Patents
Literature
149 results about "Frequency dependence" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Frequency-dependent selection occurs when the fitness of a genotype depends on its frequency. It is possible for the fitness of a genotype to increase (positively frequency-dependent) or decrease (negatively frequency-dependent) as the genotype frequency in the population increases. Examples of frequency dependence can arise in systems of mimicry:
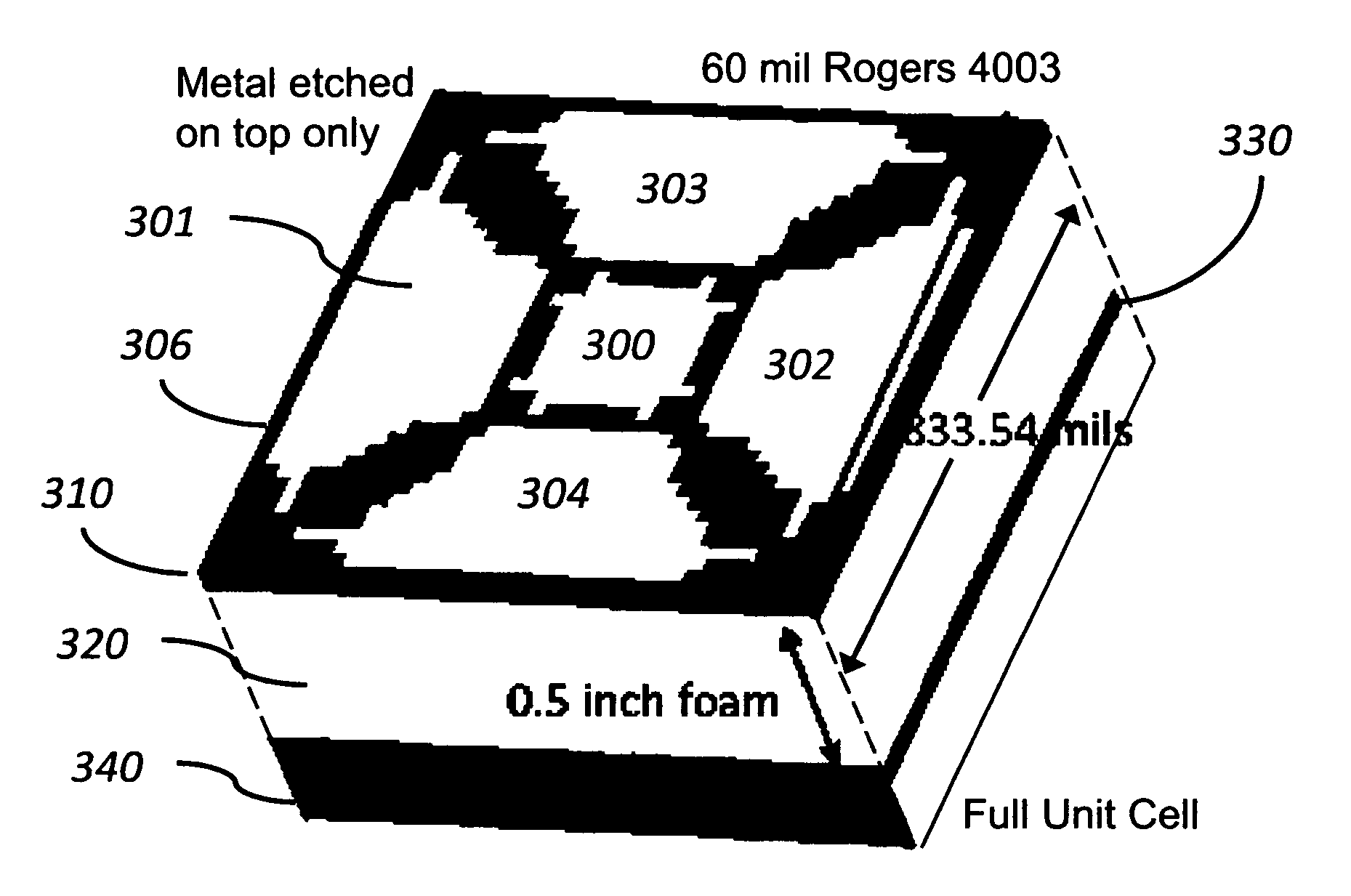
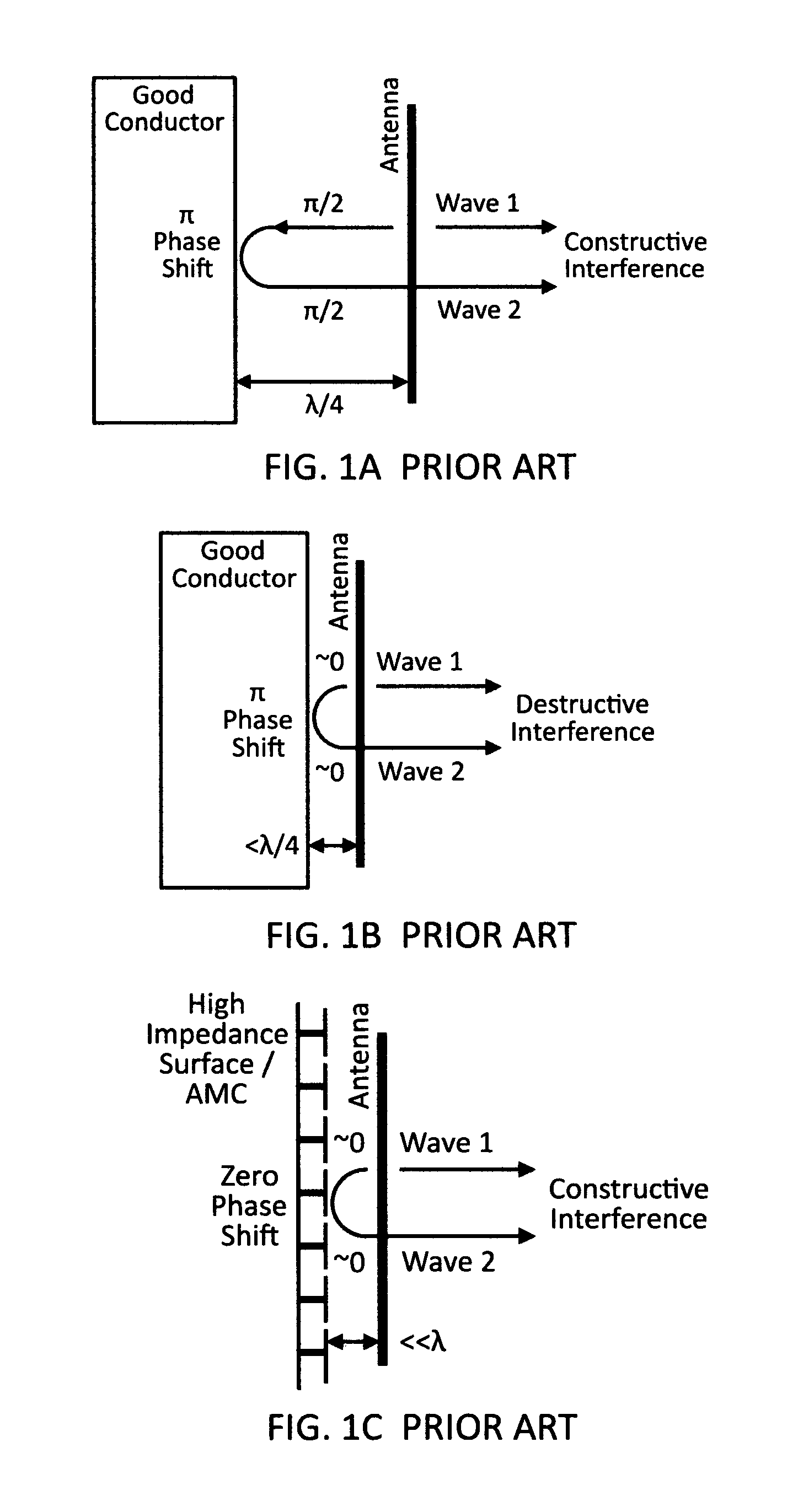
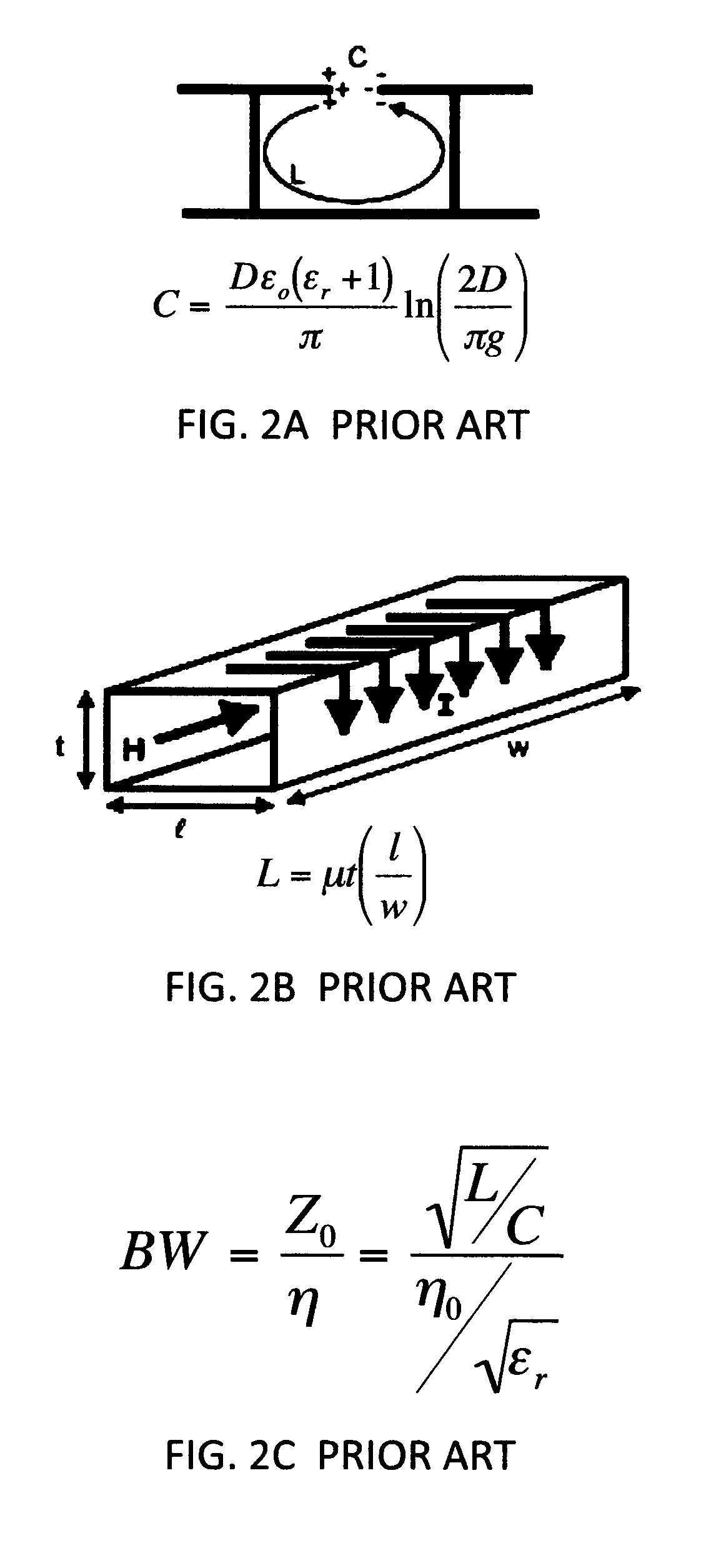
Ultra-wide band (UWB) artificial magnetic conductor (AMC) metamaterials for electrically thin antennas and arrays
InactiveUS8451189B1Maximize received power transferMinimize reflectionAntenna feed intermediatesAntenna designFractional bandwidth
This disclosure demonstrates a new class of Ultra-Wide Band (UWB) AMC with very large fractional bandwidth (>100%) even at lower frequencies (<1 GHz). This new UWB AMC is enabled by recognizing that any AMC must be an antenna in order to accept the incident radiation into the circuit. Therefore, by using UWB antenna design features, one can make wide band AMCs. Additionally, by manipulation of the UWB AMC element design, a 1 / frequency dependence can be obtained for instantiating the benefits of a quarter wave reflection over a large UWB bandwidth with a single physical thickness.
Owner:FLUHLER HERBERT U
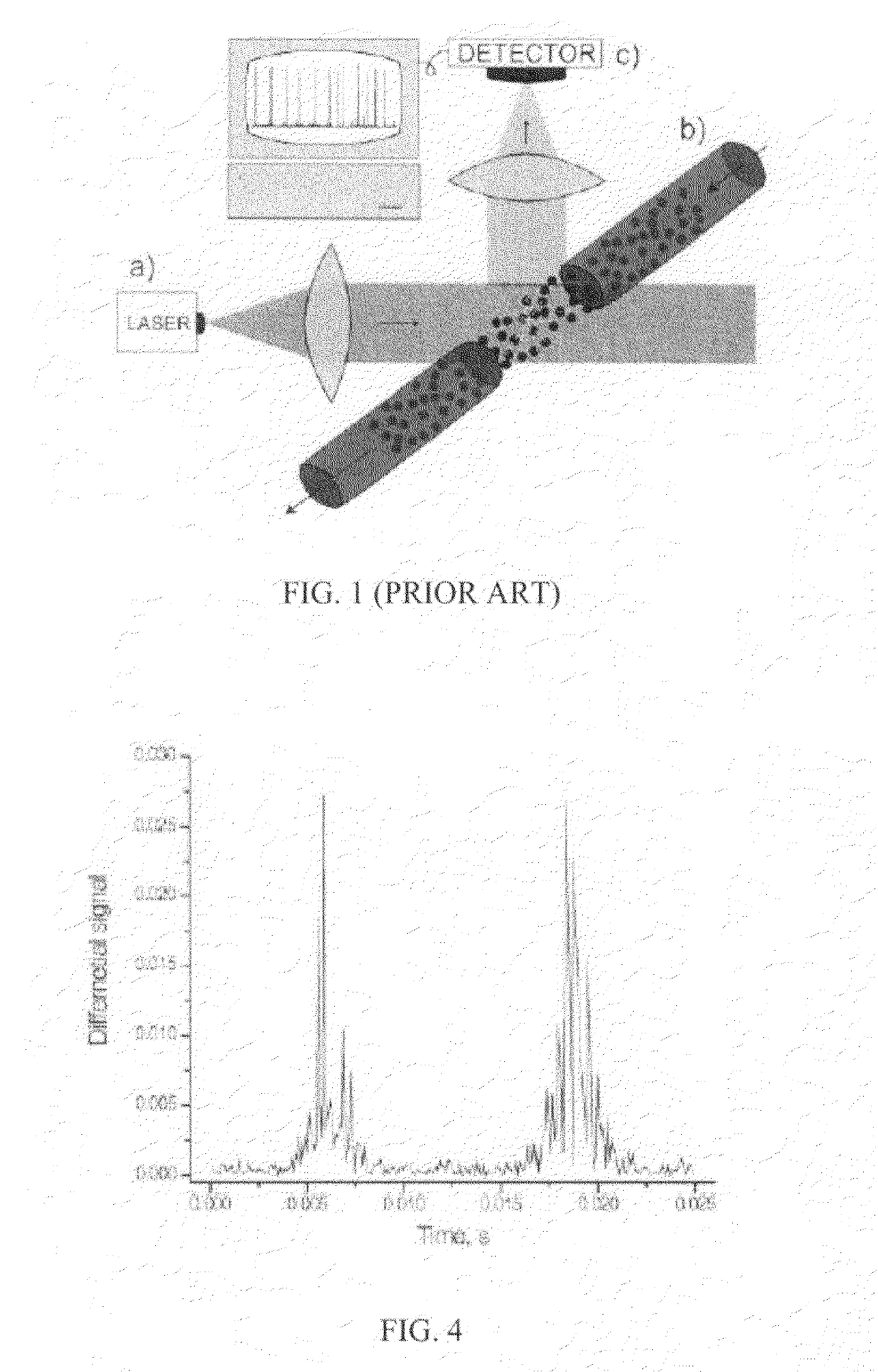
Multi-color hetereodyne interferometric apparatus and method for sizing nanoparticles
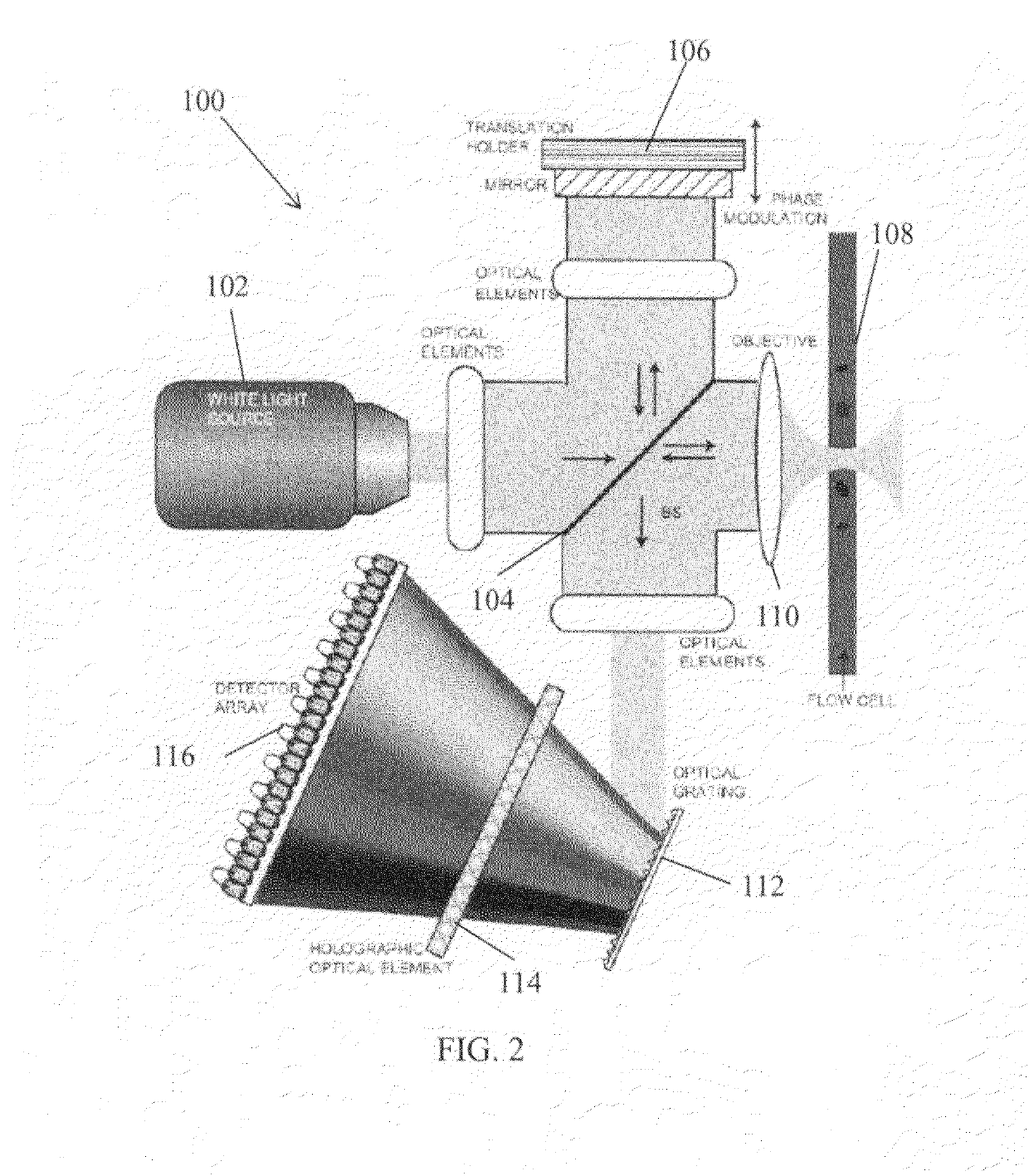
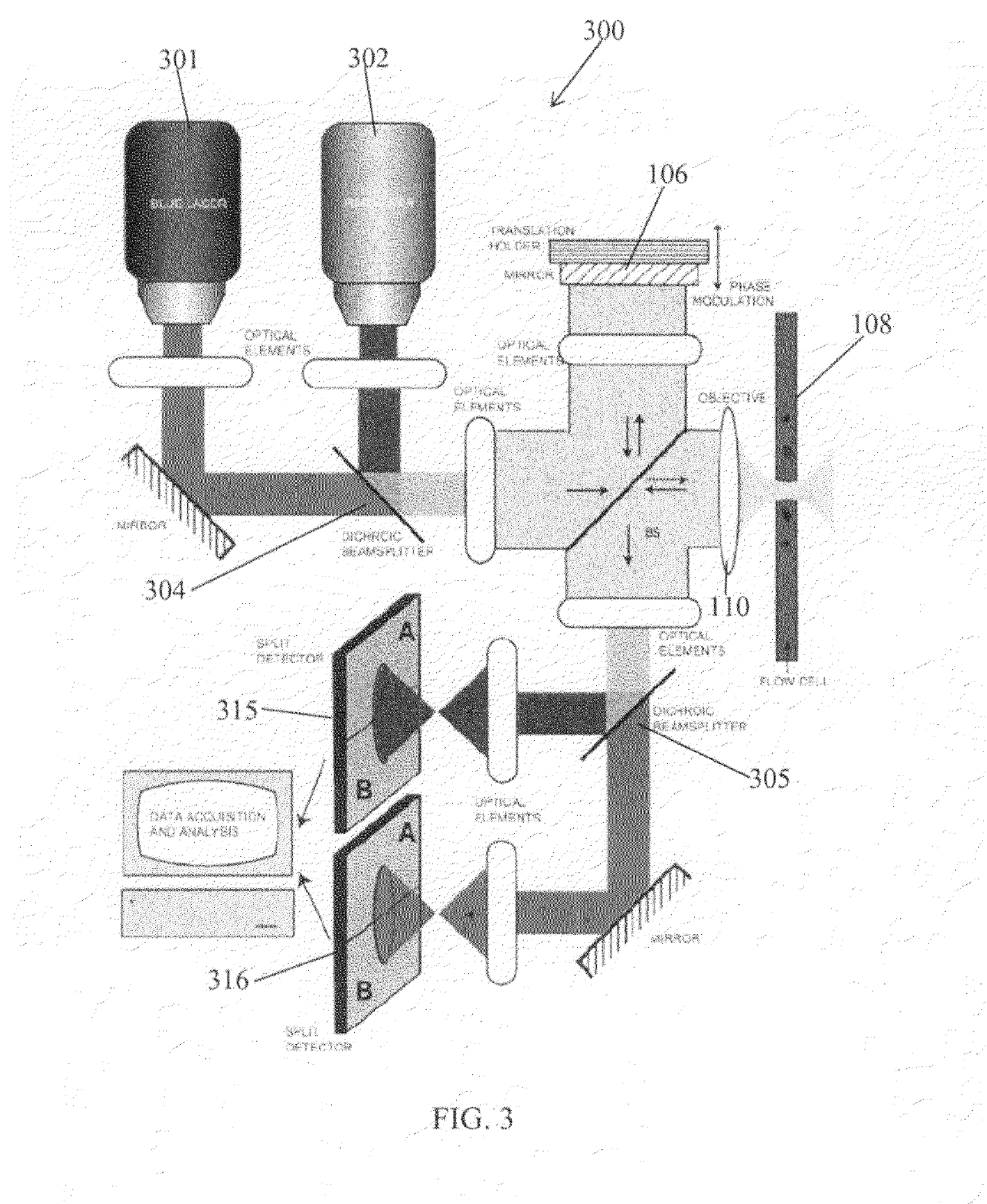
A nanoparticle sensor is capable of detecting and recognizing single nanoparticles in an aqueous environment. Such sensor may find applications in broad areas of science and technology, from the analysis of diesel engine emissions to the detection of biological warfare agents. Particle detection is based on interferometric detection of multi-color light, scattered by the particle. On the fundamental level, the detected signal has a weaker dependence on particle size (ÿ R3), compared to standard detection methods (ÿ R6). This leads to a significantly larger signal-to-noise ratio for smaller particles. By using a multi-color or white excitation light, particle dielectric properties are probed at different frequencies. This scheme samples the frequency dependence of the particle's polarizability thereby making it possible to predict the composition of the particle material. The detection scheme also employs a heterodyne or pseudoheterodyne detection configuration, which allows it to reduce or eliminate noise contribution from phase variations, which appear in any interferometric measurements.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
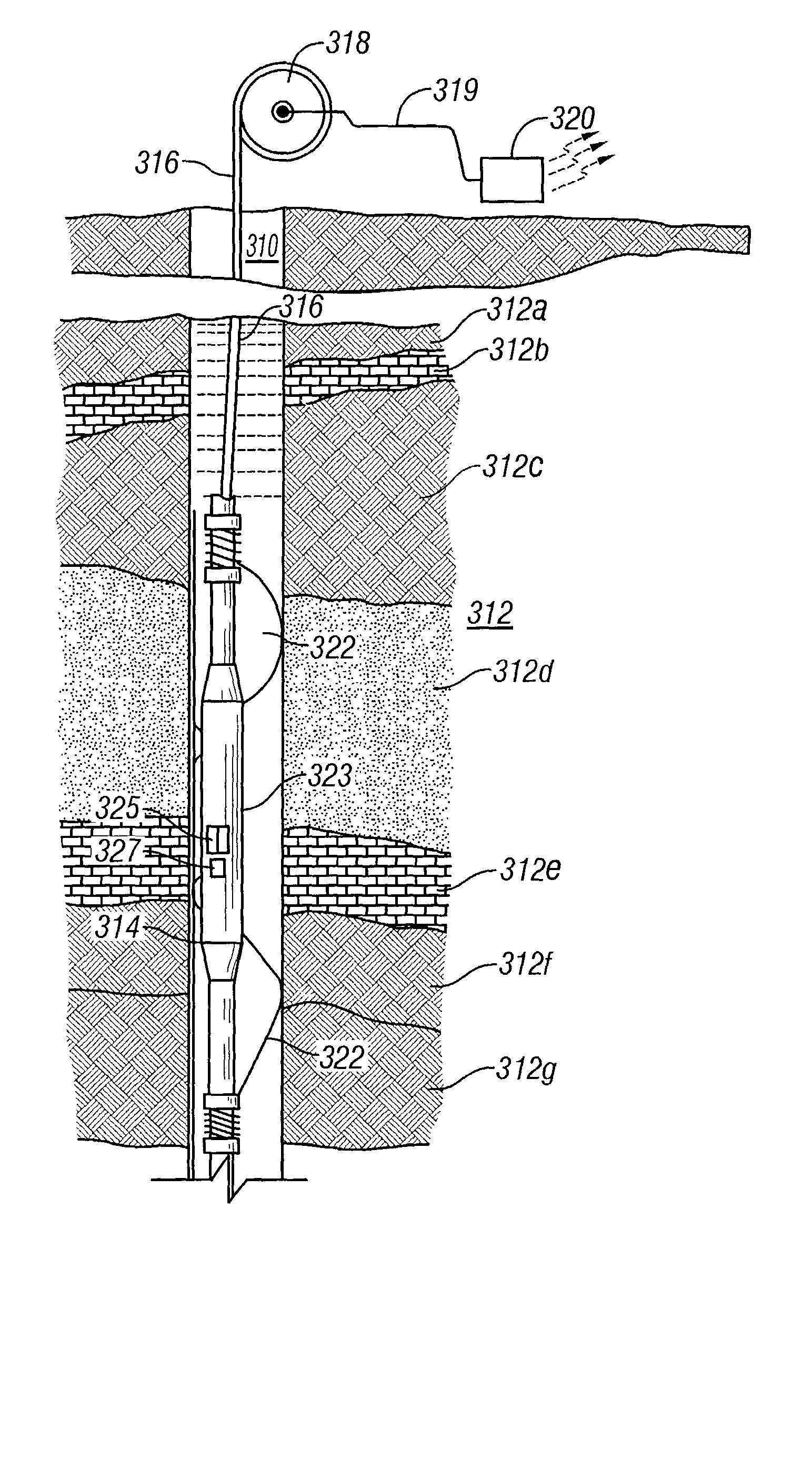
In-situ heavy-oil reservoir evaluation with artificial temperature elevation
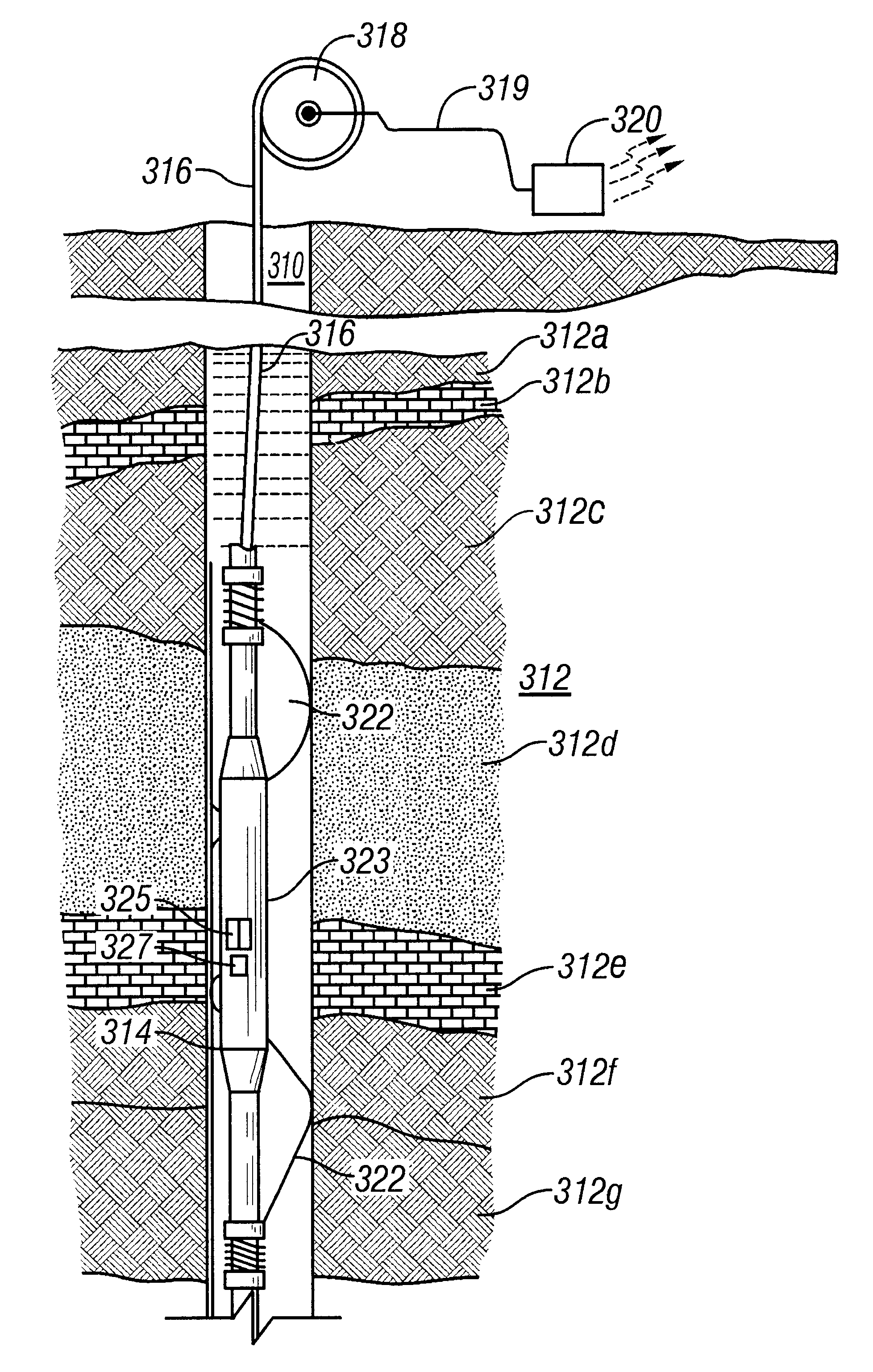
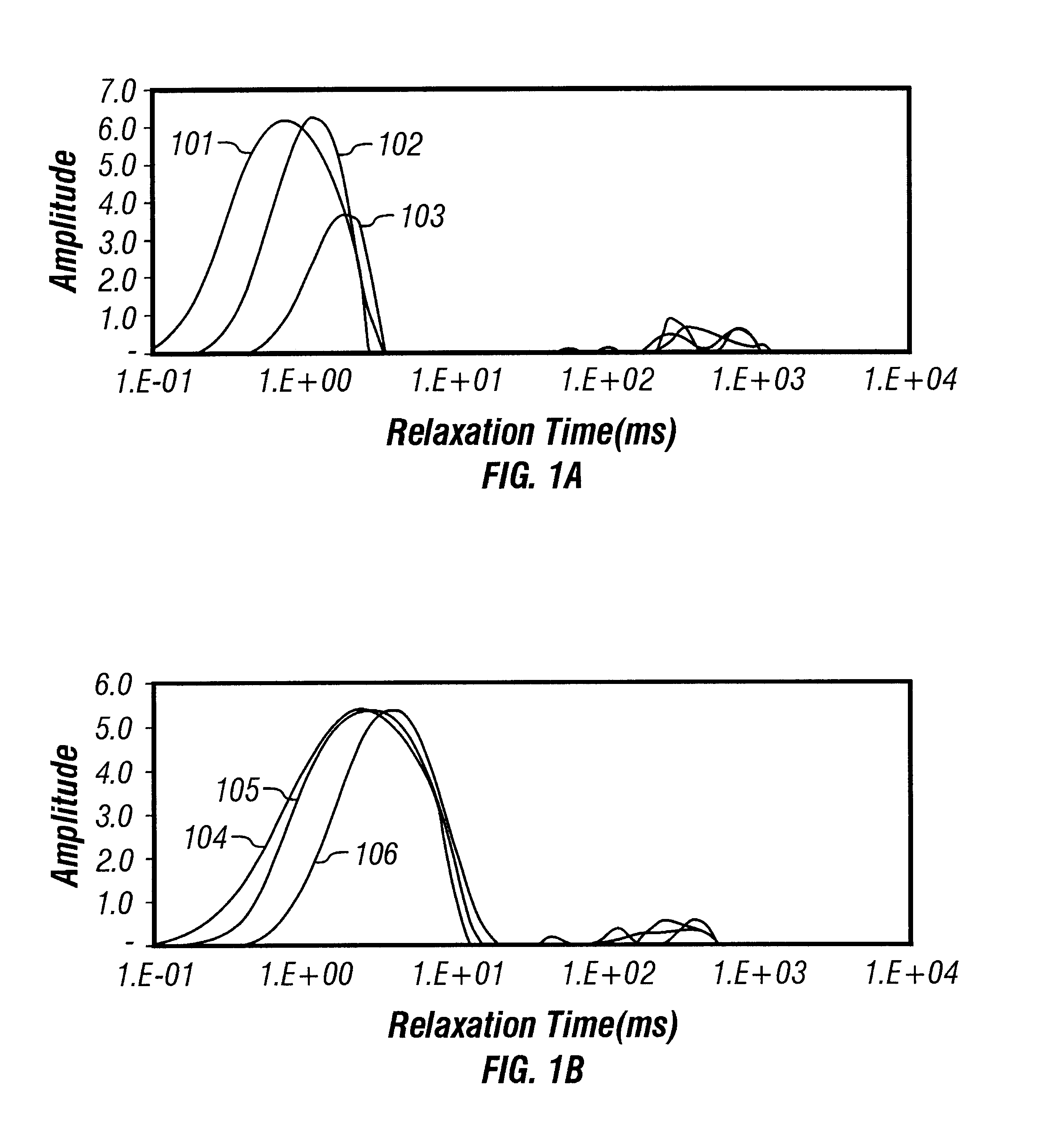
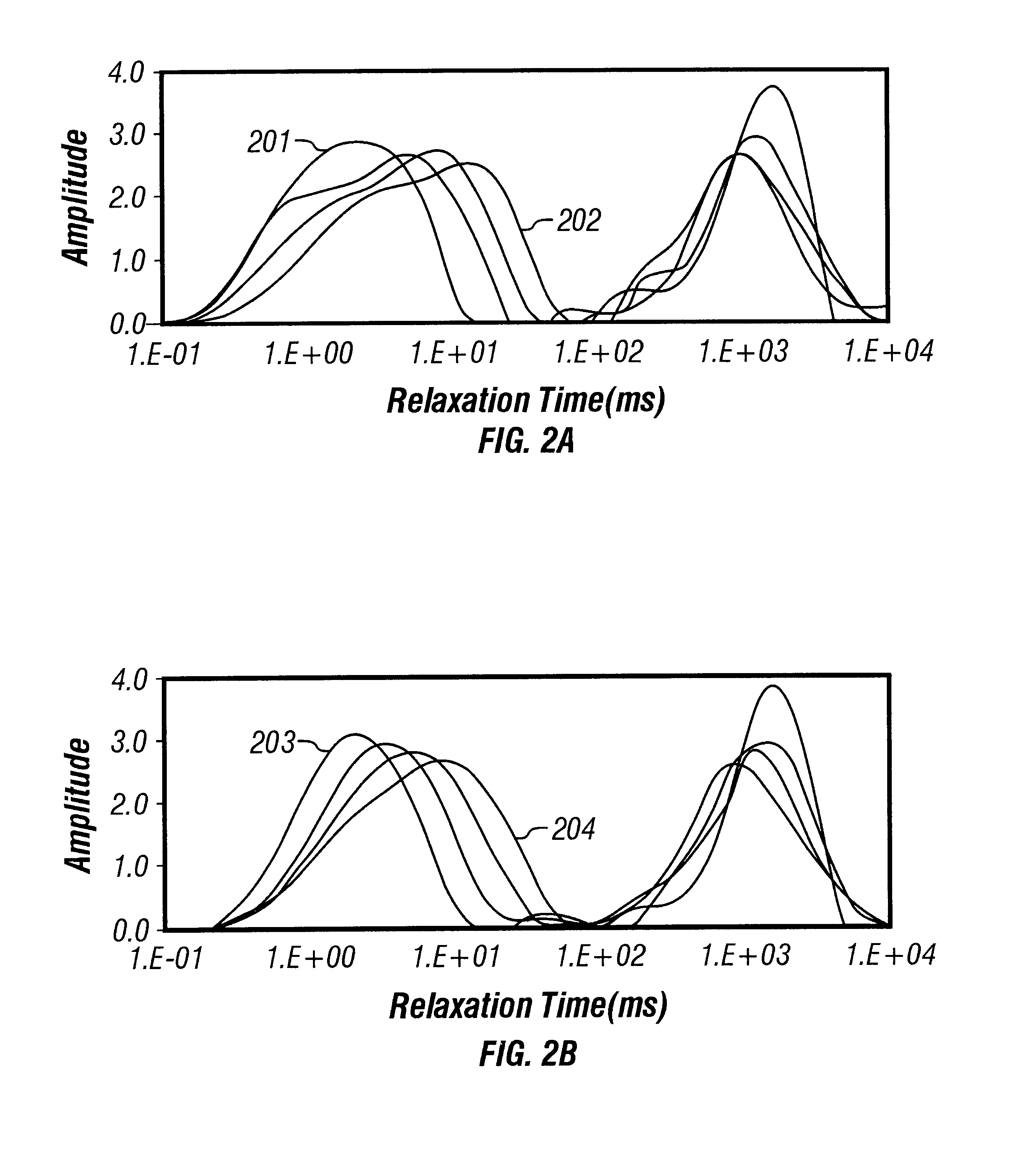
Many reservoirs of interest include heavy oil. In such reservoirs, parti at normal temperatures, many instruments commonly used for formation evaluation may not be able to distinguish between heavy oil and bound water in the formation. Passive or active heating is used to elevate the temperature of the fluids in the formation. At elevated temperatures, distinguishing between heavy oil and bound water is easier. Of particular interest is the increase in the resolvability of the transverse relaxation time T2 of NMR spin echo measurements. Additionally, the dielectric constant and the loss tangents of water and heavy oil show different temperature and frequency dependence.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES HLDG LLC
Optical waveguide structures
The purely bound electromagnetic modes of propagation supported by symmetric waveguide structures comprised of a thin lossy metal film of finite width embedded in an infinite homogeneous dielectric have been characterized at optical wavelengths. The modes supported are divided into four families depending on the symmetry of their fields. In addition to the four fundamental modes that exist, numerous higher order ones are supported as well. A nomenclature suitable for identifying all modes is discussed. The dispersion of the modes with film thickness and width has been assessed and the effects of varying the background permittivity on the characteristics of the modes determined. The frequency dependency of one of the modes has been investigated. The higher order modes have a cut-off width, below which they are no longer propagated and some of the modes have a cut-off thickness.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF OTTAWA
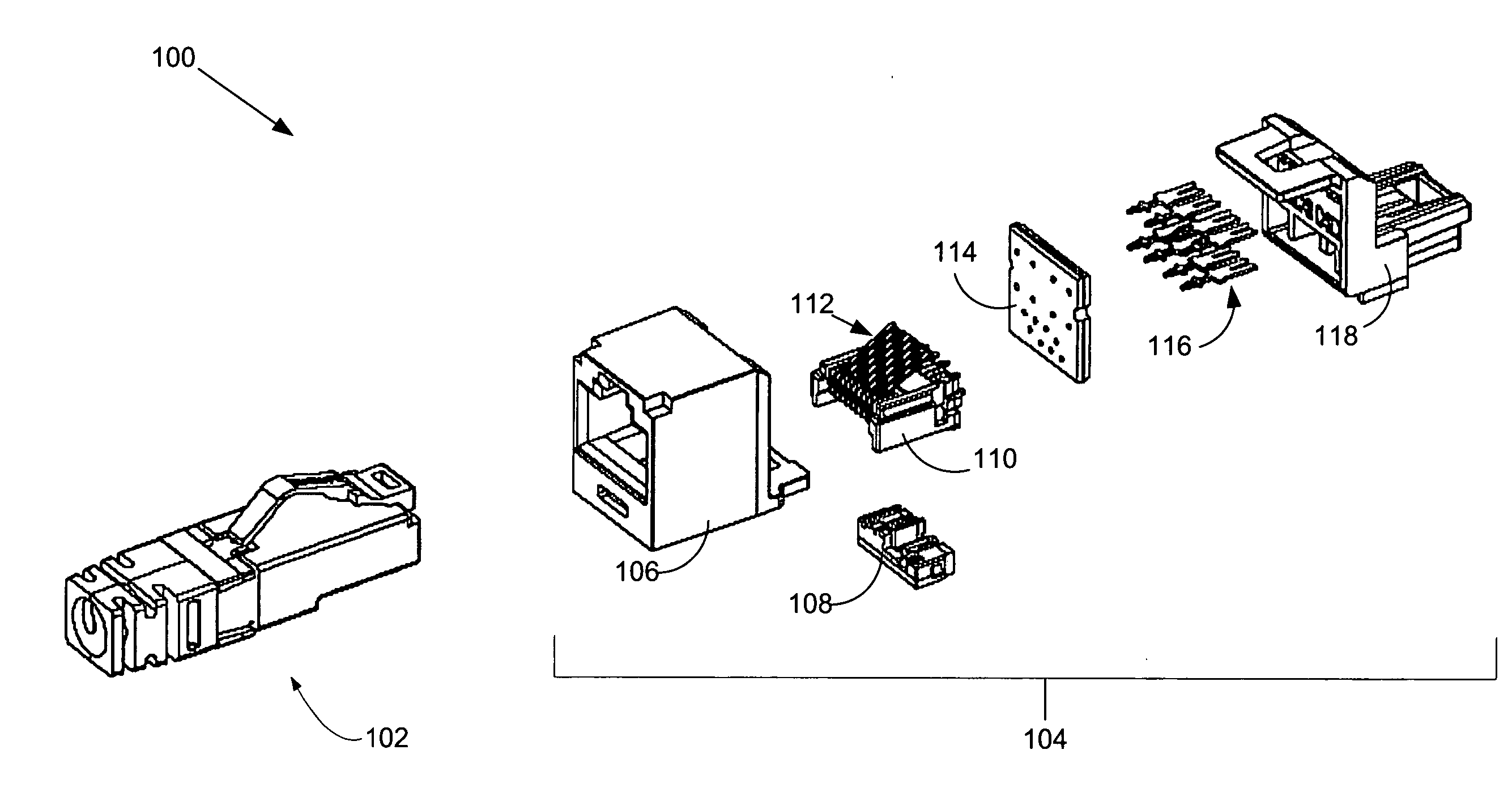
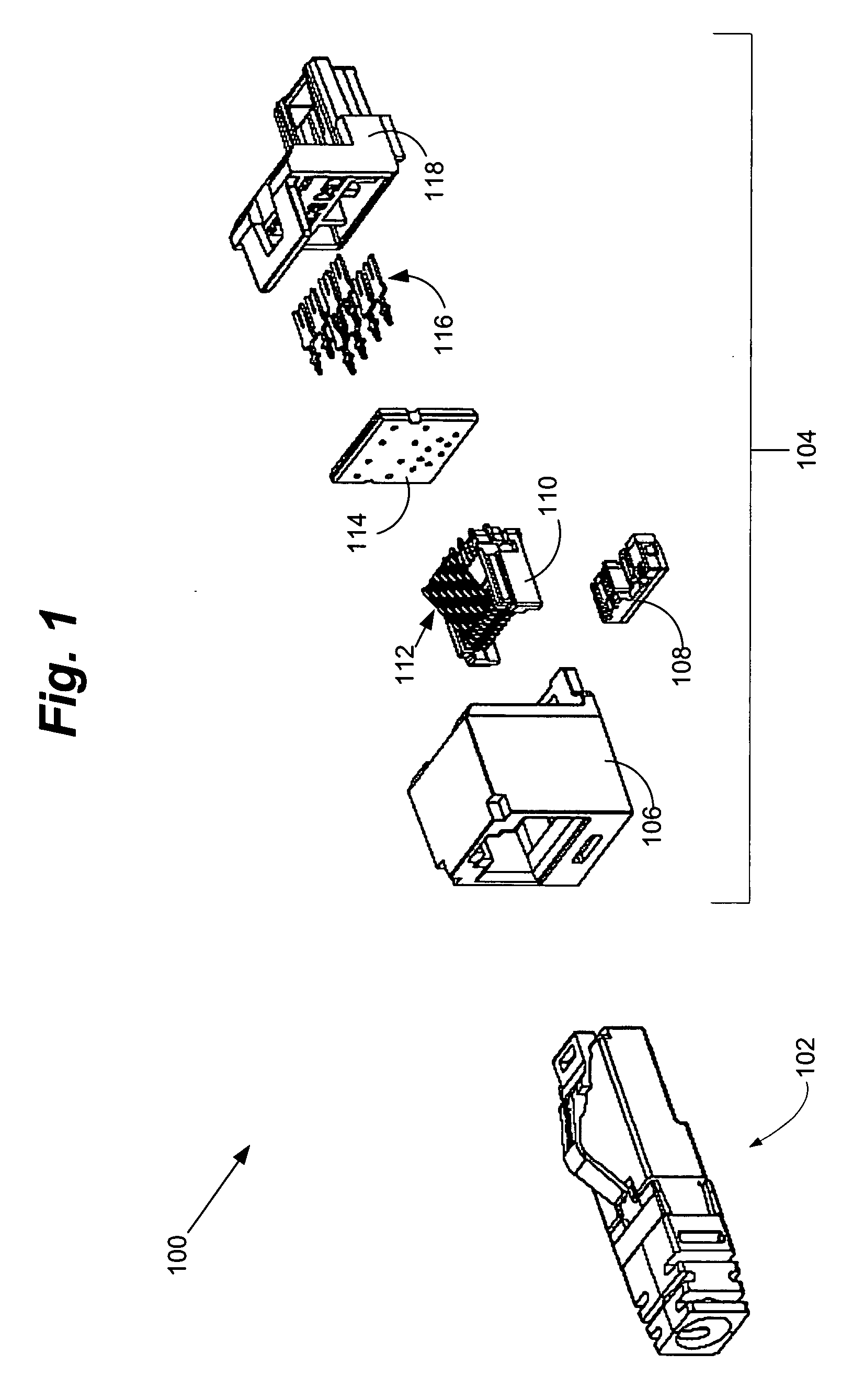
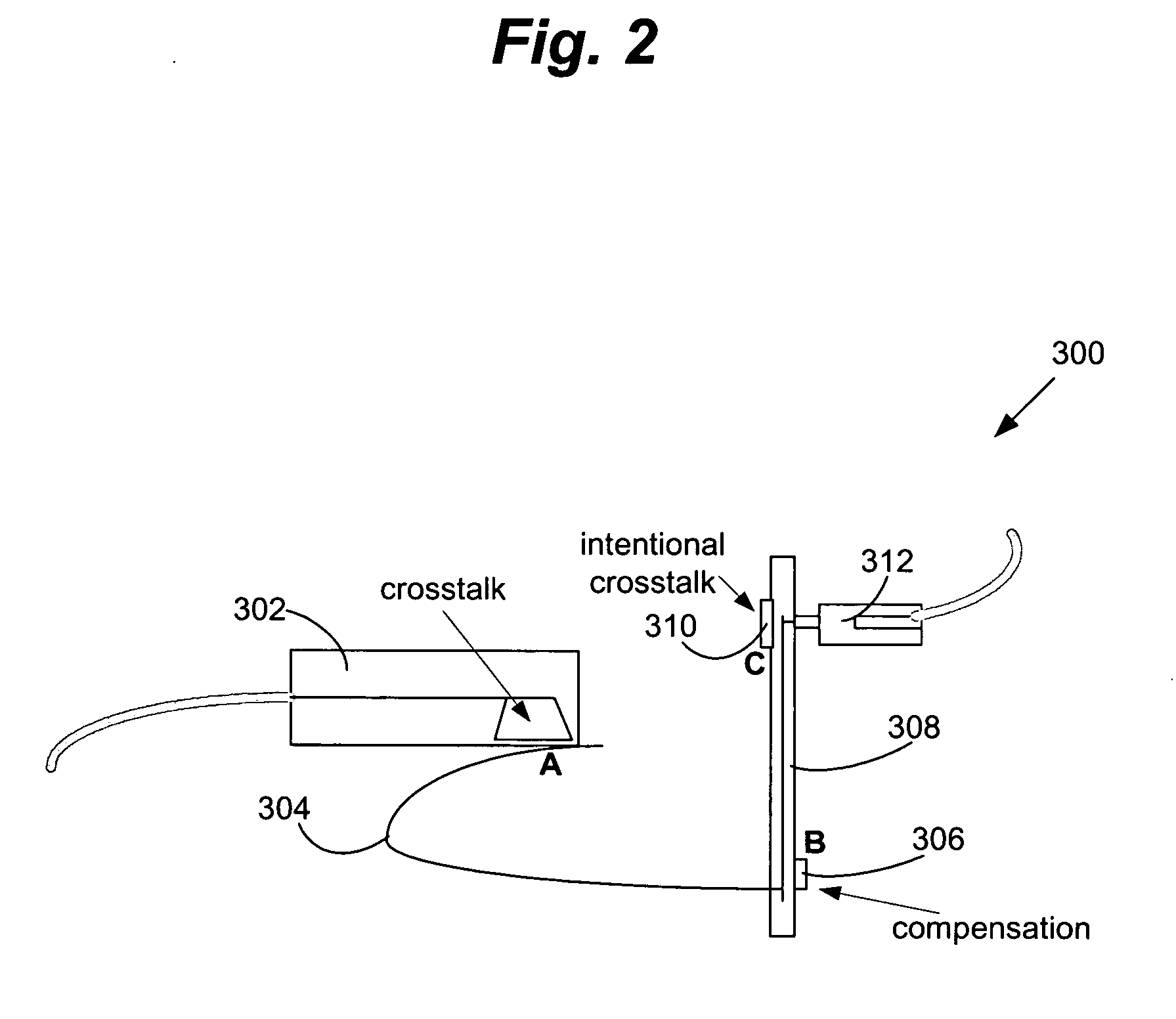
Electrical connector with improved crosstalk compensation
An electrical connector with improved crosstalk compensation is disclosed. By including at least one coupling with a different frequency dependency than other couplings in the connector, crosstalk compensation performance is improved over a greater frequency range. The different frequency dependency may, for example, be used to compensate for phase shifts caused by distances between compensation circuitry and the plug / jack interface. Embodiments for decreasing these distances are also disclosed.
Owner:PANDUIT
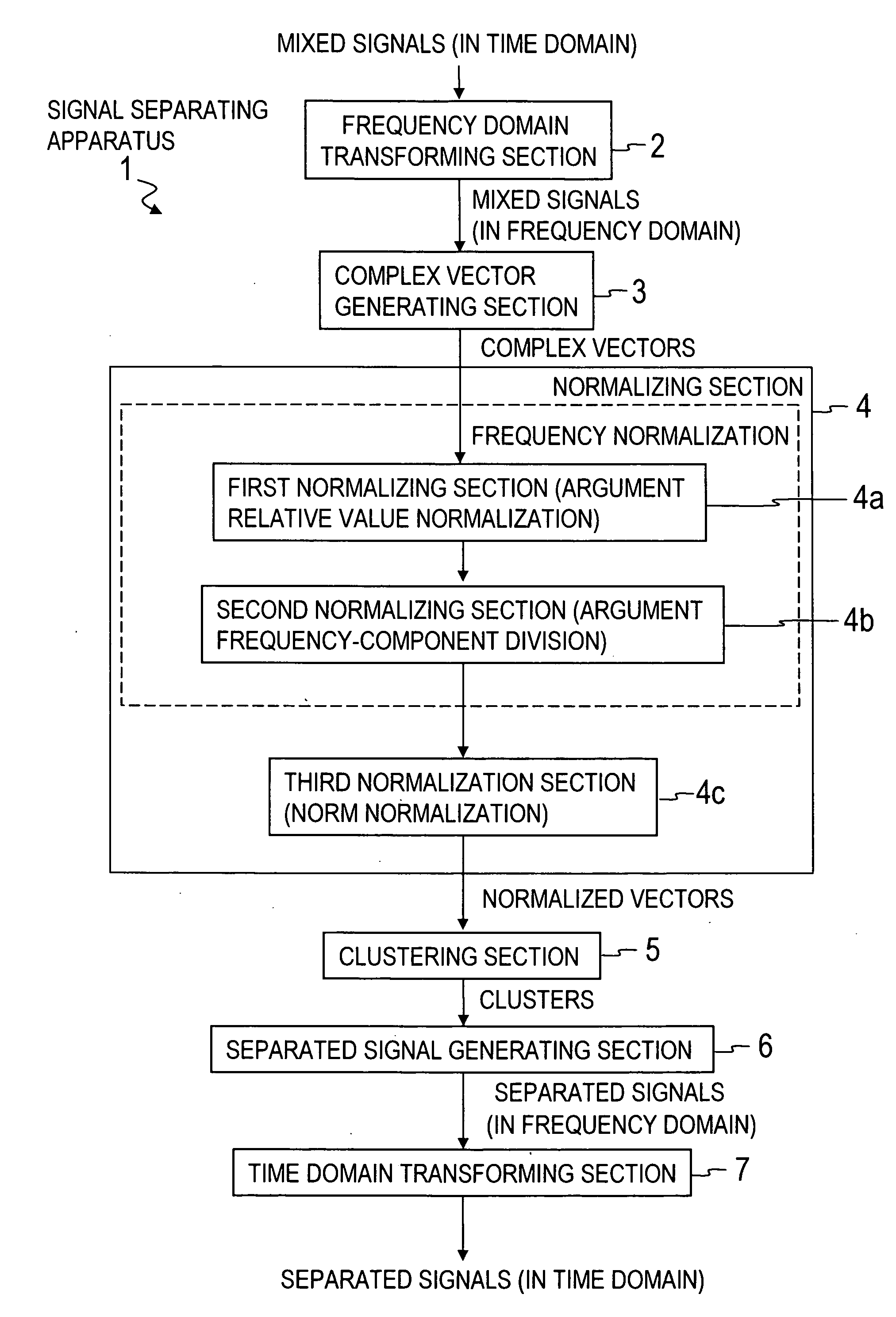
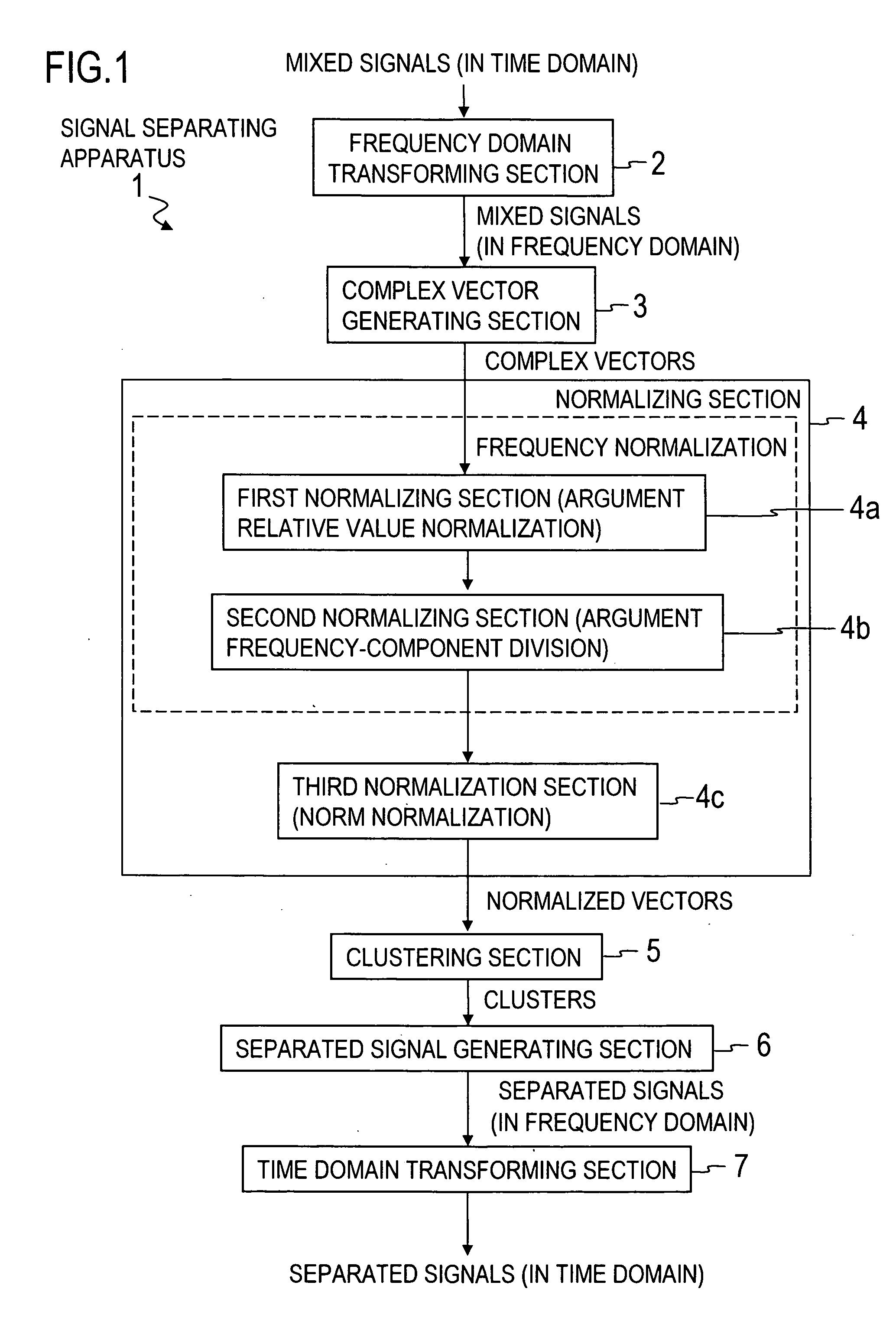
Signal Separation Device, Signal Separation Method, Signal Separation Program and Recording Medium
ActiveUS20080215651A1Simple and efficientAccurate solutionDigital data processing detailsDigital computer detailsTime domainAlgorithm
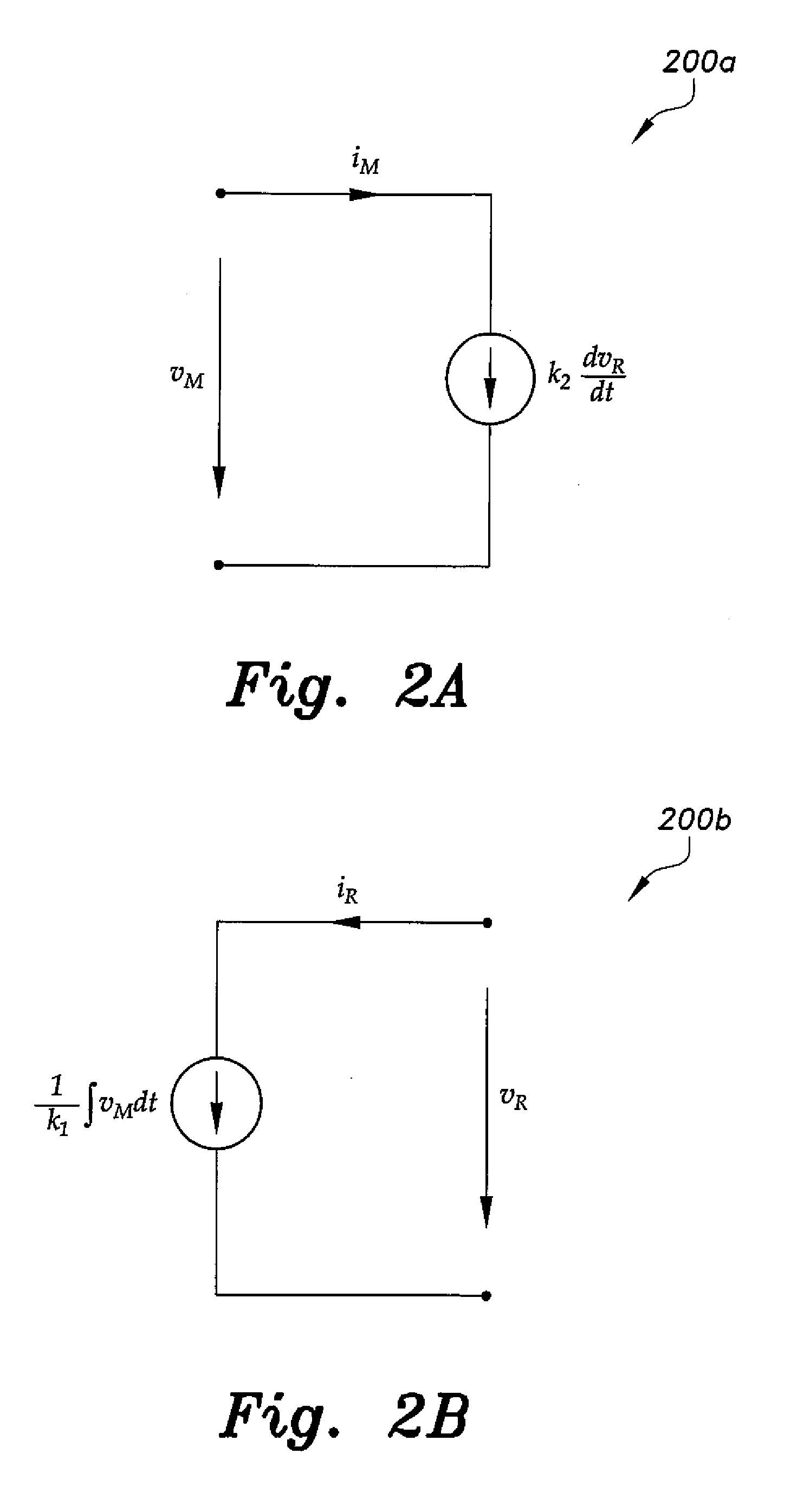
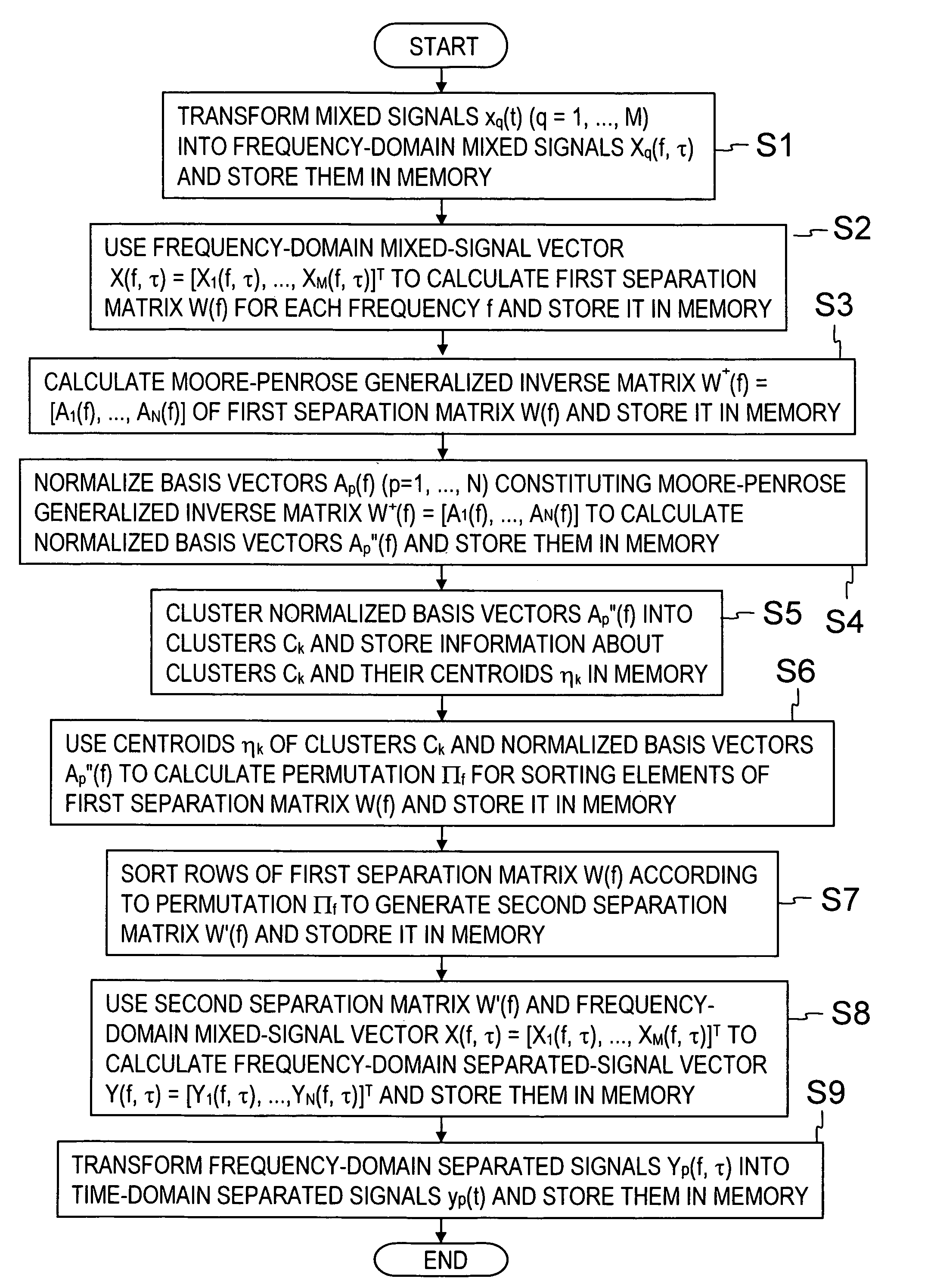
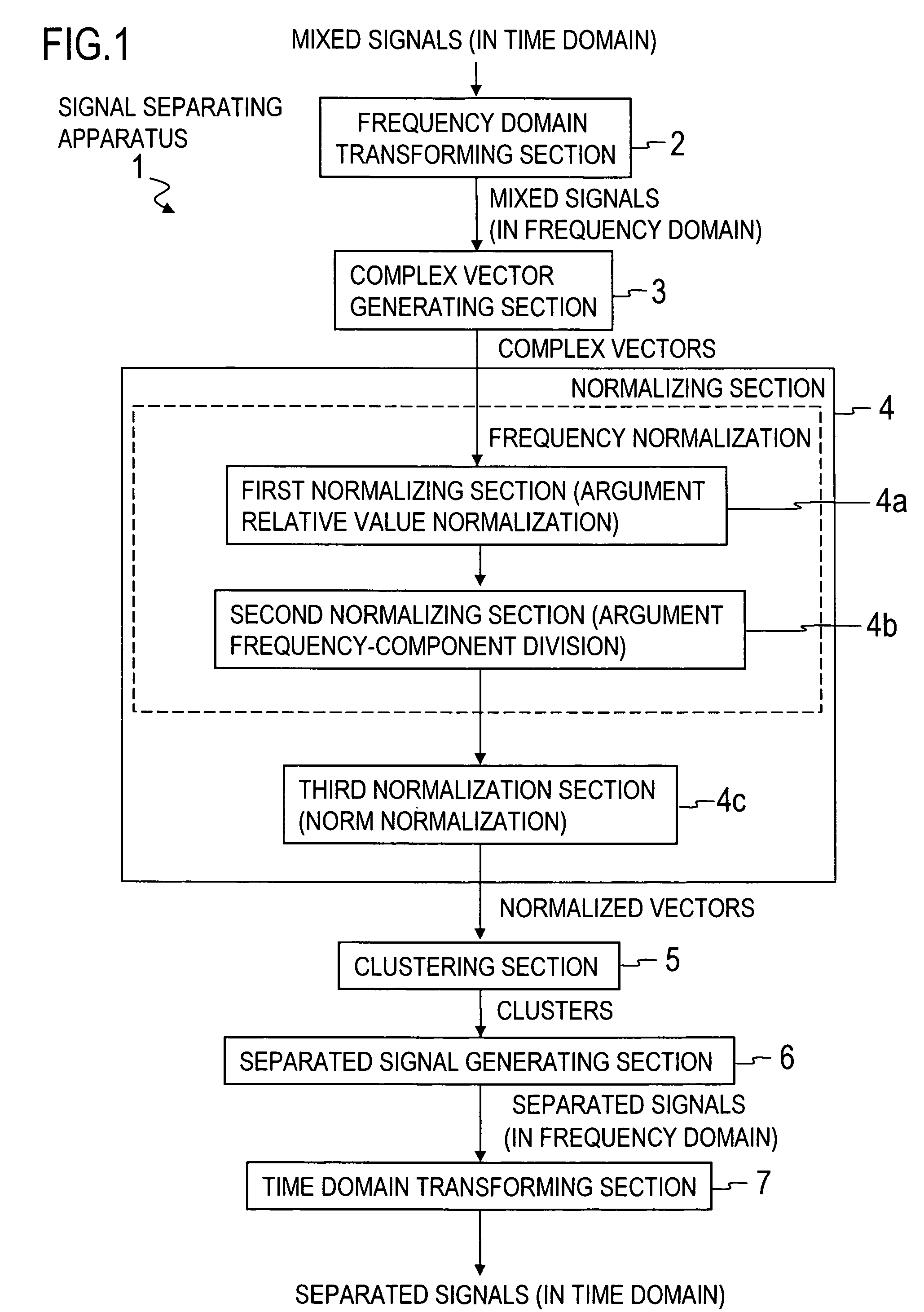
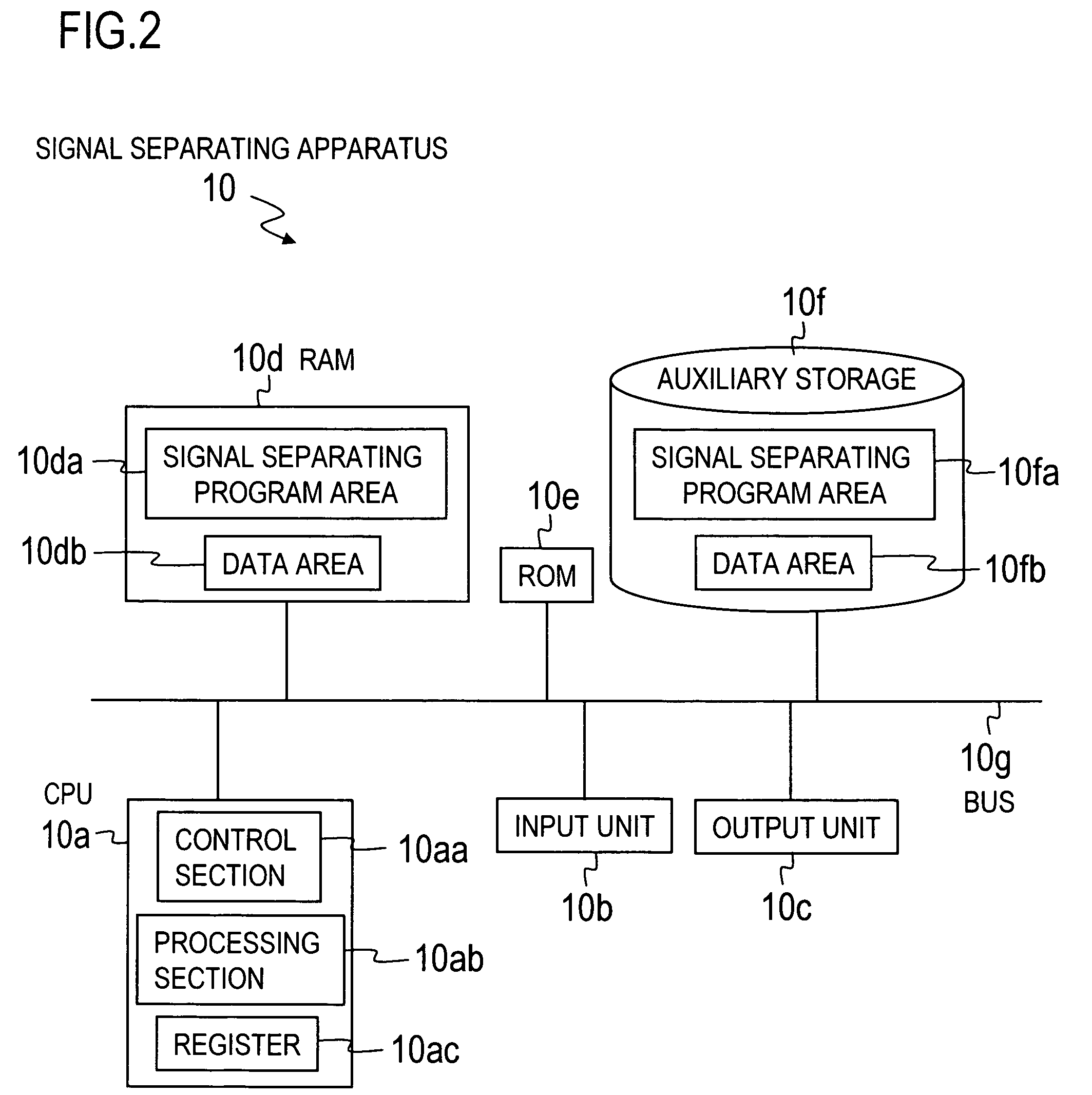
A frequency domain transforming section 2 transforms mixed signals observed by multiple sensors into mixed signals in the frequency domain, a complex vector generating section 3 generates a complex vector by using the frequency-domain mixed signals, a normalizing section 4 generates a normalized vector excluding frequency dependence of the complex vector, and a clustering section 5 clusters the normalized vectors to generate clusters. Then, a separated signal generating section 6 generates separated signals in the frequency domain by using information about the clusters and a time domain transforming section 7 transforms the separated signals in the frequency domain into separated signals in the time domain.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
System for continuously calibrating a magnetic imaging array
A calibration system and method is described to continuously measure and adjust several parameters of a magnetic imaging array. One or more non-target magnetic field source(s) are used to generate a well-defined and distinguishable spatial magnetic field distribution. The magnetic imaging array is used to measure the strength of the non-target magnetic fields and the information is used to calibrate several parameters of the array, such as, but not limited to, effective magnetometer positions and orientations, gains and their frequency dependence, bandwidth, and linearity. The calibration can happen continuously or periodically, while the imaging array is operating to create magnetic field images, if the modulation frequencies for calibration are outside the frequency window of interest.
Owner:QUSPIN
Method and apparatus for detecting optical spectral properties using optical probe beams with multiple sidebands
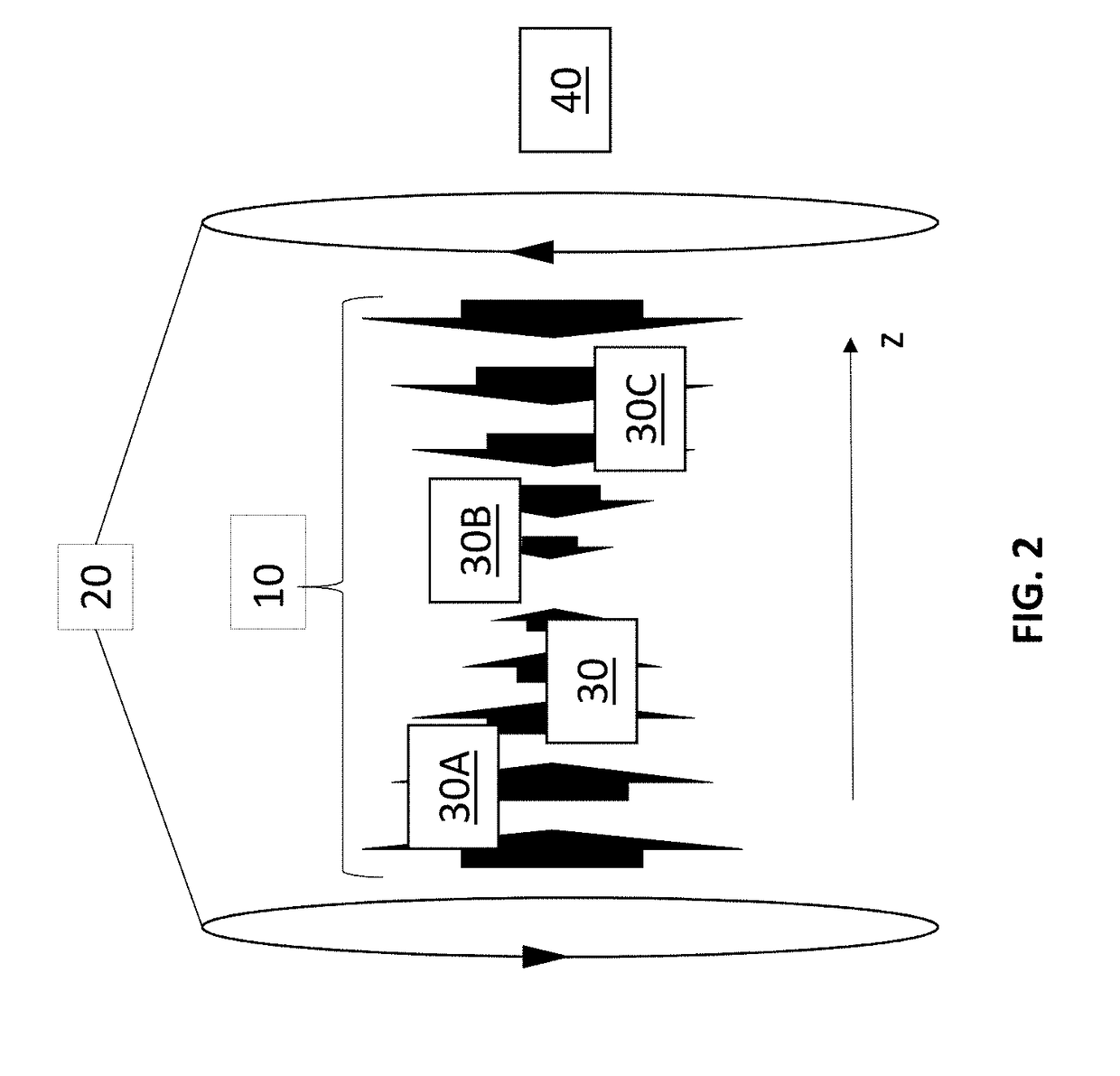
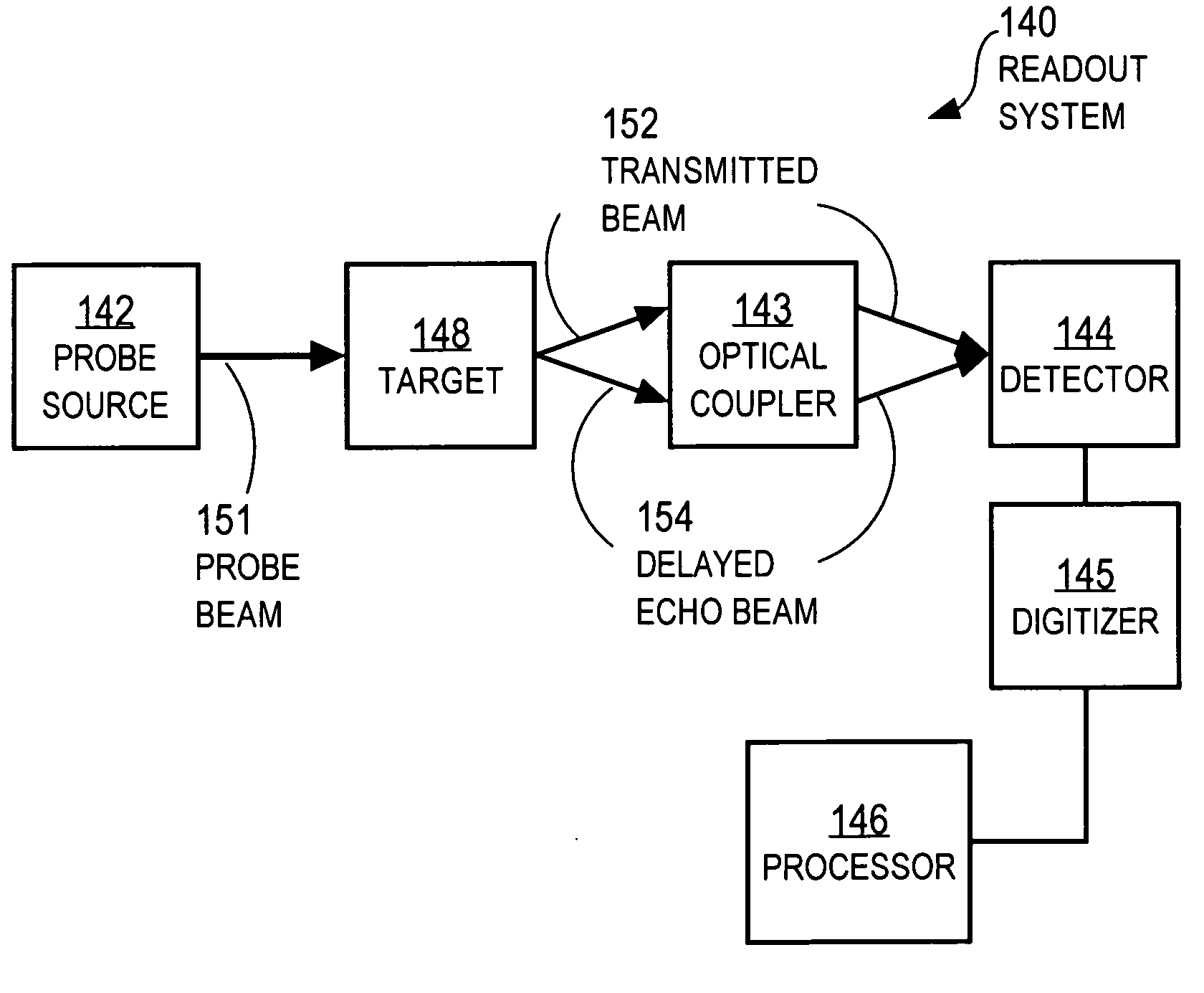
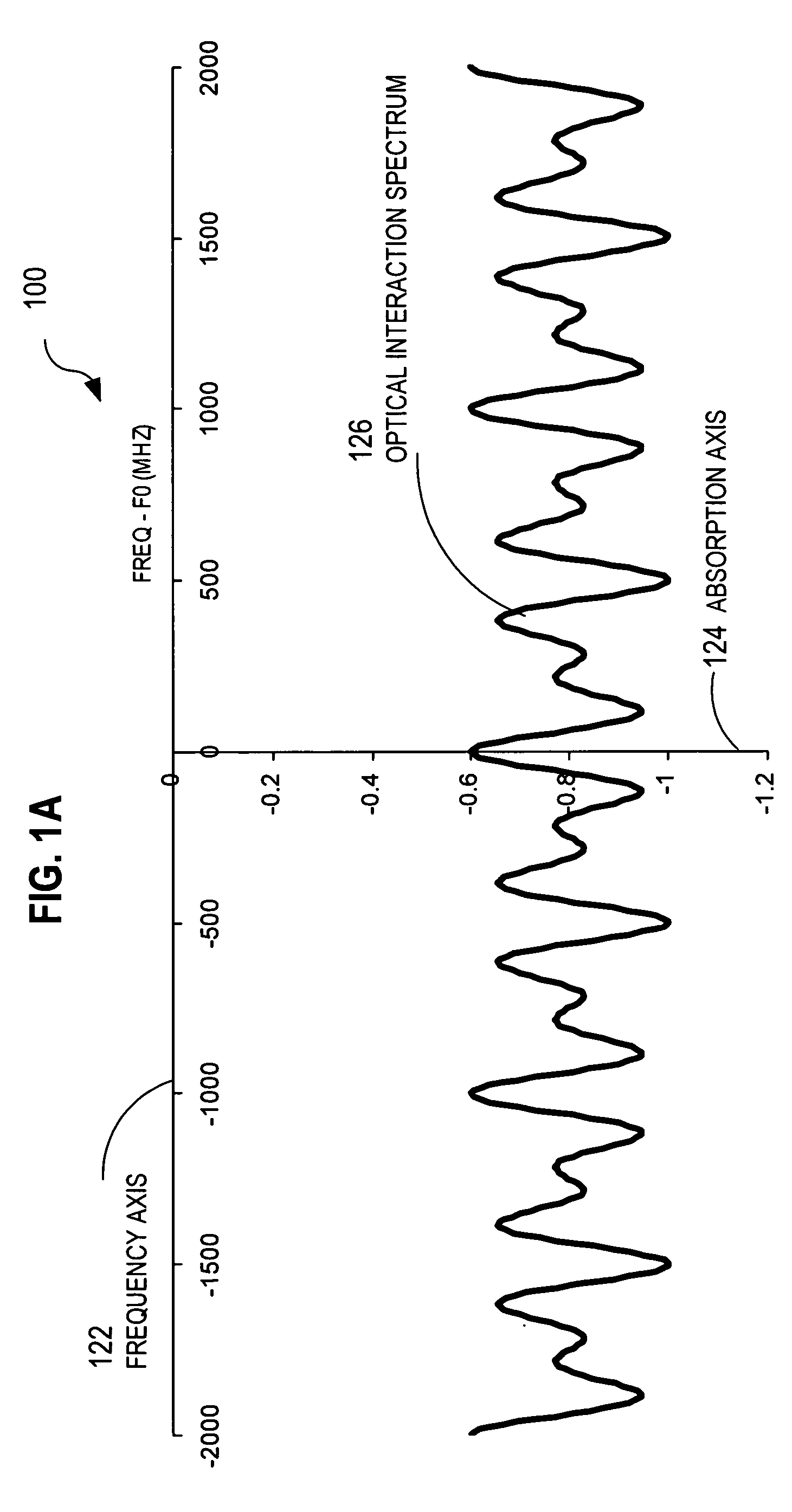
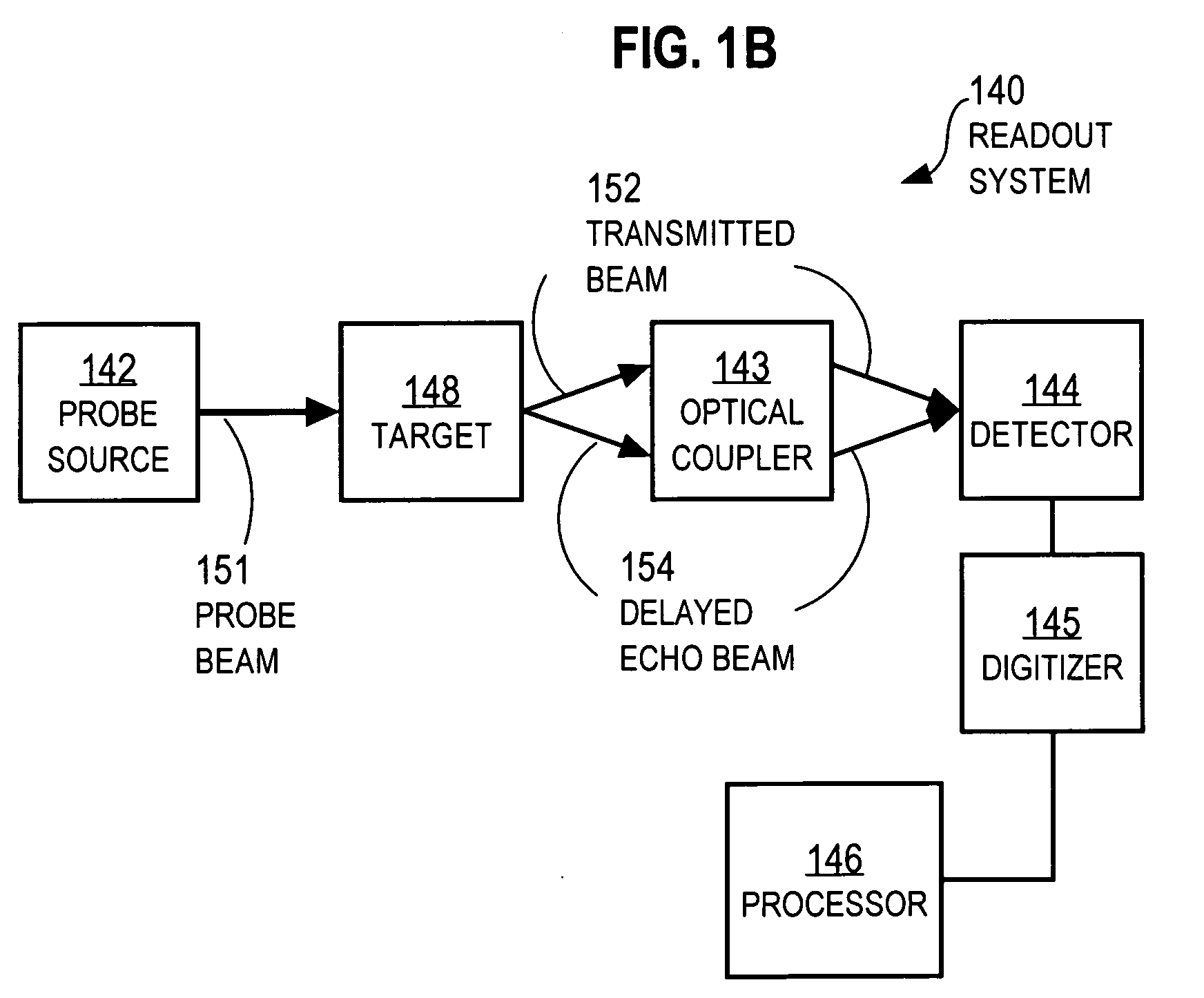
Techniques for detecting optical spectral properties of a target are described. The technique includes providing an optical carrier which has an optical frequency bandwidth which is narrow compared to the width of the narrowest spectral feature of the target to be determined. This optical carrier is then electro-optically modulated with an RF frequency chirp, creating an optical chirp probe beam with a frequency chirped optical spectrum having upper and lower frequency chirped sidebands that have amplitudes sufficient to be detected at a detector. The sidebands are frequency bands arranged symmetrically around the optical carrier frequency. The attributes of a sideband include a start frequency, bandwidth and chirp rate. A probe beam is generated with the sidebands and directed onto a target having a physical property with optical frequency dependence. An optical response signal resulting from an interaction between the probe beam and the target is detected. The optical frequency dependence of the physical property of the target is determined based on the optical response signal and the attributes of the sidebands.
Owner:MONTANA STATE UNIVERSITY
Integrated Multimodality Intravascular Imaging System that Combines Optical Coherence Tomography, Ultrasound Imaging, and Acoustic Radiation Force Optical Coherence Elastography
ActiveUS20150351722A1Low costImproved prognosisOrgan movement/changes detectionSurgeryBiomechanicsMechanical property
A method of using an integrated intraluminal imaging system includes an optical coherence tomography interferometer (OCT), an ultrasound subsystem (US) and a phase resolved acoustic radiation force optical coherence elastography subsystem (PR-RAF-OCE). The steps include performing OCT to generate a returned optical signal, performing US imaging to generate a returned ultrasound signal, performing PR-ARF-OCE to generate a returned PR-ARF-OCE signal by generating a amplitude modulated ultrasound beam or chirped amplitude modulated ultrasound beam to frequency sweep the acoustic radiation force, measuring the ARF induced tissue displacement using phase resolved OCT method, and the frequency dependence of the PR-ARF-OCE signal, processing the returned optical signal, the returned ultrasound signal and the measured frequency dependence of the returned PR-ARF-OCE optical coherence elastographic signal to quantitatively measure the mechanical properties of the identified tissues with both spectral and spatial resolution using enhanced materials response at mechanically resonant frequencies to distinguish tissues with varying stiffness, to identify tissues with different biomechanical properties and to measure structural and mechanical properties simultaneously.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Detection method using electromagnetic wave and detection apparatus
InactiveUS20080137068A1Efficient detectionImprove inspection efficiencyRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationStandard stateState variation
A detection apparatus includes a sample holding section, an irradiation means, a detection means, a calculation means, and an evaluation means. The irradiation means irradiates a substance held in the sample holding section with a THz wave. The detection unit detects a THz wave passed through or reflected from the substance. The calculation unit determines a frequency dependence of a property of the substance with respect to the irradiated THz wave and then calculates a slope of a straight line or a slope of a straight line obtained by straight-line approximation of the frequency dependence of the property of the substance. The evaluation unit evaluates the state change of the substance by comparing a previously-obtained slope of a straight line of the frequency dependence of the property of the substance in a standard state and the slope of the straight line of the substance calculated.
Owner:CANON KK +1
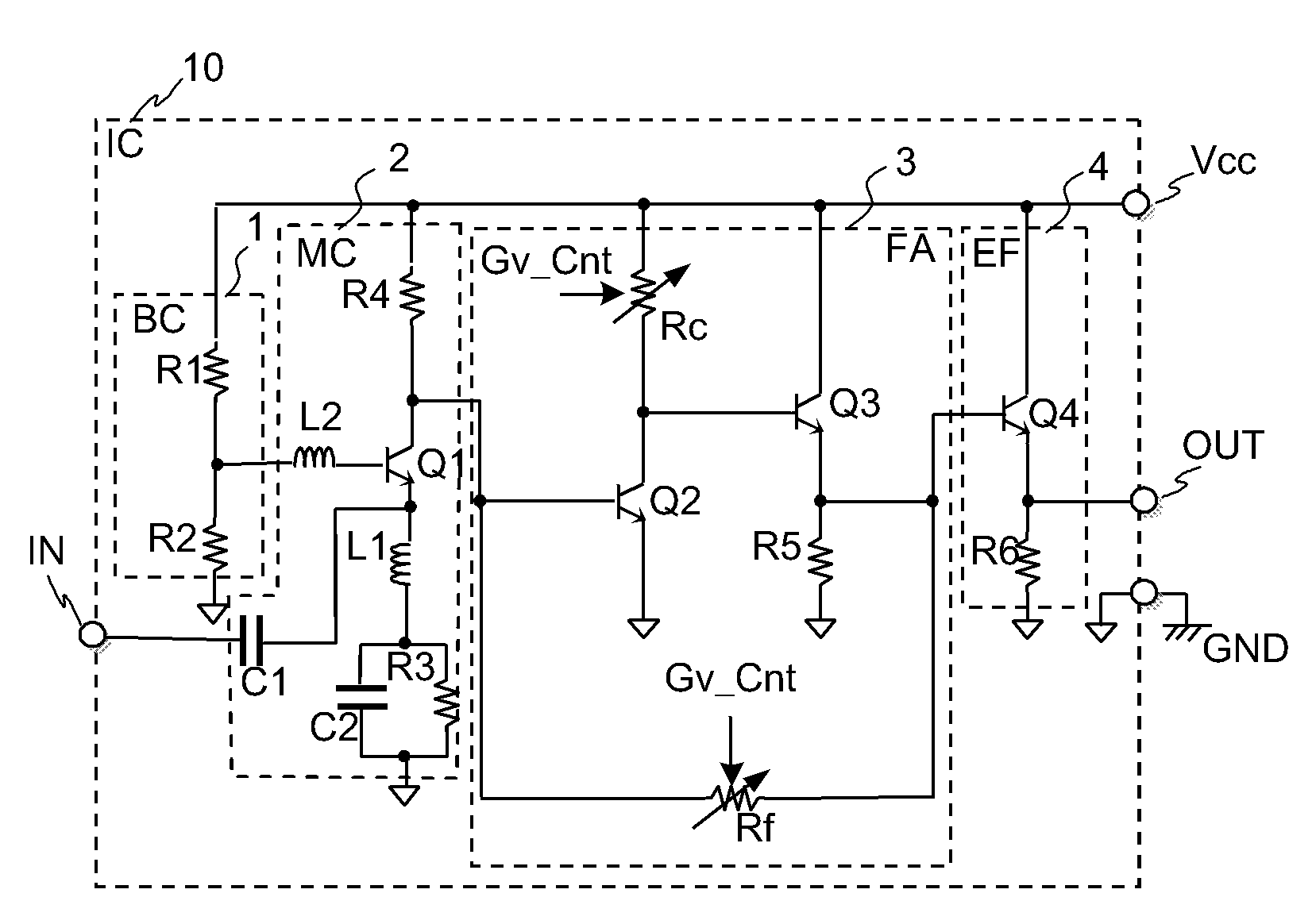
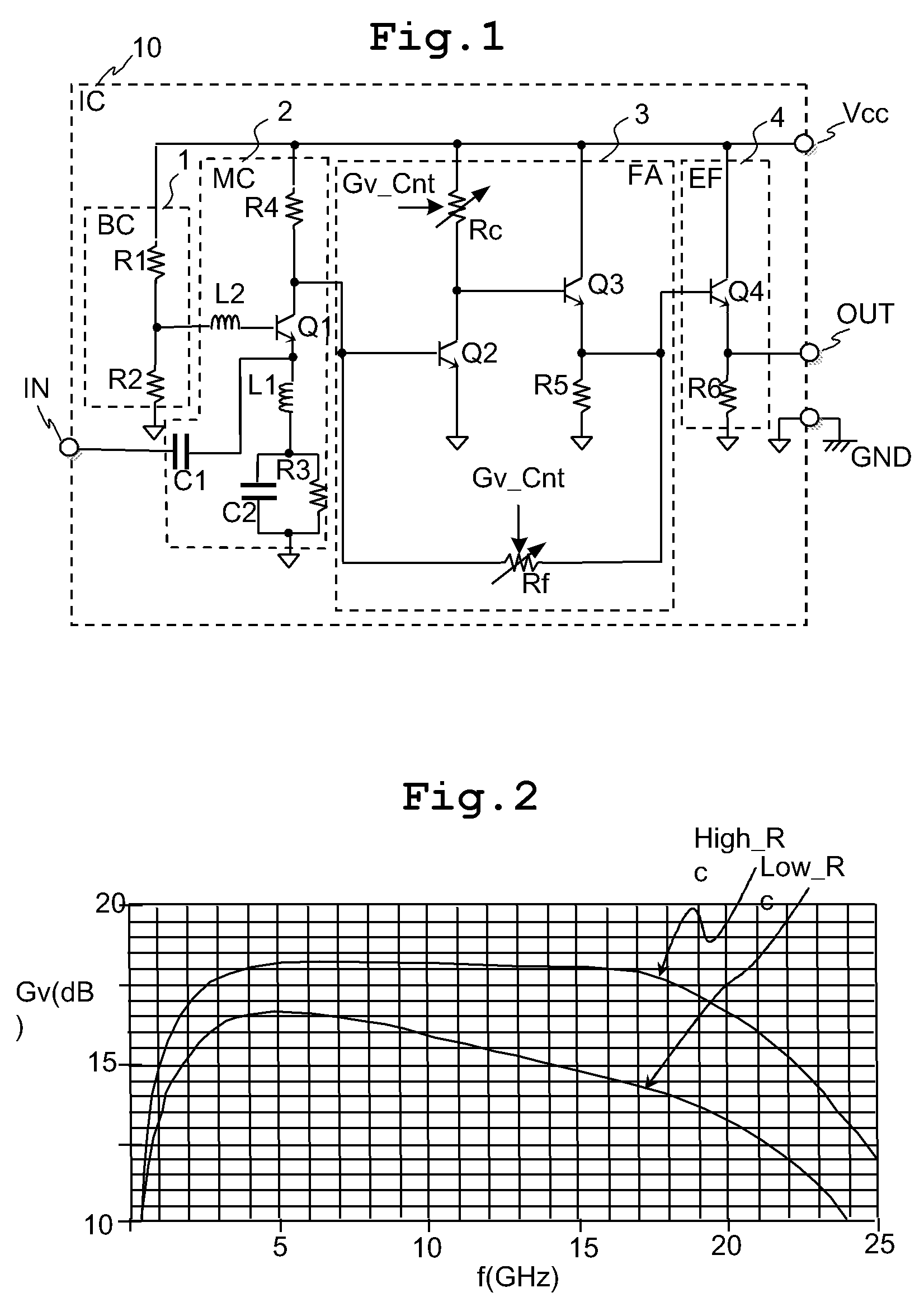
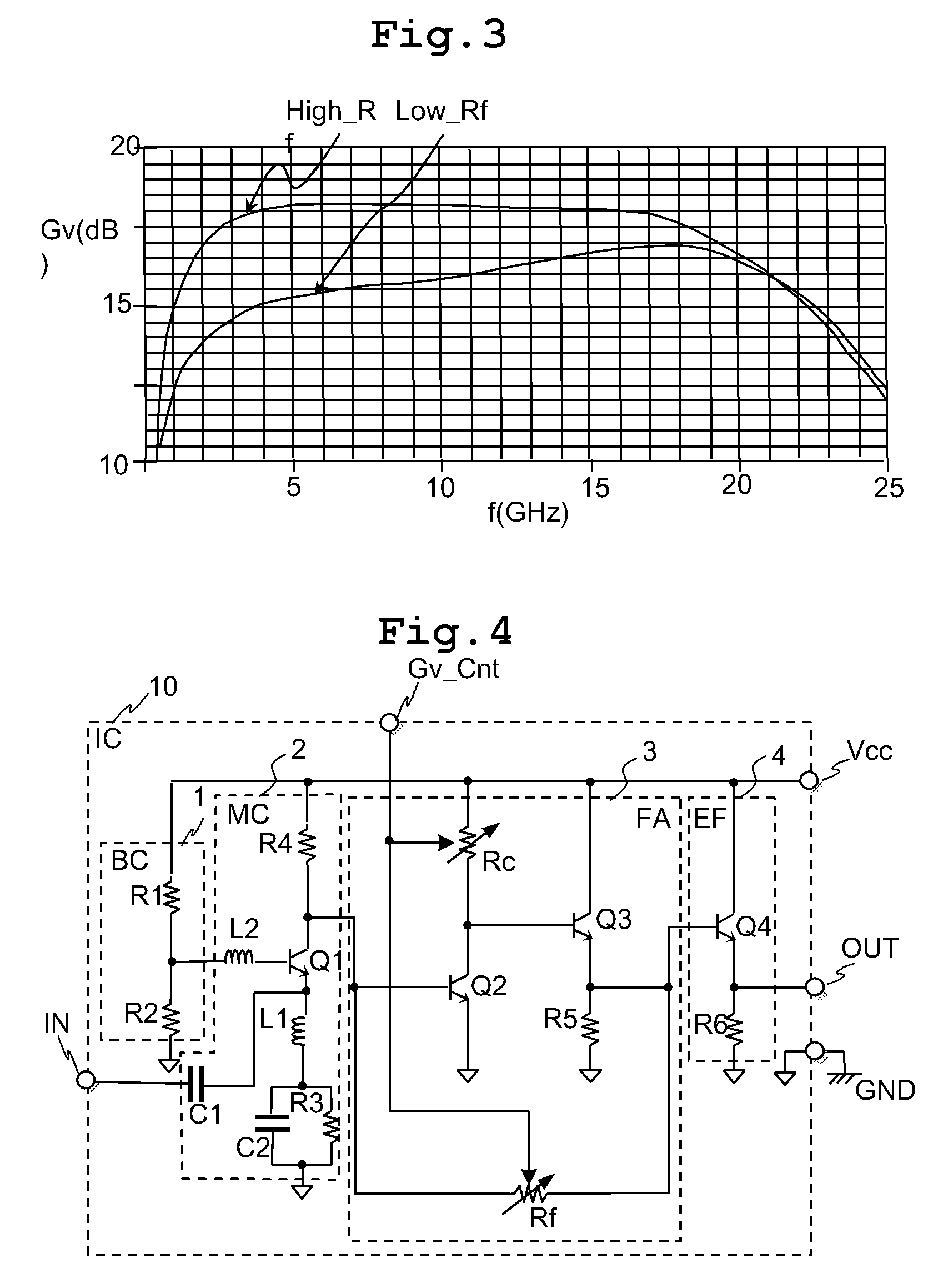
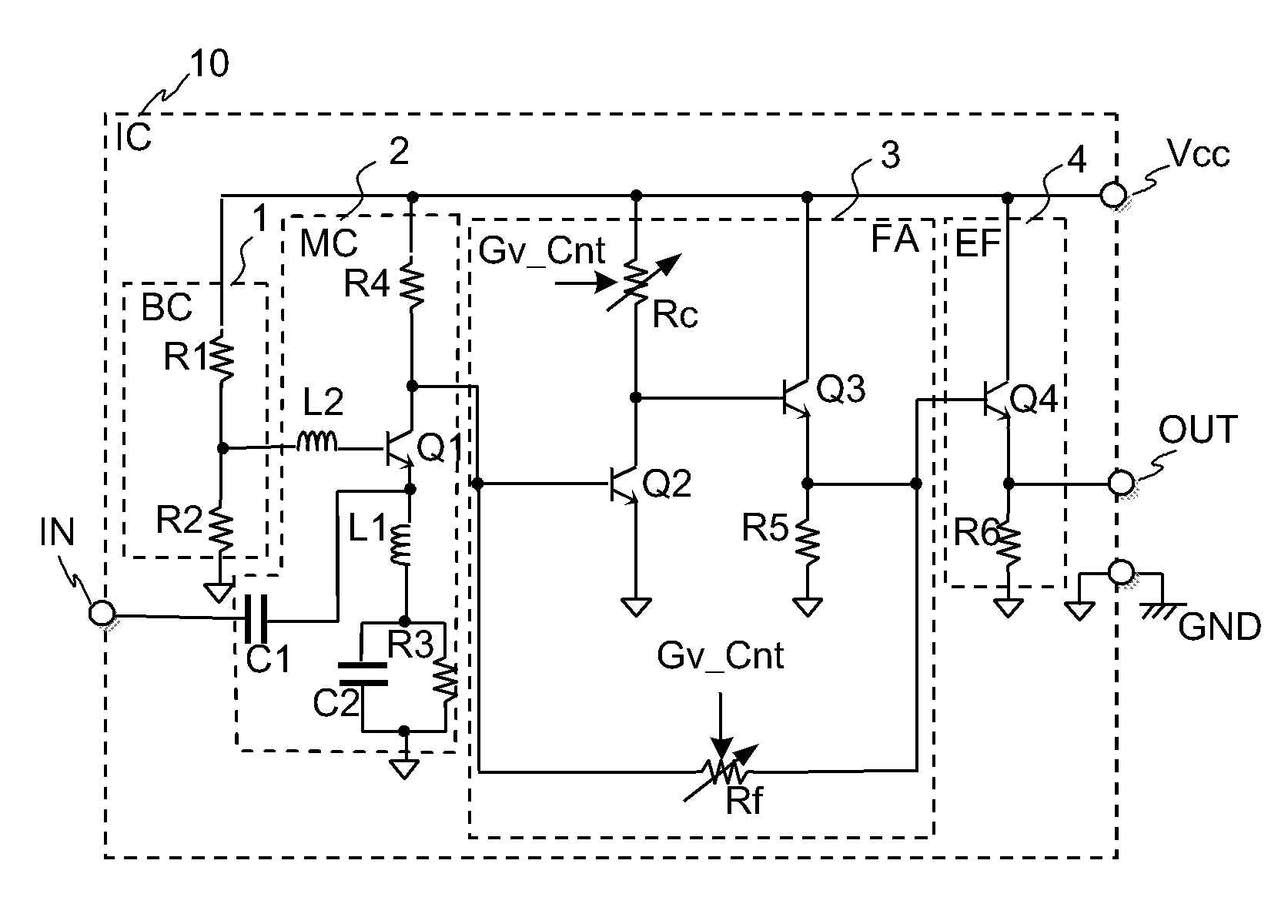
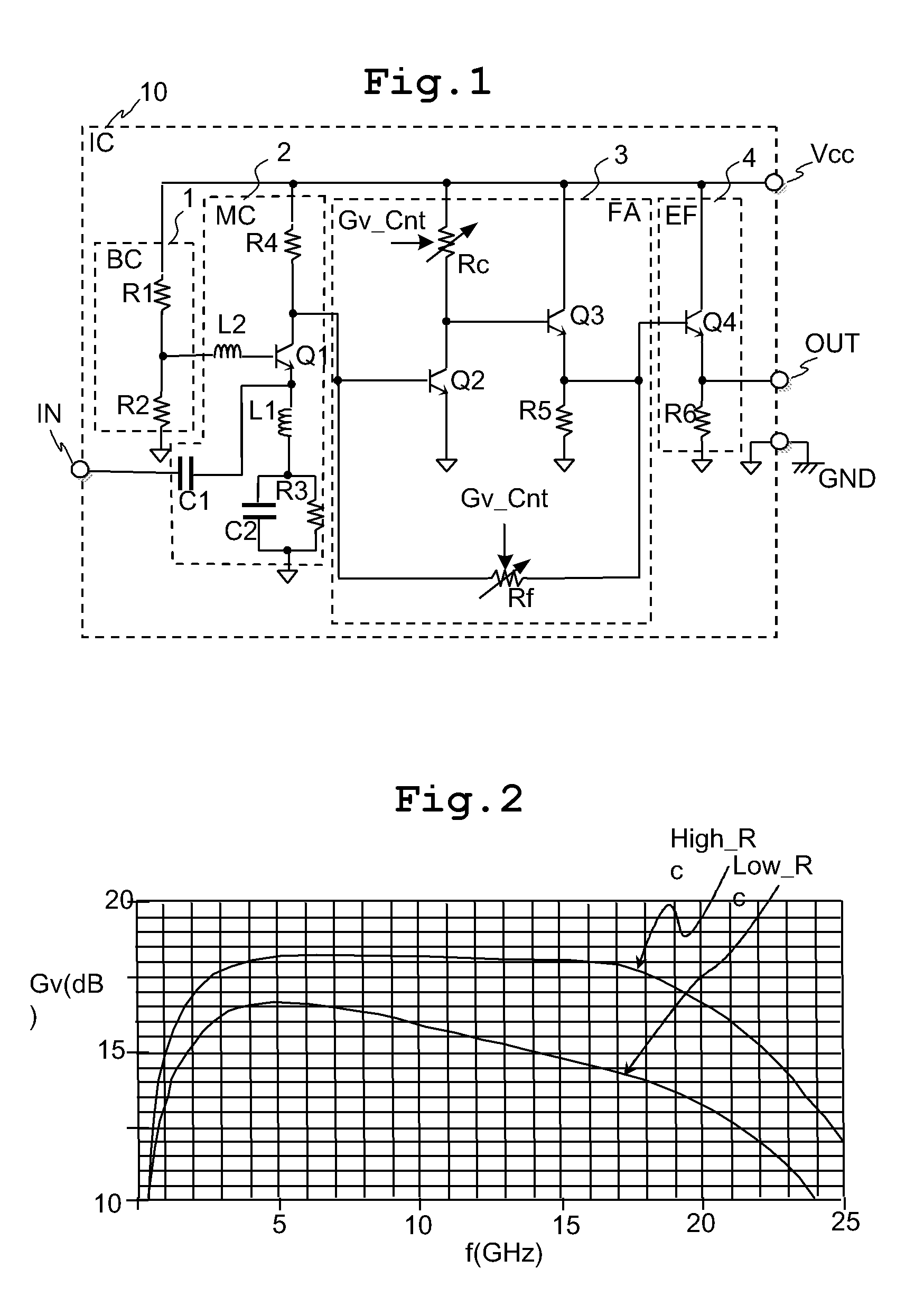
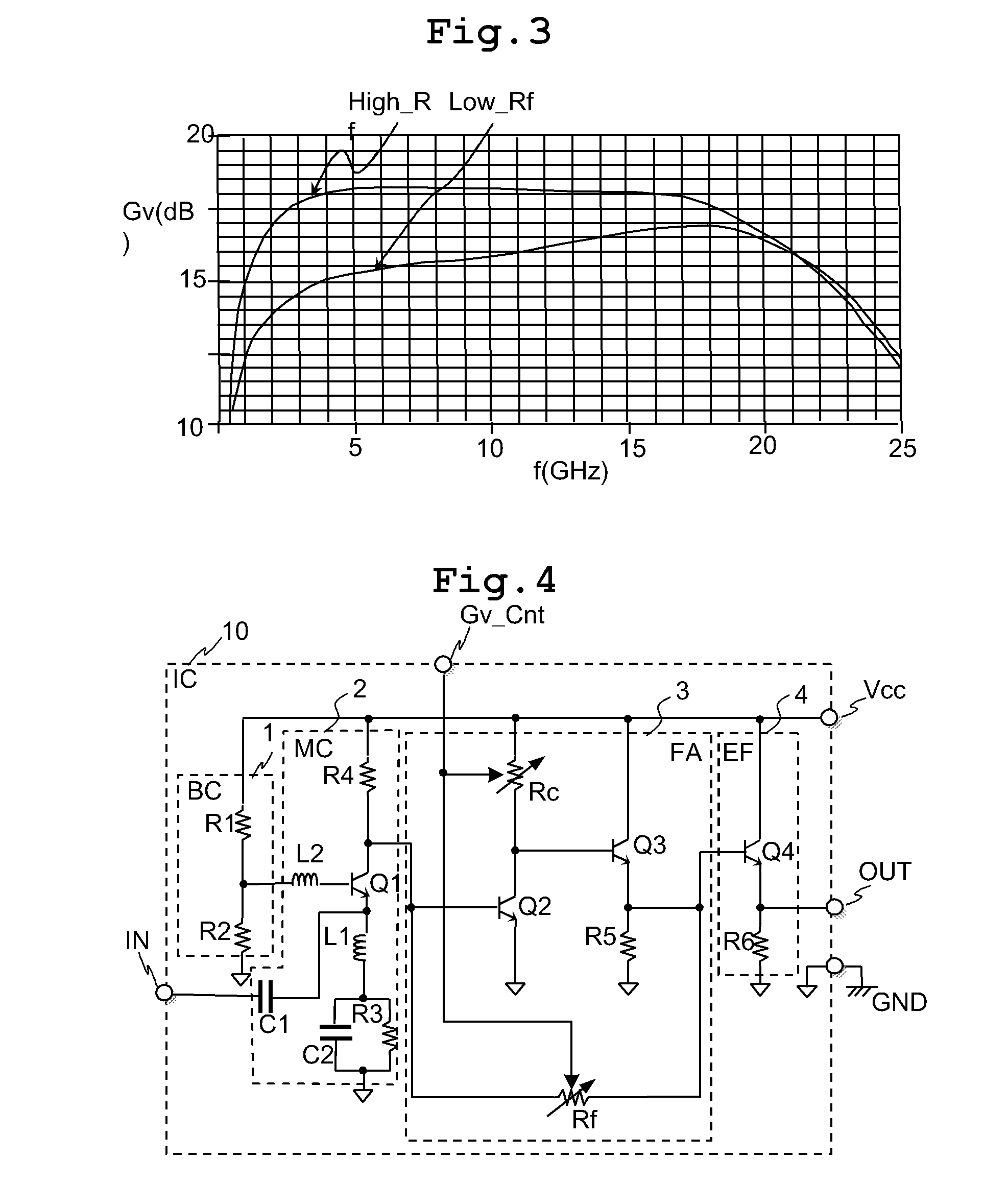
Semiconductor integrated circuit with variable gain amplifier
InactiveUS7821335B2Reduce voltageImprove noise figureNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsGain controlHigh resistanceClosed loop
The variable gain amplifier includes a bias circuit (BC) 1, a matching circuit (MC) 2, a variable gain resistive feedback amplifier (FA) 3 and an output follower (EA) 4. The resistance values of the load resistance Rc and feedback resistance Rf are changed in cooperation. In a case of making the load resistance Rc a high resistance to set the low noise amplifier to a high gain, the feedback resistance Rf is also made a high resistance, the feedback time constant τfb(c1)≈2π·RfCbe / (1+gmRc) of the closed loop of the resistive negative feedback amplifier 3 becomes substantially constant, and then the amplifier has a gain small in frequency dependency over a wide bandwidth. In a case of making the load resistance Rc a low resistance to set the low noise amplifier to a low gain, the feedback resistance Rf is also made a low resistance. The feedback resistance Rf with the low resistance increases the negative feedback quantity, and thus the amplifier is set to a low gain. Also, the load resistance Rc is made a low resistance, and the feedback time constant τfb(c1) becomes substantially constant. The gain is not lowered further in a high frequency region.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
In-situ heavy-oil reservoir evaluation with artificial temperature elevation
InactiveUS20030034777A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyBound waterRoom temperature
Many reservoirs of interest include heavy oil. In such reservoirs, parti at normal temperatures, many instruments commonly used for formation evaluation may not be able to distinguish between heavy oil and bound water in the formation. Passive or active heating is used to elevate the temperature of the fluids in the formation. At elevated temperatures, distinguishing between heavy oil and bound water is easier. Of particular interest is the increase in the resolvability of the transverse relaxation time T2 of NMR spin echo measurements. Additionally, the dielectric constant and the loss tangents of water and heavy oil show different temperature and frequency dependence.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
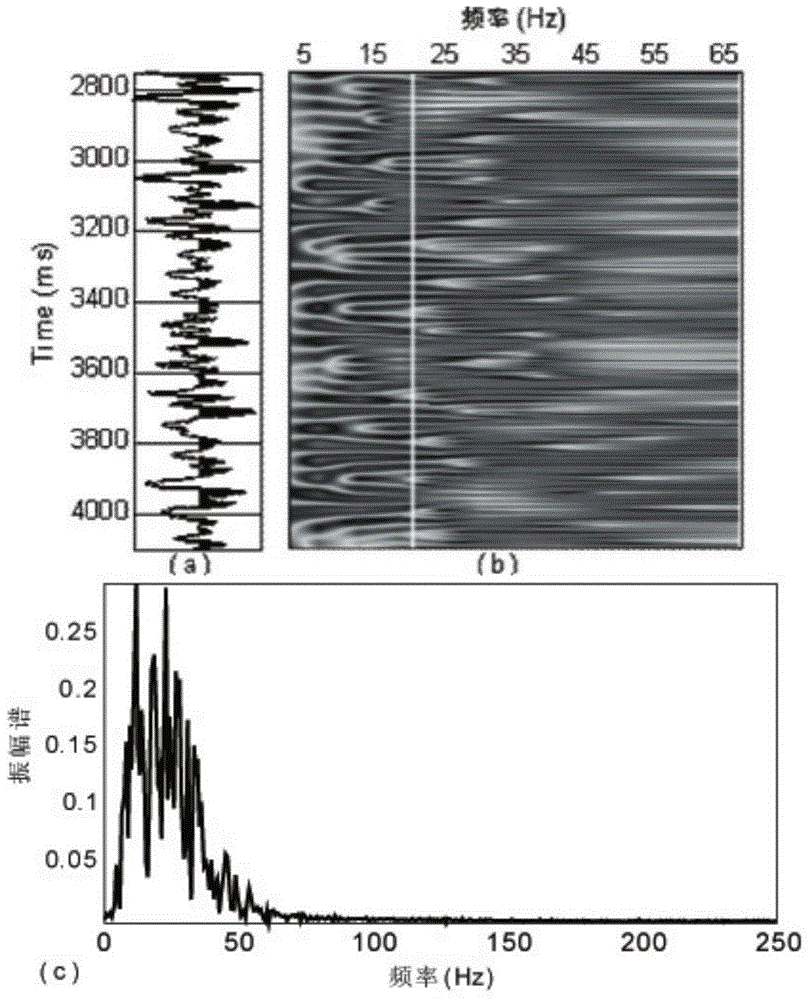
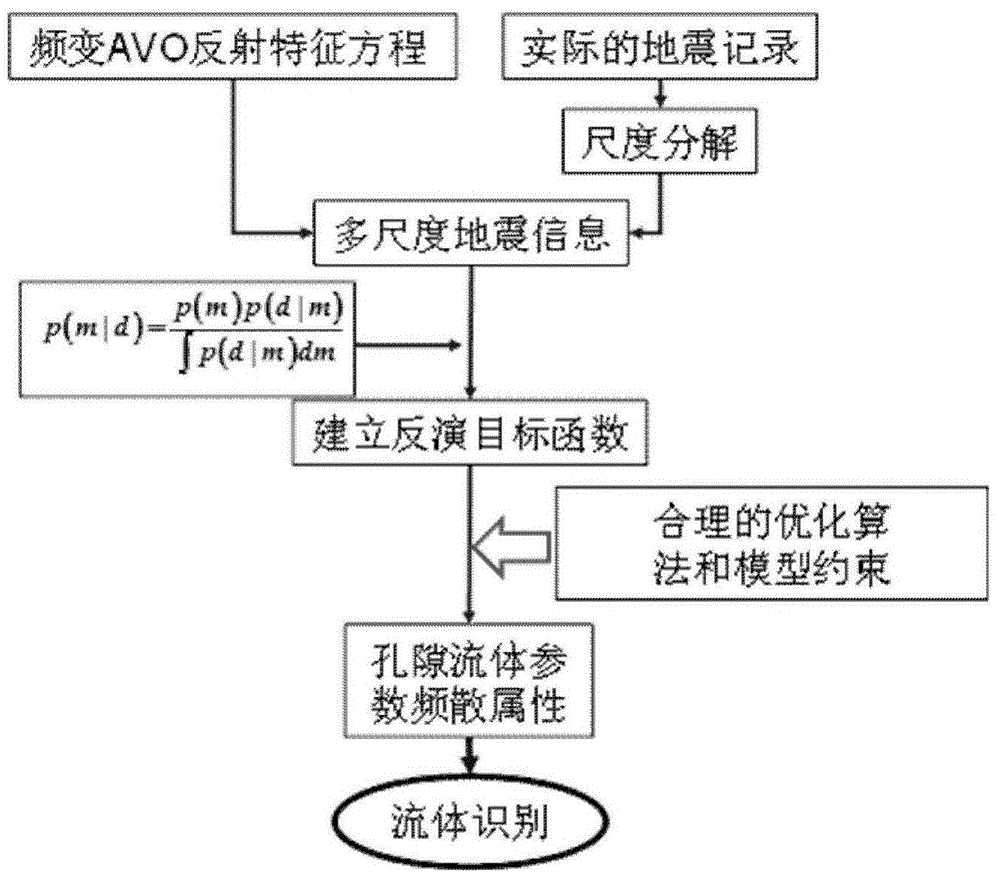
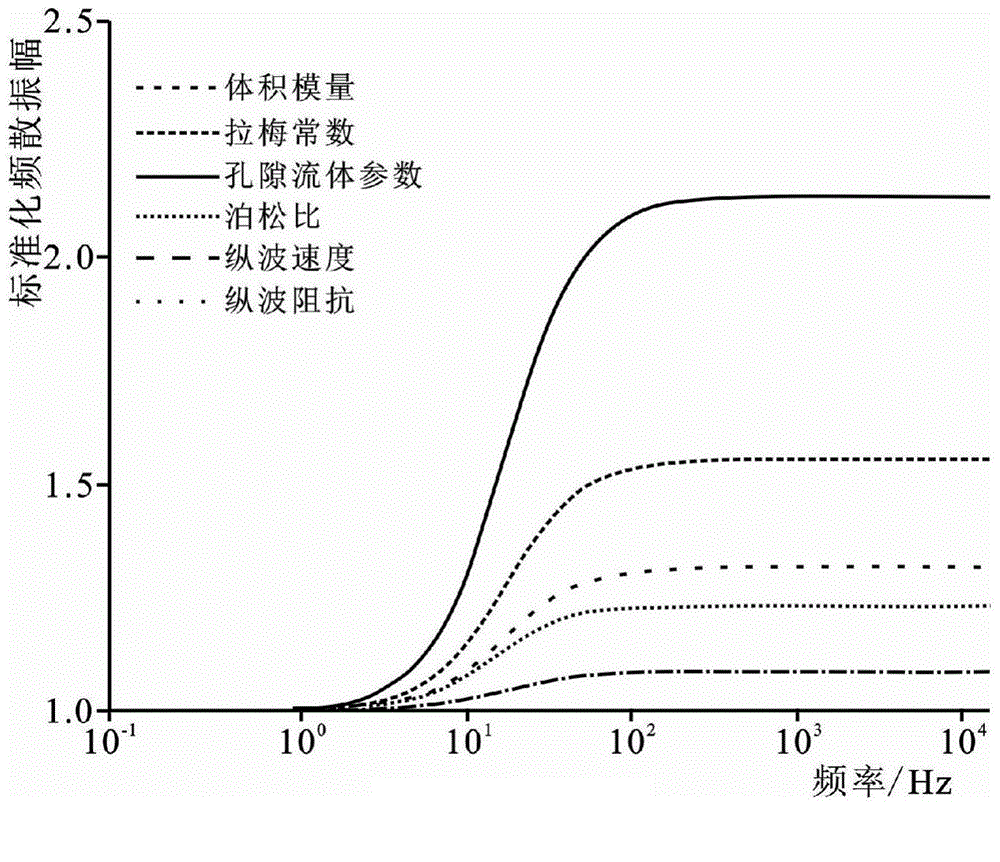
Reservoir fluid identification method based on pore fluid parameter frequency dependence inversion
InactiveCN105572727AIncreased sensitivityHigh precisionSeismic signal processingShear modulusBayesian inversion
A reservoir fluid identification method based on pore fluid parameter frequency dependence inversion is disclosed. The method comprises the following steps of carrying out amplitude preservation, denoising and offset processing on pre-stack seismic data; carrying out different-angle stack to acquire different-angle-stack seismic data of at least three angles; establishing a pore fluid parameter and a shear modulus model, extracting an angle wavelet and carrying out wavelet multi-scale frequency division processing on the different angle stack seismic data; carrying out frequency dependence attribute inversion of the pore fluid parameter; and according to a pore fluid parameter frequency dependence attribute evolution value, determining a reservoir fluid development situation. By using the method, received seismic information is used and a deceptive problem in conventional fluid identification can be well solved; a sensibility of a dependence inversion attribute of a pore-fluid sensitive parameter to a reservoir fluid is high and identification precision to the fluid is high; an Bayesian inversion theory is used to carry out inversion so that stability and reliability are high.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
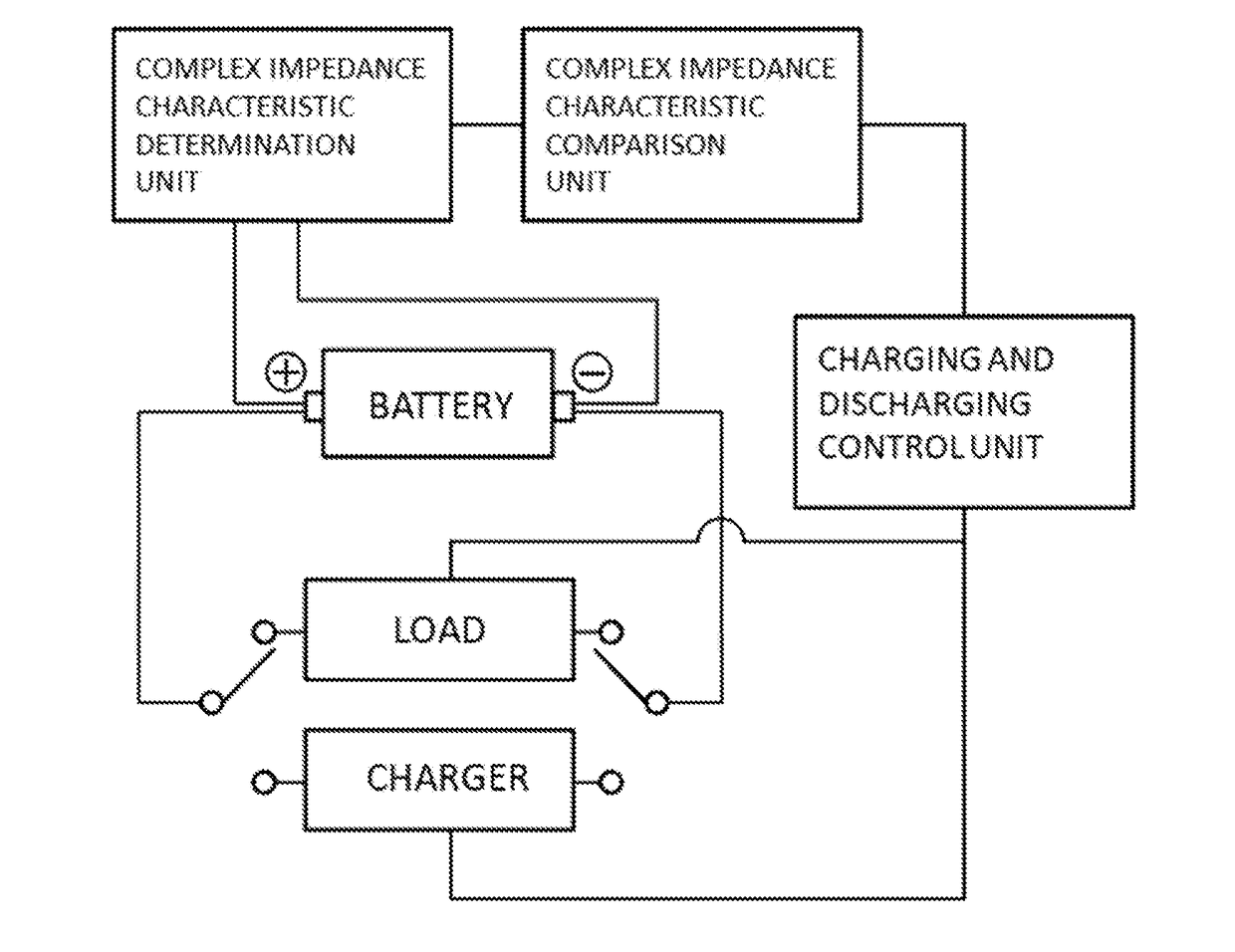
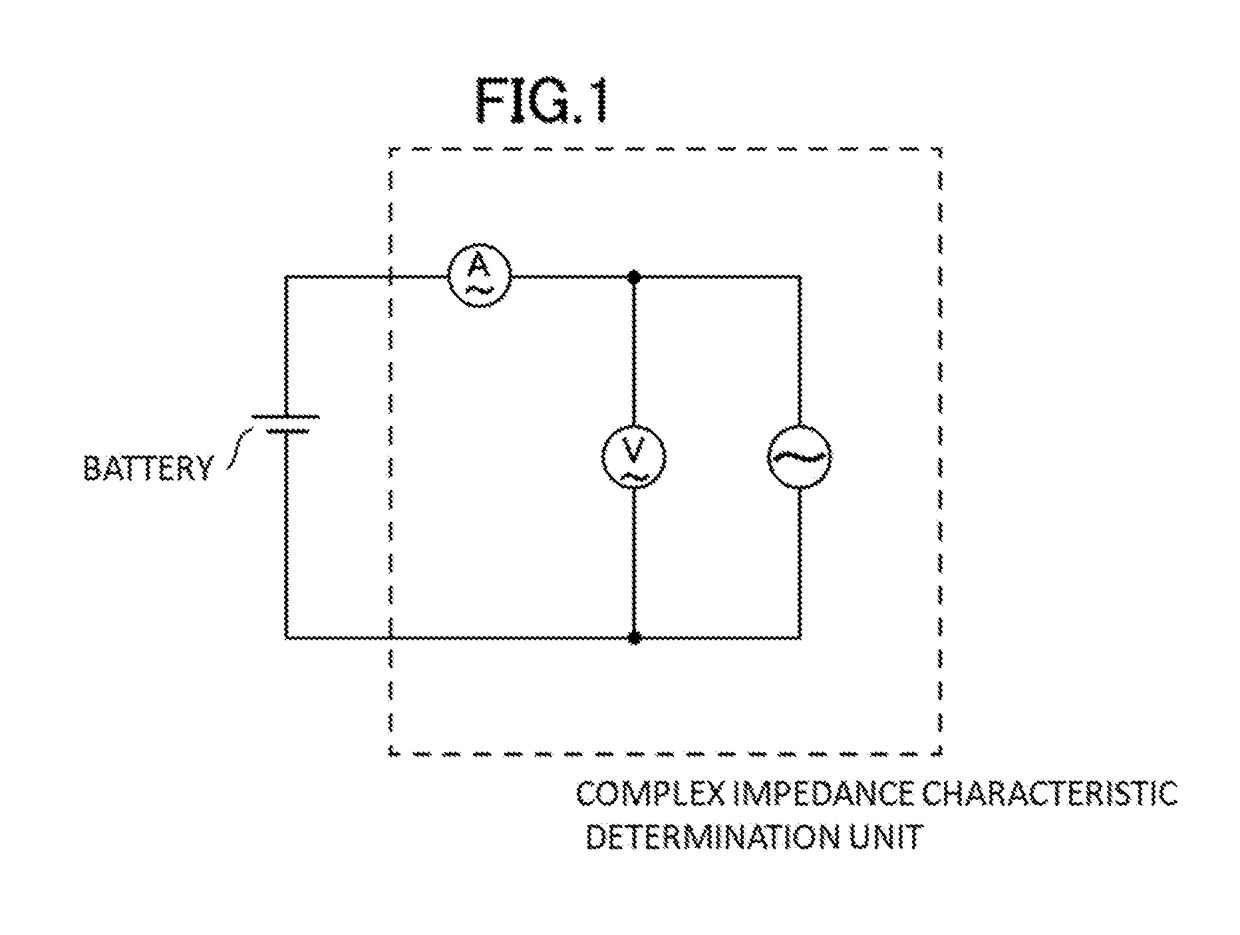
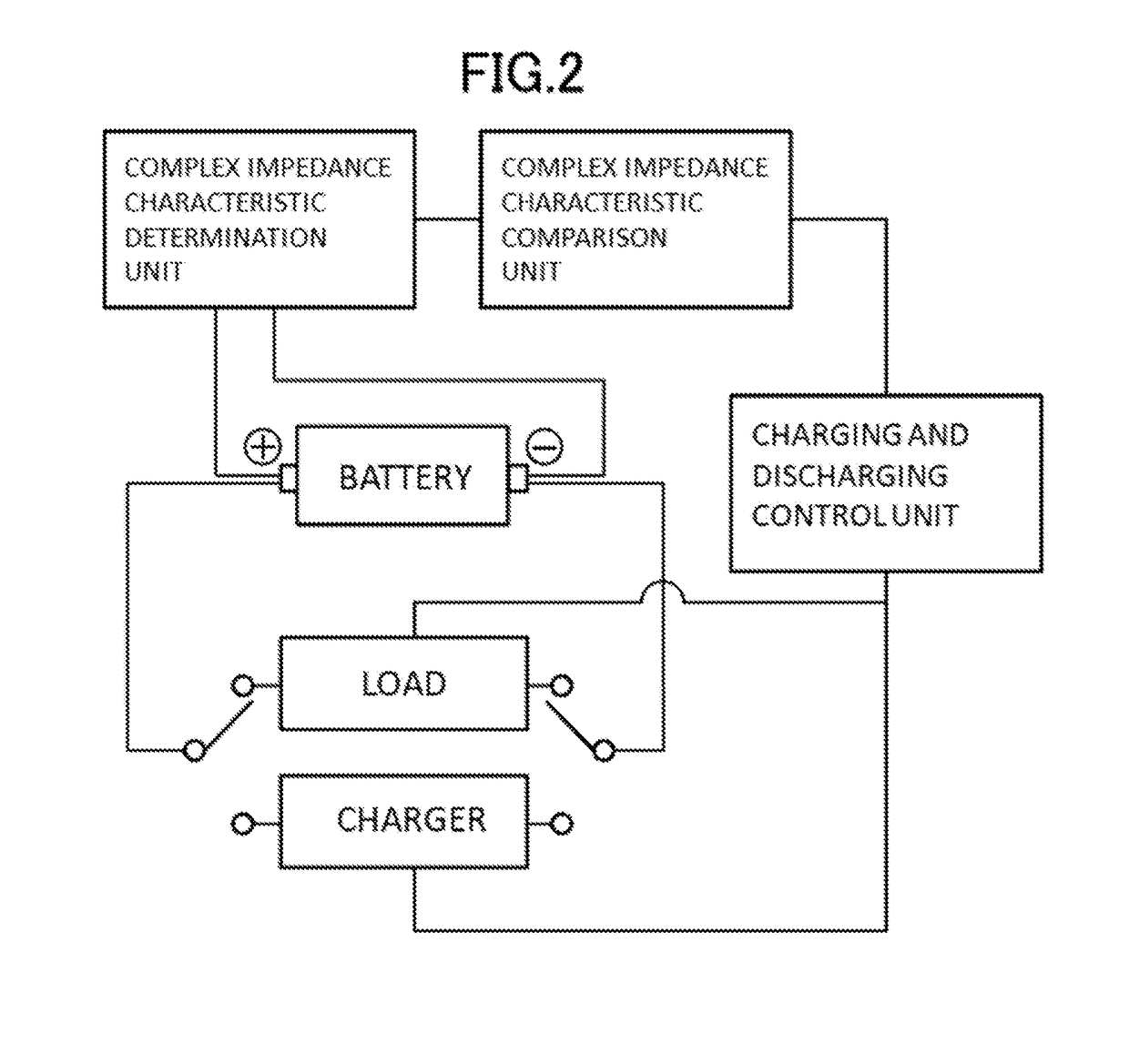
Method and system for estimating state of charge or depth of discharge of battery, and method and system for evaluating health of battery
ActiveUS20180321326A1Wide marketabilityIncrease heightCircuit monitoring/indicationElectrical testingState of chargeEngineering
It is intended to recognize the state of charge or depth of discharge of the battery more accurately than conventional technologies and to recognize health of a battery appropriately. Complex impedance between positive and negative electrodes of the battery is determined at a plurality of frequencies, and the state of charge or depth of discharge of the battery is estimated by comparing frequency dependency of Warburg impedance of the determined complex impedances with frequency dependency of Warburg impedance corresponding to a known state of charge or depth of discharge of the battery. Similarly, complex impedance is determined, and the health of the battery is evaluated by using the real part of the complex impedance at a point where the imaginary part of the complex impedance is zero on a line obtained by extending a part, which indicates frequency dependency of Warburg impedance, of a complex impedance characteristic curve representing a correlation relationship between the real and imaginary parts of the determined complex impedance.
Owner:JAPAN AEROSPACE EXPLORATION AGENCY
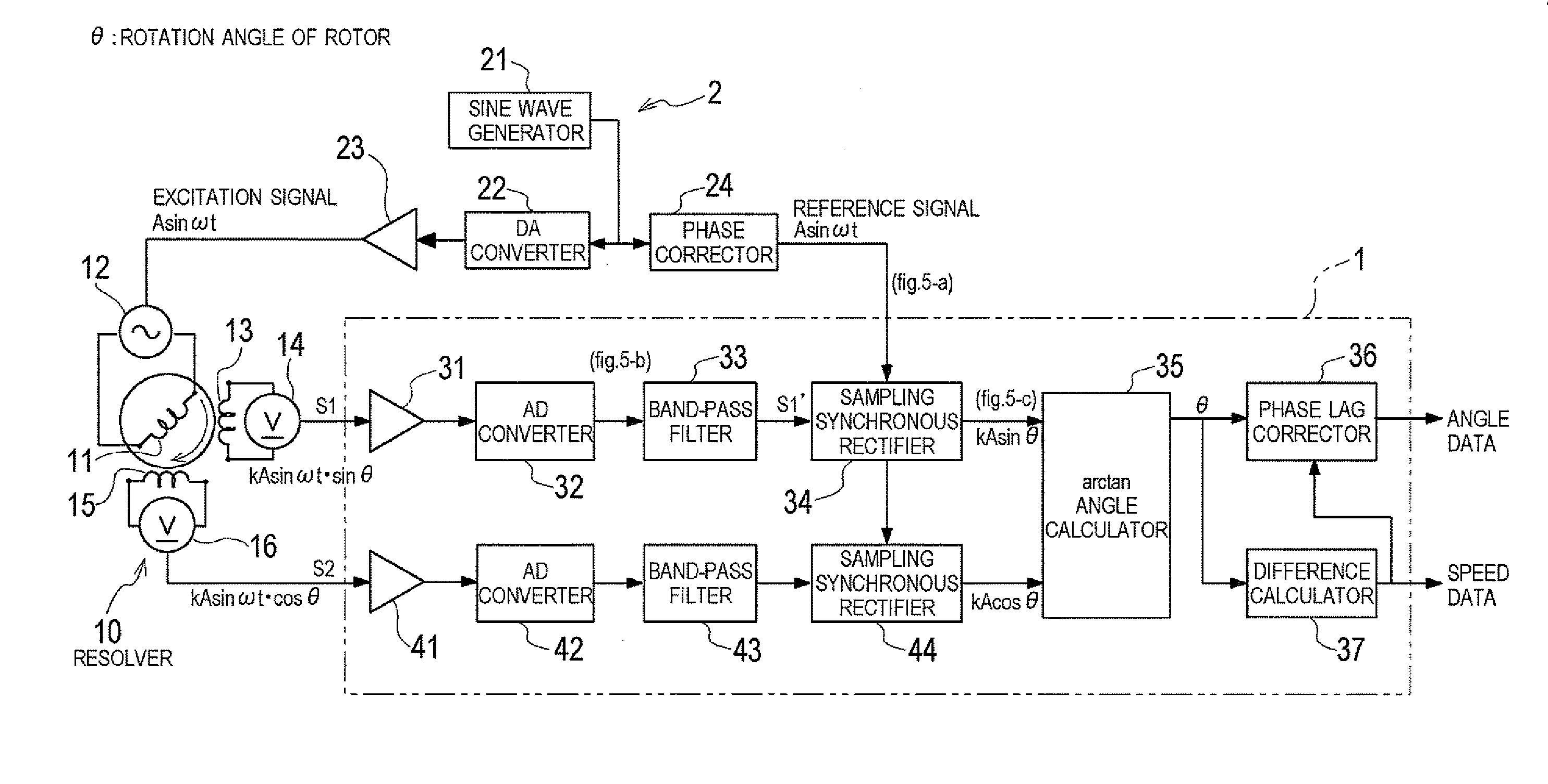
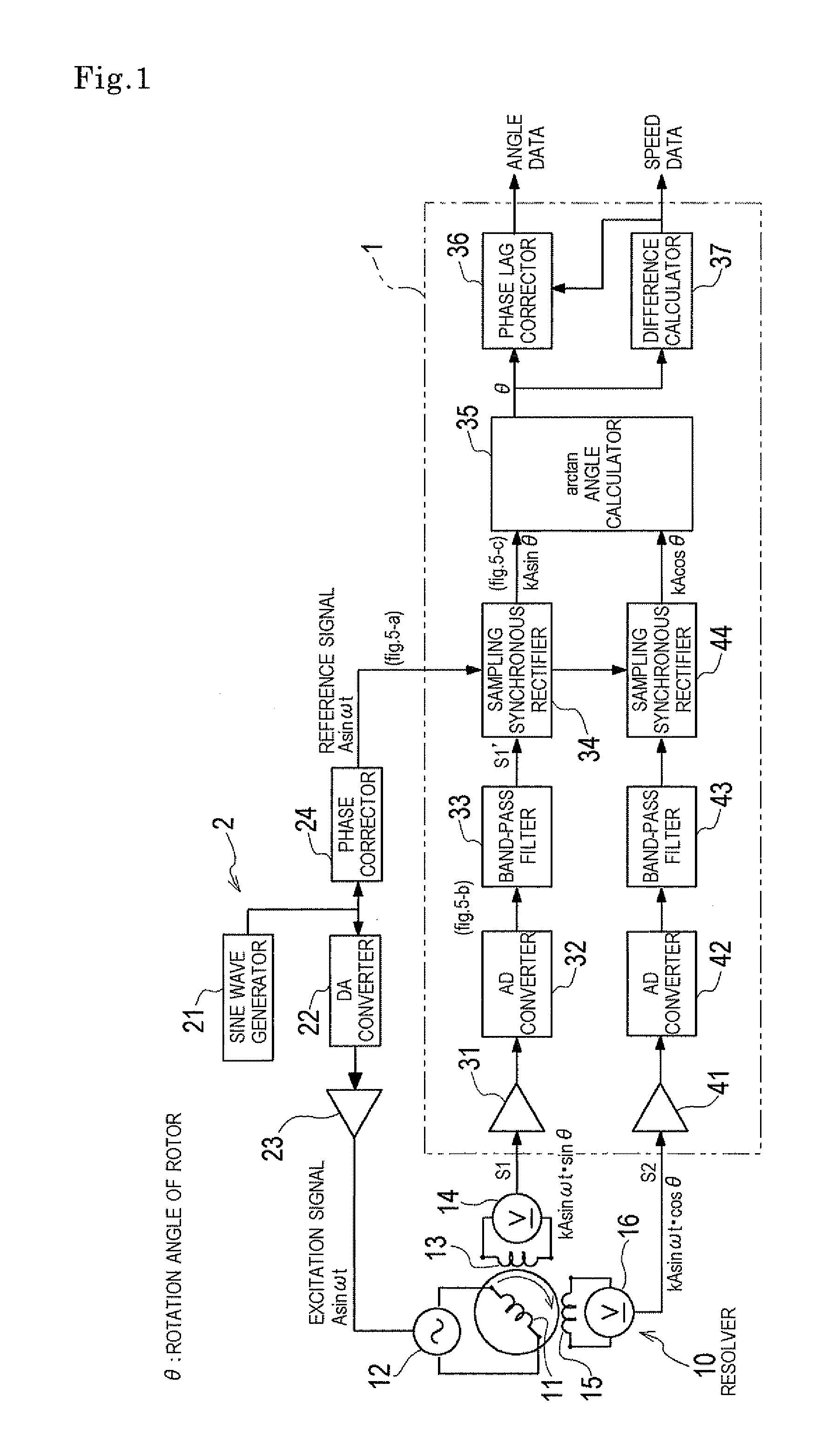
Resolver signal converter and resolver signal conversion method
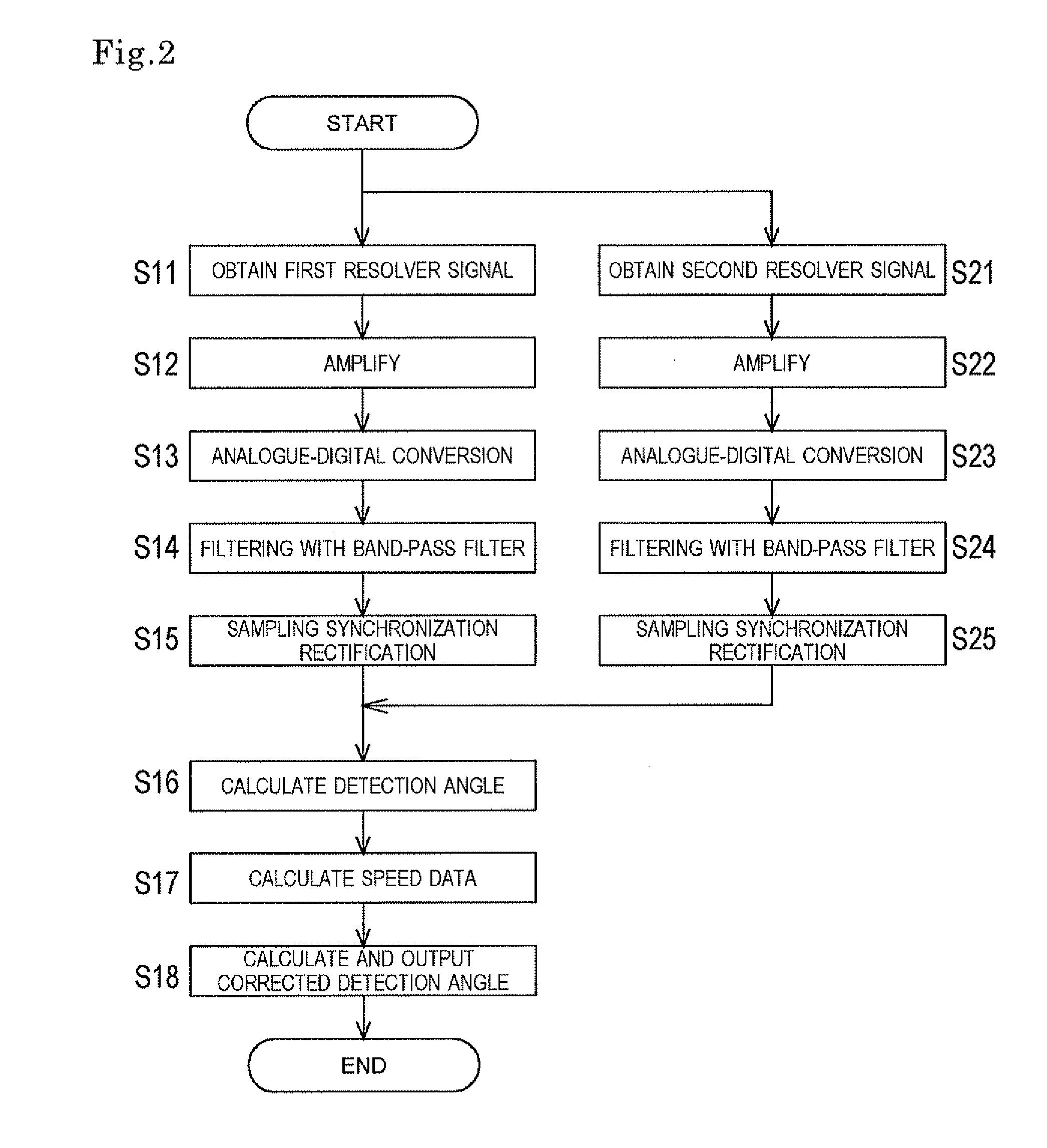
ActiveUS20120010849A1Eliminate dependenceReduce impactProgramme controlAnalogue/digital conversionBand-pass filterCenter frequency
A resolver signal converter and a resolver signal conversion method amplify and perform analogue-digital conversion on a sine wave output from a resolver; thereafter, among frequency components of the sine wave output, pass and thereby extract a predetermined bandwidth of which the center frequency is the frequency of an excitation signal, by means of a band-pass filter; sample the sine wave output while synchronizing the sine wave output with a reference signal which is based on the excitation signal; and generate a detection angle signal sine value from the sampled signal. Similarly, a detection angle signal cosine value is generated from a cosine wave output from the resolver. A detection angle is calculated based on the detection angle signal sine value and the detection angle signal cosine value. Accordingly, an influence, on an input resolver signal, of disturbance noise such as noise caused due to a magnetic field generated by a motor and switching noise caused due to PWM driving, is eliminated, and frequency dependence of arithmetic processing is eliminated. As a result, detection angle errors are reduced.
Owner:KAWASAKI HEAVY IND LTD
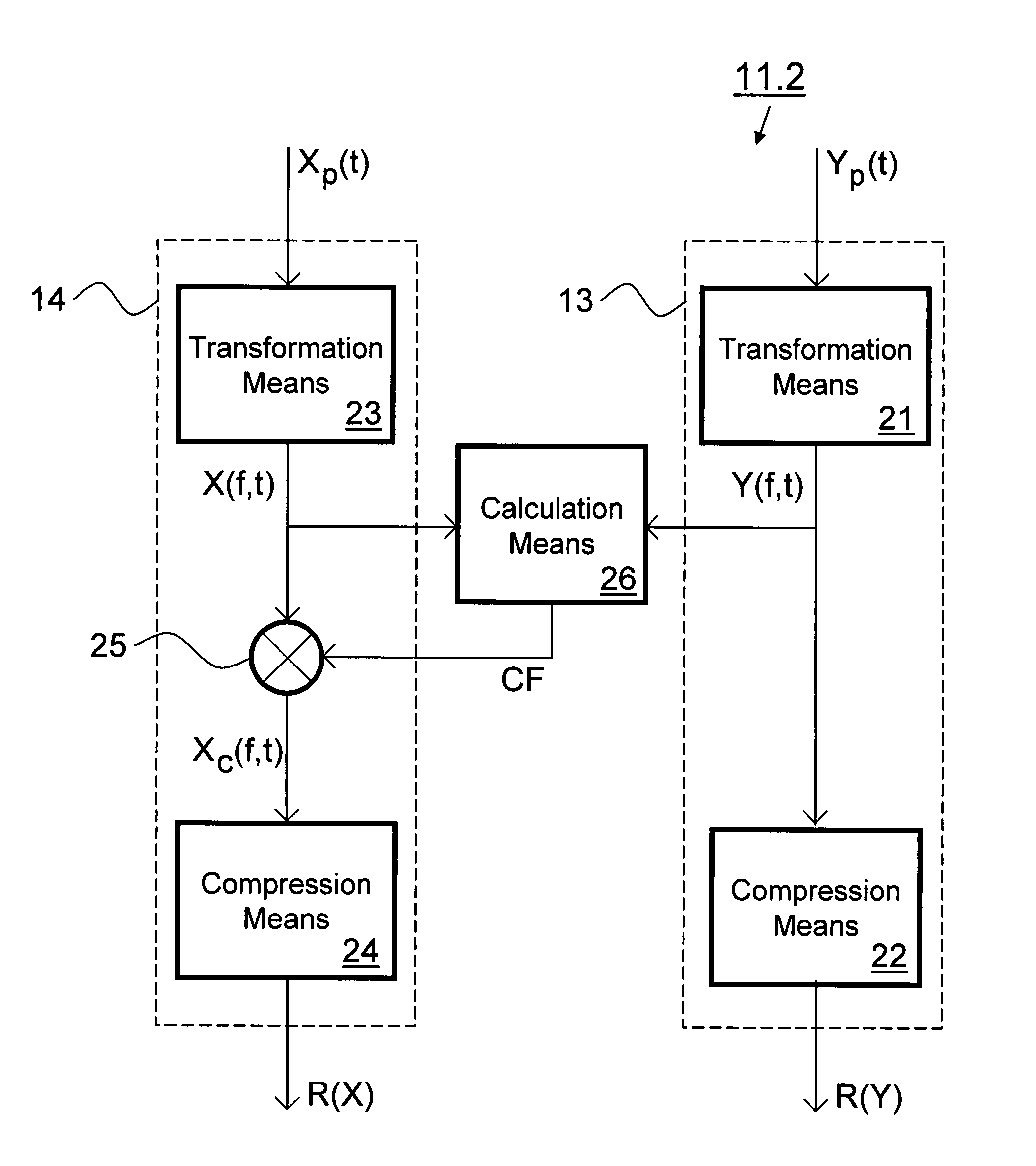
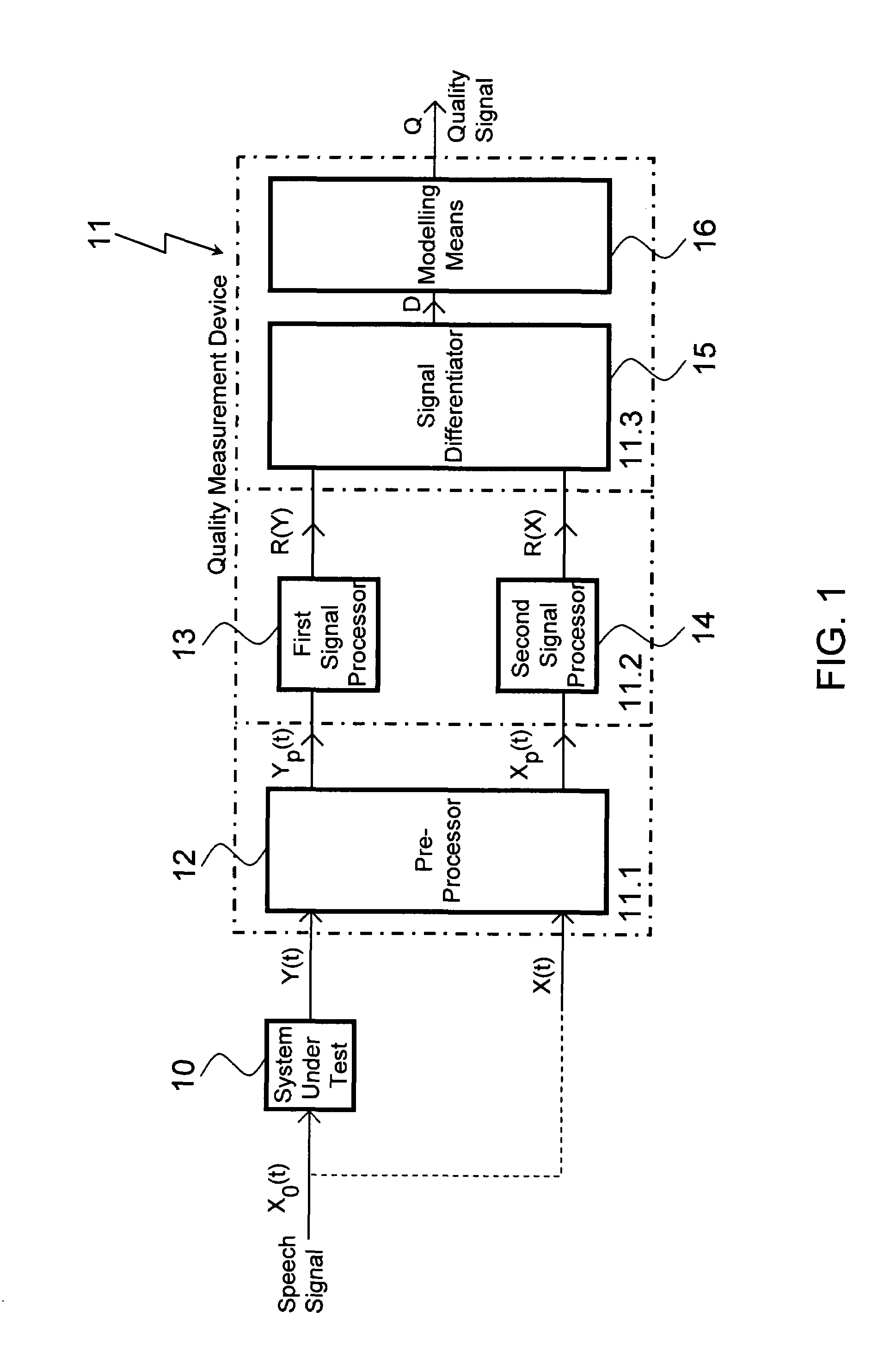
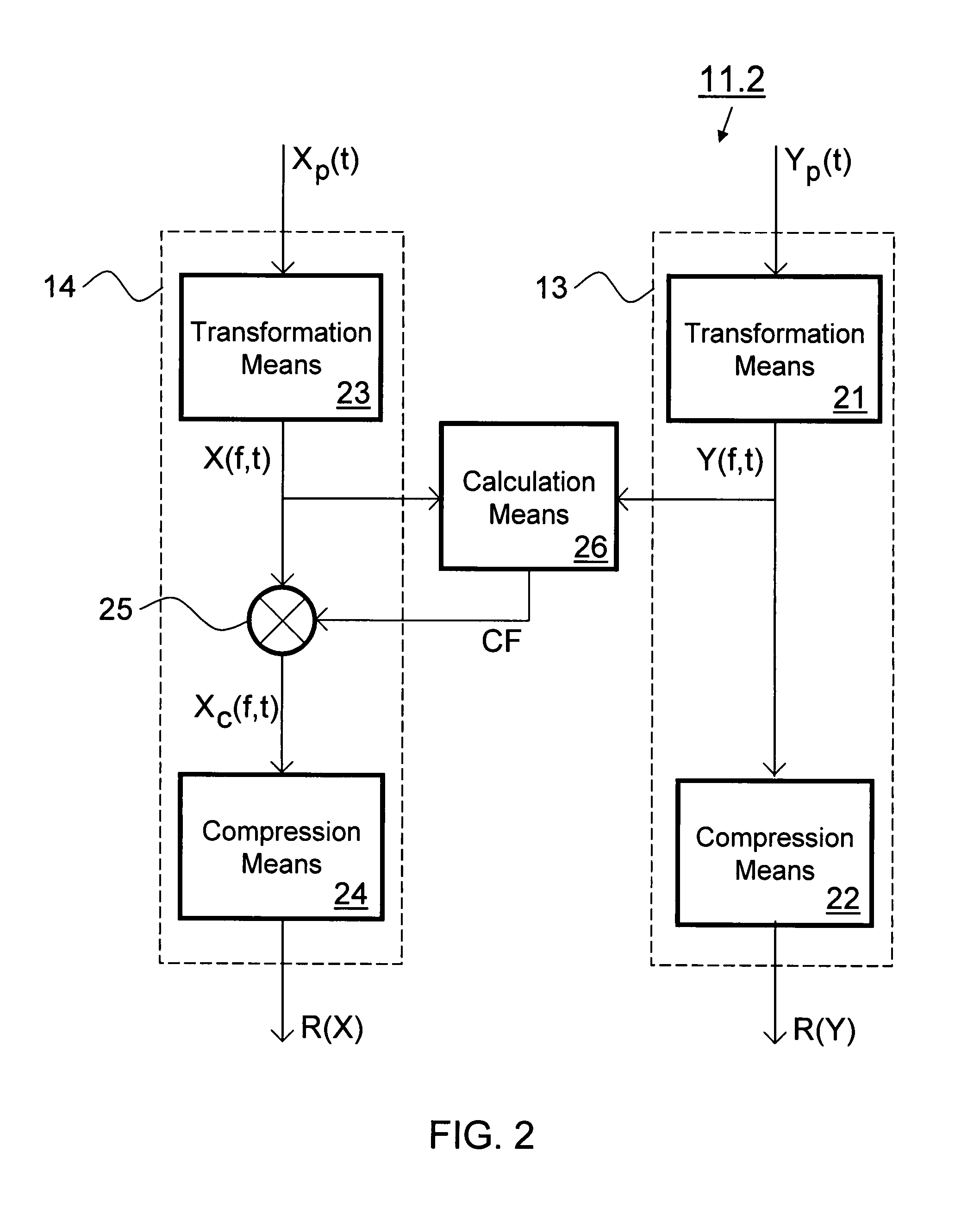
Method for determining the quality of a speech signal
Objective measurement methods and devices for predicting perceptual quality of speech signals degraded in speech processing / transporting systems have unreliable prediction results in cases where the degraded and reference signals show in between severe timbre differences. Improvement is achieved by applying a partial compensation step within in a signal processing stage using a frequency dependently clipped compensation factor for compensating power differences between the degraded and reference signals in the frequency domain. Preferably clipping values for clipping the compensation factor have larger frequency-dependency in a range of low frequencies with respect to a centre frequency of the human auditory system, than in a range of high frequencies.
Owner:KONINK KPN NV
Semiconductor integrated circuit with variable gain amplifier
InactiveUS20090102552A1Reduce voltageImprove noise figureNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsGain controlHigh resistanceClosed loop
The variable gain amplifier includes a bias circuit (BC) 1, a matching circuit (MC) 2, a variable gain resistive feedback amplifier (FA) 3 and an output follower (EA) 4. The resistance values of the load resistance Rc and feedback resistance Rf are changed in cooperation. In a case of making the load resistance Rc a high resistance to set the low noise amplifier to a high gain, the feedback resistance Rf is also made a high resistance, the feedback time constant τfb(c1)≈2π·RfCbe / (1+gmRc) of the closed loop of the resistive negative feedback amplifier 3 becomes substantially constant, and then the amplifier has a gain small in frequency dependency over a wide bandwidth. In a case of making the load resistance Rc a low resistance to set the low noise amplifier to a low gain, the feedback resistance Rf is also made a low resistance. The feedback resistance Rf with the low resistance increases the negative feedback quantity, and thus the amplifier is set to a low gain. Also, the load resistance Rc is made a low resistance, and the feedback time constant τfb(c1) becomes substantially constant. The gain is not lowered further in a high frequency region.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
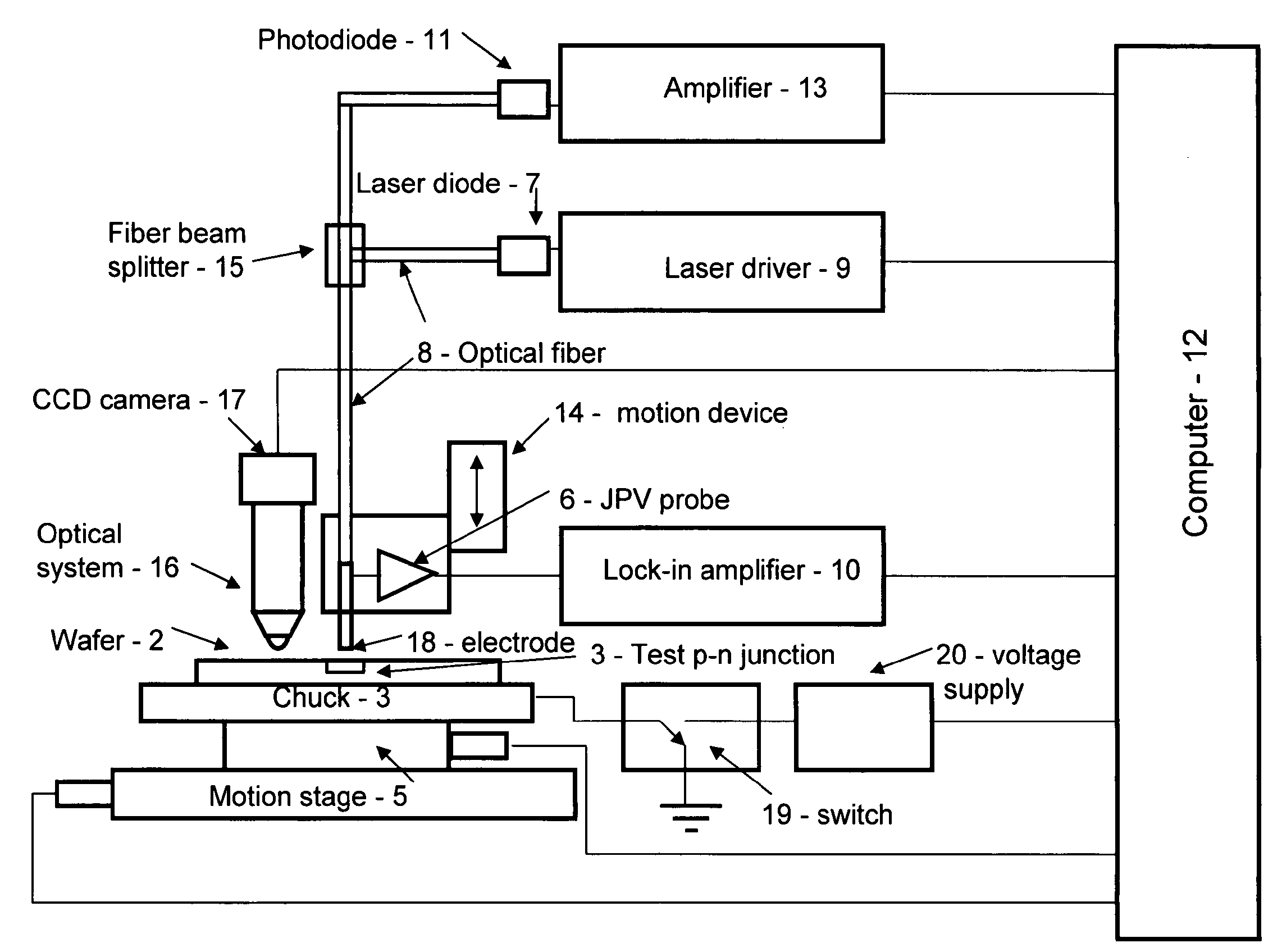
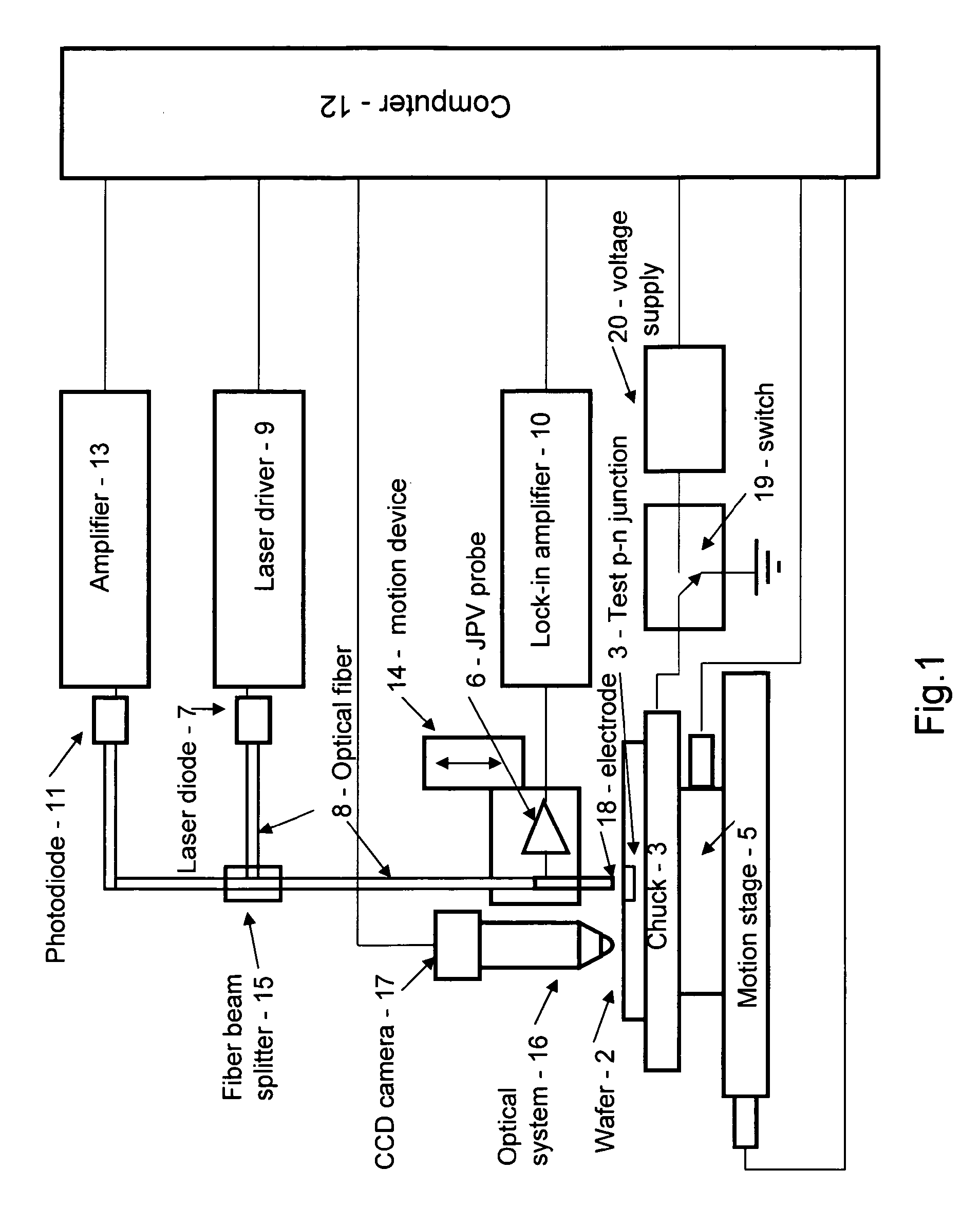
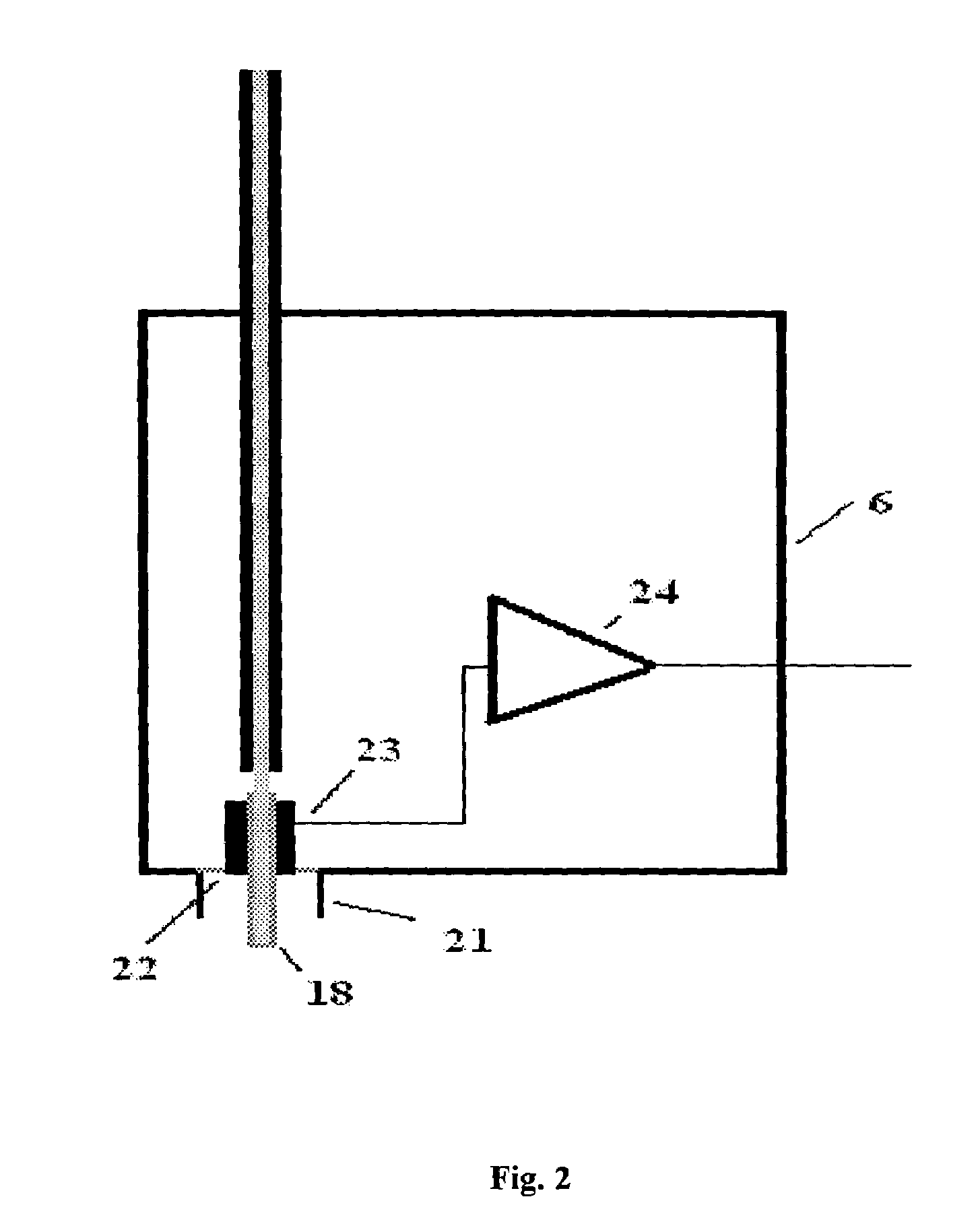
Non-contact method and apparatus for measurement of leakage current of p-n junctions in IC product wafers
InactiveUS7414409B1Improve accuracyImprove versatilityFault locationIndividual semiconductor device testingFiberCapacitance
A non-contact apparatus and method for measuring of the leakage current and capacitance of p-n junctions in test structures within scribe lanes of IC product wafers is disclosed. The apparatus has a light source optically coupled with a fiber to a transparent electrode at the end of the fiber, which is brought close to the p-n junction under test. The ac signal generated from the test p-n junction is captured by this transparent and conducting coating electrode. The leakage current of a test p-n junction is determined using the frequency dependence of junction photo-voltage signal and reference signals from a p-n junction with low leakage current and known capacitance.
Owner:AHBEE 1
Data communication circuit with equalization control
ActiveUS20090219983A1Reduce areaReduce consumptionMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsBlind equalizationTransmission channel
An adaptive equalizer comprises an adjustable equalizer circuit that allows to enhance the frequency dependence of contents of the transmitted signals which suffer from losses in the connected transmission channel. A blind equalization tuning procedure is proposed that operates without knowledge about the characteristic of transmission channel. Phase positions of transitions in the equalized signal are detected. A digital post-processing circuit evaluates a measure for spread of the detected phase positions of transitions, accumulated over a plurality of the symbol periods. The digital post-processing circuit controls the adjustable equalizer, setting the adjustable equalizer to a setting wherein the detected spread is minimized.
Owner:NXP BV
Data communication circuit with equalization control
ActiveCN101283560AModulated-carrier systemsTransmitter/receiver shaping networksPhase detectorBlind equalization
An adaptive equalizer comprises an adjustable equalizer circuit (10) that allows to enhance the frequency dependence of contents of the transmitted signals which suffer from losses in the connected transmission channel. A blind equalization tuning procedure is proposed that operates without knowledge about the characteristic of transmission channel. Phase positions of transitions in the equalized signal are detected through a transition phase detector (44). A digital post-processing circuit evaluates a measure for spread of the detected phase positions of transitions, accumulated over a plurality of the symbol periods. The digital post-processing circuit (14) controls the adjustable equalizer, setting the adjustable equalizer to a setting wherein the detected spread is minimized.
Owner:NXP BV
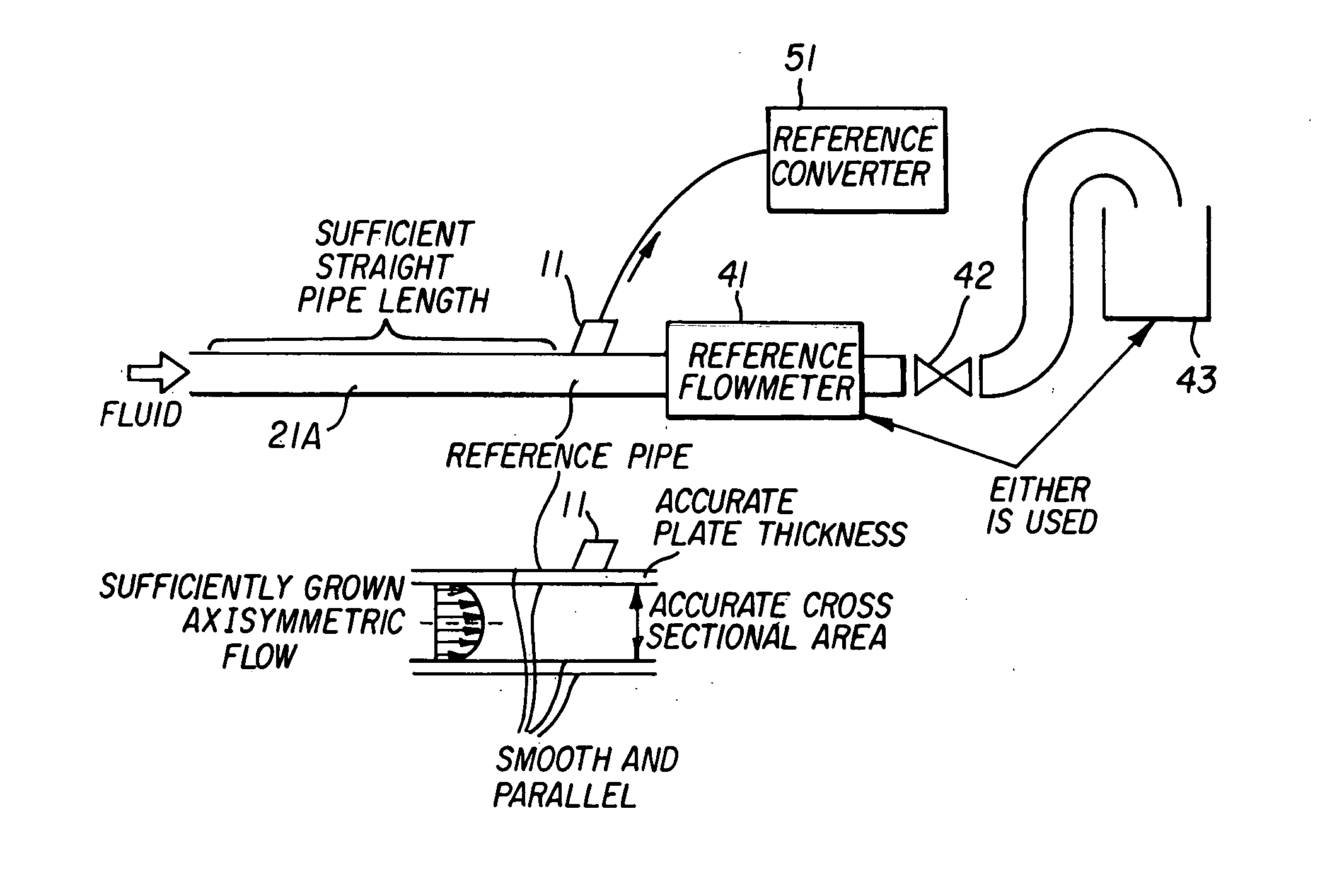
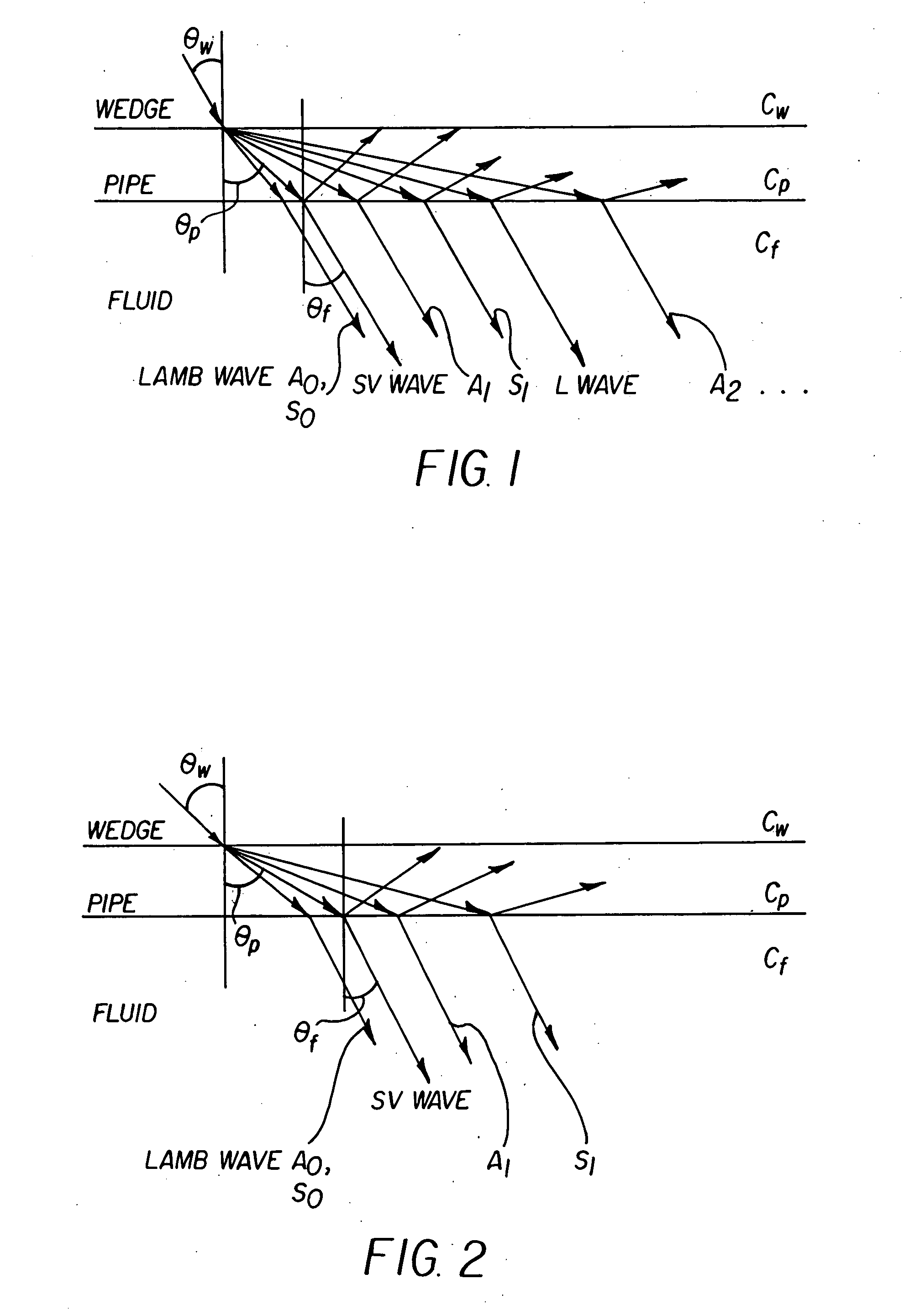
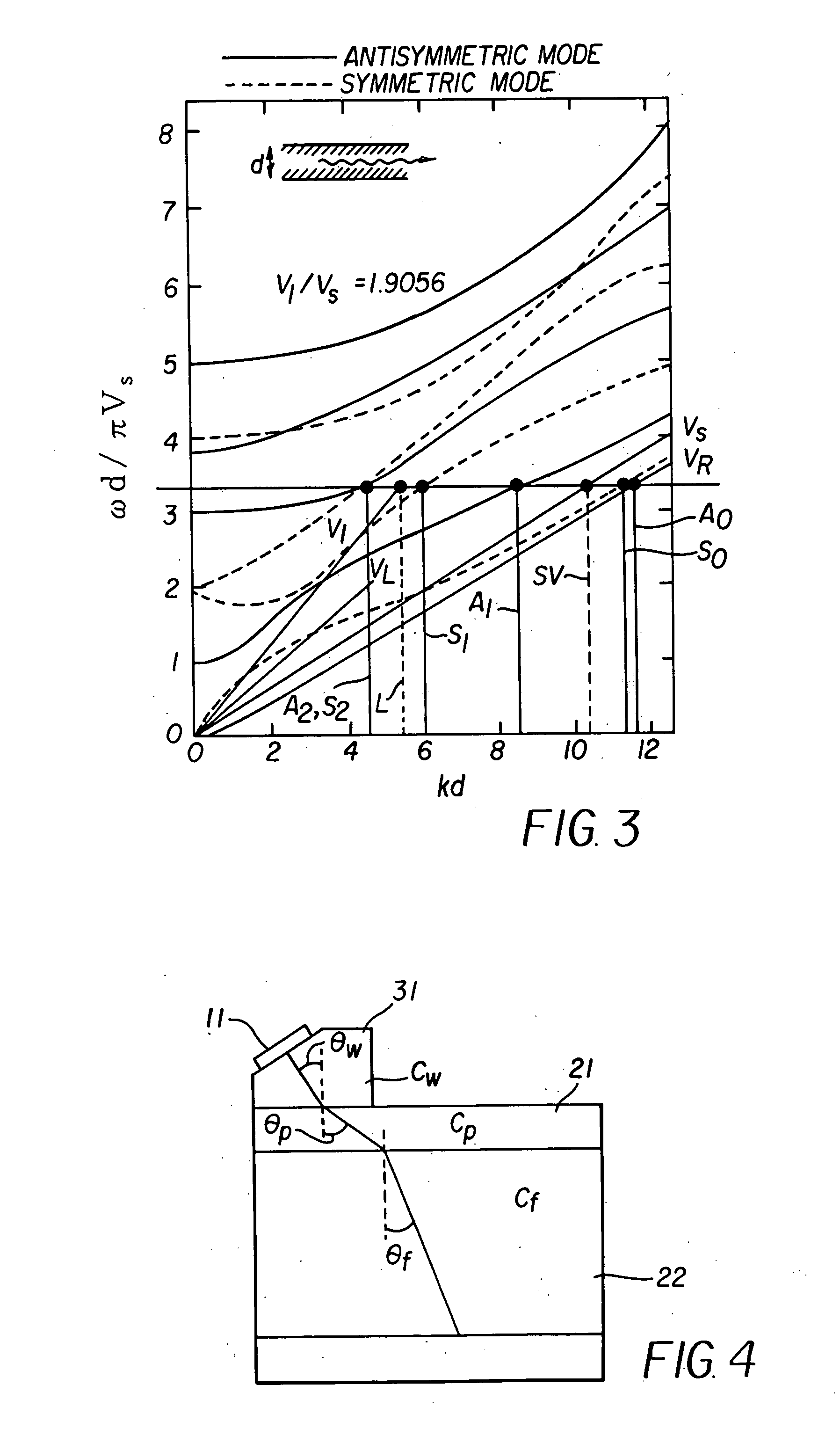
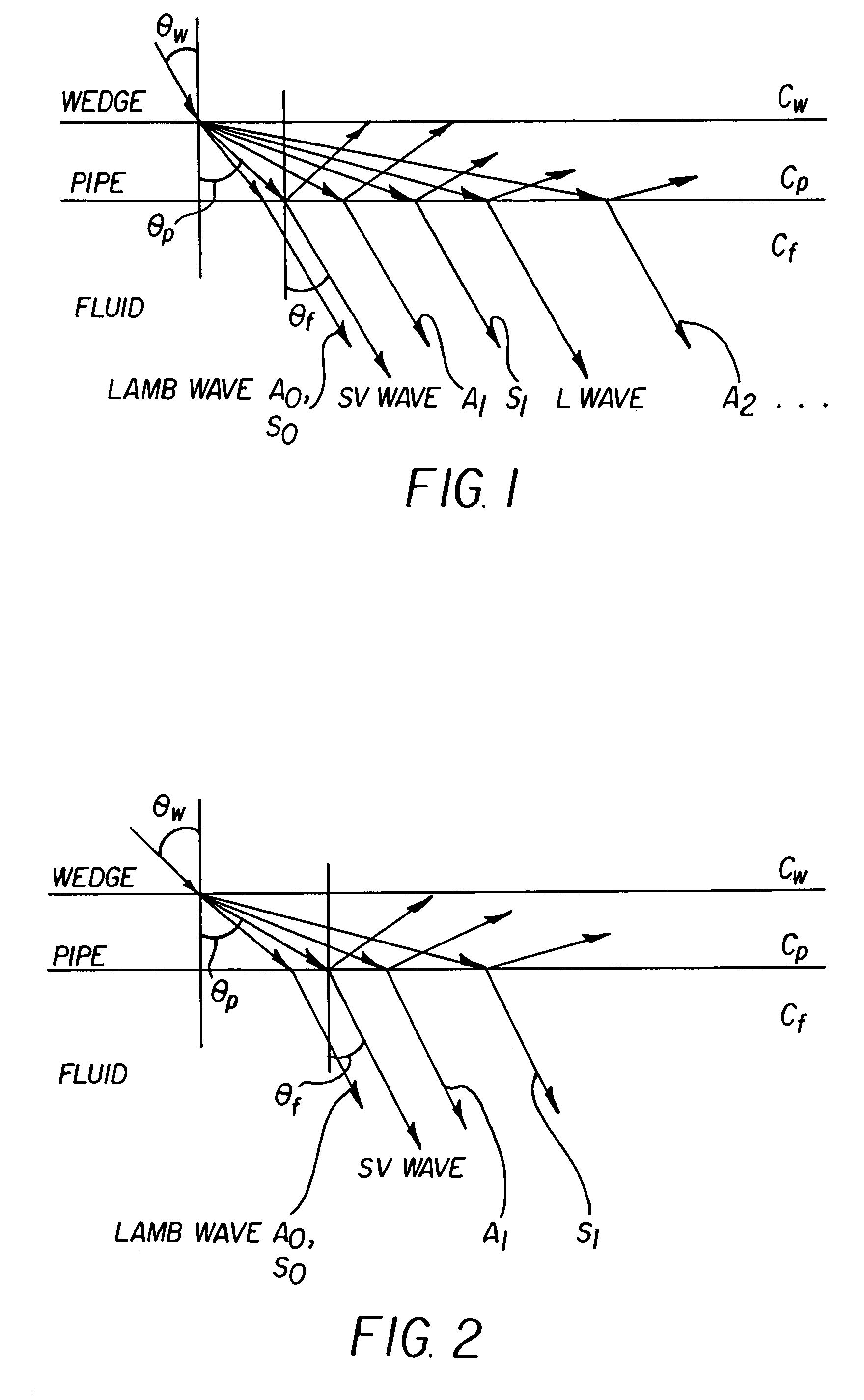
Apparatus and method for measuring a fluid flow rate profile using acoustic doppler effect
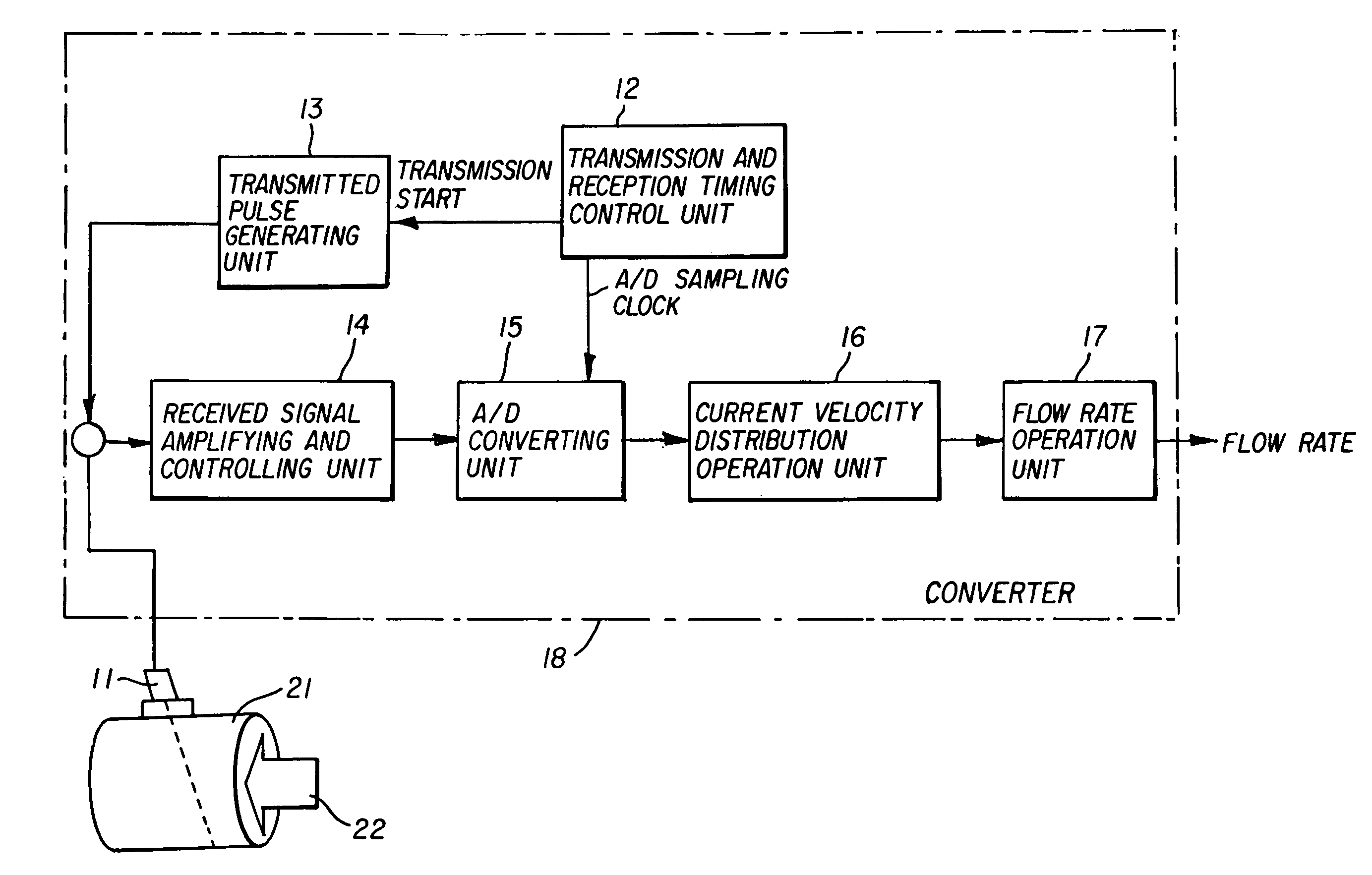
ActiveUS20060020404A1Reduced frequency dependenceReduce measurement errorFlow propertiesVolume/mass flow measurementAngle of incidenceUltrasonic sensor
An apparatus and method for measuring a flow velocity profile of fluid traveling in a pipe or conduit uses an ultrasonic wave transmitted from an ultrasonic wave transducer mounted at an angle on the outside of a pipe using a wedge, and made incident onto the fluid in the pipe to measure the fluid flow velocity profile, using the principle that a frequency of an ultrasonic wave, reflected by a reflector existing in the fluid, is changed depending on a flow velocity due to Doppler effect. The transmission frequency and the angle of incidence onto the pipe can be selected to suppress frequency dependence of a measured value due to Lamb wave and allow the flow velocity or flow rate of fluid to be measured with a greater accuracy.
Owner:FUJI ELECTRIC CO LTD
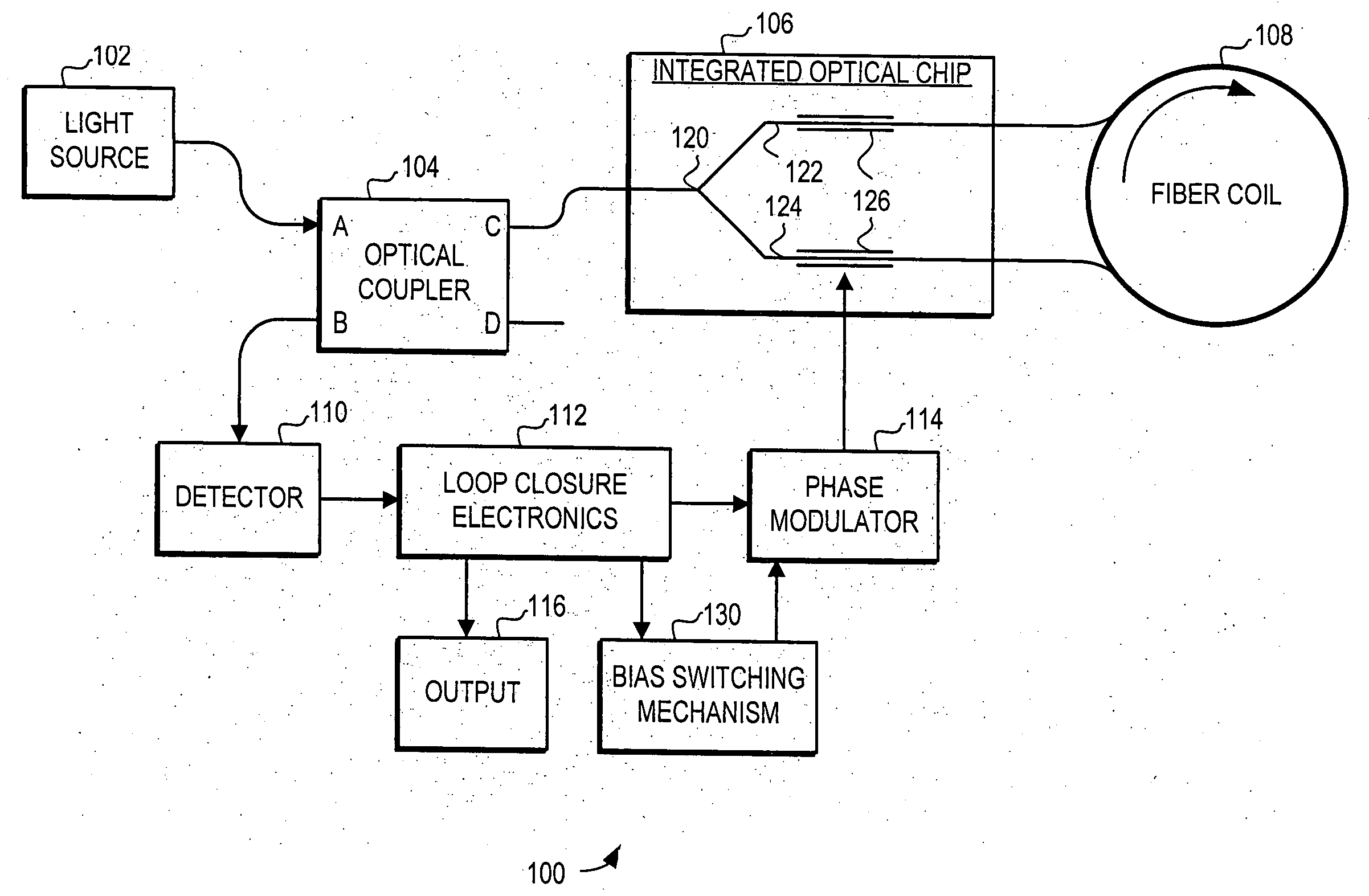
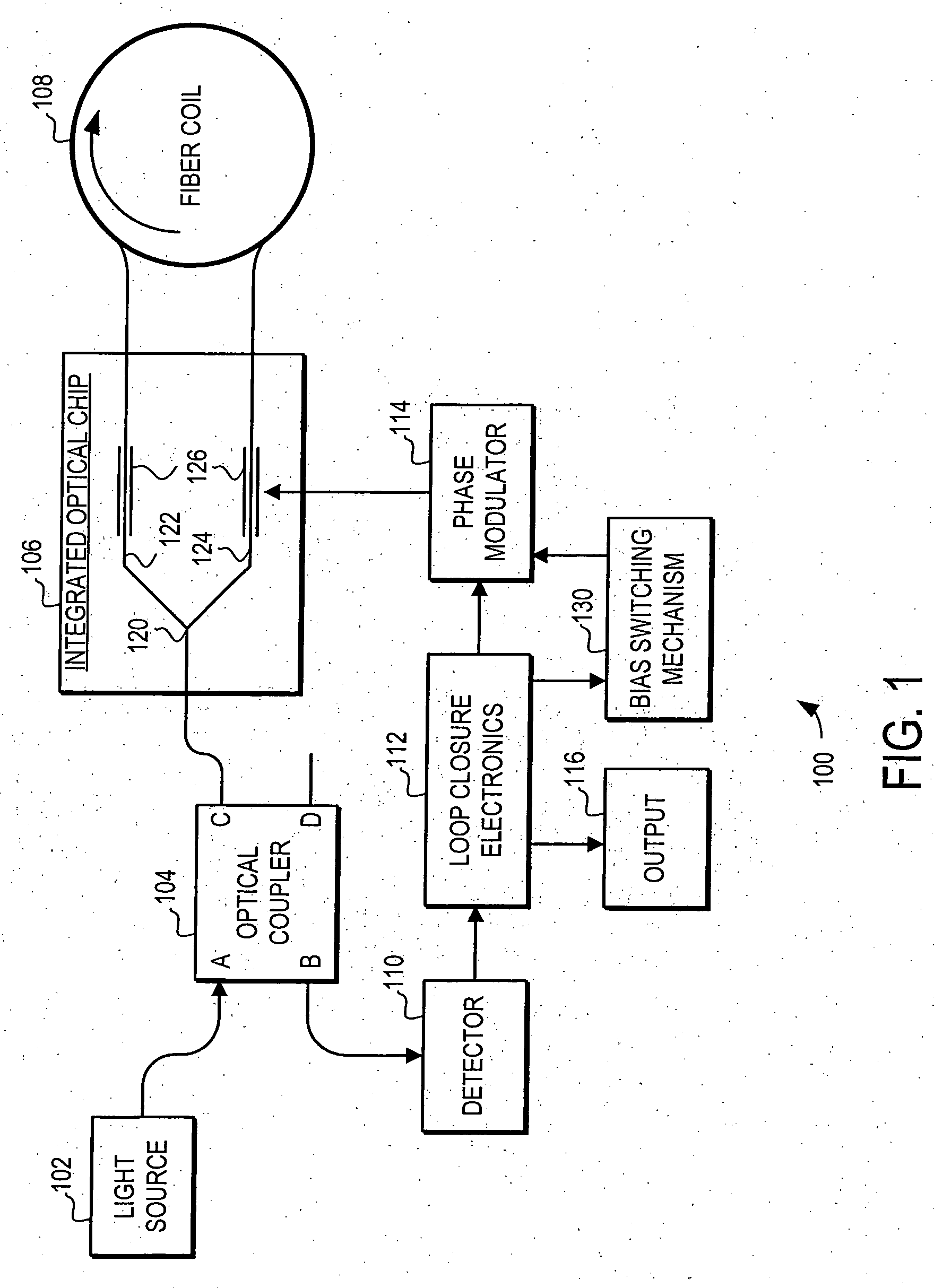
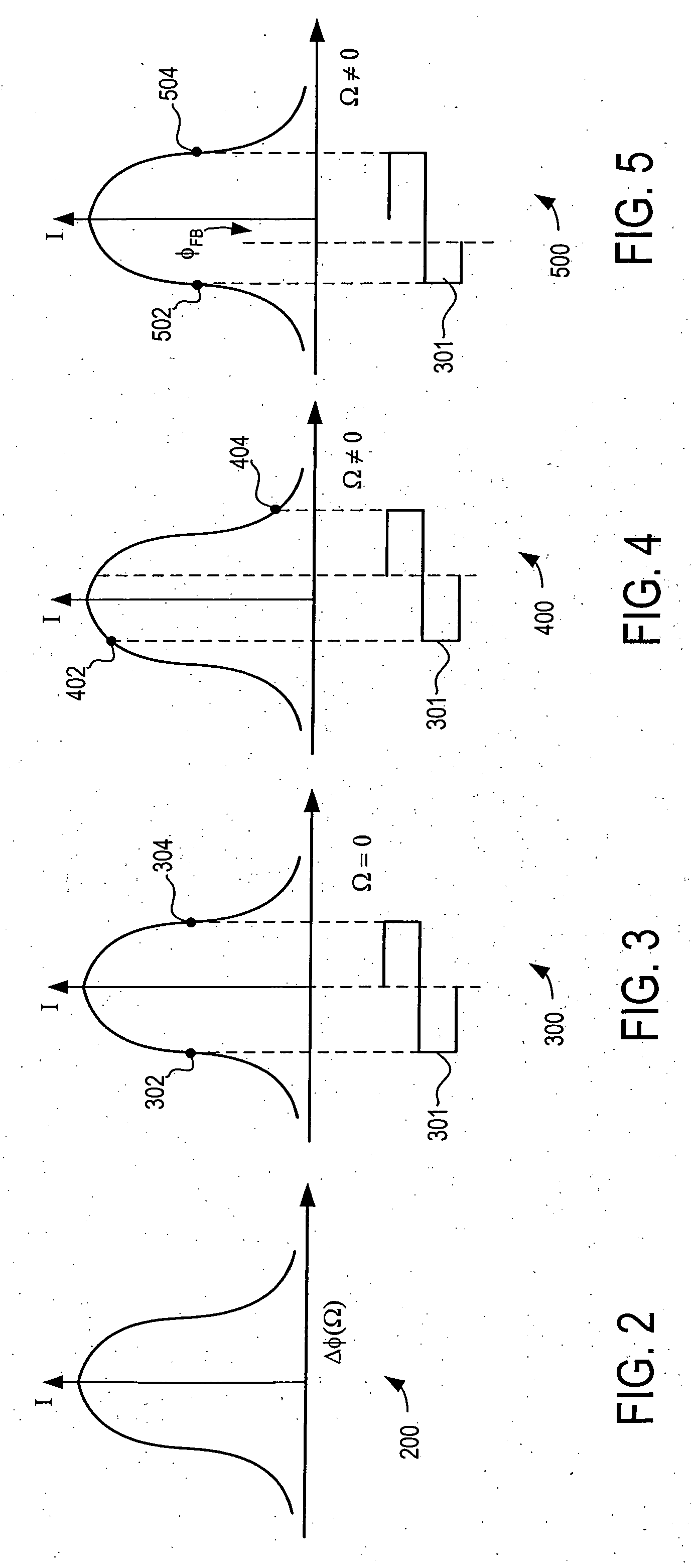
Minimal bias switching for fiber optic gyroscopes
ActiveUS20070121116A1Reduce sensitivityReducing low frequency contentSagnac effect gyrometersSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsFiberPhase shifted
A system and method is provided for reducing the sensitivity of the rotation rate measurement to the frequency dependence of the feedback modulator. Specifically, the system and method uses a minimal bias switching technique to reduce rate errors associated with the low frequency 2π resets in a closed loop fiber optic gyroscope with a phase modulator with a different phase shift associated to low and high frequencies. In general, the minimal bias switching technique reduces the low frequency components of the feedback modulation drive by increasing the frequency of the 2π resets. As a consequence, the system and method reduces the low frequency component of the feedback modulator drive to avoid errors that occur with the low frequency 2π resets.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
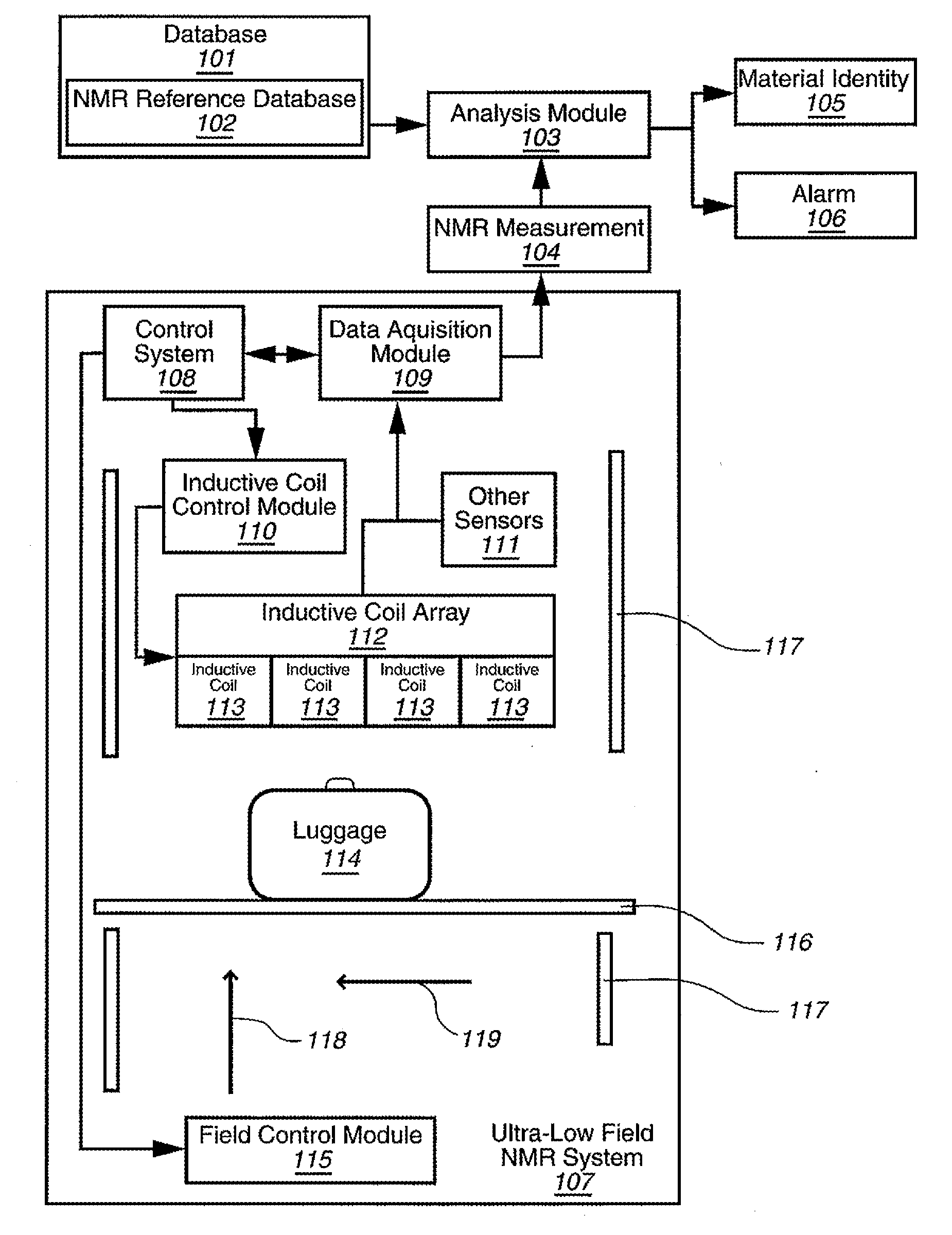
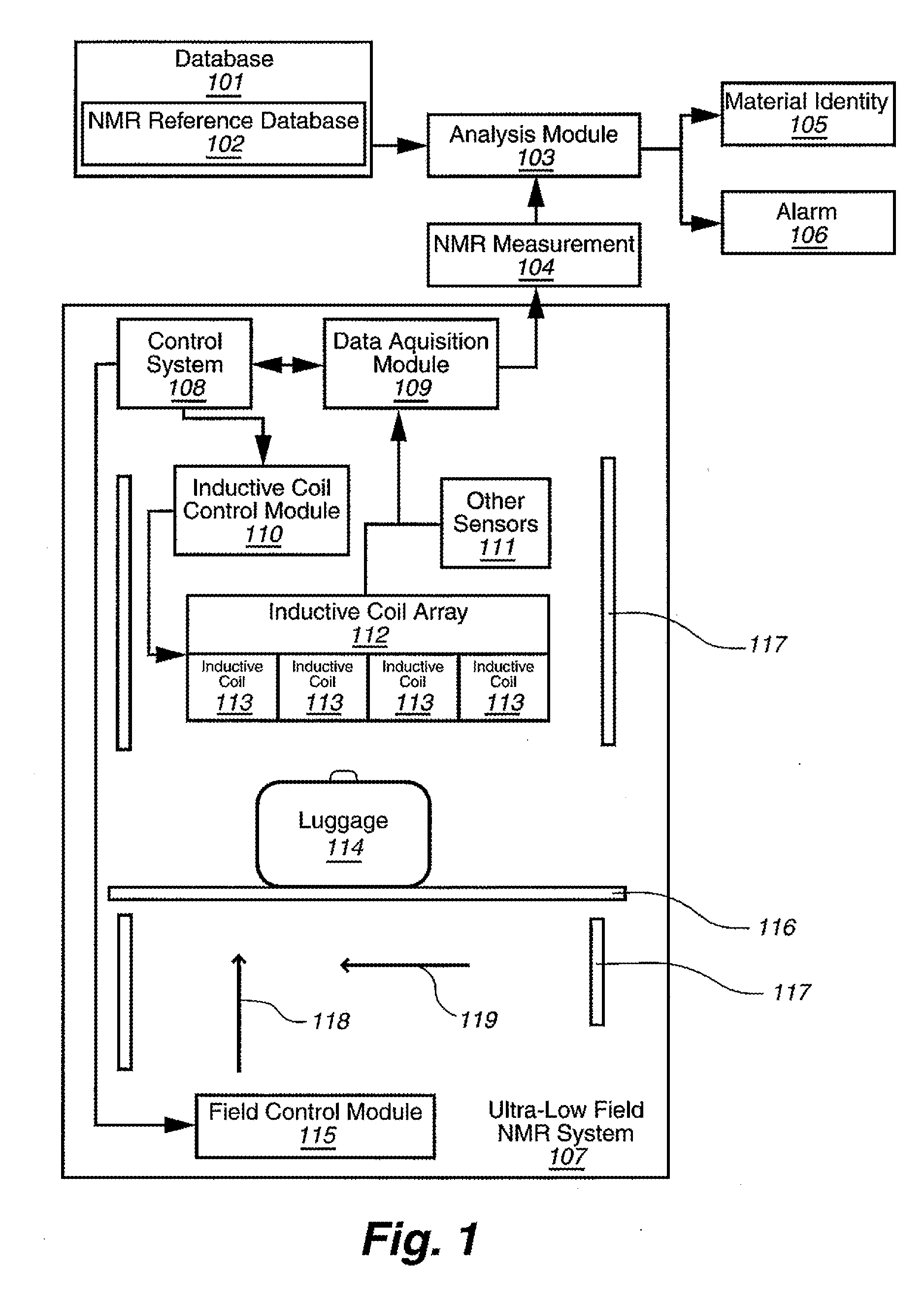
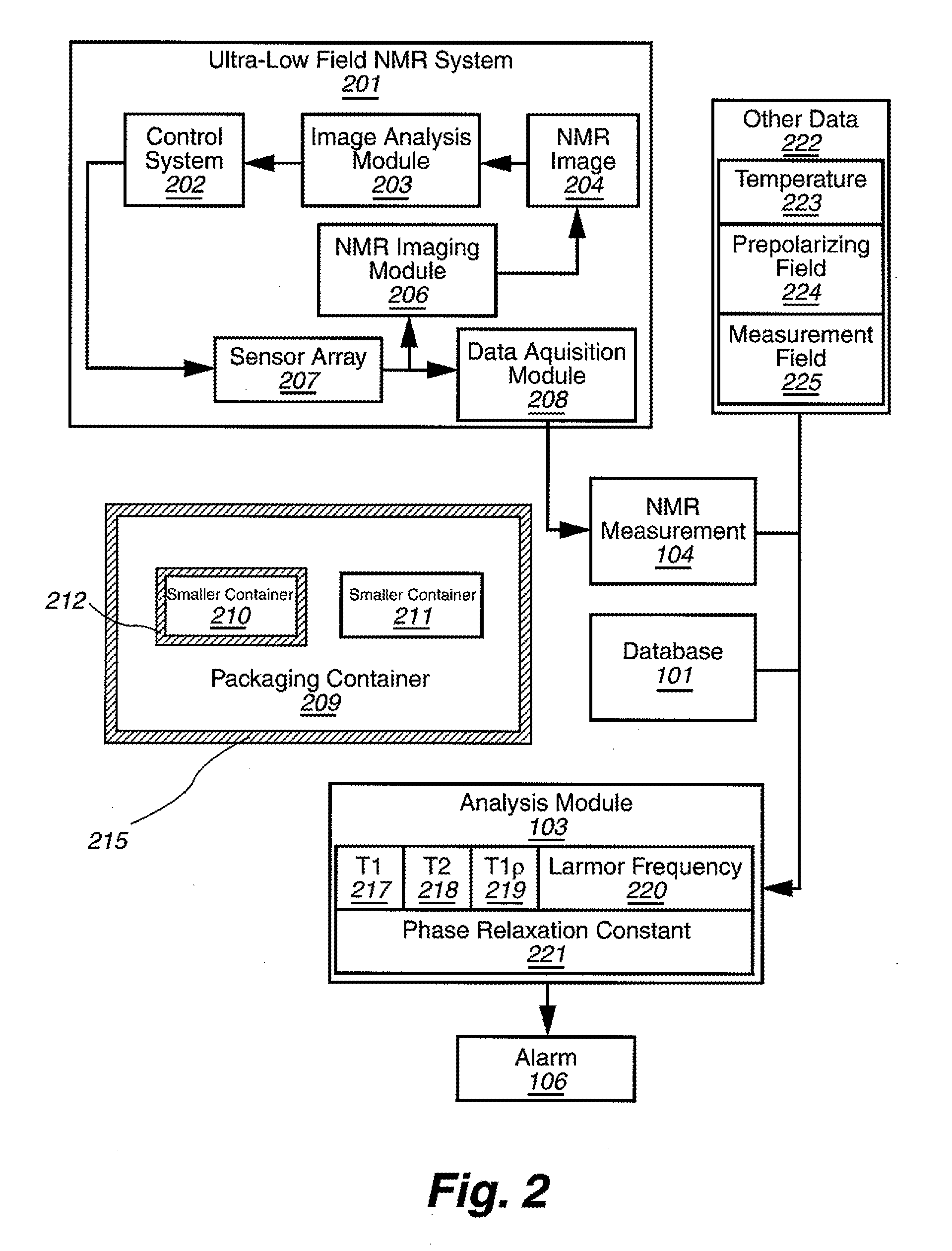
Ultra-low field nuclear magnetic resonance and magnetic resonance imaging to discriminate and identify materials
InactiveUS20100219827A1Material analysis by using resonanceElectric/magnetic detectionSolid-state nuclear magnetic resonanceNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
Method comprising obtaining an NMR measurement from a sample wherein an ultra-low field NMR system probes the sample and produces the NMR measurement and wherein a sampling temperature, prepolarizing field, and measurement field are known; detecting the NMR measurement by means of inductive coils; analyzing the NMR measurement to obtain at least one measurement feature wherein the measurement feature comprises T1, T2, T1ρ, or the frequency dependence thereof; and, searching for the at least one measurement feature within a database comprising NMR reference data for at least one material to determine if the sample comprises a material of interest.
Owner:TRIAD NAT SECURITY LLC
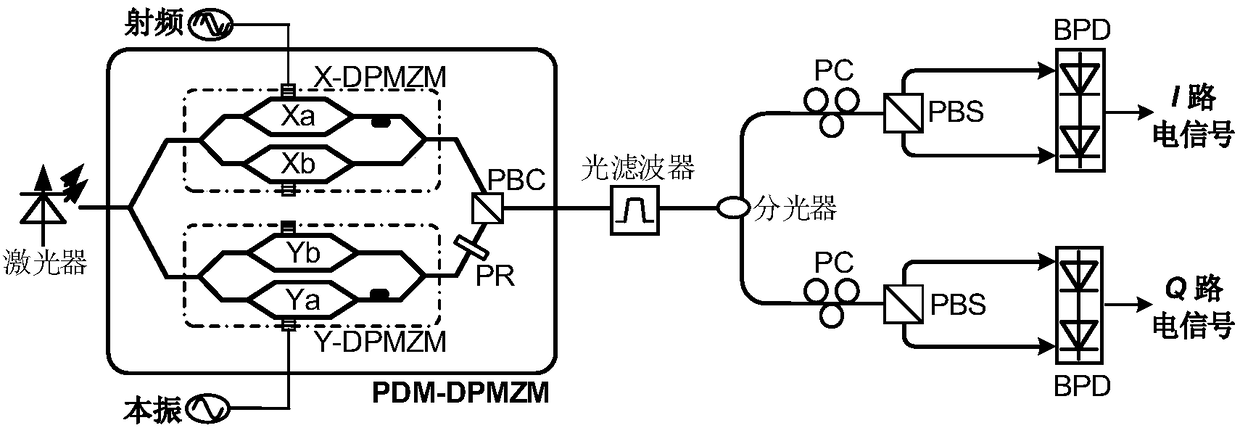
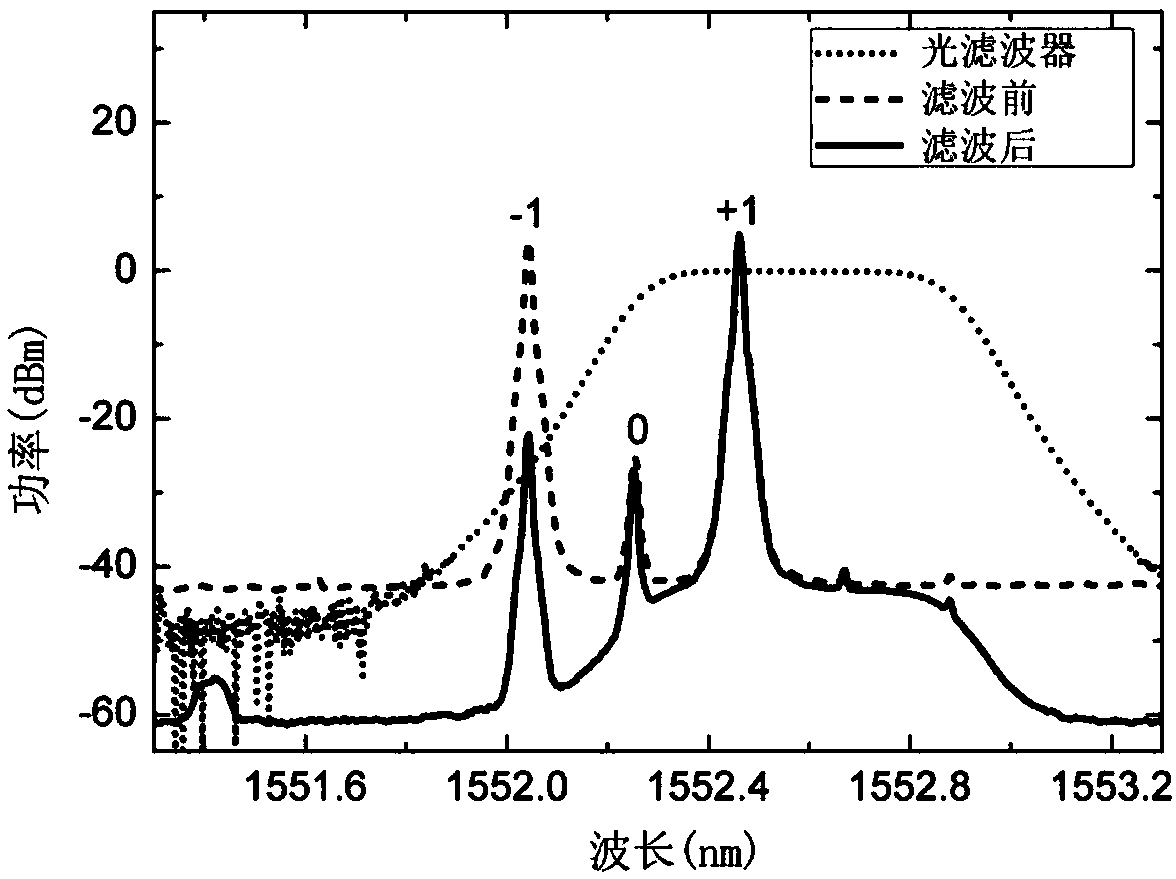
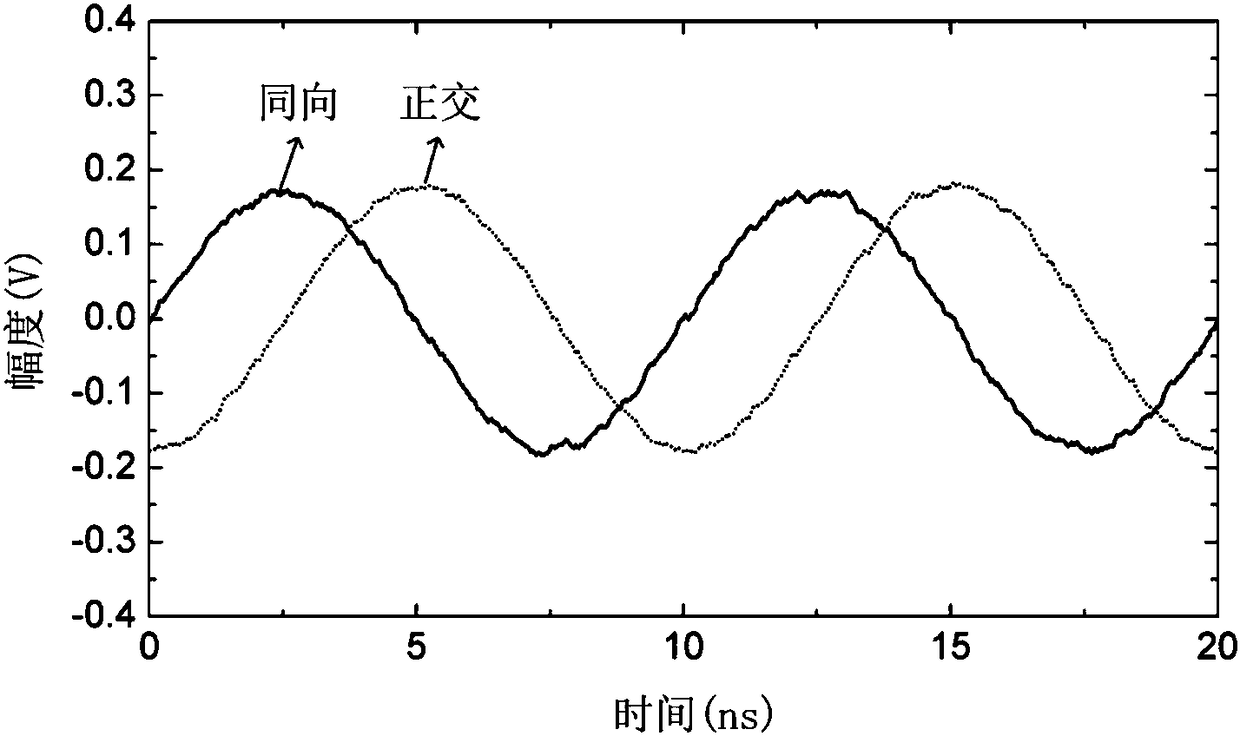
Photonics microwave I/Q down-conversion system
ActiveCN108449143AImprove balanceAvoid frequency dependenceElectromagnetic transmittersLocal oscillator signalPhase difference
The invention provides a photonics microwave I / Q down-conversion system, and relates to the technical field of optical fiber communication. The system adopts a polarization division multiplexing dual-parallel Mach-Zehnder modulator to modulate radio frequency and local oscillator signals, and by adjusting the working point of the modulator and performing optical filtering and polarization control,two paths of down-conversion channels with a phase difference of 90 degrees are constructed to achieve the microwave I / Q down-conversion. According to the photonics microwave I / Q down-conversion system provided by the invention, the radio frequency and local oscillator signals are modulated into polarization division multiplexing optical signals, and optical filtering, optical splitting, polarization control and balance detection are performed on the polarization division multiplexing optical signals to achieve the I / Q down-conversion of the radio frequency and local oscillator signals. The photonics microwave I / Q down-conversion system provided by the invention has the advantages of simple structure and high operability; and by adopting the photonics method to realize the orthogonal down-conversion of the two paths, the frequency dependence of an electronic device can be avoided, and the photonics microwave I / Q down-conversion system has the advantages of large bandwidth and high I / Qbalance degree.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Data communication circuit with equalization control
ActiveUS8396105B2Reduce areaReduce consumptionMultiple-port networksModulated-carrier systemsBlind equalizationTransmission channel
An adaptive equalizer comprises an adjustable equalizer circuit that allows to enhance the frequency dependence of contents of the transmitted signals which suffer from losses in the connected transmission channel. A blind equalization tuning procedure is proposed that operates without knowledge about the characteristic of transmission channel. Phase positions of transitions in the equalized signal are detected. A digital post-processing circuit evaluates a measure for spread of the detected phase positions of transitions, accumulated over a plurality of the symbol periods. The digital post-processing circuit controls the adjustable equalizer, setting the adjustable equalizer to a setting wherein the detected spread is minimized.
Owner:NXP BV
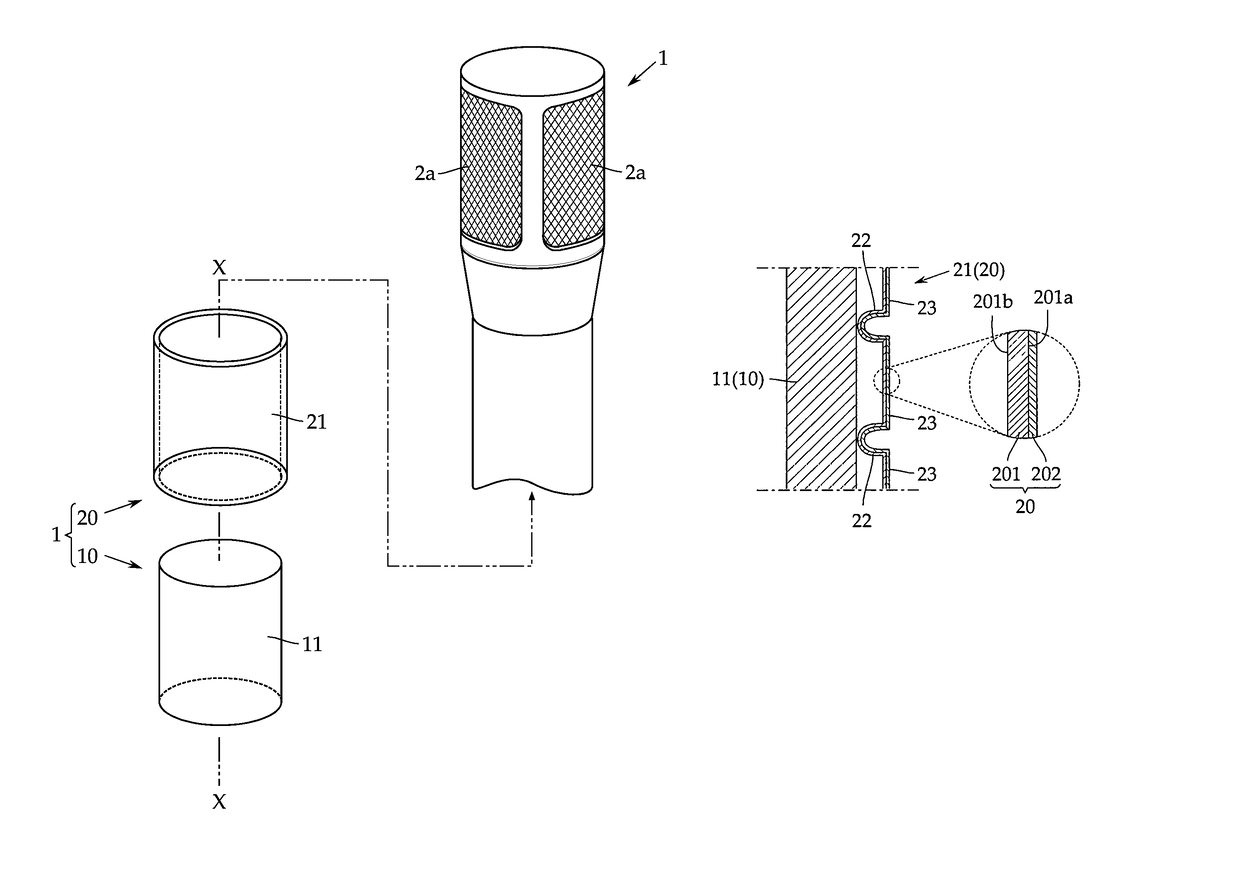
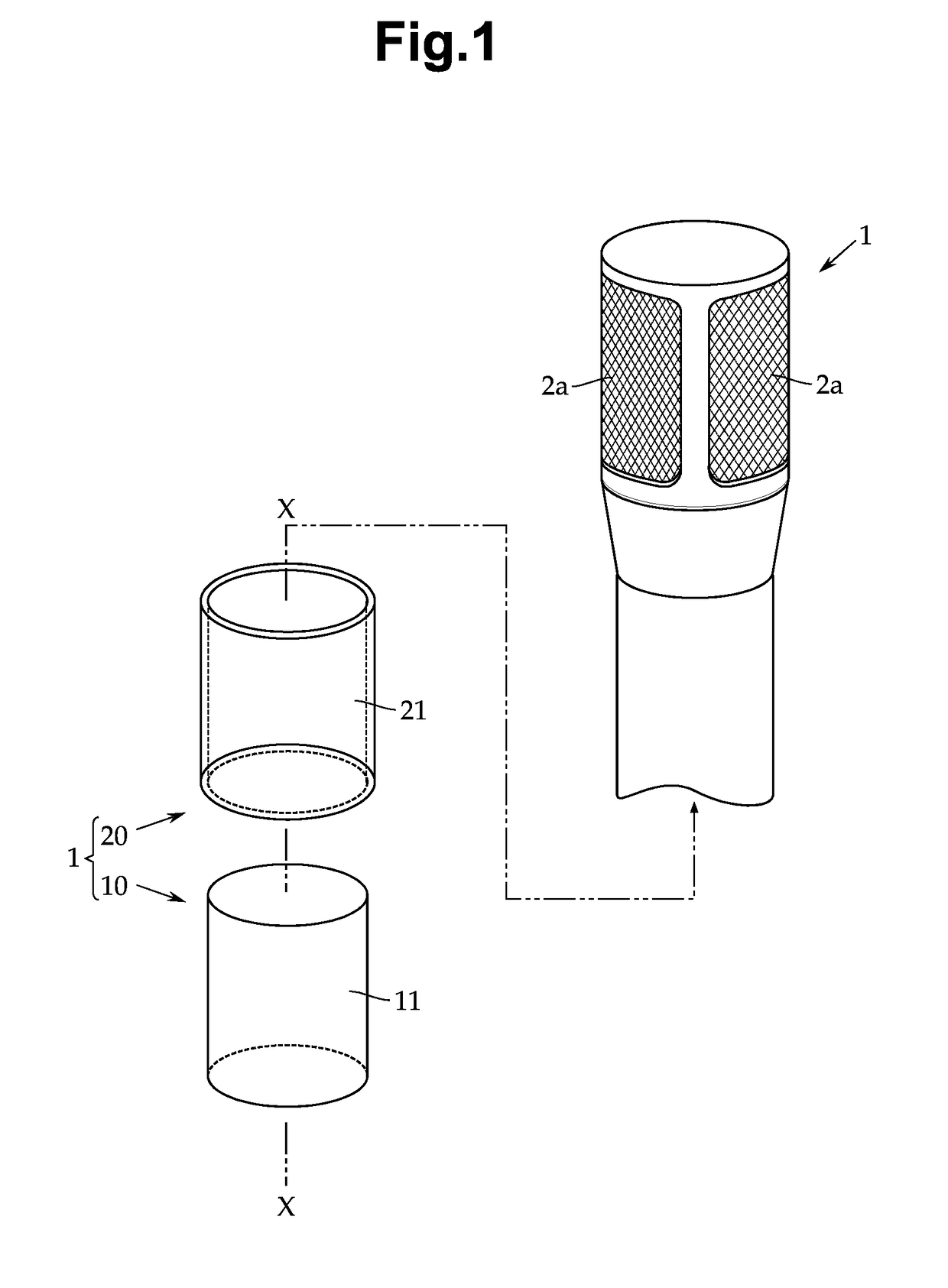
Condenser microphone unit and condenser microphone
Owner:AUDIO-TECHNICA
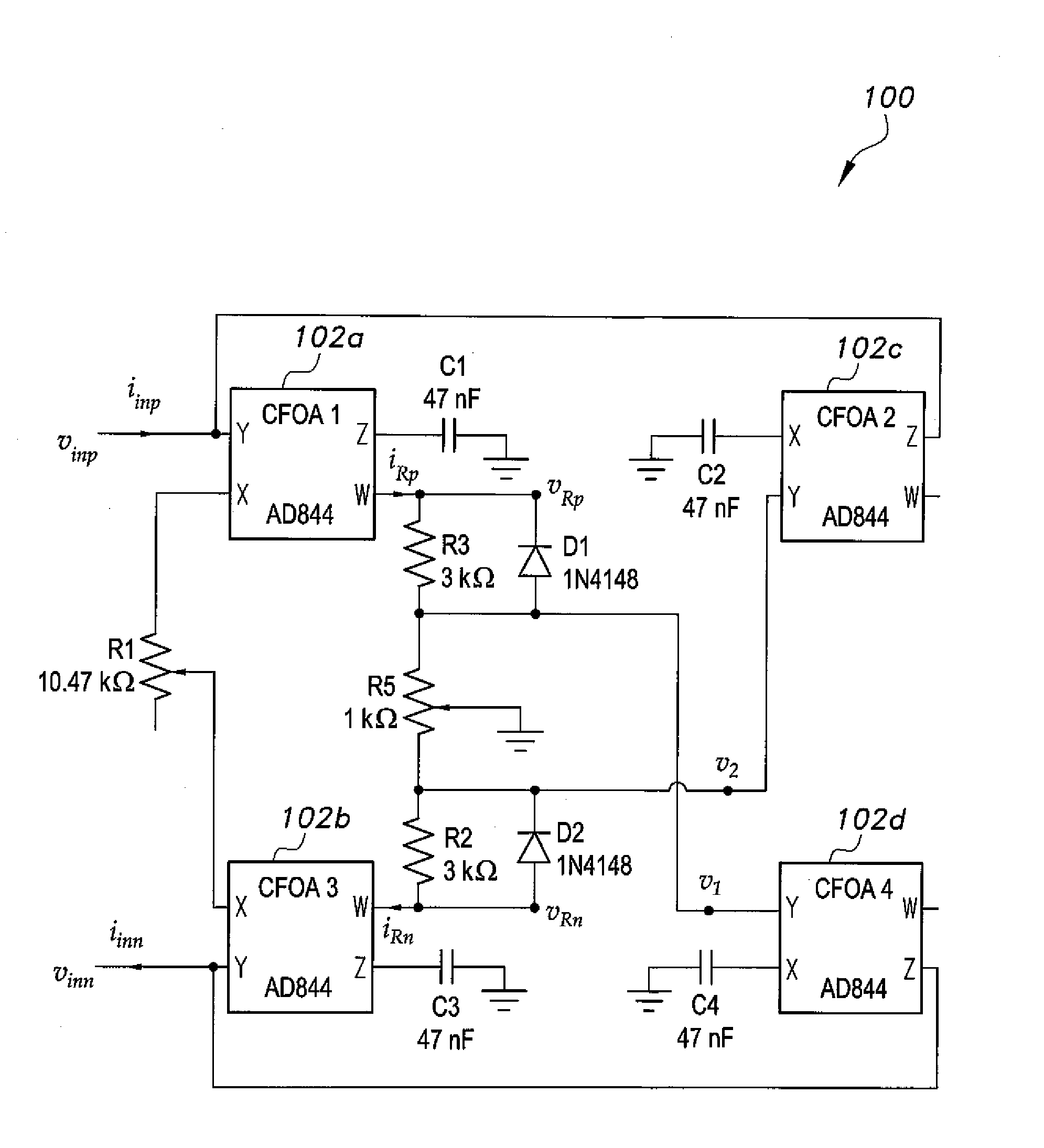
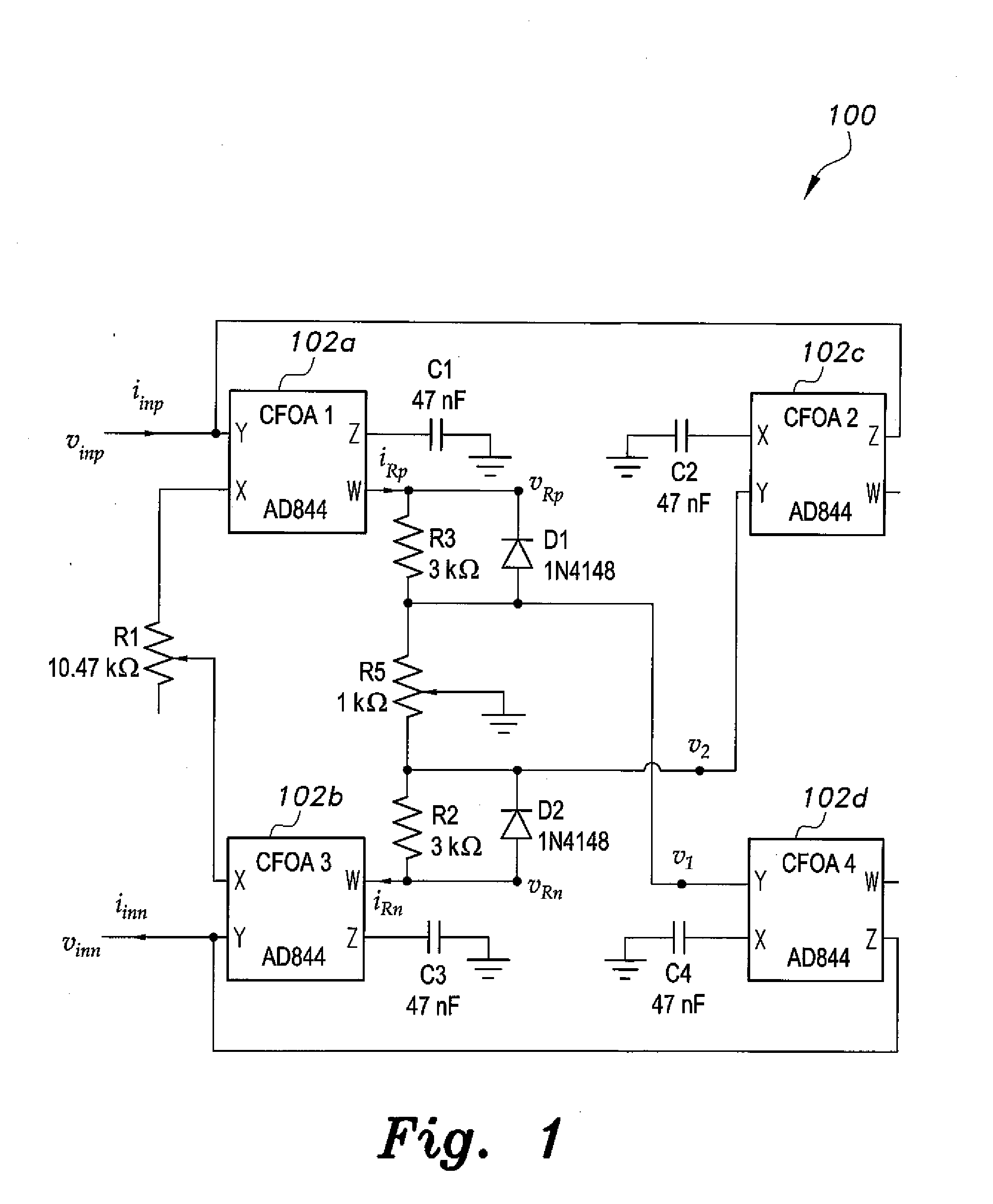
Floating memristor emulator
InactiveUS20160378896A1Cost reduction and easeReduction and ease of implementationDigital storageComputation using non-denominational number representationMemristorGrounded capacitor
The floating memristor emulator is based on a circuit implementation that uses grounded capacitors and CFOAs in addition to combinations of diodes and resistors to provide the required nonlinearity and time constants. This circuit results in low power consumption, cost reduction and ease of implementation because it avoids the use of multipliers, ADCs and RDACs. The present circuit is used in an FM demodulator, which exploits the frequency-dependence of the memristance. Successful use in the FM demodulator confirmed the functionality of the present floating memristor emulator circuit.
Owner:KING FAHD UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND MINERALS
Signal separating apparatus, signal separating method, signal separating program and recording medium
ActiveUS7647209B2Simple and efficientAccurate solutionAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDigital computer detailsTime domainAlgorithm
A frequency domain transforming section transforms mixed signals observed by multiple sensors into mixed signals in the frequency domain, a complex vector generating section generates a complex vector by using the frequency-domain mixed signals, a normalizing section generates a normalized vector excluding frequency dependence of the complex vector, and a clustering section clusters the normalized vectors to generate clusters. Then, a separated signal generating section generates separated signals in the frequency domain by using information about the clusters and a time domain transforming section transforms the separated signals in the frequency domain into separated signals in the time domain.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
Weather radar
ActiveUS20140327570A1Easy to measureRadio wave reradiation/reflectionICT adaptationWeather radarReceiving facility
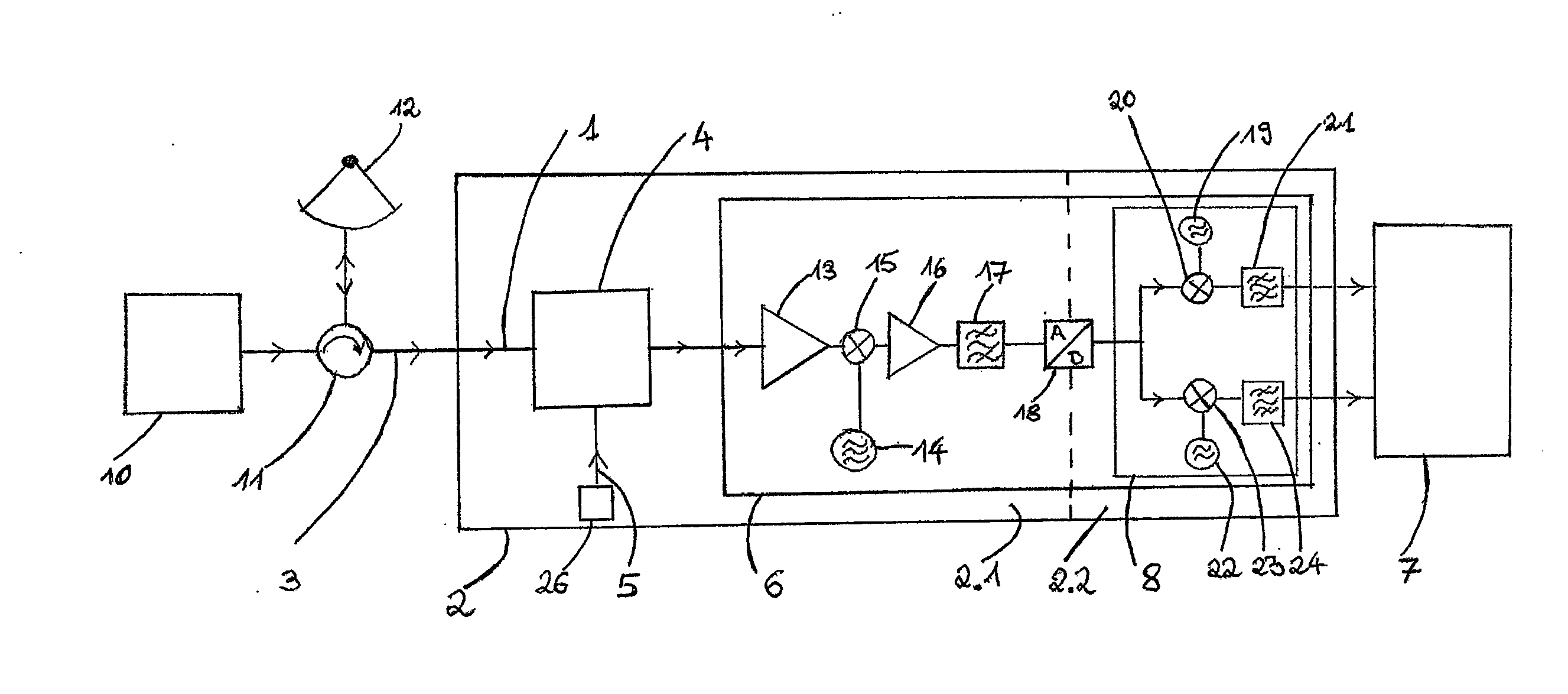
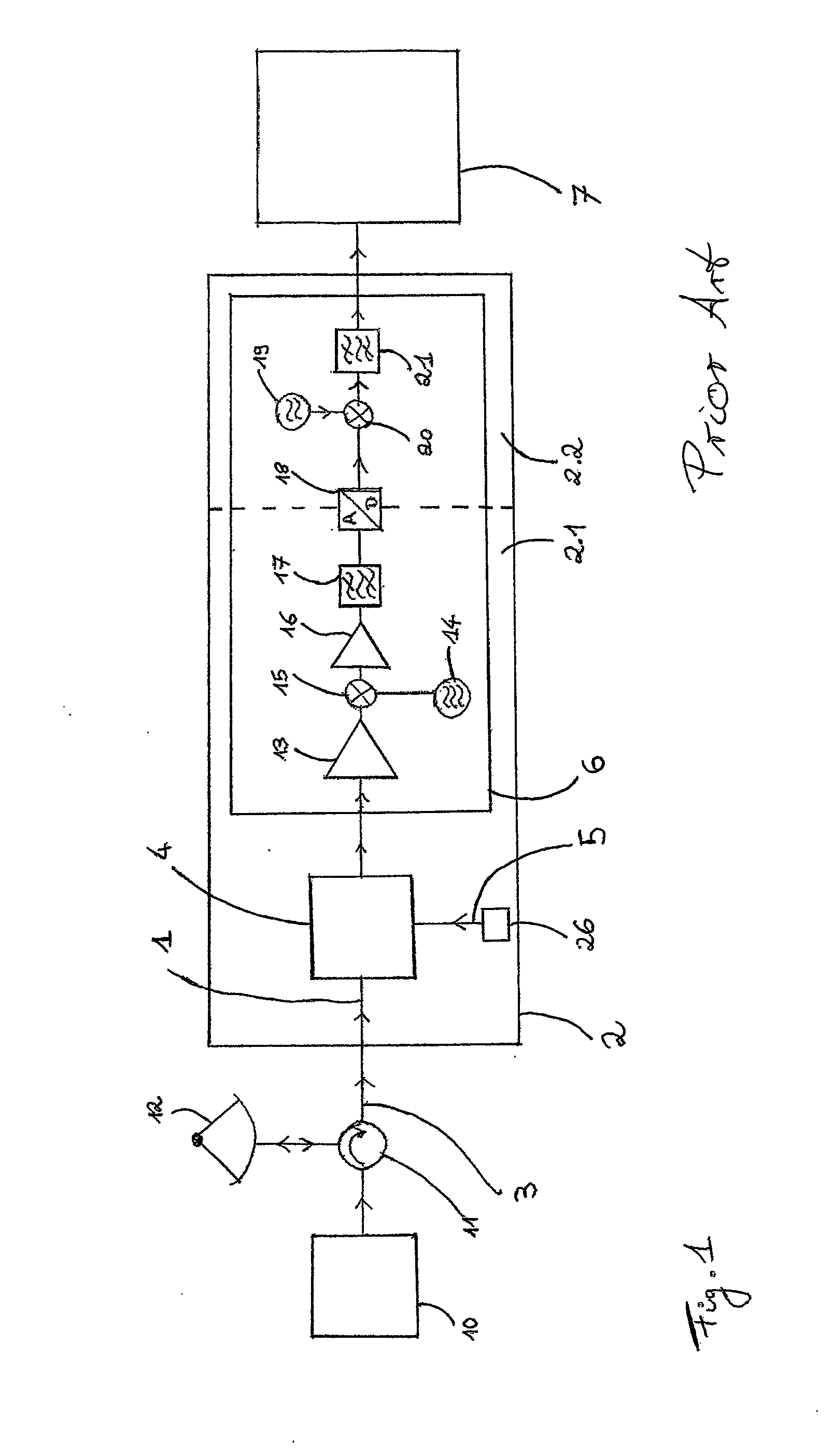
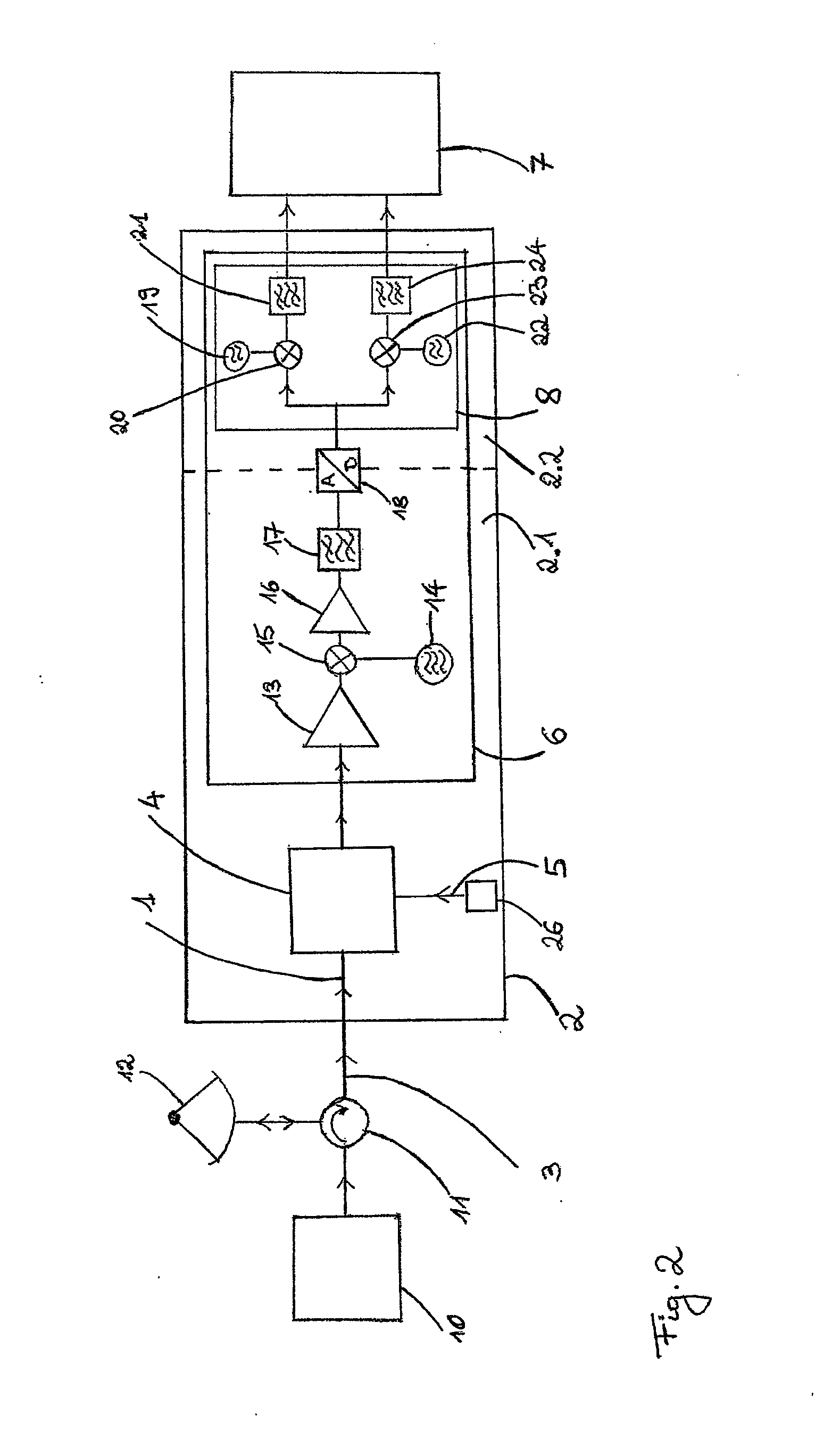
Weather radar for measuring radar signals in the GHz range with a receiver containing at least one signal path, the receiver comprising a receiving facility for an incoming radar signal, on which a test signal generated by a test signal generator is superimposed in a coupler, and a processing device to amplify, filter and convert both signals to lower frequencies, wherein for filtering a matched filter is provided, and with an evaluation device in which calibration parameters of the signal path are derived from the test signal for the frequency of the test signal in order to determine the signal strength of the received radar signal, wherein the test signal is superimposed with at least one frequency differing from the frequency of the radar signal, so that the radar signal and the test signal are processed separately from one another by the evaluation device, and the calibration parameters of the signal path for the frequency of the radar signal are determinable from the test signal through a modeling of the frequency dependence of the calibration parameters for frequencies around those of the radar signal.
Owner:LEONARDO GERMANY GMBH
Apparatus and method for measuring a fluid flow rate profile using acoustic doppler effect
ActiveUS7363174B2Reduced frequency dependenceImprove accuracyFlow propertiesVolume/mass flow measurementAngle of incidenceUltrasonic sensor
An apparatus and method for measuring a flow velocity profile of fluid traveling in a pipe or conduit uses an ultrasonic wave transmitted from an ultrasonic wave transducer mounted at an angle on the outside of a pipe using a wedge, and made incident onto the fluid in the pipe to measure the fluid flow velocity profile, using the principle that a frequency of an ultrasonic wave, reflected by a reflector existing in the fluid, is changed depending on a flow velocity due to Doppler effect. The transmission frequency and the angle of incidence onto the pipe can be selected to suppress frequency dependence of a measured value due to Lamb wave and allow the flow velocity or flow rate of fluid to be measured with a greater accuracy.
Owner:FUJI ELECTRIC CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com