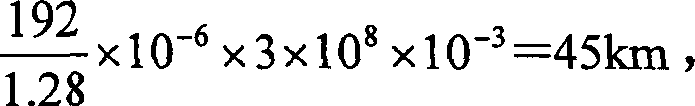Patents
Literature
148 results about "Synchronous CDMA" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
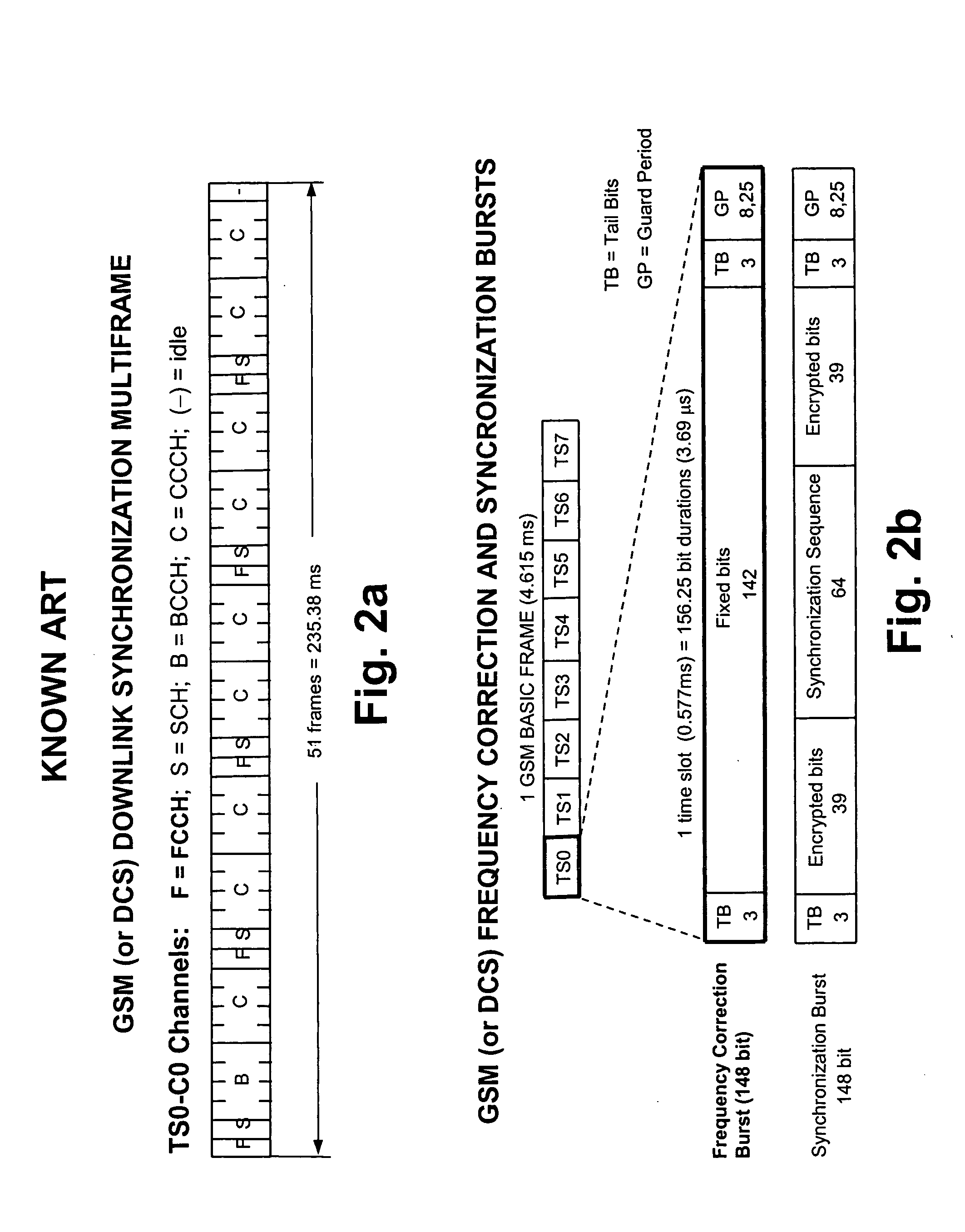
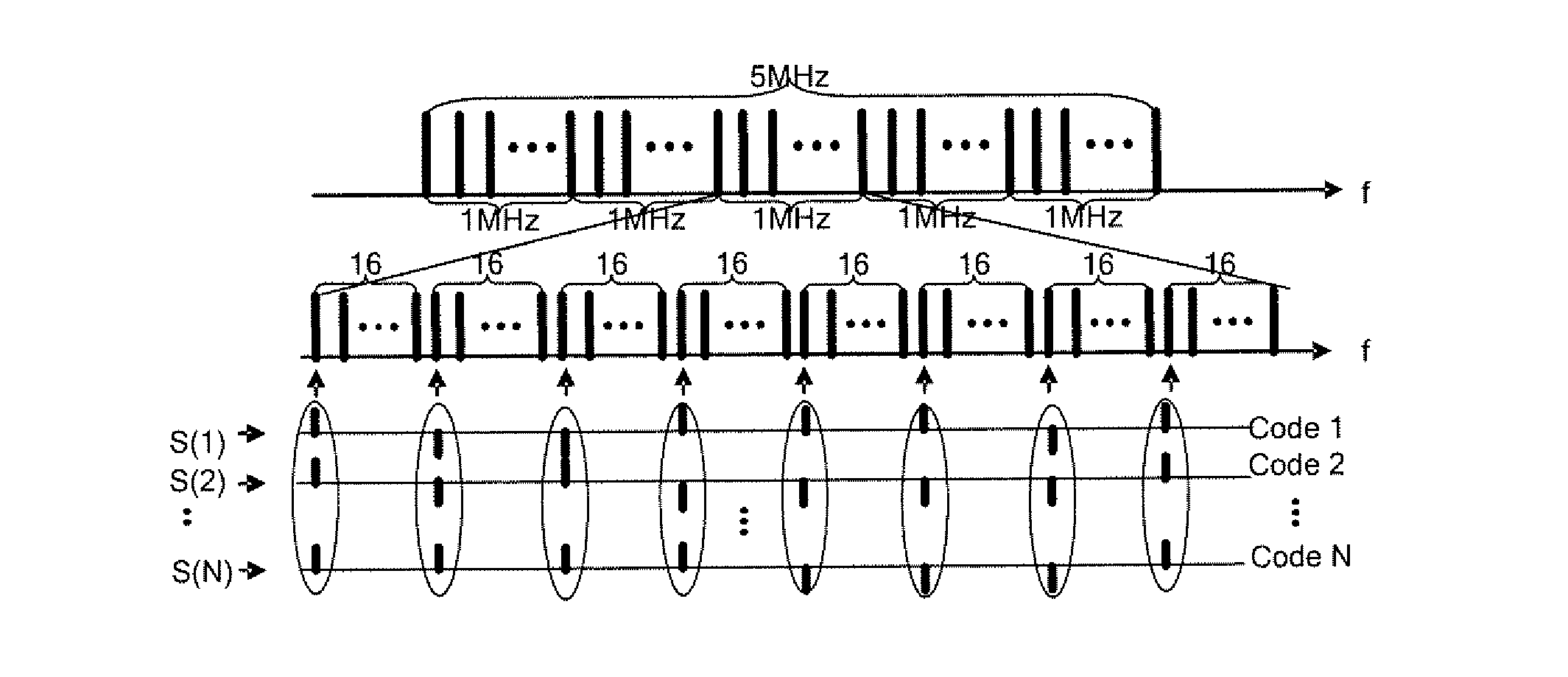
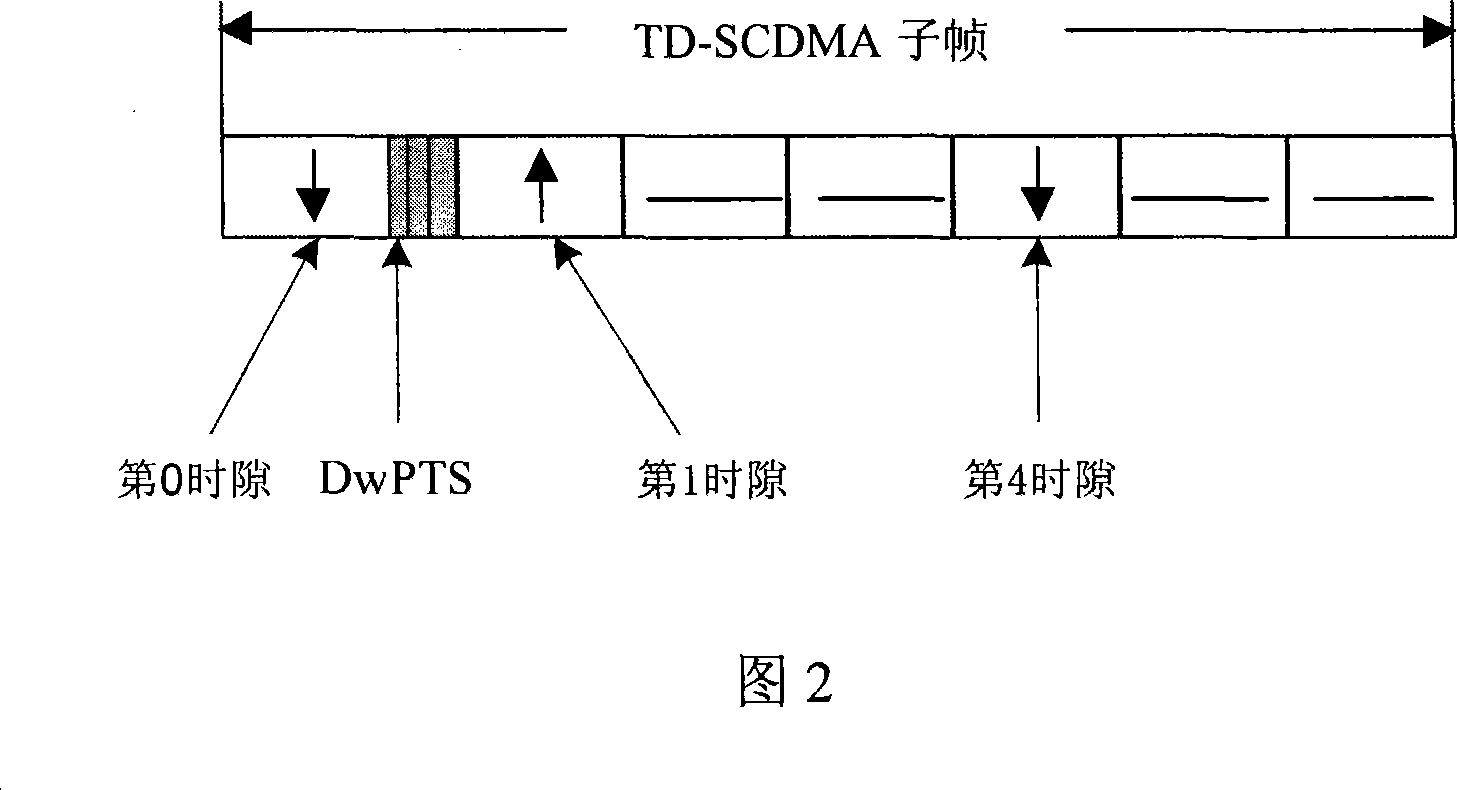
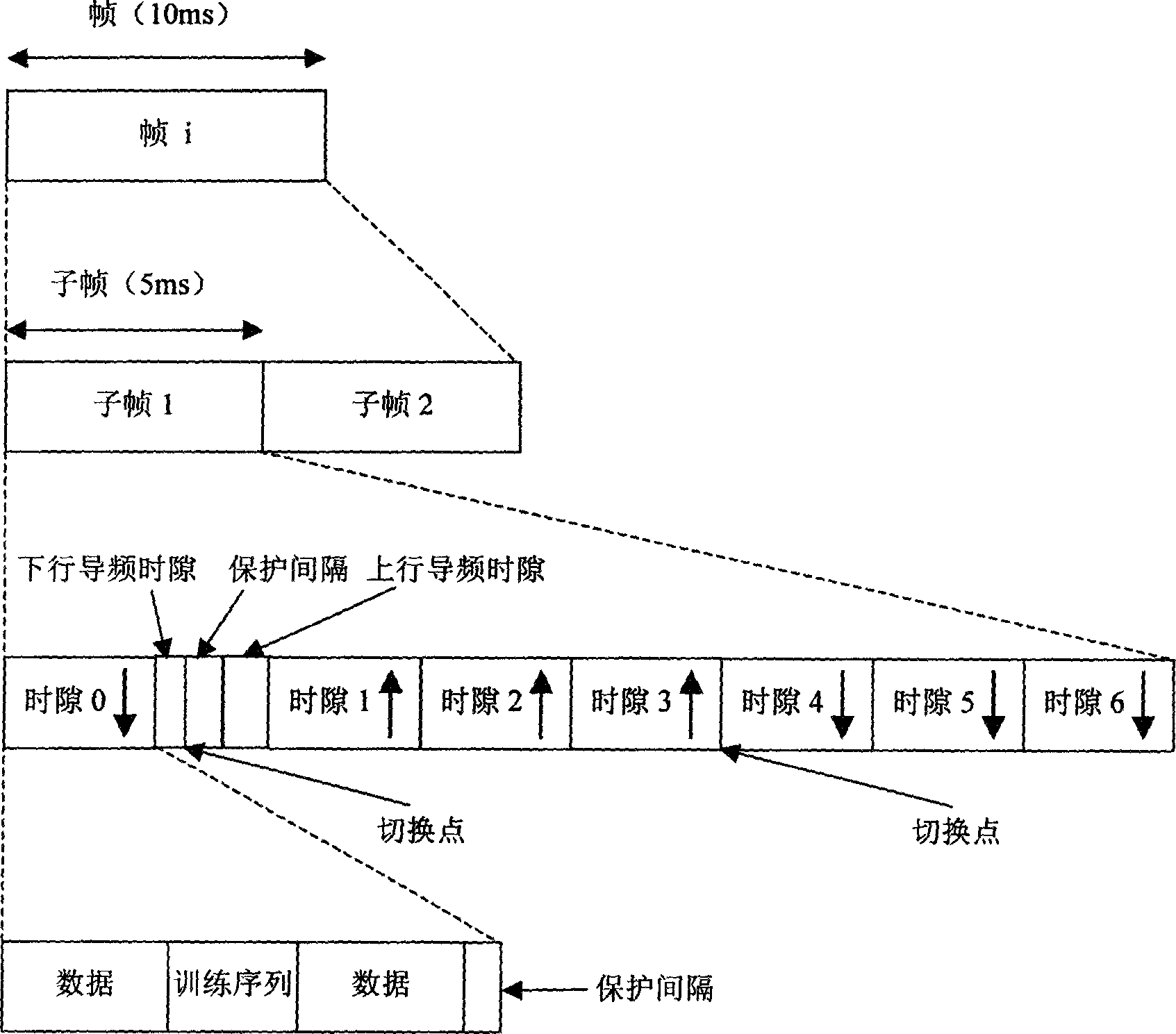
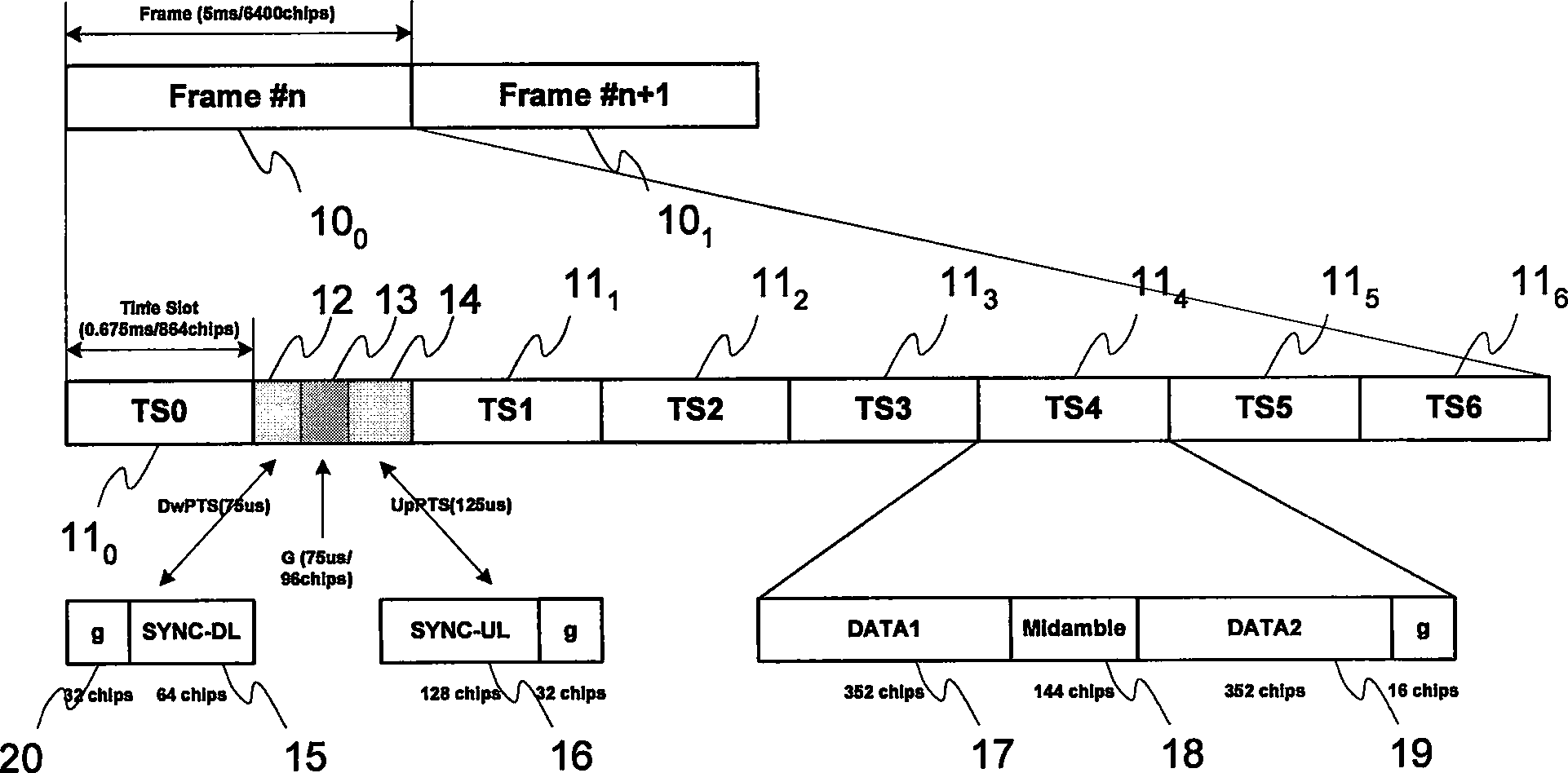
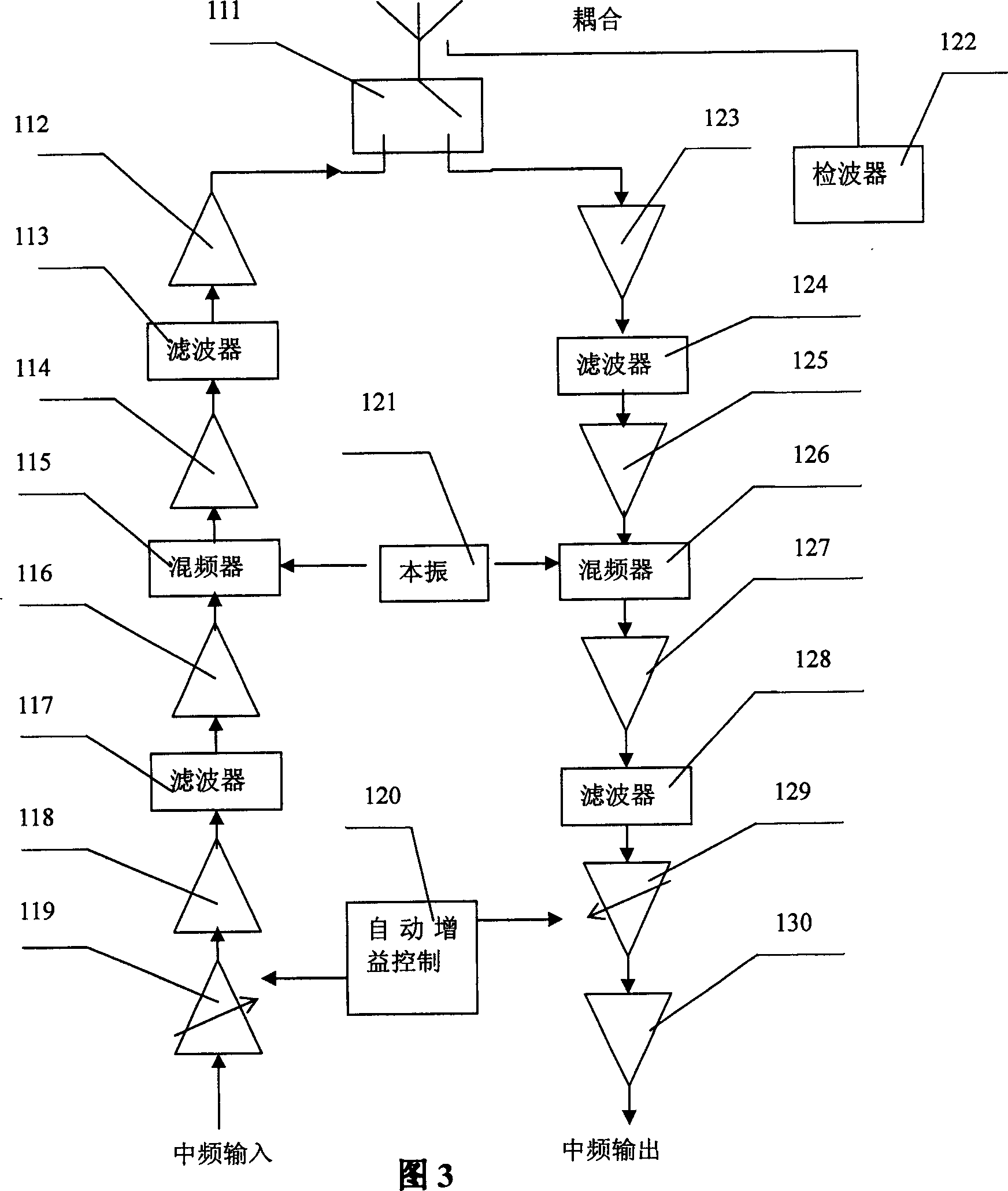
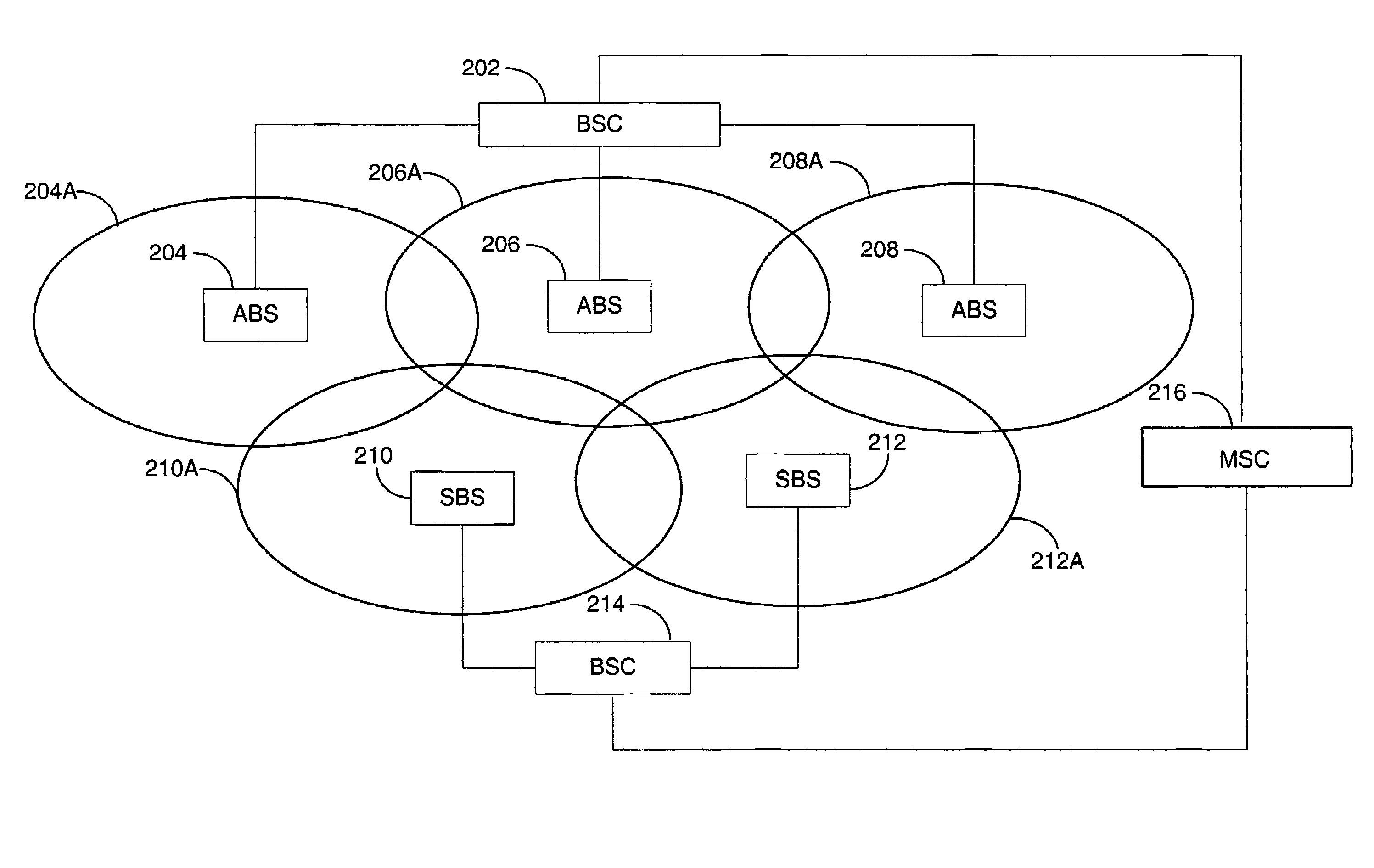
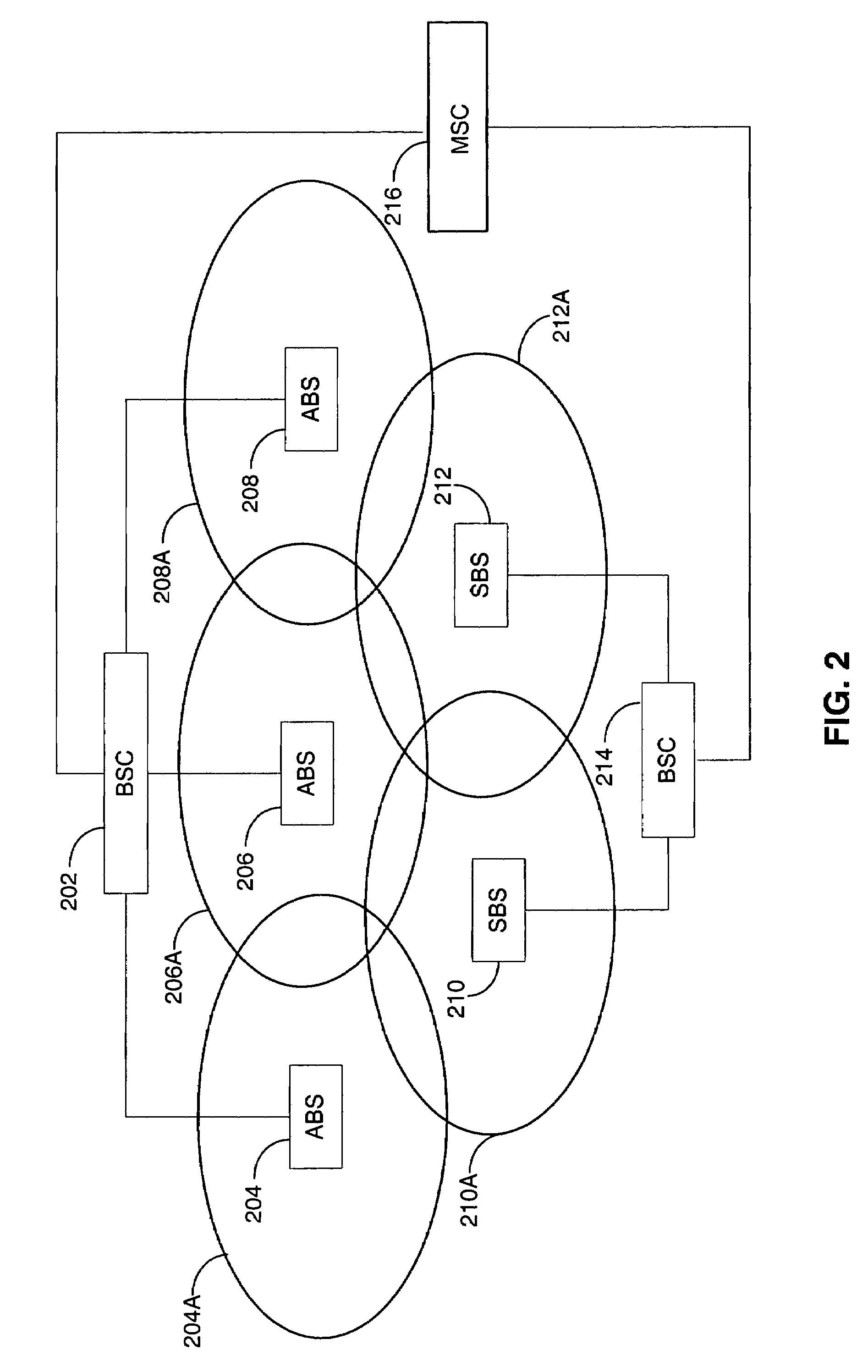
Synchronous CDMA (SCDMA) is one of the air interfaces of CDMA standards, it used the technology of TDMA to achieve the synchronization of the terminal's upload timeslot. SCDMA is the base of the UMTS-TDD LCR (Known as TDS-CDMA), and powerfully supported by the Chinese government. It's similar with the TDSCDMA of the special technology used, such as software radio and smart antenna. It belongs to the 2G (Second Generation Communication System).
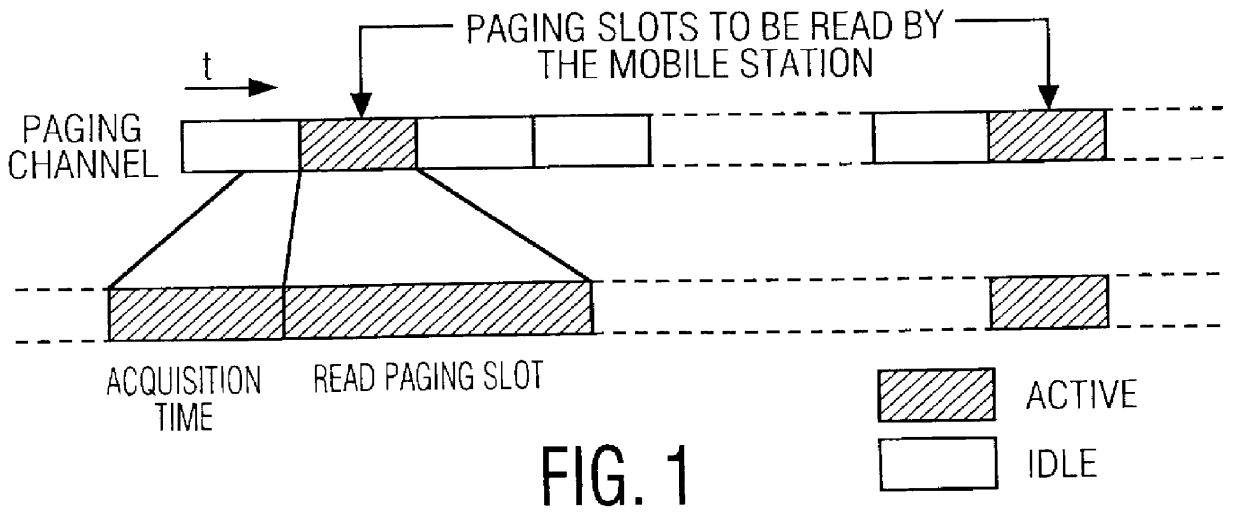
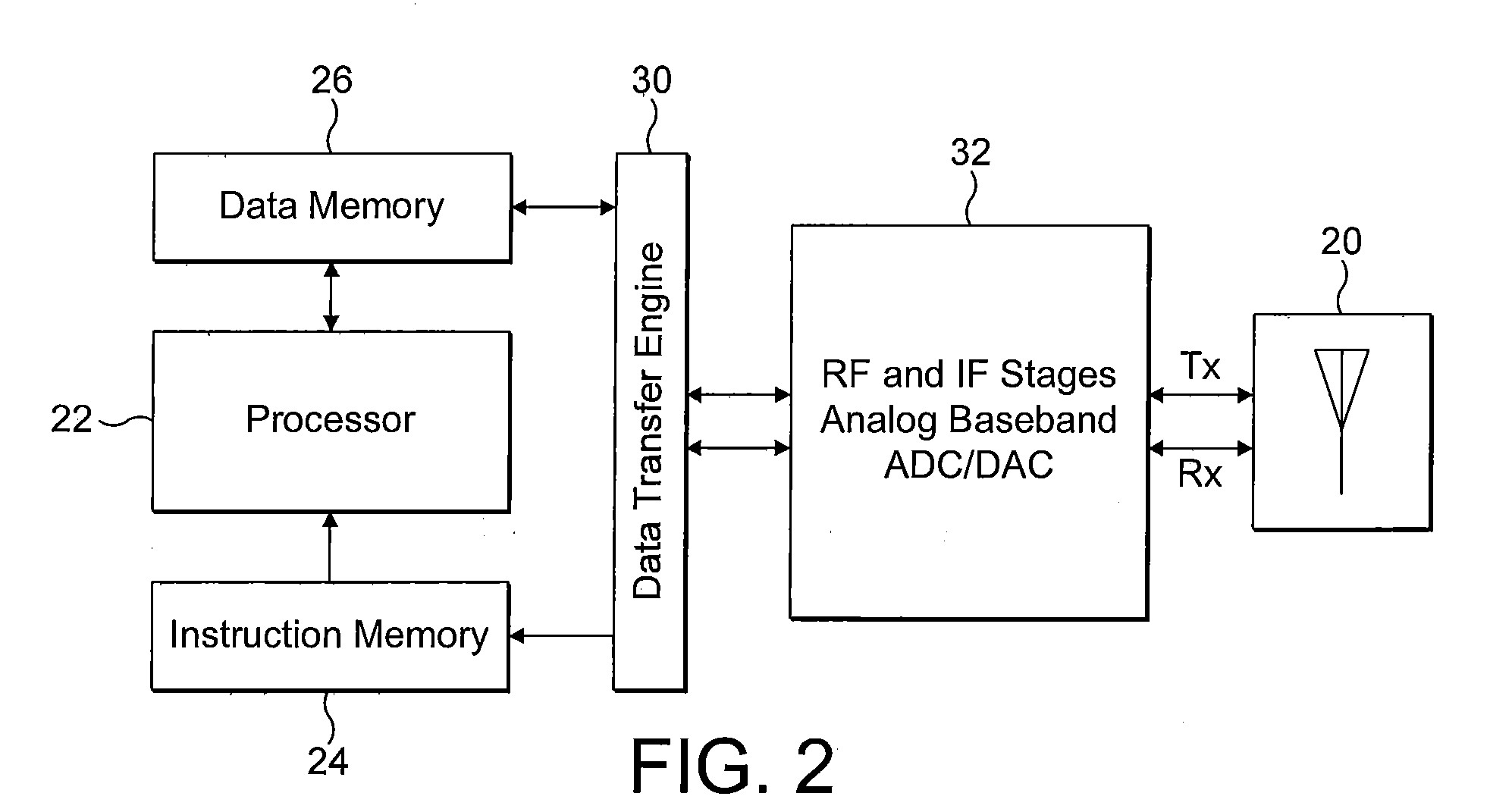
Method and mobile station to perform the initial cell search in time slotted systems
InactiveUS20050075125A1Speed up scan operationConvenient ArrangementSynchronisation arrangementAssess restrictionLow-pass filterCarrier signal
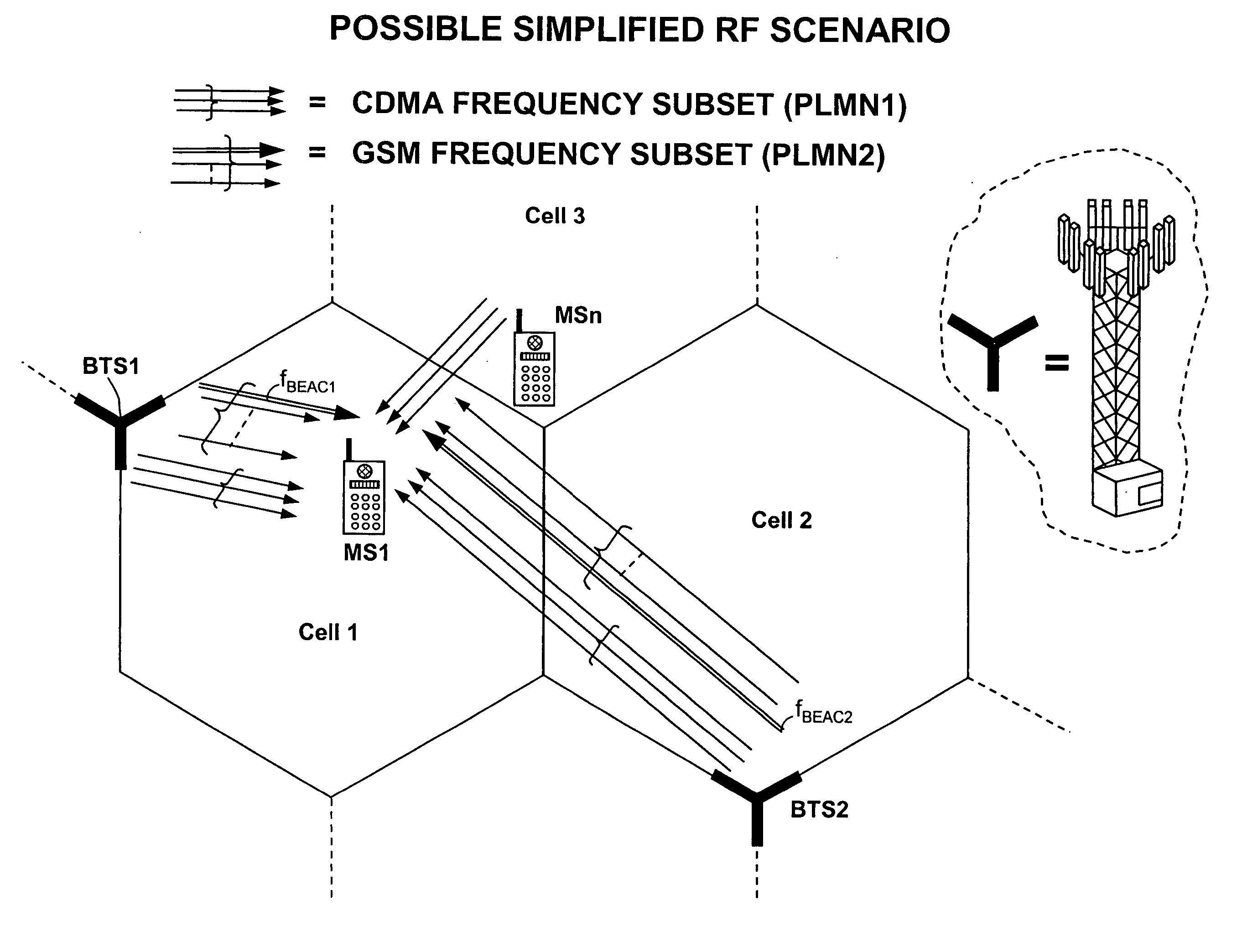
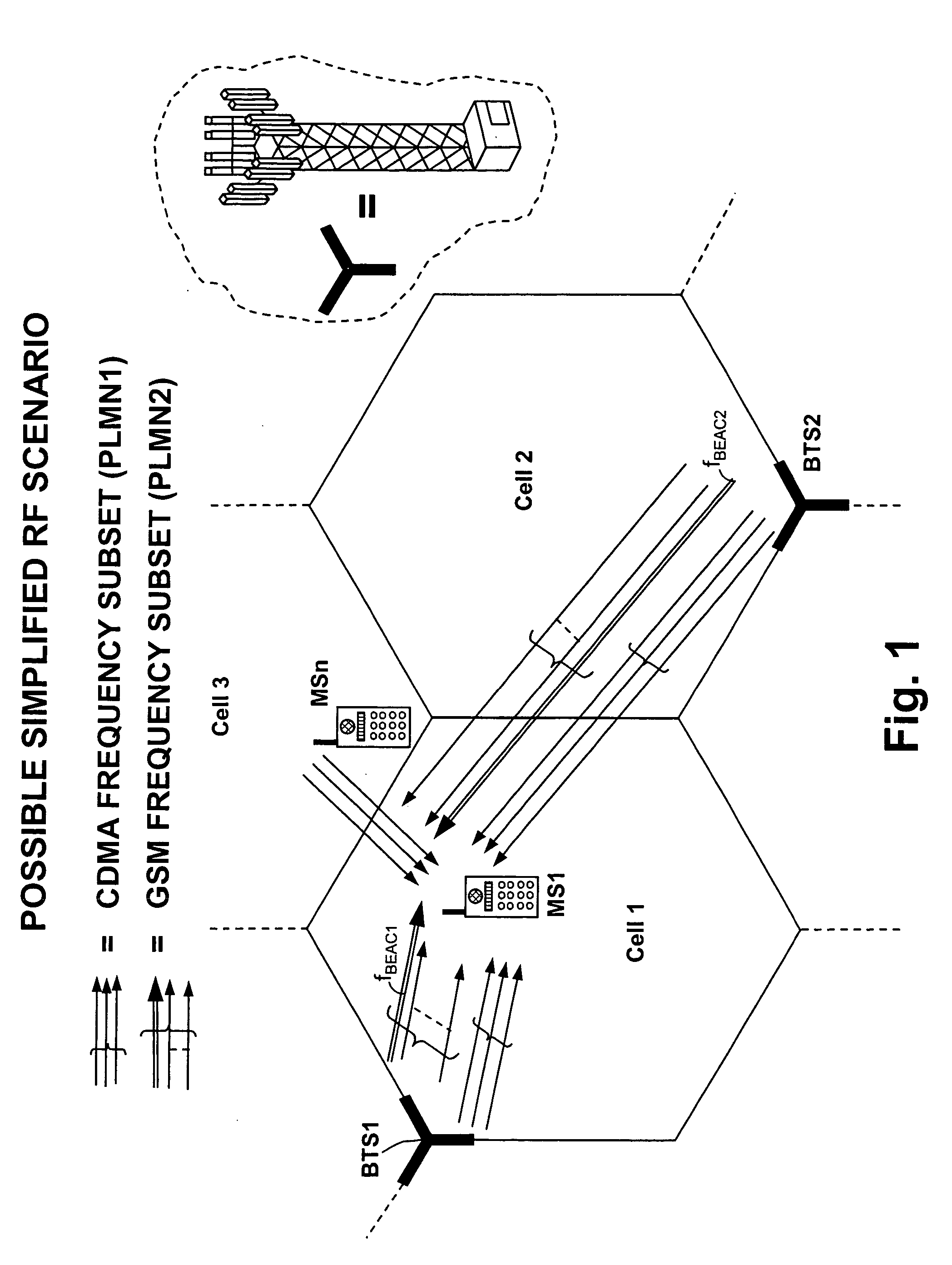
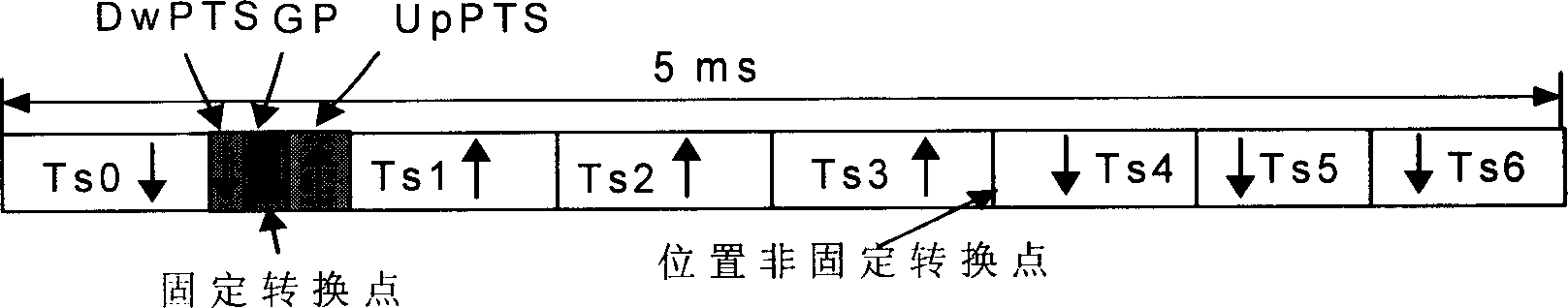
A method is disclosed that a Mobile Station MS performs at switch-on to search the most favorable target cell in UMTS systems like the 3GPP CDMA—LCR (Low Chip Rate) option at 1.28 Mcps—TDD (Time Division Duplex) mode and the equivalent TD-SCDMA (Time Division—Synchronous CDMA). Signal at the MS antenna is the sum of different RF downlink frames coming from different carriers in the assigned frequency ranges. A DL synchronization timeslot and a BCCH TS0 are both transmitted with full power in the frames, the first one includes one out of 32 SYNC codes assigned on cell basis. Following a conventional approach the absence of a common downlink pilot and without prior knowledge of the used frequencies would force the MS, for all the frequencies of the channel raster stored in the SIM card, the correlation of the received frame with all the 32 SYNCs stored in the MS, in order to detect the BSIC of a cell to which associate the power measures. Following the two-step method of the invention the power measures are performed in two-step scan of the PLMN band without interleaved correlation steps; once a final frequency is selected the respective frame is the only correlated one. At least one frame duration about 5 ms long of the whole 15 MHz bandwidth is acquired, IF converted, A / D converted and the digital set is stored. A rough scan is performed multiplying the digital set by a digital IF tuned in steps wide as the channel band (1.6 MHz) along the 15 MHz band, and filtering the baseband signal with a Root Raise Cosine low-pass filter. The 5 ms baseband signal is subdivided into 15 blocks of half timeslot (337.5 μs) and the power of each block is measured. The power of the strongest block indicates the priority of the respective frequency. The strongest power values are put in a Spectral Table together with respective frame load indicators. The load indicator is the percentage of timeslots in a frame almost equally loaded as the strongest block. The three strongest frequencies are selected for the successive scan. The second step search is performed like the first one but the IF steps are now 200 kHz wide and cover the only 1.6 MHz spectrum around a selected frequency. A final frequency is selected for the successive correlation step. Then the frequency error of the MS reference oscillator is corrected with data-aided techniques and a calibration value stored for successive connections (FIG. 9).
Owner:SIEMENS INFORMATION & COMM NEWTWORKS INC
Virtual mimo communication system
ActiveUS7508798B2Create efficientlySite diversitySpatial transmit diversityTelecommunicationsMimo transmission
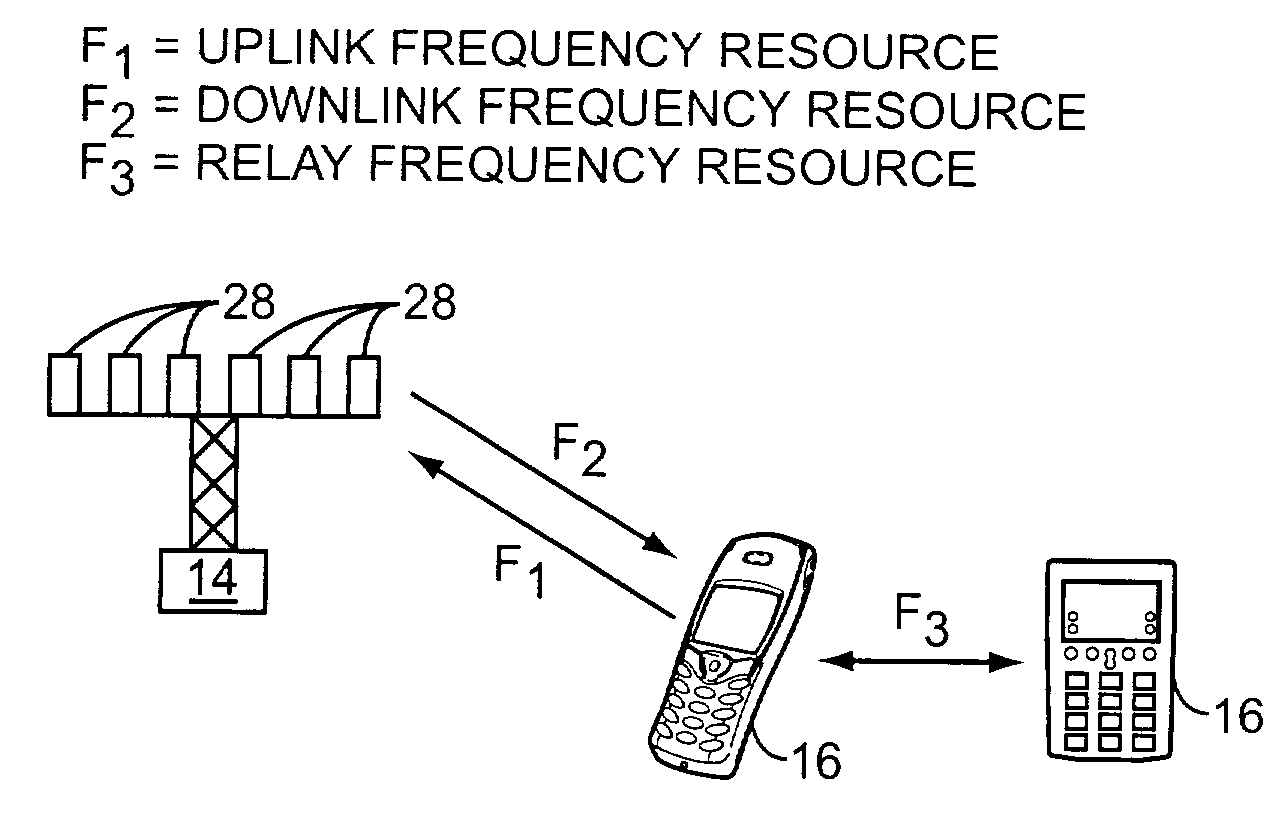
The present invention provides an effective way to create a virtual MIMO transmission system using mobile terminals that have only one transmit path and antenna. This is accomplished by assigning mobile terminals to a group and assigning certain shared resources and user-specific resources to those mobile terminals in the group. In a synchronized fashion, the mobile terminals will provide uplink transmission in concert, as if they were a single entity having multiple transmission paths and antennas. Preferably, the shared resources bear on how the data is transmitted, and the user-specific resources relate to pilot signals. The data transmitted may be encoded in any number of ways, and in one embodiment, the mobile terminals may relay their information to each other, such that uplink transmissions can incorporate STTD decoding or other space-time codes. The invention is applicable to virtually any multiple access technology, including OFDM, TDMA, and CDMA, preferably synchronous CDMA.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
Two-dimensional channel bonding in a hybrid CDMA/FDMA fixed wireless access system to provide finely variable rate channels
InactiveUS7190683B2Improve concentration efficiencyRelatively large bandwidthModulated-carrier systemsTime-division multiplexCommunications systemCode space
A communications system employs the use of both synchronous CDMA and FDMA to provide a variable bandwidth waveform with multiple bonded transmitters and receivers that are agile in both frequency and PN code to permit a variable bandwidth and variable rate multiple access system. In a first aspect the teachings provide the use of both CDMA and FDMA together to enable an improved concentration efficiency by making a larger pool of bandwidth available to each user. In a second aspect these teachings enable channel bonding across both code space and frequency space, thus making the system capable of operating within a variable (not necessarily contiguous) bandwidth and at a finely variable rate.
Owner:L 3 COMM CORP
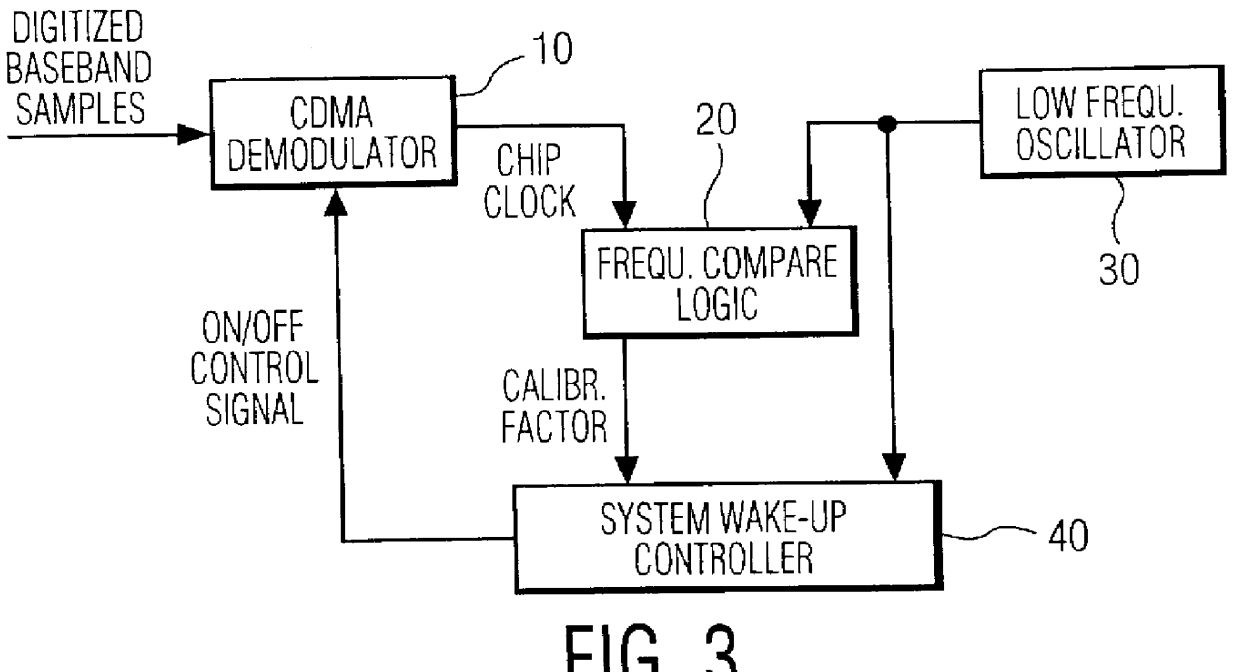
Circuit for synchronizing CDMA mobile phones
InactiveUS6028855AAccurately reacquireReduce power consumptionPower managementSynchronisation arrangementNetwork clockEngineering
A frequency calibration circuit for use in a spread spectrum receiver. The receiver includes circuitry for receiving a spread spectrum signal from a base station and for recovering a network clock signal therefrom, a low frequency oscillator for producing an oscillator clock signal, and a frequency comparator that takes as inputs the network clock signal and the oscillator clock signal and produces a calibration factor based on the difference between the clock signals. A controller coupled to the low frequency oscillator amd the frequency comparator utilizes the calibration factor together with the low frequency oscillator clock signal to output a accurate and precision timed signal thereby being able to accurately require the timing of the paging channel.
Owner:ST ERICSSON SA
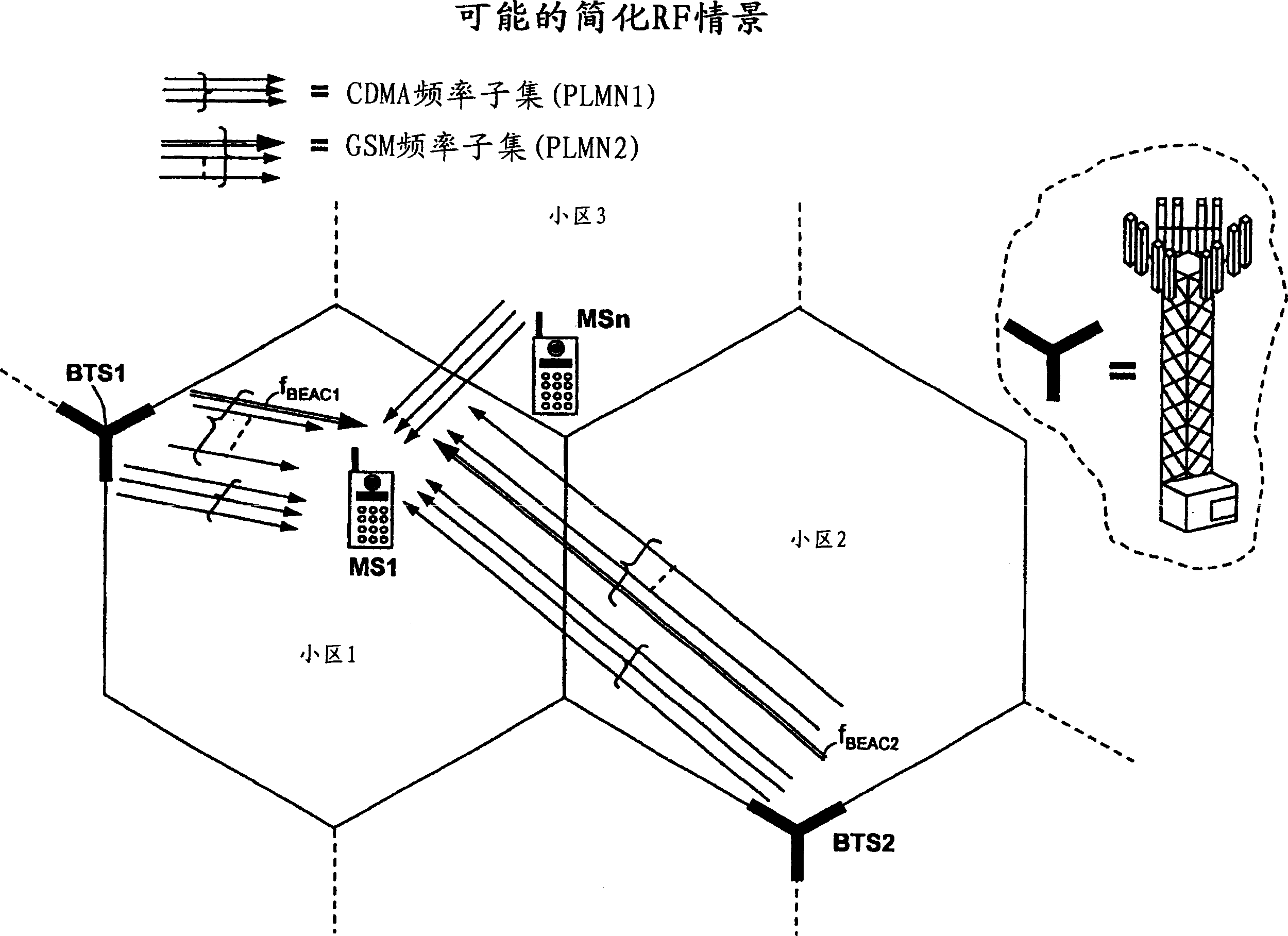
Wireless communication system based on code spreading-orthogonal frequency division multiple access and smart antenna
InactiveUS20100238846A1Avoid serious distractionsEffectively avoids disadvantageTime-division multiplexRadio transmissionFrequency spectrumTransceiver
A time division duplex wireless communication system based on Code Spreading-Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access (CS-OFDMA) and a smart antenna includes: an antenna array and multichannel transceiver, a space processor, a demodulator, an L2 processor and a modulator. The CS-OFDMA system provided by the present invention combines synchronous CDMA technique and OFDMA technique, overcomes the severe ISI caused by spectrum-spreading by the conventional CDMA system while transmitting wideband data, effectively counteracts frequency-selective fading and inter-cell interference, and is beneficial to reliable transmission of narrowband voice and wideband data and also beneficial to co-frequency networking.
Owner:BEIJING XINWEI TELECOM TECH
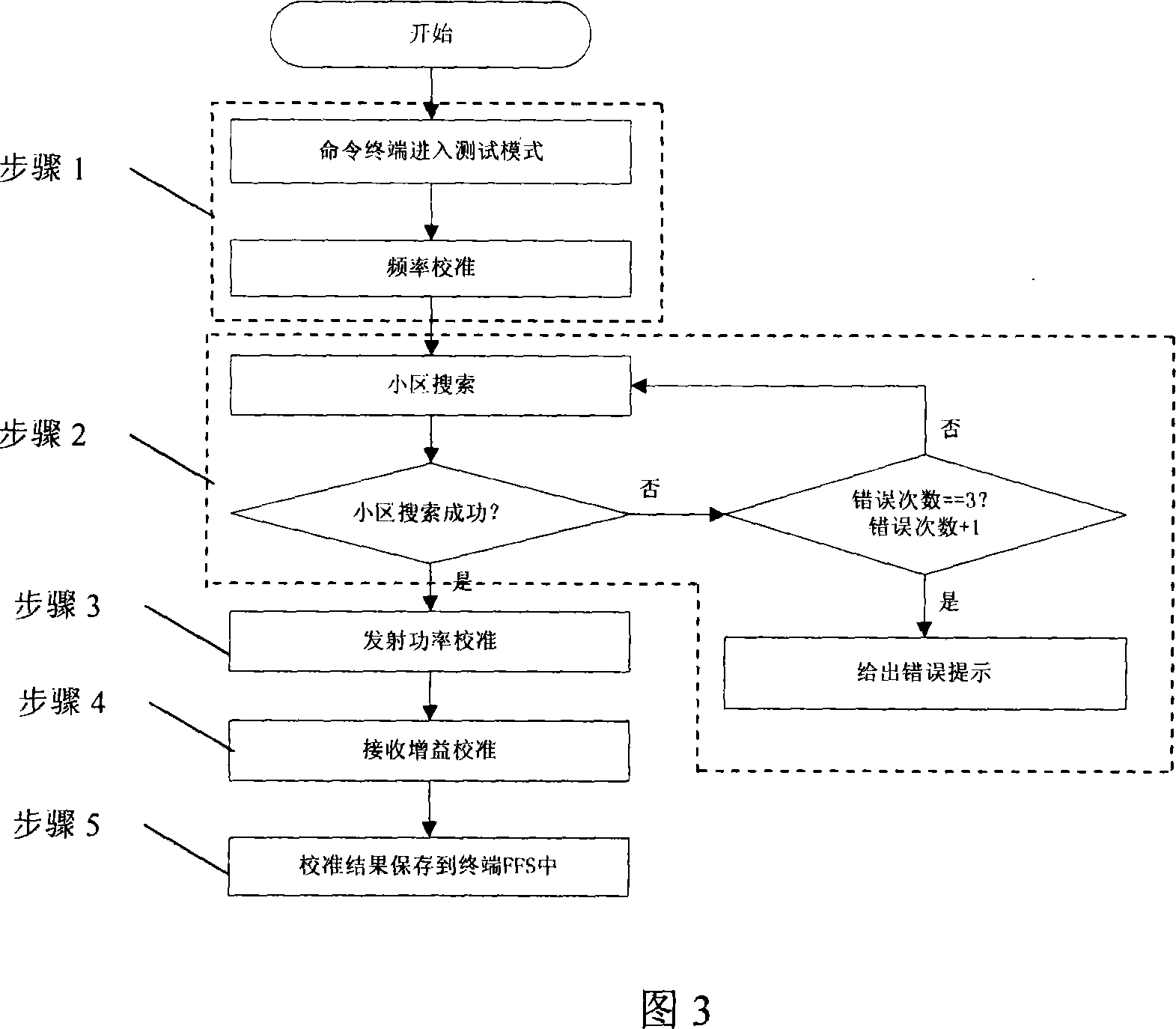
Method and device for automatic calibration of third-generation TD-SCDMA mobile terminal
InactiveCN101047915ARealize automatic calibrationImprove calibration accuracyTransmission control/equalisingCode division multiplexRadio frequencyEmission power
This invention relates to an automatic calibration method and a device for radio frequencies of TD-SCDMA / 3G mobile terminals, which can calibrate RF, emission power and received gain of mobile terminals automatically and store the calibrated results in NVRAM in the way of files with FFS. This invention can adjust the RF performance of terminals effectively mainly to current TD-SCDMA mobile terminals that their chips do not have the same control attribute.
Owner:XUANPU INDUSTRY CO LTD
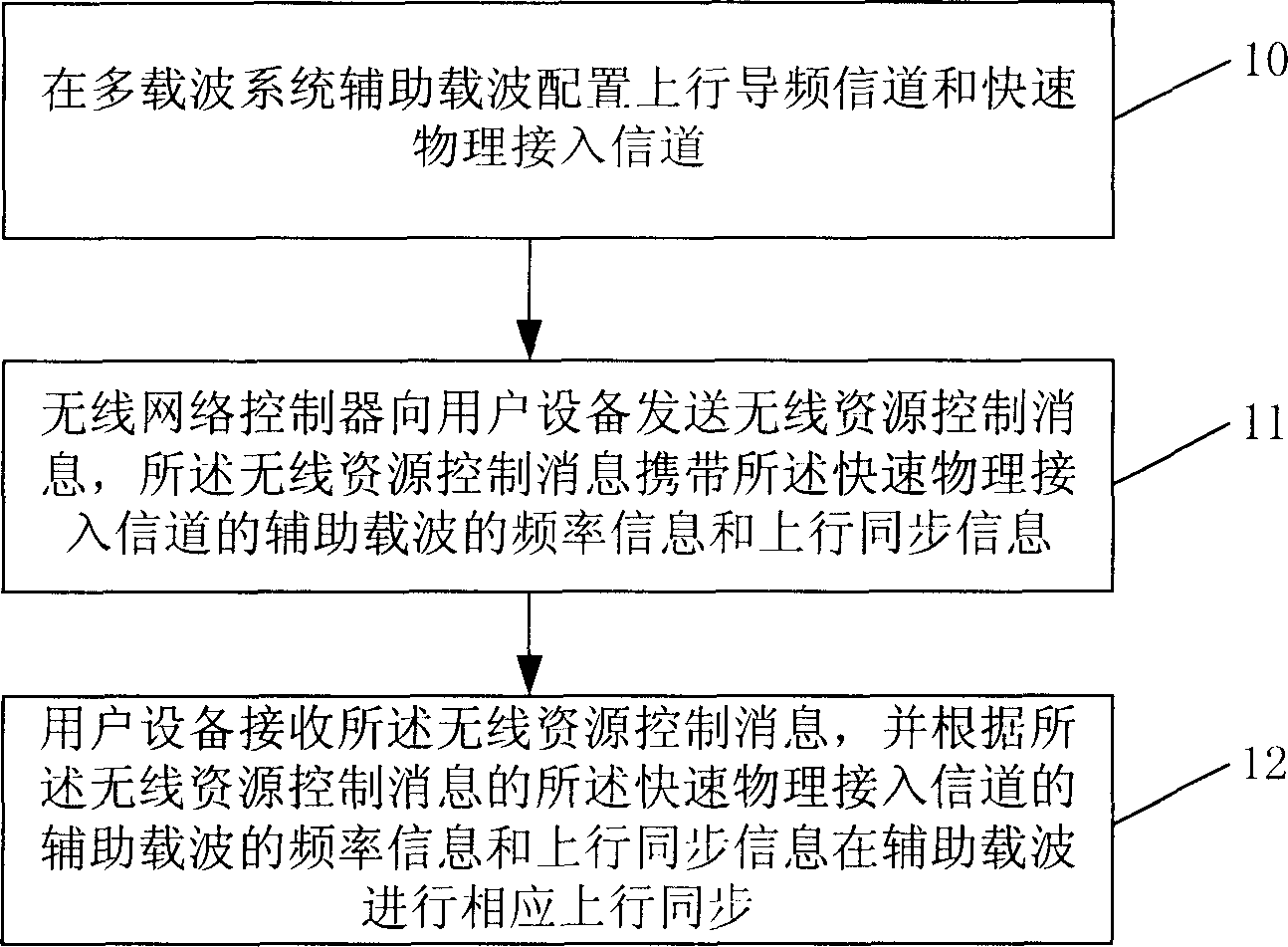
Method for realizing user equipment wireless resource control
InactiveCN1734976AIncrease capacityReduce the risk of main carrier congestionRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsRadio transmission for post communicationCarrier signalMulti carrier
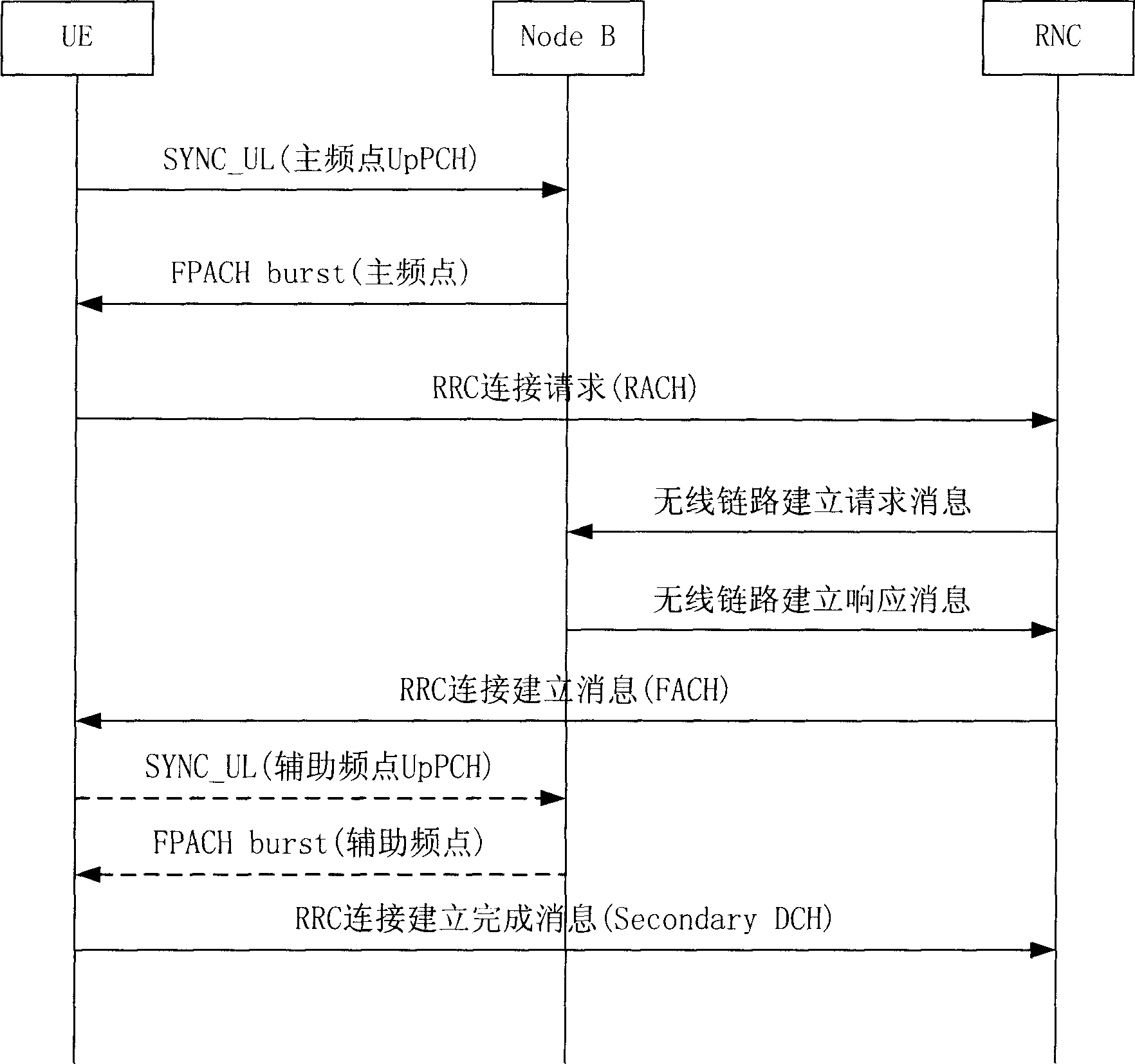
This invention discloses a method to realize control for user wireless resource for time-division synchronous CDMA multi carrier system, which comprises: a. arranging upper pilot frequency channel and quick physical access channel on auxiliary carrier wave of multi carrier system; b. the wireless network controller sends wireless resource control information with frequency information and upper synchronous information for said auxiliary carrier to user device; c. user device receives the information and executes synchronism. The invention can ensure all devices enjoying benefit from auxiliary carrier and decreases congestion hidden trouble for main carrier in early days.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
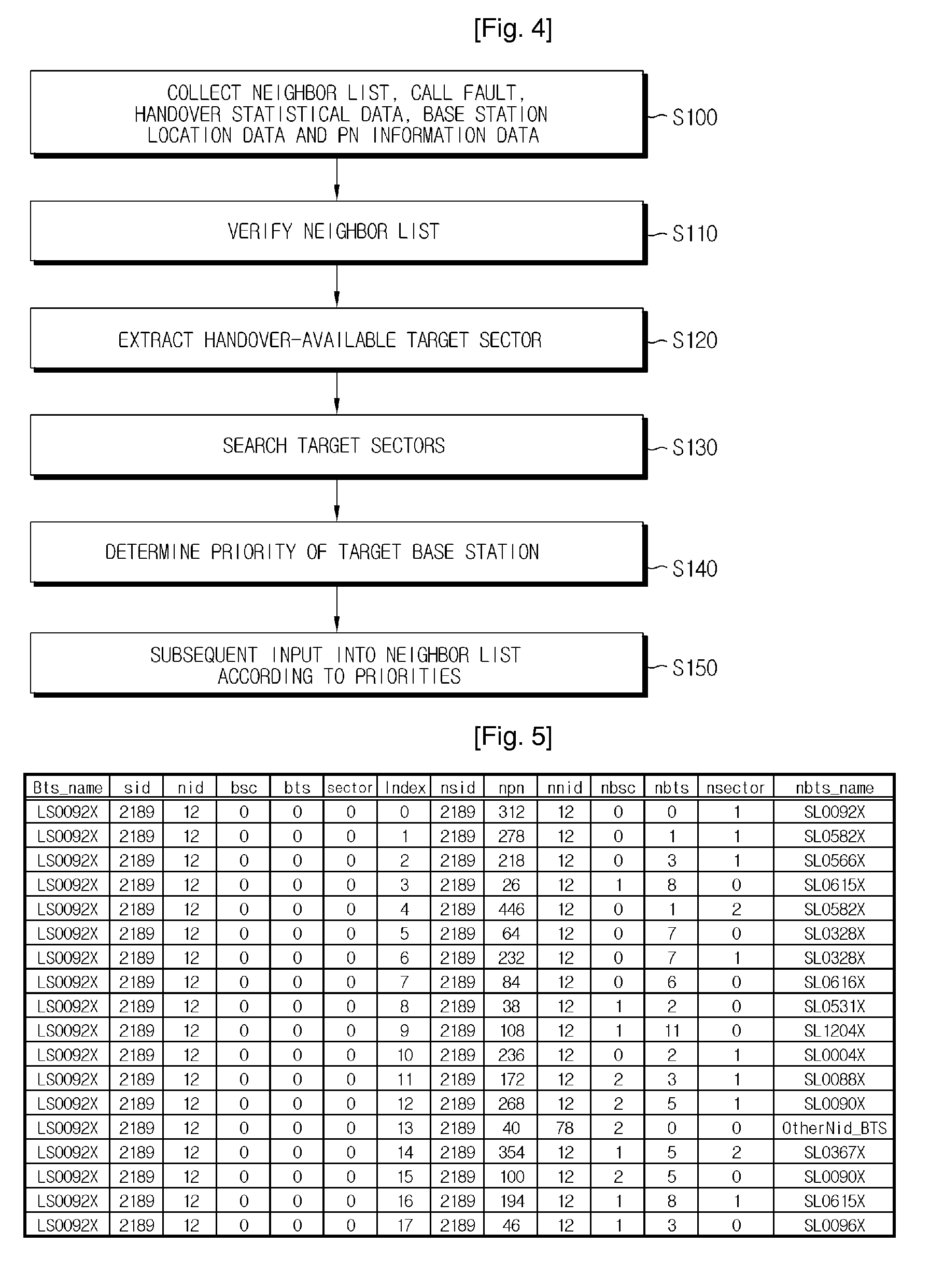
Method and Apparatus for Optimizing Neighbor List Automatically in Synchronous Cdma Network
ActiveUS20080225797A1Improve reliabilityRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsWireless commuication servicesCode division multiple accessHandover
A method for automatically optimizing a neighbor list for processing handover in a synchronous CDMA (Code Division Multiple Access) network includes the steps of: collecting neighbor list data, call fault data, handover statistical data, base station location data and PN information data of each base station sector in a nationwide network; extracting all target sectors available for handover by analyzing the collected data; endowing a weighting factor to the extracted target sectors according to importance and then sorting the target sectors according to calculated results so as to determine priorities; and subsequently inputting the target sector information to the neighbor list according to the priorities.
Owner:KT CORP
Method for reducing small-region interference in time-division synchronous CDMA accessing system
InactiveCN1816198AOptimizationReduce distractionsNetwork traffic/resource managementRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsTD-SCDMAChannel power
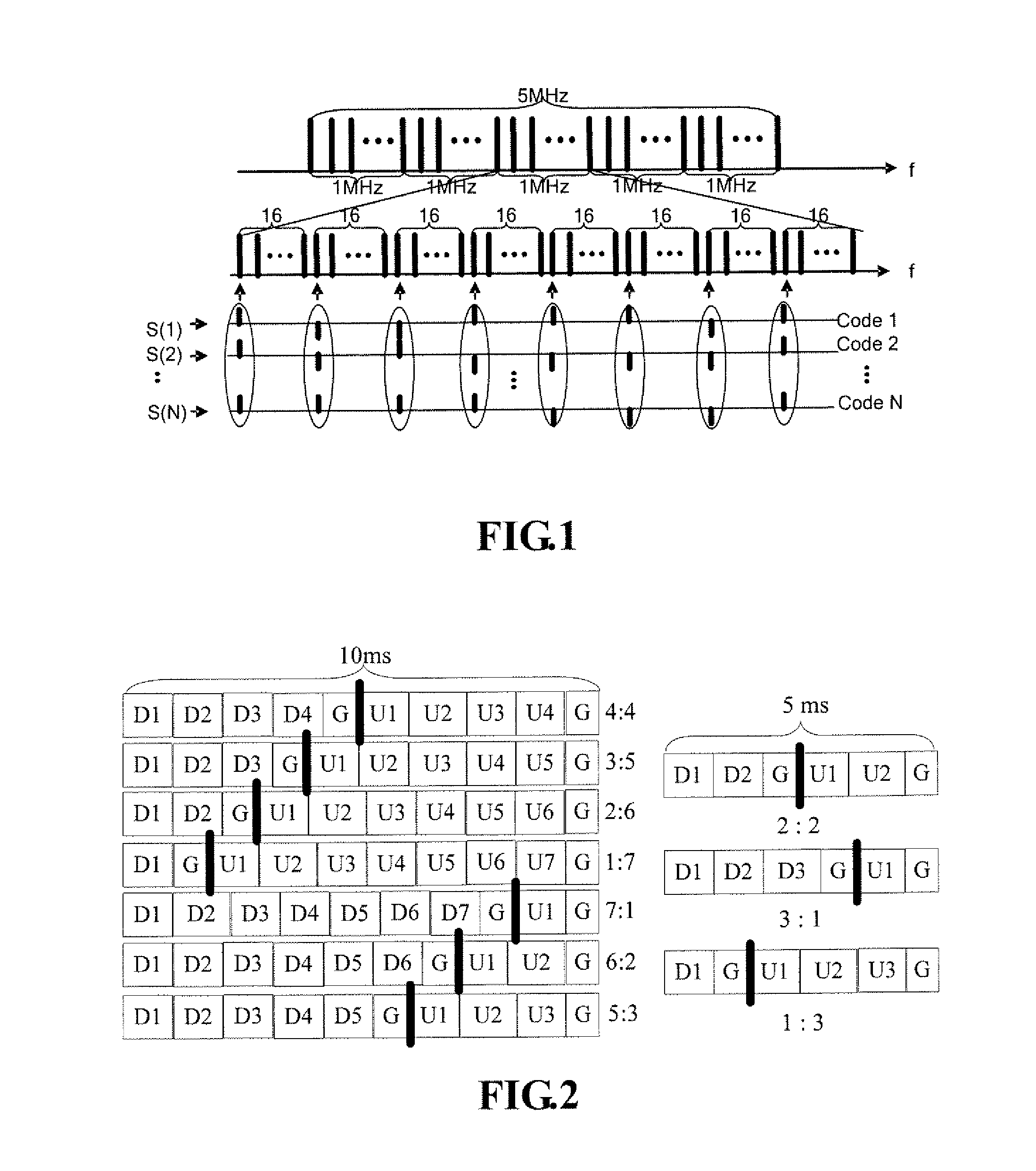
Base on different types of service in each region of system, the method allows TD-SCDMA system configures different numbers of time slots for upward and downward services for the region smartly. The said method is only applied to adjacent sub zones in configuration area, where there are different numbers of time slots for upward and downward services. Based on link estimation of investigated user device, and result report for measured channel power of interference signal up or down link, network controller determines whether a time slot is assigned to the investigated user device in order to reduce mutual interference between adjacent sub zones with different service time slots being configured. The network controller also carries out periodic monitoring for switching number inside sub zone in the said two adjacent sub zones in order to overcome influence on channel allocation caused by time varying character of interference signal so as to optimize allocation and raise capacity.
Owner:诺基亚西门子通信系统技术(北京)有限公司
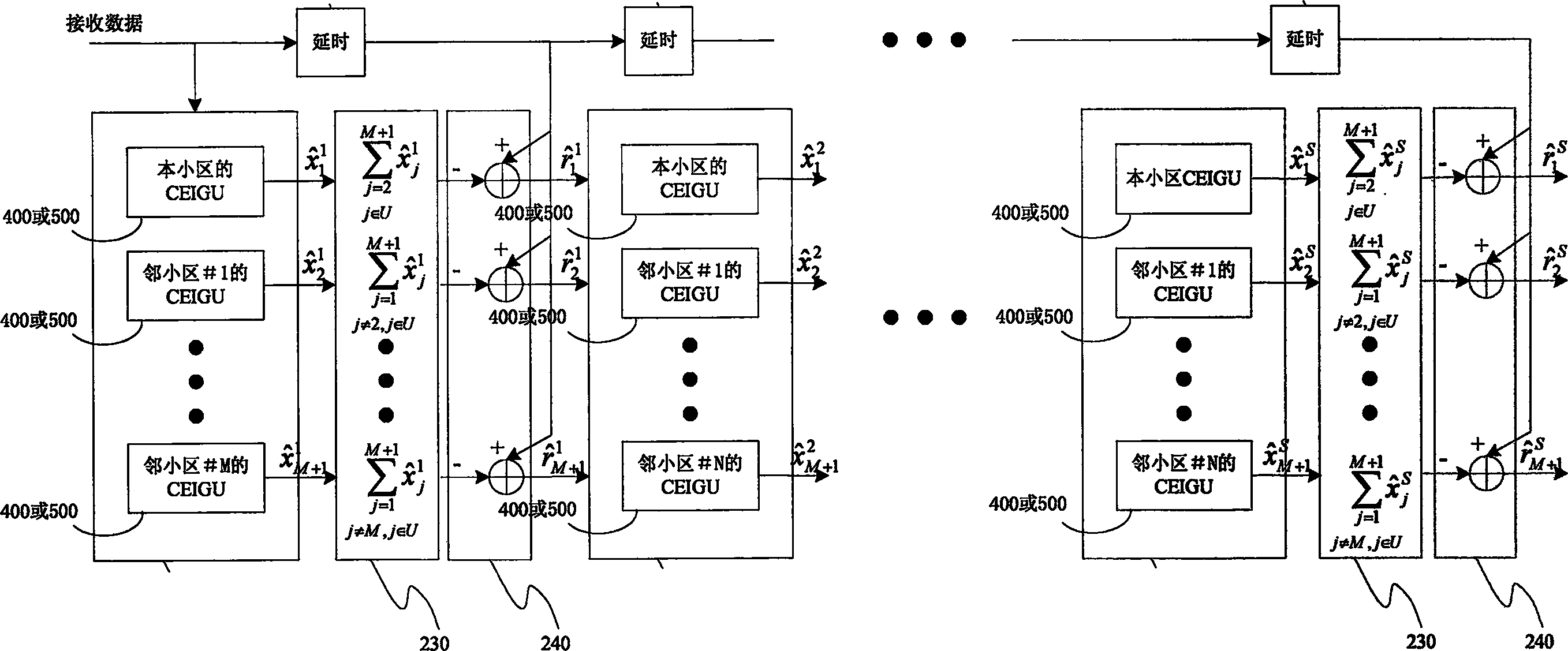
Method and device for concurrent eliminating same frequency interference in TDS-CDMA
ActiveCN1874189AEliminate the effects ofImprove reception performanceRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsRadio transmission for post communicationEngineeringMatched filter
The method and device for eliminating same frequency interference in parallel in TDS-CDMA system includes steps: based on matched filter or based on demodulation symbol generated from united detection to reconstruct interference signal of cell for each cell; superposing signals reconstructed from other interference cells; then removing superposed value of signal reconstructed from other interference cells from the received signal in order to eliminate influence on receiving signal of this cell by interference signals from adjacent cell, executing the steps repeatedly based on number of parallel stage. With lesser complexity of implementation, the method eliminates influence of signals from cells in same frequency to a considerable degree, especially, in malcondition that power of common frequency in adjacent cell is higher than this cell so as to raise performance for receiving signal of this signal.
Owner:XUANPU INDUSTRY CO LTD
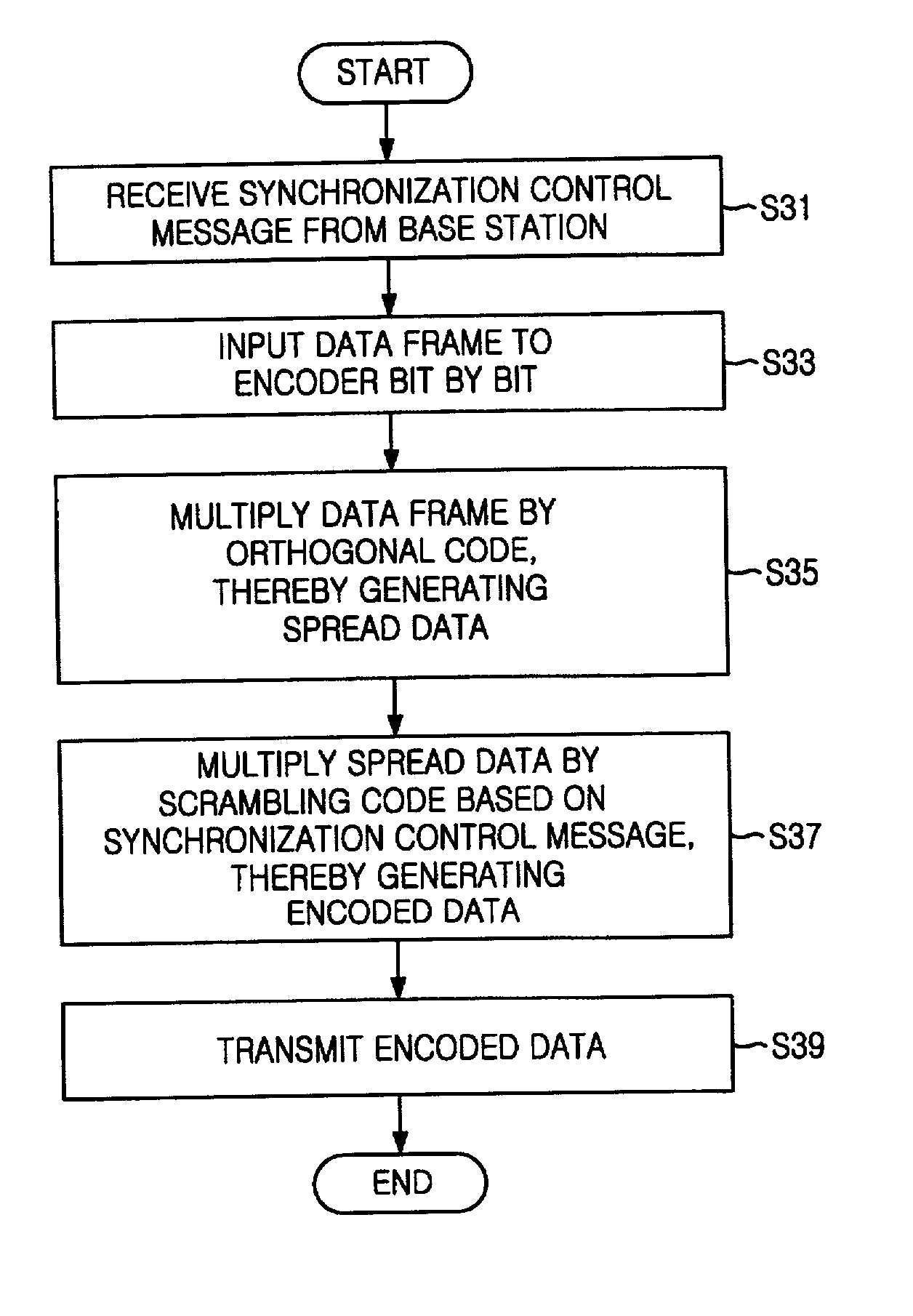
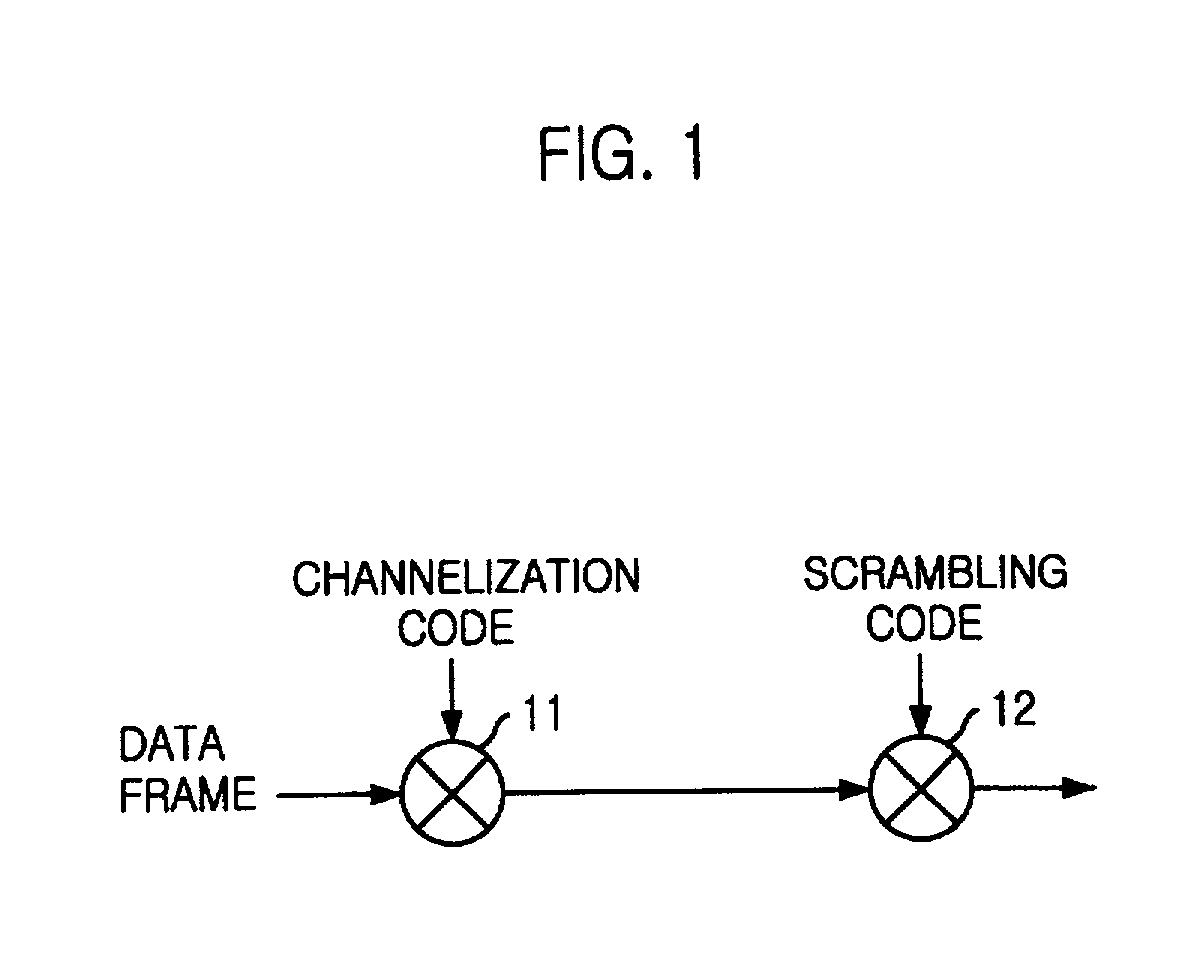
Method for assigning codes in uplink of synchronous wireless telecommunication system
InactiveUS20020003786A1Time-division multiplexConnection managementCode division multiple accessMobile station
A method for assigning codes in an uplink of a synchronous code division multiple access (CDMA) telecommunication system is disclosed. The method for assigning a code in a reverse channel of a synchronous wireless telecommunication system, comprising the steps of: a) at a mobile station, receiving time matching information of a scrambling code from a base station; b) at the mobile station, spreading data frame to be transmitted by an orthogonal code, thereby generating a spread data; and c) at the mobile station, multiplying the spread data by a scrambling code based on the time matching information of the scrambling code, thereby generating an encoded data.
Owner:SK TELECOM CO LTD
Virtual mimo communication system with uplink space-time codes of colabourated mobile terminals
The present invention provides an effective way to create a virtual MIMO transmission system using mobile terminals that have only one transmit path and antenna. This is accomplished by assigning mobile terminals to a group and assigning certain shared resources and user-specific resources to those mobile terminals in the group. In a synchronized fashion, the mobile terminals will provide uplink transmission in concert, as if they were a single entity having multiple transmission paths and antennas. Preferably, the shared resources bear on how the data is transmitted, and the user-specific resources relate to pilot signals. The data transmitted may be encoded in any number of ways, and in one embodiment, the mobile terminals may relay their information to each other, such that uplink transmissions can incorporate STTD decoding or other space-time codes. The invention is applicable to virtually any multiple access technology, including OFDM, TDMA, and CDMA, preferably synchronous CDMA.
Owner:BLACKBERRY LTD
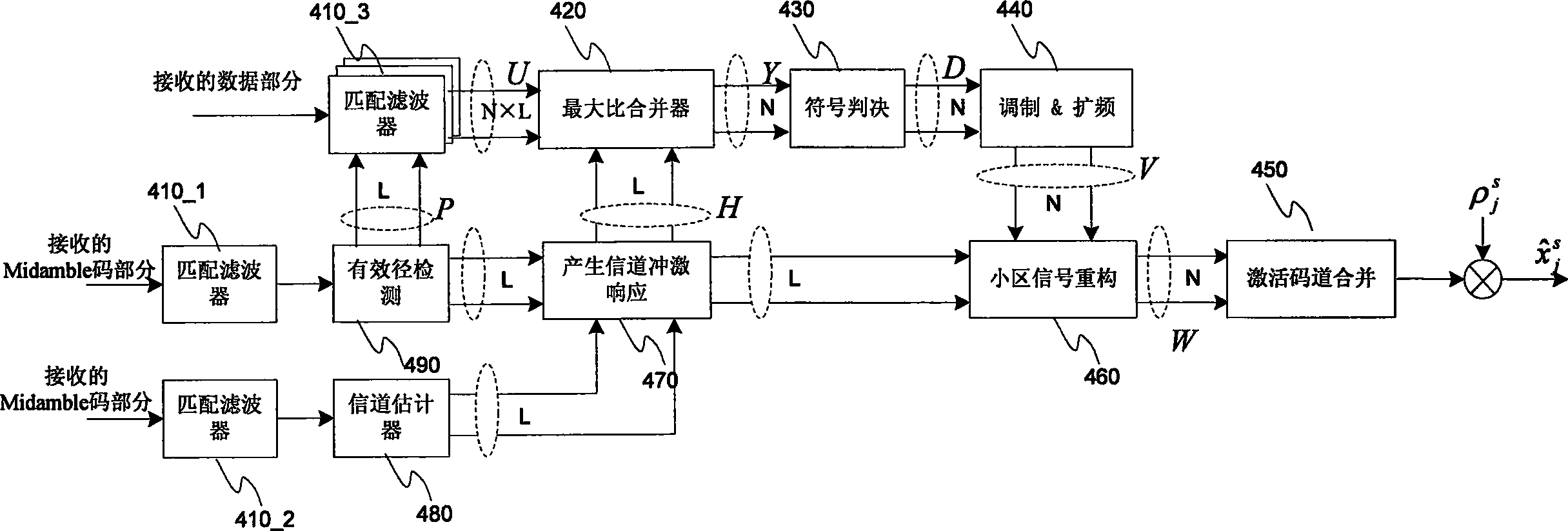
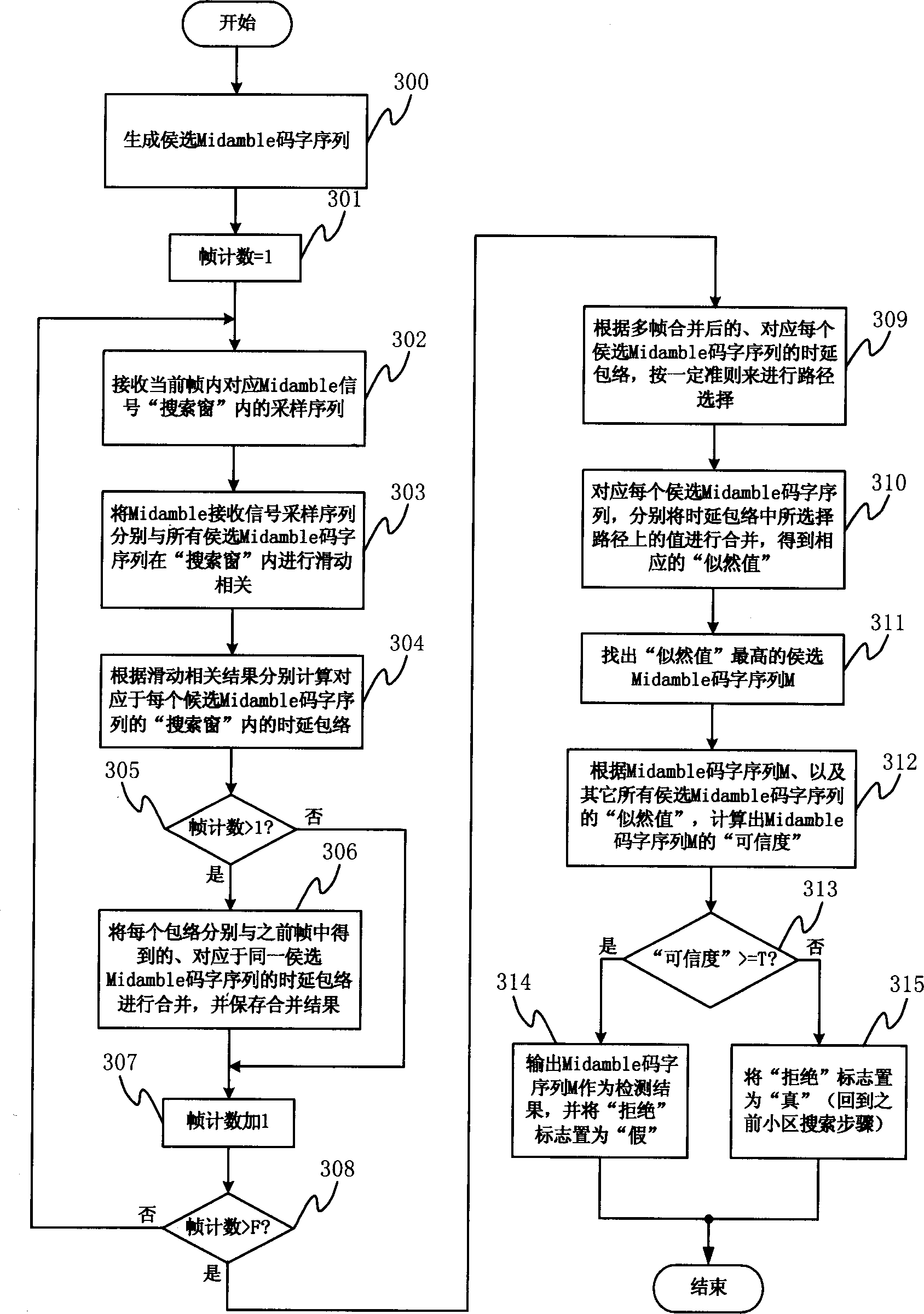
Method and equipment for detecting middle guiding code sequence in TD-SCDMA system
ActiveCN1604662AReduce false detection rateHigh-precision detectionRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsRadio transmission for post communicationSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Multiple frame
It is a kind of Midamble code sequence detection method and apparatus for TD-SCDMA mobile communication system. It can reach high detection probability and low missing probability under the condition of low signal-to-noise ratio and the under the environment of having frequency diffusion and time diffusion. It can also generate rejection mark and exclude a batch of wrong input incident, such as wrong code set sequence number input, wrong synchronous Information input and local oscillator has large frequency deviation, so to realize the reduction of initializing community research time in TD-SCDMA system. This invention includes the module and steps such as Midamble receives signal sample extraction, Midamble code sequence generation, slide association, delay envelope calculation, multi-frame combination, path selection, similar value calculation, maximum value detection, confidence level calculation and compare, the generation of detection rejection mark, and generation of detection Midamble code sequence number.
Owner:XUANPU INDUSTRY CO LTD
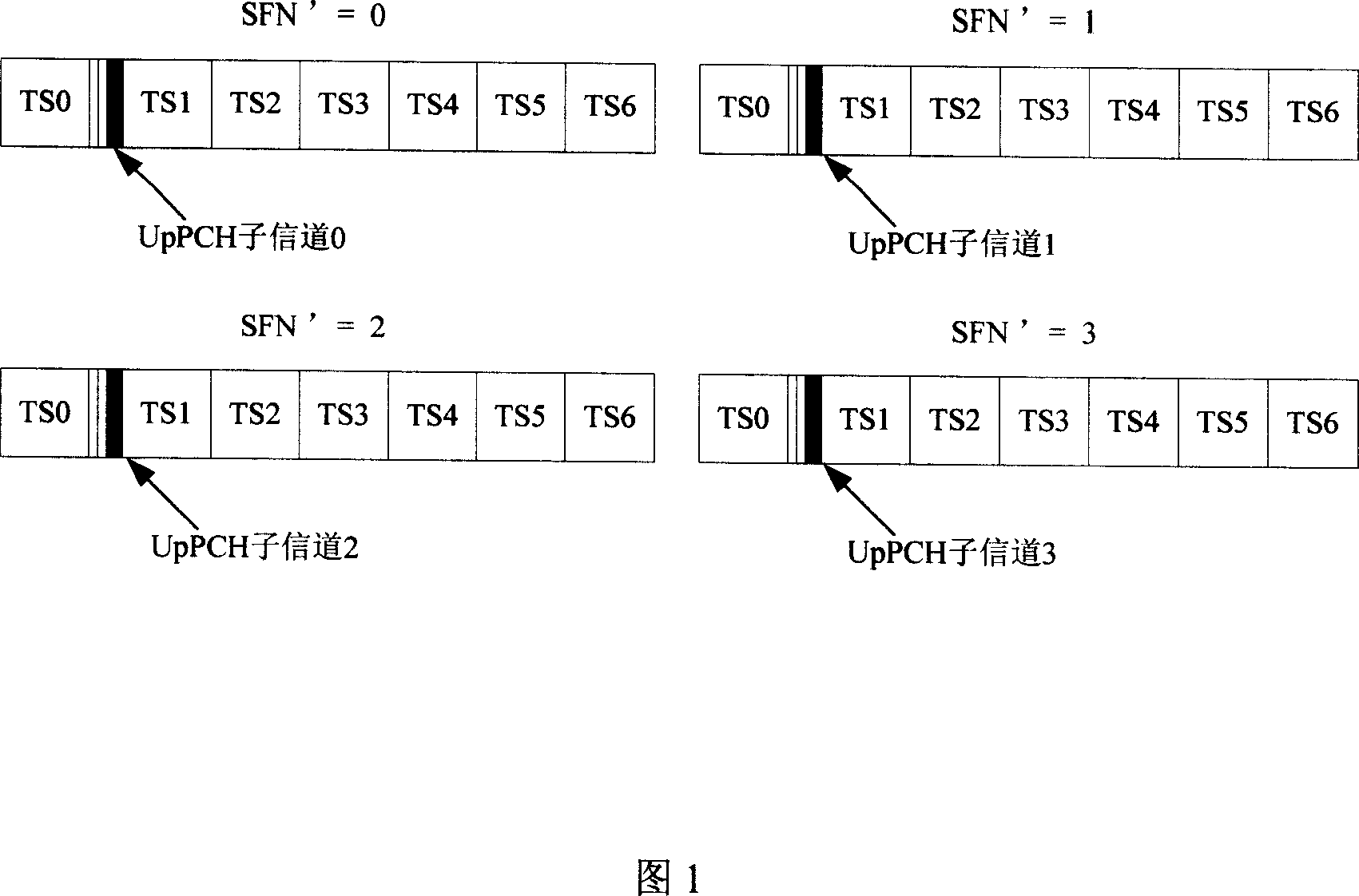
Method for identifying random access of time-division synchronous CDMA system
InactiveCN101064560AAvoid complex upgradesSave resourcesRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsRadio transmission for post communicationComputer compatibilityComputer science
The invention relates to the distinguishing method of random switch-on of time synchronization code divided multi-address system. The time synchronization code divided multi-address system can not distinguish the random switch-on. To solve the said problem, in the invention when the network distributes the channel source which switches randomly, distinguishing the random switch by synchronization code and the random switch of different business can use the different synchronization code. When the network node B detects the synchronization code, and sends the affirming information via the fast physical switch channel, and records the number of fast physical switching channel, the number of frame in the system and the synchronization code. When the terminal switches via the random channel, the node B finds the relative synchronization record, the switching type can be known by the information of synchronization code, and it is convenient to process. The invention can avoid the upgrading of software / hardware, save the system source, and reach a better compatibility backward.
Owner:田茹
Installation and system for testing data in baseband protocol in third generation mobile communication system
ActiveCN1917453AGuaranteed stabilityData switching networksSynchronization code division multiple accessBaseband
The apparatus comprises: a data exchanging interface used for intercommunication with external data; a FPGA module used for analyzing and giving out the received data, for packaging and giving out the transmitted data and for control the clock signal of the apparatus; a memory module used for buffering the data after the analyzing and before the packaging and relevant instruction data; a DSP used for reading out the data in the memory module and making relevant process, and for processing the transmitted data and transmitting it to the FPGA. The system completes the relevant testing based on the apparatus above. The invention can be used in TD=SCDMA, CDMA2000 and WCDMA system.
Owner:DATANG MOBILE COMM EQUIP CO LTD
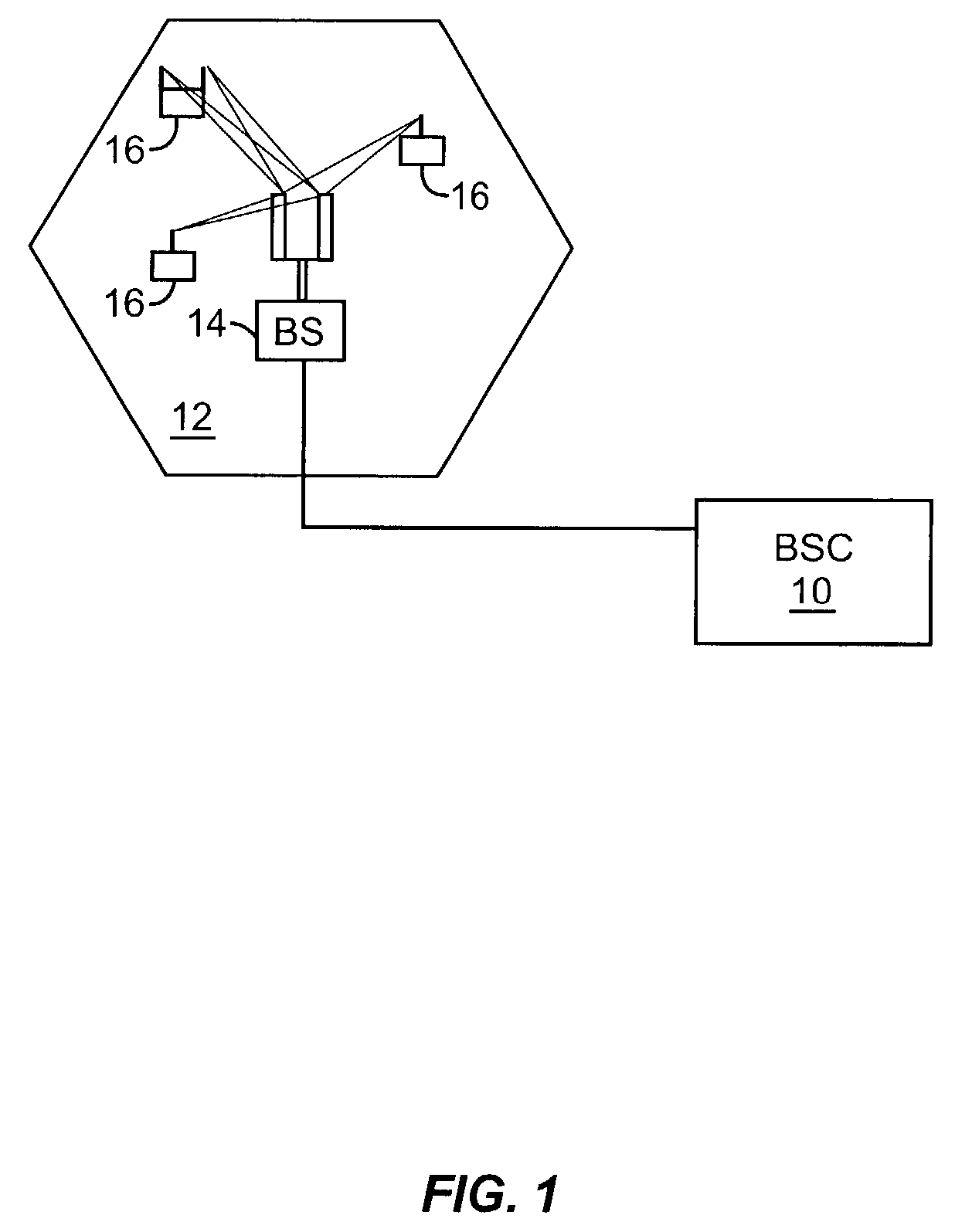
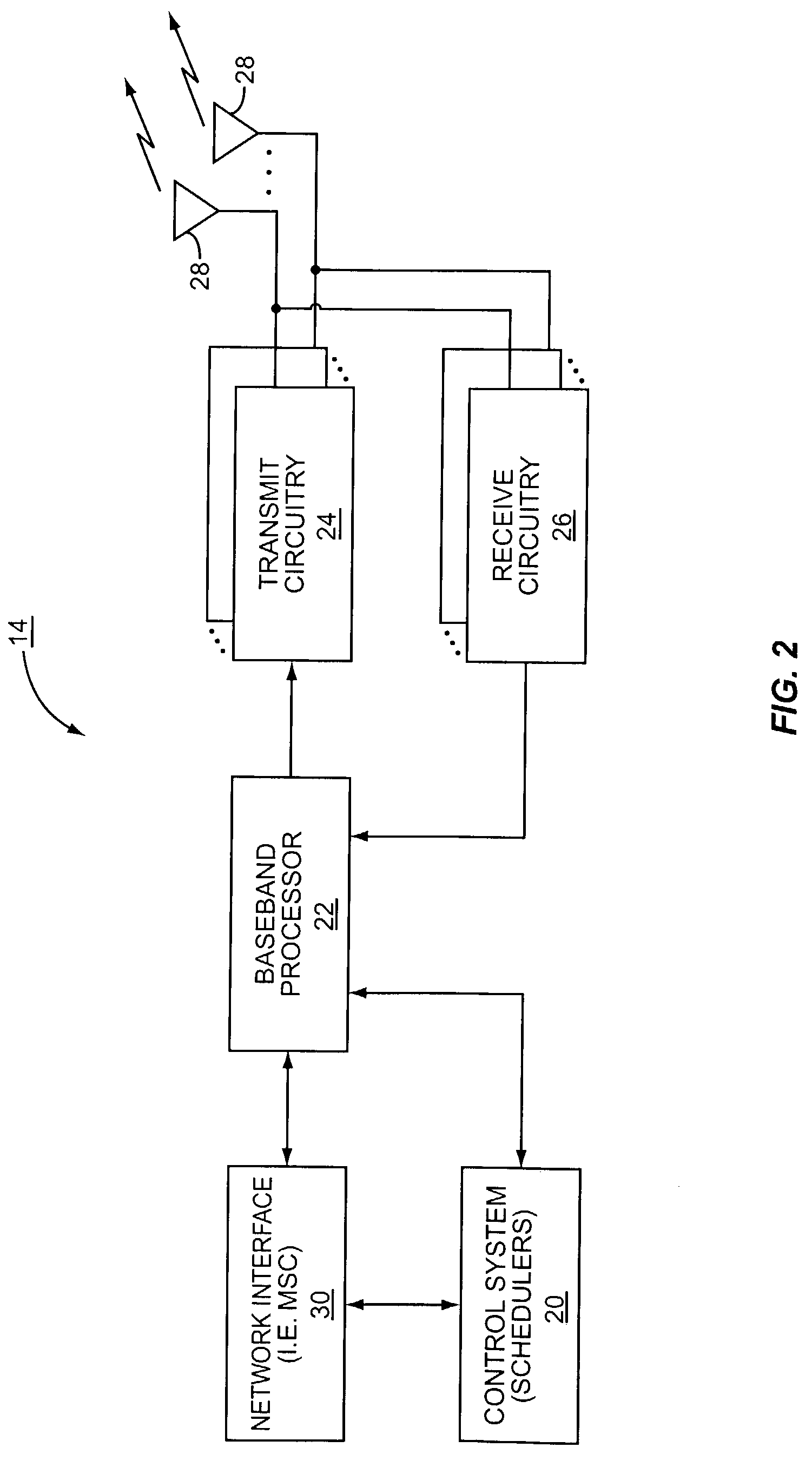
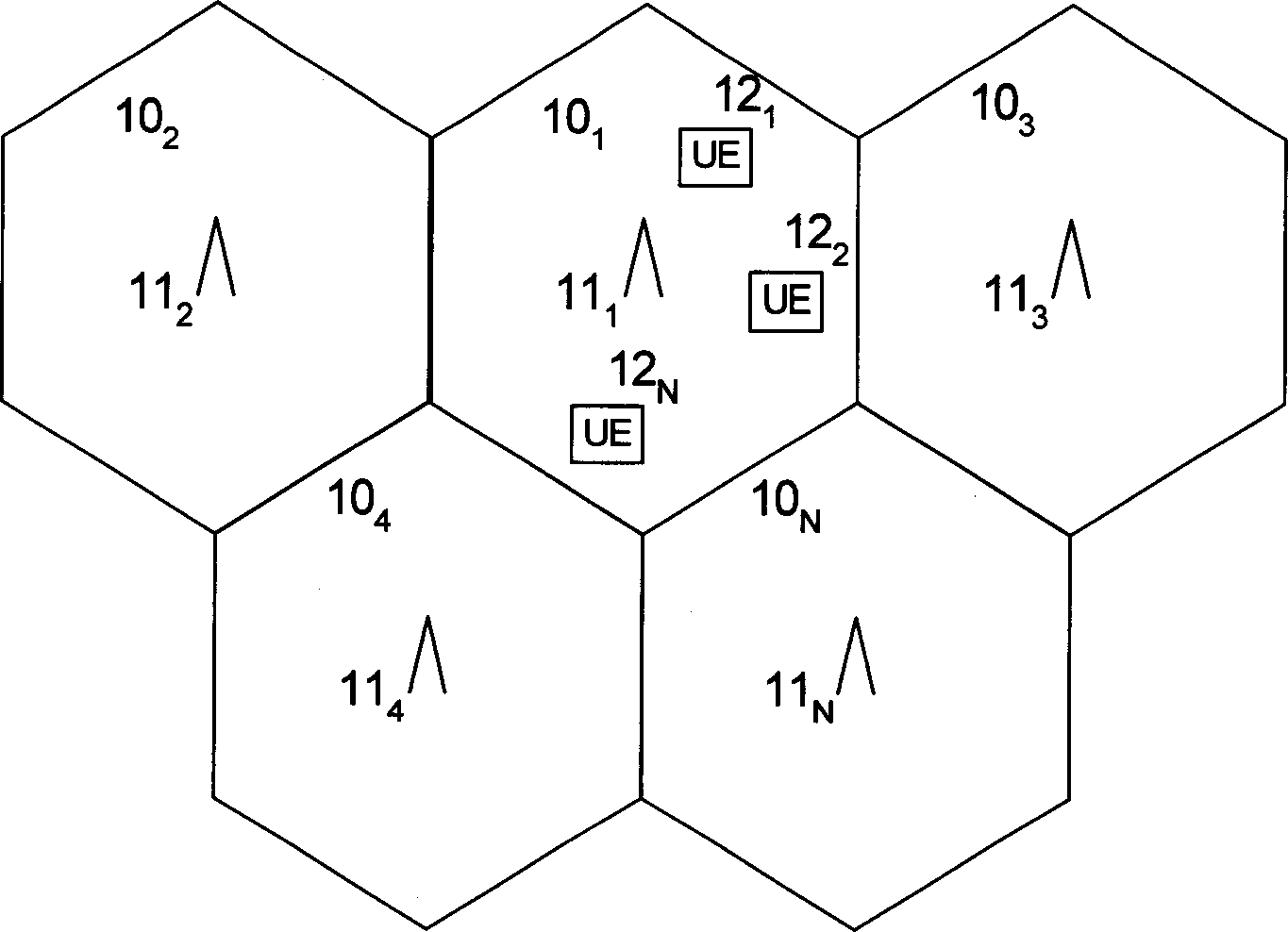
Use of wide element spacing to improve the flexibility of a circular base station antenna array in a space division/multiple access synchronous CDMA communication system
ActiveUS6956838B2Increase flexibilityReducing tower rental fees considerablyAntenna supports/mountingsBroadcast transmission systemsPhase variationCommunications system
A method is disclosed for operating a synchronous space division multiple access, code division multiple access communications system, as is a system that operates in accordance with the method. The method operates, within a coverage area of a base station (BS), to assign the same spreading code to a plurality of subscriber stations (SSs) and to transmitting signals to, and receive signals from, the SSs using an antenna array having M elements, where M>1 and where the M elements are spaced apart by more than one-half wavelength from one another. The spacing is a function of a size of an aperture of the antenna array which is a function of a signal bandwidth to carrier frequency ratio. The antenna array aperture is preferably less than k=p / 360*fc / B wavelengths, where p is a maximum acceptable phase variation over the signal bandwidth, where fc is the carrier frequency and where B is the signal bandwidth. The step of conducting communications includes steps of despreading a plurality of received signals; and beamforming the plurality of despread received signals. In a preferred embodiment individual ones of P orthogonal spreading codes are reused αM times within the coverage area, where 1 / M<α≦1.
Owner:L3 TECH INC
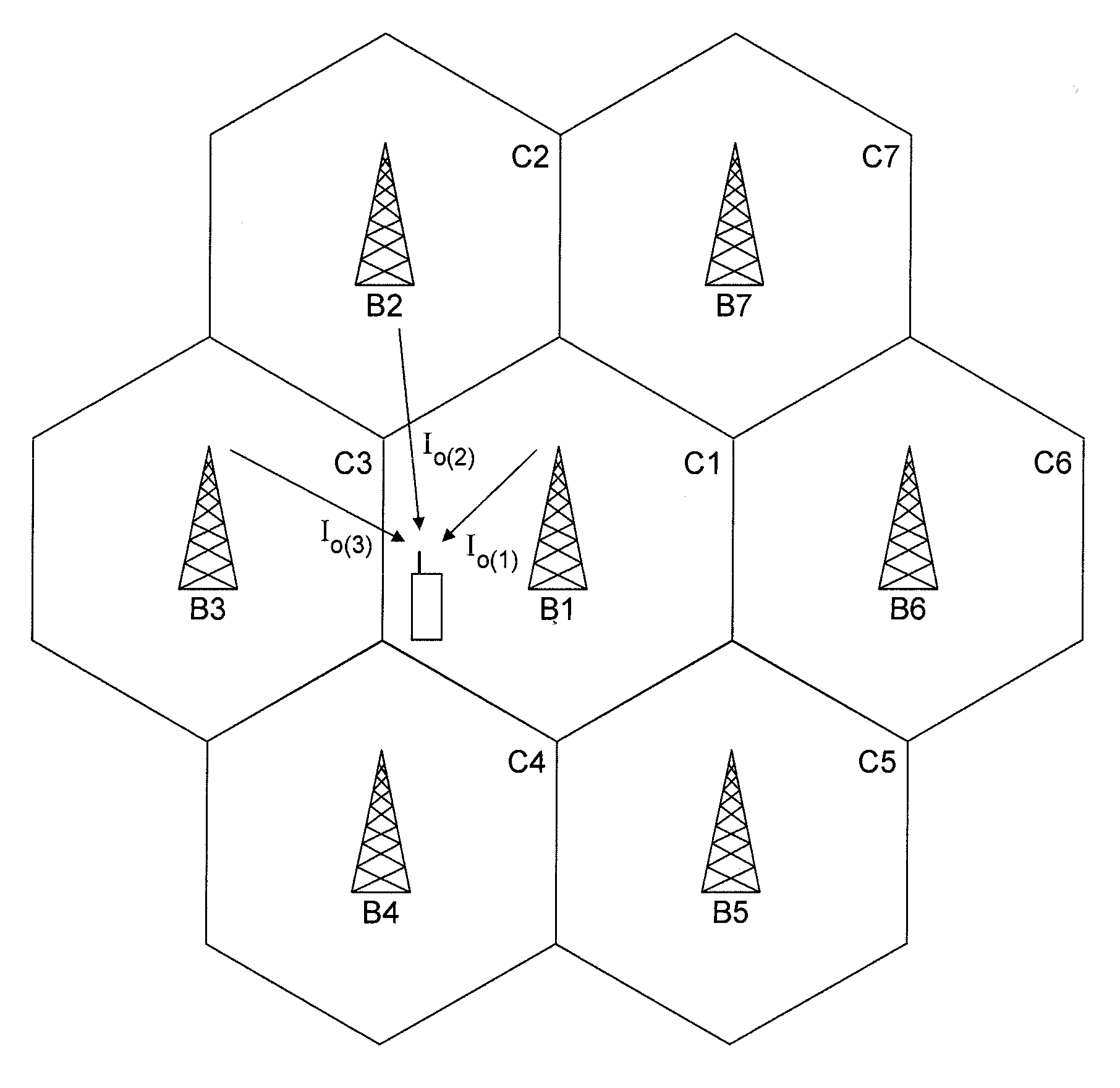
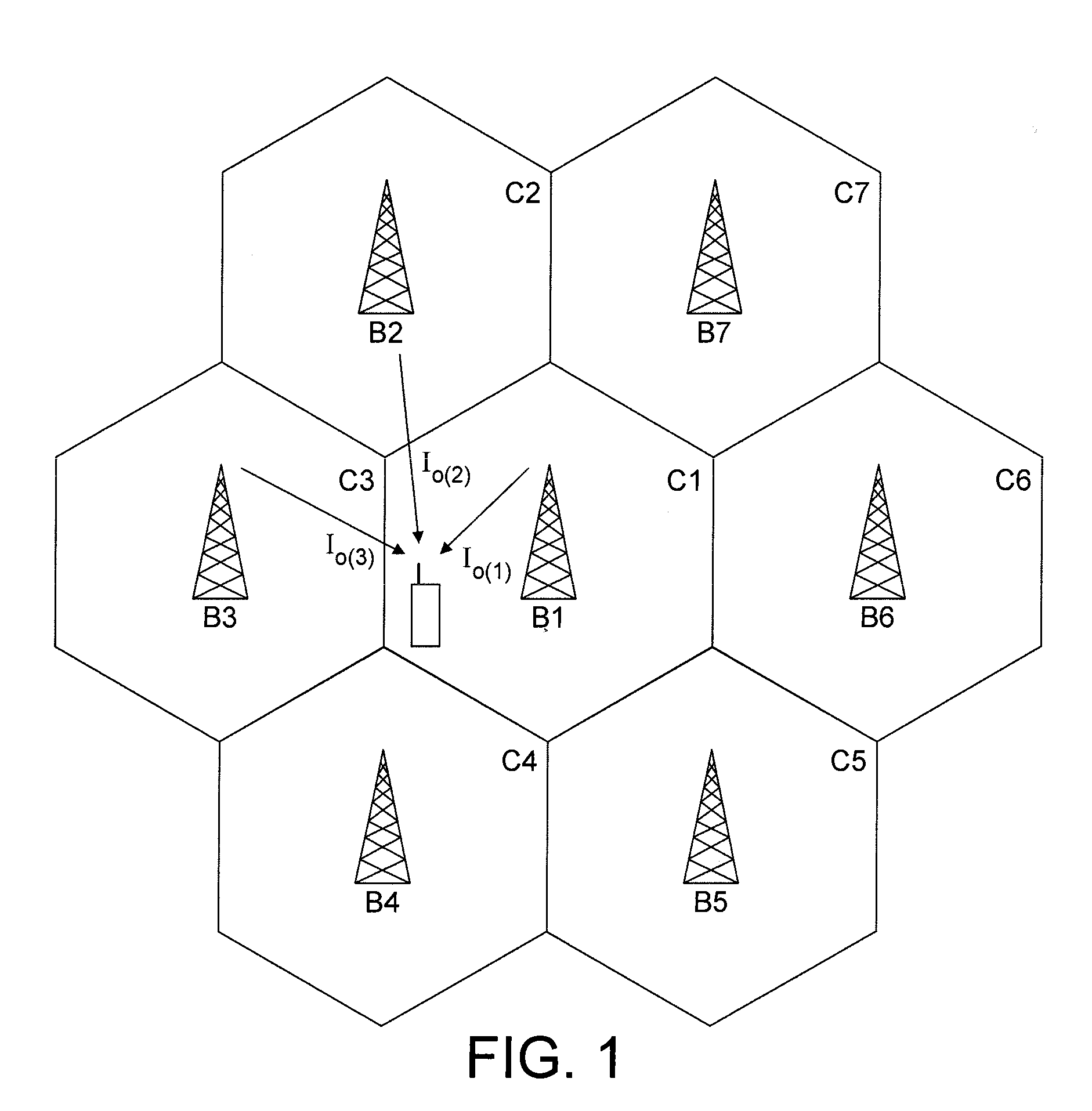
Synchronous CDMA communication system
ActiveUS20110032837A1Receivers monitoringError preventionCommunications systemWireless cellular networks
In one aspect, there is provided a method of processing a signal received using a wireless communication channel by a receiver in a wireless cellular network. In one embodiment, the method comprises receiving signal samples of a signal to be processed from a serving cell, identifying a second of dominant interfering cells generating an interfering signal, using a number of cells in the set to select an interference scenario, and using the selected interference scenario and at least one parameter related to the serving cell and the interfering cells to select a processing function for processing the signal.
Owner:ICERA INC
Method and mobile station to perform initial cell search in time slotted systems
InactiveCN1615667ASpeed up scan operationsConvenient ArrangementSynchronisation arrangementAssess restrictionFrequency spectrumGrating
A method is disclosed that a Mobile Station MS performs at switch-on to search the most favorable target cell in UMTS systems like the 3GPP CDMA LCP (Low Chip Rate) option at (1.28) Mcps TDD (Time Division Duplex) mode and the equivalent TD-SCDMA (Time Division Synchronous CDMA). Signal at the MS antenna is the surn of different RF downlink frames coming from different carriers in the assigned frequency ranges. A DL synchronization timeslot and a BCCH TS0 codes assigned on cell basis. Following a conventional approach the absence of a common downlink pilot and without prior knowledge of the used frequencies would force the MS, for all the frequencies of the channel raster stored in the SIM card, the correlation of the received frame with all the (32) sYNCs stored in the MS, in order to detect the BSIC of a cell to which associate are performed in two-step scan of the PLMN band without interleaved correlation steps; once a final frequency is selected the respective frame is the only correlated one. At least one frame duration about (5) ms long of the whole (15) MHz bandwidth is acquired, IF converted, A / D converted and the digital set is stored.
Owner:SIEMENS INFORMATION & COMM NEWTWORKS INC
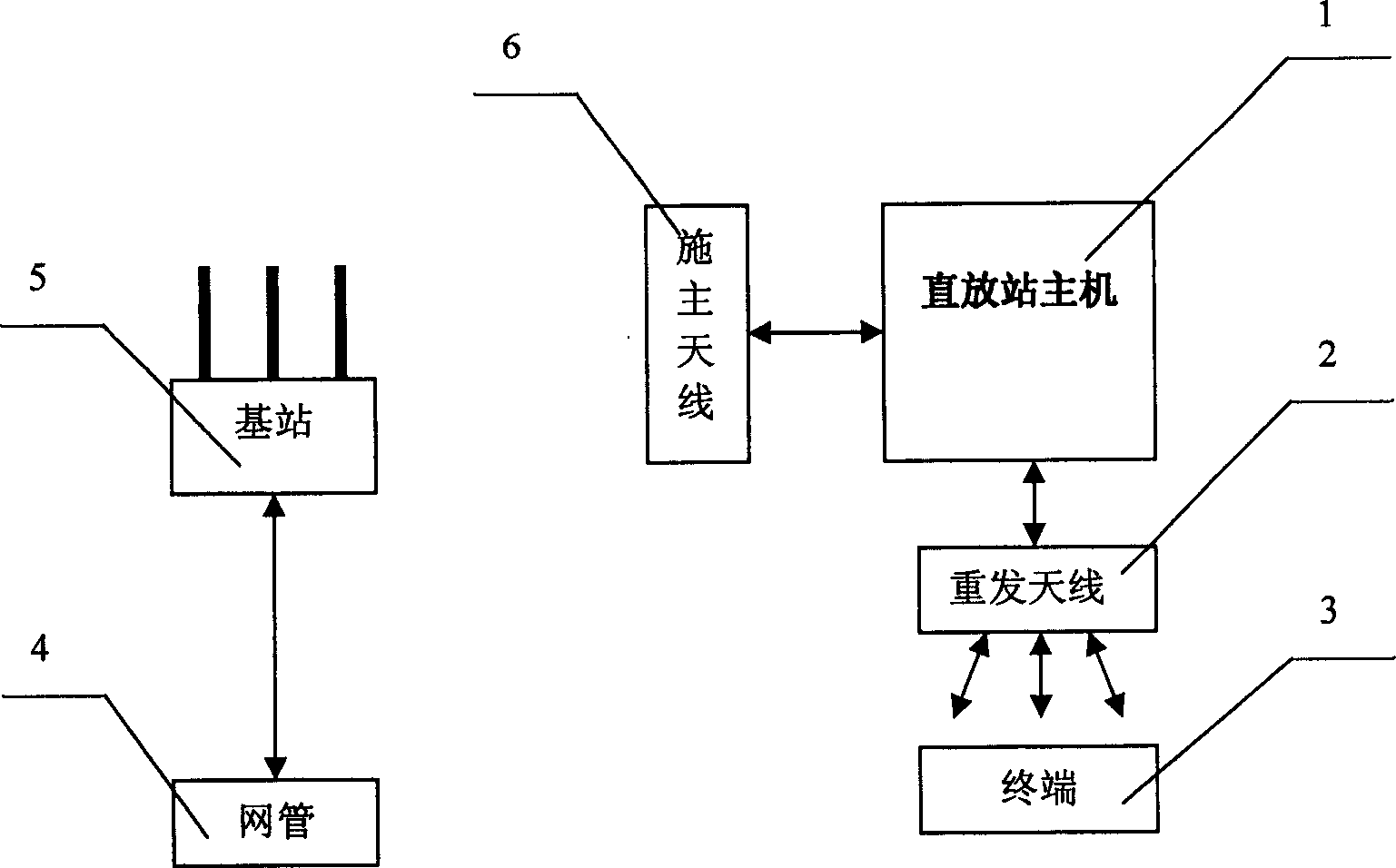
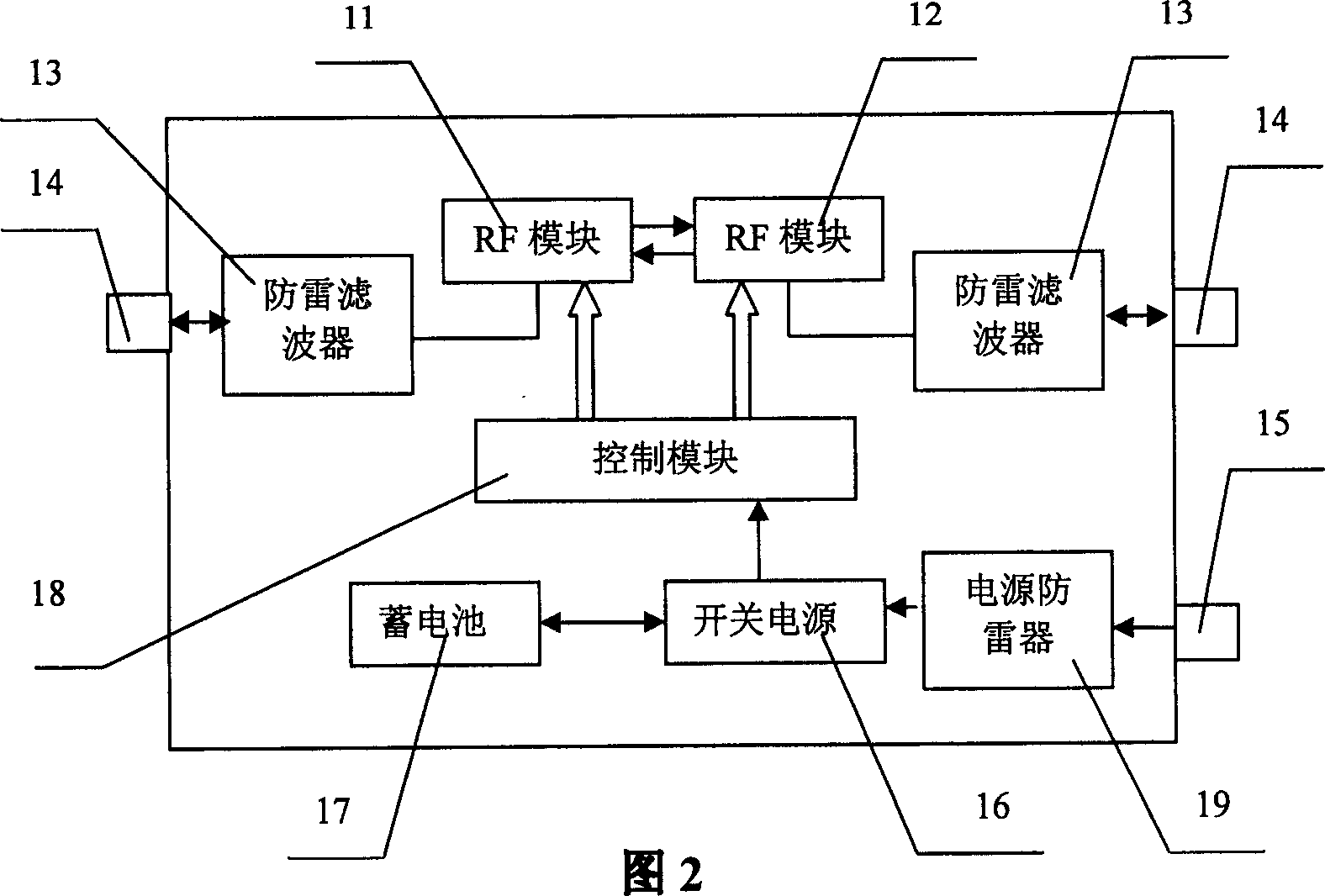
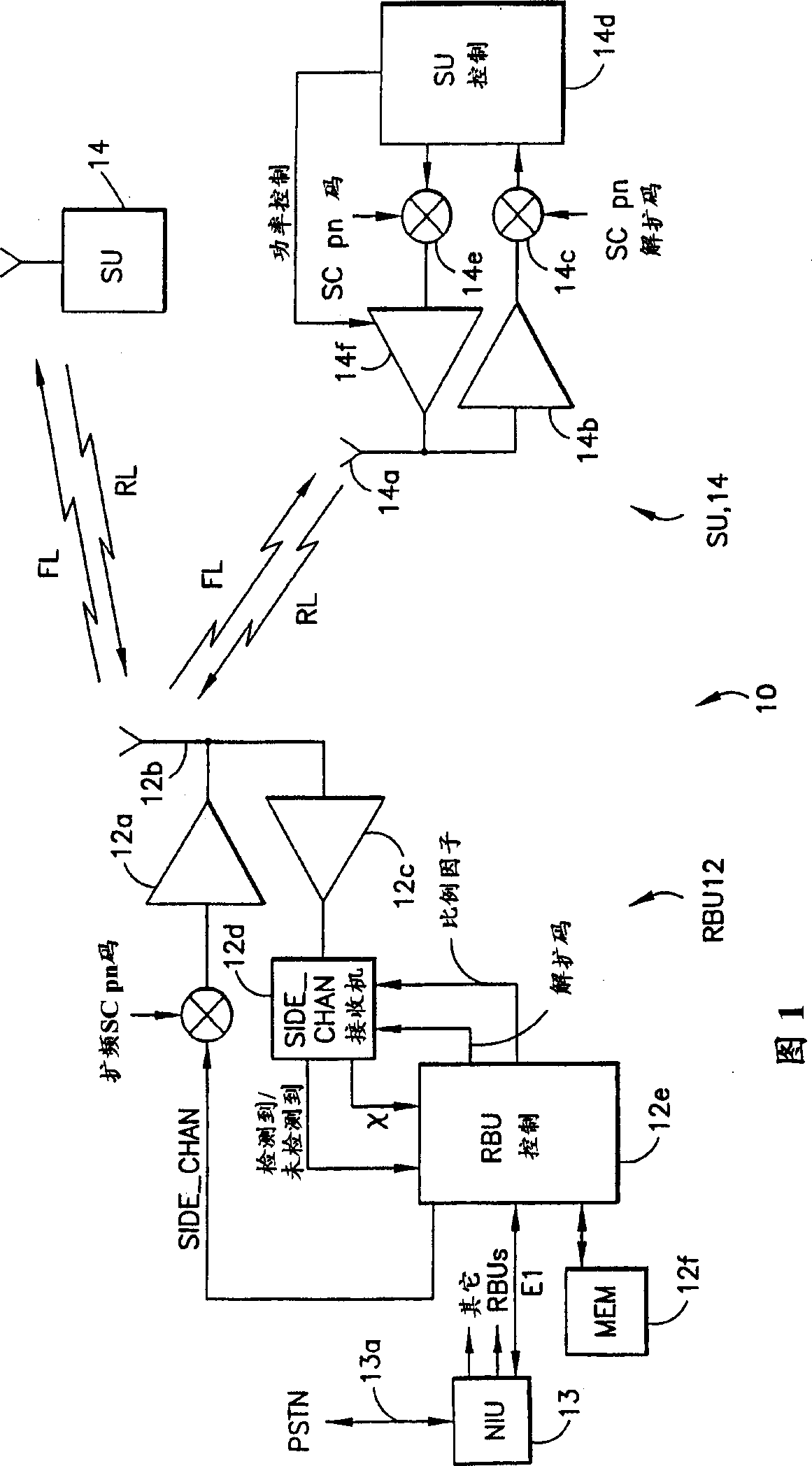
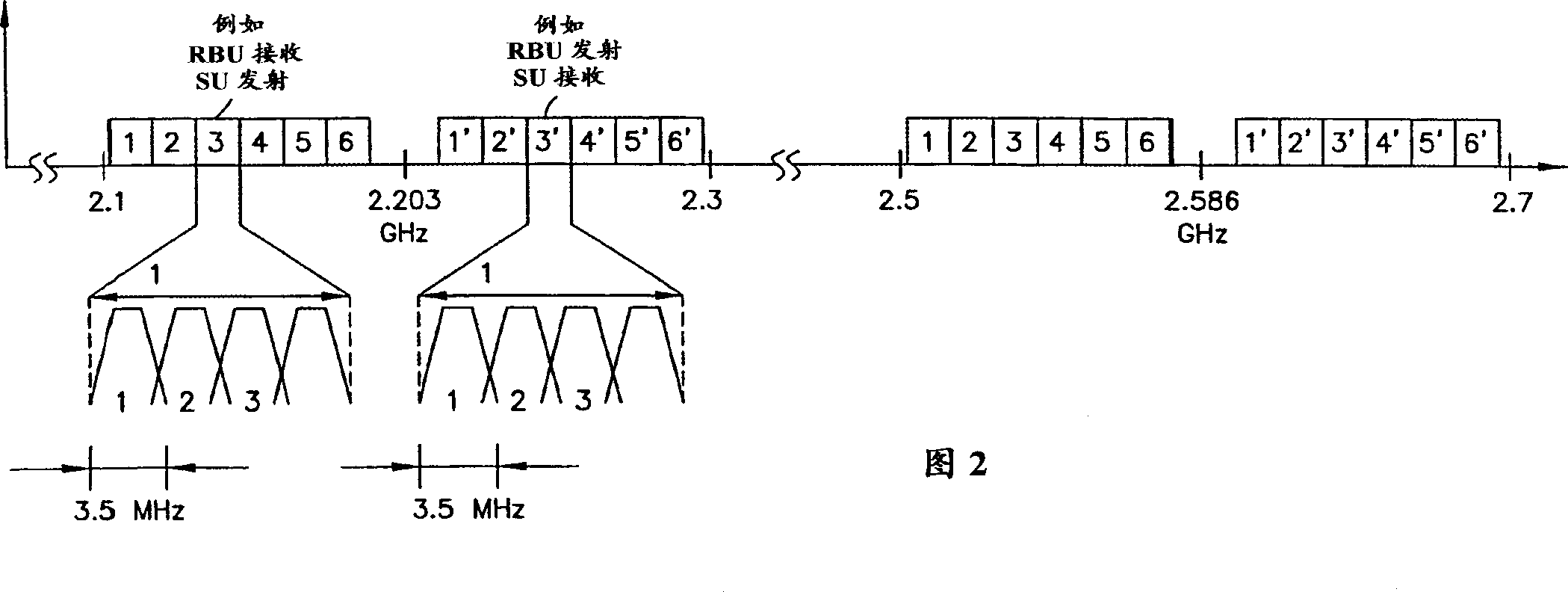
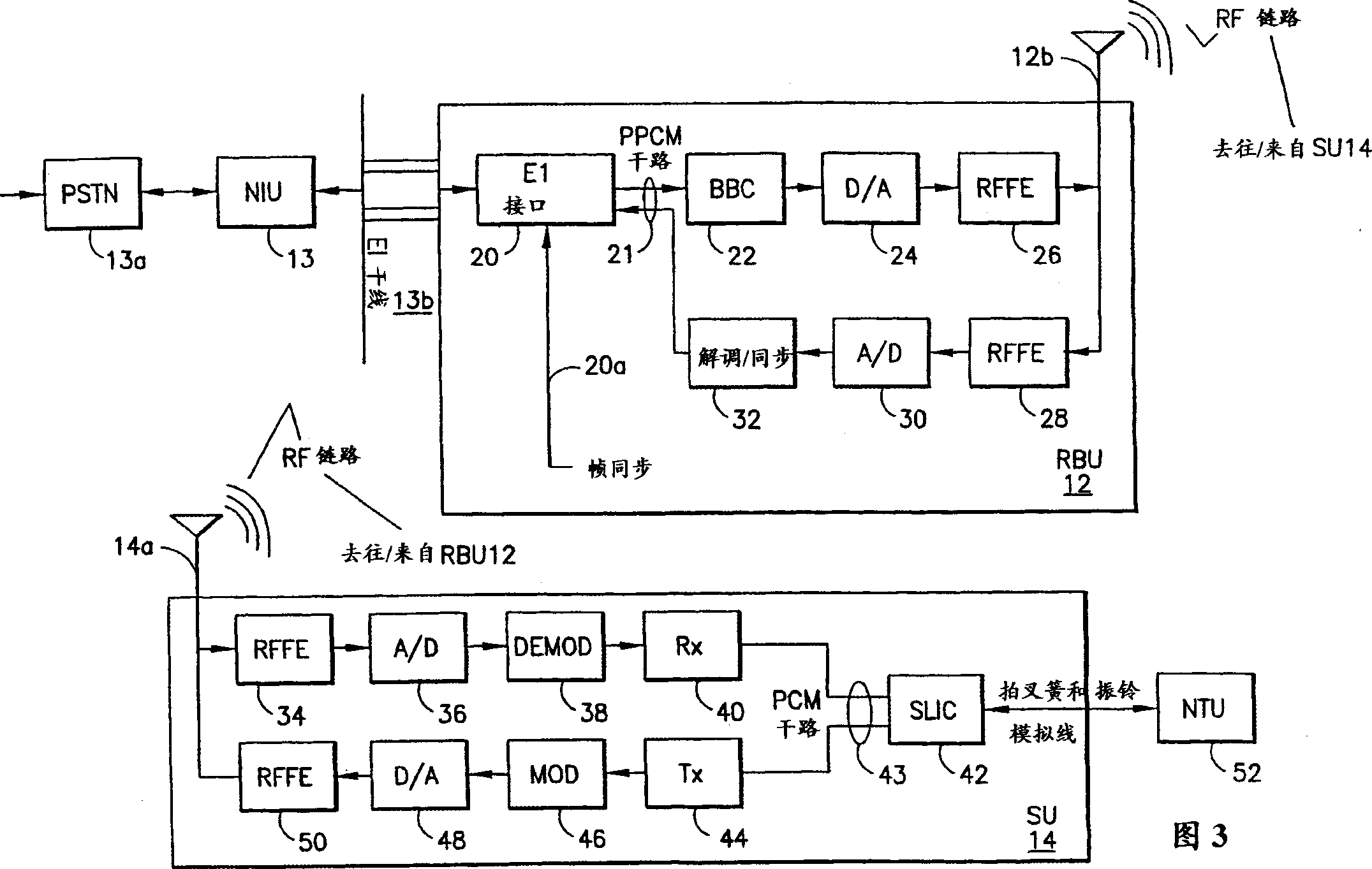
Direct transmitting station for synchronous CDMA system and its control
InactiveCN1457160ARealize the frequency conversion forwarding functionCode division multiplexRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsBlind zoneDigital analog converter
The invention discloses passing through stations in SCDMA mobile communication system and its controlling method in order to complete frequency translating transpondering function so as to solve the issue of covering blind zone for base stations in SCDMA system. The passing through station in SCDMA mobile communication includes a casing one interface for input power source, two radio frequency modules, one control module including a handset board, a digital signal processor, a field programmable gate array, a D / A and A / D converter. The controlling method of the passing through station is to control the operation of the radio frequency circuit in TDD mode controlled by DSP and FPGA.
Owner:BEIJING XINWEI TELECOM TECH
Cross-zone handover method for time division synchronous CDMA multi-frequency-point community cellular network
InactiveCN101026860AReduce the level of co-channel interferenceGuaranteed communication qualityRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsWireless communicationCommunication qualityHandover
The method includes following steps: configuring radio resources in each sector into two sorts: switching preserved resources, and not switching preserved resources, and making switching preserved resources between each adjacent sector inter orthogonal; when communicating on switching preserved resources of service sector, if terminal detects that SNR of receiving signal in adjacent sector is better than SNR at service sector, then reports the message to base station in service sector; the base station in service sector indicates the user to switch to switching preserved resources in adjacent sector, thus, the adjacent sector becomes service sector of the terminal, and the former service sector becomes adjacent sector so as to accomplish switching across sectors. The invention can reduce level of same frequency interference at edge of sector effectively so as to guarantee communication quality when mobile user is in switching procedure across sectors.
Owner:ZTE CORP
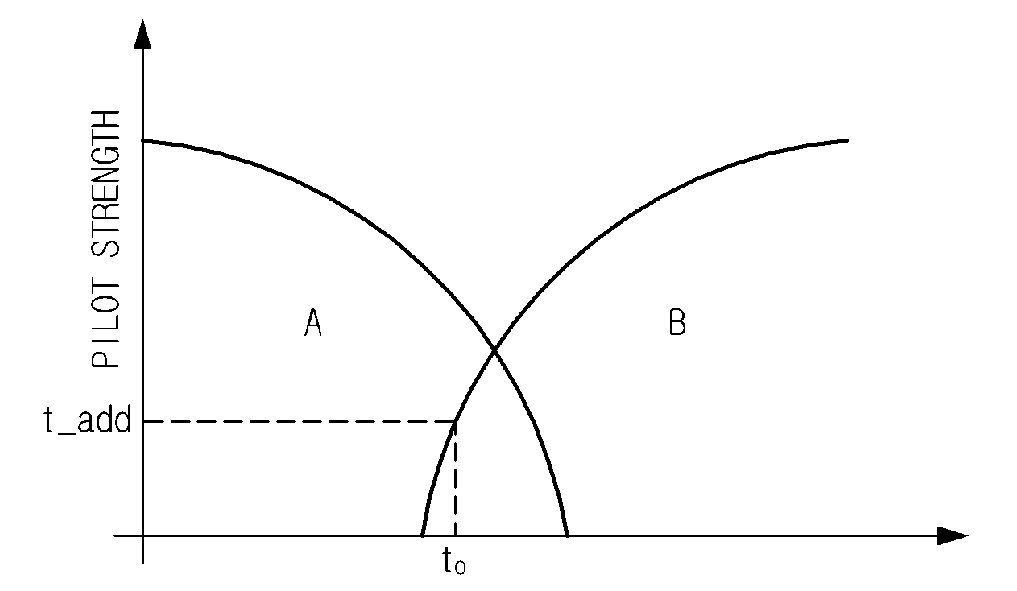
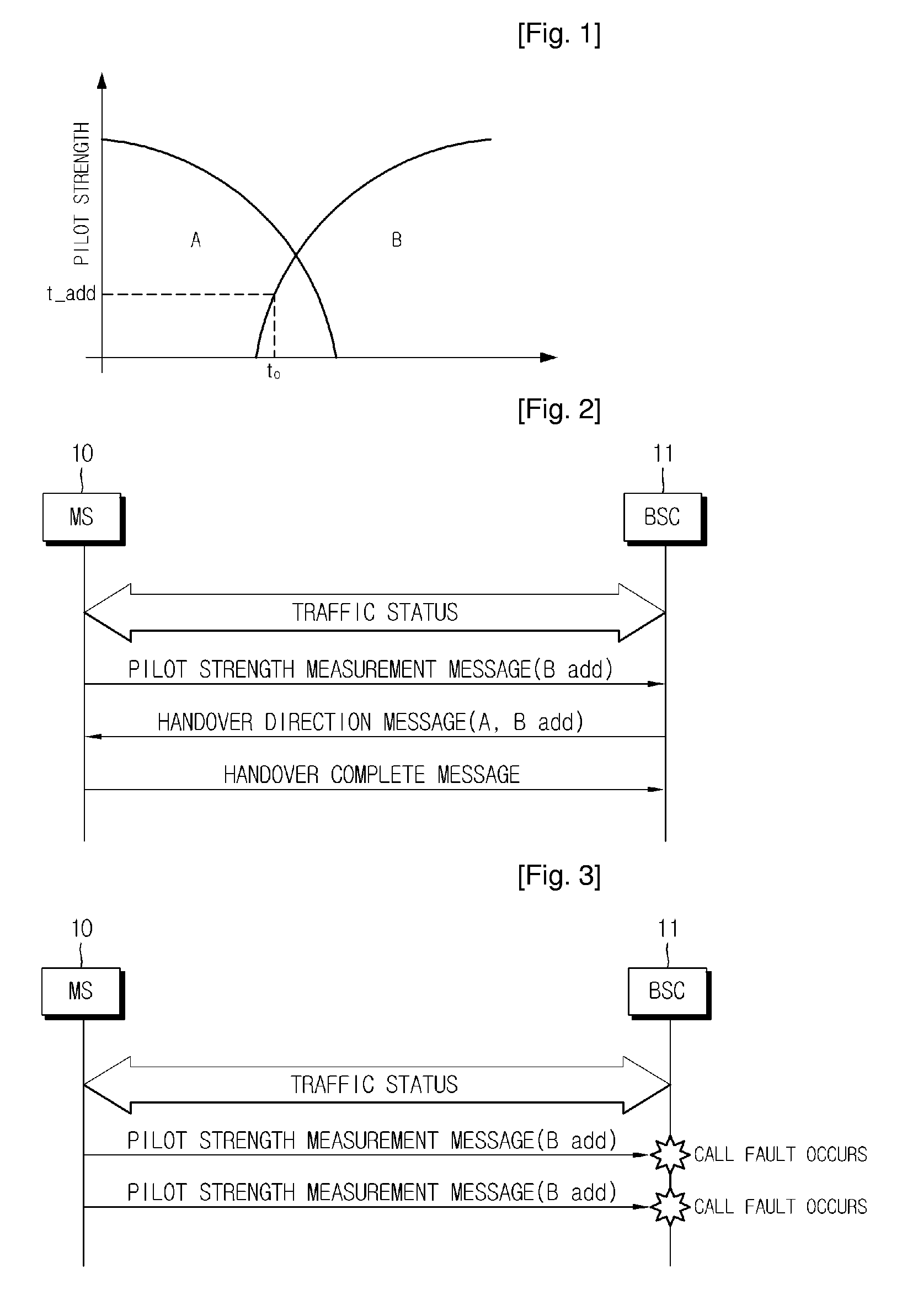
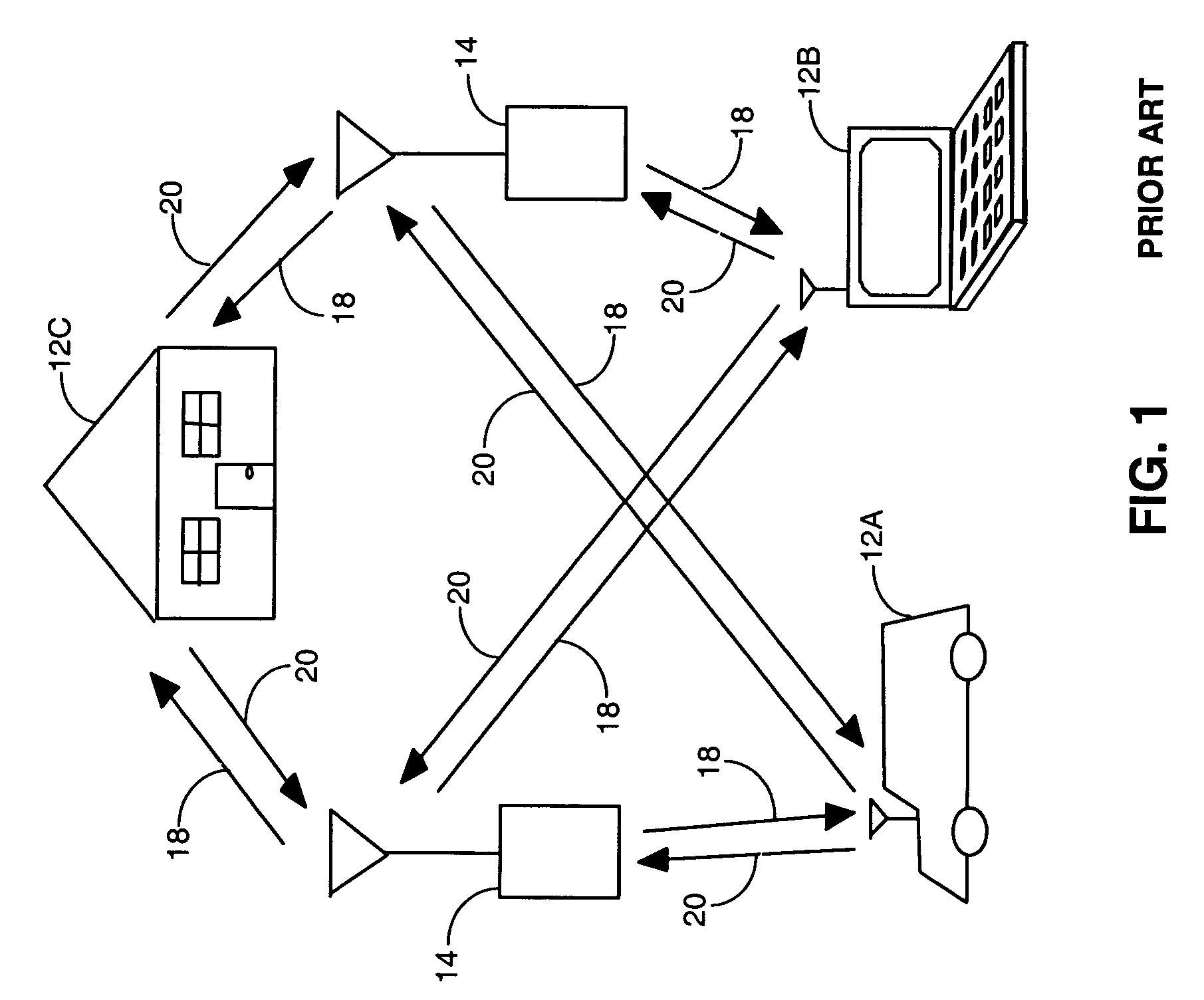
Method for handoff between an asynchronous CDMA base station and a synchronous CDMA base station
InactiveUS7391753B2Radio/inductive link selection arrangementsRadio transmissionAsynchronous cdmaTelecommunications
An improved method for facilitating handoff between an asynchronous and a synchronous base station. A method for determining a pilot channel PN offset of a pilot channel transmitted by a wireless base station. In a first embodiment, the method includes correlating a PN sequence with a received pilot signal to acquire a PN frame timing, receiving at least one search code burst aligned with the PN frame timing, the at least one search code burst signifying the pilot channel PN offset, and comparing the at least one search code burst to a set of codewords, each codeword representing a predetermined PN offset. From the search code bursts, the mobile station is able to quickly determine the PN offset of the transmitting base station, and thereby identify it. Methods for transmitting a complementary set of forward link channels are also disclosed.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
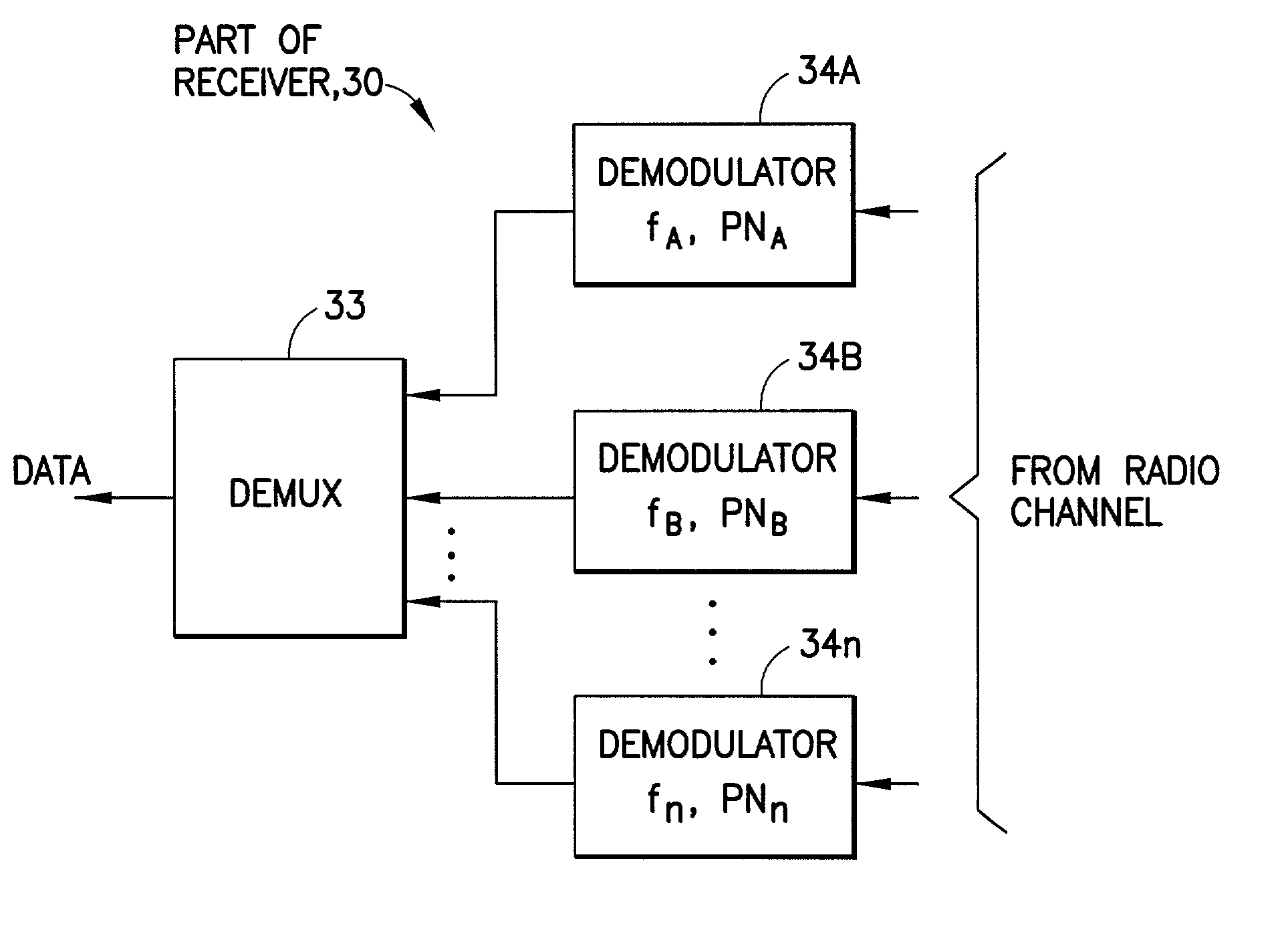
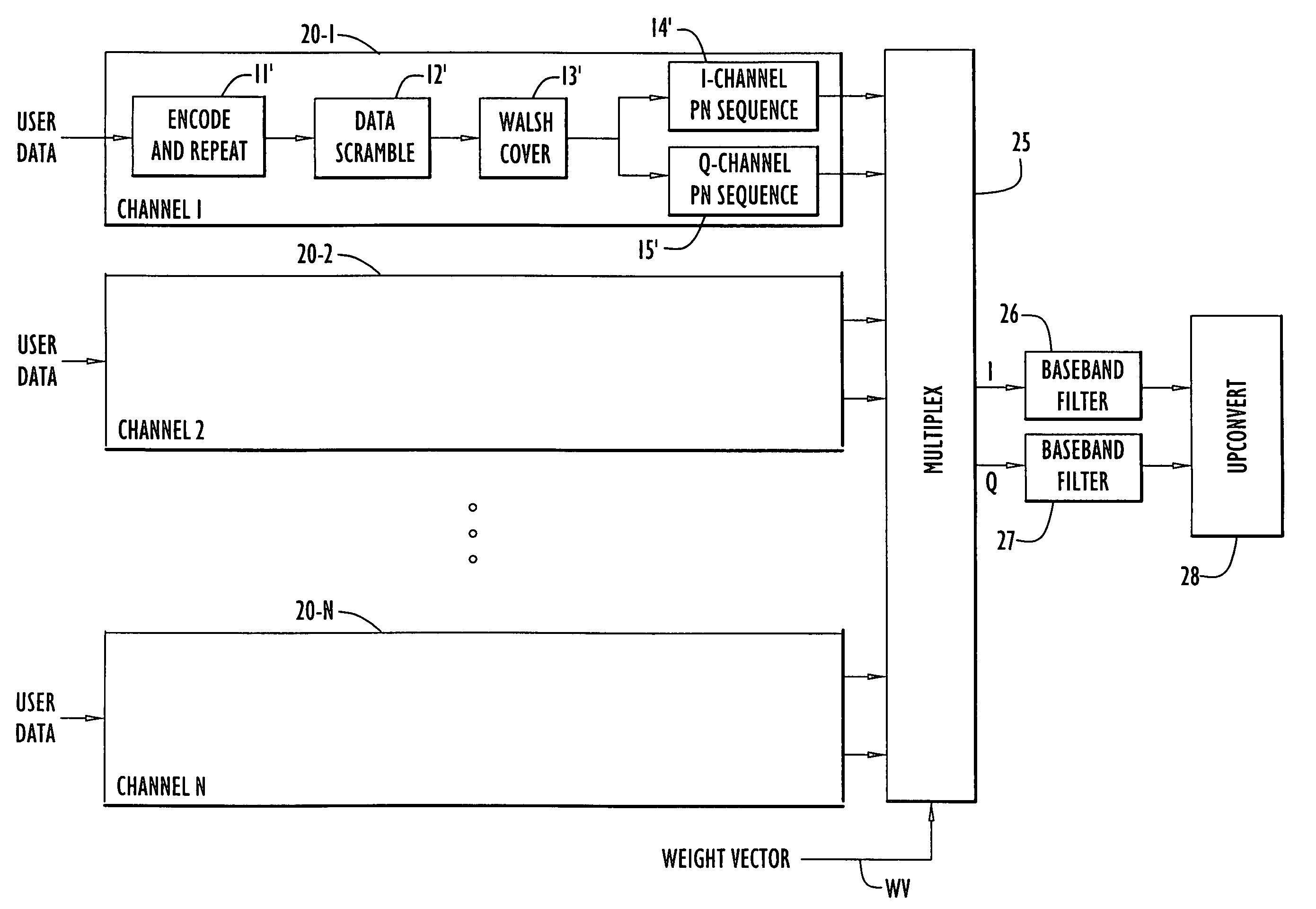
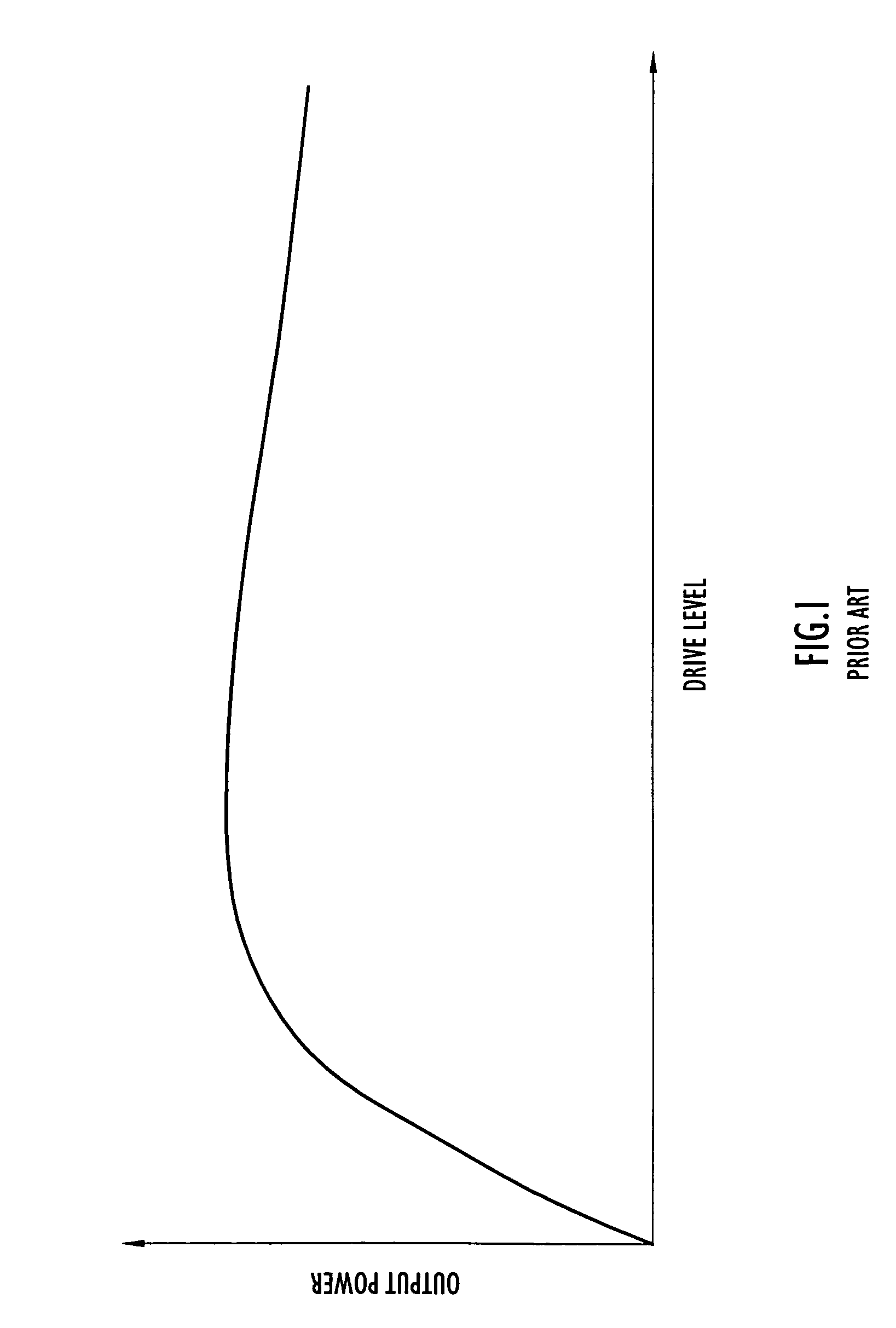
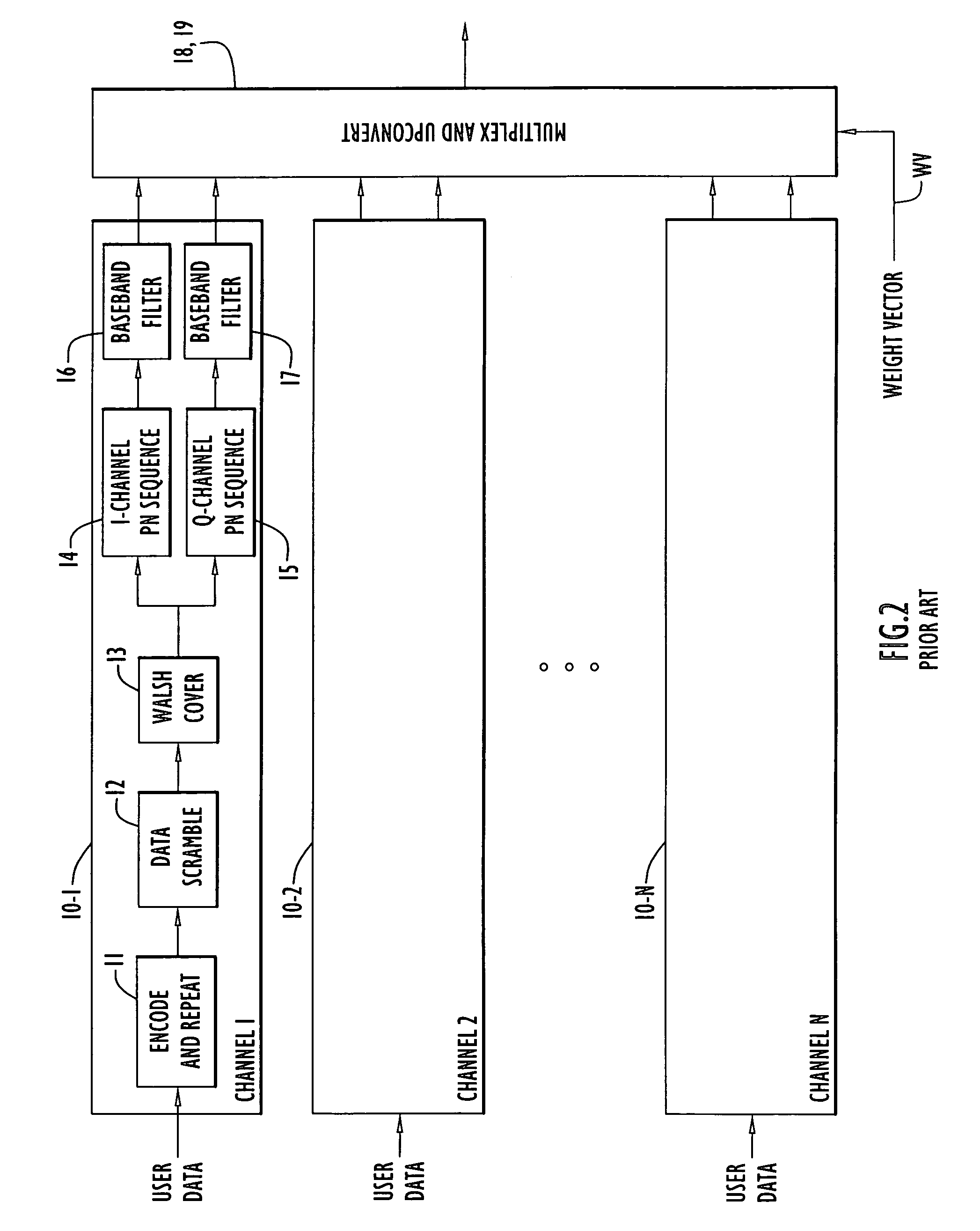
Chip-synchronous CDMA multiplexer and method resulting in constant envelope signals
InactiveUS6996080B1Reduce lossesIncrease overall effective power utilizationEnergy efficient ICTPower managementFrequency spectrumCode division multiple access
A multiplexer and a method for chip-synchronous code-division multiple access (CDMA) signals produces a constant envelope signal. The output signal of the multiplexer permits use of a saturating (Class C) high power amplifier (HPA) resulting in a net increase in effective transmitter power usage. This multiplexer applies to a variety of CDMA spread spectrum modulation formats and has many applications, such as the IS-95 forward link interface, and CDMA and CDMA / FDMA (frequency-division multiple access) applications, including general cellular base station forward traffic channels, cellular subscriber station multiple-channel reverse traffic channels (e.g. IS-95 subscriber Internet access) and satellite downlinks.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
Method for reducing interference between small zones in time-division synchronous CDMA cut-in system
This invention relates to a method for reducing reference among cells in TD-SCDMA access system. It contains respectively distributing different number up and down service time slot to different cells according to different service types, in adjacent cells with different service time slot, stopping any cell to use said service time slot and keeping another cell up and down service time slot to be unchanged. Said invention can optimize TD-SCDMA access system configuration and raise system capacity.
Owner:诺基亚西门子通信系统技术(北京)有限公司
Mobile terminal of sharing antenna of mobile phone television and movable communication module
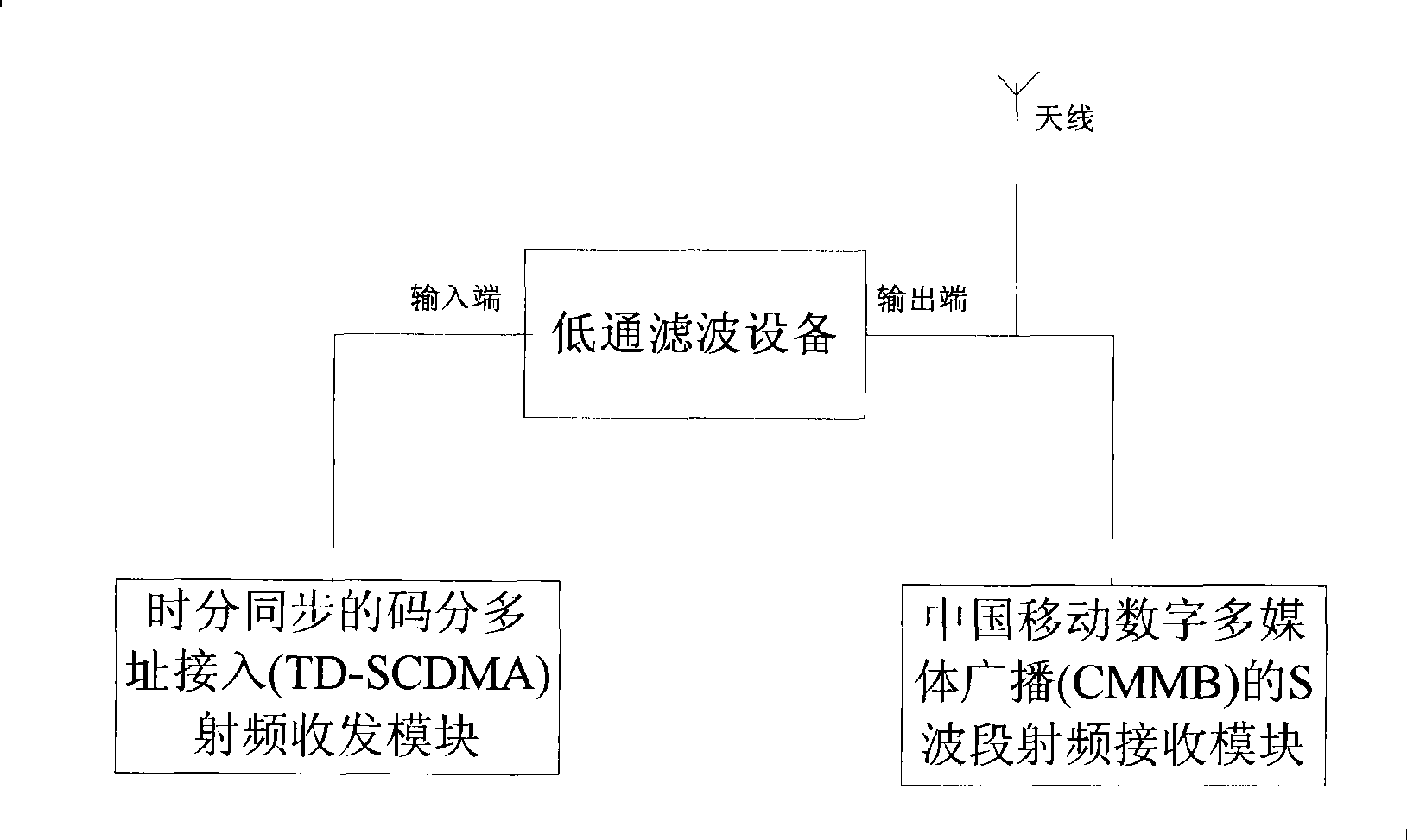
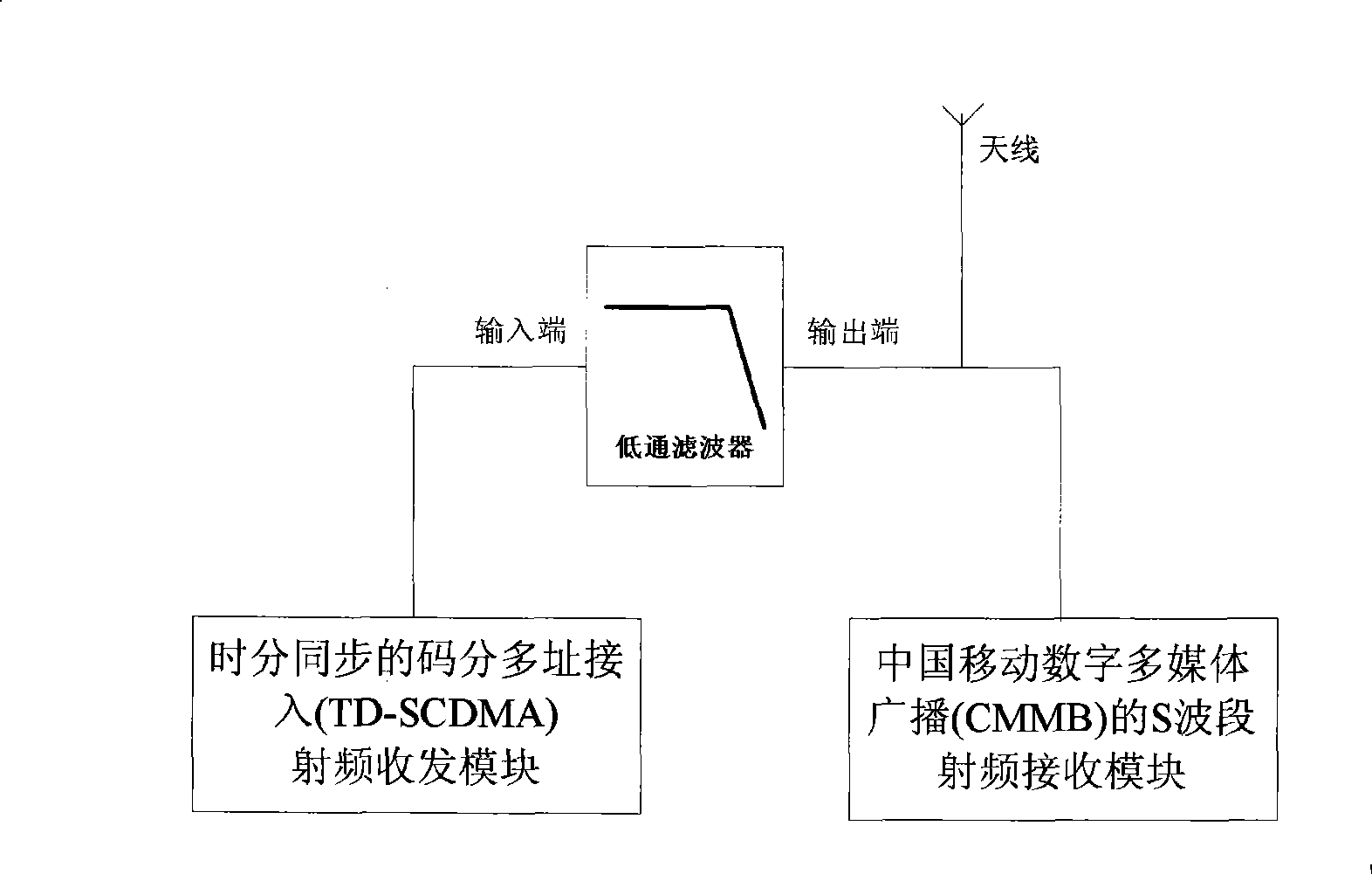
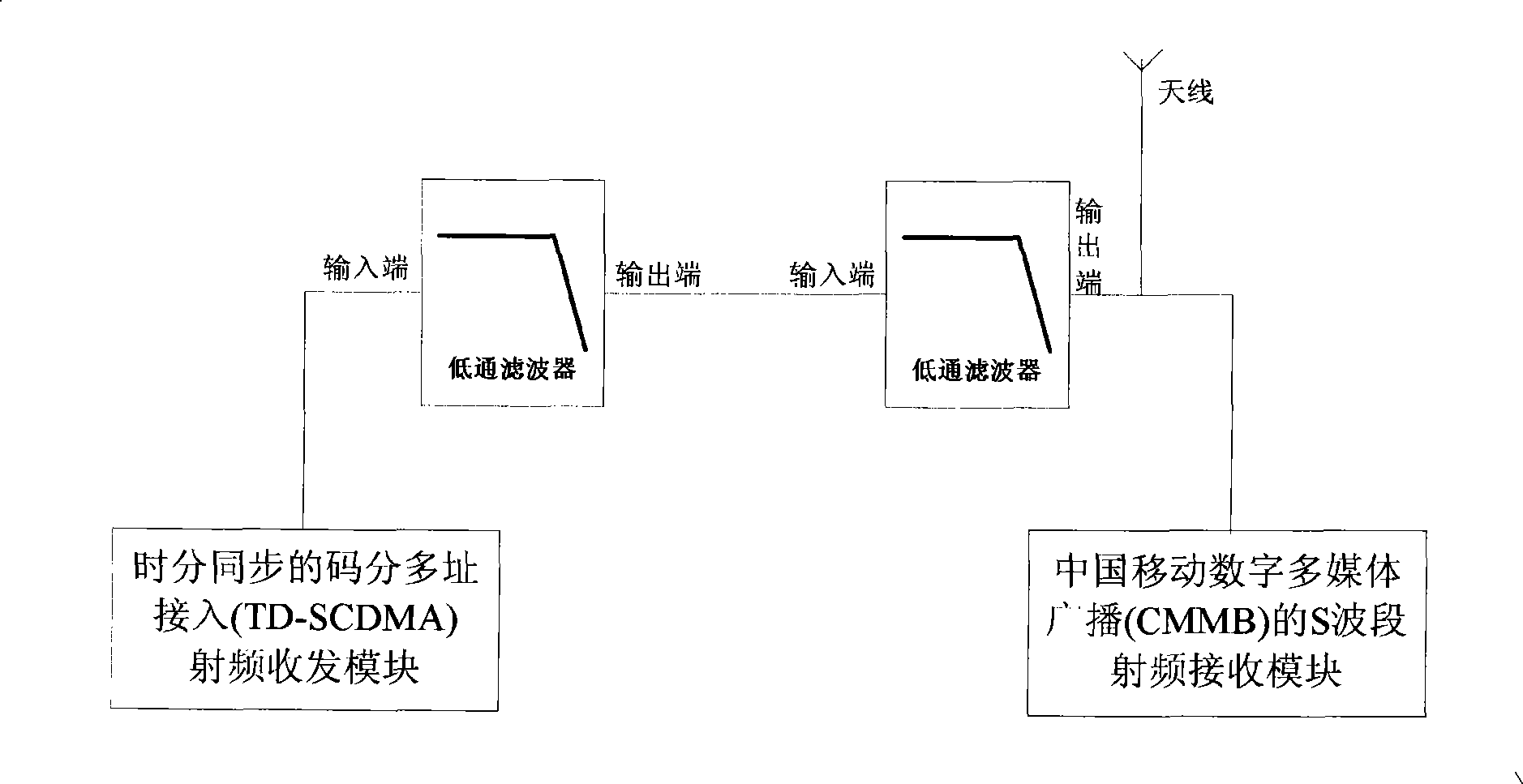
InactiveCN101369819ANo interferenceReduce difficultyRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsTransmissionLow-pass filterCode division multiple access
The invention provides a mobile terminal for an antenna shared by a mobile phone television and a mobile communication module, including a time-division synchronous CDMA access RF transmit-receive module and a China mobile digital multimedia broadcast S waveband RF receive module. The apparatus also including an antennae and a low pass filter; the input terminal of the low pass filter being connected with the time-division synchronous CDMA access RF transmit-receive module, the output terminal of the low-pass filter being connecting with the antennae, and the China mobile digital multimedia broadcast S waveband RF receive module being connected with the antennae. By means of the technical scheme of the present invention, the time-division synchronous CDMA access frequency band and the China mobile digital multimedia broadcast S waveband can share one antennae, which reduces structure difficulty and hardware cost, at the same time two RF systems can work simultaneously, and the time-division synchronous CDMA access frequency band having non interference to the China mobile digital multimedia broadcast S waveband.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Channel bandwidth dynamic configuration method for synchronous code division multiple access system
InactiveCN1812626AGuaranteed reasonable useMeet business needsNetwork traffic/resource managementRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsQuality of serviceCode division multiple access
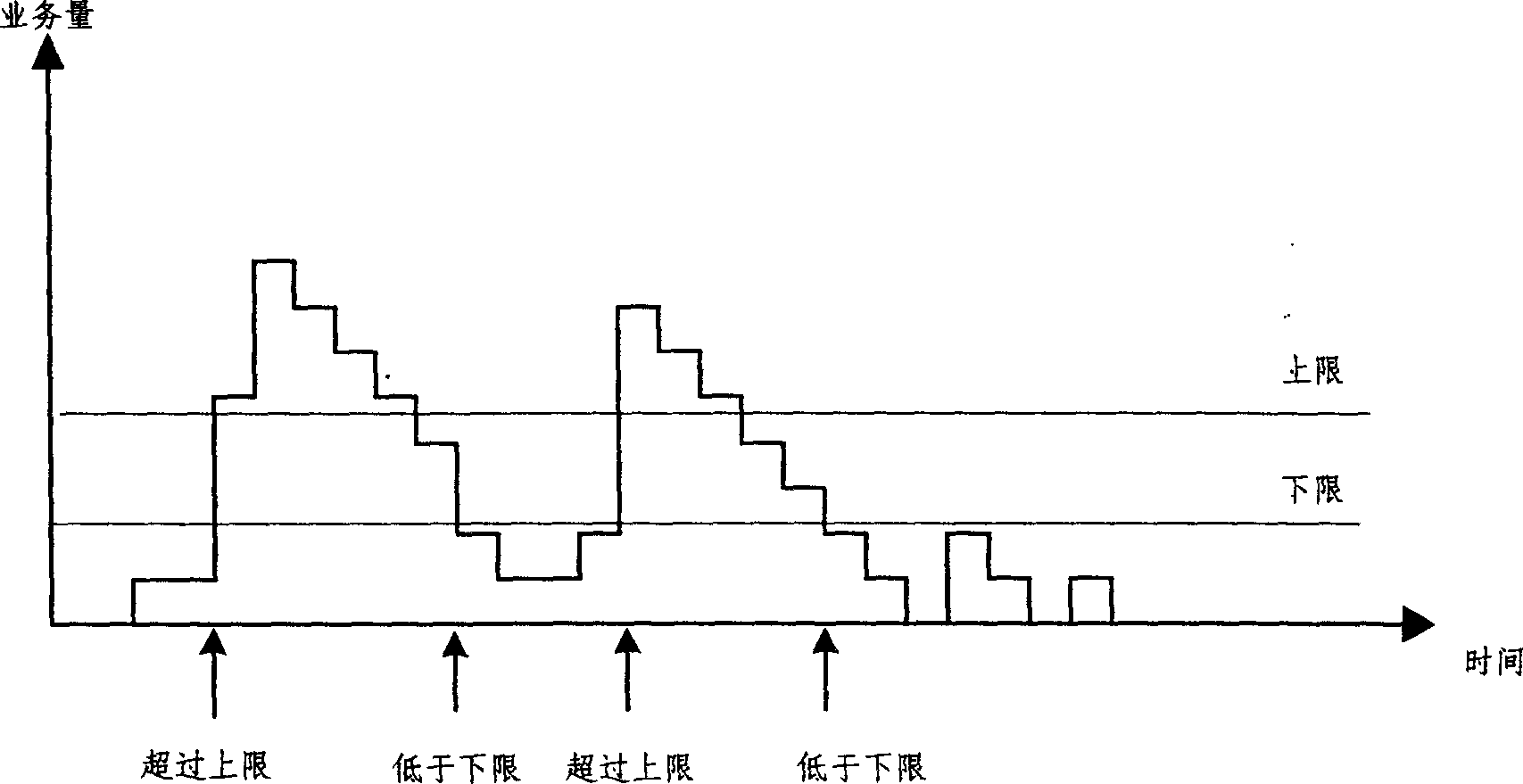
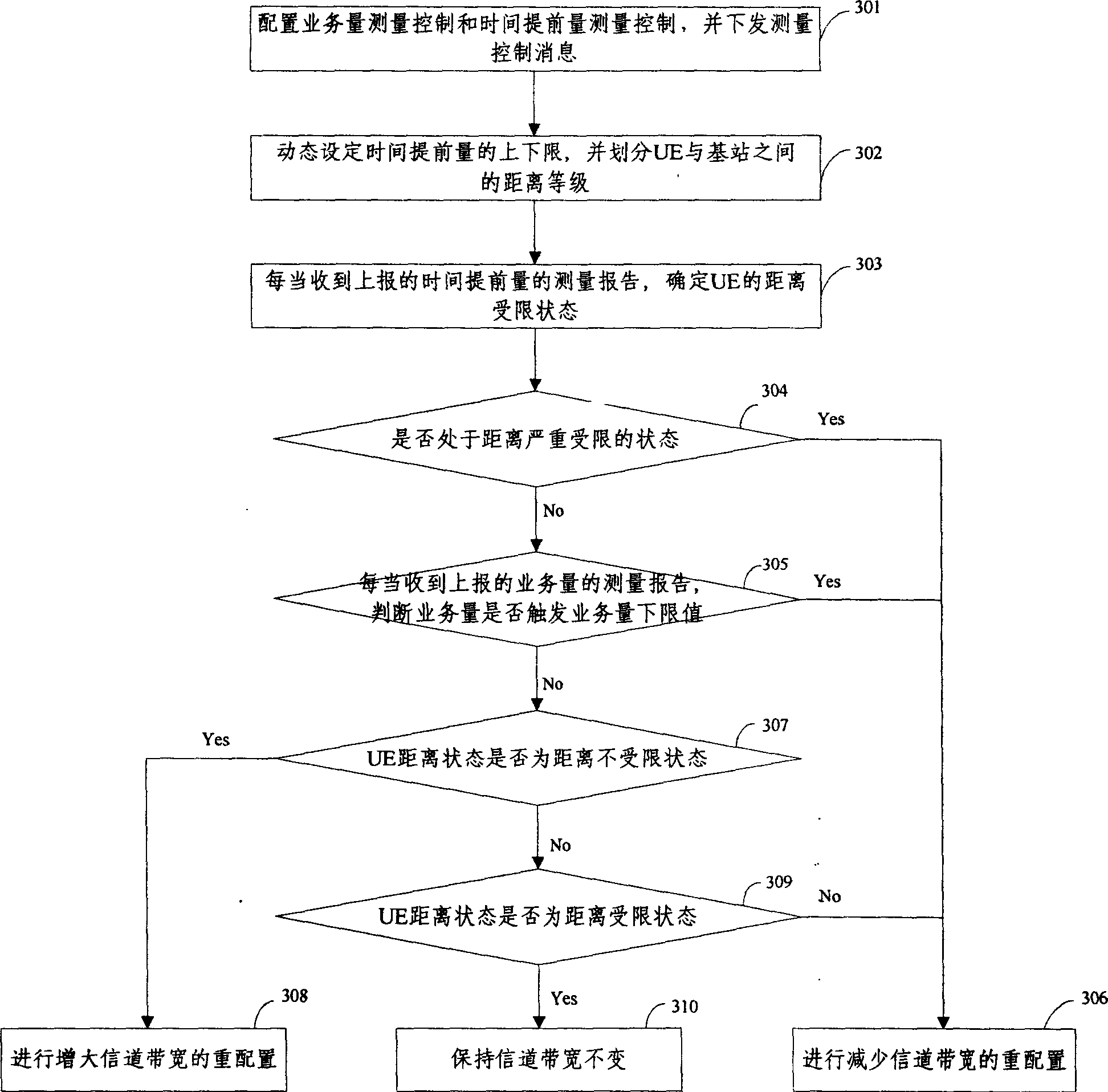
A method for dynamically configuring channel bandwidth of synchronous CDMA system includes measuring service amount of data packet service and time preact of user terminal, confirming distance restricted state between base station and user terminal according to measured time preact, reconfiguring up link or down link channel bandwidth according to said distance restricted state and said service amount.
Owner:ZTE CORP
A modulation processing method and transmission device for transmitting data in multi-carrier system
InactiveCN101262628AReduce PAR valueAvoid situations where the same dataSpatial transmit diversityTransmission control/equalisingTerminal equipmentCarrier signal
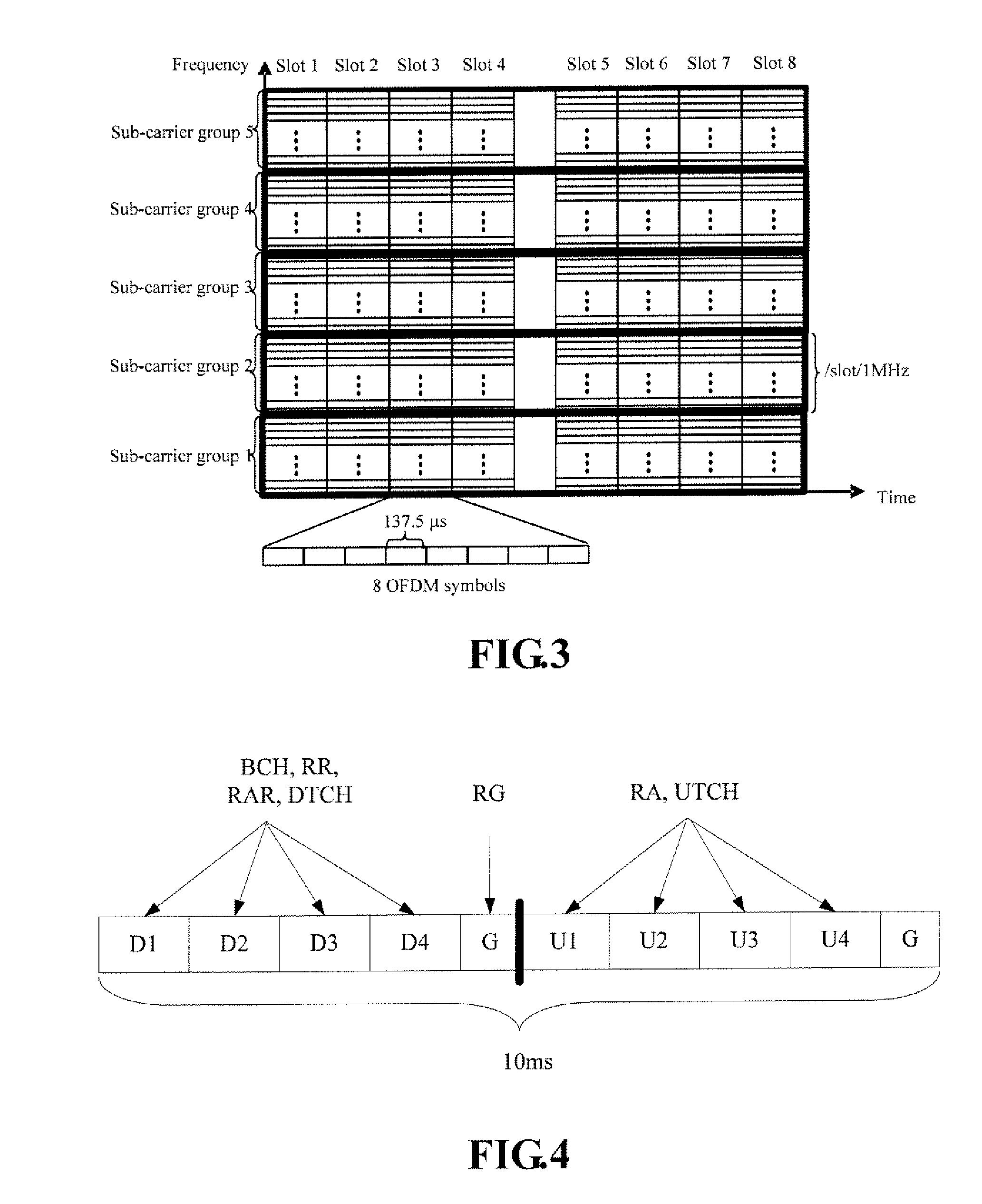
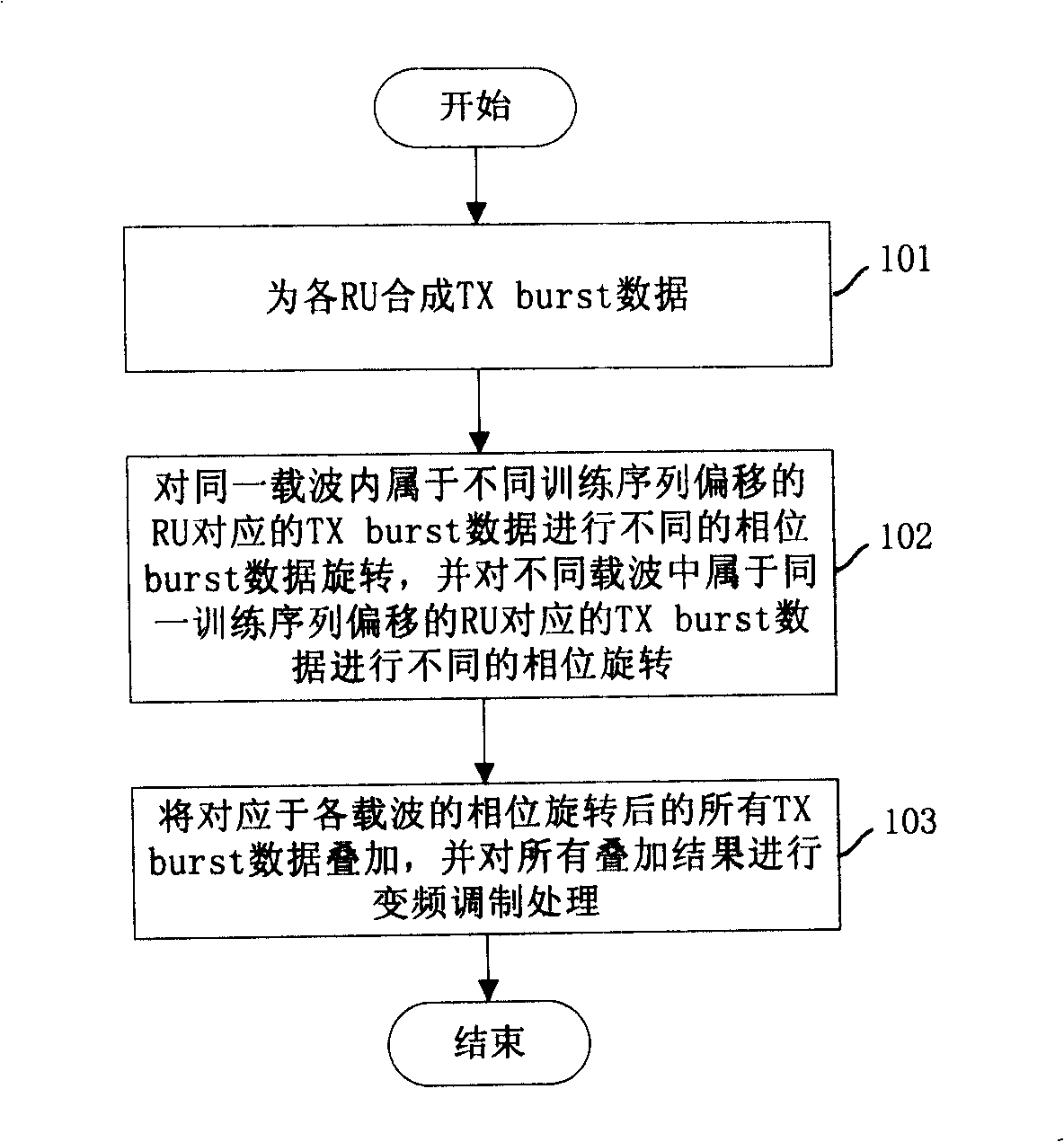
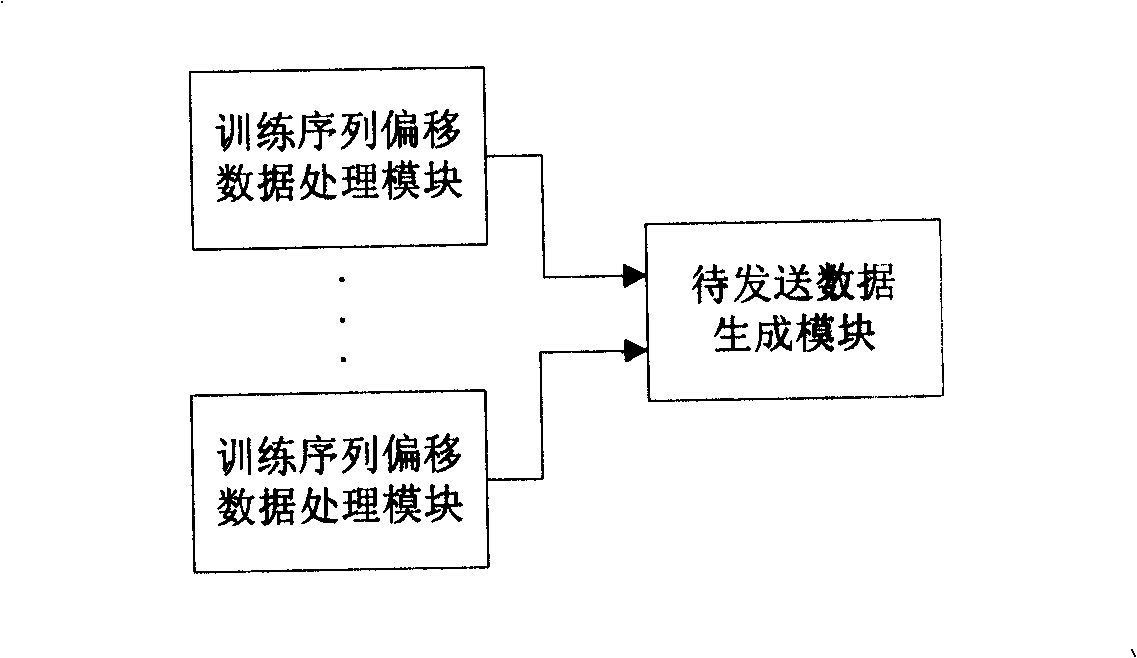
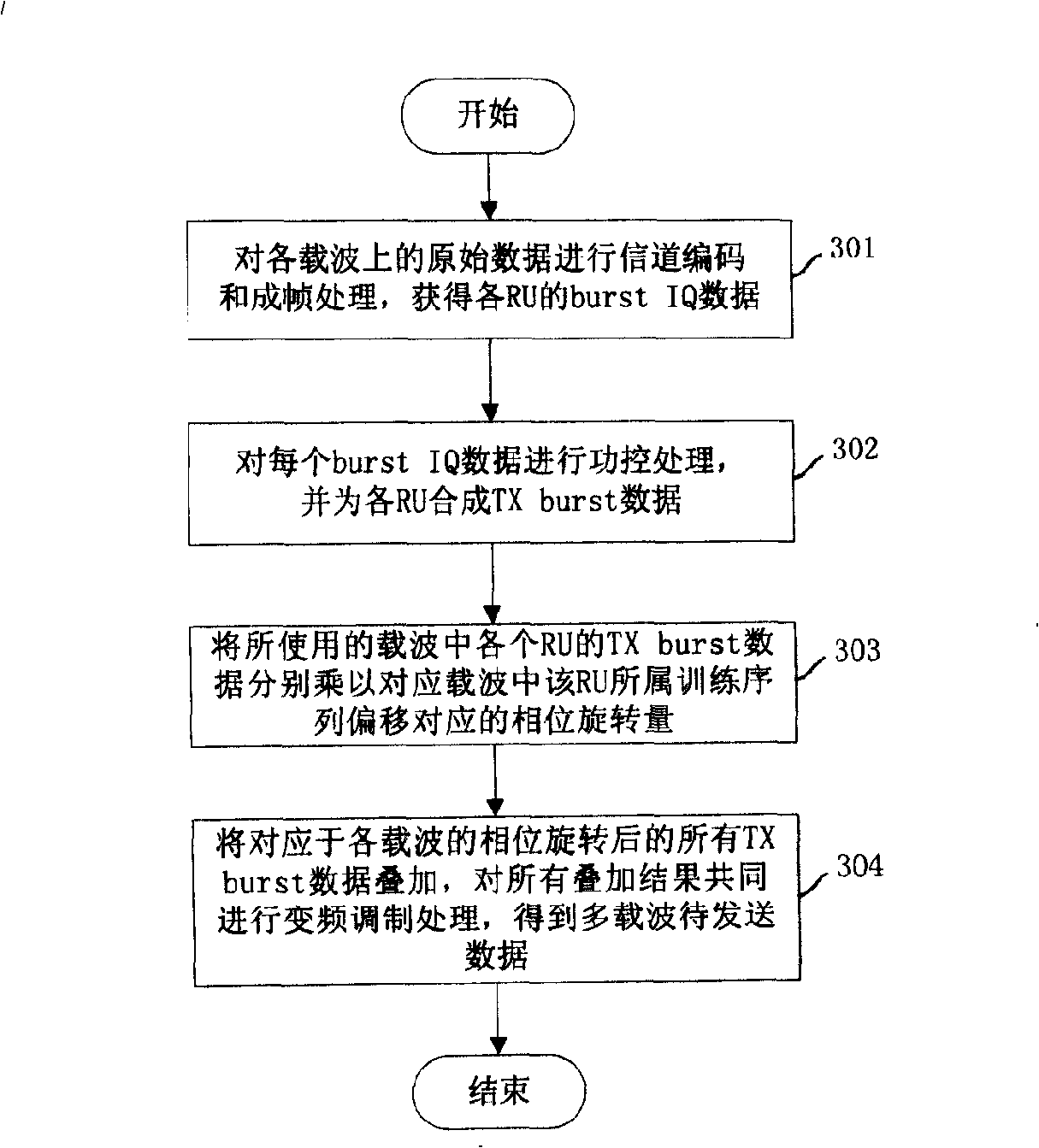
The invention discloses a modulating processing method for sending data in a multi-carrier system. The method comprises the steps that: A. TX burst data is sent for each radio unit RU, different phase rotation is carried out to the TX burst data corresponding to the RU in a same carrier but belonging to different training sequence offset as well as the TX burst data corresponding to the RU in different carriers but belonging to same training sequence offset; B. all TX burst data corresponding to each carrier and after the phase rotation is superimposed and then variable frequency modulation processing is carried out to the superimposed result. The invention also discloses a sending terminal device used for sending data modulation processing. The device comprises at least one training sequence offset data processing module and a to-be-sent data generation module. The technical proposal of the invention can effectively reduce peak-to-mean ratio in the TDD-synchronous CDMA MC system.
Owner:TD TECH COMM TECH LTD
Method for expanding time-division synchronous CDMA access system ovelay range
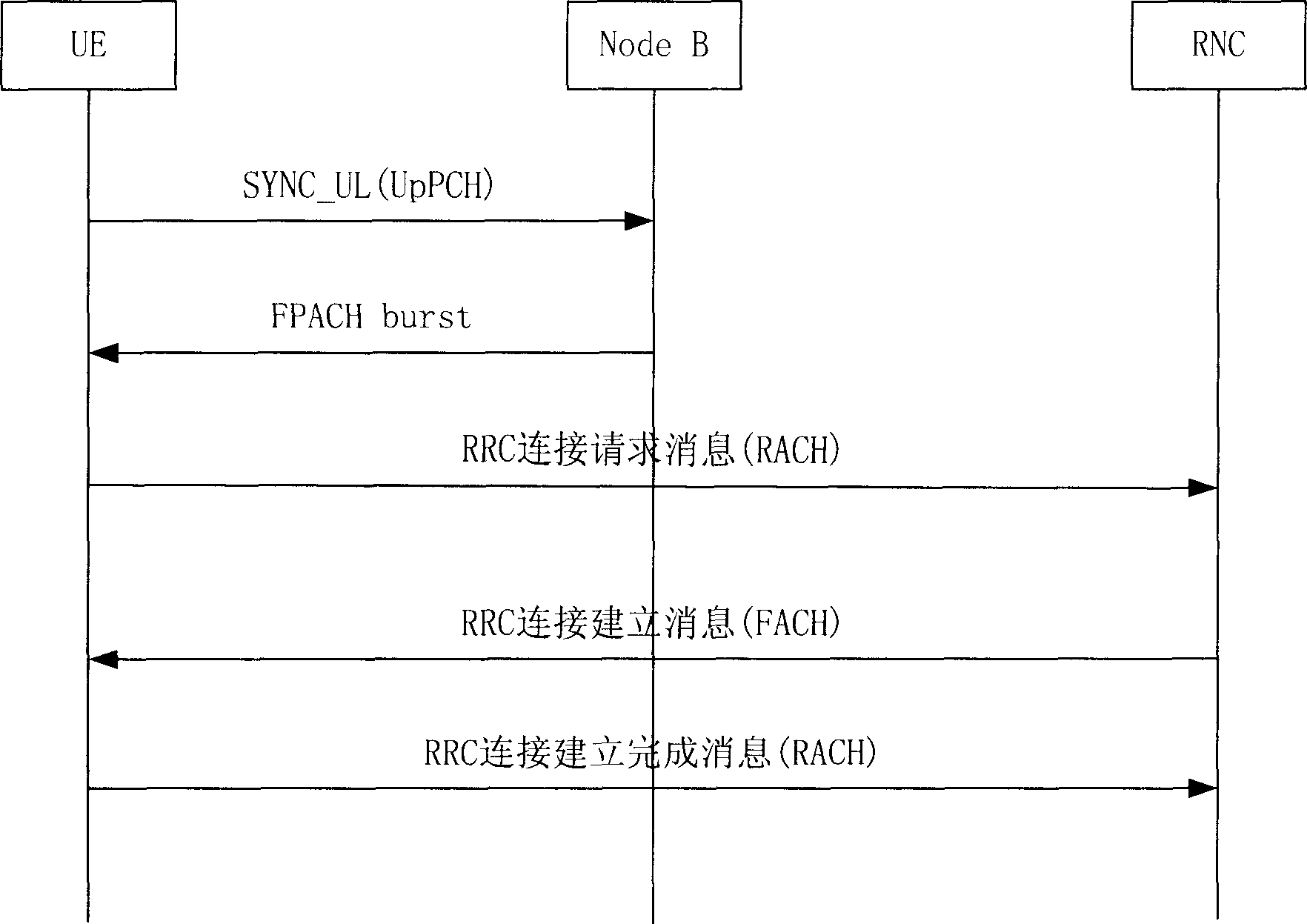
ActiveCN101075844AAchieve wide coverageSynchronisation arrangementCode division multiplexTerminal equipmentPhysical layer
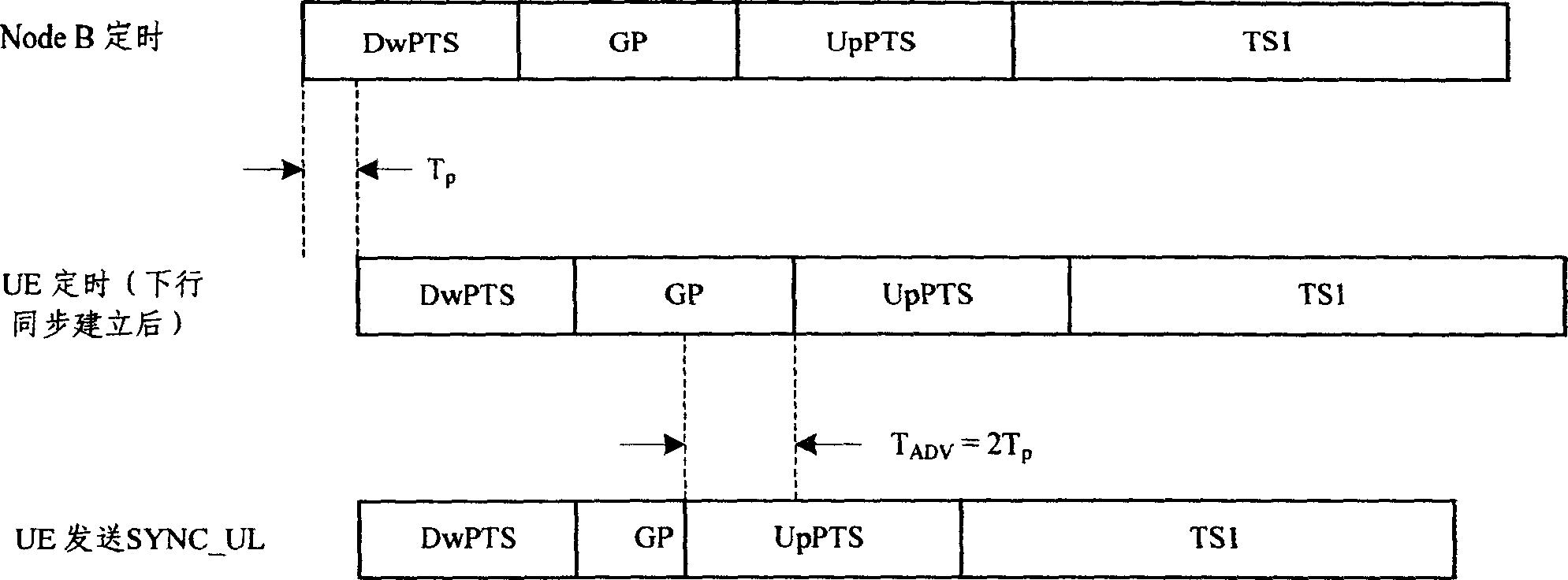
In the invention, the method of establishing uplink synchronization by the mobile terminal in the system comprises: a) based on preact of the predetermined sending time, the mobile terminal sends the uplink pilot frequency signals; b) if the mobile terminal is not able to access, the physical layer of the mobile terminal resets the preact of the sending time, and returning to step a. The invention has the following advantages: 1)realizing the wide coverage at all kinds of scenes; 2) no need to scarifying the TS1 time slot as the extra protection time slot; 3) no need to modify the currently-used base station, and only need to make slight modification for the mobile terminal 4) no need to amend the criteria and rule.
Owner:DATANG MOBILE COMM EQUIP CO LTD
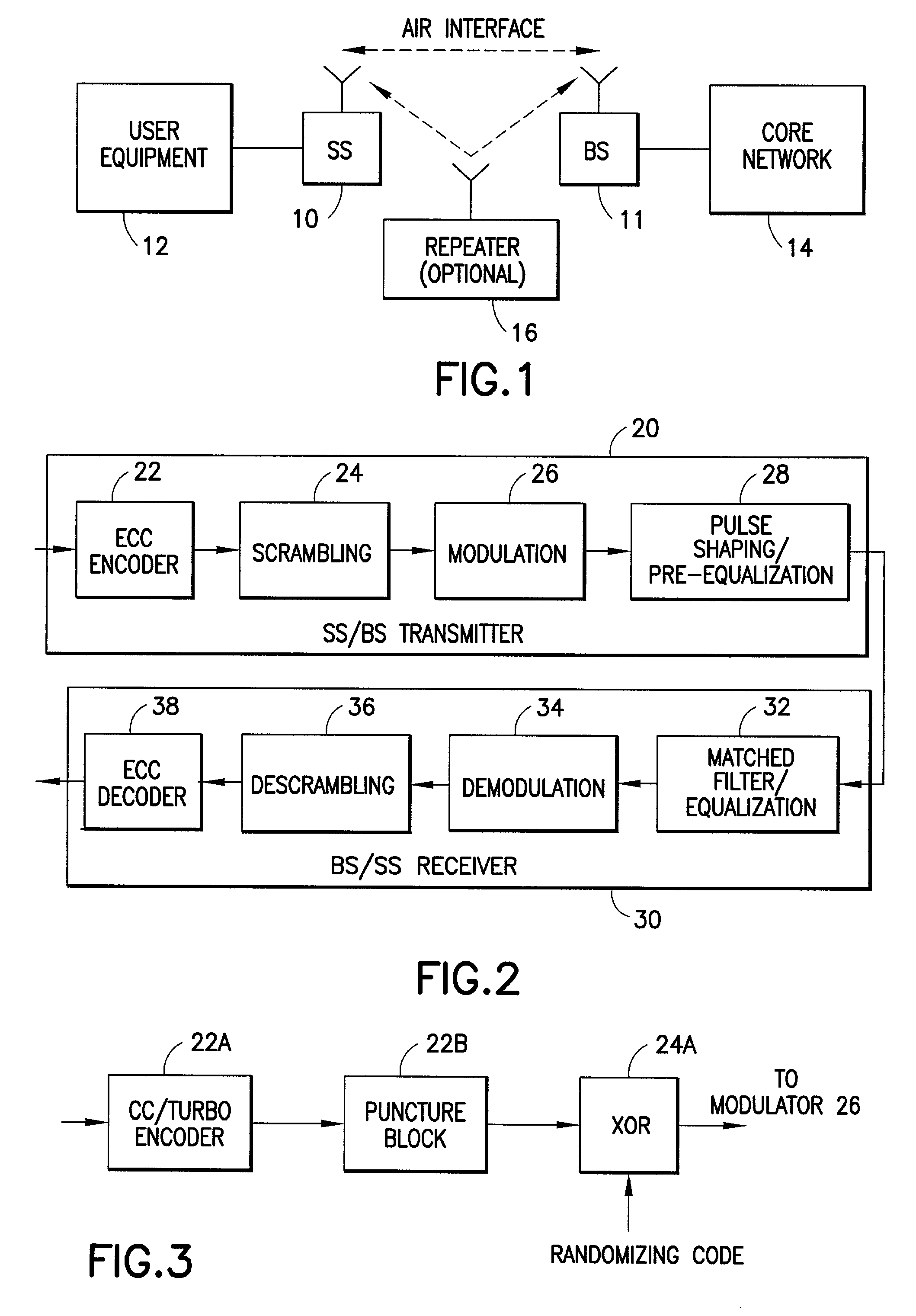
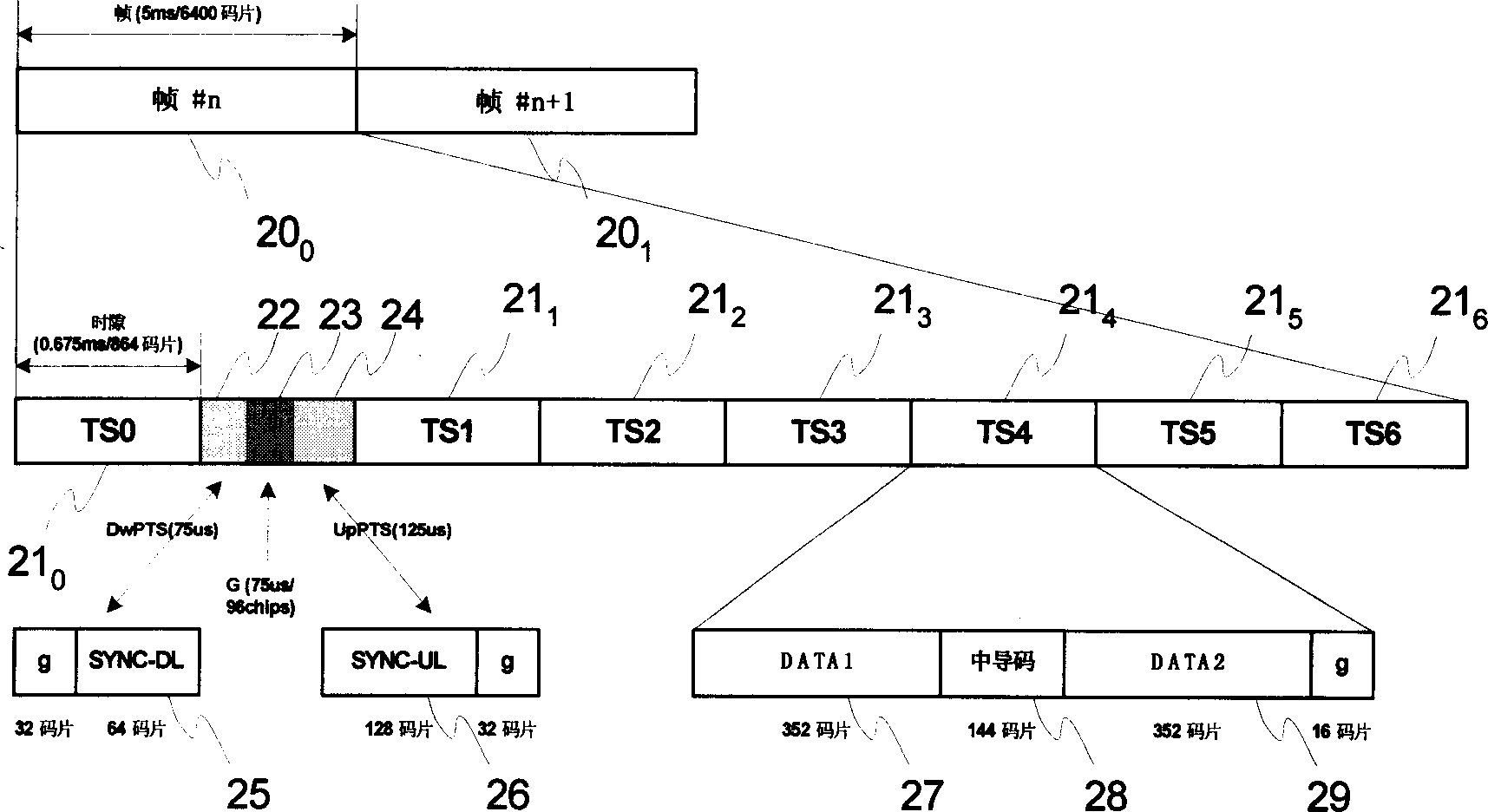
Waveform and frame structure for fixed wireless loop synchronous CDMA communications system
Disclosed is a method for transmitting information in a CDMA communication system, the method including steps of (a) multiplexing data and control information into a data stream; (b) encoding the data stream to form a stream of encoded I / Q symbol pairs; (c) inserting synchronization information into the stream of encoded I / Q symbol pairs; and (d) spreading the encoded I / Q symbol pairs and the inserted synchronization information using a same pseudonoise (pn) spreading code prior to transmission as a frame. The preferred frame structure includes an unencoded synchronization field followed by a plurality of multi-byte data fields. Individual ones of the plurality of data fields are separated by a control message field. Individual ones of the control message fields contain a single byte of a multi-byte control message frame.
Owner:L 3 COMM CORP
A method to realize time division synchronous CDMA repeater power saving
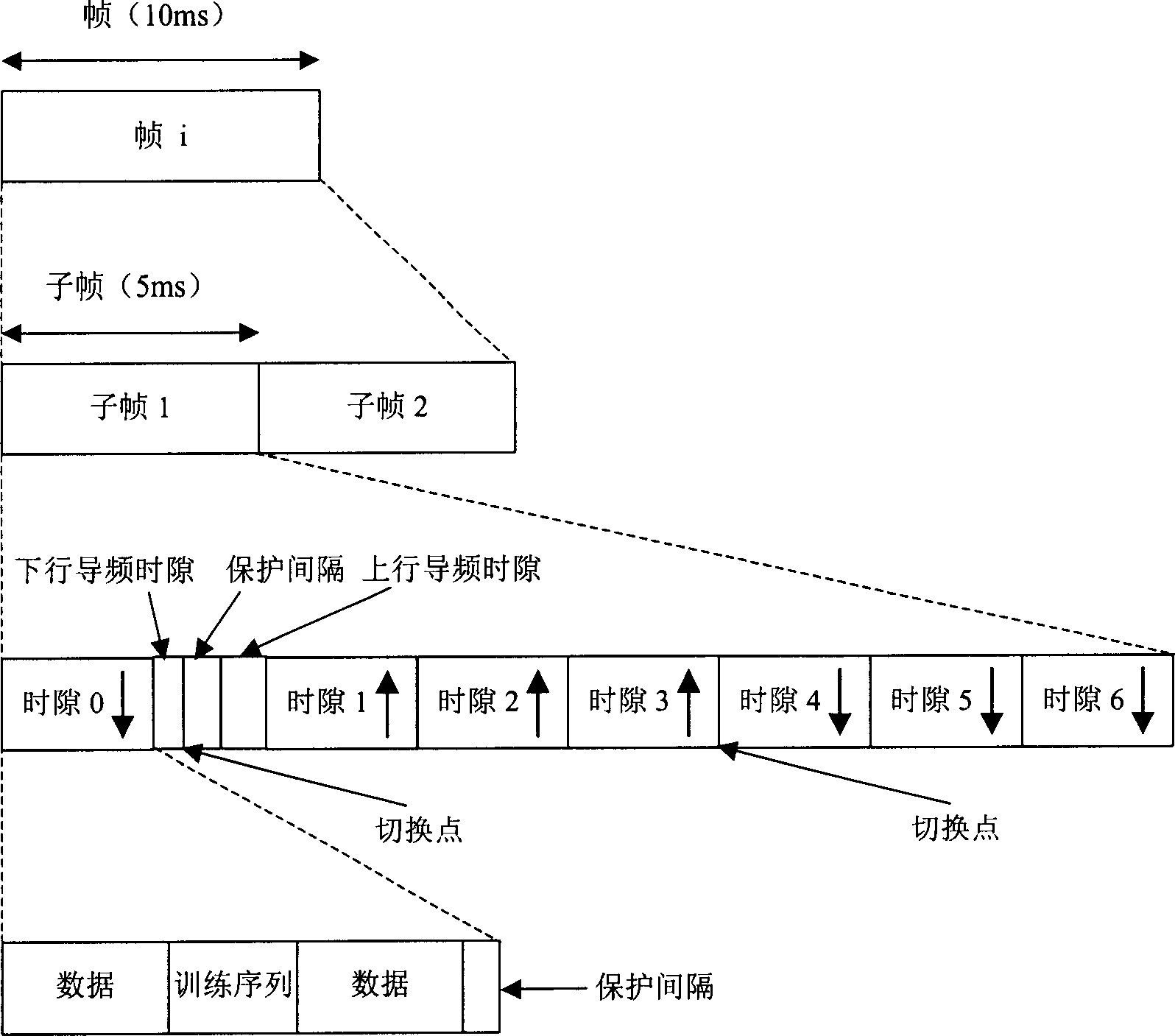
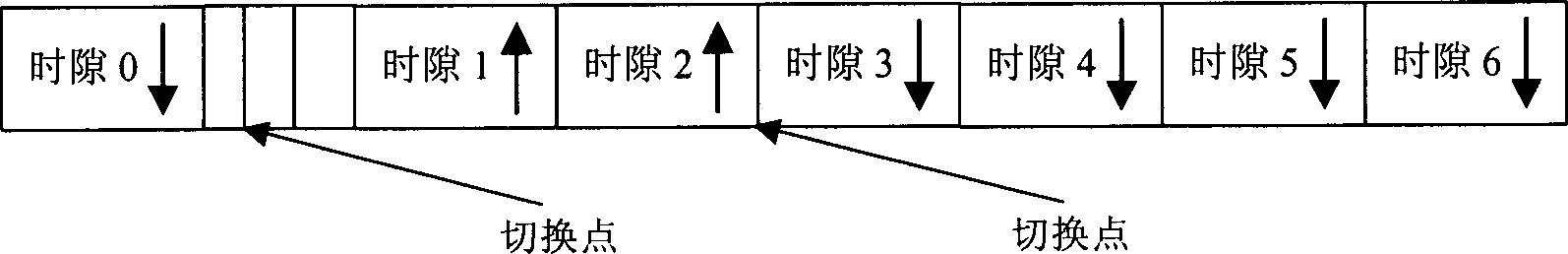
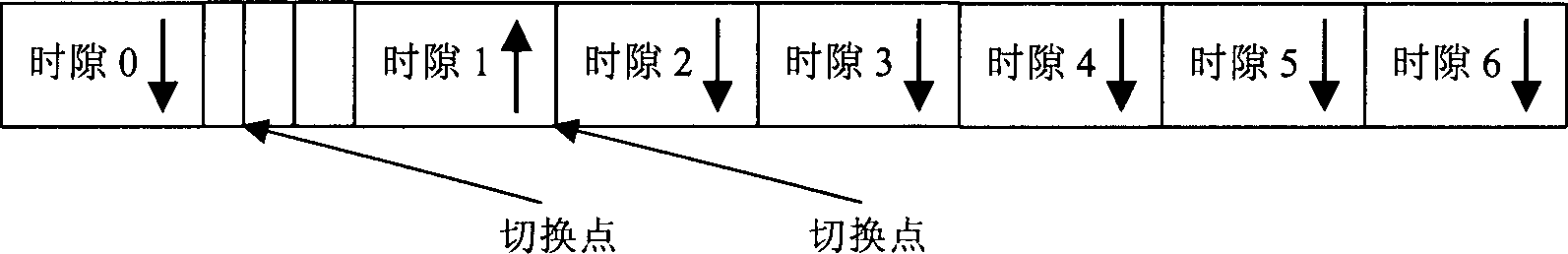
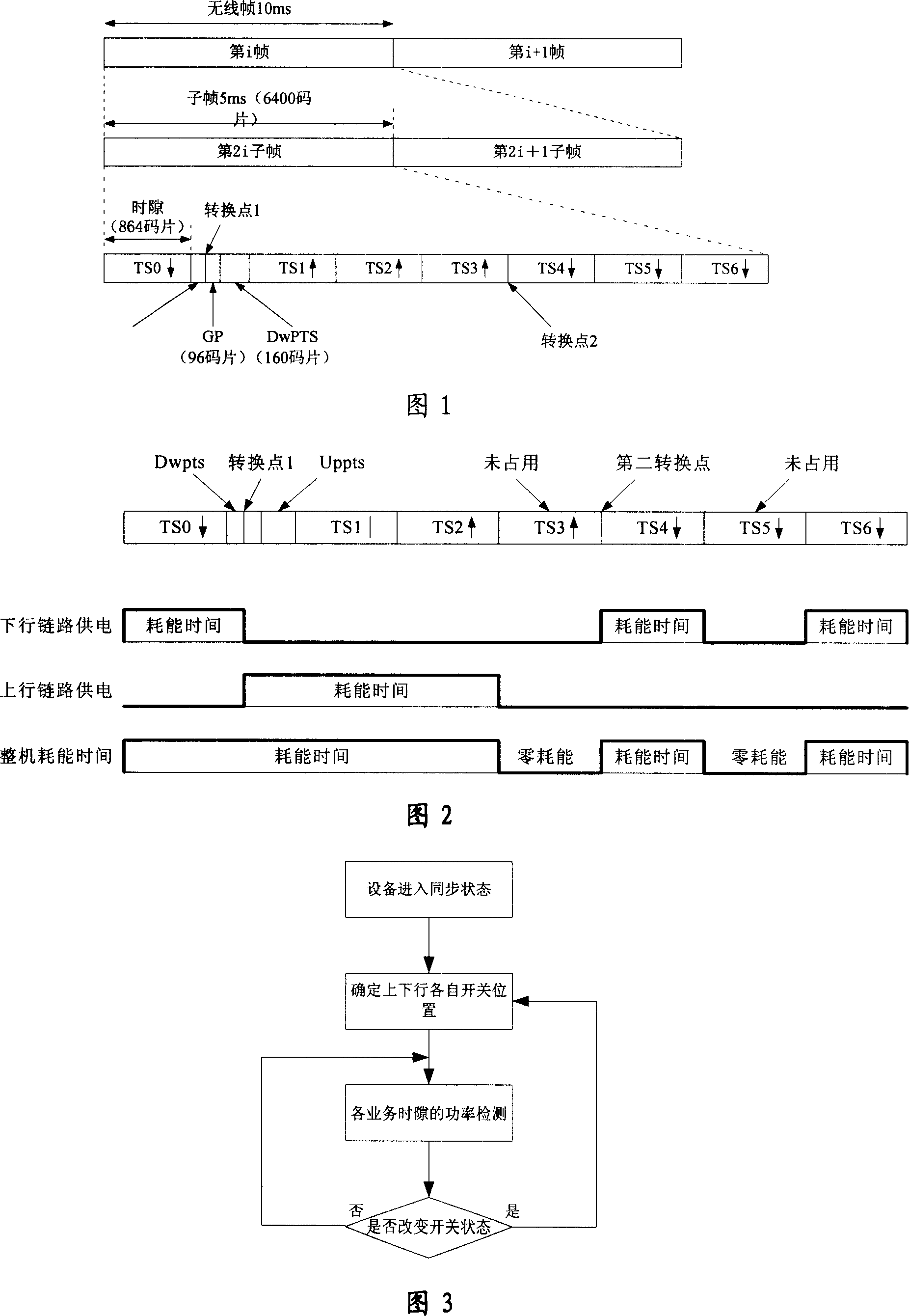
InactiveCN1964209AReduce power consumptionFever variable is smallTransmission control/equalisingRadio transmission for post communicationTD-SCDMAPower over
The related energy saving method for TD-SCDMA direct station comprises: starting direct station for signal synchronization, detecting every time slot power and the exact position of two switch points; then, using RF switch in direct station fro link circuit conversion; comparing the detected time slot power with threshold, real-time setting the business time slot into power supplying state if the slot power over threshold, or else closing power for the free time slot; re-controlling up-down switch time, and continual tracking to detect business occupancy condition. This invention reduces cost for provider and saves the direct station consumption mostly.
Owner:WUHAN HONGXIN TELECOMM TECH CO LTD
VoIP bearing method in time division synchronous CDMA access system
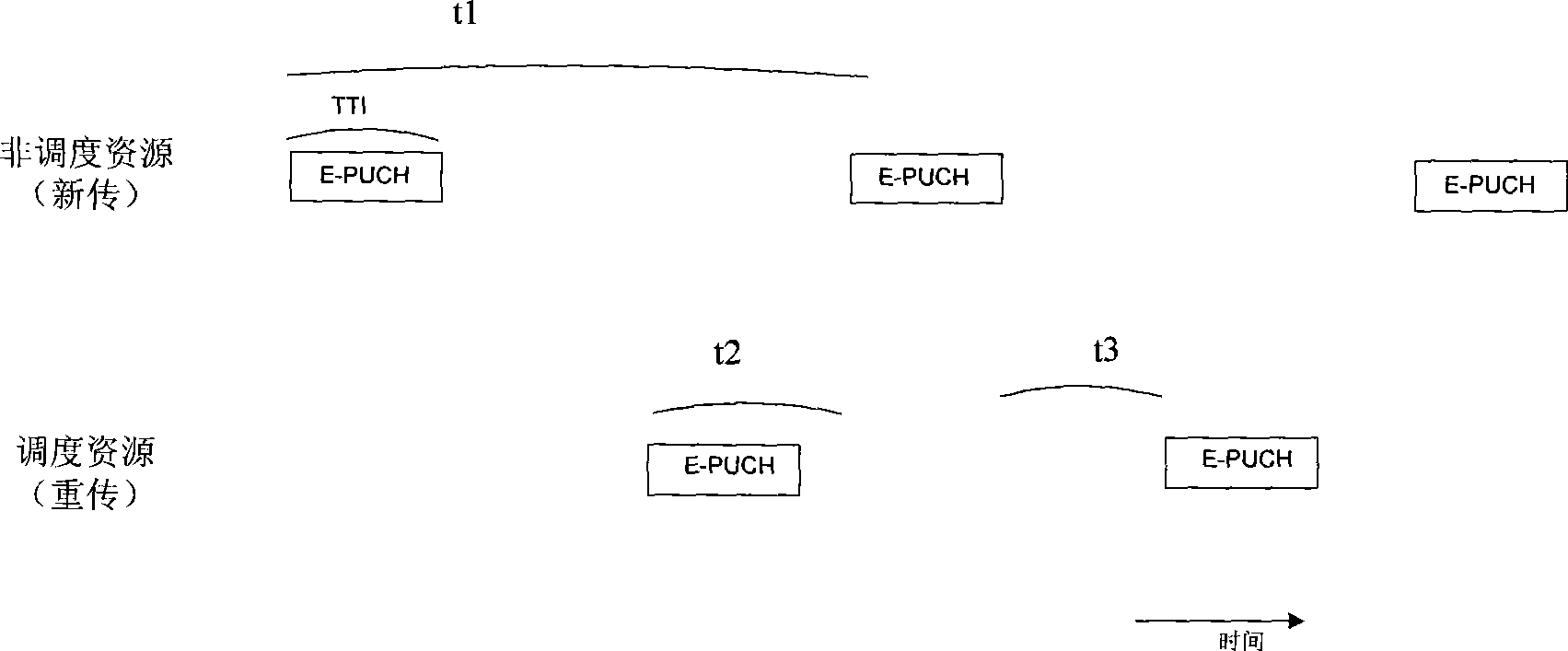
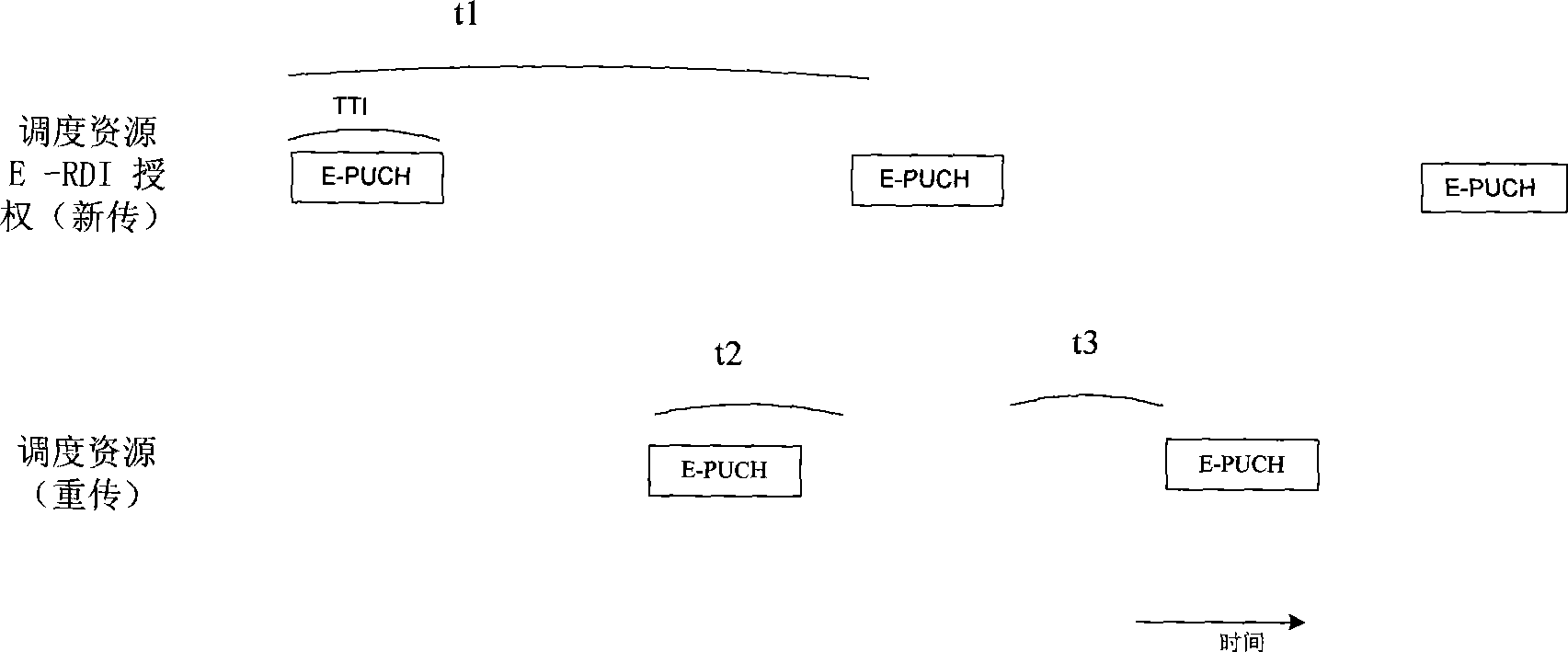
InactiveCN101399605AReduce overheadSupport VoIP transmissionError prevention/detection by using return channelRadio transmission for post communicationCode division multiple accessThe Internet
The invention provides a method for carrying an internet phone in a time division-synchronous code division multiple access system. The method comprises the following steps: (a) when an internet phone VoIP business is requested at a user terminal, a periodic uplink resource is arranged for the user terminal by a network side, and the user terminal uses the resource to upload new VoIP data; (b) after a base station receives the VoIP data and detects that the VoIP data has errors, non-acknowledge information (NACK) is fed back and authorization is retransmitted to the user terminal to allocate scheduling resources for the user terminal; and (c) after the user terminal receives the NACK information, and the VoIP data is retransmitted on the scheduling resources.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com