Patents
Literature
190 results about "FLAGS register" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
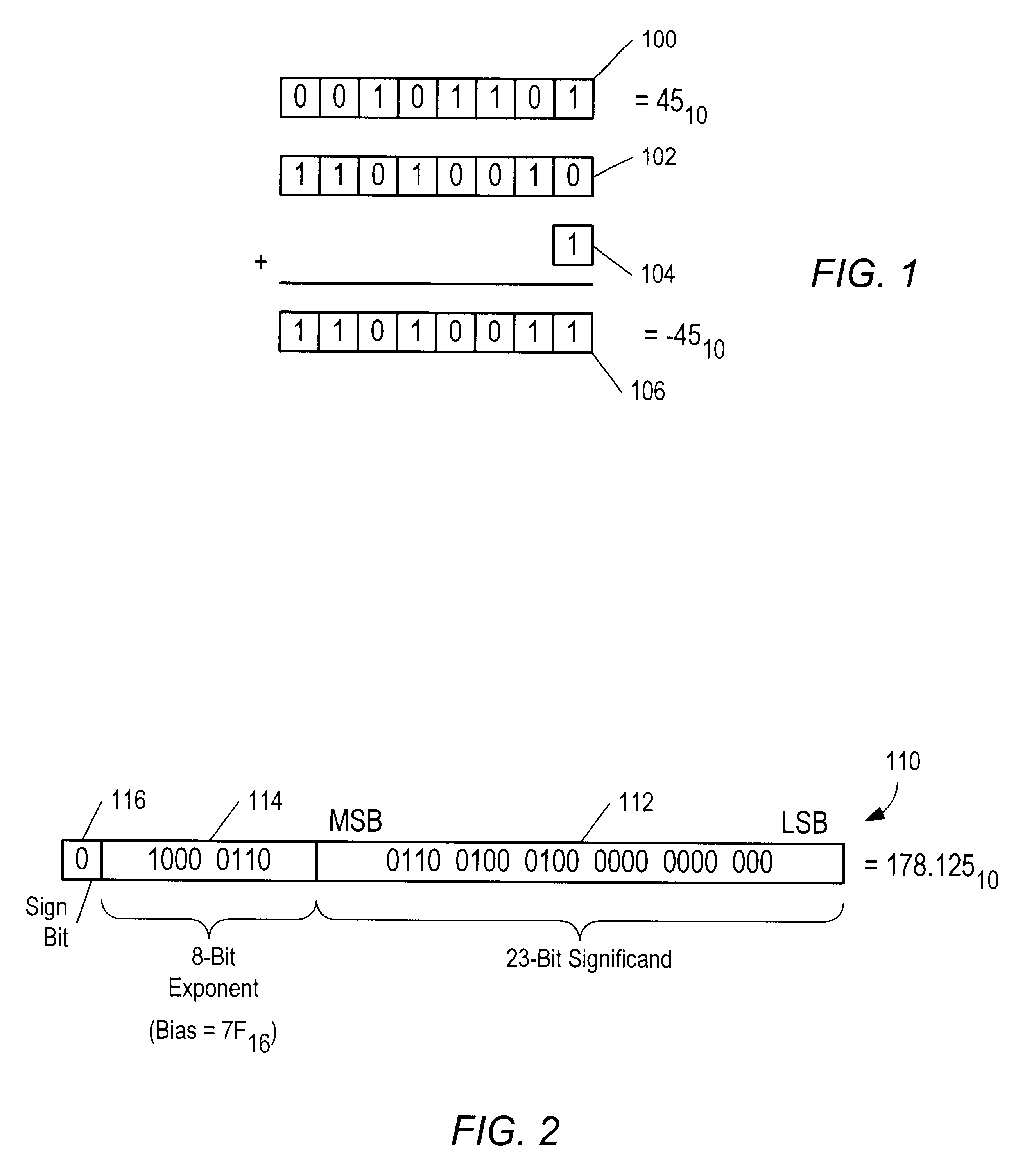
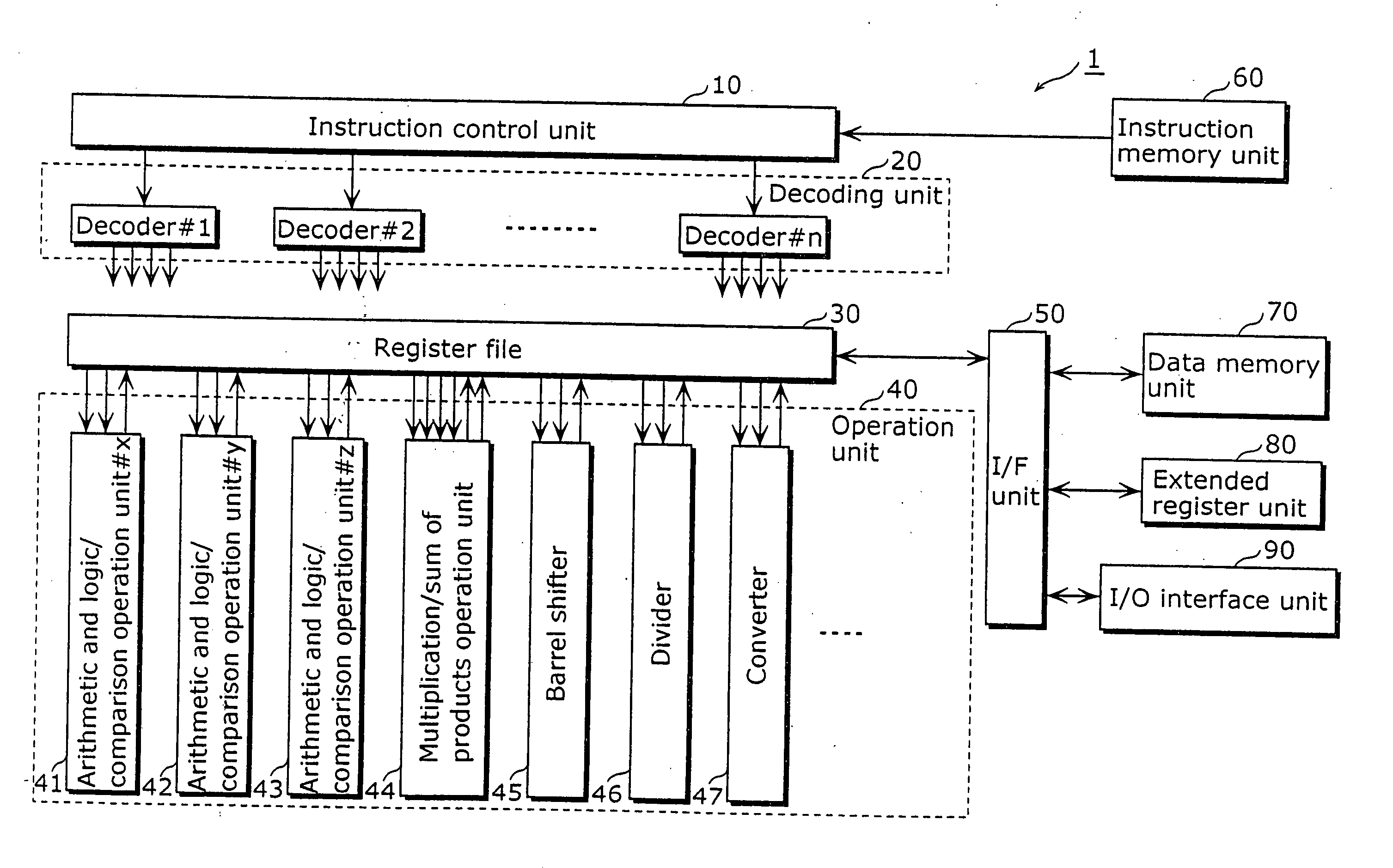
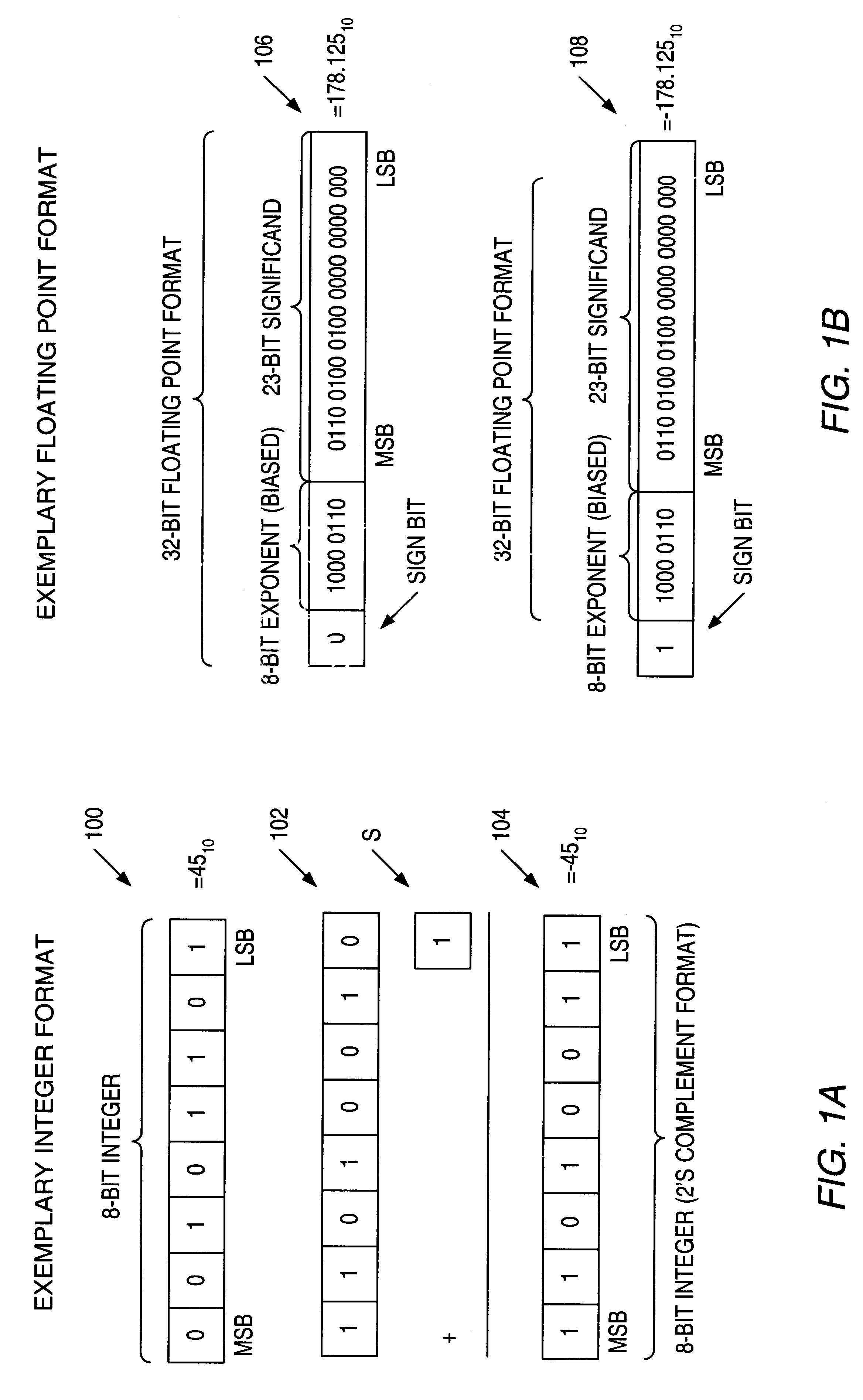
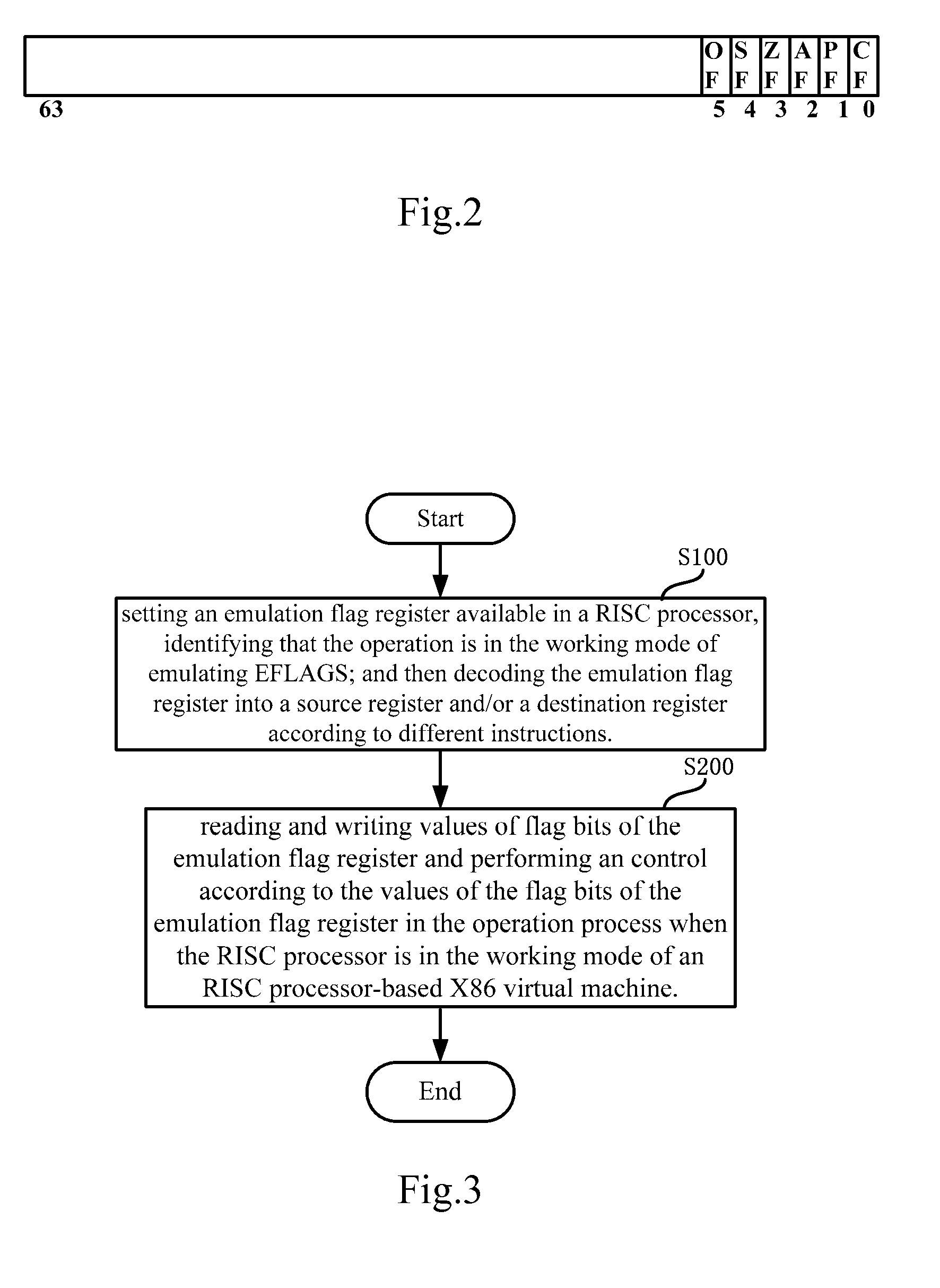
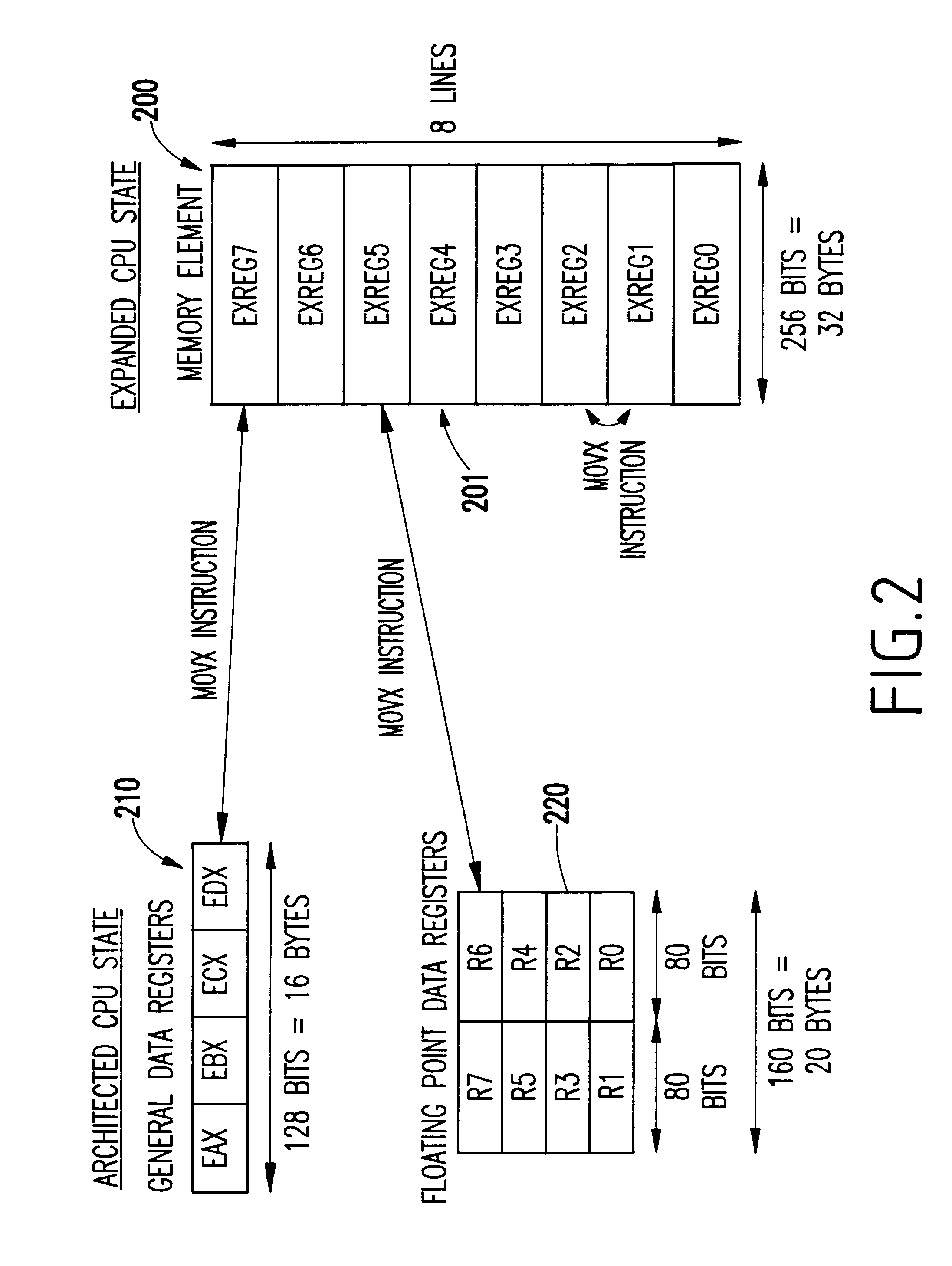
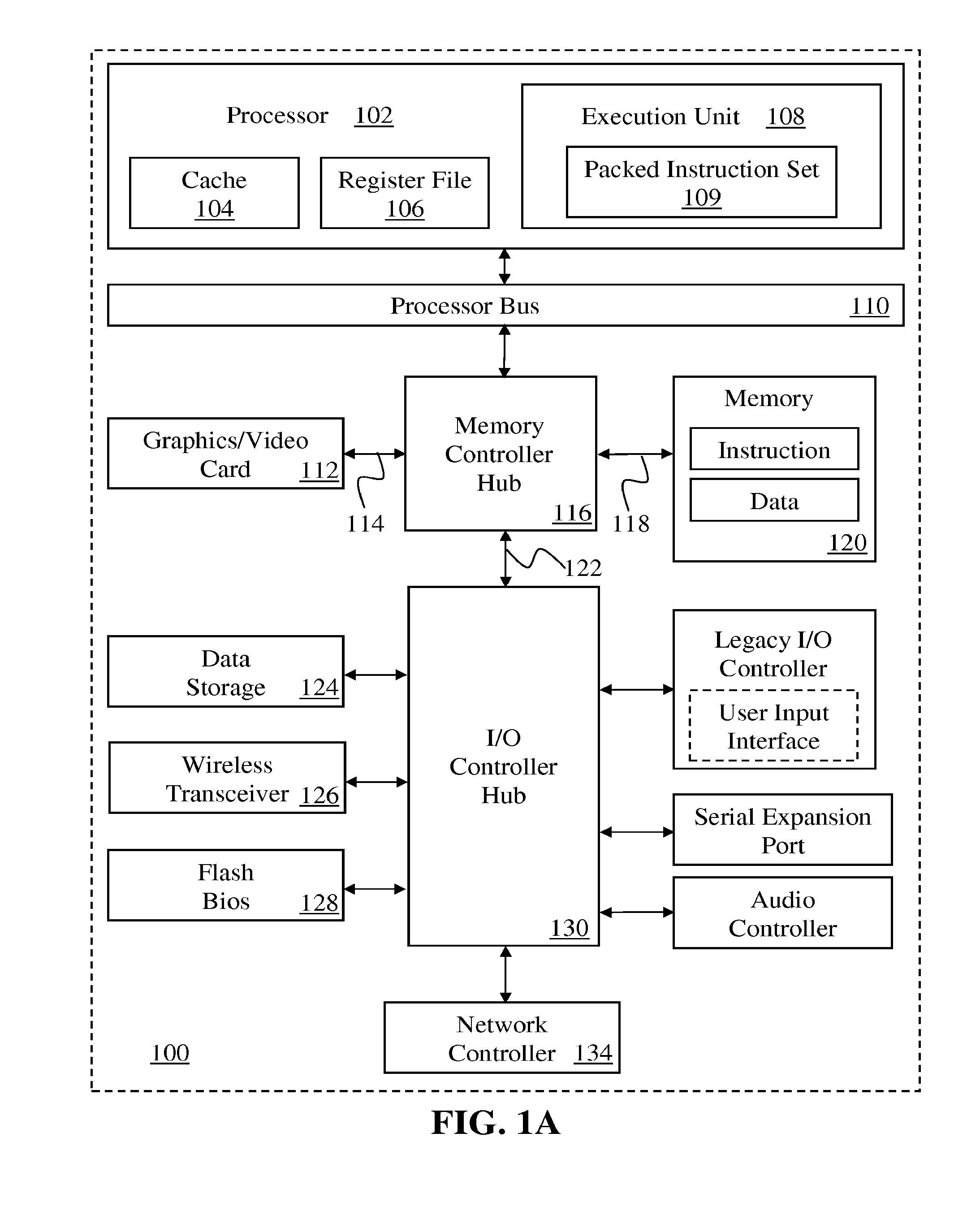
The FLAGS register is the status register in Intel x86 microprocessors that contains the current state of the processor. This register is 16 bits wide. Its successors, the EFLAGS and RFLAGS registers, are 32 bits and 64 bits wide, respectively. The wider registers retain compatibility with their smaller predecessors.
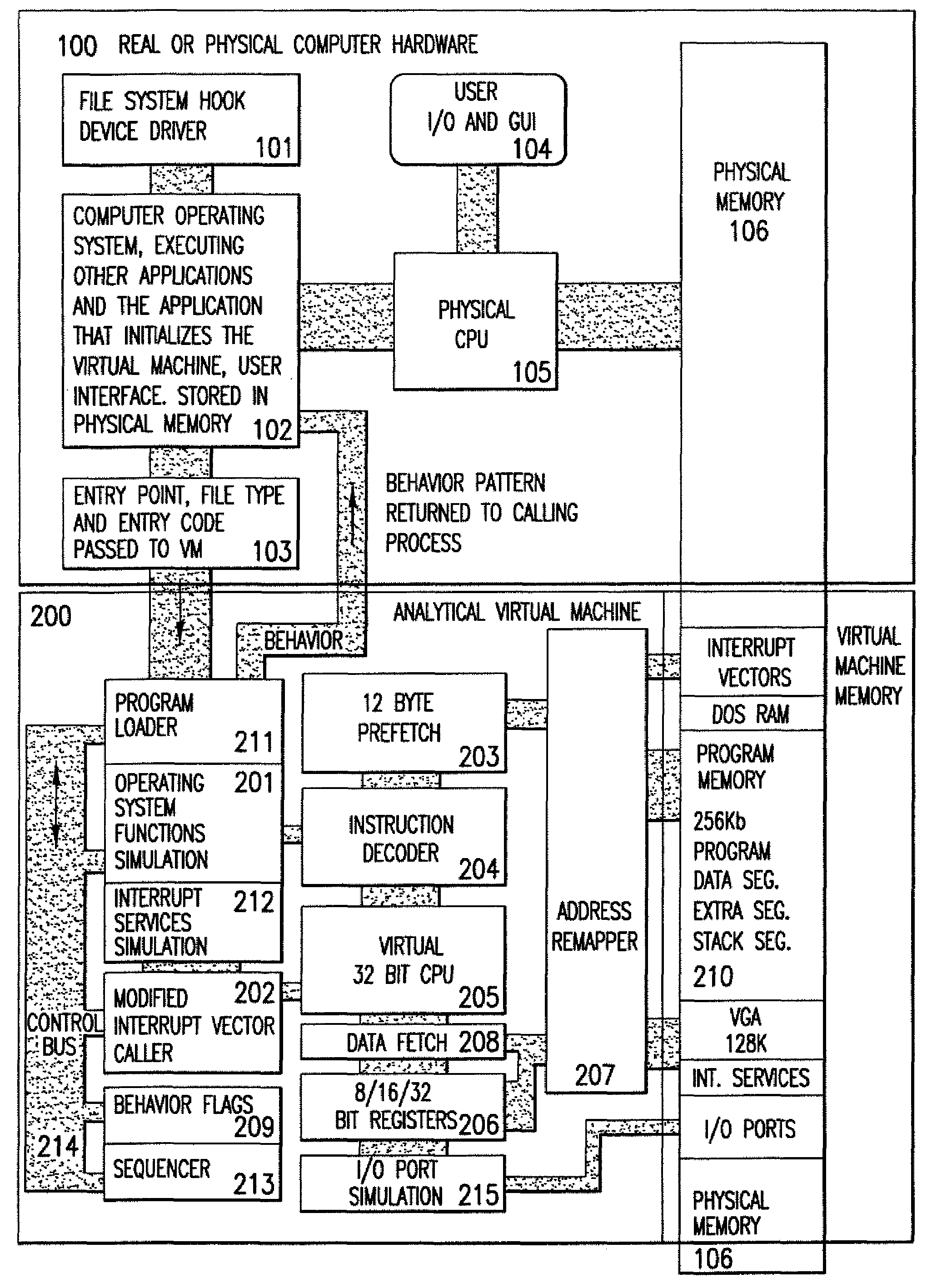
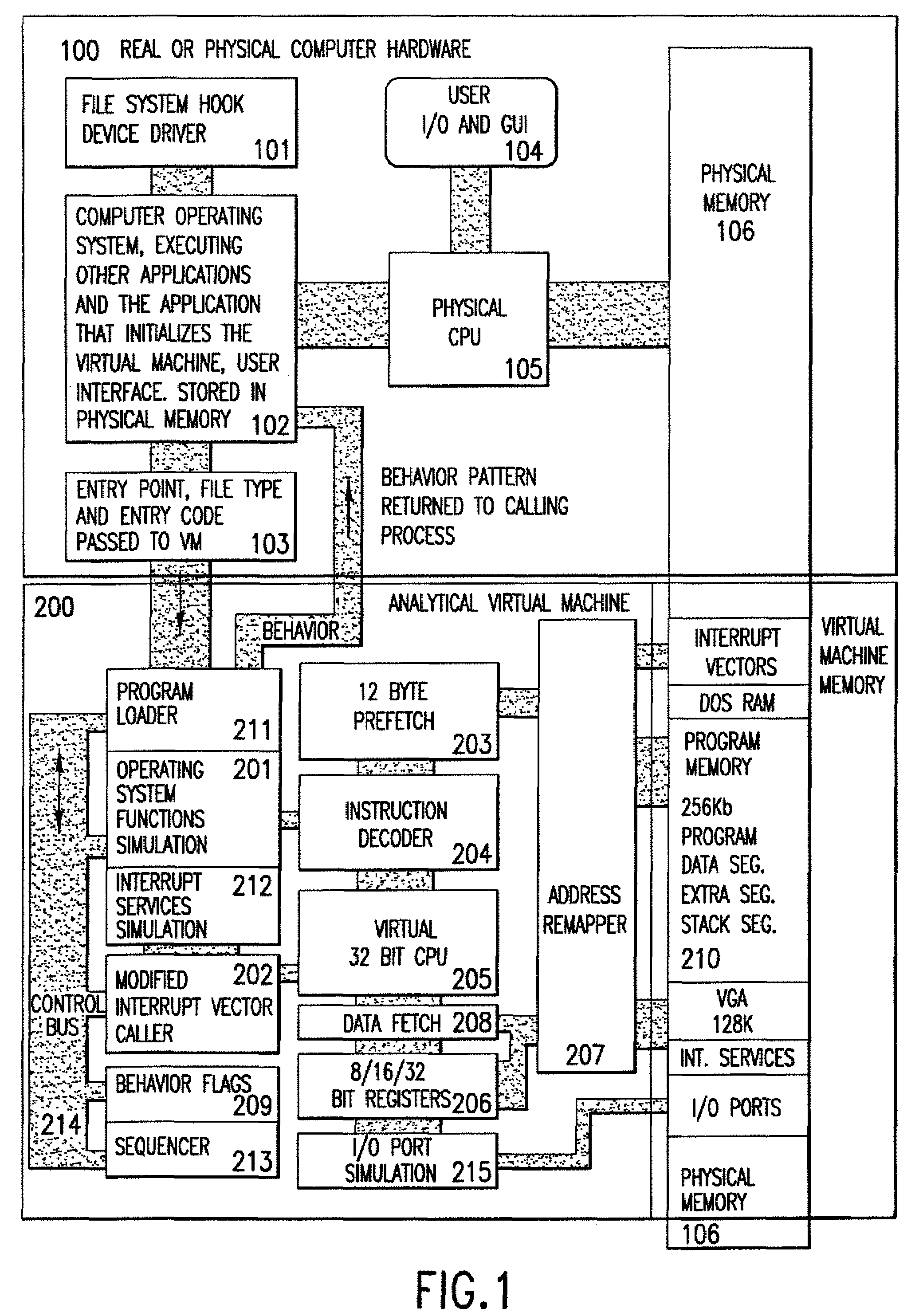
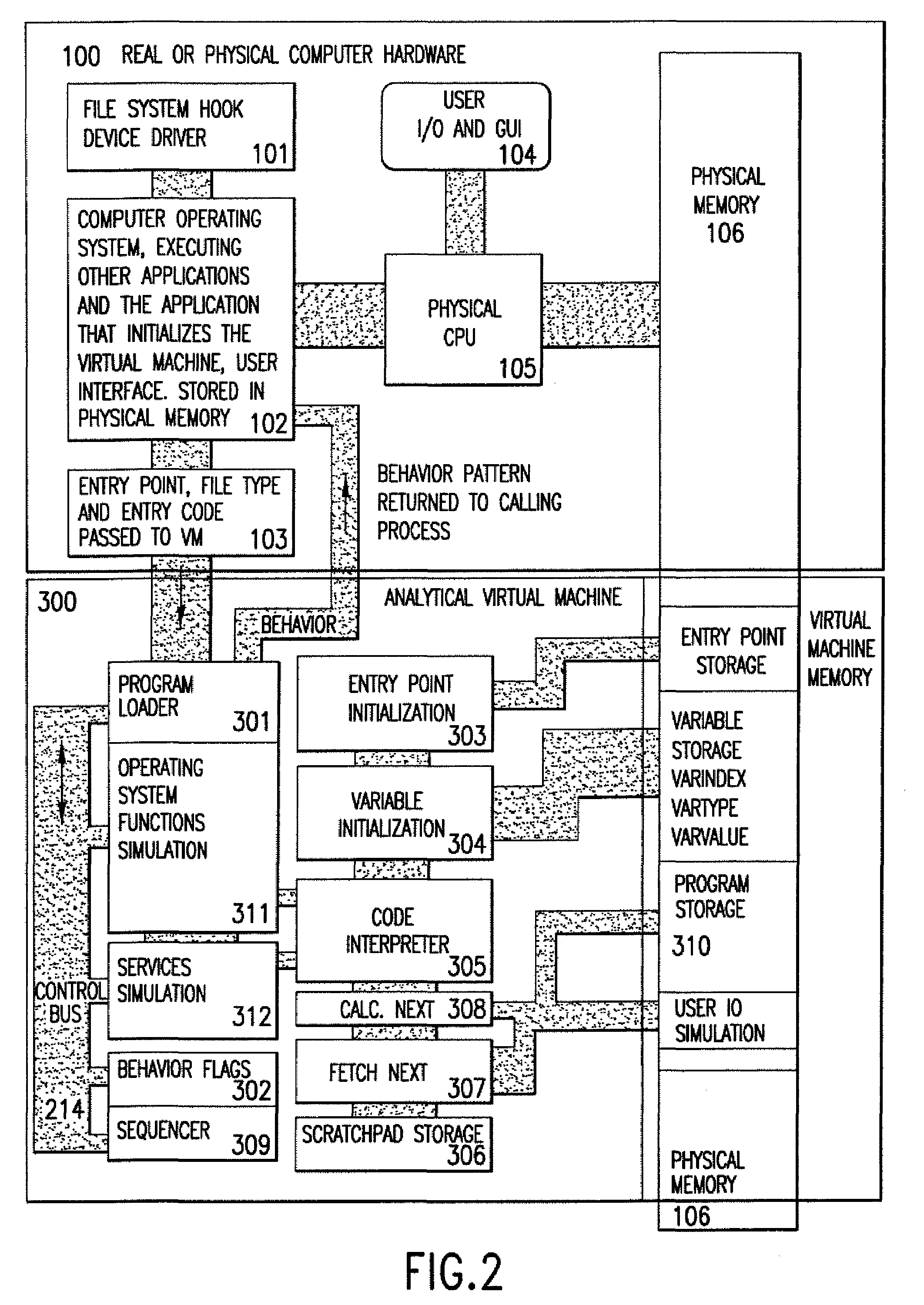
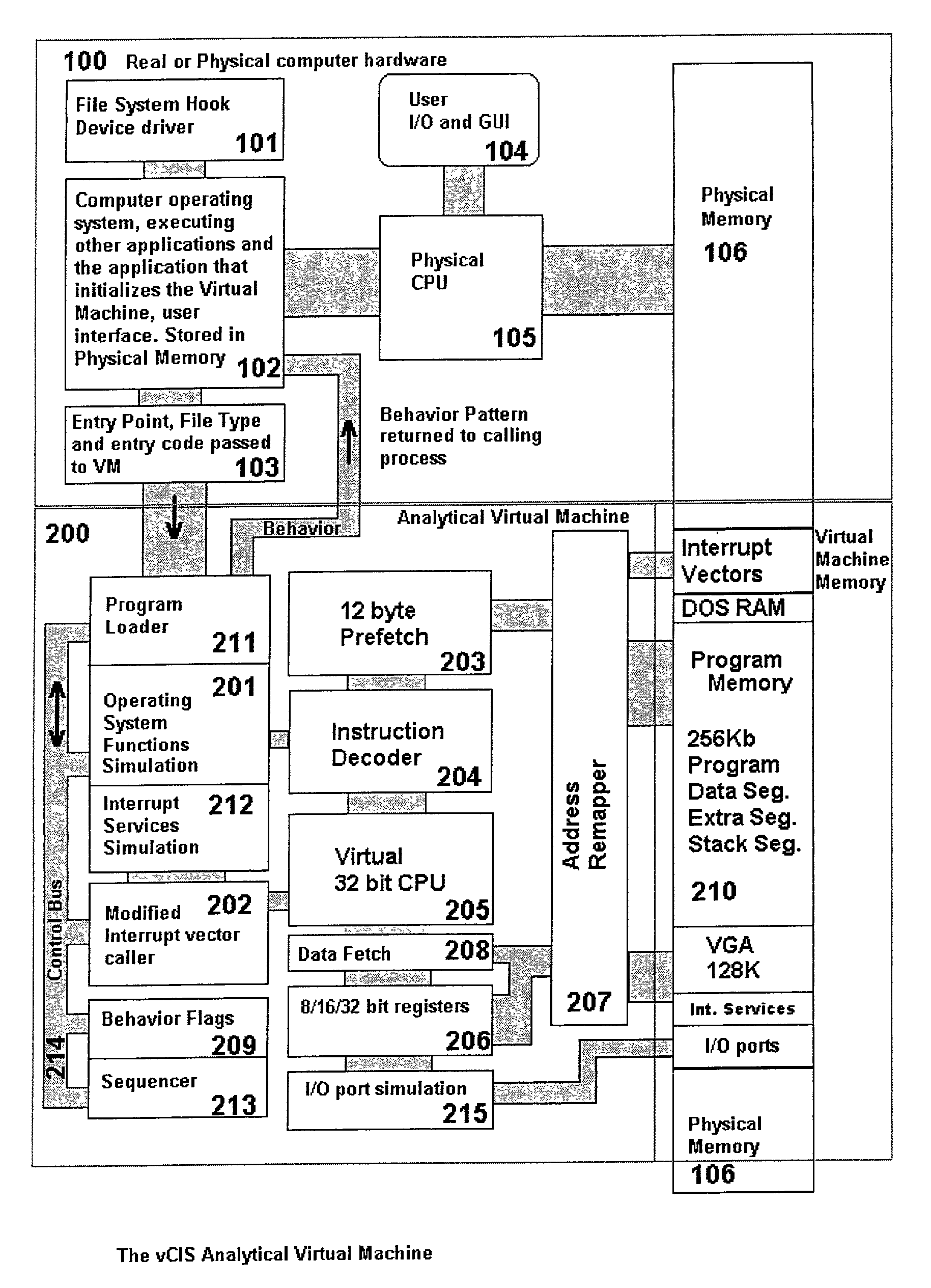
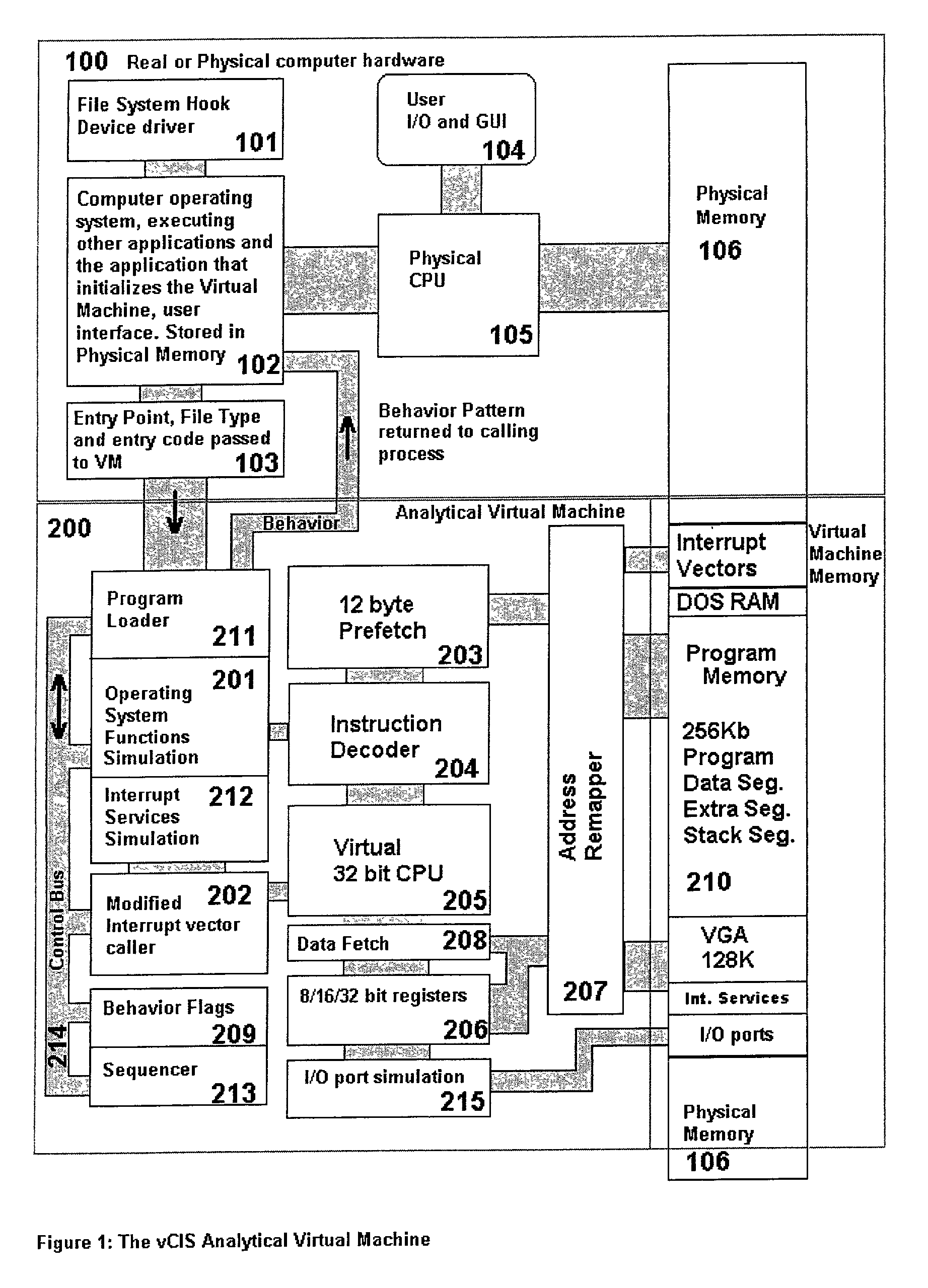
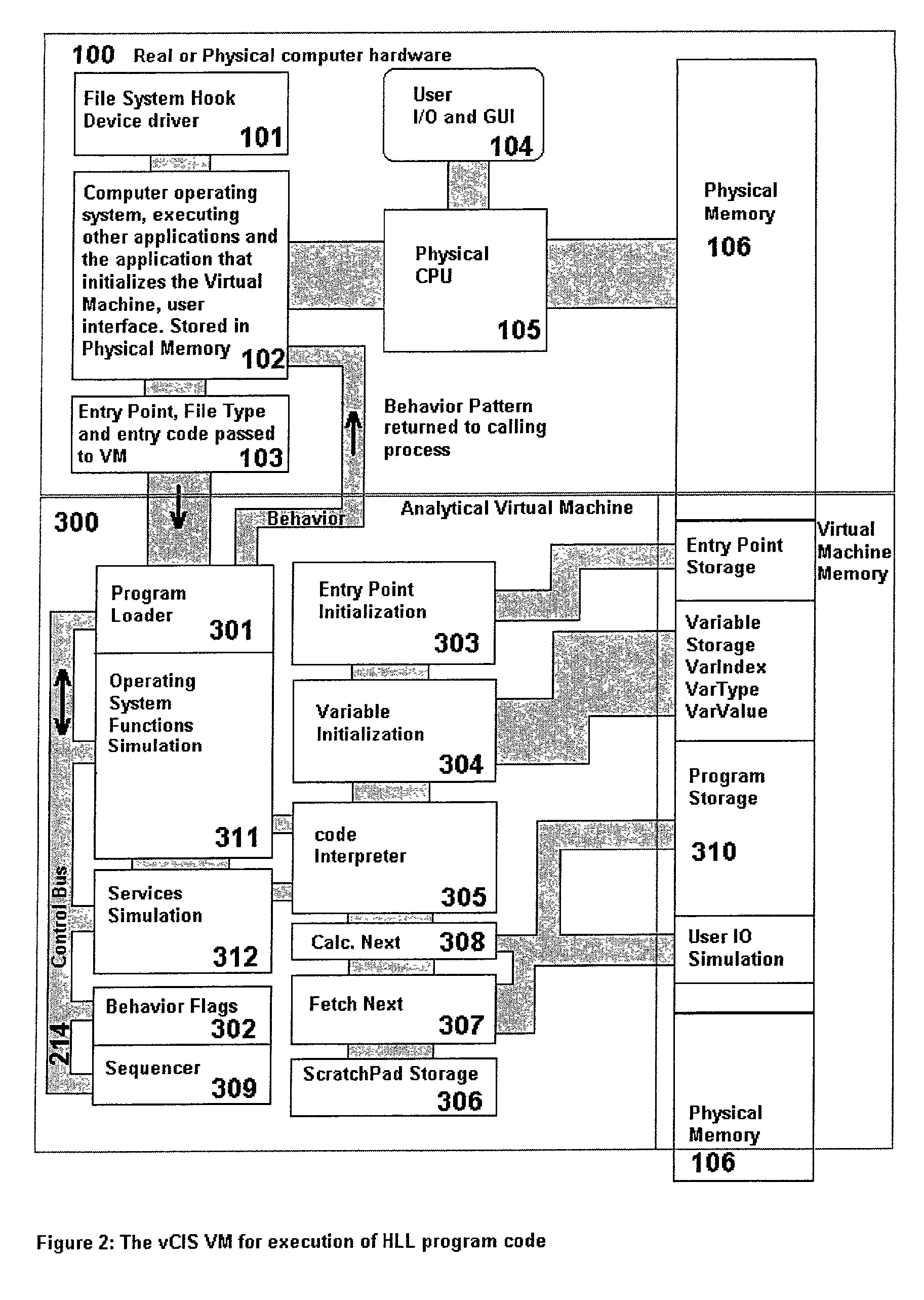
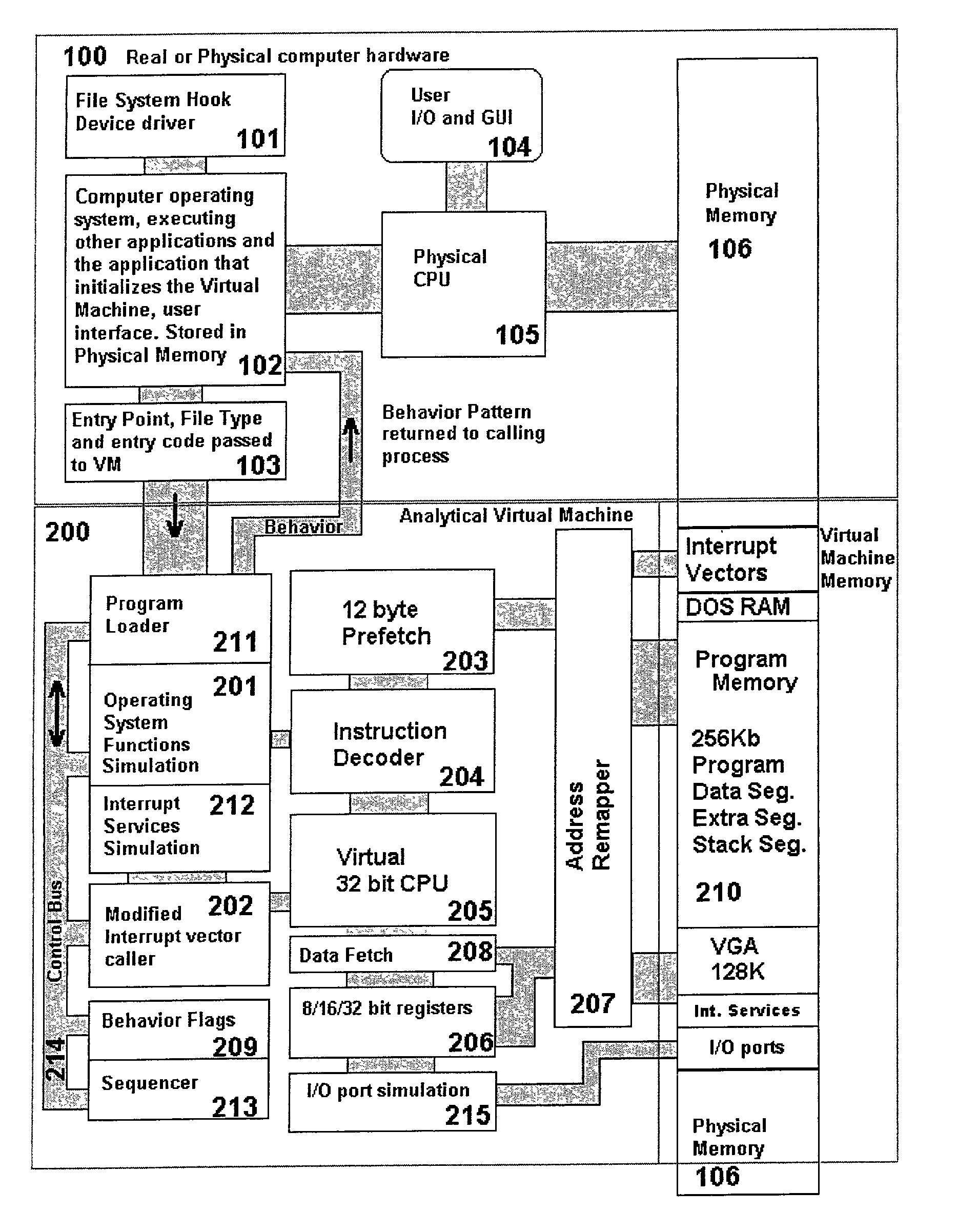
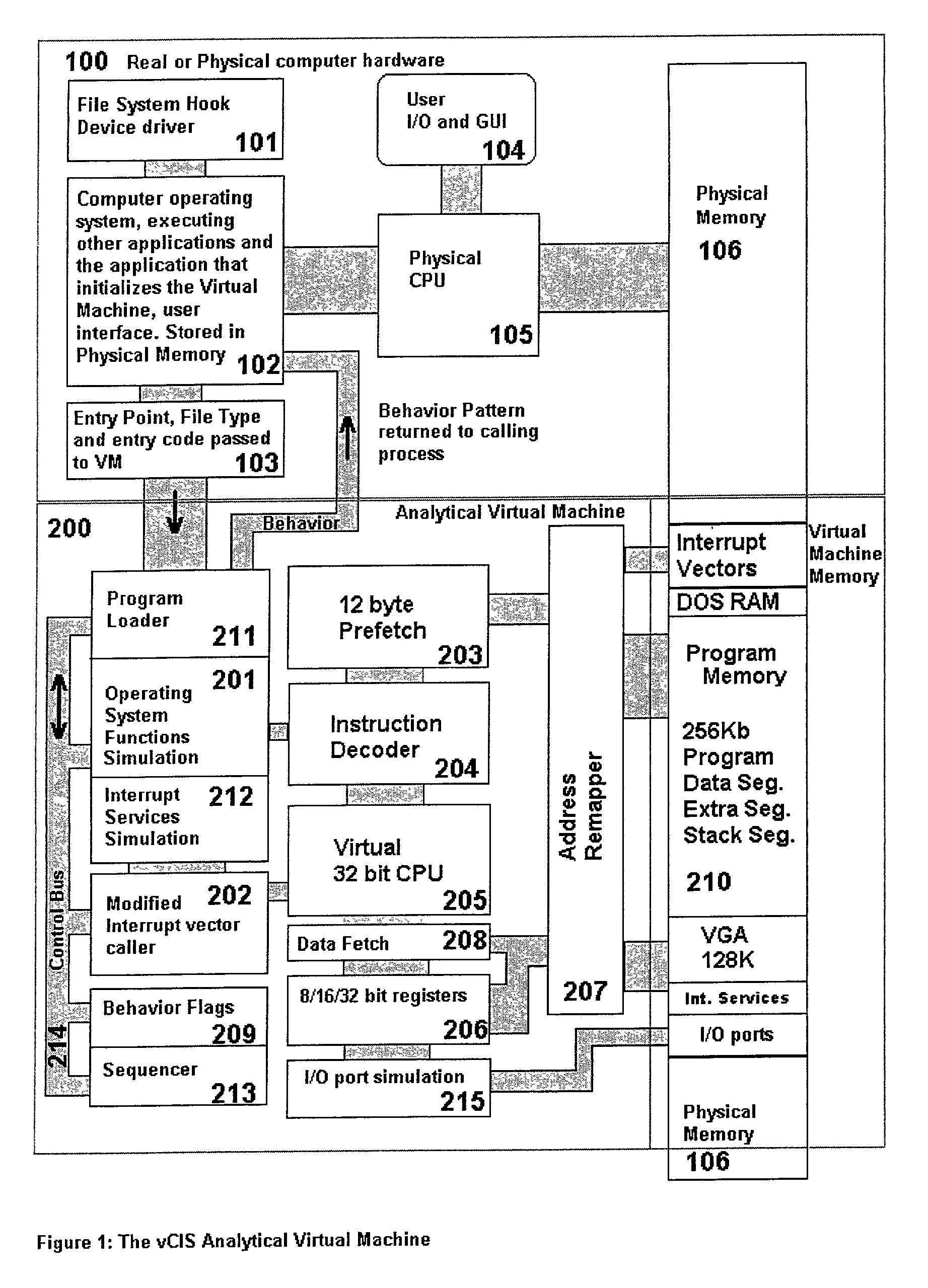
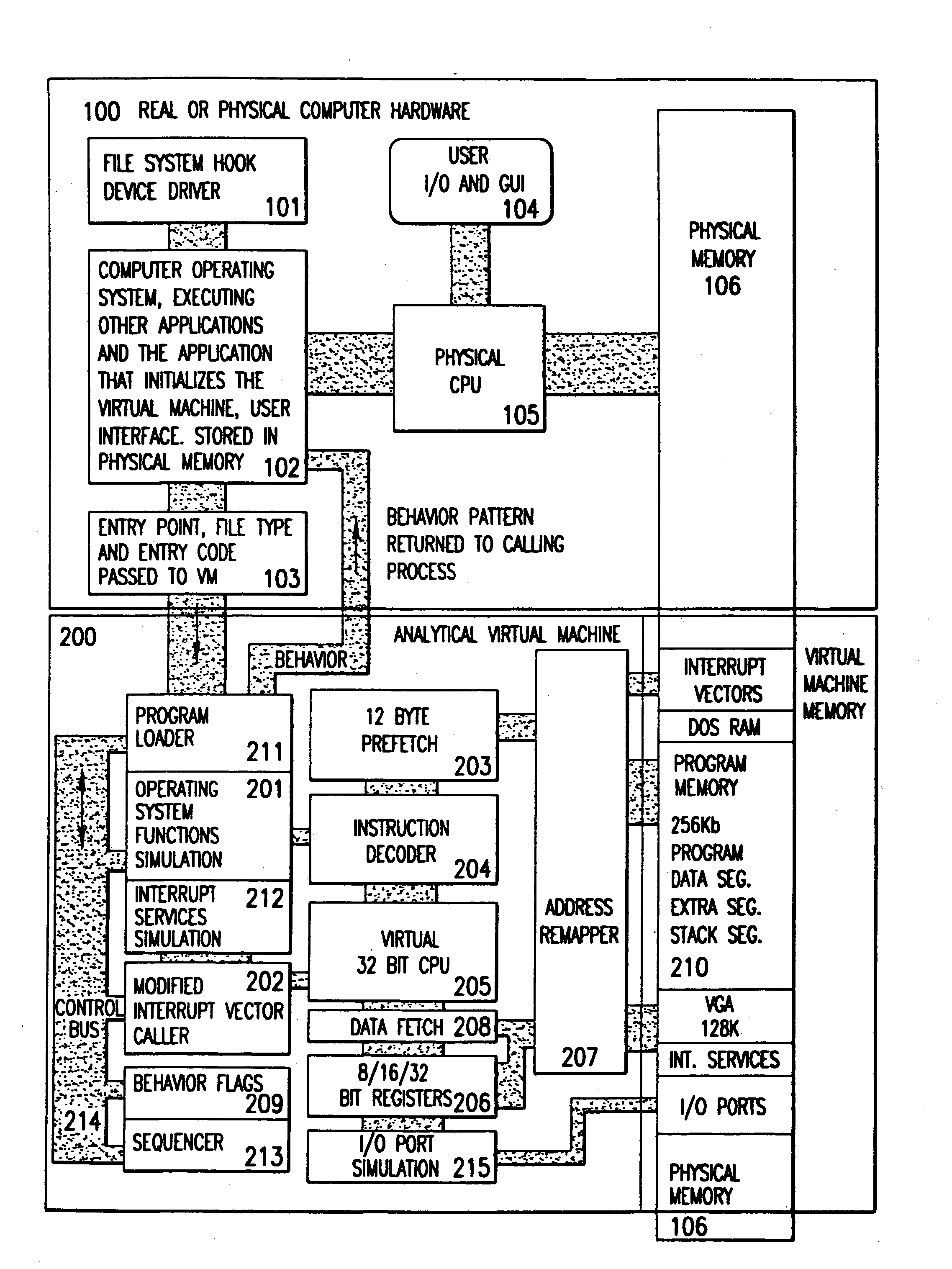
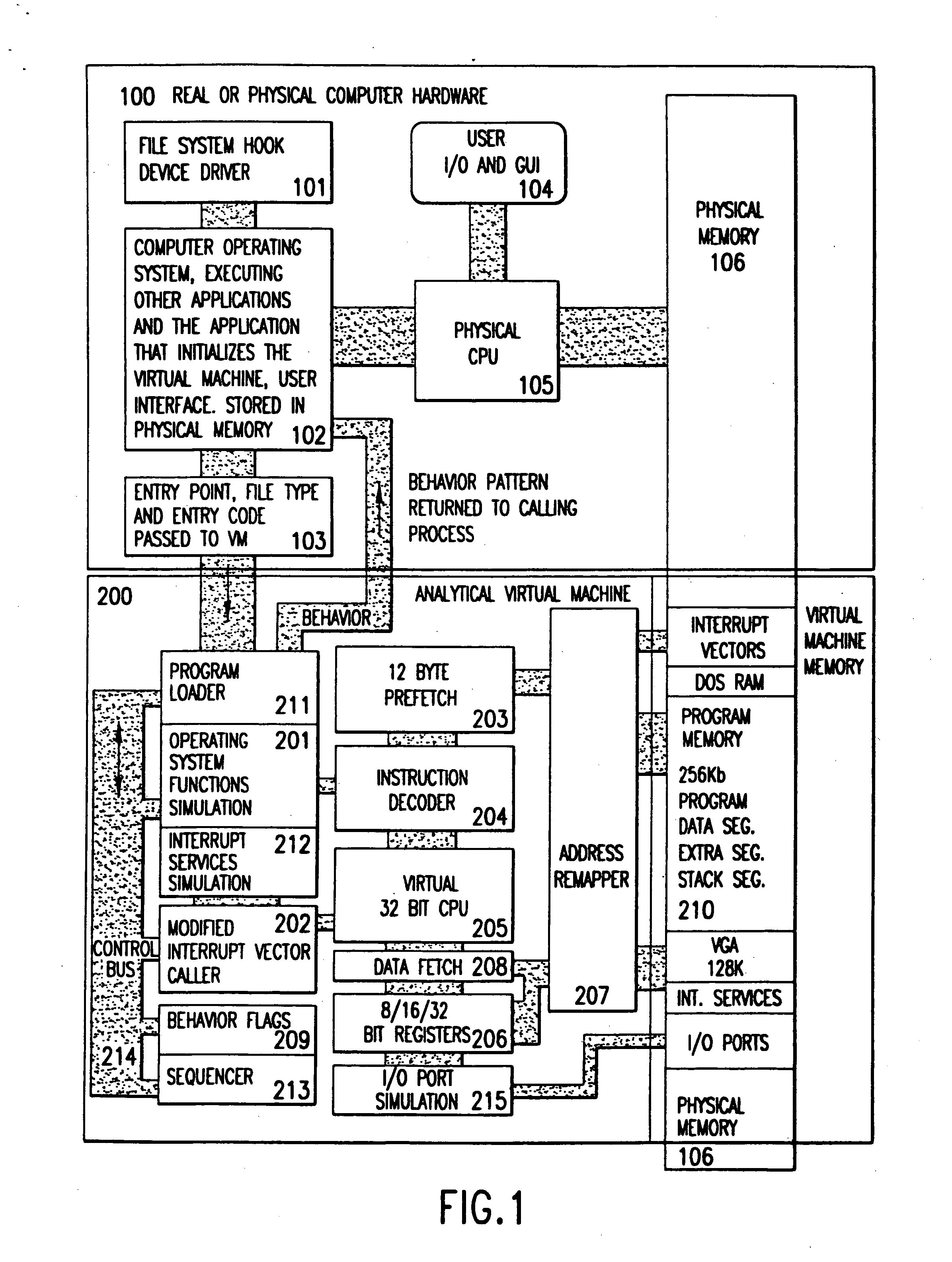
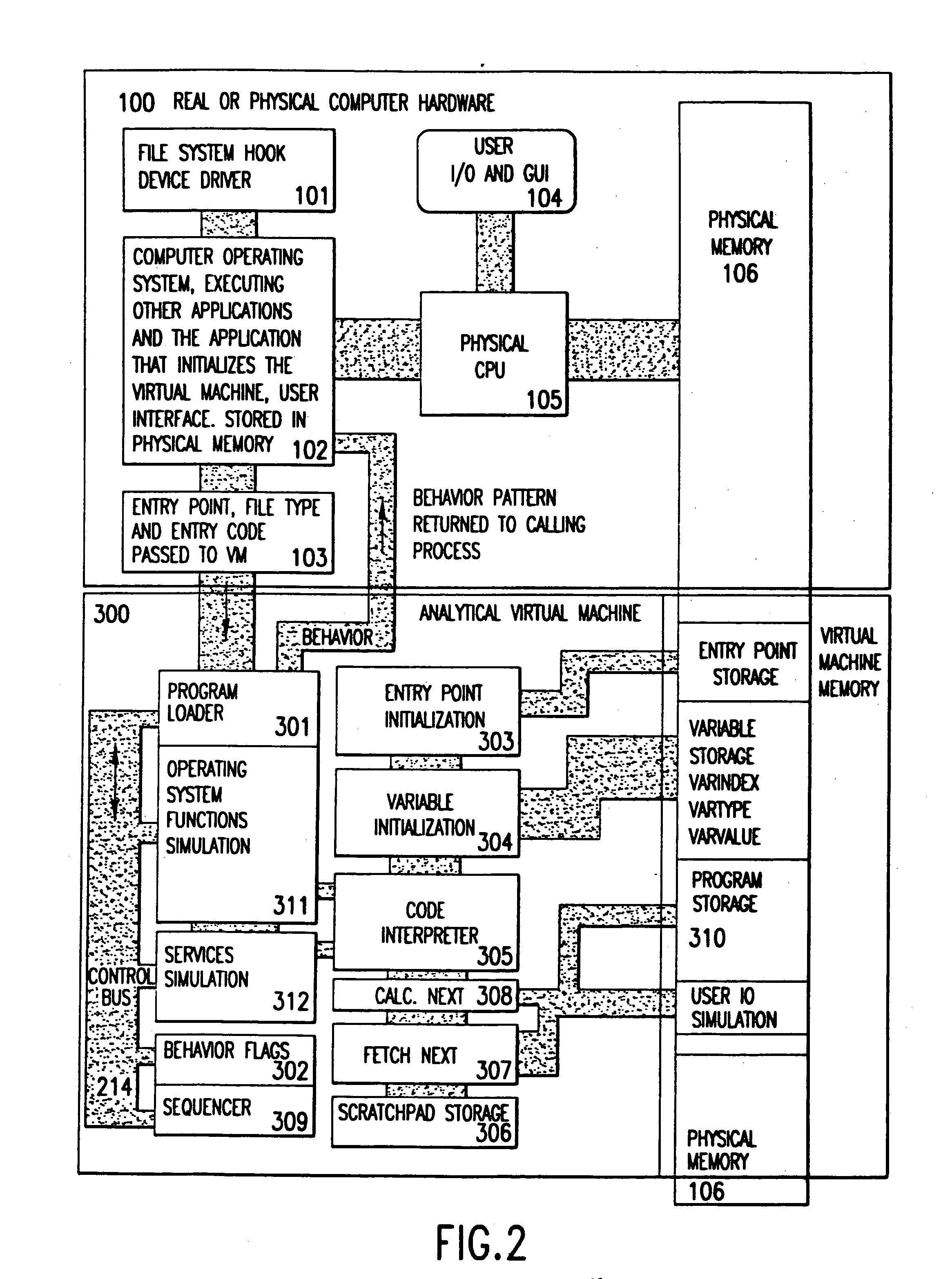
Analytical virtual machine
InactiveUS7657419B2Memory loss protectionError detection/correctionProcessor registerParallel computing
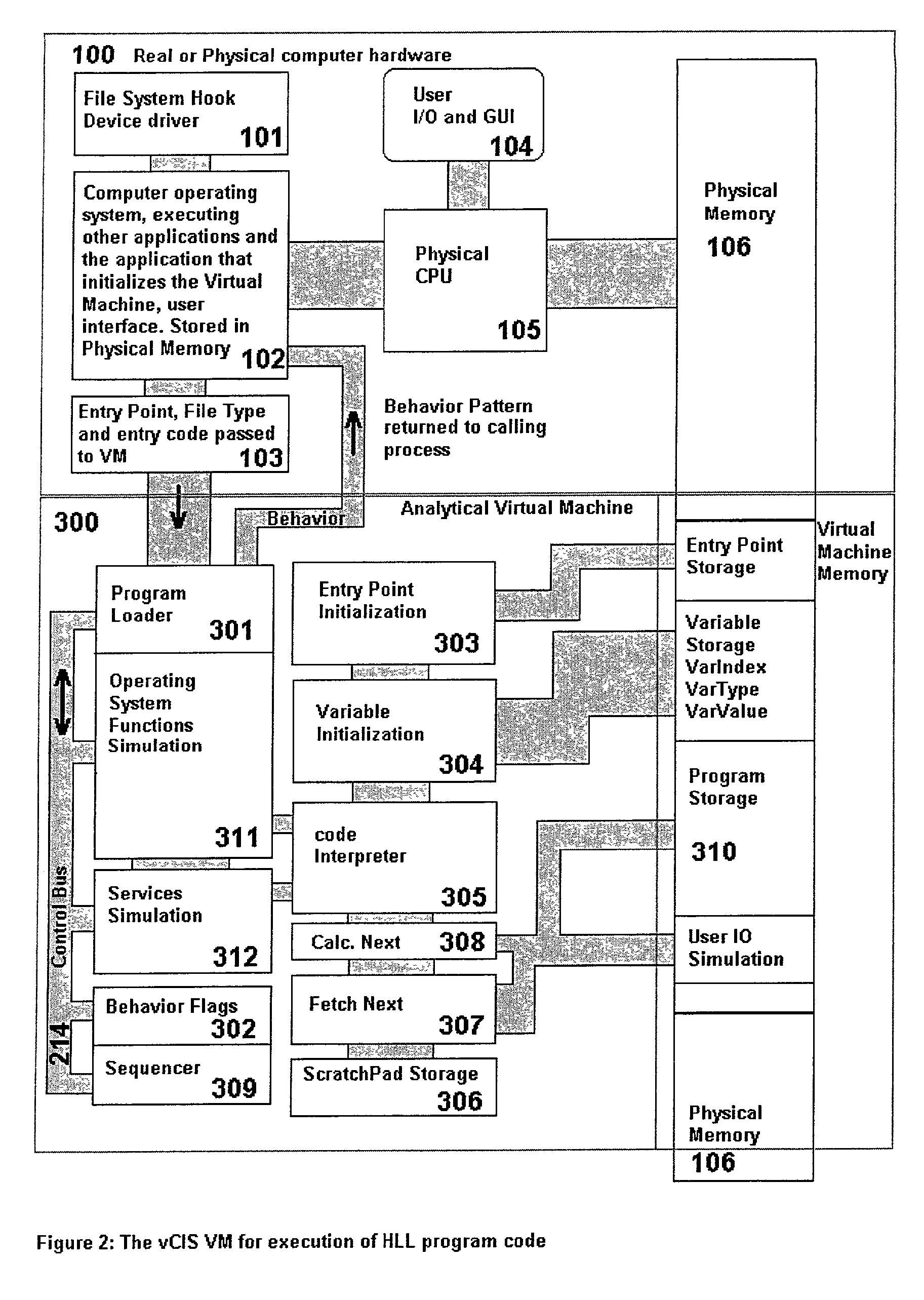
An analytical virtual machine (AVM) analyzes computer code using a software processor including a register that stores behavior flags indicative of behaviors identified by virtually executing the code within the virtual machine. The AVM includes a sequencer that stores the sequence in which behavior flags are set in the behavior flags register. The AVM analyzes machine performance by emulating execution of the code being analyzed on a fully virtual machine and records the observed behavior. When emulation and analysis are complete, the AVM returns the behavior flags register and sequencer to the real machine and terminates.
Owner:KYNDRYL INC
Analytical virtual machine
InactiveUS7146305B2Memory loss protectionDigital data processing detailsProcessor registerParallel computing
An analytical virtual machine (AVM) analyzes computer code using a software processor including a register that stores behavior flags indicative of behaviors identified by virtually executing the code within the virtual machine. The AVM includes a sequencer that stores the sequence in which behavior flags are set in the behavior flags register. The AVM analyzes machine performance by emulating execution of the code being analyzed on a fully virtual machine and records the observed behavior. When emulation and analysis are complete, the AVM returns the behavior flags register and sequencer to the real machine and terminates.
Owner:KYNDRYL INC
Analytical virtual machine
InactiveUS20020056076A1Memory loss protectionDigital data processing detailsProcessor registerParallel computing
An analytical virtual machine (AVM) analyzes computer code using a software processor including a register that stores behavior flags indicative of behaviors identified by virtually executing the code within the virtual machine. The AVM includes a sequencer that stores the sequence in which behavior flags are set in the behavior flags register. The AVM analyzes machine performance by emulating execution of the code being analyzed on a fully virtual machine and records the observed behavior. When emulation and analysis are complete, the AVM returns the behavior flags register and sequencer to the real machine and terminates.
Owner:KYNDRYL INC
Inter-thread communications using shared interrupt register
InactiveUS6971103B2Reduce overheadProgram initiation/switchingDigital computer detailsProcessor registerFLAGS register
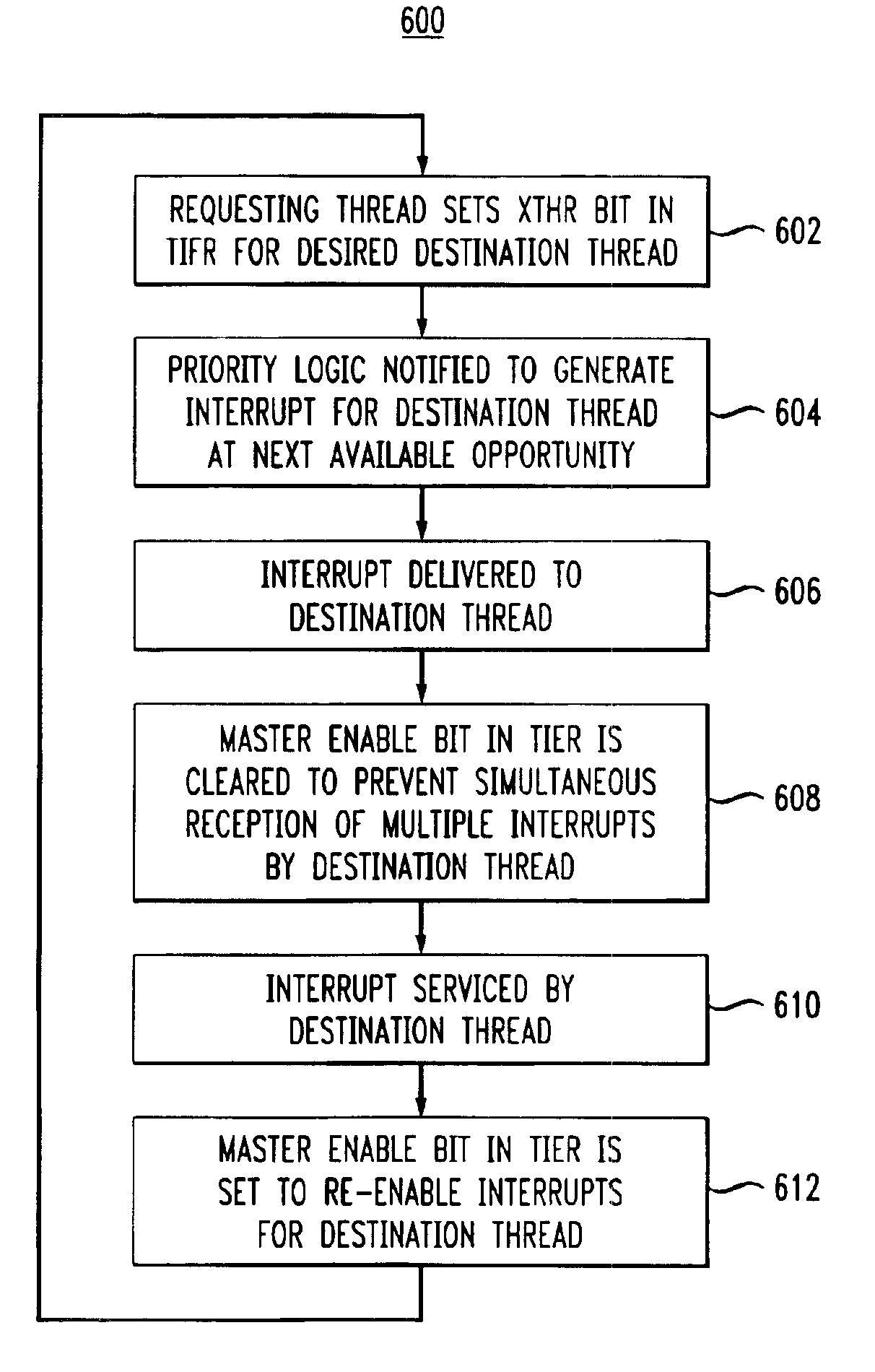
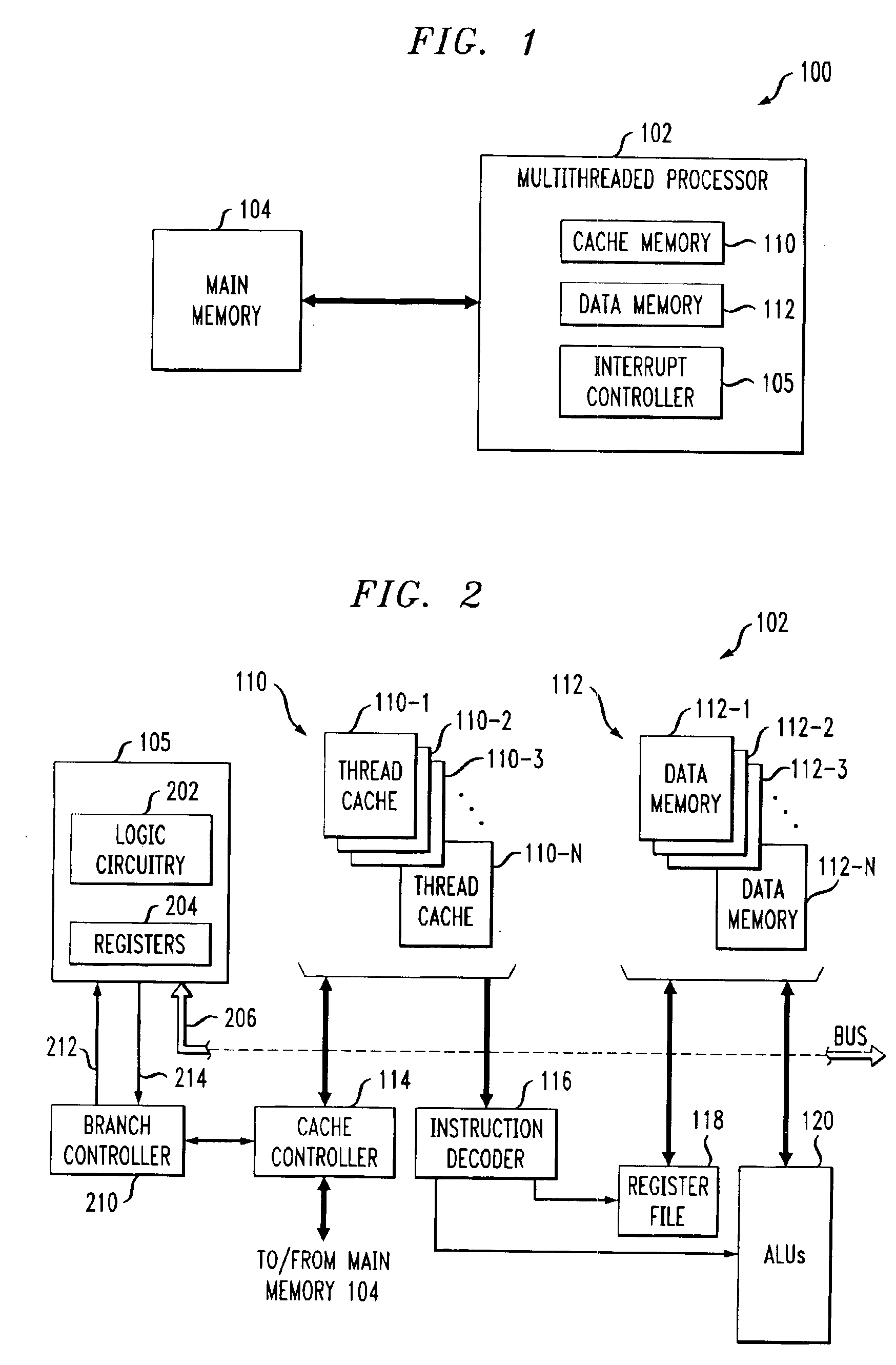
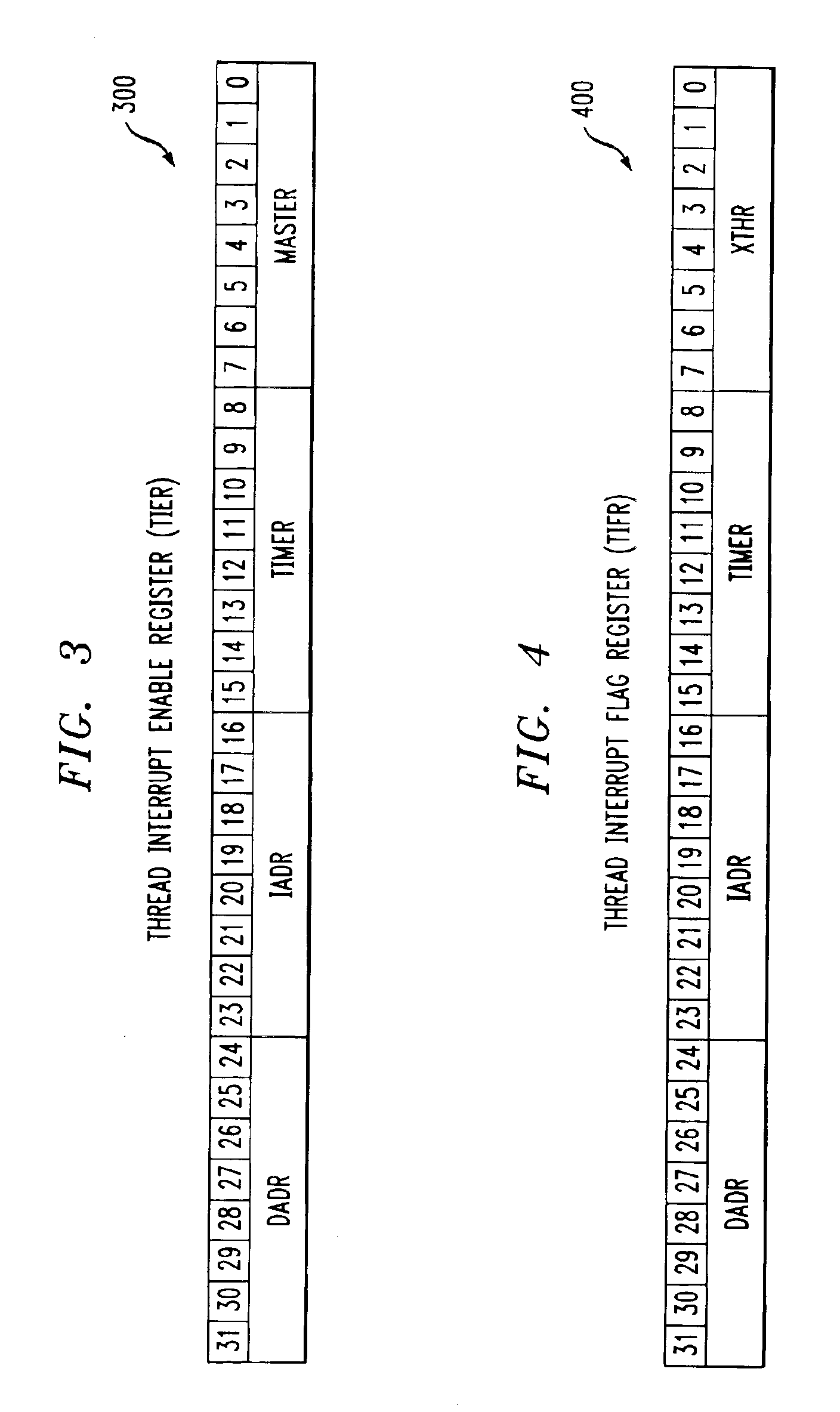
A multithreaded processor includes an interrupt controller for processing a cross-thread interrupt directed from a requesting thread to a destination thread. The interrupt controller in an illustrative embodiment receives a request for delivery of the cross-thread interrupt to the destination thread, determines whether the destination thread of the cross-thread interrupt is enabled for receipt of cross-thread interrupts, and utilizes a thread identifier to control delivery of the cross-thread interrupt to the destination thread if the destination thread is enabled for receipt of cross-thread interrupts. The requesting thread requests delivery of the cross-thread interrupt to the destination thread by setting a corresponding interrupt pending bit in a flag register of the multithreaded processor. The destination thread is enabled for receipt of cross-thread interrupts if a corresponding enable bit is set in an enable register of the multithreaded processor. The flag and enable registers may be implemented within the interrupt controller.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Shared register architecture for a dual-instruction-set CPU to facilitate data exchange between the instruction sets
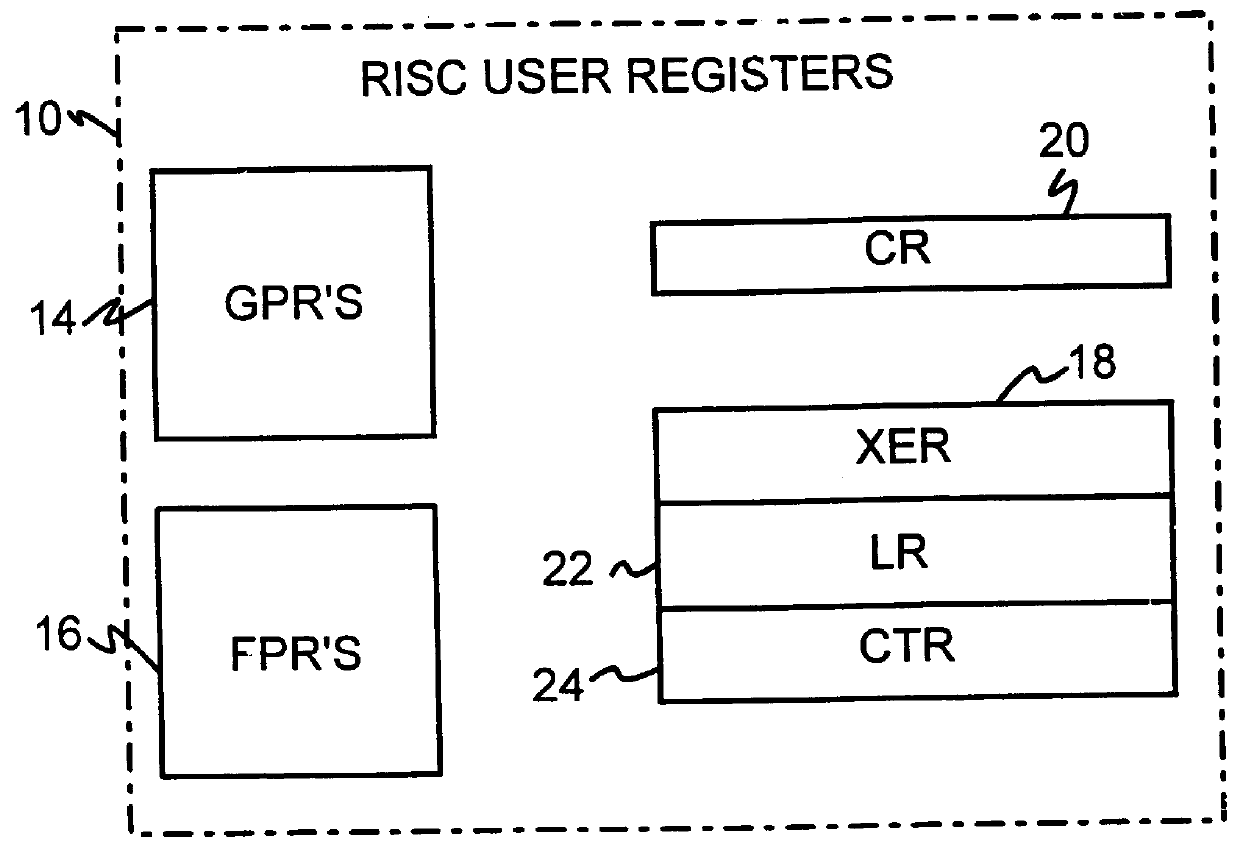
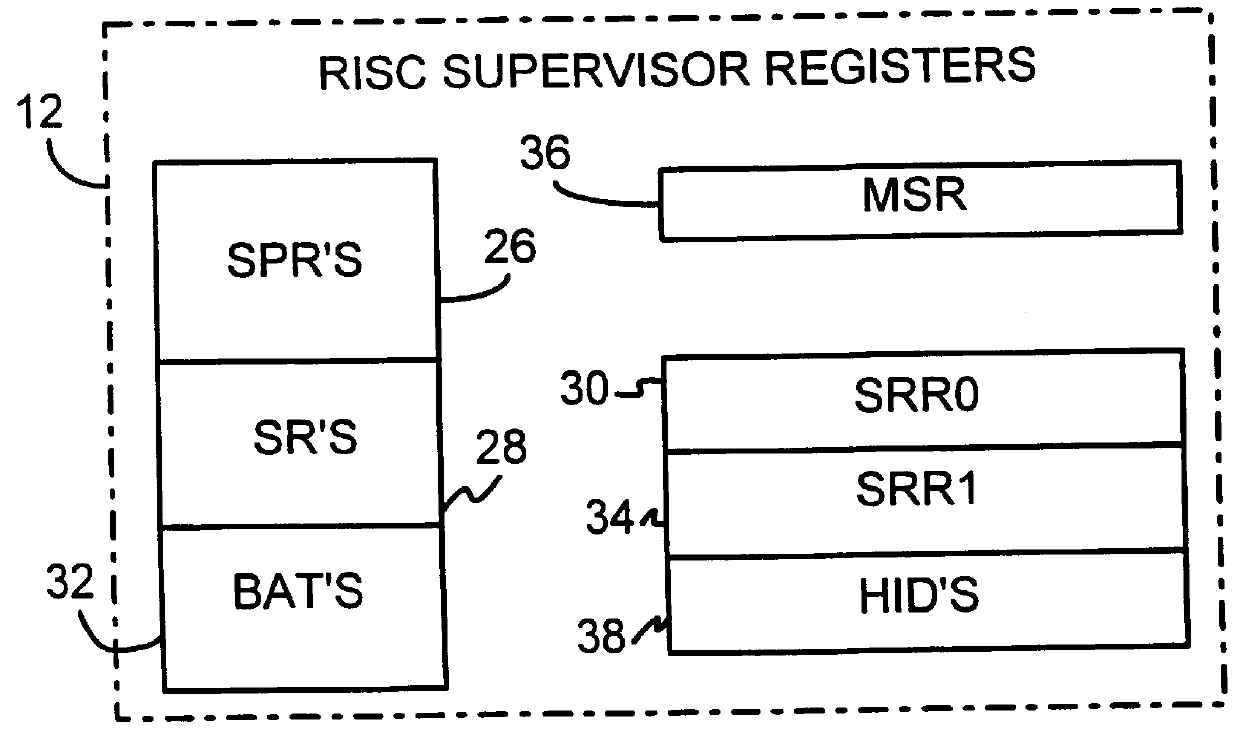
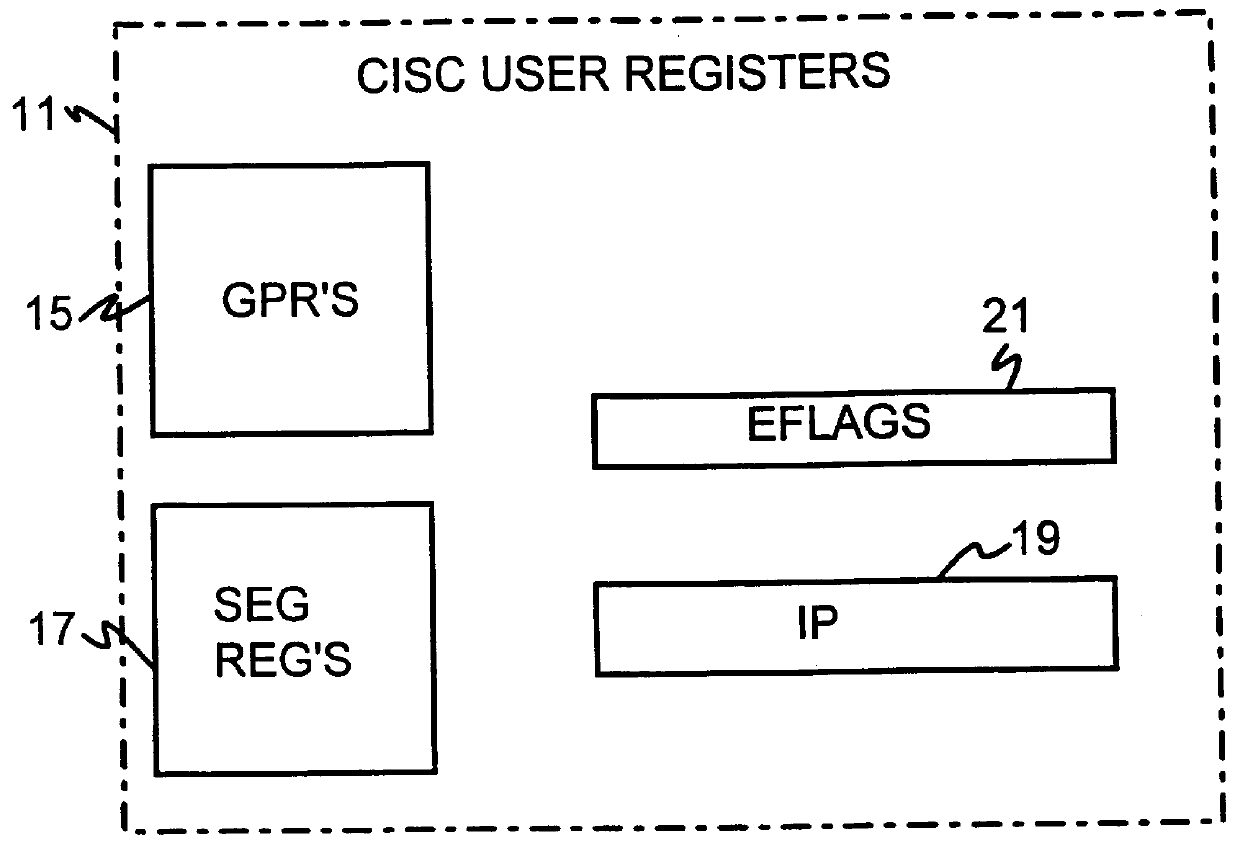
A dual-instruction set central processing unit (CPU) is capable of executing instructions from a reduced instruction set computer (RISC) instruction set and from a complex instruction set computer (CISC) instruction set. Data and address information may be to transferred from a CISC program to a RISC program running on the CPU by using shared registers. The architecturally-defined registers in the CISC instruction set are merged or folded into some of the architecturally-defined registers in the RISC architecture so that these merged registers are shared by the two instructions sets. In particular, the flags or condition code registers defined by each architecture are merged together so that CISC instructions and RISC instructions will implicitly update the same merged flags register when performing computational instructions. The RISC and CISC registers are folded together so that the CISC flags are at one end of the register while the frequently used RISC flags are at the other end, but the RISC instructions can read or write any bit in the merged register. The CISC code segment base address is stored in the RISC branch count register, while the CISC floating point instruction address is stored in the RISC branch link register. The general-purpose registers (GPR's) are also merged together, allowing a CISC program to pass data to a RISC program merely by writing one of its GPR's, switching control to the RISC program, and the RISC program reading one of its GPR's that is merged with and corresponds to the CISC GPR that was written to by the CISC program.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
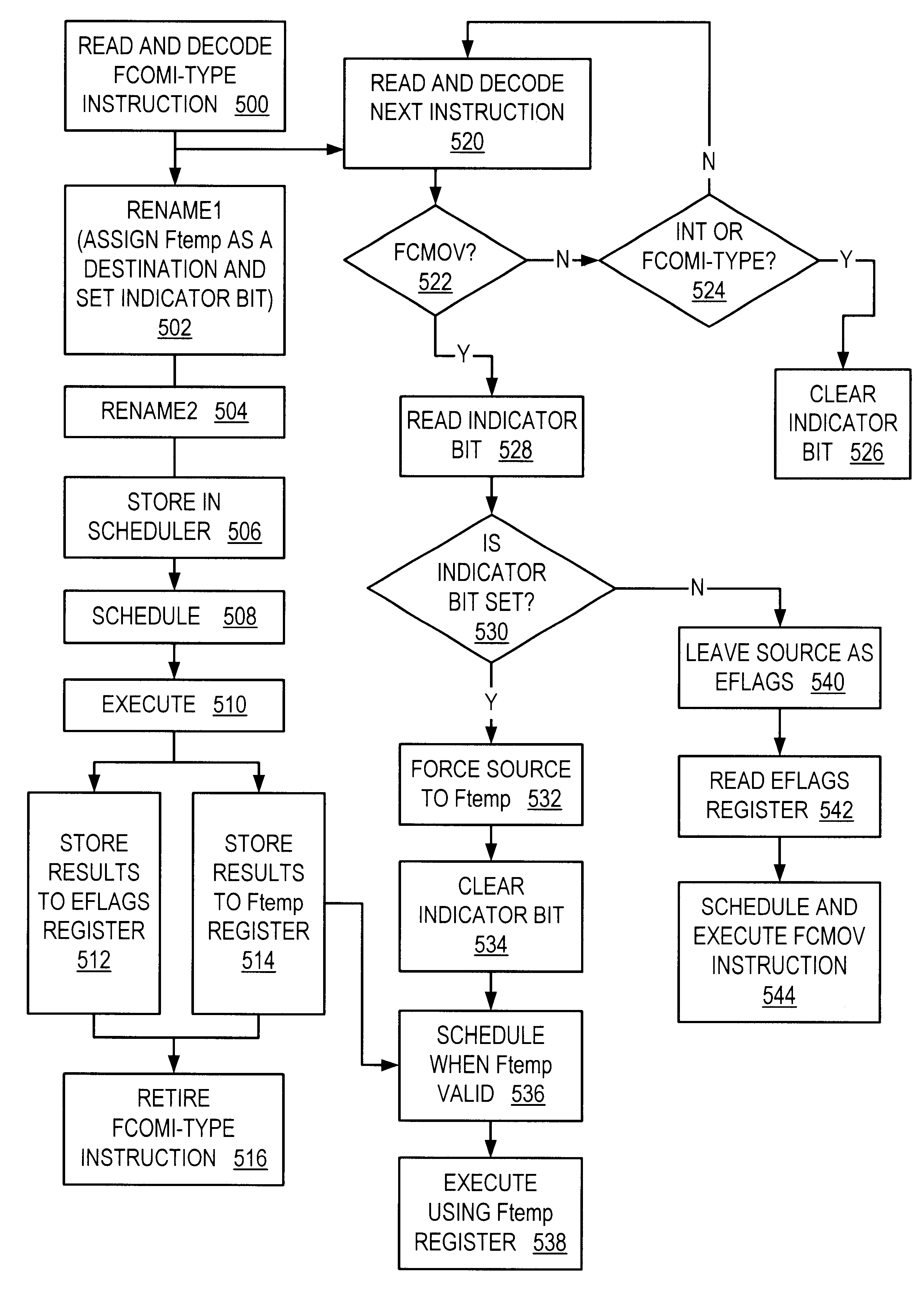
Rapid execution of FCMOV following FCOMI by storing comparison result in temporary register in floating point unit
InactiveUS6393555B1Conditional code generationGeneral purpose stored program computerProcessor registerFloating-point unit
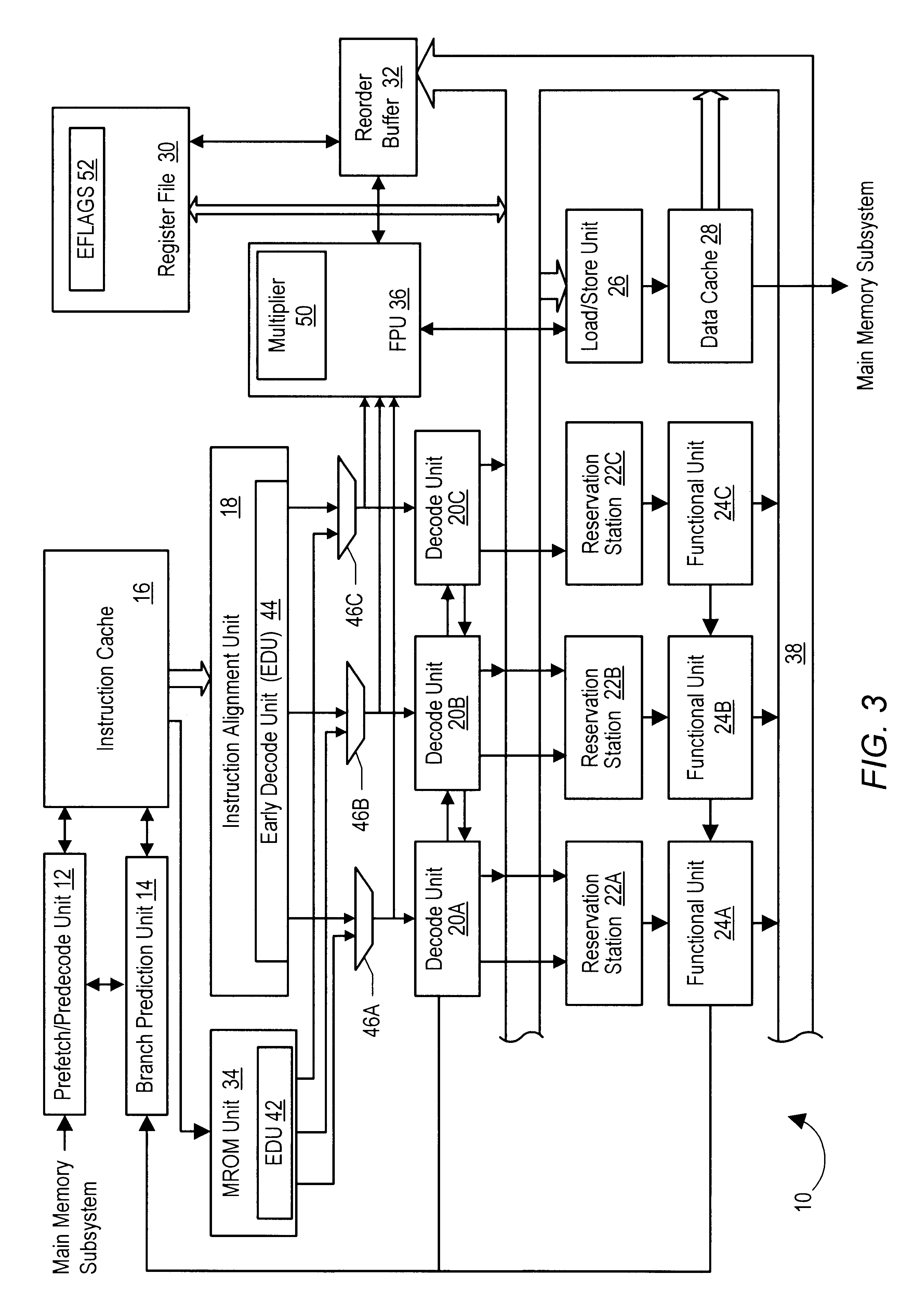
A microprocessor with a floating point unit configured to rapidly execute floating point compare (FCOMI) type instructions that are followed by floating point conditional move (FCMOV) type instructions is disclosed. FCOMI-type instructions, which normally store their results to integer status flag registers, are modified to store a copy of their results to a temporary register located within the floating point unit. If an FCMOV-type instruction is detected following an FCOMI-type instruction, then the FCMOV-type instruction's source for flag information is changed from the integer flag register to the temporary register. FCMOV-type instructions are thereby able to execute earlier because they need not wait for the integer flags to be read from the integer portion of the microprocessor. A computer system and method for rapidly executing FCOMI-type instructions followed by FCMOV-type instructions are also disclosed.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
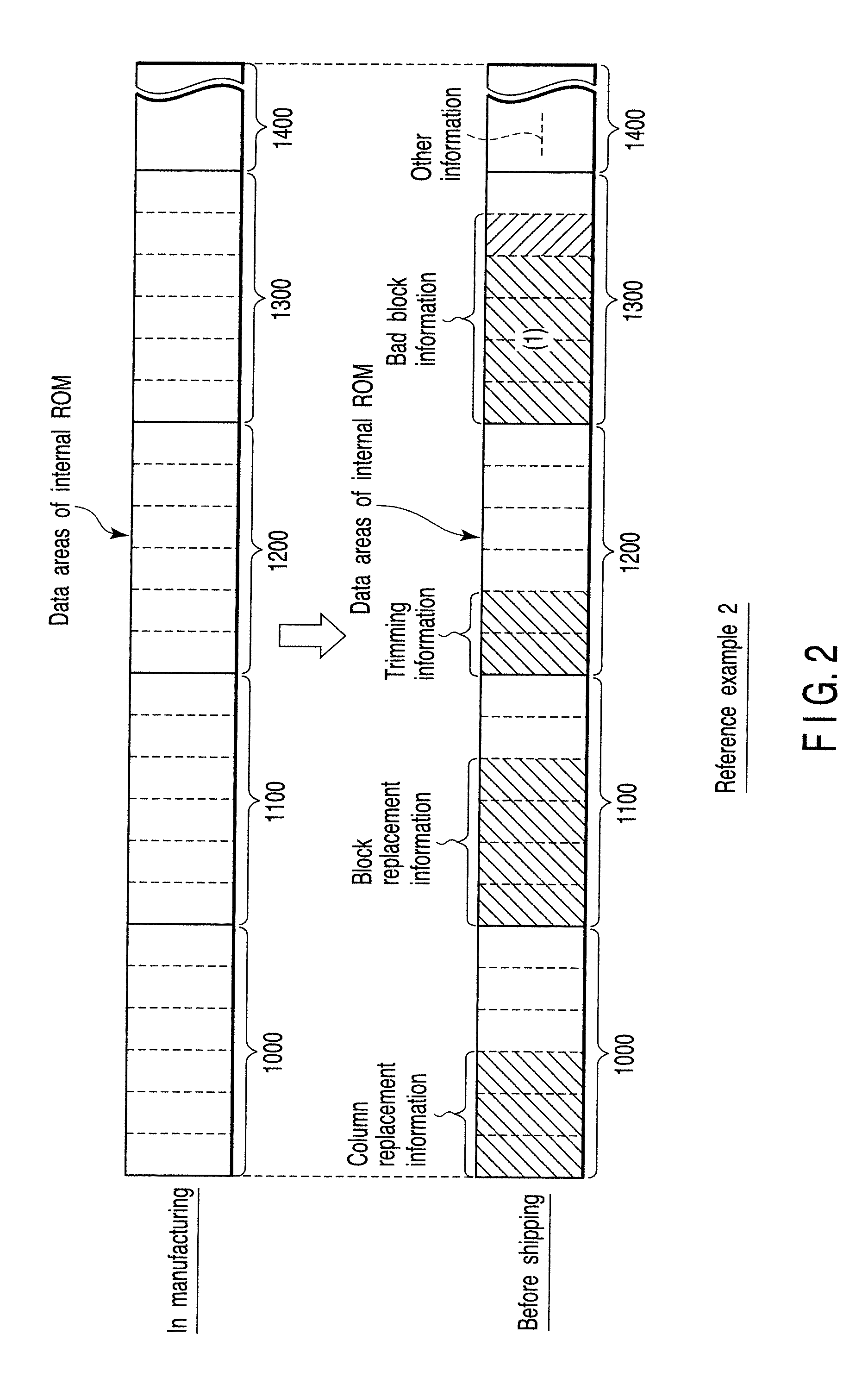
Semiconductor integrated circuit device
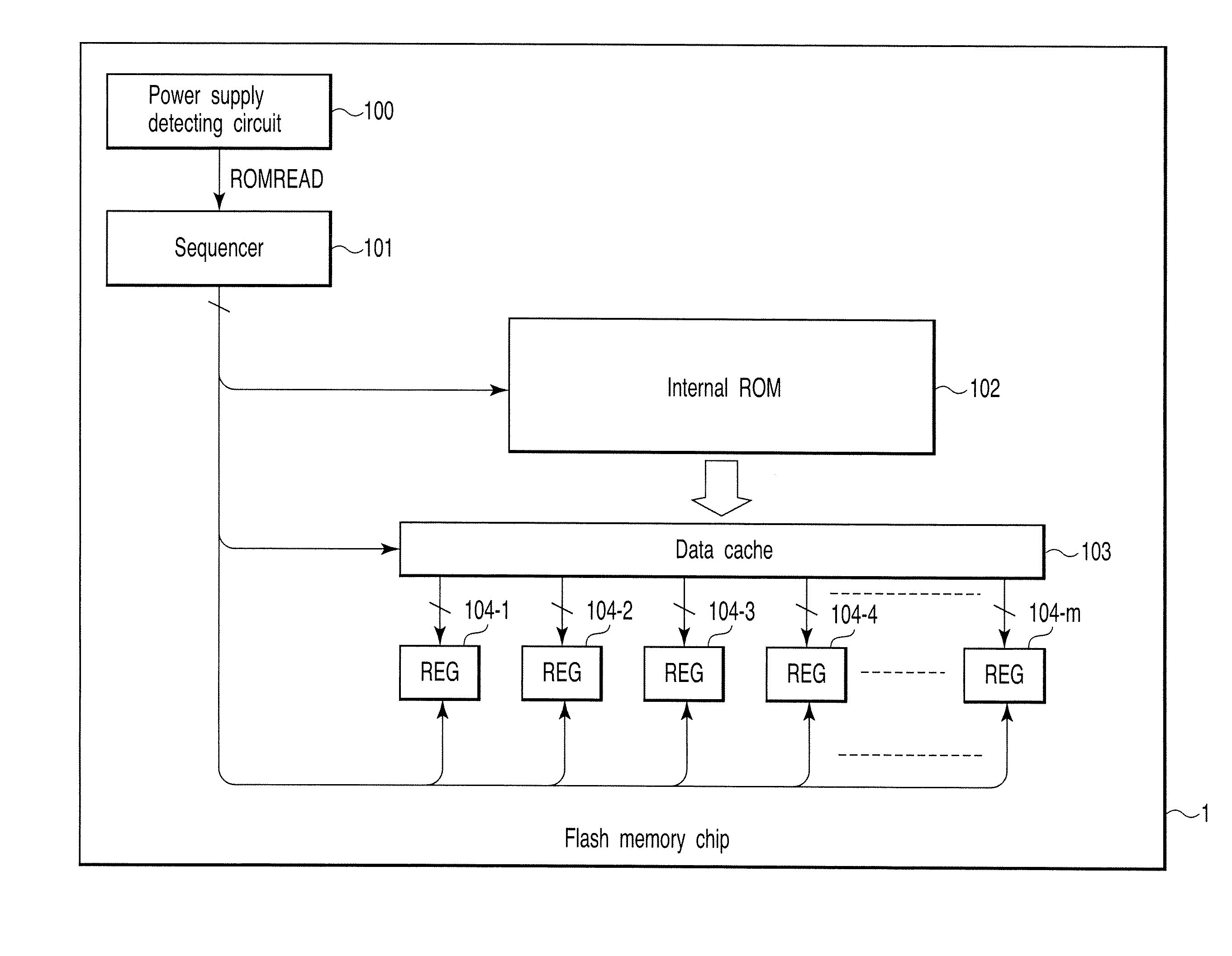
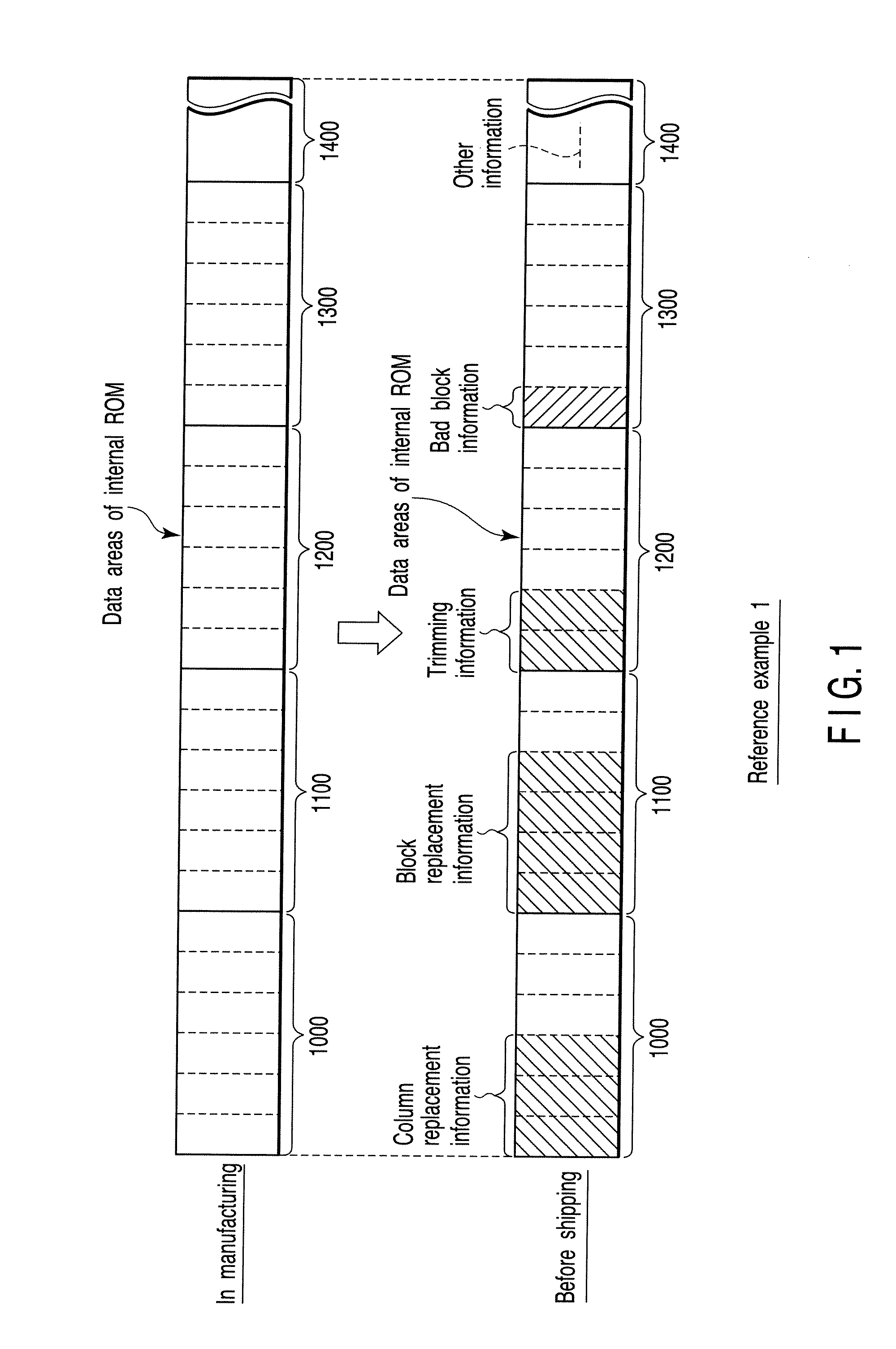
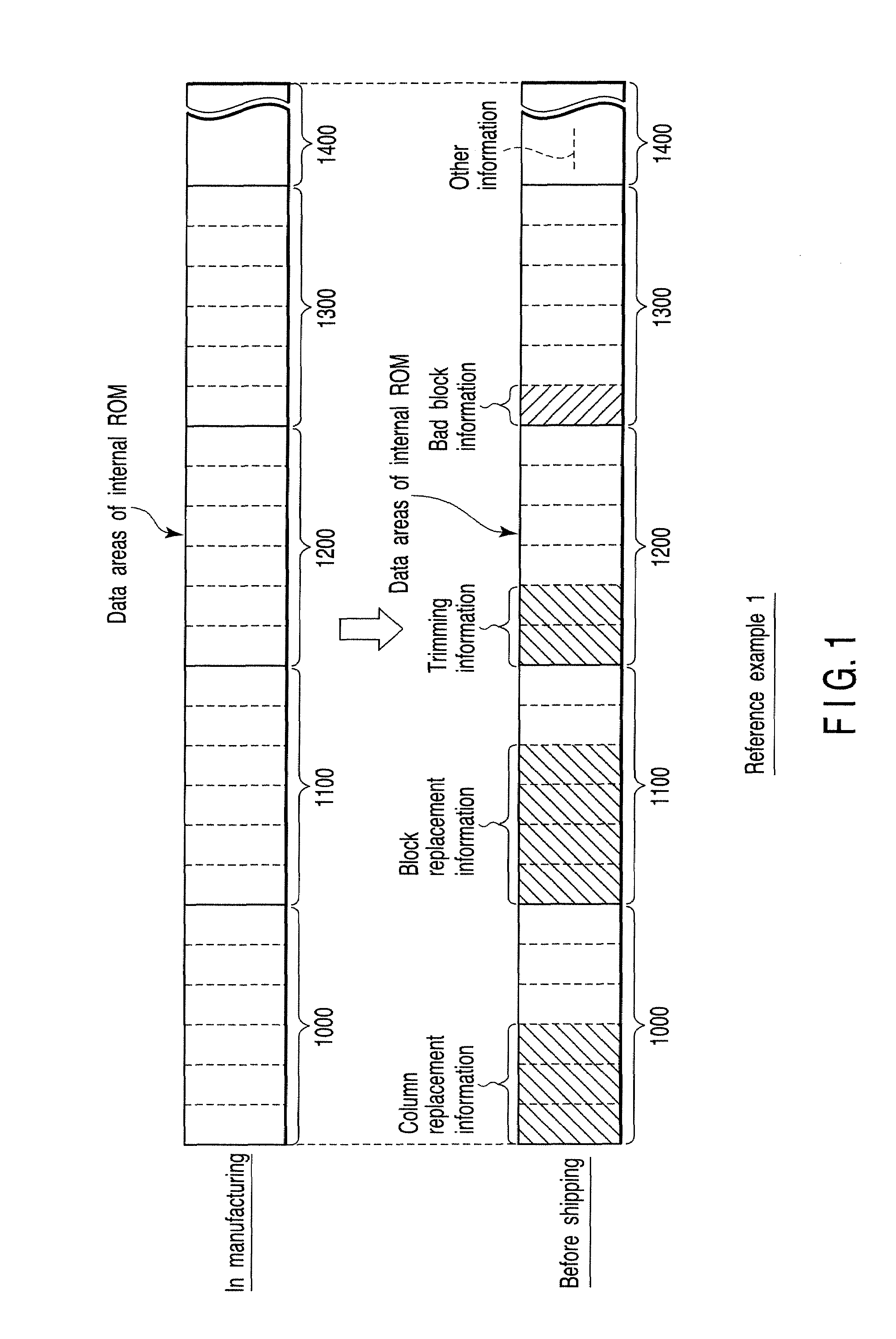
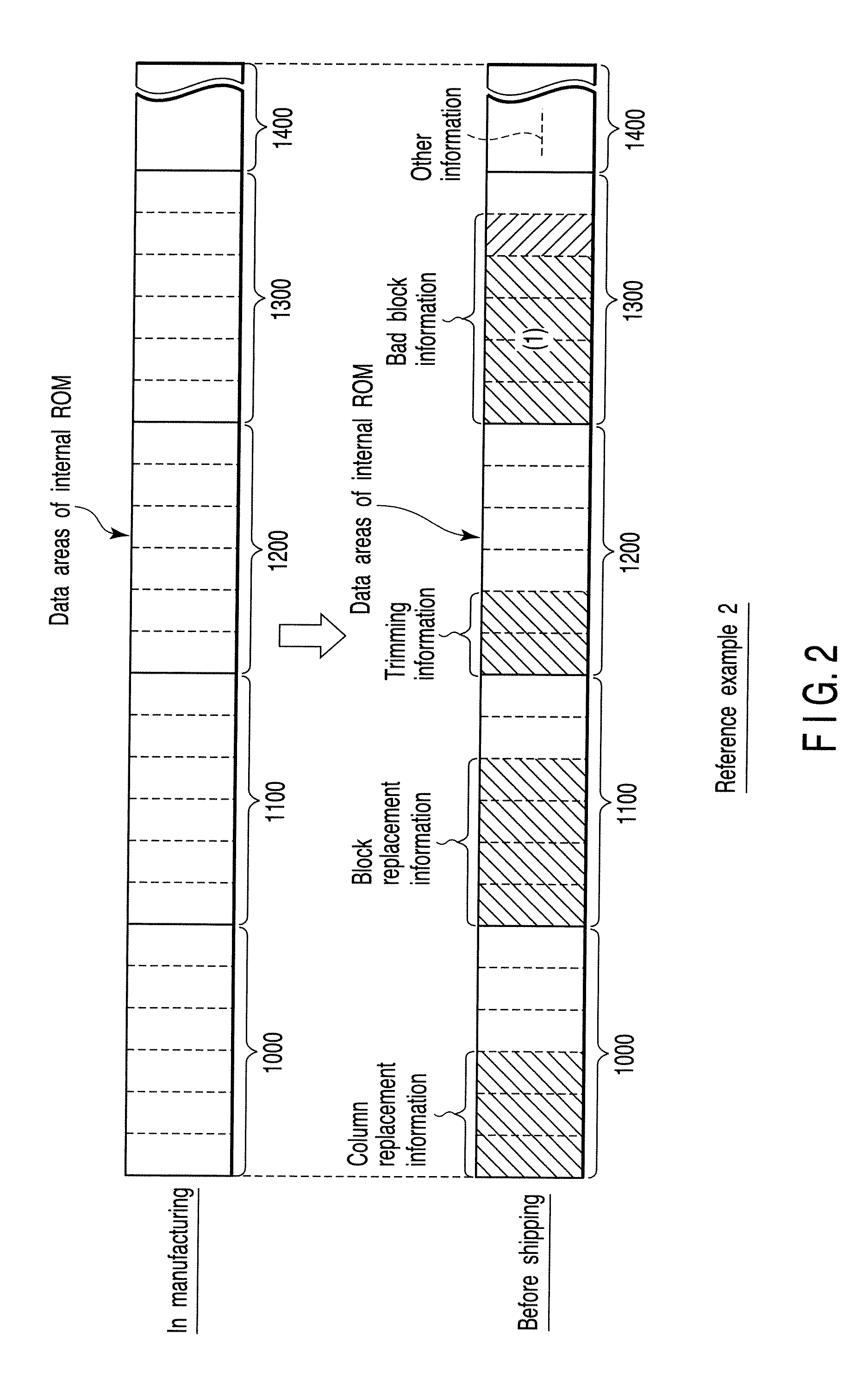
A semiconductor integrated circuit device includes a memory cell array having a plurality of blocks, a storage unit, a block replacement information register group, and a bad block flag register group. The storage unit includes a block replacement information registration area with which it is possible to register block replacement information, and a bad block information registration area with which it is possible to register bad block information. The block replacement information register group is set in accordance with the block replacement information read out of the storage unit during a boot sequence, and the bad block flag register group is set in accordance with both of the block replacement information and the bad block information read out of the storage unit during the boot sequence.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Multi-core processor control method
InactiveUS20050289286A1Shortening of system boot timeIncrease productionError detection/correctionMemory adressing/allocation/relocationMulti-core processorFLAGS register
The load / sense control of the setting value that corresponds to the processor core for CMP, etc. processors that have multi-cores realize, for such processors with multi-core structures, the shortening of system boot time during multi-core operation, flexible debugging methods, and improvement of yield with the aid of partial core quality product chips at time of semiconductor production, by equipping a core selection flag register that maintains the status of each core, and controlling the output to the core block from the processor common block through that core selection flag register status.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Processor executing SIMD instructions
InactiveUS20080046704A1Fast resultsFast processingConditional code generationInstruction analysisProcessor registerParallel computing
Owner:TANAKA TETABUYA +8
Semiconductor integrated circuit device
A semiconductor integrated circuit device includes a memory cell array having a plurality of blocks, a storage unit, a block replacement information register group, and a bad block flag register group. The storage unit includes a block replacement information registration area with which it is possible to register block replacement information, and a bad block information registration area with which it is possible to register bad block information. The block replacement information register group is set in accordance with the block replacement information read out of the storage unit during a boot sequence, and the bad block flag register group is set in accordance with both of the block replacement information and the bad block information read out of the storage unit during the boot sequence.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Semiconductor device
InactiveUS7038961B2Guaranteed uptimeRead-only memoriesDigital storagePhase-change memoryProcessor register
A phase change memory is provided with a write data register, an output data selector, a write address register, an address comparator and a flag register. Write data is not only written into a memory cell but also retained by the write data register until the next write cycle. If a read access occurs to that address before the next write cycle, data is read out from the register without reading the data from the memory cell array. Without elongating the cycle time, it is possible not only to use long time to write data into a memory cell therein but also to make longer the interval between the time when a write operation is done and the time when the subsequent read operation is made from that memory cell. As a result, data can be written reliably.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Semiconductor integrated circuit
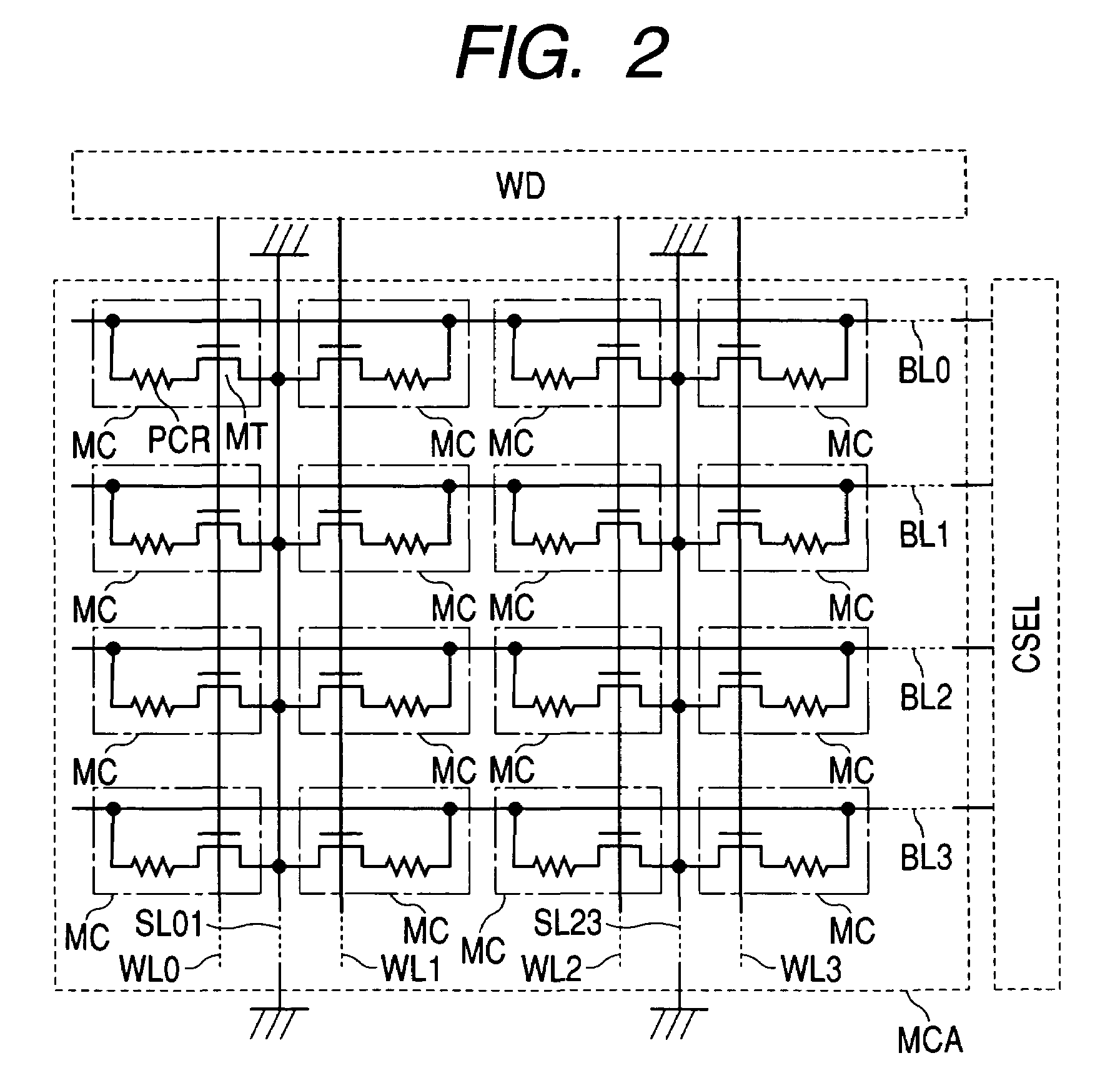
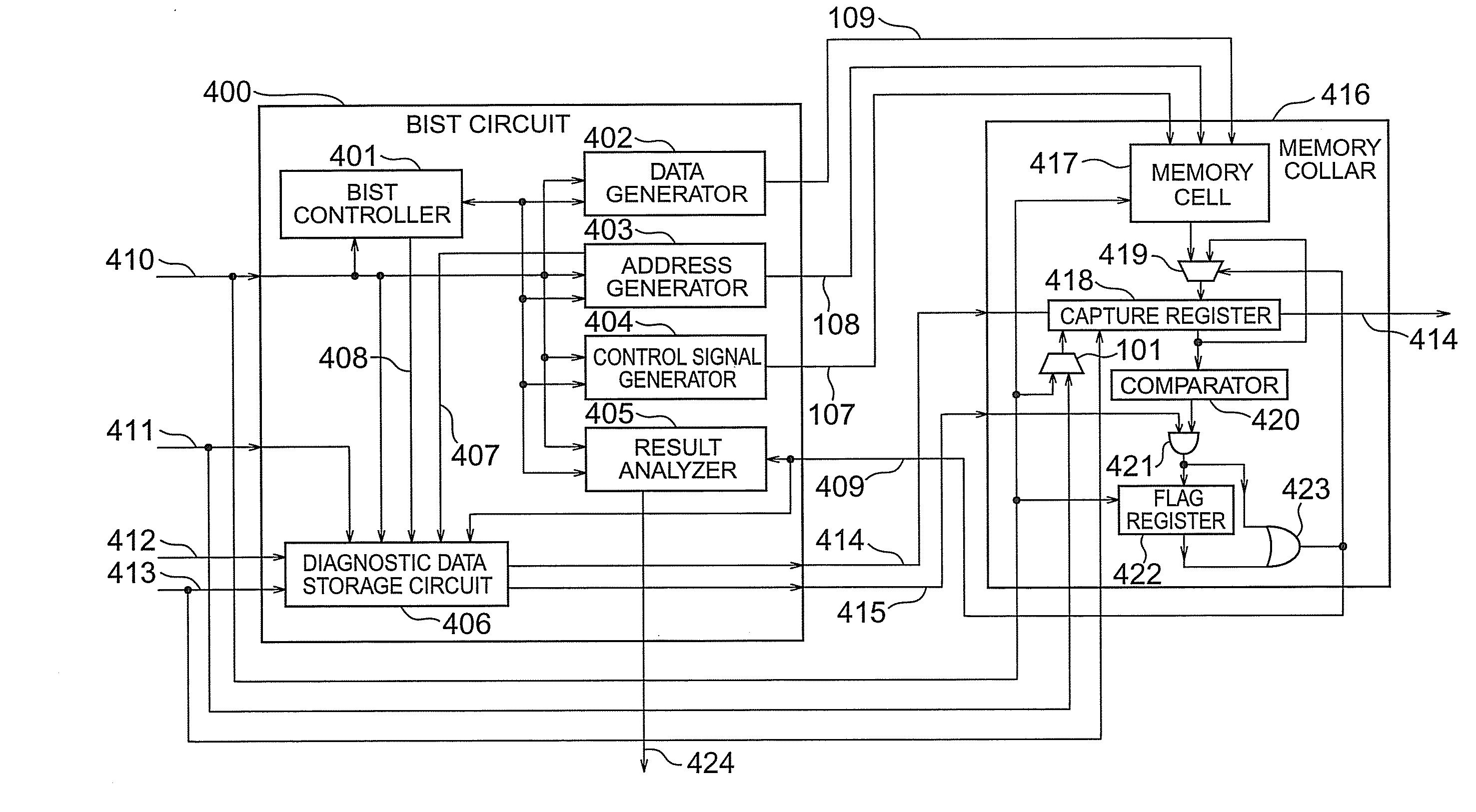
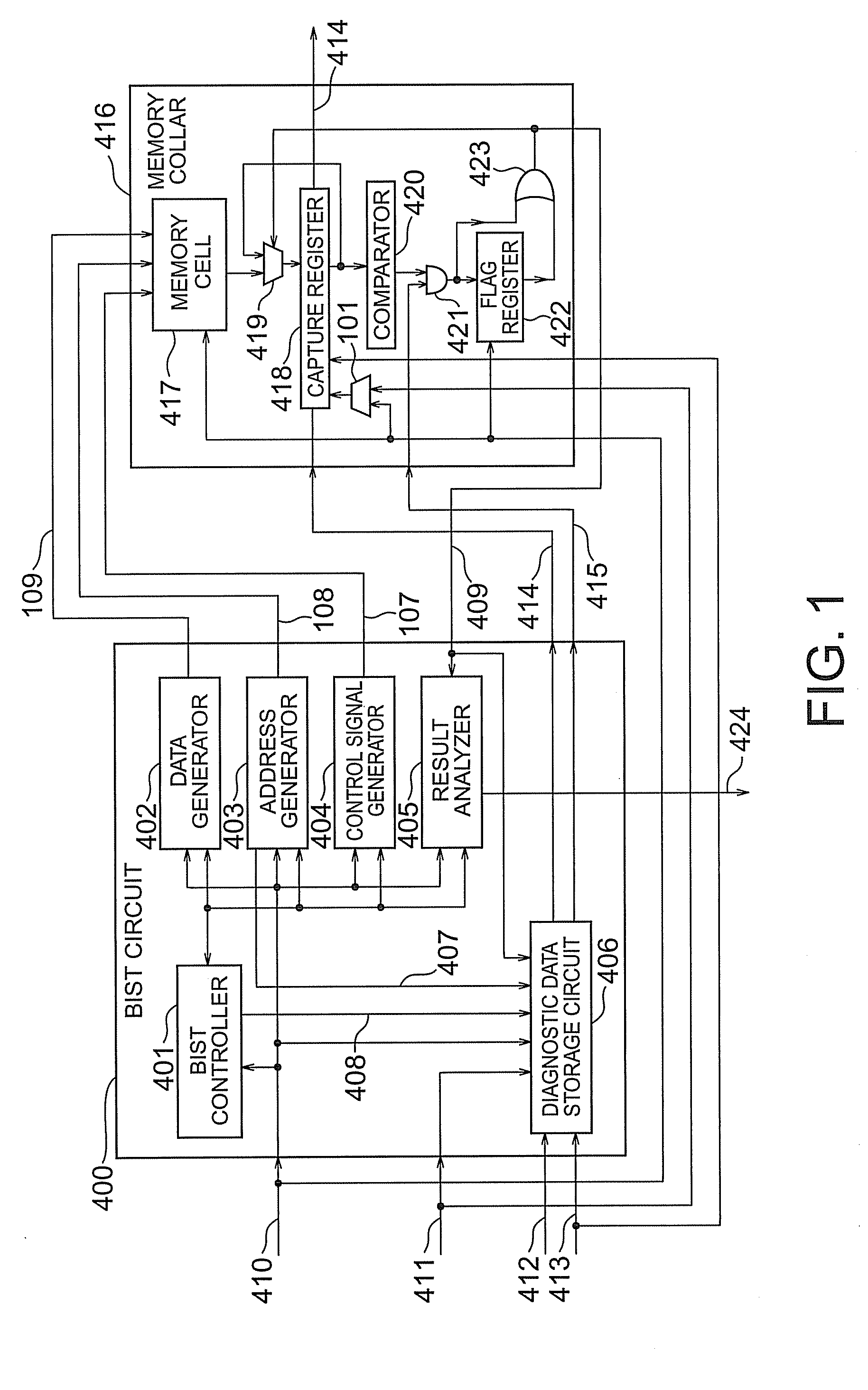
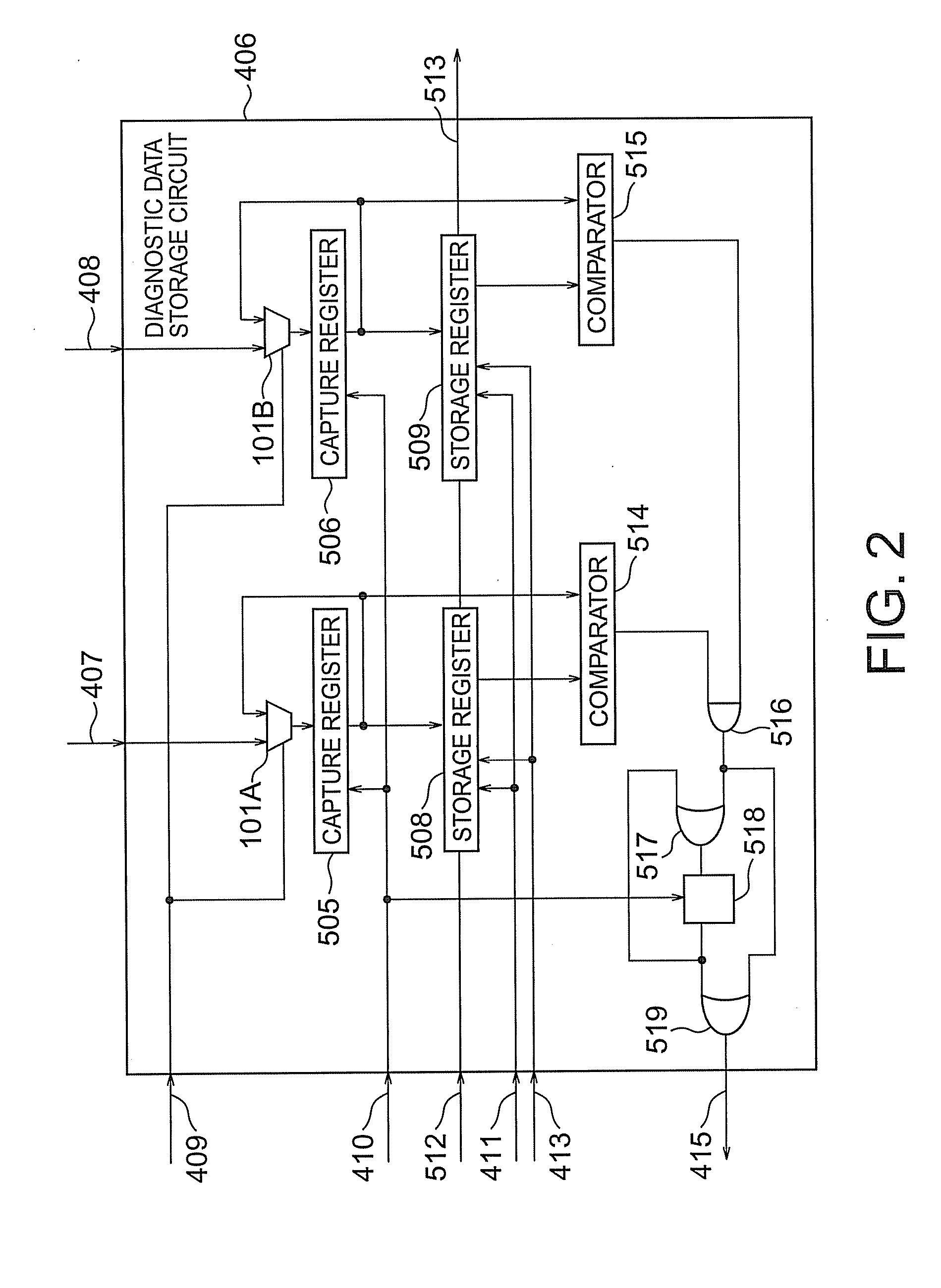
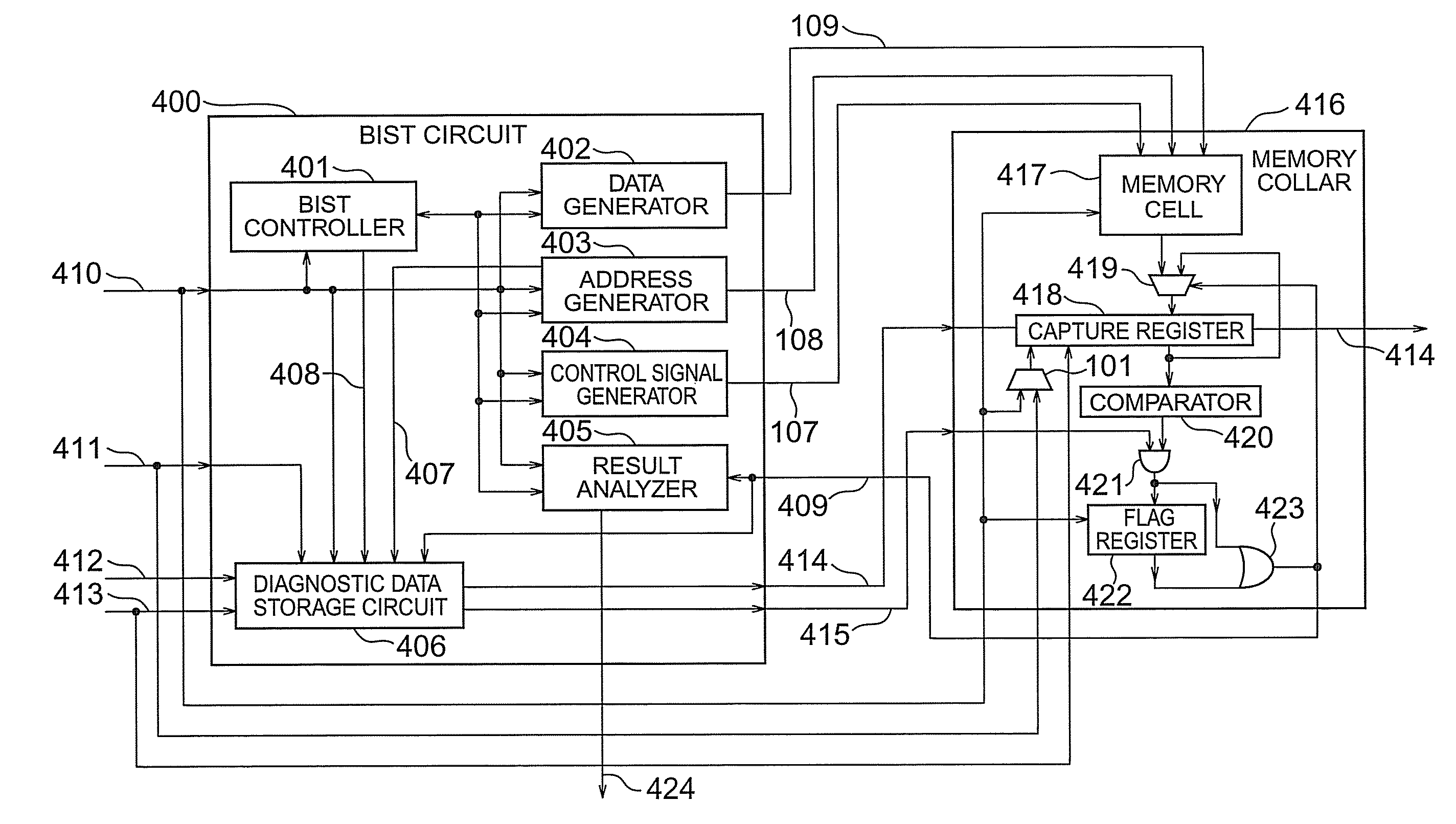
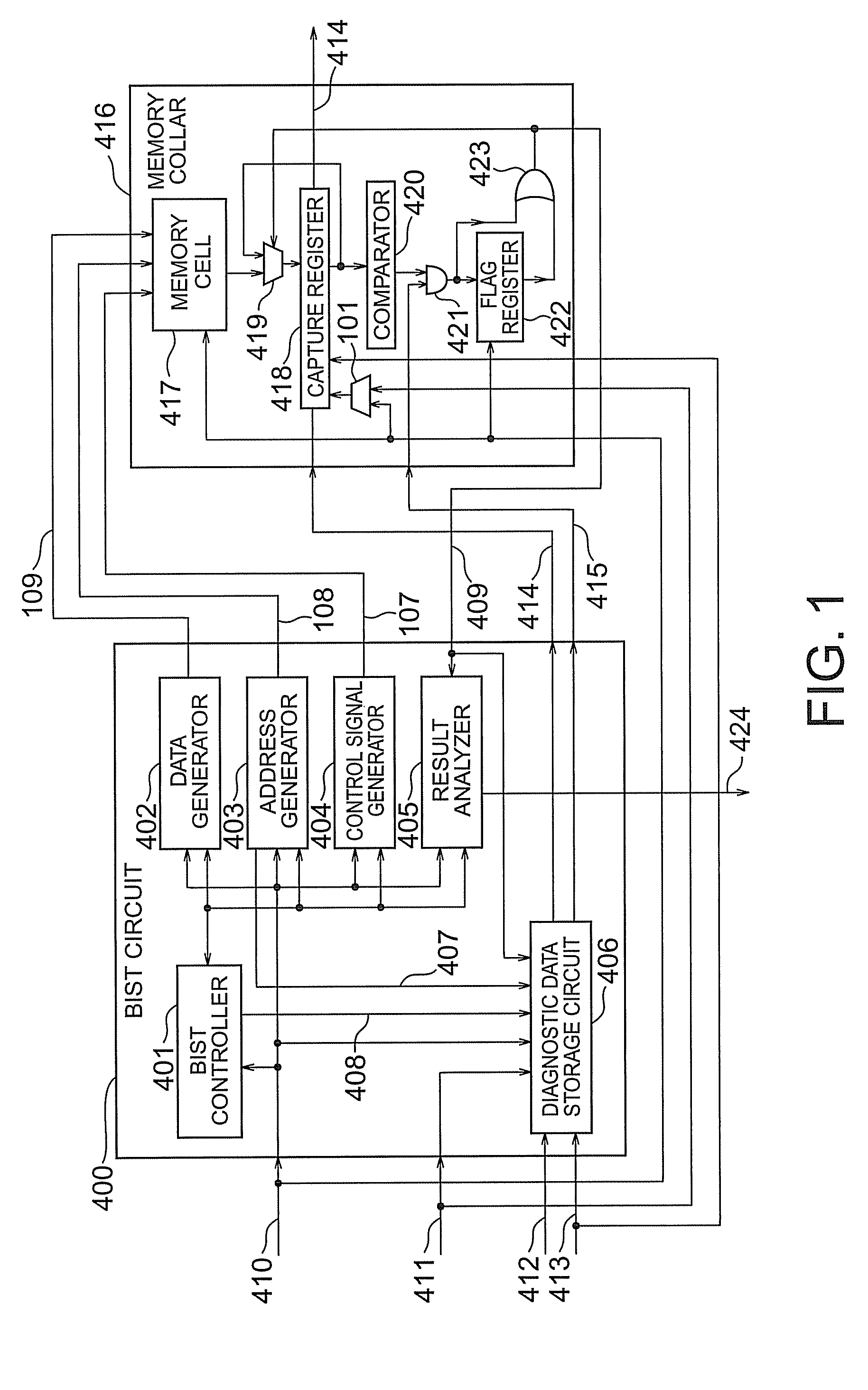
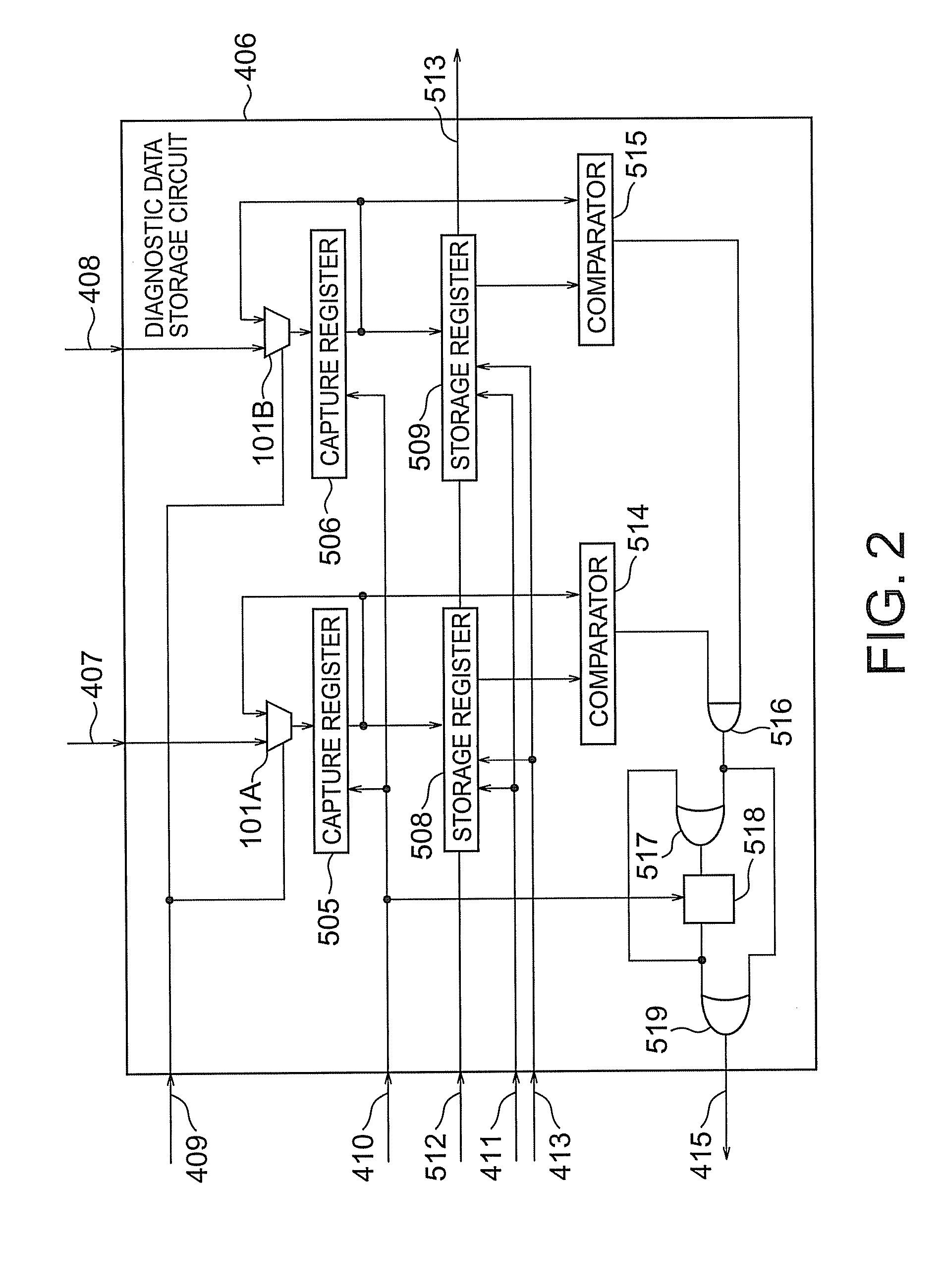
According to the present invention, there is provided a semiconductor integrated circuit having: a BIST circuit including, a data generator which generates and outputs write data to be supplied to a memory, an address generator which generates and outputs an address signal to be supplied to the memory, a control signal generator which generates and outputs a control signal for controlling the memory, a result analyzer which receives a flag signal, analyzes a result of a BIST, and outputs a BIST result signal, a BIST controller which controls operations of the data generator, the address generator, the control signal generator, and the result analyzer, and outputs a BIST state signal indicating a state of the BIST, and a diagnostic data storage circuit including a first capture register which captures and outputs, in accordance with a first clock, a latest address signal and the BIST state signal output from the BIST controller while no flag signal is supplied, and maintains outputs when the flag signal is supplied, a storage register which receive and stores the outputs from the first capture register in accordance with a second clock lower in speed than the first clock while no shift enable signal is supplied, thereby storing the address signal and the BIST signal corresponding to the supply timing of the flag signal, and outputs the stored contents outside by shifting them when the shift enable signal is supplied, and flag suppressing means for comparing the outputs from the first capture register with the stored contents of the storage register, and outputting a flag suppression signal, after the flag signal is supplied, until the latest address signal and the BIST state signal output from the first capture register match the address signal and the BIST control signal stored in the storage register; and a memory collar including, a memory cell which performs a write operation by receiving the write data, the address signal, and the control signal, and reads out and outputs the written data, in accordance with the first clock, a second capture register which captures latest data output from the memory cell while neither the shift enable signal nor the flag signal is supplied, maintains held contents when the flag signal is supplied, and outputs held contents outside by shifting the held contents when the shift enable signal is supplied, a comparator which compares the output from the second capture register with an expected value, and outputs a comparison result signal meaning failure detection if the output and the expected value do not match, and a flag register which outputs the flag signal on the basis of the comparison result signal while no flag suppression signal is supplied, and suppresses the output of the flag signal when the flag suppression signal is supplied
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Analytical virtual machine
InactiveUS20070118350A1Memory loss protectionError detection/correctionParallel computingFLAGS register
An analytical virtual machine (AVM) analyzes computer code using a software processor including a register that stores behavior flags indicative of behaviors identified by virtually executing the code within the virtual machine. The AVM includes a sequencer that stores the sequence in which behavior flags are set in the behavior flags register. The AVM analyzes machine performance by emulating execution of the code being analyzed on a fully virtual machine and records the observed behavior. When emulation and analysis are complete, the AVM returns the behavior flags register and sequencer to the real machine and terminates.
Owner:KYNDRYL INC
Apparatus and method for using checking instructions in a floating-point execution unit
InactiveUS6247117B1Digital computer detailsSpecific program execution arrangementsExecution unitOperand
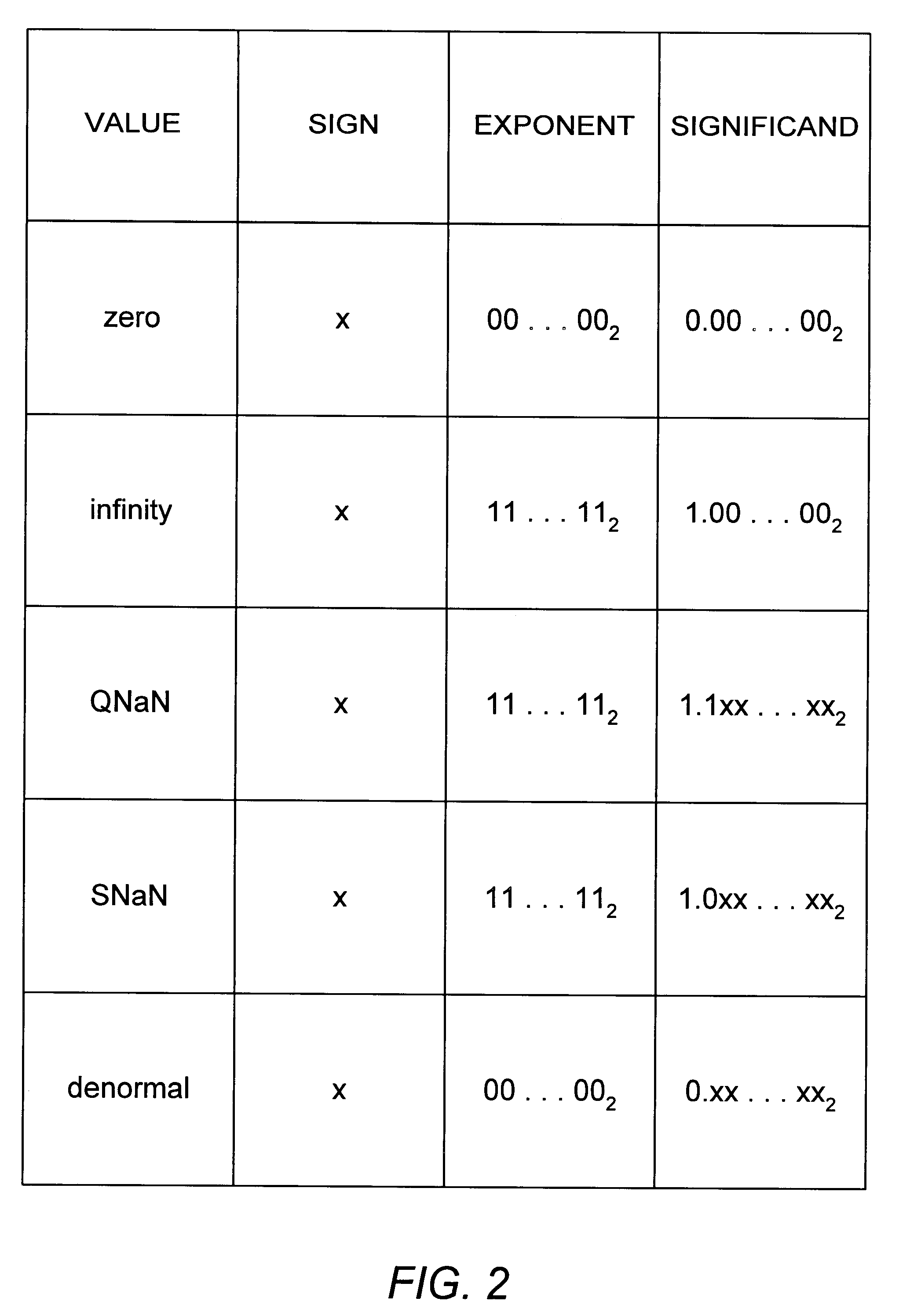
The use of checking instructions to detect special and exceptional cases of a defined data format in a microprocessor is disclosed. Generally speaking, a checking instruction is included with the microcode of floating-point instructions to detect special and exceptional cases of operand values for the floating-point instructions. A checking instruction is configured to set one or more flags in a flags register if it detects a special or exceptional case for an operand value. A checking instruction may also set the result or results of a floating-point instruction to a result value if a special or exceptional case is detected. In addition, a checking instruction may be configured to set one or more bits in status register if a special or exceptional case is detected. After a checking instruction completes execution, a subsequent microcode instruction can be executed to determine if one or more flags were set by the checking instruction. If one or more flags have been set by the checking instruction, the subsequent microcode instruction can branch to a non-sequential microcode instruction to handle the special or exceptional case detected by the checking instruction.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
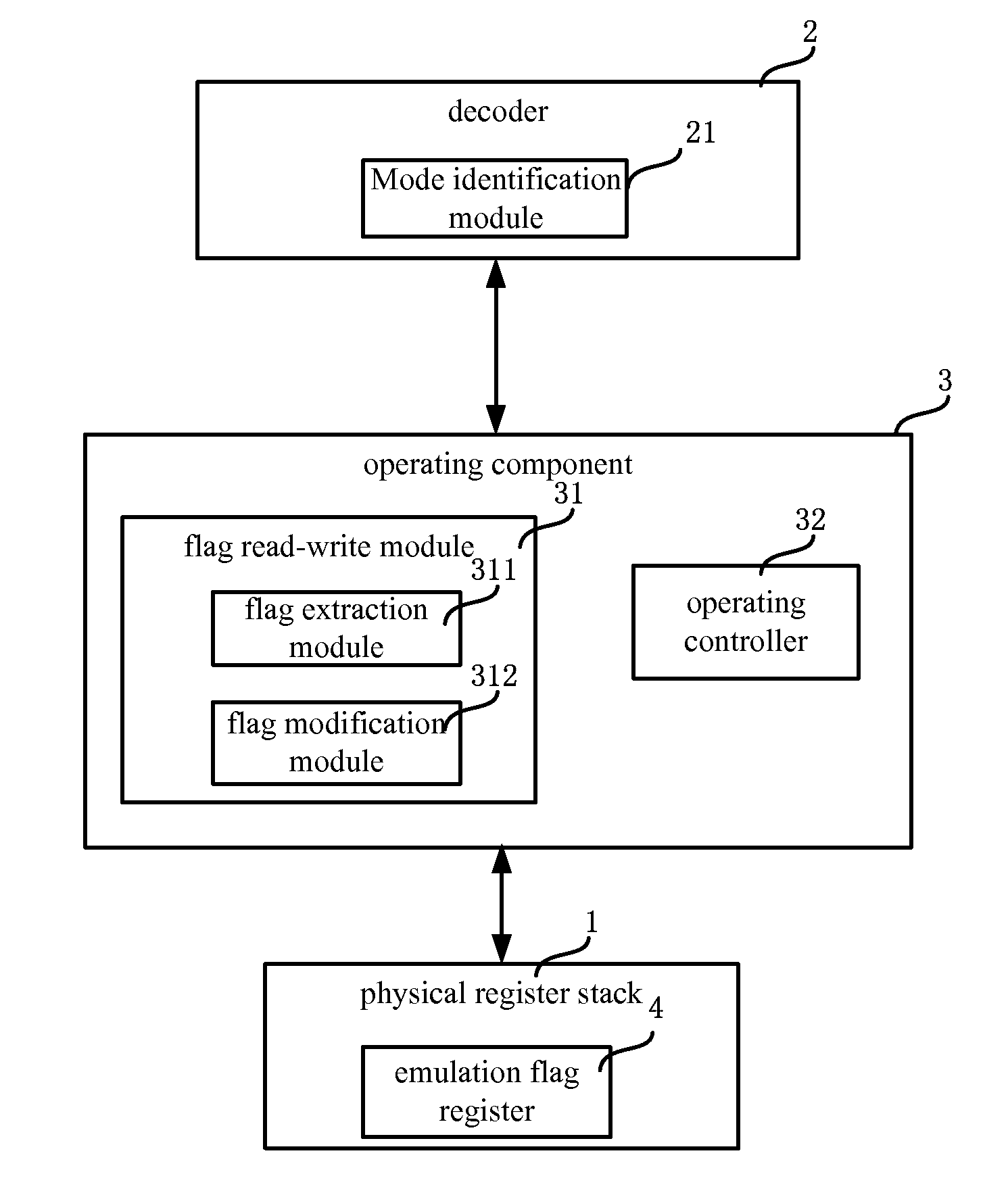
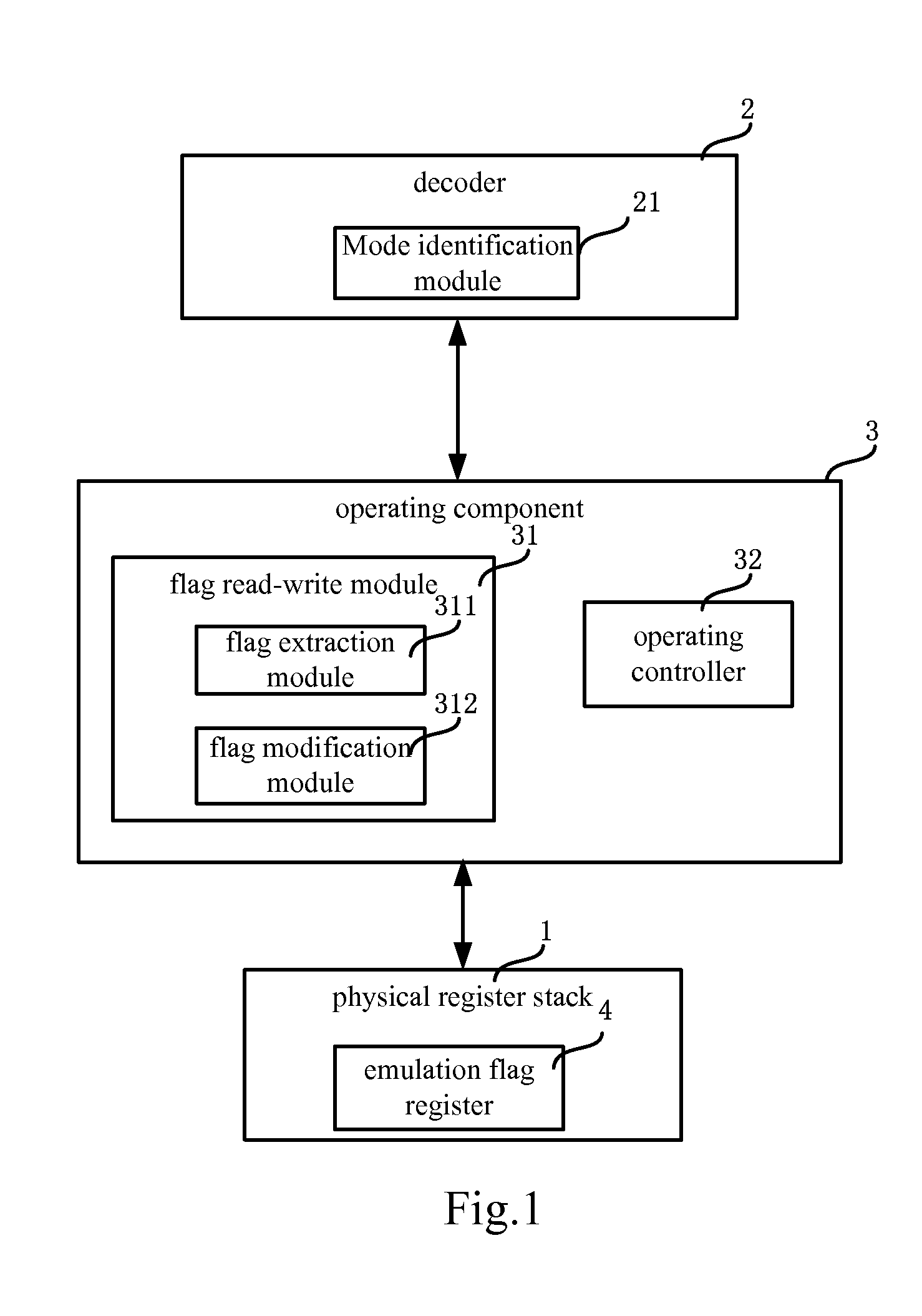
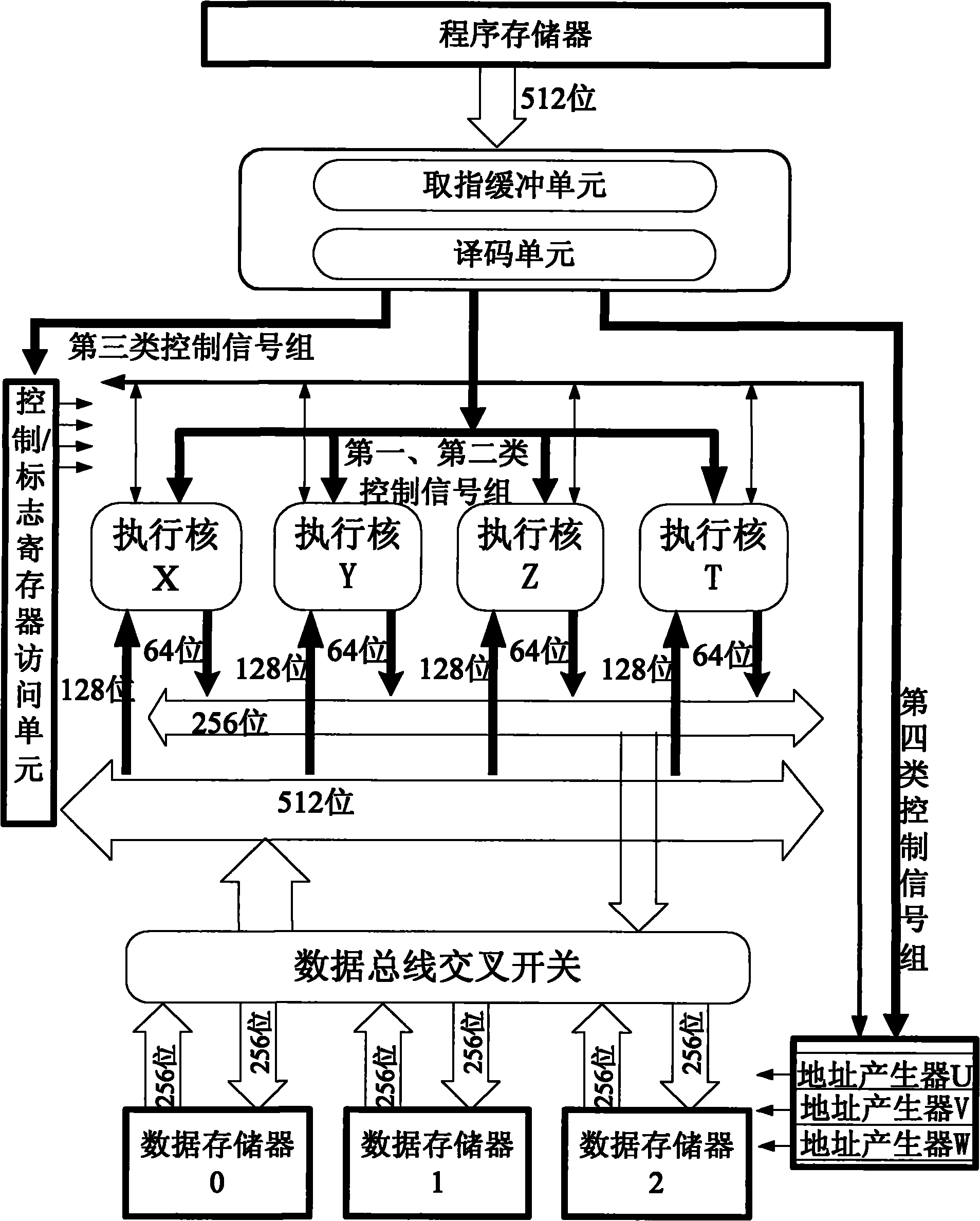
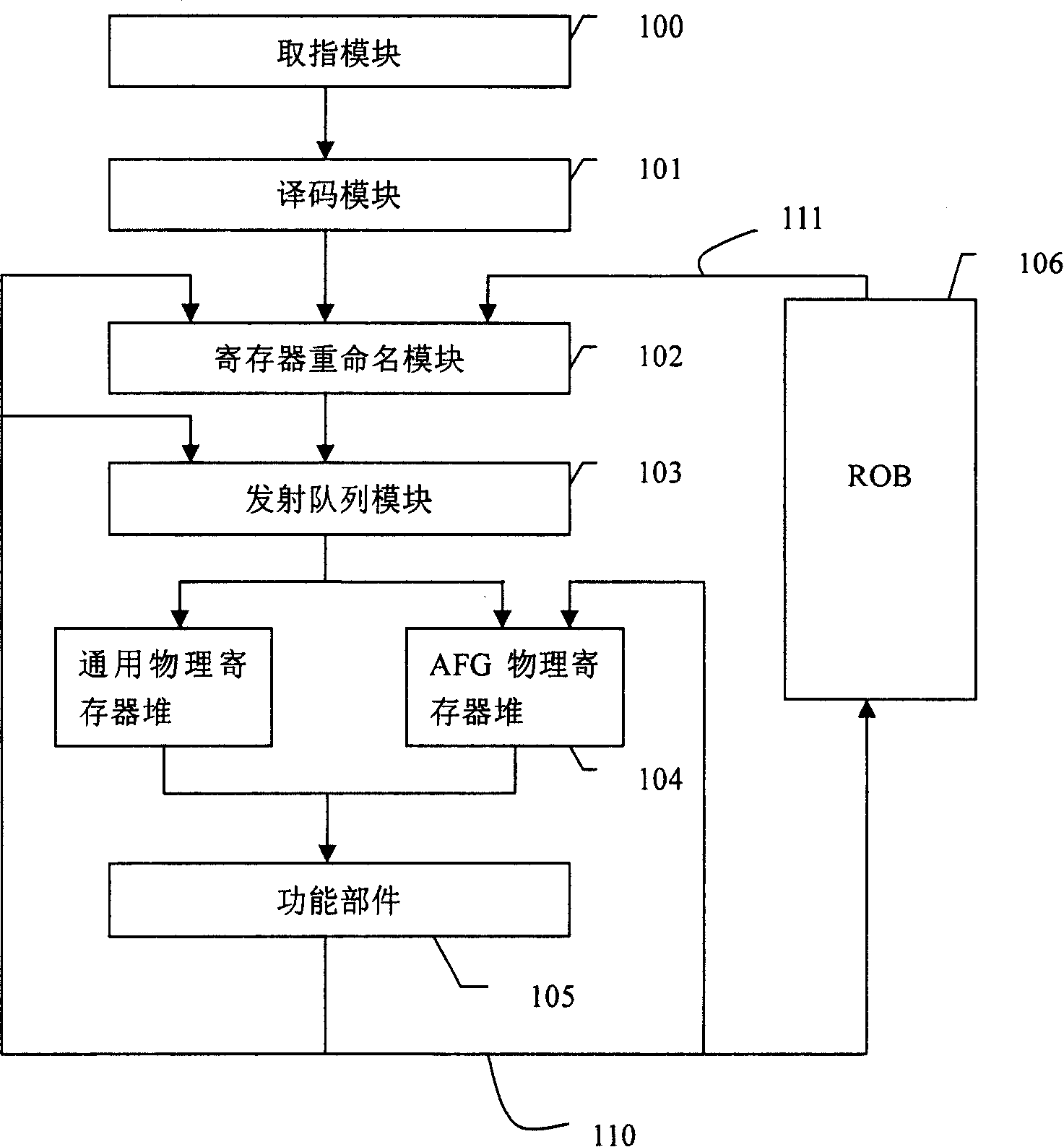
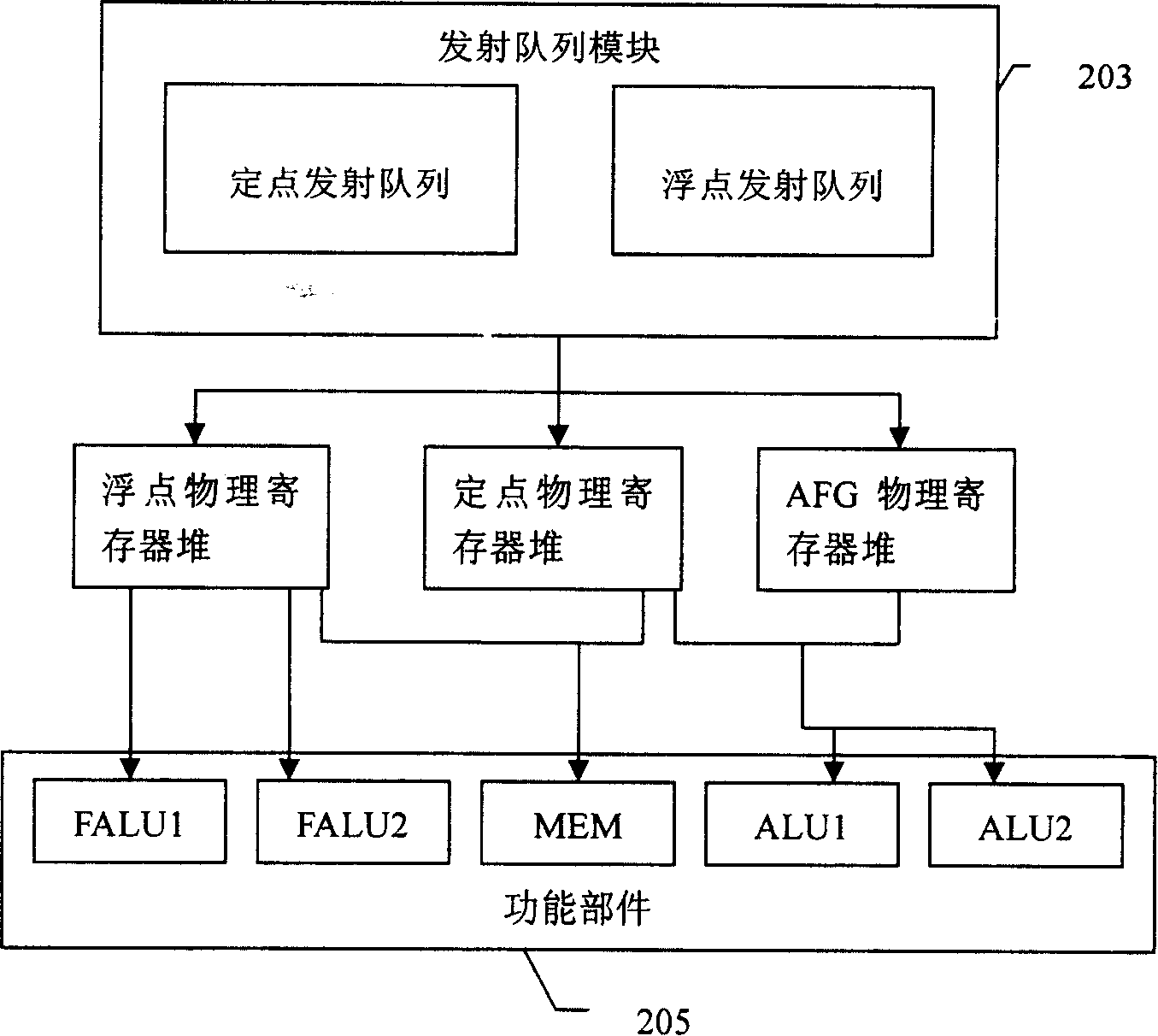
Risc processor and its register flag bit processing method
ActiveUS20100268916A1Improve performanceConditional code generationInstruction analysisProcessor registerFLAGS register
The present invention discloses a RISC processor and a method of processing flag bits of a register in the RISC processor. Said RISC processor comprises a physical register stack, an operating component connected to the physical register stack and an decoder connected to the operating component; the physical register stack comprises an emulation flag register for emulating to realize flag bits of a flag register in a CISC processor; the operating component comprises a flag read-write module for reading and writing the values of the flag bits of the emulation flag register. The operating component further comprises an operating controller for performing an operation control according to the values of the flag bits of the emulation flag register when the RISC processor is in the working mode of X86 virtual machine during an operation process.
Owner:LOONGSON TECH CORP
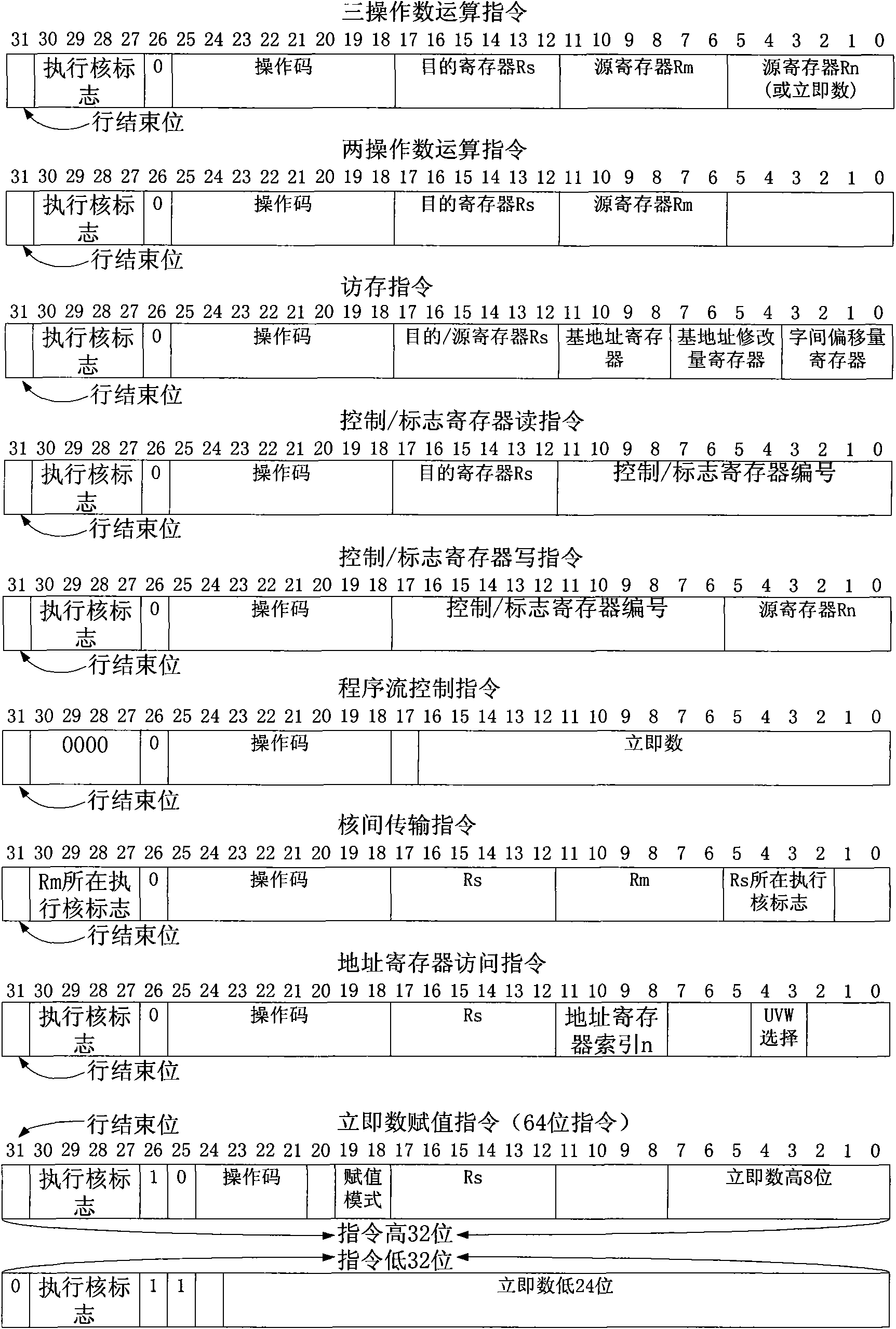
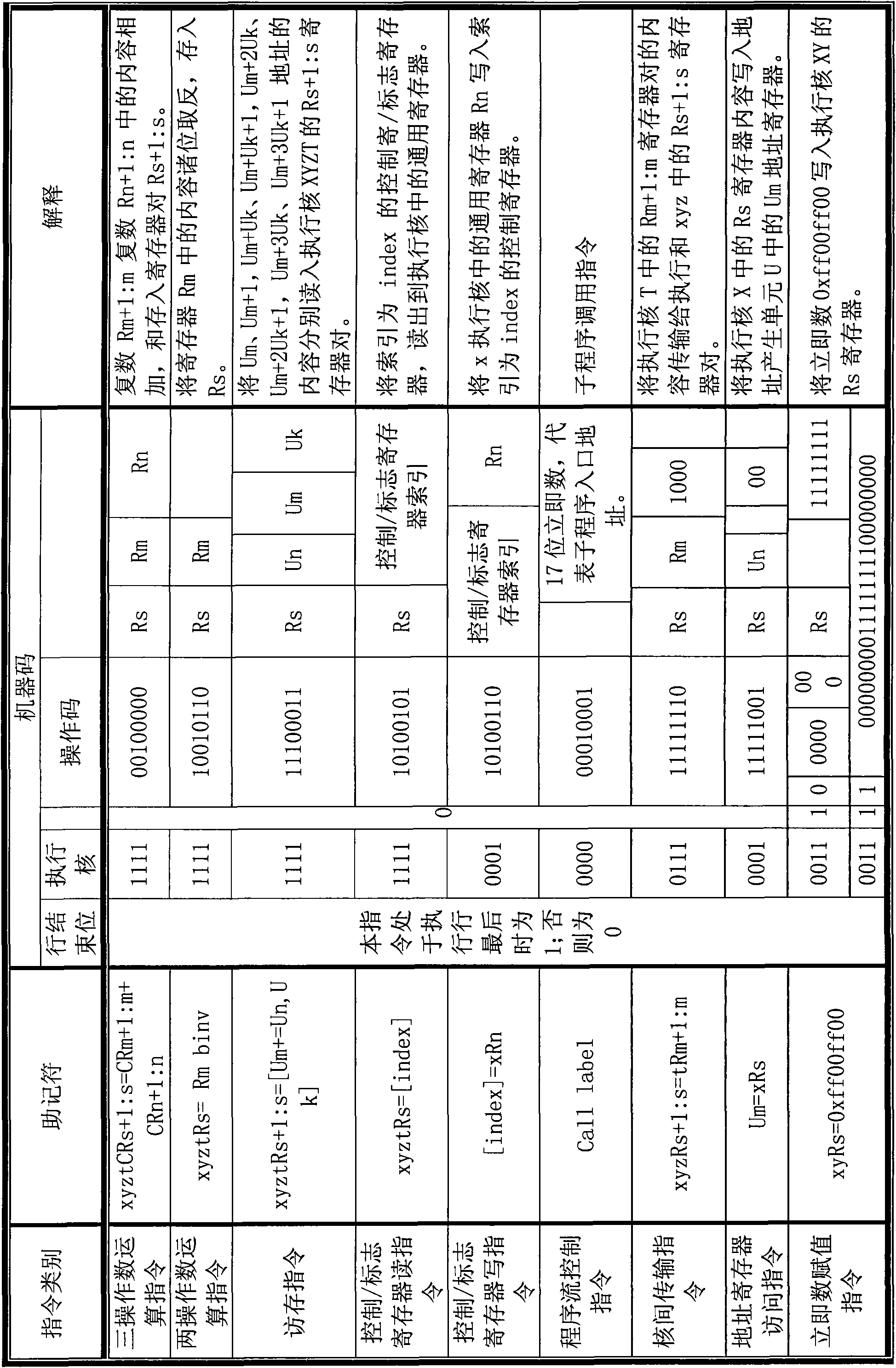
Parallel digital signal processor
ActiveCN101957743AGuaranteed data throughput requirementsData throughput requirements are metDigital data processing detailsConcurrent instruction executionControl signalProcessor register
The invention discloses a parallel digital signal processor comprising a program storage, an address-acquiring buffer unit, a decoding unit, an execution core, an address generating unit, a control / flag register access unit and a data bus, wherein the address-acquiring buffer unit is used for providing an address for the program storage, caching instructions from the program storage, splicing the instructions into parallel execution lines and then transmitting to the decoding unit; the decoding unit is used for decoding each instruction in the parallel execution line; the execution core is used for receiving a first control signal set and a second control signal set which are generated by the decoding unit, and carrying out instruction execution processing according to the states of the control signal sets; the address generating unit is used for receiving a third control signal set generated by the decoding unit and carrying out storage access processing according to the state of the control signal set; the control / flag register access unit is used for receiving a first control signal set generated by the decoding unit and carrying out control / flag register access instruction processing according to the state of the control signal set; and the data bus is used for a data storage from the read and write request of the execution core and connecting the data storage and the execution core.
Owner:安徽芯纪元科技有限公司
System and method for cooperative execution of multiple branching instructions in a processor
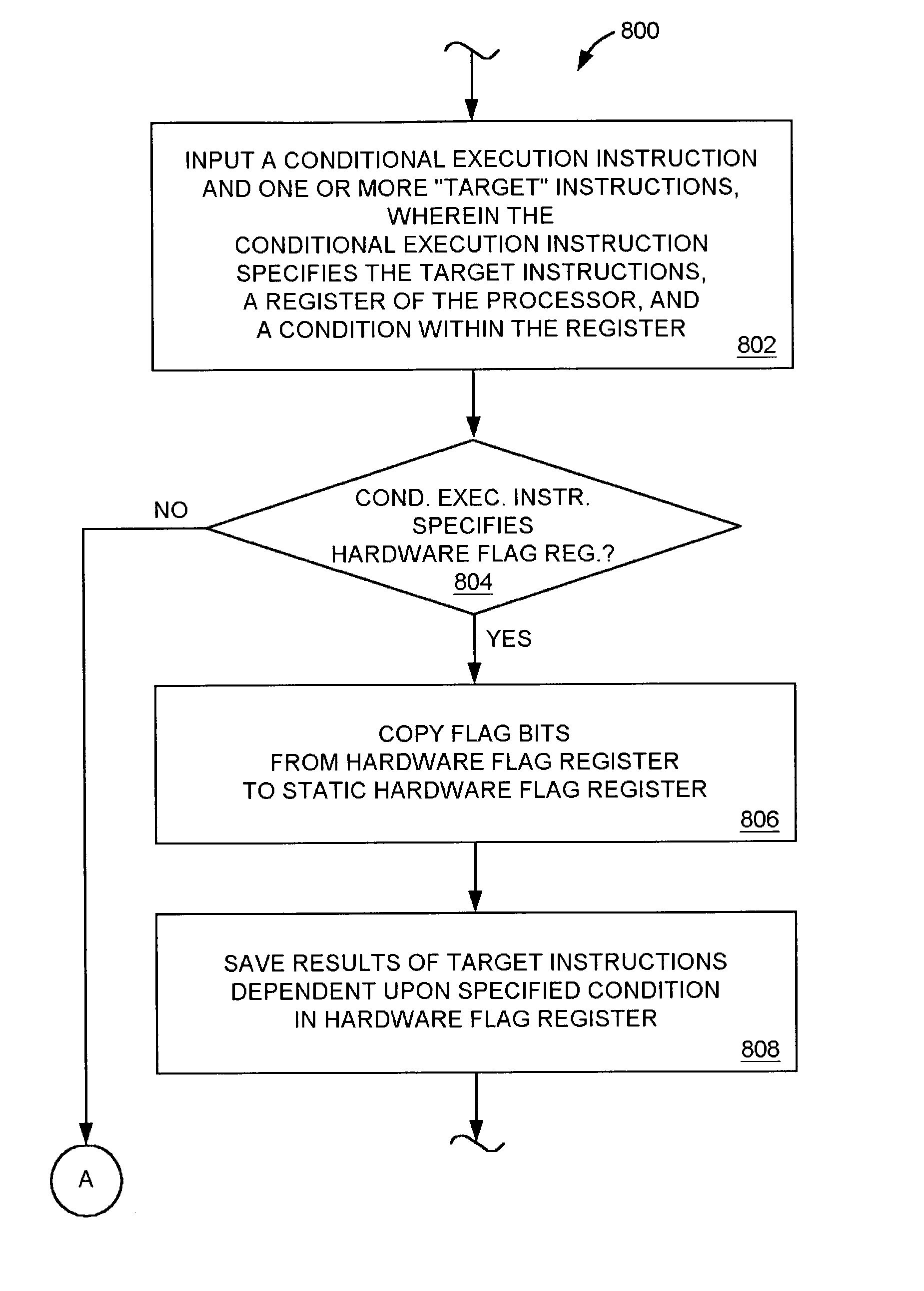
ActiveUS7299343B2Conditional code generationDigital computer detailsProcessor registerConditional execution
A system for conditionally executing an instruction depending on a previously existing condition. The system disclosed is configured to handle conditional execution instructions typically specifying at least one target instruction, a processor register, and a condition within the register. The system saves a result of each of the target instructions dependent upon the existence of the condition in the specified register during execution of the conditional execution instruction. When the conditional execution instruction specifies a first flag register, the system copies the flag bits in the first flag register to a corresponding second flag register, and saves a result of each of the target instructions dependent upon the specified condition in the first flag register during execution of the conditional execution instruction. A subsequent conditional execution instruction may then specify a condition in the second flag register in order to conditionally execute target instructions based on a previously existing condition.
Owner:VERISILICON HLDGCO LTD
Semiconductor integrated circuit having a (BIST) built-in self test circuit for fault diagnosing operation of a memory
According to the present invention, there is provided a semiconductor integrated circuit having: a BIST including a data generator, an address generator, a control signal generator, a result analyzer, a BIST controller, and a diagnostic data storage circuit including a first capture register which captures and outputs, in accordance with a first clock, a latest address signal and the BIST state signal output from said BIST controller while the flag signal is in as state that no fault is detected, and maintains outputs when the flag signal is in a state that a fault is detected. The semiconductor integrated circuit can further include a memory collar having a memory cell, a second capture register, a comparator, and a flag register. The semiconductor integrated circuit can perform a fault diagnosing operation of a memory by using a comparator type BIST circuit.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
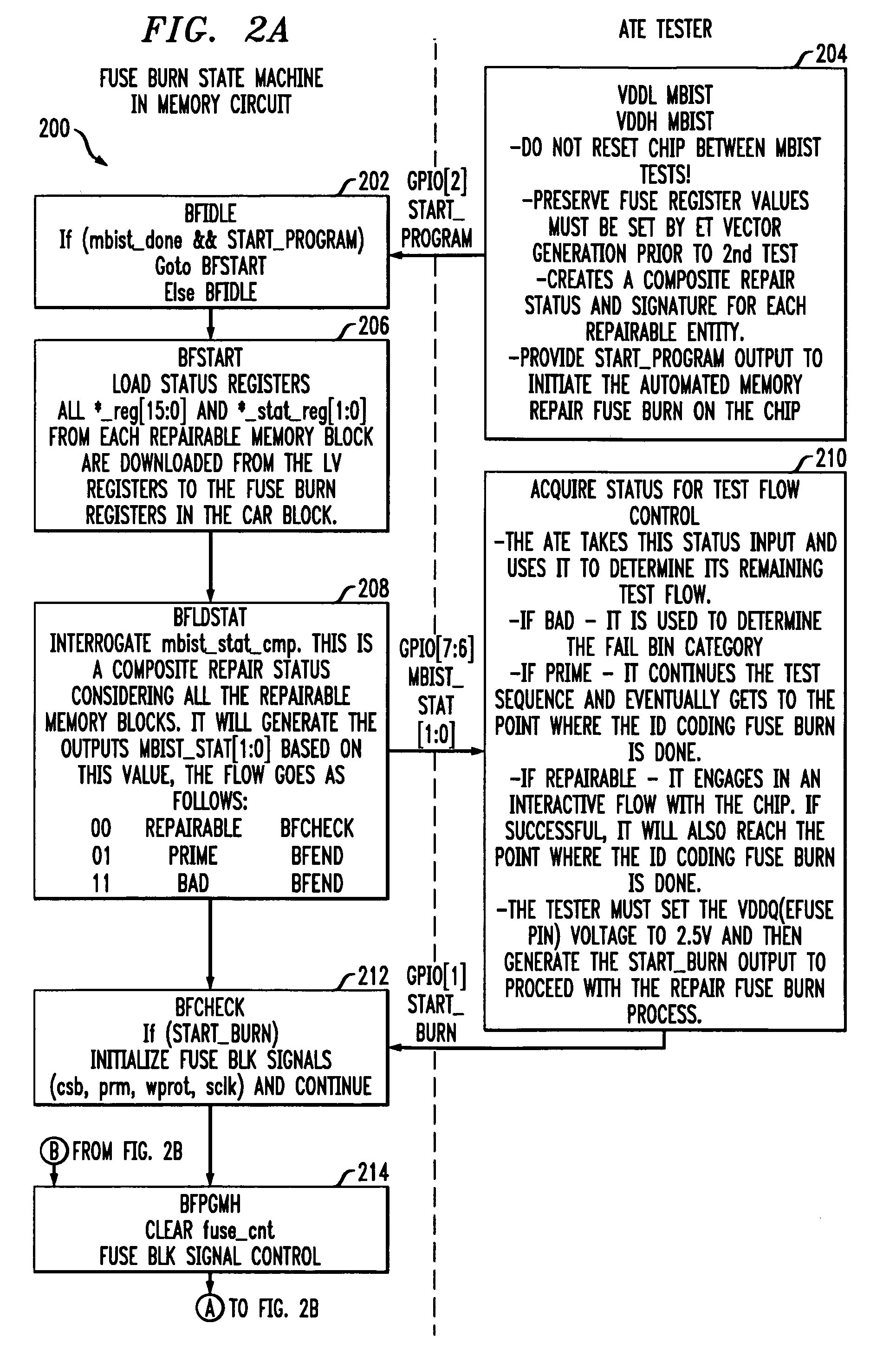
Embedded Memory Repair
InactiveUS20100157703A1Efficient repairRead-only memoriesDigital storageVoltage sourceFLAGS register
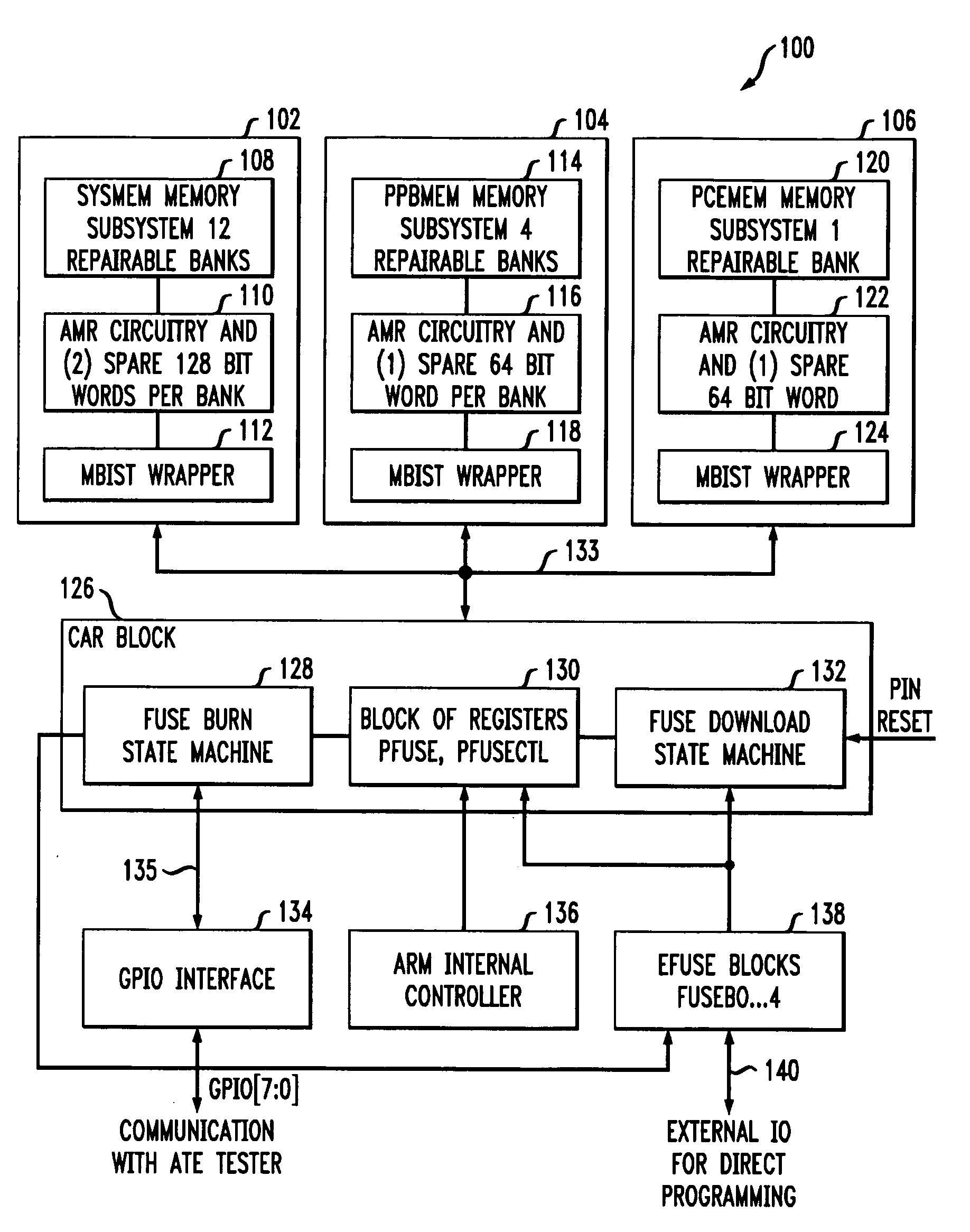
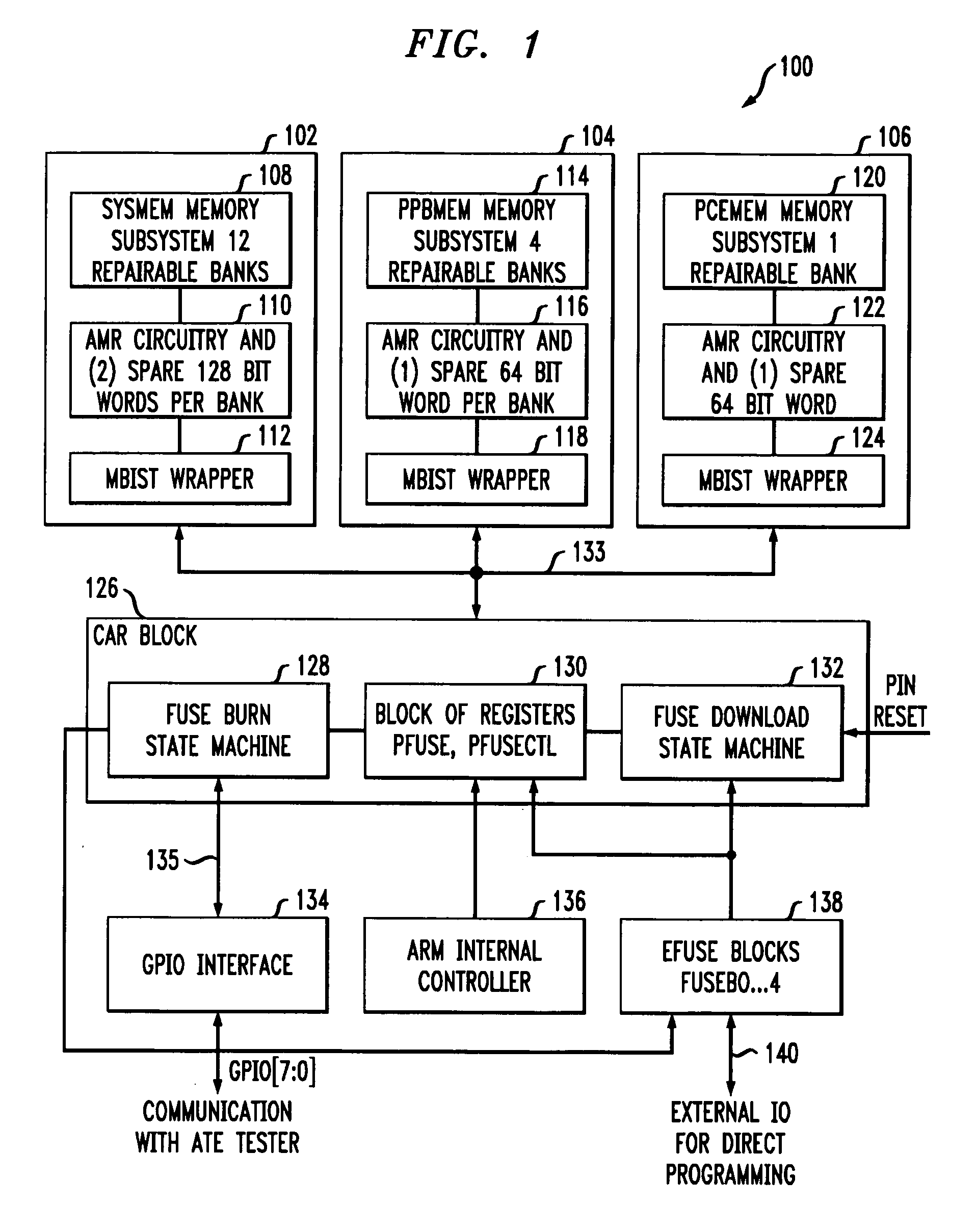
A memory repair circuit for repairing one or more failures in an embedded memory includes at least one fuse register and state machine circuitry coupled to the fuse register. The state machine circuitry implements a first state machine operative: (i) to receive status information regarding the one or more failures in the embedded memory; (ii) to determine whether the memory is repairable based on the status information; (iii) when the memory is deemed repairable, to store an address corresponding to a failed memory cell of the memory; (iv) to burn the address corresponding to the failed memory cell into the fuse register using a voltage source supplied to the memory repair circuit; and (v) to verify that the address corresponding to the failed memory cell was burned into the fuse register. The state machine circuitry further implements a second state machine operative: (i) to download information stored in the at least one fuse register into at least one repair register associated with the embedded memory; and (ii) when an address is received in the circuit corresponding to a failed memory instance in the embedded memory, to reroute access to the failed memory instance to the at least one repair register.
Owner:BROADCOM INT PTE LTD
Method for renaming state register and processor using the method
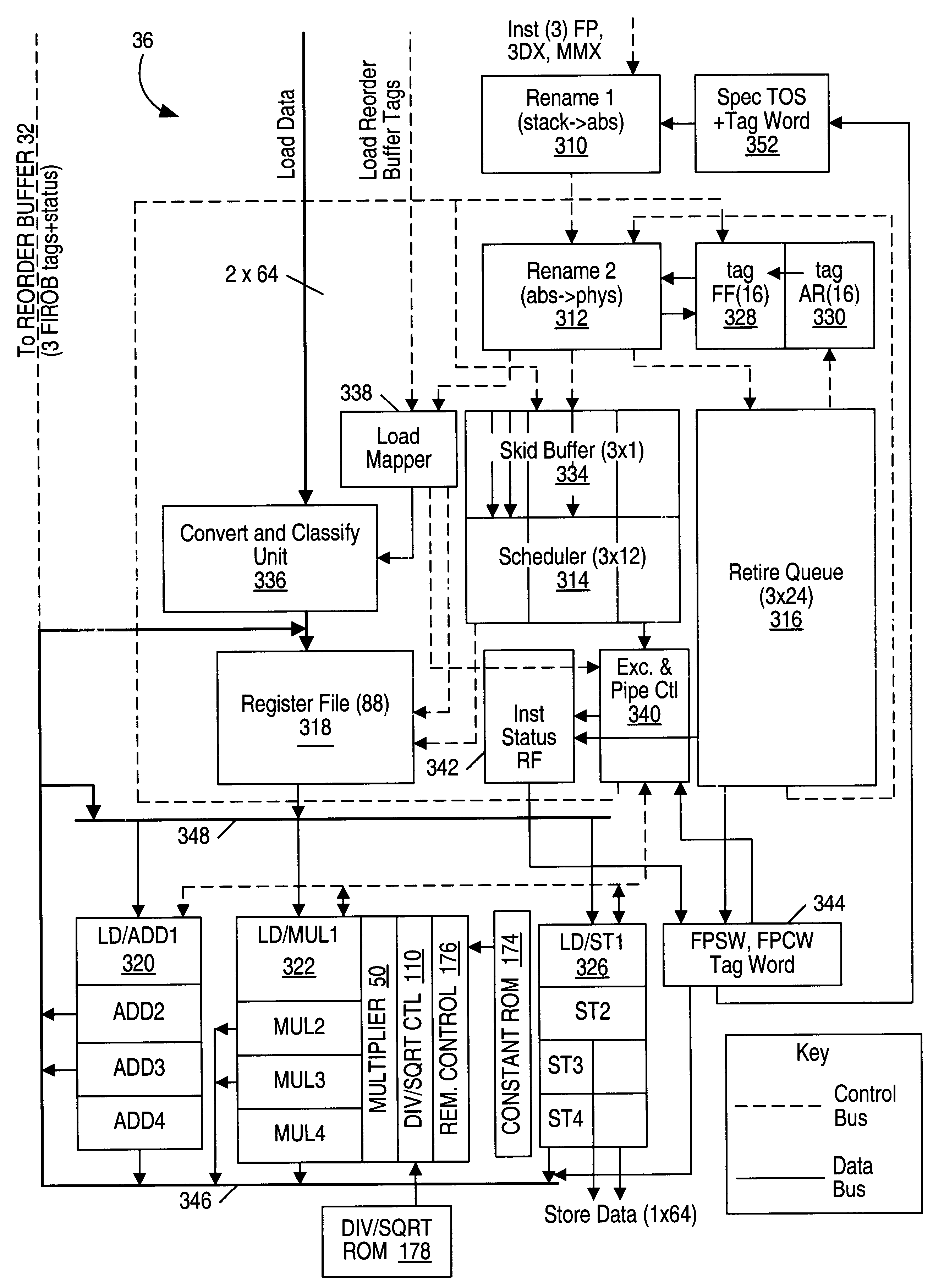
ActiveCN101169710AReduce pauseReduce congestionConcurrent instruction executionComputer scienceFLAGS register
The invention provides a method for renaming a status register in a superscalar processor with a pipeline structure, wherein the status register is a register composed of a plurality of flag bits selected from all flag bits of a flag register. The method comprises determining whether a microcode will read the status register when the microcode coded by a command reaches a register renaming module of the processor; if determining that the microcode will read the status register, allocating a nearest mapping physical register for the status register; otherwise, not allocating the physical register for the status register; determining whether the microcode will be written to the status register; if determining that the microcode will be written into the status register, allocating a new physical register with empty status to the status register; and otherwise, not allocating the physical register for the status register.
Owner:INST OF COMPUTING TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
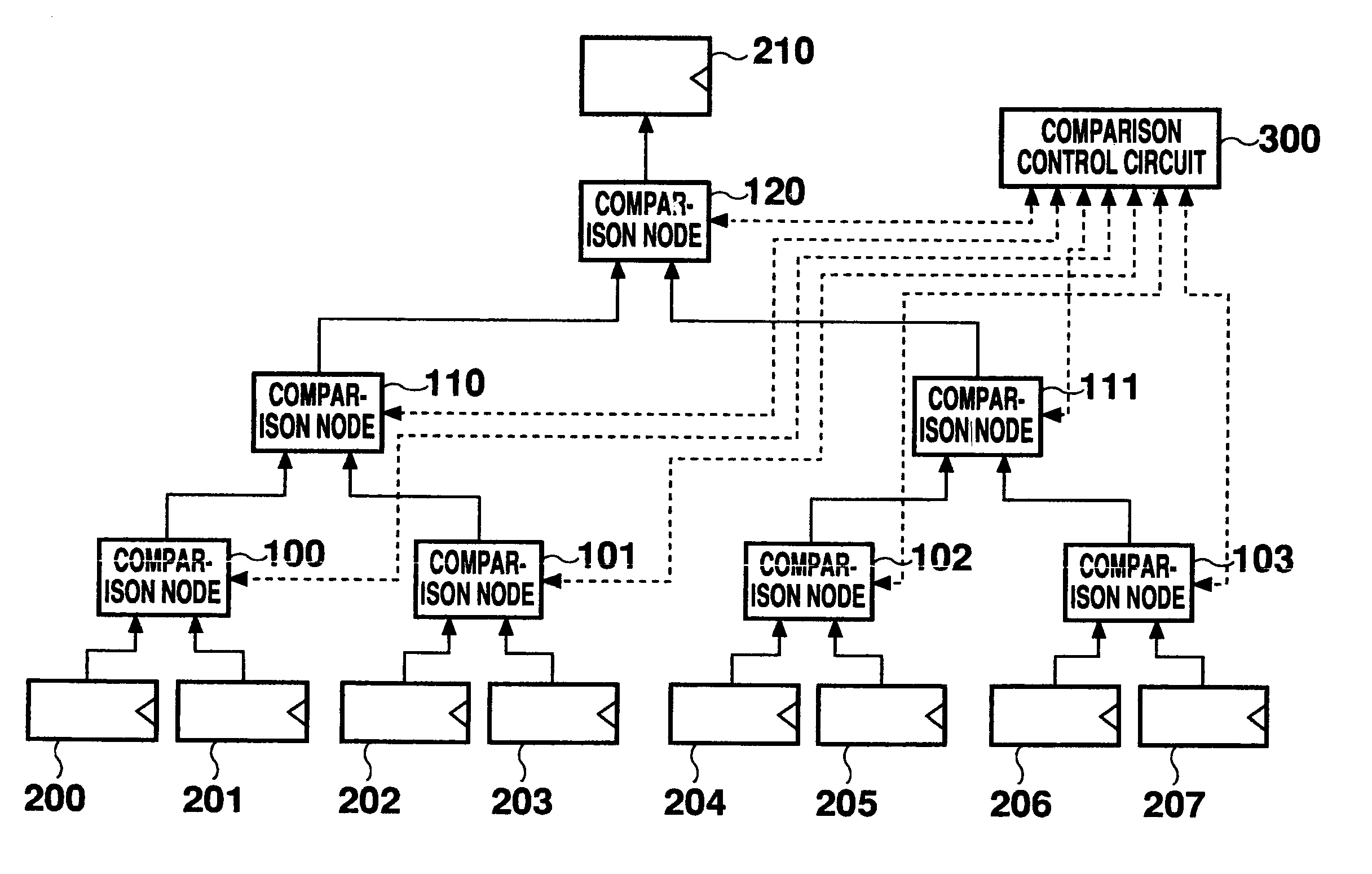
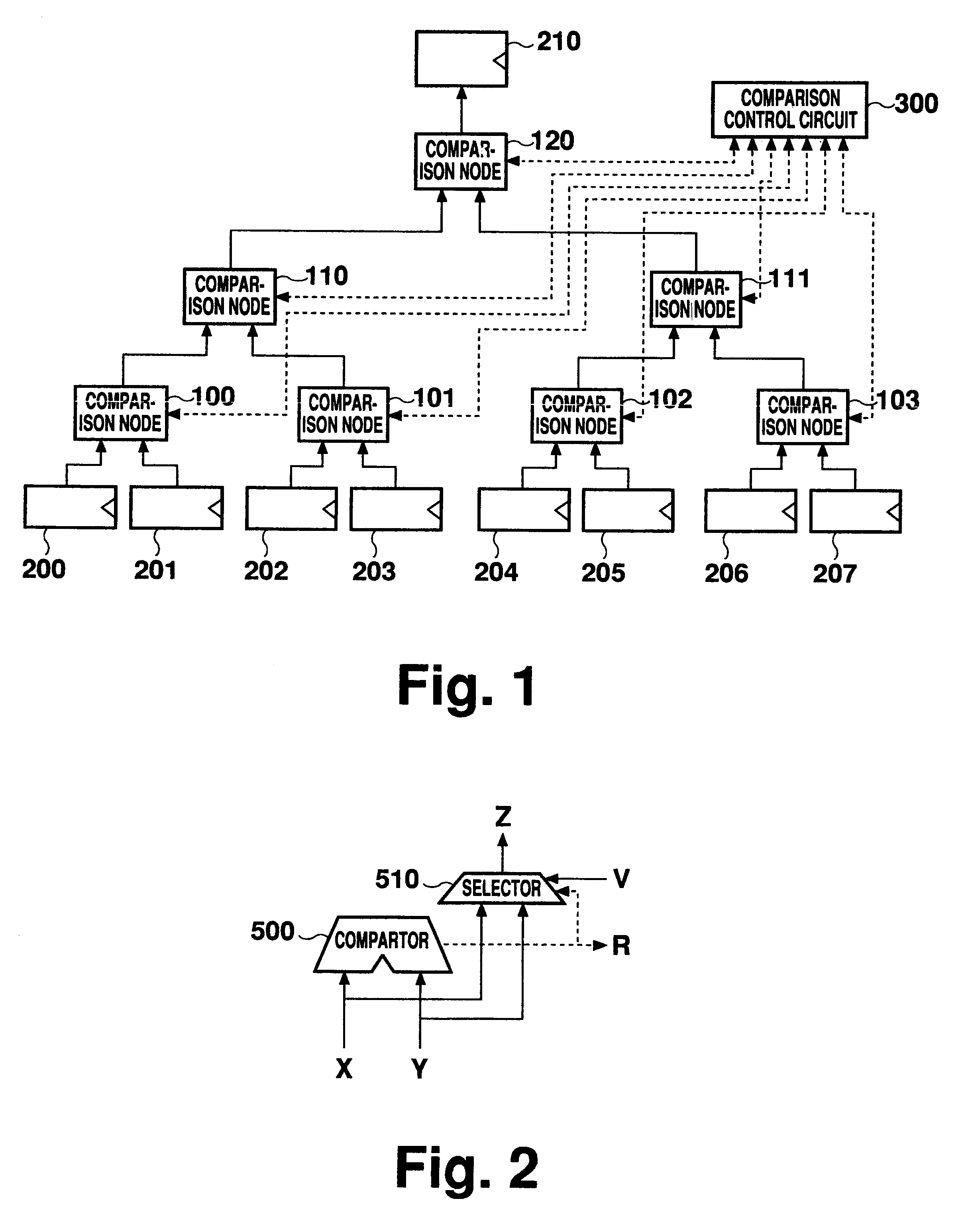
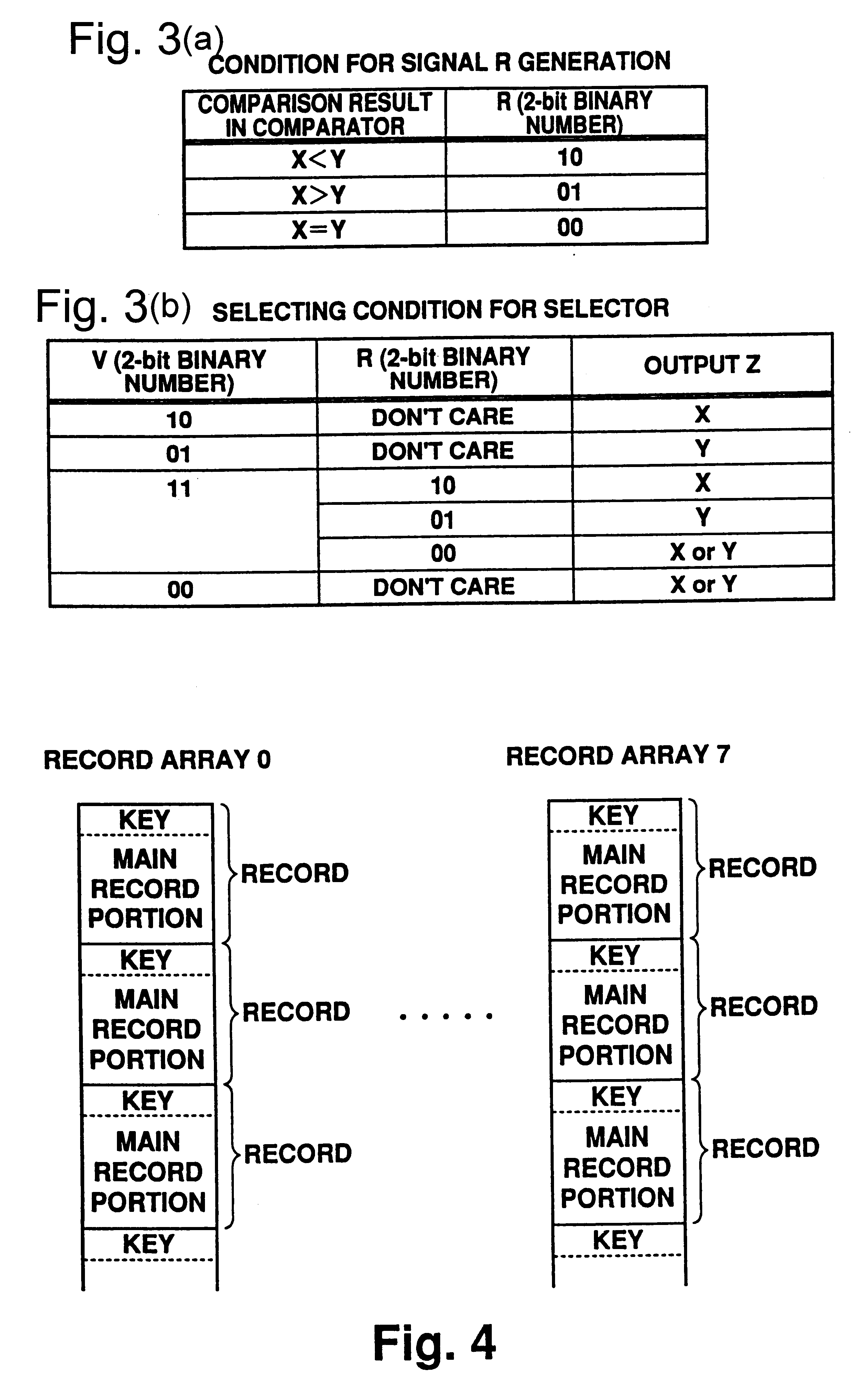
Merge sorting apparatus with comparison nodes connected in tournament tree shape
A merge sorting apparatus includes a comparison tournament circuit including comparison nodes, and a comparison control circuit for supplying to the corresponding comparison nodes validity flag information concerning the input data to each of the comparison nodes determined based on comparison results from the comparison nodes. The comparison control circuit includes comparison result registers for retaining the comparison results, validity flag registers for retaining the validity flag information, and merge member registers for retaining information as to whether the input data to each of the input registers corresponding to respective pathways should be the object of comparison in the following data comparison processing. With this arrangement, contending readouts of record arrays from a memory can be reduced and the necessity to initialize each register is eliminated, thereby speeding merge sorting.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Virtual cache registers with selectable width for accommodating different precision data formats
InactiveUS6253299B1Superior in pointImprove parallelismRegister arrangementsMemory adressing/allocation/relocationProcessor registerParallel computing
A structure and method for processing data comprises a processing unit having a base cache, base registers having a base width and being operatively connected to the processing unit, and virtual cache registers having a virtual width and being located in the base cache and operatively connected to the processing unit, wherein a base processing precision of the processing system is determined by the base width of the base registers and a selectable enhanced processing precision is determined by the virtual width of the virtual cache registers, wherein the base registers store base instructions and data and the virtual cache registers store enhanced data, the virtual width being greater than the base width, and wherein the base cache includes tags identifying a portion of the base cache as the virtual registers, the virtual cache registers being accessible by the processing unit only for execution of enhanced instructions for providing the enhanced processing precision.
Owner:IBM CORP
Microprocessor with microinstruction-specifiable non-architectural condition code flag register
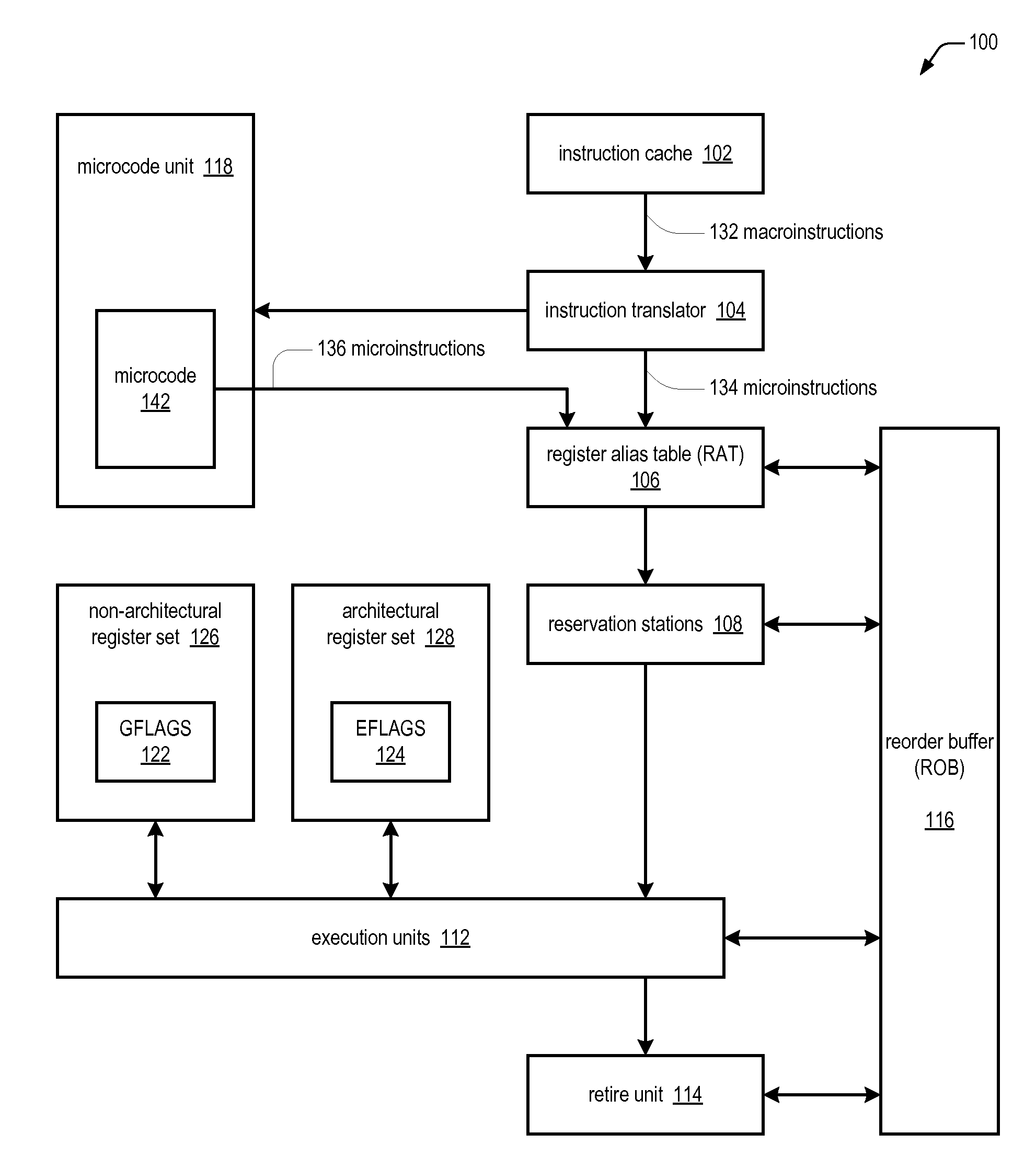
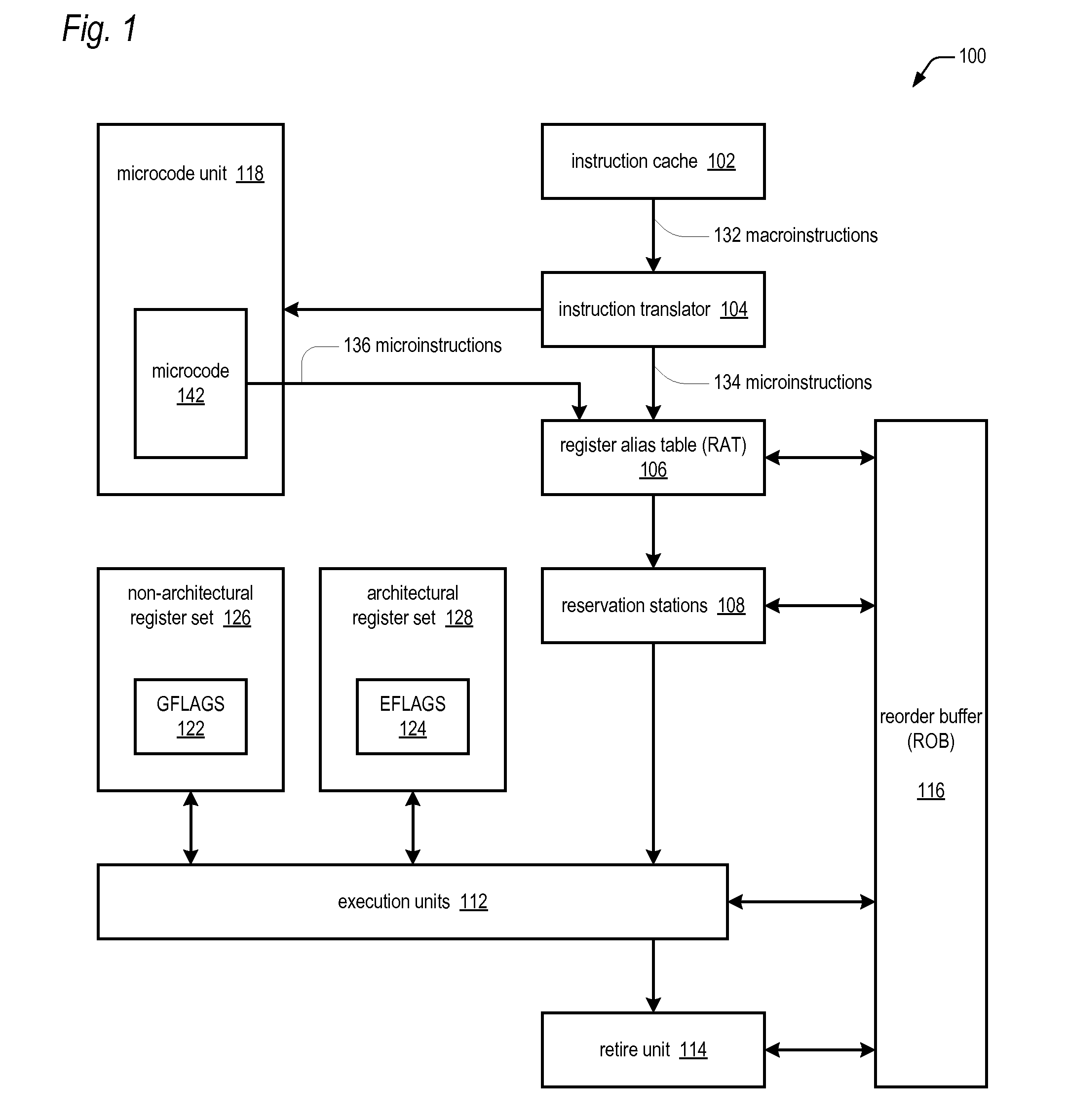
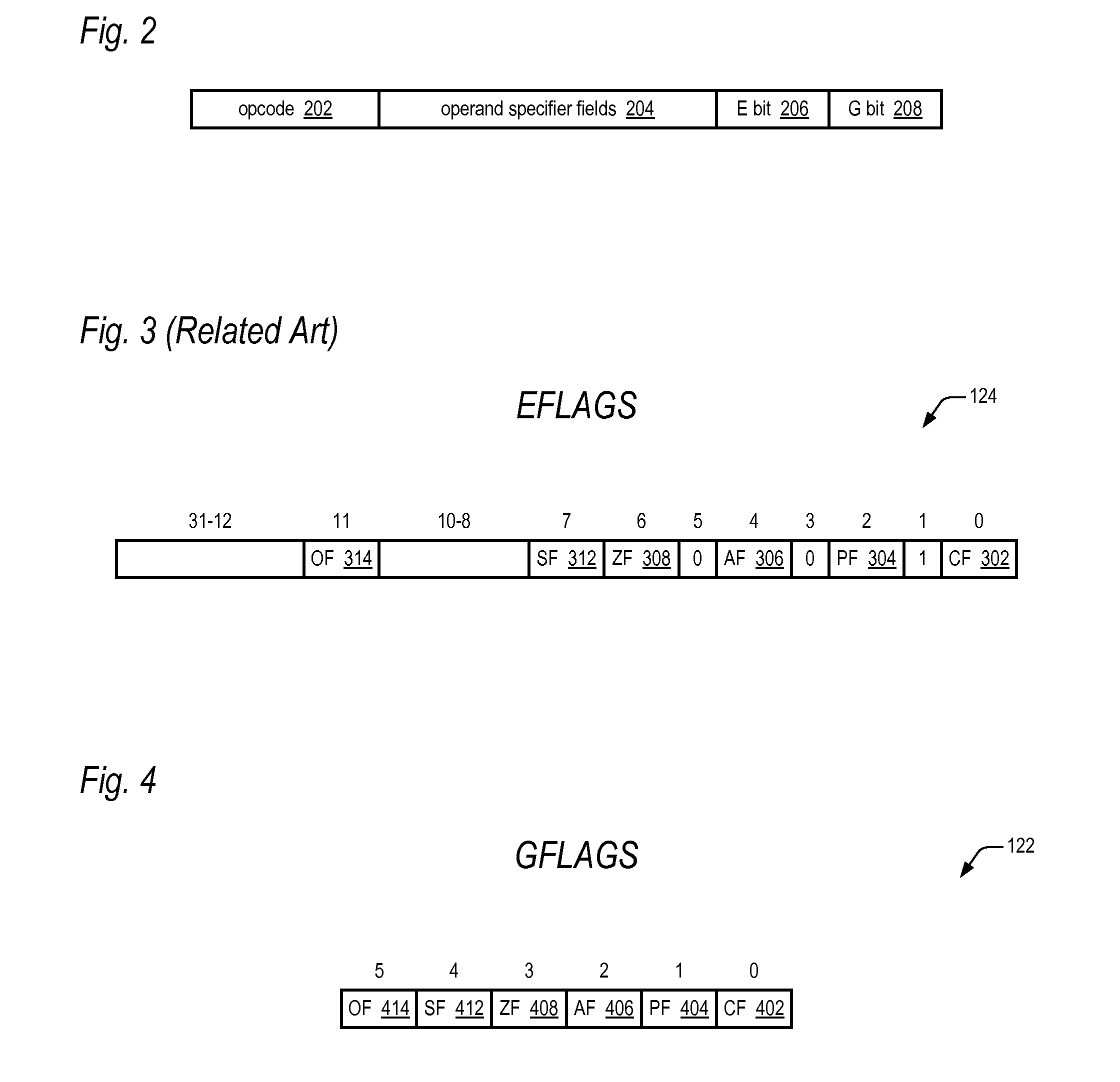
ActiveUS20100299504A1Minimal impactConditional code generationInstruction analysisCondition CodeFLAGS register
A microprocessor includes an architectural register and a non-architectural register, each having a plurality of condition code flags. A first instruction of the microarchitectural instruction set of the microprocessor instructs the microprocessor to update the plurality of condition code flags based on a result of the first instruction. The first instruction includes a field for indicating whether to update the plurality of condition code flags of the architectural or non-architectural register. A second instruction of the microarchitectural instruction set instructs the microprocessor to conditionally perform an operation based on one of the plurality of condition code flags. The second instruction includes a field for indicating whether to use the one of the plurality of condition code flags of the architectural or non-architectural register to determine whether to perform the operation.
Owner:VIA TECH INC
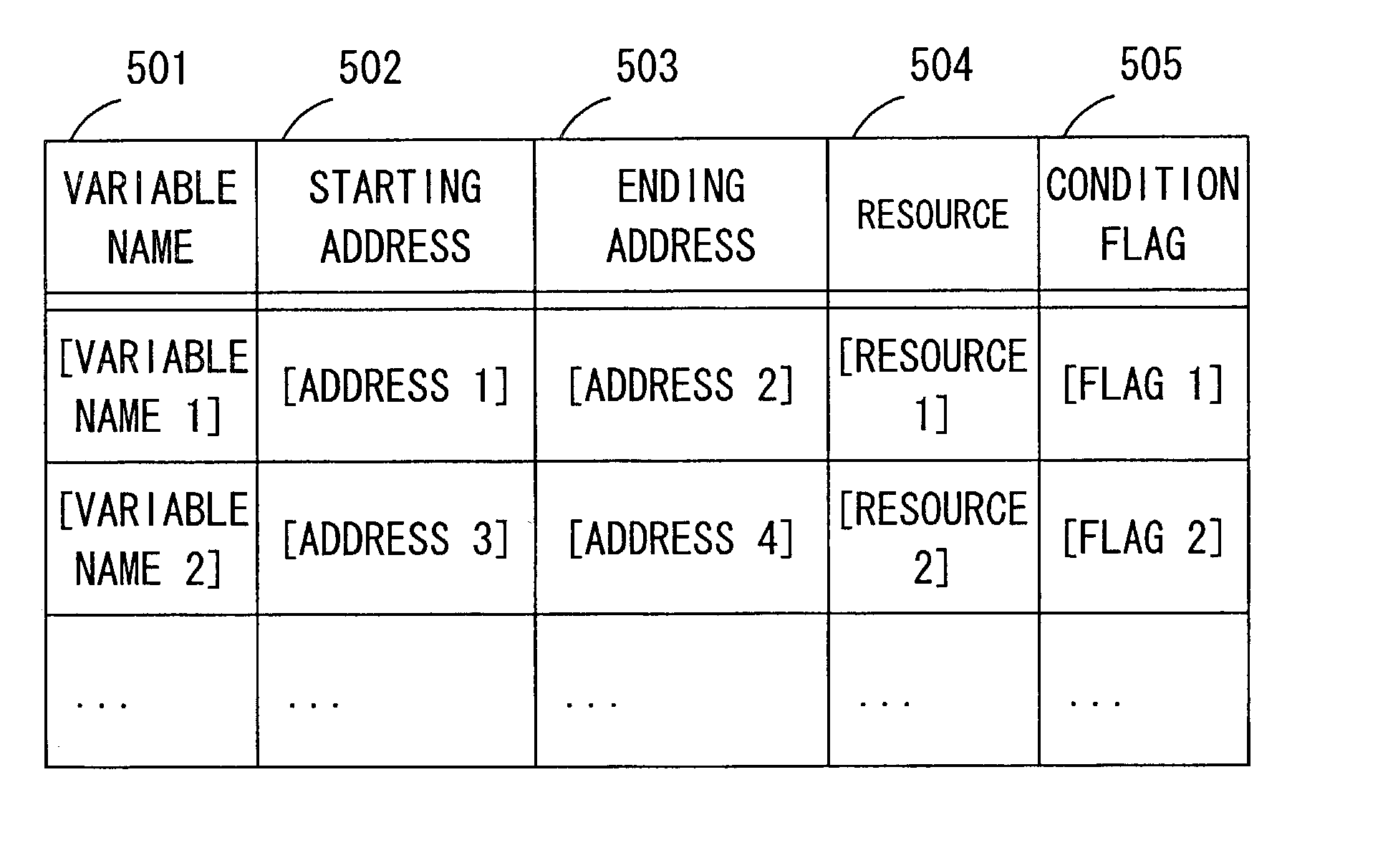
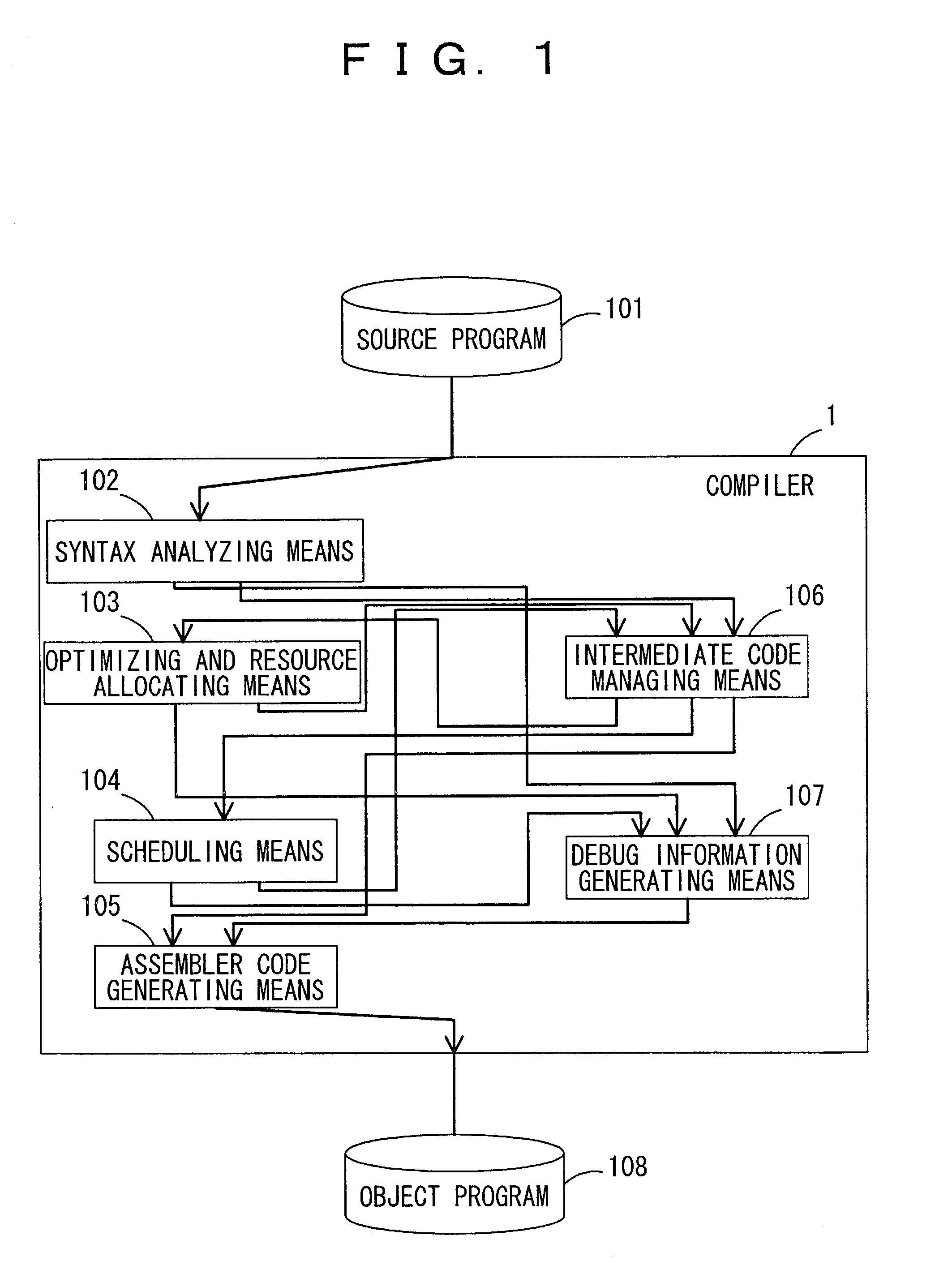
Debugging method and debugging device
ActiveUS7028291B2Accurate contentExact referenceSoftware testing/debuggingSpecific program execution arrangementsProcessor registerResource allocation
According to the present invention, a compiler generates, as debugging information on variables appearing in a source program and the allocation of hardware resources, location information made up of elements showing, for each entry of a variable, an address range within which the variable is valid, a condition flag which is made true within the address range when the variable is valid, and a resource allocated to the variable. A debugging device analyzes the debugging information and stores it. When examining the value of a variable, an entry for the valid variable is determined from the address currently being executed and the value held in the condition flag register, and the resource allocated to that variable is obtained. In this way, the contents of the variable can be referenced correctly.
Owner:SOCIONEXT INC
Instruction and logic to provide vector load-op/store-op with stride functionality
ActiveUS20140195778A1Instruction analysisGeneral purpose stored program computerMemory addressStride length
Instructions and logic provide vector load-op and / or store-op with stride functionality. Some embodiments, responsive to an instruction specifying: a set of loads, a second operation, destination register, operand register, memory address, and stride length; execution units read values in a mask register, wherein fields in the mask register correspond to stride-length multiples from the memory address to data elements in memory. A first mask value indicates the element has not been loaded from memory and a second value indicates that the element does not need to be, or has already been loaded. For each having the first value, the data element is loaded from memory into the corresponding destination register location, and the corresponding value in the mask register is changed to the second value. Then the second operation is performed using corresponding data in the destination and operand registers to generate results. The instruction may be restarted after faults.
Owner:INTEL CORP
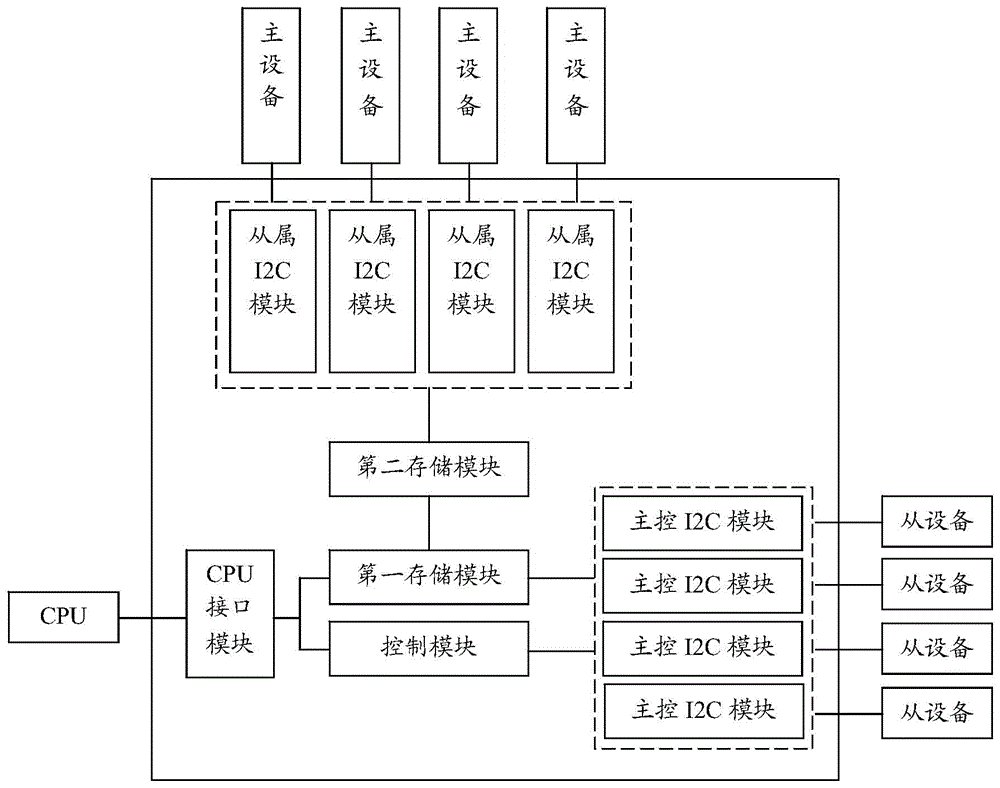
System and method for controlling I2C communication based on FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array)
InactiveCN104598418AIncrease flexibilityImprove portabilityElectric digital data processingCommunications systemProcessor register
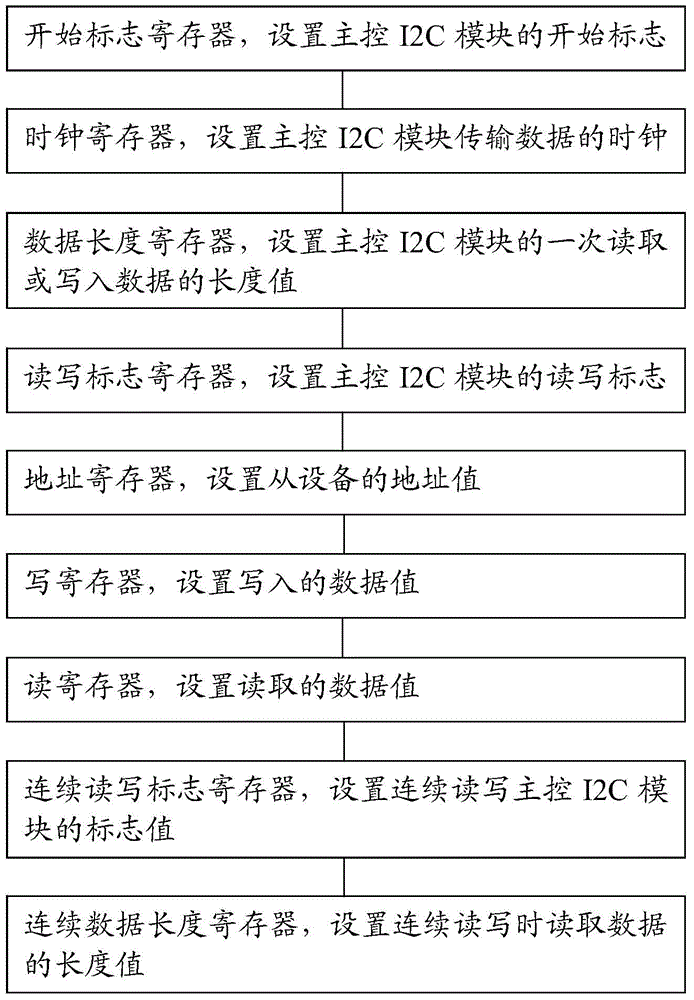
The invention discloses a system and a method for controlling I2C communication based on an FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array). The system and the method are applied to communication between slave equipment and host equipment in a communication system. MCUs (Micro Control Units) of the slave equipment are connected with the FPGA through main control I2C modules, and an FPGA unit is constructed by programming. The FPGA unit comprises the main control IC2 modules, a control module and a first storage module, wherein the main control I2C modules are connected with the control module and the first storage module respectively; the main control I2C modules comprise a leading flag register, a clock register, a data length register, a read-write flag register, an address register, a write register, a read register, a continuous read-write flag register and a continuous data length register. In the I2C modules provided by the invention, nine special registers are designed for realizing read-write functions, so that high flexibility and portability are achieved, one-time reading and writing operation can be realized, and read operation and write operation can be implemented separately.
Owner:OPWILL TECH BEIJING
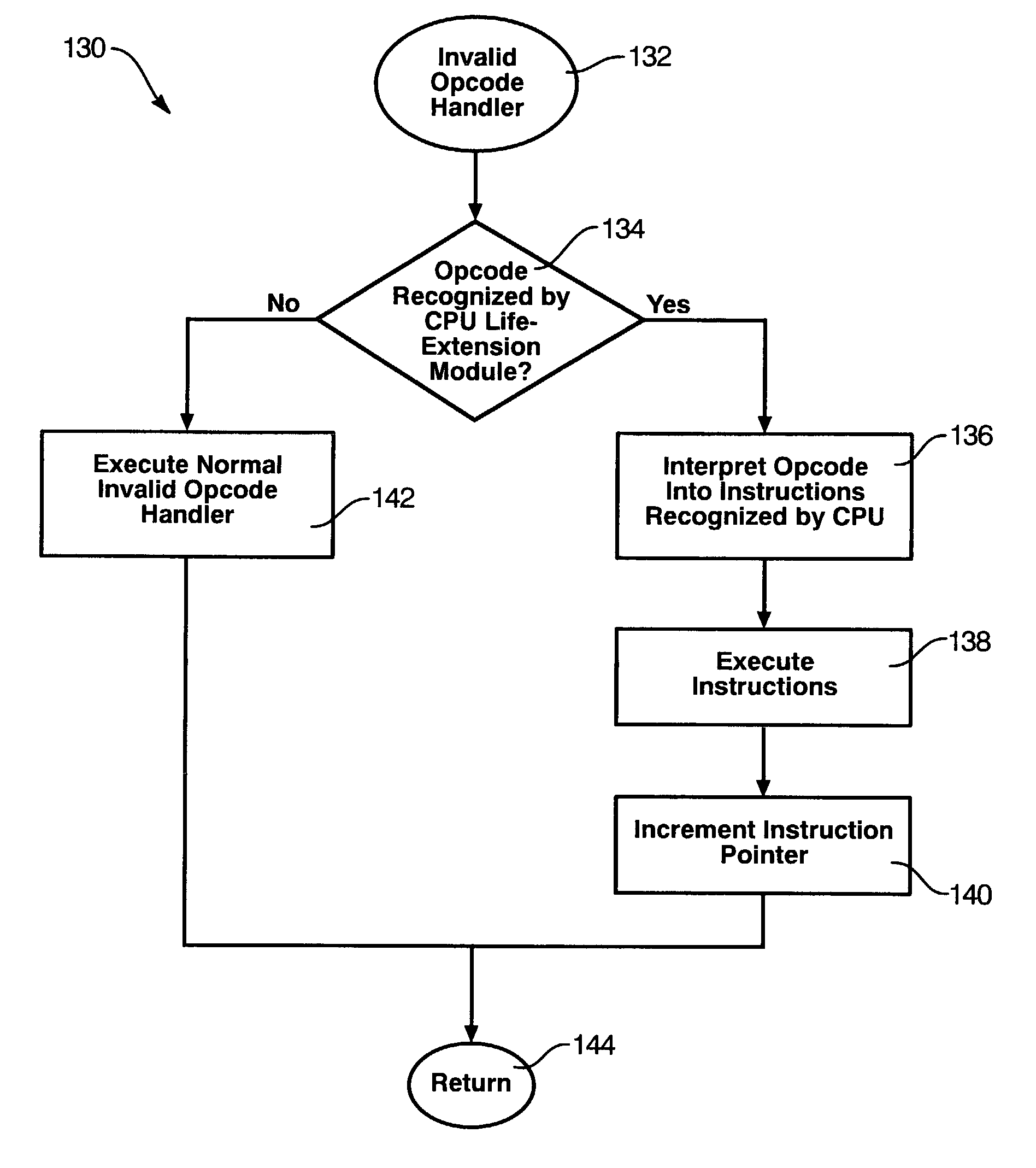
CPU life-extension apparatus and method
InactiveUS7171546B2Extended service lifeAvoid effortConditional code generationDigital computer detailsComputer moduleApplication software
A CPU life-extension apparatus and method makes a processor appear to be an upgraded CPU to substantially all software applications accessed thereby, thereby reducing the need and expense of upgrading a selected processor. A CPU life-extension module translates new instructions, intended for a CPU upgrade, into instructions recognized by the processor. In addition, the CPU life-extension module is programmed to monitor reads from and writes to a processor's flags register to modify the flags to emulate those of an upgraded CPU. The CPU life-extension module is configured to respond to interrupts generated by the processor in order to perform its various tasks.
Owner:ITE TECH INC
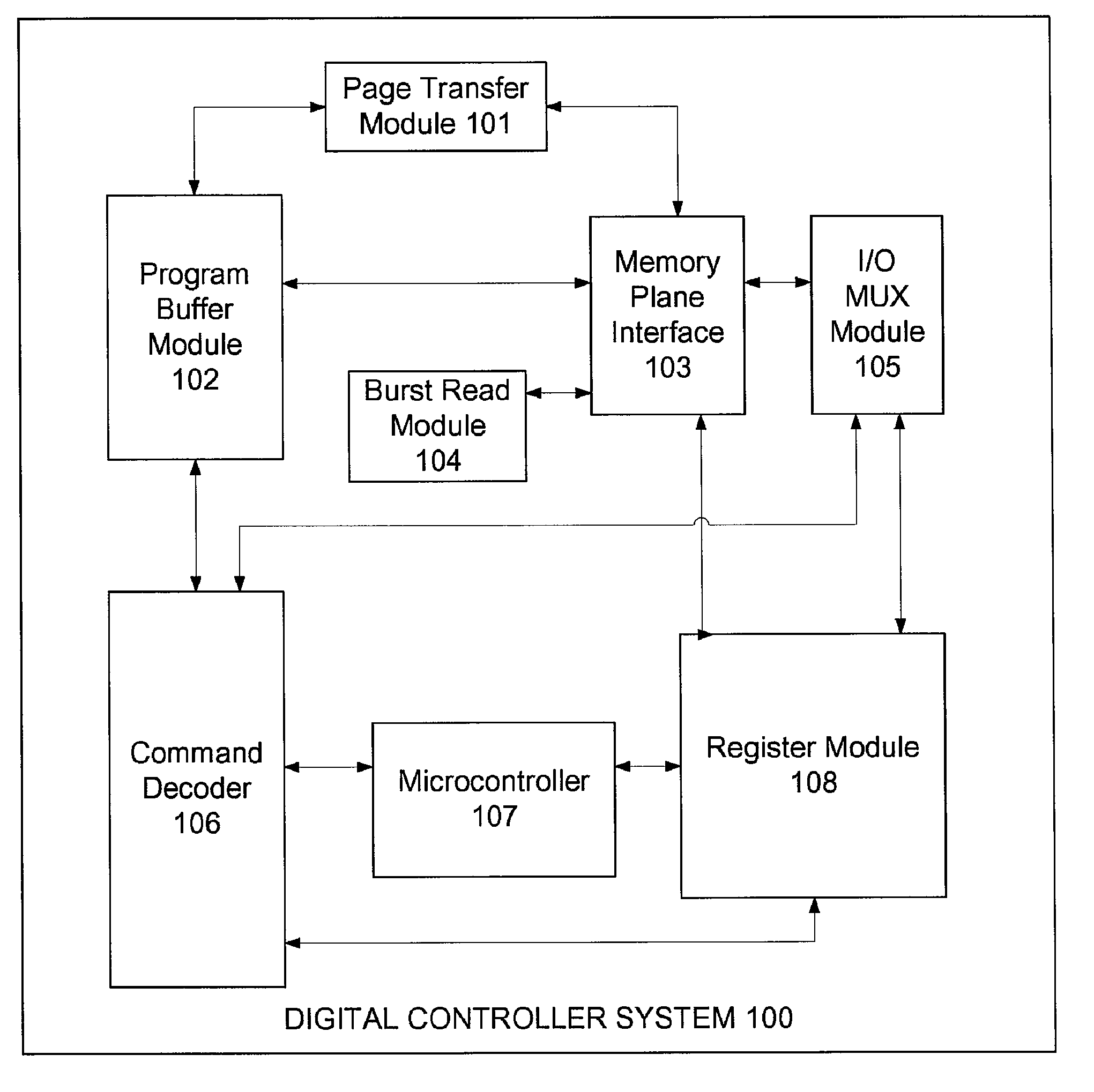
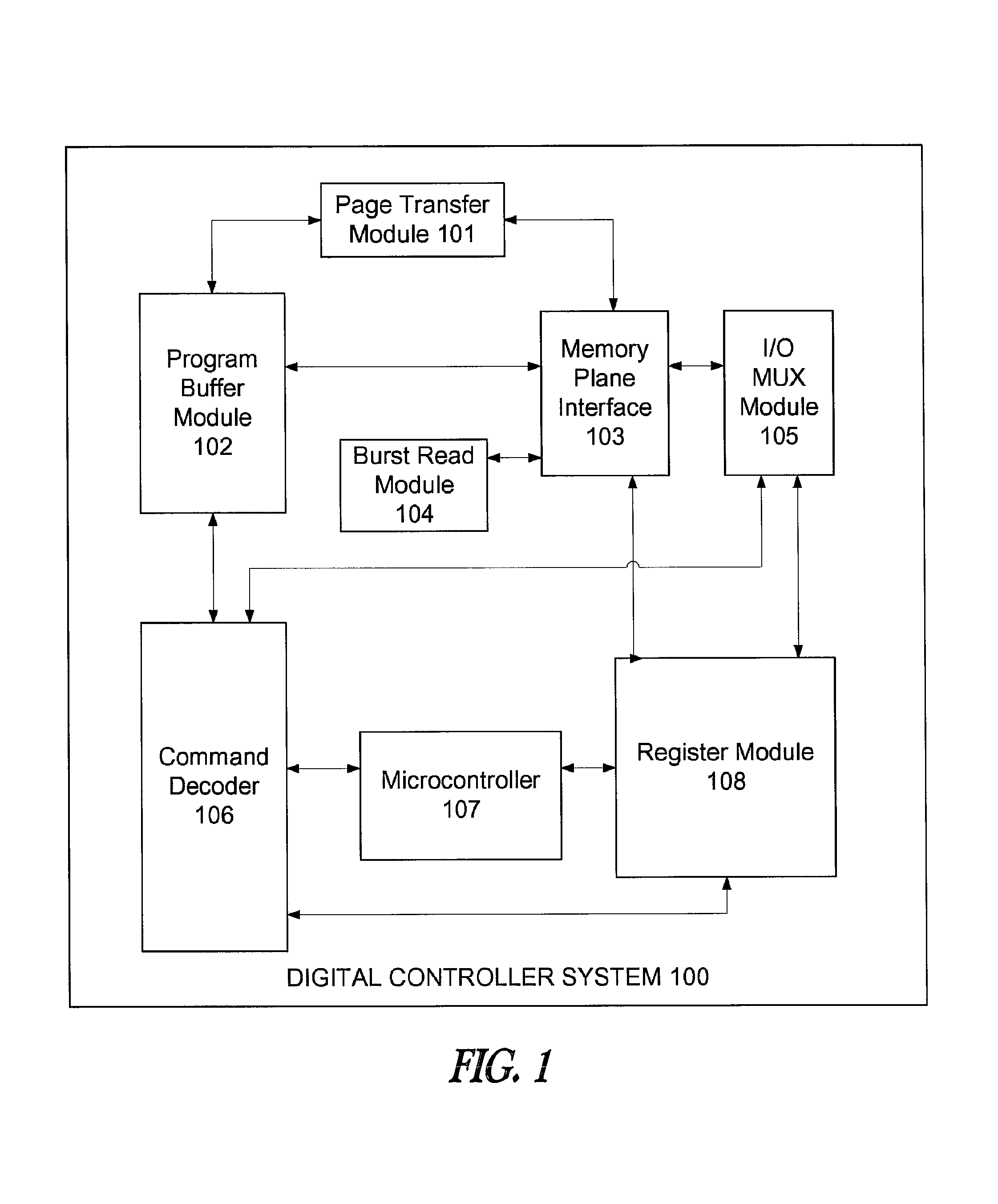
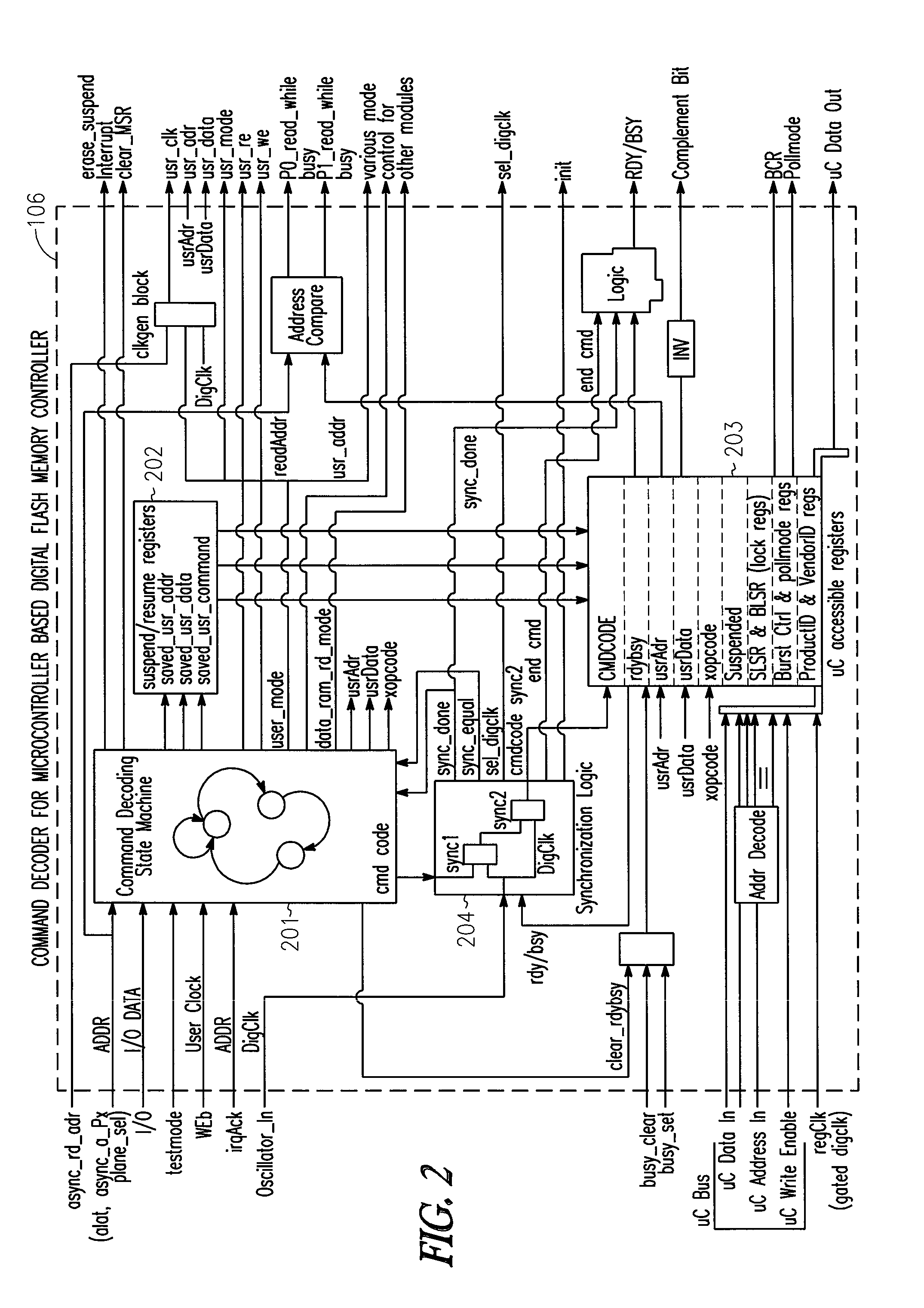
Command decoder for microcontroller based flash memory digital controller system
ActiveUS7574611B2Energy efficient ICTProgram control using stored programsMicrocontrollerProcessor register
A command decoder used for a microcontroller based Flash memory digital controller system includes multiple subsystems, including the command decoder, which serves as the main user interface for interpreting commands from a user and managing the priority of commands and command modes. The command decoder also stores crucial information including address, data, opcodes, and various flags registers that are used by other subsystems including the program buffer, burst read module, register block, and microcontroller. In addition, the command decoder contains clock synchronization logic, controls the sleep function of the microcontroller and serves as a test mode controller.
Owner:ATMEL CORP
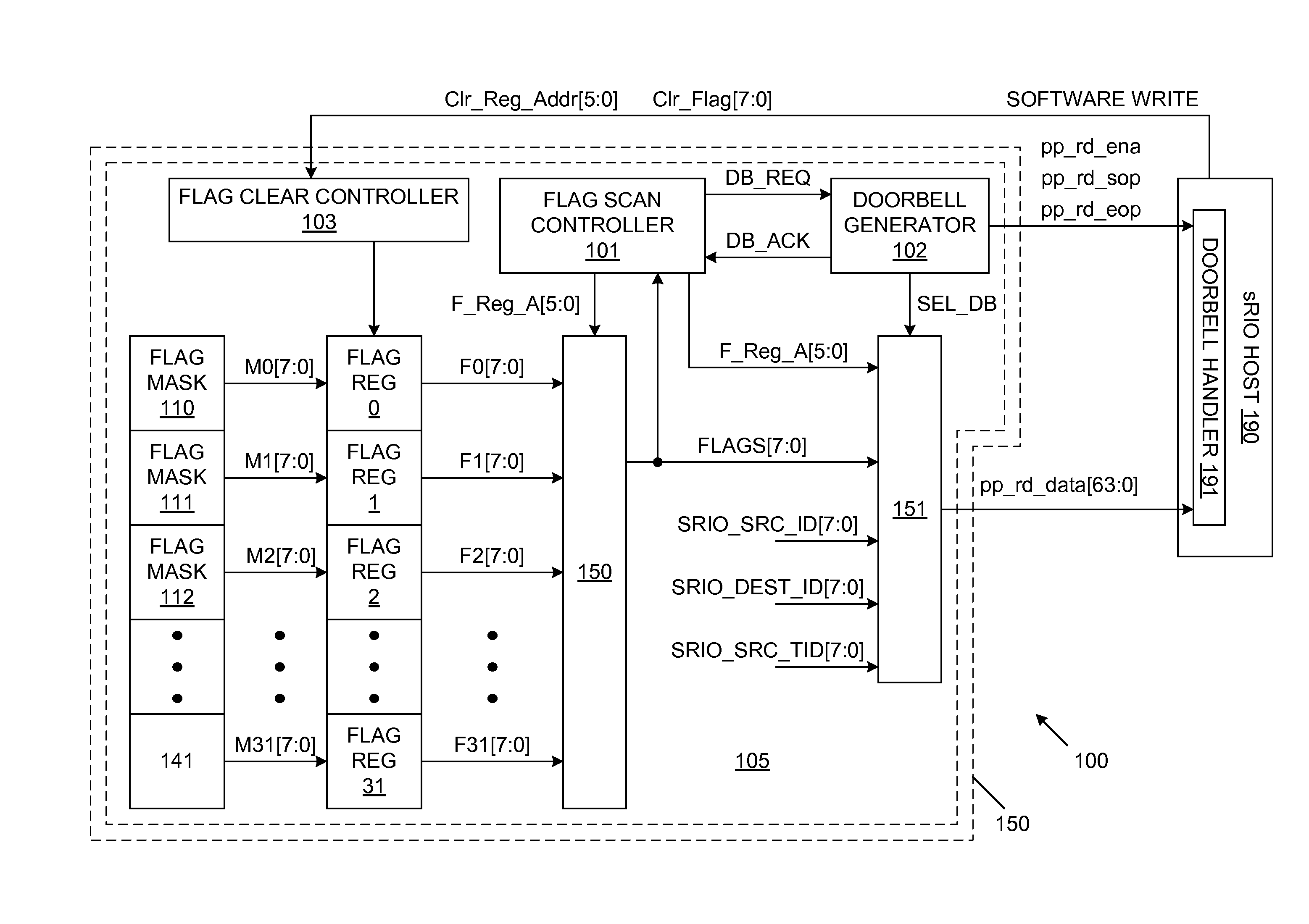
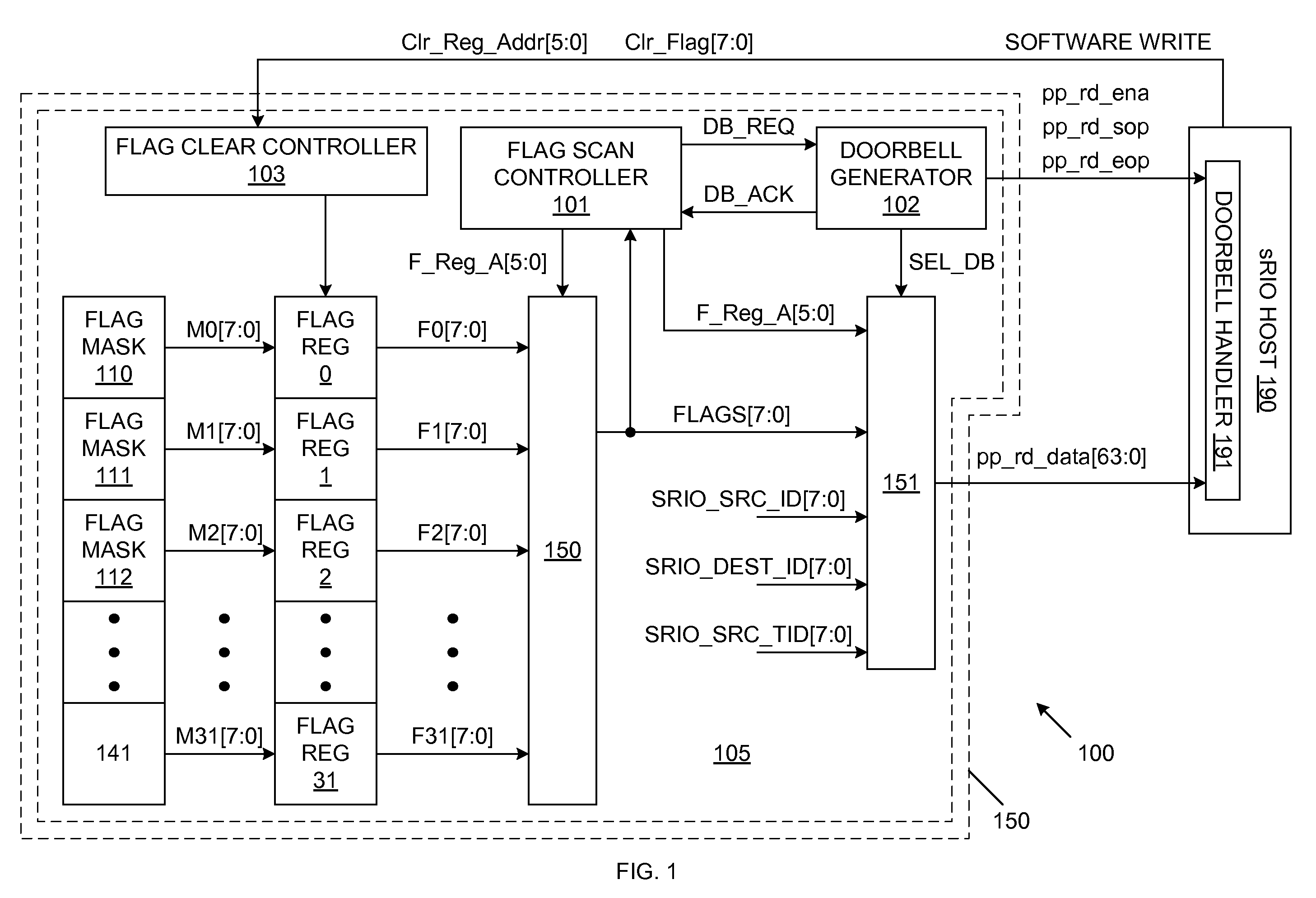
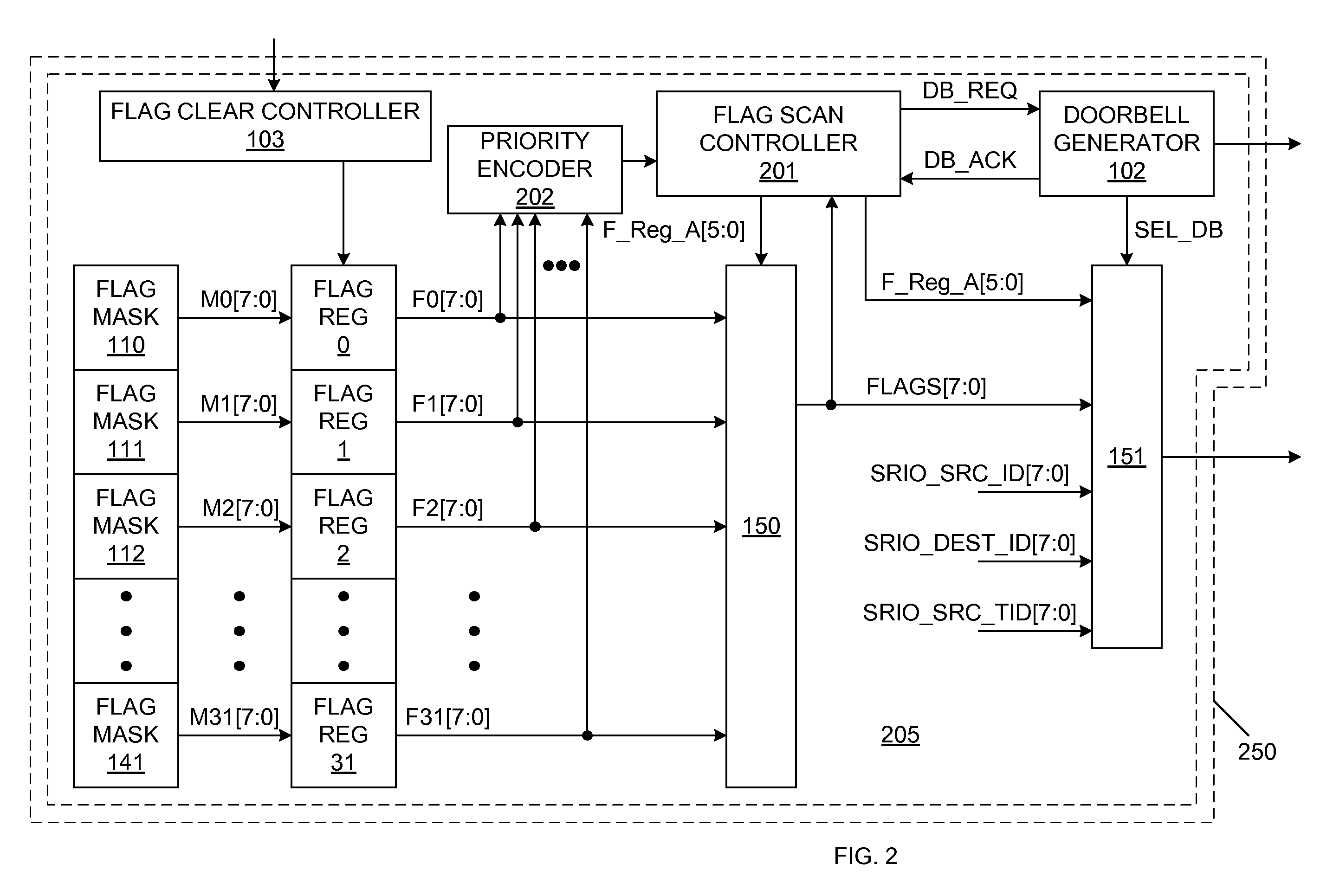
Rapid input/output doorbell coalescing to minimize CPU utilization and reduce system interrupt latency
ActiveUS7617346B2Eliminates race conditionConditional code generationMemory systemsDoorbellProcessor register
Status / error reporting is implemented using a doorbell system. A plurality of flag registers are included on a system device, such as a serial buffer. Each flag register has a corresponding address, and stores a plurality of flags. A flag scan controller accesses the flag registers in a predetermined priority order, using the flag register addresses. Upon detecting that one or more of the flags of a flag register are activated, the flag scan controller causes a doorbell command to be generated. The doorbell command includes the flag register address and the corresponding flags. A system processor receives the doorbell command and services the activated flags. Once the activated flags are serviced, the system processor performs one or more software write operations to clear the flags within the system device. The system processor can simultaneously service multiple flags. The system processor can also simultaneously clear multiple flags.
Owner:INTEGRATED DEVICE TECH INC
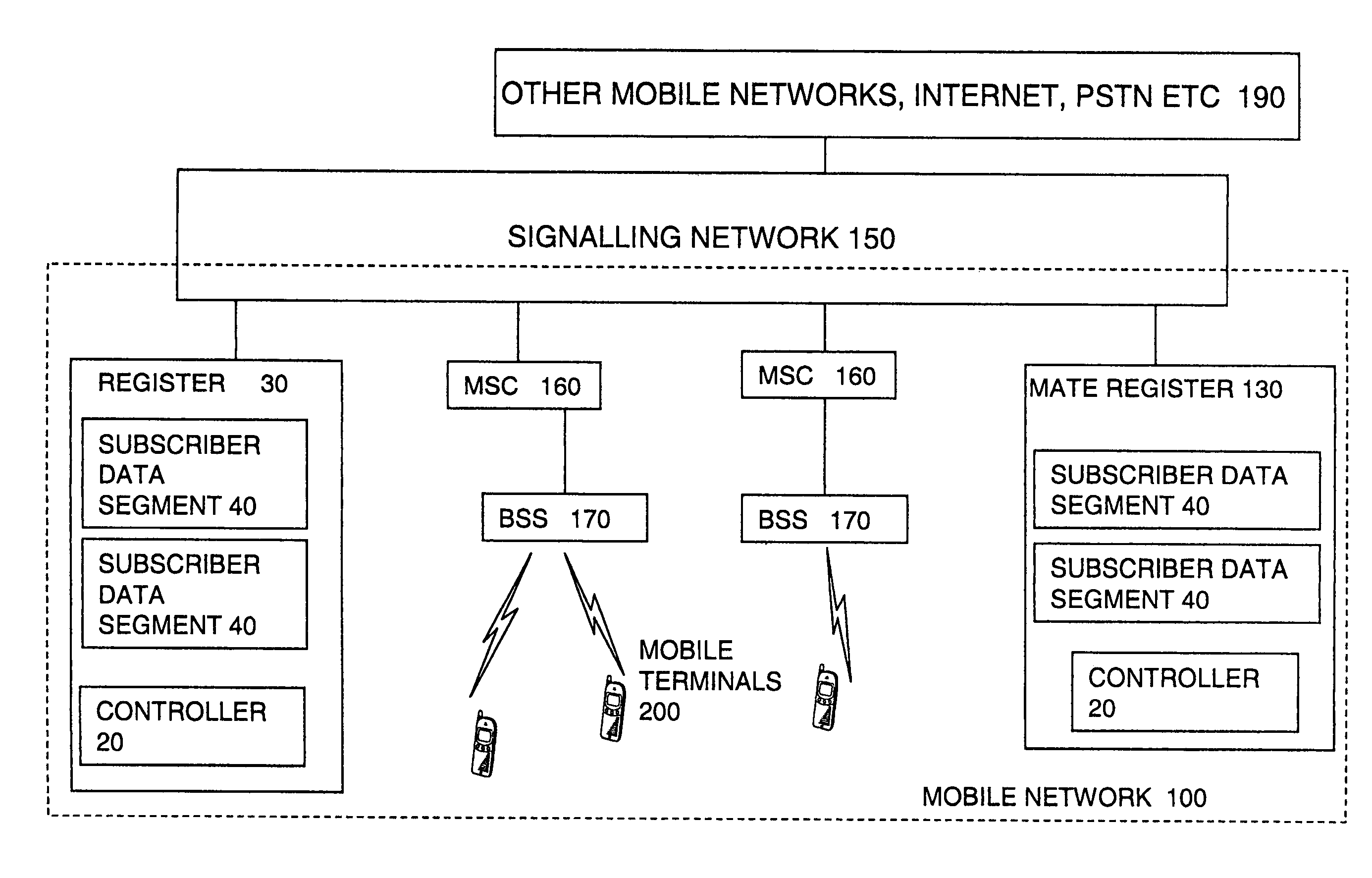
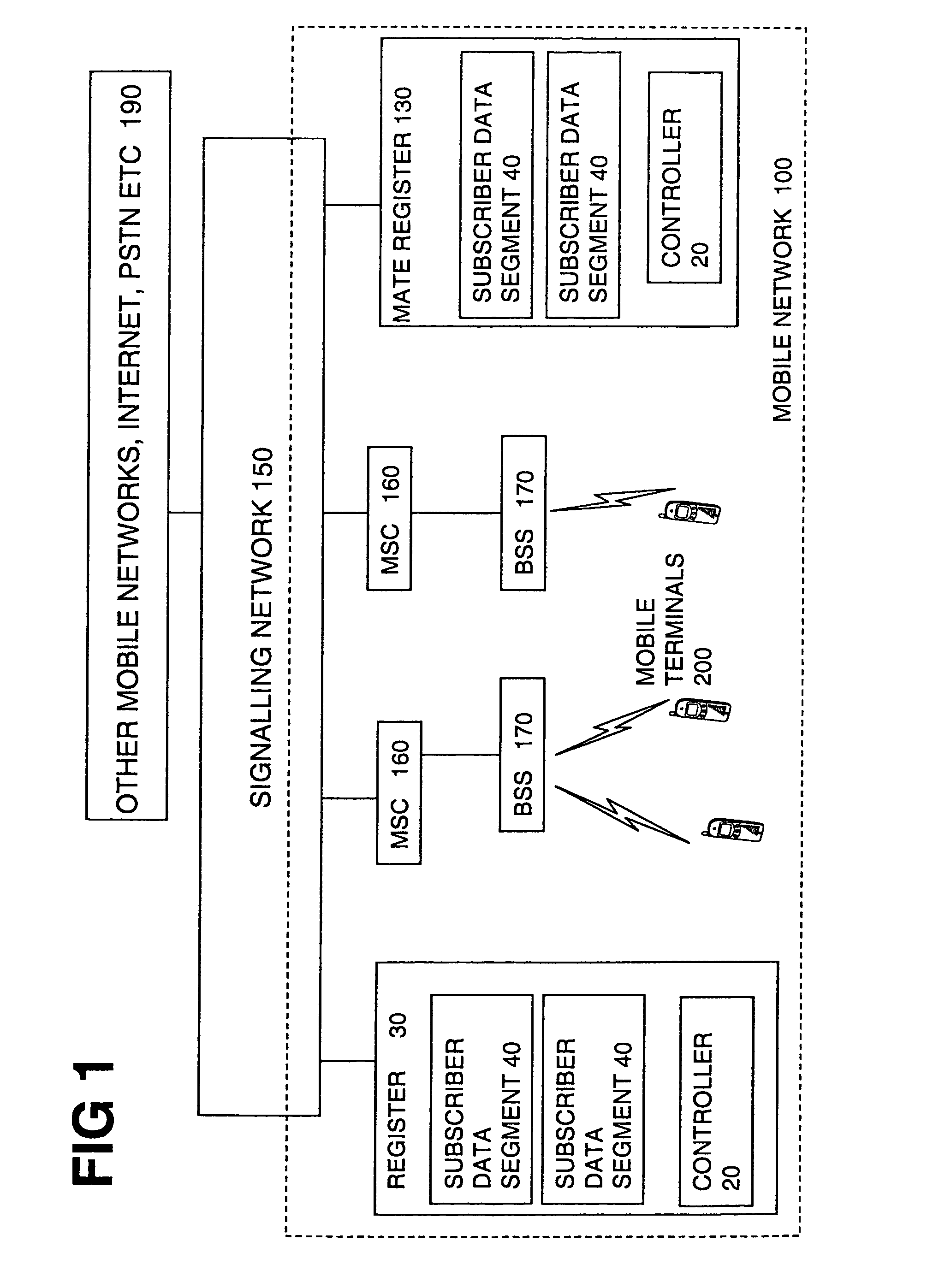
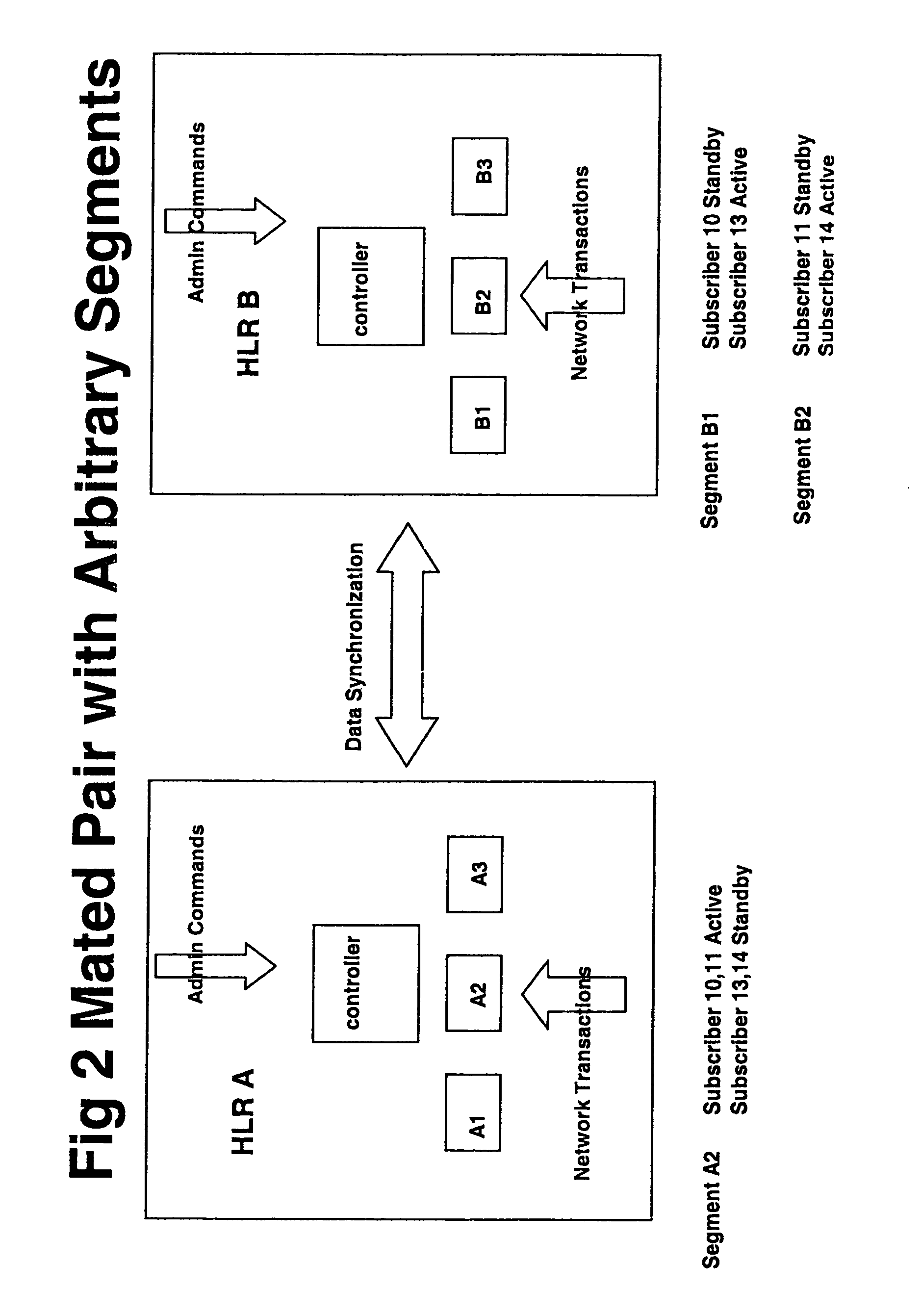
Disaster recovery for very large GSM/UMTS HLR databases
ActiveUS7039402B1Reduce riskThe process is simple and fastCommmunication supplementary servicesRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsProcessor registerData loss
An HLR register for maintaining data relating to mobile users of a network for use by the network, the register being arranged to be coupled to a mate register at a remote location for back up of the data, the register being divided into segments and arranged to carry out a partial handover to the mate register by handing over maintenance of data of one or some of the segments to the mate register temporarily. By allowing a partial handover rather than requiring a complete handover, the handover can be simpler and quicker. This can reduce the risk of loss of data or reduce an amount of down time and consequential losses of revenue. This is particularly important for larger registers. The handover can be triggered by a fault in the segment or for the purpose of planned maintenance for example. It can be triggered manually or automatically.
Owner:LENOVO INNOVATIONS LTD HONG KONG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com