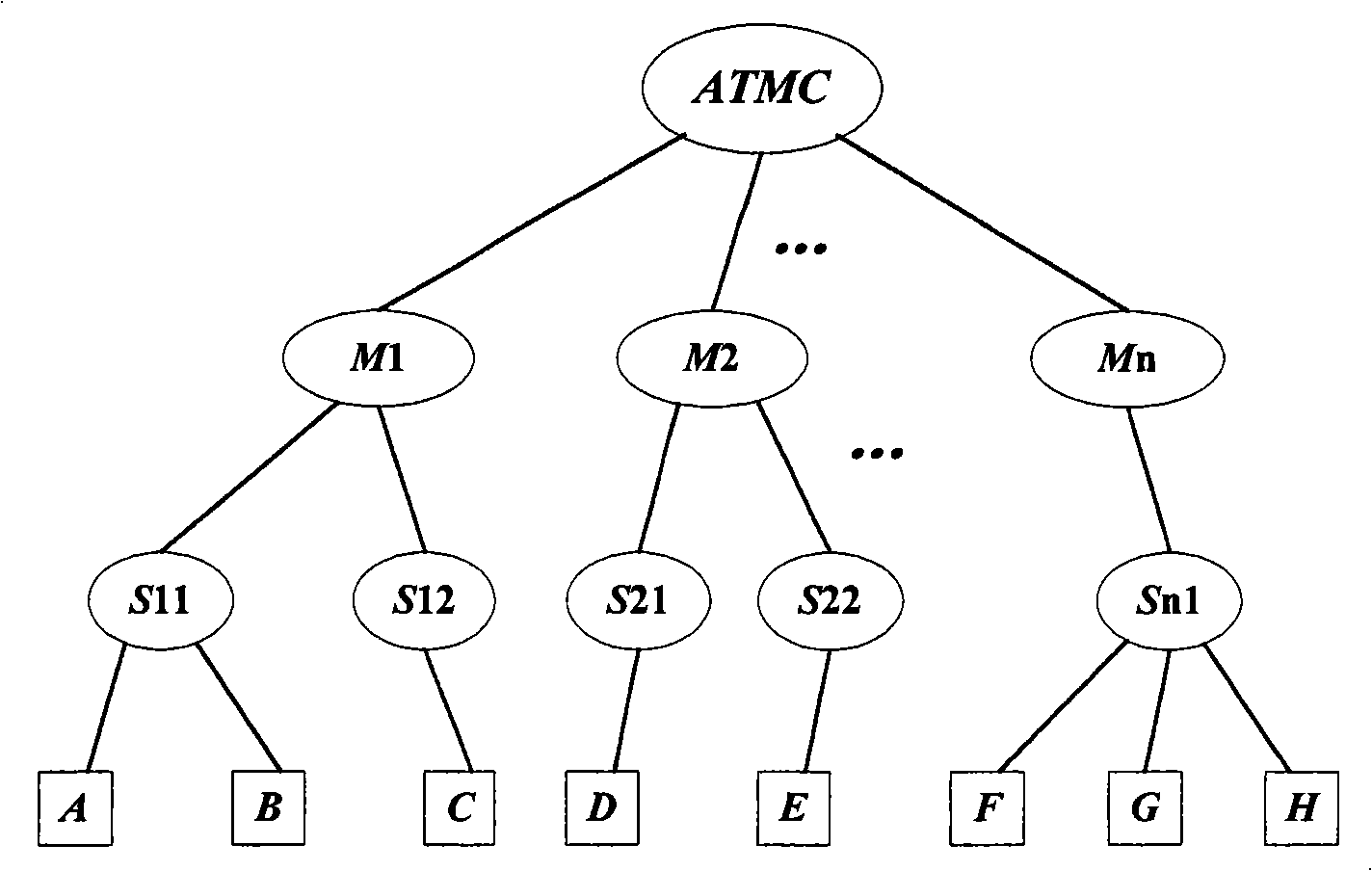
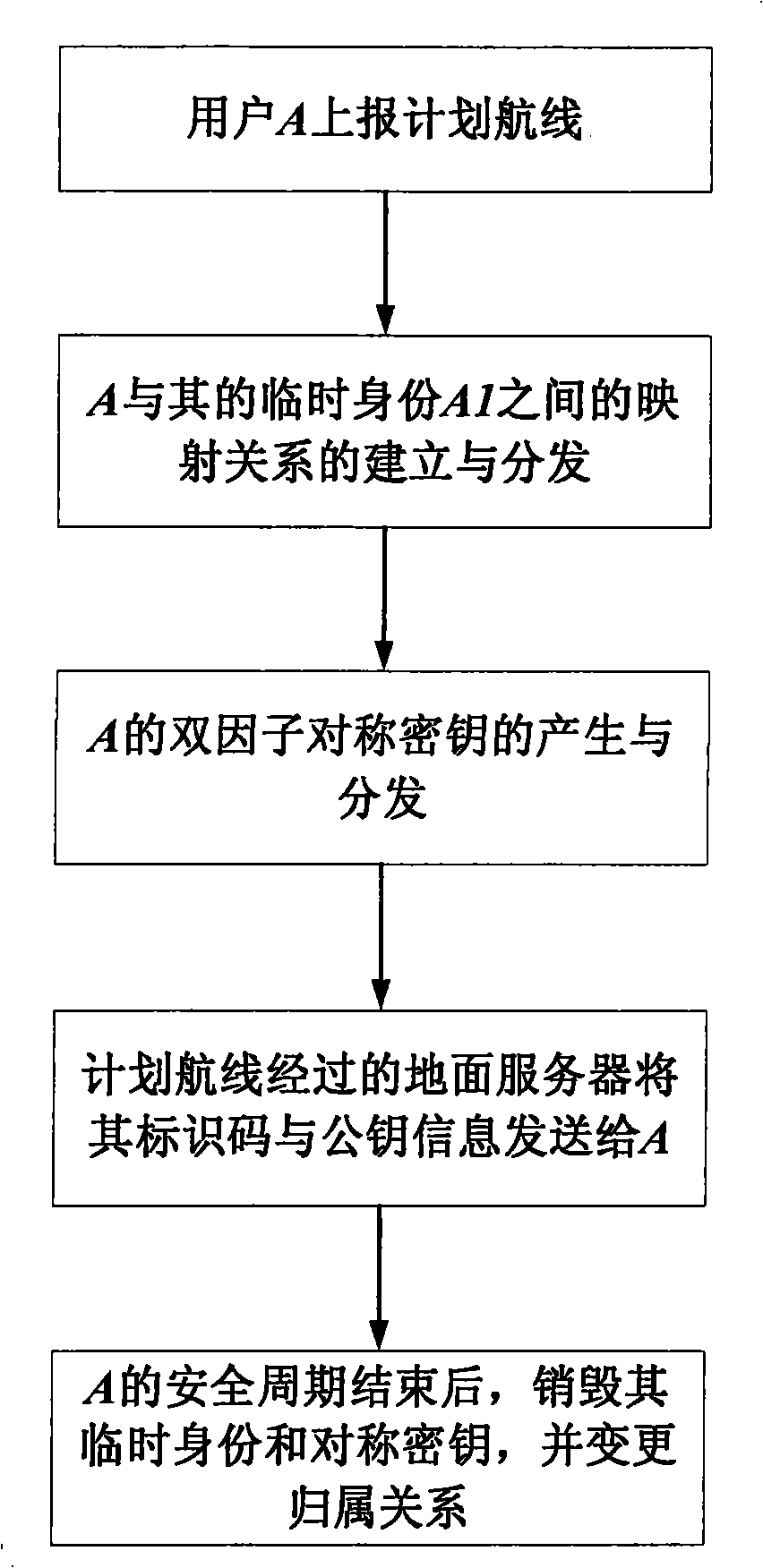
Secure transmission system for broadcast automatic monitoring information
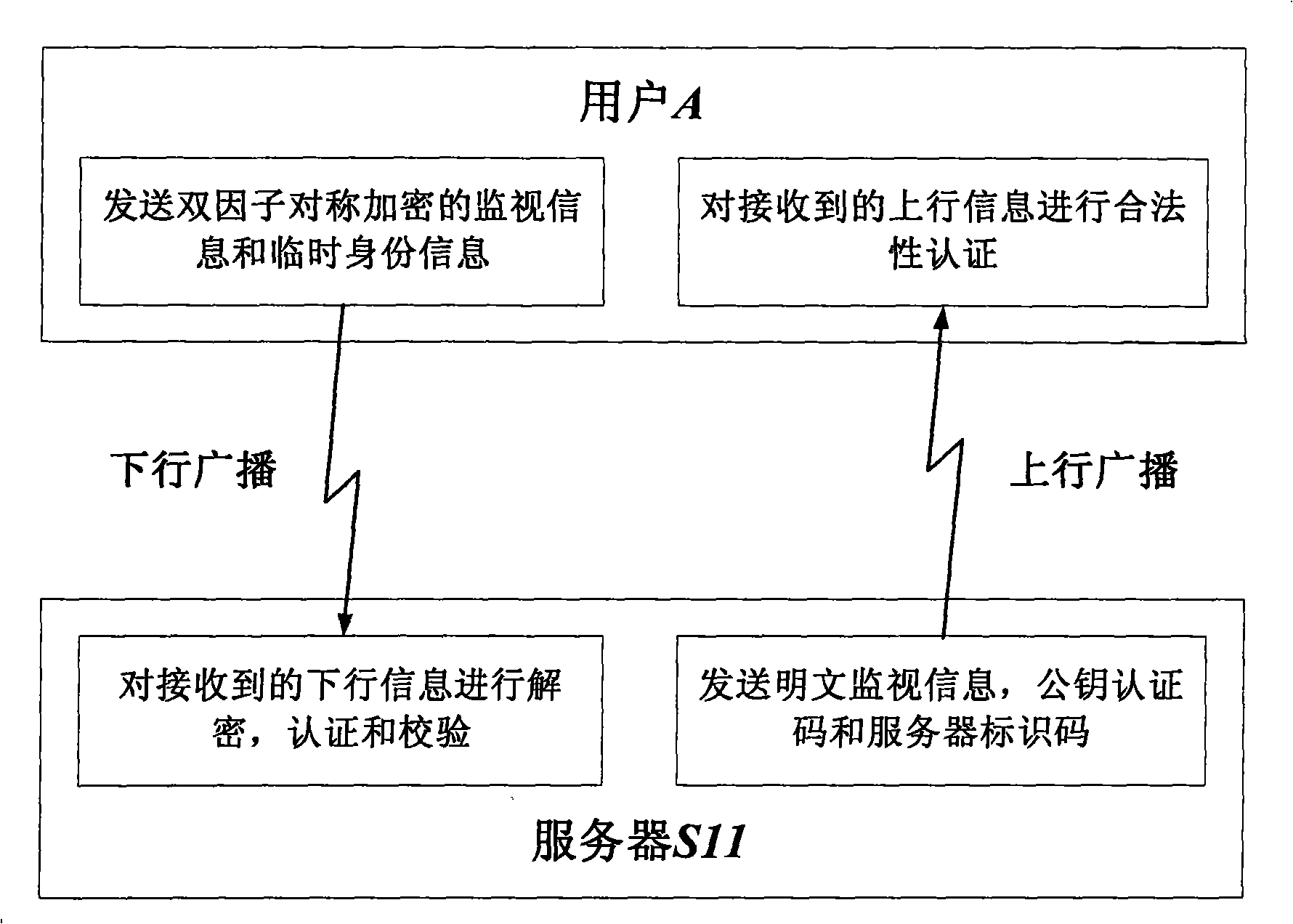
InactiveCN101261772ASecure transmissionGuaranteed normal transmissionTransmissionAircraft traffic controlThree levelInformation transmission
The method for realizing secure transmission of an Automatic Dependent Surveillance Broadcast Information includes: (1) a three-level vertical management system is constructed according to the Aviation Management & Controlling Center, the flight information region and the control area subordinated to the flight information center; the lowest level is ADS-B user belonging to each control area, and the ADS-B user communicates with the control area server that ADS-B user belongs to by means of independent mutual certification mode; (2) at the beginning stage of the planning air line safety period, the Aviation Management & Controlling Center allots a temporary identity for the ADS-B user, establishes a mapping relationship from the temporary identity to a true identity and send the mapping relationship to the administration of the flight information region which the ADS-B user planning air line passes through; before the ADS-B user takes off, the administration of the control area that the ADS-B user belongs to secretly provides the ADS-B user with the temporary user identity and double factor symmetric-key in the server, and public key information of the server identification and the server message authentication code of the ground server near the planning air line. The invention can effectively resist a plurality of active attacks, realize security certification and ensure the safety of ADS-B information transmission.
Owner:AVIATION DATA COMM +2
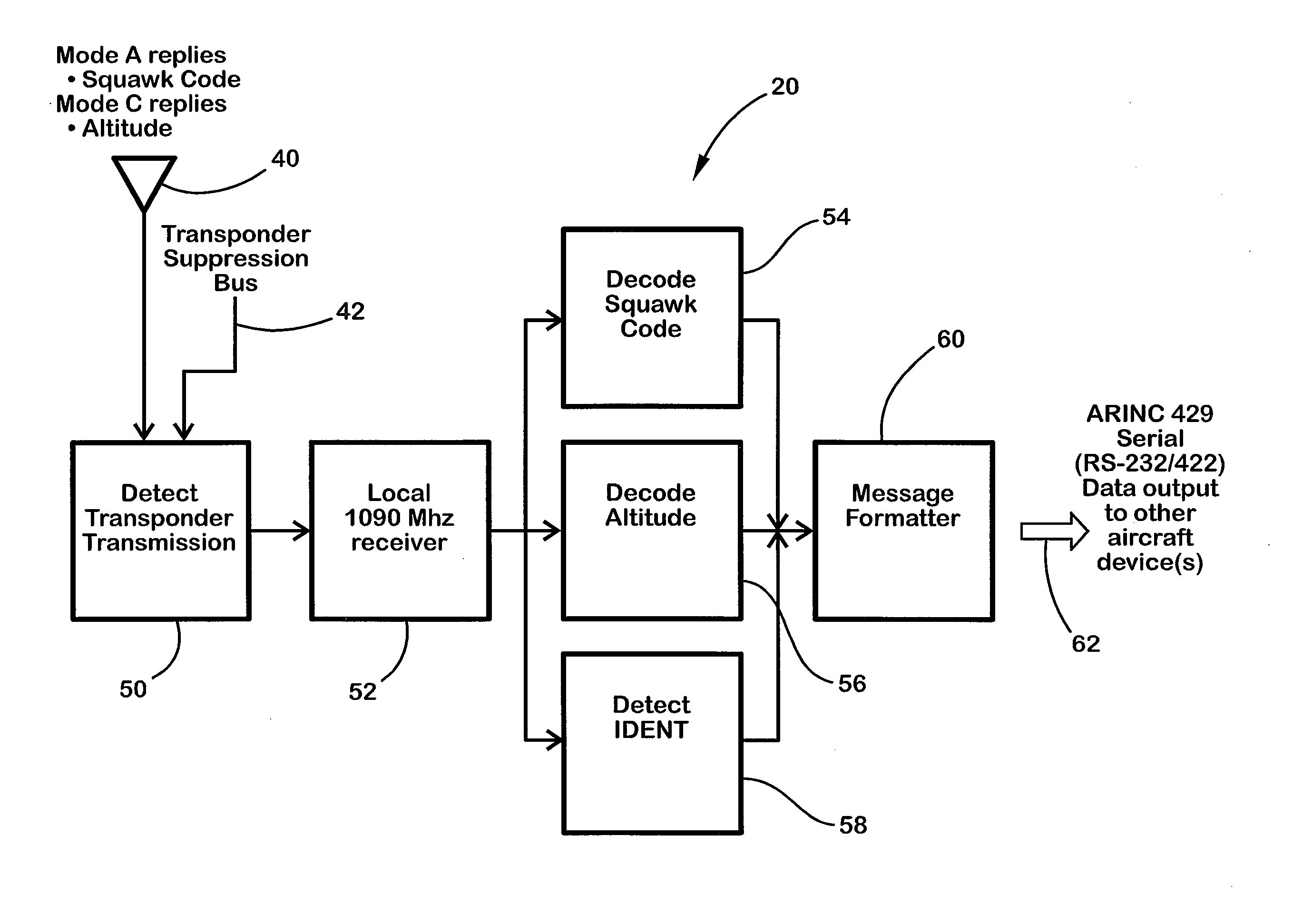
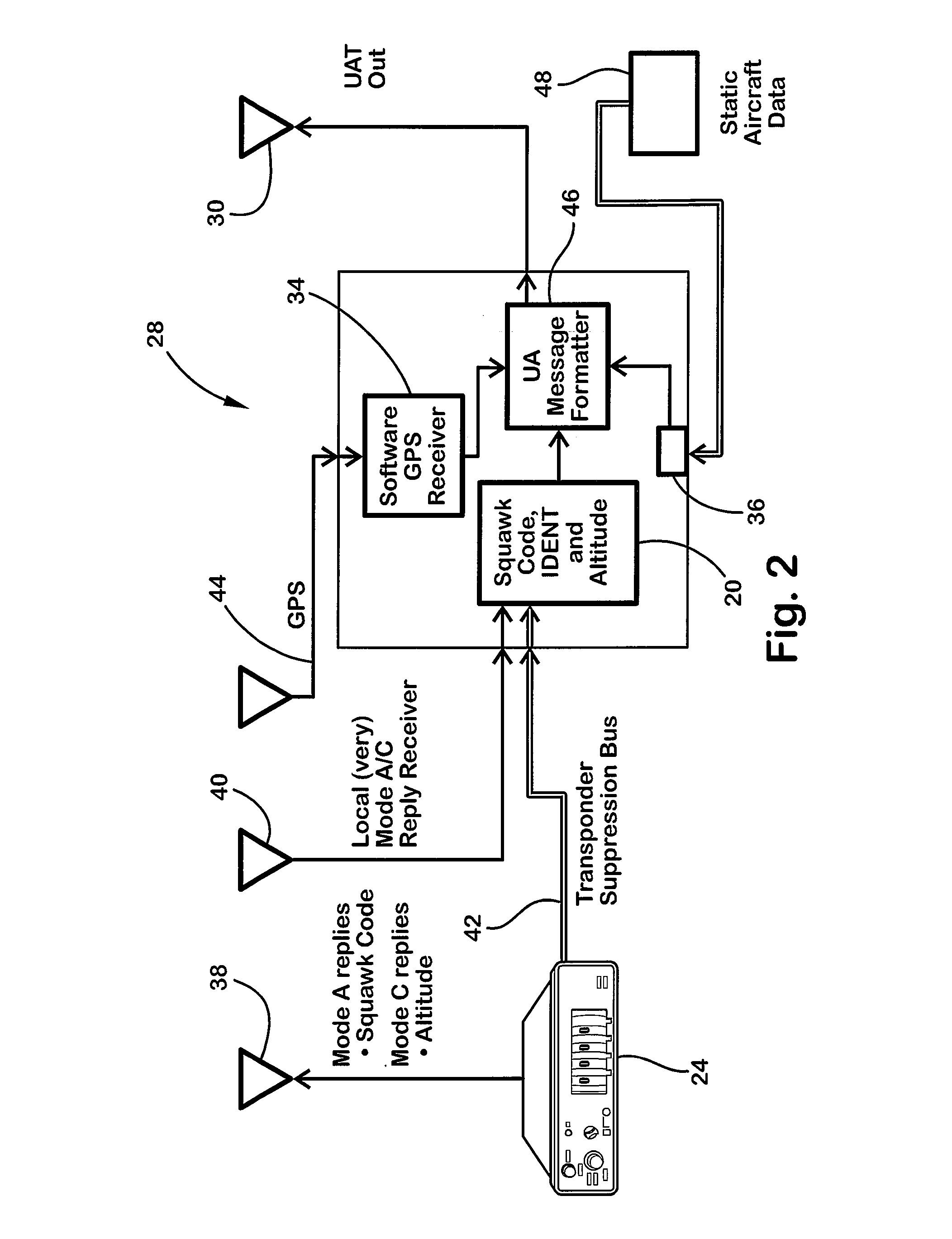
Transponder decoder
InactiveUS20120001788A1Radio wave reradiation/reflectionFlight vehicleAutomatic dependent surveillance-broadcast
An Automatic Dependent Surveillance-Broadcast (ADS-B) system for an aircraft and method of automatically harmonizing a transponder squawk code and an ADS-B system such that a squawk code broadcast by the ADS-B system matches the transponder squawk code, includes transmitting the transponder squawk code from a transponder positioned onboard an aircraft and receiving the transmitted transponder squawk code with a device positioned onboard the aircraft. The ADS-B system is updated with the received transmitter squawk code. The squawk code is transmitted using the ADS-B system.
Owner:L 3 COMM AVIONICS SYST
Correlation of flight track data with other data sources
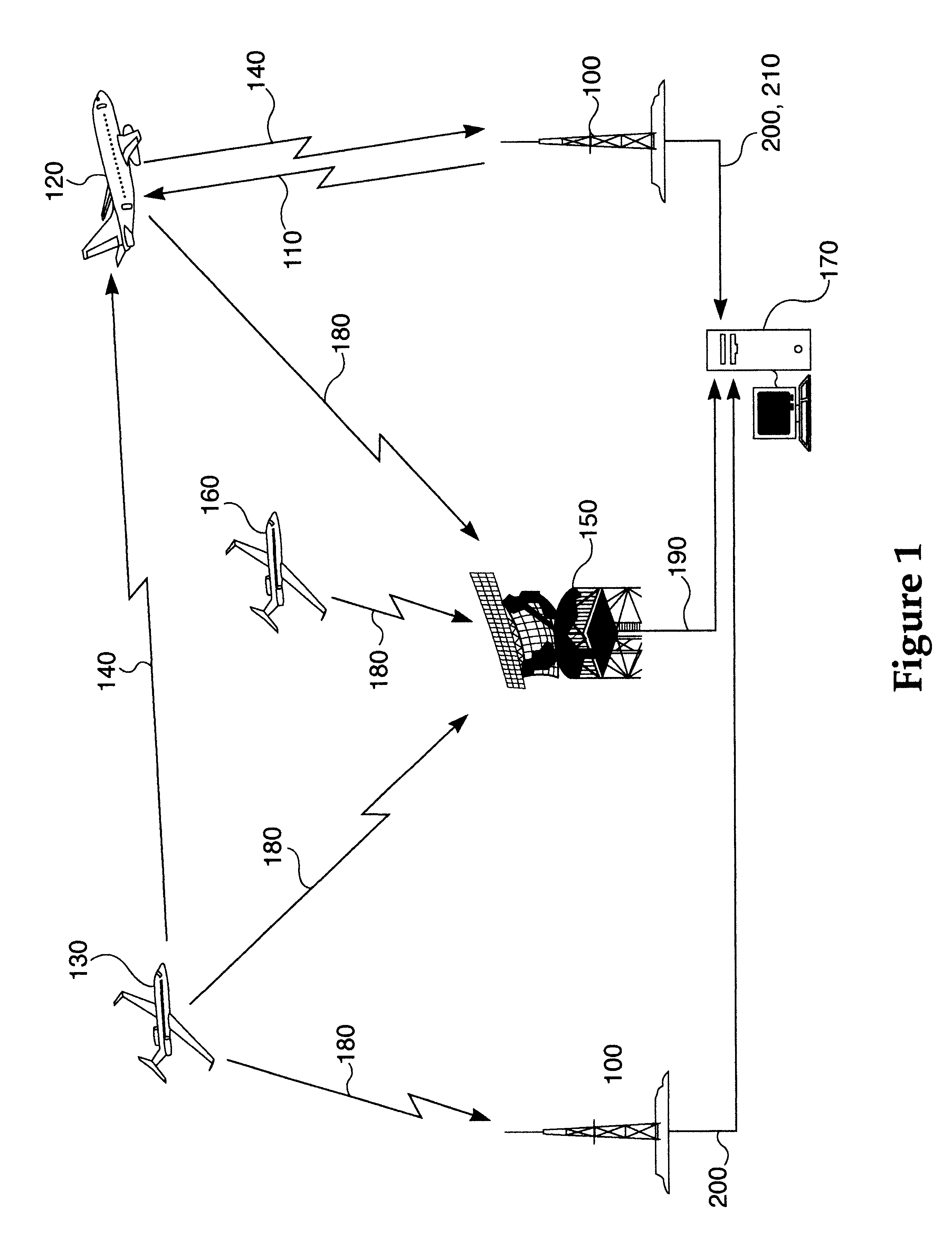
InactiveUS20050068232A1Accurately determineAccurate calculationDirection finders using radio wavesPosition fixationMonitoring systemData source
The surveillance system provides a means to augment Automatic Dependent Surveillance-Broadcast (ADS-B) with “look alike ADS-B” or “pseudo ADS-B” surveillance transmissions for aircraft which may not be ADS-B equipped. The system uses ground based surveillance to determine the position of aircraft not equipped with ADS-B, then broadcasts the identification / positional information over the ADS-B data link. ADS-B equipped aircraft broadcast their own position over the ADS-B data link. The system enables aircraft equipped with ADS-B and Cockpit Display of Traffic Information (CDTI) to obtain surveillance information on all aircraft whether or not the proximate aircraft are equipped with ADS-B.
Owner:SRA INTERNATIONAL
Automatic dependant surveillance systems and methods
InactiveUS20090146875A1Increase in sizeLarge in weightBeacon systemsSatellite radio beaconingCommunications systemMonitoring system
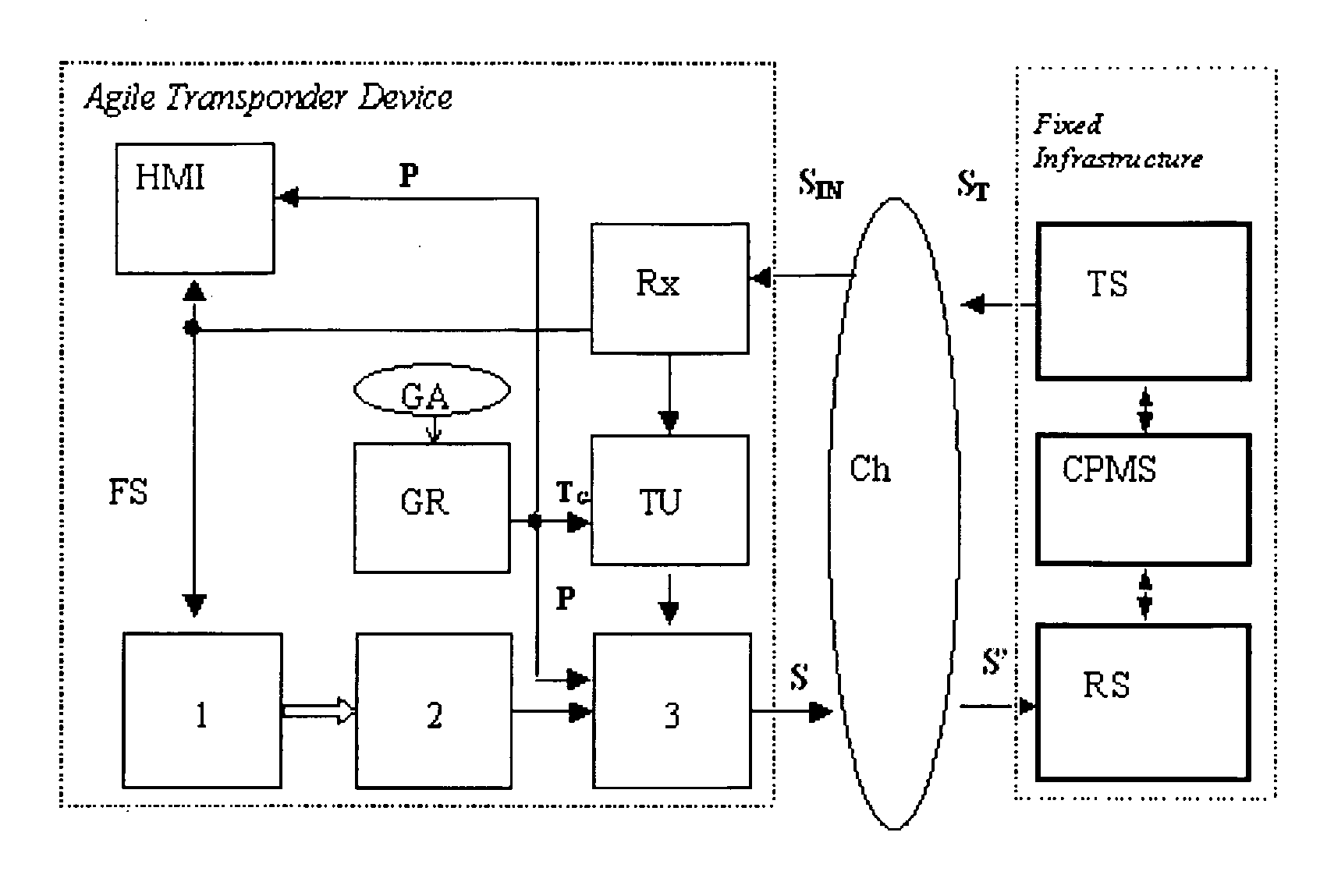
A communications system including an automated dependant surveillance-broadcast system and a global positioning system integrated into a single unit. A radio frequency receiver receives analog automated dependent surveillance-broadcast information at a selected transmission frequency and converts that information into digital form. A global positioning system receiver receives global positioning information including timing information. A processing subsystem decodes the digitized automated dependent surveillance-broadcast information in response to the timing information received by the global positioning system receiver.
Owner:HOVEY ZANE
High-Capacity Location and Identification System for Cooperating Mobiles With Frequency Agile and Time Division Transponder Device on Board
InactiveUS20080106457A1Easy to operateOvercome limitationsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionOn boardGround vehicles
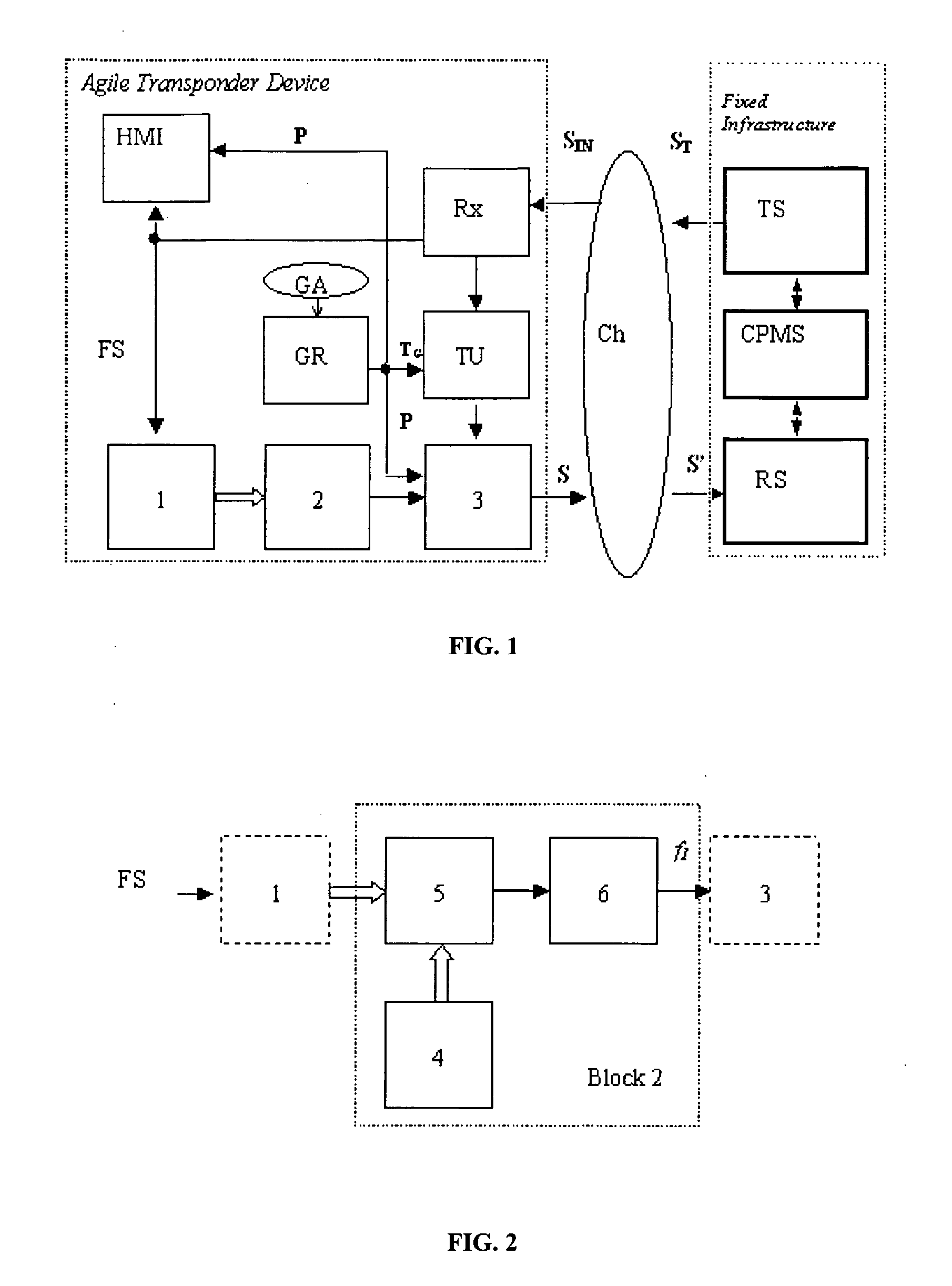
Cooperating mobiles (ground vehicles, aircraft) are located and identified by Multilateration and Automatic Dependent Surveillance-Broadcast (ADS-B) techniques using the frequency band and the format of the Secondary Surveillance Radar (SSR) signals in high traffic situations. Standard messages, transmitted by the mobile on the downlink channel, i.e. to a set of fixed receiving stations, and including the identification code, permit the location of the mobile by multiple time measurements (Multilateration) from a subset of the set of fixed receiving stations; when the message contains the position (GPS and, later, Galileo datum) the mobile may be located with the ADS-B when in view even of a few stations or of a single station. In order to overcome the problem that arises with high traffic, i.e. the superimposition of signals, called garbling.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROME TOR VERGATA
Terminal area airline safety tolerance monitoring method based on collision risk model and system thereof
ActiveCN105023468ASafety Margin MonitoringRealize monitoringAircraft traffic controlJet aeroplaneObservation data
The invention discloses a terminal area airline safety tolerance monitoring method based on a collision risk model and a system thereof, and relates to the technical field of terminal area surveillance. A lateral and vertical track deviation distribution model is established according to an automatic dependent surveillance broadcast observation data; the risk of flight collision is calculated on the basis of the collision risk model according to track deviation; and distance to an assumed parallel route, i.e. the maximum permissible airplane track deviation range, is solved through iteration by utilizing monotonicity of the risk of flight collision and a lateral and vertical safety interval under the condition of the given risk of flight collision according to the flight state of an airplane on the airline. The system comprises a data preprocessing model, a track deviation modeling module and a track safety tolerance assessment module. Terminal area airline safety tolerance monitoring is realized so that the risk of collision under a complex terminal area environment can be effectively reduced and air traffic control operation safety level and airspace capacity can be enhanced.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV +1
Systems and methods for space-time determinations with reduced network traffic
Space-time solutions are determined by exchanging pings among nodes in a network. Each ping includes a current space-time state of the transmitting node, which includes the transmitting node's currently estimated location and corrected time (as a count stamp). A particular node in the network receives pings from the other nodes in the network and uses the data in the received pings to estimate its own current position and to correct its own free-running clock relative to a common system time. As a service to the network, the particular node then transmits its corrected time (as a count stamp) and estimated position to the other nodes. In some embodiments, the space-time solutions discussed herein are used as backup to other navigation systems, such as the Automatic Dependent Surveillance-Broadcast (ADS-B) system.
Owner:DIGIMARC CORP
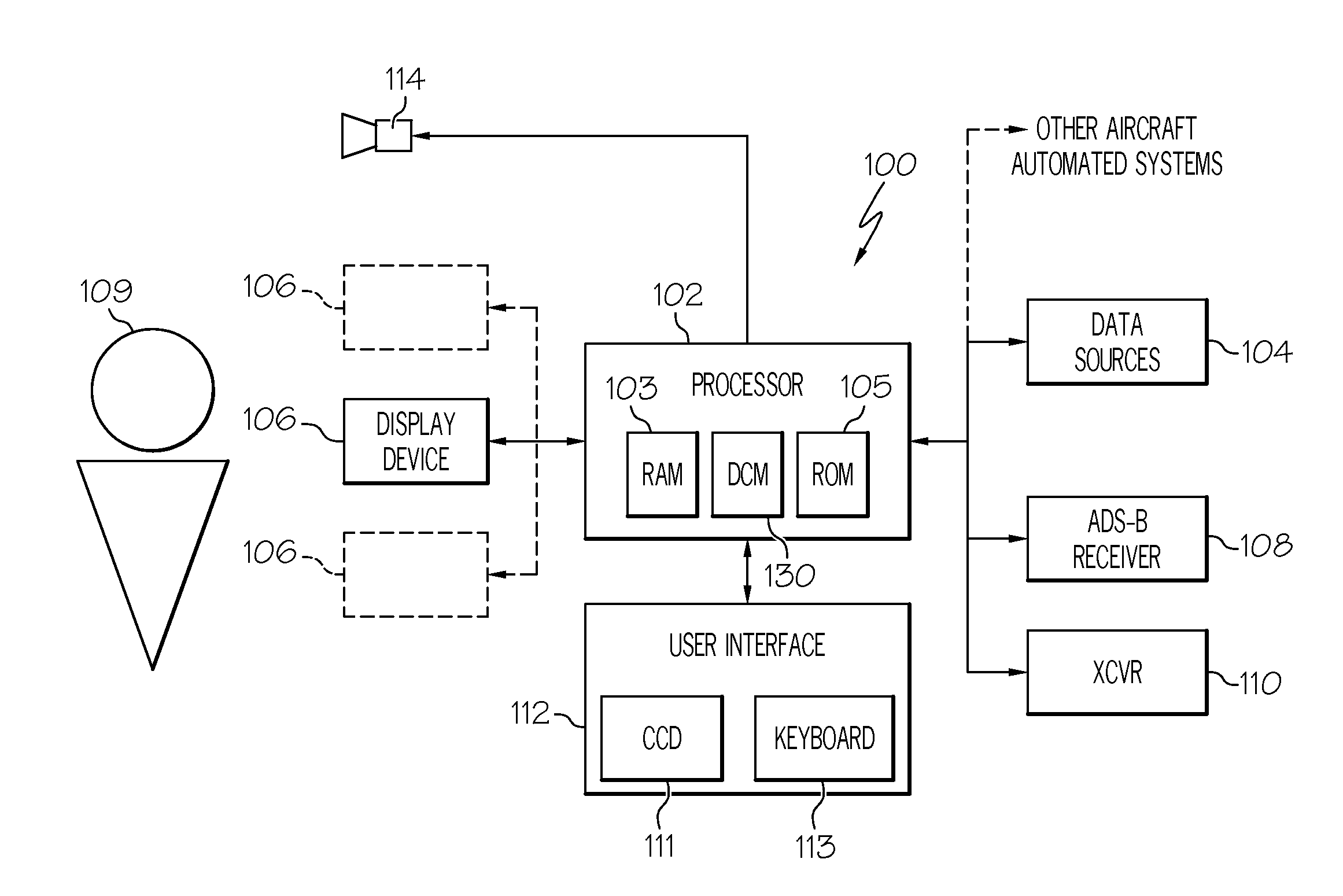
Aircraft situational awareness improvement system and method
InactiveUS20120078495A1Enhanced Situational AwarenessAnalogue computers for vehiclesAnalogue computers for trafficDisplay deviceAircraft Pilots
A system and method are provided for improving aircraft pilot situational awareness. When datalink messages and / or automatic dependent surveillance-broadcast (ADS-B) data and / or various other data are received in the aircraft, the received data are processed to generate a spatial and temporal situational model for the aircraft. At least a portion of the spatial and temporal situational model is rendered on a display device within the aircraft.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Systems and methods for correlation in an air traffic control system of interrogation-based target positional data and gps-based intruder positional data
InactiveUS20050231422A1Minimizes and eliminates displayOvercome in accuracyAnalogue computers for vehiclesAnalogue computers for trafficRoad traffic controlSimulation
An improved system and methods for correlating an interrogation-based air traffic surveillance intruder, such as an Traffic alert and Collision Avoidance System (TCAS) intruder, and a GPS-based air traffic surveillance target, such as an Automatic Dependent Surveillance Broadcast (ADS-B) target to minimize or eliminate the display of two symbols for the same intruder / target on the CDTI of an aircraft. The method comprises the steps of receiving ADS-B data at a processing unit and calculating select component deltas for the ADS-B data versus an entry in a TCAS intruder file. Progressive weights are assigned to the deltas and the progressive weights are summed, resulting in a total confidence score. Total confidence scores of ADS-B target and TCAS intruder pairs are compared to determine correlation between the ADS-B target and the TCAS intruders.
Owner:GARMIN AT
ADS-B (automatic dependent surveillance broadcast) and radar combined system error estimation method
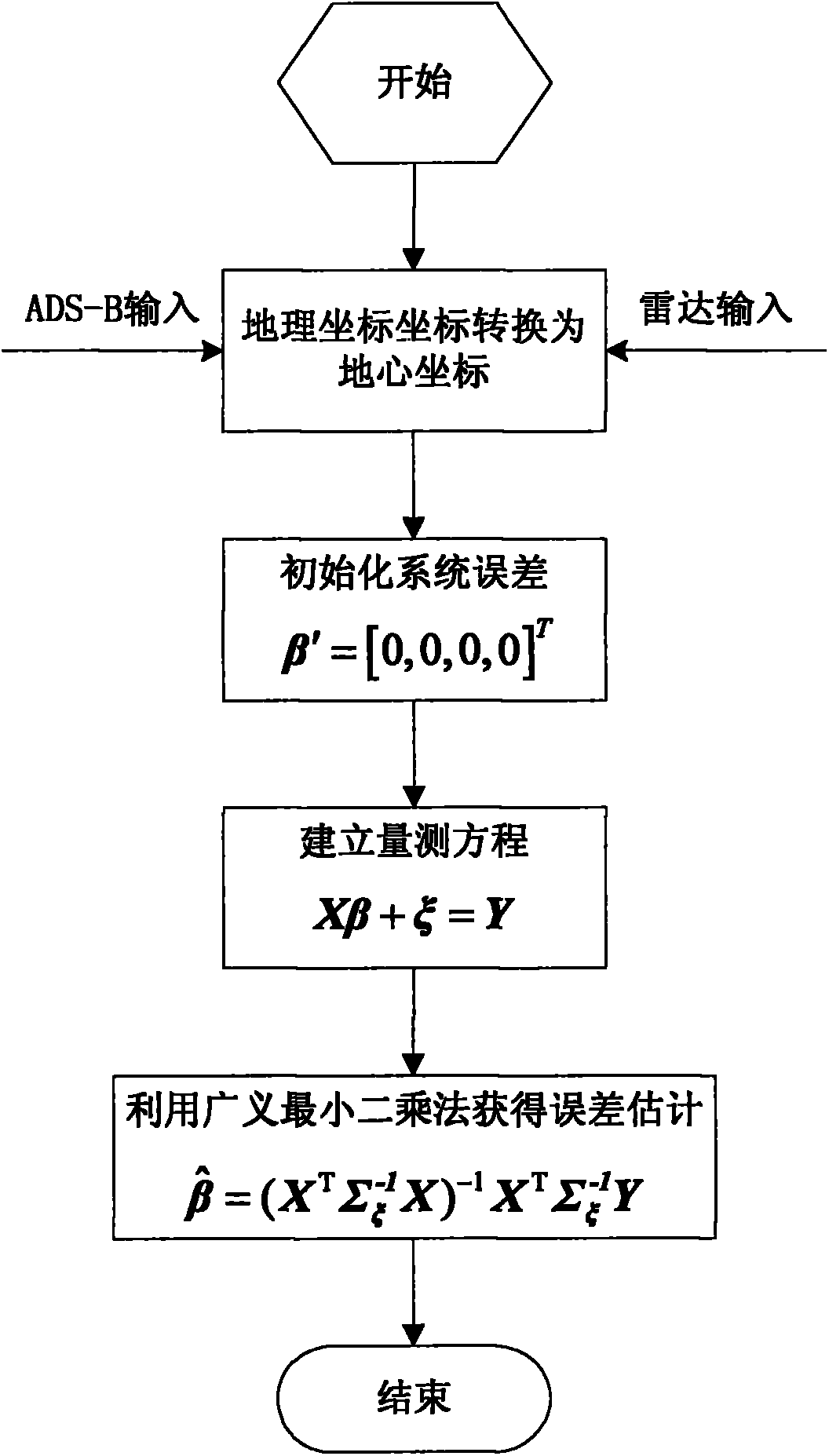
The invention discloses an ADS-B (automatic dependent surveillance broadcast) and radar combined system error estimation method, which belongs to the technical field of ADS and radar information fusion. At present, when the ADS-B equipment is used for radar calibration, the existing serious problem is that the time when the ADS-B emission equipment emits data information cannot be obtained, and no time alignment exists for the radar measuring data and the ADS-B data, so that the following error calibration is inaccurate, while all the conventional algorithms evade the problem. Aiming to effectively solve the problems of time alignment and error estimation of the radar system in the practical application, the method provided by the invention has the following steps of defining a novel ADS-B time system error based on the receiving time of the ADS-B, building the ADS-B and radar system error combined estimation model, and finally solving through the Least Squares algorithm, so that the radar can be accurately calibrated through the ADS-B.
Owner:NAVAL AERONAUTICAL & ASTRONAUTICAL UNIV PLA
Error correcting and detecting method of FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array) based S mode ADS_B (Automatic Dependent Surveillance-Broadcast) system
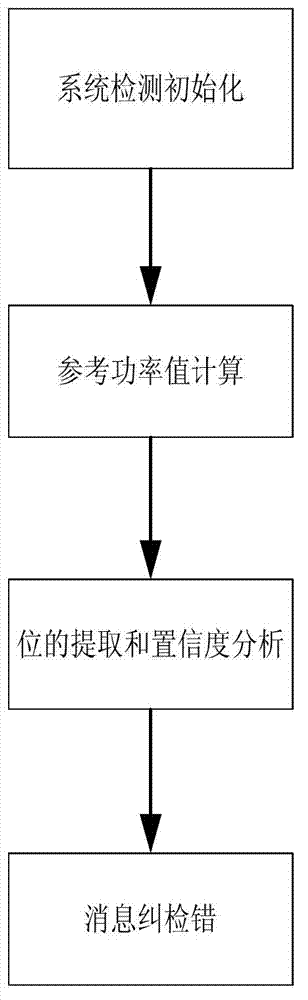
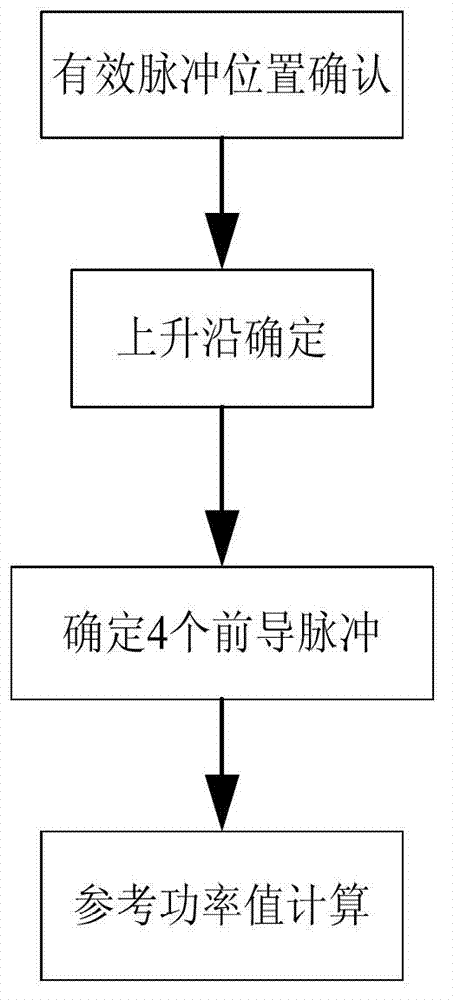
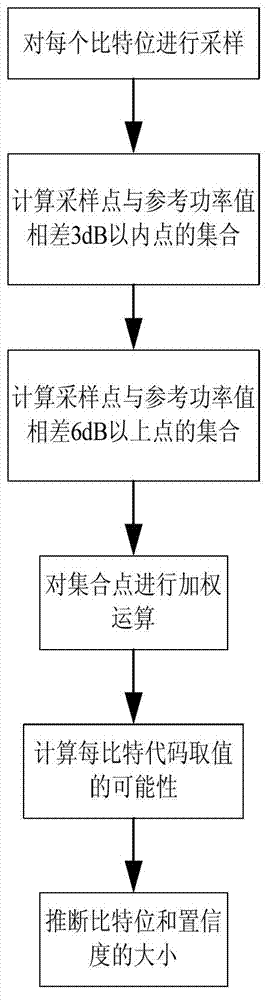
InactiveCN102831789AAccurate reference power valueEnhanced probability of error correction and detectionAircraft traffic controlError correctingField-programmable gate array
The invention relates to an error correcting and detecting method of an FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array) based S mode ADS_B (Automatic Dependent Surveillance-Broadcast) system, comprising the following steps of: S1. initializing system detection; S2. calculating reference power; S3. extracting bits, and judging confidence degree; and S4. carrying out error correction and detection on information. The error correcting and detecting method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of effectively carrying out effective bit extraction on received ADS_B information by adopting hardware treatment based on the FPGA under the condition of external disturbance and carrying out the error correction and detection on the received ADS_B information, thereby making a foreshadowing for next information decoding work.
Owner:NINGBO CHENGDIAN TAIKE ELECTRONICS INFORMATION TECH DEV
Method for detecting automatic dependent surveillance-broadcast (ADS-B) false target
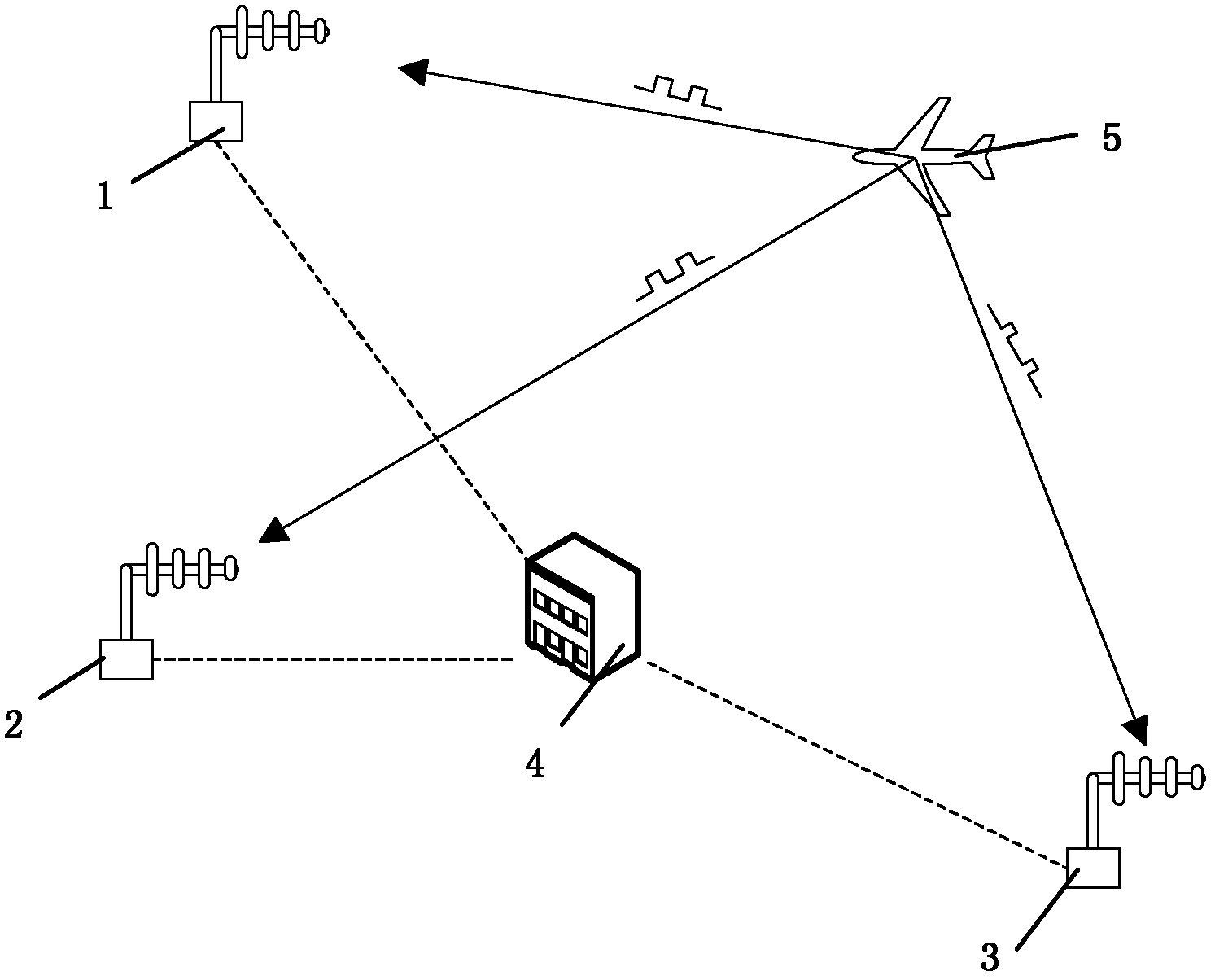
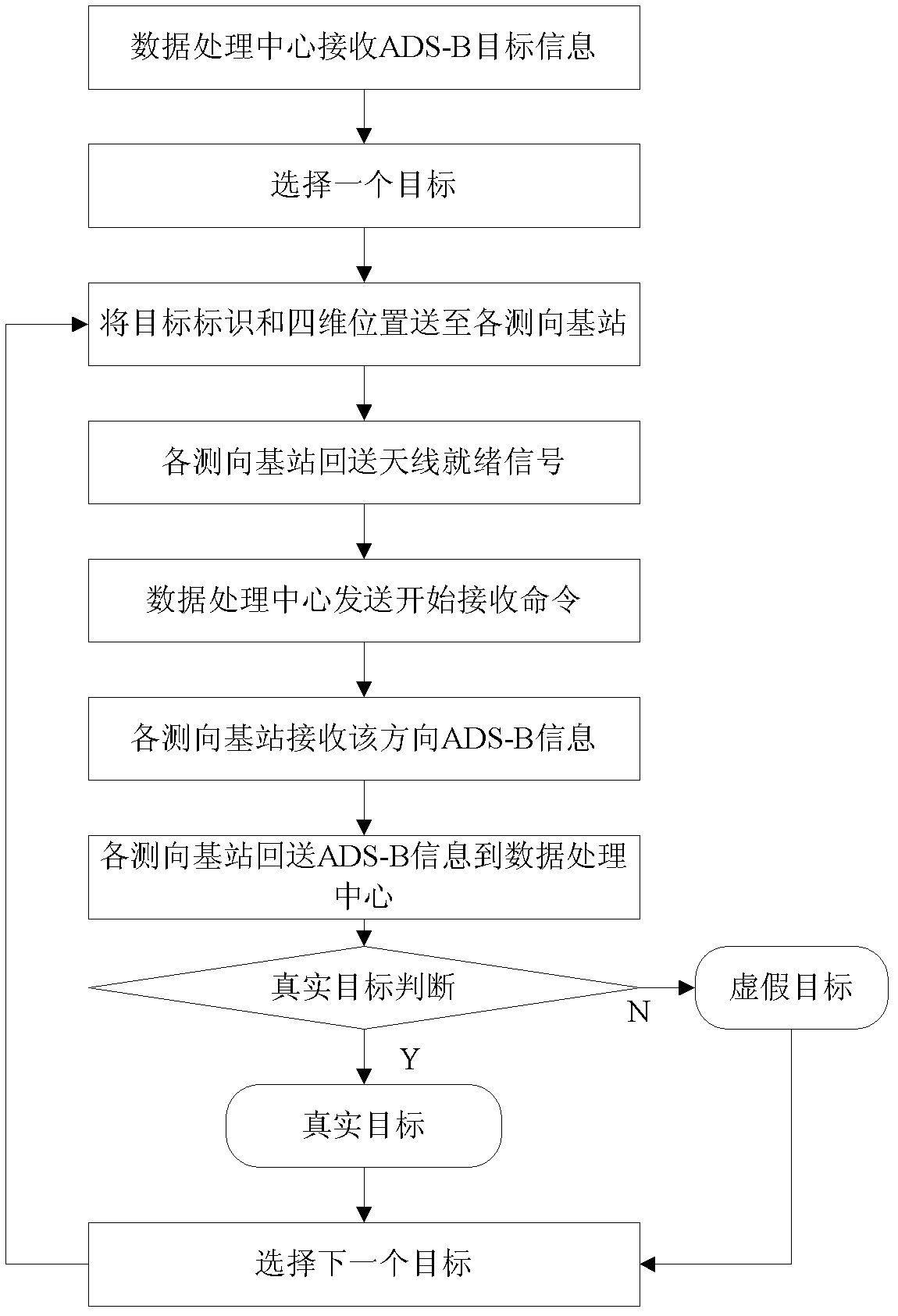
InactiveCN102323567AIncreased ability to combat unlawful interferenceEliminate hidden dangersRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsPosition fixationDirectional antennaLongitude
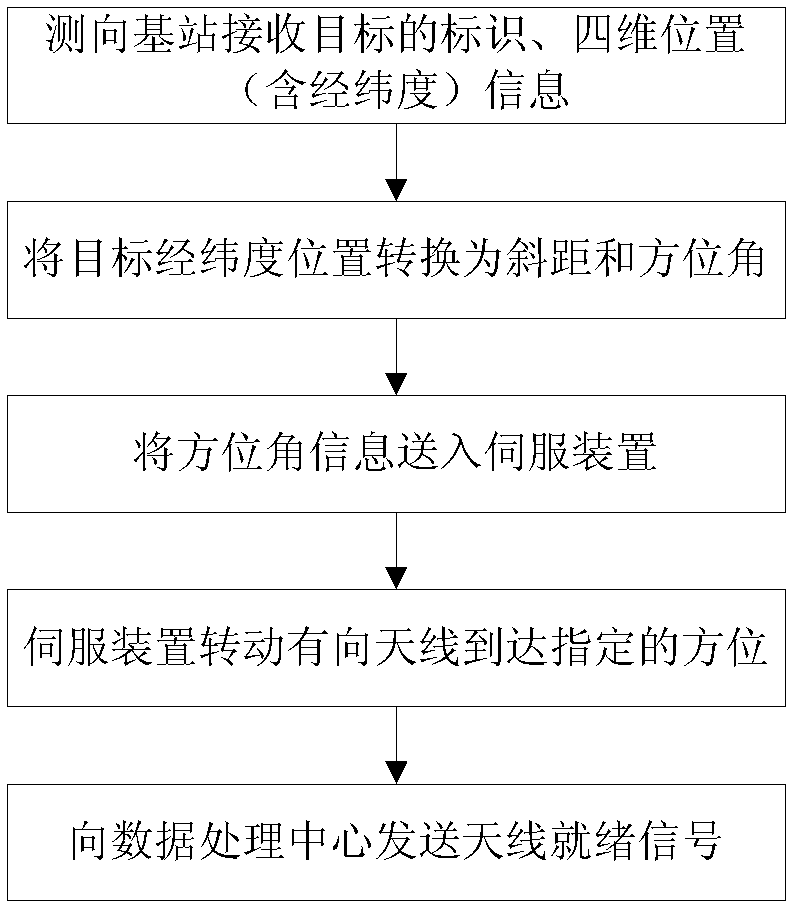
The invention relates to a method for detecting an automatic dependent surveillance-broadcast (ADS-B) false target, which belongs to a method for measuring a target location by an air traffic management system so as to judge whether a target is the false target or not and comprises the following steps: reading target representation and four-dimensional location (time, longitude and latitude, height) information output by an ADS-B system by a data processing center firstly, and respectively sending to a plurality of direction-finding base stations; firstly enabling a directional antenna to point to an orientation in which the target is located by the servo devices of all the direction-finding base stations, then, receiving target information from the direction by using an ADS-B receiving machine according to the synchronizing signal of the data processing center, and sending the target information back to the data processing center; and analyzing the results of all the direction-finding base stations by the data processing center, if more than two direction-finding base stations are capable of respectively receiving the target information, showing that the target is real; and if the target information is received by only one station or no station, showing that the target is false. In the method for detecting the ADS-B false target, a multi-station direction-finding system is formed, thereby, the false target can be accurately and effectively judged, the hidden danger is eliminated, and the air traffic safety is guaranteed.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
ECC certificate-based ADS-B data authentication method
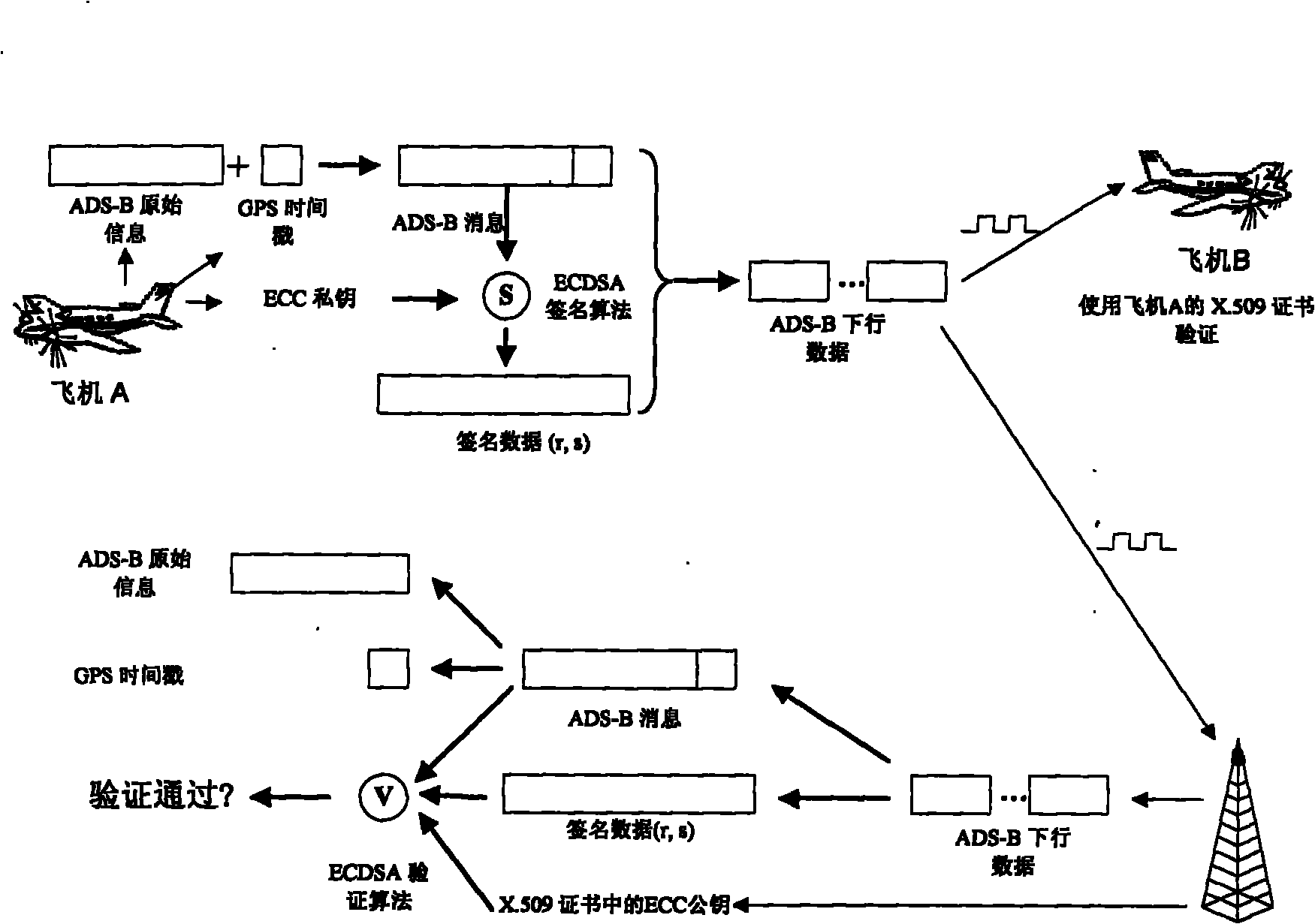
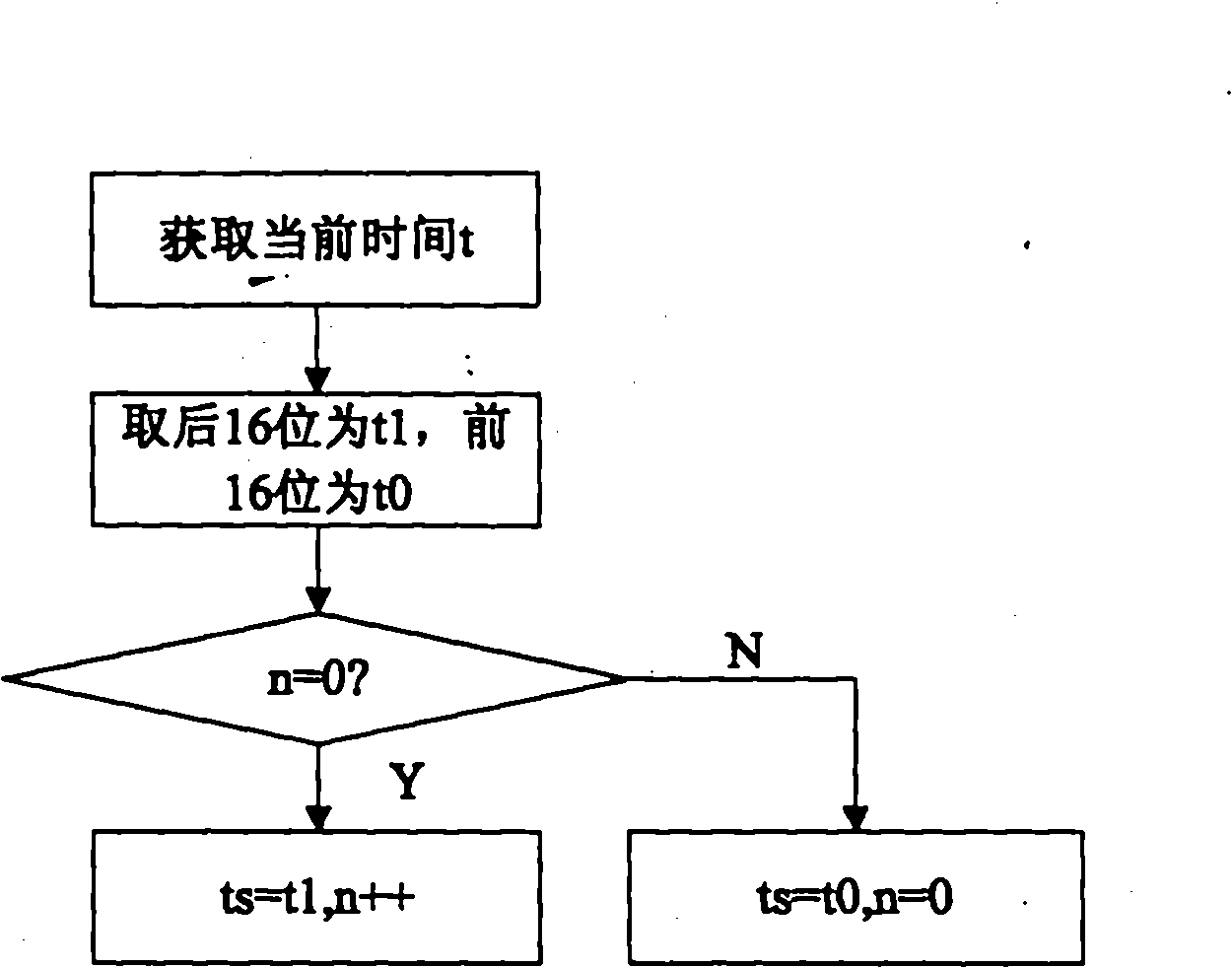
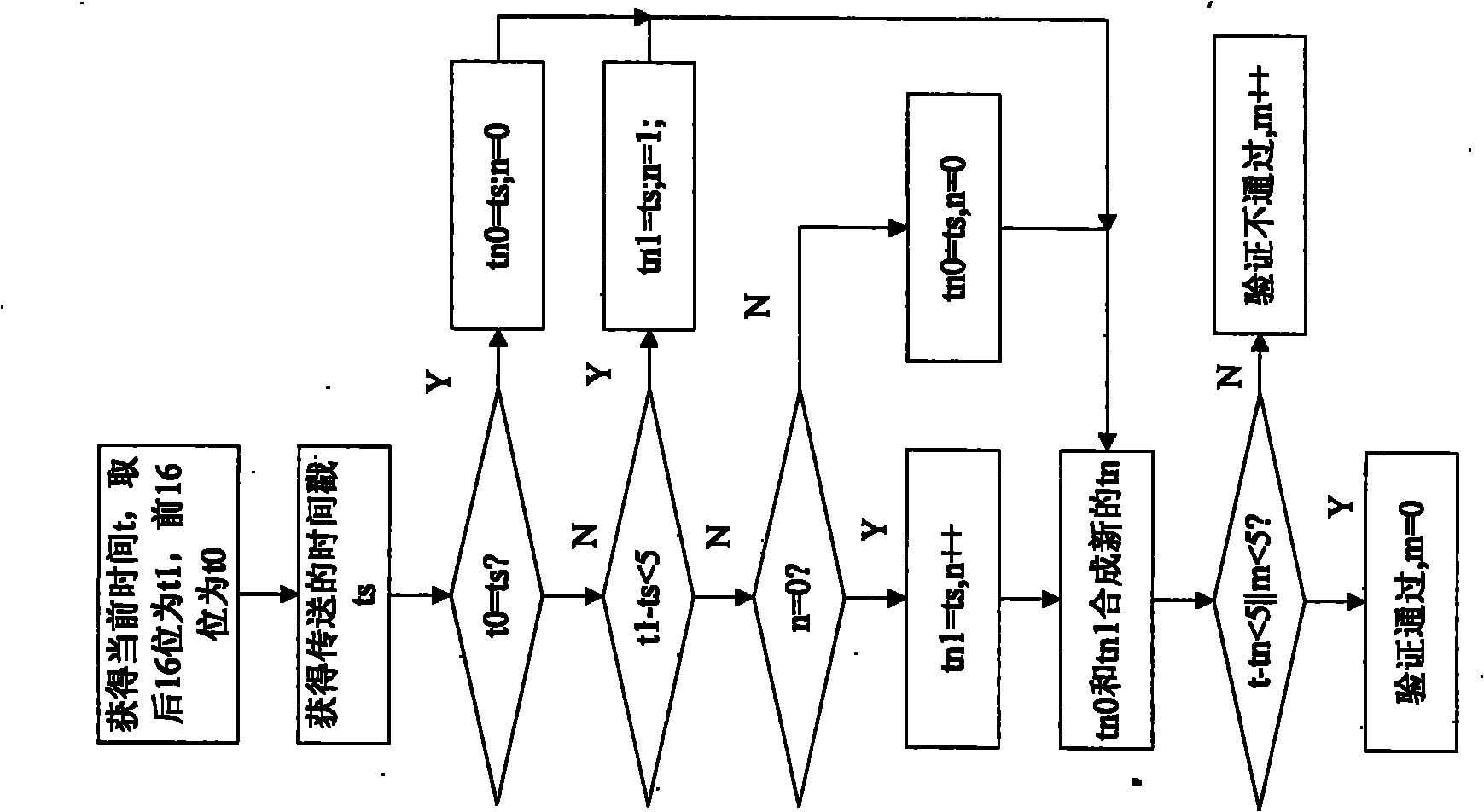
InactiveCN101917273AResistance to data spoofing attacksResistance to data replay attacksPublic key for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationTimestampTime mark
The invention relates to an ECC certificate-based ADS-B data authentication method and belongs to a method for authenticating airborne data in an automatic dependent surveillance broadcast system in the field of aviation. The method comprises the following steps of: adding a GPS timestamp into original ADS-B sending data to form an ADS-B message, and generating a signature by using an ECC private key; adding signature data into the ADS-B message, encapsulating the signature data into final ADS-B downlink data, and sending the final ADS-B downlink data through an ADS-B communication channel; and dividing ADS-B output data received by a ground station and other airplanes into two parts, wherein one part is ADS-B initial load and GPS time-scale data, and the latter is compared with the current GPS data so as to detect replay attack; and the other part is the signature data. The method can reduce the complexity of distribution and management of the private key, and resists data playback attack to ADS-B systems.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com