Patents
Literature
290 results about "Condition Code" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A coded value specifying the state of being of an entity.
Mobile terminal for displaying a rich text document comprising conditional code for identifying advertising information stored locally or on the internet
InactiveUS6892217B1Digital data information retrievalMultiple digital computer combinationsThe InternetCondition Code
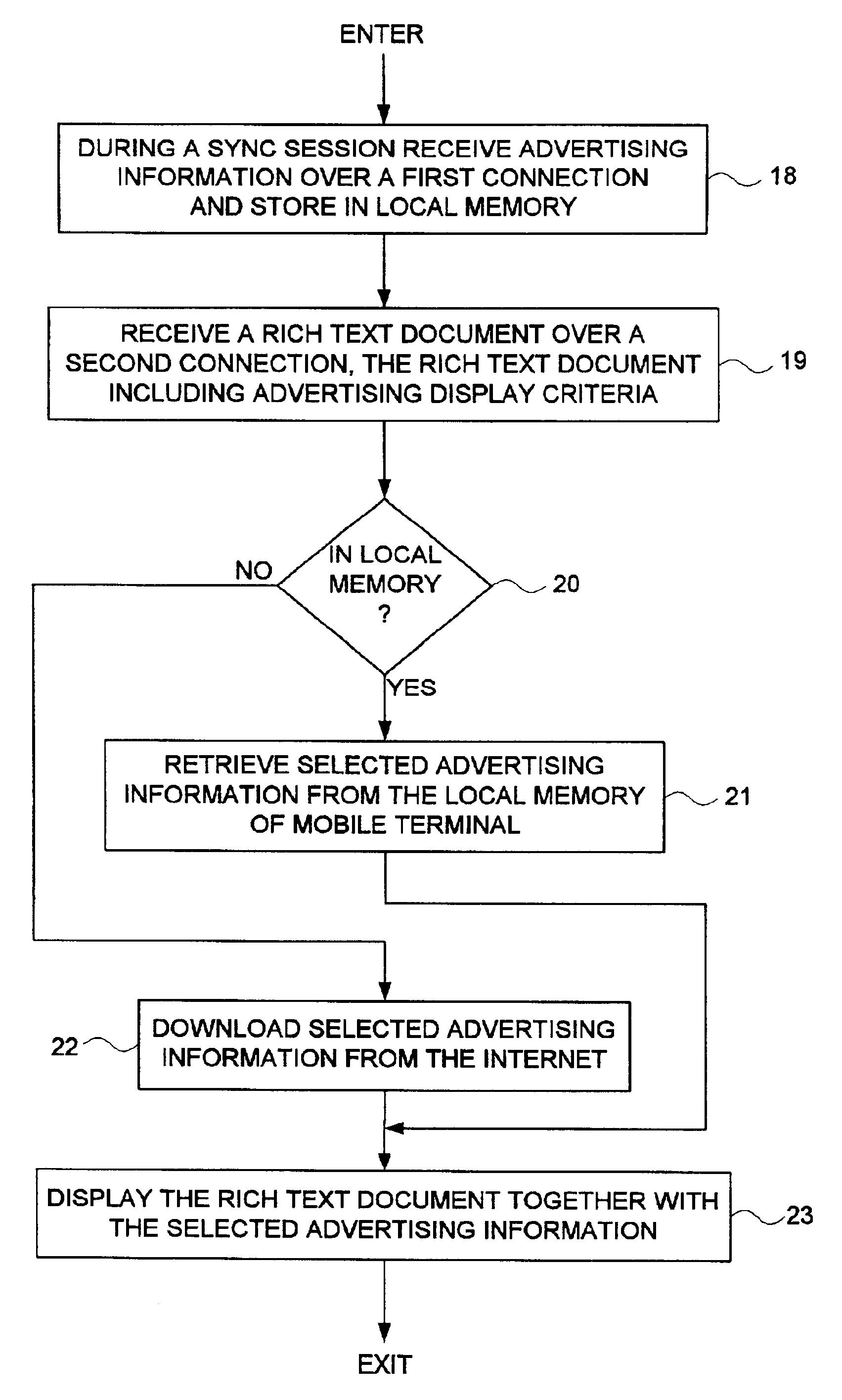
A method and apparatus are disclosed for transmitting advertising information to a mobile terminal over a first connection during a synchronization session and storing the advertising information in a local memory of the mobile terminal. A rich text document is transmitted to the mobile terminal over a second connection, wherein the rich text document comprises conditional code comprising advertising display criteria including a first identifier for retrieving selected advertising information stored in the local memory of the mobile terminal and a second identifier for downloading the selected advertising information from the Internet.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
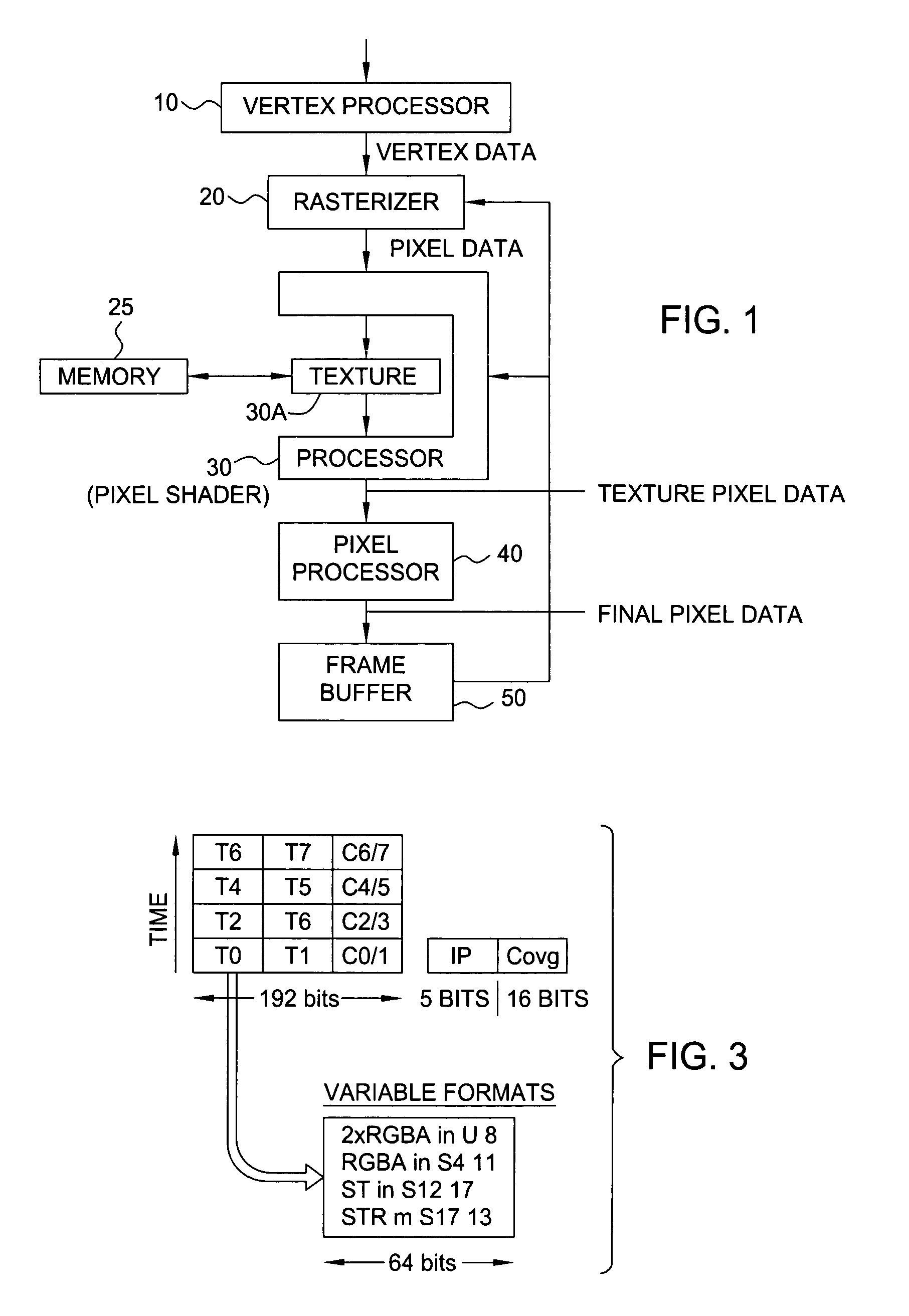
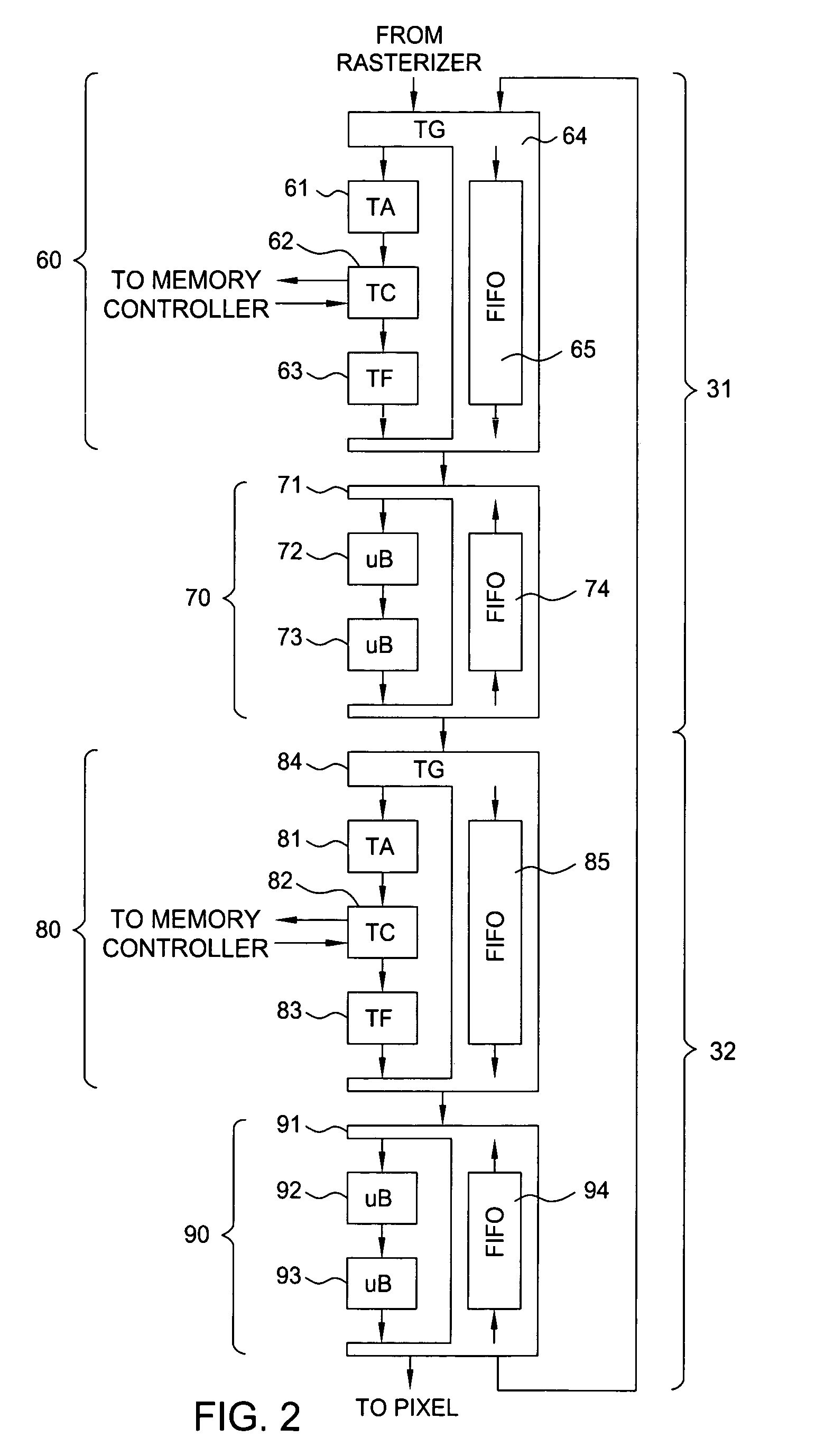
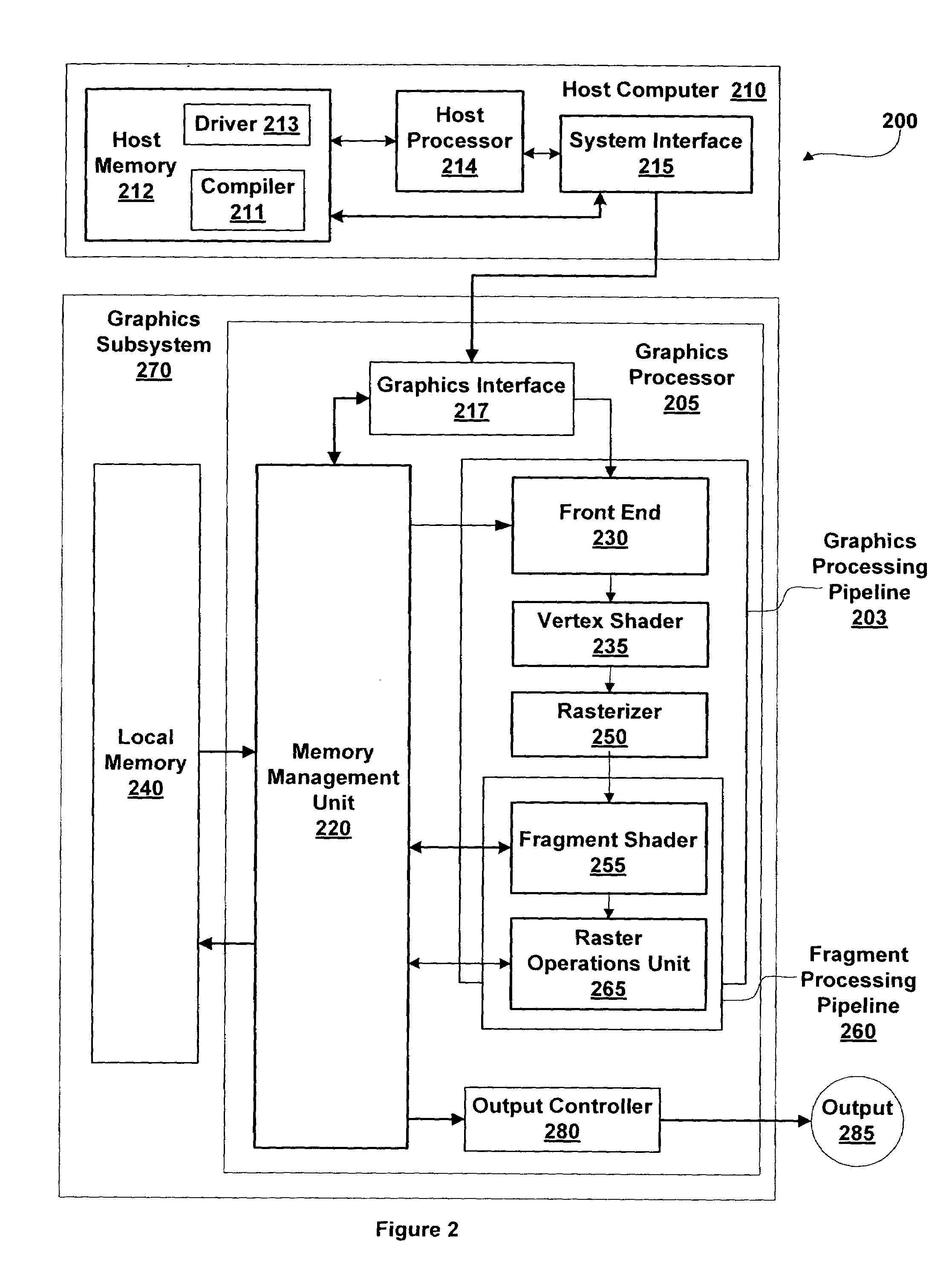
Method and system for scalable, dataflow-based, programmable processing of graphics data
ActiveUS6980209B1Improve system performanceLess system performanceCathode-ray tube indicatorsProcessor architectures/configurationArray data structureNetwork packet
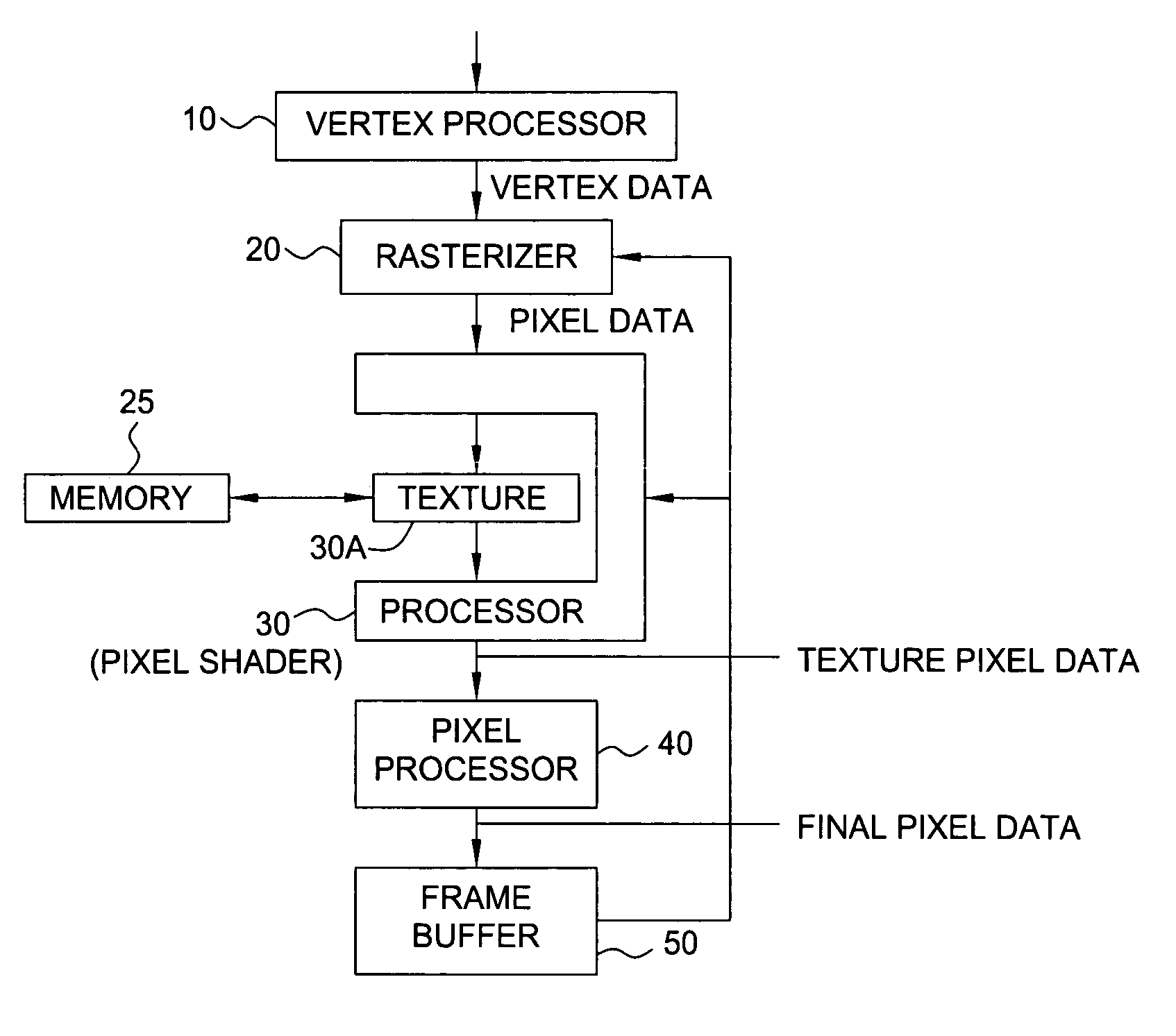
A scalable pipelined pixel shader that processes packets of data and preserves the format of each packet at each processing stage. Each packet is an ordered array of data values, at least one of which is an instruction pointer. Each member of the ordered array can be indicative of any type of data. As a packet progresses through the pixel shader during processing, each member of the ordered array can be replaced by a sequence of data values indicative of different types of data (e.g., an address of a texel, a texel, or a partially or fully processed color value). Information required for the pixel shader to process each packet is contained in the packet, and thus the pixel shader is scalable in the sense that it can be implemented in modular fashion to include any number of identical pipelined processing stages and can execute the same program regardless of the number of stages. Preferably, each processing stage is itself scalable, can be implemented to include an arbitrary number of identical pipelined instruction execution stages known as microblenders, and can execute the same program regardless of the number of microblenders. The current value of the instruction pointer (IP) in a packet determines the next instruction to be executed on the data contained in the packet. Any processing unit can change the instruction that will be executed by a subsequent processing unit by modifying the IP (and / or condition codes) of a packet that it asserts to the subsequent processing unit. Other aspects of the invention include graphics processors (each including a pixel shader configured in accordance with the invention), methods and systems for generating packets of data for processing in accordance with the invention, and methods for pipelined processing of packets of data.
Owner:PVC CONTAINER CORP +1
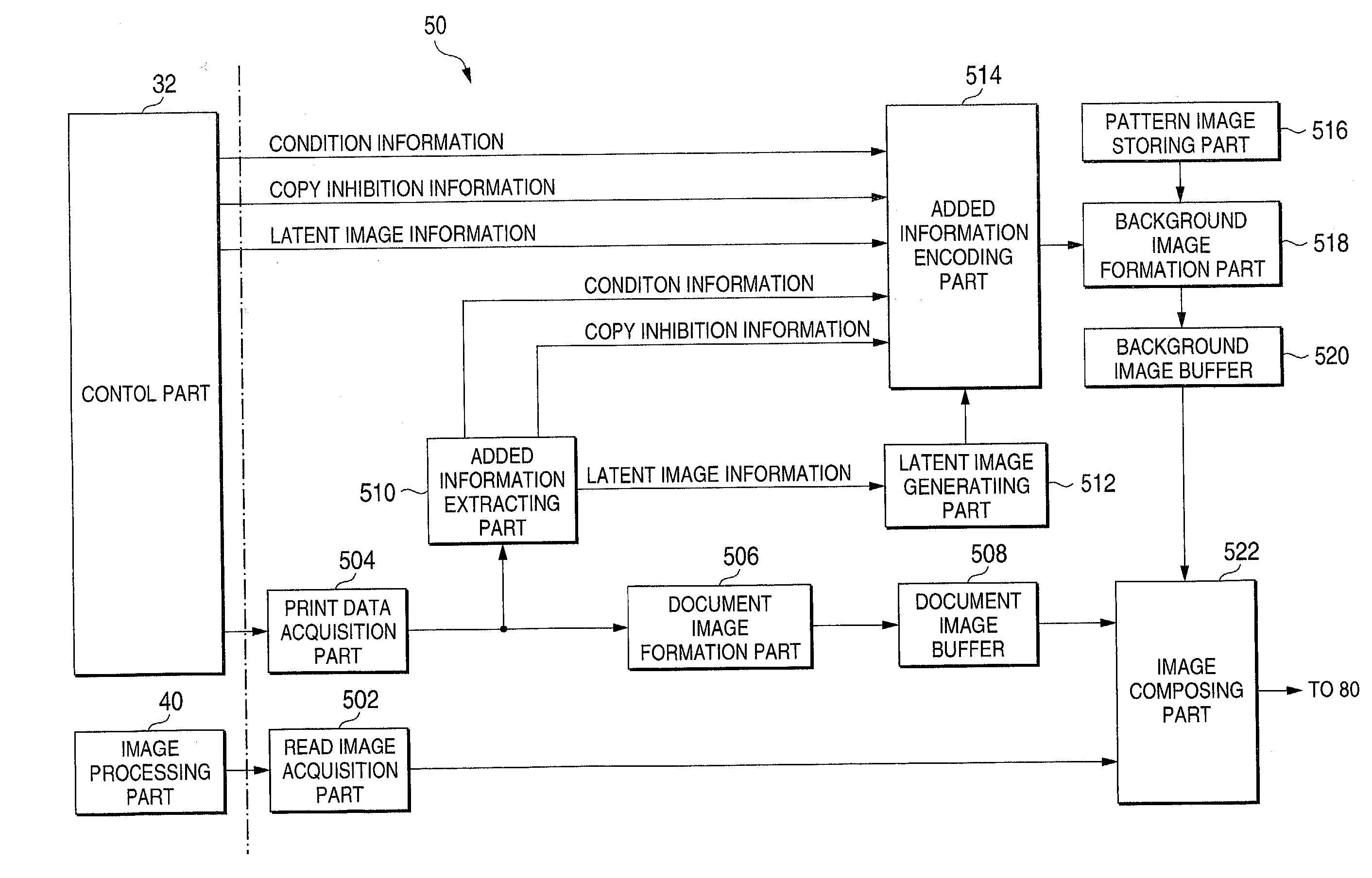
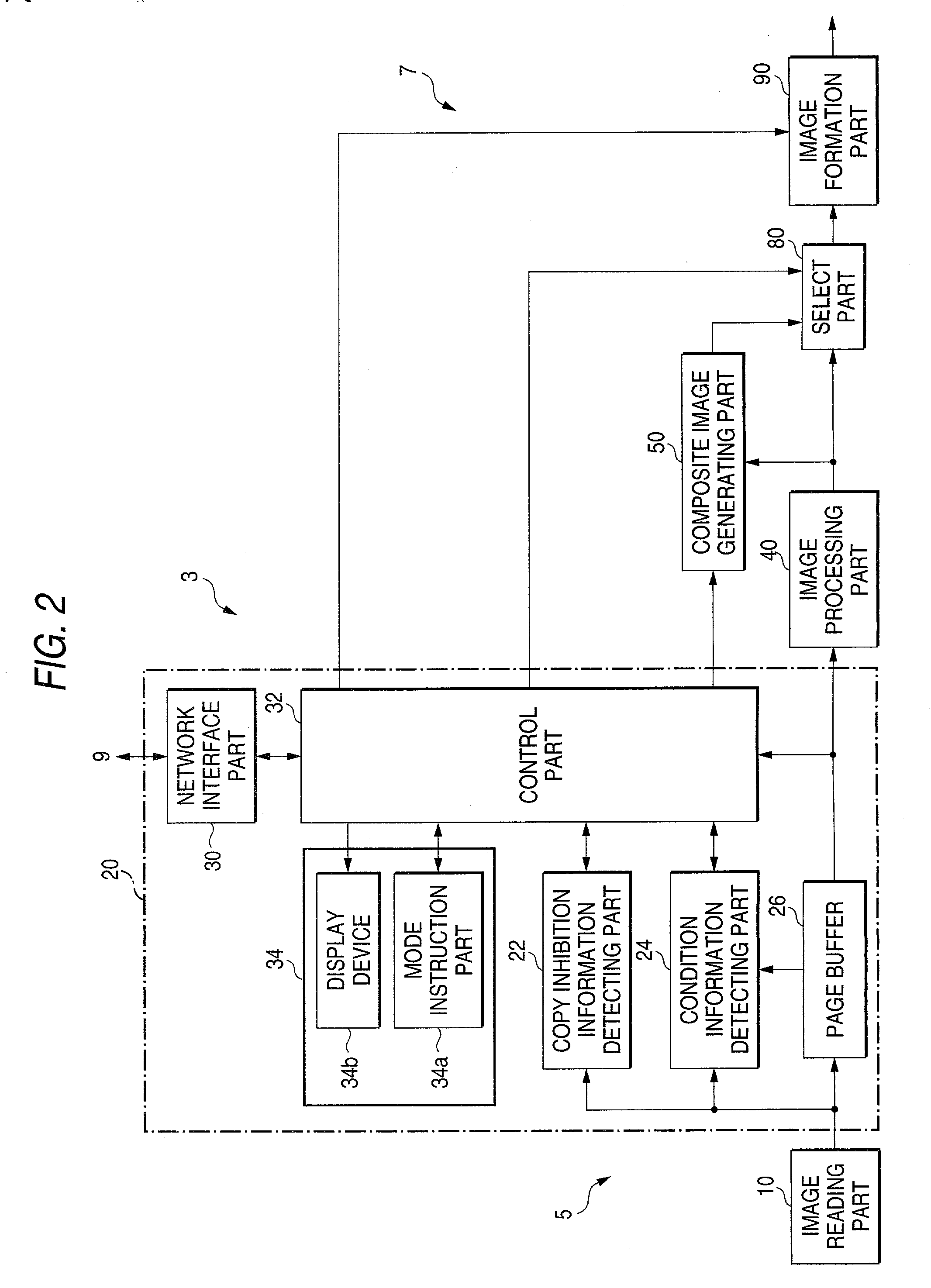
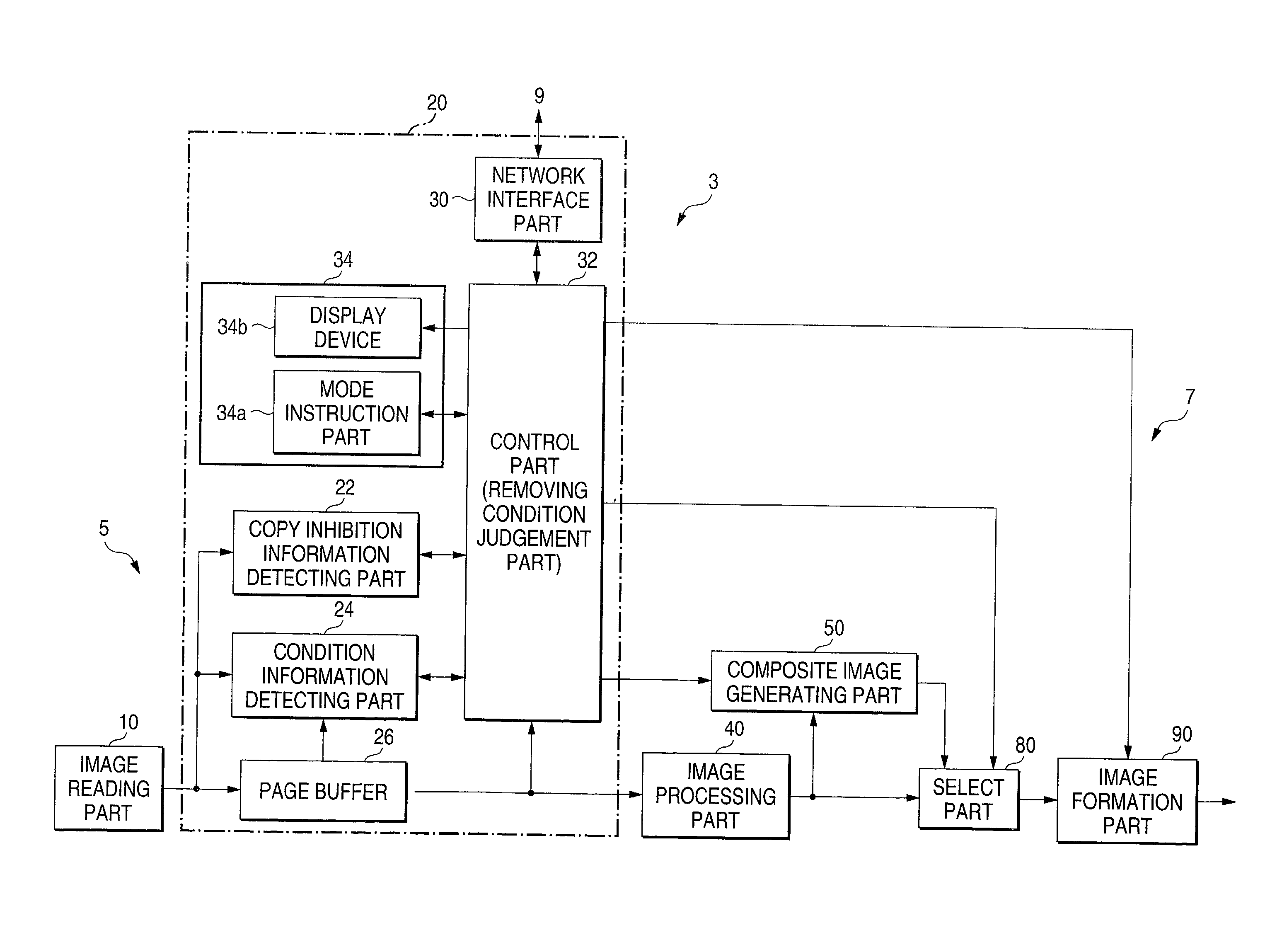
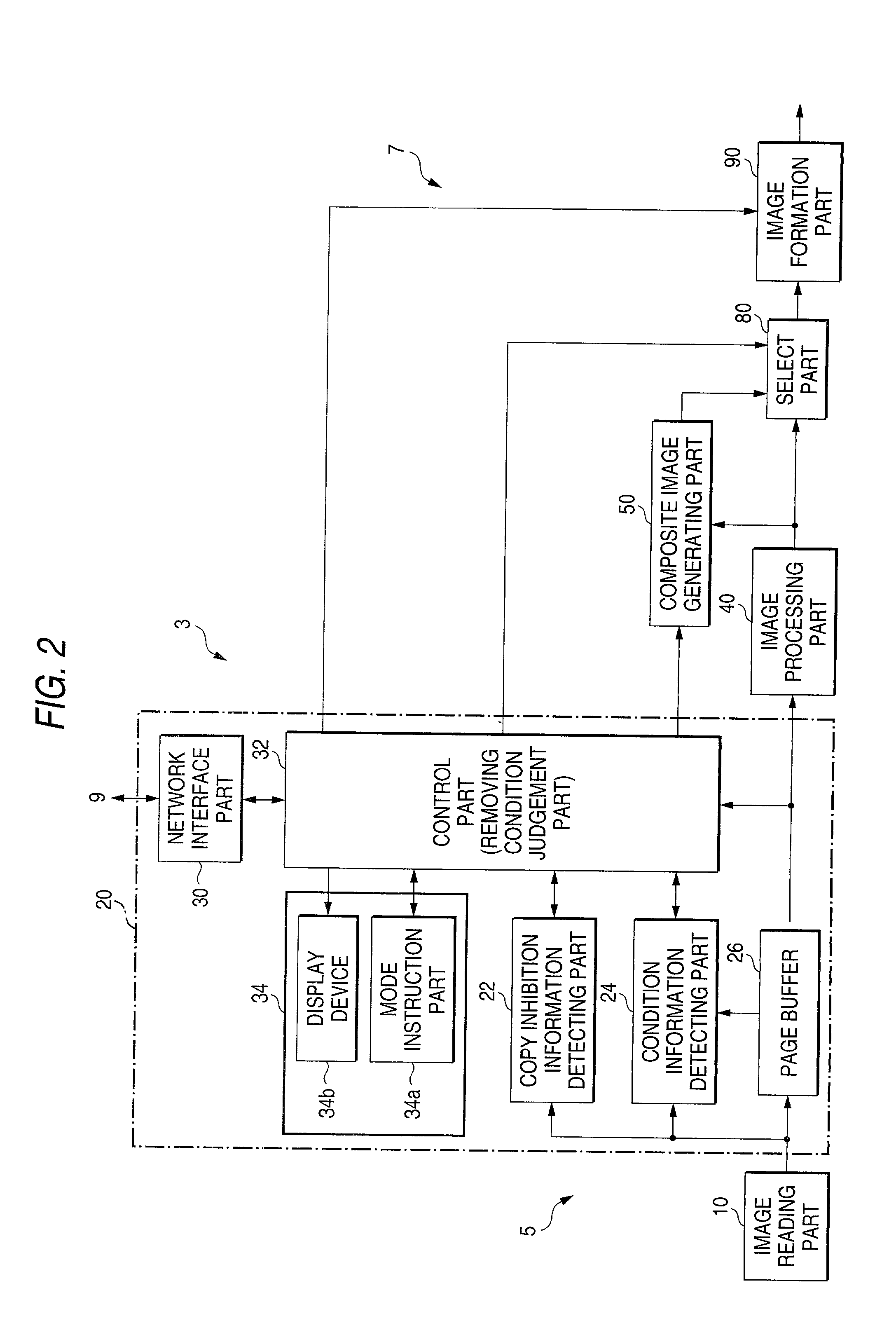
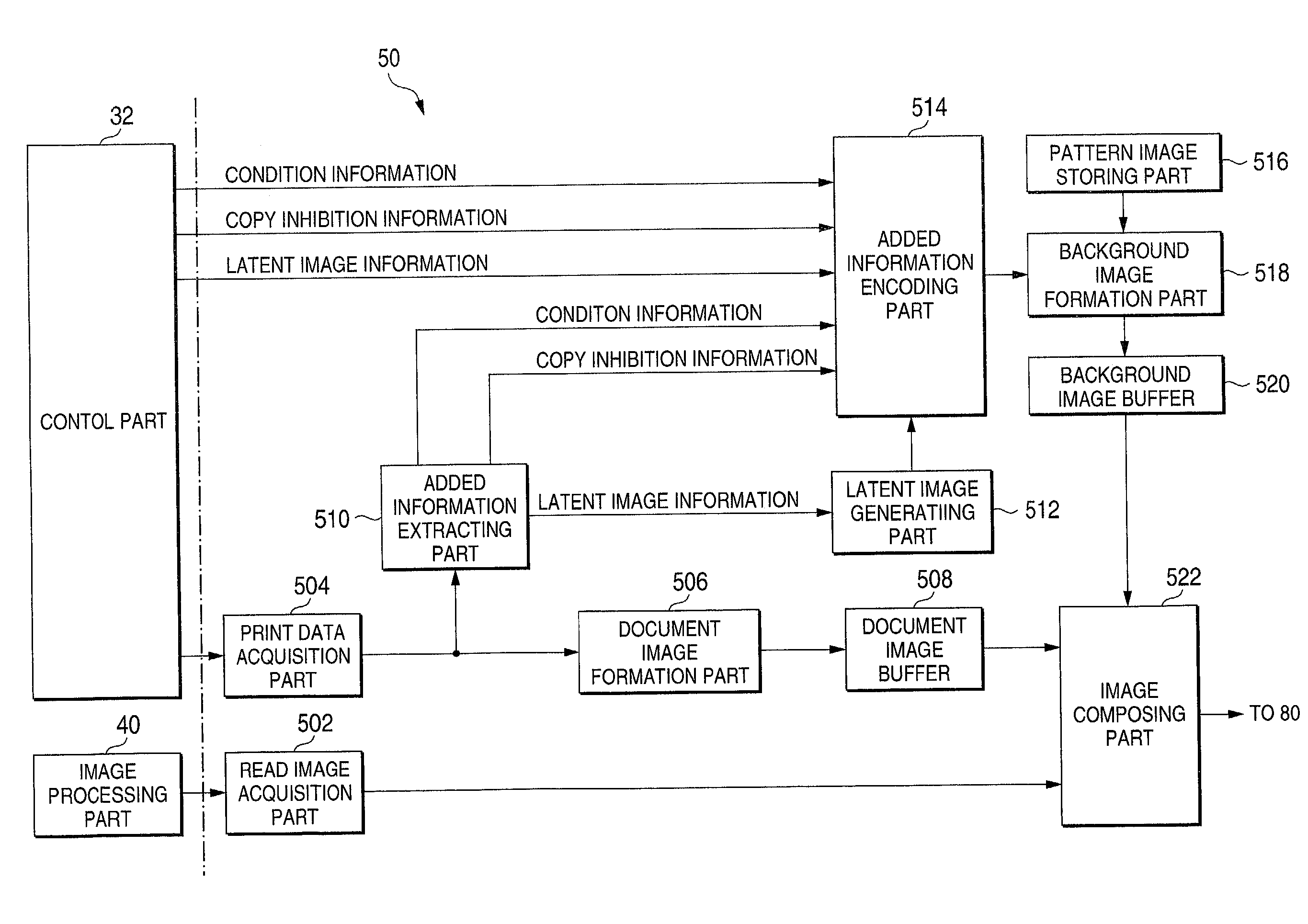
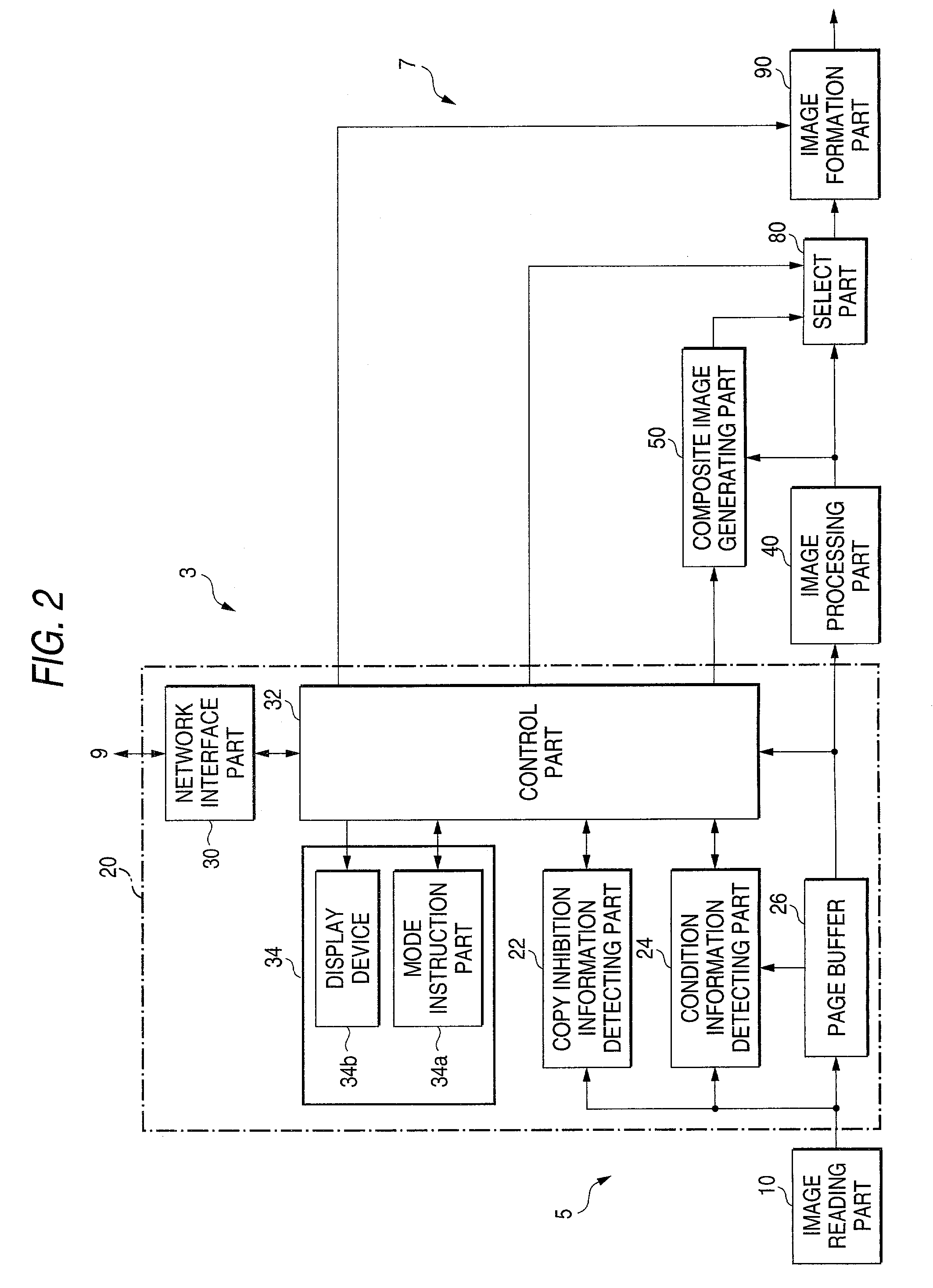
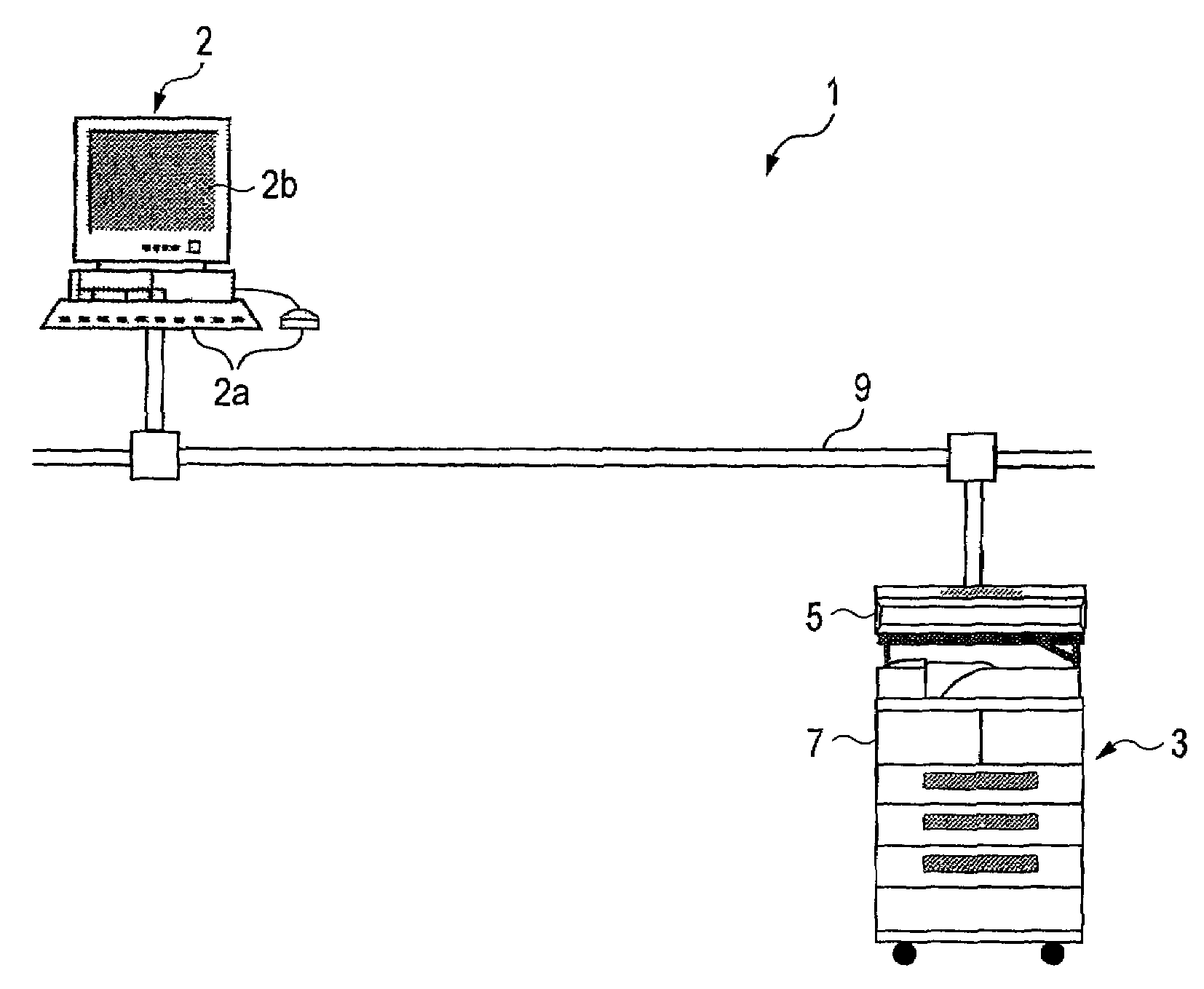
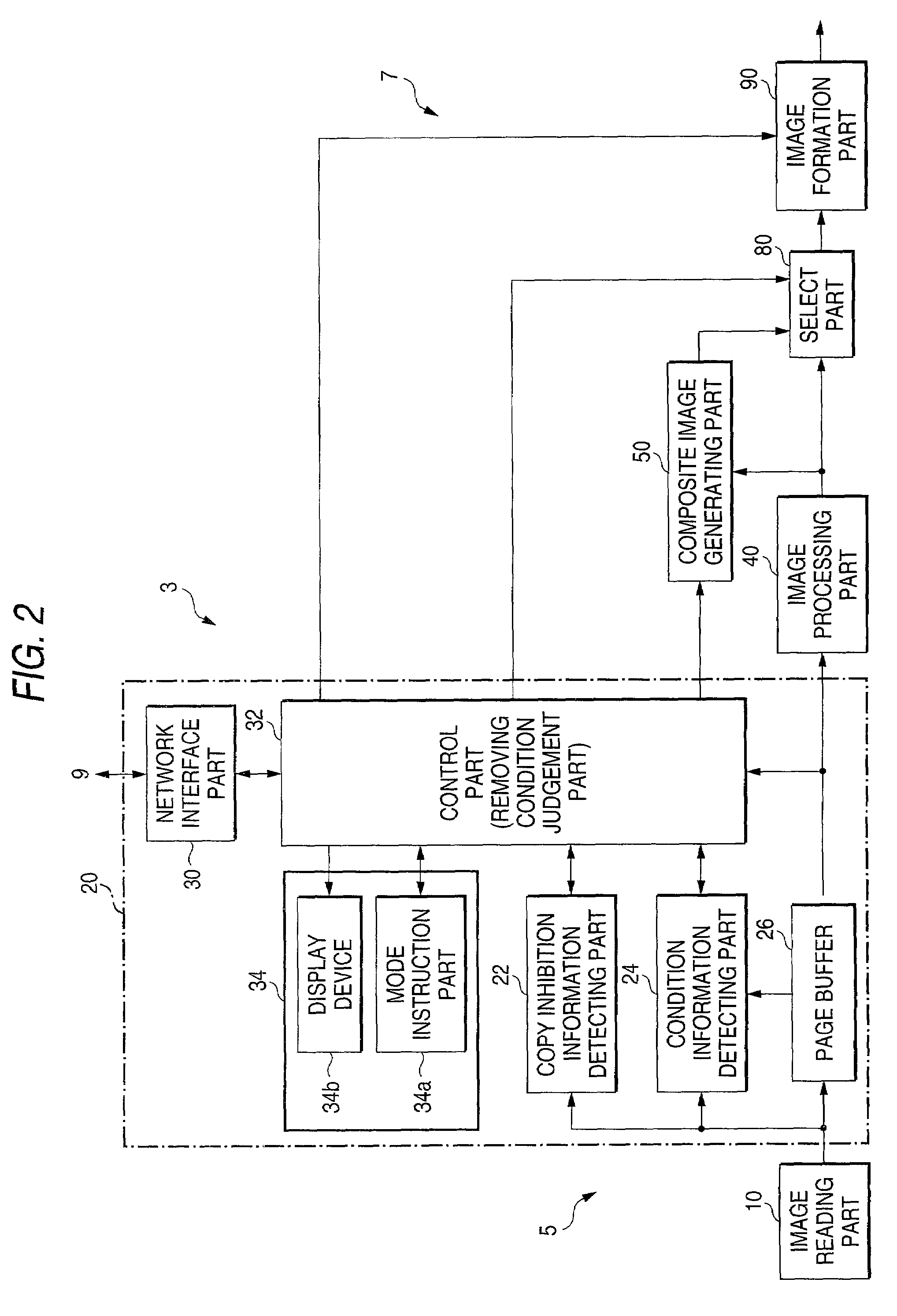
Image generating method, device and program, and illicit copying prevention system
InactiveUS20030179412A1User identity/authority verificationVisual presentation using printersComputer graphics (images)Paper document
An added information encoding part repeatedly arranges two kinds of copy inhibition code arrays of the unit two-dimensional arrays to which copy inhibition codes are assigned, and condition code arrays of the unit two-dimensional arrays to which codes for removing the copy inhibition are assigned, into a two-dimensional array according to given rules. A background image formation part generates a background image in which copy inhibition pattern image areas and condition pattern image areas are repeatedly and two-dimensionally arranged according to given rules, while referring to this array, and the pattern images corresponding to respective codes stored in the background image formation part, and stores the generated background image into a background image buffer. An image composing part reads out document images from a document image buffer, and the background image from the background image buffer, and superimposes them into a composite image.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
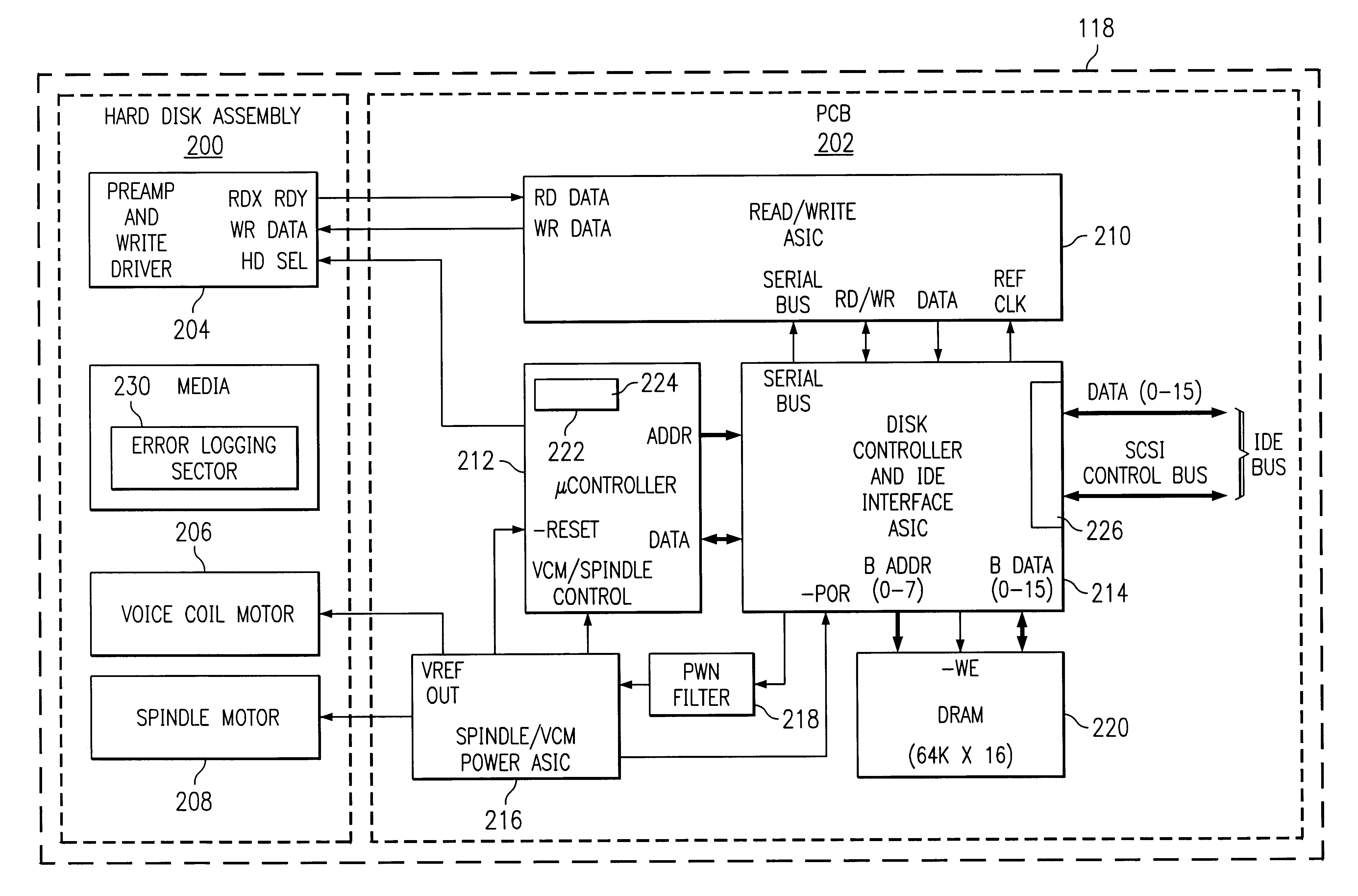
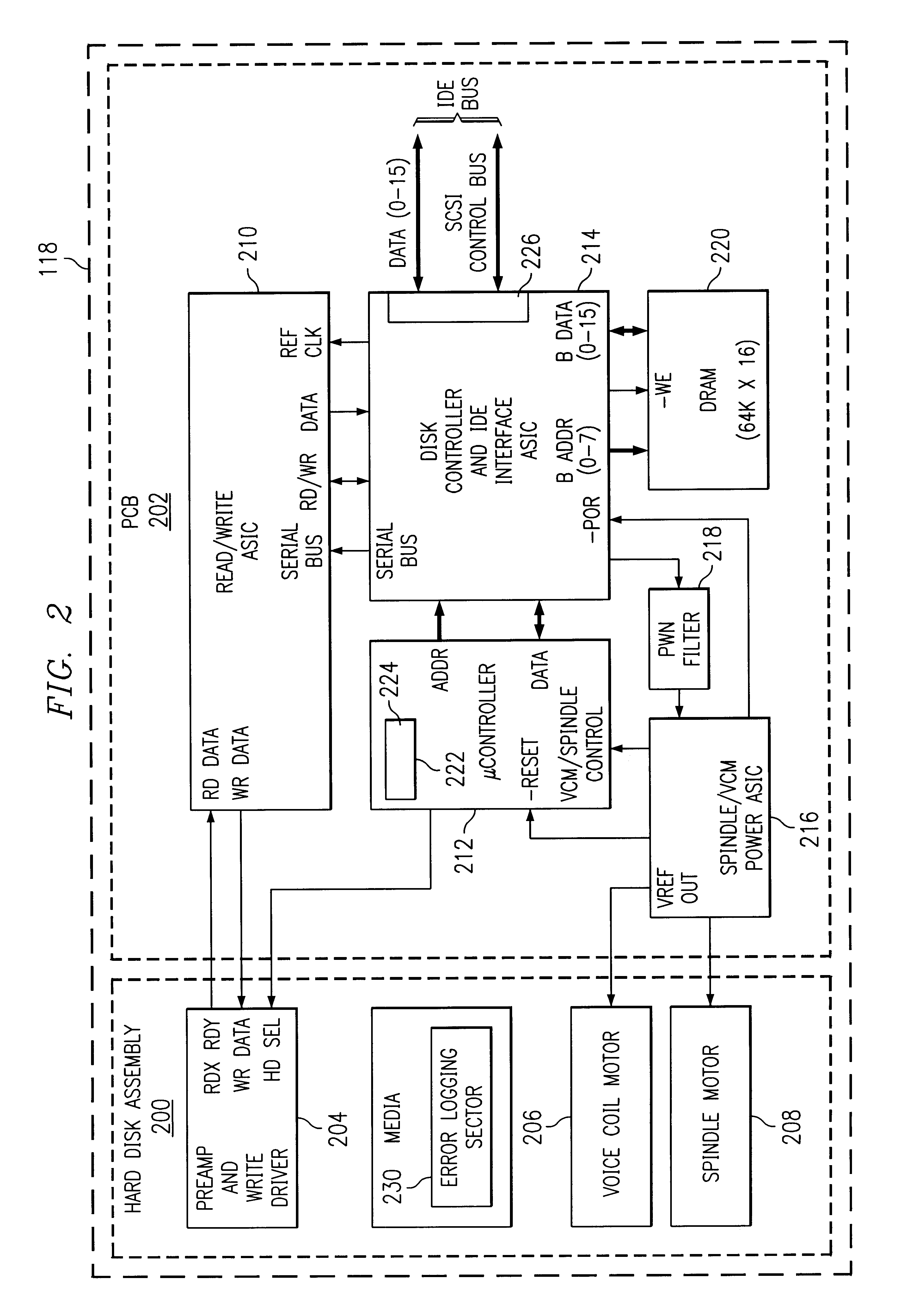
Drive error logging
A method and apparatus for logging errors in a storage device. As commands are executed by the storage device a list of previously executed commands is maintained. When an error is detected by the storage device, the previously executed commands and certain error condition codes are stored in an error log in a non-volatile memory of the storage device. The storage device is responsive to a command for reading back the values contained in the error log for diagnostic purposes.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Image reader and copier
InactiveUS20030179399A1Reliable preventionImprove processingImage enhancementImage analysisProgramming languageCondition Code
An image, in which a pattern image is arranged so as to express a control information for inhibiting copying or for removing the inhibition, is defined as an image to be read. A copy inhibition code or a condition code for removing the inhibition is assigned for the pattern image. In a "normal copy mode" of a copier, a copy inhibition information detecting part detects the copy inhibition code in an obtained image, and a controller halts the copying when the copy inhibition code is detected. A condition information detecting part detects the condition code in the obtained image. A copy mode is provided in which the copying operation is permitted when the condition matches. The controller permits copying when a condition, such as permitting a specific user to perform copying or the elapse of a predetermined day and time delimited period, is established.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
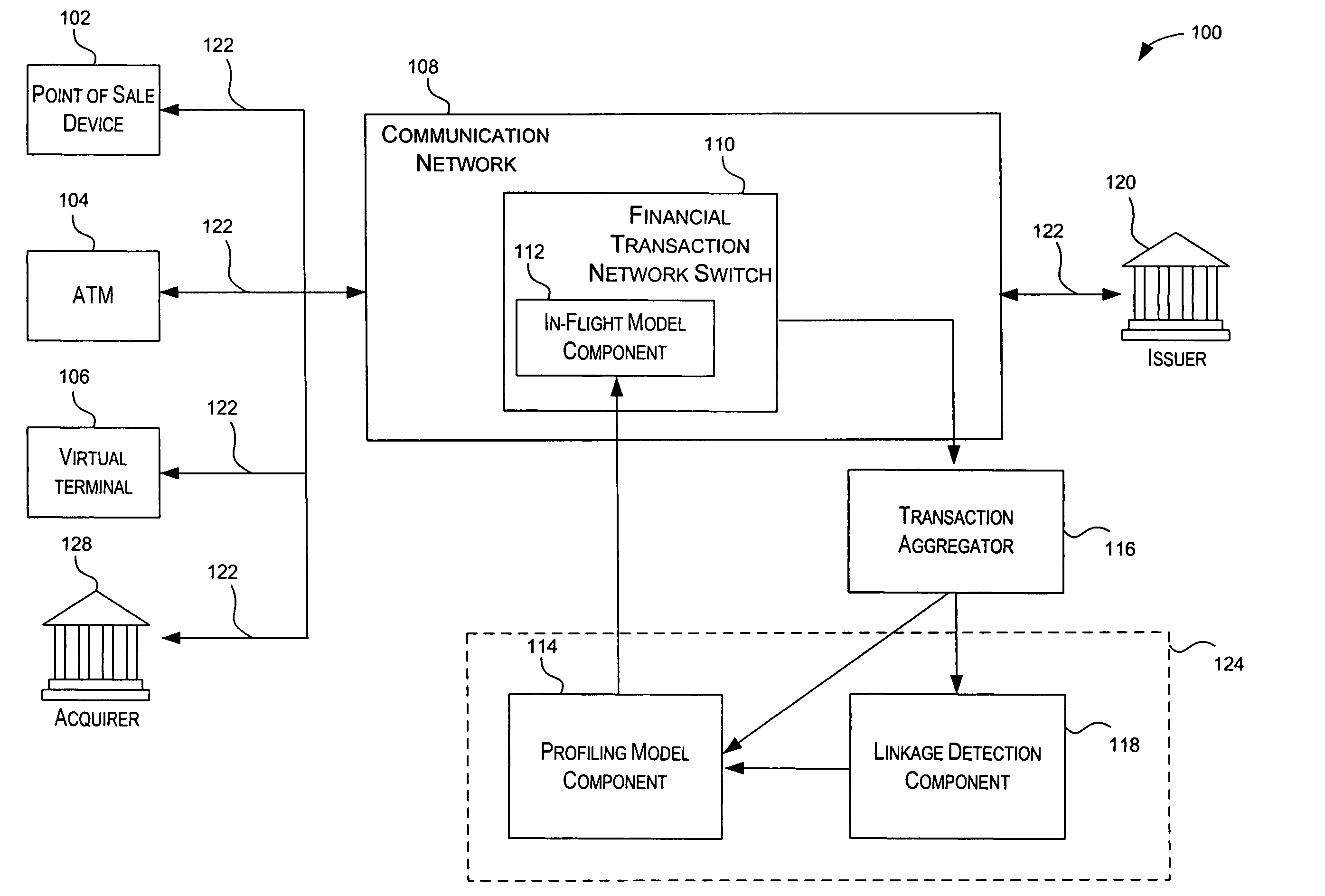
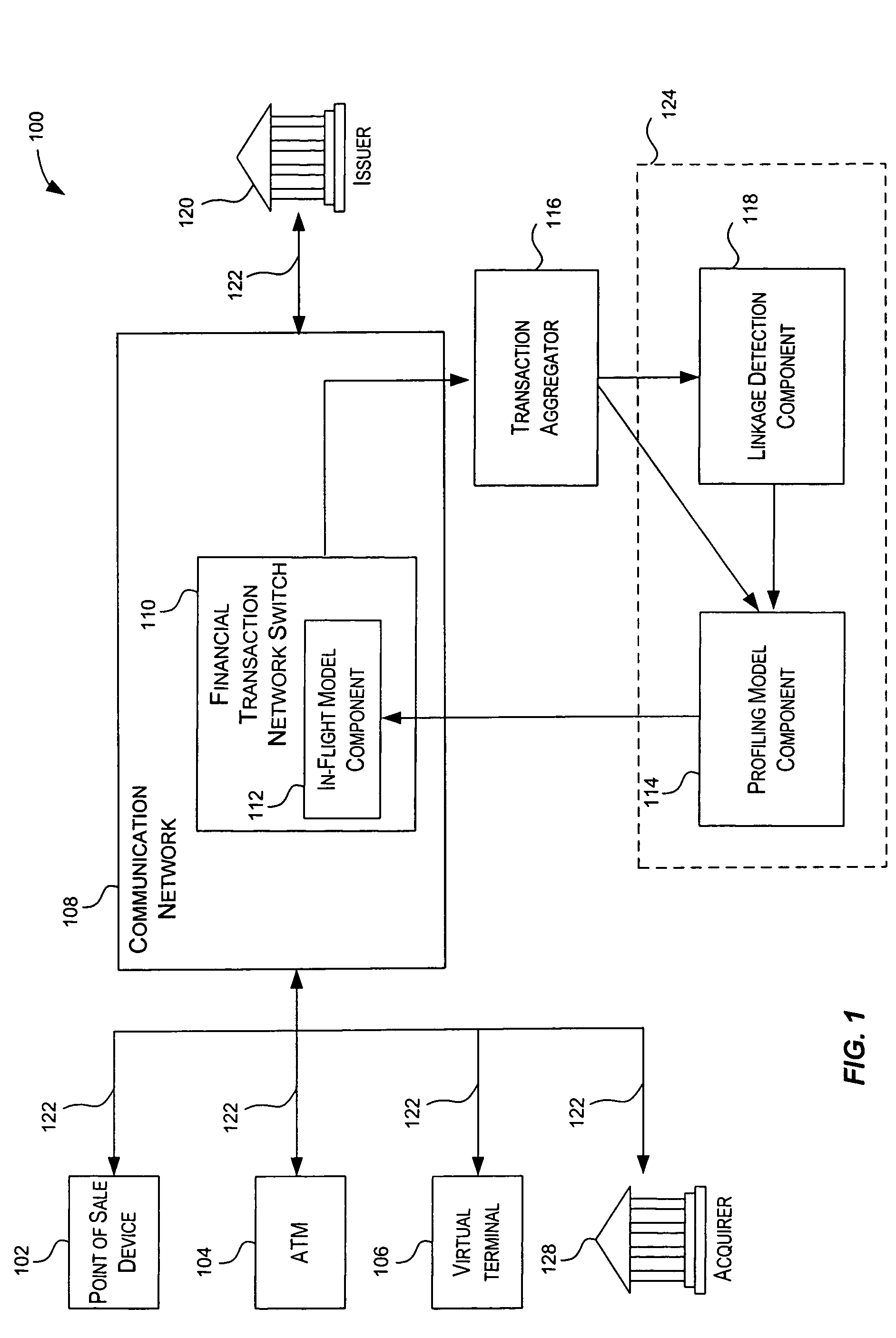
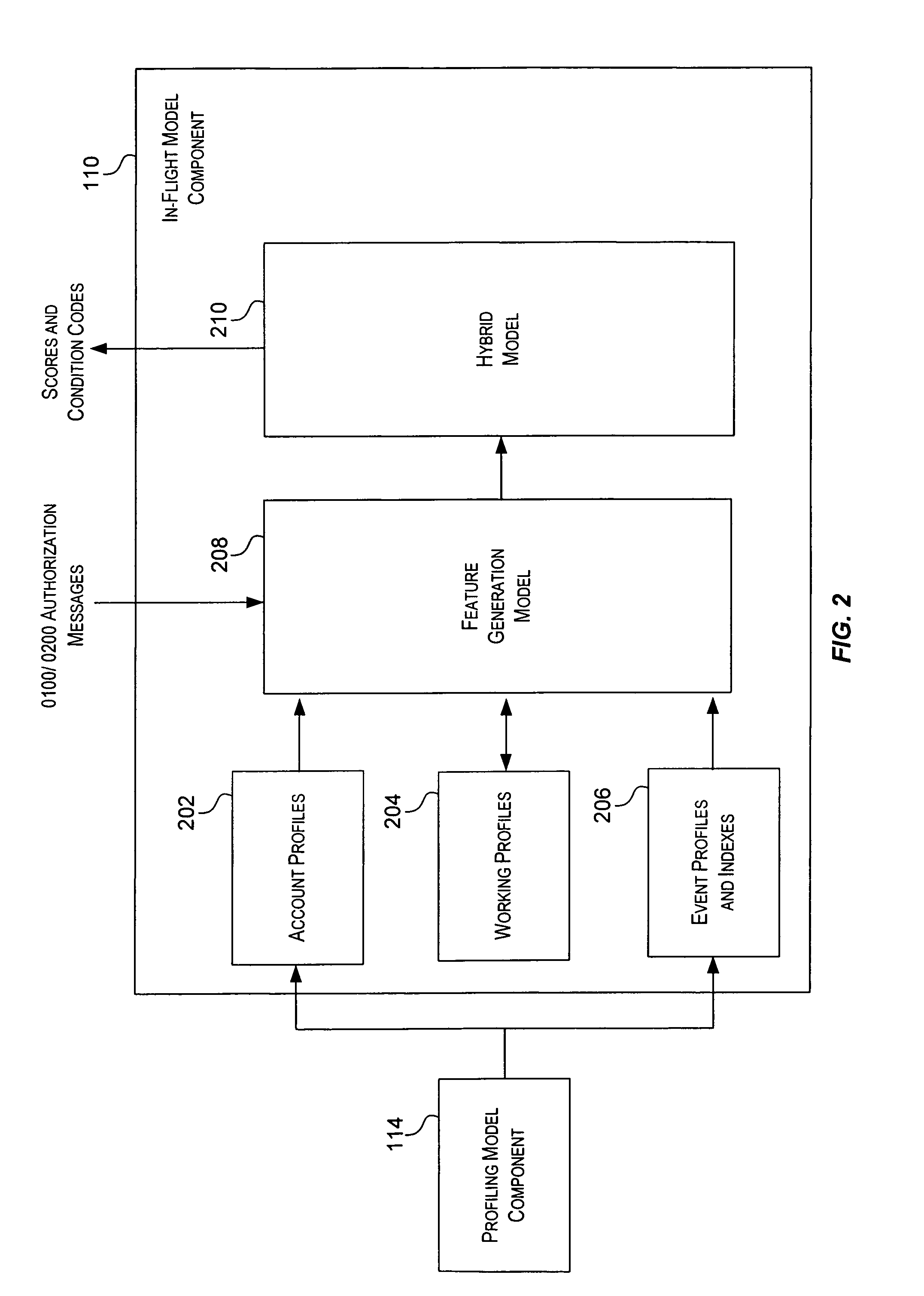
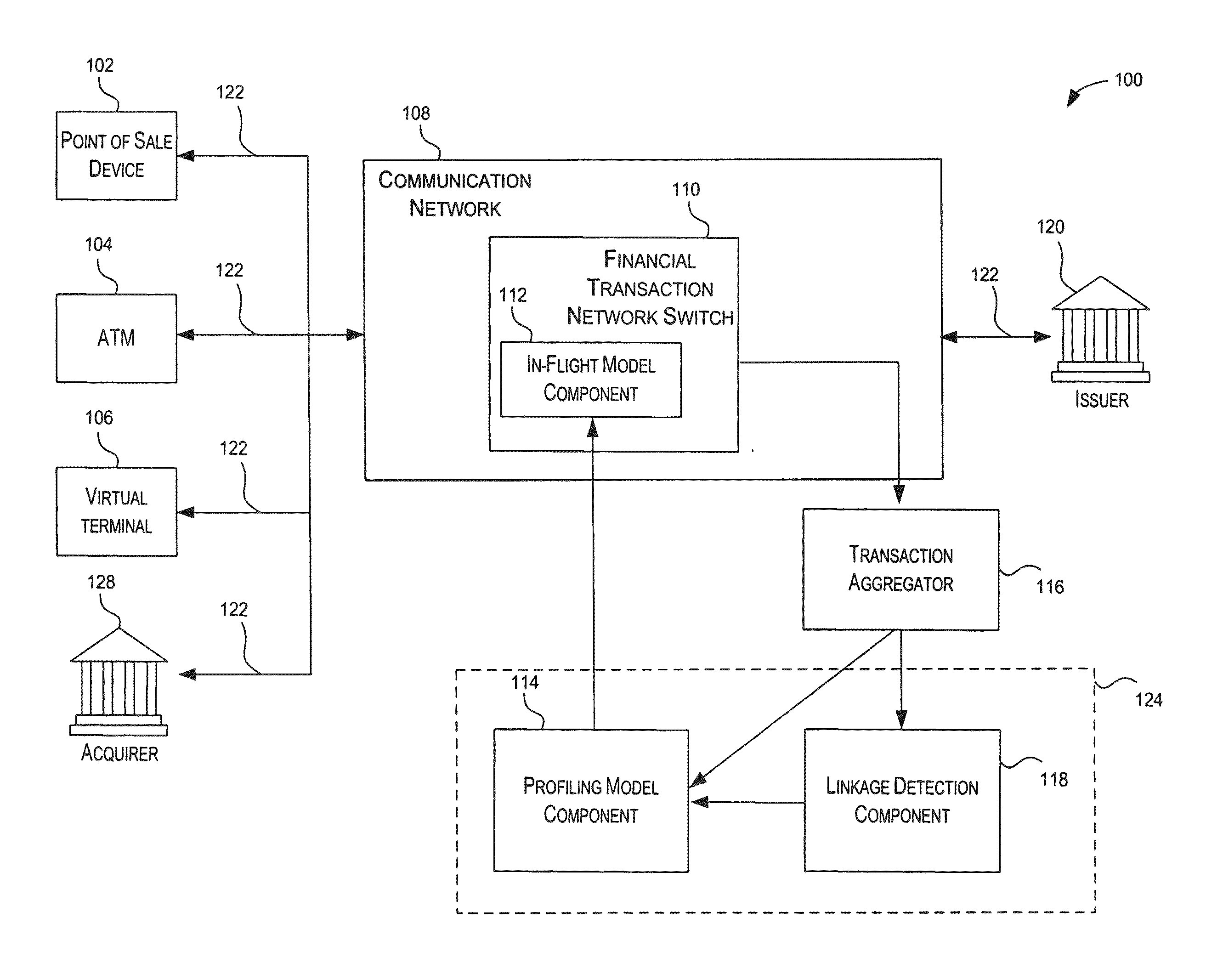
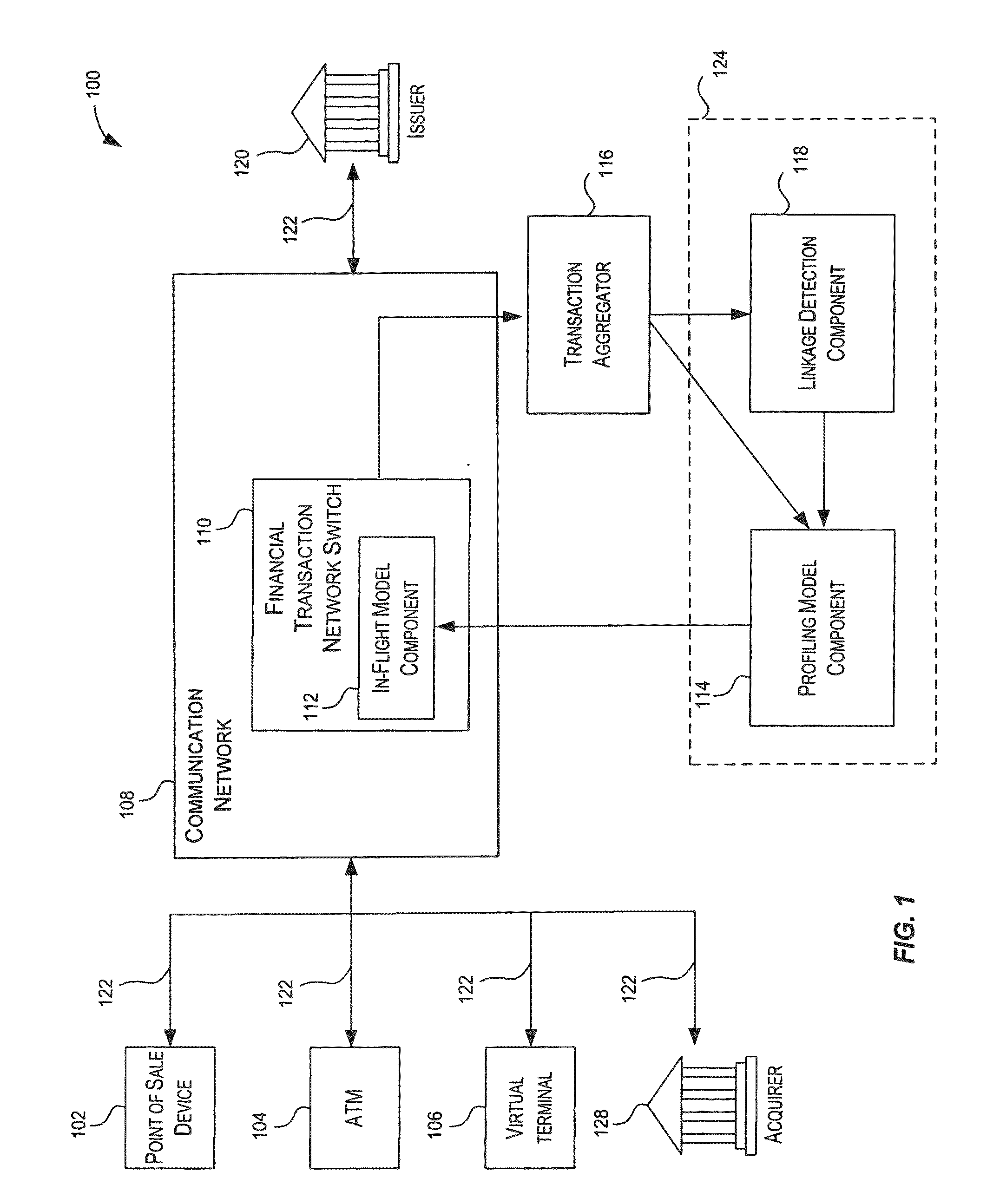
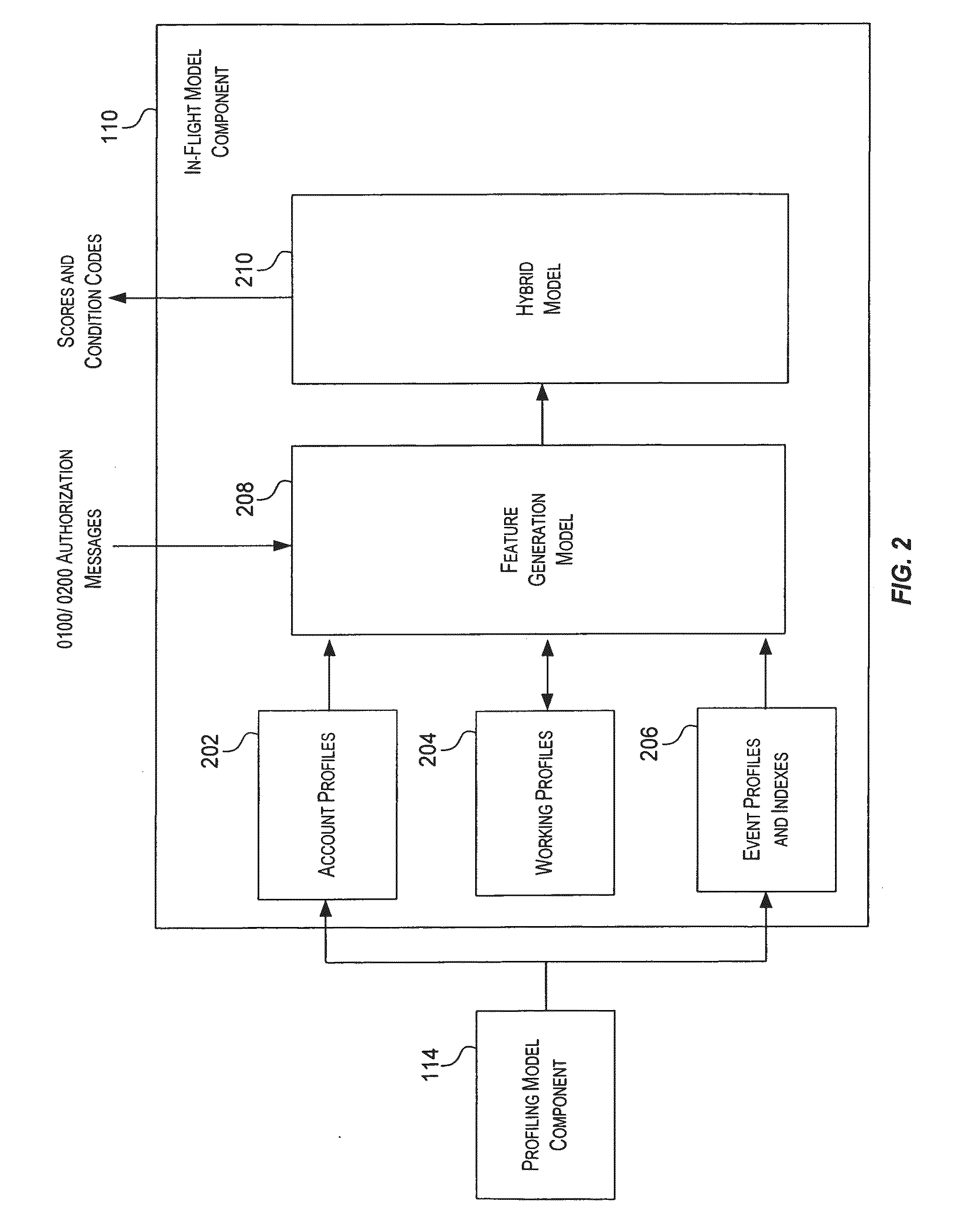
Method and system for providing risk information in connection with transaction processing
ActiveUS7809650B2Informed decisionFinanceDigital data processing detailsMultiple criteriaDecision taking
A system for providing real-time risk mitigation for an authorization system. The system receives authorization requests from multiple merchants (or their respective acquirers) and processes such requests. Each processed request is then forwarded to its corresponding issuer for further authorization. Each processed request includes an authorization message. The authorization message can include a risk score, a number of reason codes, and a number of condition codes. The use of the risk score, reason codes and condition codes allows issuers to make better informed decisions with respect to providing authorizations.
Owner:VISA USA INC (US)
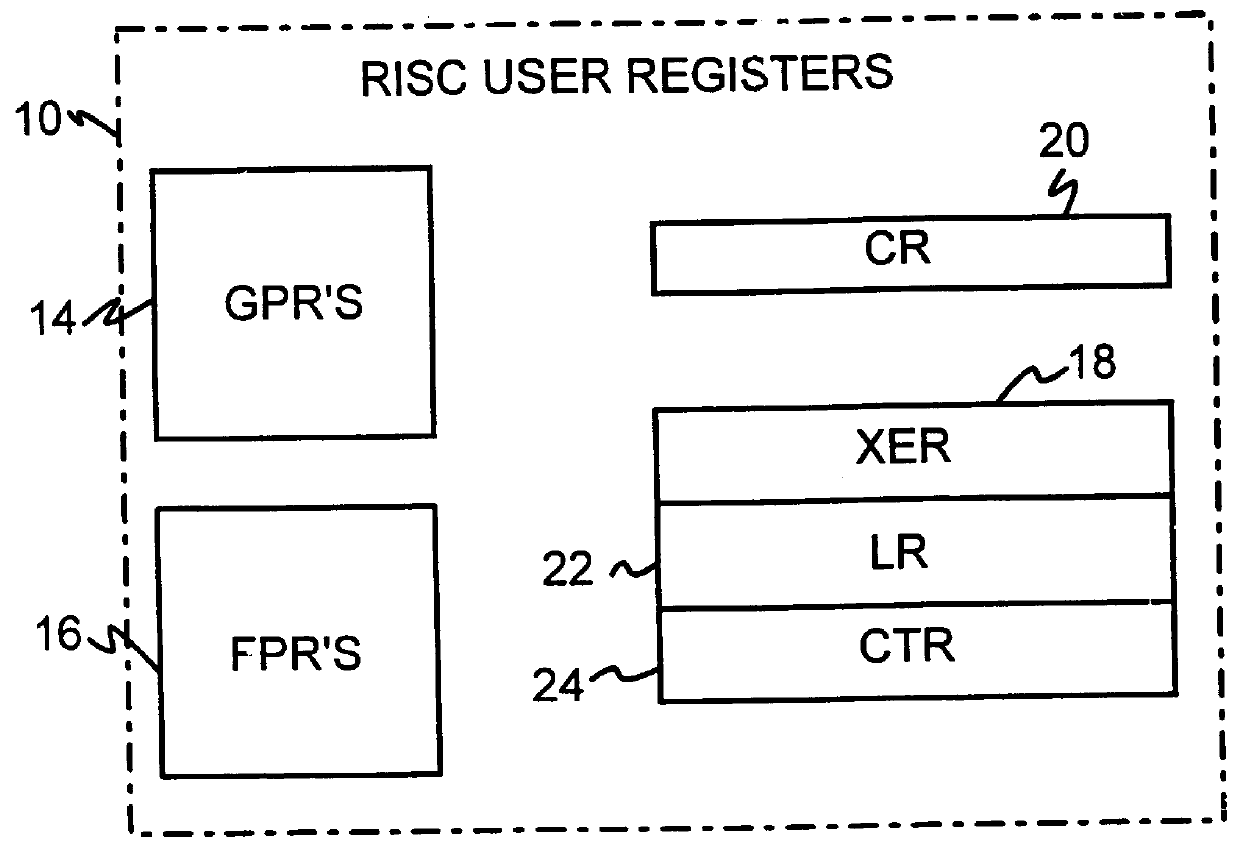
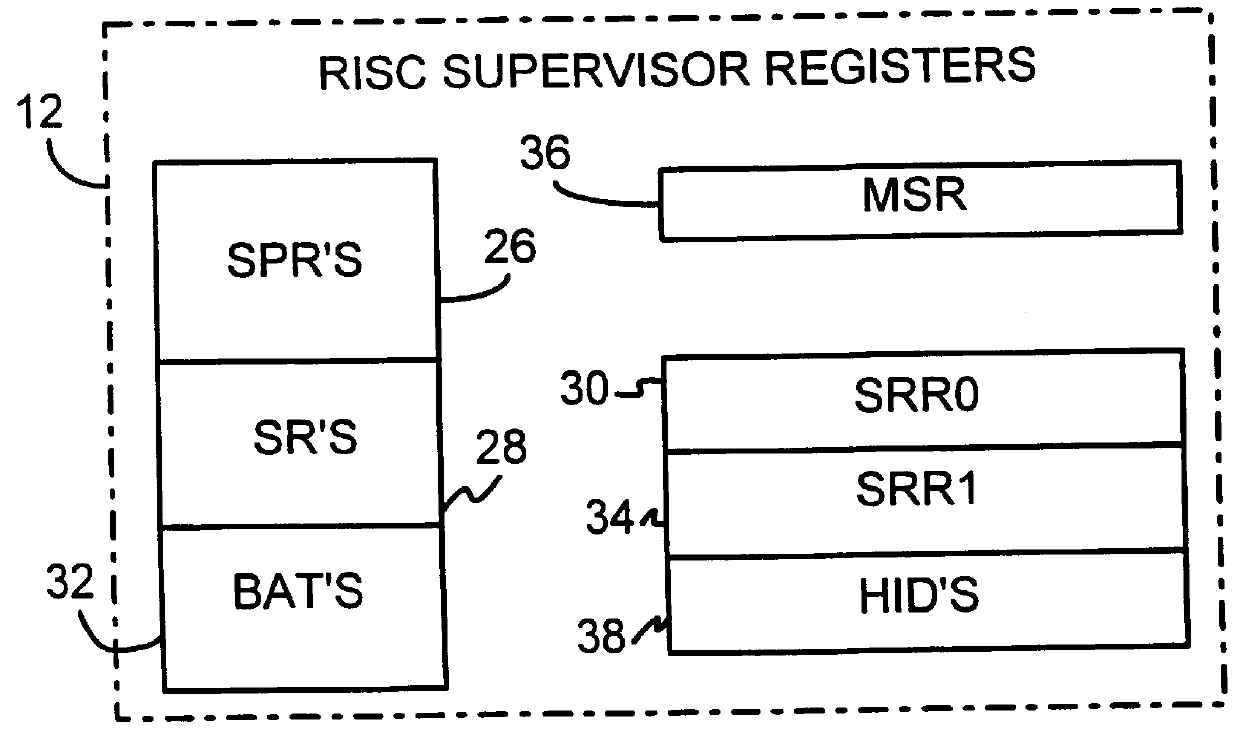
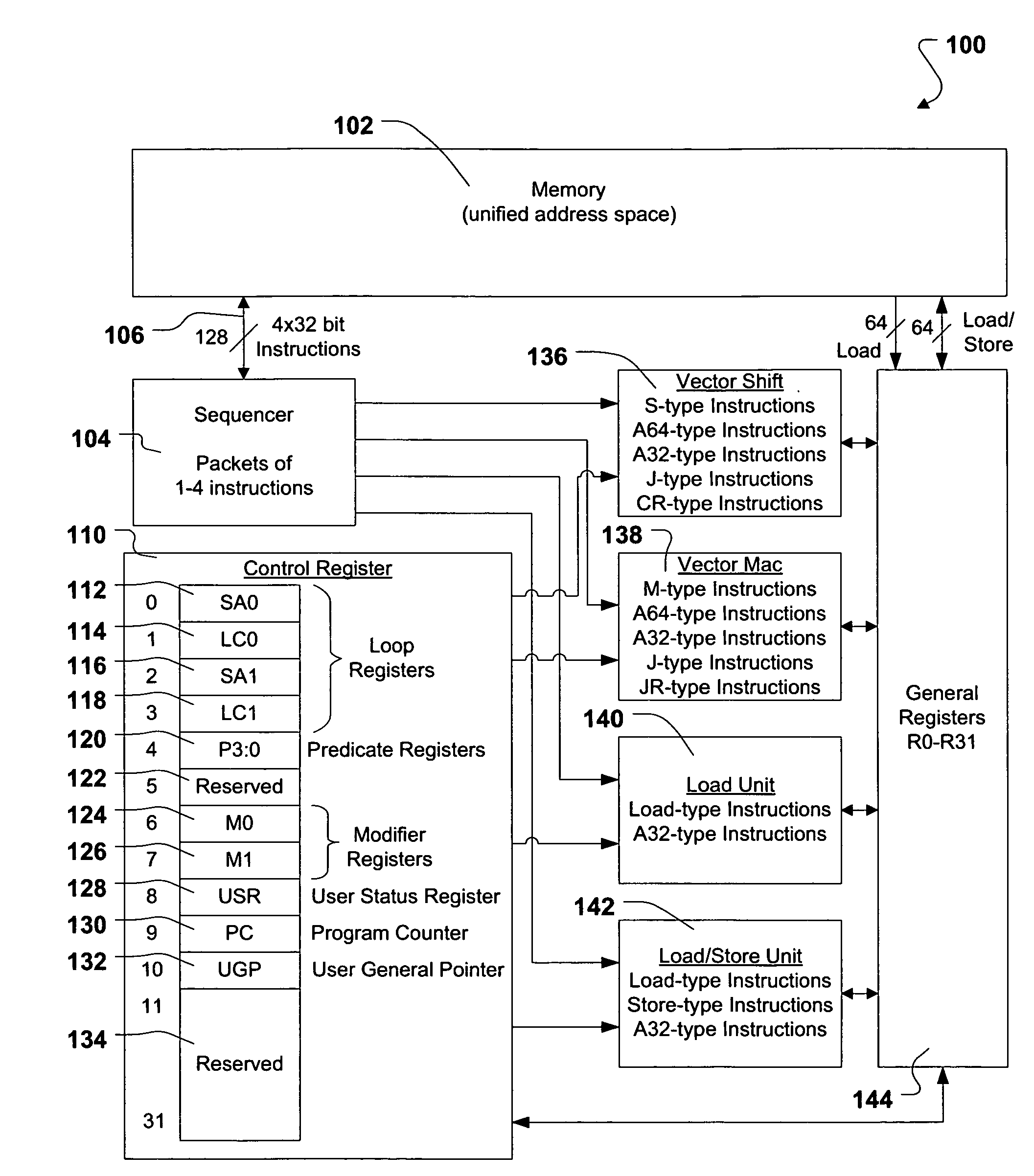
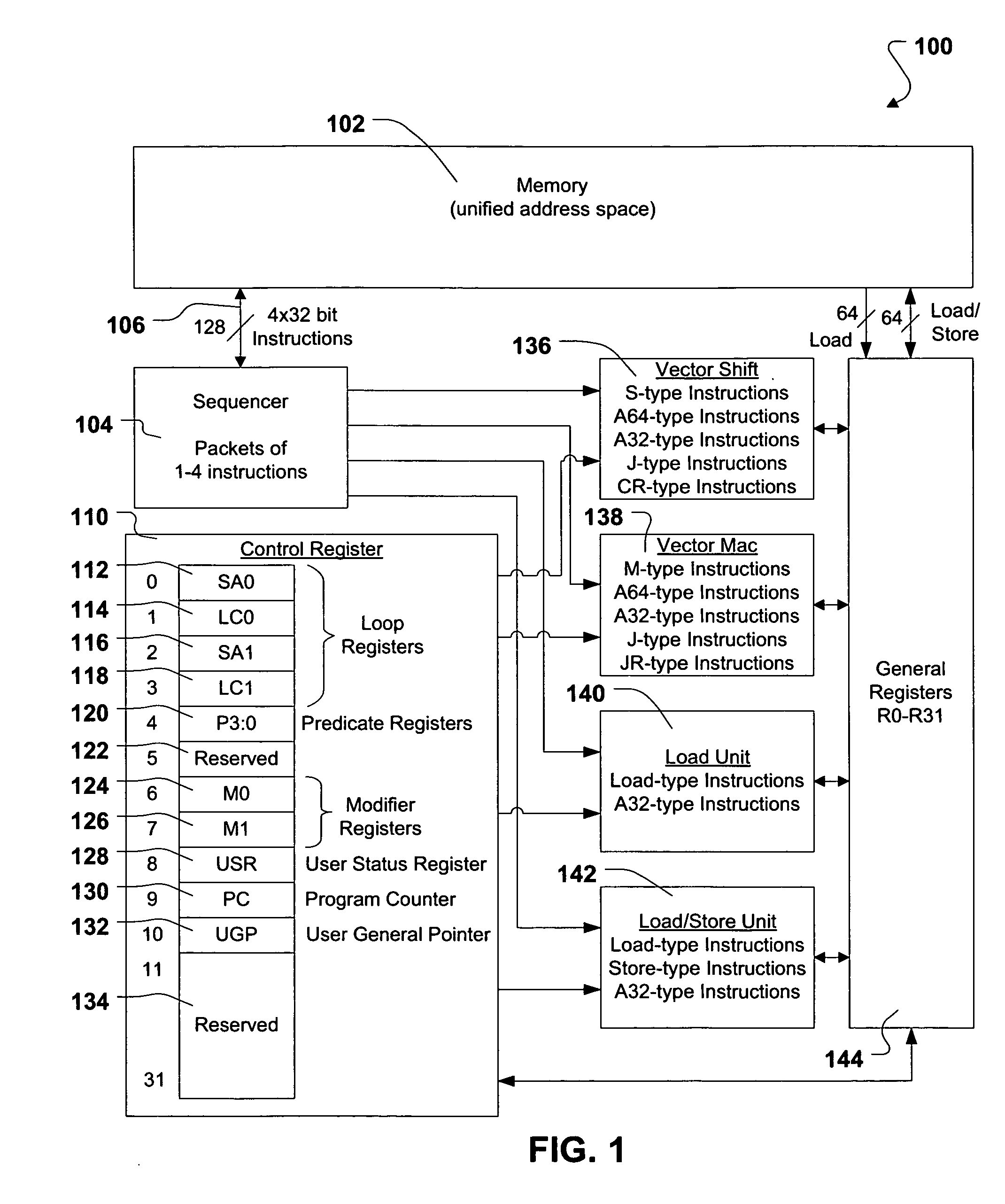
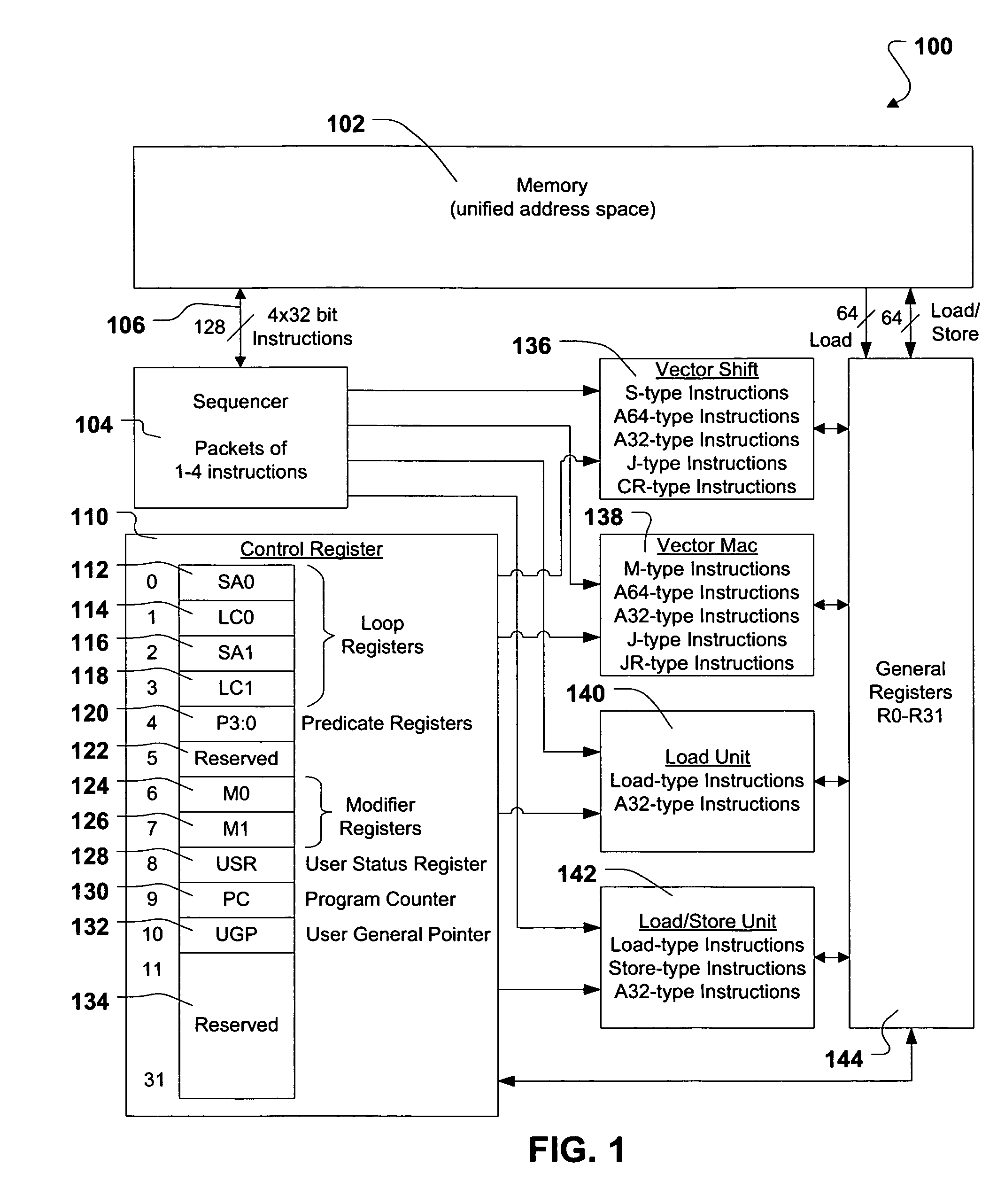
Shared register architecture for a dual-instruction-set CPU to facilitate data exchange between the instruction sets
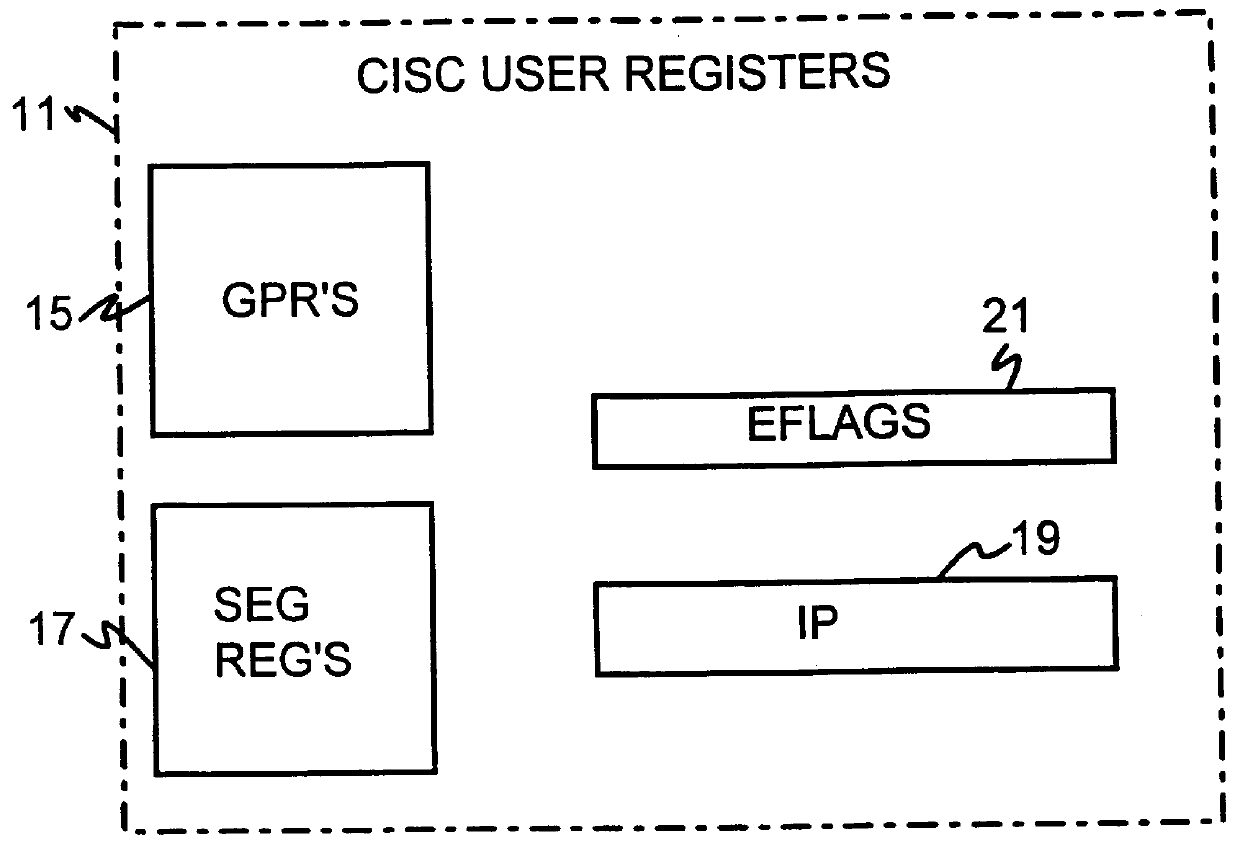
A dual-instruction set central processing unit (CPU) is capable of executing instructions from a reduced instruction set computer (RISC) instruction set and from a complex instruction set computer (CISC) instruction set. Data and address information may be to transferred from a CISC program to a RISC program running on the CPU by using shared registers. The architecturally-defined registers in the CISC instruction set are merged or folded into some of the architecturally-defined registers in the RISC architecture so that these merged registers are shared by the two instructions sets. In particular, the flags or condition code registers defined by each architecture are merged together so that CISC instructions and RISC instructions will implicitly update the same merged flags register when performing computational instructions. The RISC and CISC registers are folded together so that the CISC flags are at one end of the register while the frequently used RISC flags are at the other end, but the RISC instructions can read or write any bit in the merged register. The CISC code segment base address is stored in the RISC branch count register, while the CISC floating point instruction address is stored in the RISC branch link register. The general-purpose registers (GPR's) are also merged together, allowing a CISC program to pass data to a RISC program merely by writing one of its GPR's, switching control to the RISC program, and the RISC program reading one of its GPR's that is merged with and corresponds to the CISC GPR that was written to by the CISC program.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Processor and method that accelerate evaluation of pairs of condition-setting and branch instructions
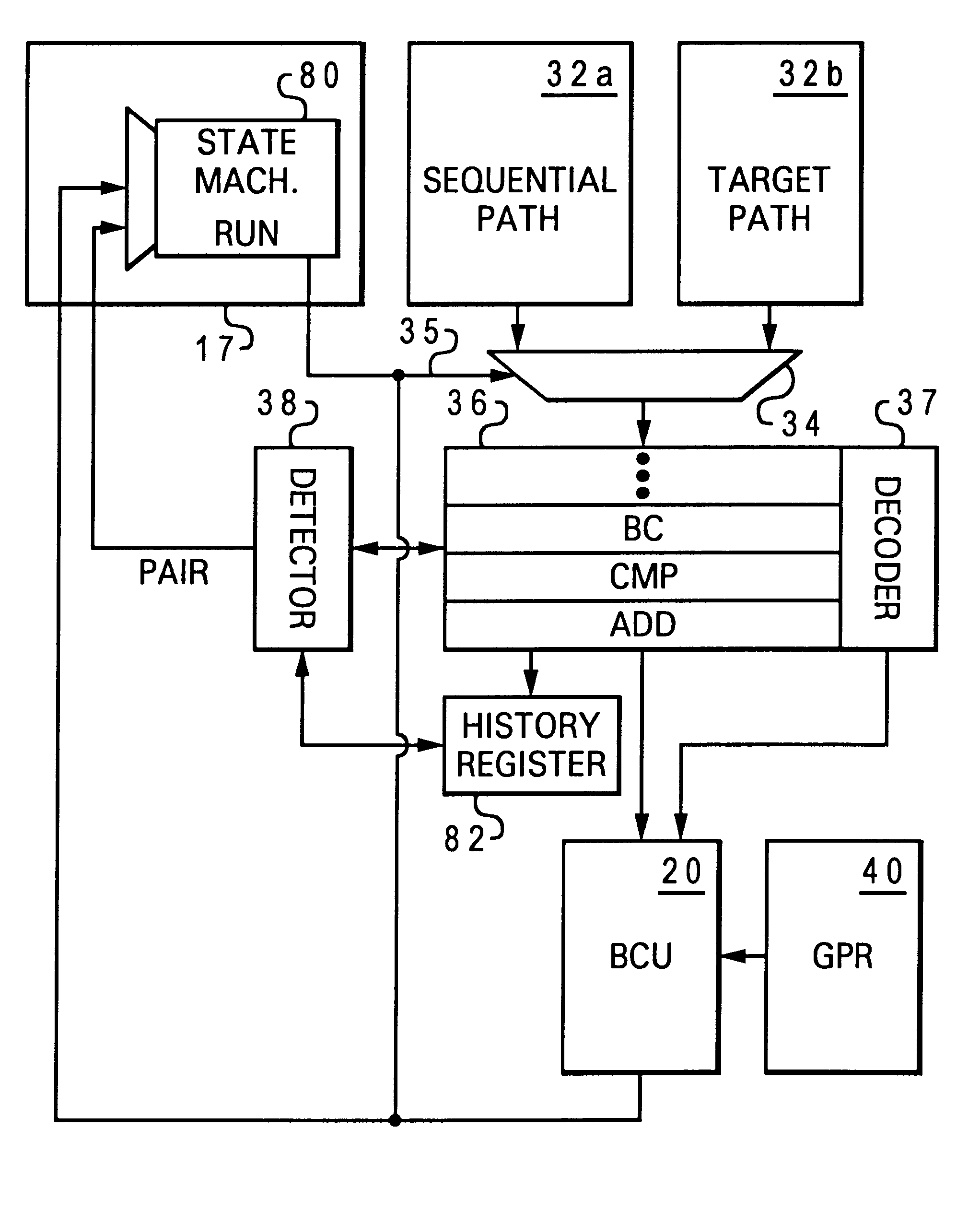
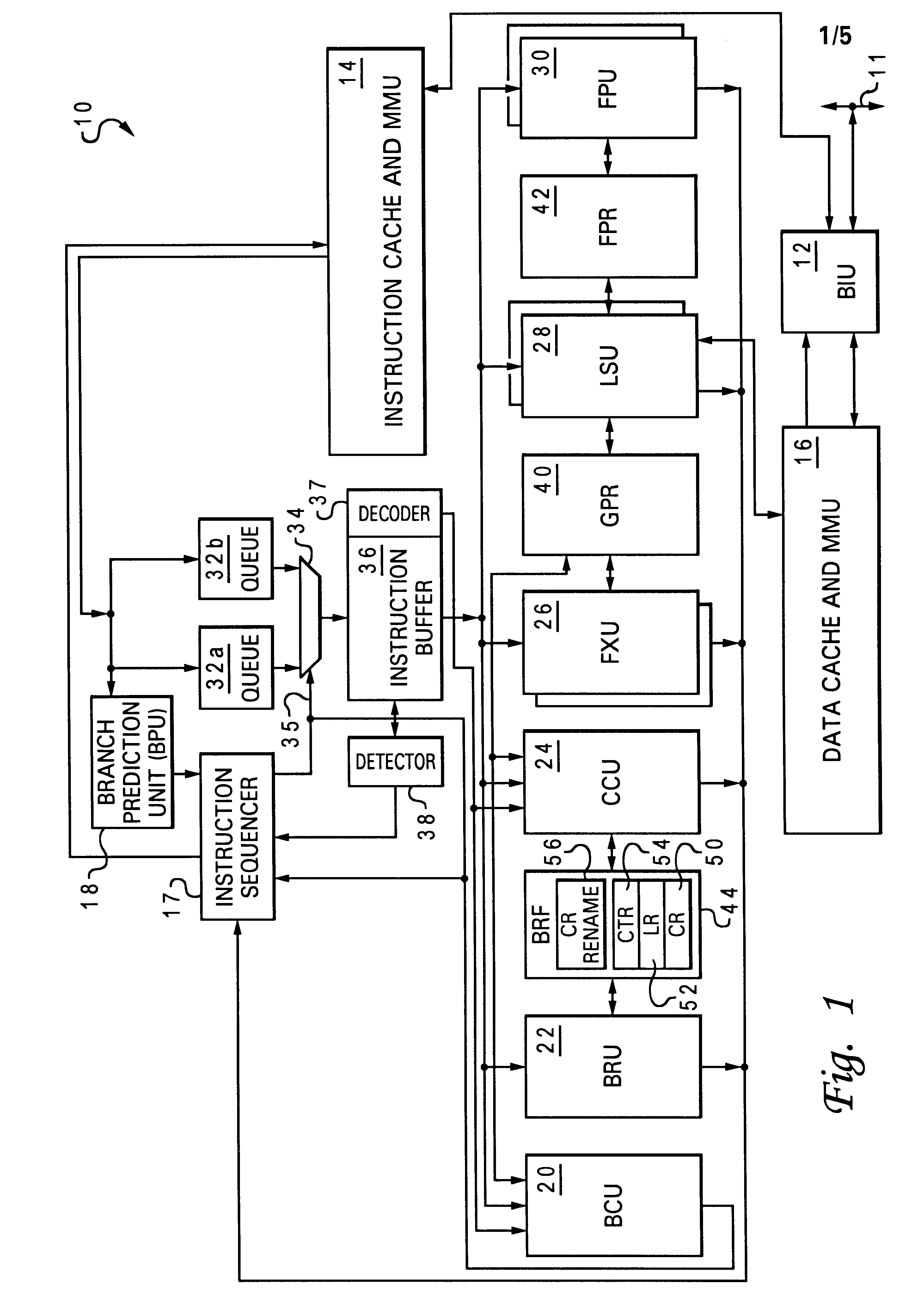
InactiveUS6598153B1Conditional code generationDigital computer detailsImage resolutionExecution unit
A processor that promotes accelerated resolution of conditional branch instructions includes an instruction sequencer that fetches a plurality of instructions and a detector that detects, among the plurality of fetched instructions, a condition-setting instruction and a conditional branch instruction that depends upon the condition-setting instruction. The processor further includes a decoder that decodes the conditional branch instruction to produce a decoded condition type and an execution unit. In response to the detection of the condition-setting instruction and the conditional branch instruction, the execution unit resolves the conditional branch instruction by evaluating the condition-setting instruction and the decoded condition type in a single operation. Because the condition code bits are not computed or stored as an intermediate result as in prior art processors, branch resolution is accelerated.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
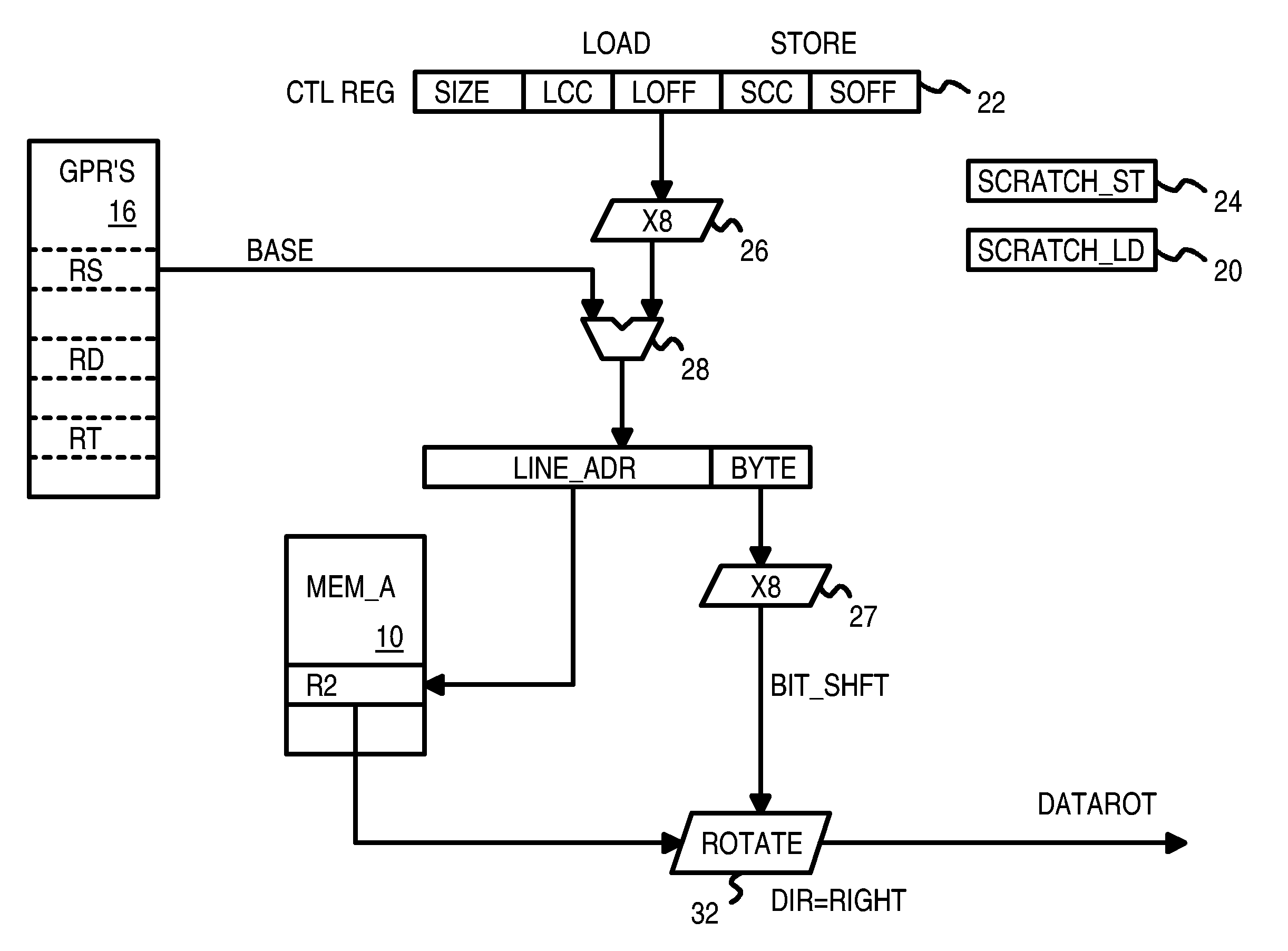
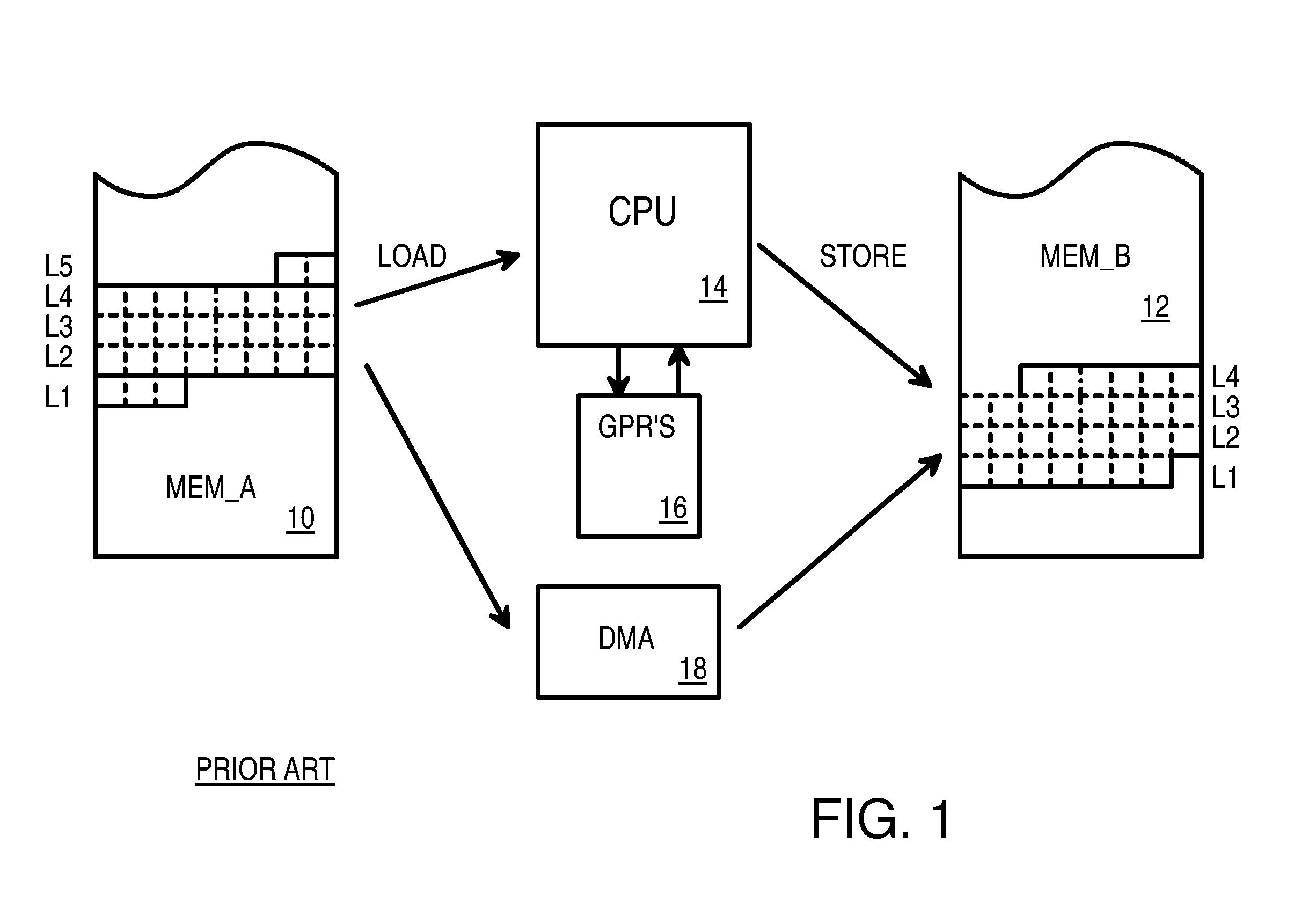
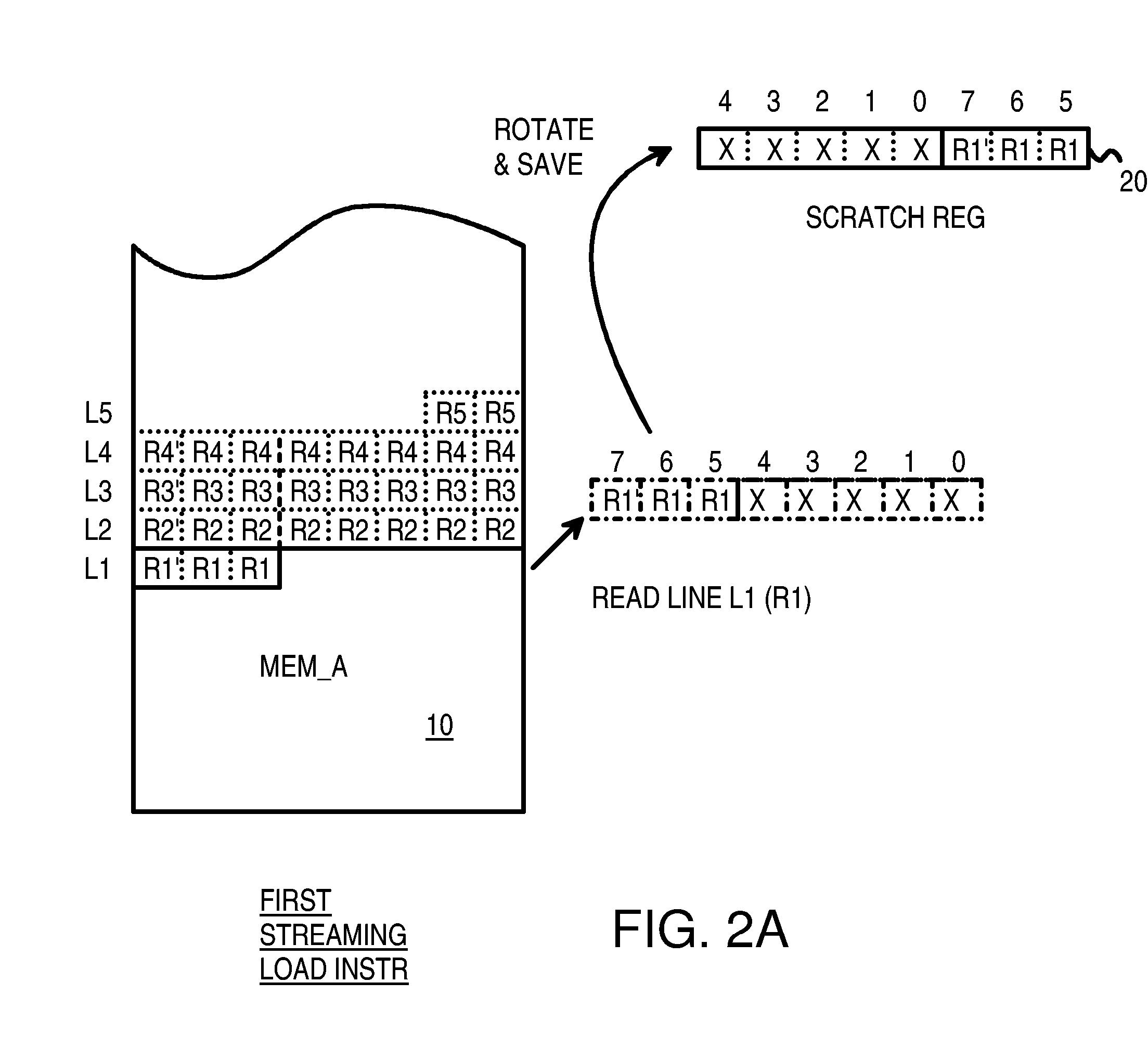
Efficient Streaming of Un-Aligned Load/Store Instructions that Save Unused Non-Aligned Data in a Scratch Register for the Next Instruction
InactiveUS20070106883A1Digital computer detailsSpecific program execution arrangementsGeneral purposeLoad instruction
A memory block with any source alignment is streamed into general-purpose registers (GPRs) as aligned data using a streaming load instruction. A streaming store instruction reads the aligned data from the GPRs and writes the data into memory with any destination alignment. Data is streamed from any source alignment to any destination alignment. Memory accesses are aligned to memory lines. The data is rotated using the offset within a memory line of the base address. The rotated data is stored in a scratch register for use by the next streaming load instruction. Rotated data just read from memory is combined with rotated data in the scratch register read by the last streaming load instruction to generate result data to load into the destination GPR. Streaming condition codes are set when the block's end is detected to disable future streaming instructions. Aligned memory accesses at full bandwidth read the un-aligned block.
Owner:AZUL SYSTEMS
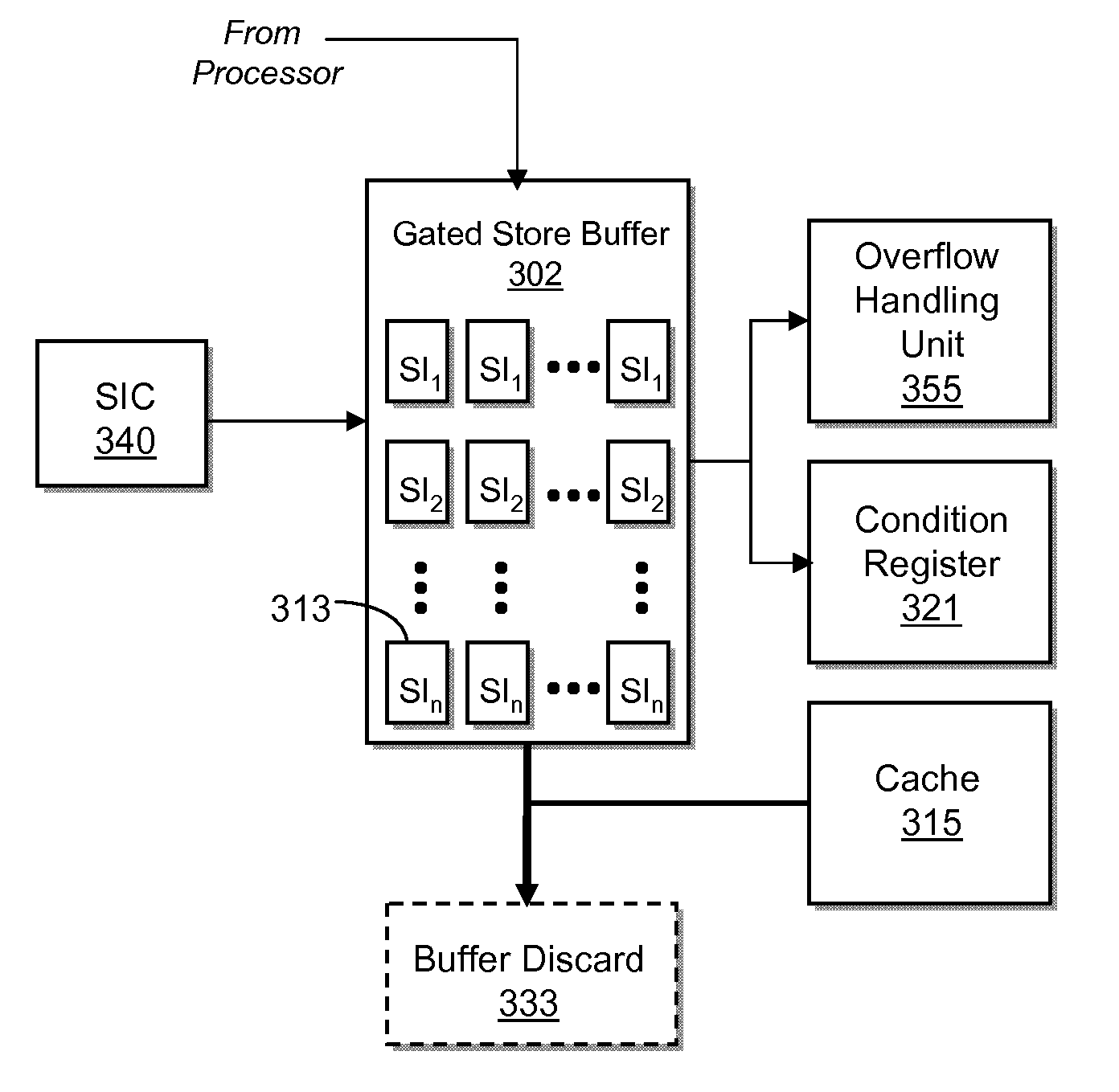
System and method for software initiated checkpoint operations
InactiveUS20110066831A1Pointing accuratelyError detection/correctionDigital computer detailsProcessor registerCondition Code
A method, system and computer program product for issuing one or more software initiated operations for creating a checkpoint of a register file and memory, and for restoring a register file and memory to the checkpointed state. At the execution of a checkpoint operation, the system returns a condition code indicating success or failure. When the condition code is set equal to one, one or more checkpoints are initiated. Contents of the register file and gated store buffer are stored each time the one or more checkpoints are initiated. When the checkpoint is created, the system notifies software when a hardware checkpoint capacity has been reached. One or more of the software checkpoint, hardware checkpoint, and handler checkpoint are utilized to provide a more precise point of restoration. During software execution, the register file and gated store buffer can be restored as defined by the one or more previous checkpoints.
Owner:IBM CORP
Image generating method, device and program, and illicit copying prevention system
InactiveUS7227661B2Reliable preventionUser identity/authority verificationVisual presentation using printersComputer graphics (images)Condition Code
An added information encoding part repeatedly arranges two kinds of copy inhibition code arrays of the unit two-dimensional arrays to which copy inhibition codes are assigned, and condition code arrays of the unit two-dimensional arrays to which codes for removing the copy inhibition are assigned, into a two-dimensional array according to given rules. A background image formation part generates a background image in which copy inhibition pattern image areas and condition pattern image areas are repeatedly and two-dimensionally arranged according to given rules, while referring to this array, and the pattern images corresponding to respective codes stored in the background image formation part, and stores the generated background image into a background image buffer. An image composing part reads out document images from a document image buffer, and the background image from the background image buffer, and superimposes them into a composite image.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
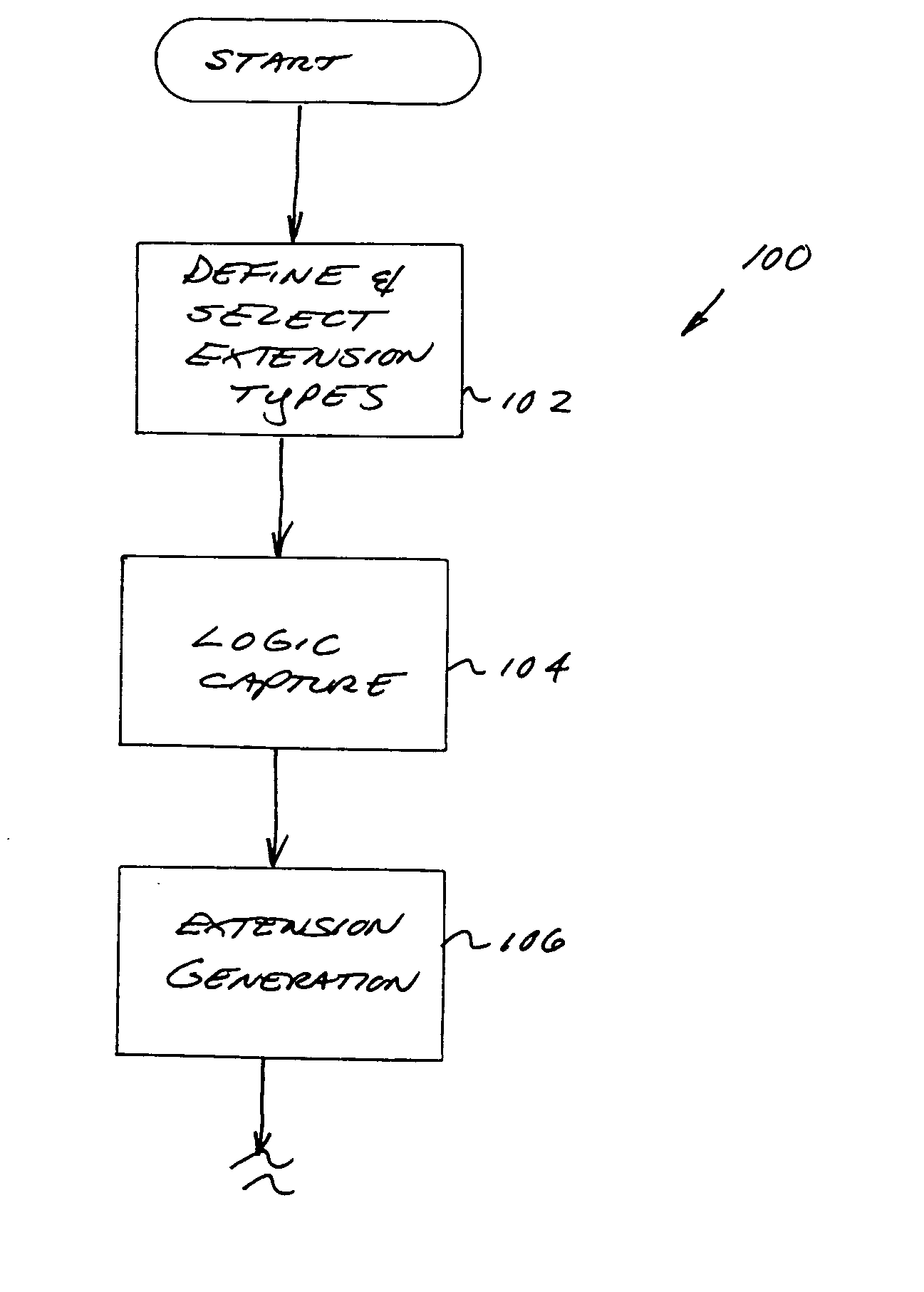
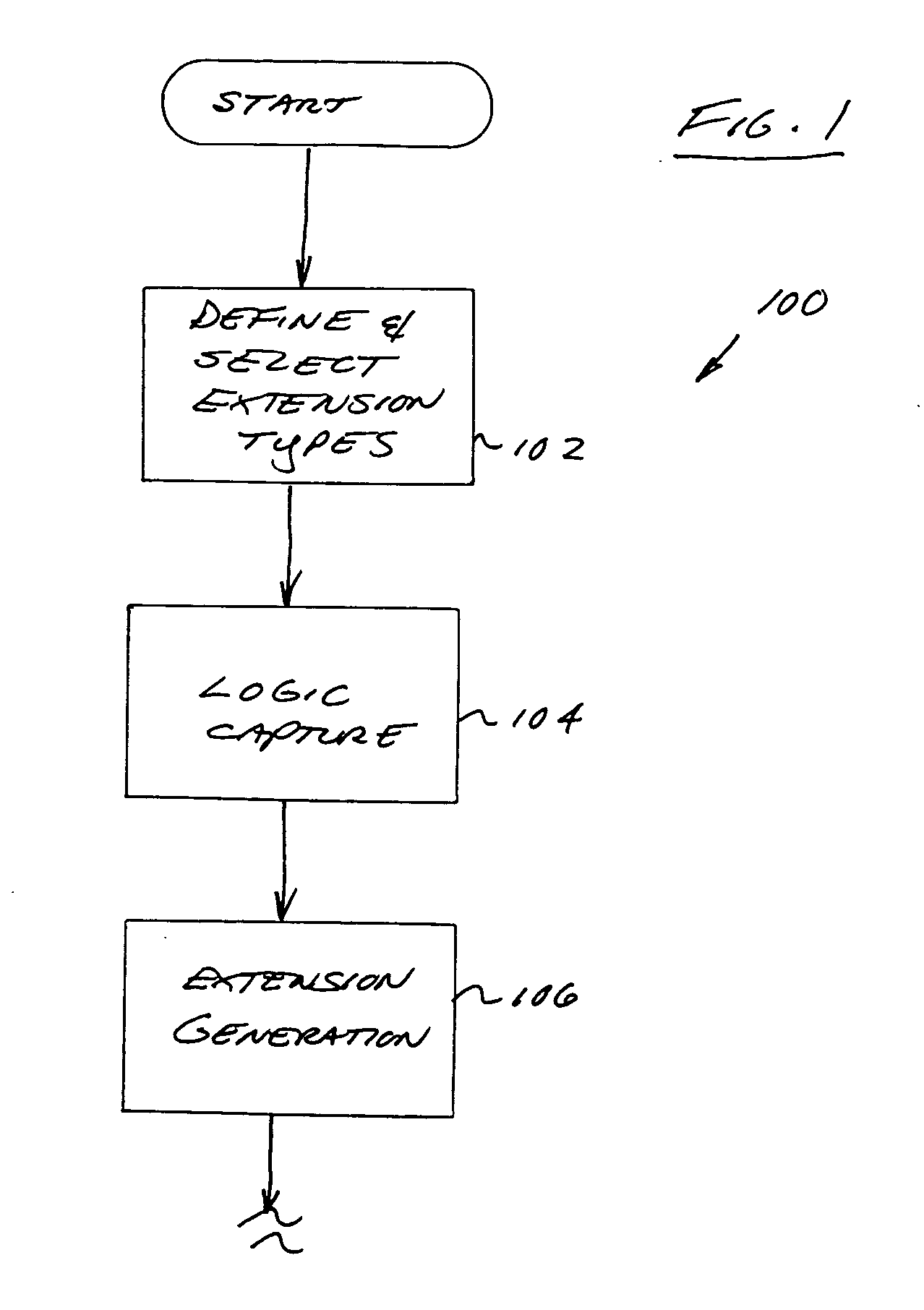
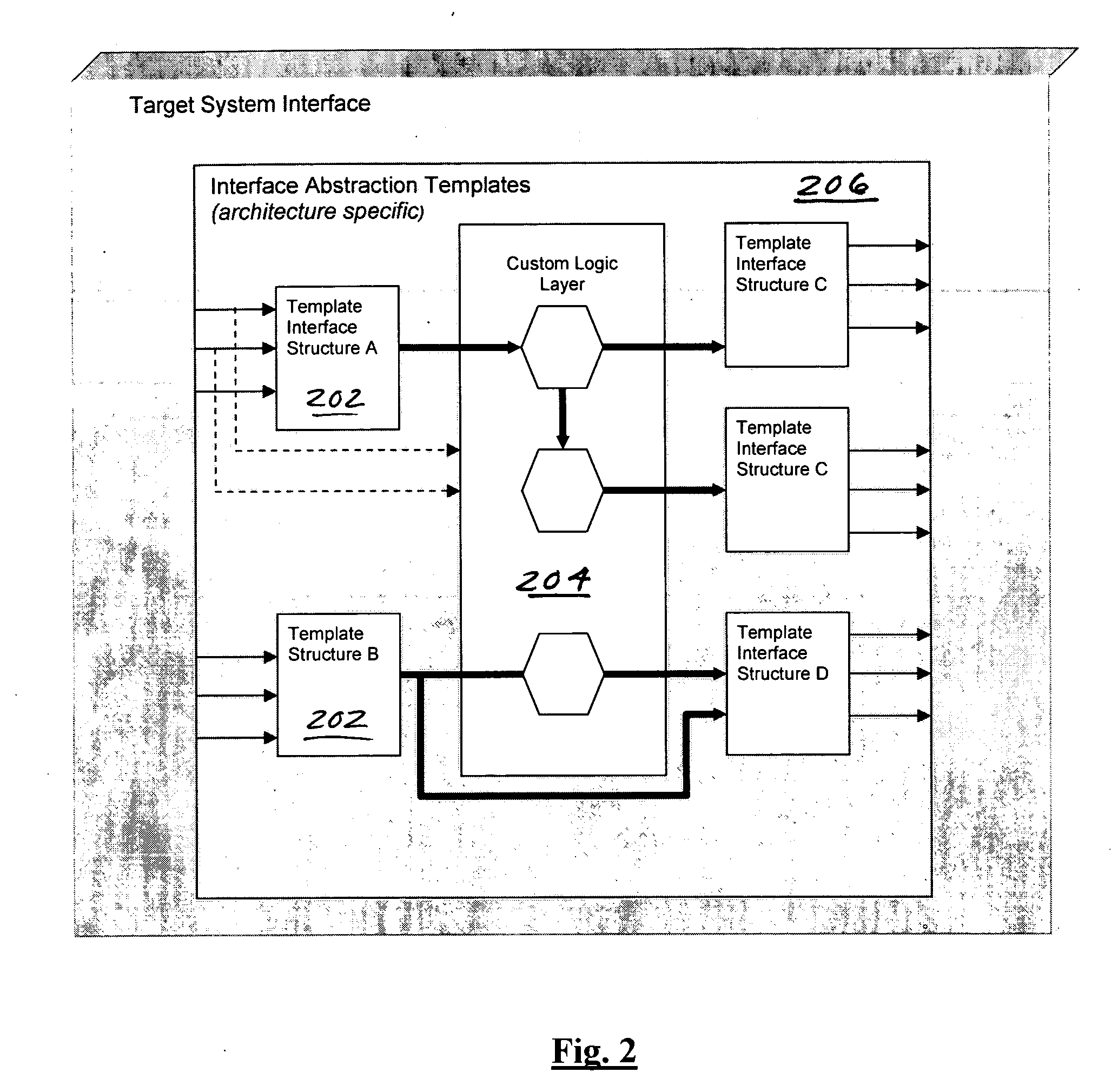
Computerized extension apparatus and methods
InactiveUS20050049843A1Effective expansionReduces extension (and processor design) generationCAD circuit designProgram controlProgramming languageCondition Code
Apparatus and methods for integrated circuit (IC) design, including the configuration and addition of extensions to the design. In one exemplary embodiment, a computer program rendered in an object-oriented language implementing the aforementioned methods for automatically adding user-customized extensions to digital processors is disclosed. The program comprises an extension tool which is adapted for varying levels of abstraction, and to significantly automate the creation and generation of various different extension types including for example ALUs, condition codes, and registers. A markup language (e.g., XML) database of abstracted extension components is utilized to permit ready addition and modification of extensions, as well as applicability of the extensions across different target architectures.
Owner:ARC INT LTD
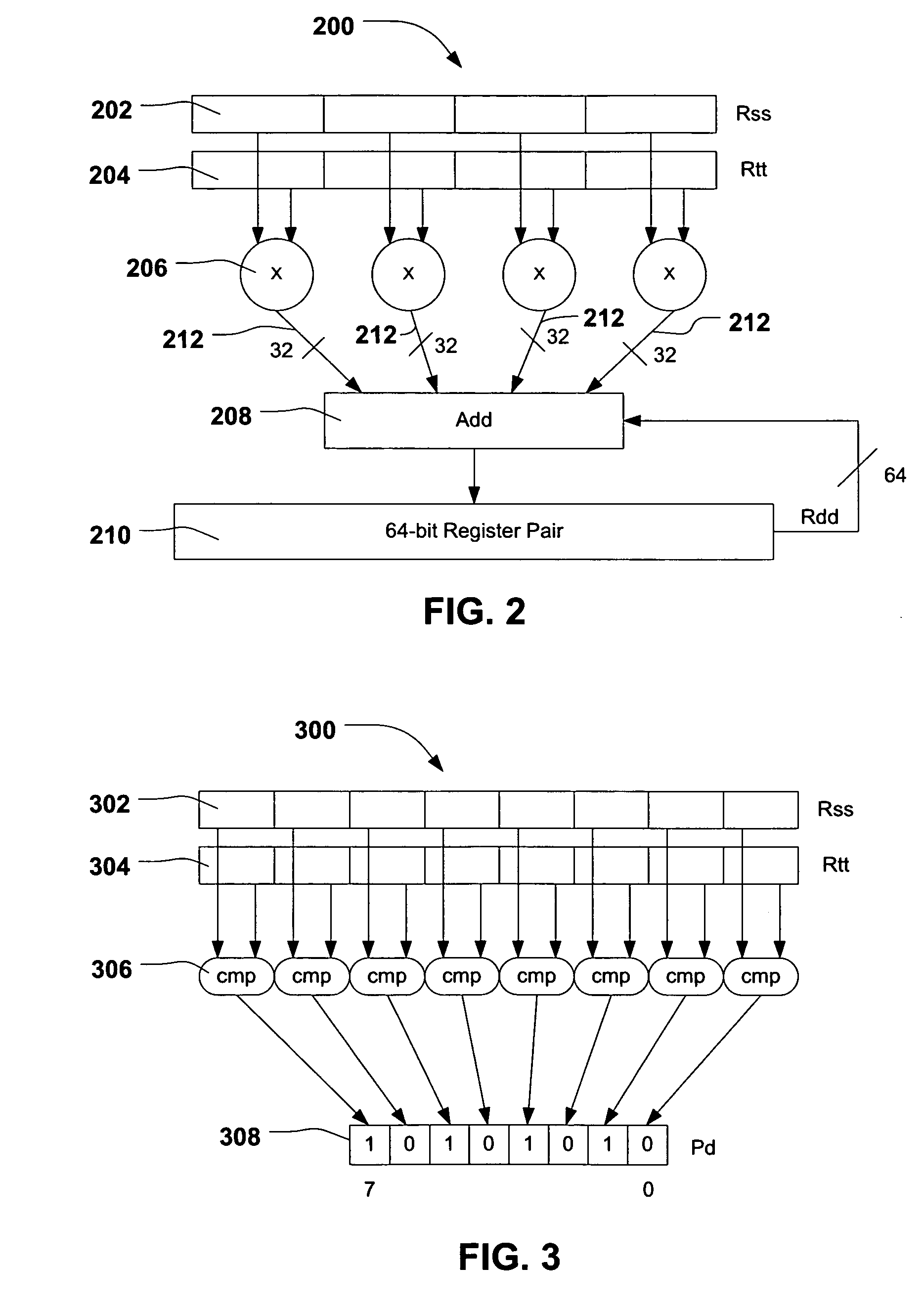
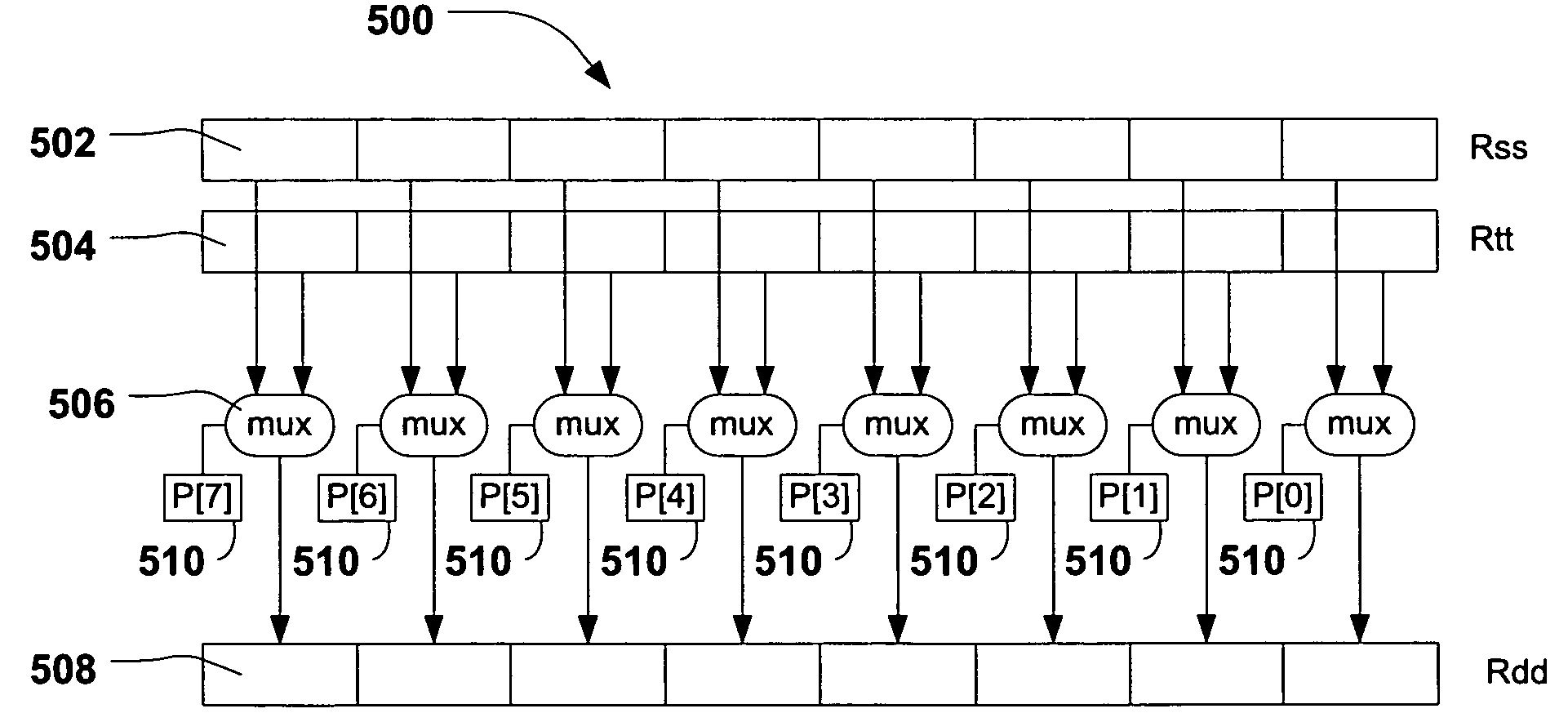
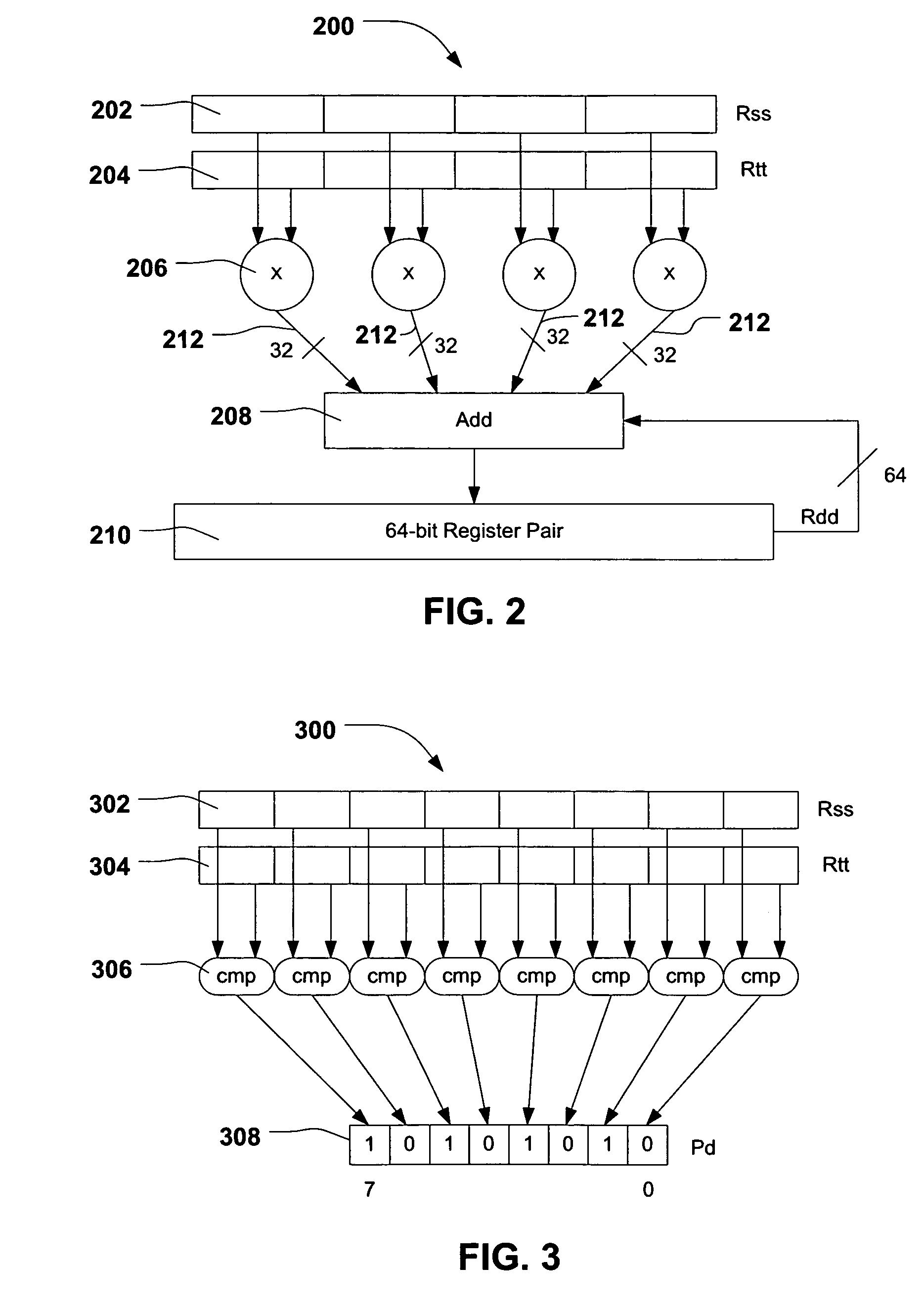
System and method of processing data using scalar/vector instructions
ActiveUS20080046683A1Improve performanceReduce power consumptionConditional code generationGeneral purpose stored program computerProcessor registerCondition Code
A processor device is disclosed that includes a register file with a combined condition code register for scalar and vector operations. The processor device utilizes the combined condition code register for scalar and vector operations. Further, a compare operation can store resulting bits in the combined condition code register and a conditional operation can utilize the combined condition code register bits for evaluating a condition.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
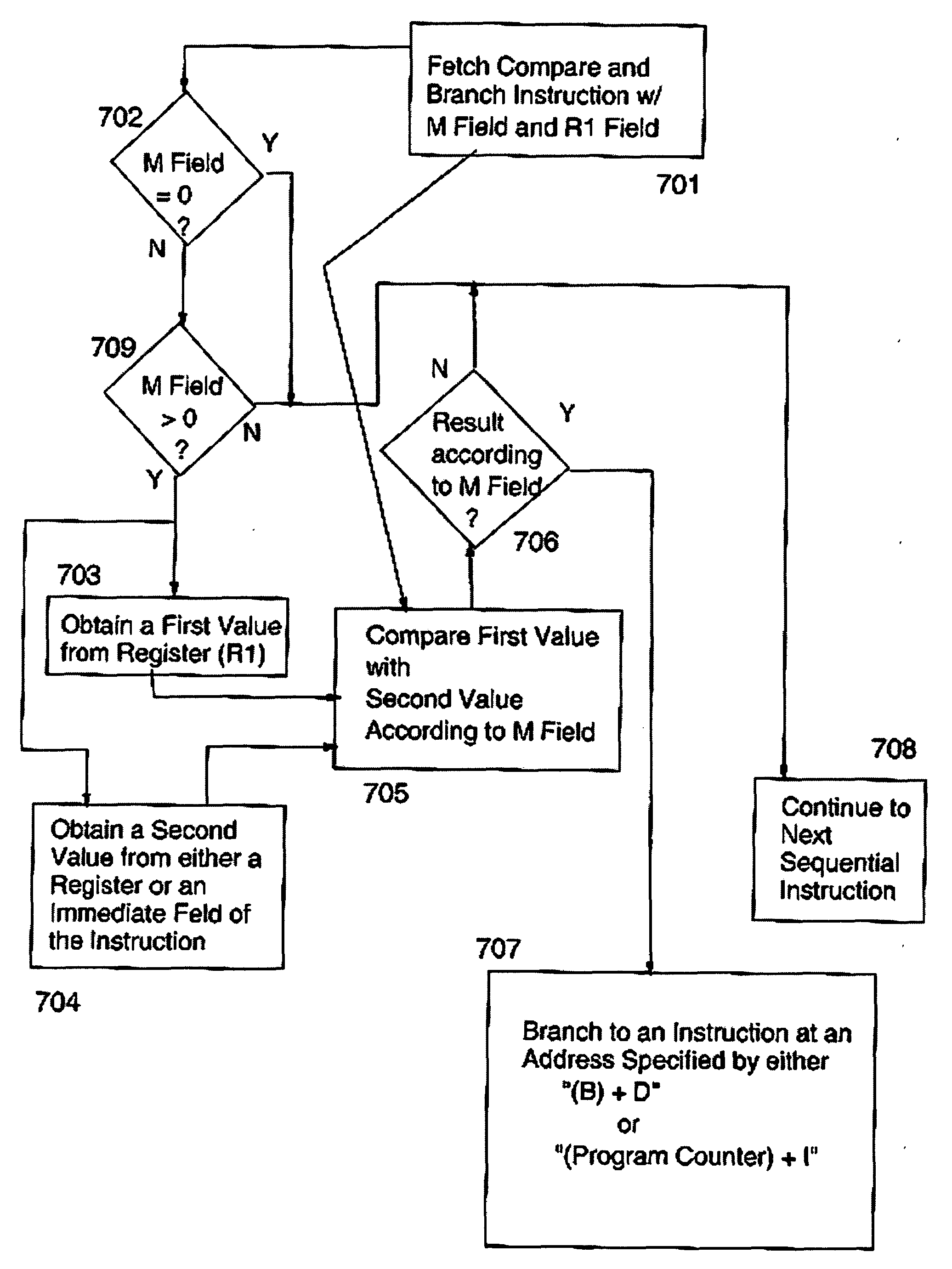
Compare and Branch Facility and Instruction Therefore
InactiveUS20090182983A1Conditional code generationDigital computer detailsCondition CodeConditional branch
An atomic compare and branch instruction is executed that combines the function of a compare instruction having an option field with a conditional branch or jump instruction such that condition codes are preserved rather than setting condition codes to a value representative of the compare results. One comparand is obtained from any one of a memory location or an immediate field and the other comparand is obtained from a register field.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method and System for Providing Risk Information in Connection with Transaction Processing
A system for providing real-time risk mitigation for an authorization system. The system receives authorization requests from multiple merchants (or their respective acquirers) and processes such requests. Each processed request is then forwarded to its corresponding issuer for further authorization. Each processed request includes an authorization message. The authorization message can include a risk score, a number of reason codes, and a number of condition codes. The use of the risk score, reason codes and condition codes allows issuers to make better informed decisions with respect to providing authorizations.
Owner:VISA USA INC (US)
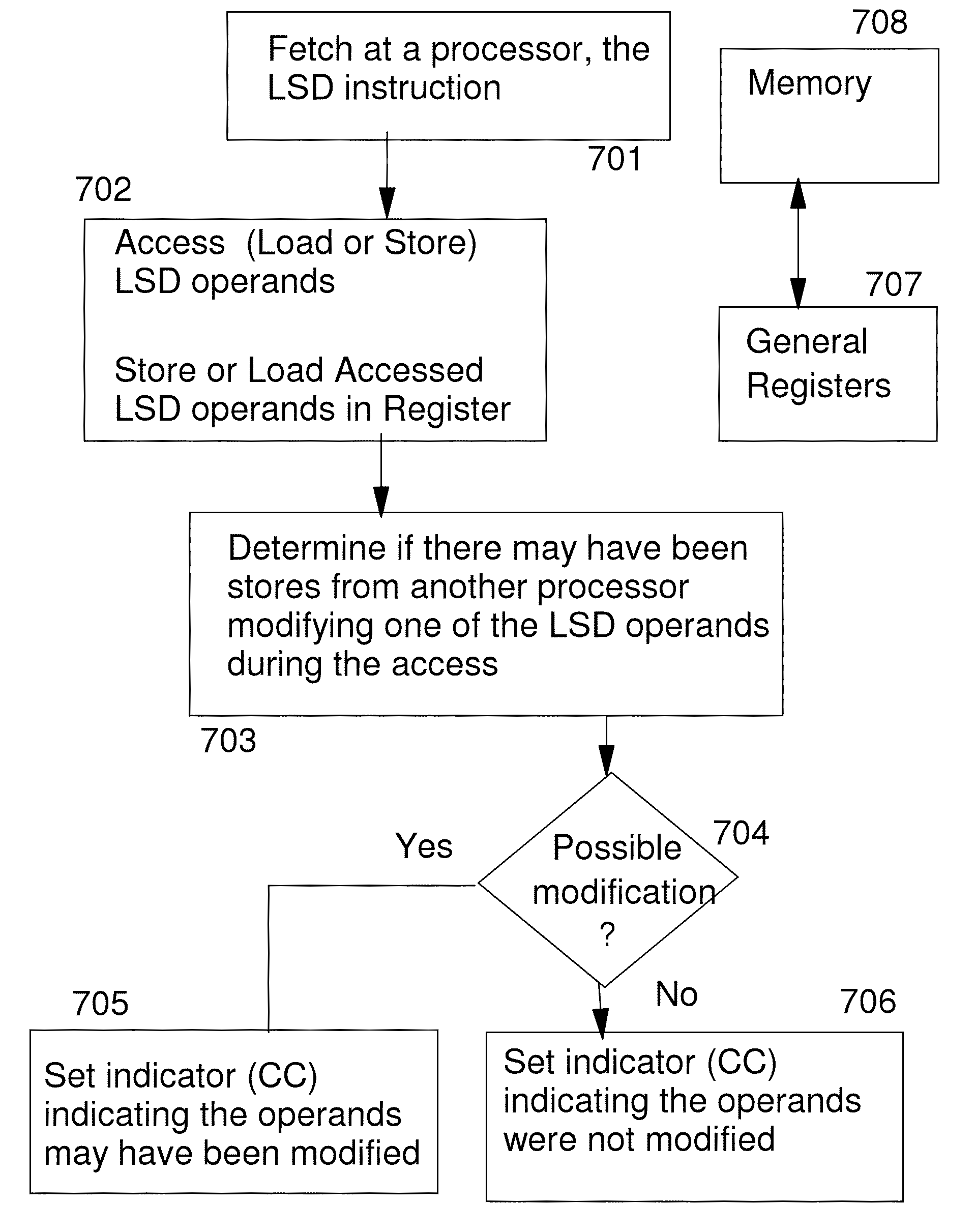
Load pair disjoint facility and instruction therefore
ActiveUS20110202748A1Memory adressing/allocation/relocationDigital computer detailsOperandCondition Code
A Load / Store Disjoint instruction, when executed by a CPU, accesses operands from two disjoint memory locations and sets condition code indicators to indicate whether or not the two operands appeared to be accessed atomically by means of block-concurrent interlocked fetch with no intervening stores to the operands from other CPUs. In a Load Pair Disjoint form of the instruction, the accesses are loads and the disjoint data is stored in general registers.
Owner:IBM CORP
System and method of processing data using scalar/vector instructions
ActiveUS7676647B2Improve performanceReduce power consumptionConditional code generationGeneral purpose stored program computerProcessor registerCondition Code
A processor device is disclosed that includes a register file with a combined condition code register for scalar and vector operations. The processor device utilizes the combined condition code register for scalar and vector operations. Further, a compare operation can store resulting bits in the combined condition code register and a conditional operation can utilize the combined condition code register bits for evaluating a condition.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
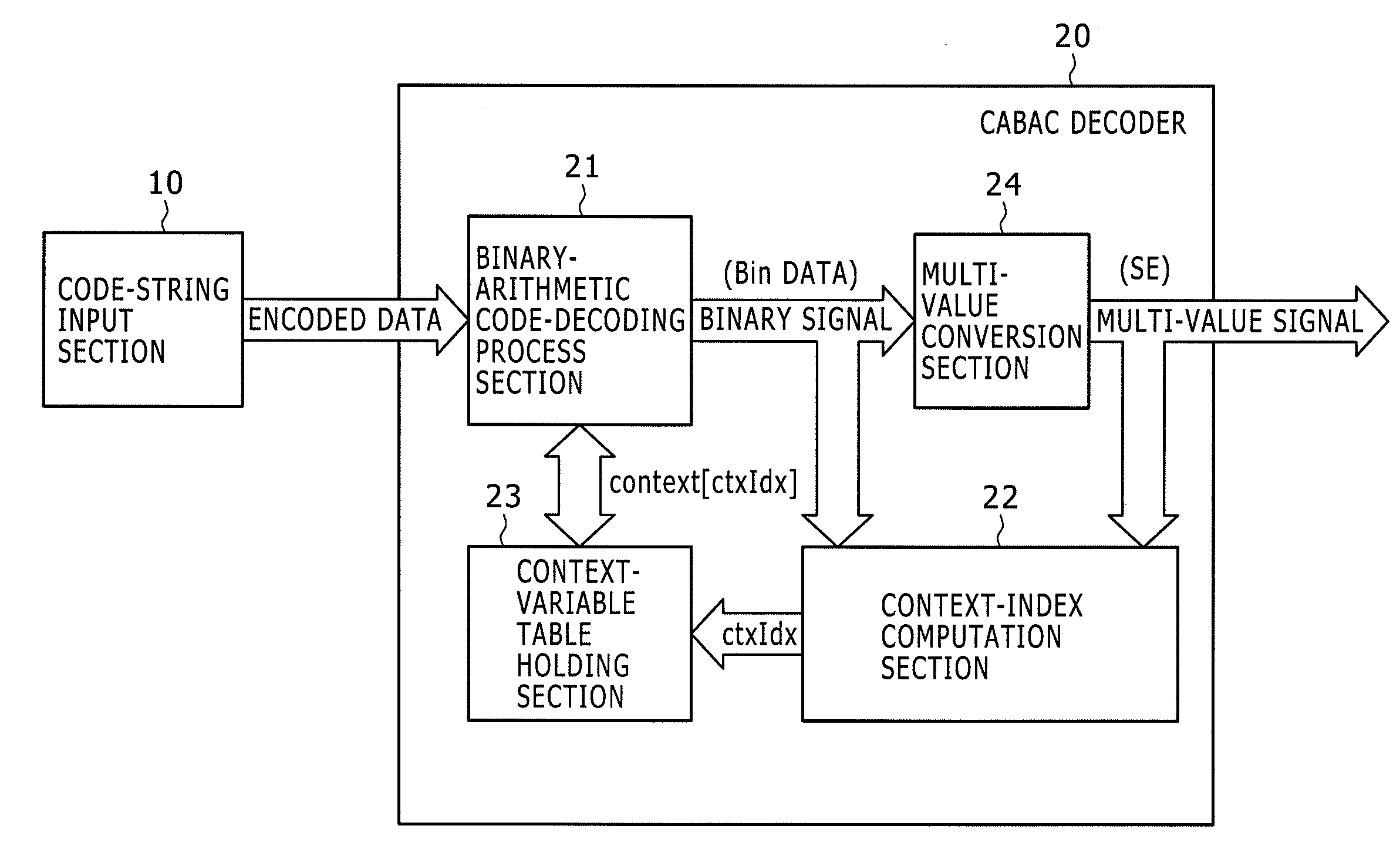
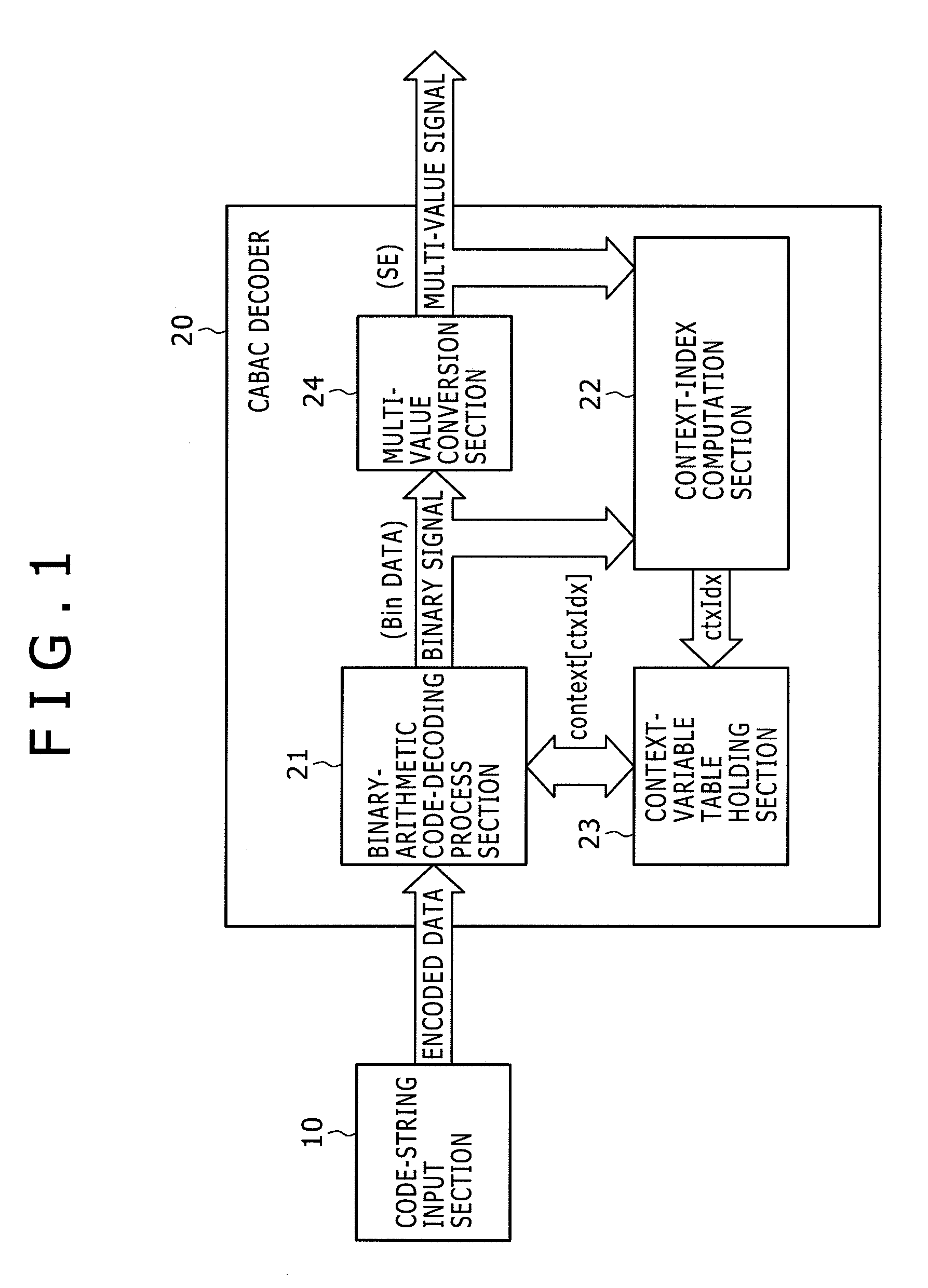
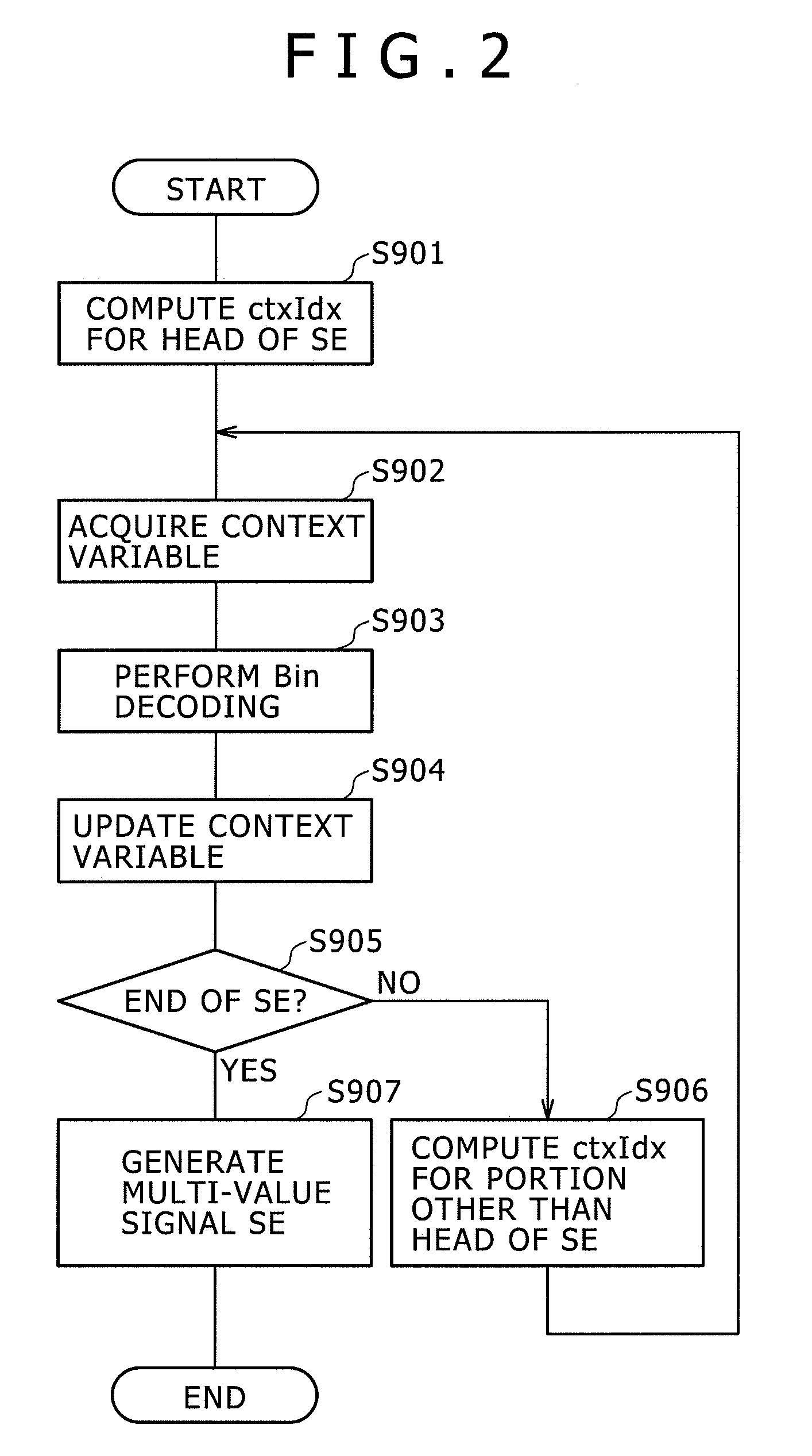
Arithmetic decoding apparatus
InactiveUS20100134330A1Excellent effect of capabilityImprove processing speedCode conversionDigital video signal modificationParallel computingArithmetic coding
Disclosed herein is an arithmetic decoding apparatus including an instruction decoder configured to decode an arithmetically encoded data decoding instruction to be executed for carrying out an arithmetic-decoding process of arithmetically decoding arithmetically encoded data into a binary signal; an execution condition code holding section configured to hold the binary signal obtained as a result of an immediately preceding arithmetic-decoding process as an execution condition code; and an arithmetic decoding execution section configured to determine whether a context number specified by the arithmetically encoded data decoding instruction is to be used as a context index as it is or the specified context number incremented by 1 is to be used as the context index in accordance with the execution condition code, and carry out the arithmetic decoding process by making use of the determined context index.
Owner:SONY CORP
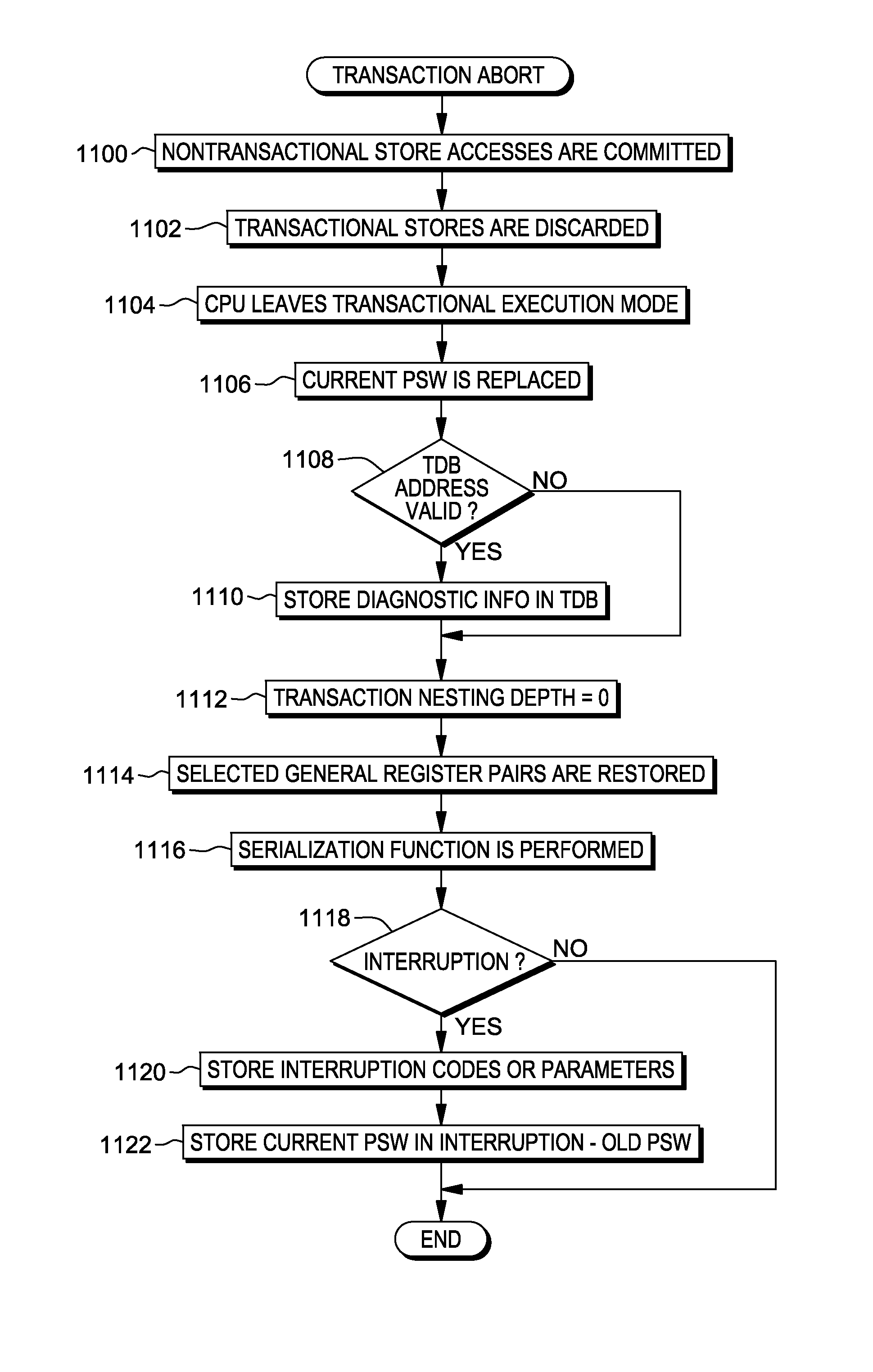
Transaction abort instruction
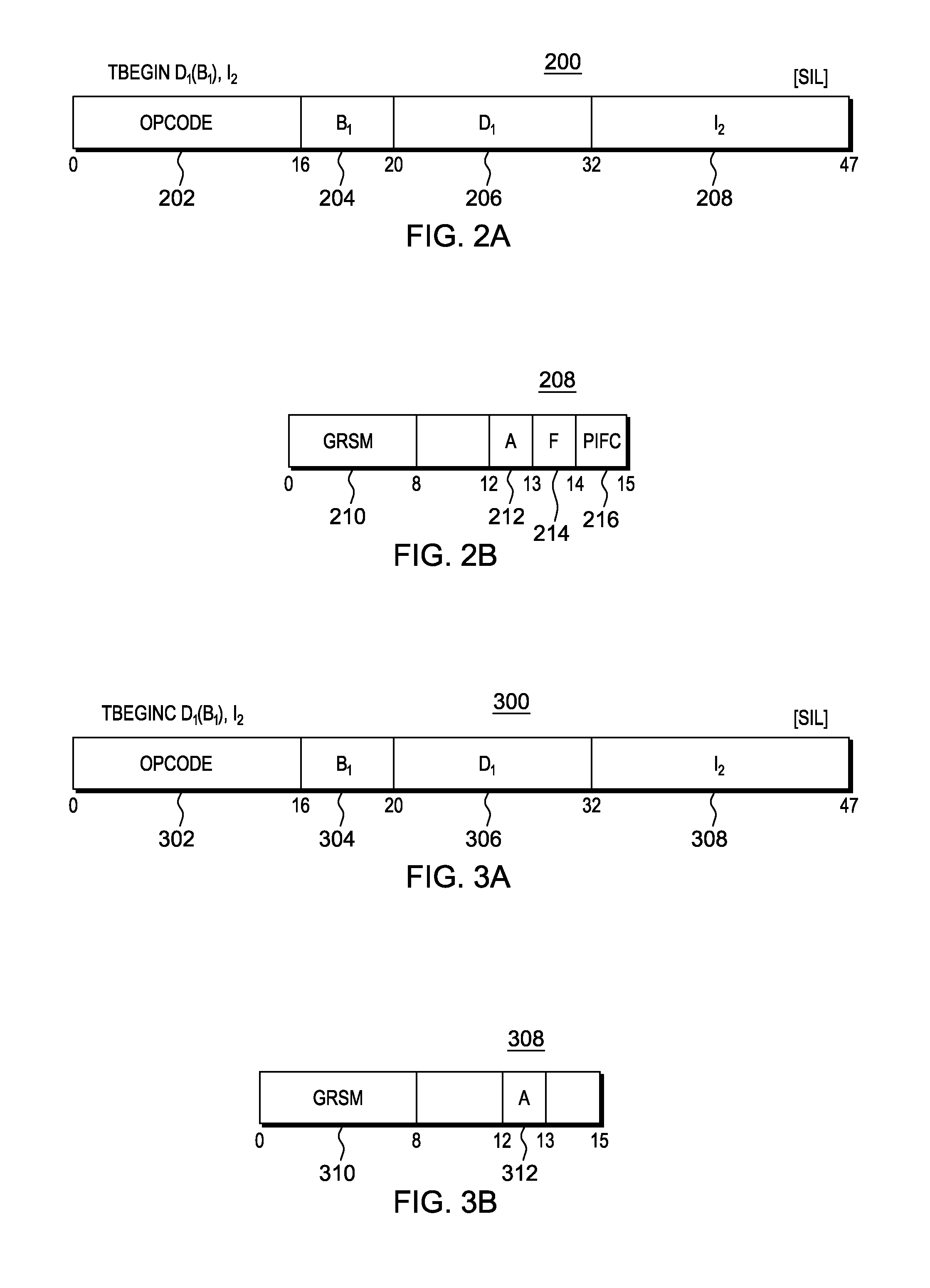
ActiveUS20130339676A1Digital computer detailsSpecific program execution arrangementsSoftware engineeringCondition Code
A TRANSACTION ABORT instruction is used to abort a transaction that is executing in a computing environment. The TRANSACTION ABORT instruction includes at least one field used to specify a user-defined abort code that indicates the specific reason for aborting the transaction. Based on executing the TRANSACTION ABORT instruction, a condition code is provided that indicates whether re-execution of the transaction is recommended.
Owner:IBM CORP
Out-of-order execution micro-processor and method of executing the related command
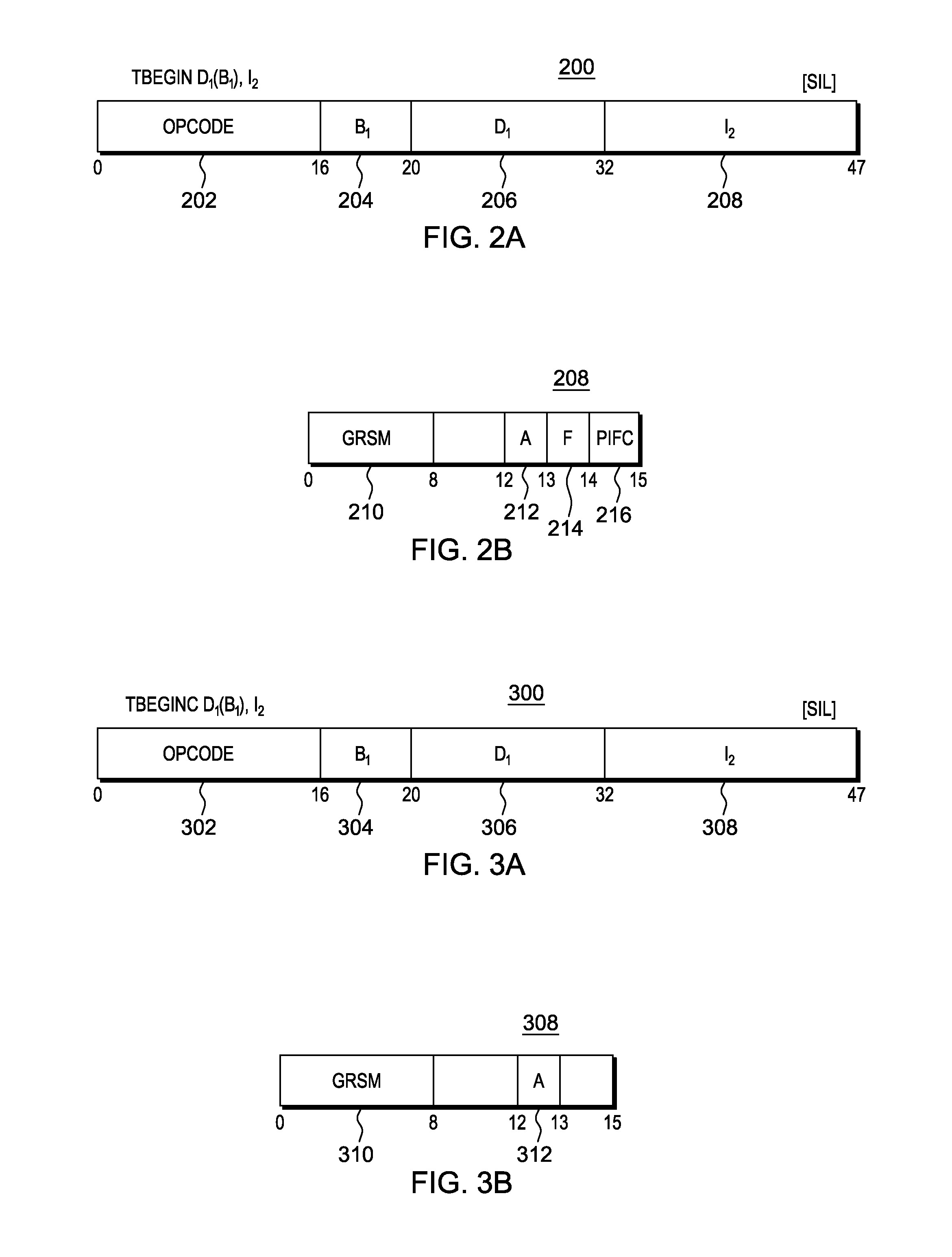
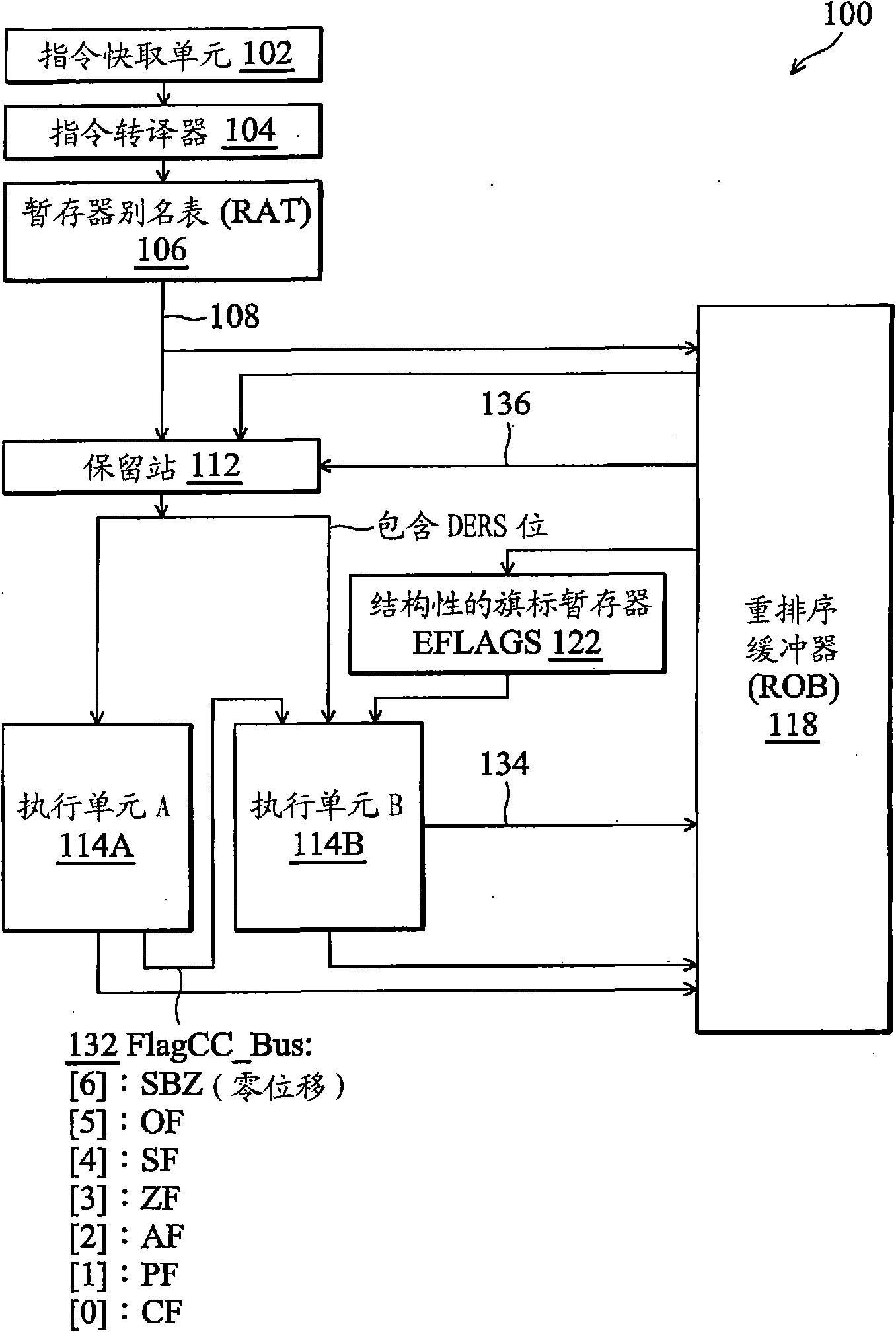
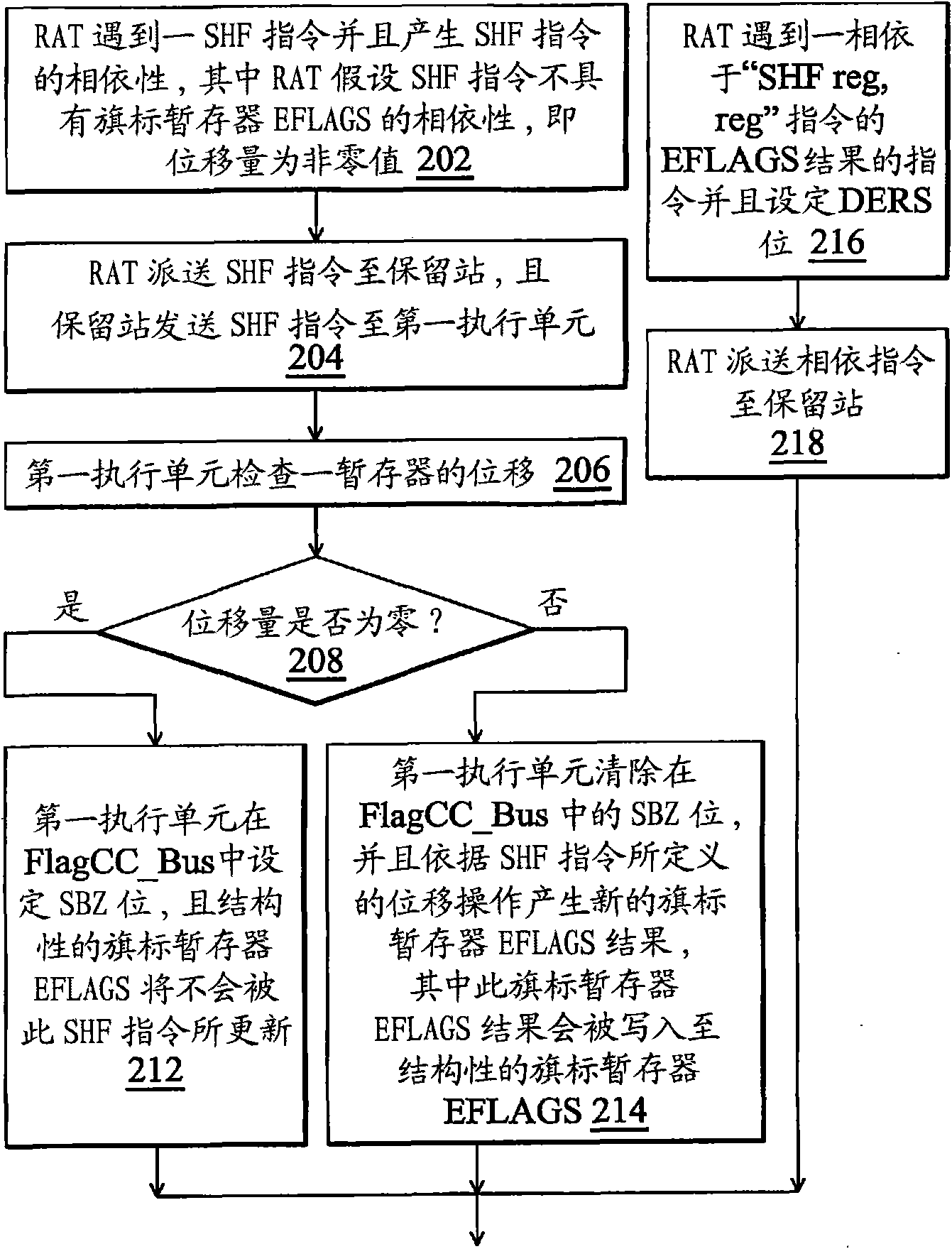
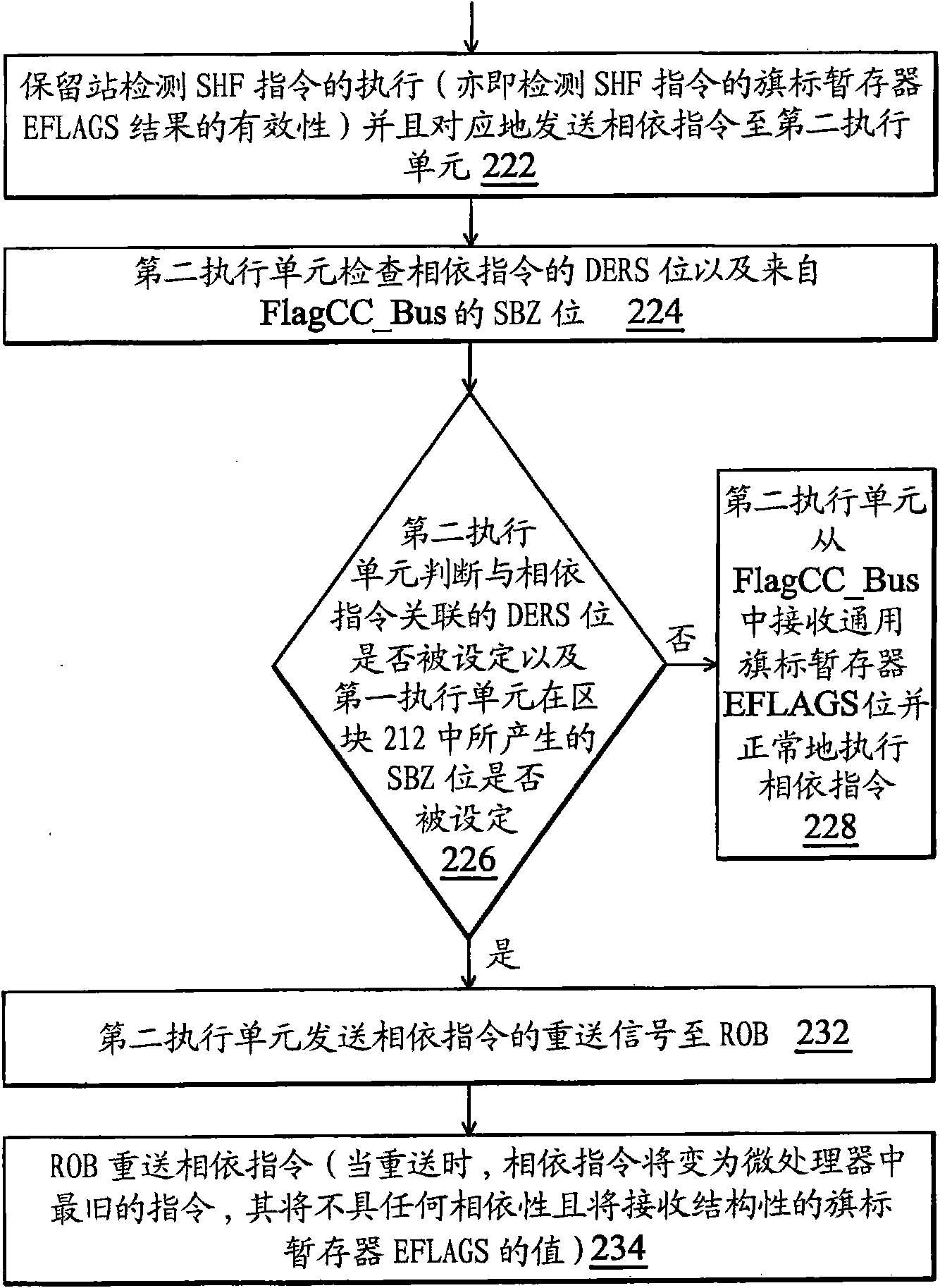
The invention provides an out-of-order execution micro-processor, comprising a temporary memory surname watch for generating a first indication for indicating whether one command depends on a condition code result of a shift command or not. A micro-processor also comprises a first execution unit for executing the shift command and generating a second indication and the second indication indicateswhether one shift amount of the shift command is zero or not. The micro-processor also comprises a second execution unit for receiving the first indication and the second indication and generating a return signal, thus when the first indication indicates that the command depends on the condition code result of the shift command and the second indication indicates that the shift amount of the shift command is zero, the command is returned.
Owner:VIA TECH INC
Image reader and copier preventing unauthorized reading and copying
InactiveUS7567355B2Reliable preventionImage enhancementUser identity/authority verificationProgramming languageCondition Code
An image, in which a pattern image is arranged so as to express a control information for inhibiting copying or for removing the inhibition, is defined as an image to be read. A copy inhibition code or a condition code for removing the inhibition is assigned for the pattern image. In a “normal copy mode” of a copier, a copy inhibition information detecting part detects the copy inhibition code in an obtained image, and a controller halts the copying when the copy inhibition code is detected. A condition information detecting part detects the condition code in the obtained image. A copy mode is provided in which the copying operation is permitted when the condition matches. The controller permits copying when a condition, such as permitting a specific user to perform copying or the elapse of a predetermined day and time delimited period, is established.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
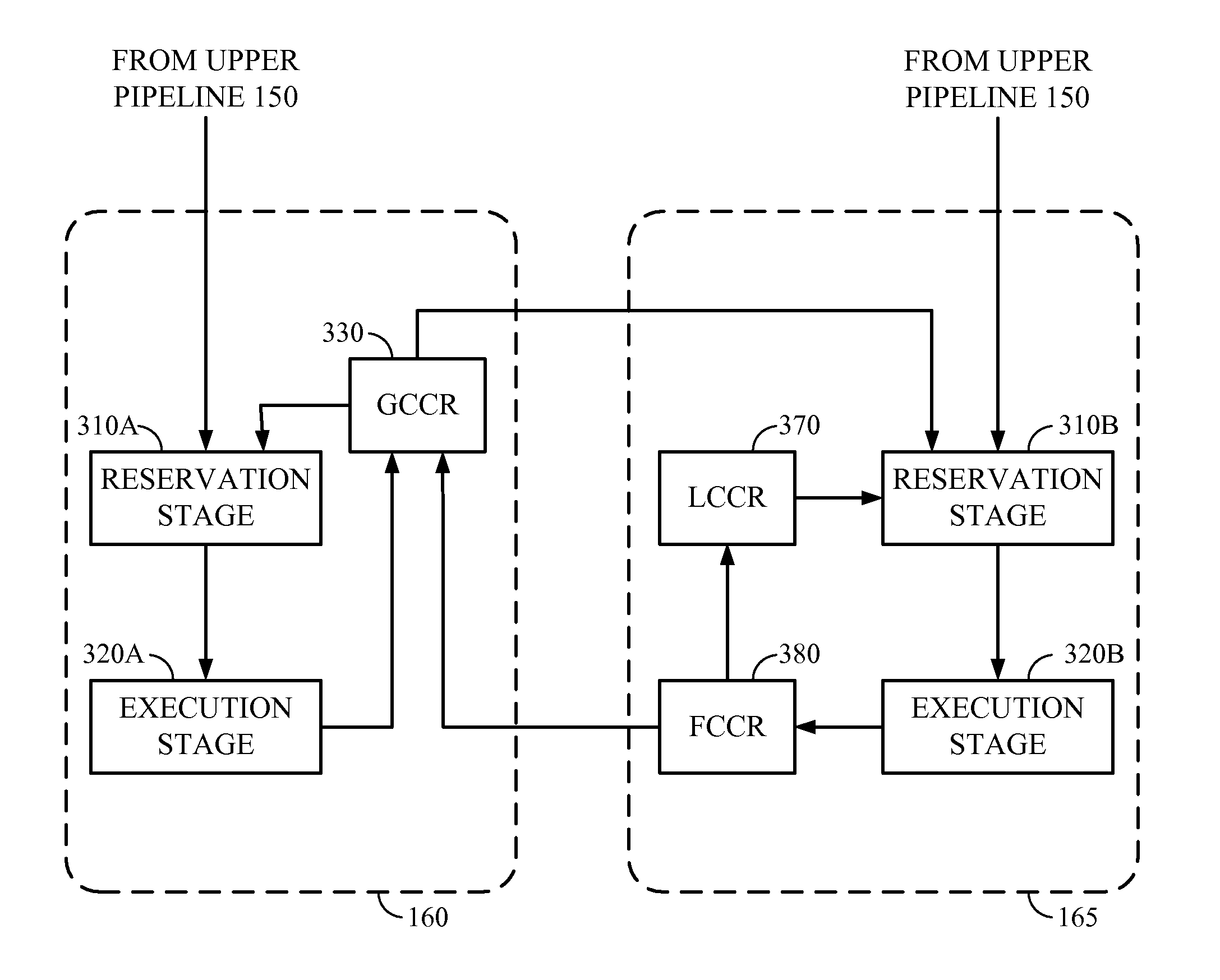
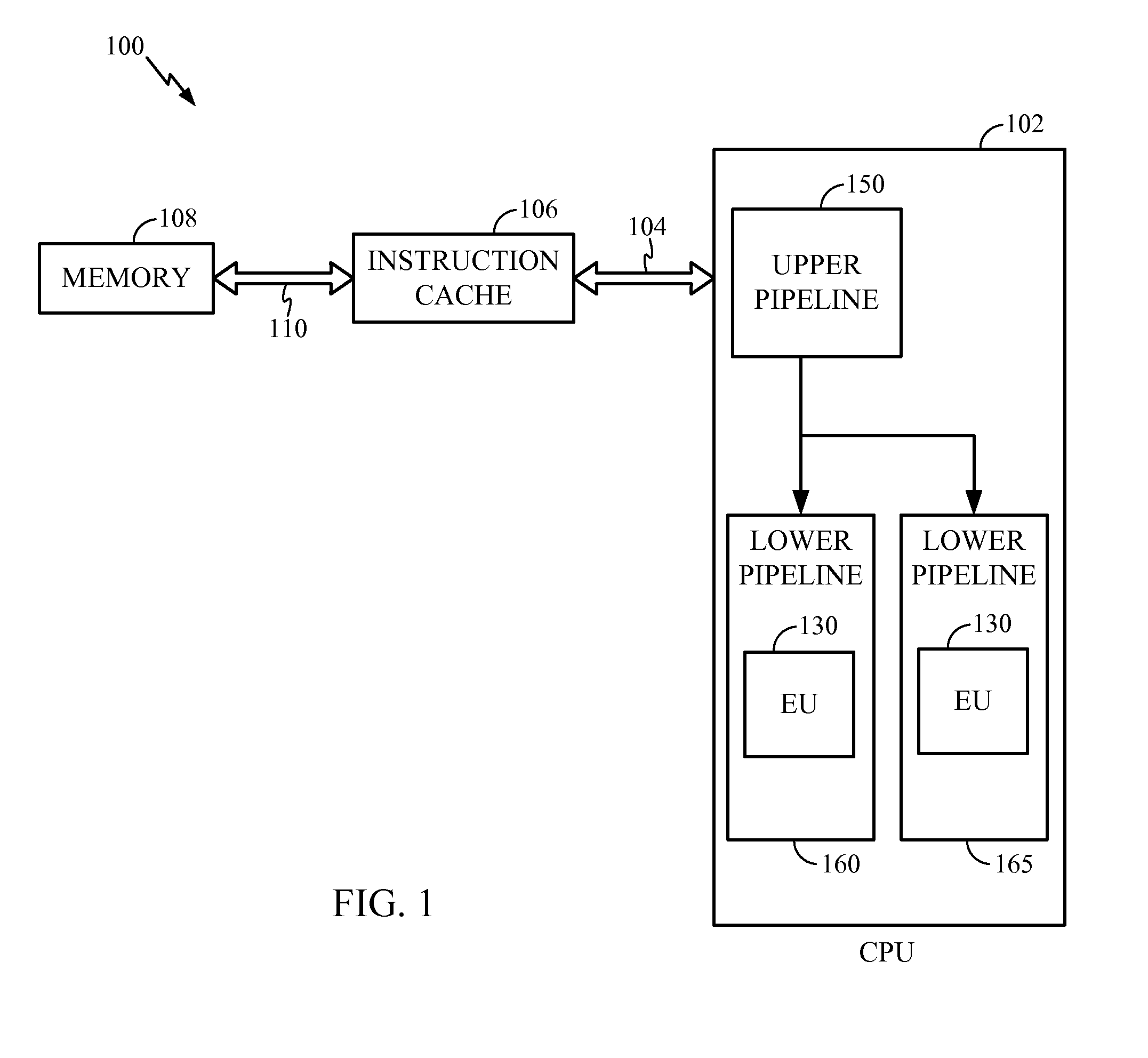
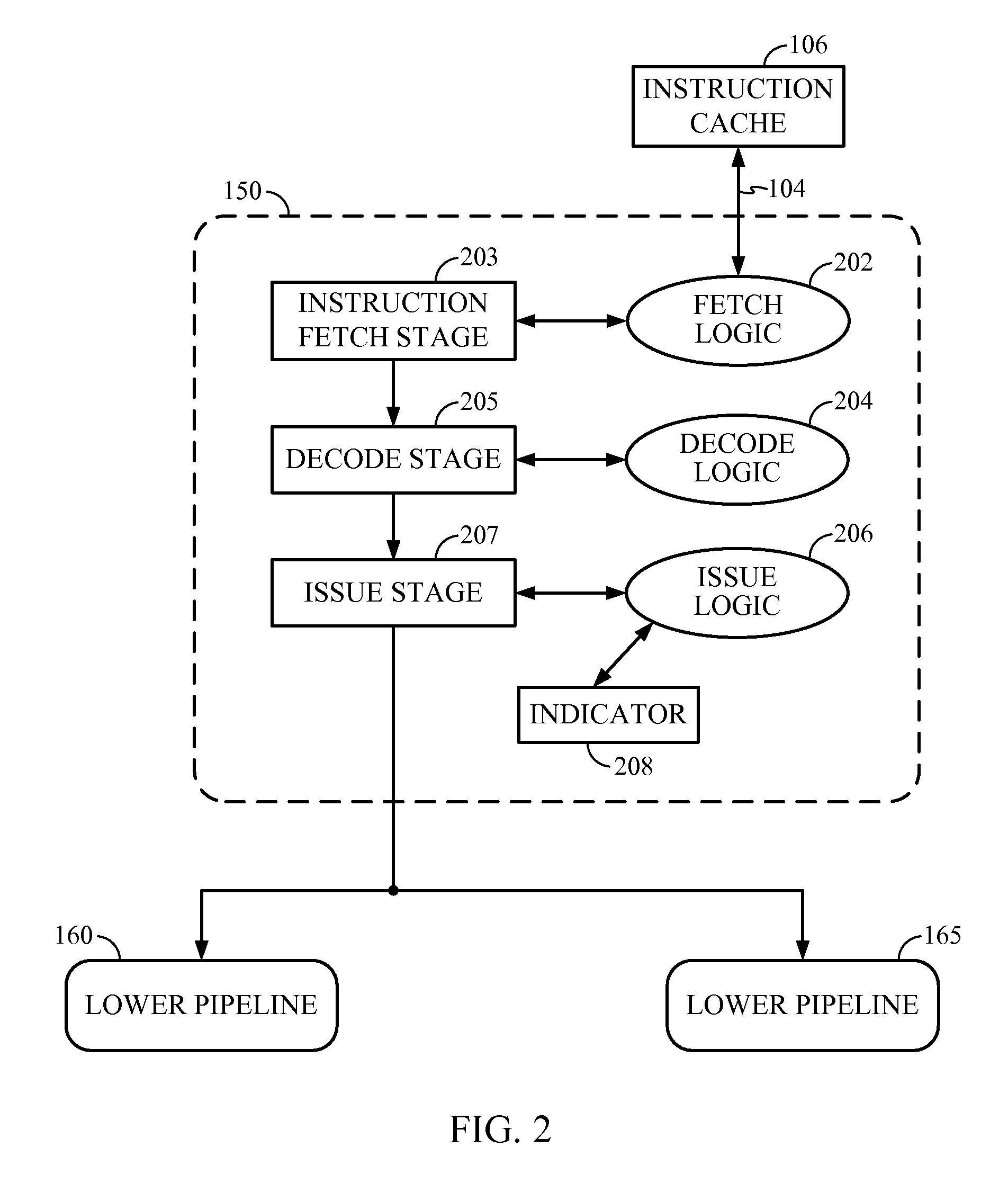
System and method for using a local condition code register for accelerating conditional instruction execution in a pipeline processor
InactiveUS8555039B2Improve executionSpeed up executionConditional code generationDigital computer detailsProcessor registerParallel computing
A method of executing a conditional instruction within a pipeline processor having a plurality of pipelines, the processor having a first condition code register associated with a first pipeline and a second condition code register associated with a second pipeline is disclosed. The method saves a most recent condition code value to either the first condition code register or the second condition code register. The method further sets an indicator indicating whether the second condition code register has the most recent condition code value and retrieves the most recent condition code value from either the first or second condition code register based on the indicator. The method uses the most recent condition code value to determine if the conditional instruction should be executed.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
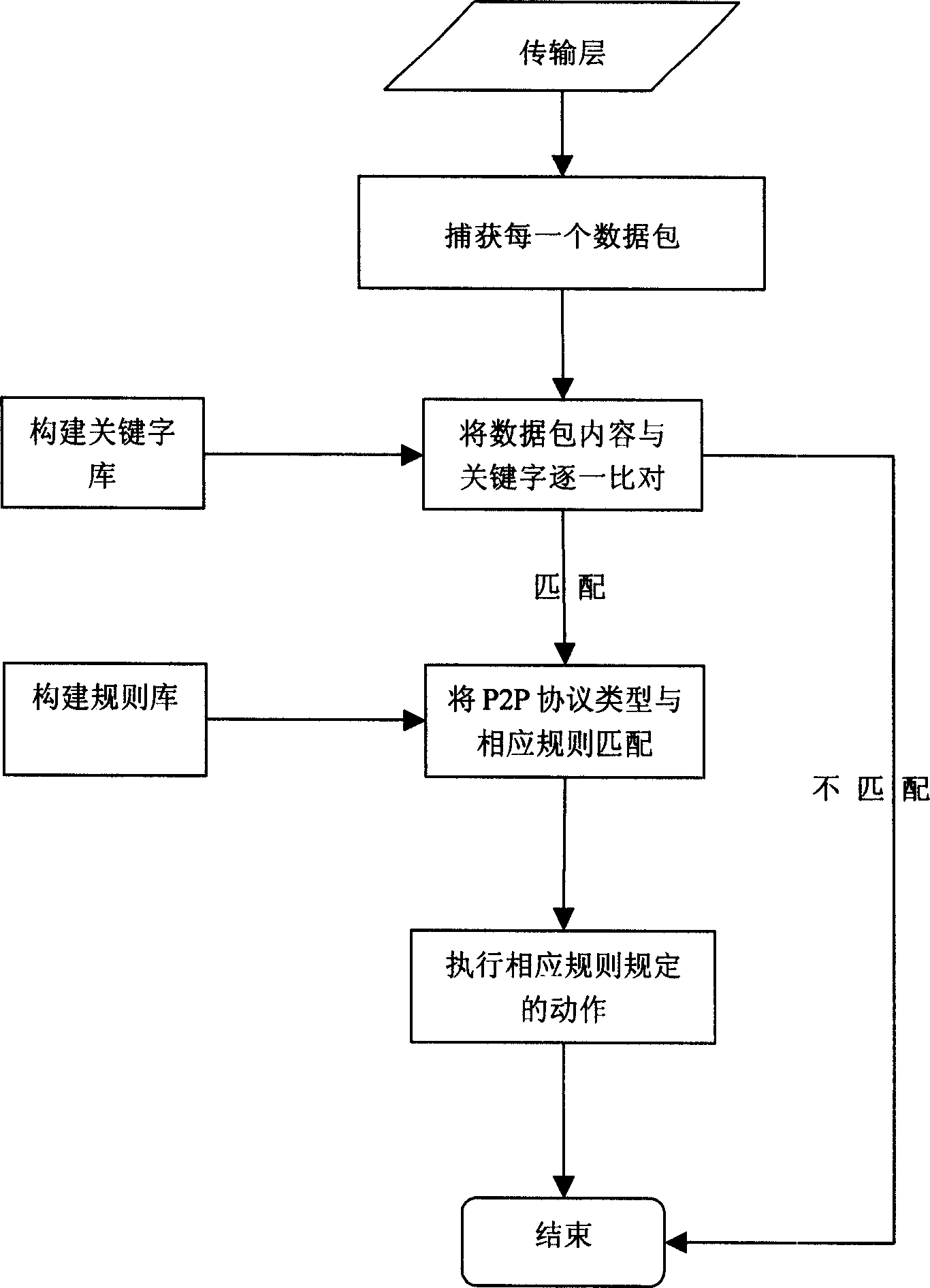
Method for discovering and controlling of producing flow based on P2P high speed unloading software
This invention relates to a method for monitoring software use, especially for finding out the flow and controlling high speed download software based on P2P, to overcome the shortage of network band width resource illegal occupying, secret disclosing and virus spreading, said invention identifies condition code (keywords) of data package to affirm high speed downloaded software type, breaking off downloading through breaking (or dropping) its TCP handshaking protocol data package.
Owner:西安交大捷普网络科技有限公司
Load Pair Disjoint Facility and Instruction Therefore
ActiveUS20130117546A1Digital computer detailsSpecific program execution arrangementsOperandCondition Code
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
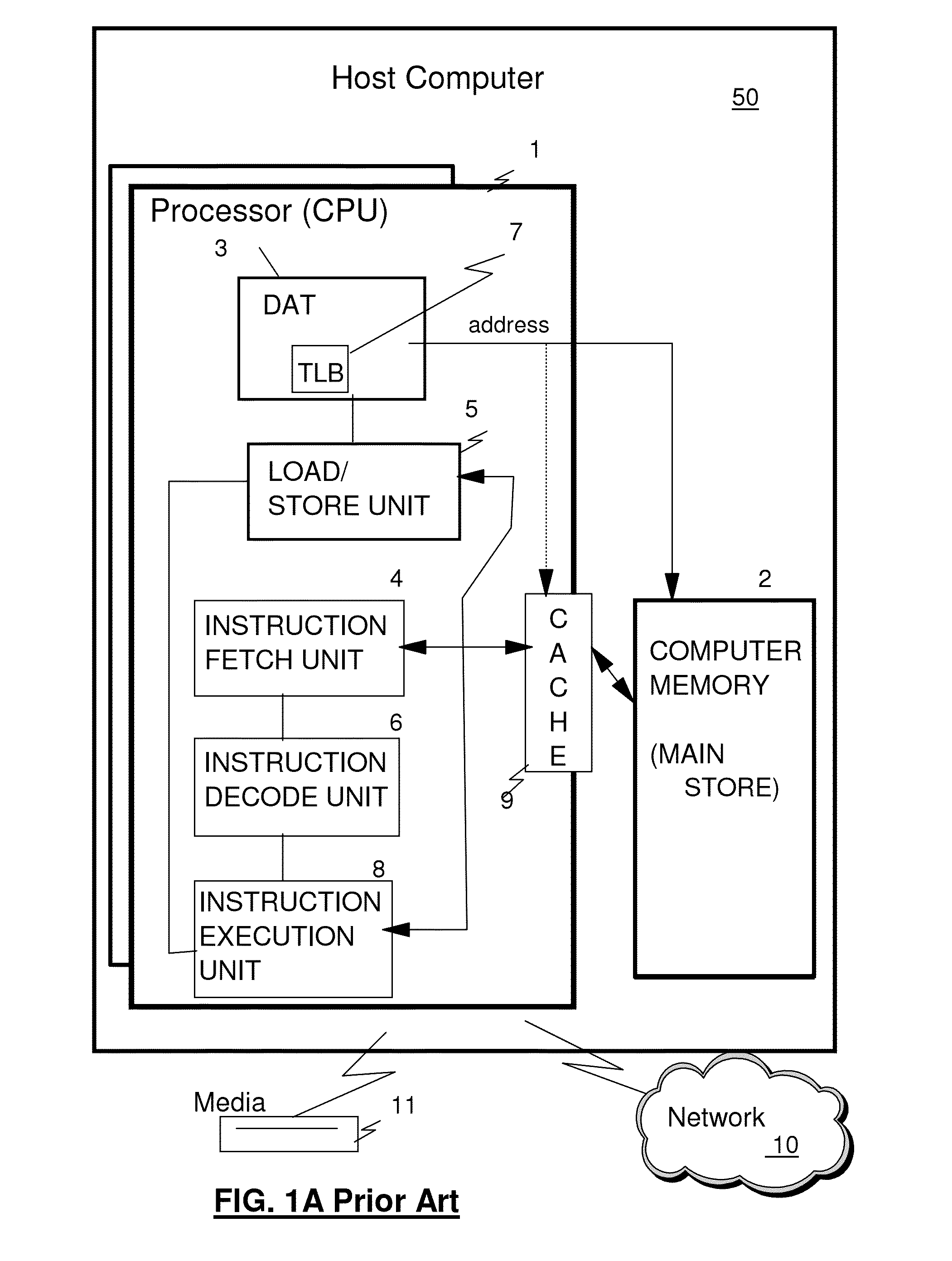
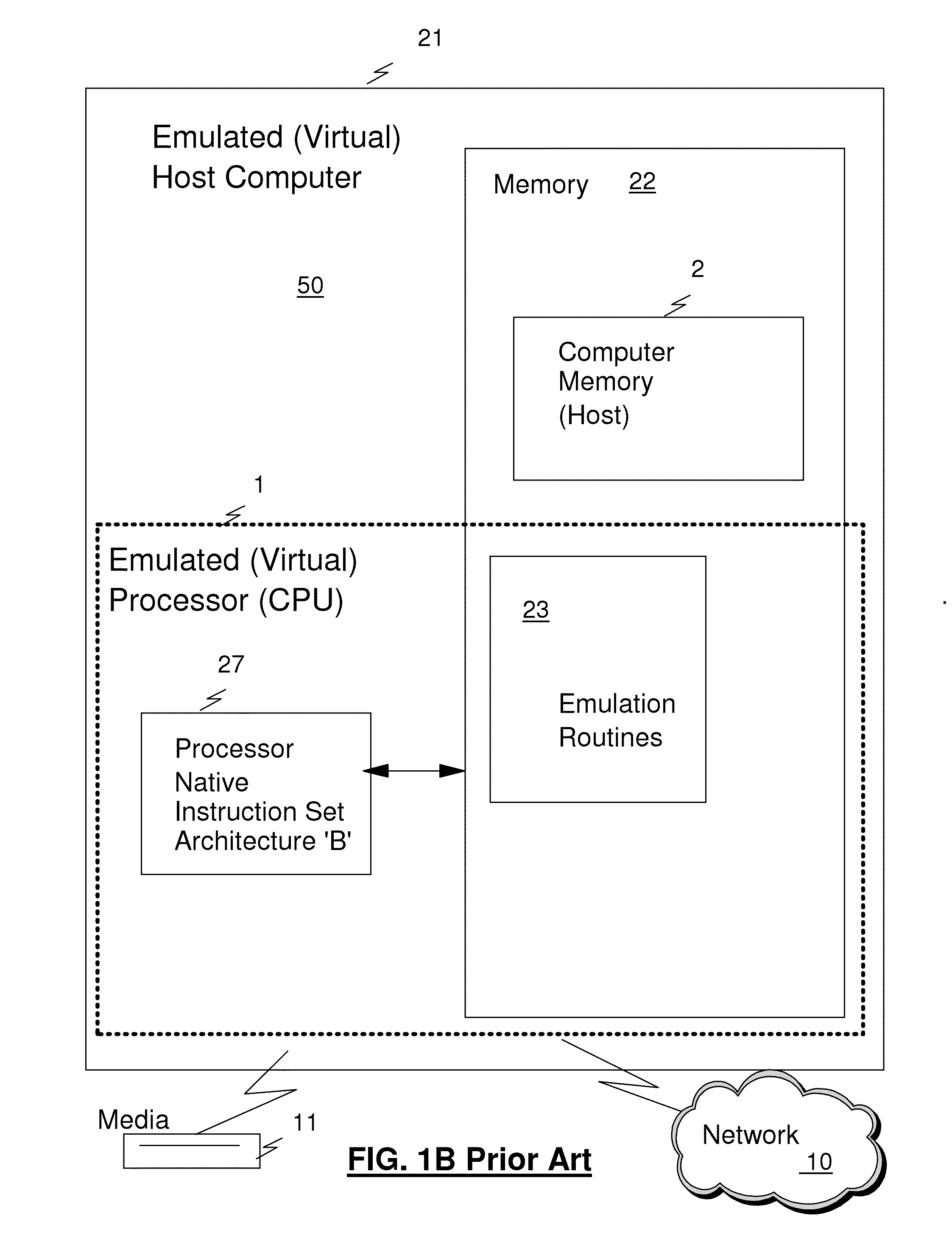
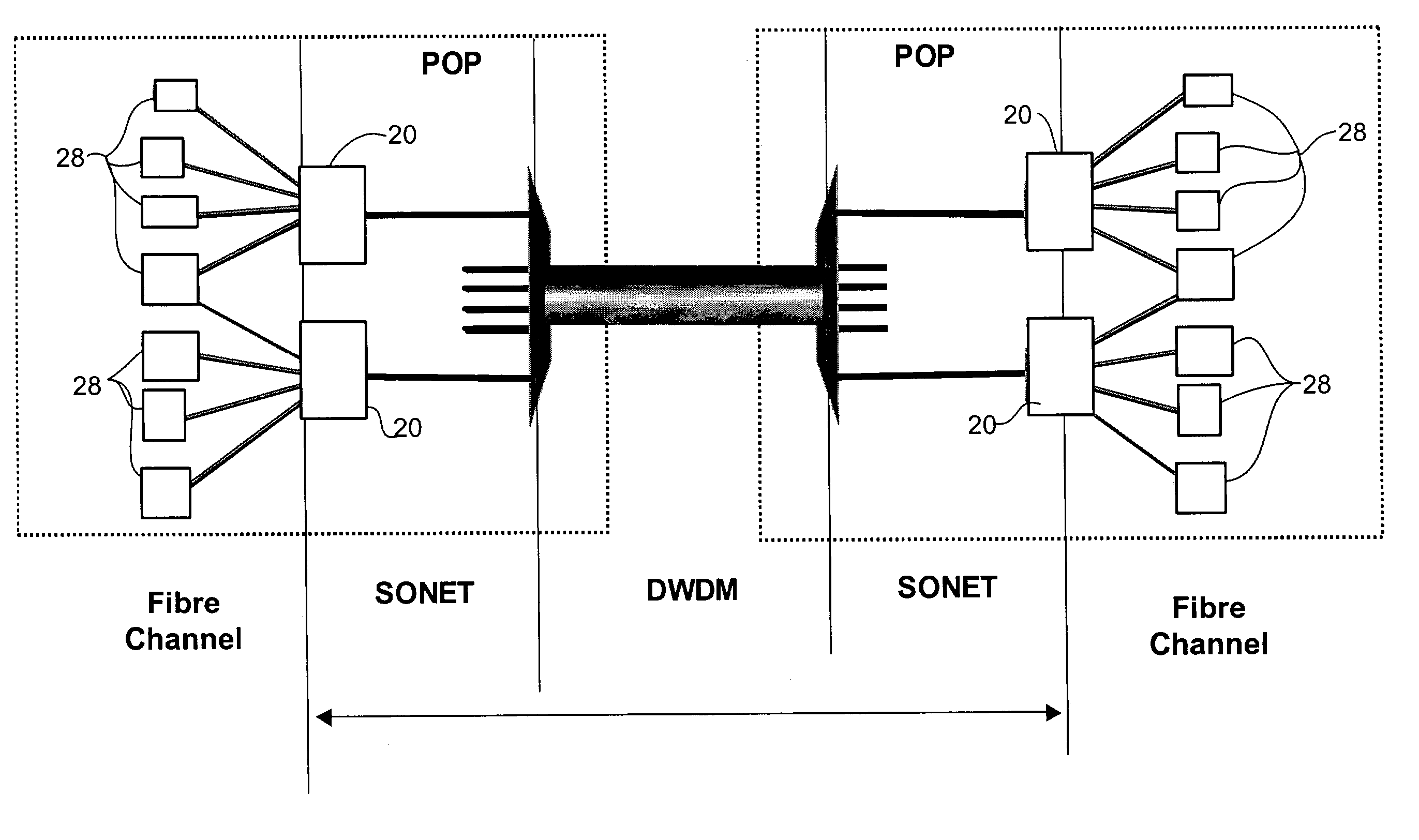
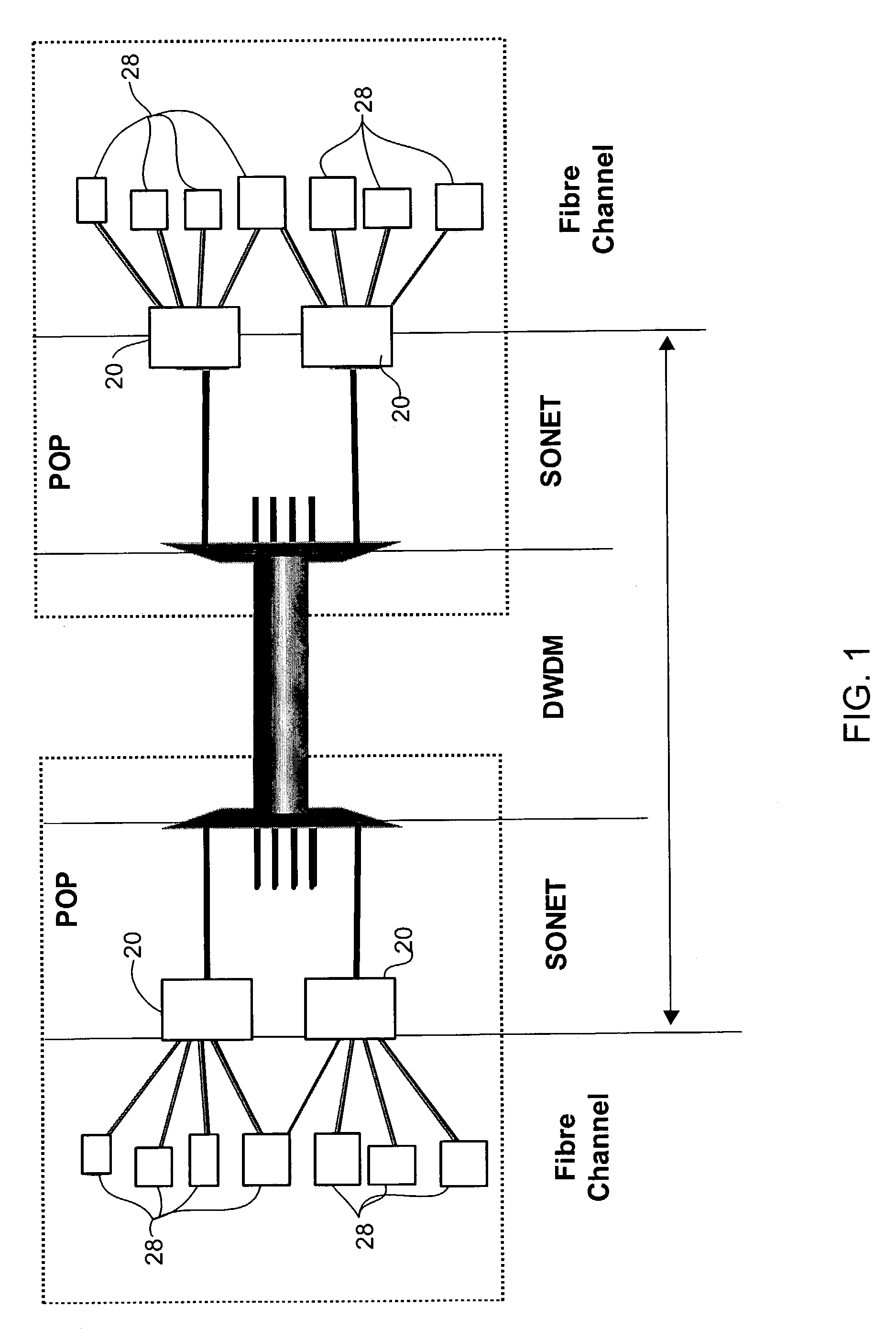
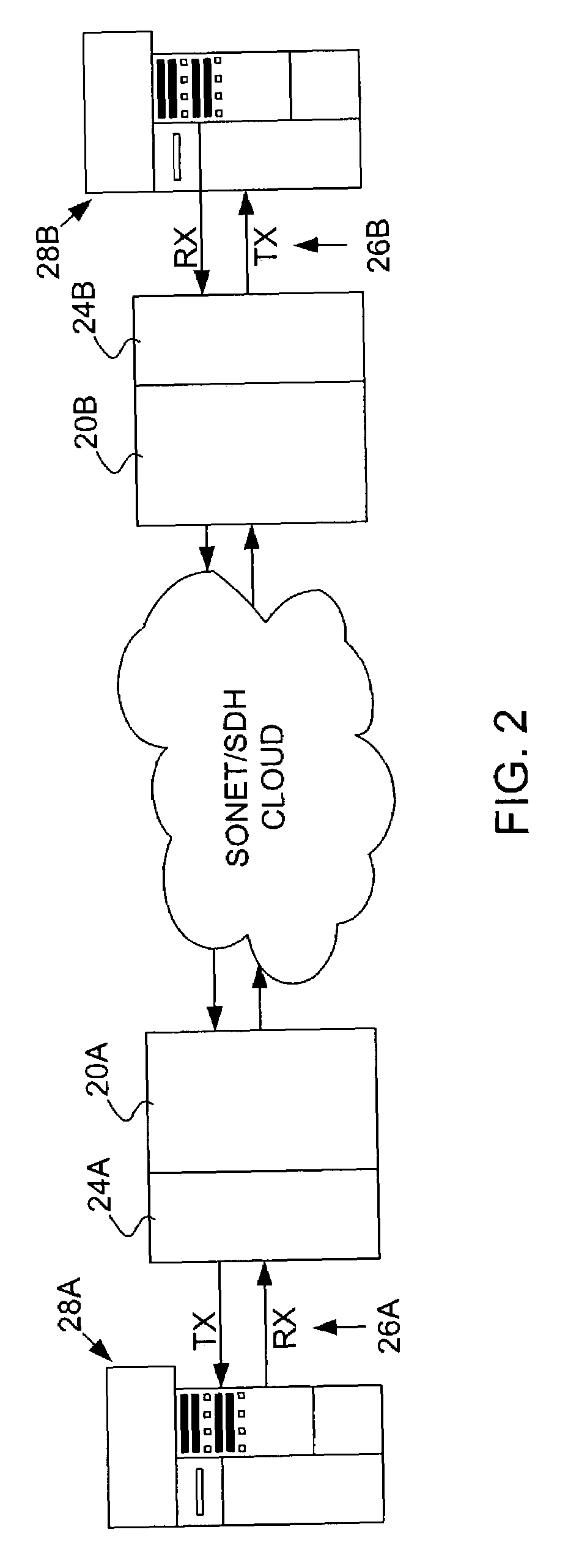
Method and system for emulating a Fiber Channel link over a SONET/SDH path
A method and system for emulating an Fibre Channel link over a SONET transport path by which Fibre Channel data is transported across the SONET / SDH transport path. To provide link integrity, techniques to handle link failures from a Fibre Channel element to its associated Fibre Channel port, or of the SONET / SDH network linking Fibre Channel ports include transmitting error condition codes over the SONET / SDH transport path overhead to a remote Fibre Channel transport interface so that the Fibre Channel link from the remote Fibre Channel transport interface to the associated remote Fibre Channel port is disabled. Timing the length of failures and return of operation of the failed links is used to handle transient conditions and to avoid link bouncing.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
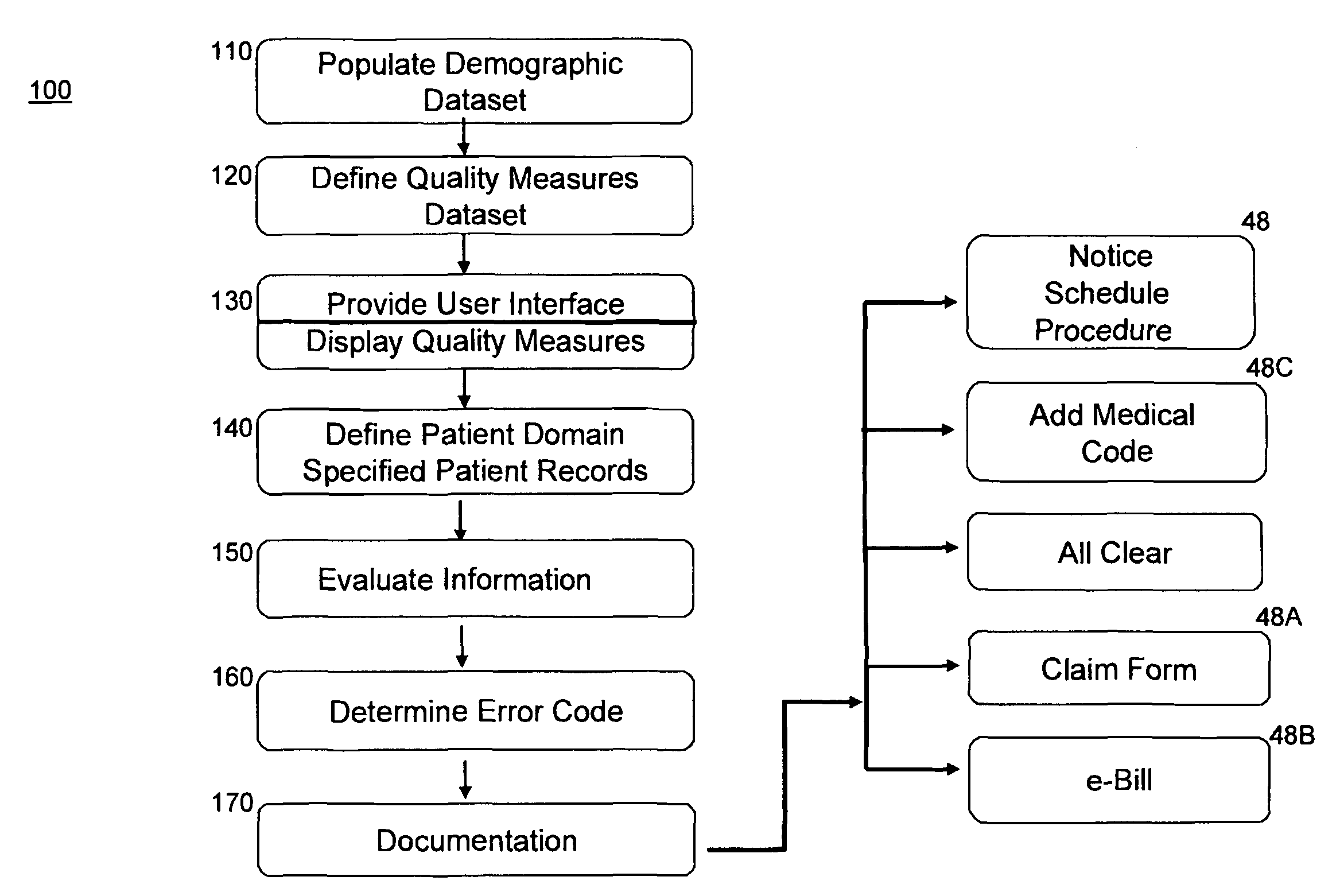
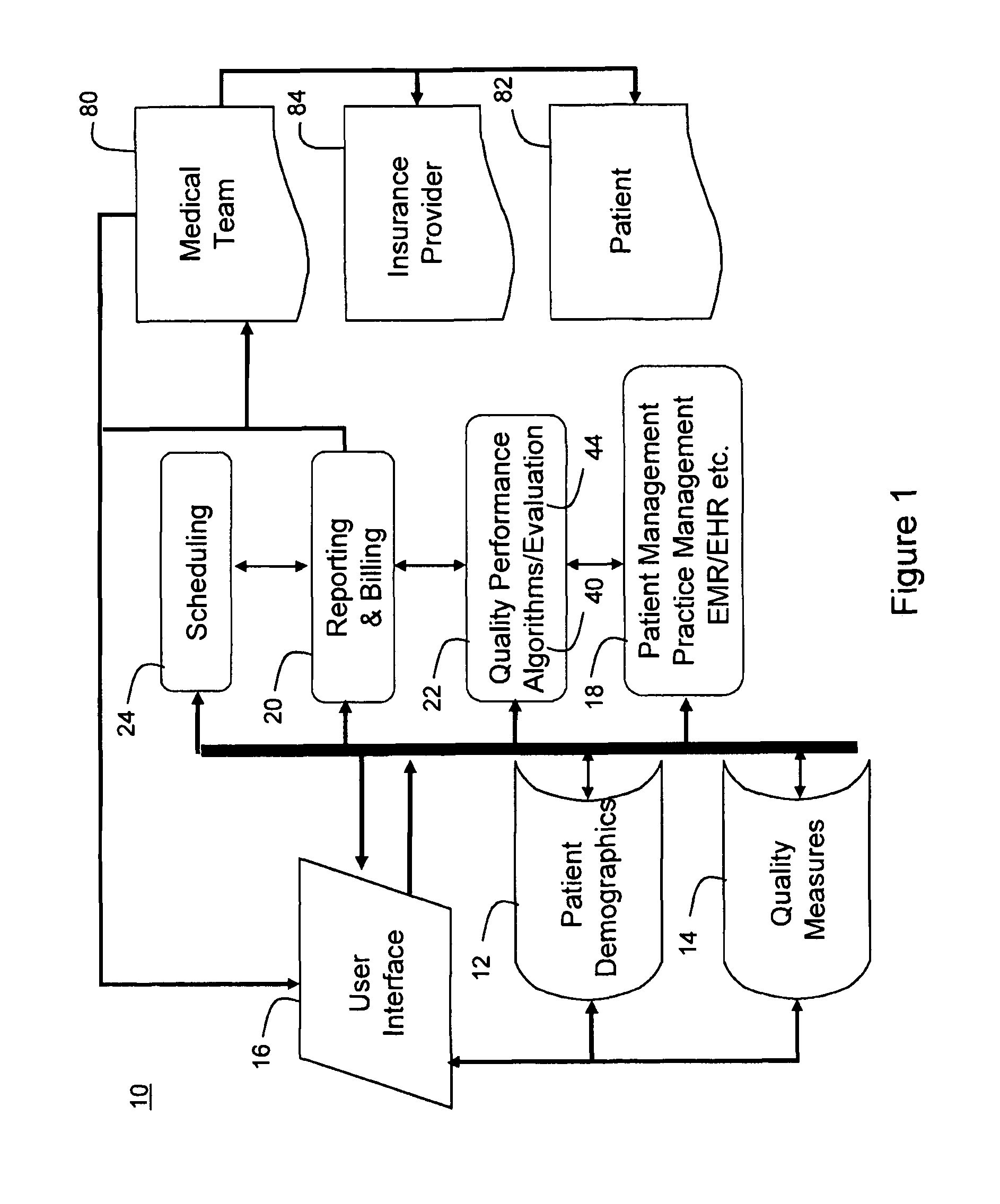
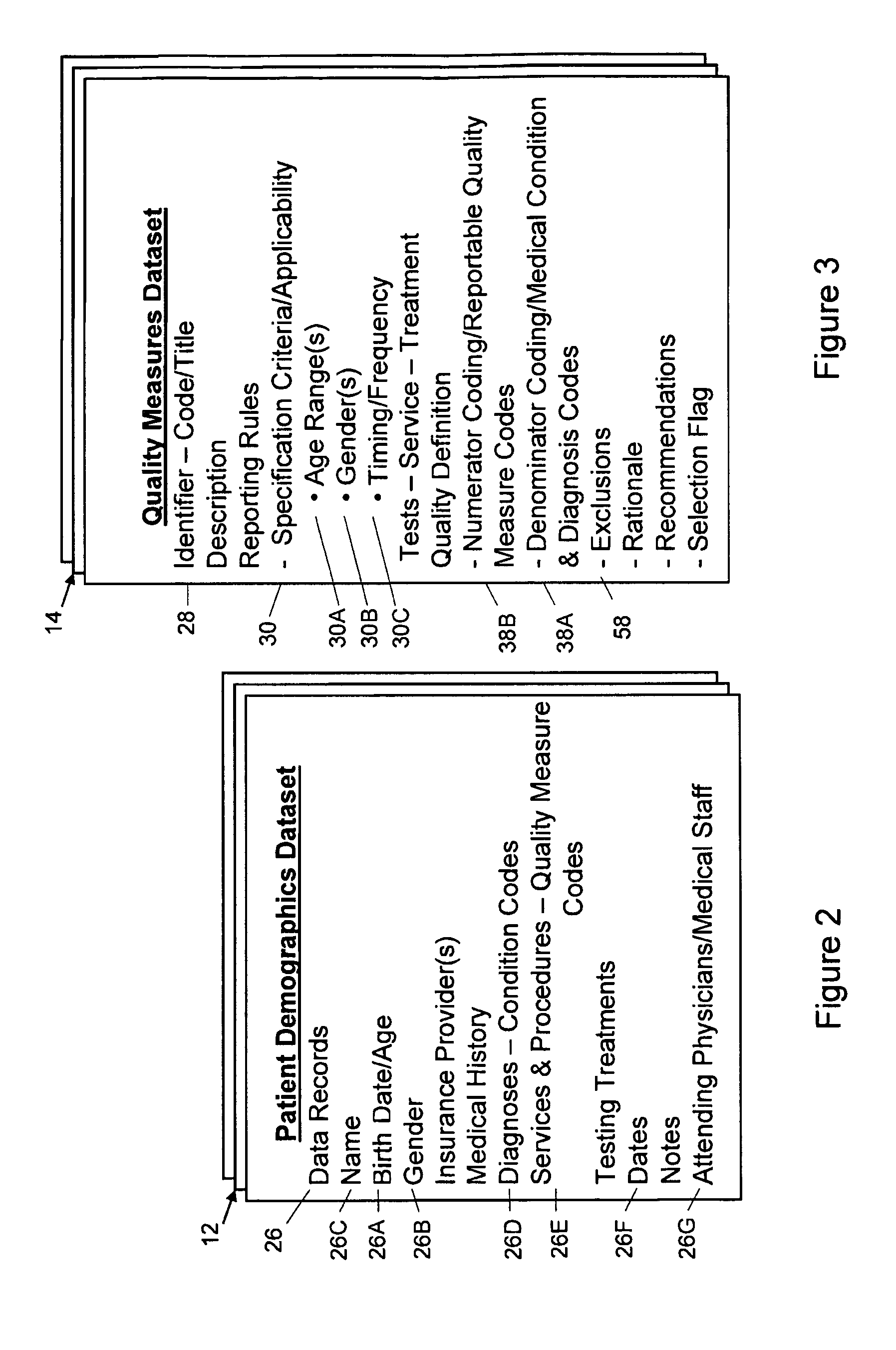
Medical quality performance measurement reporting facilitator
ActiveUS8311854B1Increase incomeDecrease personal time timePatient personal data managementOffice automationAge and genderCondition Code
A system and process evaluate the presence and absence of particular quality measure codes in a set of patient records and provide a medical service provider with options for taking corrective action when a quality measure code that should be in a patient's record is missing. Patient records are selected based on specific medical condition code combinations along with specifications with age and gender criteria. A quality measure identifier uniquely identifies a set of specification criteria, medical condition criteria, and quality measure criteria.
Owner:ALPHA II LLC
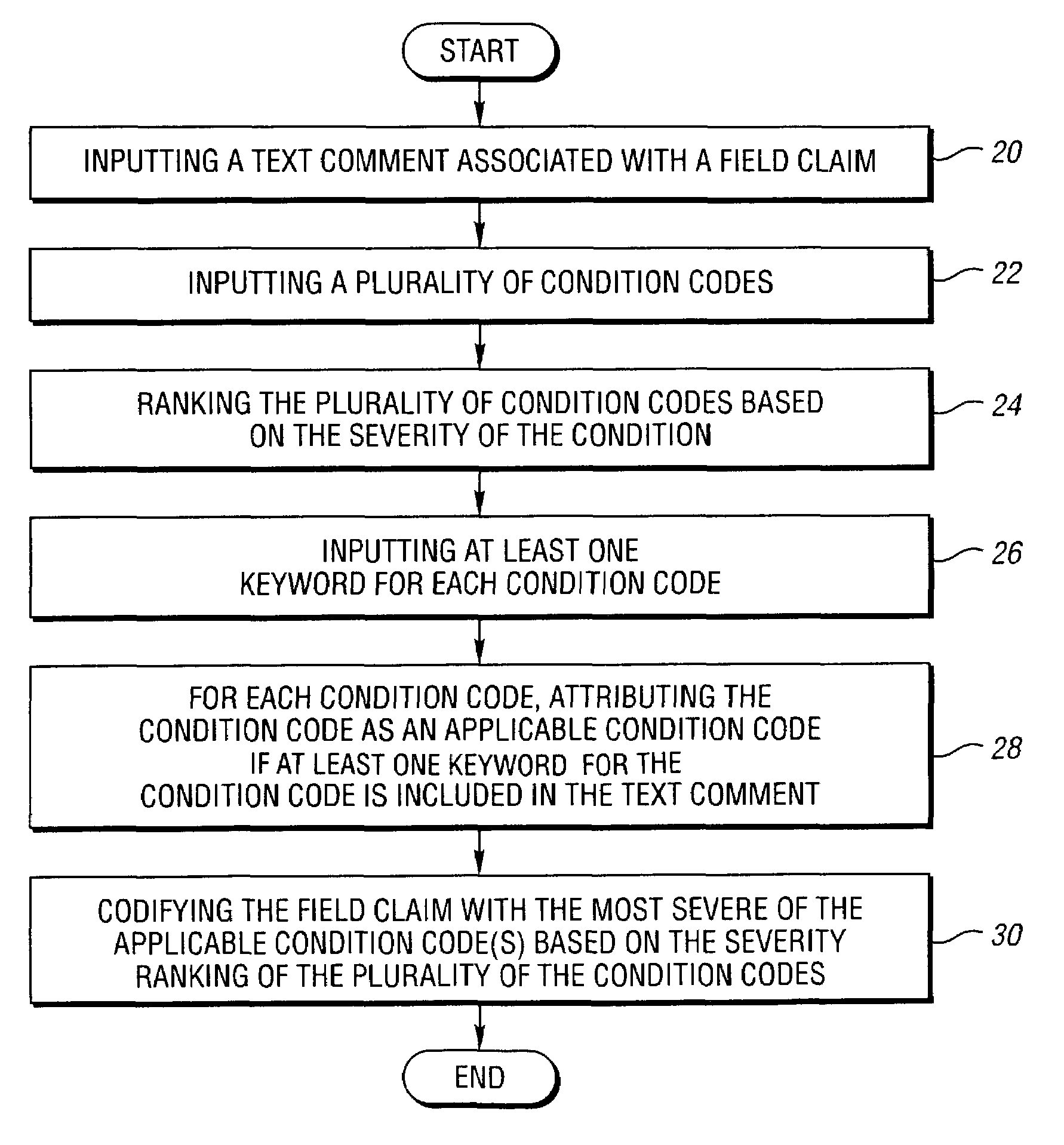
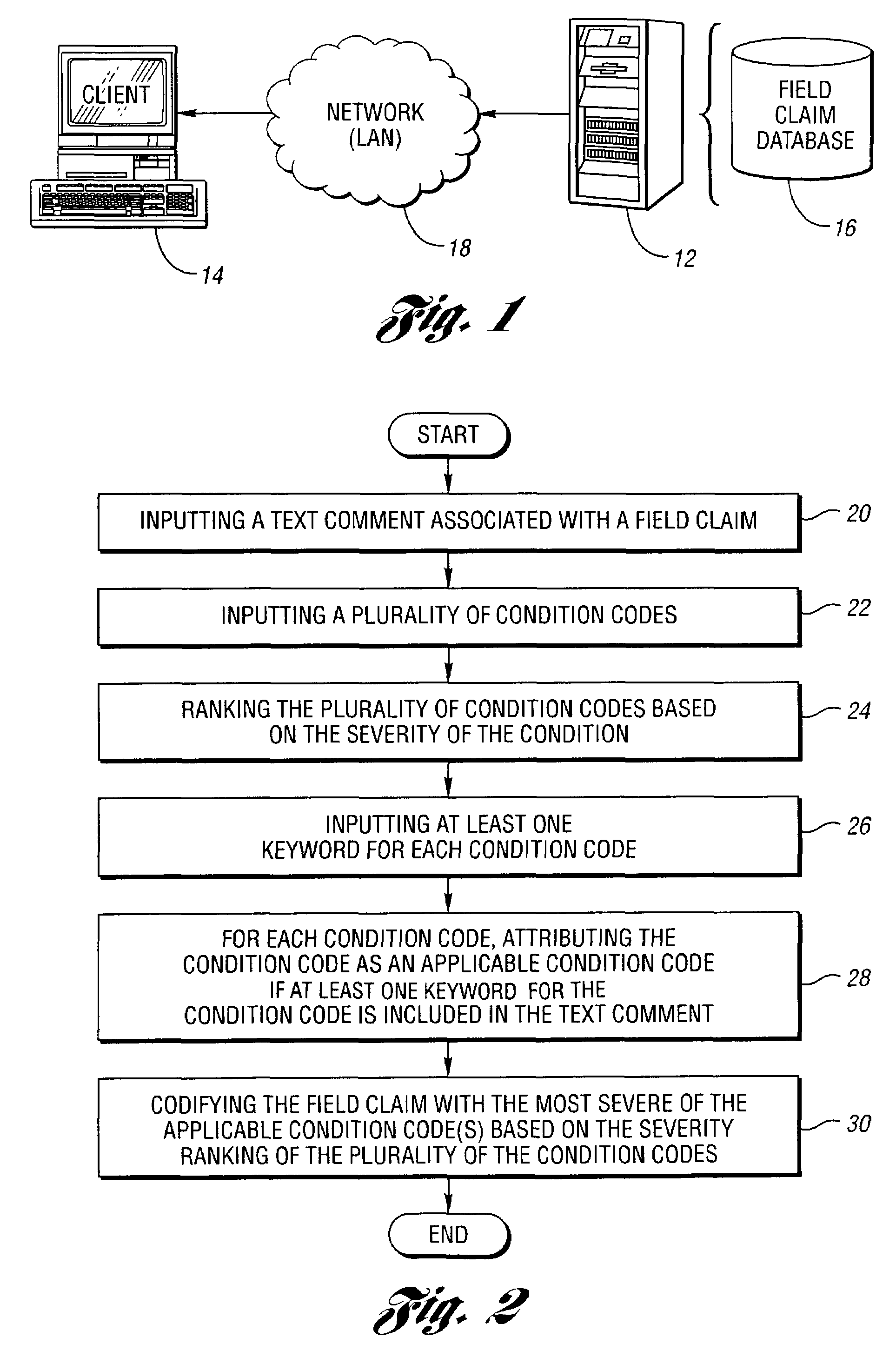
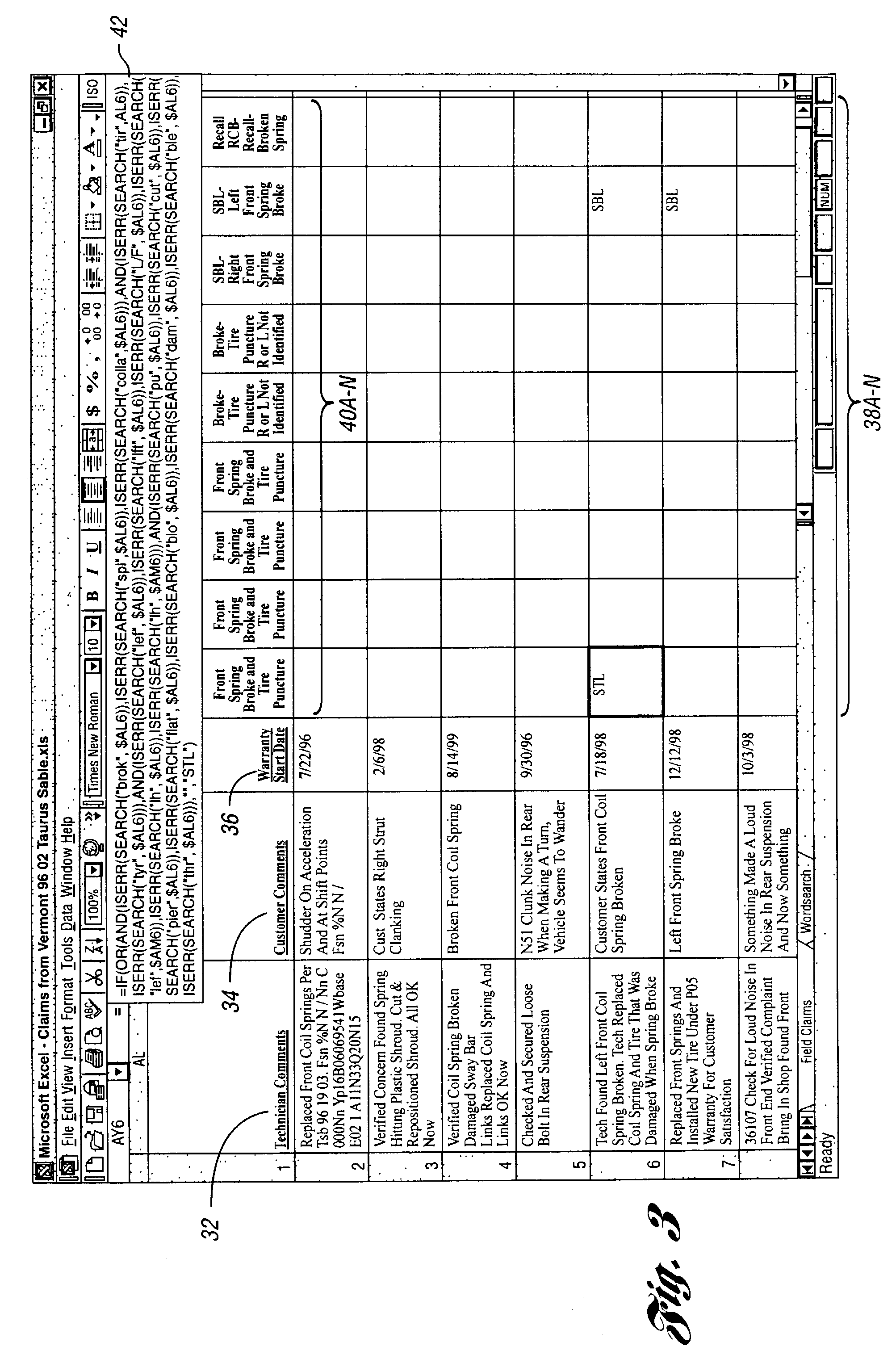
Computer-implemented method and system for attributing applicable condition codes to field claims
One aspect of the present invention is a computer-implemented method for attributing applicable condition code(s) to a field claim. One preferred method includes inputting a text comment associated with the field claim, inputting a plurality of condition codes and at least four keyword combinations of at least two non-sequential keywords for each condition code, and for each condition code, attributing the condition code as an applicable condition code if at least one keyword combination for the condition code is included in the text comment. The applicable condition code(s) can be relied upon by individuals to at least identify failure mode(s) associated with field claims.
Owner:FORD MOTOR CO
Transaction abort instruction
ActiveUS20130339709A1Digital computer detailsConcurrent instruction executionSoftware engineeringCondition Code
A TRANSACTION ABORT instruction is used to abort a transaction that is executing in a computing environment. The TRANSACTION ABORT instruction includes at least one field used to specify a user-defined abort code that indicates the specific reason for aborting the transaction. Based on executing the TRANSACTION ABORT instruction, a condition code is provided that indicates whether re-execution of the transaction is recommended.
Owner:IBM CORP
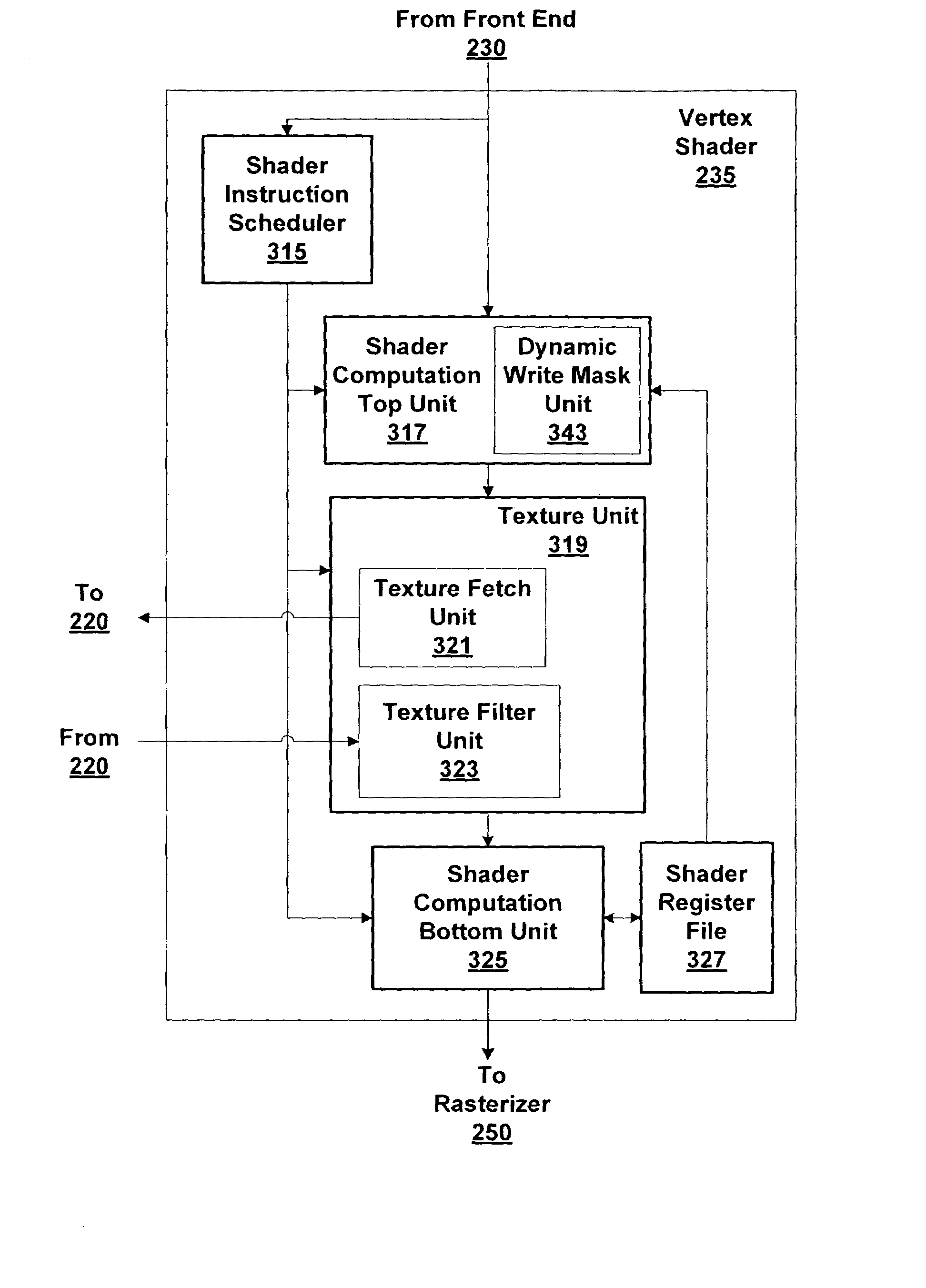
Dynamic texture fetch cancellation
ActiveUS7528843B1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsSpecific program execution arrangementsProgram instructionParallel computing
Systems and methods for dynamically canceling texture fetches may improve texture mapping performance. A shader program compiler inserts condition code writes and condition code comparison operations for shader program instructions that contribute to a texture read instruction and do not need to be executed if certain conditions are met. During execution of the shader program, the inserted condition codes are used to compute a dynamic writemask that indicates if the texture data resulting from the texture read is unnecessary. The dynamic writemask is used to cancel unnecessary texture fetches during execution of the shader program.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
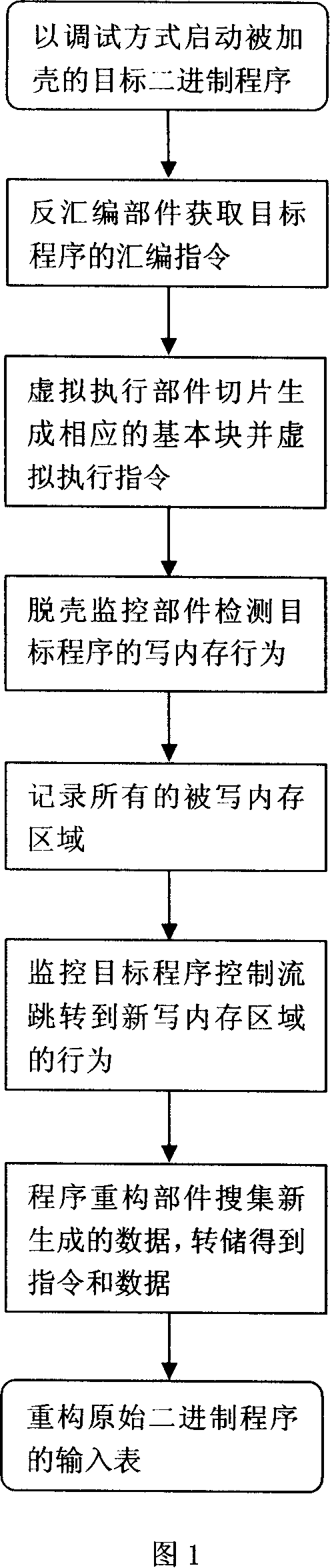
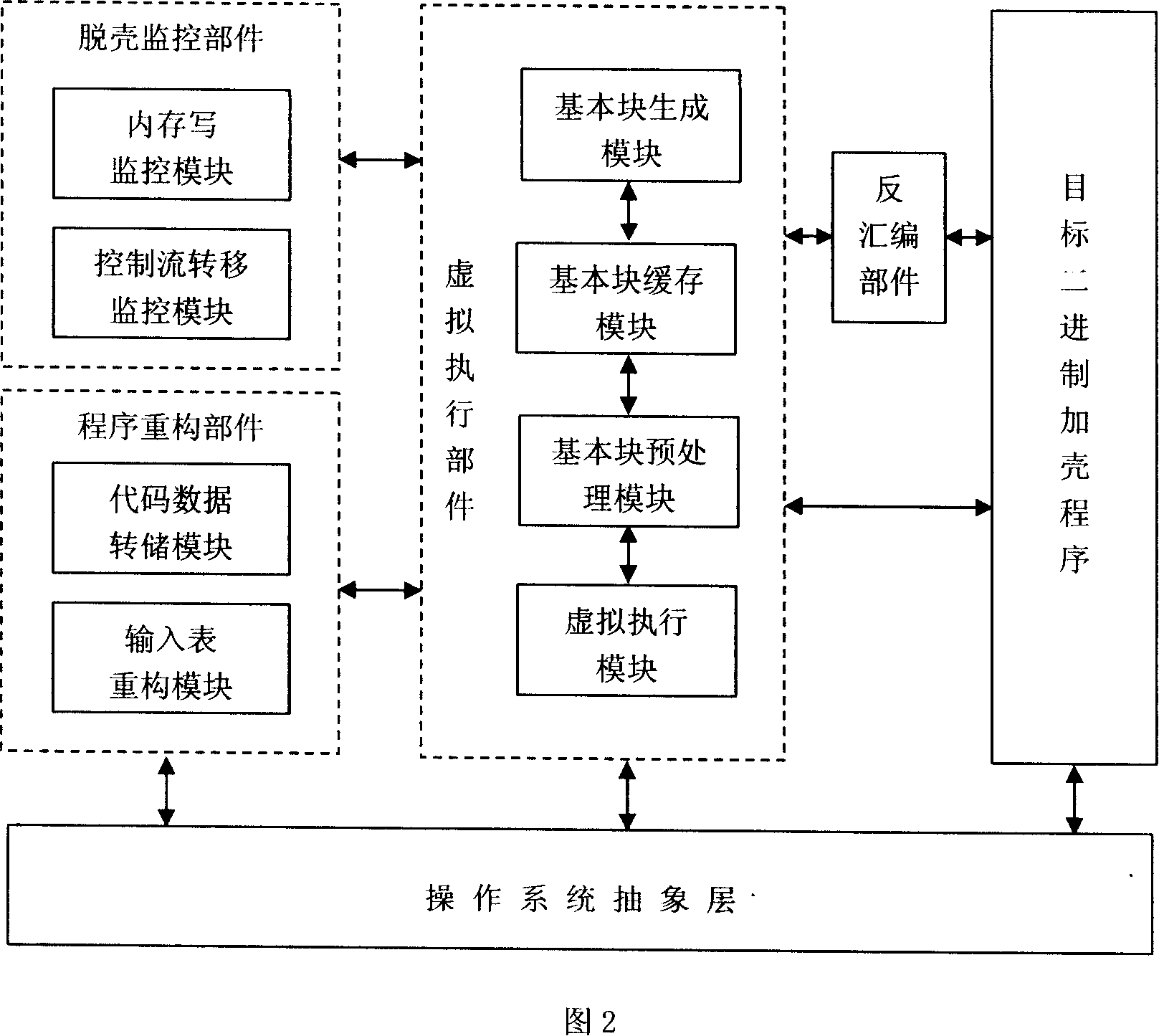
General automated shelling engine and method
InactiveCN101154259AEasy to detectReduce loadPlatform integrity maintainanceExecution unitCondition Code
The invention relates to a general automatic shelling engine and a method for computer binary shell applying program. The system consists of a disassembling unit, a virtual execution unit, a shelling monitoring unit and a program restructuring unit. The method is that: an object program is activated in a debugging mode, the disassembling unit is used for acquiring the assembler instruction of the object program, the virtual execution unit slices and generates a corresponding basic block and executes the instruction virtually, the shelling monitoring unit detects the memory writing behavior of the object program and records all memory writing regions, the shelling monitoring unit also monitors the behavior of an object program control flow jumping to a new memory writing region and accordingly judges that the shelling process ends, and the program restructuring unit is used for collecting data of all new memory writing regions and generating an original binary program through techniques such as RAM dump, input list restructuring. The invention is suitable for quick and general shelling of an unknown shell applying program and auxiliary condition code detection method without the feature of the shell applying program and with little running load.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com