Patents
Literature
236 results about "Phase variation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
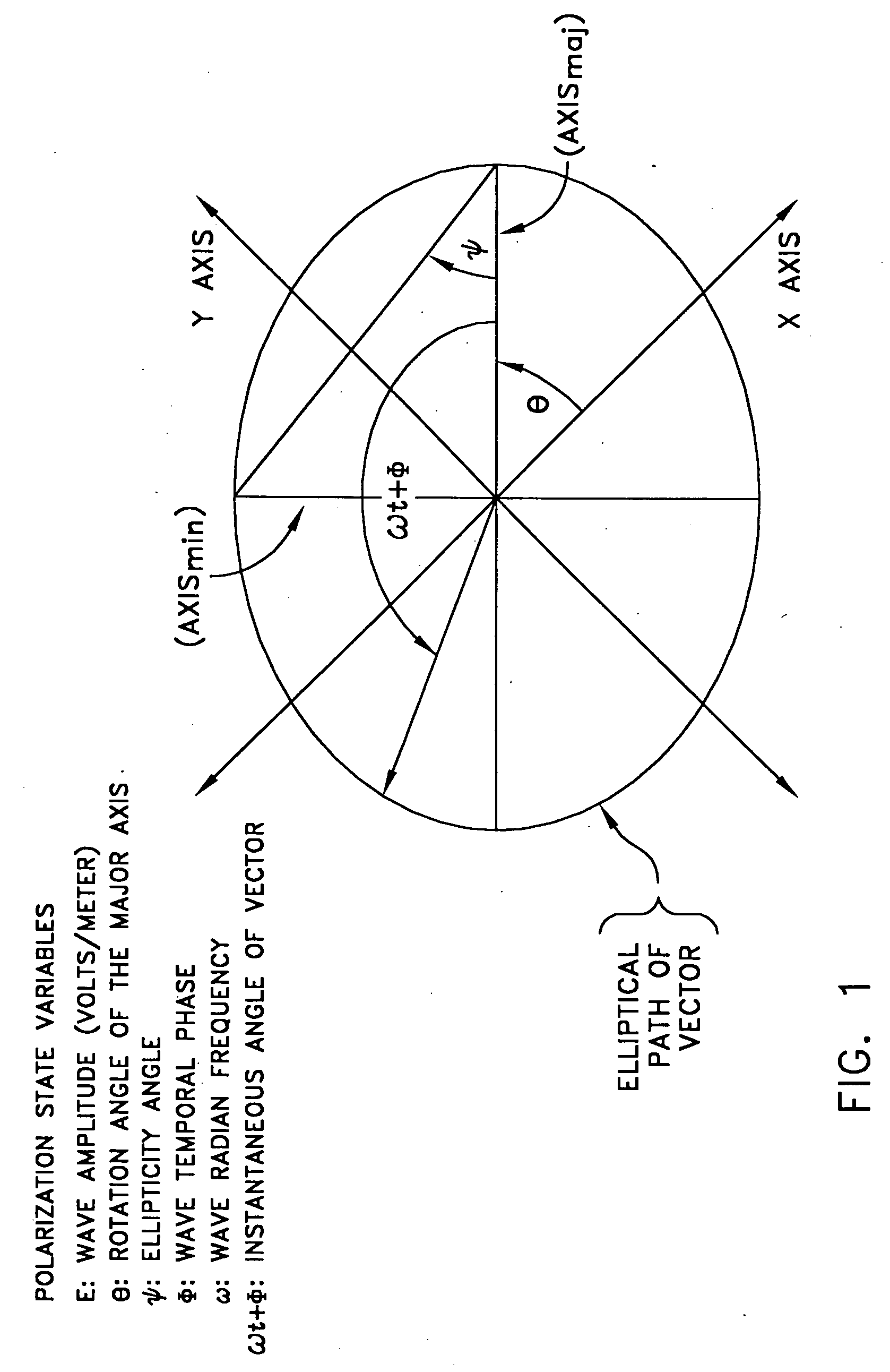
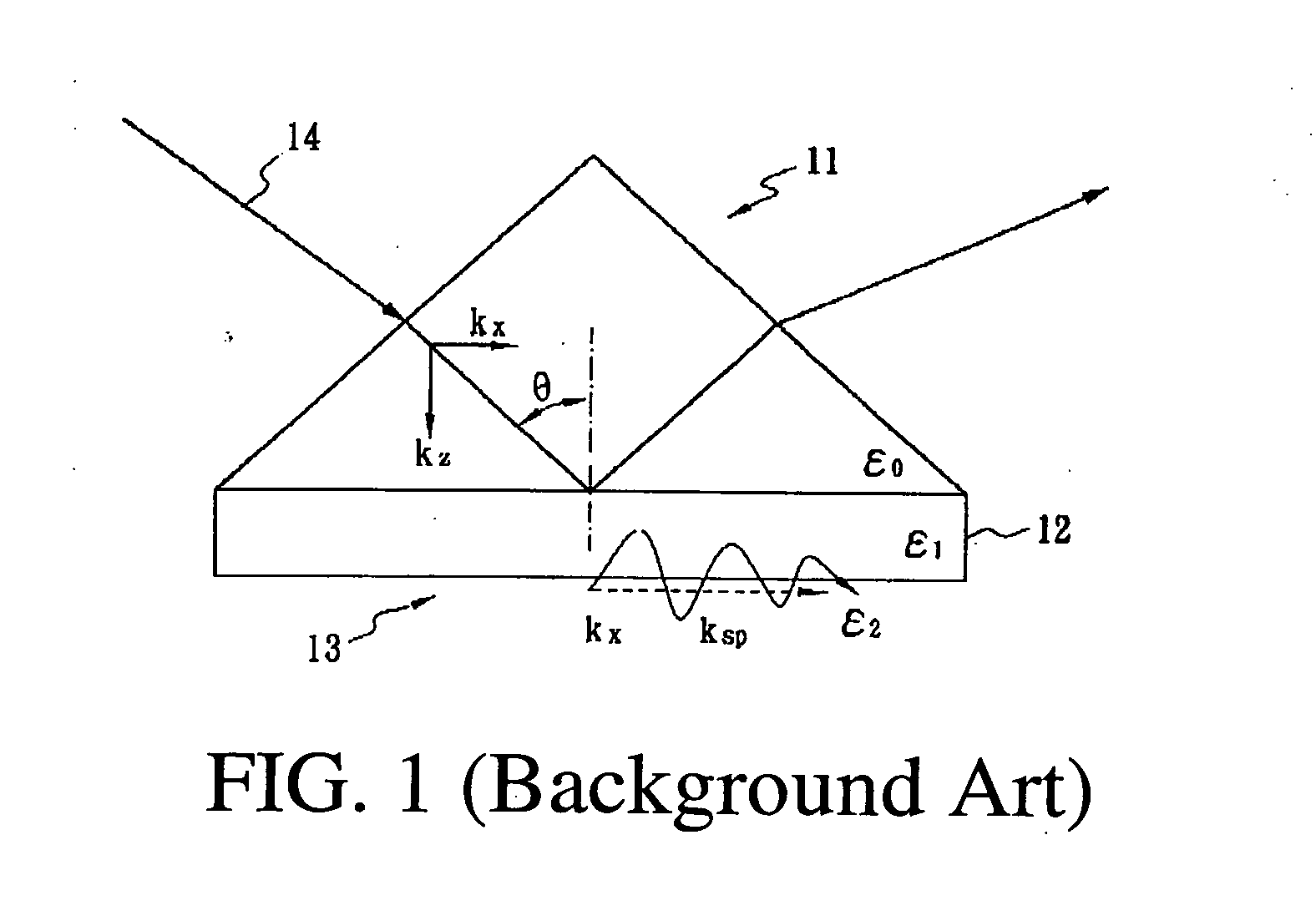
In biology, phase variation is a method for dealing with rapidly varying environments without requiring random mutation. It involves the variation of protein expression, frequently in an on-off fashion, within different parts of a bacterial population. As such the phenotype can switch at frequencies that are much higher (sometimes >1%) than classical mutation rates. Phase variation contributes to virulence by generating heterogeneity. Although it has been most commonly studied in the context of immune evasion, it is observed in many other areas as well and is employed by various types of bacteria, including Salmonella species.
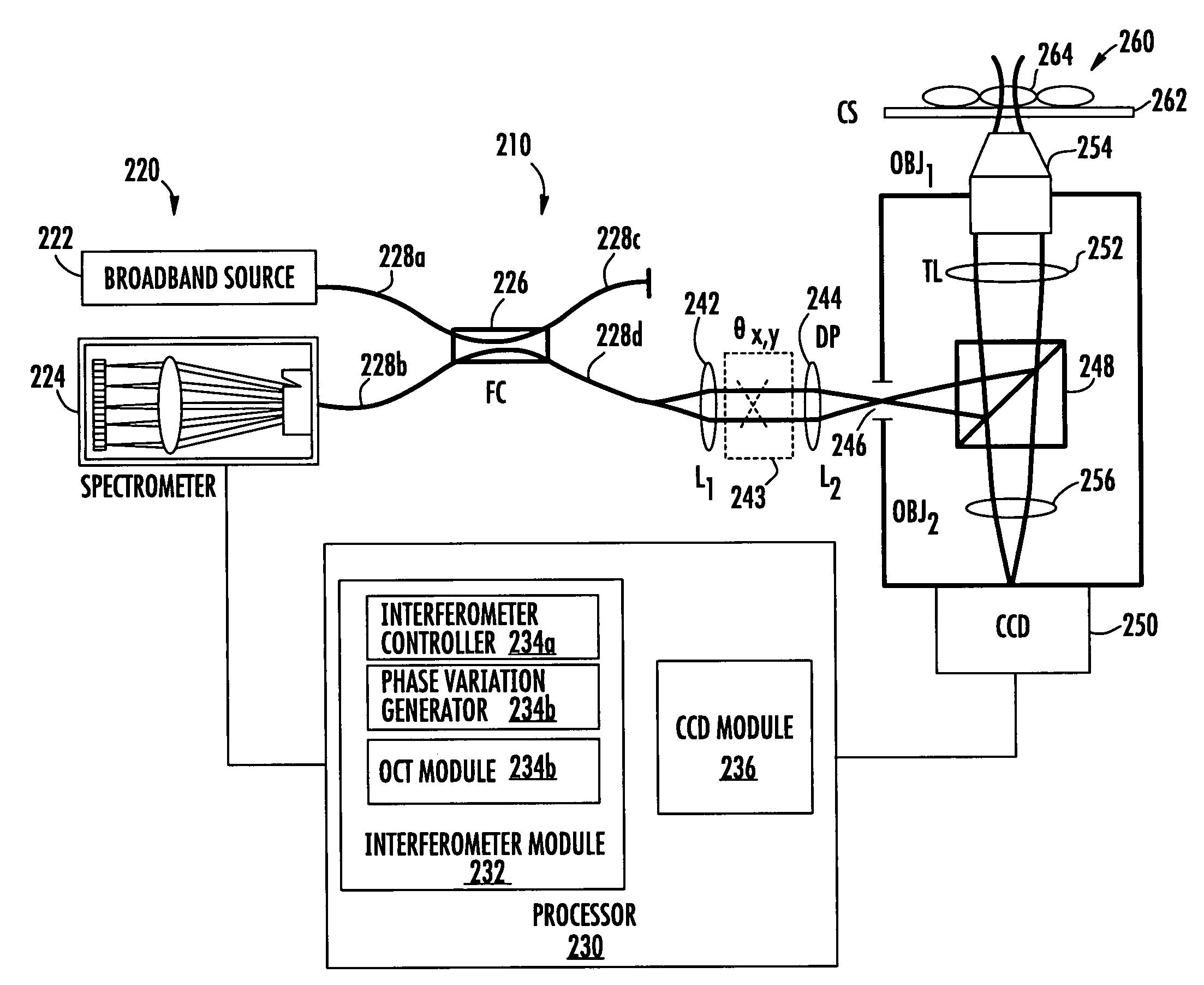
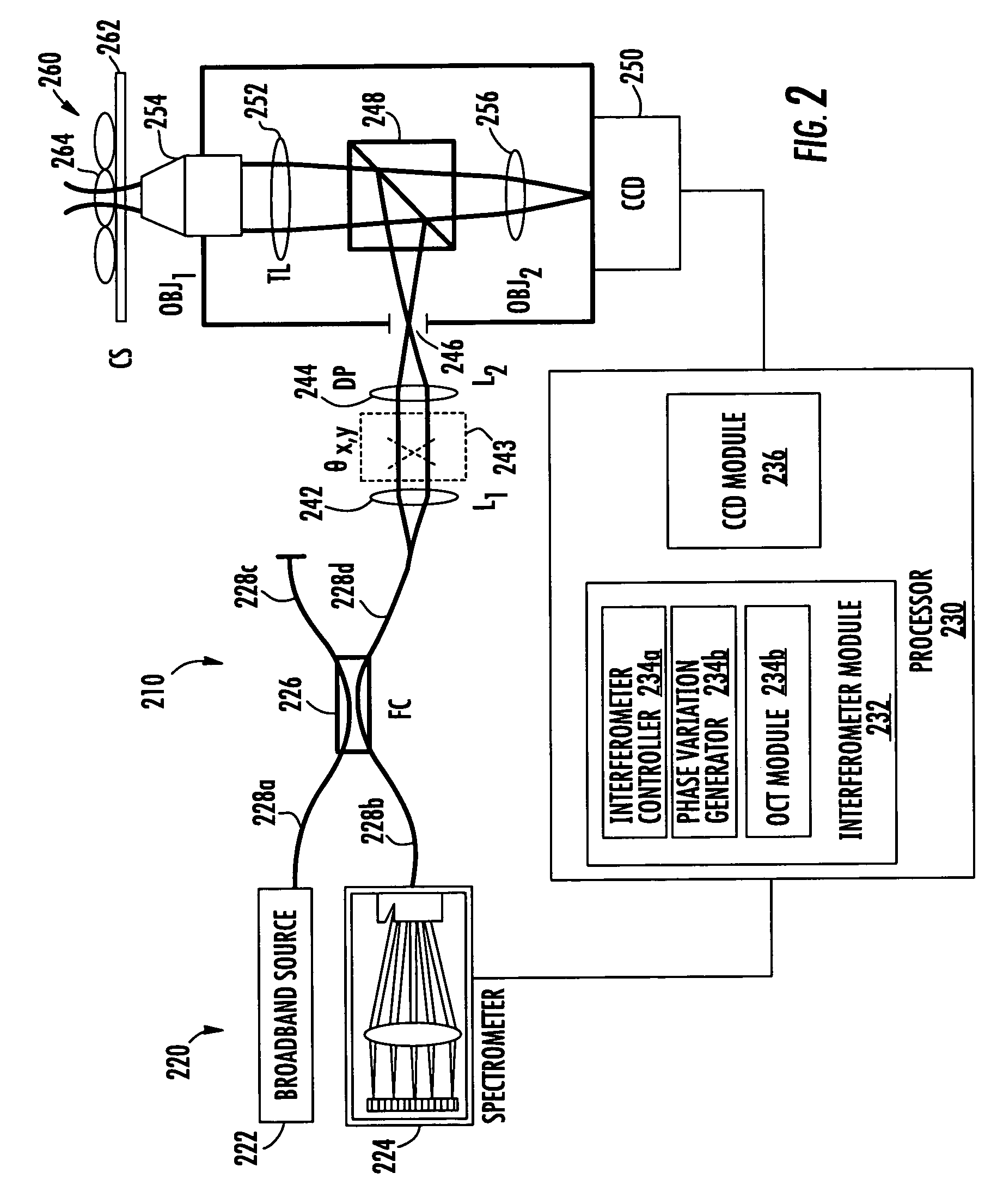
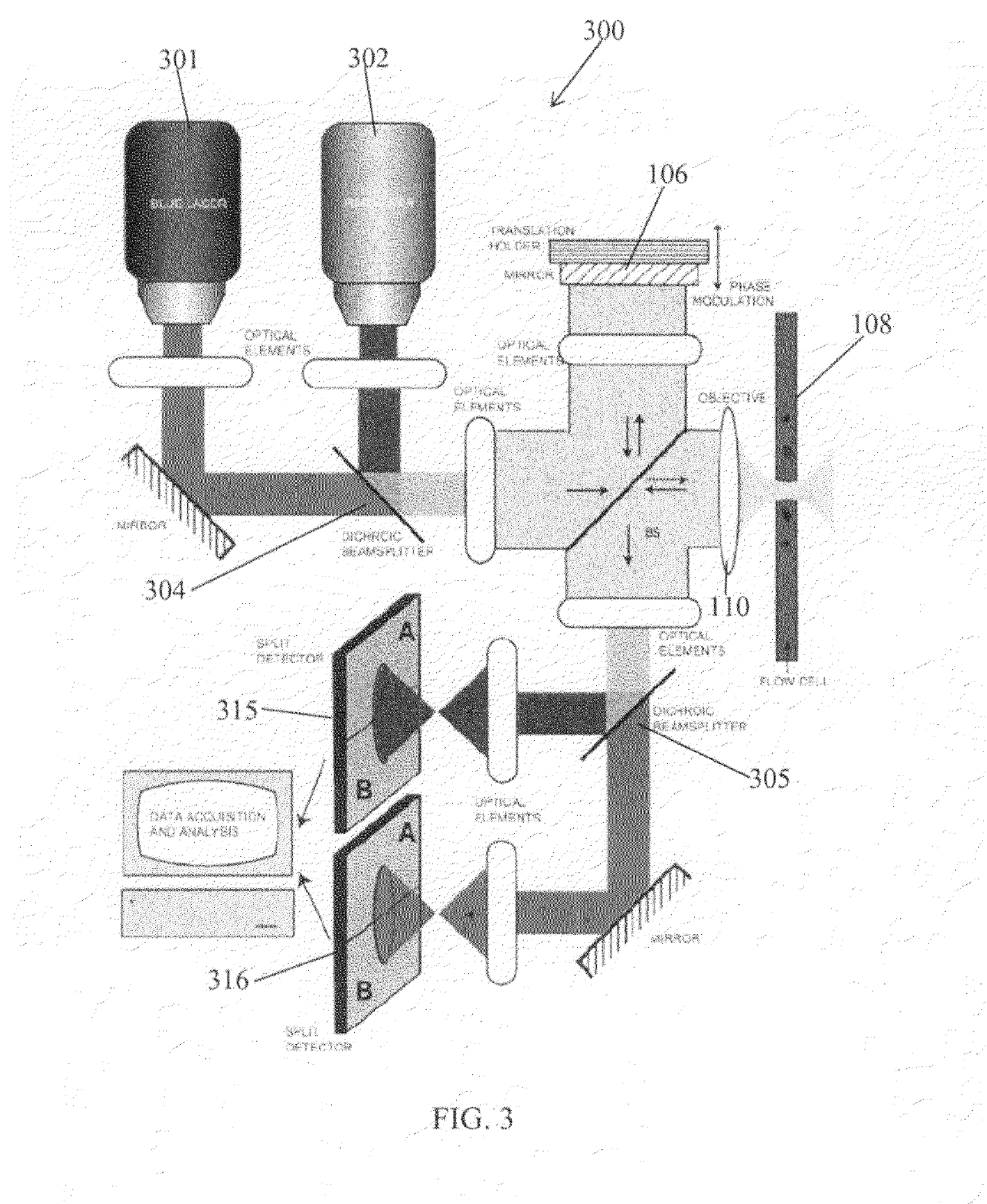
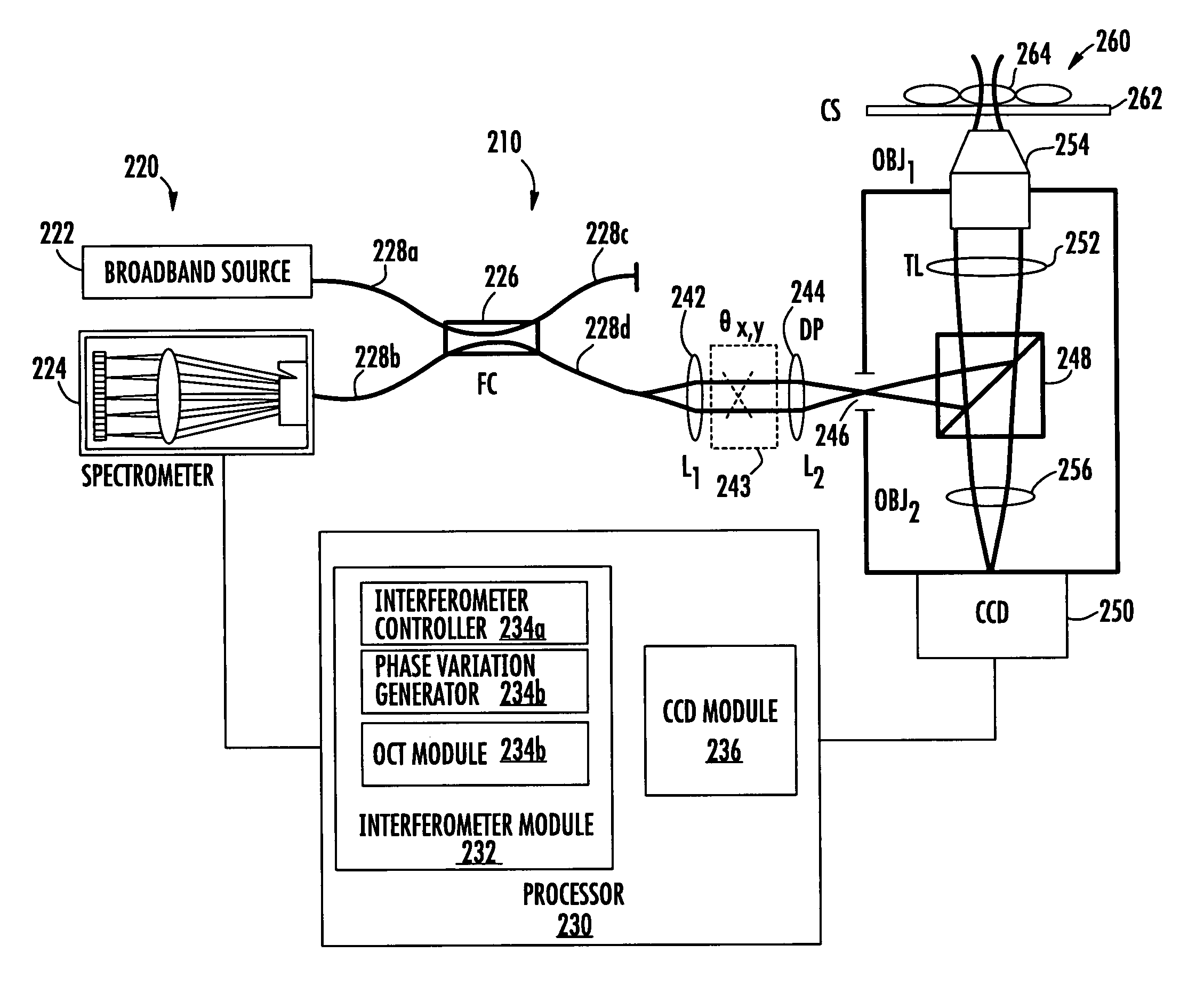
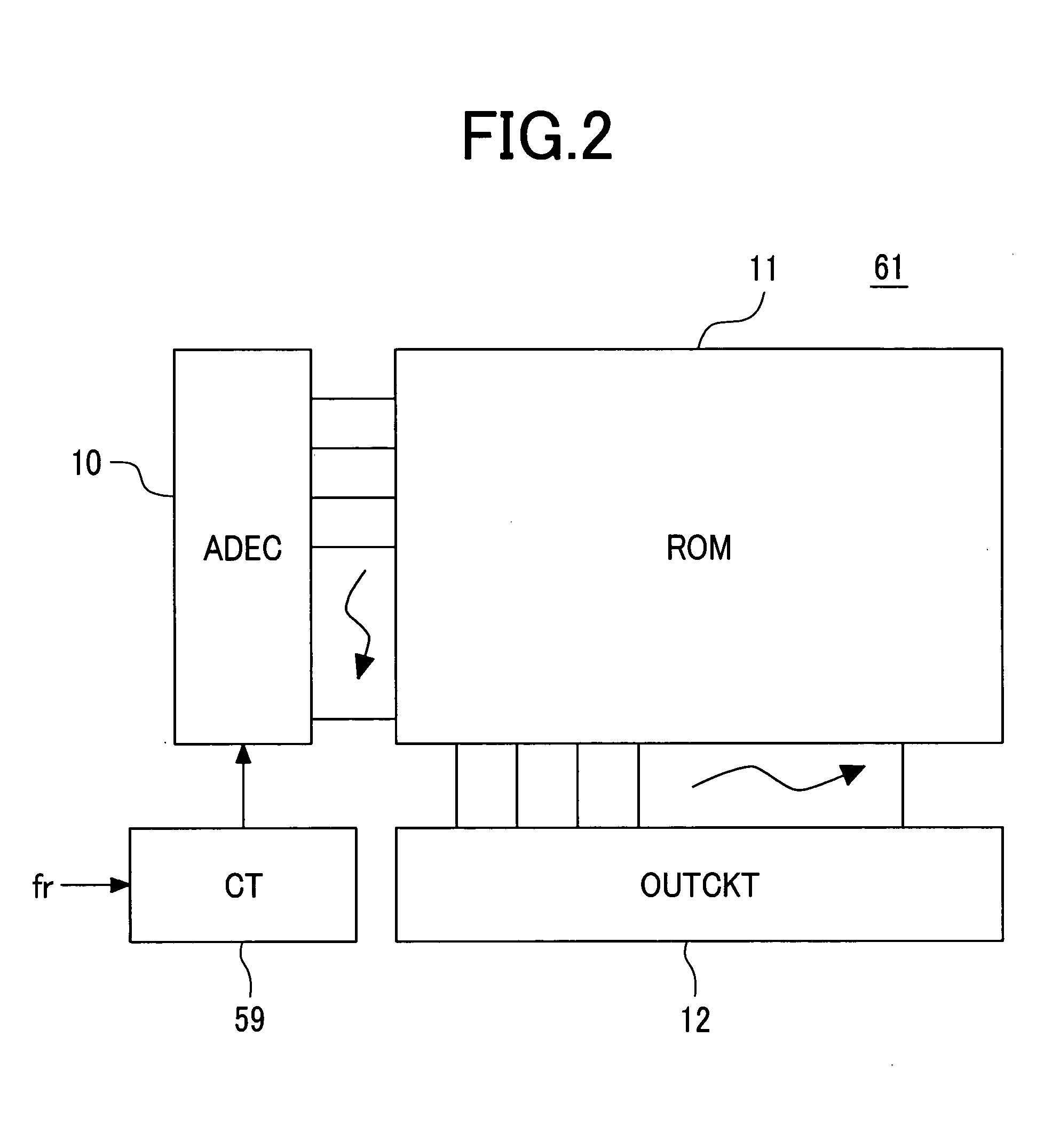
Methods, systems and computer program products for characterizing structures based on interferometric phase data
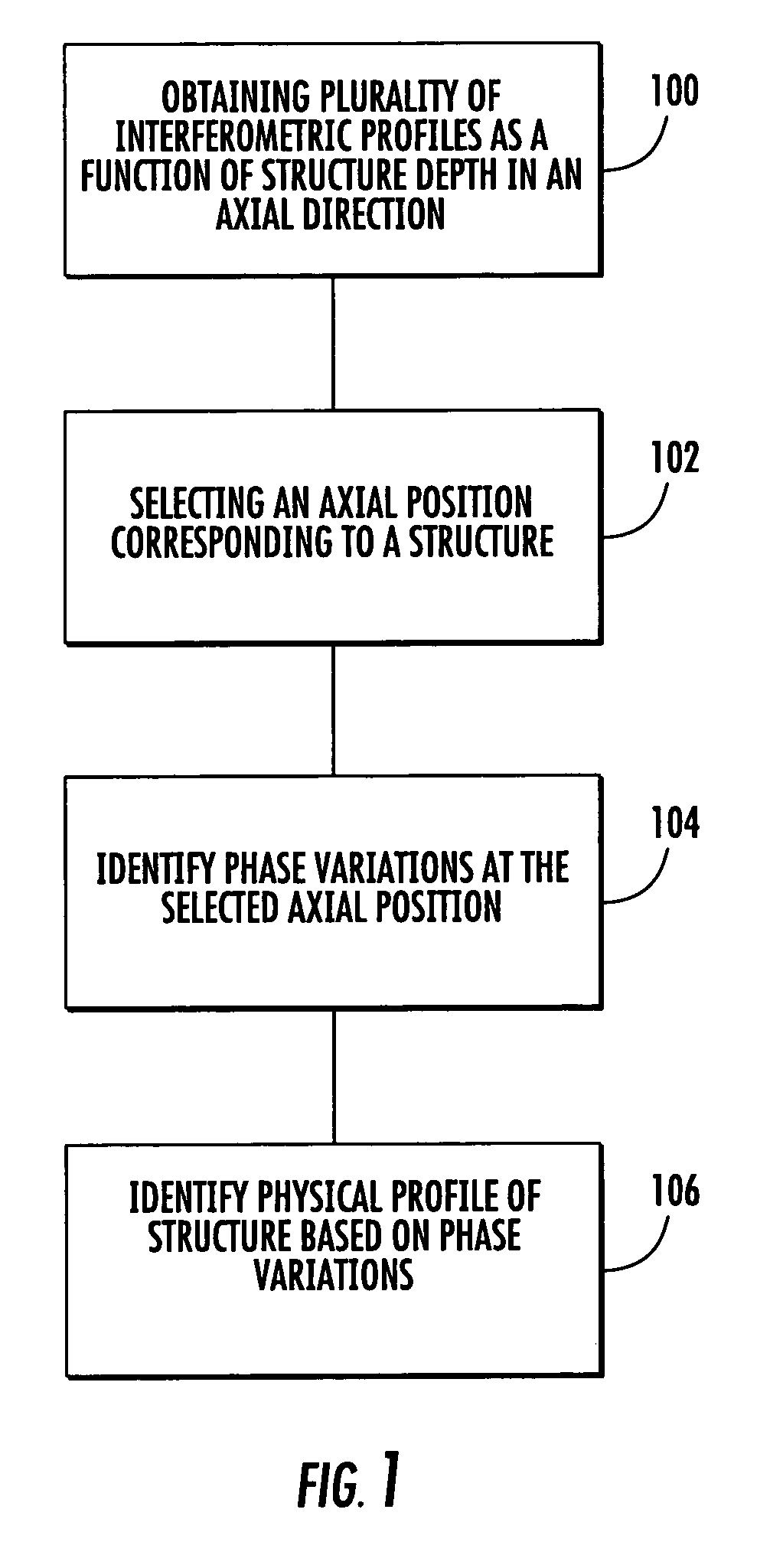
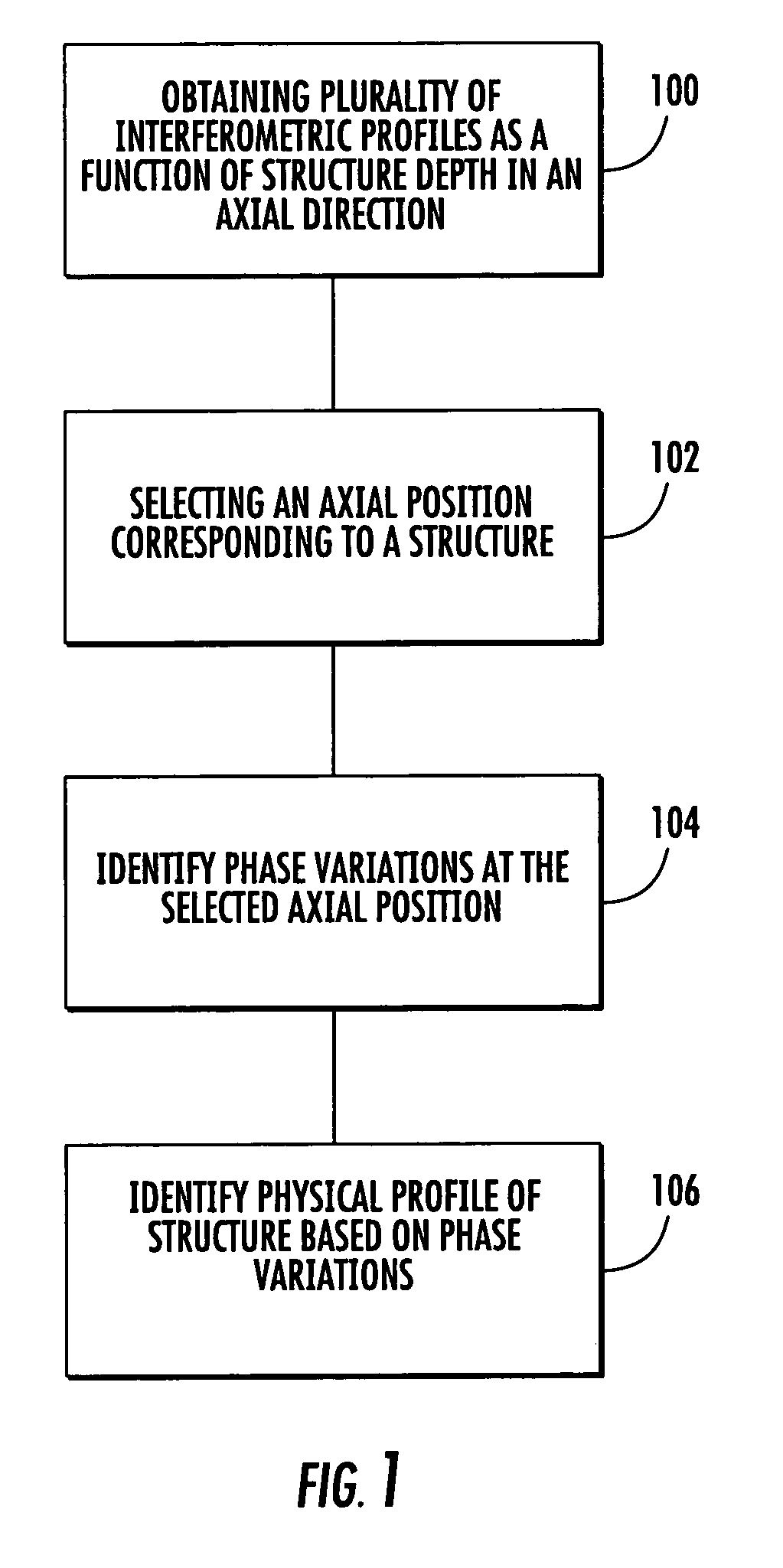
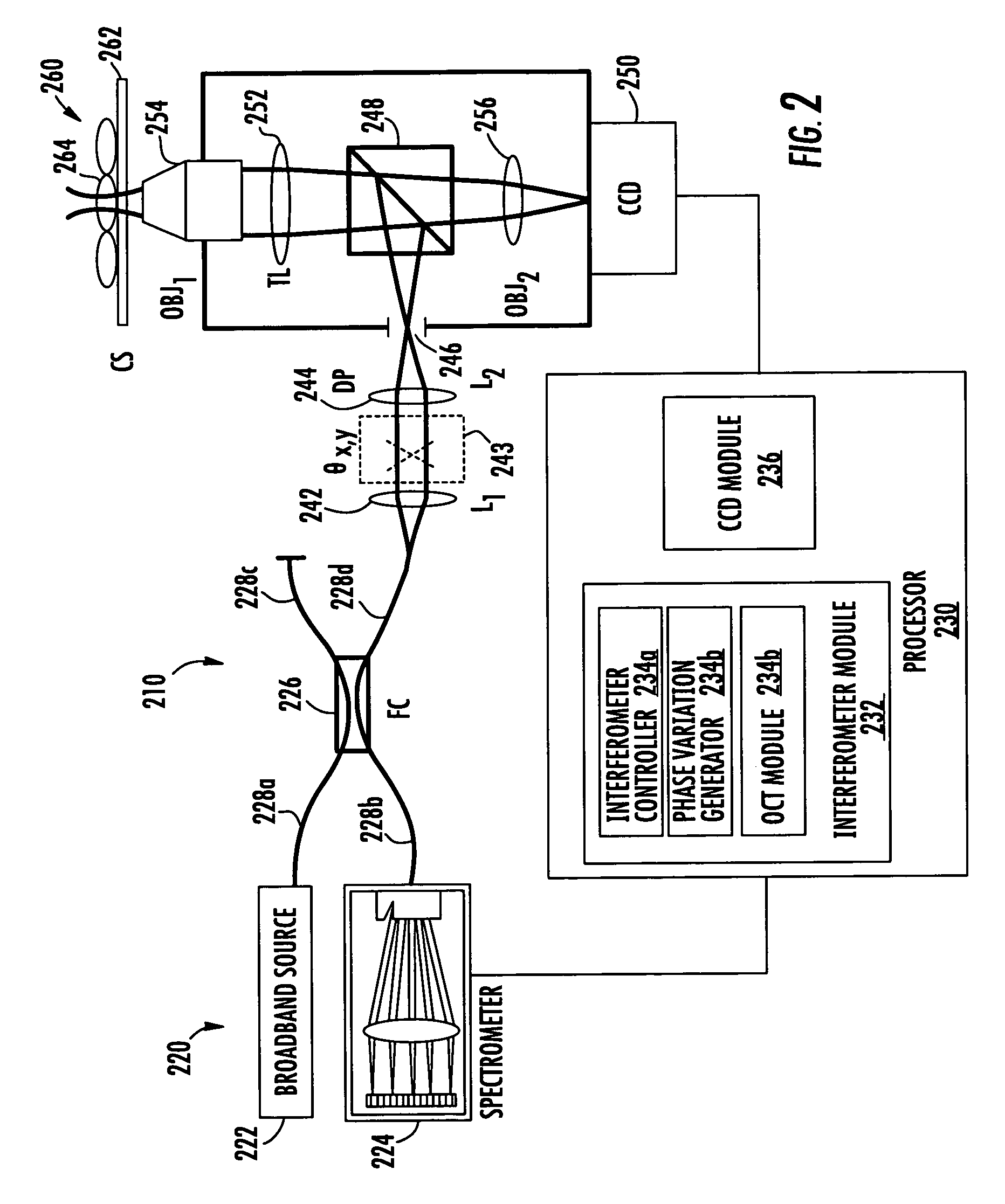
Structure profiles from optical interferometric data can be identified by obtaining a plurality of broadband interferometric optical profiles of a structure as a function of structure depth in an axial direction. Each of the plurality of interferometric optical profiles include a reference signal propagated through a reference path and a sample signal reflected from a sample reflector in the axial direction. An axial position corresponding to at least a portion of the structure is selected. Phase variations of the plurality of interferometric optical profiles are determined at the selected axial position. A physical displacement of the structure is identified based on the phase variations at the selected axial position.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
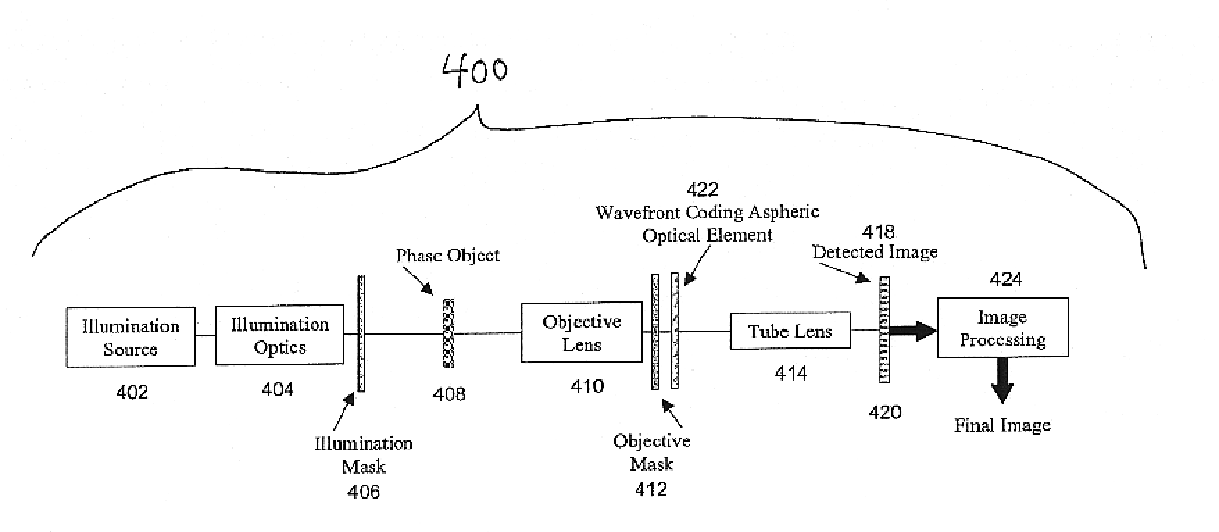
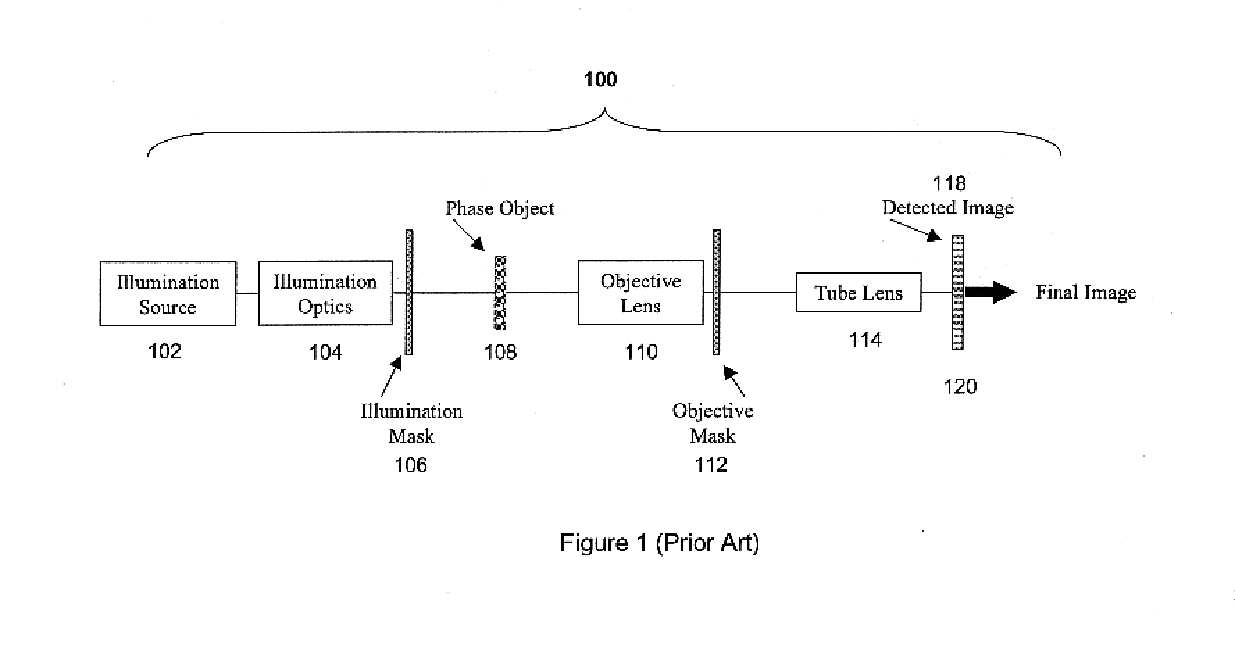
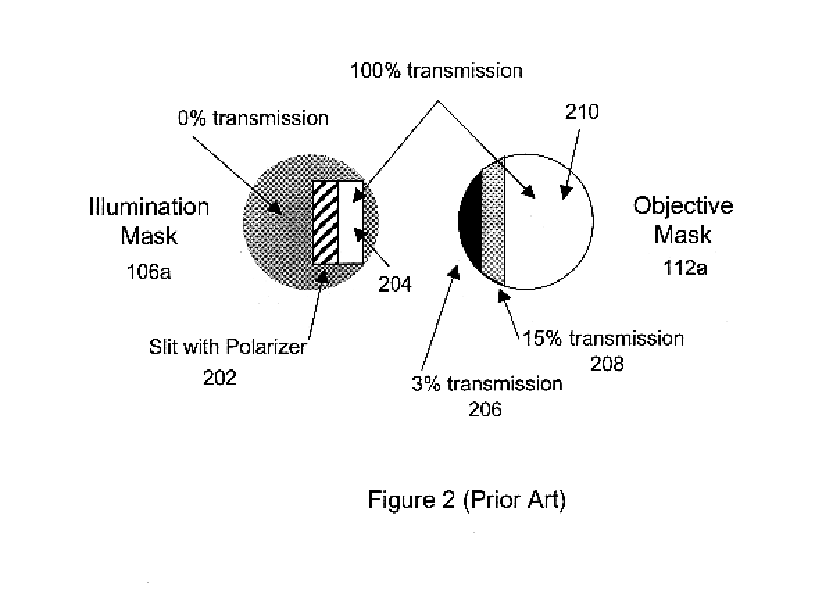
Combined wavefront coding and amplitude contrast imaging systems
InactiveUS6873733B2Enhanced contrast imageAdd depthMaterial analysis by optical meansCharacter and pattern recognitionPhase variationSignal transfer function
The present invention provides extended depth of field or focus to conventional Amplitude Contrast imaging systems. This is accomplished by including a Wavefront Coding mask in the system to apply phase variations to the wavefront transmitted by the Phase Object being imaged. The phase variations induced by the Wavefront Coding mask code the wavefront and cause the optical transfer function to remain essentially constant within some range away from the in-focus position. This provides a coded image at the detector. Post processing decodes this coded image, resulting in an in-focus image over an increased depth of field.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF +1
Multi-color hetereodyne interferometric apparatus and method for sizing nanoparticles
A nanoparticle sensor is capable of detecting and recognizing single nanoparticles in an aqueous environment. Such sensor may find applications in broad areas of science and technology, from the analysis of diesel engine emissions to the detection of biological warfare agents. Particle detection is based on interferometric detection of multi-color light, scattered by the particle. On the fundamental level, the detected signal has a weaker dependence on particle size (ÿ R3), compared to standard detection methods (ÿ R6). This leads to a significantly larger signal-to-noise ratio for smaller particles. By using a multi-color or white excitation light, particle dielectric properties are probed at different frequencies. This scheme samples the frequency dependence of the particle's polarizability thereby making it possible to predict the composition of the particle material. The detection scheme also employs a heterodyne or pseudoheterodyne detection configuration, which allows it to reduce or eliminate noise contribution from phase variations, which appear in any interferometric measurements.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
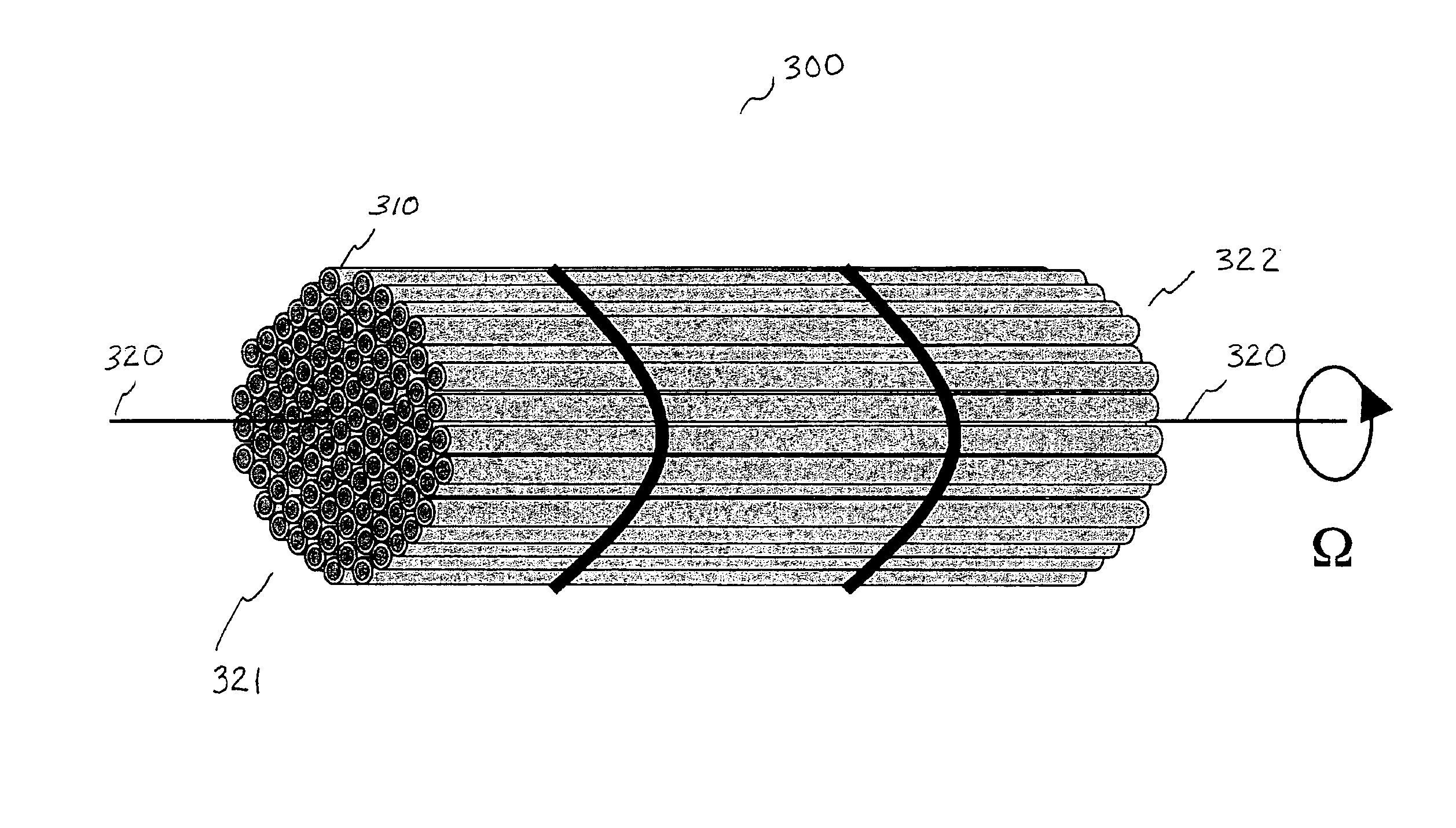
Apparatus for beam homogenization and speckle reduction
InactiveUS6895149B1Quality improvementWash out unwanted variationMaterial analysis by optical meansUsing optical meansPhase variationFiber bundle
This invention greatly improves the quality of images obtained using optical systems illuminated by coherent light. It does so by removing the undesirable psuedo-random variations in the final image due to interference speckle and inhomogeneities in the spatial intensity distribution of the light source. A bundle of light-guiding fibers is interposed between the illumination source and the imaging system. Non-uniform propagation within the fiber bundle creates a psuedo-random phase variation across the illumination beam, which gives rise to a dynamic interference speckle pattern superimposed upon the desired image acquired by the optical system. Rotating the fiber bundle around the axis of propagation, whilst simultaneously integrating the output of the photosensitive detector over a period of time, substantially removes variations due to source inhomogeneities and coherent interference.
Owner:JACOB JAMES JEFFERY +2
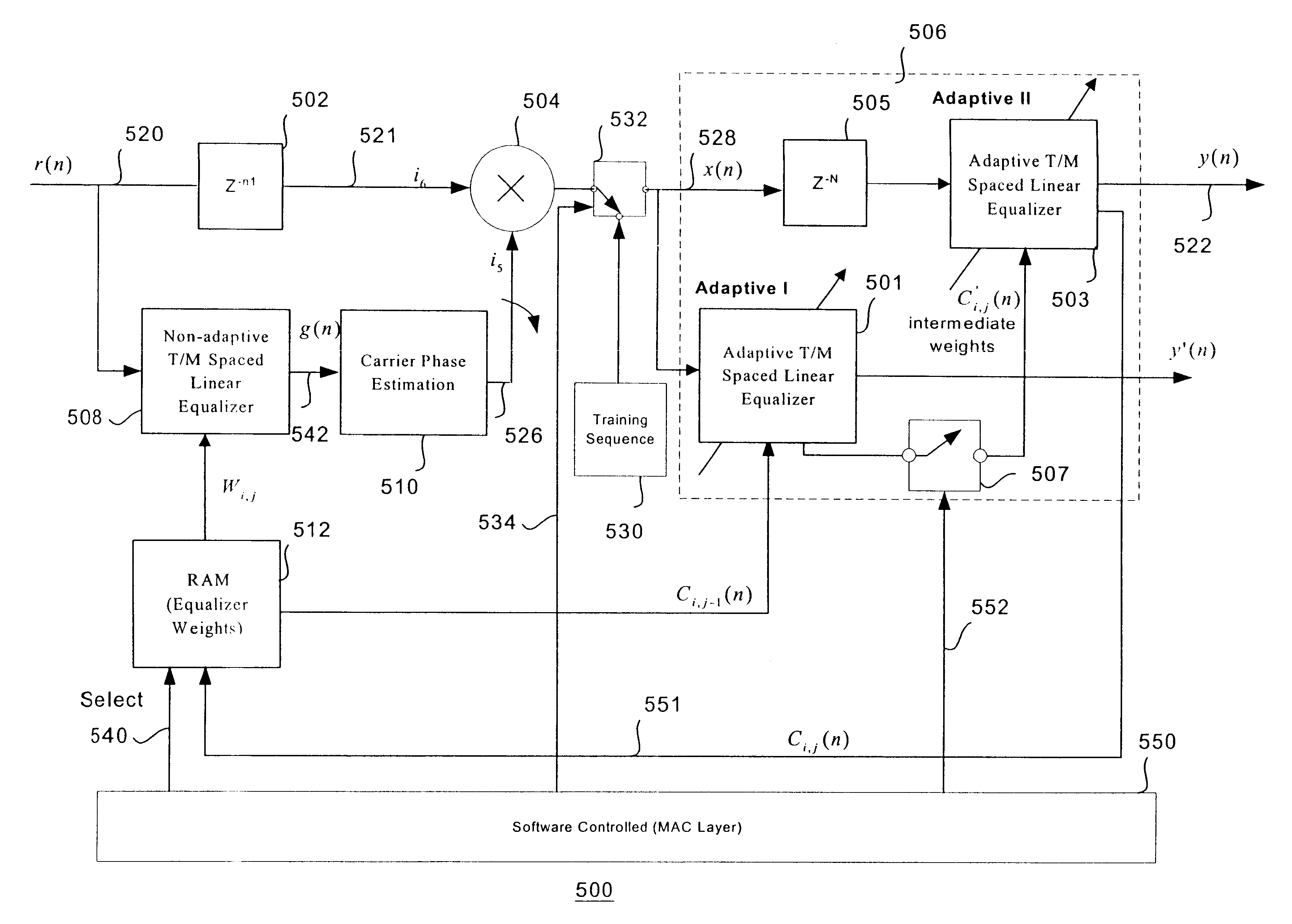
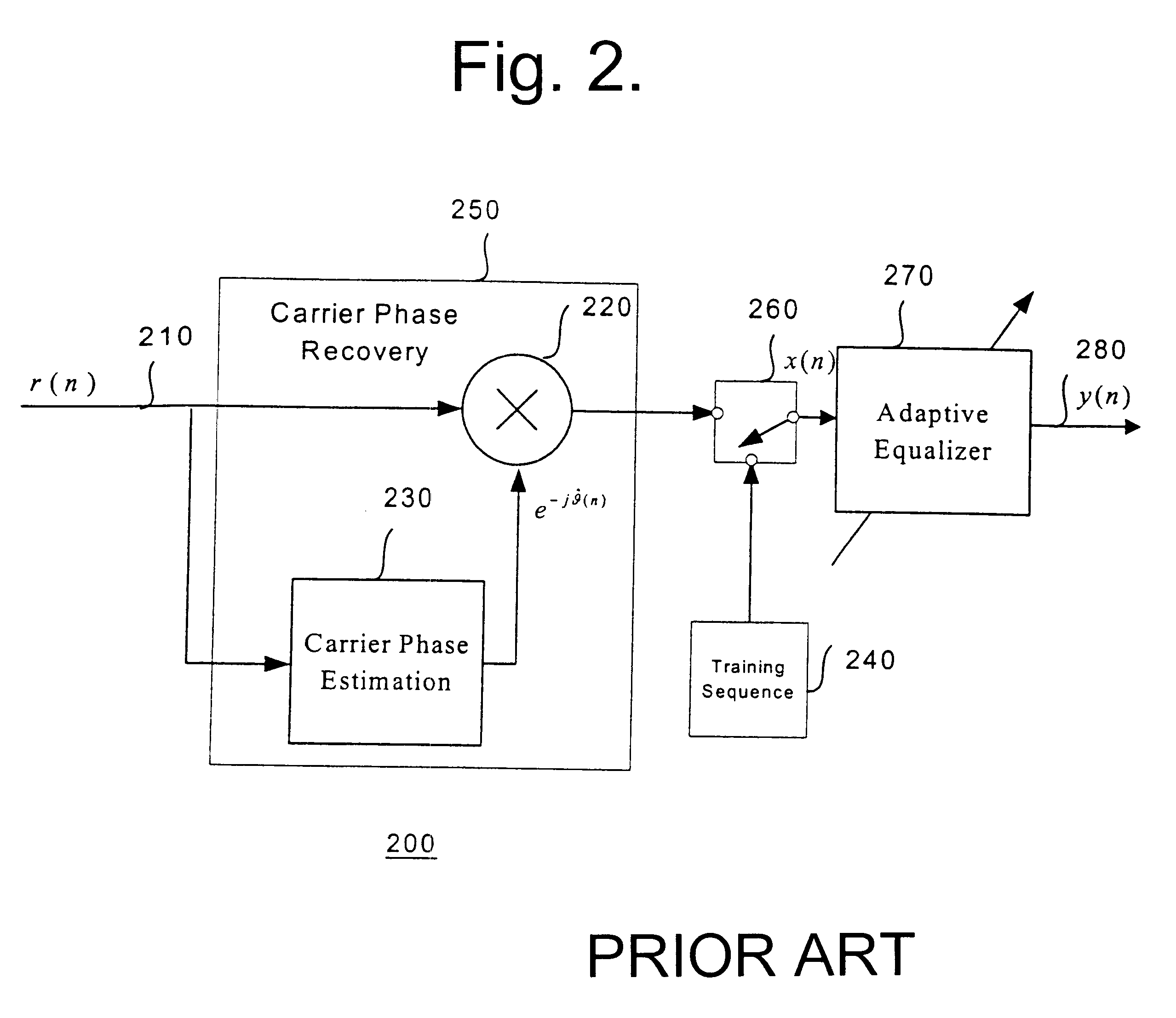
Adaptive equalizer system for short burst modems and link hopping radio networks
InactiveUS6628707B2Multiple-port networksTransmission control/equlisationPhase variationModem device
A method for an adaptive equalization apparatus in a multiple-link hopping radio system includes hopping among a plurality of radio links to receive variable-length bursts of radio signals on the plurality of radio links and equalizing amplitude and phase variations of a slow channel for each radio link from a received burst on the radio link. Further, the method includes storing the estimated tap coefficients pertinent to each radio link and using the tap weights of the current burst of the radio link to reliably pre-compensate the channel amplitude and phase distortion of a next received burst on the radio link.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Methods, systems and computer program products for characterizing structures based on interferometric phase data
ActiveUS20060256343A1Diagnostics using lightDiagnostics using tomographyPhase variationComputational physics
Structure profiles from optical interferometric data can be identified by obtaining a plurality of broadband interferometric optical profiles of a structure as a function of structure depth in an axial direction. Each of the plurality of interferometric optical profiles include a reference signal propagated through a reference path and a sample signal reflected from a sample reflector in the axial direction. An axial position corresponding to at least a portion of the structure is selected. Phase variations of the plurality of interferometric optical profiles are determined at the selected axial position. A physical displacement of the structure is identified based on the phase variations at the selected axial position.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
Spectrally tailored pulsed fiber laser oscillator
ActiveUS20100128744A1Laser using scattering effectsOptical devices for laserPhase variationOptical property
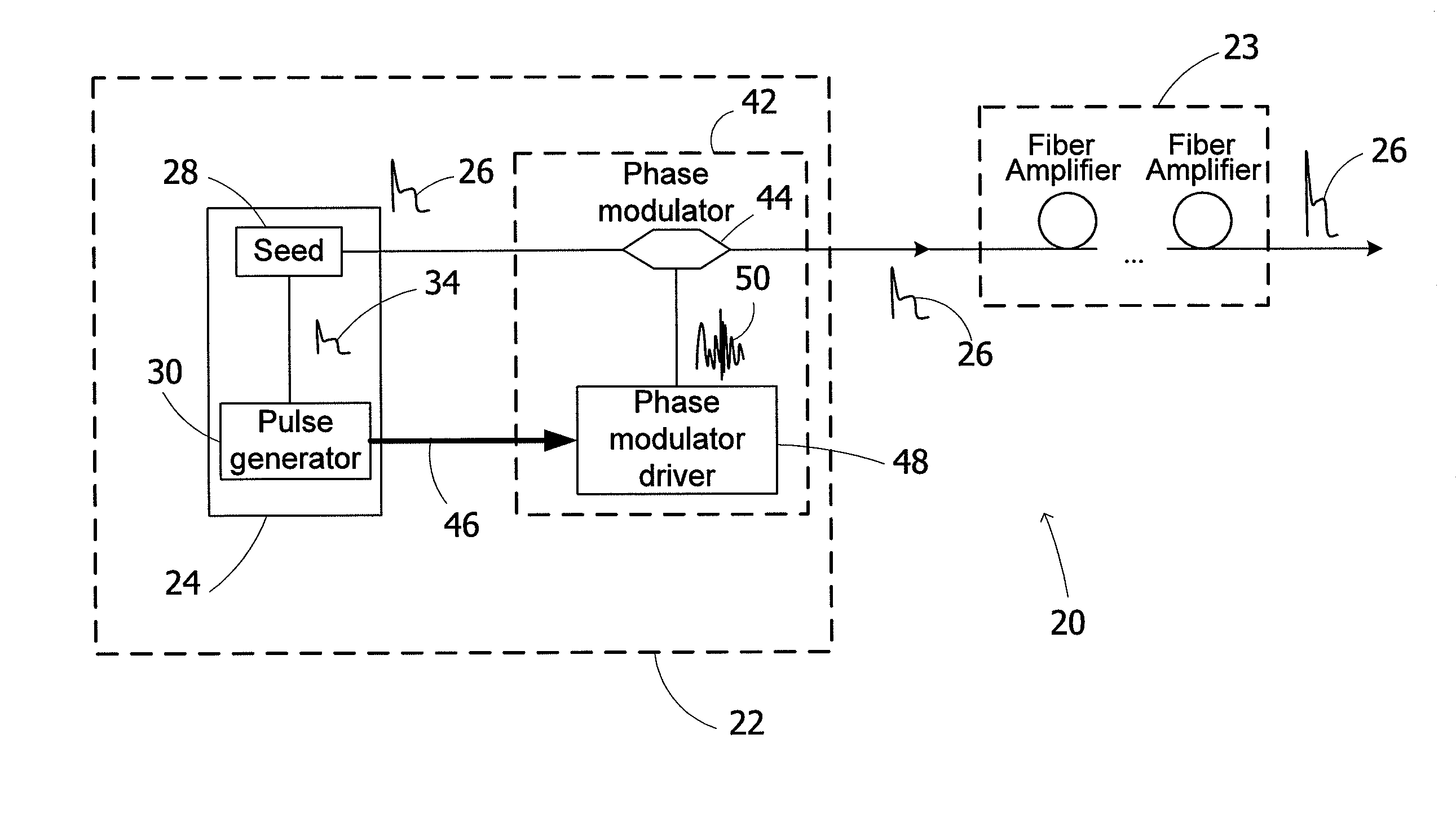
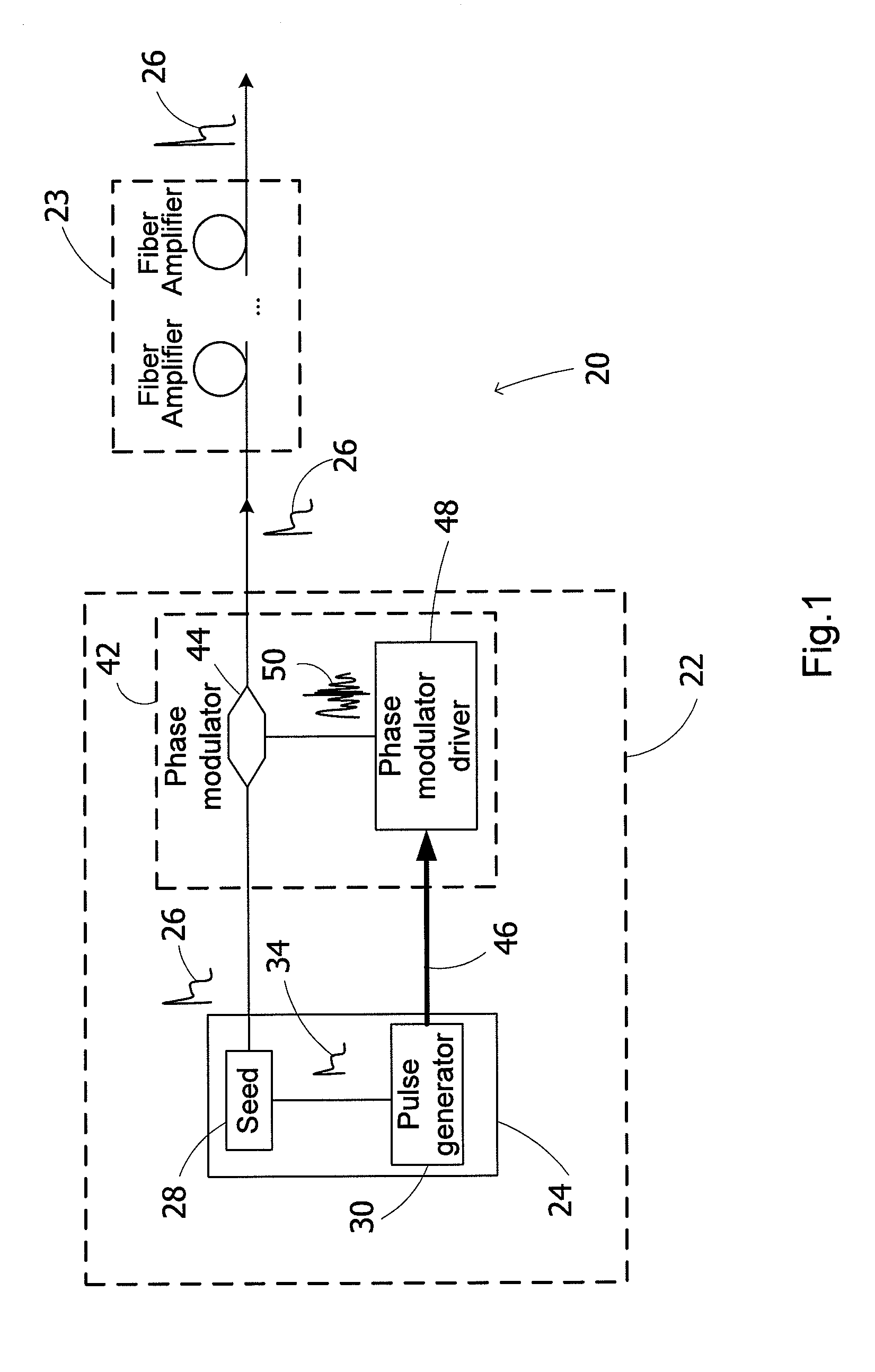
High power optical pulses generating methods and laser oscillators are provided. A light generating module generates seed optical pulses having predetermined optical characteristics. A spectrum tailoring module is then used to tailor the spectral profile of the optical pulses. The spectral tailoring module includes a phase modulator which imposes a time-dependent phase variation on the optical pulses. The activation of the phase modulator is synchronized with the passage of the optical pulse therethough, thereby efficiently reducing the RF power necessary to operate the device.
Owner:INSTITUT NATIONAL D'OPTIQUE
Adaptive equalizer system for short burst modems and link hopping radio networks
InactiveUS20020196844A1Multiple-port networksTransmission control/equlisationPhase variationModem device
A method for an adaptive equalization apparatus in a multiple-link hopping radio system includes hopping among a plurality of radio links to receive variable-length bursts of radio signals on the plurality of radio links and equalizing amplitude and phase variations of a slow channel for each radio link from a received burst on the radio link. Further, the method includes storing the estimated tap coefficients pertinent to each radio link and using the tap weights of the current burst of the radio link to reliably pre-compensate the channel amplitude and phase distortion of a next received burst on the radio link.
Owner:INTEL CORP
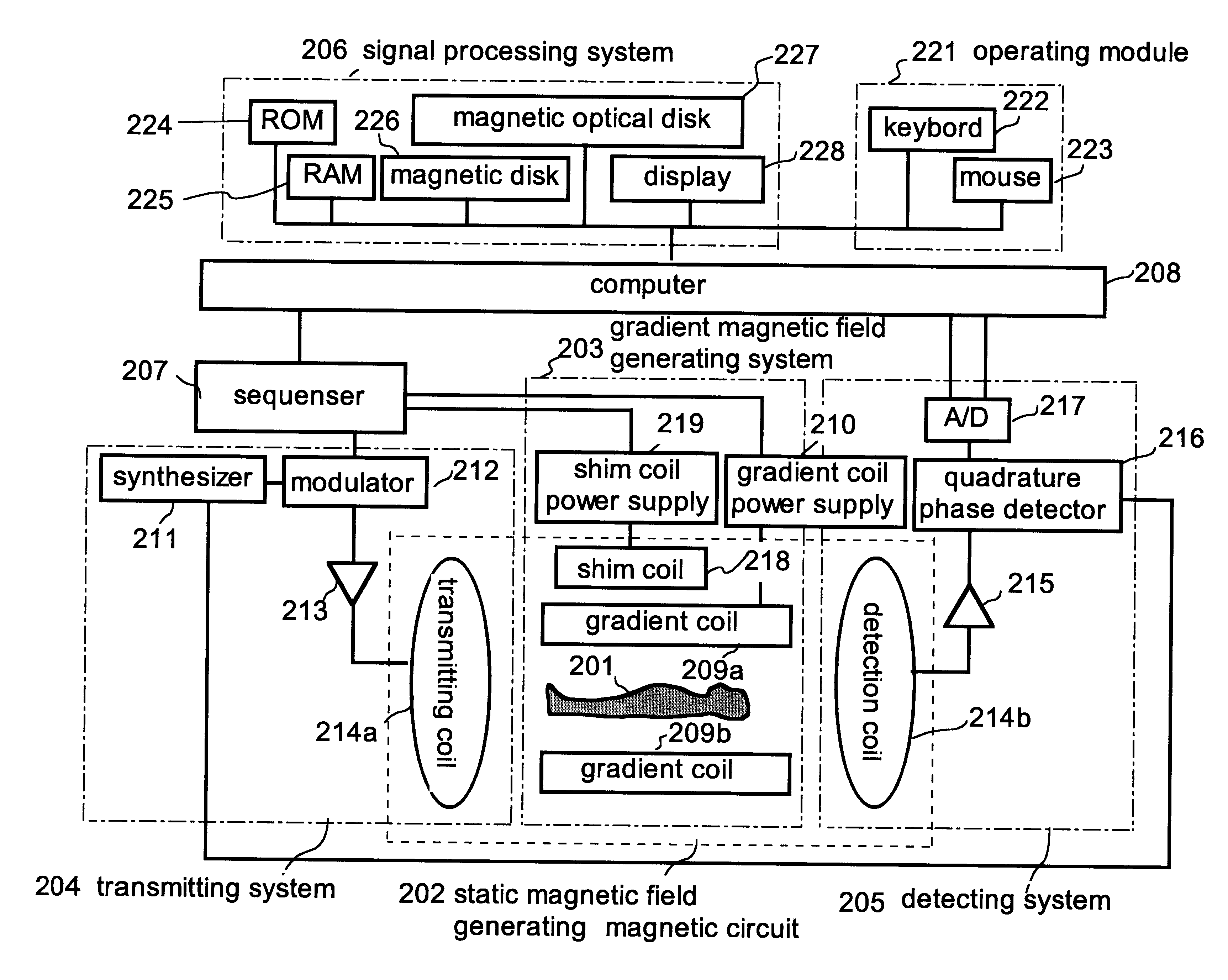
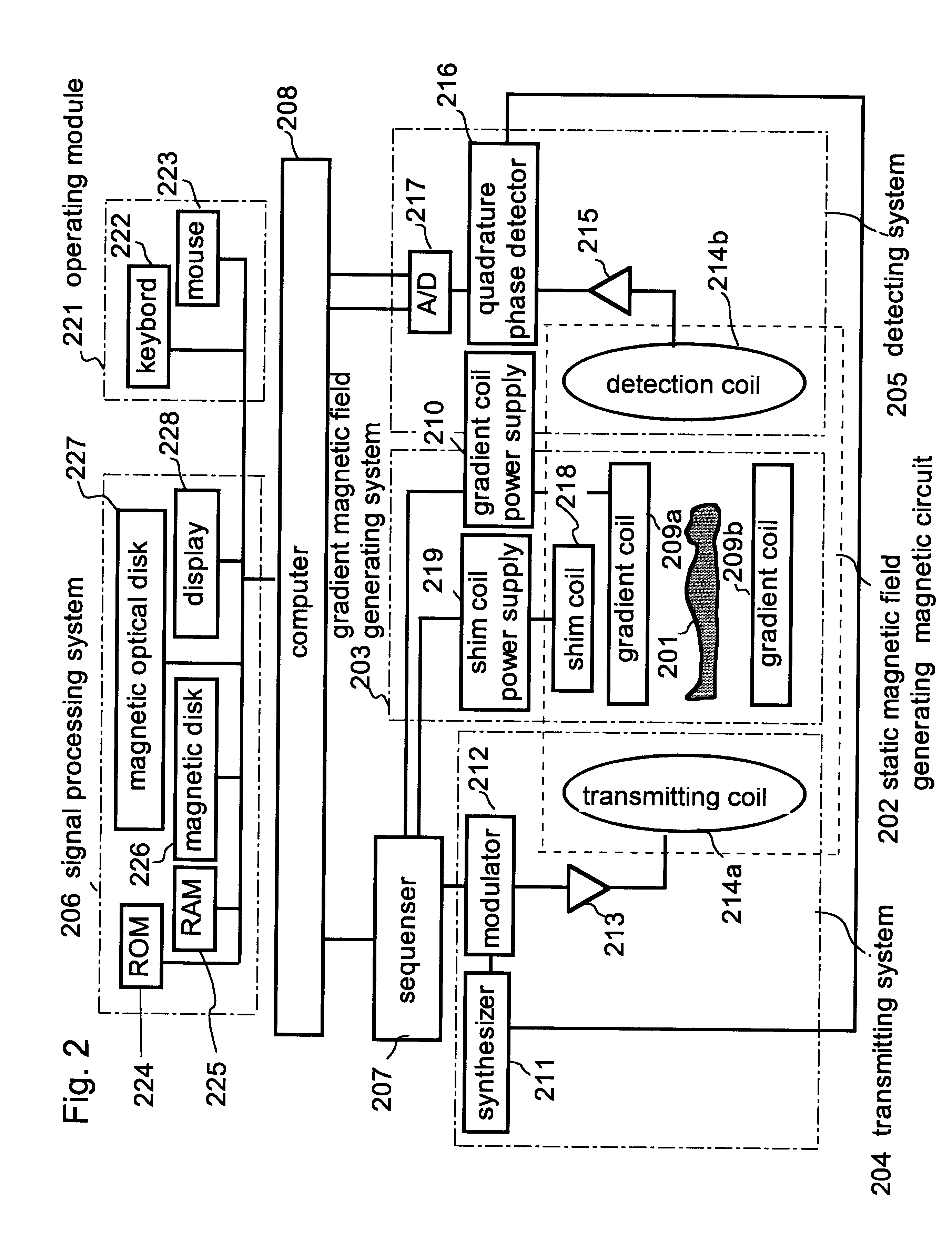
Magnetic resonance imaging device and method therefor
InactiveUS6566878B1High accurate imageDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsPhase variationCondensed matter physics
Variations in spatial phase distribution due to static magnetic field changes are corrected based on phase variations at points, specifically, at three points or a plurality of points selected by ROI, in an area where no temperature change is encountered. And a temperature distribution image is determined by using a spatial phase distribution reflecting only temperature changes after the correction, thereby high-accuracy temperature distribution image information is provided.
Owner:HITACHI MEDICAL CORP
Natural fiber span reflectometer providing a virtual phase signal sensing array capability
ActiveUS20060028636A1Low costMaterial analysis by optical meansBurglar alarmRayleigh scatteringFrequency spectrum
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
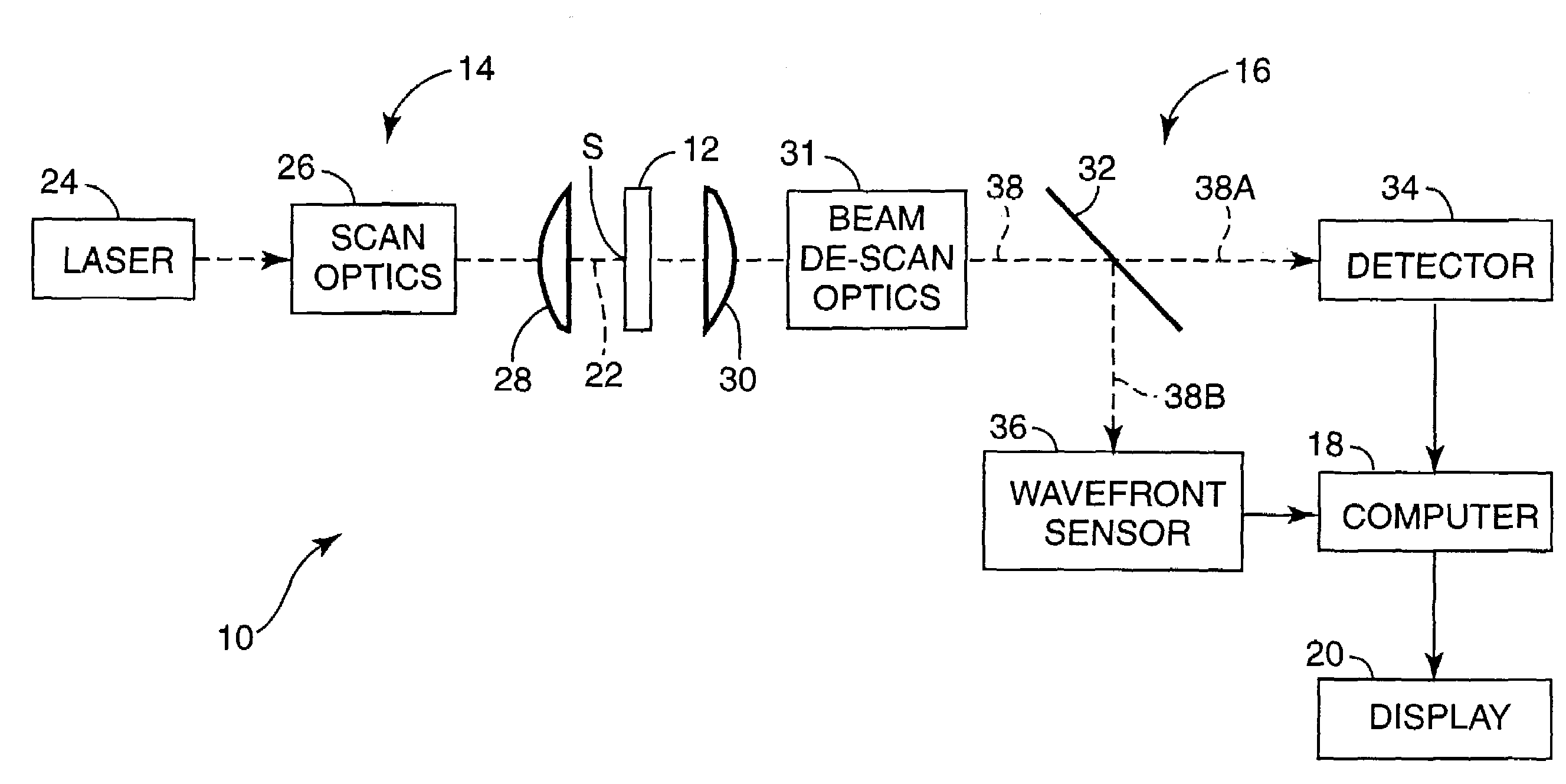
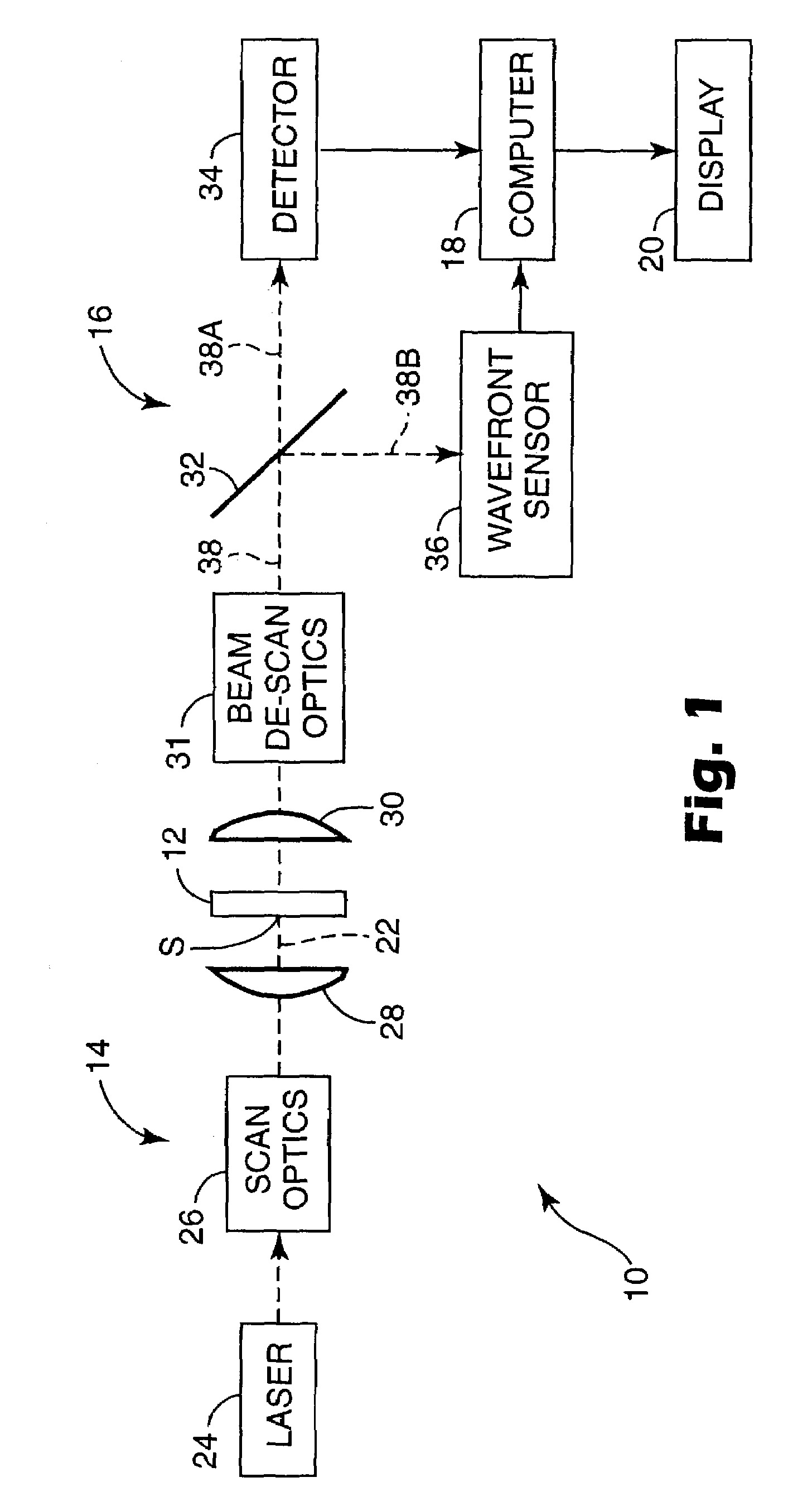
Scanning laser microscope with wavefront sensor
InactiveUS7057806B2High resolutionEnhanced resolution imagePhotometry using reference valueMaterial analysis by optical meansFrequency spectrumWavefront sensor
An enhanced resolution scanned image of an object is produced by a scanning laser microscope which includes an illumination arm for scanning an object with a focused probe beam and a detection arm for receiving light from the object. The detection arm includes a detector which collects and detects light from the object to produce pixel data for a plurality of pixels. In addition, the detection arm includes a wavefront sensor for sensing phase variations of the light from the object to produce wavefront data for scanned pixel locations. From the wavefront shape of the collected light at each pixel location, a high frequency spectrum is determined which corresponds to uncollected scattered light from small scale features of that pixel location. An enhanced resolution image of a region of interest is produced based on the high frequency spectra of the scanned pixel locations.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Hybrid inertial navigation system with improved integrity
InactiveUS6982669B2Efficient measurementPrecise positioningNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsPosition fixationKaiman filterPhase variation
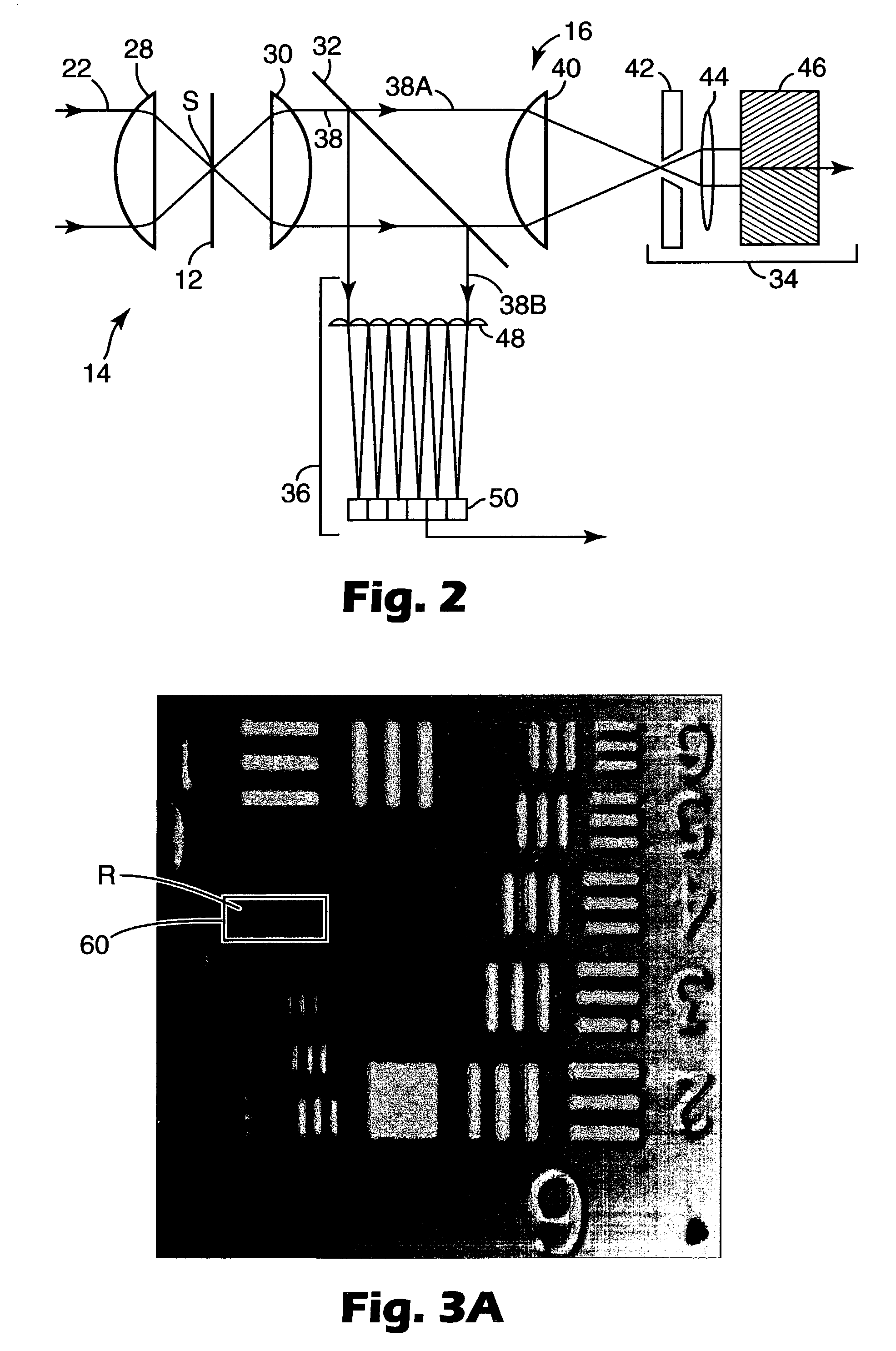
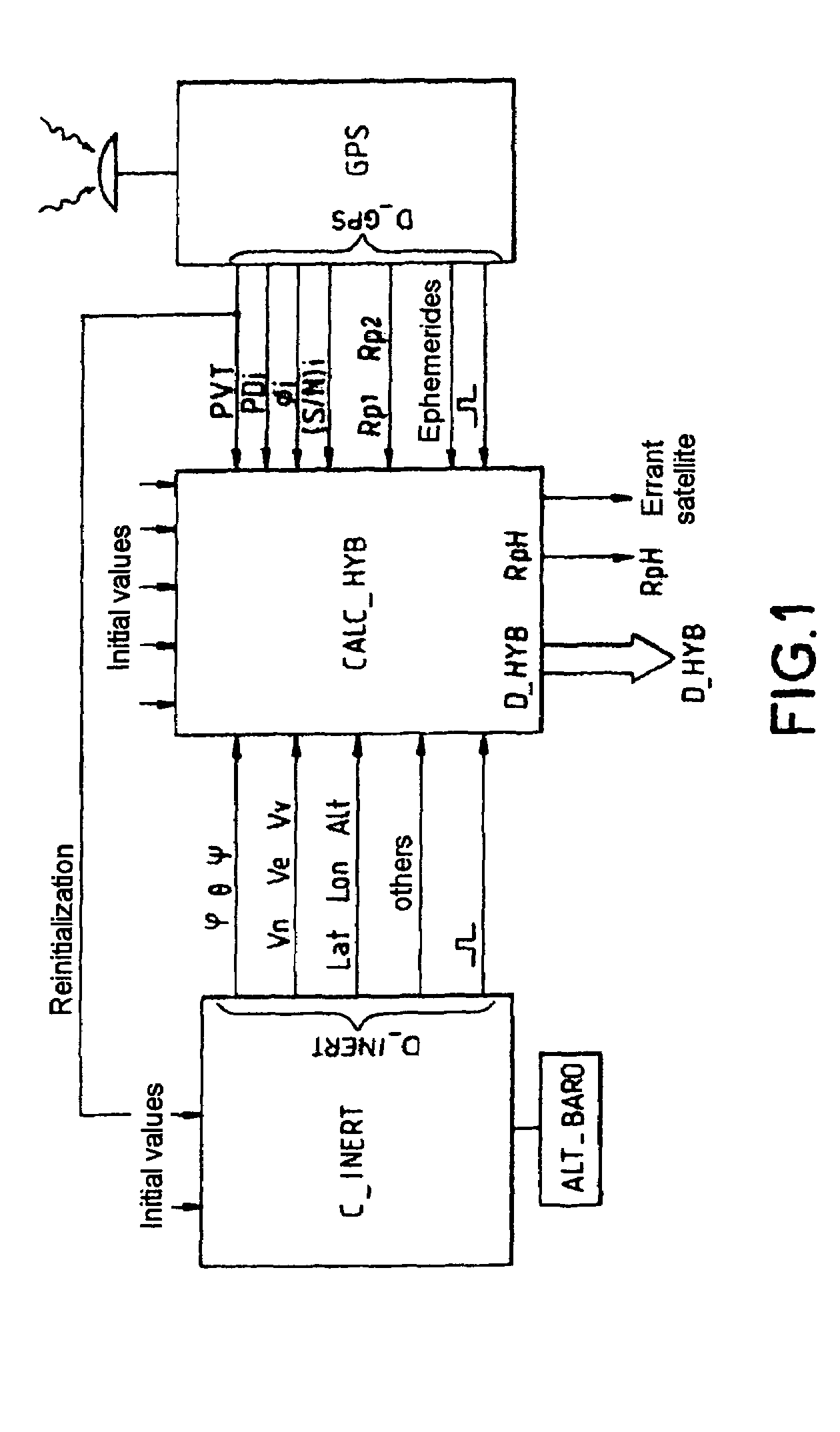
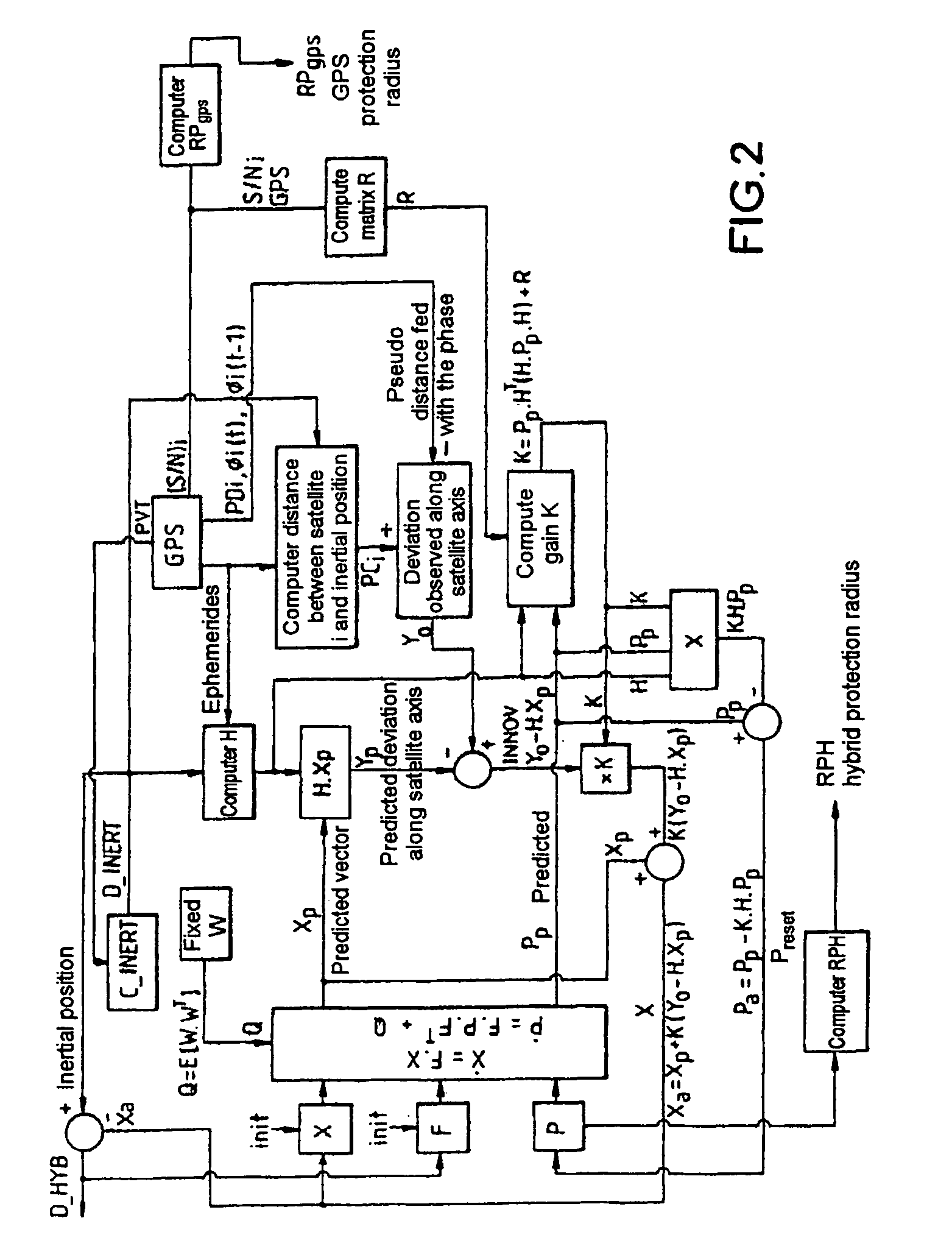
The invention relates to an internal platform hybridized with a GPS receiver. The hybridization is achieved through a Kalman filter through which a new hybrid position D-HYB is estimated on the basis of a noted deviation between pseudo-distance measure by the receiver between the receiver and the various satellites and corresponding distances computed by the inertial platform between the platform and the same satellites. In this filtering, the distance increment from one measurement instant to the next instant, between the pseudo-distance previously measured by the receiver on a satellite axis of a deviation and the new pseudo-distance measured by the receiver on a satellite axis of a deviation and the new pseudo-distance measured by the receiver on this axis, is the phase variation ΔΦ=Φ(t)−ΦI (t−1) of a digital oscillator between the two measurement instants, this variation being referred to distance along the satellite axis. The oscillator is that which makes it possible to slave the local carrier frequency in the receiver to the carrier frequency received from the satellite. Application to the measurement of position.
Owner:THALES SA
Extended depth of field optics for human vision
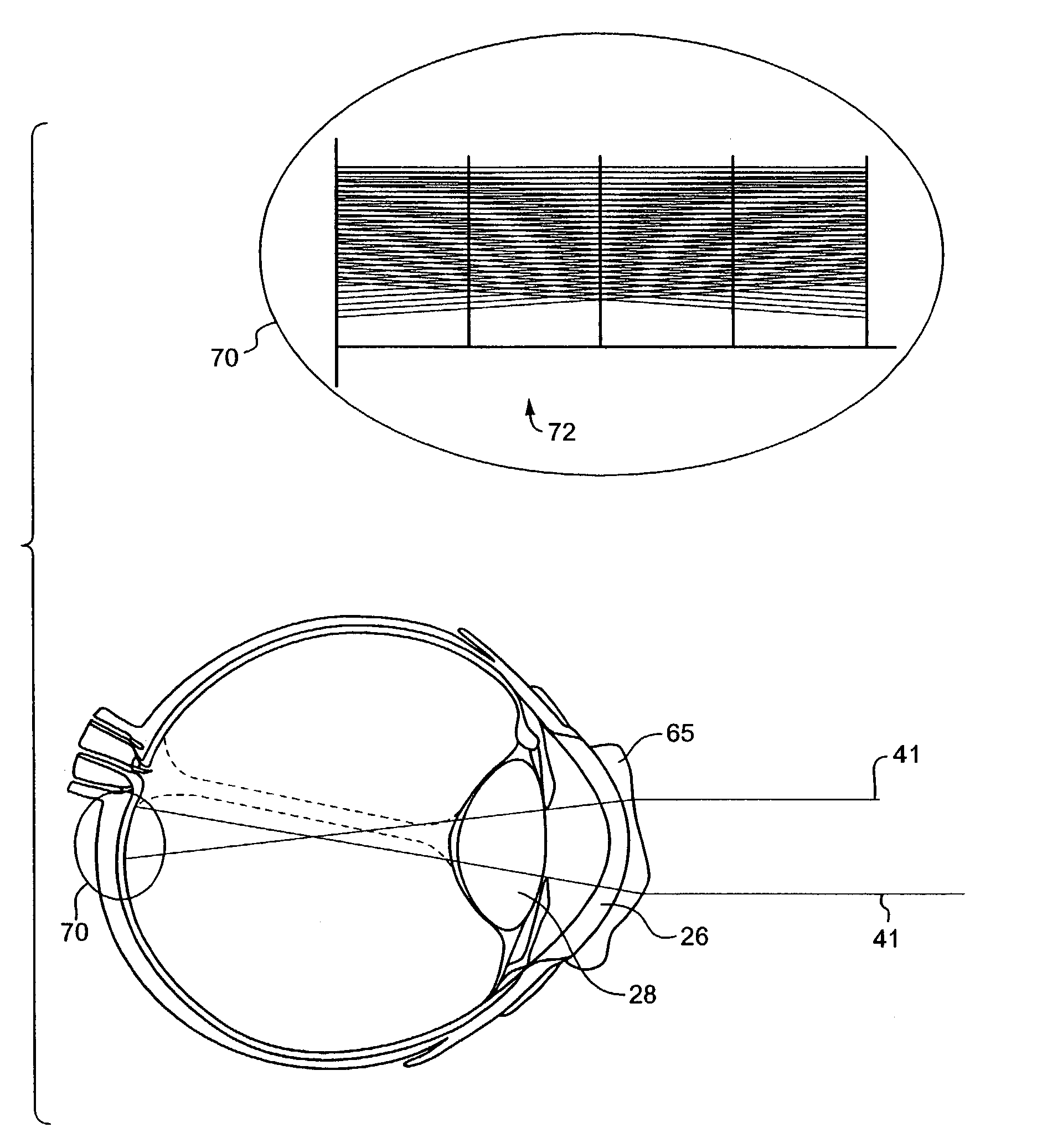
The present invention provides extended depth of field to human eyes by modifying contact lenses, intraocular implants, and / or the surface of the eye itself. This may be accomplished by applying selected phase variations to these optical elements (e.g., by varying surface thickness of the cornea of the eye). The phase variations EDF-code the wavefront and cause the optical transfer function to remain essentially constant within a range of distances from the in-focus position. This provides a coded image on the retina. The human brain decodes this coded image, resulting in an in-focus image over an increased depth of field.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
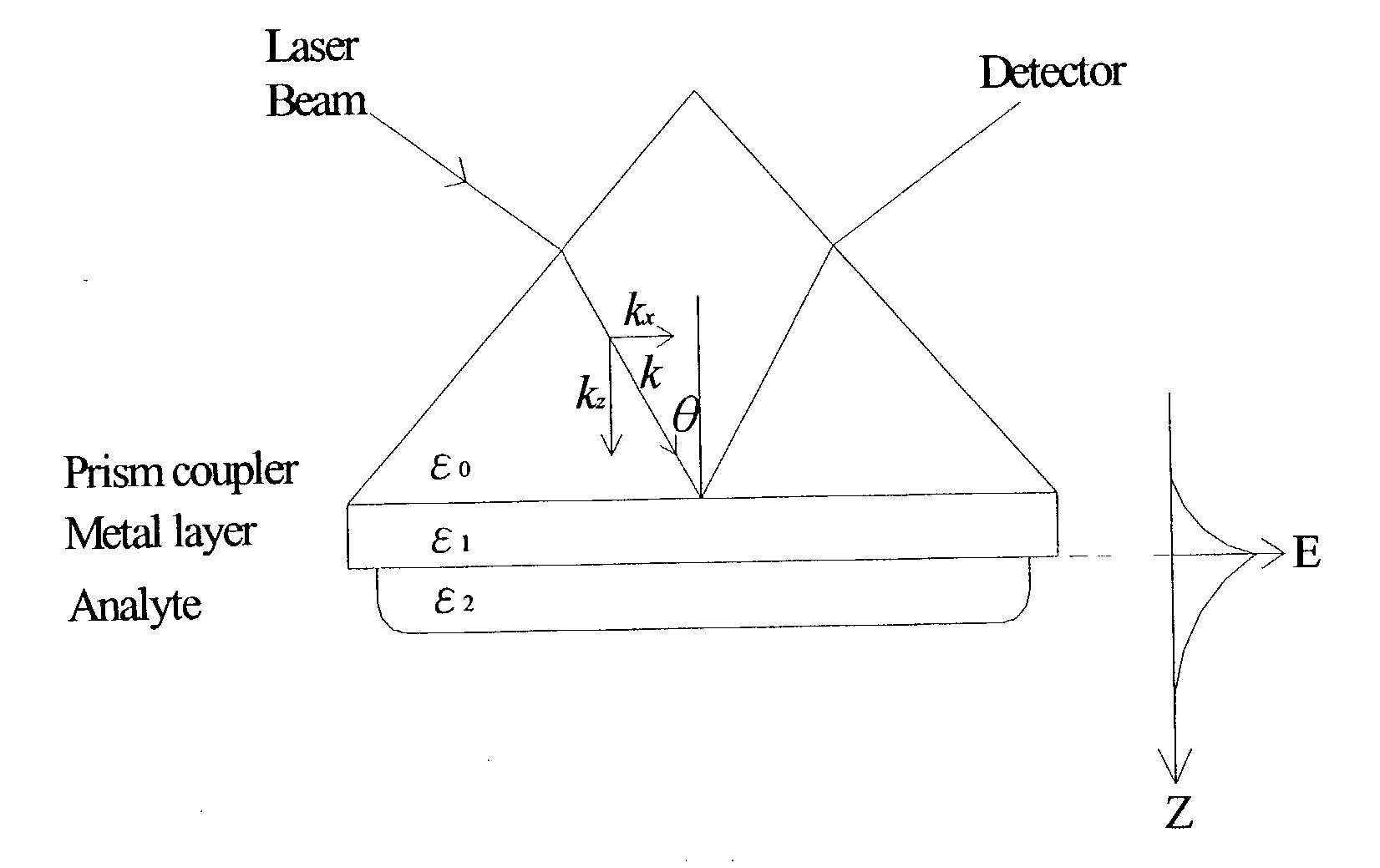
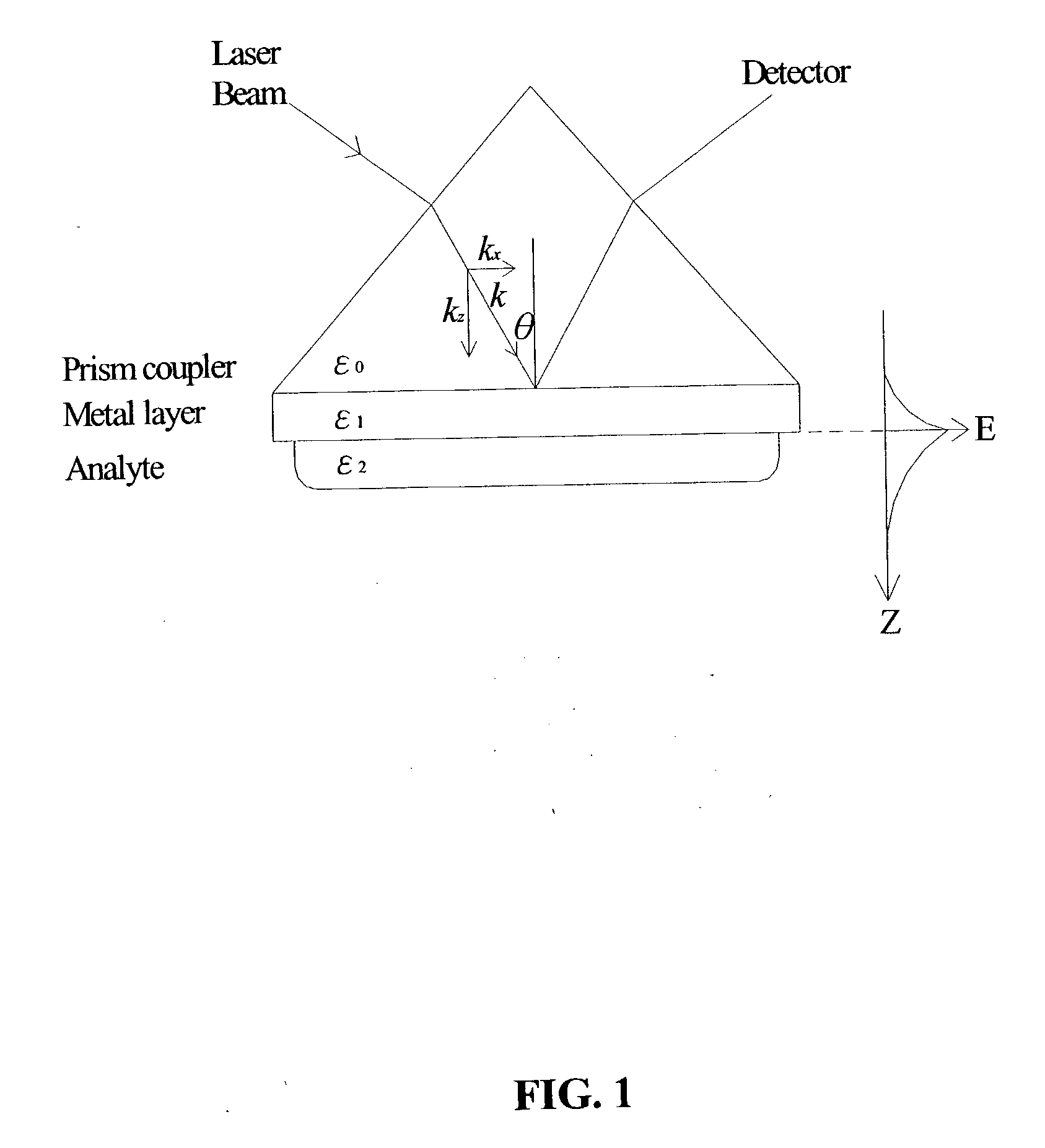
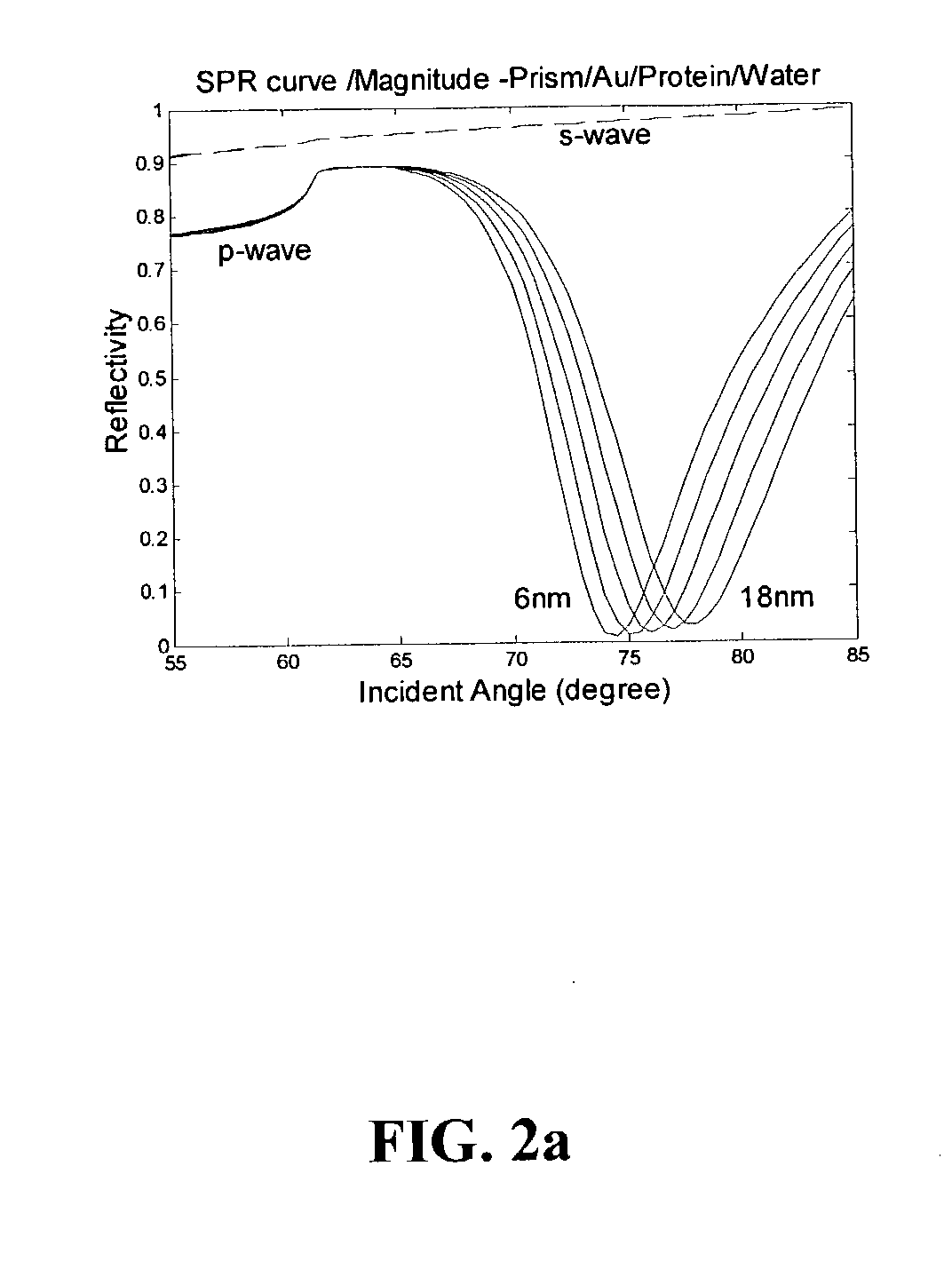
Surface plasmon resonance shifting interferometry imaging system for biomolecular interaction analysis
InactiveUS20030219809A1High resolutionHigh-throughput screening capabilityNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementReal time analysisHigh-Throughput Screening Methods
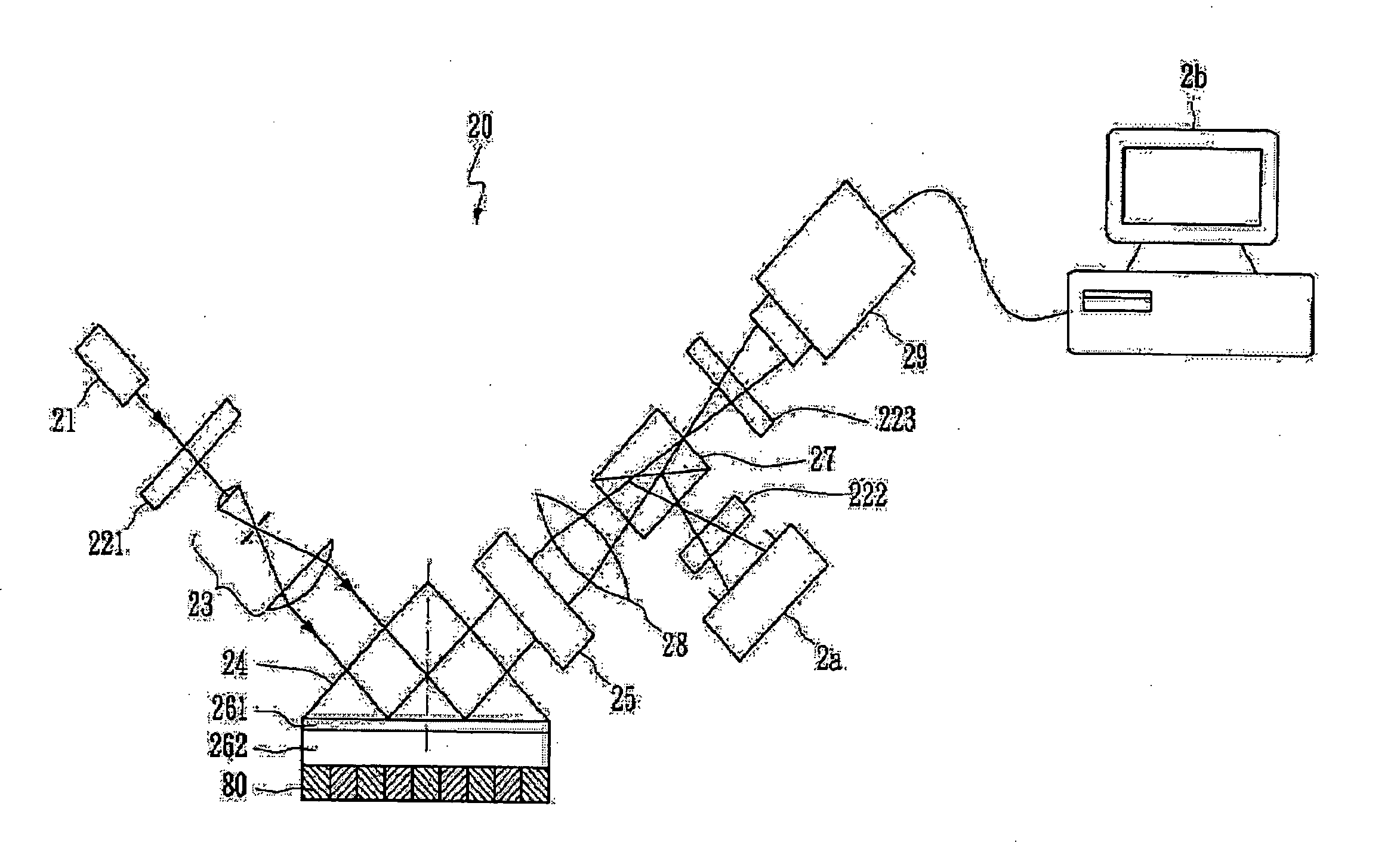
A novel surface plasmon resonance (SPR) imaging system based on modified Mach-Zehnder phase-shifting interferometry (PSI) measures the spatial phase variation of a resonantly reflected light during chemical or biological detection. The SPR microarray can diagnose the target analyte without additional labeling in the real-time analysis. Experimental results demonstrate that the detection limit of the SPR PSI imaging system is improved to about 1 pg / mm<2 >surface coverage of chemical or biological material for each individual spot over that of the conventional SPR imaging system. Therefore, the SPR PSI imaging system and its SPR microarray can provide the capability of real-time analysis, with high resolution and at high-throughput screening rates.
Owner:U VISION BIOTECH
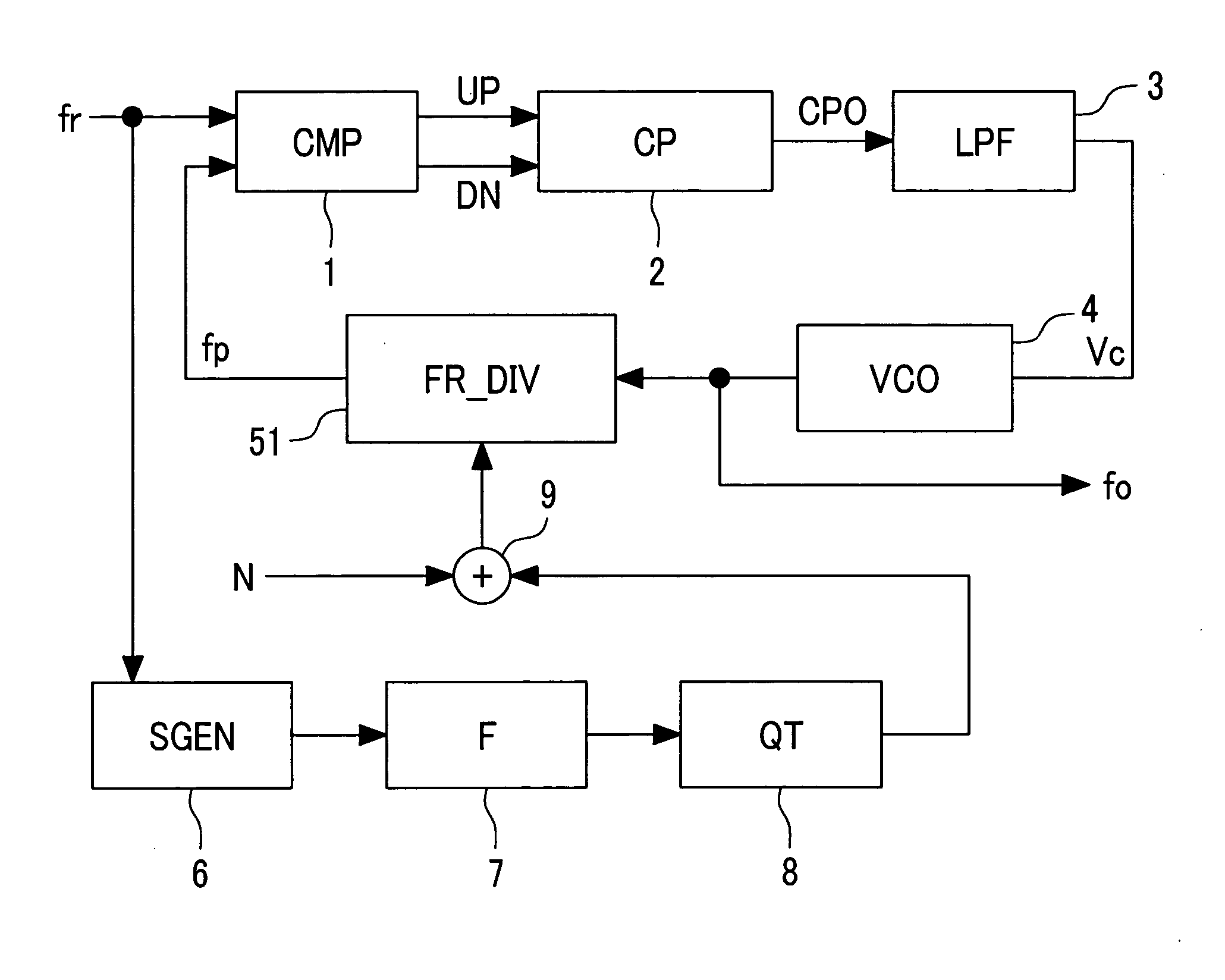
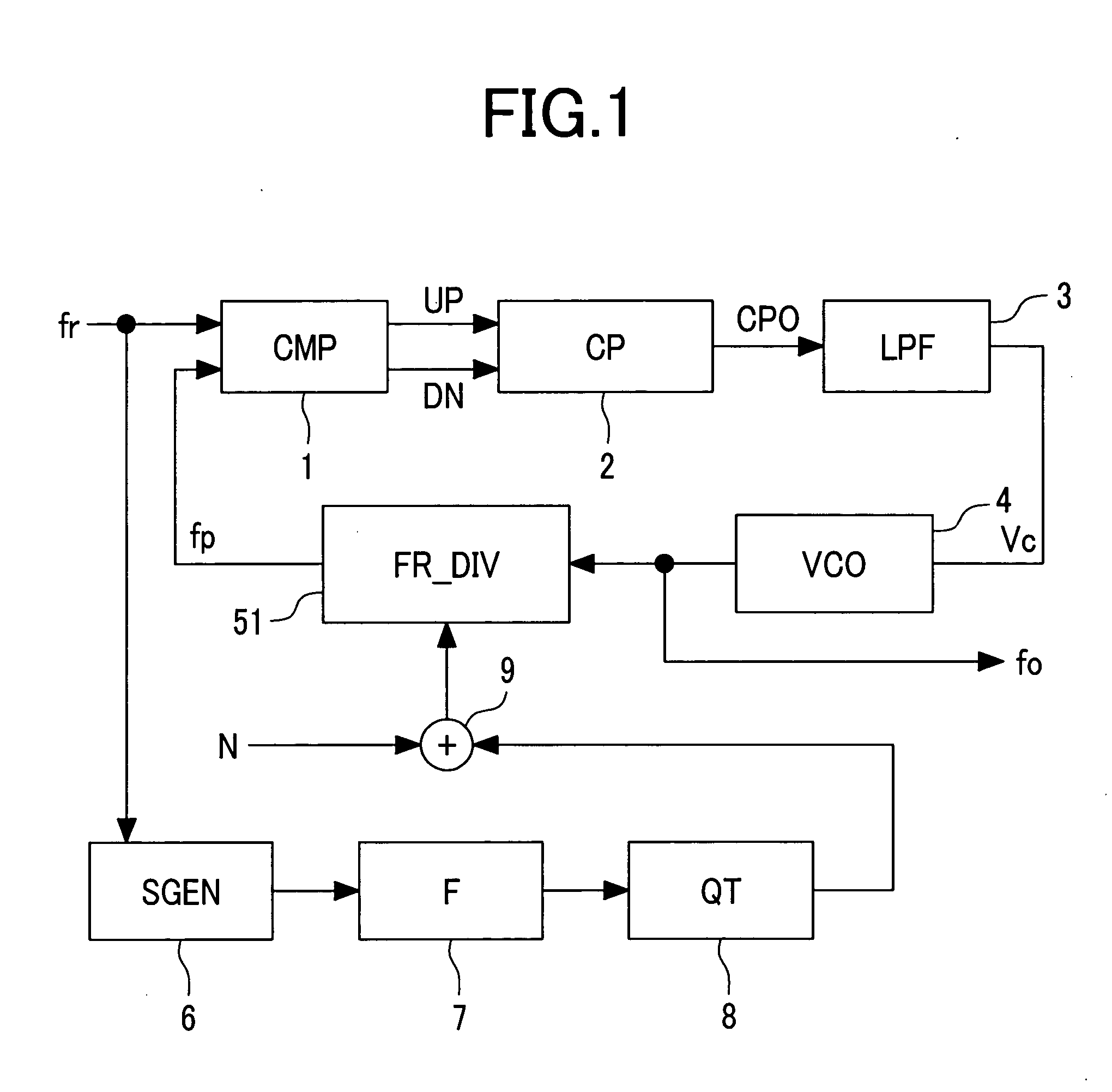
Spread spectrum clock generator and integrated circuit device using the spread spectrum clock generators
ActiveUS20050008113A1Prevents precipitous phase variationInhibitionPulse automatic controlGenerating/distributing signalsPhase variationElectromagnetic interference
The present invention provides a spread spectrum clock generator that is capable of preventing phase jumps and jitters and suppressing the occurrence of Electro Magnetic Interference components and that can easily be applied to large scale integrated circuits. The spread spectrum clock generator can be configured with a filter, quantizer, fractional divider, and other elements. Also, this clock generator circuitry can be configured by combination of a delta-sigma ΔΣ quantizer and factional divider so that sine wave modulation and random number modulation can be realized. Thereby, control with digital values can be performed. This clock generator prevents precipitous phase variations in the output high frequency clock and makes fine phase control possible. Consequently, EMI reduction by 20-30 dB can be expected.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
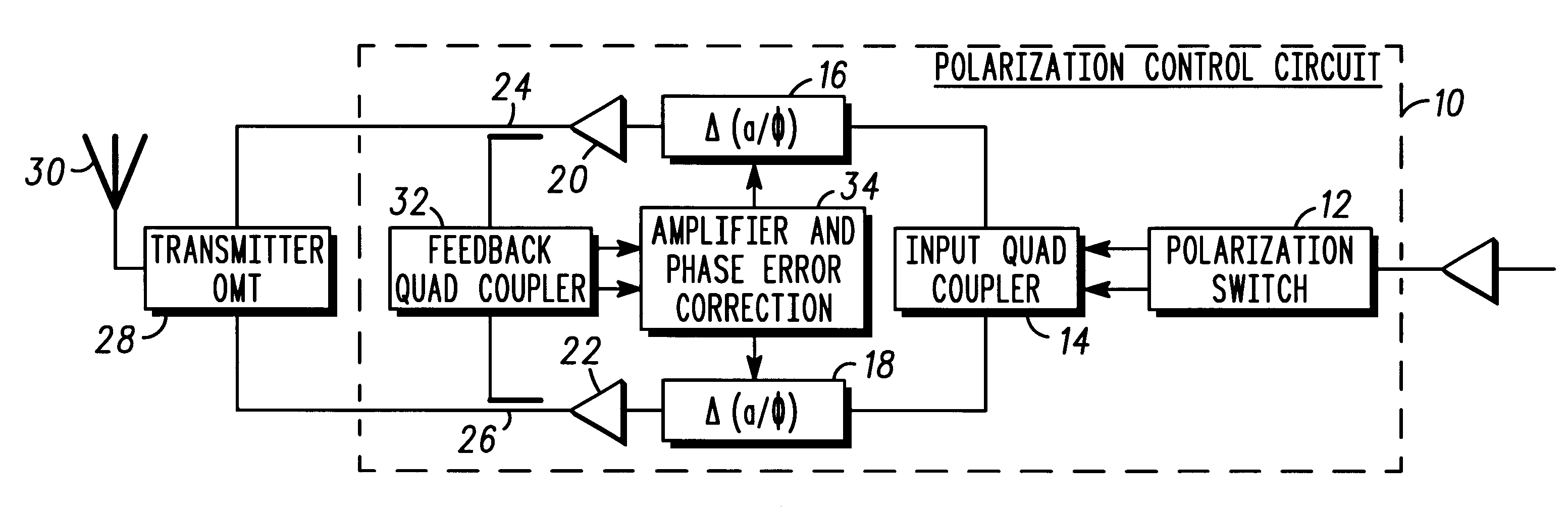
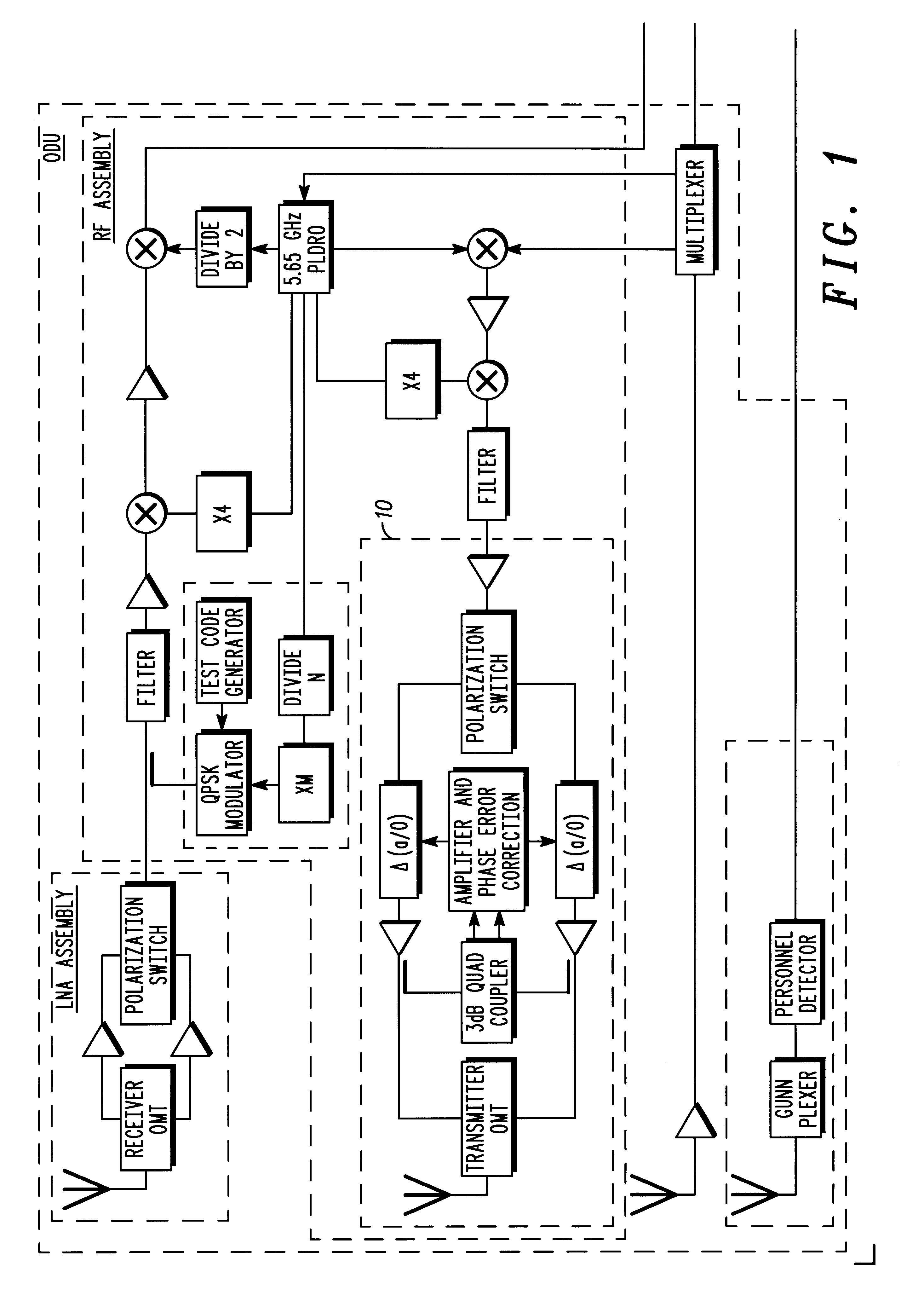
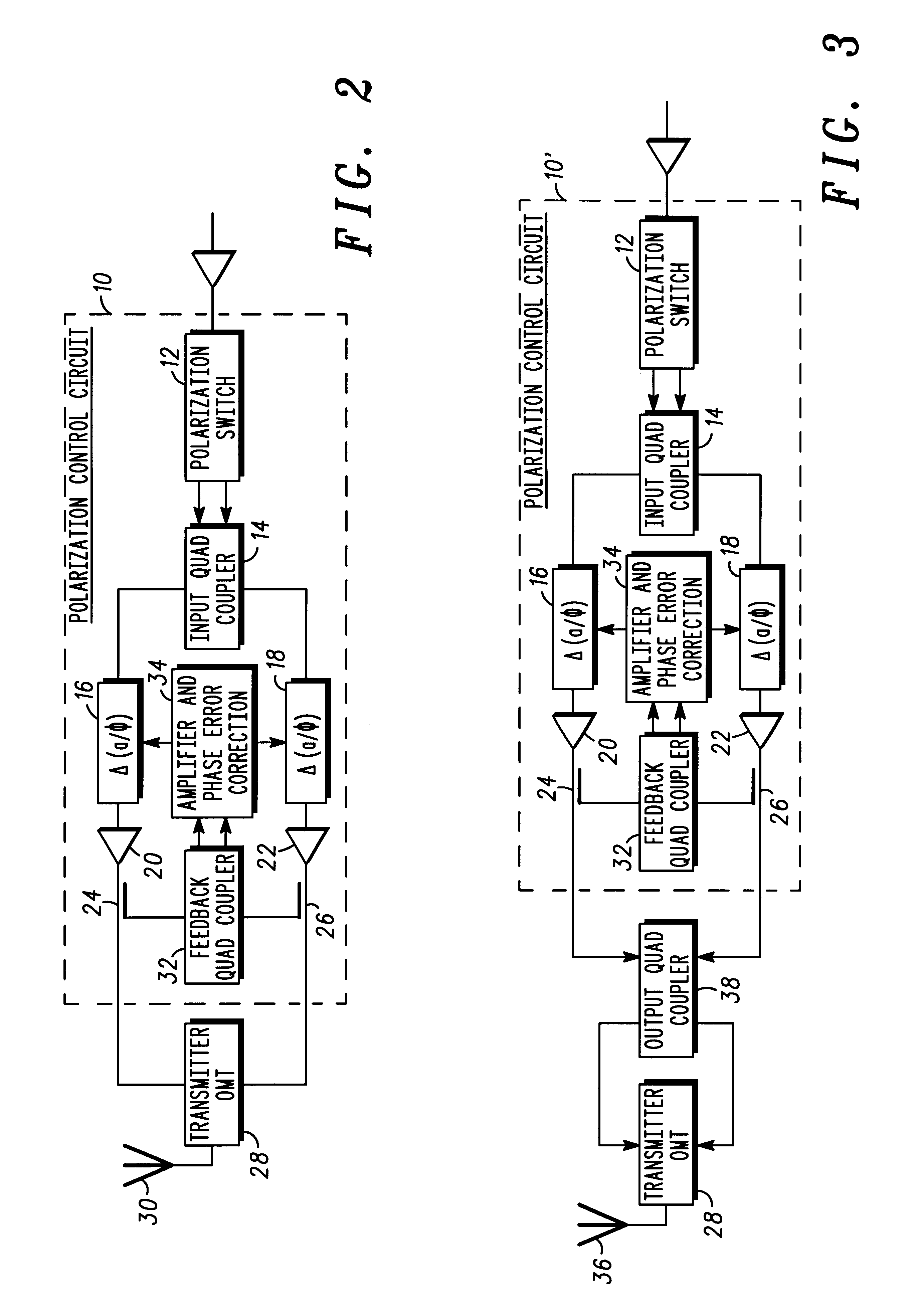
Method for efficiently generating selectable antenna polarization
InactiveUS6262690B1Polarisation/directional diversityPolarised antenna unit combinationsPhase detectorPhase variation
An antenna system (10) capable of transmitting electromagnetic radiation using the technique of combining two quadrature signals for either right hand circular polarization or left hand circular polarization using a circularly polarized antenna (30), or alternately, either horizontal or vertical polarization using a linearly polarized antenna (36) while incorporating feedback for automatically correcting for amplitude and phase variations in the quadrature paths using a switch (12) which selects the sense of the polarization and electronic optimization of the transmit antenna (30, 36). The antenna system includes a control circuit having a polarization switch (12) for receiving a transmission signal. The switch (12) generates first and second output signals which are substantially similar to the transmission signal, and determines whether to apply the transmission signal to one of a first or a second switch output. A coupler (14) receives the first and second switch outputs and generates first and second output signals having a predetermined phase difference. A variable detector (16, 18) detects and adjusts a relative amplitude and phase of the respective first and second output signals. An error correction circuit (34) determines an adjustment to the variable phase detector to vary the phase and amplitude of the first and second output signals in accordance with the relative amplitude and phase of the respective first and second output signals.
Owner:CDC PROPRIETE INTELLECTUELLE
Spread spectrum receiving apparatus
InactiveUS6882681B2Spatial transmit diversityPolarisation/directional diversityPhase variationEngineering
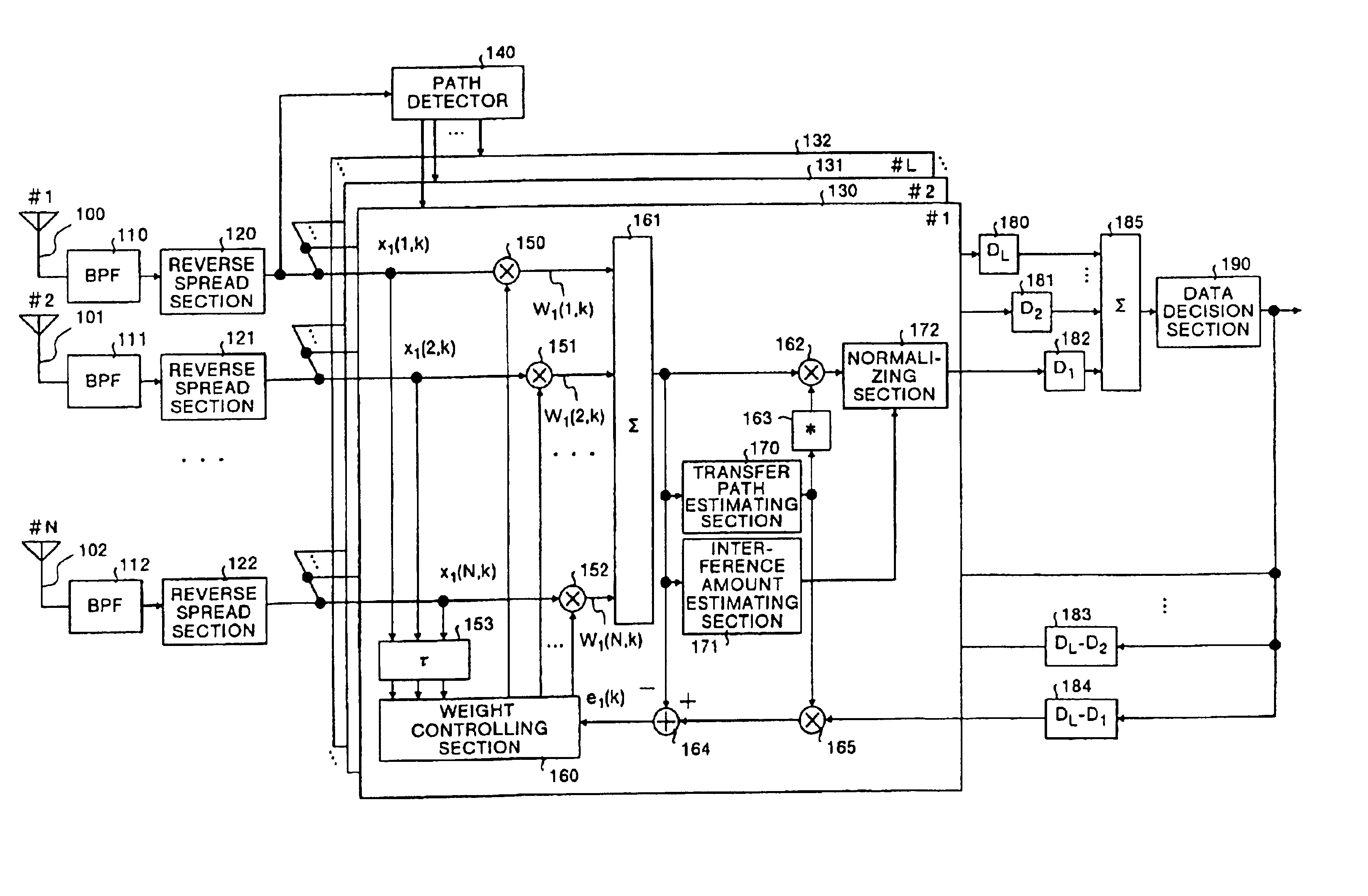
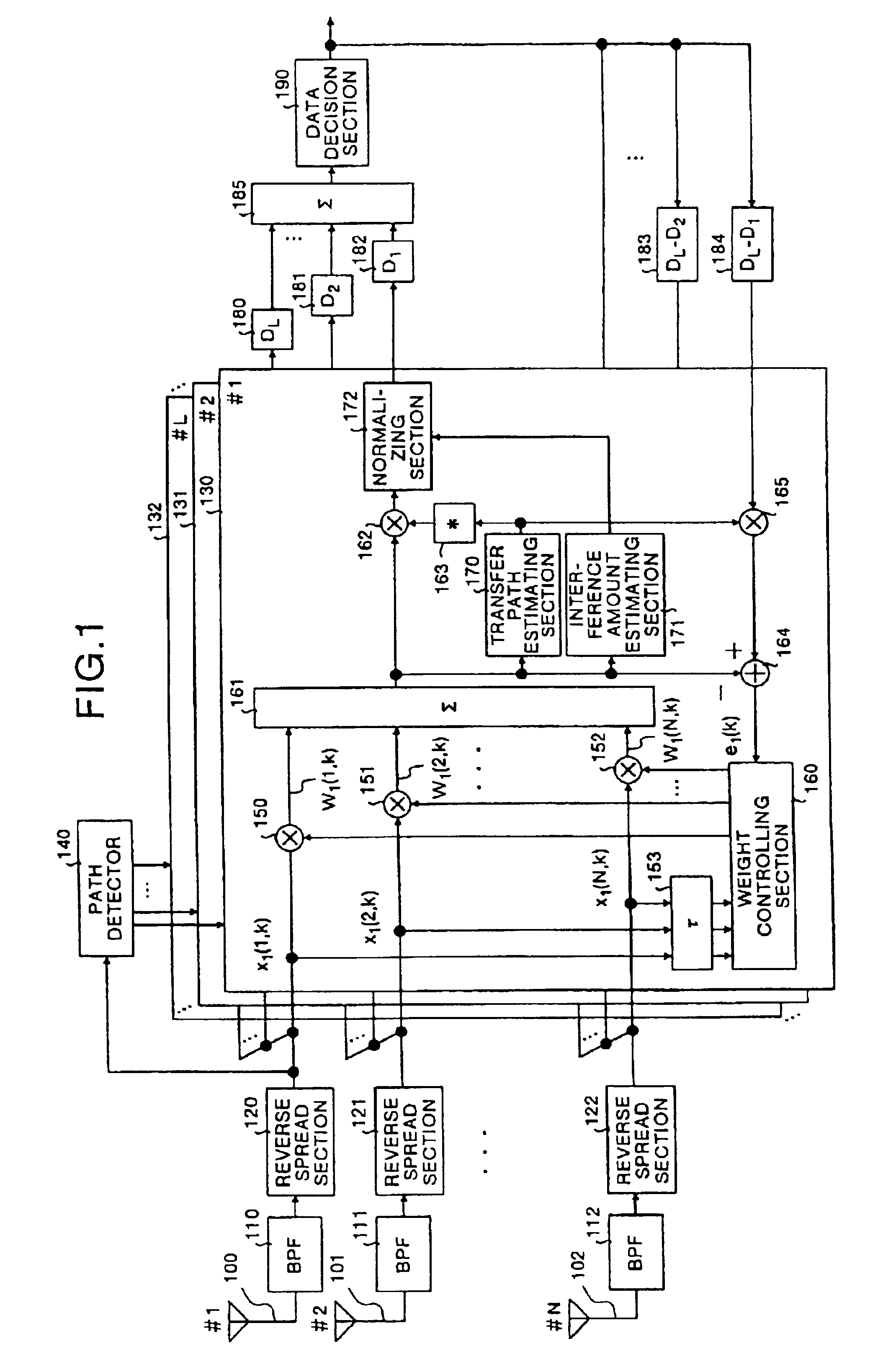
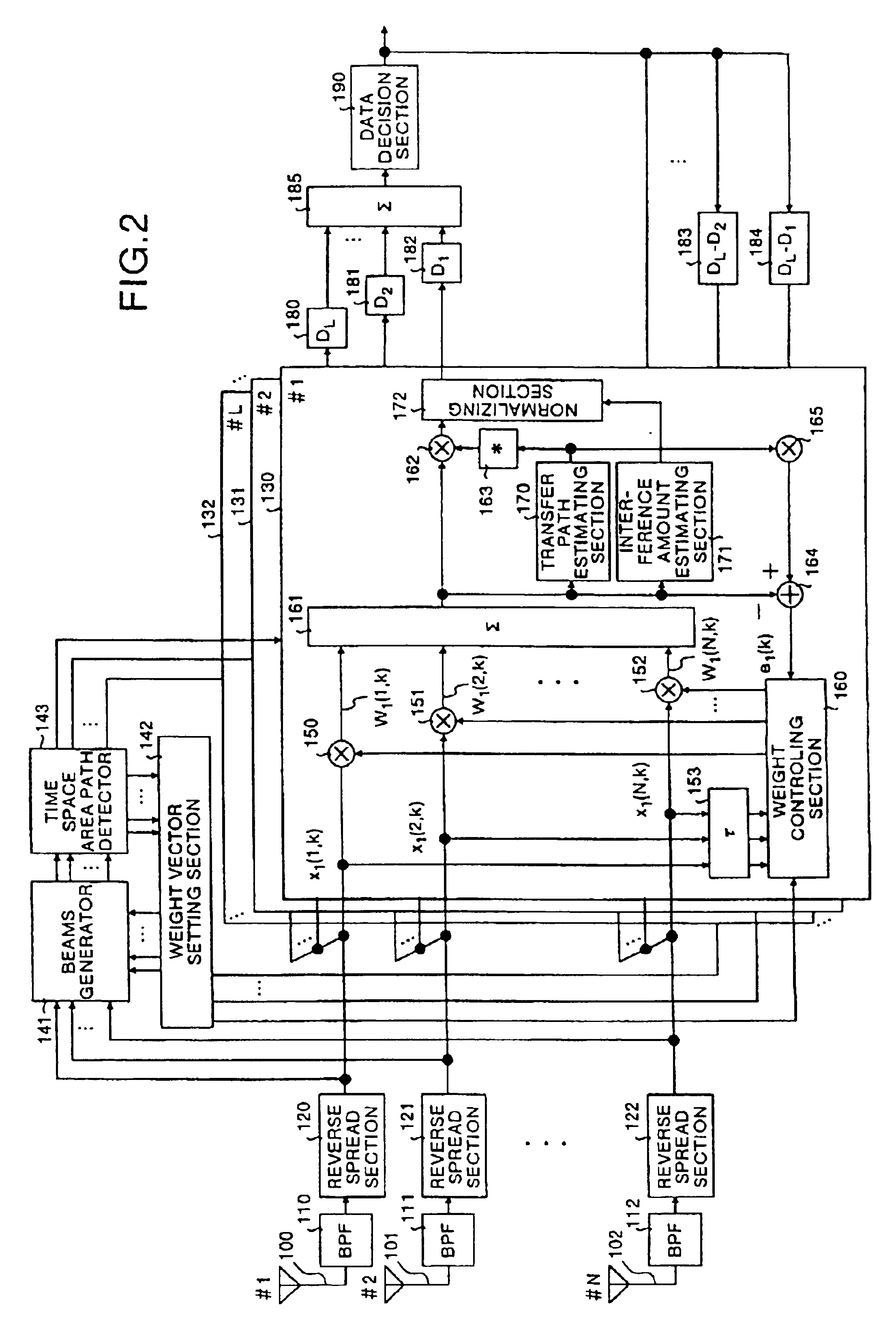
A path detector (140) detects a plurality of multi-path waves that have satisfied a predetermined standard from reverse spread signals, a plurality of adders (161) form beams on the basis of a path, a plurality of transfer path estimating sections (170) and complex conjugate calculators (163) calculate a transfer path estimation value, and based upon the result of the estimation, carry out a weighting process in accordance with the signal amplitude and a removing process of the phase variations. Moreover, a plurality of interference amount estimating sections (171) extract the amount of interference, a plurality of normalizing sections (172) normalize the signals that have been subjected to the phase variation removing process based upon the amount of interference, an adder (185) combines all the signals that have been normalized, and a data determining section (190) determines the signal that have been combined.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Surface plasmon resonance microscope using common-path phase-shift interferometry
InactiveUS20060119859A1Polarisation-affecting propertiesPhase-affecting property measurementsRefractive indexPhase shift interferometry
The present invention integrates the surface plasmon resonance and common-path phase-shift interferometry techniques to develop a microscope for measuring the two-dimensional spatial phase variation caused by biomolecular interactions on a sensing chip without the need for additional labeling. The common-path phase-shift interferometry technique has the advantage of long-term stability, even when subjected to external disturbances. Hence, the developed microscope meets the requirements of the real-time kinetic studies involved in biomolecular interaction analysis. The surface plasmon resonance microscope of the present invention using common-path phase-shift interferometry demonstrates a detection limit of 2×10−7 refractive index change, a long-term phase stability of 2.5×10−4π rms over four hours, and a spatial phase resolution of 10−3 π with a lateral resolution of 100 μm.
Owner:PHALANX BIOTECH GROUP
Reflectarray antenna system
InactiveUS20120162010A1Simple methodShorten the setting timeUnderwater structuresAntennasPhase variationRadiating element
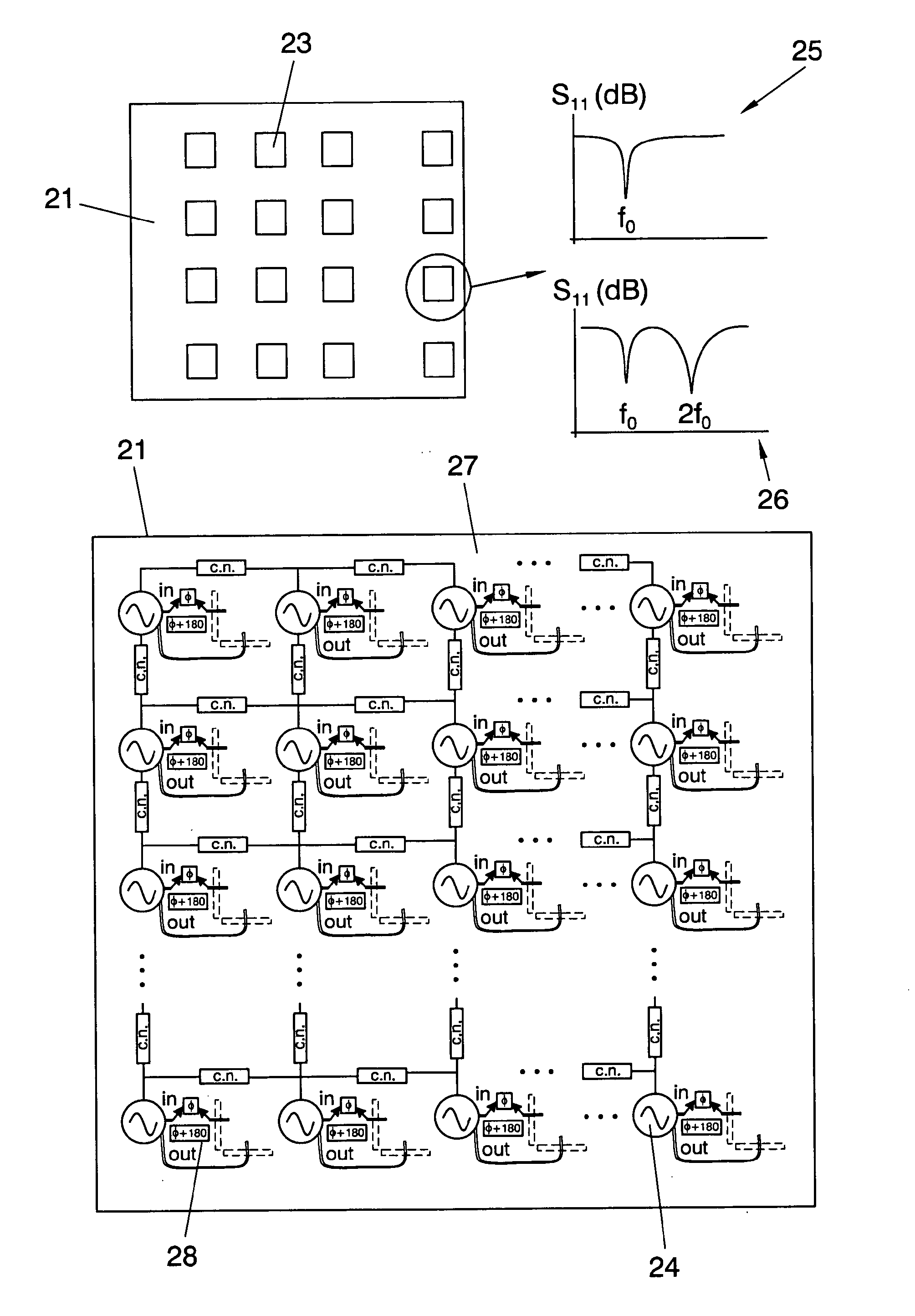
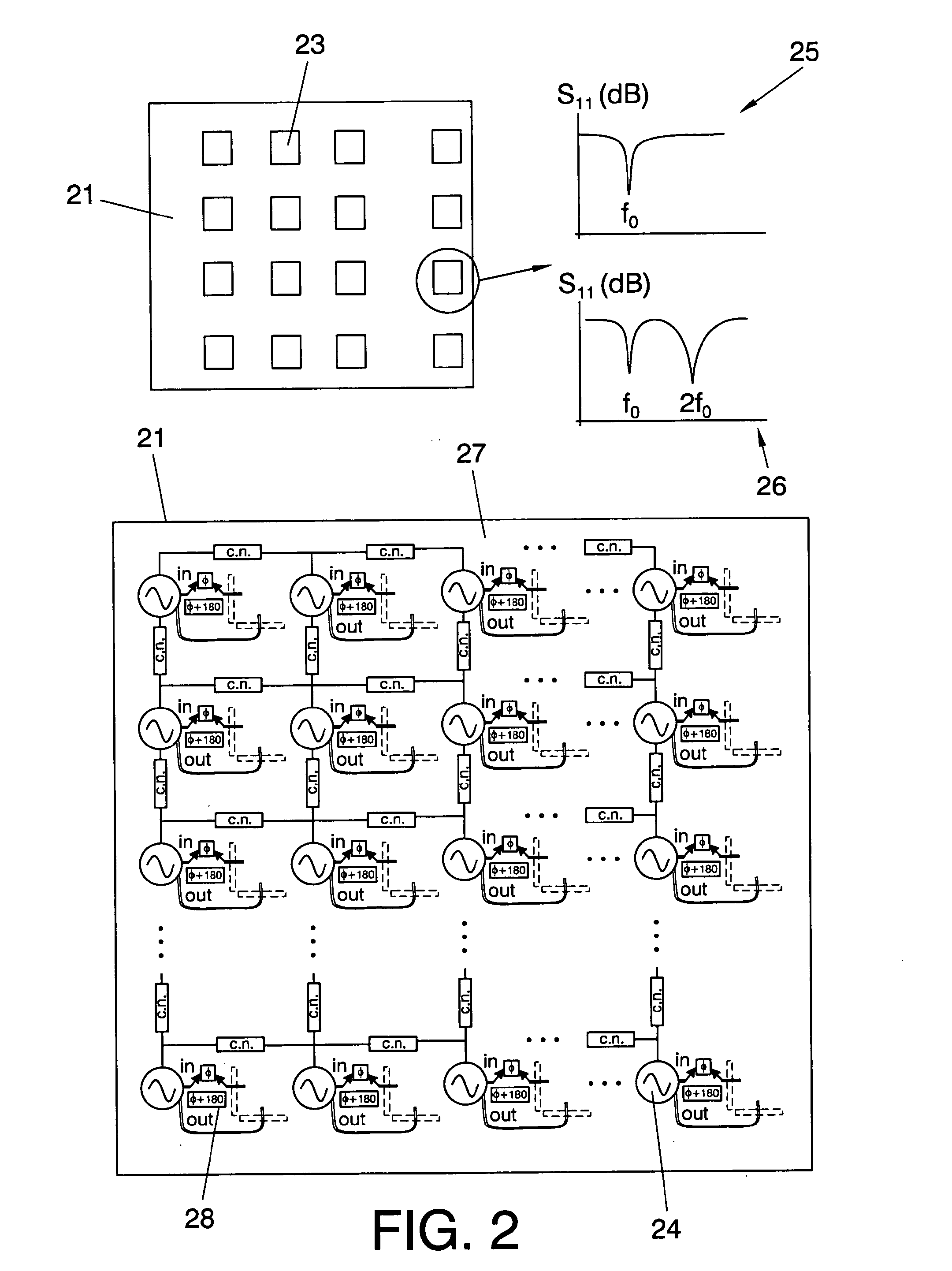
The reflectarray includes a plurality of cells integrated in a PCB and externally illuminated by an input signal from a feeding source at a frequency fi, and an output signal is reflected, where each cell of the reflectarray is an AIA formed by a passive radiating element connected to an active circuit, which can be either an oscillator, or a push-push oscillator or a SOM, where the passive radiating circuit is placed on a reflective surface forming a side of the reflectarray and the active circuit is placed on the reverse side, the active circuit producing an output signal with a frequency related to the input frequency fi and the oscillation frequency fosc of said active circuit. This phase relationship is determined by an output phase variation, which is controlled by electronic means integrated in the reflectarray system, which allows an output phase variation interval even higher than 180°.
Owner:FUNDACIO PRIVADA CENT TECNOLOGIC DE TELECOMUNICACIONS DE CATALUNYA
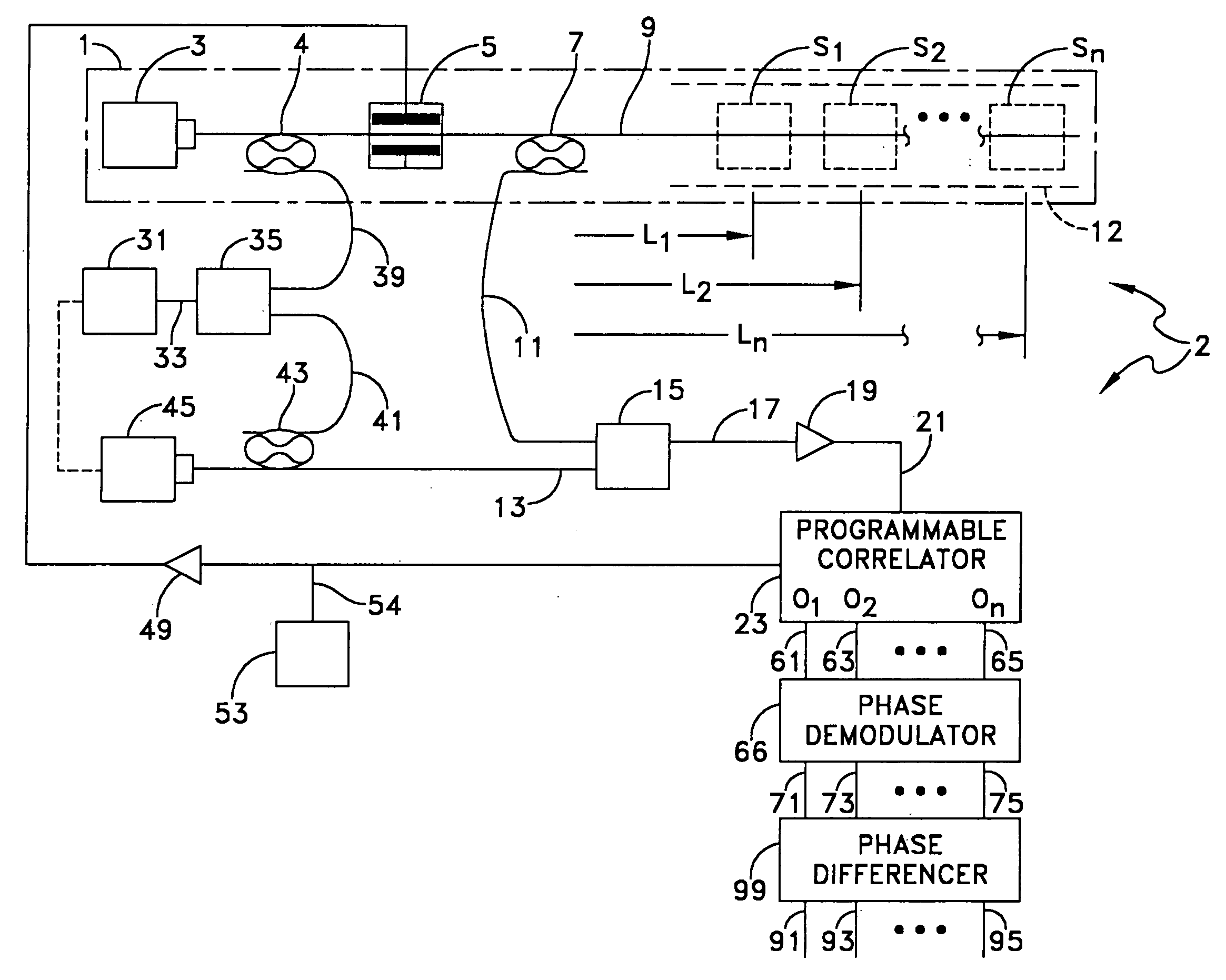
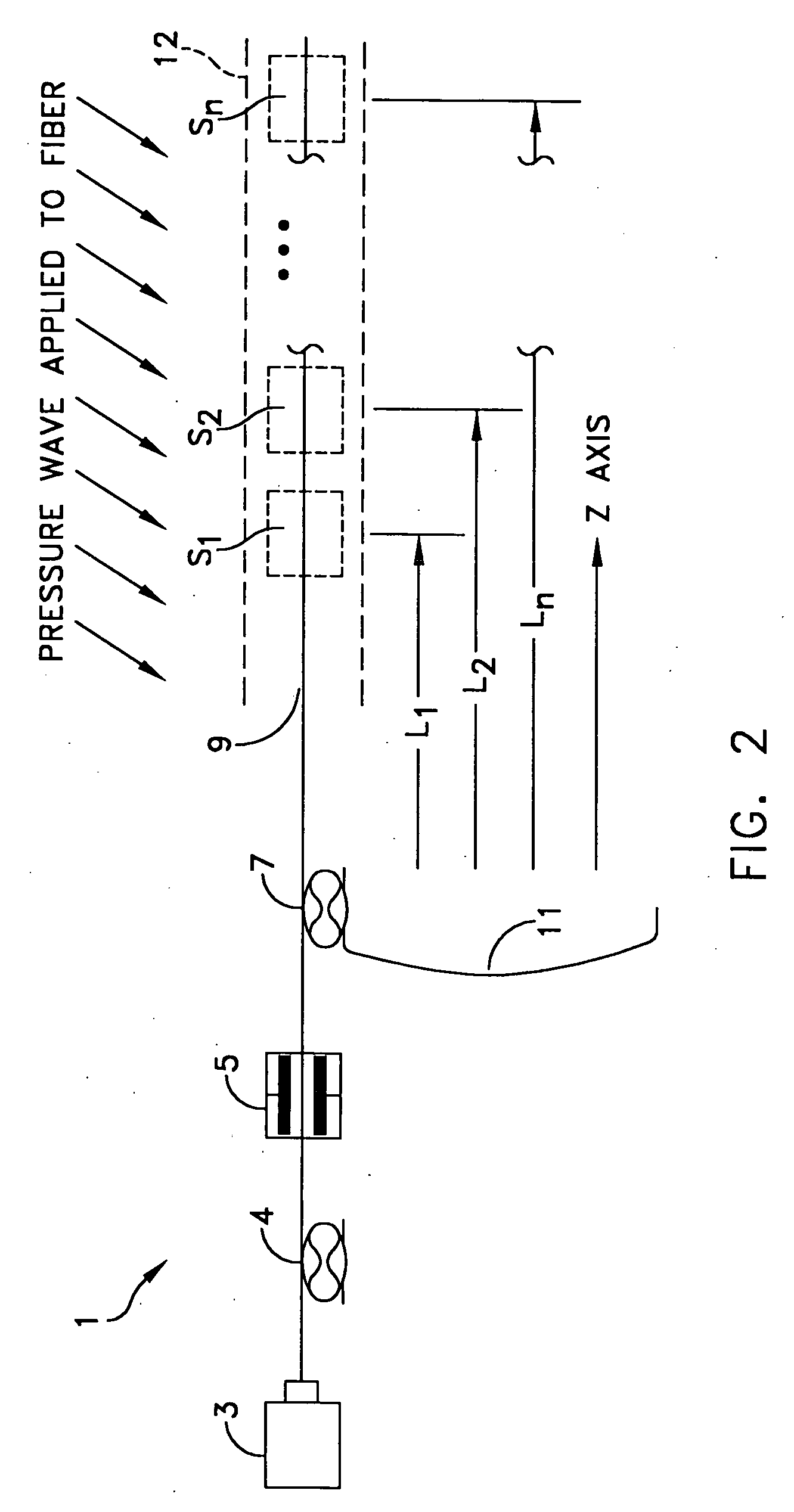
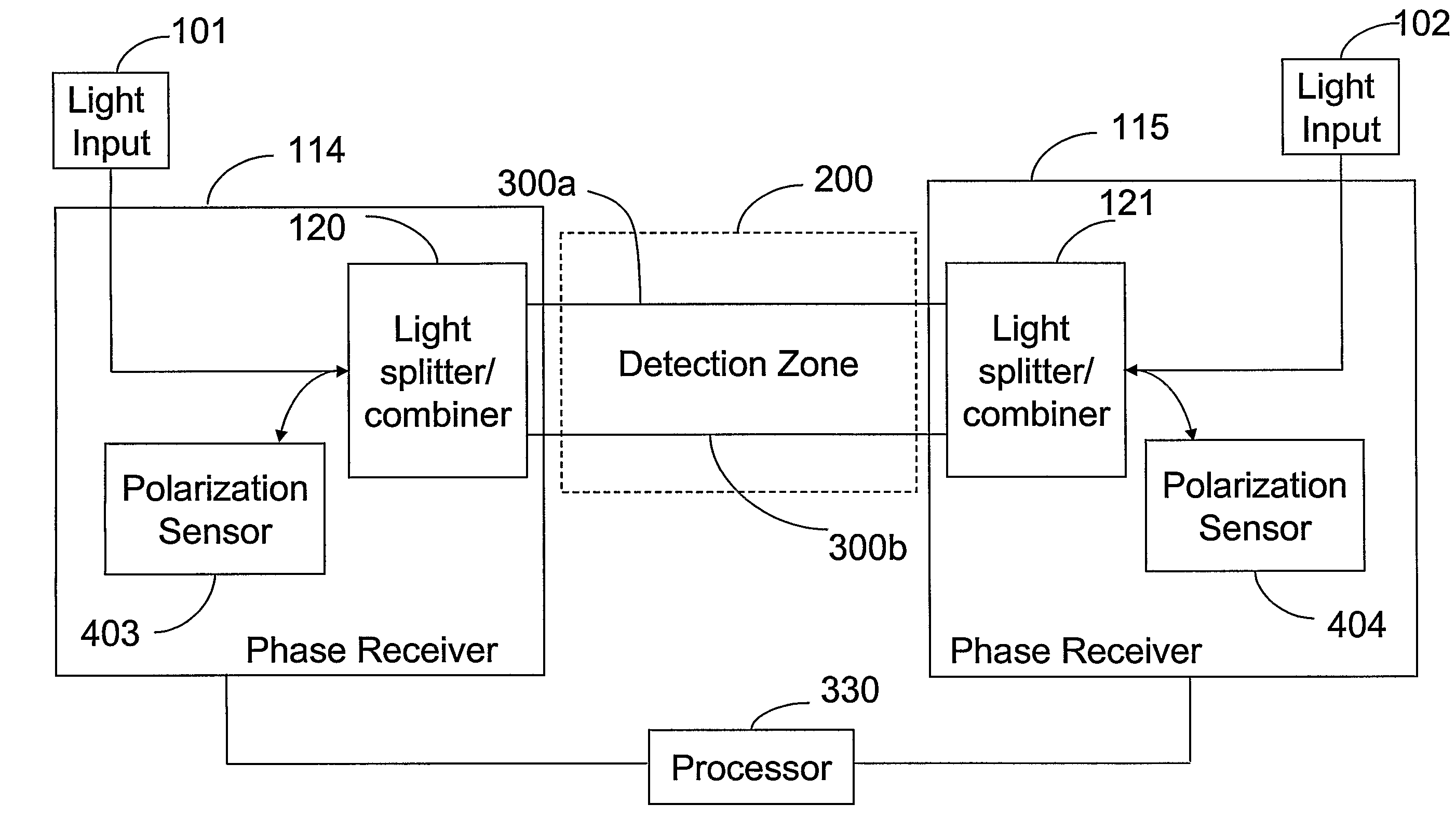
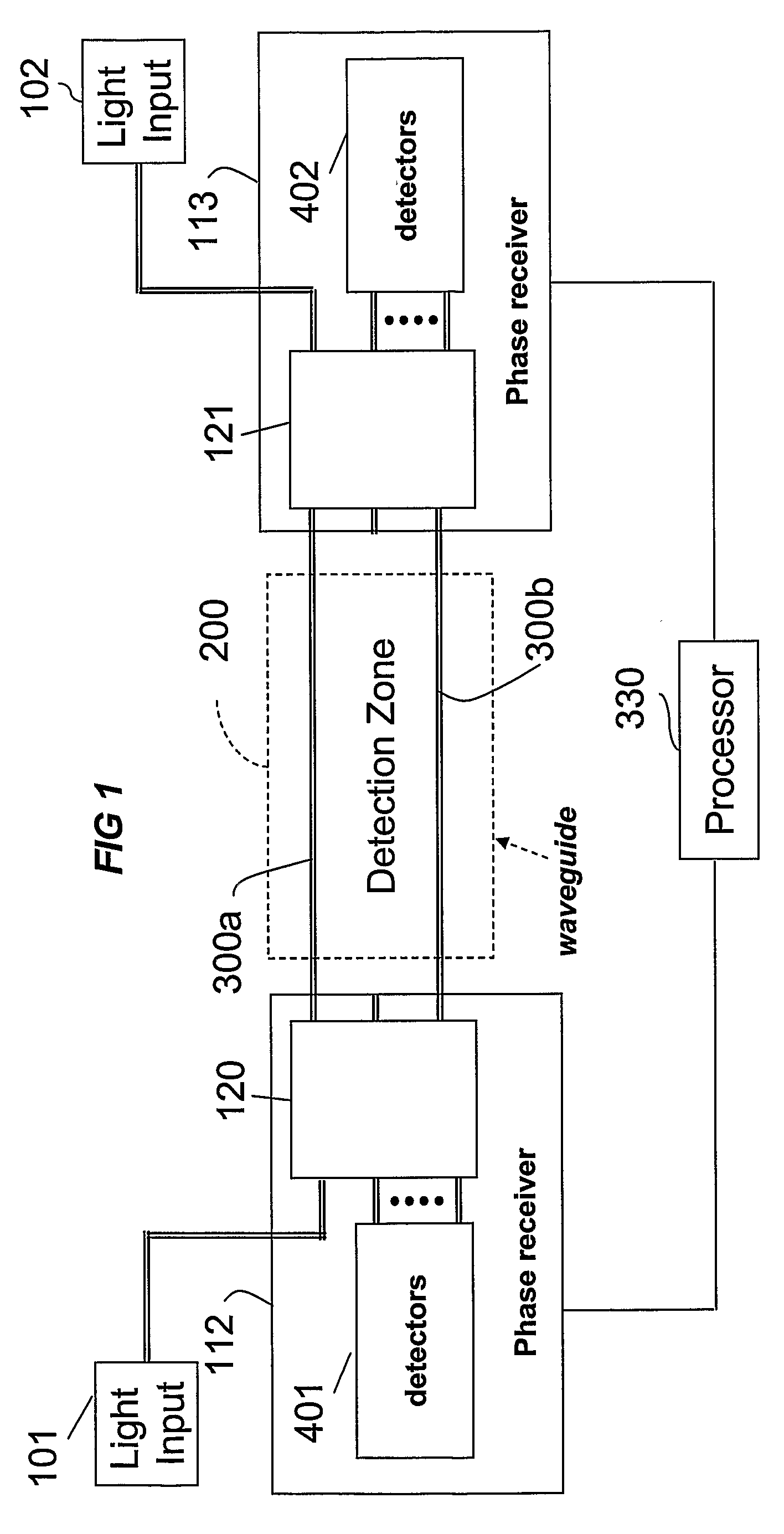
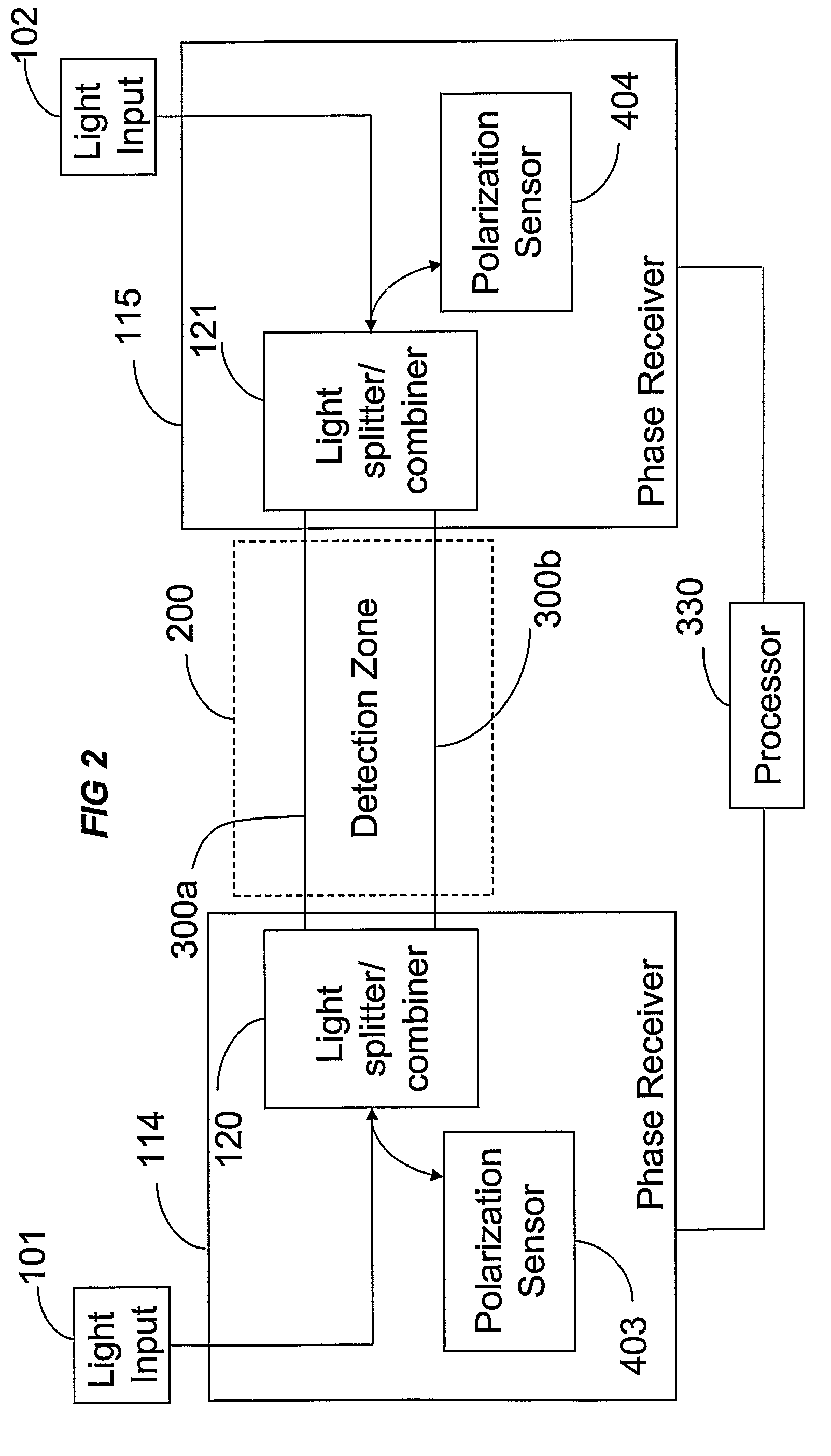
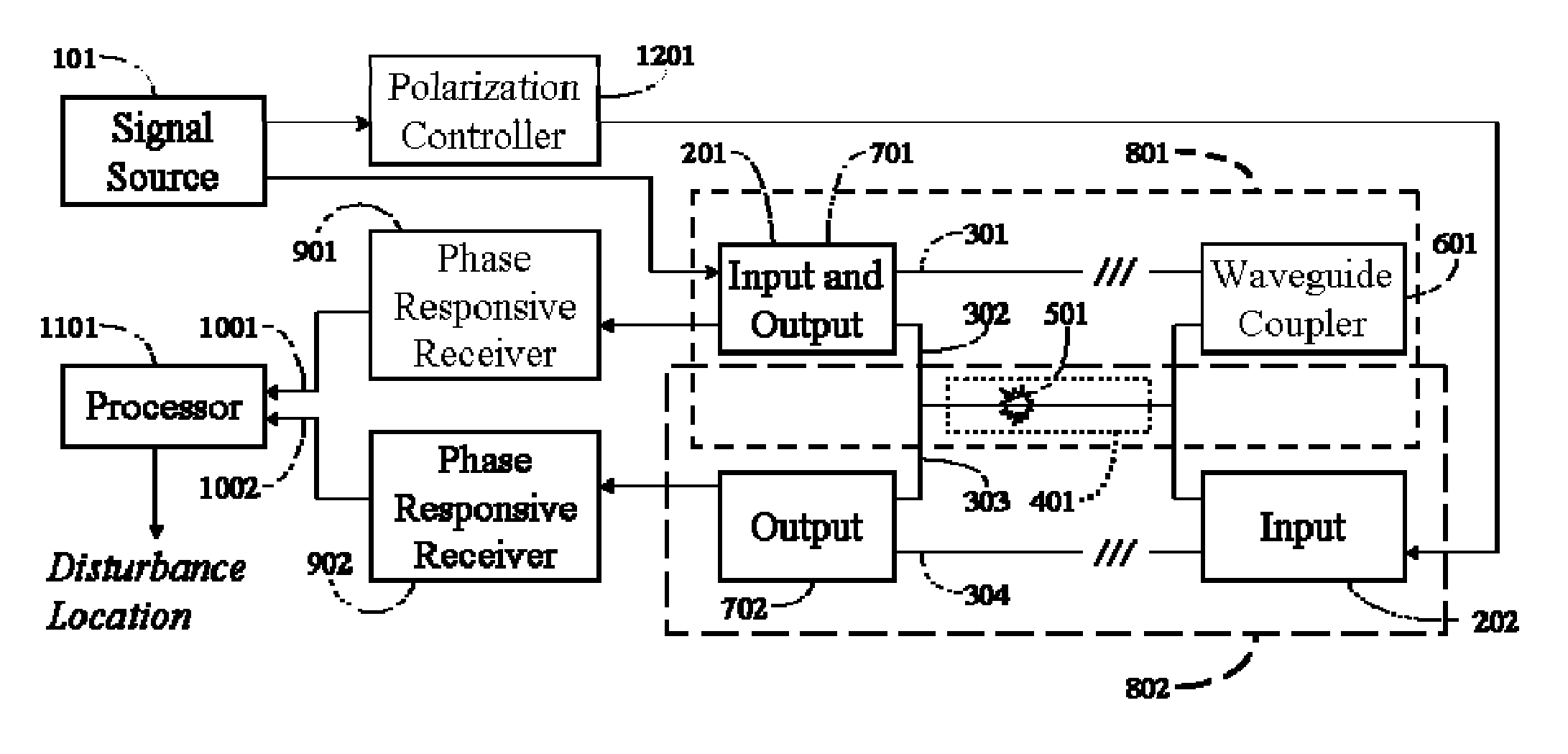
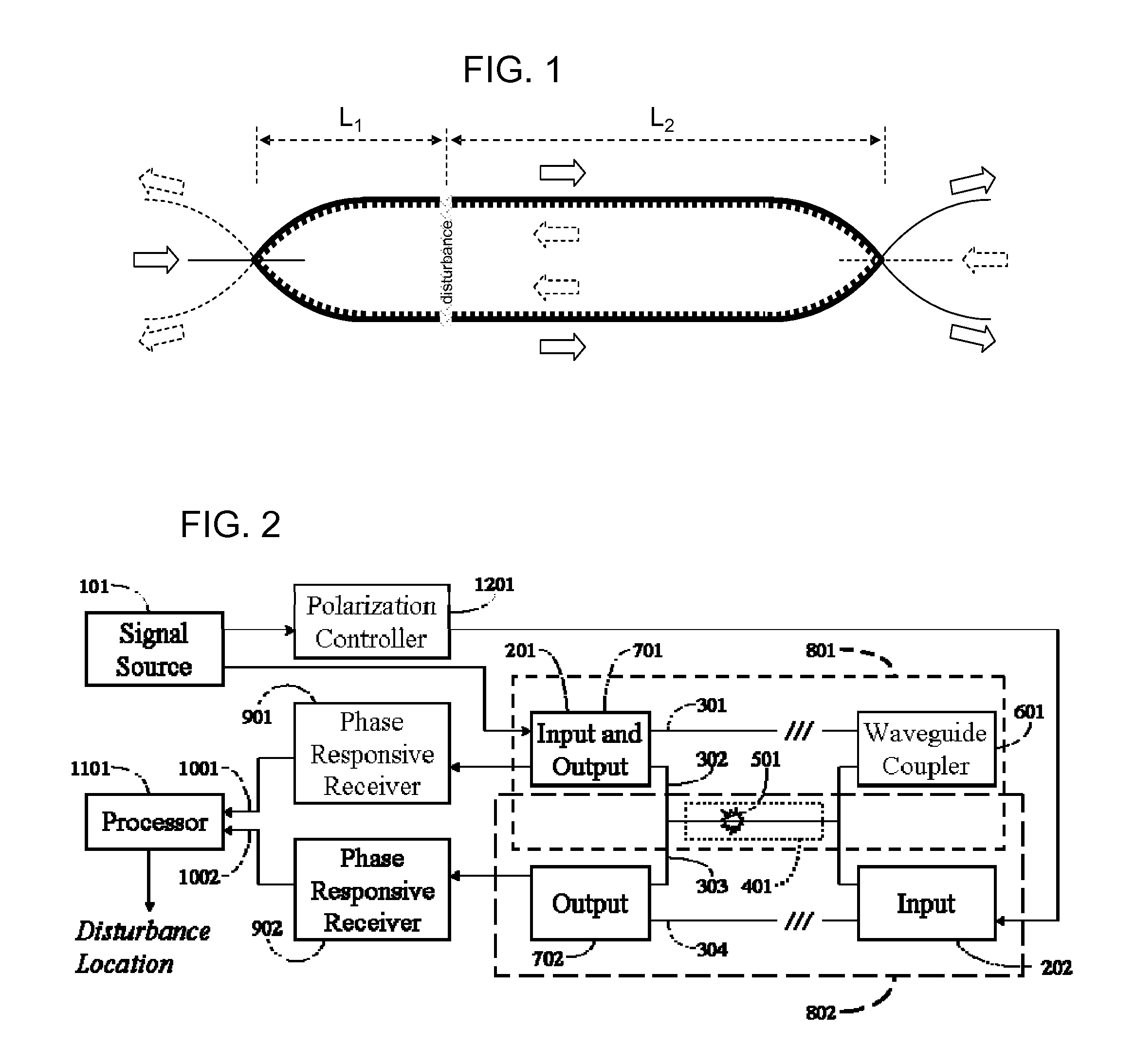
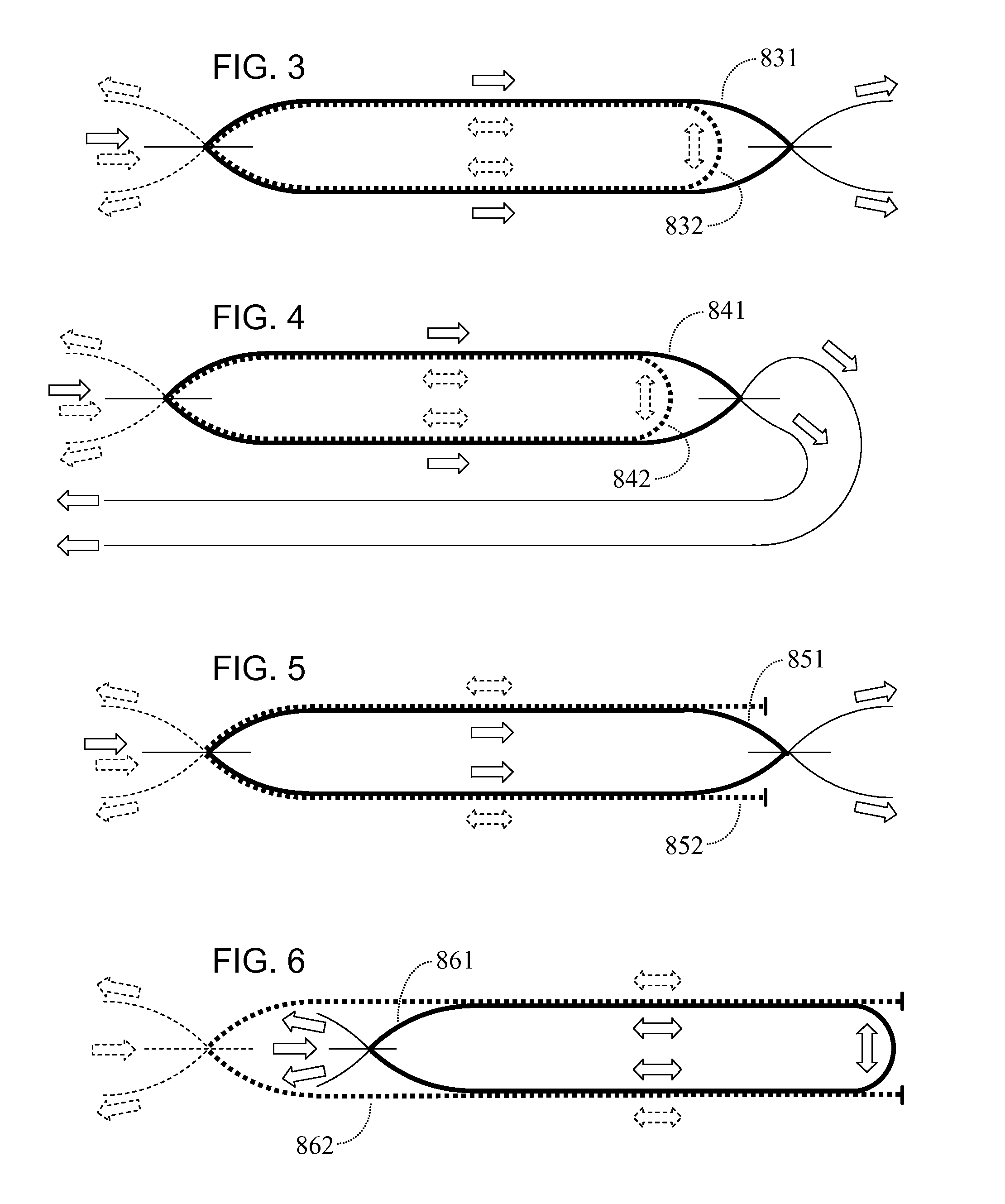
Phase Responsive Optical Fiber Sensor
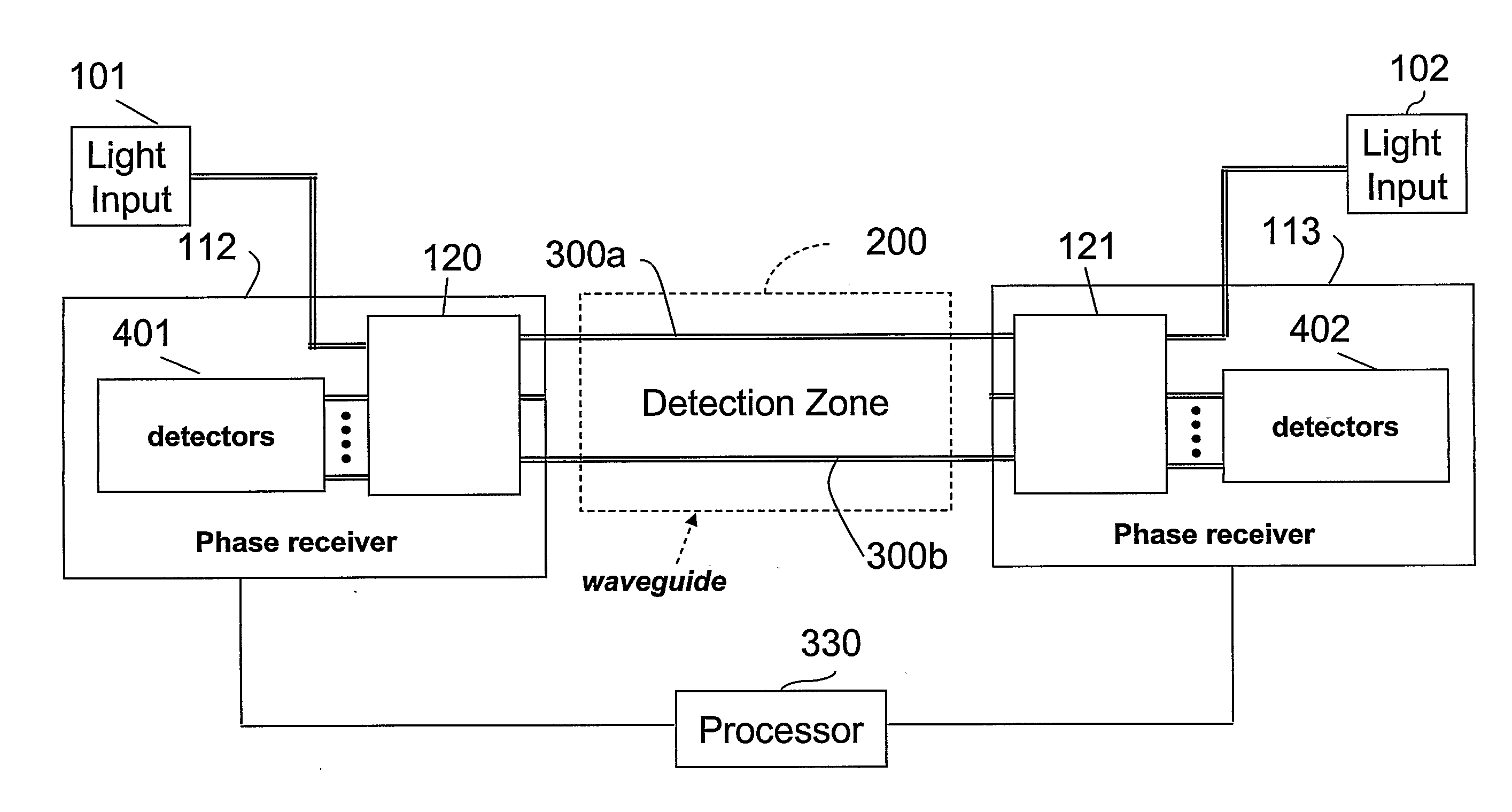
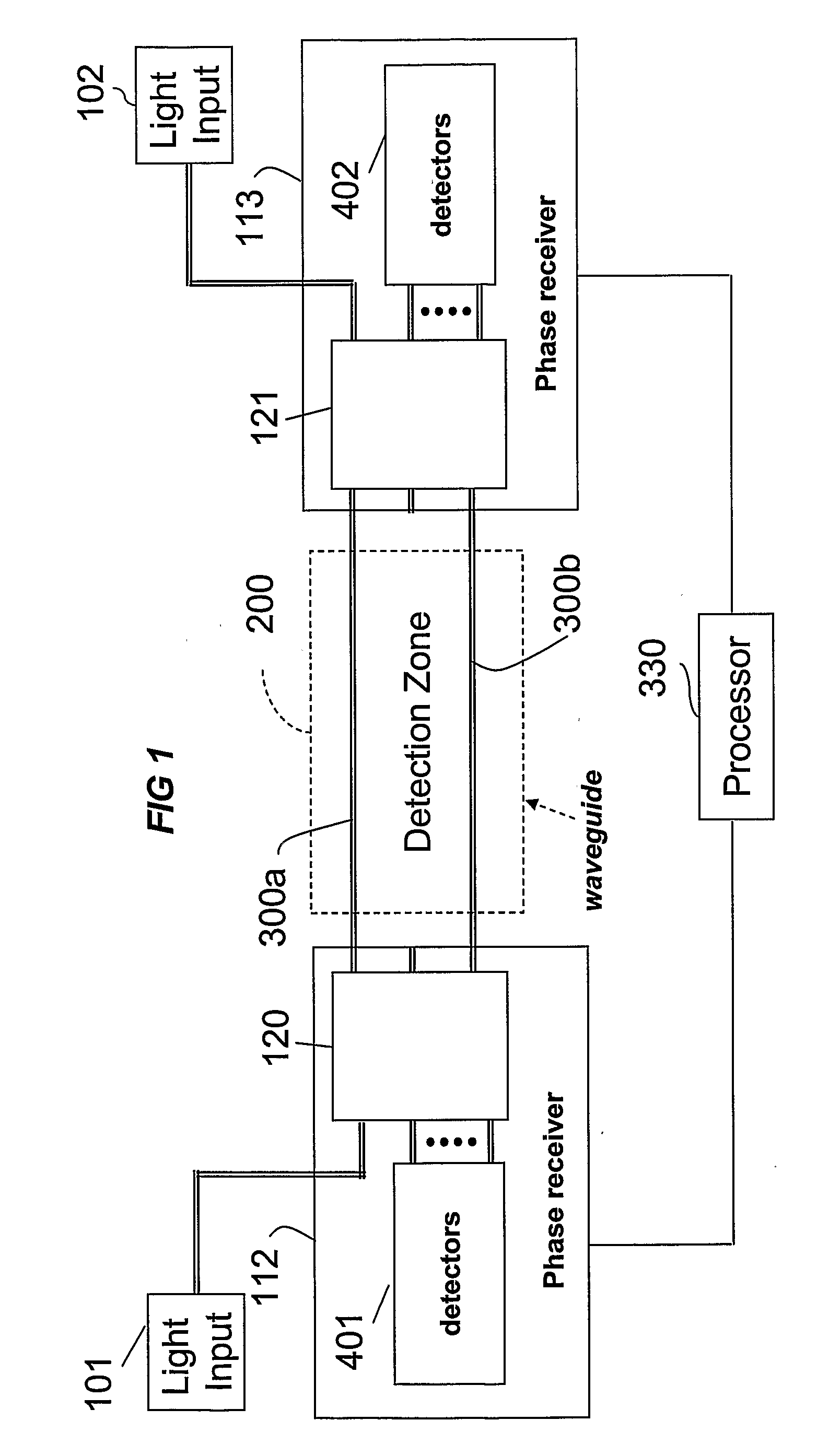
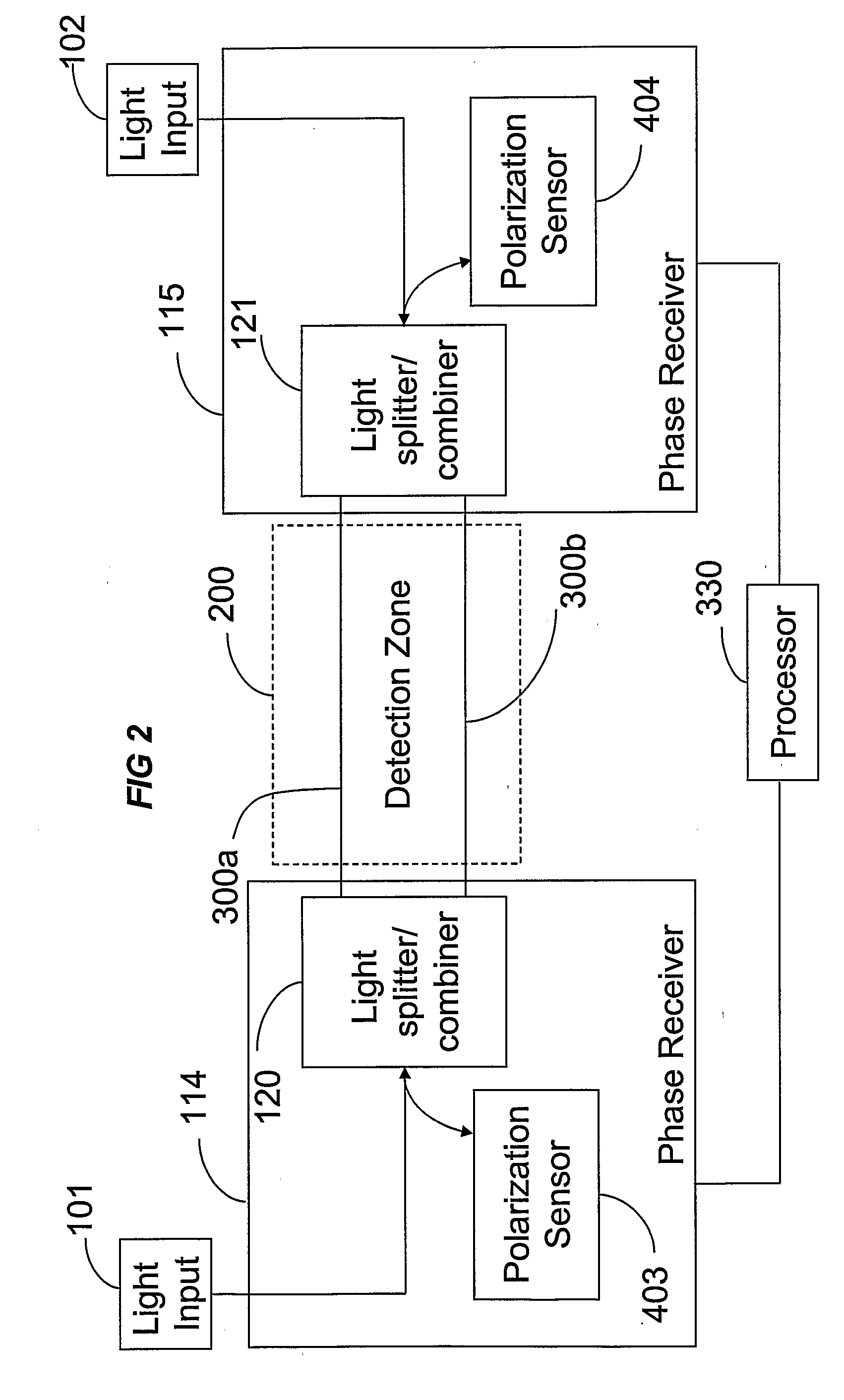
The location of a physical disturbance along an optical waveguide is determined by measuring different propagation times for the resulting phase variation to propagate to phase responsive receivers at ends of bidirectional signal paths. Each receiver can have a coupler that functions as a beam combiner and as a beam splitter inserting the opposite signal. On each receiving end, the coupler provides one or more detectors with signals from which phase related independent variable values are taken, processed and mapped to phase angles. Relative phase angle versus time is derived for each opposite signal pair and correlated at a time difference, i.e., a difference in propagation time from which the location of the disturbance is resolved. Polarization sensitive and polarization insensitive examples are discussed with various optical fiber arrangements.
Owner:OPTELLIOS
Phase responsive optical fiber sensor
The location of a physical disturbance along an optical waveguide is determined by measuring different propagation times for the resulting phase variation to propagate to phase responsive receivers at ends of bidirectional signal paths. Each receiver can have a coupler that functions as a beam combiner and as a beam splitter inserting the opposite signal. On each receiving end, the coupler provides one or more detectors with signals from which phase related independent variable values are taken, processed and mapped to phase angles. Relative phase angle versus time is derived for each opposite signal pair and correlated at a time difference, i.e., a difference in propagation time from which the location of the disturbance is resolved. Polarization sensitive and polarization insensitive examples are discussed with various optical fiber arrangements.
Owner:OPTELLIOS
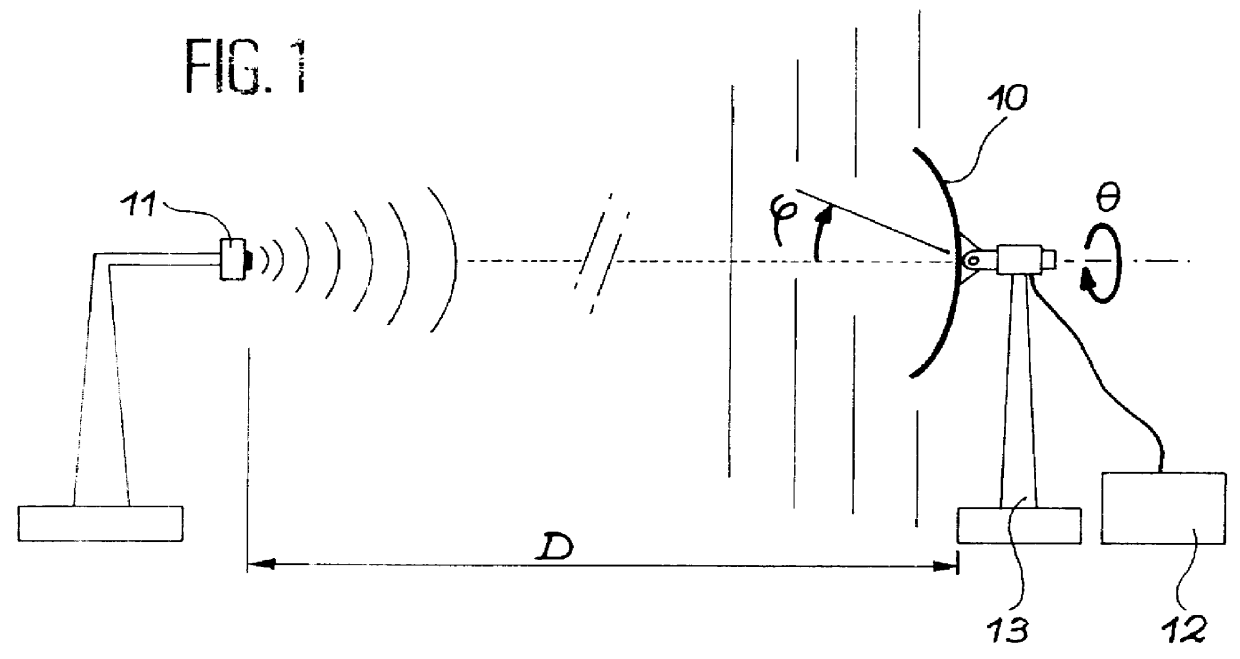
Antenna pattern measurement method and device
PCT No. PCT / FR96 / 01490 Sec. 371 Date Aug. 27, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Aug. 27, 1998 PCT Filed Sep. 24, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 12253 PCT Pub. Date Apr. 3, 1997This invention relates to a process for measuring an antenna diagram in which: the antenna (30) is connected to a receiver (33) capable of supplying C / No measures (the ratio of the useful signal power to the noise power spectral density) and possibly phase variation measurements; the antenna (30) is placed at the end of a mast (32) or a carrier satellite facing towards the sky to track the satellites in a constellation, the antenna reception band being included in the satellite antenna transmission band; the C / No ratio and phase variations are automatically recorded for a given period; the diagram for the said antenna is deduced by calculation.
Owner:CENT NAT DETUD SPATIALES C N E S
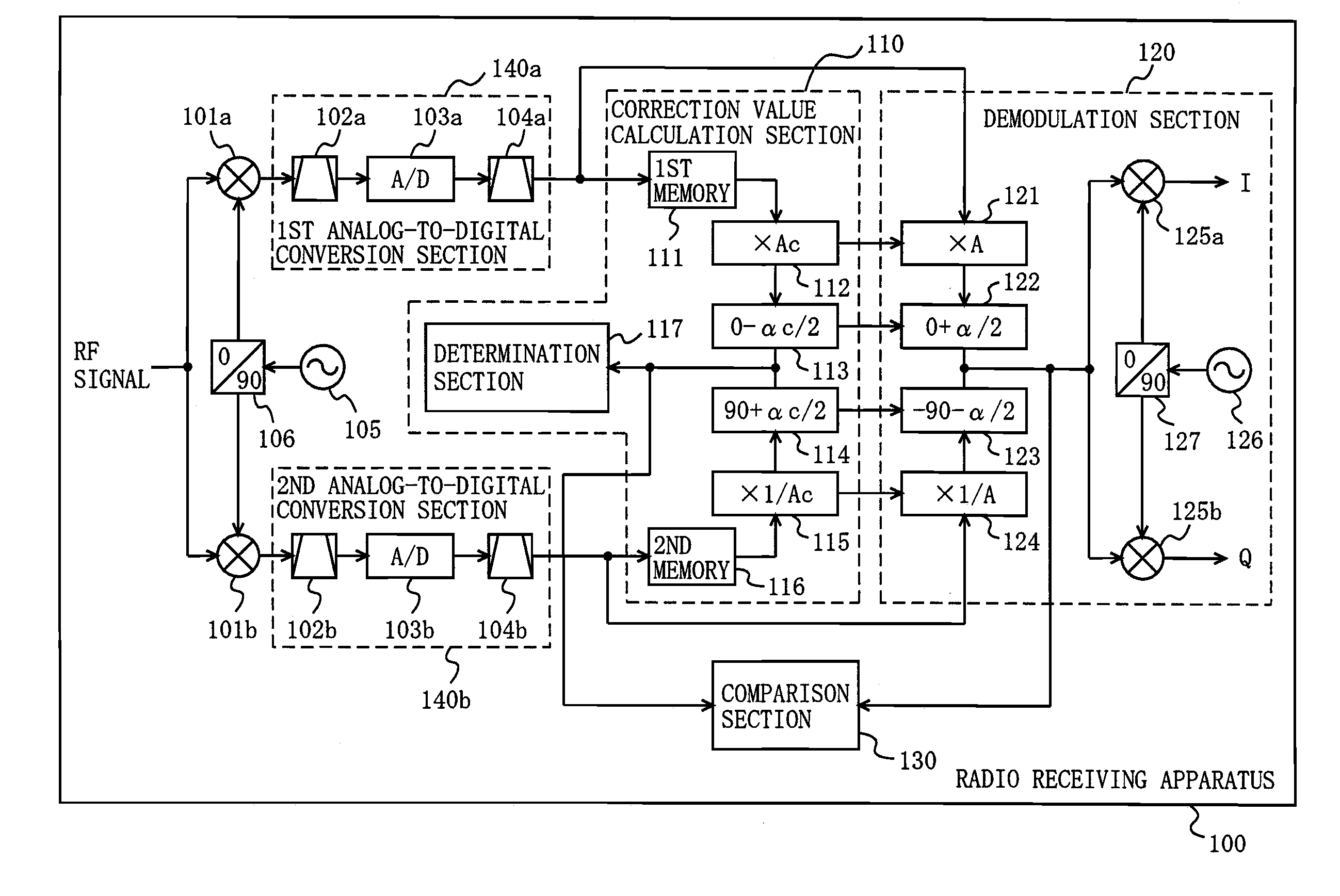
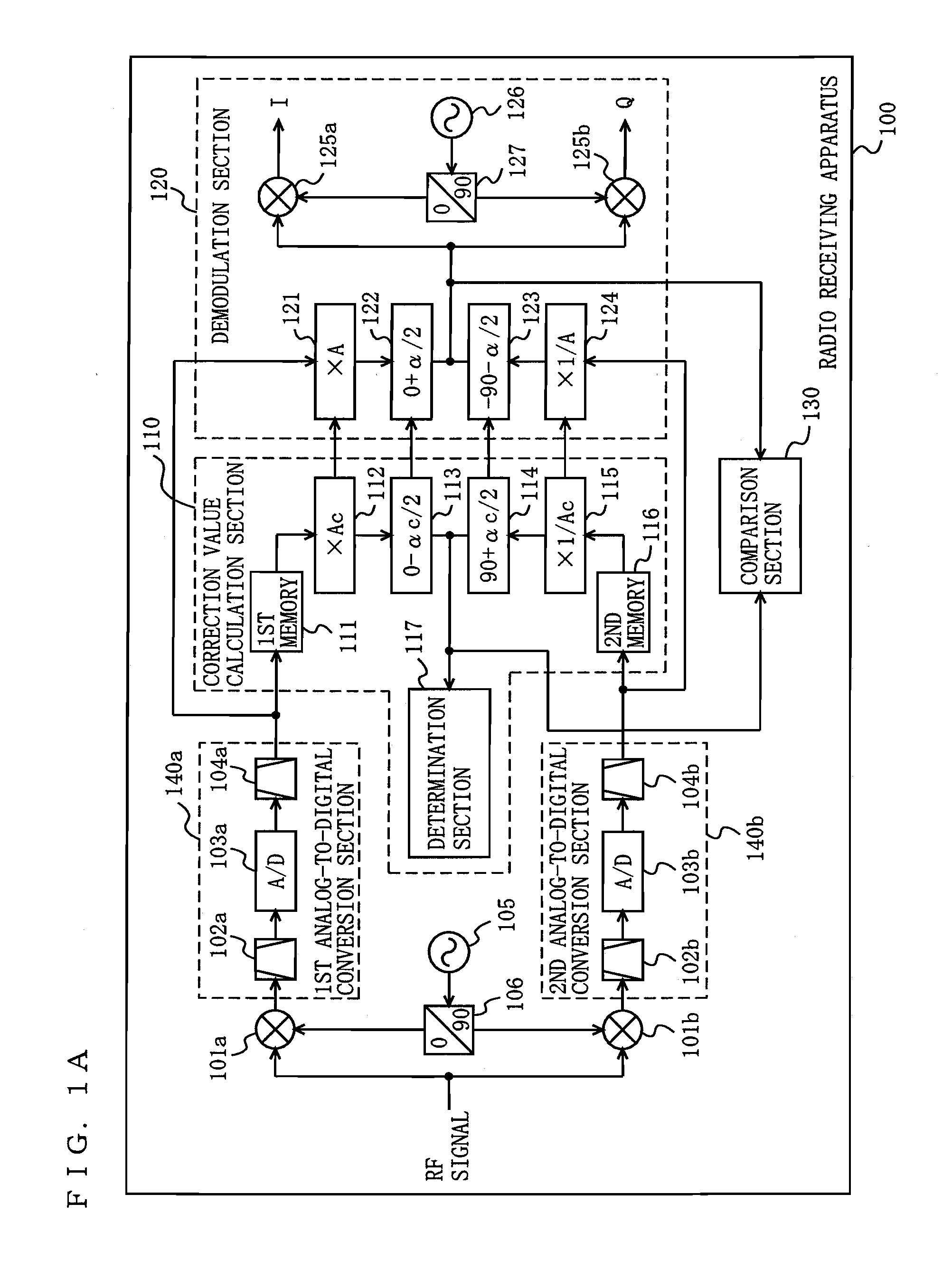
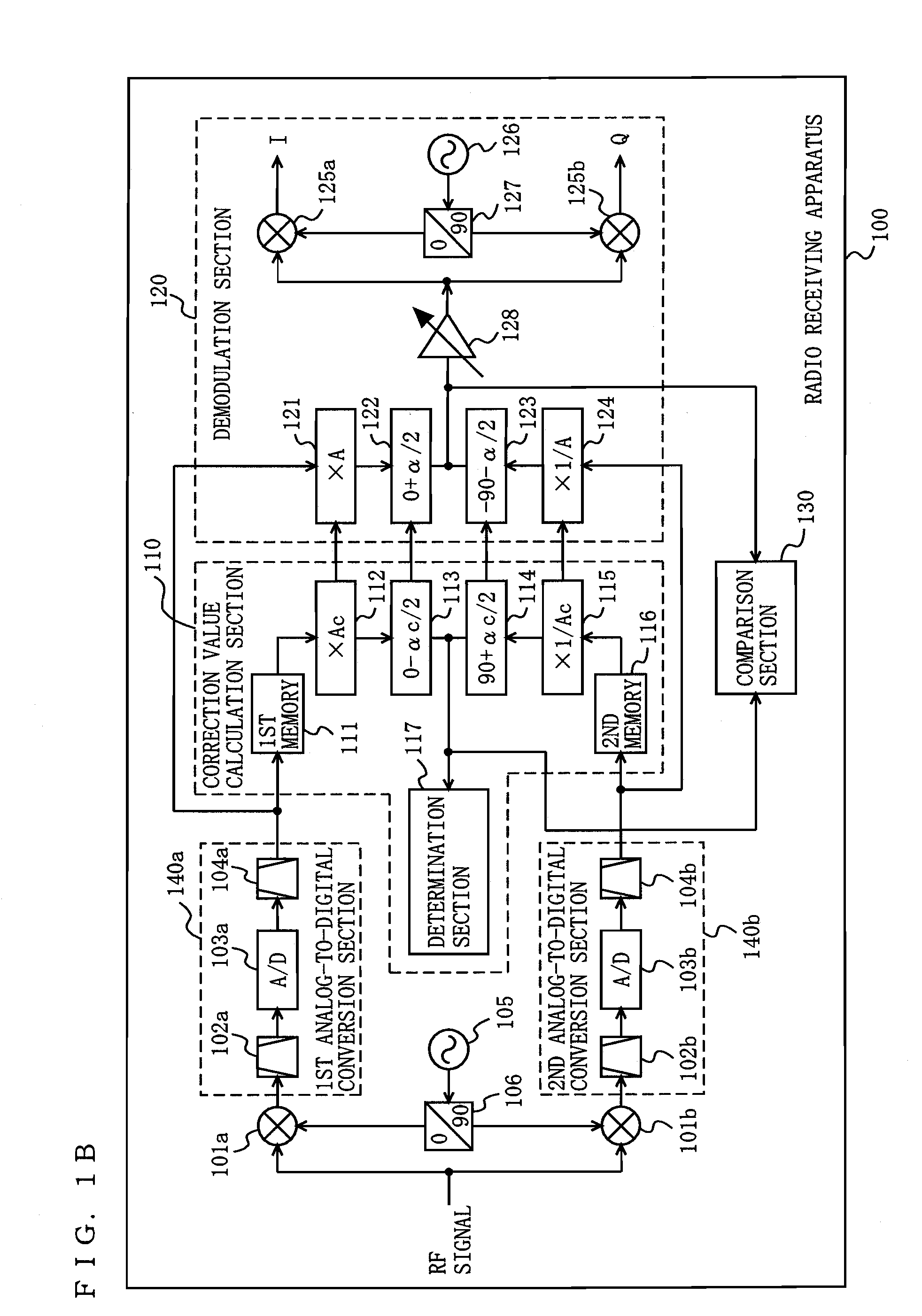
Radio receiving device
ActiveUS20100189197A1Suppress image noiseAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsAmplitude demodulationPhase correctionPhase variation
A radio receiving apparatus capable of making compensation for both amplitude variations and phase variations and of suppressing image interference in a short period of time is provided.A correction value calculation section (110) combines a signal, obtained by multiplying a first digital signal by an amplitude correction candidate value and rotating the phase of the first digital signal, with a signal obtained by multiplying a second digital signal by a multiplicative inverse of the amplitude correction candidate value and performing, for the second digital signal, phase rotation which is in a quadrature relationship to phase rotation performed for the first digital signal, so as to obtain a first combined signal, obtain an inflection point of the first combined signal, and input, to a demodulation section (120), the amplitude correction candidate value and a phase correction candidate value, which correspond to the inflection point, as an amplitude correction value and a phase correction value, respectively. The demodulation section (120) makes compensation for the amplitudes and the phases and suppresses image interference, based on the amplitude correction value and the phase correction value.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Detection and location of boundary intrusion, using composite variables derived from phase measurements
A disturbance, such as vibration from human activity, is located along a fiberoptic waveguide configuration (301-304) with two interferometers (801, 802) of the same or different types, such as Mach-Zehnder, Sagnac, and Michelson interferometers. Carrier signals from a source (101) are split at the interferometer inputs (201, 202) and re-combined at the outputs (701, 702) after propagating through the detection zone (401), where phase variations are induced by the disturbance (501). Phase responsive receivers (901, 902) detect phase relationships (1001, 1002) between the carrier signals over time. A processor (1101) combines the phase relationships into composite signals according to equations that differ for different interferometer configurations, with a time lag between or a ratio of the composite signals representing the location of the disturbance. The detected and composite values are unbounded, permitting phase displacement to exceed the carrier period and allowing disturbances of variable magnitudes to be located.
Owner:OPTELLIOS
Portable mobile terminal and transmission unit
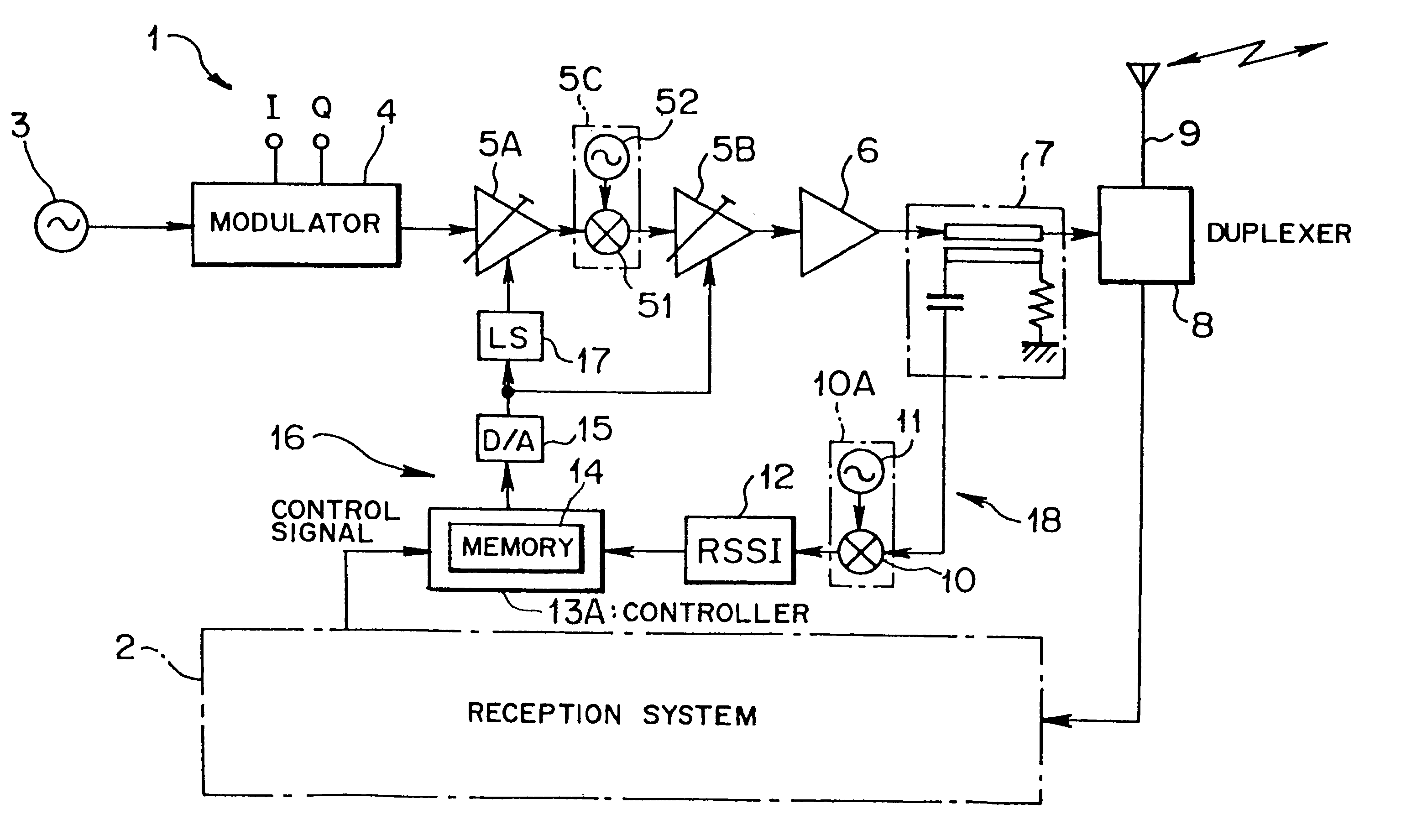
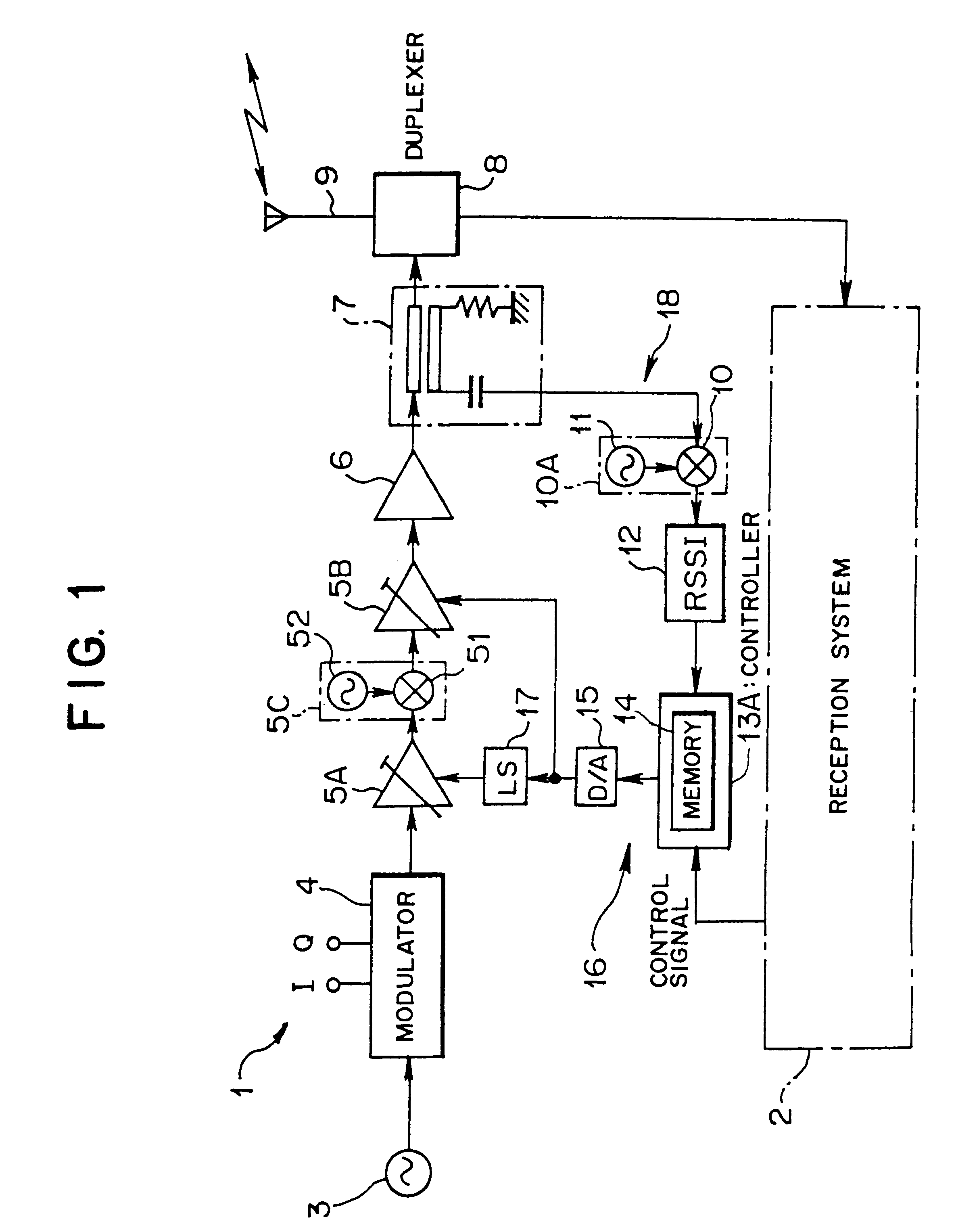
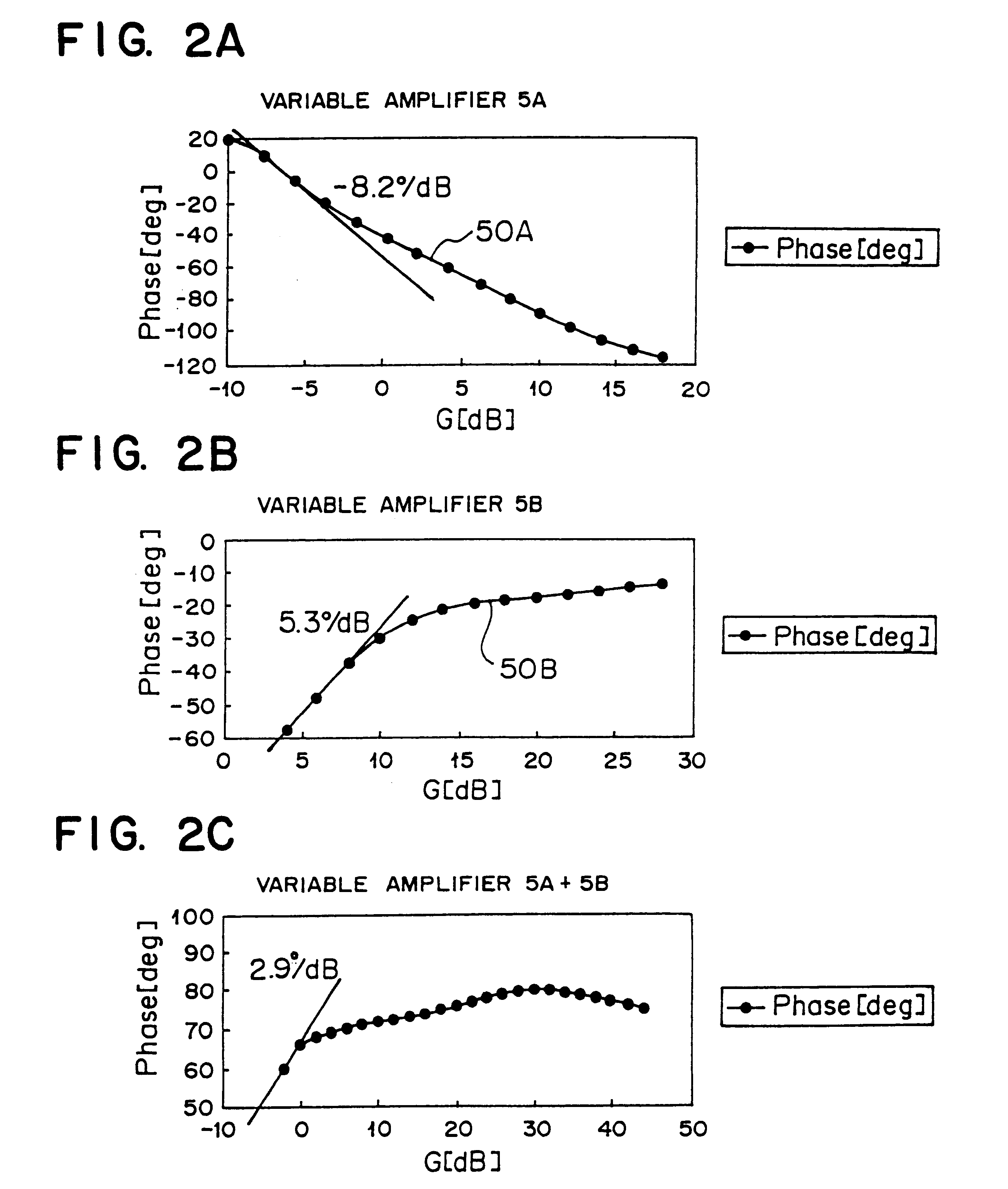
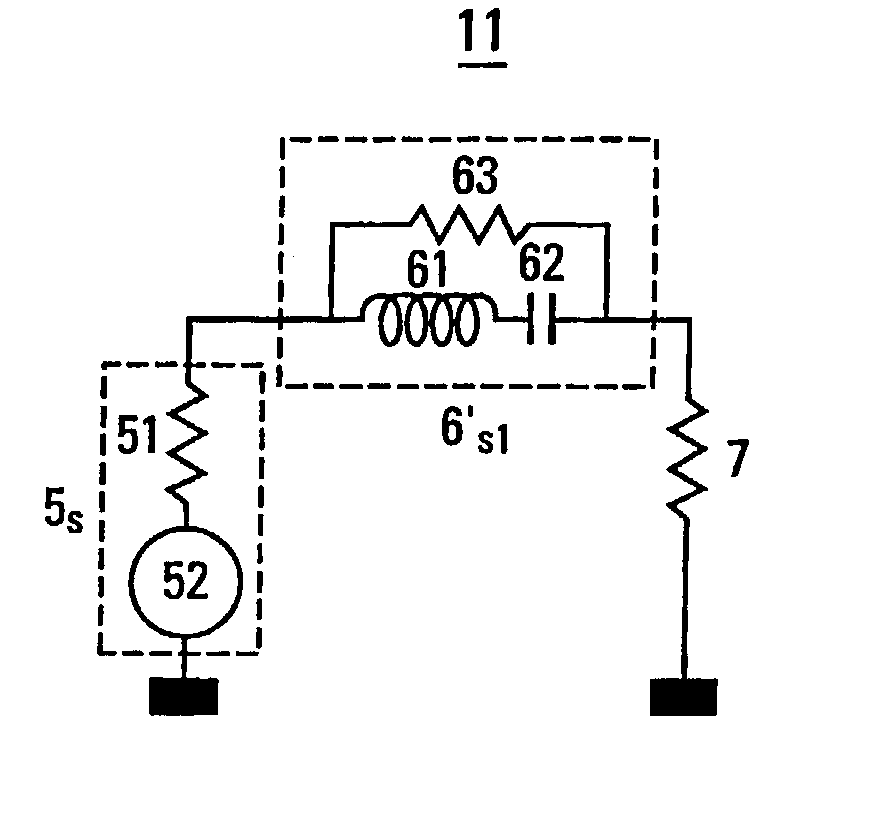
A portable mobile terminal or a transmission unit, applicable to multiplex radiocommunication systems including a CDMA, comprises a modulating section for modulating a transmission signal by using a spectrum spread system, an amplifying section for amplifying the modulated transmission signal to a needed transmission power, a plurality of variable gain units provided between the modulating section and the amplifying section to be connected in series to each other to provide an ability of changing a gain of the transmission signal modulated by the modulating section, and respectively having gain-to-phase characteristics set to cancel a phase variation of the transmission signal to the entire gain variation, and a control section for controlling a gain of each of the variable gain units. The portable mobile terminal and the transmission unit can control the transmission power in multistage throughout a wide range, and can minimize the phase variation of the transmission signal at that time.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Continuous-time integrating filter with minimum phase variation, and bandpass sigma delta modulator using such a filter
The disclosure pertains to continuous-time filtering. More particularly, it relates to filtering in a feedback control loop, for example in a sigma-delta (SigmaDelta) modulator. The making of a filter for this type of application comes up against a major problem linked to the relativity between the amplitude and phase responses. This limits the possibilities of choice in order to take steps against the instability of the loop. A continuous-time filter with minimum phase variation carries out the bandpass integration of the signal presented at its input. The making of the continuous-time filter as a bandpass integrator raises the problem of achieving a compromise between gain variations and phase variations close to the -1 critical point, This compromise must lead to the stability of the loop. This problem is resolved by using a continuous-time bandpass integrating filter comprising at least one resonance device with minimum phase variation.
Owner:THALES SA
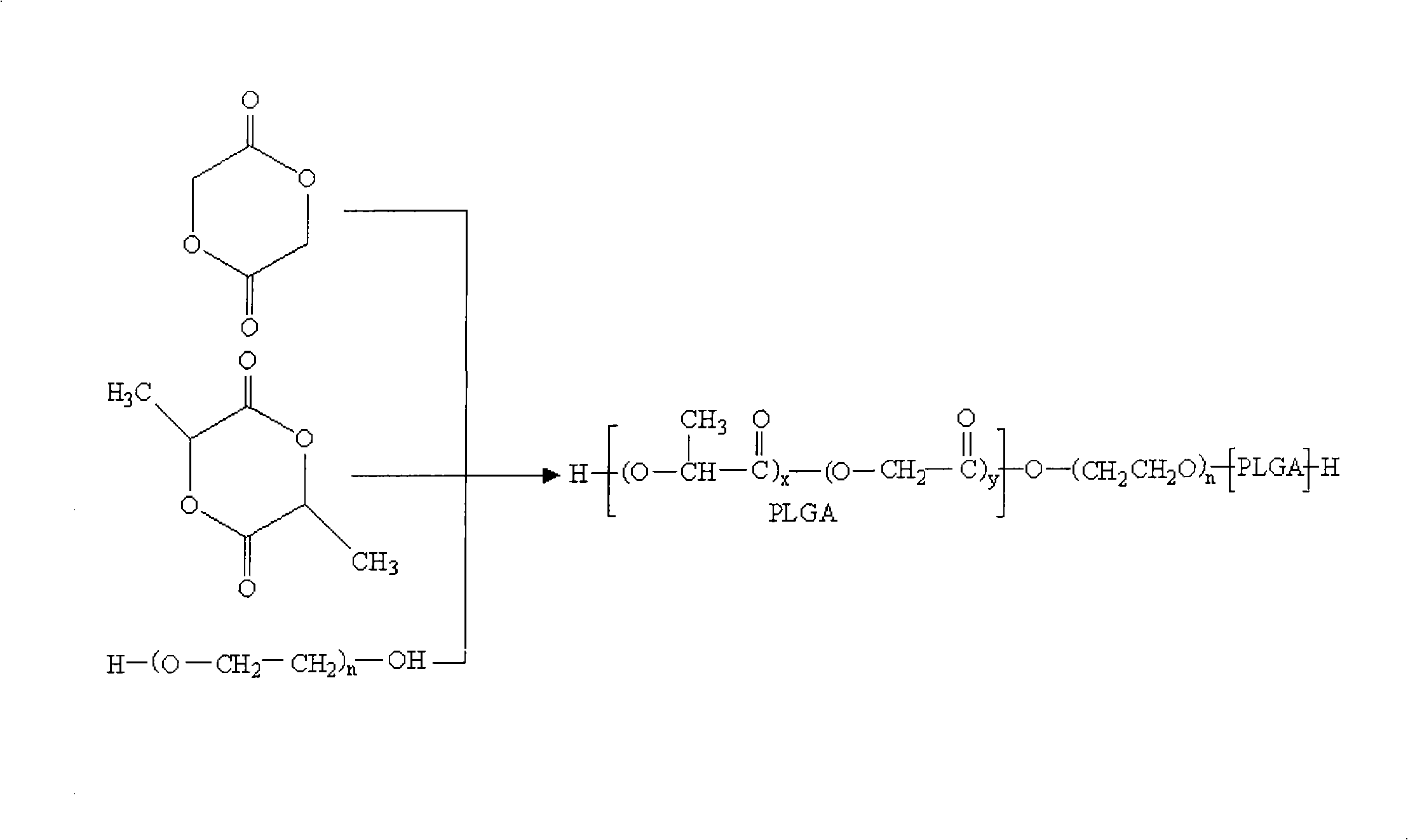
Copolymer with temperature/PH dual-sensibility and preparation and application thereof
InactiveCN101538368AAvoid disadvantagesImprove responsivenessPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsPolyethylene glycolCopolymer
The invention relates to a novel temperature / PH dual-sensibility self-assembly segmented copolymer, i.e. polyhistidine-polylactic-co-glycolic acid-polyethyleneglycol-polylactic-co-glycolic acid-polyhistidine (OLH-b-PLGA-b-PEG-b-PLGA-b-OLH), belonging to the technical field of medicine. The self-assembly segmented copolymer accords with the structural features of a temperature / PH unika polymer, and a molecular structure of the self-assembly segmented copolymer respectively comprises a polylactic-co-glycolic acid-polyethyleneglycol-polylactic-co-glycolic acid (PLGA-b-PEG-b-PLGA) chain link which responds to temperature change and a low polyhistidine chain link which responds to PH change; copolymers can be dissolved into water under room temperature to form a free-pouring micellar solution,and when the temperature and the PH of an external environment change, the copolymers with different structural proportions are respectively expressed as follows: (1) the phase variation of solution-gelatin, and (2) the response action of the dissociation of a micellar structure, wherein the copolymer with the response action of the (1) can be taken as a carrier of an injection type sustained controlled-release drug delivery system, and the copolymer with the response action of the (2) can be taken as a carrier of a micellar target drug delivery system.
Owner:SHENYANG PHARMA UNIVERSITY
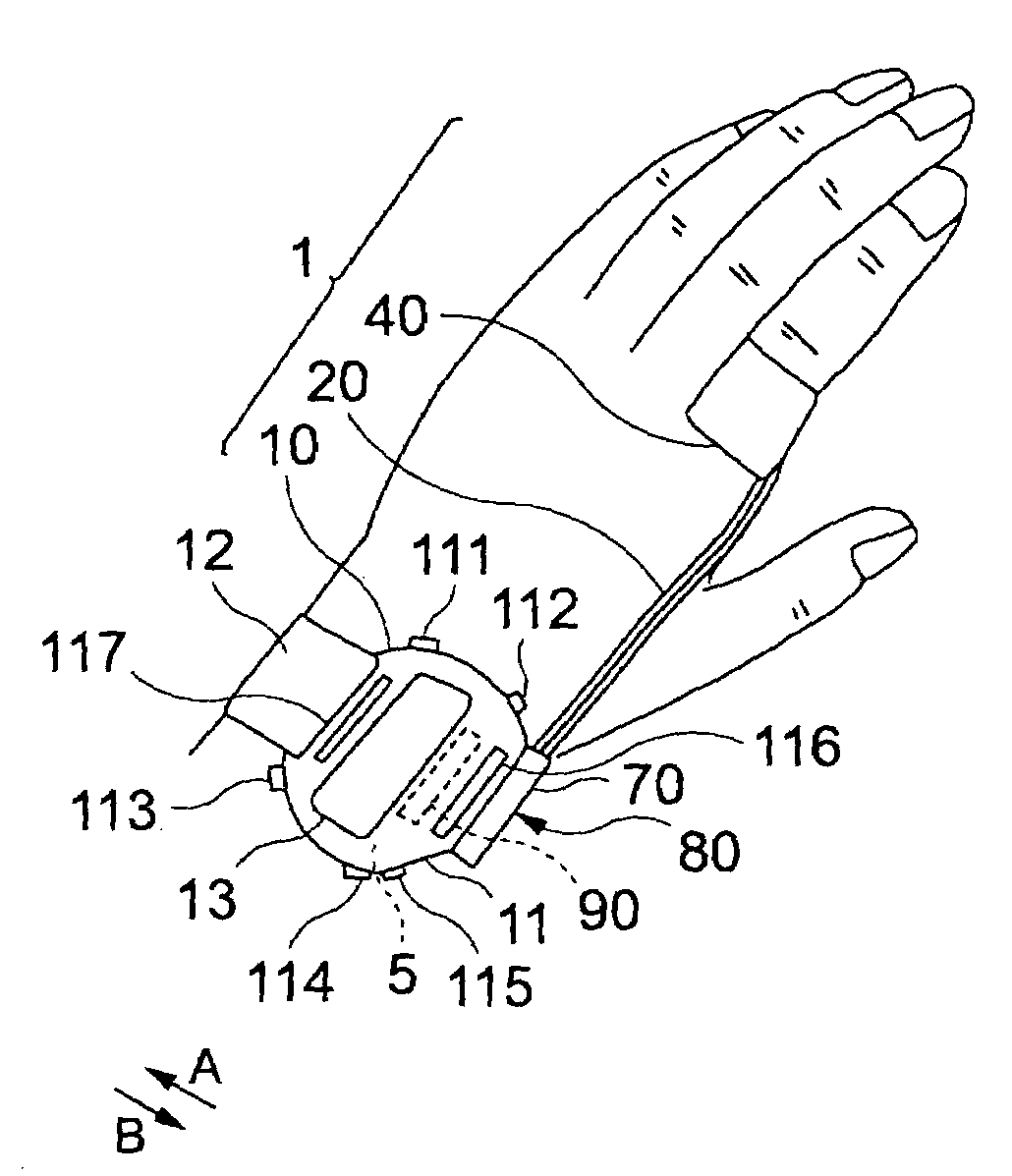
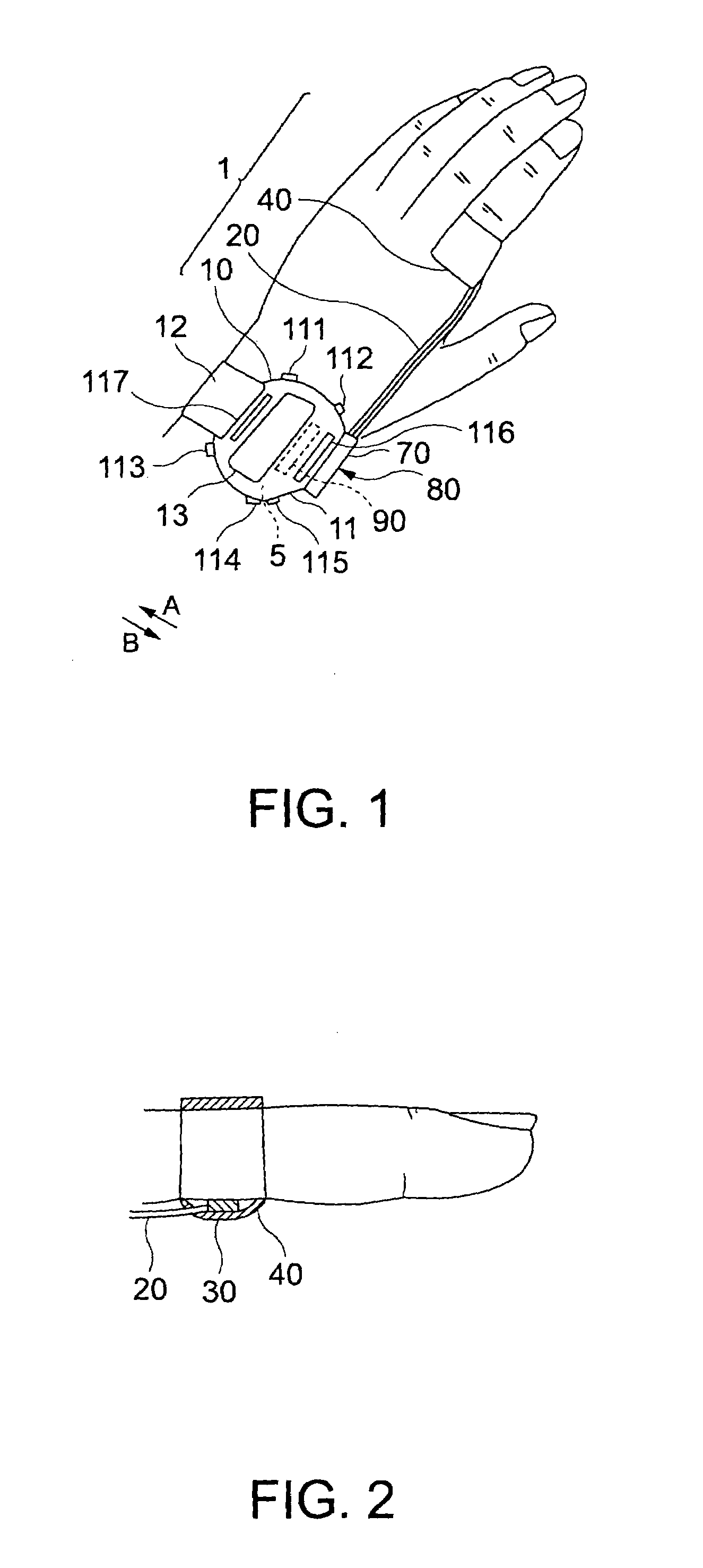
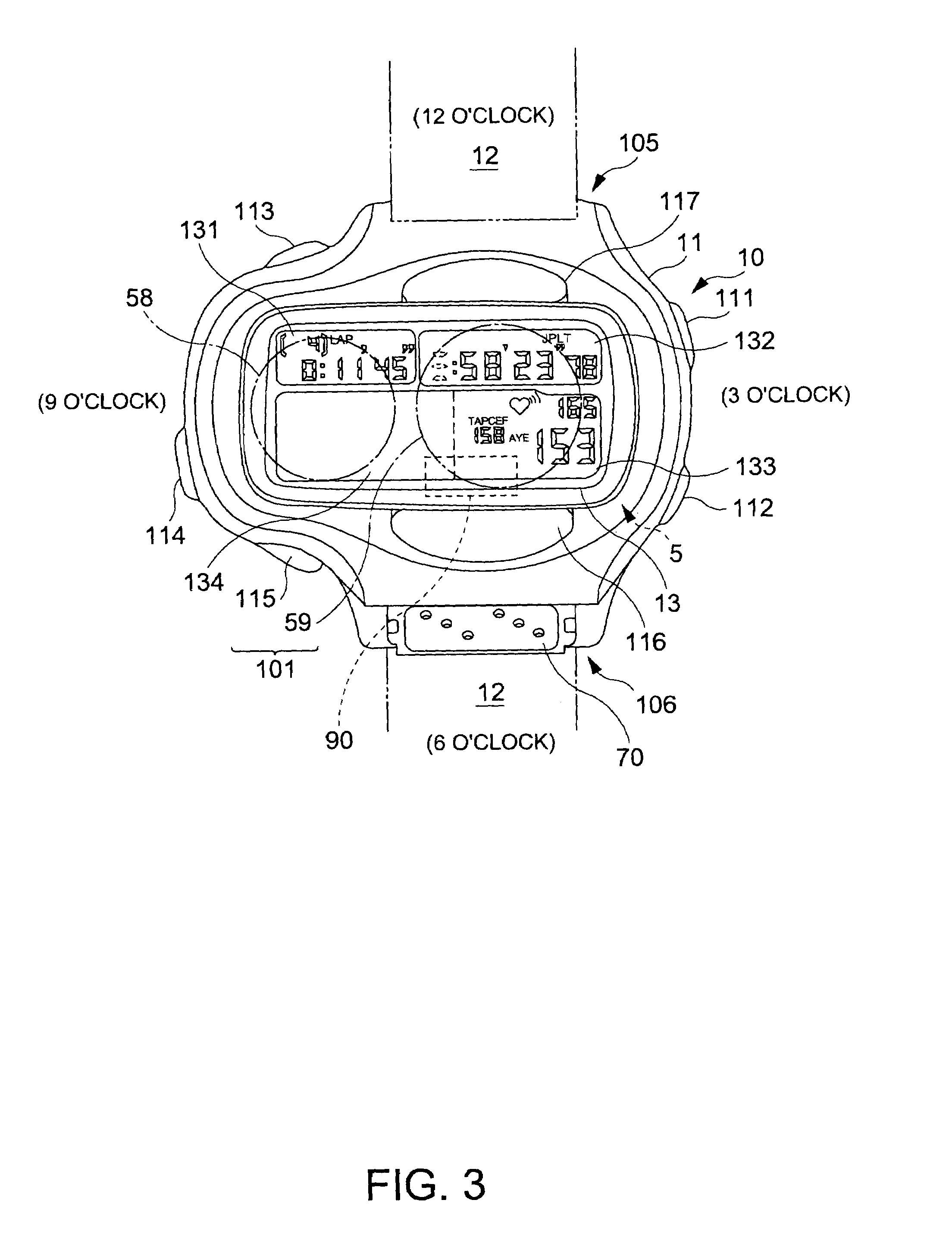
Pulsimeter, control method for pulsimeter, wristwatch information device, control program, and recording medium
A frequency analyzer carries out a frequency analysis on a pulse wave signal output from a pulse wave detector. A candidate extractor extracts candidate spectrum peaks from a frequency analysis result of the frequency analyzer. A phase variation calculator calculates variations in phase angle of each of the extracted candidate spectrum peaks, and a spectrum peak selector selects a target spectrum peak from among the extracted candidate spectrum peaks based on their respective variations in phase angle. A pulse rate is calculated using the target spectrum peak.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
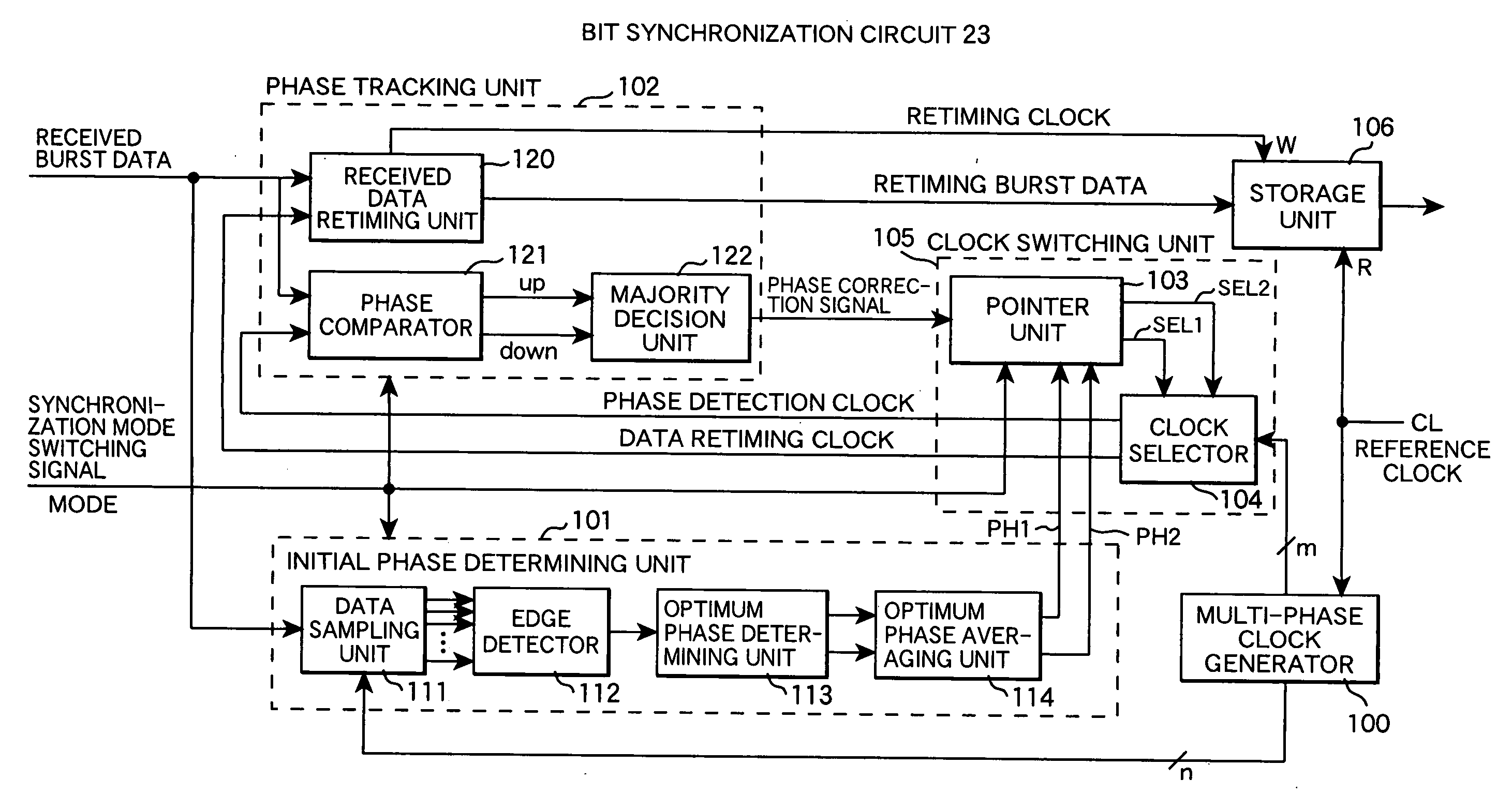
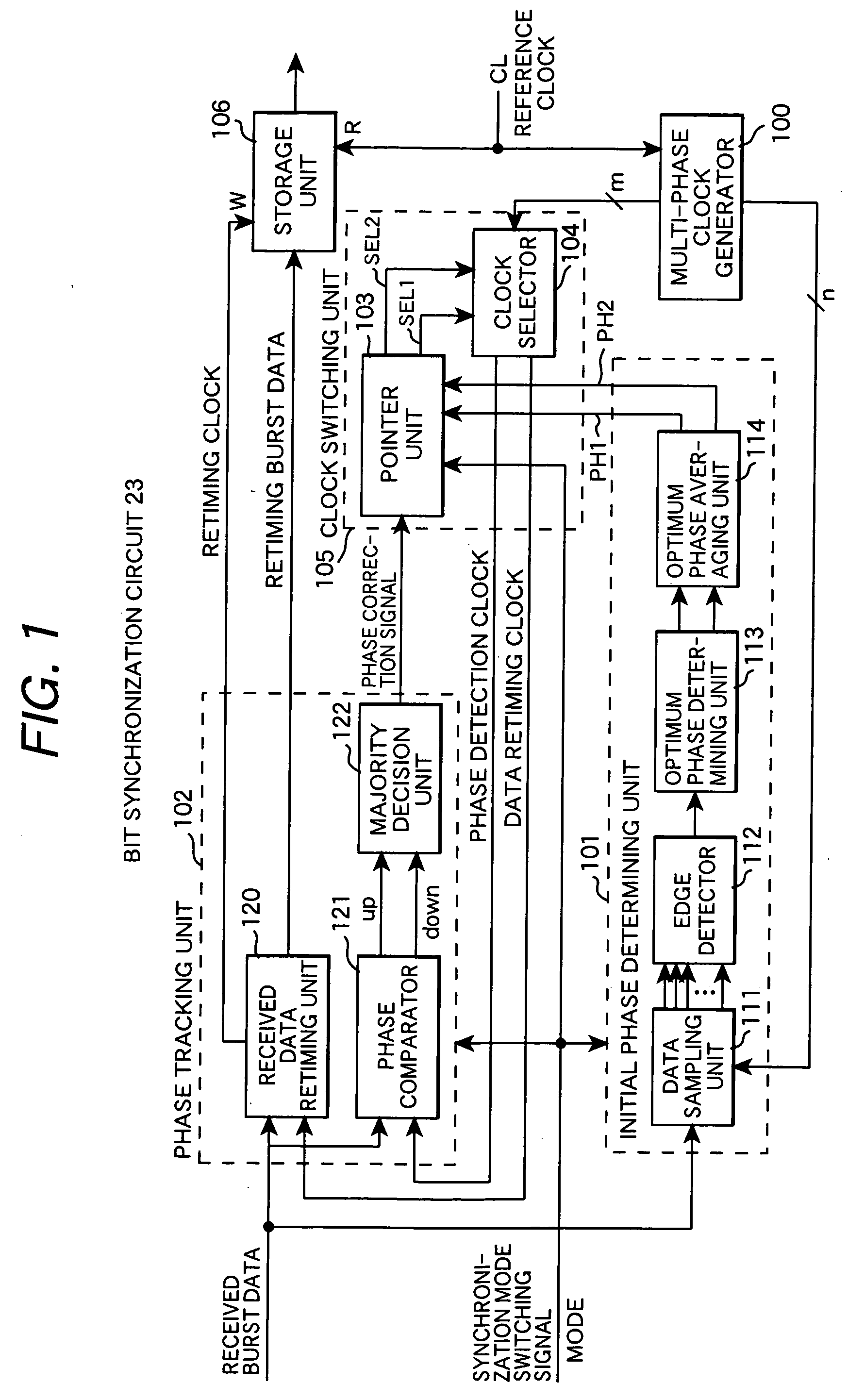
Bit synchronization circuit with phase tracking function
InactiveUS20070030937A1Reduce power consumptionQuick fixReceiver initialisationPulse automatic controlData synchronizationPhase relation
A bit synchronization circuit comprising an initial phase determining unit for rapidly determining, during a period of receiving a preamble of burst data, a clock with a phase synchronized with received burst data from among multi-phase clocks having the same frequency as an internal reference clock and a phase tracking unit for modifying the synchronized phase clock responsive to phase variation of received data during a period of receiving a payload of burst data by taking the synchronized phase clock determined by the initial phase determining unit as an initial phase. The bit synchronization circuit retimes burst data with a data retiming clock having a predetermined phase relation with the synchronized phase clock and outputs the burst data in synchronization with the internal reference clock.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
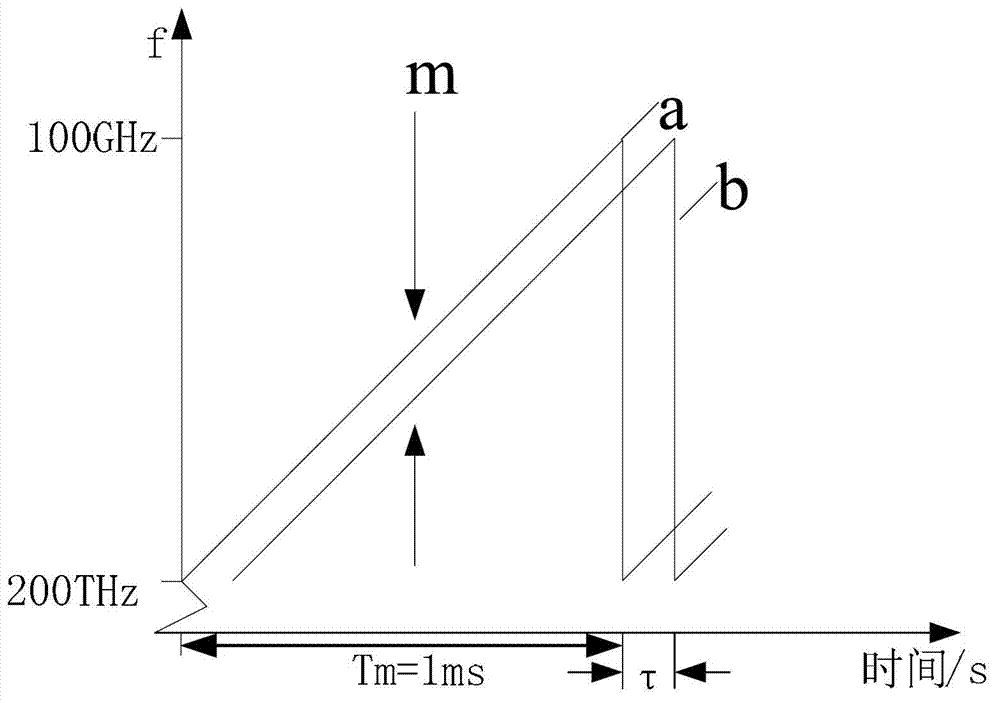
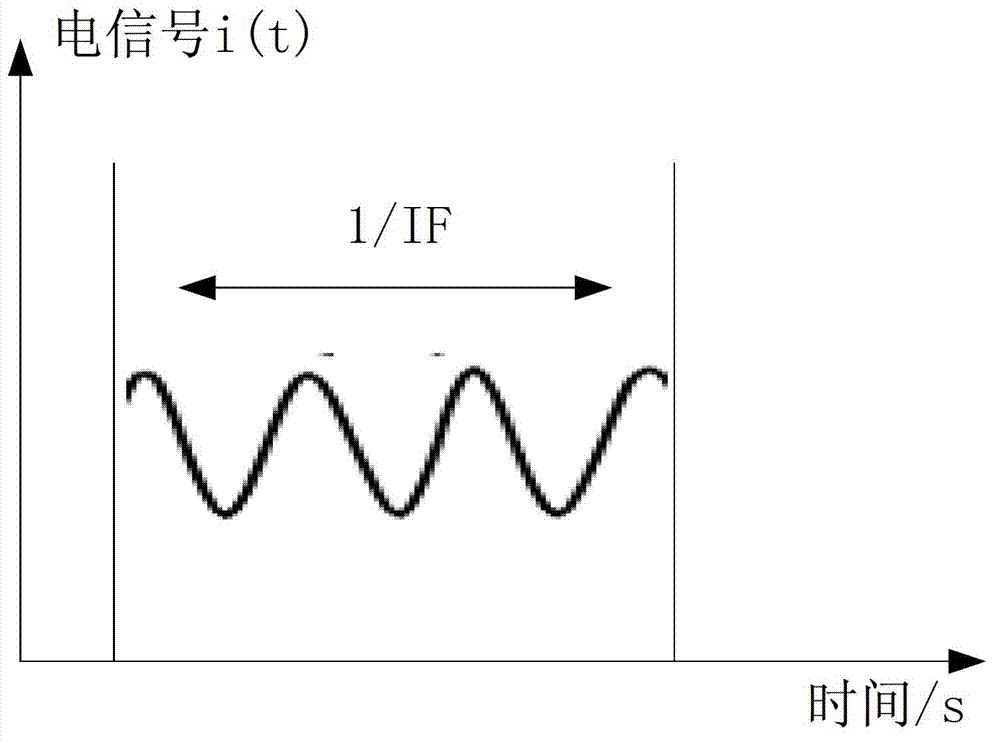
Frequency modulated continuous wave (FMCW) laser radar high-accuracy signal measurement method based on phase demodulation method
InactiveCN103163513AOvercoming problems affected by nonlinearity of laser frequency modulationOvercoming Signal Quality ShortcomingsWave based measurement systemsSignal qualityMeasurement precision
The invention discloses a frequency modulated continuous wave (FMCW) laser radar high-accuracy signal measurement method based on a phase demodulation method, relates to a signal demodulation method for resisting laser frequency modulation nonlinear interference, and aims to the problem of low measurement accuracy due to the influence of laser frequency modulation nonlinearity of a beat frequency signal frequency demodulation technology in a conventional FMCW-technology-based laser radar signal measurement method for detecting the appearance of a workpiece, and due to the limitation of signal quality in the whole sampling time period on signal subdividing number during the extraction of beat frequency signal frequency. By using the phase demodulation method, a relationship between a beat frequency signal phase variation in a frequency modulation laser radar light path and the time delay tau of a measurement light path relative to a reference light path is obtained, a measured distance value R is calculated, and the FMCW laser radar high-accuracy signal measurement method is implemented. The method is applied to the field of high-accuracy FMCW laser radar distance measurement.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com