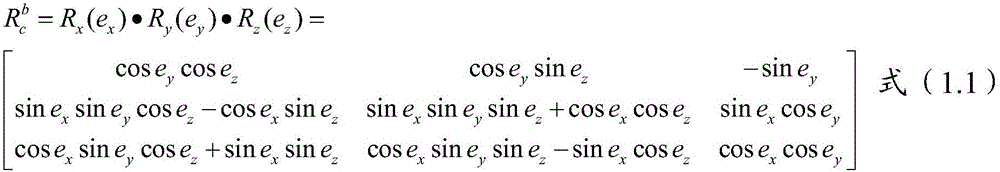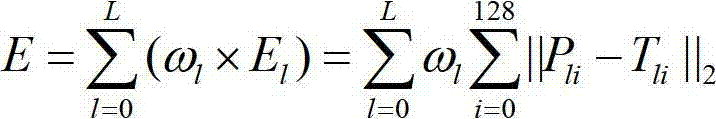Patents
Literature
97 results about "Absolute orientation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Absolute orientation. [′ab·sə‚lüt ȯr·ē·ən′tā·shən] (navigation) The adjusting to proper scale, orientating of the model datum parallel to sea level or another given vertical datum, and positioning of the model with reference to the horizontal datum of a stereoscopic model or group of models.
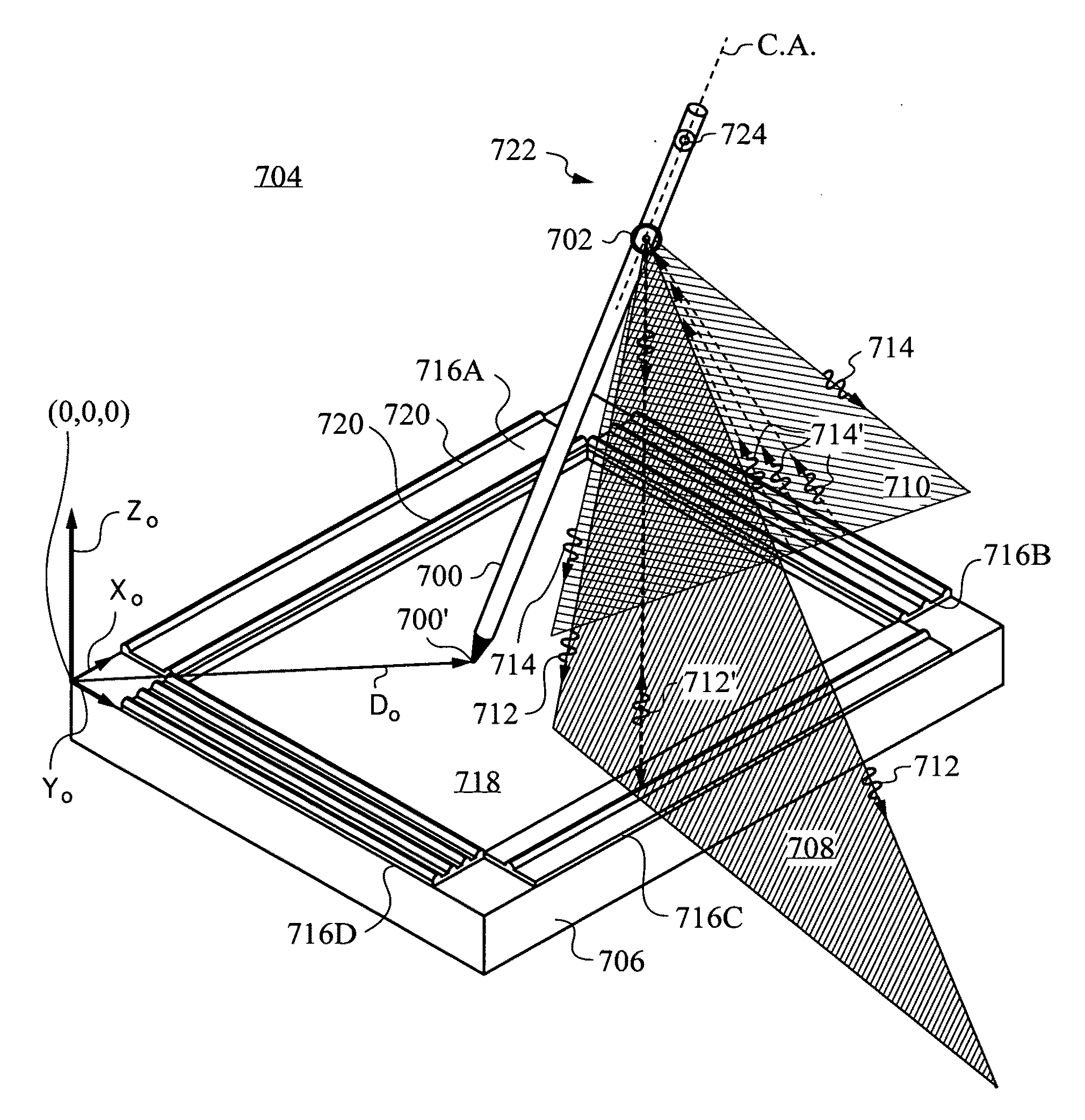
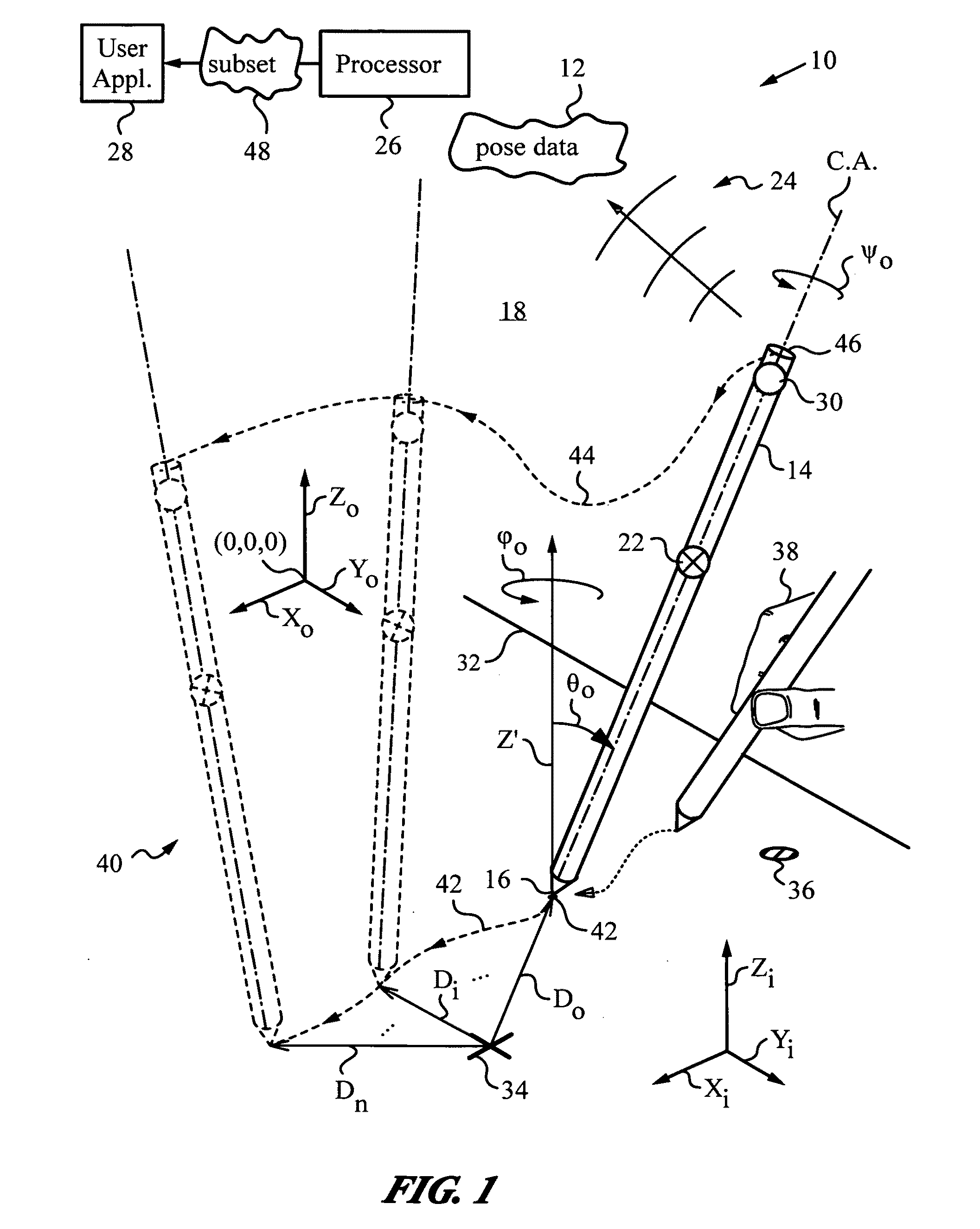
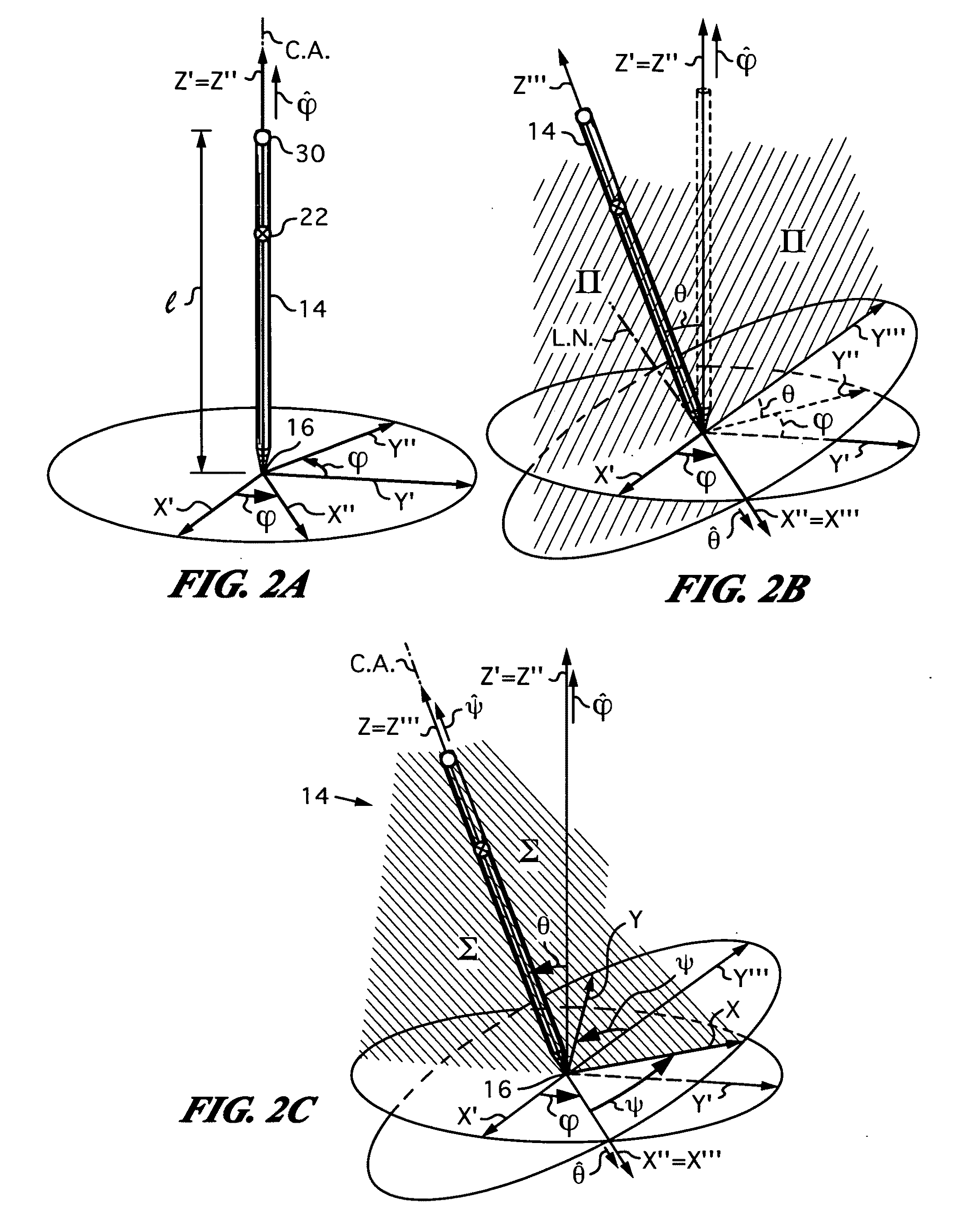
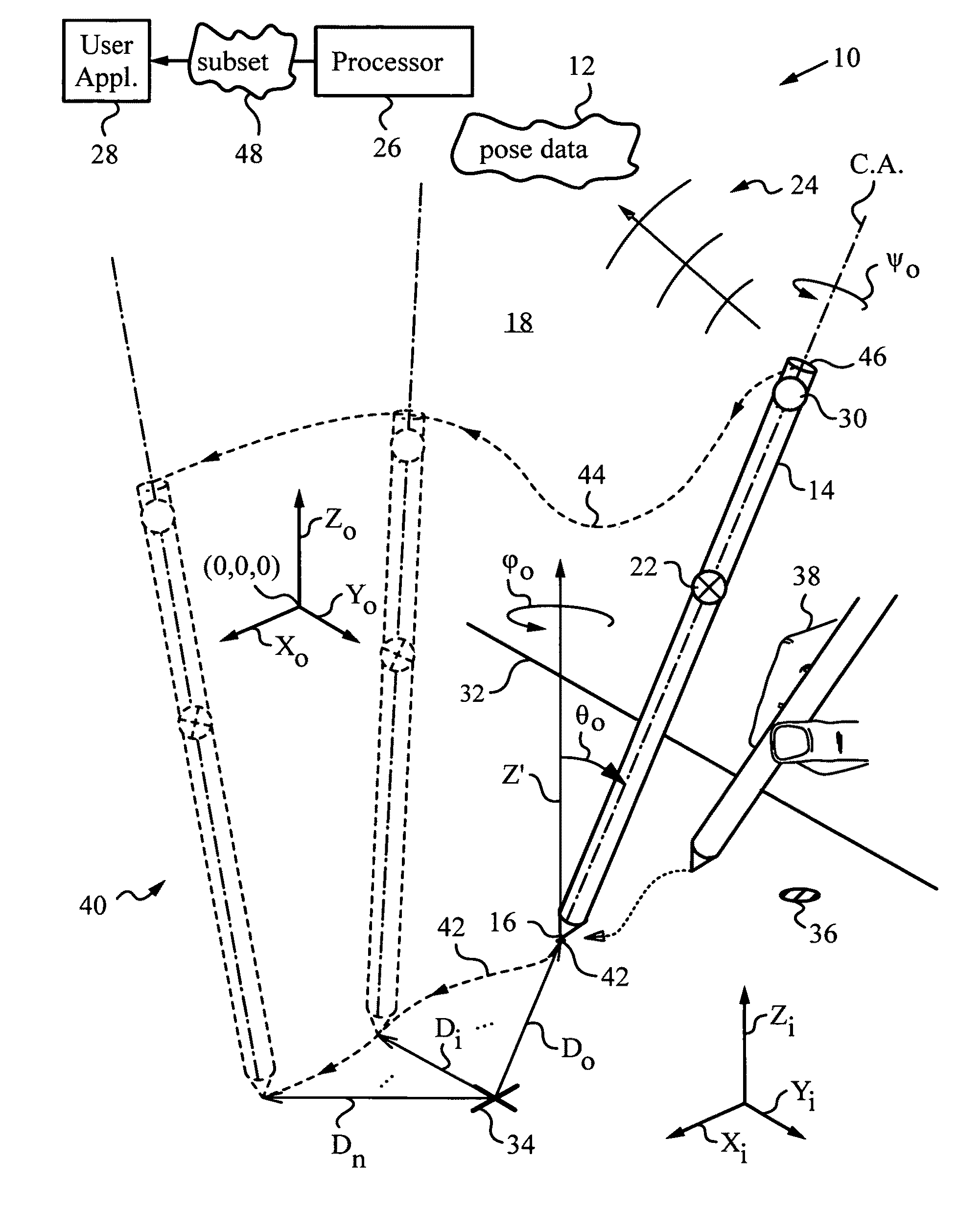
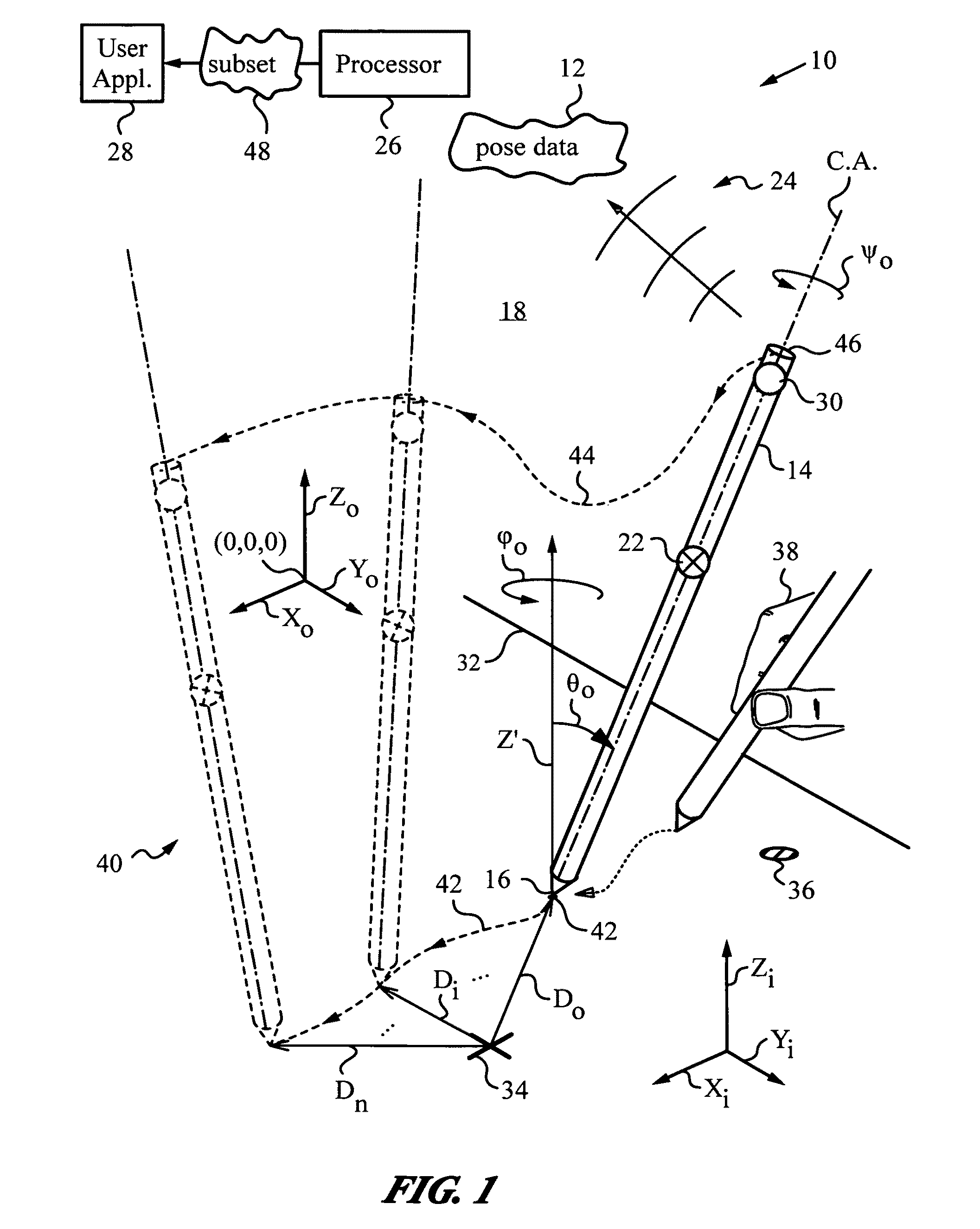
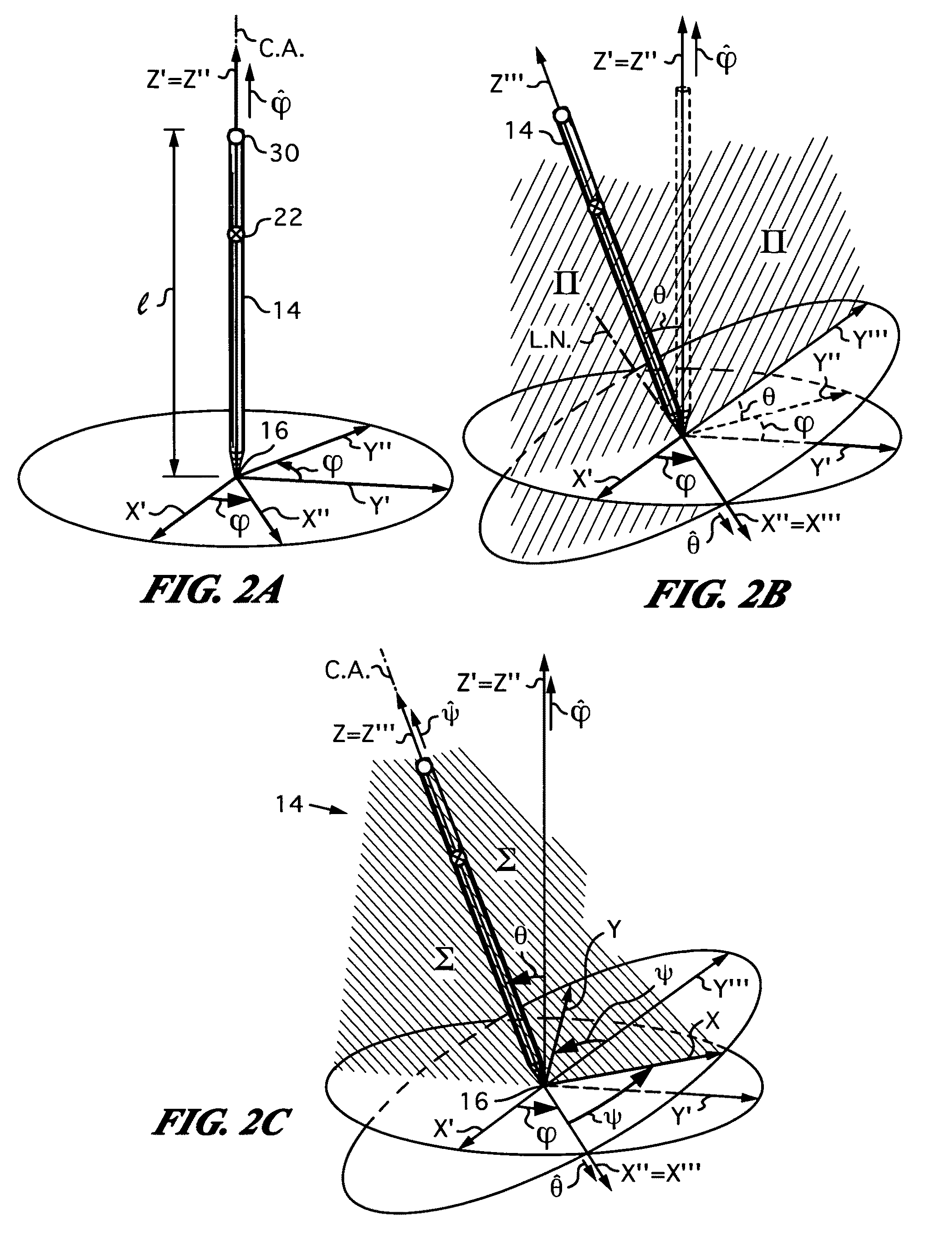
Computer interface employing a manipulated object with absolute pose detection component and a display
ActiveUS20100013860A1Good choiceInput/output for user-computer interactionImage enhancementPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
Owner:ELECTRONICS SCRIPTING PRODS
Computer interface employing a manipulated object with absolute pose detection component and a display
ActiveUS7961909B2Input/output for user-computer interactionImage enhancementPhotovoltaic detectorsRemote control
A system that has a remote control, e.g., a wand, equipped with a relative motion sensor that outputs data indicative of a change in position of the wand. The system also has one or more light sources and a photodetector that detects their light and outputs data indicative of the detected light. The system uses one or more controllers to determine the absolute position of the wand based on the data output by the relative motion sensor and by the photodetector. The data enables determination of the absolute pose of the wand, which includes the absolute position of a reference point chosen on the wand and the absolute orientation of the wand. To properly express the absolute parameters of position and / or orientation of the wand a reference location is chosen with respect to which the calculations are performed. The system is coupled to a display that shows an image defined by a first and second orthogonal axes such as two axes belonging to world coordinates (Xo,Yo,Zo). The one or more controllers are configured to generate signals that are a function of the absolute position of the wand in or along a third axis for rendering the display. To simplify the mapping of a real three-dimensional environment in which the wand is operated to the cyberspace of the application that the system is running, the third axis is preferably the third Cartesian coordinate axis of world coordinates (Xo,Yo,Zo).
Owner:ELECTRONICS SCRIPTING PRODS
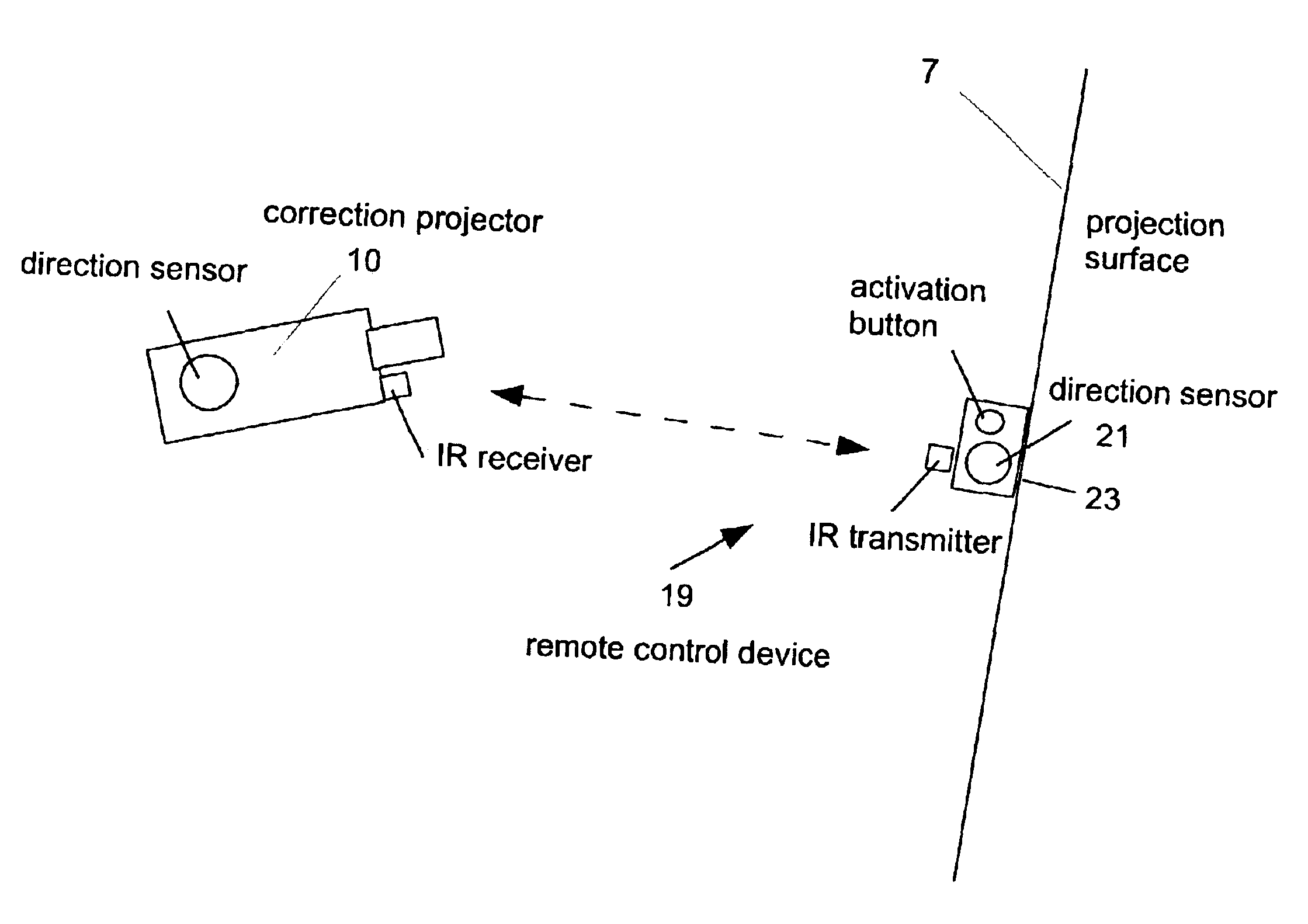
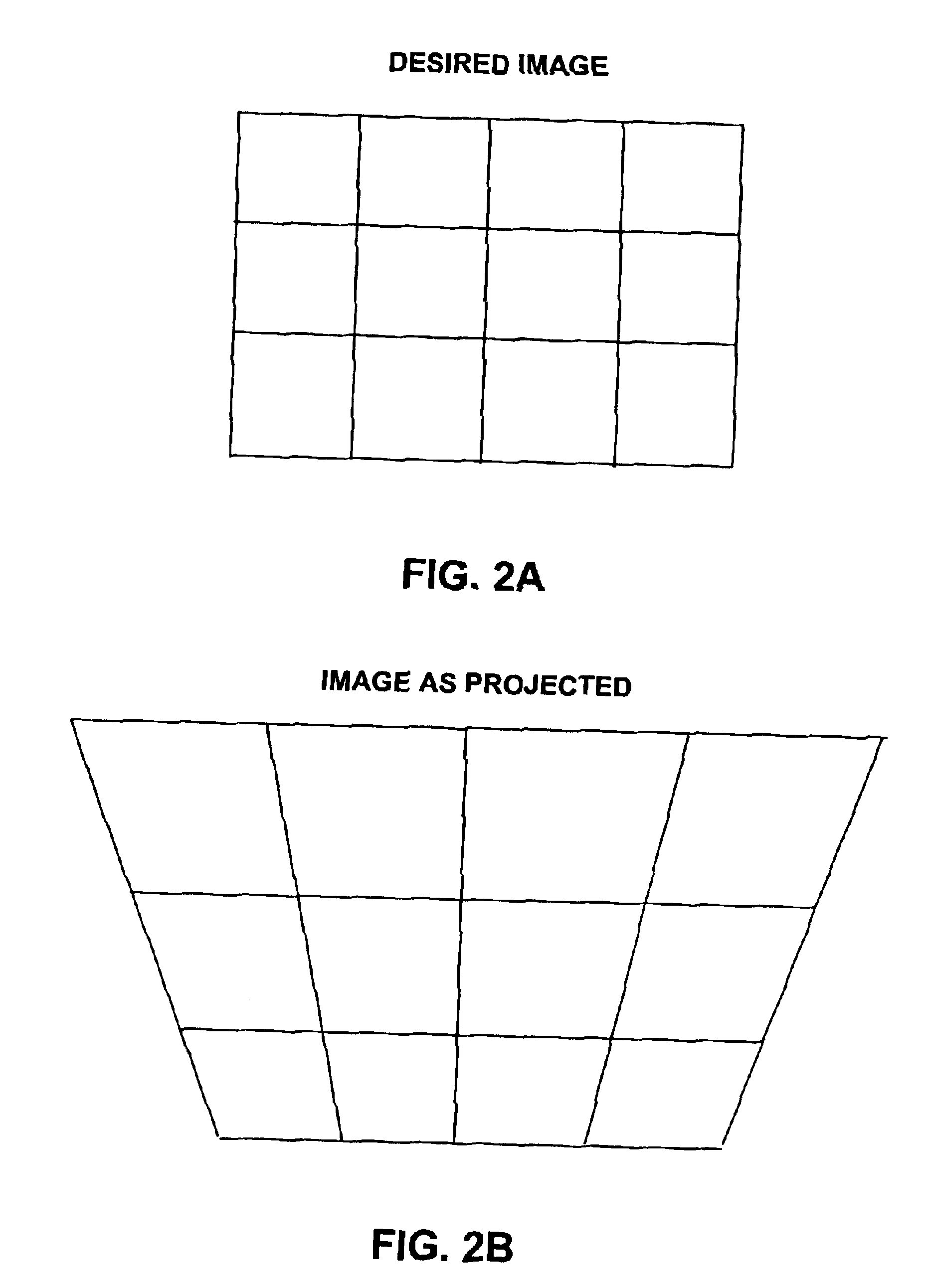
Automatic keystone correction system and method
A projector assembly and method for automatically correcting keystone distortion includes an image correction engine, a light engine, a projection lens having a projection axis, a processor, a directional sensor and an inclination sensor. The sensors determine the absolute vertical and horizontal direction of the projection axis. The inclination sensor determines the vertical zero reference. The direction sensor is used to determine the horizontal zero reference. The processor calculates vertical and horizontal difference angles between the absolute directions and zero reference values in the vertical and horizontal directions. Using difference angles, the processor calculates the keystone distortion and instructs the image correction engine to apply geometric and brightness correction to the image data proportional and inverse to the keystone distortion and lens parameters (field of view, focal length, imperfections, etc) such that the image projected onto a viewing screen, is free from keystone distortion.
Owner:GEO SEMICONDUCTOR INC
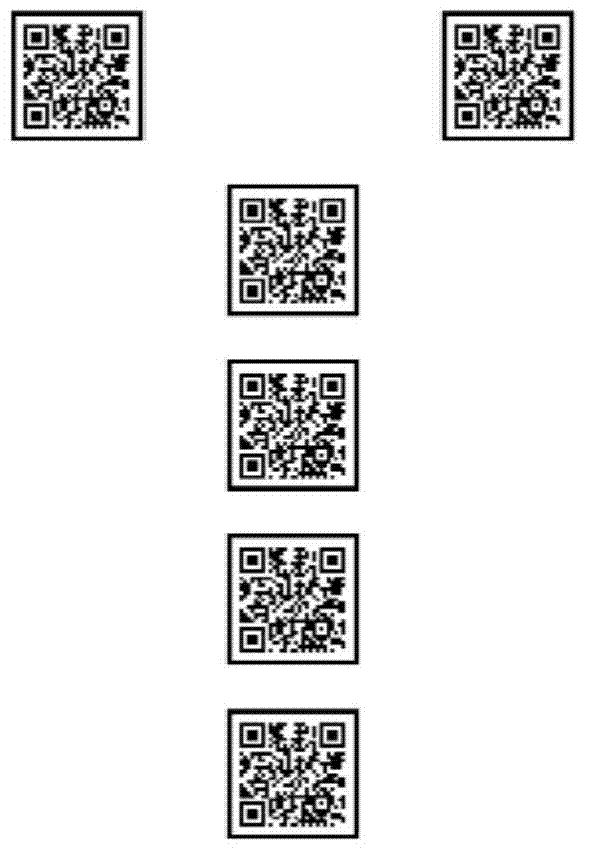
Two-dimensional code and vision-inert combined navigation system and method for robot
ActiveCN104848858AImprove screening efficiencyImprove computing efficiencyNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsAbsolute orientationNavigation system
The invention provides a two-dimensional code and a vision-inert combined navigation system and method for a robot. A sealed assistant frame is arranged at the periphery of the two-dimensional code, and the sealed assistant frame and the two-dimensional code are both applied to vision navigation. The two-dimensional code is used in the vision-inert combined navigation system for the robot; the vision-inert combined navigation method for the robot comprises the following steps: paving a plurality of two-dimensional codes with the sealed assistant frames at the peripheries on a ground; when the robot walks forwards, taking images by using imaging equipment; acquiring the absolute position and the absolute direction angle of the imaging equipment, and acquiring the absolute coordinates of the two-dimensional codes, and the absolute position and the absolute direction angle of the imaging equipment; confirming the relative position of the robot relative to a present starting point and the relative direction angle of the robot relative to a present starting direction angle; acquiring the absolute position of the robot, and taking the absolute position as a next starting point; acquiring the absolute direction angle of the robot, and taking the absolute direction angle as a next starting direction angle.
Owner:BEIJING JIZHIJIA TECH CO LTD
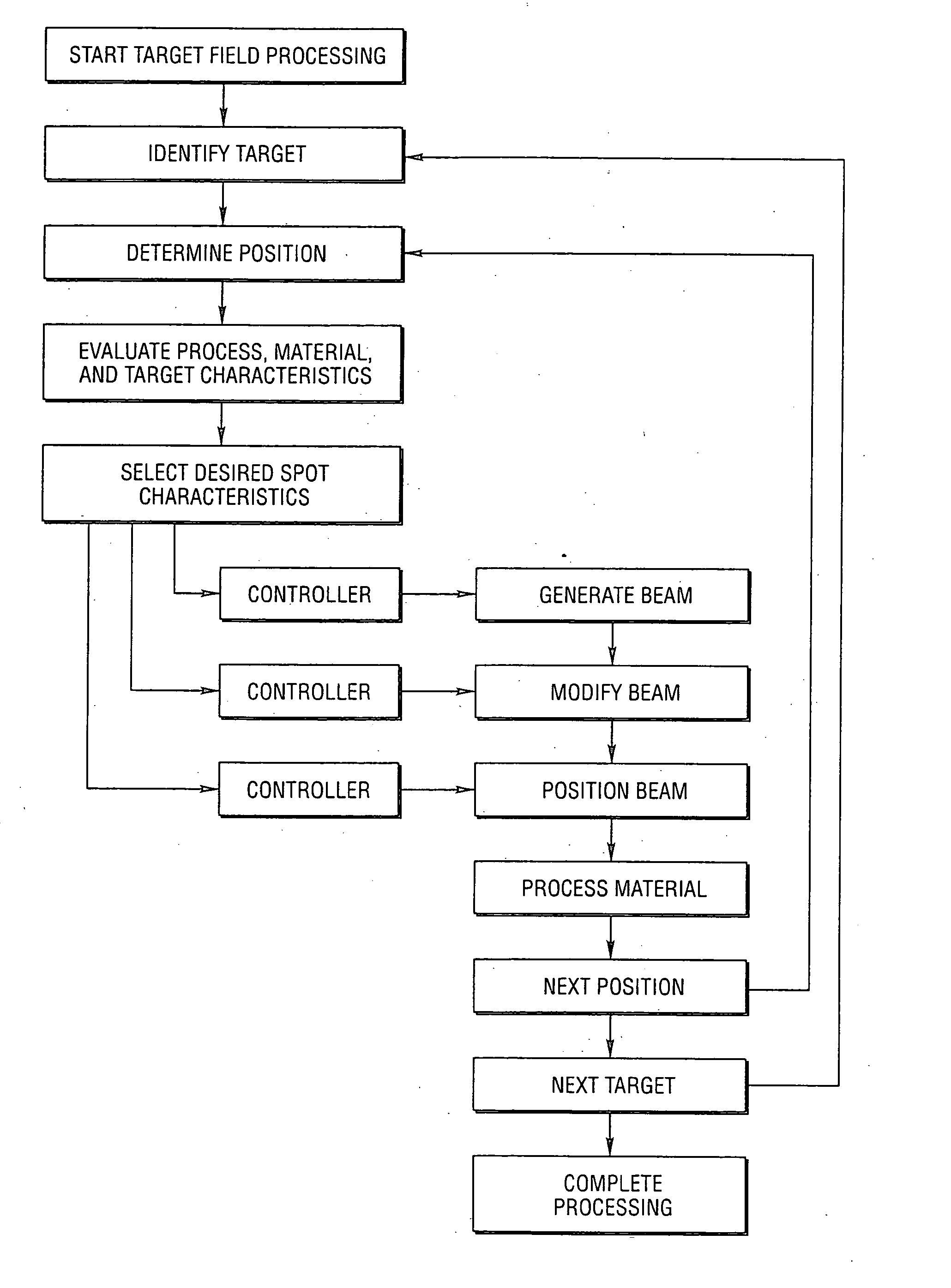
High-speed, precision, laser-based method and system for processing material of one or more targets within a field
InactiveUS20050017156A1Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsIlluminanceOptical axis
A precision, laser-based method and system for high-speed, sequential processing of material of targets within a field are disclosed that control the irradiation distribution pattern of imaged spots. For each spot, a laser beam is incident on a first anamorphic optical device and a second anamorphic optical device so that the beam is controllably modified into an elliptical irradiance pattern. The modified beam is propagated through a scanning optical system with an objective lens to image a controlled elliptical spot on the target. In one embodiment, the relative orientations of the devices along an optical axis are controlled to modify the beam irradiance pattern to obtain an elliptical shape while the absolute orientation of the devices controls the orientation of the elliptical spot.
Owner:ELECTRO SCI IND INC
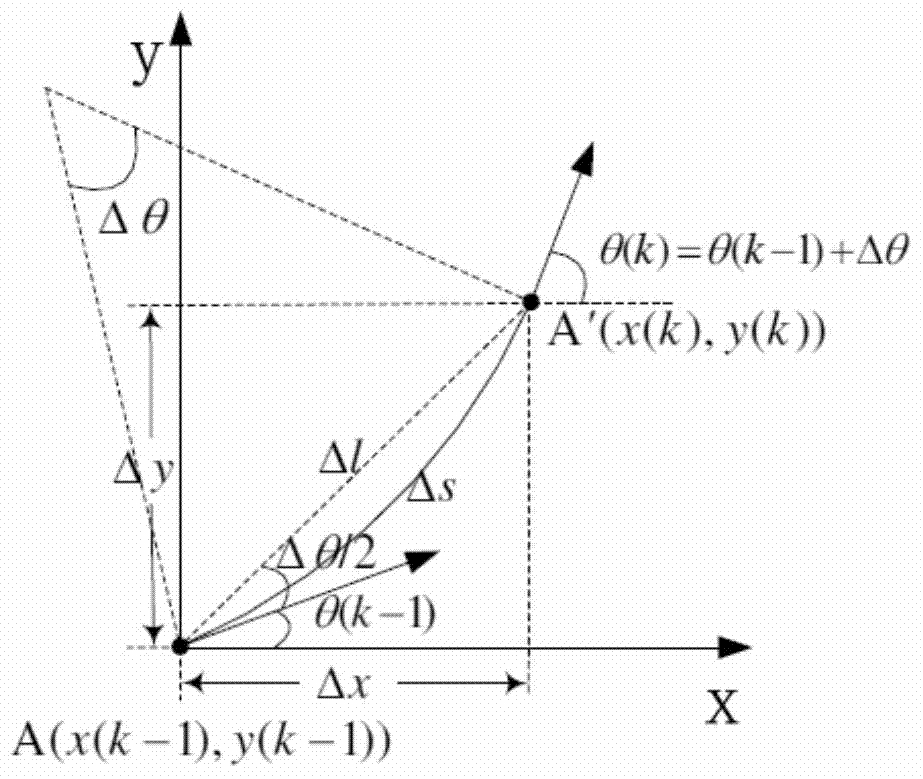
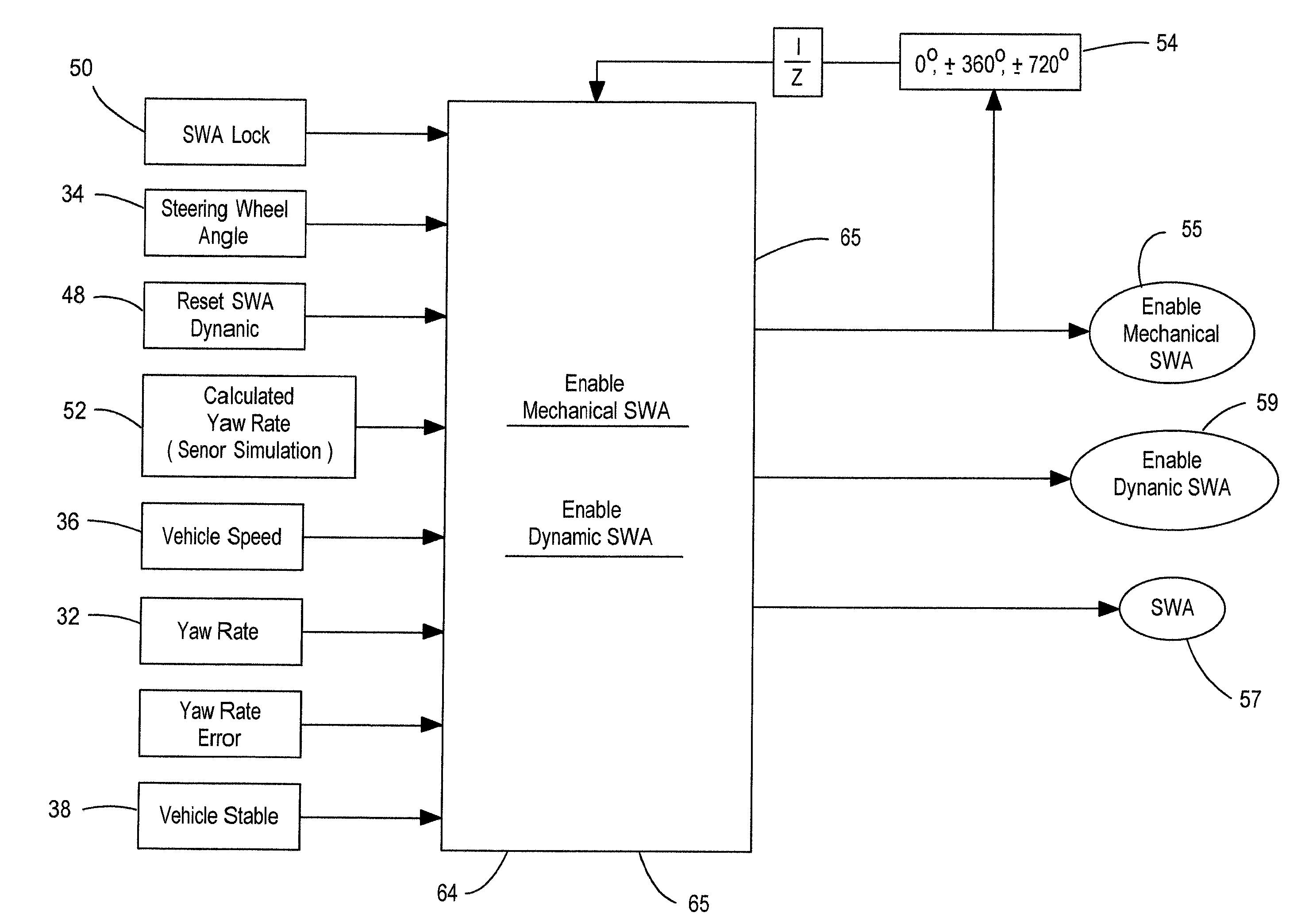
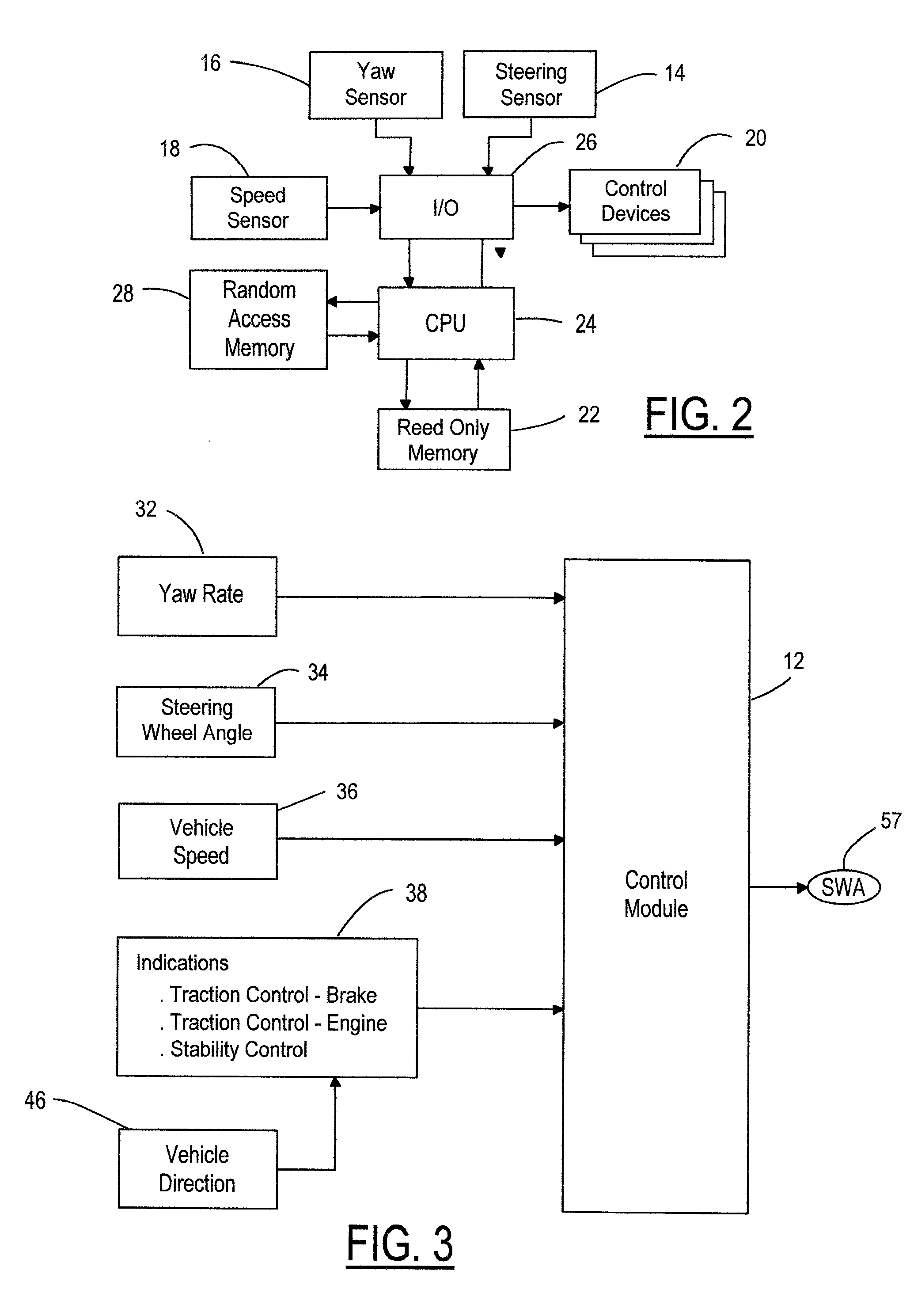
Determining the direction of travel of an automotive vehicle from yaw rate and relative steering wheel angle
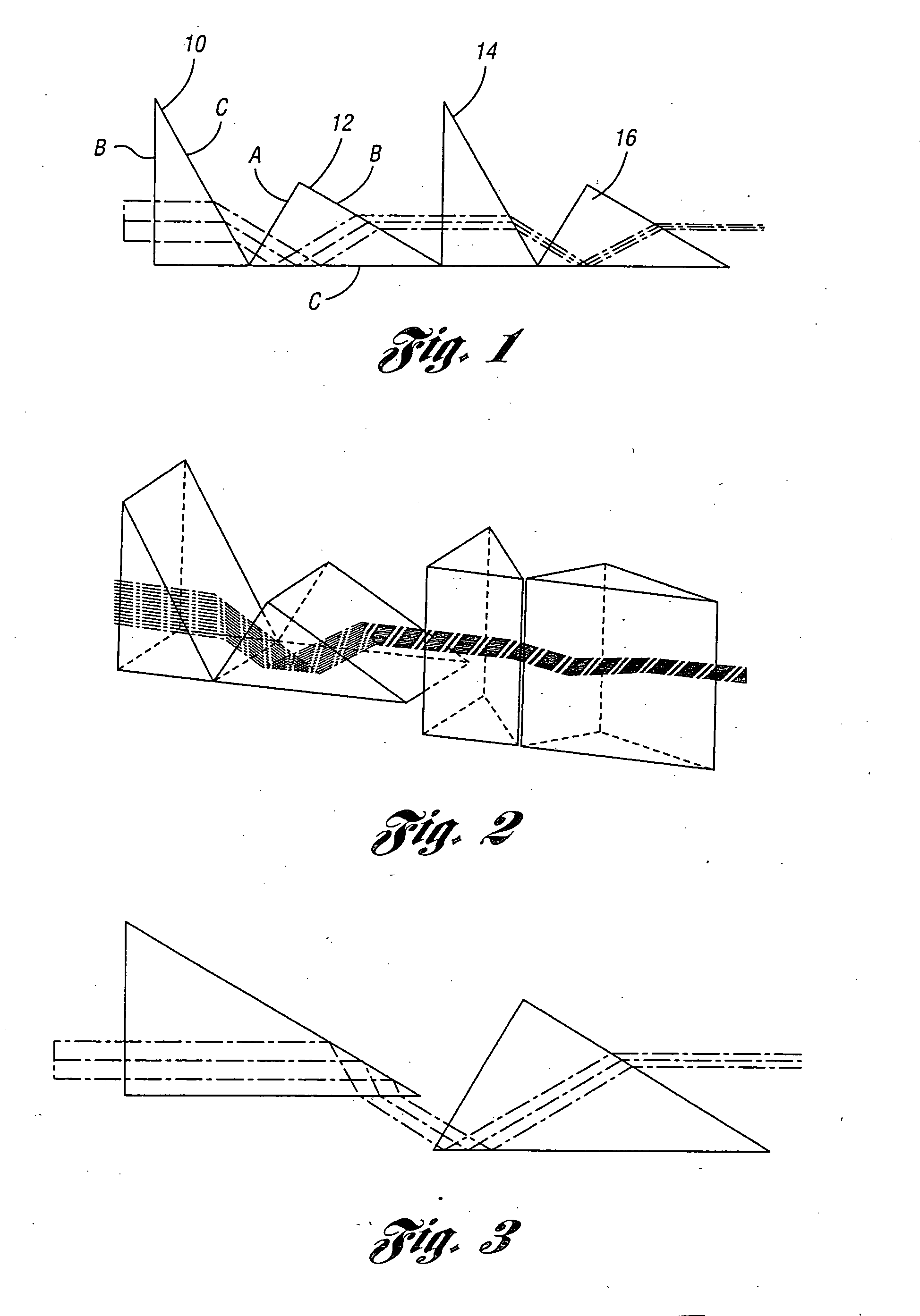
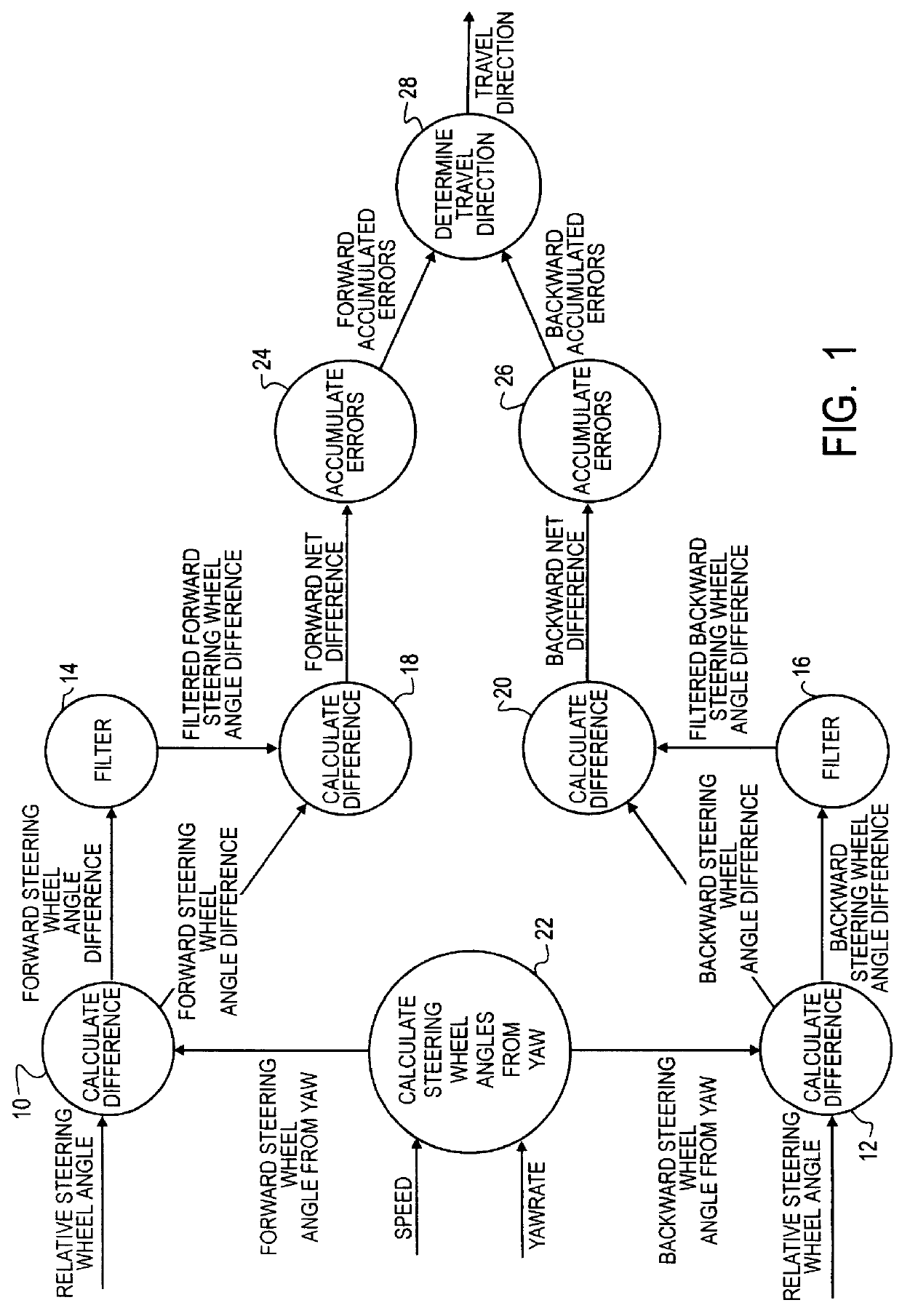
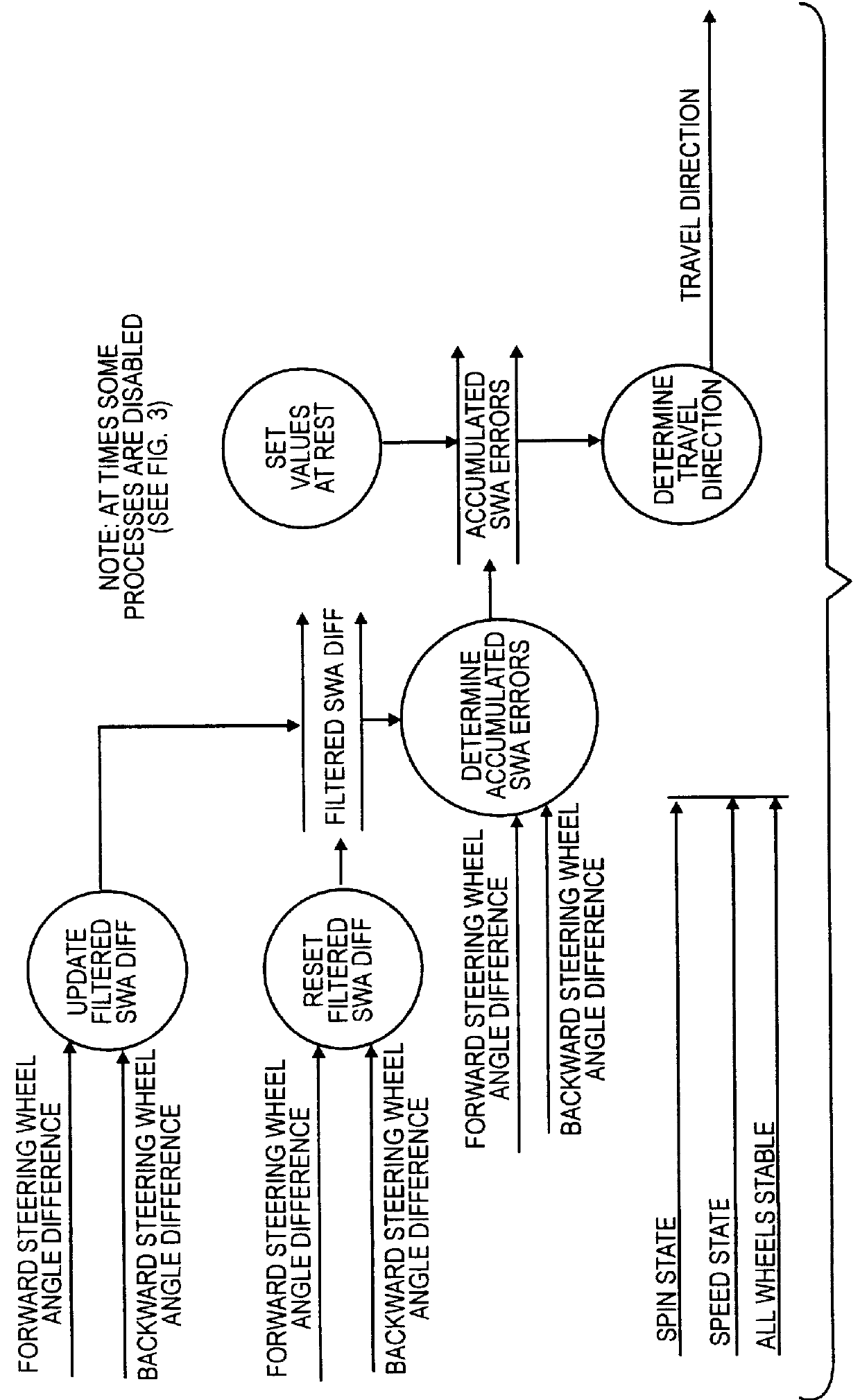
A method of using relative steering wheel angle of an automotive vehicle, vehicle yaw rate, and vehicle speed to determine whether the vehicle is traveling forward or backward. Forward and backward steering wheel angles are calculated from vehicle speed and yaw rate (22). A difference between relative steering wheel angle and forward steering wheel angle (10), and a difference between relative steering wheel angle and backward steering wheel angle (12) are calculated. The difference between relative steering wheel angle and forward steering wheel angle is filtered (14), and a difference between the filtered and the unfiltered difference between relative steering wheel angle and forward steering wheel angle is calculated to obtain a forward net difference (18). The difference between relative steering wheel angle and backward steering wheel angle is filtered (16), and a difference between the filtered and the unfiltered difference between relative steering wheel angle and backward steering wheel angle is calculated to obtain a backward net difference (20). While repeatedly performing the foregoing steps, forward net difference values derived from the forward net differences are accumulated (24), and backward net difference values derived from the backward net differences are accumulated (26). The travel direction is determined by comparing the accumulation of forward net difference values and the accumulation of backward net difference values (28). Absolute steering wheel angle and road bank angle can also be calculated.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
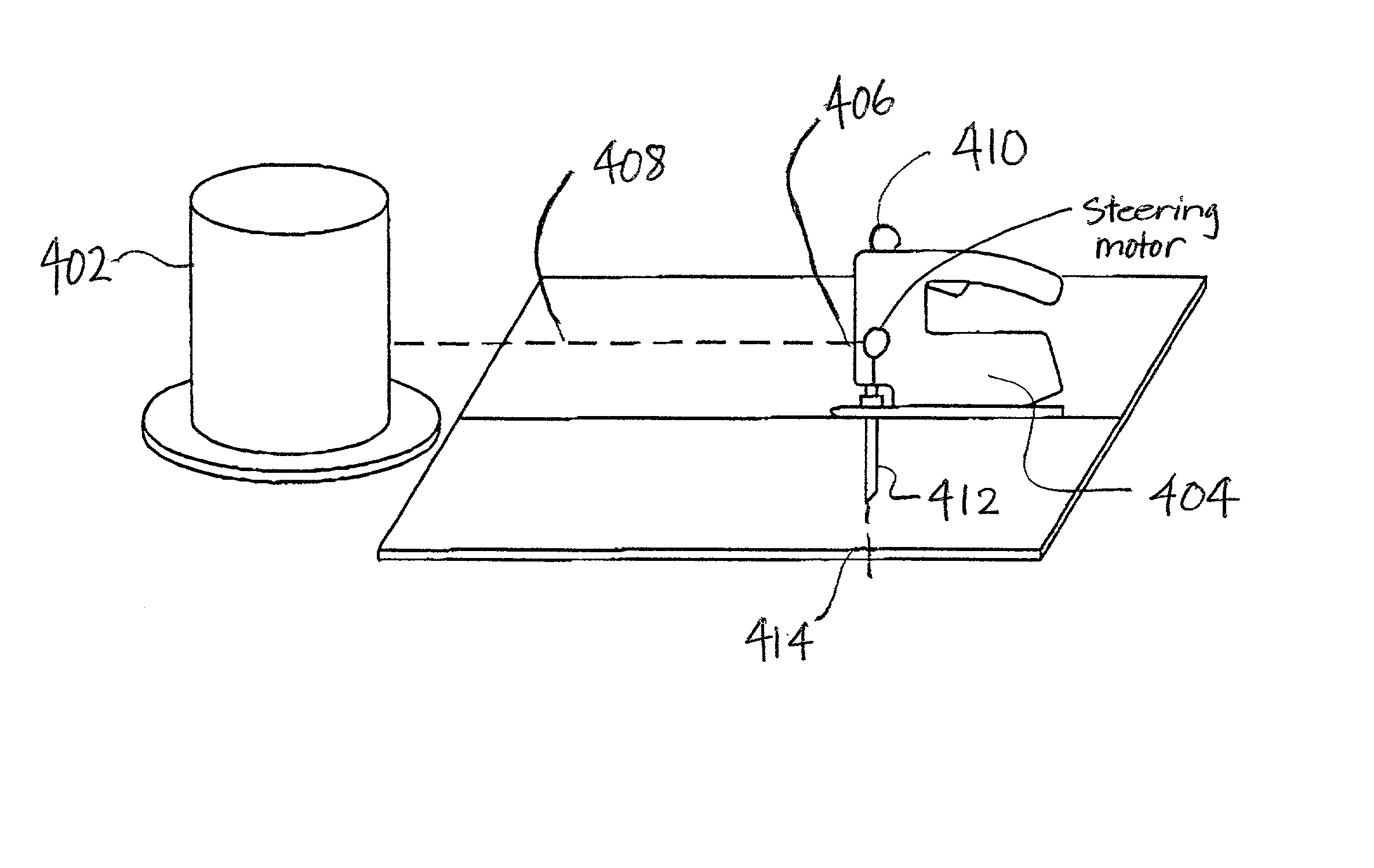
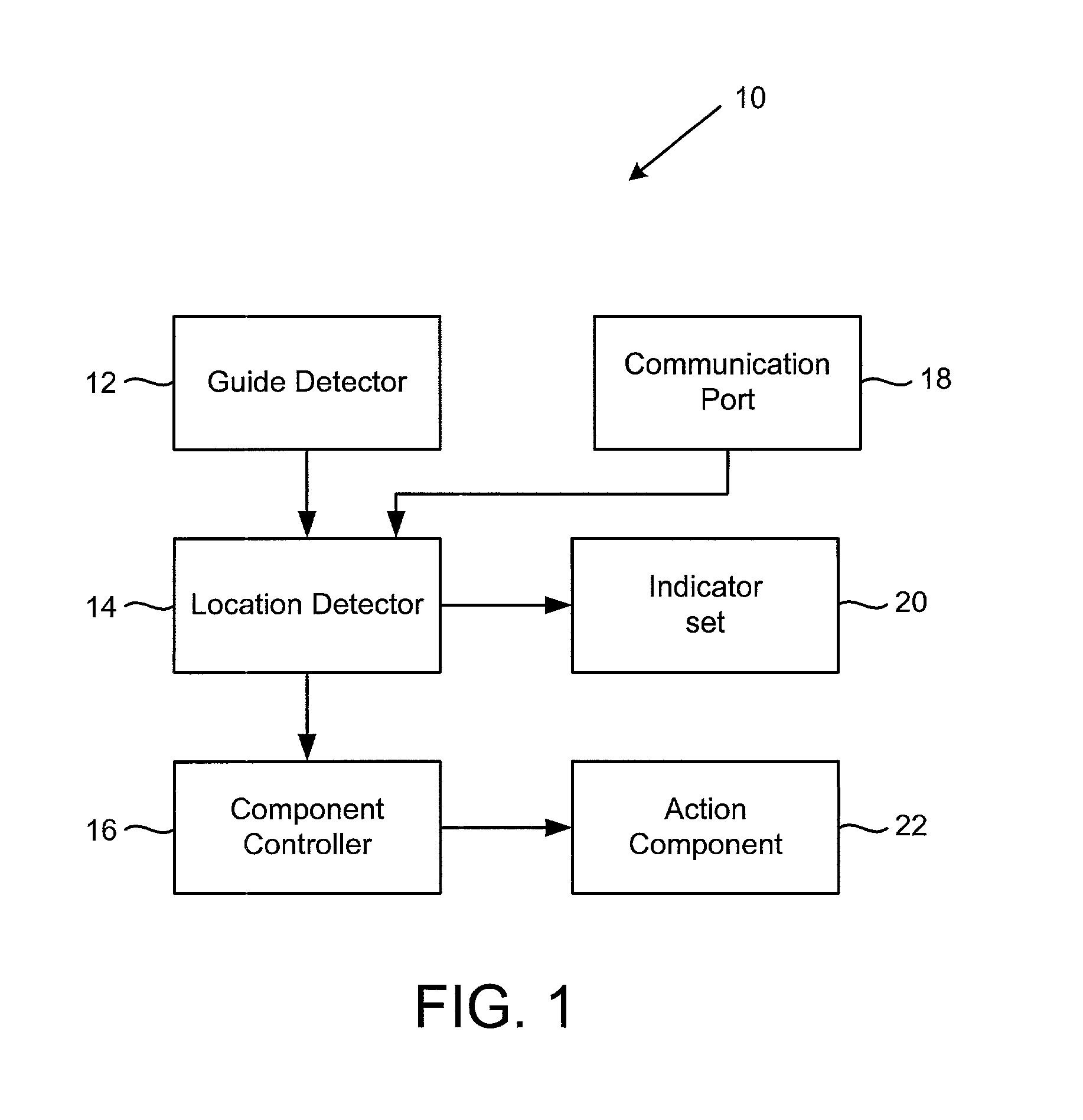
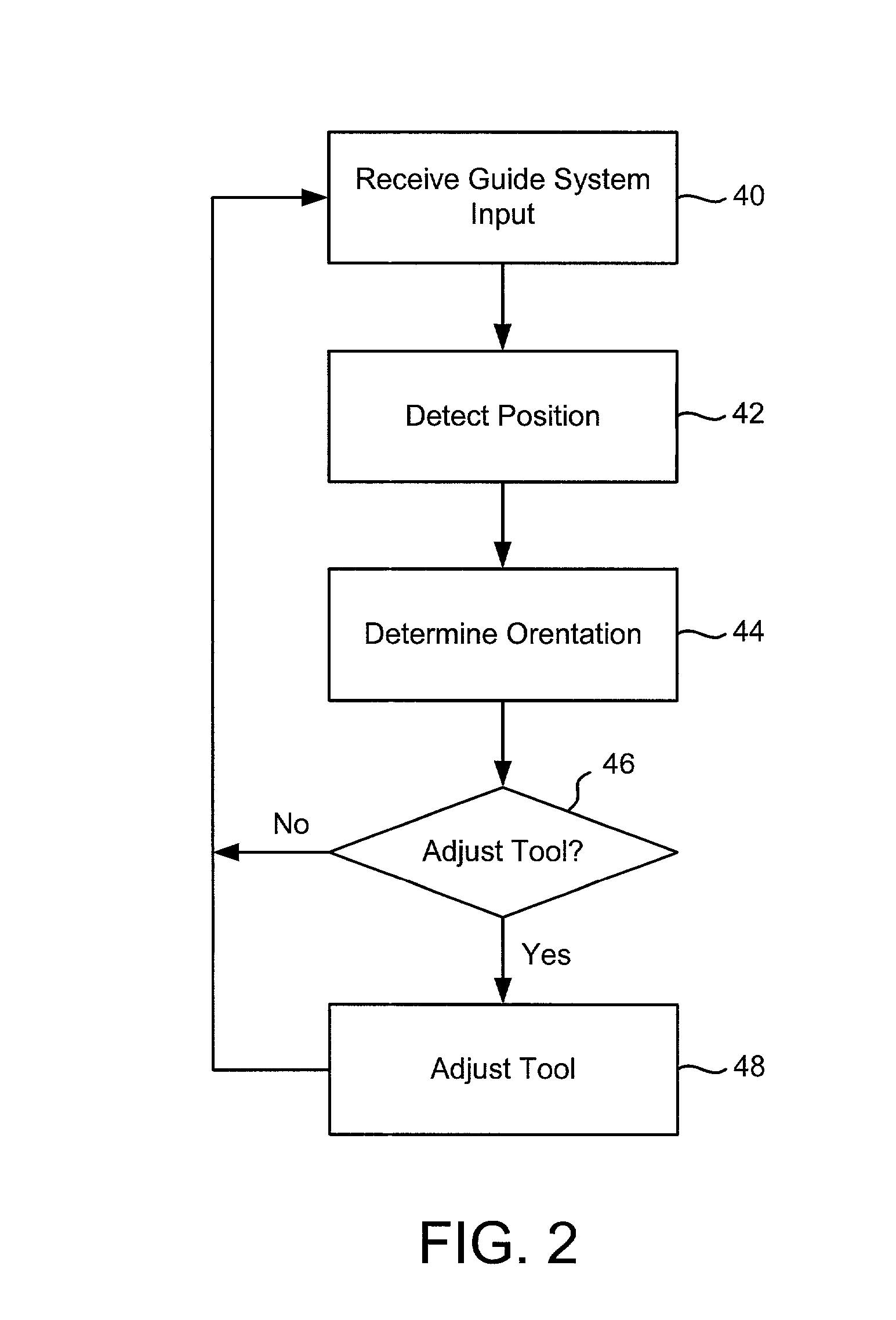
Tools with orientation detection
InactiveUS20030000355A1Stapling toolsDrilling/boring measurement devicesAbsolute orientationEngineering
A tool operates with a guide system to identify the orientation of a tool on a work piece. In one implementation, the tool identifies its orientation with respect to a guide signal supplied by the guide system. In an alternate embodiment, the tool determines its absolute orientation, such as a (x, y) coordinate. The tool includes an action component adapted to alter the work piece, such as a cutting head in a router. A guide detector in the tool detects a position of a guide signal from the guide system. A location detector in the tool receives the position data and employs it to determine the tool's orientation. Based on the detected orientation, the tool decides whether any tool adjustments are necessary. Examples of tool adjustments include the following: adjusting the position of the action component, enabling or disabling the action component, and providing operating indicators to direct a tool operator's use of the tool.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH CO LTD
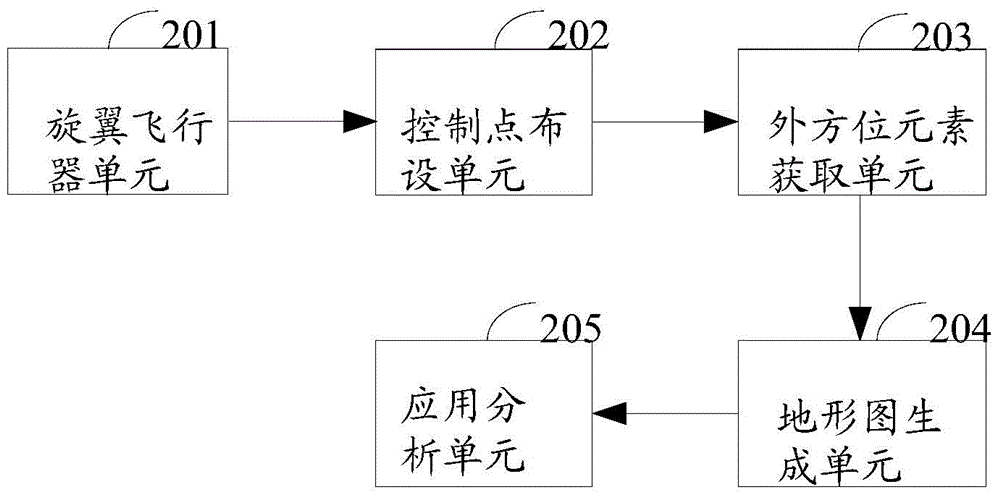
Photogrammetry and remote sensing comprehensive teaching method and system
The invention discloses a photogrammetry and remote sensing comprehensive teaching method and a system. The method comprises the following steps that aerial images of a preset flight planning area are obtained and pre-treated, control points are distributed in the flight planning area according to the pretreated aerial images and control point distributing standards, the geographical coordinate measuring is conducted, exterior orientation factors of all the images are obtained by according to the measured geographical coordinate information of the control points and the aerial images by aerial triangulation, relative orientation and absolute orientation are conducted on all the images in an all-digital photogrammetry working station according to the obtained exterior orientation factors of all the images, a three-dimensional model is built, the topography and feature data collection is conducted in the built three-dimensional model, a digital surveying and mapping product is generated according to the collected topography and feature data, and the three-dimensional modeling and space analysis are conducted by using the generated digital surveying and mapping product based on the project application needs. The teaching efficiency can be improved, and the teaching effect can be improved.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF URBAN CONSTR +1
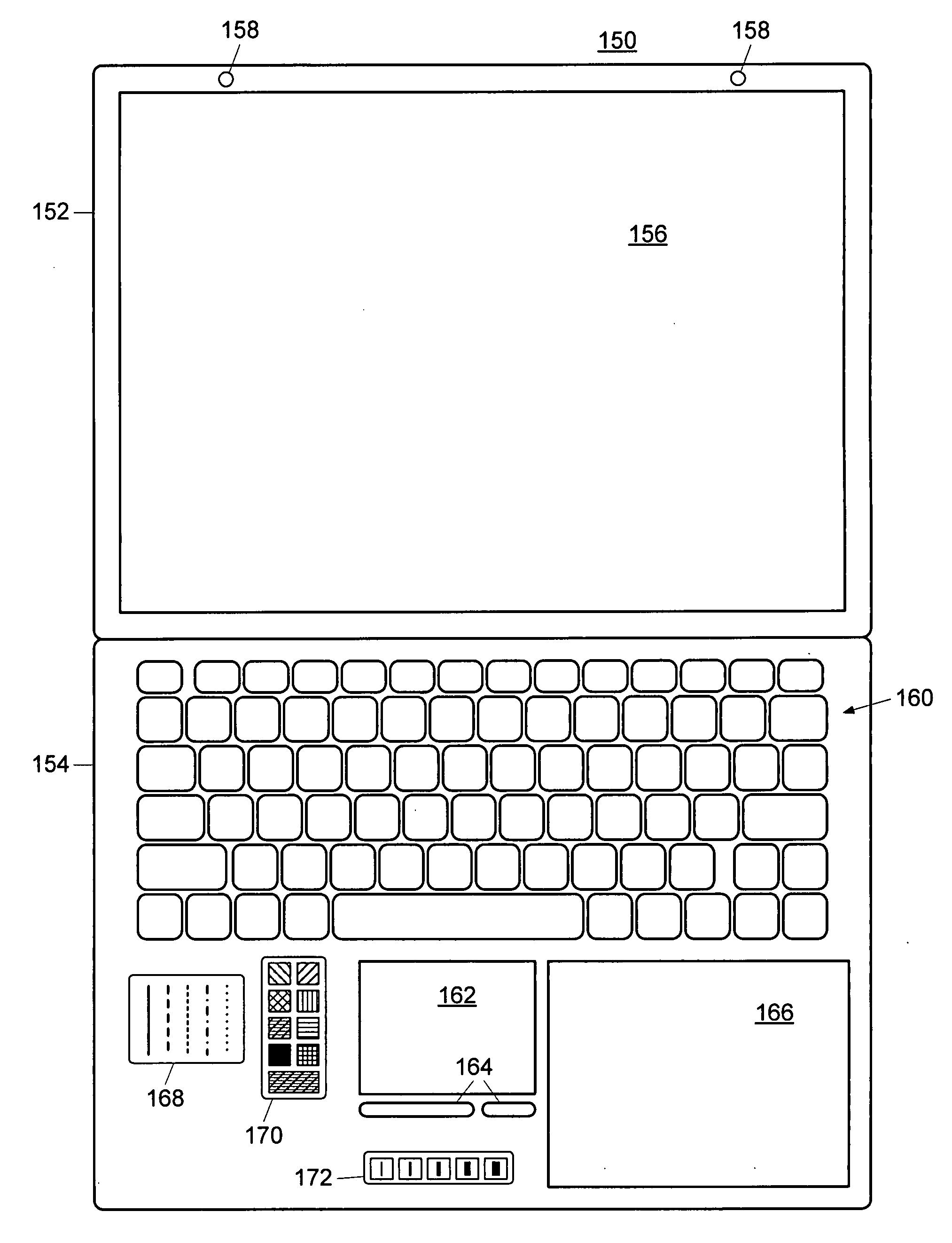
Relative-position, absolute-orientation sketch pad and optical stylus for a personal computer
InactiveUS20070285405A1Accessed faster and moreEasy to addDetails for portable computersInput/output processes for data processingAbsolute orientationEngineering
A notebook computer is upgraded by providing stylus-cooperating indicia near the keyboard and an optical stylus that can recognize the indicia. The indicia includes a sketch pad area that cooperates with the optical stylus to transmit movement data to the computer. The movement data is relative in position and absolute in orientation, providing ΔX and ΔY in the sketch pad's coordinate plane rather than the stylus's. Other indicia represents tool buttons recognized by both humans and the stylus. A stylus and stickers kits is used to upgraded existing notebook computers. New ones can be manufactured with the stylus-cooperating indicia in place or the indicia may be provided on a substrate that may be attached to any notebook computer, as selected and positioned by the end user. The stickers or substrate is thin enough to permit the notebook computer to be closed as usual. In an alternative embodiment, the indicia is printed on a mouse pad or other surface to provide tablet and stylus functionality to other kinds of personal computers as well.
Owner:REHM PETER H
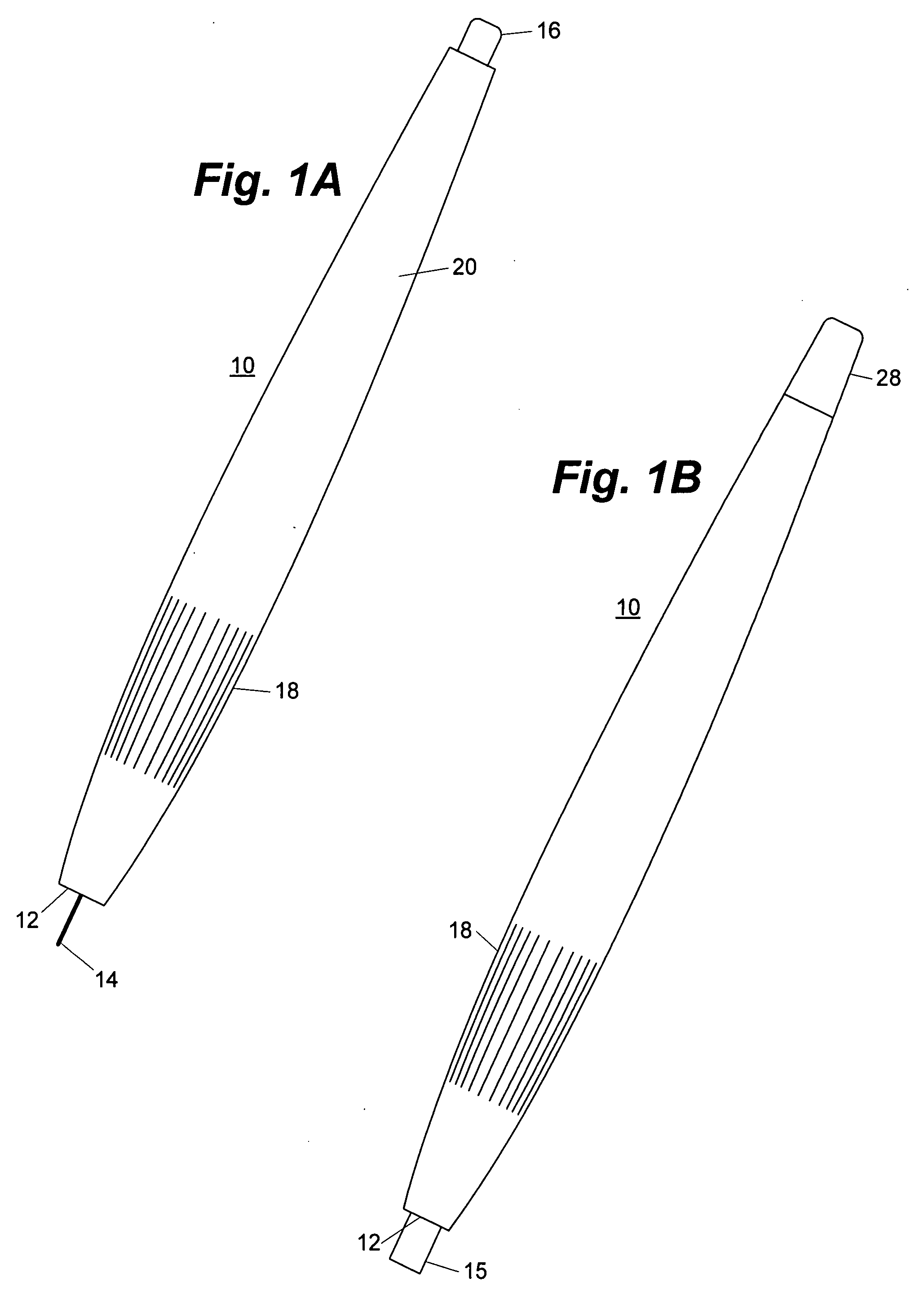
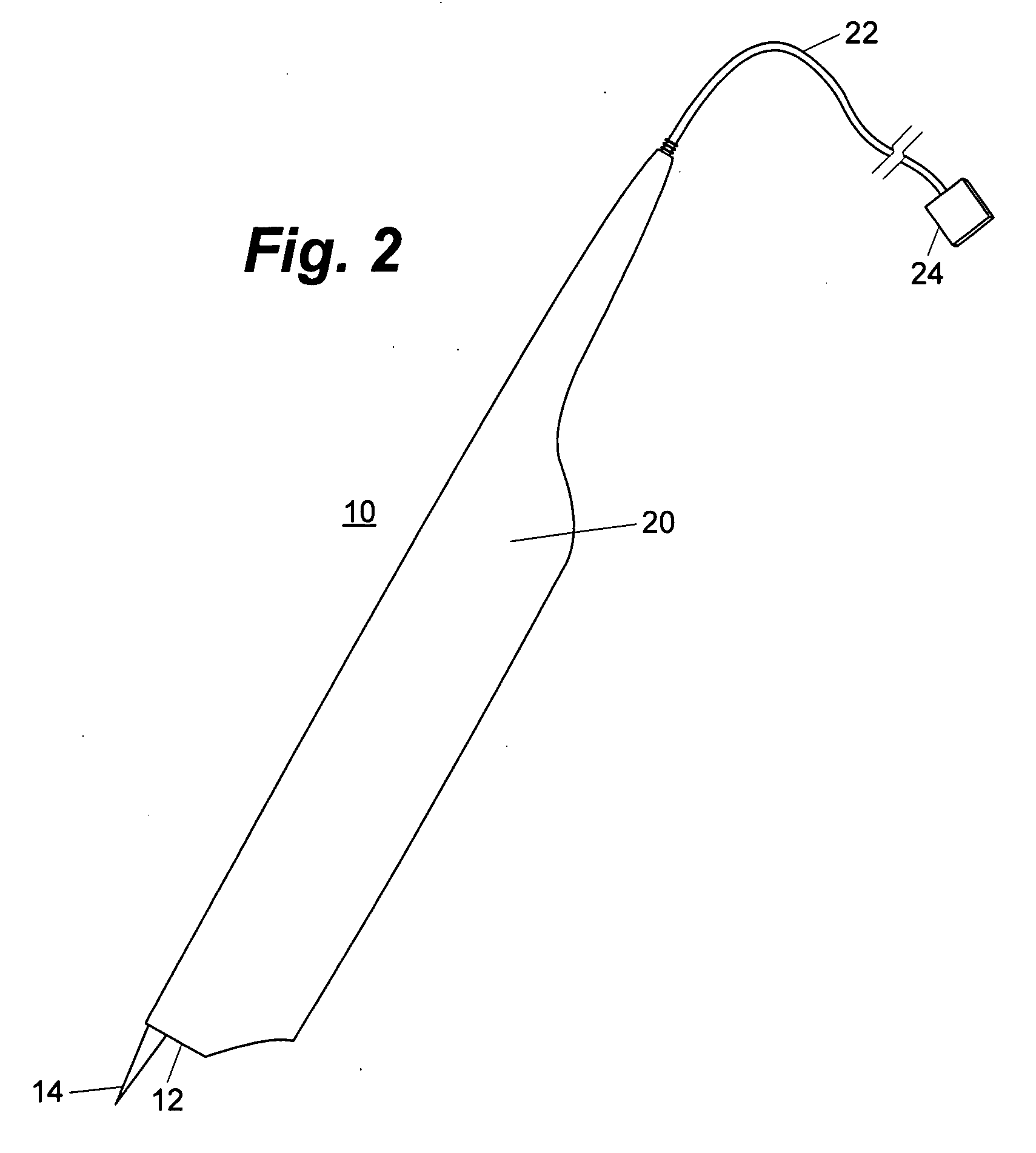
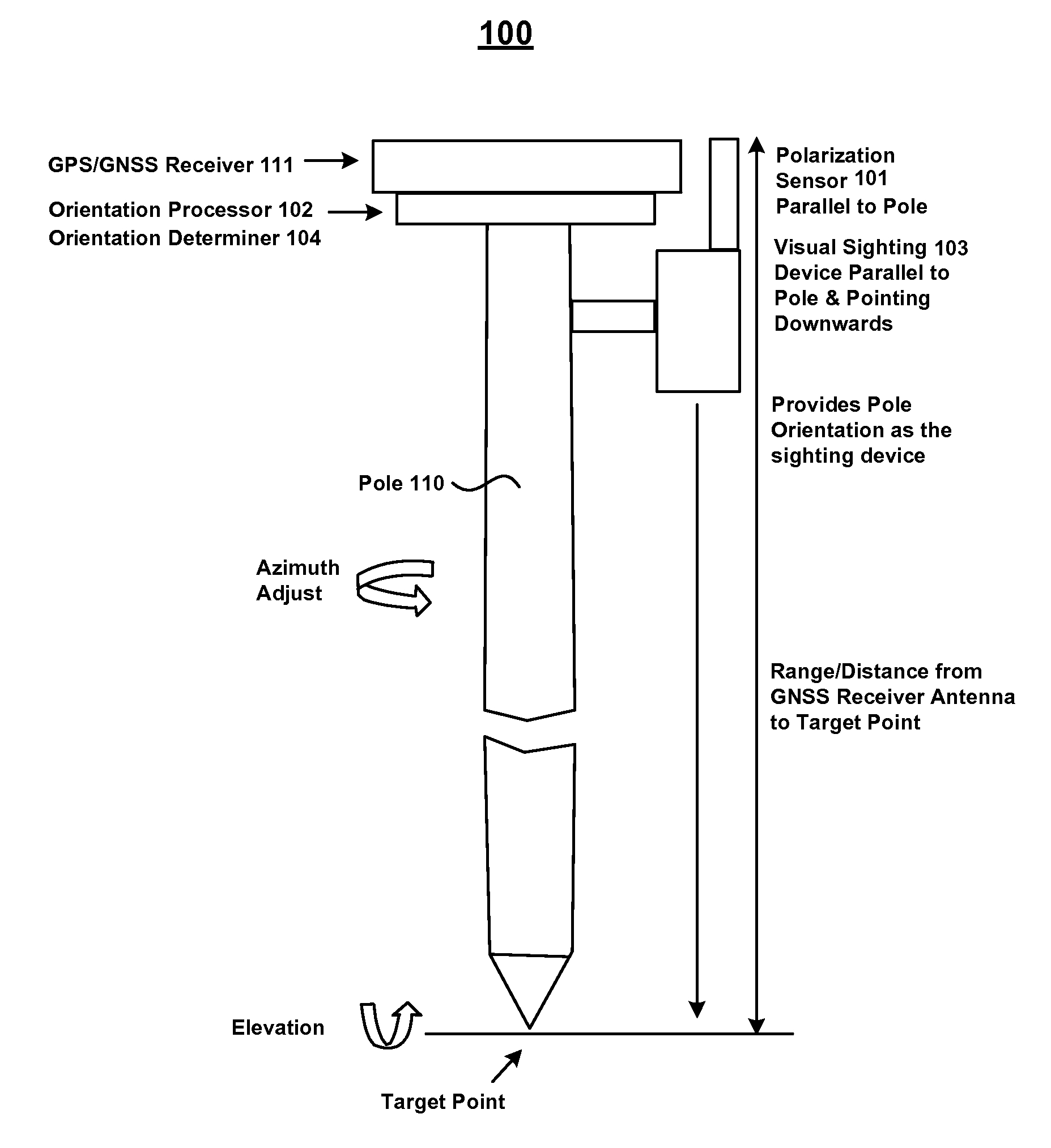
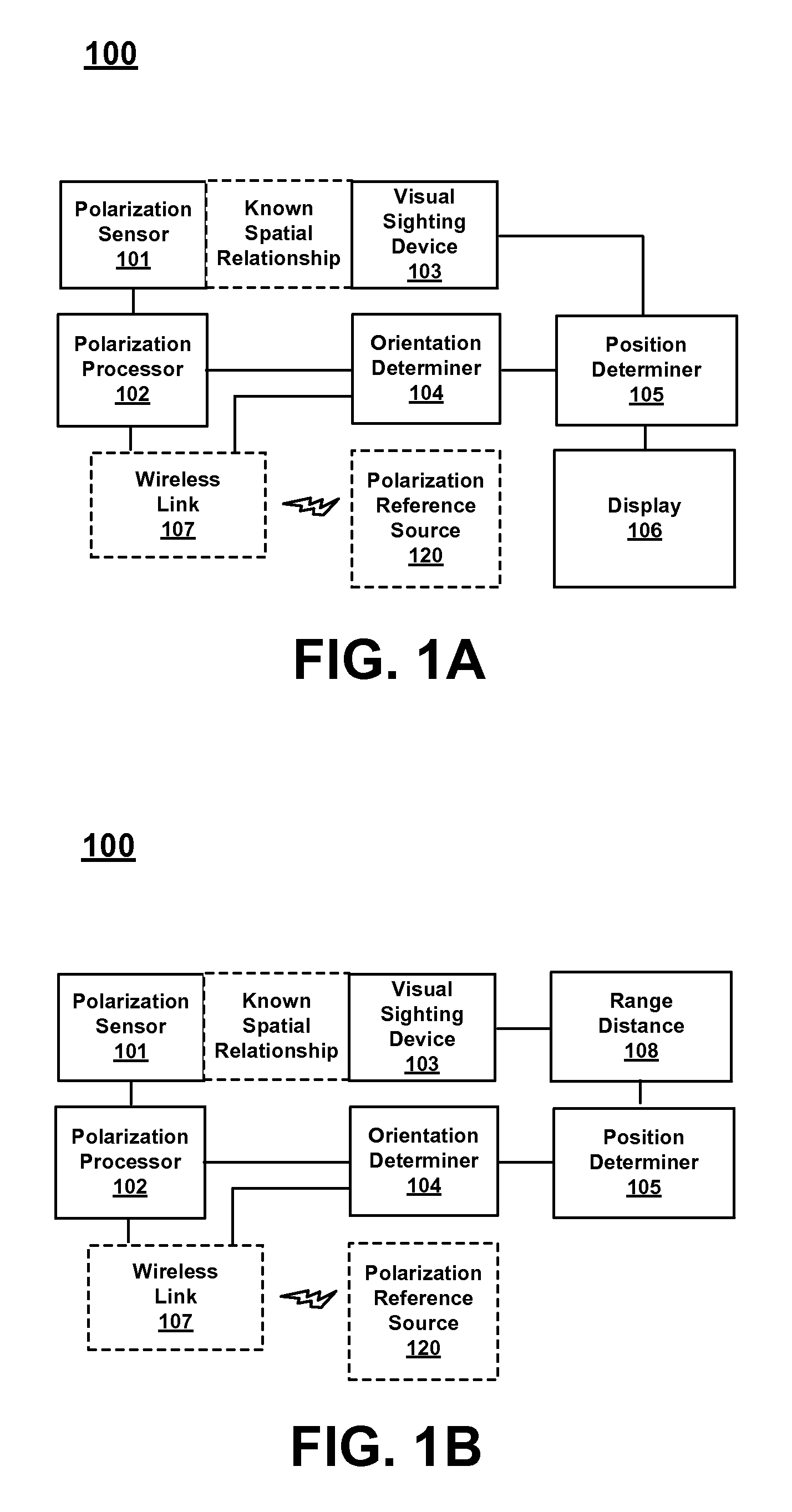
Use of a sky polarization sensor for absolute orientation determination in position determining systems
A method for determining absolute orientation of a platform is disclosed. In one embodiment, a first sky polarization data set for a first time Ti is measured using a sky polarization sensor disposed on a platform. A second sky polarization data set is obtained at a second time Tj. A difference in orientation between the first sky polarization data set and the second sky polarization data set is determined using an orientation determiner. The difference in orientation is provided as at least one orientation parameter for the platform at time Tj. The at least one orientation parameter is used to provide a direction relative to a reference point on the platform.
Owner:TRIMBLE INC
Angular motion tracking sensor
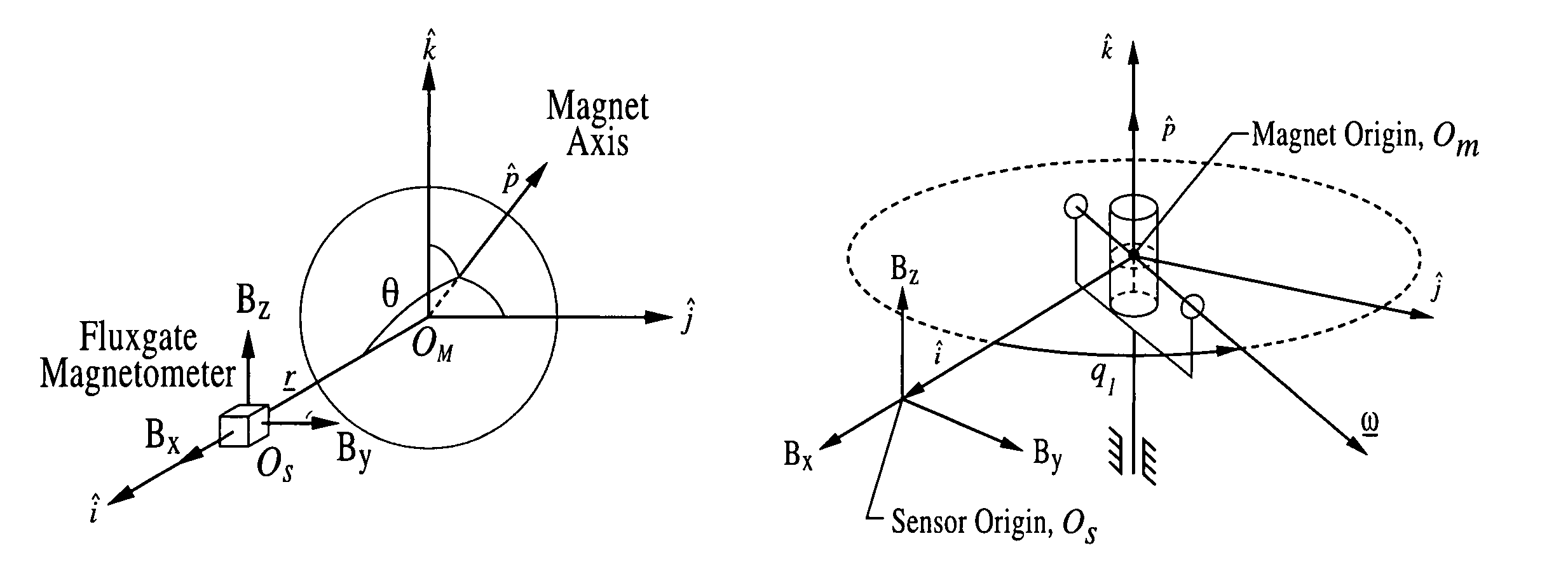
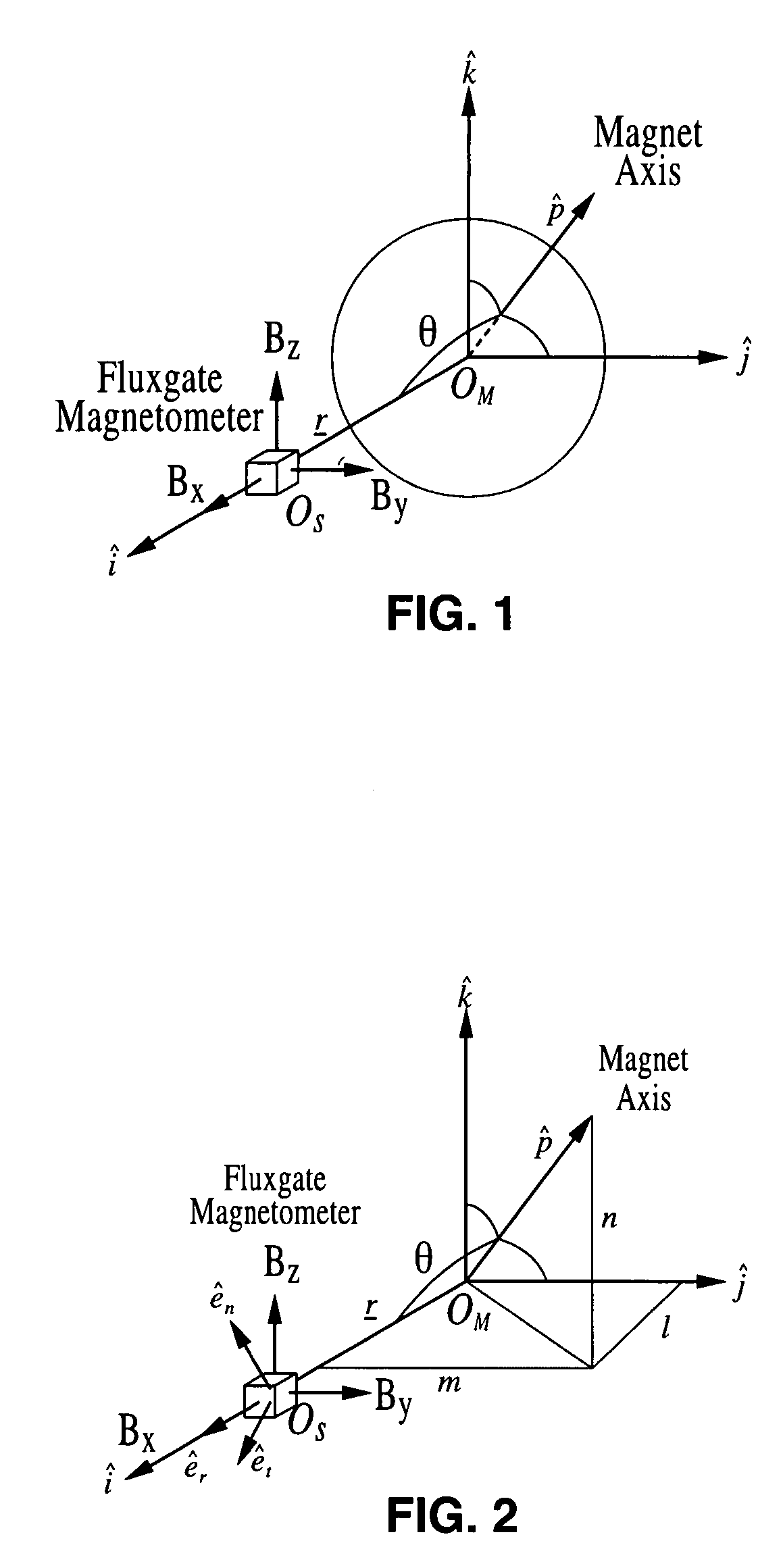
ActiveUS7868610B2Using electrical meansAcceleration measurementAbsolute orientationClassical mechanics
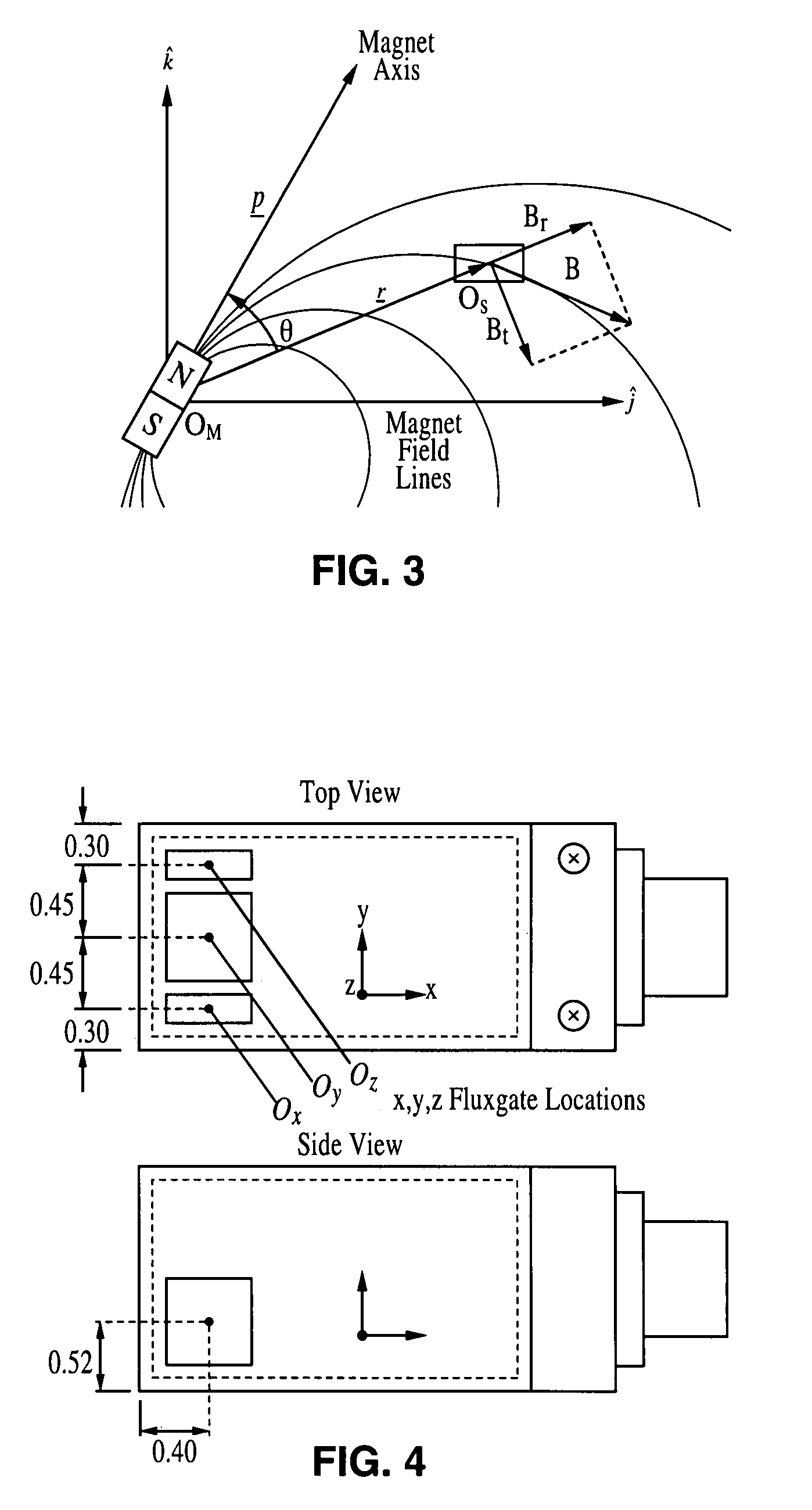
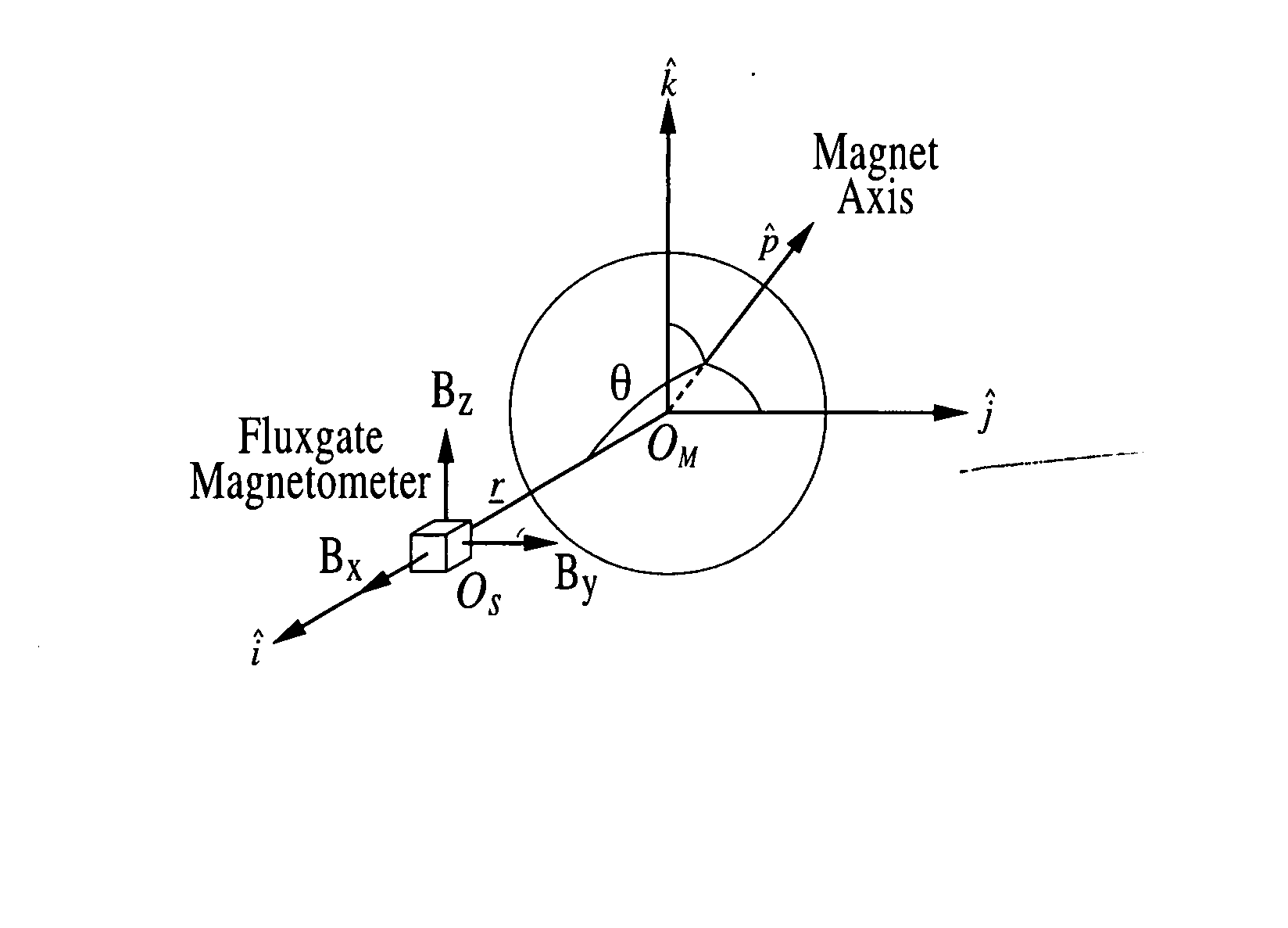
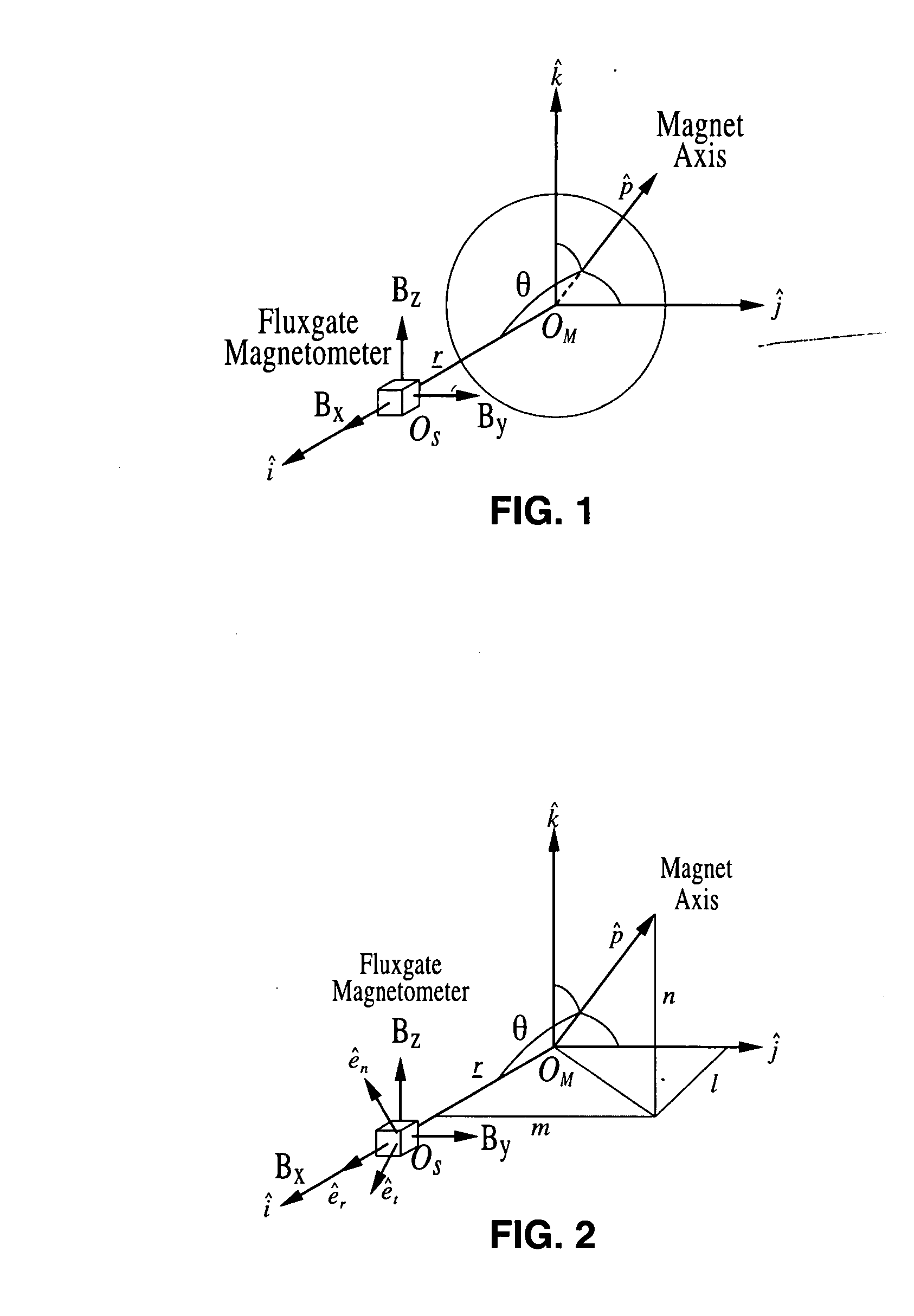
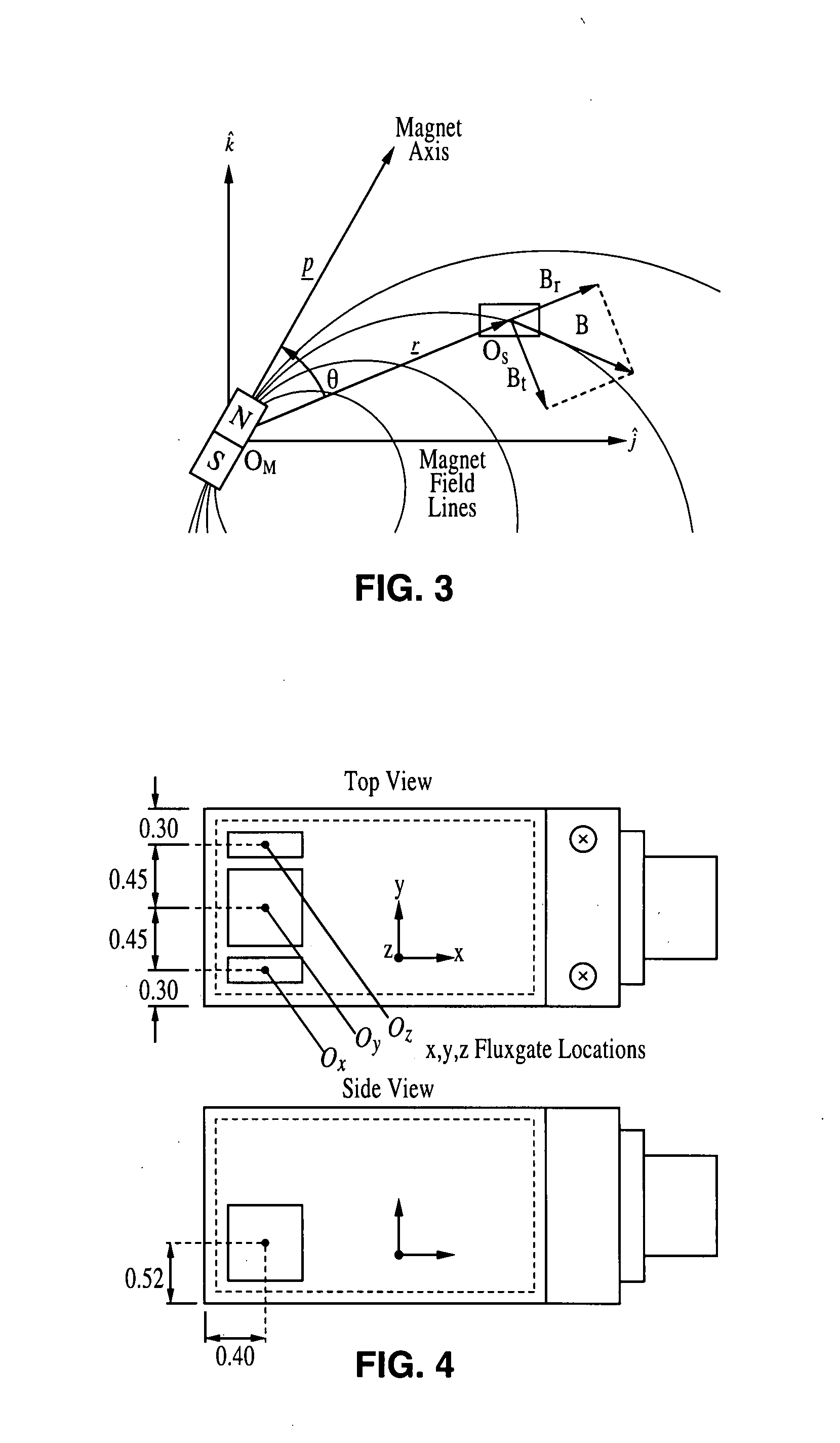
A motion tracking sensor apparatus configured for real-time, three-dimensional angular motion tracking that can determine the absolute orientation, axis of rotation and angular speed of a body rotating about a point, which is fixed relative to the sensor, without contacting the rotating body. The sensor obtains measurements of the three-dimensional magnetic field of a dipole fixed on the body. In one embodiment, a permanent magnet is embedded in the center of the rotating body, and the time-varying magnetic field is measured as the magnet rotates, and then the instantaneous magnet orientation from the field data is determined. The apparatus is particularly suited for use with devices that are based on a sphere rotating in a cradle such as spherical motors or spherical variable transmissions.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Three-dimensional, non-contacting, angular motion sensor
A three-dimensional non-contacting angular motion sensor, based on magnetometry, has been developed for velocity feedback in the ball wheel mechanism, which serves as the drivetrain for a class of omnidirectional mobile platforms. More generally, this scheme tracks rigid-body rotation about a fixed point with an undefined axis of rotation. The approach involves tracking the time-varying magnetic field of a permanent disc magnet, embedded at the center of the sphere. This data is then used to determine the absolute orientation of the magnet axis. Finally, an approach based on the natural invariants of rigid-body motion is used to determine the instantaneous axis of rotation and the angular speed of the sphere about this axis.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Navigation system, method of position estimation and method of providing navigation information
InactiveUS20130054130A1Correction capabilityImprove accuracyRoad vehicles traffic controlDigital computer detailsLine sensorAbsolute orientation
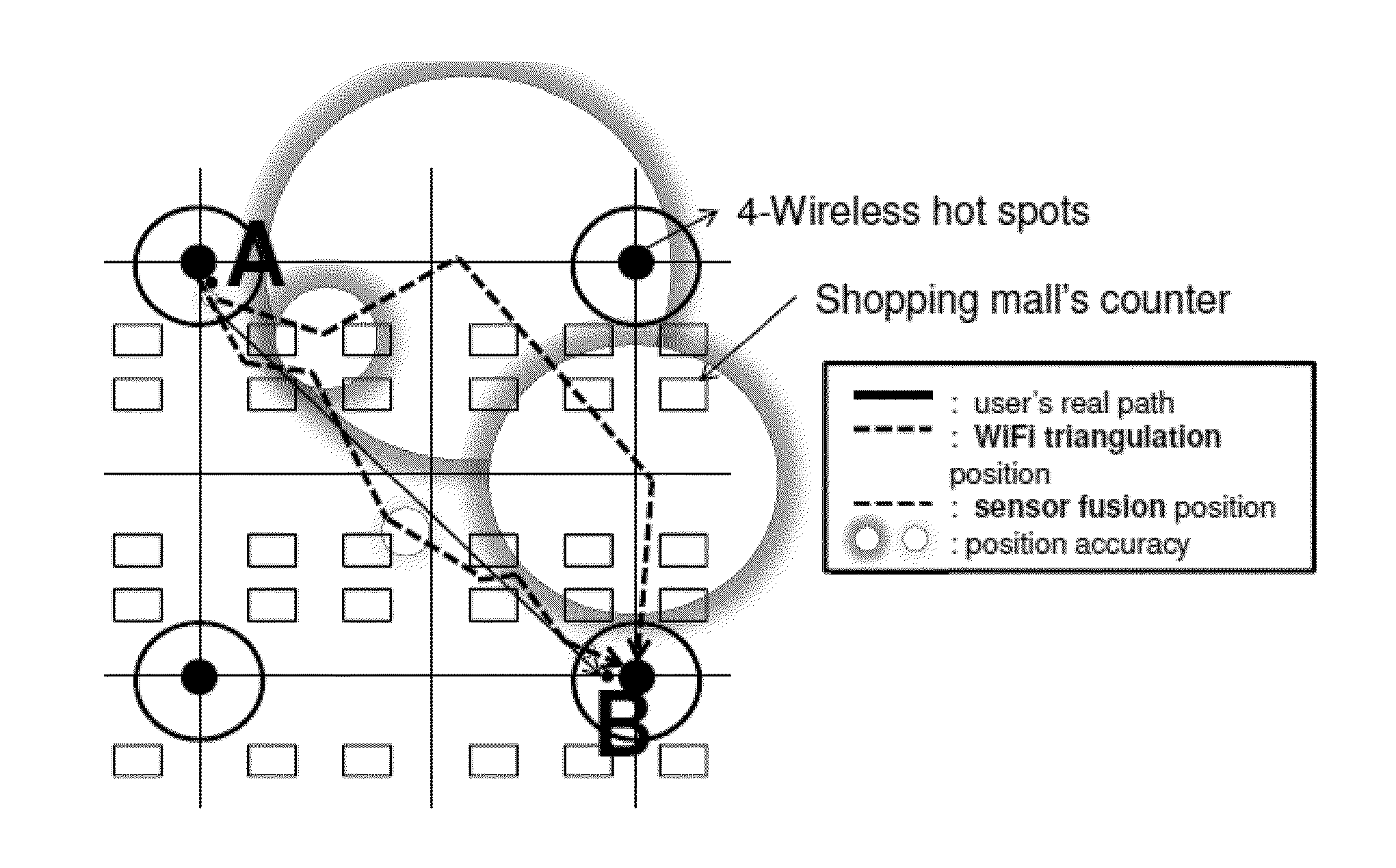
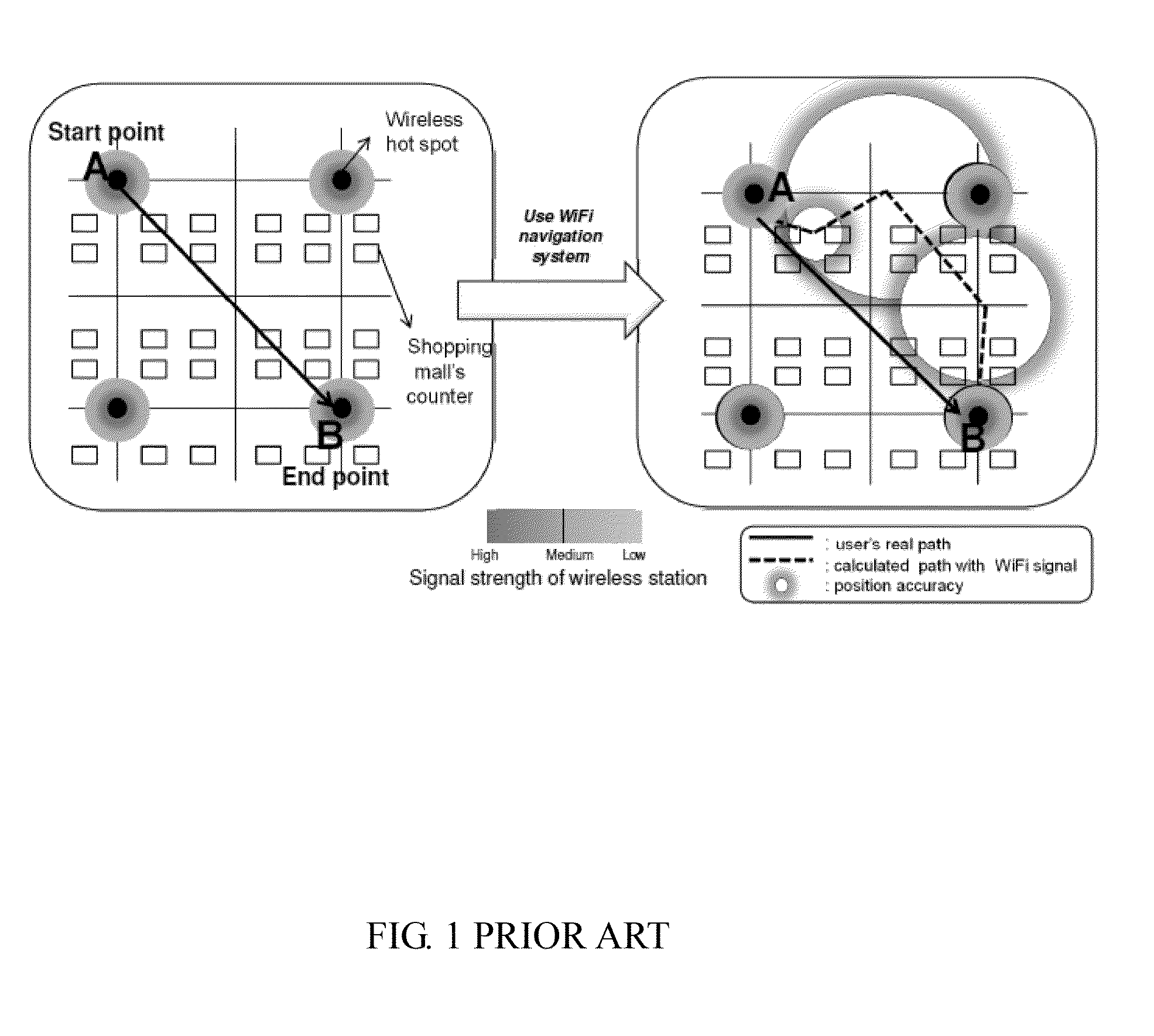
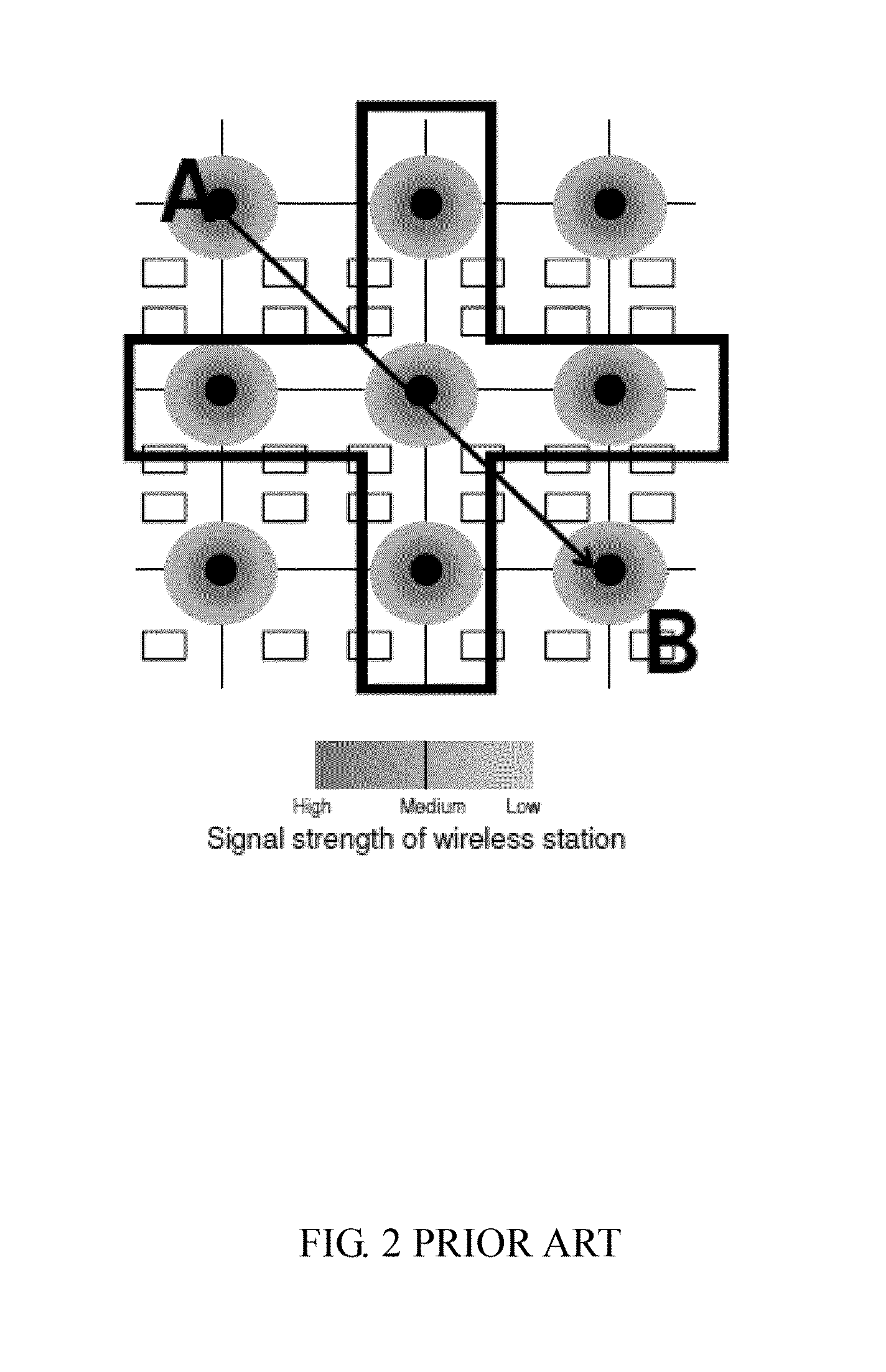
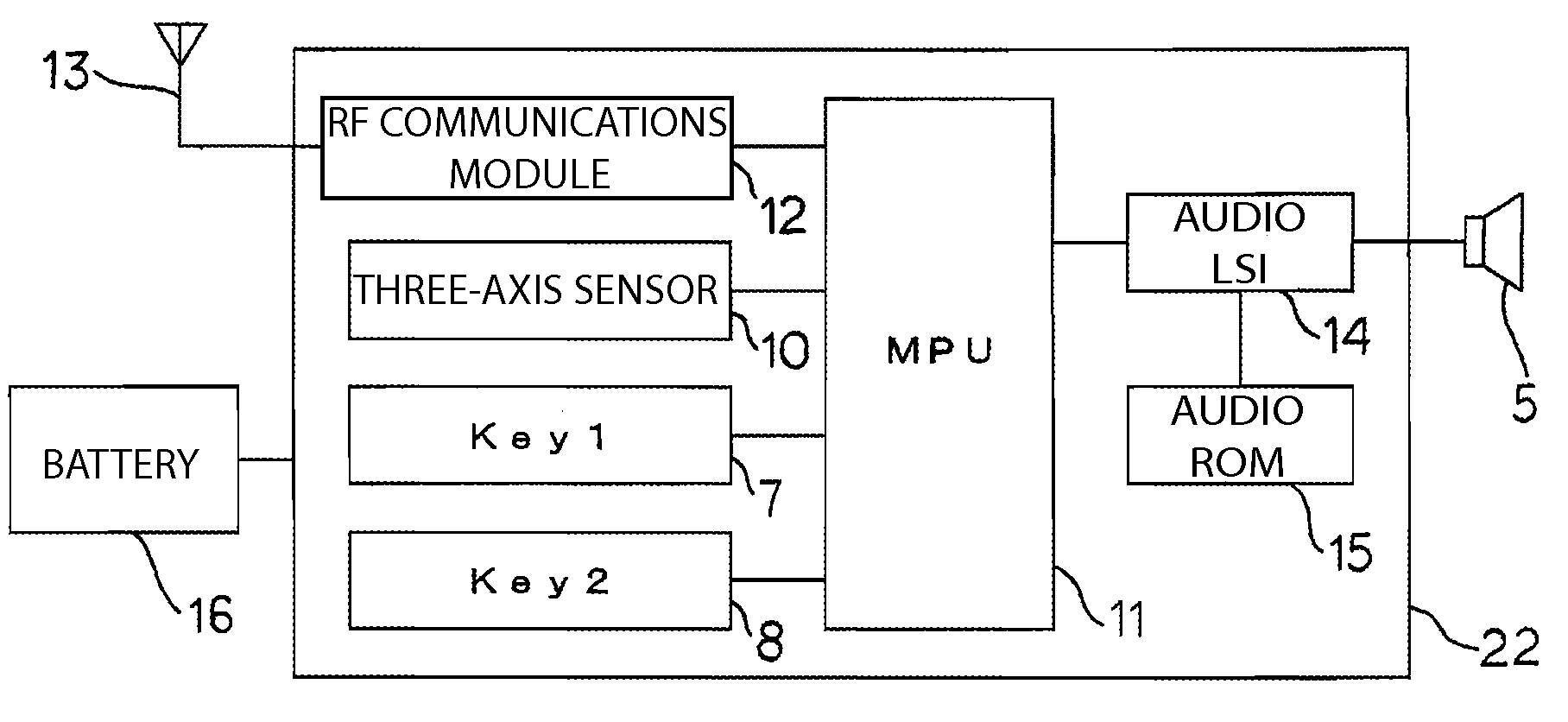
A hybrid-computing navigation system worn by a user includes a modified motion sensor group which includes 9-axis or 10-axis motion sensors that are built-in, and a host device configured for providing navigation information, in which the modified motion sensor group is worn on the user so that a moving direction of the user is the same as a heading direction calculated from the modified motion sensor group. The modified motion sensor group provides step counting and absolute orientation in yaw, roll and pitch using a sensor fusion technique. The navigation system further includes at least one wireless sensor at wifi hot spot to perform sensor fusion for obtaining an absolute position of an estimated position of the user. Sensor fusion combining with location map are used to perform location map matching and fingerprinting. A method of position estimation of a user using the navigation system is also disclosed.
Owner:CM HK LTD
Remote control transmitter
InactiveUS20090267897A1Simple structureTelevision system detailsTelemetry/telecontrol selection arrangementsAbsolute orientationRemote control
A remote control transmitter detects motion in a specific direction or in a rotational direction around a specific axis: The transmitter includes a battery placed on a bottom surface side within a case containing circuitry of the transmitter. The bottom surface side has a convex surface, with a center of curvature C coincident in the upward direction of the force of gravity above a center of gravity G of the transmitter. When placed on a flat surface, the transmitter assumes a stable orientation such that when the transmitter is grasped in order to perform a motion-based operation, it can be can be assumed that the vertical direction is the direction of the line joining the center of curvature C of the stable portion to the center of mass G, as an absolute direction for reference in detecting the motion operation.
Owner:SMK CORP
Device And Method For Measuring Wave Motion
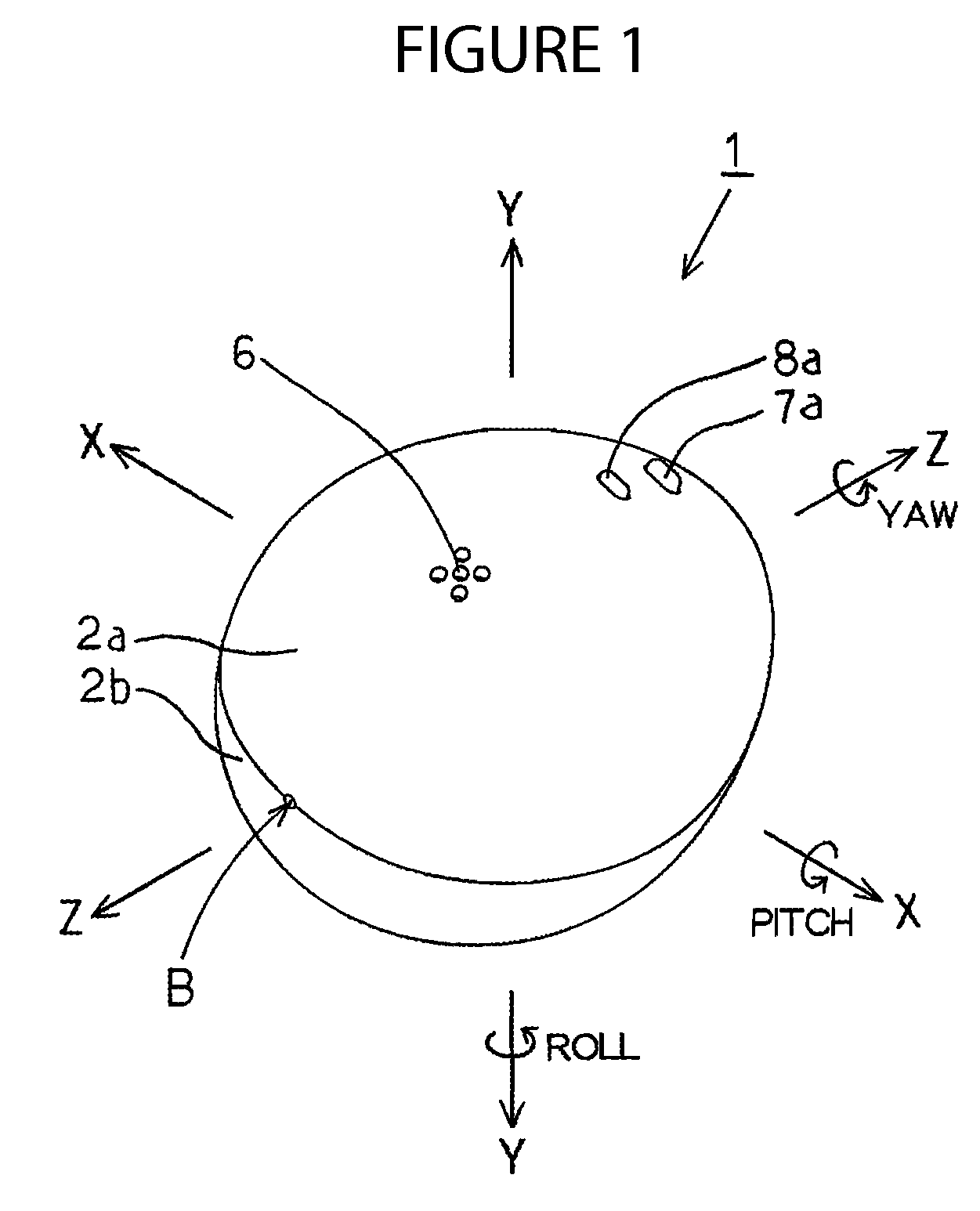
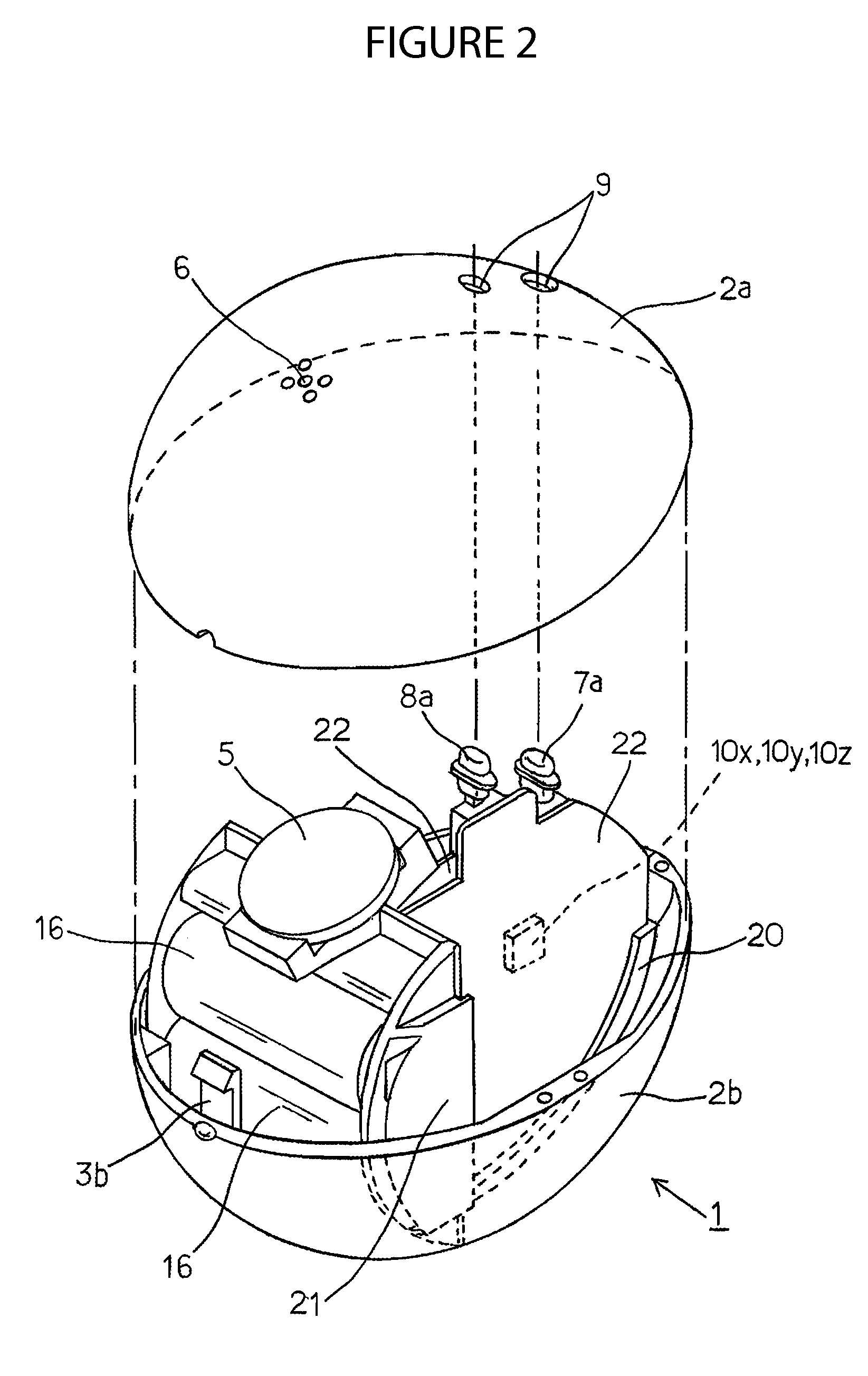
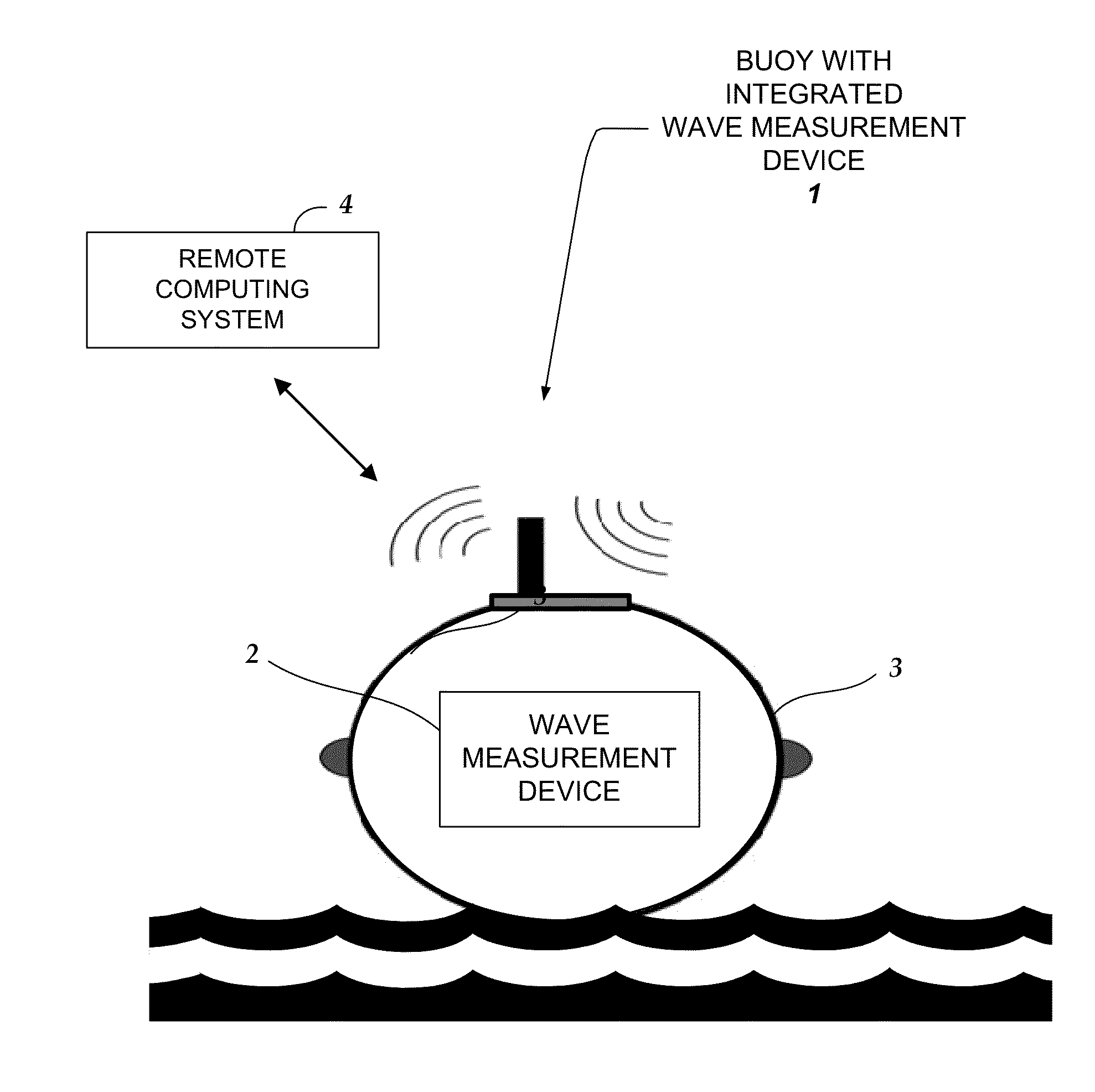
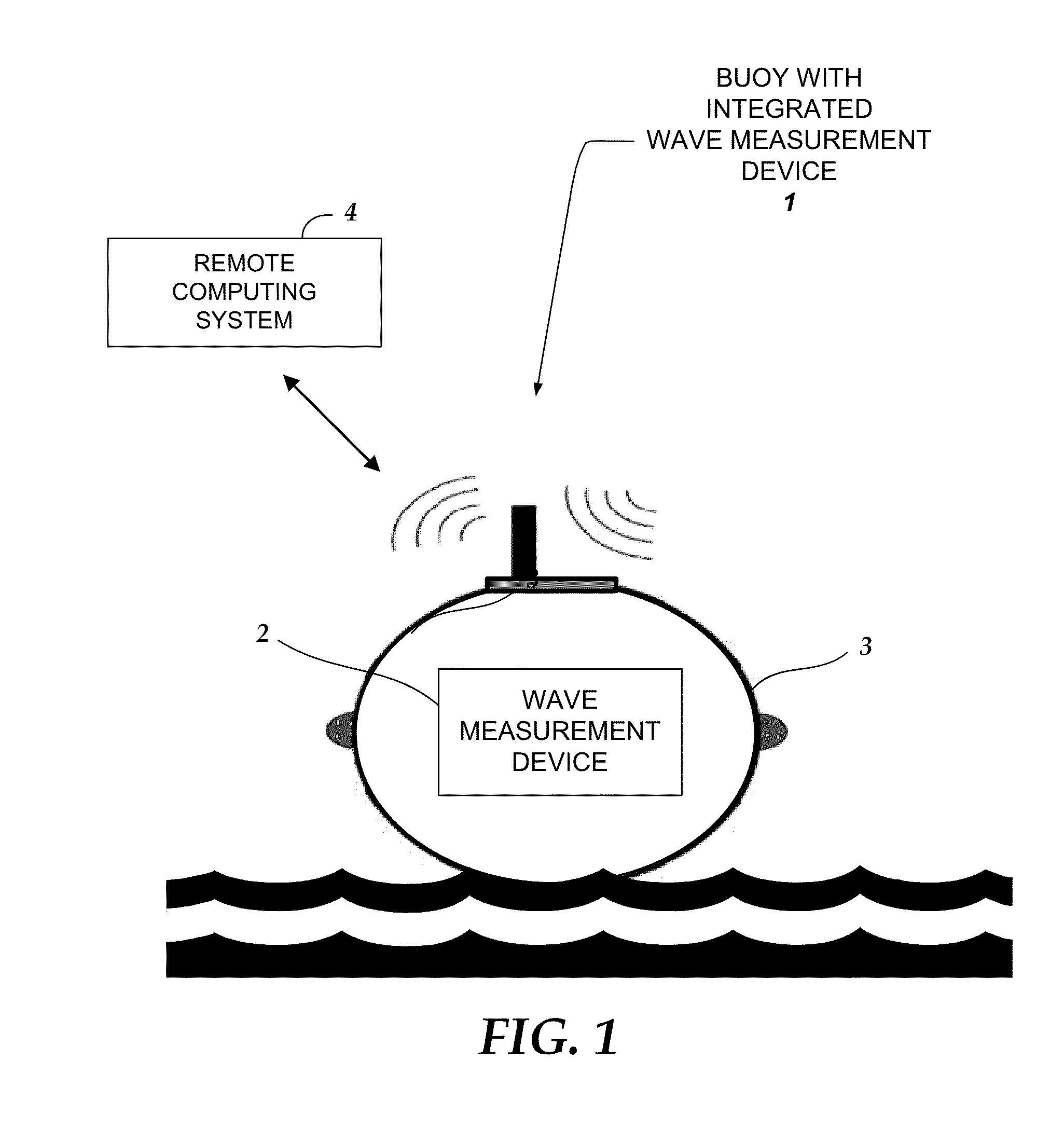
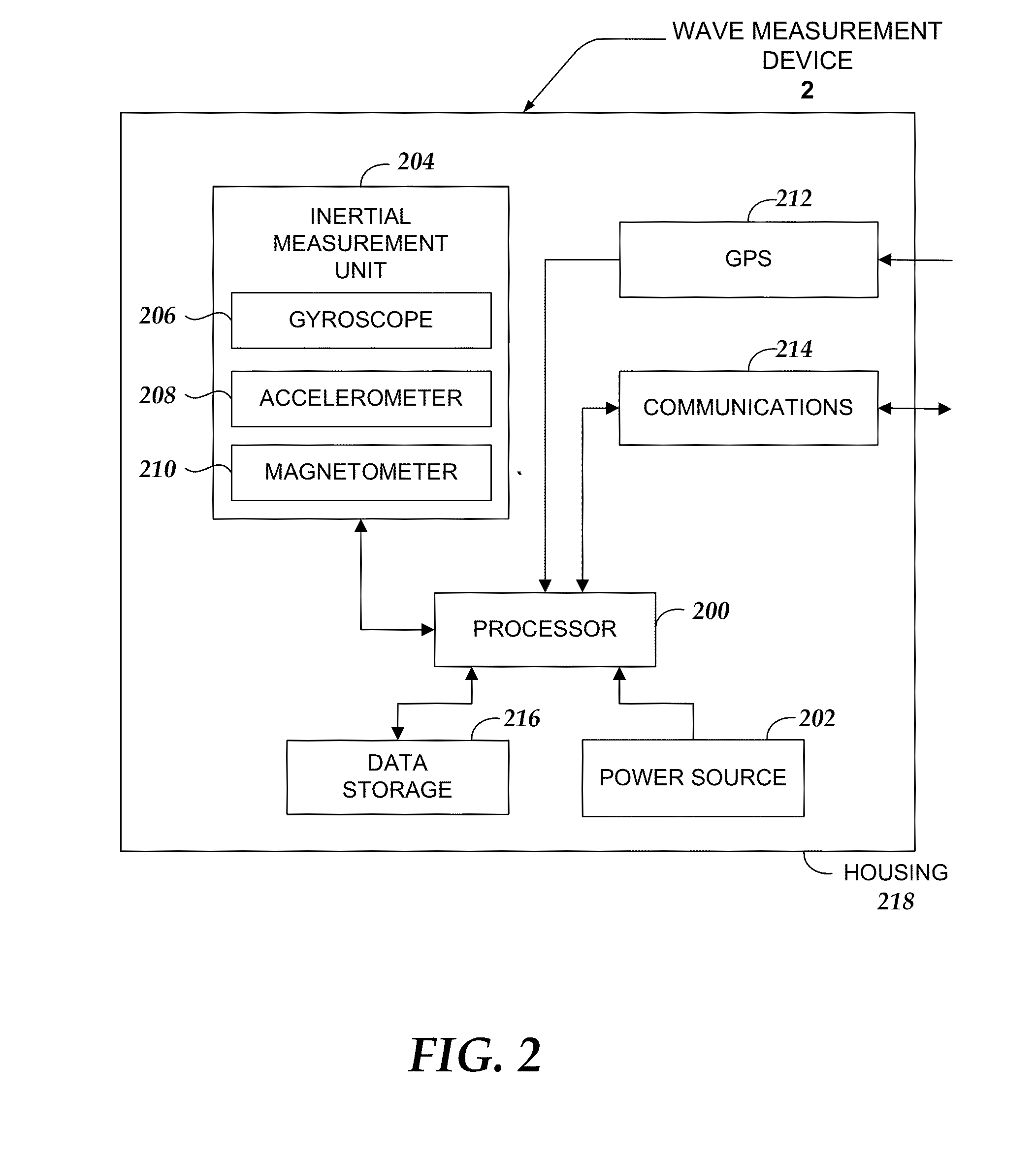
InactiveUS20150025804A1Accurate wave motion informationMeasuring open water movementSpecial data processing applications3d sensorMeasurement device
Embodiments are directed towards a wave measuring electronics device that is integrated within a buoy and the buoy is moored in an ocean. The wave measurement device performs a computer-implemented method for estimating wave motion, including receiving 3D sensor data from each of an accelerometer and a gyroscope, determining, an absolute orientation of the buoy based on said 3D sensor data; and estimating, the true earth acceleration of the buoy over a specified time interval.
Owner:SEA ENG
Method for determining absolute steering wheel angle from a single-turn steering wheel angle sensor
ActiveUS20090287375A1Rule out the possibilitySteering initiationsDigital data processing detailsSteering wheelAbsolute orientation
A method and algorithm for determining a steering wheel angle of a vehicle steering mechanism upon power up of a vehicle using a single-turn steering wheel angle sensor by eliminating plausible steering wheel angles until one and only one steering wheel angle possibility remains.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
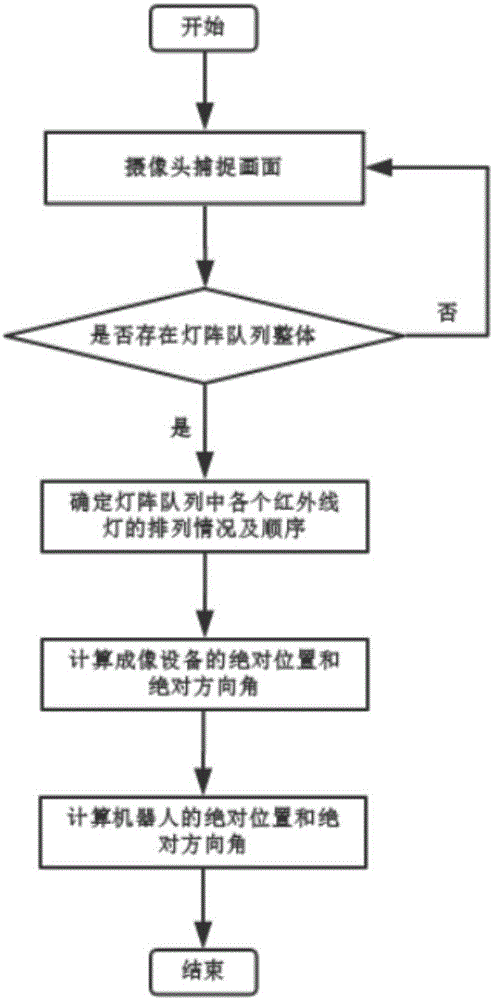
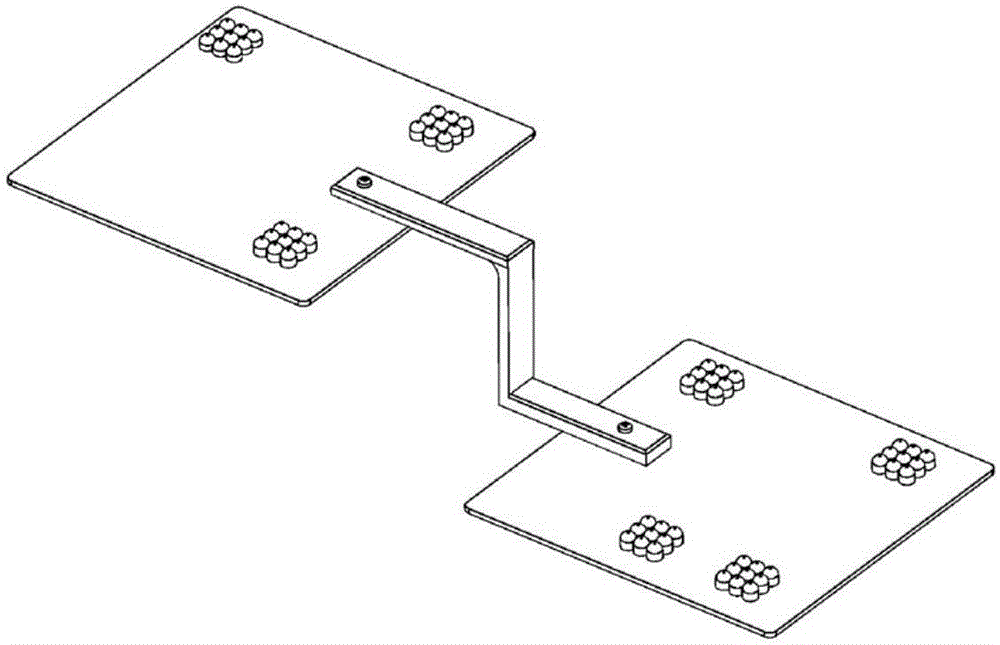
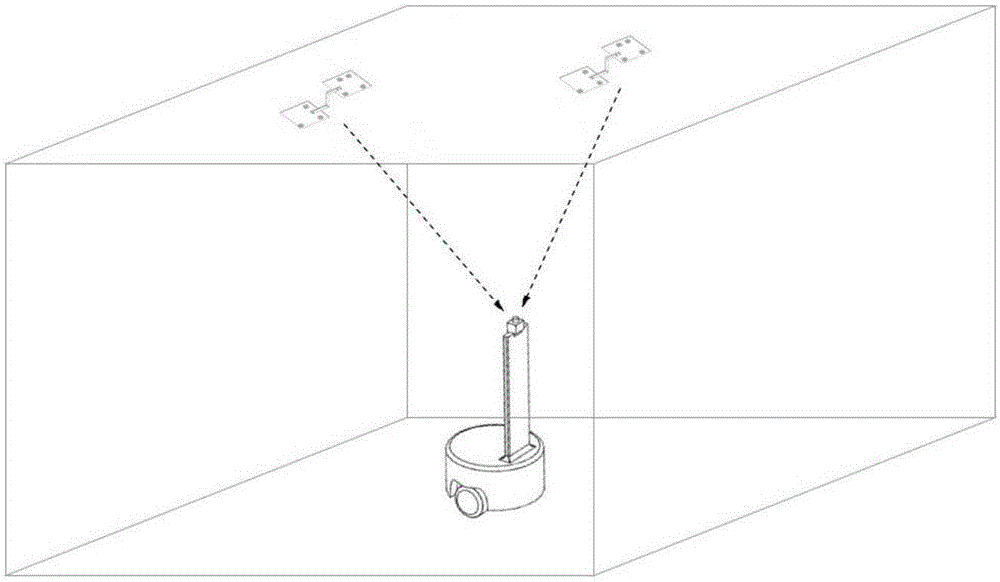
Robot positioning method based on infrared lamp three-dimensional arrays
ActiveCN107436422AEasy numberingPrecise positioningNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsPosition fixationAbsolute orientationInfrared lamp
The invention discloses a robot positioning method based on infrared lamp three-dimensional arrays, and the method comprises the steps: arranging a plurality of infrared lamp three-dimensional arrays with different arrangement modes in an environment; enabling infrared imaging equipment installed on a robot to capture the images of the infrared lamp three-dimensional arrays on a moving path of the robot when the robot is in moving; determining the region where the infrared lamp three-dimensional arrays are located based on the images of the infrared lamp three-dimensional arrays, and obtaining the absolute position and absolute direction angle of the robot; determining the relative position of the robot relative to a robot start point and a relative direction of the robot relative to the robot start point through a coder and an inertia sensor on the robot; and verifying the absolute position and absolute direction angle of the robot. The method provided by the invention is high in positioning precision.
Owner:HANGZHOU HUICANG INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
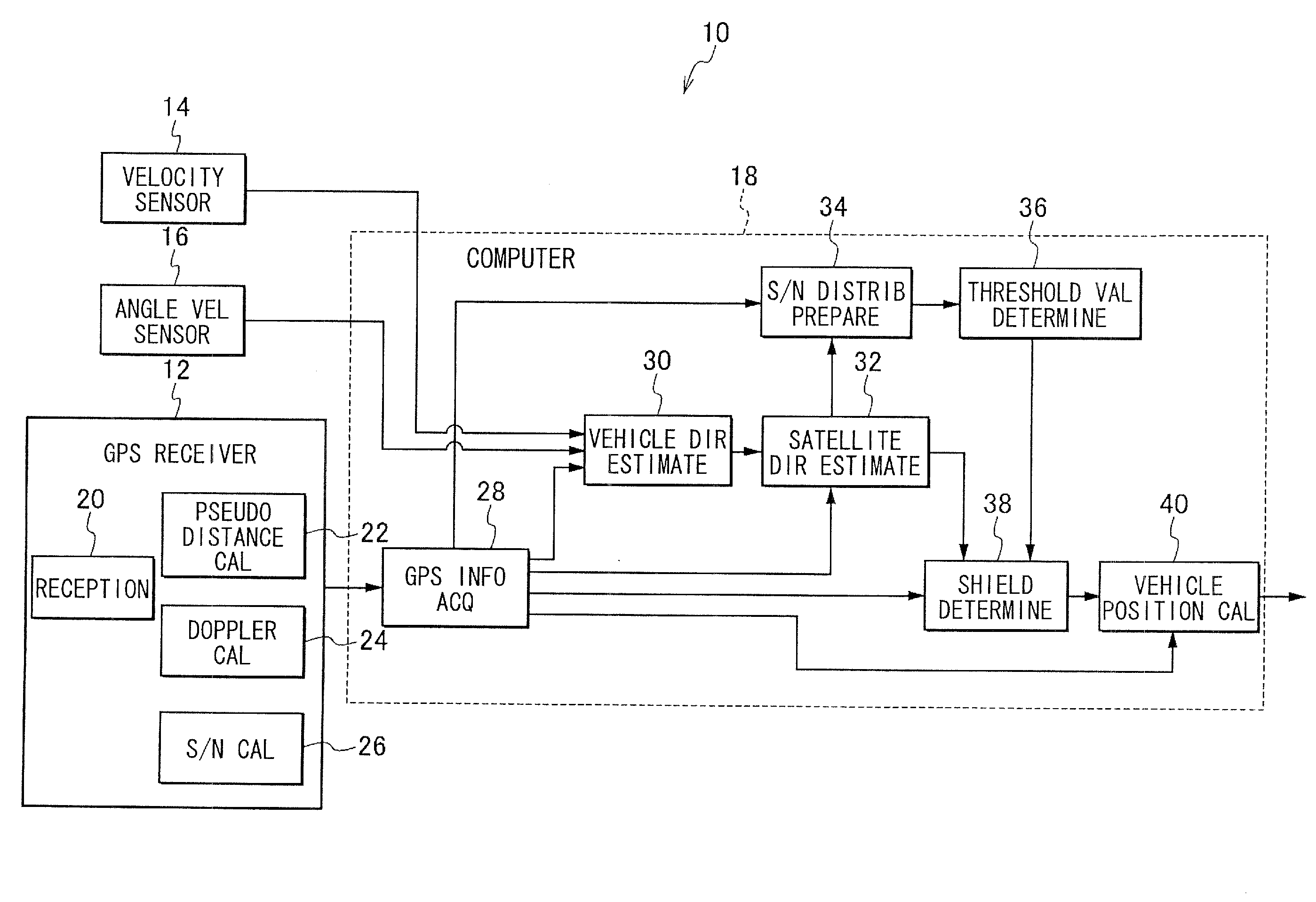
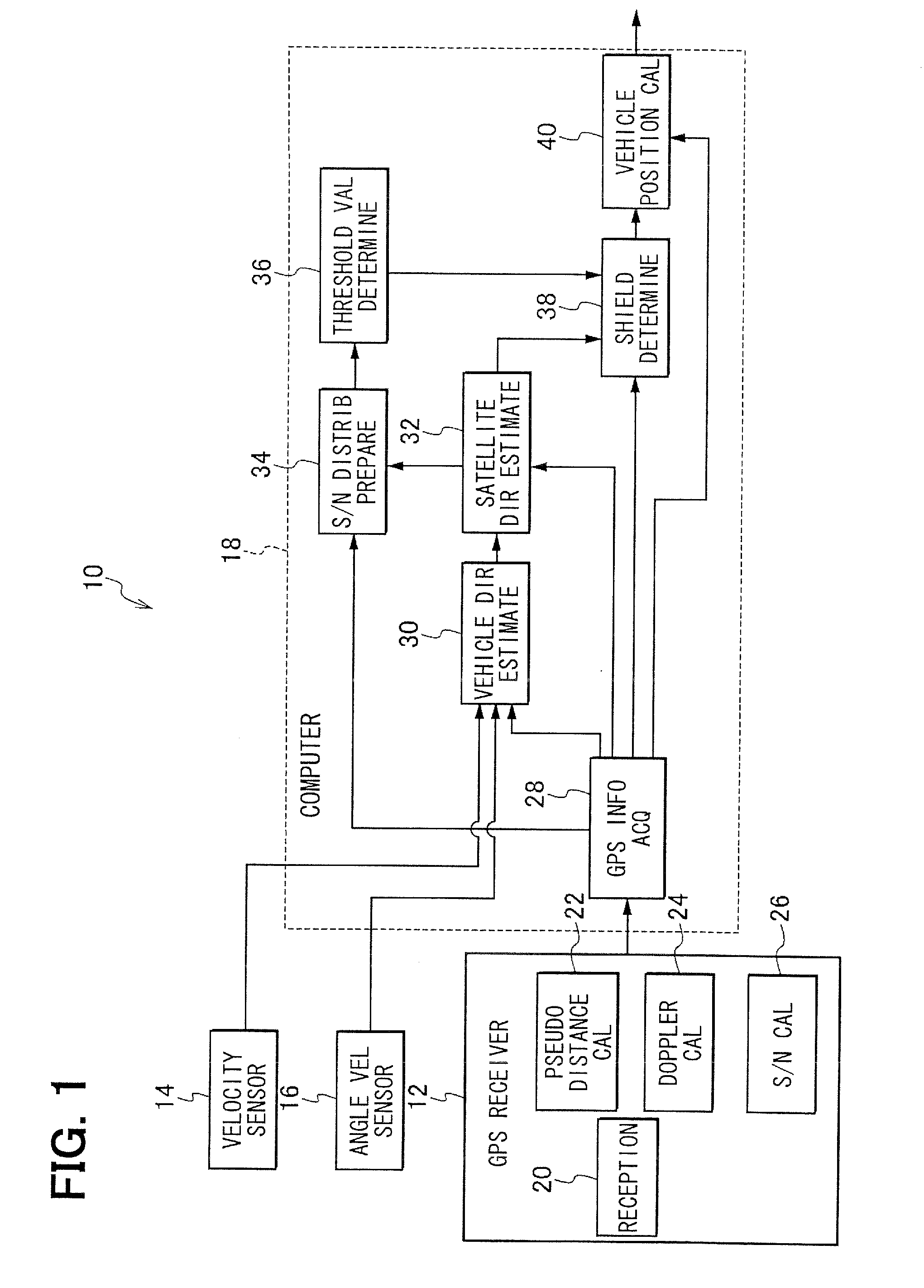
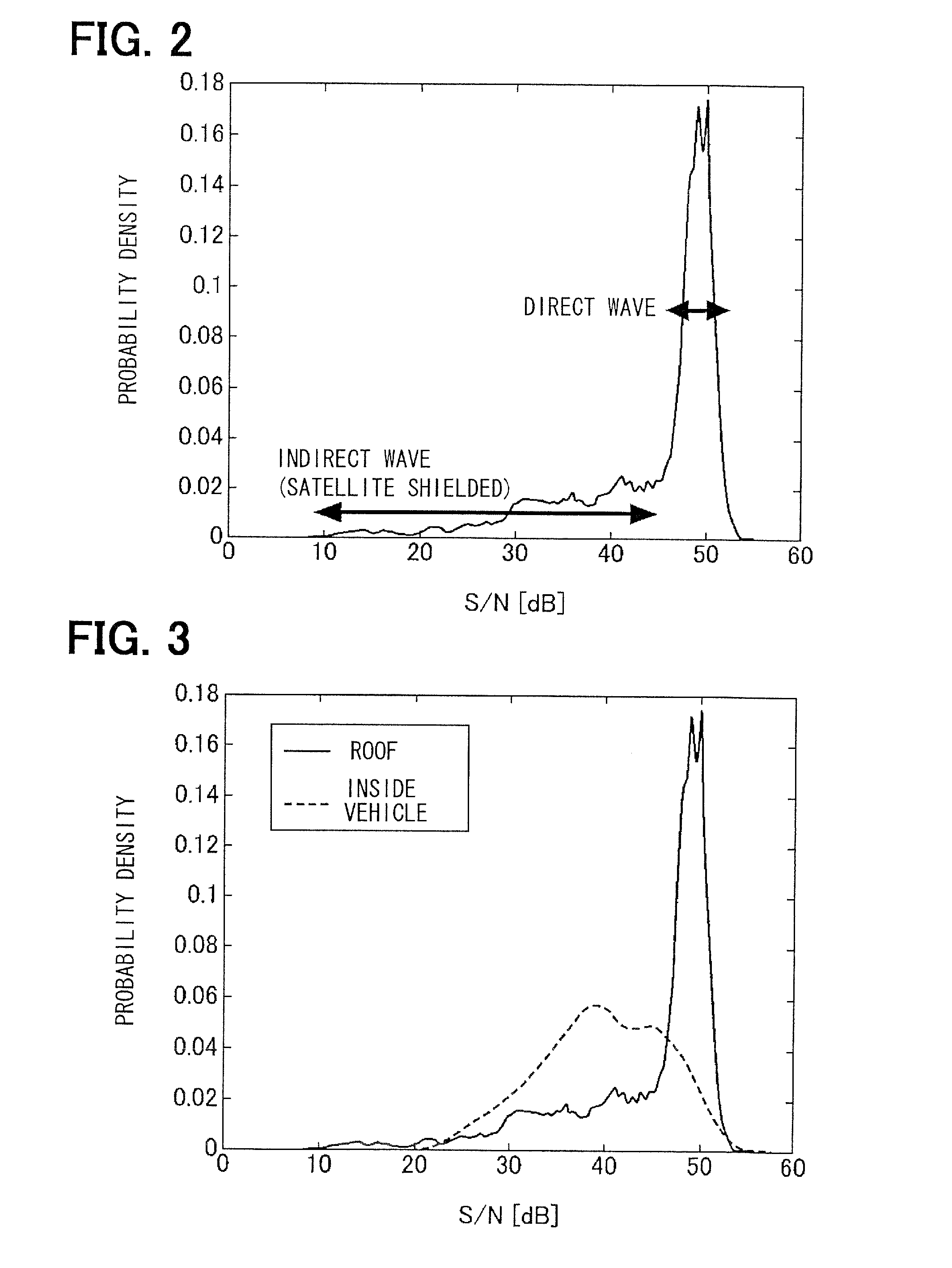
Satellite signal determination apparatus
ActiveUS20120105271A1Improve accuracySatellite radio beaconingRadio wave reradiation/reflectionNatural satelliteAbsolute orientation
A vehicle direction estimation section estimates an absolute direction of a heading direction of a vehicle based on GPS information and vehicle information. A satellite direction estimation section estimates an absolute direction of a target satellite of several satellites for positioning based on corresponding GPS information, and estimates a relative direction of the target satellite with respect to the heading direction based on the estimated absolute direction of the heading direction and the estimated absolute direction of the target satellite. A shield determination section determines a shielded state of the target satellite by determining whether a signal strength of a satellite signal from the target satellite is greater than a threshold value relative to a target partition of several partitions into which a three-dimensional sphere with respect to the heading direction is divided, the target partition which the calculated relative direction of the target satellite belongs to.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Precise surveying and mapping method of 0.25m contour interval of flat ground with large scale of 1:500 to 1:200
The invention relates to a precise surveying and mapping method of a 0.25m contour interval of a flat ground with a large scale of 1:500 to 1:200, which adopts the aerial and ground combining mode of an aerial survey and a ground survey, complements advantages of each other and ensures the high precision of the 0.25m contour interval. The invention comprises the following steps of: acquiring an image by utilizing a DMC (Digital Micro-Circuit) aerial digital camera; collecting topographic map data by combining the aerial survey and the ground survey; utilizing all horizontal and vertical field distribution points for all photo control points; and aerially triangulating and improving the absolute orientation precision of mapping.
Owner:煤航(香港)有限公司
Positioning method and equipment for cleaning robot
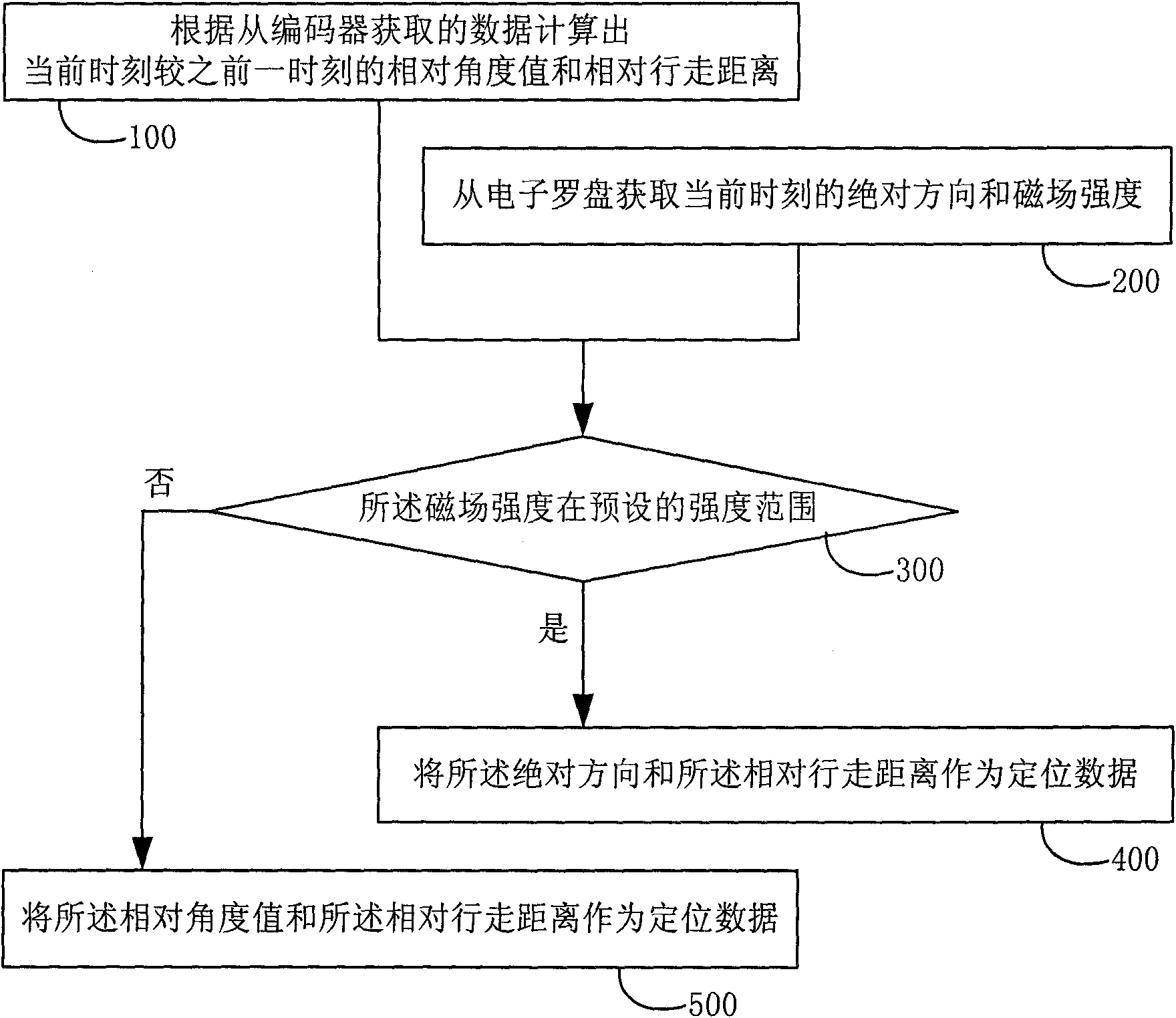
ActiveCN102138768AAvoid influenceAvoid Cumulative ErrorsMachine detailsNavigation by terrestrial meansAbsolute orientationEngineering
The invention provides a positioning method and equipment for a cleaning robot. The method comprises the following steps of: calculating a relative angle value and a relative travel distance of a current moment relative to a previous moment according to data acquired from an encoder; acquiring absolute direction and magnetic field strength of the current moment from an electronic compass; taking the absolute direction and the relative travel distance as positioning data if the magnetic field strength is in a preset strength range; and taking the relative angle value and the relative travel distance as the positioning data if the magnetic field strength is not in the preset strength range. In the positioning method for the cleaning robot, the magnetic field strength of the electronic compass is acquired as confidence of the absolute direction of the current moment of the electronic compass, so that accumulated error caused by positioning of the encoder can be avoided to a certain extent, the influence of interference of an external magnetic field on the positioning data of the robot can also be avoided, and the positioning accuracy is greatly improved at a lower hardware cost.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH +1
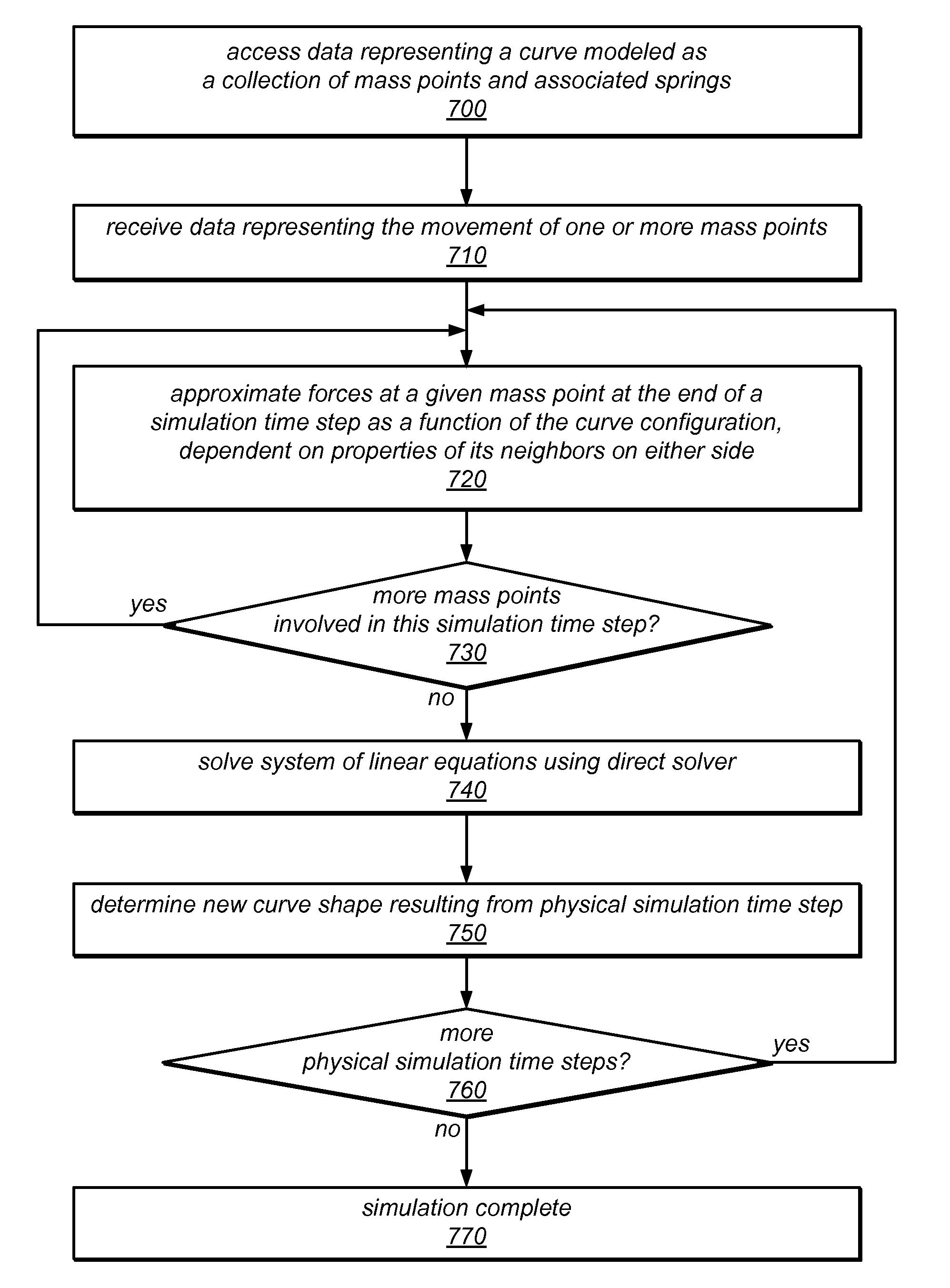
System and Method for Physically Based Curve Editing
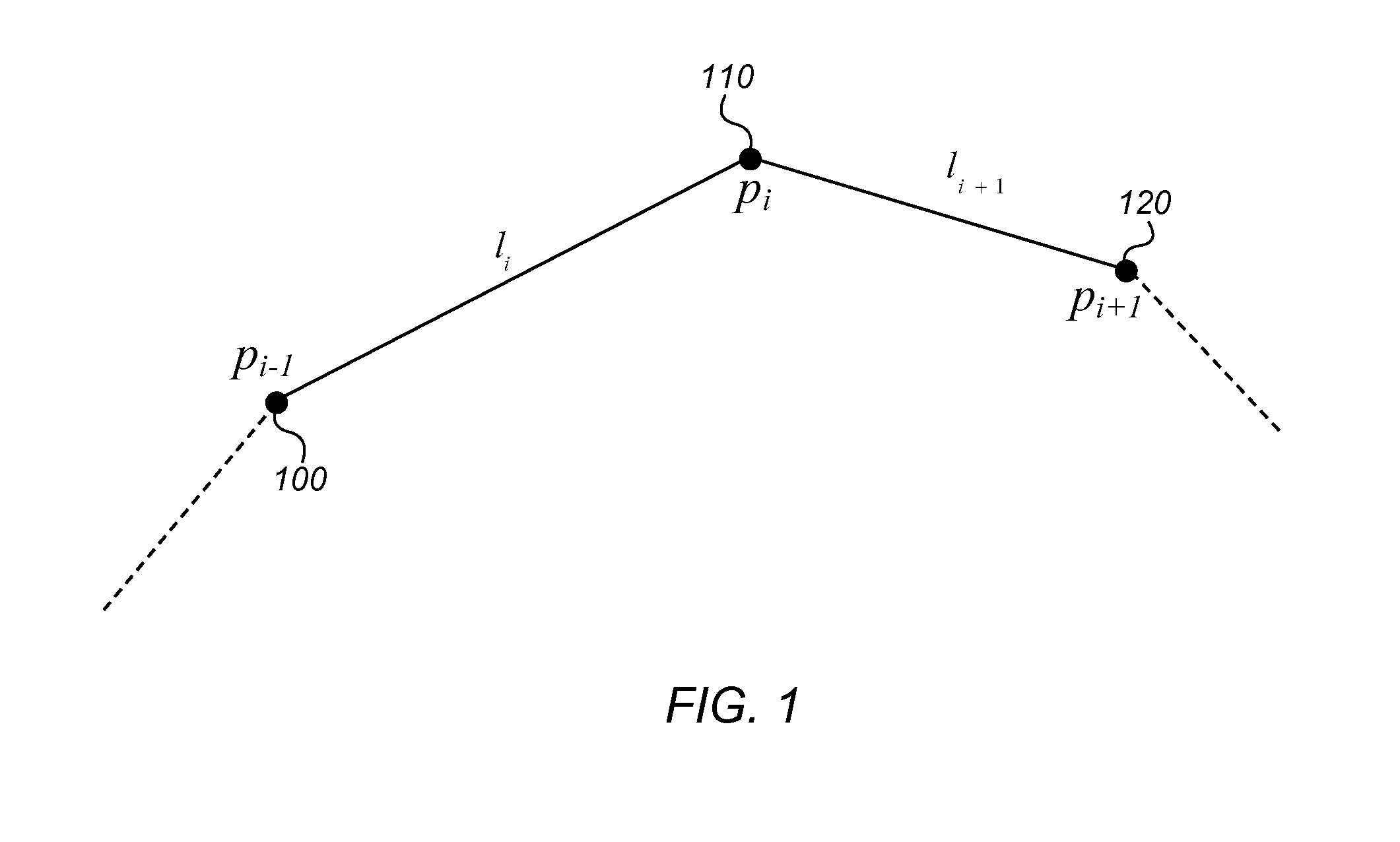
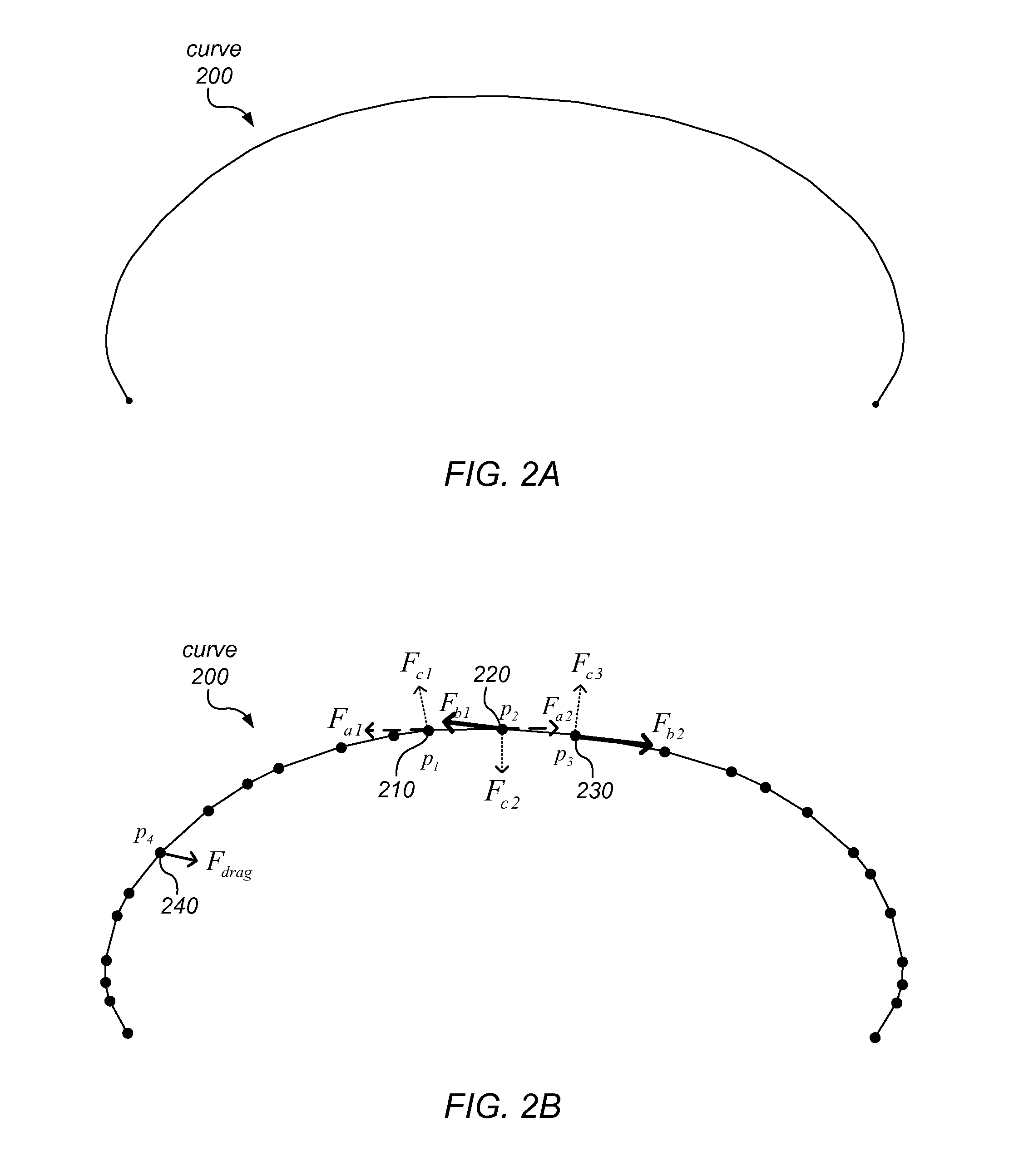
ActiveUS20130132051A1Fine granularityDrawing from basic elementsCathode-ray tube indicatorsAbsolute orientationSpring force
A curve editor may model a continuous curve as a finite collection of discrete mass points (among which the curve's mass is distributed) and associated springs. The springs may include damped axial springs between pairs of consecutive mass points, and damped bending springs representing interactions between sets of three consecutive mass points. In response to manipulation of the curve at various mass points, the curve editor may determine new positions and / or velocities of one or more mass points using a real time physical simulation of the spring forces acting at mass points involved in the editing operation. The simulation may be dependent on viscous drag forces and / or on constraints applied to individual mass points, angles defined by consecutive mass points, or an absolute direction of a segment between two mass points. Mass points may be added to or removed from the model by adaptive resampling, and the mass redistributed accordingly.
Owner:ADOBE INC
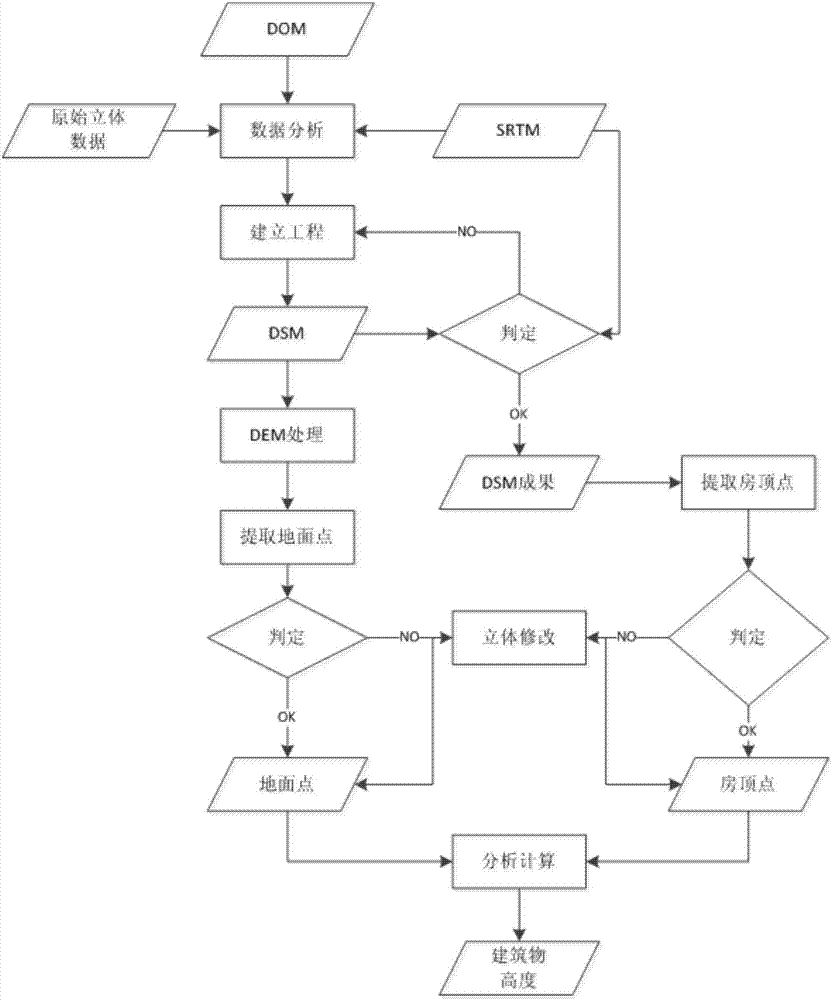
Method for automatically extracting height of building based on stereoscopic satellite image
ActiveCN106871864AEfficient extractionPicture taking arrangementsHeight/levelling measurementCheck pointAbsolute orientation
The invention discloses a method for automatically extracting height of a building based on a stereoscopic satellite image, and relates to the field of satellite image interpretation. The method comprises the following steps of obtaining an original stereoscopic satellite image pair, SRTM data and DOM data of a target building; pre-processing the original stereoscopic satellite image pair, and performing relative orientation and absolute orientation in sequence to generate an epipolar image used for extracting DSM data; extracting initial DSM data of the target building, referring to a DLG data road image layer, a landform image layer and the DOM data of the target building to obtain a check point which meets the requirements; obtaining DEM data in which elevation information of the target building is removed by filtering; integrating the data; performing stereoscopic checking and correcting on a top point elevation value and a foundation elevation value of the target building; subtracting the foundation elevation value of the building from the top point elevation value of the building to obtain the elevation information of the building by combining a house image layer of the target building in DOM and DLG. The method can be used for extracting the elevation information of the building more quickly and more efficiently.
Owner:MAPUNI TECH CO LTD
Method and wearable device for performing actions using body sensor array
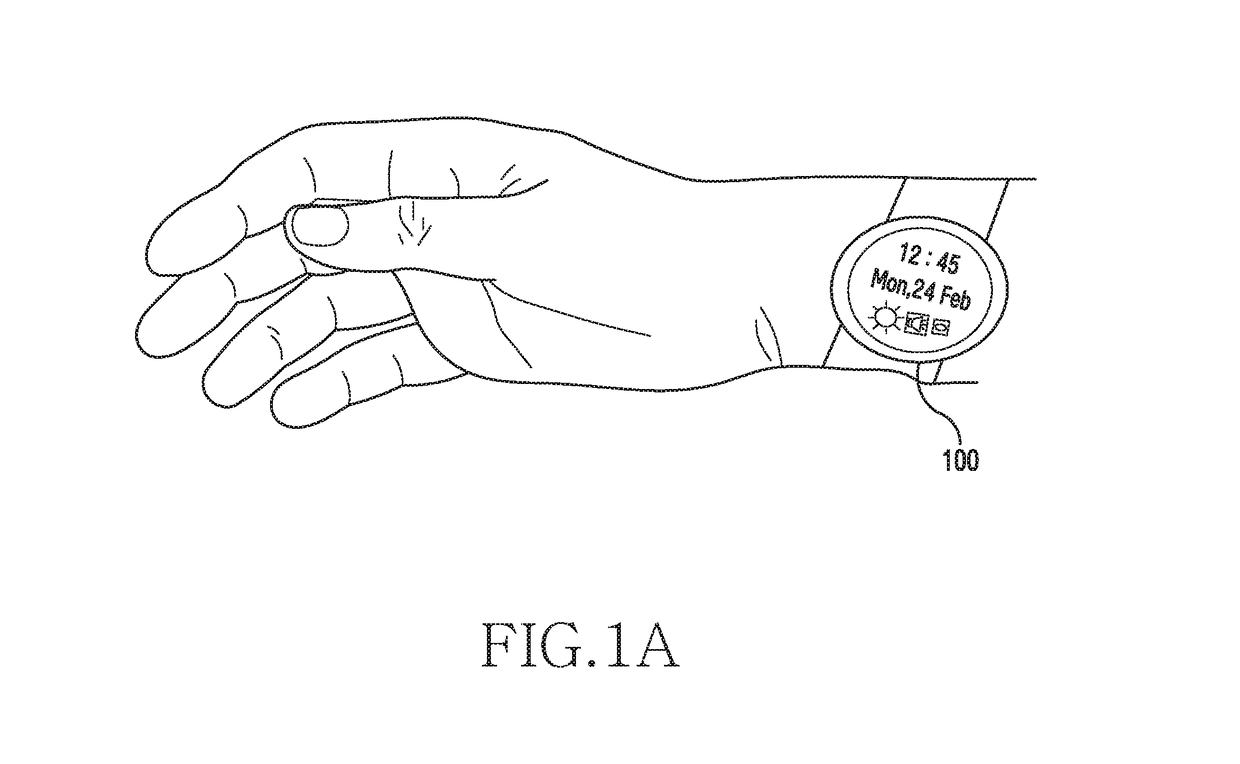
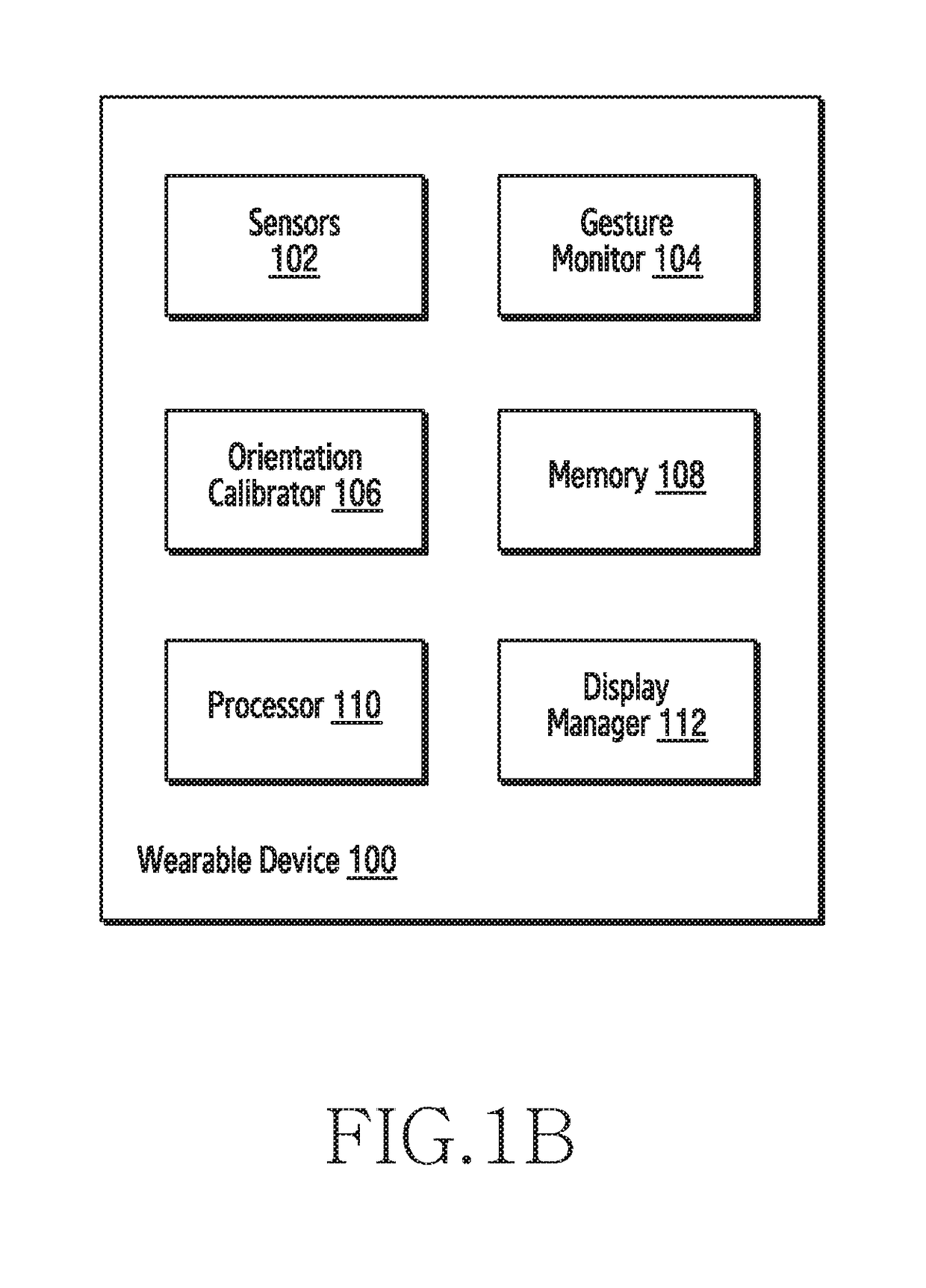
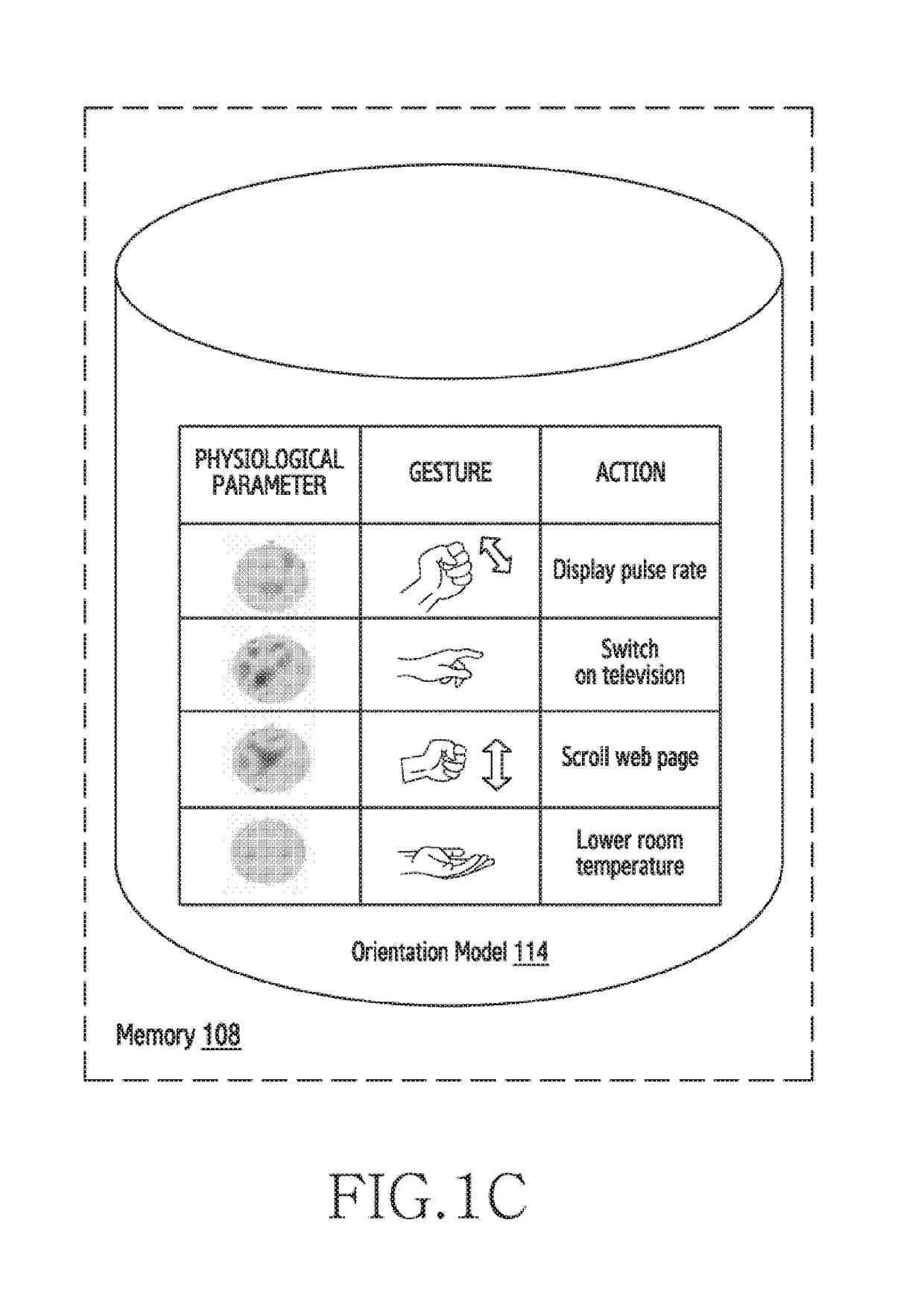
ActiveUS20180338720A1Input/output for user-computer interactionElectromyographySensor arrayAbsolute orientation
A method for performing actions by a wearable device is provided. The method includes detecting at least one signal indicating a movement of a muscle of the wrist, via an array of biometric sensors exposed through an inner peripheral surface of a substantially circular band of the wearable device, identifying an orientation of the wearable device corresponding to the at least one signal, and providing, based at least in part on the identification, a function corresponding to the orientation of the wearable device. The method further includes detecting, by the wearable device, an absolute orientation of the wearable device using at least one of an inertial sensor and the one or more body sensors. The method further includes dynamically performing an action, by the wearable device, based on a pre-stored mapping of the at least one physiological parameter and the absolute orientation of the wearable device.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
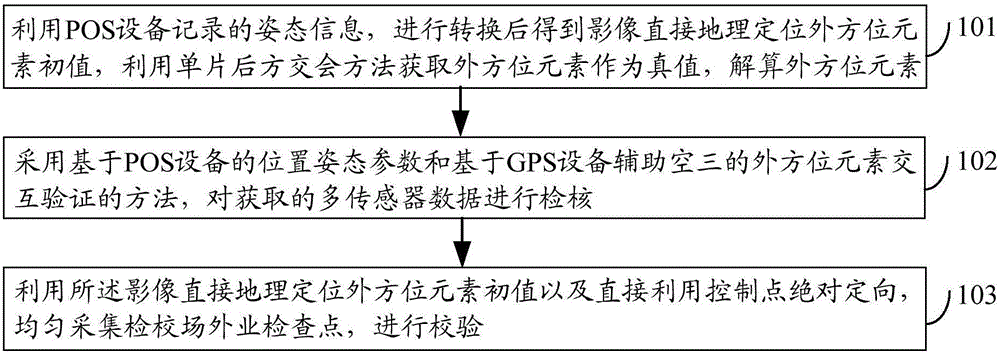
Verifying method and apparatus based on POS equipment and digital aerial survey camera
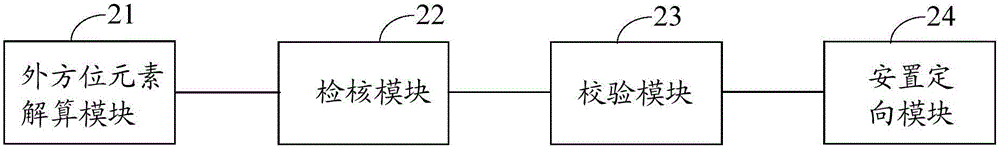
Embodiments of the invention disclose a verifying method and apparatus based on POS equipment and digital aerial survey camera, related to measurement and remote sensing technology and capable of effectively verifying system integration errors. The verifying method based on POS equipment and digital aerial survey camera comprises: using POS equipment to record attitude information, converting to obtain image direct geographical positioning exterior orientation element initial value, acquiring exterior orientation elements as true values by using a single-photograph resection method, and resolving exterior orientation elements; validating acquired multi-sensor data by using a cross-validation method of POS equipment-based positional attitude parameters and GPS equipment-supported aerotriangulation exterior orientation elements; using the image direct geographical positioning exterior orientation element initial value and directly using control point absolute orientation to evenly acquire and validate off-site surveillance check points for verification. The invention is applied to verification of exterior orientation elements.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF URBAN CONSTR +2
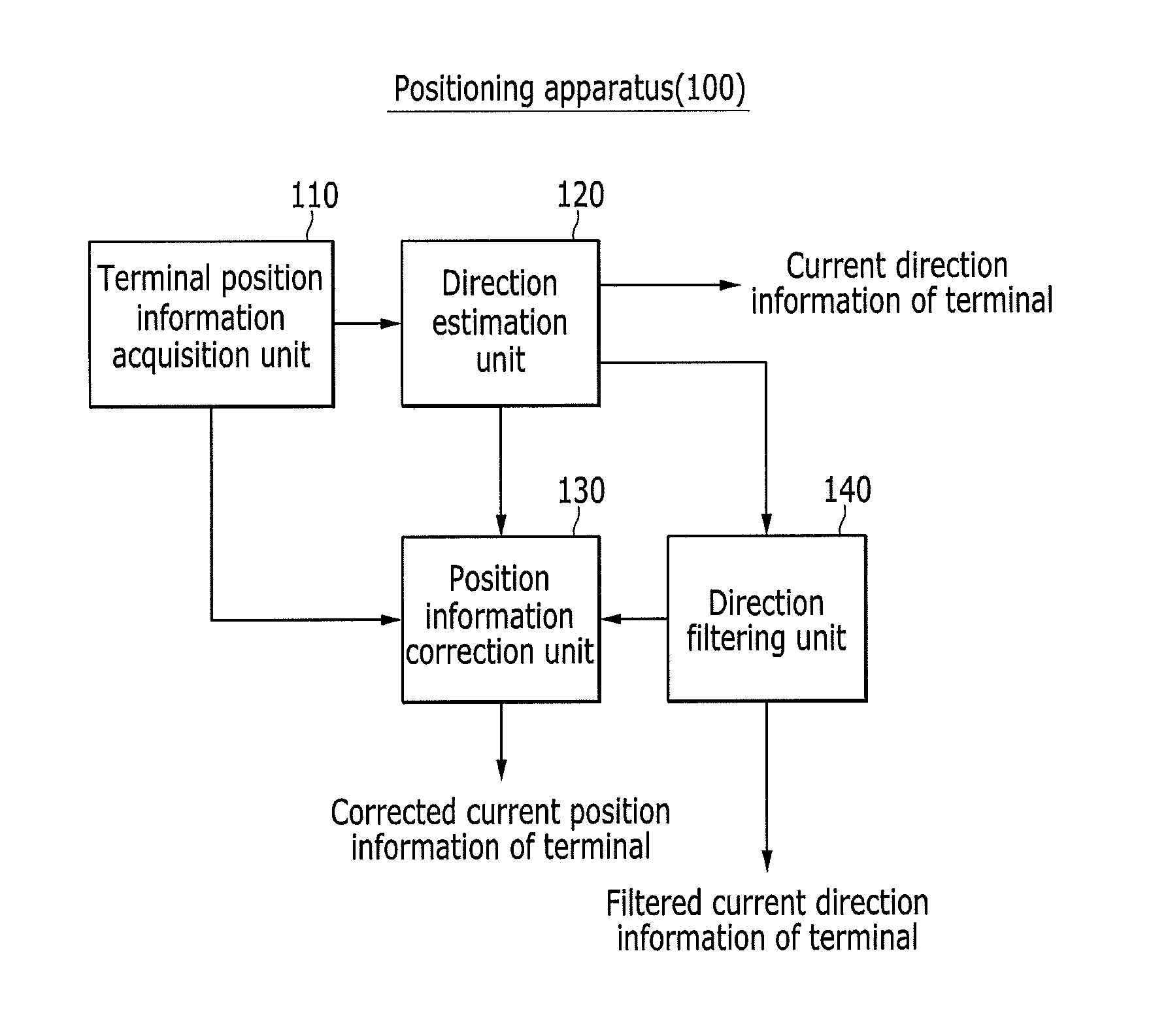
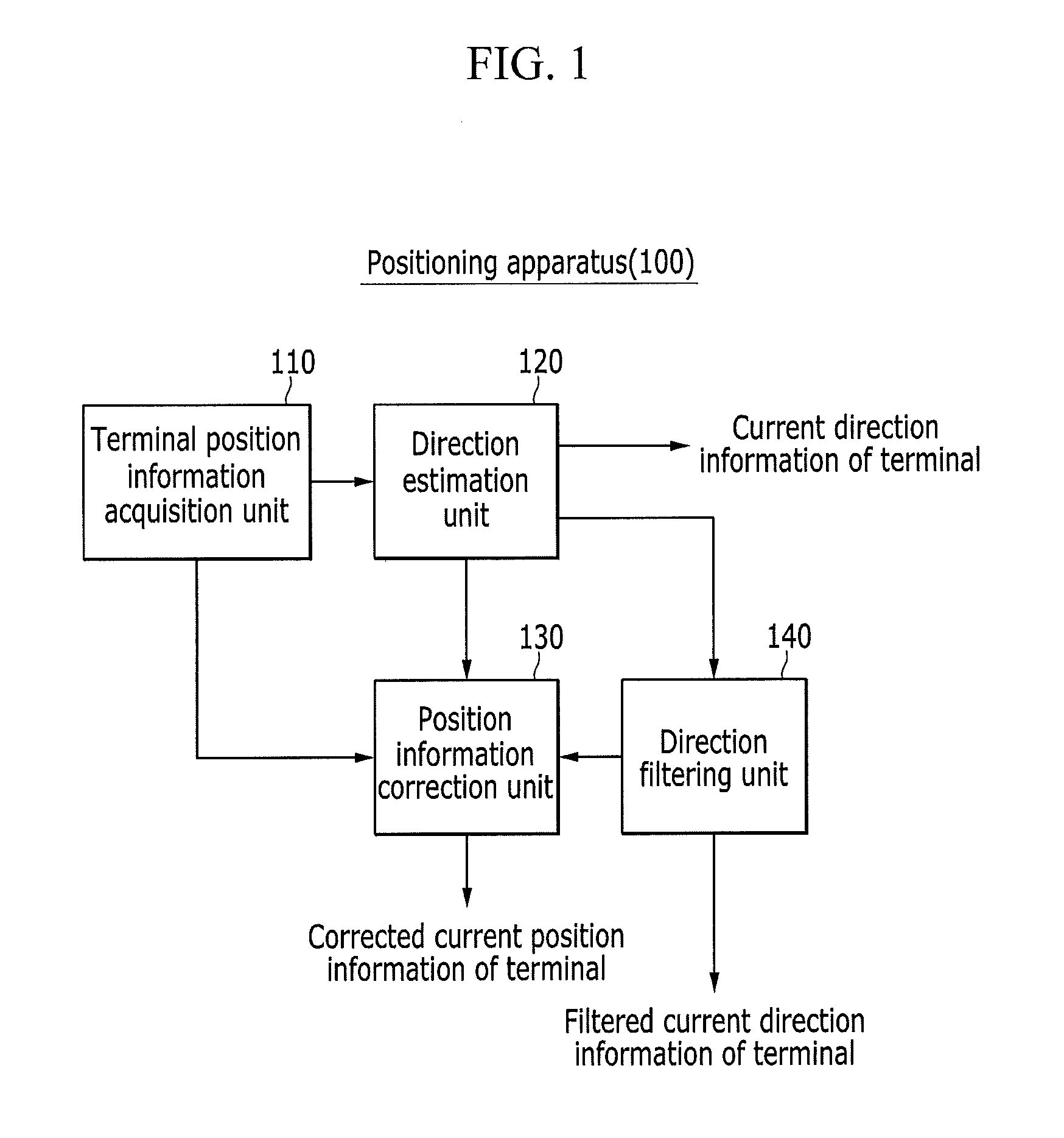
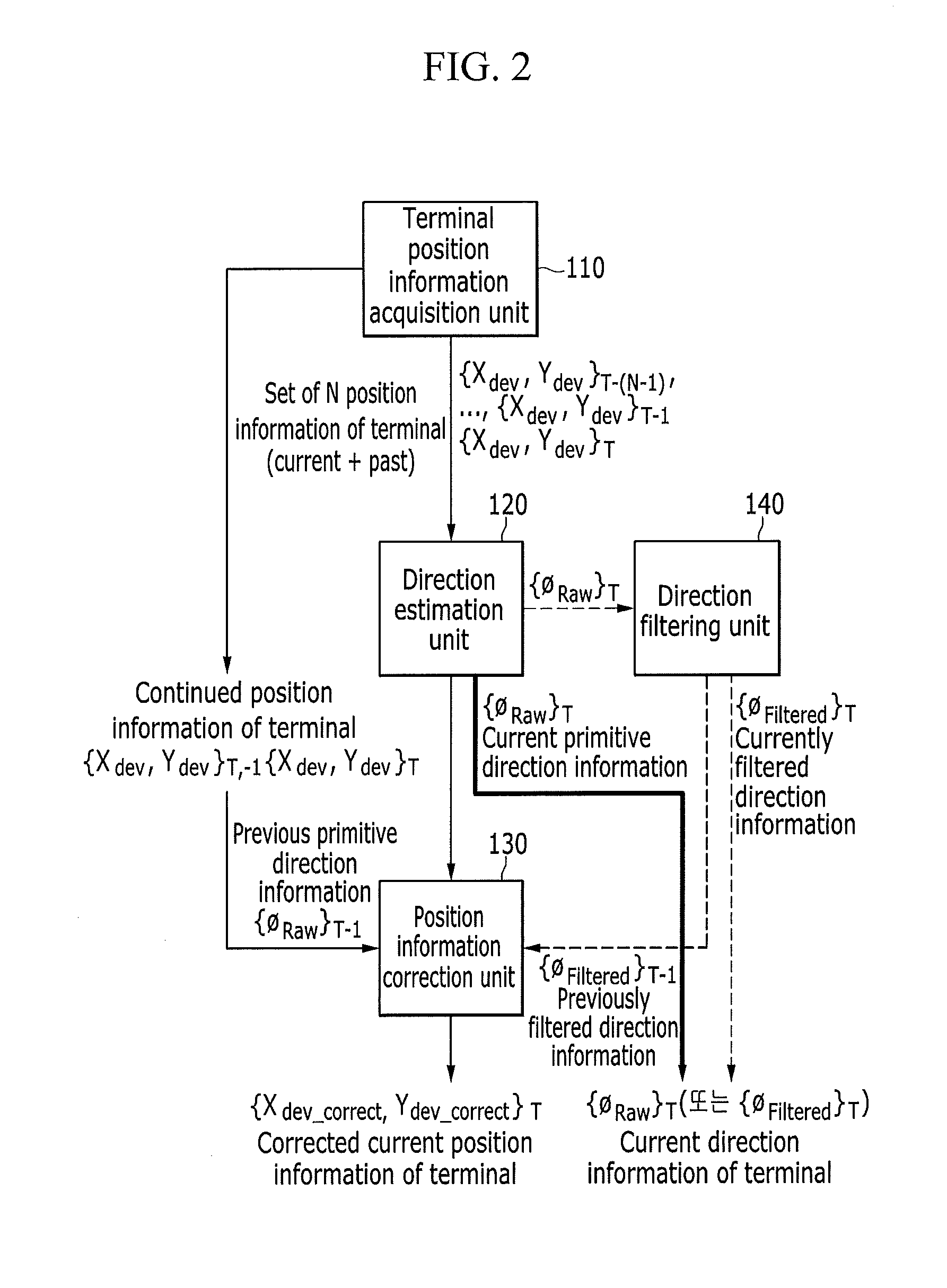
Method for determining moving direction of terminal and correcting position thereof, and positioning apparatus using the method
InactiveUS20150282116A1Position fixationWireless communicationAbsolute orientationDirection information
Provided are a method for determining a moving direction of a terminal and correcting a position thereof, and a positioning apparatus using the same. Relative direction information is estimated based on N pieces of position information of the terminal, and distortion information is removed from the relative direction information to acquire relative direction information without direction integrity. Further, the relative direction information is transmitted into absolute direction information to acquire a moving path direction of the terminal. Next, the position information of the terminal is corrected based on the moving path direction of the terminal.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
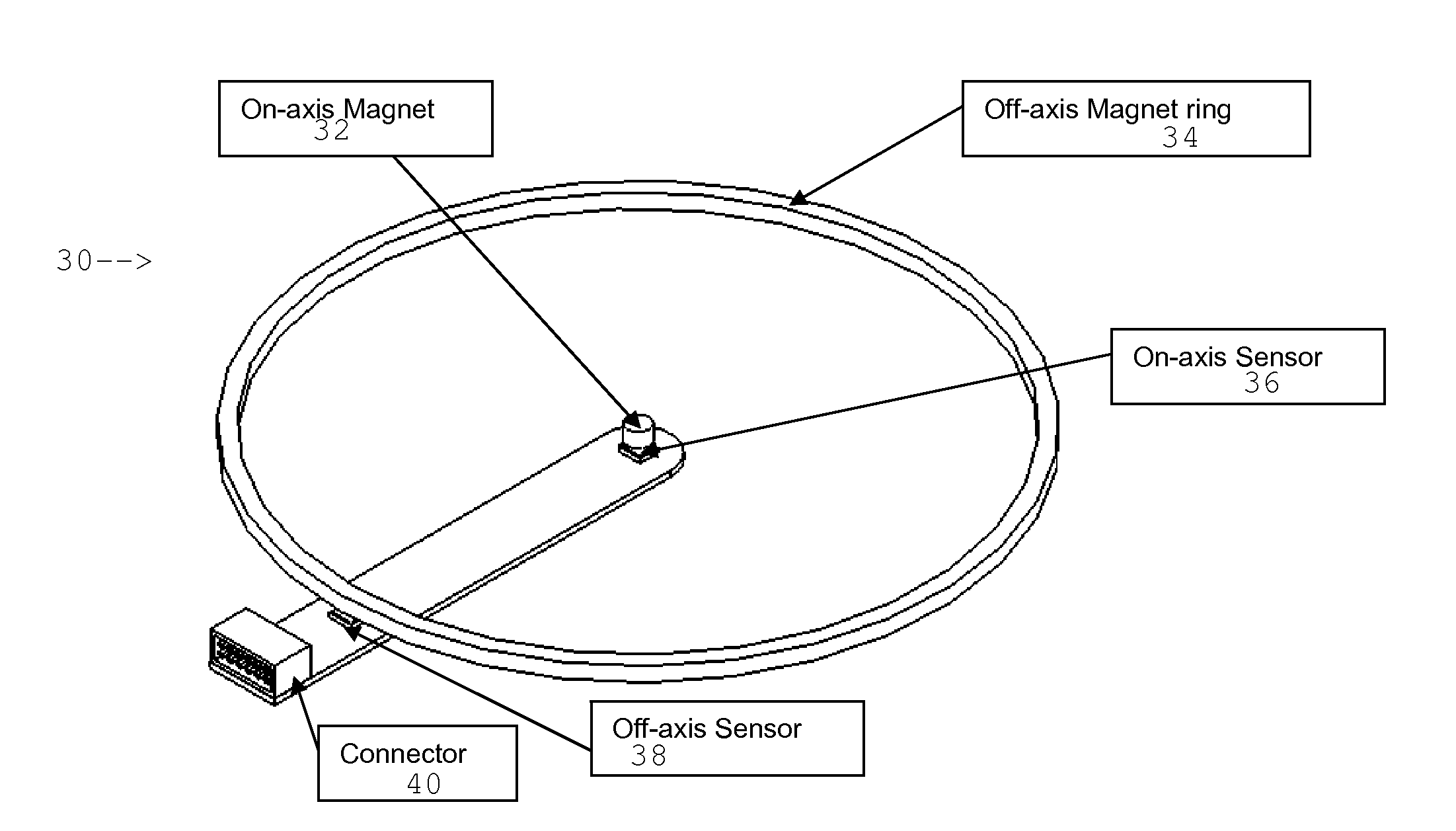
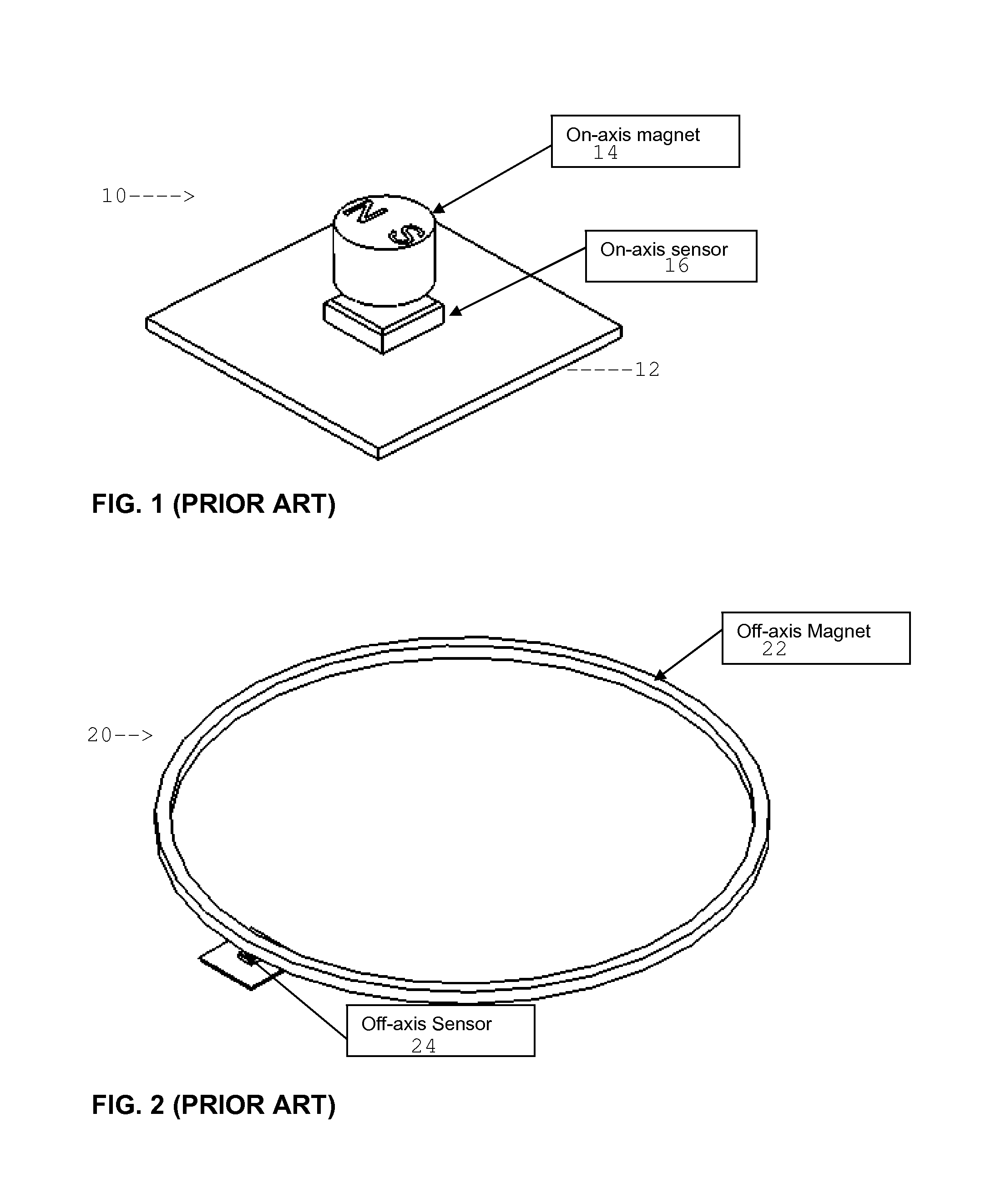
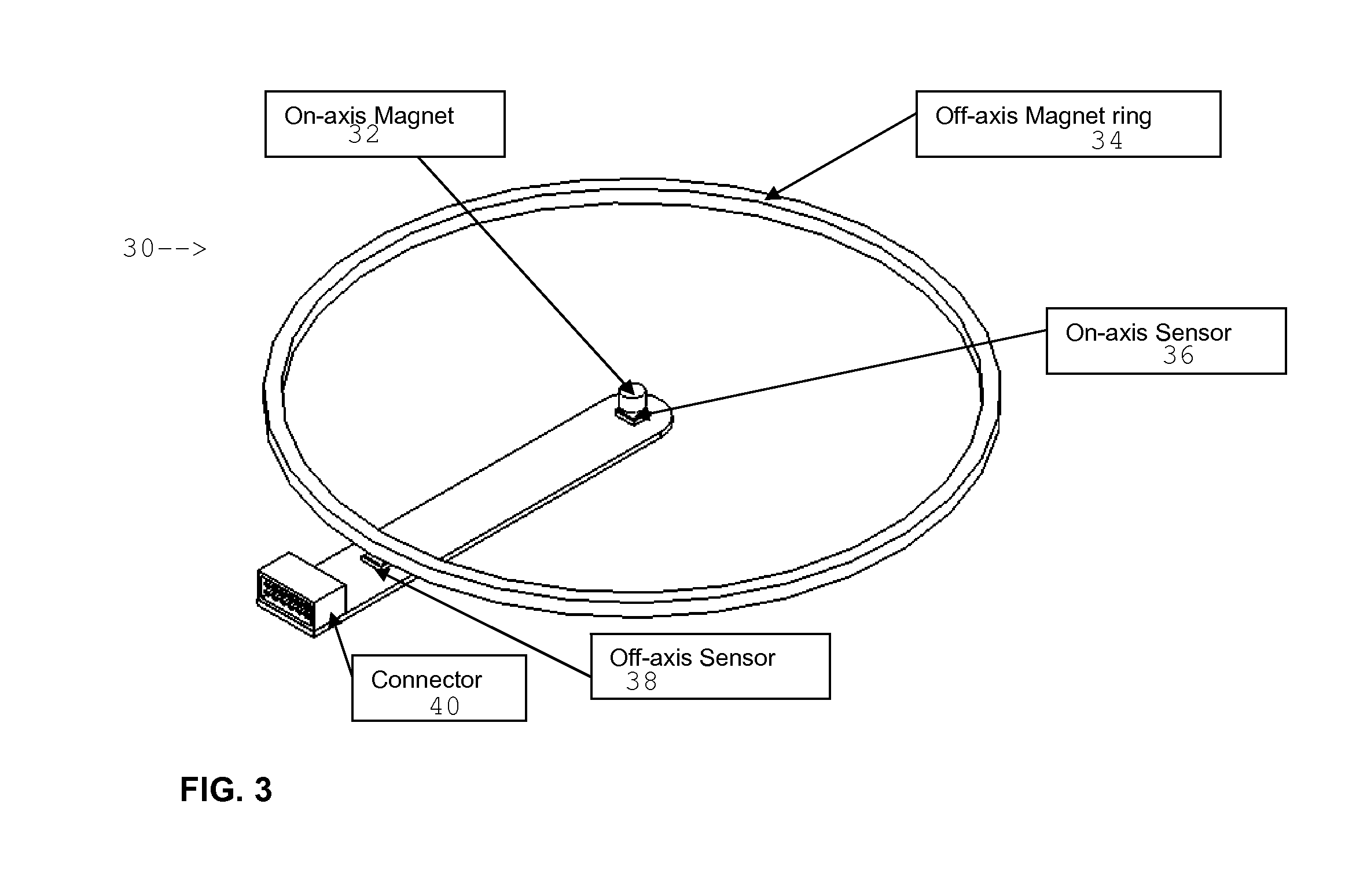
High resolution absolute orientation rotary magnetic encoder
ActiveUS20120217956A1Using electrical meansConverting sensor outputRotational axisAbsolute orientation
A rotary encoder includes a magnet disposed on a rotational axis of the encoder. The magnet is polarized transversely to the rotational axis. A first magnetic sensor is disposed on the rotational axis proximate the on-axis magnet. A magnet ring is disposed rotationally coaxially with the rotational axis and has a selected diametric distance from the axis. The magnet ring has a plurality of alternatingly polarized magnets. A number of pole pairs in the magnet ring is selected to match an angular resolution of the first magnetic sensor. A second magnetic sensor is disposed proximate the magnet ring.
Owner:DEXTER MAGNETIC TECH
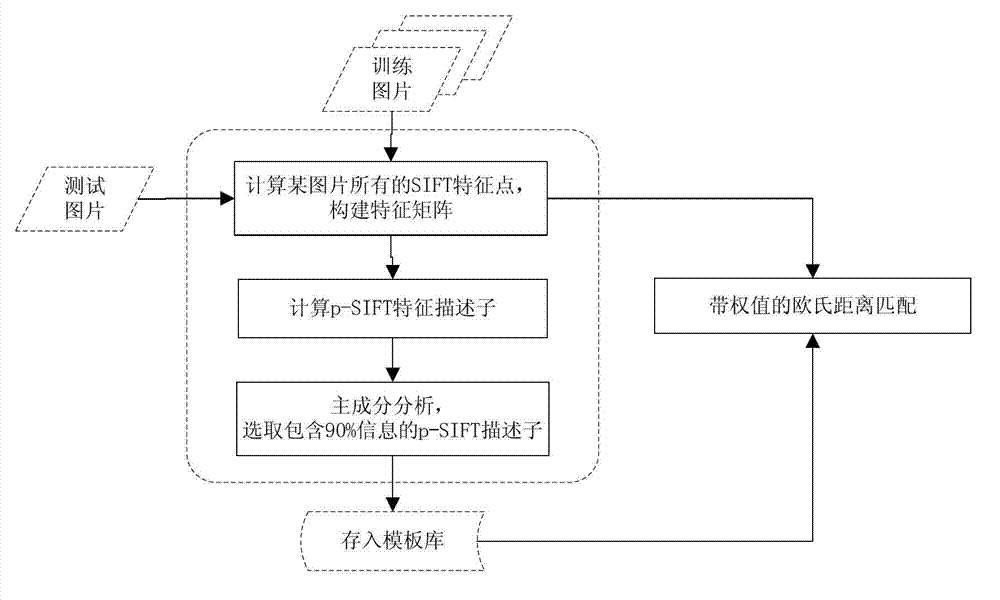
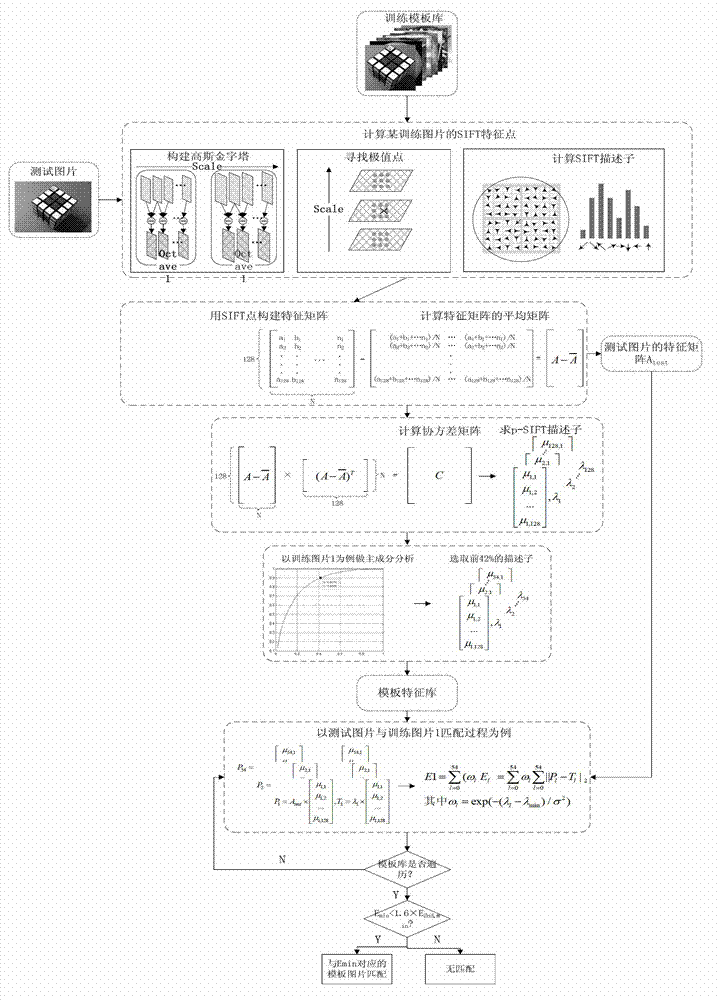
Object identification method based on p-SIFT (Scale Invariant Feature Transform) characteristic
ActiveCN102930292AImprove computing efficiencyCharacter and pattern recognitionTraining phaseScale-invariant feature transform
The invention provides an object identification method based on a p-SIFT (Scale Invariant Feature Transform) characteristic. The object identification method comprises a template library training phase and a test picture matching phase. The template library training phase comprises the following steps of: respectively calculating an SIFT characteristic point of each training picture in a template library to obtain a characteristic matrix; and calculating a covariance matrix of the characteristic matrix to obtain a p-SIFT characteristic descriptor. The test picture matching phase comprises the following steps of: calculating an SIFT characteristic matrix of a test picture; and calculating the similarity of the test picture and the characteristic matrix of a template library training picture. According to the object identification method disclosed by the invention, the characteristic points described by the p-SIFT characteristic are the region relativity and the direction relativity, so that the characteristic points are changed into a relative direction and a relative direction from an absolute position and an absolute direction, and the identification accuracy is improved.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
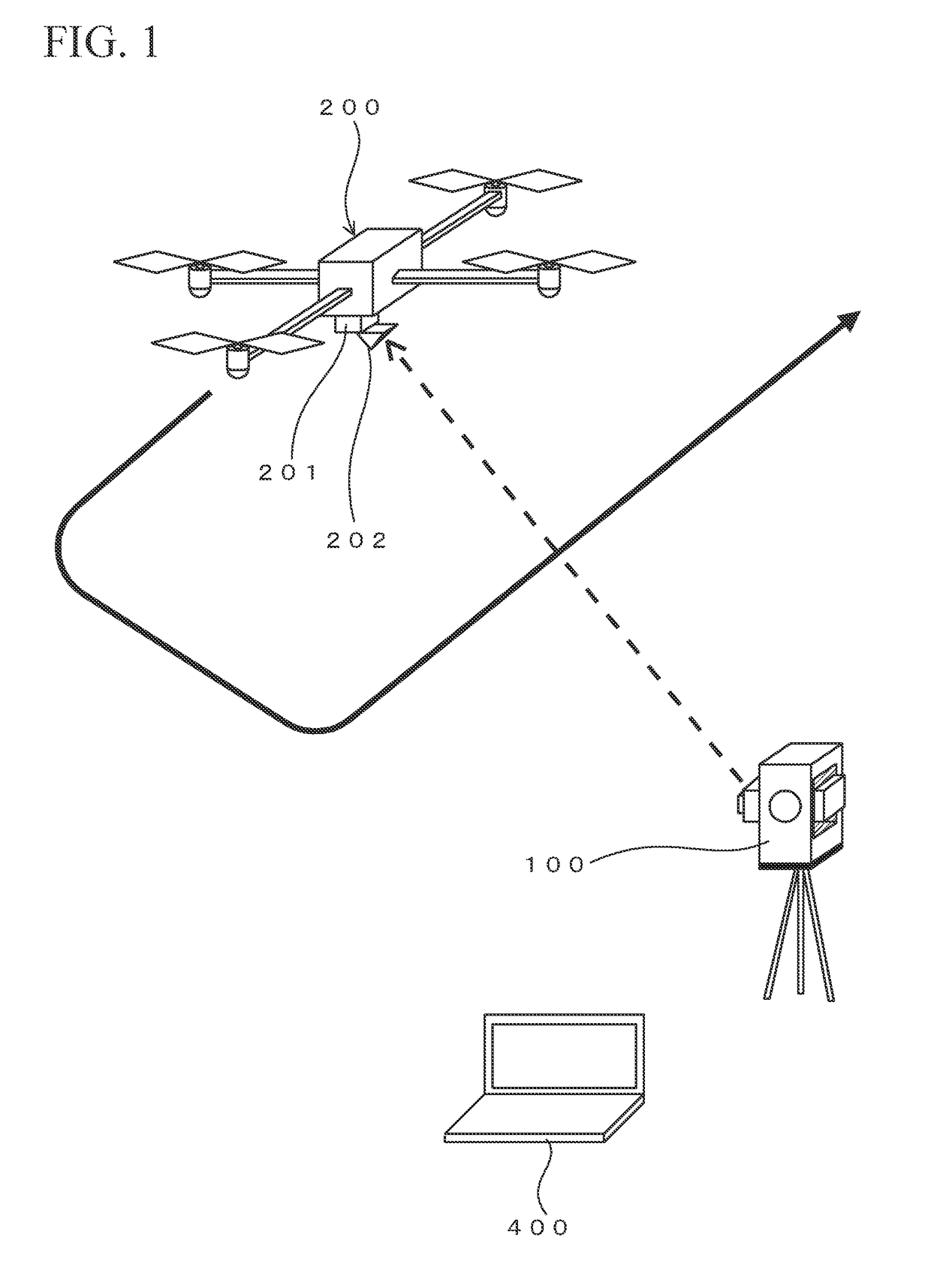
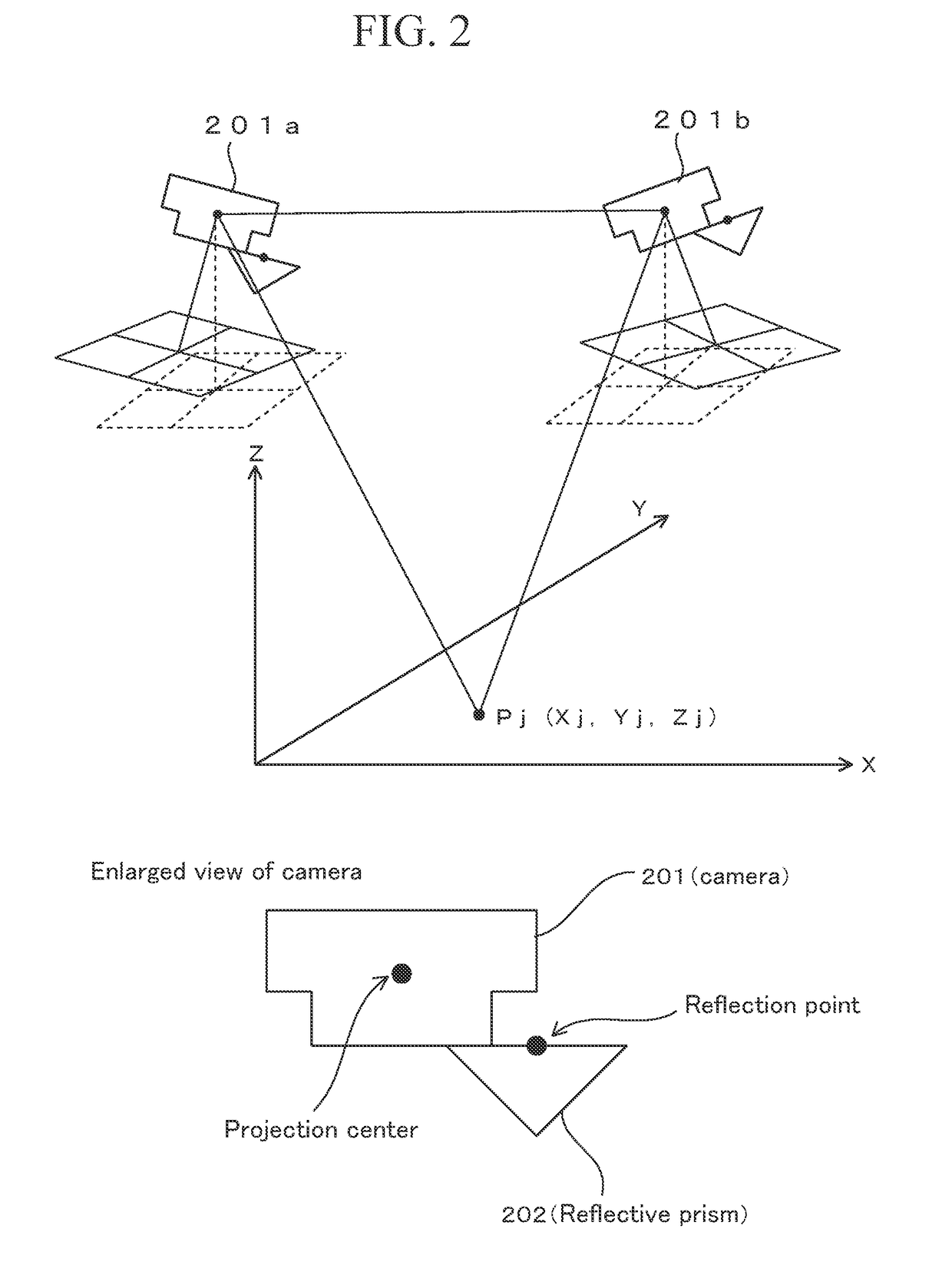
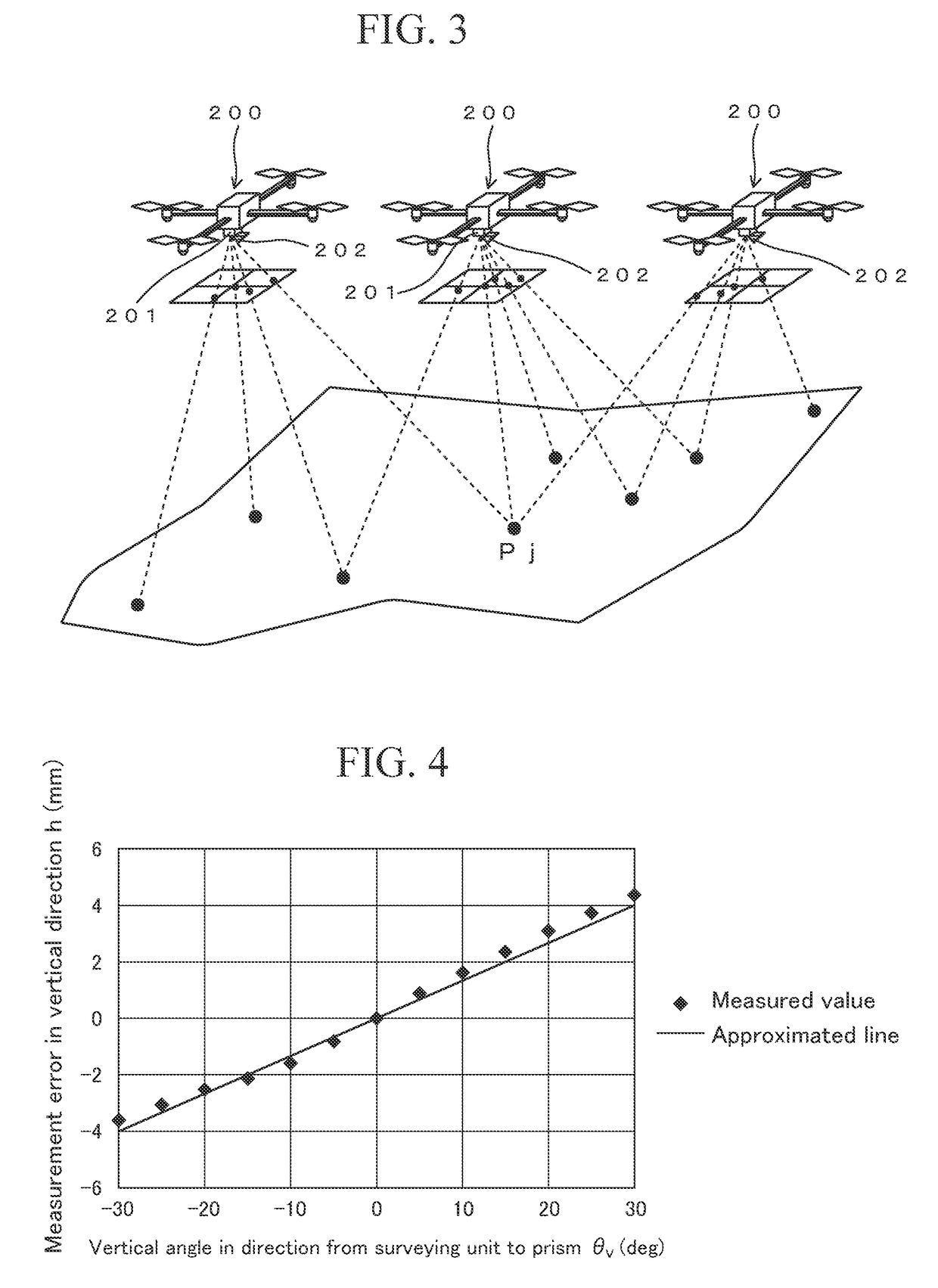
Survey data processing device, survey data processing method, and survey data processing program
A technique is provided to enable reduction in cost relating to installation of orientation targets in aerial photogrammetry. A survey data processing device includes a positioning data receiving unit, a relative orientation unit, an absolute orientation unit, and an adjustment calculation executing unit. The positioning data receiving unit receives positioning data obtained by tracking and positioning a reflective prism of an aerial vehicle by a total station. The aerial vehicle also has a camera. The relative orientation unit calculates relative exterior orientation parameters of the camera by relative orientation using photographed images taken by the camera. The absolute orientation unit provides a true scale to the relative exterior orientation parameters by absolute orientation using the positioning data and the relative exterior orientation parameters. The adjustment calculation executing unit corrects the relative exterior orientation parameters having the true scale, by using a positional relationship between the camera and the reflective prism.
Owner:KK TOPCON
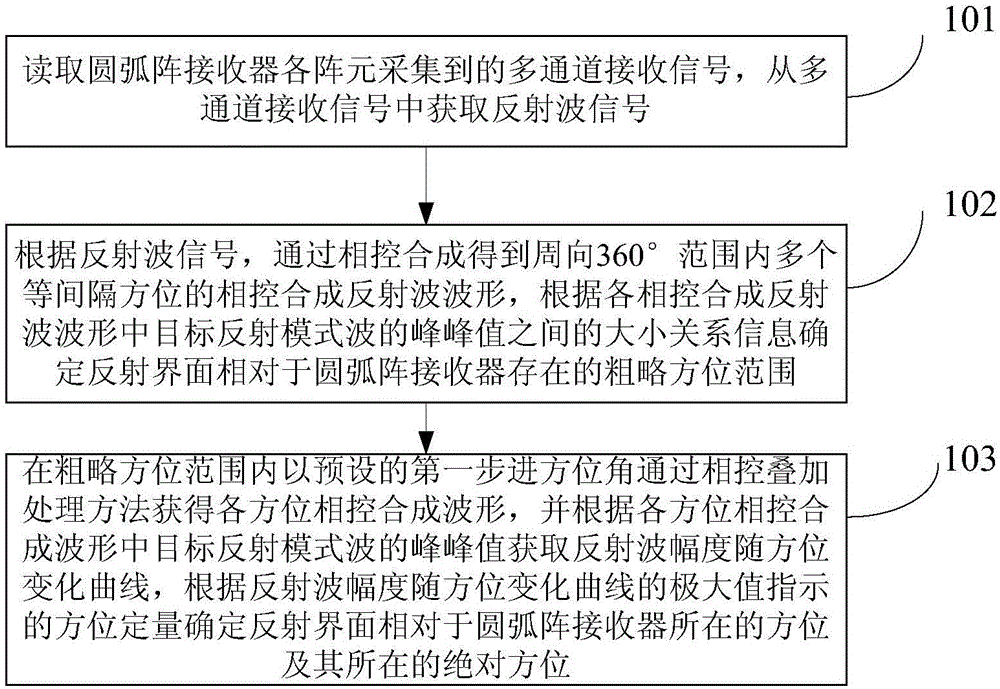
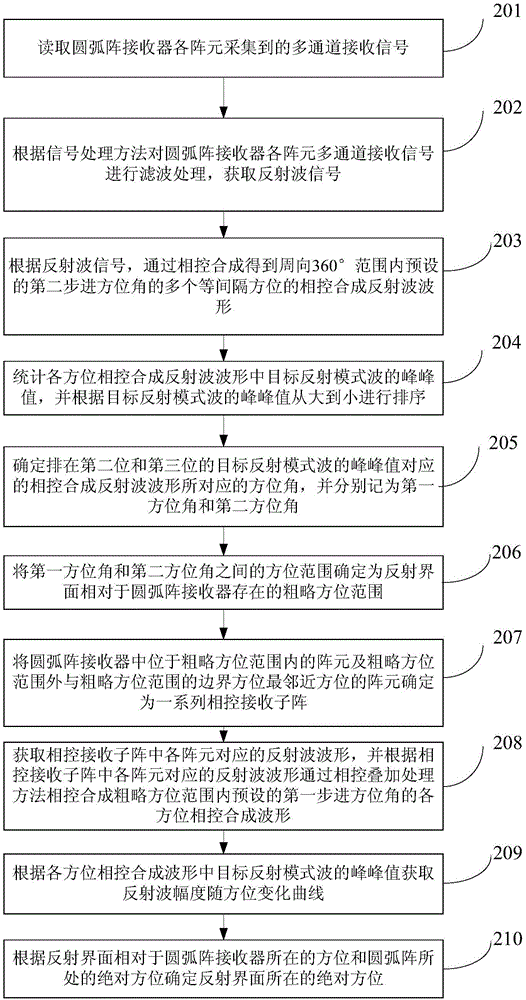
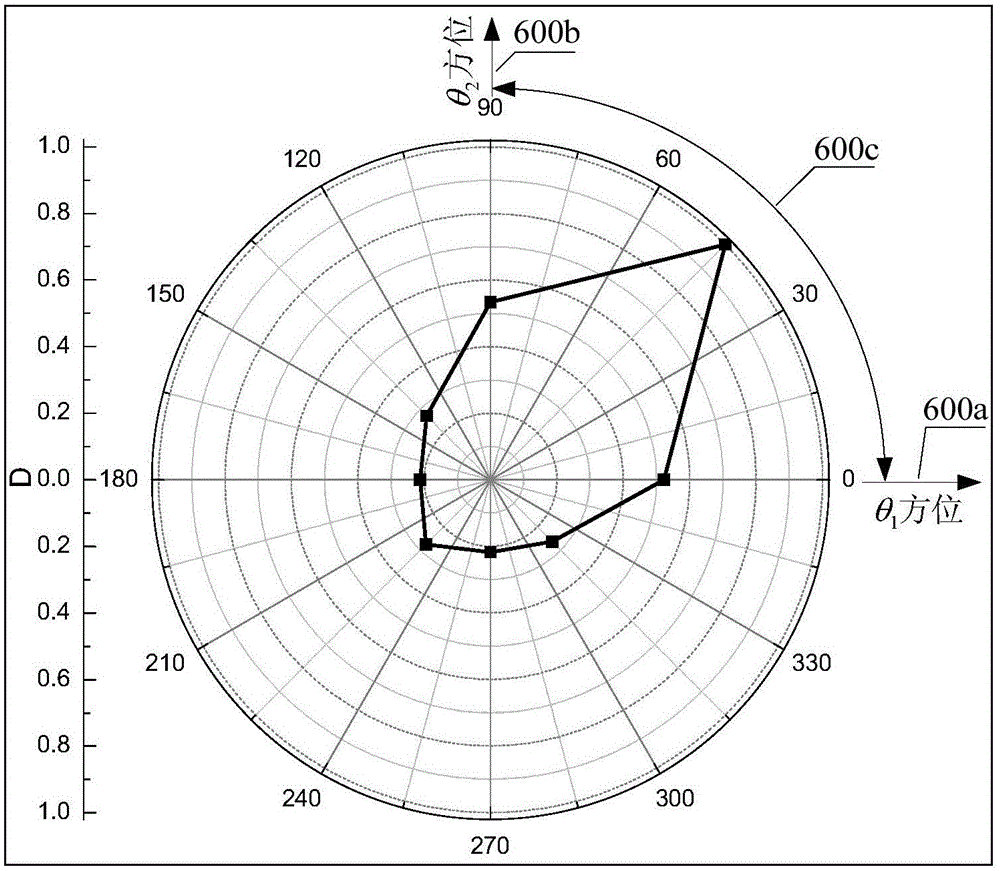
Reflecting interface orientation quantitative decision method based on phased receiving directivity and device thereof
ActiveCN105044779AResolve uncertaintyDetermine accurate quantificationSeismic signal processingSeismology for water-loggingReflected wavesArray element
The invention provides a reflecting interface orientation quantitative decision method based on phased receiving directivity and a device thereof and relates to the field of petroleum geophysical exploration and acoustic wave signal processing technologies. The method comprises the following steps: a multichannel receipt signal acquired by each array element of an arc array receiver is read and a reflected wave signal is obtained; according to the reflected wave signal, phased synthetic reflected waveforms in multiple equally-spaced orientations within the range of circumferentially 360 degrees through phased synthesis, and a rough orientation range of a reflecting interface relative to the arc array receiver is determined according to size relation between peak-to-peak values of target reflection mode wave in each phased synthetic reflected waveform; and phased synthetic waveform in each orientation is obtained through a phased superposition treatment method in the preset first stepping orientation within the rough orientation range, an orientation variation curve of reflected wave amplitude is obtained according to the peak-to-peak value of the target reflection mode wave in each phased synthetic reflected waveform, and orientation and absolute orientation of the reflecting interface relative to the arc array receiver are quantitatively determined according to the orientation indicated by the maximum value of the curve.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com