Patents
Literature
10178 results about "Photodetector" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Photodetectors, also called photosensors, are sensors of light or other electromagnetic radiation. A photo detector has a p–n junction that converts light photons into current. The absorbed photons make electron–hole pairs in the depletion region. Photodiodes and photo transistors are a few examples of photo detectors. Solar cells convert some of the light energy absorbed into electrical energy.
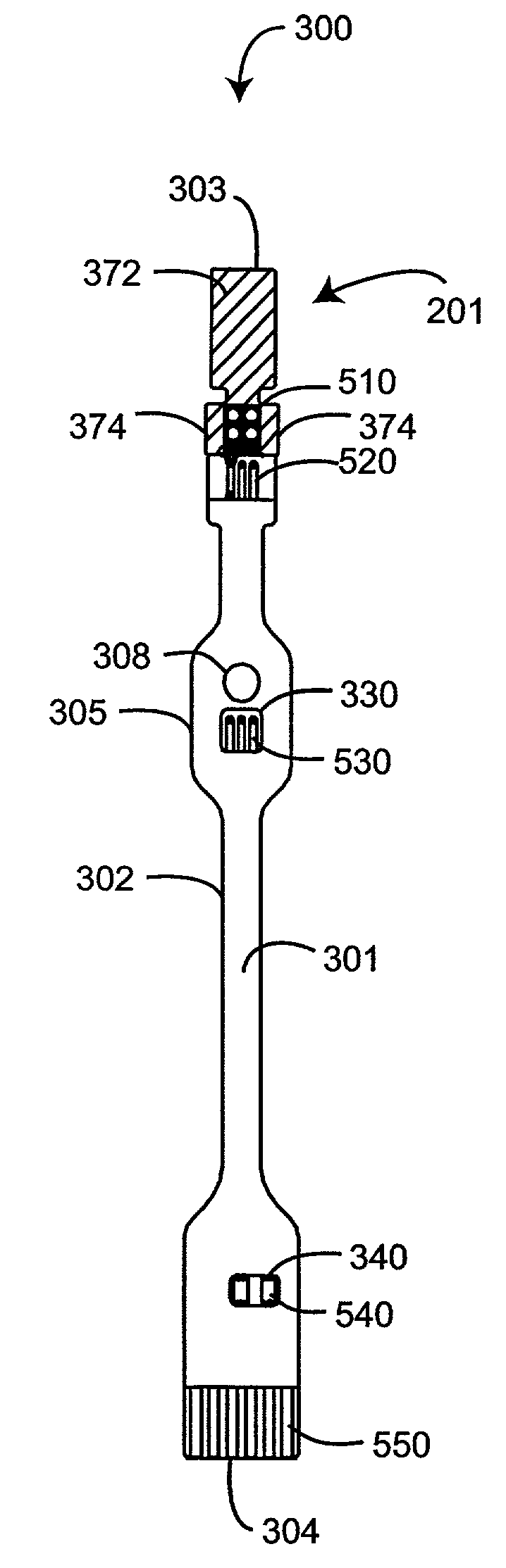
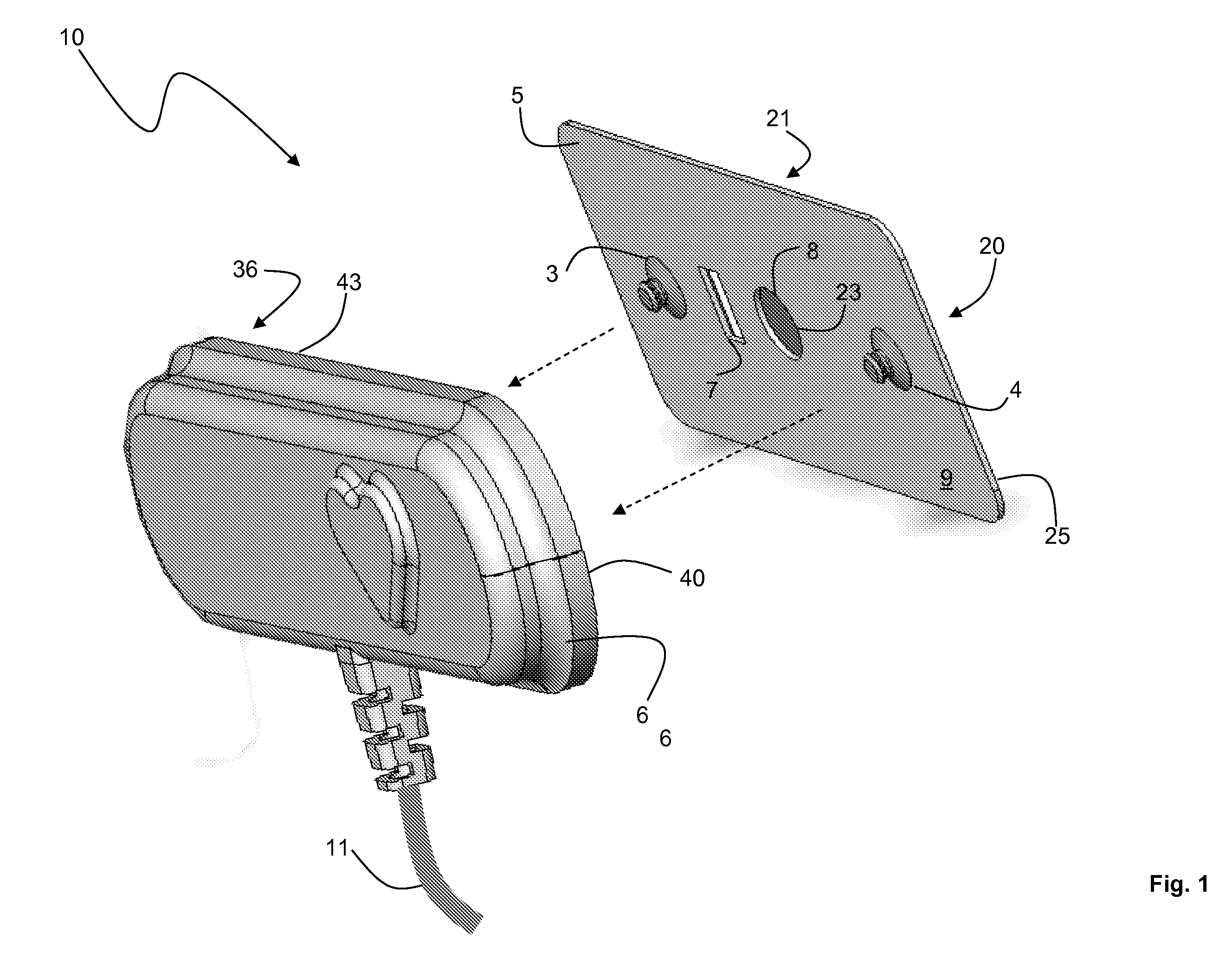
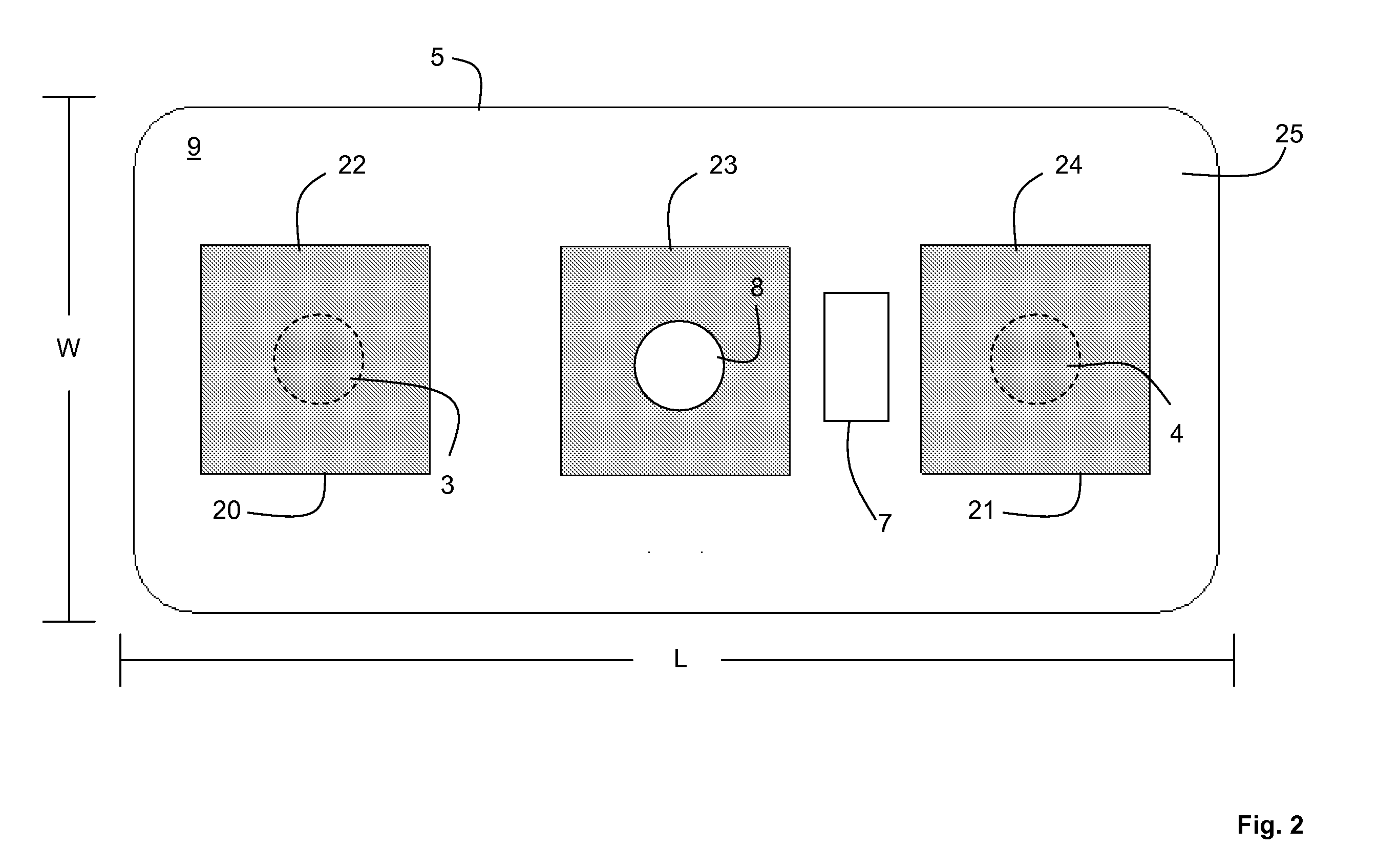
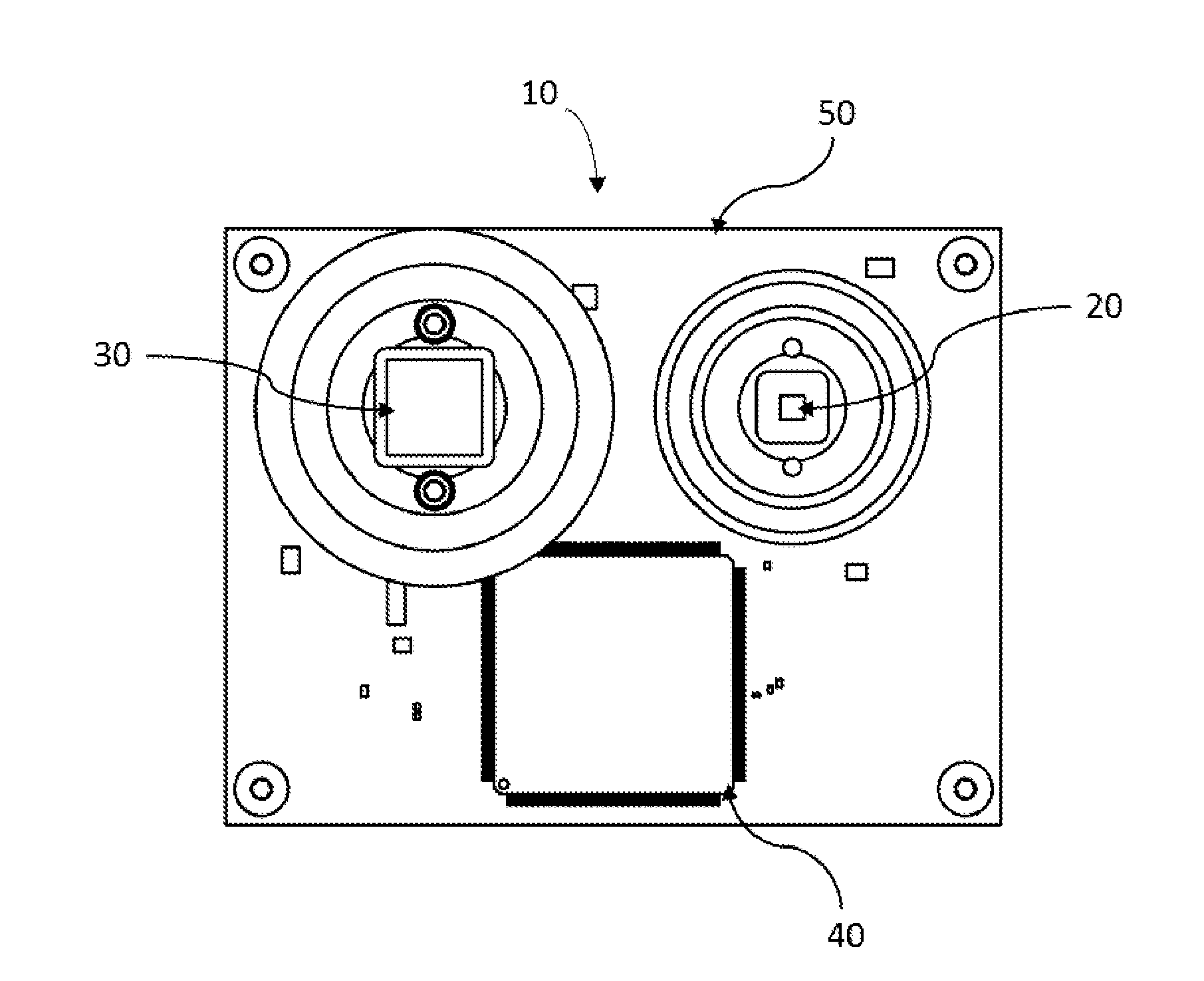
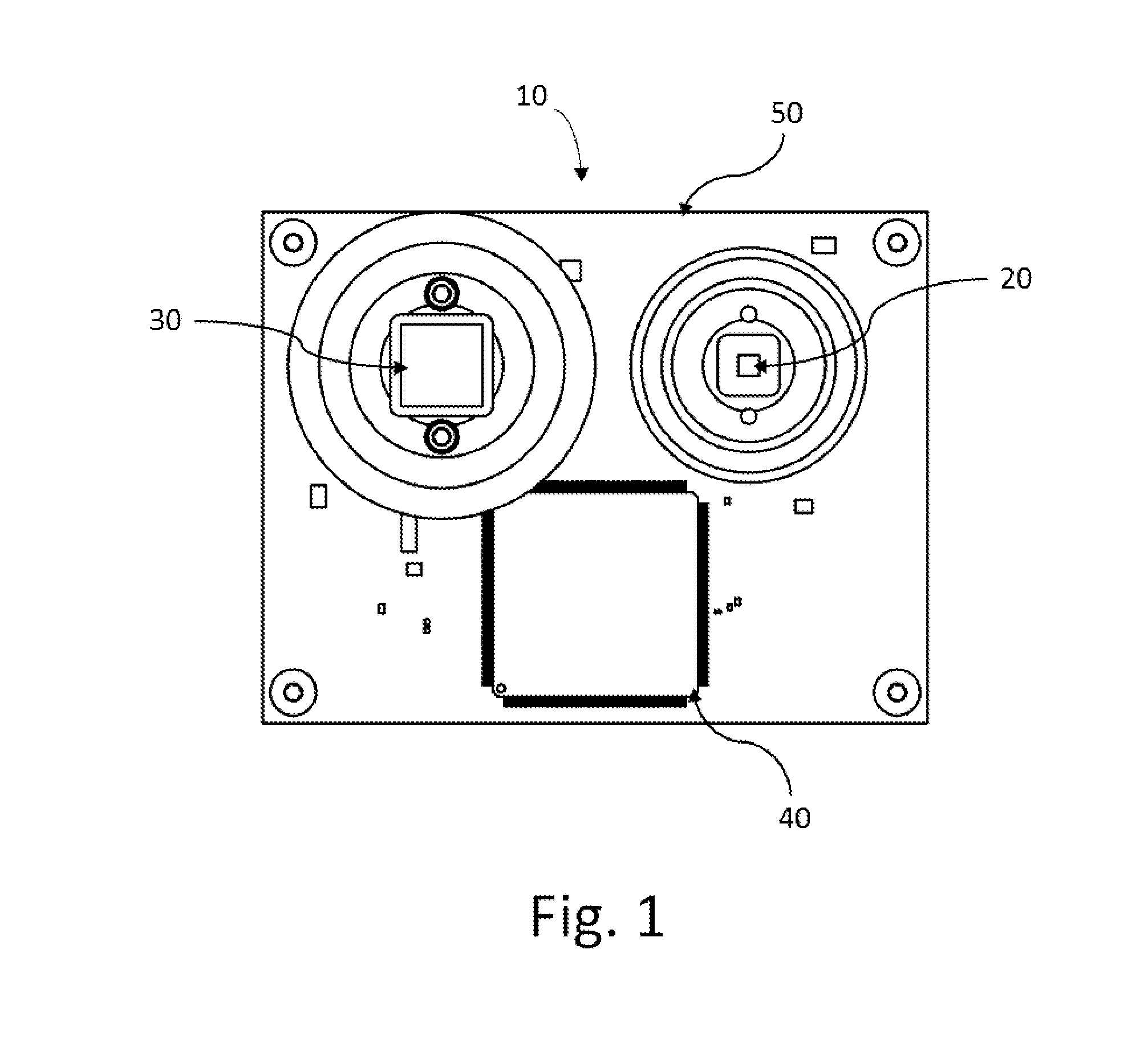
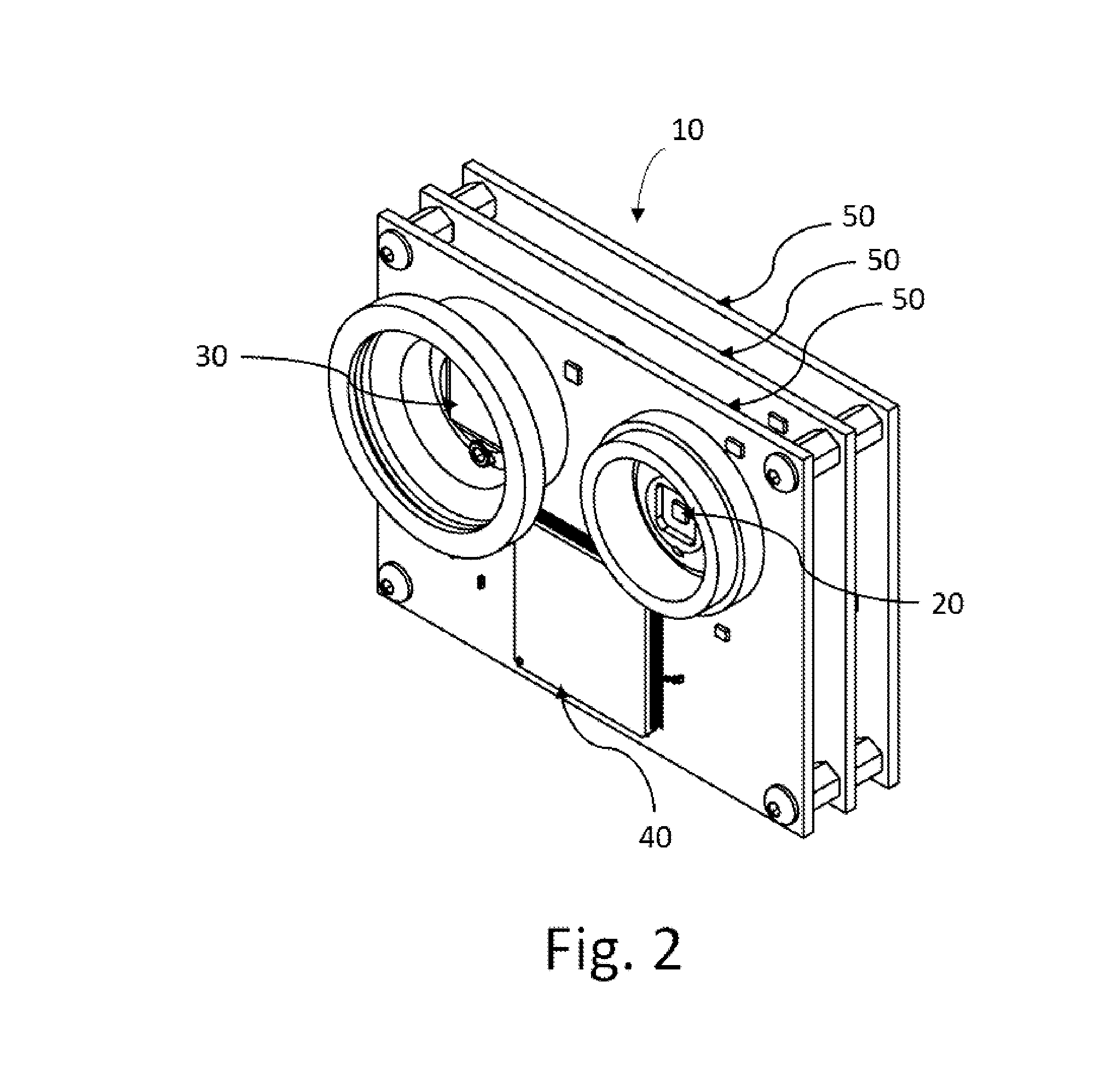
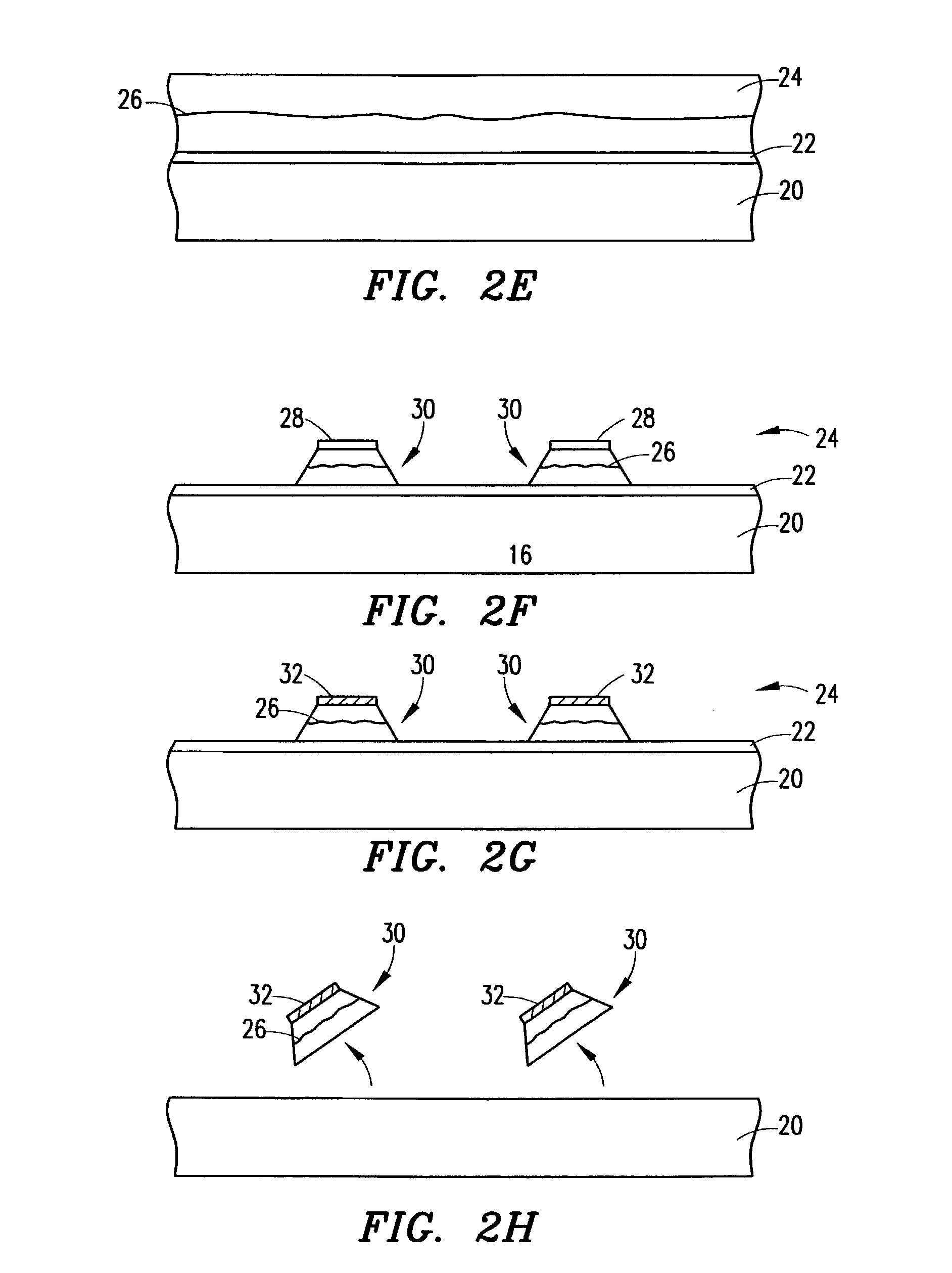
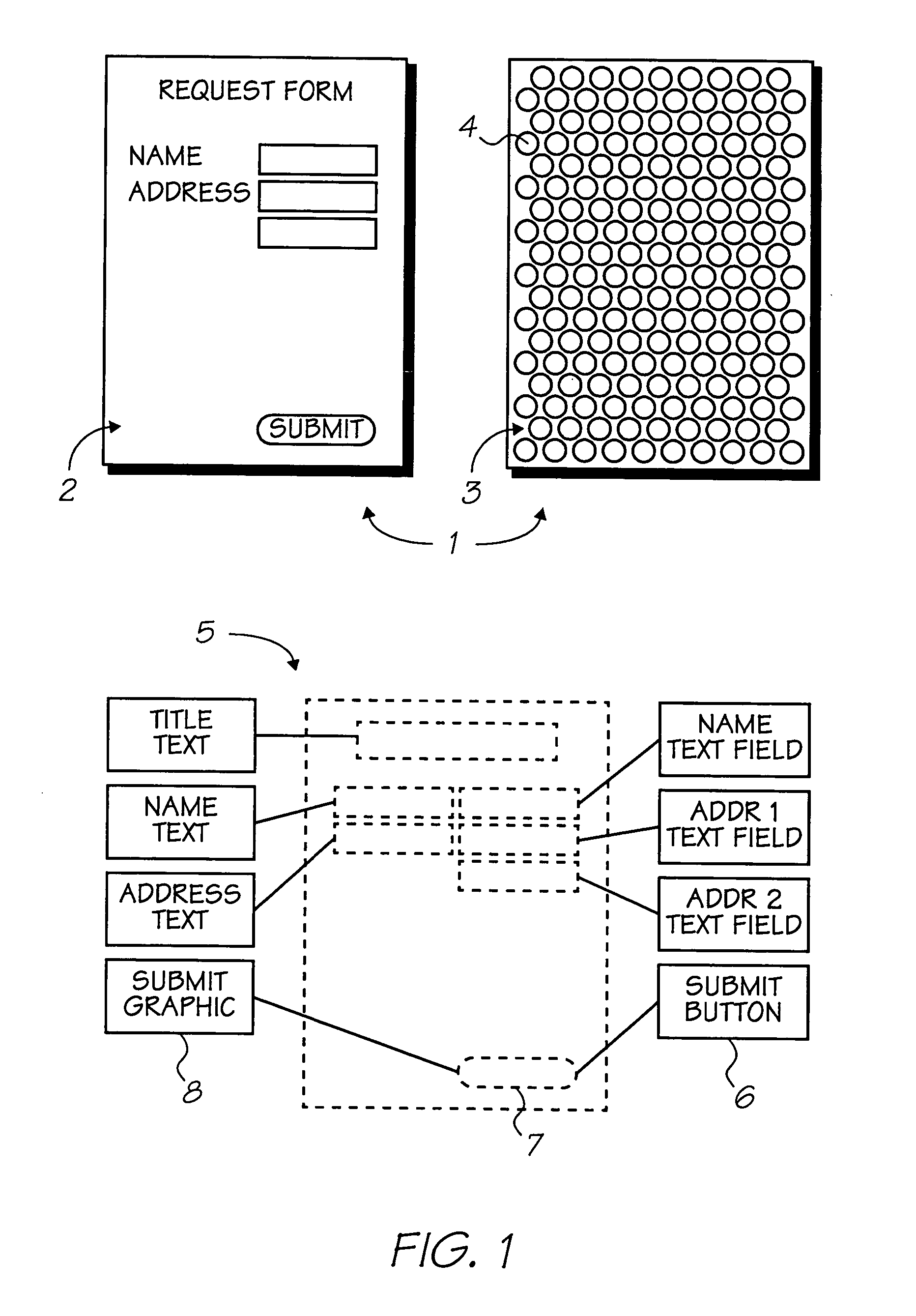
Flex circuit shielded optical sensor
InactiveUS6985764B2Cross-talk/noise/interference reductionColor/spectral properties measurementsPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
A flex circuit optical sensor has an integrated Faraday shield. A conductive trace layer disposed on a substrate is used to form a conductive grid which shields the face of a photodetector. A conductive ink layer is formed on a substrate side opposite the trace layer. The back and sides of the detector are shielded by flex circuit flaps that have the conductive ink layer but substantially exclude the trace layer so as to fold over and closely adhere to the detector body. The shielded substrate flaps advantageously eliminate a separate detector shield, which is typically fabricated with an etched copper part that must be attached to a flex circuit before mounting the detector.
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
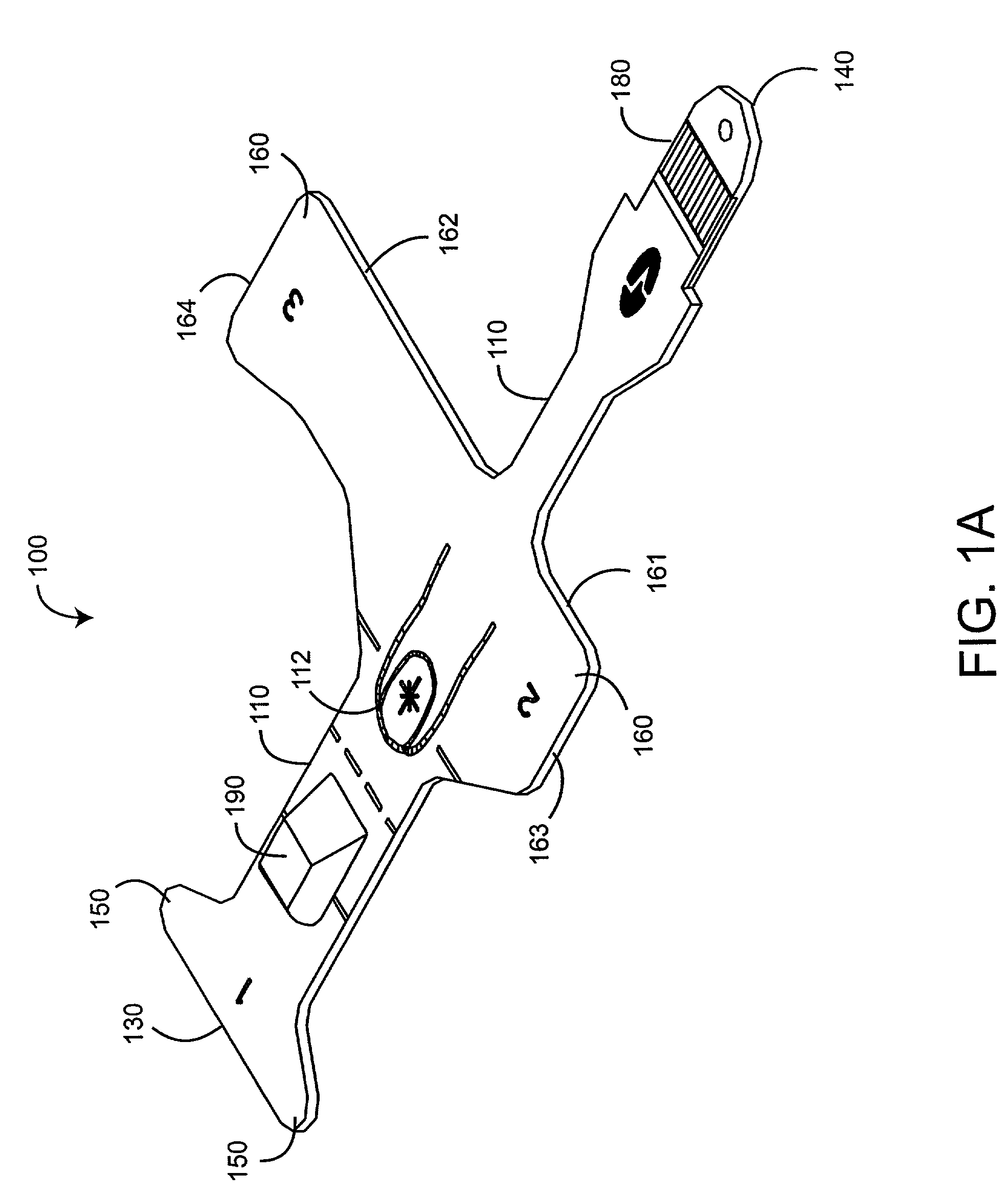
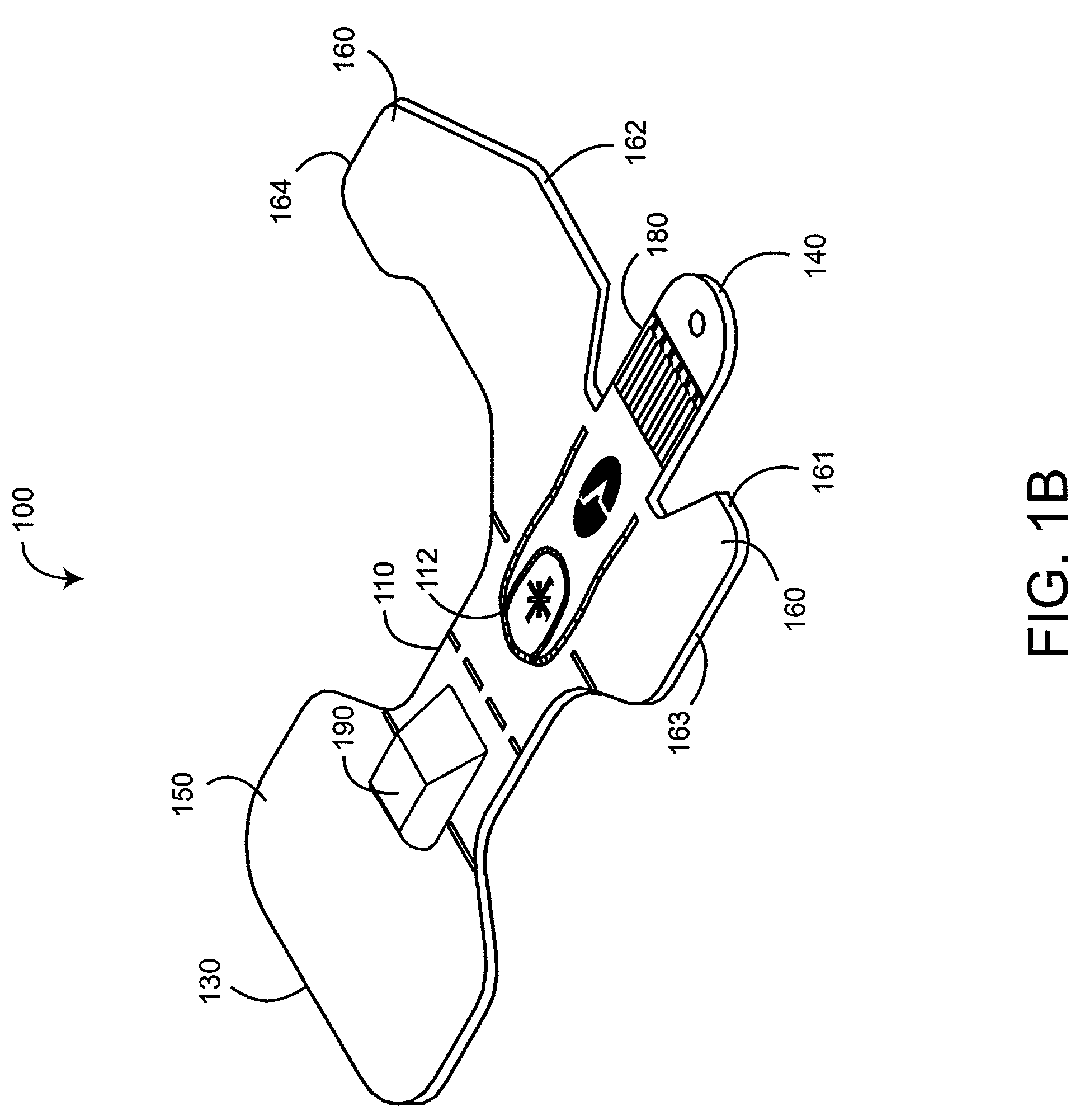
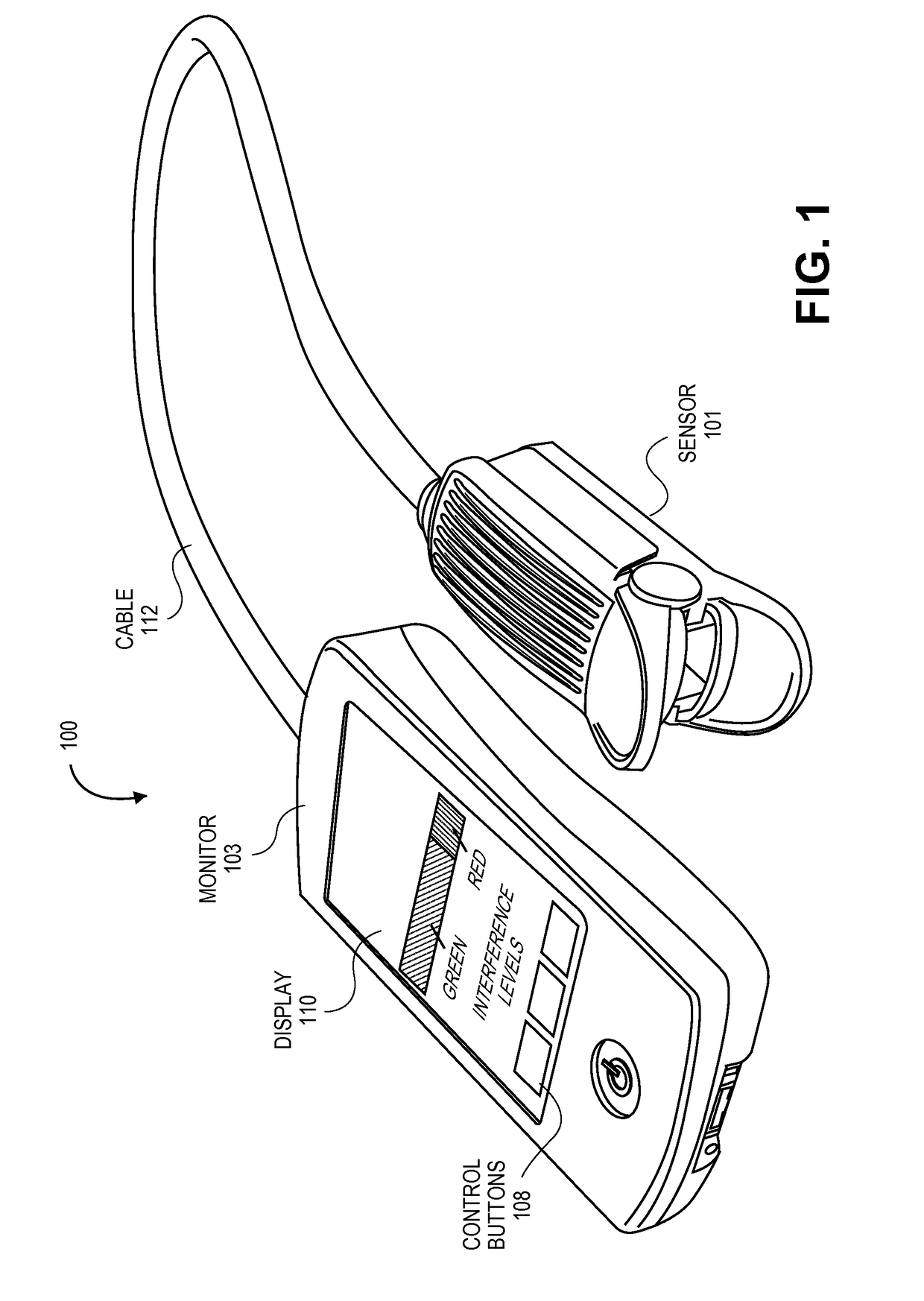
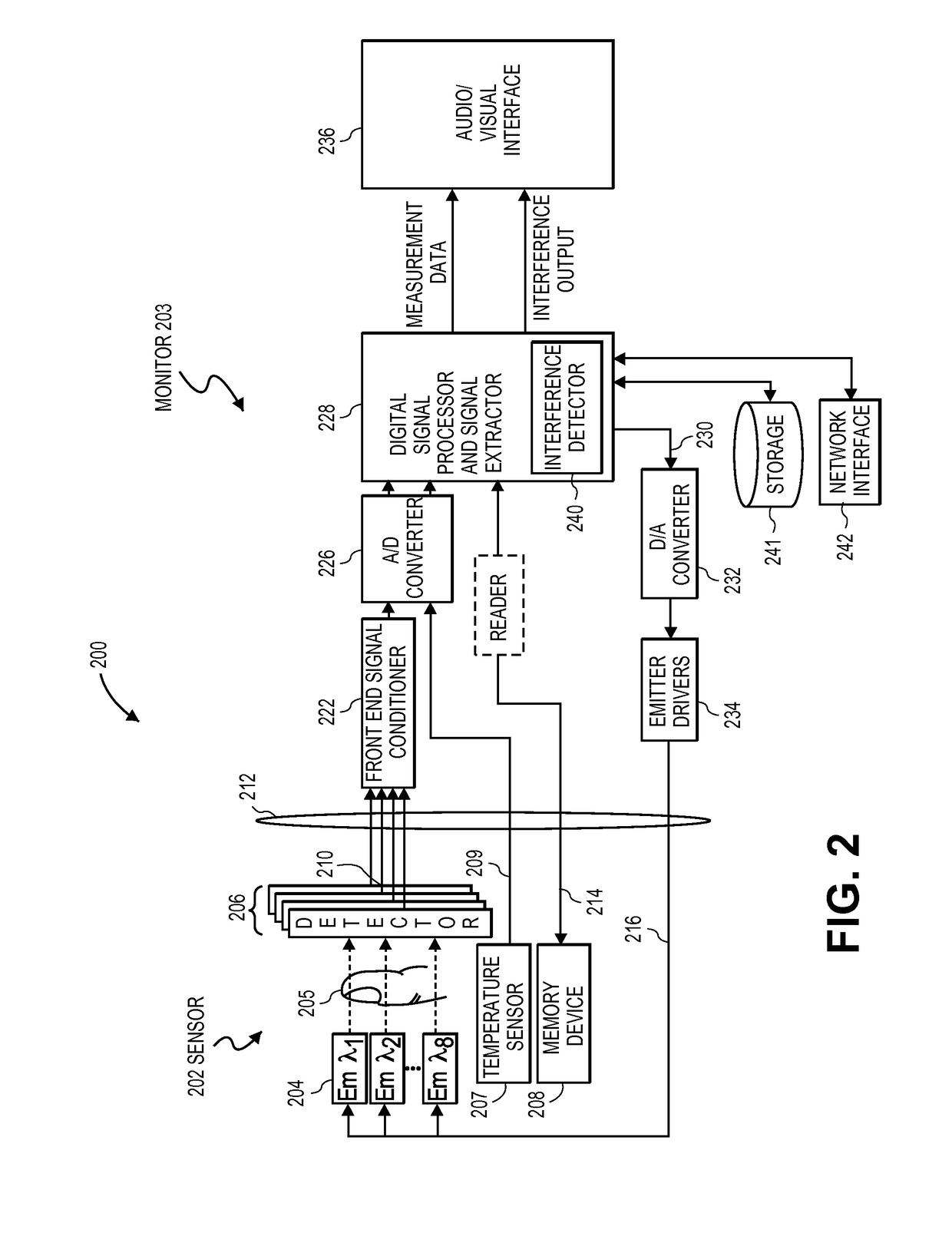
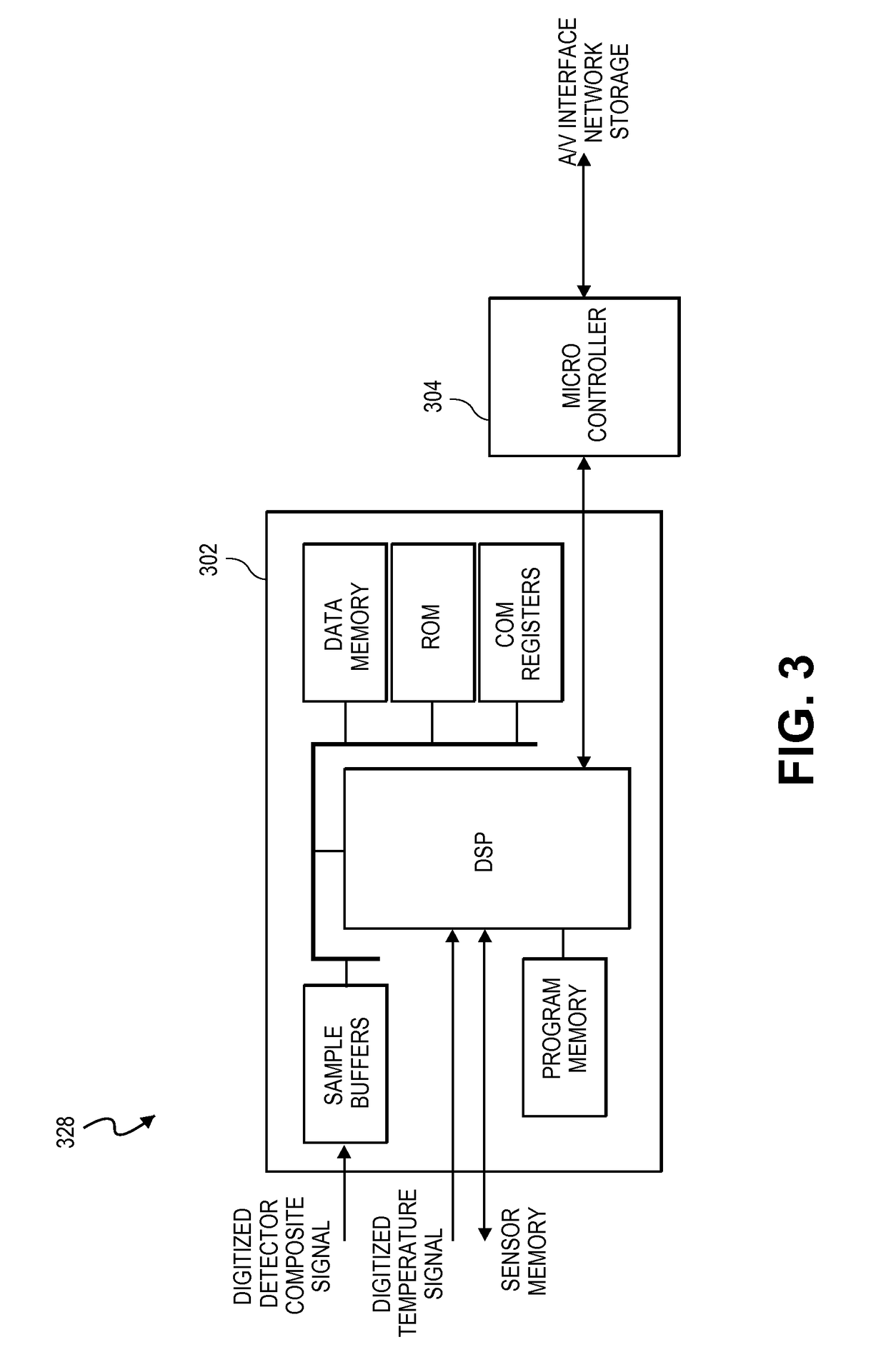
Interference detector for patient monitor
ActiveUS8471713B2Quickly informedQuickly alertedNoise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementElectric testing/monitoringEnvironmental noiseMedical equipment
A system is disclosed for detecting and calculating the level of ambient and / or environmental noise, such as electromagnetic interference generated by electric power lines, ambient lights, light dimmers, television or computer displays, power supplies or transformers, and medical equipment. In some embodiments, the system performs frequency analysis on the interference signal detected by light photodetectors and determines the power of the interference signal concentrated in the analyzed frequency bands. The worst-case interference level can be determined by selecting the maximum from the computed power values. In some embodiments, the determined interference signal power can be compared with the noise tolerance of a patient monitoring system configured to reliably and non-invasively detect physiological parameters of a user. The results of the comparison can be presented to the user audio-visually. In some embodiments, the system can be used to perform spot check measurements of electromagnetic interference.
Owner:MASIMO CORP
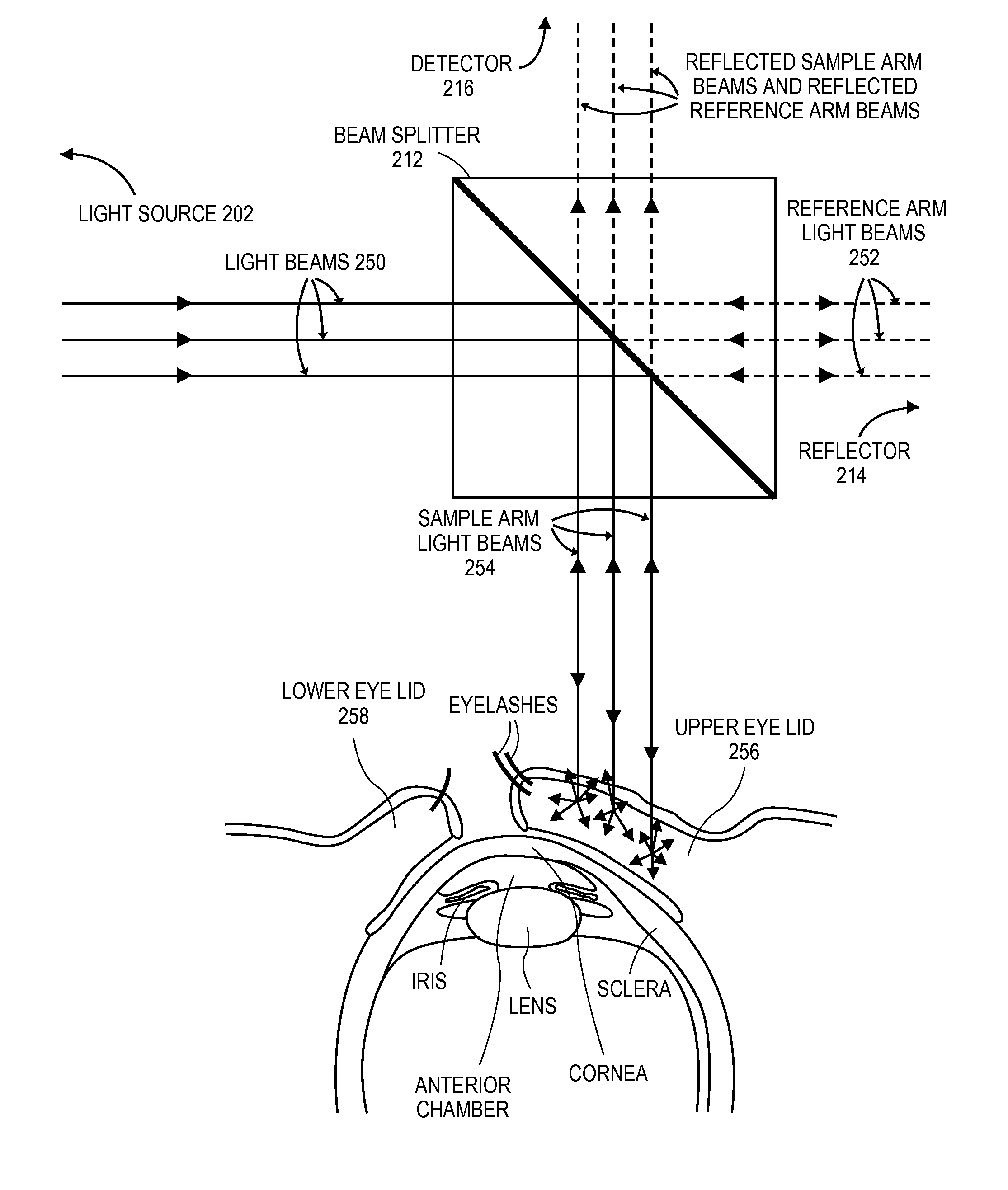
Patient monitor for monitoring microcirculation
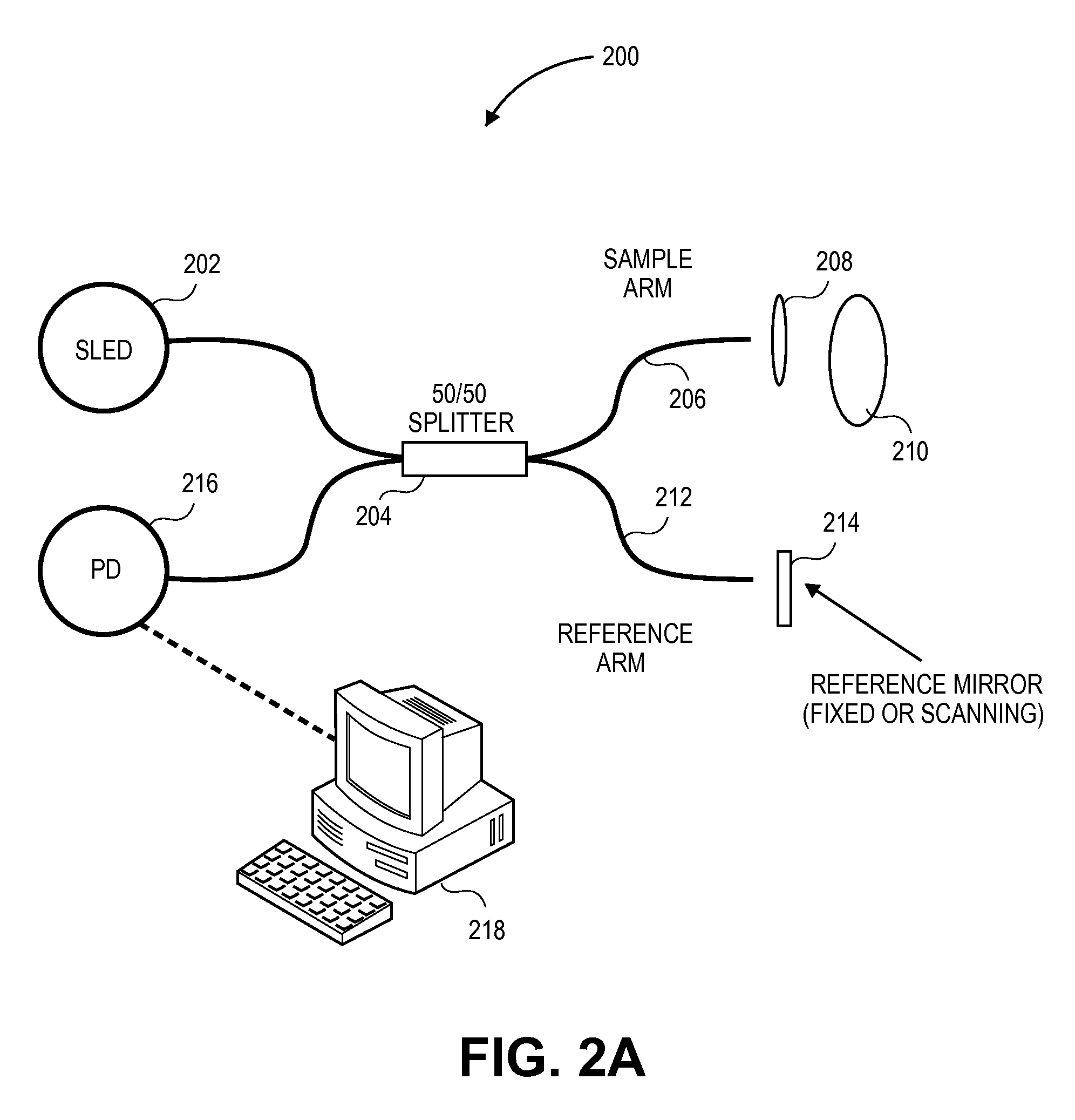
A patient monitor capable of measuring microcirculation at a tissue site includes a light source, a beam splitter, a photodetector and a patient monitor. Light emitted from the light source is split into a reference arm and a sample arm. The light in the sample arm is directed at a tissue site, such as an eyelid. The reflected light from the tissue site is interfered with the light from the reference arm. The photodetector measures the interference of the light from both the sample arm and the reference arm. The patient monitor uses the measurements from the photodetector to calculate the oxygen saturation at the tissue site and monitor the microcirculation at the tissue site.
Owner:MASIMO CORP
Control of an optical fiber scanner
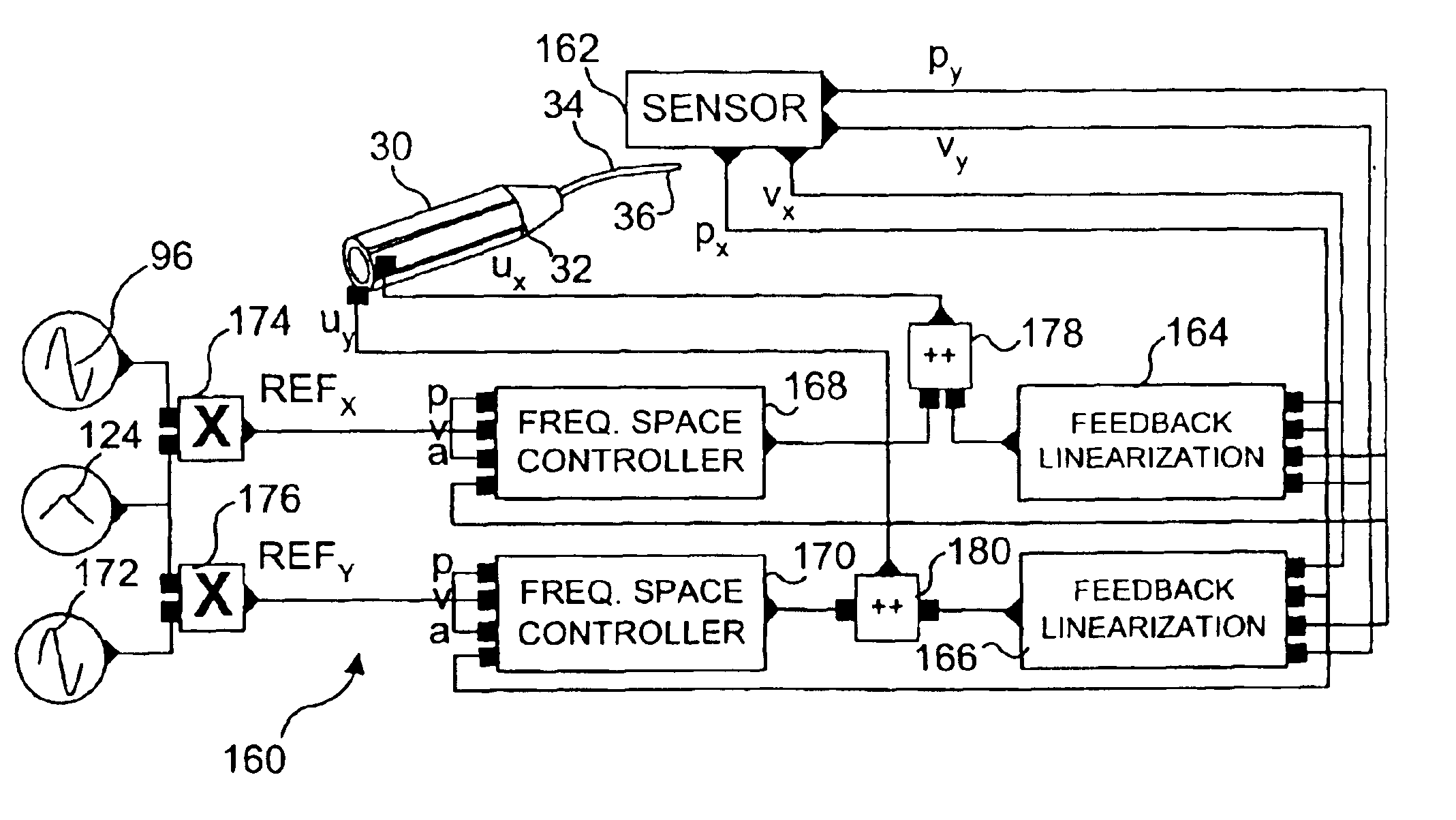
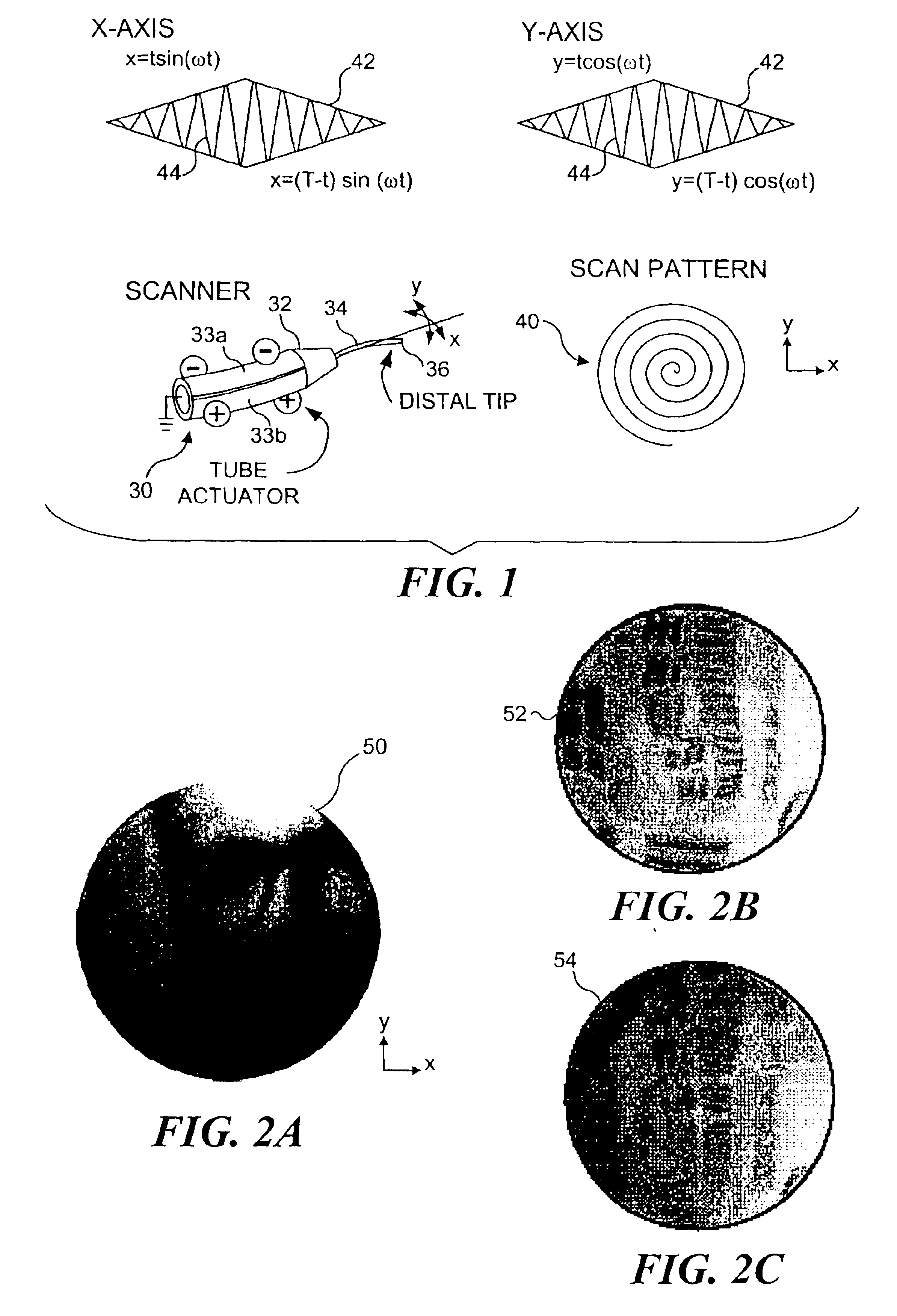
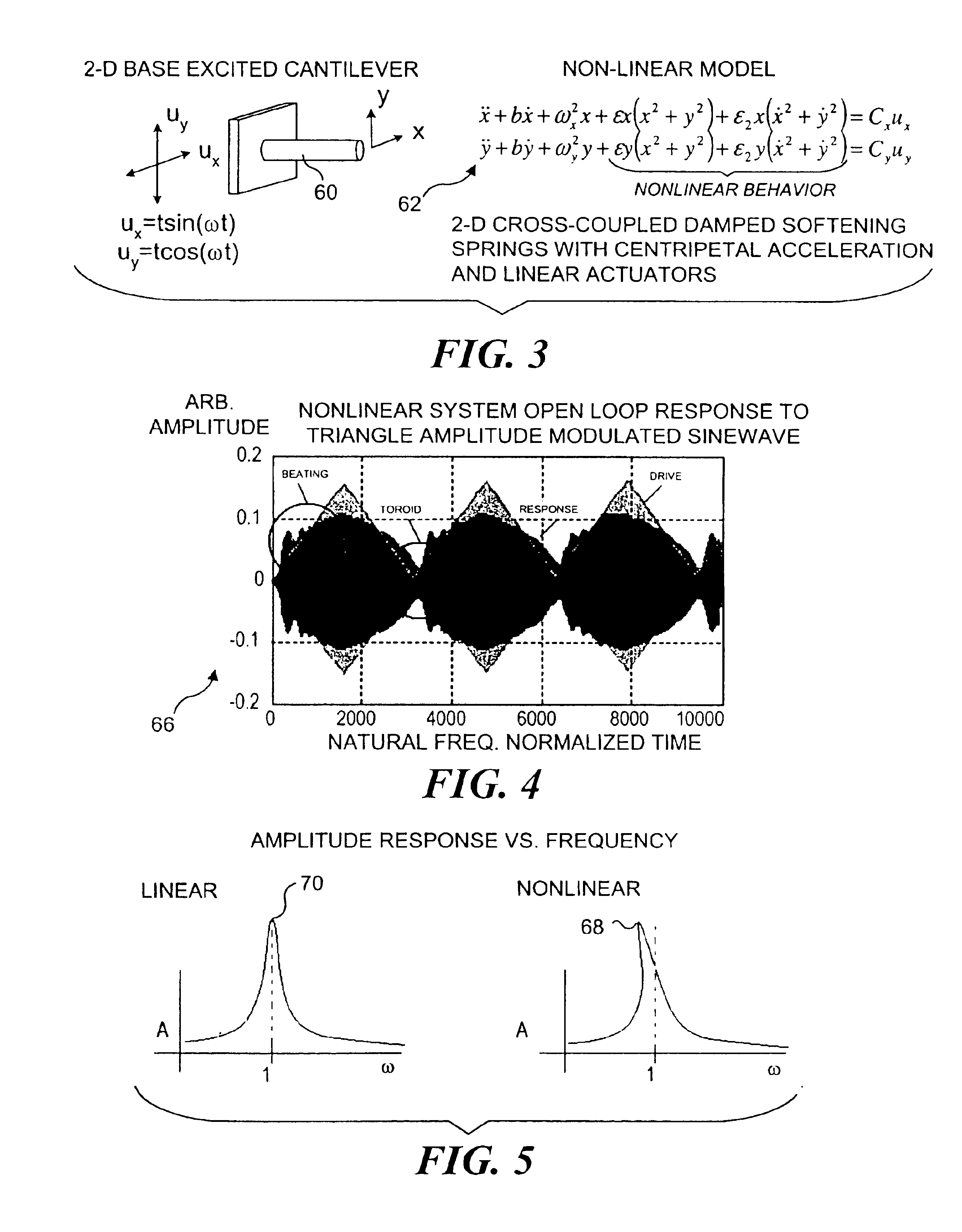
InactiveUS6845190B1Remove nonlinear behaviorRobust cancellationSurgeryEndoscopesOptical scannersPhotodetector
Controls for an optical scanner, such as a single fiber scanning endoscope (SFSE) that includes a resonating optical fiber and a single photodetector to produce large field of view, high-resolution images. A nonlinear control scheme with feedback linearization is employed in one type of control to accurately produce a desired scan. Open loop and closed loops controllers are applied to the nonlinear optical scanner of the SFSE. A closed loop control (no model) uses either phase locked loop and PID controllers, or a dual-phase lock-in amplifier and two PIDs for each axis controlled. Other forms of the control that employ a model use a frequency space tracking control, an error space tracking control, feedback linearizing controls, an adaptive control, and a sliding mode control.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Semiconductor components, in particular photodetectors, light emitting diodes, optical modulators and waveguides with multilayer structures grown on silicon substrates
InactiveUS6403975B1Cost advantagePromote absorptionNanoopticsNon-linear opticsPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
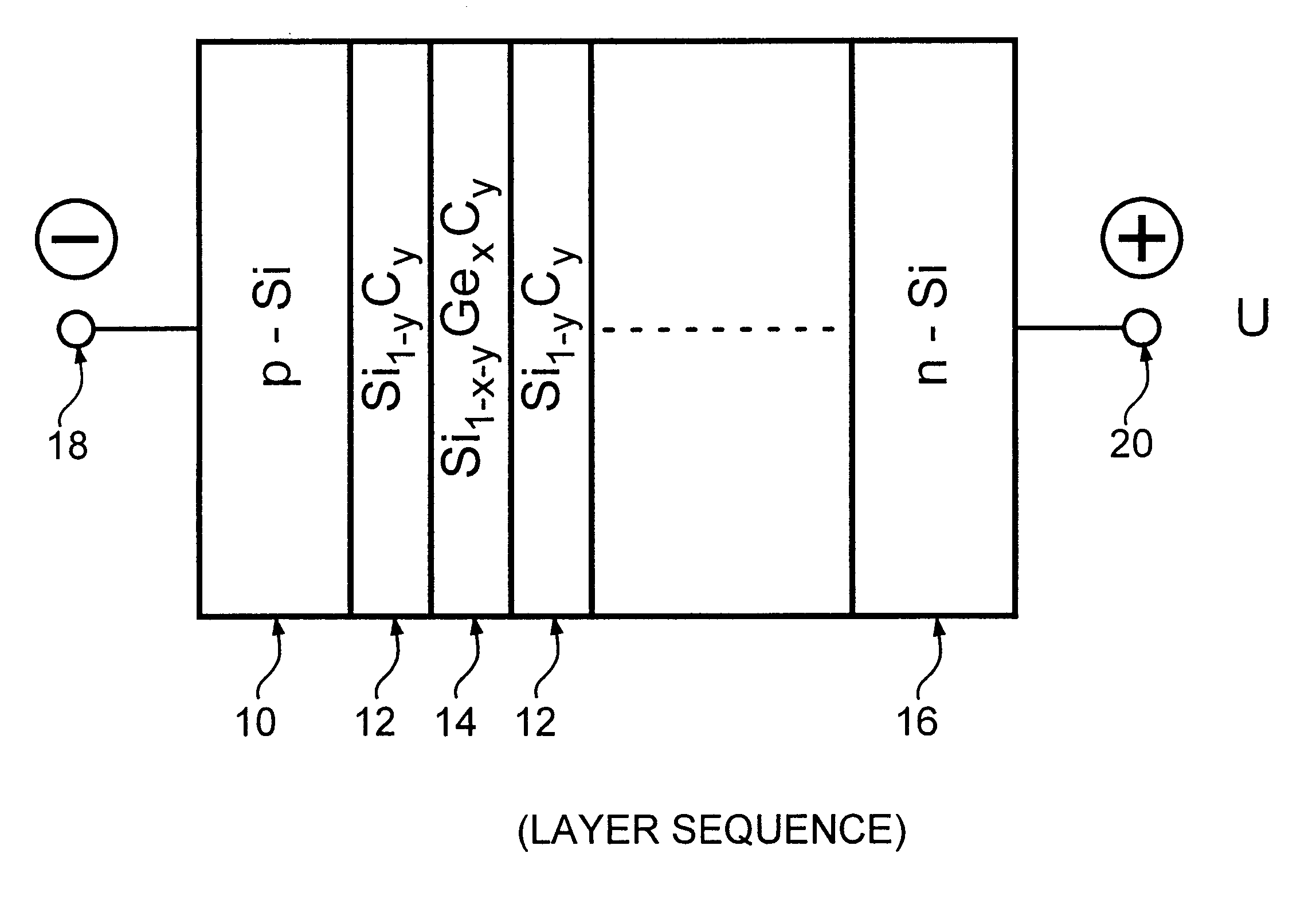
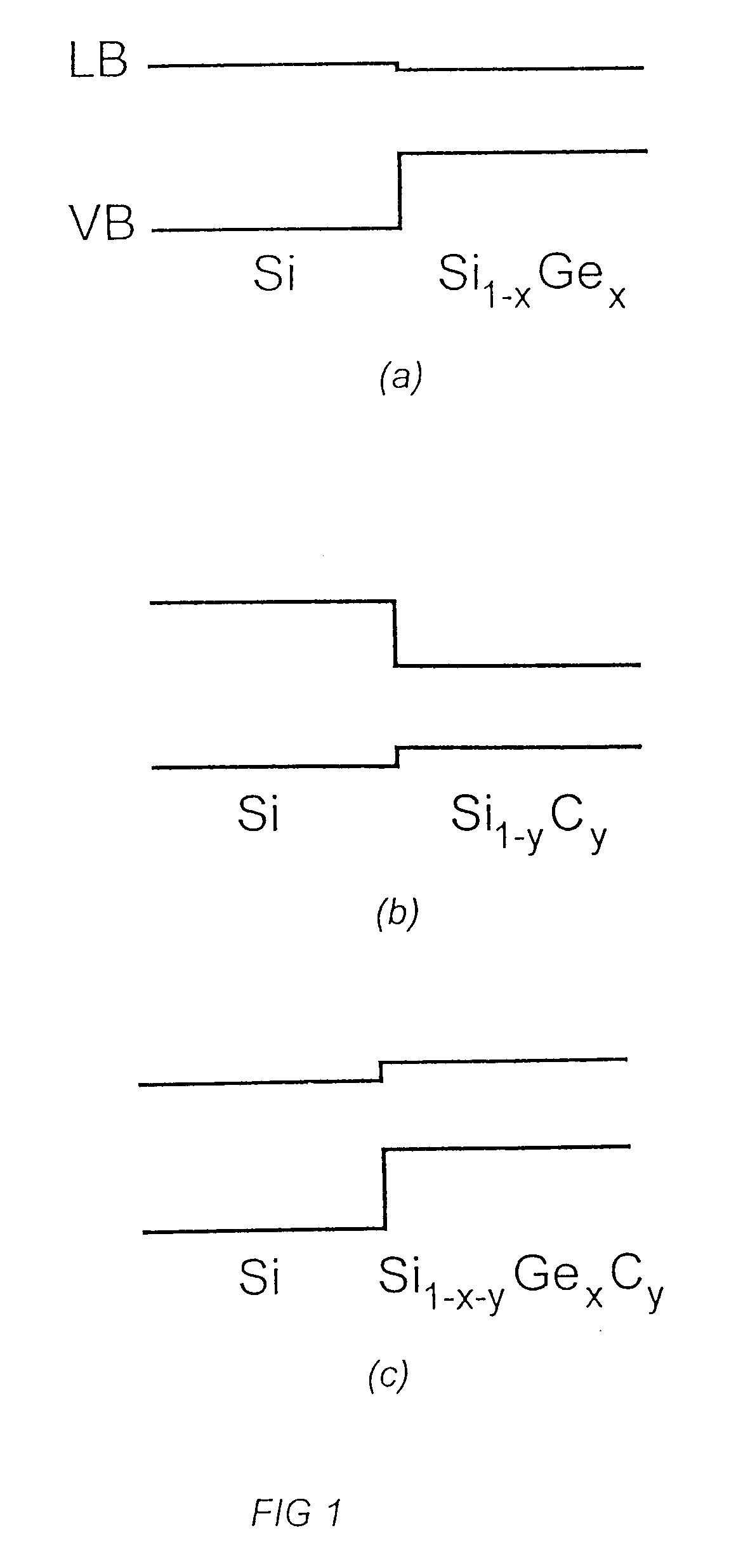
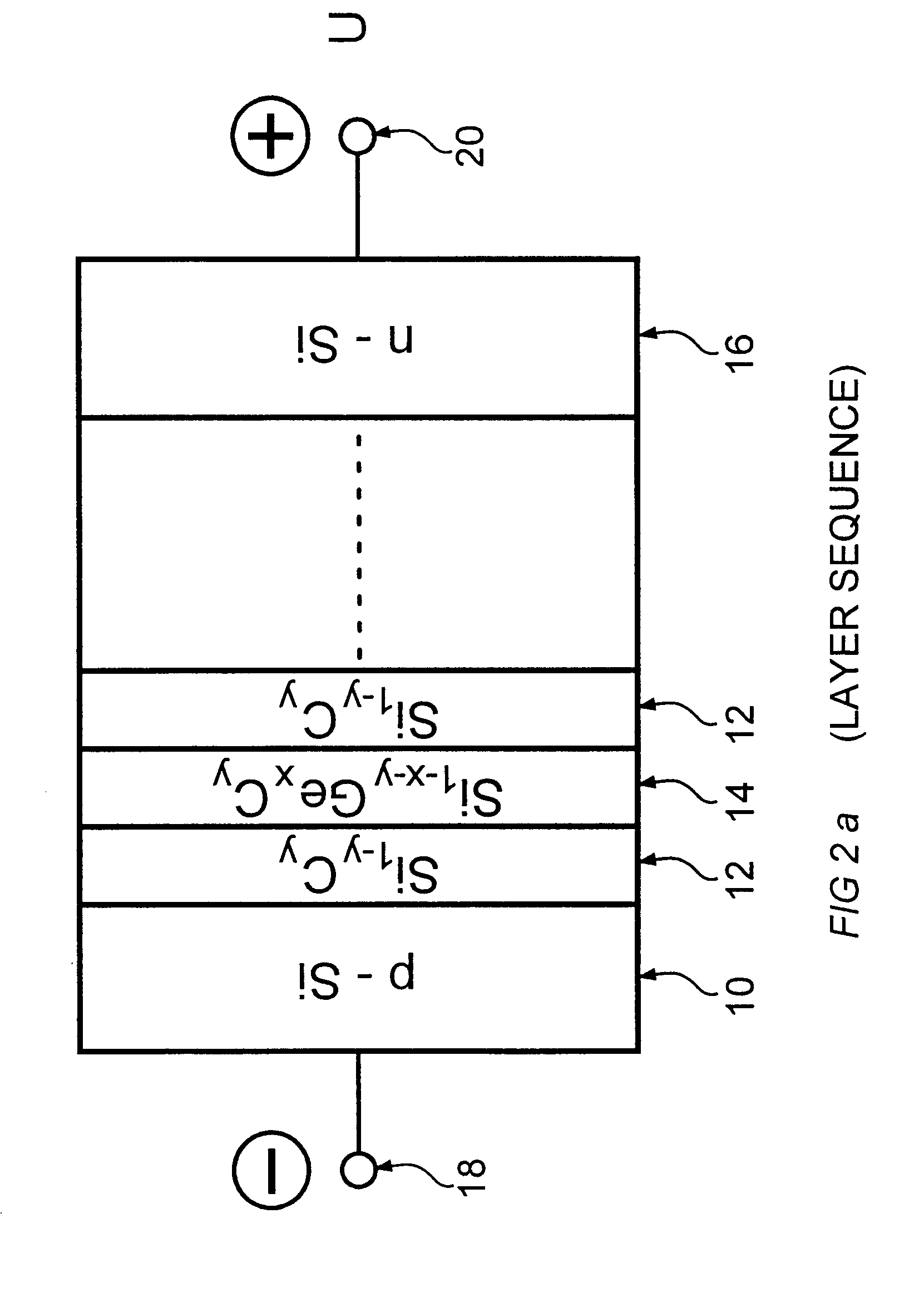
A semiconductor component, selected from the group comprising a photodetector, a light emitting diode, an optical modulator and a waveguide. The semiconductor component comprises an Si substrate, an active region formed on said substrate, and an Si capping layer on said active region. In one embodiment the active region is a superlattice comprising alternating layers of Si1-yCy and Si1-x-yGexCy, with the atomic fraction y of the Si1-x-yGexCy layers being equal to or different from the atomic fraction y of the Si1-yCy layers. In another embodiment it is a superlattice comprising a plurality of periods of a three-layer structure comprising Si, Si1-yCy and Si1-xGex layers. In a third embodiment it is a superlattice comprising a plurality of periods of a three-layer structure comprising Si, Si1-yCy and Si1-x-yGexCy layers, with the atomic fraction y of the Si1-x-yGexCy layers being equal to or different from the atomic fraction y of the Si1-yCy layers. The components have faborable optical and electrical properties and are suitable for integration on a Si substrate.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
Near infrared spectroscopy device with reusable portion
InactiveUS7706853B2Small sizeFirmly attachedMaterial analysis by optical meansDiagnostic recording/measuringSurgical operationHigh energy
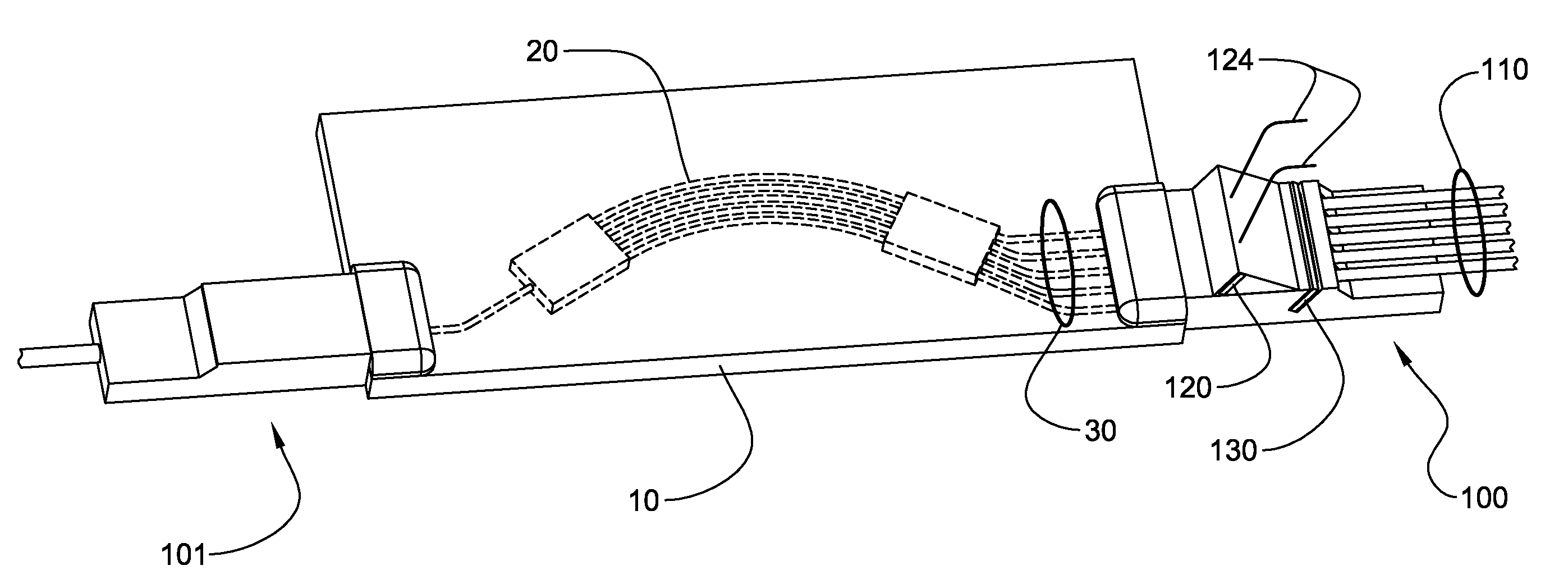
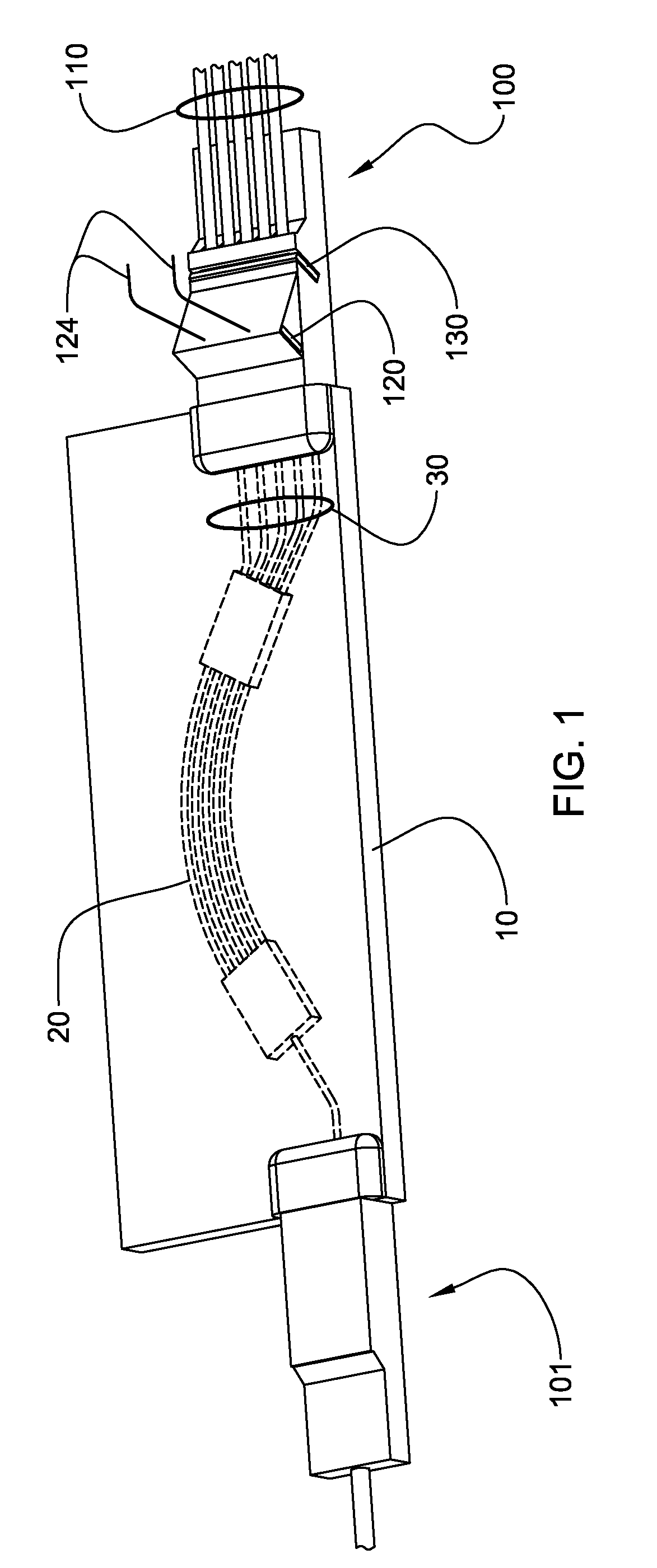
A NIRS sensor device for brain monitoring is small in size, provides reliable attachment to a patient, blocks ambient light, is easy to use, is hygienic, and supports data integration with surgical and monitoring systems. The sensor device is coupled to a remote near infrared light source via a hybrid cable. Since the light source is remotely located, a source adapted for providing high energy, short pulses can easily be used so that there is less chance of interference by superficial non-brain tissues and less interference from ambient light. In addition, the remote location avoids changes in output of local light sources experienced in the prior art during hypothermia procedures (e.g., bandwidth shifts in LEDs as a result of lowered temperature). The higher energy may be achieved by the use of laser diodes as opposed to locally-mounted LEDs typically used in the prior art. The sensor device is a two-piece design comprising a reusable portion containing the photodetector(s) and a disposable portion that receives the light from the reusable portion and bends it to direct the light into the brain.
Owner:TERUMO CARDIOVASCULAR SYST CORP
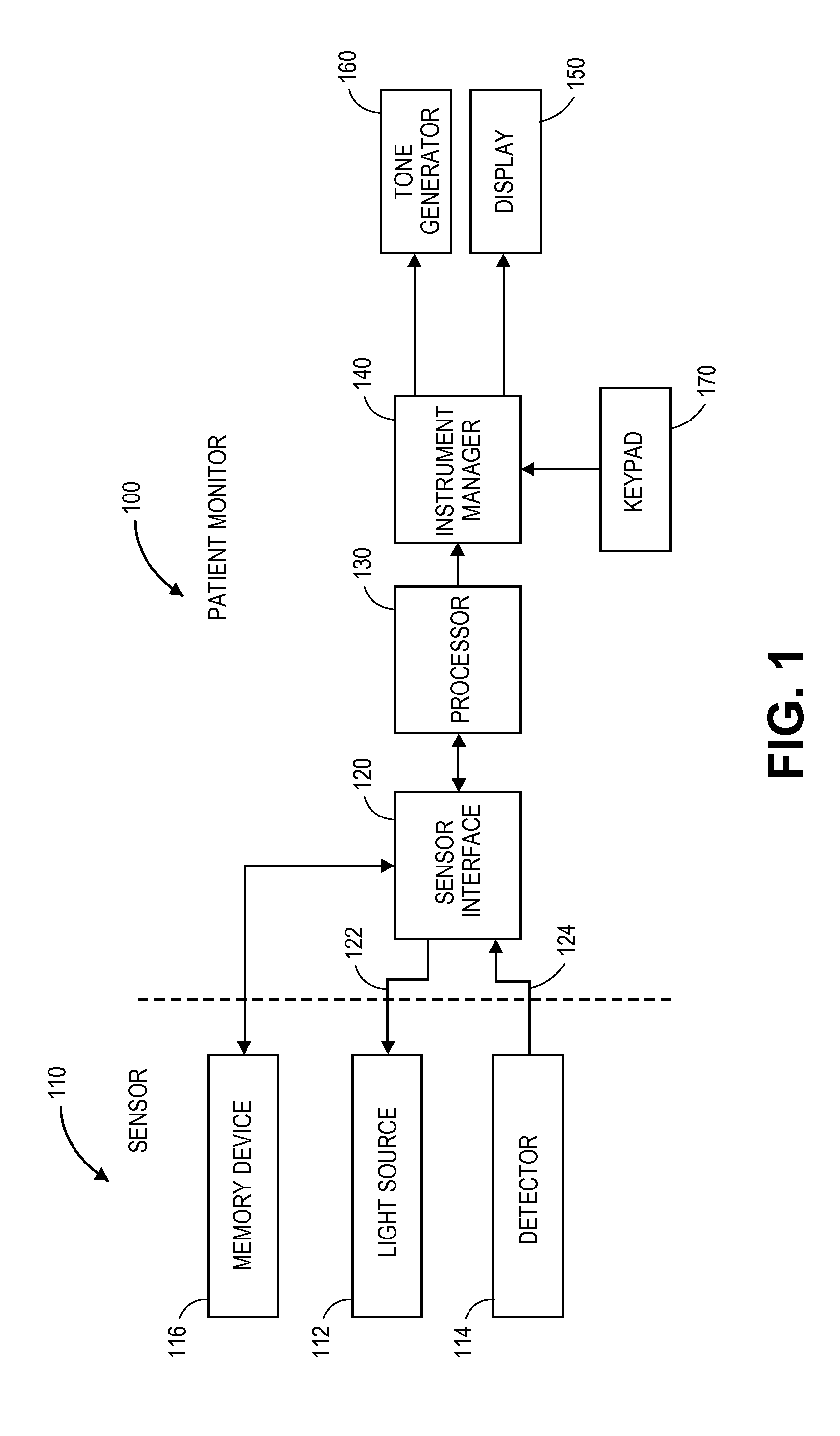
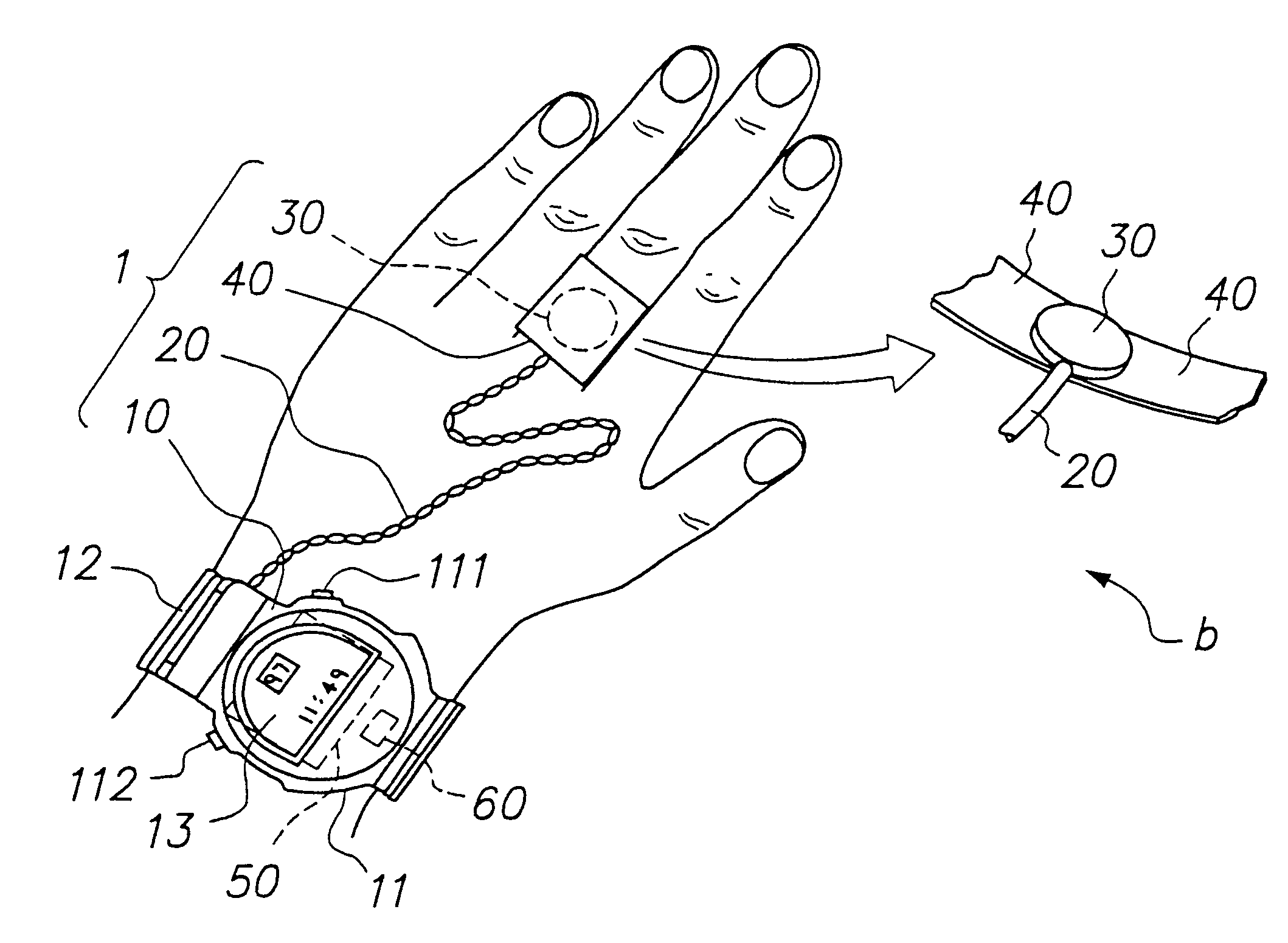
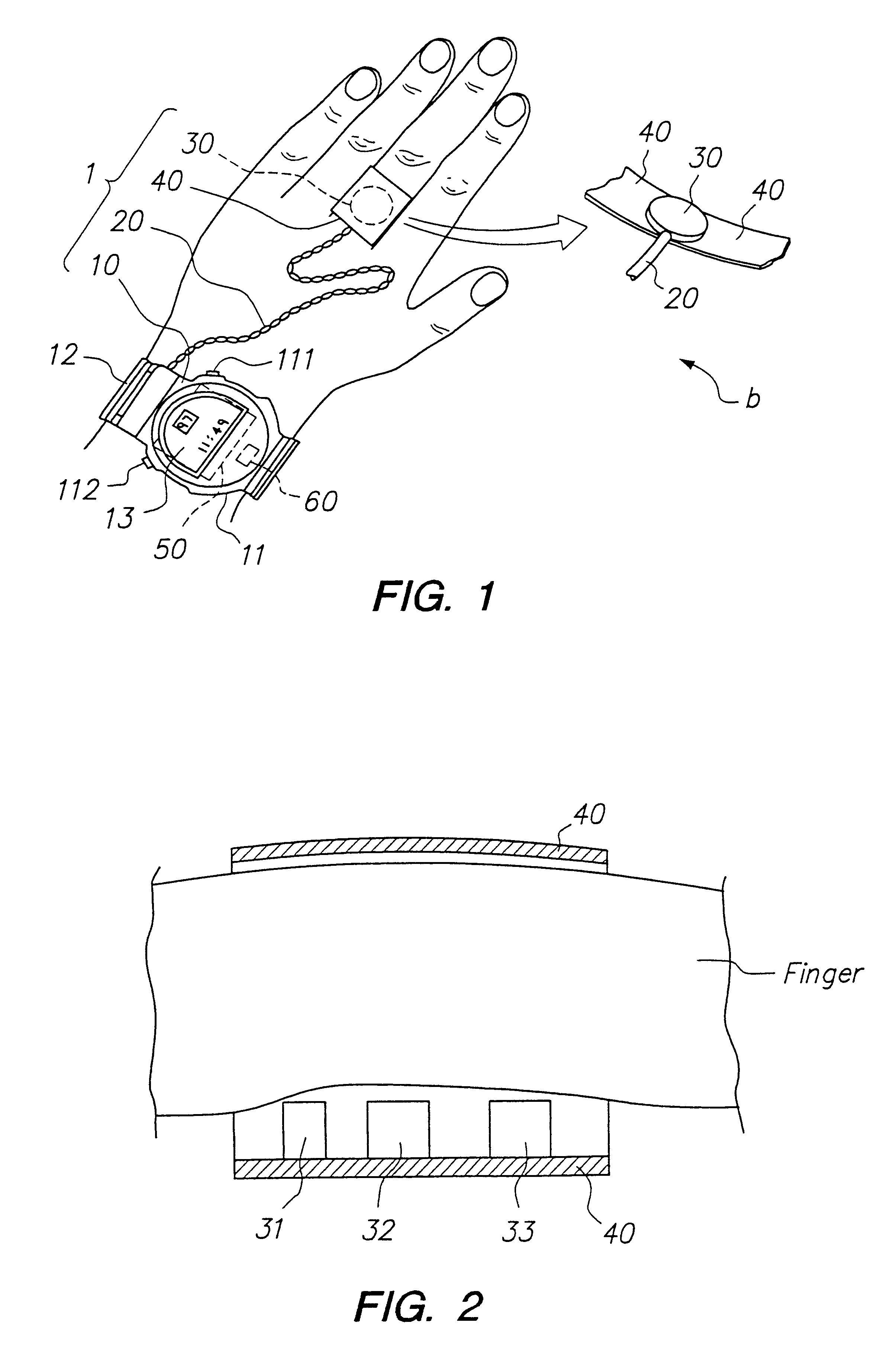
Reflection photodetector and biological information measuring instrument
InactiveUS6198951B1Inertial sensorsMeasuring/recording heart/pulse ratePower flowAudio power amplifier
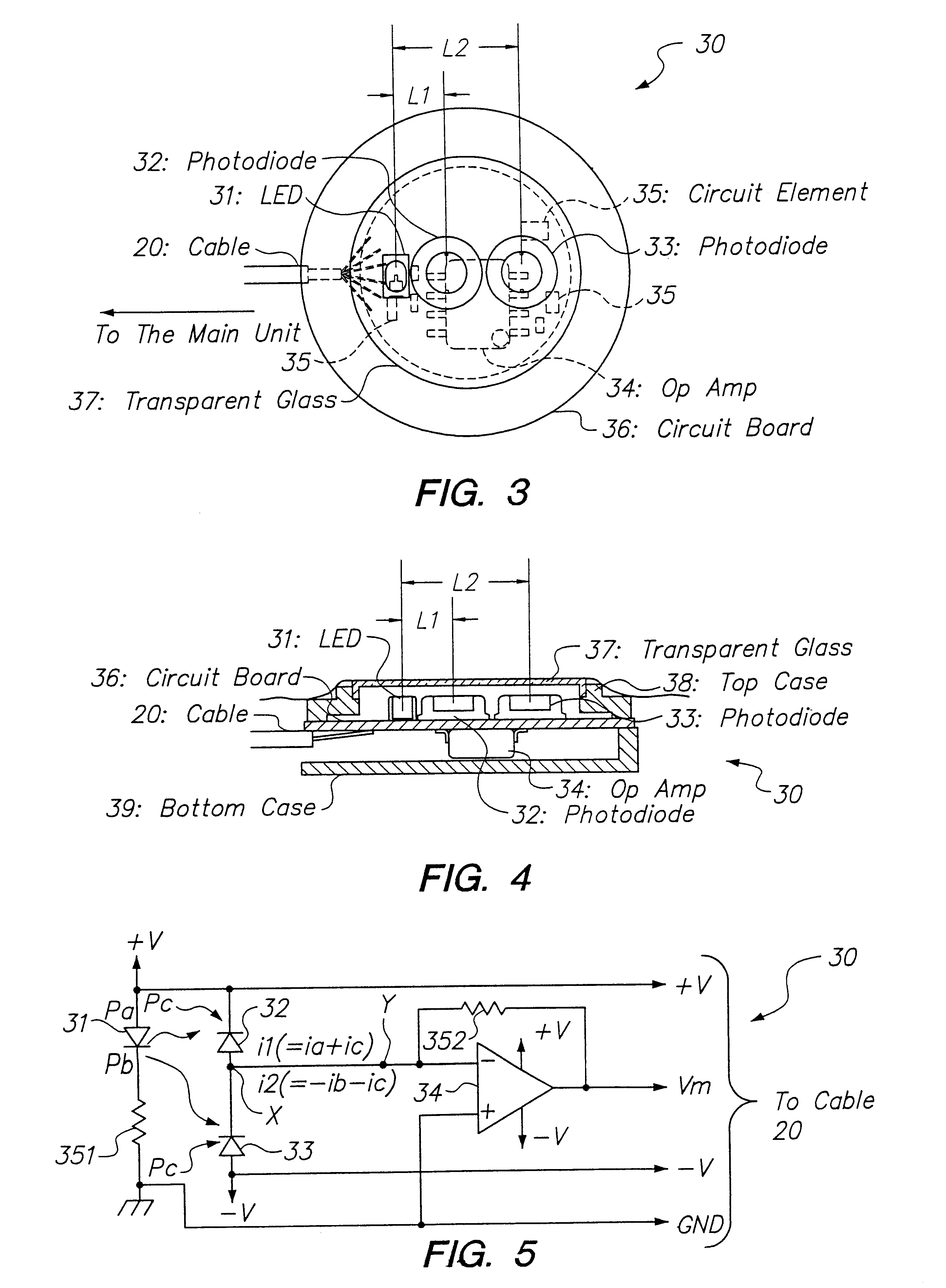
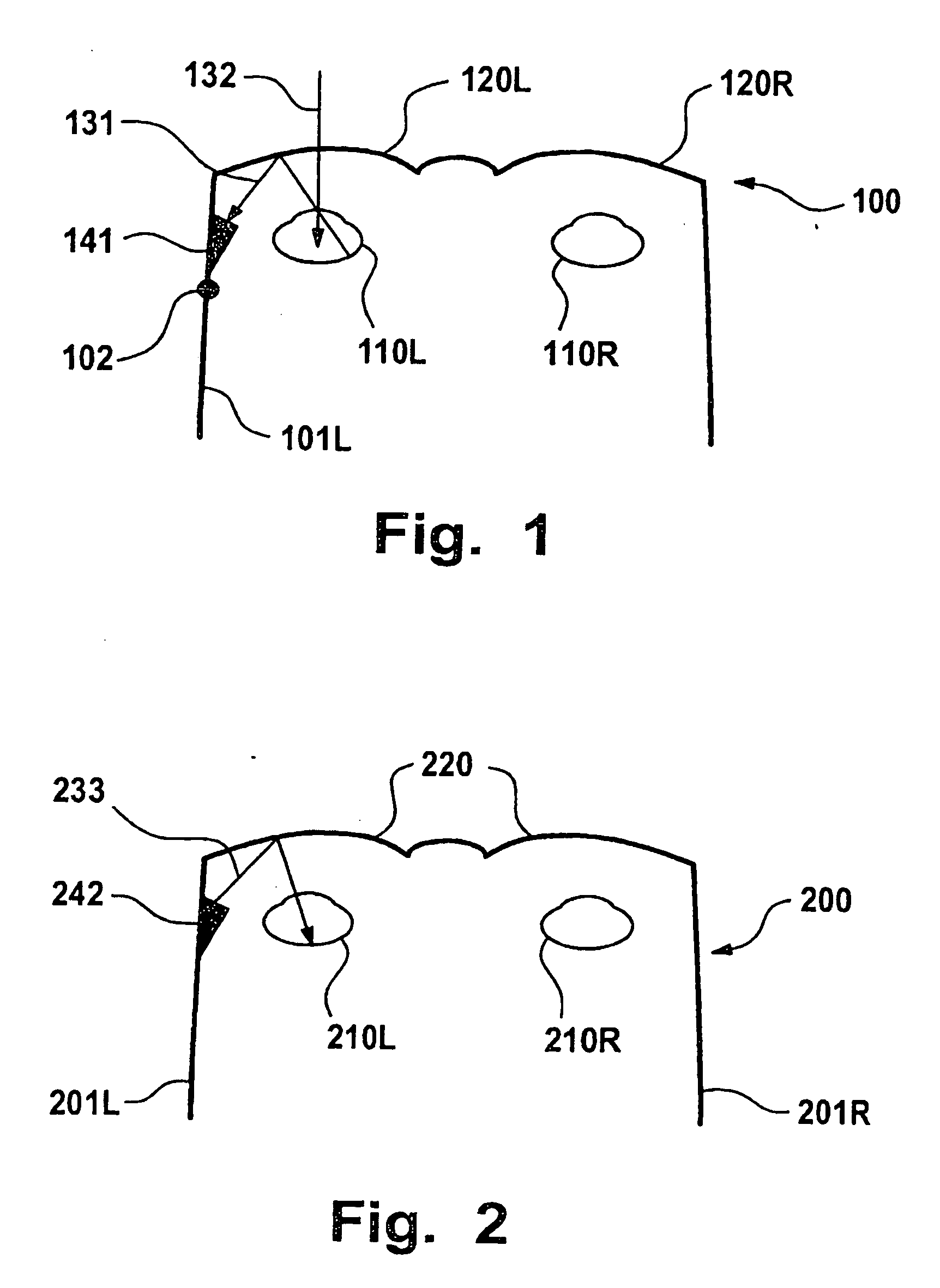
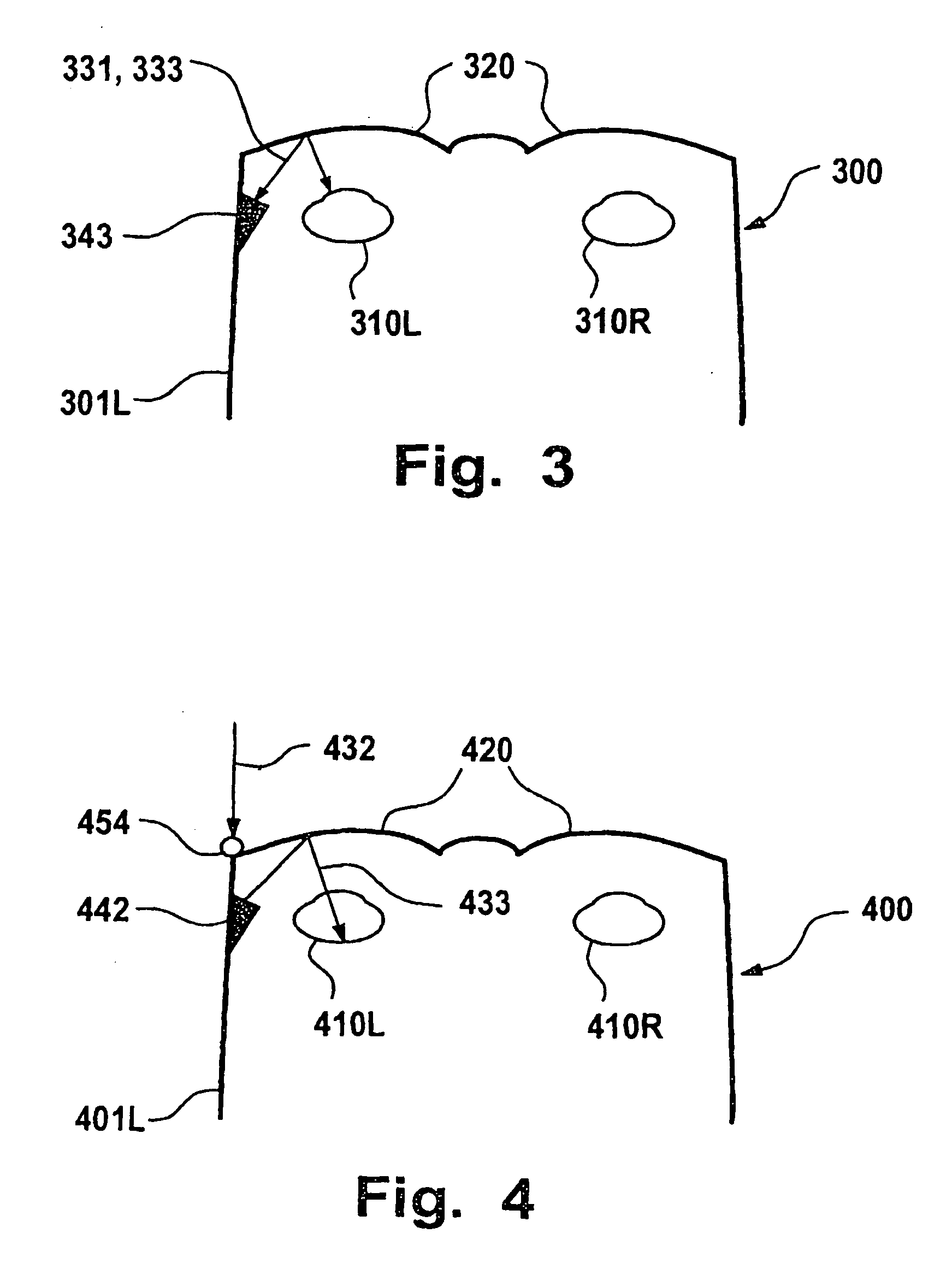
When emitted light from LED 31 is incident on photodiodes 32 and 33 with luminance Pa and Pb, currents ia and ib are generated according to luminance Pa and Pb. When outside light is incident through the finger tissues on photodiodes 32 and 33 with luminance Pc, current ic is produced. The current i1 (=ia+ic) generated by photodiode 32, and the current i2 (=-ib-ic) generated by photodiode 33, are added at node X, and the current ic corresponding to outside light is thus cancelled. In addition, photodiodes 32 and 33 are disposed at different distances from LED 31. As a result, the current flowing to opamp 34 is current ia corresponding to luminance Pa because luminance Pb is extremely low. The opamp 34 then applies a current voltage conversion to generate pulse wave signal Vm.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Small-scale, vital-signs monitoring device, system and method
InactiveUS20050228244A1Quick measurementLow costEvaluation of blood vesselsCatheterPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
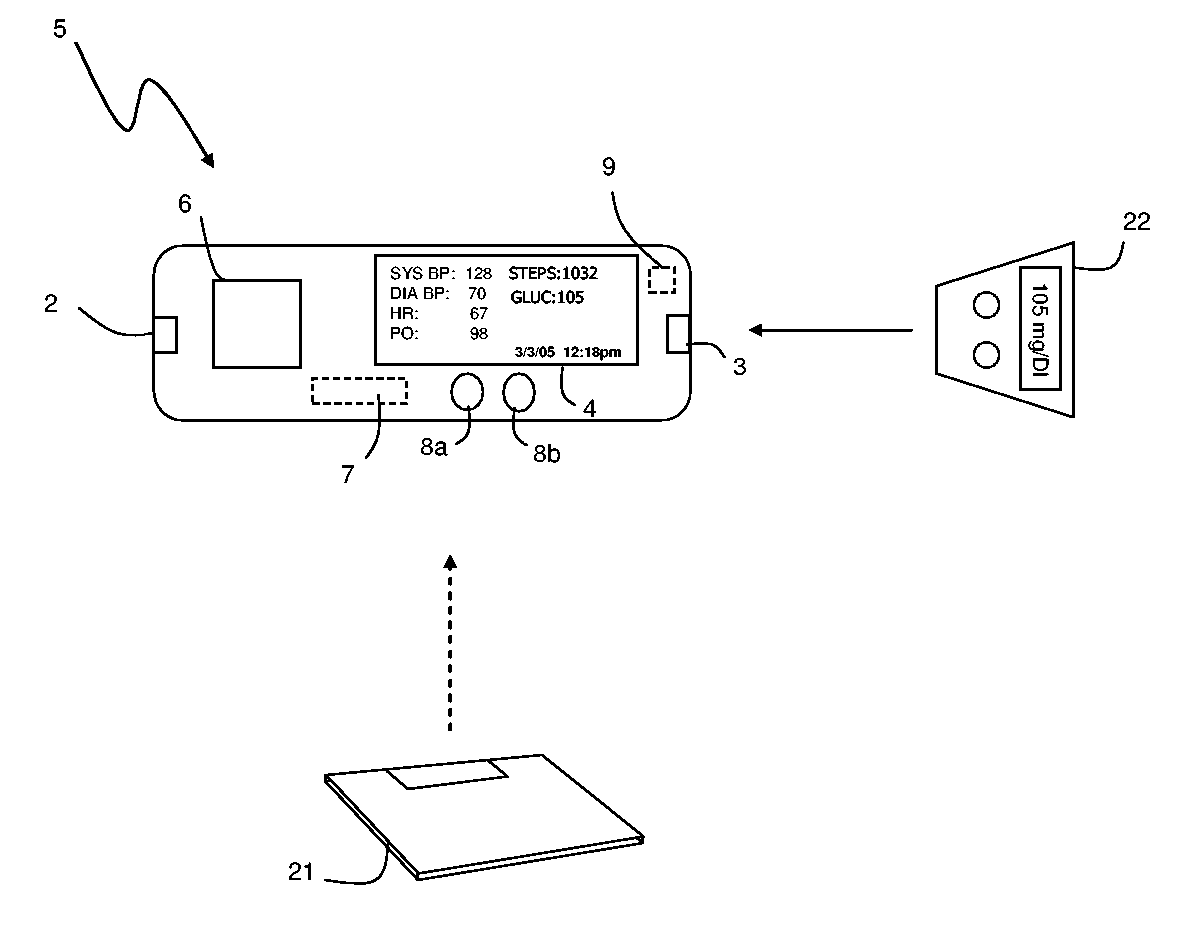
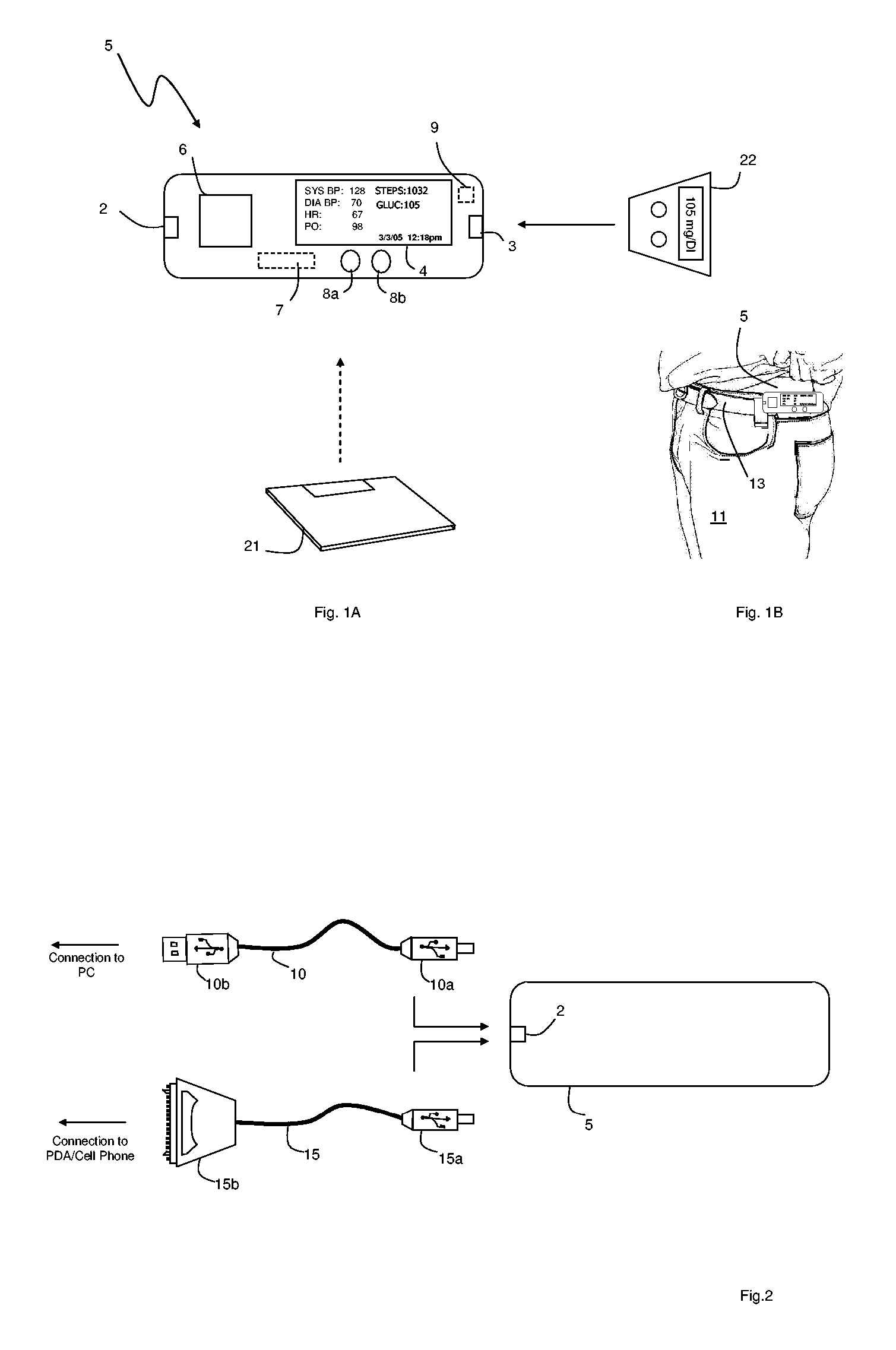
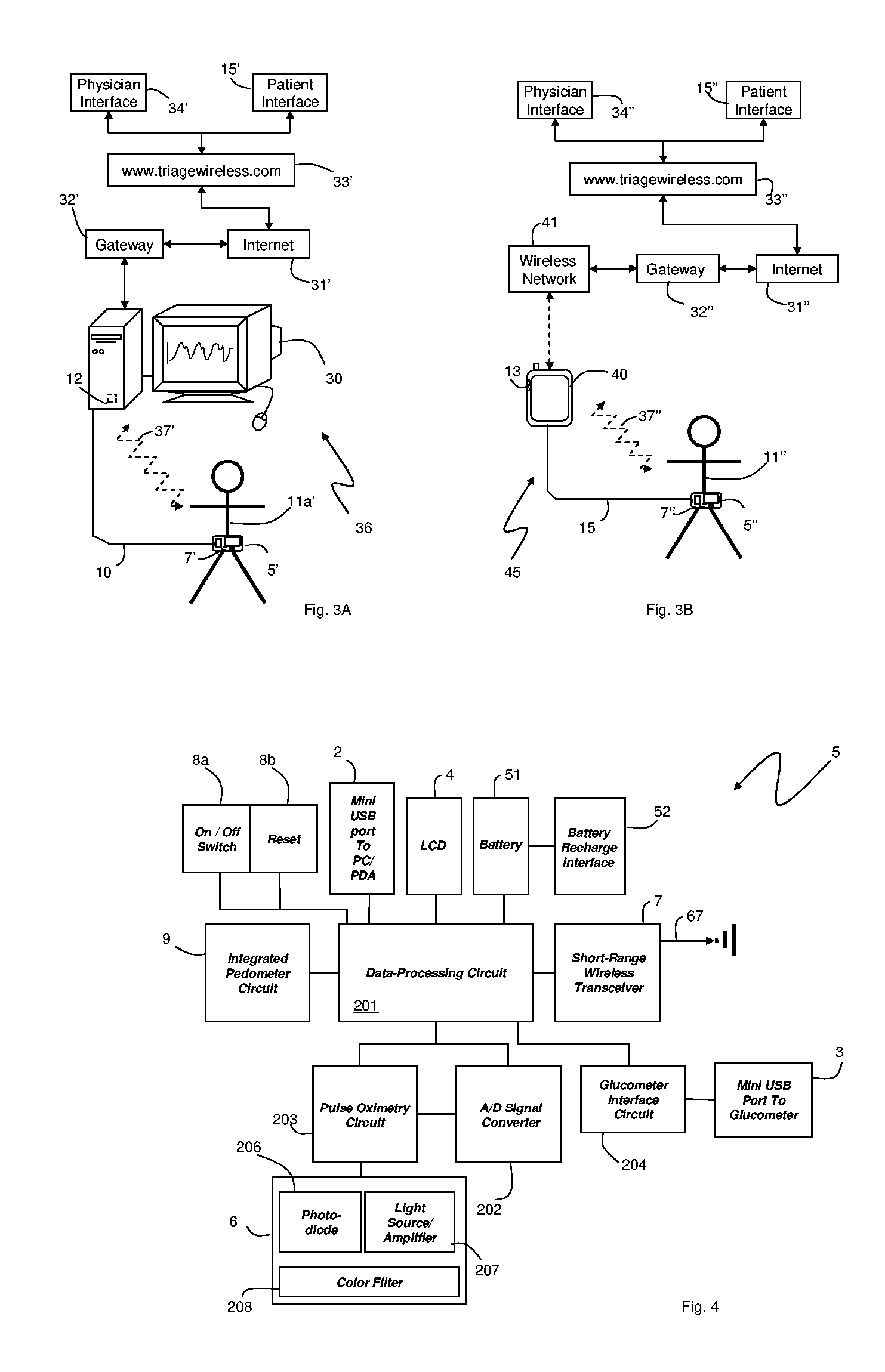
The invention provides a monitoring device featuring: 1) a housing having a first surface; 2) a sensor pad, positioned on the first surface, that includes a first LED emitting red light, a second LED emitting infrared light, and a photodetector; 3) a data-processing circuit that analyzes a signal from the photodetector to generate a blood pressure value; and 4) means for transmitting the blood pressure value to an external device.
Owner:TRIAGE WIRELESS
LED light communication system
InactiveUS20080310850A1Easy to transportFirmly connectedPower distribution line transmissionElectric/electromagnetic visible signallingTransceiverPhotovoltaic detectors
An LED light and communication system includes at least one optical transceiver, the optical transceiver including a light support and a processor. The light support has a plurality of light emitting diodes and at least one photodetector attached thereto, the light emitting diodes receiving power from a power source. The processor is in communication with the light emitting diodes and the at least one photodetector, the processor capable of illuminating the light emitting diodes to simultaneously create at least one first light signal, and at least one second light signal, the first light signal being observable to the unaided eyes of an individual and the second light signal not being observable to the unaided eyes of the individual. The second light signal includes at least one data packet. The at least one data packet comprises global positioning system (GPS) location information.
Owner:FEDERAL LAW ENFORCEMENT DEV SERVICES
Two-part patch sensor for monitoring vital signs
ActiveUS20080114220A1Quick measurementLittle and no discomfortUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsElectrocardiographyOptical radiationPhotodetector
A two-component monitoring device and system for monitoring blood pressure from a patient is disclosed herein. The two-component monitoring device includes a disposable component and a main component. The disposable component features: i) a backing structure having a first aperture; and ii) first and second electrodes, each electrode connected to the backing structure and including an electrical lead and a conductive electrode material, and configured to generate an electrical signal that passes through the electrical lead when the conductive electrode material contacts the patient. The main component includes: i) first and second connectors configured to connect to the first and second electrical leads to receive the first and second electrical signals; and ii) an optical component comprising a light source that generates optical radiation and a photodetector that detects the optical radiation. The optical component inserts into the first aperture of the disposable component. The main component optionally includes an acoustic sensor. The system utilizes a processing device, connected to the monitoring device by a cable which receives and processes a plurality of signals to determine real-time blood-pressure values for the patient.
Owner:SOTERA WIRELESS
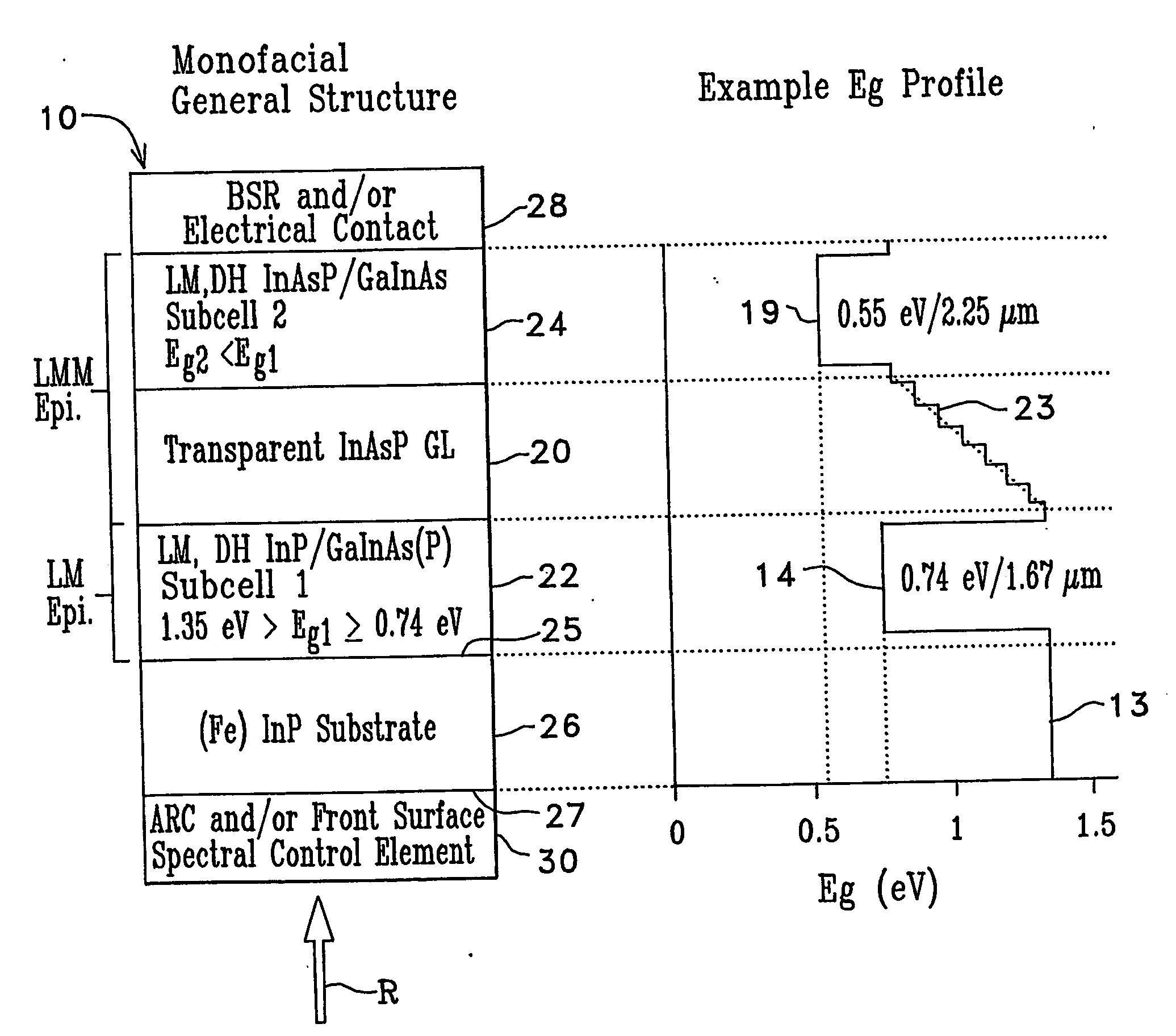
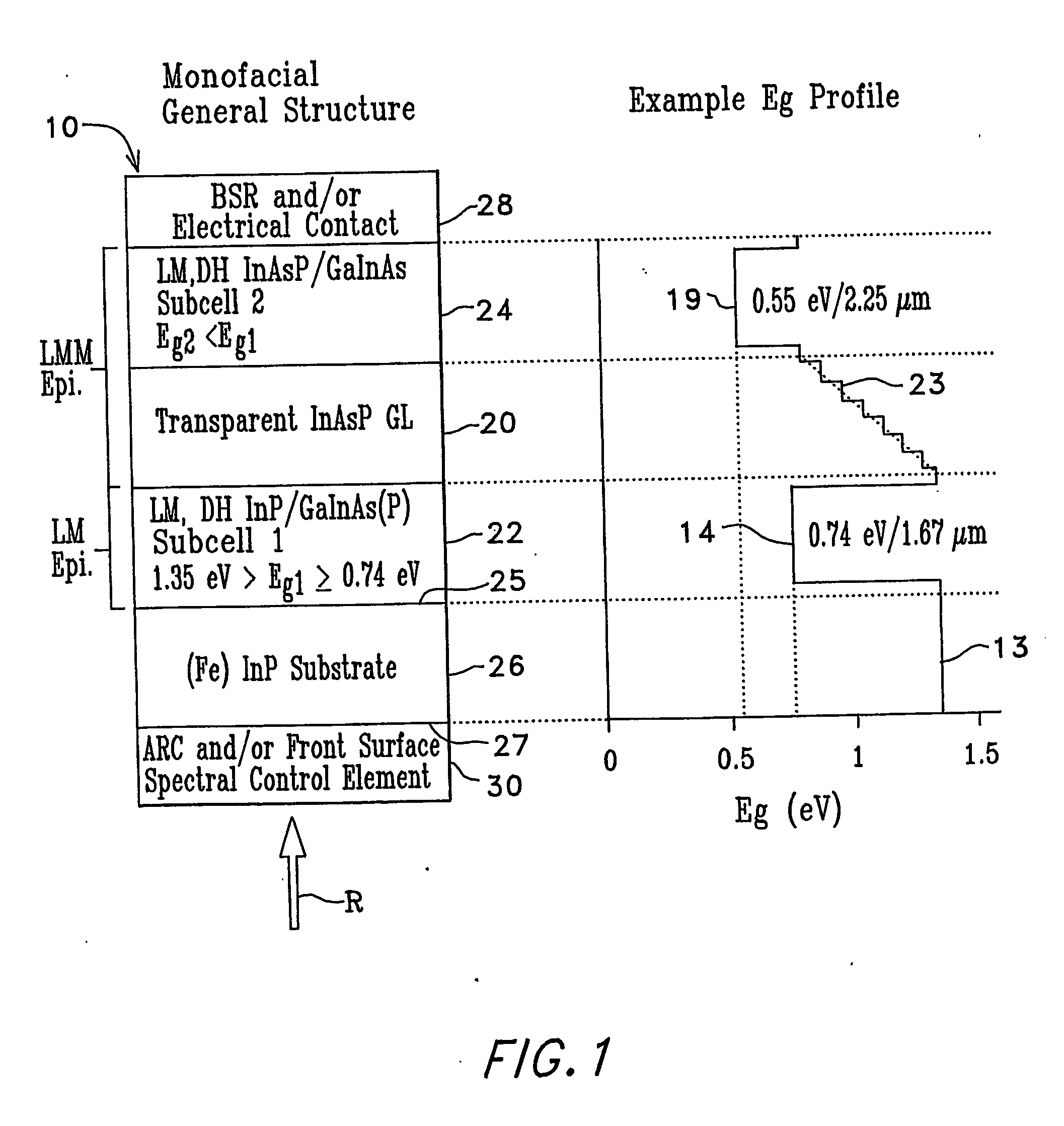
Low bandgap, monolithic, multi-bandgap, optoelectronic devices
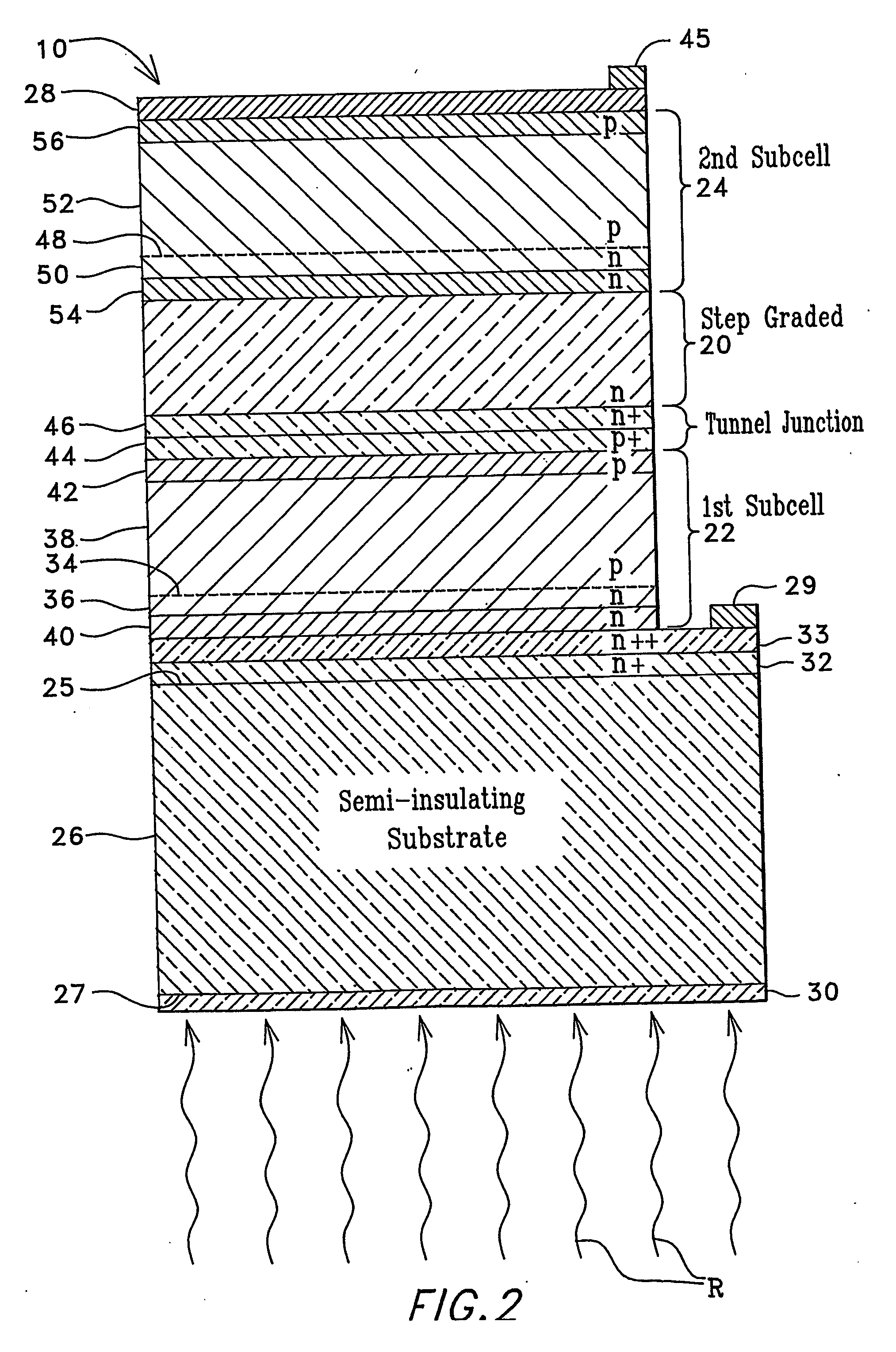
InactiveUS20060162768A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic energy generationPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
Low-bandgap, monolithic, multi-bandgap, optoelectronic devices (10), including PV converters, photodetectors, and LED's, have lattice-matched (LM), double-heterostructure (DH), low-bandgap GaInAs(P) subcells (22, 24) including those that are lattice-mismatched (LMM) to InP, grown on an InP substrate (26) by use of at least one graded lattice constant transition layer (20) of InAsP positioned somewhere between the InP substrate (26) and the LMM subcell(s) (22, 24). These devices are monofacial (10) or bifacial (80) and include monolithic, integrated, modules (MIMs) (190) with a plurality of voltage-matched subcell circuits (262, 264, 266, 270, 272) as well as other variations and embodiments.
Owner:ALLIANCE FOR SUSTAINABLE ENERGY
Camera Adapter Based Optical Imaging Apparatus
ActiveUS20110043661A1Cancel noiseLow costTelevision system detailsInterferometersSpectral bandsFrequency spectrum
The invention describes several embodiments of an adapter which can make use of the devices in any commercially available digital cameras to accomplish different functions, such as a fundus camera, as a microscope or as an en-face optical coherence tomography (OCT) to produce constant depth OCT images or as a Fourier domain (channelled spectrum) optical coherence tomography to produce a reflectivity profile in the depth of an object or cross section OCT images, or depth resolved volumes. The invention admits addition of confocal detection and provides simultaneous measurements or imaging in at least two channels, confocal and OCT, where the confocal channel provides an en-face image simultaneous with the acquisition of OCT cross sections, to guide the acquisition as well as to be used subsequently in the visualisation of OCT images. Different technical solutions are provided for the assembly of one or two digital cameras which together with such adapters lead to modular and portable high resolution imaging systems which can accomplish various functions with a minimum of extra components while adapting the elements in the digital camera. The cost of such adapters is comparable with that of commercial digital cameras, i.e. the total cost of such assemblies of commercially digital cameras and dedicated adapters to accomplish high resolution imaging are at a fraction of the cost of dedicated stand alone instruments. Embodiments and methods are presented to employ colour cameras and their associated optical sources to deliver simultaneous signals using their colour sensor parts to provide spectroscopic information, phase shifting inferometry in one step, depth range extension, polarisation, angular measurements and spectroscopic Fourier domain (channelled spectrum) optical coherence tomography in as many spectral bands simultaneously as the number of colour parts of the photodetector sensor in the digital camera. In conjunction with simultaneous acquistion of a confocal image, at least 4 channels can simultaneously be provided using the three color parts of conventional color cameras to deliver three OCT images in addition to the confocal image.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF KENT
LED array package with internal feedback and control
ActiveUS7252408B2Electric circuit arrangementsLighting heating/cooling arrangementsDriver circuitElectricity
A packaged LED array for high temperature operation comprises a metal base, the metal base including an underlying thermal connection pad. One or more layers of ceramic overly the metal base. The array includes a plurality of LED dice, each LED die having electrodes. And, the LED thermally coupled to the metal base. A driver circuit is electrically connected to the LED die electrodes and controls the LED array current. An LED driver is mounted within the LED array package, and thermally coupled to the metal base. In a second embodiment, one or more of the LED dice can be switched from the driver to a measurement circuit and used as a photodetector to measure the light output of the LED array. The measured photodetector signal can further be used as a feedback signal to control the LED array light output.
Owner:LIGHTING SCI GROUP
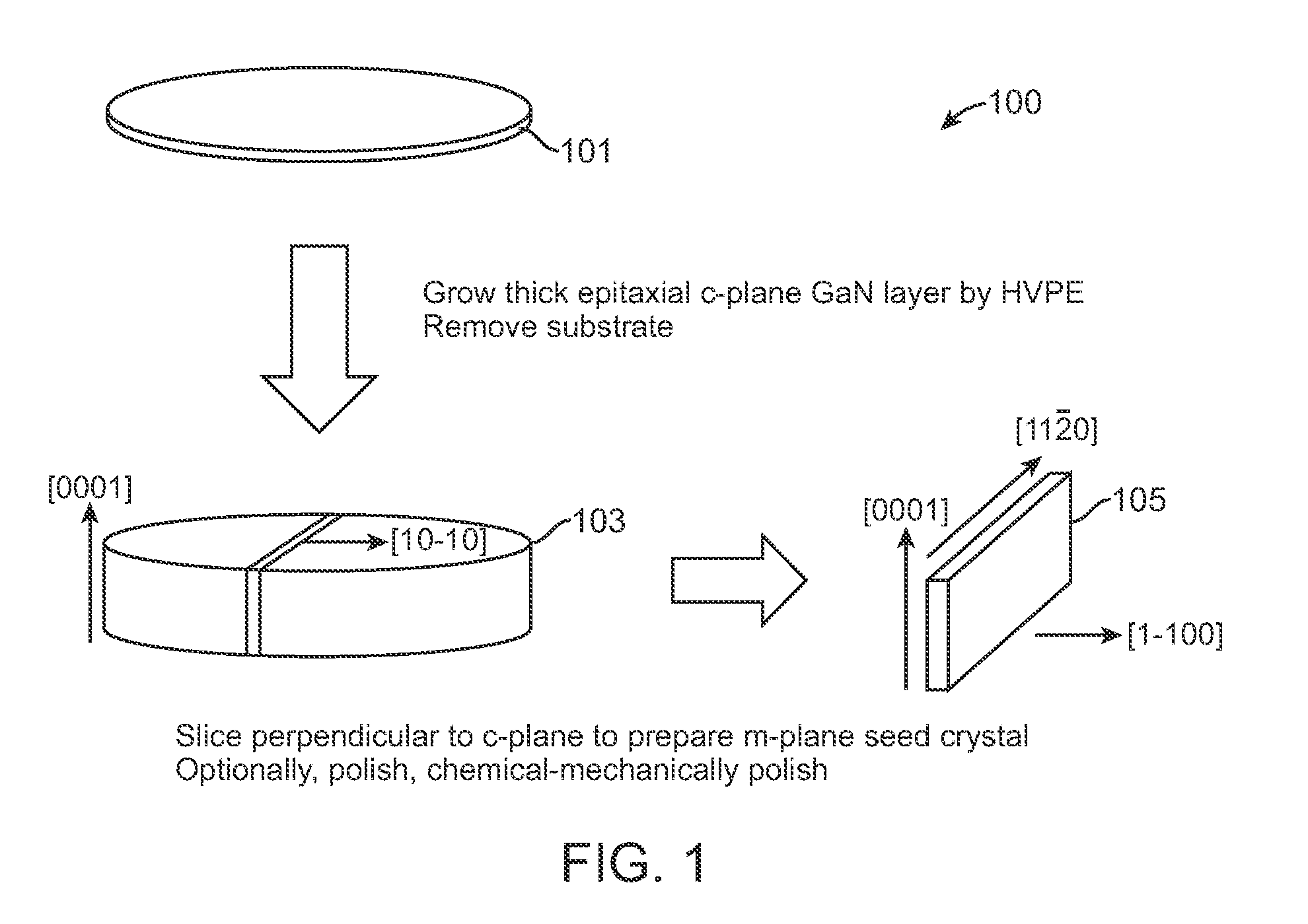
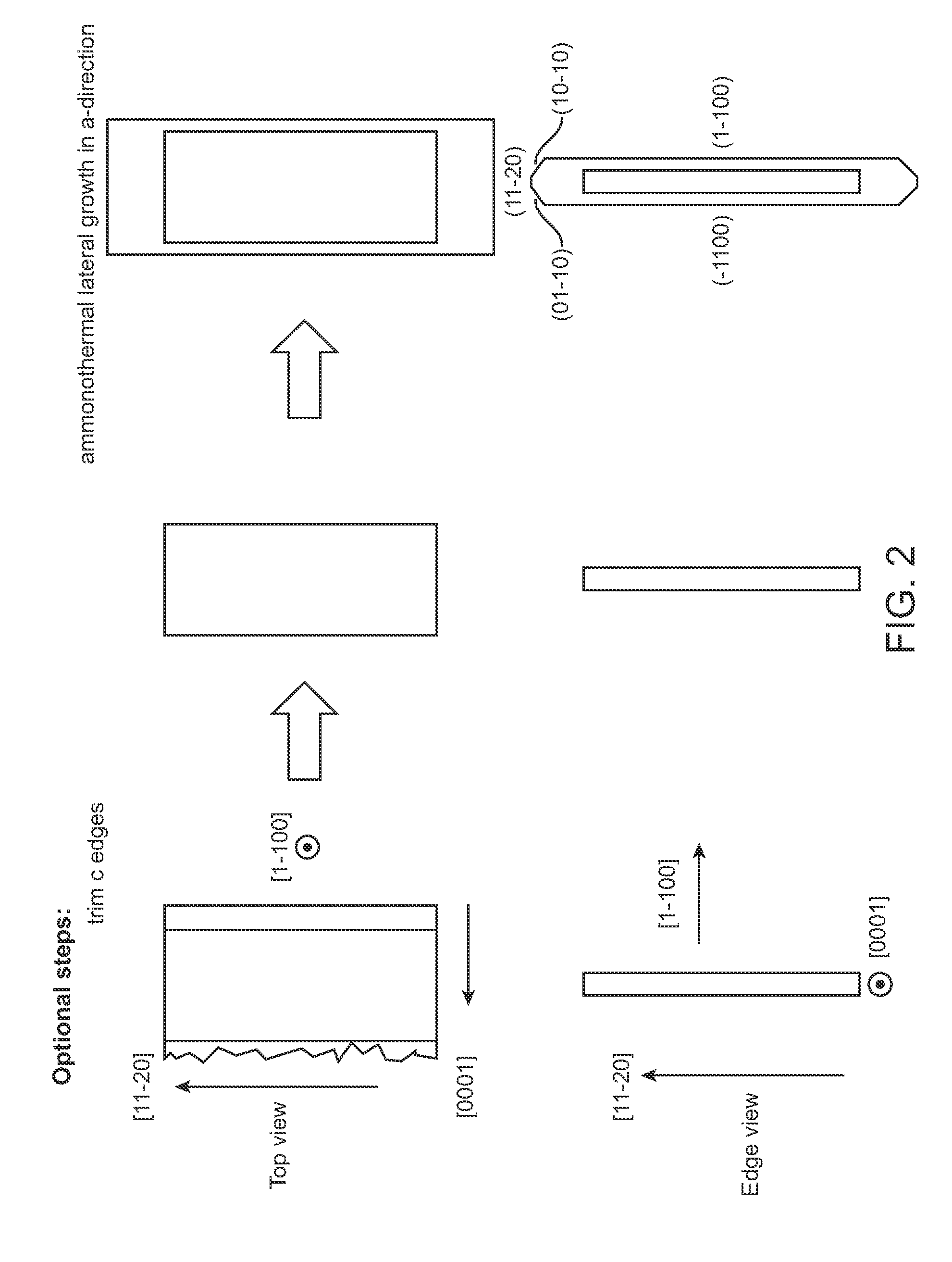
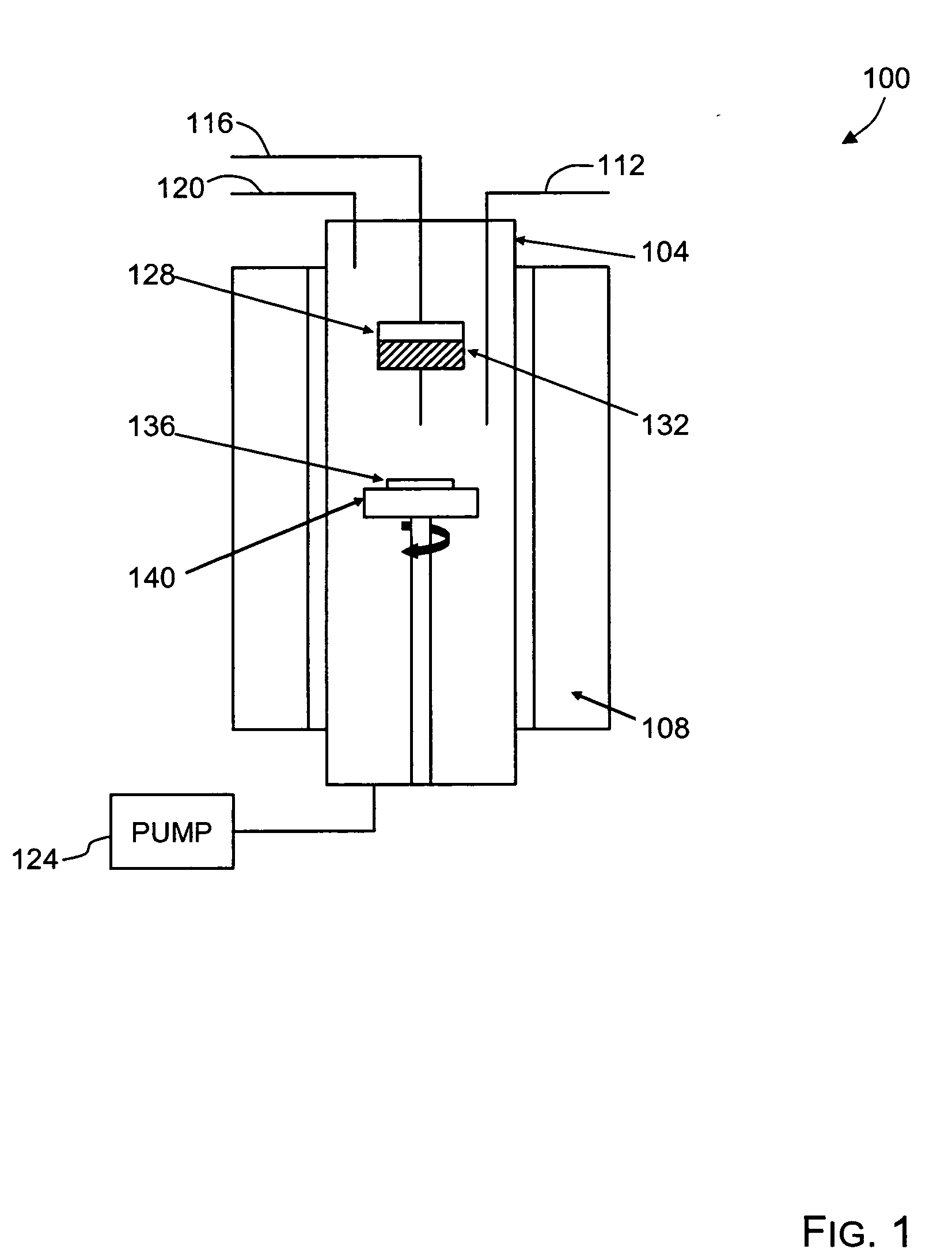
High quality large area bulk non-polar or semipolar gallium based substrates and methods
InactiveUS20100003492A1Great area of substrateCost-effective manufacturingPolycrystalline material growthConductive materialPhotodetectorSolar cell
A large area nitride crystal, comprising gallium and nitrogen, with a non-polar or semi-polar large-area face, is disclosed, along with a method for making. The crystal is useful as a substrate for a light emitting diode, a laser diode, a transistor, a photodetector, a solar cell, or for photoelectrochemical water splitting for hydrogen generation.
Owner:SORAA
Group III Nitride Articles and Methods for Making Same
ActiveUS20100044718A1Promote formationEasy to fillPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
Owner:KYMA TECH
Monitoring device with an accelerometer, method and system
ActiveUS8172761B1Light weightComfortable to wearCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringAccelerometerPhotodetector
A monitoring device for monitoring the vital signs of a user is disclosed herein. The monitoring device is preferably comprises an article, an optical sensor, an accelerometer and processor. The optical sensor preferably comprises a photodetector and a plurality of light emitting diodes. A sensor signal from the optical sensor is processed with a filtered accelerometer output signal from the accelerometer to create a filtered vital sign signal used to generate a real-time vital sign for a user.
Owner:FRX POLYMERS LLC +1
Optical phased array lidar system and method of using same
A lidar-based system and method are used for the solid state beamforming and steering of laser beams using optical phased array (OPA) photonic integrated circuits (PICs) and the detection of laser beams using photodetectors. Transmitter and receiver electronics, power management electronics, control electronics, data conversion electronics and processing electronics are also included in the system and used in the method.Laser pulses beamformed by the OPA PIC reflect from objects in the field of view (FOV) of said OPA, and are detected by a detector or a set of detectors.A lidar system includes at least one lidar, and any subset and any number of complementary sensors, data processing / communication / storage modules, and a balance of system for supplying power, protecting, connecting, and mounting the components of said system.Direct correlation between the 3D point cloud generated by the lidar and the color images captured by an RGB (Red, Green, Blue) video camera can be achieved by using an optical beam splitter that sends optical signals simultaneously to both sensors.A lidar system may contain a plurality of lidar sensors, a lidar sensor may contain a plurality of optical transmitters, and an optical transmitter may contain a plurality of OPA PICs.
Owner:QUANERGY SOLUTIONS INC
Color LiDAR scanner
Owner:VELODYNE LIDAR USA INC
Multilayer organic photodetectors with improved performance
ActiveUS20050110007A1Reduce dark currentTotal current dropSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
The present invention generally relates to organic photodetectors. Further, it is, directed to an optimized organic photodetector having reduced dark current and high efficiency and response time.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
Computer interface employing a manipulated object with absolute pose detection component and a display
ActiveUS20100013860A1Good choiceInput/output for user-computer interactionImage enhancementPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
Owner:ELECTRONICS SCRIPTING PRODS
Light absorption and filtering properties of vertically oriented semiconductor nano wires
InactiveUS9000353B2Optical radiation measurementMaterial nanotechnologyPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
A nanowire array is described herein. The nanowire array comprises a substrate and a plurality of nanowires extending essentially vertically from the substrate; wherein: each of the nanowires has uniform chemical along its entire length; a refractive index of the nanowires is at least two times of a refractive index of a cladding of the nanowires. This nanowire array is useful as a photodetector, a submicron color filter, a static color display or a dynamic color display.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE +1
Optical excitation/detection device and method for making same using fluidic self-assembly techniques
InactiveUS20040222357A1Solid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansCMOSPhotovoltaic detectors
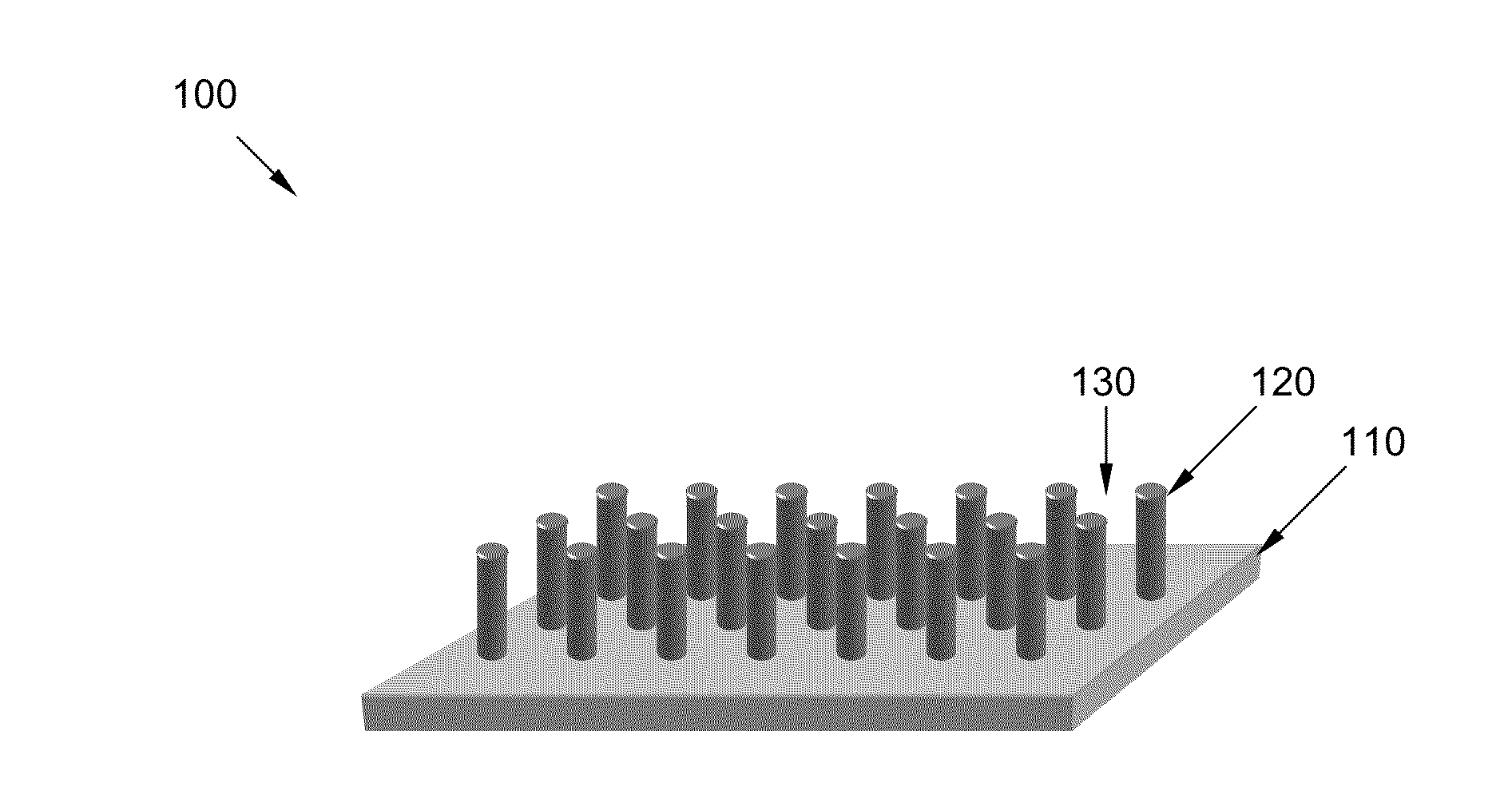
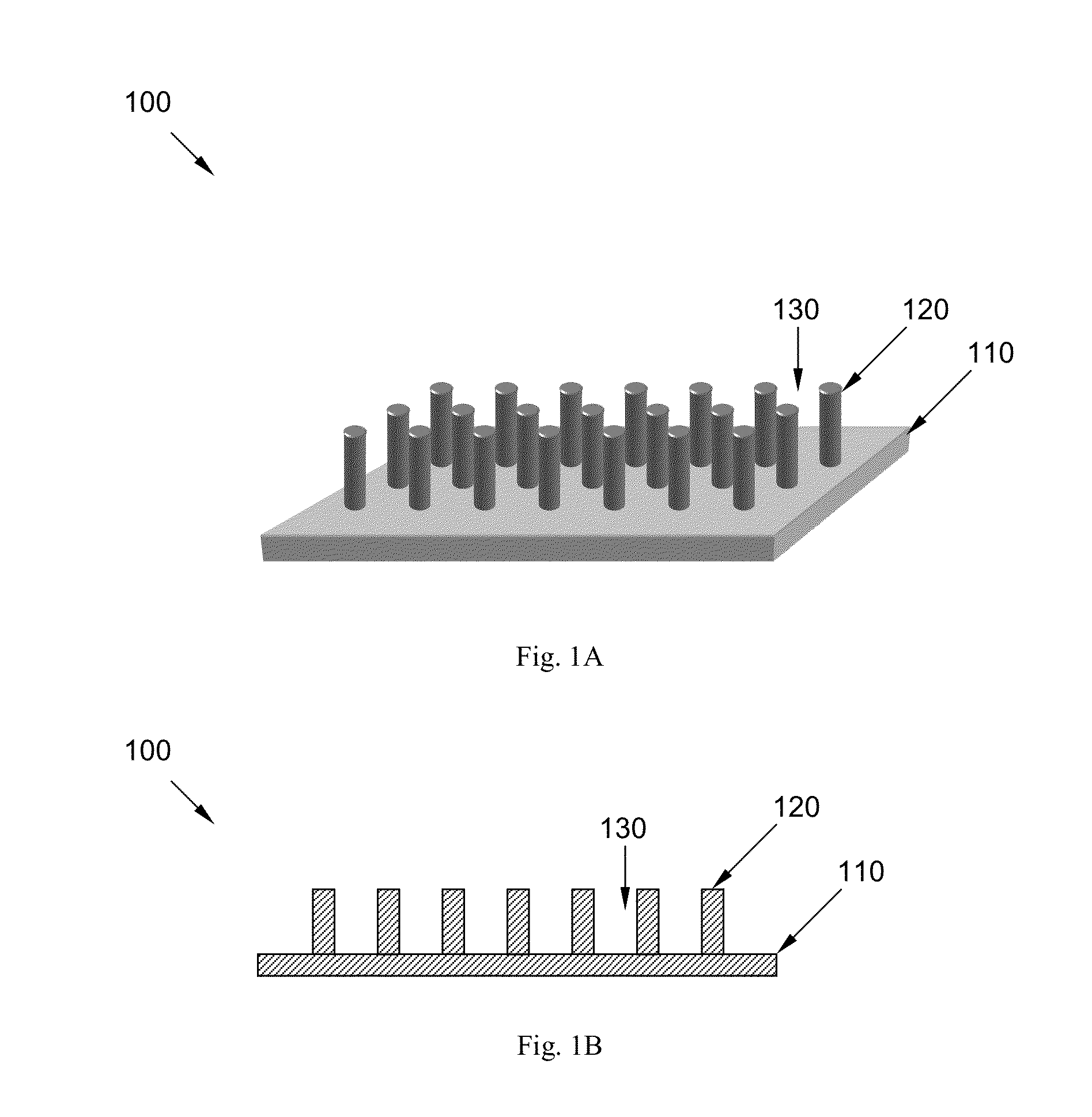
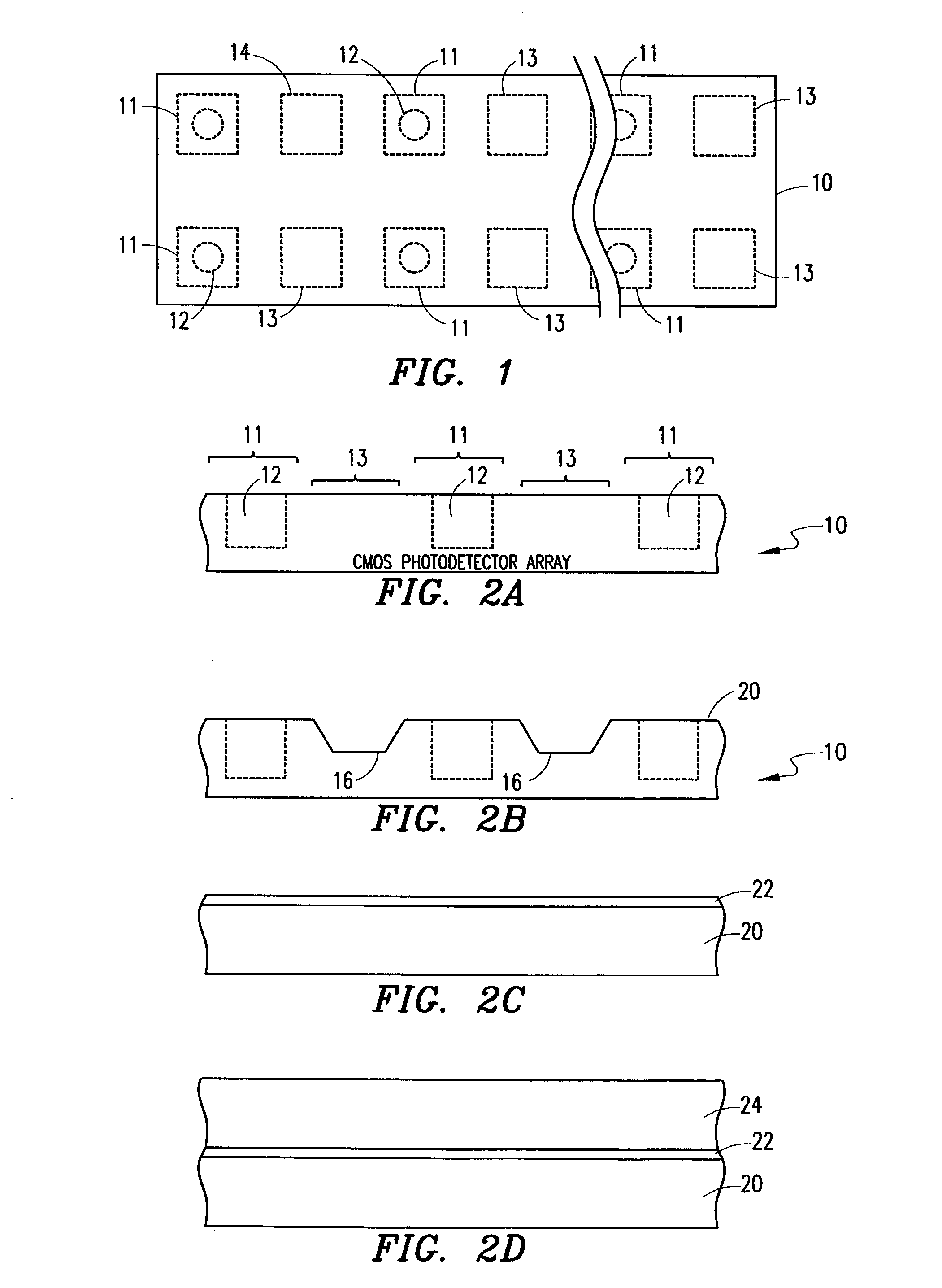
The disclosure is directed toward an optical excitation / detection device that includes an arrayed plurality of photodetectors and separately formed photoemitters, as well as a method for making such a device. A CMOS fabricated photodetector array including a plurality of individual photoreceptors is selectively etched back between photoreceptor locations to reveal a plurality of recessed regions having a certain geographic profile. A plurality of semiconductor blocks, each having light emitting capability and each having a certain geometric profile that is complementary in size and shape to the certain geometric profile of the recessed regions, are separately fabricated. These blocks are included within a fluid to form a slurry. The slurry is then flowed over the CMOS fabricated photodetector array in accordance with a fluidic self-assembly technique, and the included semiconductor blocks are individually deposited within each of the plurality of recessed regions in the CMOS fabricated photodetector array. The deposited blocks are then attached within the recessed regions to form the optical excitation / detection device from an arrayed plurality of photodetectors and separately formed photoemitters.
Owner:SANOFI AVENTIS DEUT GMBH
Patient identification using physiological sensor
InactiveUS20070073116A1Help positioningDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
A patient information tracking system is disclosed that implements a physiological sensor system used to acquire information related to the wearer of a physiological sensor. The sensor system includes a physiological sensor adapted to be attached to a patient and includes at least one emitter and a photodetector. The sensor system further includes a positioning element to position the sensor such that the at least one emitter is sufficiently proximate the detector to acquire information from an identification element worn by the patient. A method for using a physiological sensor system to acquire information related to the wearer of a sensor is also provided. The sensor may also include a securing portion configured to couple to the sensor portion of the wearer. The sensor may also include a security wire and a memory device for retaining the wearer's information.
Owner:MASIMO CORP
Sensor, method and device for optical blood oximetry
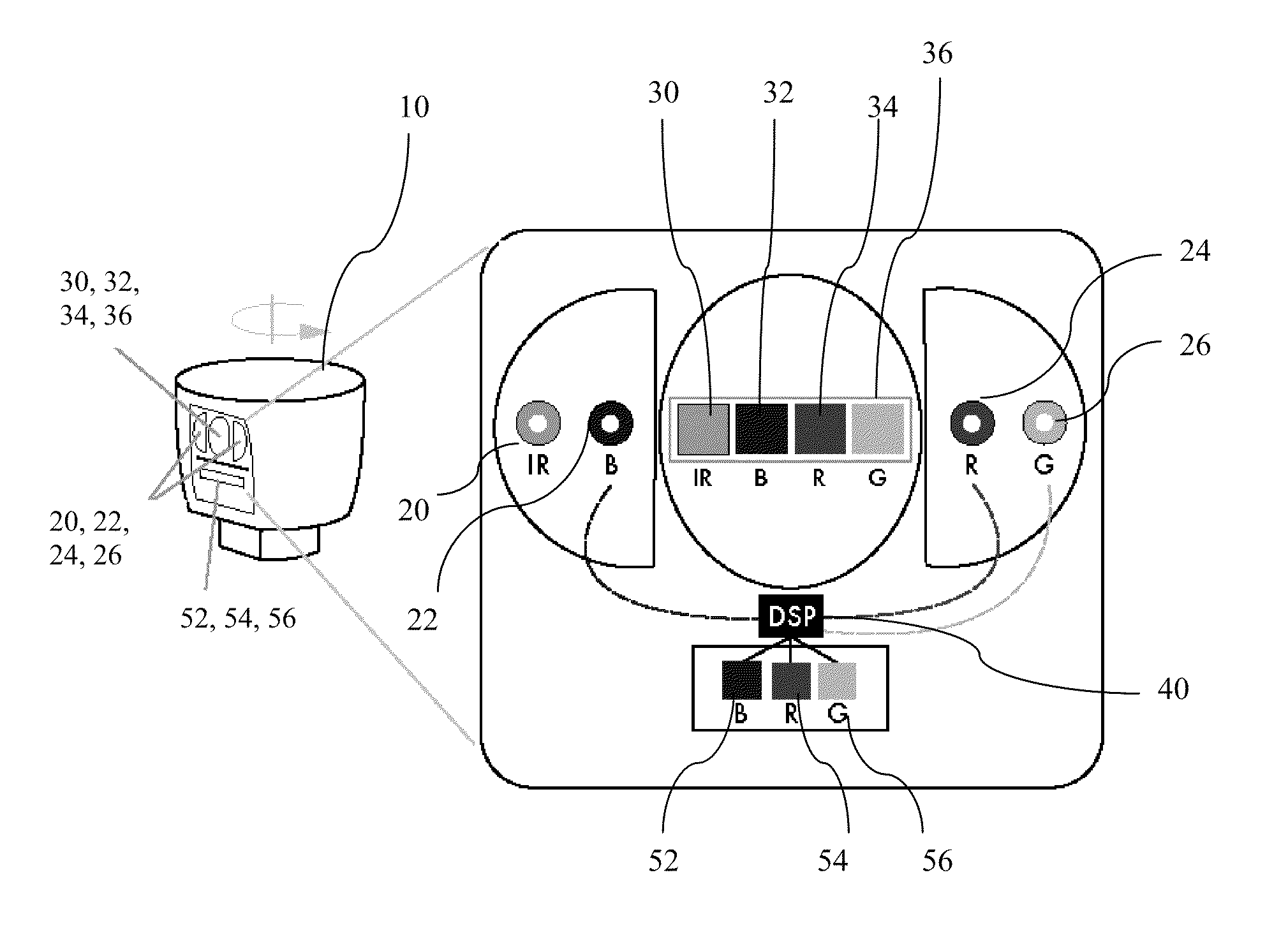
InactiveUS6031603AIncrease the areaImprove acquisitionSurgeryVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
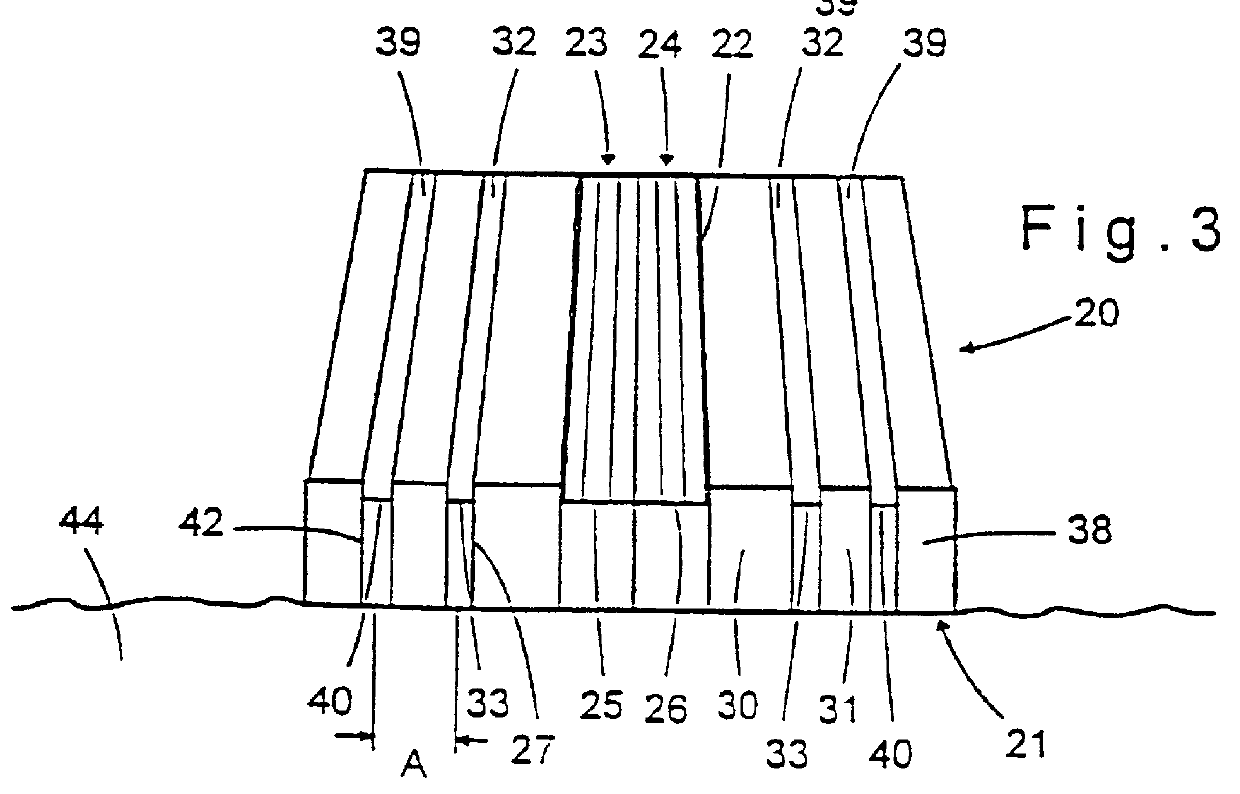
PCT No. PCT / IL96 / 00006 Sec. 371 Date Jul. 9, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Jul. 9, 1998 PCT Filed Jun. 6, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO96 / 41566 PCT Pub. Date Dec. 27, 1996There is described a new sensor for optical blood oximetry as well as a method and apparatus in which the new sensor is used. The new sensor includes two point-like light emitters (23,24) positioned in the center of the device in close proximity to each other and at least one and preferably two annular detector terminals (32,39) concentrically surrounding the light emitters. The light sources may, for example, be two laser diodes emitting each monochromatic light within the range of 670 nm to 940 nm. The detector devices are, for example, photodetectors.
Owner:T M M ACQUISITIONS
Scanning device for coded data
InactiveUS7128270B2Input/output for user-computer interactionDigital data processing detailsPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
A scanning device for scanning coded data indicative of a plurality of locations disposed on a surface is provided. The device generates interaction data based on the sensed coded data. The scanning device comprises a laser source for exposing a coded data portion, a photodetector, an analog to digital converter, a framestore, an image processor and a host processor.
Owner:SILVERBROOK RES PTY LTD
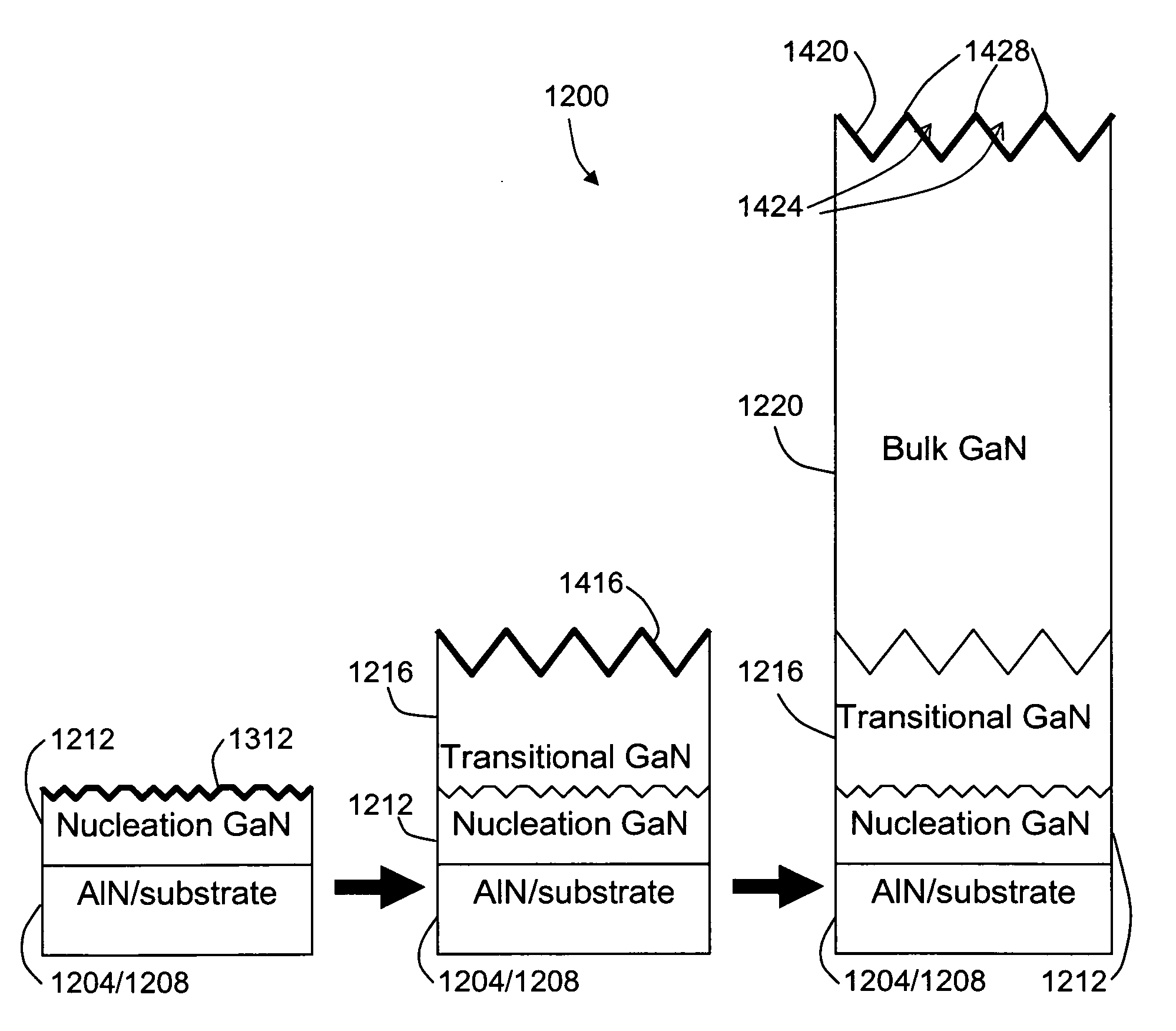
Group iii-nitride growth on silicon or silicon germanium substrates and method and devices therefor
InactiveUS20080128745A1Laser detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
A structure including a Si1-xGex substrate and a distributed Bragg reflector layer disposed directly onto the substrate. The distributed Bragg reflector layer includes a repeating pattern that includes at least one aluminum nitride layer and a second layer having the general formula AlyGa1-yN. Another aspect of the present invention is various devices including this structure. Another aspect of the present invention is directed to a method of forming such a structure comprising providing a Si1-xGex substrate and depositing a distributed Bragg reflector layer directly onto the substrate. Another aspect of the present invention is directed to a photodetector or photovoltaic cell device, including a Si1-xGex substrate device, a group III-nitride device and contacts to provide a conductive path for a current generated across at least one of the Si1-xGex substrate device and the group III-nitride device upon incident light.
Owner:NAVY U S A AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE THE
Computer interface employing a manipulated object with absolute pose detection component and a display
ActiveUS7961909B2Input/output for user-computer interactionImage enhancementPhotovoltaic detectorsRemote control
A system that has a remote control, e.g., a wand, equipped with a relative motion sensor that outputs data indicative of a change in position of the wand. The system also has one or more light sources and a photodetector that detects their light and outputs data indicative of the detected light. The system uses one or more controllers to determine the absolute position of the wand based on the data output by the relative motion sensor and by the photodetector. The data enables determination of the absolute pose of the wand, which includes the absolute position of a reference point chosen on the wand and the absolute orientation of the wand. To properly express the absolute parameters of position and / or orientation of the wand a reference location is chosen with respect to which the calculations are performed. The system is coupled to a display that shows an image defined by a first and second orthogonal axes such as two axes belonging to world coordinates (Xo,Yo,Zo). The one or more controllers are configured to generate signals that are a function of the absolute position of the wand in or along a third axis for rendering the display. To simplify the mapping of a real three-dimensional environment in which the wand is operated to the cyberspace of the application that the system is running, the third axis is preferably the third Cartesian coordinate axis of world coordinates (Xo,Yo,Zo).
Owner:ELECTRONICS SCRIPTING PRODS
Blood-pressure monitoring device featuring a calibration-based analysis
Owner:TRIAGE WIRELESS
Information system and method for providing information using a holographic element
ActiveUS20070109619A1Improve relationshipThe relationship is accurateInput/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsAngle of incidencePhotodetector
In the following, the essential points are summarized again by means of groups of characteristics which each individually and in combination with one another characterize the invention specifically: 1. Information system for providing information in correlation with light incident on an eye, having a holographic element disposed in front of the eye, and an optical scanning device which detects light incident on the eye by way of the holographic element. 2. Information system according to Point 1, wherein the optical scanning device is at a fixed predetermined angular ratio with respect to the holographic element. 3. Information system according to Point 1 or 2, wherein the optical scanning device detects light which is refracted by the holographic element before it impinges on the eye and does not enter the eye. 4. Information system according to one of the preceding points, wherein the optical scanning device detects light which was first reflected back from the eye and was then refracted by the holographic element. 5. Information system according to one of the preceding points, wherein the holographic element refracts light originating from the field of vision of the eye only at several discrete wavelengths in the visible range before the light impinges on the eye for the detection by the optical scanning device, and refracts light reflected back from the eye only at one discrete wavelength in the infrared range for the detection by the optical scanning device. 6. Information system according to one of the preceding points, wherein the holographic element refracts light originating from the field of vision of the eye at fewer than 20, fewer than 10 or fewer than 5 discrete wavelengths in the visible range either before the light impinges on the eye or after its backscattering as a result of the eye for the detection by the optical scanning device. 7. Information system according to one of the preceding points, wherein the holographic element refracts light originating from the field of vision of the eye at a discrete wavelength in the infrared range either before the light impinges on the eye or after its backscattering as a result of the eye for the detection by the optical scanning device. 8. Information system according to one of the preceding points, wherein the holographic element refracts light reflected back by the eye only at a discrete wavelength in the infrared range for the detection by the optical scanning device. 9. Information system according to one of the preceding points, wherein the holographic element refracts light of one or several discrete wavelengths, at which the optical scanning device has a high sensitivity. 10. Information system according to one of the preceding points, wherein the holographic element refracts light a several discrete wavelengths such that the refracted light is guided to a common point, and the angle of incidence of the light on this point permits a clear optionally also wavelength-independent conclusion on the angle of incidence of the light upon the holographic element. 11. Information system according to one of the preceding points, having an optical projection device which projects light into the eye by way of the holographic element. 12. Information system according to Point 11, wherein the light detected by the optical detection device and the light projected in front of the optical projection device run in the opposite direction through a common light guiding lens system and can be focused such by the optical scanning device or projection device that their respective beams describe the same path from or into the eye. 13. Information system for providing information in correlation with information obtained from an eye, having a holographic element disposed in front of the eye, and an optical projection device which projects light into the eye by way of the holographic element. 14. Information system according to one of Points 11 to 13, wherein the optical projection device projects light only at one or several discrete wavelengths in the visible range and / or at a wavelength in the infrared range. 15. Information system according to one of Points 11 to 14, wherein the holographic element refracts the wavelengths of the projected light. 16. Information system according to one of Points 11-15, wherein the optical projection device is in a fixed predetermined angular ratio with respect to the holographic element. 17. Information system according to Point 16, wherein the holographic element comprises one or more optical flags, whose light reflection characteristics can be used by the information system by means of a photodetector for calibrating a projection angle of the optical projection device and / or a light guiding device. 18. Information system according to Point 17, including Point 12, wherein the information system uses the light reflection characteristics of the optical flags for calibrating a scanning angle of the optical scanning device and / or a light guiding device. 19. Information system according to Point 17, wherein the optical flags are generated in that reflecting elements are imaged during the creating of the holographic element such in the holographic element that they (something is missing) reflect light of one or several wavelengths which, corresponding to the predetermined angular ratio with respect to the optical projection device is incident on the holographic element, back along the path of incidence. 20. Information system according to Point 19, wherein the photodetector device has a splitter mirror which is arranged such in the light beam of the optical projection device that it guides a portion of the light, which impinges on the splitter mirror against the projection direction, in the direction of a photodetector which detects in at least two areas situated concentrically around one another. 21. Information system according to one of the preceding points, wherein the holographic element has light-refracting characteristics at one or several discrete wavelengths, which correspond to a reflection on the concave side of an area constructed according to the curvature of a rotationally symmetrical ellipsoid. 22. Information system according to one of the preceding points, wherein the holographic element has light refracting characteristics at one or several discrete wavelengths, which correspond to a refraction on the concave side of an area constructed according to the curvature of a rotationally symmetrical ellipsoid, which refraction corresponds to a reflection on a respective conical surface which is rotationally symmetrical about the axis of rotation of the ellipsoid and is perpendicular with respect to the ellipsoid at the site of the refraction. 23. Method of providing information in correlation with light incident on an eye, whereby a holographic element is disposed in front of the eye, and an optical scanning device detects the light incident on the eye by means of the holographic element. 24. Method according to Point 23, whereby the optical scanning device is at a fixed predetermined angular ratio with respect to the holographic element. 25. Method according to Point 23 or 24, whereby the optical scanning device detects light which is refracted by the holographic element before impinging on the eye and does not enter the eye. 26. Method according to one of Points 23 to 25, whereby the optical scanning device detects light which was first reflected back from the eye and was then refracted by the holographic element. 27. Method according to one of Points 23 to 26, whereby the holographic element refracts light originating from the field of vision of the eye only at several discrete wavelengths in the visible range before its impinging on the eye for the detection by the optical scanning device and refracts light reflected back from the eye only at a discrete wavelength in the infrared range for the detection by the optical scanning device. 28. Method according to one of Points 23 to 27, whereby the holographic element refracts light originating from the field of vision of the eye at fewer than 20, fewer than 10 or fewer than 5 discrete wavelengths in the visible range either before its impinging on the eye or after its backscattering as a result of the eye for the detection by the optical scanning device. 29. Method according to one of Points 23 to 28, whereby the holographic element refracts light originating from the visual field of the eye at a discrete wavelength in the infrared range either before its impinging on the eye or after its backscattering as a result of the eye for the detection by the optical scanning device. 30. Method according to one of Points 23 to 29, whereby the holographic element refracts light reflected back from the eye only at a discrete wavelength in the infrared range for the detection by the optical scanning device. 31. Method according to one of Points 23 to 30, whereby the holographic element refracts light of one or several discrete wavelengths, at which the optical scanning device has a high sensitivity. 32. Method according to one of Points 23 to 31, whereby the holographic element refracts light at several discrete wavelengths such that the refracted light is guided to a common point, an the angle of incidence of the light onto this point allows a clear, optionally also wavelength-independent conclusion on the angle of incidence of the light upon the holographic element. 33. Method according to one of Points 23 to 32, whereby an optical projection device projects light by way of the holographic element into the eye. 34. Method according to Point 33, whereby the light detected by the optical scanning device and the light projected in front of the optical projection device run in the opposite direction through a common light guiding lens system and can be focused such by the optical scanning device or projection device that their respective beams describe the same path from or into the eye. 35. Method of providing information in correlation with information obtained from an eye, whereby a holographic element is disposed in front of the eye, and an optical projection device projects light by way of the holographic element into the eye. 36. Method according to points 33 to 35, whereby the optical projection device projects light only at one or several discrete wavelengths in the visible range and / or at a wavelength in the infrared range. 37. Method according to one of Points 33 to 36, whereby the holographic element refracts the wavelengths of the projected light. 38. Method according to one of Points 33 to 37, whereby the optical projection device is in a fixed predetermined angular ratio with respect to the holographic element. 39. Method according to Point 38, whereby the holographic element is equipped with one or more optical flags, whose light reflection characteristics can be used by means of a photodetector device for calibrating a projection angle of the optical projection device and / or a light guiding device. 40. Method according to Point 39, including Point 34, whereby the light reflection characteristics of the optical flags are used for calibrating a scanning angle of the optical scanning device and / or a light guiding device. 41. Method according to Point 39, whereby the optical flags are generated in that reflecting elements are imaged during the creating of the holographic element such in the holographic element that they beam light of one or more wavelengths which, corresponding to the predetermined angular ratio with respect to the optical projection device is incident on the holographic element, back along the incidence path. 42. Method according to Point 41, whereby the photodetector device is equipped with a photodetector detecting in at least two areas situated concentrically around one another, and a splitter mirror which is arranged such in the light beam of the optical projection device that it directs a portion of the light impinging on the splitter mirror against the projecting direction, in the direction of the photodetector. 43. Method according to one of Points 23 to 42, whereby the holographic element has light-refracting characteristics at one or several discrete wavelengths which correspond to a reflection on the concave side of an area constructed according to a curvature of a rotationally symmetrical ellipsoid. 44. Method according to one of Points 23 to 43, whereby the holographic element has light-refracting characteristics at one or several discrete wavelengths, which correspond to a refraction on the concave side of an area constructed according to a curvature of a rotationally symmetrical ellipsoid, which refraction corresponds to a reflection on a respective conical surface rotationally symmetrical about the axis of rotation of the ellipsoid, which conical surface is perpendicular with respect to the ellipsoid at the site of the refraction. While the preceding description with respect to the title is limited to embodiments falling under the initially mentioned generic terms “scanning information system” and “projecting information system”, each individual discussed characteristic of their disclosure can also be used in an embodiment of the systems, devices and methods initially identified by reference to their full content. The applications by the same applicant and / or the same inventors mentioned in the present application should be considered to be a correlated invention complex.
Owner:APPLE INC
Fiber array unit with integrated optical power monitor
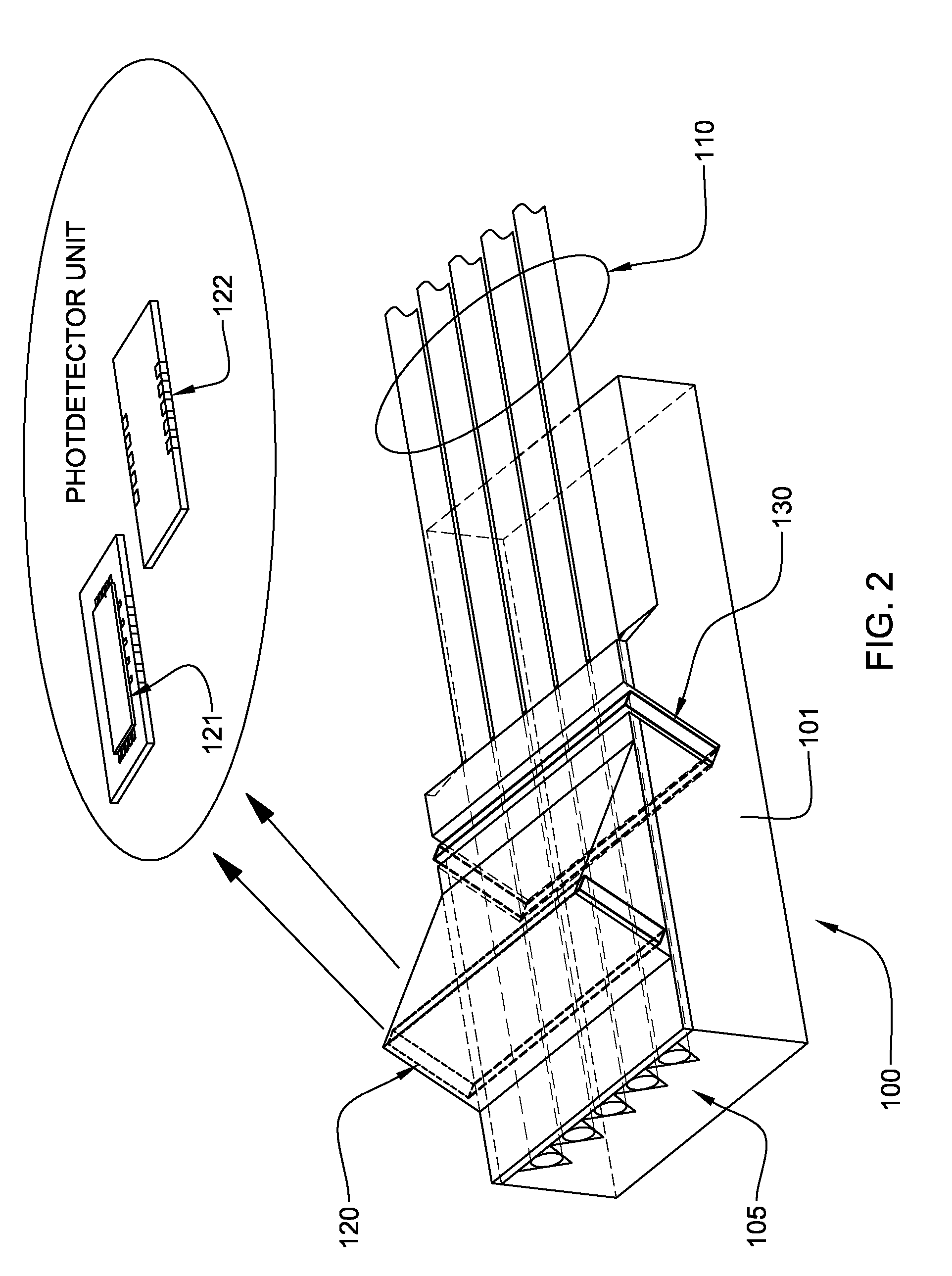
A technique for monitoring optical power in a fiber array unit having a plurality of optical transmission waveguides terminating at an edge thereof for carrying optical signals to and / or from a PLC. A tapping filter is placed within a slit formed in the substrate and interrupting the transmission channels, thereby tapping at least some of the optical power from the channels and directing the tapped optical power toward respective photodetector channels for detection, while allowing other optical power to continue transmission in the at least one channel of the fiber array unit.
Owner:ZHU HAI BEN JIA TECH CO LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com