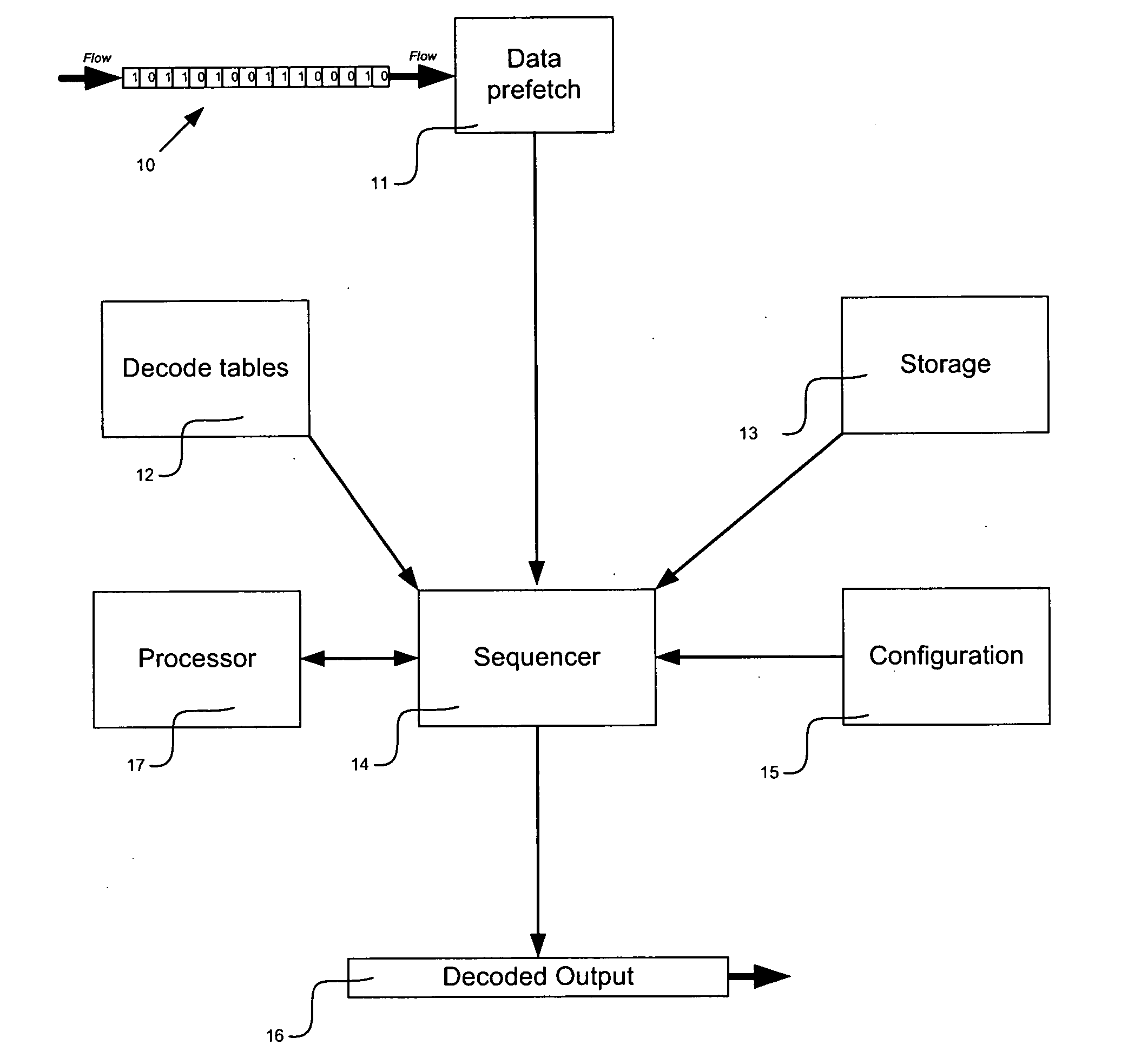
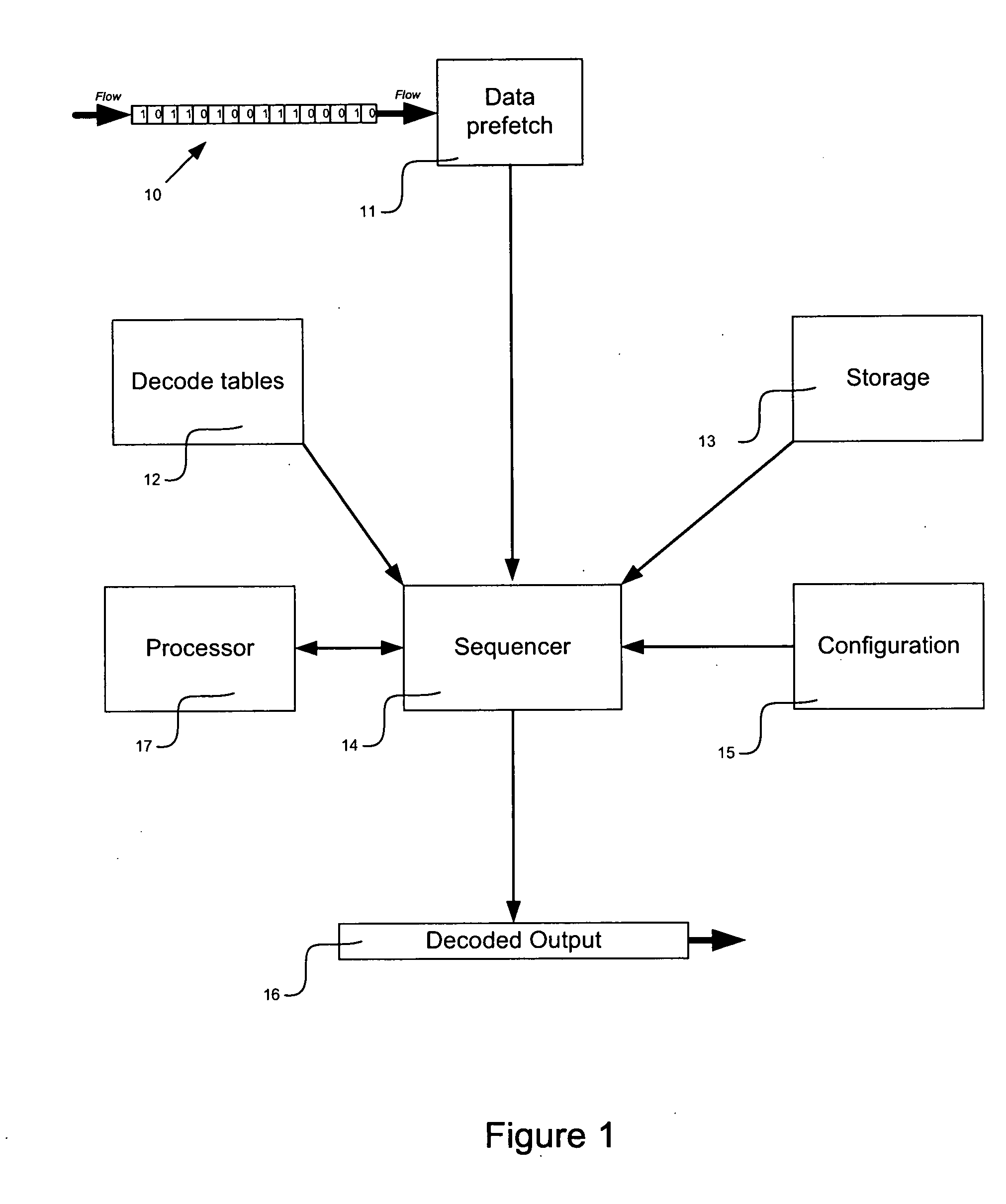
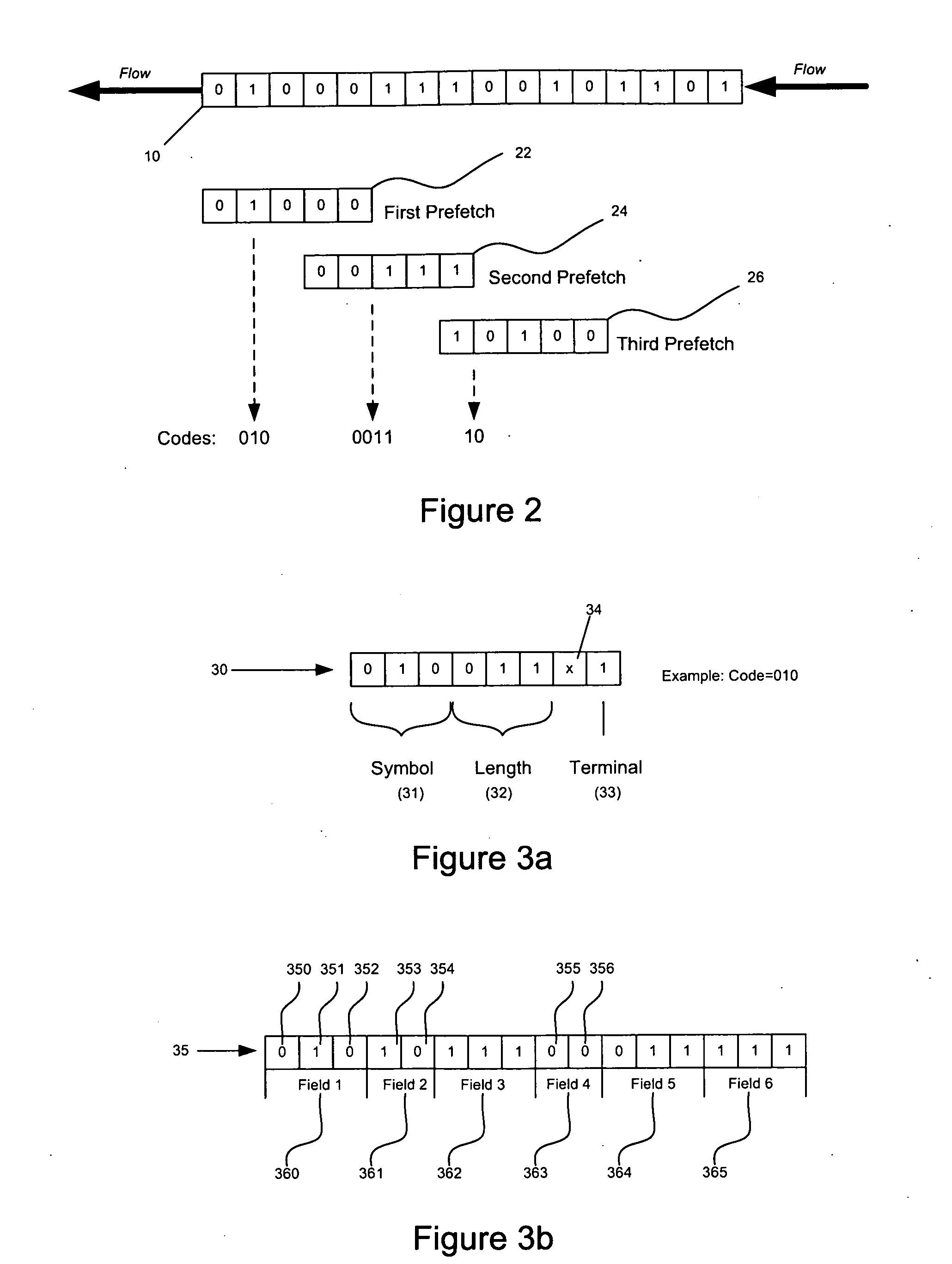
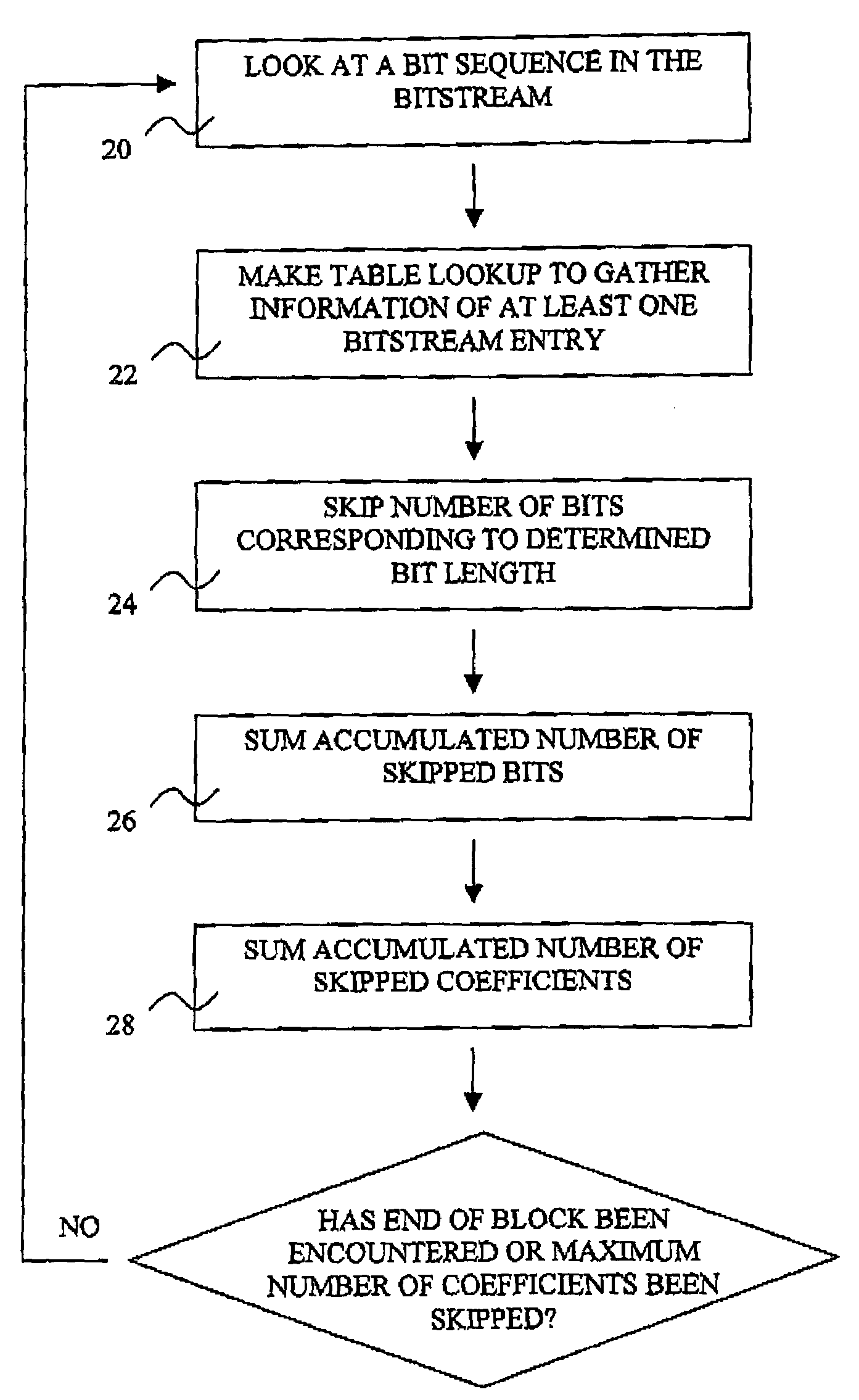
Patents
Literature
376 results about "Huffman coding" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
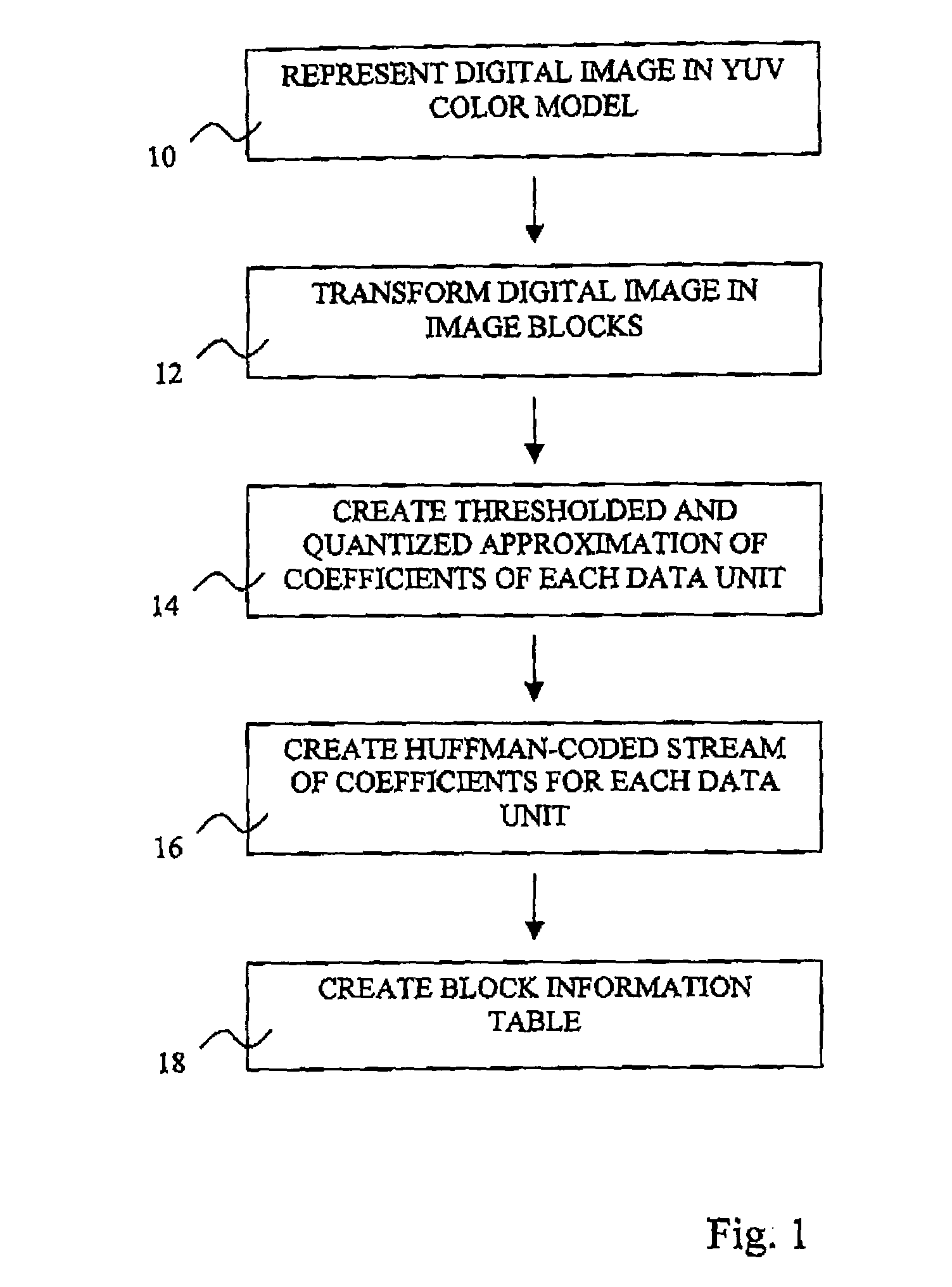
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In computer science and information theory, a Huffman code is a particular type of optimal prefix code that is commonly used for lossless data compression. The process of finding or using such a code proceeds by means of Huffman coding, an algorithm developed by David A. Huffman while he was a Sc.D. student at MIT, and published in the 1952 paper "A Method for the Construction of Minimum-Redundancy Codes".
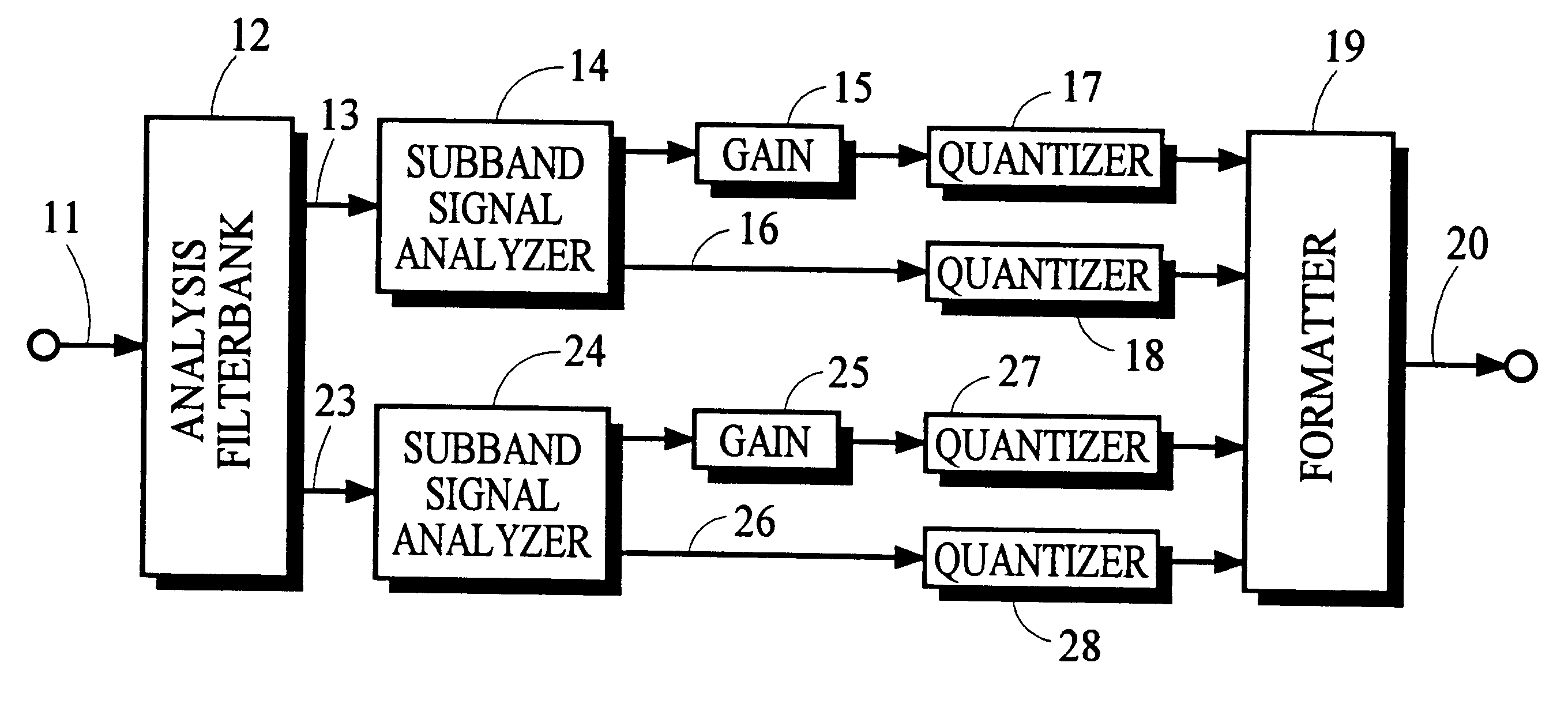
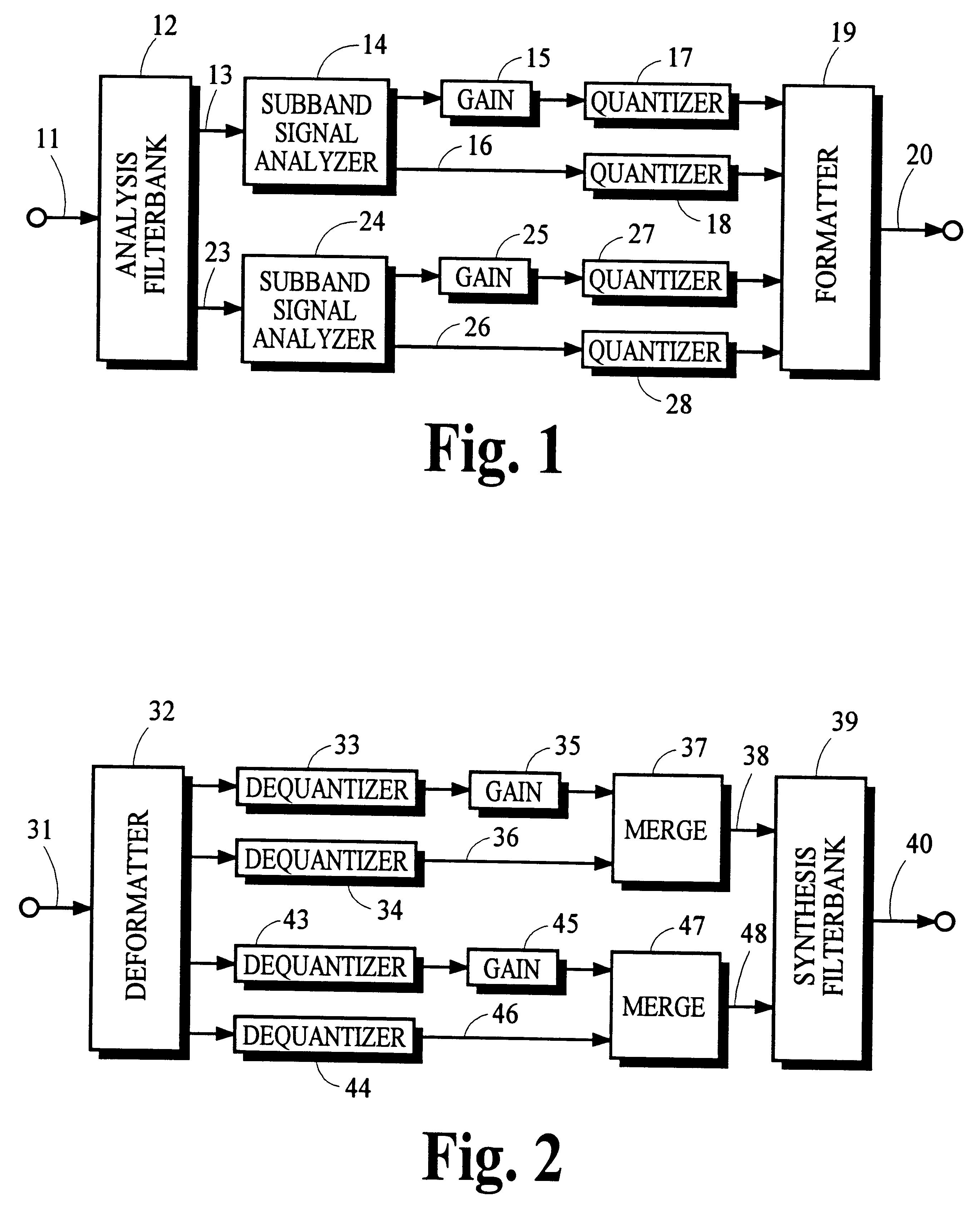
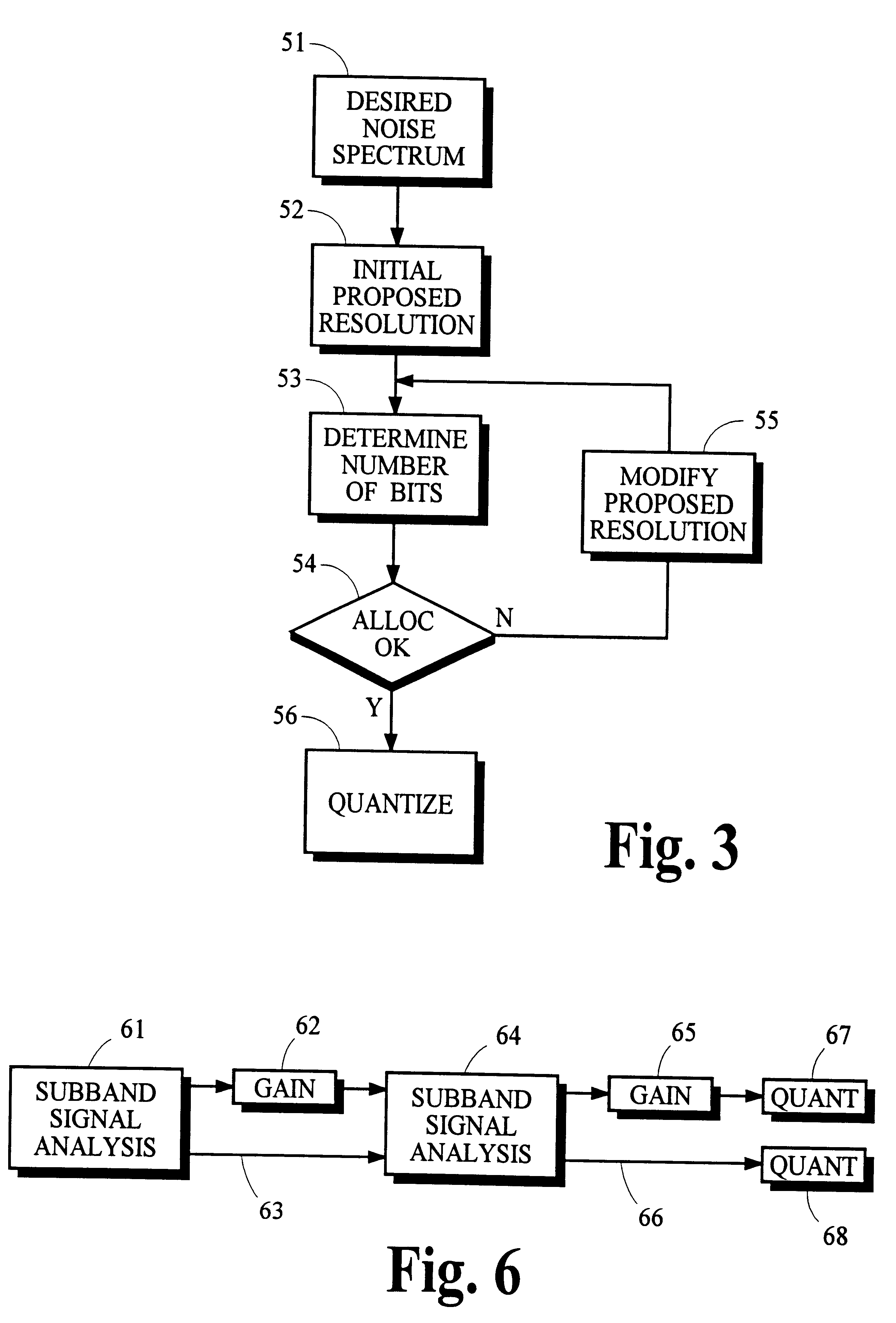
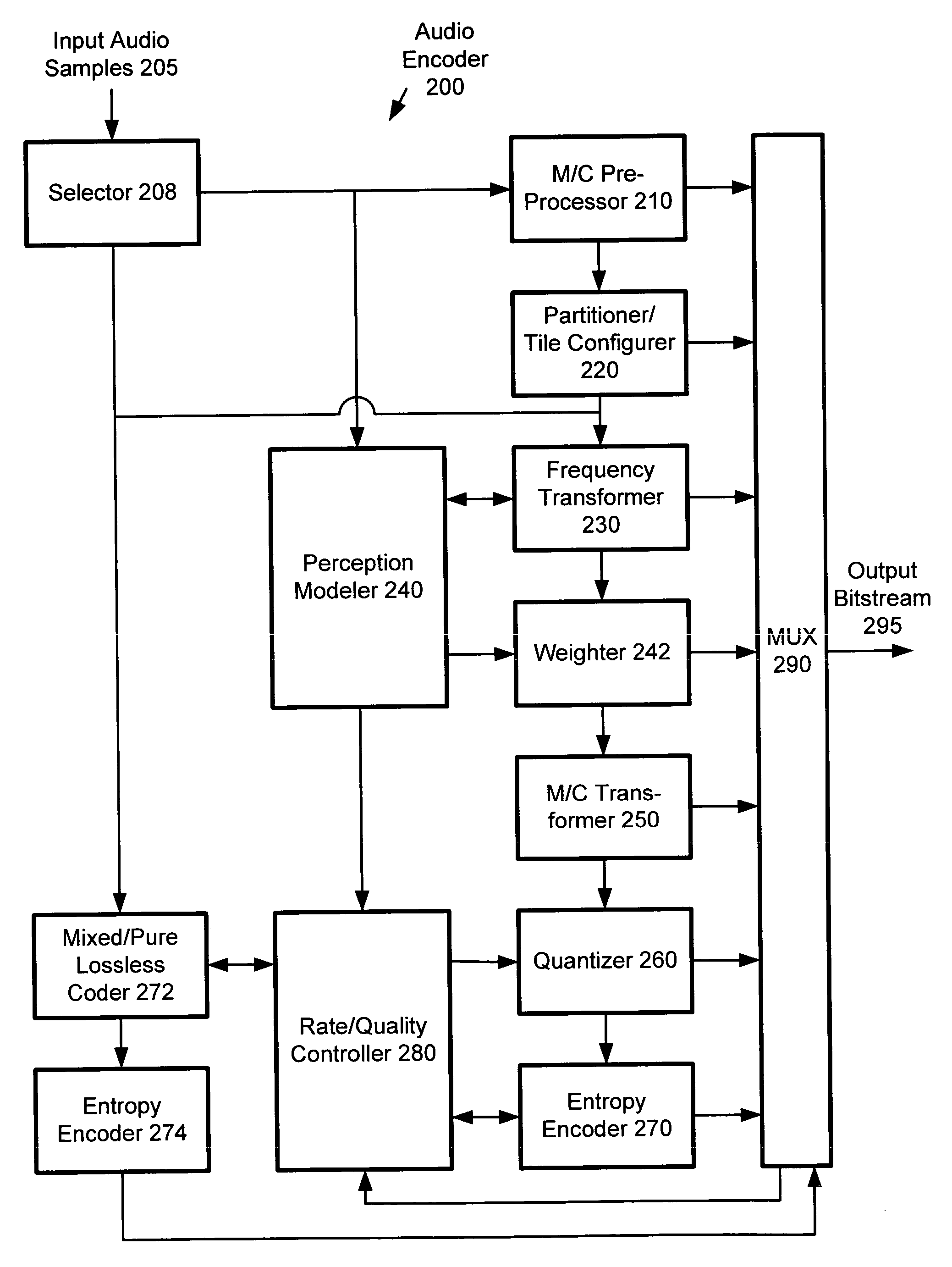
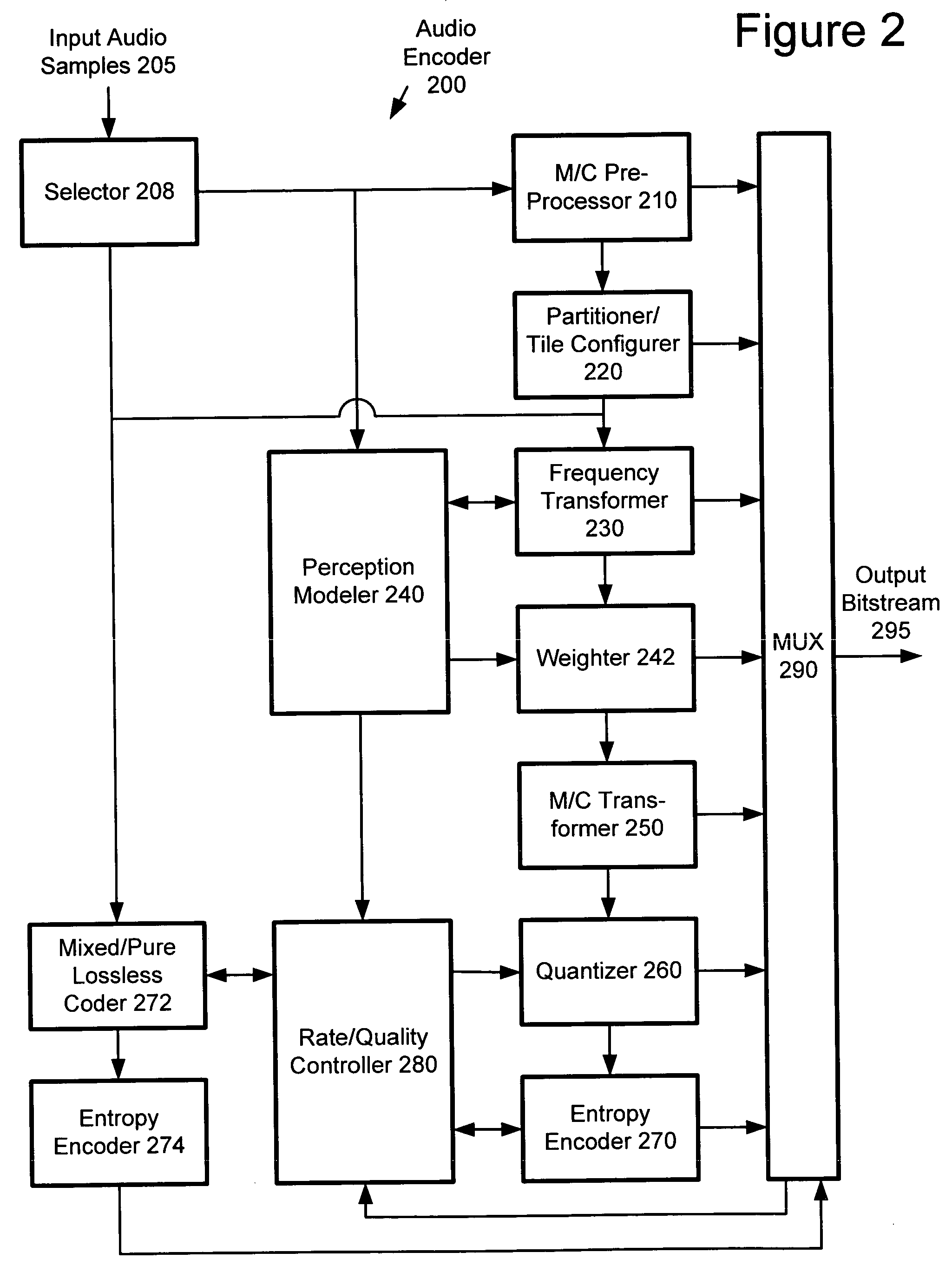
Using gain-adaptive quantization and non-uniform symbol lengths for improved audio coding
InactiveUS6246345B1Good coding gainEfficient executionColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionNormal densityIntra-frame
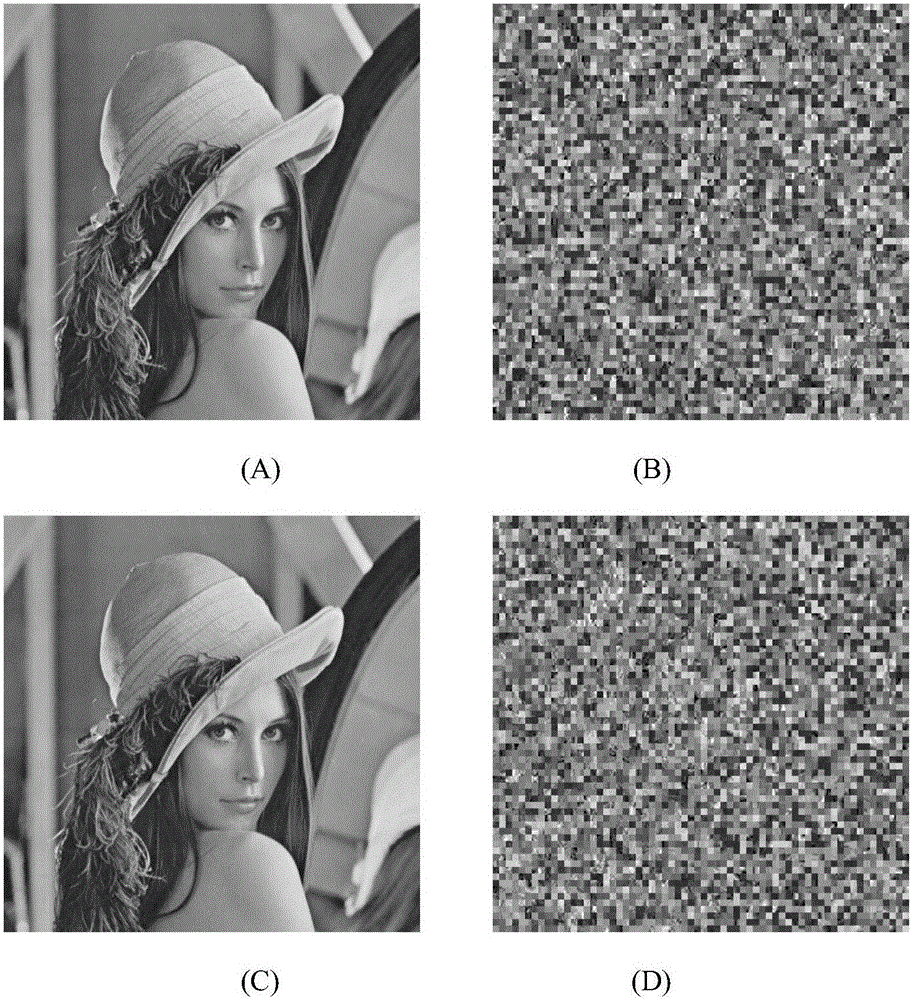
Techniques like Huffman coding can be used to represent digital audio signal components more efficiently using non-uniform length symbols than can be represented by other coding techniques using uniform length symbols Unfortunately, the coding efficiency that can be achieved by Huffman coding depends on the probability density function of the information to be coded and the Huffman coding process itself requires considerable processing and memory resources. A coding process that uses gain-adaptive quantization according to the present invention can realize the advantage of using non-uniform length symbols while overcoming the shortcomings of Huffman coding. In gain-adaptive quantization, the magnitudes of signal components to be encoded are compared to one or more thresholds and placed into classes according to the results of the comparison. The magnitudes of the components placed into one of the classes are modified according to a gain factor that is related to the threshold used to classify the components. Preferably, the gain factor may be expressed as a function of only the threshold value. Gain-adaptive quantization may be used to encode frequency subband signals in split-band audio coding systems. Additional features including cascaded gain-adaptive quantization, intra-frame coding, split-interval and non-overloading quantizers are disclosed.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
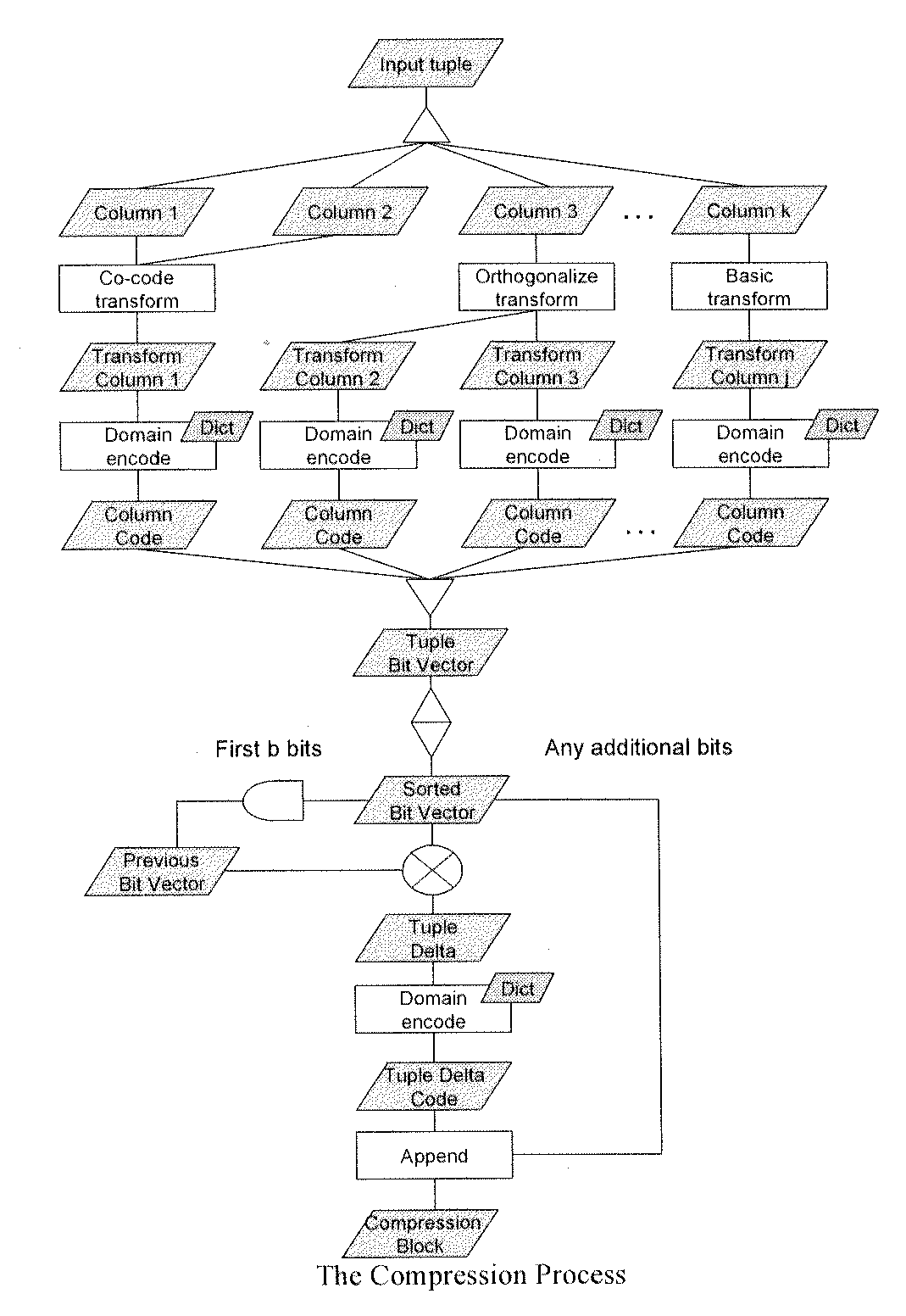
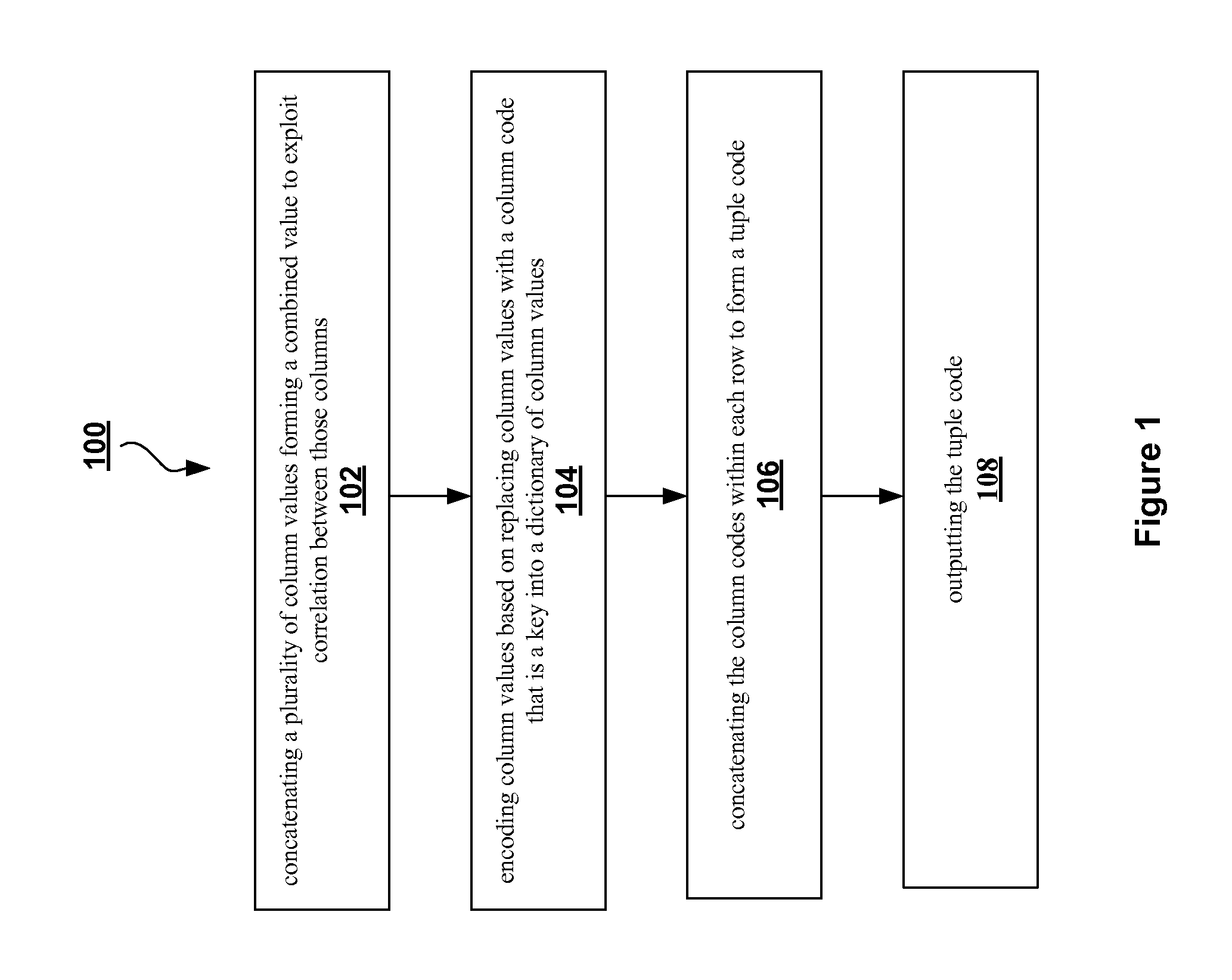
Compression method for relational tables based on combined column and row coding
InactiveUS20090006399A1Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsVariable-length codeTheoretical computer science
A robust method to compress relations close to their entropy while still allowing efficient queries. Column values are encoded into variable length codes to exploit skew in their frequencies. The codes in each tuple are concatenated and the resulting tuplecodes are sorted and delta-coded to exploit the lack of ordering in a relation. Correlation is exploited either by co-coding correlated columns, or by using a sort order that can leverage the correlation. Also presented is a novel Huffman coding scheme, called segregated coding, that preserves maximum compression while allowing range and equality predicates on the compressed data, without even accessing the full dictionary. Delta coding is exploited to speed up queries, by reusing computations performed on nearly identical records.
Owner:IBM CORP
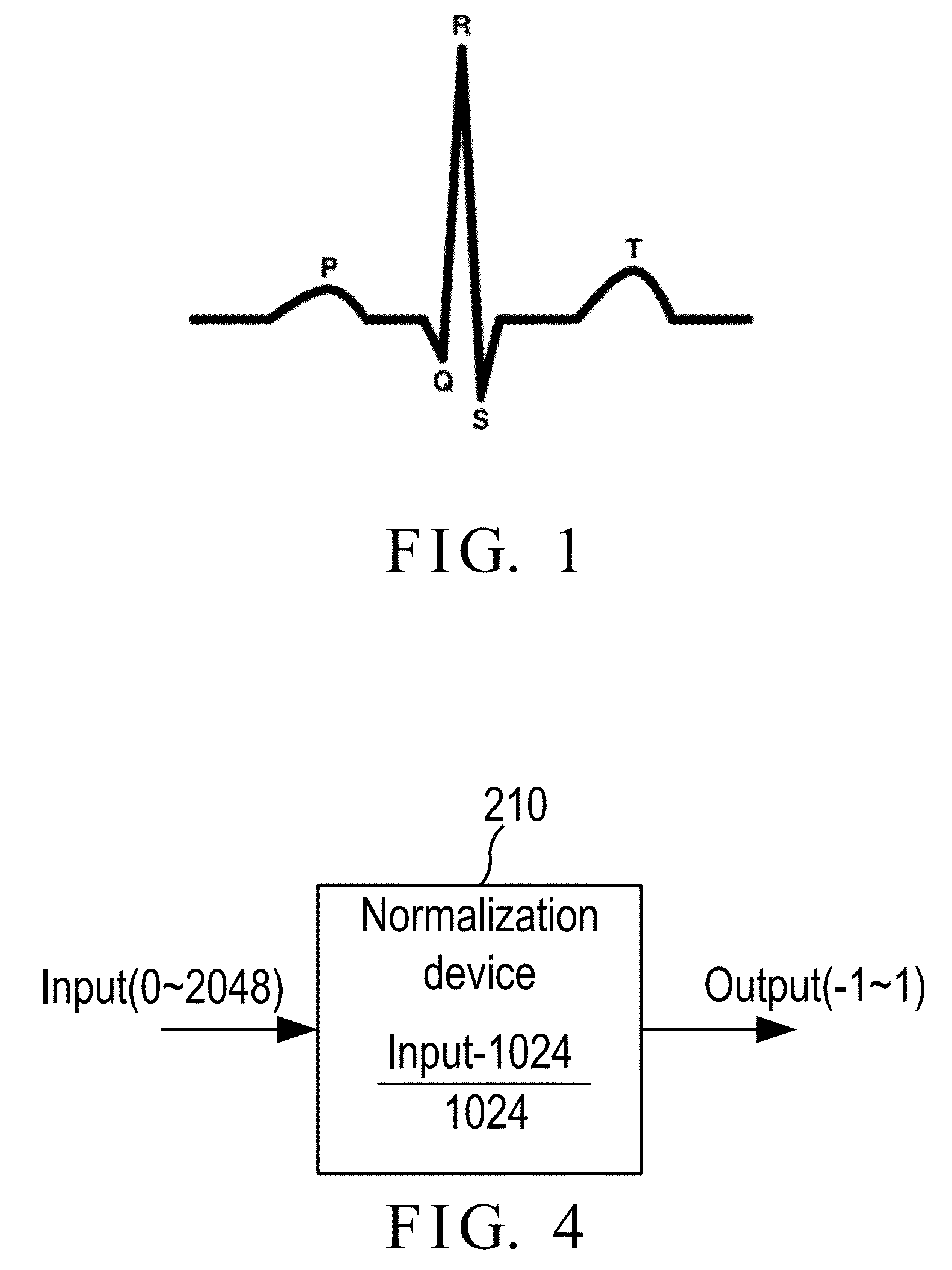
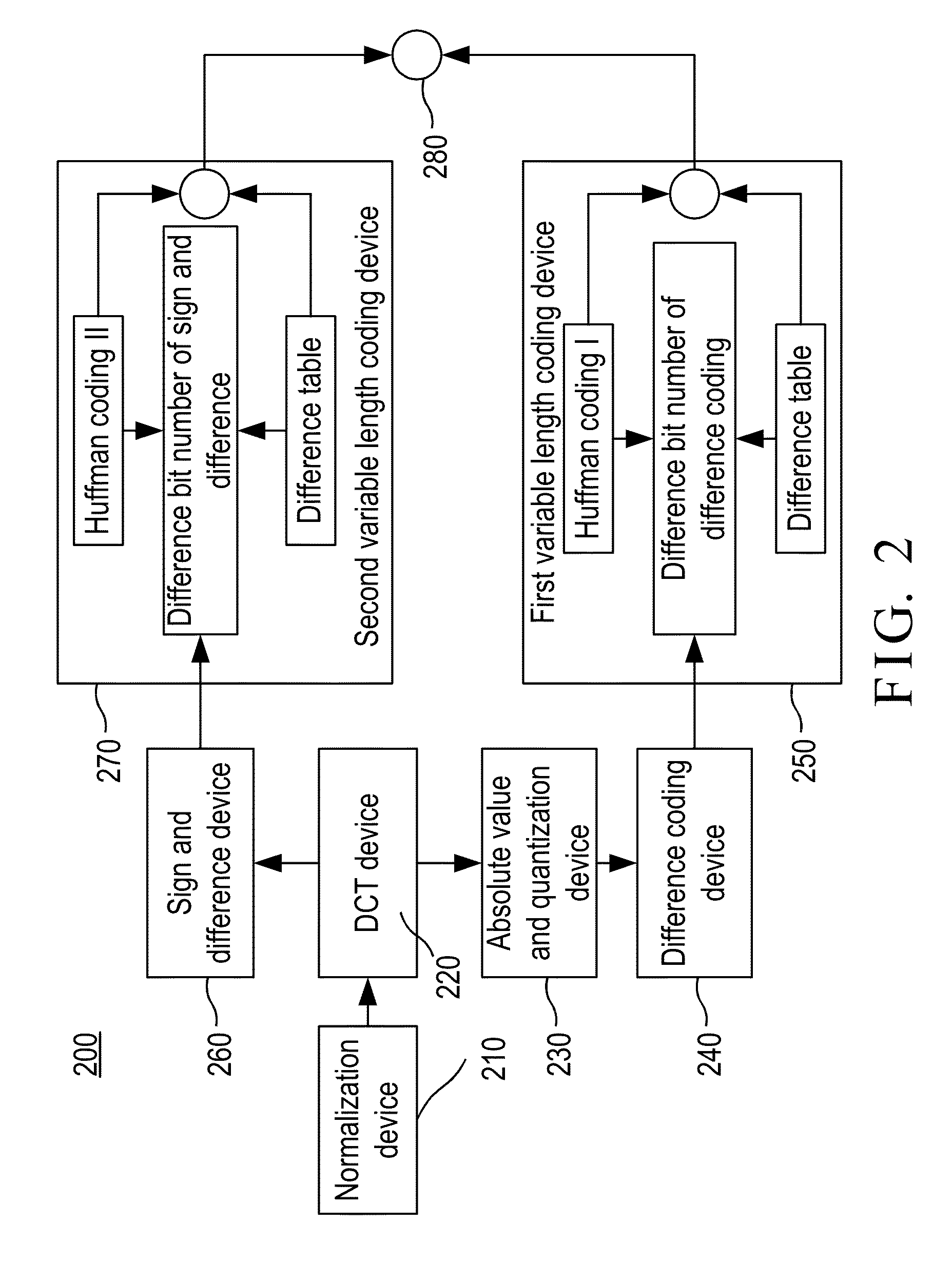
Electrocardiogram signal compression and de-compression system
InactiveUS20130243105A1Improve quality scoreLow distortion rateCode conversionComputer-assisted medical data acquisitionEcg signalFrequency spectrum
The invention provides an electrocardiogram signal compression and de-compression system. The invention uses the sign characteristics of the coefficients of the discrete cosine transform type IV and the characteristics of quantization of spectrum to perform the differential pulse code modulation of the spectrum for preserving the high frequency characteristics of the spectrum of the discrete Fourier transform. The invention also uses the Huffman coding to increase the compression ratio. Different from the conventional compression technology, the invention uses the fact that the quantization values of the spectrum in the high frequency are almost the same to increase the compression ratio and preserve the characteristics of high frequency components of the spectrum.
Owner:NAT CHENG KUNG UNIV
Entropy coding by adapting coding between level and run-length/level modes
An audio encoder performs adaptive entropy encoding of audio data. For example, an audio encoder switches between variable dimension vector Huffman coding of direct levels of quantized audio data and run-level coding of run lengths and levels of quantized audio data. The encoder can use, for example, context-based arithmetic coding for coding run lengths and levels. The encoder can determine when to switch between coding modes by counting consecutive coefficients having a predominant value (e.g., zero). An audio decoder performs corresponding adaptive entropy decoding.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
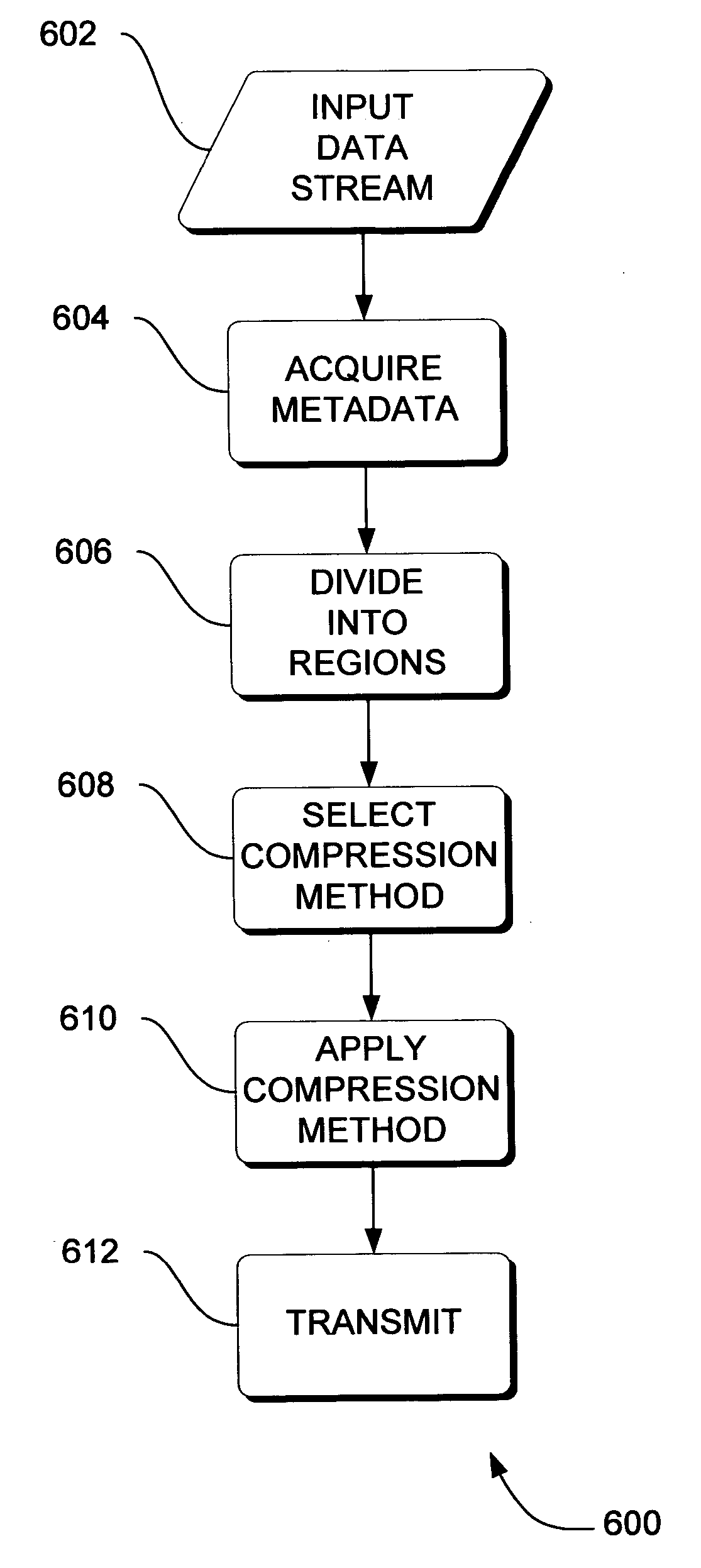
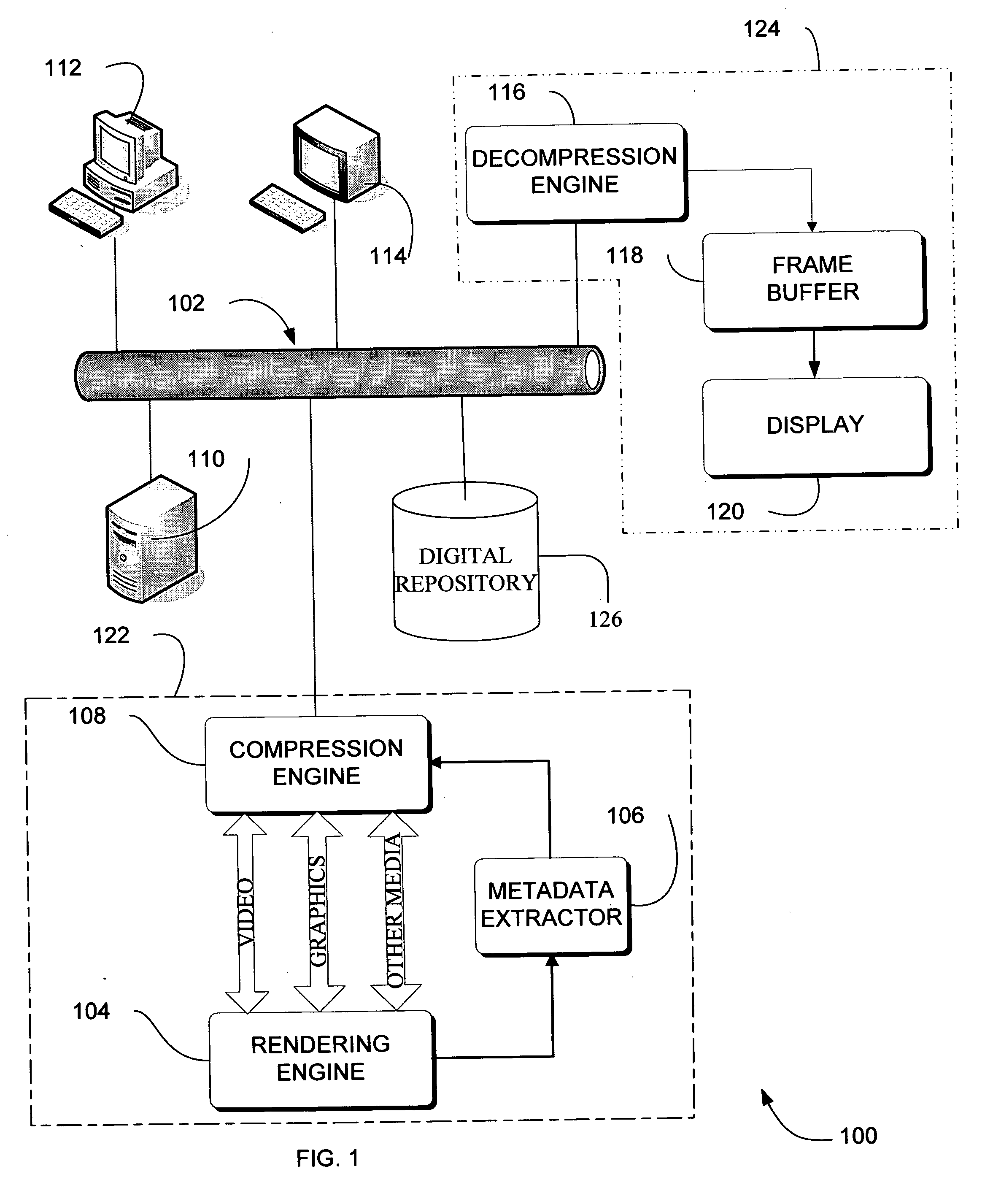
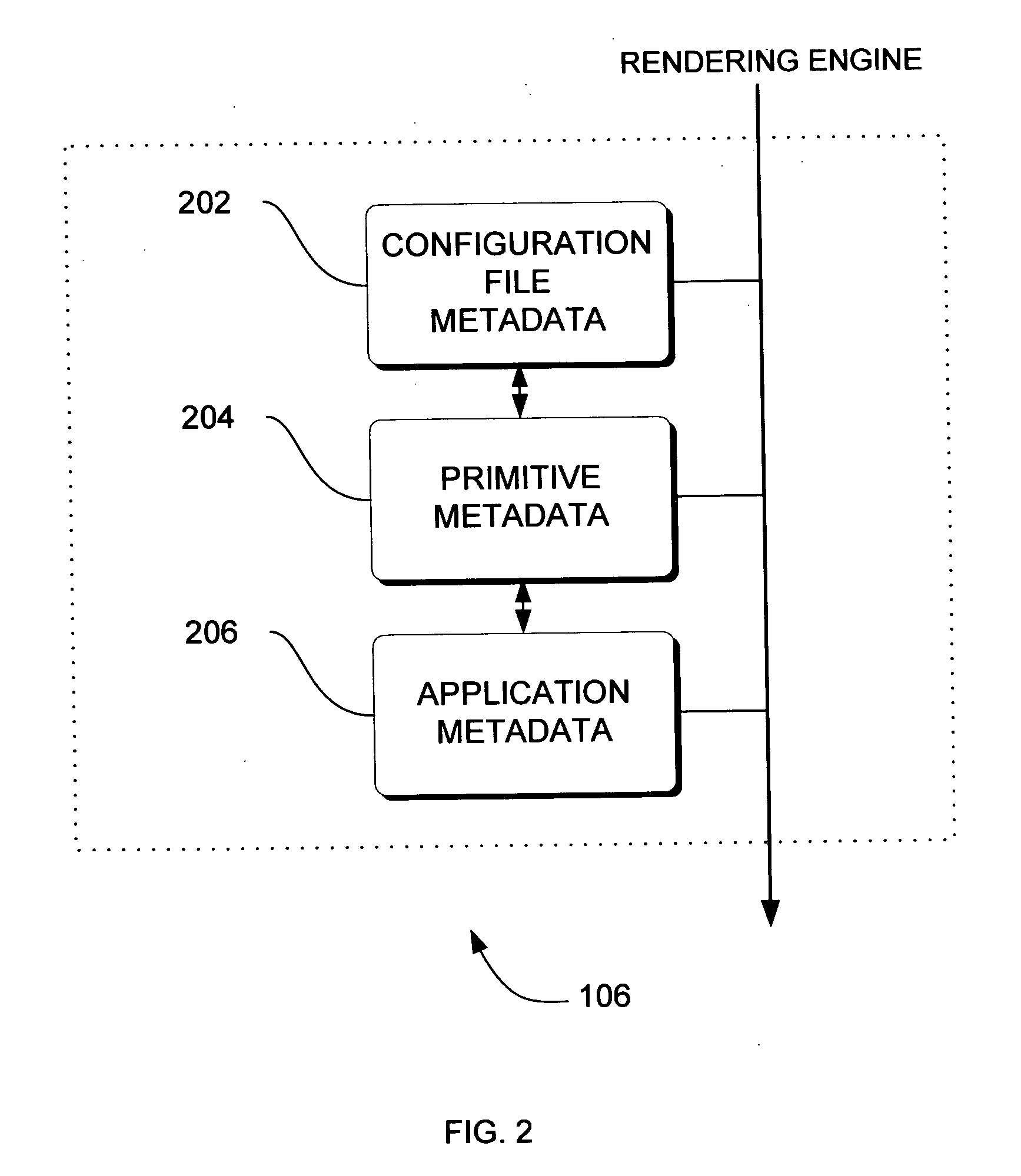
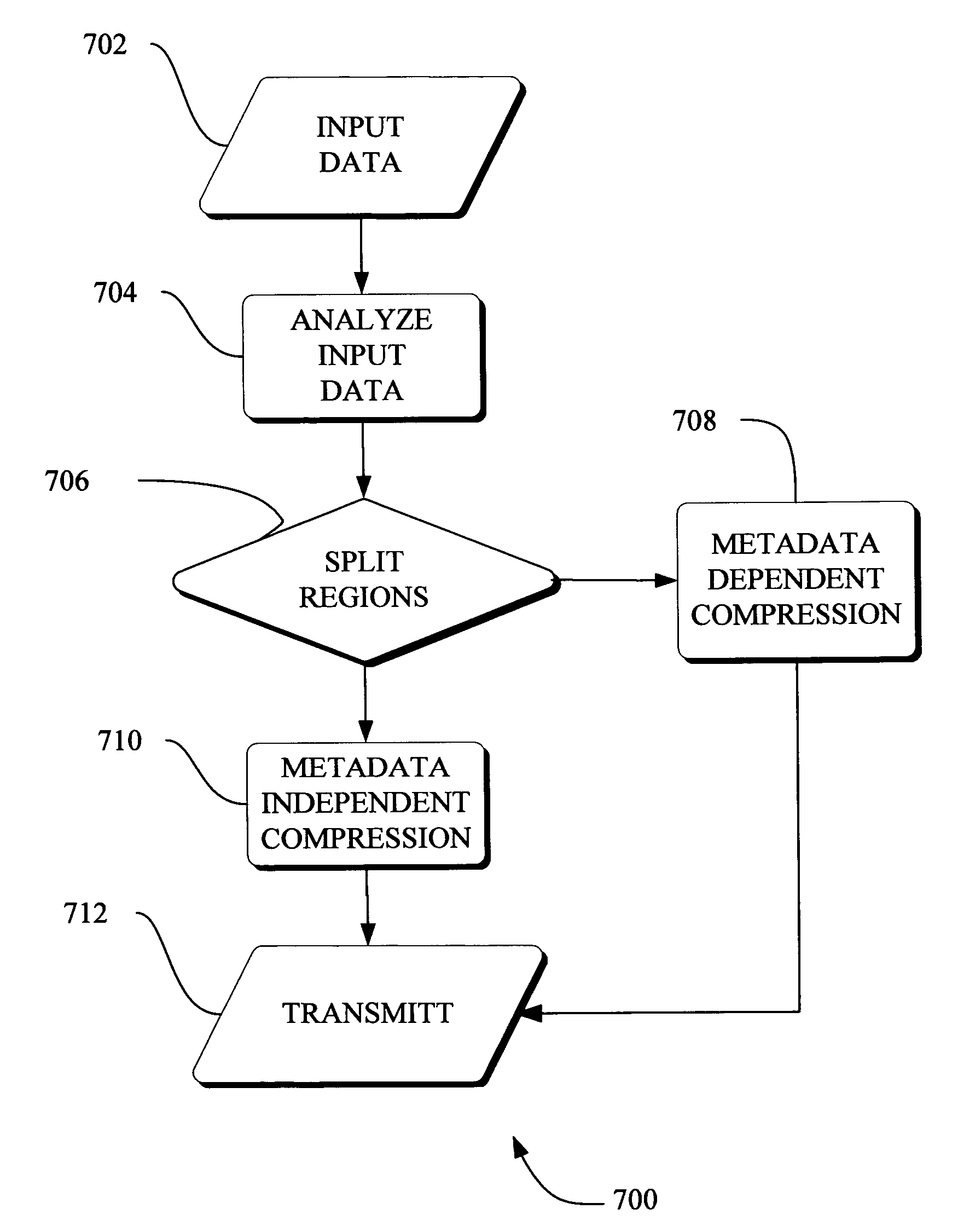
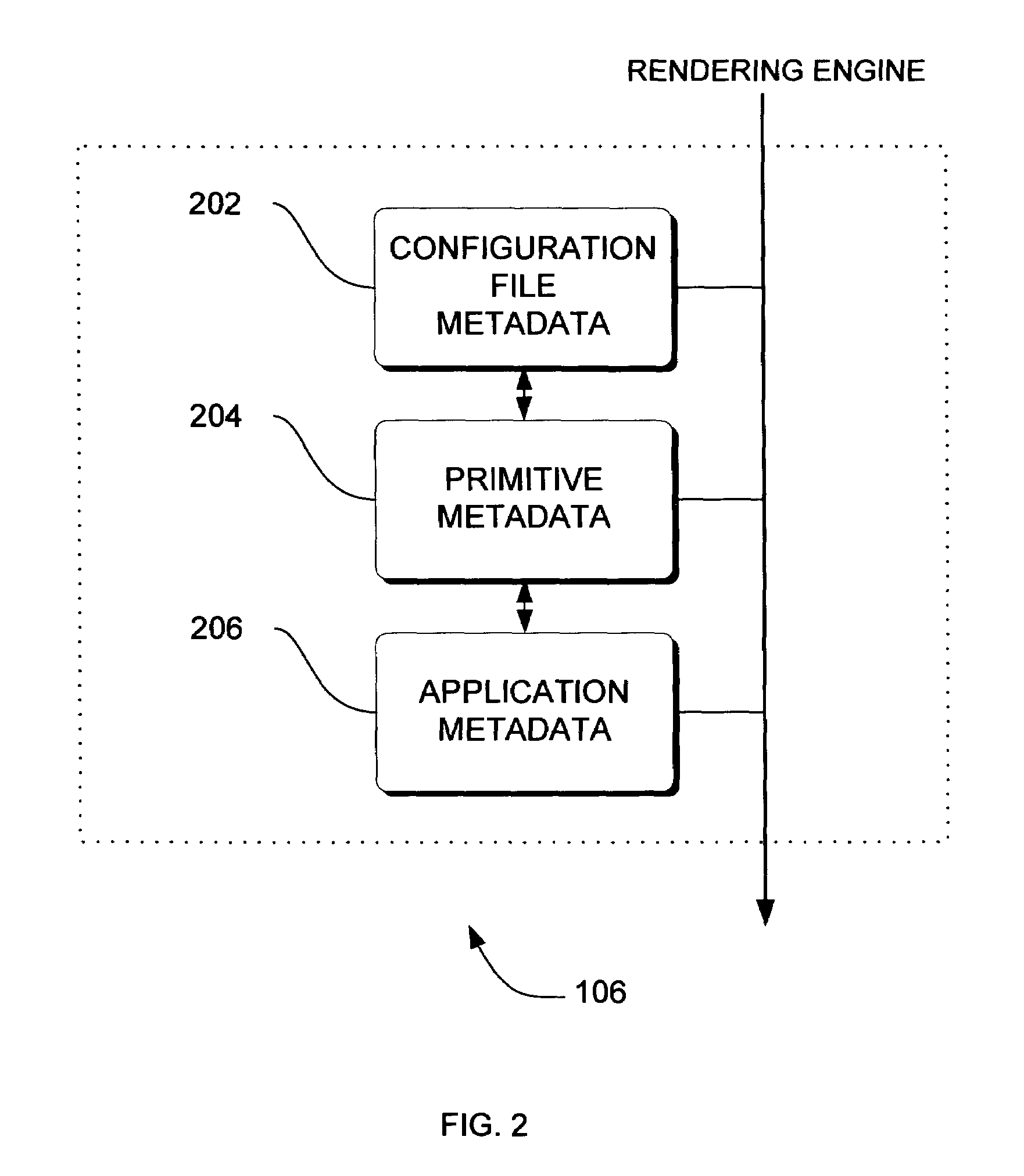
Adaptive video compression of graphical user interfaces using application metadata
InactiveUS20060294125A1Digital data processing detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionData streamDisplay device
Systems, methods and computer accessible medium are provided through which an input data stream consisting one or more media regions before entering a network to be rendered by a display coupled a remote video frame buffer is compressed on the basis of one or more configuration file metadata, source primitive metadata, and application high-level metadata of identified media regions. The input data stream is compressed by using one or more MPEG compression, JPEG compression, vector graphics compression, Huffman coding, or user defined compression scheme.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
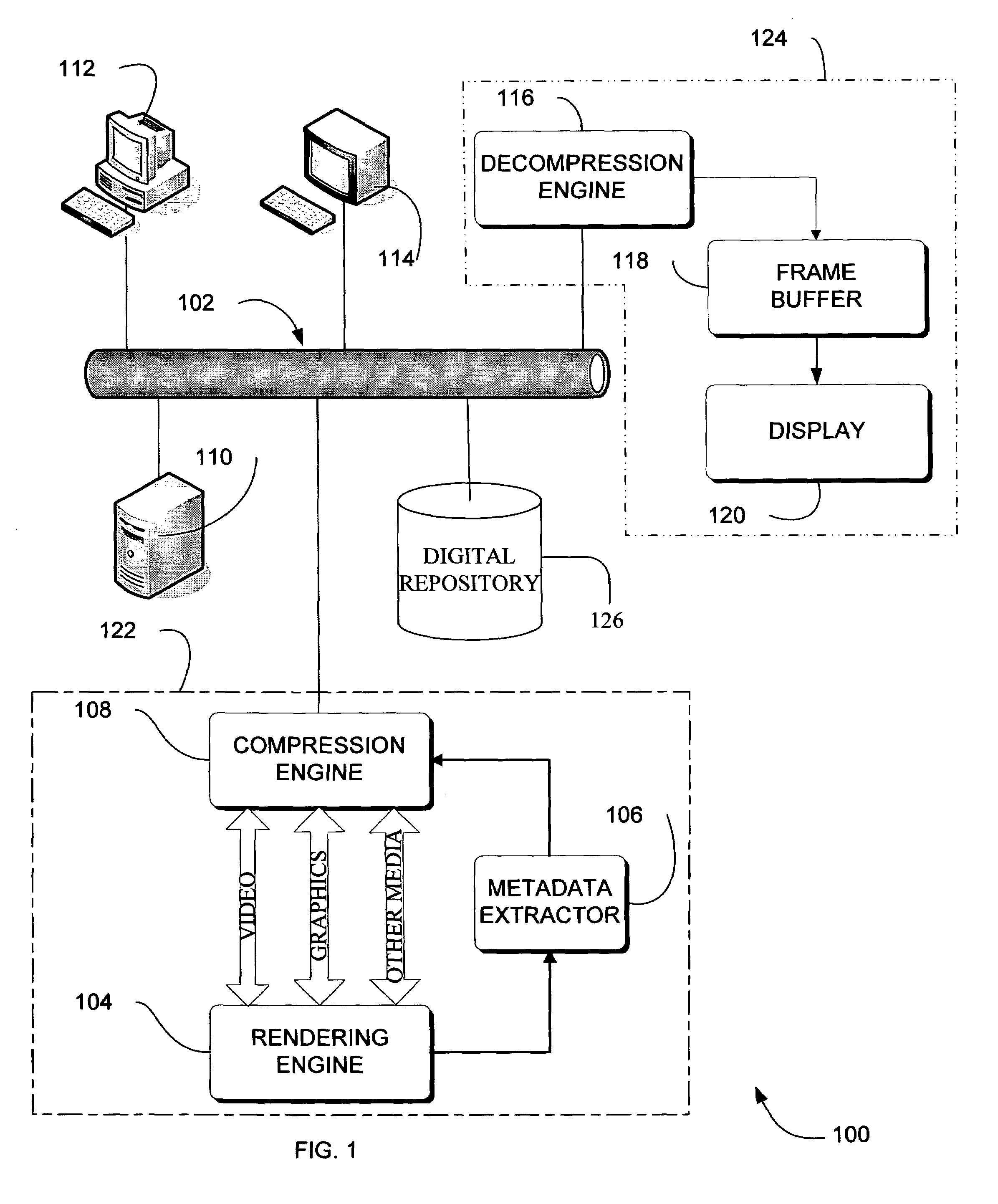
Adaptive video compression of graphical user interfaces using application metadata
InactiveUS7548657B2Character and pattern recognitionDigital video signal modificationData streamDisplay device
Systems, methods and computer accessible medium are provided through which an input data stream consisting one or more media regions before entering a network to be rendered by a display coupled a remote video frame buffer is compressed on the basis of one or more configuration file metadata, source primitive metadata, and application high-level metadata of identified media regions. The input data stream is compressed by using one or more MPEG compression, JPEG compression, vector graphics compression, Huffman coding, or user defined compression scheme.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Methods and devices for coding or decoding an audio signal or bit stream
InactiveUS6975254B1Increase probabilityConvenient amountBroadcast with distributionSpeech analysisFrequency spectrumGrating
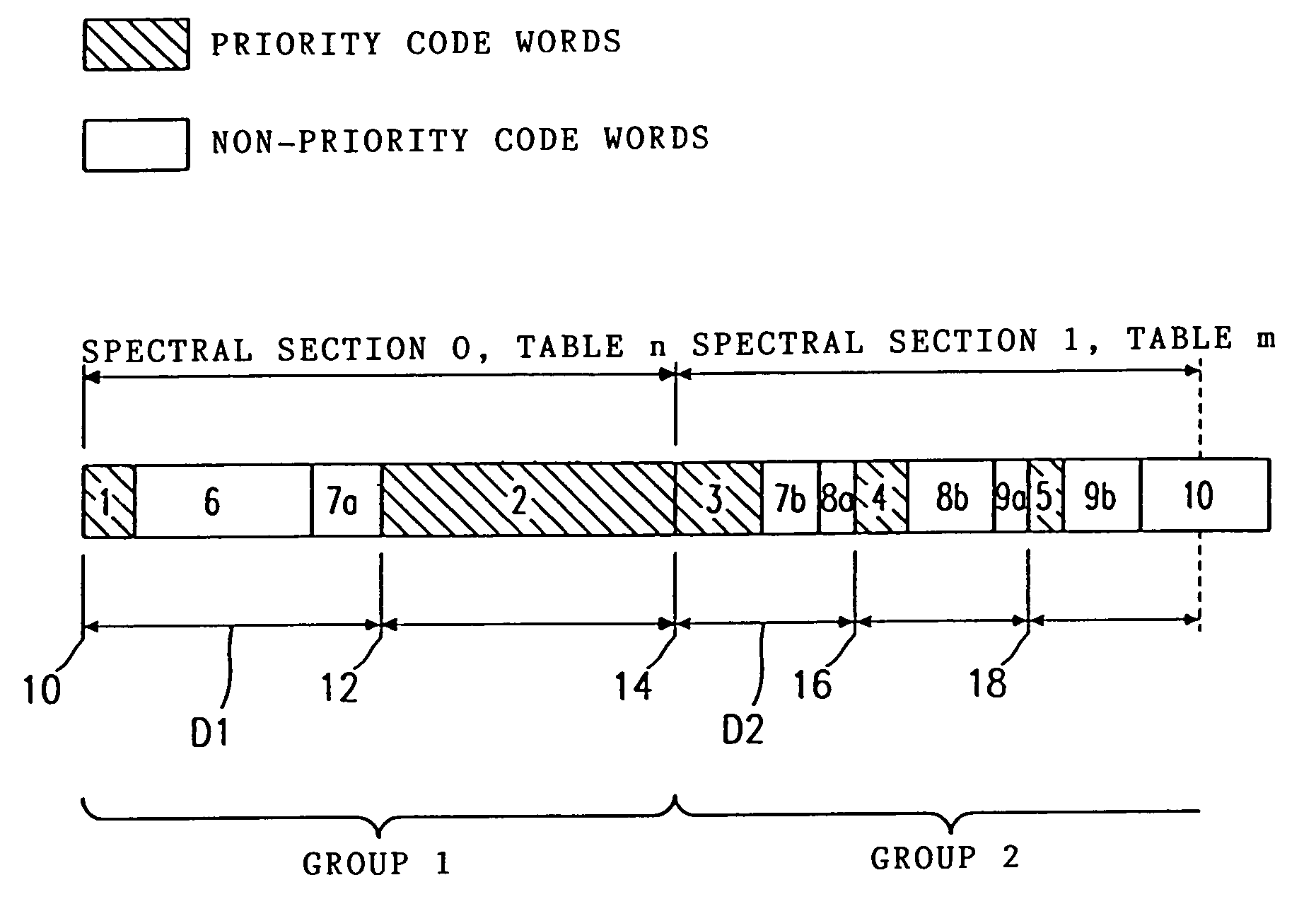
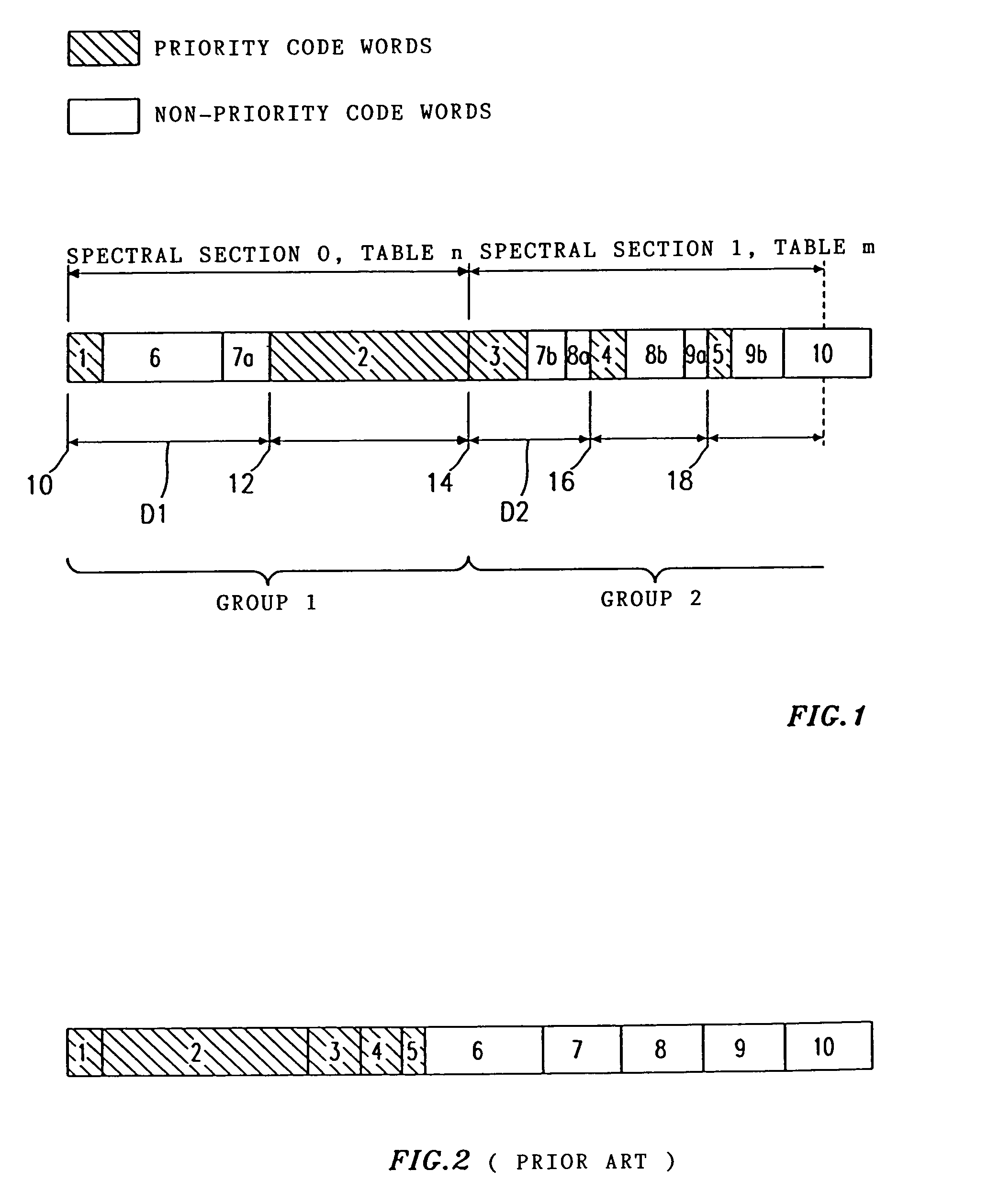
In a method for coding an audio signal to obtain a coded bit stream, discrete-time samples of the audio signal are transformed into the frequency domain to obtain spectral values. The spectral values are coded with a code table having a limited number of code words of different lengths to obtain spectral values coded by code words, the length of a code word assigned to a spectral value being that much shorter the higher the probability of occurrence of the spectral value is. A raster is then specified for the coded bit stream, the raster having equidistant raster points and the distance between the raster points depending on the code table(s) used. In order to obtain error-tolerant Huffman coding, priority code words, which represent particular spectral values which are psychoacoustically more important than other spectral values, are so arranged in the raster that the start of each priority code word coincides with a raster point.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
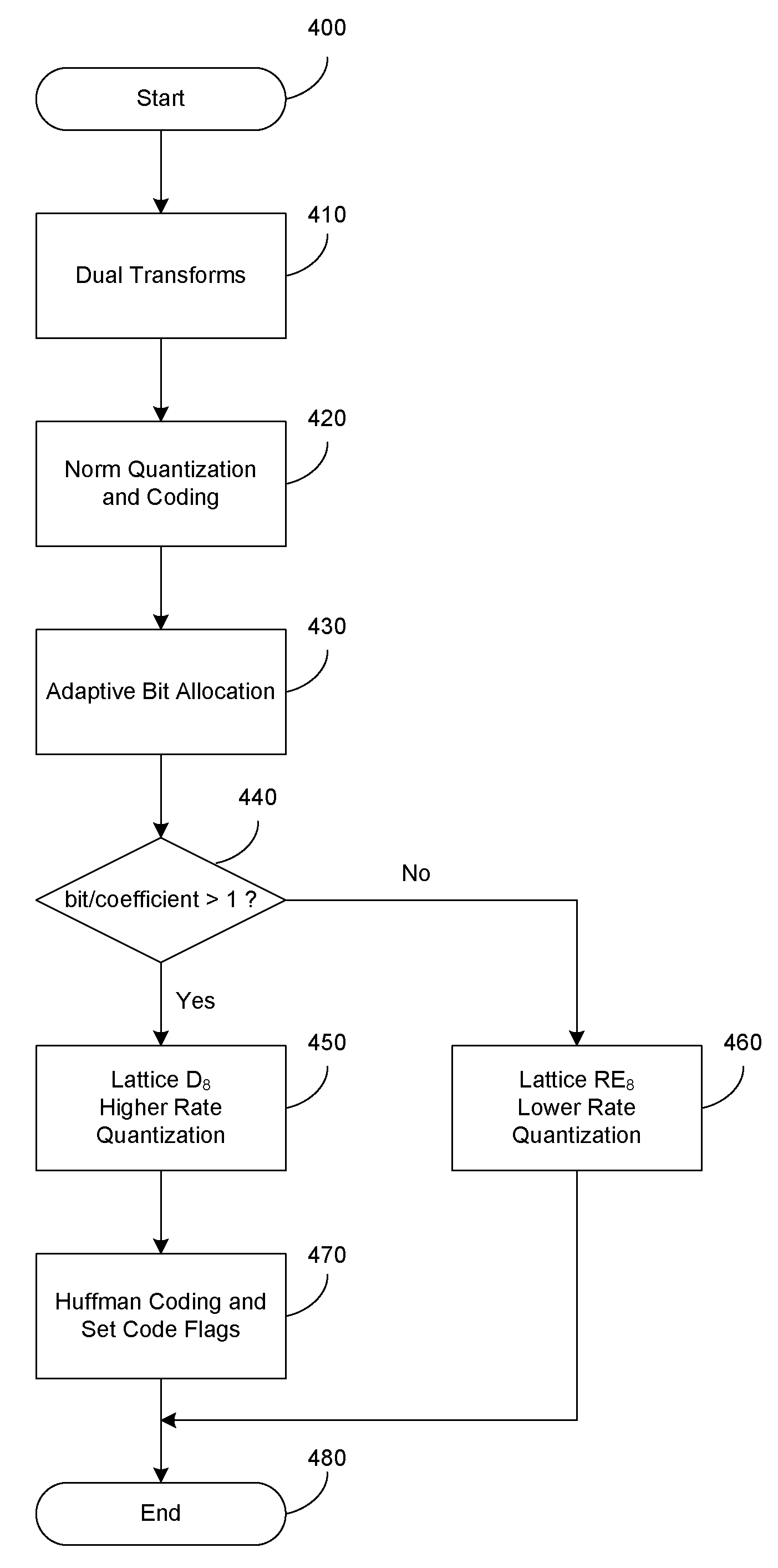
Dual-transform coding of audio signals
Methods, devices, and systems for coding and decoding audio are disclosed. At least two transforms are applied on an audio signal, each with different transform periods for better resolutions at both low and high frequencies. The transform coefficients are selected and combined such that the data rate remains similar as a single transform. The transform coefficients may be coded with a fast lattice vector quantizer. The quantizer has a high rate quantizer and a low rate quantizer. The high rate quantizer includes a scheme to truncate the lattice. The low rate quantizer includes a table based searching method. The low rate quantizer may also include a table based indexing scheme. The high rate quantizer may further include Huffman coding for the quantization indices of transform coefficients to improve the quantizing / coding efficiency.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
System and method for compressing data
InactiveUS6839624B1Improve decoding speedSave memory spaceNavigational calculation instrumentsPosition fixationTheoretical computer scienceSubject matter
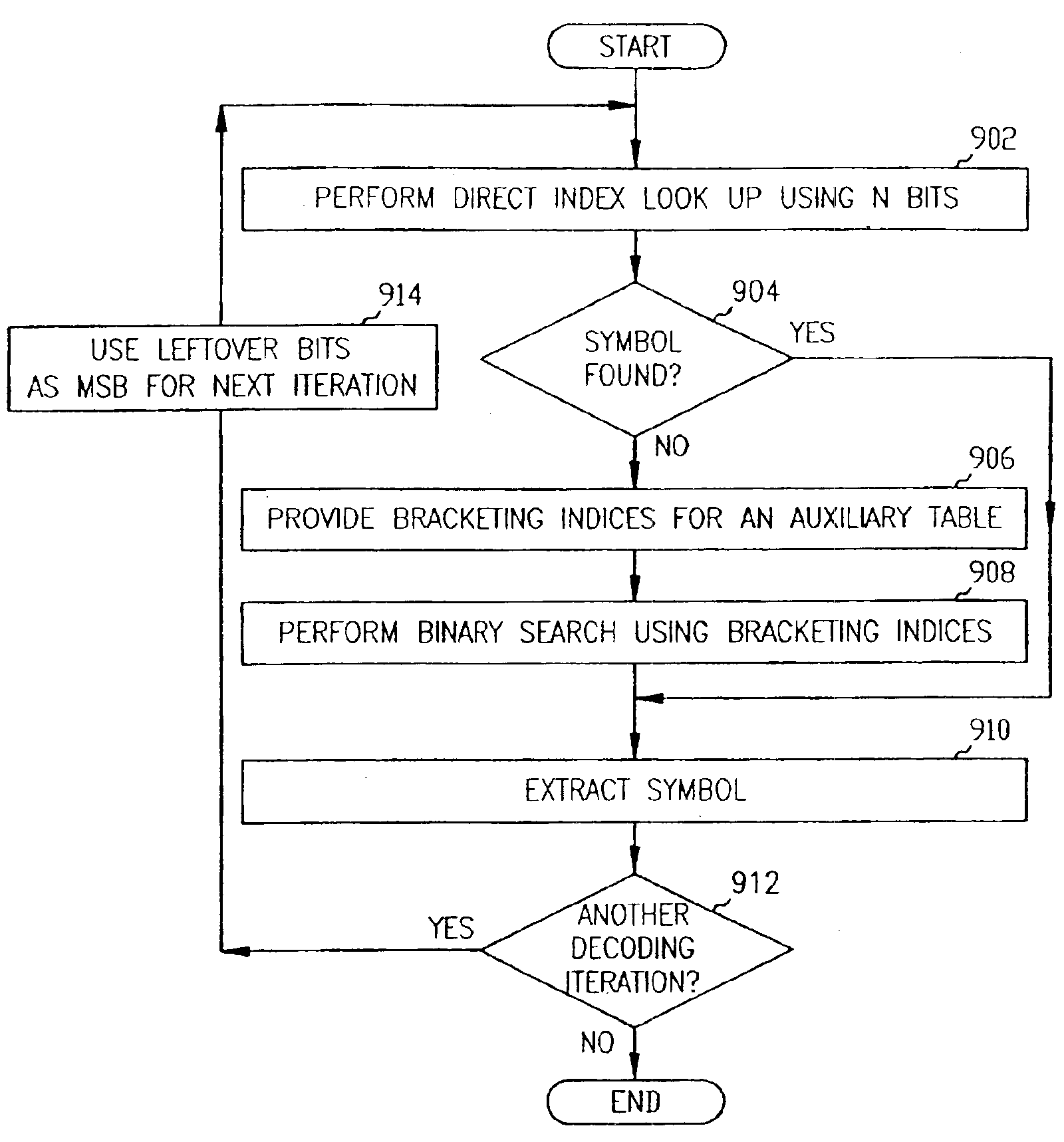
Systems, devices and methods are provided to compress data, and in particular to code and decode data. One aspect of the present subject matter is a data structure. The data structure includes a field representing a decoding structure to decode canonical Huffman encoded data, and a field representing a symbol table. The decoding structure includes a field representing an accelerator table to provide a 2N-deep direct-index lookup to provide high-frequency symbols for high-frequency data and to provide bracketing indices for low-frequency data. The decoding structure also includes a field for a binary search table to provide a low-frequency symbol index using a binary search bounded by the bracketing indices provided by the accelerator table. The symbol table is adapted to provide a symbol associated with the low-frequency index.
Owner:GARMIN
Data compression, control program for controlling the data compression
InactiveUS6940900B2Increase the compression ratioReduce the amount of codePulse modulation television signal transmissionPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesData signalTheoretical computer science
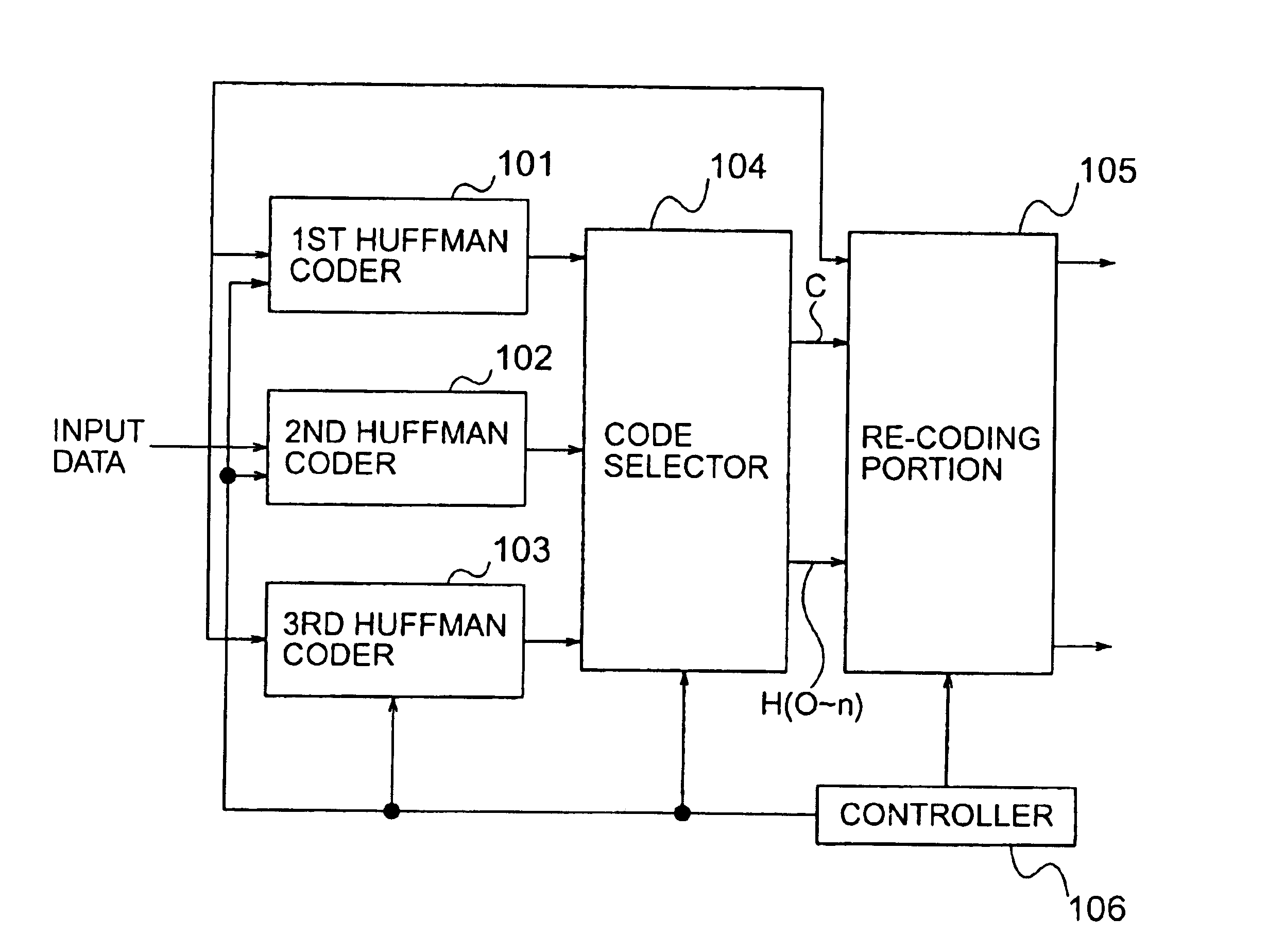
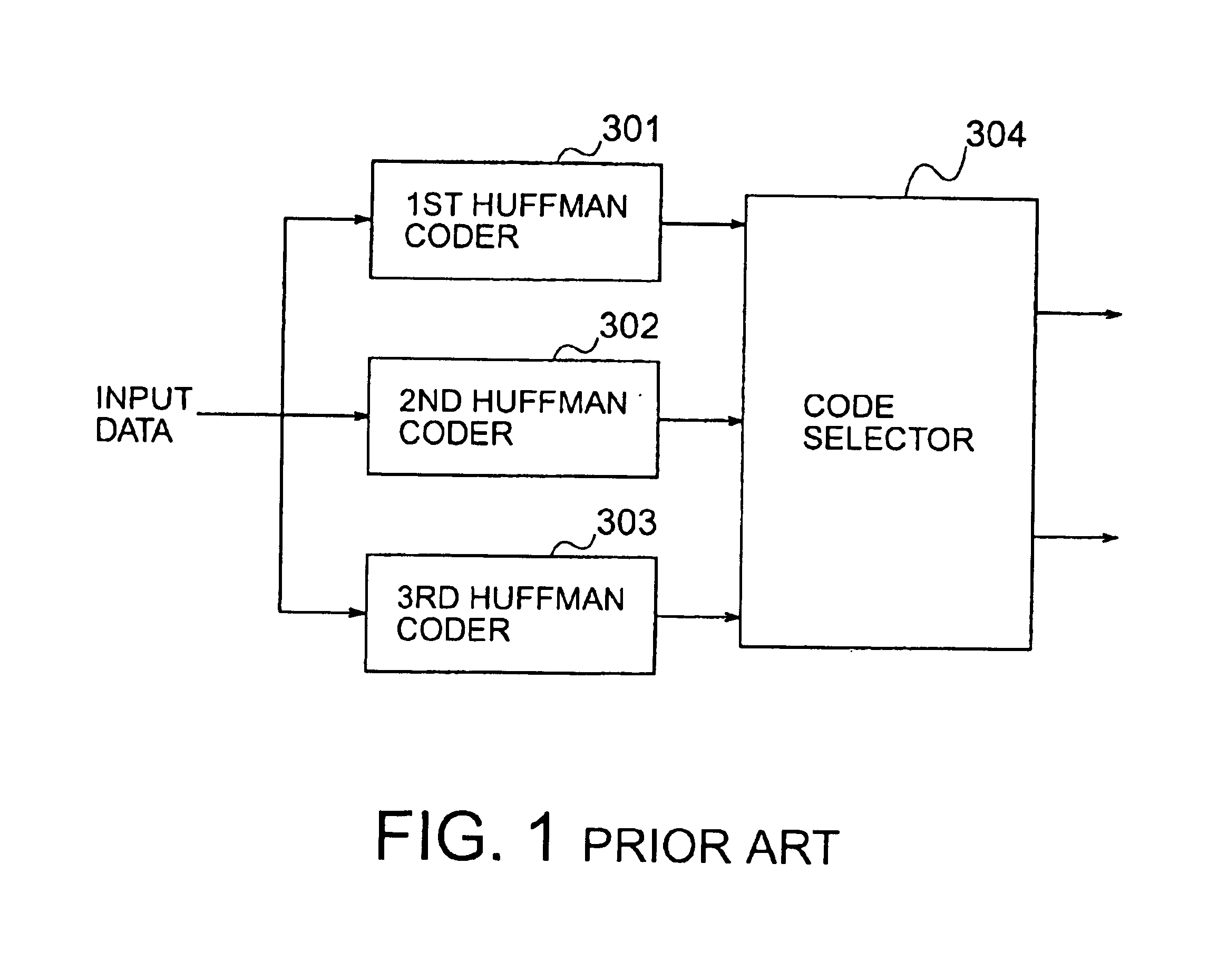
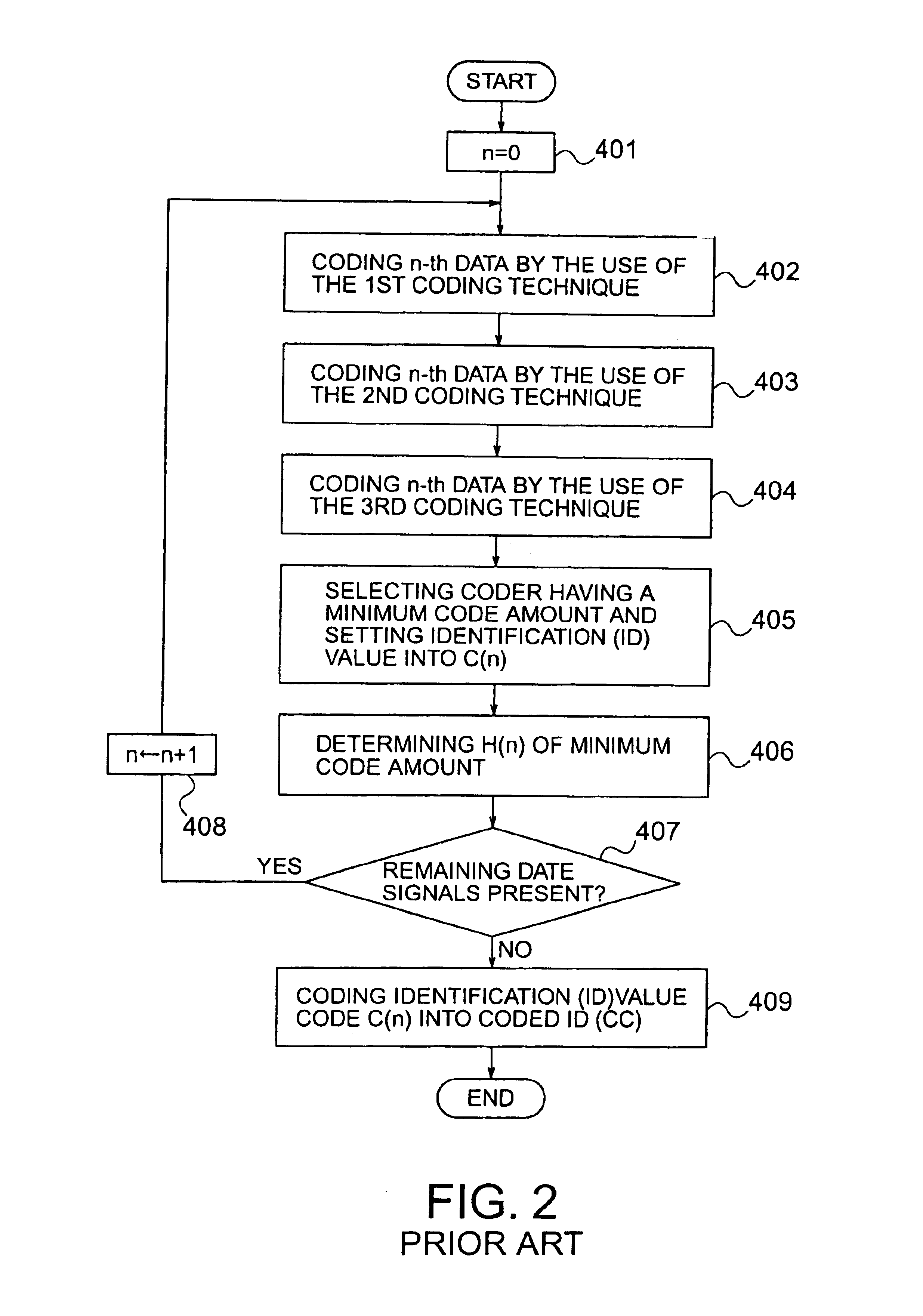
In a data compression device having a plurality of Huffman coders given identification (ID) values, respectively, to produce Huffman codes together with the corresponding ID codes obtained from the ID values, a re-coding portion is included to change a sequence of the ID values so that a reduction is accomplished about a code amount of the Huffman codes and the ID codes obtained from the ID value sequence and is operable to re-code an input data sequence again by Huffman coders indicated by the changed ID values. Such re-coded Huffman codes and ID codes based on the changed ID values are produced as output data signals.
Owner:NEC CORP
Surveillance system
InactiveUS6842540B1Increased evidenceEasy to separateTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionSurveillance cameraDiscrete cosine transform
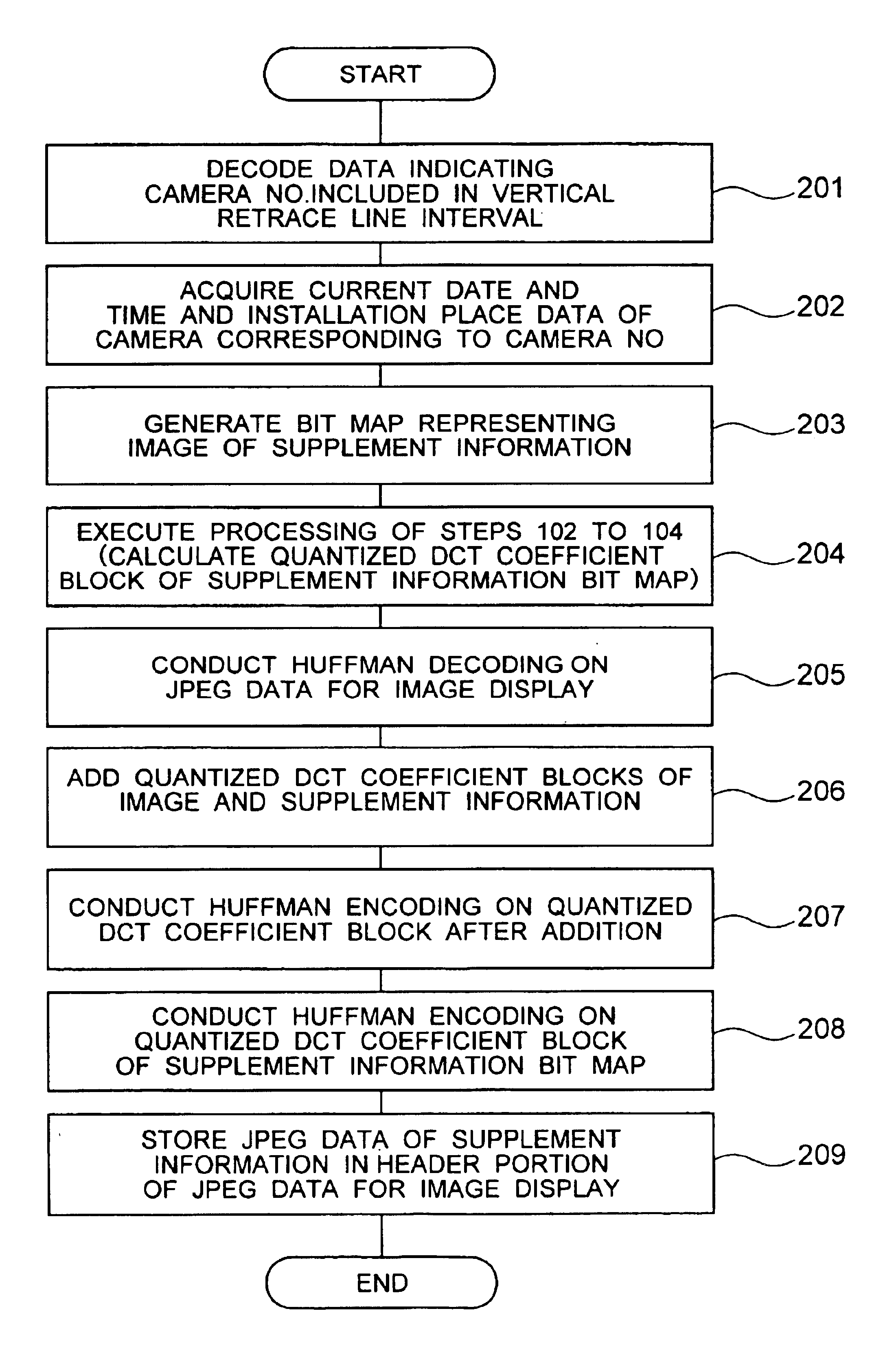
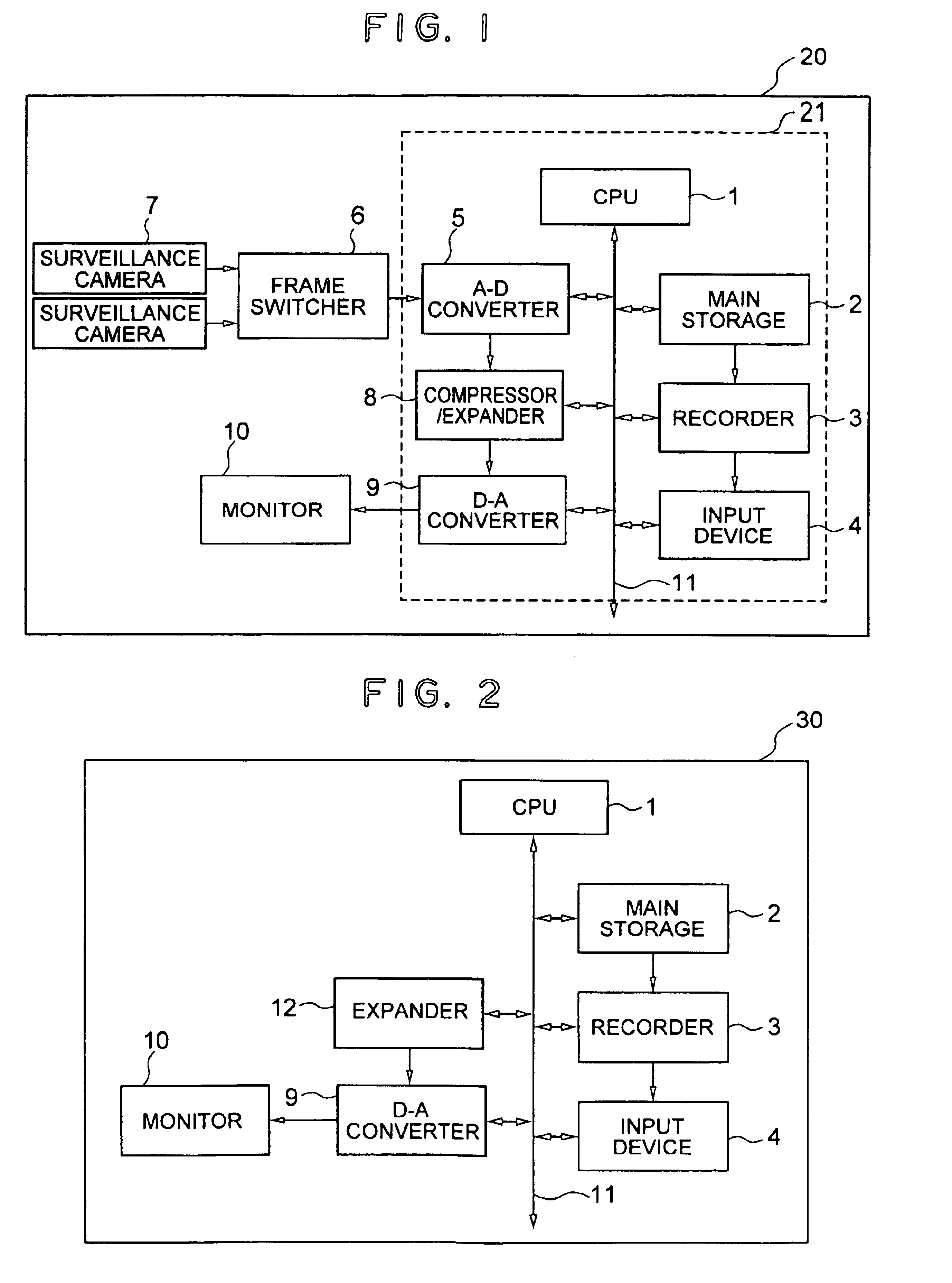
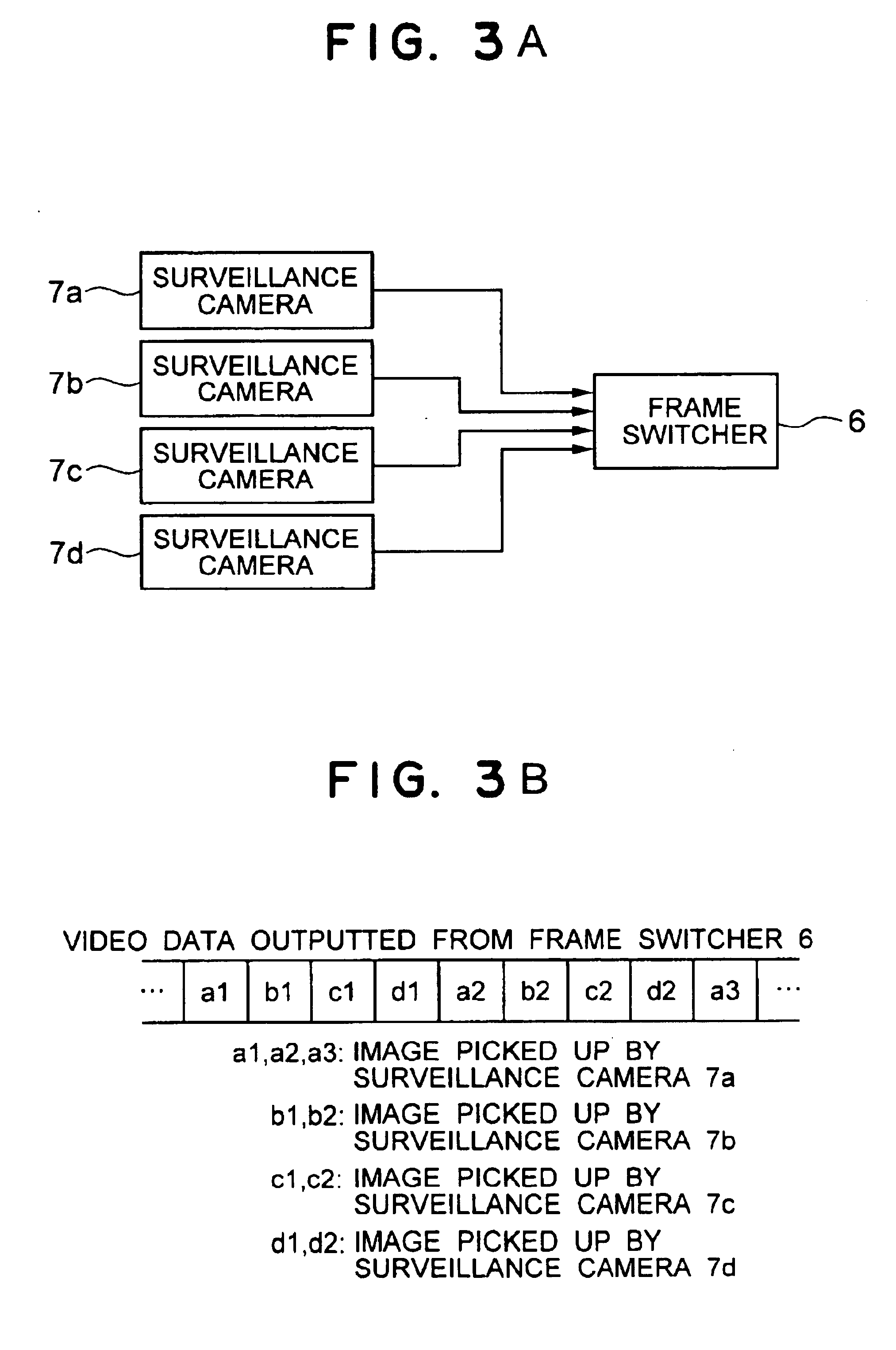
A surveillance image is acquired from a surveillance camera. Supplement information (such as date and time, and surveillance camera number) relating to the surveillance image is acquired. By imaging the supplement information, supplement information image data is generated. A quantized discrete cosine transform coefficient block obtained by conducting discrete cosine transform and then quantization on surveillance image data of the surveillance image is added to a quantized discrete cosine transform coefficient block obtained by conducting discrete cosine transform and then quantization on the supplement information image data. A resultant sum is subjected to Huffman encoding. The result is recorded.
Owner:MAXELL HLDG LTD
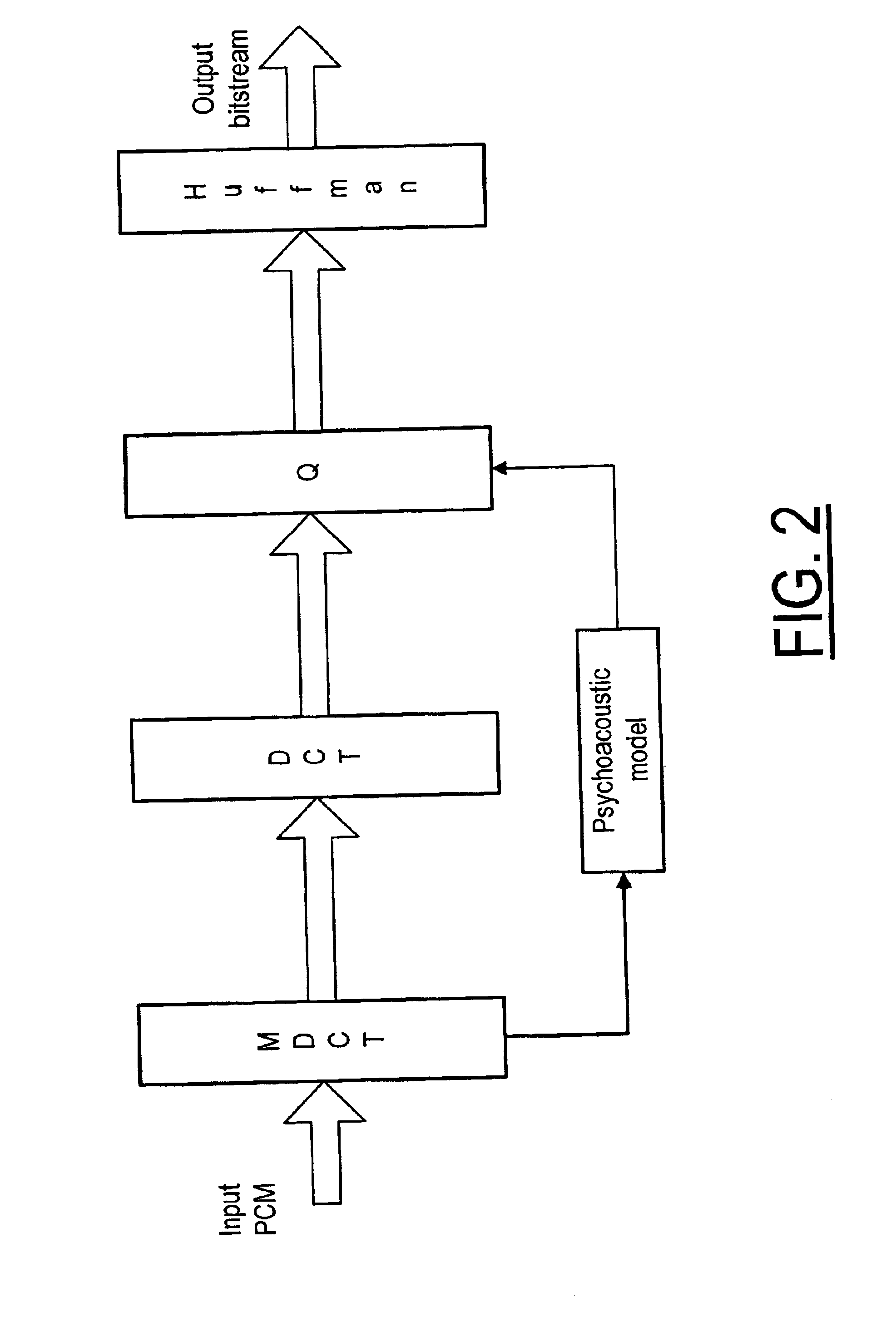
Method and system for inter-channel signal redundancy removal in perceptual audio coding
InactiveUS6934676B2Improve efficiencyReduce the amount requiredBroadcast information characterisationSpeech analysisVocal tractMasking threshold
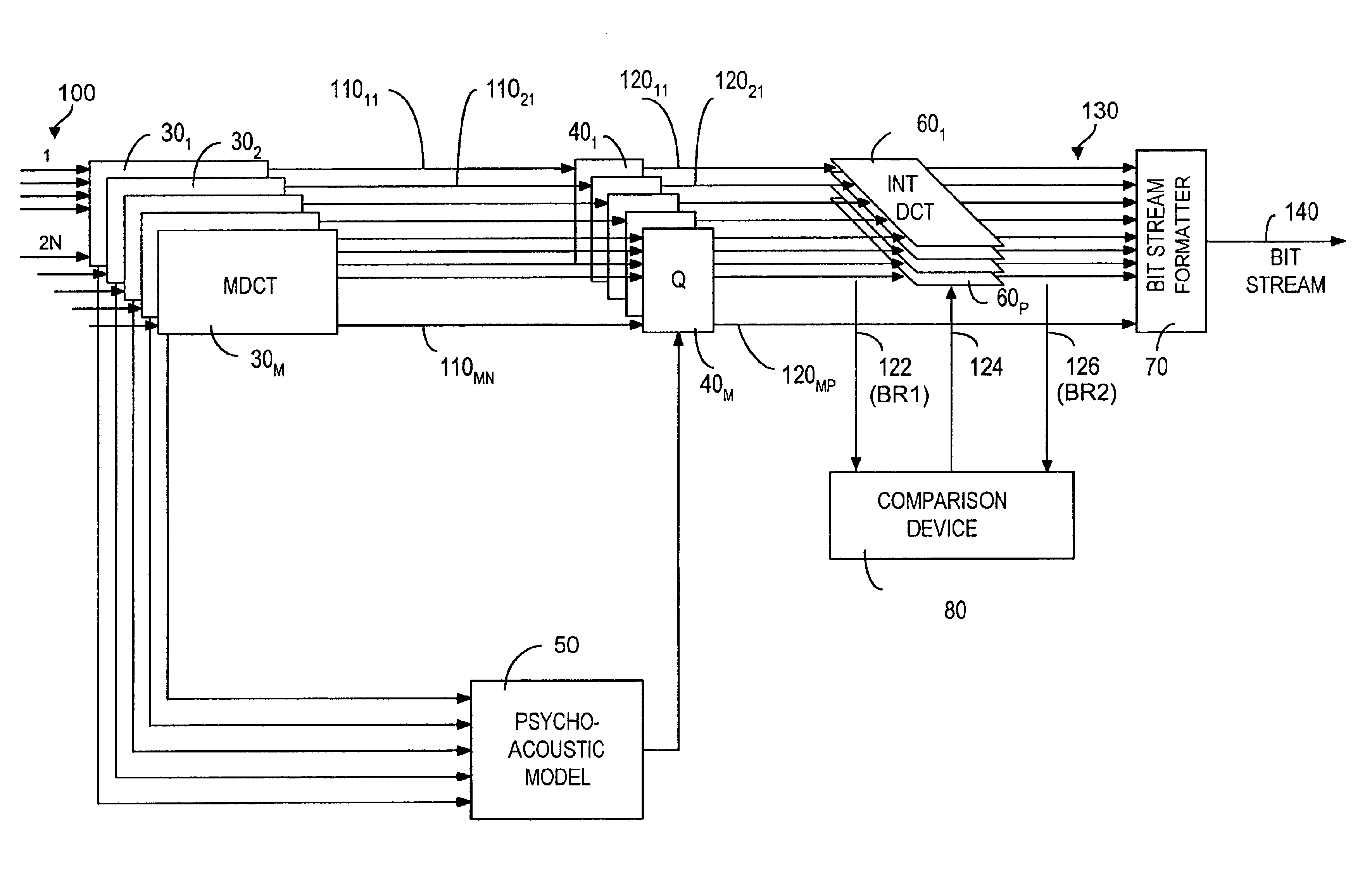
A method and system for coding audio signals in a multi-channel sound system, wherein a plurality of MDCT units are used to reduce the audio signals for providing a plurality of MDCT coefficients. The MDCT coefficients are quantized according to the masking threshold calculated from a psychoacoustic model and a plurality of INT (integer-to-integer) DCT modules are used to remove the cross-channel redundancy in the quantized MDCT coefficients. The output from the INT-DCT modules is Huffman coded and written to a bitstream for transmission or storage.
Owner:UBER TECH INC
Fast lattice vector quantization
InactiveUS20080097755A1Improve sound qualityReduce data loadCode conversionSpeech recognitionTime domainHigh rate
Methods, devices, and systems for coding and decoding audio are disclosed. Digital samples of an audio signal are transformed from the time domain to the frequency domain. The resulting transform coefficients are coded with a fast lattice vector quantizer. The quantizer has a high rate quantizer and a low rate quantizer. The high rate quantizer includes a scheme to truncate the lattice. The low rate quantizer includes a table based searching method. The low rate quantizer may also include a table based indexing scheme. The high rate quantizer may further include Huffman coding for the quantization indices of transform coefficients to improve the quantizing / coding efficiency.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
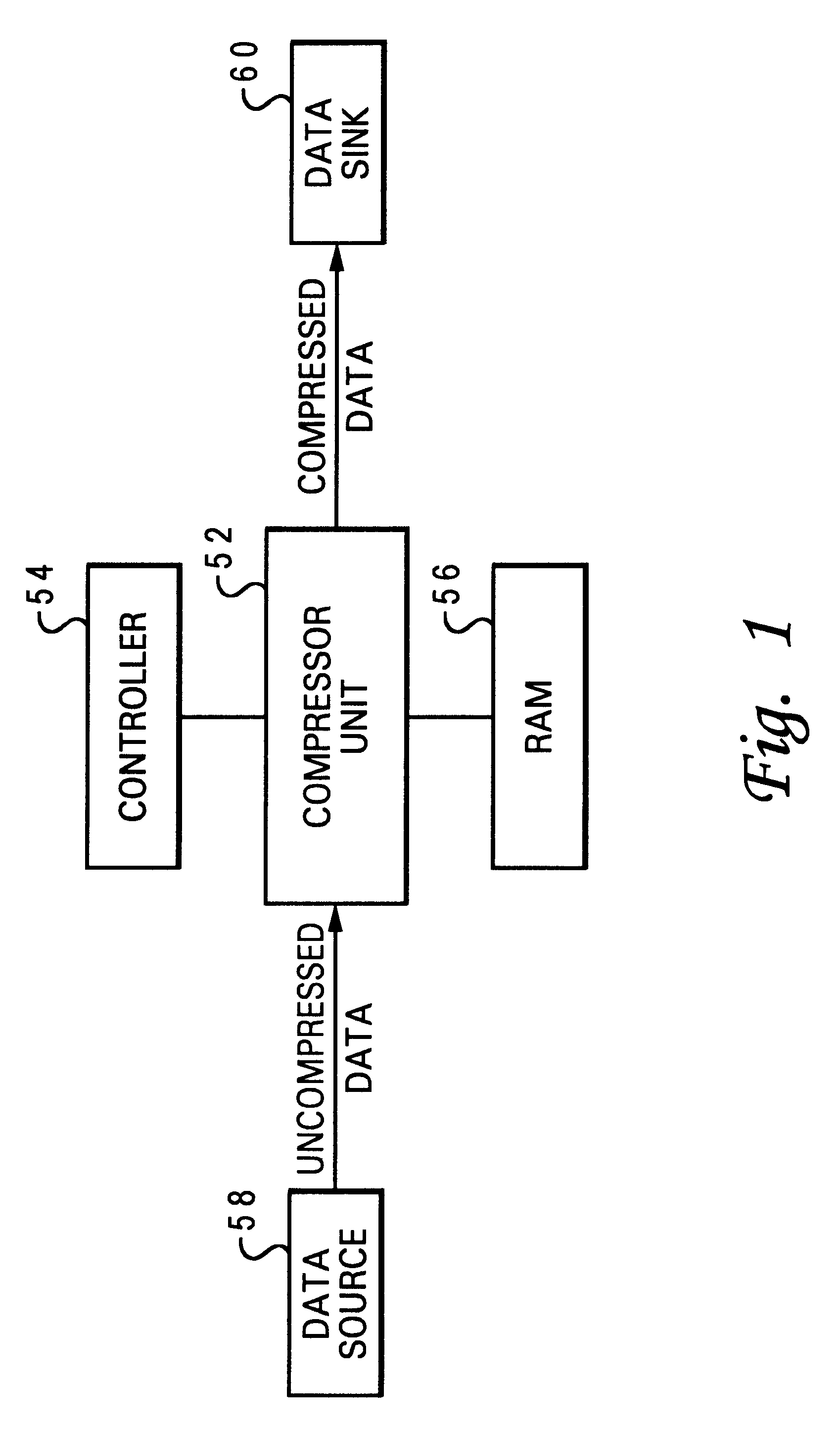
Real-time reduction of CPU overhead for data compression
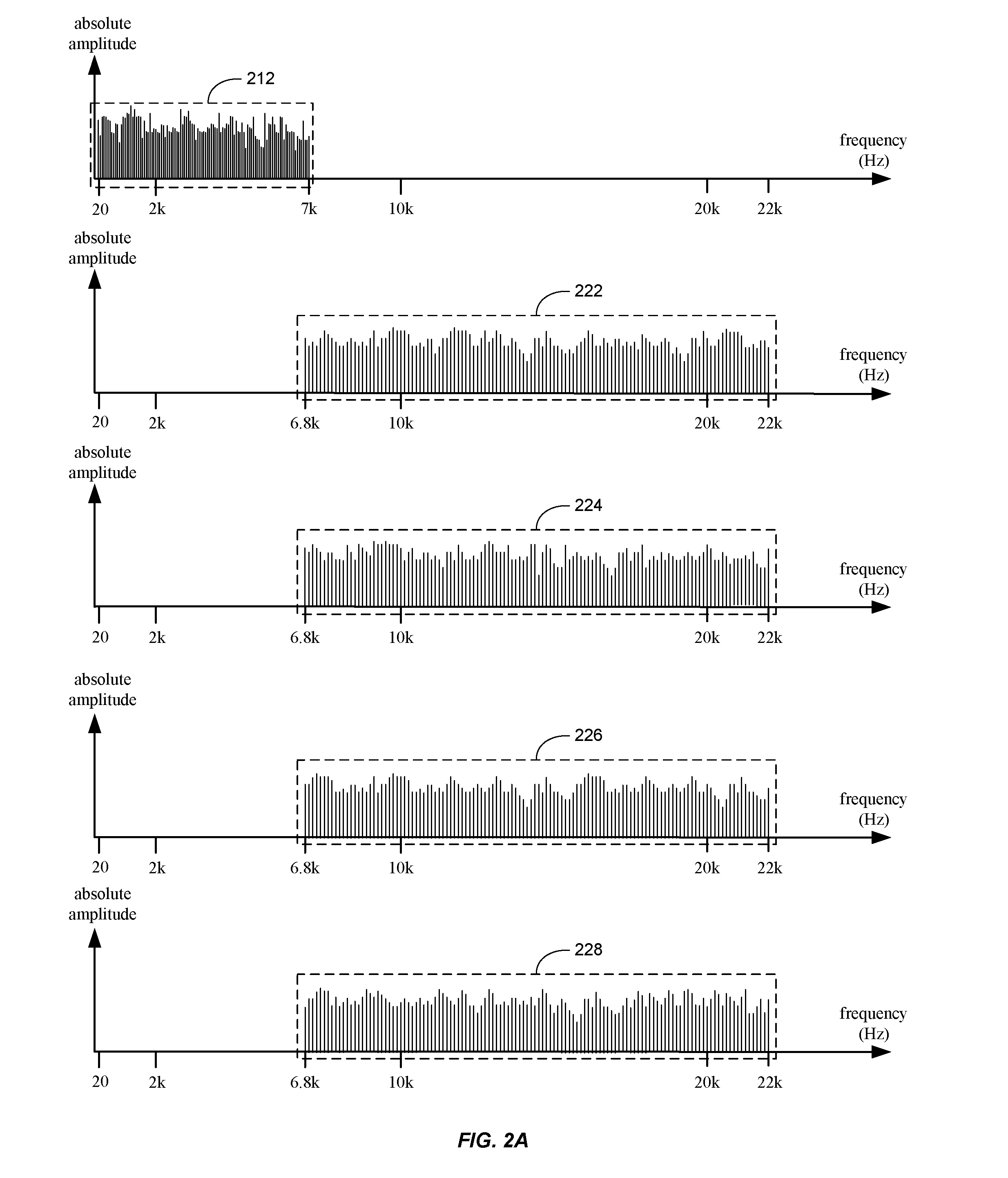
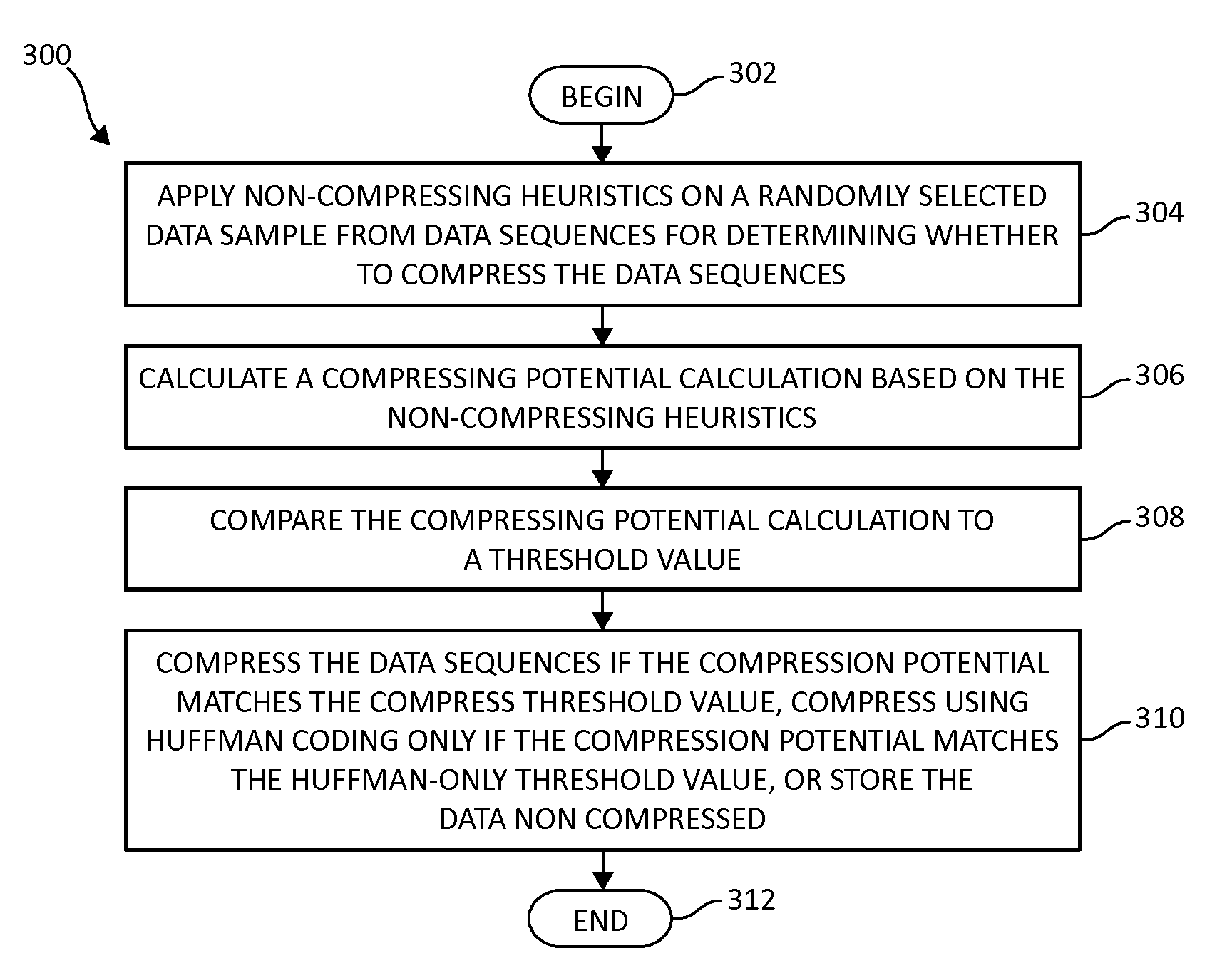
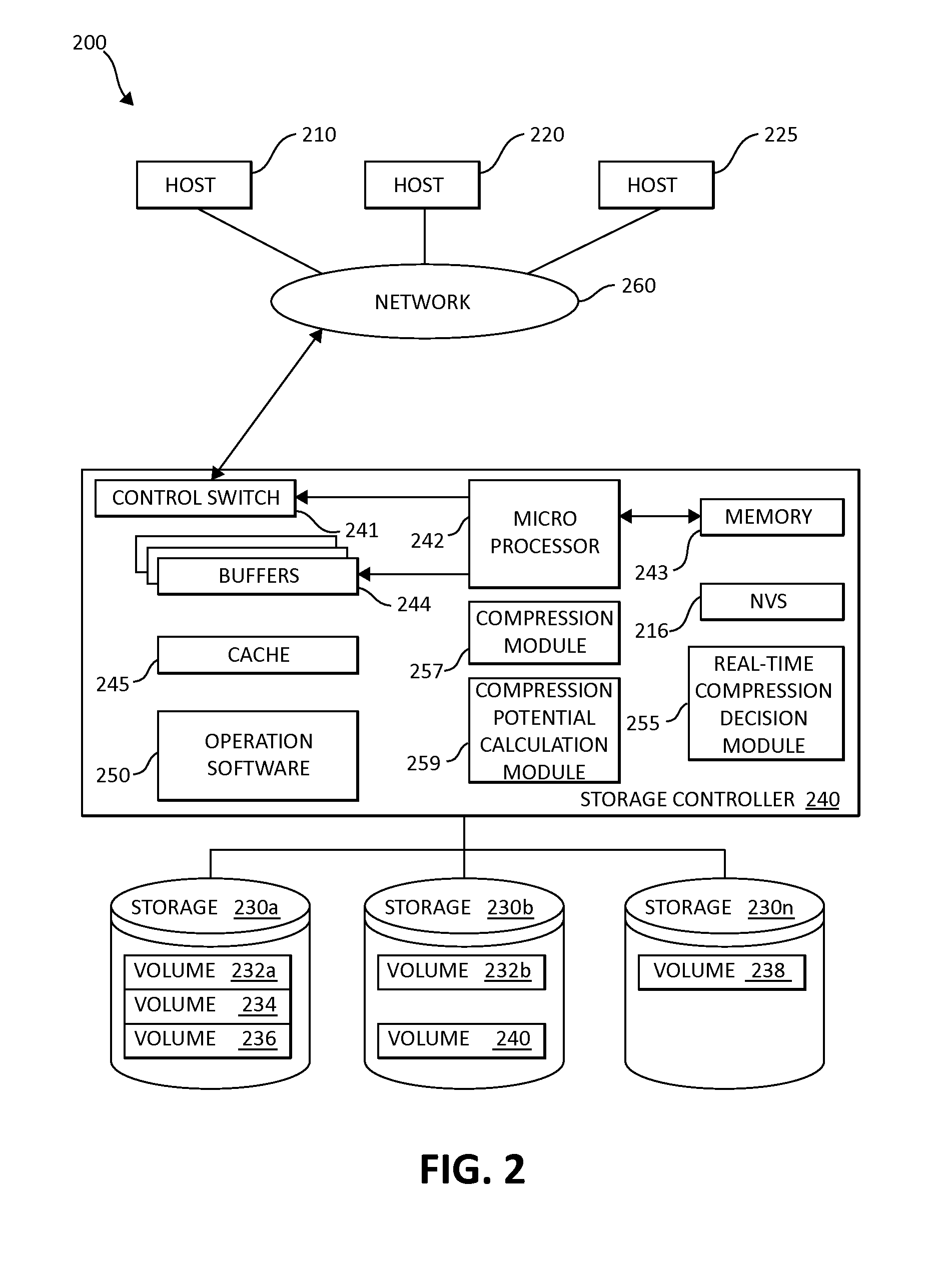
InactiveUS20140195498A1Reduce CPU overheadWell formedDigital data processing detailsCode conversionHeuristicData sequences
Real-time reduction of CPU overhead for data compression is performed by a processor device in a computing environment. Non-compressing heuristics are applied on a randomly selected data sample from data sequences for determining whether to compress the data sequences. A compression potential is calculated based on the non-compressing heuristics. The compression potential is compared to a threshold value. The data sequences are either compressed if the compress threshold is matched, compressed using Huffman coding if Huffman coding threshold is matched, or stored without compression.
Owner:IBM CORP
Image encoding apparatus, and image processing apparatus and its control method
InactiveUS20050276500A1Data generationDeterioration of precisionCharacter and pattern recognitionTelevision systemsImaging processingJPEG
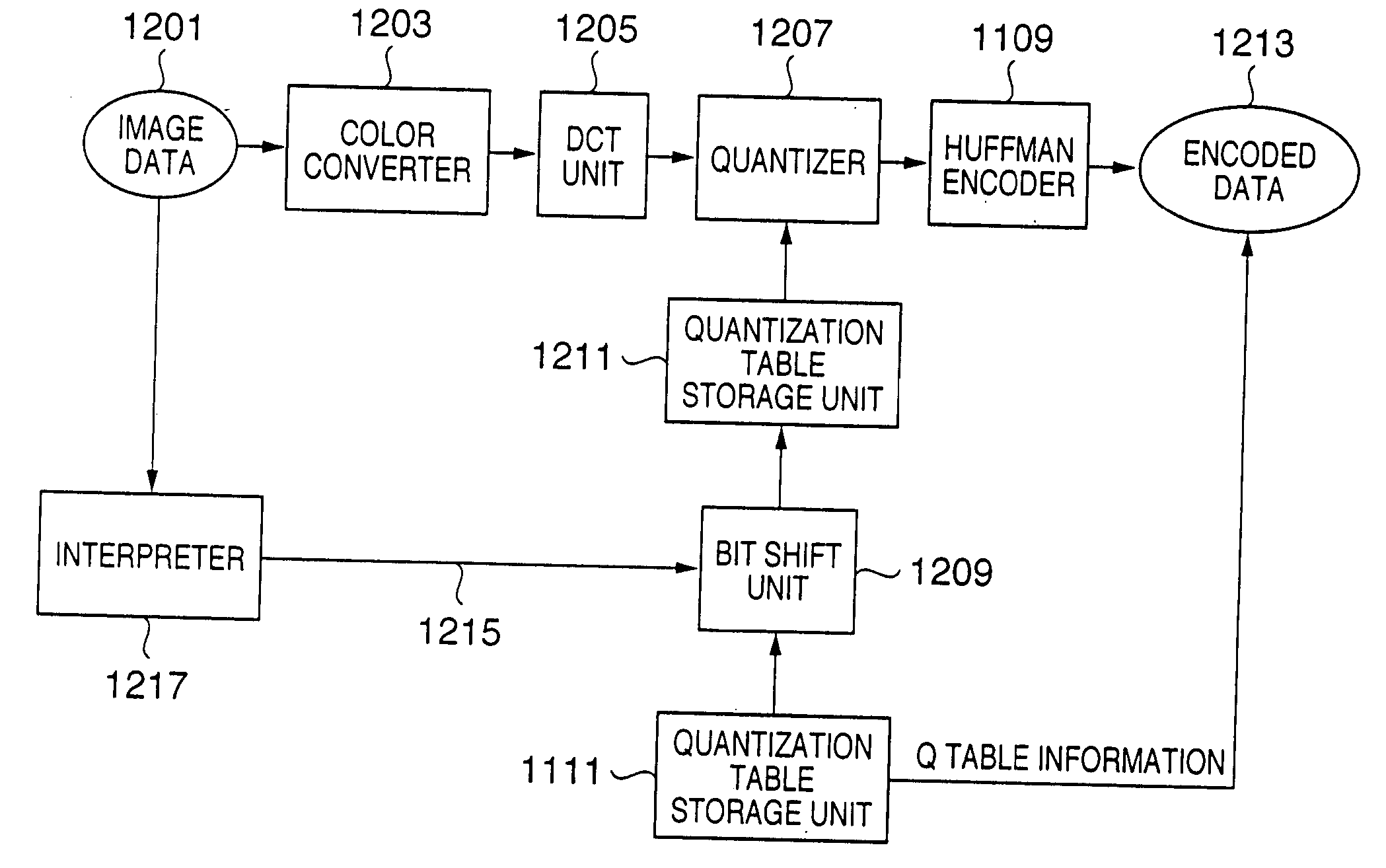
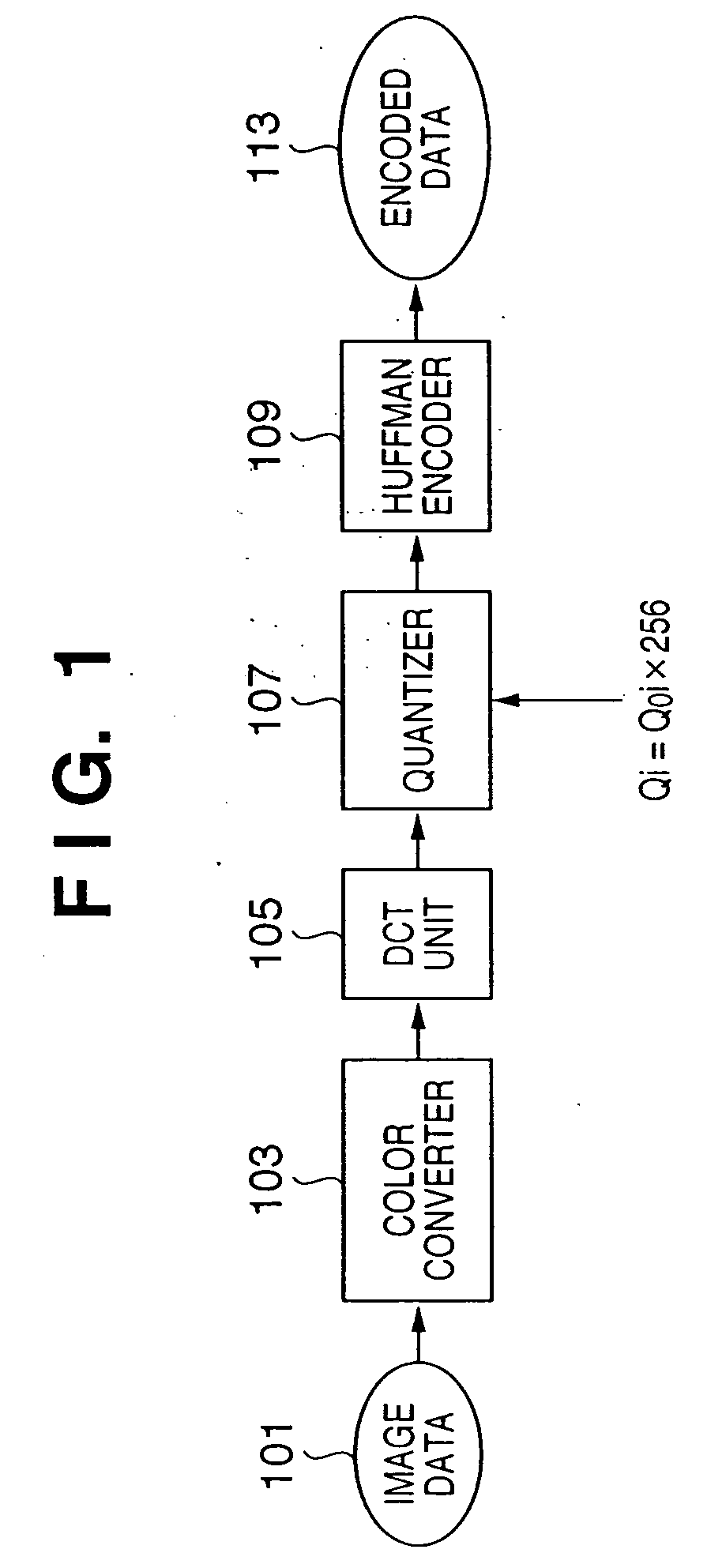
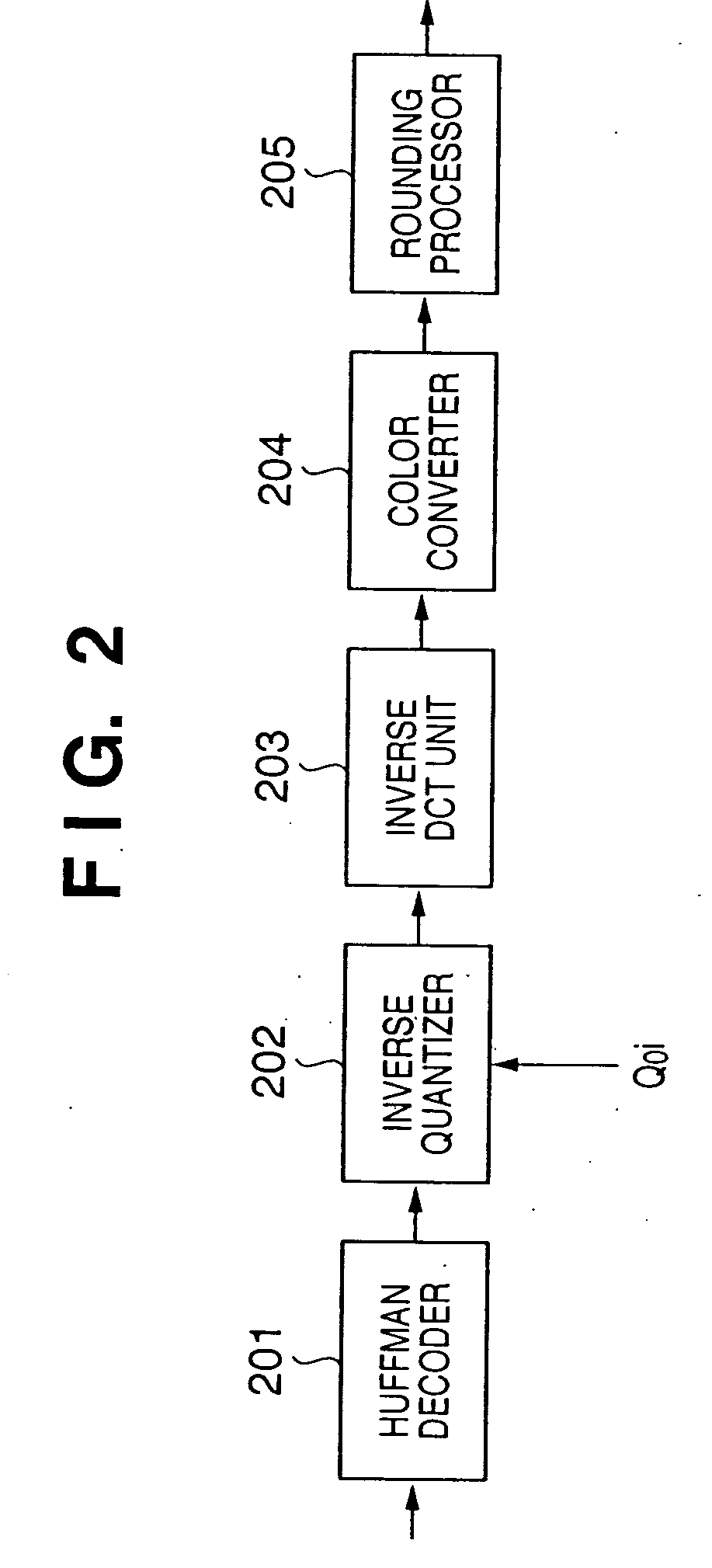
This invention generates target encoded data by suppressing an arithmetic precision drop by executing processes such as orthogonal transformation and the like using the number of bits of an input image in place of reducing the number of bits at the time of input upon encoding an image. Upon generating baseline JPEG encoded data, a quantization table for an 8-bit image is stored in a quantization table storage unit. When an interpreter outputs information indicating that each color component per pixel of input image data is 16 bits, a bit shift unit multiplies the quantization table stored in the quantization table storage unit by the 8th power of 2 or {8th power of 2+1}. A quantizer quantizes coefficients output from a DCT unit on the basis of the quantization table stored in the quantization table storage unit, and a Huffman encoder encodes the quantization result to Huffman codes. A header is created by setting information indicating baseline JPEG and the quantization table stored in the quantization table storage unit, thus generating encoded data.
Owner:CANON KK
Fast JPEG huffman encoding and decoding
InactiveUS6373412B1Electric signal transmission systemsCharacter and pattern recognitionData streamJPEG
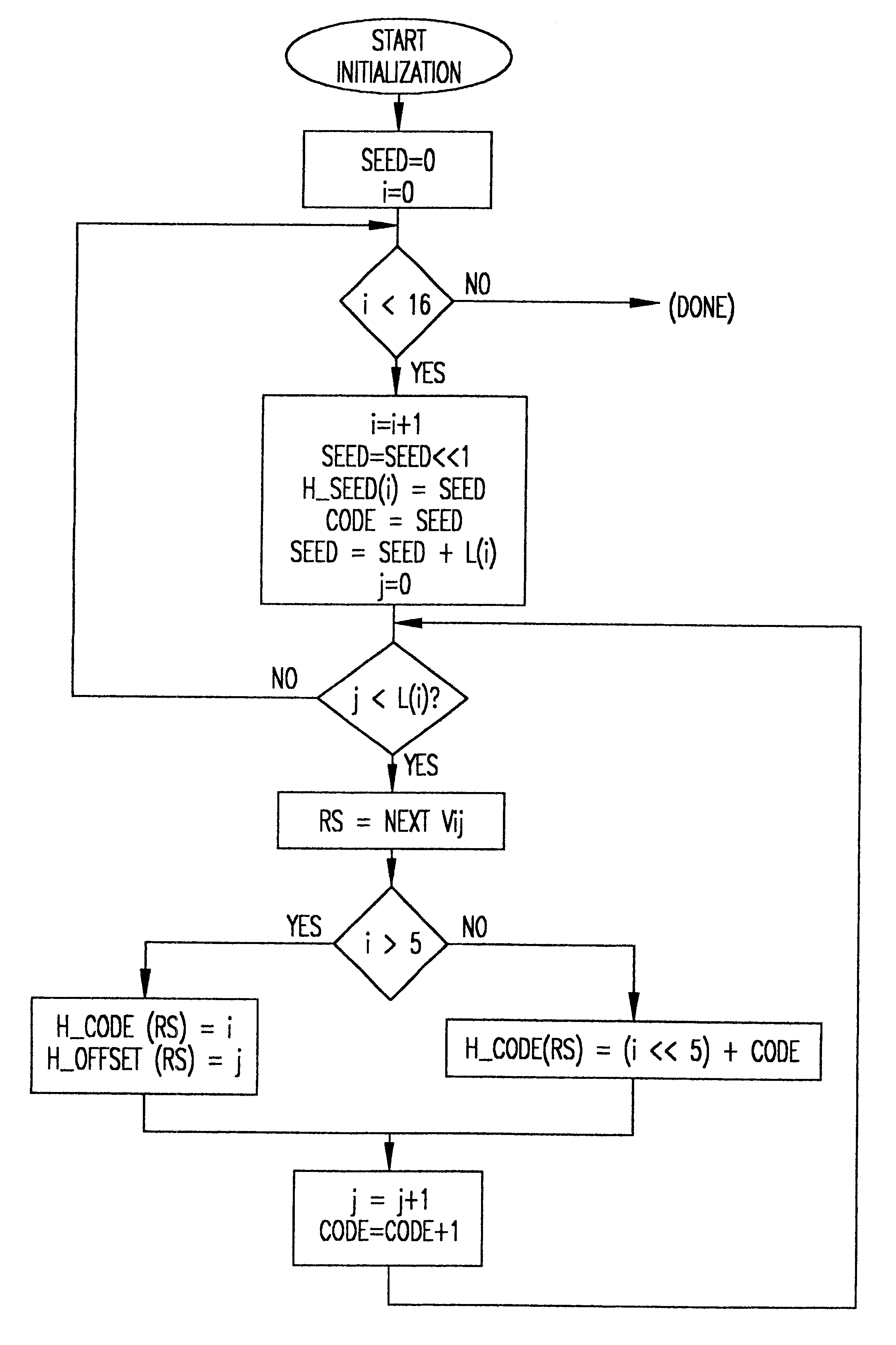
Huffman encoding, particularly from a packed data format, is simplified by using two different table formats depending on code length. Huffman tables are also reduced in size thereby. Decoding is performed in reduced time by testing for the length of valid Huffman codes in a compressed data stream and using an offset corresponding to a test criterion yielding a particular test result to provide a direct index into Huffman table symbol values while greatly reducing the size of look-up tables used for such a purpose.
Owner:IBM CORP
Object and fractal-based binocular three-dimensional video compression coding and decoding method
InactiveCN101980537AReduce compression timeReduce blockinessTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationIndependent motionDecoding methods
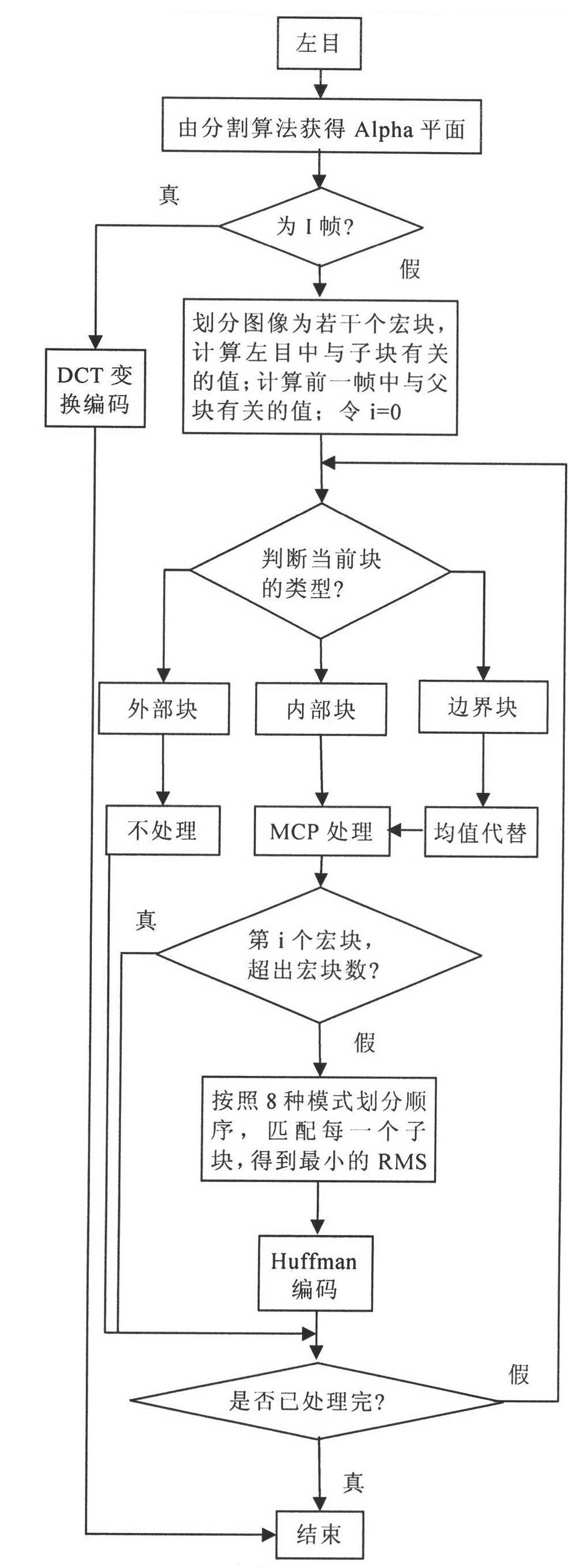
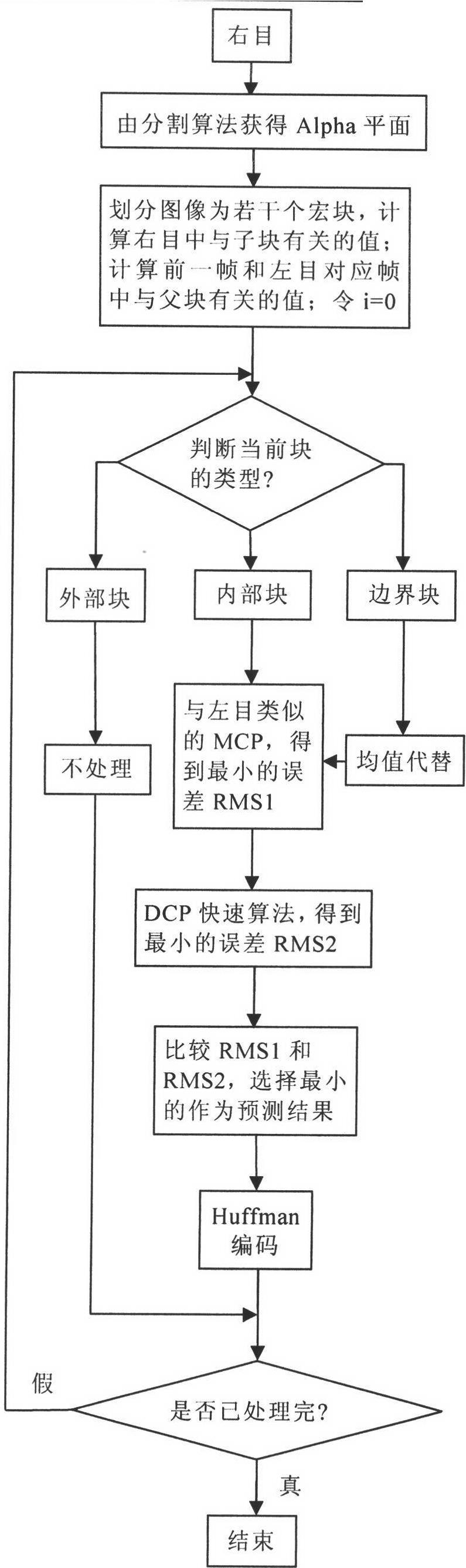
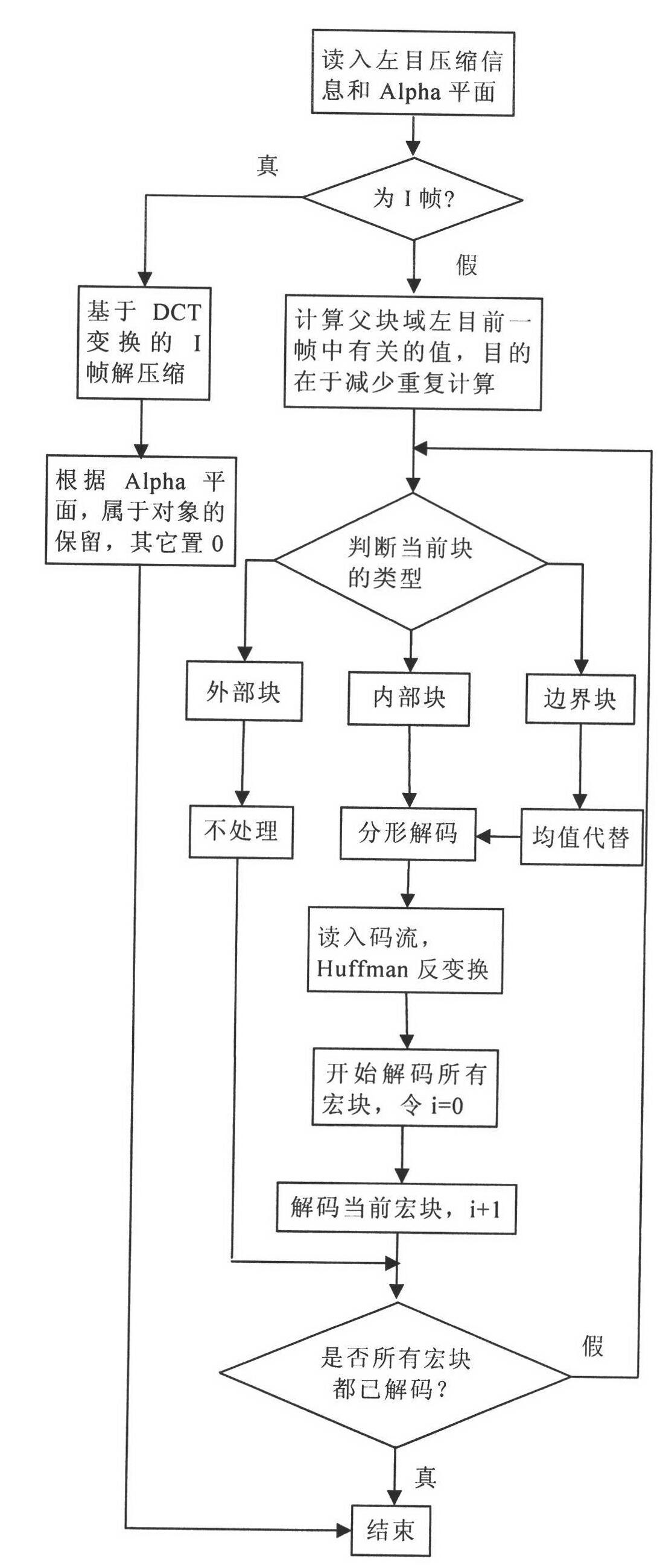
The invention provides an object and fractal-based binocular three-dimensional video compression and decompression method. In binocular three-dimensional video coding, a left channel is used as a basic layer, a right channel is used as an enhancement layer, and the left channel is encoded by an independent motion compensation prediction (MCP) mode. The object and fractal-based binocular three-dimensional video compression coding method comprises the following steps of: firstly, acquiring a video object partition plane, namely an Alpha plane by a video partition method, encoding the initial frame of a left eye through block discrete cosine transformation (DCT), and performing block motion estimation / compensation coding on a non-I frame of the left eye; secondly, determining the area attribute of an image block by utilizing the Alpha plane, and if the block is not within a video object area of the current code, not processing an external block, and if the block is within the video object area of the current code completely, searching the most similar matching block by a full-searching method in a previous frame of an internal block, namely a reference frame searching window of a left eye video; and finally, compressing coefficients of an iterated function system by a Huffman coding method, and if part of pixels of the block are within the video object area of the current code, and the other part of pixels are not within the video object area of the current code, processing a boundary block independently. The right channel is encoded by a MCP mode and a disparity compensation prediction (DCP) mode, the MCP is similar to the processing of the left eye, and the block with the minimum error is used as a prediction result. When the DCP coding mode is performed, the polarization and directionality in a three-dimensional parallel camera structure are utilized fully.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
System and method for realizing parallel decompression of hardware
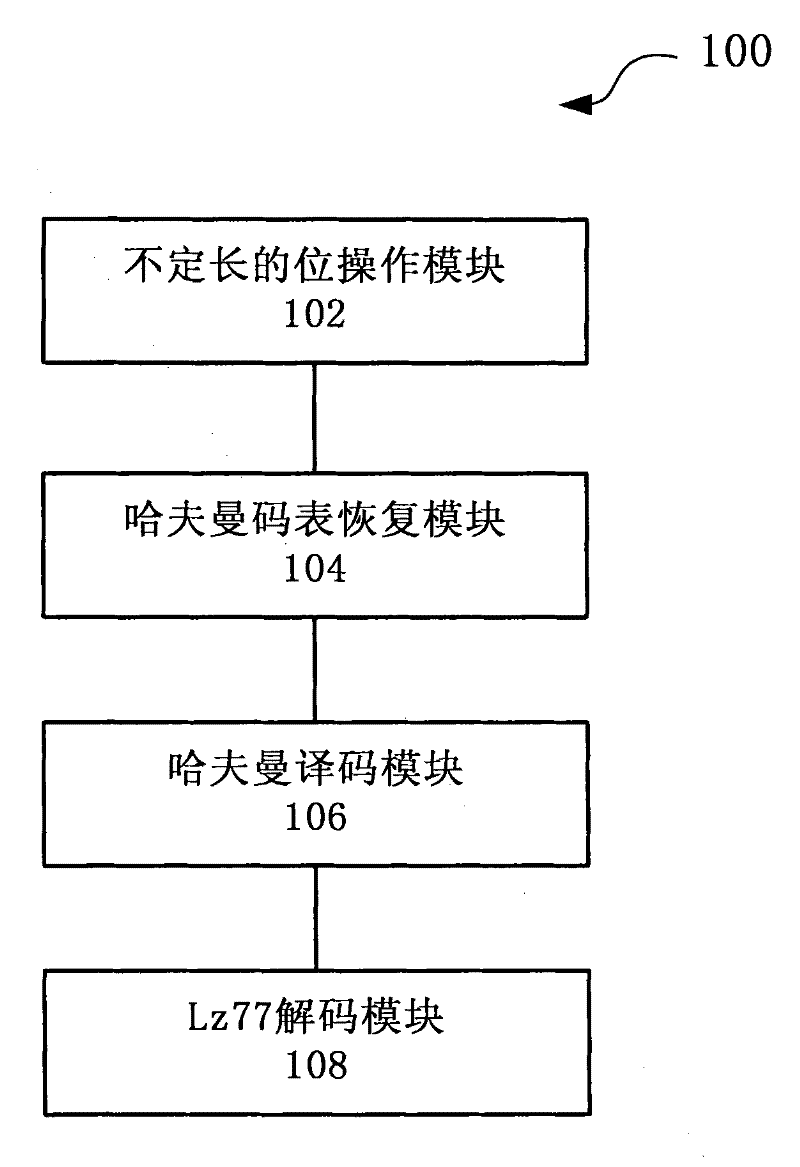
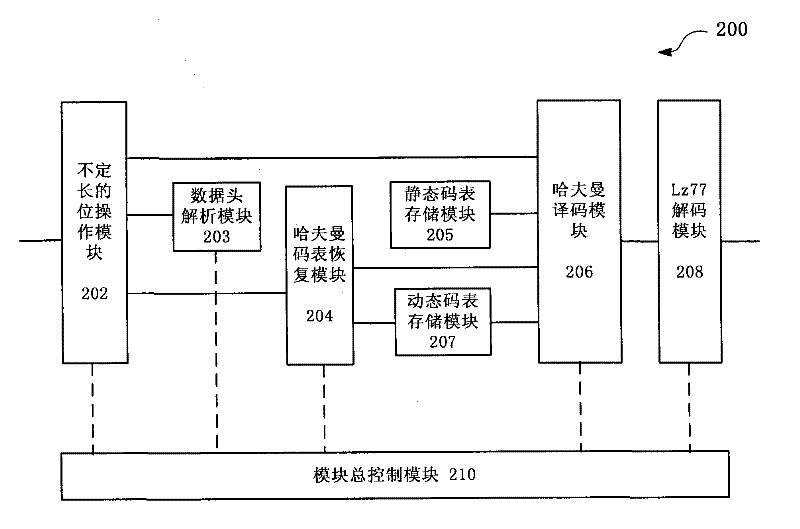
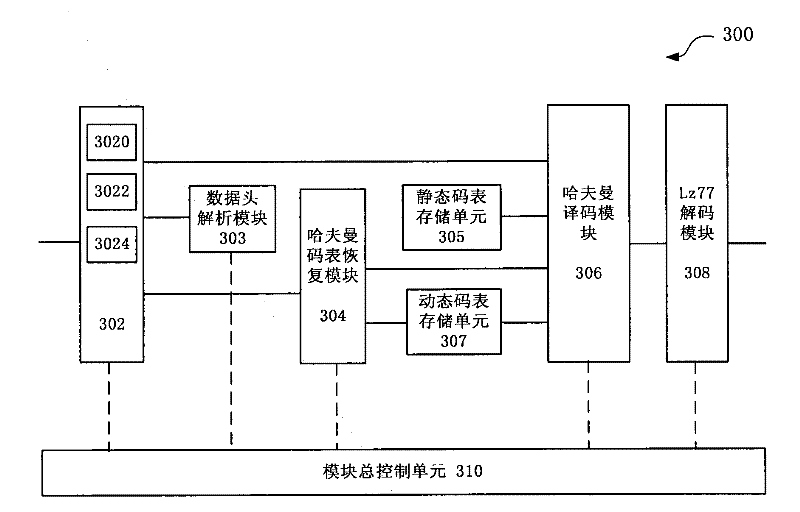
The invention discloses a system and method for realizing parallel decompression of hardware. The system comprises a variable-length bit manipulation module, a Huffman table recovery module, a Huffman coding module and a decoding module, wherein the variable-length bit manipulation module is used for carrying out variable-length bit manipulation on to-be-decompressed data to acquire variable-length data; the Huffman table recovery module is used for recovering a Huffman table in accordance with the variable-length data; the Huffman coding module is used for executing Huffman coding in parallel in accordance with the Huffman table; and the decoding module is used for carrying out decoding in accordance with the Huffman coding result. According to the system and method for realizing the parallel decompression of hardware, an FPGA (field programmable gate array) is utilized to realize a Gzip decompressing function, a parallel decompression algorithm is utilized and a hardware circuit structure suitable for the algorithm is designed, thus improving the processing efficiency of the decompression greatly.
Owner:BAIDU ONLINE NETWORK TECH (BEIJIBG) CO LTD
Efficient decoding of n-tuple variable bit length symbols
ActiveUS7372378B2Improve processing efficiencyRequires minimizationCode conversionData streamParallel computing
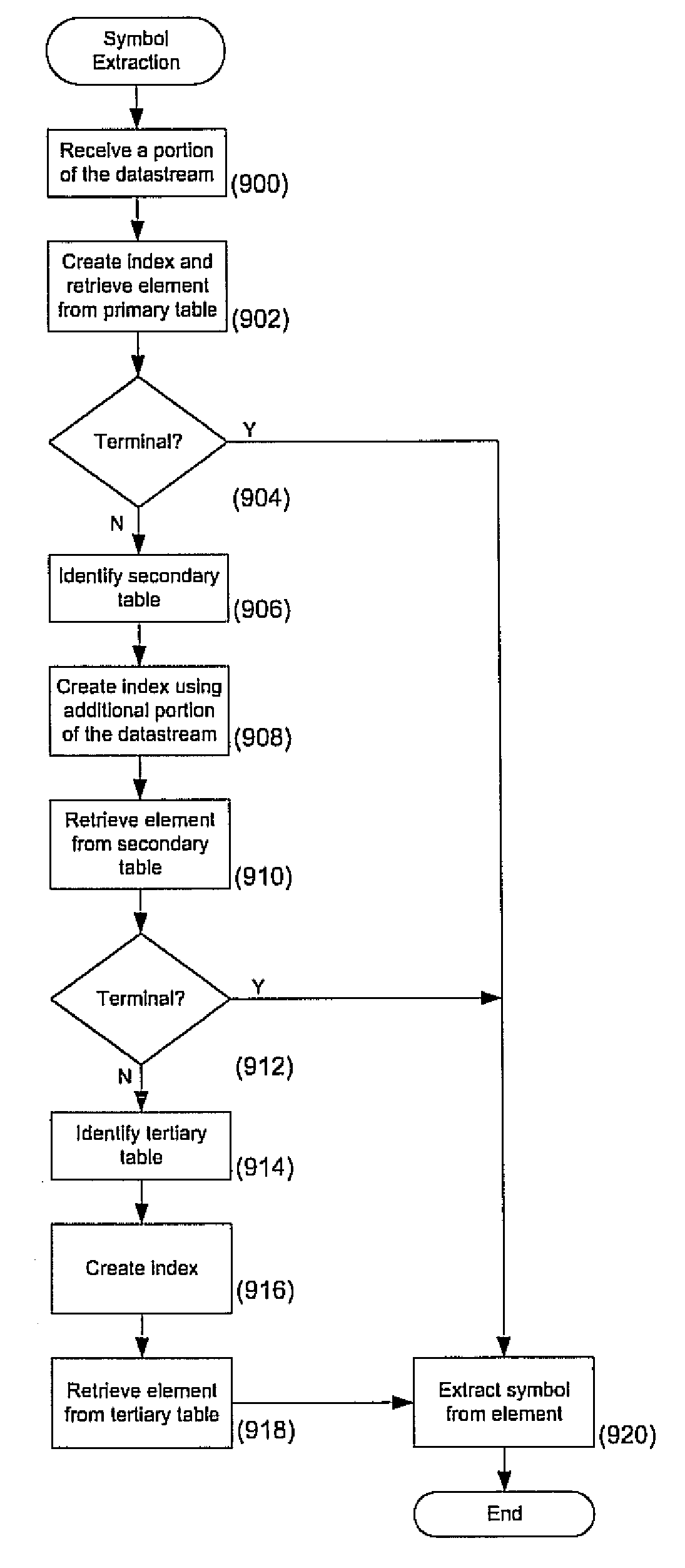
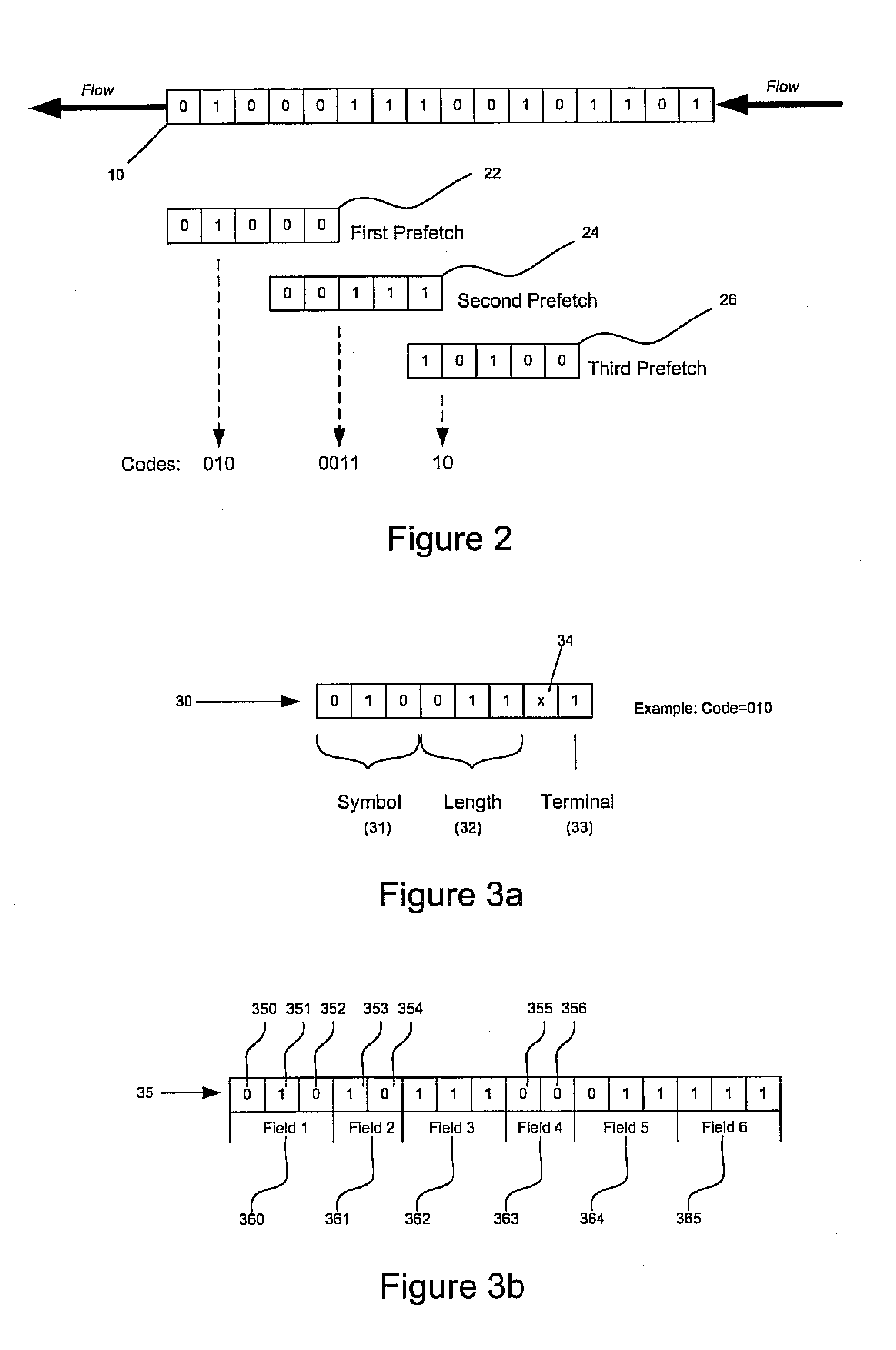
Methods and systems that leverage the advantages of Huffman coding to increase processing efficiency of a data-stream while simultaneously minimizing storage requirements are provided. Decoding efficiency and table storage requirements can be balanced to produce systems that can be adapted for use in high-end network infrastructure applications and for low-resourced portable consumer devices. The systems and methods are operative in decoding data streams using multi-symbol codes and sign information, including AAC and MP3 data streams. A hierarchical structure of tables is described as having primary tables, secondary tables, tertiary tables and so on. Optimization balances processing requirements, table storage requirements and the described systems and methods may be implemented on a variety of processing platforms.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Variable-length, high-speed asynchronous decoder circuit
InactiveUS6865668B1Improve throughputDigital data processing detailsDigital computer detailsVariable-length codeComputational logic
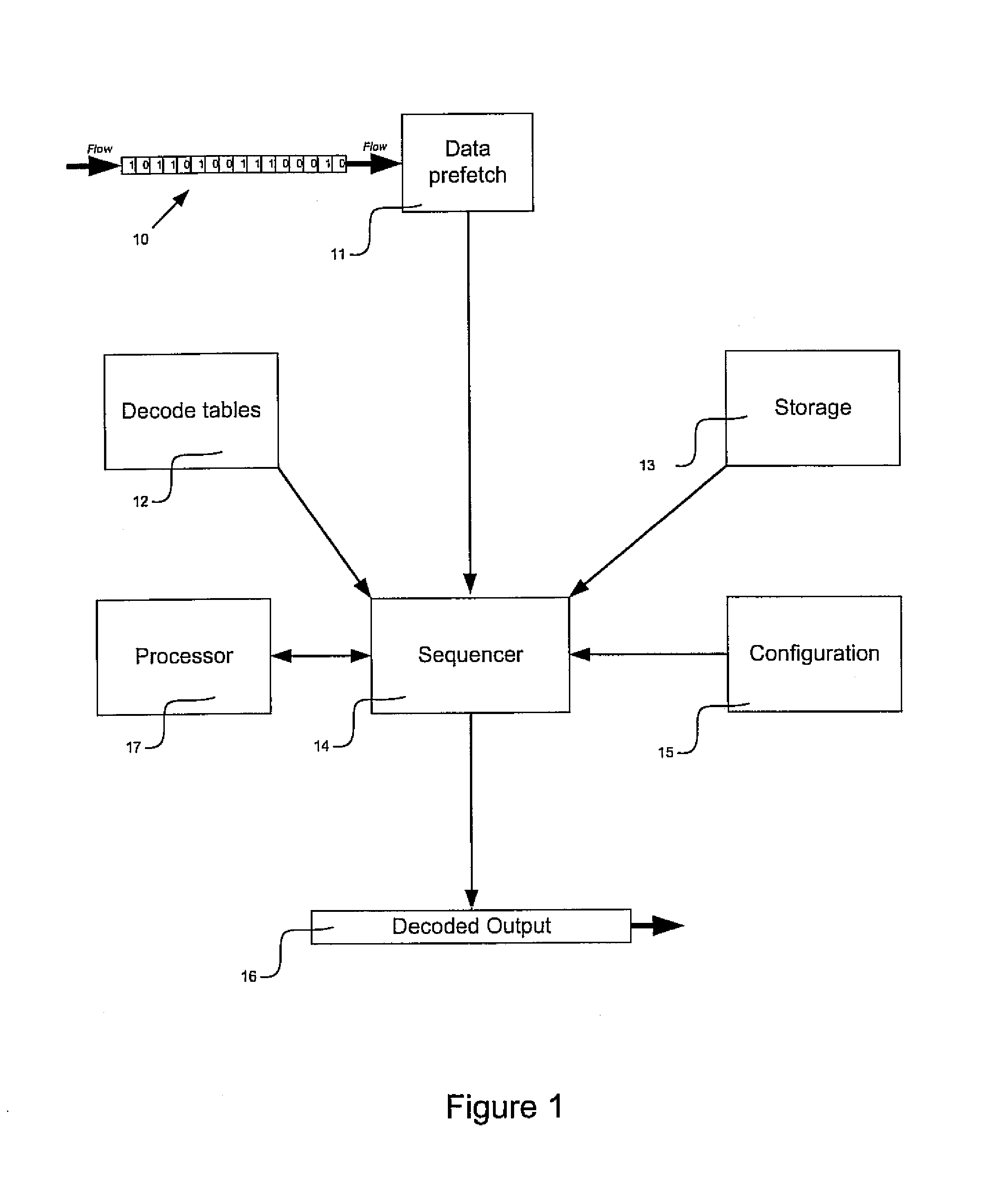
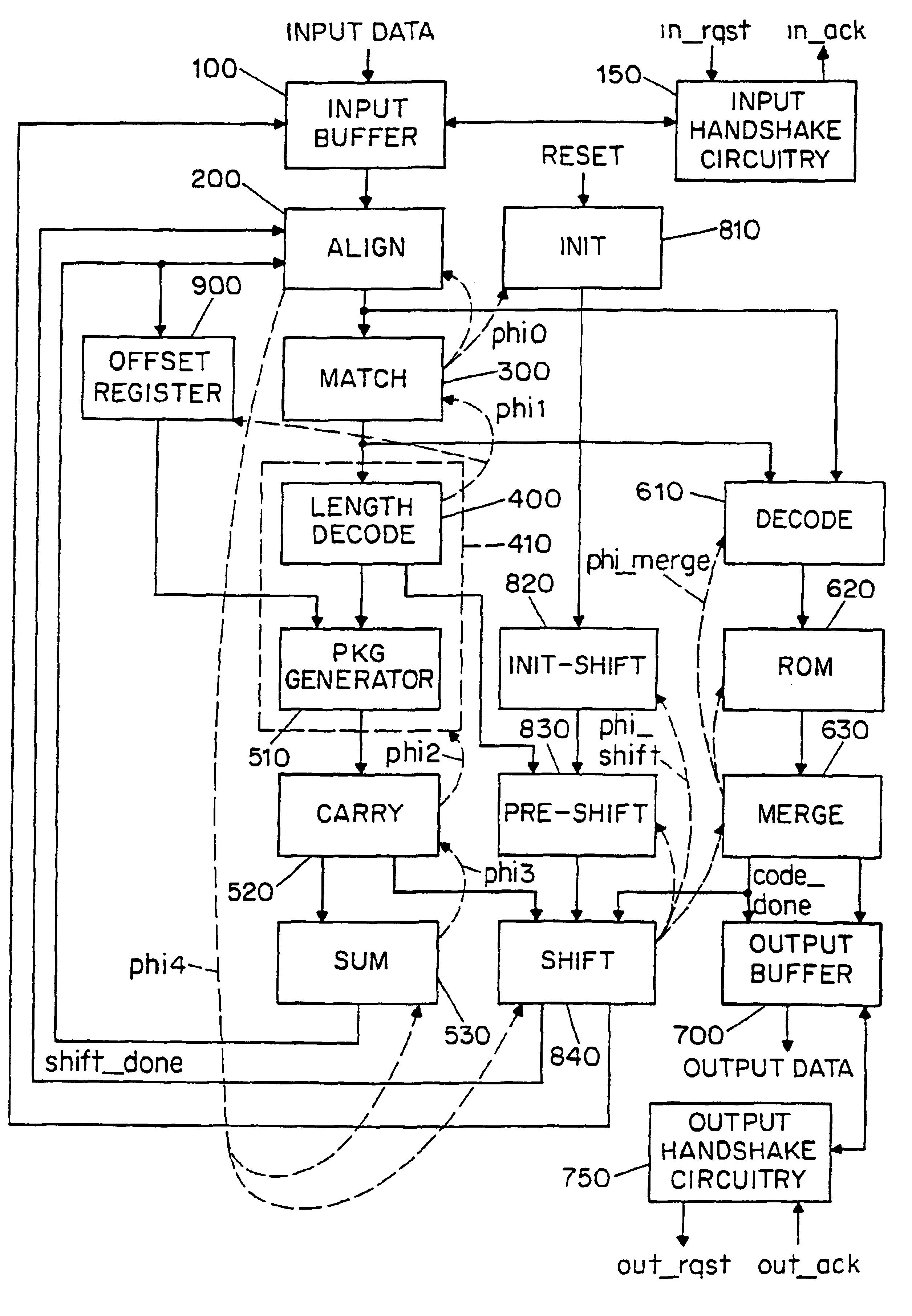
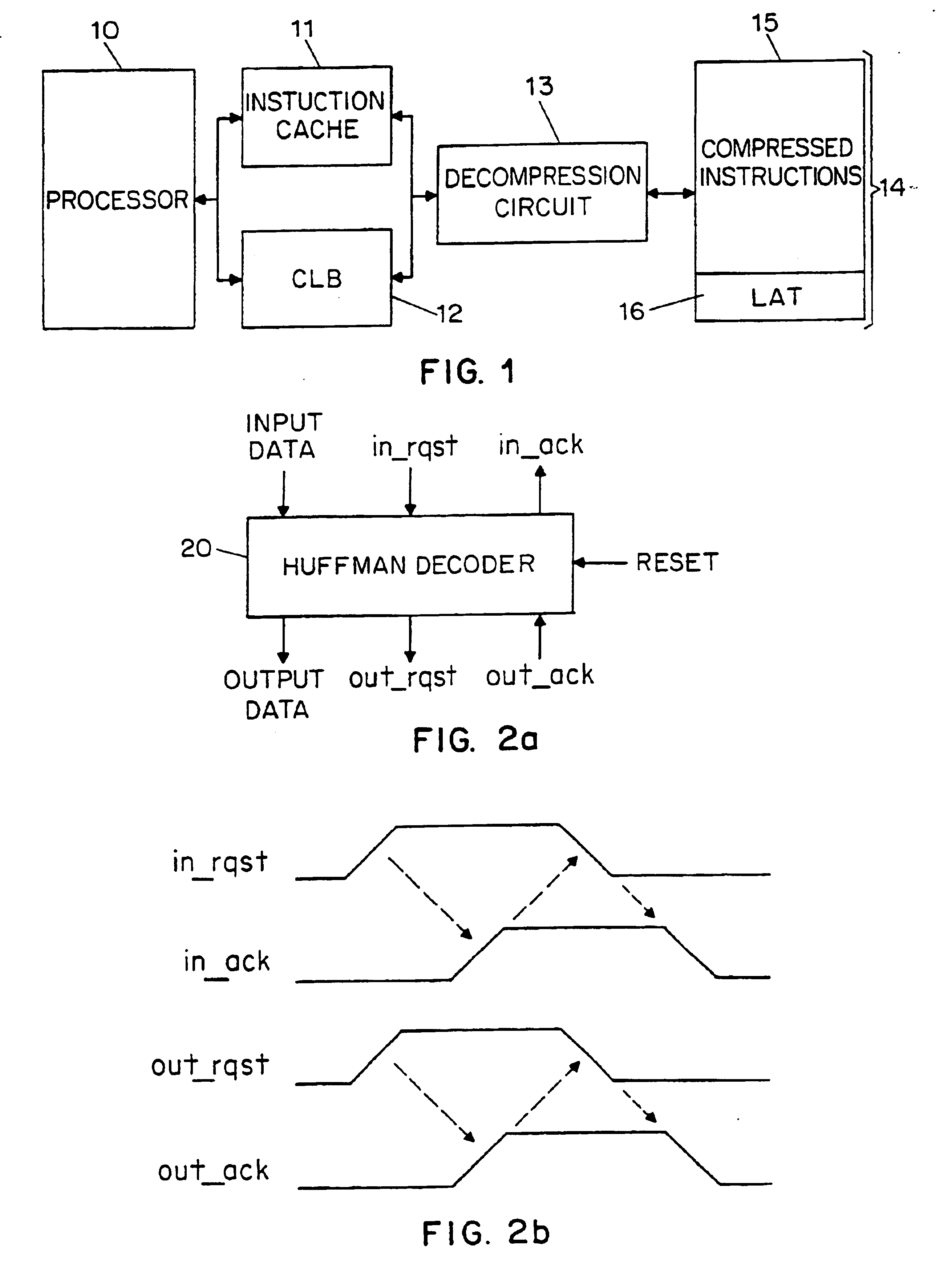
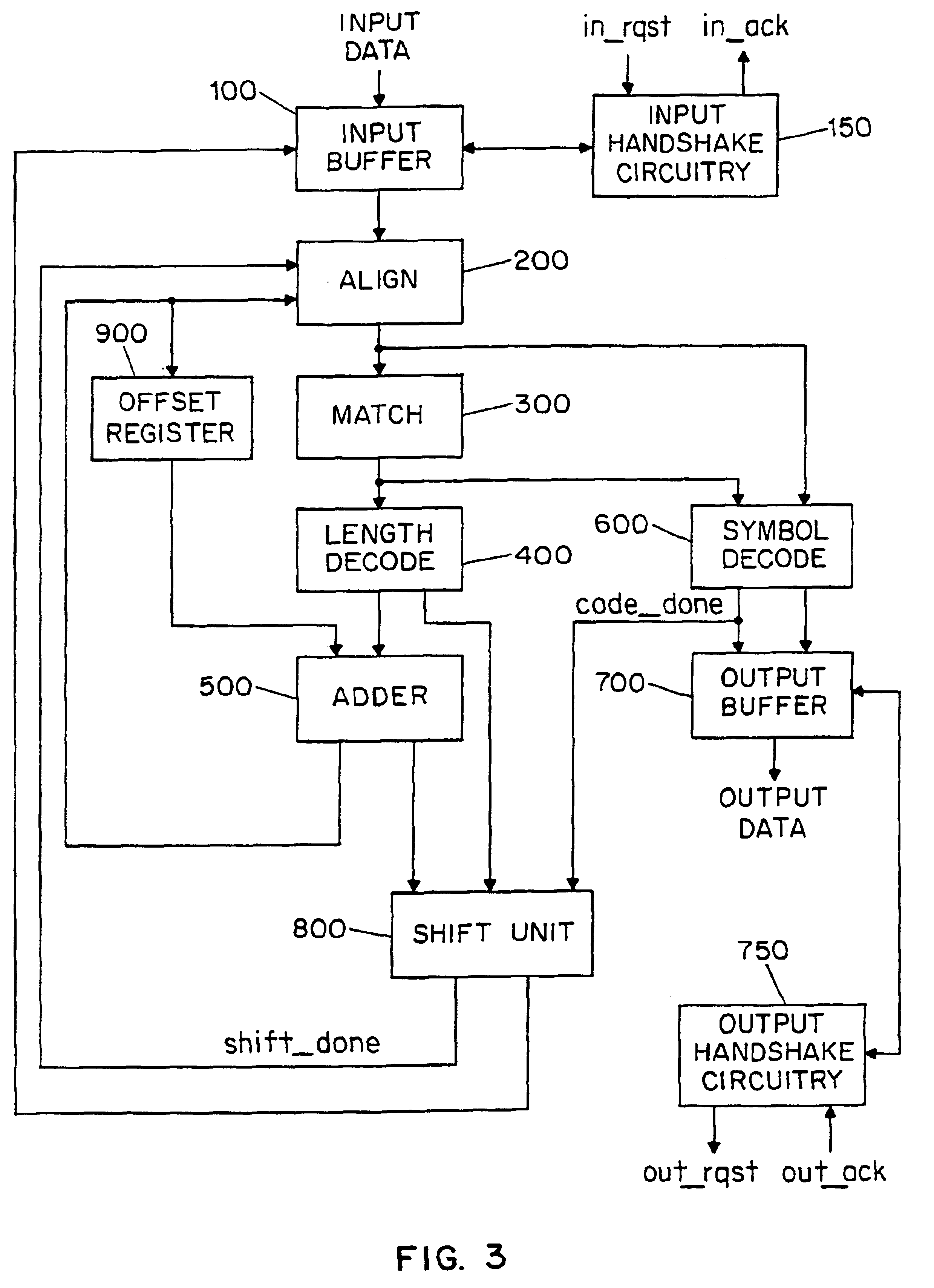
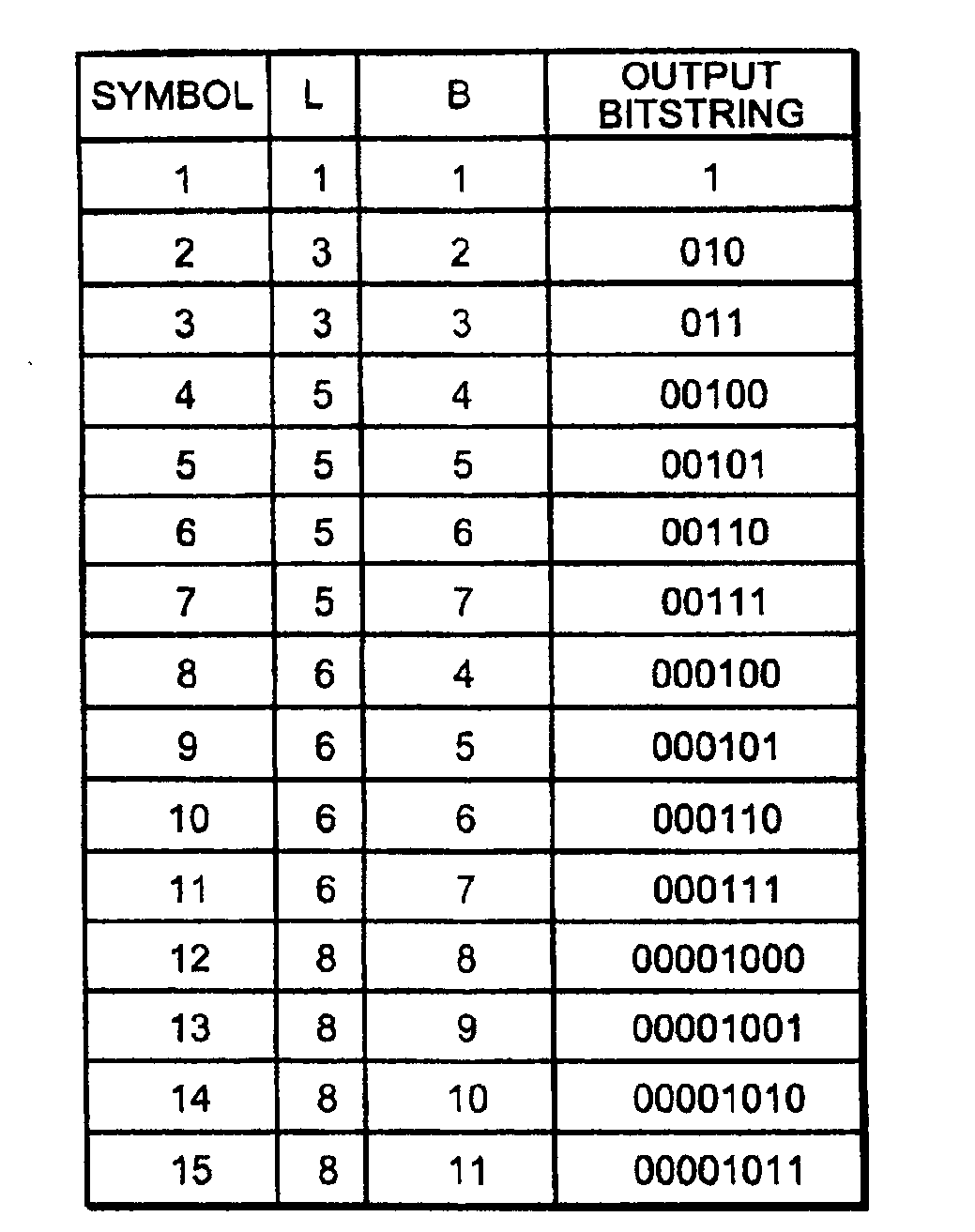
There is disclosed a decoder circuit (20) for decoding input data coded using a variable length coding technique, such as Huffman coding. The decoder circuit (20) comprises an input buffer (100), a logic circuit (150) coupled to the input buffer (100), and an output buffer (700) coupled to the logic circuit (750). The logic circuit (750) includes a plurality of computational logic stages for decoding the input data, the plurality of computational logic stages arranged in one or more computational threads. At least one of the computational threads is arranged as a self-timed ring, wherein each computational logic stage in the ring produces a completion signal indicating either completion or non-completion of the computational logic of the associated computational logic stage. Each completion signal is coupled to a previous computational logic stage in the ring. The previous computational logic stage performs control operations when the completion signal indicates completion and performs evaluation of its inputs when the completion signal indicates non-completion.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
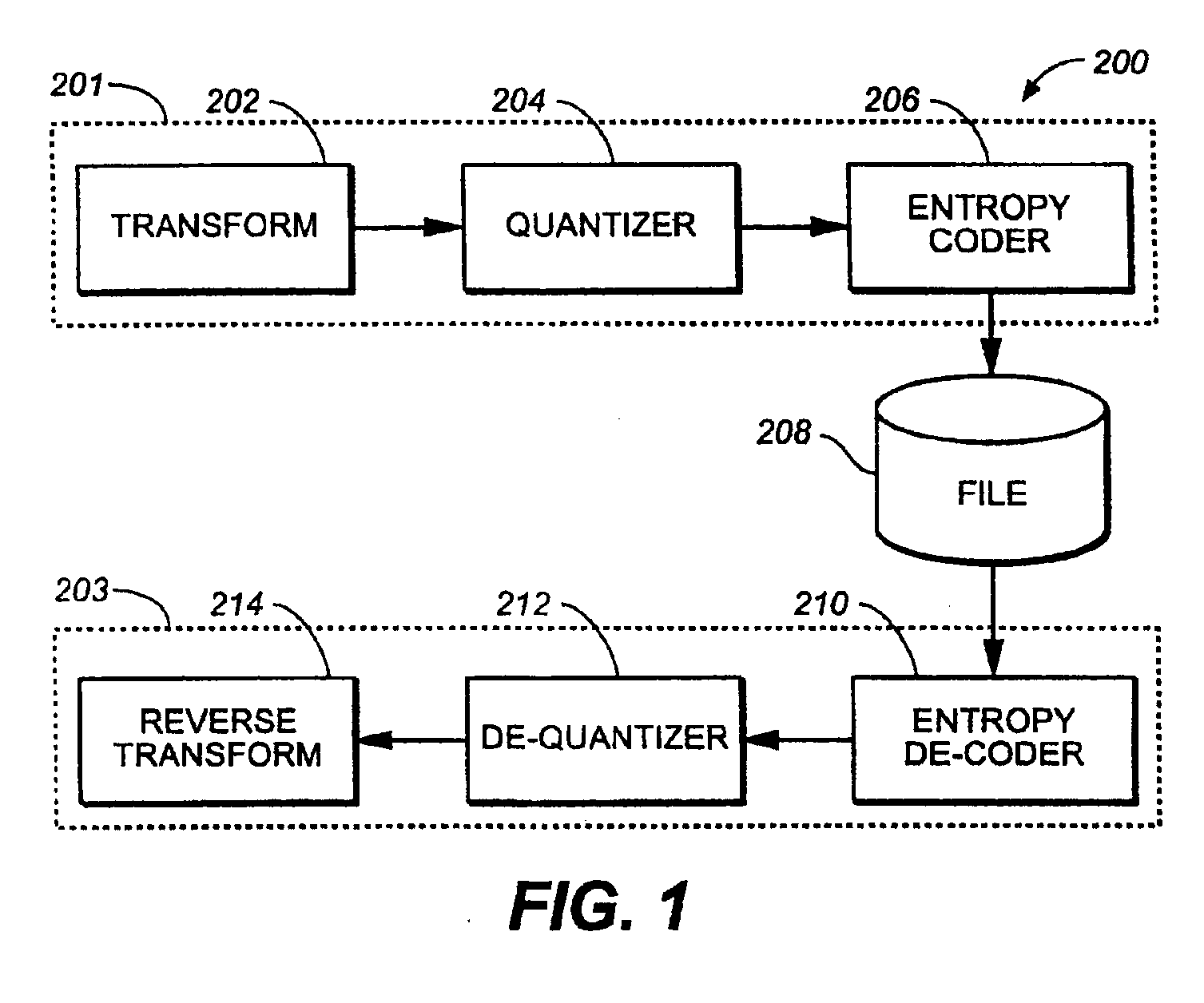
Multiple Technique Entropy Coding System And Method
InactiveUS20090080788A1Accurate descriptionFast computerCode conversionCharacter and pattern recognitionAlgorithmLookup table
A system, method and computer program product having optimal matching to a known or measured probability distribution encodes data without the use of an excessively large lookup table. An encoder constructed according to the present invention uses two or more different encoding methods in combination. In one embodiment, Huffman coding by table lookup is combined with computational generation, such as by using an exponential Golomb equation. The most commonly occurring elements are looked up in a small Huffman table, while the remaining elements are coded with the equation. In another embodiment, data is encoded using two or more equations. In yet another embodiment, data is encoded using multiple tables in conjunction with one or more equations.
Owner:DROPLET TECH
Time-of-flight measuring device
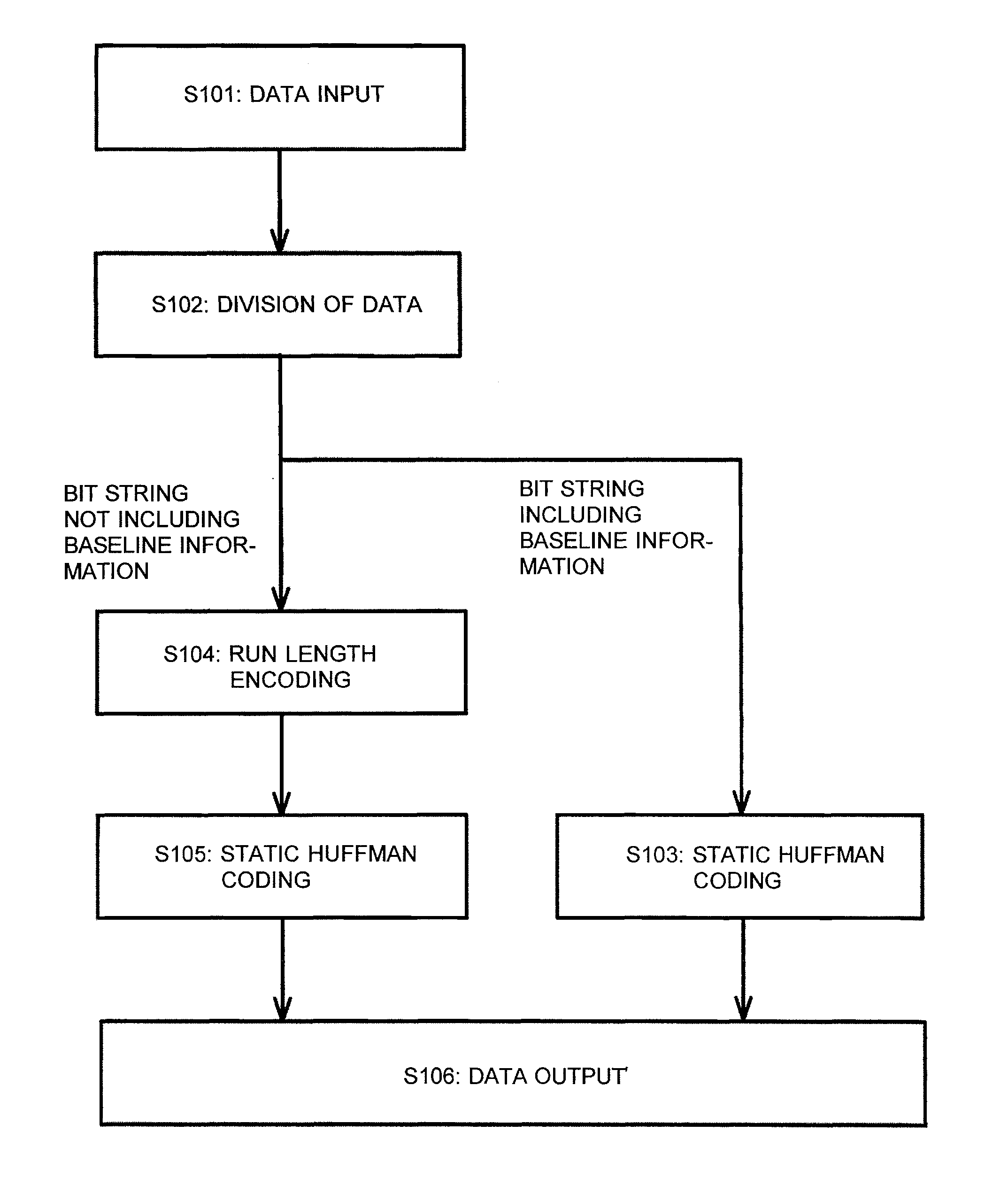
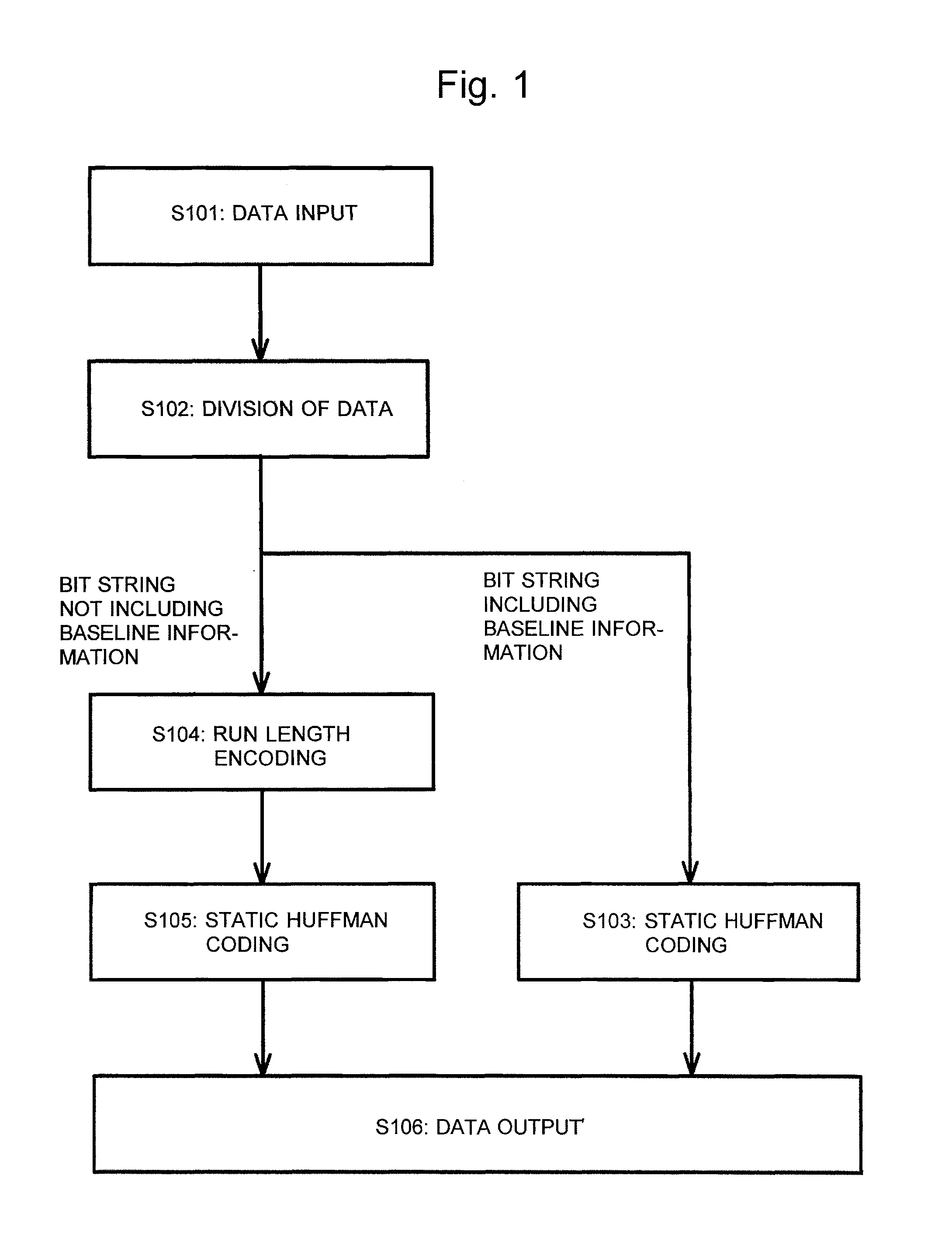
InactiveUS8004432B2Shorten the time periodEasy to processTime-of-flight spectrometersCode conversionComputer hardwareData treatment
A time-of-flight measuring device for performing a hardware-based high-speed data compression process before transferring the data from a signal recorder to a data processor is provided. A time-series digital signal recorded by a signal recorder is converted to a plurality of time-series digital signals by being divided into a bit string including baseline information and a bit string not including the baseline information. Then, the time-series digital signal consisting of a bit string not including the baseline information is compressed by run-length encoding, such as zero length encoding or switched run-length encoding. Subsequently, static Huffman coding is performed on each of the time-series digital signals to reduce the data amount.
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP
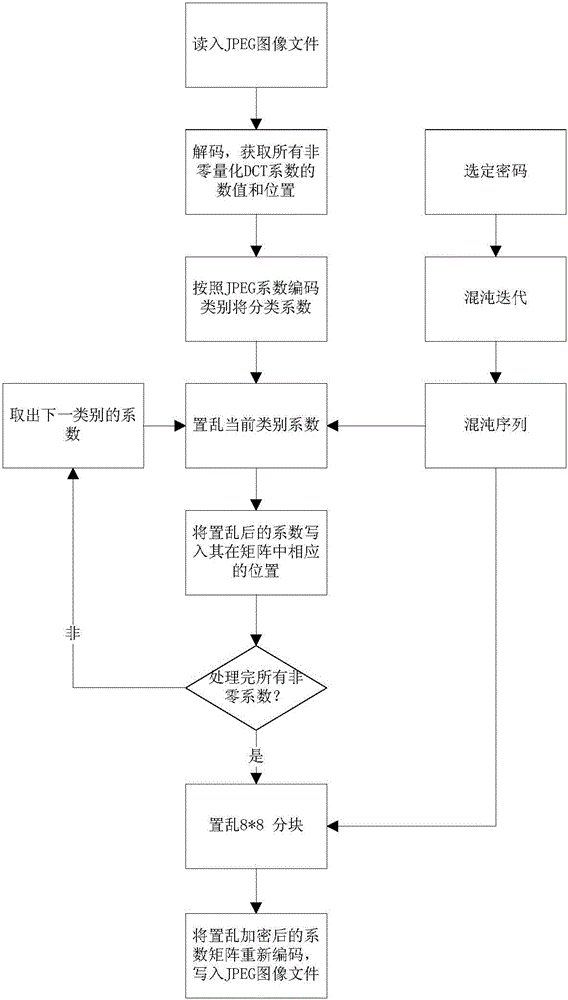
Intra-class coefficient scrambling-based JPEG image encryption method
InactiveCN105975866AIncrease the compression ratioExpand the key spaceImage codingDigital data protectionPlaintextAc coefficient
The invention relates to an intra-class coefficient scrambling-based JPEG image encryption method. The method comprises the following steps: firstly reading in a JPEG image file, acquiring a Huffman coding table and image data which undergoes JPEG coding compression, carrying out decoding to acquire all the non-zero quantized DCT coefficient numerical values and positions and carrying out classification; selecting a password, carrying out chaotic iteration by utilizing the password, so as to generate a chaotic sequence, and scrambling the non-zero coefficients and 8*8 block of each class by utilizing the chaotic sequence; and carrying out entropy coding on a scrambled quantized DCT coefficient matrix, and writing the coded data into the JPEG image file so as to complete intra-class coefficient scrambling-based JPEG image encryption. According to the method disclosed in the invention, scrambling is carried out on different classes of quantized DCT coefficients through the chaotic sequence, and the quantized DC coefficients and the non-zero AC coefficients are processed by directly using one encryption scheme, so that the safety and the high efficiency are both considered; and the encrypted images are similar to clear text image files in the aspect of size, and have high compression ratios.
Owner:CHANGAN UNIV
Efficient one-pass cache-aware compression
InactiveUS20150113220A1Well formedMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationTheoretical computer scienceByte
Exemplary method, system, and computer program product embodiments for efficient one-pass cache-aware compression are provided. In one embodiment, by way of example only, an output of a fast compressor to Huffman encoding for achieving the one-pass cache-aware compression by using a predetermined Huffman-tree upon determining by the fast compressor a final representation of each data byte.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Efficient decoding of n-tuple variable bit length symbols
ActiveUS20070126608A1Improve processing efficiencyStorage requirement is minimizedCode conversionData streamParallel computing
Methods and systems that leverage the advantages of Huffman coding to increase processing efficiency of a data-stream while simultaneously minimizing storage requirements are provided. Decoding efficiency and table storage requirements can be balanced to produce systems that can be adapted for use in high-end network infrastructure applications and for low-resourced portable consumer devices. The systems and methods are operative in decoding data streams using multi-symbol codes and sign information, including AAC and MP3 data streams. A hierarchical structure of tables is described as having primary tables, secondary tables, tertiary tables and so on. Optimization balances processing requirements, table storage requirements and the described systems and methods may be implemented on a variety of processing platforms.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Method for processing a digital image and image representation format
InactiveUS7480418B2Easy to analyzeEasily be manipulatedGeometric image transformationCharacter and pattern recognitionZeroth orderDigital image
Owner:NOKIA TECH OY
Fast loss less image compression system based on neighborhood comparisons
InactiveUS20040008896A1Reduce varianceEasy to compressCode conversionCharacter and pattern recognitionPixel value differenceImage compression
A fast loss less image compression system based on neighborhood comparisons compares pixel value differences with neighboring pixels and replaces such pixel values with the minimum of the differences. A marker is attached to a block of pixels, such that all the pixels in that block are compared with neighbors of one direction. The marker indicates how all of the pixels in that block are compared. Intermittent Huffman-tree construction is used such that one tree is used for several frames. Huffman coding is used to compress the resulting frame. A single Huffman-tree is constructed once every predetermined number of frames. The frequency of Huffman-tree construction can be performed according to the instantaneous availability of processor time to perform the construction. When more processing time is available, the Huffman-trees are computed more frequently. Such frequency variation can be implemented by using an input video frame buffer. If the buffer is a certain size, then processor time for Huffman-tree construction is available.
Owner:ZAXEL SYST
Method, apparatus and recording medium for data compression
InactiveUS7003171B1Fast and efficient data compressionComputational loadCharacter and pattern recognitionDigital video signal modificationBit allocationBinary classification
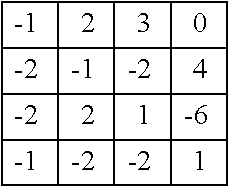
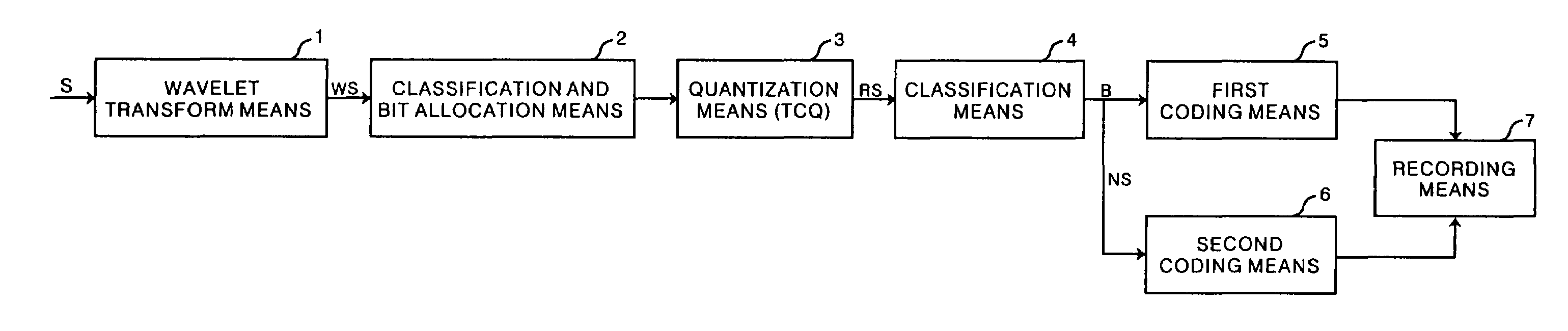
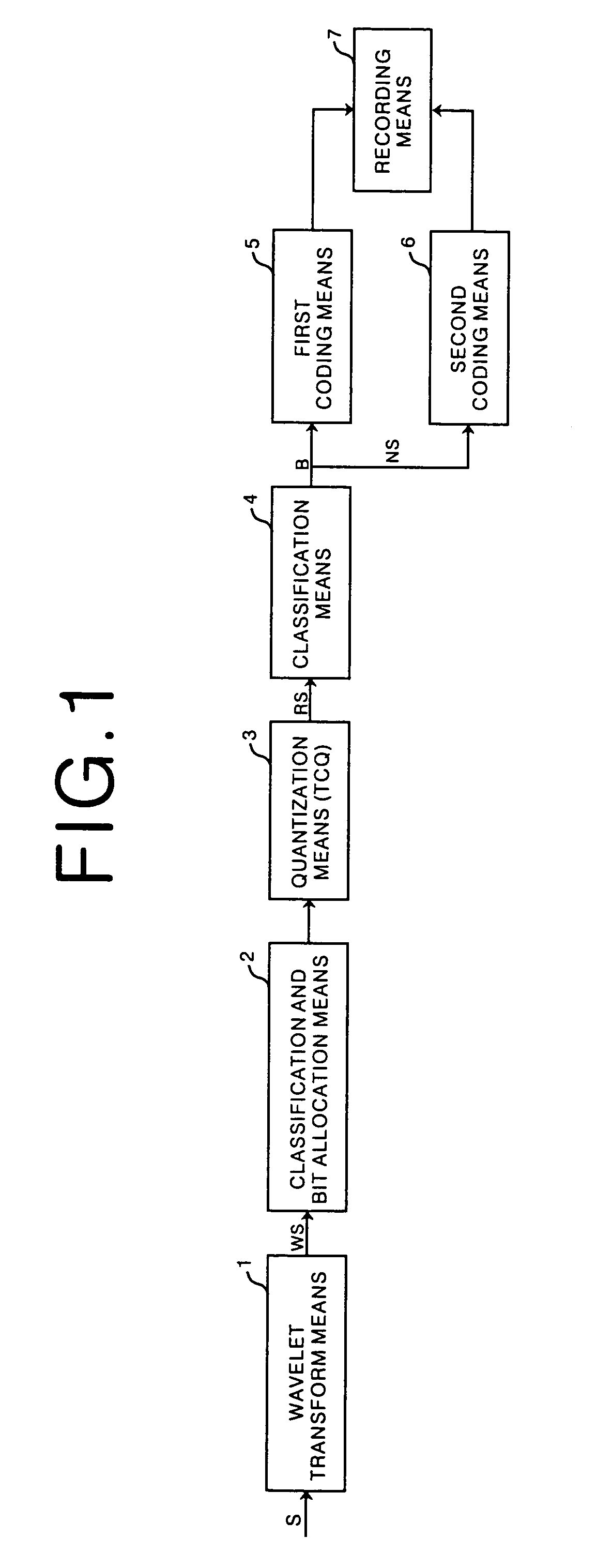
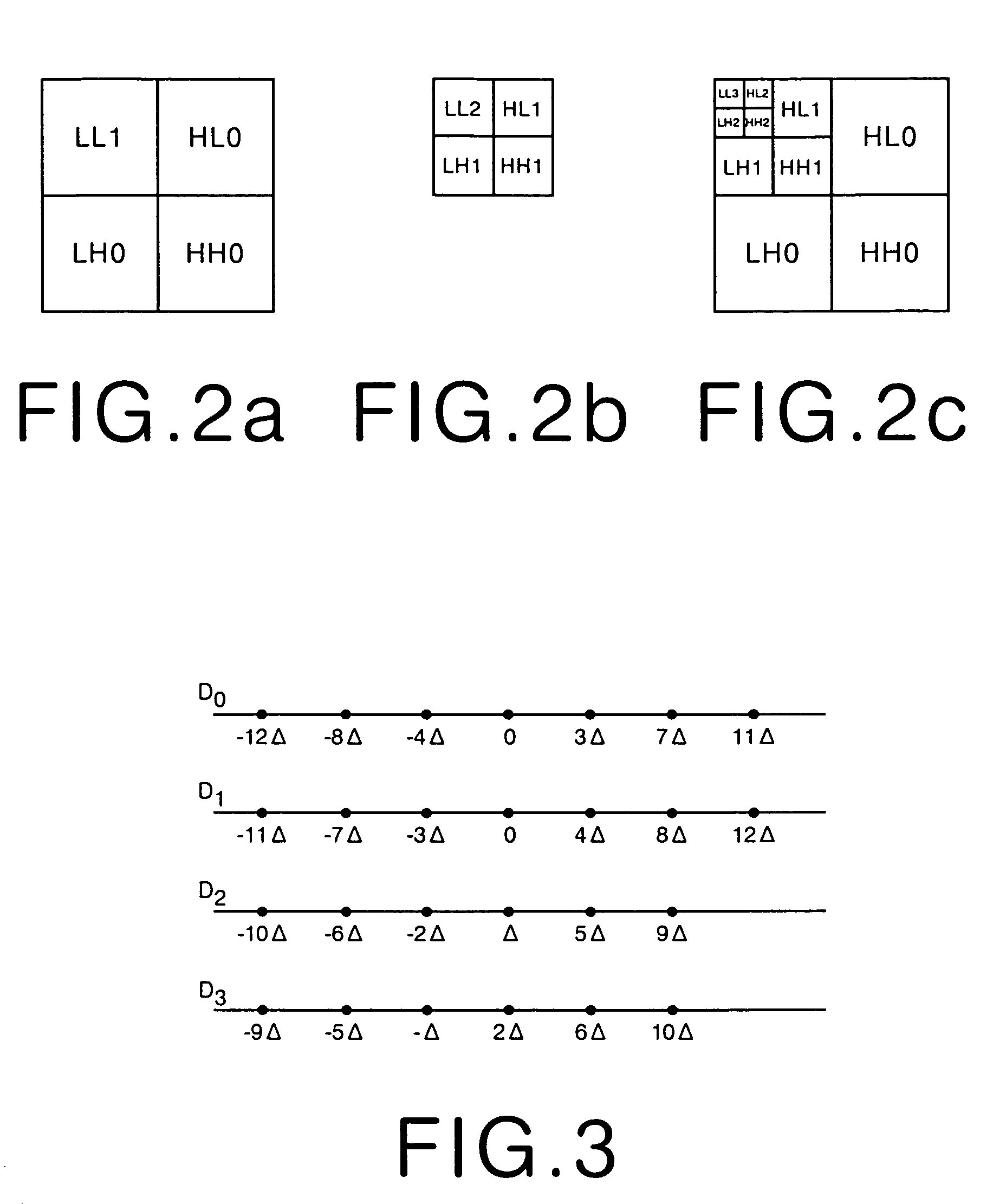
Fast and efficient data compression can be carried out. Original image data are subjected to wavelet transform. The obtained wavelet-transformed data are classified and bit allocation is determined. Based on the determined bit allocation, the wavelet-transformed data are quantized and quantized data are obtained. The quantized data are classified into 0 data and non-zero data. Binary classification information data indicating this classification are also obtained. The classification information data are coded according to a coding method having a comparatively simple operation, such as Huffman coding and run length coding. The multi-valued, non-zero data are coded according to a coding method having a high compression efficiency although having a comparatively complex operation, such as universal coding and Golomb-Rice coding.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
Demura data lossless compression and decompression method of OLED screen
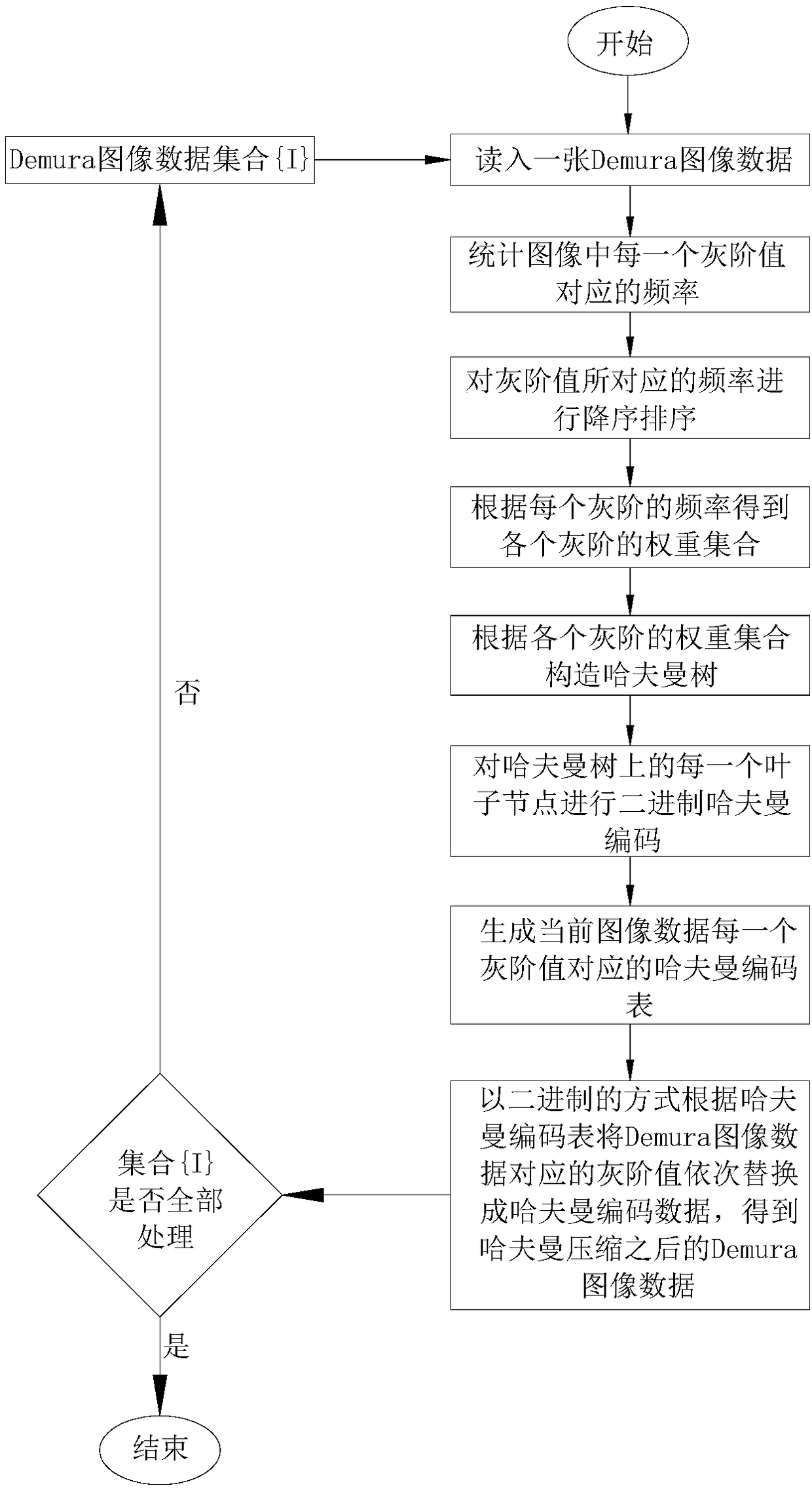
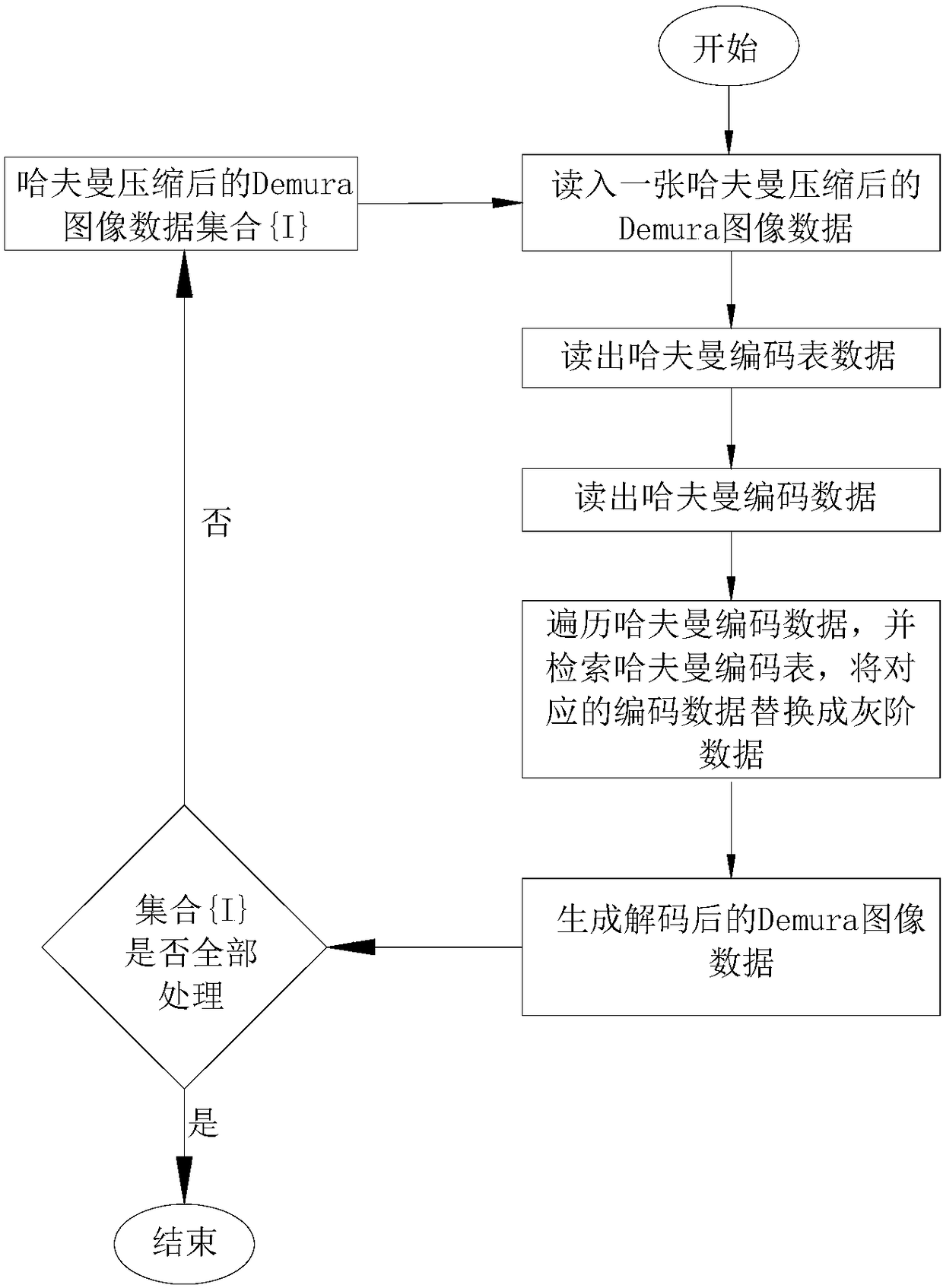
InactiveCN108259911AGuaranteed accuracy requirementsIncrease the compression ratioDigital video signal modificationGray levelFrequency of occurrence
A Demura data lossless compression method of an OLED screen comprises performing Demura data Huffman coding lossless compression for R, G, B. The data compression method comprises the steps of: analyzing the gray scale of the read Demura image data, and counting the frequency of occurrence of each gray scale; performing the construction of the Huffman tree according to the frequency of each gray scale sorted according to the current Demura image data; performing a binary Huffman encoding on the constructed Huffman tree; and replacing the corresponding gray scale value in the original Demura image data with a Huffman encoded value. The invention adopts Huffman coding lossless compression to ensure the accuracy requirement in the Deumra process. Due to the characteristics such as the particularity of Demura data, relatively concentrated gray scale distribution and a higher ratio of the gray scale data with high frequency, the compression ratio of the encoded data is relatively high, andthe cost is saved.
Owner:苏州佳智彩光电科技有限公司
Method and system for compressing reduced instruction set computer (RISC) executable code
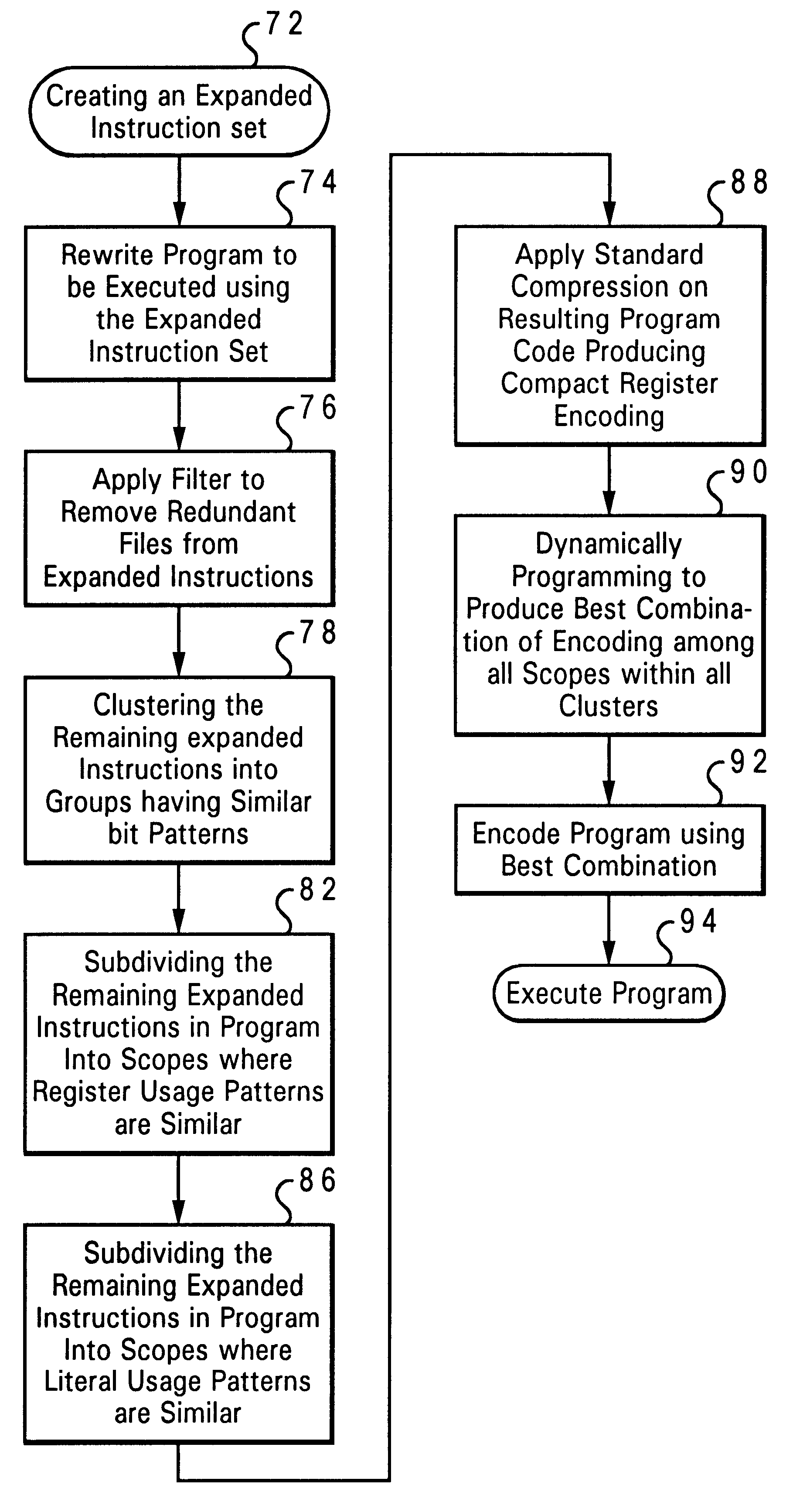
InactiveUS6442680B1Eliminate redundancySoftware engineeringDigital computer detailsPowerPCProcessor register
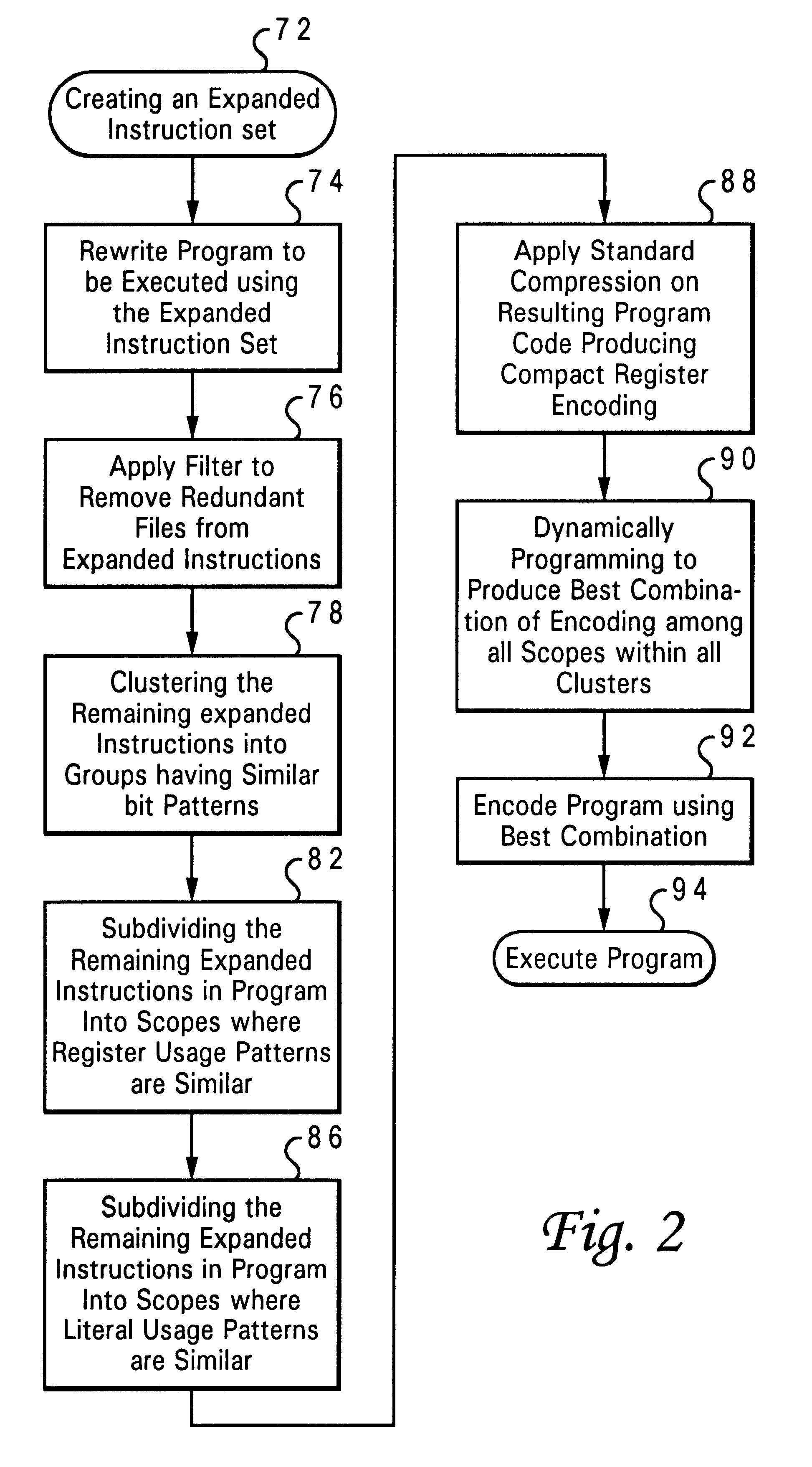
A method and system for a compression scheme used with program executables that run in a reduced instruction set computer (RISC) architecture such as the PowerPC is disclosed. Initially, a RISC instruction set is expanded to produce code that facilitates the removal of redundant fields. The program is then rewritten using this new expanded instruction set. Next, a filter is applied to remove redundant fields from the expanded instructions. The expanded instructions are then clustered into groups, such that instructions belonging to the same cluster show similar bit patterns. Within each cluster, the scopes are created such that register usage patterns within each scope are similar. Within each cluster, more scopes are created such that literals within each instruction scope are drawn from the same range of integers. A conventional compression technique such as Huffman encoding is then applied on each instruction scope within each cluster. Dynamic programming techniques are then used to produce the best combination of encoding among all scopes within all the different clusters. Where applicable, instruction scopes are combined that use the same encoding scheme to reduce the size of the resulting dictionary. Similarly instruction clusters are combined that use the same encoding scheme to reduce the size of the resulting dictionary.
Owner:IBM CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com