Patents
Literature
432 results about "Frequency space" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
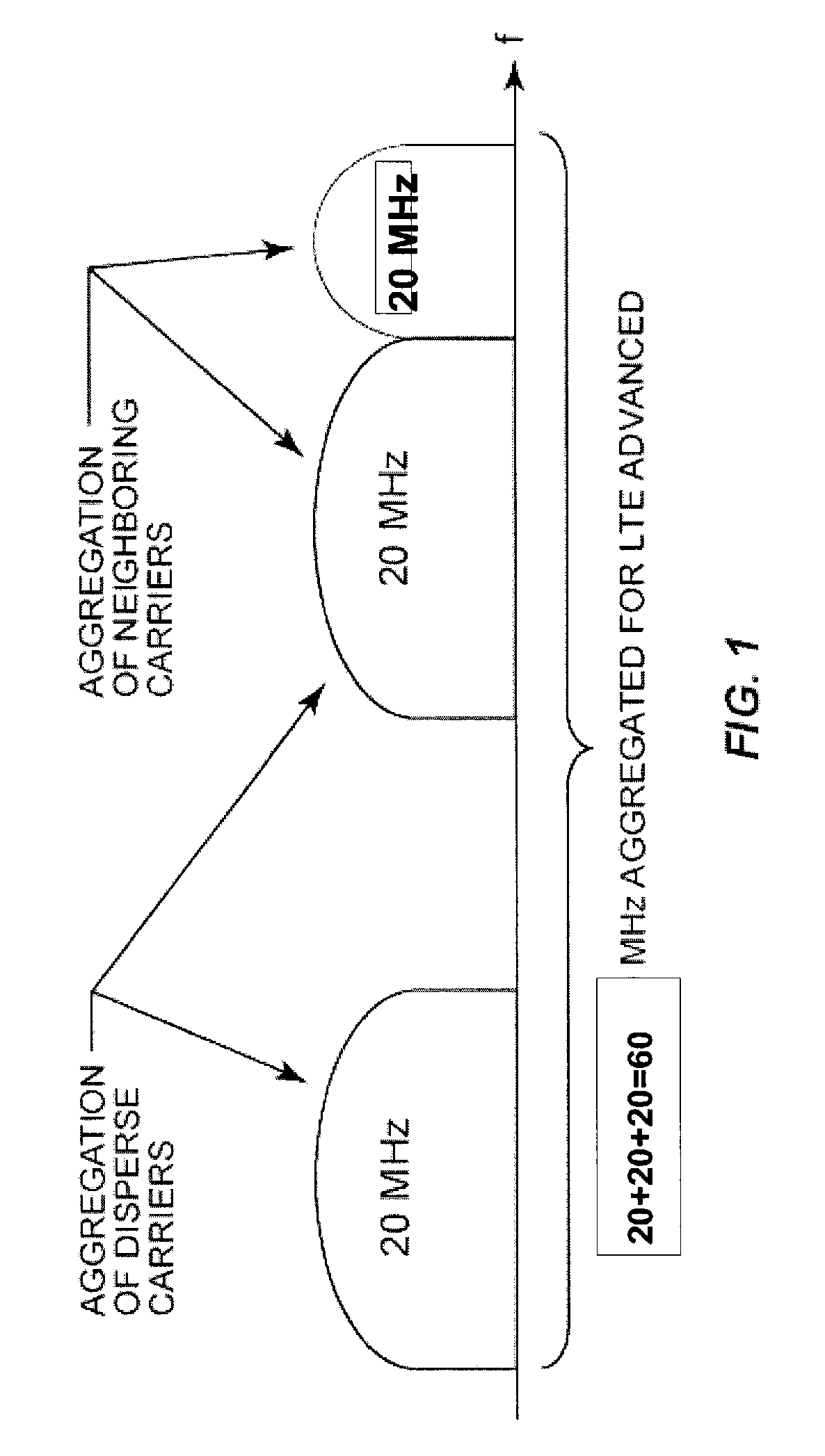
Frequency is important in wireless communications, where the frequency of a signal is mathematically related to the wavelength. If f is the frequency of an electromagnetic field in free space as measured in megahertz, and w is the wavelength as measured in meters, then. w = 300/f. and conversely.
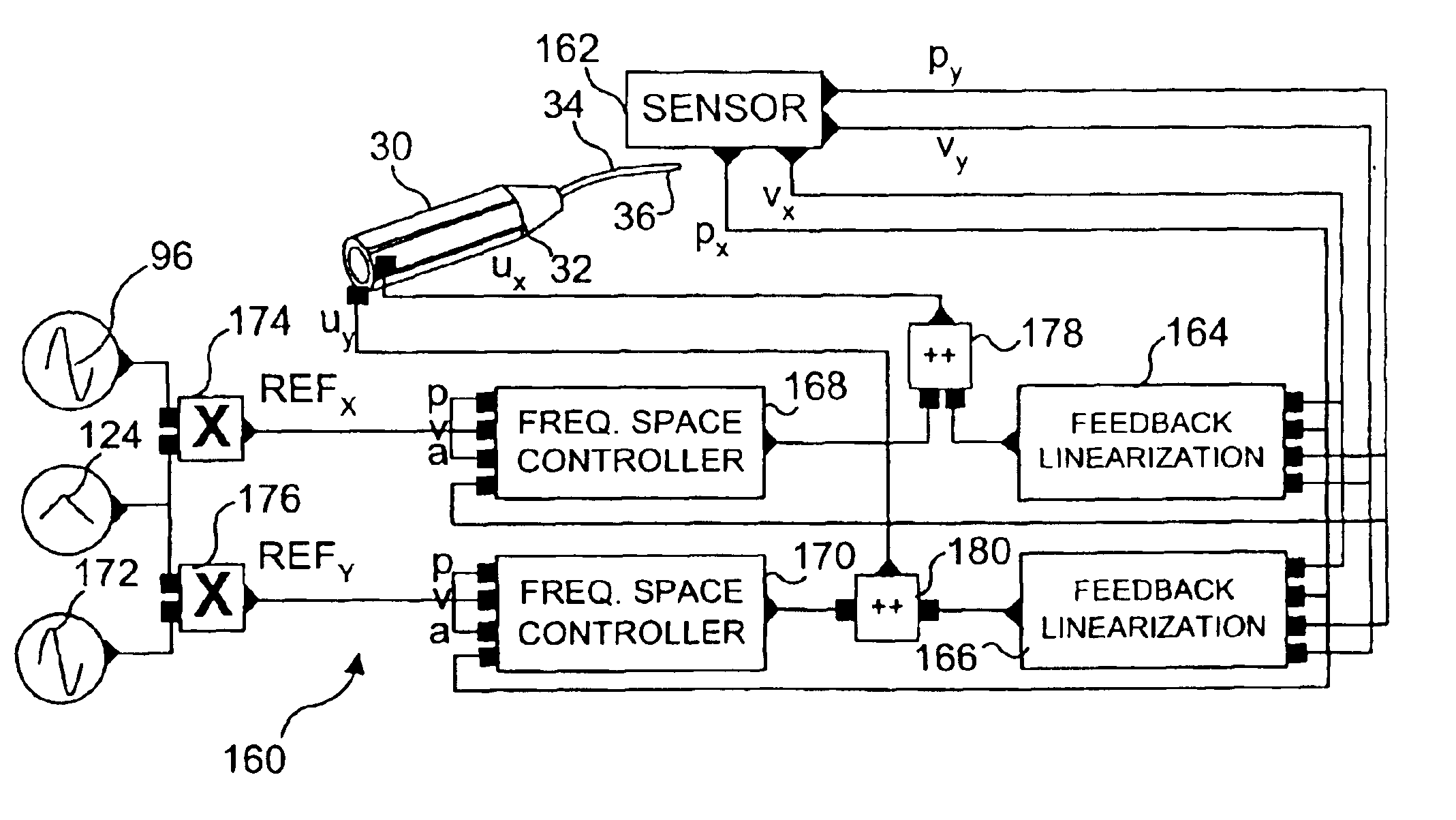
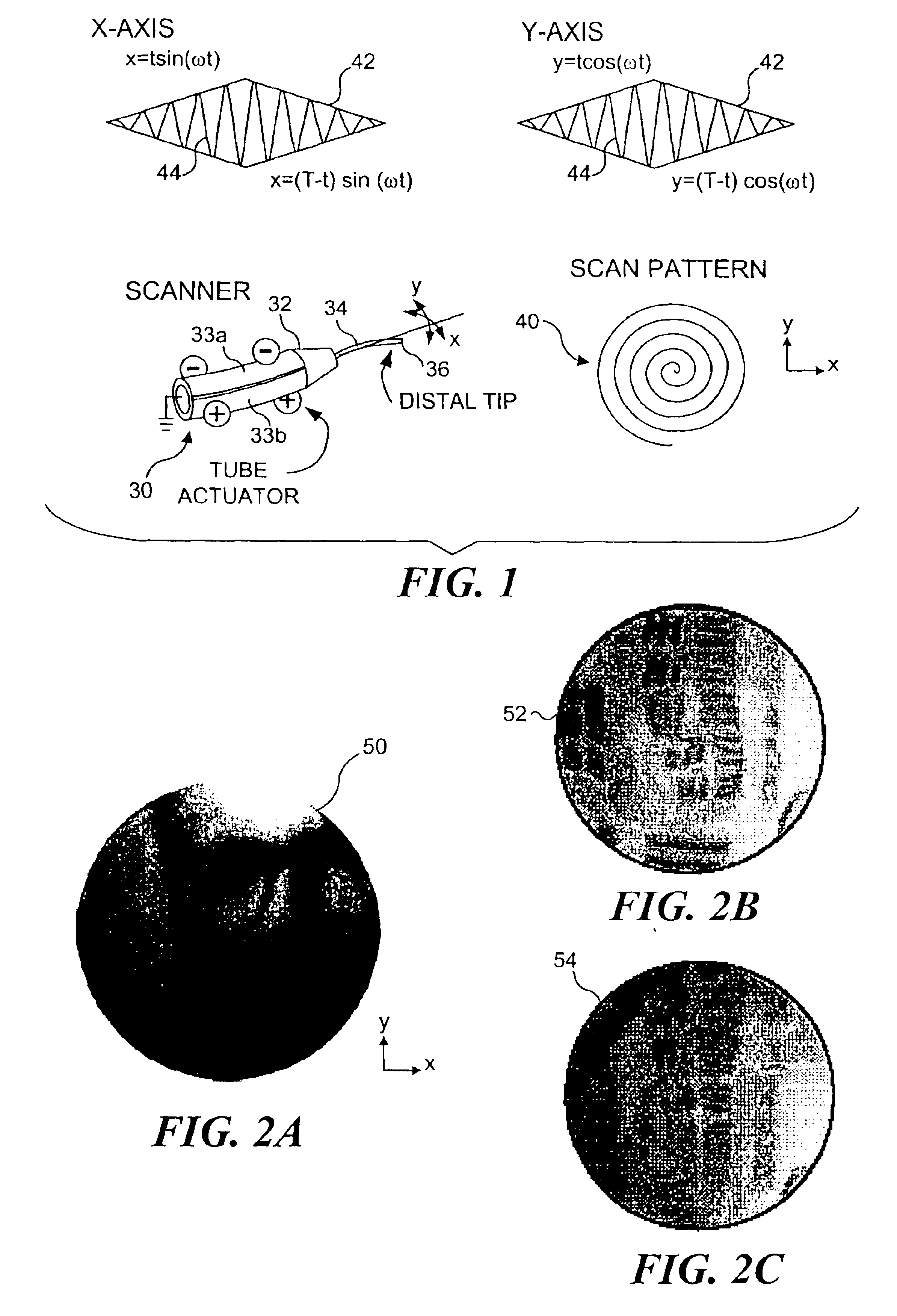
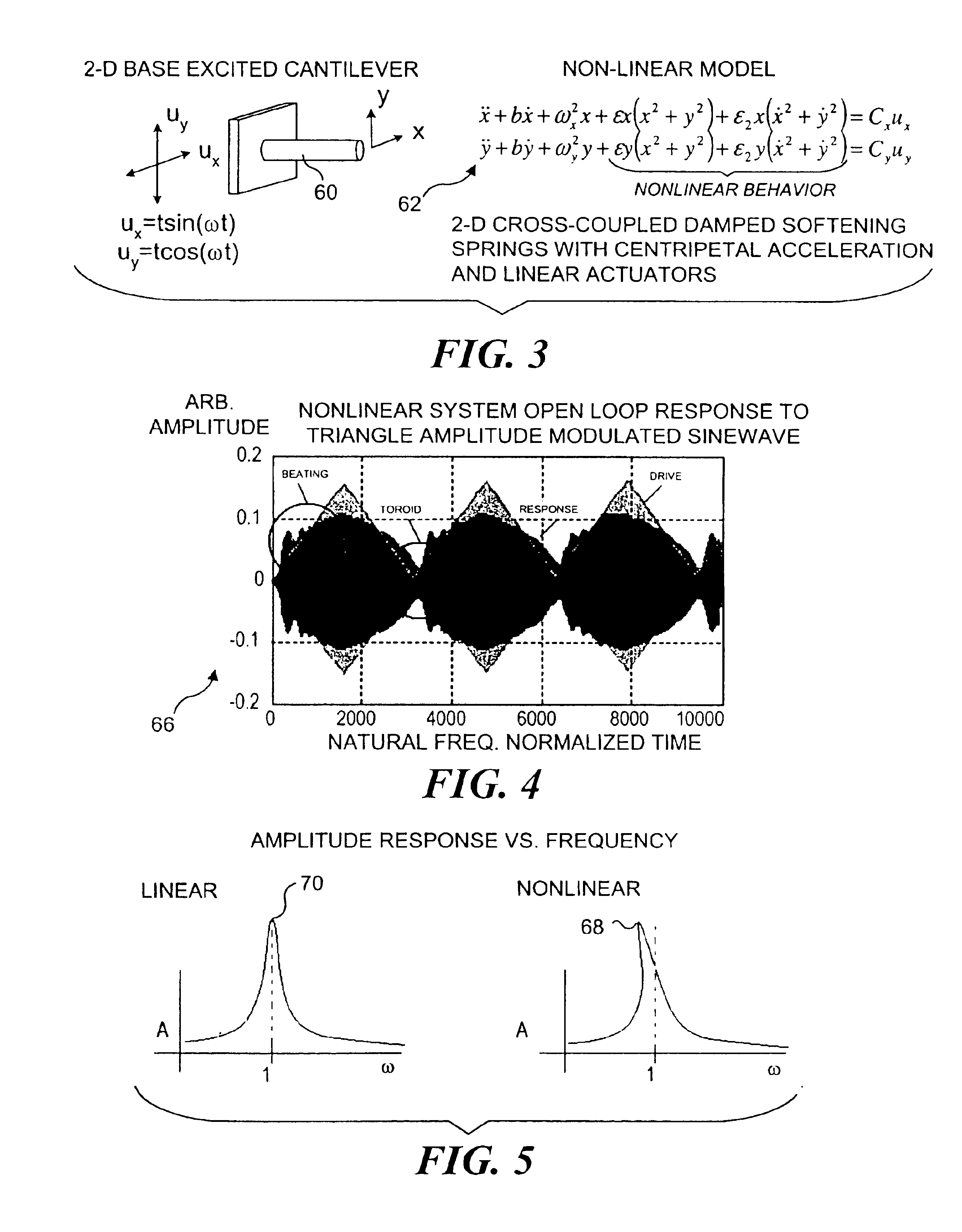
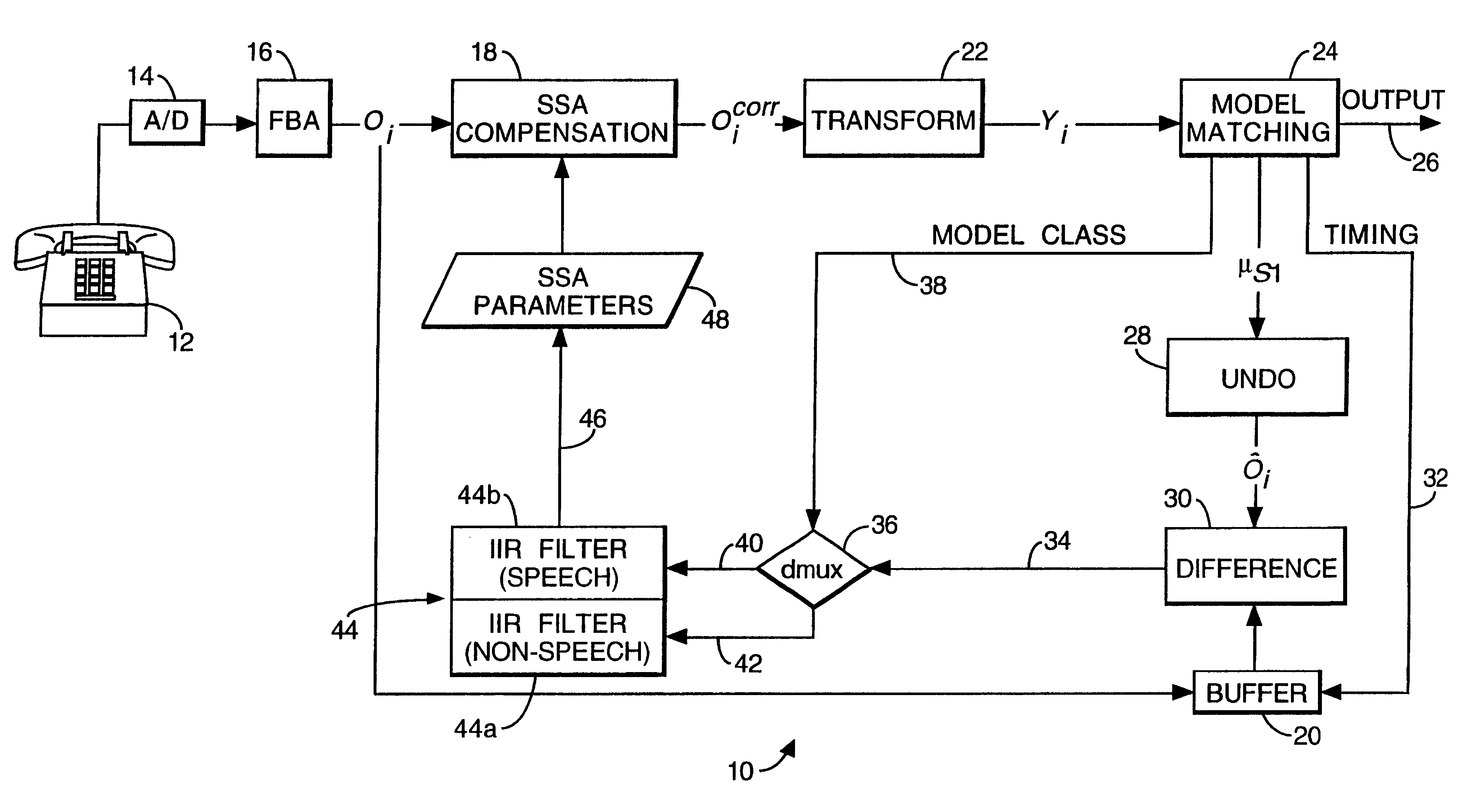
Control of an optical fiber scanner
InactiveUS6845190B1Remove nonlinear behaviorRobust cancellationSurgeryEndoscopesOptical scannersPhotodetector
Controls for an optical scanner, such as a single fiber scanning endoscope (SFSE) that includes a resonating optical fiber and a single photodetector to produce large field of view, high-resolution images. A nonlinear control scheme with feedback linearization is employed in one type of control to accurately produce a desired scan. Open loop and closed loops controllers are applied to the nonlinear optical scanner of the SFSE. A closed loop control (no model) uses either phase locked loop and PID controllers, or a dual-phase lock-in amplifier and two PIDs for each axis controlled. Other forms of the control that employ a model use a frequency space tracking control, an error space tracking control, feedback linearizing controls, an adaptive control, and a sliding mode control.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
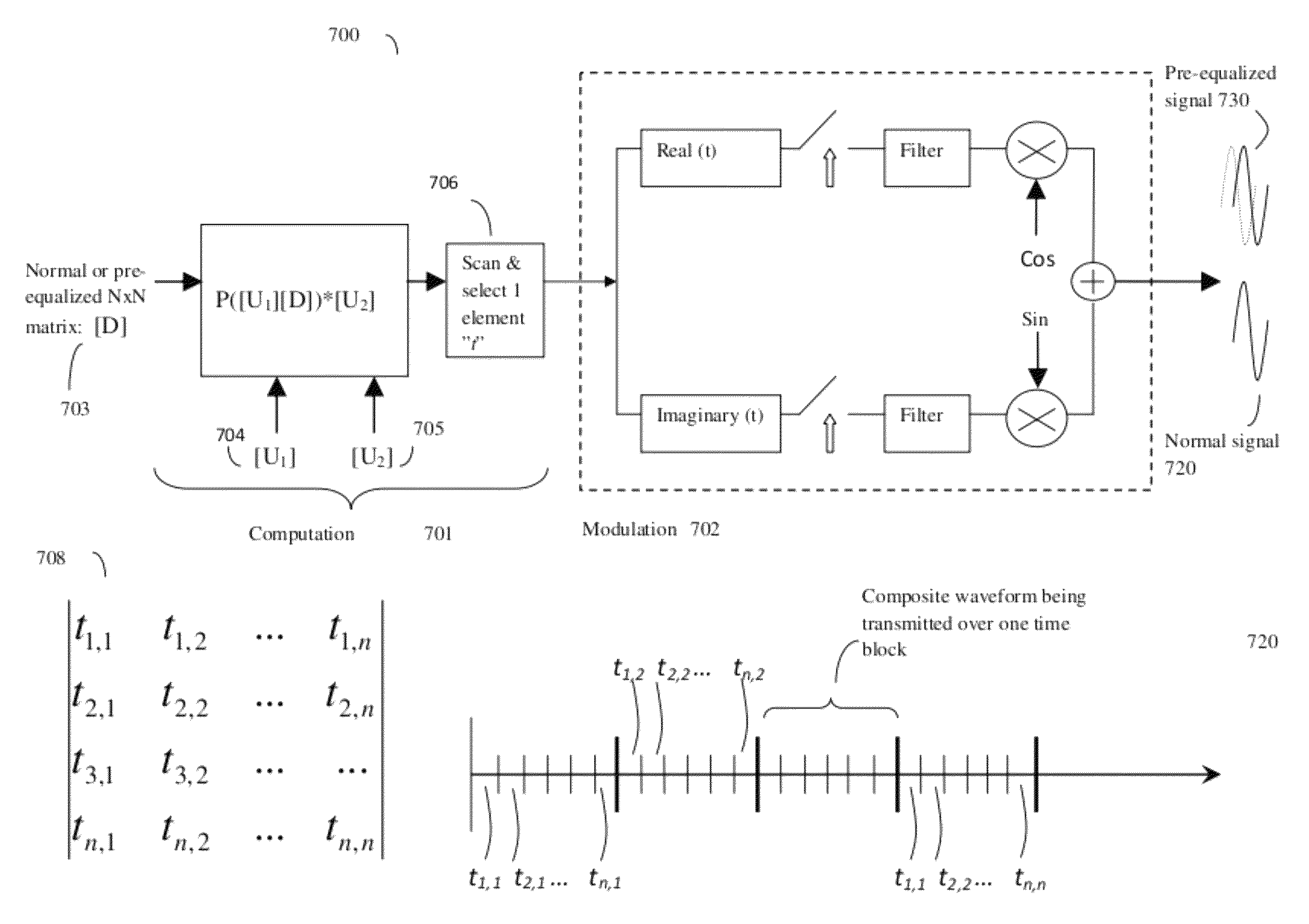
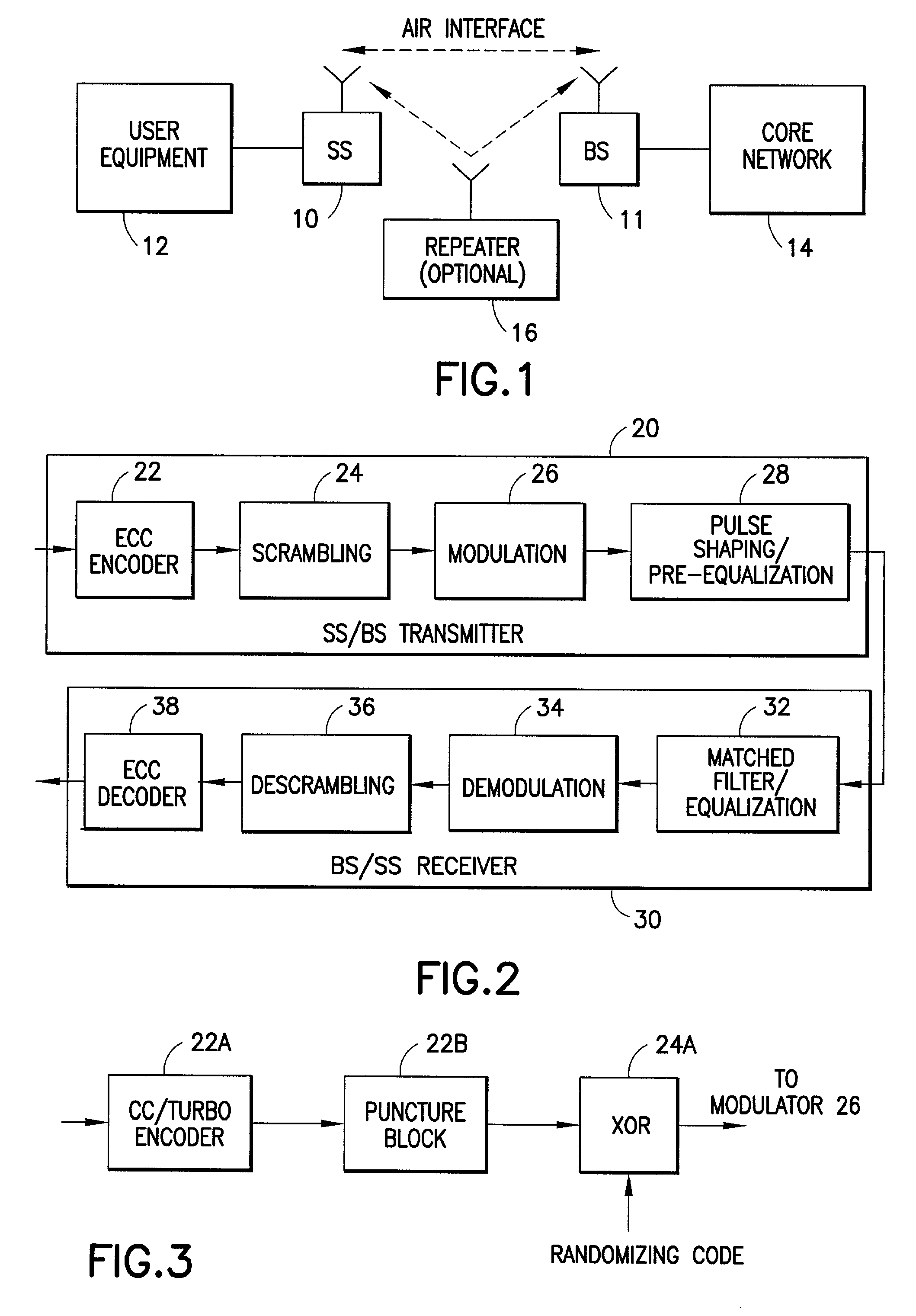
Signal modulation method resistant to echo reflections and frequency offsets
ActiveUS9083595B2Improve performancePromote decompositionNetwork traffic/resource managementMulti-frequency code systemsHigh rateEngineering
A method of modulating communications signals, such as optical fiber, wired electronic, or wireless signals in a manner that facilitates automatic correction for the signal distortion effects of echoes and frequency shifts, while still allowing high rates of data transmission. Data symbols intended for transmission are distributed into N×N matrices, and used to weigh or modulate a family of cyclically time shifted and cyclically frequency shifted waveforms. Although these waveforms may then be distorted during transmission, their basic cyclic time and frequency repeating structure facilitates use of improved receivers with deconvolution devices that can utilize the repeating patterns to correct for these distortions. The various waveforms may be sent in N time blocks at various time spacing and frequency spacing combinations in a manner that can allow interleaving of blocks from different transmitters. Applications to channel sounding / characterization, system optimization, and also radar are also discussed.
Owner:COHERE TECH
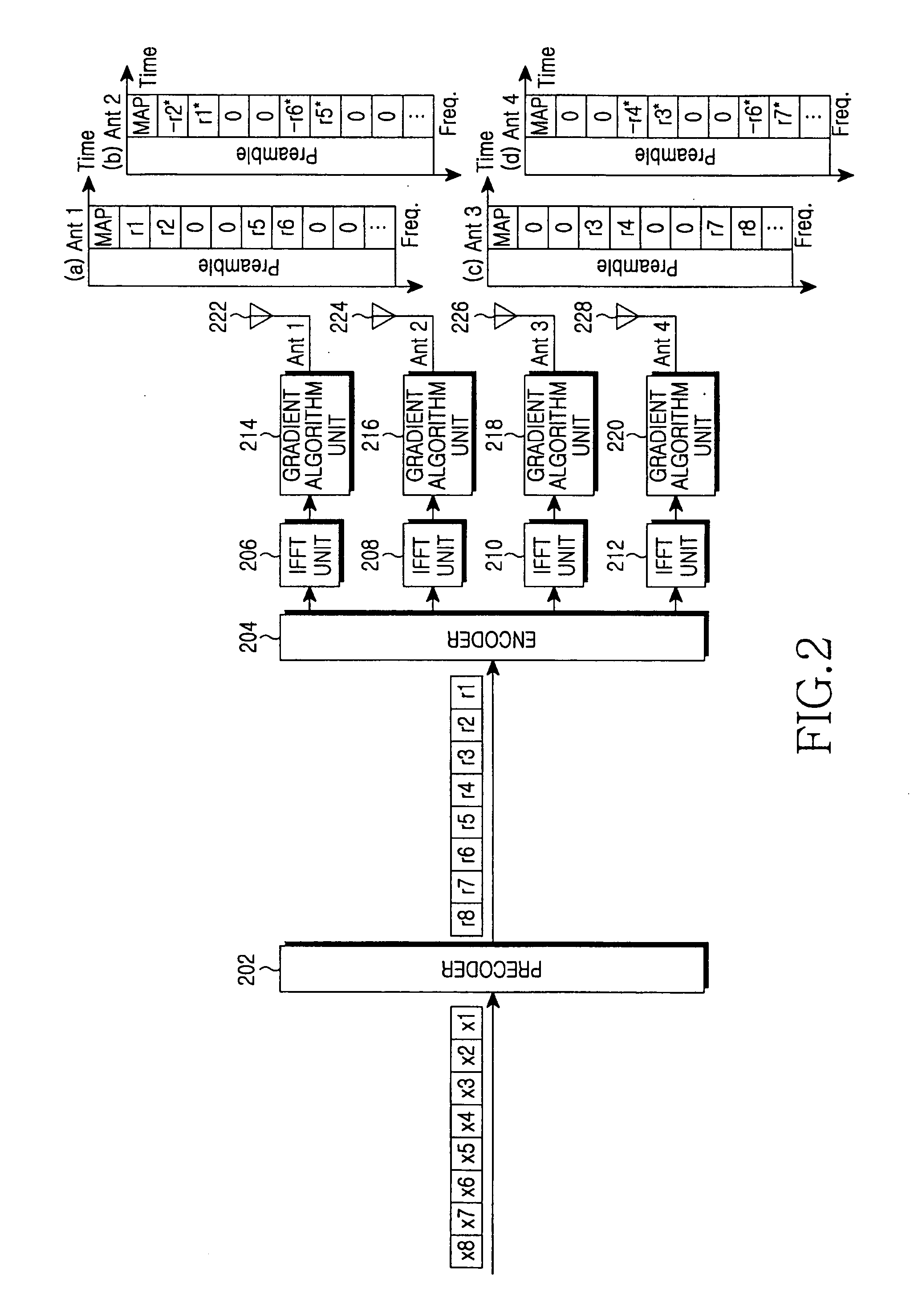
Apparatus and method for minimizing a PAPR in an OFDM communication system
InactiveUS20060078066A1Reduce PAPRMinimizes power ratioSpatial transmit diversityPolarisation/directional diversitySpatial mappingFourier transform on finite groups
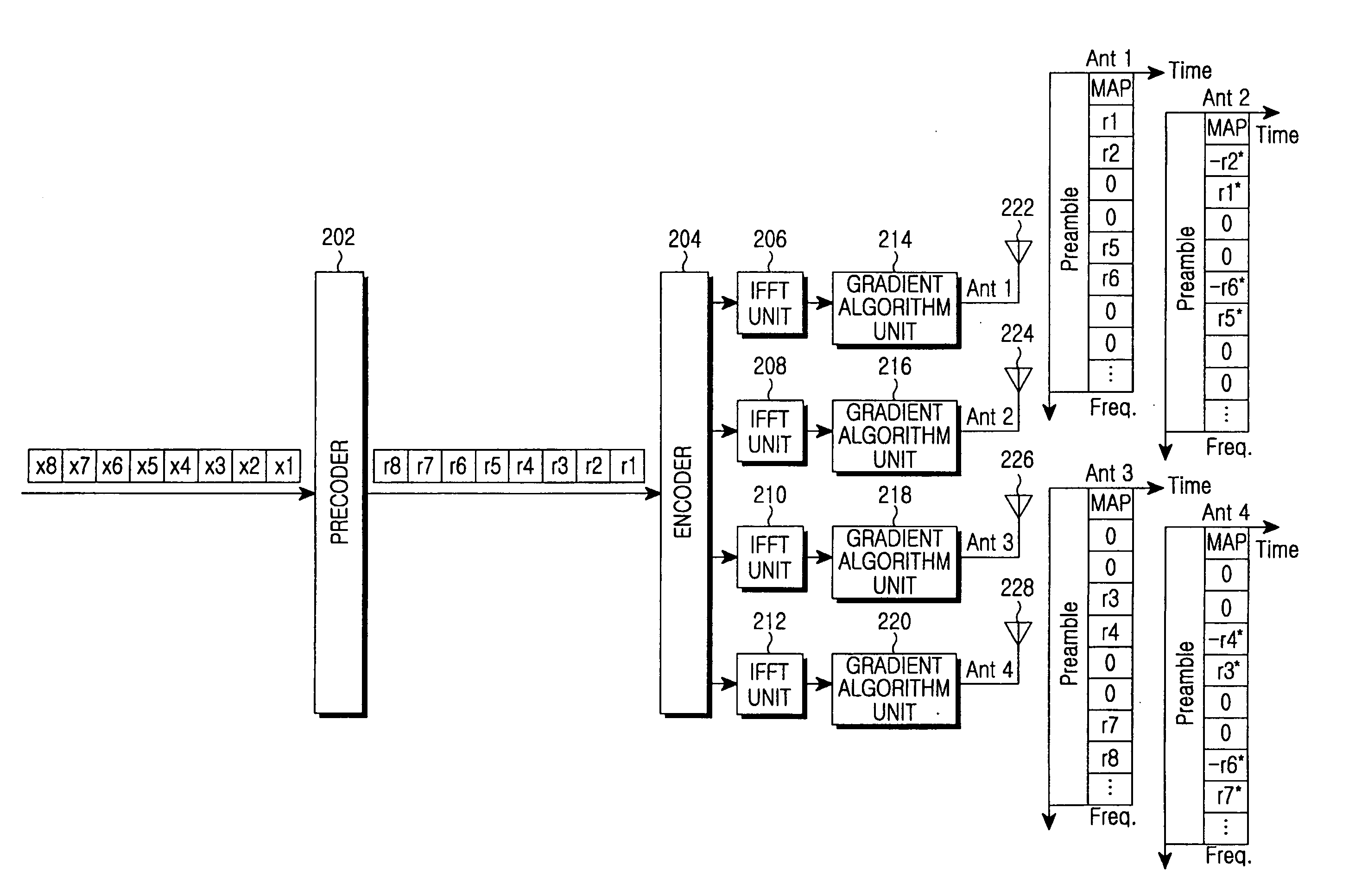
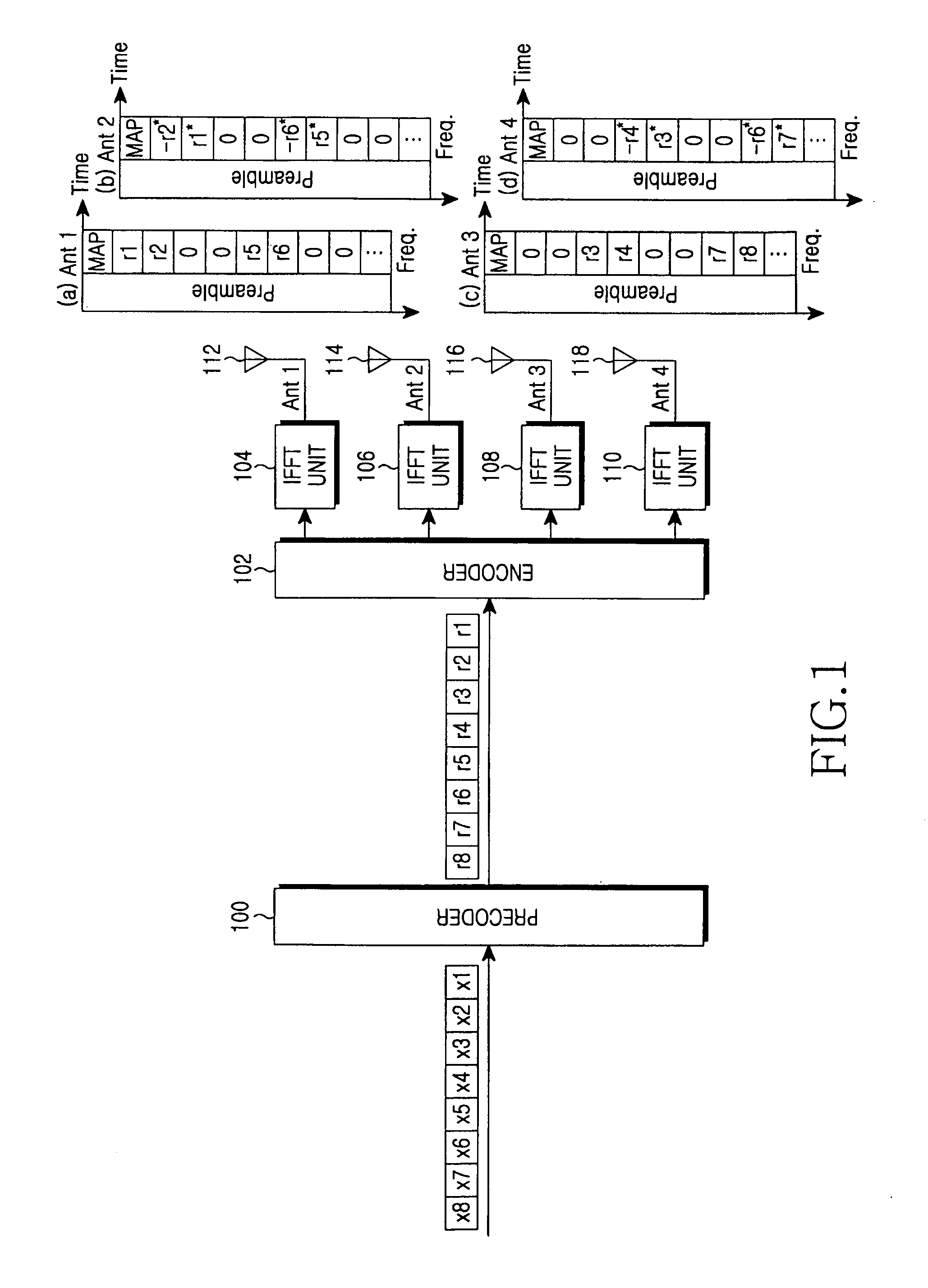
A transmitter for minimizing a PAPR in OFDM communication system. The transmitter includes: a precoder for coding input symbols so that a signal rotation is generated, and generating a complex vector including the coded symbols; an encoder for performing a frequency-space mapping for the symbols generated as the complex vector according to a predetermined scheme; a random mapper for randomly mapping the symbols for which the frequency-space mapping has been performed on a frequency plane through at least one transmit antenna; an Inverse Fast Fourier Transform (IFFT) unit for performing an IFFT for the symbols for which the frequency-space mapping has been performed; and a gradient algorithm unit for receiving IFFTed signals from the IFFT unit and reducing the PAPR.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
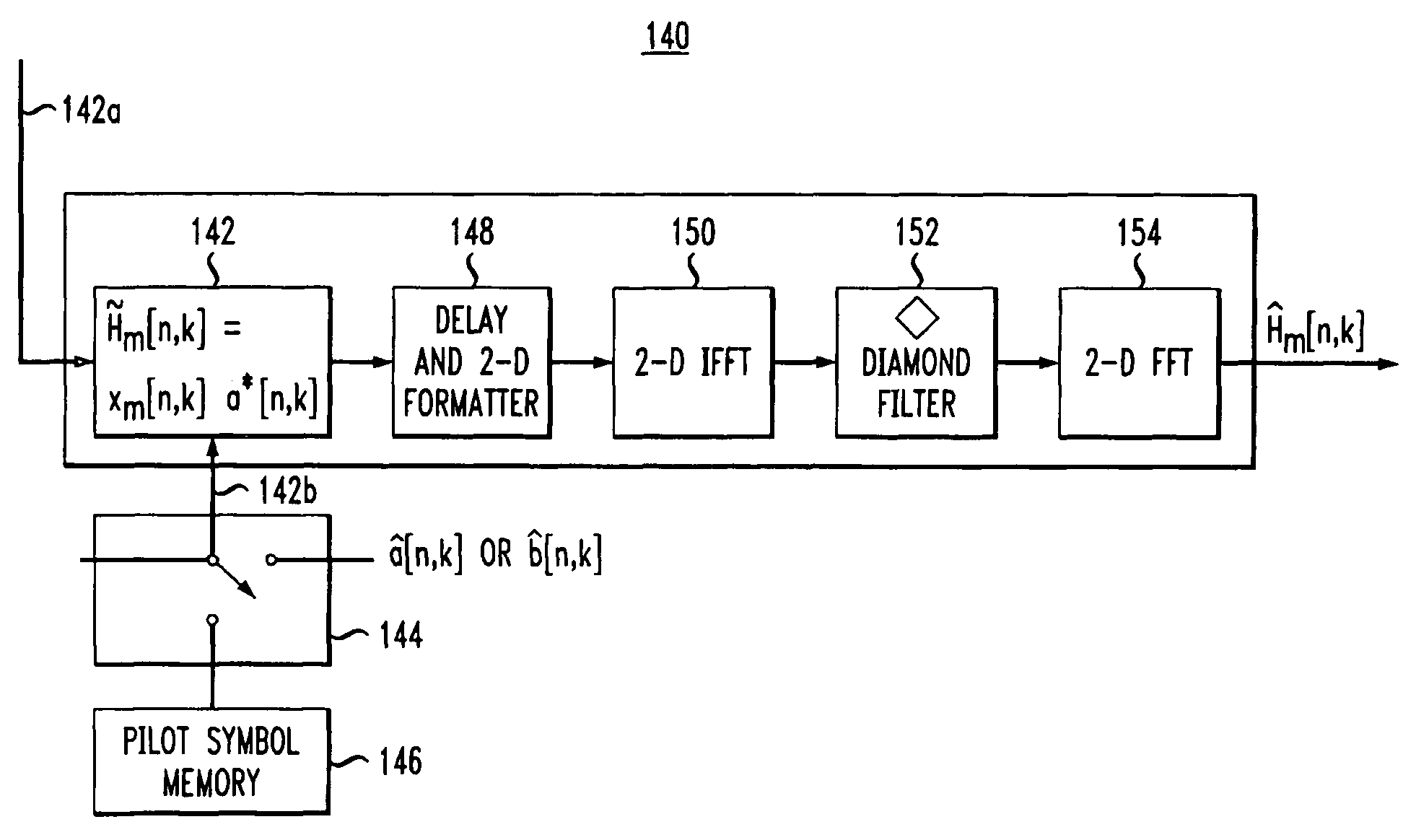
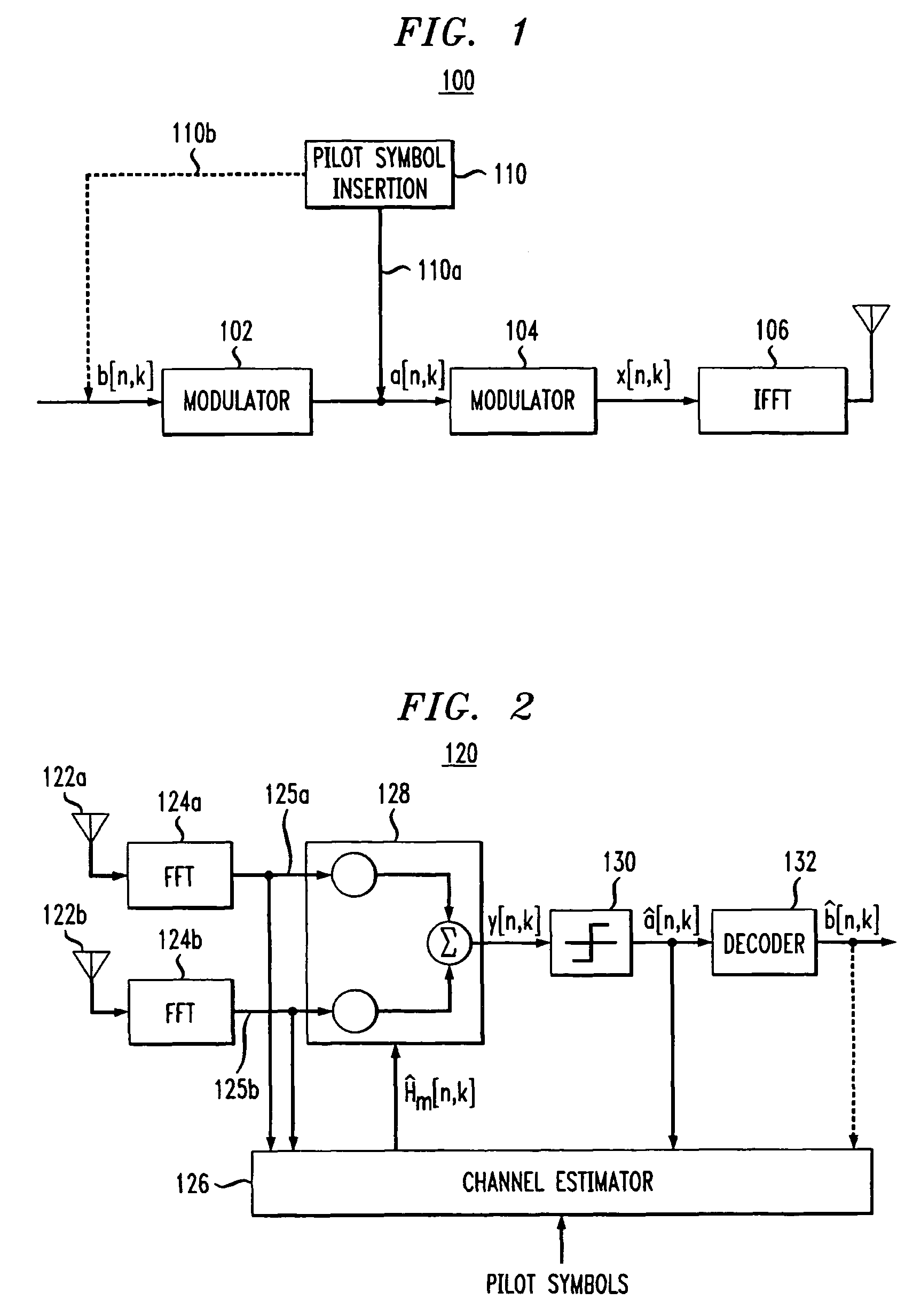
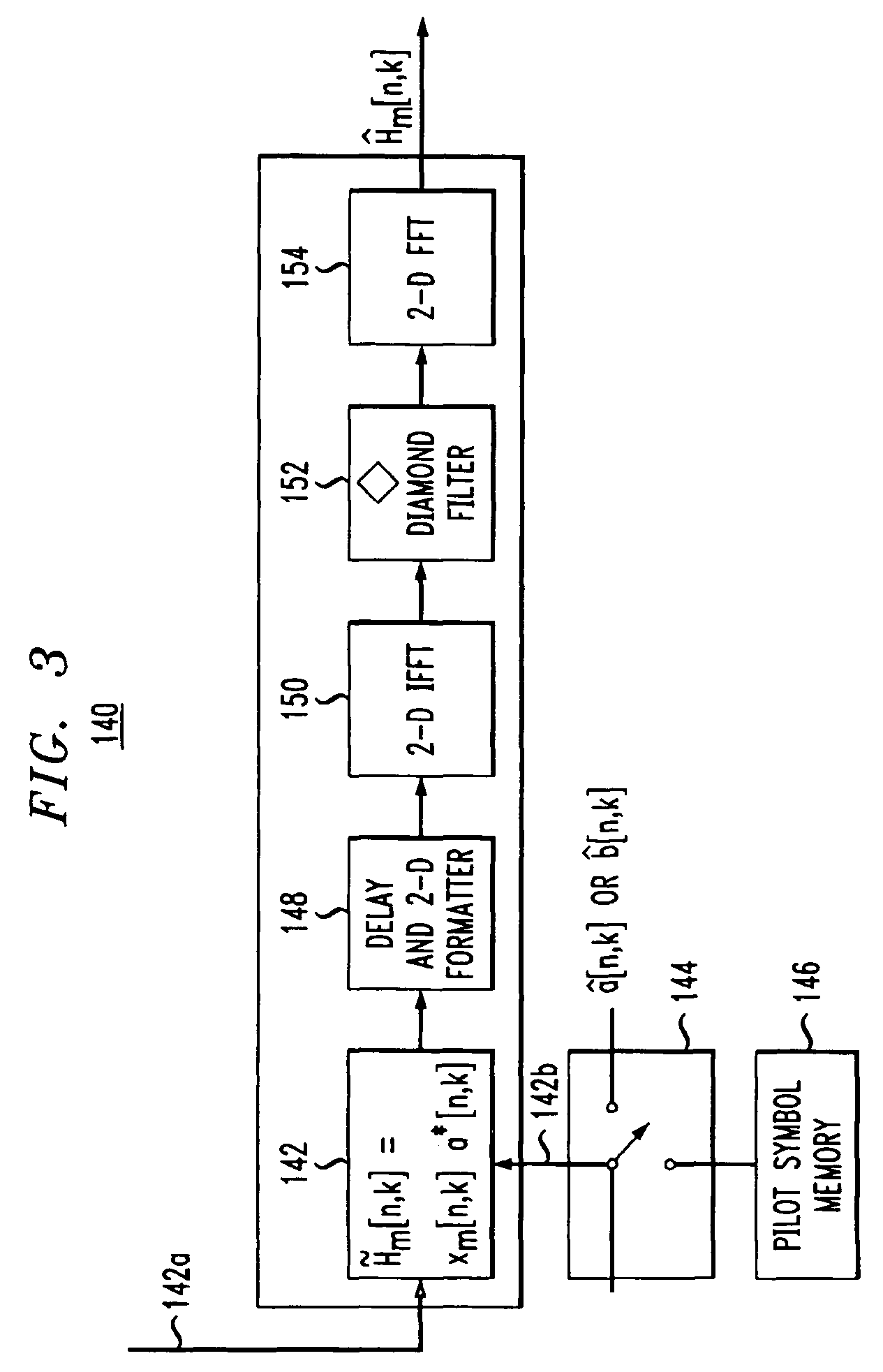
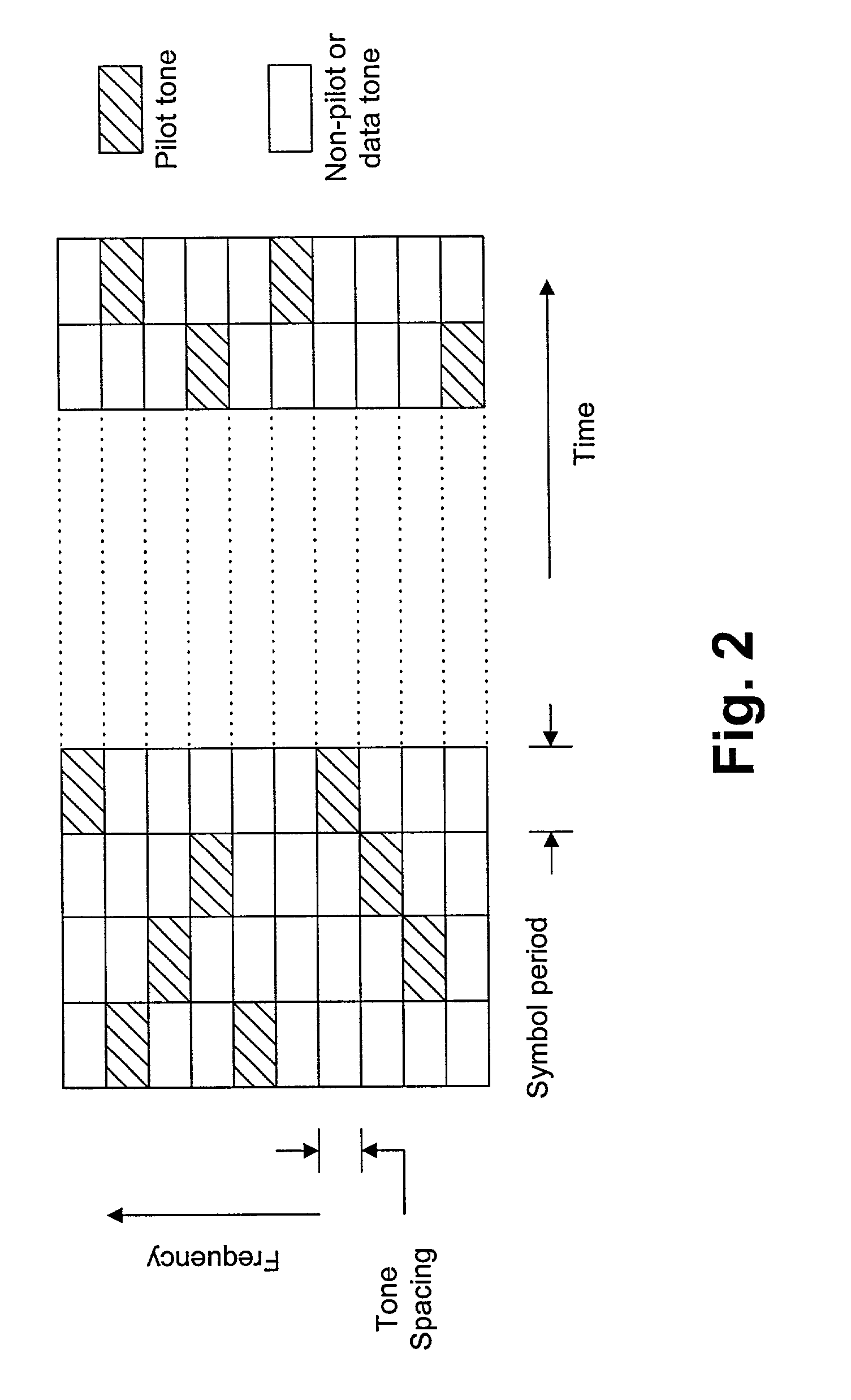
Pilot-aided channel estimation for OFDM in wireless systems
InactiveUS7292651B2Robust parameter estimationNoise-reduced channelFrequency-division multiplex detailsSecret communicationCommunications systemFourier transform on finite groups
A method and apparatus for pilot-symbol aided channel estimation in a wireless digital communication system which transmits packets of N OFDM data blocks, each data block comprising a set of K orthogonal carrier frequencies. At the transmitter, pilot symbols are inserted into each data packet at known positions so as to occupy predetermined positions in the time-frequency space. At the receiver, the received signal is subject to a two-dimensional inverse Fourier transform, two-dimensional filtering and a two-dimensional Fourier transform to recover the pilot symbols so as to estimate the channel response.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
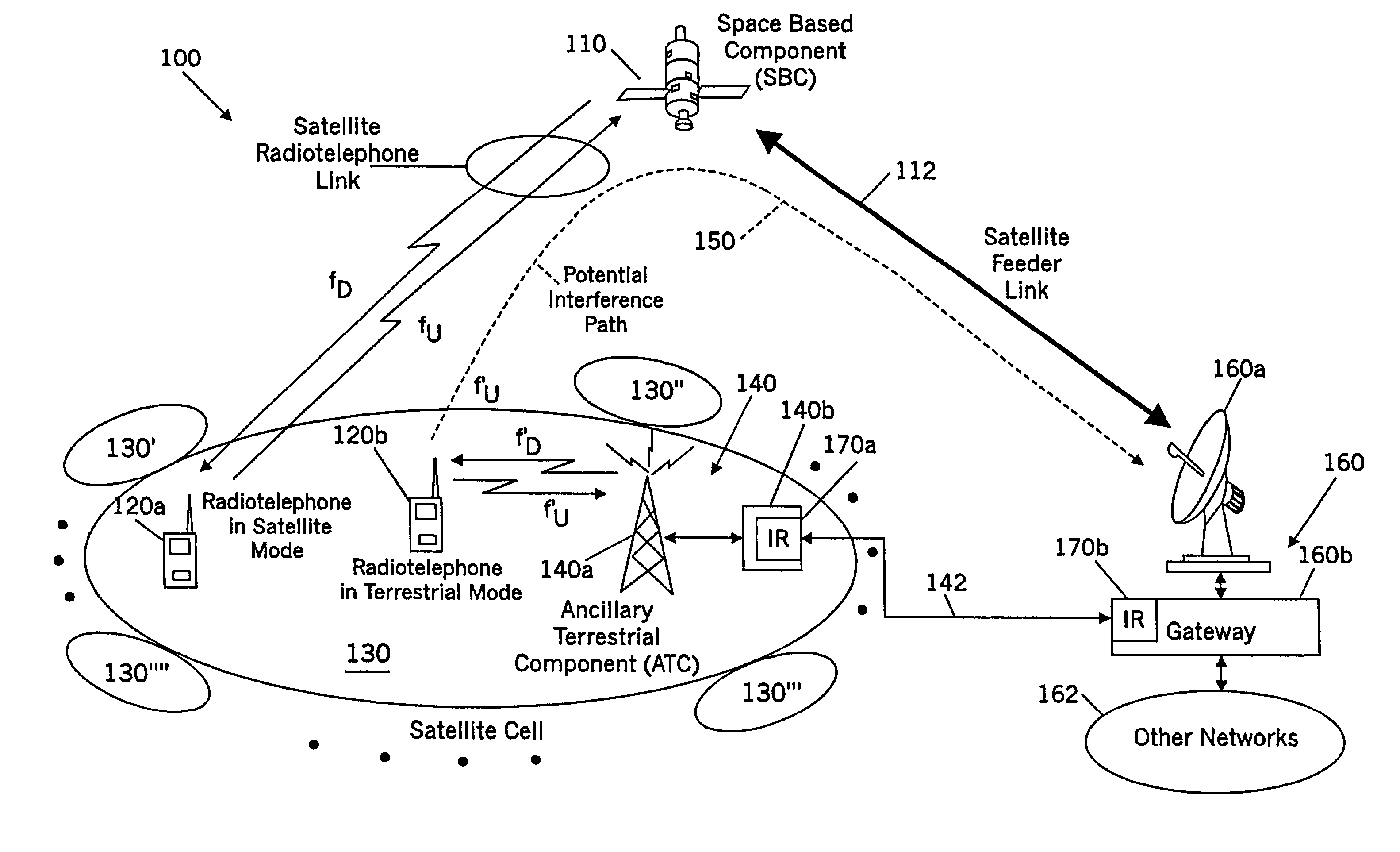
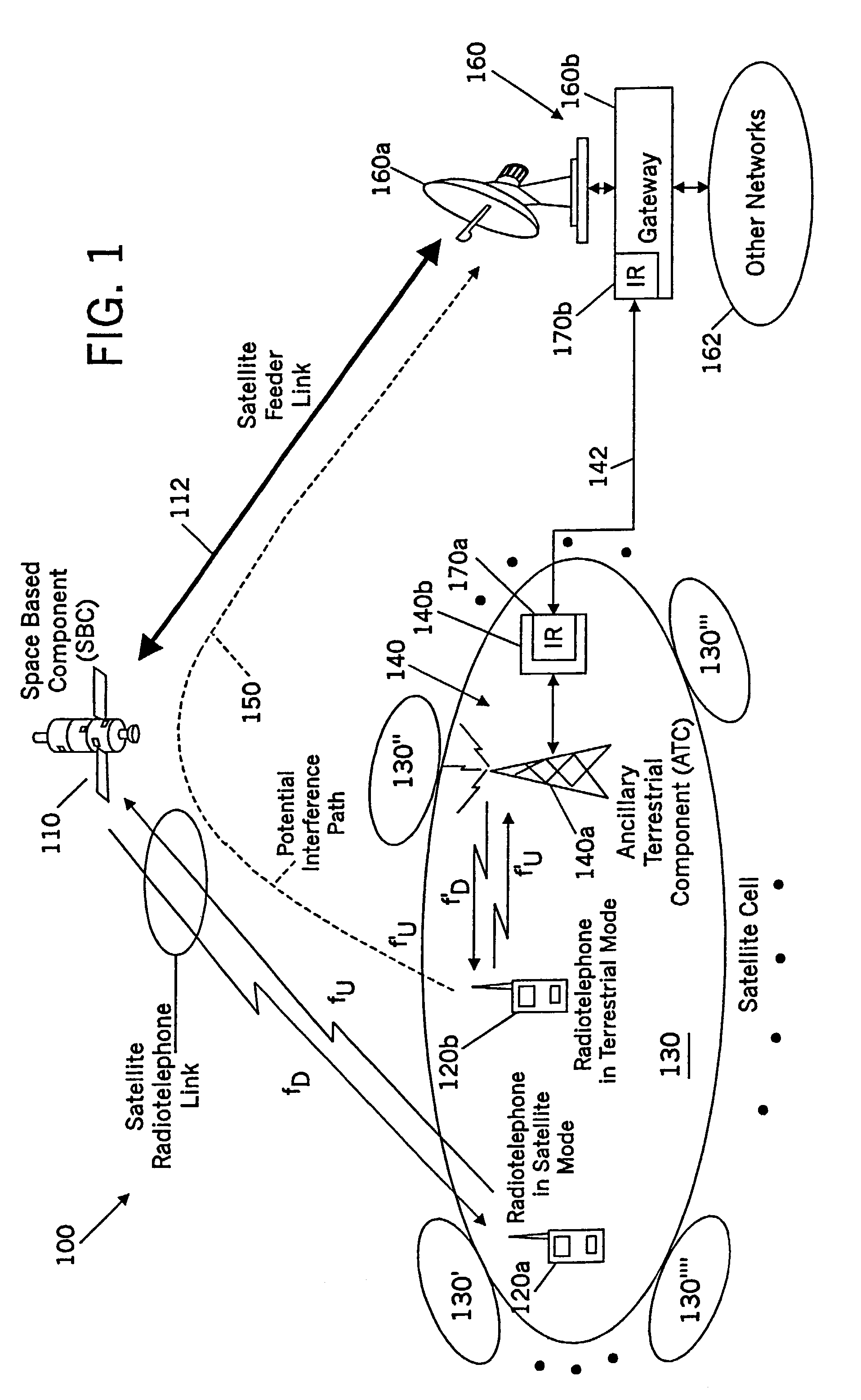
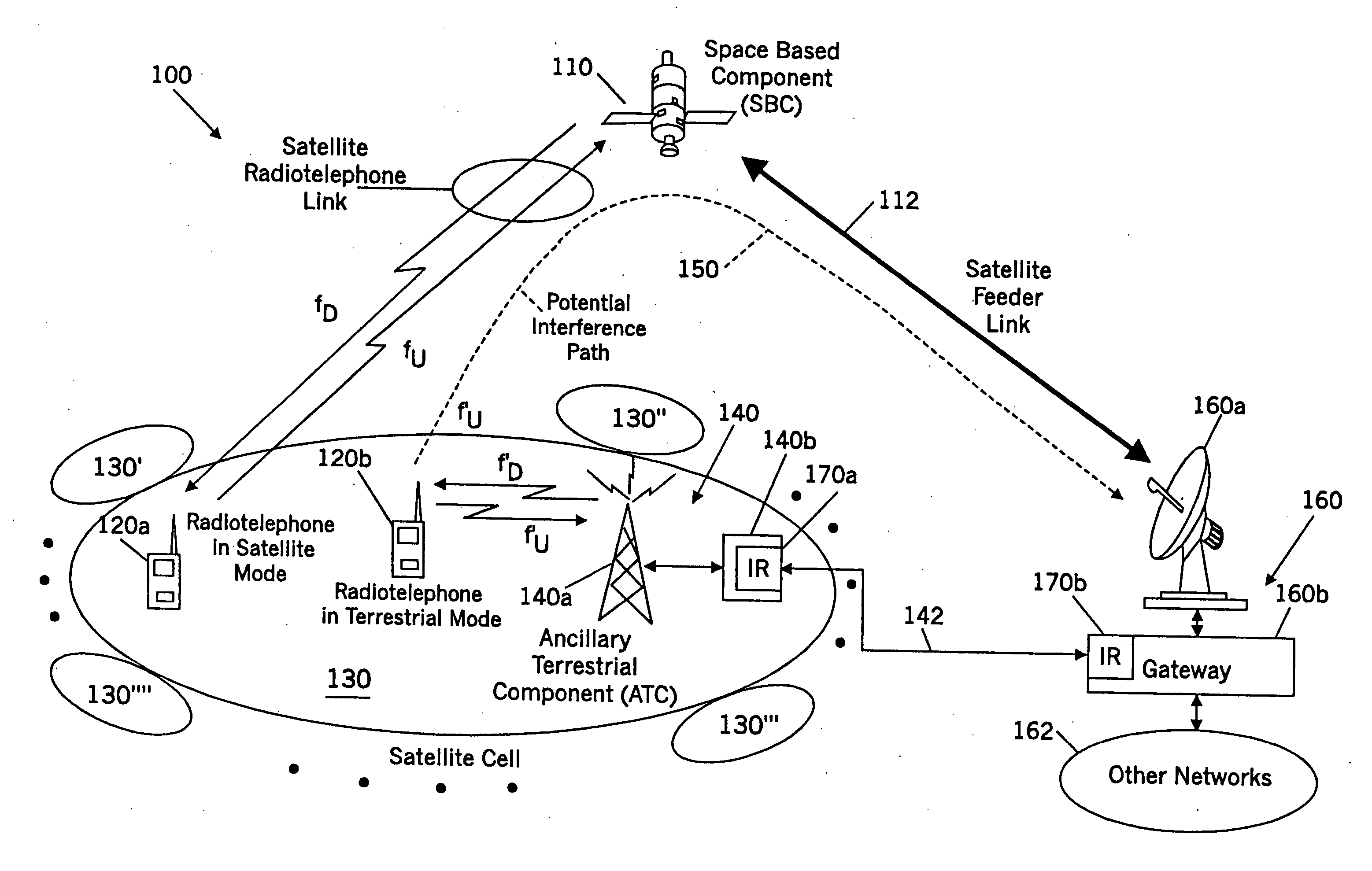
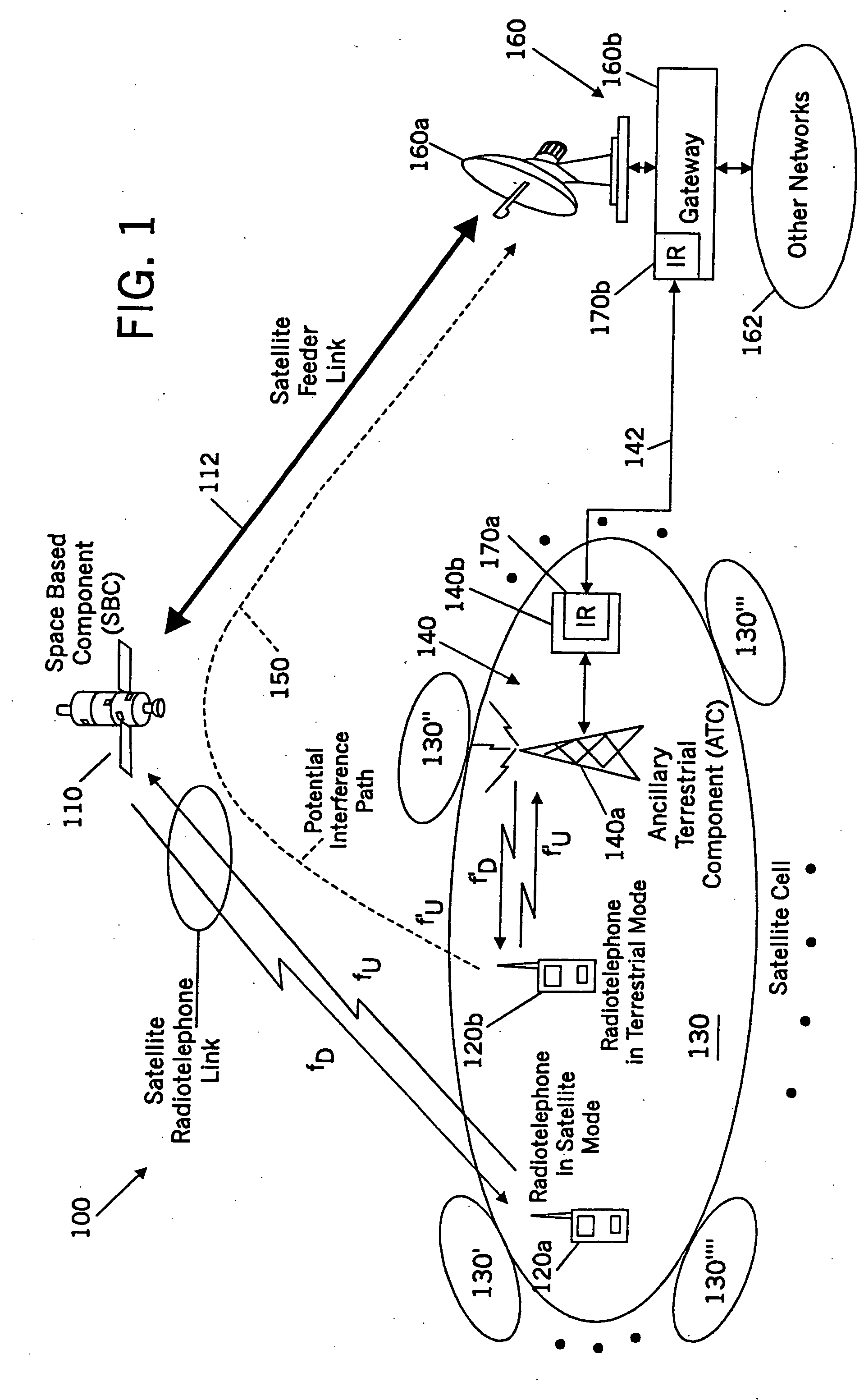
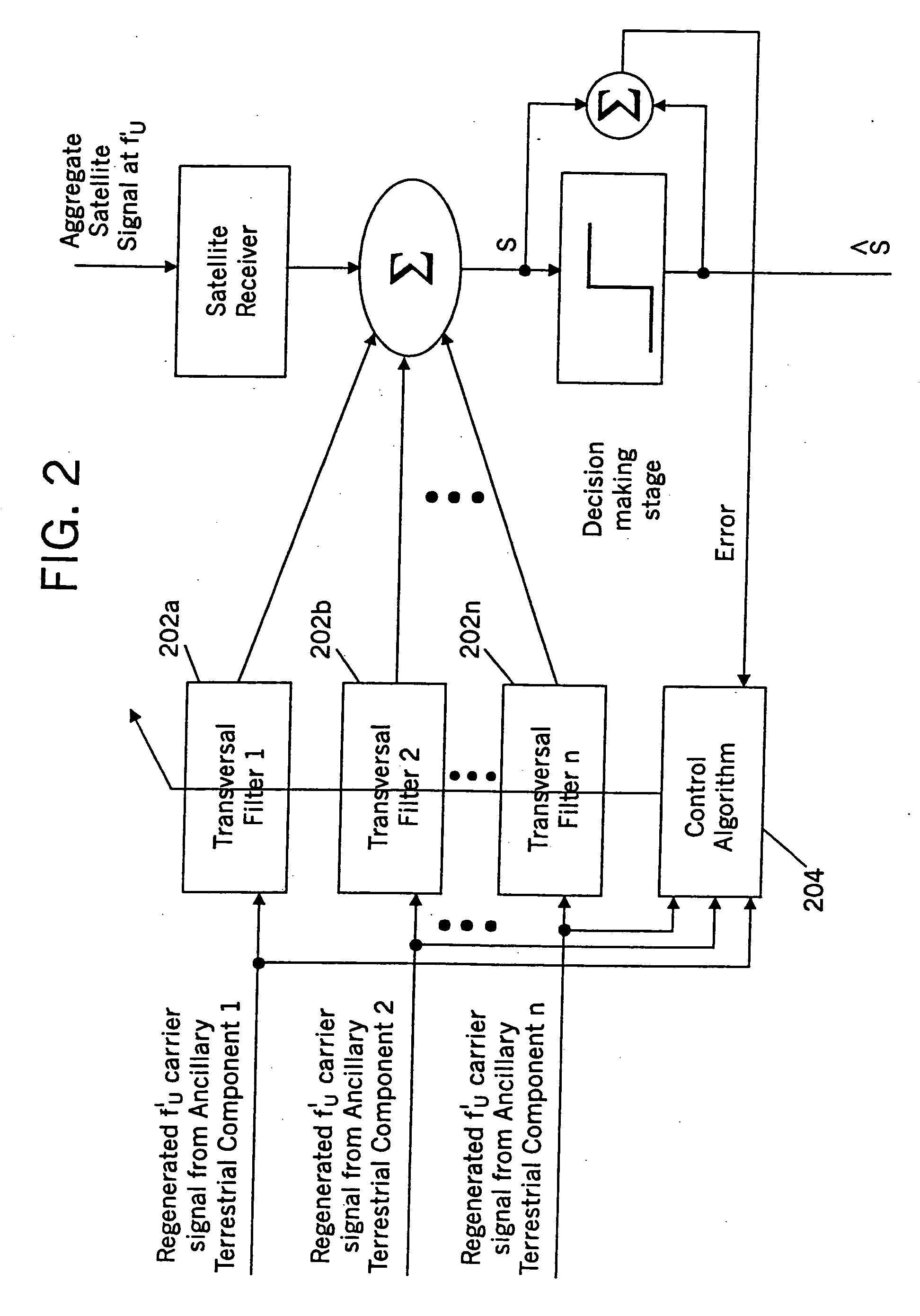
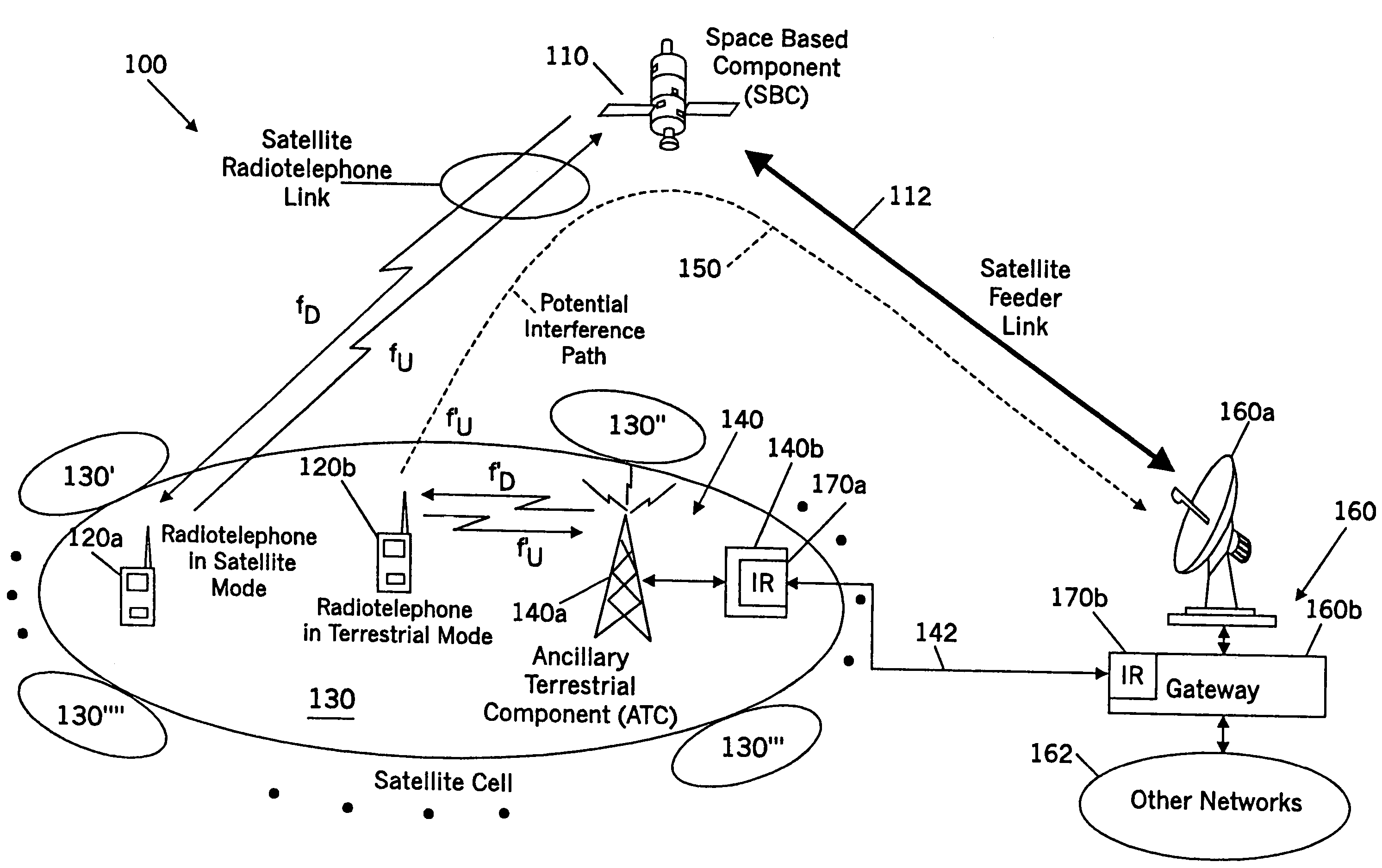
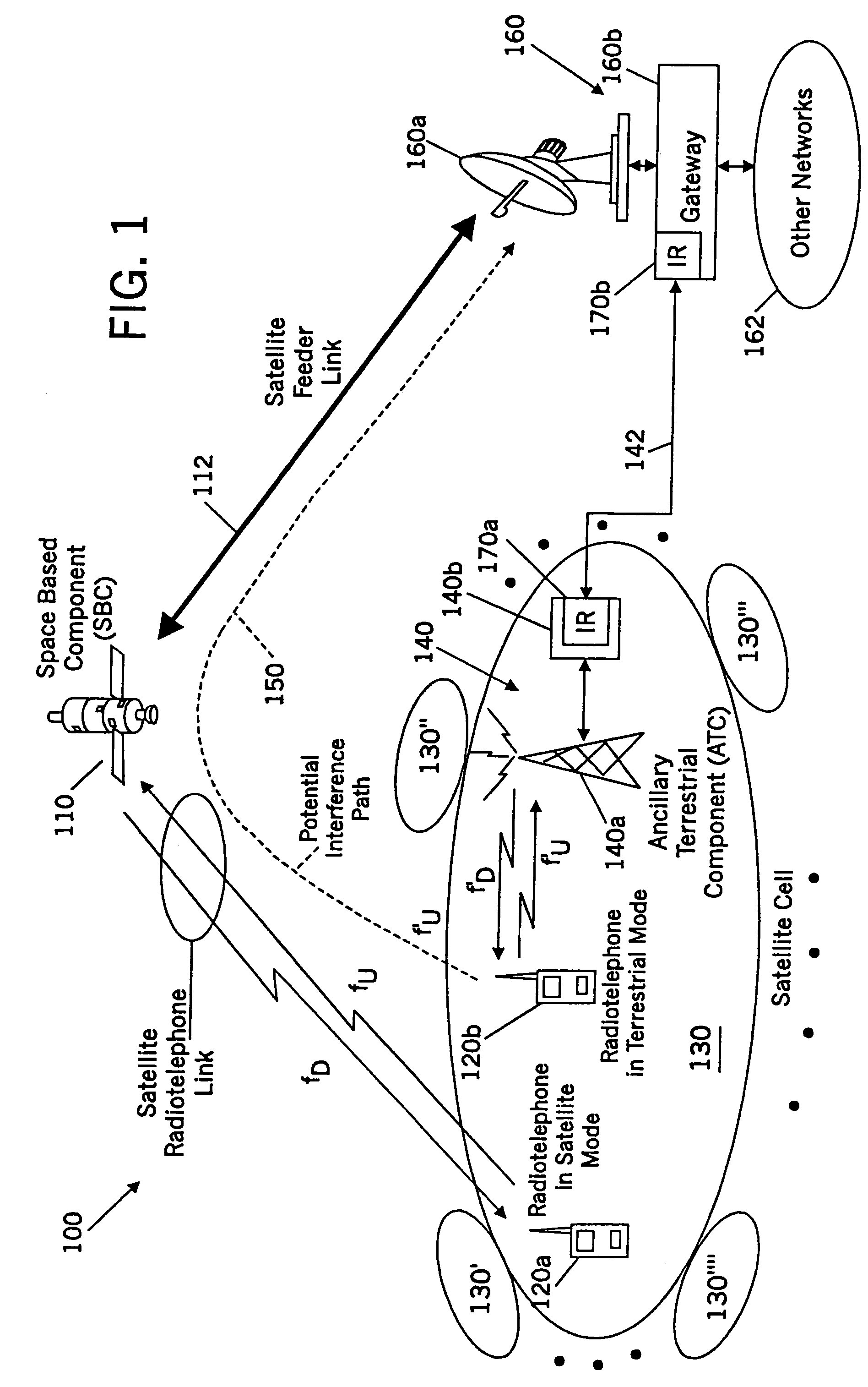
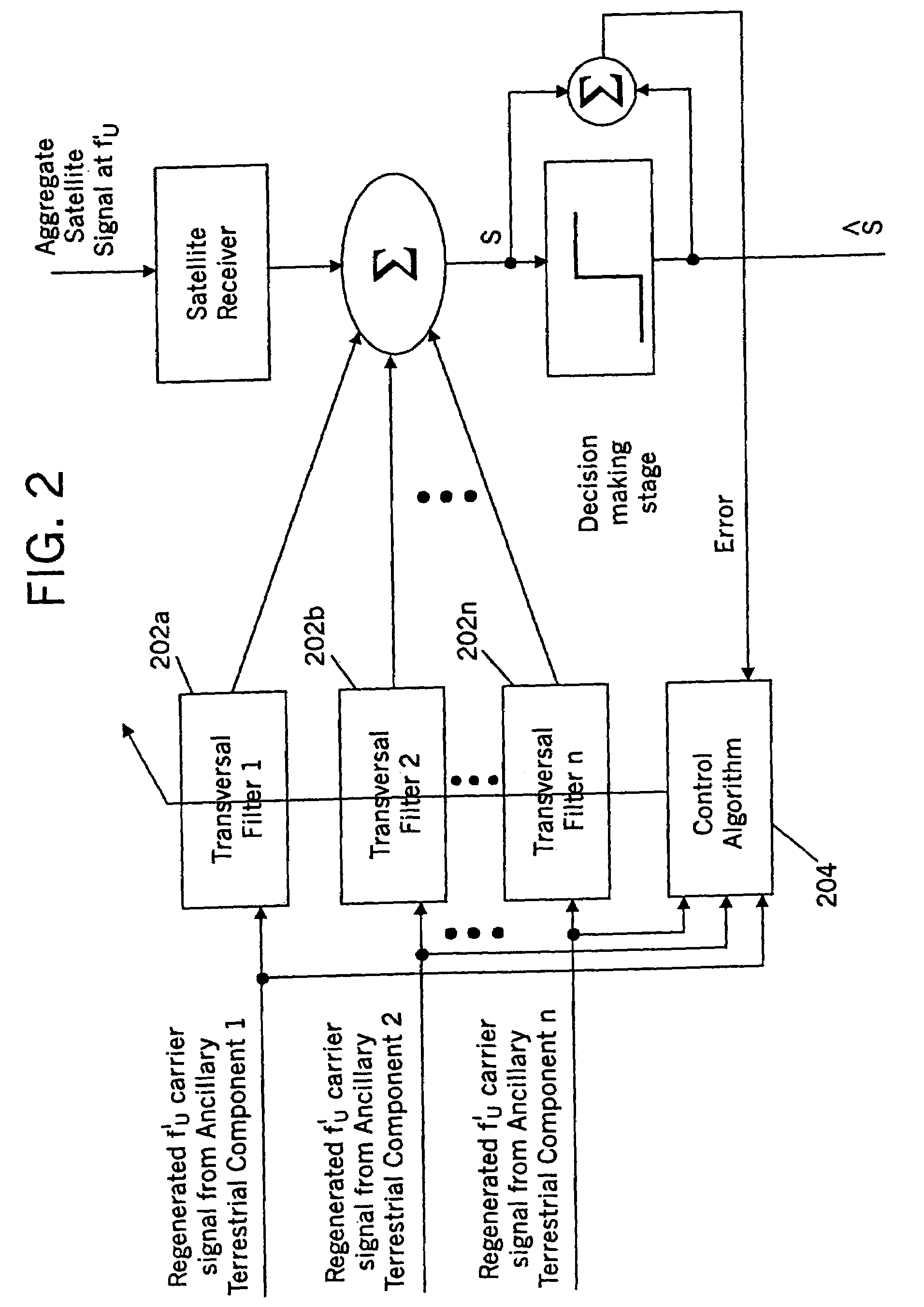
Methods and systems for modifying satellite antenna cell patterns in response to terrestrial reuse of satellite frequencies
InactiveUS7062267B2Reduce distractionsDegraded radiation patternUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionEavesdropping prevention circuitsSatellite antennasCell pattern
Space-based wireless radiotelephone communications are provided in a satellite footprint over a satellite radiotelephone frequency band. The satellite footprint is divided into satellite cells in which satellite radiotelephone frequencies of the satellite radiotelephone frequency band are spatially reused. At least one of the satellite radiotelephone frequencies that is assigned to a given satellite cell in the satellite footprint is terrestrially reused outside the given satellite cell. A radiation pattern of at least the given satellite cell is modified to reduce interference with the at least one of the satellite radiotelephone frequencies that is terrestrially reused outside the given satellite cell.
Owner:ATC TECH LLC
Signal modulation method resistant to echo reflections and frequency offsets
ActiveUS20120201322A1Improve performancePromote decompositionModulated-carrier systemsNetwork traffic/resource managementHigh rateFrequency shift
A method of modulating communications signals, such as optical fiber, wired electronic, or wireless signals in a manner that facilitates automatic correction for the signal distortion effects of echoes and frequency shifts, while still allowing high rates of data transmission. Data symbols intended for transmission are distributed into N×N matrices, and used to weigh or modulate a family of cyclically time shifted and cyclically frequency shifted waveforms. Although these waveforms may then be distorted during transmission, their basic cyclic time and frequency repeating structure facilitates use of improved receivers with deconvolution devices that can utilize the repeating patterns to correct for these distortions. The various waveforms may be sent in N time blocks at various time spacing and frequency spacing combinations in a manner that can allow interleaving of blocks from different transmitters. Applications to channel sounding / characterization, system optimization, and also radar are also discussed.
Owner:COHERE TECH
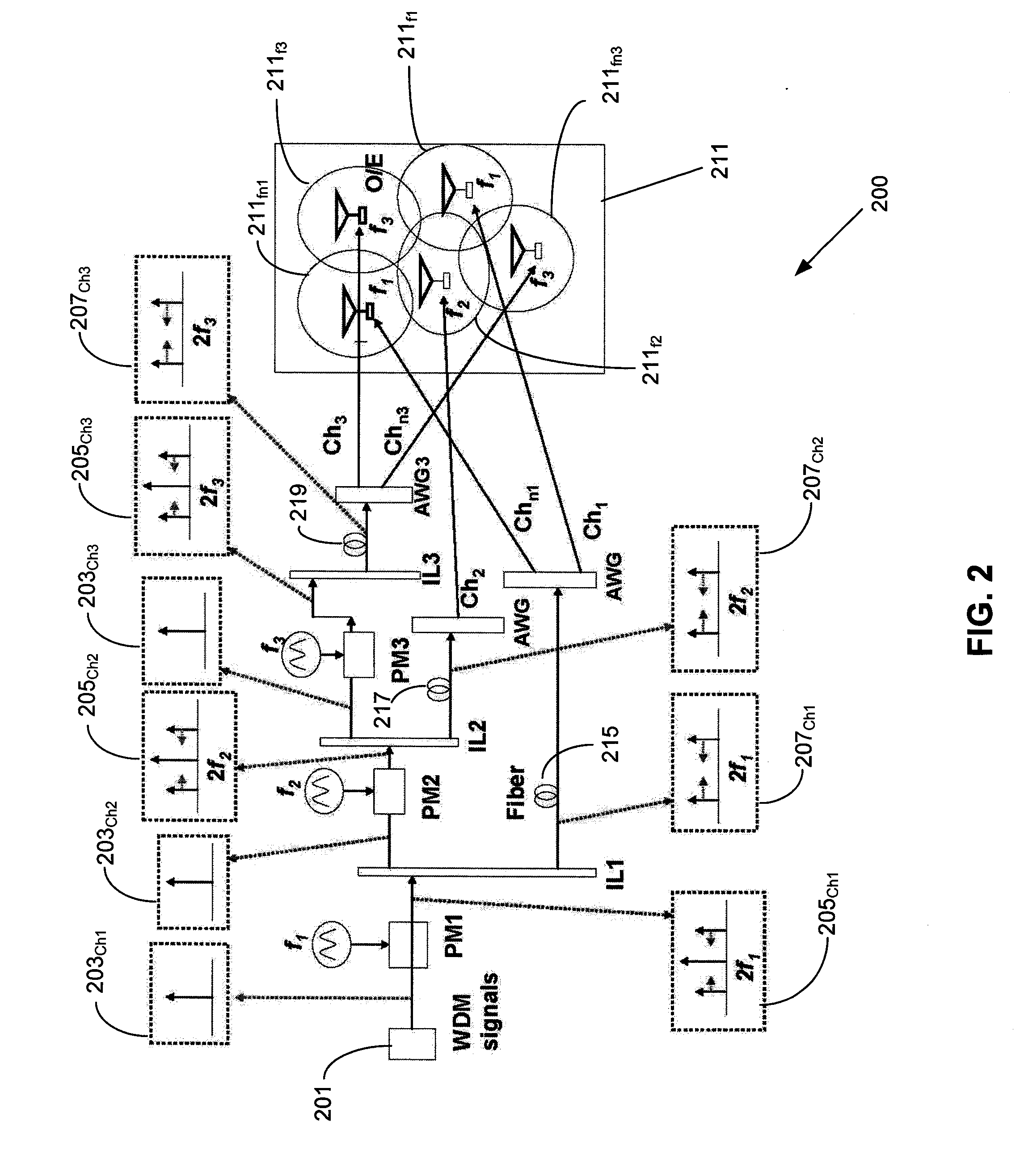
Optical Re-Modulation in DWDM Radio-Over-Fiber Network
InactiveUS20070292143A1Reduce distractionsElectromagnetic transmittersRadio over fiberWireless transmission
An apparatus includes multiple signal paths for optically converting an optical signal to multiples of the optical signal at different respective carrier frequencies for reducing interference between wireless transmissions of the multiples of the optical signal. Preferably, the converting includes a first modulator for modulating the optical signal into a first optical carrier and an initial first-order sideband signal with a frequency spacing twice that of the first optical carrier and a first interleaver for separating the first optical carrier and the initial first-order sideband signal. The converting also includes a second phase modulator for modulating the first optical carrier into a second optical carrier and a second first-order sideband signal with a frequency spacing twice that of the second optical carrier.
Owner:NEC LAB AMERICA
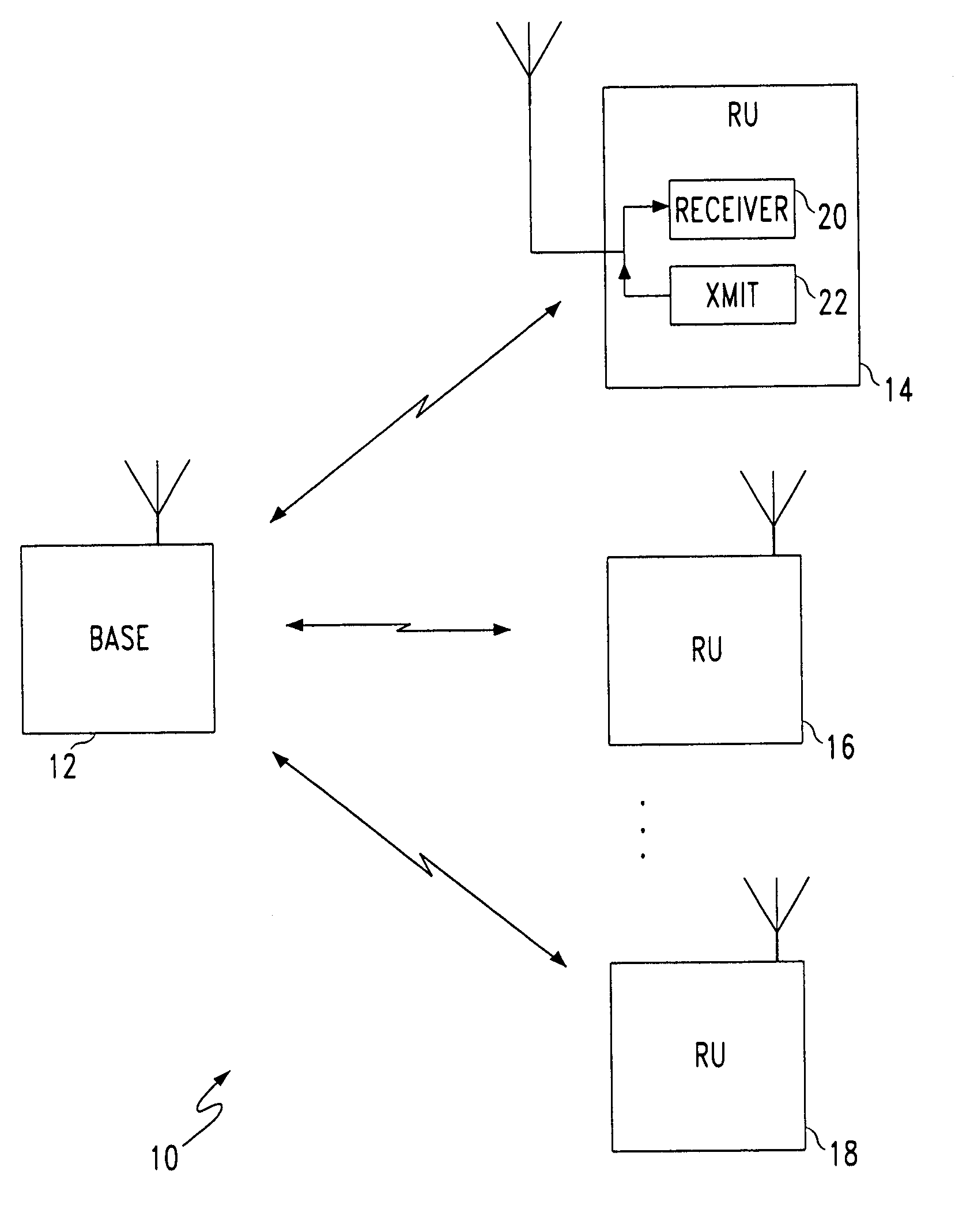
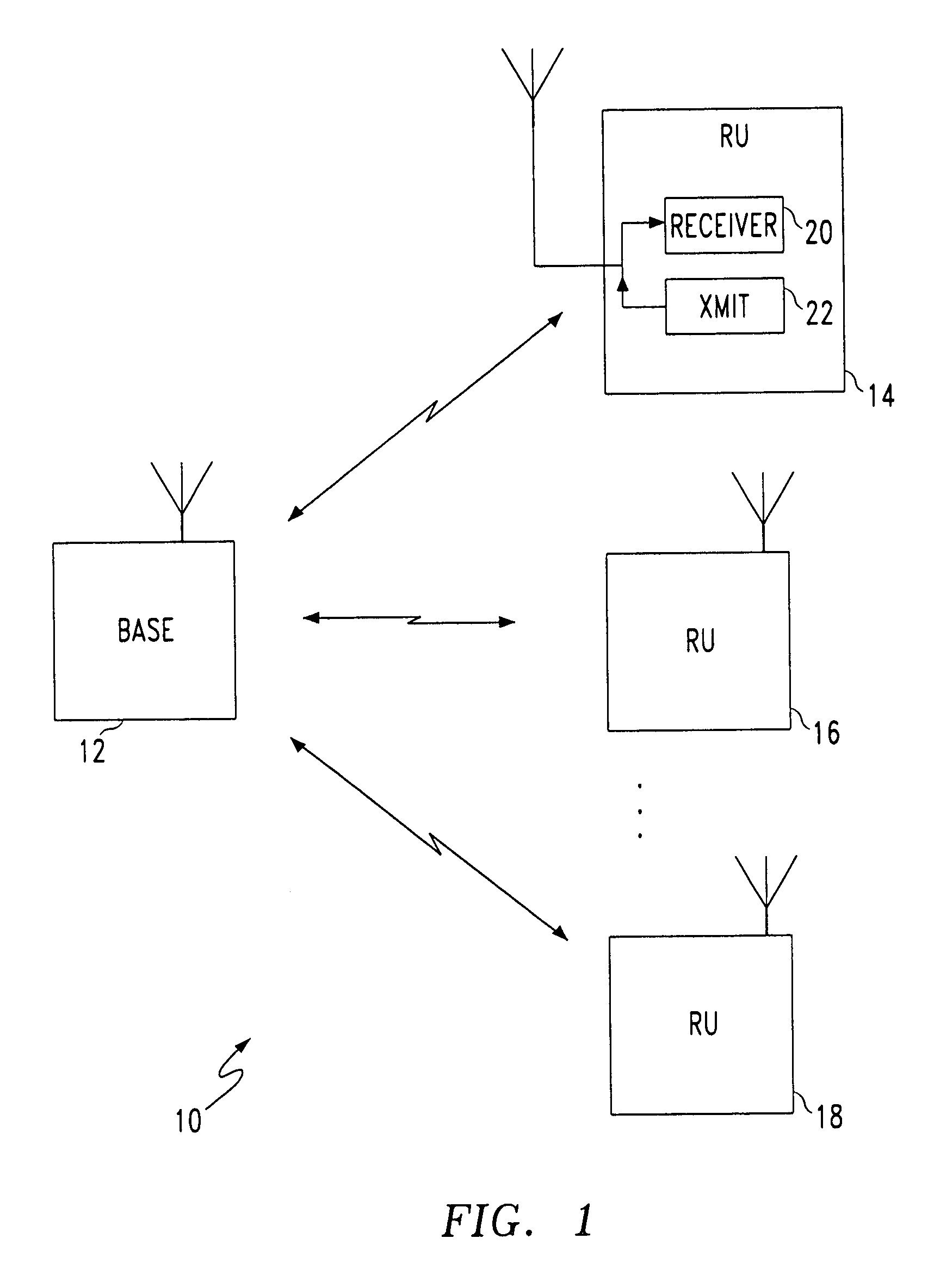
Collision-free multiple access reservation scheme for multi-tone modulation links
InactiveUS6967937B1Network traffic/resource managementTransmission path divisionCommunications systemOfdm communication system
A method is provided for multiple remote units (RU)s to efficiently utilize resources on a shared OFDM high speed data channel without collisions. A collision occurs when two or more RUs transmit on the same frequency at the same time. The method defines two distinct states for accessing the channel. These are the Arbitration state and the Data Transfer state. A base station transmits a flag on the downlink to notify the RUs of which state is in effect. RUs having a data message notify the base station by transmitting a frequency tone, which acts as a request to transmit data, during the arbitration state. The tone frequencies are frequency spaced to be mutually orthogonal, so that the base station can receive all the uplink requests simultaneously. Upon receiving the uplink request signals, the base station establishes the data transfer state and orders the uplink data messages from the remote units is a non-interfering sequence. A system for preventing uplink data message collisions in an OFDM communications system is also provided.
Owner:AT&T WIRELESS SERVICES
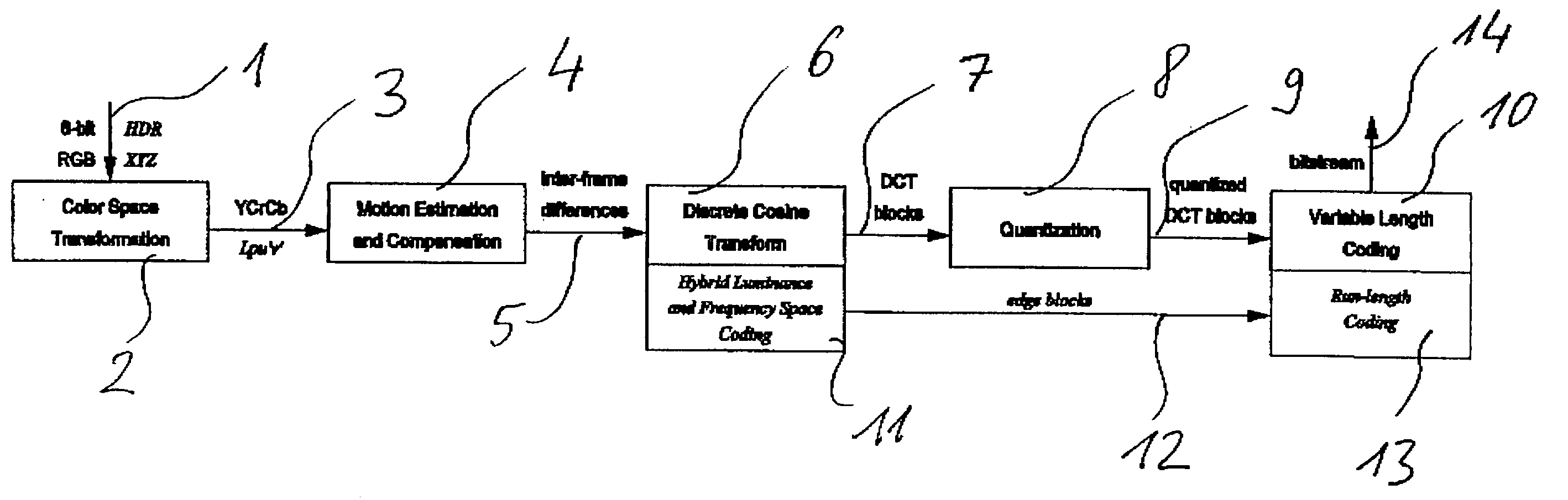
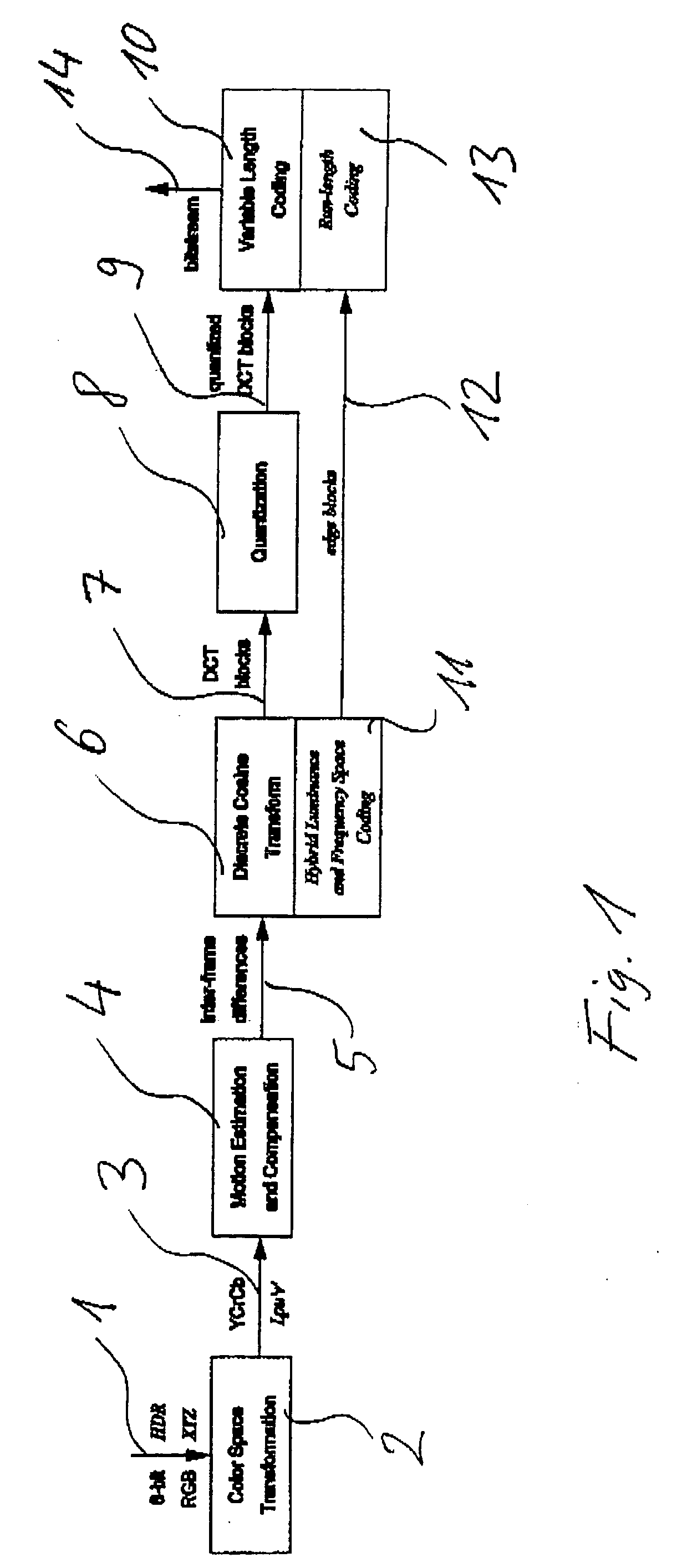
Method and apparatus for encoding high dynamic range video
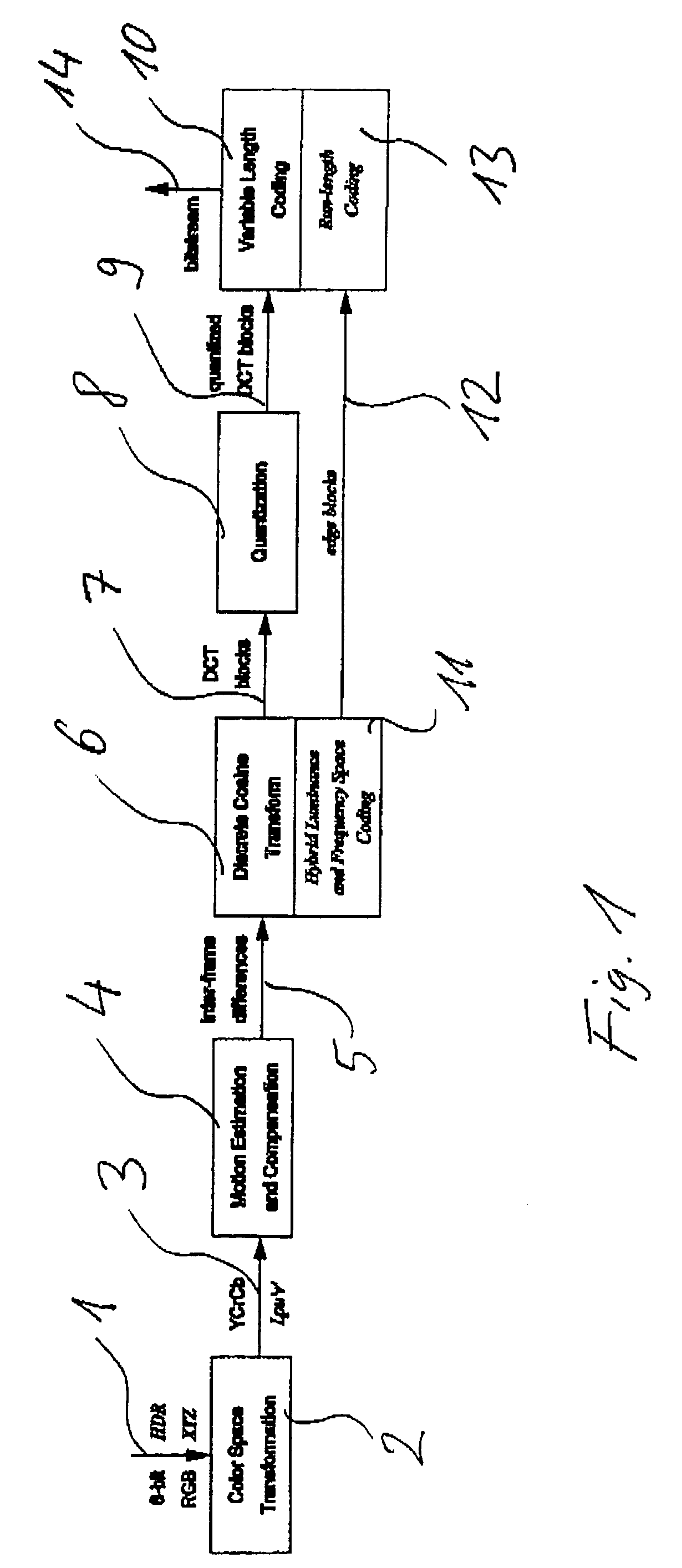
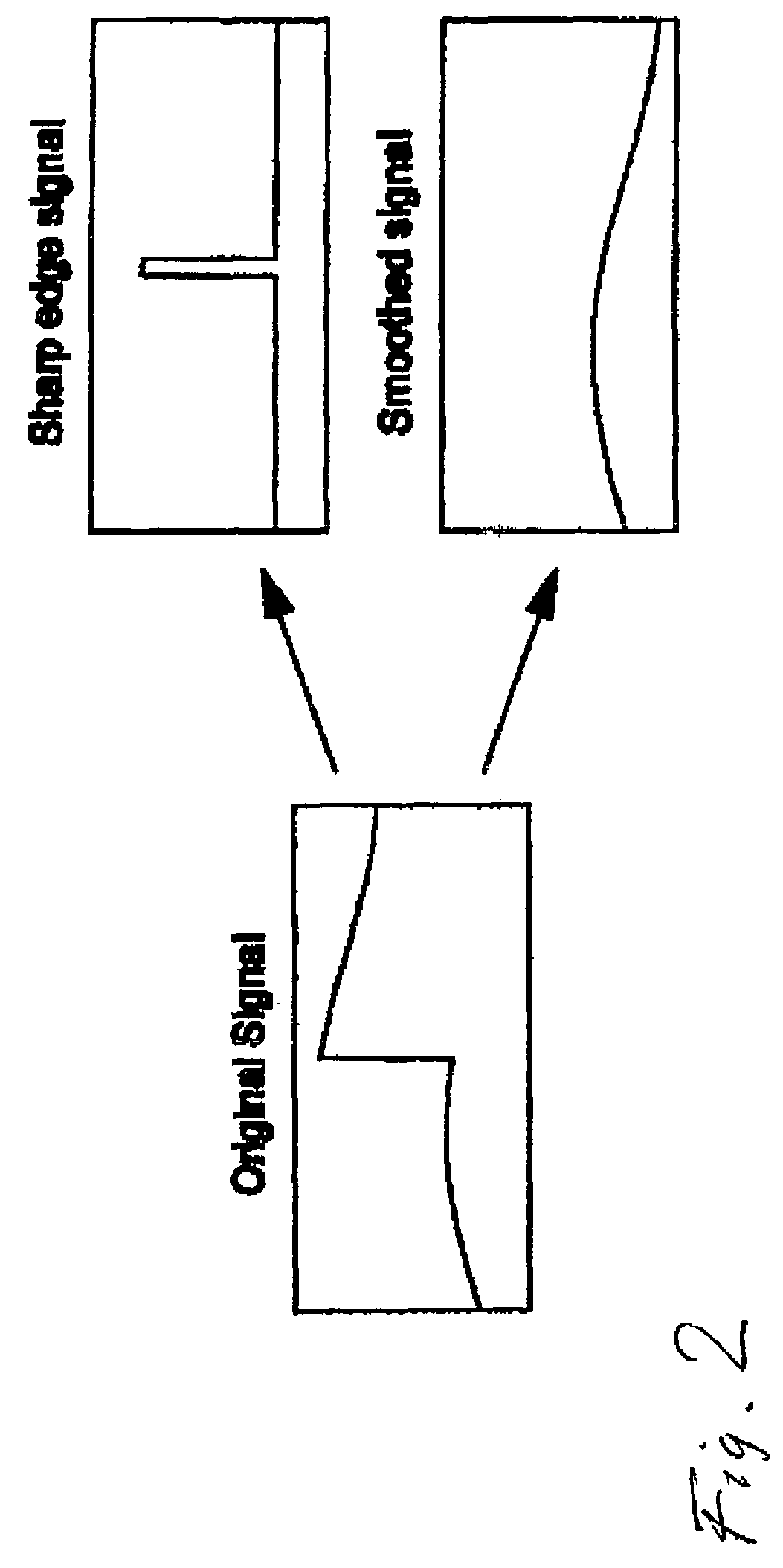
InactiveUS20060002611A1Good colorIncrease rangeColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionPattern recognitionData stream
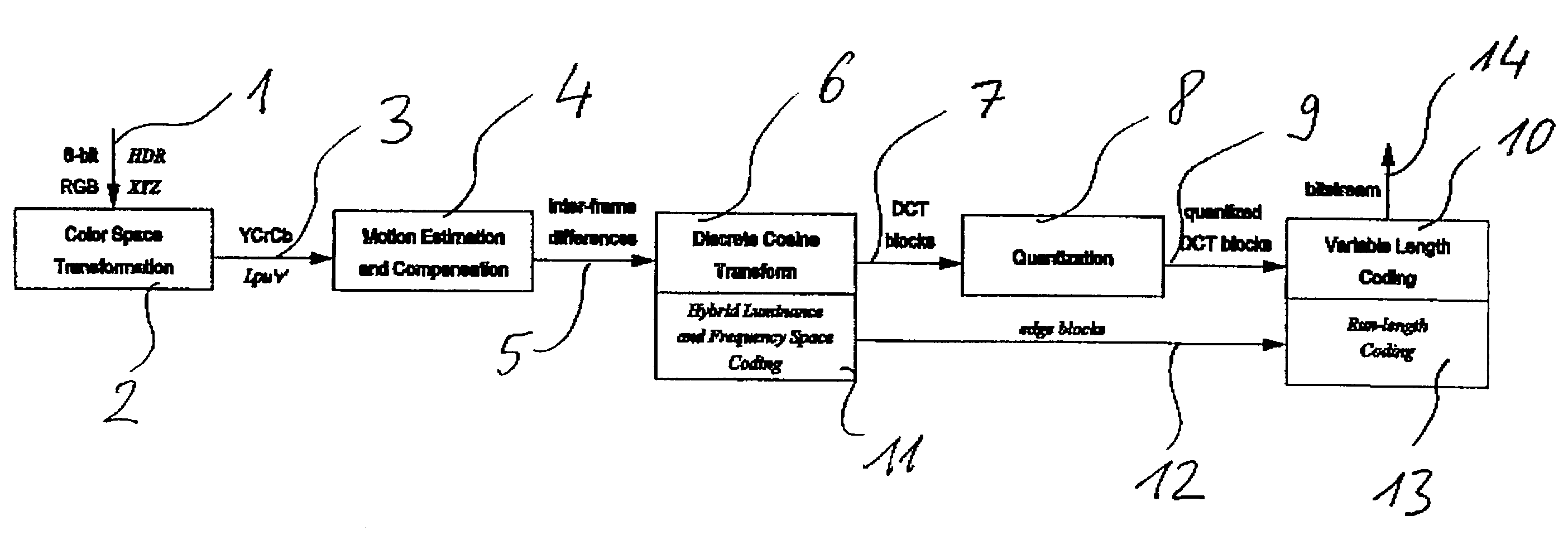
A method and apparatus for encoding high dynamic range video by means of video compression is shown. The method comprises the steps of providing high dynamic range (HDR) tristimulus color data (XYZ) for each frame of the video and threshold versus intensity data for a human observer; constructing a perceptually conservative luminance transformation from continuous luminance data (Y) to discrete values (Lp) using said threshold versus intensity data for the human observer; transforming the HDR tristimulus color data into perceptually linear color data of three color channels (Lp, u′, v′) for obtaining visually lossless compressed frames; estimating motion vector of said consecutive frames of the video and compensating the difference of the tristimulus color data for performing an inter-frame encoding and an inter-frame compression; transforming the compensated differences of the tristimulus color data to frequency space data; quantizing said frequency space data; variable-length encoding of the quantized frequency space data and storing or transmitting a stream of visual data resulting from the encoded quantized frequency space data;
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
Method and system for multi-carrier stochastic access
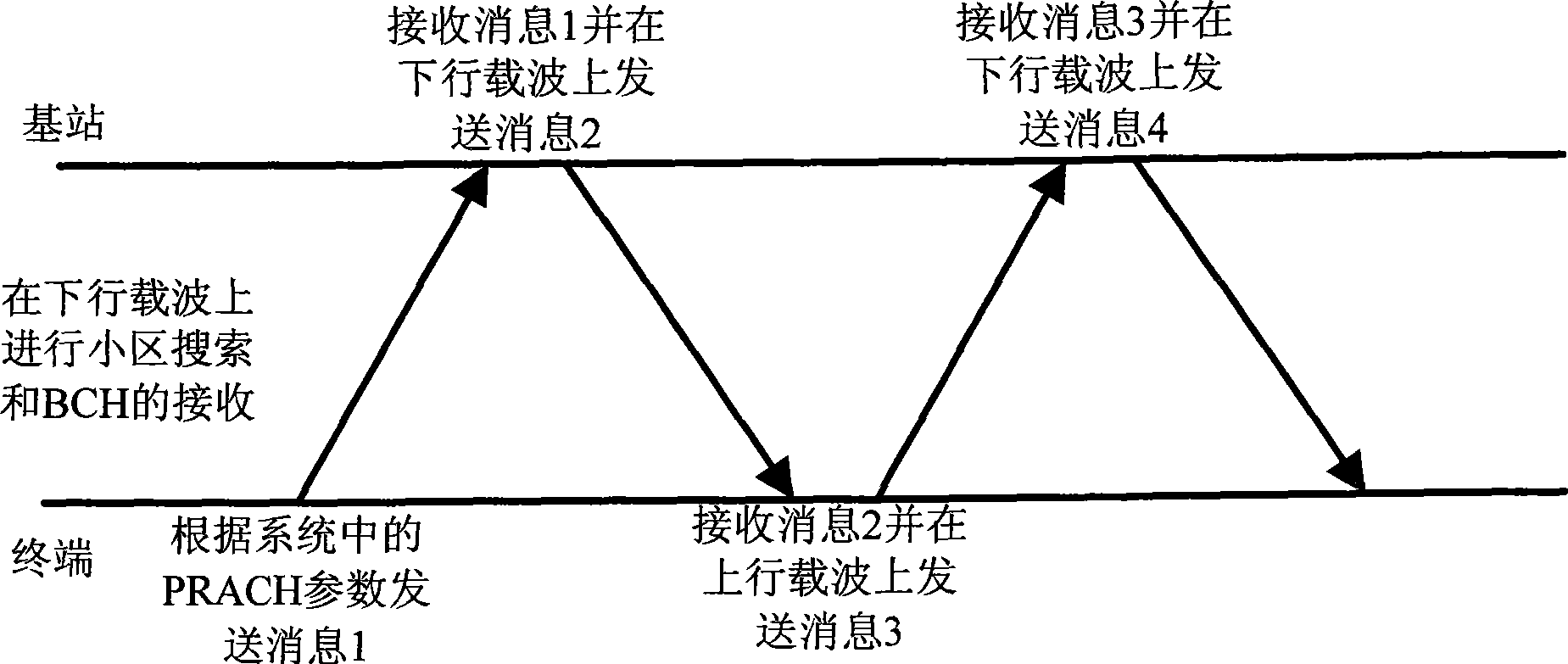
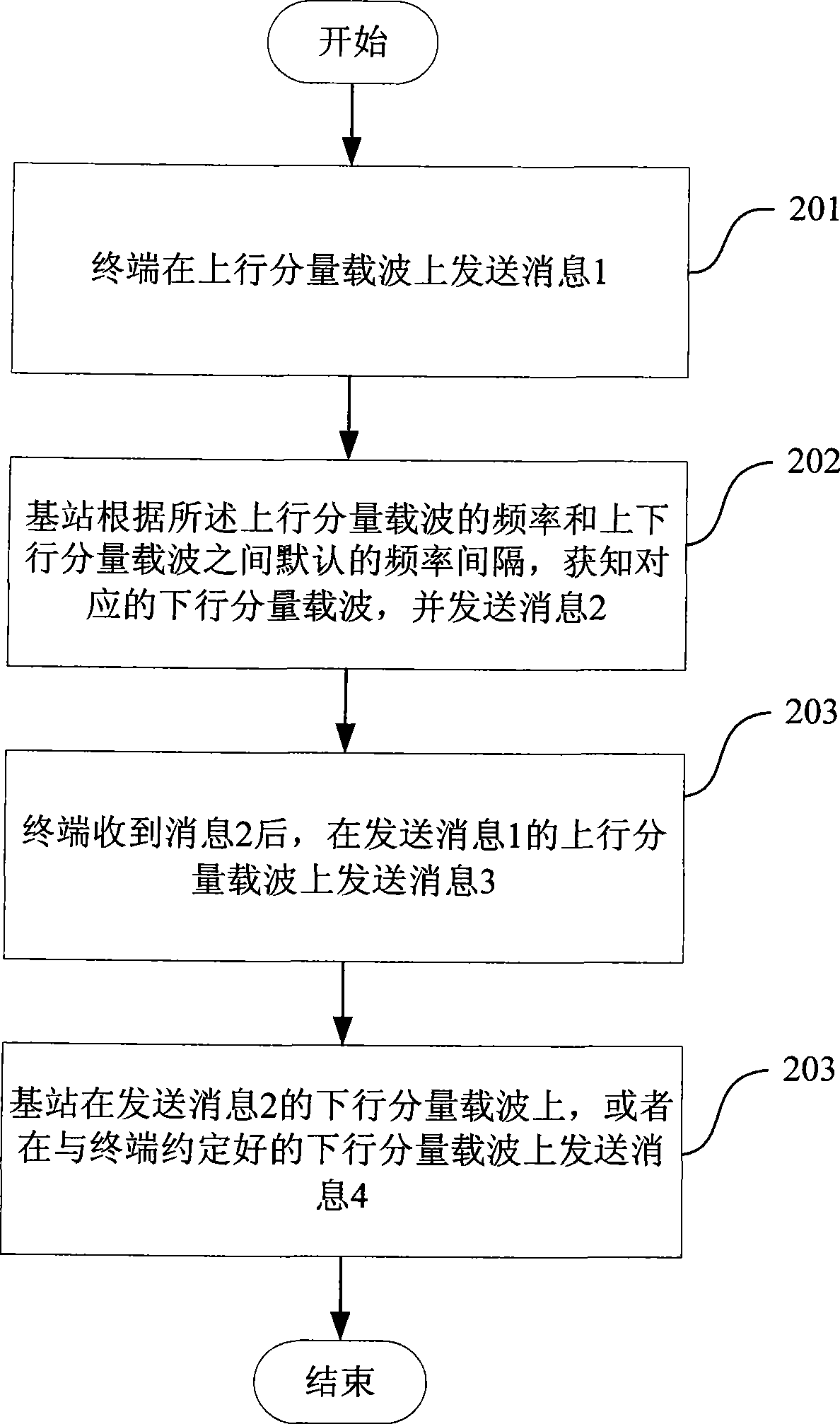
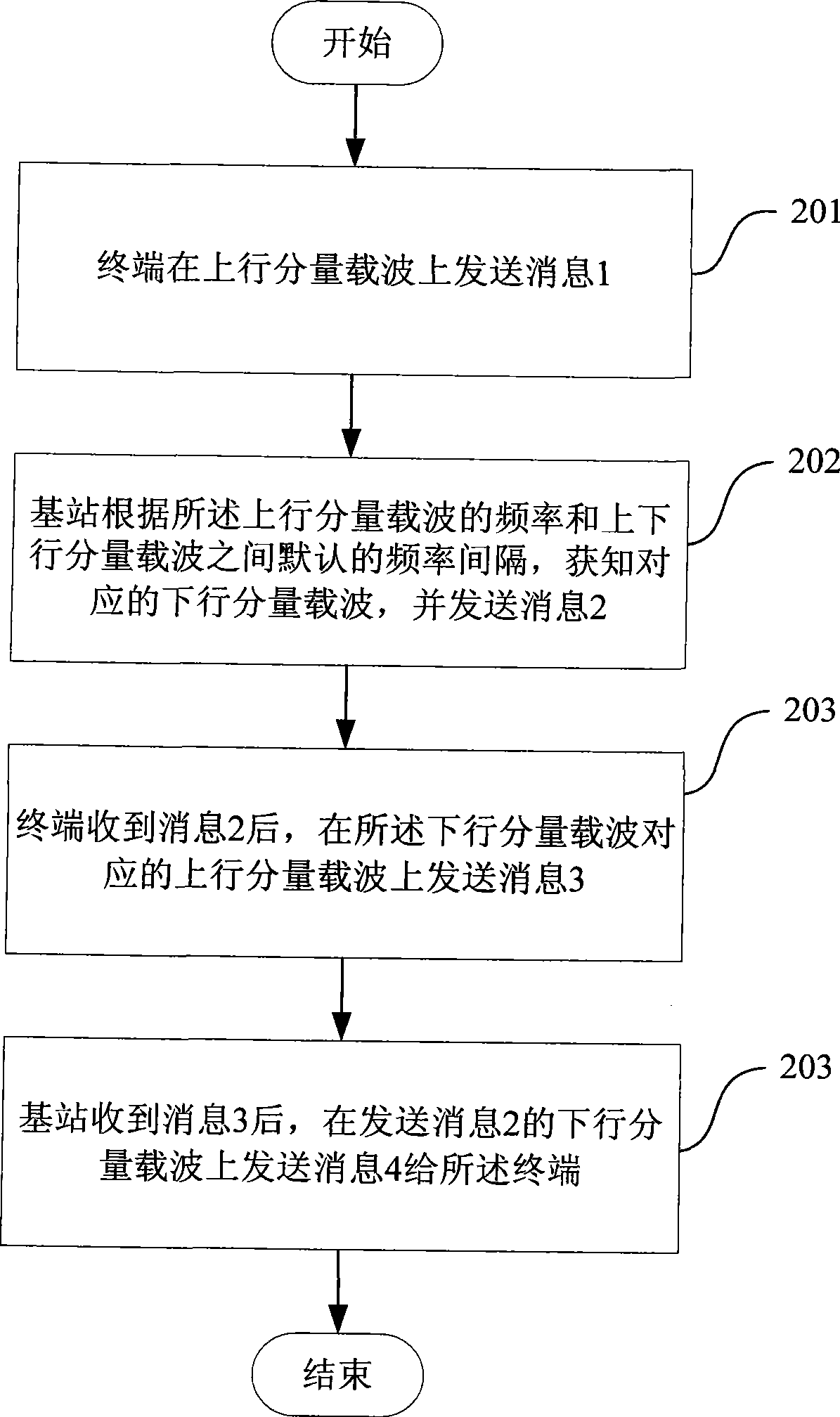
InactiveCN101505538ASolving the Uncertainty Problem of Downlink Component CarriersBackward Compatibility GuaranteedWireless communicationCarrier signalRandom-access channel
The invention discloses a method for random access of multiple carriers, which is applied to the condition of asymmetrical configuration of uplink and downlink carriers of an advanced long term evolution LTE-A system. The method comprises that: after receiving a leader sequence, a base station acquires a downlink component carrier corresponding to an uplink component carrier sending the leader sequence according to the frequency of the uplink component carrier and default frequency space between the uplink and downlink component carriers, sends random access channel RACH response messages on the downlink component carrier to a terminal, and sends competition resolving messages on the downlink component carrier sending the RACH response messages or the downlink component carrier agreed with the terminal to the terminal. The method can solve the problem of uncertainty of the downlink component carrier sending the RACH response messages and the competition resolving messages, and can maintain backward compatibility with LTE.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Methods and systems for configuring satellite antenna cell patterns in response to terrestrial use of satellite frequencies
InactiveUS20060135060A1Reduce distractionsReduce radiationRadio transmissionTransmission noise suppressionSatellite antennasCell pattern
Space-based wireless radiotelephone communications are provided in a satellite footprint over a satellite radiotelephone frequency band. The satellite footprint is divided into satellite cells in which satellite radiotelephone frequencies of the satellite radiotelephone frequency band are spatially reused. At least one of the satellite radiotelephone frequencies that is assigned to a given satellite cell in the satellite footprint is terrestrially reused outside the given satellite cell. A radiation pattern of at least the given satellite cell is modified to reduce interference with the at least one of the satellite radiotelephone frequencies that is terrestrially reused outside the given satellite cell.
Owner:ATC TECH LLC
Methods and systems for configuring satellite antenna cell patterns in response to terrestrial use of satellite frequencies
InactiveUS7295807B2Reduce distractionsReduce radiationRadio transmissionWireless commuication servicesSatellite antennasCell pattern
Space-based wireless radiotelephone communications are provided in a satellite footprint over a satellite radiotelephone frequency band. The satellite footprint is divided into satellite cells in which satellite radiotelephone frequencies of the satellite radiotelephone frequency band are spatially reused. At least one of the satellite radiotelephone frequencies that is assigned to a given satellite cell in the satellite footprint is terrestrially reused outside the given satellite cell. A radiation pattern of at least the given satellite cell is modified to reduce interference with the at least one of the satellite radiotelephone frequencies that is terrestrially reused outside the given satellite cell.
Owner:ATC TECH LLC
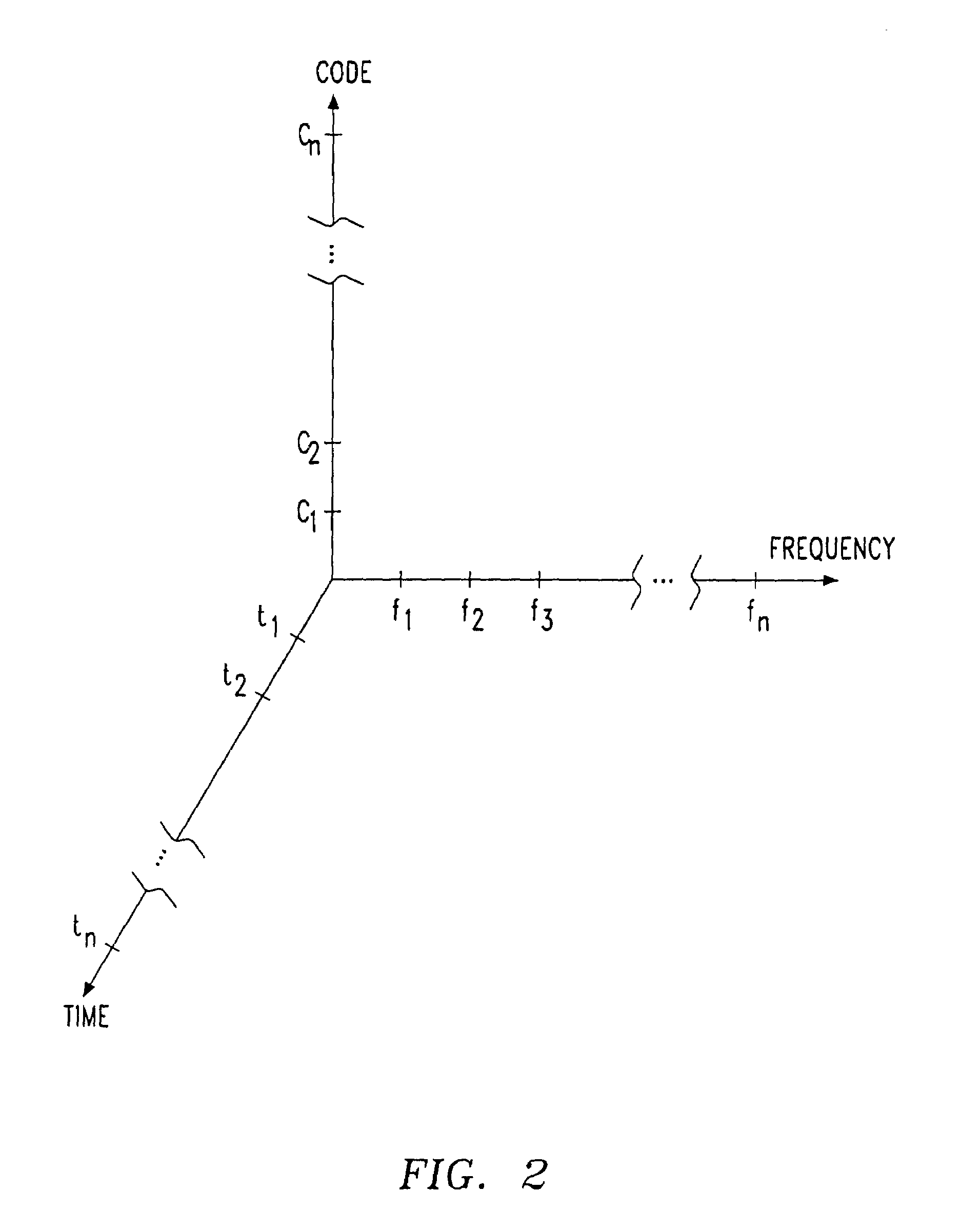
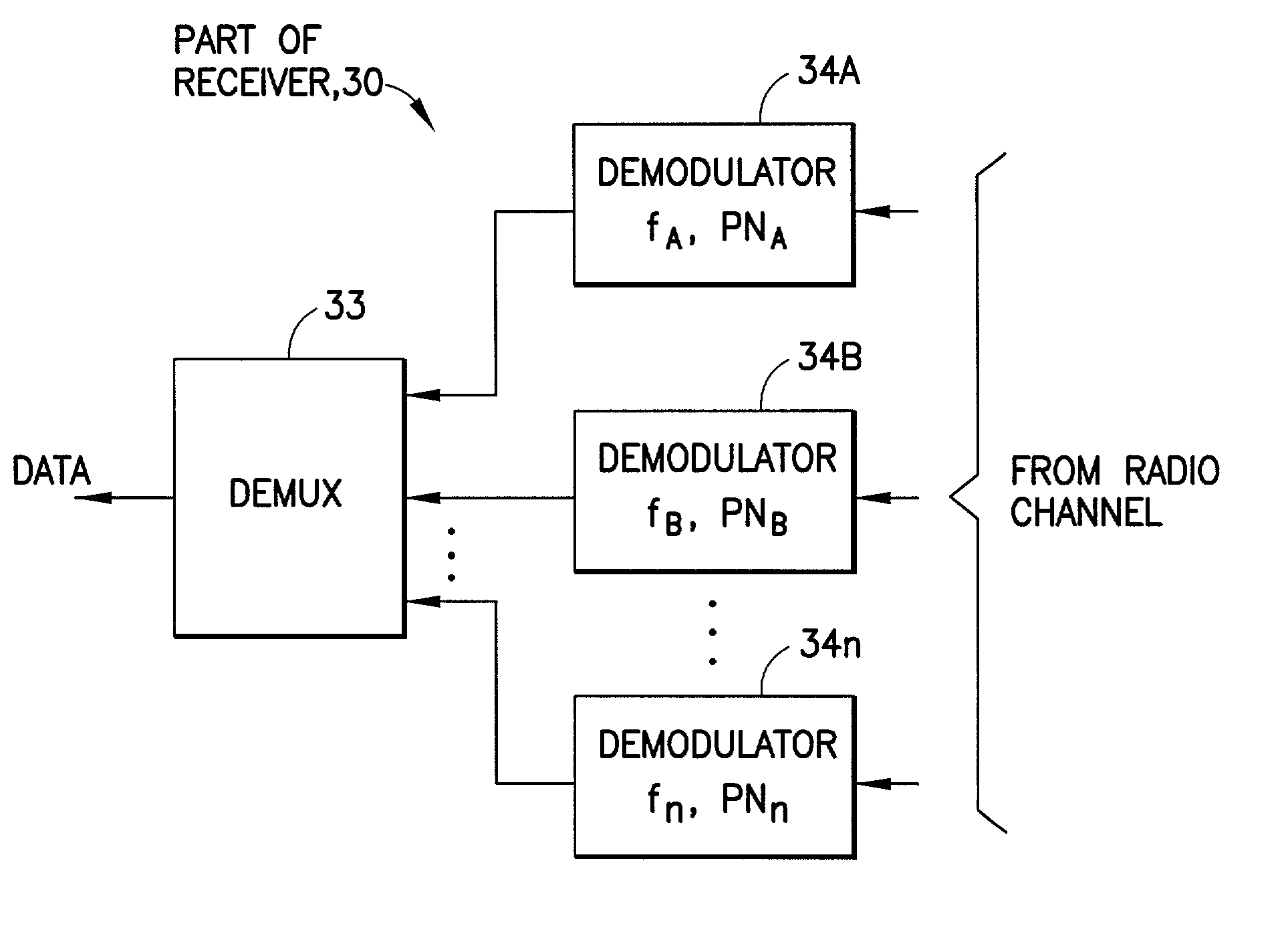
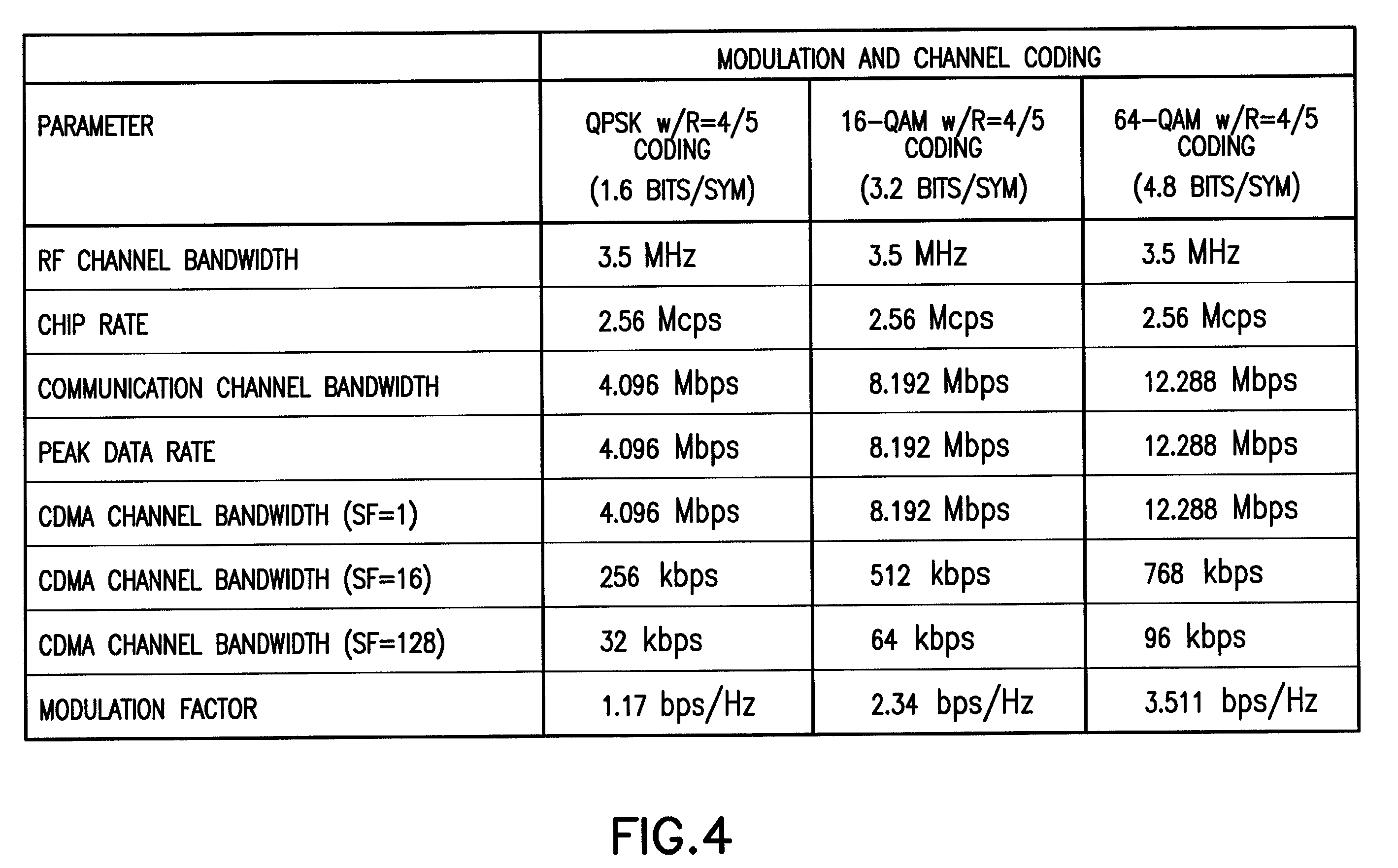
Two-dimensional channel bonding in a hybrid CDMA/FDMA fixed wireless access system to provide finely variable rate channels
InactiveUS7190683B2Improve concentration efficiencyRelatively large bandwidthModulated-carrier systemsTime-division multiplexCommunications systemCode space
A communications system employs the use of both synchronous CDMA and FDMA to provide a variable bandwidth waveform with multiple bonded transmitters and receivers that are agile in both frequency and PN code to permit a variable bandwidth and variable rate multiple access system. In a first aspect the teachings provide the use of both CDMA and FDMA together to enable an improved concentration efficiency by making a larger pool of bandwidth available to each user. In a second aspect these teachings enable channel bonding across both code space and frequency space, thus making the system capable of operating within a variable (not necessarily contiguous) bandwidth and at a finely variable rate.
Owner:L 3 COMM CORP
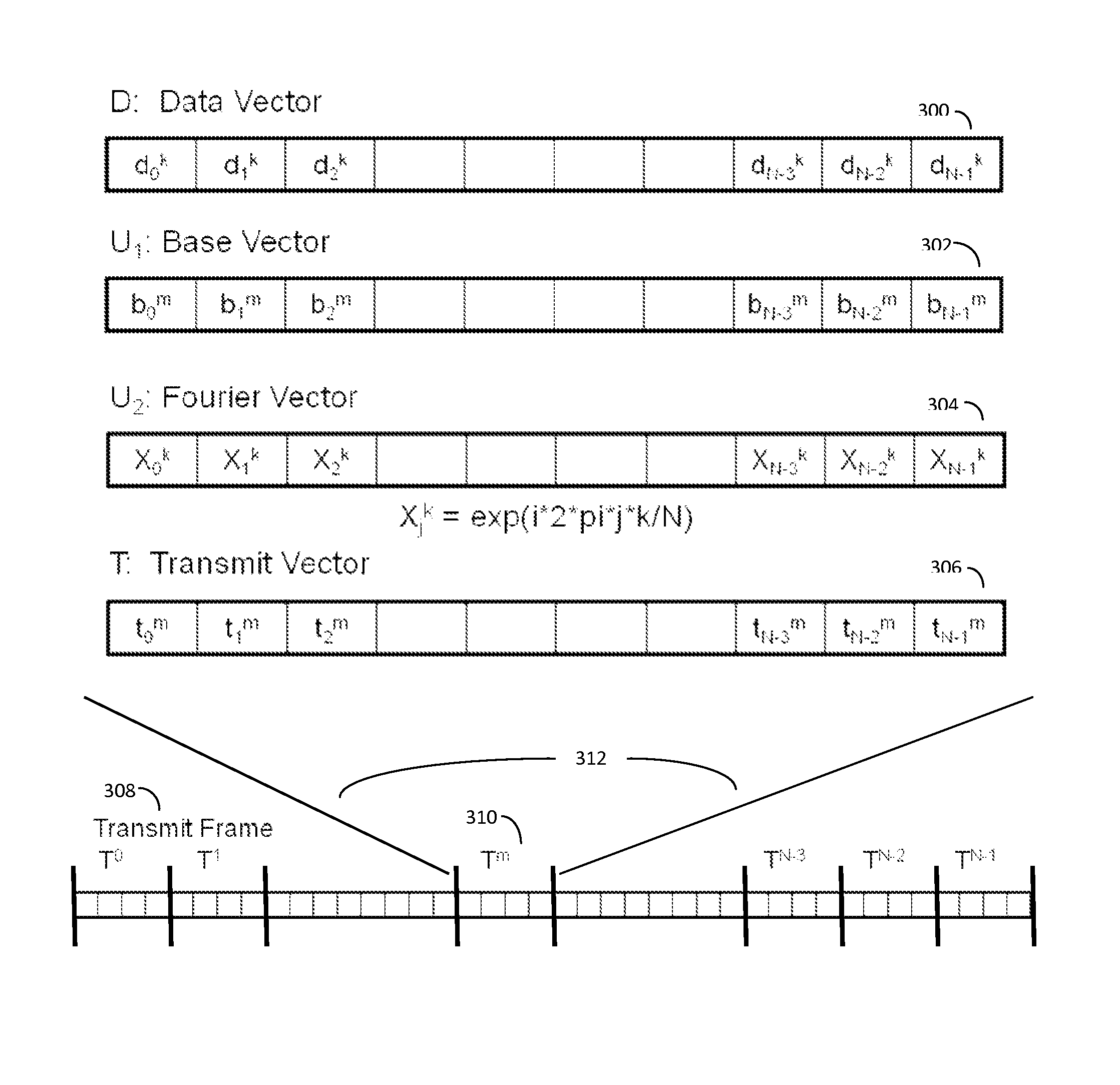
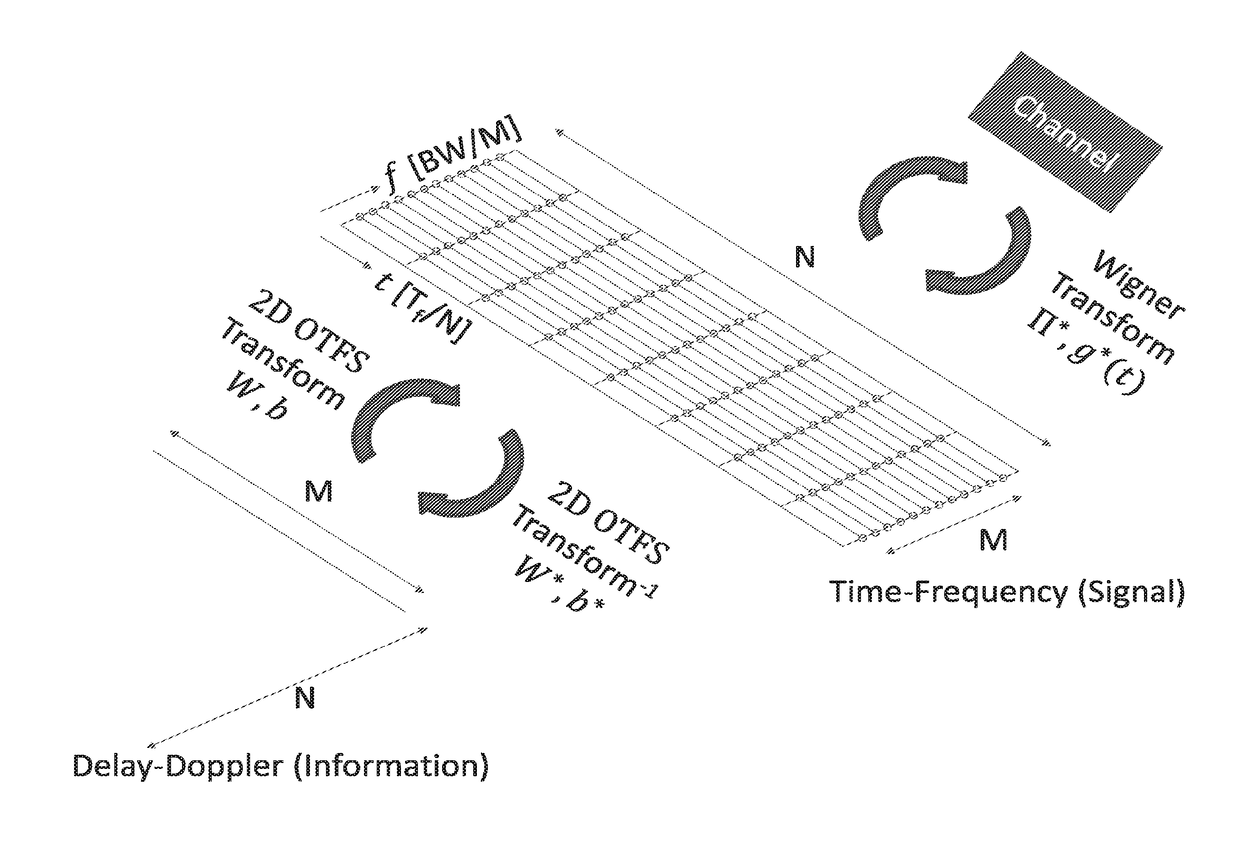
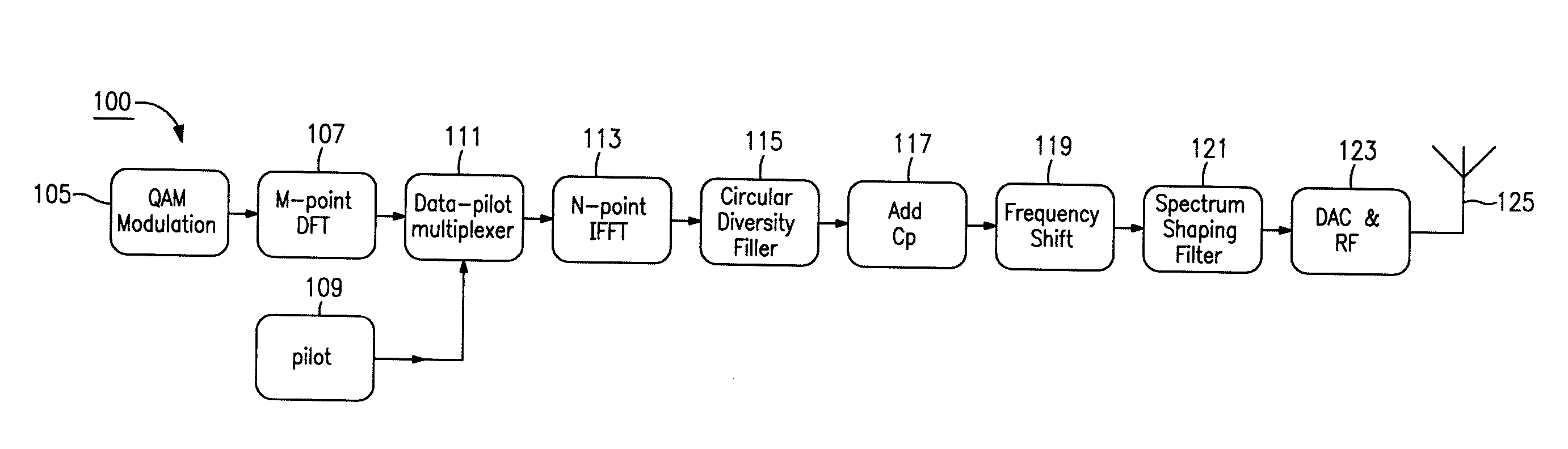
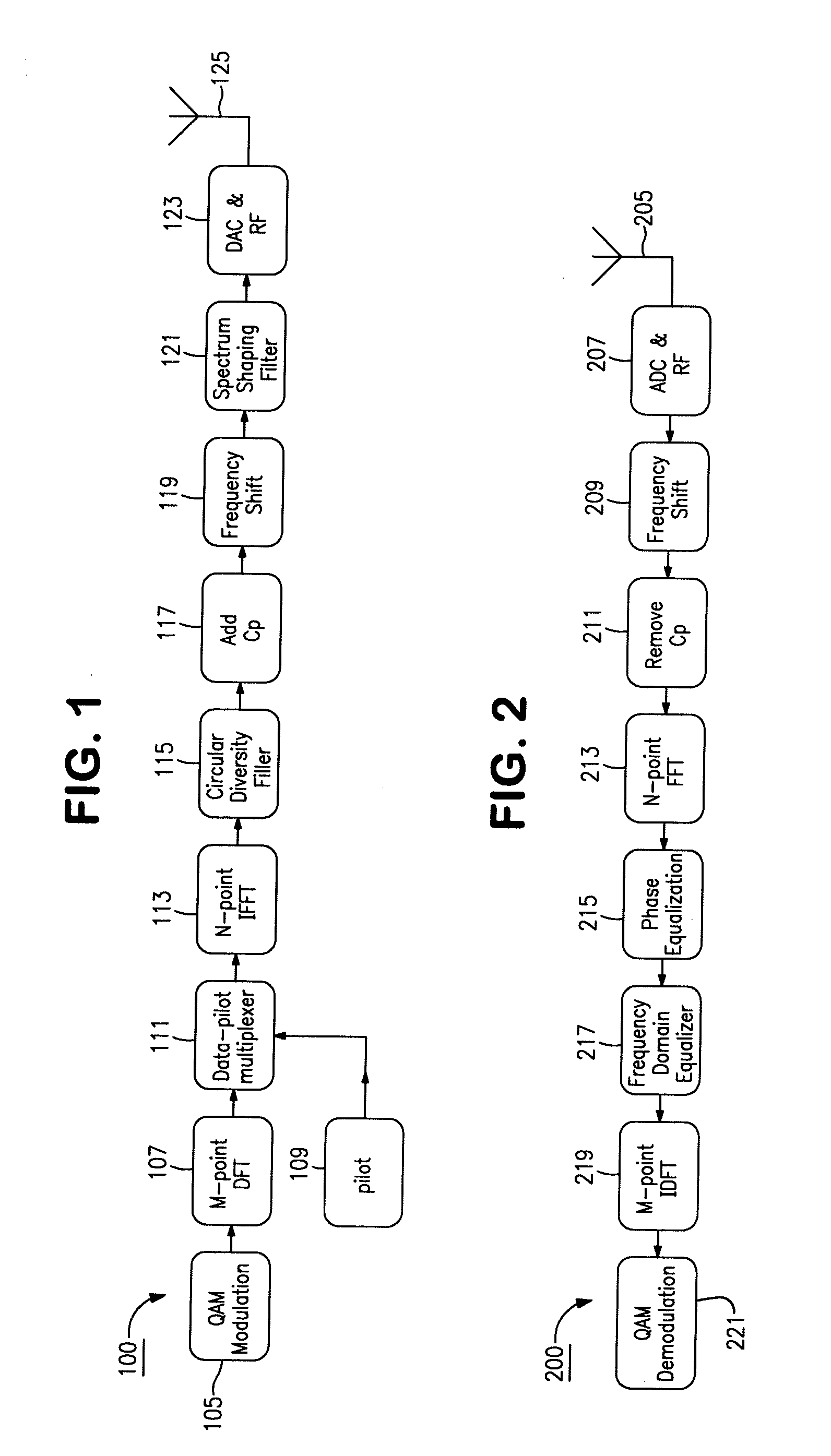
Orthogonal time frequency space modulation over a plurality of narrow band subcarriers
ActiveUS20180205481A1Huge economic benefitsGood removal effectMulti-frequency code systemsOrthogonal multiplexOriginal dataCarrier signal
An Orthogonal Time Frequency Space Modulation (OTFS) modulation scheme that maps data symbols, along with optional pilot symbols, using a symplectic-like transformation such as a 2D Fourier transform and optional scrambling operation, into a complex wave aggregate and be backward compatible with legacy OFDM systems, is described. This wave aggregate may be processed for transmission by selecting portions of the aggregate according to various time and frequency intervals. The output from this process can be used to modulate transmitted waveforms according to various time intervals over a plurality of narrow-band subcarriers, often by using mutually orthogonal subcarrier “tones” or carrier frequencies. The entire wave aggregate may be transmitted over various time intervals. At the receiver, an inverse of this process can be used to both characterize the data channel and to correct the received signals for channel distortions, thus receiving a clear form of the original data symbols.
Owner:COHERE TECH
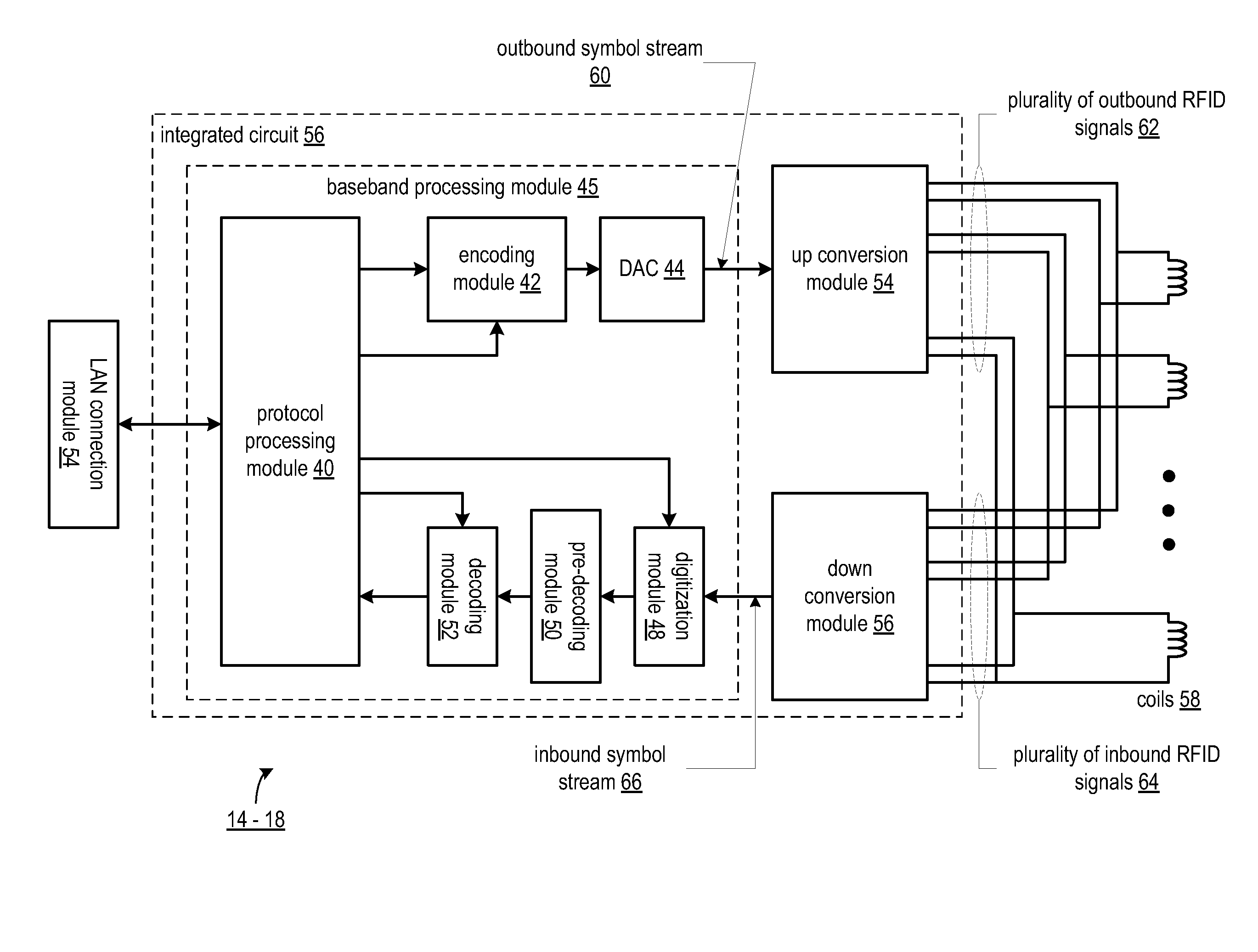
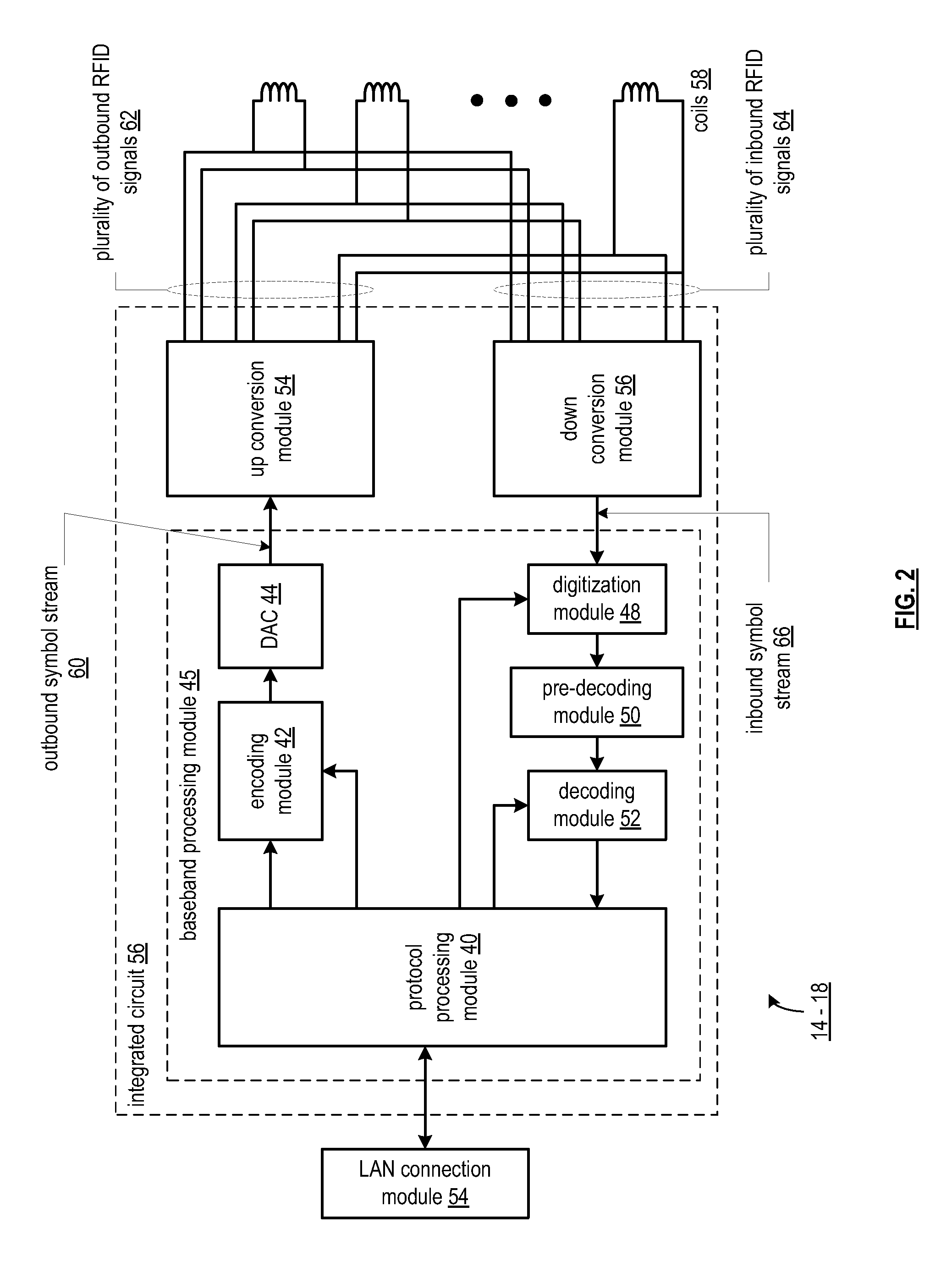
Near field communication front-end
ActiveUS20080238625A1Electric signal transmission systemsDigital data processing detailsEngineeringUp conversion
A near field communication front-end includes an up conversion module, a plurality of coils, and a down conversion module. The up conversion module is coupled to convert an outbound symbol stream into a plurality of outbound signals based on a frequency-space encoding scheme. The plurality of coils is coupled to electromagnetically transmit the plurality of outbound signals and to electromagnetically receive a plurality of inbound signals in accordance with the frequency-space encoding scheme. The down conversion module is coupled to convert the plurality of inbound signals into an inbound symbol stream in accordance with the frequency-space encoding scheme.
Owner:NXP USA INC
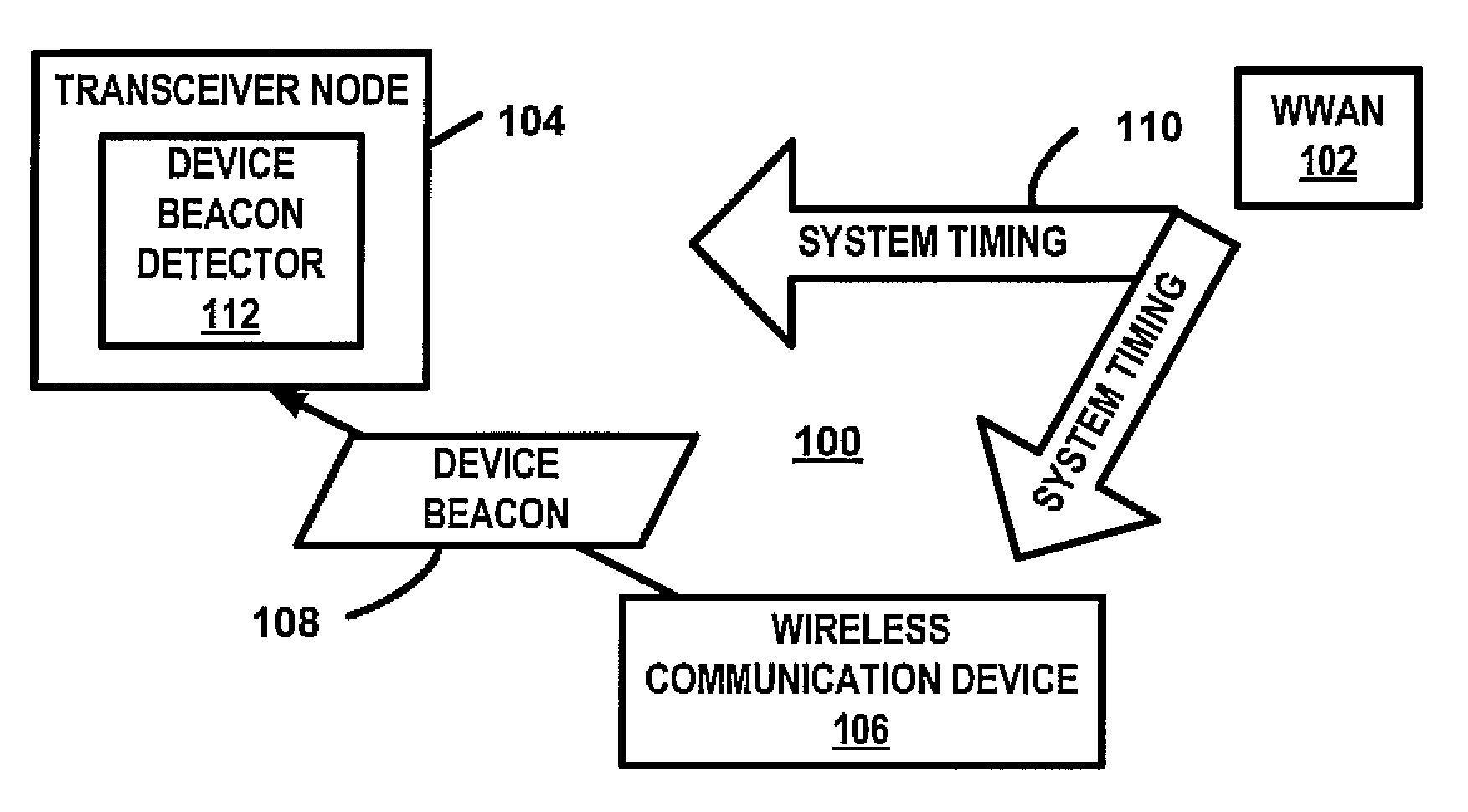
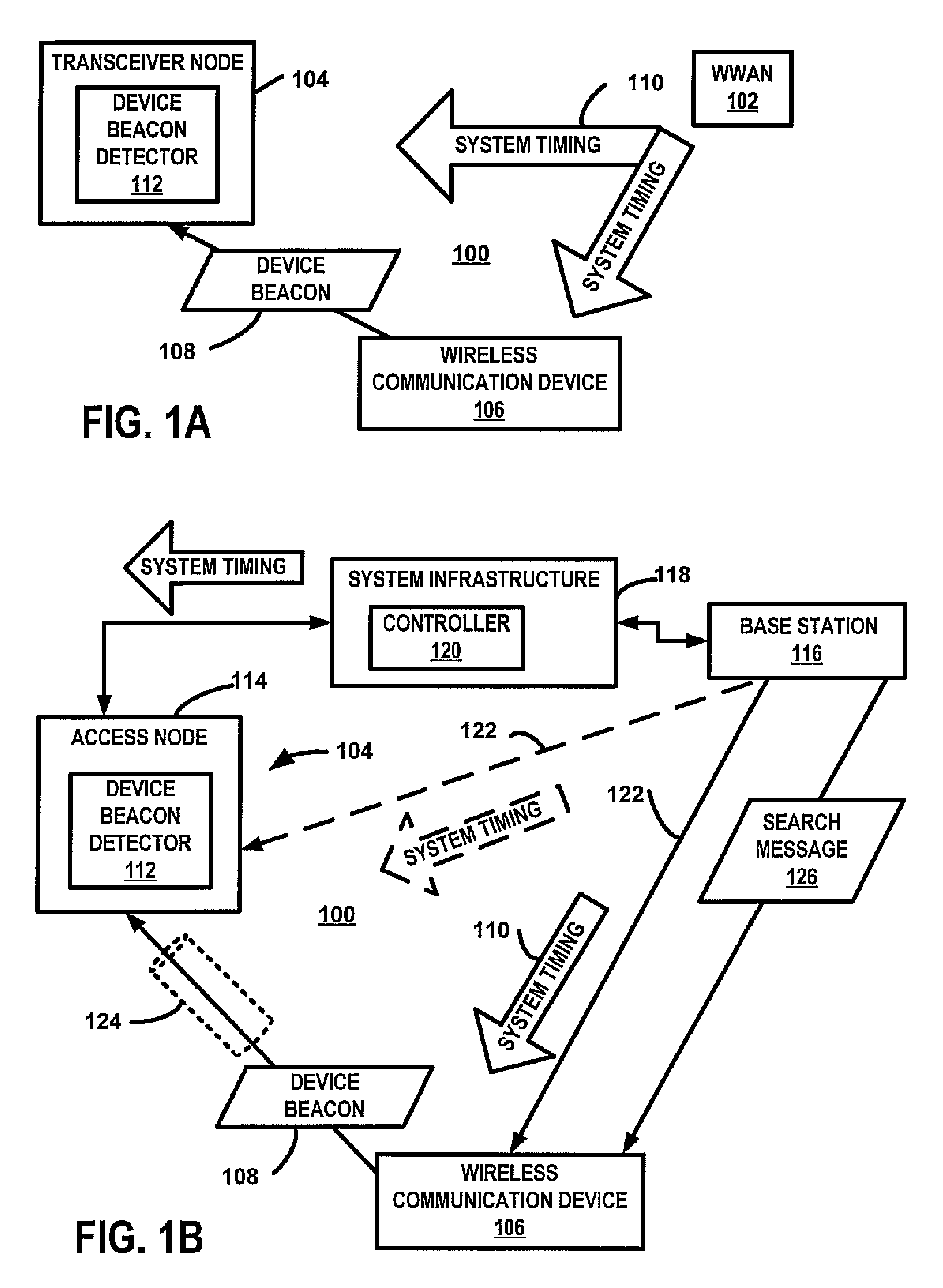
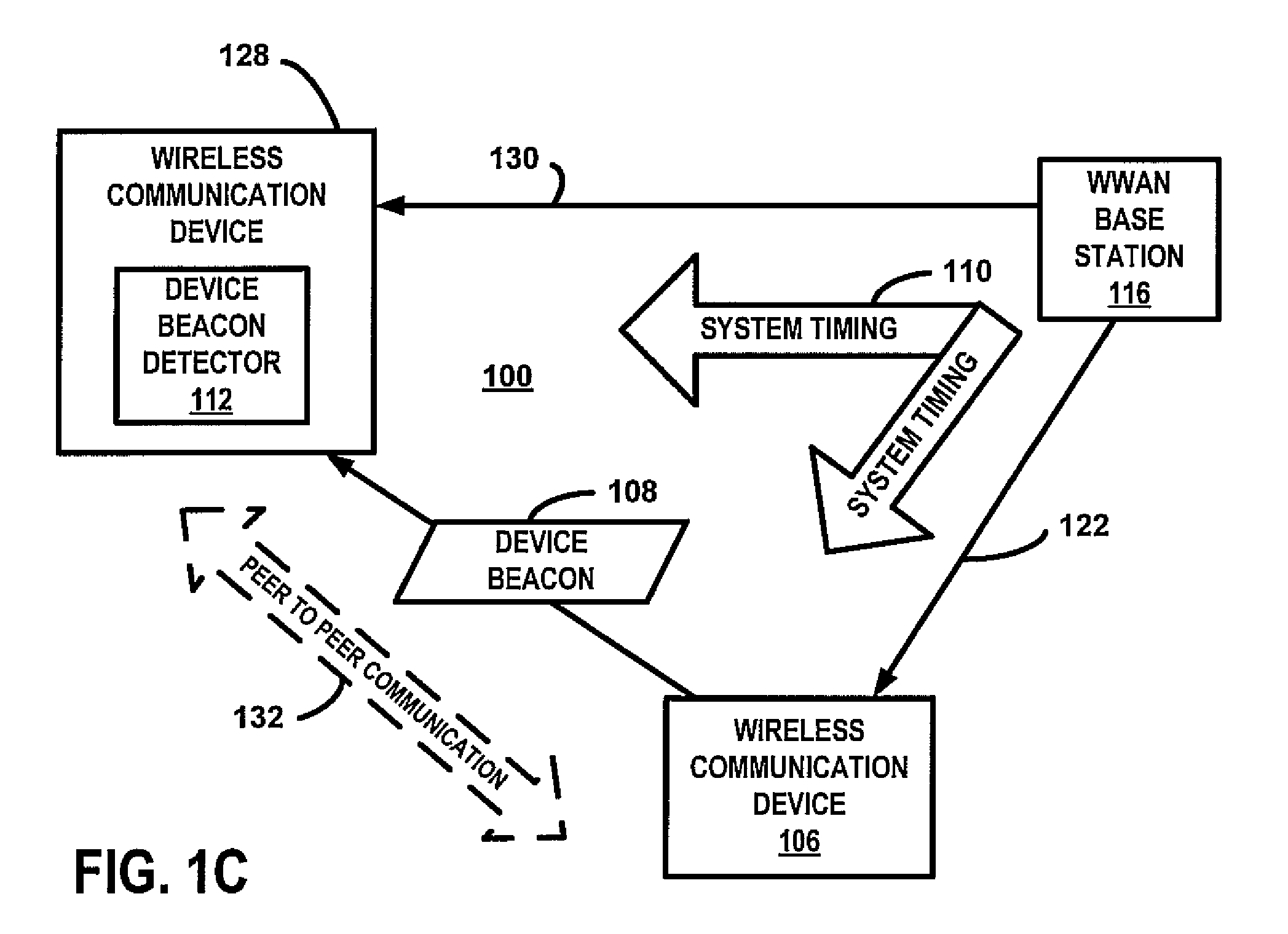
Device beacon for communication management for peer to peer communications
InactiveUS20100118834A1Synchronisation arrangementModulated-carrier systemsCommunication deviceWide area network
A wireless communication device transmits a device beacon in accordance with a system timing of a wireless wide area network (WWAN). For one example, the beacon is transmitted relative to WWAN uplink channels of the time-frequency space of the uplink WWAN channel assignment. In response to the reception of the device beacon by another wireless communication device, a peer to peer communication session is established.
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
Optical performance monitor
ActiveUS7130505B2Wavelength-division multiplex systemsCoupling light guidesOptical performance monitoringPhotodiode
Owner:LUMENTUM OPERATIONS LLC
Method and apparatus for encoding high dynamic range video
InactiveUS7483486B2Good colorIncrease rangeColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionPattern recognitionMotion vector
A method and apparatus for encoding high dynamic range video by means of video compression is shown. The method comprises the steps of providing high dynamic range (HDR) tristimulus color data (XYZ) for each frame of the video and threshold versus intensity data for a human observer; constructing a perceptually conservative luminance transformation from continuous luminance data (Y) to discrete values (Lp) using said threshold versus intensity data for the human observer; transforming the HDR tristimulus color data into perceptually linear color data of three color channels (Lp, u′, v′) for obtaining visually lossless compressed frames; estimating motion vector of said consecutive frames of the video and compensating the difference of the tristimulus color data for performing an inter-frame encoding and an inter-frame compression; transforming the compensated differences of the tristimulus color data to frequency space data; quantizing said frequency space data; variable-length encoding of the quantized frequency space data and storing or transmitting a stream of visual data resulting from the encoded quantized frequency space data.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
Synchronization of a pilot assisted channel estimation orthogonal frequency division multiplexing system
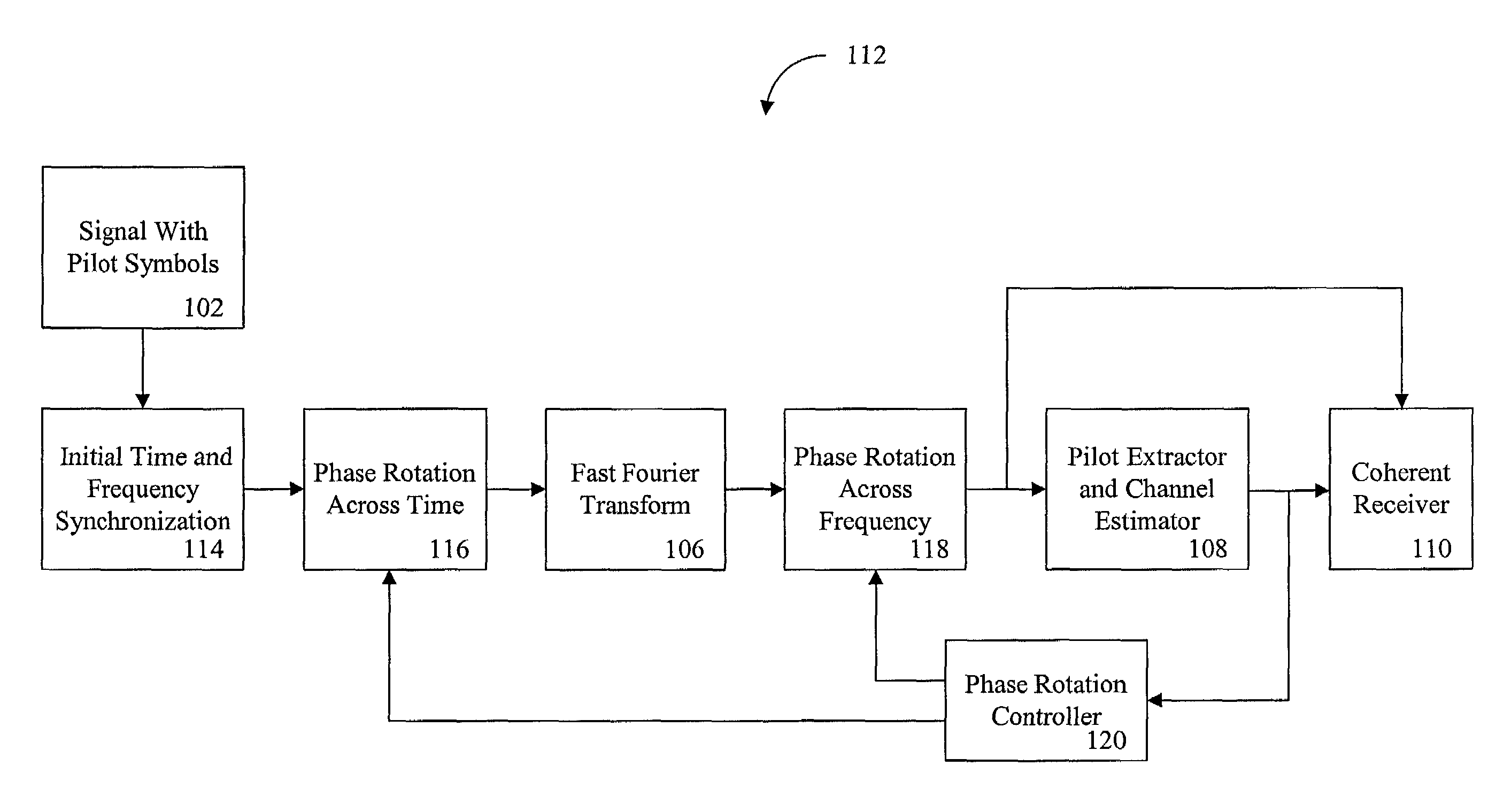
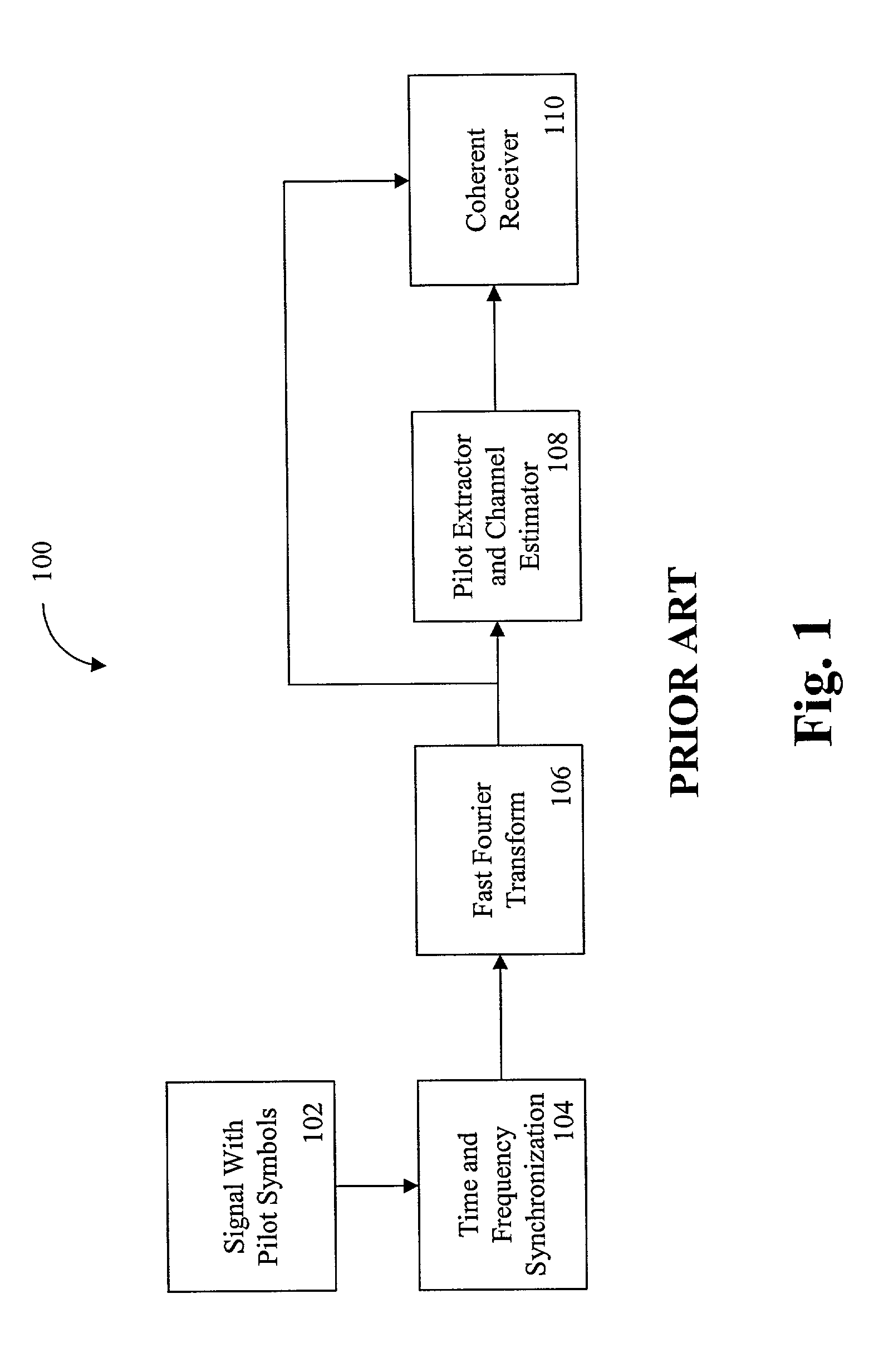
ActiveUS7023928B2Minimize estimated channel errorSensitive to frequencyBaseband system detailsAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsPhase differenceCarrier signal
A synchronization of a pilot assisted channel estimation orthogonal frequency division multiplexing can be achieved by receiving a signal containing pilot symbols, providing an initial time and frequency synchronization to the signal, phase rotating the signal across time, transforming the signal with a fast Fourier transformation, phase rotating the signal across frequency, extracting the pilot symbols and generating a channel estimator. The phase rotating across time and the phase rotating across frequency are controlled by a phase rotation controller in accordance with the channel estimator. The initial time and frequency synchronization synchronizes the signal such that intercarrier interference effects and intersymbol interference effects are negligible. The signal may include plural carrier frequencies each having an arrival timing offset and a frequency offset. The signal may also include delay spread or Doppler spread. The phase rotation controller measures a phase different between the channel estimator at times k and k+Δk, where k is time and Δk is a symbol period and measures a phase difference between the channel estimator at frequencies n and n+Δn, where n is tone frequency and Δn is a frequency spacing between adjacent tones.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
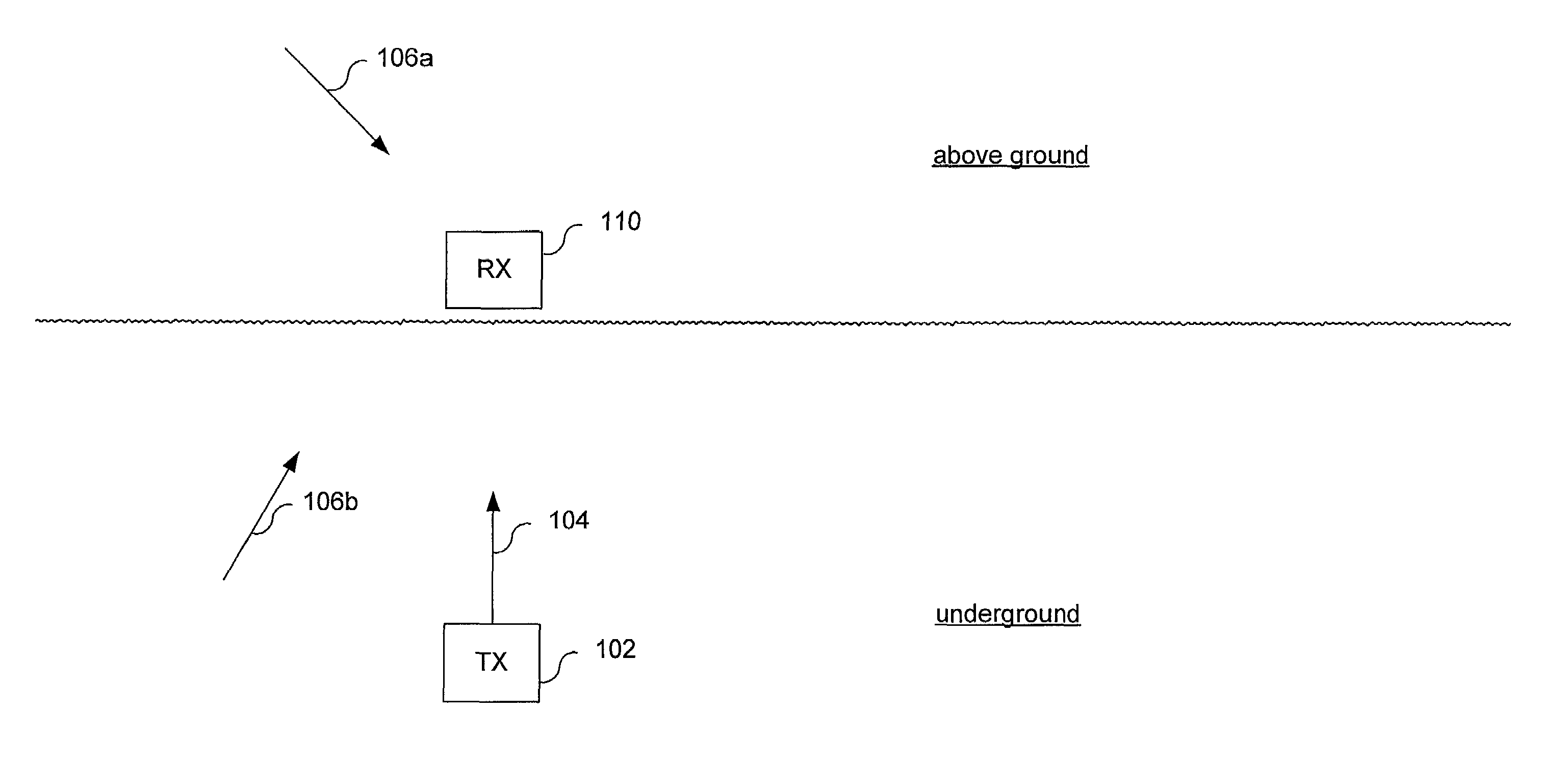
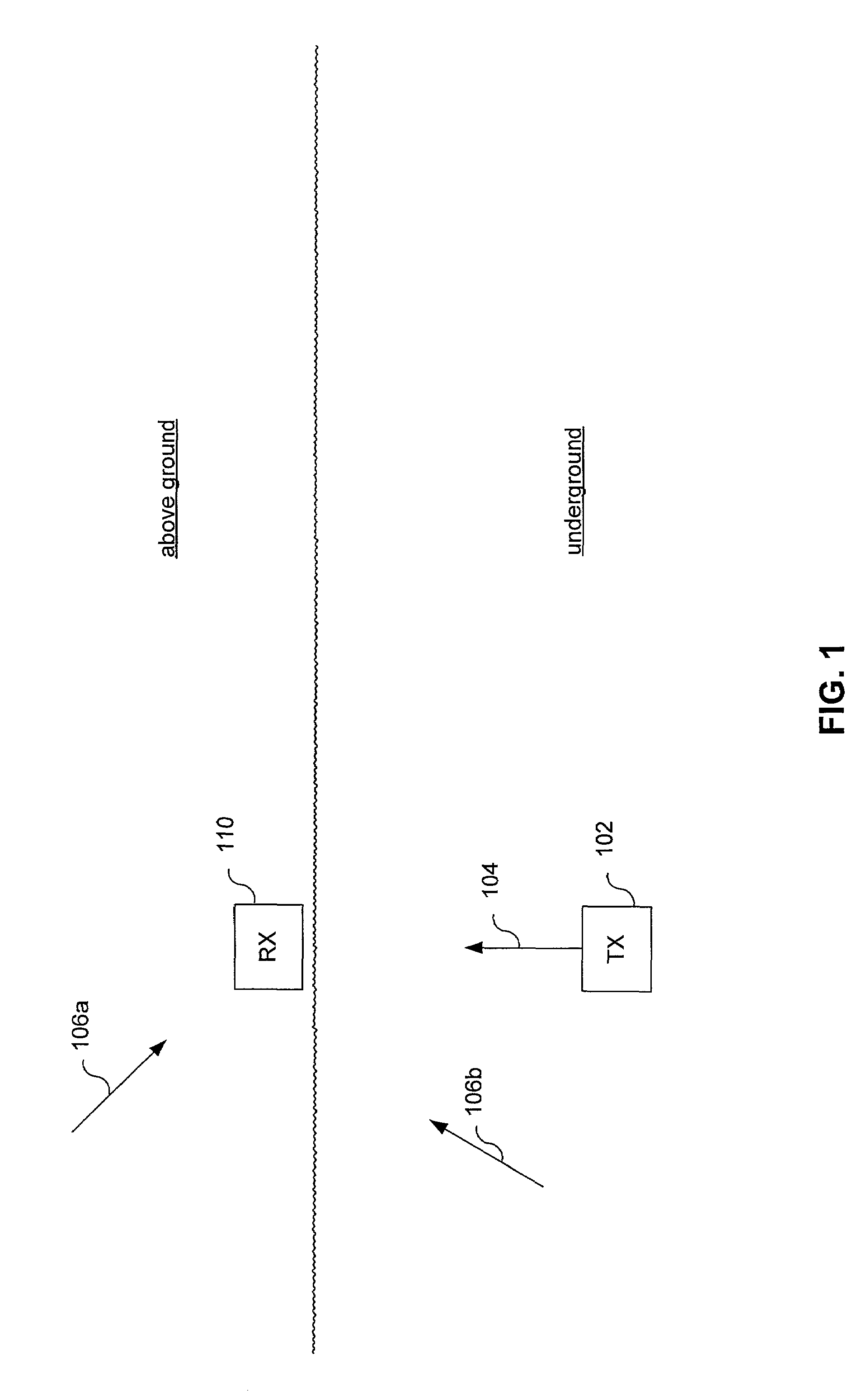
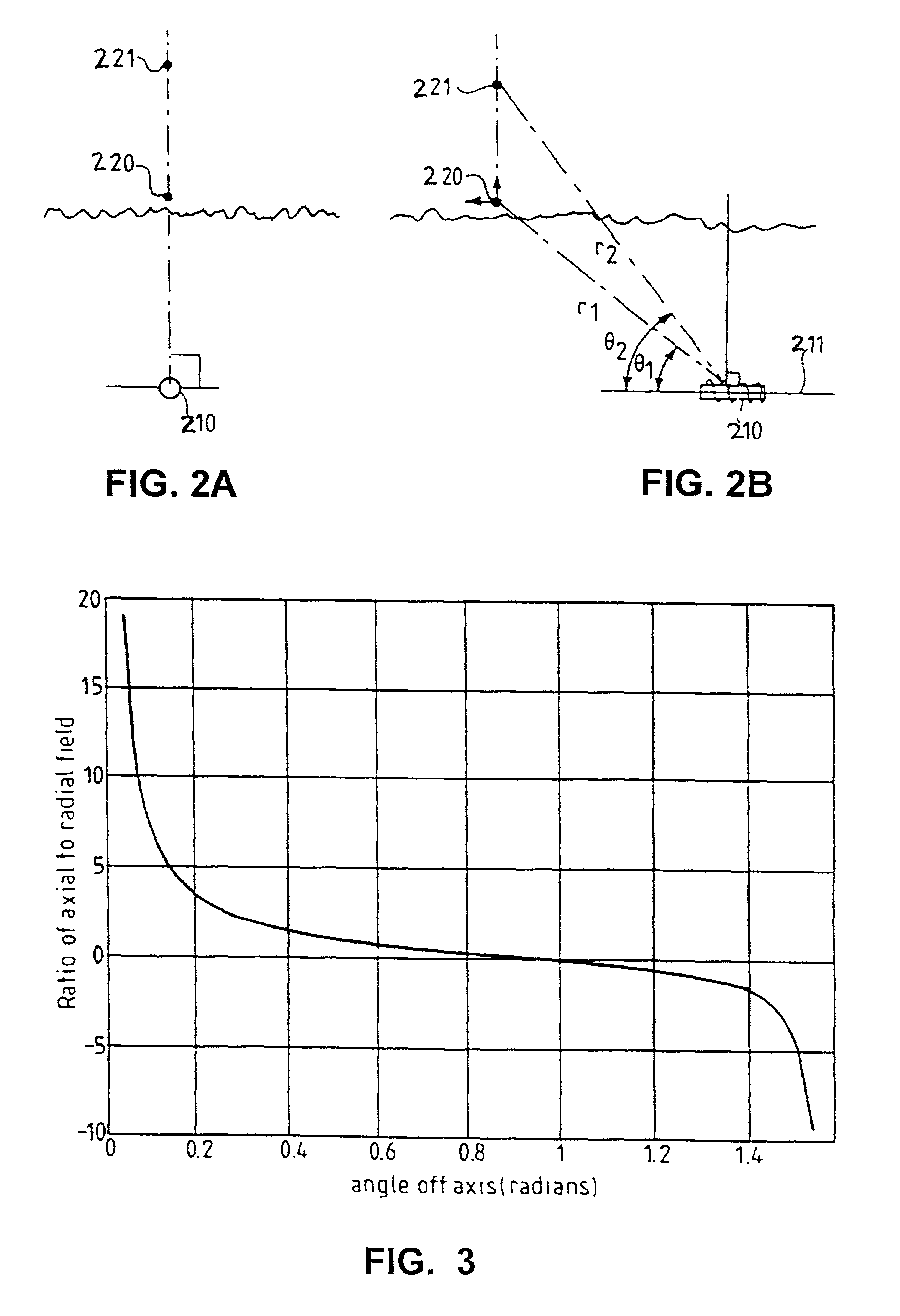
Method and system for producing a magnetic field signal usable for locating an underground object
Transmitted magnetic field signals useable for locating an underground object, and methods and systems for generating the same. The magnetic field signal has desired spectral characteristics. More specifically, the transmitted magnetic field signal includes a carrier component useable for locating an underground object. The carrier component has a carrier component frequency substantially equal to an integer multiple of 300 Hz. This guarantees that the carrier component frequency is substantially equal to an integer multiple of both 50 Hz and 60 Hz. Such a carrier component allows use of maximum information sidebands in environments that often include harmonically derived interference signals at regular 50 Hz (±0.1 Hz) or 60 Hz (±0.1 Hz) intervals caused by power lines. The transmitted magnetic field signal may also include at least one information sideband including sideband energy. A substantial portion of the sideband energy is contained between the carrier component frequency and a frequency spaced 50 Hz from the carrier component frequency.
Owner:RADIODETECTION
Recognition system
InactiveUS6671666B1Reduce dimensionalityAdd dimensionImage analysisDigital technique networkFrequency spectrumFilter bank
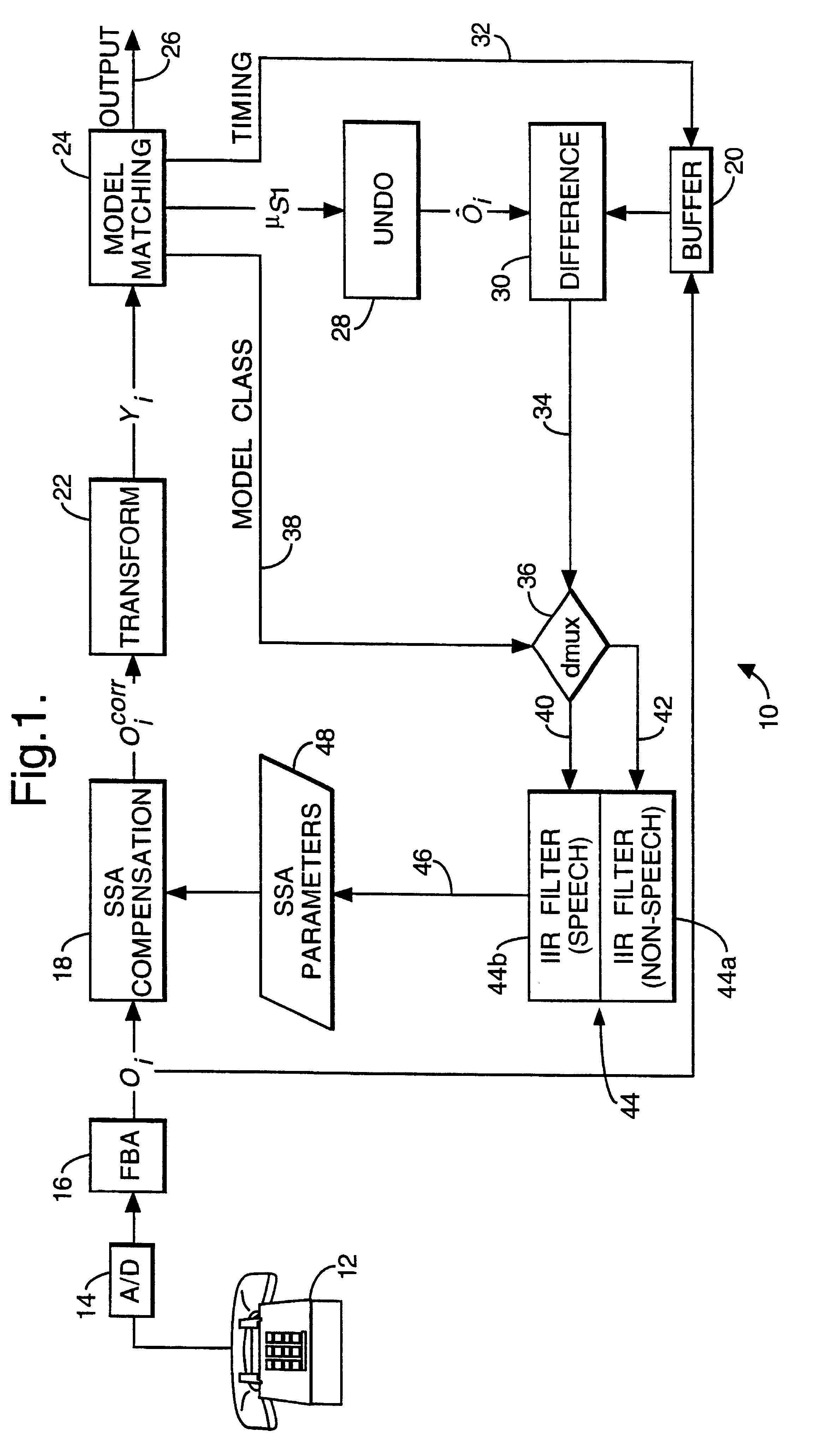
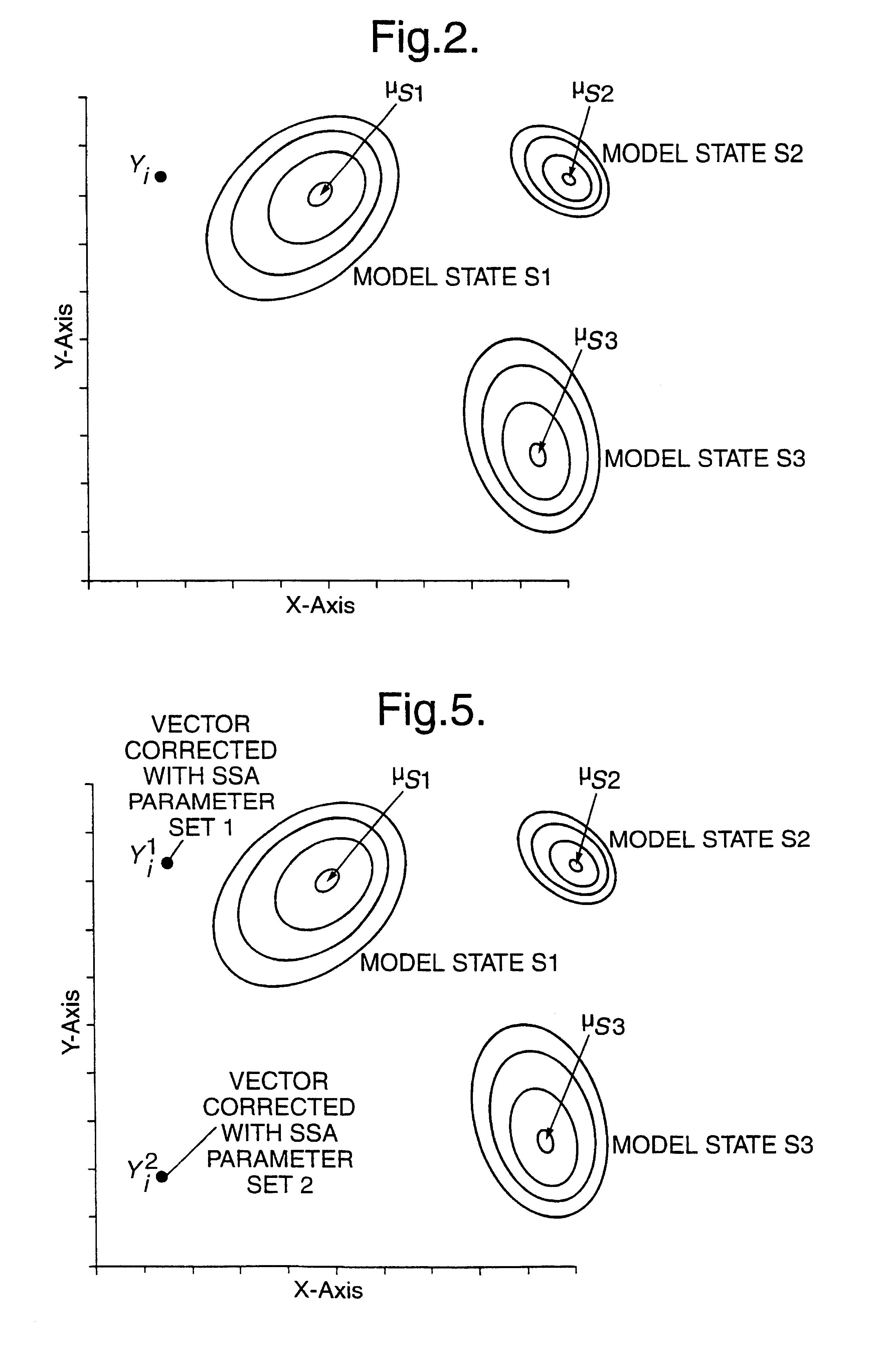
A recognition system (10) incorporates a filterbank analyser (16) producing successive data vectors of energy values for twenty-six frequency intervals in a speech signal. A unit (18) compensates for spectral distortion in each vector. Compensated vectors undergo a transformation into feature vectors with twelve dimensions and are matched with hidden Markov model states in a computer (24). Each matched model state has a mean value which is an estimate of the speech feature vector. A match inverter (28) produces an estimate of the speech data vector in frequency space by a pseudo-inverse transformation. It includes information which will be lost in a later transformation to frequency space. The estimated data vector is compared with its associated speech signal data vector, and infinite impulse response filters (44) average their difference with others. Averaged difference vectors so produced are used by the unit (18) in compensation of speech signal data vectors.
Owner:AURIX
Wireless communication methods and receivers for receiving and processing multiple component carrier signals
InactiveUS20090257517A1Save spaceReduce effective subcarrier spacingTransmission path divisionSecret communicationFast Fourier transformCommunications system
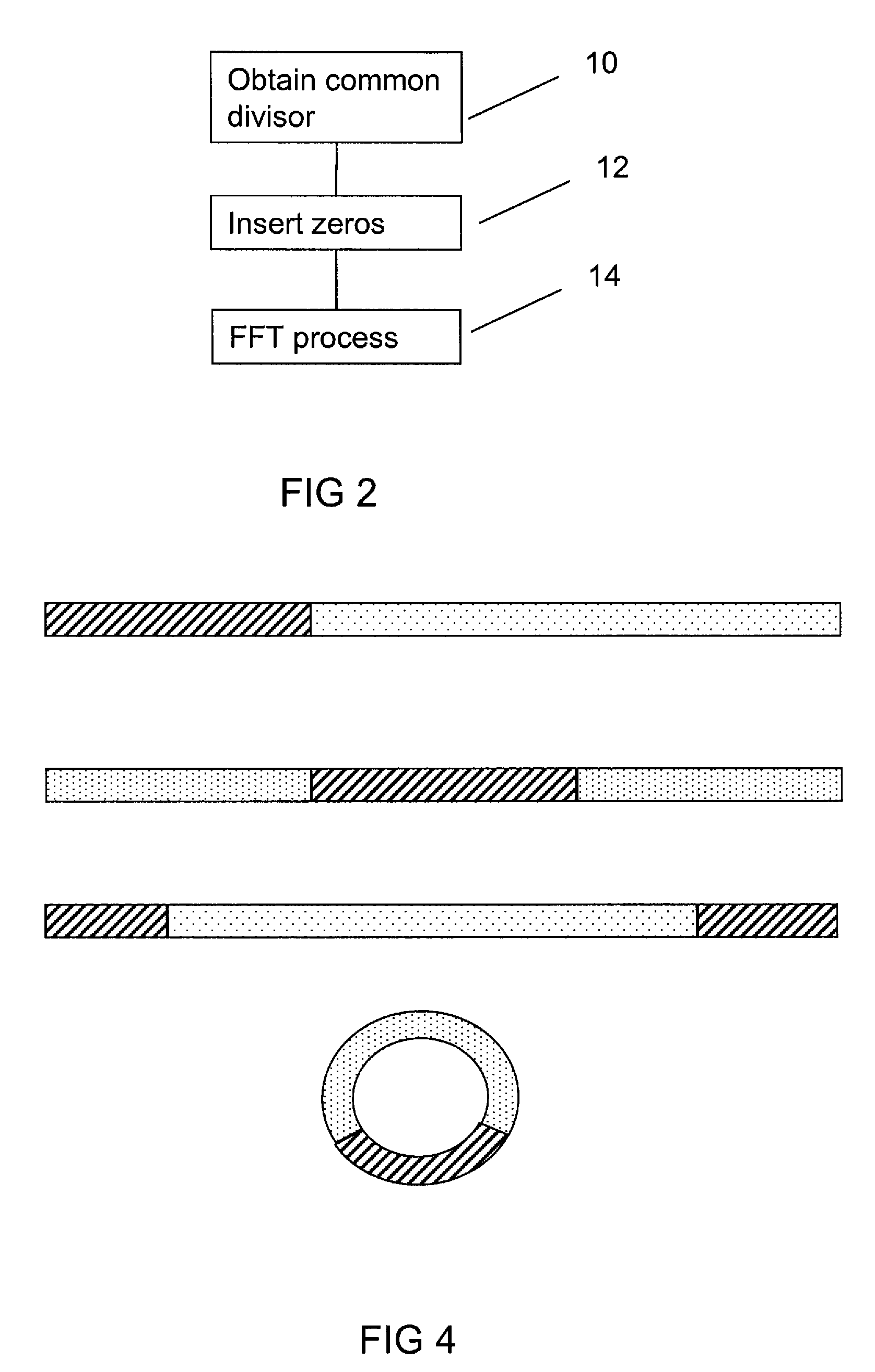
A wireless communication system receiver receives and processes a signal comprising at least two component carriers carrying data scheduled to the receiver and having center frequencies spaced apart by at least one component carrier frequency difference. Each component carrier comprises a number of subcarriers spaced apart by a system subcarrier frequency spacing. A common divisor is obtained for the at least one component carrier frequency difference and the system subcarrier frequency spacing. A symbol is received on the subcarriers of the component carriers and downconverted to baseband to produce a baseband symbol. A block of padding values is inserted in the baseband symbol to produce a padded symbol. The length of the block of padding values is such that intermediate subcarriers are inserted to yield a subcarrier frequency spacing for the padded symbol equal to the common divisor. Finally the padded symbol is Fast Fourier Transform, FFT, processed.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
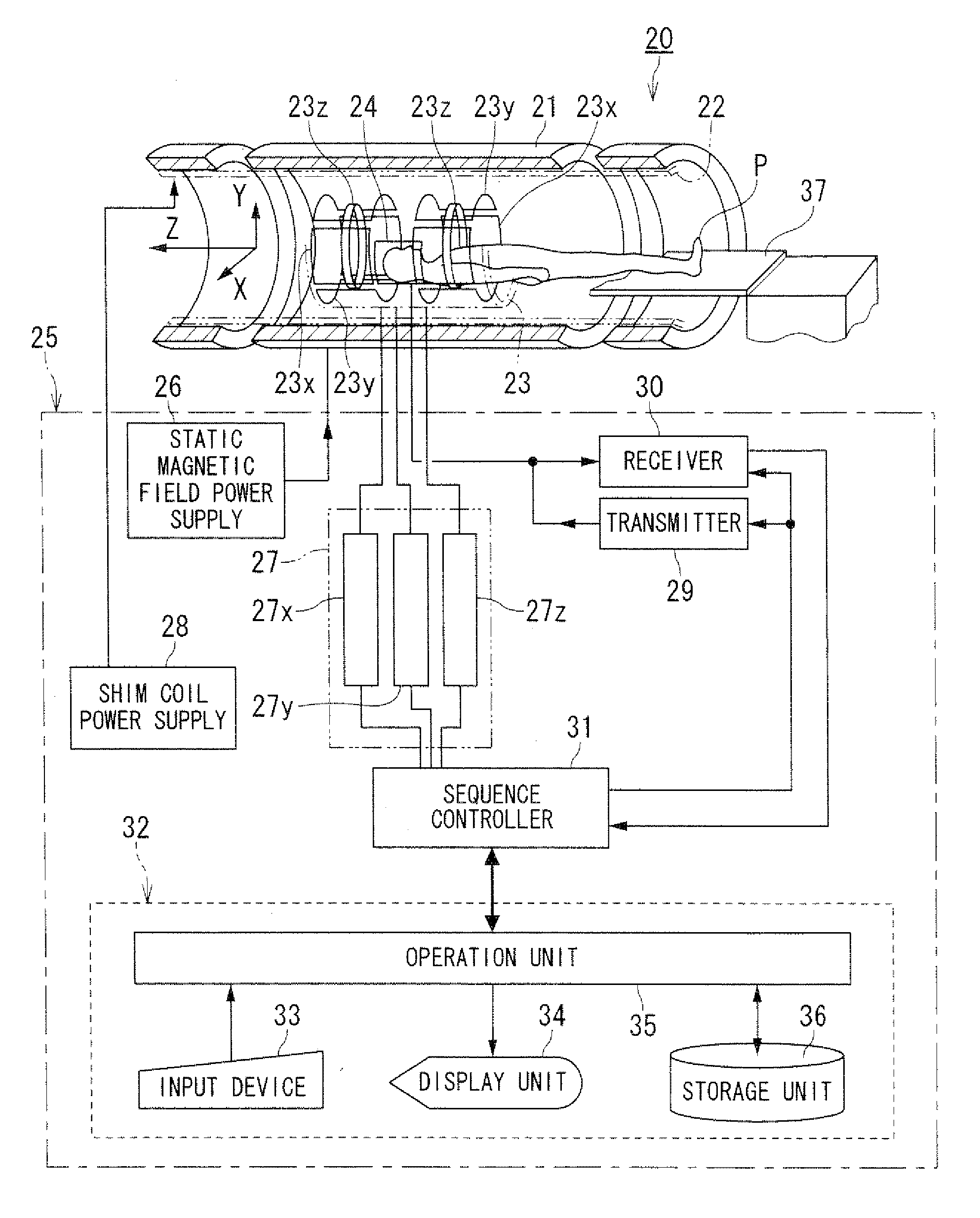
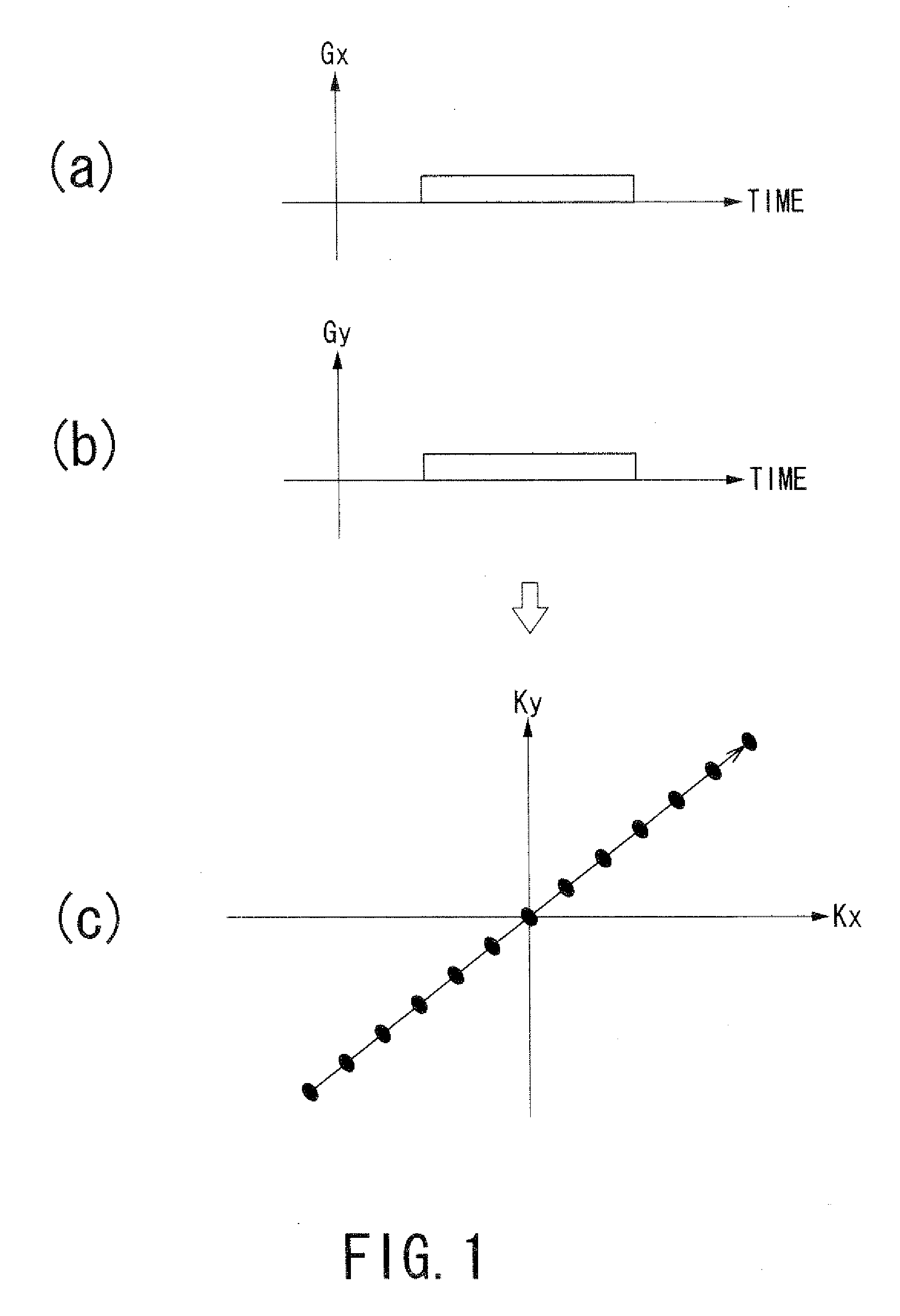
Magnetic resonance imaging apparatus and magnetic resonance imaging method
ActiveUS20090115794A1Suppress artifactsReduce frequencyMagnetic measurementsCharacter and pattern recognitionResonanceComputer science
A magnetic resonance imaging apparatus includes an acquisition unit, a calculation unit, a recalculation unit, a correction unit and a generating unit. The acquisition unit acquires data from plural slices in an object by rotating a zonary region in frequency space by every repetition time. The calculation unit calculates correction parameters for motion correction. The recalculation unit recalculates at least a part of the correction parameters based on relationship between values of the correction parameters and at least one of real-spatial positions and times at which the data is acquired. The correction unit corrects the data using correction parameters including recalculated correction parameters. The generating unit generates image data based on corrected data.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
Capacitive micromachined acoustic transducer
ActiveUS7152481B2Wide bandwidthHigh sensitivitySemiconductor electrostatic transducersDeaf-aid setsMembrane anchorTransducer
A micromachined capacitive acoustic transducer including an electrode formed by a perforated plate and another electrode formed by a shallowly corrugated membrane anchored at one or more positions on the substrate which also supports the said perforated plate is described. Also disclosed includes: a fixed perforated plate; a movable shallowly corrugated membrane having holes to form acoustic filter to a certain frequency or a range of frequencies spaced from the perforated plate that is anchored in one or more location but loose at other locations; a support structure in the perforated plate maintaining the minimum separation between the membrane and the perforated plate near the perimeter.
Owner:NEOMEMS TECH INC WUXI CHINA
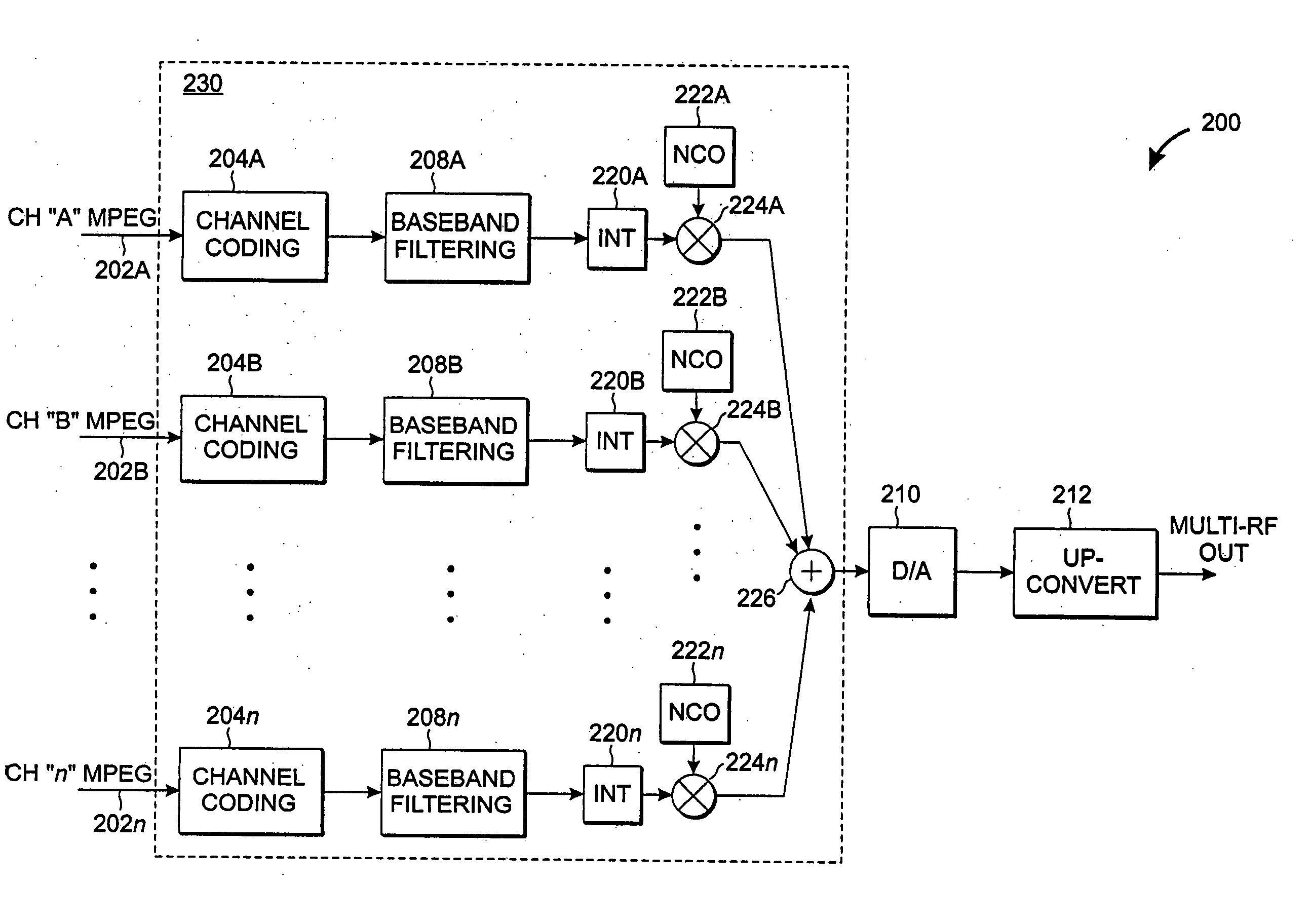
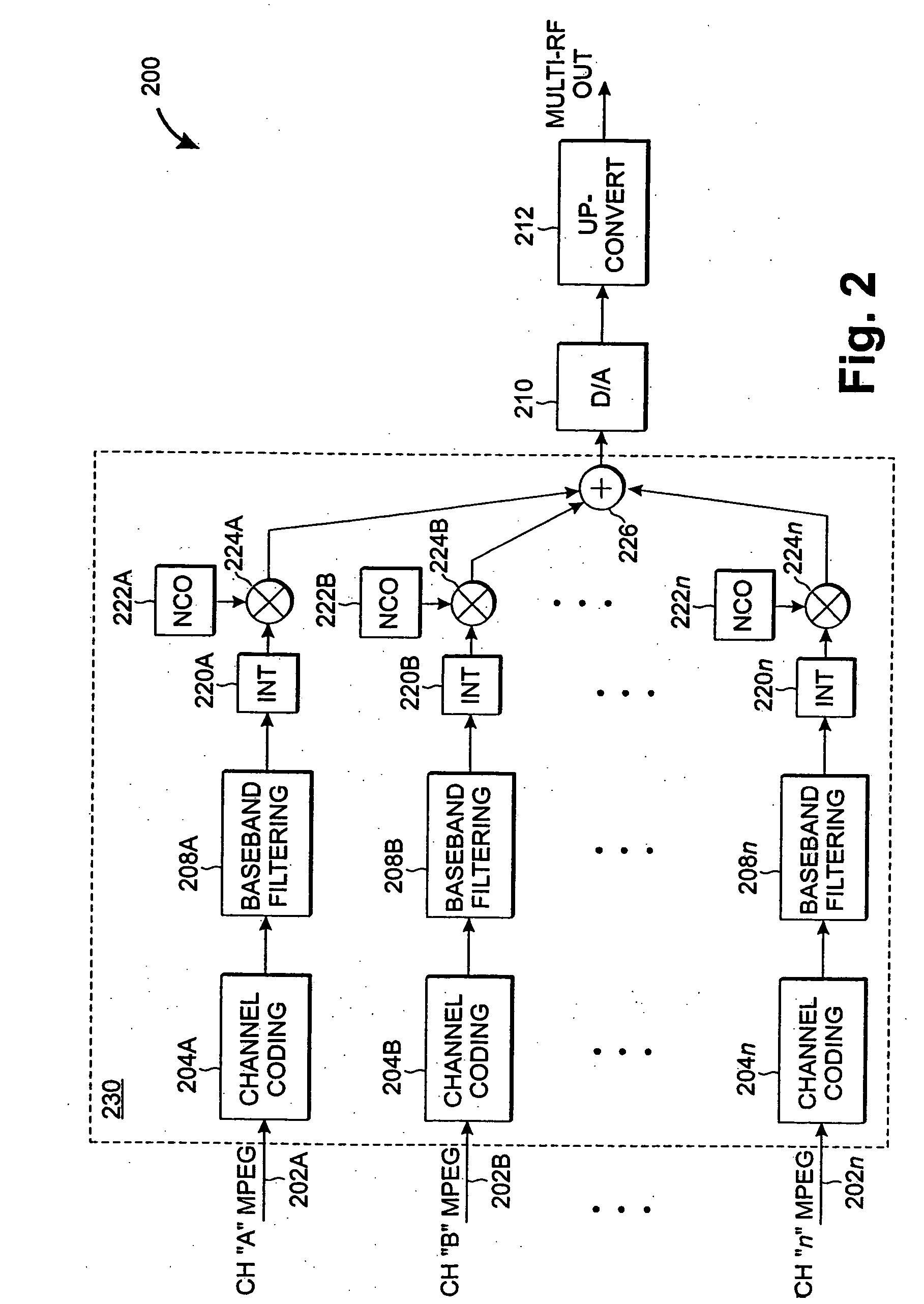
Cost-effective multi-channel quadrature amplitude modulation
A highly-efficient, cost-effective technique for multi-channel QAM modulation is described. The technique employs an inverse fast-Fourier transform (IFFT) as a multi-channel modulator. QAM encoding expresses QAM symbols as constellation points in the complex plane such that each QAM symbol represents a specific phase and amplitude of a carrier frequency to which it is applied. In multi-channel systems, the carrier frequencies are generally uniformly spaced at a channel-spacing frequency (6 MHz, for digital cable systems in the United States). The IFFT accepts a set of complex frequency inputs, each representing the complex frequency specification (i.e., phase and amplitude) of a particular frequency. The inputs are all uniformly spaced, so assuming that the IFFT is sampled at a rate to provide the appropriate frequency spacing between its frequency-domain inputs, the IFFT will produce a time domain representation of QAM symbols applied to its various inputs modulated onto carriers with the desired channel separation. Since the channel spacing and the symbol rate are different due to excess channel bandwidth, interpolation is used to rectify the difference. An efficient scheme for combining this interpolation with baseband filtering and anti-imaging filtering is described.
Owner:RGB NETWORKS
Method and apparatus for high speed data transmission modulation and demodulation
ActiveUS20110182332A1Transmission path divisionSecret communicationWireless transmissionCarrier signal
A method and apparatus for communicating wirelessly comprising creating a plurality of sub-carrier signals by quadrature amplitude modulating data onto a plurality of sub-carrier frequencies spaced apart by a sub-carrier frequency spacing interval, frequency shifting the sub-carrier signals by one half of the sub-carrier frequency spacing interval, and modulating the sub-carrier signals onto a radio frequency carrier wave for wireless transmission.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
Hybrid one-way and full-way wave equation migration
ActiveUS8116168B1Reduce background noiseSave computing resourcesSeismologyImaging qualityWave equation
A migration method using hybrid one-way and full-way (HOF) wave equation propagation. The HOF method extrapolates seismic wavefields in less complex media with a one-way wave equation propagator and extrapolates seismic wavefields in extremely complex media with a full-way wave equation propagator. For prestack depth migration, the HOF extrapolates source-side and receiver-side wavefields independently. Frequency-space domain and time-space domain imaging conditions are applied to the one-way and the full-way extrapolated wavefields, respectively. A suitable amplitude matching factor is introduced to combine the one-way and full-way images. The HOF method is a cost-effective migration that produces superior image quality with less noises and less computational resources.
Owner:LANDMARK GRAPHICS
Technique for optically converting wavelengths in a multi-wavelength system
InactiveUS20020118415A1Increase heightIncreasing down-convertersWavelength-division multiplex systemsLength waveMulti wavelength
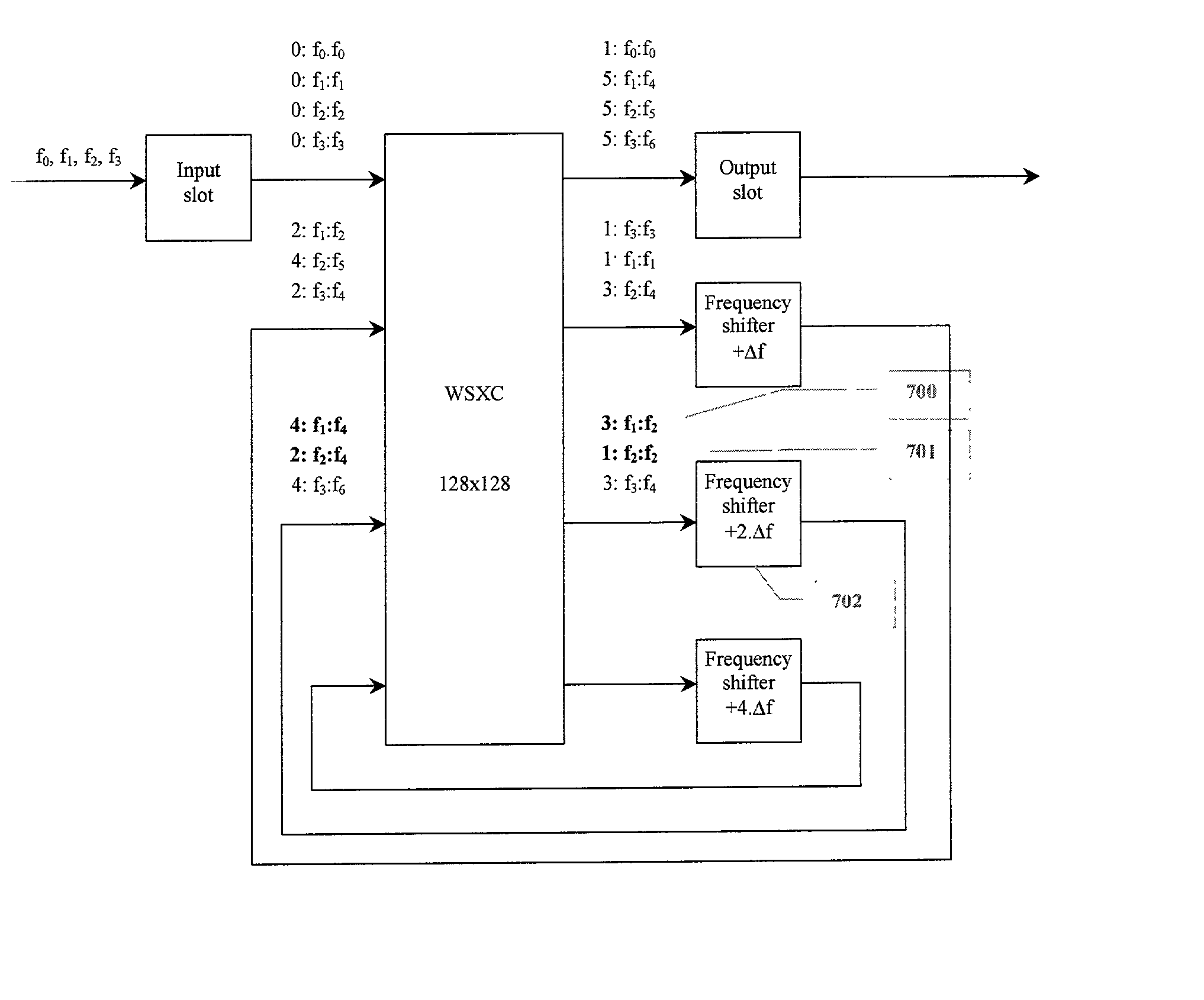
A technique for optically converting wavelengths in a multi-wavelength system is disclosed. In one embodiment, wherein the multi-wavelength system has W wavelength channels, wherein W=2N, the technique is realized by selectively directing a received frequency channel corresponding to a respective wavelength channel based upon a predetermined frequency mapping. Then, the frequency of the selectively directed frequency channel is shifted at least once by an amount defined by ±21DELTAf, wherein DELTAf is the frequency spacing between adjacent frequency channels, and i=0, 1, . . . N-1.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Optical fibre fourier transformation white light interferometric method
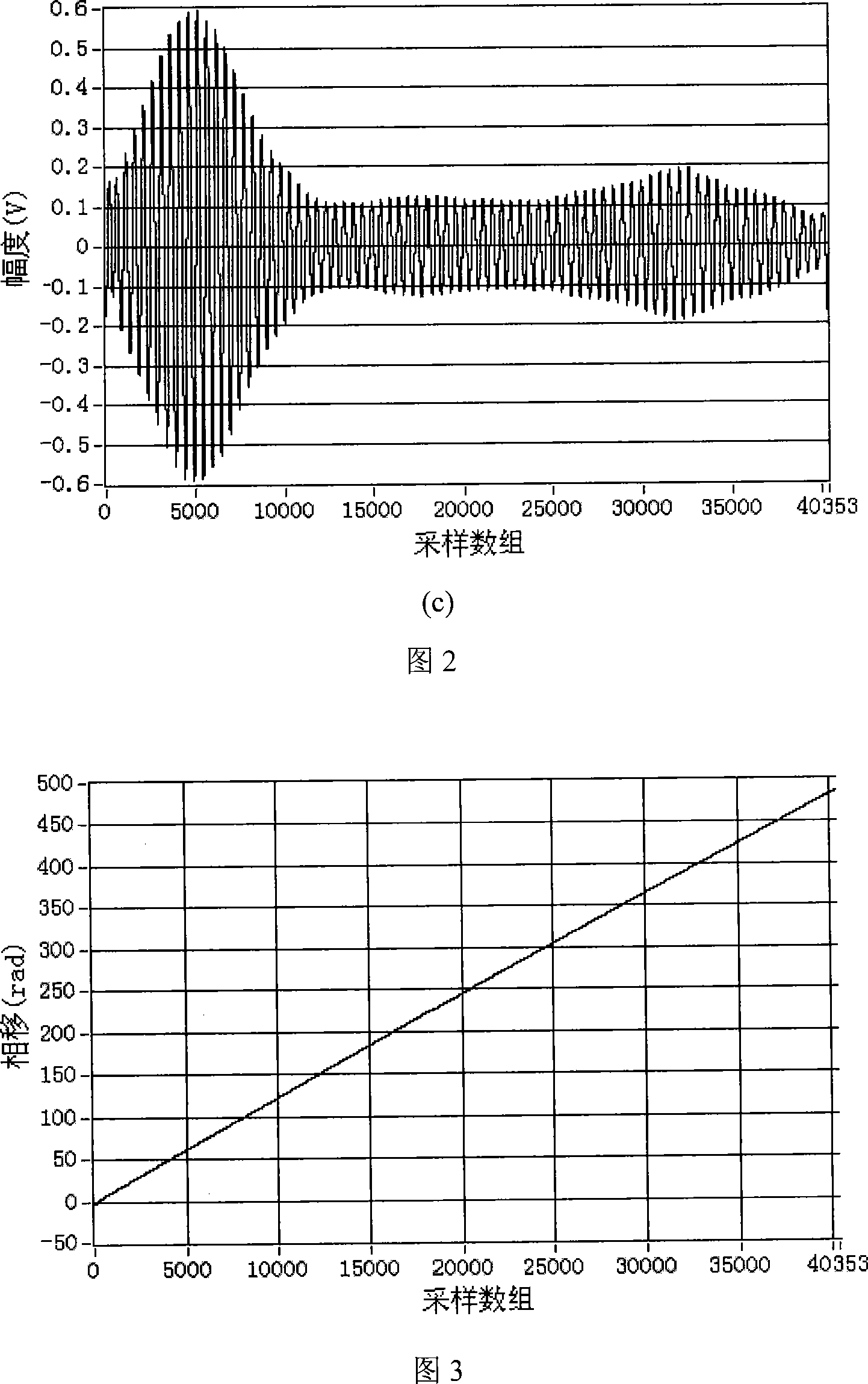
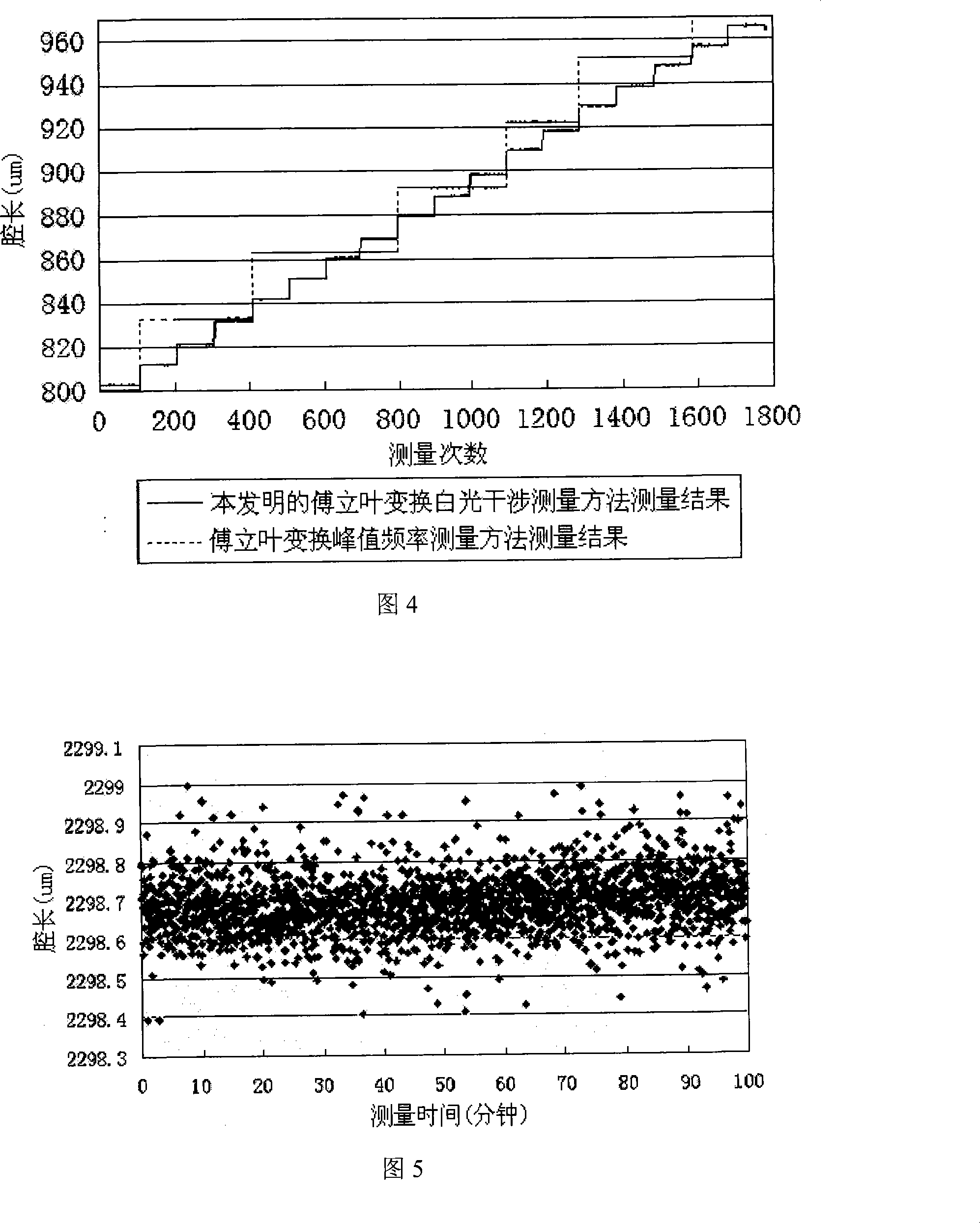
ActiveCN101158602AHigh measurement accuracyOptical measurementsInterferometric spectrometryWhite light interferometryFrequency measurements
An optical fiber Fourier measurement with switching white light interferometer implements Fourier transforms on white light spectrum output from transducer interferometer, the carrier frequency is Fourier spectrum defined by interferometer optical path difference, two sets of carrier frequency components are separated and symmetrical in the frequency space; one set of components is filtered for anti-Fourier transforms and plural logarithm operation, phase information of the transducer interferometer is set as an imaginary part of signals and separated from the background formed by lighting source spectrum outline and interference fringes contrast; the phase information of the transducer interferometer is limited within (minus Pi, Pi) according to operation procedure, the 2 Pi phases polarize of phase information is phase unwrapped, the measuring range is not limited with the 2 Pi phase; absolute optical path difference of transducer interferometer is calculated from phase information, thus realizing testing. The method of the invention prominently increases accuracy of white light spectrum peak measuring method and Fourier peak value frequency switching method.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
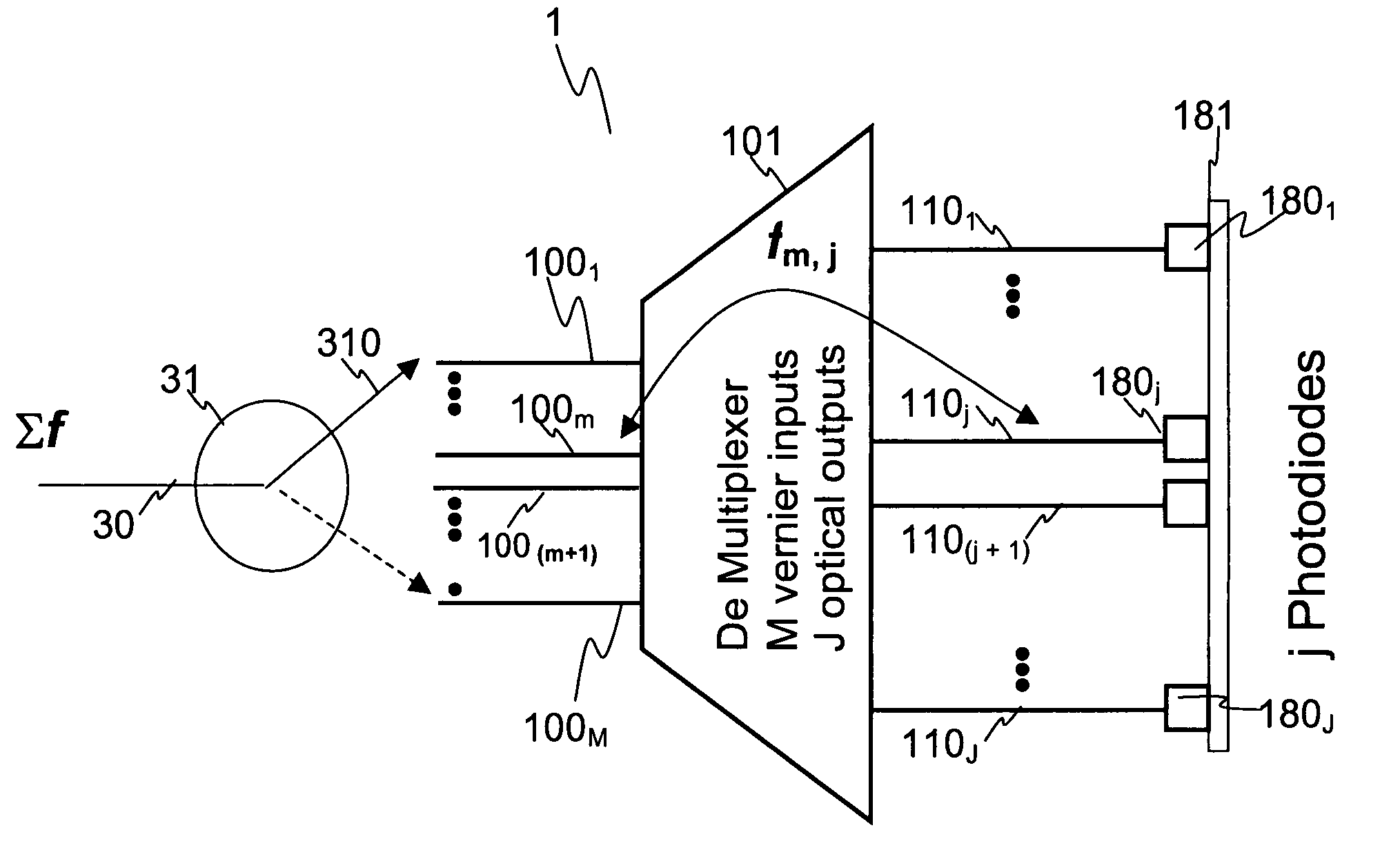
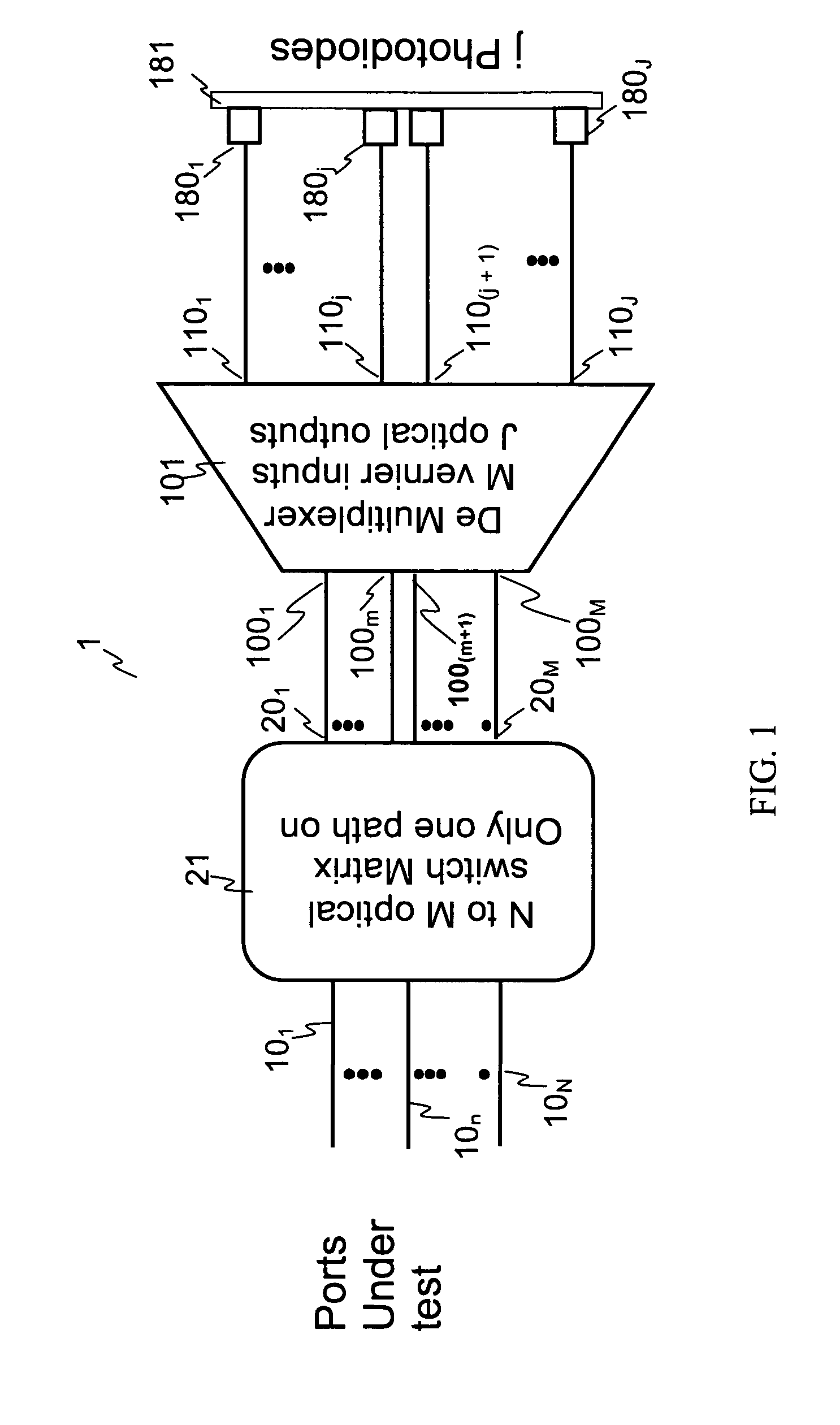
Optical performance monitor
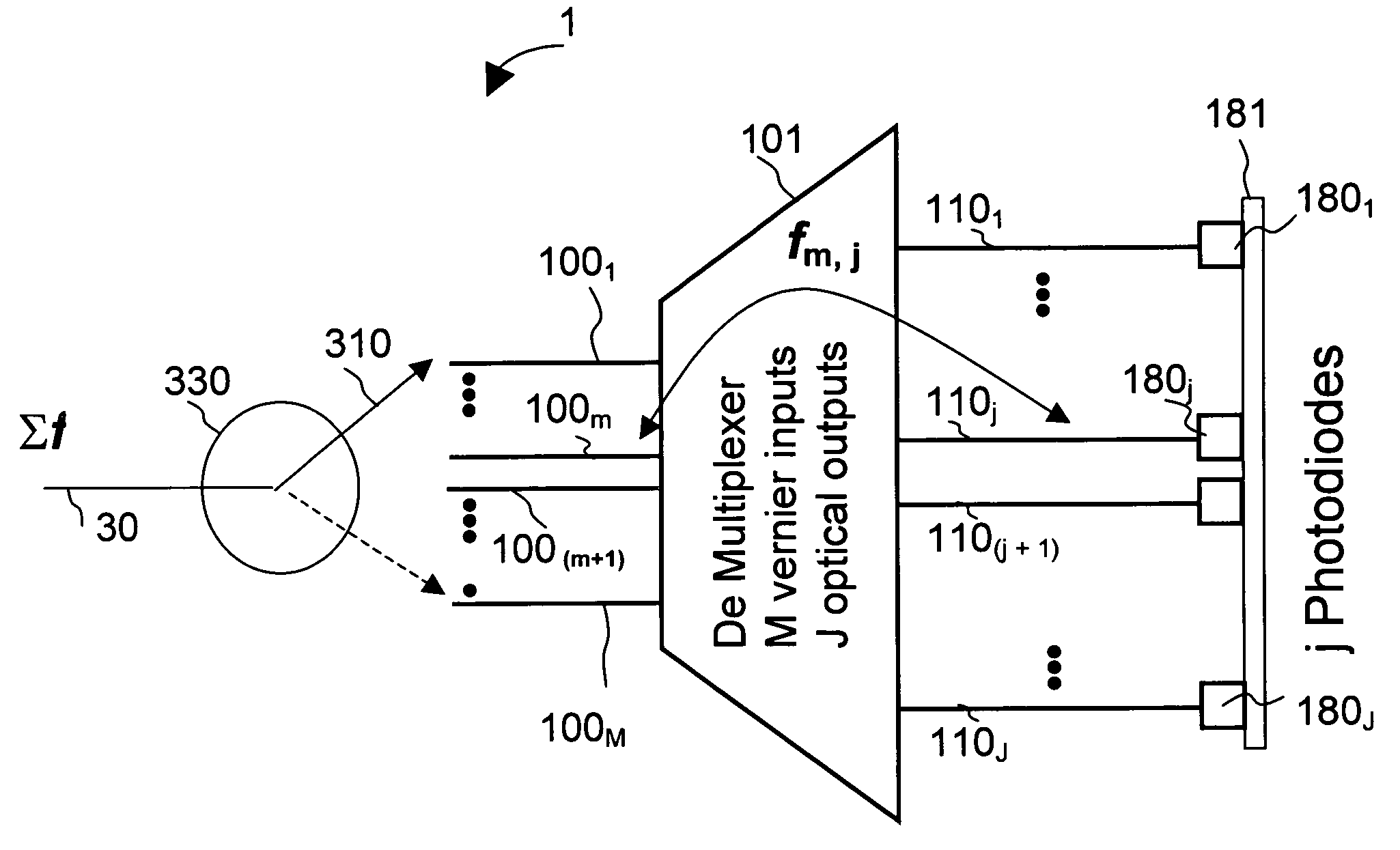
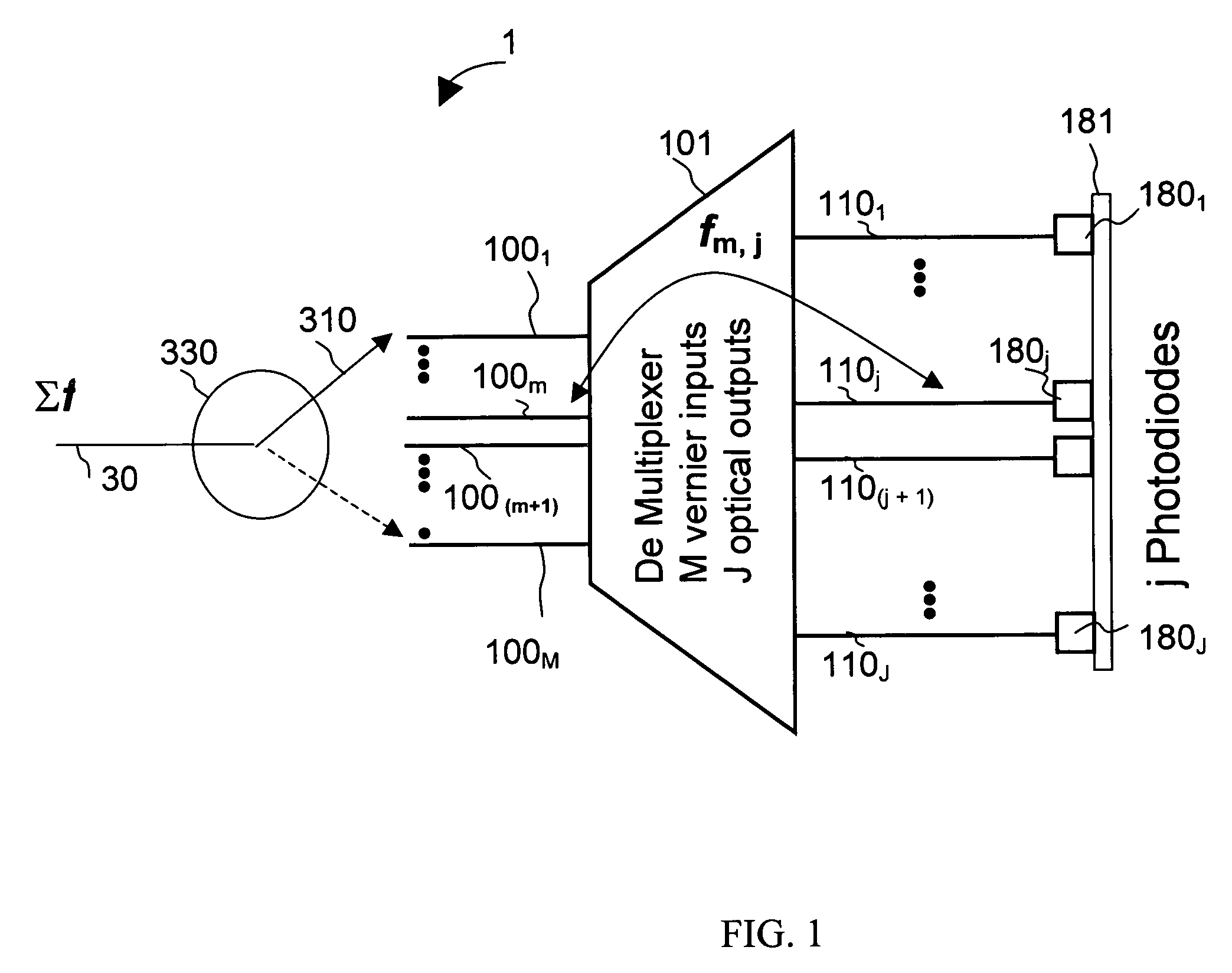
An apparatus for monitoring an input optical signal at a plurality of distinct optical frequencies is disclosed wherein a demultiplexing arrayed waveguide grating (AWG) having a plurality of M>1 Vernier input ports is disposed between an optical switch and a photodiode array coupled to the output ports of the AWG. In operation, the optical switch sequentially provides the input optical signal into each of the Vernier ports, and signals detected by photodiodes are stored in a memory unit. The apparatus is capable of monitoring the input optical signal with a frequency step which is M times smaller than a frequency spacing between the AWG transmission bands, and obtain M frequency-resolved readings from each photodiode.
Owner:LUMENTUM OPERATIONS LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com