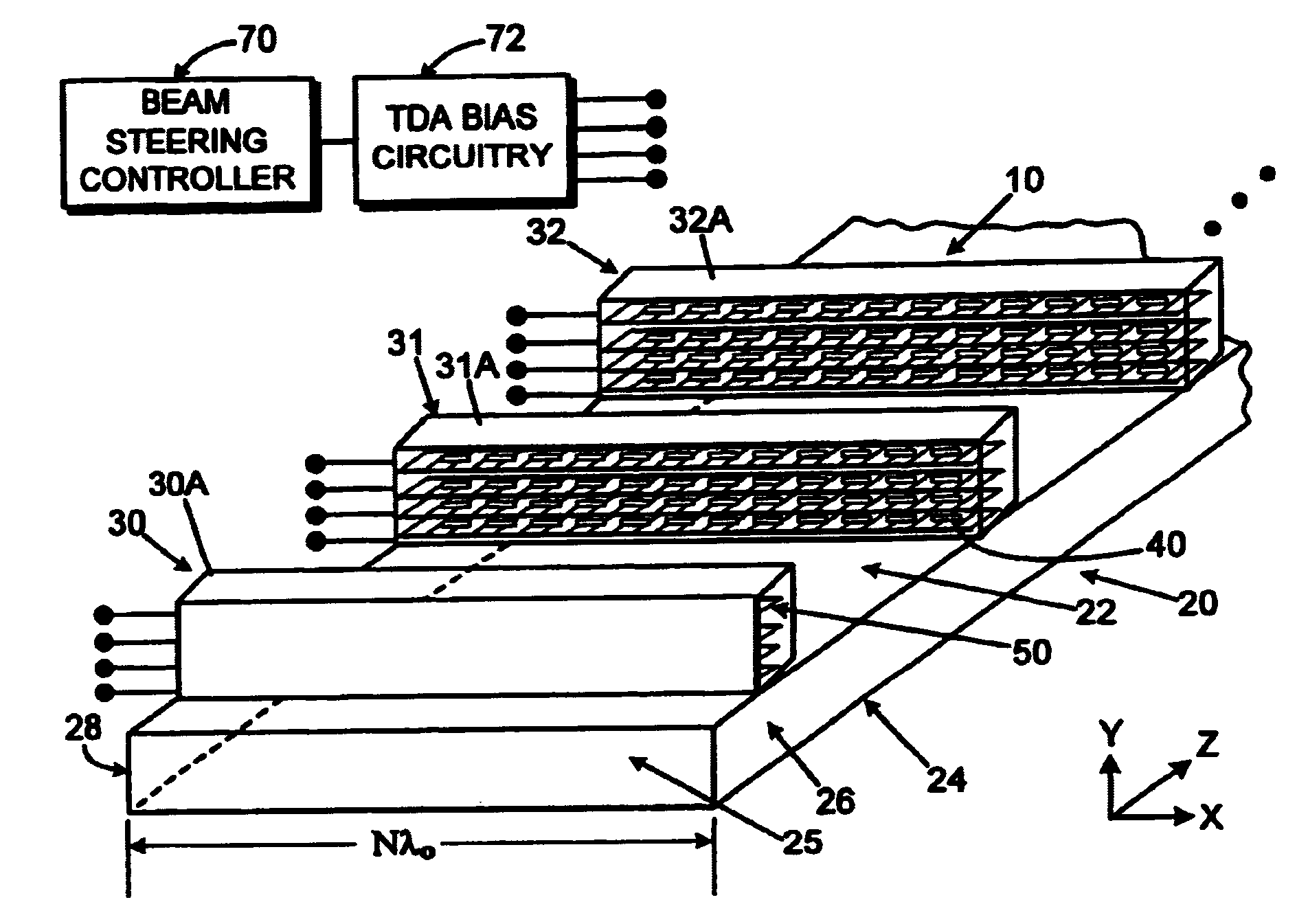
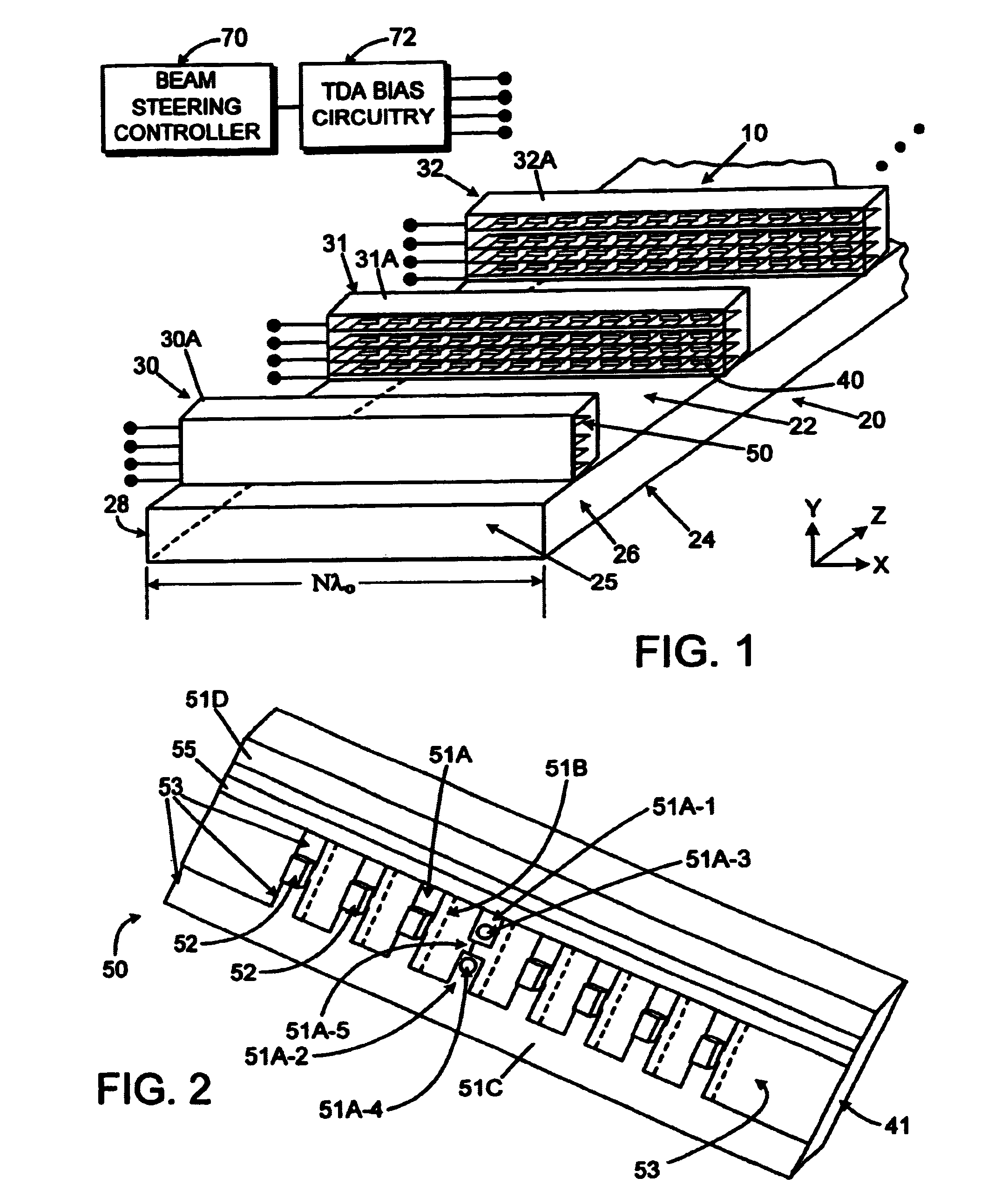
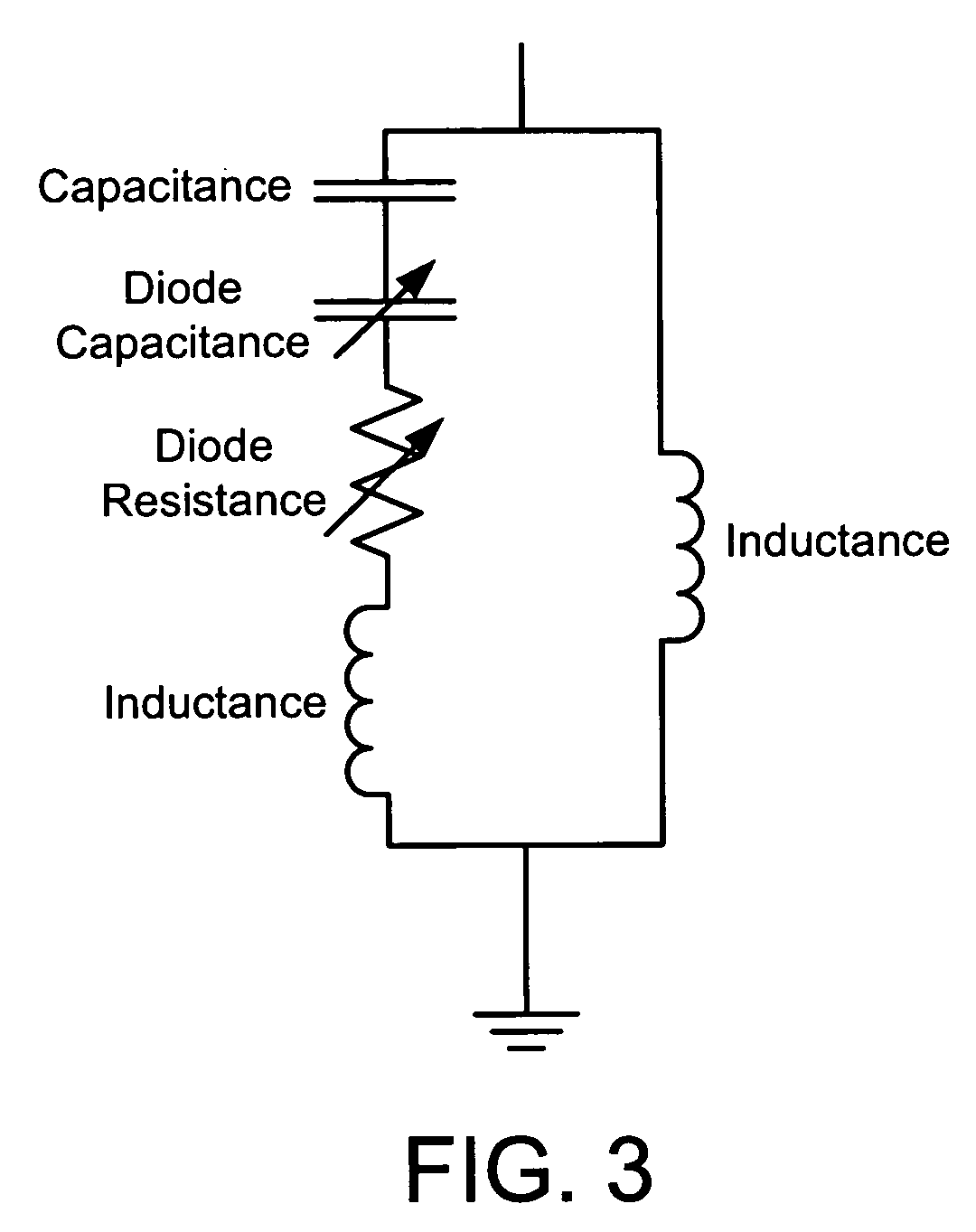
Patents
Literature
8742 results about "Antenna array" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An antenna array is a set of individual antennas used for transmitting and/or receiving radio waves, connected together in such a way that their individual currents are in a specified amplitude and phase relationship. This allows the array to act as a single antenna, generally with improved directional characteristics than would be obtained from the individual elements. The resulting array in fact is often referred to and treated as "an antenna," particularly when the elements are in rigid arrangement with respect to each other, and when the ratio of currents are fixed. On the other hand, a steerable array may be fixed physically but has electronic control over the relationship between those currents, allowing for adjustment of the antenna's directionality without requiring physical motion. The array uses electromagnetic wave interference to enhance the radiative signal in one desired direction at the expense of other directions. It may also be used to null the radiation pattern in one particular direction, especially for a receiving antenna in the face of a particular interfering source.
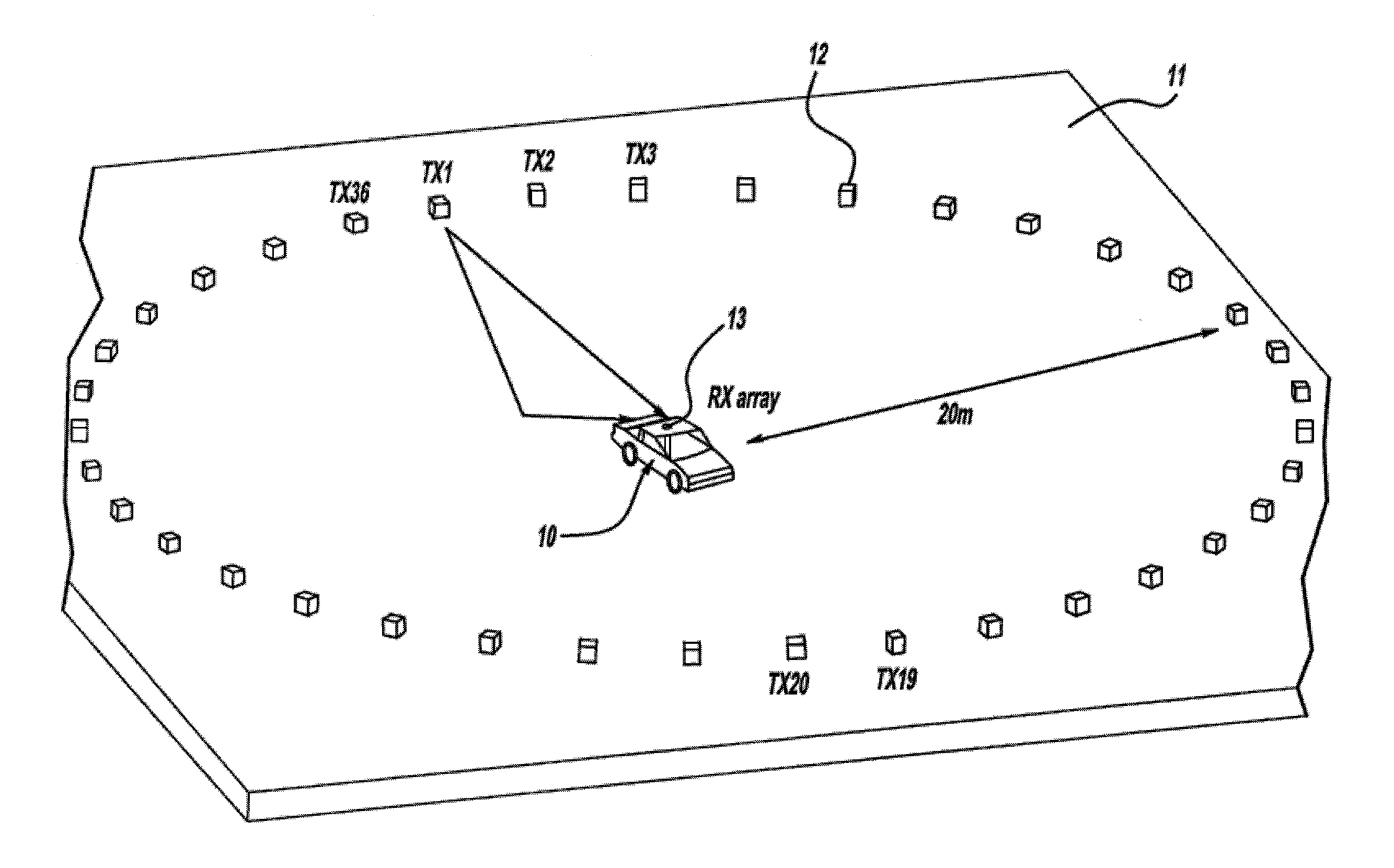
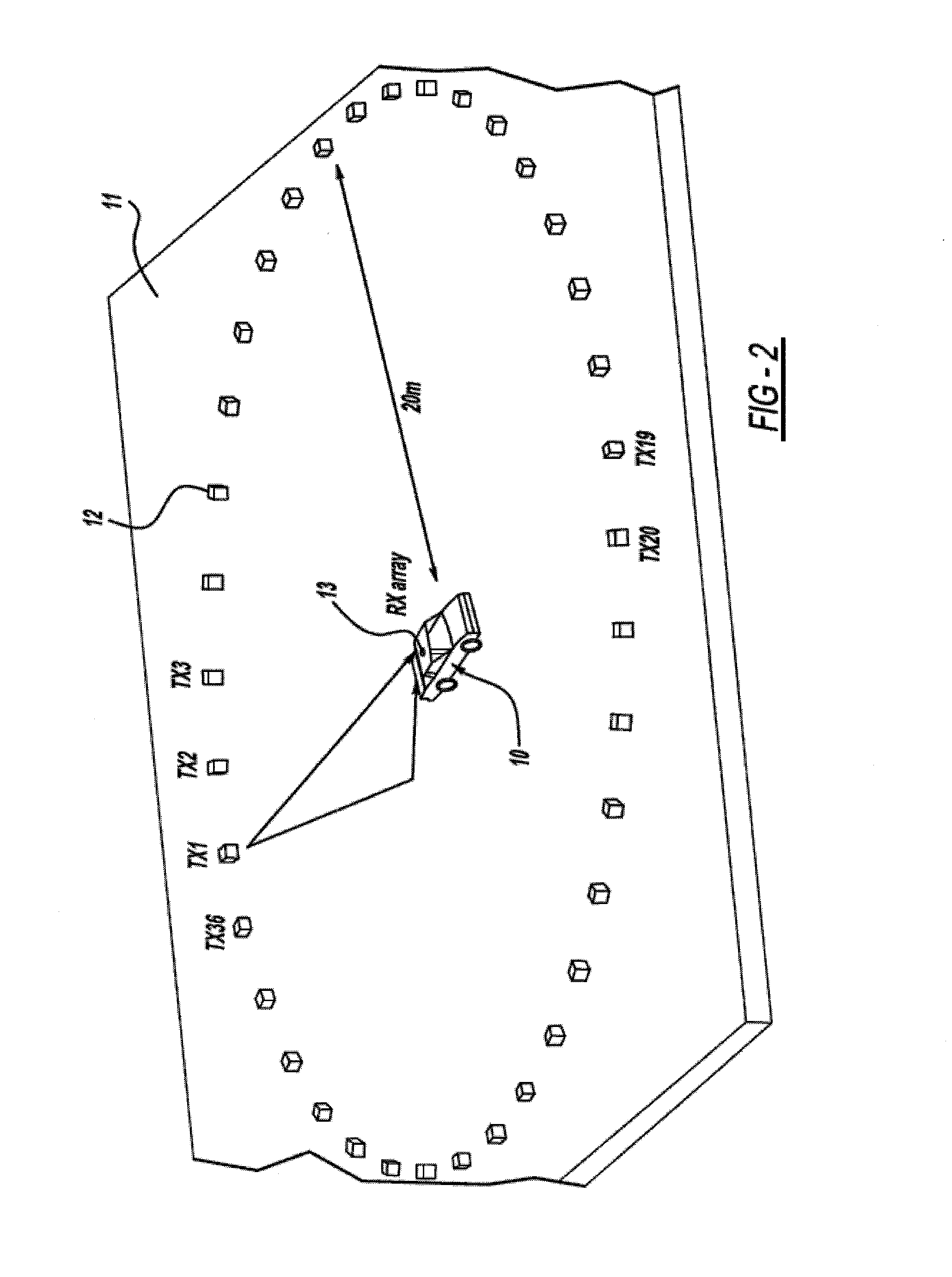
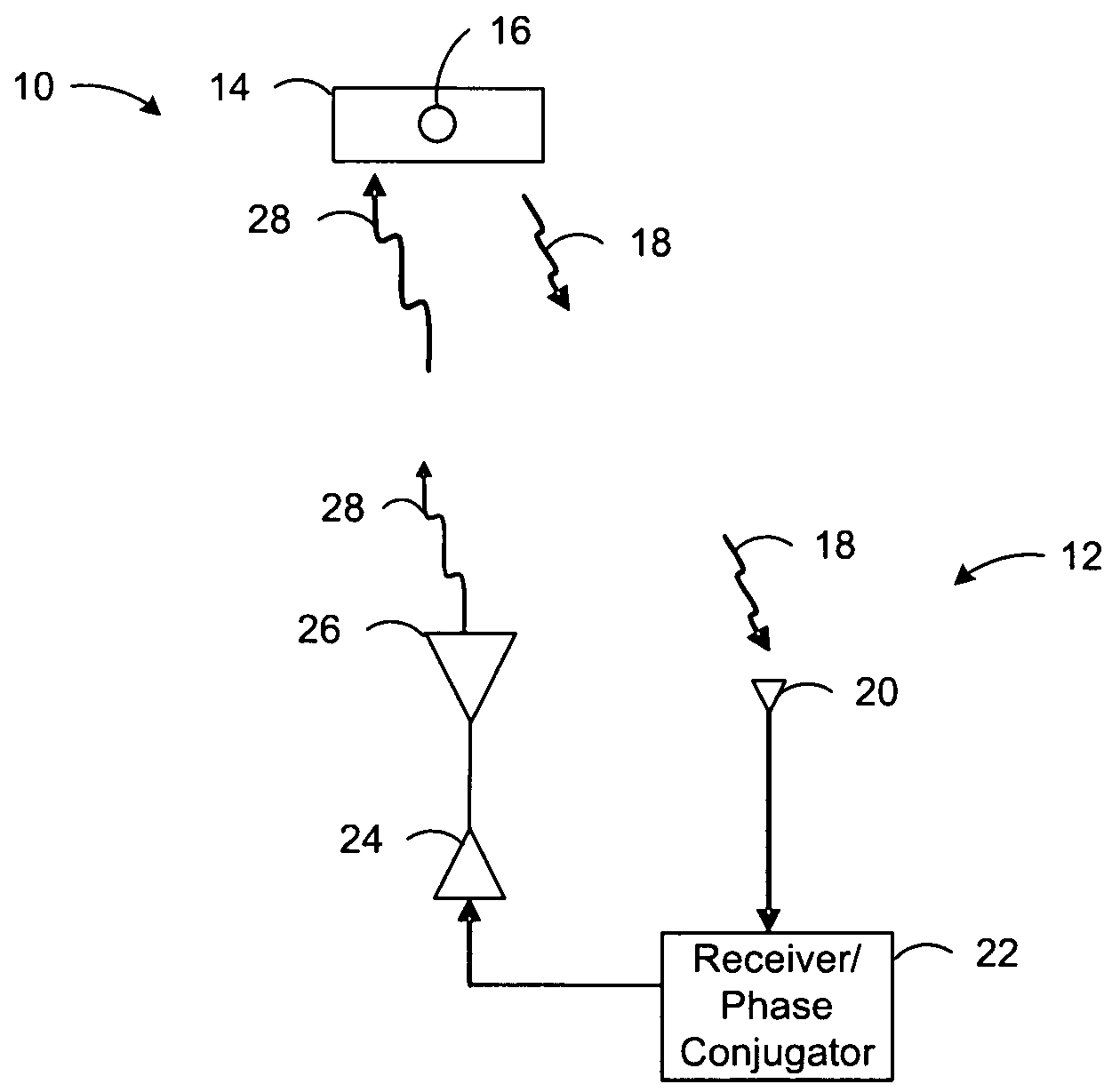
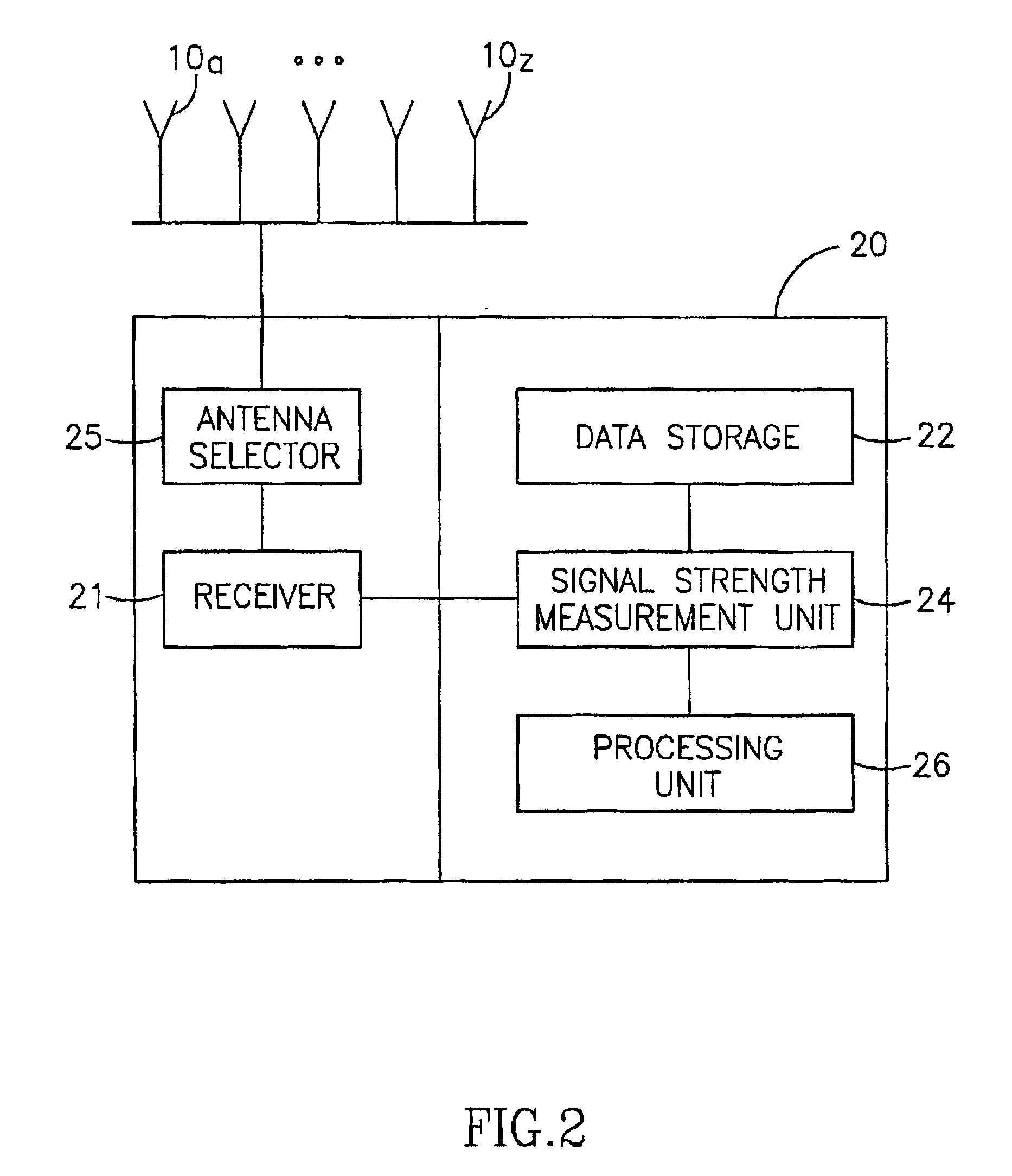
Automotive direction finding system based on received power levels
InactiveUS20110148578A1Road vehicles traffic controlElectric/electromagnetic visible signallingDigital dataMicrocontroller
A system is provided for locating a vehicle. The system comprises a transmission device such as a key fob for transmission and receiving of a signal. Typically the key fob has a plurality of indicators such as LED indicators arranged in a circle. The key fob is adapted to transmit a radio frequency or microwave frequency transmission signal. An antenna array is positioned on or in a vehicle. The array comprises a plurality of antennas, generally arranged in a circular pattern. The array is adapted to receive the transmission signal from the transmission device which is converted to be analyzed by a microcontroller unit (MCU). The MCU is adapted to: (i) receive digital data converted from the transmission signal, (ii) calculate an angle of arrival (AOA) or direction of arrival (DOA) based on known components and an algorithm, and (iii) transmit a selection signal back to the key fob. A signal processing unit is coupled to the plurality of antennas and the MCU. The signal processing unit is adapted to receive the signal transmission from each antenna, convert the signal to digital data, and transmit the digital data to the MCU.
Owner:OAKLAND UNIVESITY
Wireless power transmission system and method
ActiveUS20100259447A1Minimal energyOvercomes drawbackElectromagnetic wave systemCircuit arrangementsElectric power transmissionEngineering
A wireless power transmission system including at least one source of electromagnetic radiation, a plurality of wireless power receivers that receive radiated electromagnetic energy, a beacon collocated with each wireless power receiver, wherein the beacon generates and radiates a pilot signal when the beacon is in an active state, and an array of transmitting antennas connected to the source of electromagnetic radiation that radiates the electromagnetic radiation in the direction of the beacon in the active state. The electromagnetic radiation can be electronically steered from one wireless power receiver to another by activating and deactivating the beacons collocated with each wireless power receiver.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
System and method for powering vehicle using radio frequency signals and feedback
ActiveUS20100044123A1Improve power efficiencyCharging stationsElectromagnetic wave systemChannel state informationRadio frequency signal
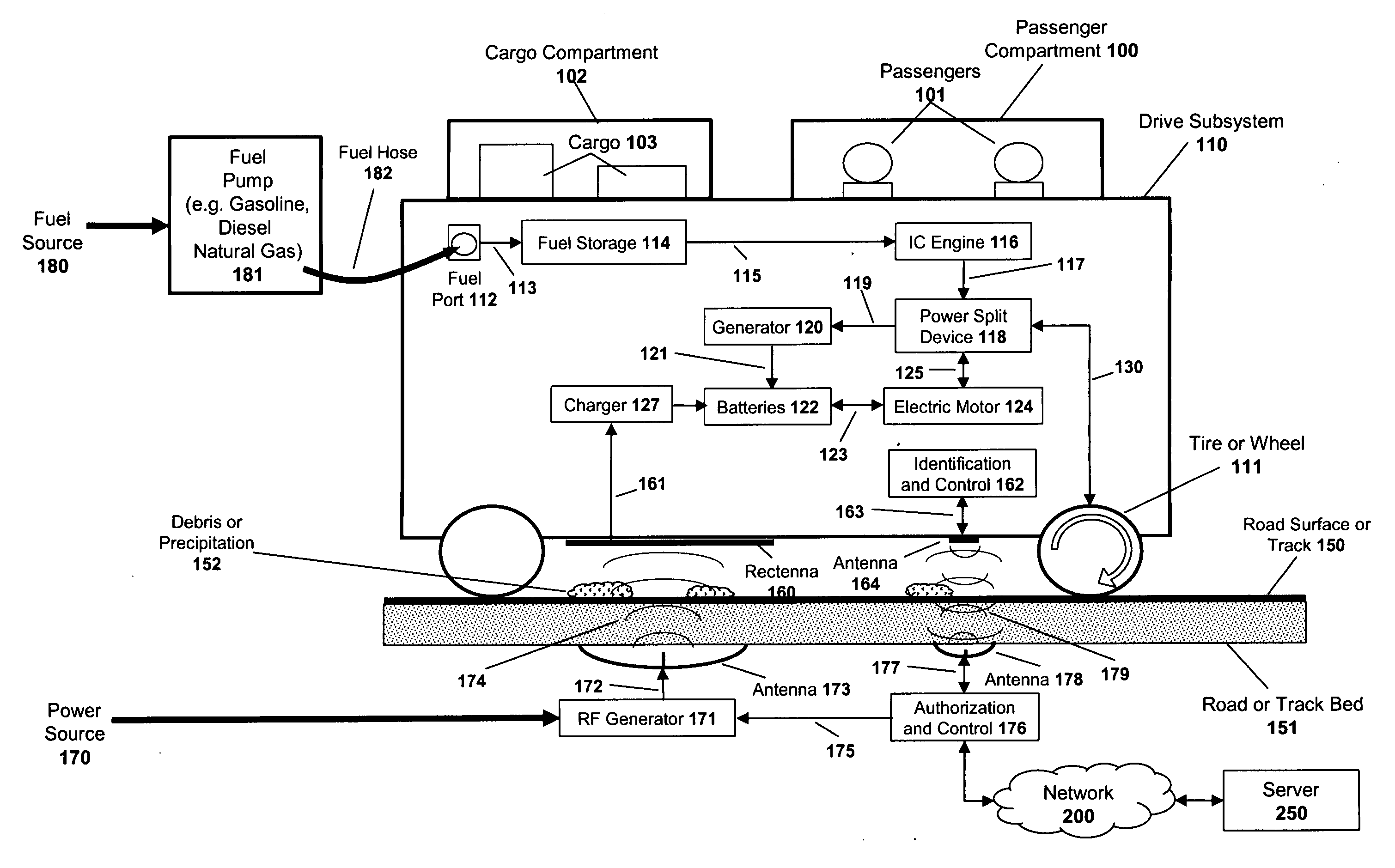
A system and method are described for powering a vehicle using radio frequency (“RF”) signals. For example, a method according to one embodiment of the invention comprises: positioning an antenna array beneath or on the road surface of a roadway, the antenna array configured to transmit RF signals responsive to RF processing logic and / or circuitry; coupling a rectenna array to a vehicle, the rectenna array configured to receive the RF signals transmitted from the antenna array and to generate power from the RF signals; providing feedback signals from the vehicle to the RF processing logic and / or circuitry, the feedback signals including channel state information (CSI) defining a current state of the channels between the antenna array and the rectenna array, the RF processing logic and / or circuitry using the channel state information to adjust the RF signal transmissions from the antenna array to improve the efficiency of the power generated by the rectenna array; and using the power generated by the rectenna array to power the vehicle.
Owner:REARDEN
Apparatus and method for spatial division duplex (SDD) for millimeter wave communication system
ActiveUS20110243040A1Antenna arraysFrequency-division multiplex detailsMillimeter wave communication systemsMobile communication systems
An apparatus and method for full-duplex millimeter wave mobile wireless communication are provided. The apparatus includes a Spatial Division Duple (SDD) mobile communication system using millimeter waves, the SDD mobile communication system including a first wireless terminal having a first transmit antenna array having a plurality of first transmit antennas for transmitting a spatially beamformed first transmit beam, and a first receive antenna array having a plurality of first receive antennas for forming a spatially beamformed first receive beam and a second wireless terminal including a second transmit antenna array having a plurality of second transmit antennas for transmitting a spatially beamformed second transmit beam directed towards a receive beam of the first wireless terminal, and a second receive antenna array having a plurality of second receive antennas for forming a spatially beamformed second receive beam directed toward the transmit beam of the first terminal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Wireless transmission using an adaptive transmit antenna array
ActiveUS20050117660A1Spatial transmit diversityBroadcast transmission systemsWireless transmissionClosed loop
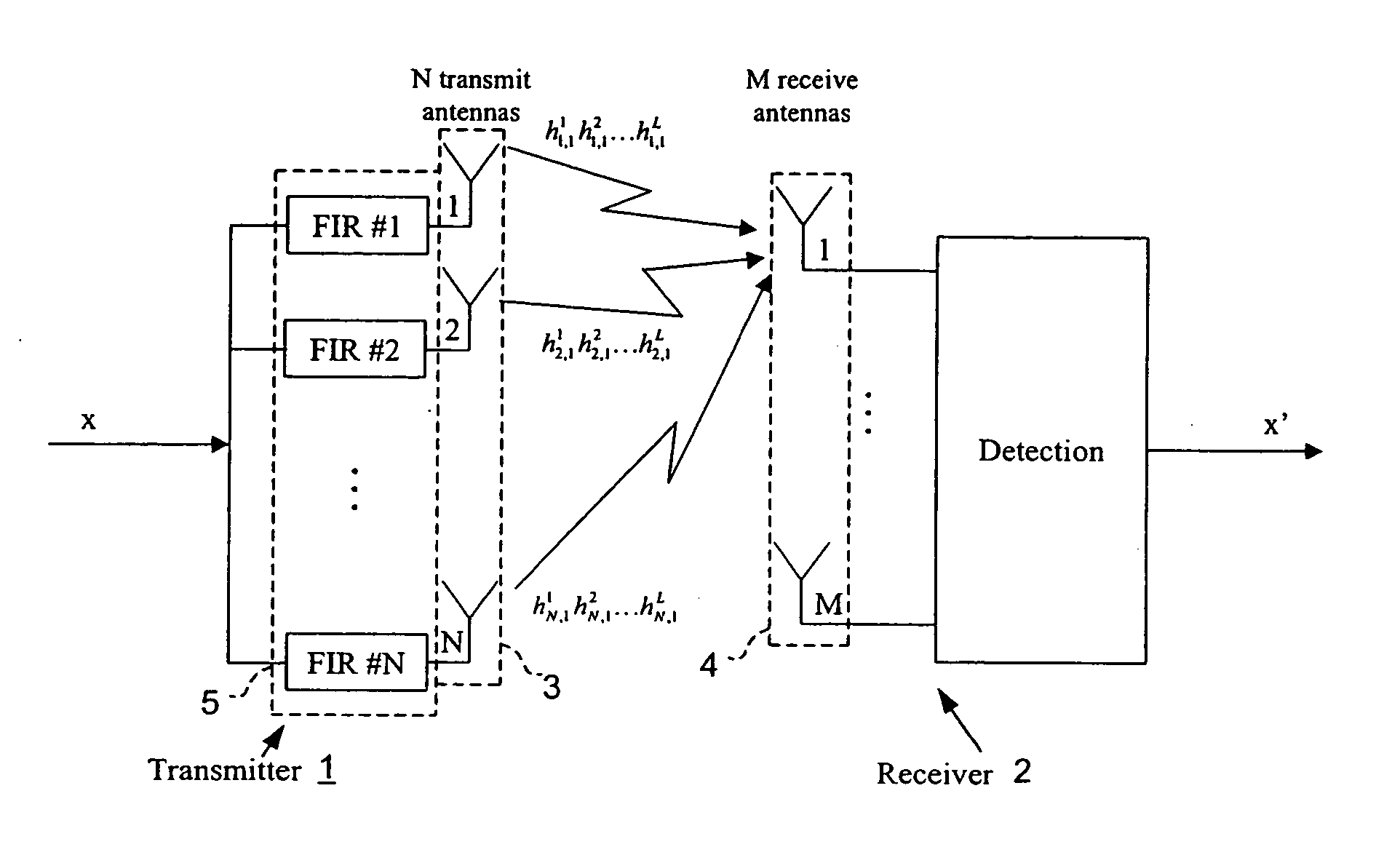
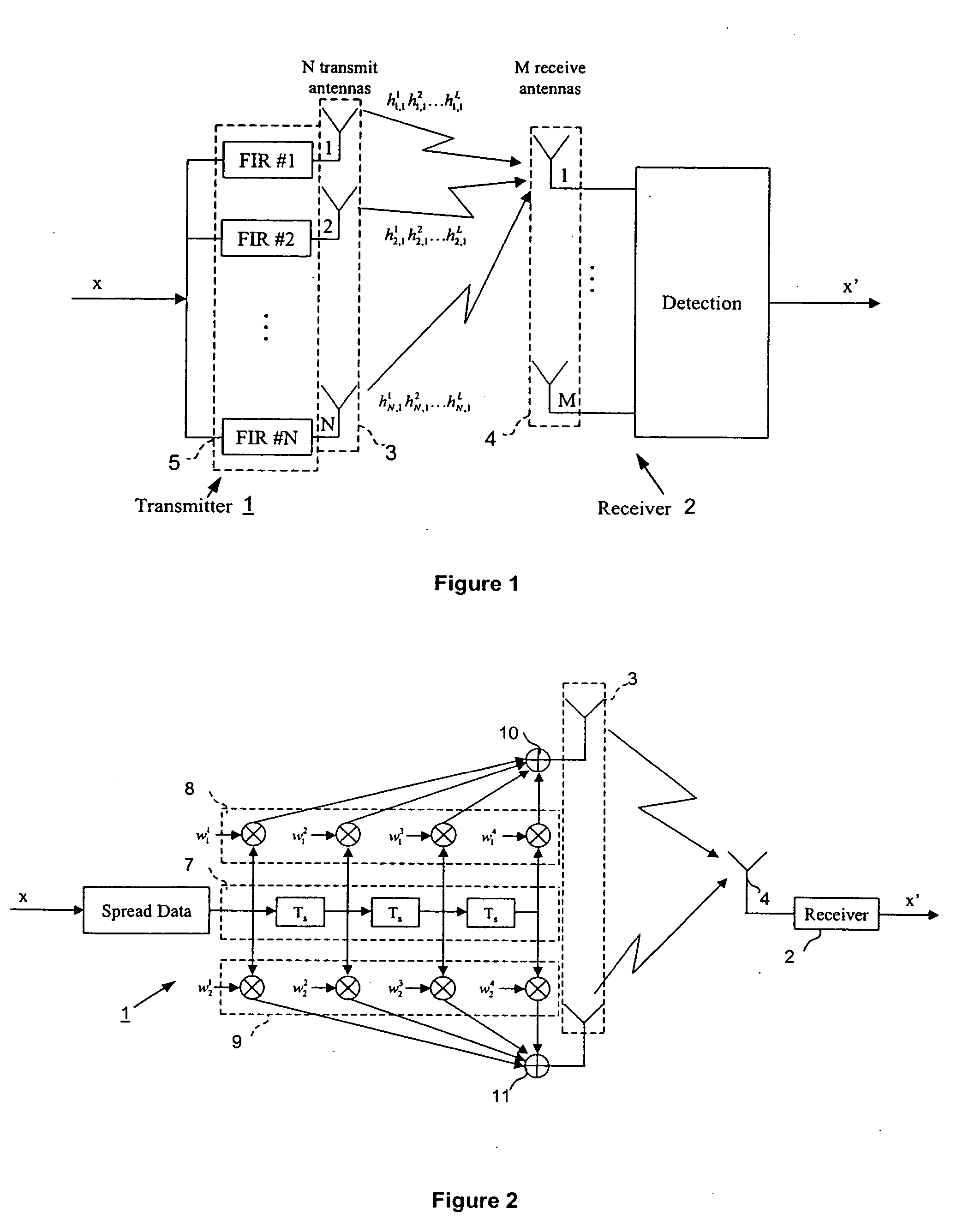
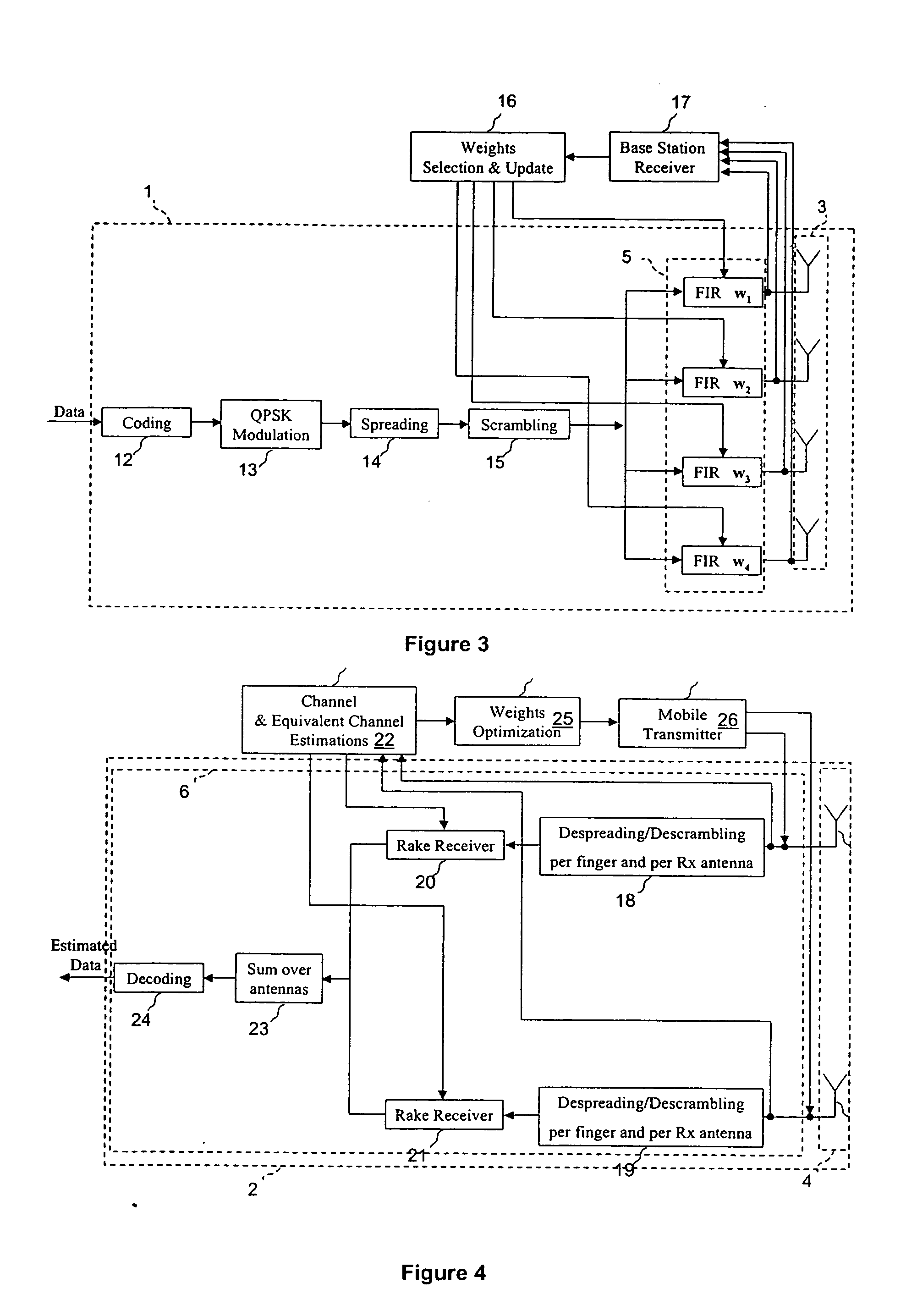
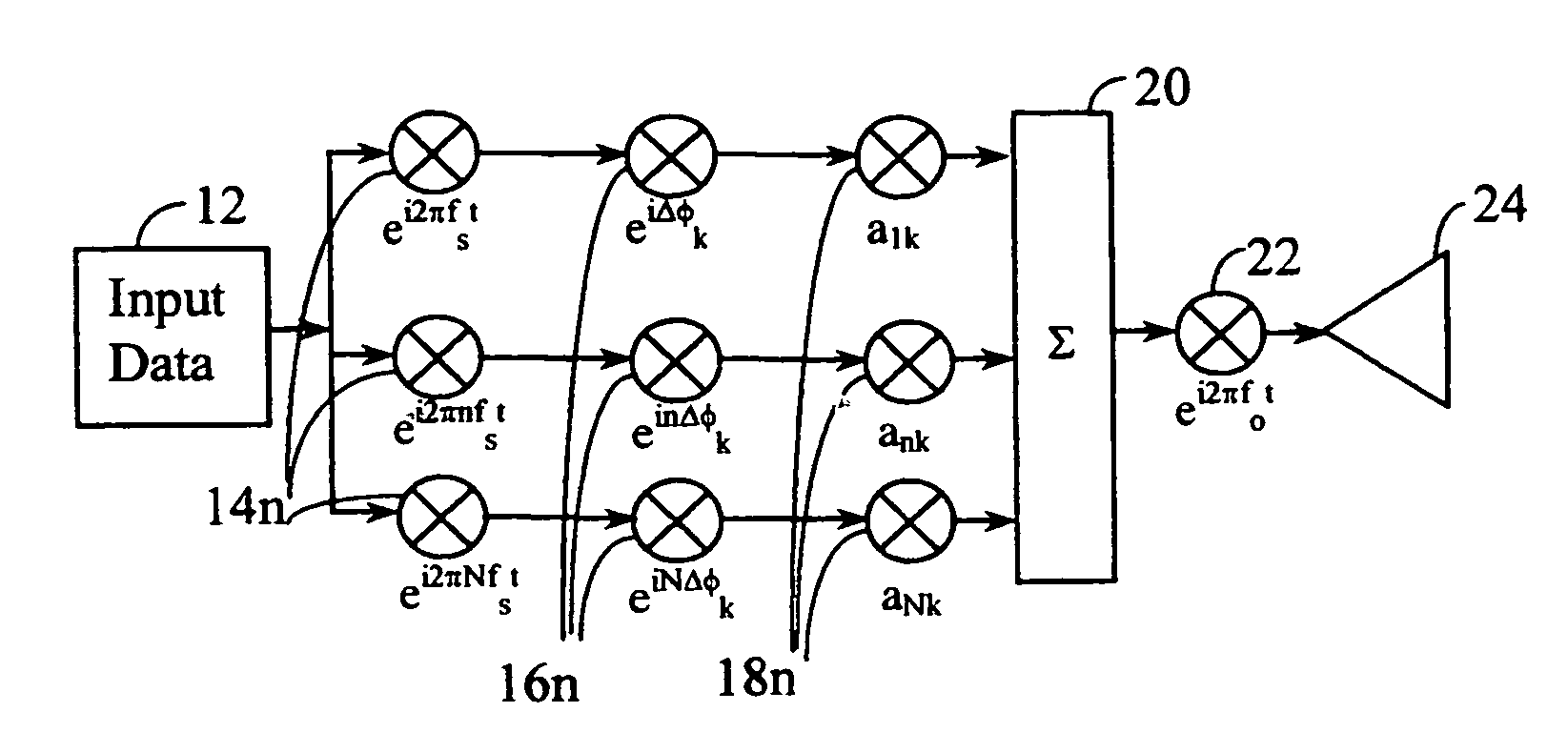
Closed loop wireless communication of signals using an adaptive transmit antenna array (3), in which a plurality of copies of signals to be transmitted by the transmit antenna array (3) are produced with delays and weights (wnj) that are functions of the multi-path transmission channel characteristics (H) from the transmit antenna array (3) to a receive antenna array (4) of a receiver (2) and are combined before transmission by the transmit antenna array. The delays and weights (wnj) of the transmit copies for each transmit antenna element are functions of the respective multi-path transmission channel characteristics (hn,m=1l=1,… ,hn,m=Ml=L)from that transmit antenna element to the receive antenna array (4) ssuch that the multi-path signal components propagated to each receiver element are received with distinguishable delays according to the propagation path. The receiver (2) combines the received signal components from each receive antenna element with delays and weights (u) that are respective functions of the multi-path transmission channels. Preferably, the receiver comprises a multi-finger RAKE receiver (6) that copies the received signals from the receive antenna array with delays and weights (u) that are respective functions of the multi-path transmission channels and combines the copied received signals.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Multiple access method and system
InactiveUS7010048B1Reduce decreaseLower Level RequirementsFrequency diversityWavelength-division multiplex systemsFiberPulse envelope
A wireless communication system transmits data on multiple carriers simultaneously to provide frequency diversity. Carrier interference causes a narrow pulse in the time domain when the relative phases of the multiple carriers are zero. Selection of the frequency separation and phases of the carriers controls the timing of the pulses. Both time division of the pulses and frequency division of the carriers achieves multiple access. Carrier interferometry is a basis from which other communication protocols can be derived. Frequency hopping and frequency shifting of the carriers does not change the pulse envelope if the relative frequency separation and phases between the carriers are preserved. Direct sequence CDMA signals are generated in the time domain by a predetermined selection of carrier amplitudes. Each pulse can be sampled in different phase spaces at different times. This enables communication in phase spaces that are not detectable by conventional receivers. The time-dependent phase relationship of the carriers provides automatic scanning of a beam pattern transmitted by an antenna array. In waveguide communications, the carrier frequencies and phase space may be matched to the chromatic dispersion of an optical fiber to increase the capacity of the fiber.
Owner:DEPARTMENT 13 INC
Array system and method for locating an in vivo signal source
A system and method for localizing an in vivo signal source using a wearable antenna array having at least two antenna elements. The signal is received and a signal strength is measured at two or more antenna elements. An estimated coordinate set is derived from the signal strength measurements.
Owner:GIVEN IMAGING LTD
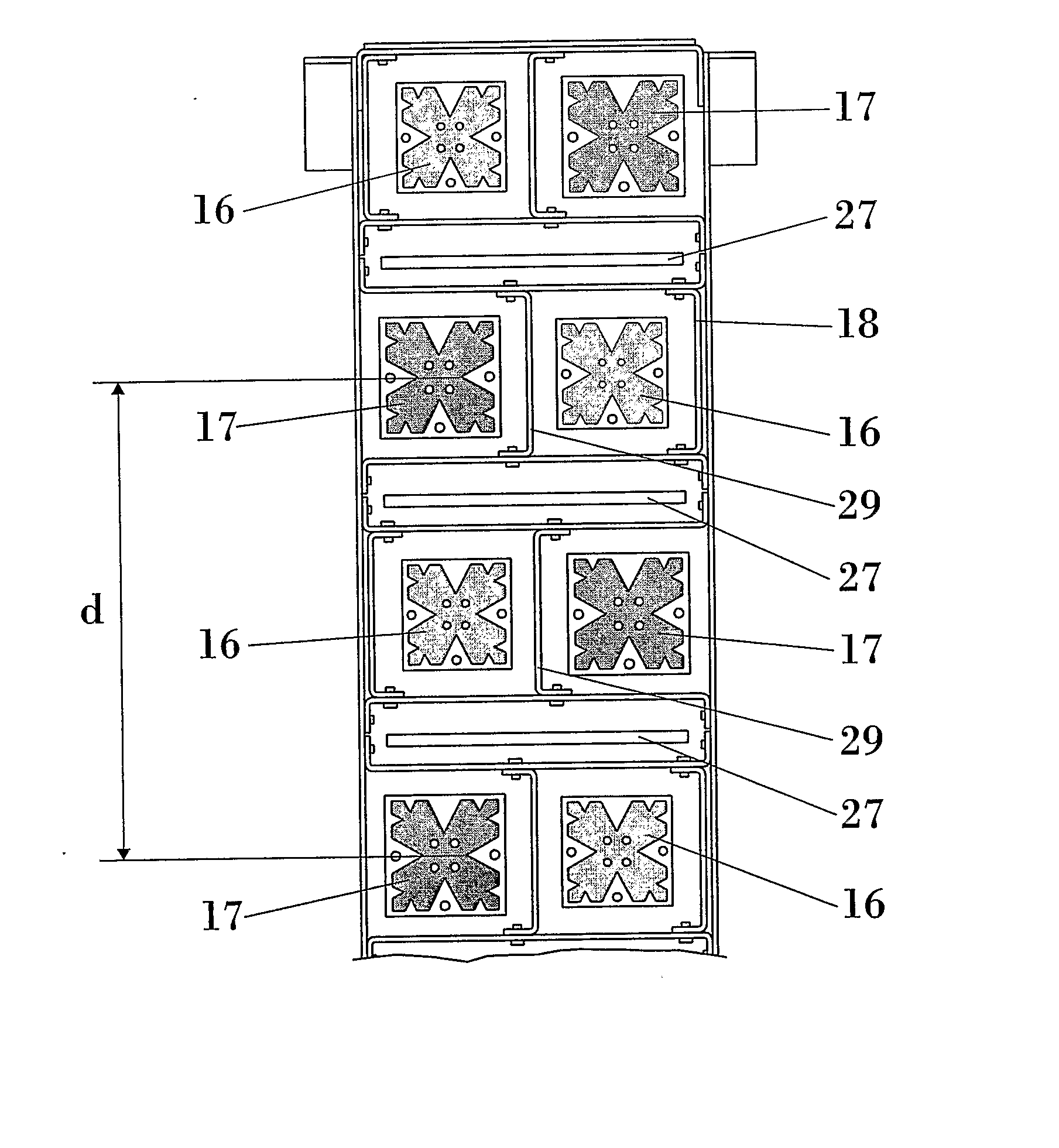
Slim Multi-Band Antenna Array For Cellular Base Stations
InactiveUS20080062062A1Reduce widthMinimizes overall network impactSimultaneous aerial operationsIndividually energised antenna arraysMulti bandEngineering
This invention is in the field of base station antennas for wireless communications. The present invention refers to a slim multi-band antenna array for cellular base stations, which provides a reduced width of the base station antenna and minimizes the environmental and visual impact of a network of cellular base station antennas, in particular in mobile telephony and wireless service networks. A multiband antenna array comprises a first set of radiating elements operating at a first frequency band and a second set of radiating elements operating at a second frequency band, said radiating elements being smaller than λ / 2 or smaller than λ / 3, being (λ) the longest operating wavelength. The ratio between the largest and the smaller of said frequency bands is smaller than 2.
Owner:COMMSCOPE TECH LLC
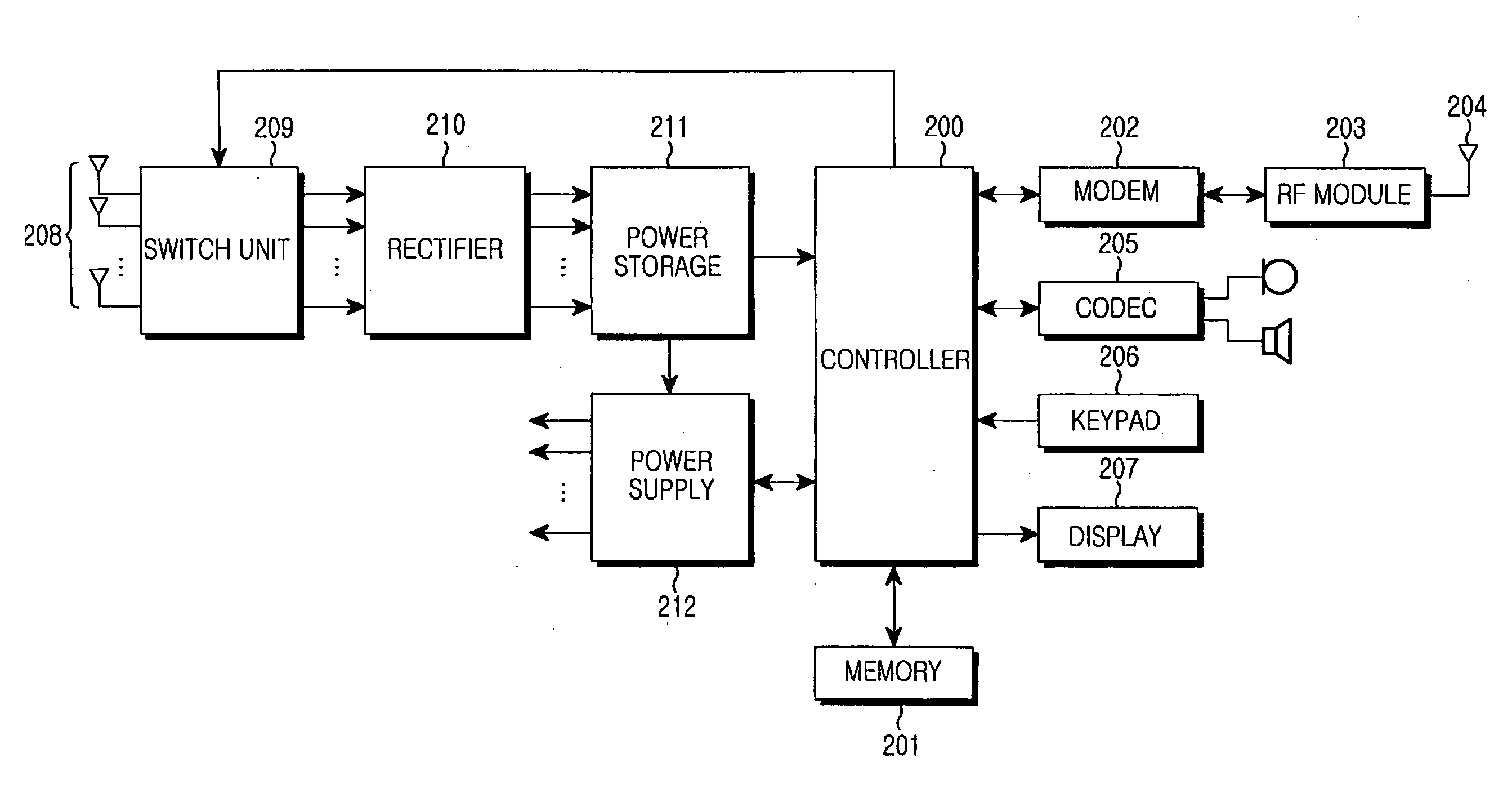
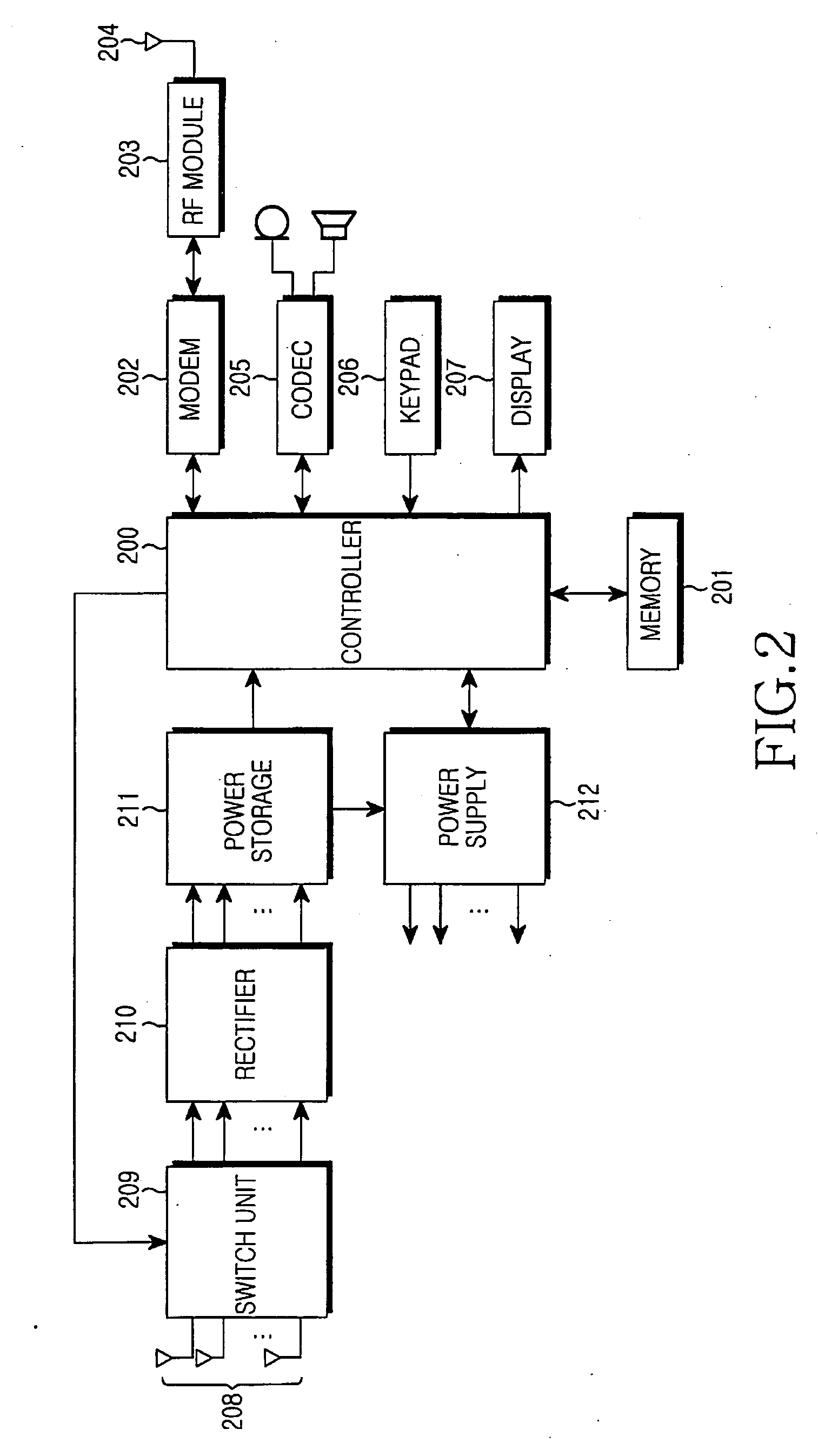
Apparatus and method for using ambient RF power in a portable terminal
An apparatus and method for using ambient RF power in a portable terminal are provided. In the charging apparatus, an antenna array receives RF signals left derelict in the air, a rectifier rectifies the RF signals to DC voltages, and a power storage stores the DC voltages as power.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
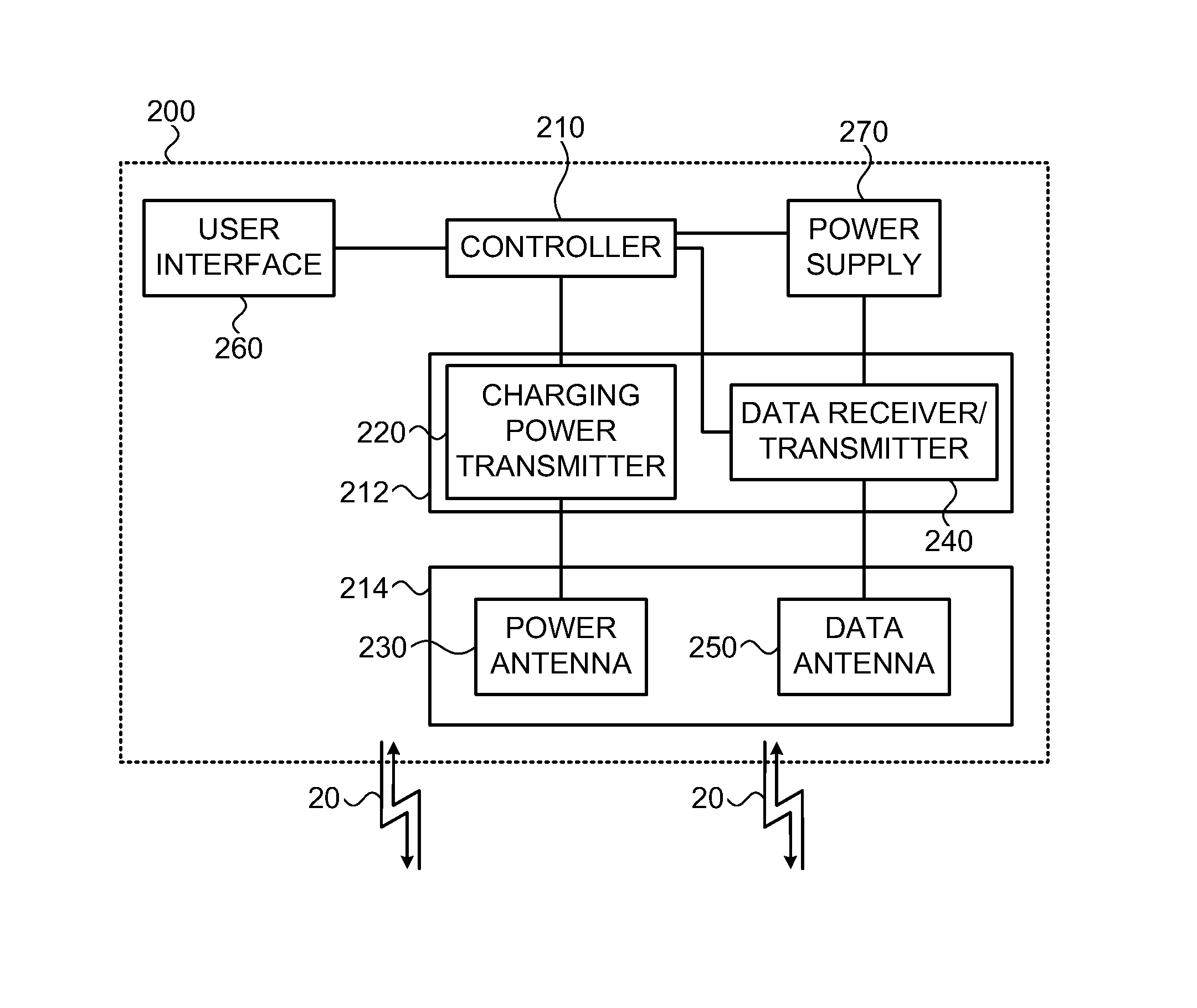
Remote charging system
ActiveUS20140375261A1Effective remote chargingIndicating/monitoring circuitsElectric powerDirectional antennaEngineering
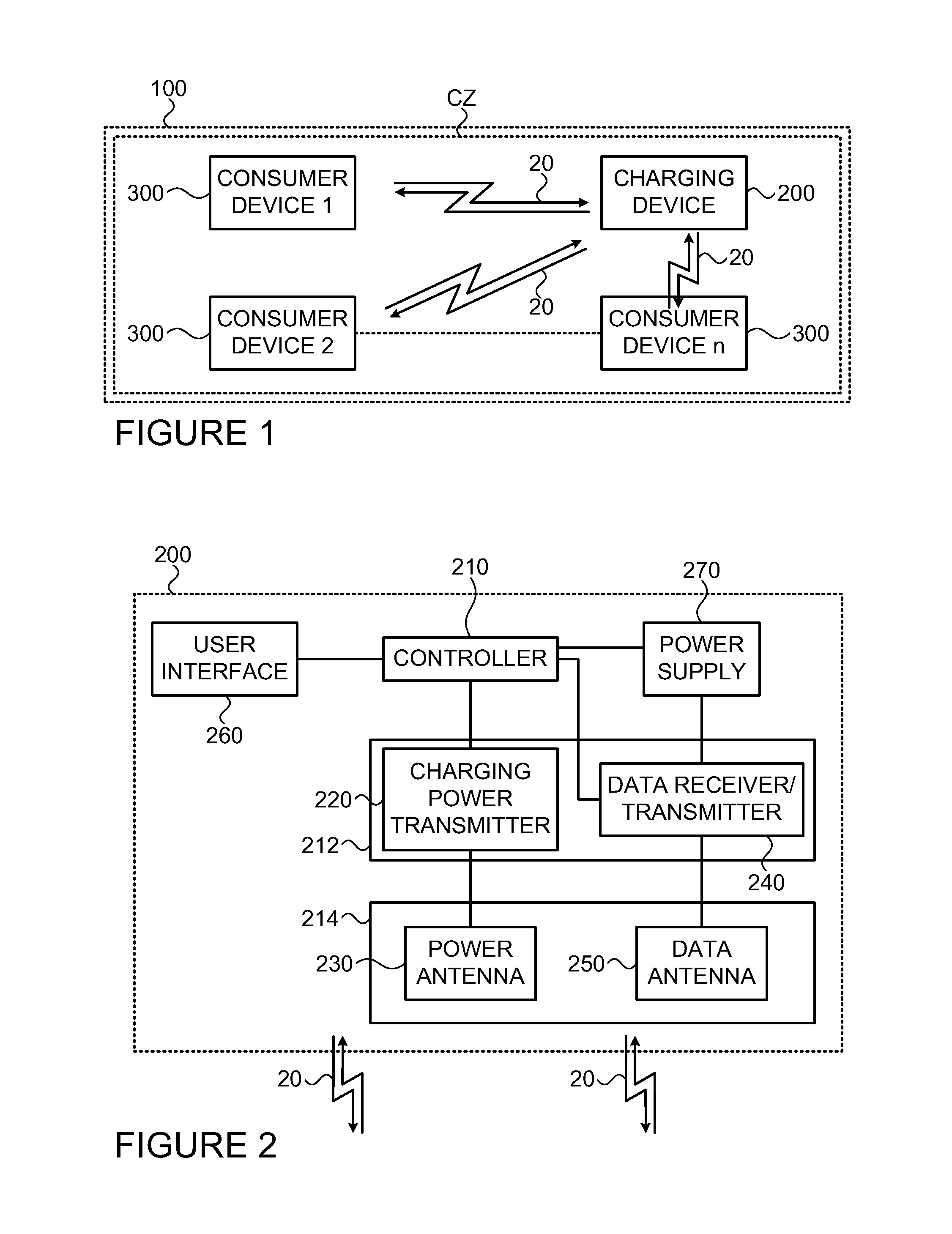
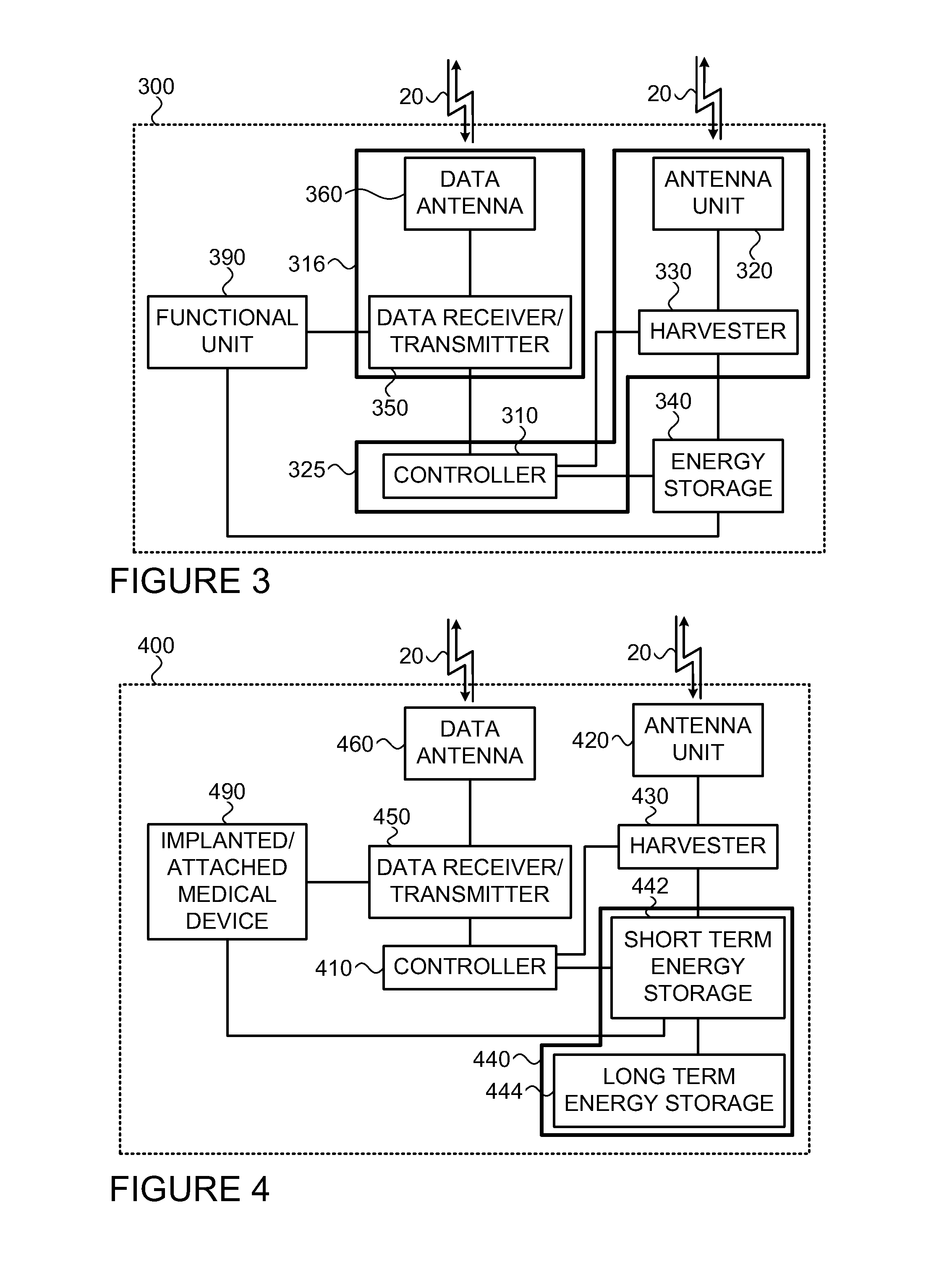
A charging device (200) is provided for communicating with one or more consumer devices (300) for remotely charging at least one of them upon demand of the consumer. The charging device (200) comprises a transmitter unit associated with an antenna unit comprising a power antenna configured to define at least one charging zone for transmitting charging power to the at least one charging zone; a receiver for receiving signals from consumers (300) located within the charging zone; and a controller unit. The controller is configured and operable to be responsive to a request signal from a consumer (300) indicative of demand for charging, to initiate a charging process of the consumer by radiation from the power antenna toward said consumer (300) to supply power required for operating a functional unit of said consumer (300). The power antenna may comprise an array of directional antenna elements, each defining the charging zone within a different angular segment of entire charging space defined by a radiation pattern of the antenna array.
Owner:HUMAVOX
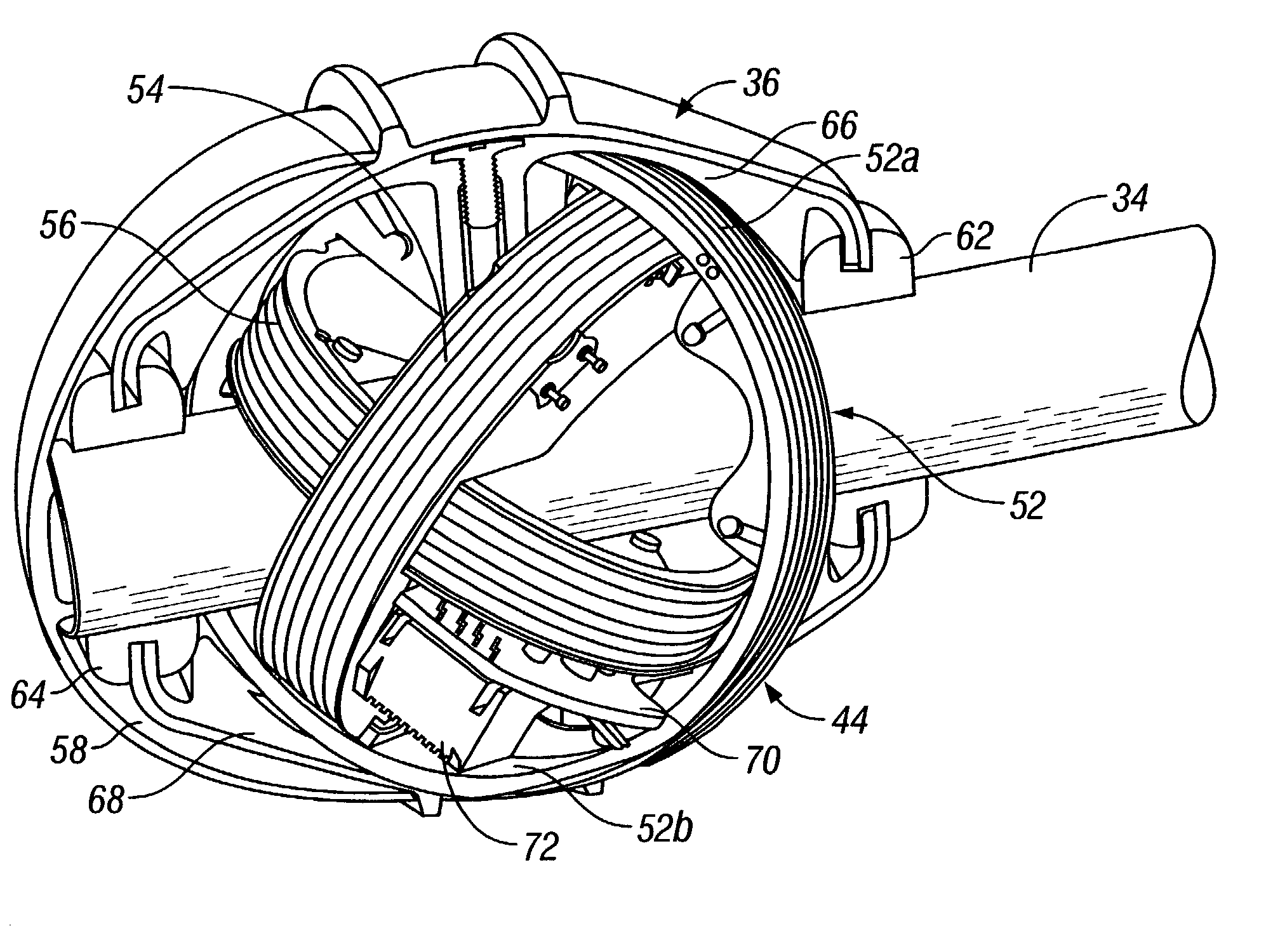
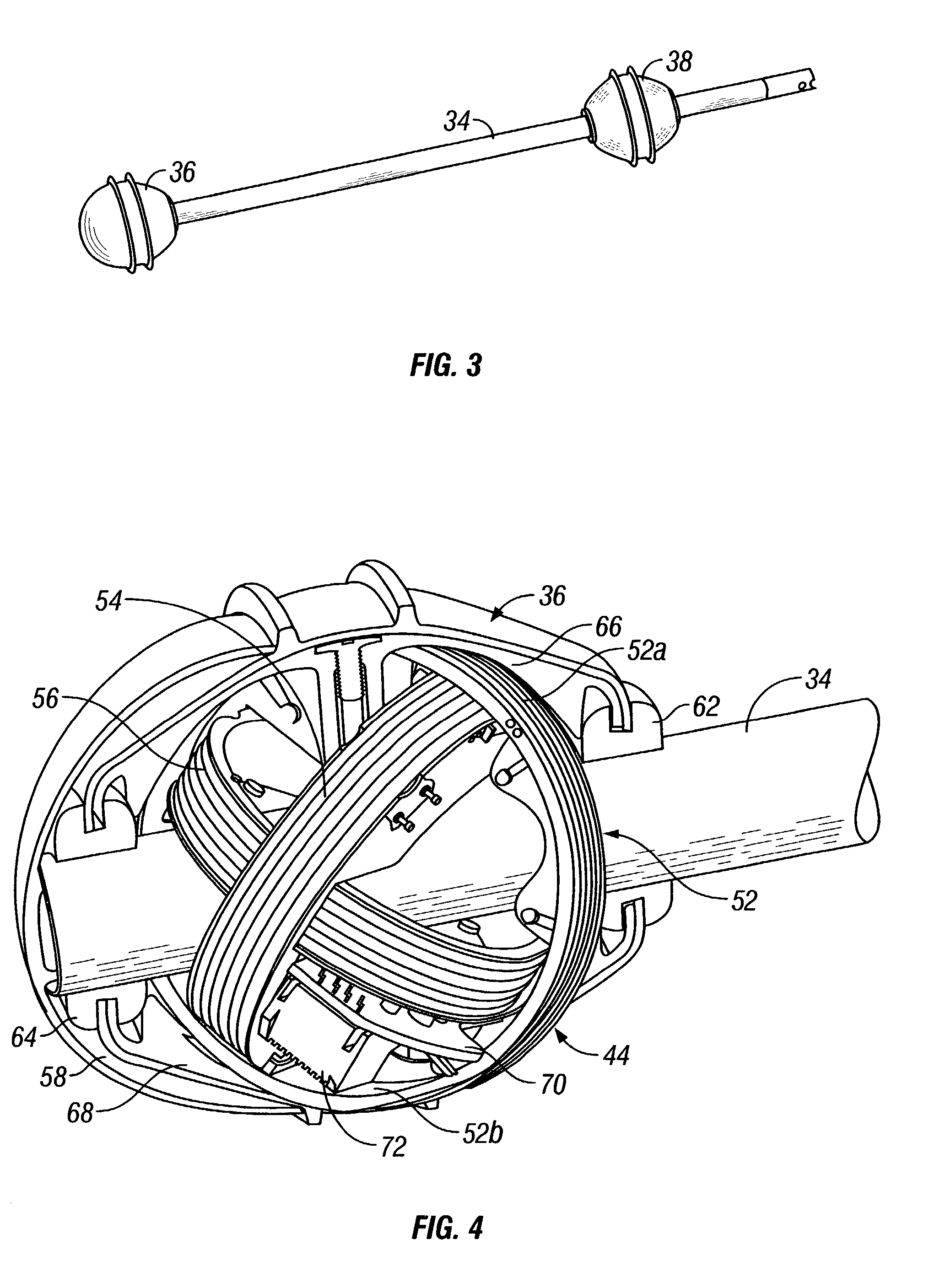
Electronically agile dual beam antenna system
InactiveUS6768456B1Reduce needSimple and reliable processAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesIndividually energised antenna arraysDual beamMulti beam
The present invention provides an improved antenna system that, in one embodiment, includes an antenna array comprised of a plurality of elements, each of which is capable of providing a signal. Also included in the improved antenna system is a multi-beam beamformer for producing two spatially independent overlapping beams from the signals provided by two different subsets of the antenna array. The phase of the two beams is compared to realize an interferometer that can provide high or fine resolution data on the position of an object relative to the antenna system. The amplitude of the two beams can also be compared to obtain coarse data on the position of the object. The beamformer includes a switching network for selecting which elements of the antenna array form the two subsets. This permits, for example, the position of the beams to moved, the baseline of the two beams to be varied, and / or the beam width of the beams to be altered. To reduce adverse aerodynamic effects in certain applications, the antenna array is located conformal to the exterior surface of the body on which the array is mounted. Further, to reduce temperature related problems associated with high speed movement of the body on which the array is located, the array is located on the side of the body, as opposed to the front of the body. The side location also provides space for other types of sensors that are preferably located adjacent to the front surface of the body.
Owner:BALL AEROSPACE & TECHNOLOGIES
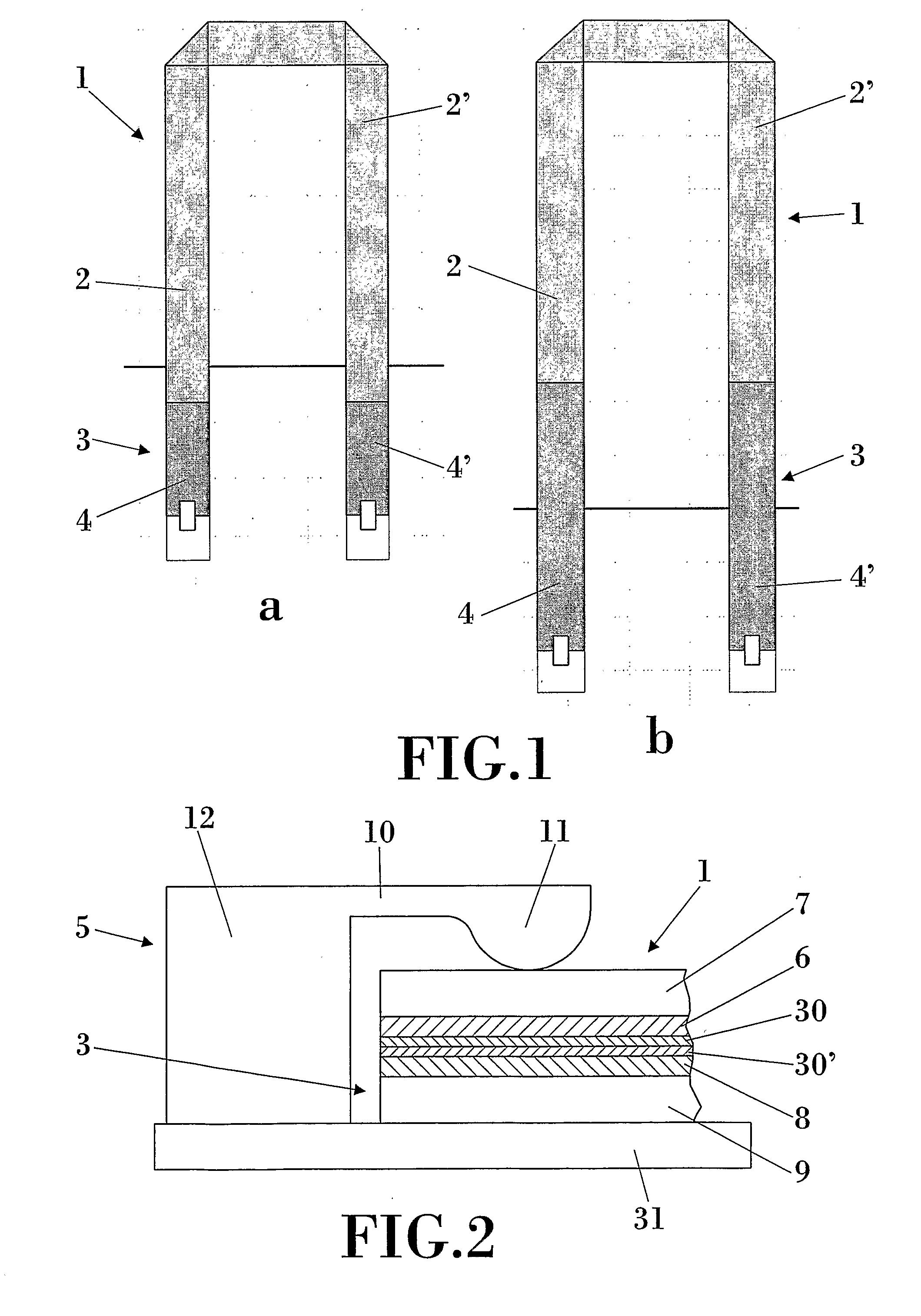
Antenna arrays formed of spiral sub-array lattices
InactiveUS6842157B2Improve bindingWider antenna bandwidthSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsEngineeringGrating lobe
A antenna array (20) includes a plurality of periodic or aperiodic arranged sub-arrays (22). Each sub-array (22) includes a plurality of antenna elements (32) arranged in the form of a spiral (30). The sub-arrays (22) can comprise various spiral shapes to provide the required physical configuration and operational parameters to the antenna array (20). The elements (32) of each sub-array (22) are arranged to minimize the number of such elements (32) that intersect imaginary planes perpendicular to the spiral and passing through the spiral center. Such an orientation of the elements (32) minimizes grating lobes in the antenna pattern.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
Omnidirectional sonde and line locator
InactiveUS7009399B2Easy to useSimple methodAlarmsElectric/magnetic detection for transportElectromagnetic shieldingGraphical user interface testing
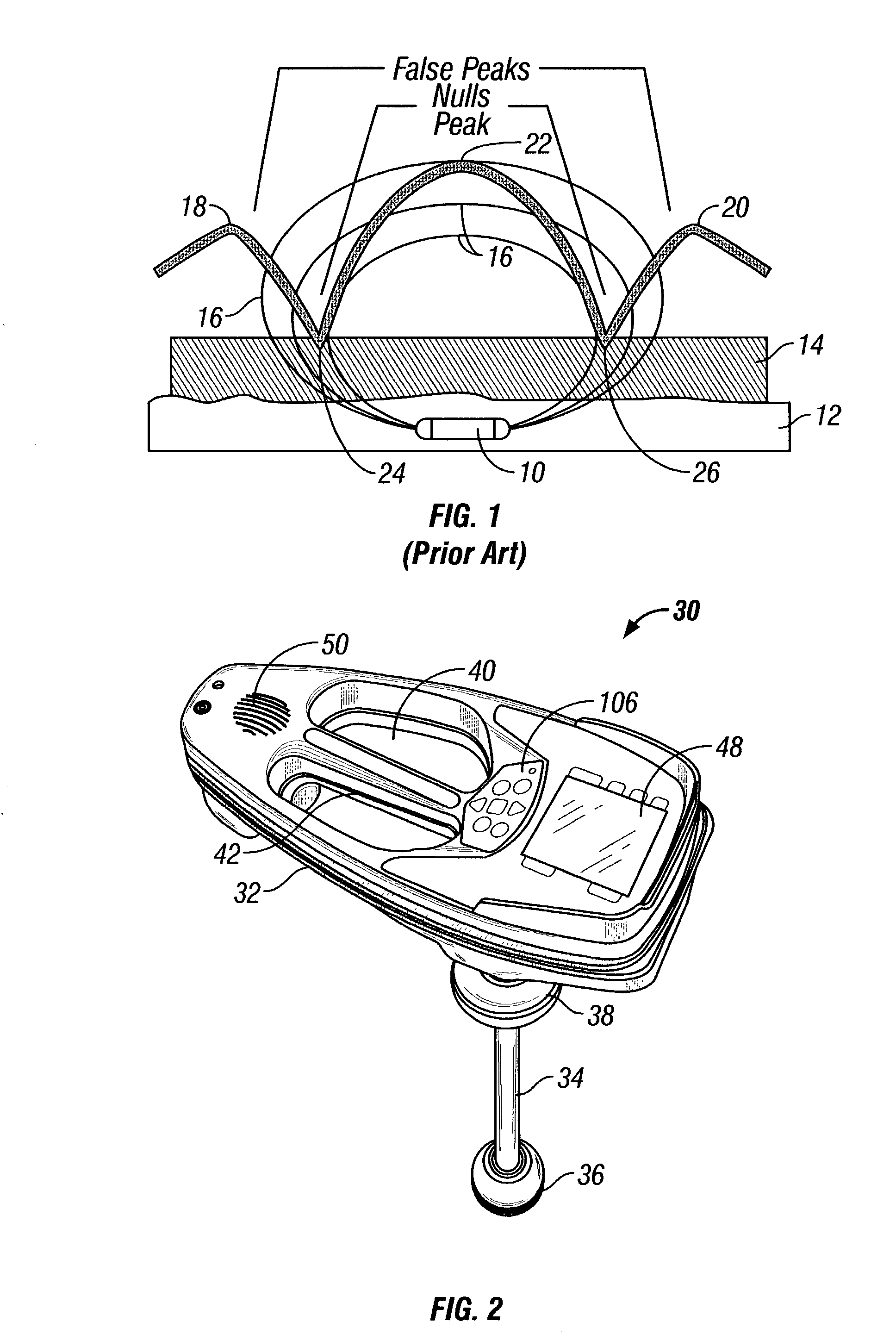
At least one antenna array including three mutually orthogonal antennas each sharing a common center point senses an electromagnetic signal emitted by a buried object such as a utility line, pipe or sonde. A circuit at least partially mounted in a housing is connected to the array and determines a location of the buried object by measuring signal strength and field angles in three dimensions without having to align the antenna array relative to the buried object while eliminating nulls and false peaks. A graphical user interface (GUI) has user-friendly icons, symbols, menus, numbers and graphical and auditory representation of signal strength. A SEARCH view indicates signal strength by showing a rotating strength indicator, a trace mode MAP view in which line location is shown by a line that moves side-to-side, and a sonde mode MAP view in which sonde location is shown by a moving line, pole and equator.
Owner:SEEK TECH
Millimeter-wave quasi-optical integrated dielectric lens antenna and array thereof
InactiveCN101662076AWith quasi-optical Gaussian beam radiation characteristicsGuaranteed normal transmissionAntenna arraysDielectric resonator antennaDielectric substrate
The invention relates to the technical field of radar, in particular to a millimeter-wave quasi-optical integrated dielectric lens antenna and an array thereof. The array consists of a microstrip integrated antenna, a dielectric lens, an objective lens, an array base, a reflecting mirror, a protective cover and a beam transfer switch; one end face of the dielectric lens is a hemisphere or an ellipsoid, while the other end face is a cylindrical section; the microstrip integrated antenna is generated by an dielectric substrate, the front surface of the dielectric substrate is closely adhered tothe cylindrical section of the dielectric lens and serves as a feed source, and the back surface is grounded; the hemispherical or ellipsoidal end face of the dielectric lens is an antenna radiating surface; the length of the cylindrical part of the dielectric lens can be changed; the antenna array is arranged into a linear array or an area array; the array base and the reflecting mirror have conical quasi-optical reflecting mirror surfaces; the focus of the objective lens of the linear array or the area array aligns with the central line of the dielectric lens; the protective cover is arranged outside; and the antenna array is controlled by the beam transfer switch. The antenna structure has strong shock resistance and dust prevention, and is suitable for millimeter-wave radars for planes, automobiles and ships, and receiving / emitting sensing of communication equipment.
Owner:阮树成
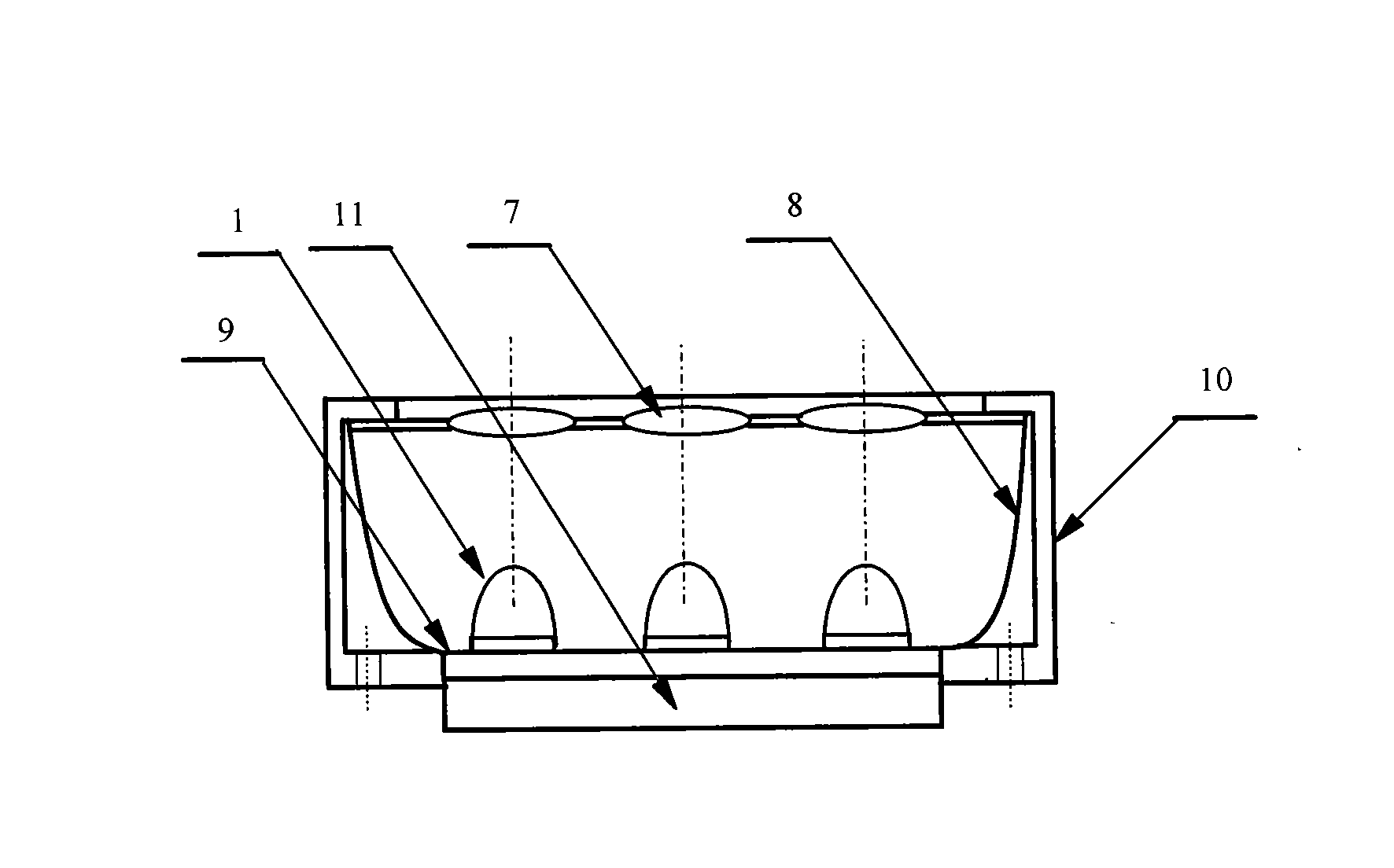
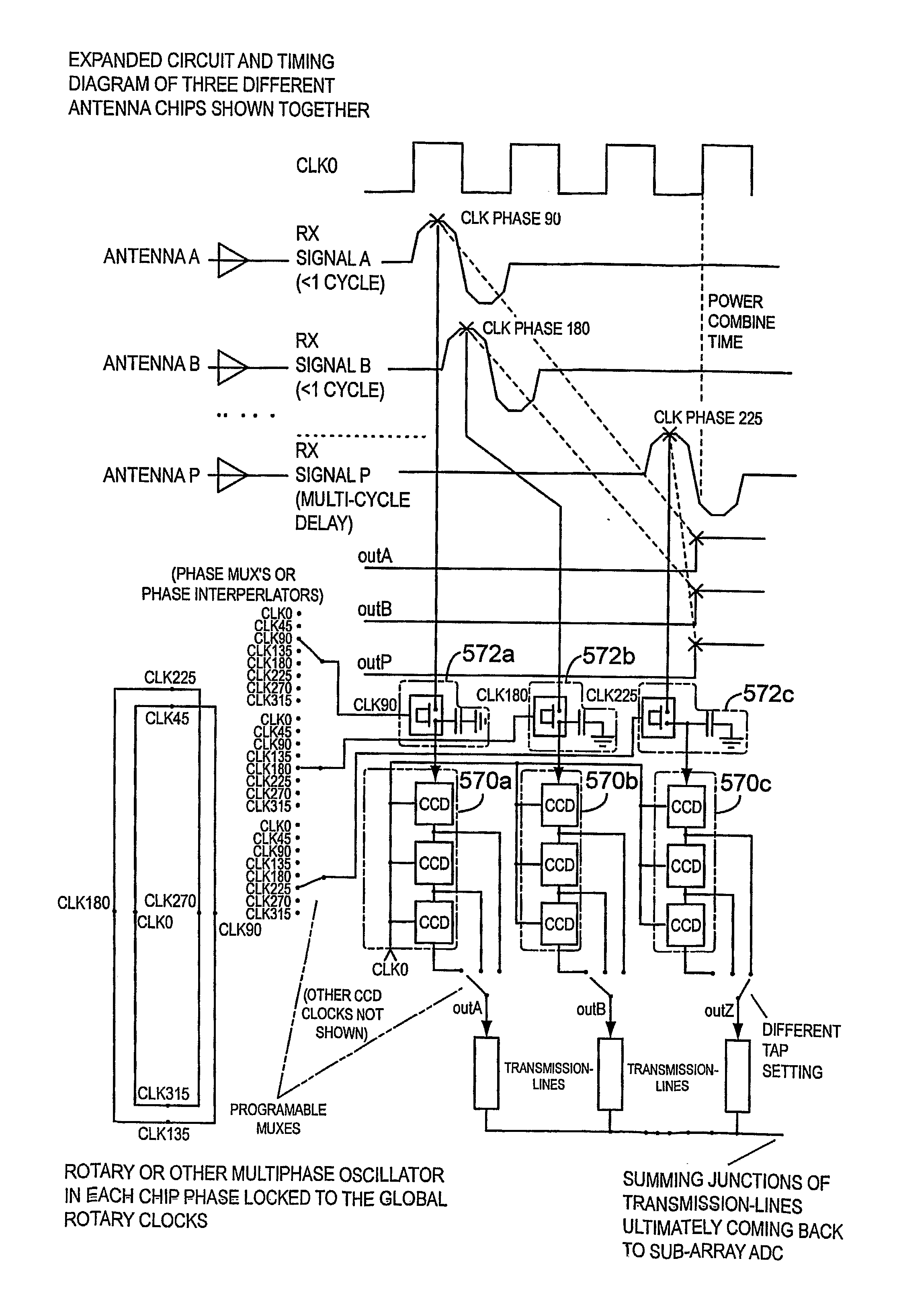
True time delay phase array radar using rotary clocks and electronic delay lines
ActiveUS20120039366A1Forming accuratelyEasy to moveAntenna arraysPulse automatic controlTime delaysAnalog delay line
Local oscillator circuitry for an antenna array is disclosed. The circuitry includes an array of rotary traveling wave oscillators which are arranged in a pattern over an area and coupled so as to make them coherent. This provides for a set of phase synchronous local oscillators distributed over a large area. The array also includes a plurality of phase shifters each of which is connected to one of the rotary oscillators to provide a phase shifted local oscillator for the array. The phase shifter optionally includes a cycle counter that is configured to count cycles of the rotary oscillator to which it is connected and control circuitry that is then operative to provide a shifted rotary oscillator output based on the count from the cycle counter. A system and method for operating a true-time delay phased array antenna system. The system includes a plurality of antenna element circuits for driving or receiving an rf signal from the elements of the array. Each element circuit has a transmit and a receive path and a local multiphase oscillator, such as a rotary traveling wave oscillator. Each path has an analog delay line for providing a true-time delay for the antenna element. Preferably, the analog delay line is a charge coupled device whose control nodes are connected to phases of the local multiphase oscillator to implement a delay that is an integer number local multiphase oscillator periods. A fractional delay is also included in the path by using a sample and hold circuit connected to a particular phase of the oscillator. By delaying each antenna element by a true time delay, broadband operation of the array is possible.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
High dielectric antenna array
InactiveUS20150042526A1Small sizeReduce distanceNear-field transmissionCircuit arrangementsDielectricPhased array
A system and method for wirelessly transmitting signals via antenna phased array. In order to decrease the distance between individual antennae in the array, the antennae are submersed in a high dielectric material in addition to being arranged at right angles to one another, both features precluding one or more antennae from coupling. Furthermore, wires are covered in high dielectric material in order to refract RF signals around them, allowing antennae towards the center of the array to successfully transmit signals past other layers.
Owner:OSSIA
Antenna array with asymmetric elements
ActiveUS20150122886A1Particular array feeding systemsIndividually energised antenna arraysNon symmetricAntenna element
An RFID reader is provided that includes an antenna array comprising multiple antenna elements circumferentially distributed around a longitudinal axis of the antenna array. Each antenna element includes multiple patch elements disposed above one or more underlying substrates, wherein the patch elements of each antenna element are disposed on an outer side of the antenna element. Further, one or more of the antenna elements is an asymmetric antenna element, wherein a first end of the asymmetric antenna element is wider than a second, opposite end of the asymmetric antenna element, wherein a first patch element disposed proximate to the first end of the asymmetric antenna element is larger than a second patch element disposed proximate to the second end of the asymmetric antenna element, and wherein a resonant frequency associated with the first patch element is approximately the same as a resonant frequency associated with the second patch element.
Owner:SYMBOL TECH LLC
System and methods for direction finding using a handheld device
ActiveUS20070197229A1Position fixationNear-field for read/write/interrrogation/identification systemsRelevant informationEngineering
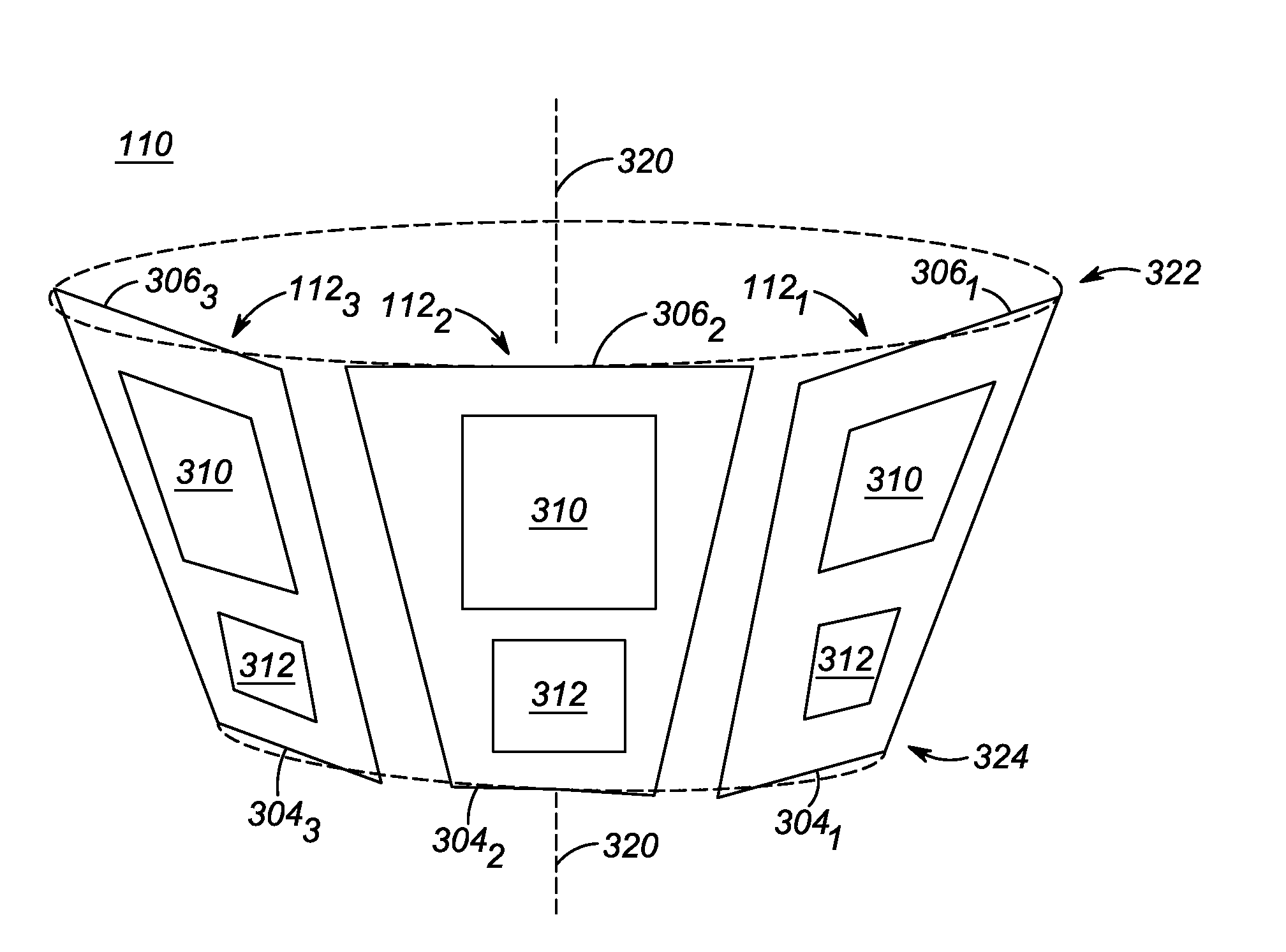
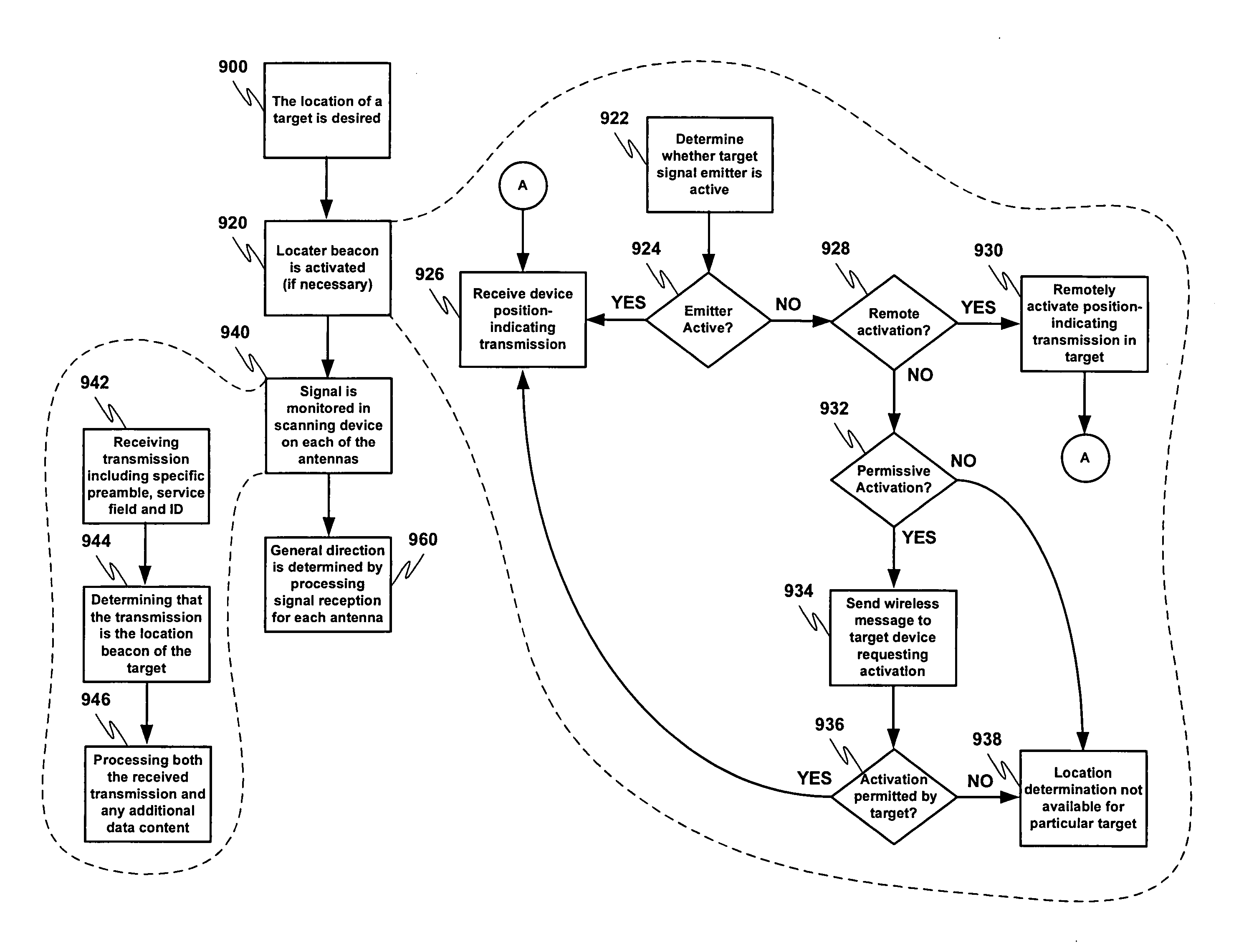
A system for indicating the relative direction of a target object or location as determined from the current position of a wireless communication device. The system employs Direction of Arrival determination using an antenna array for indicating the direction of a target device and includes facilities to activate a location-indicating transmission in a target device, the ability to request that a location-indicating transmission be activated in a remote target device, relevant information reception from a target device and the display of all potential target devices within effective transmission range of the wireless communication device.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
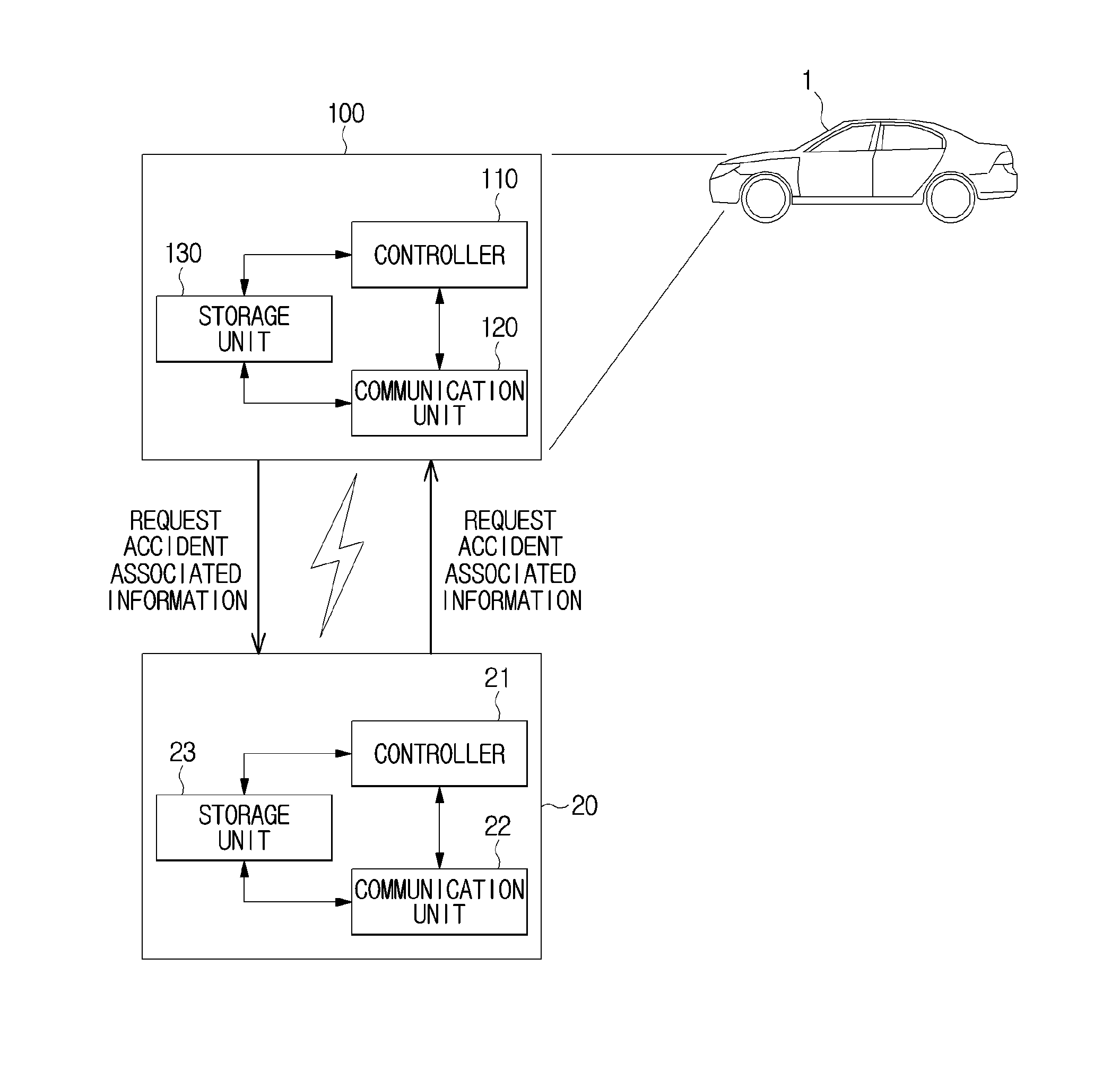
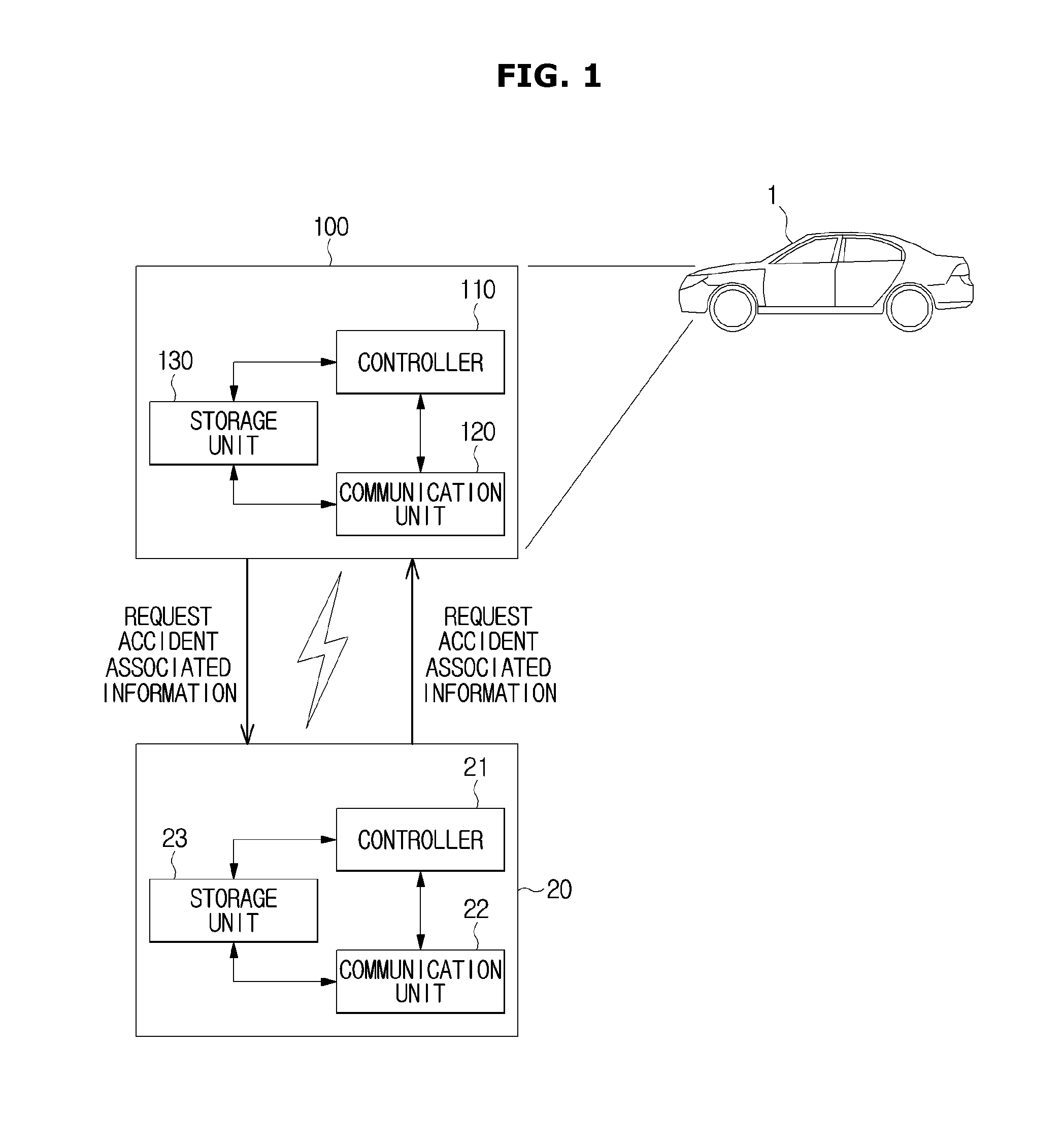
Accident information management apparatus, vehicle including accident information management apparatus, and accident information management method
InactiveUS20160277911A1Emergency connection handlingData processing applicationsCommunication unitControl communications
A vehicle includes a communication unit including an antenna array having a plurality of antenna elements for transmitting and receiving a signal and a beamformer for forming a beam pattern focused in a specific direction by adjusting a phase of the signal transmitted from the plurality of antenna elements, and a controller for controlling the communication unit to transmit a request signal of accident associated information by focusing the beam pattern onto a peripheral vehicle.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD
MMW electronically scanned antenna
A millimeter wave (MMW) antenna array includes a continuous transverse stub (CTS) radiating aperture comprising a set of spaced continuous transverse stubs, each having a longitudinal extent. A series feed system is coupled to an excitation source for exciting the stubs with MMW electromagnetic energy having a linear phase progression along the longitudinal extent of the stubs to produce an array beam which can be scanned over a beam scan range by changing the excitation frequency.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO +1
Enhanced Receiver for Wireless Power Transmission
ActiveUS20150326069A1Reduce power levelAdjusting operationBatteries circuit arrangementsElectromagnetic wave systemMicrocontrollerConverters
An enhanced receiver for wireless power transmission is disclosed. The receiver may be able to convert RF waves into continuous, stable and suitable voltage or power that can be used for charging or powering an electronic device. The receiver may include an antenna array for extracting and rectifying power from RF waves or pockets of energy. An input boost converter in the receiver may step up and stabilize the rectified voltage, while charging a storage element in the receiver. An output boost converter in the receiver may step up the output voltage of the storage element to deliver continuous and suitable power or voltage to a load. A microcontroller in the receiver may perform power measurements at different nodes or sections to adjust the operation of the input and output boost converters so that load power requirements can be satisfied at all times.
Owner:ENERGOUS CORPORATION
Adaptive antenna for use in same frequency networks
InactiveUS6404386B1Spatial transmit diversityAntenna supports/mountingsEngineeringCellular communication systems
An antenna apparatus which can increase capacity in a cellular communication system. The antenna operates in conjunction with a mobile subscriber unit and provides a plurality of antenna elements, each coupled to a respective signal control component such as a switch. The switch position of each antenna element is programmed for optimum reception during, for example, an idle mode which receives a pilot signal. The antenna array creates a beamformer for signals to be transmitted from the mobile subscriber unit, and a directional receiving array to more optimally detect and receive signals transmitted from the base station. By directionally receiving and transmitting signals, multipath fading is greatly reduced as well as intercell interference. Various techniques for determining the proper arrangement of signal control components for each antenna element are accommodated.
Owner:IPR LICENSING INC
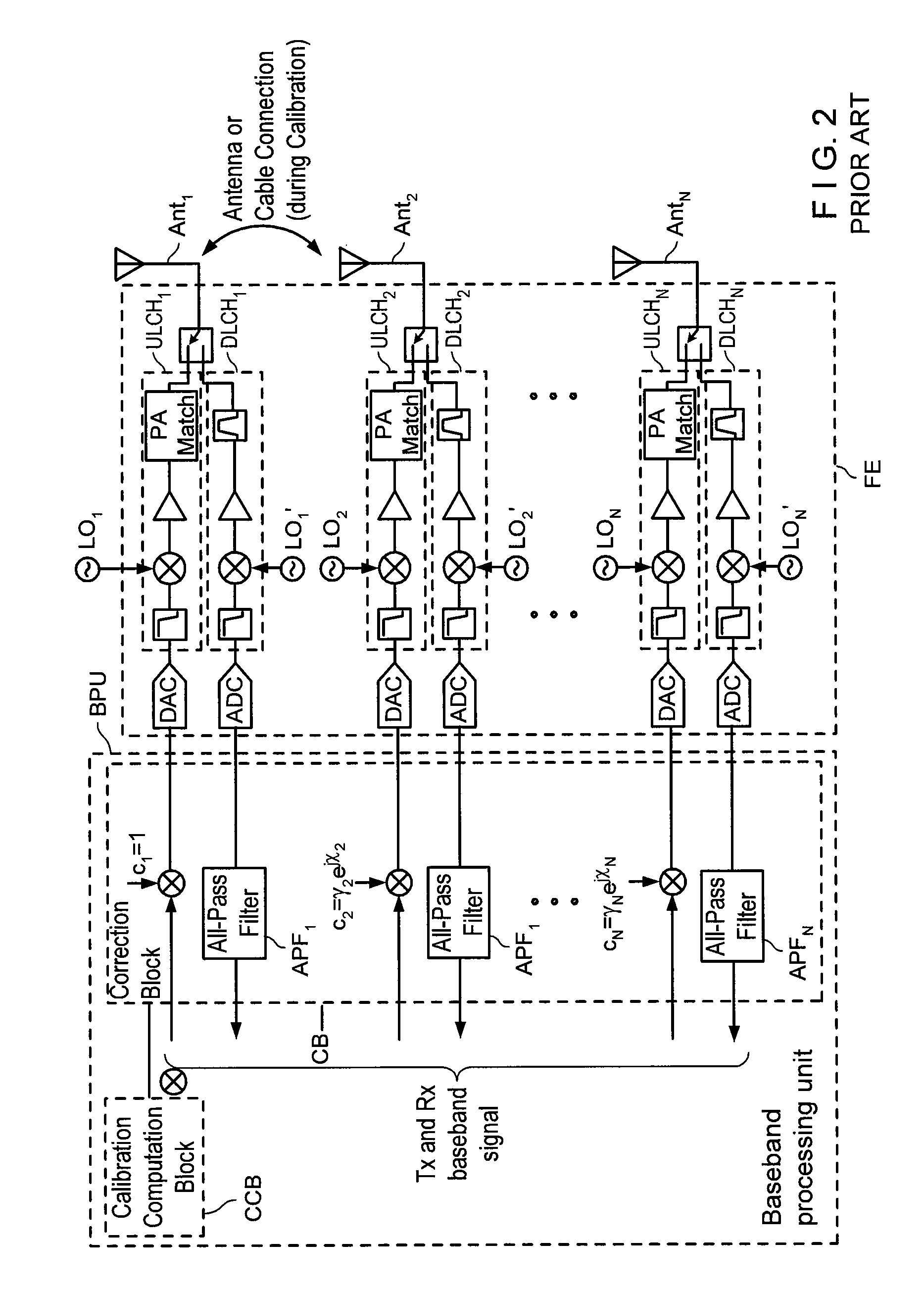
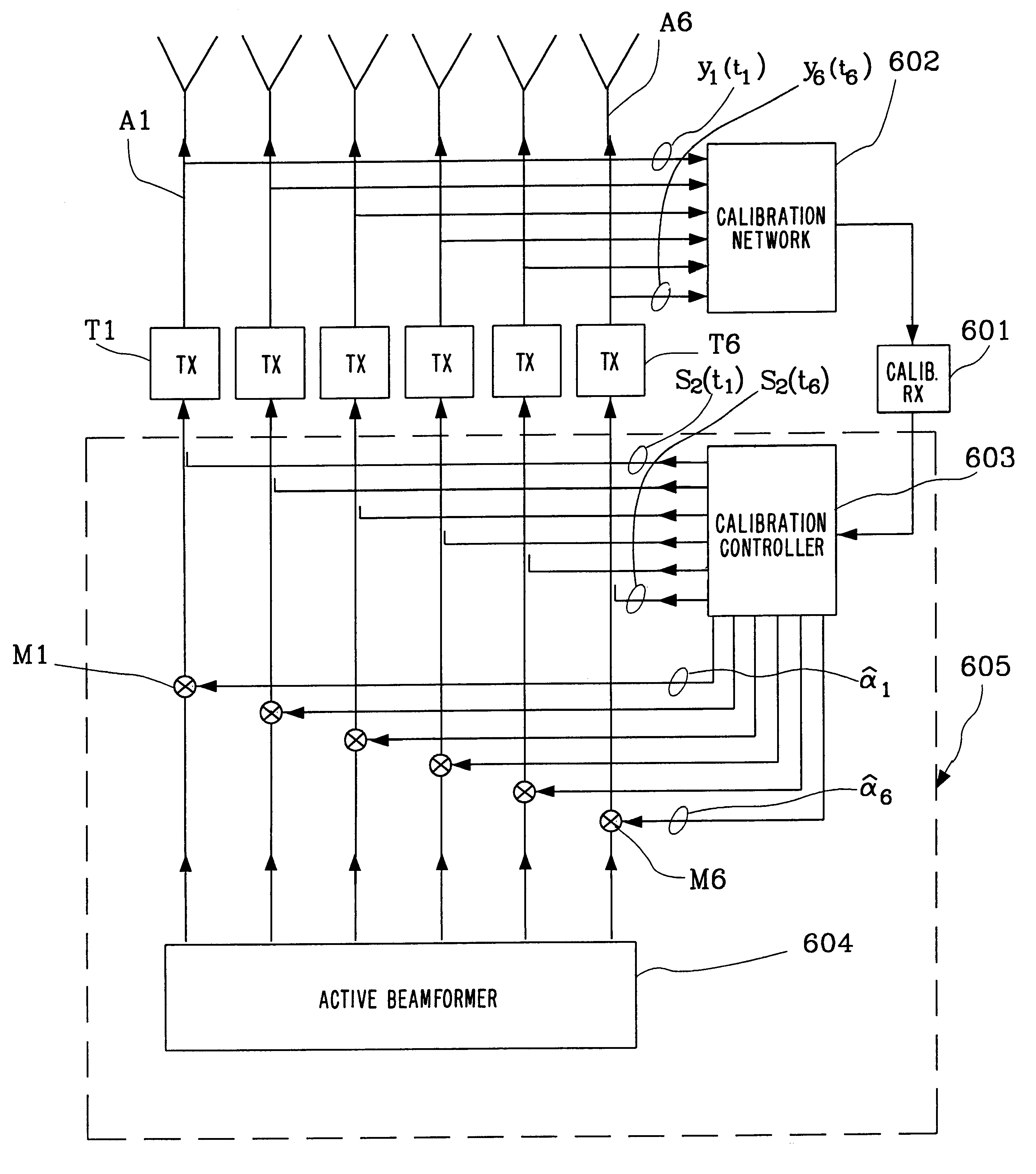
MULTI-TRANSCEIVER ARCHITECTURE FOR ADVANCED Tx ANTENNA MONITORING AND CALIBRATION IN MIMO AND SMART ANTENNA COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS
ActiveUS20100093282A1Lower performance requirementsTransmitters monitoringReceivers monitoringWireless transceiverAir interface
Exemplary embodiments of system and method are provided for measuring signal amplitude, phase and / or delay offsets between multiple transmit signals fed through the transmit signal processing chains and wirelessly transmitted over the transceive antennas of separate transceiver modules, wherein transmit signal coupling between the transmit antennas of said transceiver modules' transmit signal processing chains may be used for synchronizing the transmit signals and calibrating their amplitude, phase and / or delay parameters. The exemplary embodiments further provide a front end arrangement of a wireless transceiver device which can comprise at least two independently controllable transceiver modules, each connected to an associated spatial diversity transceive antenna and comprising at least one associated transmit signal processing chain and at least one associated receive signal processing chain coupled to a common baseband processing unit. The exemplary transceiver architecture can be executed on an antenna loop between the transmit signal processing chain of a first transceiver module and the transmit signal processing chain of a second transceiver over the air interface and relies on an adaptive antenna concept which facilitates a wireless transmission of data via a plurality of wireless communication channels utilizing an array of transceive antennas, receiving feedback information via at least one of said communication channels using such antenna loop and modifying a transmission mode based on the received feedback information.
Owner:RPX CORP
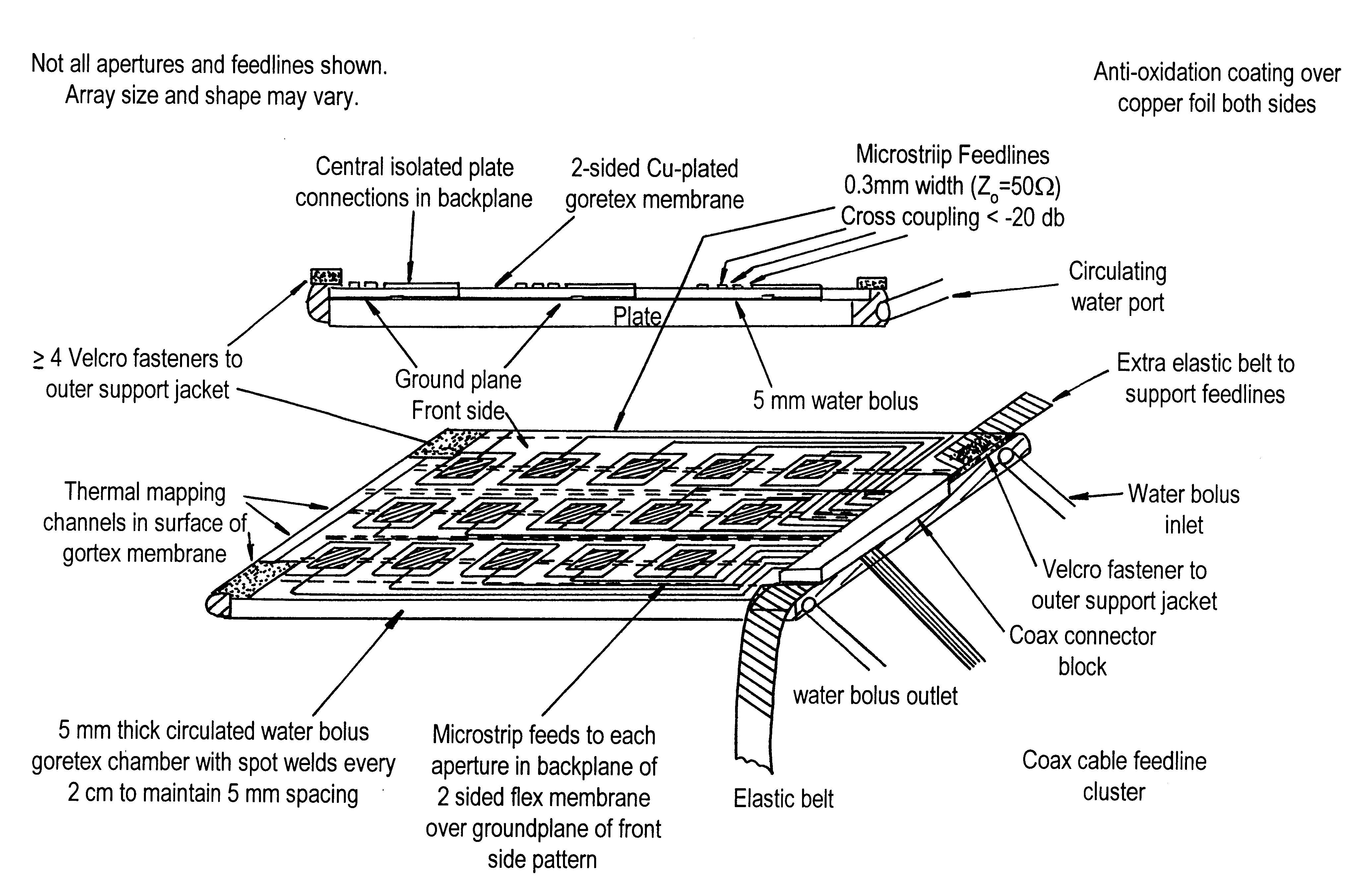
Microwave garment for heating and/or monitoring tissue
InactiveUS6330479B1Reduce manufacturing costImproved patient comfortElectrotherapyMicrowave therapyDielectric substrateEngineering
A flexible microwave applicator and method of use thereof. The applicator includes a flexible, dielectric-containing compartment (e.g. temperature regulated water or oil) having a variable contour, tissue-engaging surface and an opposite non-tissue-engaging surface and an antenna array adjacent to a non-tissue-engaging surface. The antenna array includes at least one flexible printed circuit board having a front metal surface, a dielectric substrate, a back metal surface, a connection structure for connecting the antenna array to at least one external microwave device, at least one dual concentric conductor aperture on the front surface, and at least one microstrip feedline in communication with the dual concentric conductor aperture and the connection structure. The microwave applicator also includes flexible attachment material for placement over the antenna array and dielectric compartment to allow the microwave applicator to be attached to a subject like a garment which closely conforms to the anatomy portion to be heated. The flexible attachment material may be configured such that the microwave applicator is configured as an appropriately-shaped type of garment, for example, a vest, jacket, cap, hood, blanket, custom shaped conformal wrap, sleeve, or as a pair of shorts.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
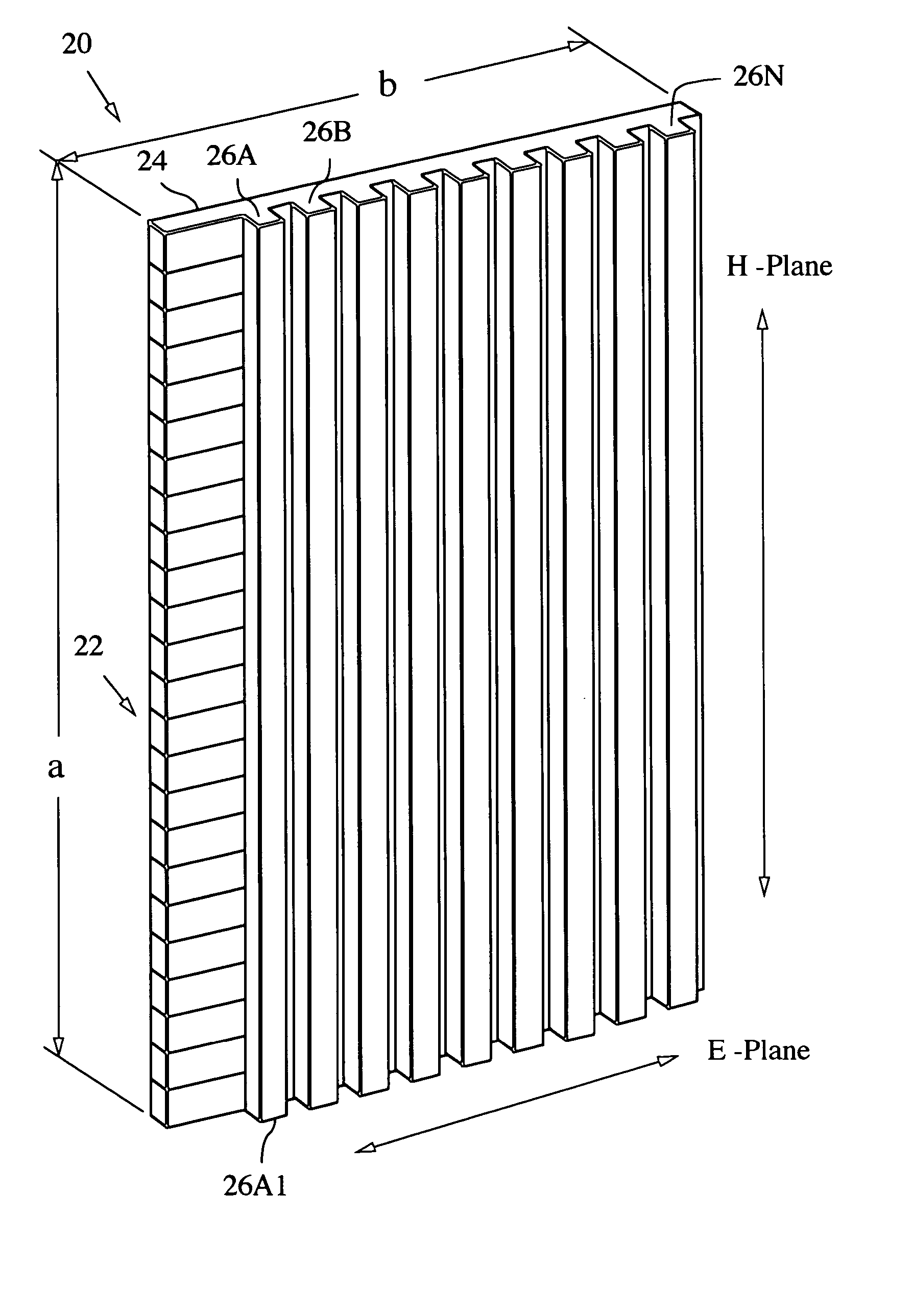
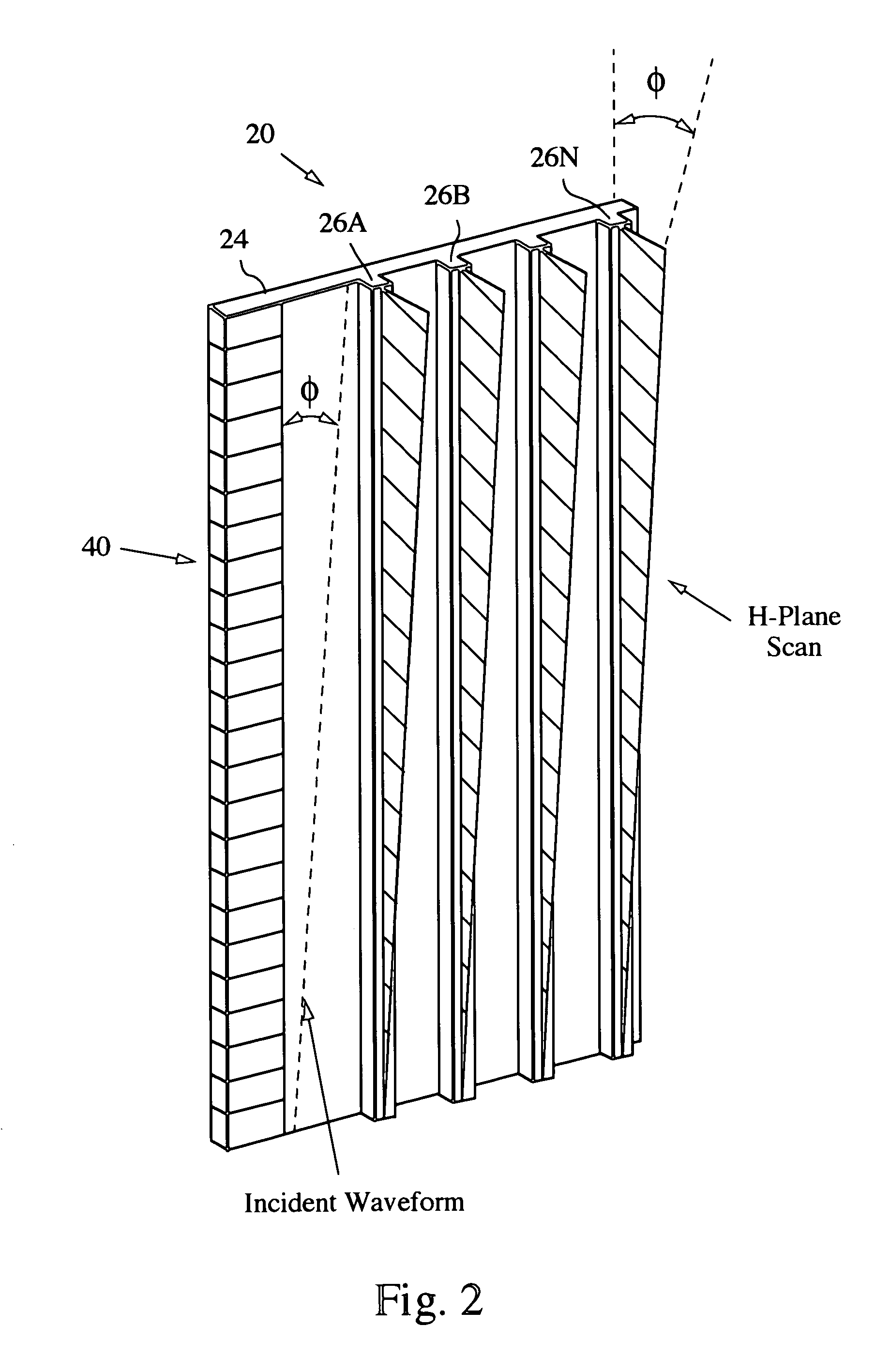
Transverse device array radiator ESA
An antenna array employing continuous transverse stubs as radiating elements is described, which includes an upper conductive plate structure comprising a set of continuous transverse stubs, and a lower conductive plate structure disposed in a spaced relationship relative to the upper plate structure. The upper plate structure and the lower plate structure define an overmoded waveguide medium for propagation of electromagnetic energy. For each of the stubs, one or more transverse device array phase shifters are disposed therein.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
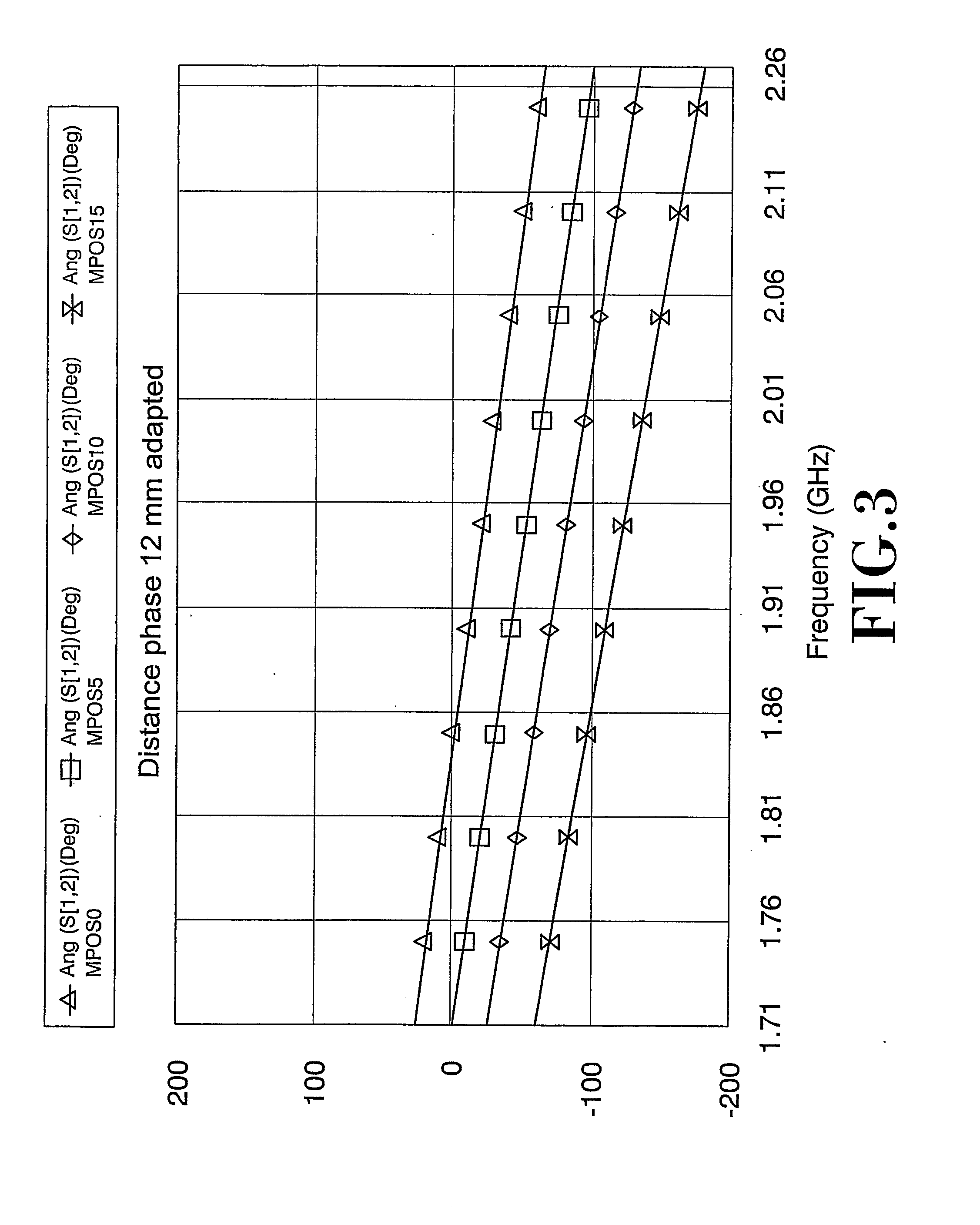
Antenna array calibration
InactiveUS6339399B1Improve performanceImprove accuracyWave based measurement systemsAntennasAmplitude distortionCellular communication systems
A method and a system for calibrating the reception and transmission of an antenna array for use in a cellular communication system is disclosed. The calibration of the reception of the antenna array is performed by injecting a single calibration signal into each of a number of receiving antenna sections, in parallel. The signals are collected after having passed receiving components that might have distorted the phase and amplitude. Correction factors are generated and applied to received signals. The calibration of the transmission of the antenna array is preformed in a similar way. A single calibration signal is generated and injected into each of a number of transmitting antenna sections, one at a time. The signals are collected, one at a time, after having passed transmitting components that might have distorted the phase and amplitude. Correction factors are generated and applied to signals that are to be transmitted.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
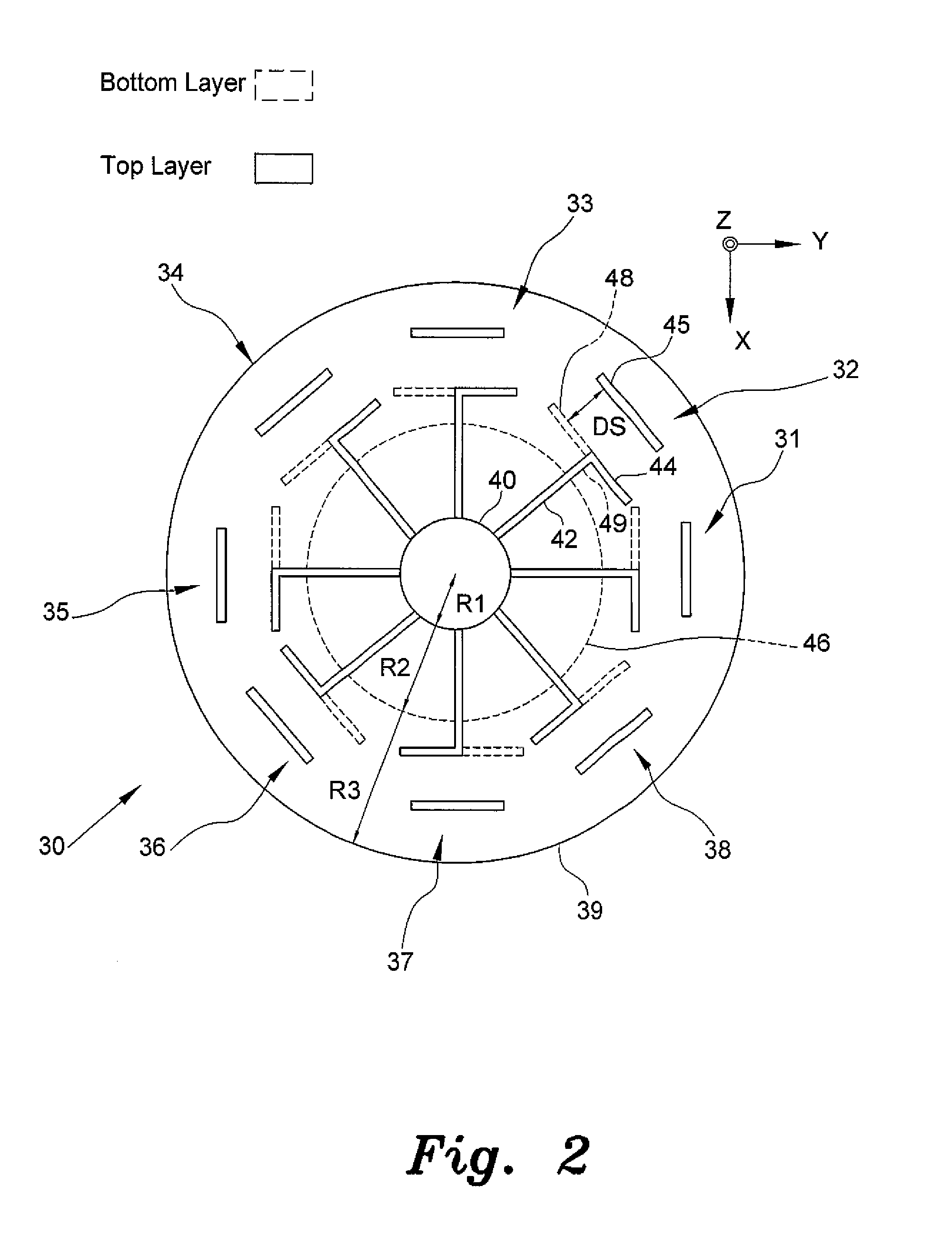
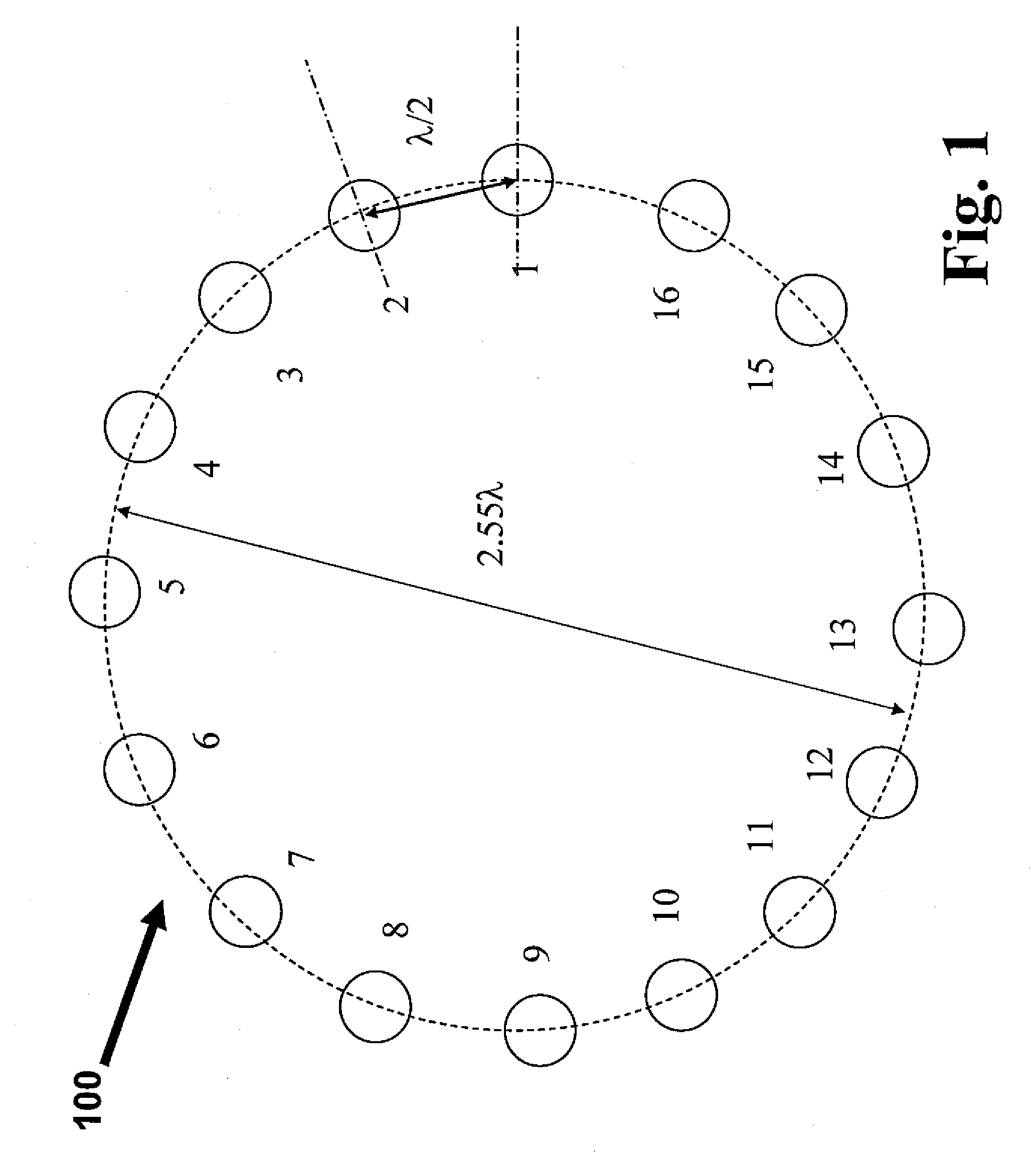
Circular antenna array for vehicular direction finding
InactiveUS9082307B2Road vehicles traffic controlRadiating elements structural formsCircular discIn vehicle
The circular antenna array for vehicular direction finding applications is a circular disc having a plurality of microstrip antennas radially spaced around the disc at equal angles. In one embodiment, the circular antenna array includes V-shaped antennas, and in another embodiment, the antennas are Yagi antennas. The circular antenna array can operate under two modes, switched and phased, in the 2.45 GHz band with an operating bandwidth of at least 100 MHz. The circular antenna array is configured to be installed in vehicles. Selective transmittal of an RF signal from a key fob generates a response signal from a specific antenna element receiving the RF signal in line with the direction of origin thereof. An LED panel indicates proximity and direction to the vehicle being located.
Owner:KING FAHD UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND MINERALS
Array structure for the application to wireless switch of WLAN and wman
InactiveUS20070257858A1Improve efficiencyLow budgetIndoor communication adaptationIndividually energised antenna arraysArea networkArray data structure
The present invention provides an antenna array structure which includes multiple array elements, and the antenna array structure is using for the application of the WLAN (wireless local area network) or WMAN (wireless metro area network.) Furthermore, the array elements of the present invention are phased arrays or attenuated arrays, and when configuration with different type of the array element is used, the corresponding BFN (beam forming network) can also be implemented in various possibilities. With all the configuration of the present invention, the manufacturers can have a stable array structure for their applications.
Owner:ACCTON TECHNOLOGY CORPORATION
Dual staggered vertically polarized variable azimuth beamwidth antenna for wireless network
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
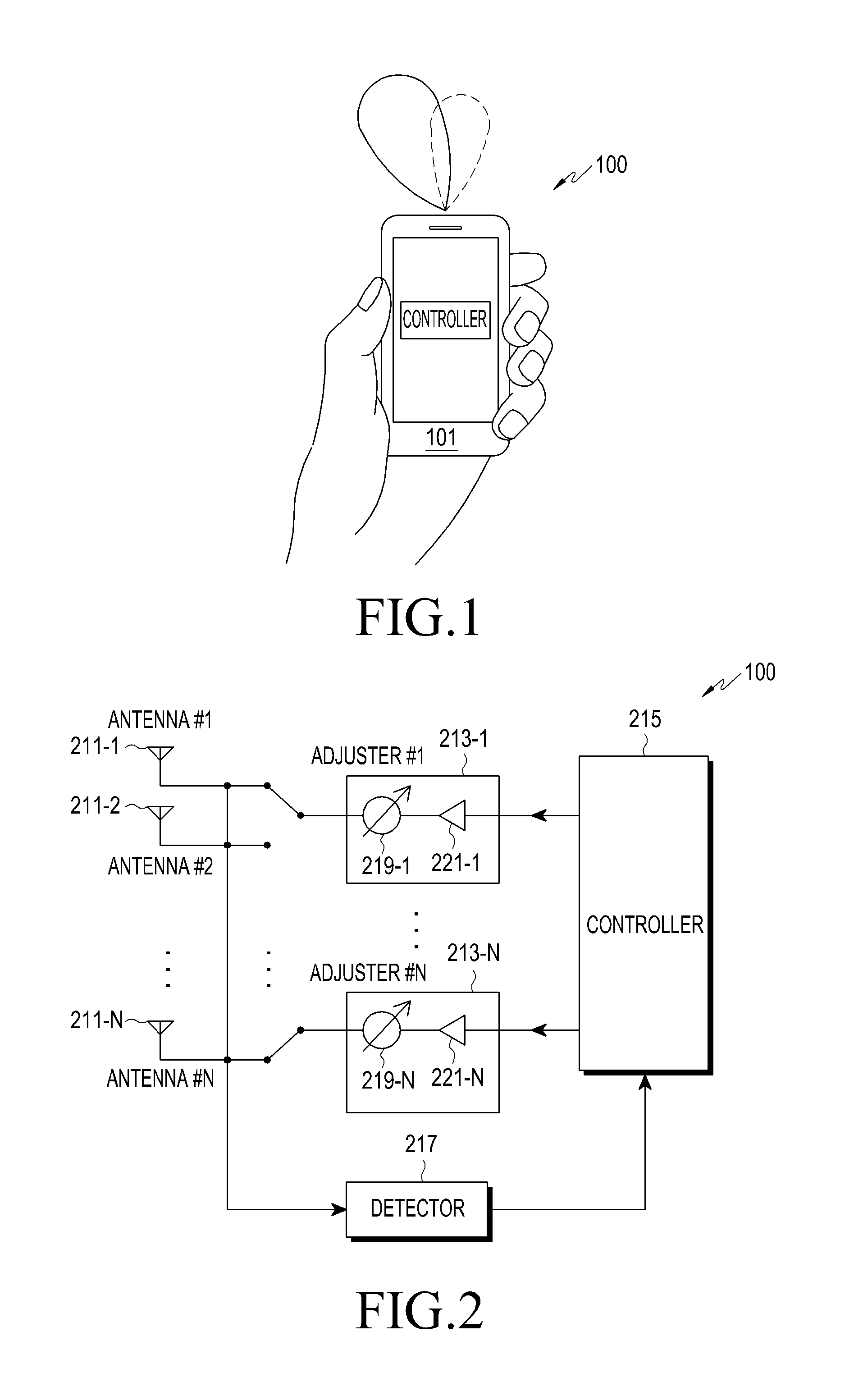
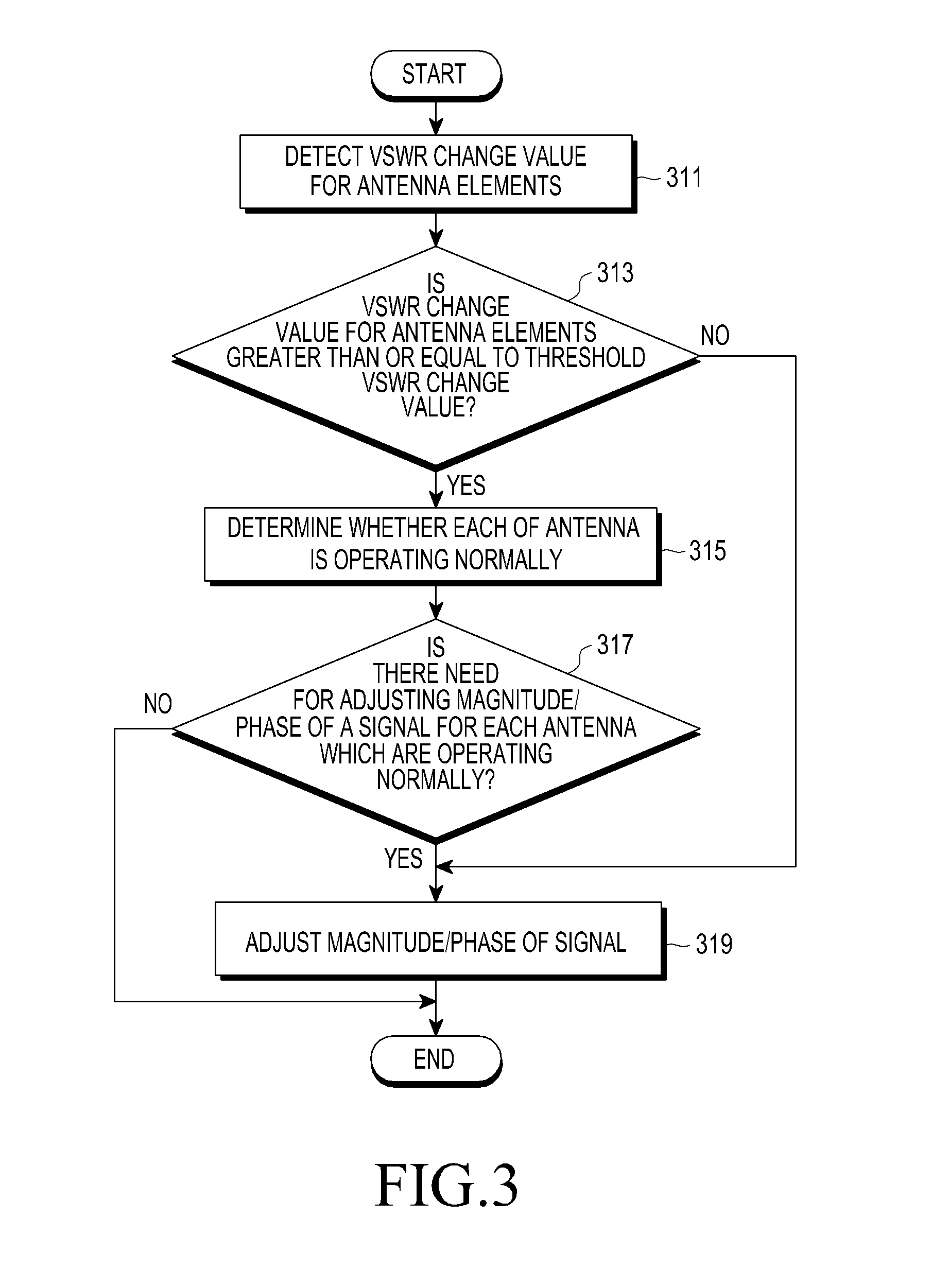
Apparatus and method for adjusting beam pattern in communication system supporting beam division multipile access scheme
ActiveUS20150318610A1Reduce degradationImprove communication system performanceTransmitters monitoringSpatial transmit diversityCommunications systemBeam pattern
A method for adjusting a beam pattern in a beam pattern adjusting apparatus in a communication system supporting a Beam Division Multiple Access (BDMA) scheme is provided. The method includes determining whether a Voltage Standing Wave Ratio (VSWR) value for each antenna included in an antenna array included in the beam pattern adjusting apparatus is greater than or equal to a threshold VSWR value, if it is determined that an antenna of the antenna array has a VSWR value that is greater than or equal to the threshold VSWR, detecting whether each of the antenna elements is operable, and if it is determined that at least one of the antennas is inoperable, adjusting a beam pattern of at least one of the antennas that is operable.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com