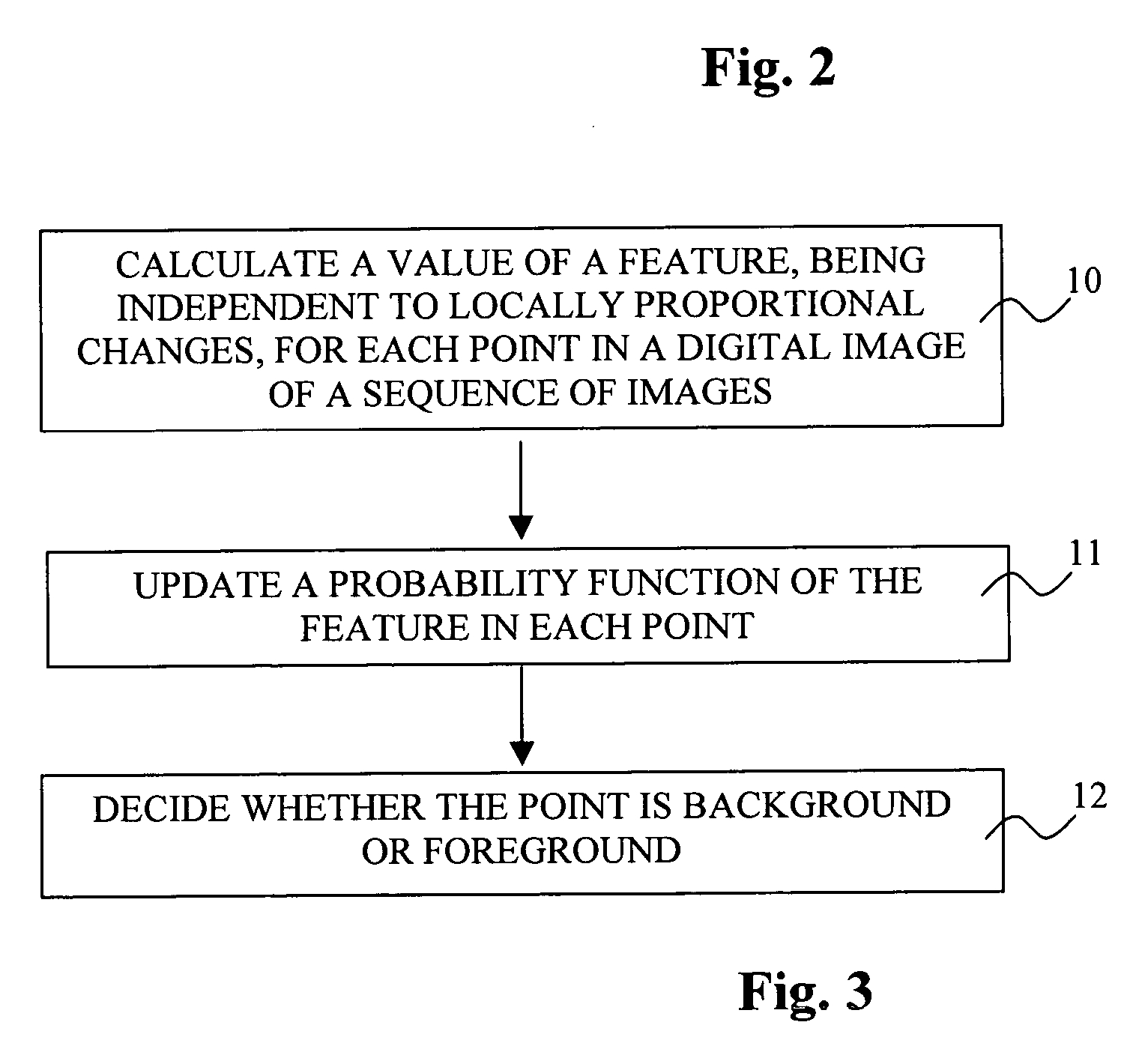
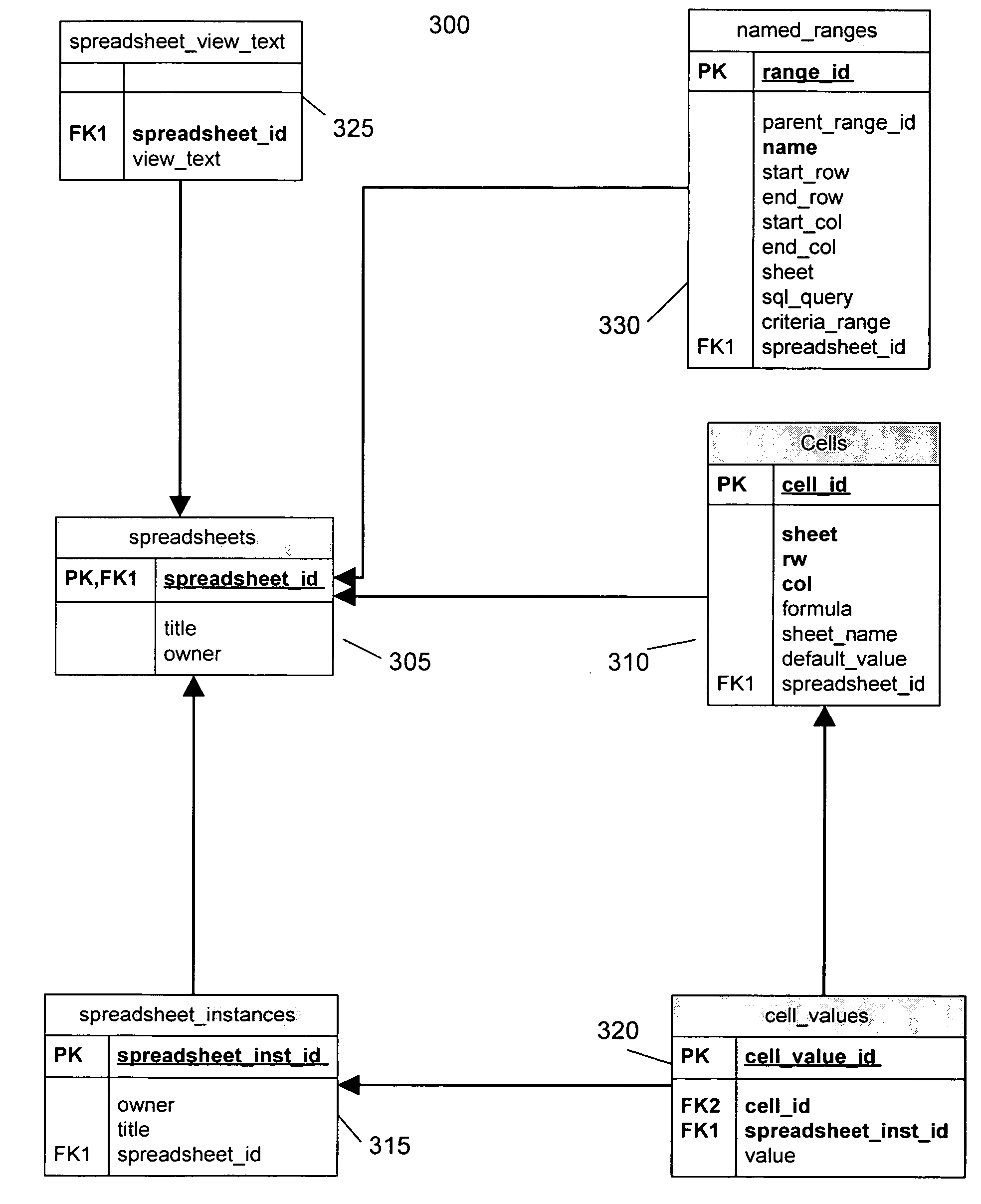
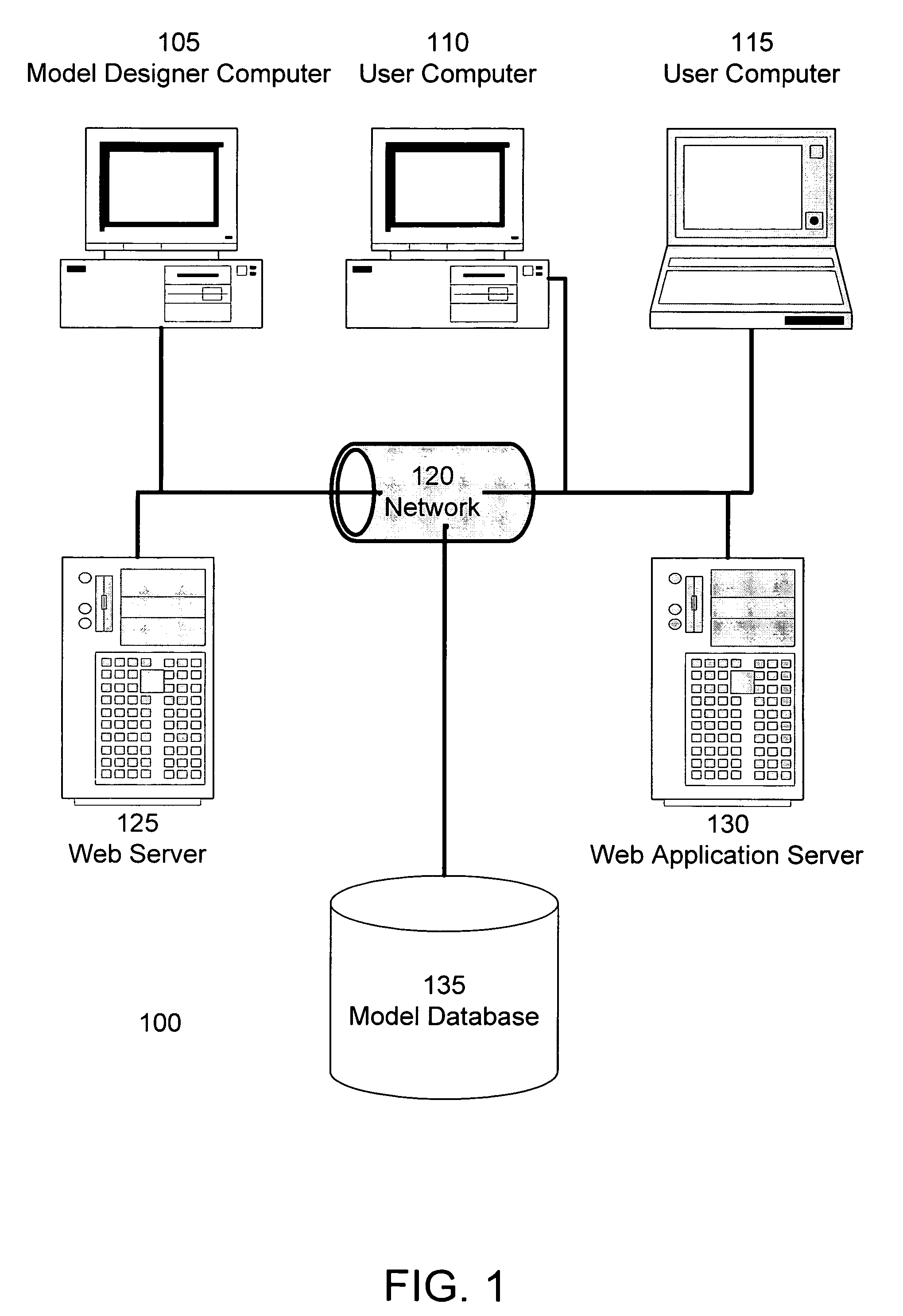
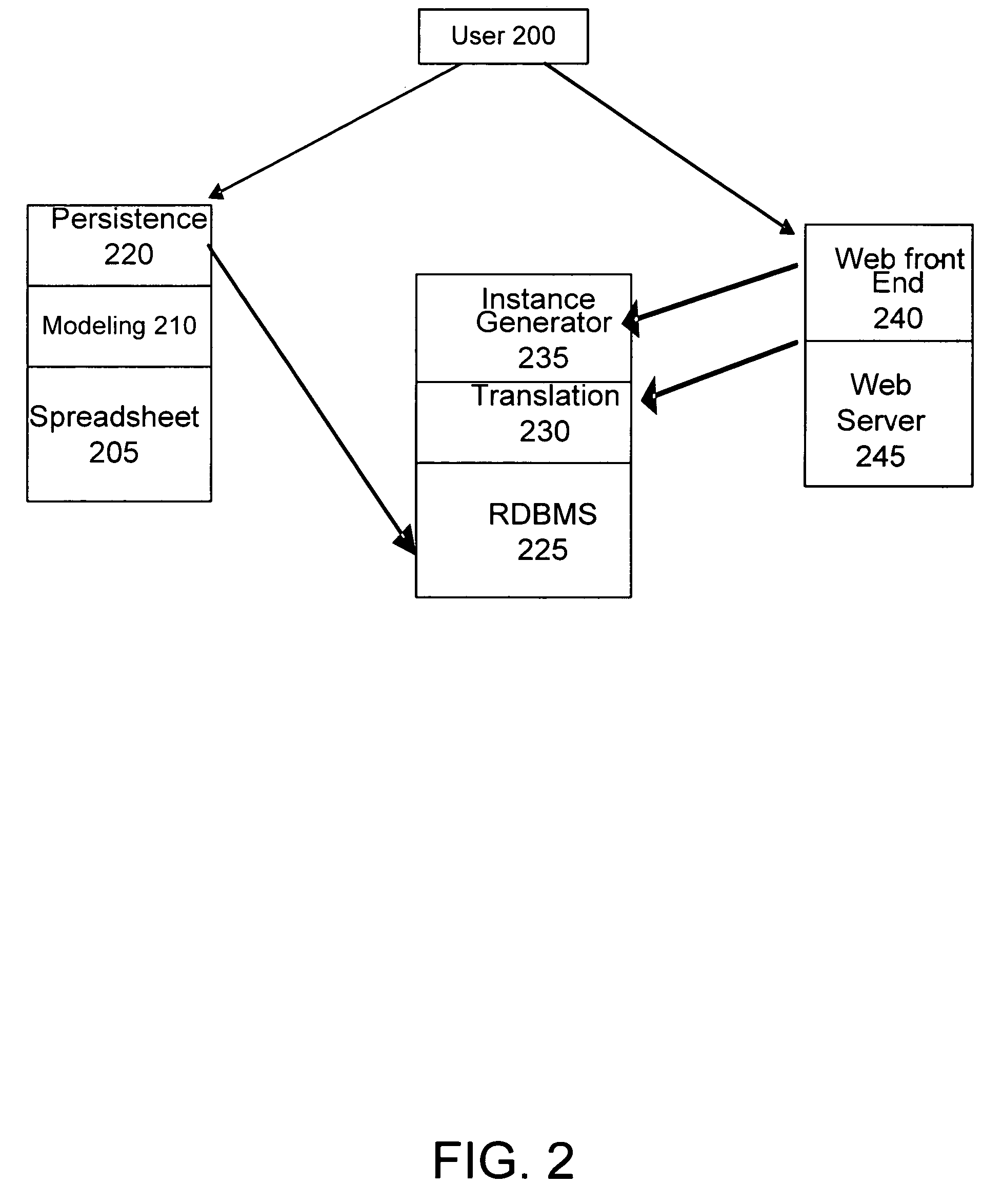
Patents
Literature
183results about How to "Fast computer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
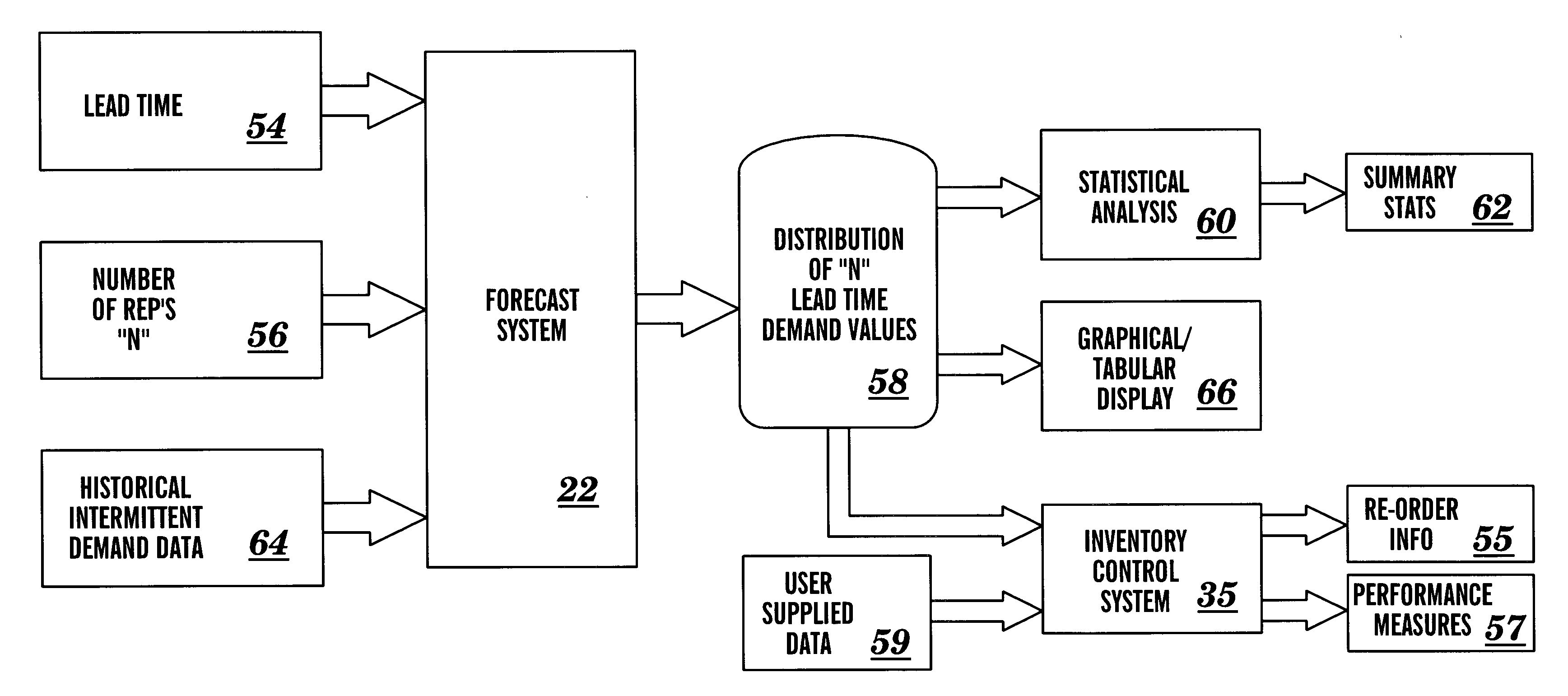
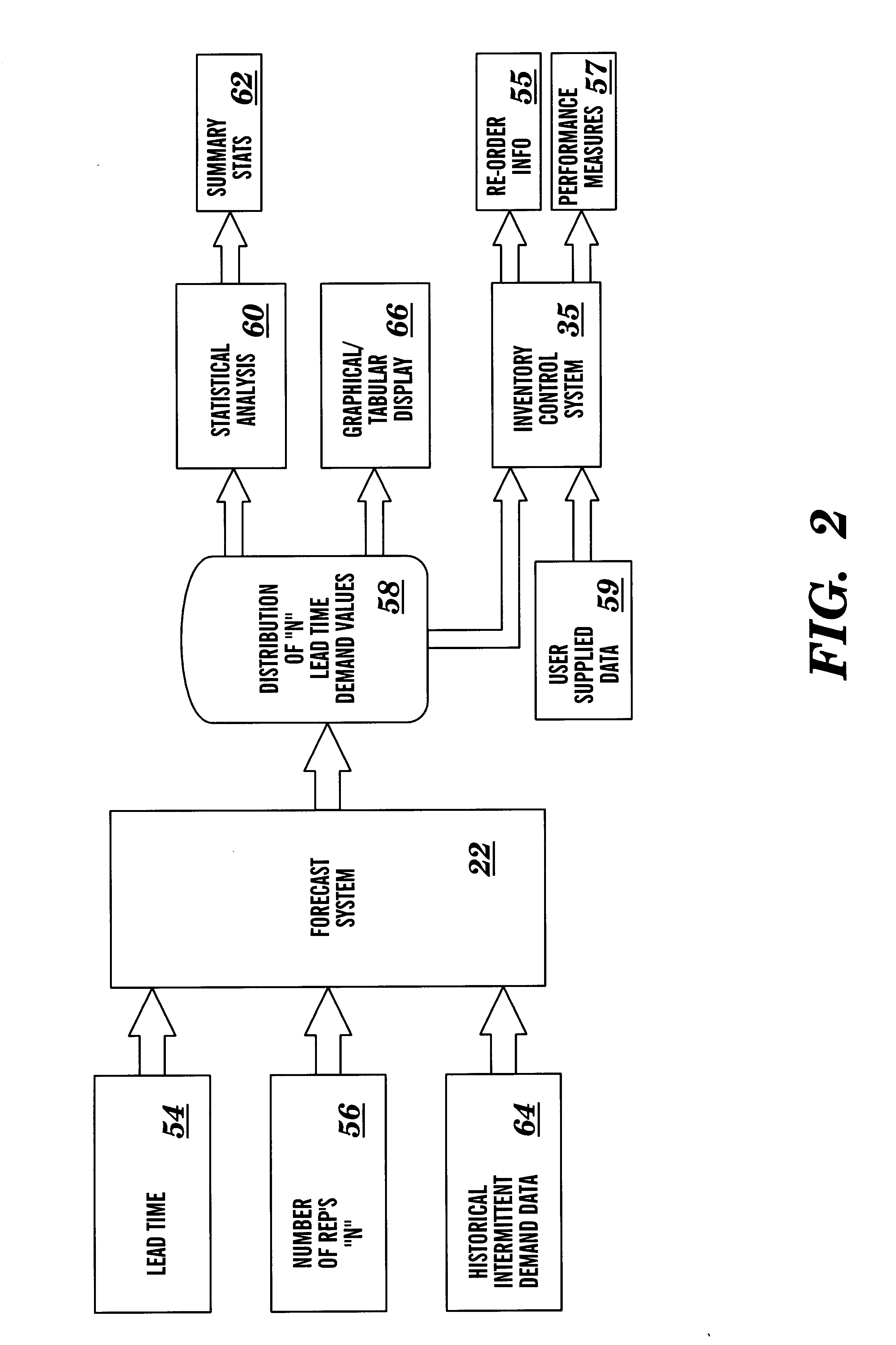
System and method for forecasting intermittent demand
InactiveUS6205431B1Convenient and accurateImprove accuracyForecastingResourcesControl systemEngineering
Owner:SMART SOFTWARE
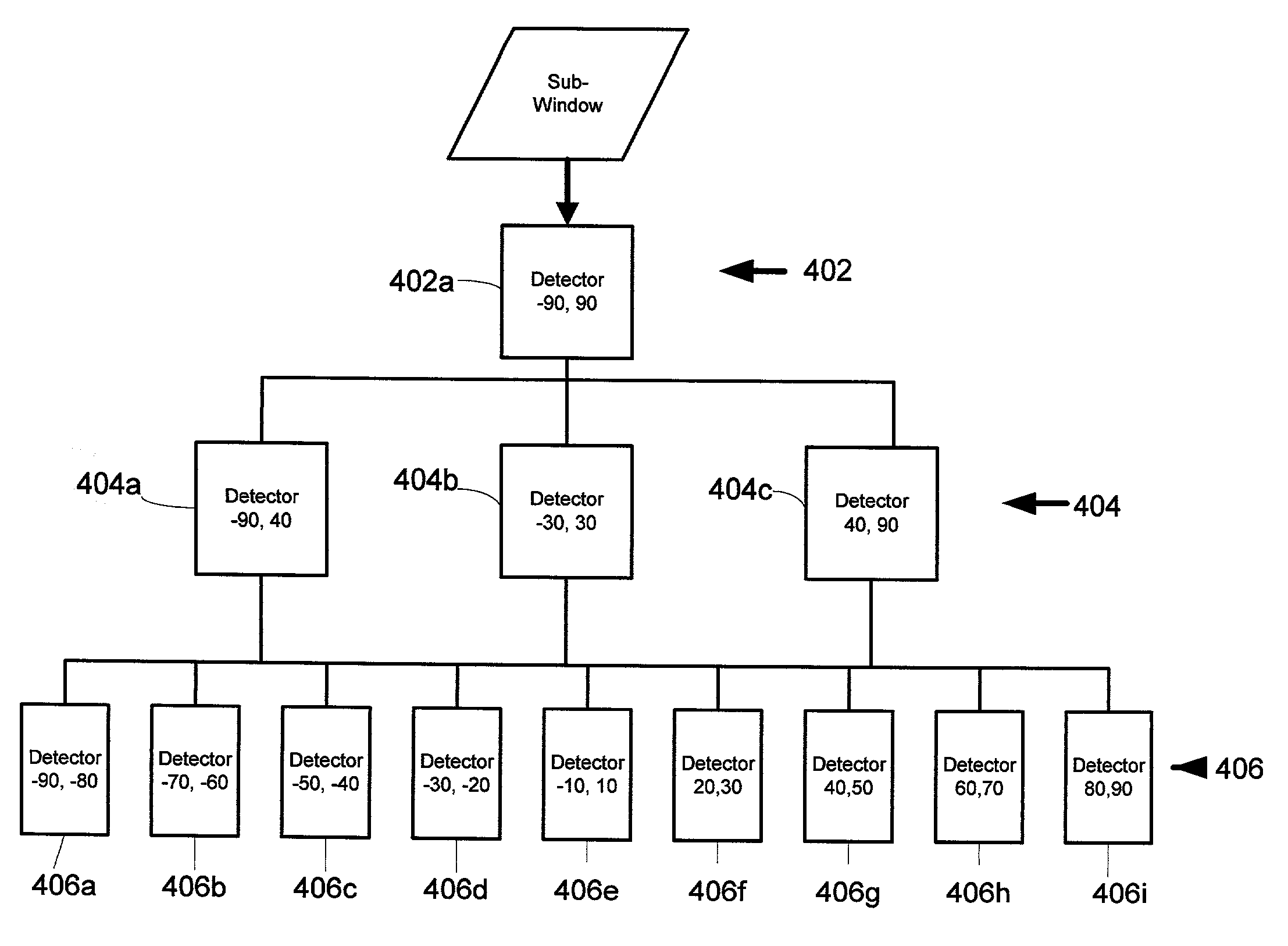
System and method for multi-view face detection
InactiveUS7050607B2Overcome limitationsOptimization rangeCharacter and pattern recognitionFace detectionState of art
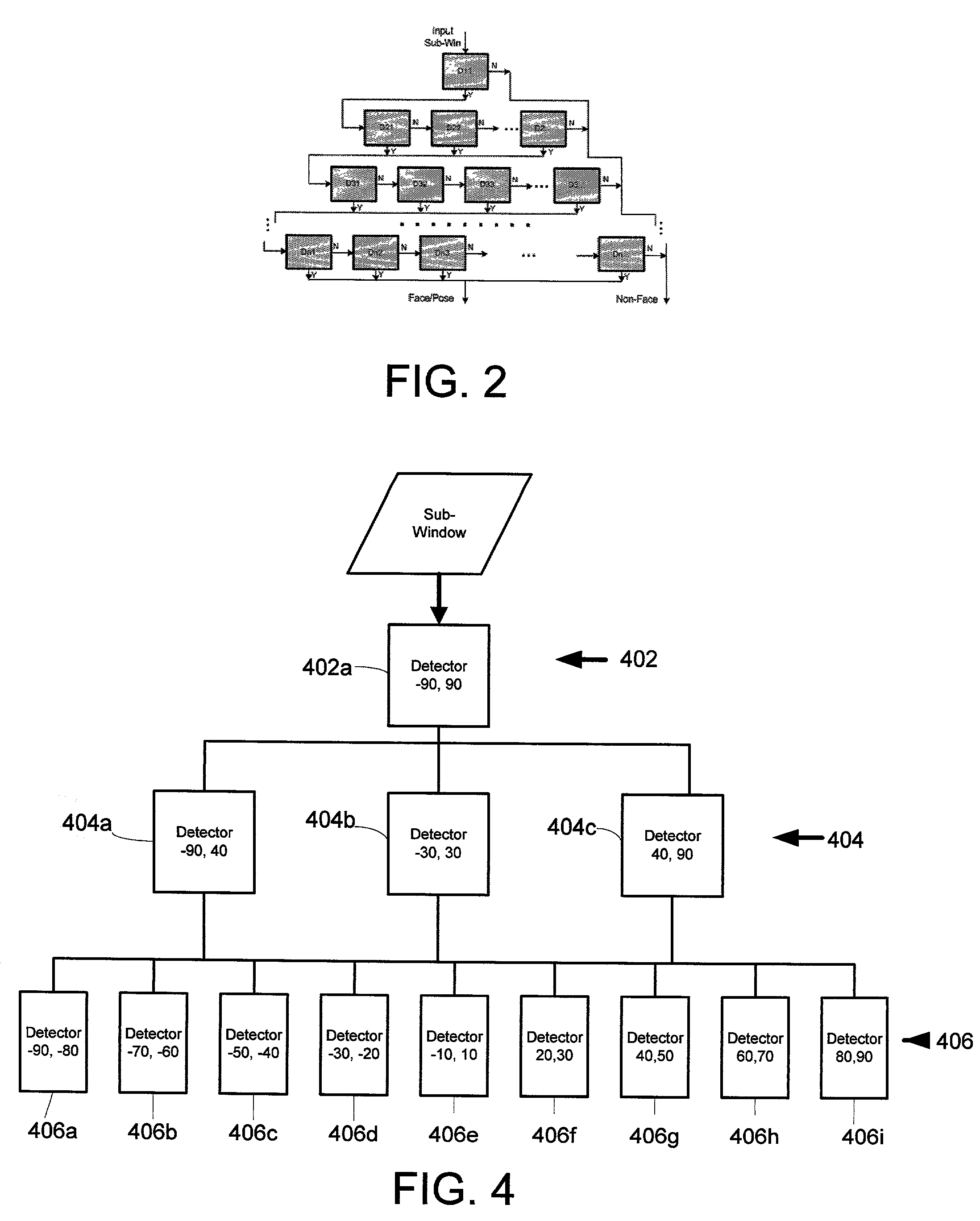
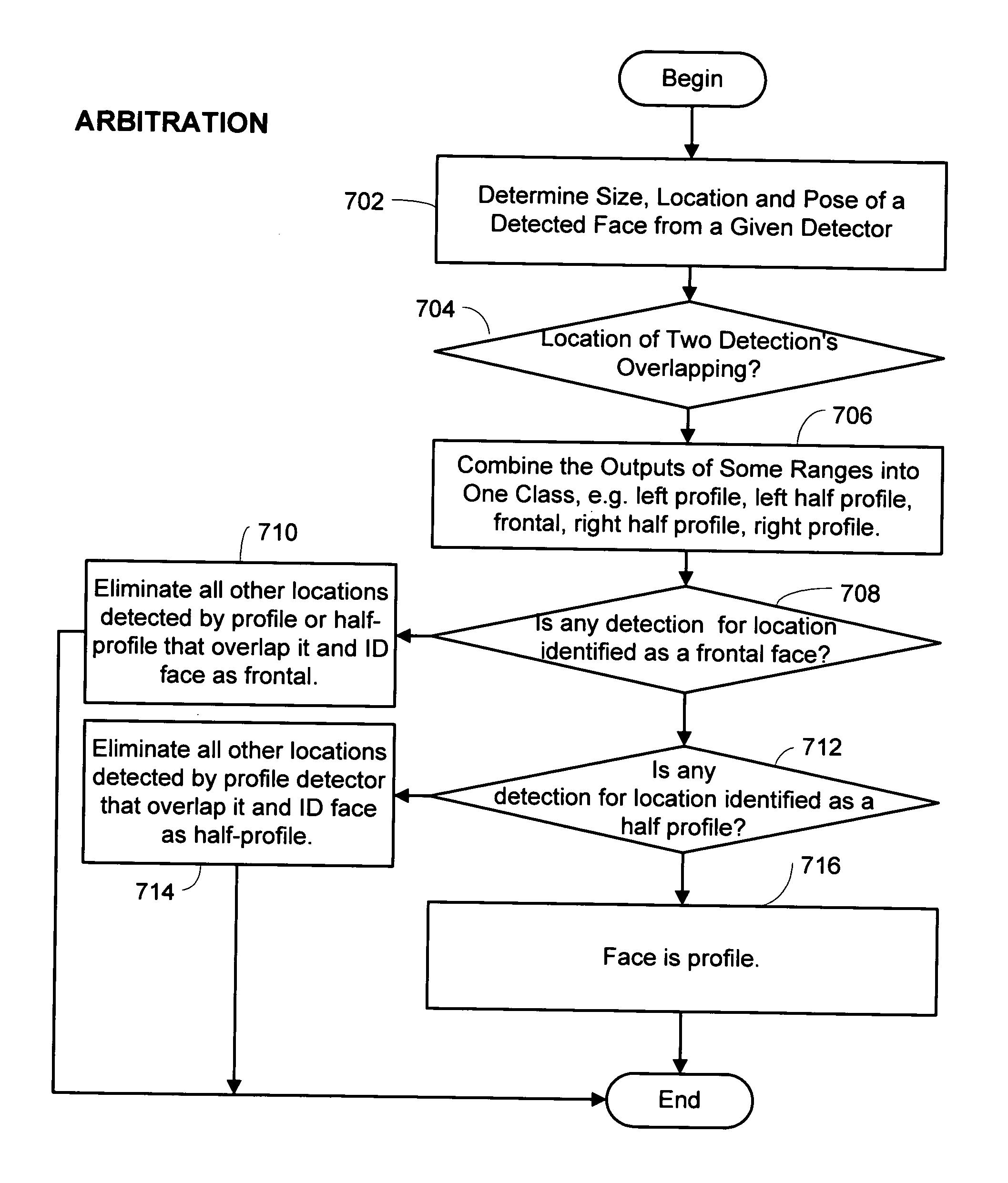
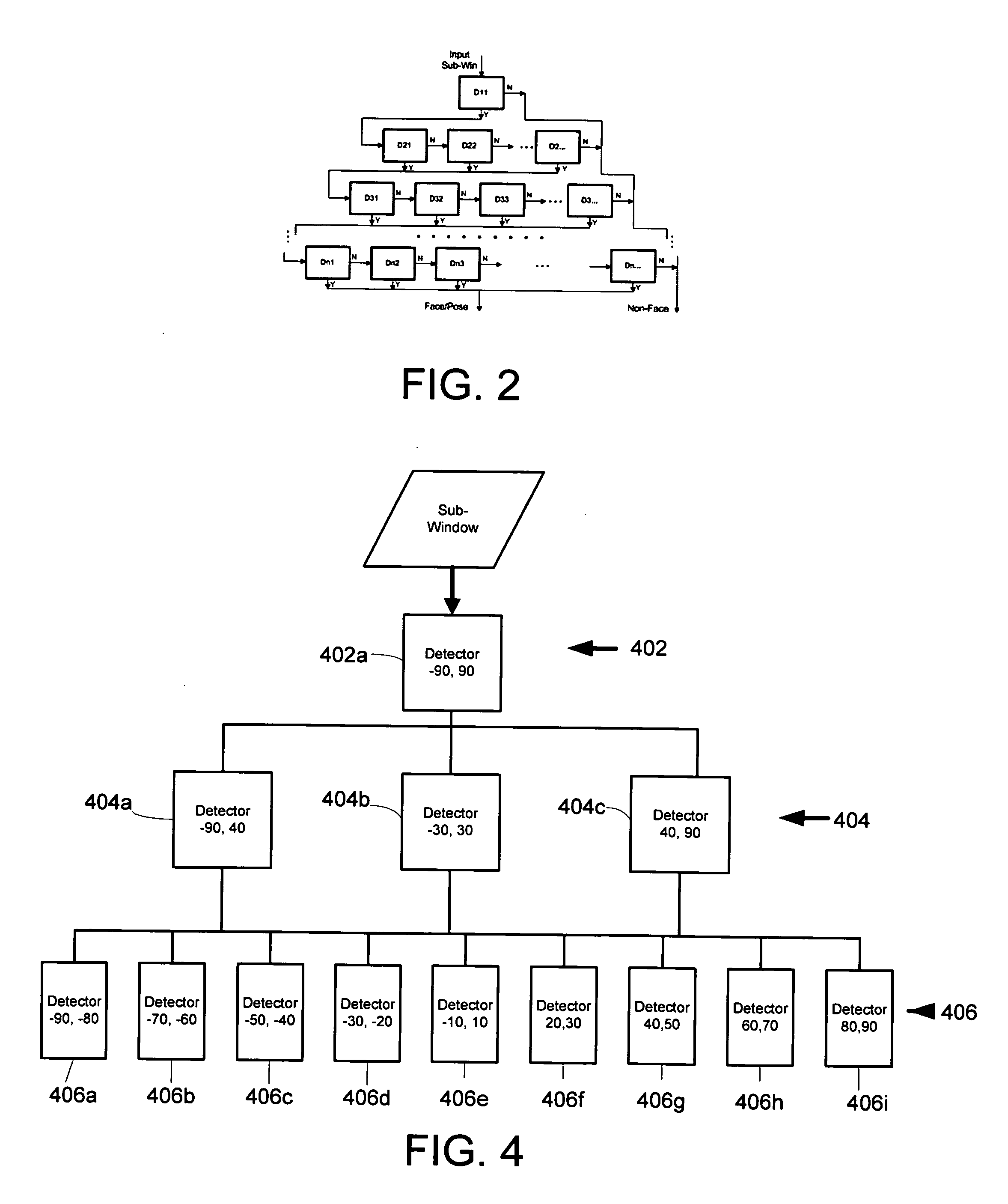
A system and method for real-time multi-view (i.e. not just frontal view) face detection. The system and method uses a sequence of detectors of increasing complexity and face / non-face discriminating thresholds to quickly discard non-faces at the earliest stage possible, thus saving much computation compared to prior art systems. The detector-pyramid architecture for multi-view face detection uses a coarse-to-fine and simple-to-complex scheme. This architecture solves the problem of lengthy processing that precludes real-time face detection effectively and efficiently by discarding most of non-face sub-windows using the simplest possible features at the earliest possible stage. This leads to the first real-time multi-view face detection system which has the accuracy almost as good as the state-of-the-art system yet 270 times faster, allowing real-time performance.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Methods of imaging based on wavelet retrieval of scenes
InactiveUS6751363B1Fast computerComputation taskData processing applicationsCharacter and pattern recognitionFeature vectorObject based
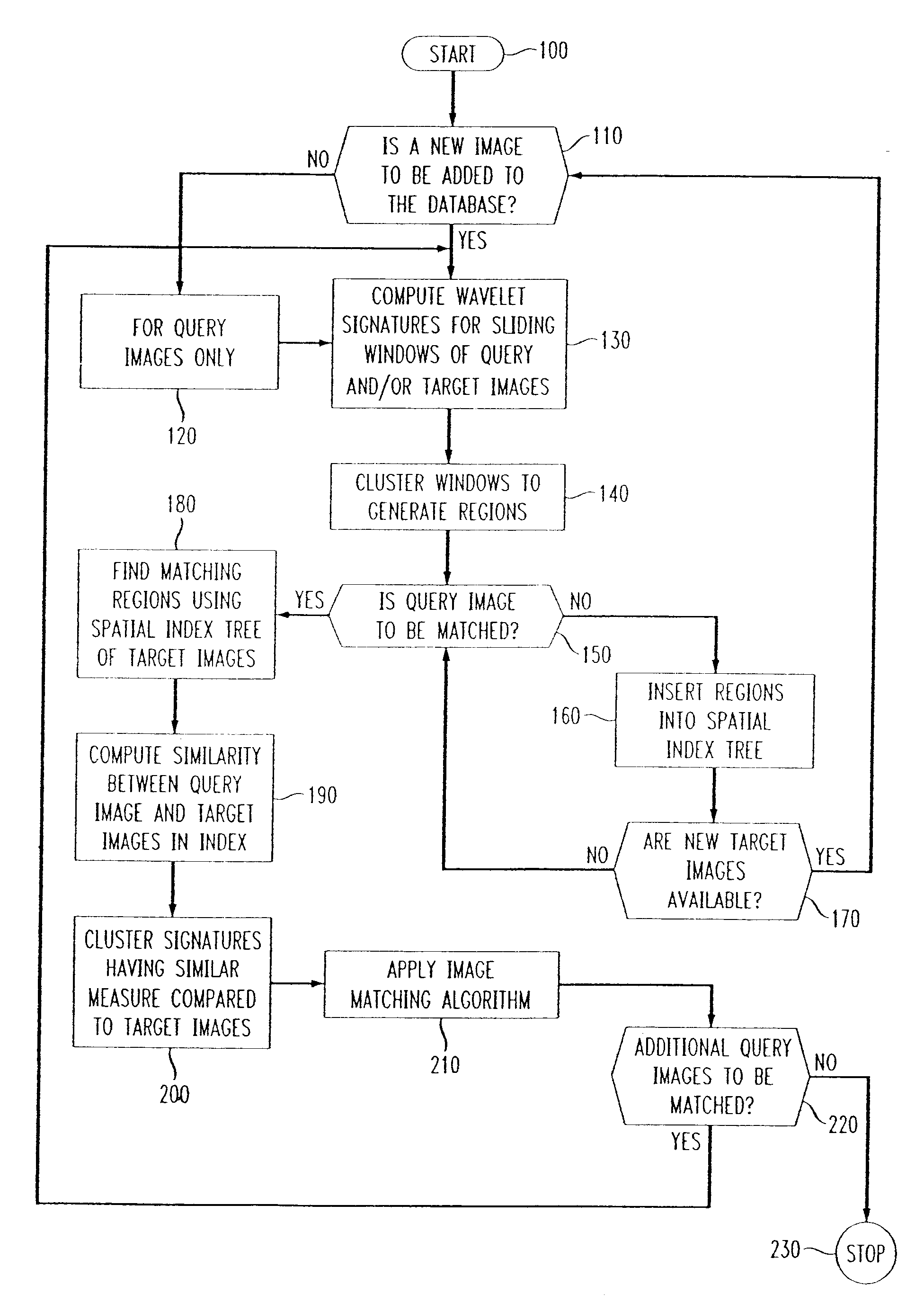
Methods of imaging objects based on wavelet retrieval of scenes utilize wavelet transformation of plural defined regions of a query image. By increasing the granularity of the query image to greater than one region, accurate feature vectors are obtained that allow for robust extraction of corresponding regions from a database of target images. The methods further include the use of sliding windows to decompose the query and target images into regions, and the clustering of the regions utilizing a novel similarity metric that ensures robust image matching in low response times.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC +1
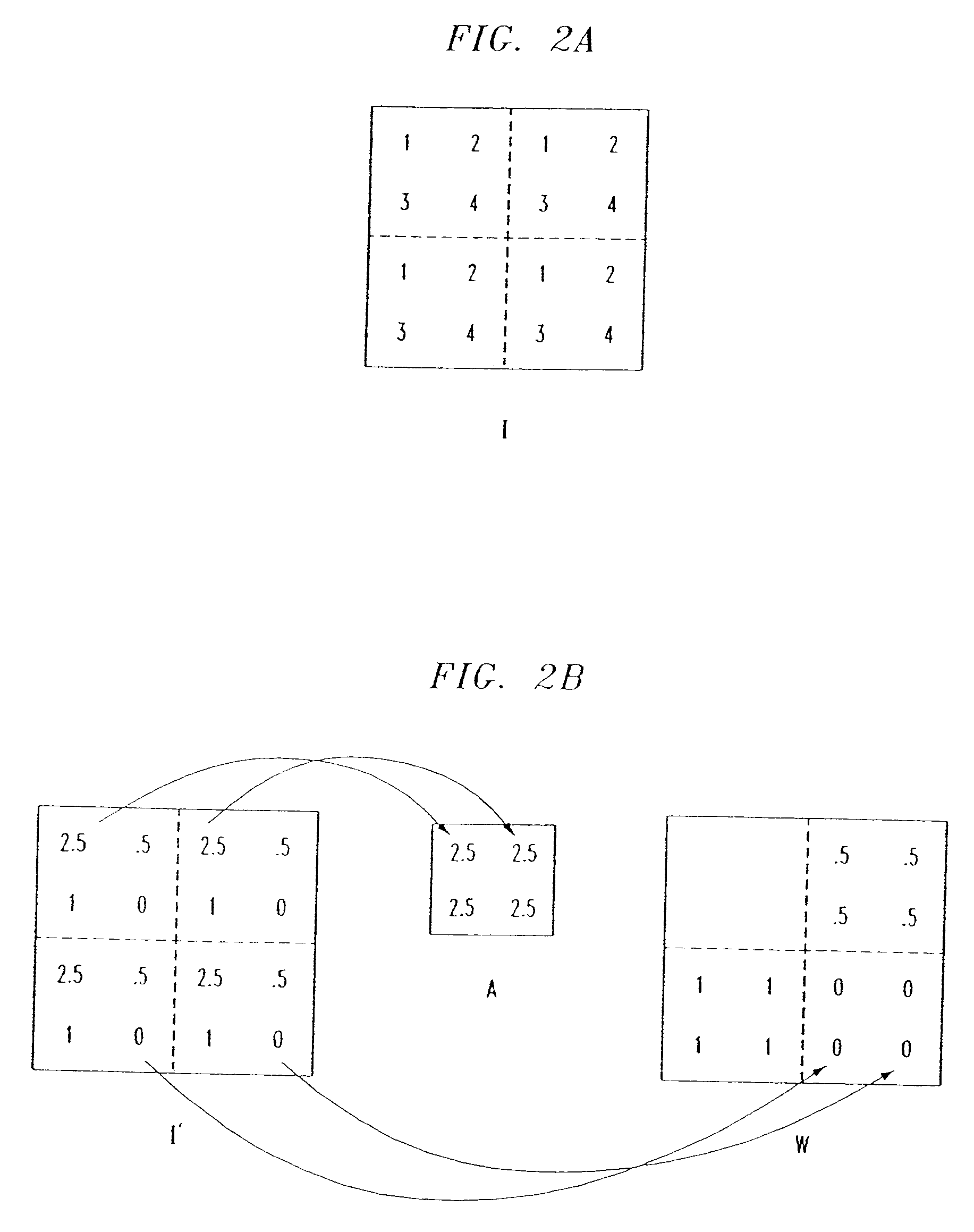
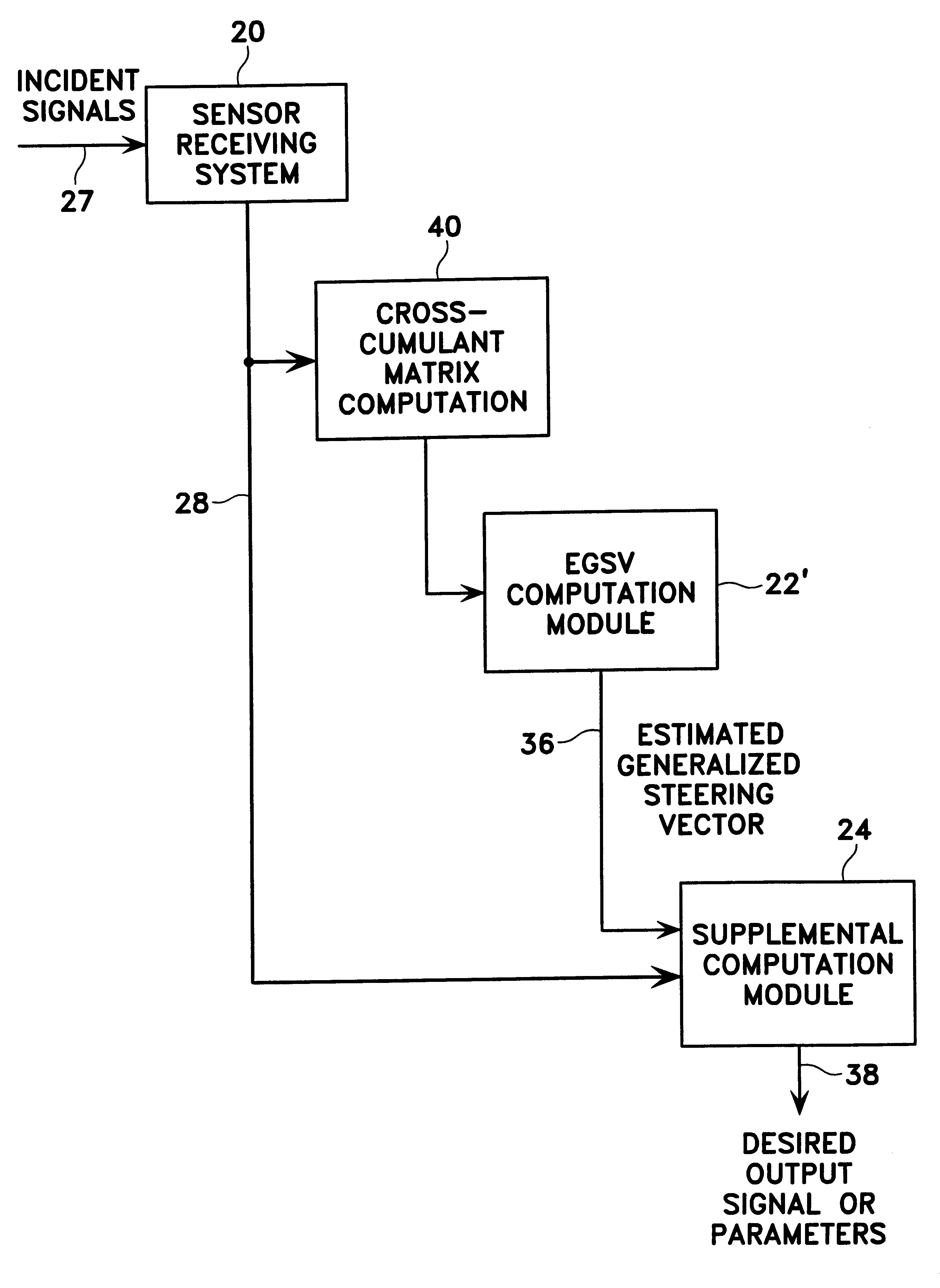
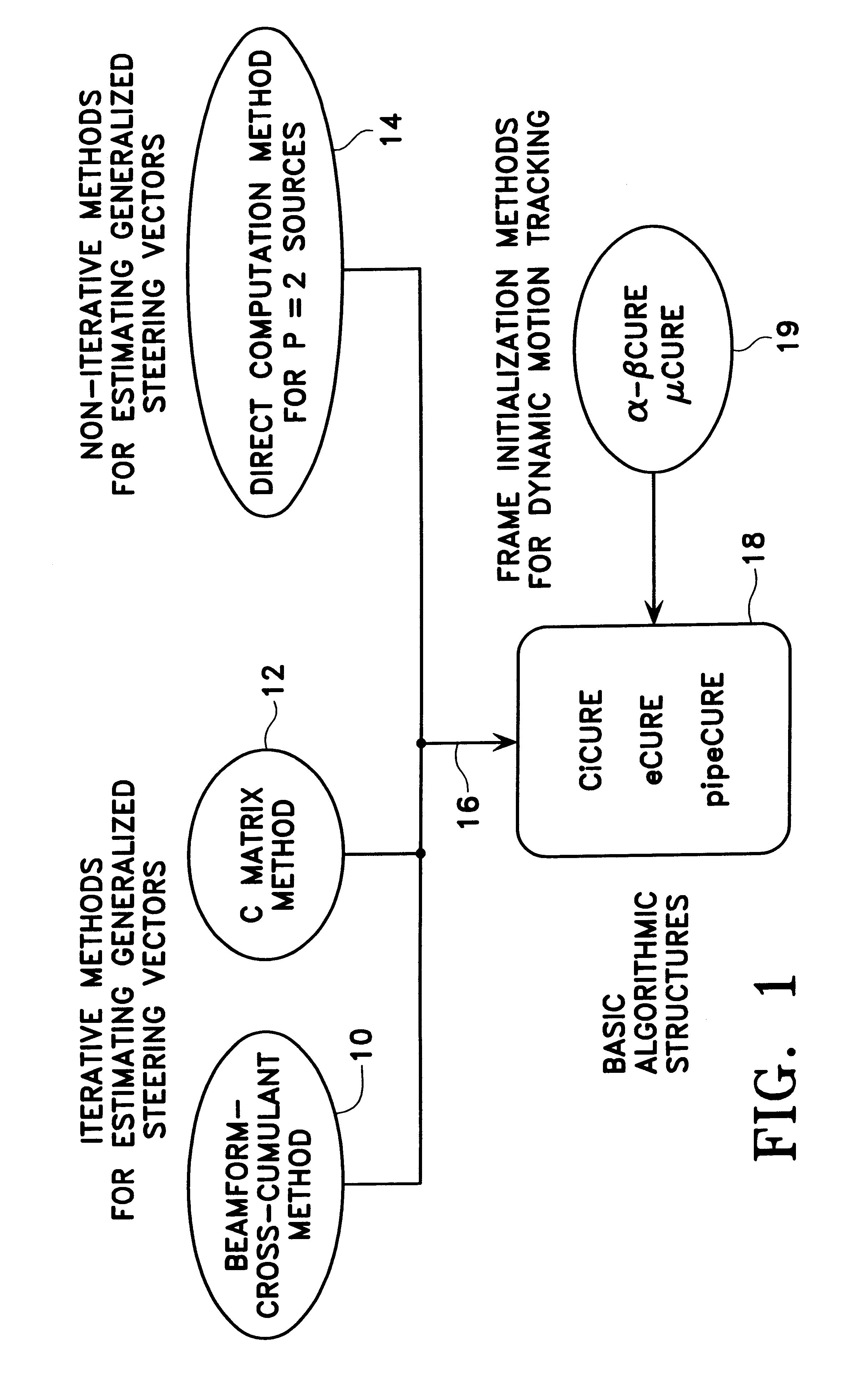
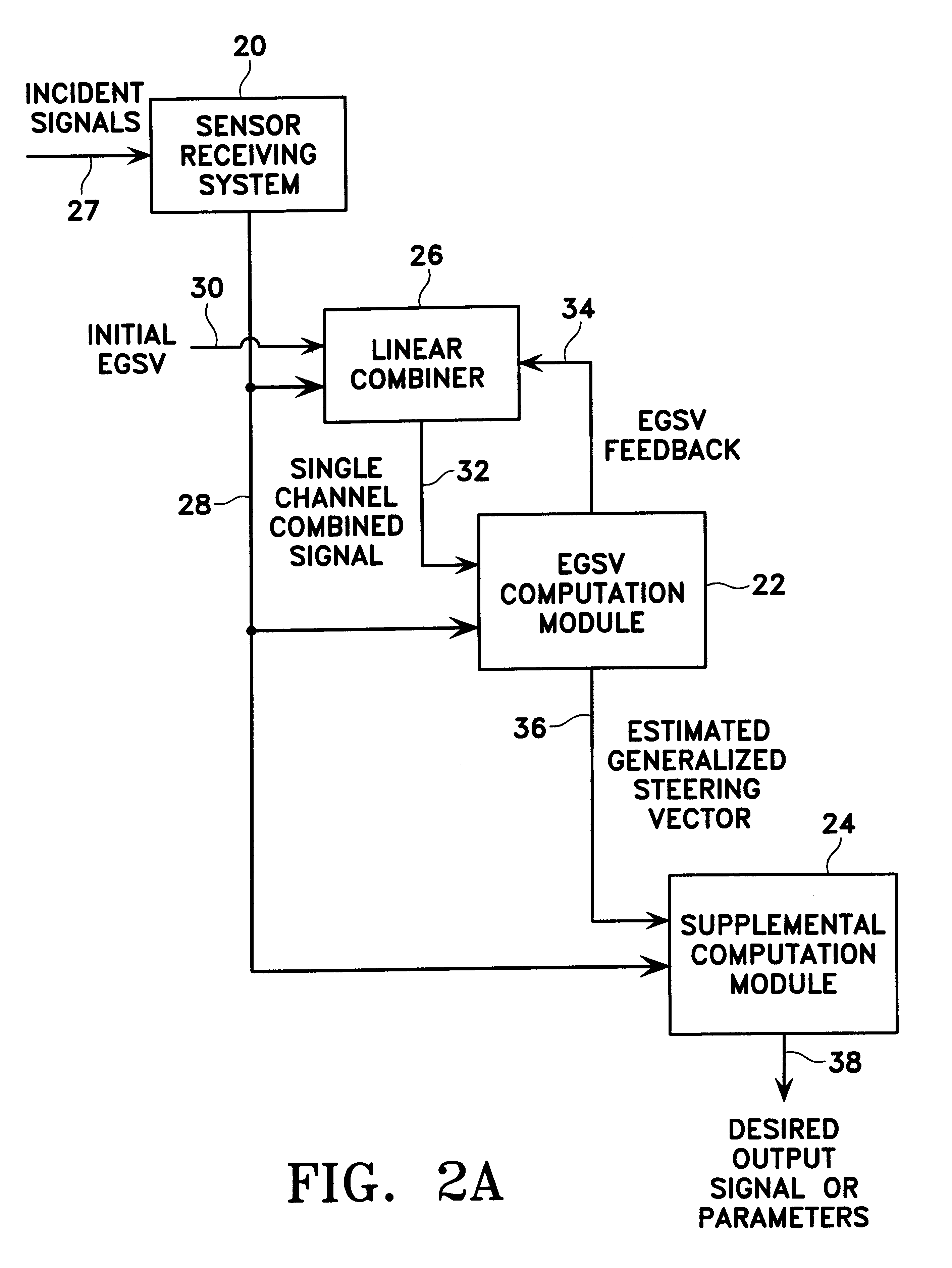
Method for processing radio signals that are subject to unwanted change during propagation
InactiveUS6208295B1Acquisition stableStable captureSpatial transmit diversityRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsRadio signalTransmitter
A method for processing received radio signals that are subject to unwanted change during propagation through the atmosphere, from a transmitter to a receiver array. The multiple signals are received as cochannel signals at the antenna array, and are processed to eliminate the effects of modification of the signals during propagation, wherein the processing step includes cumulant-based signal recovery without regard for the geometrical properties of the antenna array. In the invention as disclosed, two different information signals having two different polarization states are transmitted, and at least one of the transmitted signals is subjected to an unwanted change of its polarization state. The received signals are processed to separate and recover the two information signals without regard to their polarization states.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
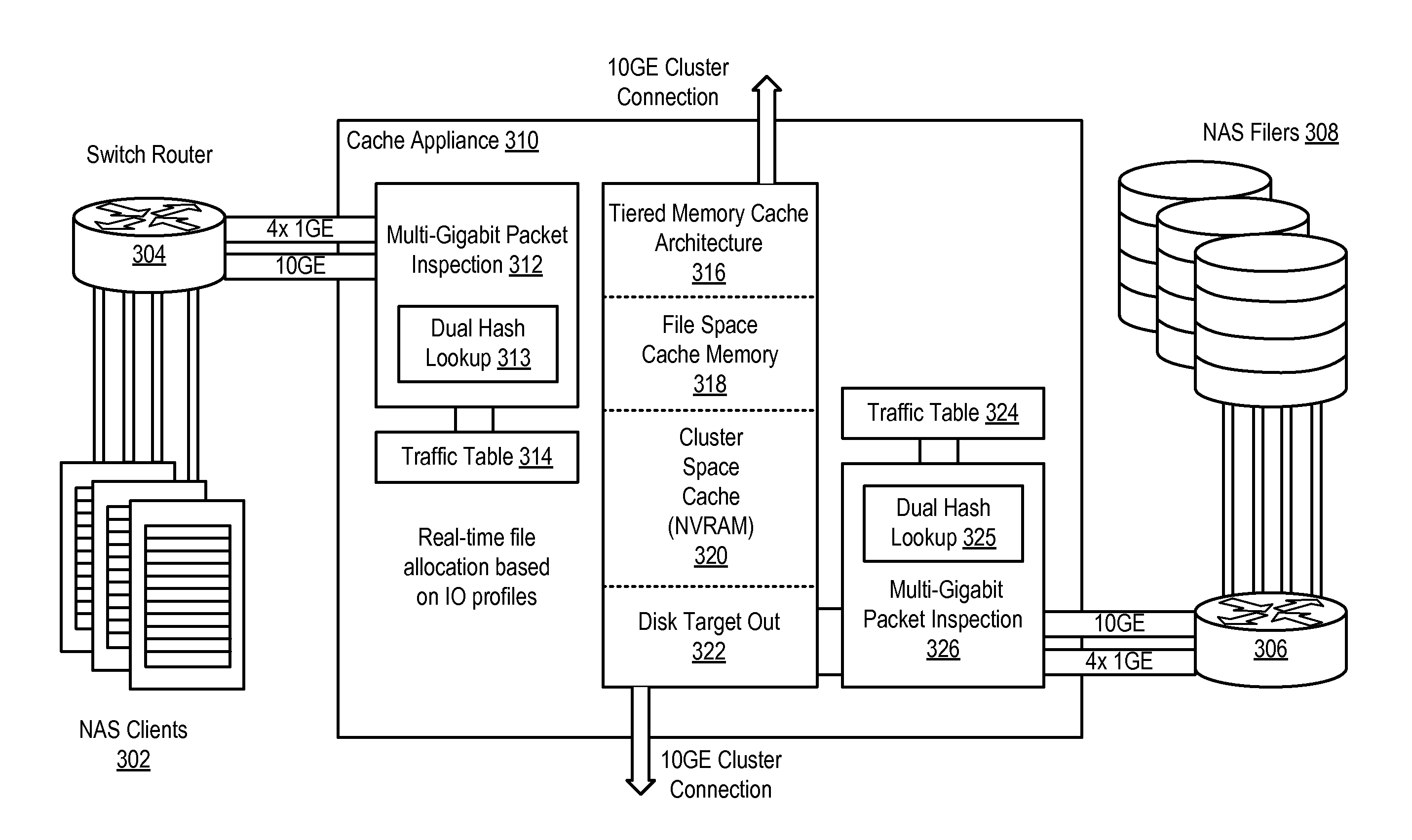
Dual Hash Indexing System and Methodology
ActiveUS20100023726A1Fixed processing costFast computerMemory adressing/allocation/relocationData switching by path configurationTraffic capacityClient-side
A method, system and program are disclosed for accelerating data storage in a cache appliance that transparently monitors NFS and CIFS traffic between clients and NAS subsystems and caches files in a cache memory by using a dual hash technique to rapidly store and / or retrieve connection state information for cached connections in a plurality of index tables that are indexed by hashing network protocol address information with a pair of irreducible CRC hash algorithms to obtain an index to the memory location of the connection state information.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
Robust interest point detector and descriptor
ActiveUS20090238460A1Fast computerNot sacrificing performanceImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionInterest point detection
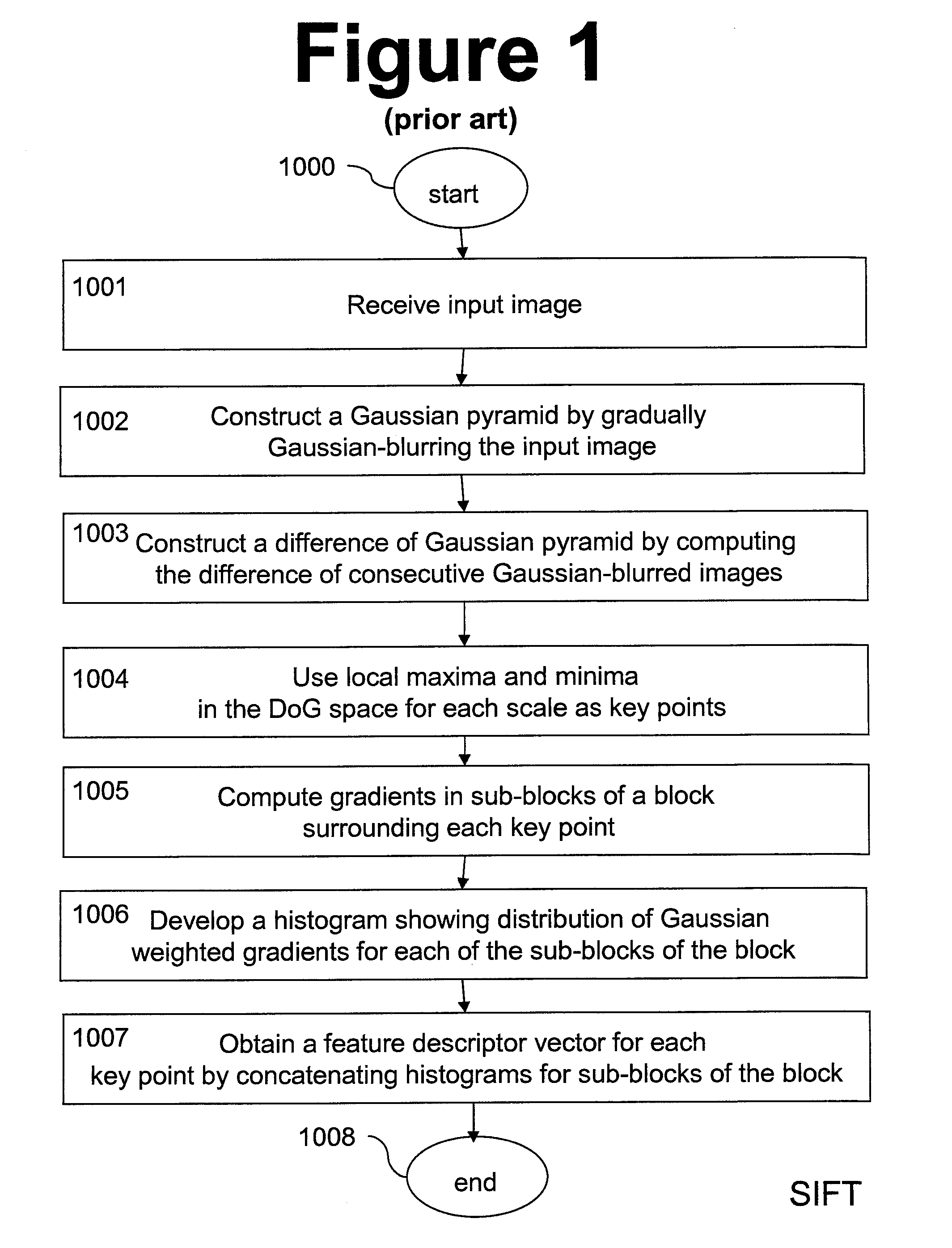
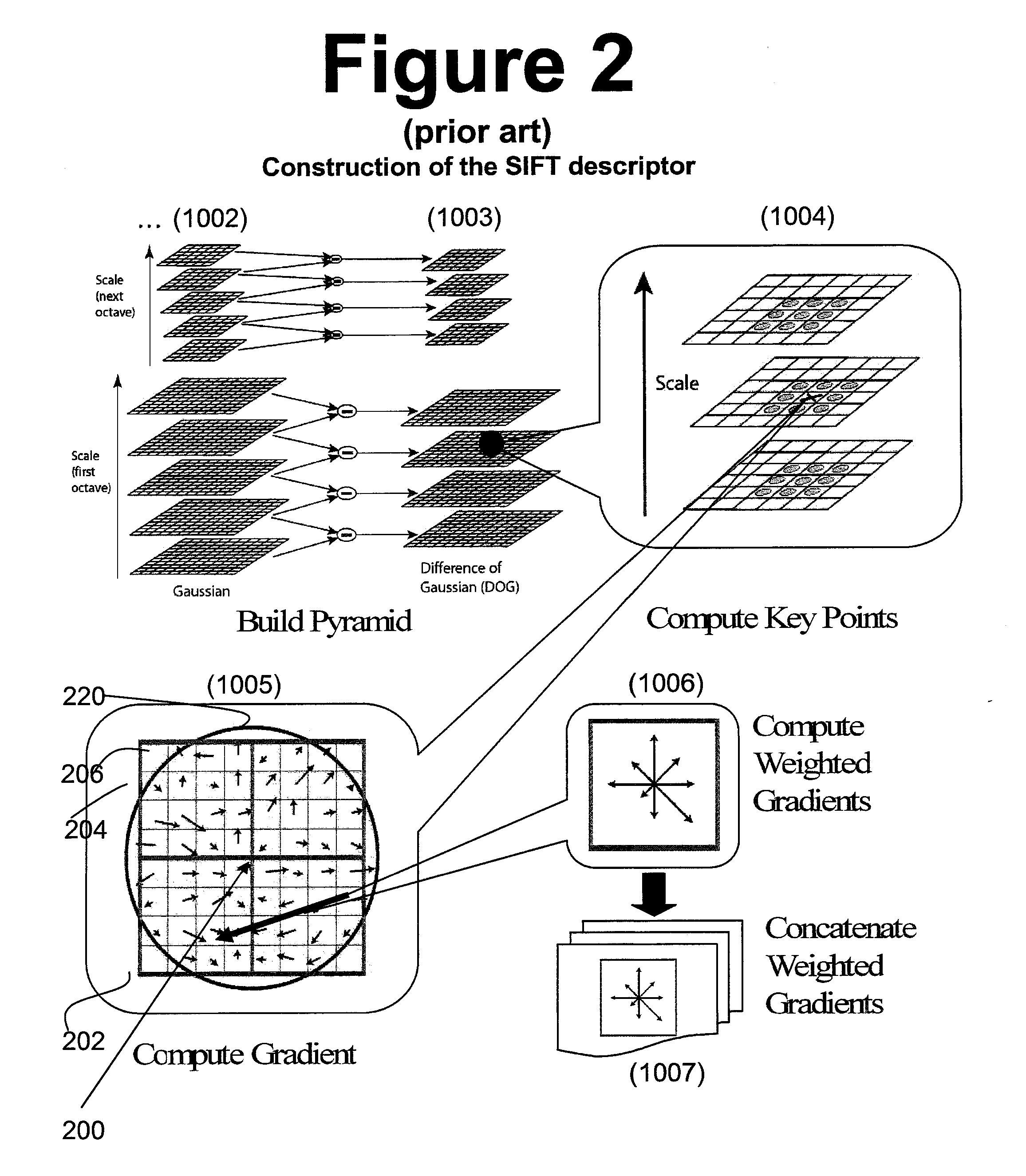
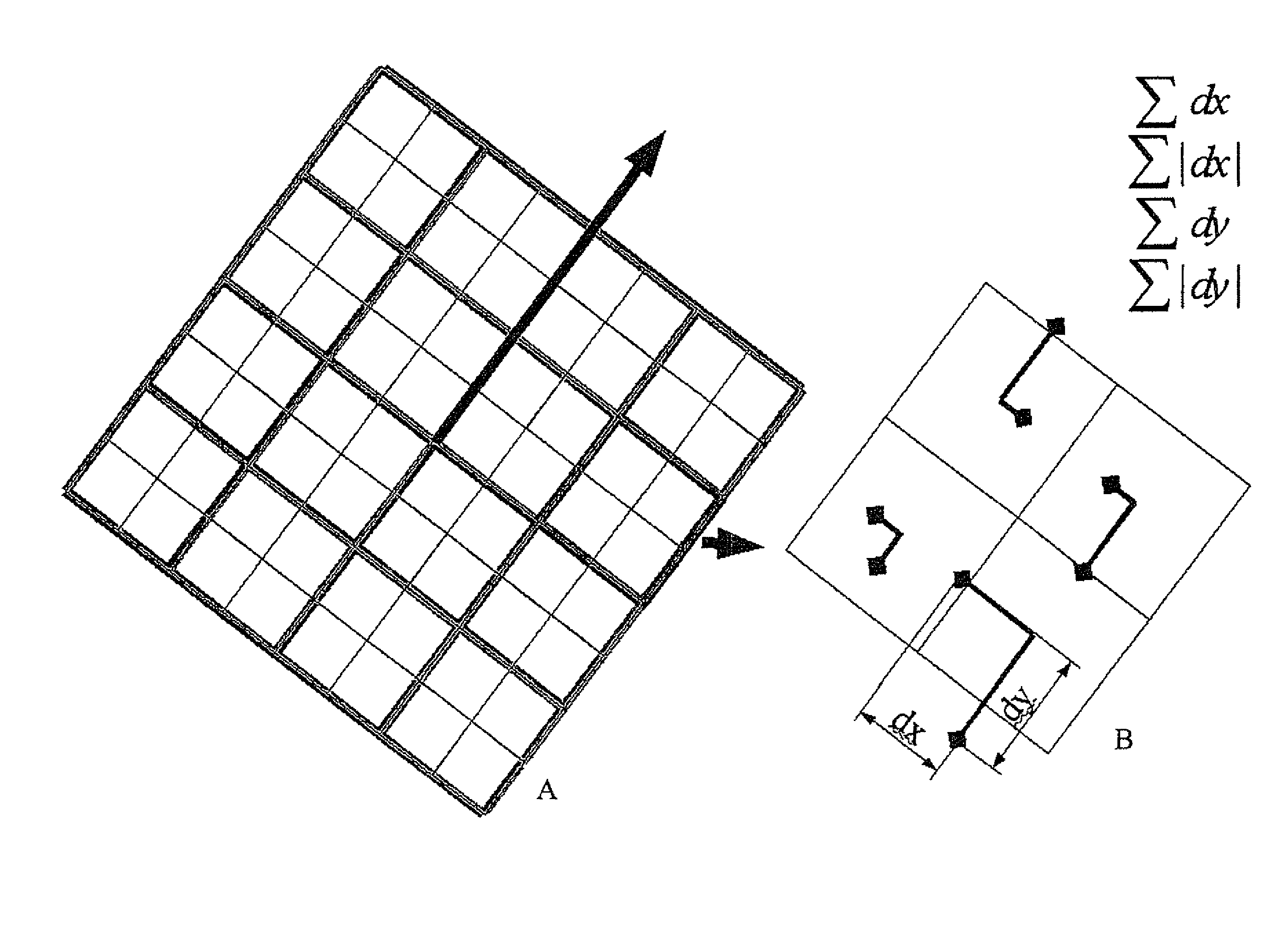
Methods and apparatus for operating on images are described, in particular methods and apparatus for interest point detection and / or description working under different scales and with different rotations, e.g. for scale-invariant and rotation-invariant interest point detection and / or description. The present invention can provide improved or alternative apparatus and methods for matching interest points either in the same image or in a different image. The present invention can provide alternative or improved software for implementing any of the methods of the invention. The present invention can provide alternative or improved data structures created by multiple filtering operations to generate a plurality of filtered images as well as data structures for storing the filtered images themselves, e.g. as stored in memory or transmitted through a network. The present invention can provide alternative or improved data structures including descriptors of interest points in images, e.g. as stored in memory or transmitted through a network as well as datastructures associating such descriptors with an original copy of the image or an image derived therefrom, e.g. a thumbnail image.
Owner:K U LEUVEN RES & DEV +2
Force display master interface device for teleoperation
InactiveUS6435794B1Fast computerInput/output for user-computer interactionGripping headsHigh speed controlRemote control
A force display master interface is provided for interaction with teleoperated robotic slave manipulators or virtual slave entities. The device provides a de-coupled actuator that permits selective engagement between the actuator and the fingertip. A method for high speed control of force display masters is disclosed, which includes determination of a pre-contact state of the slave entity and an object in the slave environment. Operation on the pre-contact state information is used to pre-position the actuator into an appropriate position to represent the contact to the operator, before slave contact is made. In one embodiment, the force display master provides a hand mounted linkage assembly, in combination with a remote control assembly that measures fingertip motion and selectively provides resistance thereto. In another embodiment the invention includes general linkage-actuator arrangements that can be used singly or in combination to provide a variety of master interface devices.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
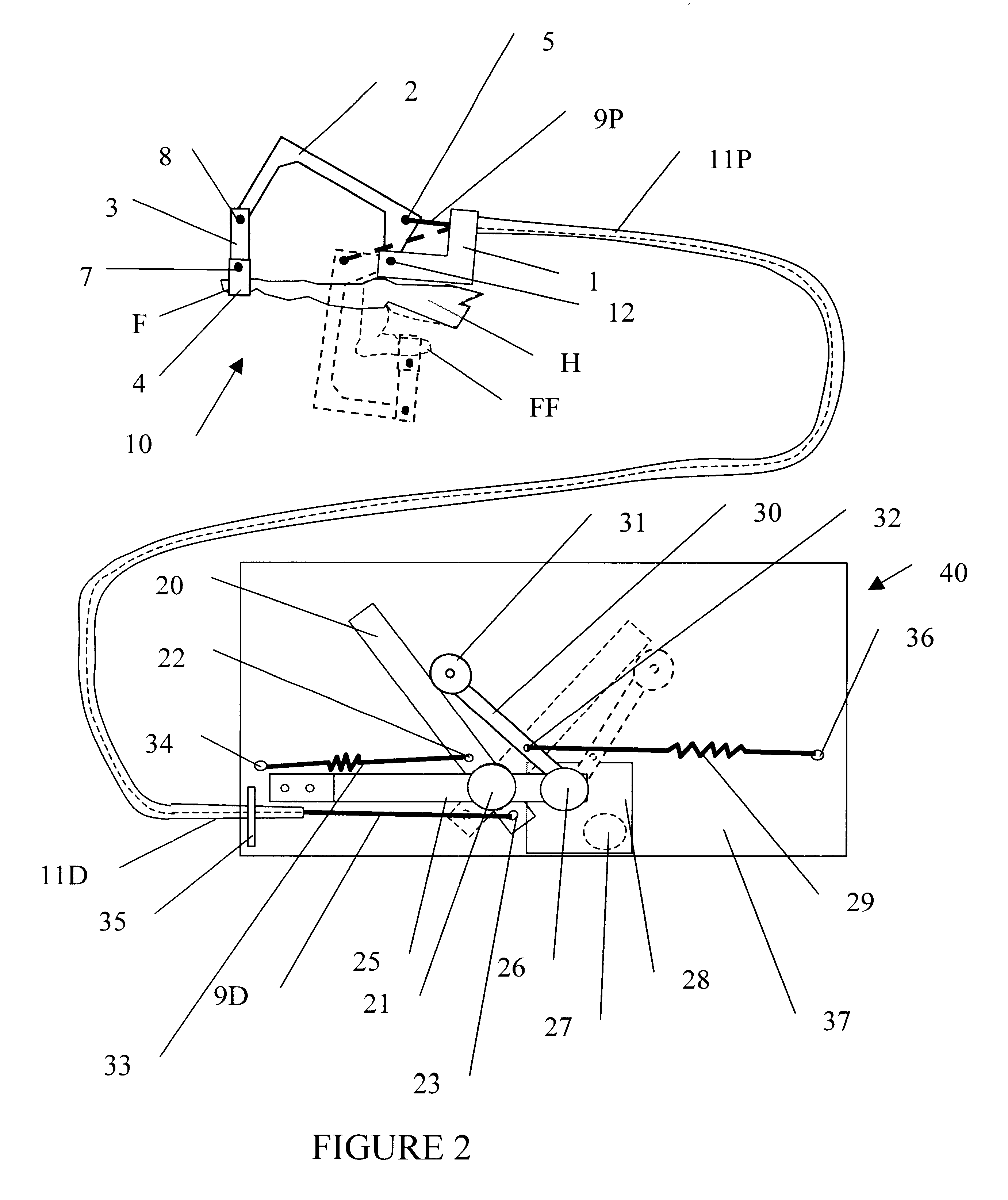
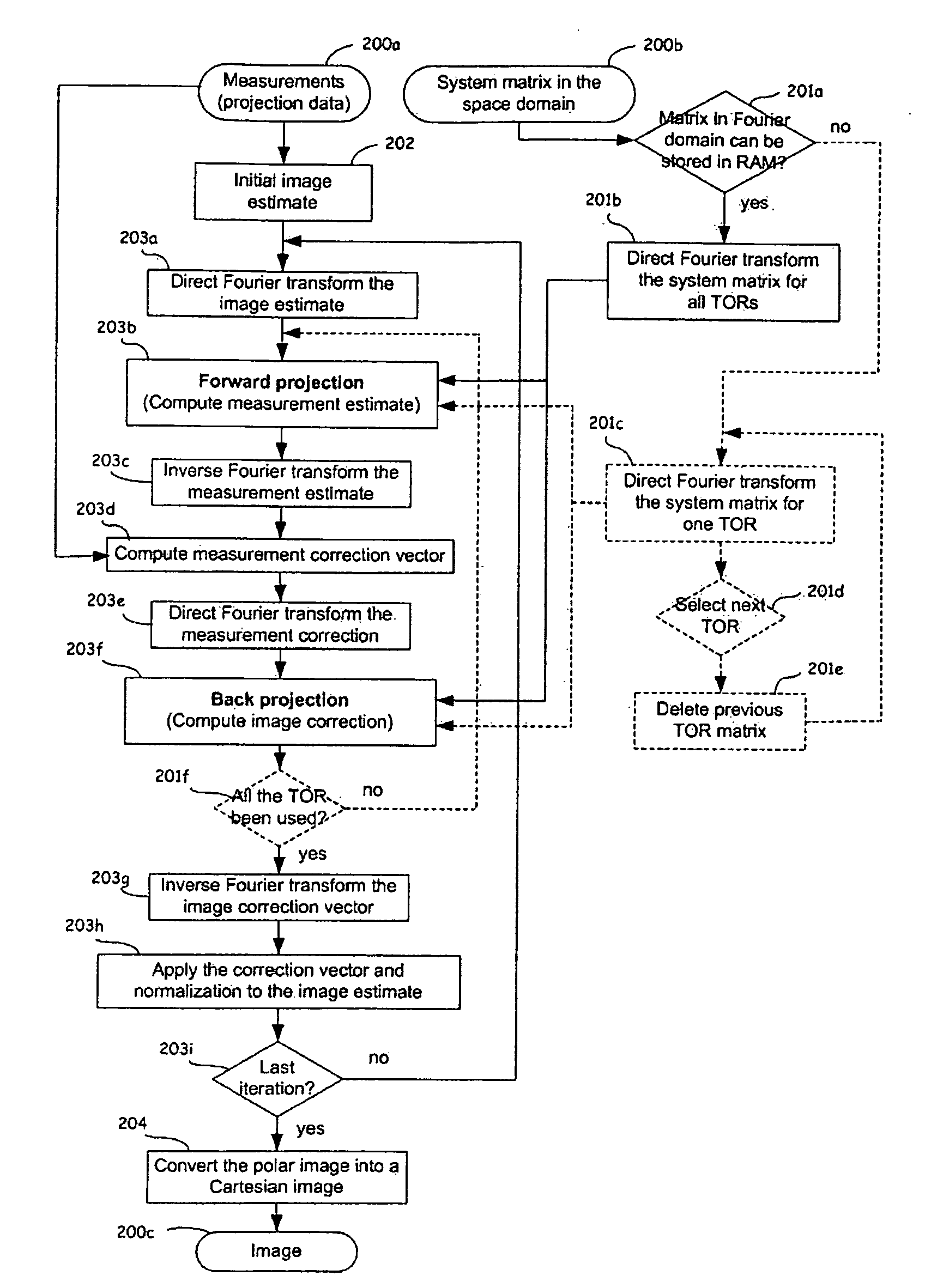
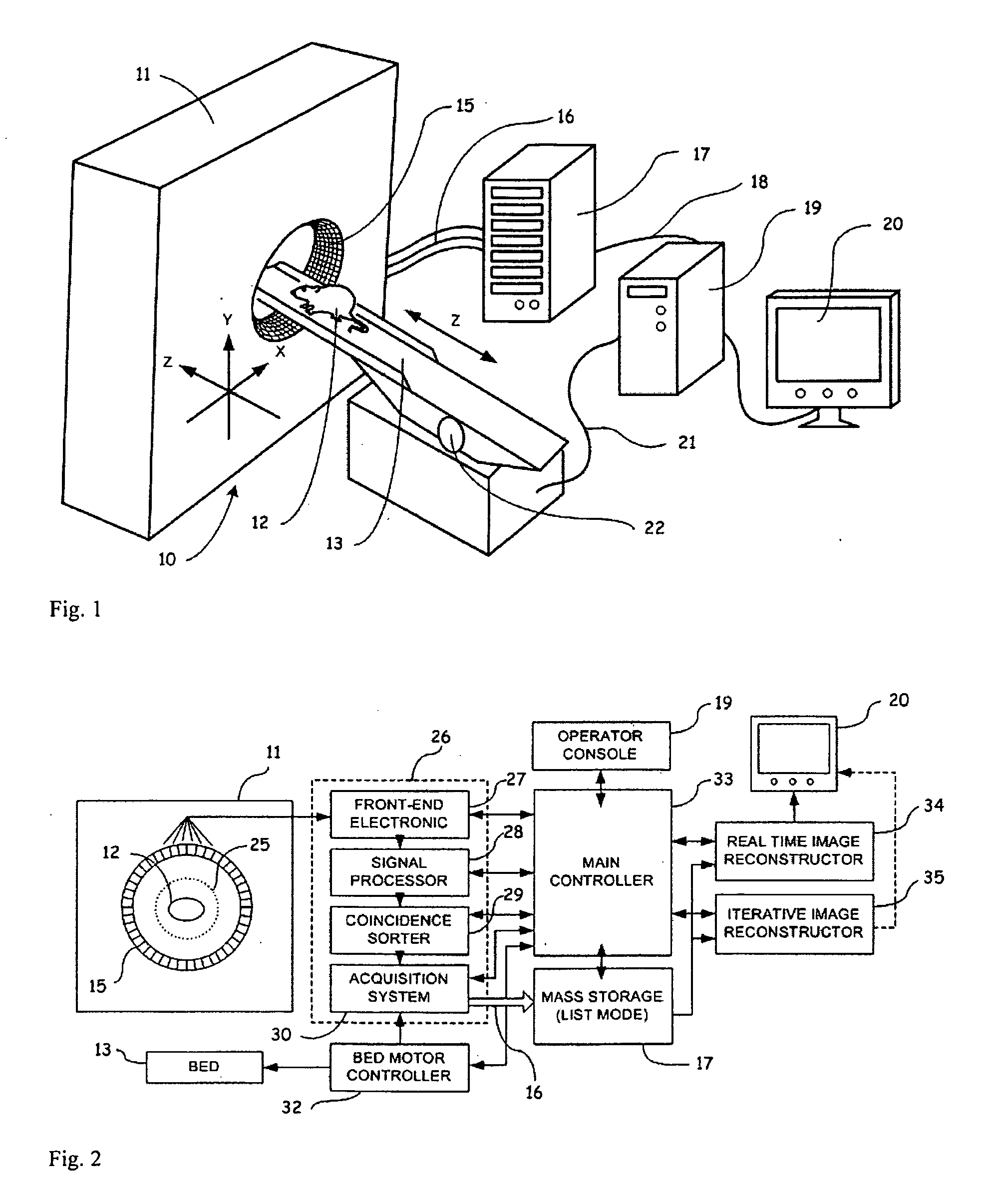
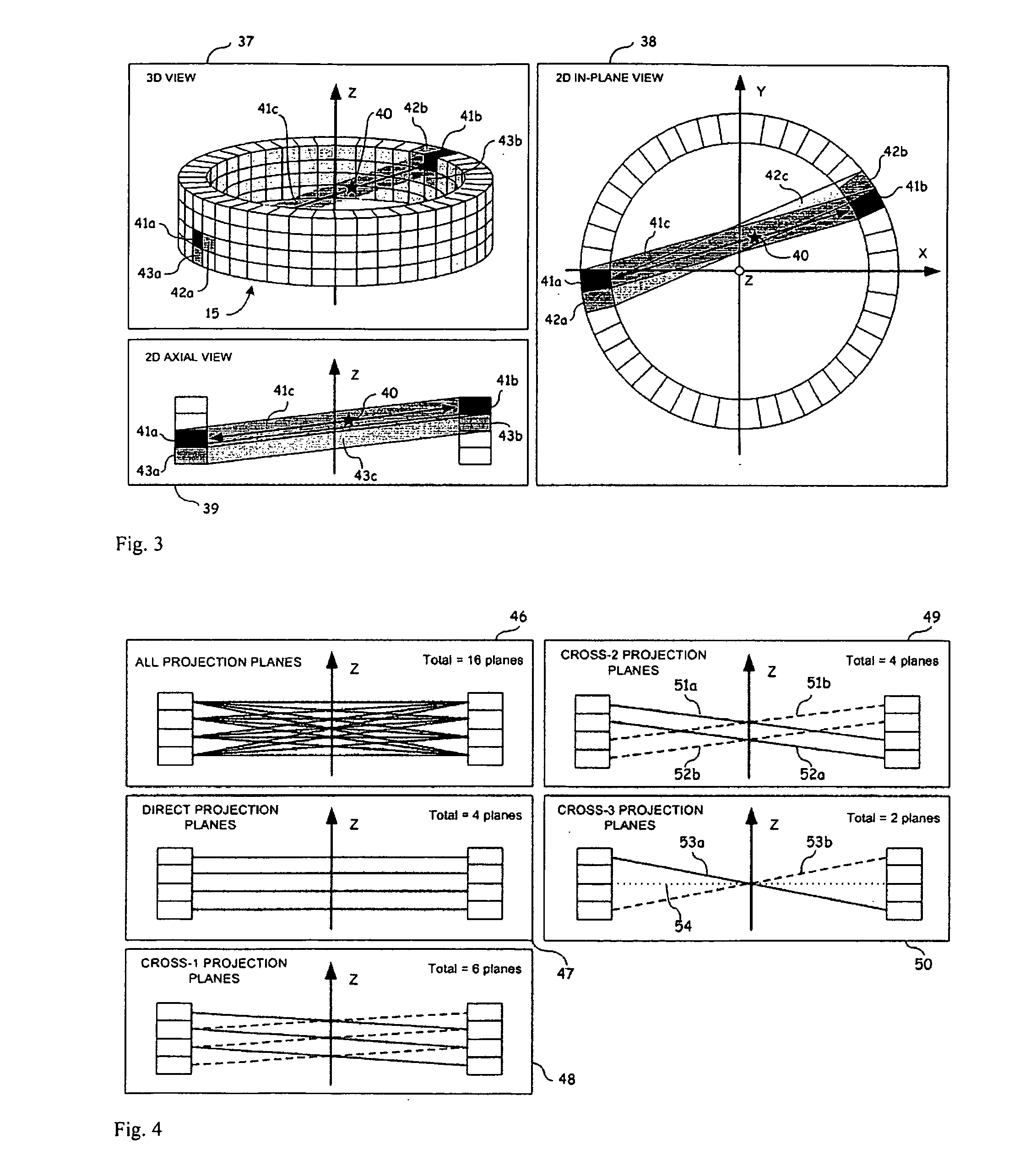
Image Reconstruction Methods Based on Block Circulant System Matrices
InactiveUS20090123048A1Minimized in sizeFast computerReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationIn planeLines of response
An iterative image reconstruction method used with an imaging system that generates projection data, the method comprises: collecting the projection data; choosing a polar or cylindrical image definition comprising a polar or cylindrical grid representation and a number of basis functions positioned according to the polar or cylindrical grid so that the number of basis functions at different radius positions of the polar or cylindrical image grid is a factor of a number of in-plane symmetries between lines of response along which the projection data are measured by the imaging system; obtaining a system probability matrix that relates each of the projection data to each basis function of the polar or cylindrical image definition; restructuring the system probability matrix into a block circulant matrix and converting the system probability matrix in the Fourier domain; storing the projection data into a measurement data vector; providing an initial polar or cylindrical image estimate; for each iteration; recalculating the polar or cylindrical image estimate according to an iterative solver based on forward and back projection operations with the system probability matrix in the Fourier domain; and converting the polar or cylindrical image estimate into a Cartesian image representation to thereby obtain a reconstructed image.
Owner:SOCPRA SCI SANTE & HUMAINES S E C
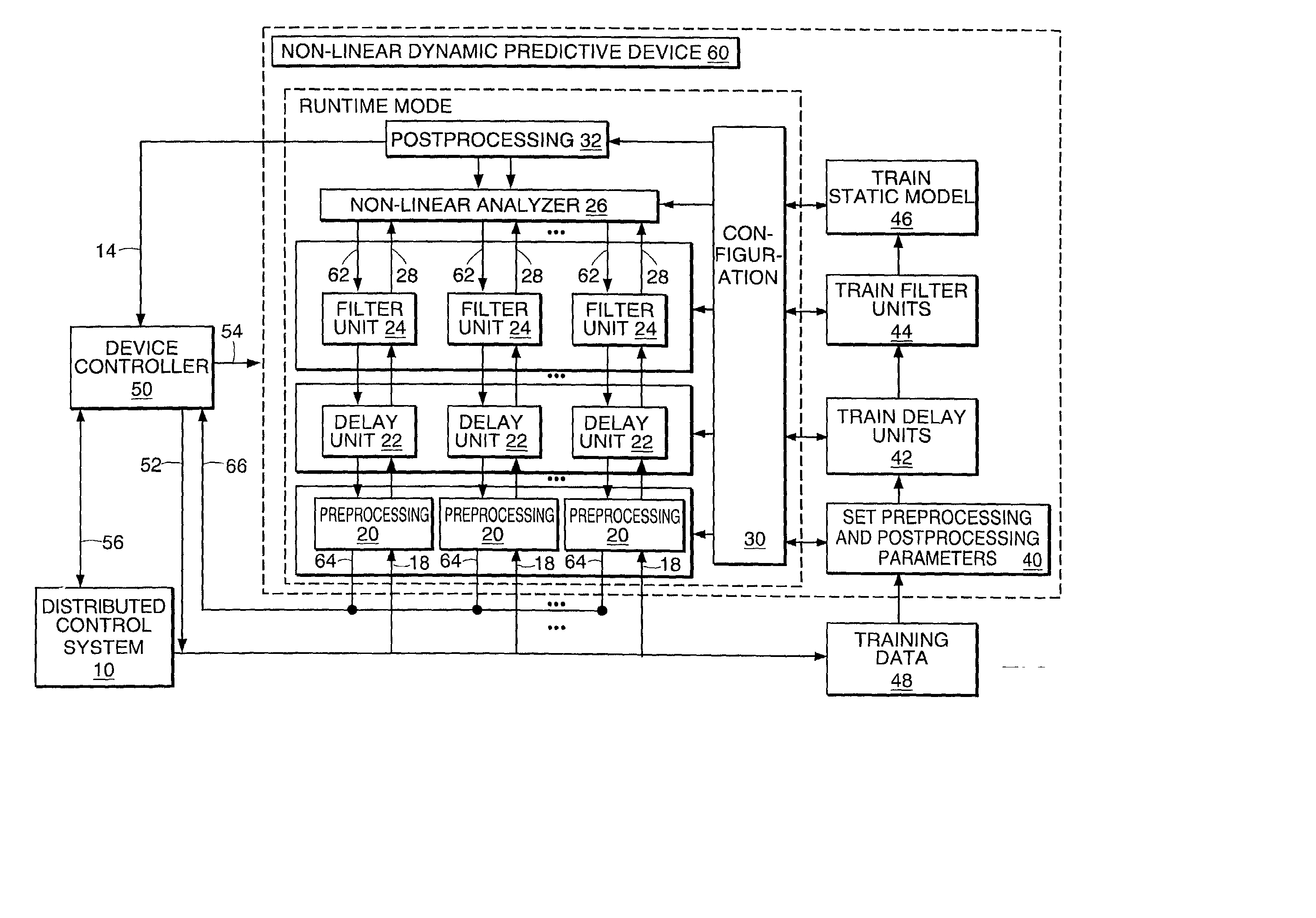
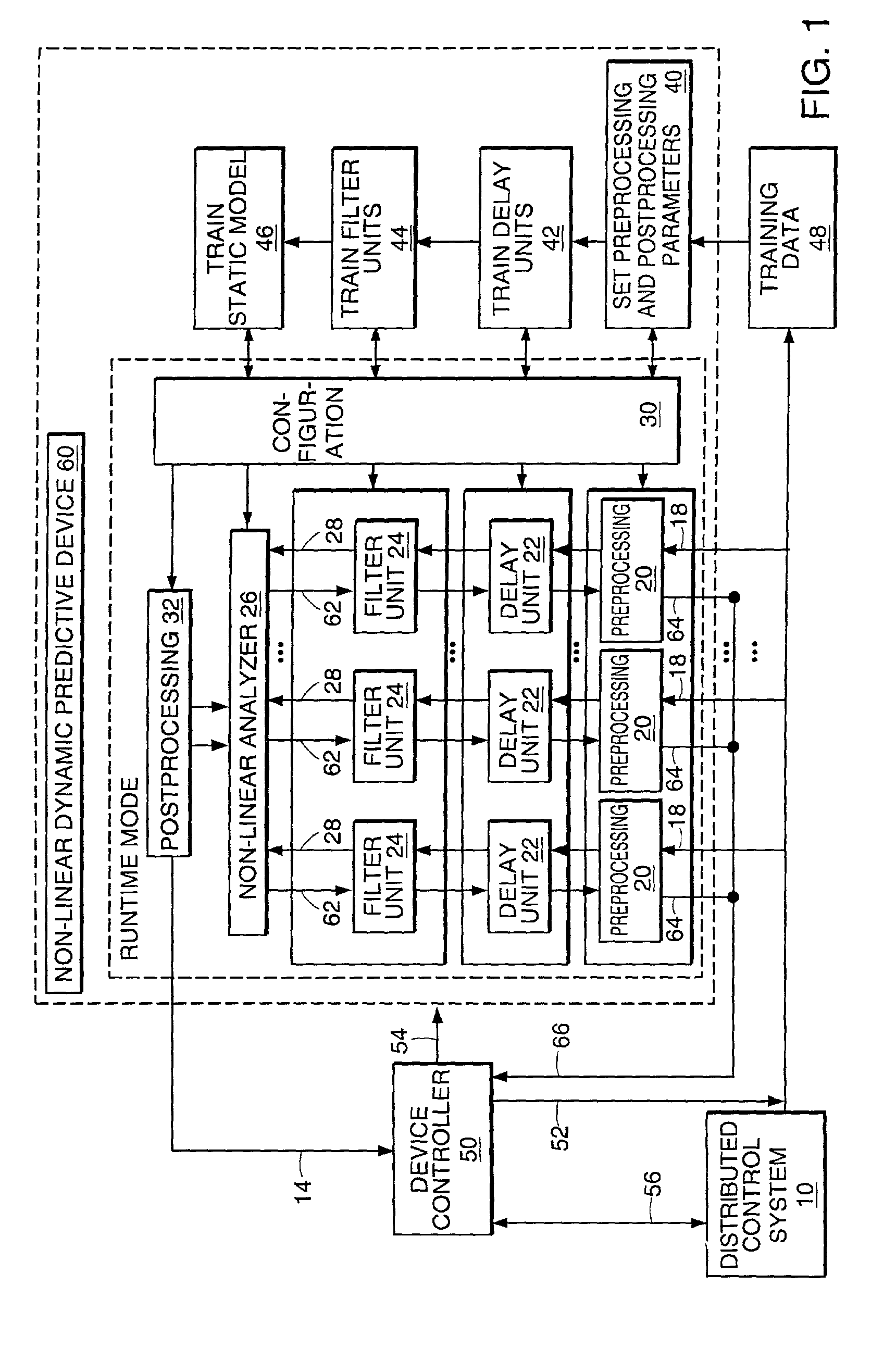
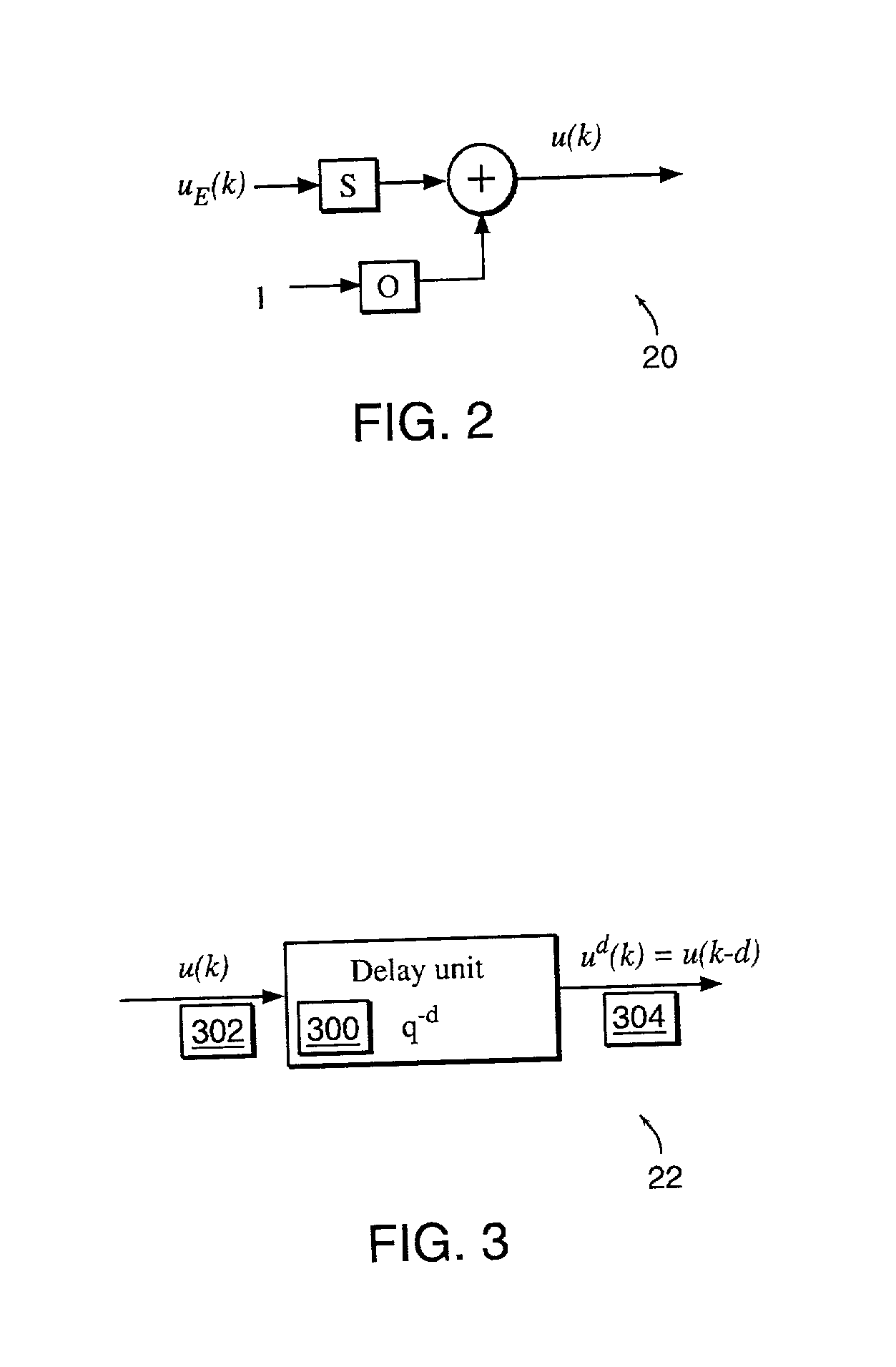
Non-linear dynamic predictive device
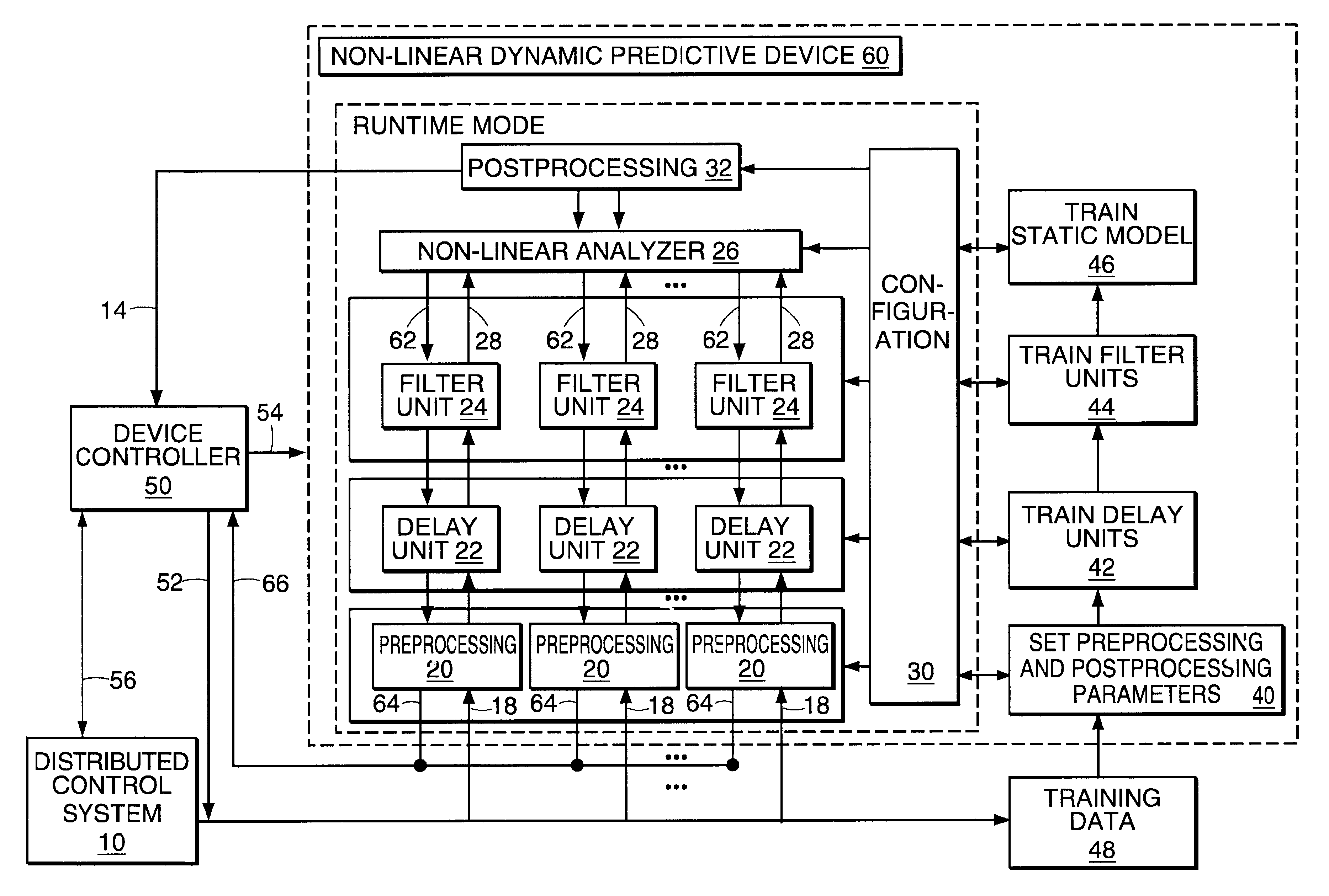
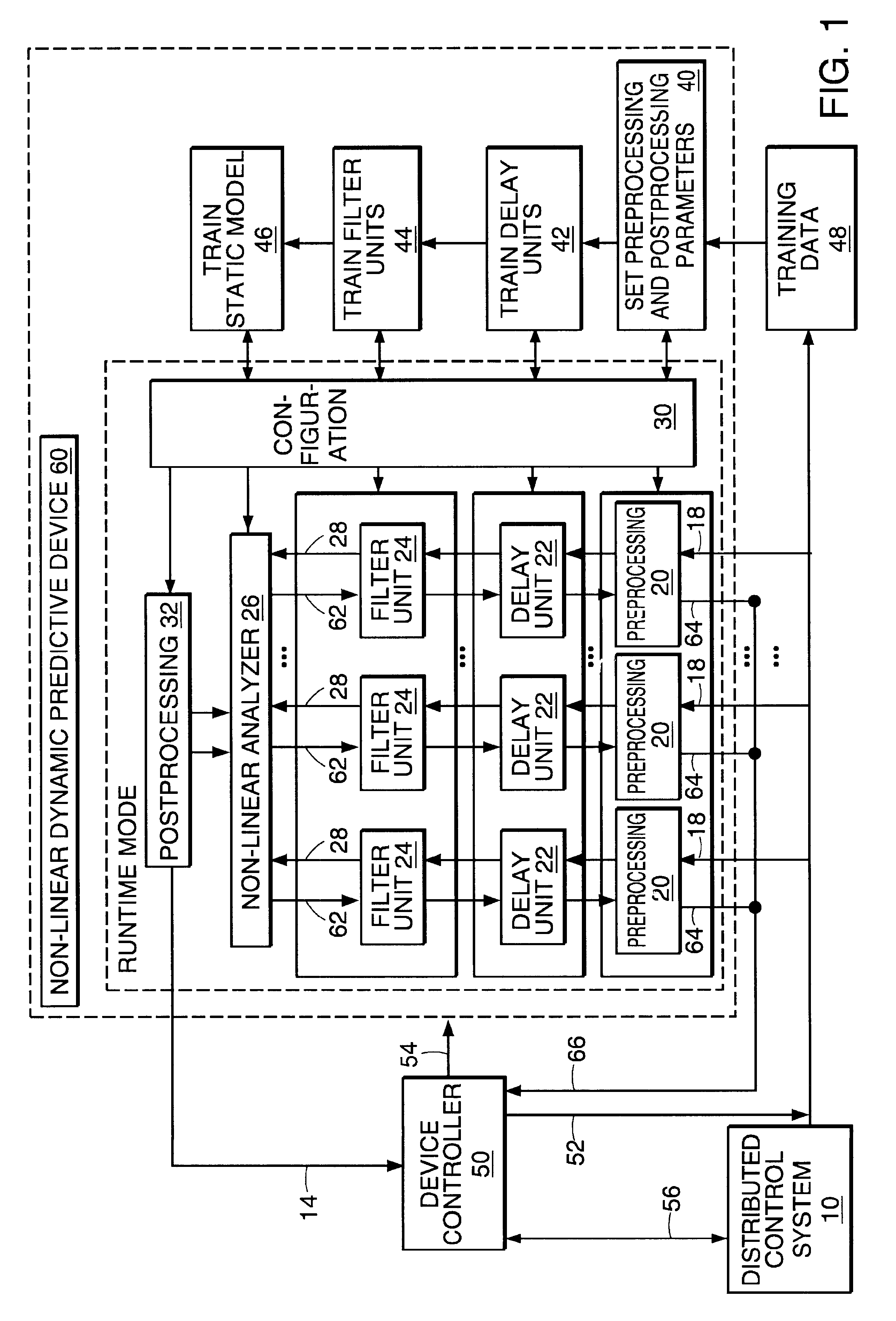
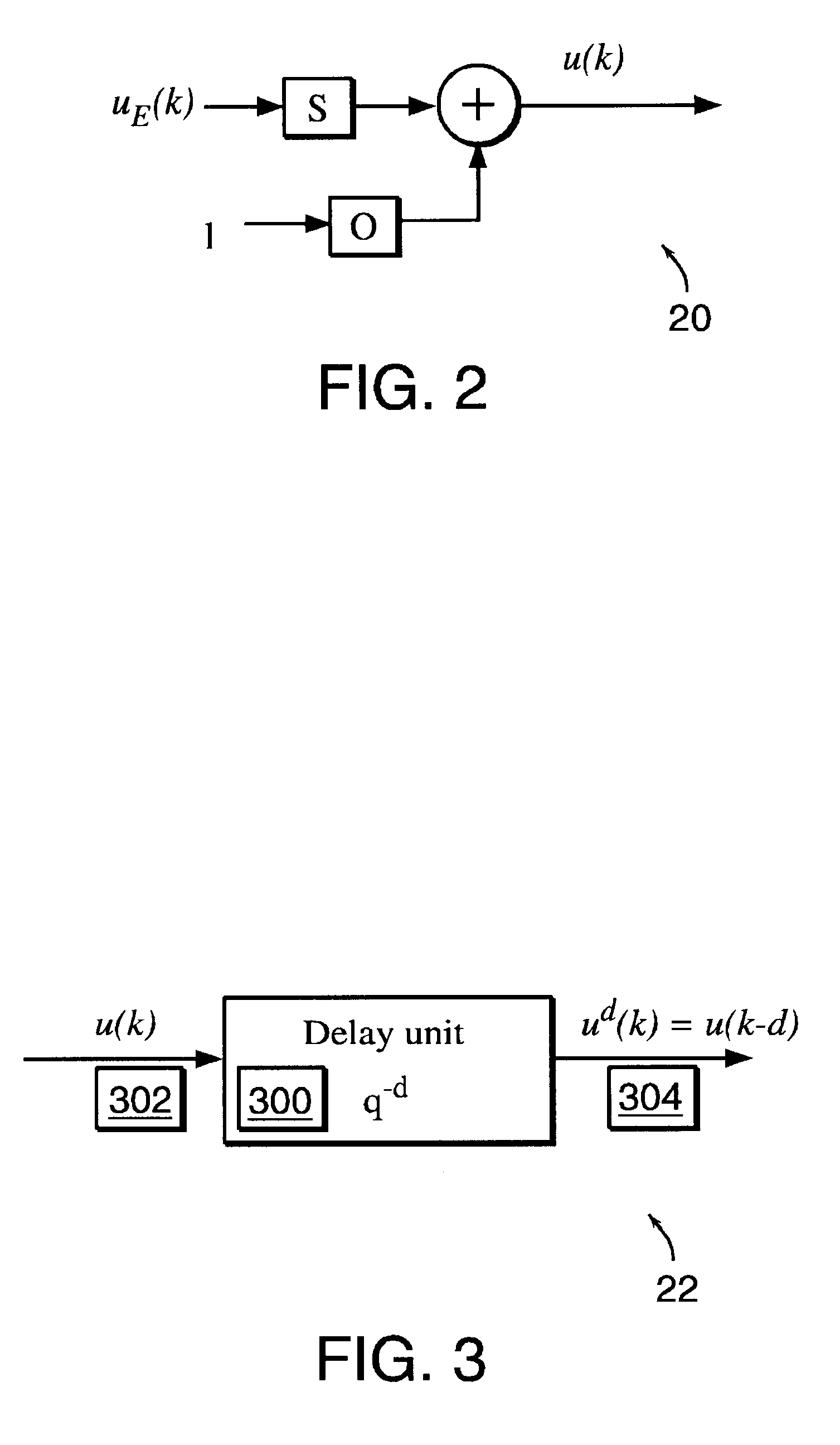
InactiveUS6453308B1Improve accuracyFast computerSimulator controlElectric testing/monitoringHorizonDead time
A non-linear dynamic predictive device (60) is disclosed which operates either in a configuration mode or in one of three runtime modes: prediction mode, horizon mode, or reverse horizon mode. An external device controller (50) sets the mode and determines the data source and the frequency of data. In prediction mode, the input data are such as might be received from a distributed control system (DCS) (10) as found in a manufacturing process; the device controller ensures that a contiguous stream of data from the DCS is provided to the predictive device at a synchronous discrete base sample time. In prediction mode, the device controller operates the predictive device once per base sample time and receives the output from the predictive device through path (14). In horizon mode and reverse horizon mode, the device controller operates the predictive device additionally many times during base sample time interval. In horizon mode, additional data is provided through path (52). In reverse horizon mode data is passed in a reverse direction through the device, utilizing information stored during horizon mode, and returned to the device controller through path (66). In the forward modes, the data are passed to a series of preprocessing units (20) which convert each input variable (18) from engineering units to normalized units. Each preprocessing unit feeds a delay unit (22) that time-aligns the input to take into account dead time effects such as pipeline transport delay. The output of each delay unit is passed to a dynamic filter unit (24). Each dynamic filter unit internally utilizes one or more feedback paths that are essential for representing the dynamic information in the process. The filter units themselves are configured into loosely coupled subfilters which are automatically set up during the configuration mode and allow the capability of practical operator override of the automatic configuration settings. The outputs (28) of the dynamic filter units are passed to a non-linear analyzer (26) which outputs a value in normalized units. The output of the analyzer is passed to a post-processing unit (32) that converts the output to engineering units. This output represents a prediction of the output of the modeled process. In reverse horizon mode, a value of 1 is presented at the output of the predictive device and data is passed through the device in a reverse flow to produce a set of outputs (64) at the input of the predictive device. These are returned to the device controller through path (66). The purpose of the reverse horizon mode is to provide essential information for process control and optimization. The precise operation of the predictive device is configured by a set of parameters. that are determined during the configuration mode and stored in a storage device (30). The configuration mode makes use of one or more files of training data (48) collected from the DCS during standard operation of the process, or through structured plant testing. The predictive device is trained in four phases (40, 42, 44, and 46) correspo
Owner:ASPENTECH CORP
System and method for multi-view face detection
InactiveUS20060120572A1Overcome limitationsOptimization rangeCharacter and pattern recognitionFace detectionState of art
A system and method for real-time multi-view (i.e. not just frontal view) face detection. The system and method uses a sequence of detectors of increasing complexity and face / non-face discriminating thresholds to quickly discard non-faces at the earliest stage possible, thus saving much computation compared to prior art systems. The detector-pyramid architecture for multi-view face detection uses a coarse-to-fine and simple-to-complex scheme. This architecture solves the problem of lengthy processing that precludes real-time face detection effectively and efficiently by discarding most of non-face sub-windows using the simplest possible features at the earliest possible stage. This leads to the first real-time multi-view face detection system which has the accuracy almost as good as the state-of-the-art system yet 270 times faster, allowing real-time performance.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Computer modeling and animation of natural phenomena
InactiveUS20060087509A1Fast computerEasy to controlCathode-ray tube indicatorsAnimationGraphicsAnimation
3D graphics animation is increasingly used in movies and virtual reality computer games to produce realistic visual simulations of physical and natural phenomena. The animation of diffuse liquids such as gases is an indispensable component in such special effects. The present system and methods utilize physically-based and more intuitive procedurally-based simulation techniques to simulate and render natural phenomena in computer graphics. The present invention facilitates user interaction in order to generate a variety of gas effects, for example, waves within water, plumes within hot gas, and flames within fire. Improved user interaction is achieved by improving rendering performance and introducing a new method of high-level control for Eulerian simulations.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Search using graph colorization and personalized bookmark processing
ActiveUS20050216533A1Fast computerInformation can be usedData processing applicationsWeb data indexingPersonalizationBookmarking
In a search processing system, identifying input authority weights for a plurality of pages, wherein an input authority weight represents a user's weight of a page in terms of interest; distributing a page's input authority weight over one or more pages that are linked in a graph to the page; and using a resulting authority weight for a page in effecting a search result list. The search result list might comprise one or more of reordering search hits and highlighting search hits.
Owner:R2 SOLUTIONS
Novel descriptor for image corresponding point matching
ActiveUS20100080469A1Reduce complexityReduce dimensionalityCharacter and pattern recognitionImage gradientImage identification
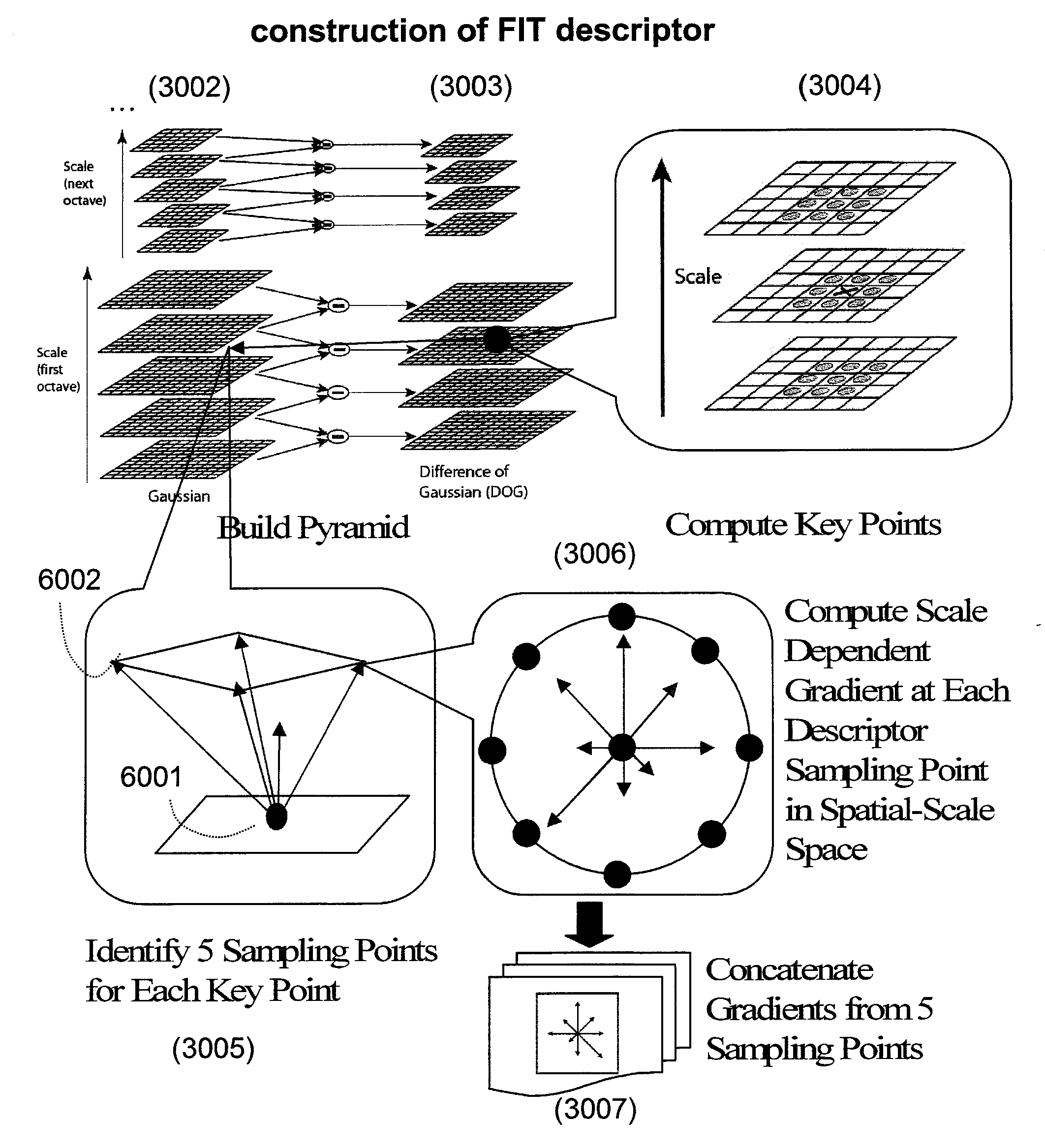
System and method of generating feature descriptors for image identification. Input image is Gaussian-blurred at different scales. A difference of Gaussian space is obtained from differences of adjacent Gaussian-blurred images. Key points are identified in the difference-of-Gaussian space. For each key point, primary sampling points are defined with three dimensional relative positions from key point and reaching into planes of different scales. Secondary sampling points are identified for each primary sampling point. Secondary image gradients are obtained between an image at a primary sampling point and images at secondary sampling points corresponding to this primary sampling point. Secondary image gradients form components of primary image gradients at primary sampling points. Primary image gradients are concatenated to obtain a descriptor vector for input image. Descriptor vector thus obtained is scale invariant and requires a number of additions equal to number of primary sampling points multiplied by a number of secondary sampling points.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
Robust interest point detector and descriptor
ActiveUS8165401B2Fast computerNot sacrificing performanceImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionInterest point detection
Methods and apparatus for operating on images are described, in particular methods and apparatus for interest point detection and / or description working under different scales and with different rotations, e.g. for scale-invariant and rotation-invariant interest point detection and / or description. The present invention can provide improved or alternative apparatus and methods for matching interest points either in the same image or in a different image. The present invention can provide alternative or improved software for implementing any of the methods of the invention. The present invention can provide alternative or improved data structures created by multiple filtering operations to generate a plurality of filtered images as well as data structures for storing the filtered images themselves, e.g. as stored in memory or transmitted through a network. The present invention can provide alternative or improved data structures including descriptors of interest points in images, e.g. as stored in memory or transmitted through a network as well as data structures associating such descriptors with an original copy of the image or an image derived therefrom, e.g. a thumbnail image.
Owner:K U LEUVEN RES & DEV +2
Method for tracking objects in a scene
ActiveUS20060215880A1Accurate decisionQuick calculationCharacter and pattern recognitionHide markov modelDigital image
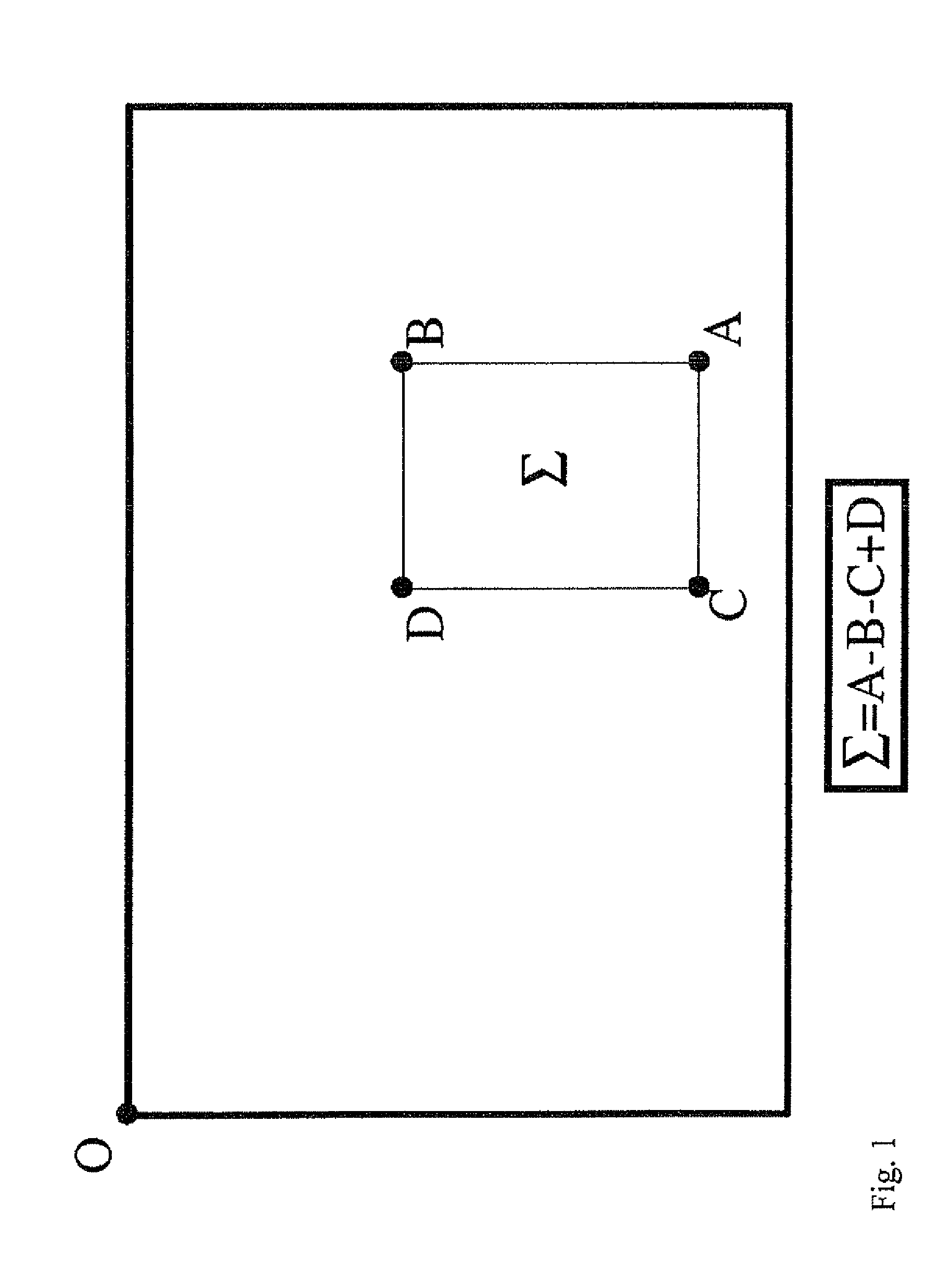
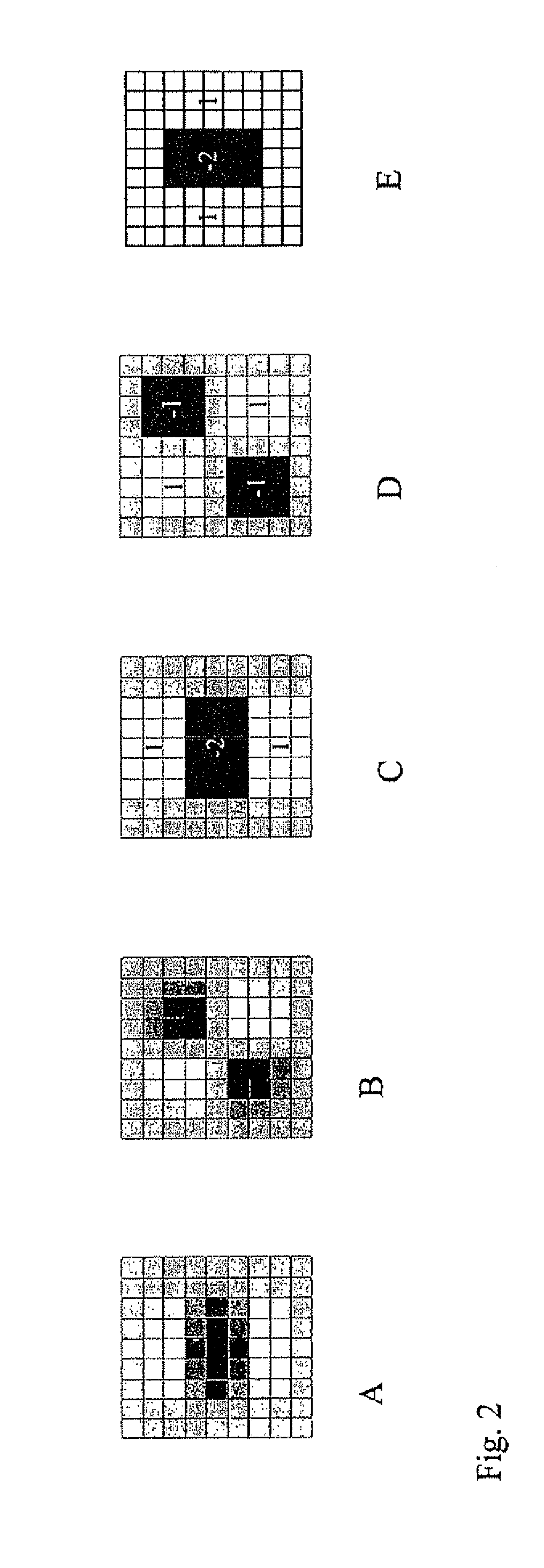
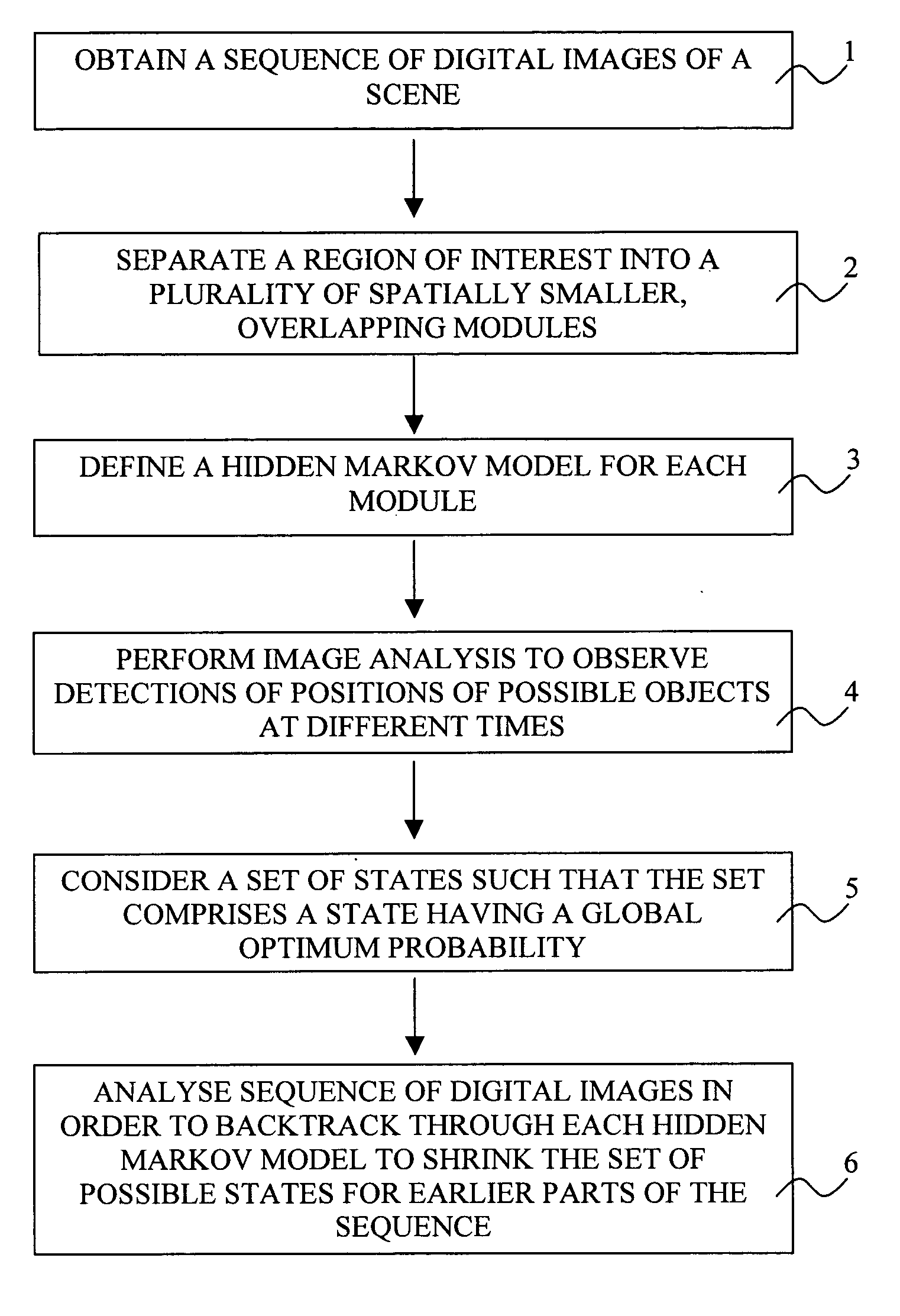
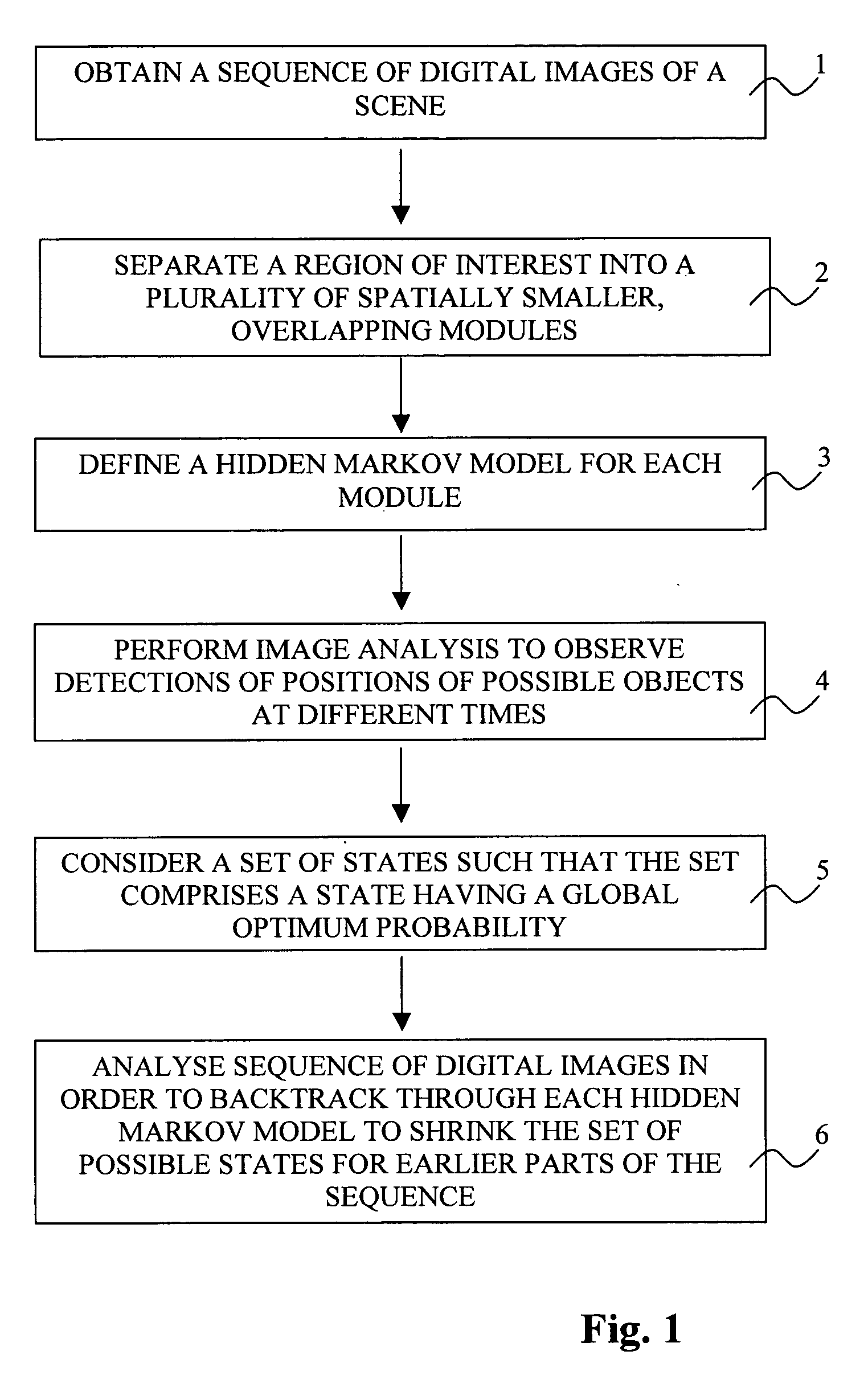
A method for tracking objects in a scene being viewed by a sequence of digital images comprises: separating a region of interest in the digital images into a plurality of spatially smaller, overlapping modules, and defining a hidden Markov model for each module. The method further comprises observing detections of positions of possible objects at different times, considering a set of states at a point of time (t1) such that the set of states comprises a state having a global optimum probability, and backtracking through the sequence of digital images for each hidden Markov model to shrink the set of states that are possible for earlier parts of the sequence of digital images, such that a single optimal state is found for an earlier point of time (t2<t1), whereby tracks of detected objects through the scene are determined up to the earlier point of time (t2).
Owner:AXIS
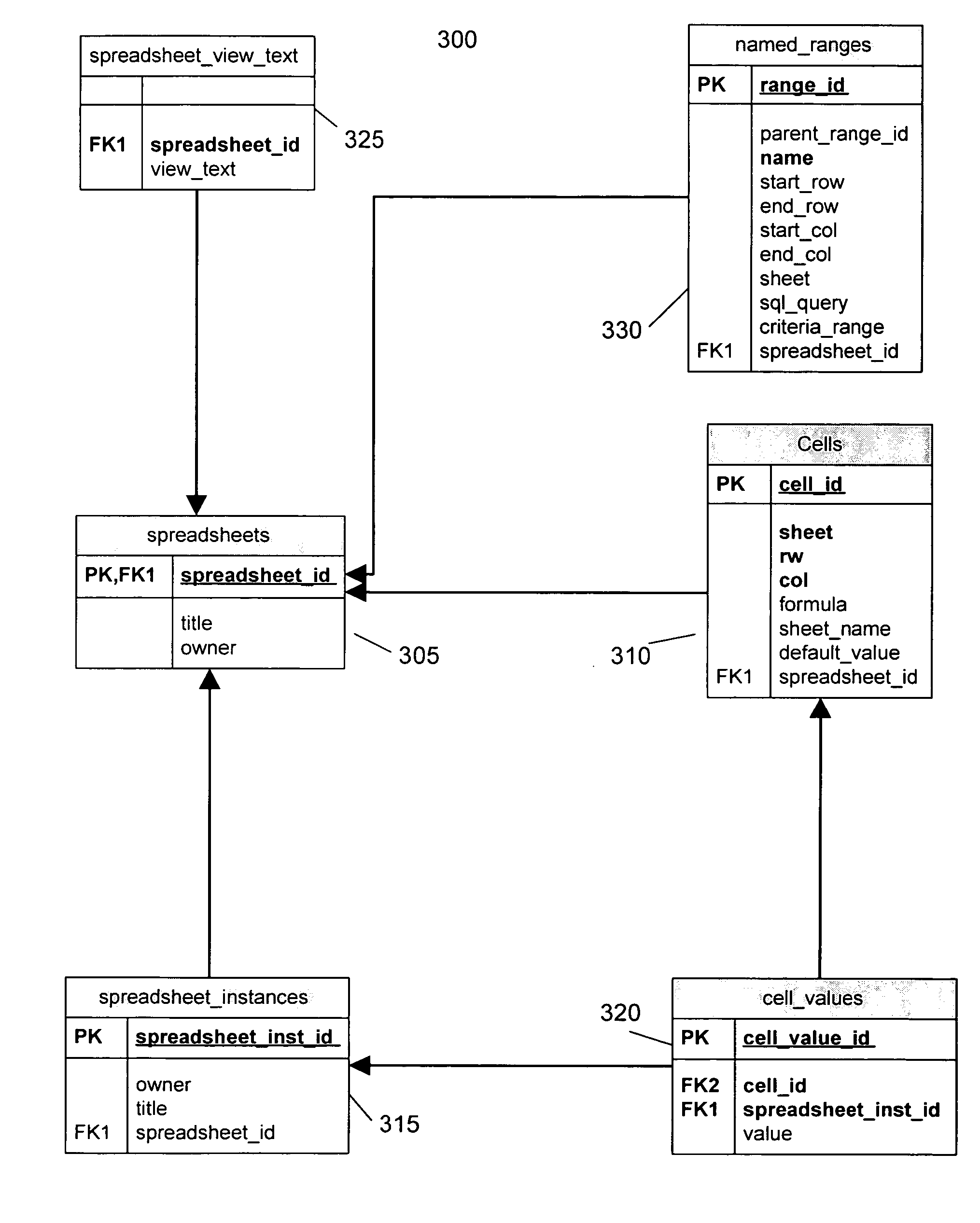
Spreadsheet to SQL translation
ActiveUS20050039114A1Eliminate needEasy to useDigital data information retrievalData processing applicationsWeb browserData set
Users can create computational models in a spreadsheet application and automatically apply the model to data stored in a relational database. By importing a sample of the data from a database table into the spreadsheet application, users can build spreadsheet models that perform analysis and computations on the sample data. Once the model is complete, the spreadsheet model is translated into an SQL format model understood by the database. The SQL model can operate on the entire data set in the database, rather than just the sample data used to construct the model. The SQL model and its associated data are stored in the database, and the model can be executed on a different sets of data. A web browser based front-end allows model users to access the SQL model via a web browser, eliminating the need for model users to have a spreadsheet application.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Network global expectation model for multi-tier networks
InactiveUS20050197993A1Quick costRapidly needWavelength-division multiplex systemsFuzzy logic based systemsSensitivity analysisNetwork cost
In the Network Global Expectation Model, expectation values evaluated over the entire network are used as a multi-moment description of the required quantities of key network and network element (NE) resources and commensurate network costs. The Network Global Expectation Model naturally and analytically connects the global (network) and local (network element) views of the communication system, and thereby may be used as a tool to gain insight and very quickly provide approximate results for the preliminary evaluation and design of dynamic networks. Further, the Network Global Expectation Model may serve as a valuable guide in the areas of network element feature requirements, costs, sensitivity analyses, scaling performance, comparisons, product definition and application domains, and product and technology roadmapping. The network is arranged as a multiple tier network of nodes in order to apply the analysis methods of the Network Global Expectation Model. The analytical method is developed to include non-uniform demands on the network.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
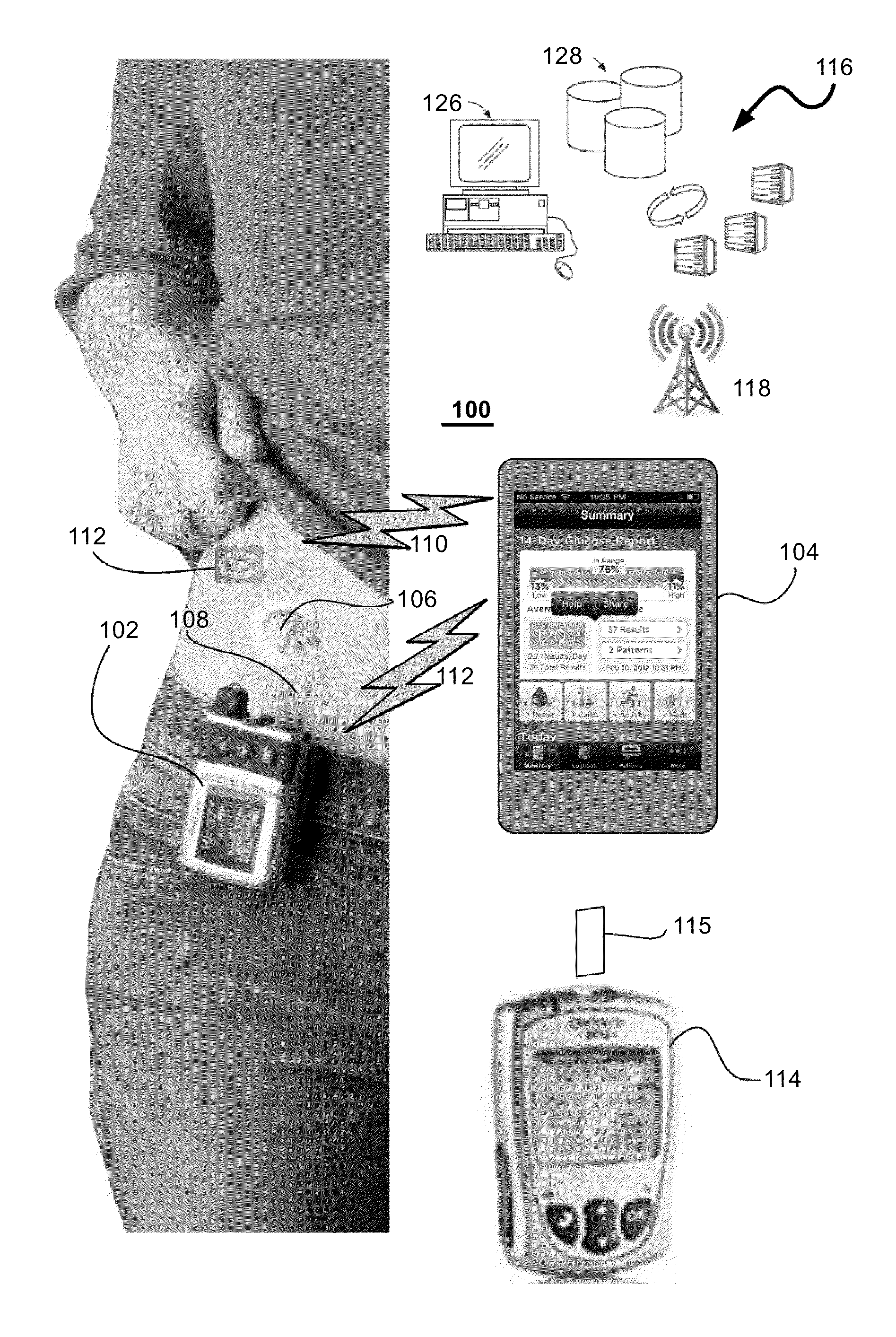
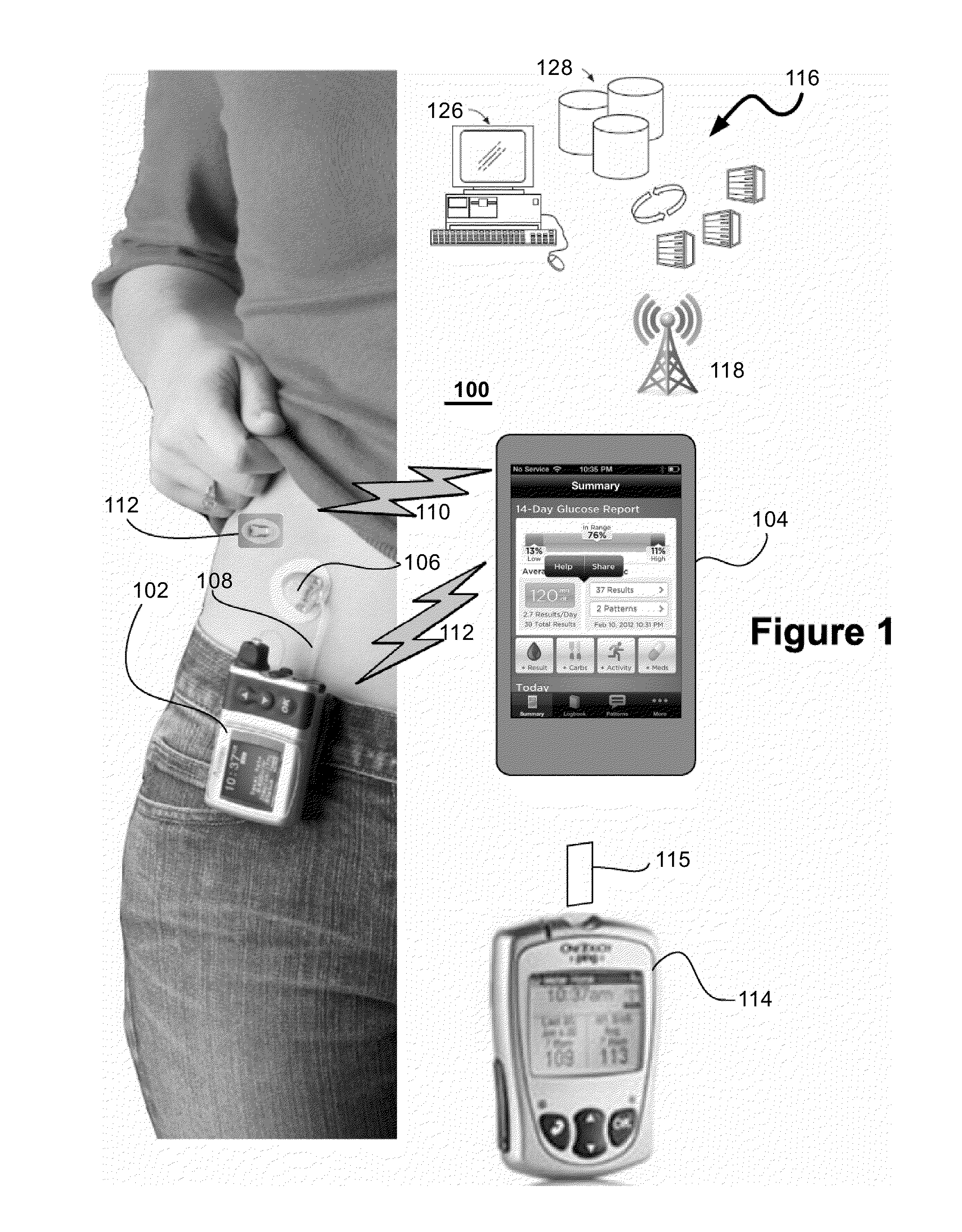
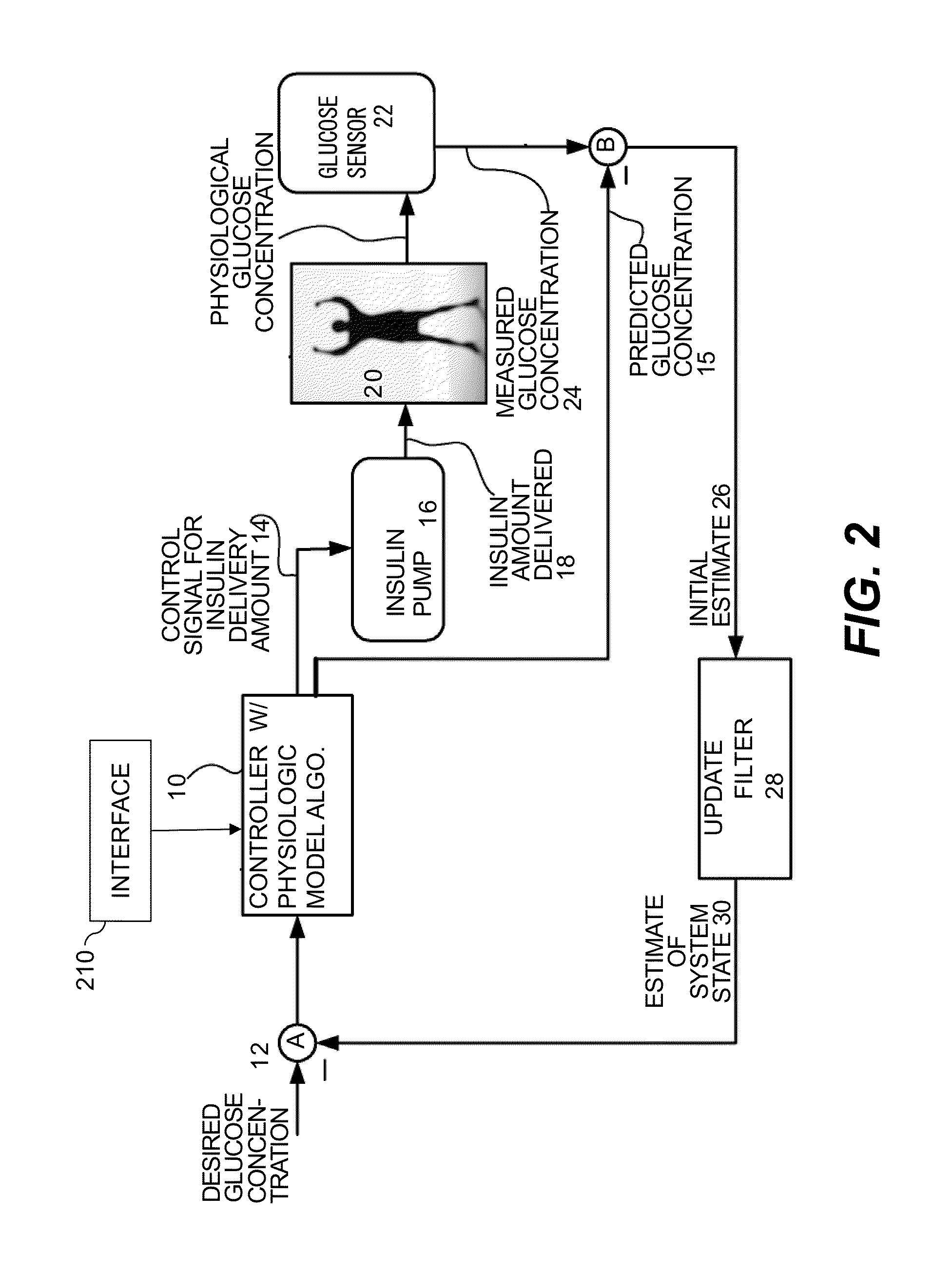
Method and System for Closed-Loop Control of an Artificial Pancreas
ActiveUS20140276555A1Reduce error contributedReduce truncation errorDrug and medicationsMedical devicesInsulin pumpClosed loop
A local extremum of a function ƒ is determined by computing a Jacobian of ƒ at a test point x by adding an imaginary part to x and a Hessian of ƒ by adding two imaginary parts to a multicomplex copy of x and extracting a third imaginary part. Solving a system of equations defined by the Jacobian and Hessian yields a delta; the process is repeated until convergence. This method is used in each of a series of time intervals to compute an insulin-delivery amount for an insulin pump. ƒ is a model-predictive-control cost function; x is a set of successive candidate insulin delivery amounts beginning from a selected time interval. A system includes a glucose monitor and a controller using glucose measurement data therefrom to determine an insulin delivery amount for a time interval by minimizing ƒ; an insulin pump provides insulin corresponding to the delivery amount.
Owner:ANIMAS CORP +1
Computation of page authority weights using personalized bookmarks
ActiveUS7343374B2Fast computerInformation can be usedData processing applicationsWeb data indexingPersonalizationBookmarking
In a search processing system, identifying input authority weights for a plurality of pages, wherein an input authority weight represents a user's weight of a page in terms of interest; distributing a page's input authority weight over one or more pages that are linked in a graph to the page; and using a resulting authority weight for a page in effecting a search result list. The search result list might comprise one or more of reordering search hits and highlighting search hits.
Owner:R2 SOLUTIONS
Accelerated ray-object intersection
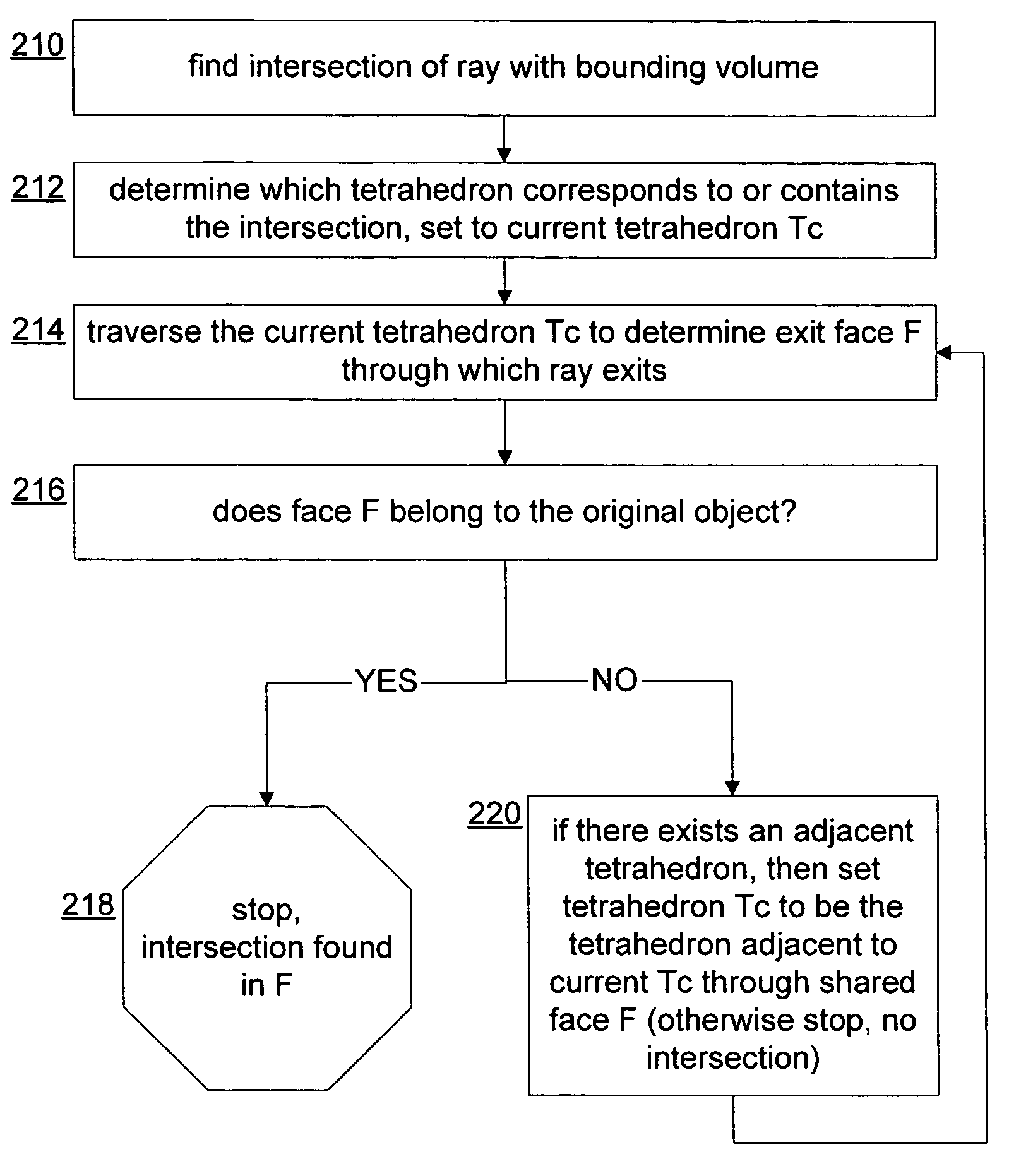
ActiveUS7483024B2Simple calculationQuickly and accurately find3D-image rendering3D modellingComputer visionBounding surface
An original mesh is provided with a bounding surface and a convex hull surface. A first tessellation links the convex hull to the original mesh, and a second tessellation links the bounding surface to the convex hull. Using the tessellations to find a first intersection between a ray and the original mesh by finding a first intersected polygon of the bounding surface, and then traversing adjacent intersected polygons starting from the first intersection until the intersection is found. When the ray is moved, a second ray-surface intersection can be found by finding a polygon locally near the first intersection and containing a first intersection with the moved ray, traversing out from the local polygon through adjacent polygons intersected by the moved ray, and determining whether traversed polygons are unoccluded based on whether they are part of the convex hull surface.
Owner:AUTODESK INC
Non-linear dynamic predictive device
InactiveUS20020178133A1Fast computerImprove accuracySimulator controlElectric testing/monitoringNonlinear approximationDead time
A non-linear dynamic predictive device (60) is disclosed which operates either in a configuration mode or in one of three runtime modes: prediction mode, horizon mode, or reverse horizon mode. An external device controller (50) sets the mode and determines the data source and the frequency of data. In the forward modes (prediction and horizon), the data are passed to a series of preprocessing units (20) which convert each input variable (18) from engineering units to normalized units. Each preprocessing unit feeds a delay unit (22) that time-aligns the input to take into account dead time effects. The output of each delay unit is passed to a dynamic filter unit (24). Each dynamic filter unit internally utilizes one or more feedback paths that provide representations of the dynamic information in the process. The outputs (28) of the dynamic filter units are passed to a non-linear approximator (26) which outputs a value in normalized units. The output of the approximator is passed to a post-processing unit (32) that converts the output to engineering units. This output represents a prediction of the output of the modeled process. In reverse horizon mode, data is passed through the device in a reverse flow to produce a set of outputs (64) at the input of the predictive device. These are returned to the device controller through path (66). The purpose of the reverse horizon mode is to provide information for process control and optimization. The predictive device approximates a large class of non-linear dynamic processes. The structure of the predictive device allows it to be incorporated into a practical multivariable non-linear Model Predictive Control scheme, or used to estimate process properties.
Owner:ASPENTECH CORP
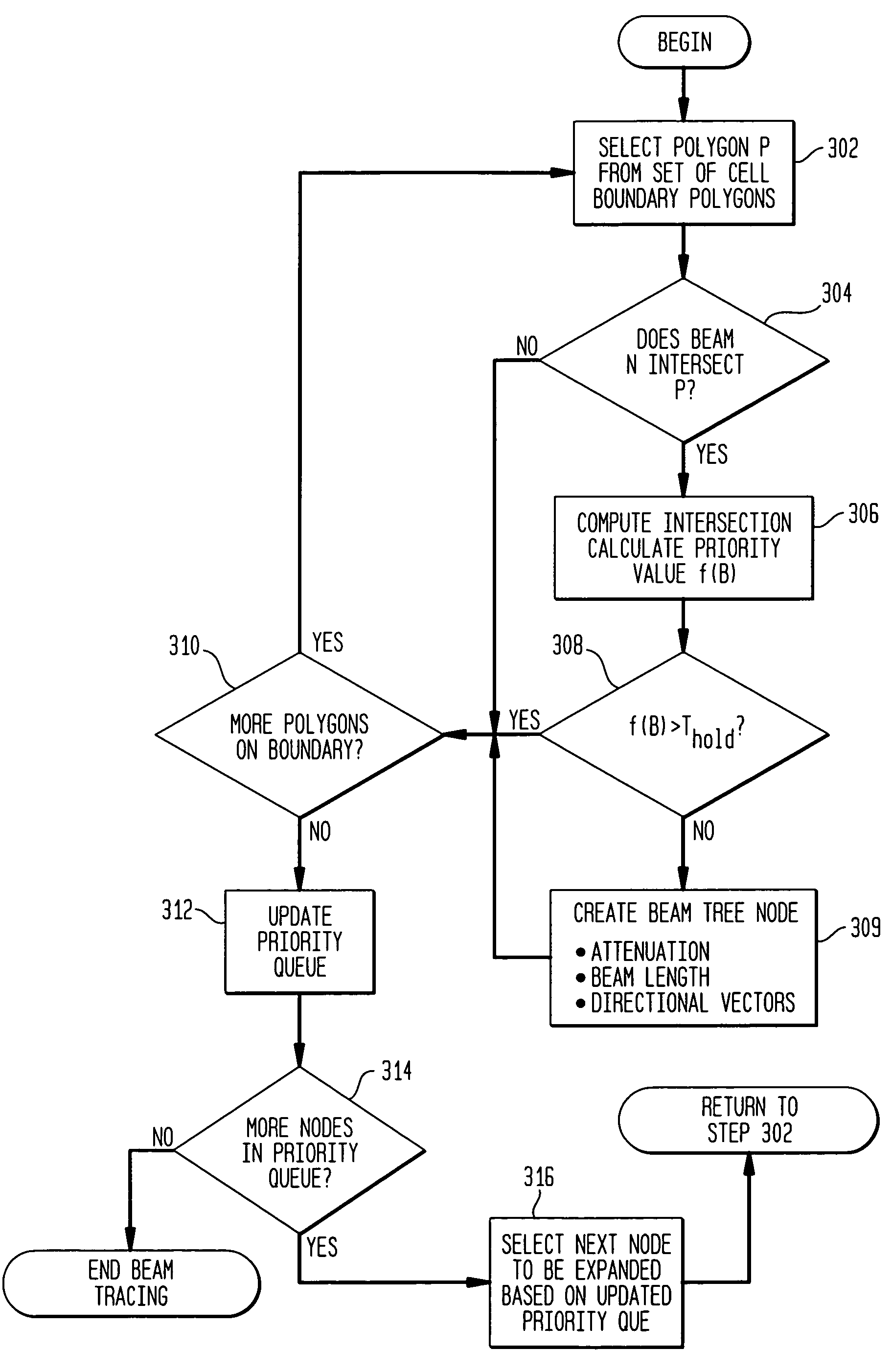
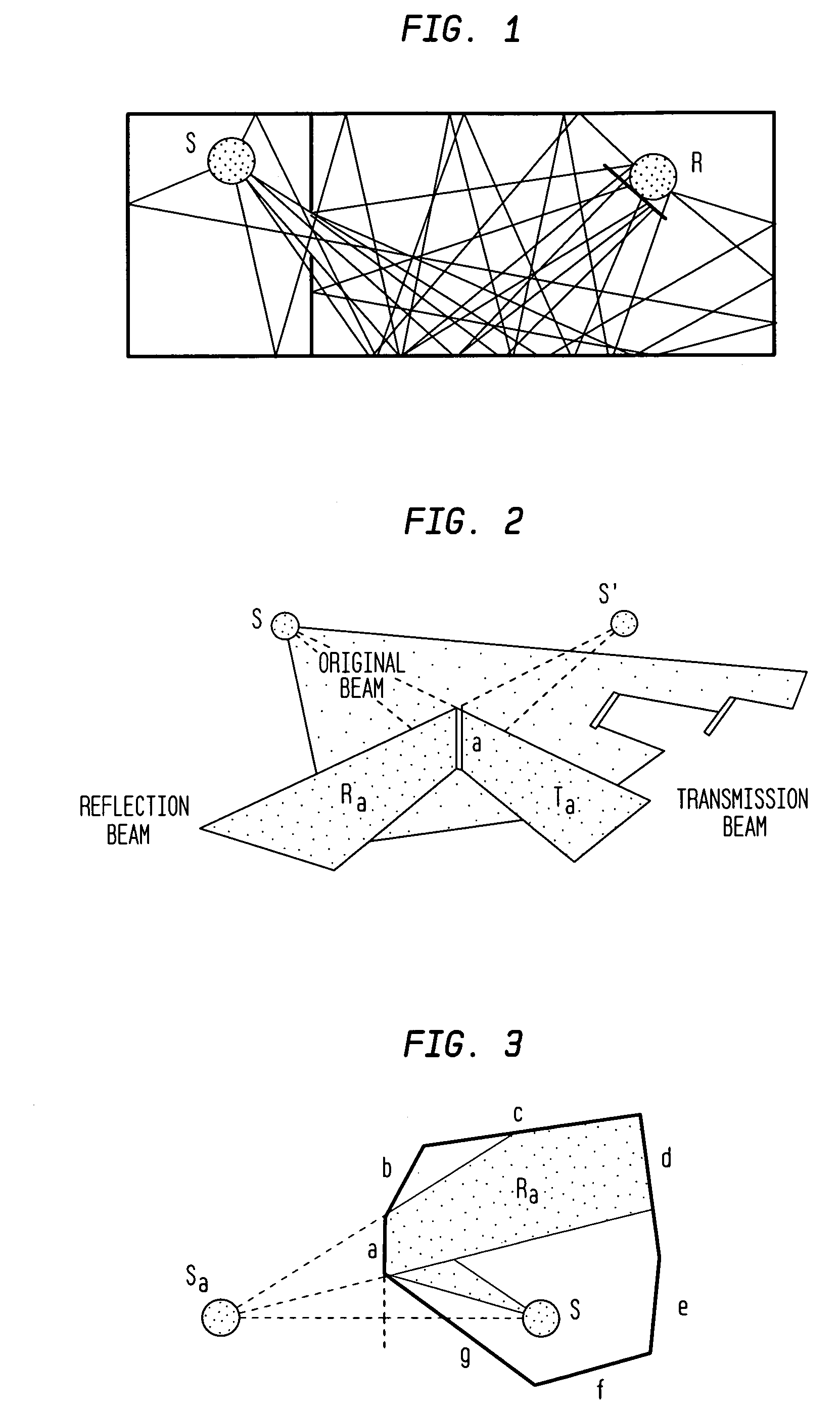
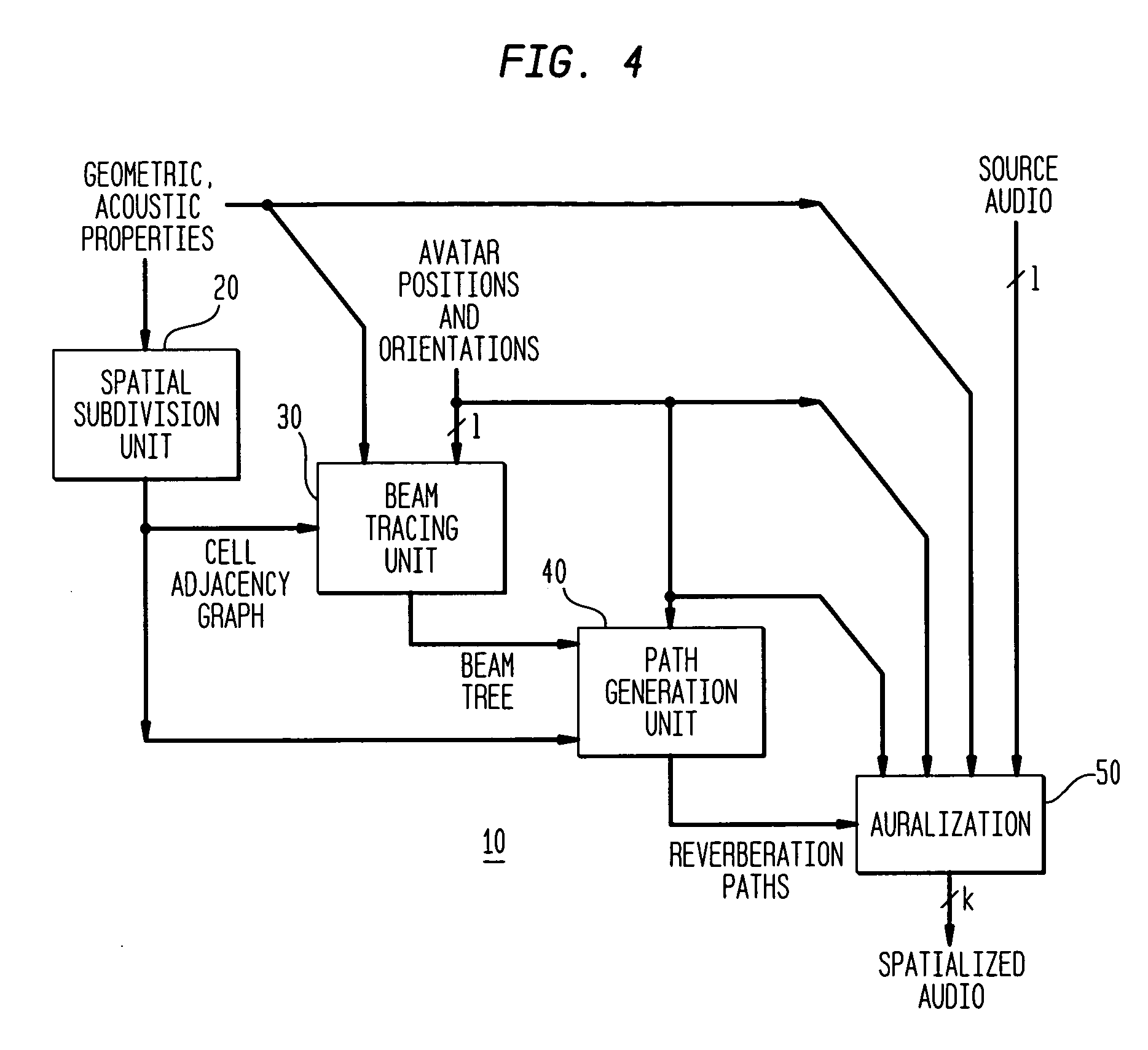
Acoustic modeling apparatus and method using accelerated beam tracing techniques
InactiveUS7146296B1Rapidly auralizedFast modelingGain controlAnalogue computers for electric apparatusBeam tracingTree (data structure)
An acoustic modeling system and an acoustic modeling method use beam tracing techniques that accelerate computation of significant acoustic reverberation paths in a distributed virtual environment. The acoustic modeling system and method perform a priority-driven beam tracing to construct a beam tree data structure representing “early” reverberation paths between avatar locations by performing a best-first traversal of a cell adjacency graph that represents the virtual environment. To further accelerate reverberation path computations, the acoustic modeling system and method according to one embodiment perform a bi-directional beam tracing algorithm that combines sets of beams traced from pairs of avatar locations to efficiently find viable acoustic reverberation paths.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC +1
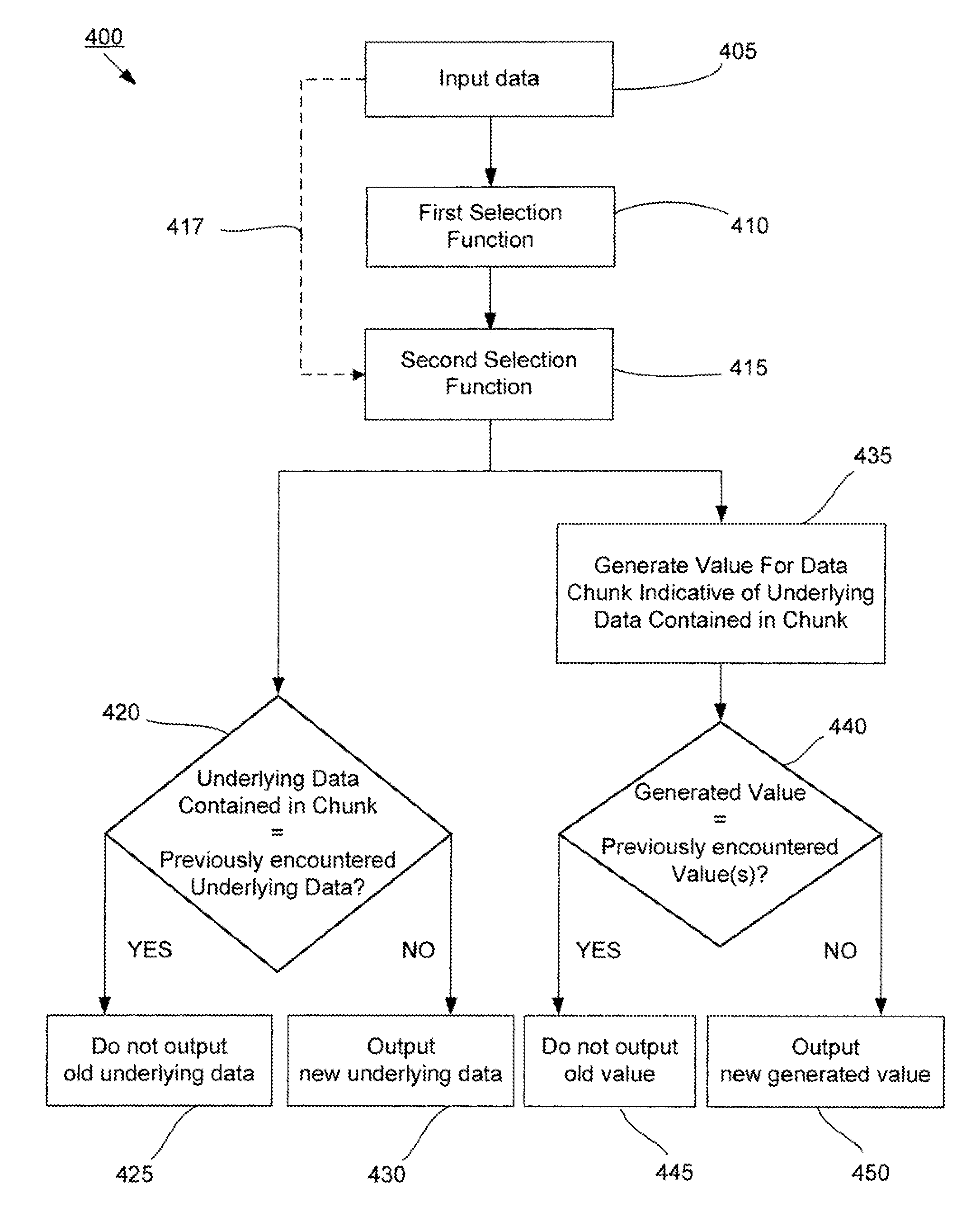
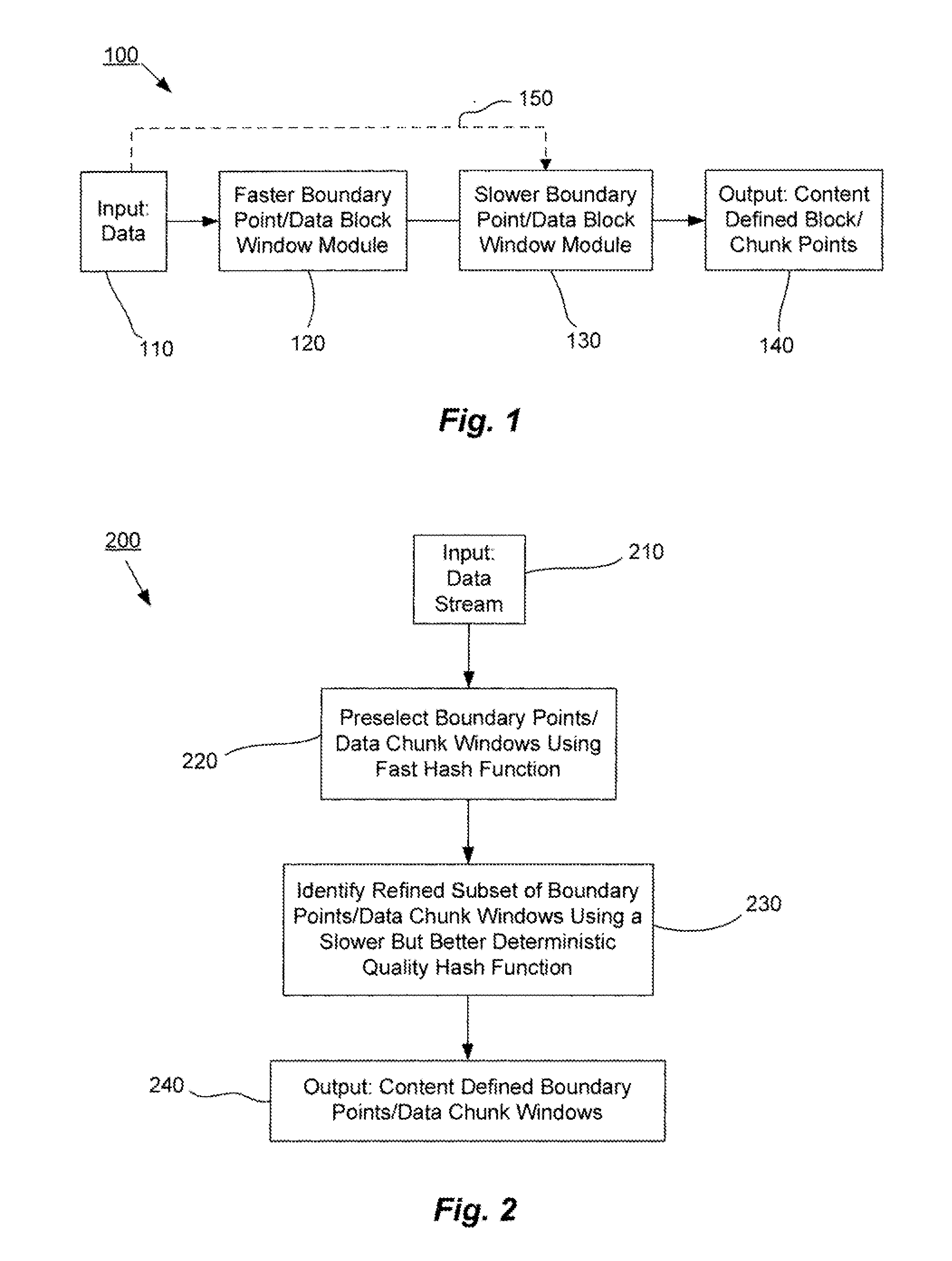
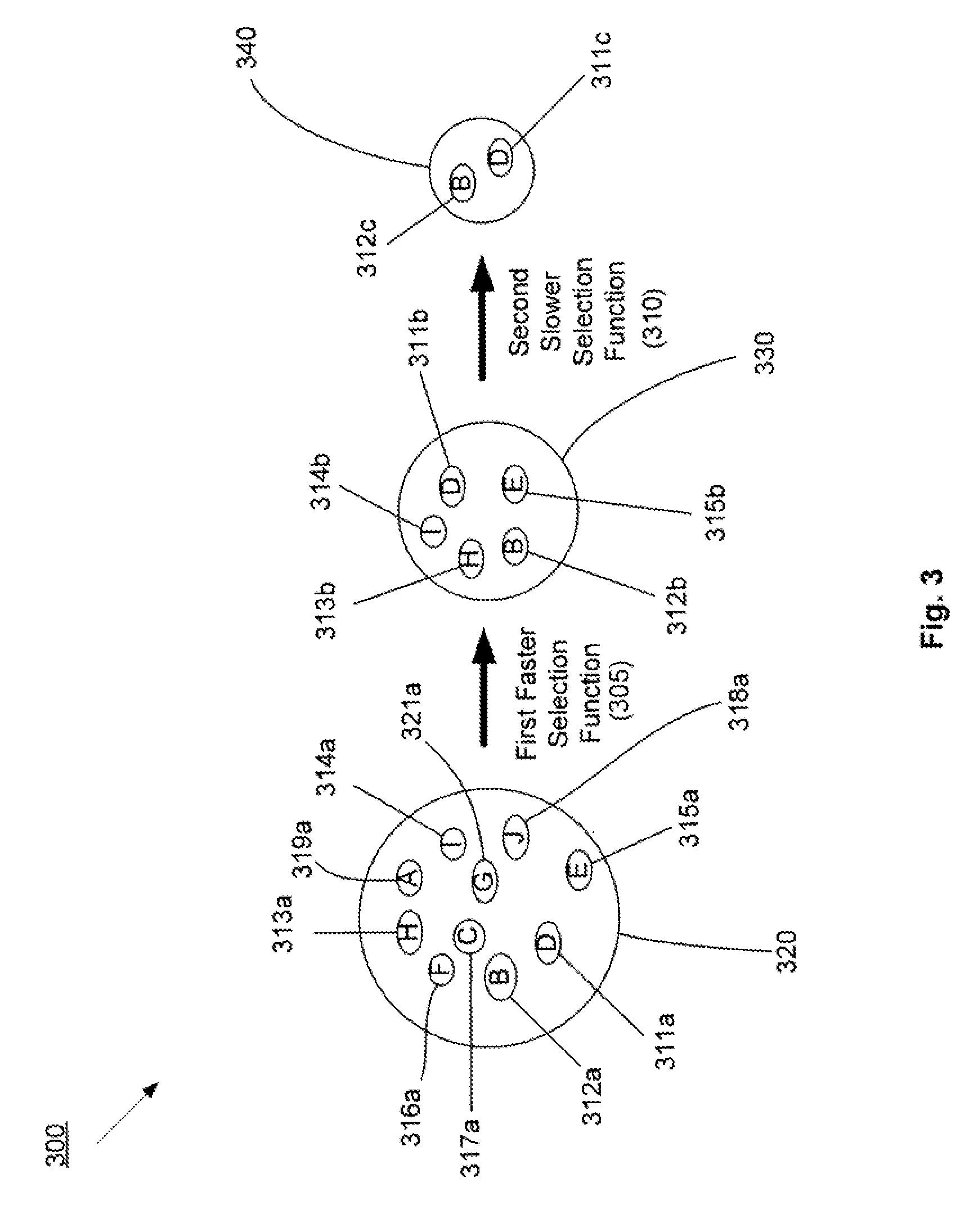
Methods and systems for data management using multiple selection criteria
ActiveUS20080133446A1Improve data processing speedReduce quality problemsDigital data information retrievalProgram control using stored programsData setHash function
Systems and methods for data management and data processing are provided. Embodiments may include systems and methods relating to fast data selection with reasonably high quality results, and may include a faster data selection function and a slower data selection function. Various embodiments may include systems and methods relating to data hashing and / or data redundancy identification and elimination for a data set or a string of data. Embodiments may include a first selection function is used to pre-select boundary points or data blocks / windows from a data set or data stream and a second selection function is used to refine the boundary points or data blocks / windows. The second selection function may be better at determining the best places for boundary points or data blocks / windows in the data set or data stream. In various embodiments, data may be processed by a first faster hash function and slower more discriminating second hash function.
Owner:NEC CORP
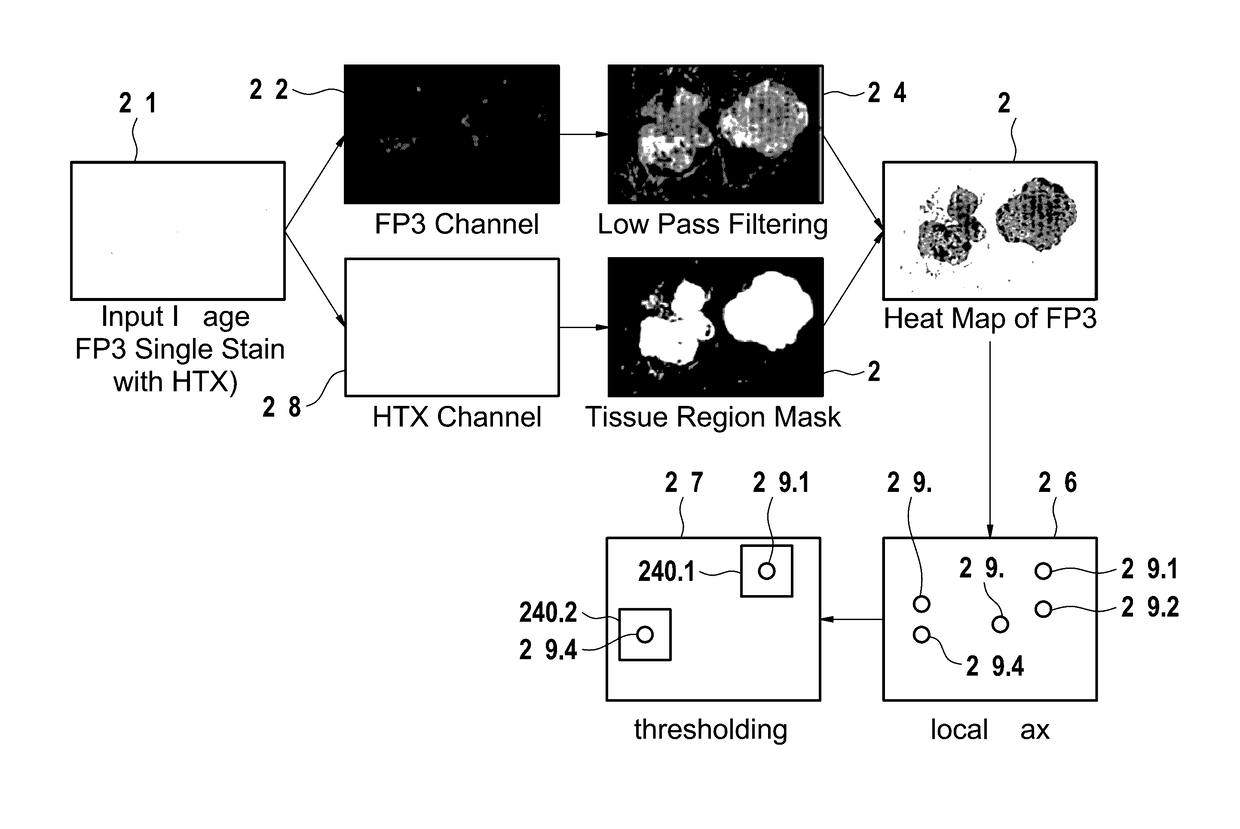
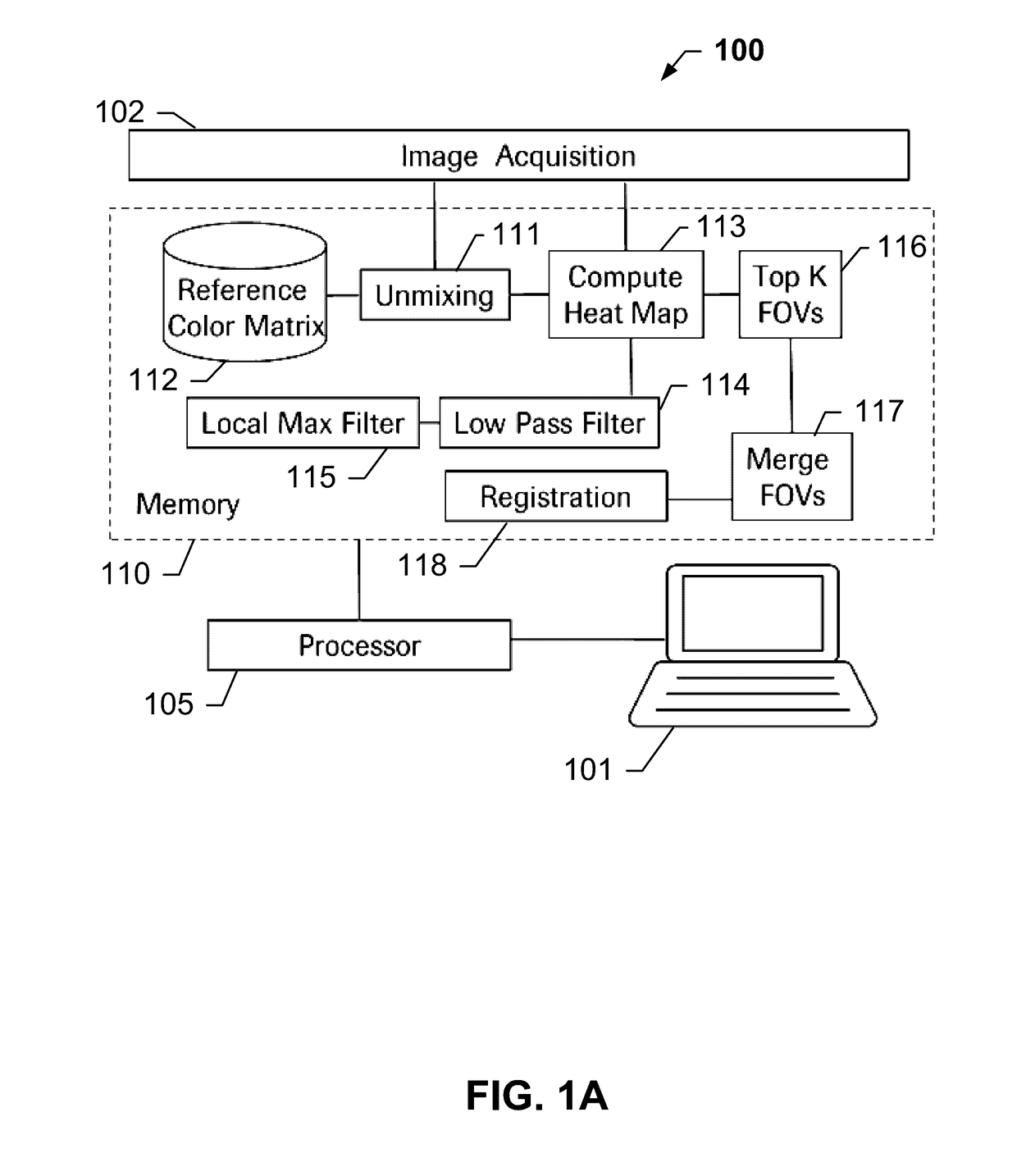
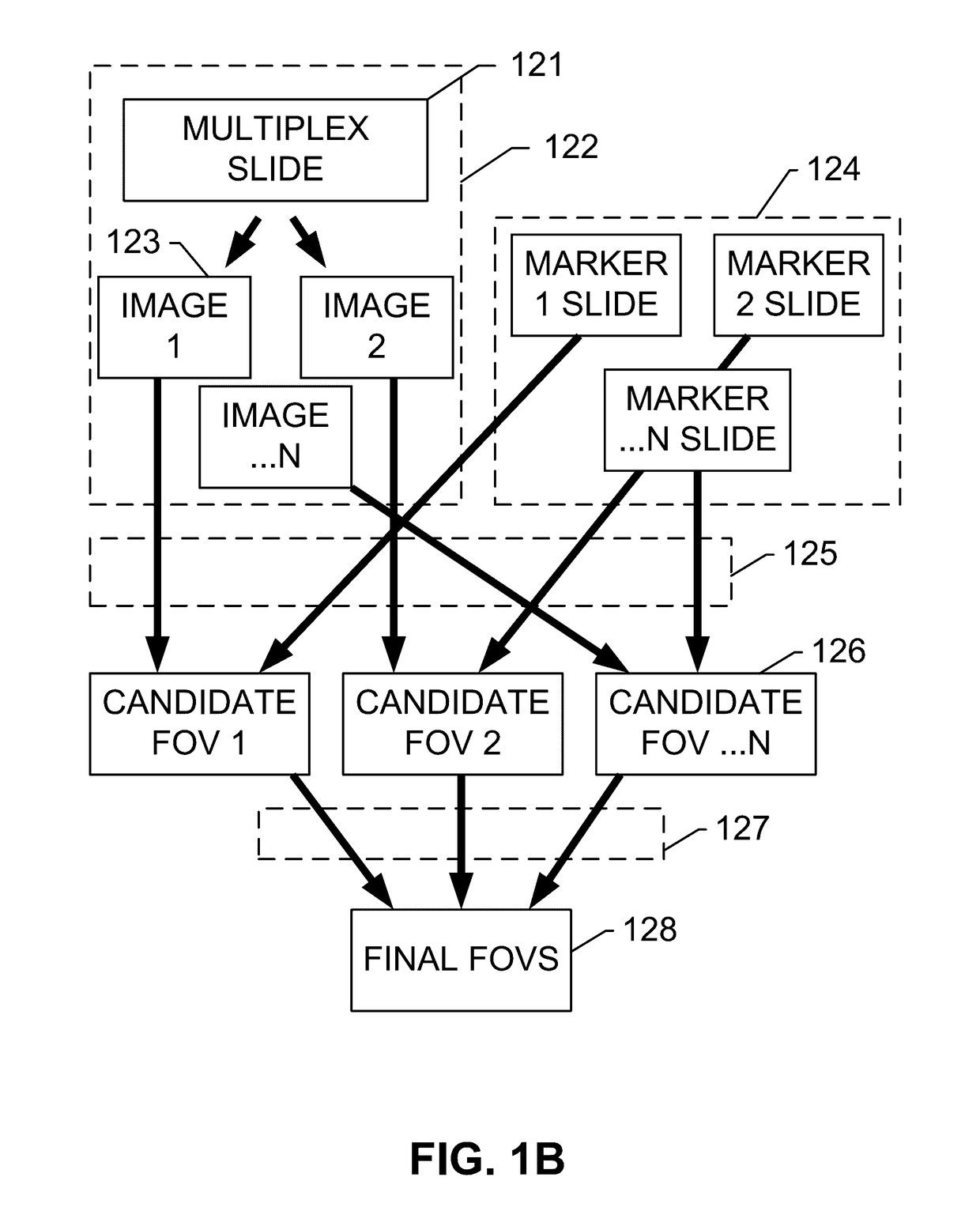
Image processing method and system for analyzing a multi-channel image obtained from a biological tissue sample being stained by multiple stains
ActiveUS20170154420A1High resolutionImprove reliabilityImage enhancementImage analysisImaging processingLow-pass filter
Systems and methods for automatic FOV selection in immunoscore computation that involve reading images for individual markers from an unmixed multiplex slide or single stain slides, and computing the tissue region mask from the individual marker image. The heat map of each marker is determined by applying the low pass filter on the individual marker image channel and selecting the top K highest intensity regions from the heat map as the candidate FOVs for each marker. The candidate FOVs from the individual marker images are merged together in the same coordinate system by either adding all of the FOVs together or by only adding the FOVs from the selected marker images depending on the user's choice, and registering all the individual marker images to a common coordinate system and transferring the FOVs back to the original images.
Owner:PROVIDENCE HEALTH SYST OREGON +1
Message processing protocol which mitigates optimistic messaging behavior
ActiveUS20180183901A1Increase transaction volumeMaintain performanceFinanceData switching networksMessage processingMessage passing
The disclosed embodiments relate to implementation, such as by a message processing system architecture, of a message handling system and / or protocol which mitigates optimistic messaging behavior. As used herein optimistic messaging behavior may at least refer to the transmission, in whole or in part, of a message, or of one or more messages of a sequence thereof, to a receiving system, such as the system implemented by the disclosed embodiments, prior to the sender determining that the message(s) is / are desired, alone or in conjunction with subsequently canceling or otherwise invalidating the message(s) once it has been determined that it is not desired. The disclosed embodiments mitigate such behavior by detecting and taking action with respect to these types of messages to deter optimizing behavior which may or may not be manipulative, while maintaining reliable message handling under increasing processing loads with minimal impact on users being able to send messages to the system.
Owner:CHICAGO MERCANTILE EXCHANGE
Accelerated occlusion culling using directional discretized occluders and system therefore
InactiveUS6574360B1Increase frame rateFast computerDigital computer detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionViewpointsComputer graphics (images)
An occlusion culling method for image processing and system therefor. The culling method first determines which polygons are hidden, or occluded, by other objects. These hidden or occluded polygons will not contribute to the final scene and, therefore, need not be rendered. In the first major step, the input models are preprocessed to build a hierarchical data structure which is as an approximation to the input models. Simple polygonal occluders are determined for substitution in place of the complex image geometry in successive visibility queries. Once the first preprocessing step is complete, the second step may be executed at run-time, while a user is inspecting, or visualizing, the input. In the second step, the occluders, determined in the first step, are used to selectively forego rendering shapes or shape portions that are unseen from the current viewpoint.
Owner:IBM CORP
Electrosurgical generator and method for simulating output signals
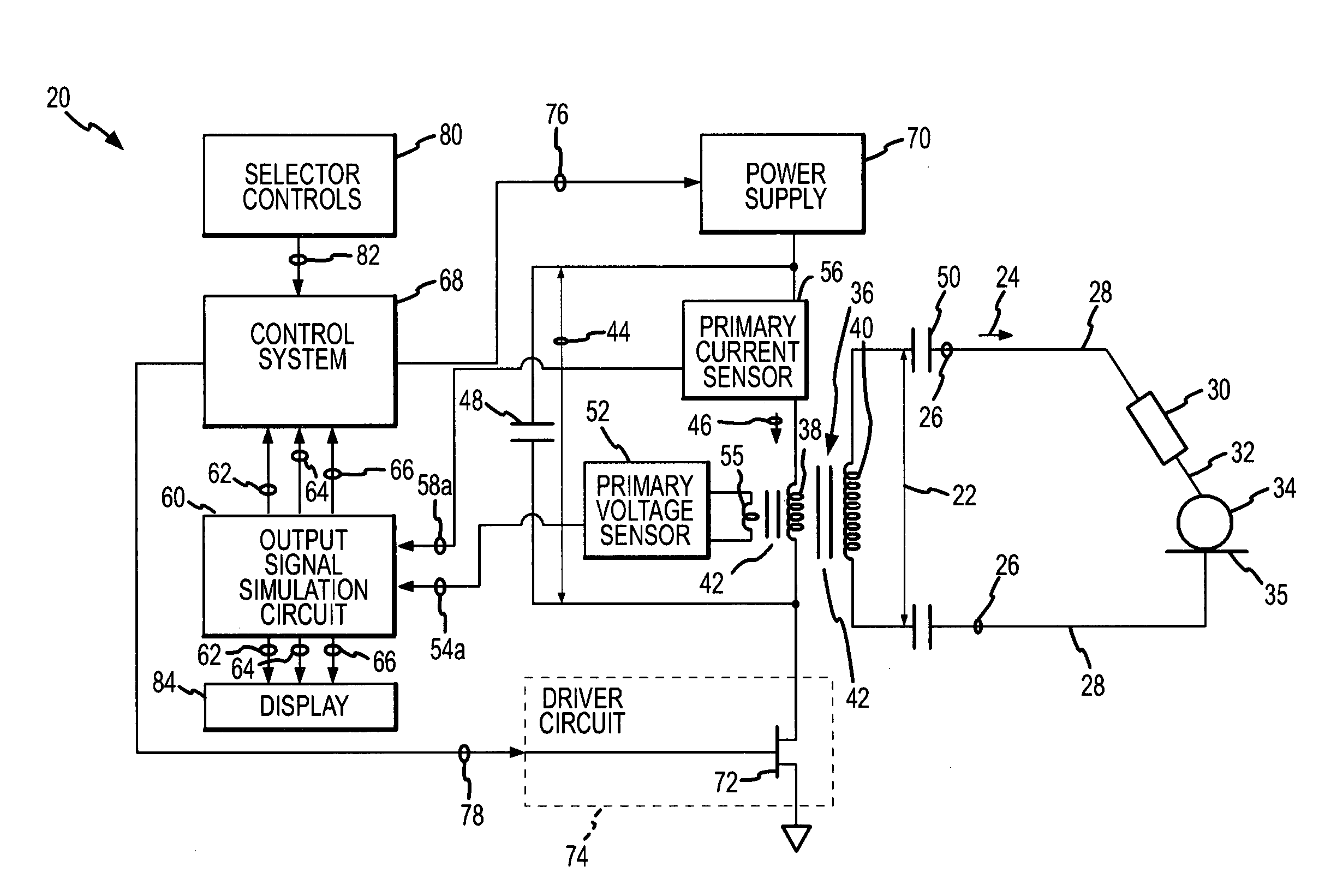
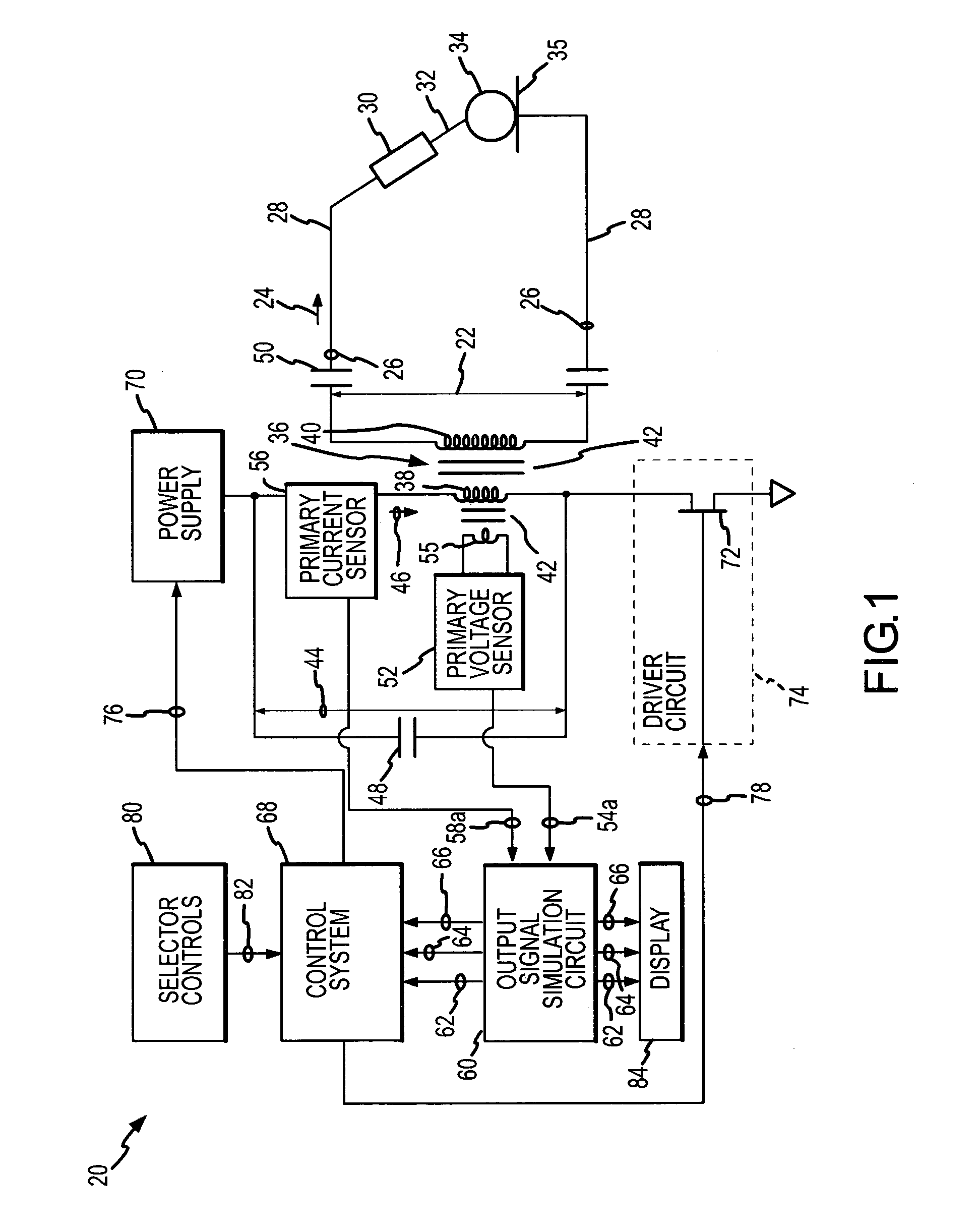
ActiveUS7736358B2Easy to monitorHigh power controlSurgical instruments for heatingPower flowTransformer
Owner:CONMED CORP
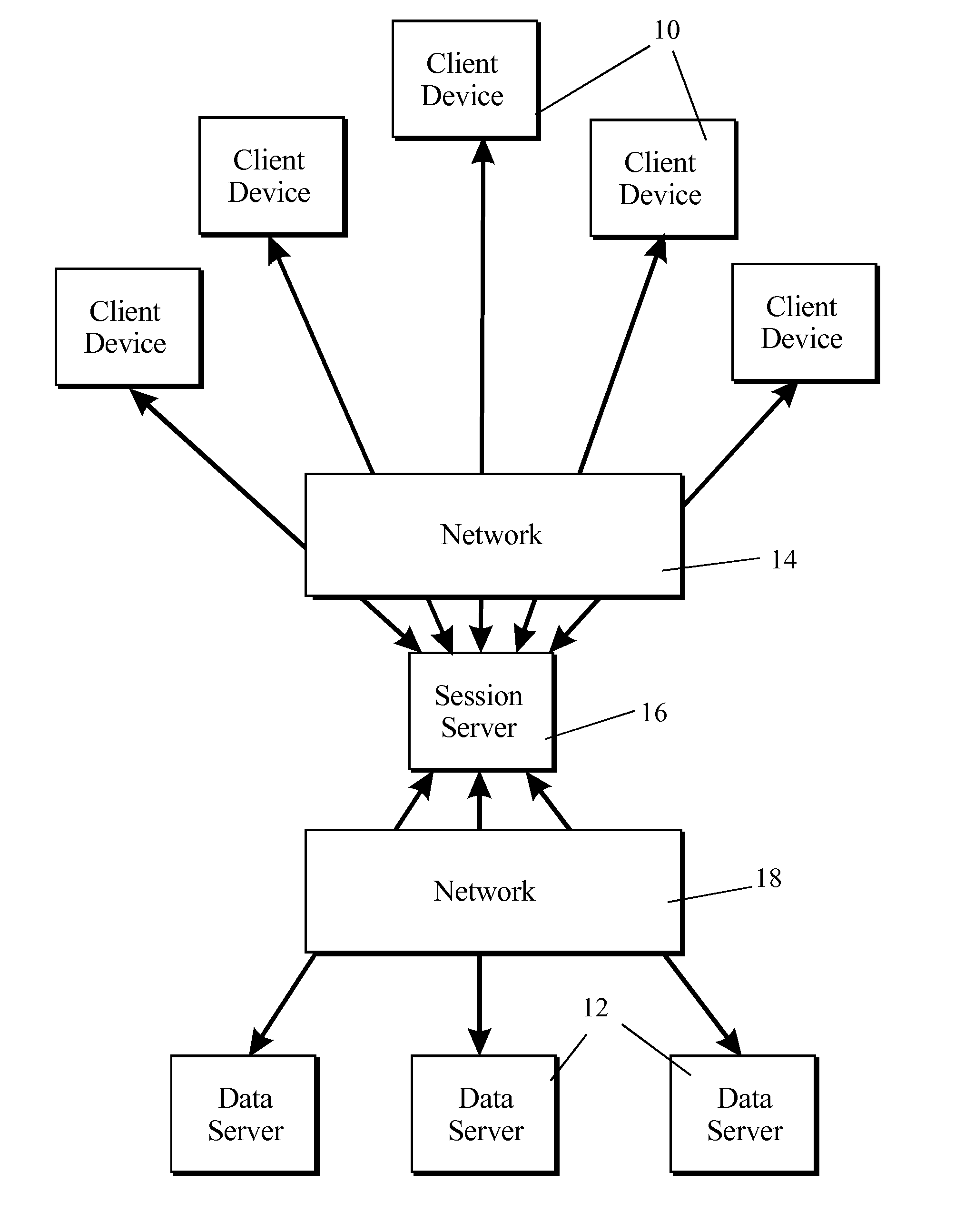
System for viewing and interacting with a virtual 3-d scene
InactiveUS20140108967A1Minimal processing powerGuaranteed uptimeCAD network environmentVideo gamesUser equipmentUser interface
A system is described for enabling one or more user devices to view and interact with a three-dimensional (3-D) scene. The system comprises a data server 12 having a processor executing a program to create a virtual 3-D scene, and a user device 10 communicating remotely with the data server by way of a wired or wireless network. The user device 10 runs a user interface program for transmitting commands to the data server to modify the virtual 3-D scene and for displaying on a user screen an image that includes image data received from the data server as an encoded stream. The data server 12 is operative additionally to transmit commands to the user device for the purpose of altering the user interface.
Owner:MARKHAM STEVEN +1
Spreadsheet to SQL translation
ActiveUS7299223B2Eliminate needEasy to useData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalWeb browserData set
Users can create computational models in a spreadsheet application and automatically apply the model to data stored in a relational database. By importing a sample of the data from a database table into the spreadsheet application, users can build spreadsheet models that perform analysis and computations on the sample data. Once the model is complete, the spreadsheet model is translated into an SQL format model understood by the database. The SQL model can operate on the entire data set in the database, rather than just the sample data used to construct the model. The SQL model and its associated data are stored in the database, and the model can be executed on a different sets of data. A web browser based front-end allows model users to access the SQL model via a web browser, eliminating the need for model users to have a spreadsheet application.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
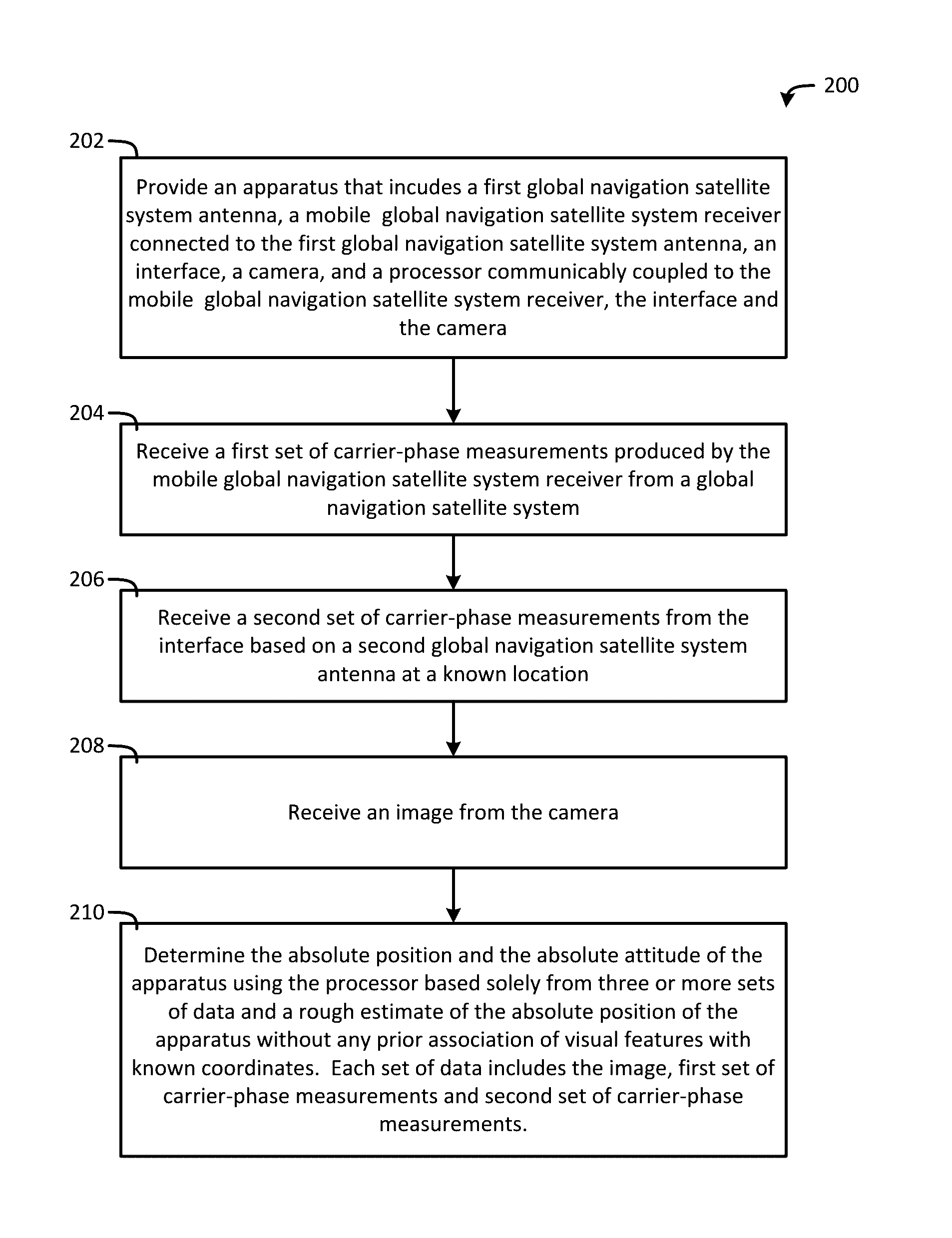
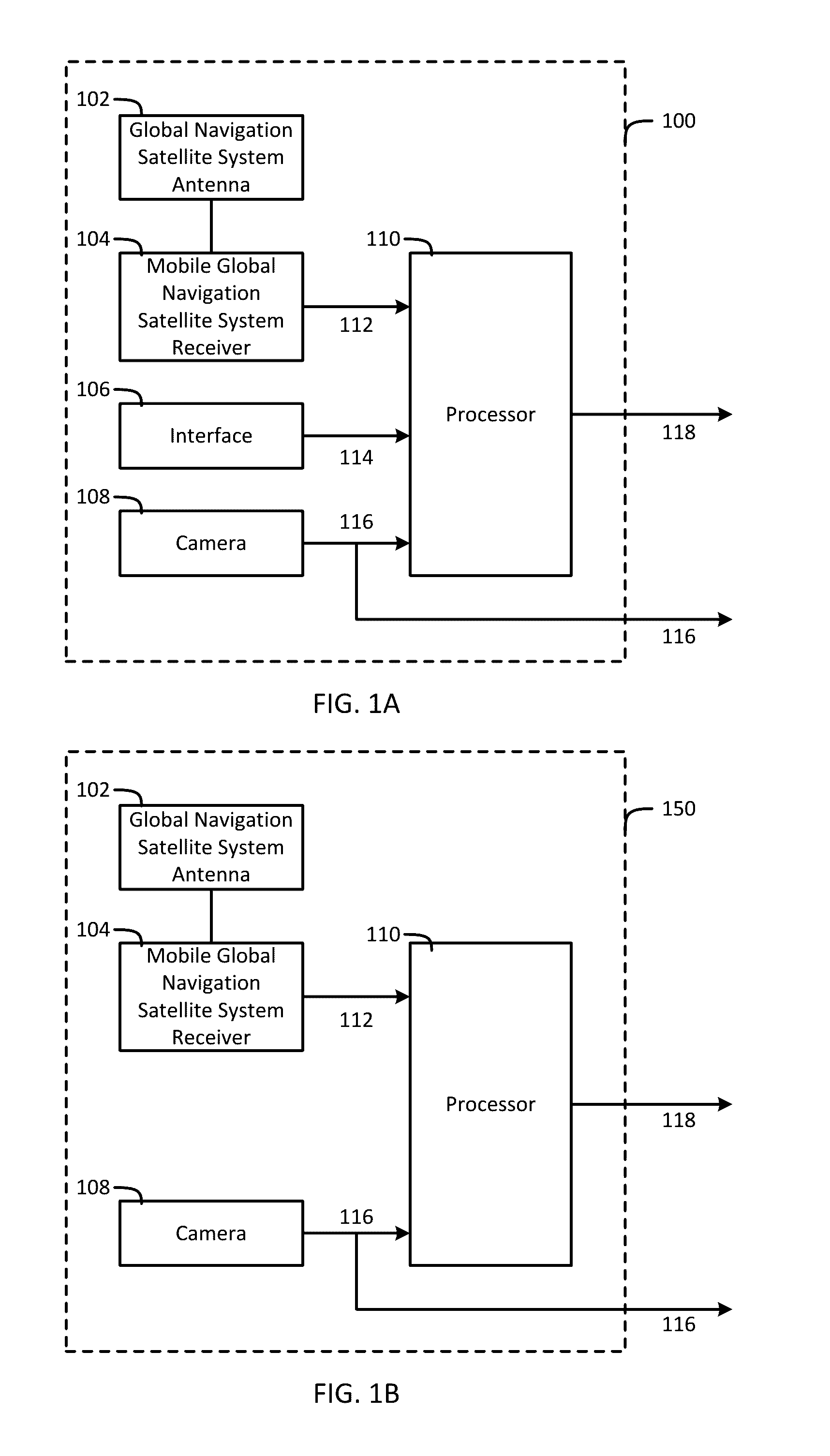
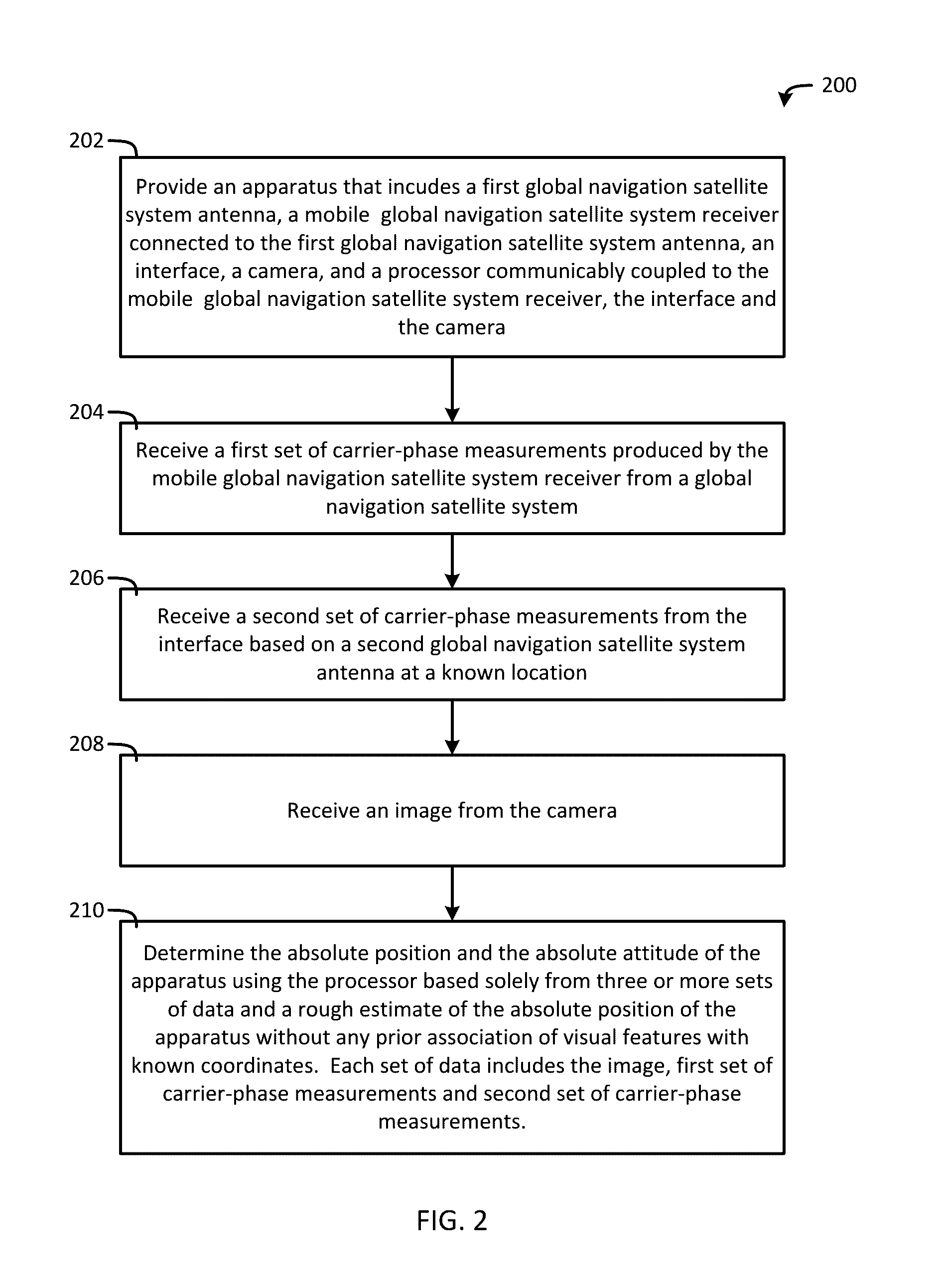
System and method for fusion of camera and global navigation satellite system (GNSS) carrier-phase measurements for globally-referenced mobile device pose determination
InactiveUS20160327653A1Quick fixFaster and robust and accuratePosition fixationSatellite radio beaconingNatural satelliteComputer vision
An apparatus including a global navigation satellite system (GNSS) antenna, a mobile GNSS receiver connected to the GNSS antenna, a camera operable to produce an image, and a processor communicably coupled to the mobile GNSS receiver and the camera. The mobile GNSS receiver is operable to produce a set of carrier-phase measurements from a GNSS. The processor is operable to receive the image and the set of carrier-phase measurements, extract point feature measurements from the image, model the point feature measurements based on the image to produce a point feature model, model the set of carrier-phase measurements to produce a carrier-phase model, execute a cost function including the point feature measurements, the carrier-phase measurements, the point feature model, and the carrier-phase model, and determine a state associated with the apparatus based on the executed cost function.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com