Patents
Literature
380 results about "Relative direction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The most common relative directions are left, right, forward(s), backward(s), up, and down. No absolute direction corresponds to any of the relative directions. This is a consequence of the translational invariance of the laws of physics: nature, loosely speaking, behaves the same no matter what direction one moves. As demonstrated by the Michelson-Morley null result, there is no absolute inertial frame of reference. There are definite relationships between the relative directions, however. left and right, forward and backward, and up and down are three pairs of complementary directions, each pair orthogonal to both of the others. Relative directions are also known as egocentric coordinates.
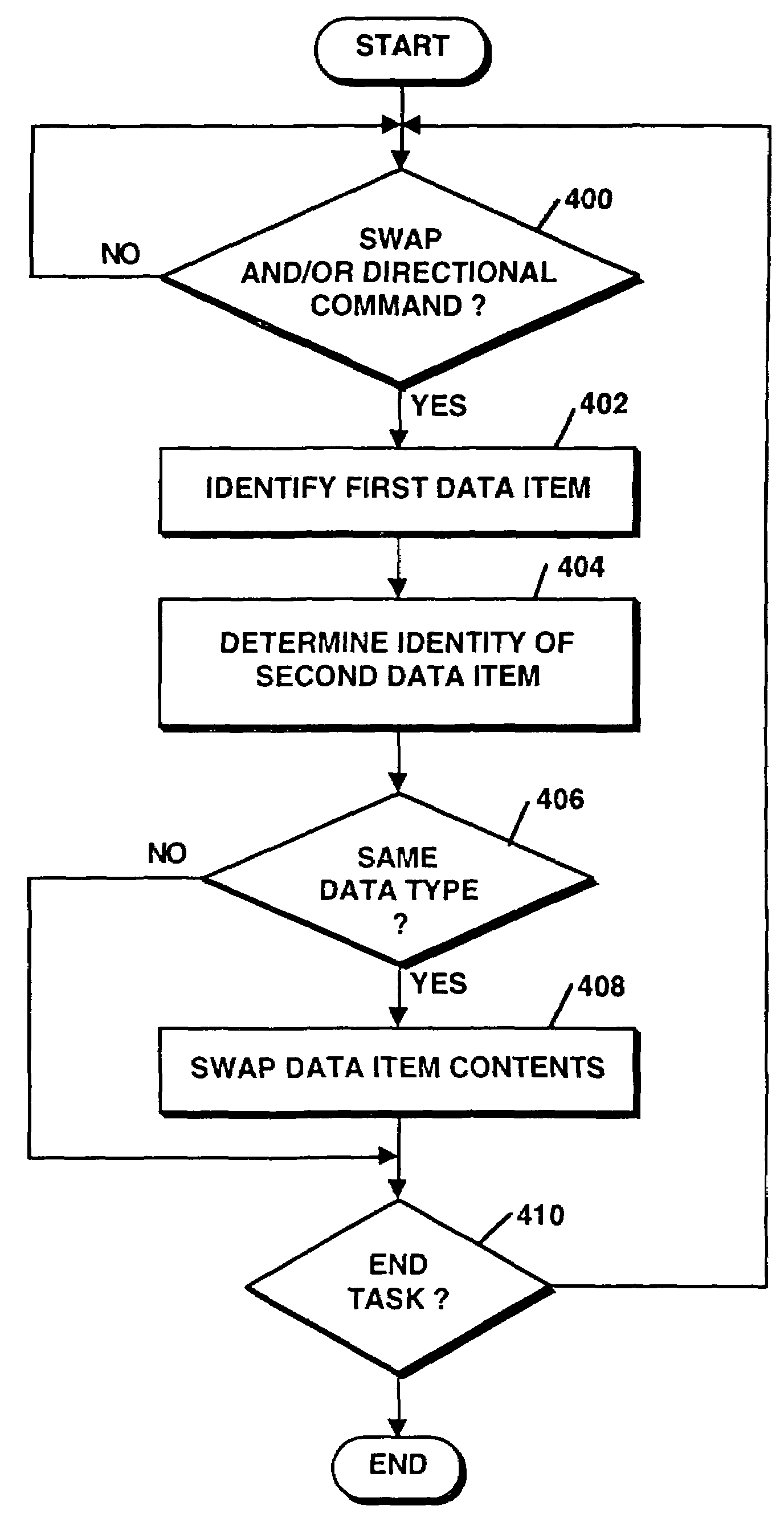
Method and apparatus for reordering data items
InactiveUS7017118B1Sure easyInput/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsGraphicsSeries data
A swapping utility enables directional commands from a graphic user interface and / or keyboard to be utilized to swap data items associated with lists, tables or other series of data items. Upon receipt of both a directional command, e.g. up, down, left, or right, and a swap command, the utility uses the current position of the cursor or a selected entity to identify a first data item to be swapped and the relative direction thereto to identify a second, adjacent data item to be swapped. If both identified data items are of the same data type, their respective contents are exchanged within the ordered list or table without the need to cut and paste the content. In alternative embodiments, multiple adjacent data items may be swapped, or, in an embodiment which utilizes multiple selection icons, single or multiple nonadjacent entities may be directly swapped.
Owner:IBM CORP
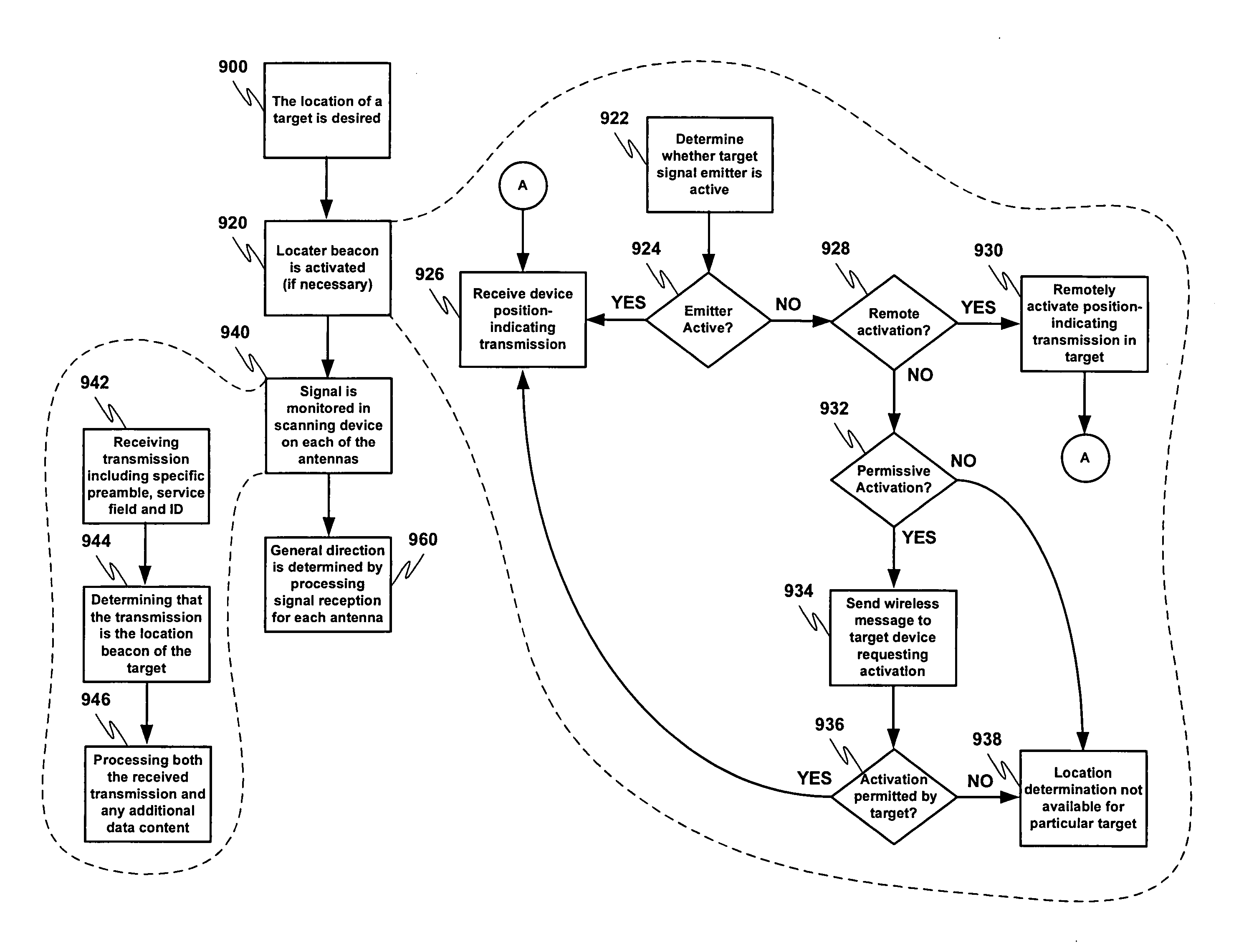
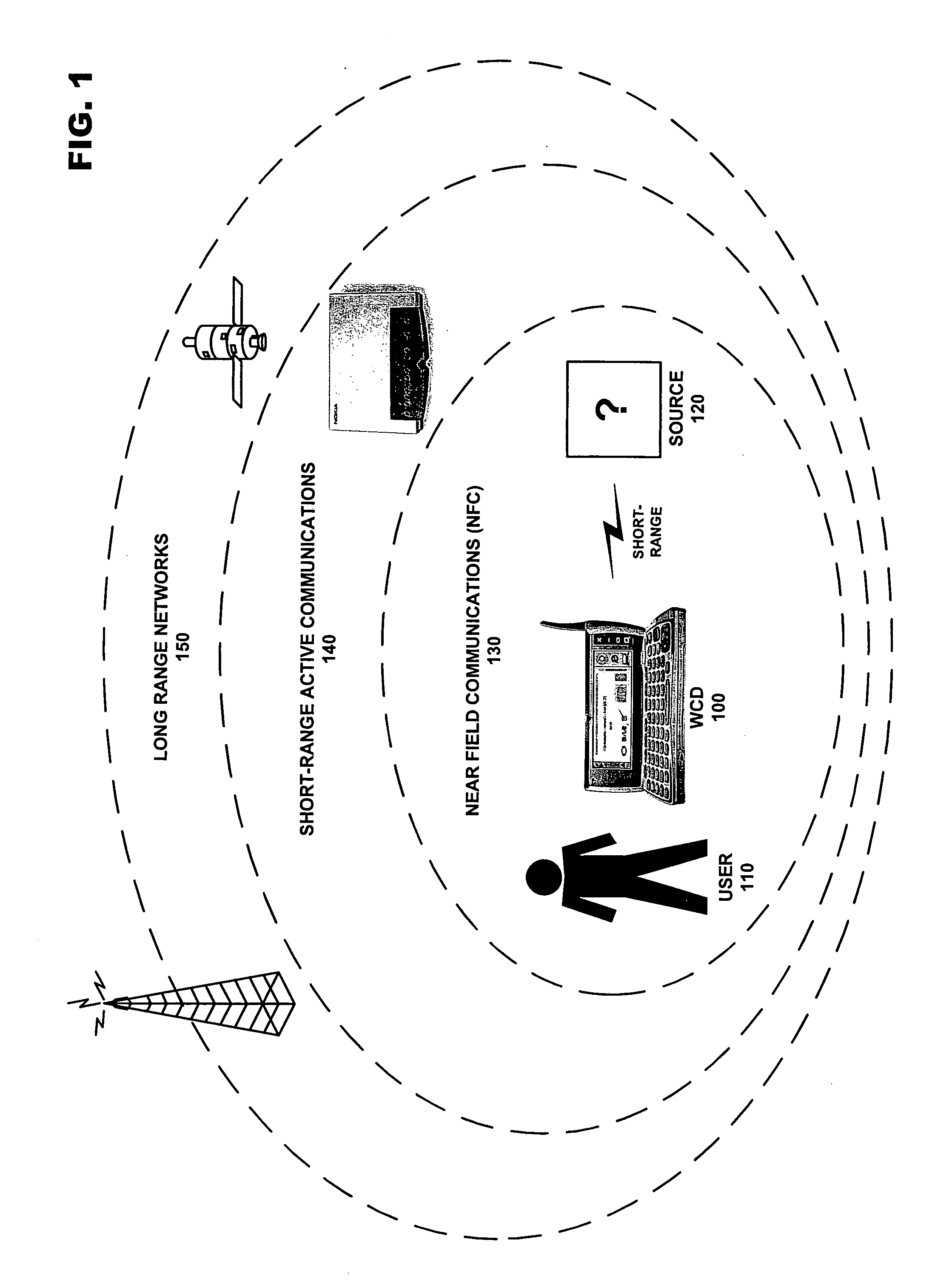
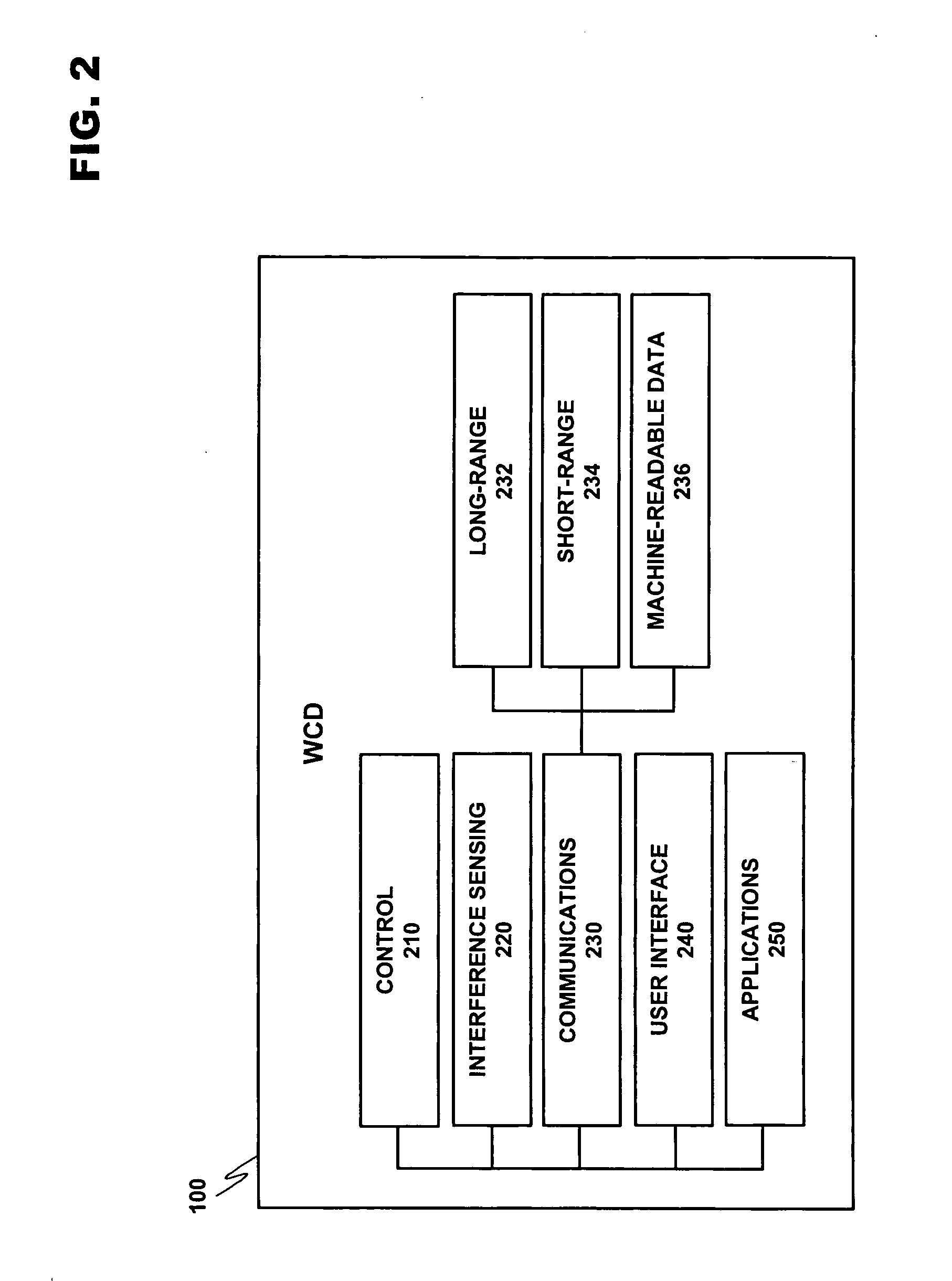
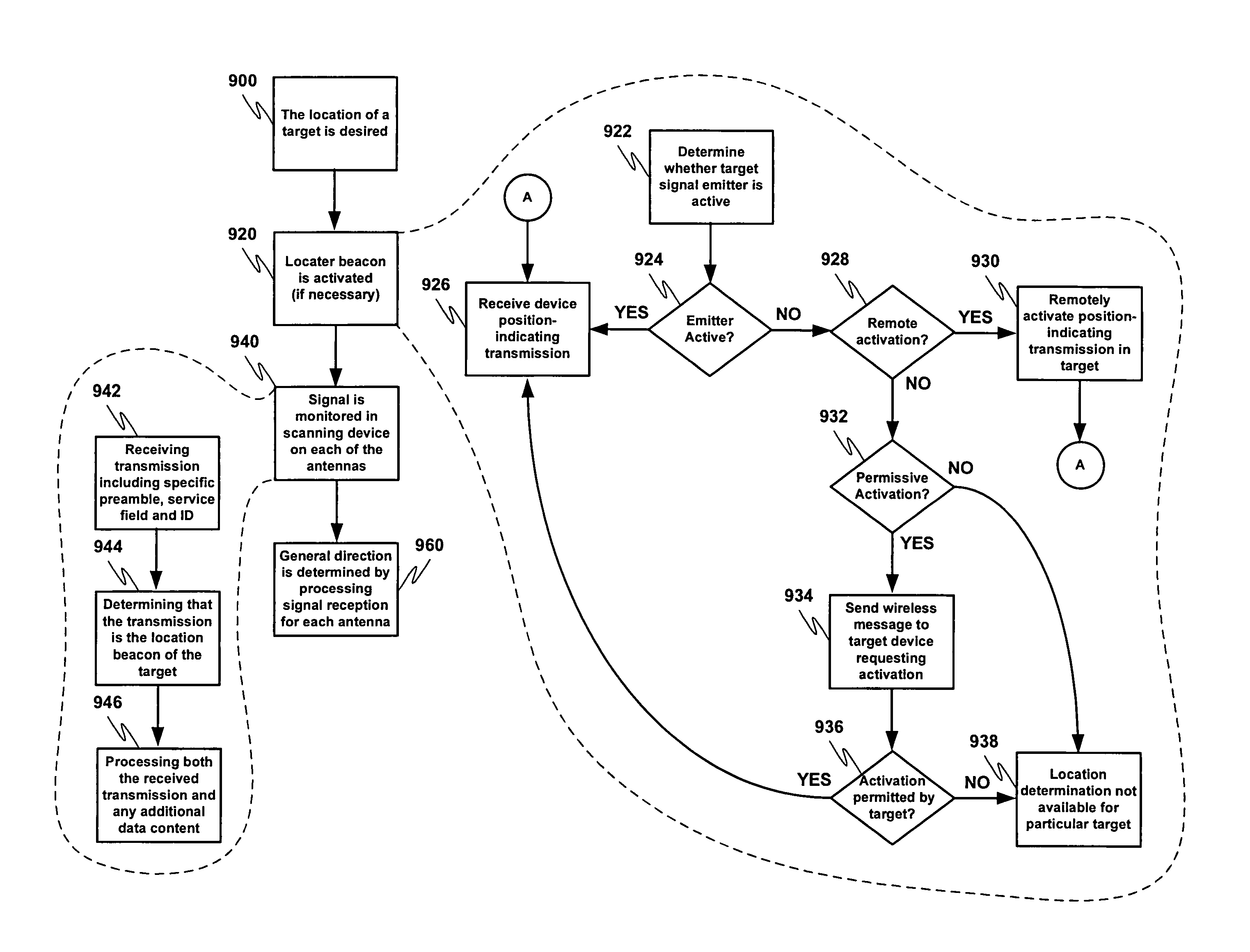
System and methods for direction finding using a handheld device
ActiveUS20070197229A1Position fixationNear-field for read/write/interrrogation/identification systemsRelevant informationEngineering
A system for indicating the relative direction of a target object or location as determined from the current position of a wireless communication device. The system employs Direction of Arrival determination using an antenna array for indicating the direction of a target device and includes facilities to activate a location-indicating transmission in a target device, the ability to request that a location-indicating transmission be activated in a remote target device, relevant information reception from a target device and the display of all potential target devices within effective transmission range of the wireless communication device.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
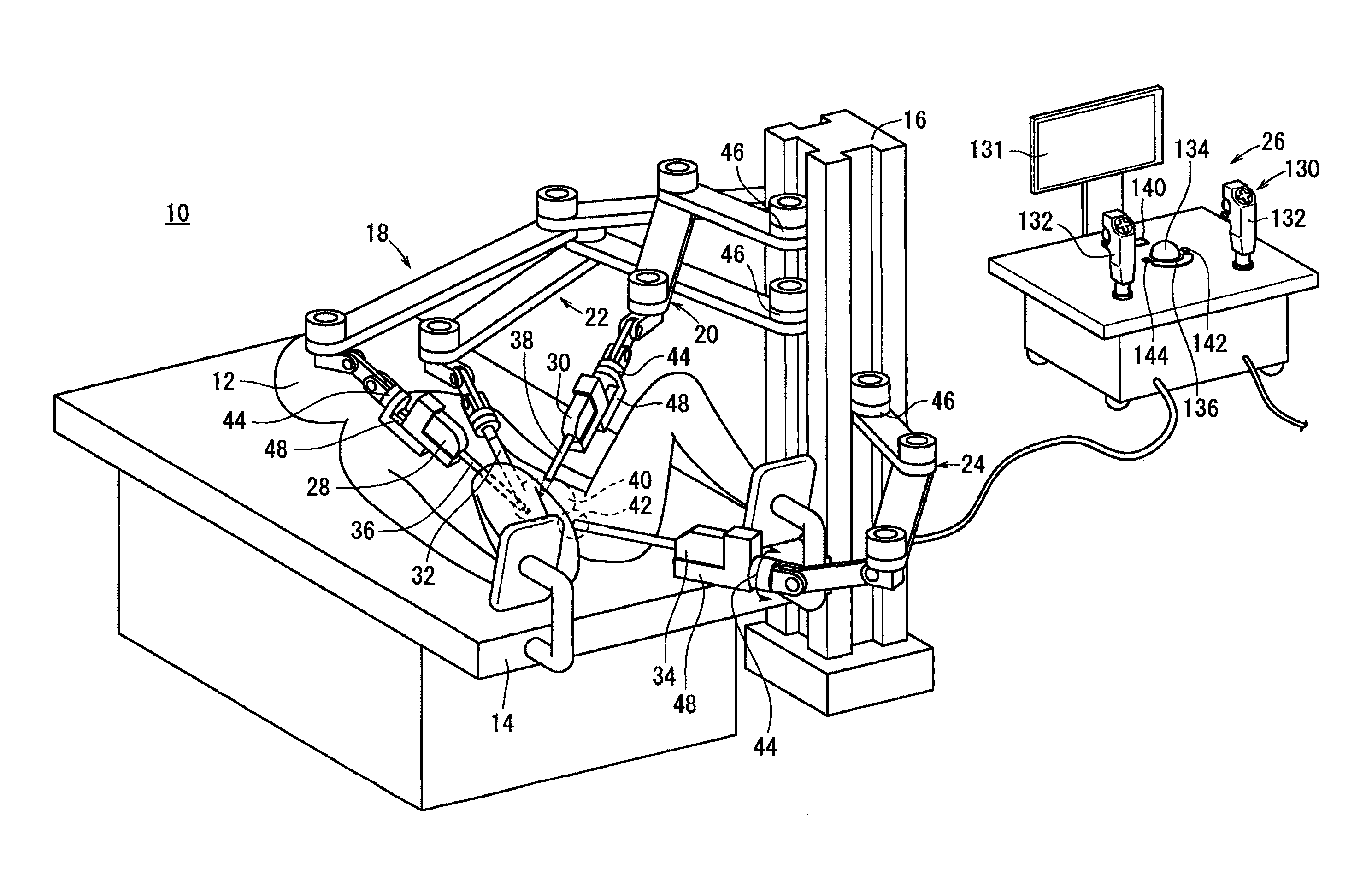
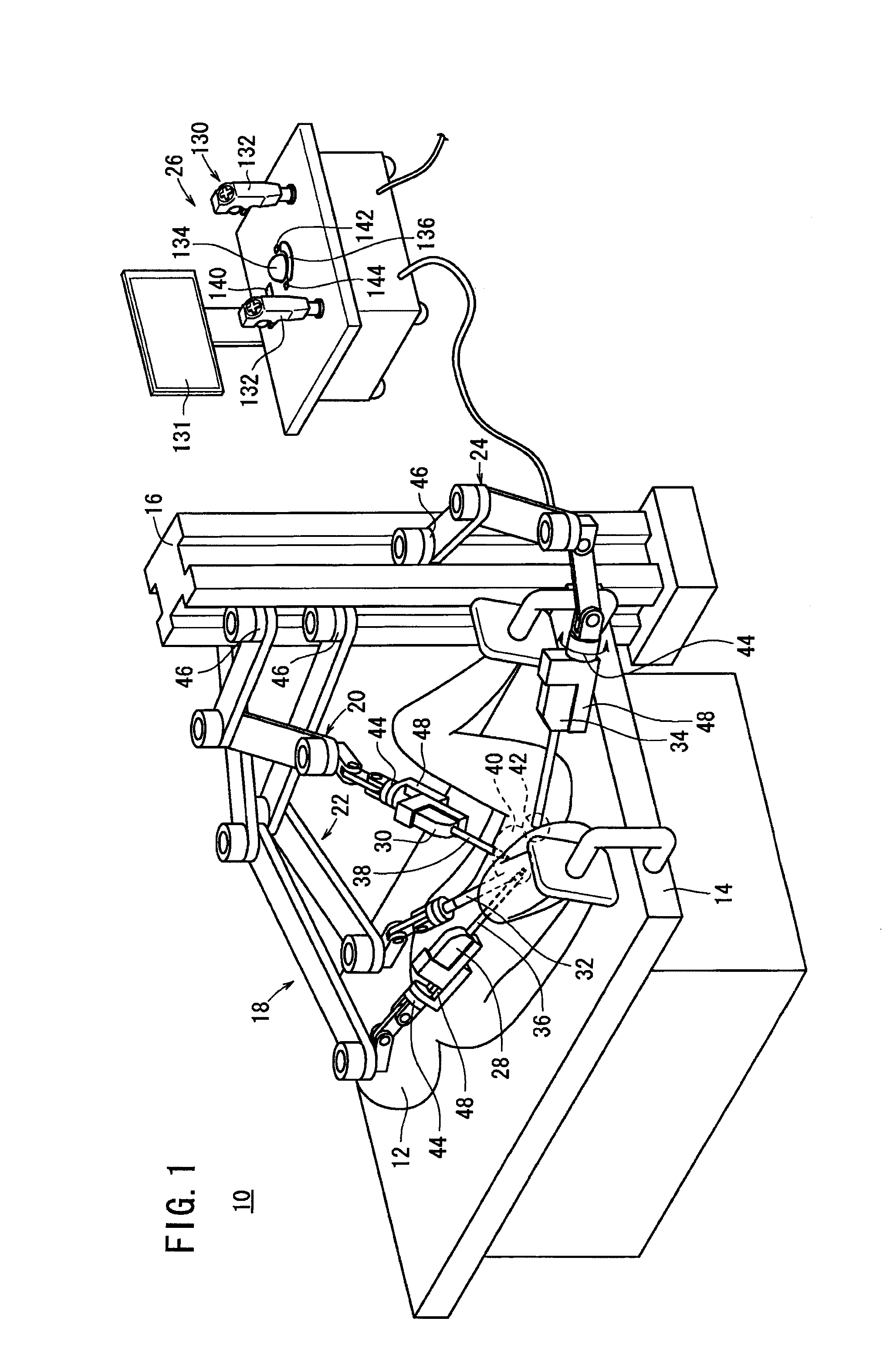
Medical robot system for supporting an organ in a position suitable for a medical treatment
ActiveUS20100331859A1Reduce the numberAvoid problemsDiagnosticsSurgical manipulatorsRobotic systemsMedical robot
Provided is a medical robot system which includes a medical manipulator capable of handling organs such as a uterine of different shapes and sizes. The medical robot system includes a robot arm, a medical manipulator which is detachably provided in the robot arm and supports an organ to a predetermined position, and a controller unit operable by an operator to control the robot arm and the medical manipulator. The medical manipulator also includes a first arm portion in a base side thereof, a second arm portion in a front side thereof for supporting the organ, and a connection portion connecting the first arm portion with the second arm portion. The control unit adjusts a relative direction of the second arm portion and the first arm portion and a length of the second arm portion in a telescopic manner thereby being suitable for organs of various shapes and sizes.
Owner:KARL STORZ GMBH & CO KG
Multi-axial orthopedic device and system
Embodiments of an orthopedic implant device and system, and methods for implanting them, are disclosed. The implant may include a receiver member having a channel for accommodating an elongated rod or other longitudinal member, a bone anchoring member such as a screw or hook, and a base member rotatable with respect to the receiver member for retaining the bone anchoring member in the receiver member. The base member is configured to allow at least two different degrees of maximum angulation of the bone anchoring member with respect to the receiver member. The number and relative direction of such angulations are independent of the orientation of the channel or other part of the receiving member.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
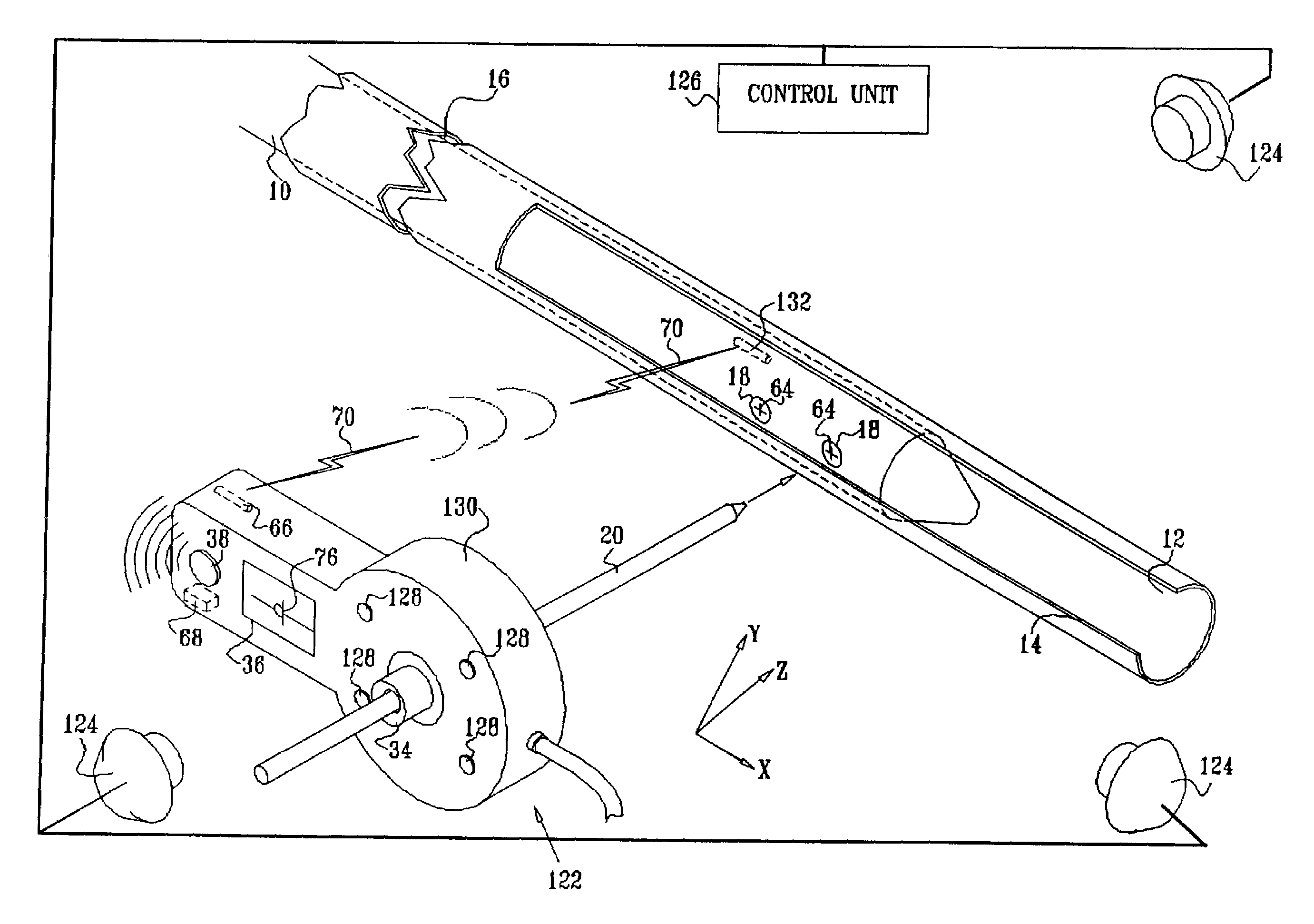
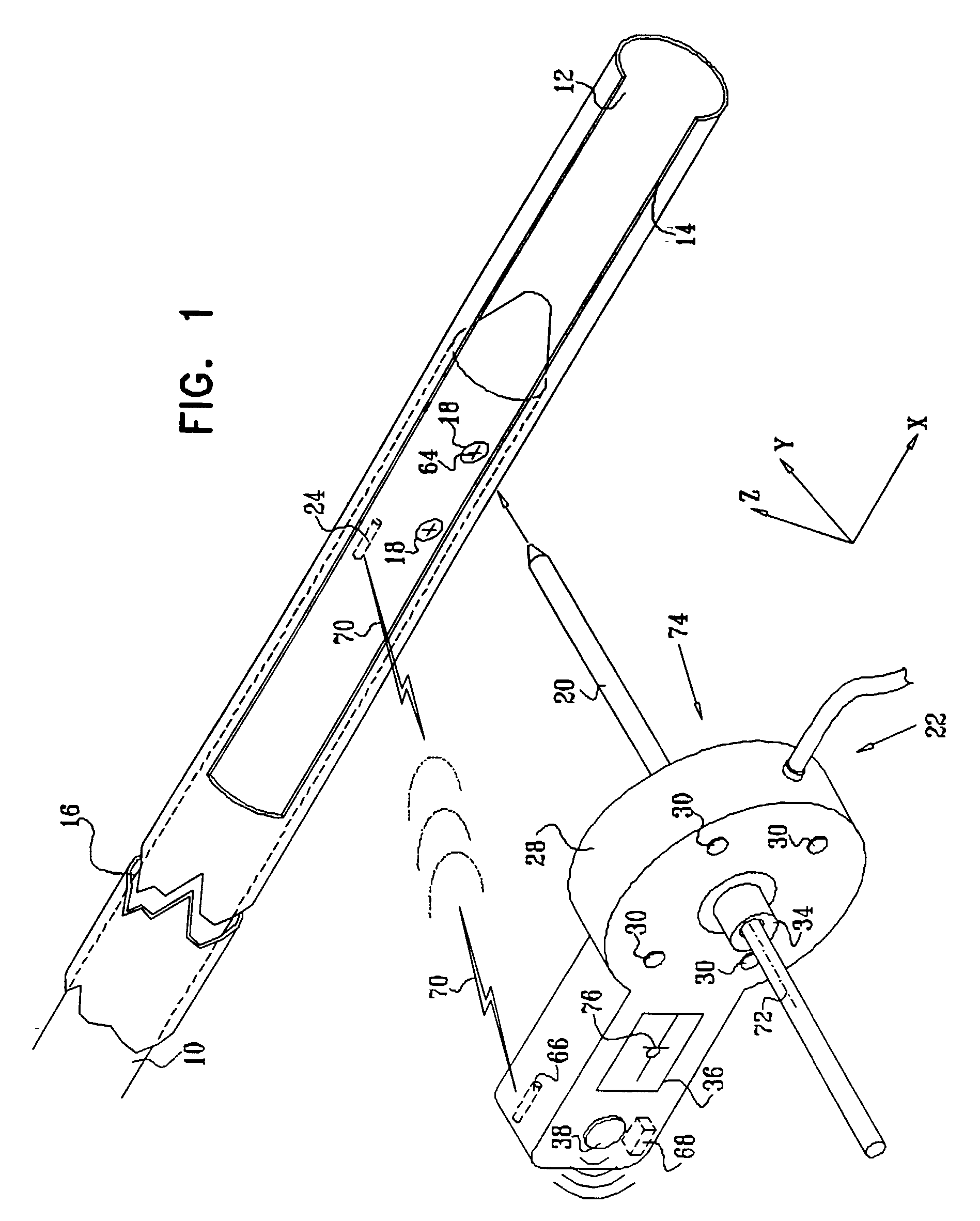
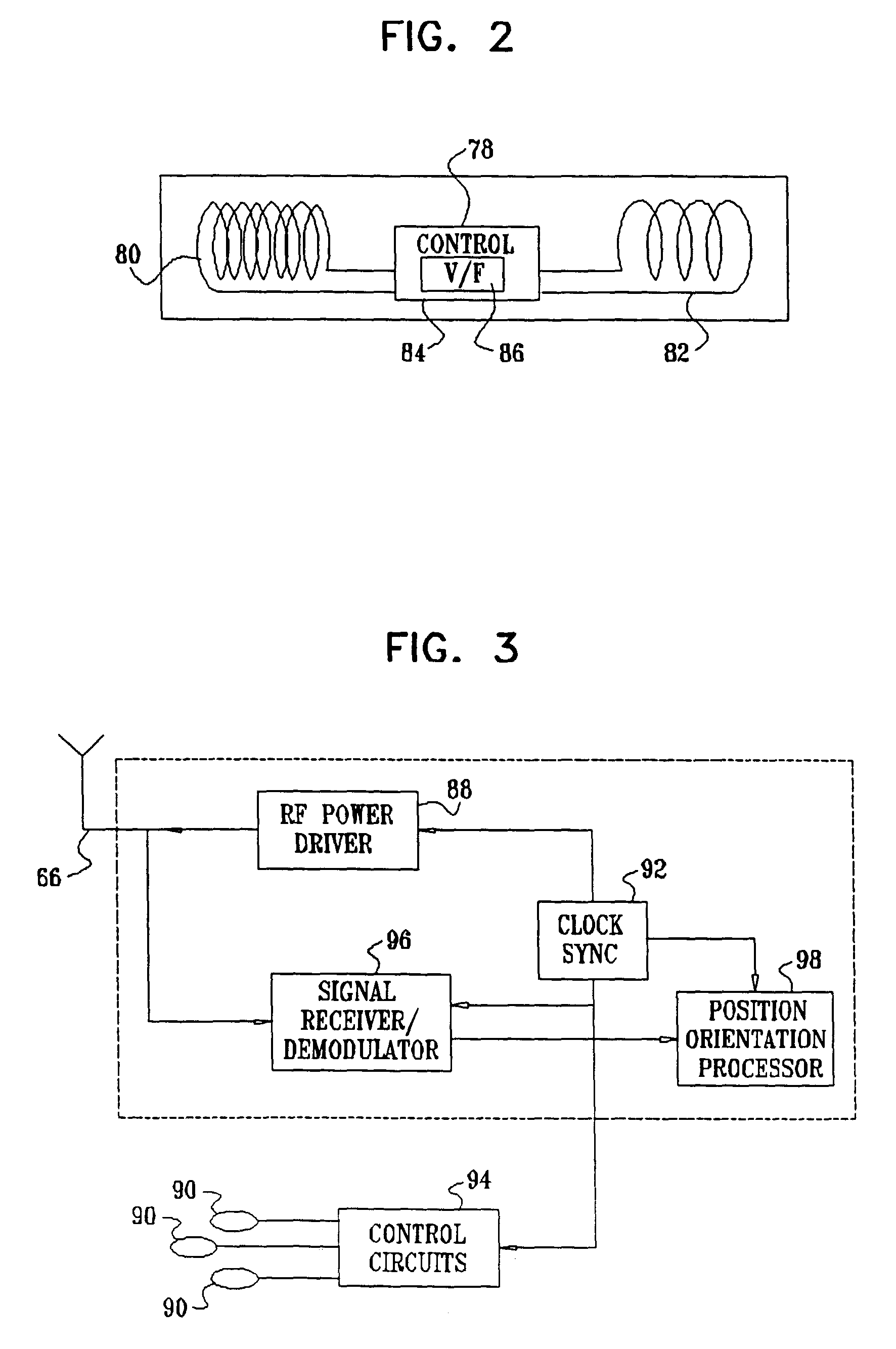
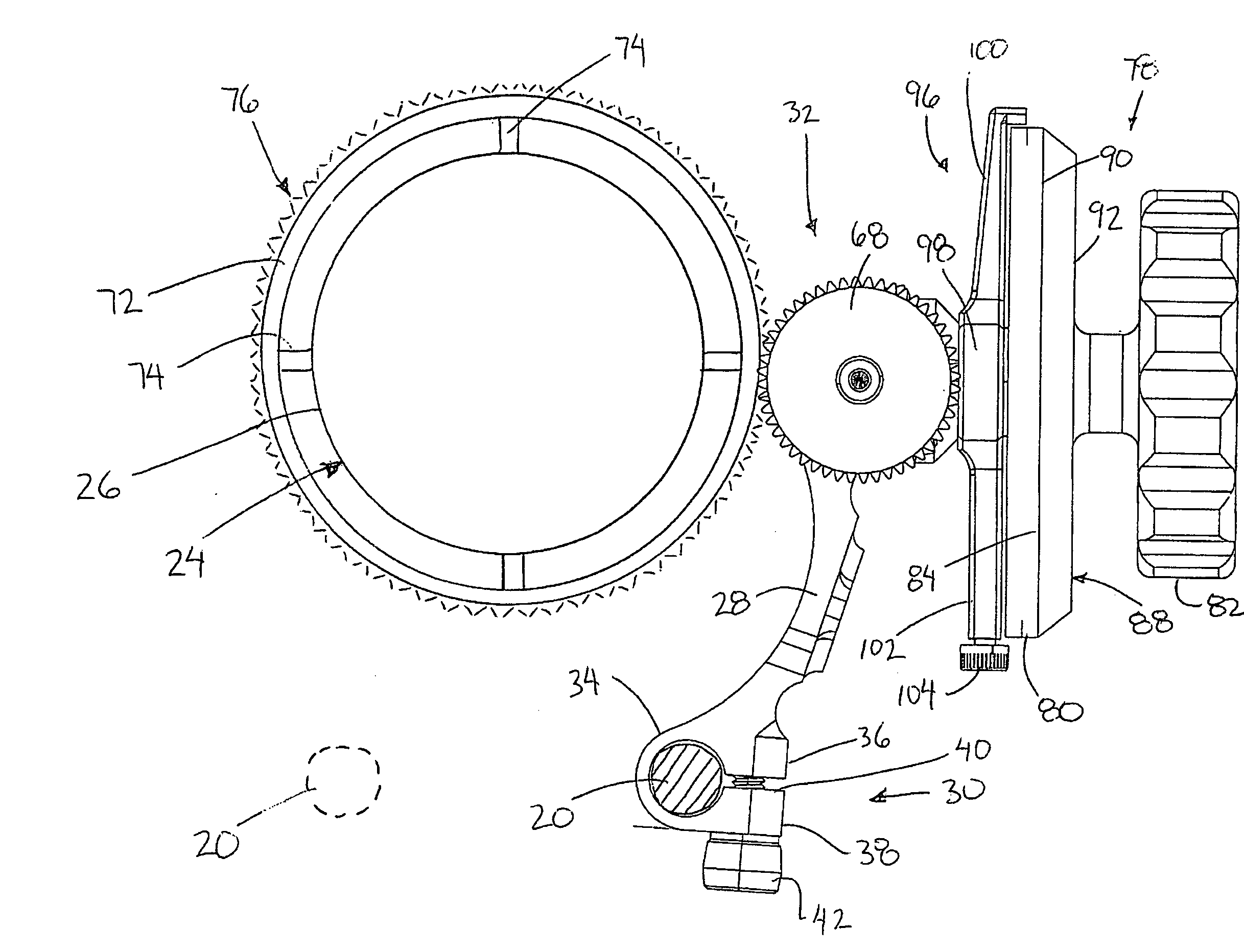
Distal targeting of locking screws in intramedullary nails
In a distal targeting system a hand-held location pad is integral with a guide section for a drill or similar surgical instrument, and has a plurality of magnetic field generators. A sensor, such as a wireless sensor, having a plurality of field transponders, is disposed in an orthopedic appliance, such as an intramedullary nail. The sensor is capable of detecting and discriminating the strength and direction of the different fields generated by the field generators. Control circuitry, preferably located in the location pad is responsive to a signal of the sensor, and determines the displacement and relative directions of an axis of the guide section, and a bore in the orthopedic appliance. A screen display and optional speaker in the location pad provide an operator-perceptible indication that enables the operator to adjust the position of the guide section so as to align its position and direction with the bore.
Owner:BIOSENSE
Apparatus method and system for docking a trailer to a towing vehicle
InactiveUS20050128059A1Precise positioningFunction increaseVehicle with living accommodationOptical signallingVehicle drivingTowing
A system for docking a vehicle to a trailer includes a scanning module affixed to the rear of a vehicle that scans the area behind the vehicle to locate and measure the distance to a trailer, utilizing a reflector affixed to the trailer. A display module in the cab of the vehicle receives distance and direction data from the scanning module and uses a graphical display to graphically depict the distance and relative orientation between the vehicle and trailer. In one embodiment the graphical depiction is an overhead view with an icon indicating the position of the trailer hitch. The present invention enables an unassisted vehicle operator to align and position a vehicle for docking with a trailer.
Owner:VAUSE DOUGLAS
Apparatus and method for determining the relative position and orientation of neurostimulation leads
ActiveUS20060122653A1Spinal electrodesDiagnostic recording/measuringPotential measurementSpinal column
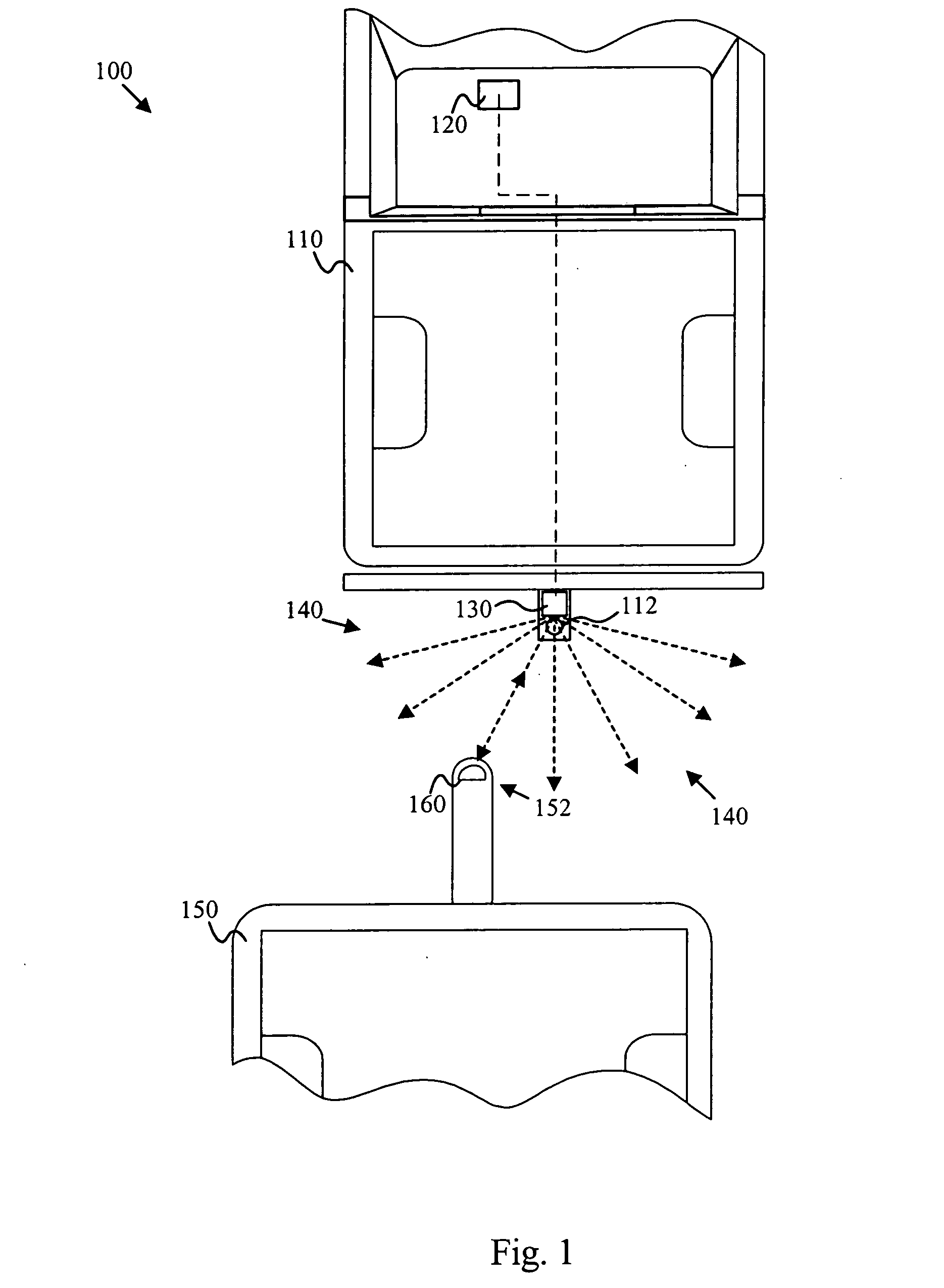
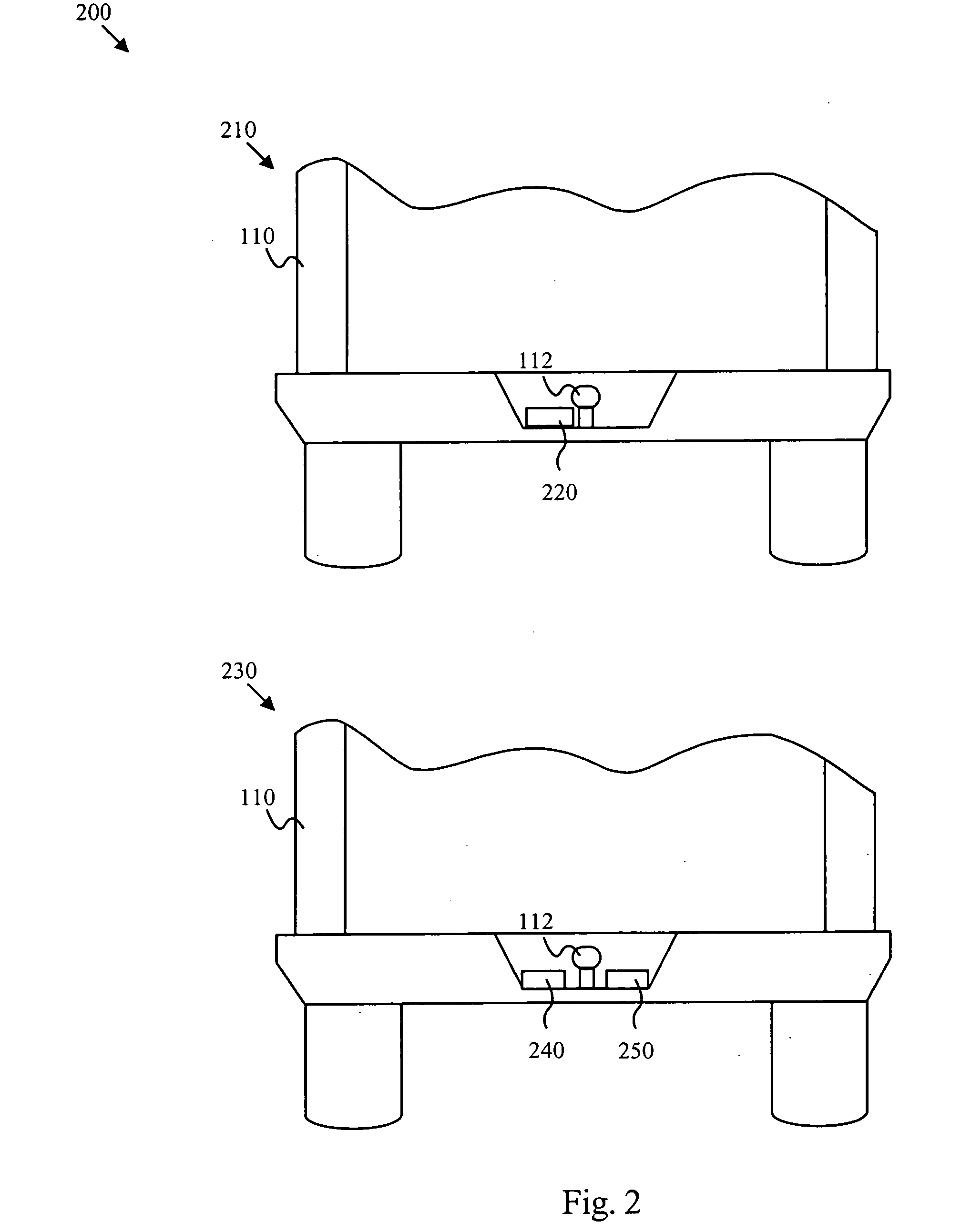
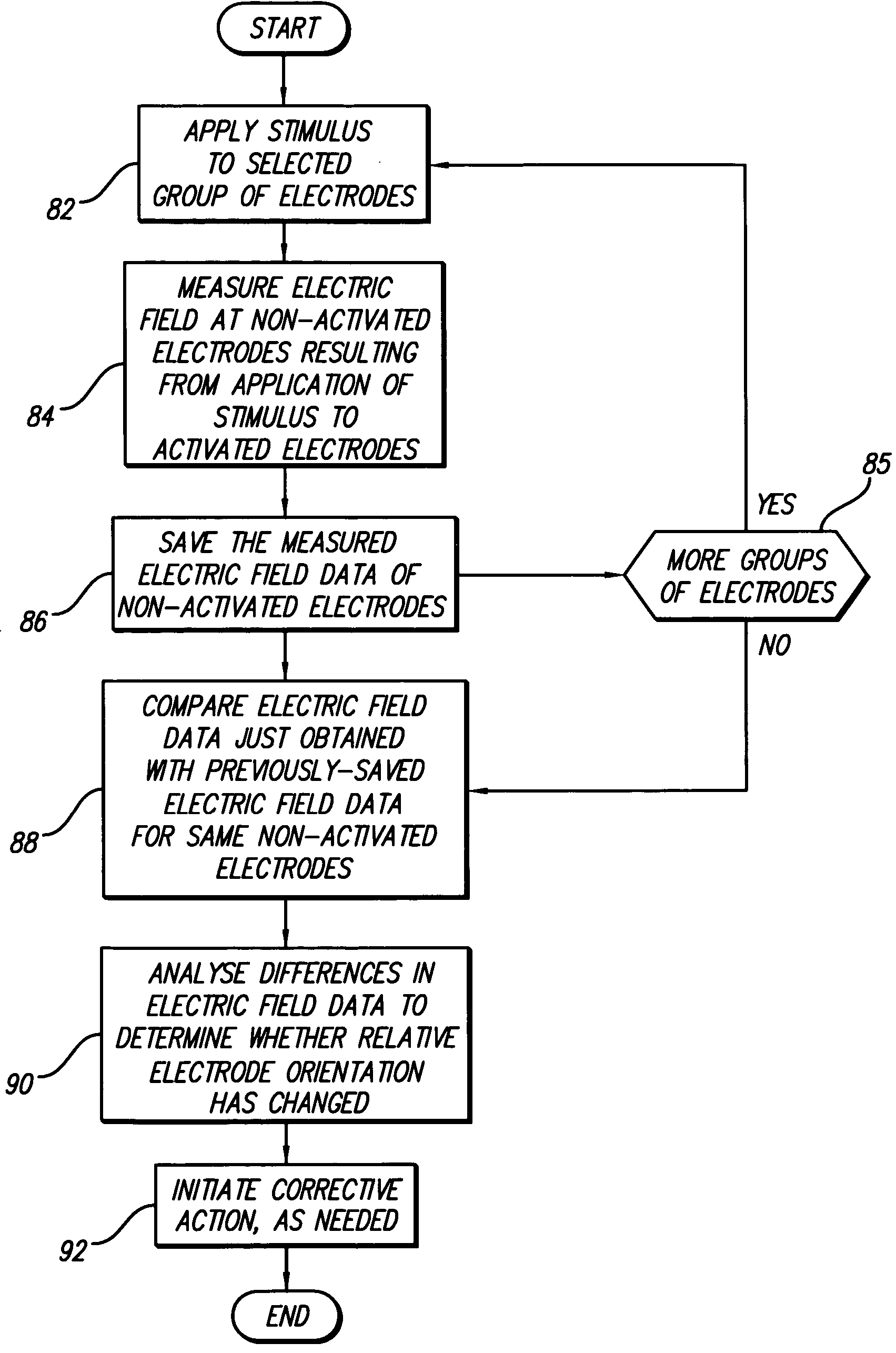
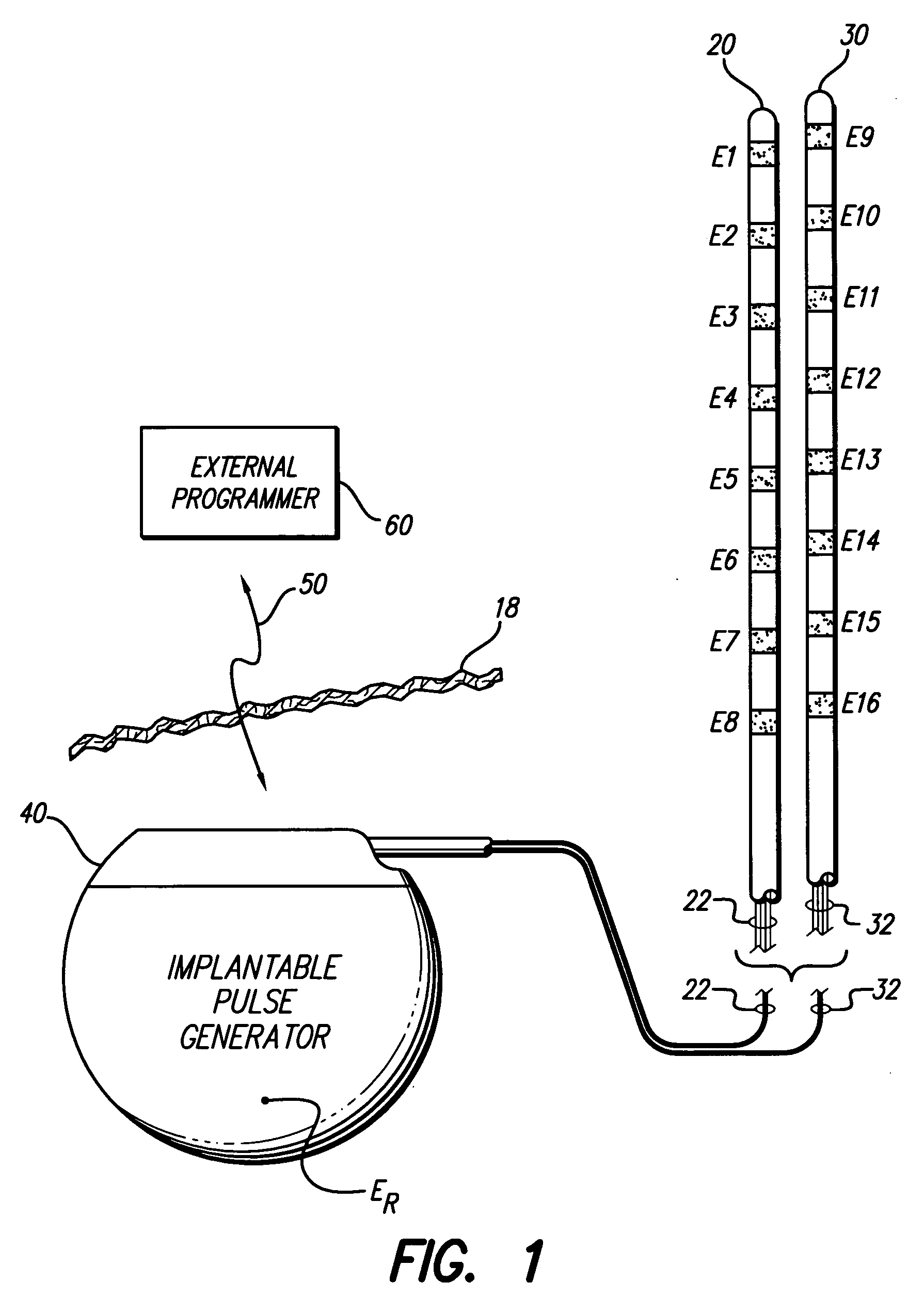
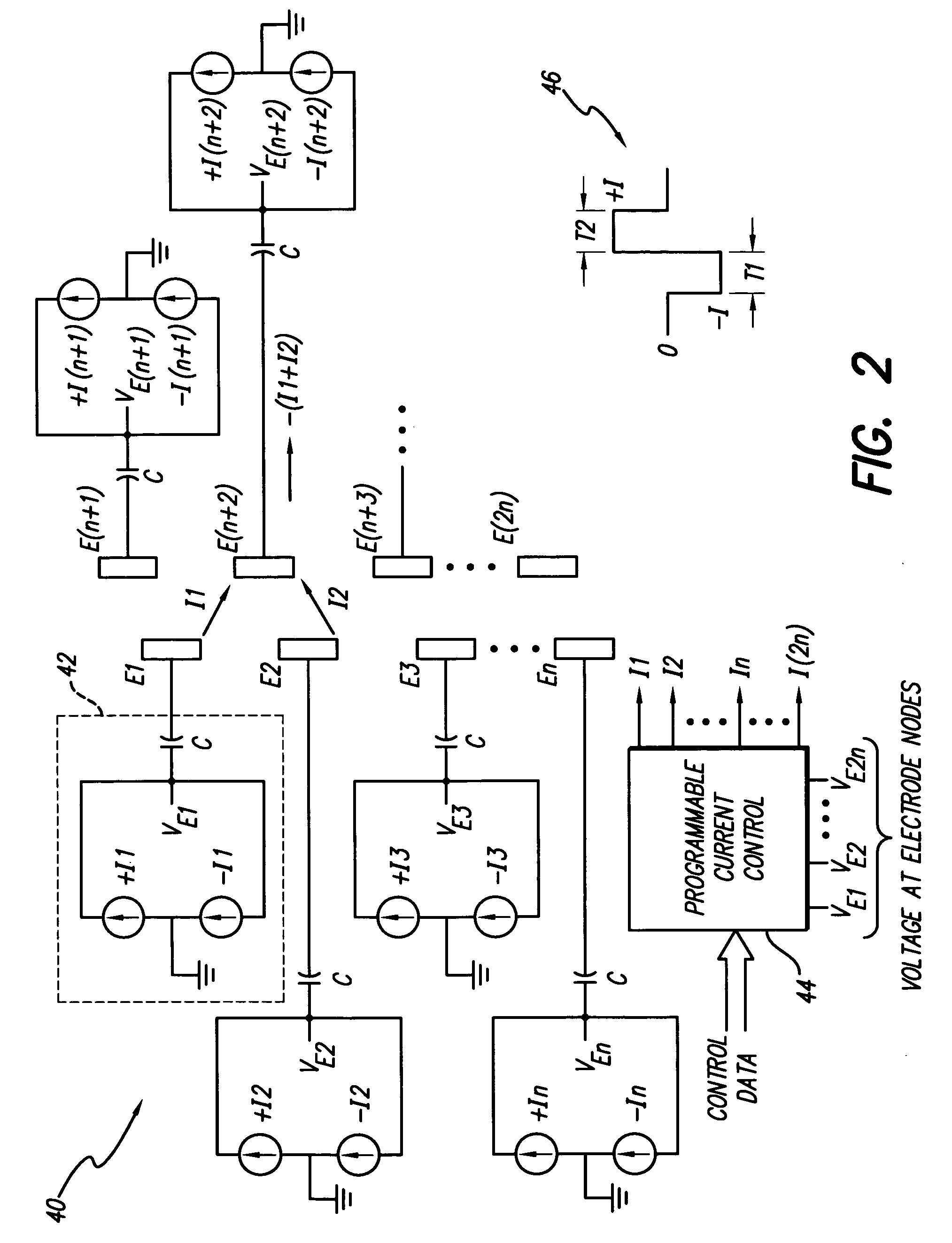
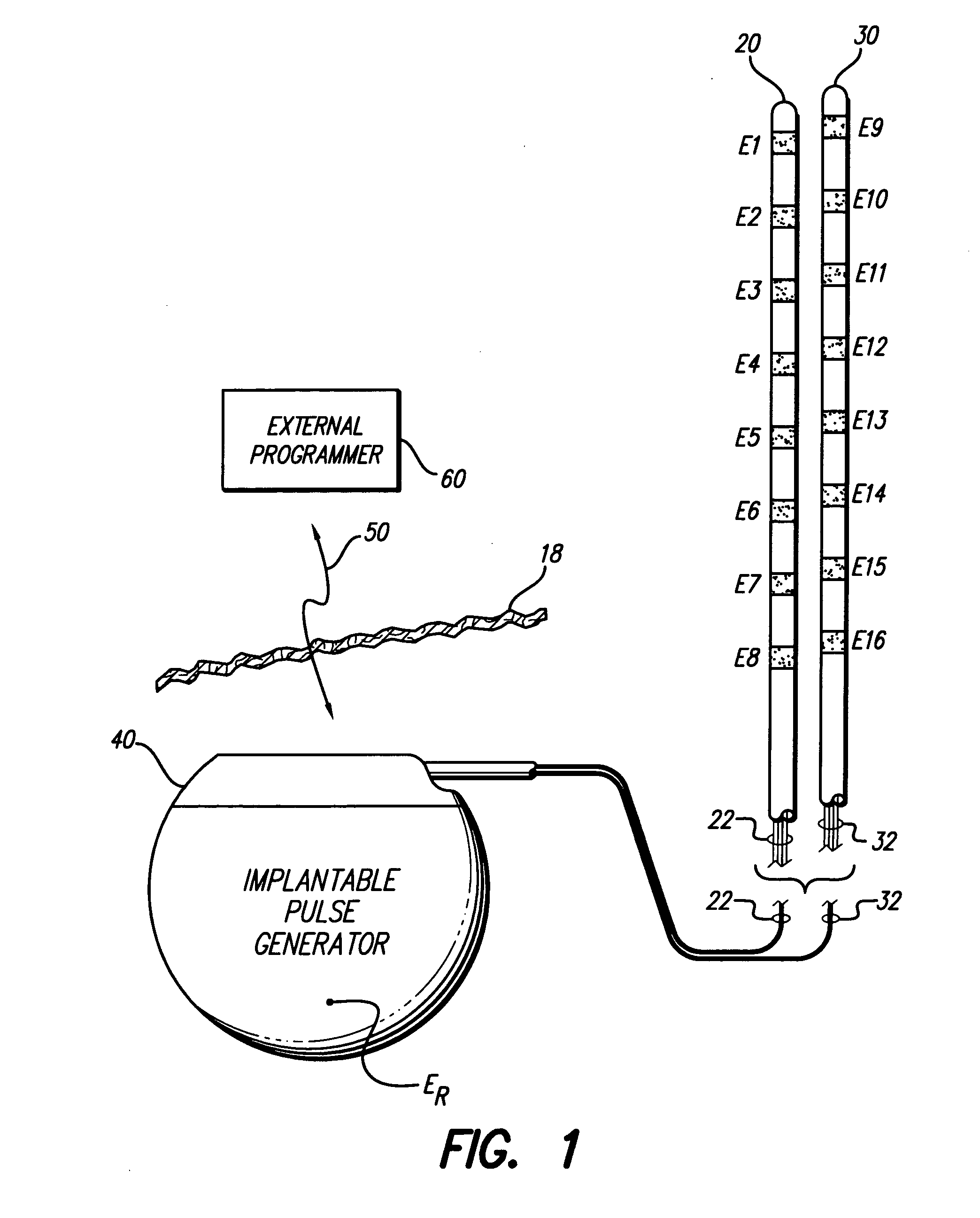
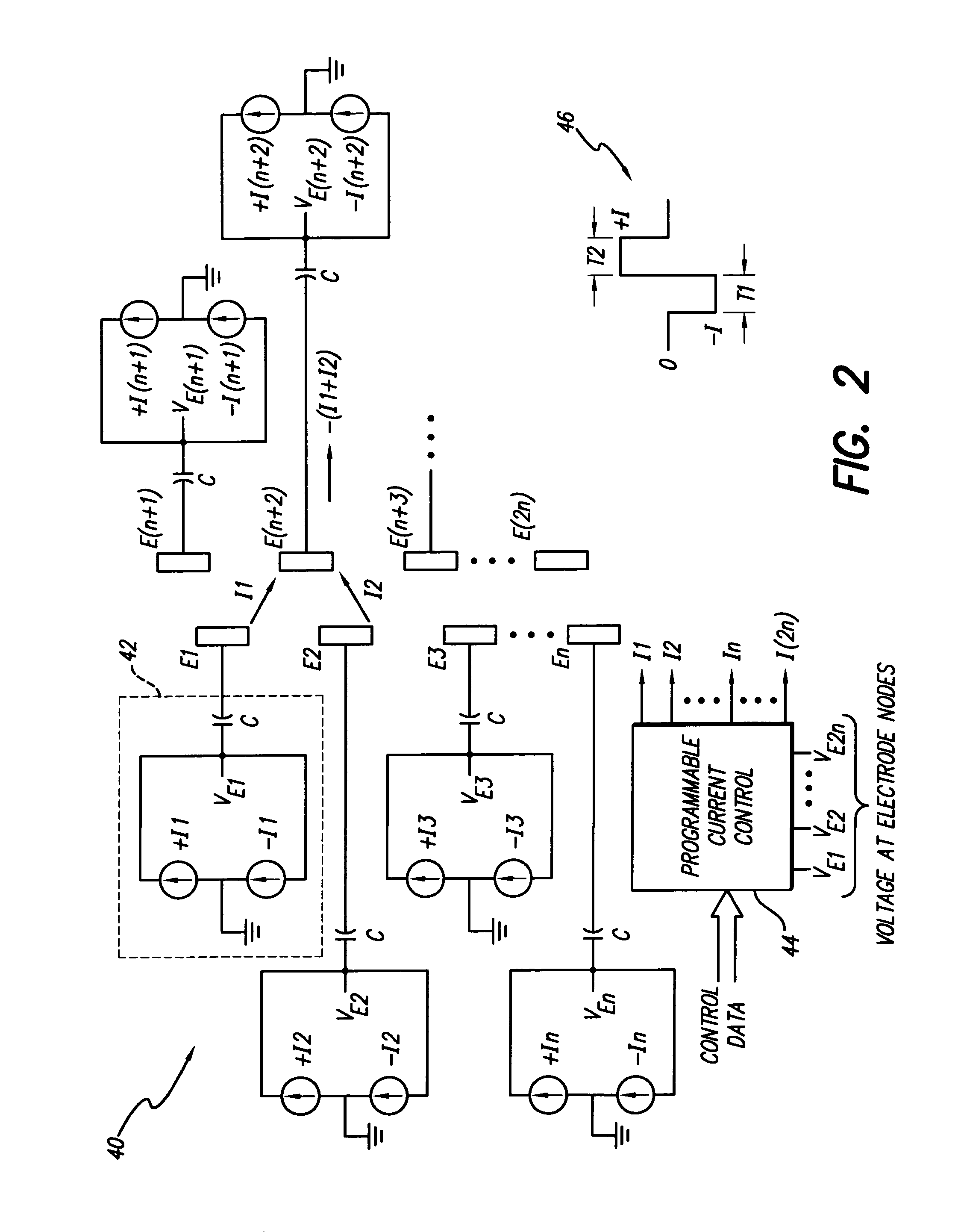
Interelectrode impedance or electric field potential measurements are used to determine the relative orientation of one lead to other leads in the spinal column or other body / tissue location. Interelectrode impedance is determined by measuring impedance vectors. The value of the impedance vector is due primarily to the electrode-electrolyte interface, and the bulk impedance between the electrodes. The bulk impedance between the electrodes is, in turn, made up of (1) the impedance of the tissue adjacent to the electrodes, and (2) the impedance of the tissue between the electrodes. In one embodiment, the present invention makes both monopolar and bipolar impedance measurements, and then corrects the bipolar impedance measurements using the monopolar measurements to eliminate the effect of the impedance of the tissue adjacent the electrodes. The orientation and position of the leads may be inferred from the relative minima of the corrected bipolar impedance values. These corrected impedance values may also be mapped and stored to facilitate a comparison with subsequent corrected impedance measurement values. Such comparison allows a determination to be made as to whether the lead position and / or orientation has changed appreciably over time. In another embodiment, one or more electrodes are stimulated and the resulting electric field potential on the non-stimulated electrodes is measured. Such field potential measurements provide an indication of the relative orientation of the electrodes. Once known, the relative orientation may be used to track lead migration, to setup stimulation configurations and parameters for nominal stimulation and / or navigation. Also, such measurements allow automatic adjustment of stimulation energy to a previously-defined optimal potential field in the case of lead migration or postural changes.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
Apparatus and method for determining the relative position and orientation of neurostimulation leads
ActiveUS20060122654A1Spinal electrodesDiagnostic recording/measuringPotential measurementSpinal column
Interelectrode impedance or electric field potential measurements are used to determine the relative orientation of one lead to other leads in the spinal column or other body / tissue location. Interelectrode impedance is determined by measuring impedance vectors. The value of the impedance vector is due primarily to the electrode-electrolyte interface, and the bulk impedance between the electrodes. The bulk impedance between the electrodes is, in turn, made up of (1) the impedance of the tissue adjacent to the electrodes, and (2) the impedance of the tissue between the electrodes. In one embodiment, the present invention makes both monopolar and bipolar impedance measurements, and then corrects the bipolar impedance measurements using the monopolar measurements to eliminate the effect of the impedance of the tissue adjacent the electrodes. The orientation and position of the leads may be inferred from the relative minima of the corrected bipolar impedance values. These corrected impedance values may also be mapped and stored to facilitate a comparison with subsequent corrected impedance measurement values. Such comparison allows a determination to be made as to whether the lead position and / or orientation has changed appreciably over time. In another embodiment, one or more electrodes are stimulated and the resulting electric field potential on the non-stimulated electrodes is measured. Such field potential measurements provide an indication of the relative orientation of the electrodes. Once known, the relative orientation may be used to track lead migration, to setup stimulation configurations and parameters for nominal stimulation and / or navigation. Also, such measurements allow automatic adjustment of stimulation energy to a previously-defined optimal potential field in the case of lead migration or postural changes.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
Sensor Fusion Algorithm
ActiveUS20130232280A1Well formedInput/output for user-computer interactionBuilding braking devicesAlgorithmComputer vision
Sensor fusion algorithm techniques are described. In one or more embodiments, behaviors of a host device and accessory devices are controlled based upon an orientation of the host device and accessory devices, relative to one another. A combined spatial position and / or orientation for the host device may be obtained based on raw measurements that are obtained from at least two different types of sensors. In addition, a spatial position and / or orientation for an accessory device is ascertained using one or more sensors of the accessory device. An orientation (or position) of the accessory device relative to the host computing device may then be computed based on the combined spatial position / orientation for the host computing device and the ascertained spatial position / orientation for the accessory device. The relative orientation that is computed may then be used in various ways to control behaviors of the host computing device and / or accessory device.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Two-dimensional code and vision-inert combined navigation system and method for robot
ActiveCN104848858AImprove screening efficiencyImprove computing efficiencyNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsAbsolute orientationNavigation system
The invention provides a two-dimensional code and a vision-inert combined navigation system and method for a robot. A sealed assistant frame is arranged at the periphery of the two-dimensional code, and the sealed assistant frame and the two-dimensional code are both applied to vision navigation. The two-dimensional code is used in the vision-inert combined navigation system for the robot; the vision-inert combined navigation method for the robot comprises the following steps: paving a plurality of two-dimensional codes with the sealed assistant frames at the peripheries on a ground; when the robot walks forwards, taking images by using imaging equipment; acquiring the absolute position and the absolute direction angle of the imaging equipment, and acquiring the absolute coordinates of the two-dimensional codes, and the absolute position and the absolute direction angle of the imaging equipment; confirming the relative position of the robot relative to a present starting point and the relative direction angle of the robot relative to a present starting direction angle; acquiring the absolute position of the robot, and taking the absolute position as a next starting point; acquiring the absolute direction angle of the robot, and taking the absolute direction angle as a next starting direction angle.
Owner:BEIJING JIZHIJIA TECH CO LTD
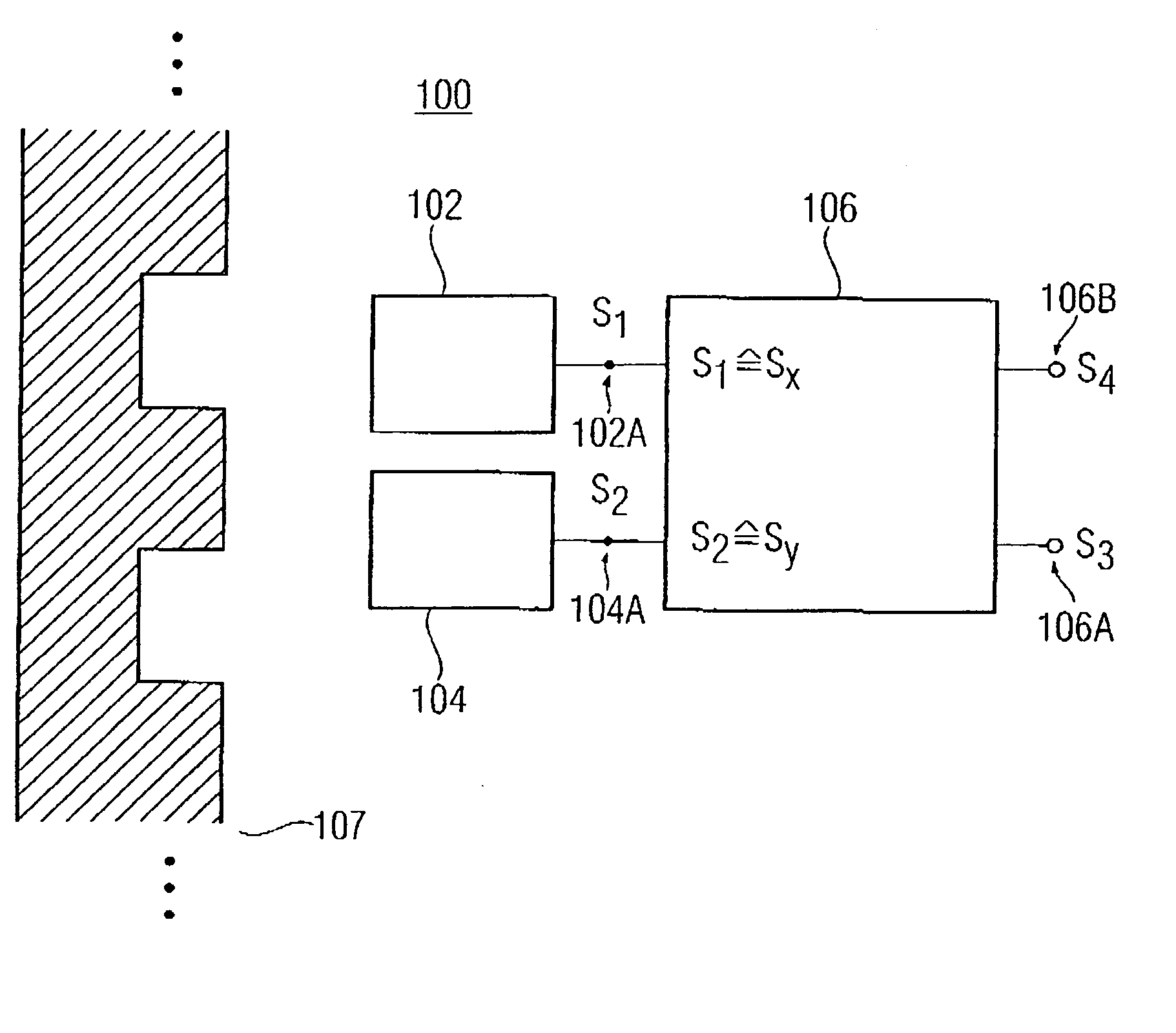
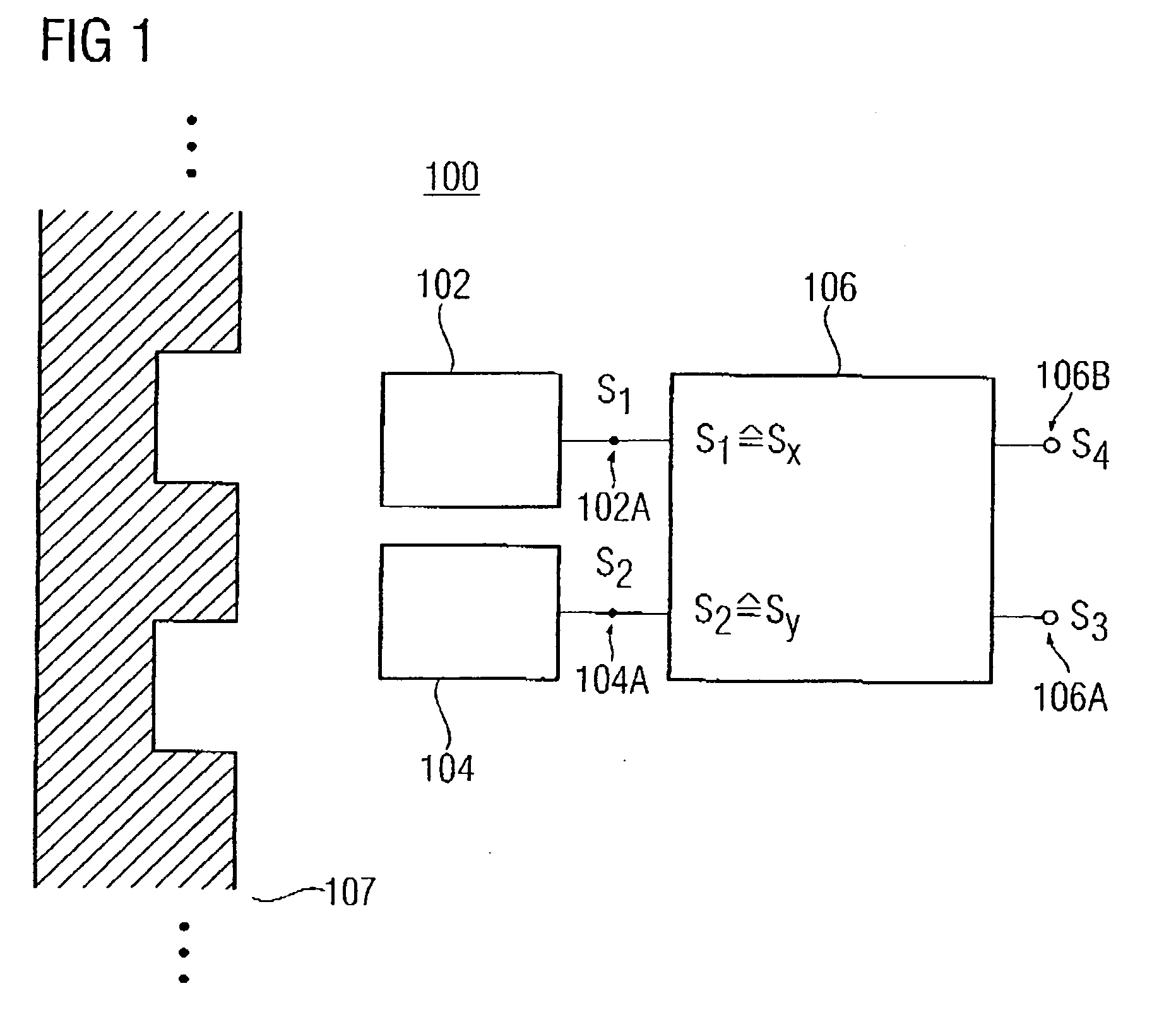
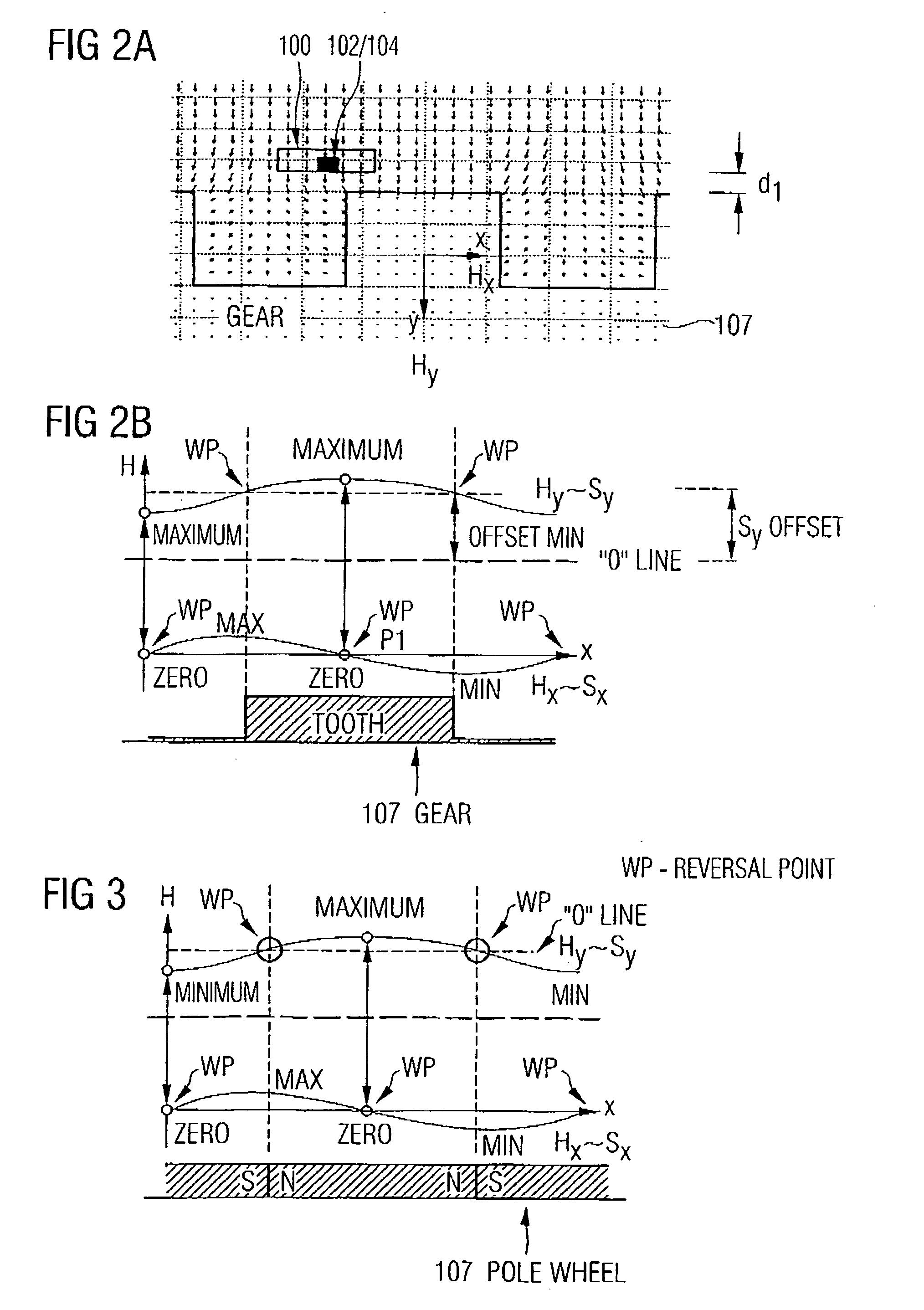
Apparatus and method for the determination of a direction of an object
InactiveUS20050258820A1Advanced conceptMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesMagnetic fieldNuclear magnetic resonance
An apparatus for the determination of a momentary relative direction of an indicator object depending on a magnetic field influenced or generated by the indicator object includes first means for sensing a course of a first magnetic field component of the magnetic field, second means for sensing a course of a second magnetic field component of the magnetic field, and means for evaluating the course of the first magnetic field component and the second magnetic field component in order to determine the momentary, relative direction of the indicator object, the first magnetic field component and the second magnetic field component being offset in angle with respect to each other.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
Wireless communication terminals and methods that display relative direction and distance therebetween responsive to acceleration data
InactiveUS20090221298A1Improve accuracyNavigation by terrestrial meansPosition fixationTerminal operationAcceleration Unit
Wireless communication terminals are disclosed that display the direction and distance between them so that users can, for example, travel away from each other and then later find one another. The terminals are configured to track their movement using acceleration data. Some of the terminals may operate as slave terminals in which they transmit their movement data to a master terminal which determines therefrom the relative direction and distance between the terminals. The master terminal may then transmit the relative direction and distance data to the slave terminals where it can be displayed to their users.
Owner:SONY ERICSSON MOBILE COMM AB
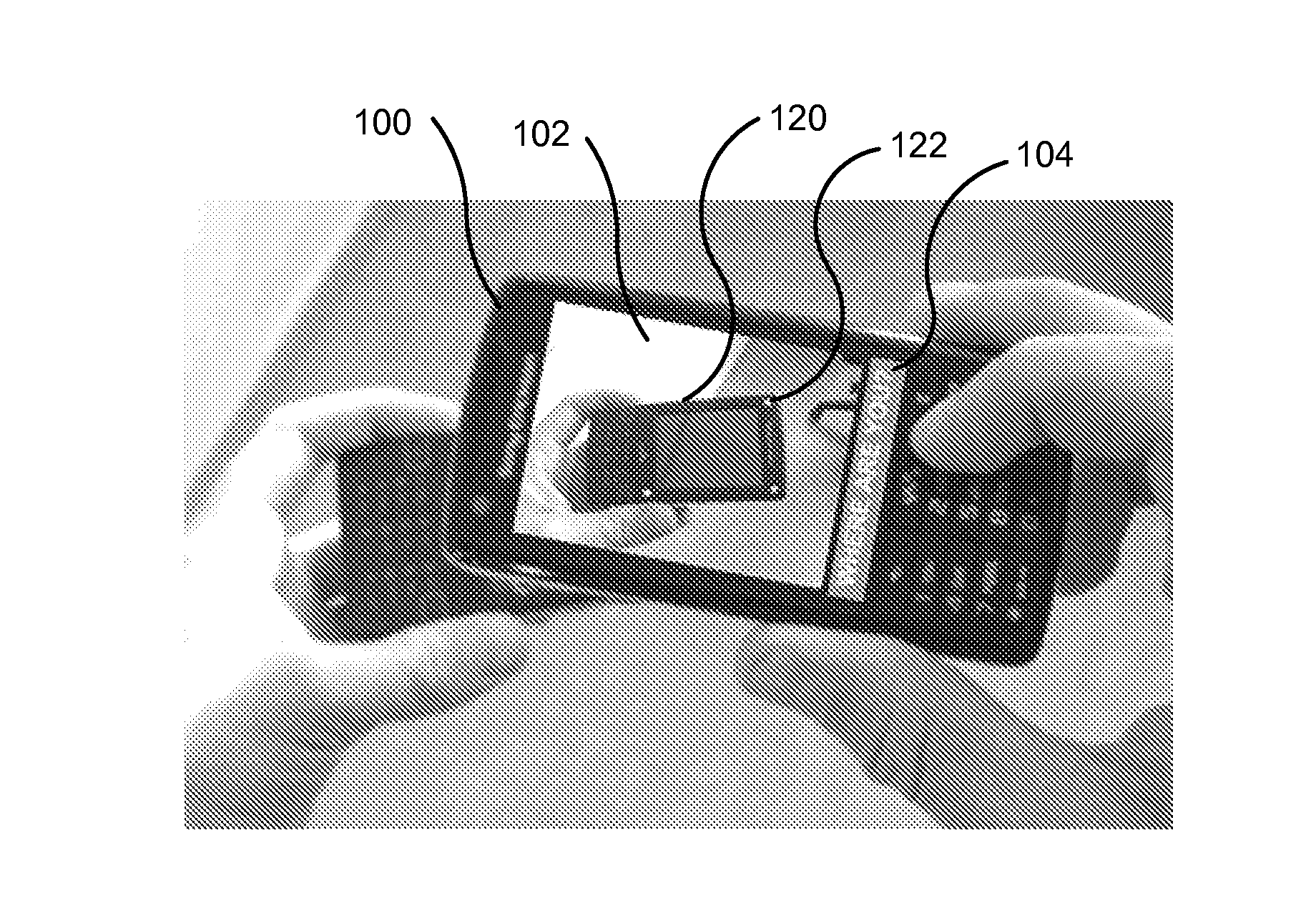
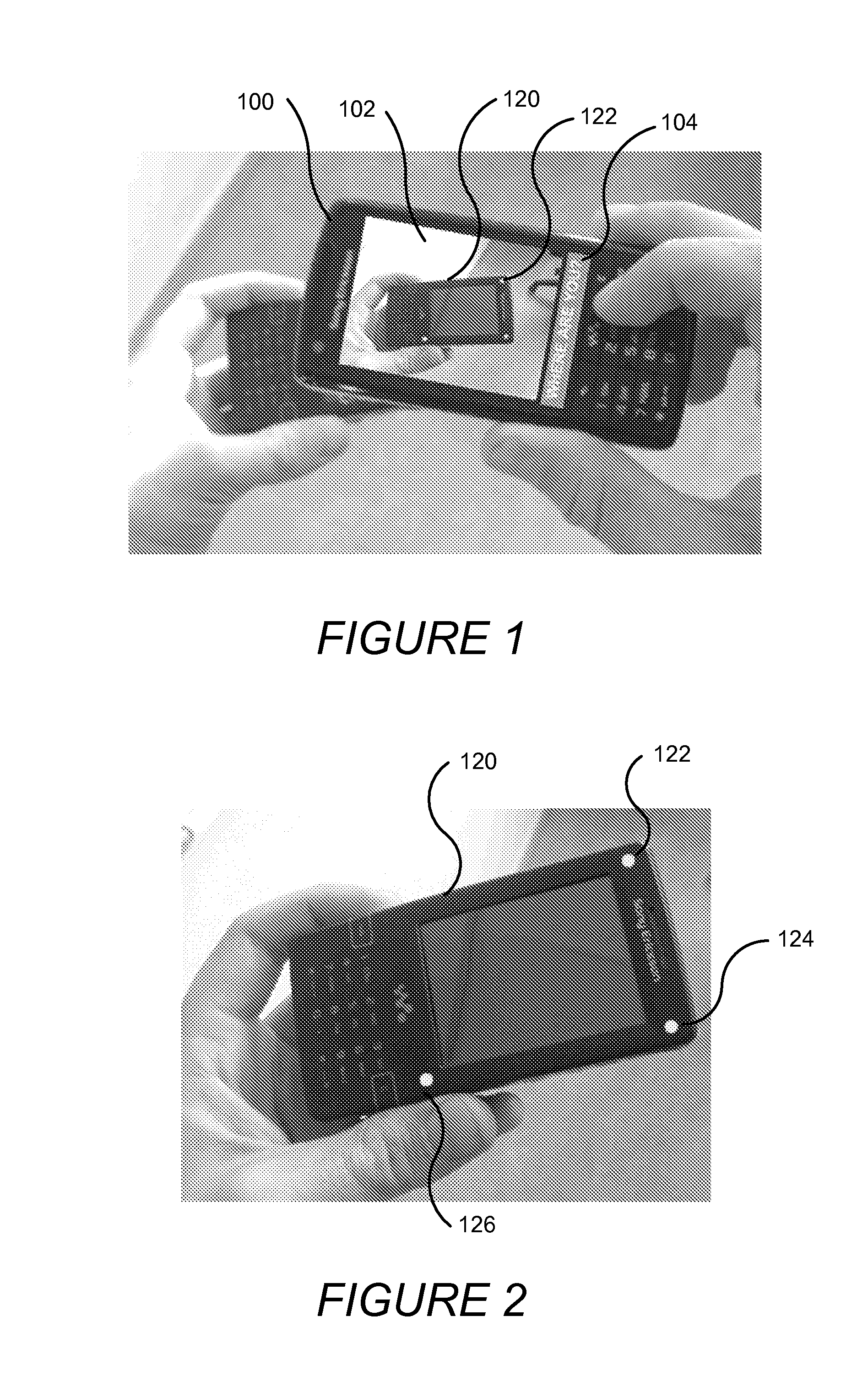
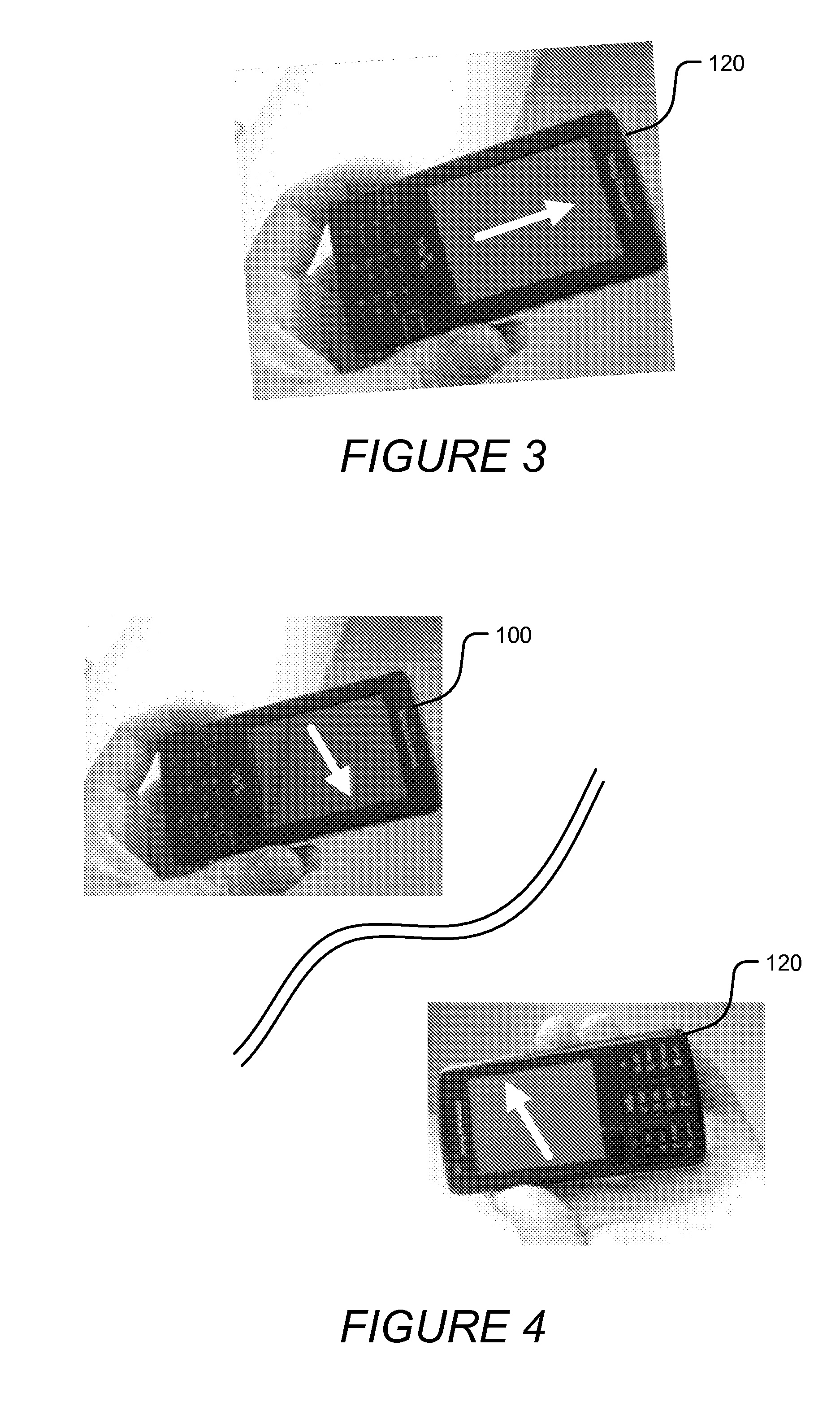
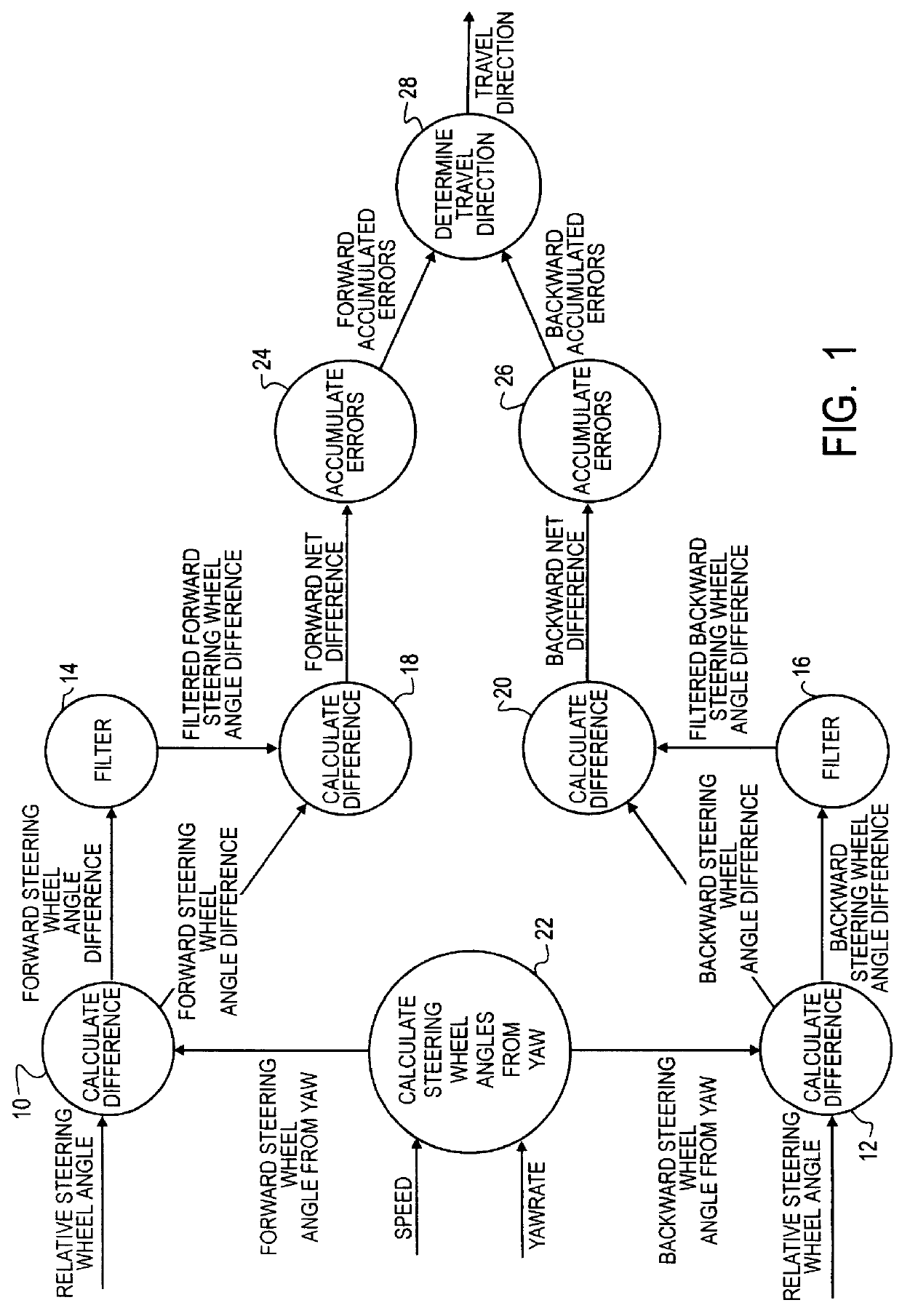
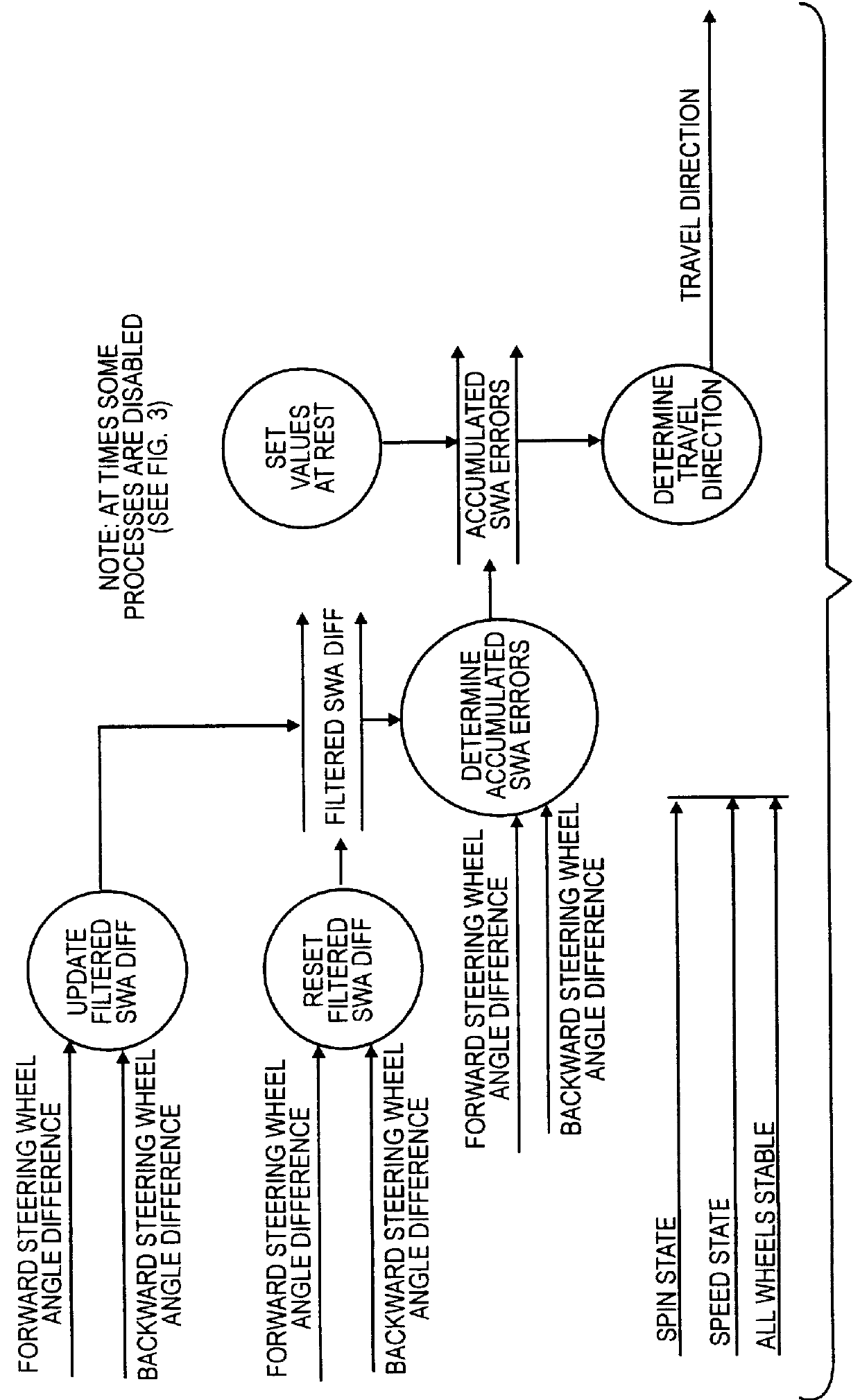
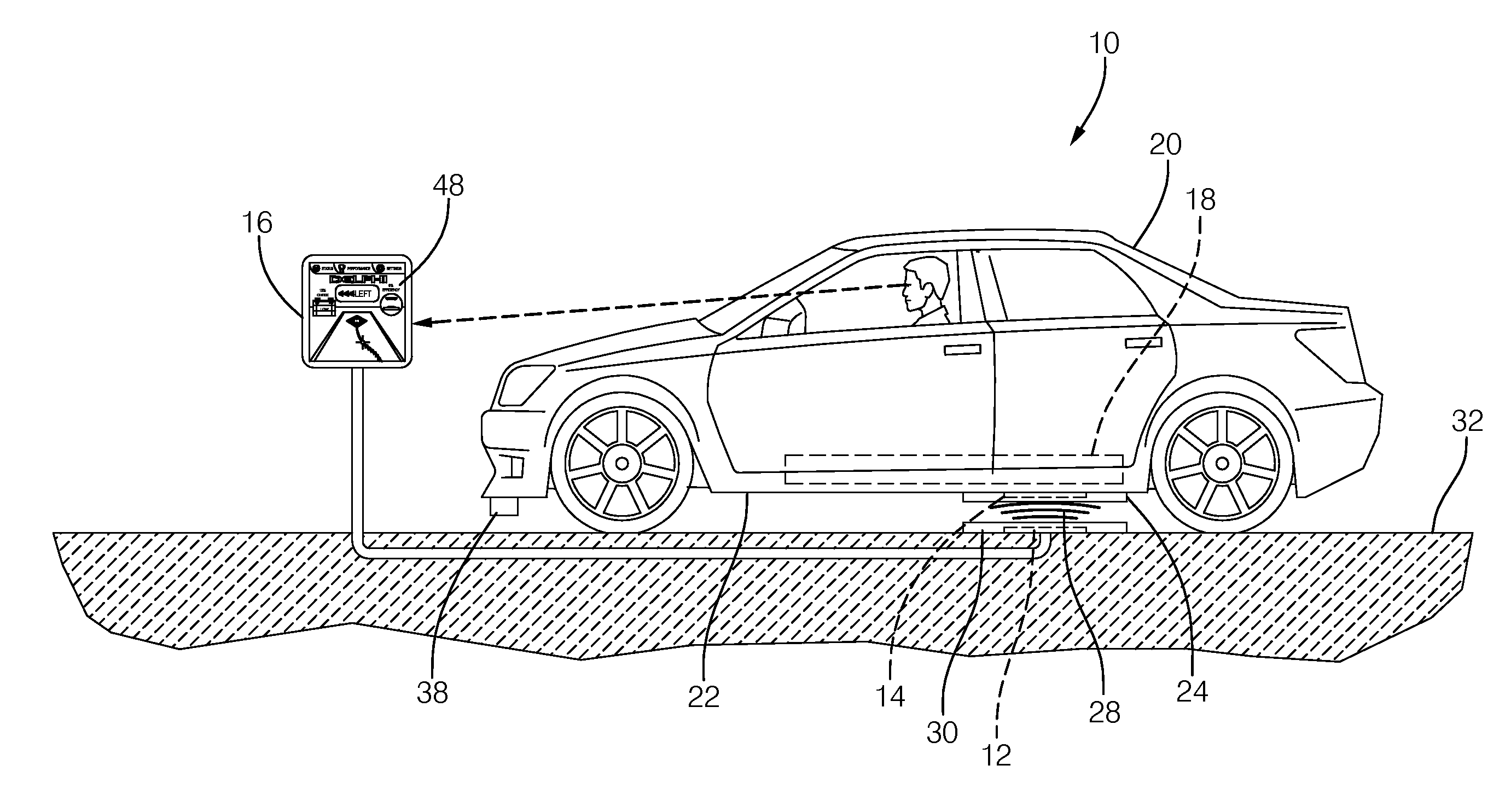
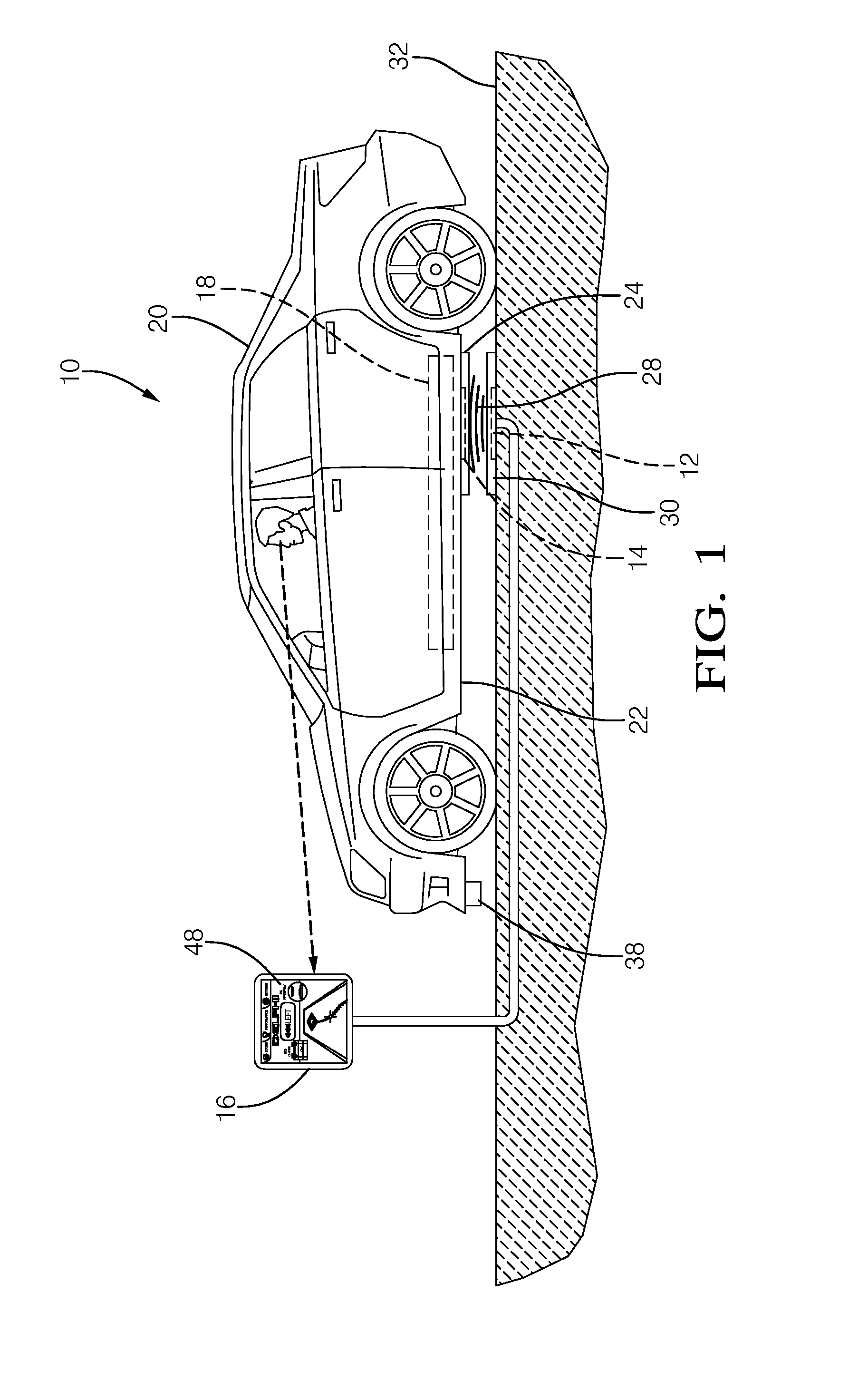
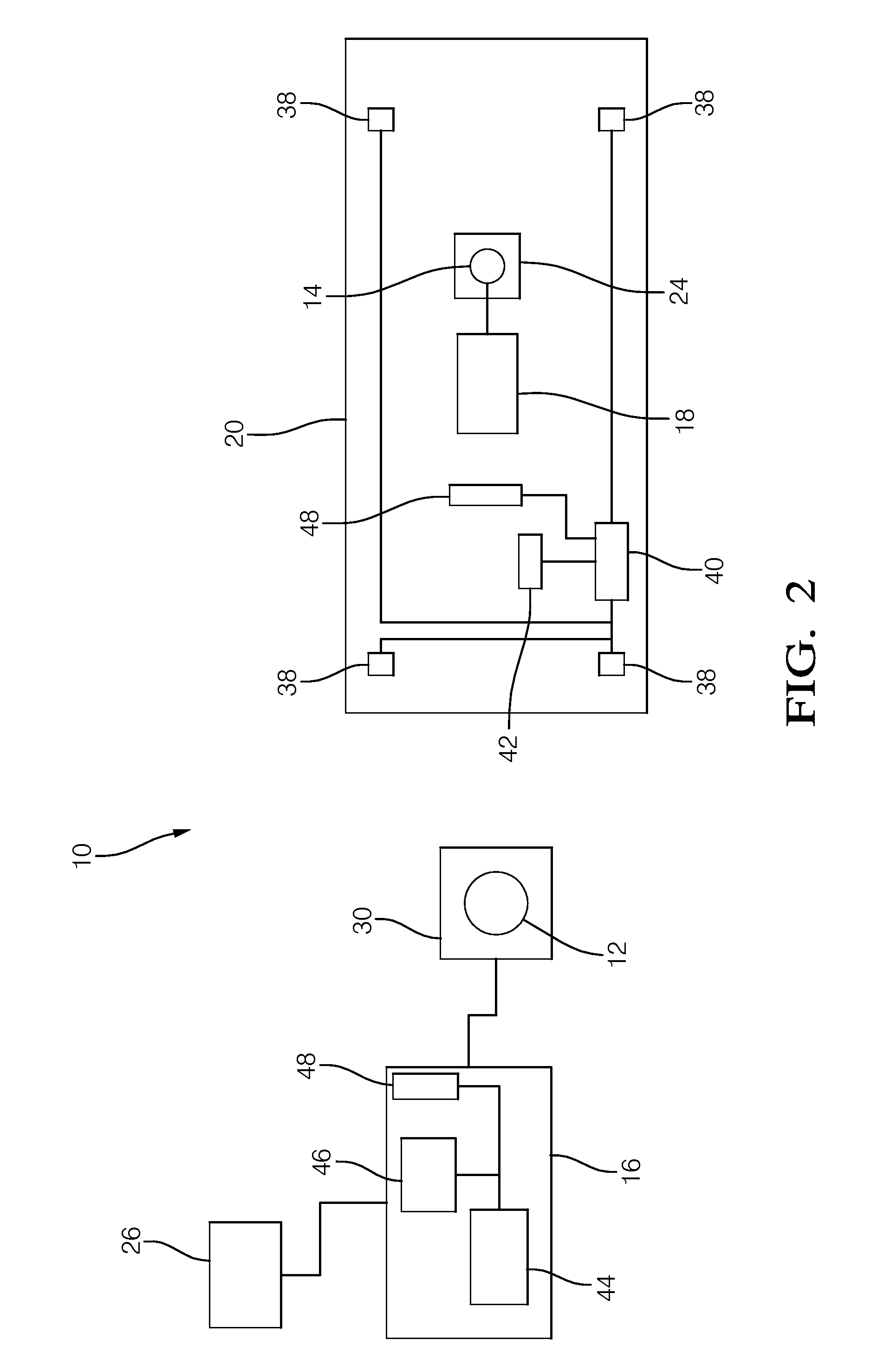
Determining the direction of travel of an automotive vehicle from yaw rate and relative steering wheel angle
A method of using relative steering wheel angle of an automotive vehicle, vehicle yaw rate, and vehicle speed to determine whether the vehicle is traveling forward or backward. Forward and backward steering wheel angles are calculated from vehicle speed and yaw rate (22). A difference between relative steering wheel angle and forward steering wheel angle (10), and a difference between relative steering wheel angle and backward steering wheel angle (12) are calculated. The difference between relative steering wheel angle and forward steering wheel angle is filtered (14), and a difference between the filtered and the unfiltered difference between relative steering wheel angle and forward steering wheel angle is calculated to obtain a forward net difference (18). The difference between relative steering wheel angle and backward steering wheel angle is filtered (16), and a difference between the filtered and the unfiltered difference between relative steering wheel angle and backward steering wheel angle is calculated to obtain a backward net difference (20). While repeatedly performing the foregoing steps, forward net difference values derived from the forward net differences are accumulated (24), and backward net difference values derived from the backward net differences are accumulated (26). The travel direction is determined by comparing the accumulation of forward net difference values and the accumulation of backward net difference values (28). Absolute steering wheel angle and road bank angle can also be calculated.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
System and method to align a source resonator and a capture resonator for wireless electrical power transfer
ActiveUS20140132208A1Circuit monitoring/indicationDifferent batteries chargingElectric power transmissionElectrical battery
A system and a method to provide alignment between a source resonator and a capture resonator. The system and method may be used to align a vehicle having a capture resonator to the source resonator of a wireless inductive battery charging system for an electric vehicle. The system includes a display device, a sensor to determine a location of the source resonator relative to the capture resonator, and a controller in communication with the source resonator, the capture resonator, the sensor, and the display device. The controller is programmed to determine a relative distance and a relative direction between the source resonator and the capture resonator, determine a transfer efficiency of electrical power between the source resonator and the capture resonator. The display device is configured to indicate the relative distance and the relative direction between the source resonator and the capture resonator and indicate the transfer efficiency.
Owner:APTIV TECH LTD
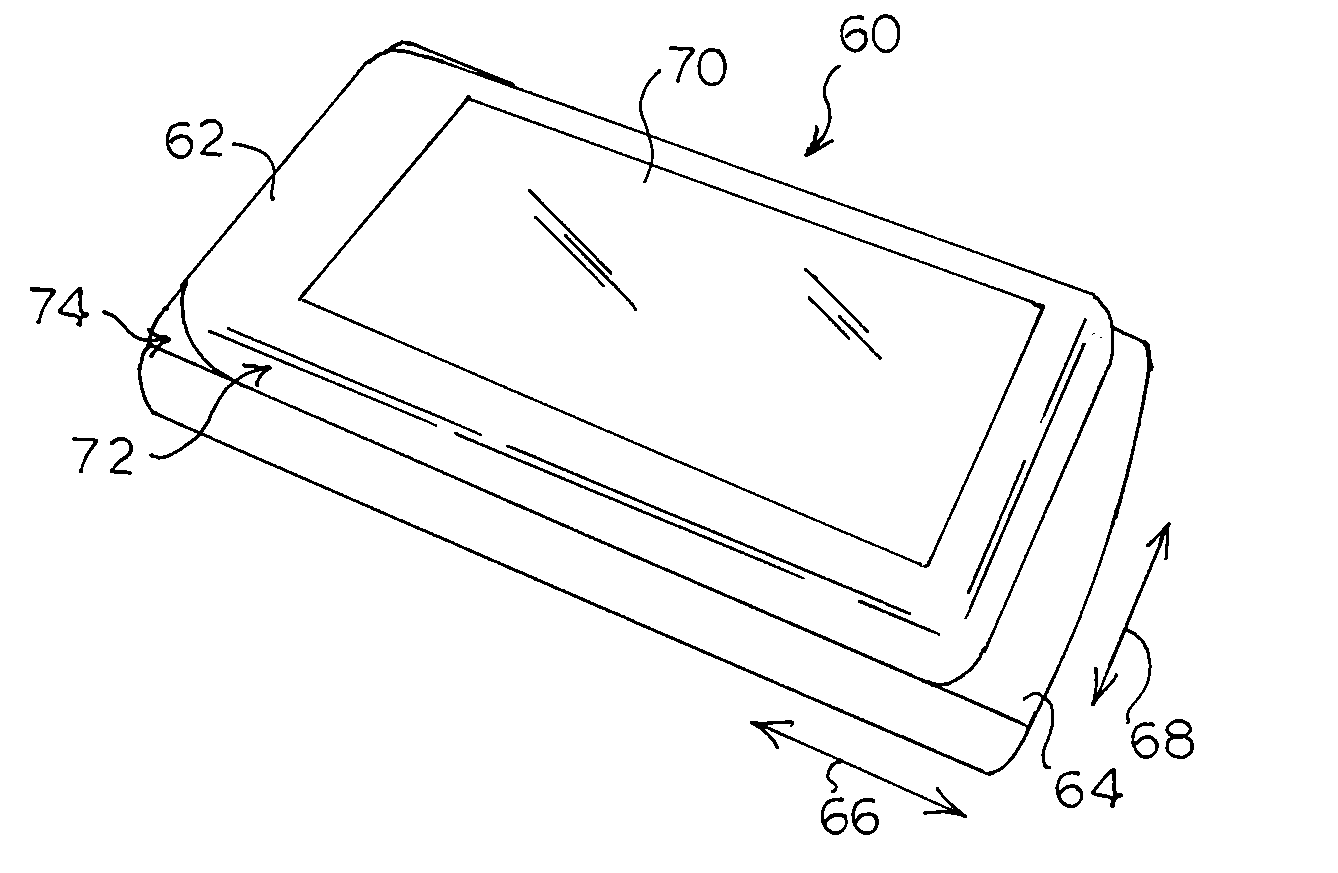
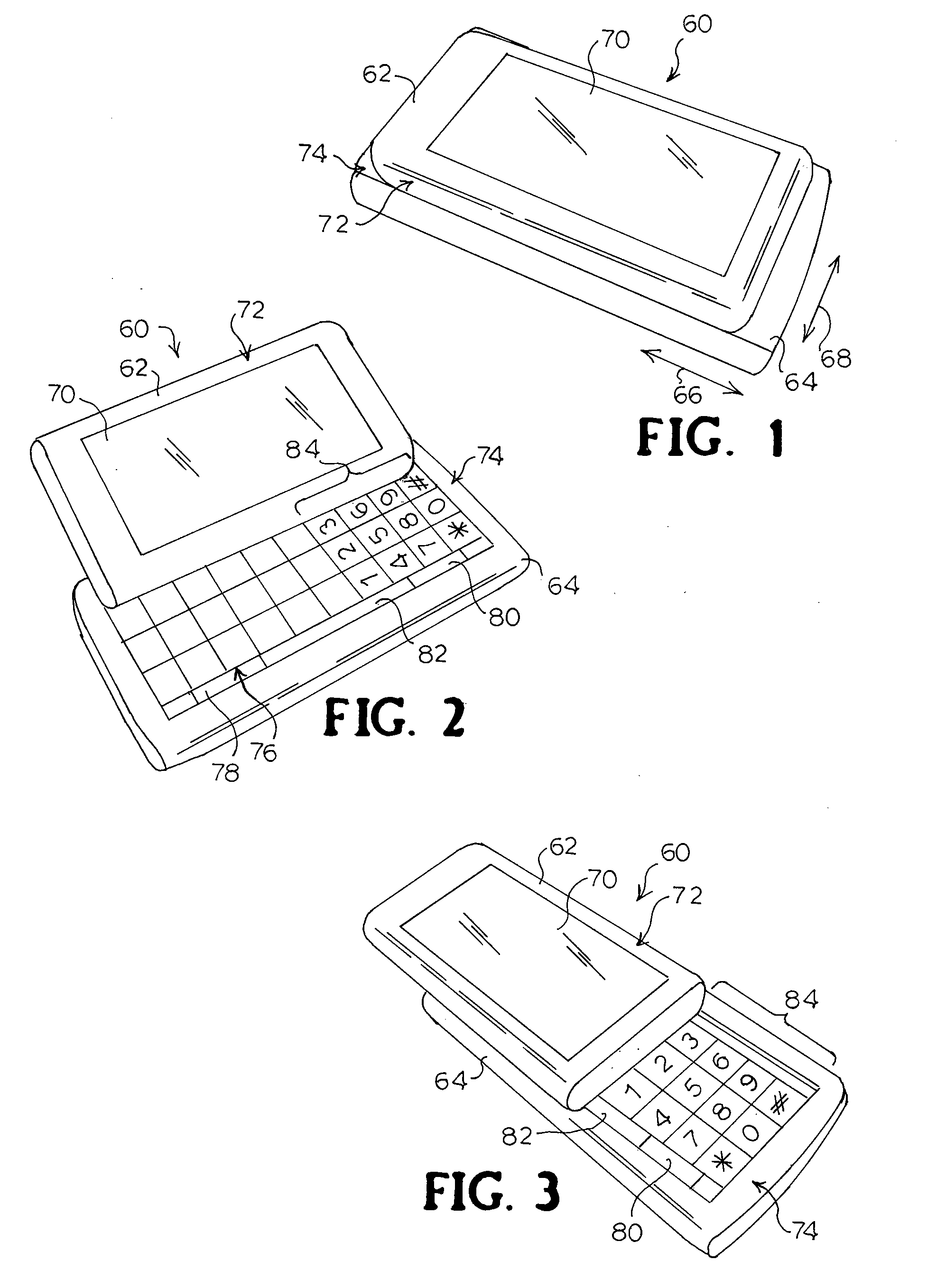
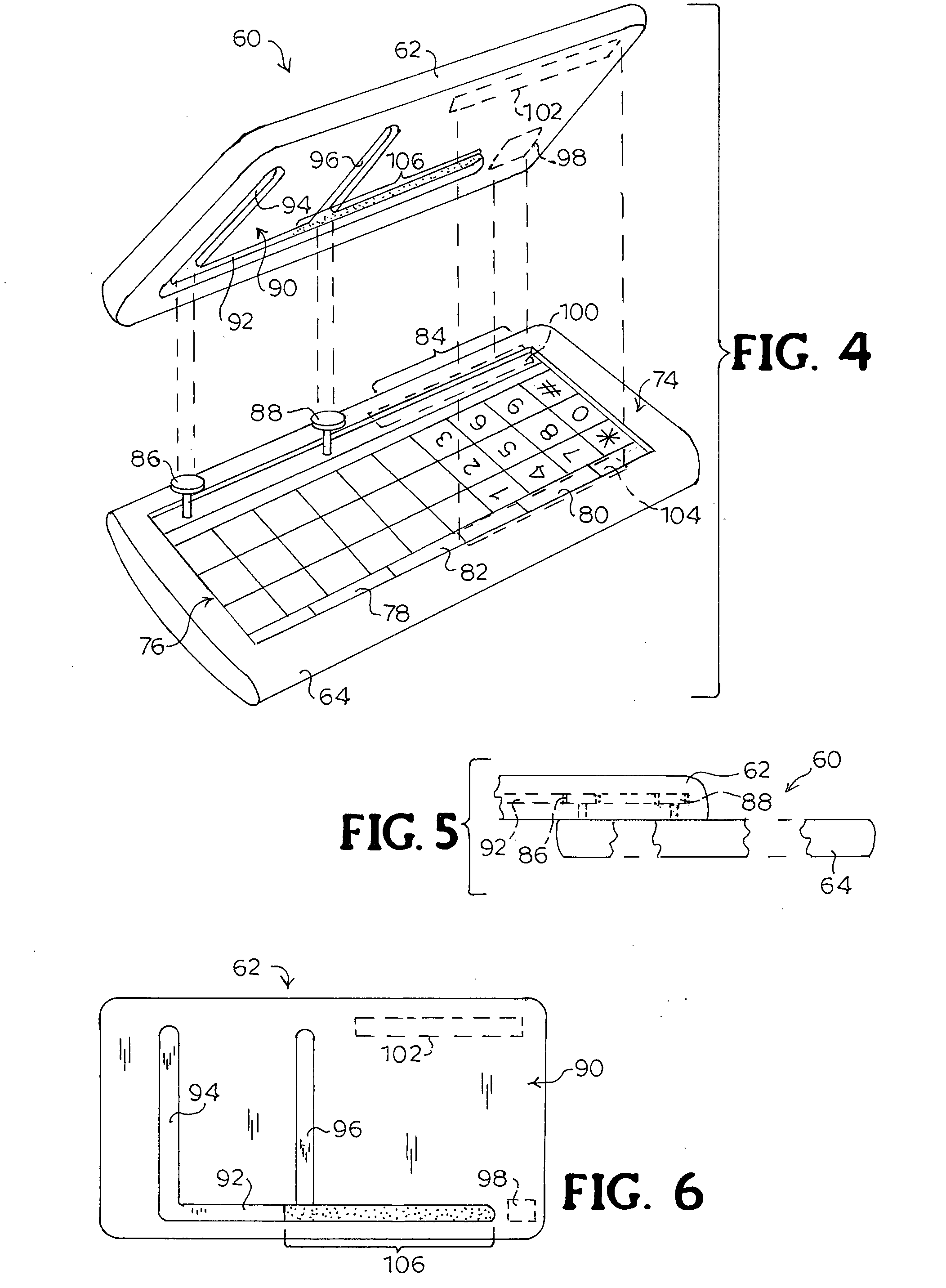
Two-way sliding mobile terminal
A mobile terminal that allows sliding between housings in two directions. The housings may slide in longitudinal and lateral relative directions. One position, for example, may be for PDA use with an alphanumeric keypad exposed and another position may be for phone use with a numeric keypad exposed. One housing may include pins that extend from one surface and another housing may include grooves in an opposing surface to receive the pins. At least one longitudinal groove may be provided, and in one embodiment two lateral grooves are provided to accommodate two longitudinally aligned pins. An overlay may be provided that may be exposed to cover keys with numbers or navigation indications when the housings slide longitudinally and may remain hidden when the housings slide laterally with respect to each other. A casing may be provided that substantially encloses the bottom housing when in the closed position.
Owner:SONY CORP
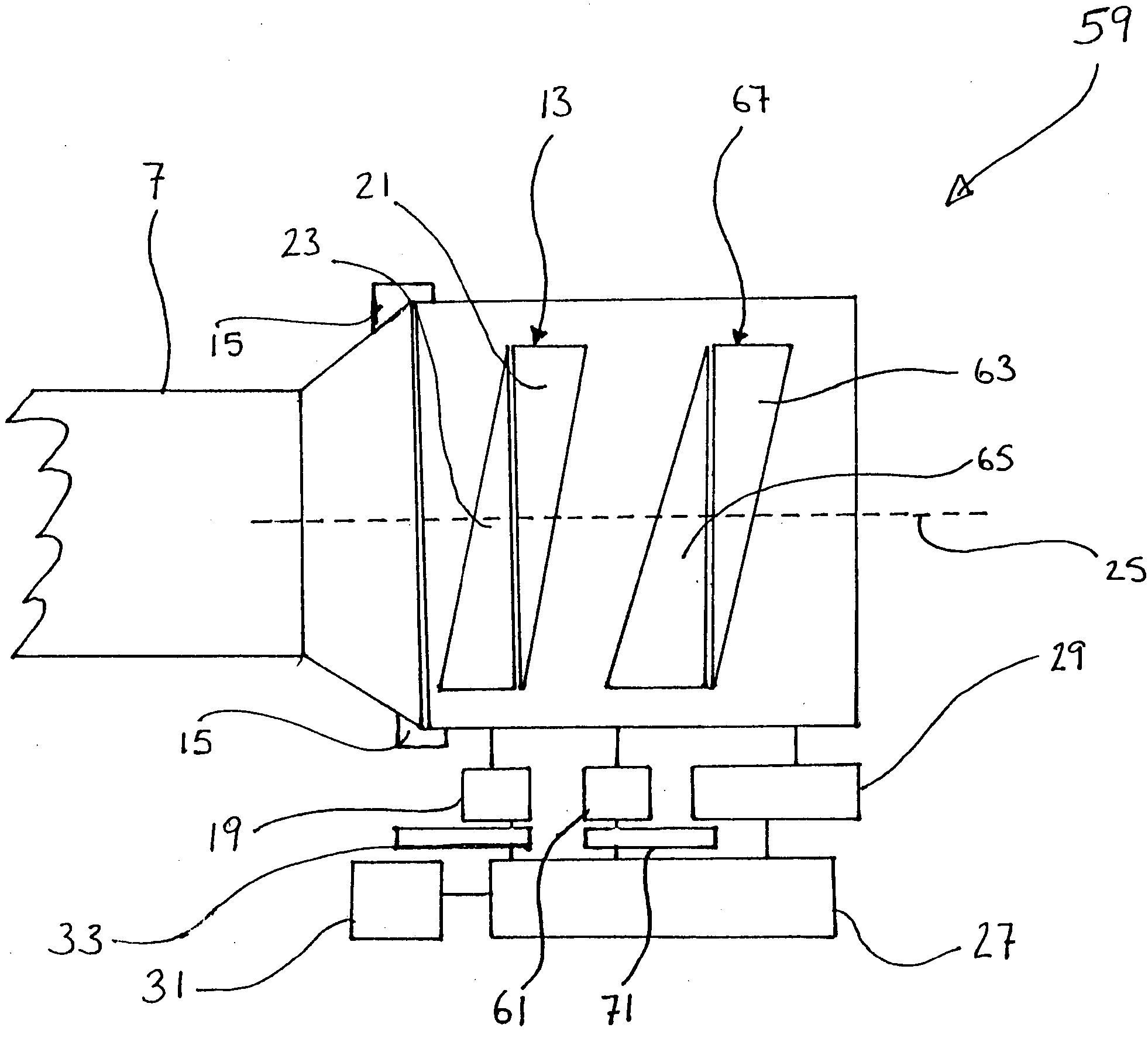
Gun sight compensator
A range compensator for a gun sight for an associated gun is provided. The compensator includes at least one Risley prism pair that is rotatable in opposite relative directions about a common axis; mounting means for mounting the Risley prism pair to the sight between the sight and a target at a distance; and, a respective rotator associated with the Risley prism pair for rotating each prism in the Risley prism pair about the axis that is generally aligned with the path. The prisms are rotatable between an unrefracted range finding position in which a “line of departure” required to ensure the projectile strikes the target is determined and a refracted firing position in which the path of light extending between the sight and the target is refractively deviated to maintain the target centered with the sight when the gun is positioned along the required “line of departure”.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF WATERLOO
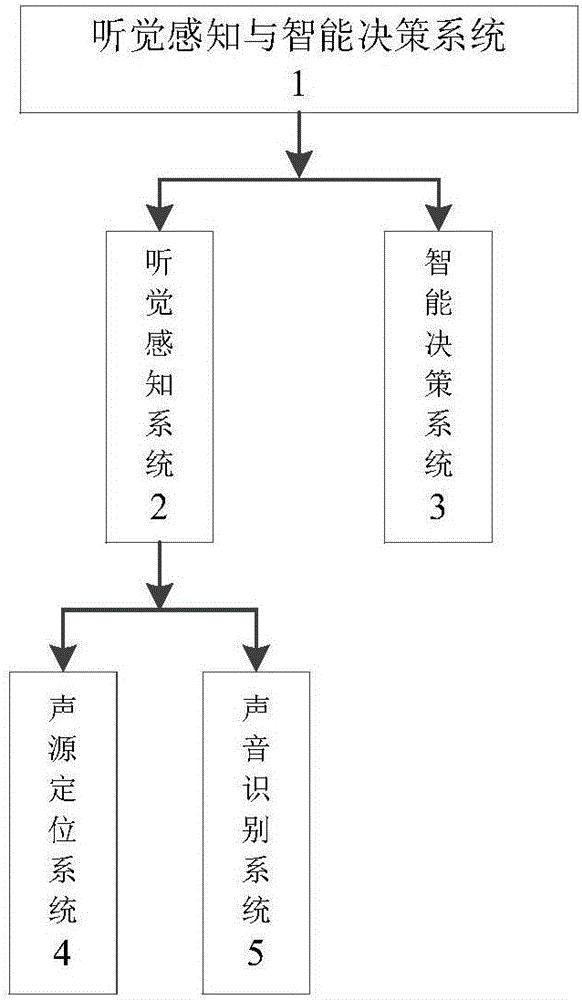
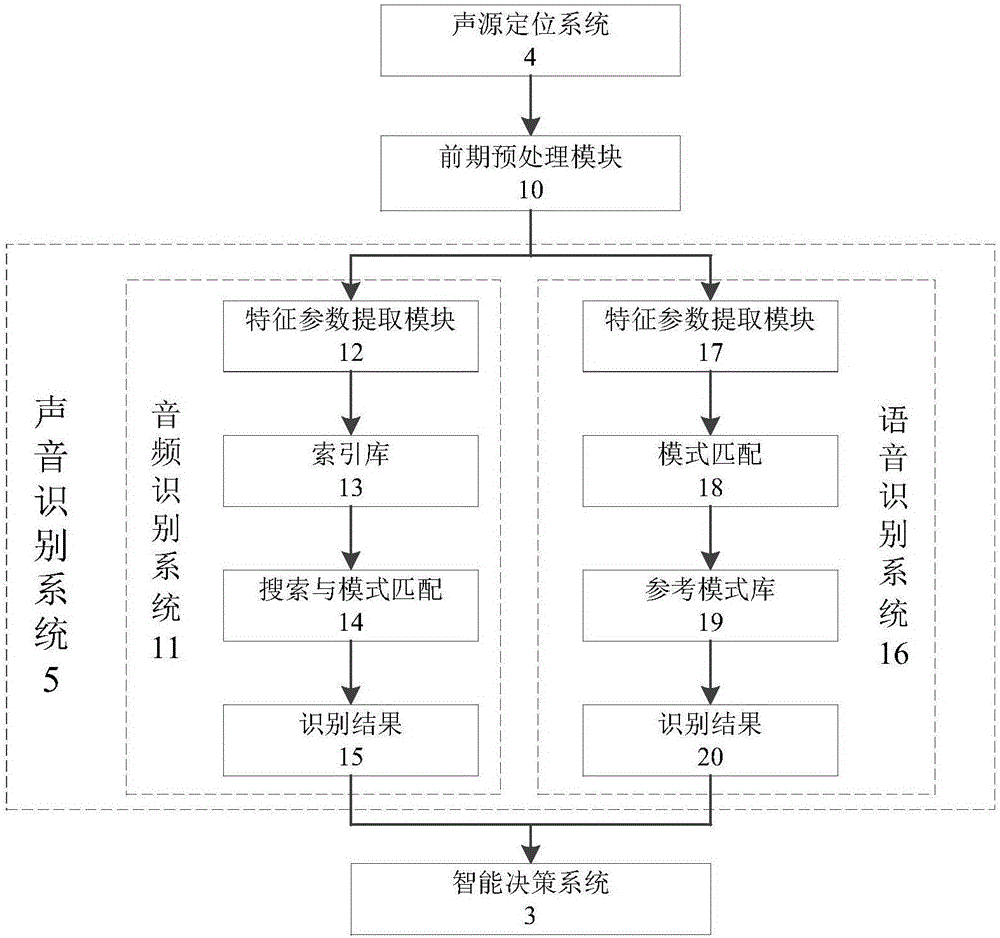
Auditory perception and intelligent decision making system of unmanned vehicle
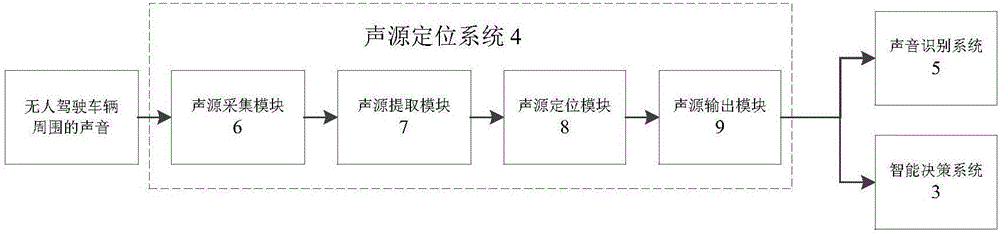
ActiveCN105938657ARoad vehicles traffic controlSpeech recognitionInformation processingSound sources
The invention discloses an auditory perception and intelligent decision making system of an unmanned vehicle. The auditory perception and intelligent decision making system includes an auditory perception system and an intelligent decision making system; the auditory perception system includes a sound source positioning system and a sound identification system. The sound source positioning system positions the location and relative direction of a sound emitting source and transmits positioning results to the sound identification system and the intelligent decision making system; the sound identification system classifies and identifies sound source positioning information and transmits results to the intelligent decision making system; the information acquisition module of the intelligent decision making system receives sound information transmitted by the sound source positioning system and the sound identification system; an information processing and decision making module analyzes and processes the sound information and calculates lane changing and avoidance schemes of the unmanned vehicle; and a control execution module controls the behaviors of the unmanned vehicle and makes effective response.
Owner:CHANGZHOU JIAMEI TECH CO LTD
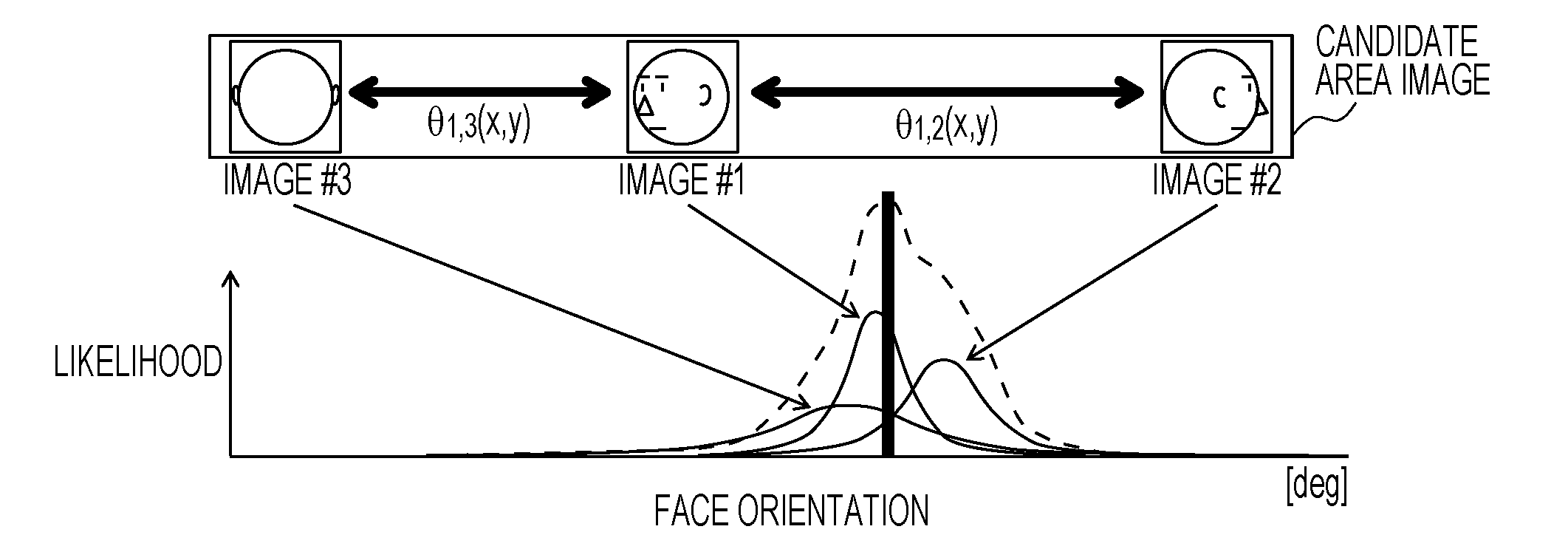
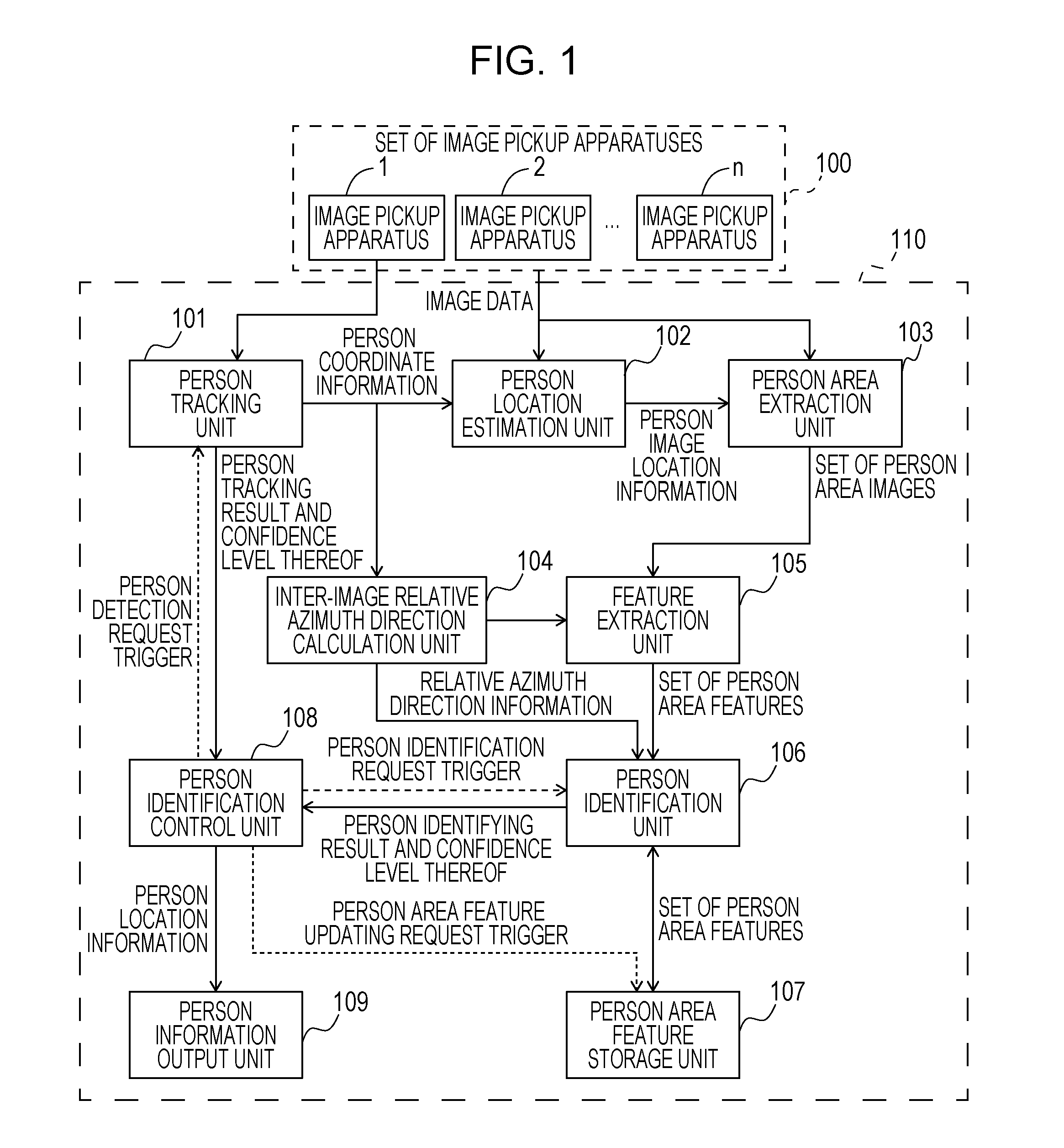
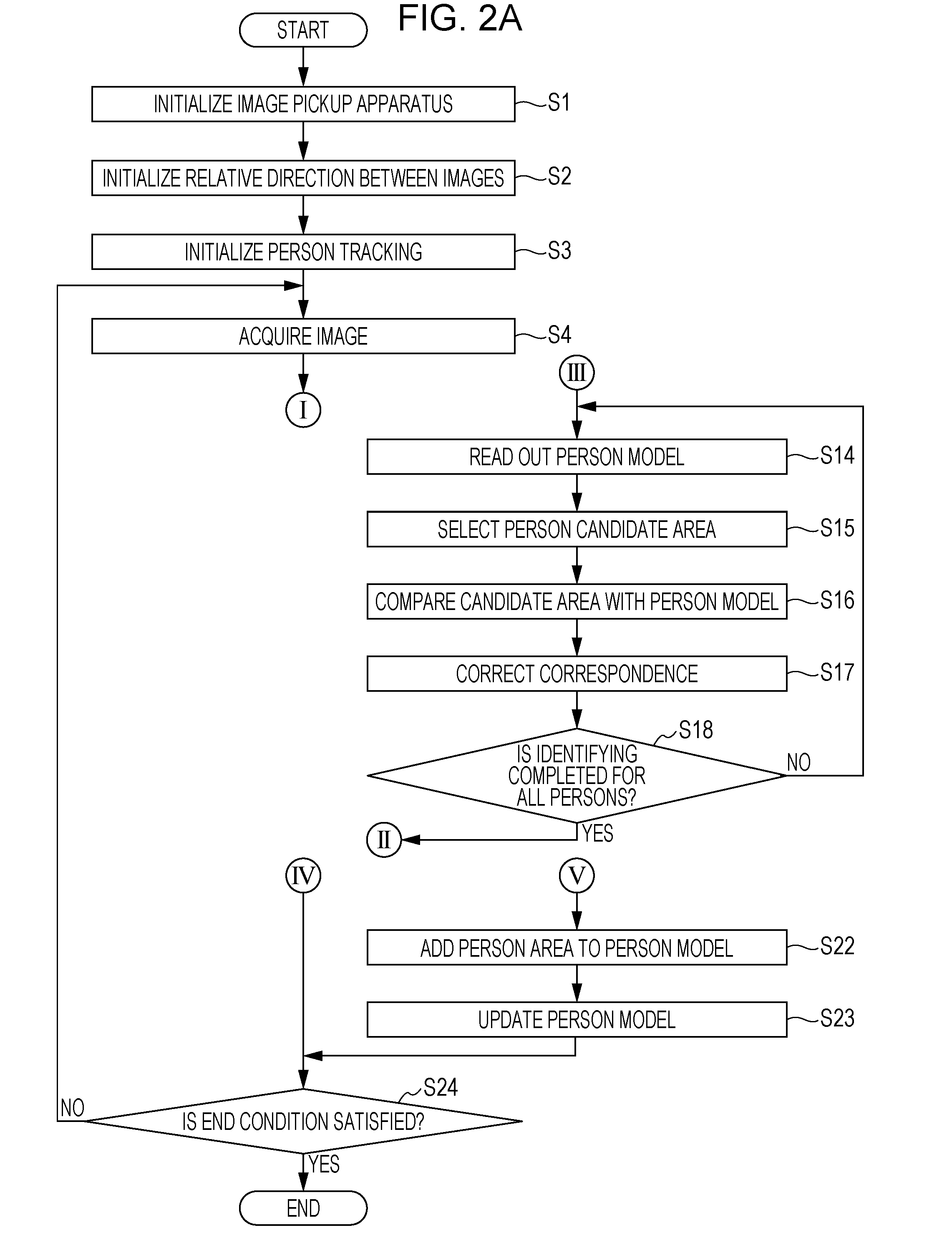
Image recognition system, image recognition apparatus, image recognition method, and computer program
ActiveUS20150363636A1Quick identificationTelevision system detailsImage enhancementComputer graphics (images)Recognition system
A relative direction relationship is acquired between first and second input area images of a particular person taken from different directions. The particular person is identified by comparing a feature of the first input area image with a feature of a first one of registered area images of the particular person or another person taken from at least three directions, comparing a feature of the second input area image with a feature of a second registered area image of the same person as the person of the first registered area image, and determining whether the person in the first and second input area images is the same person in the first and second registered area images. The first and second registered area images are selected such that the relation between the first and second registered area images is similar to the relation between the first and second input area images.
Owner:CANON KK
Measuring overlay and profile asymmetry using symmetric and anti-symmetric scatterometry signals
ActiveUS20060274310A1Easy extractionPhotomechanical apparatusMaterial analysis by optical meansGratingPolarizer
Systems and methods are disclosed for using ellipsometer configurations to measure the partial Mueller matrix and the complete Jones matrix of a system that may be isotropic or anisotropic. In one embodiment two or more signals, which do not necessarily satisfy any symmetry assumptions individually, are combined into a composite signal which satisfies a symmetry assumption. The individual signals are collected at two or more analyzer angles. Symmetry properties of the composite signals allow easy extraction of overlay information for any relative orientation of the incident light beam with respect to a ID grating target, as well as for targets comprising general 2D gratings. Signals of a certain symmetry property also allow measurement of profile asymmetry in a very efficient manner. In another embodiment a measurement methodology is defined to measure only signals which satisfy a symmetry assumption. An optional embodiment comprises a single polarization element serving as polarizer and analyzer. Another optional embodiment uses an analyzing prism to simultaneously collect two polarization components of reflected light.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
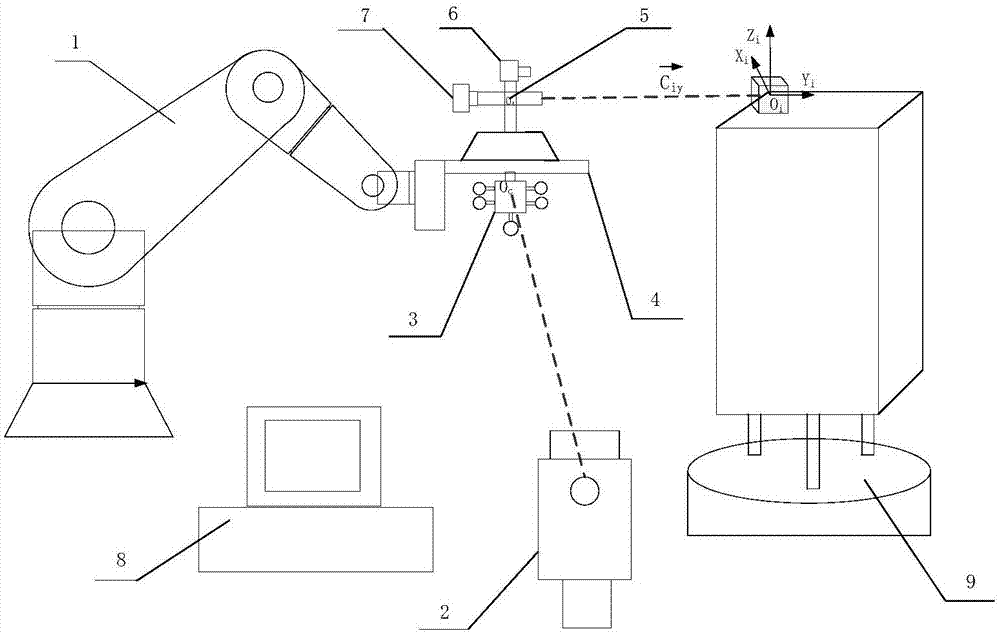
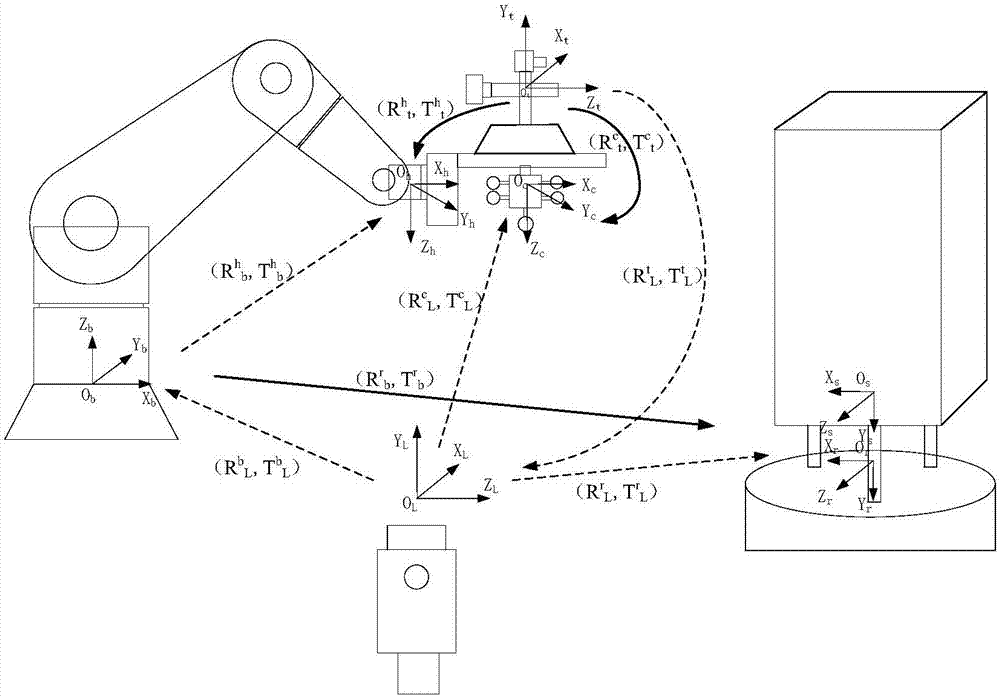
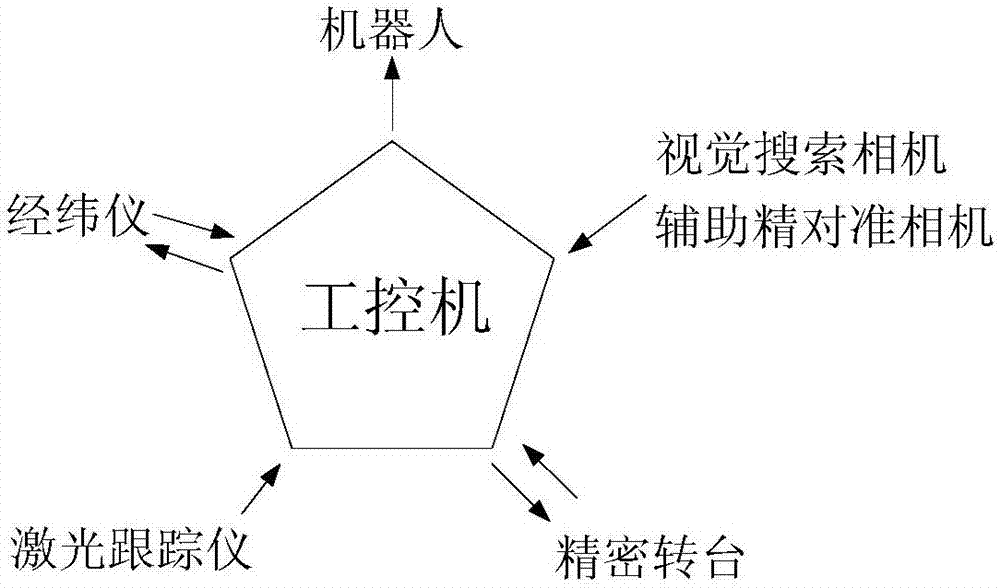
Automatic collimation measurement system, collimation method and measurement method for spacecraft devices
ActiveCN107543495ARealize automatic levelingExcellent leveling accuracyUsing optical meansTheodolitesTheodoliteAutocollimation
The invention discloses a collimation measurement system for attitudes and angles among spacecraft devices based on the combination between a robot and a theodolite. The system herein includes a robot, a laser tracker, a laser tracking target (T-MAC), a robot terminal tool, and the like. The system searches a to-be-tested datum cube mirror which is disposed on a spacecraft device by conducting mode identification, and computes the relations of phase position and direction of the datum cube mirror with respect to the theodolite. The laser tracker is intended for calibrating the relative direction relation in a coordinate system of respective spacecraft devices and integrating the measurement results of the theodolite at different measurement positions to the same coordinate system. Based onthe calibration relation and the relative relation, the laser tracker is guided to real-timely track the robot terminal tool and establish the relative relation between the laser track and the robotterminal tool. And eventually, the attitude relation matrix of the spacecraft is computed. According to the invention, the automatic measurement of the attitude relation among different devices is realized, the measurement efficiency can reach one time per half-minute, the measurement precision can be higher than 30'', on-site measurement flexibility is higher, and construction and measurement indifferent places can be much easier.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF SPACECRAFT ENVIRONMENT ENG
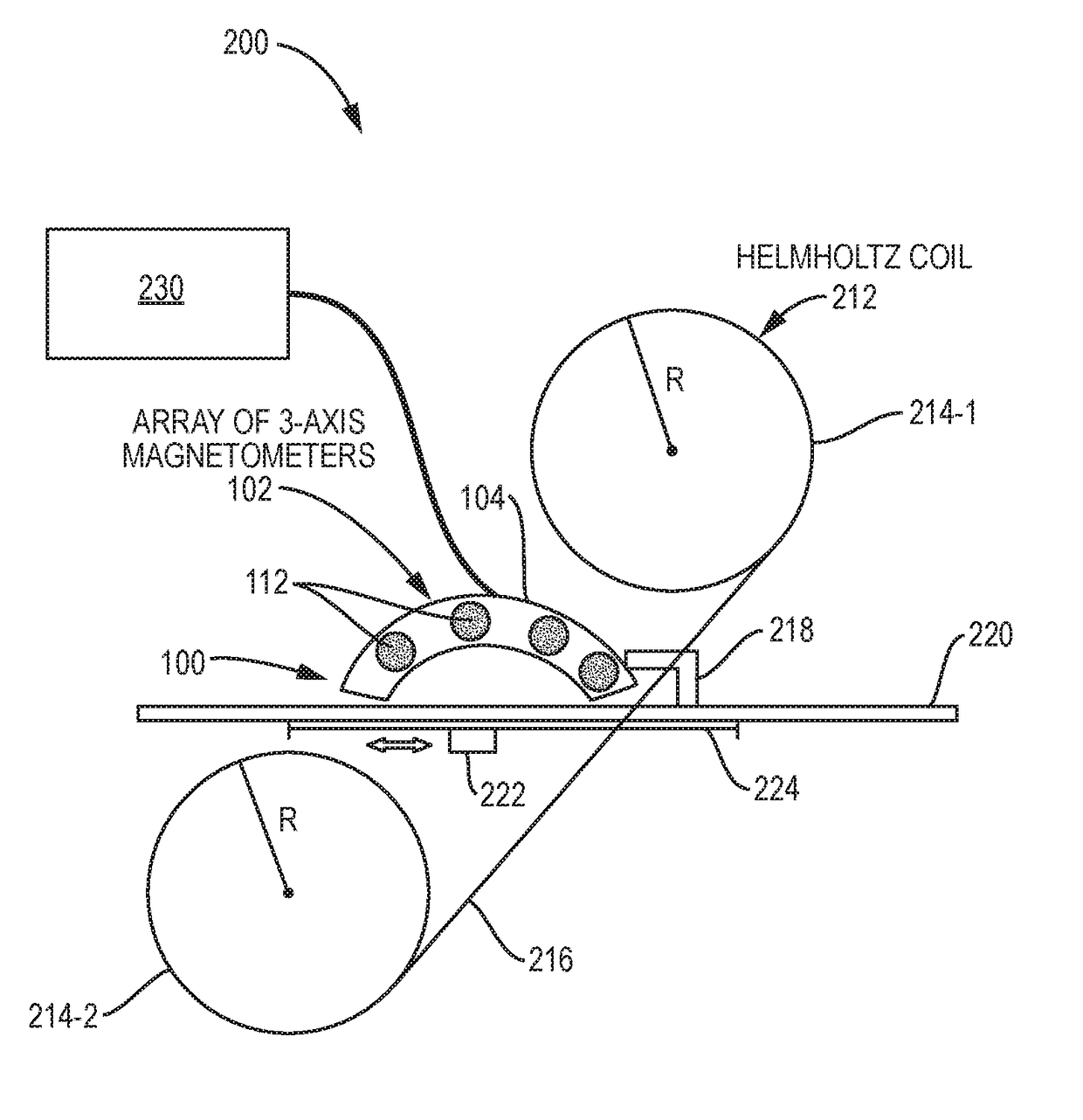
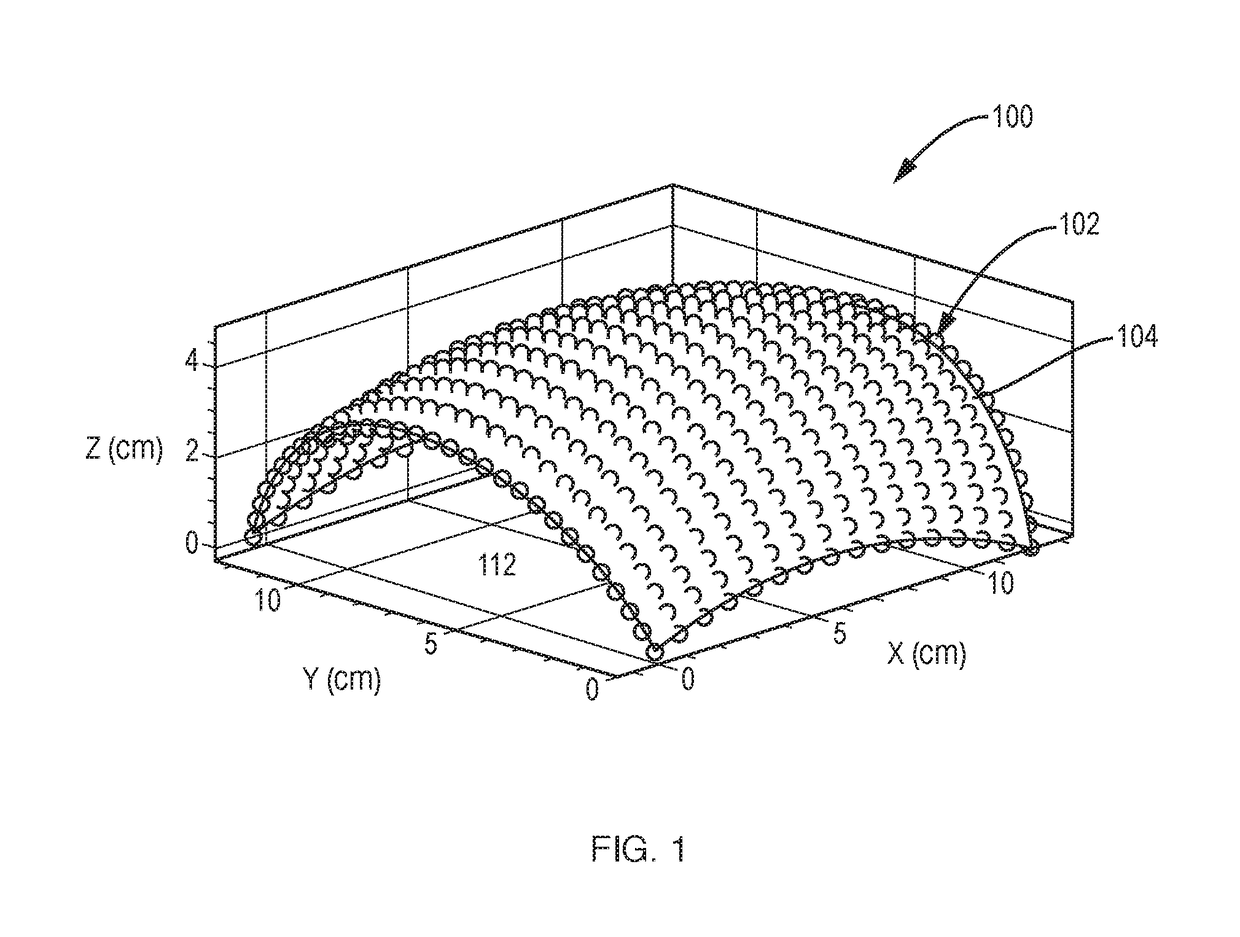
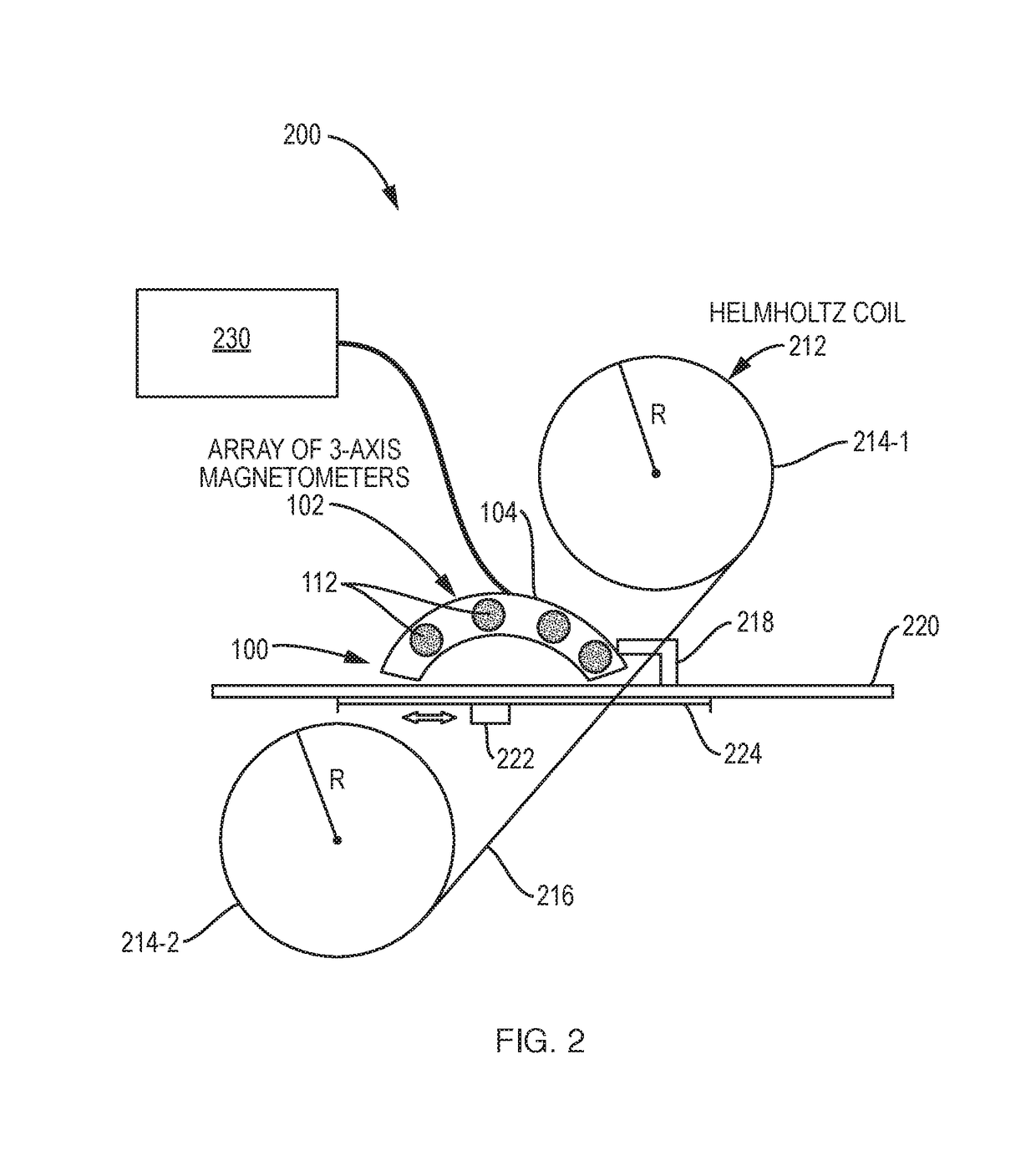
Calibration and Monitoring for 3-Axis Magnetometer Arrays of Arbitrary Geometry
ActiveUS20180003777A1Good reproducibilityShorten the timeElectrical measurementsThree-component magnetometersMagnetic tension forceMagnetometer
A system and method for calibrating rigid and non-rigid arrays of 3-axis magnetometers as disclosed. Such arrays might be used to analyze structures containing ferromagnetic material. The calibration determines scale factor and bias parameters of each magnetometer in the array, and the relative orientation and position of each magnetometer in the array. Once the parameters are determined, the actual magnetic field value at the magnetometer location can be simply related to magnetometer measurements. The method and system can be used to calibrate an array of 3-axis magnetometers in aggregate as opposed to individual magnetometers. This is critical in large arrays to increasing reproducibility of the calibration procedure and decreasing time required to complete calibration procedure.
Owner:CHARLES STARK DRAPER LABORATORY
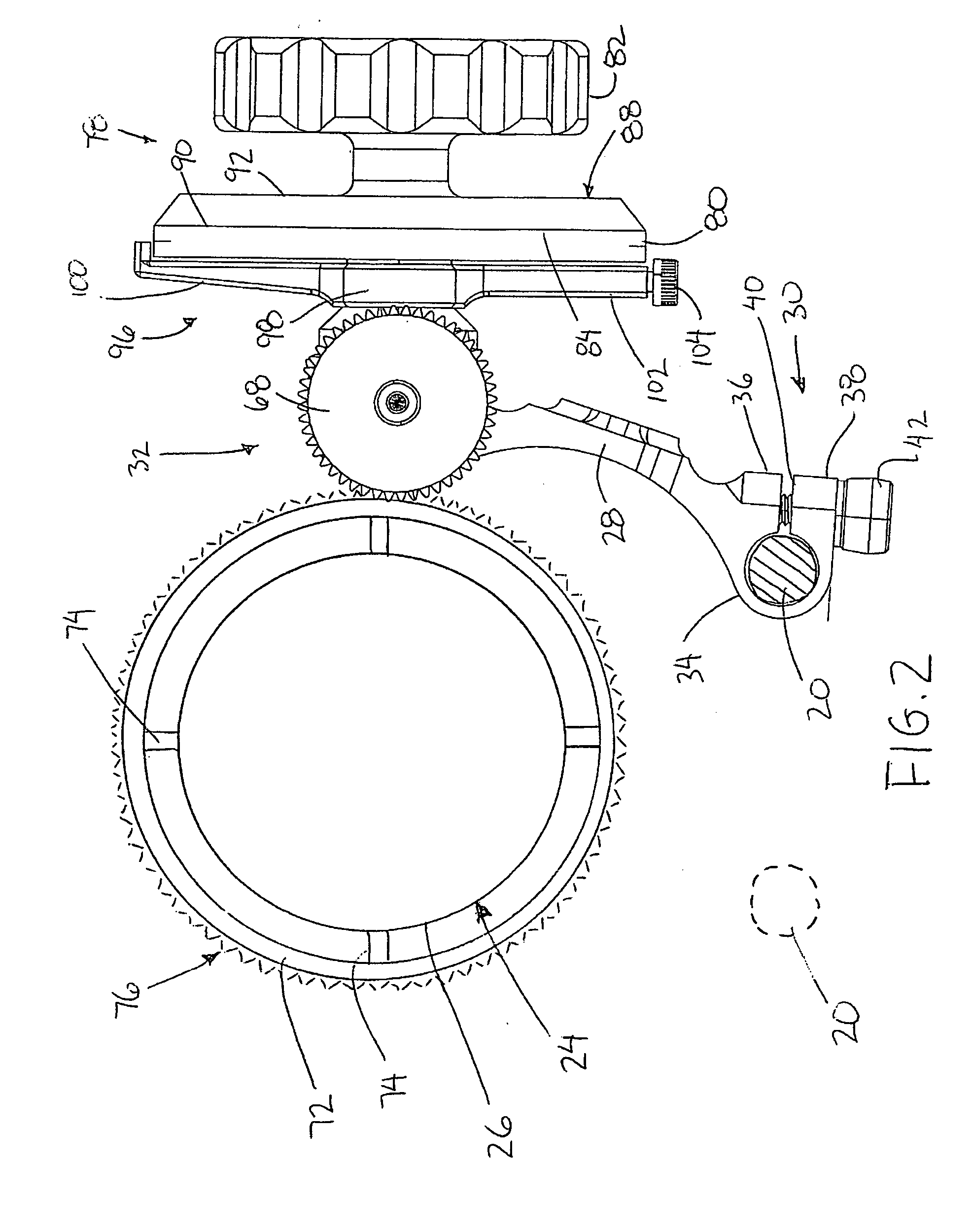
Follow Focus Camera Accessory Device
InactiveUS20100259669A1Simple structureAvoid mistakesTelevision system detailsColor television detailsEngineeringRelative direction
A focussing accessory device comprises a focussing ring rotatable with a focussing control of a video camera rotatable responsive to rotation of a control knob. A main body of the device is supported on a single mounting rail of a camera assembly for relative pivotal movement to adjust an orientation of the device relative to the camera. The control knob is coupled to an input of a transmission on the main body. An output of the transmission meshes in engagement with the focussing ring. The transmission is reversibly supported on the main body to reverse the location and orientation of the output. An index marker is provided for rotation about an axis of the control knob independently therefrom. An annular indexing member is selectively coupled for rotation with the control knob relative to the index marker by magnetic elements which permit mounting in only one relative orientation.
Owner:WOOD DENNIS
Rowing exercise machine with self-aligning pivoting user support
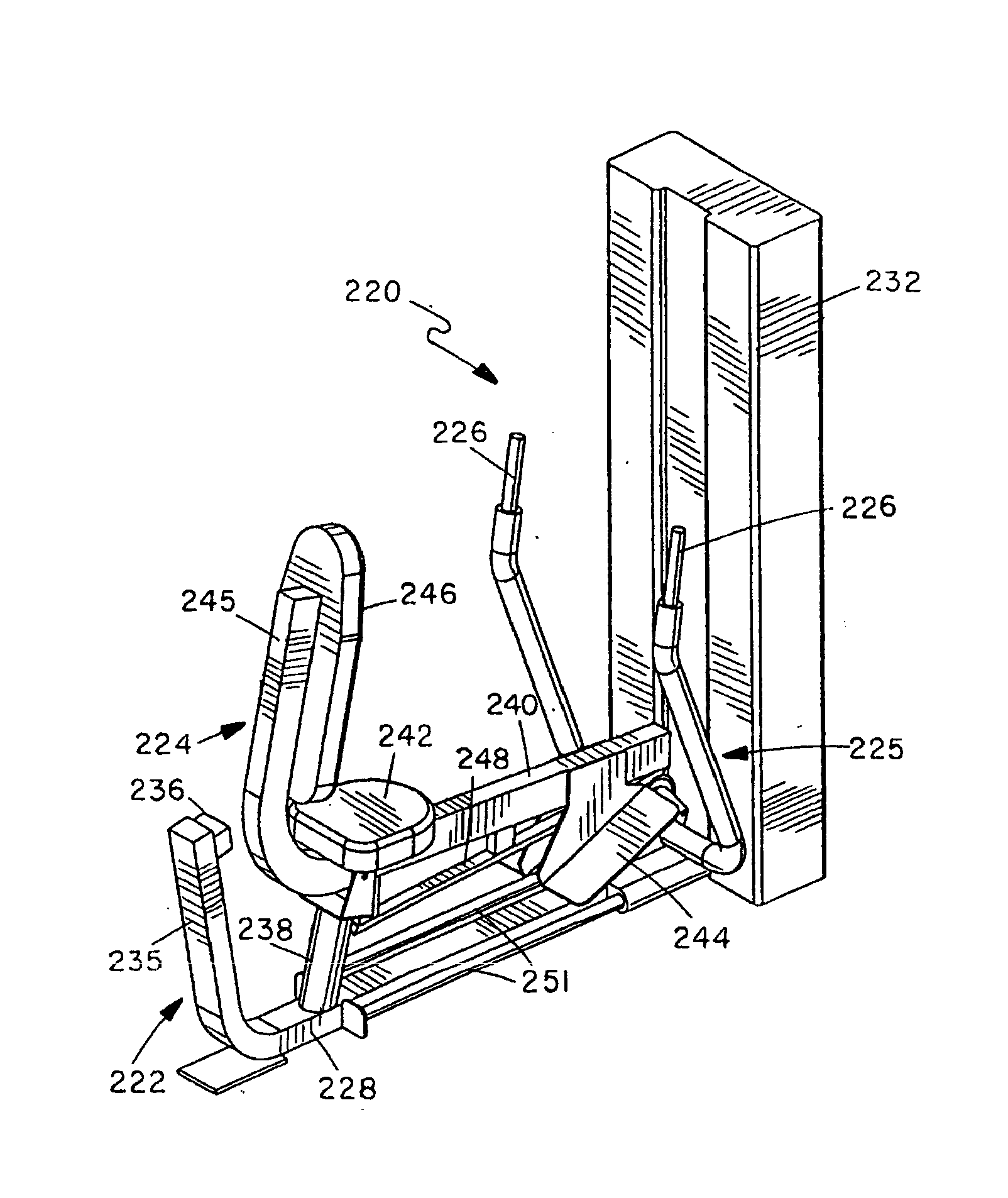
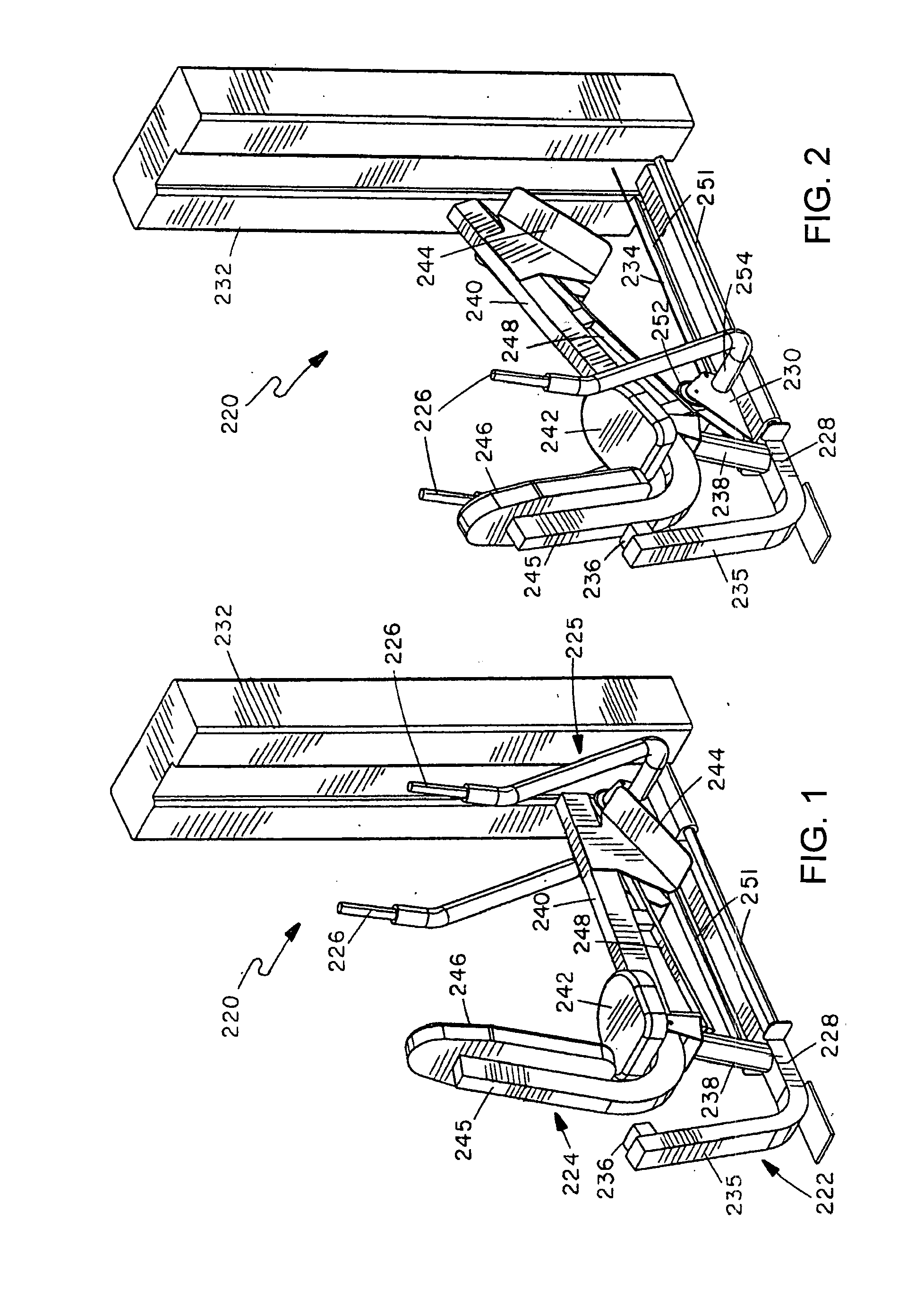
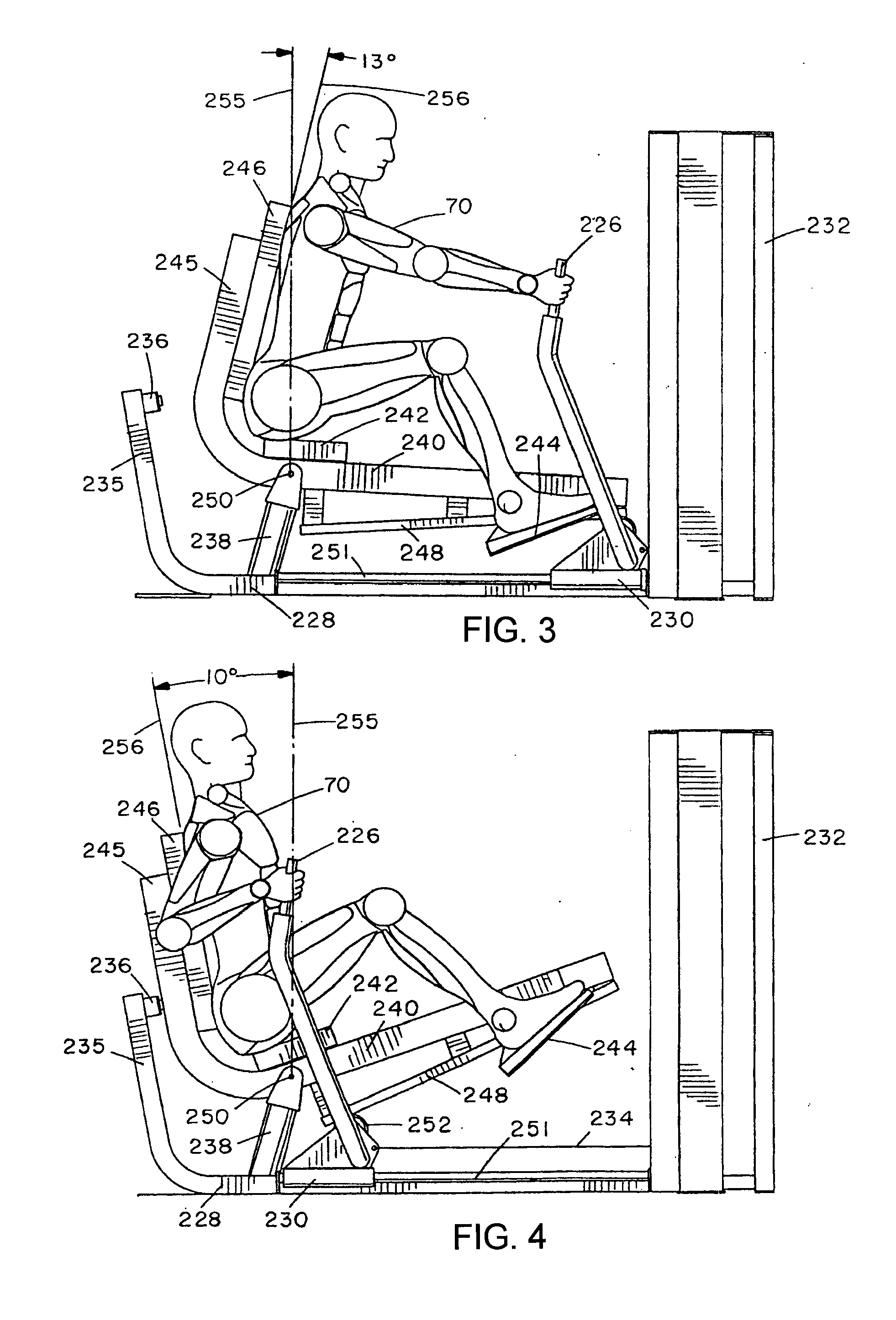
ActiveUS20080214365A1Reduces initial lifting resistanceReduce resistanceMuscle exercising devicesMovement coordination devicesBraced frameEngineering
A rowing or mid-row exercise machine has a main frame and a user support frame pivotally mounted relative to the main frame for rotation between start and end positions. The user support frame supports spaced positions on a user's body in the same relative orientation throughout an exercise movement. A user engagement device is movably mounted relative to the frames and has at least one handle gripped by the user in performing exercises. The handle is movable in a predetermined rowing exercise path between a start position spaced in front of a user's chest and an end position closer to the chest. A connecting linkage translates movement of the user engagement device to rotational movement of the user support frame. A load resists movement of at least one of the user support, user engagement device, and connecting linkage.
Owner:HOIST FITNESS SYST
System and methods for direction finding using a handheld device
ActiveUS7667646B2Position fixationNear-field for read/write/interrrogation/identification systemsRelevant informationEngineering
A system for indicating the relative direction of a target object or location as determined from the current position of a wireless communication device. The system employs Direction of Arrival determination using an antenna array for indicating the direction of a target device and includes facilities to activate a location-indicating transmission in a target device, the ability to request that a location-indicating transmission be activated in a remote target device, relevant information reception from a target device and the display of all potential target devices within effective transmission range of the wireless communication device.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
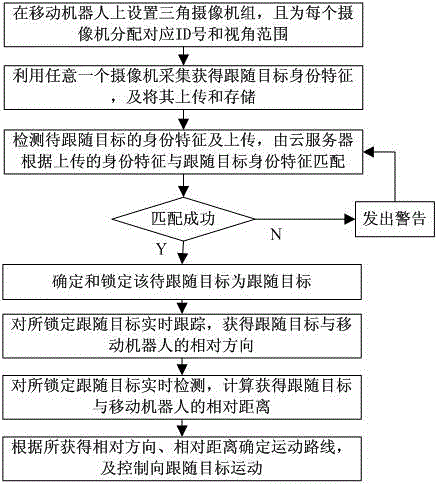
Target following control method of mobile robot
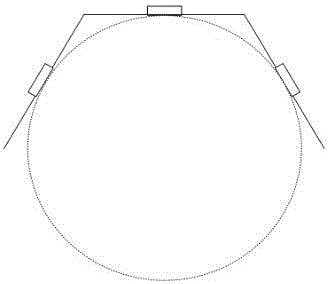
ActiveCN106094875AEnhanced target following functionHigh Feature Detection CapabilitiesTelevision system detailsImage enhancementAutomatic controlFeature detection
The invention discloses a target following control method of a mobile robot. The target following control method comprises the steps of arranging a triangular camera set on the mobile robot, and distributing a corresponding ID number and a visual angle range; acquiring an identity characteristic of a following target, and performing uploading and storage of the identity characteristic; detecting the identity characteristic of a to-be-followed target and uploading the identity characteristic of the to-be-followed target to a cloud server, performing characteristic matching by the cloud server, when matching succeeds, determining and locking the to-be-followed target as the following target; tracking the locked following target by a person, and obtaining relative direction between the following target and the mobile robot; performing real-time detection on the locked following target for obtaining a relative distance through calculation; determining a moving route according to the obtained relative directions and relative distance between the following target and the mobile robot, and making the mobile robot move to the following object according to the moving route. The target following control method has higher characteristic detecting function and higher automatic control function. Furthermore the target following control method can be well used for a robot tracking process.
Owner:NANJING NANYOU INST OF INFORMATION TECHNOVATION CO LTD
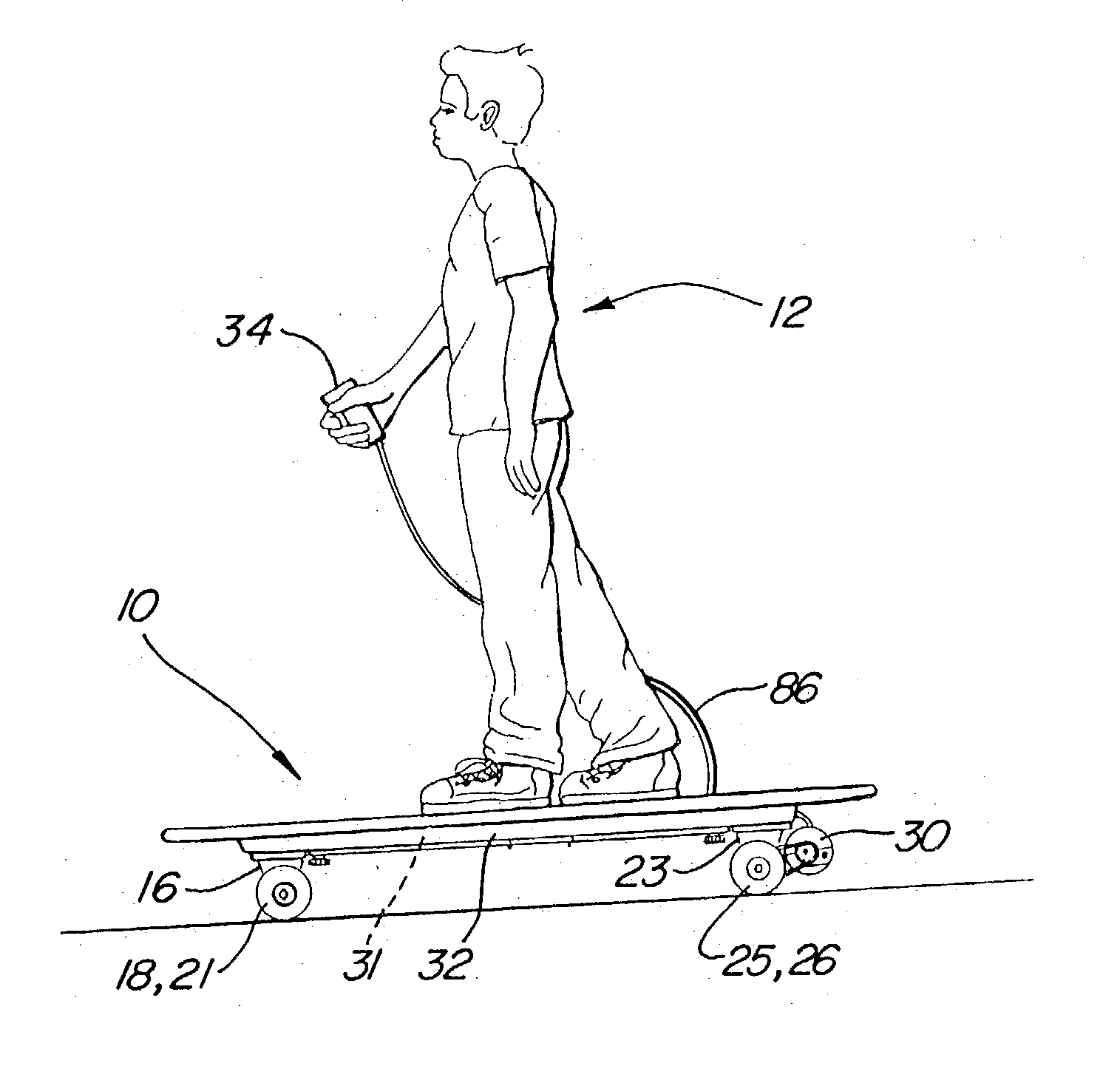
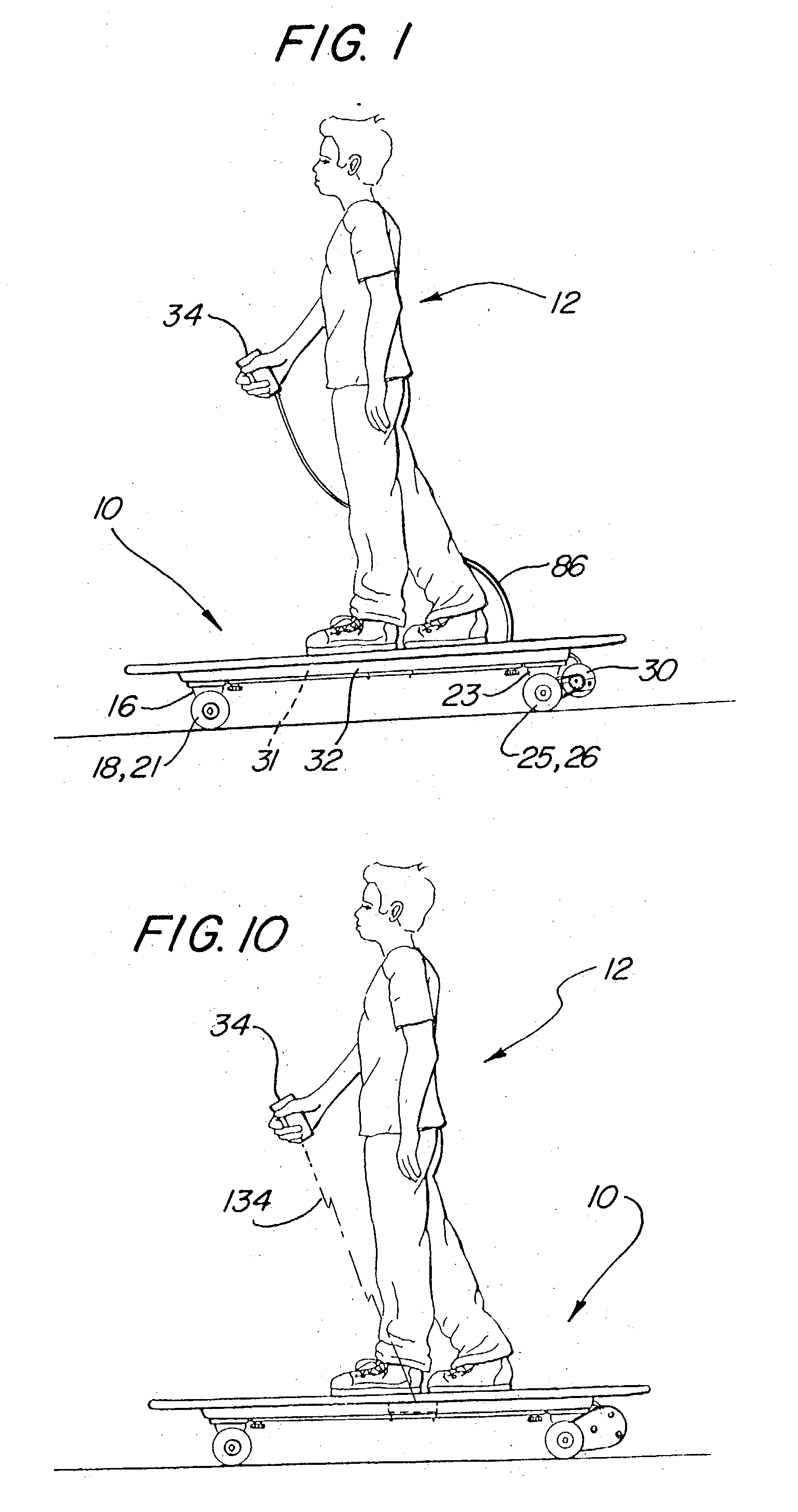
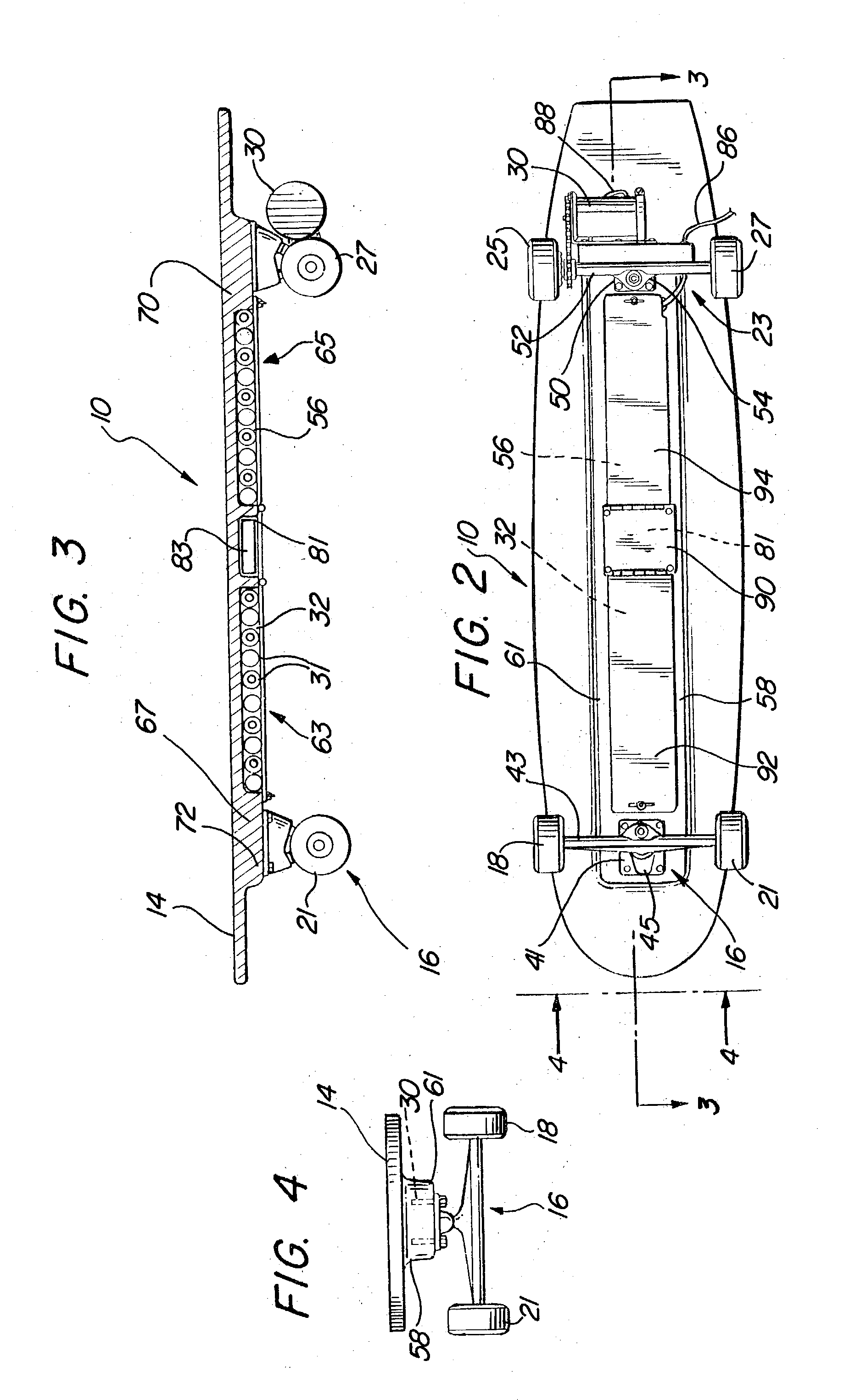
Skateboard with remote controlled motive power
A vehicle for transporting a rider includes a platform for supporting the rider and at least one skate truck coupled to the platform and including a housing. An axel included in the skate truck extends through the housing to support a wheel having a rotational relationship with both the housing and the platform. Motive power rotates the wheel relative to the platform a free-wheel bearing includes first portions coupled to the wheel and second portions coupled to the motive power. The second portions of the bearing have a fixed relationship with the first portions of the bearing when rotated in a first relative direction, and have a free-wheeling relationship with the first portions of the bearing when rotated in a second relative direction opposite to the first relative direction. When the motive power comprises a motor, portions of the platform can be adapted to receive a battery.
Owner:HILLMAN ROGER
Image acquisition and positioning method and image acquisition and positioning system
ActiveCN103557859AHigh precisionOptical rangefindersNavigational calculation instrumentsComputer scienceInformation acquisition
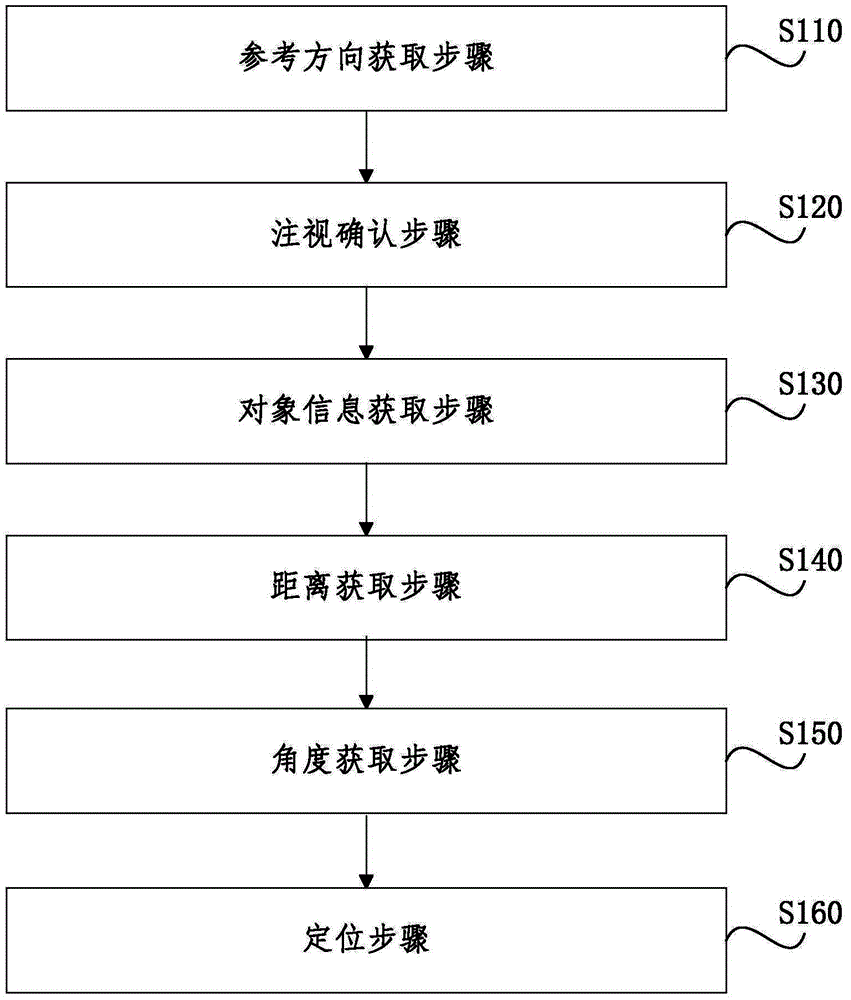
The invention discloses an image acquisition and positioning method and an image acquisition and positioning system. The method comprises the following steps: acquisition of a reference direction: a step of acquiring the reference direction corresponding to a user; confirmation of staring: a step of confirming that the eyes of the user are staring at a positioning assistant object; acquisition of object information: a step of acquiring the position information of the positioning assistant object; acquisition of distance: a step of acquiring the distance between the user and the positioning assistant object; acquisition of an angle: a step of acquiring the angle between the staring direction of the user and the reference direction; and positioning: a step of acquiring the position information of the user on the basis of the position information of the positioning assistant object, the distance between the user and the positioning assistant object, the reference direction and the angle between the staring direction of the user and the reference direction. According to the invention, accurate positioning of the position of the user is realized by acquiring the distance between and the relative direction of the positioning assistant object stared by the eyes of the user and the user, and image acquisition and positioning precision is improved.
Owner:BEIJING ZHIGU RUI TUO TECH
Thermally assisted magnetic head with optical waveguide and light shield
ActiveUS20090052077A1Good yieldEffective lightingRecord information storageRecording/reproducing/erasing methodsHigh densityLens hood
A thermally assisted magnetic head which can realize high-density writing onto magnetic recording media is provided.The thermally assisted magnetic head includes a magnetic head part having a medium-opposing surface and a back face opposing the medium-opposing surface. The magnetic head part has a recording head part, an optical waveguide, and light shields. The optical waveguide extends along the opposing direction of the medium-opposing surface and back face. Each of the light shields extends along the opposing direction of the medium-opposing surface and back face and inhibits laser light from passing between the medium-opposing surface and back face. The optical waveguide and light shields are arranged on a first line when seen from the back face. When seen from the back face, the light shields oppose each other while interposing the first line therebetween and are arranged on a second line substantially orthogonal to the first line.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Method and apparatus for determining a relative orientation of points on a rigid body
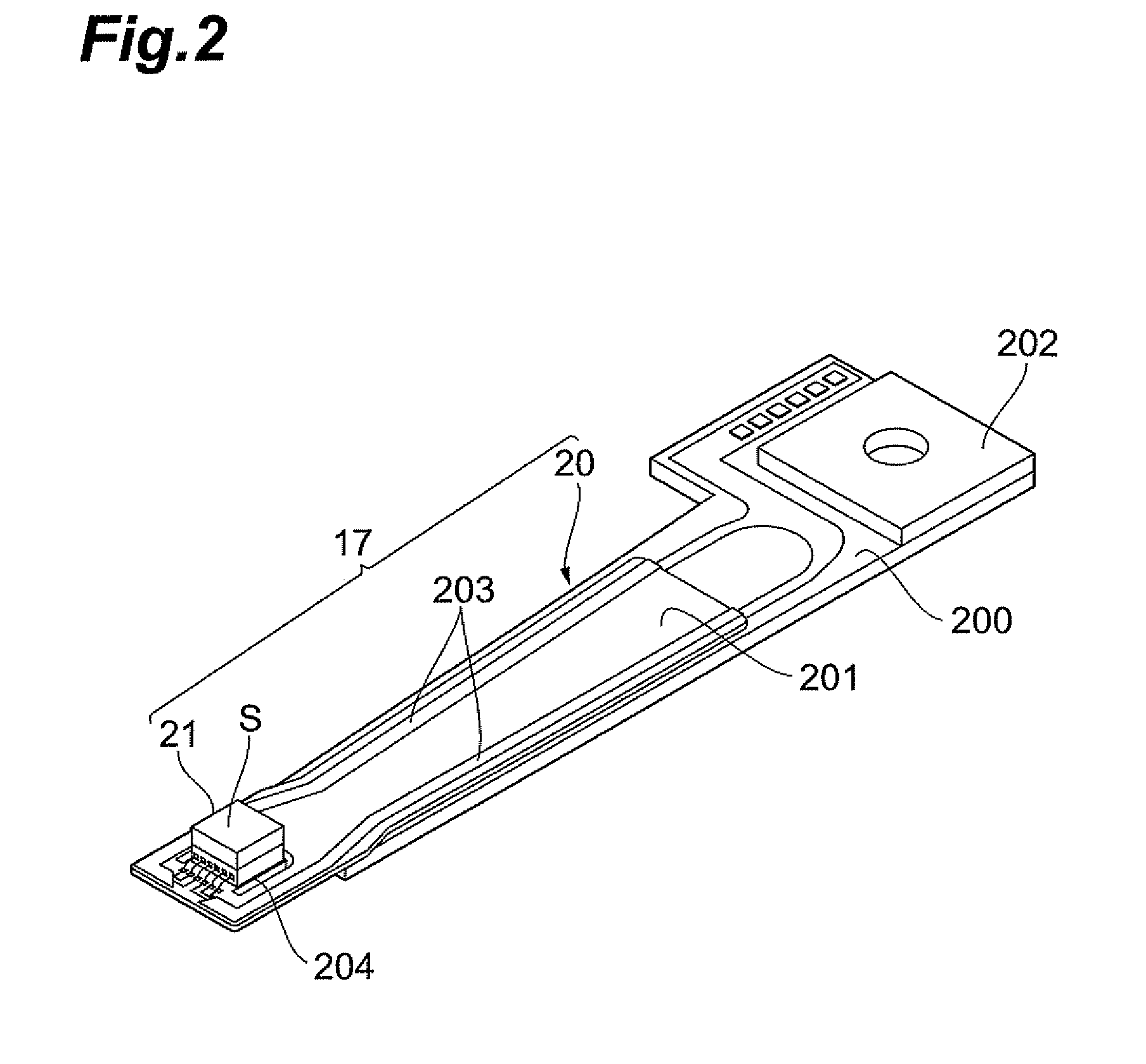
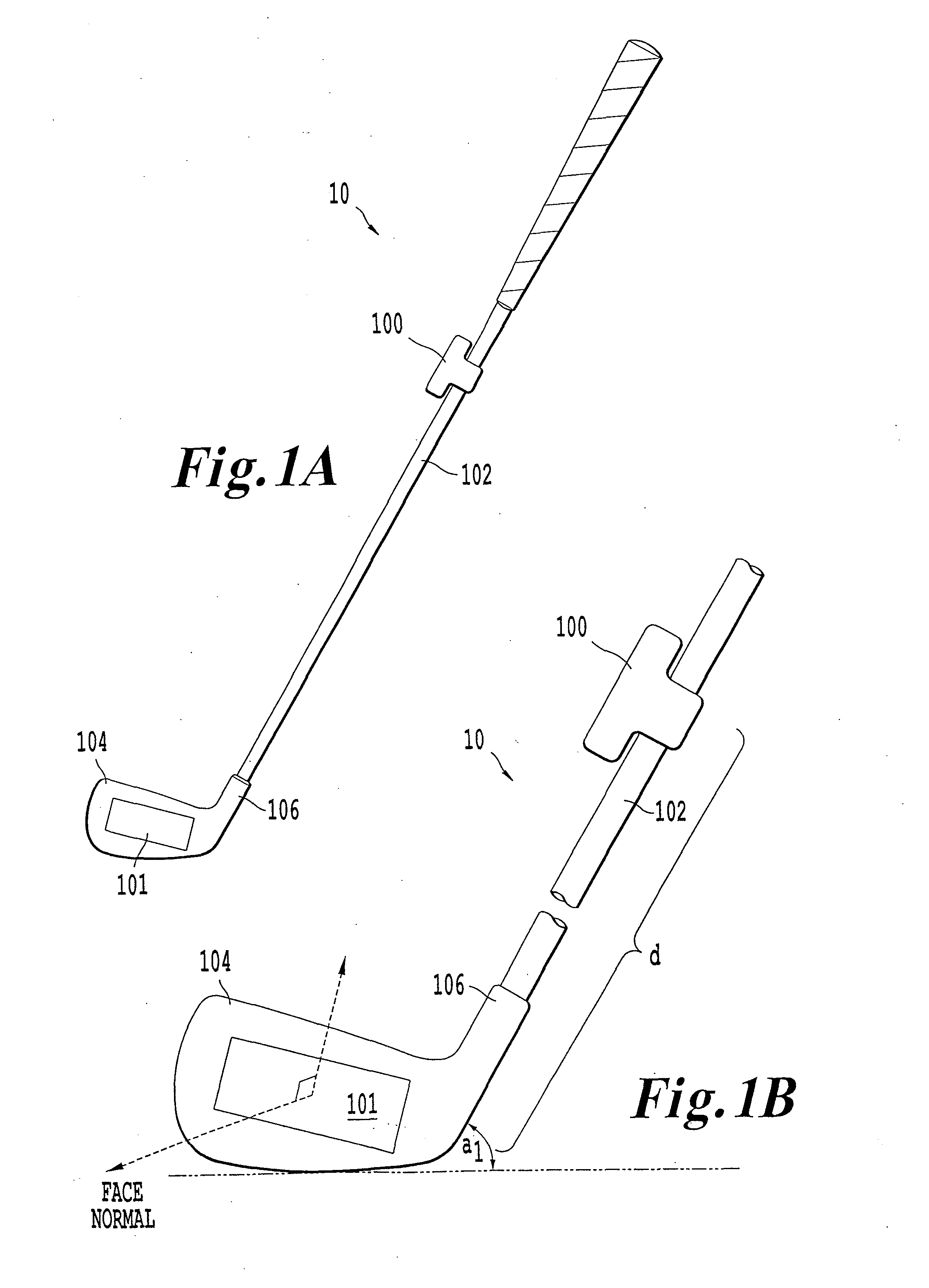
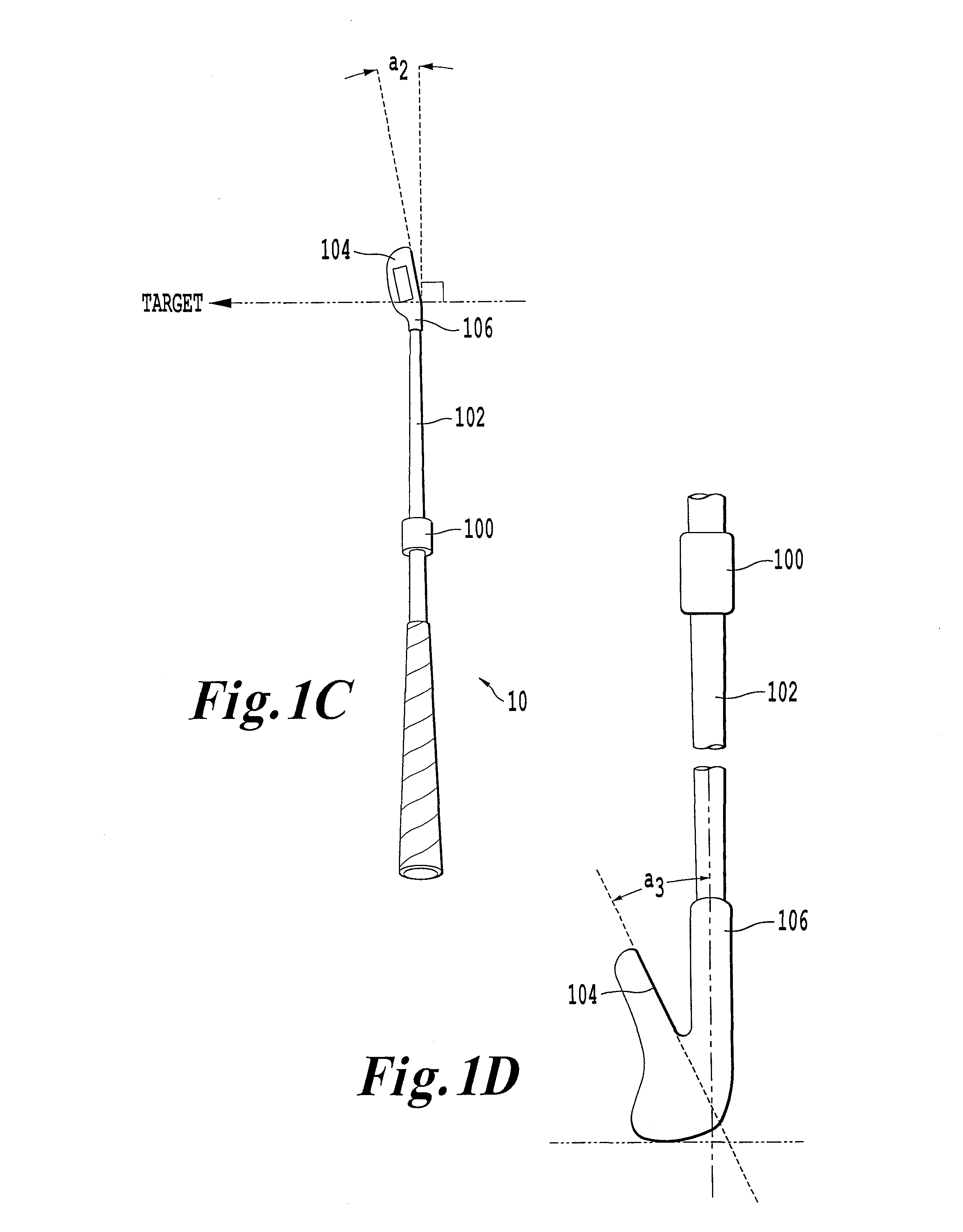
ActiveUS20140200092A1Improve accuracyGolfing accessoriesAcceleration measurement in multiple dimensionsCommunication unitGyroscope
An inertial measurement unit is affixed to a rigid body. The inertial measurement includes a gyroscope that measures a first angular velocity and an angular acceleration; a first accelerometer that measures a first acceleration; a communications unit that receives a measurement signal, the measurement signal including a second acceleration transmitted from a second accelerometer, the second accelerometer being affixed to the rigid body; and a controller that calculates a relative orientation of the inertial measurement unit and the second accelerometer, and a distance separating the inertial measurement unit and the second accelerometer.
Owner:PPG TECH
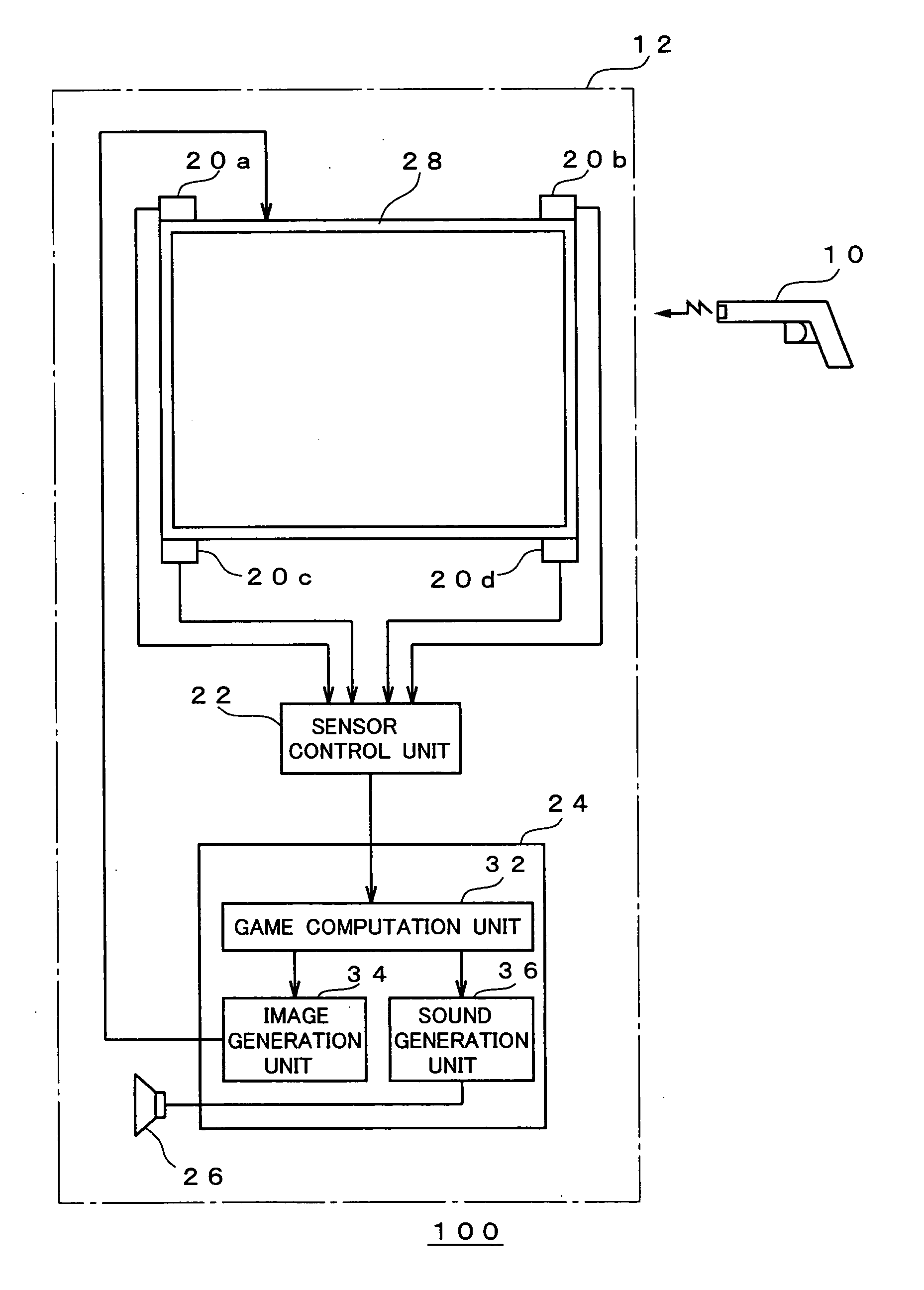
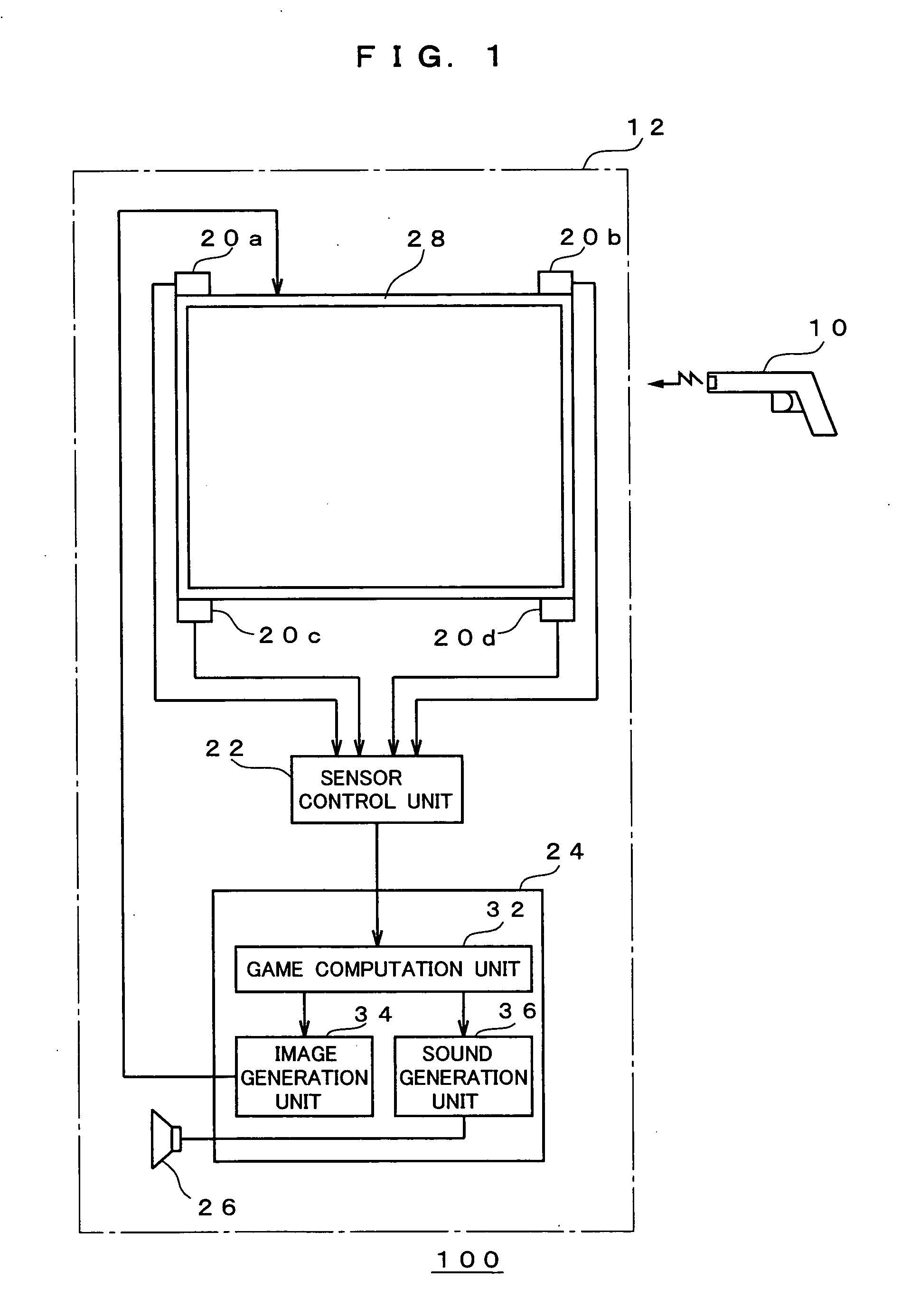
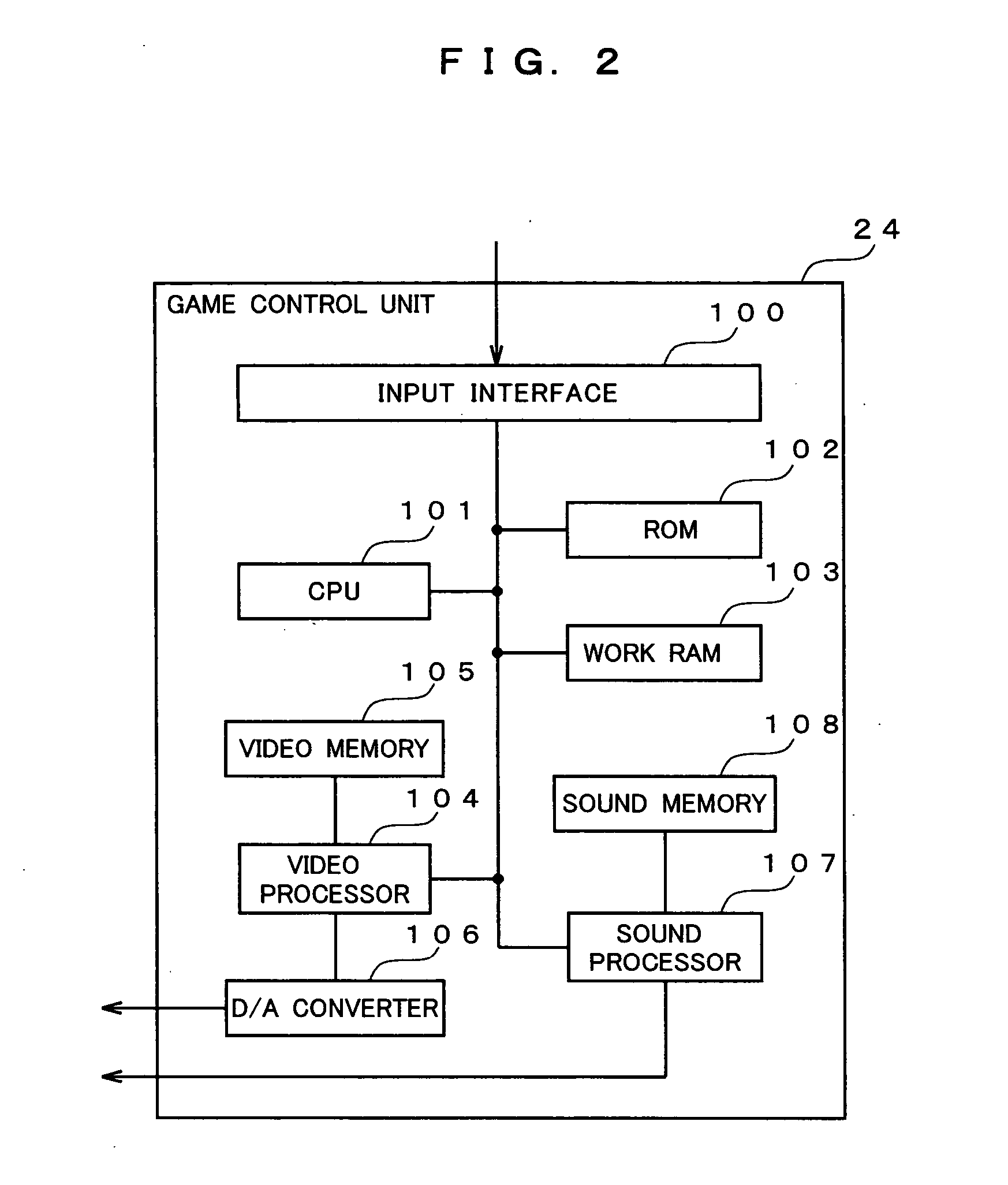
Image generation device, image display method and program product
InactiveUS20050272506A1Precise processEfficient expressionVideo gamesSpecial data processing applicationsComputer graphics (images)Virtual space
Upon projecting the inside of a virtual space on a prescribed projection plane and generating a two-dimensional image, foremost, the relative position of the operational unit and the relative direction designated with such operational unit are acquired, and these are substituted with the position and direction in the virtual space. Next, the position of the operational unit in the virtual space is shifted a prescribed amount horizontally and / or vertically to set the starting point, and an ending point is set on a virtual line extending along the direction designated by the operational unit in the virtual space. Next, a virtual viewpoint which approximately matches the position and direction of the operational unit in the virtual space is set and subject to projective transformation, and a two-dimensional image containing the trajectory image corresponding to a part or the entirety of the zone connecting the starting point and ending point is generated thereby.
Owner:SEGA CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com