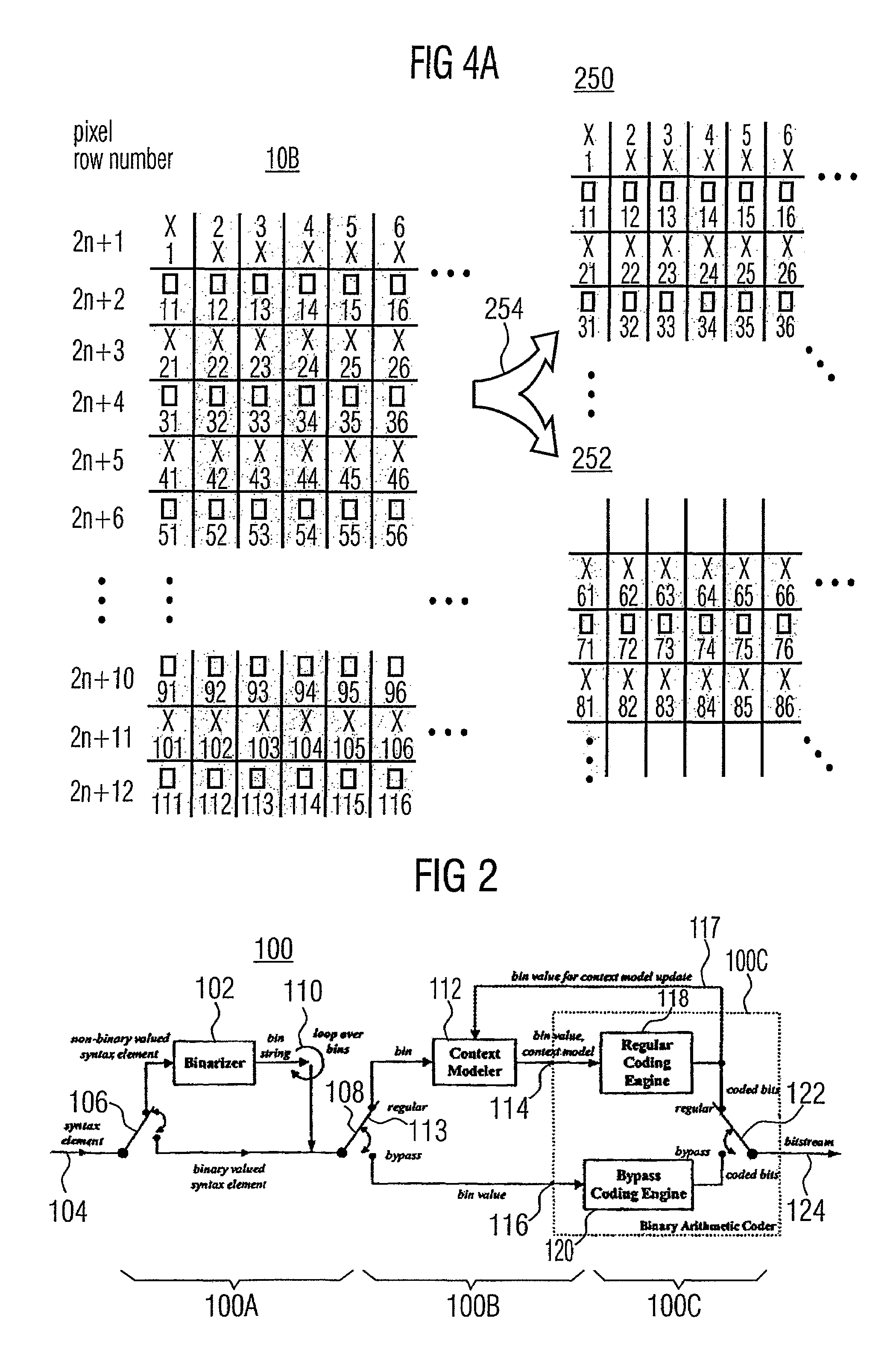
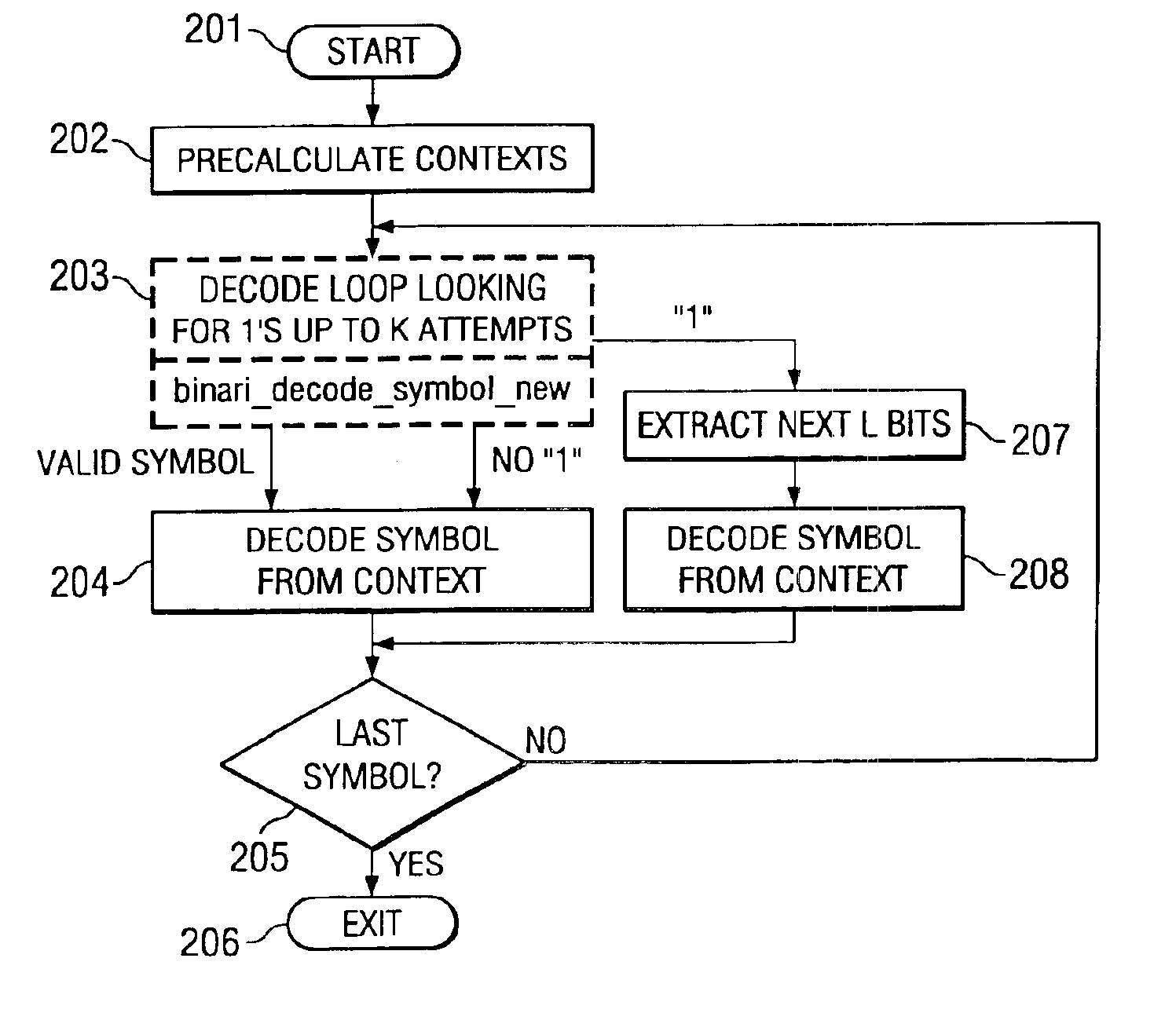
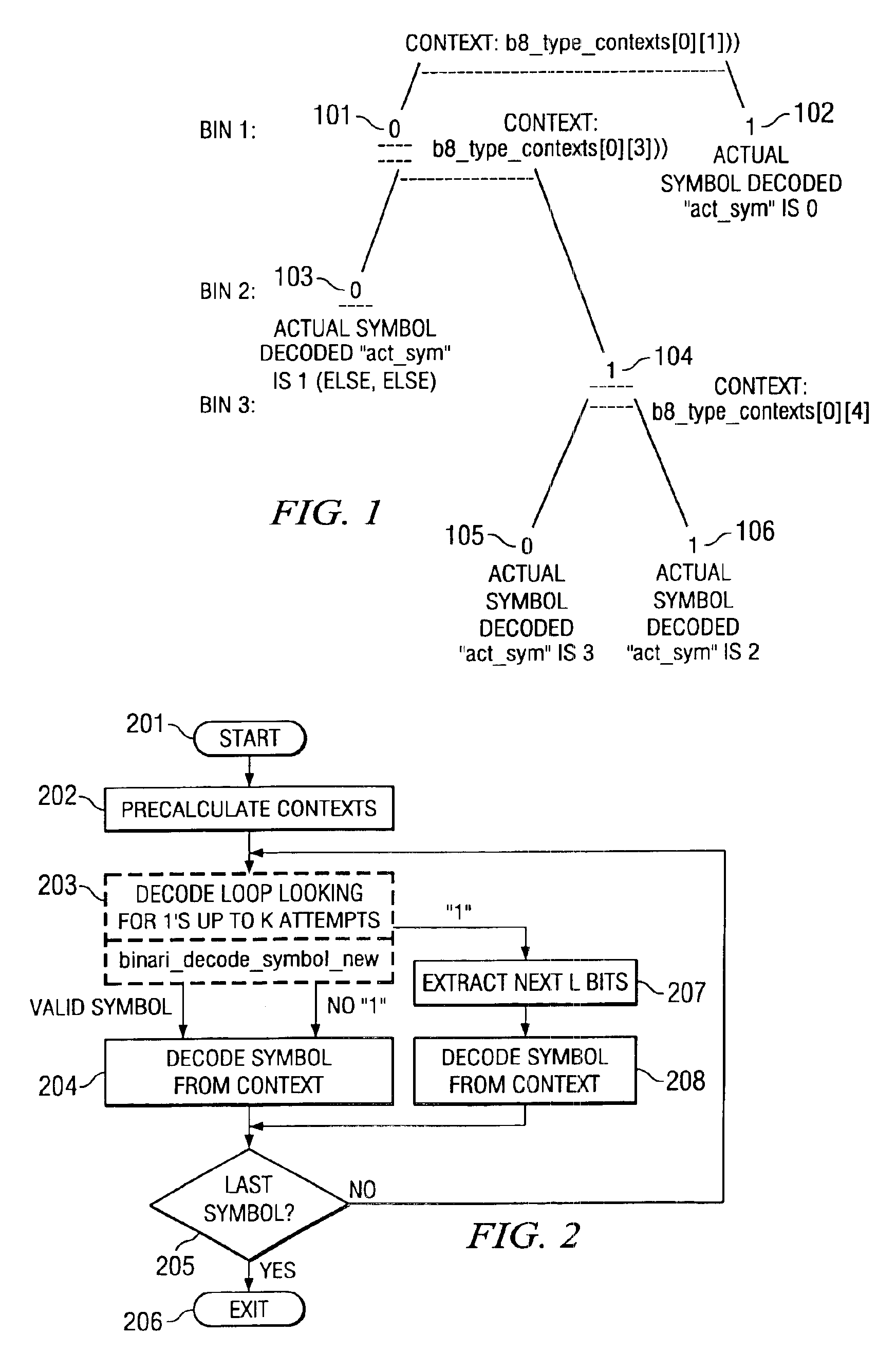
Patents
Literature
571 results about "Arithmetic coding" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
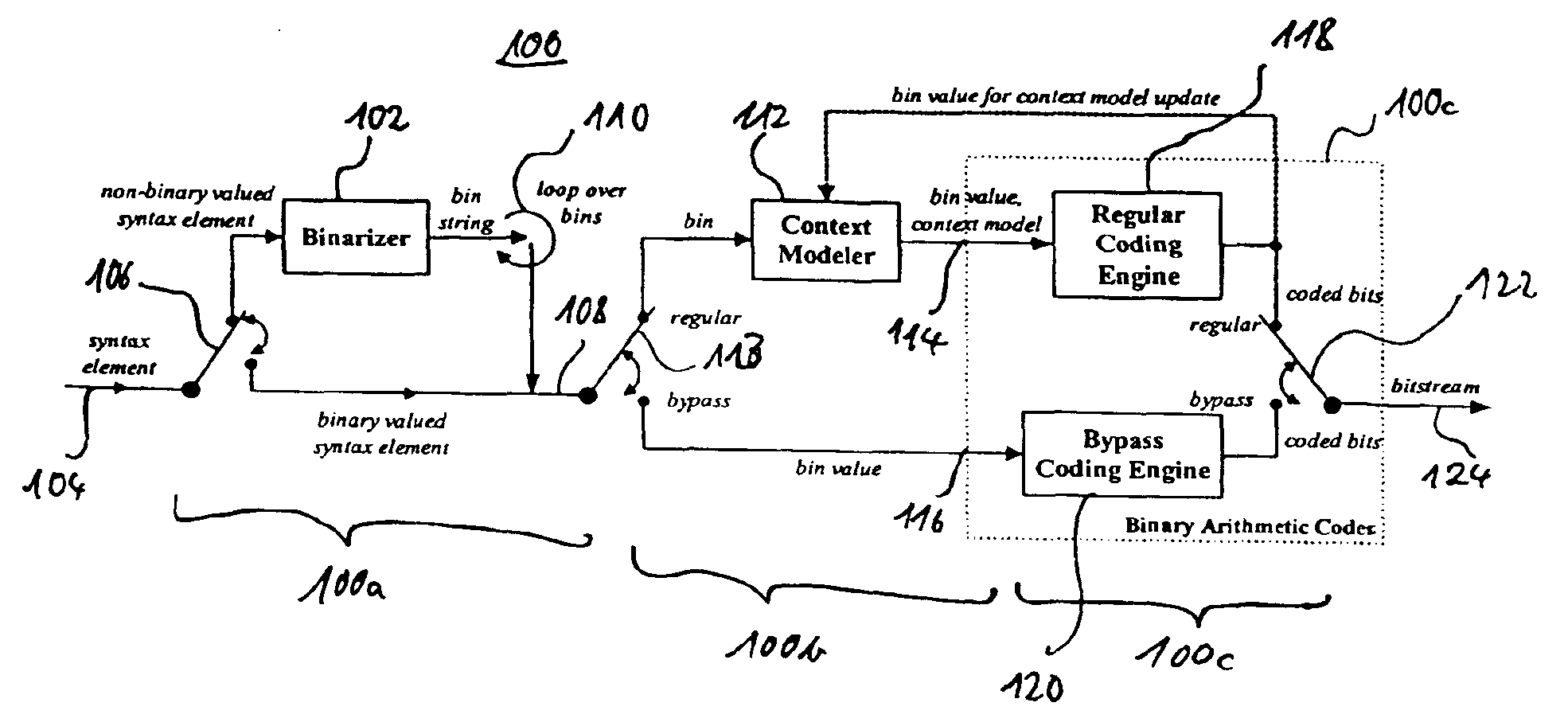
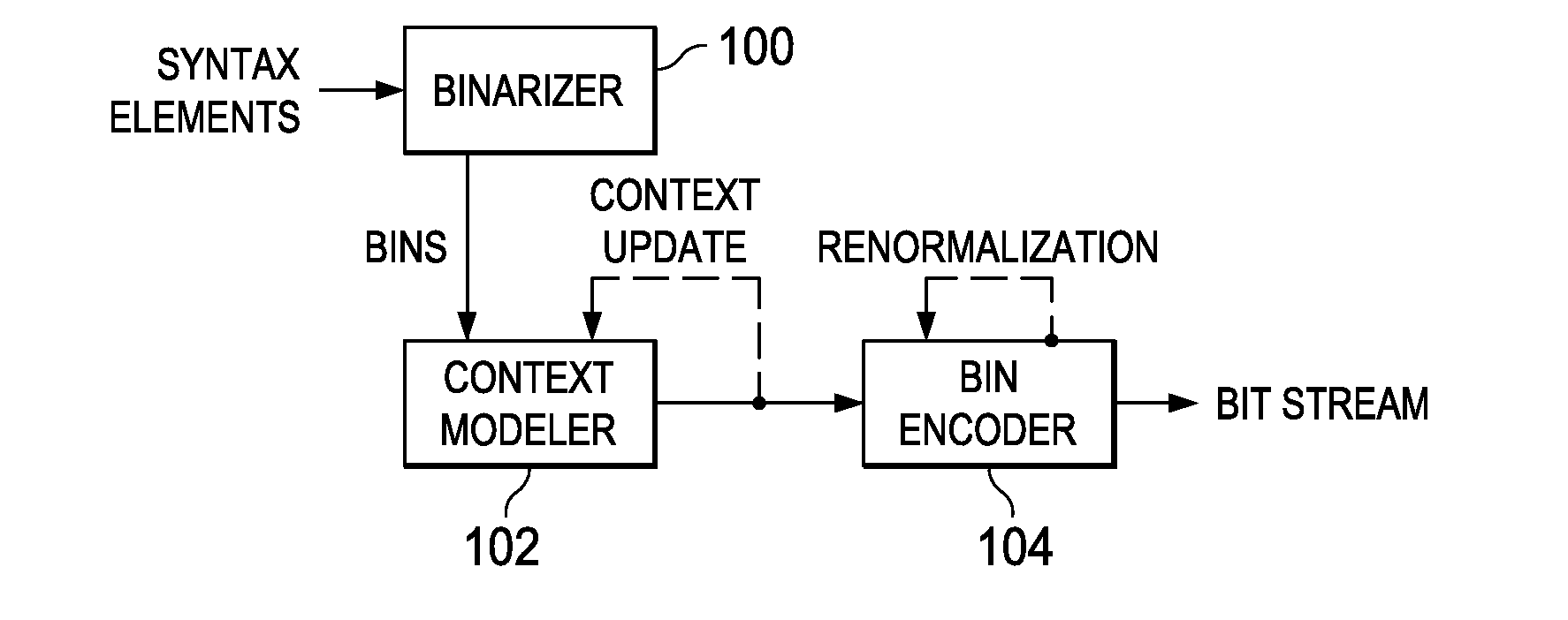
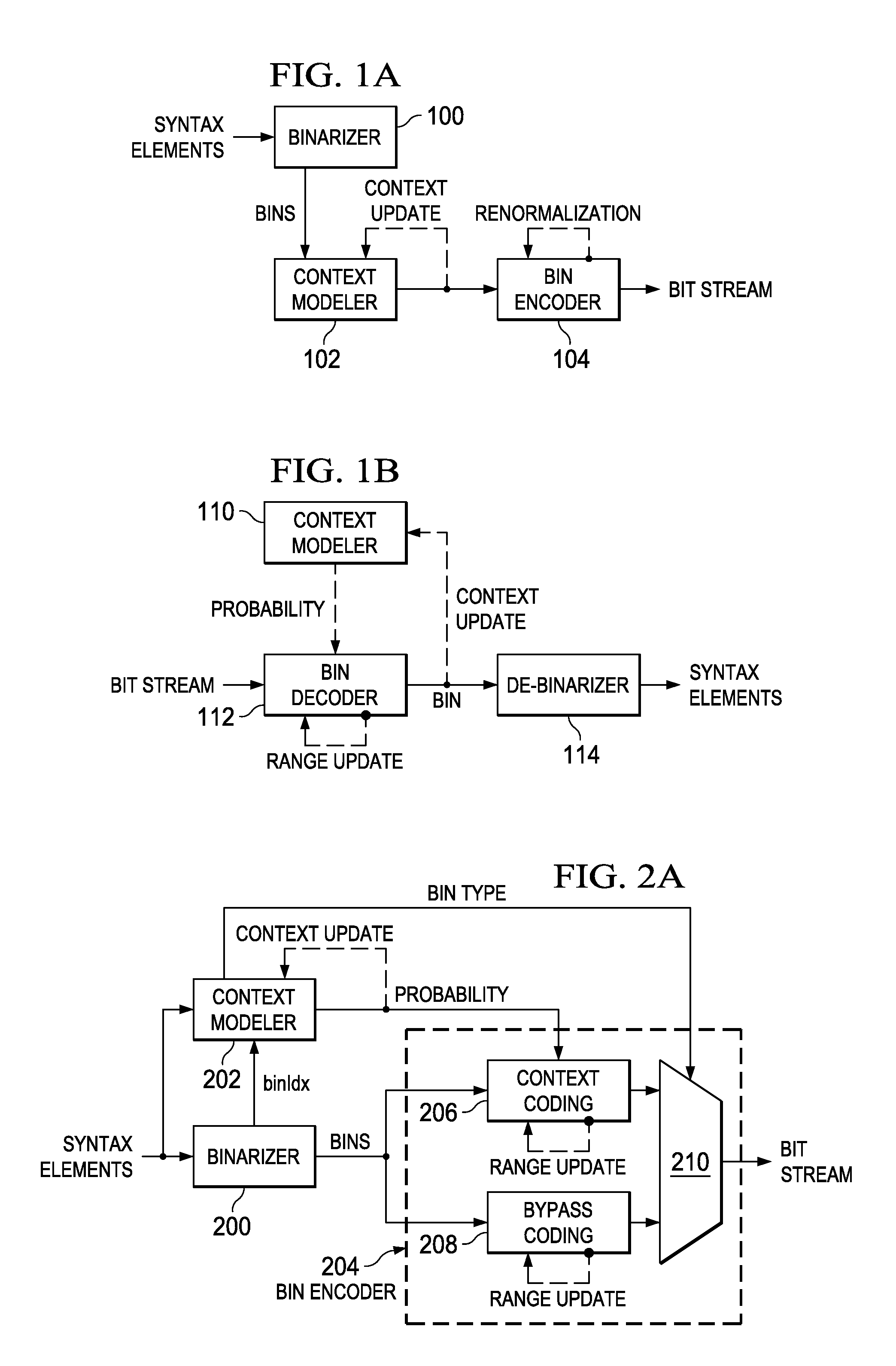
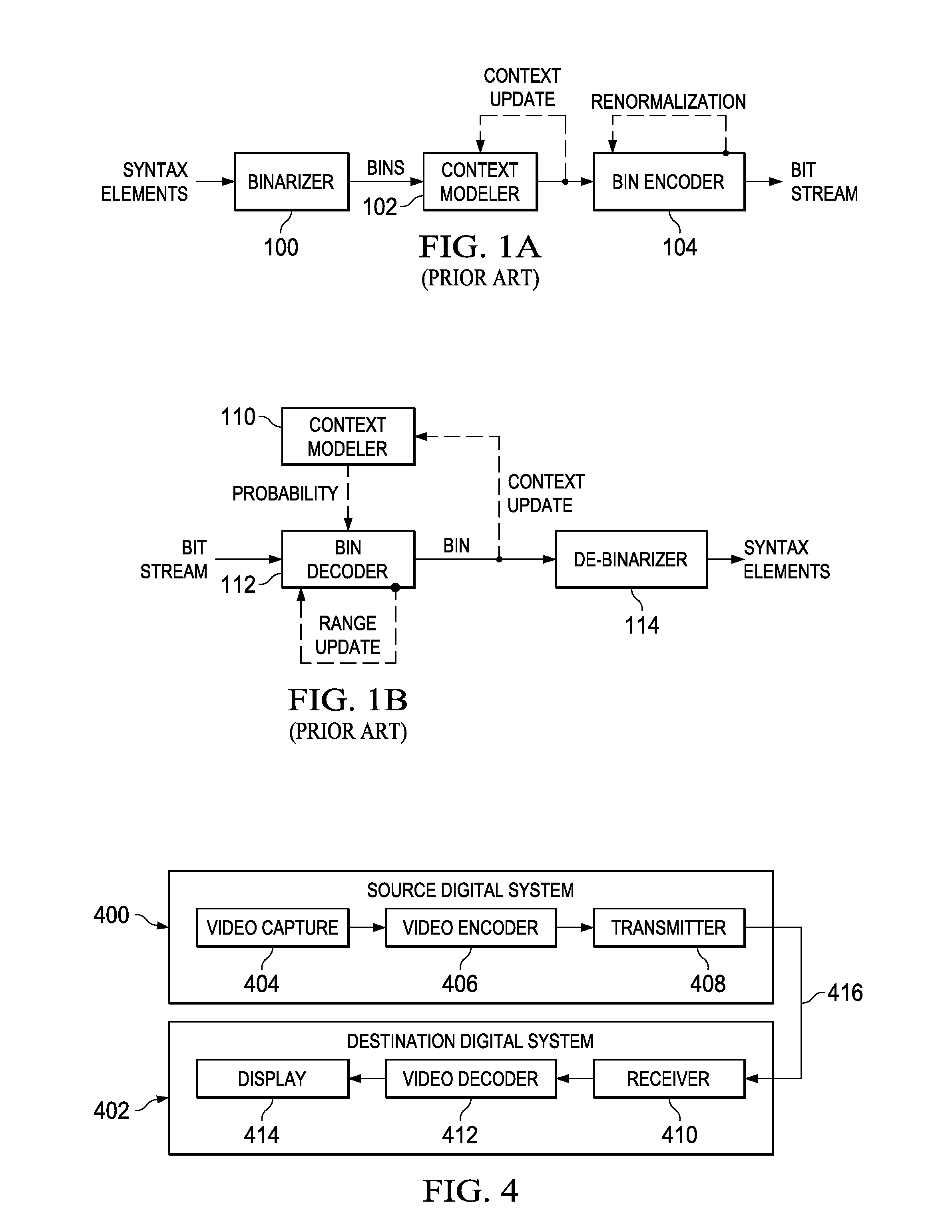
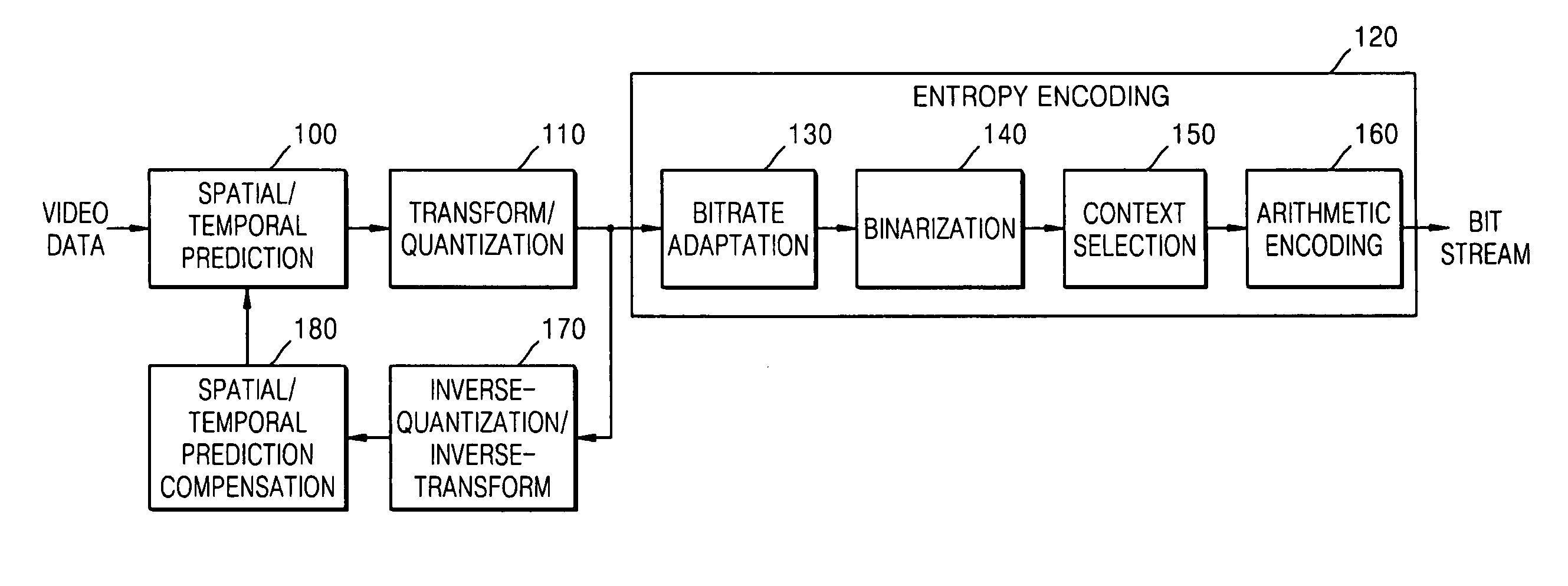
Arithmetic coding is a form of entropy encoding used in lossless data compression. Normally, a string of characters such as the words "hello there" is represented using a fixed number of bits per character, as in the ASCII code. When a string is converted to arithmetic encoding, frequently used characters will be stored with fewer bits and not-so-frequently occurring characters will be stored with more bits, resulting in fewer bits used in total. Arithmetic coding differs from other forms of entropy encoding, such as Huffman coding, in that rather than separating the input into component symbols and replacing each with a code, arithmetic coding encodes the entire message into a single number, an arbitrary-precision fraction q where 0.0 ≤ q < 1.0. It represents the current information as a range, defined by two numbers. Recent family of entropy coders called asymmetric numeral systems allows for faster implementations thanks to directly operating on a single natural number representing the current information.
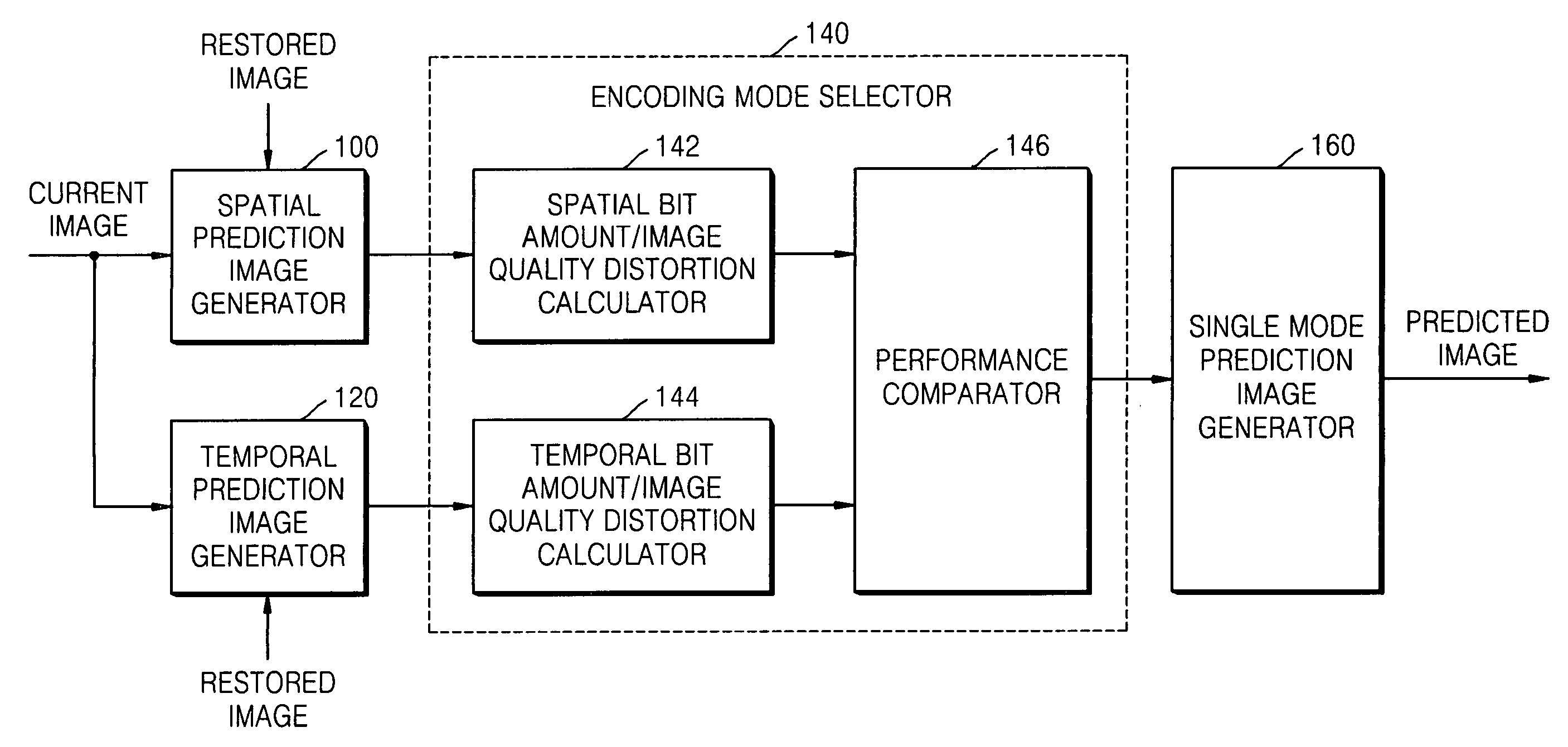
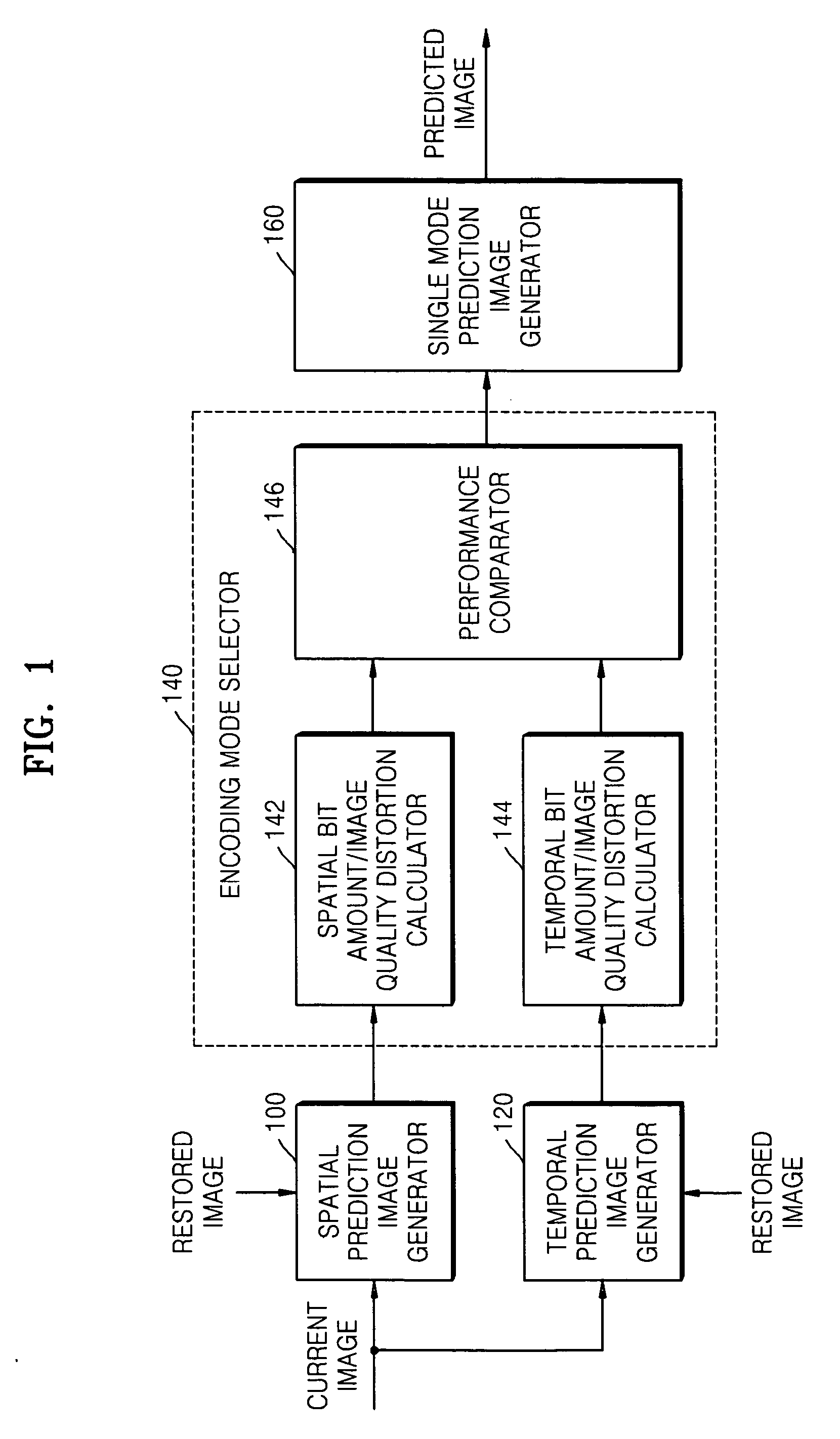
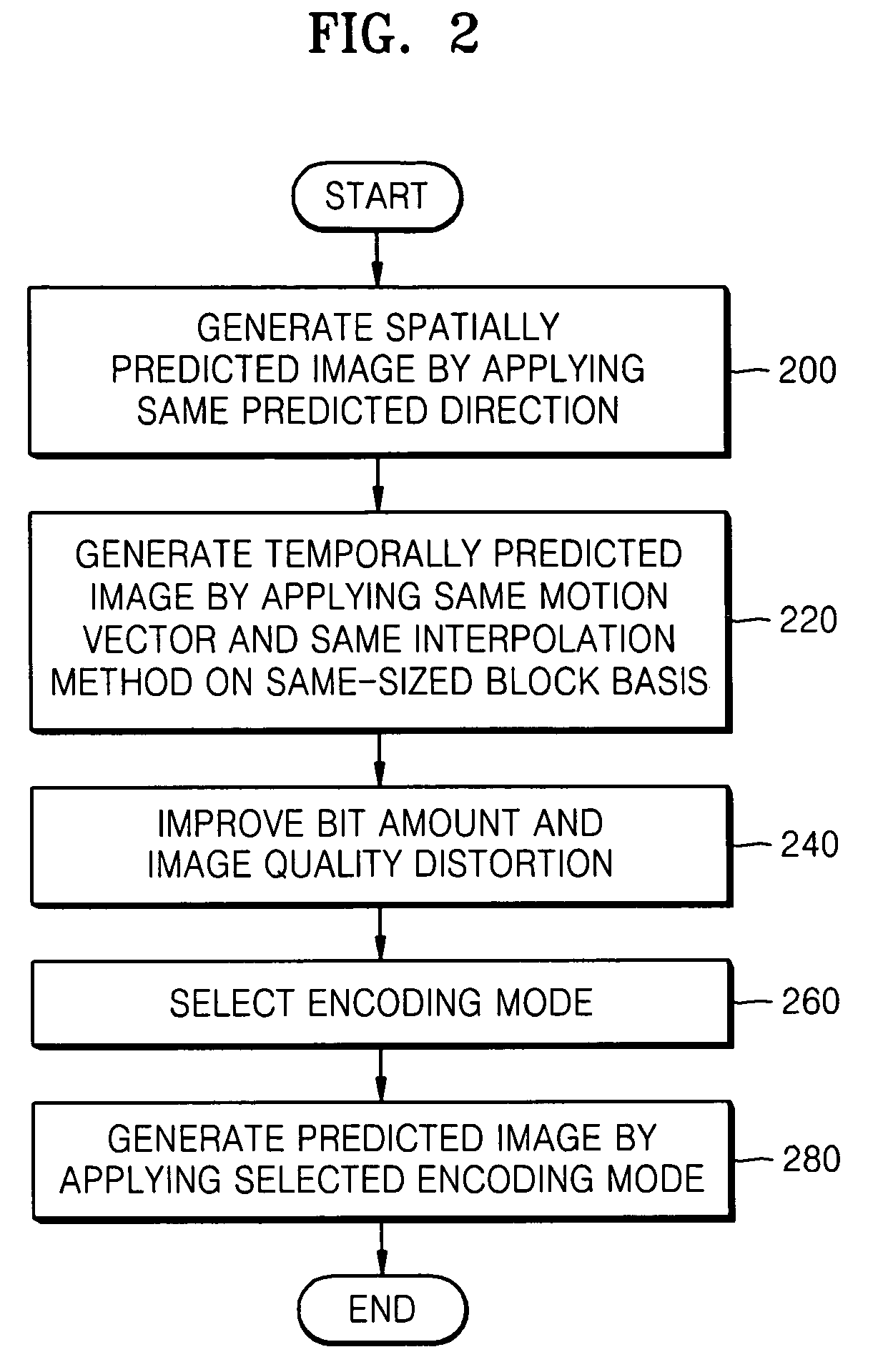
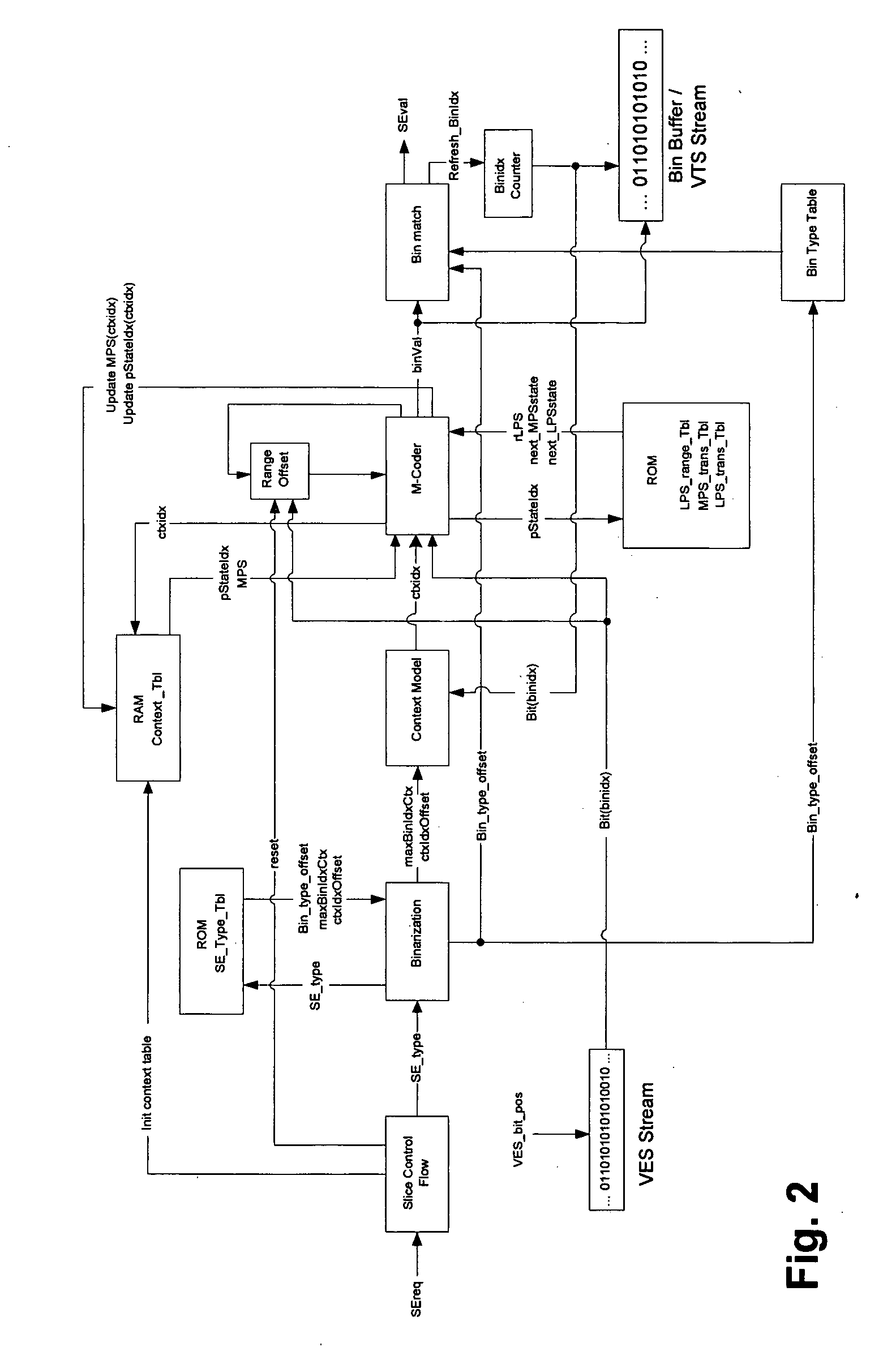
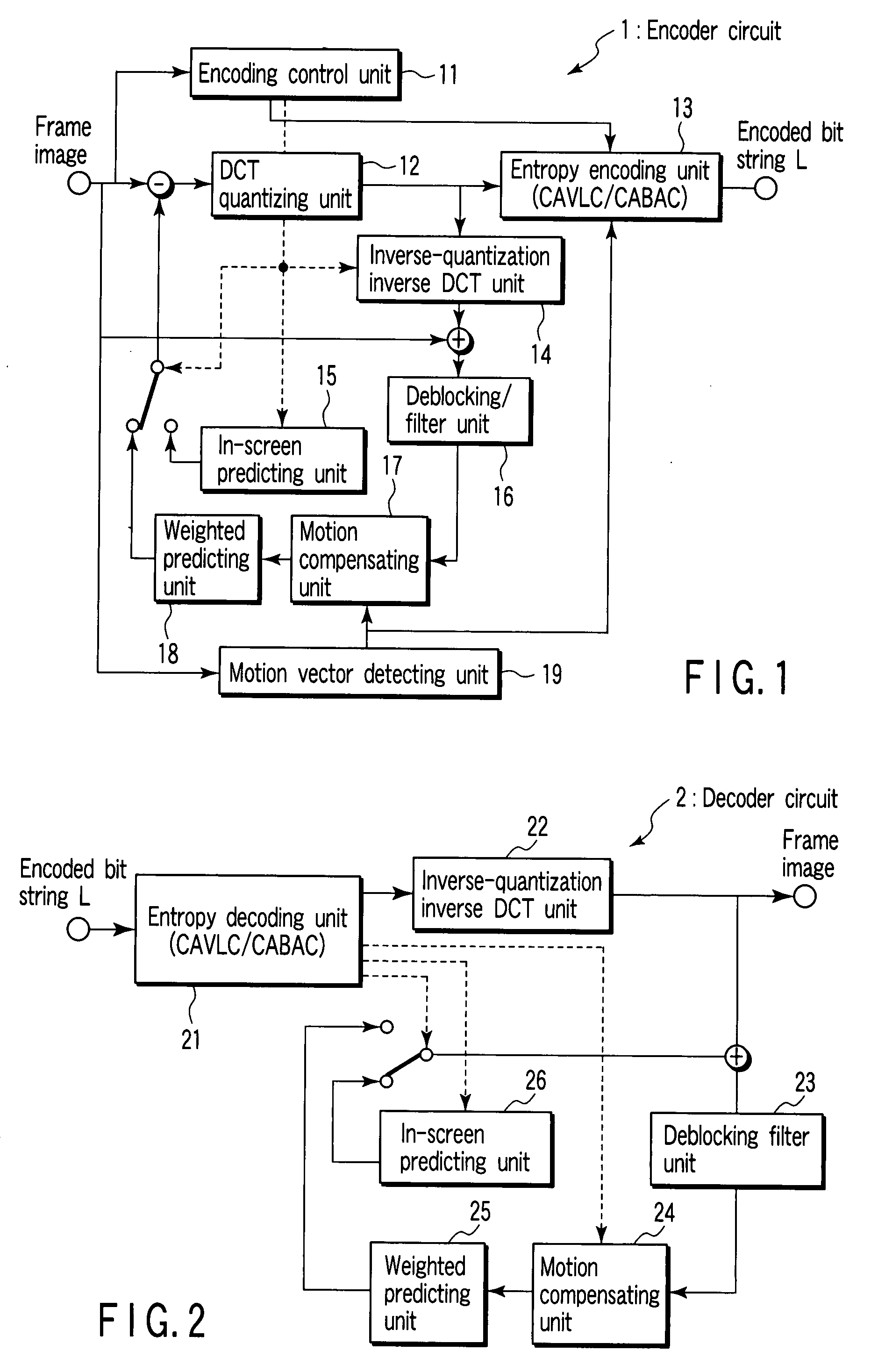
Method, medium, and apparatus encoding and/or decoding an image using the same coding mode across components
ActiveUS20070110153A1Improve efficiencyImprove image qualityColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionPattern recognitionArithmetic coding
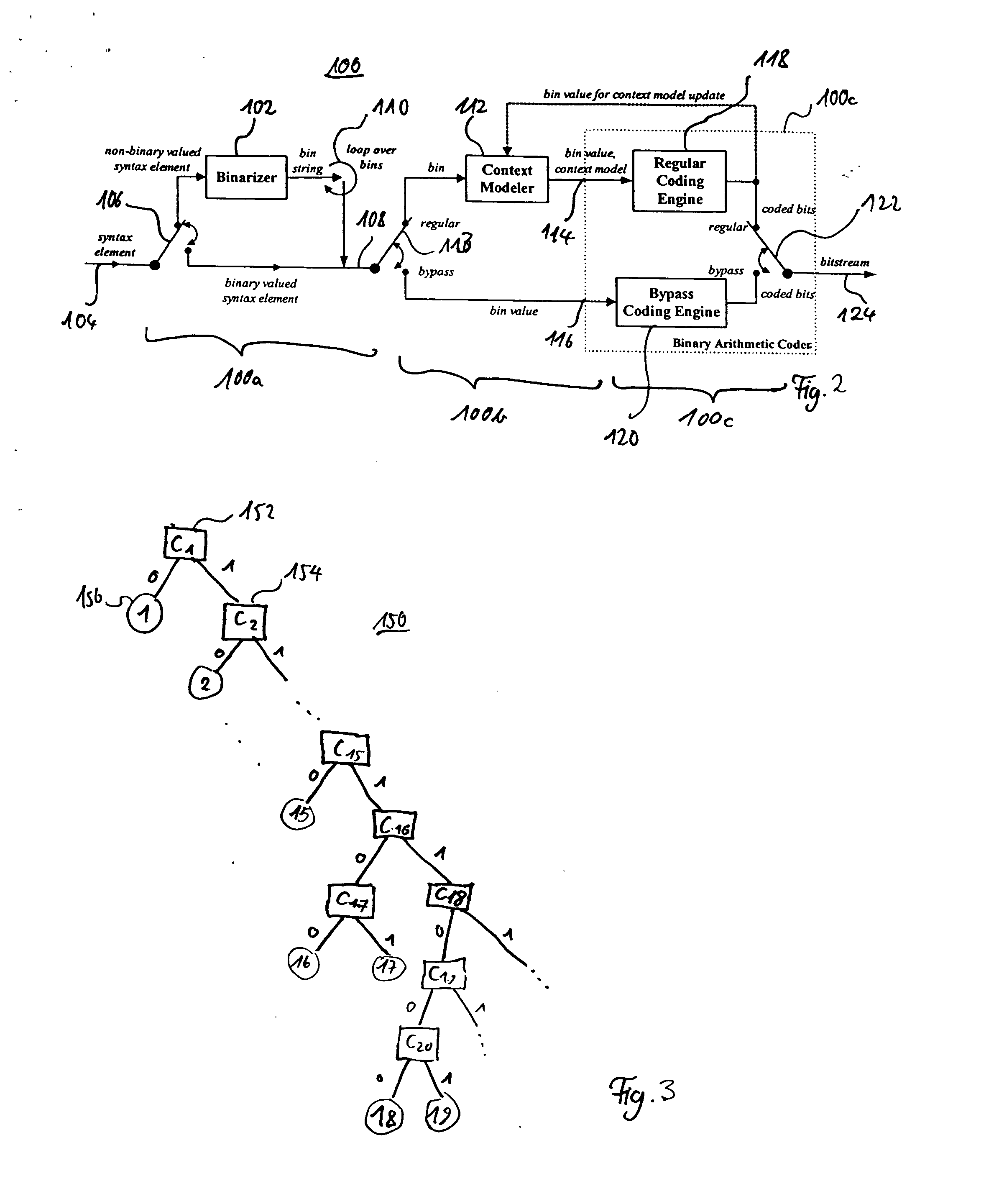
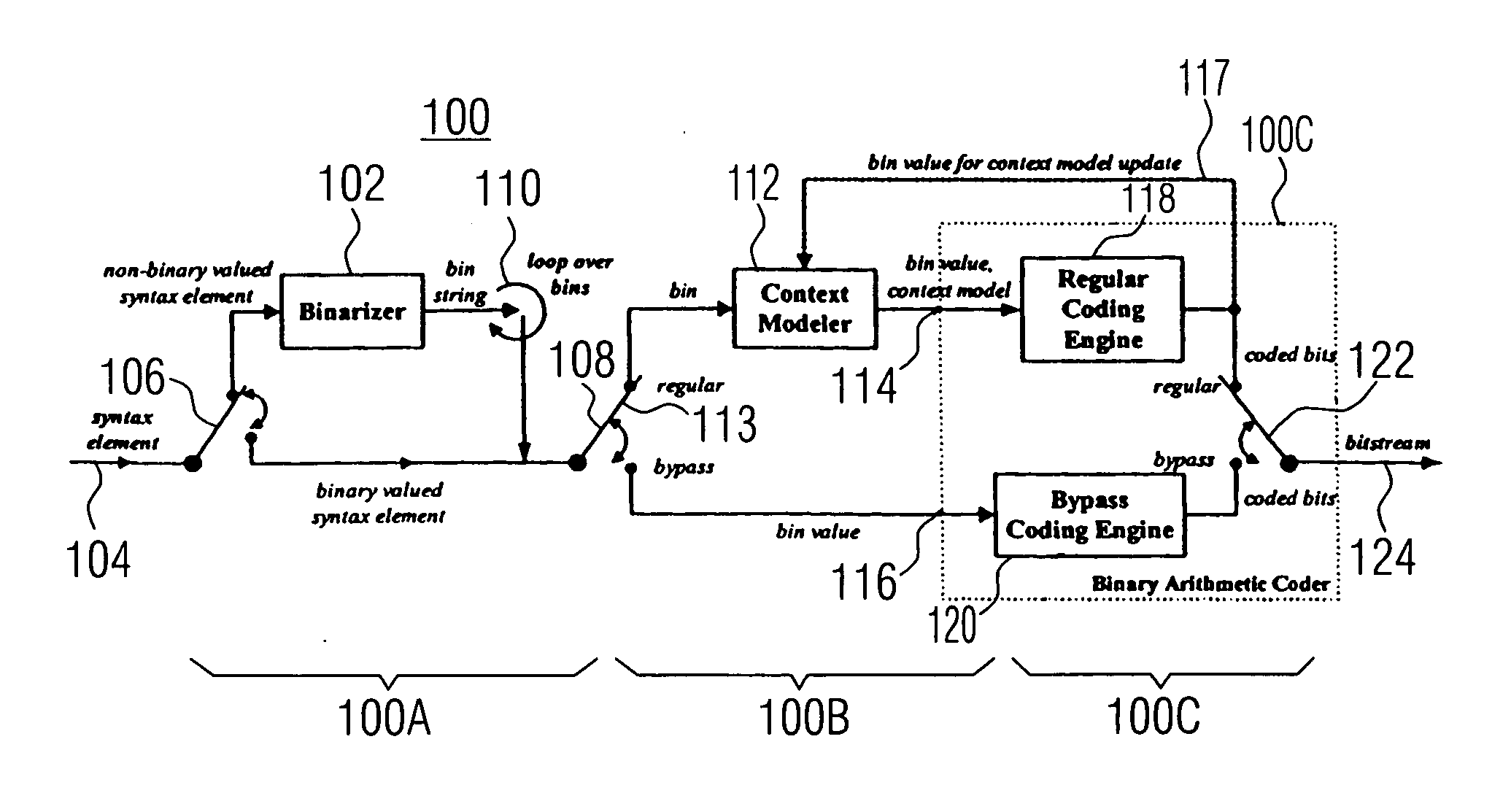
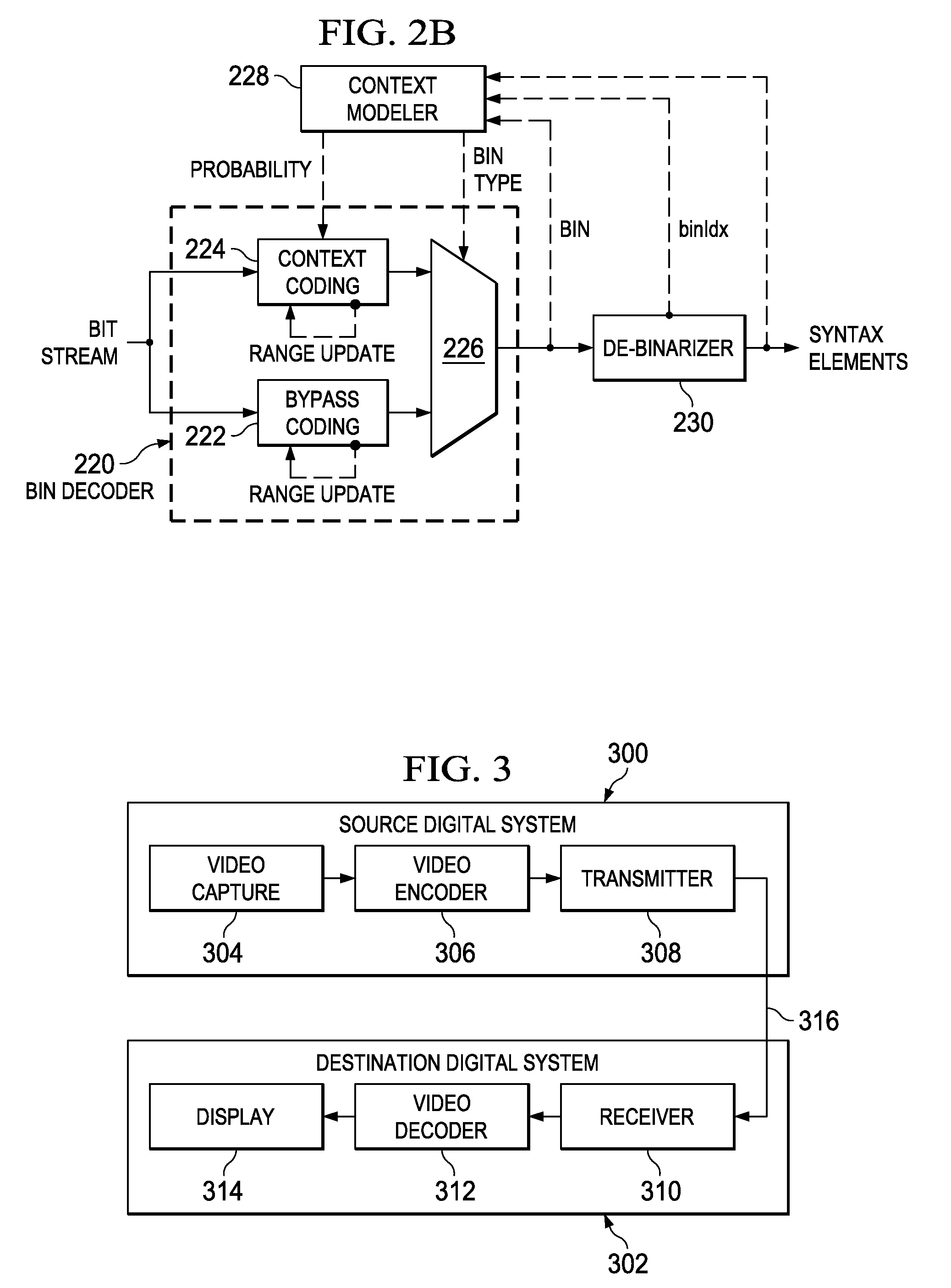
A method, medium, and apparatus encoding and / or decoding an image in order to increase encoding and decoding efficiency by performing binary-arithmetic coding / decoding on a binary value of a syntax element using a probability model having the same syntax element probability value for respective context index information of each of at least two image components.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
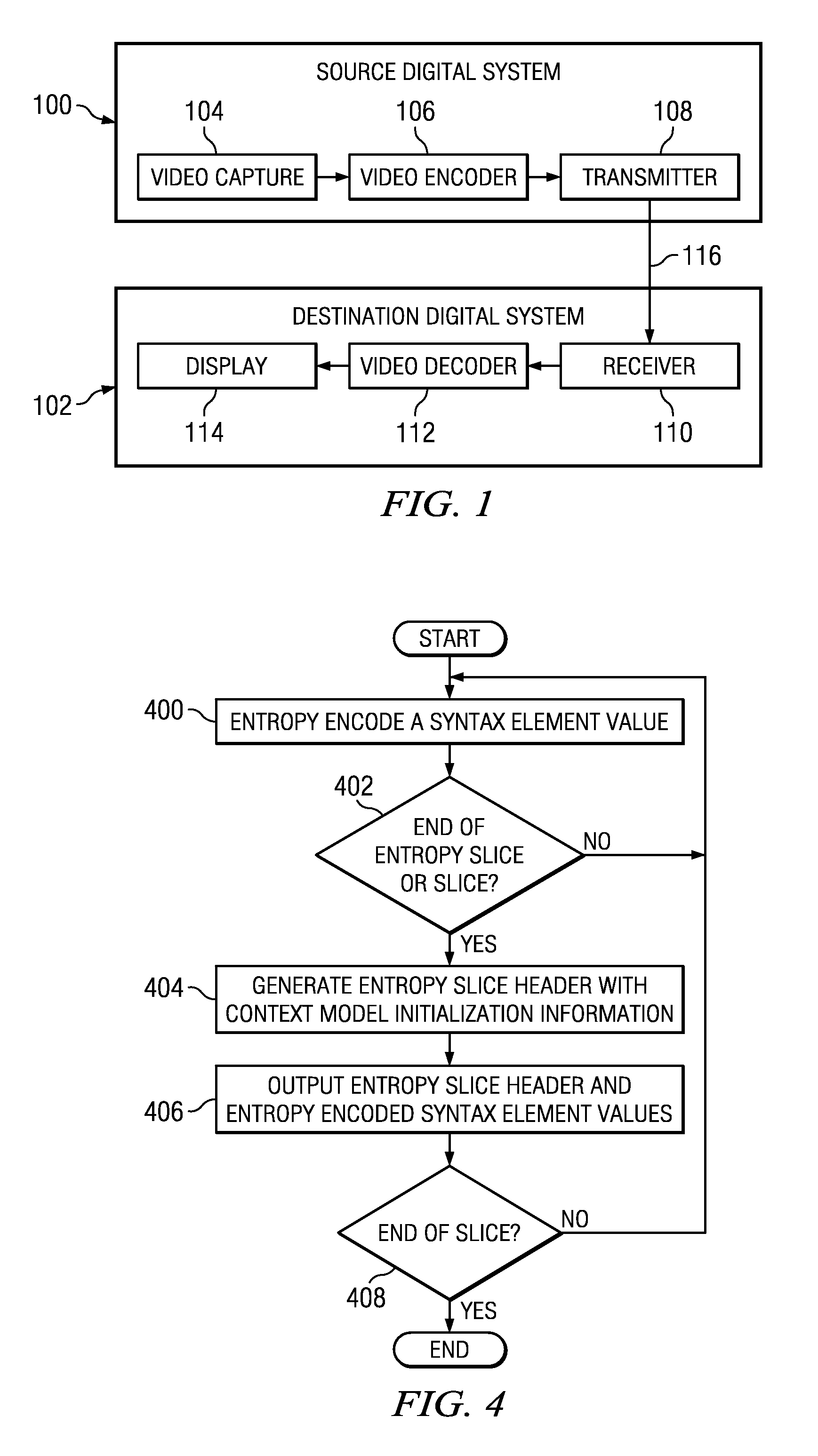
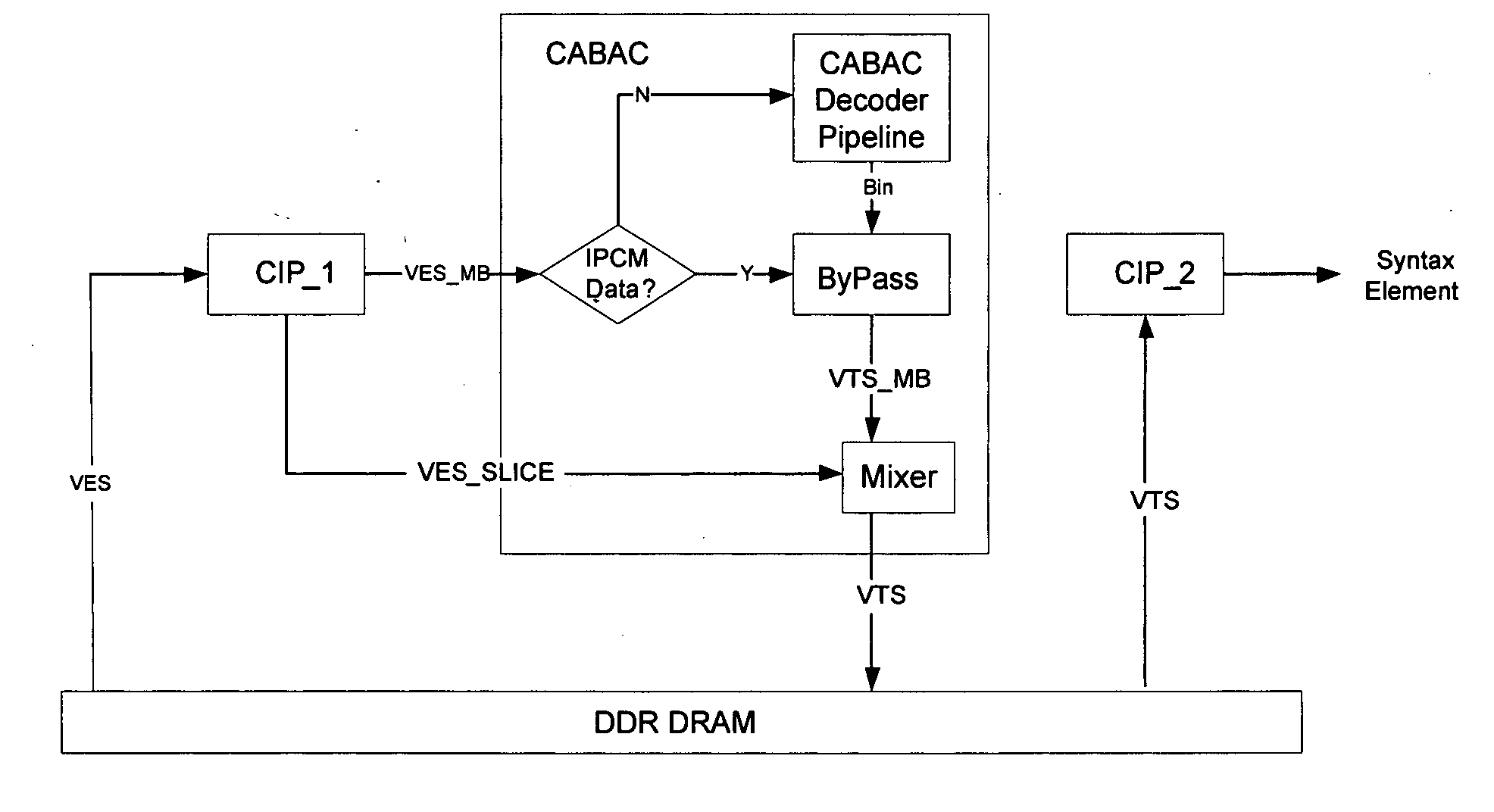
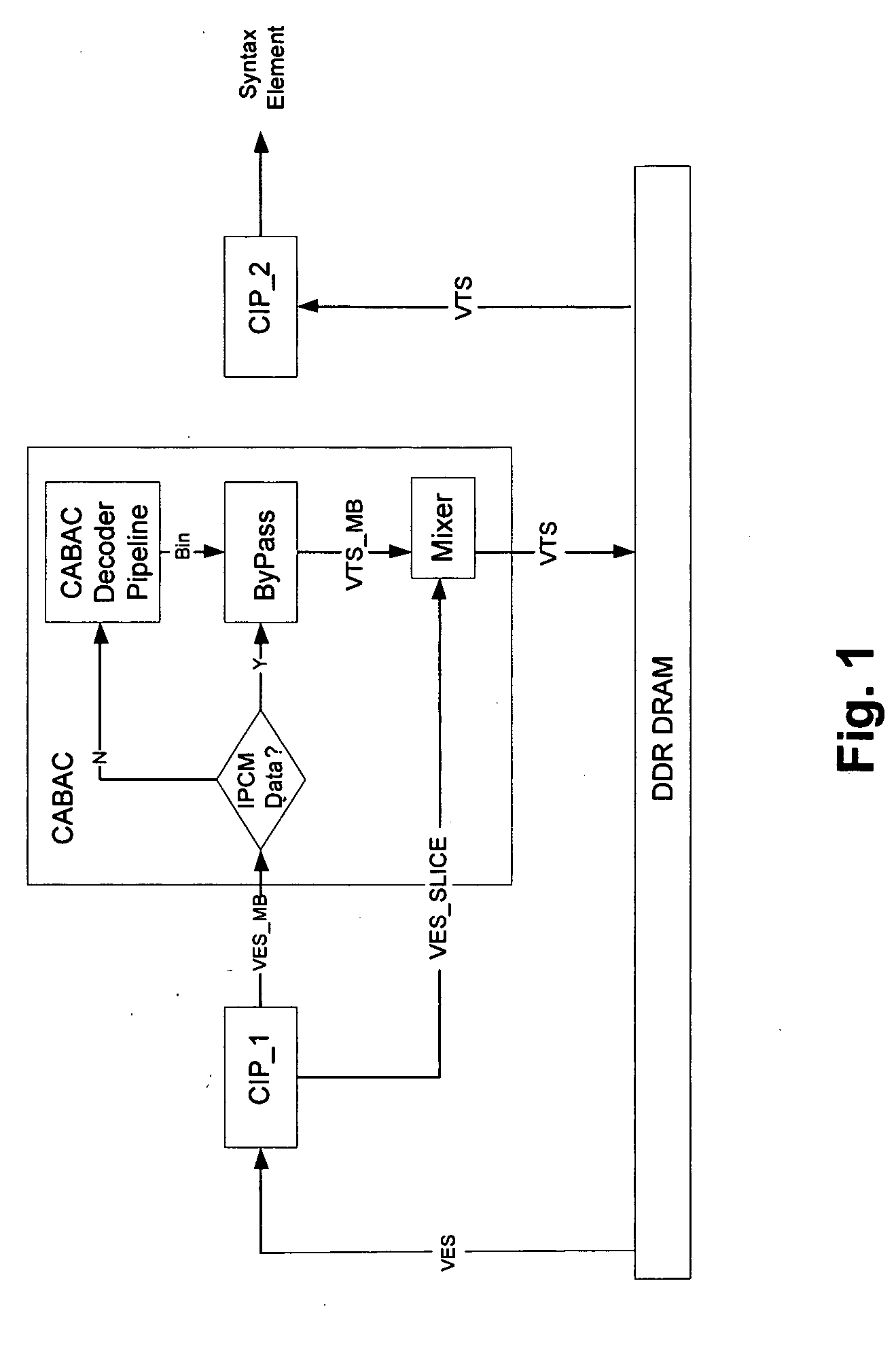
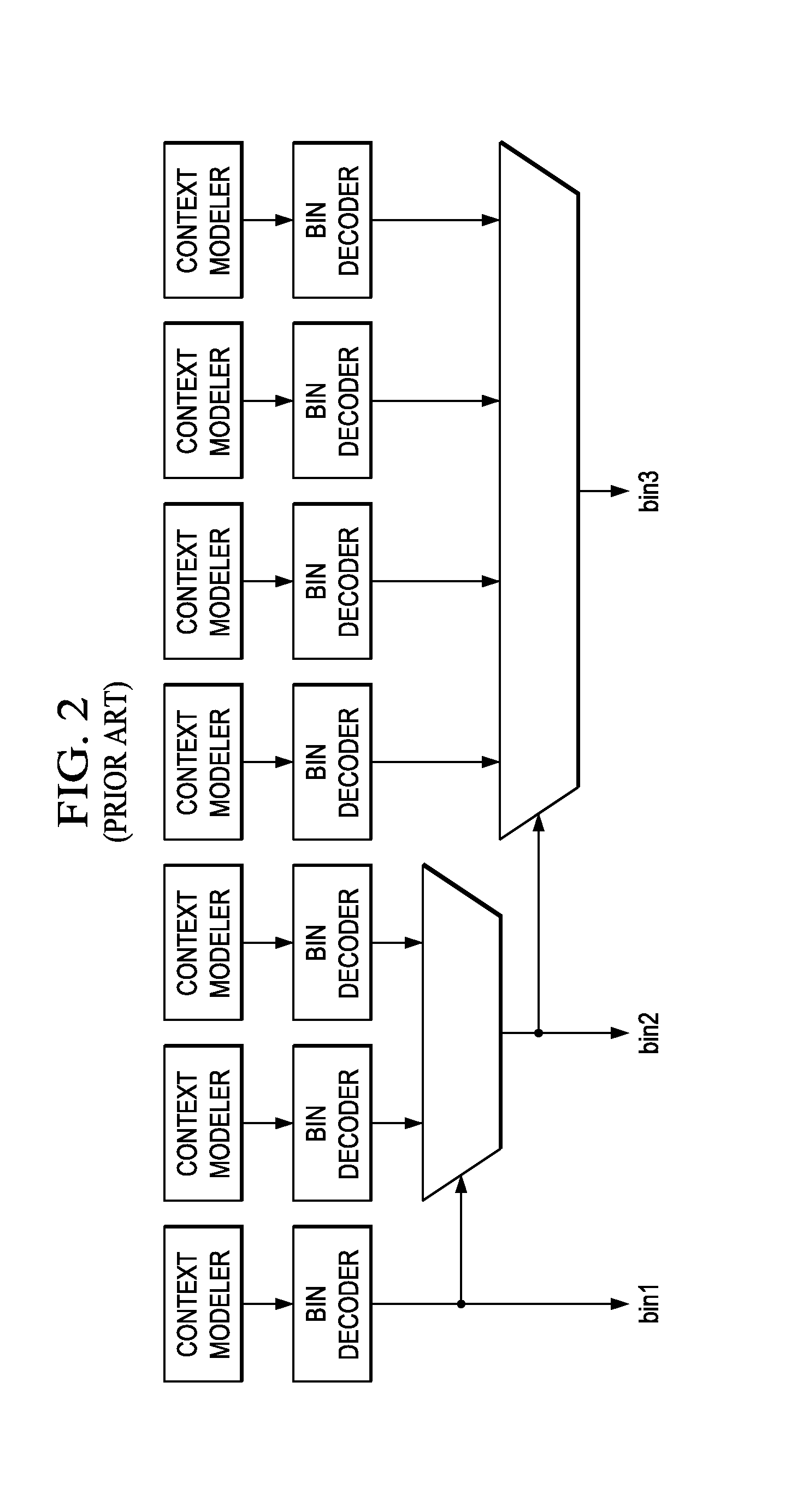
Parallel CABAC Decoding Using Entropy Slices
InactiveUS20100098155A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionVideo encodingContext model
A method of video encoding is provided that includes performing context-adaptive binary arithmetic coding (CABAC) on a plurality of syntax element values in a slice to generate a plurality of entropy-encoded syntax element values, generating an entropy slice header to identify the plurality of entropy-encoded syntax element values as an entropy slice, wherein the entropy slice header comprises context model initialization information, and outputting the entropy slice header and the plurality of entropy encoded syntax element values.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
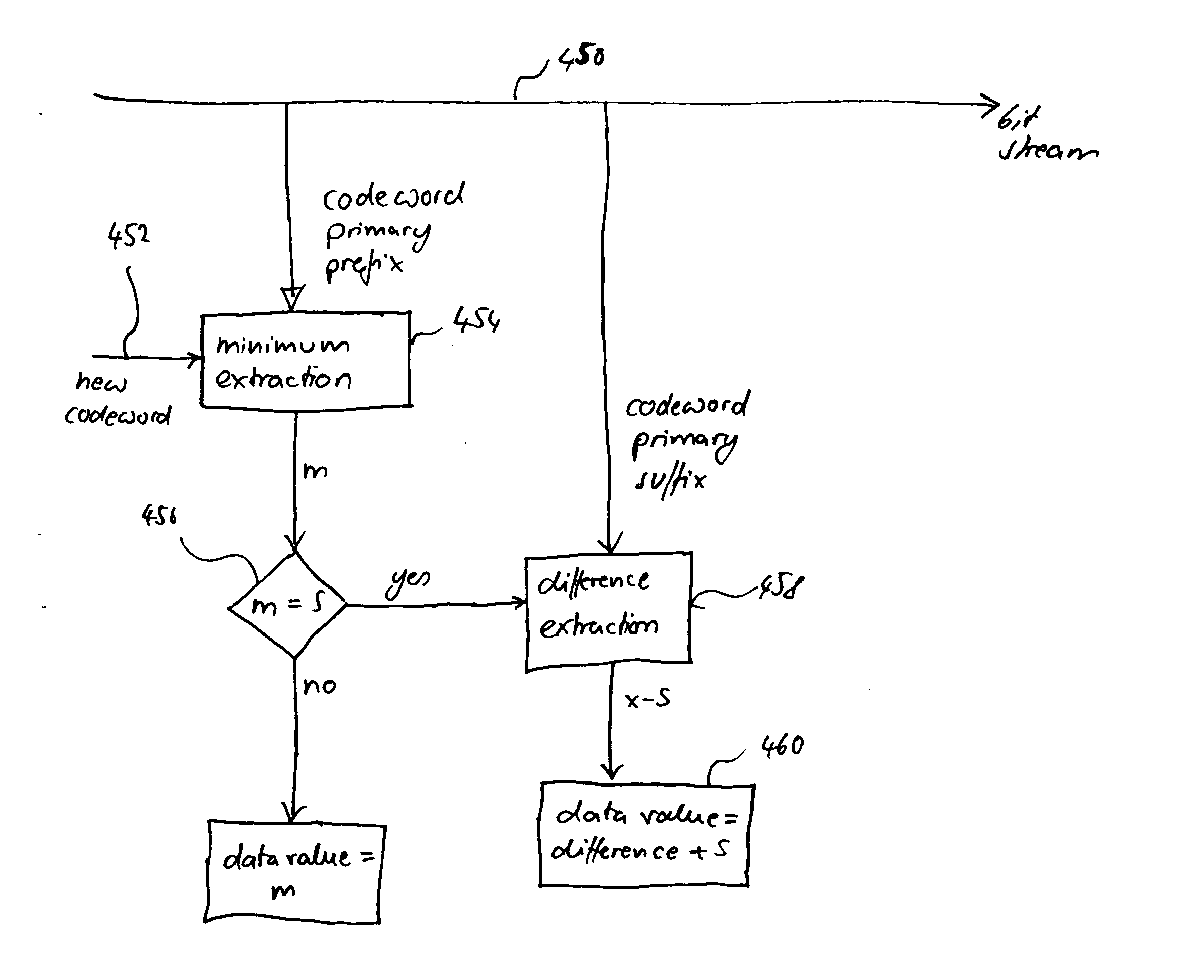
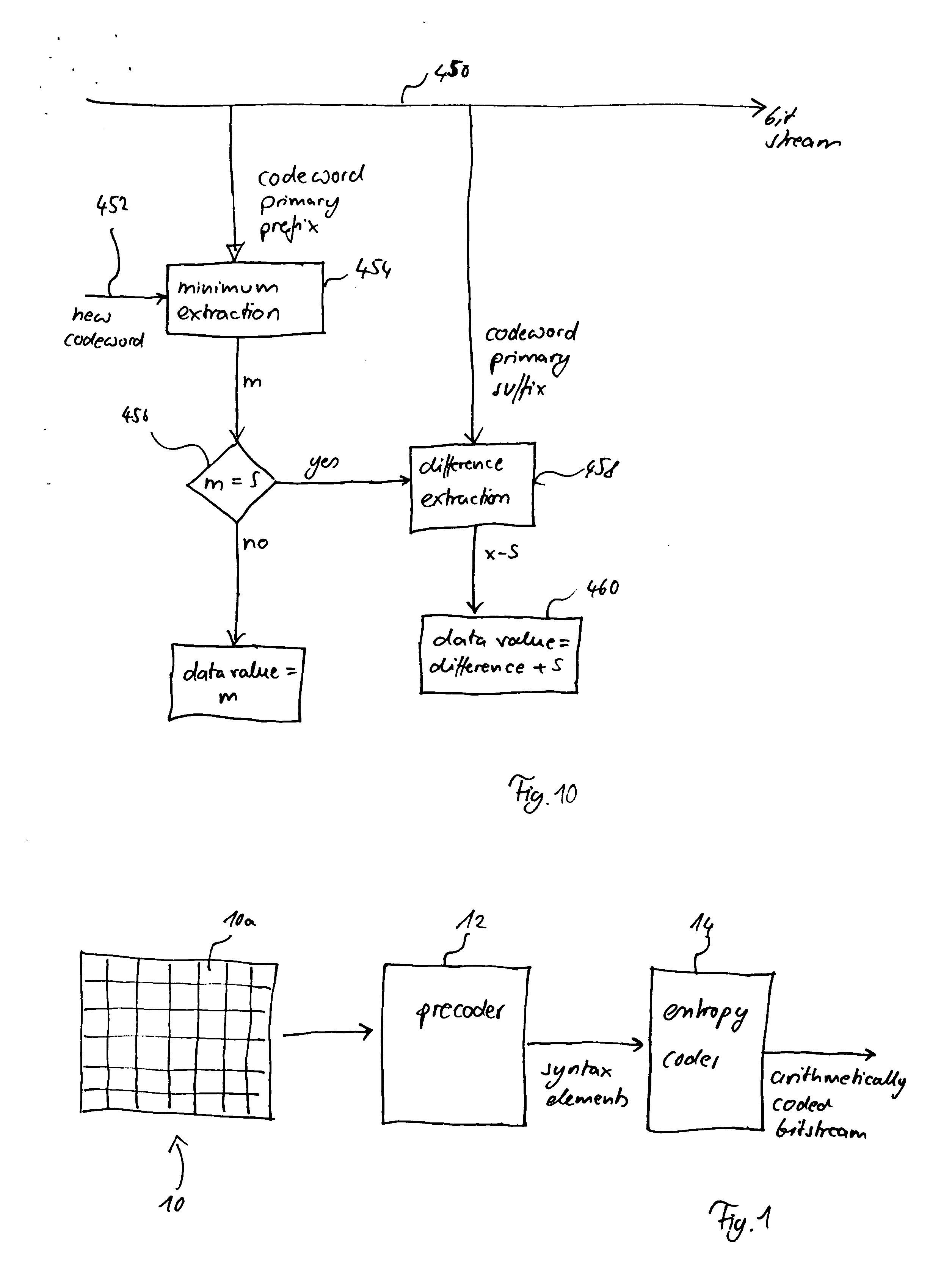
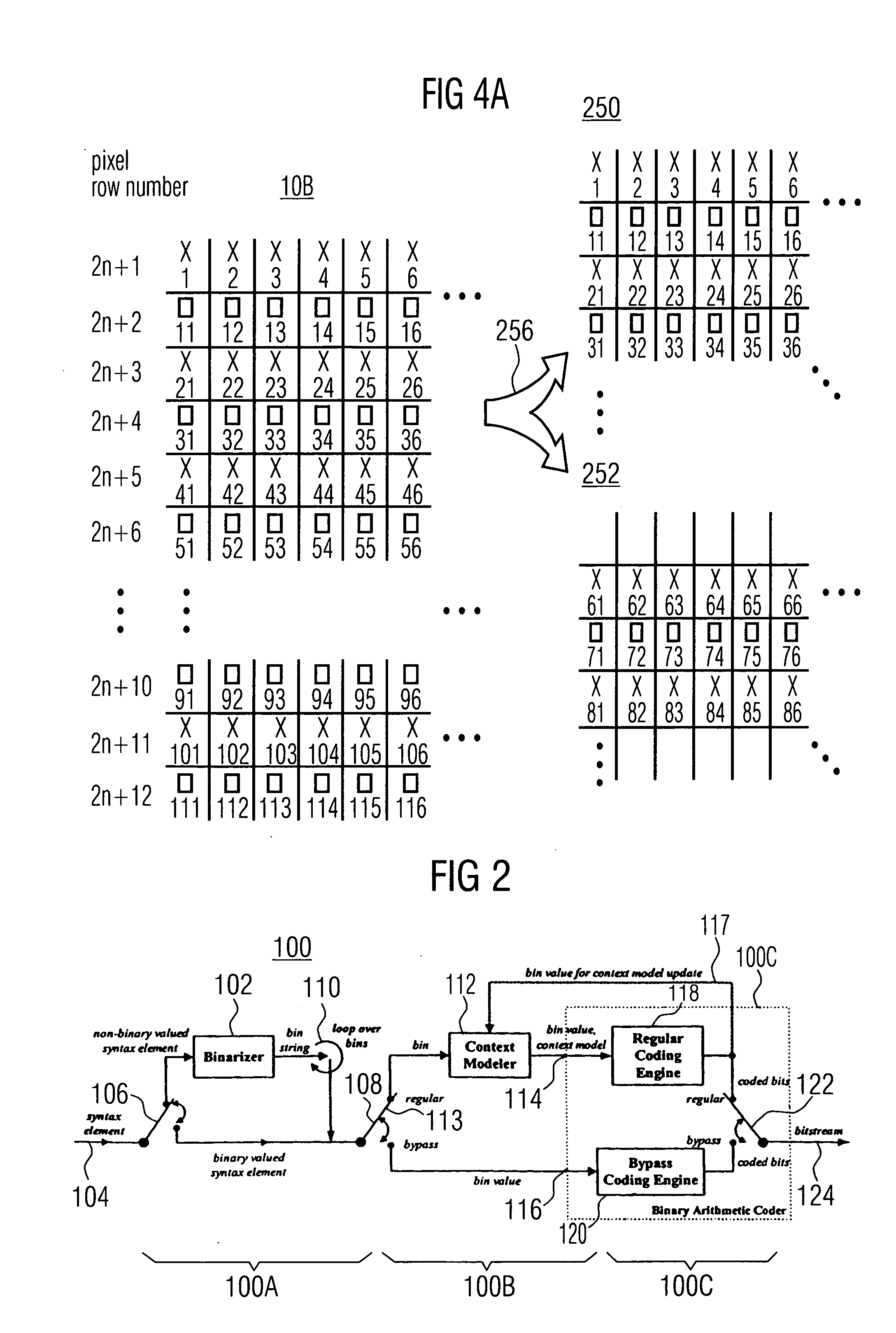
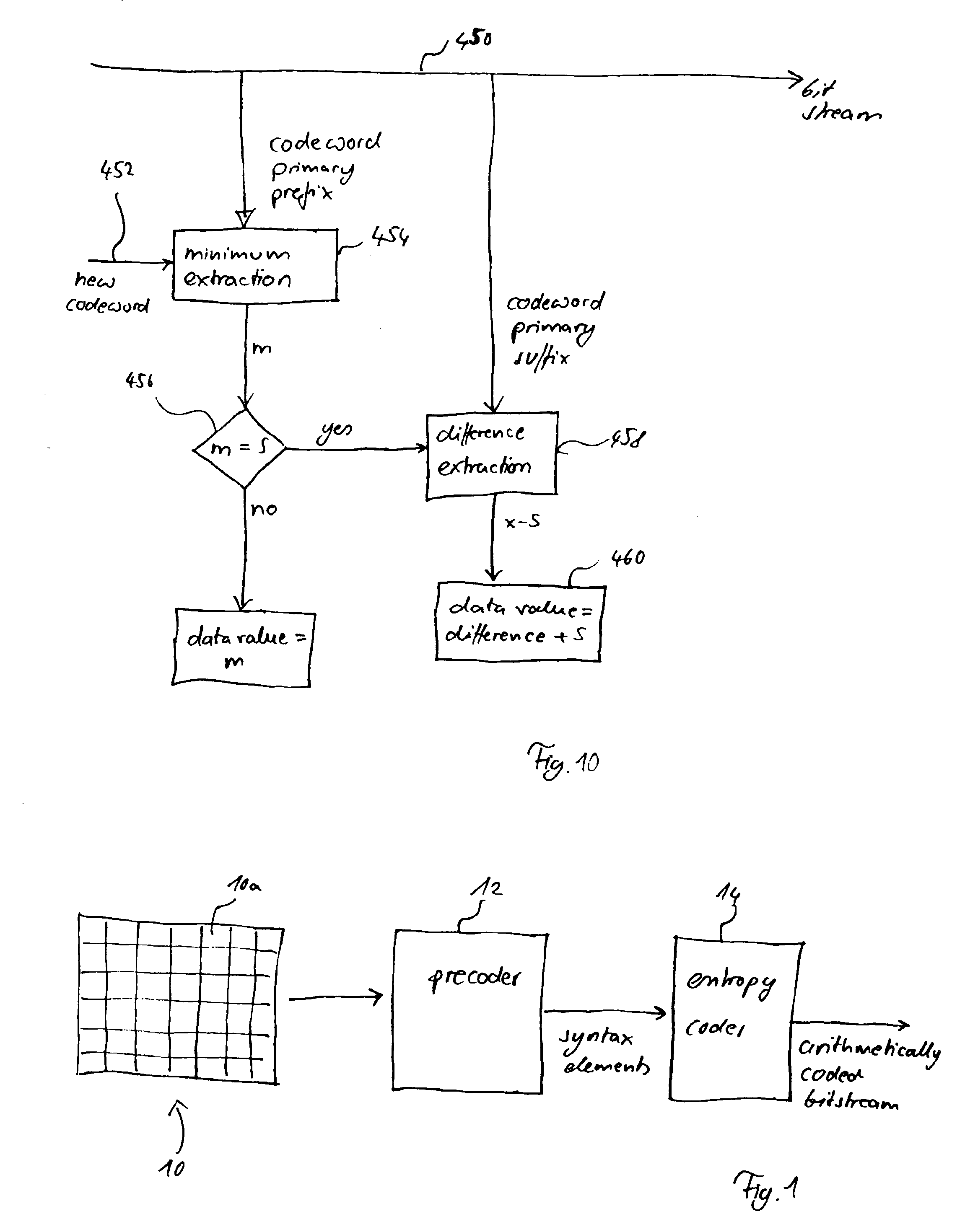
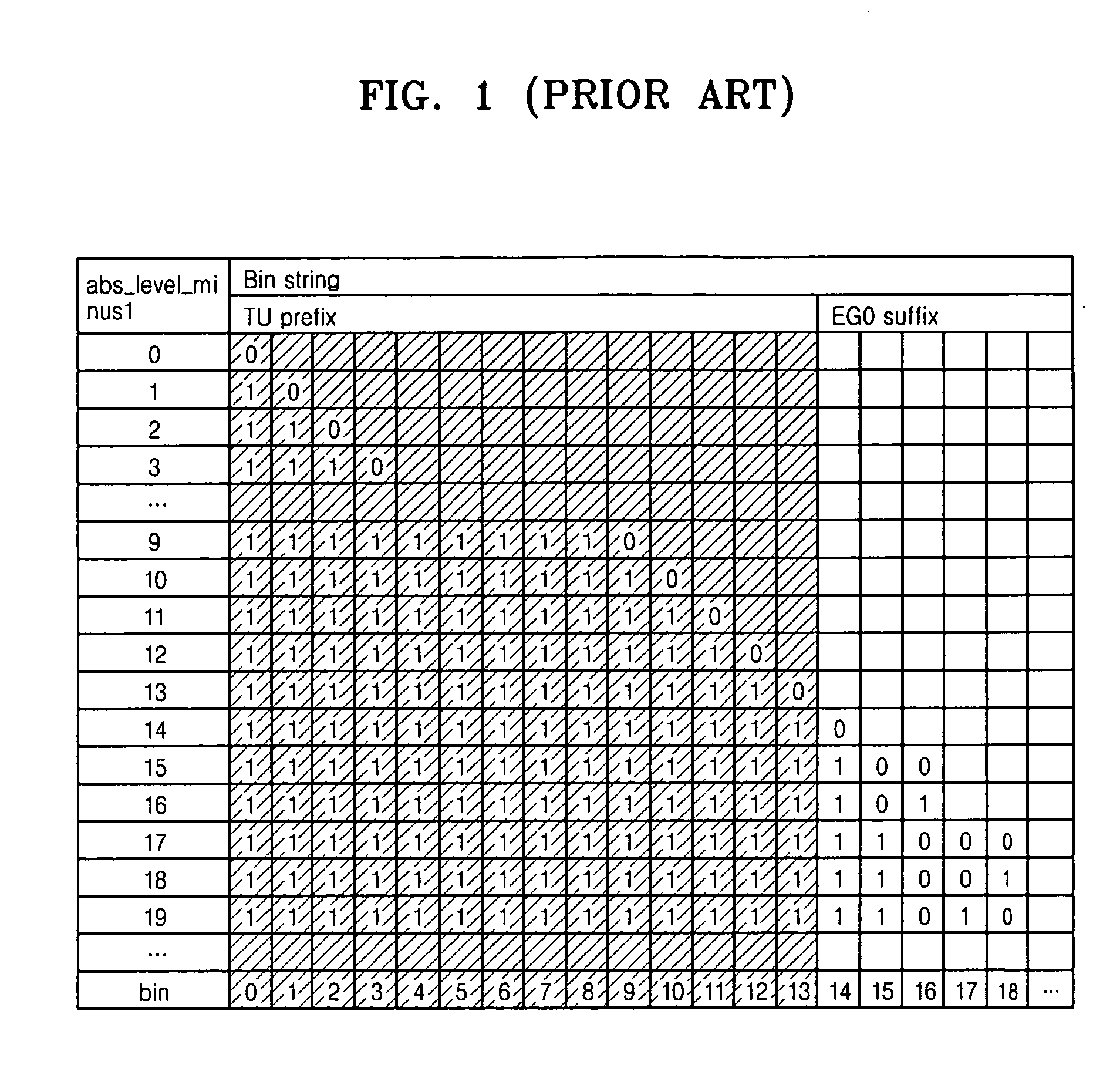
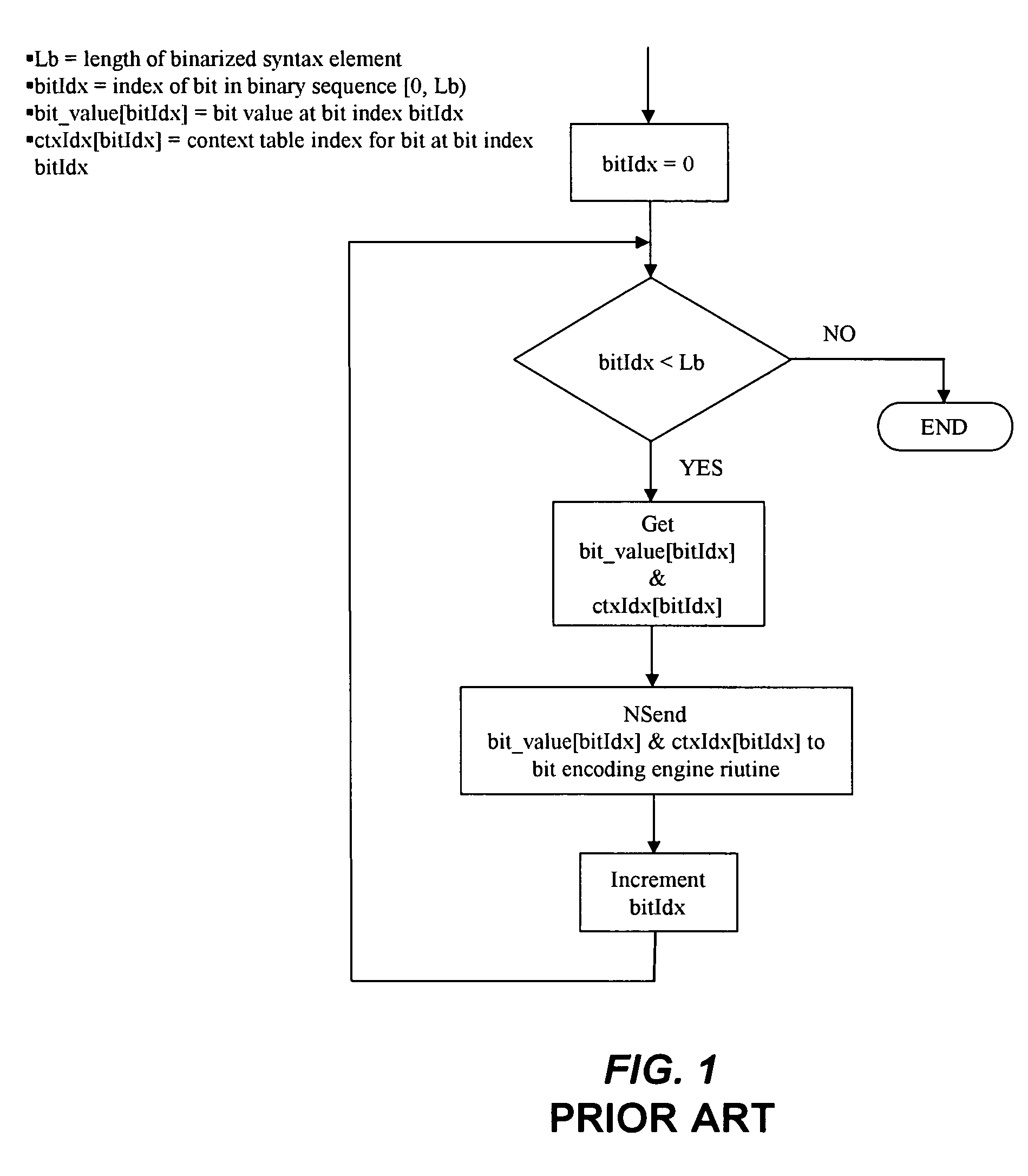
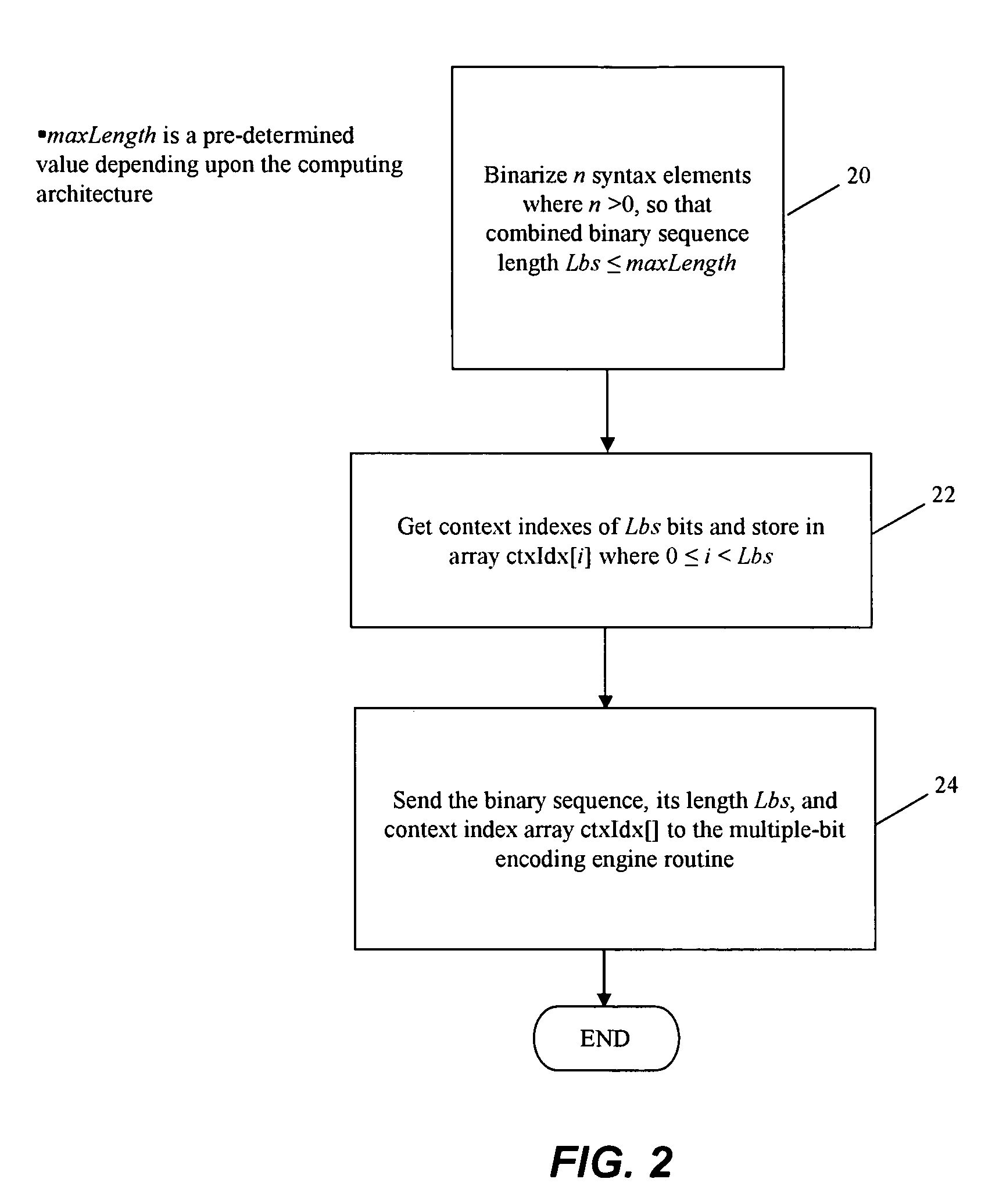
Method and apparatus for binarization and arithmetic coding of a data value
ActiveUS20050038837A1Moderate computational overheadEfficient compressionDigital data processing detailsDigital computer detailsComputer architectureCut off value
Binarization a data value comprises binarizing the minimum of the data value and a predetermined cut-off value in accordance with a first binarization scheme, in order to yield a primary prefix. If the data value is greater than the cut-off value, binarizing a difference of the data value minus the predetermined cut-off value in accordance with a second binarization scheme to obtain a binary suffix, the first binarization scheme being different from the second binarization scheme, and appending the primary suffix to the primary prefix is performed. A very effective compression of data values may be achiever by using the binarization scheme for preparing the syntax elements for the arithmetic coding, the binarization scheme substantially being a combination of two different binarization schemes, and by using binary arithmetic coding instead of m-ary arithmetic coding for coding the binarized syntax elements.
Owner:GE VIDEO COMPRESSION LLC
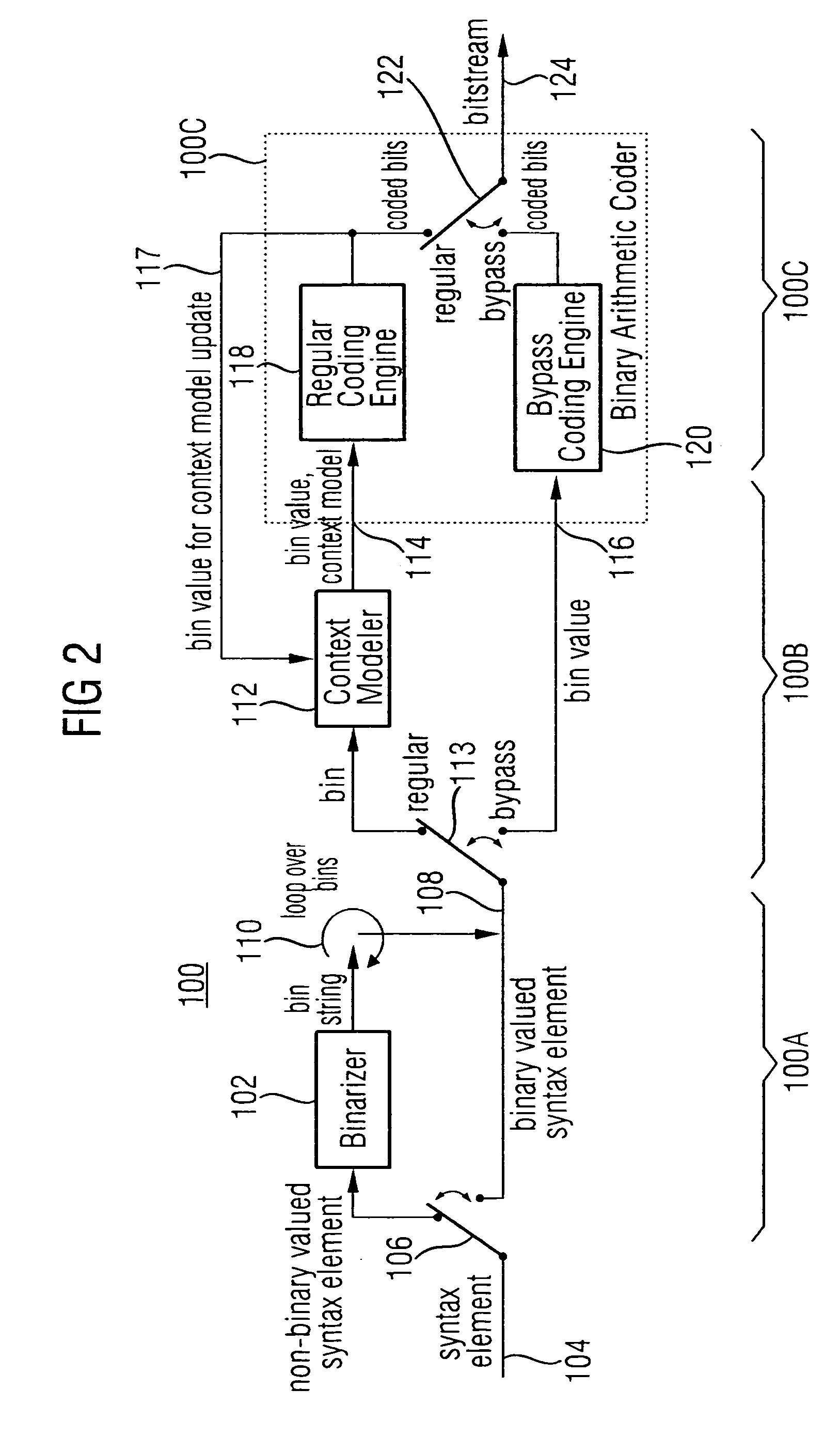
Method and system for context-based adaptive binary arithmetic coding
InactiveUS6856701B2Improve coding efficiencyCode conversionCharacter and pattern recognitionMultiple contextContext based
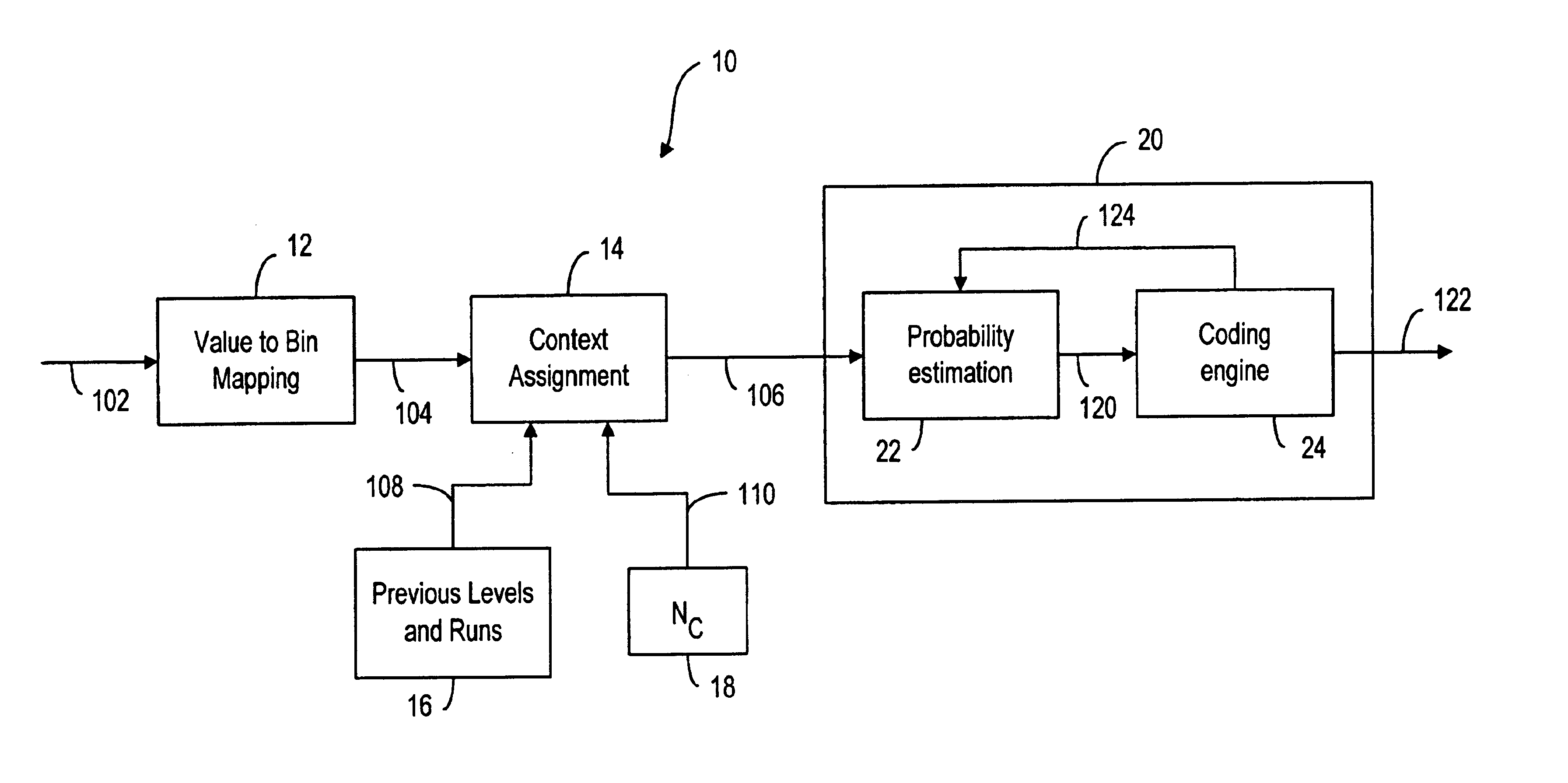
A method and system for image coding, wherein an image is divided into a plurality of blocks for scanning. The pixels values in the scanned block are represented by a plurality of level-run value pairs, wherein the level value is indicative of a non-zero pixel value and the run value is indicative of the number of consecutive zero pixel values preceding the non-zero pixel value. A plurality of contexts indicative of the level-run value pairs are conveyed to a decoder for allowing the decoder to reconstruct the image based on the contexts. The assignment of the contexts is also based on the level value of a preceding level-run pair. Additionally, instead of an end-of-block symbol, the number of non-zero coefficients is provided to the decoder prior to conveying the contexts thereto.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
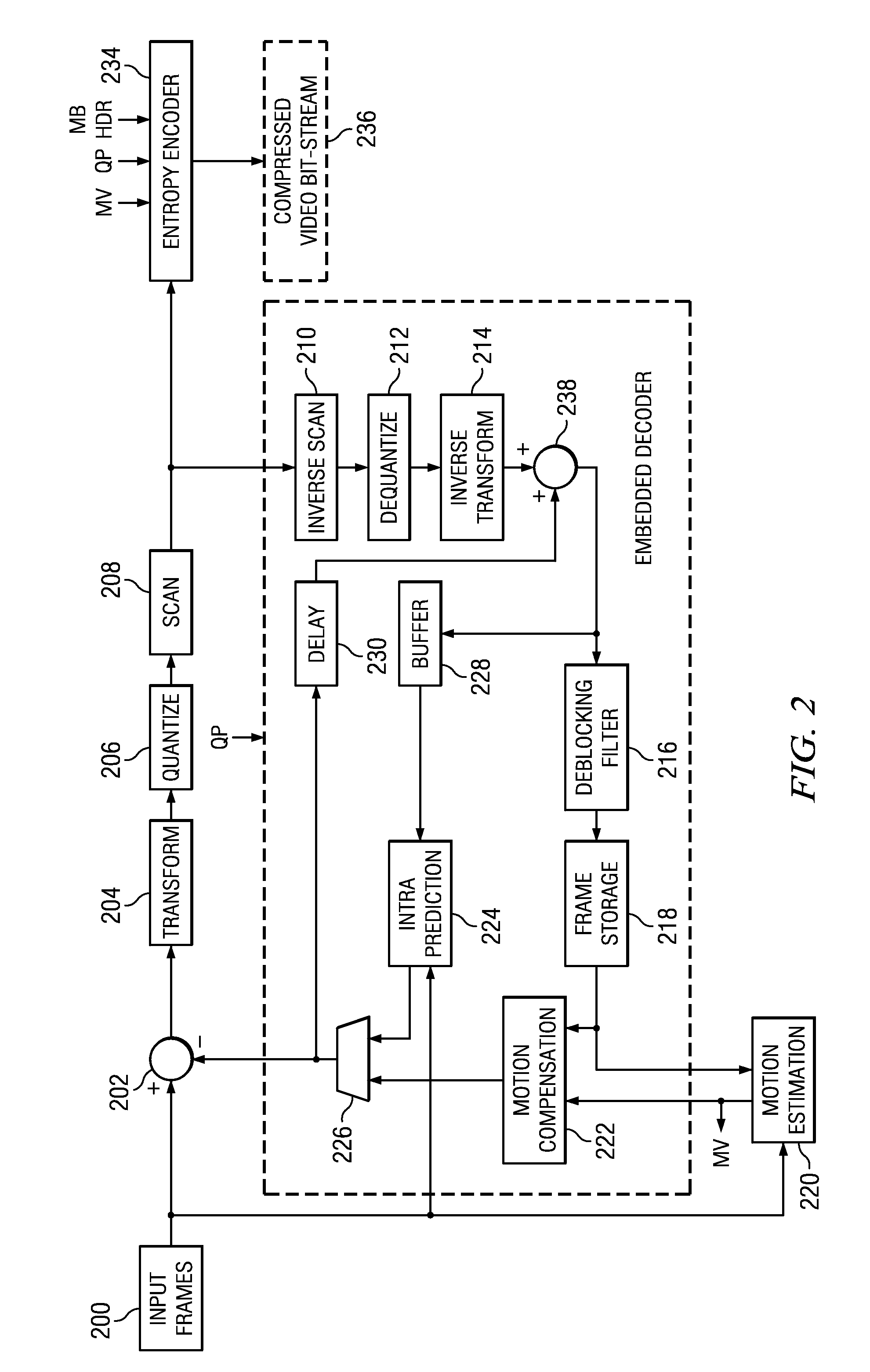
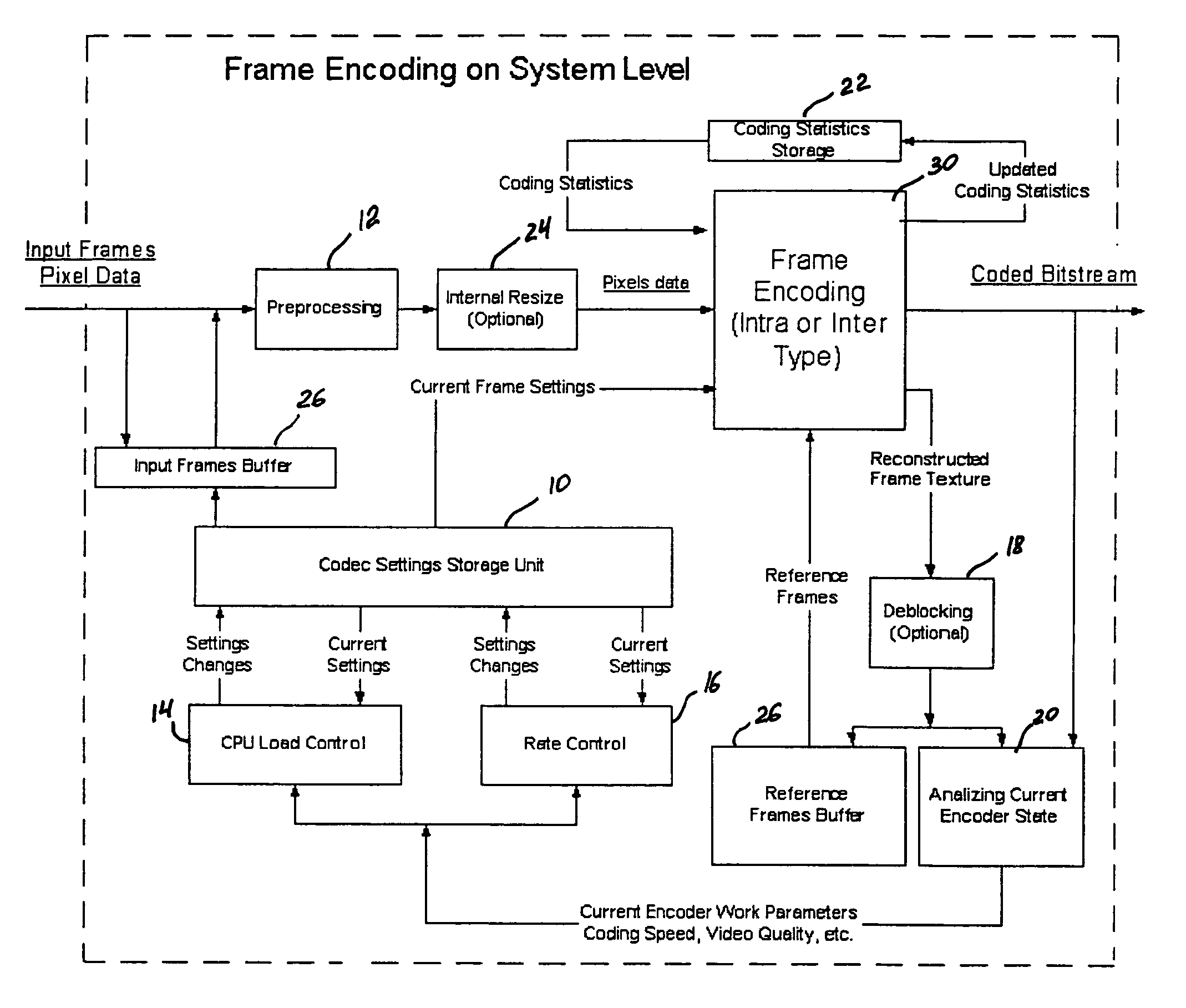
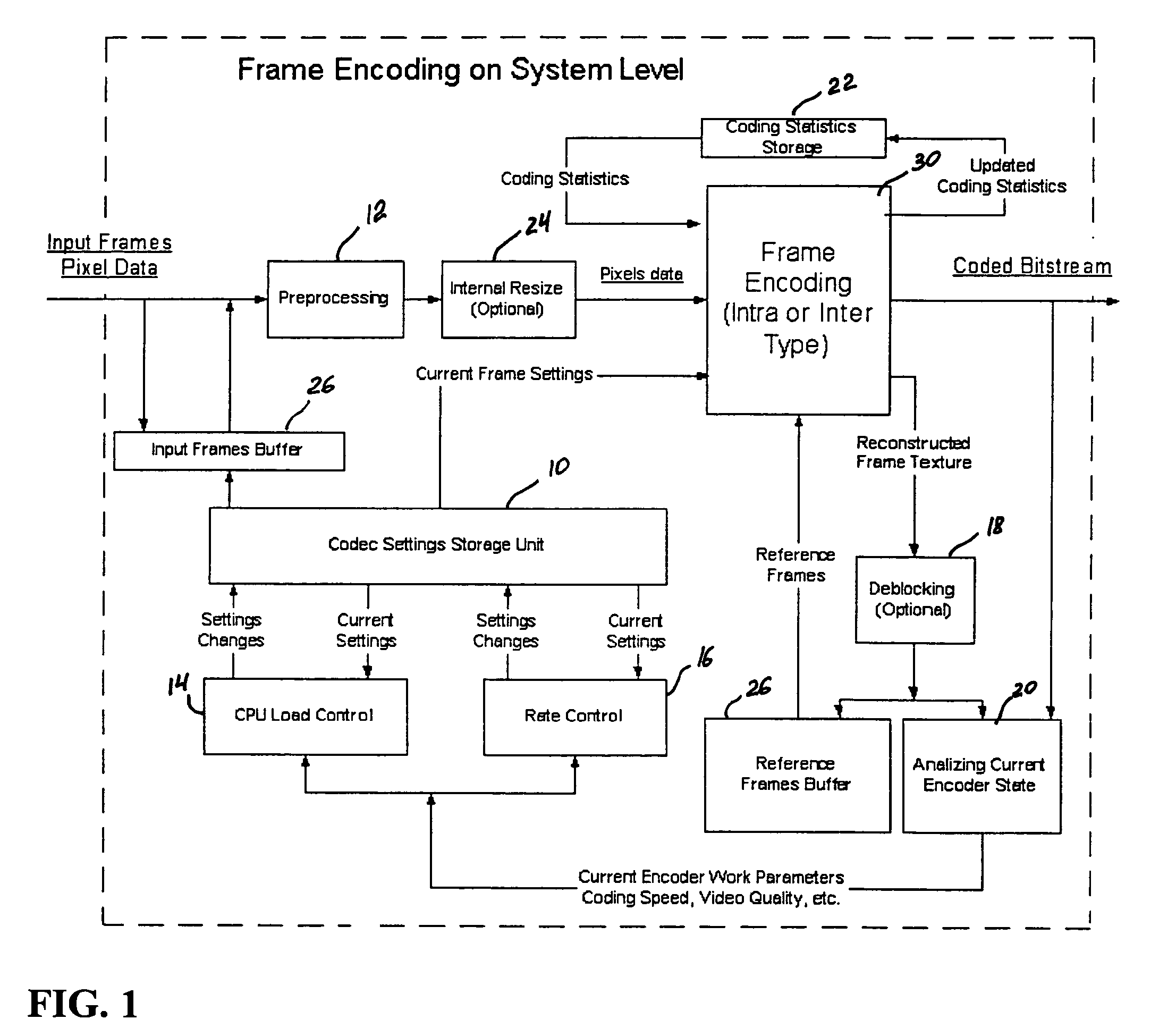
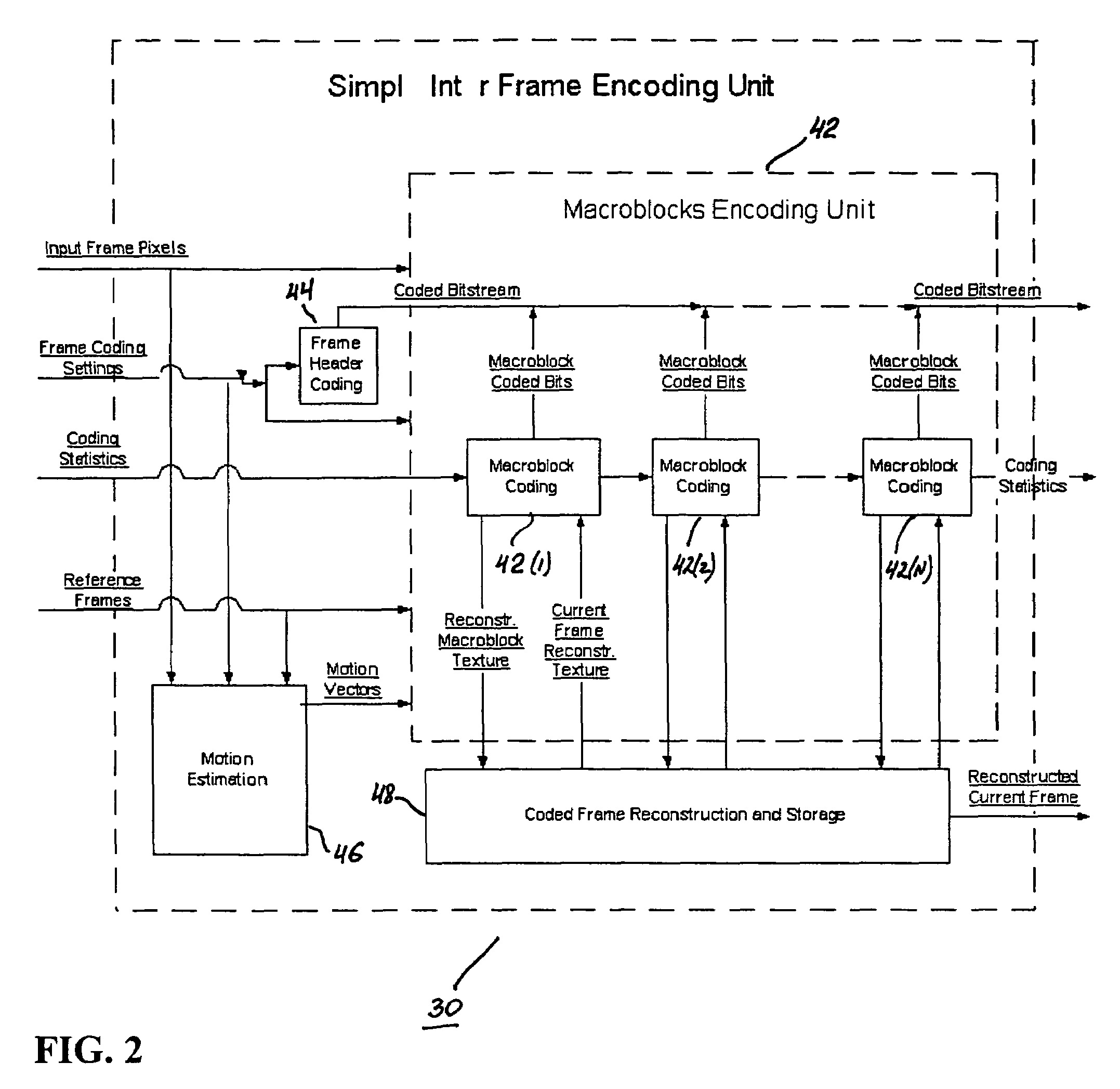
Real-time video coding/decoding
ActiveUS20050276323A1Picture reproducers using cathode ray tubesCode conversionMotion vectorDownscaling
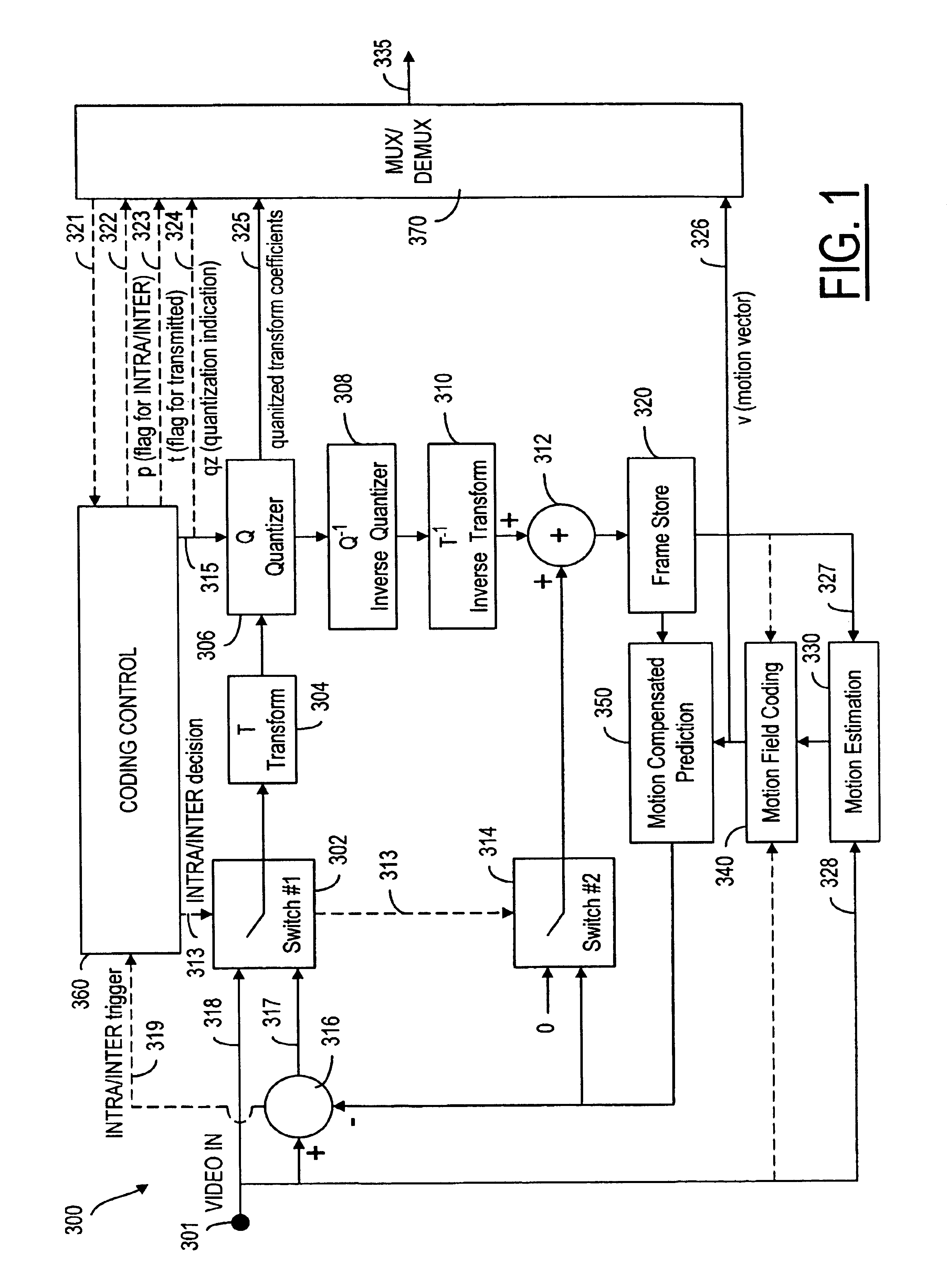
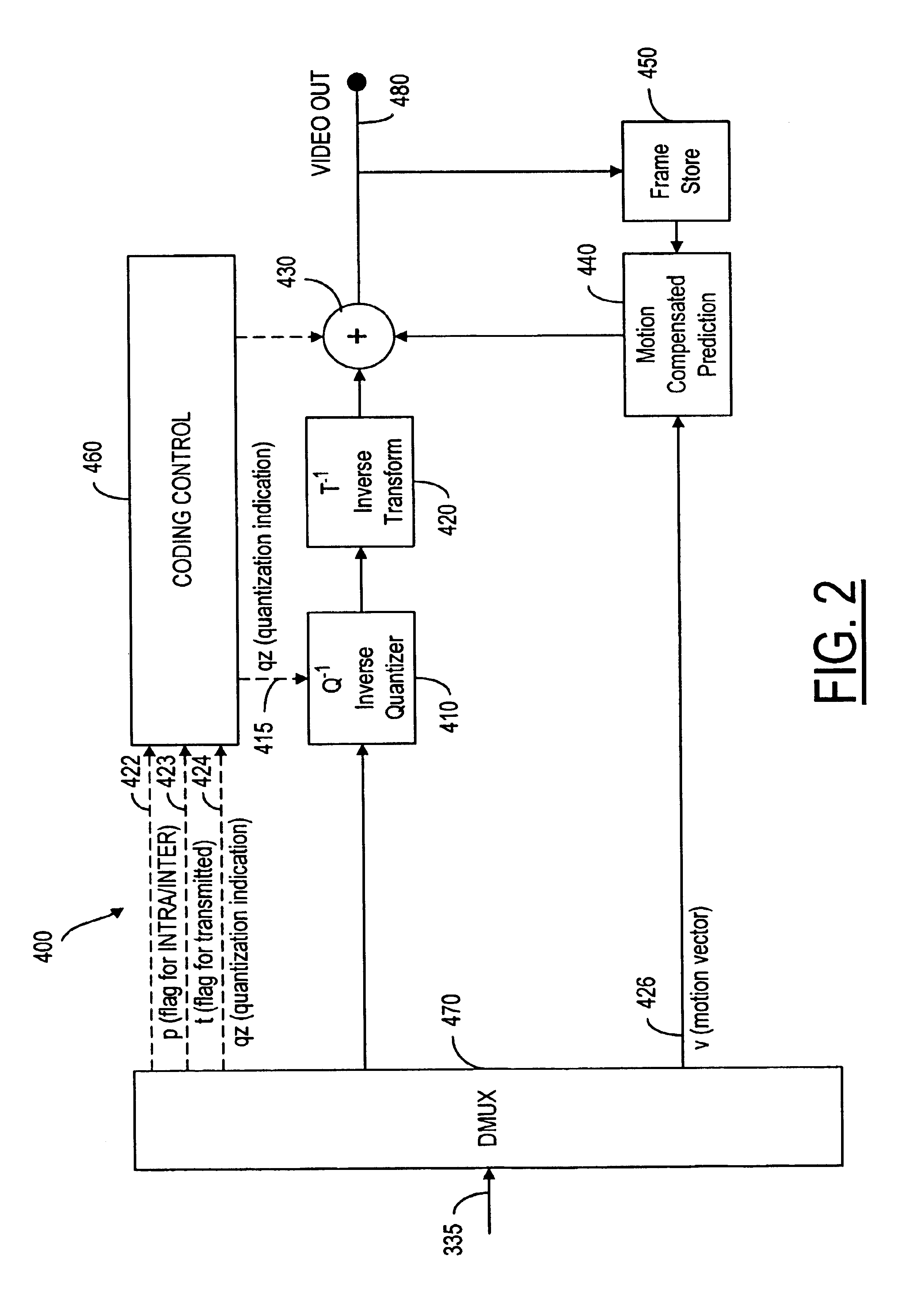
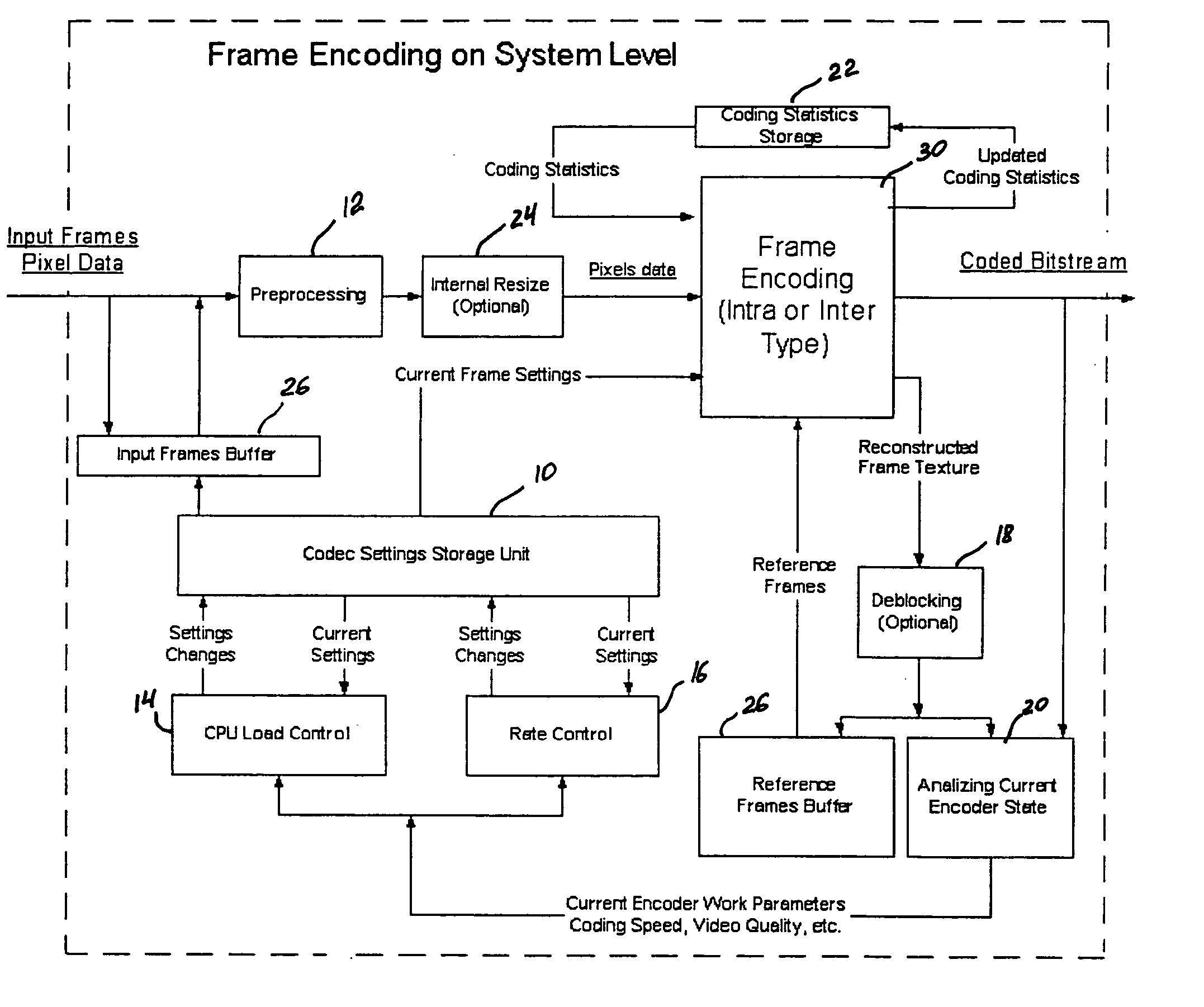
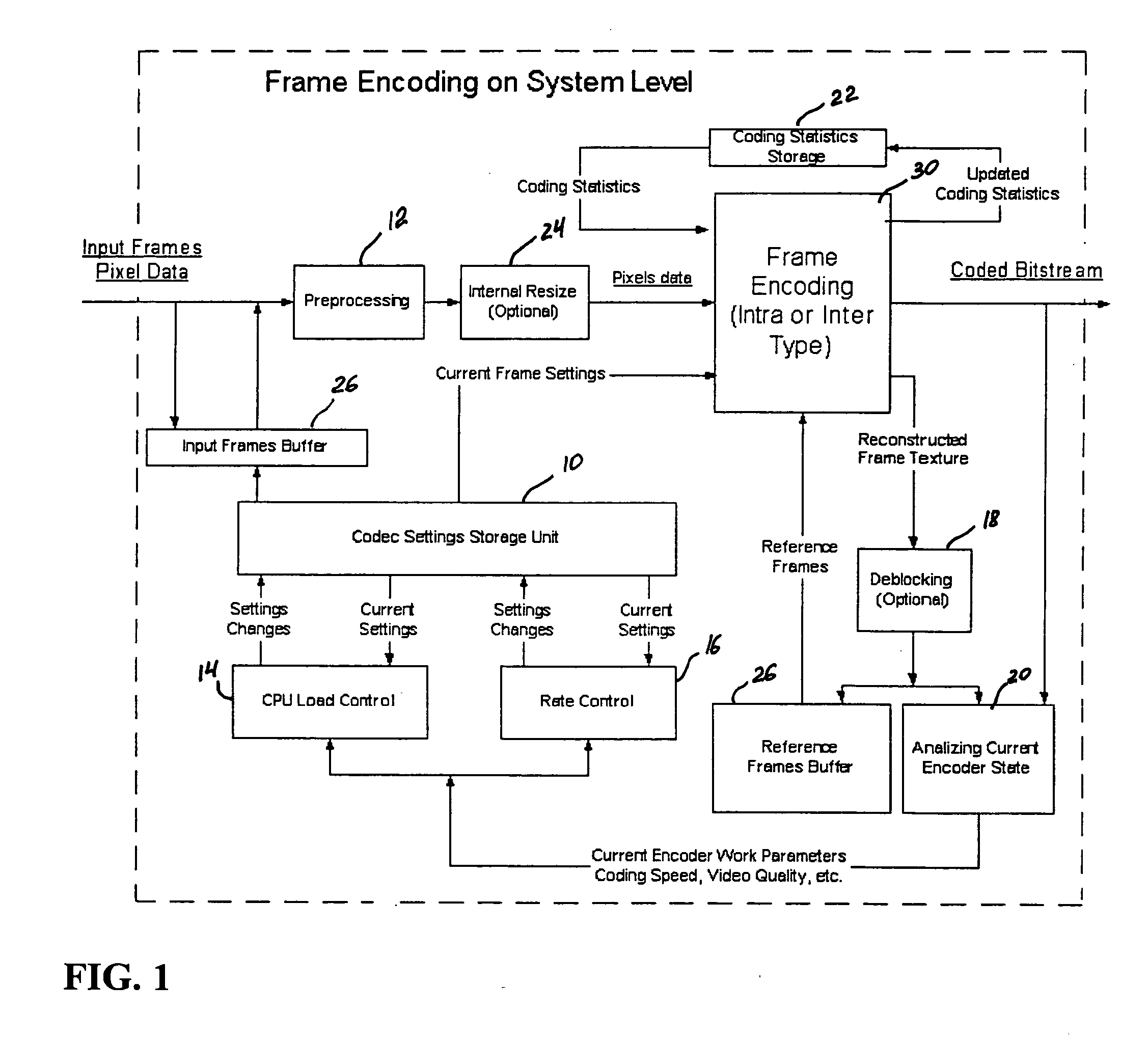
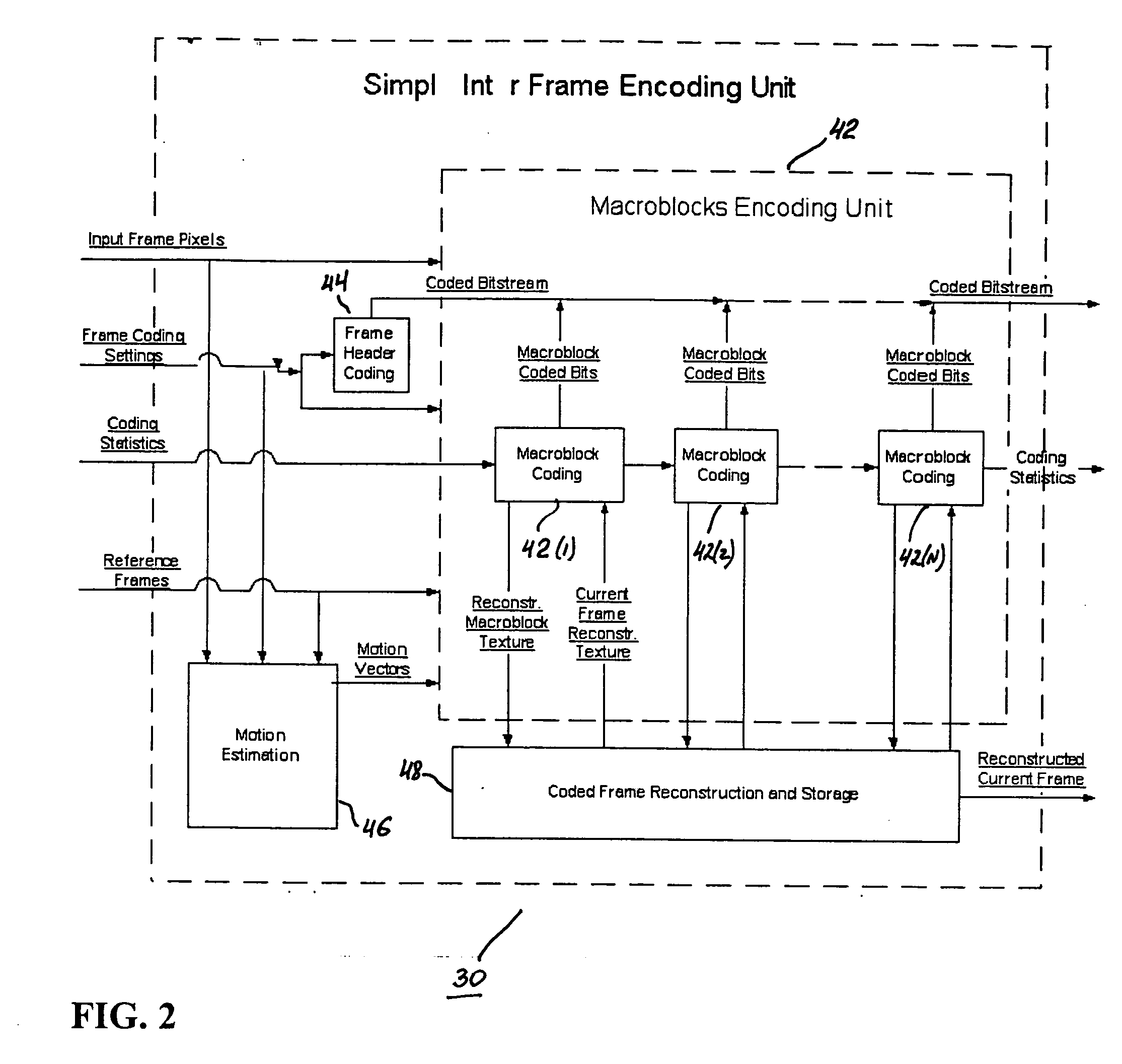
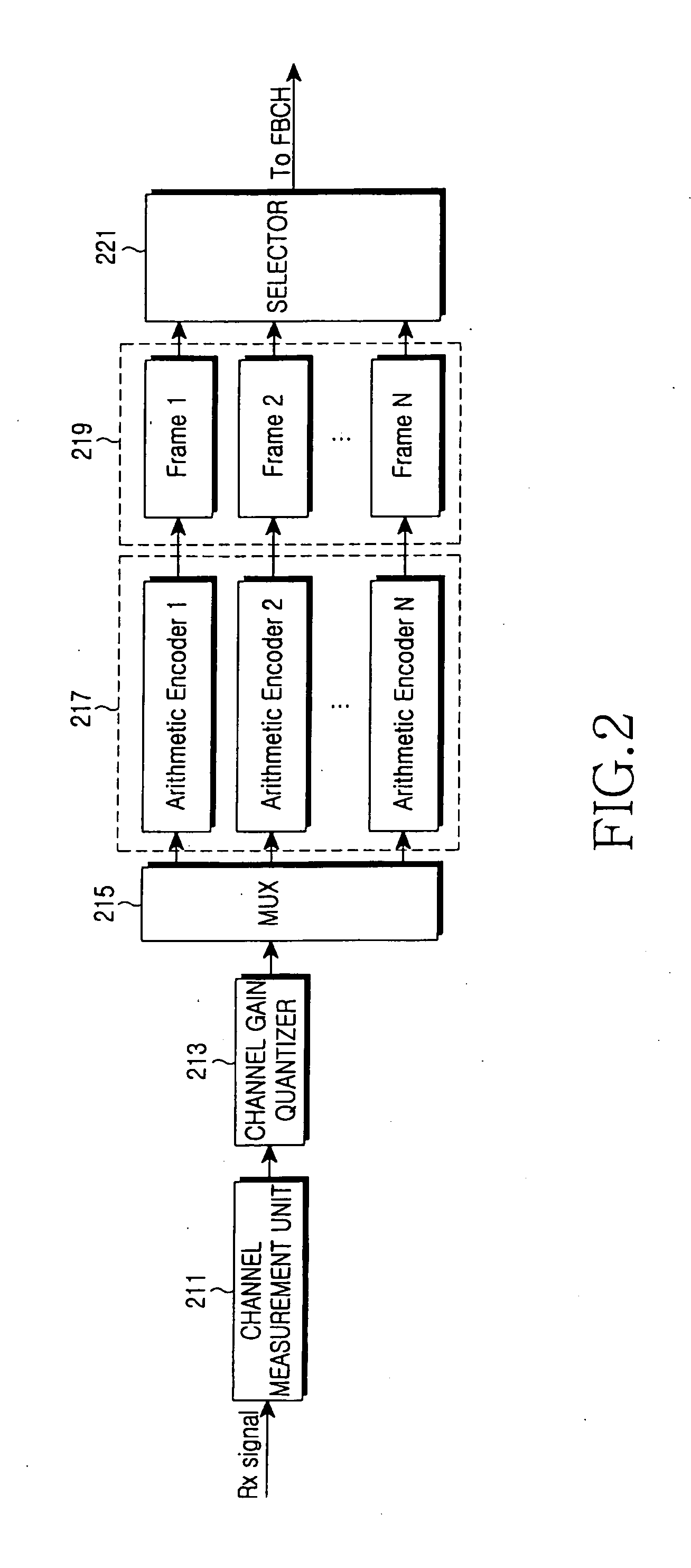
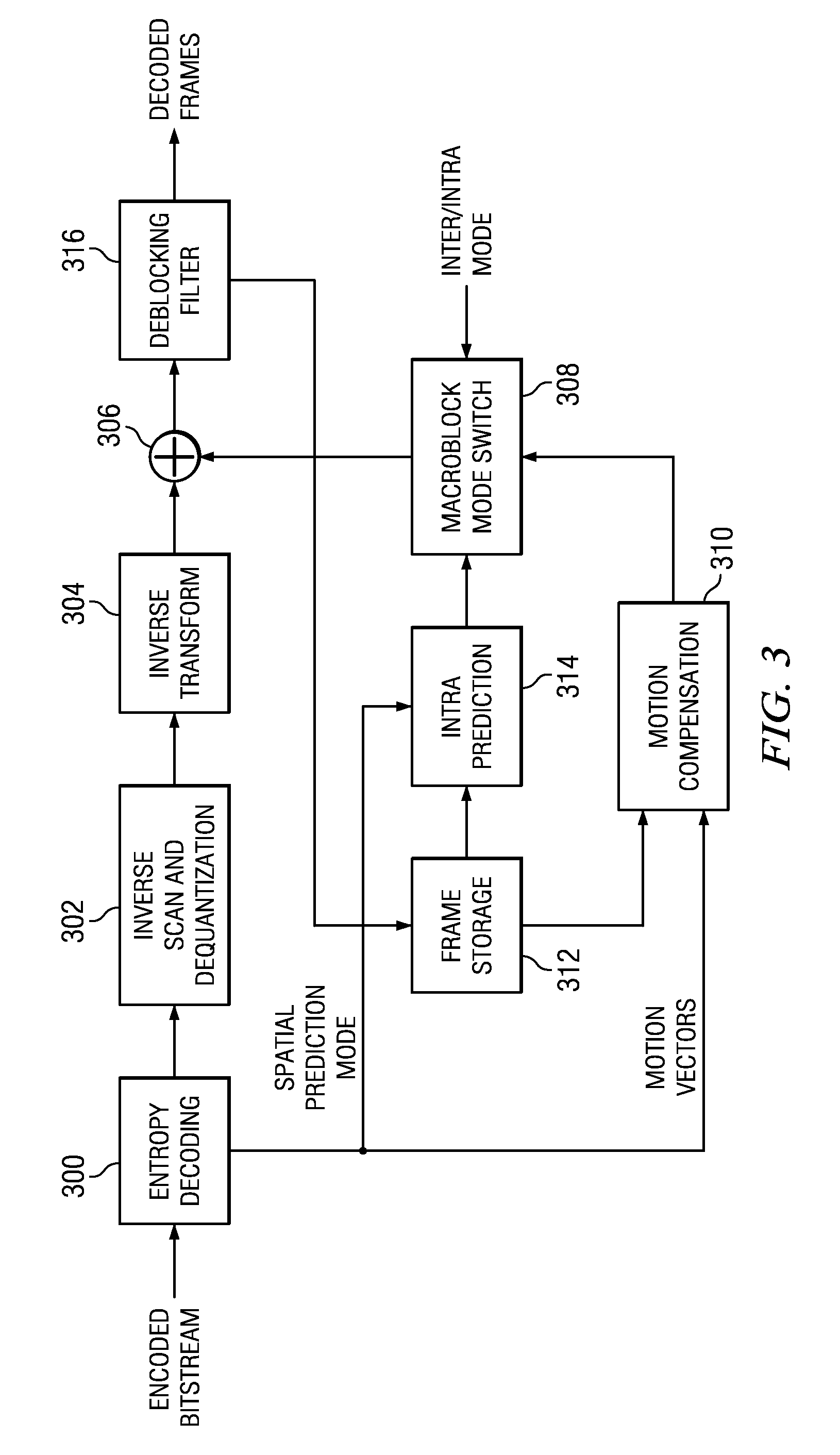
A video codec for real-time encoding / decoding of digitized video data with high compression efficiency, comprising a frame encoder receiving input frame pixels; a codec setting unit for setting and storing coding setting parameters; a CPU load controller for controlling desired frame encoding time and CPU loading; a rate controller for controlling frame size; a coding statistics memory for storing frequency tables for arithmetic coding of bitstream parameters and a reference frame buffer for storing reference frames. The frame encoder comprises a motion estimation unit, a frame head coding unit, a coded frame reconstruction and storage unit and a macroblock encoding unit. The macroblock encoding unit provides calculation of texture prediction and prediction error, transforming texture prediction error and quantization of transform coefficient, calculation of motion vector prediction and prediction error and arithmetic context modeling for motion vectors, header parameters and transform coefficients. The codec also includes a deblocking unit for processing video data to eliminate blocking effect from restored data encoded at high distortion level, which may be a part of encoder or decoder, an internal resize unit, providing matching downscaling of a frame before encoding and upscaling of decoded frame according to the coding setting parameters, and a noise suppression unit.
Owner:BEAMR IMAGING LTD
Arithmetic coding for transforming video and picture data units
ActiveUS7379608B2Improve compression efficiencyIncrease the compression ratioCharacter and pattern recognitionTelevision systemsProbability estimationContext model
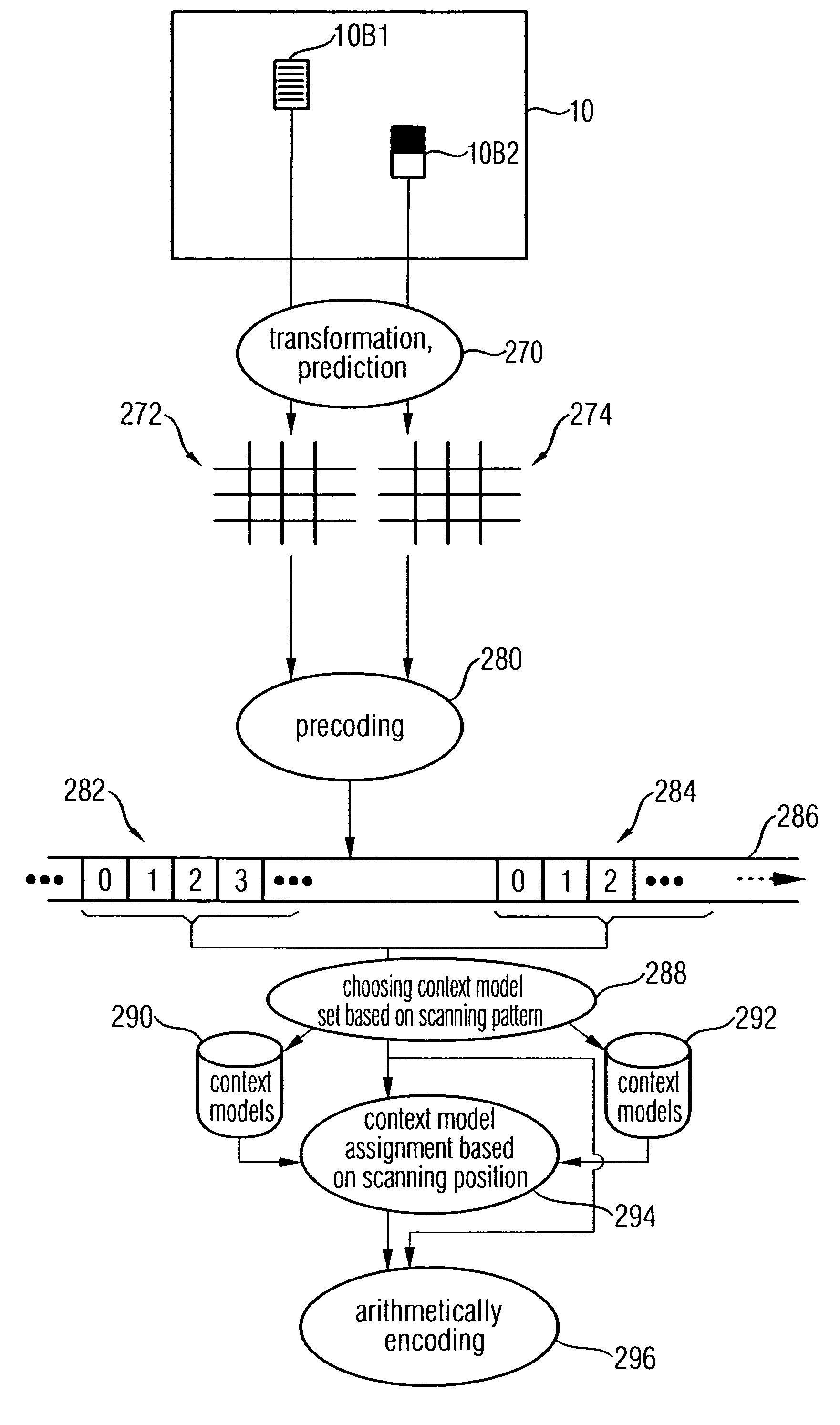
A method for encoding a video frame or picture comprises dividing up the video frame or the picture in portions of a first type associated with a first scanning pattern, and portions of a second type associated with a second scanning pattern. Data corresponding to a predetermined of the portions of the video frame or picture is transformed into a two-dimensional transform coefficient array. Fhe transform coefficients are precoded in order to obtain transform data units. One of a first and a second set of context models is chosen depending on as to whether the predetermined portion is a portion of a type being associated with the first or the second scanning pattern. One context model of the chosen one of the first and the second set of context models is assigned to the transform data unit based on the scanning position assigned to the predetermined transform coefficient. Finally, the transform data unit or a sub-unit thereof is arithmetically encoded into a coded bit stream based on the probability estimation with which the assigned context model is associated.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Two pass architecture for H.264 CABAC decoding process
InactiveUS20060126744A1Eliminate dependenciesHigh performance throughputColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionHigh-definition televisionComputer architecture
An architecture capable of stream parsing of the H.264 Content Based Adaptive Binary Arithmetic Coding (CABAC) format is disclosed. The architecture employs a two pass dataflow approach to implement the functions of CABAC bit parsing and decoding processes (based on the H.264 CABAC algorithm). The architecture can be implemented, for example, as a system-on-chip (SOC) for a video / audio decoder for use high definition television broadcasting (HDTV) applications. Other such video / audio decoder applications are enabled as well.
Owner:MICRONAS
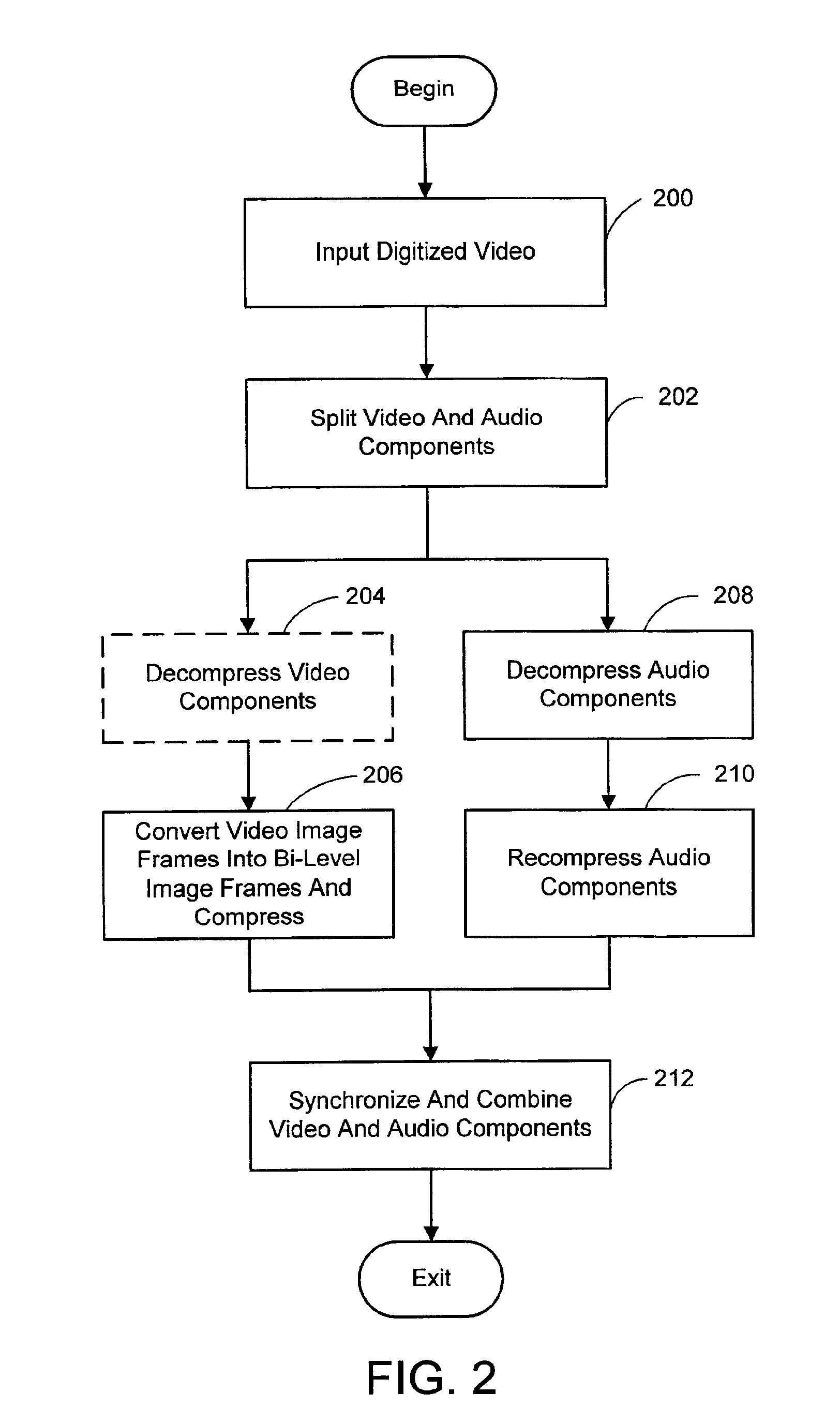
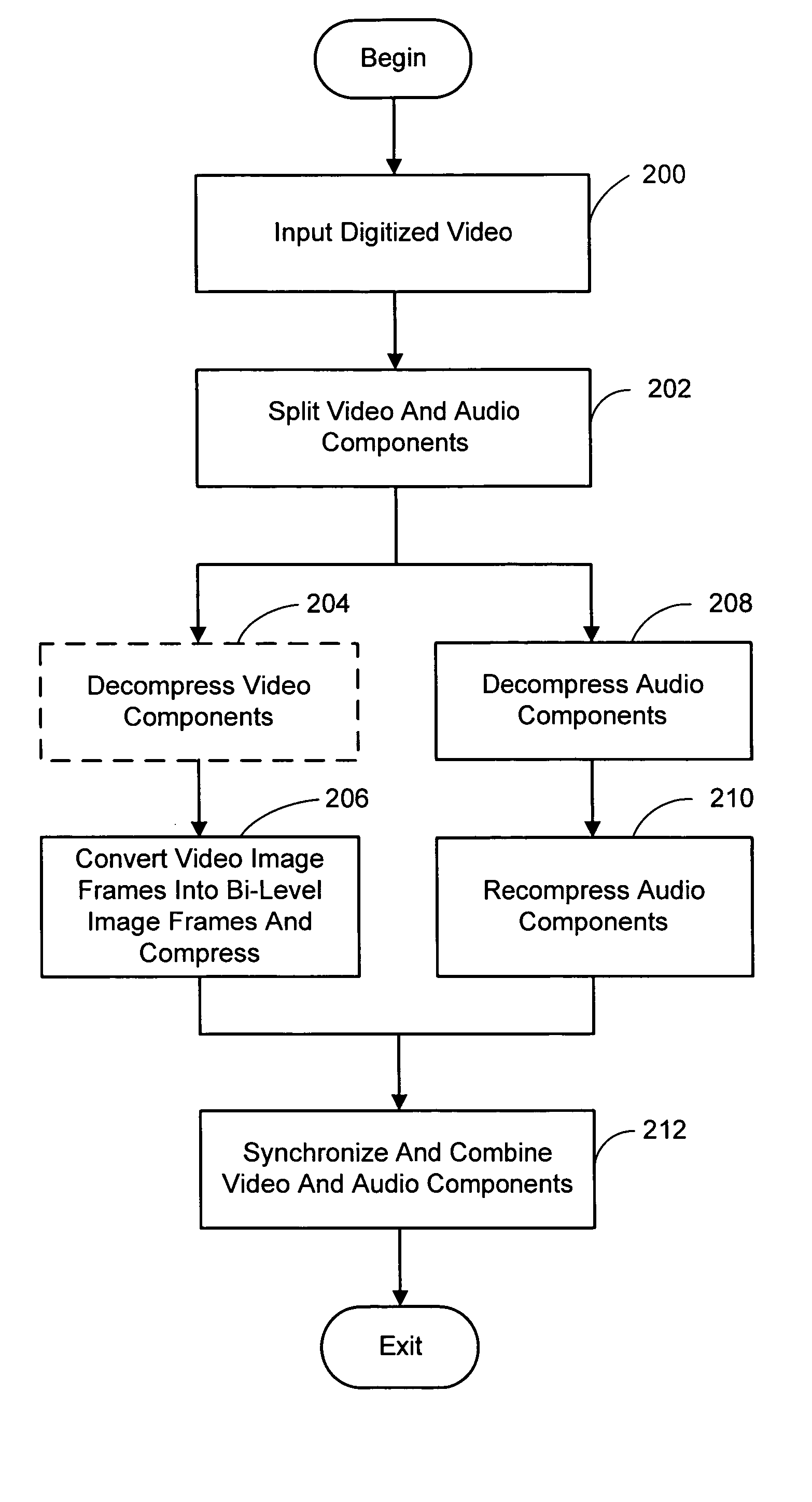
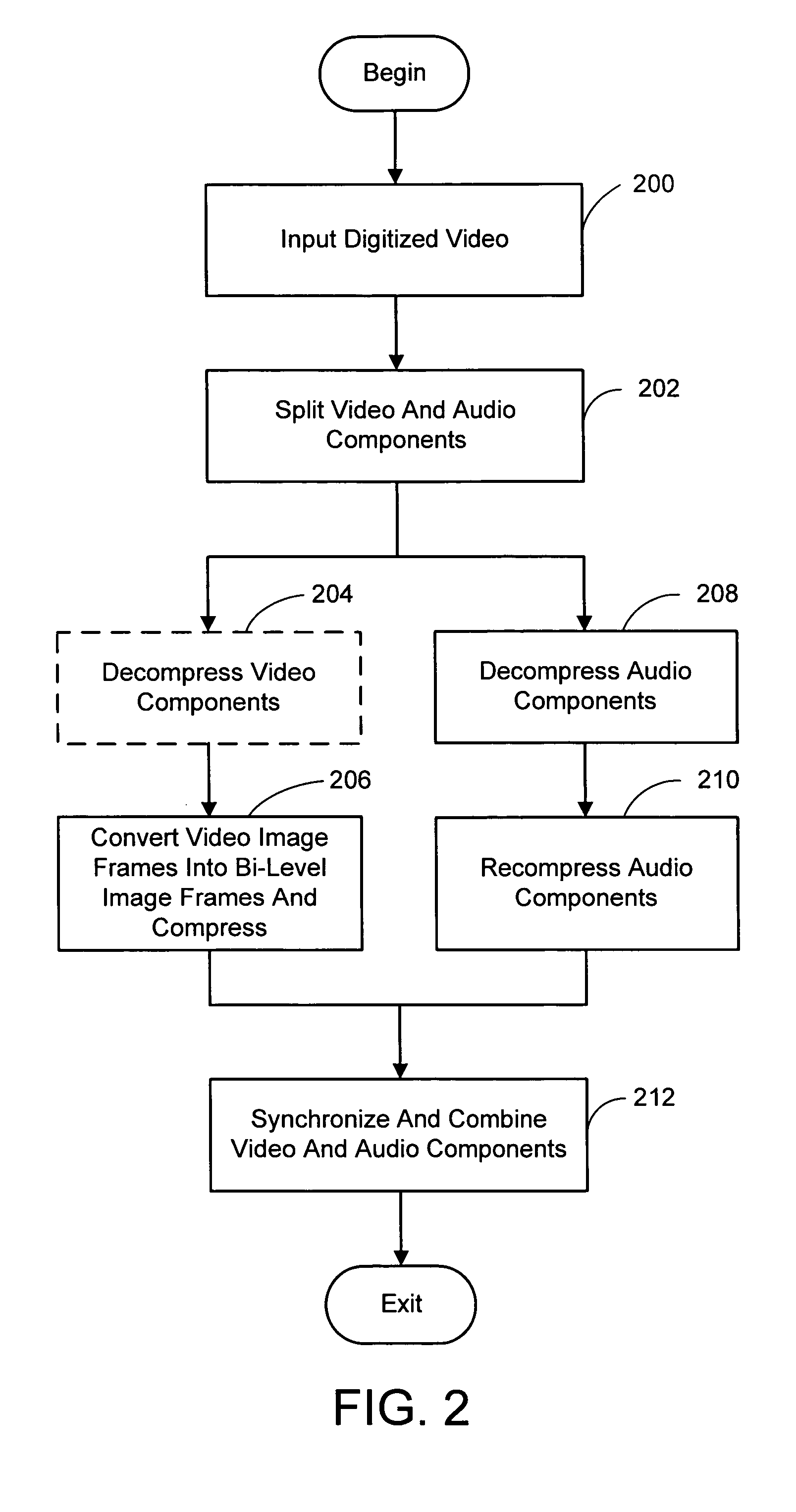
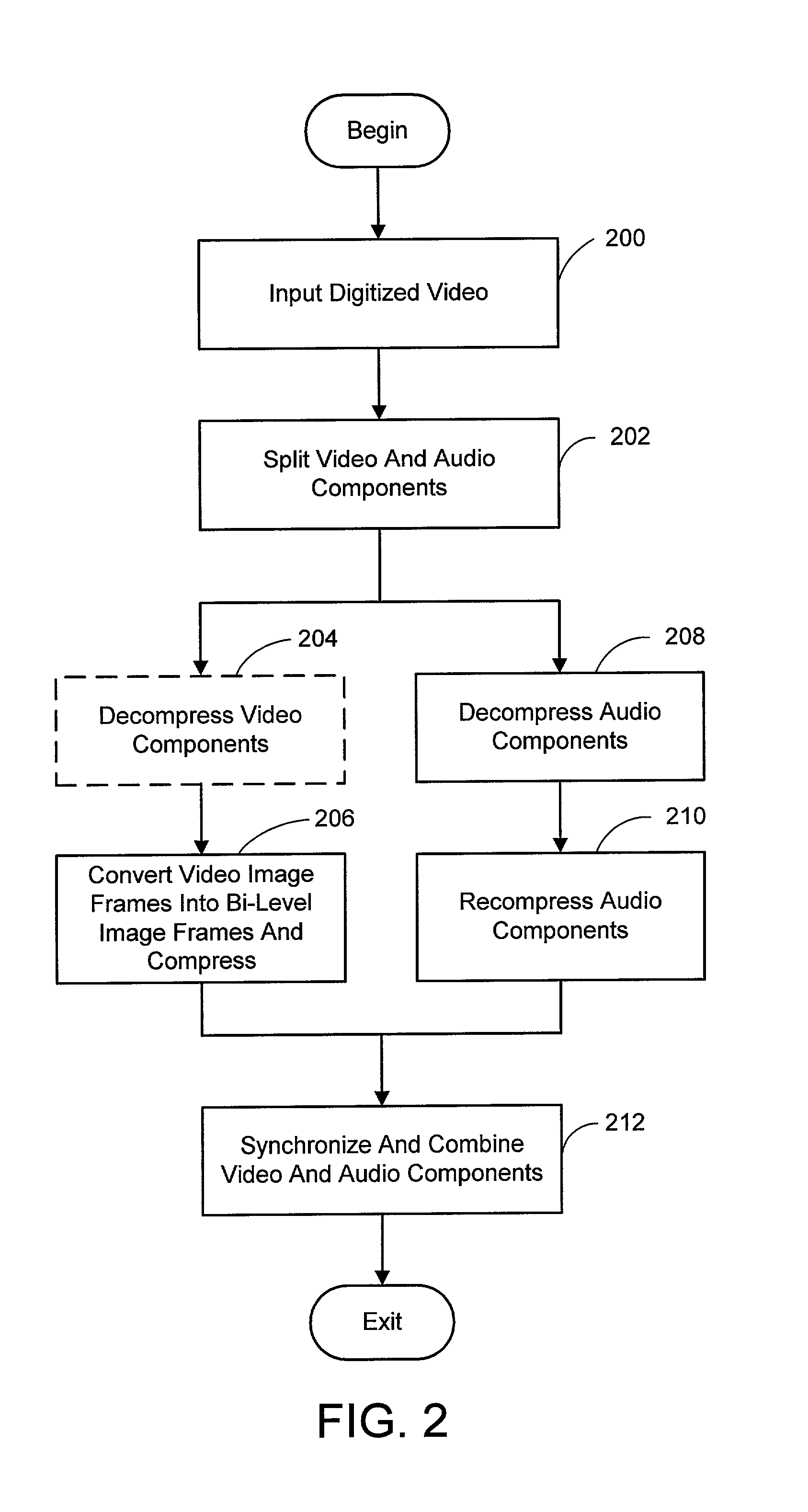
System and process for broadcast and communication with very low bit-rate bi-level or sketch video
InactiveUS6888893B2Clear imagingLow bandwidthPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningComputer graphics (images)Arithmetic coding
A system and process for broadcast and communication with bi-level or sketch video at extremely low bandwidths is described. Essentially, bi-level and sketch video presents the outlines of the objects in a scene being depicted. Bi-level and sketch video provides a clearer shape, smoother motion, shorter initial latency and cheaper computational cost than do conventional DCT-based video compression methods. This is accomplished by converting each color or gray-scale image frame to bi-level or sketch image frame using adaptive thresholding method, compressing bi-level or sketch image frames into bi-level or sketch video using adaptive context-based arithmetic coding method. Bi-level or sketch video is particularly suitable to such small devices as Pocket PCs and mobile phones that possess small display screen, low bandwidth connection, and light computational power.
Owner:ZHIGU HLDG
Method and arrangement for coding transform coefficients in picture and/or video coders and decoders and a corresponding computer program and a corresponding computer-readable storage medium
ActiveUS20040114683A1Picture reproducers using cathode ray tubesCode conversionComputer graphics (images)Video encoding
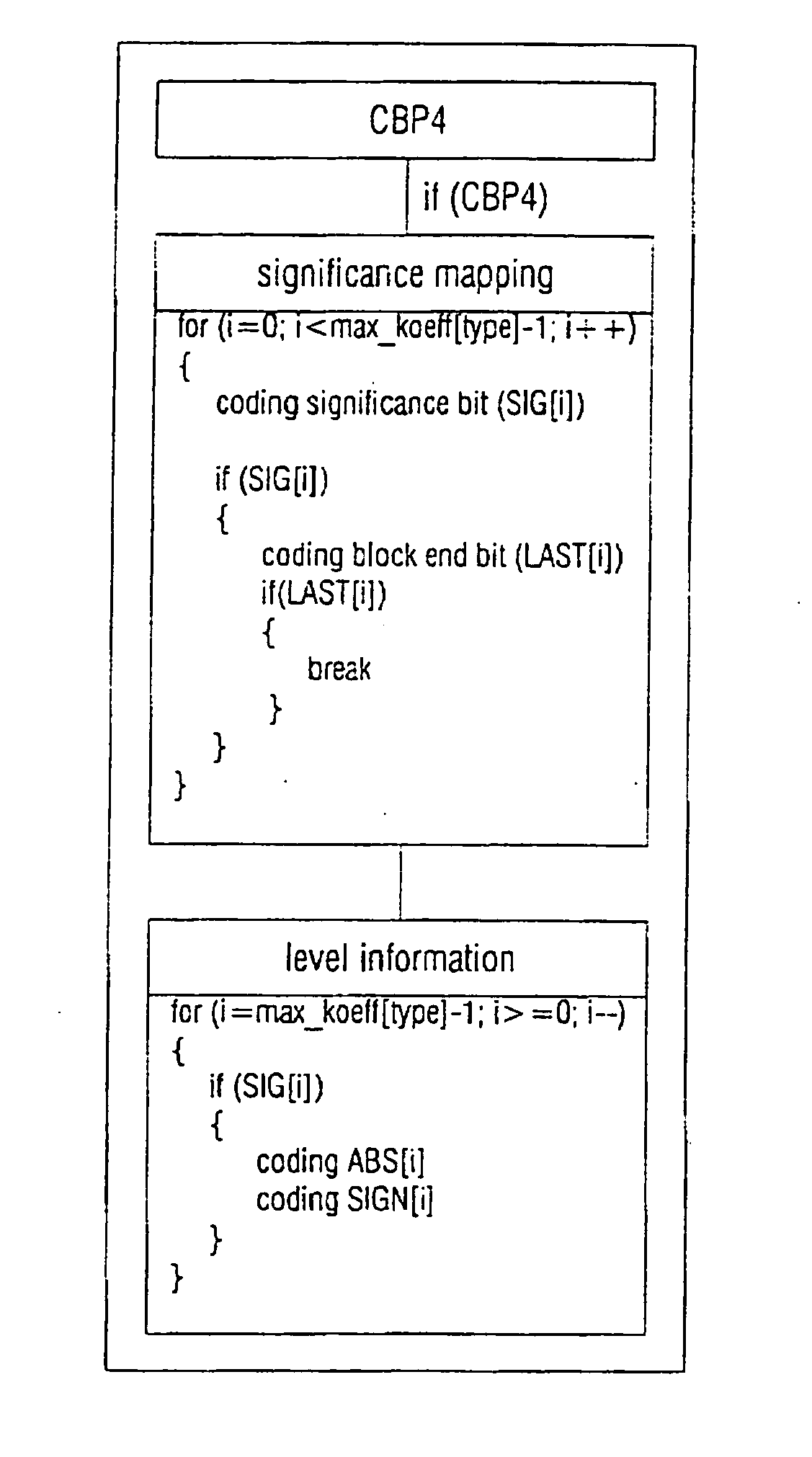
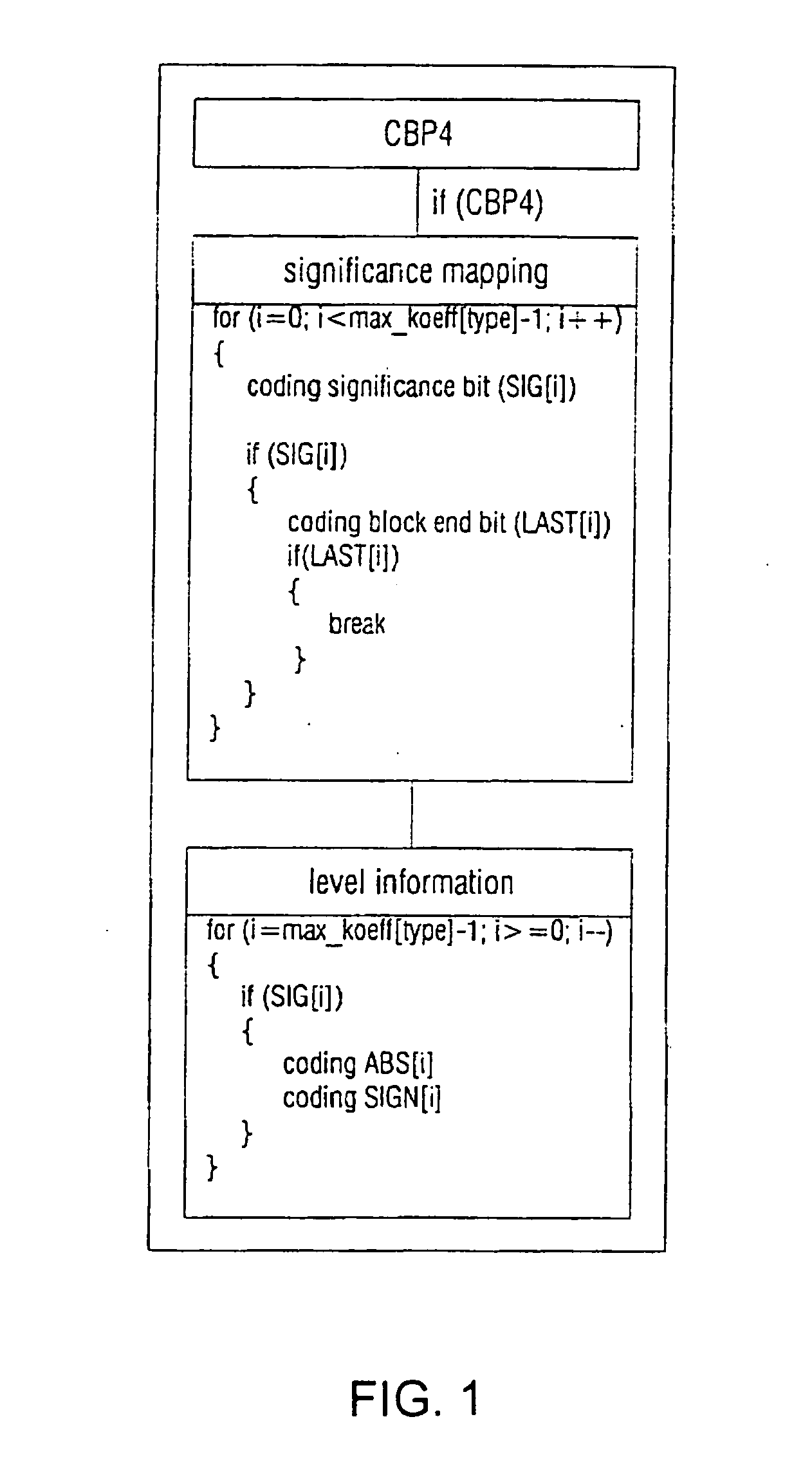
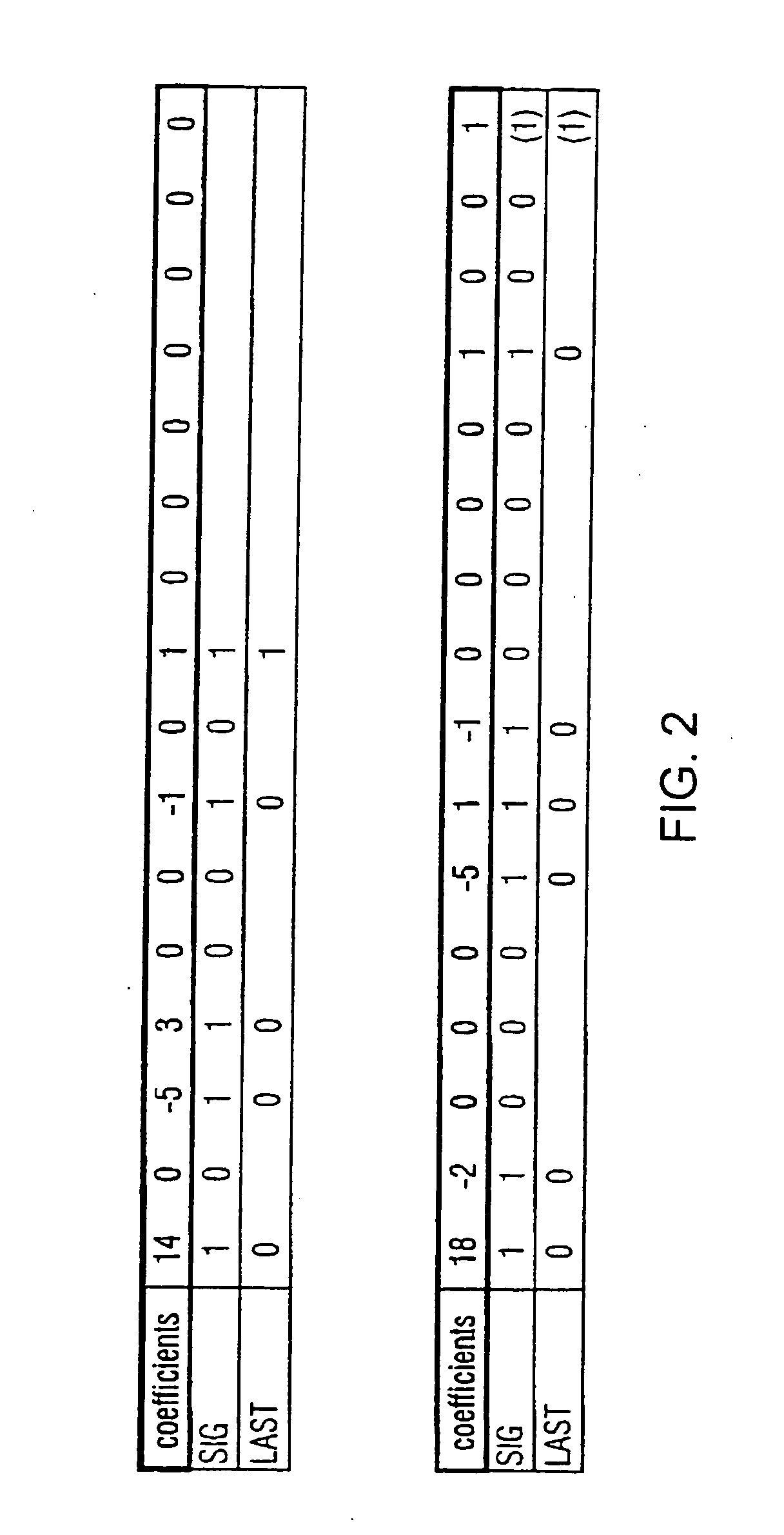
The present invention describes a method and an arrangement for coding transform coefficients in picture and / or video coders and decoders and a corresponding computer program and a corresponding computer-readable storage medium, which can particularly be employed as a novel efficient method for binary-arithmetic coding transform coefficients in the field of video coding. For this, it is suggested that, for blocks of (video) pictures containing significant transform coefficients, coding of the transform coefficients takes place in such a way that, for each block in a scan process, the positions of significant transform coefficients in the block and subsequently, in a reverse scan order-starting from the last significant transform coefficient within the block-the values (levels) of the significant transform coefficients are determined and coded.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
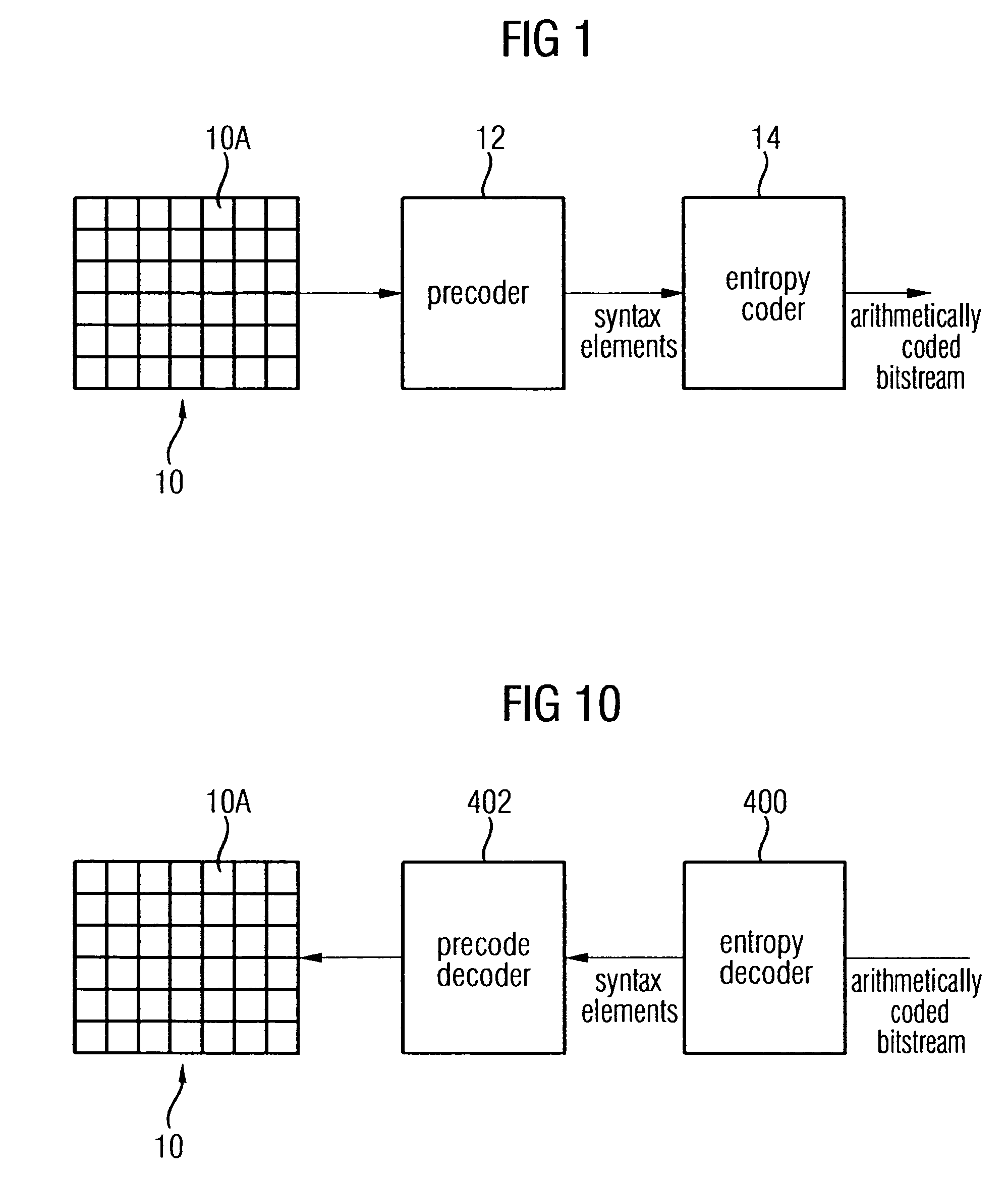
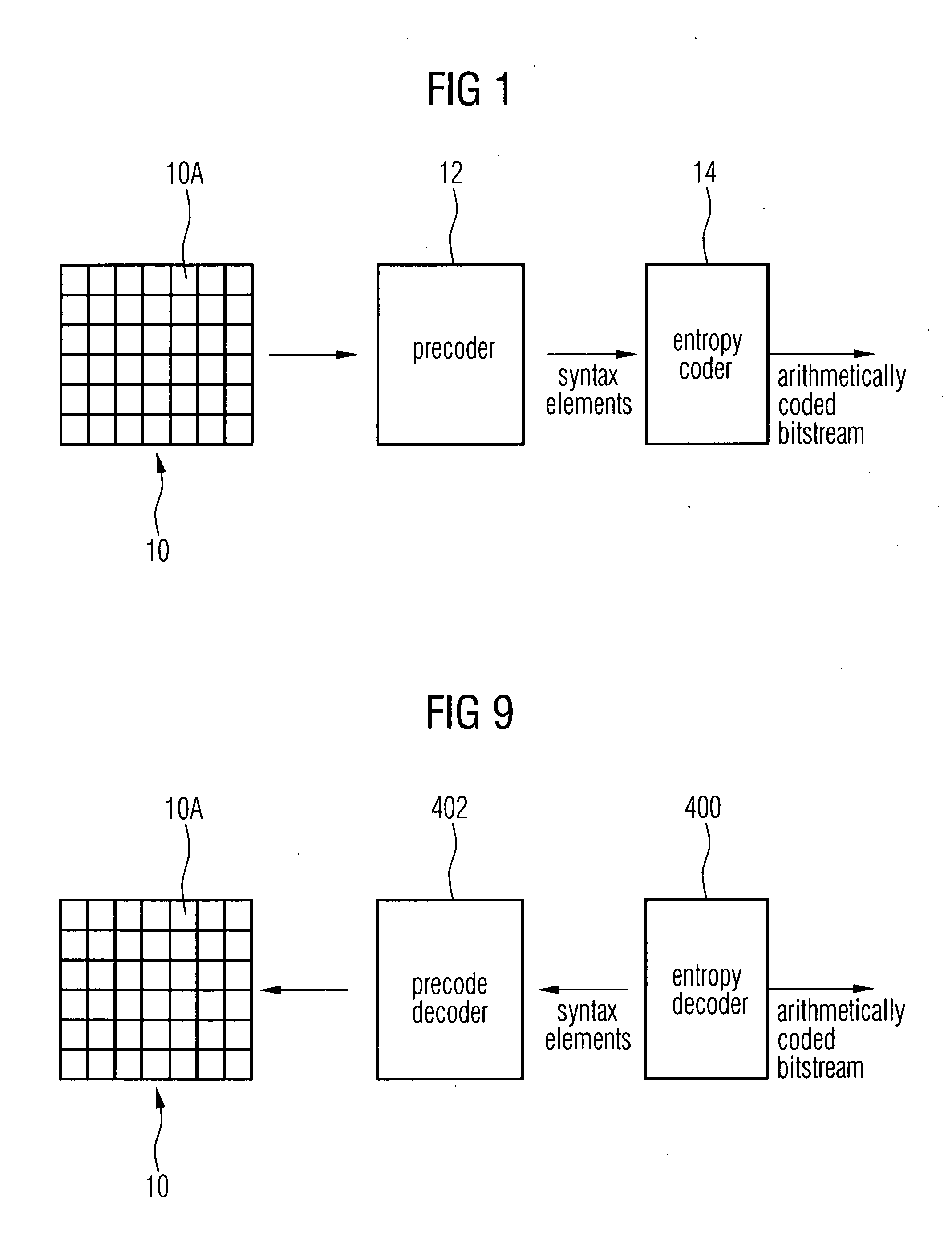
Coding of a syntax element contained in a pre-coded video signal
ActiveUS20050074176A1Increase the compression ratioImprove approximationCode conversionCharacter and pattern recognitionPrecodingPattern recognition
A method for encoding a syntax element contained in a precoded video signal into a coded bit stream, the precoded video signal representing at least one video frame, the syntax element being associated with a predetermined portion of the video frame and being indicative of as to whether the predetermined portion of the video frame is precoded in a first or a second way into the precoded video signal is described. The method comprises investigating as to whether a neighboring portion of the video frame neighboring the predetermined portion is precoded in the first way or the second way, in order to obtain a binary value; assigning one of at least two context models to the predetermined portion of the video frame based on the binary value, wherein each context model is associated with a different probability estimation; and arithmetically encoding the syntax element into the coded bit stream based on the probability estimation with which the assigned context model is associated.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
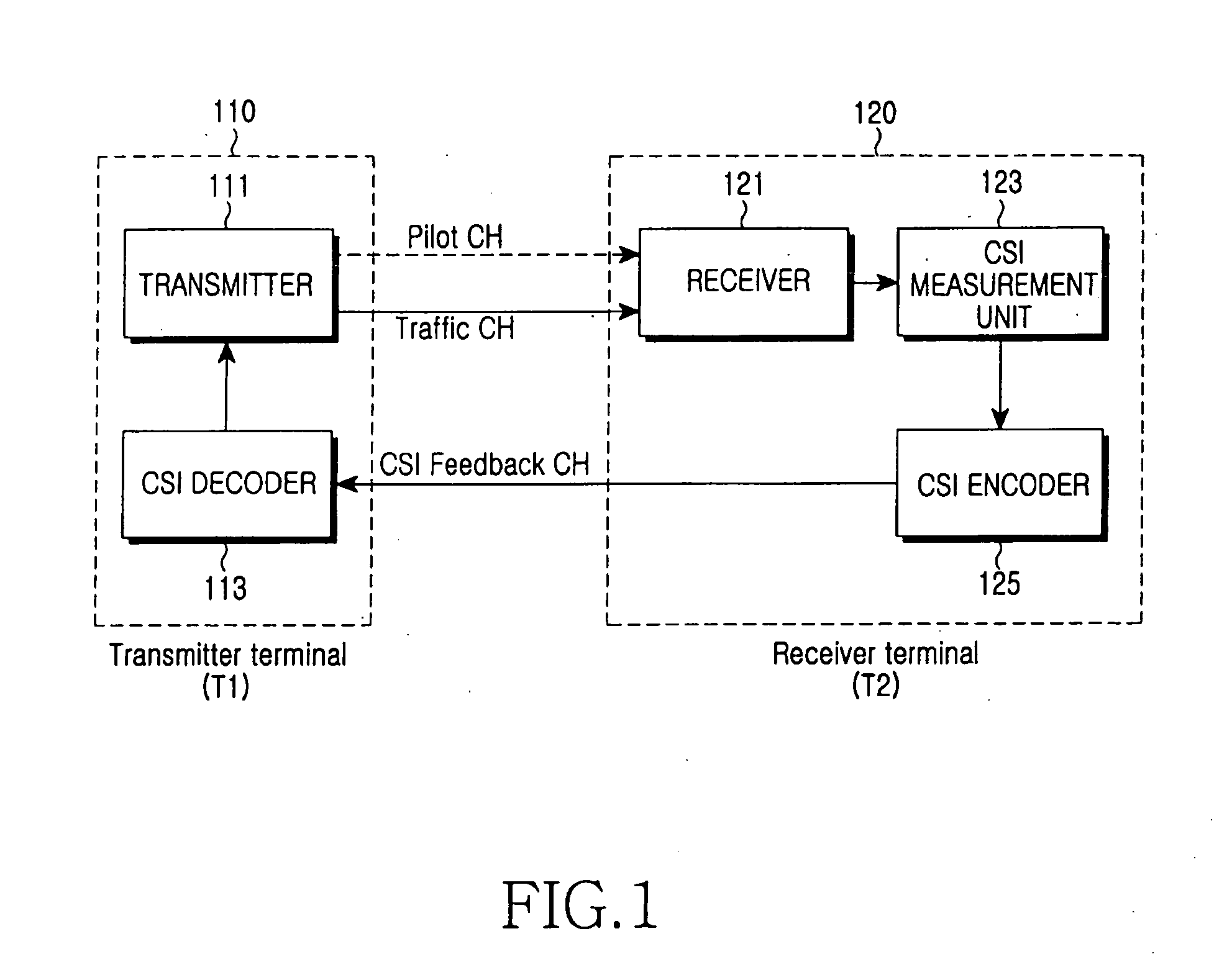
Method and apparatus for channel state feedback using arithmetic coding
ActiveUS20050265436A1Reduce the impactImprove system performanceModulated-carrier systemsFrequency-division multiplex detailsCommunications systemArithmetic coding
Disclosed are the design and implementation of a CSI feedback channel in a multi-carrier wireless communication system. An apparatus and a method for channel state feedback using arithmetic coding are provided to ensure efficiency and reliability of a system by transmitting the CSI while compressing the CSI with a predetermined compression rate selected depending on a channel state. The apparatus for CSI feedback in a wireless communication system performing channel estimation at a transmitter or a receiver by using a communication channel includes a transmitter terminal transmitting a signal for CSI measurement by using the communication channel, and a receiver terminal receiving the signal from the transmitter terminal, checking a channel state based on the received signal, and transmitting the signal to the transmitter terminal after compressing the signal according to the channel state.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Real-time video coding/decoding
Owner:BEAMR IMAGING LTD
System and process for broadcast and communication with very low bit-rate bi-level or sketch video
ActiveUS20050041739A1Eliminating the unwanted backgroundColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionBi layerComputer graphics (images)
A system and process for broadcast and communication with bi-level or sketch video at extremely low bandwidths is described. Essentially, bi-level and sketch video presents the outlines of the objects in a scene being depicted. Bi-level and sketch video provides a clearer shape, smoother motion, shorter initial latency and cheaper computational cost than do conventional DCT-based video compression methods. This is accomplished by converting each color or gray-scale image frame to bi-level or sketch image frame using adaptive thresholding method, compressing bi-level or sketch image frames into bi-level or sketch video using adaptive context-based arithmetic coding method. Bi-level or sketch video is particularly suitable to such small devices as Pocket PCs and mobile phones that possess small display screen, low bandwidth connection, and light computational power.
Owner:ZHIGU HLDG
Method and apparatus for binarization and arithmetic coding of a data value
ActiveUS6900748B2Efficient compressionModerate computational overheadDigital data processing detailsDigital computer detailsComputer architectureCut off value
Binarization a data value comprises binarizing the minimum of the data value and a predetermined cut-off value in accordance with a first binarization scheme, in order to yield a primary prefix. If the data value is greater than the cut-off value, binarizing a difference of the data value minus the predetermined cut-off value in accordance with a second binarization scheme to obtain a binary suffix, the first binarization scheme being different from the second binarization scheme, and appending the primary suffix to the primary prefix is performed. A very effective compression of data values may be achieve by using the binarization scheme for preparing the syntax elements for the arithmetic coding, the binarization schemes substantially being a combination of two different binarization schemes, and by using binary arithmetic coding instead of m-ary arithmetic coding for coding the binarized syntax elements.
Owner:GE VIDEO COMPRESSION LLC
Coding of a syntax element contained in a pre-coded video signal
ActiveUS7286710B2Increase the compression ratioImprove approximationCode conversionCharacter and pattern recognitionPrecodingPattern recognition
A method for encoding a syntax element contained in a precoded video signal into a coded bit stream, the precoded video signal representing at least one video frame, the syntax element being associated with a predetermined portion of the video frame and being indicative of as to whether the predetermined portion of the video frame is precoded in a first or a second way into the precoded video signal is described. The method comprises investigating as to whether a neighboring portion of the video frame neighboring the predetermined portion is precoded in the first way or the second way, in order to obtain a binary value; assigning one of at least two context models to the predetermined portion of the video frame based on the binary value, wherein each context model is associated with a different probability estimation; and arithmetically encoding the syntax element into the coded bit stream based on the probability estimation with which the assigned context model is associated.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
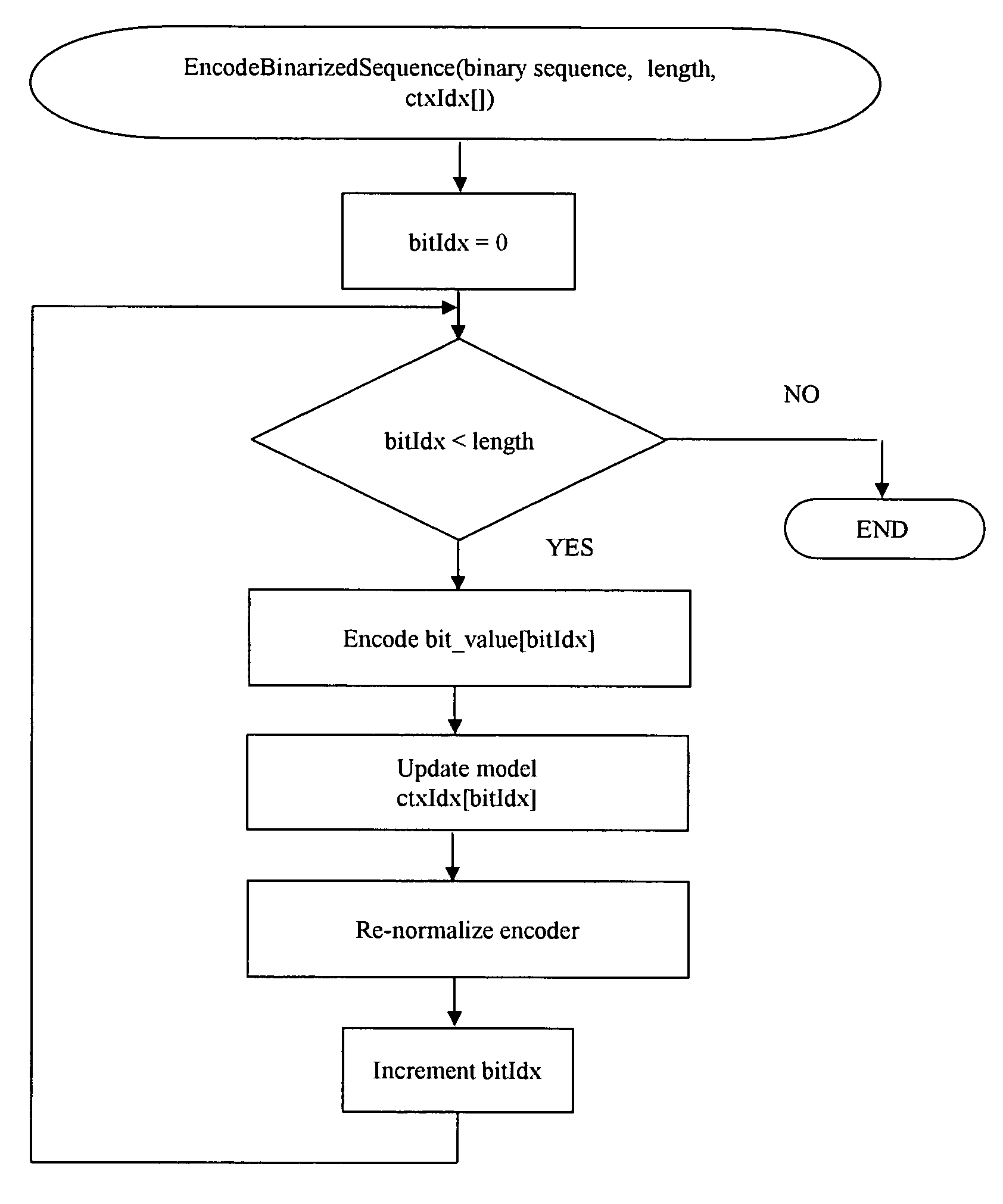
Method of context based adaptive binary arithmetic decoding with two part symbol decoding
ActiveUS6876317B2Data representation error detection/correctionCode conversionComputer hardwareSymbol decoding
This invention is method of decoding a context based adaptive binary arithmetic encoded bit stream. The invention determines a maximum number of iterations for decoding a next symbol. This preferably employs a left most bit detect command. The invention considers the bit stream bit by bit until detection of a bit having a first digital state of the maximum number of iterations. If the maximum number of iterations occurs first, the invention decodes the considered bits. If a bit having the first digital state occurs first, the invention selects a number of next bits from the bit stream dependent upon the determined position within the coding table and decodes a symbol corresponding to the maximum number of bits and the selected number of next bits. The invention preferably pre-calculates an order symbol contexts corresponding to an order of determination of a code tree encompassing all possible codes and decodes symbols dependent upon a current context within the pre-calculated.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
System and process for broadcast and communication with very low bit-rate bi-level or sketch video
InactiveUS20020126755A1Clear imagingLow bandwidthColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputer graphics (images)Arithmetic coding
A system and process for broadcast and communication with bi-level or sketch video at extremely low bandwidths is described. Essentially, bi-level and sketch video presents the outlines of the objects in a scene being depicted. Bi-level and sketch video provides a clearer shape, smoother motion, shorter initial latency and cheaper computational cost than do conventional DCT-based video compression methods. This is accomplished by converting each color or gray-scale image frame to bi-level or sketch image frame using adaptive thresholding method, compressing bi-level or sketch image frames into bi-level or sketch video using adaptive context-based arithmetic coding method. Bi-level or sketch video is particularly suitable to such small devices as Pocket PCs and mobile phones that possess small display screen, low bandwidth connection, and light computational power.
Owner:ZHIGU HLDG
Reducing Context Coded and Bypass Coded Bins to Improve Context Adaptive Binary Arithmetic Coding (CABAC) Throughput
ActiveUS20130272389A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionArithmetic codingSyntax
Techniques for context-adaptive binary arithmetic coding (CABAC) coding with a reduced number of context coded and / or bypass coded bins are provided. Rather than using only truncated unary binarization for the syntax element representing the delta quantization parameter and context coding all of the resulting bins as in the prior art, a different binarization is used and only part of the resulting bins are context coded, thus reducing the worst case number of context coded bins for this syntax element. Further, binarization techniques for the syntax element representing the remaining actual value of a transform coefficient are provided that restrict the maximum codeword length of this syntax element to 32 bits or less, thus reducing the number of bypass coded bins for this syntax element over the prior art.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Entropy coding by adapting coding between level and run-length/level modes
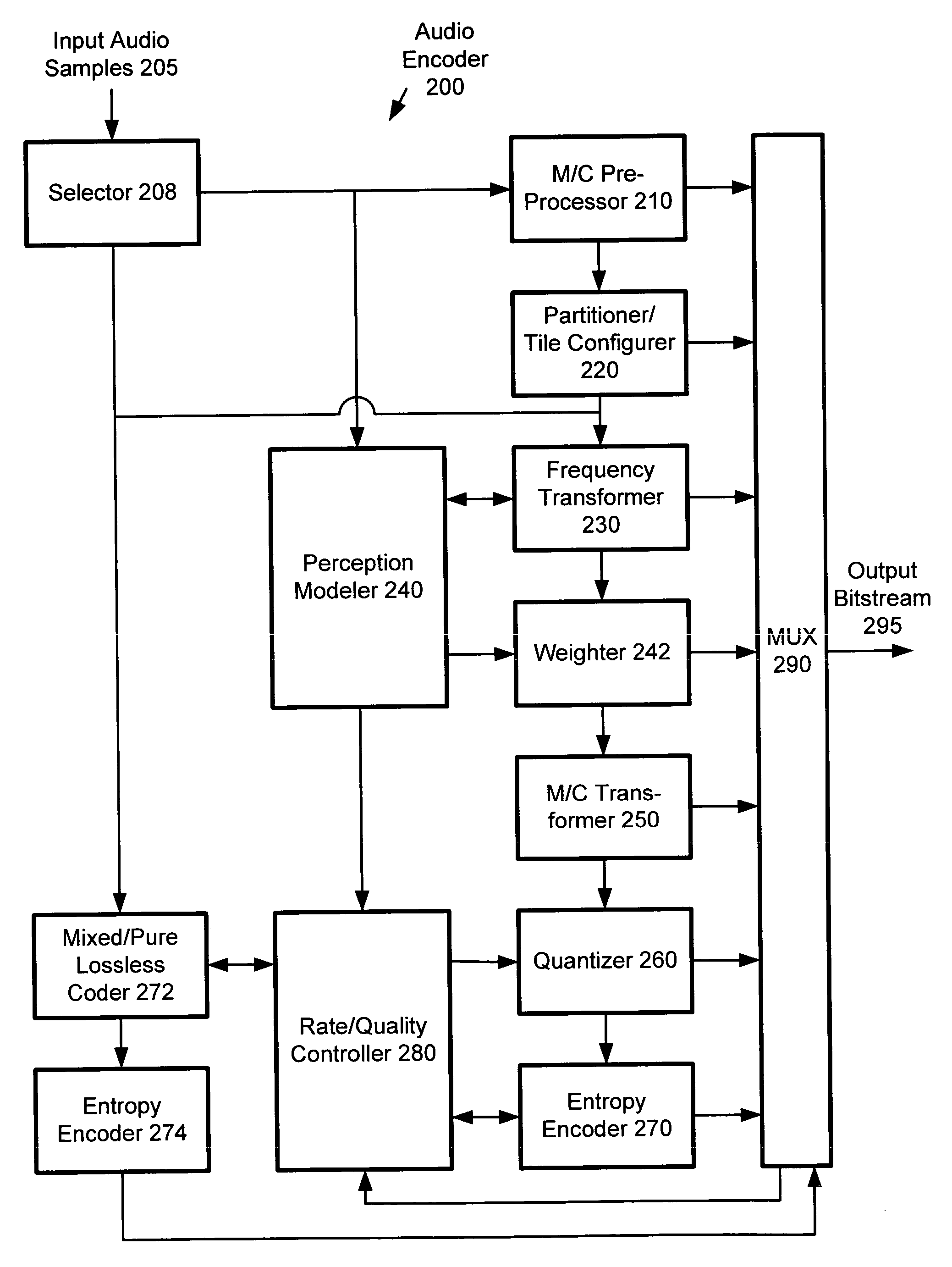
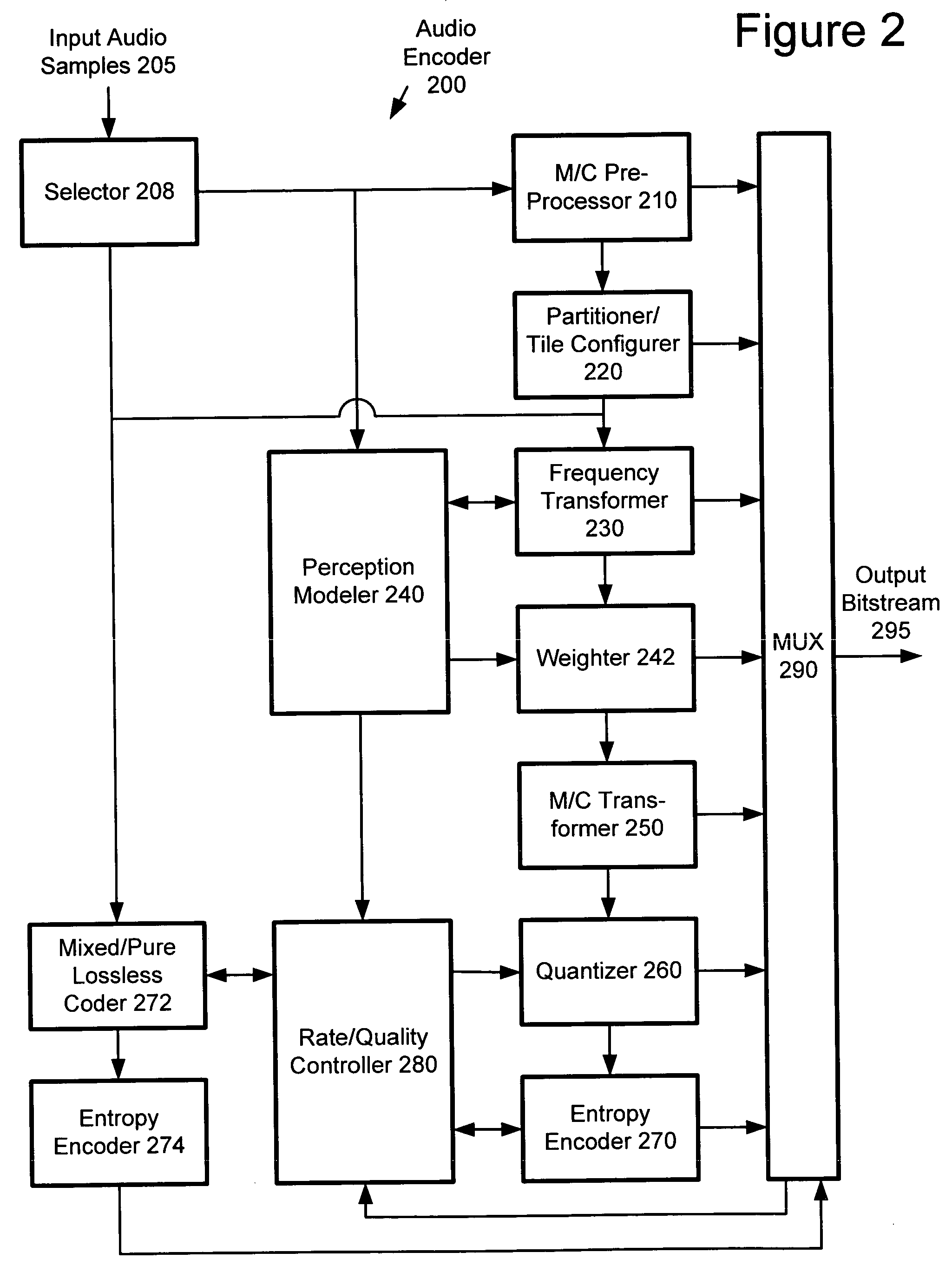
An audio encoder performs adaptive entropy encoding of audio data. For example, an audio encoder switches between variable dimension vector Huffman coding of direct levels of quantized audio data and run-level coding of run lengths and levels of quantized audio data. The encoder can use, for example, context-based arithmetic coding for coding run lengths and levels. The encoder can determine when to switch between coding modes by counting consecutive coefficients having a predominant value (e.g., zero). An audio decoder performs corresponding adaptive entropy decoding.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Parallel CABAC decoding for video decompression
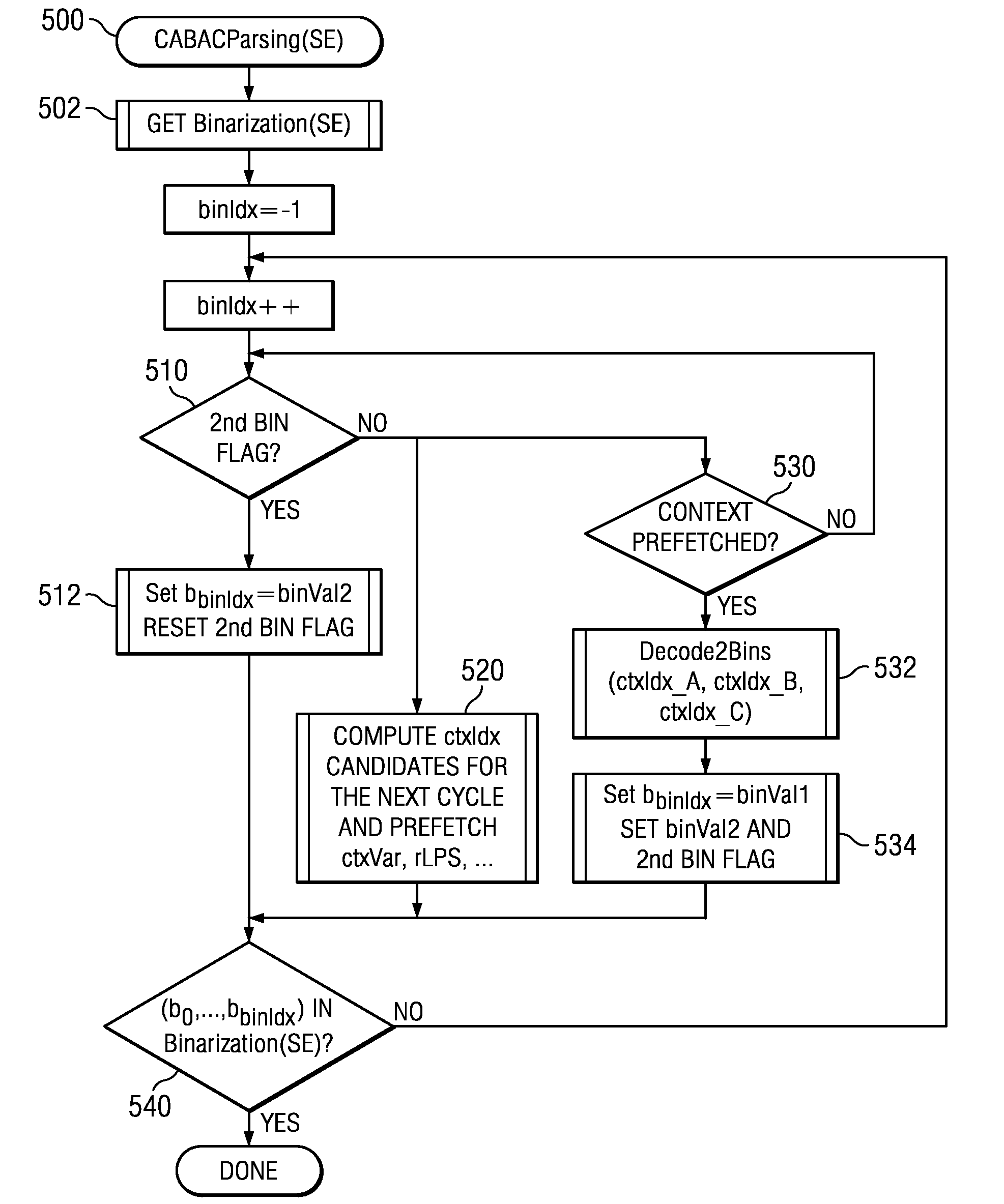
A method of video decoding is provided that includes receiving a data stream comprising a sequence of syntax elements that were compressed using context-adaptive binary arithmetic coding (CABAC), such that the encoding of each bin of a bin string representative of a syntax element was performed by arithmetic encoding. Two consecutive bins of a syntax element are decoded in parallel. Speculative computation and prefetching is used to reduce the critical path and thereby improve processing speed.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
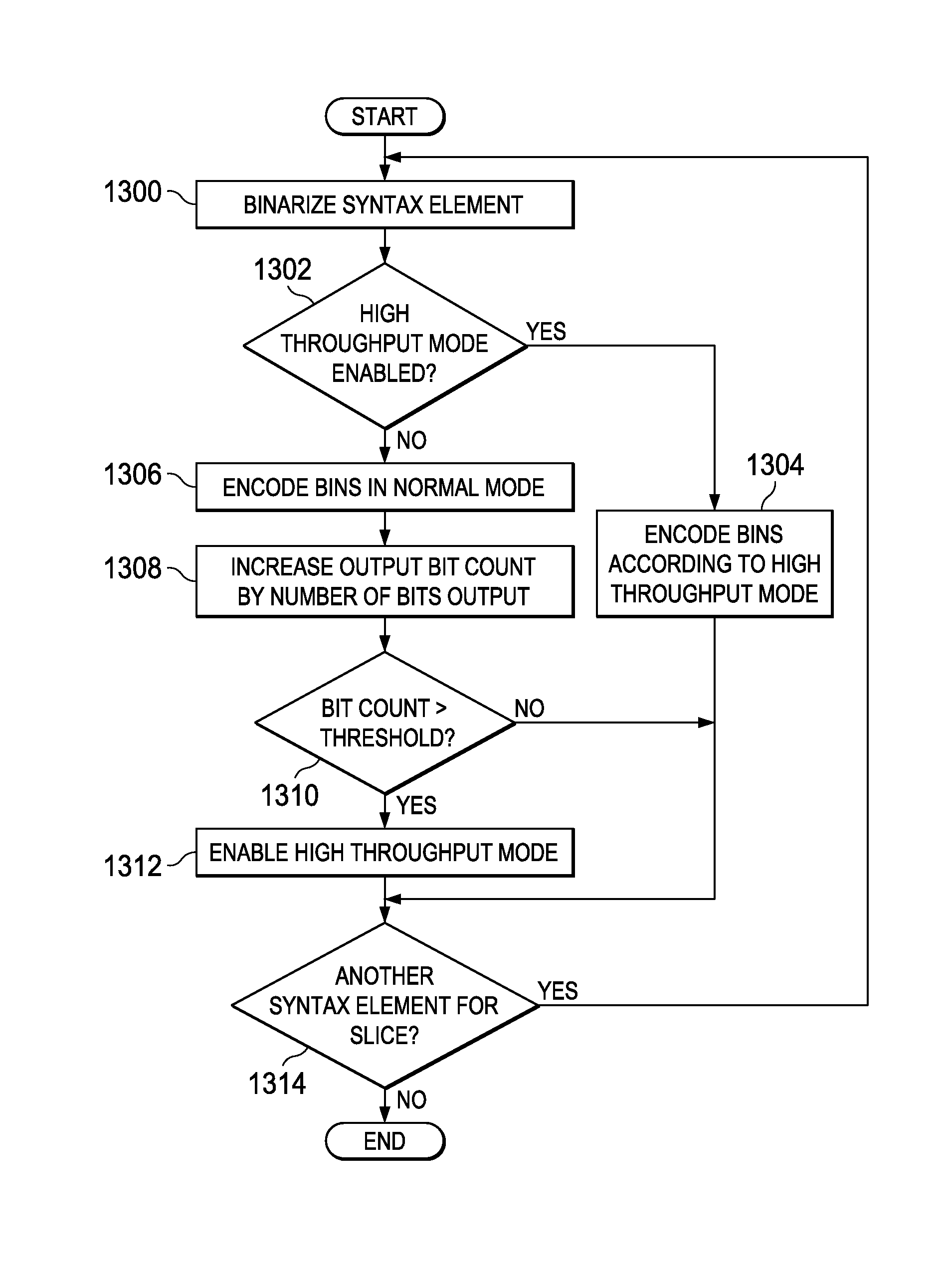
Context Adaptive Binary Arithmetic Coding (CABAC) with Scalable Throughput and Coding Efficiency
ActiveUS20130177069A1Reduce in quantityColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputer architectureVideo sequence
A method for encoding a video sequence is provided that includes entropy encoding syntax elements representative of transform coefficients generated as the video sequence is processed, wherein entropy encoding syntax elements representative of a transform coefficient includes binarizing the syntax elements representative of the transform coefficient to generate a plurality of binary symbols (bins), coding a portion of the plurality of bins in context coding mode, and coding a remaining portion of the plurality of bins in bypass coding mode. The method further includes reducing the number of bins that are coded in context coding mode for each transform coefficient in a plurality of subsequent transform coefficients that are entropy encoded after a specified number of transform coefficients have been entropy encoded.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
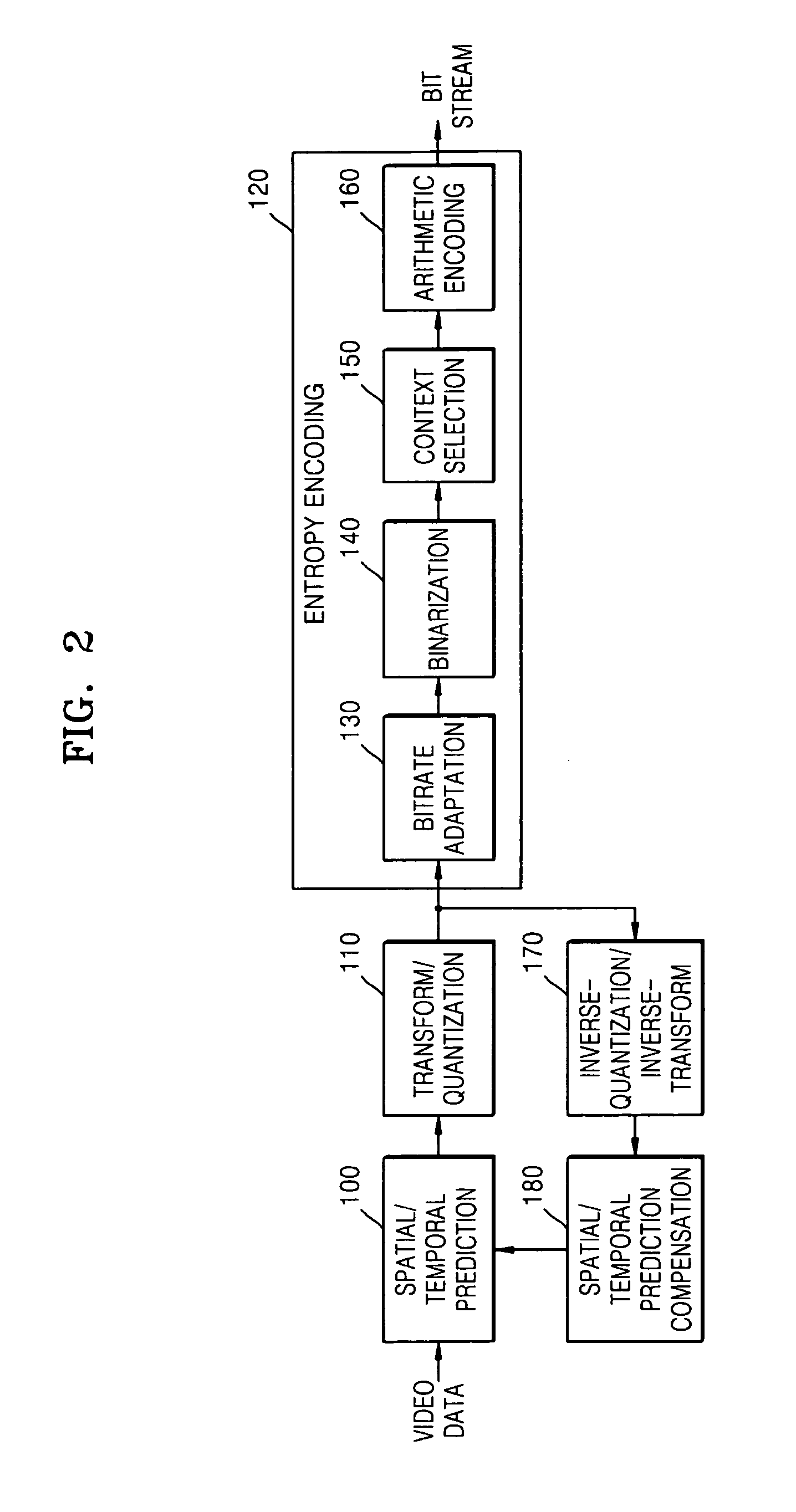
Method, medium, and system encoding/decoding video data using bitrate adaptive binary arithmetic coding
InactiveUS20070171985A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionPattern recognitionArithmetic coding
A method, medium, and system encoding / decoding video data using a binary arithmetic coding adaptive to a compression bit rate of the video data. The system may include a bitrate adaptation unit determining a maximum length of a prefix using a compression bitrate of the video data, a binarization unit dividing the video data into a prefix and a suffix according to the determined maximum length of the prefix and binarizing the video data, and an arithmetic encoding unit performing an arithmetic encoding on the binarized video data. The video data may be encoded / decoded using binary arithmetic encoding / decoding by determining the maximum length of the prefix, an order of an exponential Golomb code, and the number of contexts based on the compression bitrate. Accordingly, it is possible to obtain high encoding efficiency regardless of a range of the desired compression bitrate.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
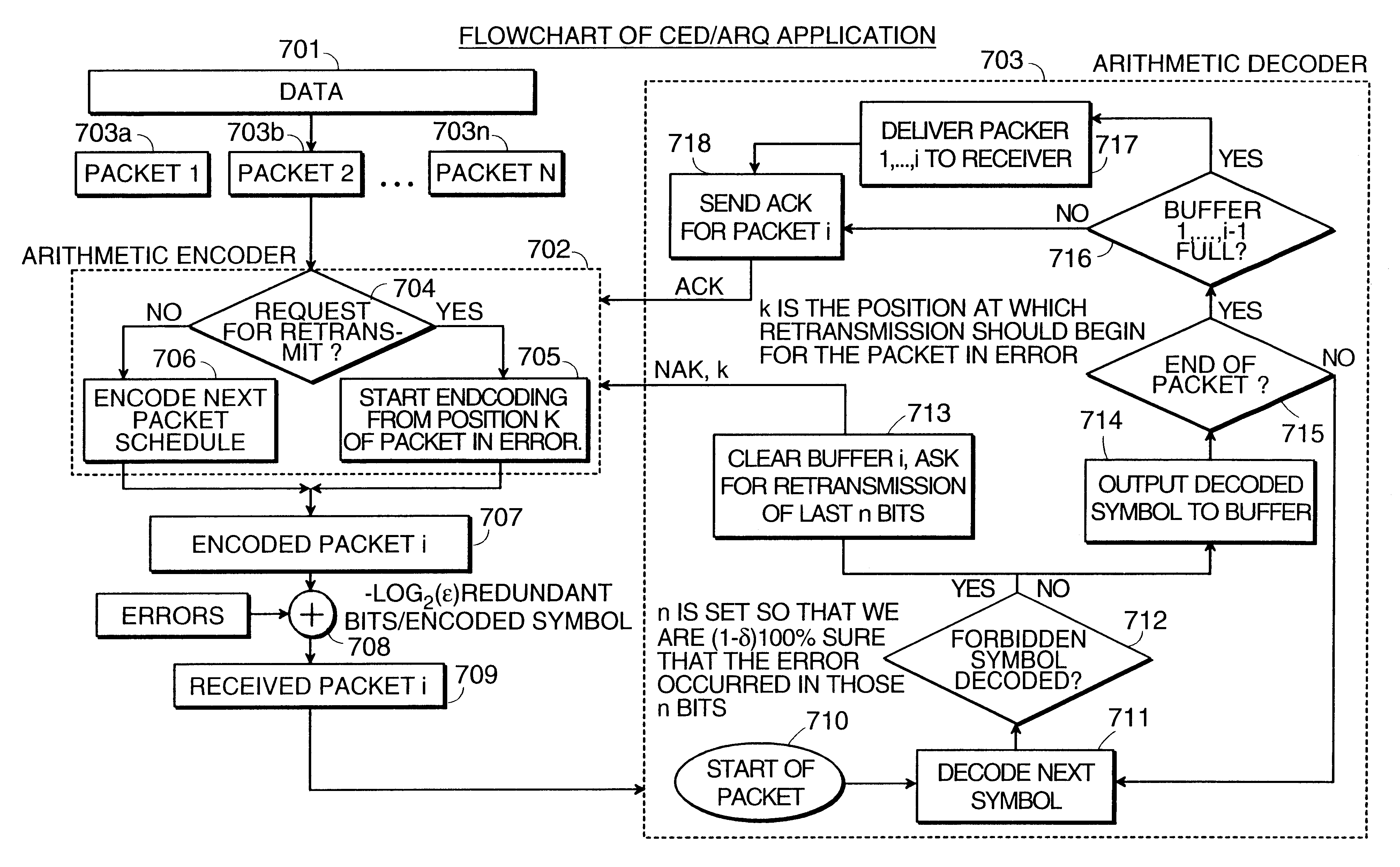
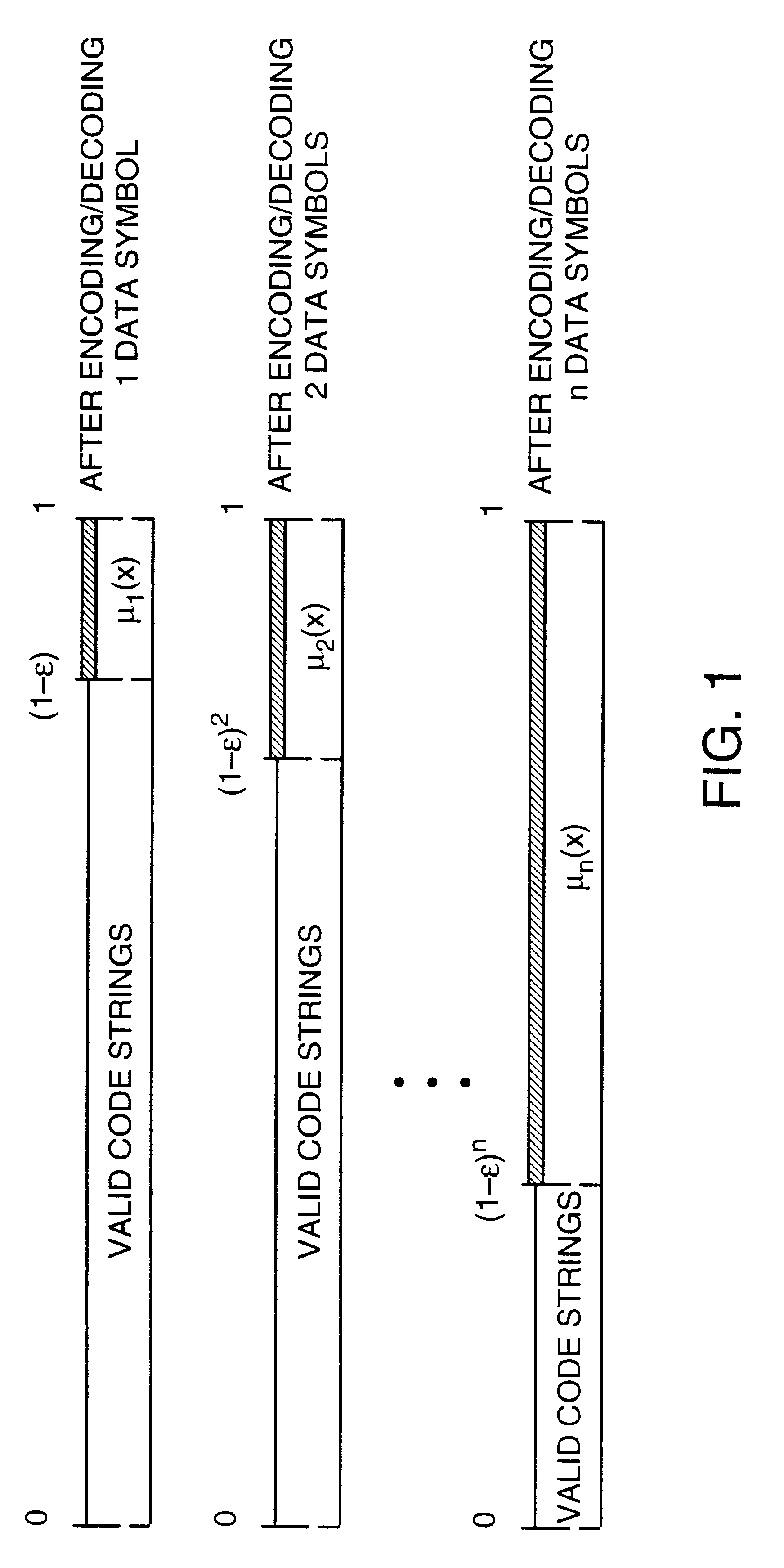
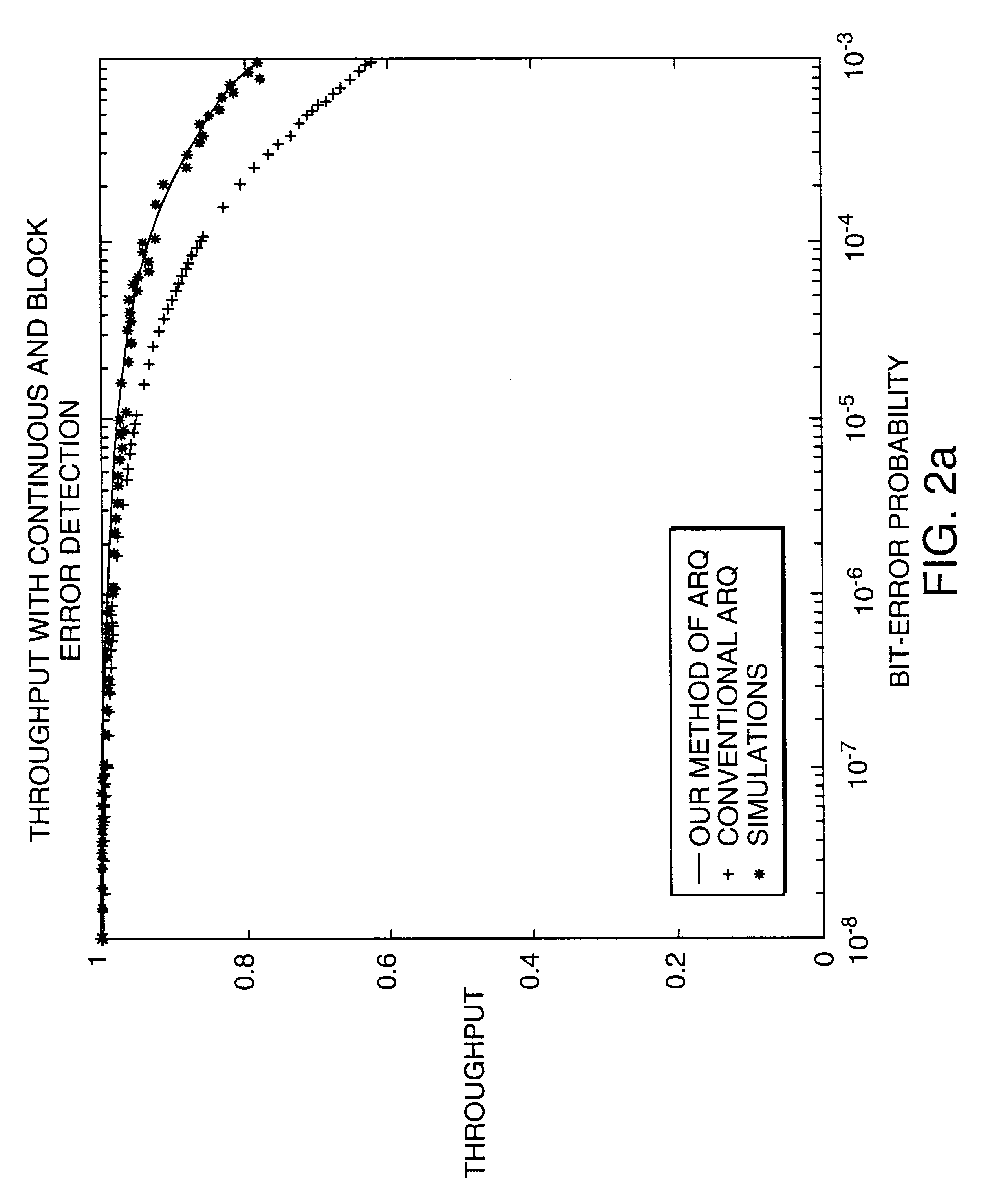
Data transmission using arithmetic coding based continuous error detection
InactiveUS6418549B1Error prevention/detection by using return channelTransmission systemsAutomatic repeat requestTrade offs
Method and apparatus for image transmission using arithmetic coding, based on continuous error detection uses a controlled amount of added redundancy. A continuous error detection scheme is provided, wherein there is a trade-off between the amount of added redundancy and the time needed to detect an error once it occurs. Herein, there is no need for the cyclic redundancy check (CRC) to wait until an entire block of data has been received and processed before an error can be detected. The invention can be used to great advantage both in the automatic repeat request (ARQ) and other concatenated coding schemes. Errors in the received bit stream are detected by introducing added redundancy, e.g., a forbidden symbol, in the arithmetic coding operation. The forbidden symbol is never intended to be encoded. The redundancy error causes loss of synchronization, which is used to detect errors. If a forbidden symbol gets decoded, it means that an error has occurred. In this invention, there is direct control over the amount of redundancy added vs. the amount of time it takes to detect an error. For image compression systems, by using the invention and ARQ, only one device would suffice both for source compression and channel coding.
Owner:MERU NETWORKS
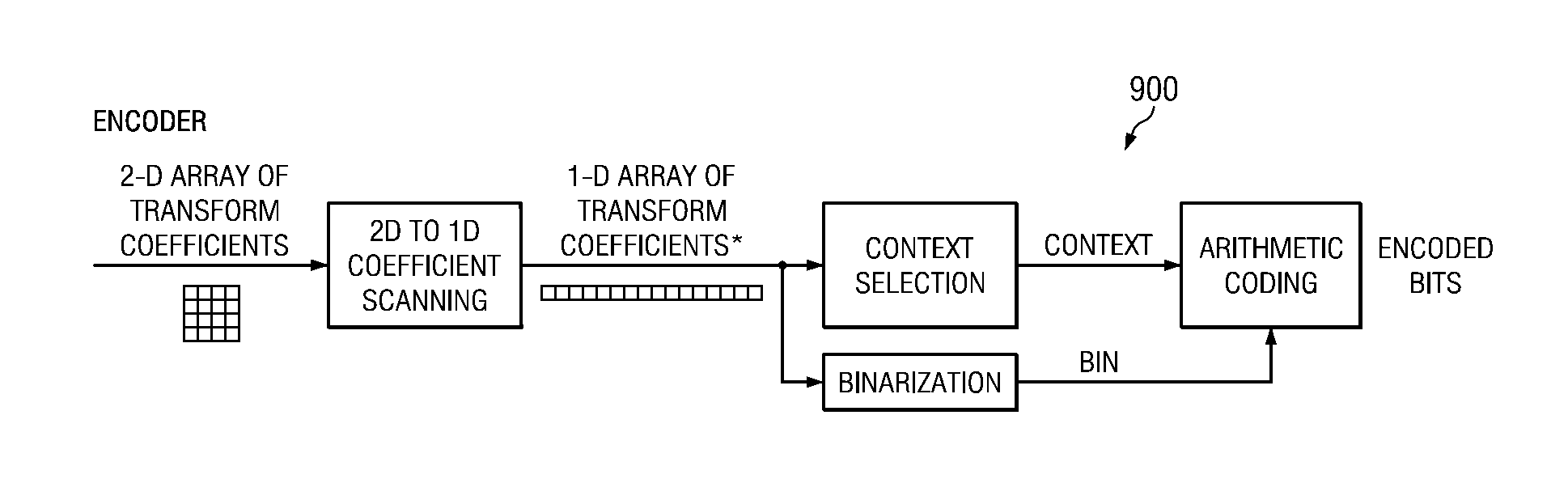
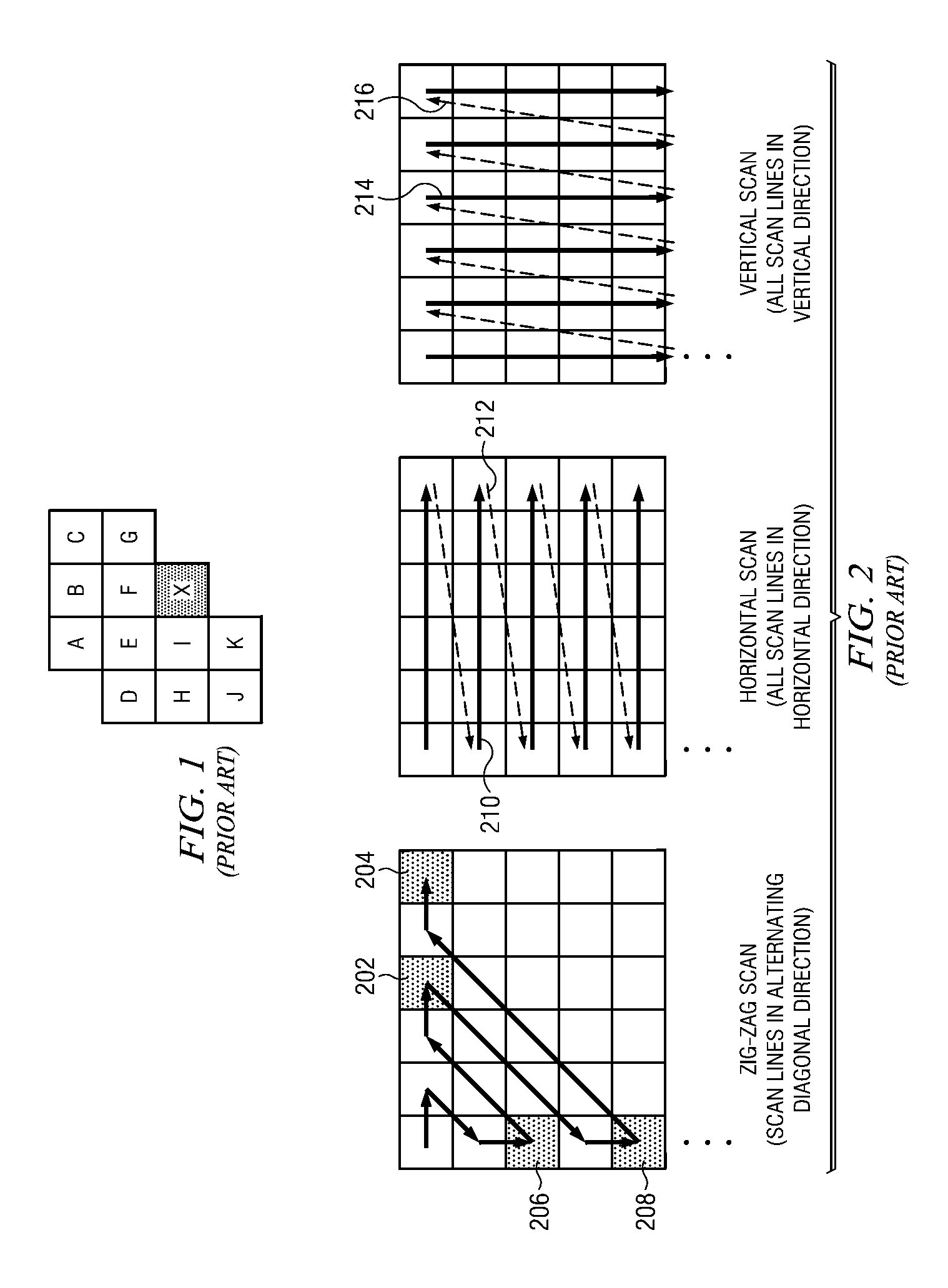
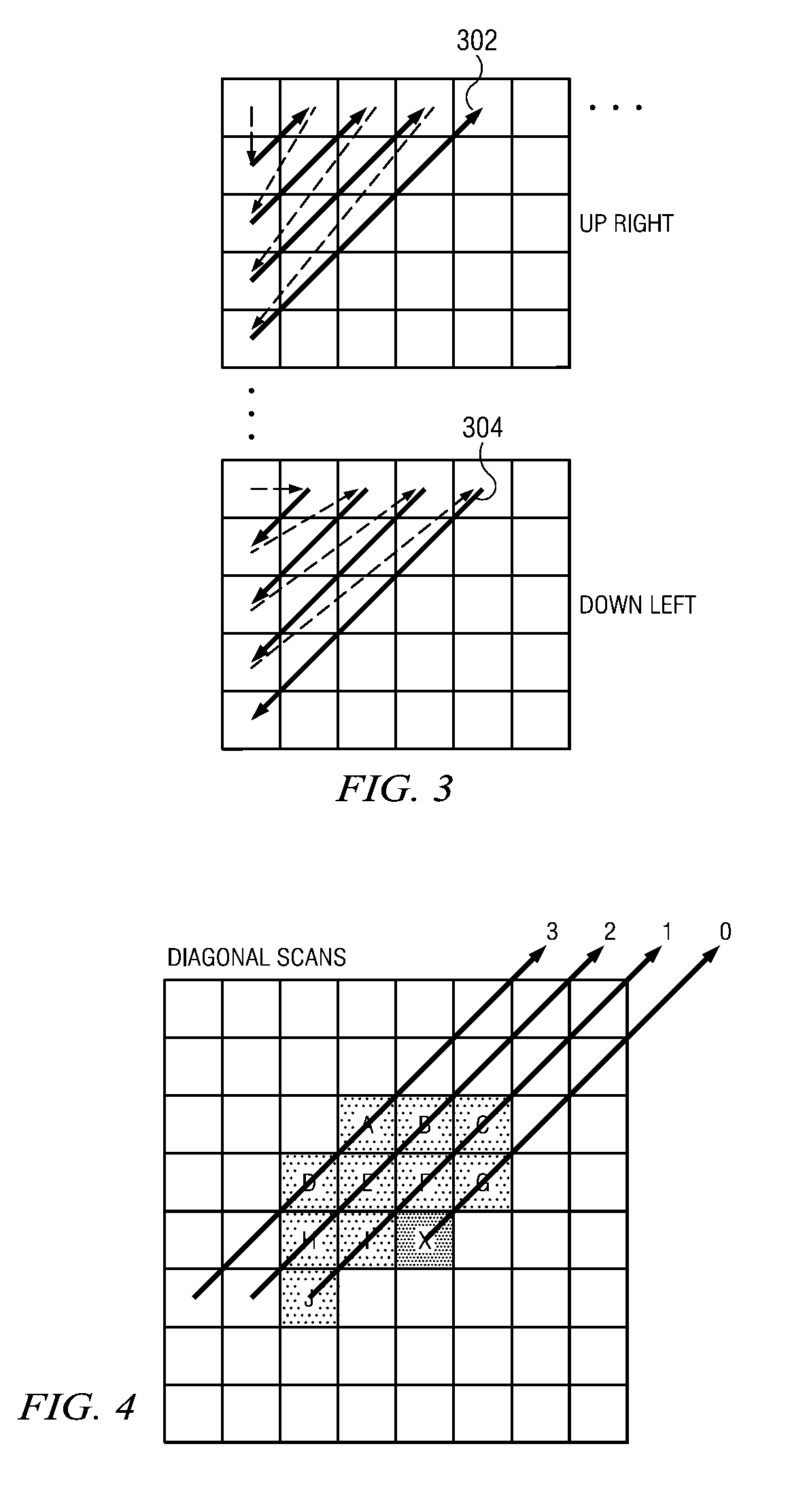
Method and apparatus for diagonal scan and simplified context selection for parallel entropy coding of significance map of transform coefficients
ActiveUS20120082233A1Reduce dependenceReduced neighboring dependencyColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionTheoretical computer scienceArithmetic coding
A method and apparatus for encoding bit code utilizing context dependency simplification to reduce dependent scans. The method includes retrieving at least one 2 dimensional array of transform coefficient, transforming the at least one 2 dimensional array of the significance map of the transform coefficient to a 1 dimensional coefficient scanning and determining at least one of scan direction, coding unit type and slice type assigned to transform coefficient, selecting neighbors based on at least one of scan direction and coding unit type and slice type, computing context index based on the values of the selected neighbors for context selection, and performing arithmetic coding to generate coded bit utilizing the computed context index and binarization.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
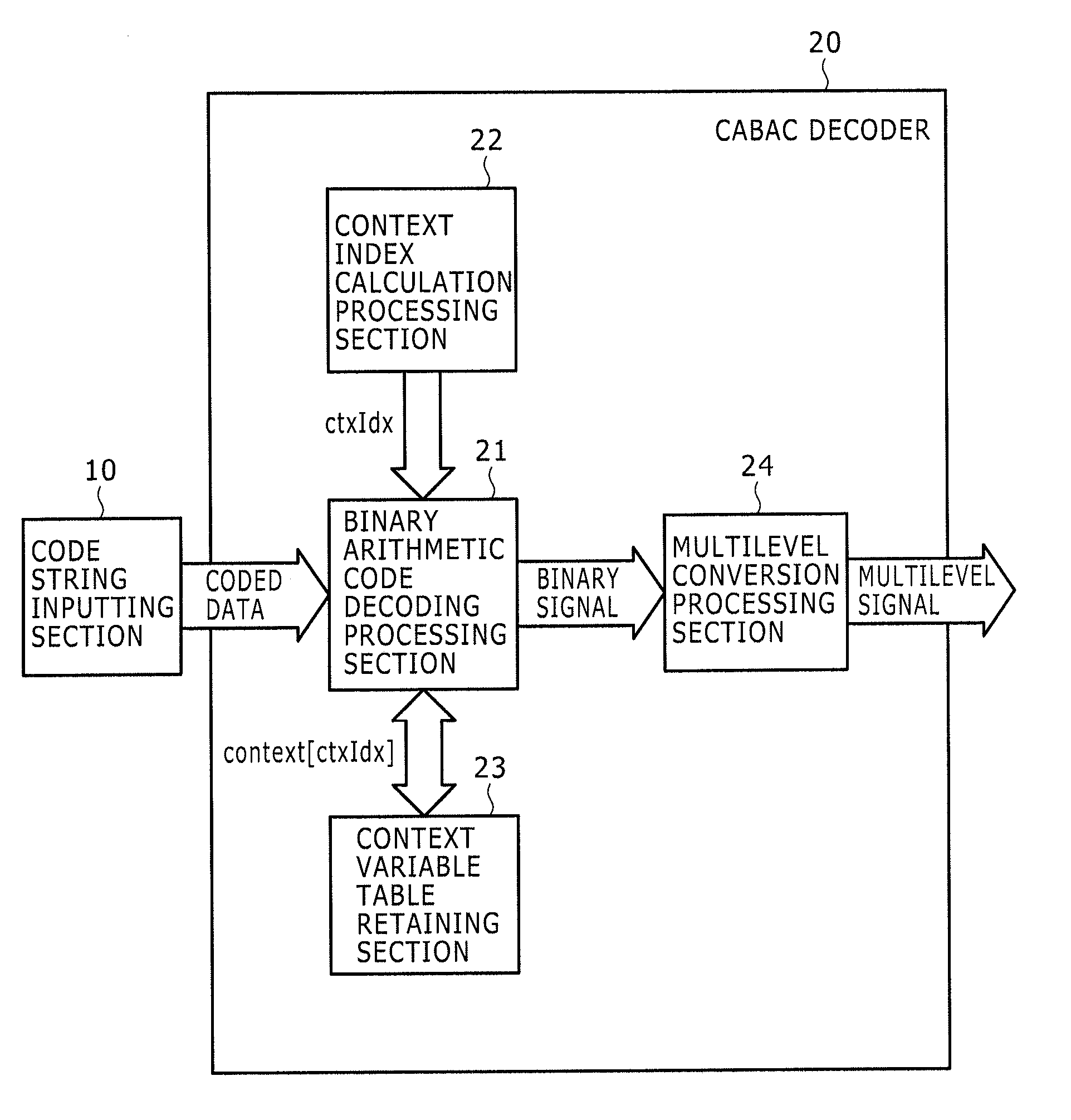
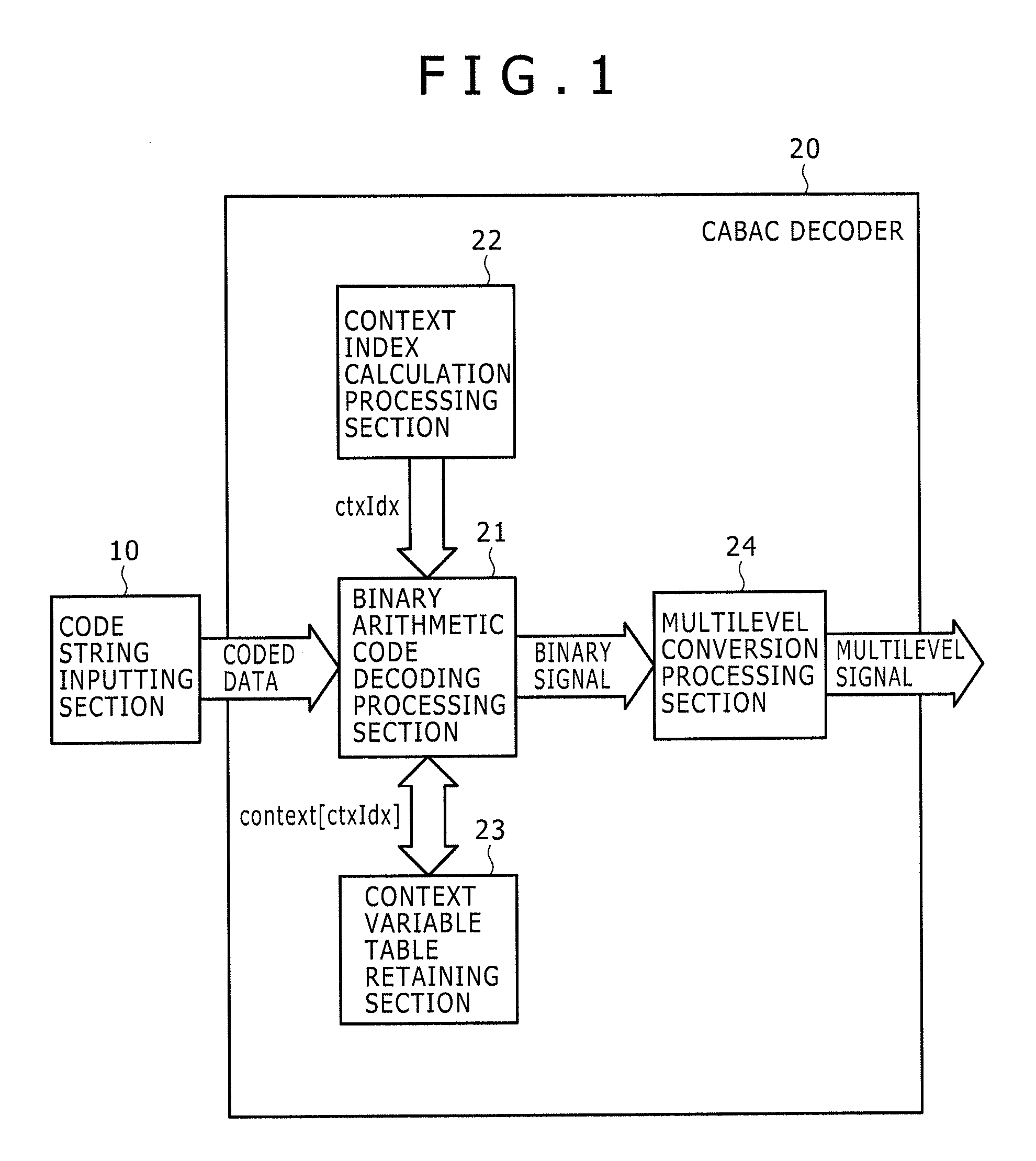
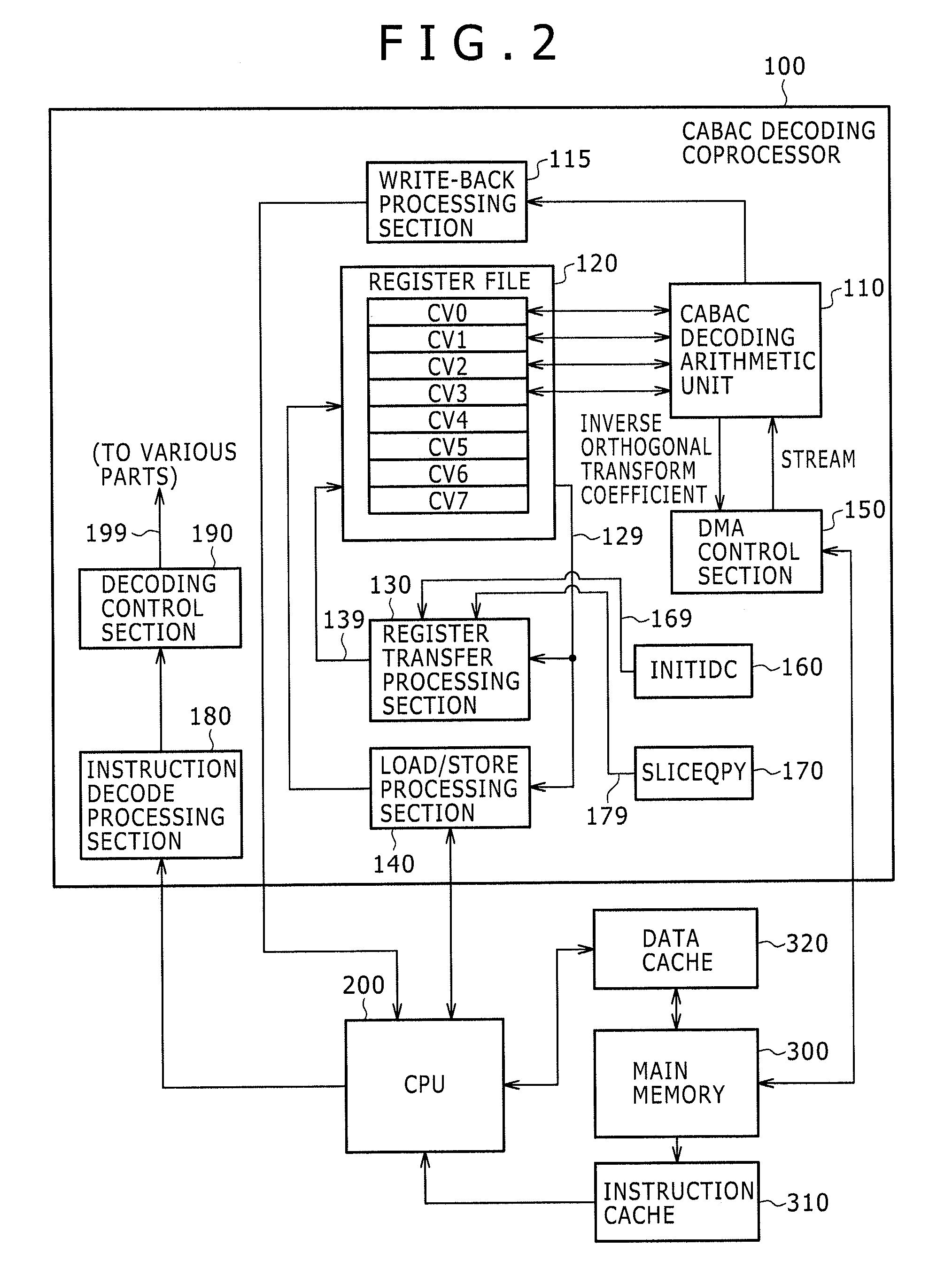
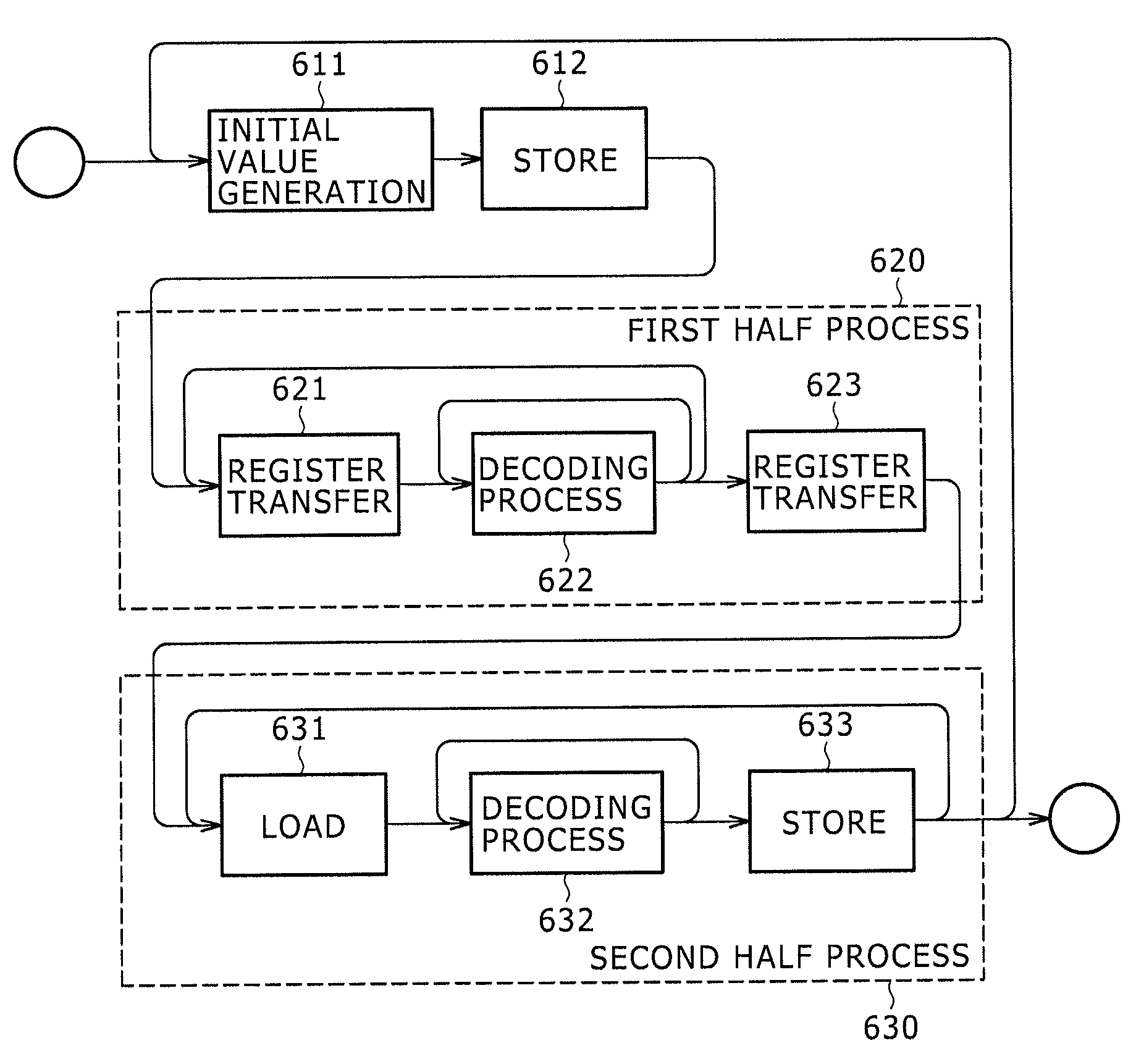
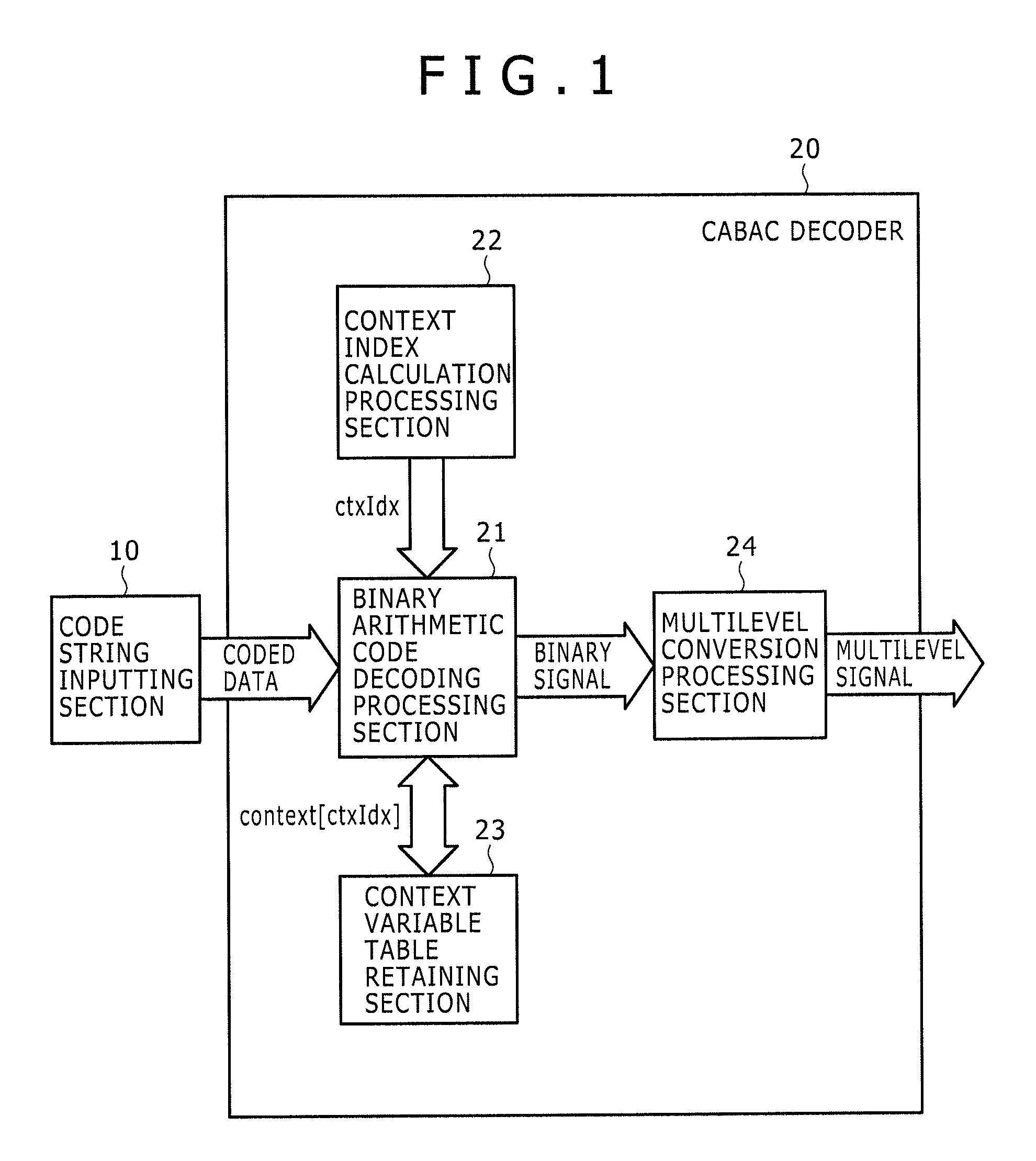
Arithmetic decoding device
InactiveUS20090273491A1Good effectImprove processing speedCode conversionDigital video signal modificationParallel computingArithmetic coding
Disclosed herein is an arithmetic decoding device including: an arithmetic decoding unit configured to decode coded data resulting from arithmetic coding on a basis of a context variable indicating a probability state and a most probable symbol; a plurality of arithmetic registers configured to supply the context variable to the arithmetic decoding unit and retain a result of operation by the arithmetic decoding unit; and a plurality of save registers configured to save contents retained in the arithmetic registers.
Owner:SONY CORP
Arithmetic decoding device
InactiveUS7884743B2Improve processing speedCode conversionDigital video signal modificationProcessor registerParallel computing
Disclosed herein is an arithmetic decoding device including: an arithmetic decoding unit configured to decode coded data resulting from arithmetic coding on a basis of a context variable indicating a probability state and a most probable symbol; a plurality of arithmetic registers configured to supply the context variable to the arithmetic decoding unit and retain a result of operation by the arithmetic decoding unit; and a plurality of save registers configured to save contents retained in the arithmetic registers.
Owner:SONY CORP
Method for selection of contexts for arithmetic coding of reference picture and motion vector residual bitstream syntax elements
ActiveUS7469070B2Faster and accurate adaptationEasy to compressCode conversionCharacter and pattern recognitionMultiple contextDigital video
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
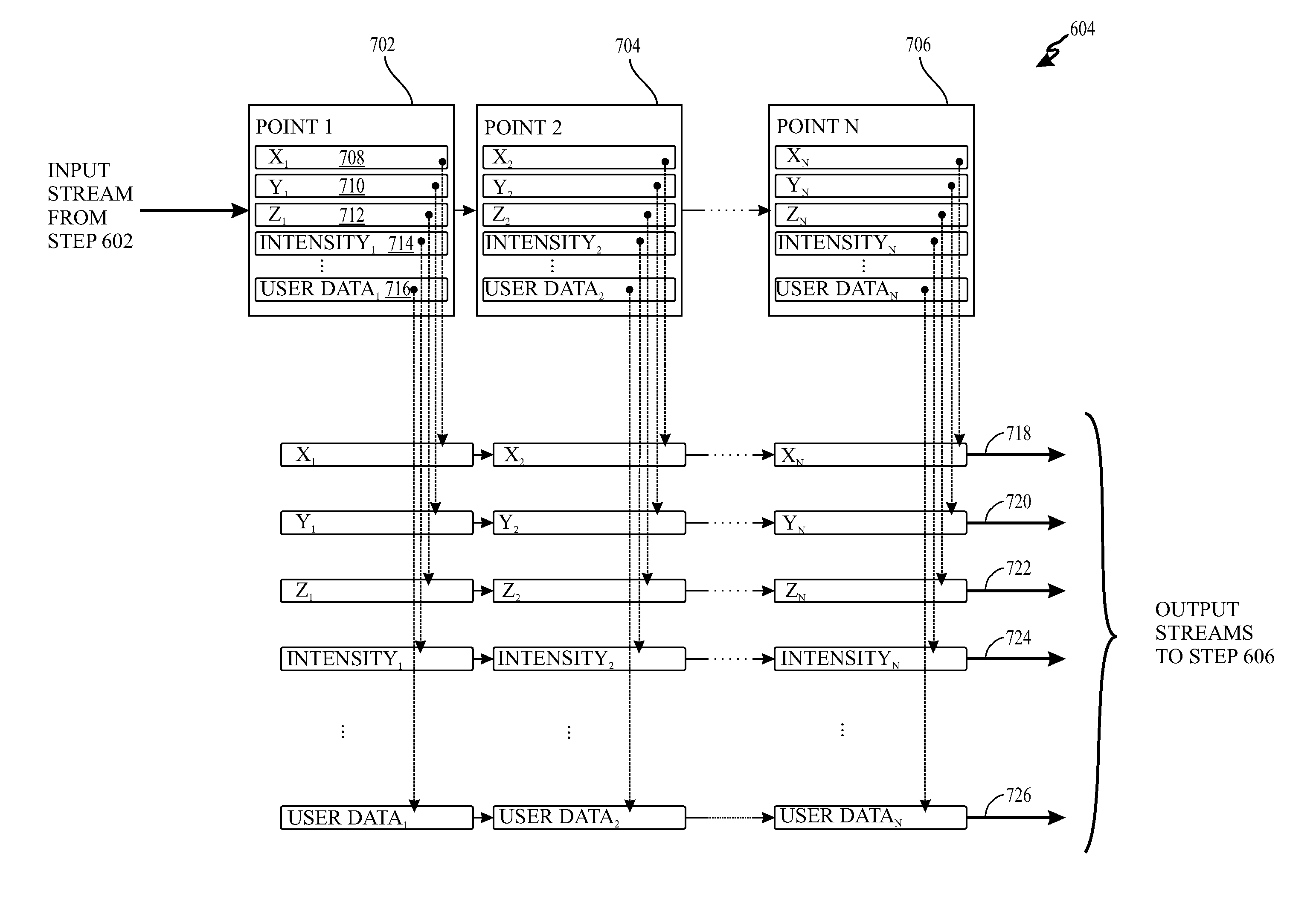
LIGHT DETECTION AND RANGING (LiDAR)DATA COMPRESSION AND DECOMPRESSION METHODS AND APPARATUS
ActiveUS20120124113A1Digital data processing detailsDigital computer detailsData compressionScalar Value
Methods and apparatus for lossless LiDAR LAS file compression and decompression are provided that include predictive coding, variable-length coding, and arithmetic coding. The predictive coding uses four different predictors including three predictors for x, y, and z coordinates and a constant predictor for scalar values, associated with each LiDAR data point.
Owner:UNIV OF MARIBOR LAB FOR GEOMETRIC MODELLING & MULTIMEDIA ALGORITHMS
Method and system for fast context based adaptive binary arithmetic coding
InactiveUS7221296B2Improve the level ofReduce overheadCode conversionCharacter and pattern recognitionParallel computingFloating point
A method and processor for providing context-based adaptive binary arithmetic CABAC coding. Binarization is performed on one or more syntax elements to obtain a binary sequence. Data bits of the said binary sequence are provided to an arithmetic encoding unit in bulk. Binarization is performed on one or more syntax elements to generate exp Golomb code by converting mapped syntax-element values to corresponding floating point type values. Re-normalization of CABAC encoding is performed by restructuring the re-normalization into two processing units including an arithmetic encoding unit and a bit writing unit. The bit writing unit is configured to format signal bits into a multiple-bit sequence, and write multiple bits simultaneously during an execution of a bit writing loop.
Owner:STREAMING NETWORKS PVT
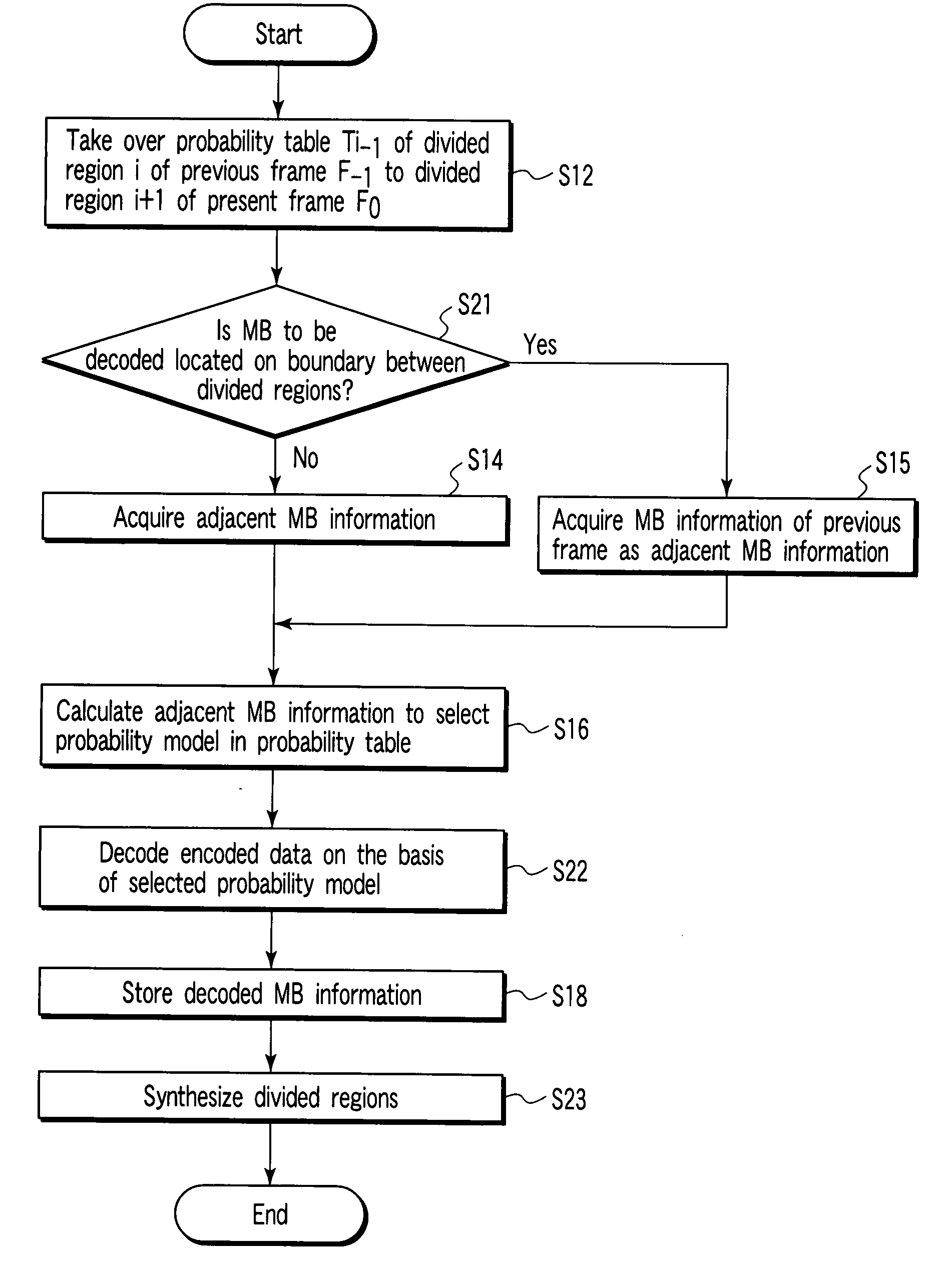
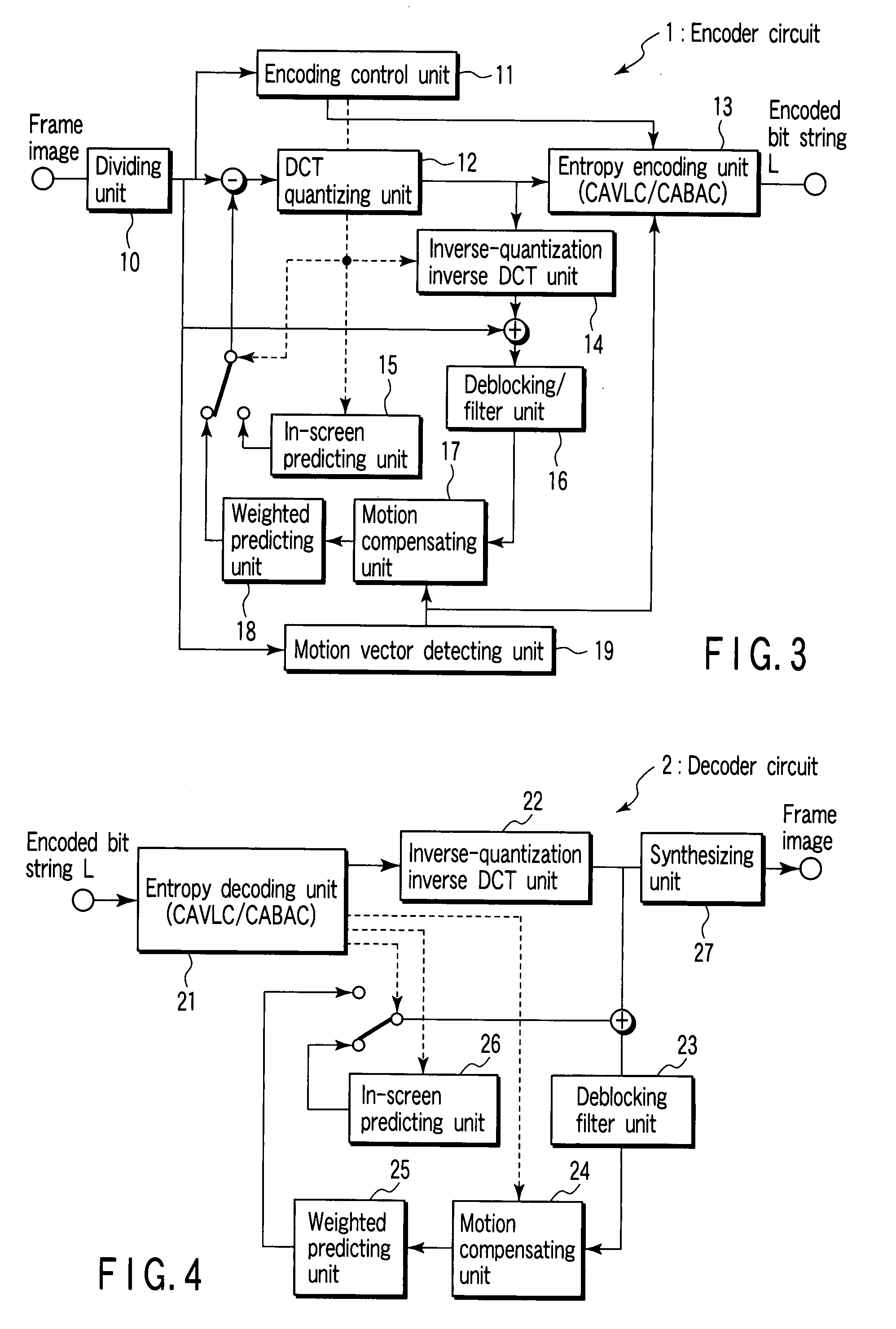
Encoding circuit, decoding circuit, encoder circuit, decoder circuit, and CABAC processing method
InactiveUS20080001796A1Code conversionDigital video signal modificationPattern recognitionArithmetic coding
According to one embodiment, an encoding circuit includes a taking-over unit which takes over probability tables of divided regions of a previous frame image of a frame image having divided regions to divided regions of a present frame image, respectively, an acquiring unit which acquires a parameter of an adjacent macro block of the previous frame image when the macro block is located on a boundary between the divided regions, a selecting unit which calculates the parameter of the macro block to select one of probability models in the probability table, and an encoding unit which arithmetically encodes a residual signal in the frame image on the basis of the selected probability model to generate an encoded bit string.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com