Patents
Literature
1609 results about "Multithreading" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
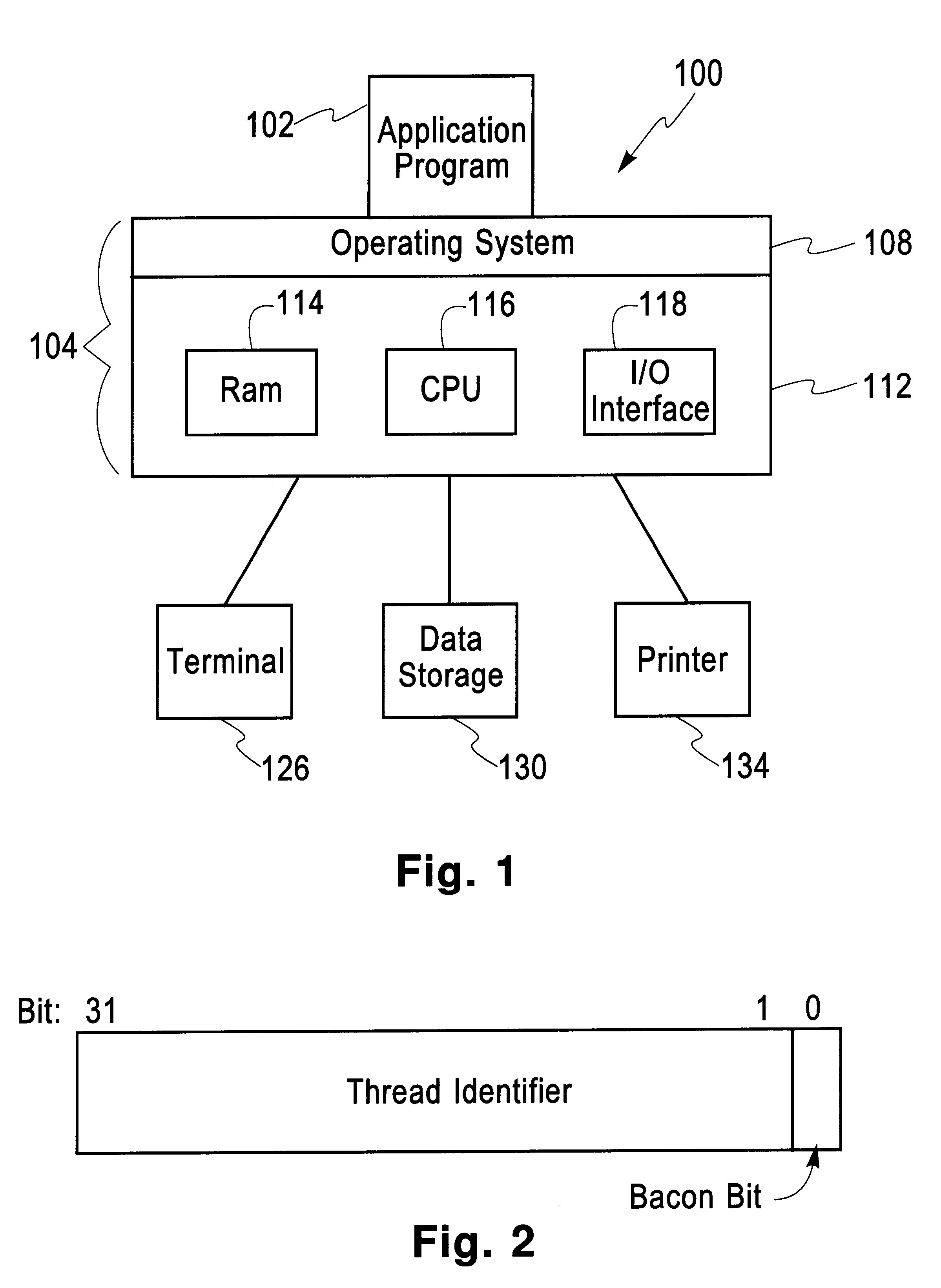
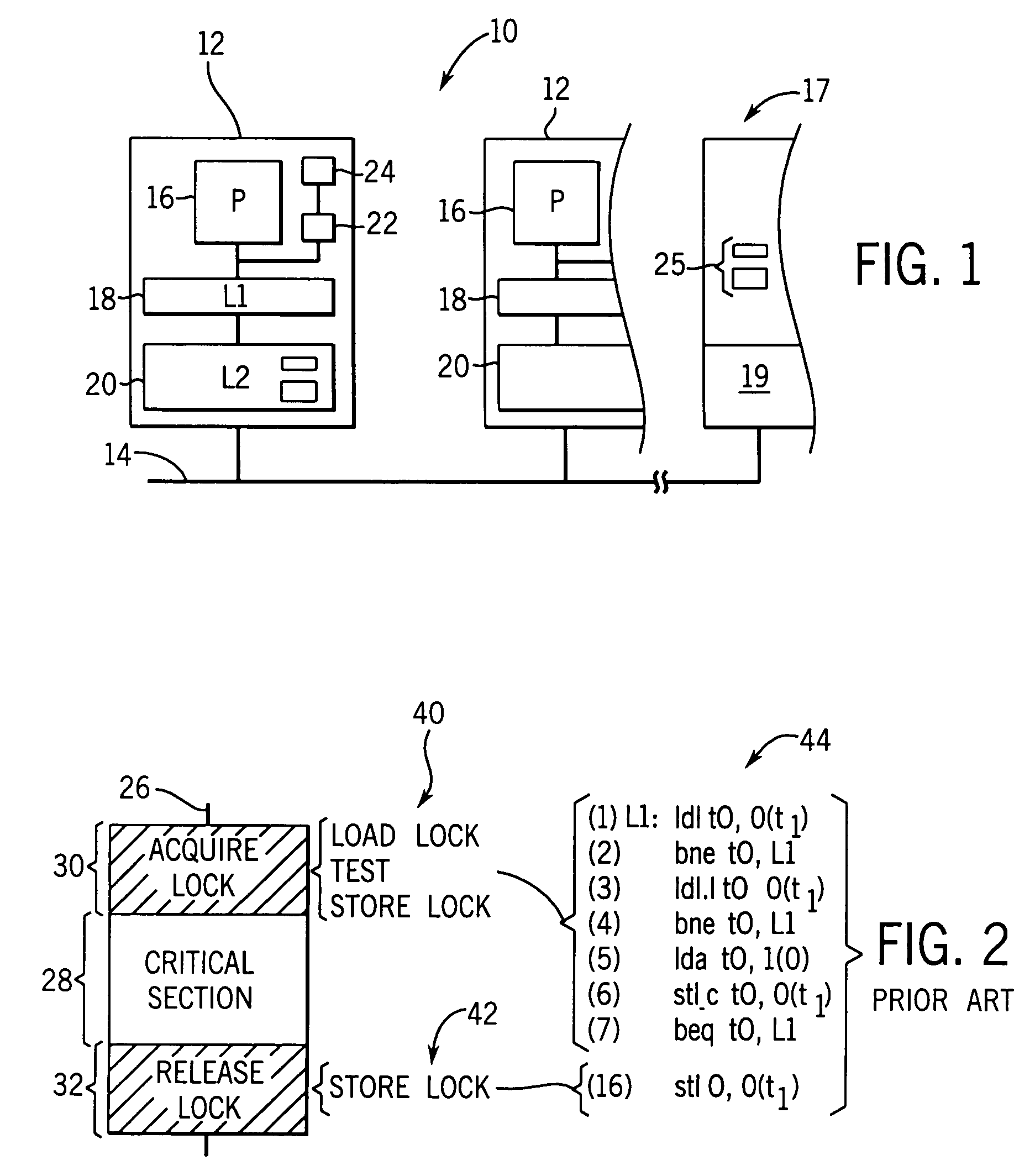
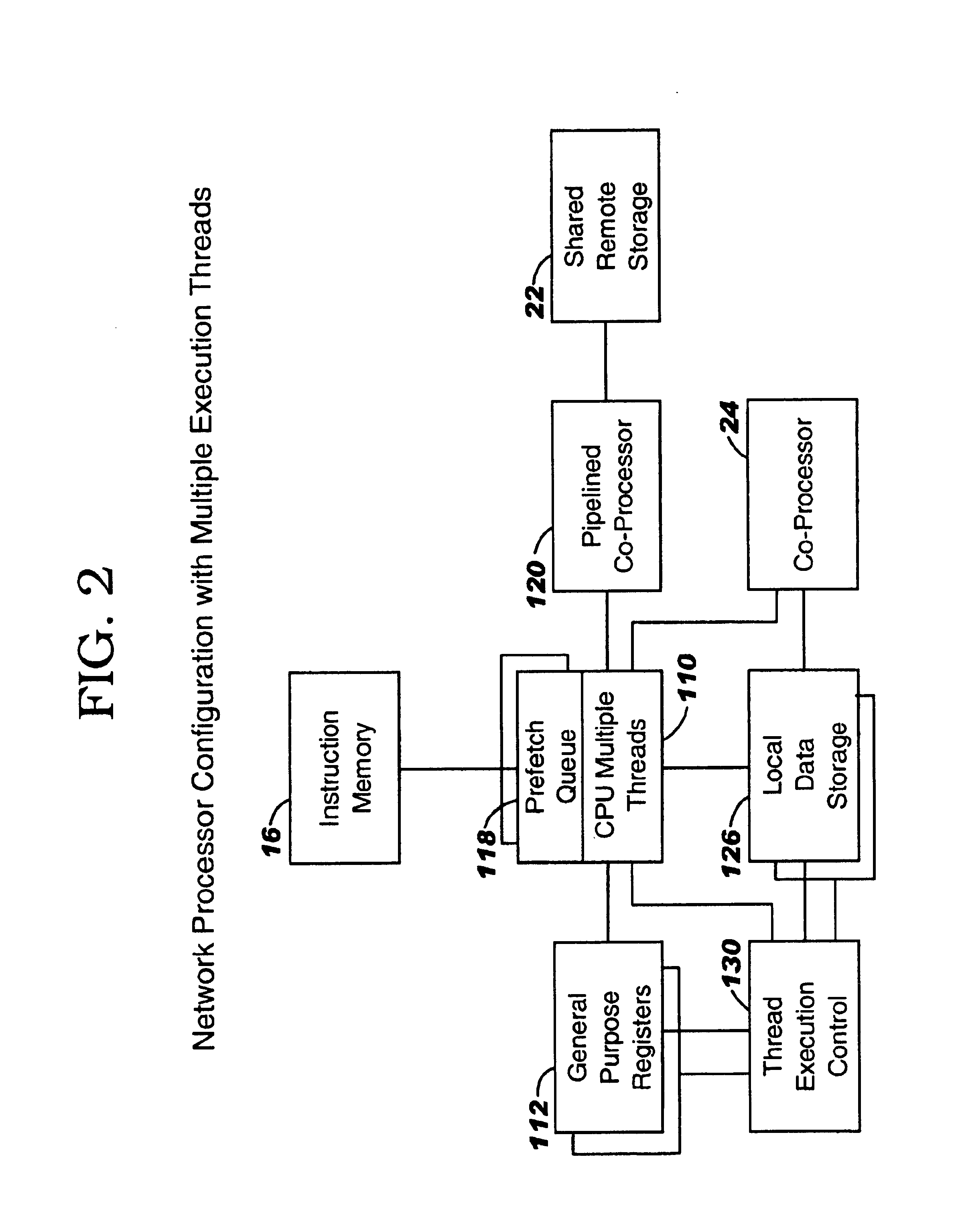
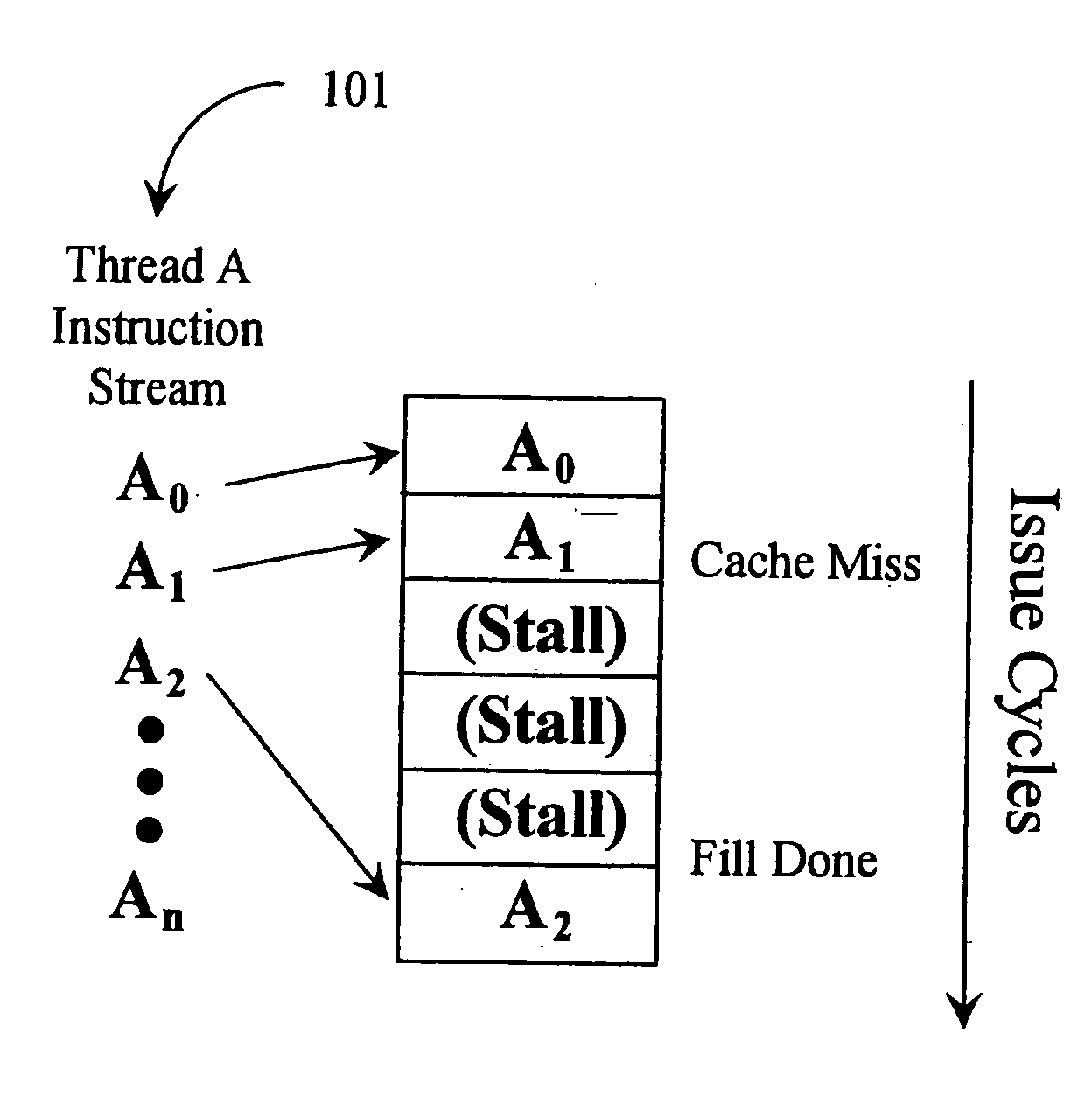
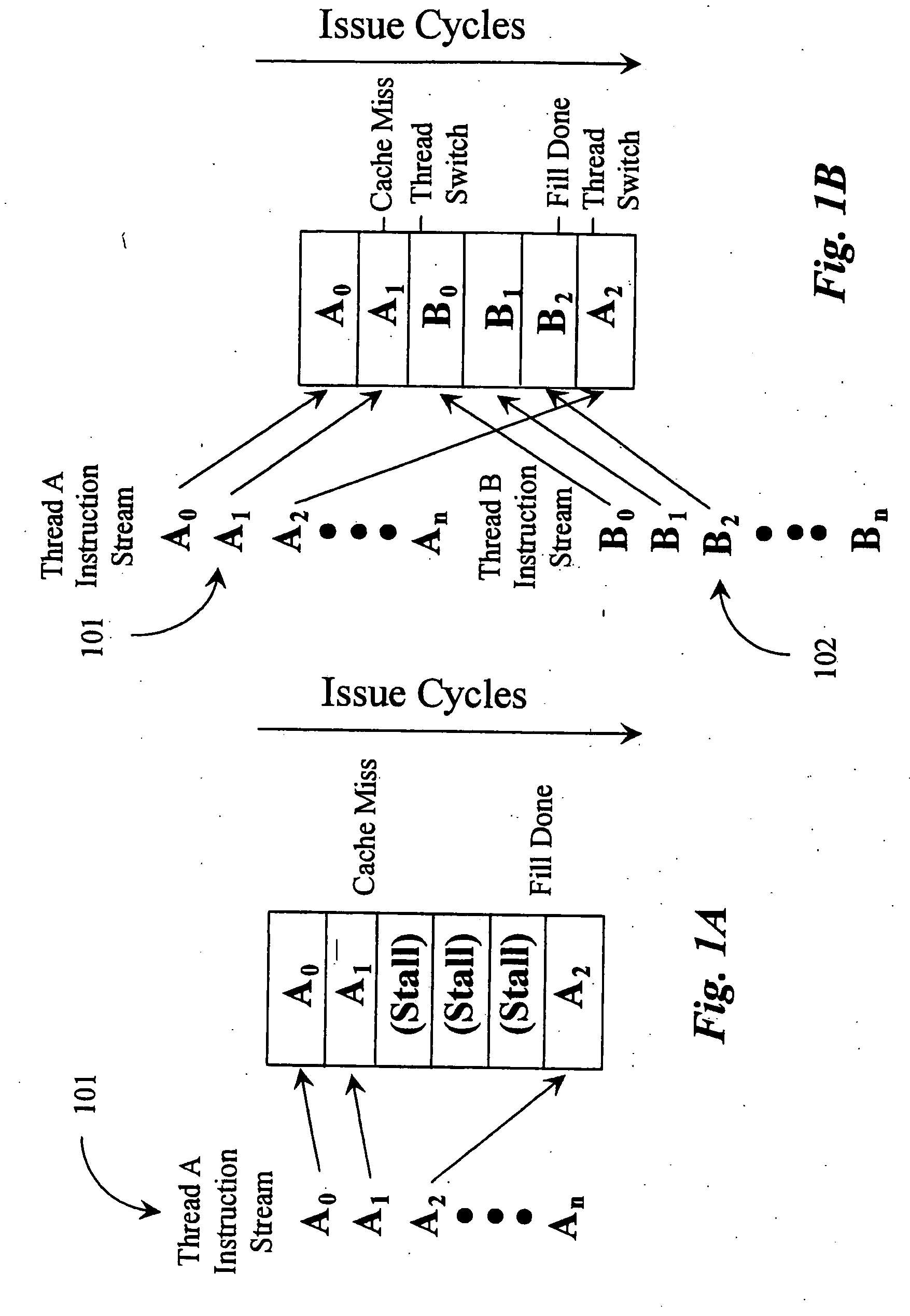
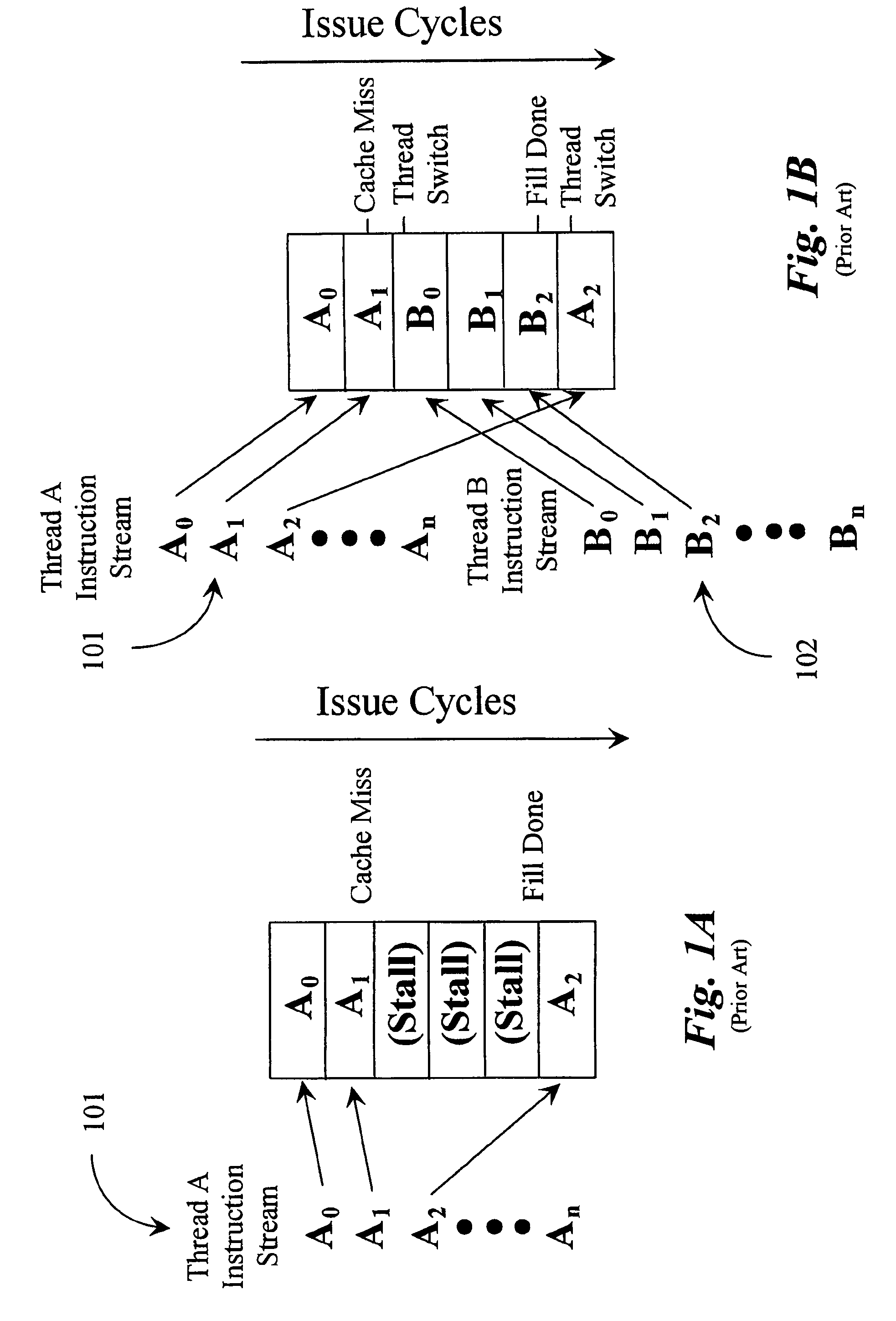
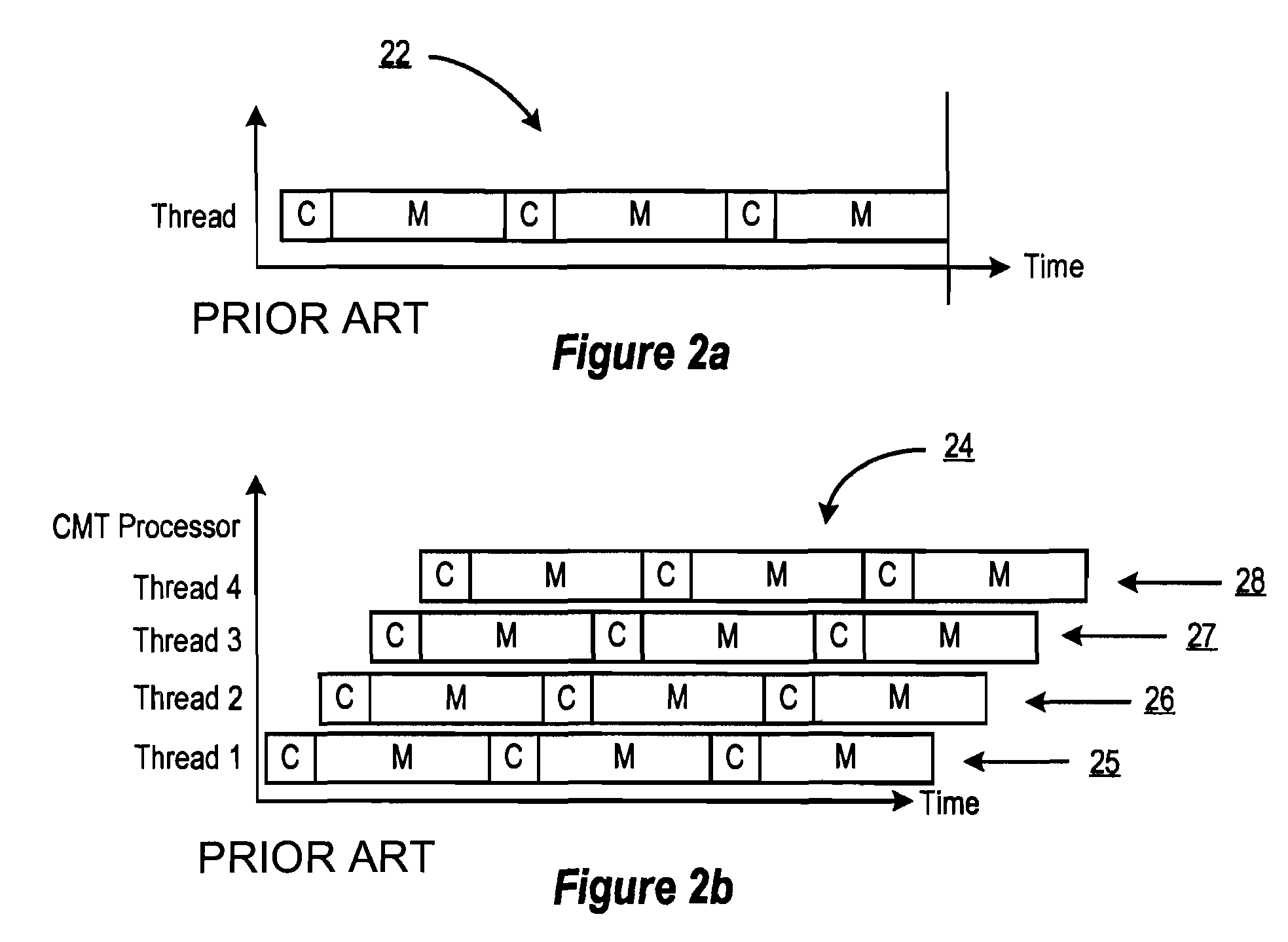
In computer architecture, multithreading is the ability of a central processing unit (CPU) (or a single core in a multi-core processor) to provide multiple threads of execution concurrently, supported by the operating system. This approach differs from multiprocessing. In a multithreaded application, the threads share the resources of a single or multiple cores, which include the computing units, the CPU caches, and the translation lookaside buffer (TLB).
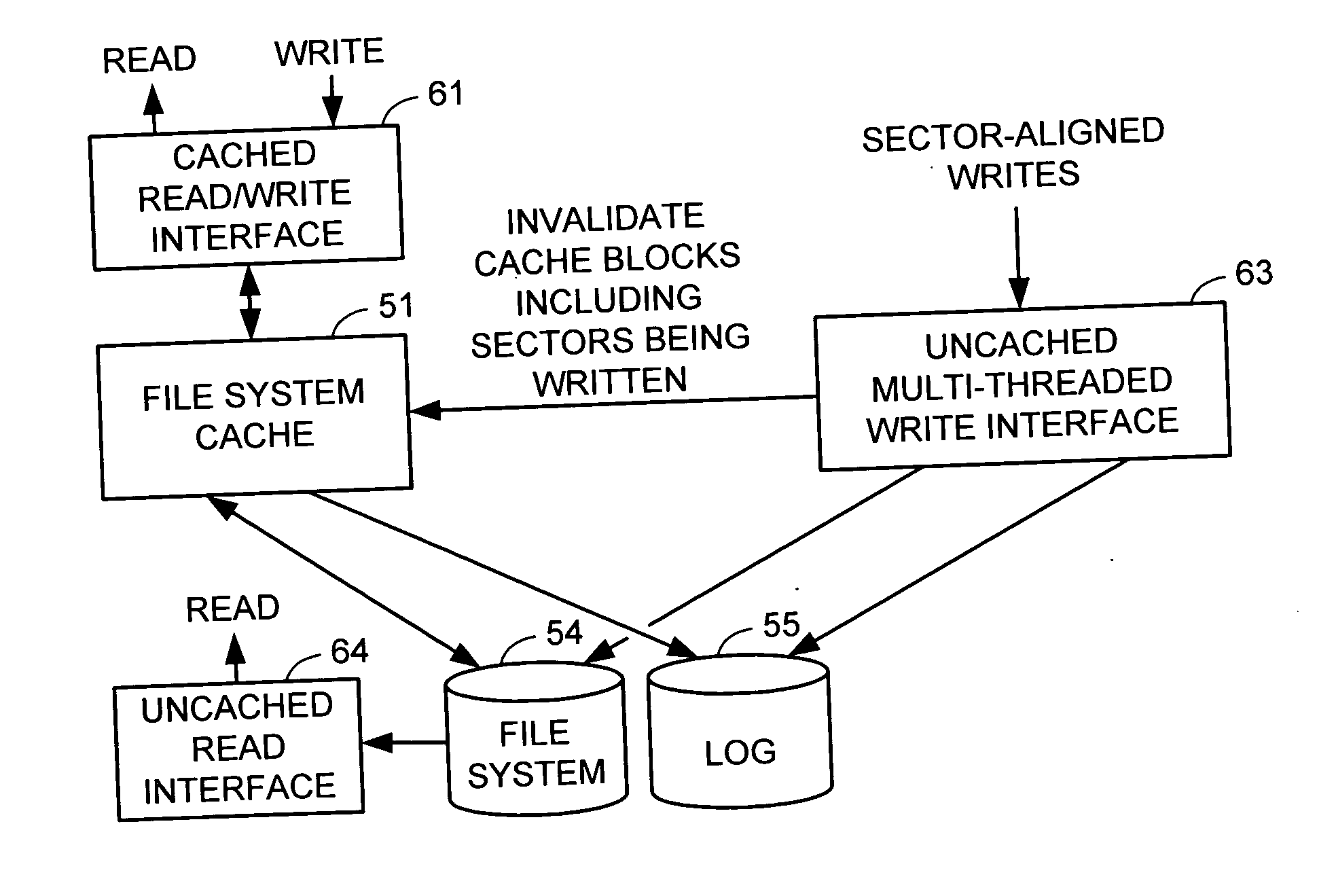
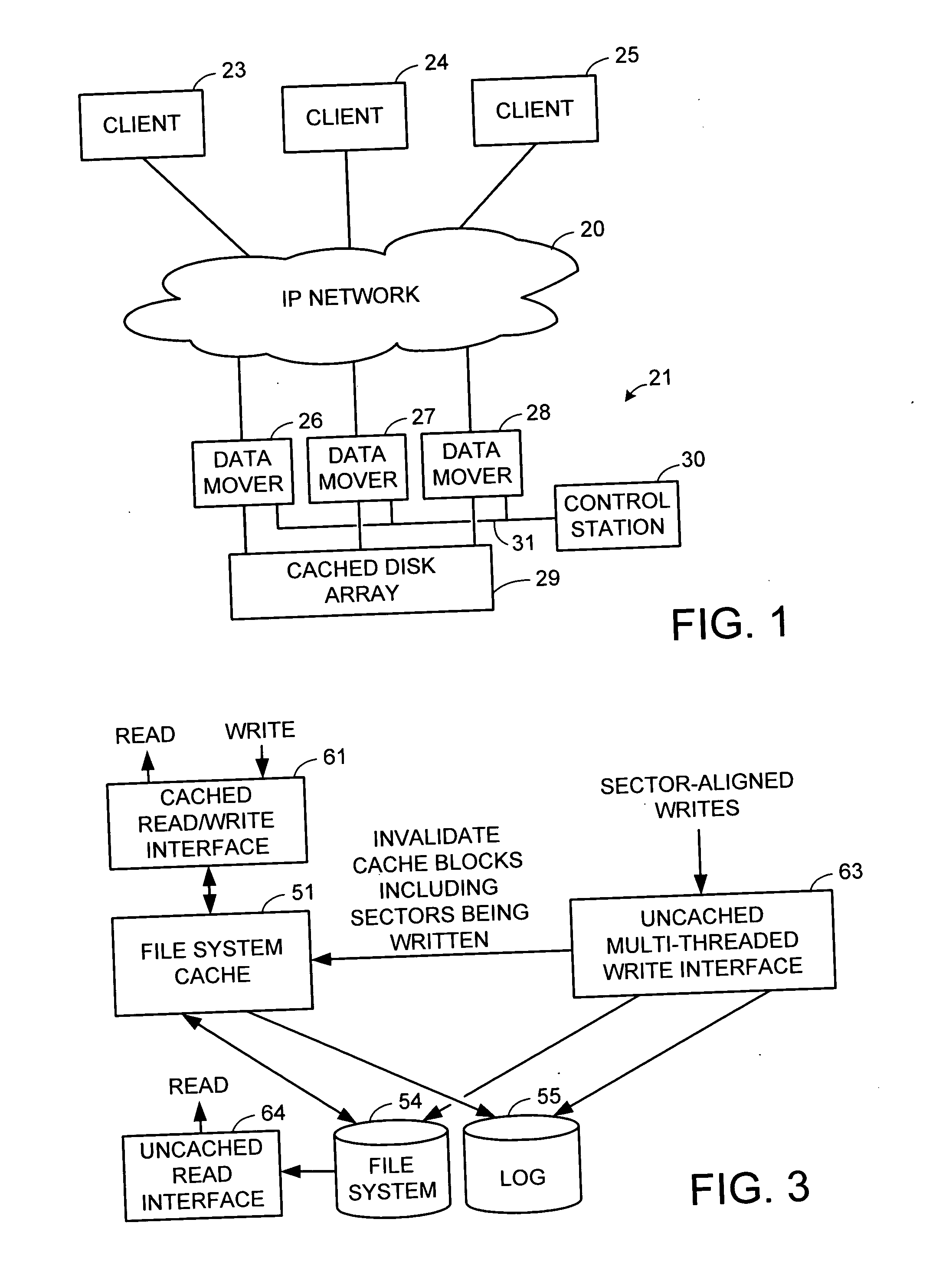
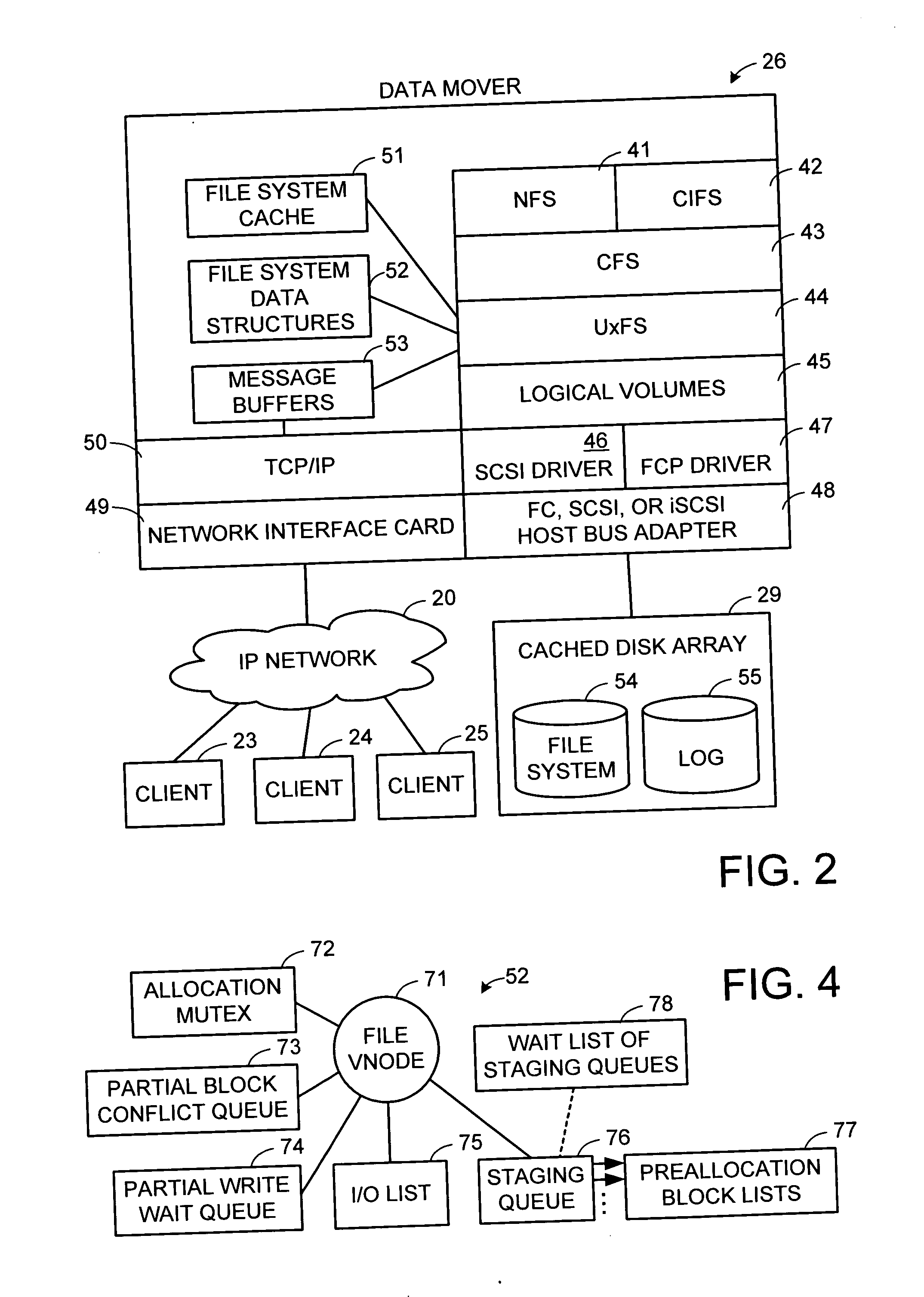
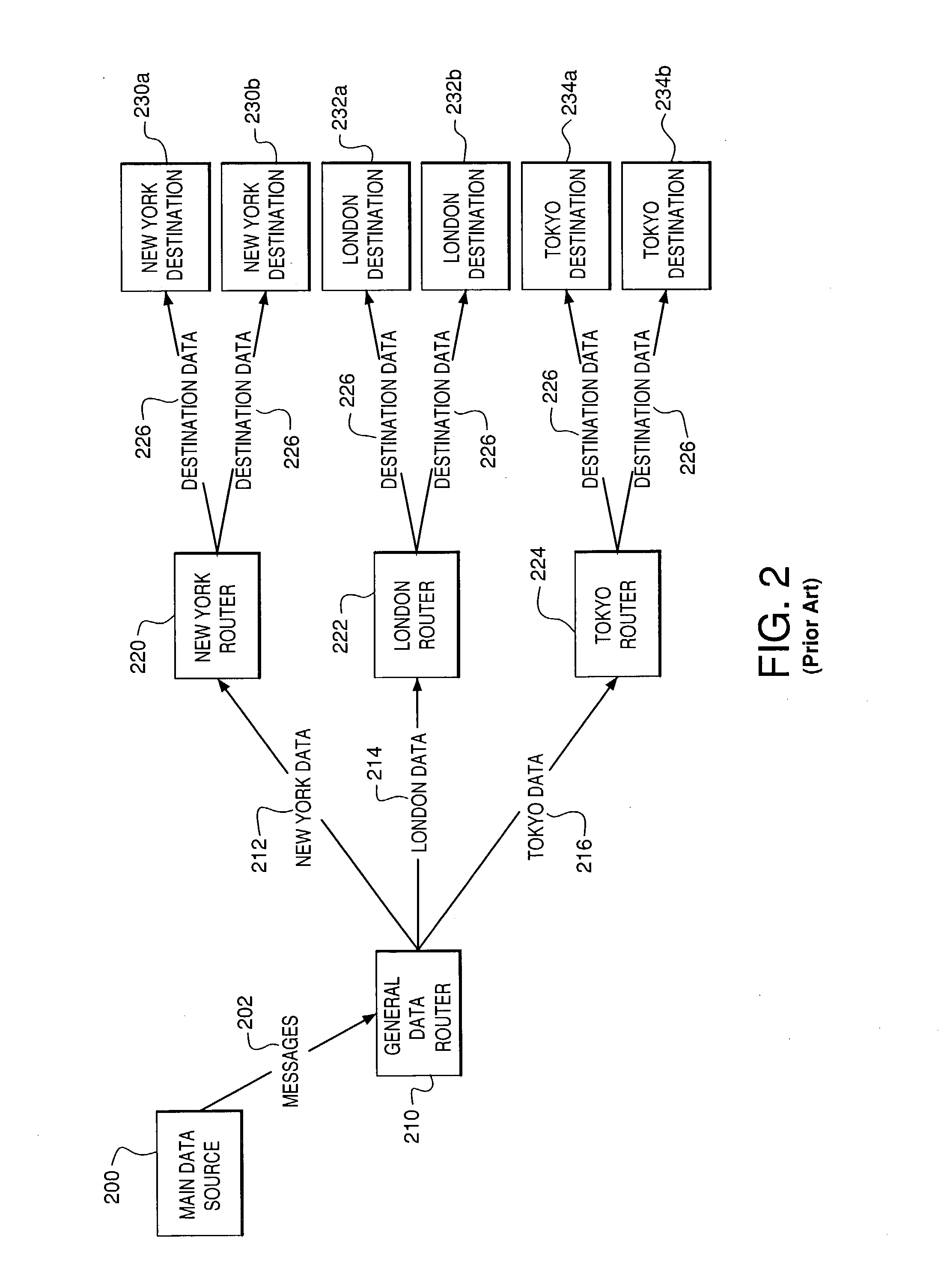
Multi-threaded write interface and methods for increasing the single file read and write throughput of a file server
ActiveUS20050066095A1Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsData integrityFile allocation
A write interface in a file server provides permission management for concurrent access to data blocks of a file, ensures correct use and update of indirect blocks in a tree of the file, preallocates file blocks when the file is extended, solves access conflicts for concurrent reads and writes to the same block, and permits the use of pipelined processors. For example, a write operation includes obtaining a per file allocation mutex (mutually exclusive lock), preallocating a metadata block, releasing the allocation mutex, issuing an asynchronous write request for writing to the file, waiting for the asynchronous write request to complete, obtaining the allocation mutex, committing the preallocated metadata block, and releasing the allocation mutex. Since no locks are held during the writing of data to the on-disk storage and this data write takes the majority of the time, the method enhances concurrency while maintaining data integrity.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
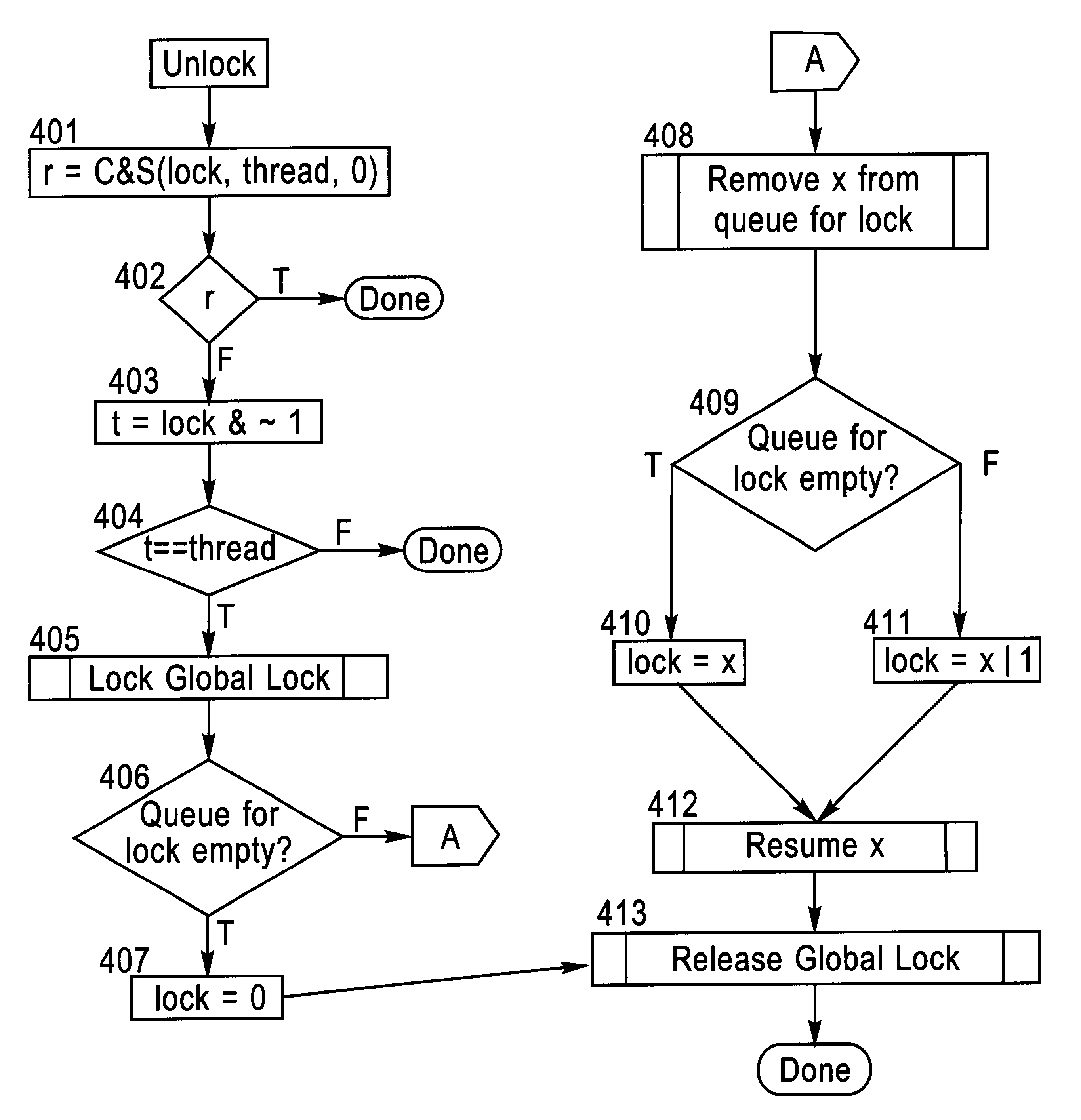
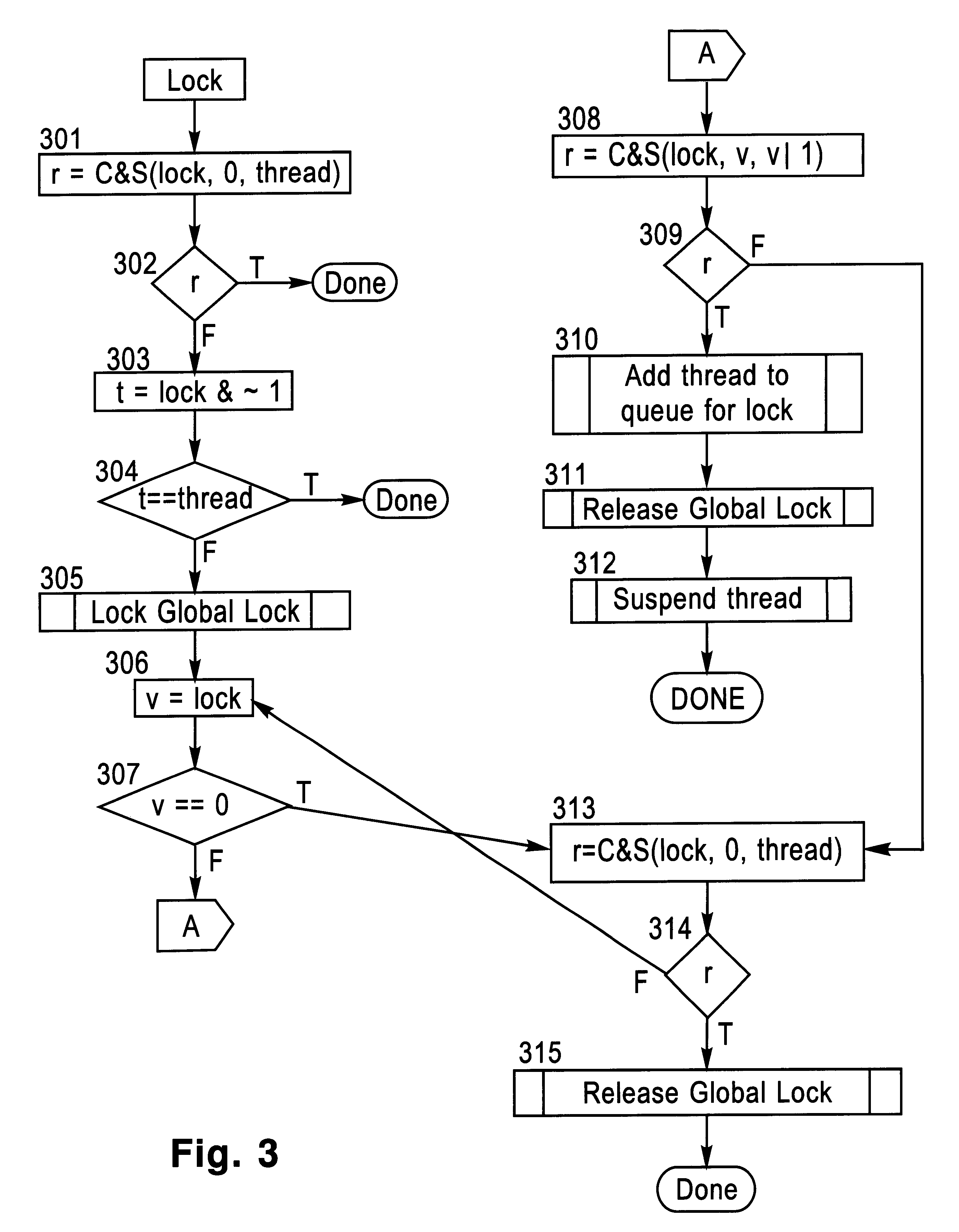
Locking and unlocking mechanism for controlling concurrent access to objects
InactiveUS6247025B1Data processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalNormal caseSpin locks
A lock / unlock mechanism to control concurrent access to objects in a multi-threaded computer processing system comprises two parts: a thread pointer (or thread identifier), and a one-bit flag called a "Bacon bit". Preferably, when an object is not locked (i.e., no thread has been granted access to the object), the thread identifier and Bacon bit are set to 0. When an object is locked by a particular thread (i.e., the thread has been granted access to the object), the thread identifier is set to a value that identifies the particular thread; if no other threads are waiting to lock the object, the Bacon bit is set to 0; however, if other threads are waiting to lock the object, the Bacon bit is set to "1', which indicates the there is a queue of waiting threads associated with the object. To lock an object, a single CompareAndSwap operation is preferably used, much like with spin-locks; if the lock is already held by another thread, enqueueing is handled in out-of-line code. To unlock an object, in the normal case, a single CompareAndSwap operation may be used. This single operation atomically tests that the current thread owns the lock, and that no other threads are waiting for the object (i.e., the Bacon bit is "0'). A global lock is preferably used to change the Bacon bit of the lock. This provides an lock / unlock mechanism which combines many of the desirable features of both spin locking and queued locking, and can be used as the basis for a very fast implementation of the synchronization facilities of the Java language.
Owner:IBM CORP
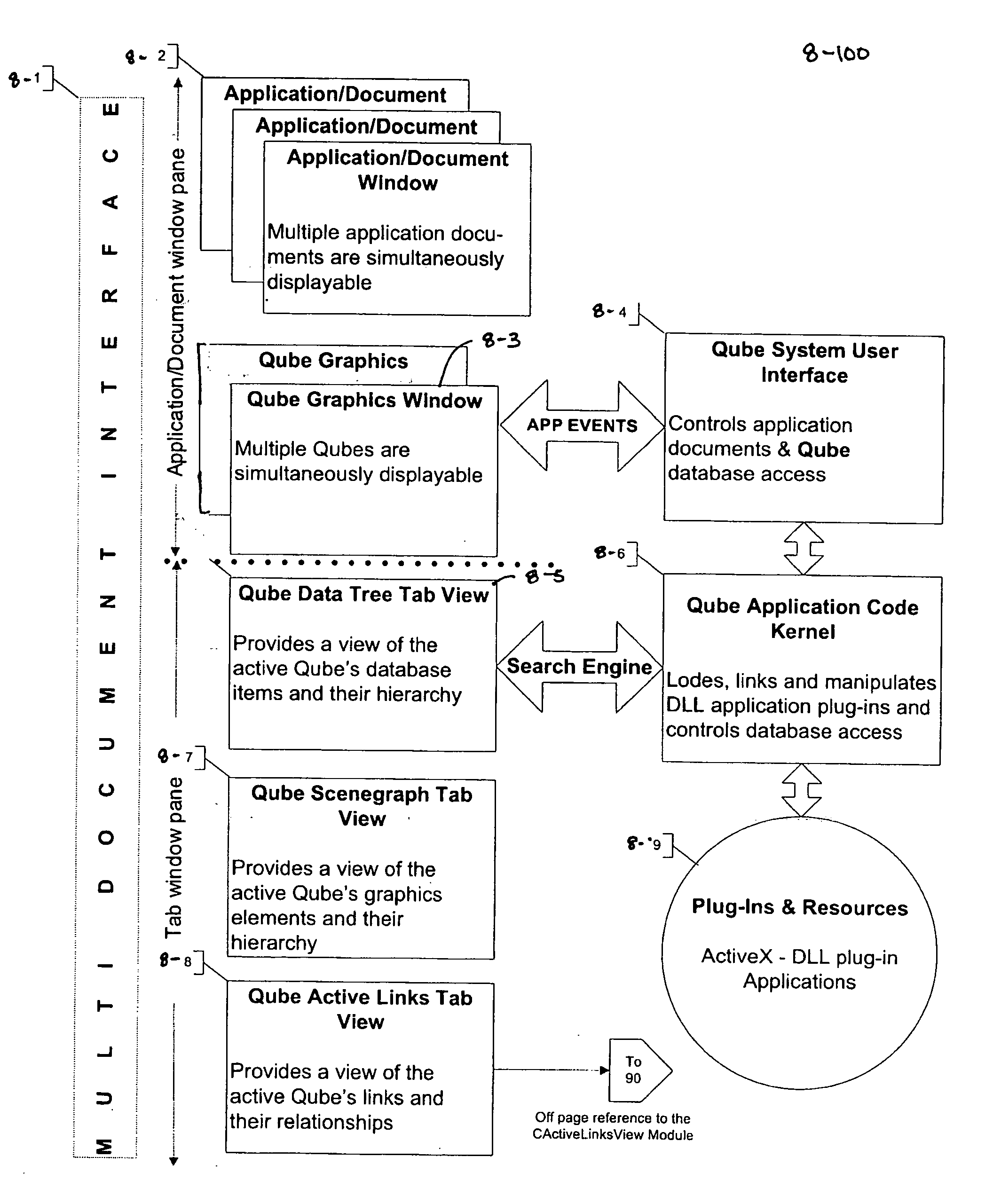
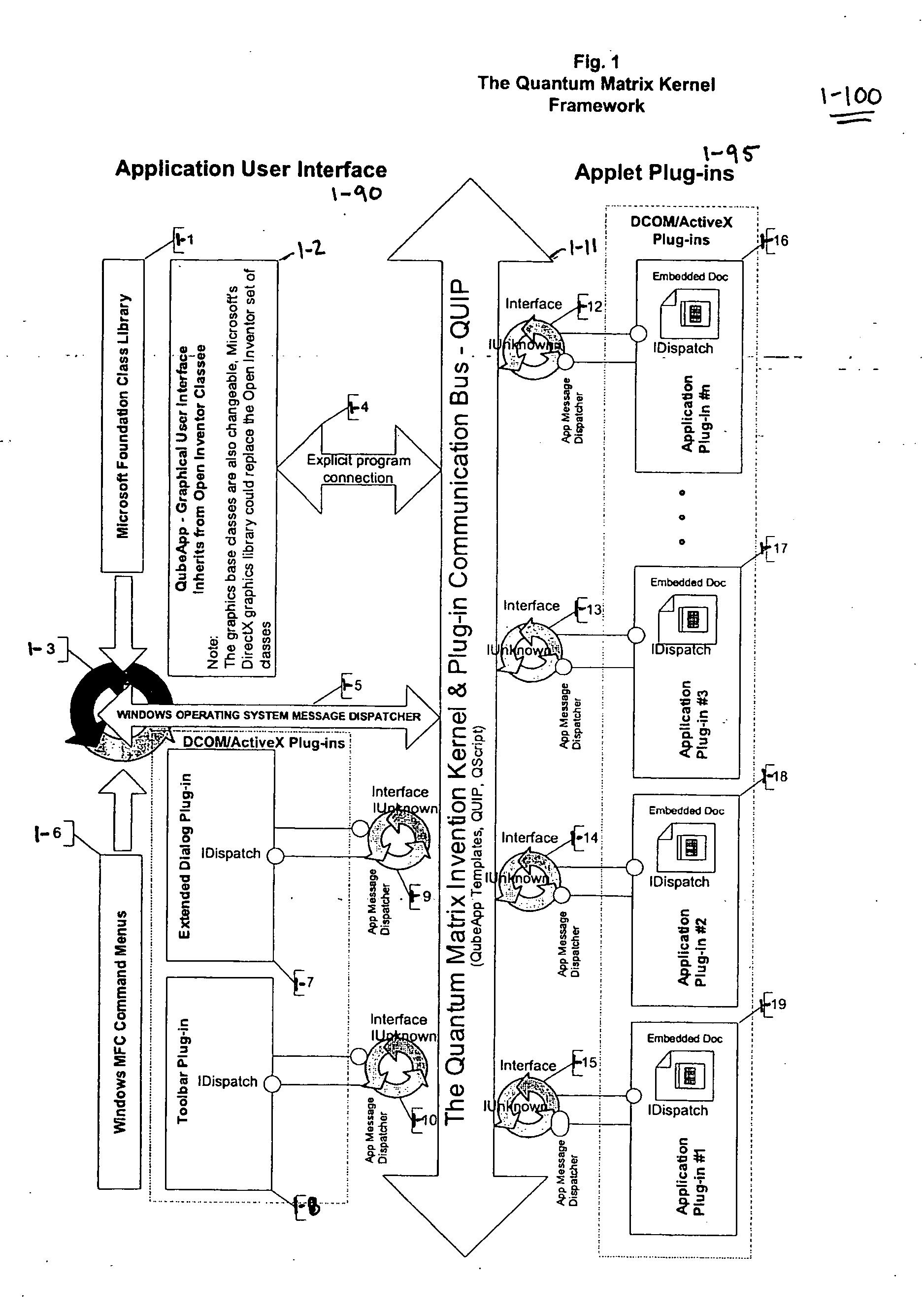
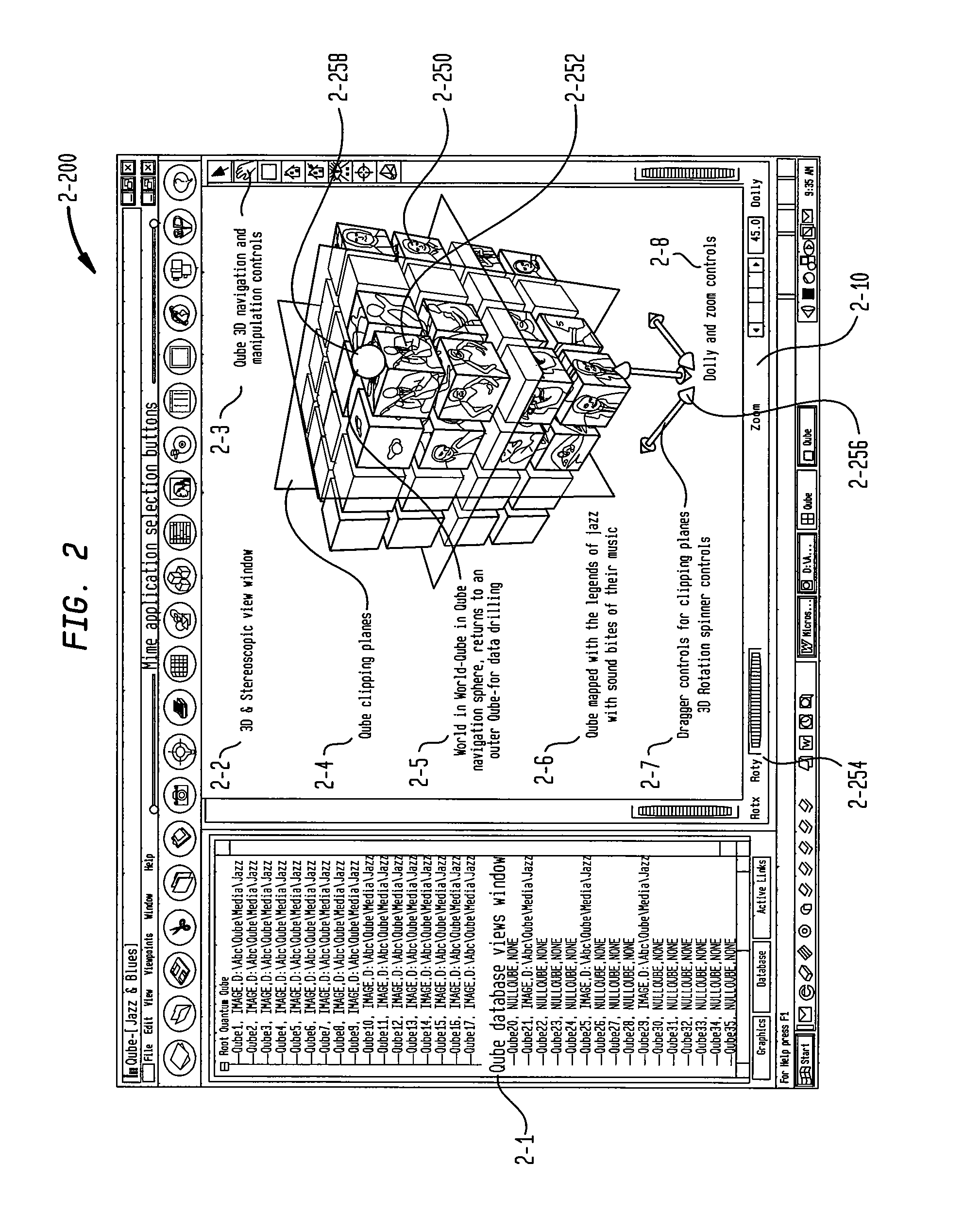
System and method for multi-dimensional organization, management, and manipulation of data
ActiveUS20050131924A1Data processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsScripting languageFile system
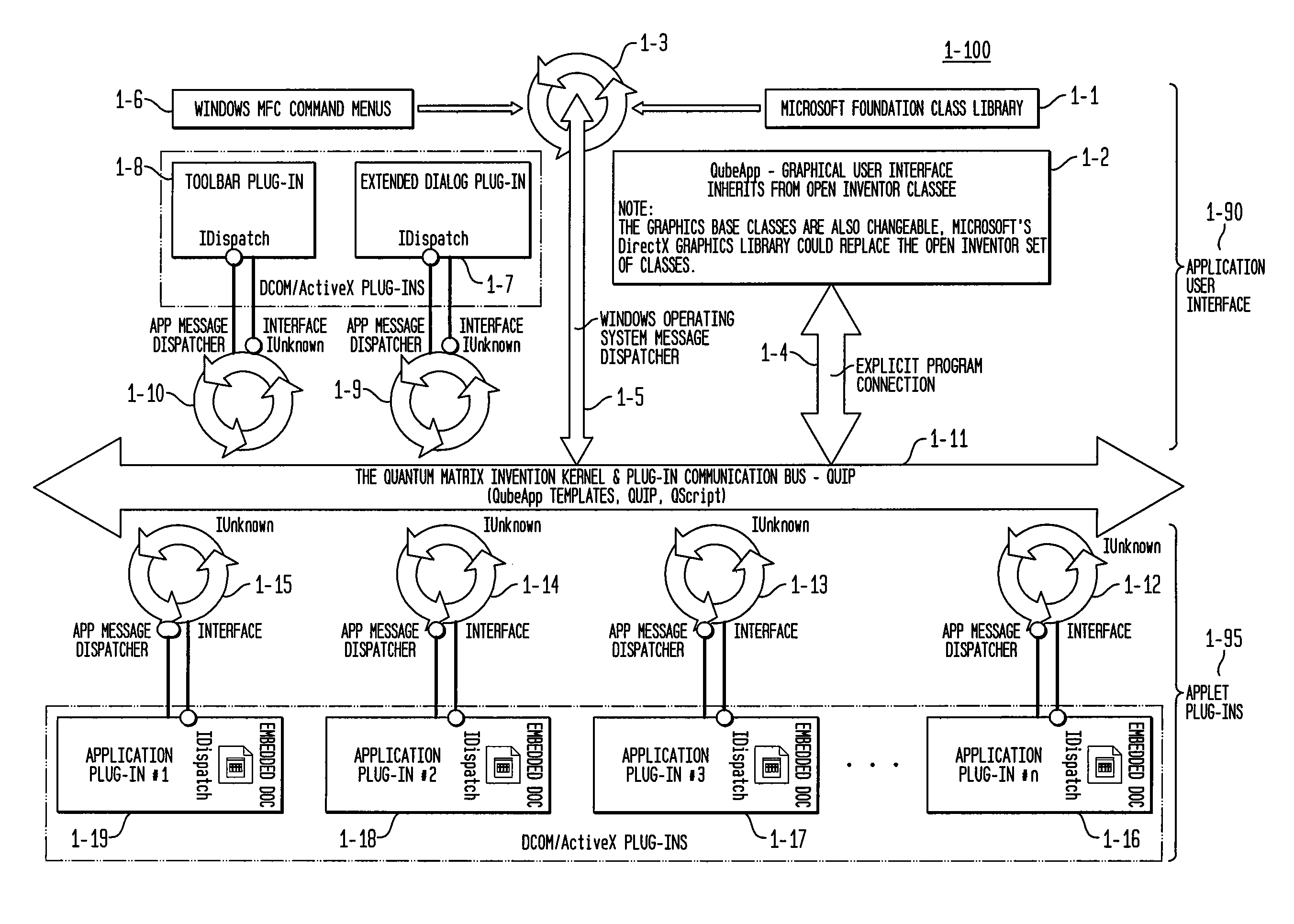
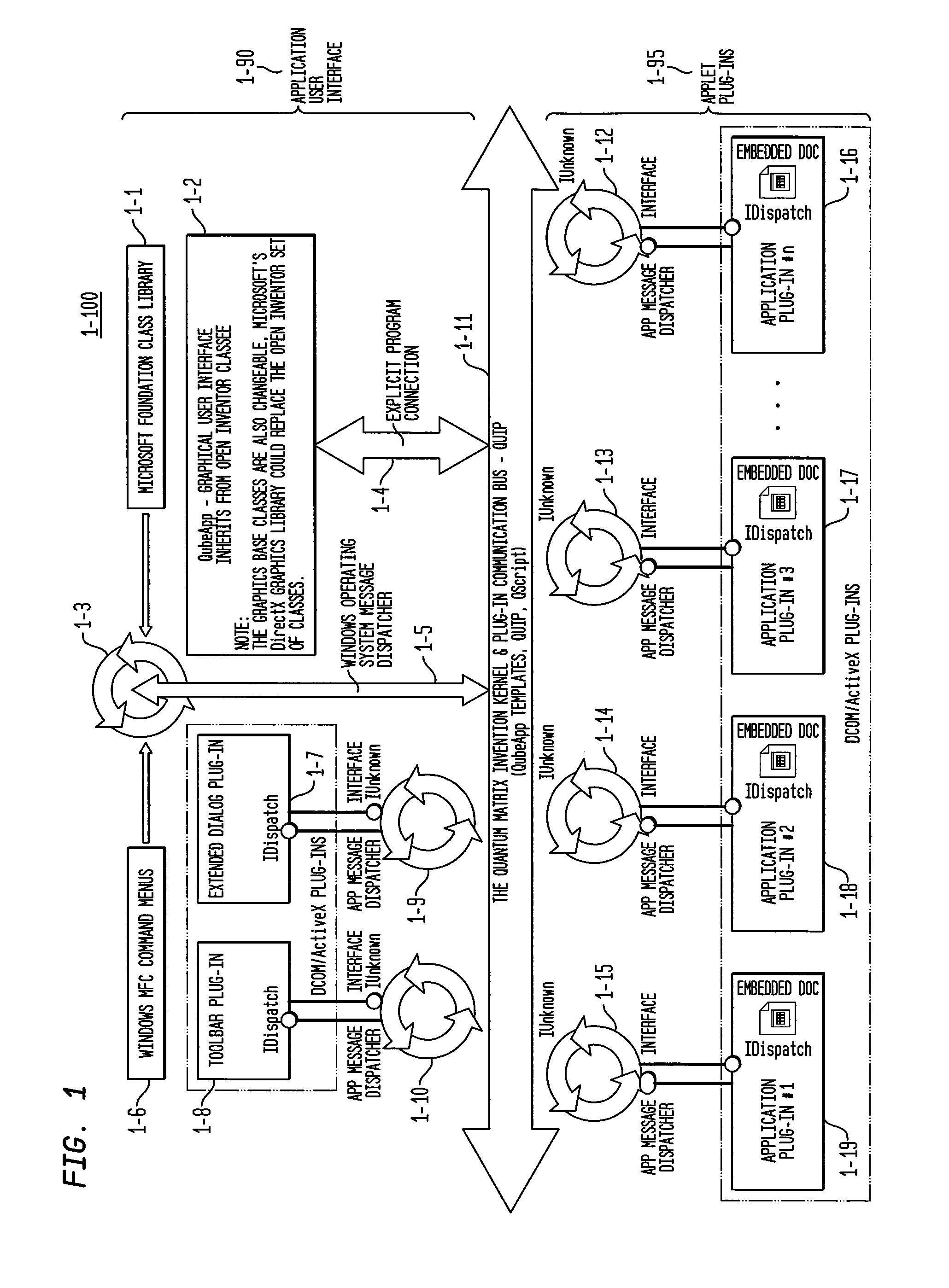
The Quantum Matrix system is a multi-dimensional, multi-threaded exchange environment for data organization, management, and manipulation. Data is organized into a multi-dimensional structure of nodes. Nodes may represent data, absence of data, or another set of nodes. The multi-dimensional structure or portions of it can be automatically created from a file system. One or more associations are also defined for the multi-dimensional structure. An association indicates a relationship between a node and another node, data, or a set of nodes. The multi-dimensional structure is then displayed three-dimensionally and navigated. Relational logic, Boolean algebra, or a scripting language can be applied to the nodes, data, and associations to produce a resultant set of nodes. Furthermore, portions of the multi-dimensional structure can be isolated with the use of planes to ease navigation. Furthermore, Avatars may be displayed and used for collaborative purposes and to automate the navigation of the multi-dimensional structure.
Owner:QUANTUM MATRIX HLDG
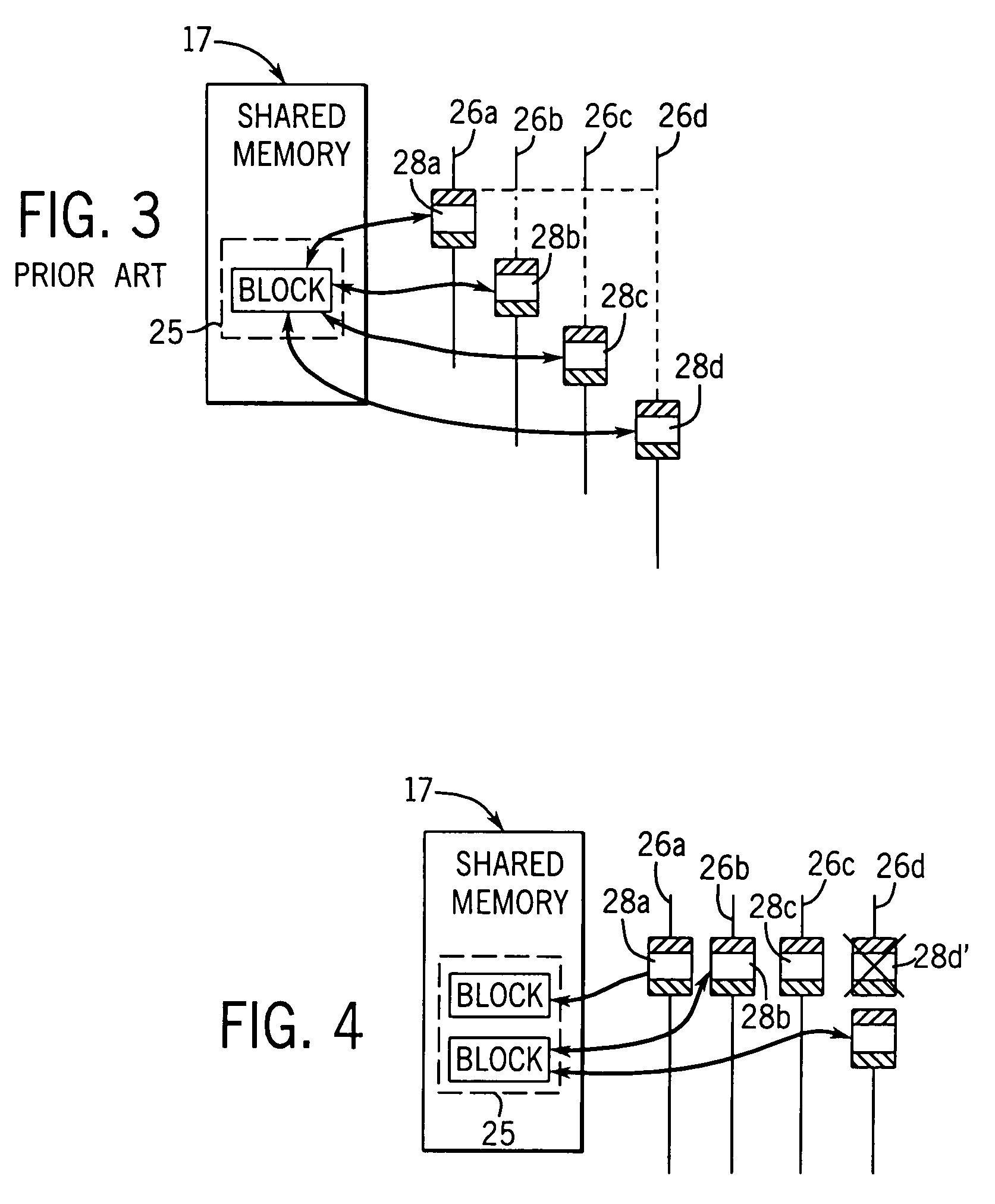
Converting program code with access coordination for a shared memory
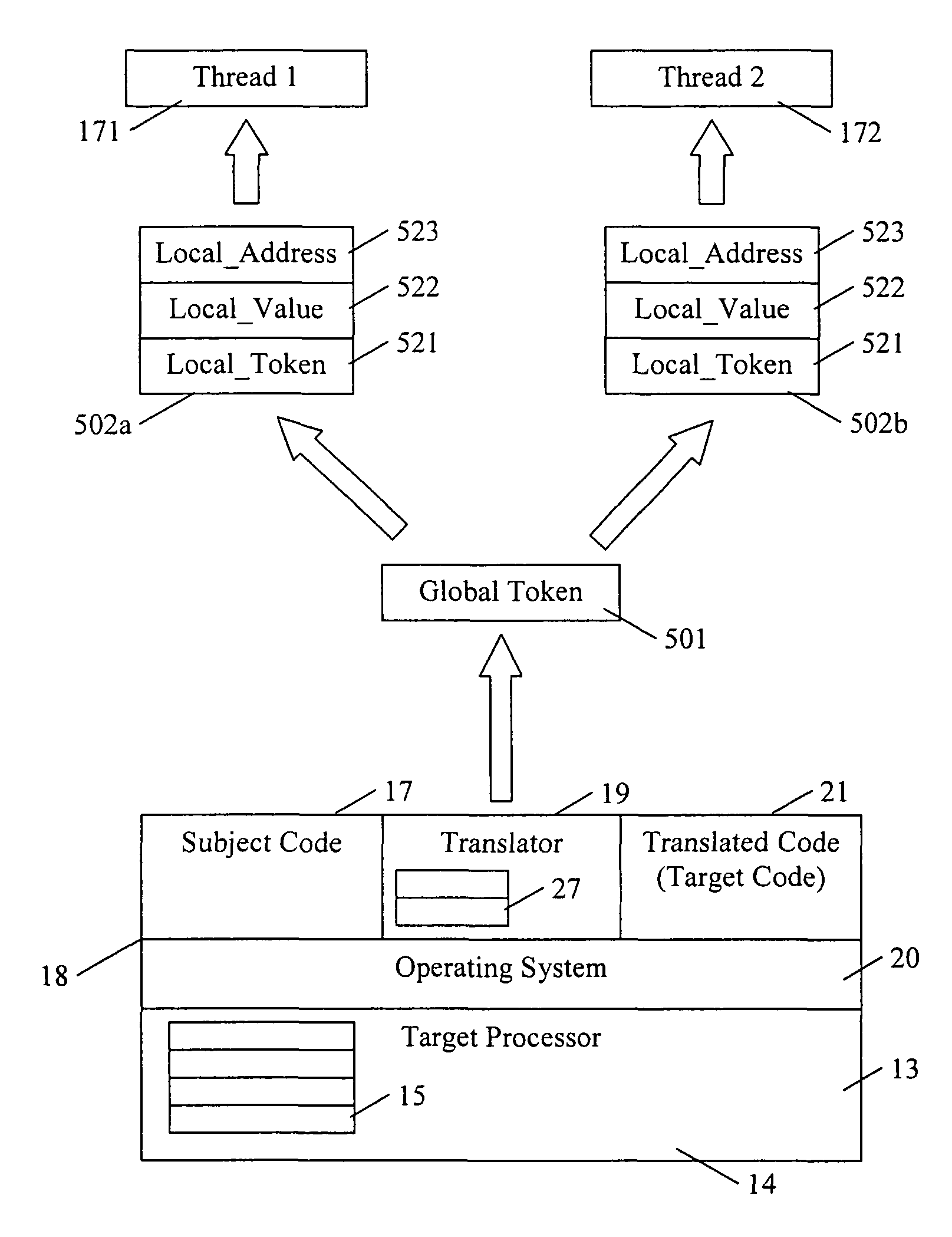
A dynamic binary translator 19 converts a subject program 17 into target code 21 on a target processor 13. For a multi-threaded subject environment, the translator 19 provides a global token 501 common to each thread 171, 172, and one or more sets of local data 502, which together are employed to coordinate access to a memory 18 as a shared resource. Adjusting the global token 501 allows the local datastructures 502a,b in each thread to detect potential interference with the shared resource 18.
Owner:IBM CORP
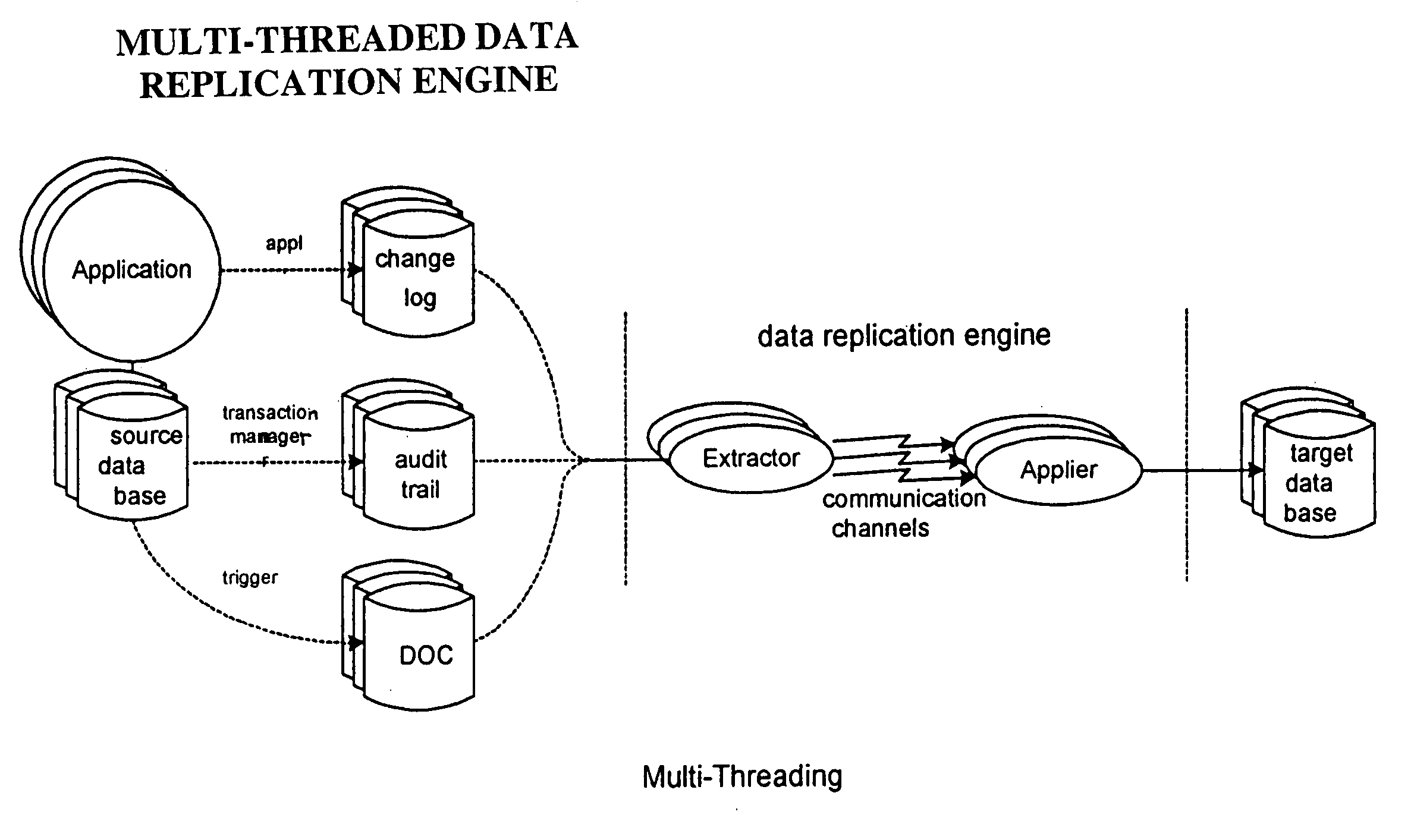
Method for ensuring referential integrity in multi-threaded replication engines
ActiveUS20050021567A1Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsTransaction dataLoad capacity
During replication of transaction data from a source database to a target database via a change queue associated with the source database, one or more multiple paths are provided between the change queue and the target database. The one or more multiple paths cause at least some of the transaction data to become unserialized. At least some of the unserialized data is reserialized prior to or upon applying the originally unserialized transaction data to the target database. If the current transaction load is close or equal to the maximum transaction load capacity of a path between the change queue and the target database, another path is provided. If the maximum transaction threshold limit of an applier associated with the target database has been reached, open transactions may be prematurely committed.
Owner:INTEL CORP
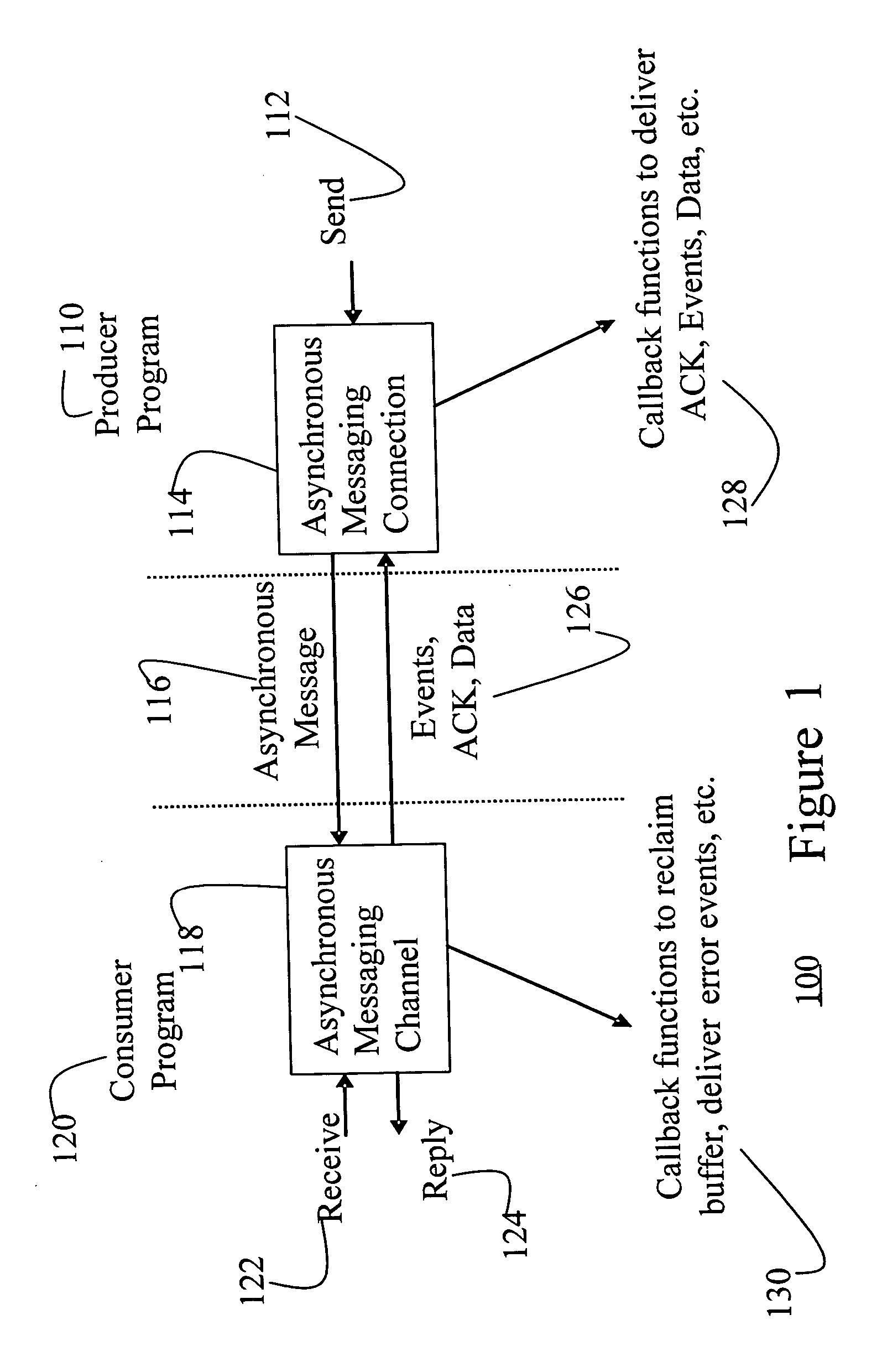
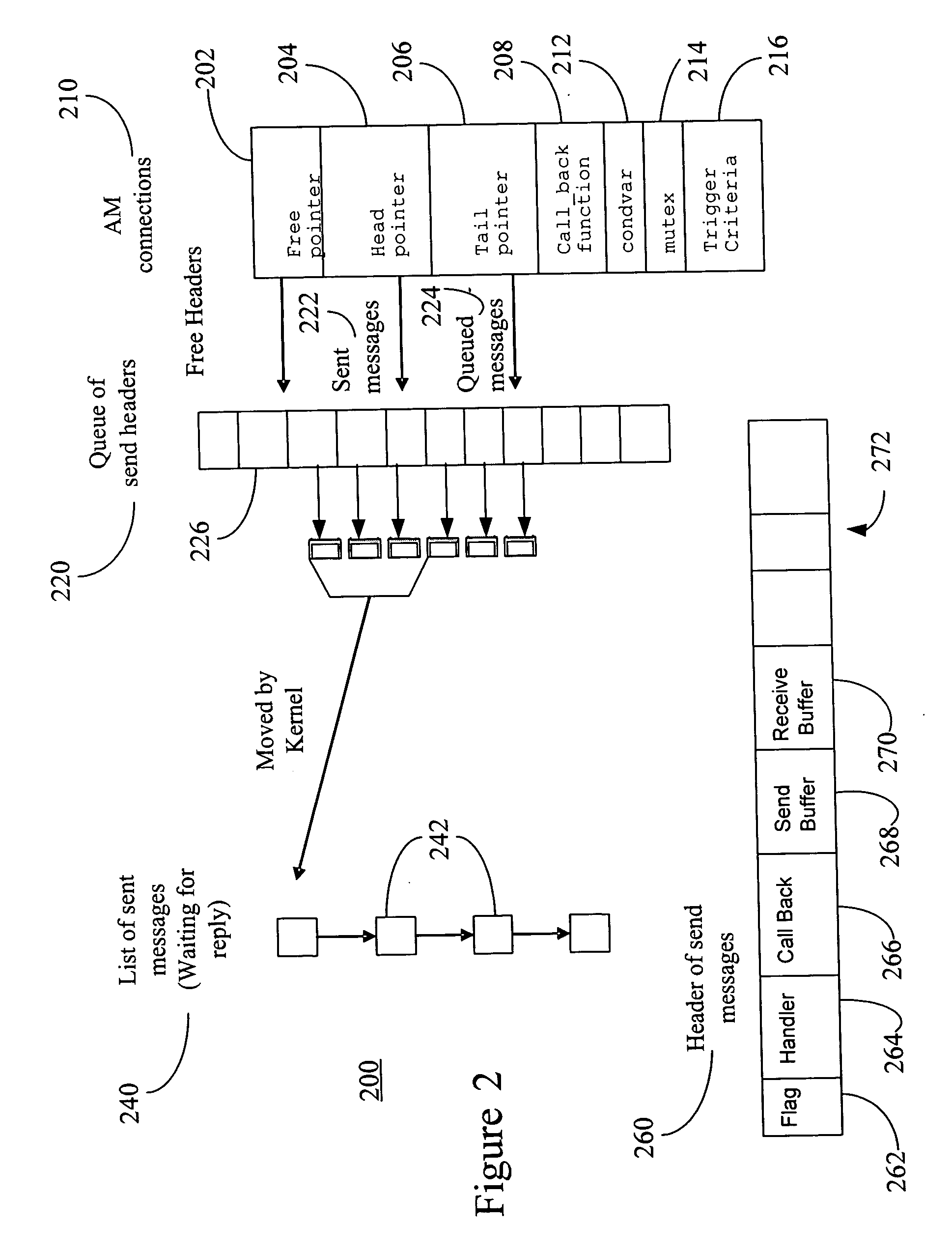
Fast and memory protected asynchronous message scheme in a multi-process and multi-thread environment
ActiveUS20060182137A1Speeding up queue operationSlow performanceTime-division multiplexStore-and-forward switching systemsComputer hardwareData transmission
An asynchronous message passing mechanism that allows for multiple messages to be batched for delivery between processes, while allowing for full memory protection during data transfers and a lockless mechanism for speeding up queue operation and queuing and delivering messages simultaneously.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
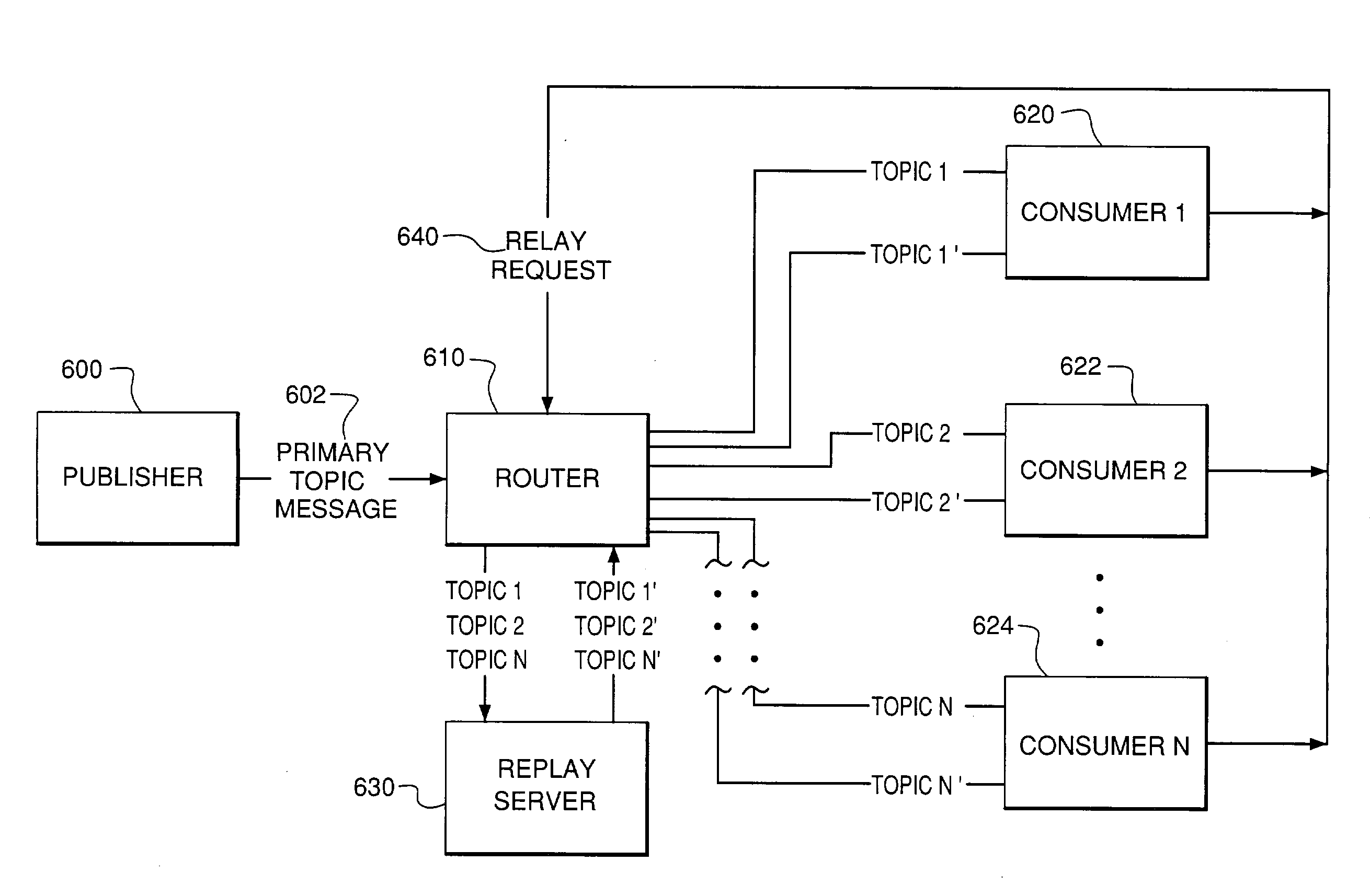
System and method for message processing and routing
InactiveUS20050021836A1Precise and reliable loggingMultiple digital computer combinationsProgram controlLoggingMessage routing
A message routing system that allows applications at either end of the system to run as-is without modification. The system functions in a multithreaded environment and is capable of handling complex routing rules and message transformation. It is also capable of learning and executing new routing rules and message transformations in formats previously unrecognized by the system. The system enables precise and reliable logging of messages throughout processing and supports publication of enterprise-wide broadcast messages. The system further preferably employs cooperating inbound and outbound transport processes for consuming, routing, processing, safely storing and publishing messages in batches of logical units of work to ensure that the logical units of work are not lost in system transactions. The system also preferably utilizes a replay server for preserving and replaying messages that might otherwise fail to reach their intended destinations.
Owner:GOLDMAN SACHS & CO LLC
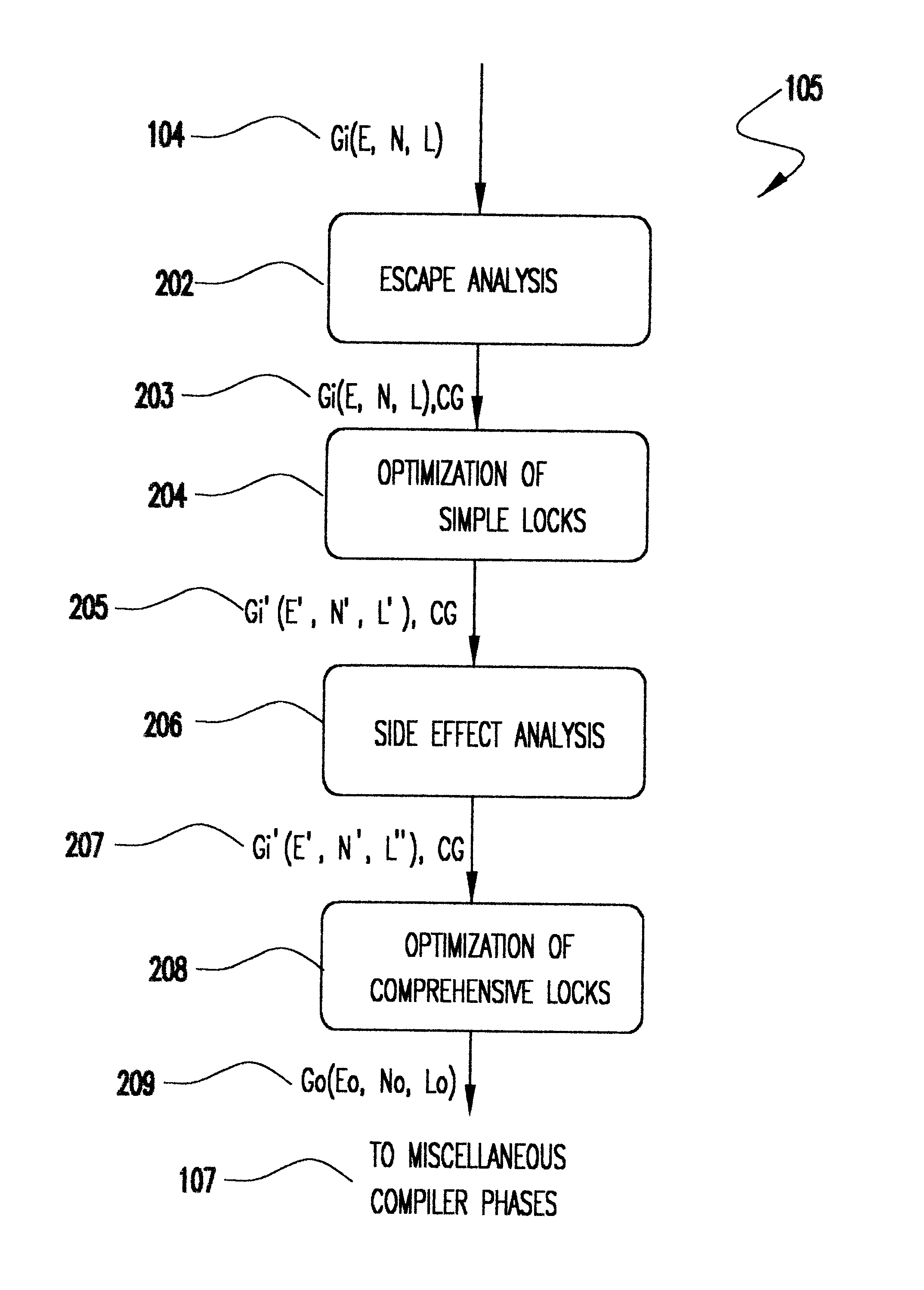
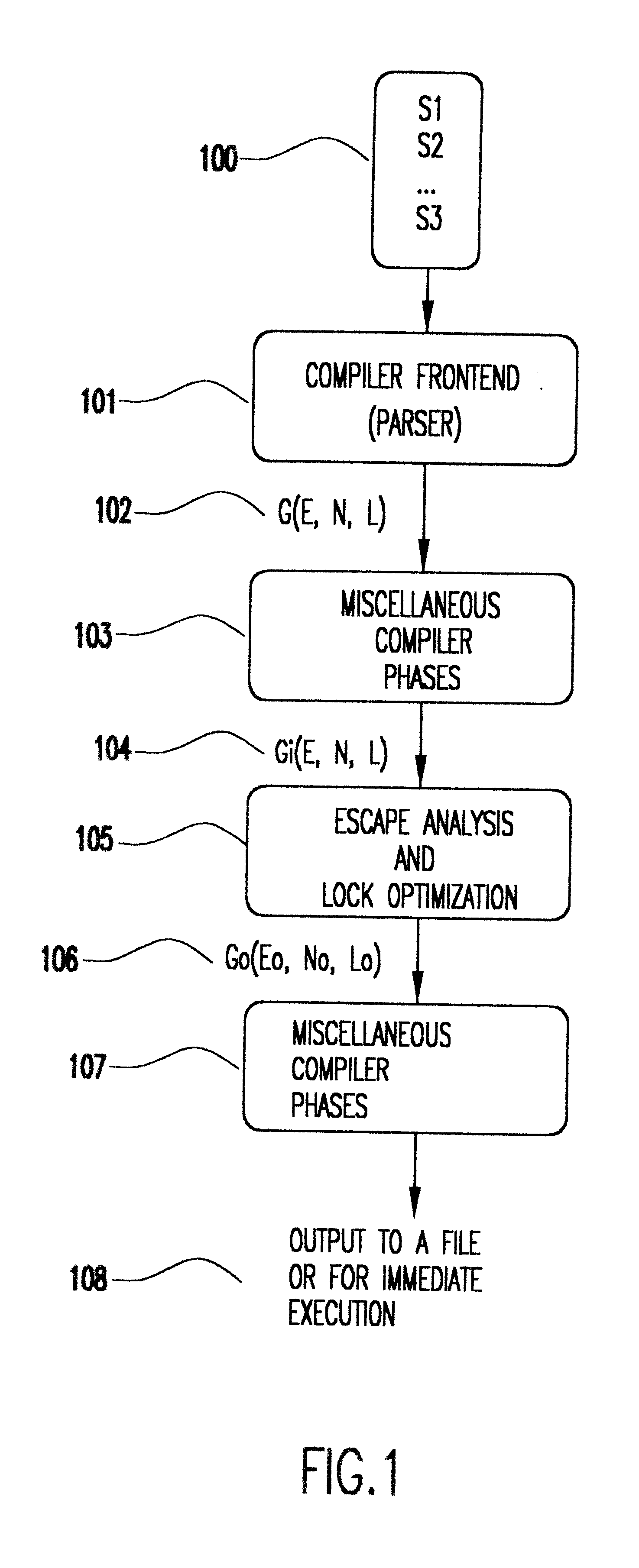
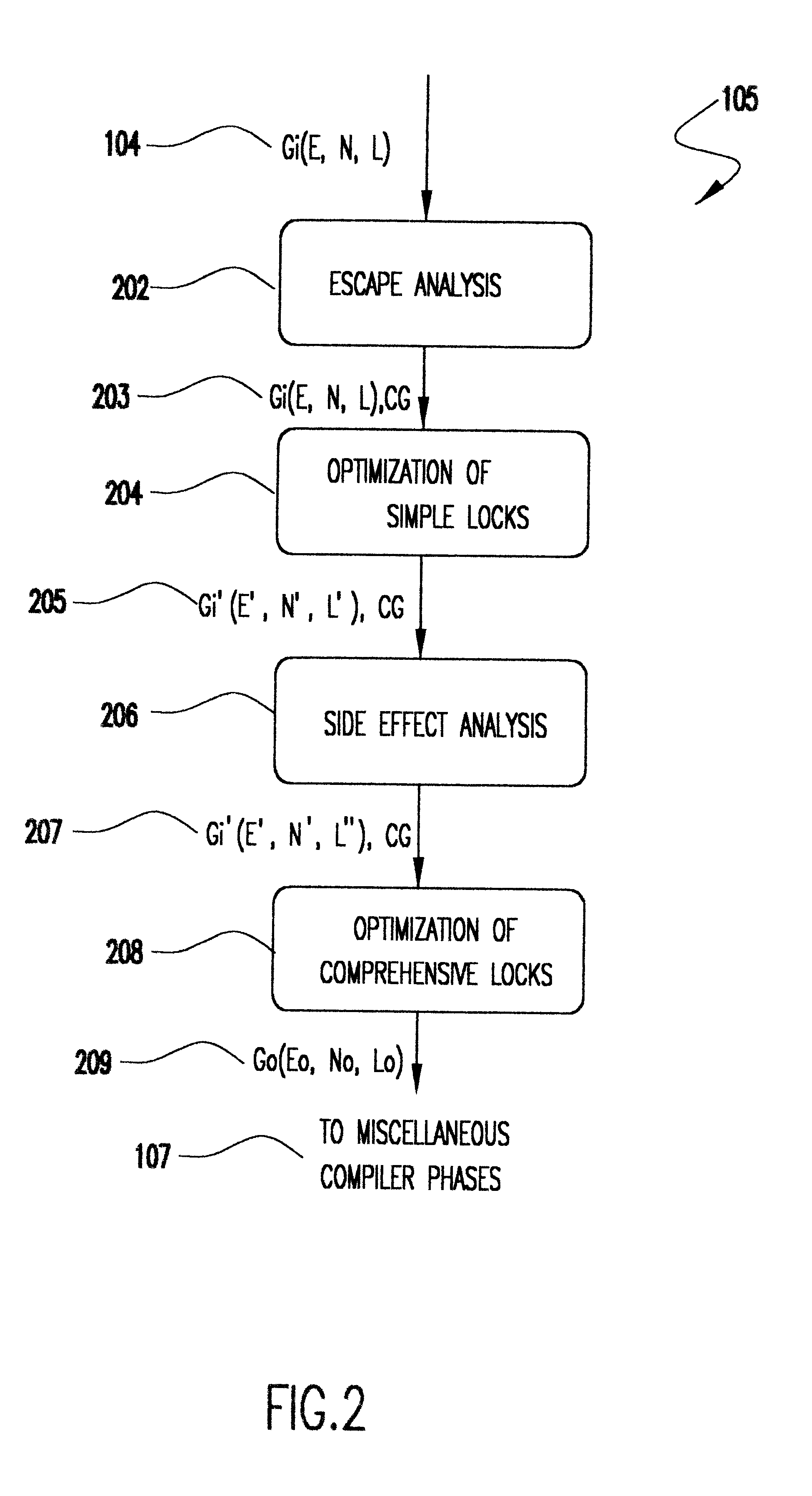
Method for optimizing locks in computer programs
InactiveUS6530079B1Easy to operateProgram synchronisationSoftware engineeringProgram planningSemantics
A method and several variants for using information about the scope of access of objects acted upon by mutual exclusion, or mutex, locks to transform a computer program by eliminating locking operations from the program or simplifying the locking operations, while strictly performing the semantics of the original program. In particular, if it can be determined by a compiler that the object locked can only be accessed by a single thread it is not necessary to perform the "acquire" or "release" part of the locking operation, and only its side effects must be performed. Likewise, if it can be determined that the side effects of a locking operation acting on a variable which is locked in multiple threads are not needed, then only the locking operation, and not the side effects, needs to be performed. This simplifies the locking operation, and leads to faster programs which use fewer computer processor resources to execute; and programs which perform fewer shared memory accesses, which in turn not only causes the optimized program, but also other programs executing on the same computing machine to execute faster. The method also describes how information about the semantics of the locking operation side effects and the information about the scope of access can also be used to eliminate performing the side effect parts of the locking operation, thereby completely eliminating the locking operation. The method also describes how to analyze the program to compute the necessary information about the scope of access. Variants of the method show how one or several of the features of the method may be performed.
Owner:IBM CORP
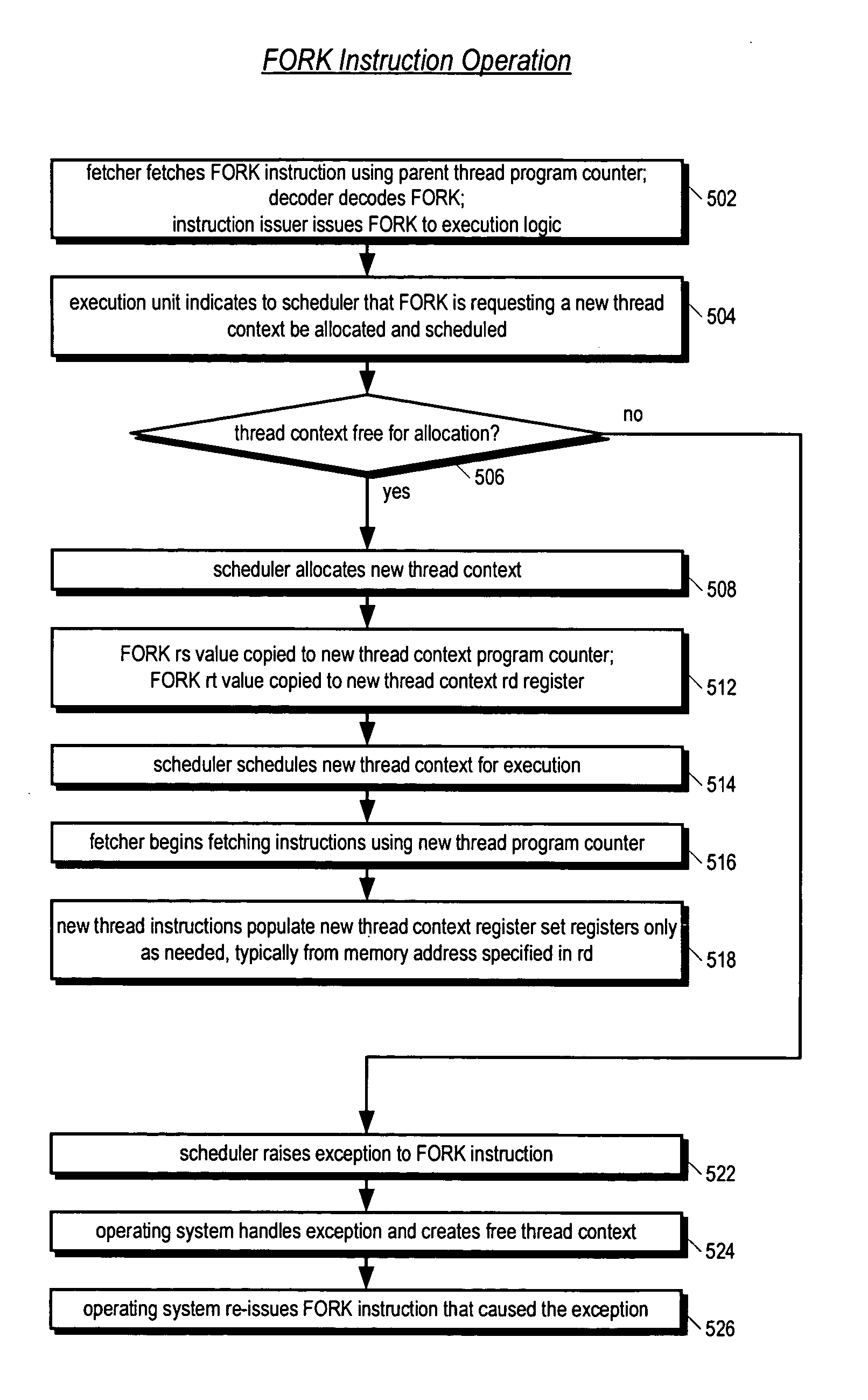
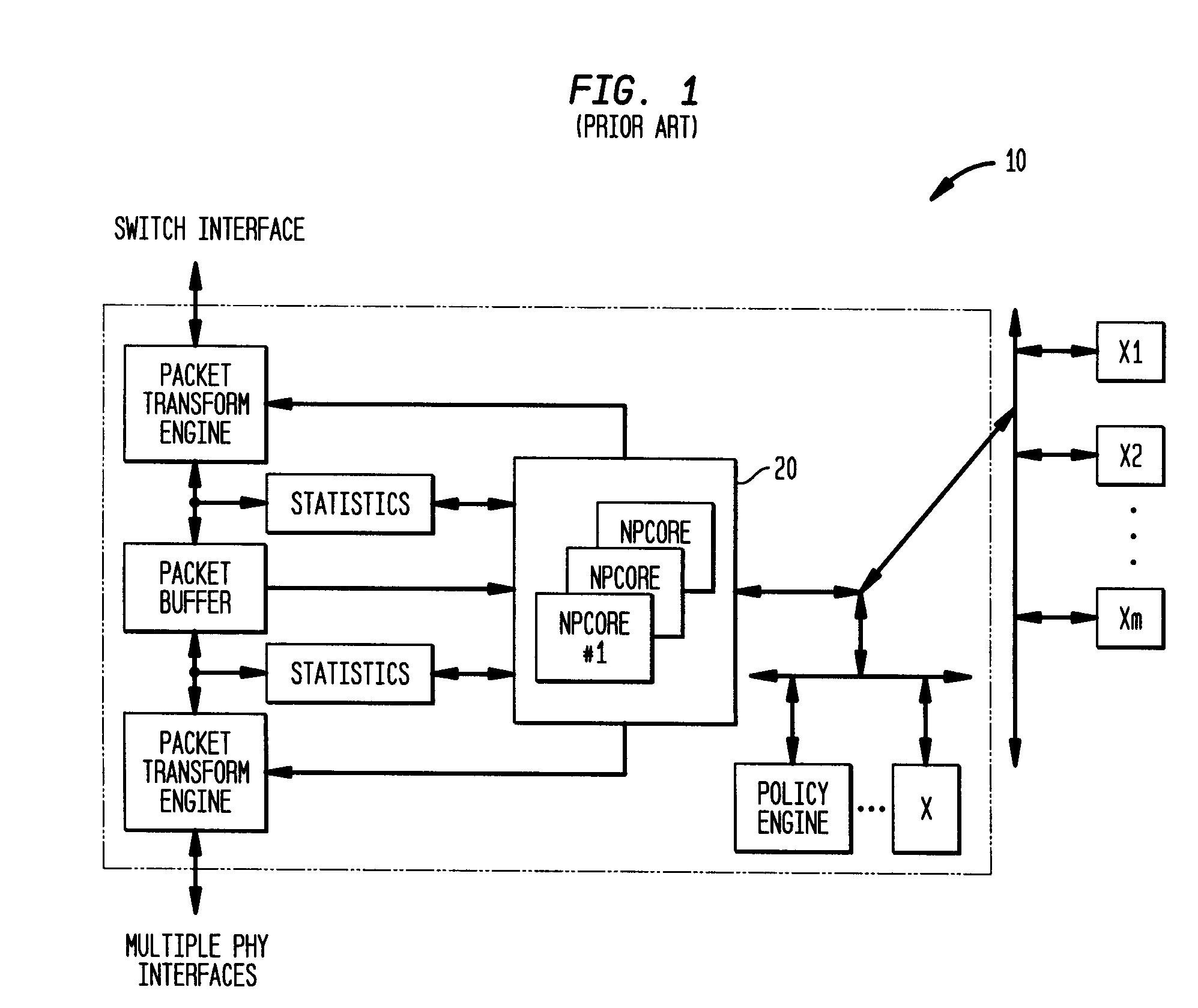
Apparatus, method, and instruction for initiation of concurrent instruction streams in a multithreading microprocessor
ActiveUS20050120194A1Reduce overheadAvoid wasting energyProgram initiation/switchingSoftware engineeringGeneral purposeComputer architecture
A fork instruction for execution on a multithreaded microprocessor and occupying a single instruction issue slot is disclosed. The fork instruction, executing in a parent thread, includes a first operand specifying the initial instruction address of a new thread and a second operand. The microprocessor executes the fork instruction by allocating context for the new thread, copying the first operand to a program counter of the new thread context, copying the second operand to a register of the new thread context, and scheduling the new thread for execution. If no new thread context is free for allocation, the microprocessor raises an exception to the fork instruction. The fork instruction is efficient because it does not copy the parent thread general purpose registers to the new thread. The second operand is typically used as a pointer to a data structure in memory containing initial general purpose register set values for the new thread.
Owner:MIPS TECH INC
Multitask process monitoring method and system in distributed system environment
ActiveCN102360310AEfficient parallel processingGood for load balancingResource allocationFiltrationMonitoring system
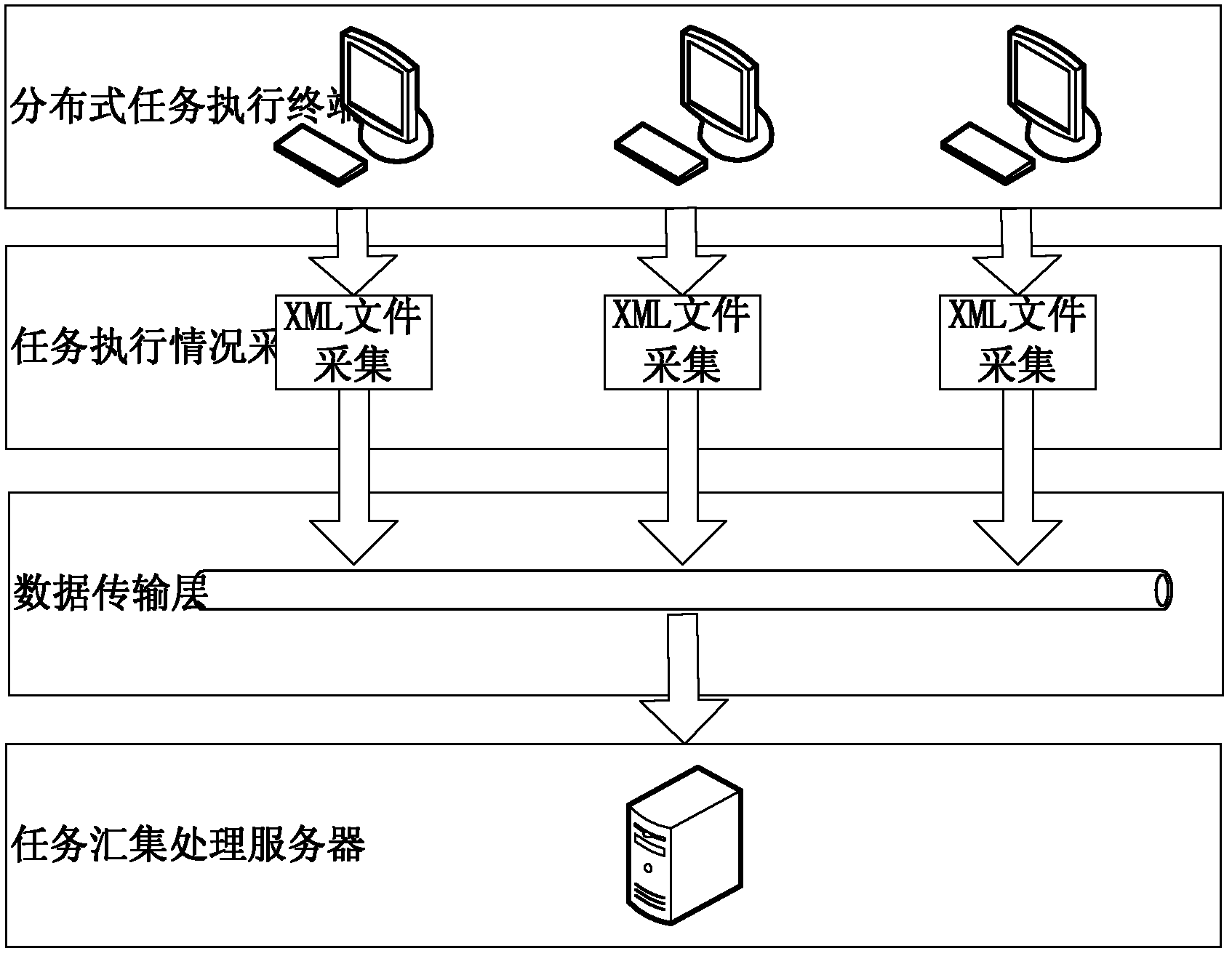
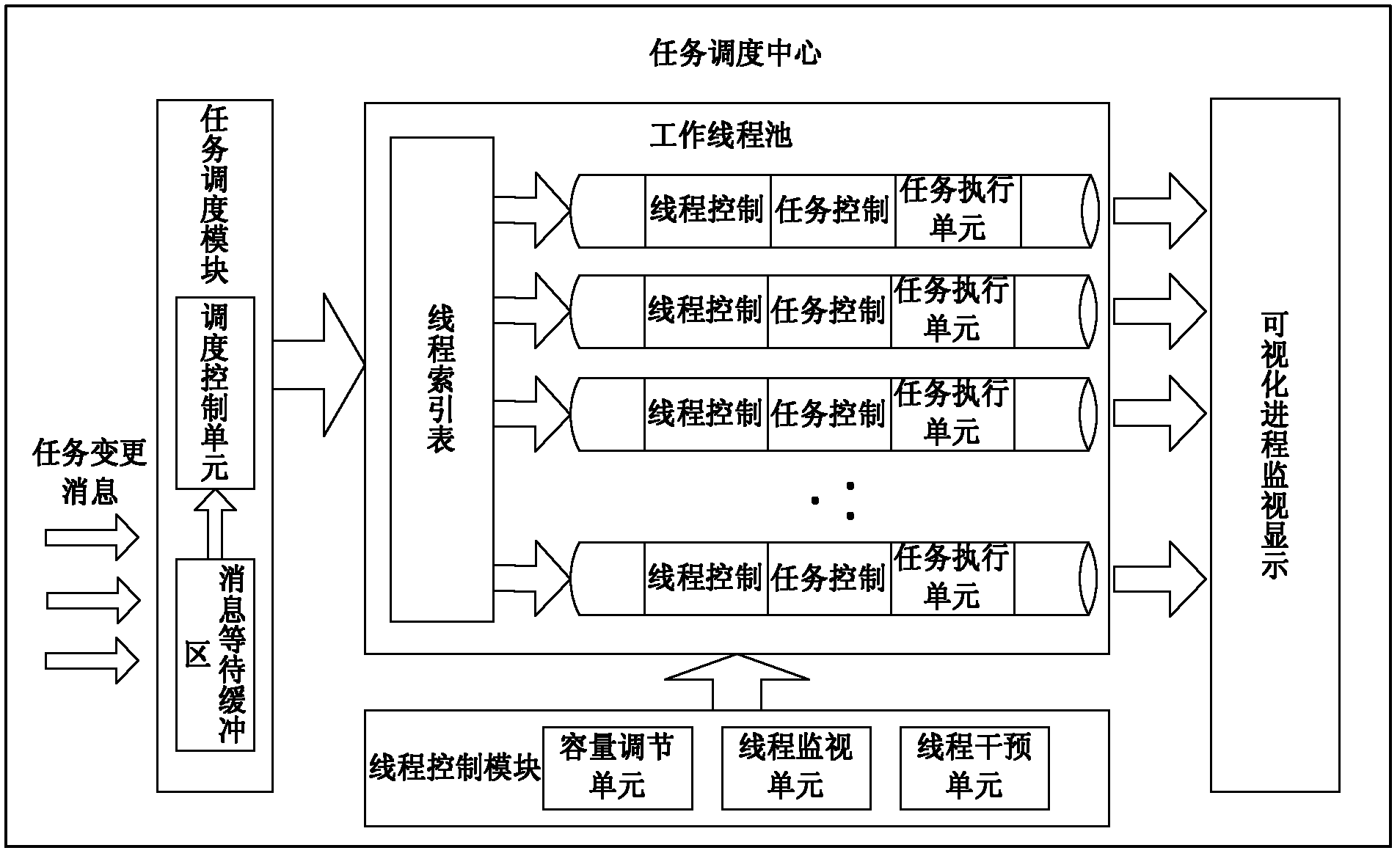
The invention discloses a multitask process monitoring method in the distributed system environment. The method comprises the following steps that: five states of the task execution process of each task execution terminal in the distributed system environment are monitored; an XML (eXtensible markup language) format description file is transported to a task collecting and processing server, the task execution conditions after filtration are written in a database and simultaneously task change information is sent to notify a task scheduling center; the task scheduling center directly submits the information to a task scheduling module after receiving the task change information and the task scheduling module adds the received information to information waiting queues; a scheduling control unit searches for a thread index table for threads of execution of the task and gives the threads of execution to the threads to be executed; and a thread control module monitors a plurality of threads in a work thread pool in real time in the system operation process. The invention also discloses a multitask process monitoring system. The system comprises a plurality of distributed task execution terminals, the task collecting and processing server and the task scheduling center.
Owner:THE 28TH RES INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GROUP CORP
System and method for multi-dimensional organization, management, and manipulation of data
ActiveUS7433885B2Data processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsScripting languageFile system
The Quantum Matrix system is a multi-dimensional, multi-threaded exchange environment for data organization, management, and manipulation. Data is organized into a multi-dimensional structure of nodes. Nodes may represent data, absence of data, or another set of nodes. The multi-dimensional structure or portions of it can be automatically created from a file system. One or more associations are also defined for the multi-dimensional structure. An association indicates a relationship between a node and another node, data, or a set of nodes. The multi-dimensional structure is then displayed three-dimensionally and navigated. Relational logic, Boolean algebra, or a scripting language can be applied to the nodes, data, and associations to produce a resultant set of nodes. Furthermore, portions of the multi-dimensional structure can be isolated with the use of planes to ease navigation. Furthermore, Avatars may be displayed and used for collaborative purposes and to automate the navigation of the multi-dimensional structure.
Owner:QUANTUM MATRIX HLDG
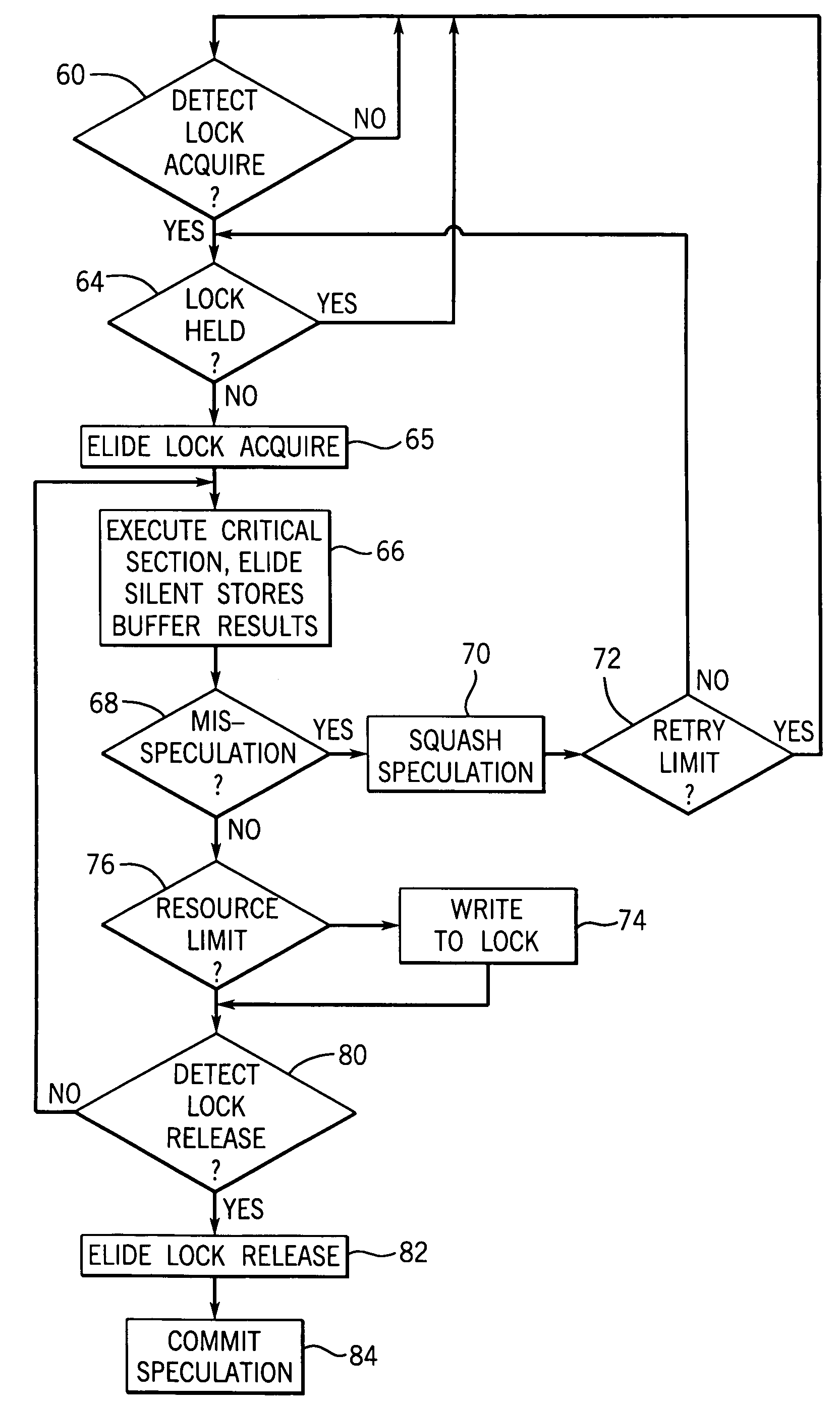
Concurrent execution of critical sections by eliding ownership of locks
ActiveUS7120762B2Ensure correct executionEfficient executionMemory architecture accessing/allocationProgram synchronisationSpeculative executionCritical section
Critical sections of multi-threaded programs, normally protected by locks providing access by only one thread, are speculatively executed concurrently by multiple threads with elision of the lock acquisition and release. Upon a completion of the speculative execution without actual conflict as may be identified using standard cache protocols, the speculative execution is committed, otherwise the speculative execution is squashed. Speculative execution with elision of the lock acquisition, allows a greater degree of parallel execution in multi-threaded programs with aggressive lock usage.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
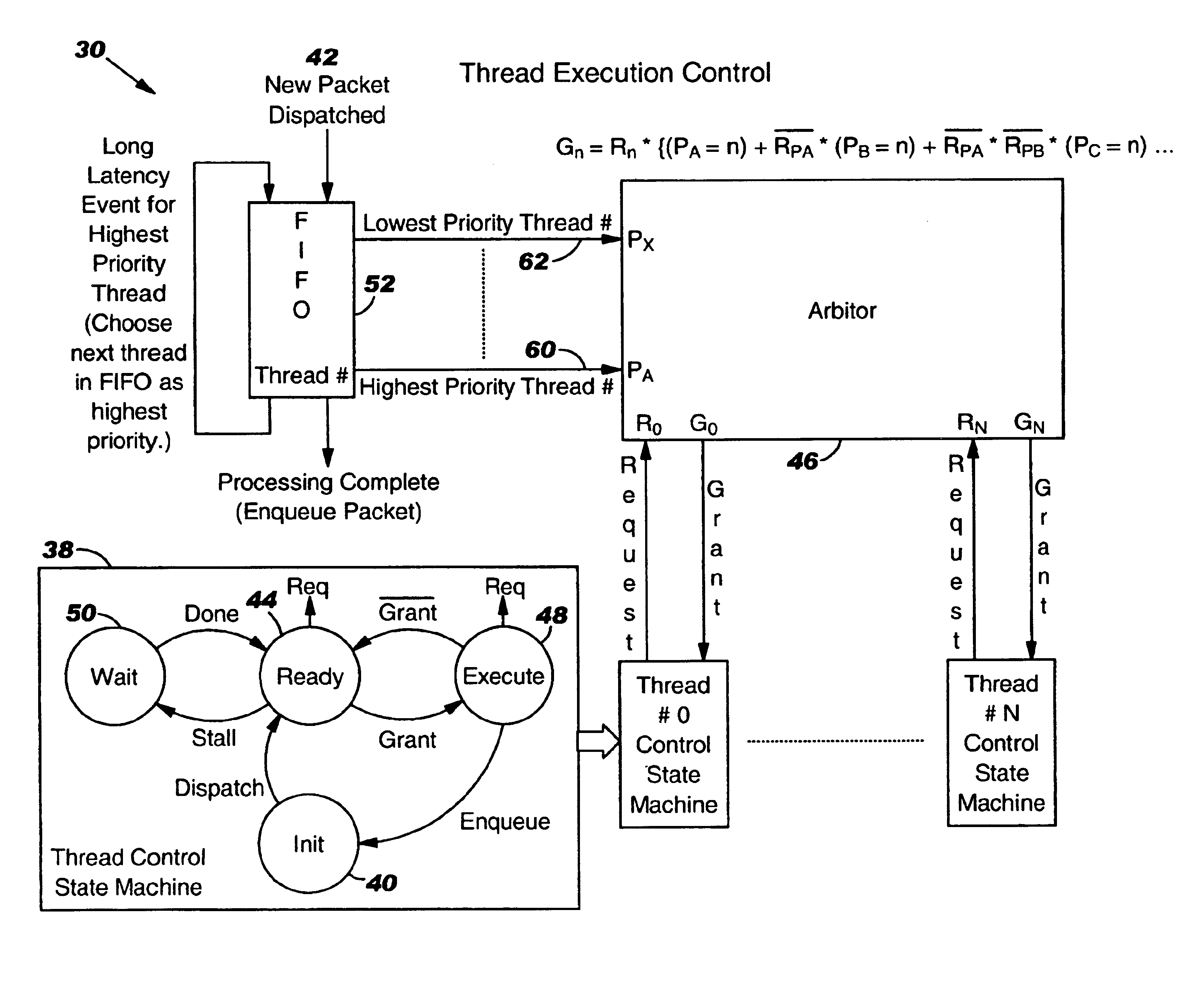
Controller for multiple instruction thread processors
InactiveUS6931641B1Efficient comprehensive utilizationProgram initiation/switchingProgram synchronisationFistLong latency
A mechanism controls a multi-thread processor so that when a fist thread encounters a latency event to a first predefined time interval temporary control is transferred to an alternate execution thread for duration of the first predefined time interval and then back to the original thread. The mechanism grants full control to the alternate execution thread when a latency event for a second predefined time interval is encountered. The first predefined time interval is termed short latency event whereas the second time interval is termed long latency event.
Owner:INTEL CORP
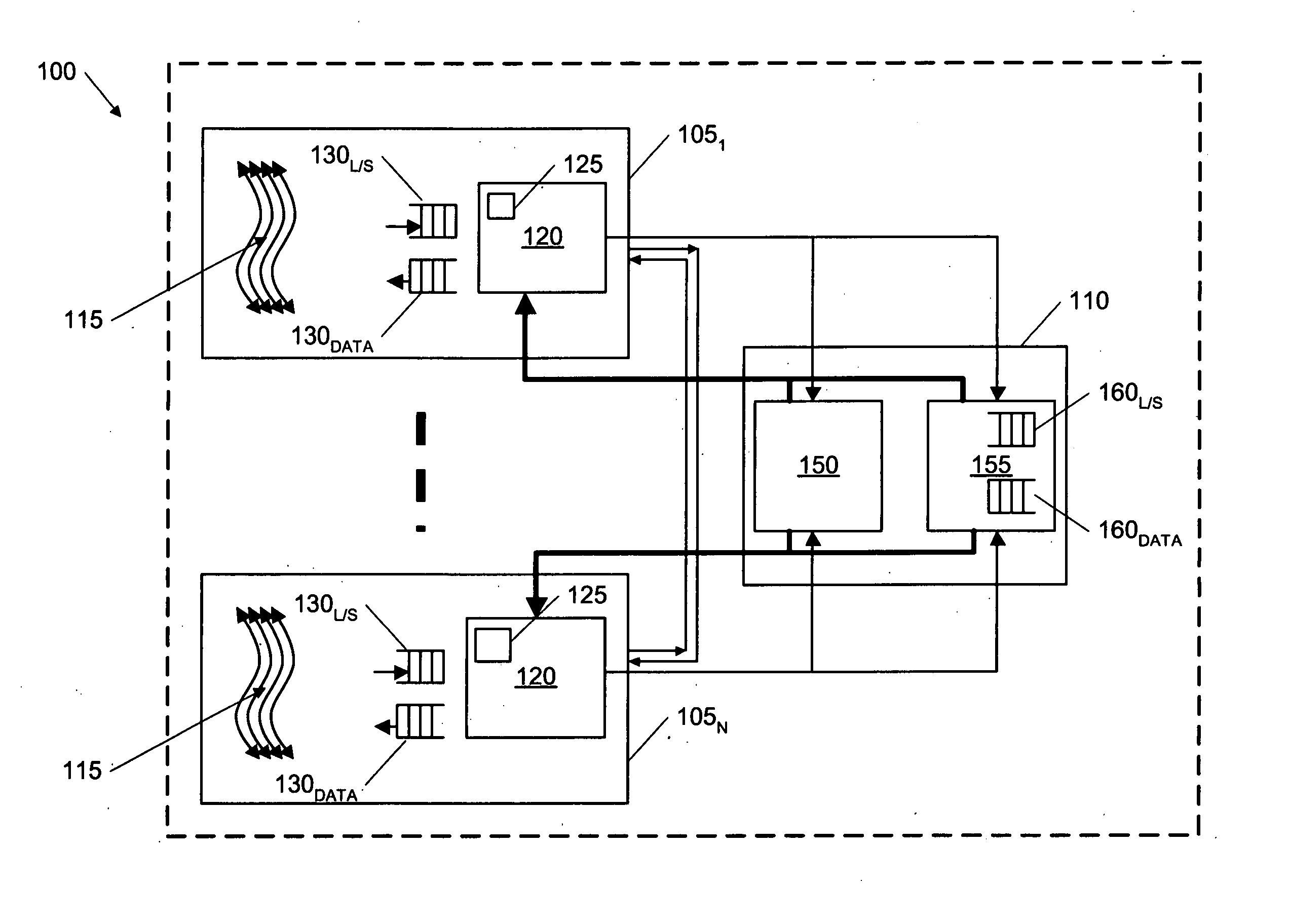
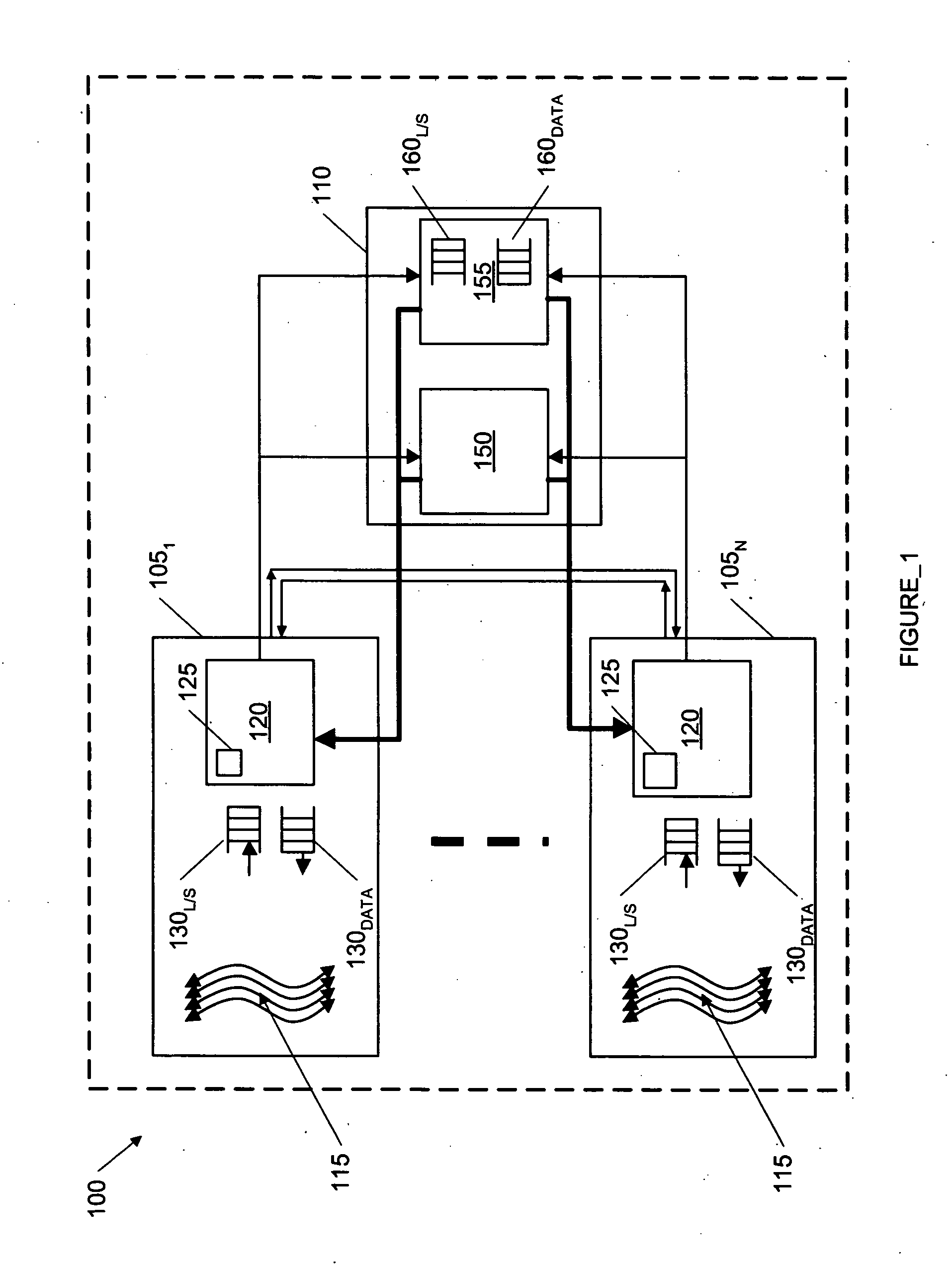
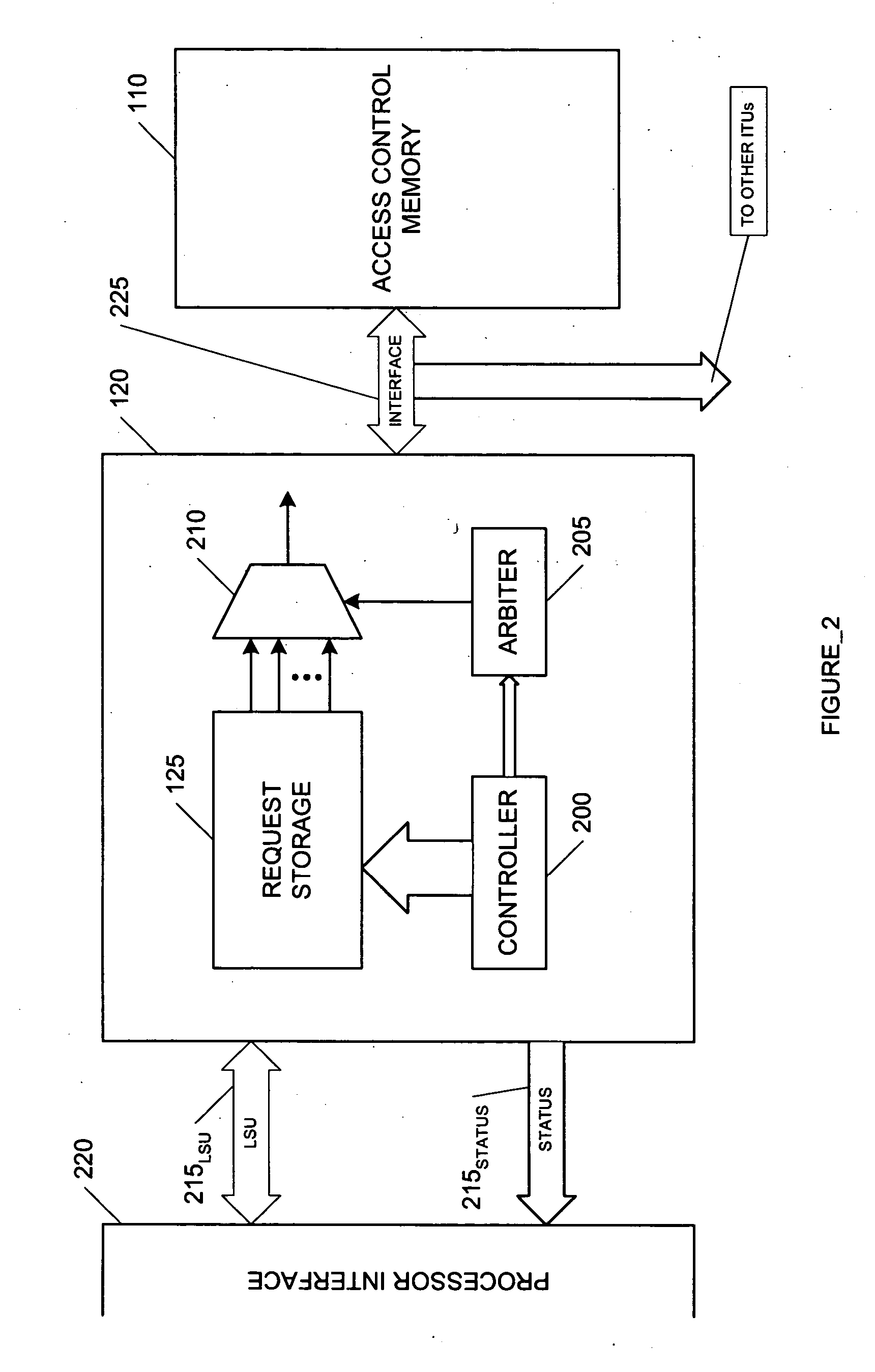
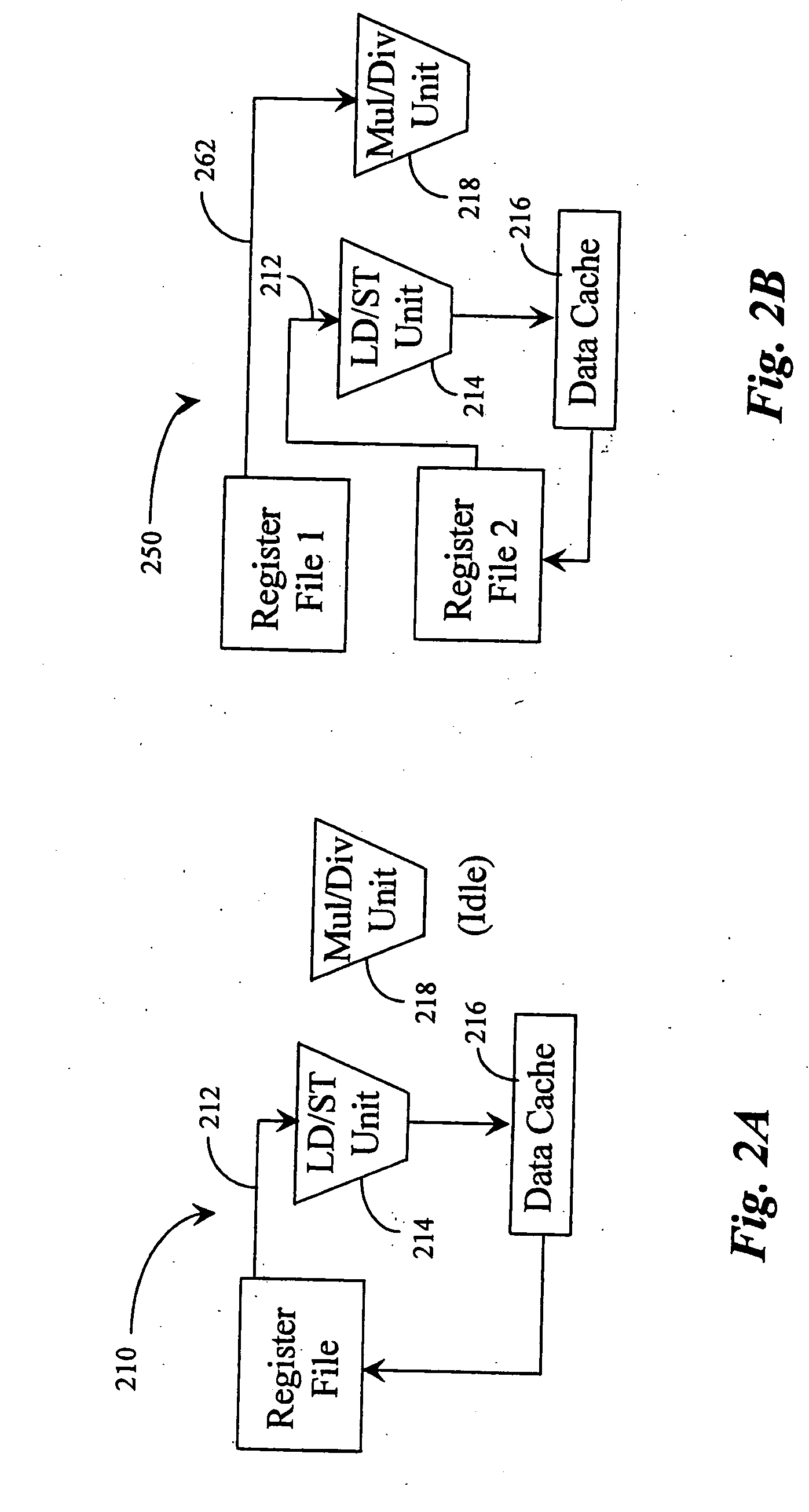
Smart memory based synchronization controller for a multi-threaded multiprocessor SoC
A memory interface for use with a multiprocess memory system having a gating memory, the gating memory associating one or more memory access methods with each of a plurality of memory locations of the memory system wherein the gating memory returns a particular one access method for a particular one memory location responsive to a memory access instruction relating to the particular one memory location, the interface including: a request storage for storing a plurality of concurrent memory access instructions for one or more of the particular memory locations, each the memory access instruction issued from an associated independent thread context; an arbiter, coupled to the request storage, for selecting a particular one of the memory access instructions to apply to the gating memory; and a controller, coupled to the request storage and to the arbiter, for: storing the plurality of memory access instructions in the request storage; initiating application of the particular one memory access instruction selected by the arbiter to the gating memory; receiving the particular one access method associated with the particular one memory access method from the gating memory; and initiating a communication of the particular access method to the thread context associated with the particular one access instruction.
Owner:MIPS TECH INC
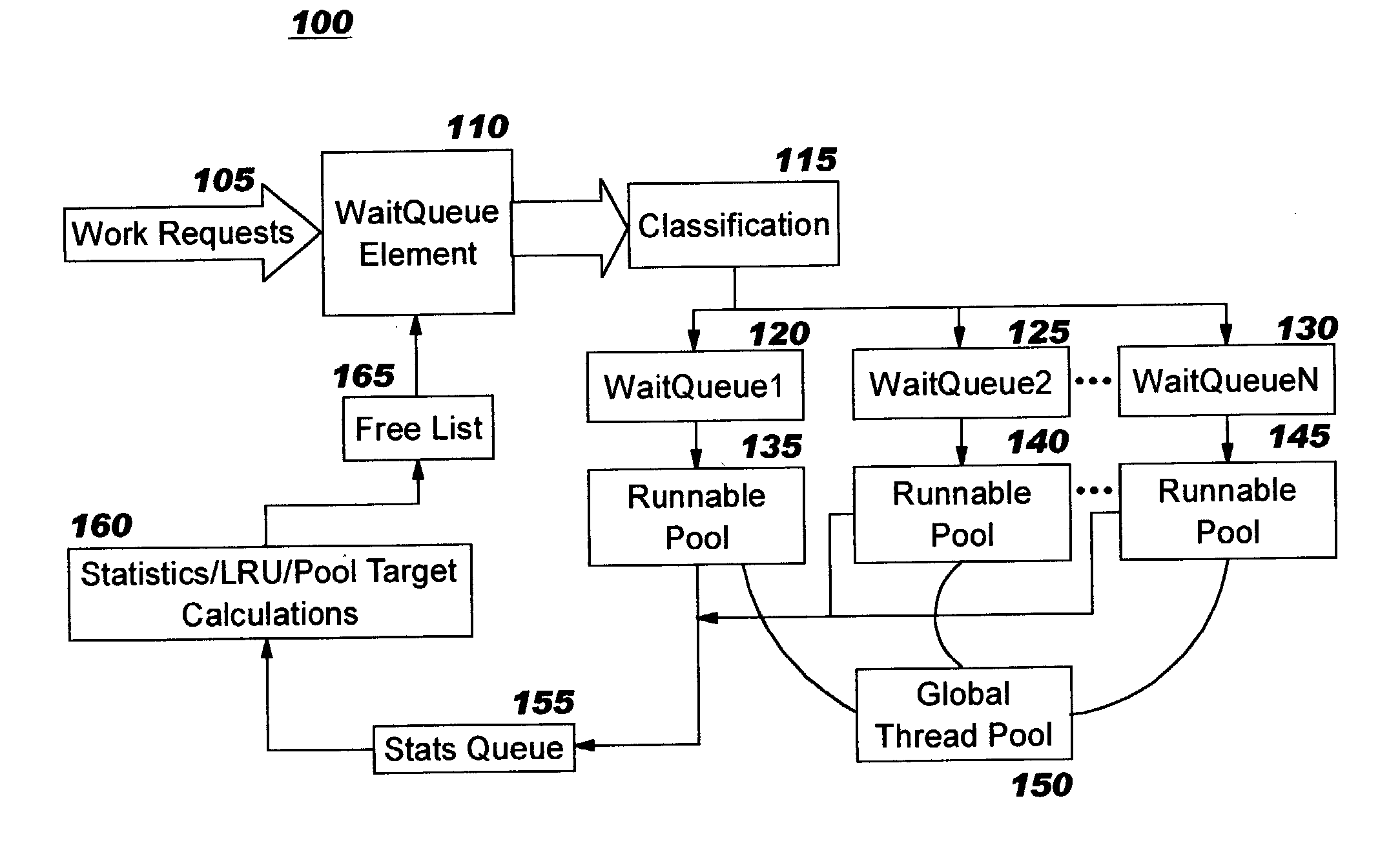
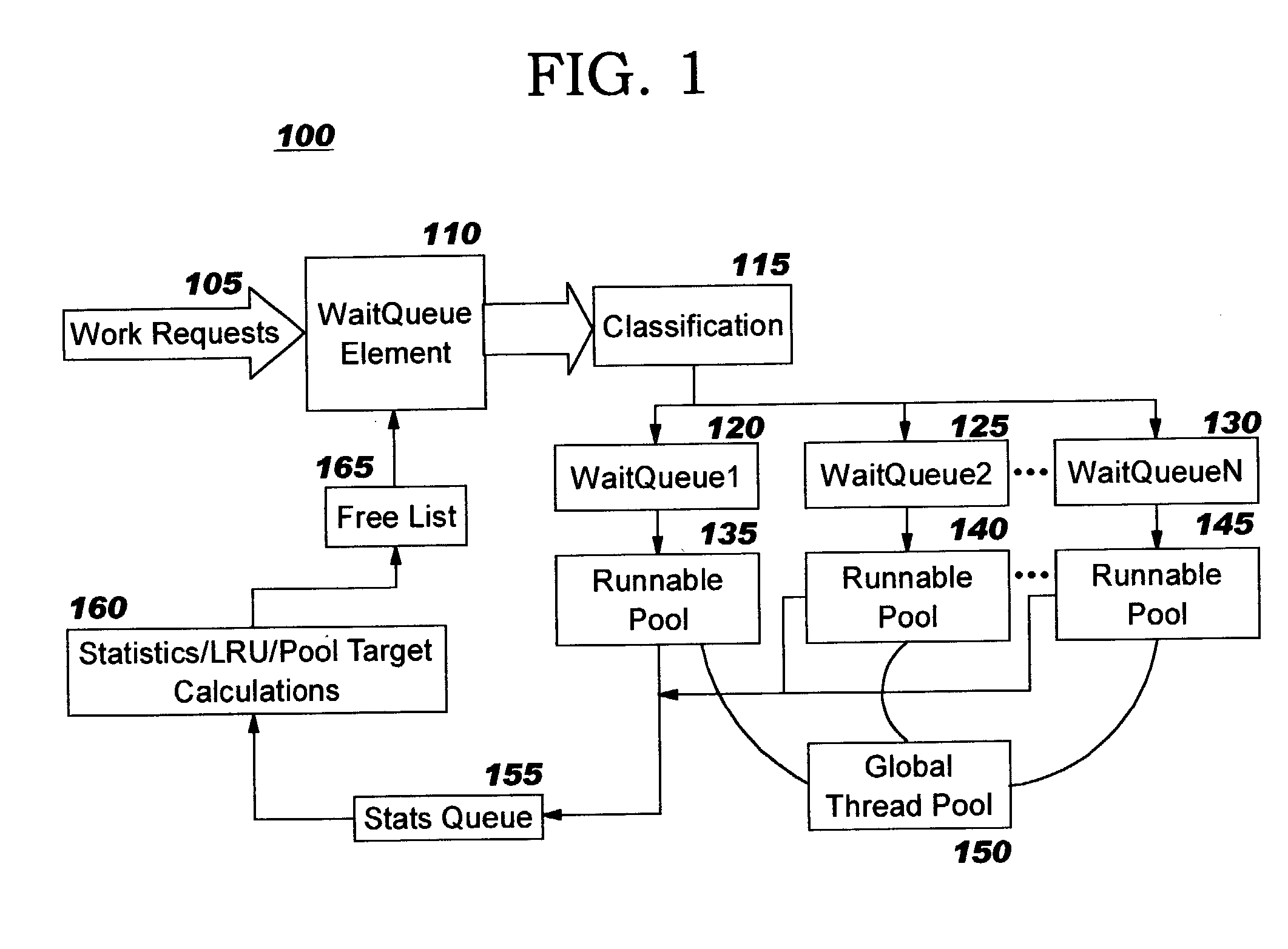
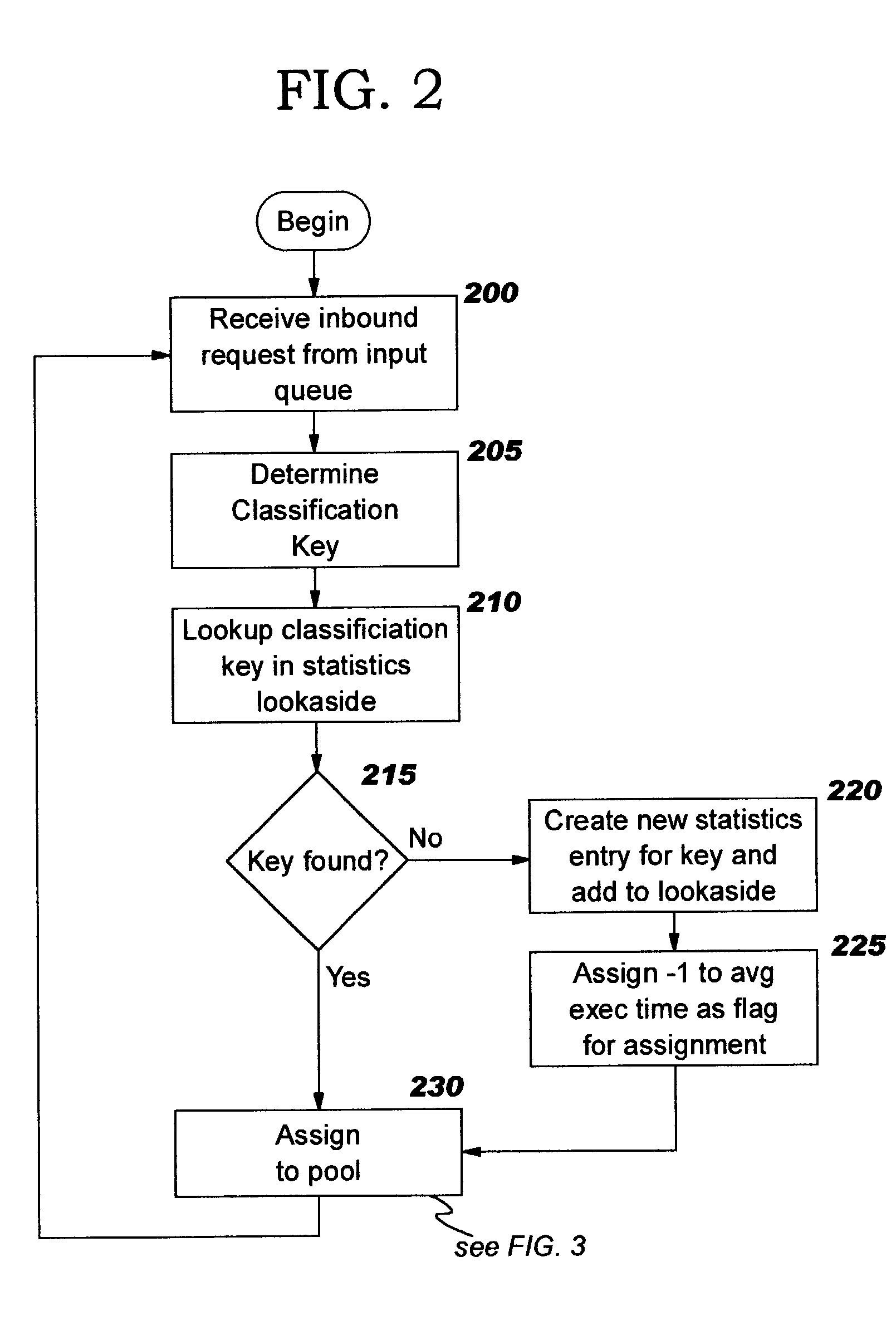
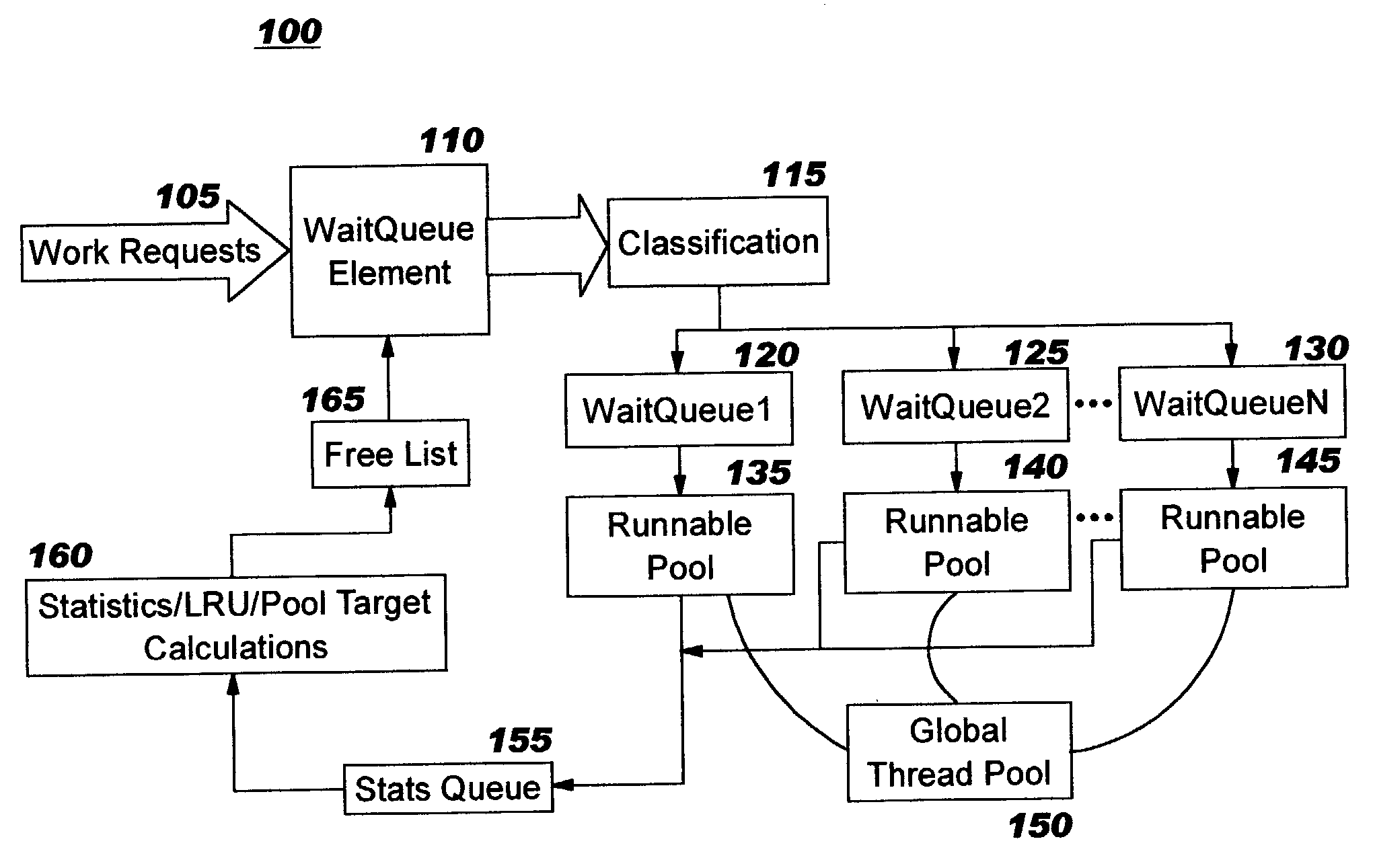
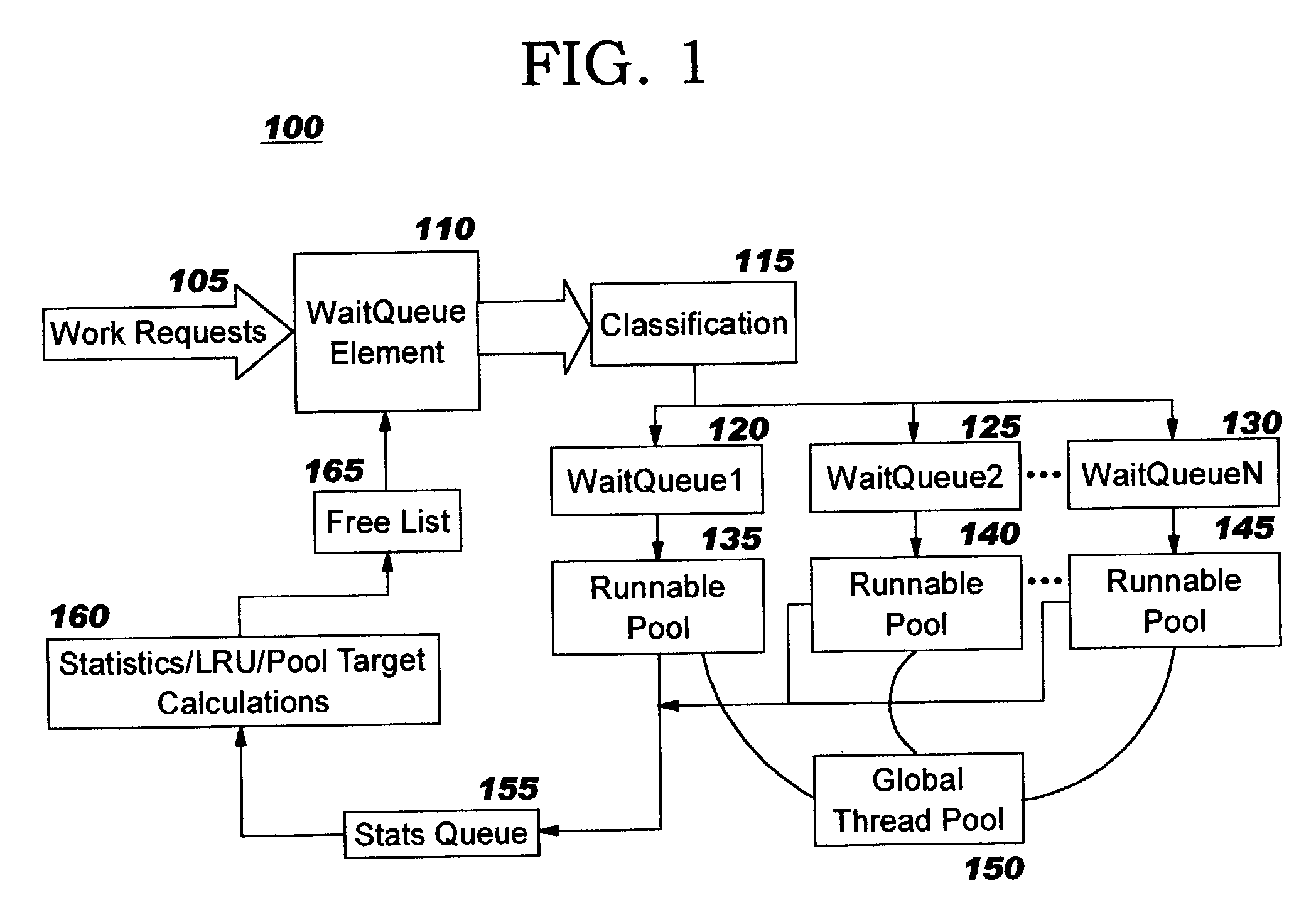
Dynamic thread pool tuning techniques
InactiveUS20040139434A1Improve performanceSimple technologyProgram initiation/switchingResource allocationParallel computingEngineering
Thread pools in a multithreaded server are programmatically adjusted, based on observed statistics from the server's inbound workload. In a multithreaded server environment, response time to end users is improved while increasing the efficiency of software execution and resource usage. Execution time and wait / queued time are tracked, for various types of requests being serviced by a server. Multiple logical pools of threads are used to service these requests, and inbound requests are directed to a selected one of these pools such that requests of similar execution-time requirements are serviced by the threads in that pool. The number and size of thread pools may be adjusted programmatically, and the distribution calculation (i.e., determining which inbound requests should be assigned to which pools) is a programmatic determination. In preferred embodiments, only one of these variables is adjusted at a time, and the results are monitored to determine whether the effect was positive or negative. The disclosed techniques also apply to tracking and classifying requests by method name (and, optionally, parameters).
Owner:IBM CORP
Integrated mechanism for suspension and deallocation of computational threads of execution in a processor
ActiveUS20050125795A1Valuable opcode spaceLittle overheadProgram initiation/switchingSoftware engineeringOperandProgram Thread
A yield instruction for execution in a multithreaded microprocessor is disclosed. The yield instruction includes an operand. If the operand is zero the microprocessor terminates the program thread including the yield instruction. If the operand is −1 the microprocessor unconditionally reschedules the program thread. If the operand is a positive integer the microprocessor views the operand as a bit vector specifying one or more yield qualifier inputs, such as interrupt signals, and conditionally reschedules the thread based on the qualifier inputs and bit vector values. The microprocessor also includes a mask register that specifies a bit vector of the qualifier inputs. If the operand specifies a qualifier input not also specified in the mask register, an exception to the instruction is raised. The instruction returns a value specifying the values of the qualifier inputs qualified by the mask register value.
Owner:MIPS TECH INC
Inter-thread communications using shared interrupt register
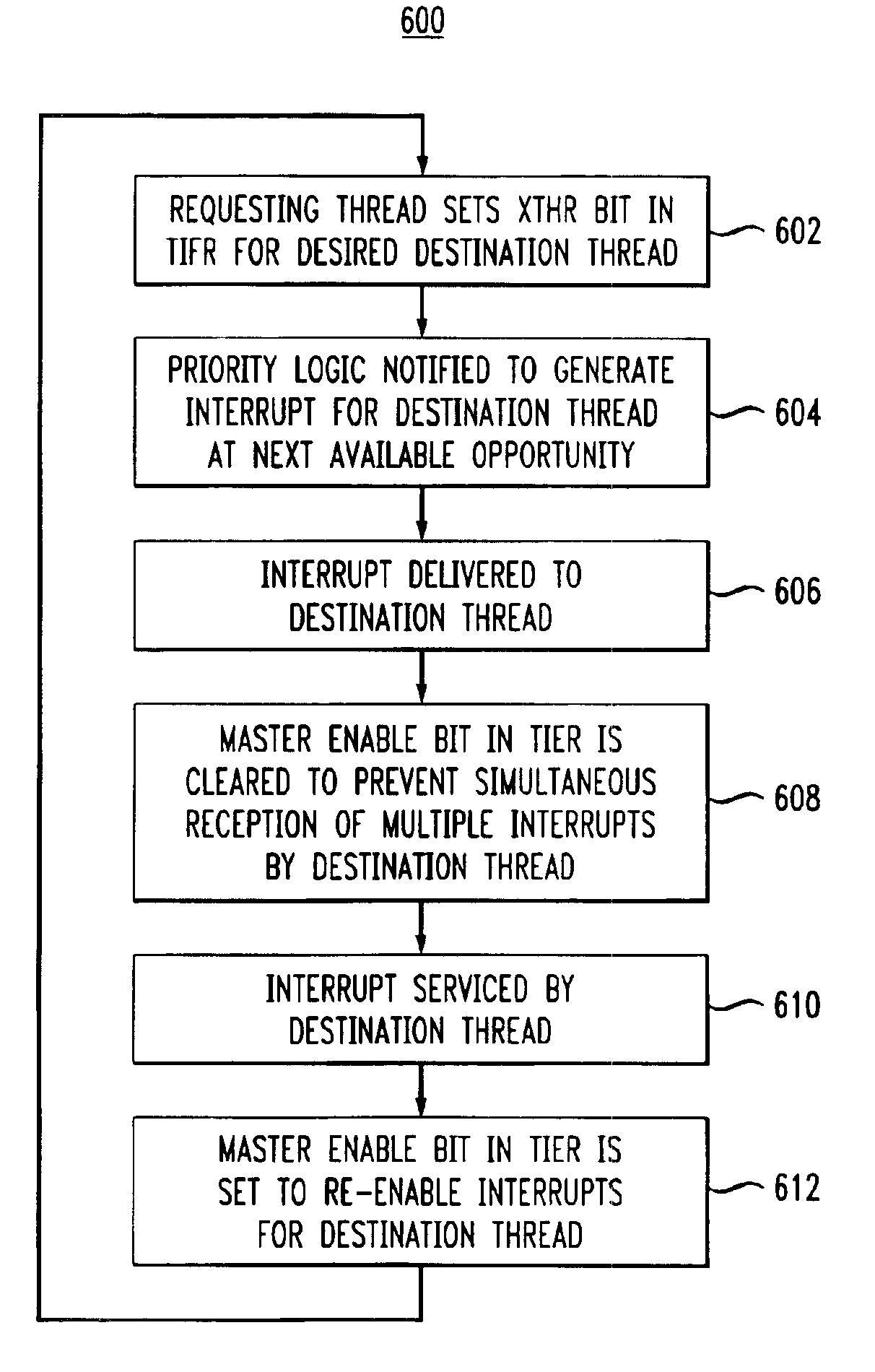
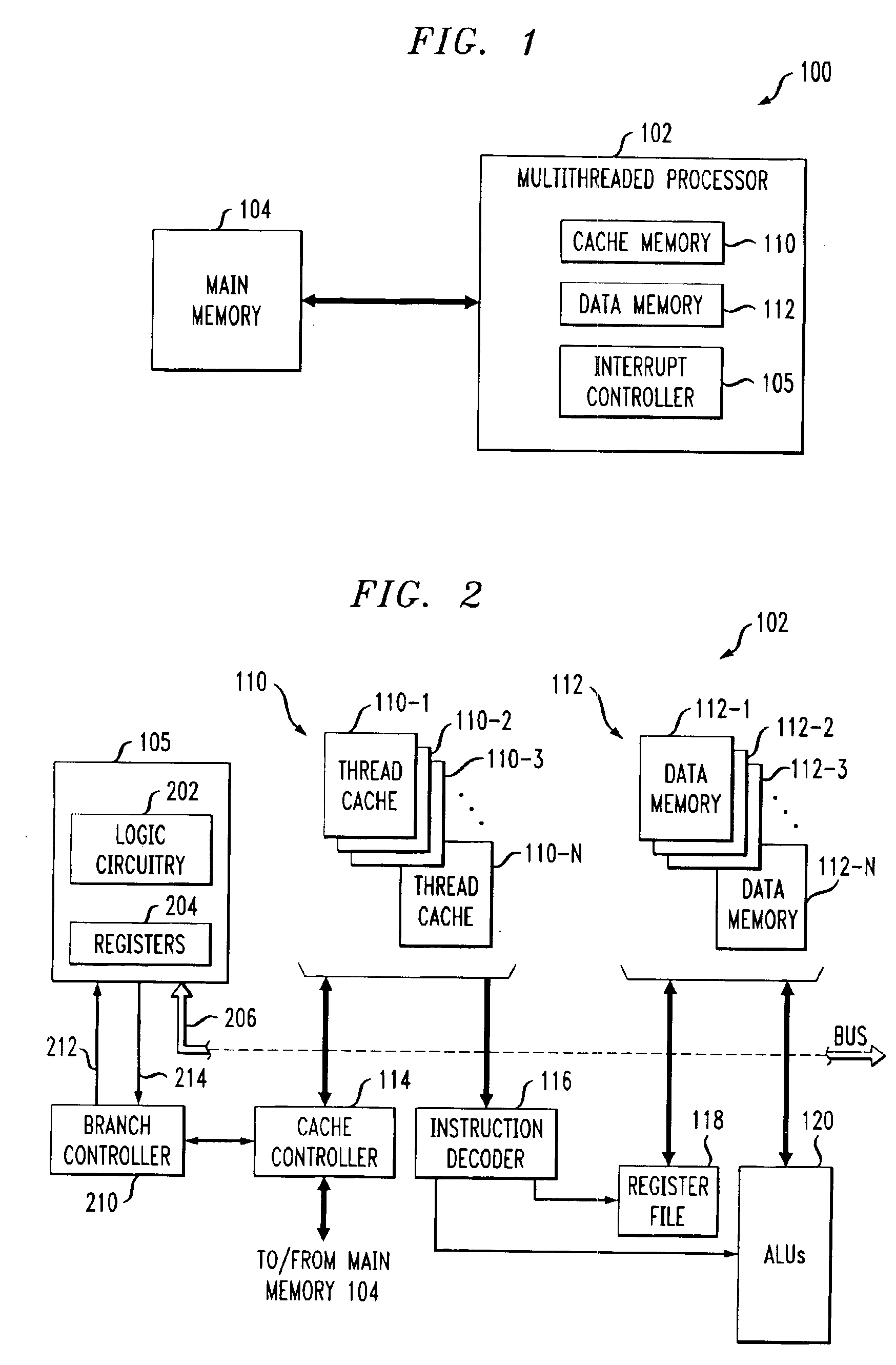
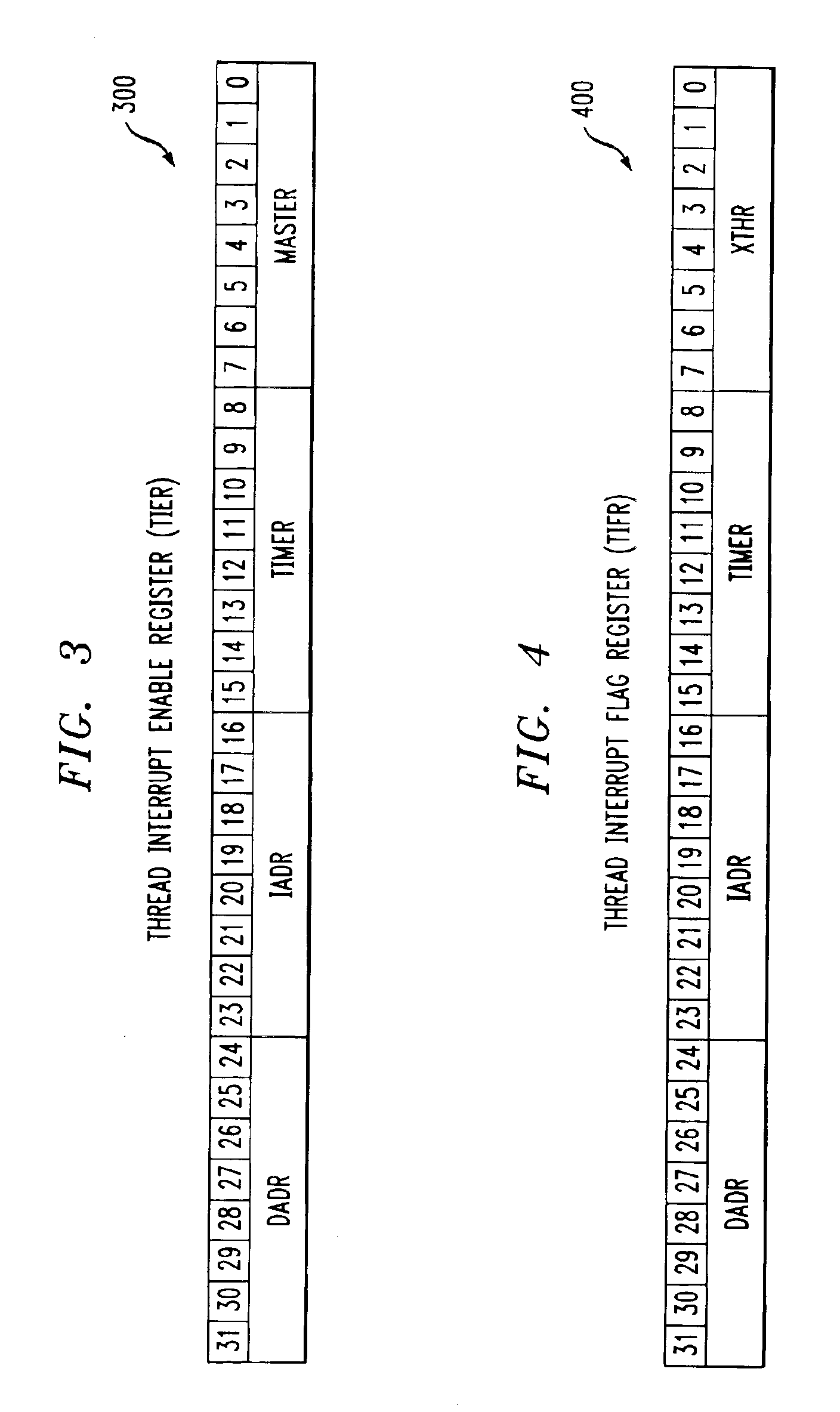
InactiveUS6971103B2Reduce overheadProgram initiation/switchingDigital computer detailsProcessor registerFLAGS register
A multithreaded processor includes an interrupt controller for processing a cross-thread interrupt directed from a requesting thread to a destination thread. The interrupt controller in an illustrative embodiment receives a request for delivery of the cross-thread interrupt to the destination thread, determines whether the destination thread of the cross-thread interrupt is enabled for receipt of cross-thread interrupts, and utilizes a thread identifier to control delivery of the cross-thread interrupt to the destination thread if the destination thread is enabled for receipt of cross-thread interrupts. The requesting thread requests delivery of the cross-thread interrupt to the destination thread by setting a corresponding interrupt pending bit in a flag register of the multithreaded processor. The destination thread is enabled for receipt of cross-thread interrupts if a corresponding enable bit is set in an enable register of the multithreaded processor. The flag and enable registers may be implemented within the interrupt controller.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Self-contained processor subsystem as component for system-on-chip design
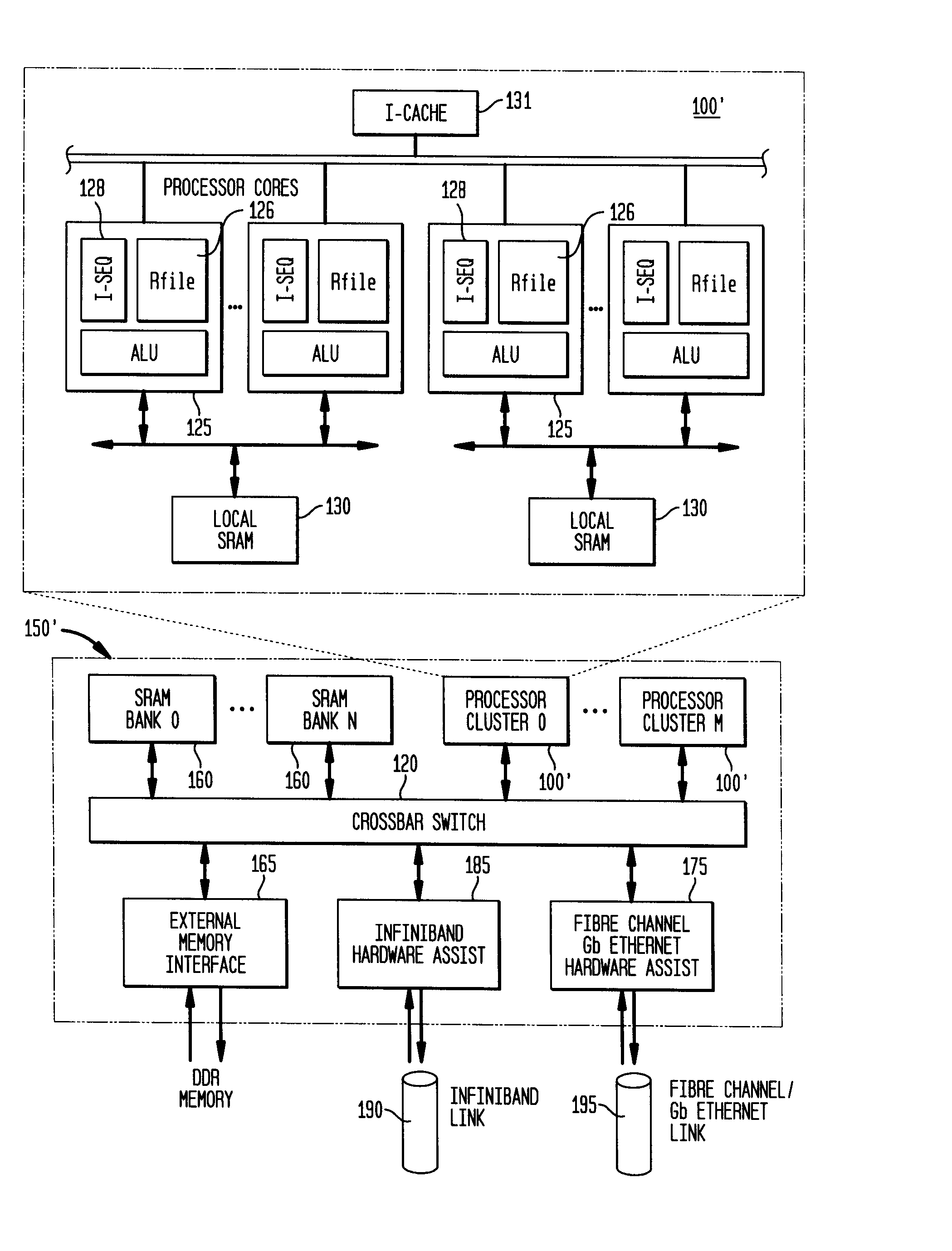
ActiveUS20050021871A1Processor speed be improveCache latency be reduceMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionLocal memoriesSwitched fabric
A System-on-Chip (SoC) component comprising a single independent multiprocessor subsystem core including a plurality of multiple processors, each multiple processor having a local memory associated therewith forming a processor cluster; and a switch fabric means connecting each processor cluster within an SoC integrated circuit (IC). The single SoC independent multiprocessor subsystem core is capable of performing multi-threading operation processing for SoC devices when configured as a DSP, coprocessor, Hybrid ASIC, or network processing arrangements. The switch fabric means additionally interconnects a SoC local system bus device with SoC processor components with the independent multiprocessor subsystem core.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
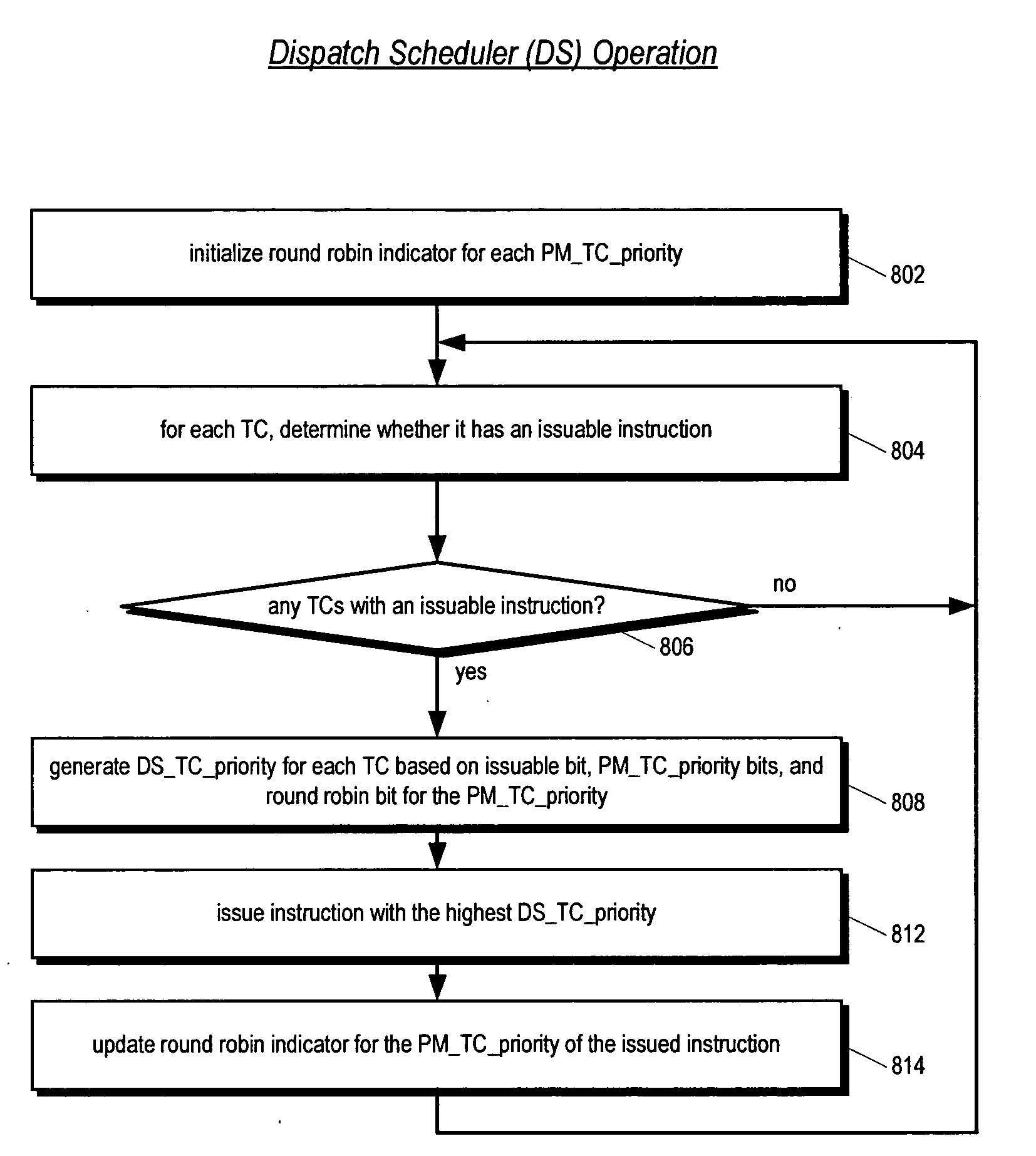
Multithreading processor including thread scheduler based on instruction stall likelihood prediction
ActiveUS20060179280A1Increase processor efficiencyReduce in quantityDigital computer detailsMultiprogramming arrangementsLoad instructionScheduling instructions
An apparatus for scheduling dispatch of instructions among a plurality of threads being concurrently executed in a multithreading processor is provided. The apparatus includes an instruction decoder that generate register usage information for an instruction from each of the threads, a priority generator that generates a priority for each instruction based on the register usage information and state information of instructions currently executing in an execution pipeline, and selection logic that dispatches at least one instruction from at least one thread based on the priority of the instructions. The priority indicates the likelihood the instruction will execute in the execution pipeline without stalling. For example, an instruction may have a high priority if it has little or no register dependencies or its data is known to be available; or may have a low priority if it has strong register dependencies or is an uncacheable or synchronized storage space load instruction.
Owner:ARM FINANCE OVERSEAS LTD
Mechanisms for assuring quality of service for programs executing on a multithreaded processor
ActiveUS7376954B2Program initiation/switchingError detection/correctionQuality of serviceProcessor register
A mechanism for assuring quality of service for a context in a digital processor has a first scheduling register dedicated to the context, the register having N out of M bits set, and a first scheduler that consults the register to assign issue slots to the context. The first scheduler grants issue slots for the context by referencing the N bits in the first register, and repeats a pattern of assignments of issue slots after referencing the M bits of the first register.
Owner:MIPS TECH INC
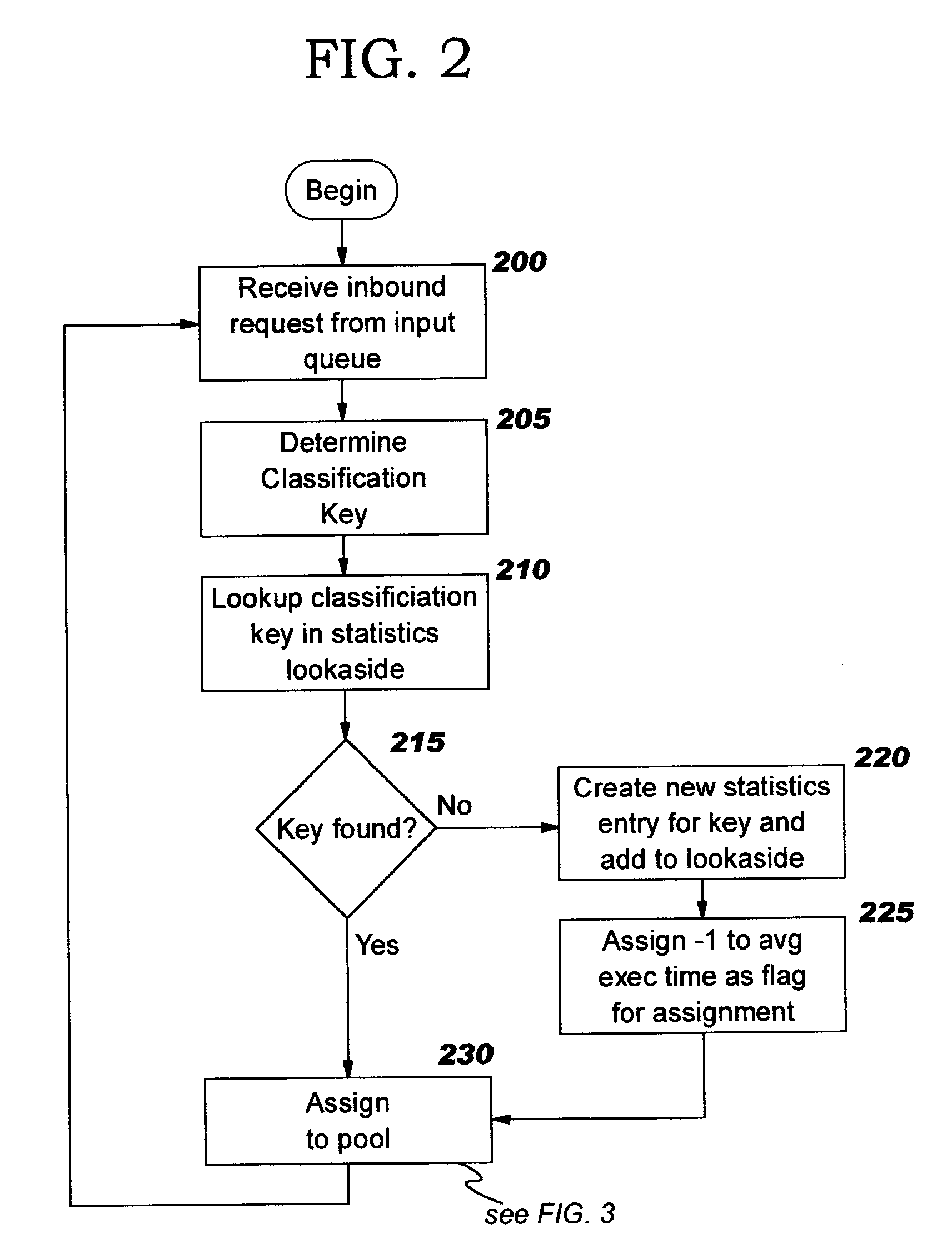
Programmatic response-time based workload distribution techniques
InactiveUS20040139433A1Improve performanceSimple technologyProgram initiation/switchingElectric devicesQueue timeWorkload
Workload is programmatically distributed across a set of execution resources. In a multithreaded server environment, response time to end users is improved while increasing the efficiency of software execution and resource usage. Execution time and wait / queued time are tracked, for various types of requests being serviced by a server. Multiple logical pools of threads are used to service these requests, and inbound requests are directed to a selected one of these pools such that requests of similar execution-time requirements are serviced by the threads in that pool. The number and size of thread pools may be adjusted programmatically, and the distribution calculation (i.e., determining which inbound requests should be assigned to which pools) is a programmatic determination. In preferred embodiments, only one of these variables is adjusted at a time, and the results are monitored to determine whether the effect was positive or negative. The disclosed techniques also apply to tracking and classifying requests by method name (and, optionally, parameters).
Owner:IBM CORP
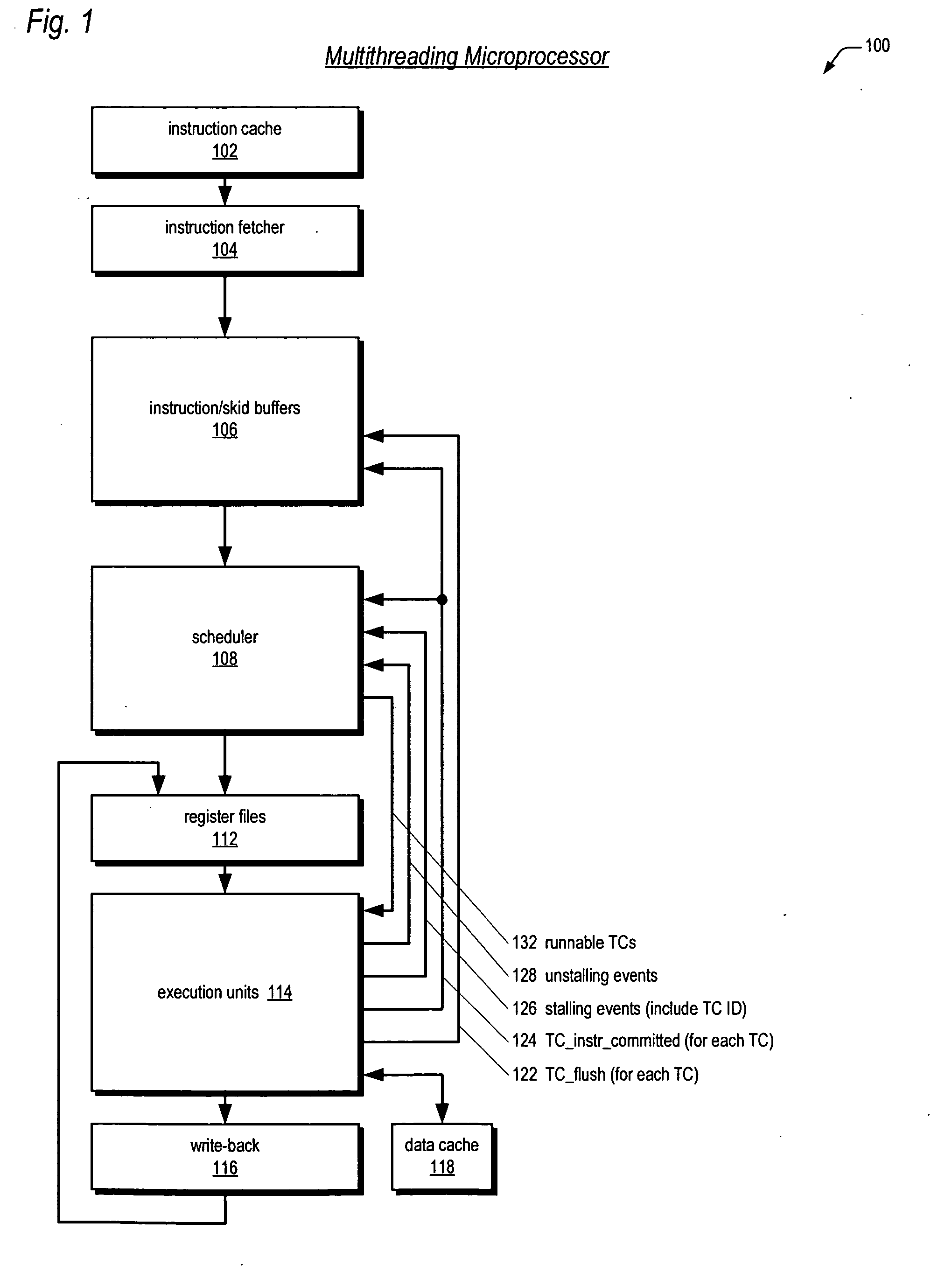
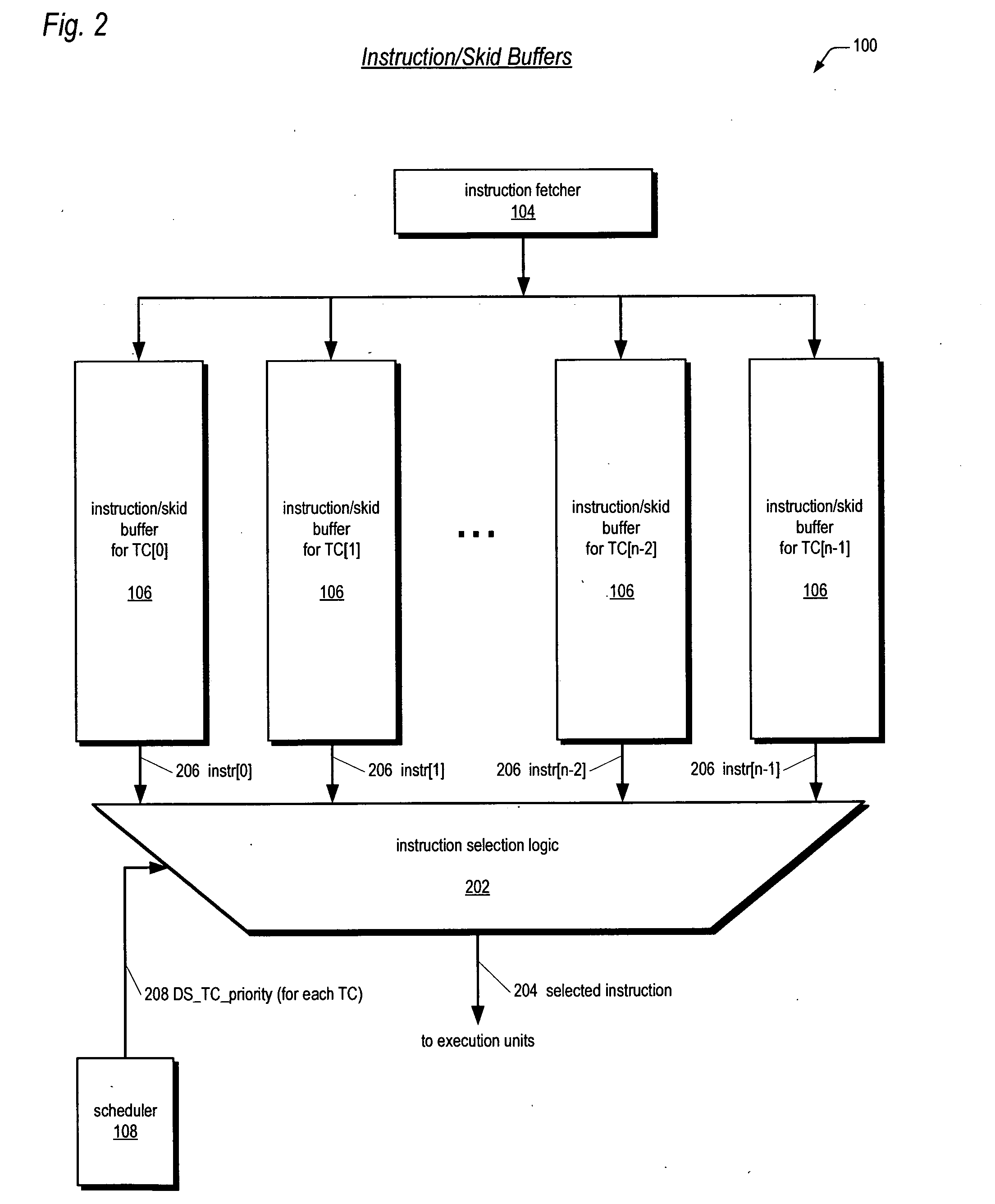
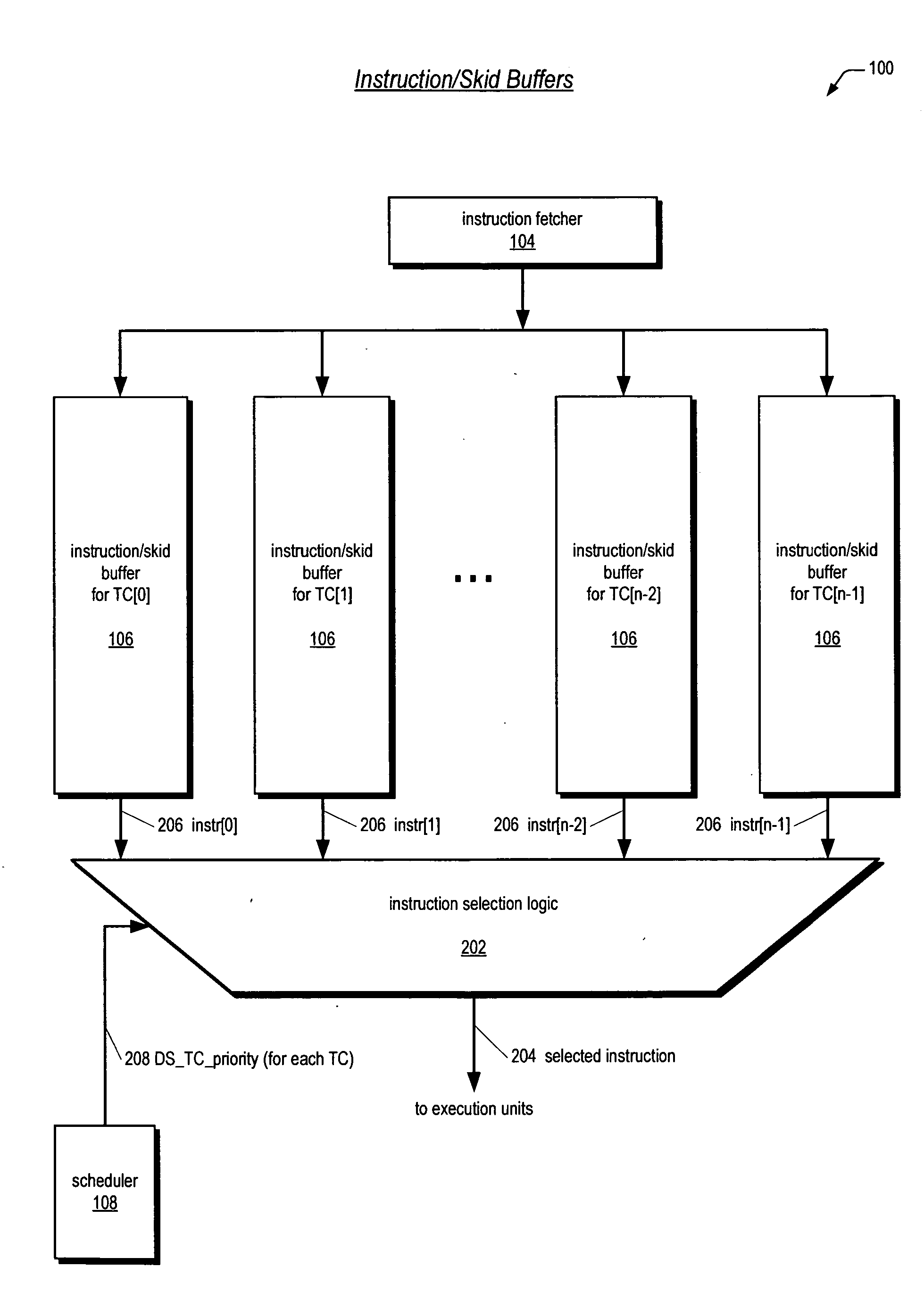
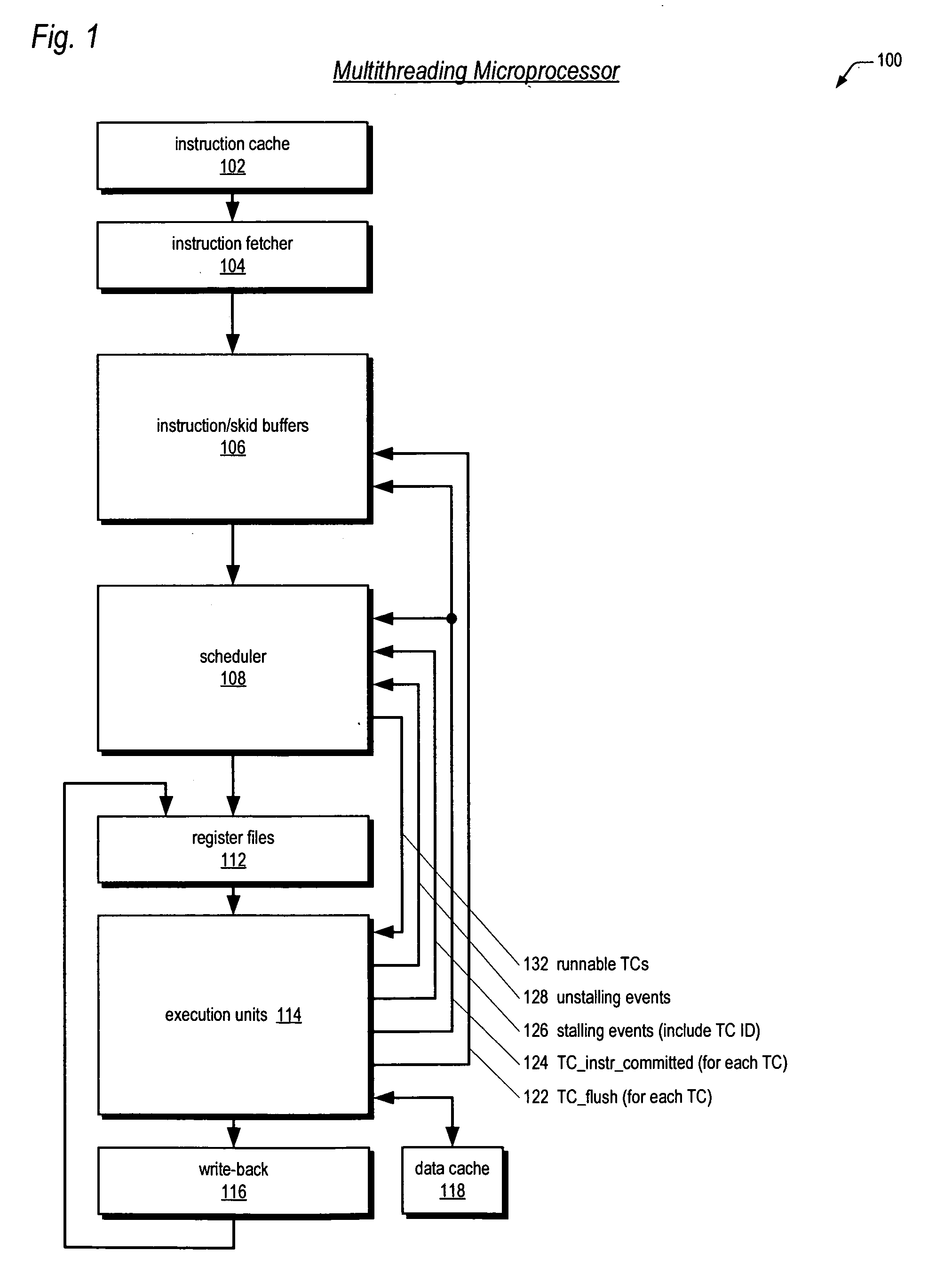
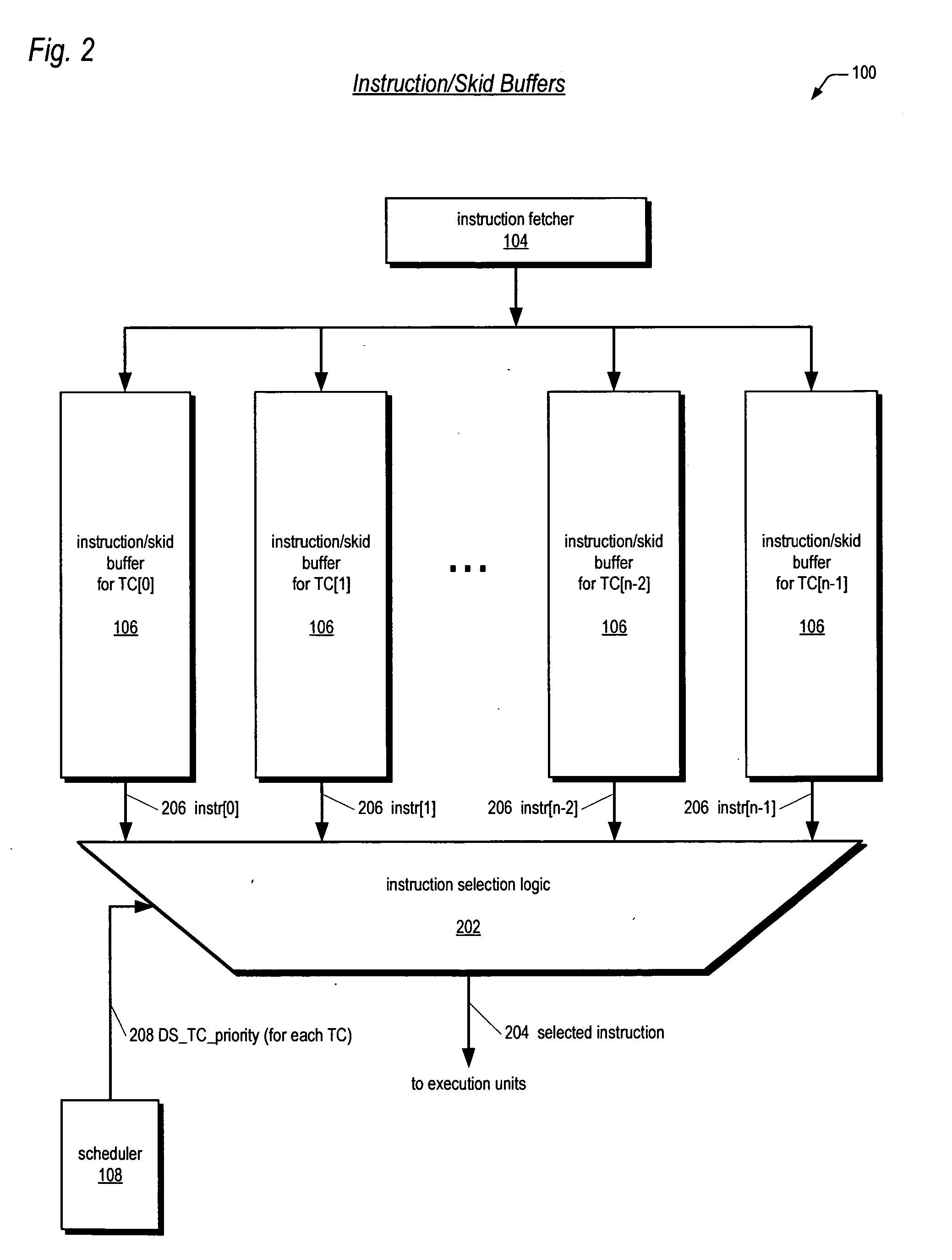
Instruction/skid buffers in a multithreading microprocessor
ActiveUS20060179274A1Reduce the amount requiredImprove processor performanceDigital computer detailsMemory systemsParallel computingControl logic
An apparatus for reducing instruction re-fetching in a multithreading processor configured to concurrently execute a plurality of threads is disclosed. The apparatus includes a buffer for each thread that stores fetched instructions of the thread, having an indicator for indicating which of the fetched instructions in the buffer have already been dispatched for execution. An input for each thread indicates that one or more of the already-dispatched instructions in the buffer has been flushed from execution. Control logic for each thread updates the indicator to indicate the flushed instructions are no longer already-dispatched, in response to the input. This enables the processor to re-dispatch the flushed instructions from the buffer to avoid re-fetching the flushed instructions. In one embodiment, there are fewer buffers than threads, and they are dynamically allocatable by the threads. In one embodiment, a single integrated buffer is shared by all the threads.
Owner:MIPS TECH INC
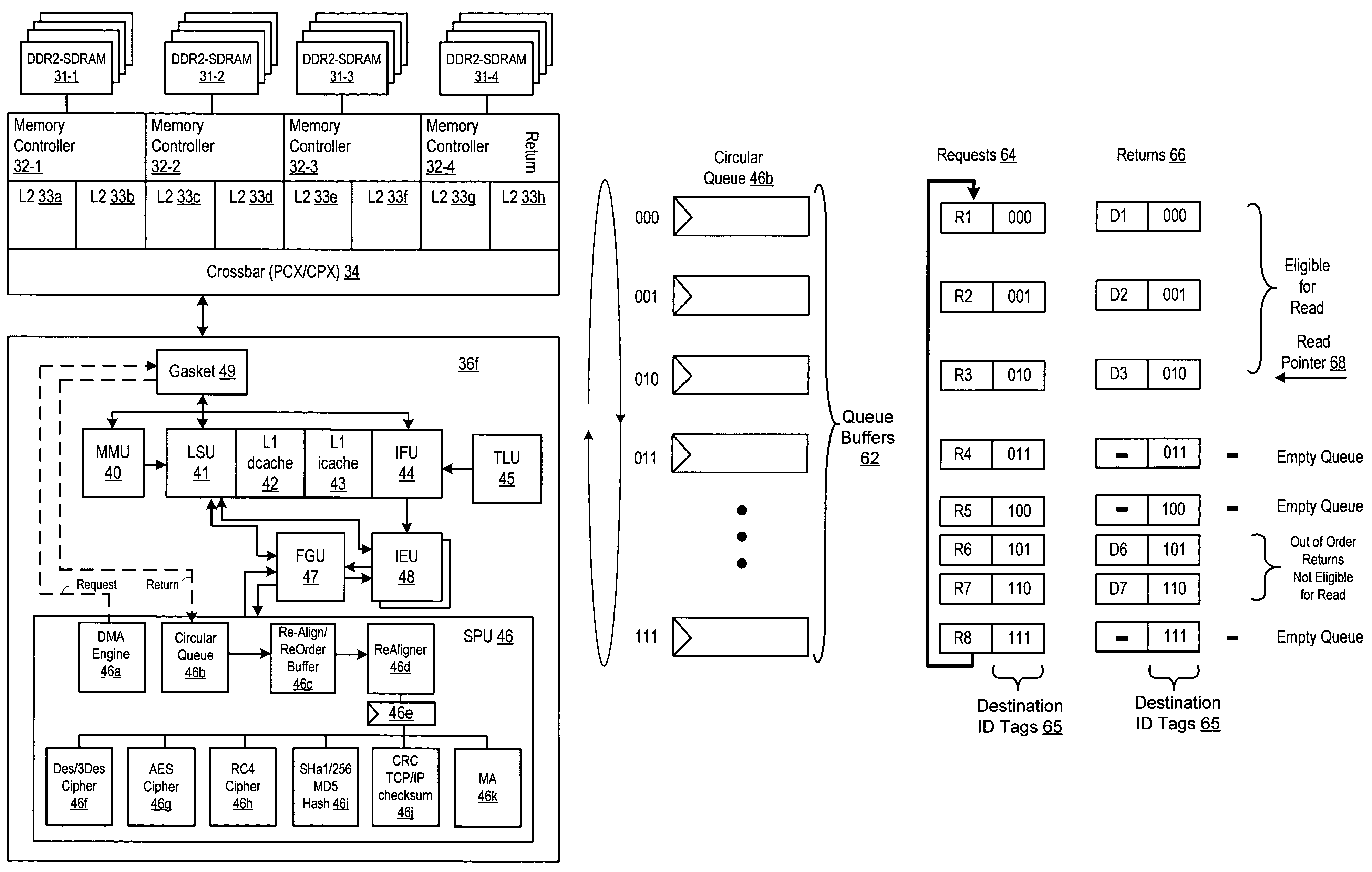
Out-of-order memory transactions in a fine-grain multithreaded/multi-core processor
ActiveUS7571284B1Improve performanceEfficient processingGeneral purpose stored program computerMultiprogramming arrangementsProcessing coreMulti-core processor
A method and apparatus for implementing out-of-order memory transactions in a multithreaded, multicore processor. In the present invention, circular queue comprising a plurality of queue buffers is used to store load data returned by a memory unit in response to a request issued by a processing module, such as a stream processing unit, in a processing core. As requests are issued, a destination queue buffer ID tag is transmitted as part of the request. When the request is returned, that destination number is reflected back and is used to control which queue within the circular queue will be used to store the retuned load data. Separate pointers are used to indicate the order of the queues to be read and the order of the queues to be written. The method and apparatus implemented by the present invention allows out-of-order data to be processed efficiently, thereby improving the performance of a fine grain multithreaded, multi-core processor.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Method for securing video images
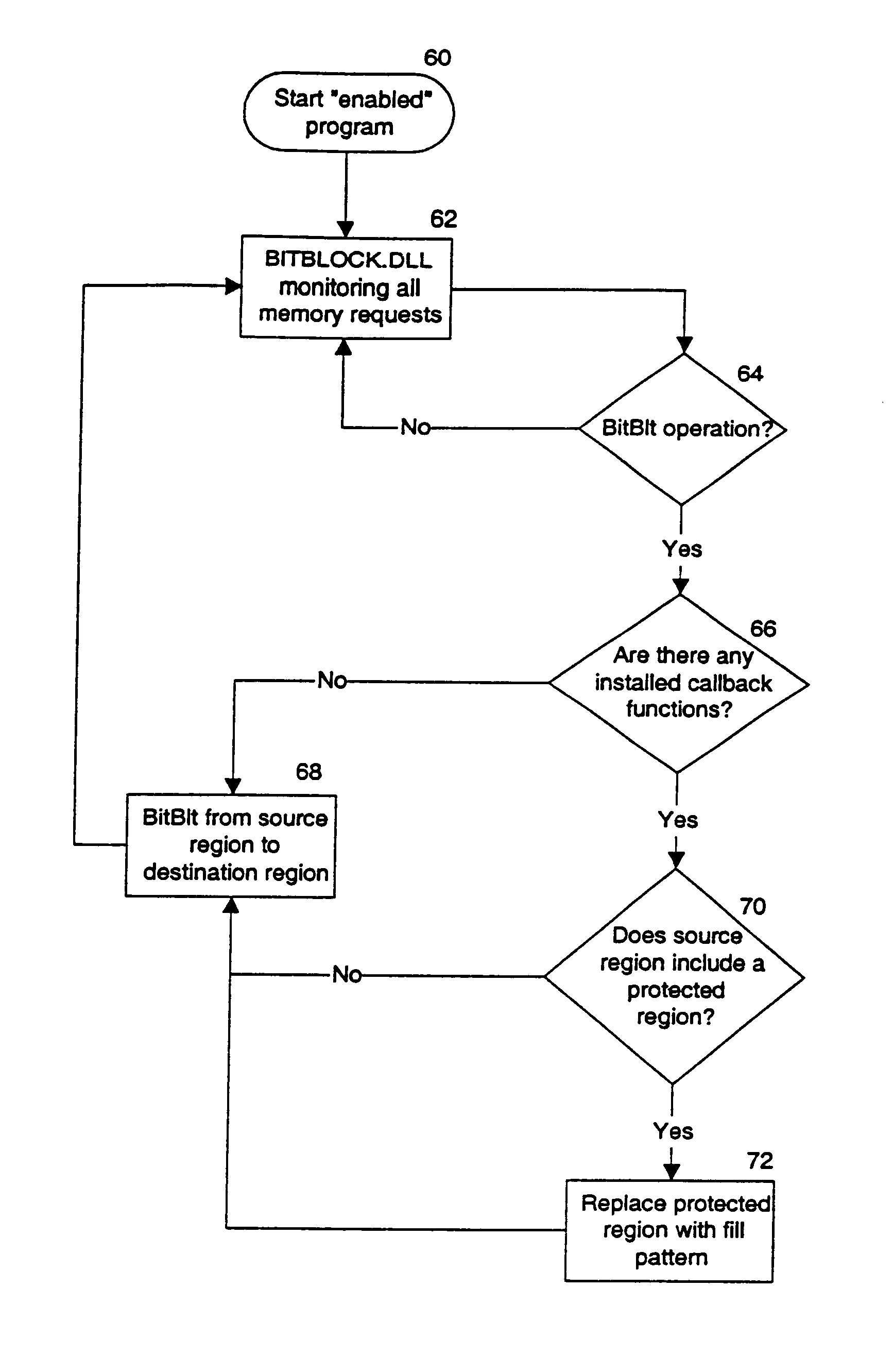
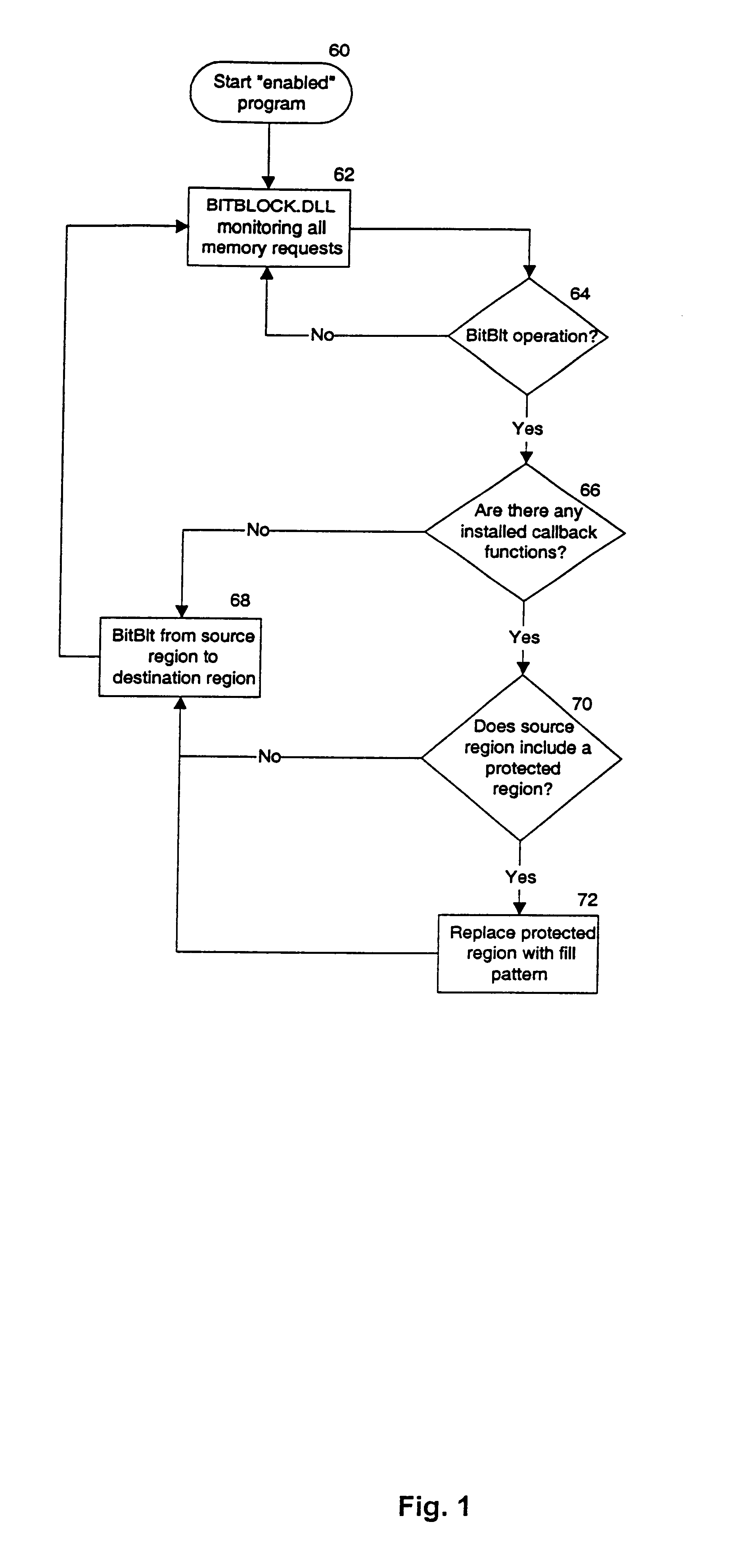
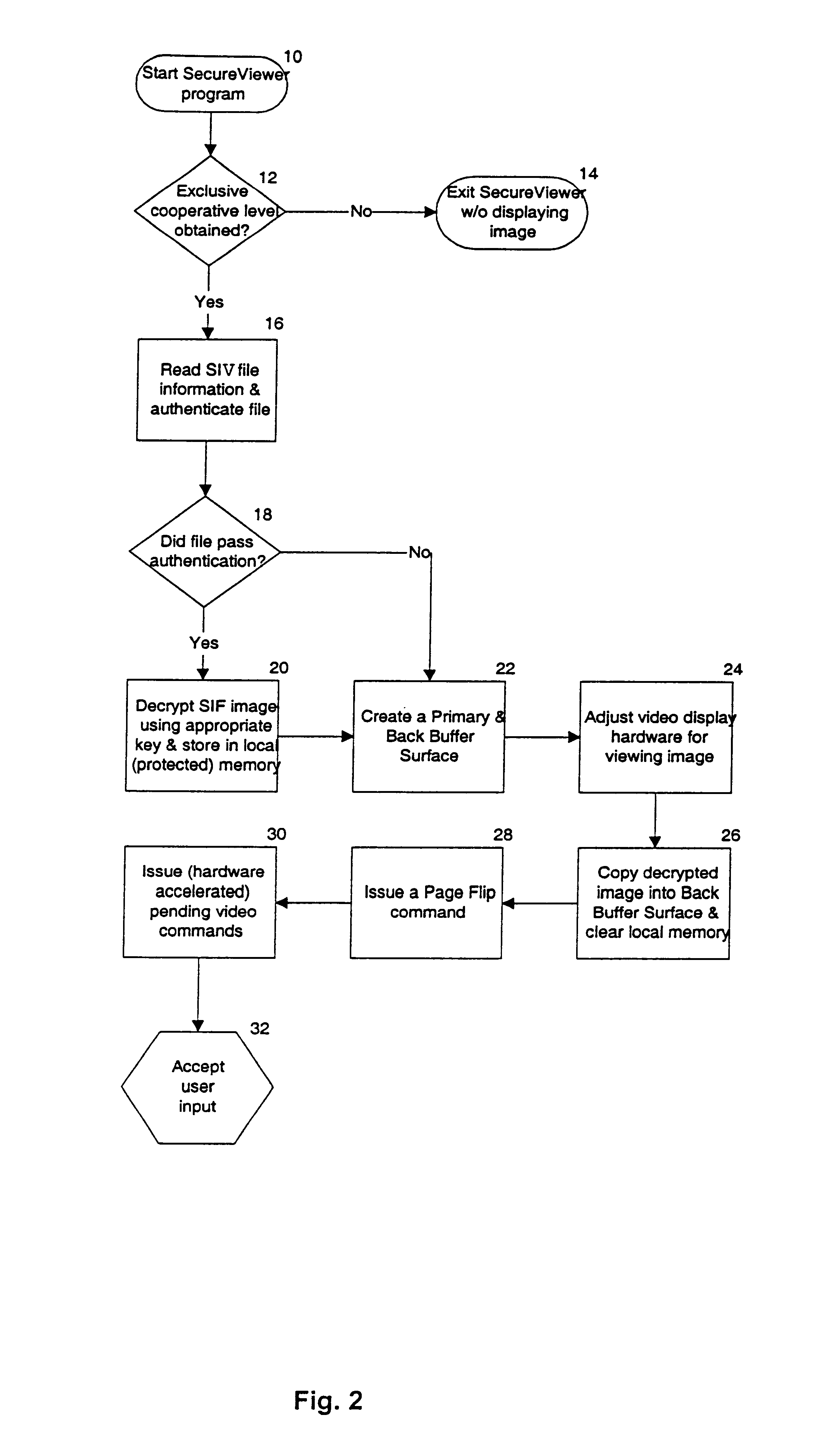
A method for protecting the video memory on a computer system from being illicitly copied. The invention decrypts a previously encrypted image and displays it on the video screen. During the time the image is displayed, the invention protects it from being copied by other running applications. This is accomplished in multithreaded operating systems by first issuing a multithreaded locking primitive to the video memory resource, and then inserting a pending video hardware request that will take precedence over any subsequent video memory access requests. The pending request serves the purpose of destroying the contents of video memory. The pending request is passive in that it does not execute unless a malicious program has removed the video memory lock.
Owner:HANGER SOLUTIONS LLC +1
Method and apparatus for testing performances of solid state disks
InactiveCN103578568AImprove test efficiencyMeet high-quality testing requirementsStatic storageTest efficiencyTest performance
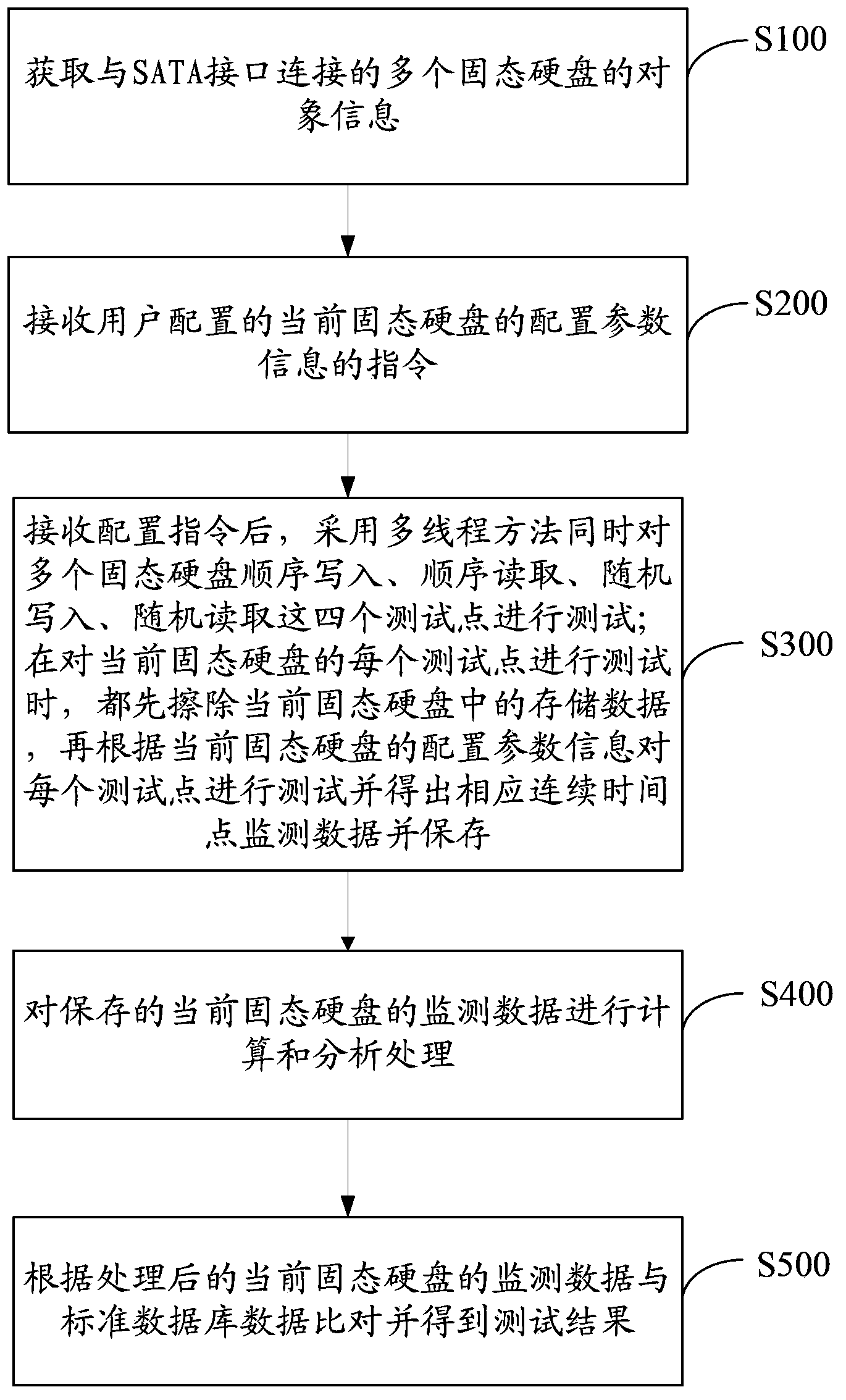
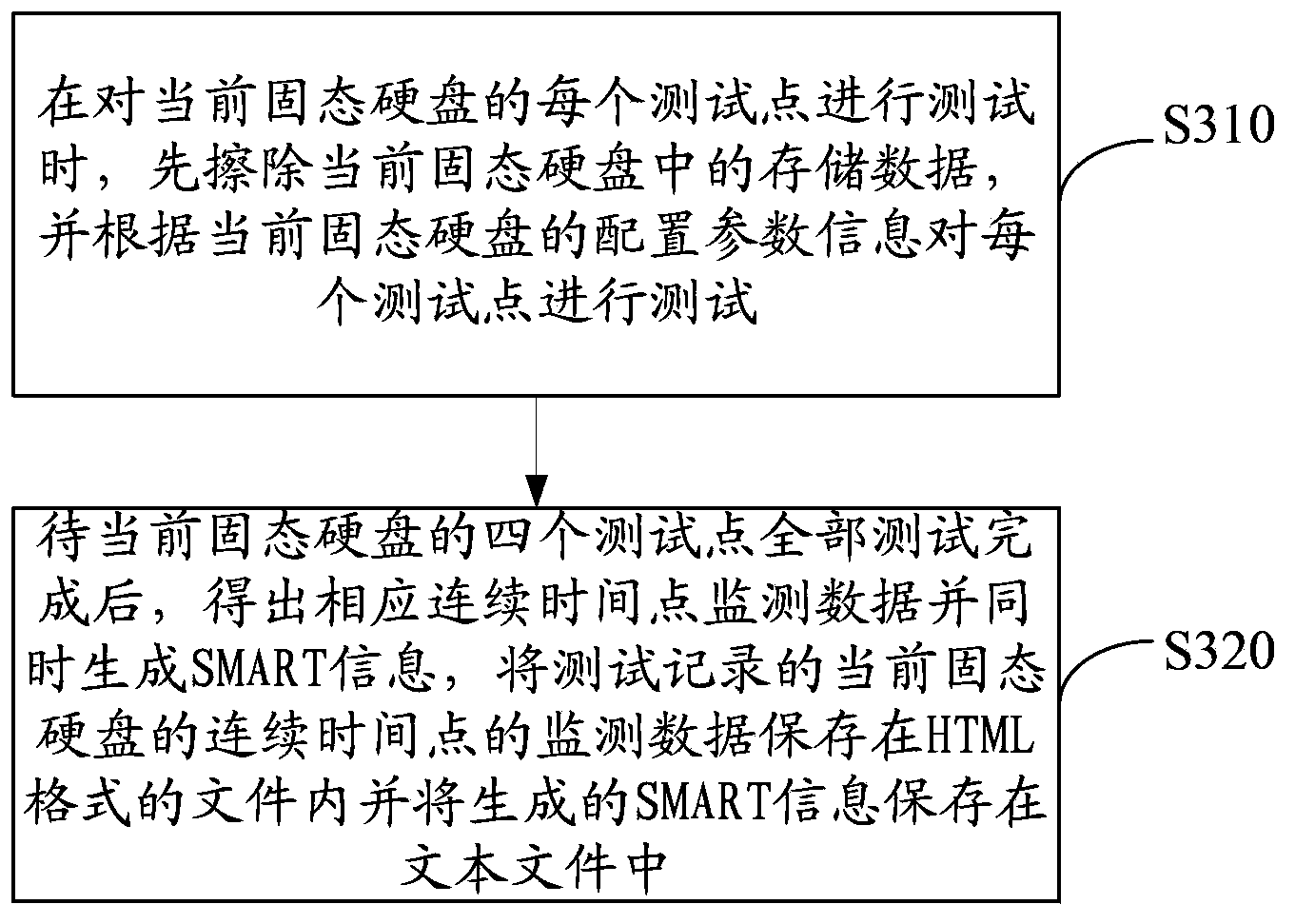
The invention discloses a method and an apparatus for testing performances of solid state disks, wherein the method is used to realize automatic test processing on multiple solid state disks. The method comprises the following steps: step S100, acquiring object information of the multiple solid state disks connected with SATA interfaces; step S200, receiving an instruction about the current solid state disk configuration parameter information configured by a user, and employing a multithreading method to perform test on four test points such as sequential write, sequential read, random write and random read of the multiple solid state disks; step S300, obtaining corresponding continuous time point monitor data; step S400, performing calculation and analysis on the monitor data; and step S500, comparing the monitor data with standard data in a standard data base to obtain a test result. The provided method and the apparatus for testing performances of the solid state disks are capable of improving test efficiency of the solid state disks, providing an extremely detailed abnormal time point test report for the user and guaranteeing the accuracy of solid state disk performance test information.
Owner:南京潜海智能科技有限公司
Method for checkpointing instruction groups with out-of-order floating point instructions in a multi-threaded processor
InactiveUS20060179346A1Error detection/correctionDigital computer detailsFloating-point unitStorage cell
A method and apparatus are provided for dispatch group checkpointing in a microprocessor, including provisions for handling partially completed dispatch groups and instructions which modify system coherent state prior to completion. An instruction checkpoint retry mechanism is implemented to recover from soft errors in logic. The processor is able to dispatch fixed point unit (FXU), load / store unit (LSU), and floating point unit (FPU) or vector multimedia extension (VMX) instructions on the same cycle. Store data is written to a store queue when a store instruction finishes executing. The data is held in the store queue until the store instruction is checkpointed, at which point it can be released to the coherently shared level 2 (L2) cache.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method and system for automated analysis of the performance of remote method invocations in multi-tier applications using bytecode instrumentation
ActiveUS20070169055A1Minimal disruptionError detection/correctionSpecific program execution arrangementsSerializationClient-side
Provided is a method and system for monitoring and diagnosing the performance of remote method invocations using bytecode instrumentation in distributed multi-tier applications. The provided method and system involves automated instrumentation of client application bytecode and server application bytecode with sensors for measuring performance of remote method invocations and operations performed during remote method invocations. Performance information is captured for each remote method invocation separately, allowing performance diagnosis of multithreaded execution of remote method invocations, so that throughput and response time information are accurate even when other threads perform remote method invocations concurrently. This makes the present invention suitable for performance diagnosis of remote method invocations on systems under load, such as found in production and load-testing environments. The captured performance metrics include throughput and response time information of remote method invocation, object serialization, and transport. The performance metrics are captured per remote method invocation. The above performance metrics enable developers and administrators to optimize their programming code for performance. Performance metrics are preferably further sent to a processing unit for storage, analysis, and correlation.
Owner:DYNATRACE
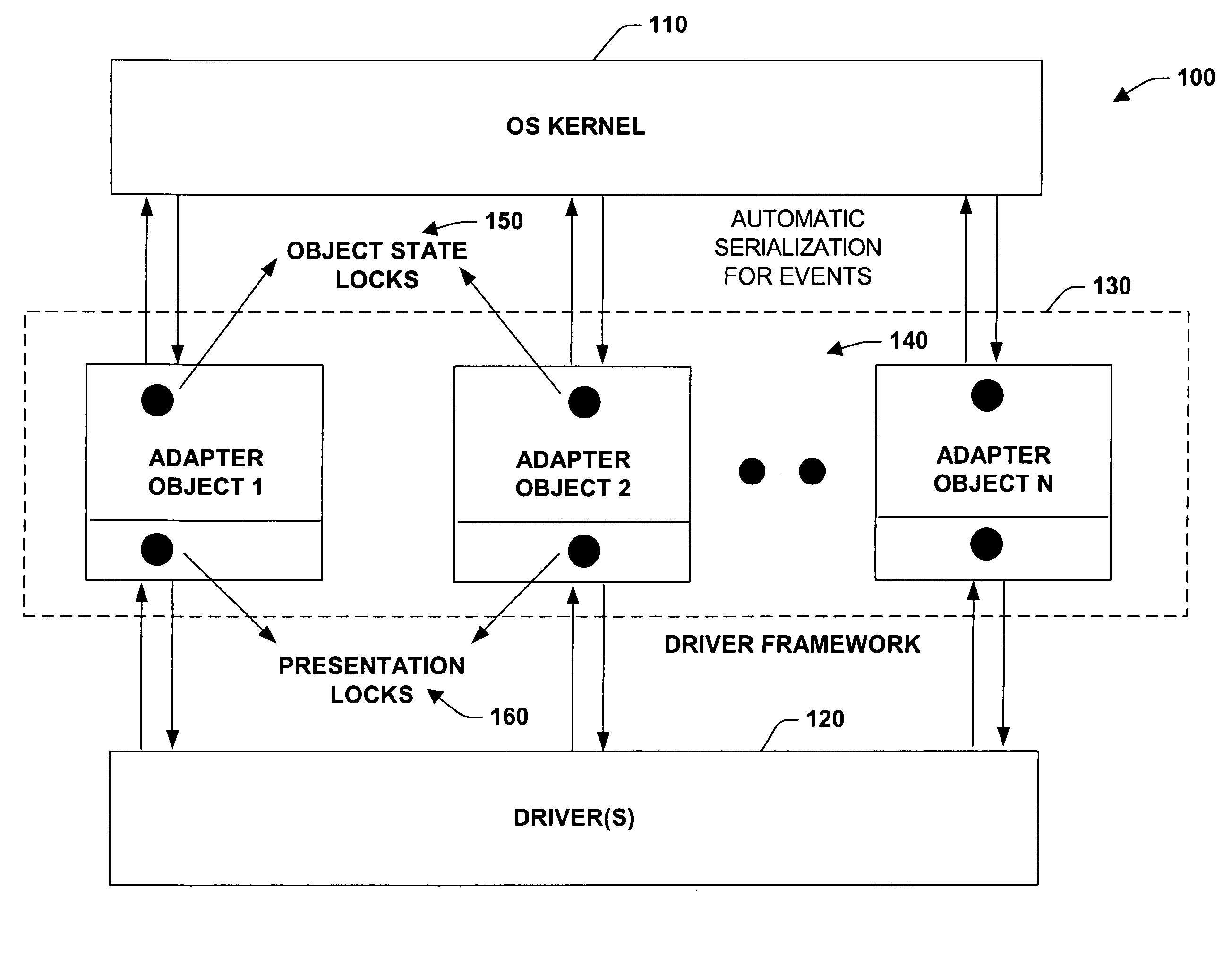
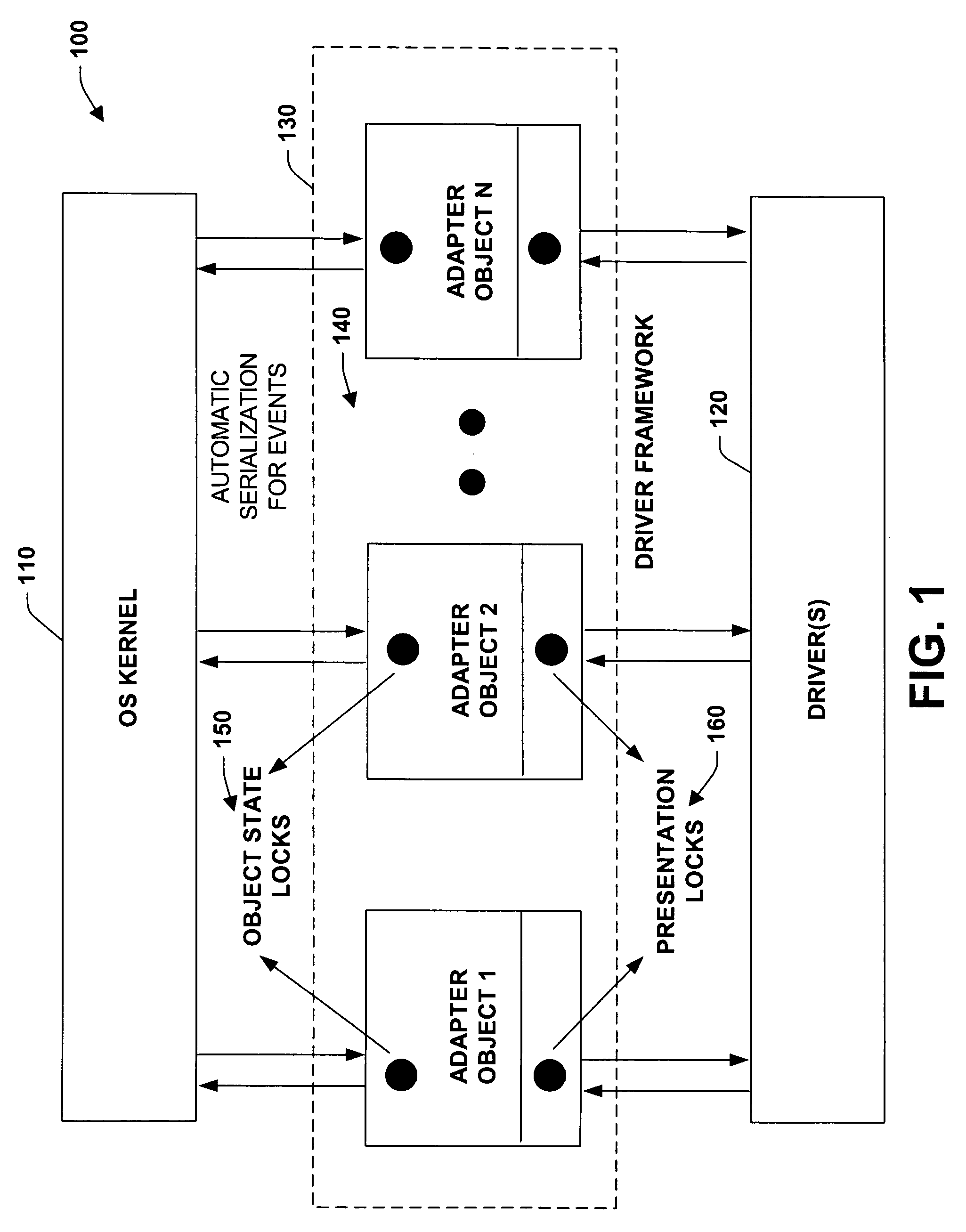
Driver framework component for synchronizing interactions between a multi-threaded environment and a driver operating in a less-threaded software environment
InactiveUS7406698B2Improve scalabilityLess threadingDigital data processing detailsUnauthorized memory use protectionProgram managementOperational system
The present invention relates to a system and methodology to facilitate automatic interactions between a highly threaded software environment such as an operating system kernel and a module operating in a less threaded environment. This is achieved by supplying adapter objects that employ various automated locking components to synchronize interactions between the environments such as processing of events or interrupts that may be generated in the system. In one aspect, a driver management system is provided that includes a driver framework component (DFC) that is separate from a driver or other type module, wherein the DFC generates objects that facilitate seamless interactions between the driver and a highly threaded system. A presentation component associated with the DFC selectively exposes objects to the driver in a multi-threaded environment.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Multithreaded processor efficiency by pre-fetching instructions for a scheduled thread
InactiveUS6965982B2Ensure proper implementationMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationComputer architectureFlip-flop
Owner:INTEL CORP
Multi-thread parallel processing method based on multi-thread programming and message queue
ActiveCN102902512AFast and efficient multi-threaded transformationReduce running timeConcurrent instruction executionComputer architectureConcurrent computation
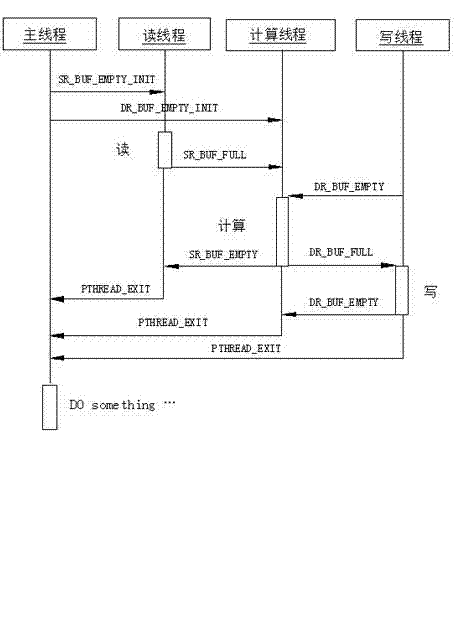
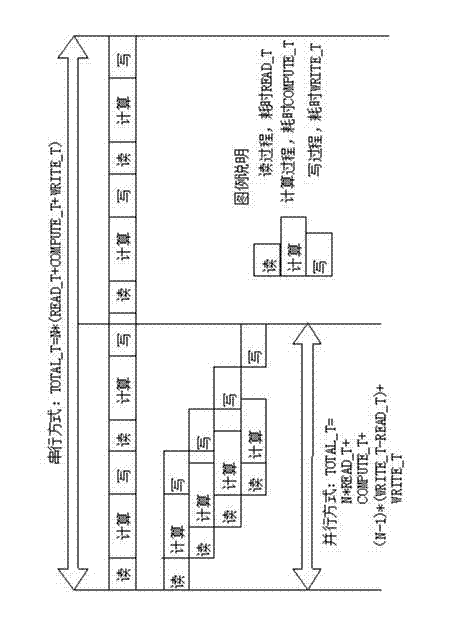
The invention provides a multi-thread parallel processing method based on a multi-thread programming and a message queue, belonging to the field of high-performance computation of a computer. The parallelization of traditional single-thread serial software is modified, and current modern multi-core CPU (Central Processing Unit) computation equipment, a pthread multi-thread parallel computing technology and a technology for realizing in-thread communication of the message queue are utilized. The method comprises the following steps of: in a single node, establishing three types of pthread threads including a reading thread, a computing thread and a writing thread, wherein the quantity of each type of the threads is flexible and configurable; exploring multi-buffering and establishing four queues for the in-thread communication; and allocating a computing task and managing a buffering space resource. The method is widely applied to the application field with multi-thread parallel processing requirements; a software developer is guided to carry out multi-thread modification on existing software so as to realize the optimization of the utilization of a system resource; and the hardware resource utilization rate is obviously improved, and the computation efficiency of software and the whole performance of the software are improved.
Owner:LANGCHAO ELECTRONIC INFORMATION IND CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com