Patents
Literature
571 results about "Reservoir fluid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Reservoir fluids are the fluids (including gases and solids) that exist in a reservoir. The fluid type must be determined very early in the life of a reservoir (often before sampling or initial production) because fluid type is the critical factor in many of the decisions that must be made about producing the fluid from the reservoir.
Coating and/or treating hydraulic fracturing proppants to improve wettability, proppant lubrication, and/or to reduce damage by fracturing fluids and reservoir fluids
InactiveUS20050244641A1Reduce conductivityEfficient arrangementSynthetic resin layered productsCellulosic plastic layered productsFracturing fluidCompound (substance)
Surface modified oil and gas well hydraulic fracturing proppants for improving wettability, altering chemical reactivity, altering surface topography, imparting lubricity or controlling relative permeability to flow of fluids of such proppants. The use and preparation of such coated proppants in hydraulic fracturing of subterranean formations is also described.
Owner:CARBO CERAMICS
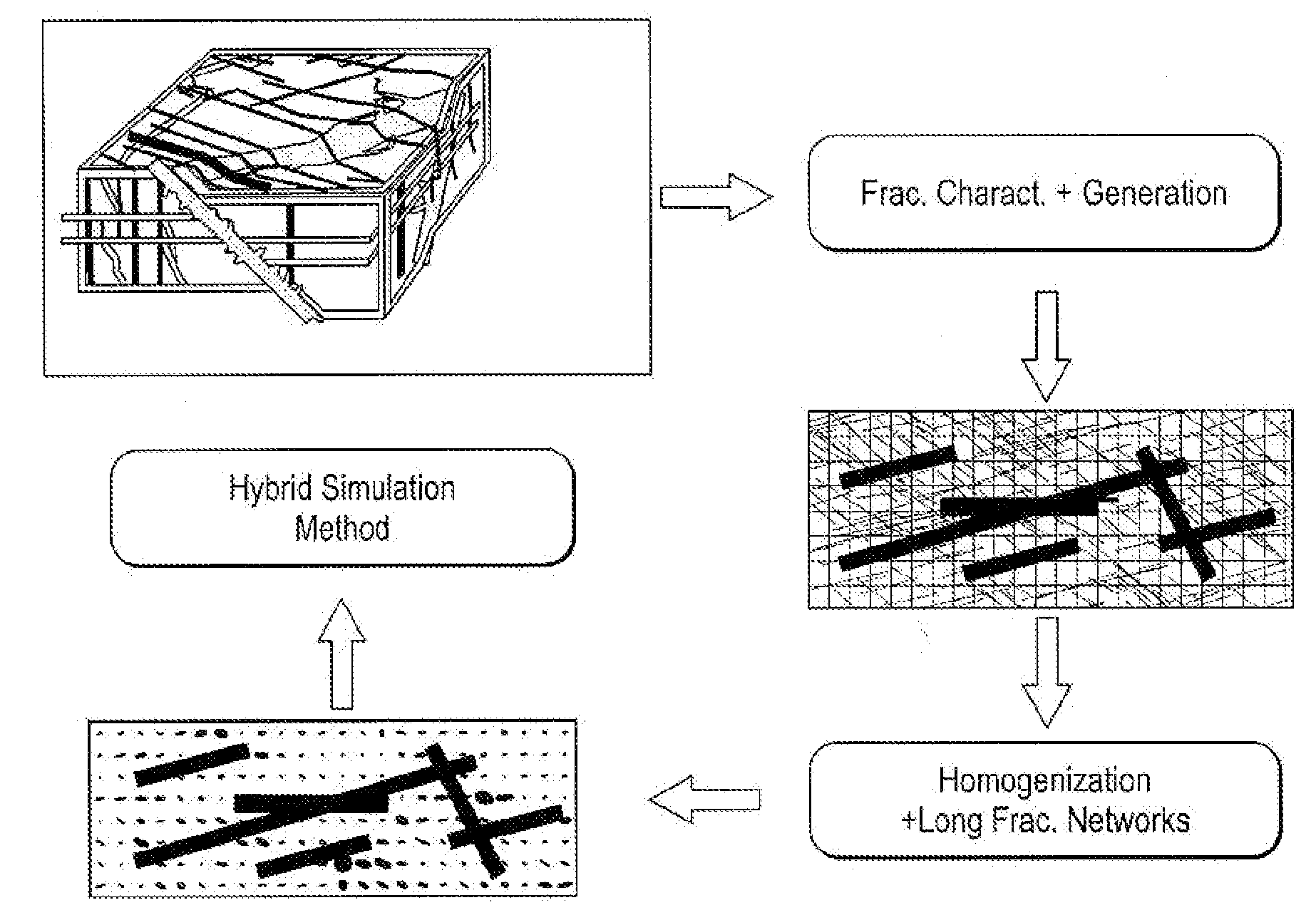
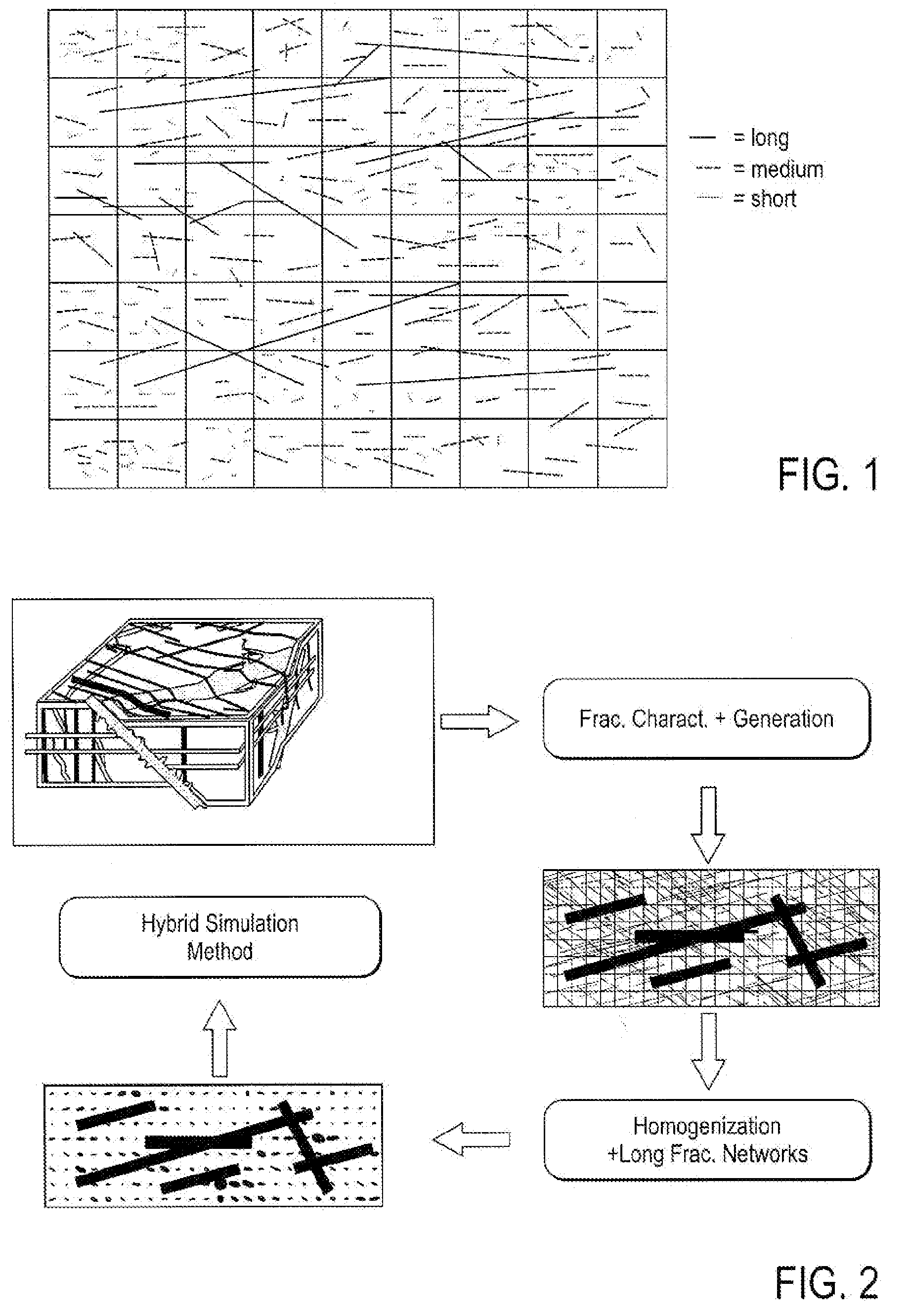
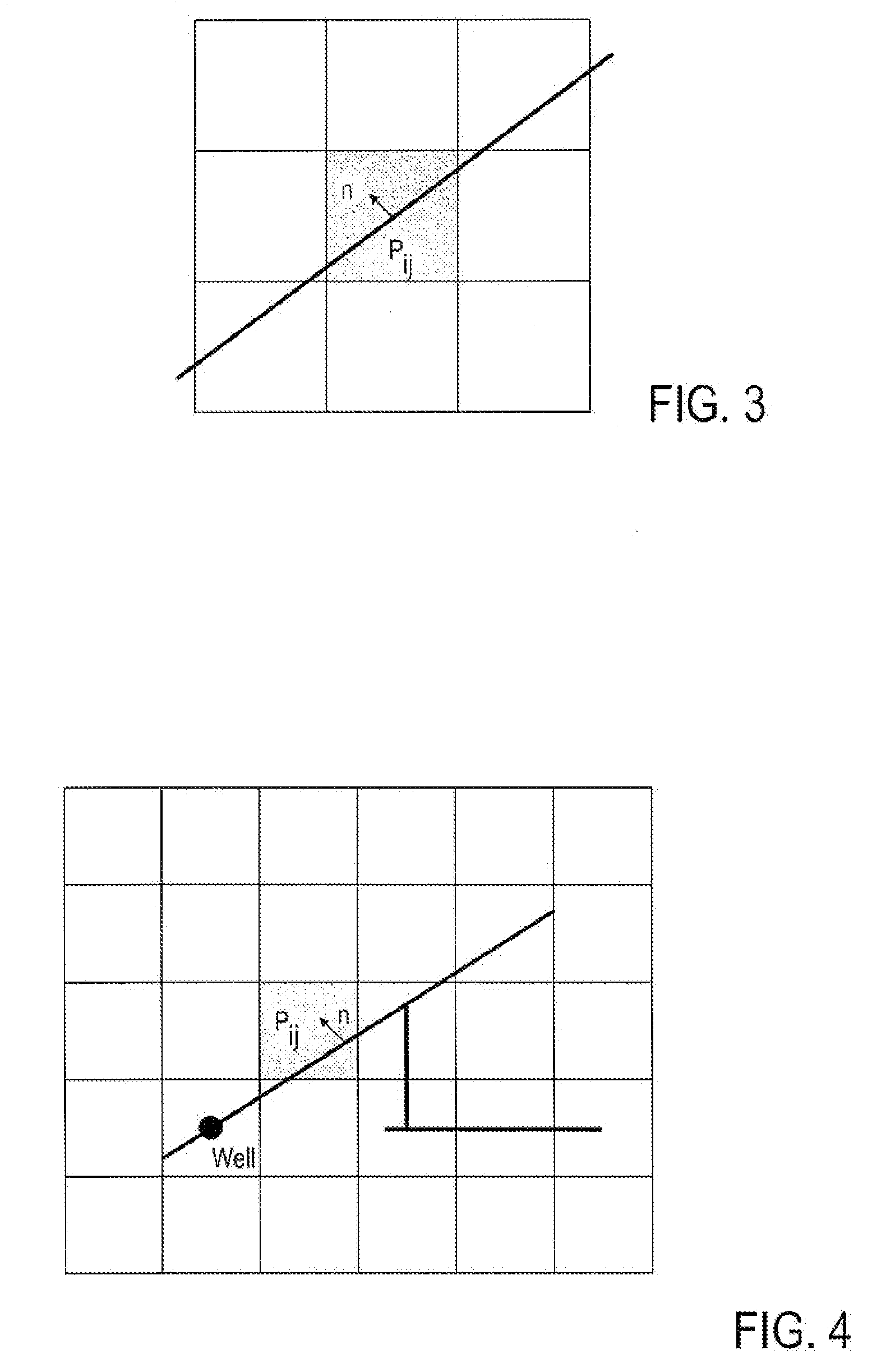
Method, System and Apparatus for Simulating Fluid Flow in a Fractured Reservoir Utilizing A Combination of Discrete Fracture Networks and Homogenization of Small Fractures
ActiveUS20080133186A1Increase the number ofImprove stabilitySurveySeismologyEnvironmental geologyReservoir fluid
The present invention includes a method, system and apparatus for simulating fluid flow in a fractured subterranean reservoir. A three-dimensional hybrid reservoir model representative of a fractured subterranean reservoir is created. The model includes porous matrix blocks and a network of long fractures overlying the matrix blocks. The networks of long fractures include two-dimensional fracture blocks. Matrix and fracture flow equations for fluid flow in the matrix and fracture blocks are obtained. The effective fluid flow transmissibilities between the matrix blocks and the fracture blocks are determined. The matrix and fracture flow equations are coupled via the effective fluid flow transmissibilities. The matrix and fracture flow equations are then solved simultaneously for flow responses. Two-dimensional fracture blocks are used which ideally overly and are fluidly connect to underlying matrix blocks. The long fractures may be in direct in fluid communication with one or more intersecting wells. Where long fractures intersect with one another, the intersection of the long fractures may be modeled as a point source to enhance numerical stability during simulation. The hybrid reservoir model may utilize networks of fractures in conjunction with an underlying grid of matrix blocks wherein fracture characteristics such as (1) orientation; (2) fracture aperture; (3) fracture length; and (4) fracture height are more realistically modeled than in previously known reservoir models.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
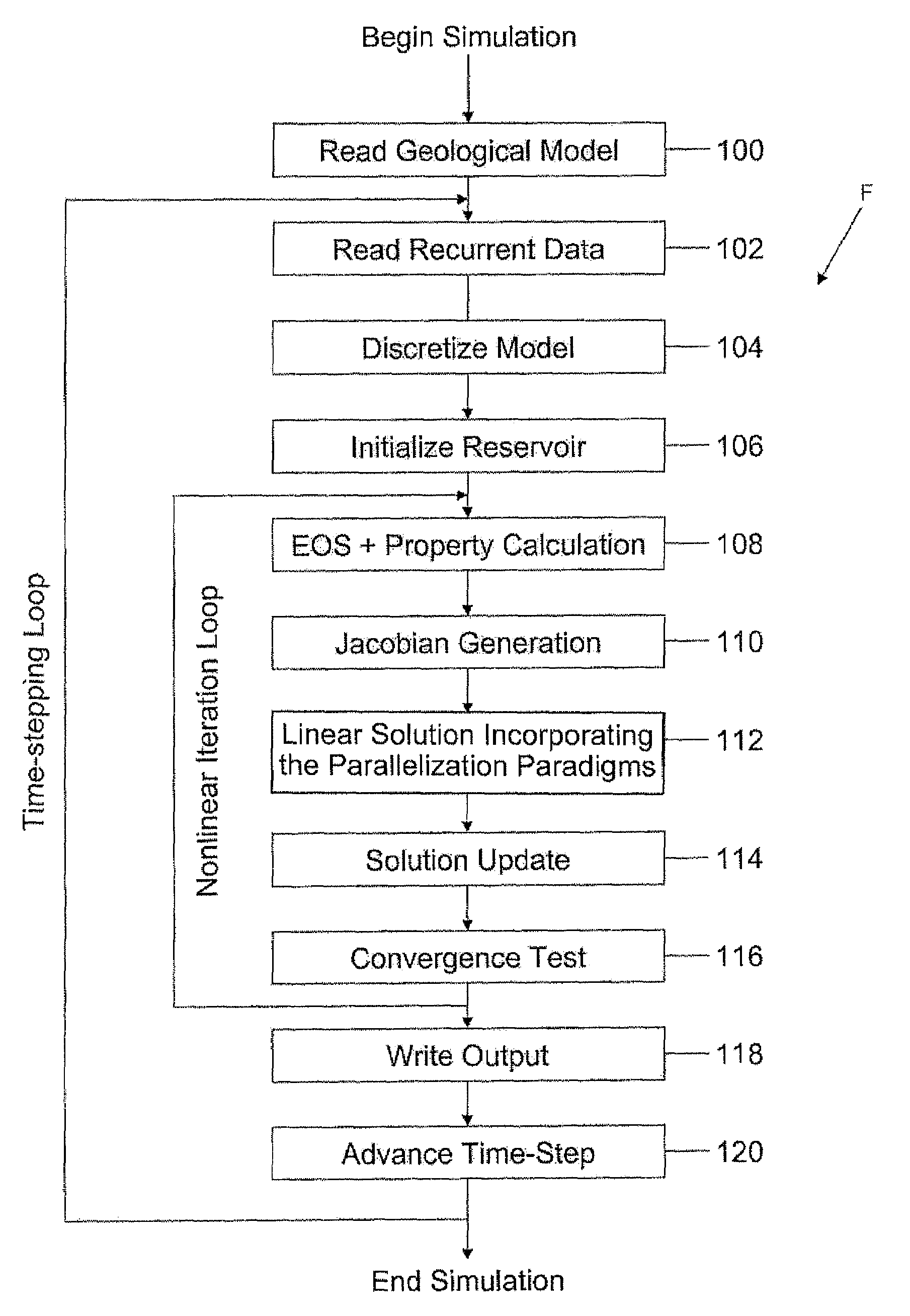
Highly-parallel, implicit compositional reservoir simulator for multi-million-cell models
ActiveUS7526418B2Reduce processing timeElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingPermeability/surface area analysisSupercomputerDistributed memory
A fully-parallelized, highly-efficient compositional implicit hydrocarbon reservoir simulator is provided. The simulator is capable of solving giant reservoir models, of the type frequently encountered in the Middle East and elsewhere in the world, with fast turnaround time. The simulator may be implemented in a variety of computer platforms ranging from shared-memory and distributed-memory supercomputers to commercial and self-made clusters of personal computers. The performance capabilities enable analysis of reservoir models in full detail, using both fine geological characterization and detailed individual definition of the hydrocarbon components present in the reservoir fluids.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
Well device for throttle regulation of inflowing fluids
A flow arrangement (10, 12) for use in a well through one or more underground reservoirs, and where the arrangement (10, 12) is designed to throttle radially inflowing reservoir fluids produced through an inflow portion of the production tubing in the well, the production tubing in and along this inflow portion being provided with one or more arrangements (10, 12). Such an arrangement (10, 12) is designed to effect a relatively stable and predictable fluid pressure drop at any stable fluid flow rate in the course of the production period of the well, and where said fluid pressure drop will exhibit the smallest possible degree of susceptibility to influence by differences in the viscosity and / or any changes in the viscosity of the inflowing reservoir fluids during the production period. Such a fluid pressure drop is obtained by the arrangement (10, 12) comprising among other things one or more short, removable and replaceable flow restrictions such as nozzle inserts (44, 62), and where the individual flow restriction may be given the desired cross section of flow, through which reservoir fluids may flow and be throttled, or the flow restriction may be a sealing plug.
Owner:RESLINK
Flow control device for choking inflowing fluids in a well
A flow arrangement (10, 12) for use in a well through one or more underground reservoirs, and where the arrangement (10, 12) is designed to throttle radially inflowing reservoir fluids produced through an inflow portion of the production tubing in the well, the production tubing in and along this inflow portion being provided with one or more arrangements (10, 12) Such an arrangement (10, 12) is designed to effect a relatively stable and predictable fluid pressure drop at any stable fluid flow rate in the course of the production period of the well, and where said fluid pressure drop will exhibit the smallest possible degree of susceptibility to influence by differences in the viscosity and / or any changes in the viscosity of the inflowing reservoir fluids during the production period. Such a fluid pressure drop is obtained by the arrangement (10, 12) comprising among other things one or more short, removable and replaceable flow restrictions such as nozzle inserts (44, 62), and where the individual flow restriction may be given the desired cross section of flow, through which reservoir fluids may flow and be throttled, or the flow restriction may be a sealing plug.
Owner:RESLINK
Facilitating oilfield development with downhole fluid analysis
InactiveUS20080040086A1Eliminate needSimple processElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSeismology for water-loggingModeling softwareData acquisition
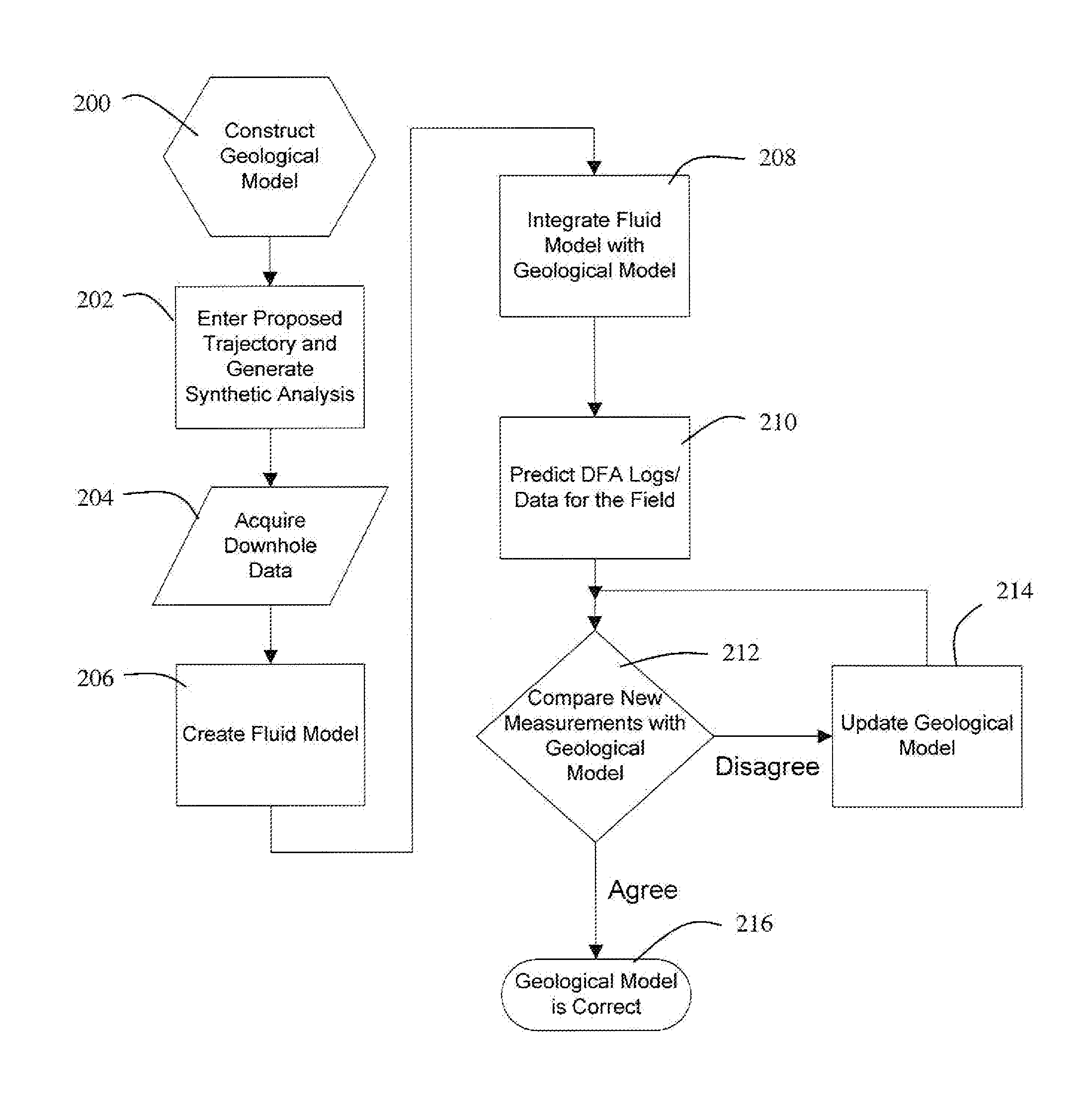
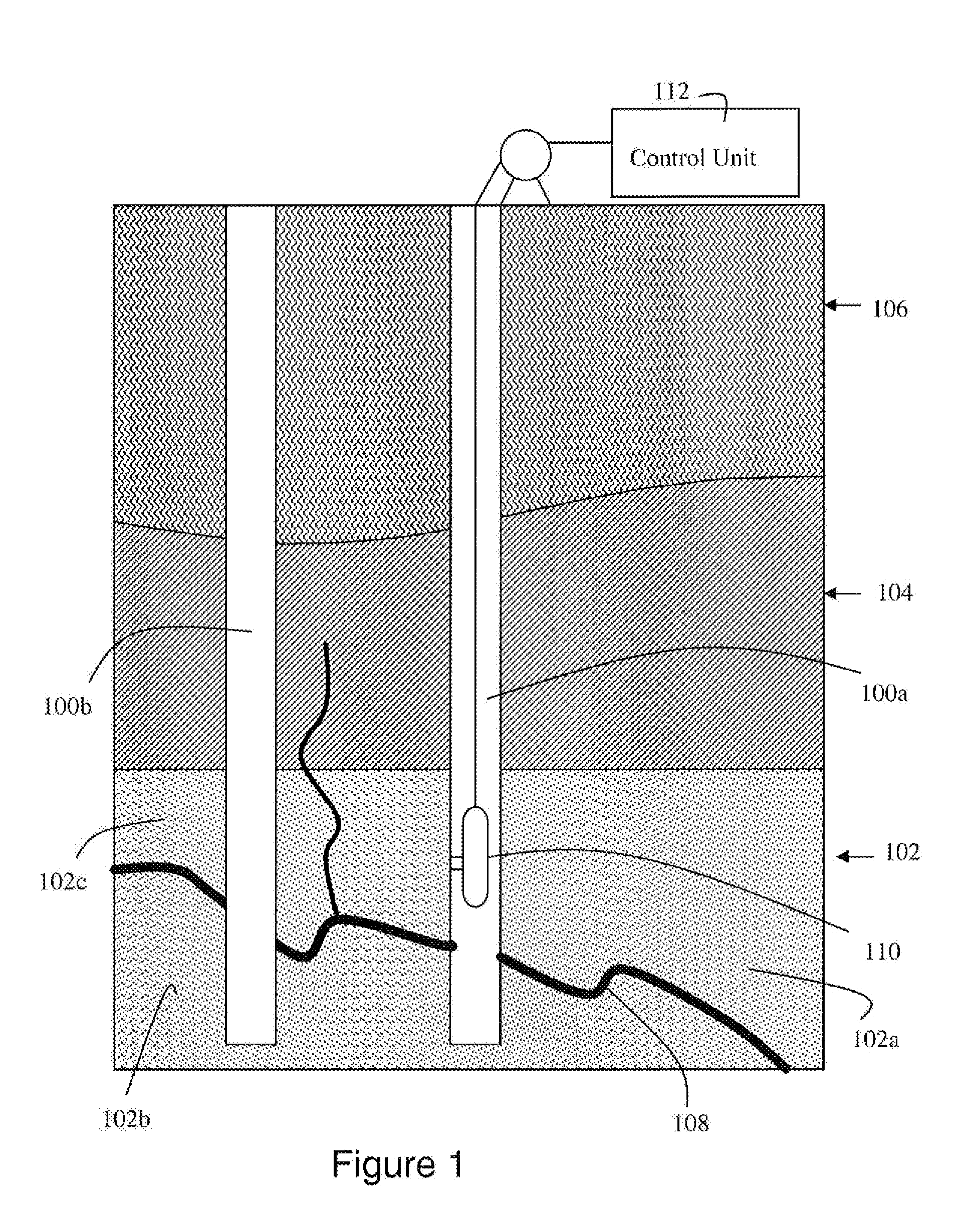
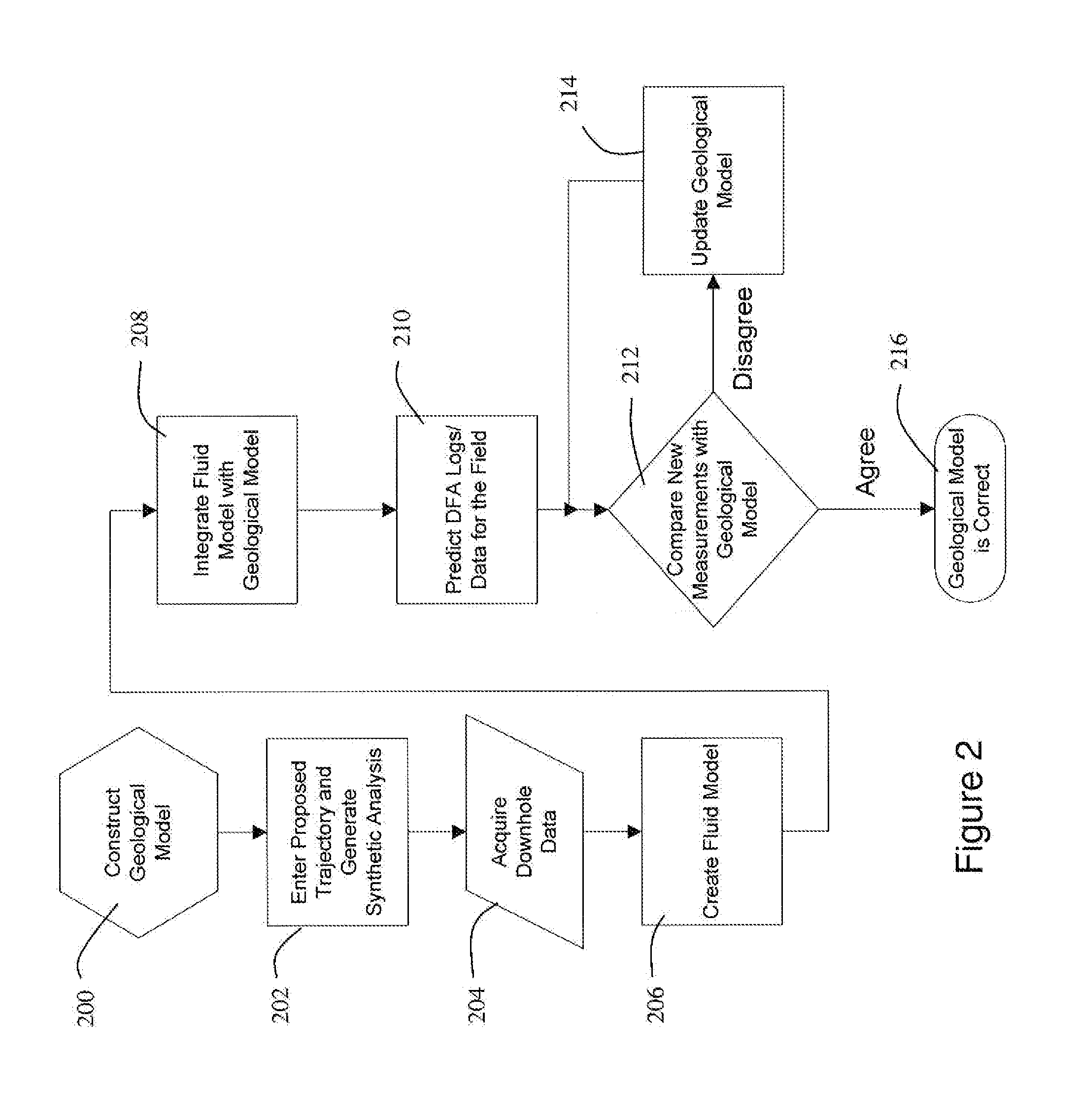
Formation fluid data based on measurements taken downhole under natural conditions is utilized to help identify reservoir compartments. A geological model of the reservoir including expected pressure and temperature conditions is integrated with a predicted fluid model fitted to measured composition and PVT data on reservoir fluid samples or representative analog. Synthetic downhole fluid analysis (DFA) logs created from the predictive fluid model can be displayed along the proposed borehole trajectory by geological modeling software prior to data acquisition. During a downhole fluid sampling operation, actual measurements can be displayed next to the predicted logs. If agreement exists between the predicted and measured fluid samples, the geologic and fluid models are validated. However, if there is a discrepancy between the predicted and measured fluid samples, the geological model and the fluid model need to be re-analyzed, e.g., to identify reservoir fluid compartments. A quantitative comparative analysis of the sampled fluids can be performed against other samples in the same borehole or in different boreholes in the field or region to calculate the statistical similarity of the fluids, and thus the possible connectivity between two or more reservoir regions.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Highly-parallel, implicit compositional reservoir simulator for multi-million-cell models
ActiveUS20060036418A1Reducing computer processing timeReduce processing timeElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingPermeability/surface area analysisSupercomputerDistributed memory
A fully-parallelized, highly-efficient compositional implicit hydrocarbon reservoir simulator is provided. The simulator is capable of solving giant reservoir models, of the type frequently encountered in the Middle East and elsewhere in the world, with fast turnaround time. The simulator may be implemented in a variety of computer platforms ranging from shared-memory and distributed-memory supercomputers to commercial and self-made clusters of personal computers. The performance capabilities enable analysis of reservoir models in full detail, using both fine geological characterization and detailed individual definition of the hydrocarbon components present in the reservoir fluids.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
Tight Gas Stimulation by In-Situ Nitrogen Generation
InactiveUS20130126169A1Avoid reactionIncrease ratingsInsulationFluid removalHydrostatic pressureNitrogen
Provided is a method and composition for the in-situ generation of synthetic sweet spots in tight-gas formations. The composition can include nitrogen generating compounds, which upon activation, react to generate heat and nitrogen gas. The method of using the composition includes injecting the composition into a tight-gas formation such that upon activation, heat and nitrogen gas are generated. Upon the generation of nitrogen gas and heat within the formation, microfractures are produced within the formation and the hydrostatic pressure within the reservoir is reduced to less than the reservoir fluid pressure, such that the rate of production of hydrocarbons from the formation is increased.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
Real-time measurement of reservoir fluid properties
ActiveUS20110040501A1Eliminates long delayImprove securitySurveyFlow propertiesLine tubingReal time analysis
A system, method, and fluid analysis module are provided for the real-time analysis of multiphase fluids. The system generally comprises means for directing a fluid stream from a flow line to a fluid analysis module, a processor and communication means. The fluid analysis module comprises sensor for measurement of at least one property of the fluid. The processor processes the measurement data from the sensor, and the communication means communicates the processed data to a central acquisition unit or computer.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Methods, systems and apparatus for coiled tubing testing
A method and apparatus for testing a multi-zone reservoir while reservoir fluids are flowing from within the wellbore. The method and apparatus enables isolation and testing of individual zones without the need to pull production tubing. This abstract allows a searcher or other reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the disclosure. It may not be used to interpret or limit the scope or meaning of the claims.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Method and apparatus for downhole fluid analysis for reservoir fluid characterization
InactiveUS20050205256A1Interfere with measurementSurveyParticle separator tubesResidual gas analyzerSorbent
A formation fluid sample is exposed to a rigidly-supported semi-permeable membrane such as silicone rubber to permit diffusion of gases and vapors from the formation fluid into a vacuum chamber, while at the same time, blocking the passage of any liquids. The membrane-transmitted gas is analyzed in the vacuum chamber by a residual gas analyzer. An ion pump or sorbent is associated with the evacuated chamber to maintain the vacuum. The ion pump or sorbent removes gases and vapors from the chamber that diffuse into the chamber from the reservoir sample that is on the opposite side of the semi-permeable membrane.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
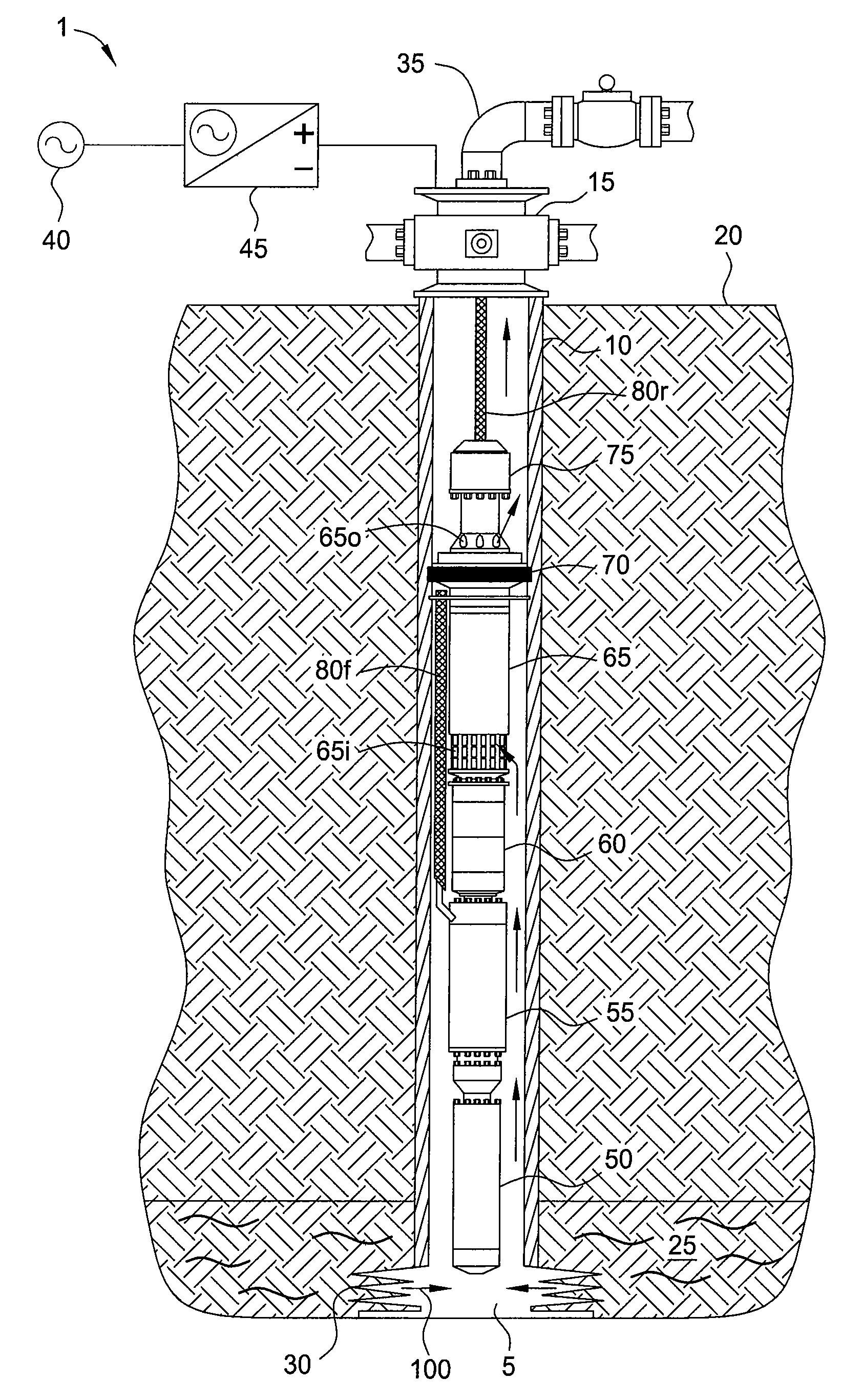
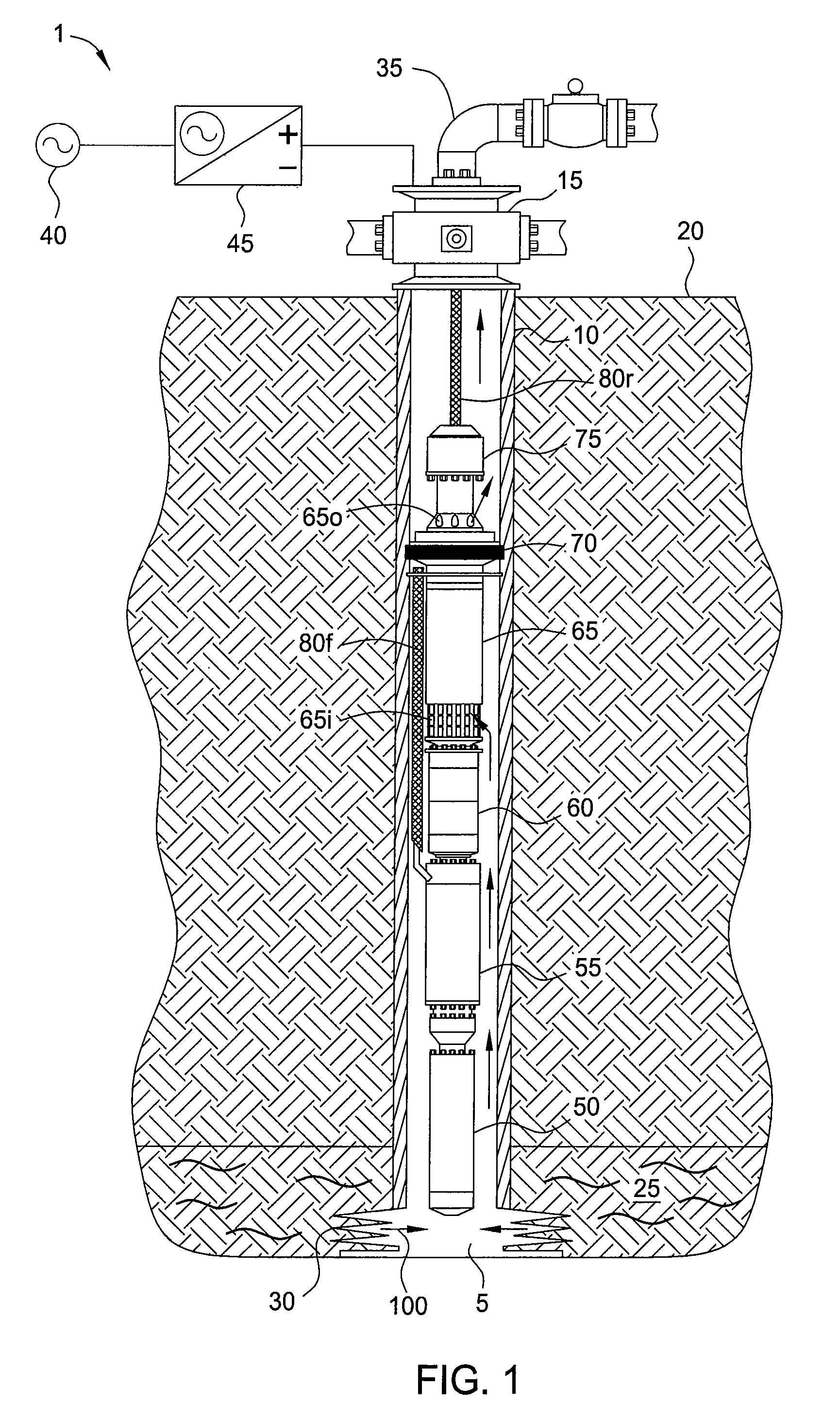
Cable suspended pumping system
Embodiments of the present invention generally relate to a cable suspended pumping system. In one embodiment, a method of producing fluid from a reservoir includes deploying a pumping system into a wellbore to a location proximate the reservoir using a cable. The pump assembly includes a motor, an isolation device, a pump, and a power conversion module (PCM). The method further includes setting the isolation device, thereby rotationally fixing the pumping system to a tubular string disposed in the wellbore and isolating an inlet of the pump from an outlet of the pump; supplying a DC power signal from the surface to the PCM via the cable; and supplying a second power signal to the motor, thereby operating the pump and pumping reservoir fluid from the reservoir to the surface.
Owner:ZEITECS
Acoustic/Pressure Wave-Driven Separation Device
InactiveUS20080053787A1Thermal non-catalytic crackingGeneral water supply conservationChemistryReservoir fluid
An acoustic / pressure wave-driven device for separating a first component from a mixture of the first component and a second fluid component. The device comprises a rich reservoir, a lean reservoir, a pump reservoir, a bridge structure, and an acoustic / pressure wave source. The rich reservoir is for containing a fluid mixture having an elevated concentration of the first component. The lean reservoir is for containing a fluid mixture having a lesser concentration of the first component that is leaner than the concentration of the first component in fluid mixture of the rich reservoir. The pump reservoir contains a fluid mixture of the first component and the second fluid component. The bridge structure has a sidewall defining a gradient channel in fluid communication with the rich reservoir and the lean reservoir and a length extending there between. The gradient channel is for containing a fluid having a concentration gradient of the first component along its length. A diffusion portion of the sidewall disposed between the gradient channel and the pump reservoir is adapted to permit diffusion of at least the first component between the gradient channel and the pump reservoir while preventing fluid flow there between. The acoustic / pressure wave source provides acoustic waves into the pump reservoir to cause pressure oscillations in the fluid mixture therein adjacent to the diffusion portion to move molecules of the target component against the concentration gradient from the lean reservoir into the rich reservoir.
Owner:THE BOARD OF RGT UNIV OF OKLAHOMA
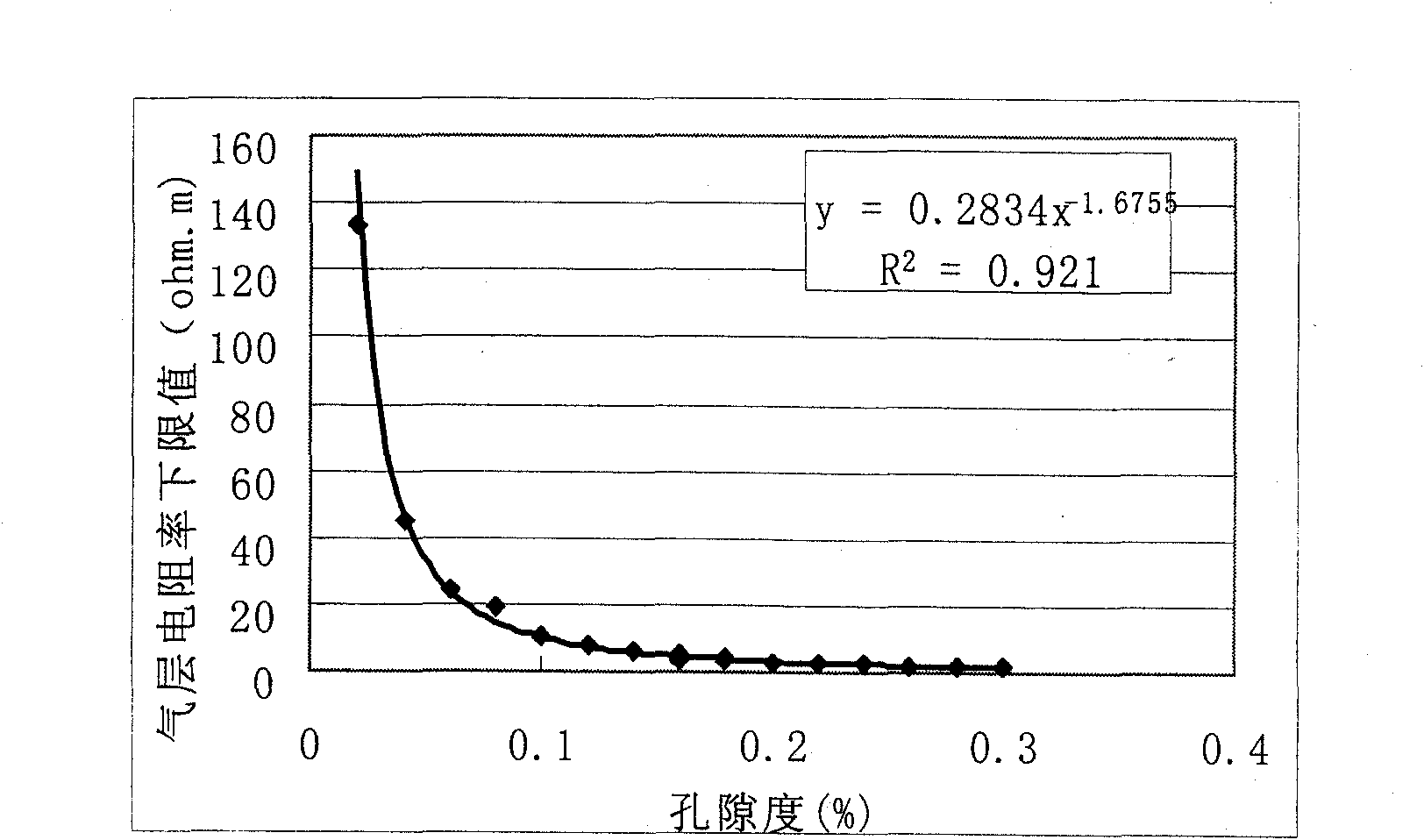
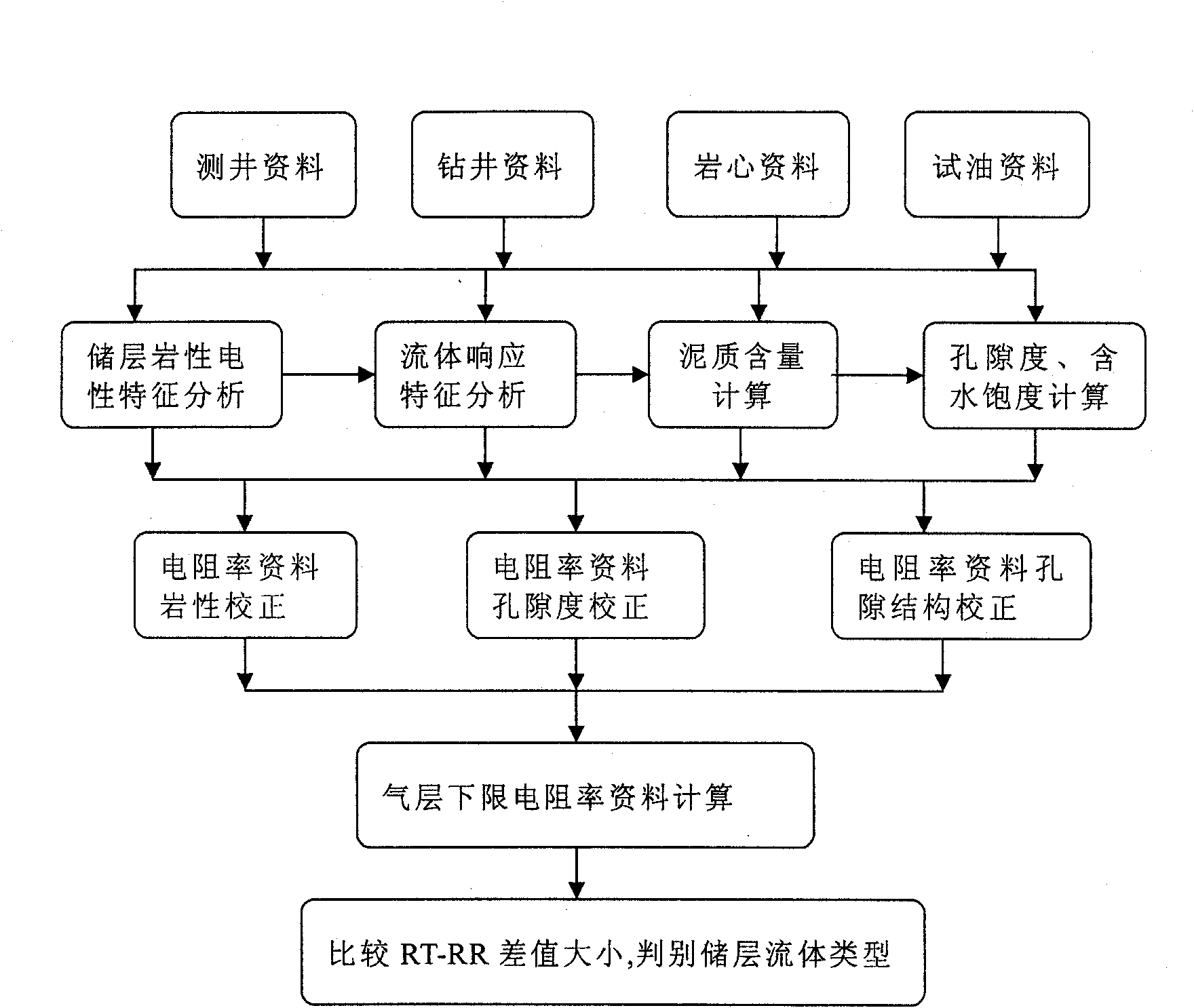
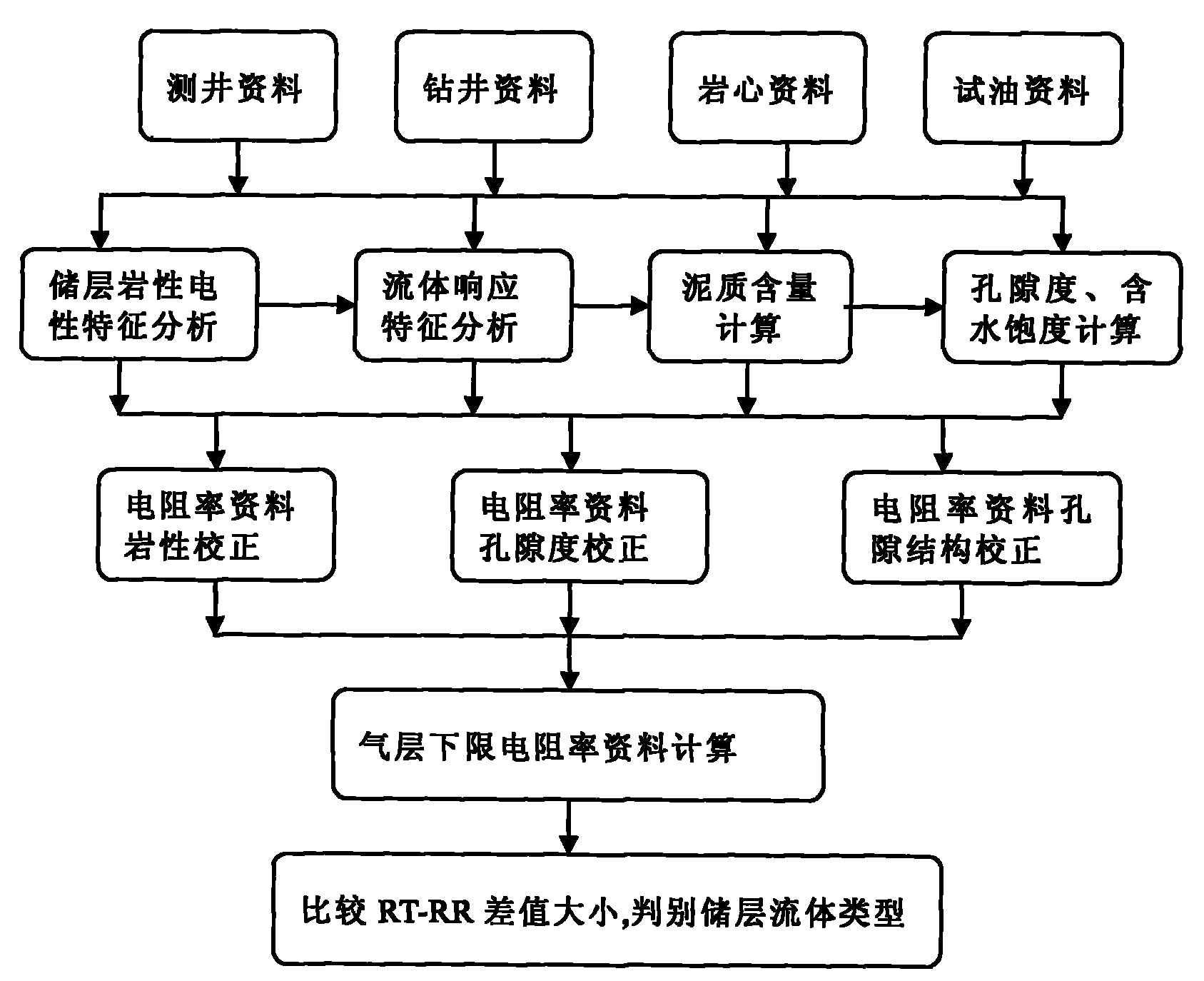
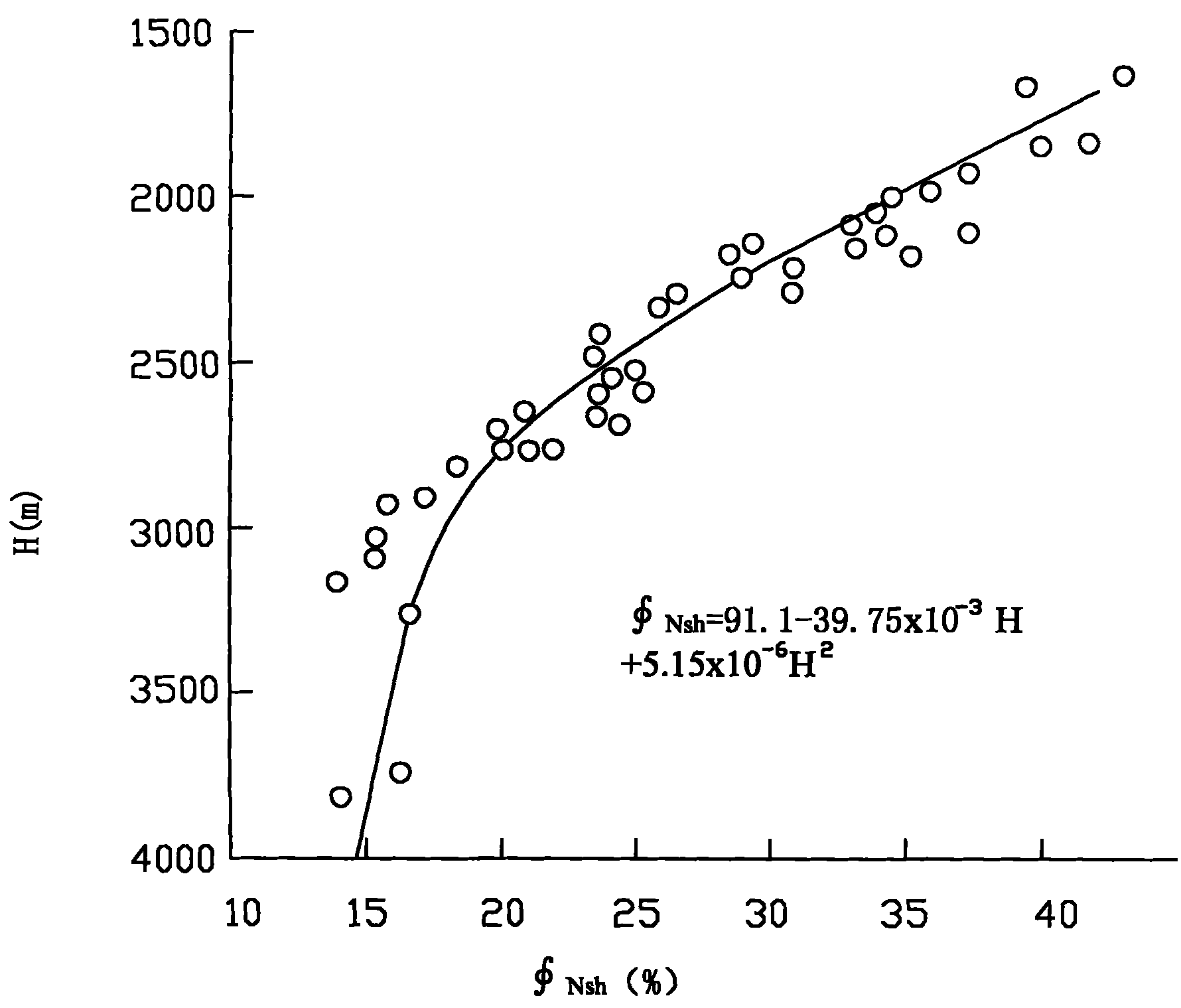
Method for distinguishing reservoir fluid type by adopting resistivity data
ActiveCN101930082AMastering Real Response PropertiesImprove the identification rateElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMaterial resistancePorosityLower limit
The invention discloses a method for distinguishing a reservoir fluid type by adopting resistivity data, relating to the technological field of petroleum and gas logging, geology and core test analysis. The method comprises the following steps of: a. logging by utilizing core data scales and accurately calculating reservoir shale content, rock constituent and porosity; b. eliminating the influence of rock characters and the porosity on resistivity; c. utilizing a core test to obtain the parameters of m, a, n and b reflecting a pore structure, calculating the resistivity lower limit RR of an air layer and eliminating the influence of the pore structure on the resistivity; and d. distinguishing the reservoir fluid type by comparing a deep-induction and deep- lateral resistivity value RT andthe resistivity lower limit RR of the air layer obtained in the step c. The invention eliminates the influence of non-fluid factors of the rock characters, the porosity, the pore structure and the like on the resistivity, and maintains and utilizes the response characteristics of fluids with different resistivities so as to greatly enhance the coincidence rate for distinguishing the reservoir fluid type.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
Fluid property sensors
InactiveUS7434457B2Analysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesConstructionsElectrical conductorEngineering
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
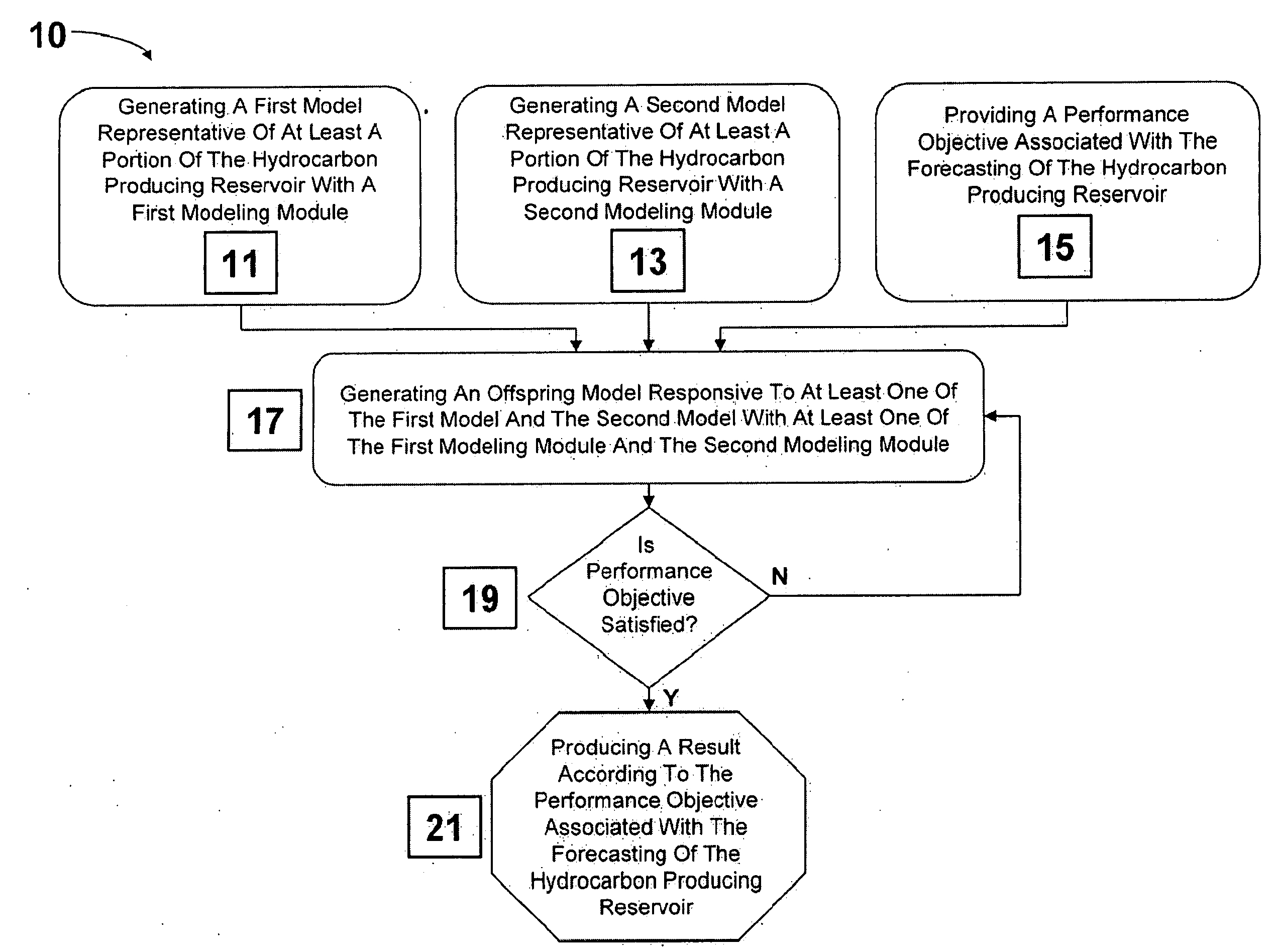
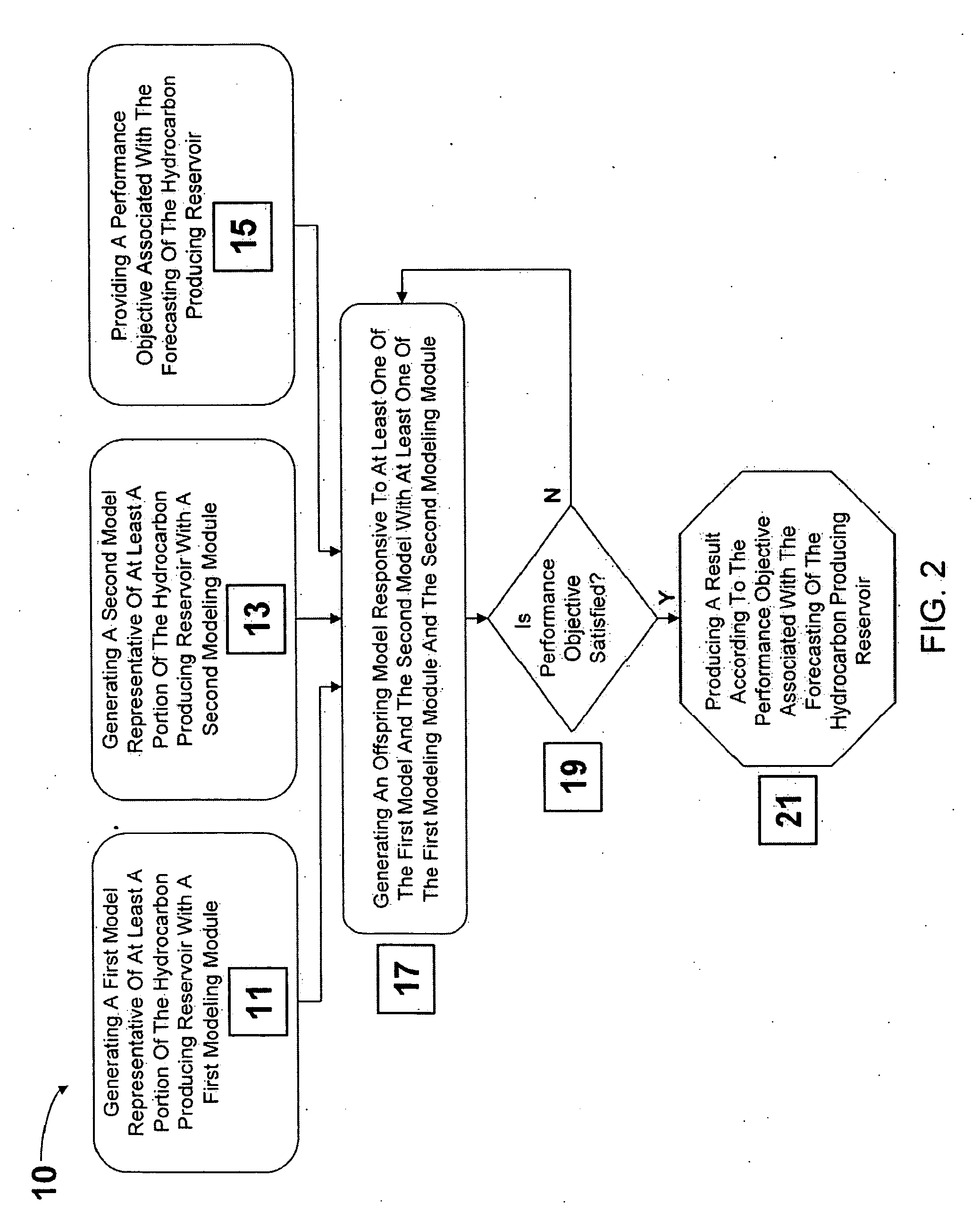
System and method for forecasting production from a hydrocarbon reservoir
A system and method is taught to substantially automate forecasting for a hydrocarbon producing reservoir through integration of modeling module workflows. A control management module automatically generates static and dynamic offspring models, with static and dynamic modeling software, until a performance objective associated with the forecasting of the reservoir is satisfied. The performance objective can include an experimental design table to determine a sensitivity of a particular parameter or can be directed towards reservoir optimization, i.e., ultimate hydrocarbon recovery, net present value, reservoir percentage yield, reservoir fluid flow rate, or history matching error.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
Method and apparatus for downhole fluid analysis for reservoir fluid characterization
InactiveUS7219541B2Interfere with measurementSurveyParticle separator tubesResidual gas analyzerSorbent
A formation fluid sample is exposed to a rigidly-supported semi-permeable membrane such as silicone rubber to permit diffusion of gases and vapors from the formation fluid into a vacuum chamber, while at the same time, blocking the passage of any liquids. The membrane-transmitted gas is analyzed in the vacuum chamber by a residual gas analyzer. An ion pump or sorbent is associated with the evacuated chamber to maintain the vacuum. The ion pump or sorbent removes gases and vapors from the chamber that diffuse into the chamber from the reservoir sample that is on the opposite side of the semi-permeable membrane.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Method and apparatus for simulating PVT parameters
InactiveUS7249009B2Improve statistical accuracyImprove estimation accuracyElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSamplingWell loggingWell drilling
A method and apparatus for converting downhole wireline logging measurements of pressure gradient, formation pressure and temperature into estimates of petroleum fluid PVT properties unaffected by oil-based drilling mud, without the need for retrieving actual petroleum samples from the borehole for laboratory analysis at the surface. The statistical accuracy of the PVT properties of reservoir fluids are enhanced with geochemical information of the fluids expected from a given reservoir.
Owner:BAKER GEOMARK
Method for judging reservoir fluid type of difference between density porosity and neutron porosity
ActiveCN101832133AImprove the identification rateImprove guidanceBorehole/well accessoriesLithologyRock core
The invention discloses a method for judging the reservoir fluid type of a difference between density porosity and neutron porosity and relates to the technical fields of oil and gas logging and geology and core test analysis. The method comprises the following steps: 1) accurately calculating the shale content, the rock composition, the density porosity and the neutron porosity of a reservoir bycore data calibrating logging and logging data environmental correction; 2) removing the influence of factors of lithology, well diameter and mud invasion on density and neutron data; and 3) establishing standards for judging the reservoir fluid type by utilizing the response difference of the density and the neutron data to gas and formation water and by comparing the values of the density porosity and the neutron porosity. When the invention judges the reservoir fluid type by utilizing the density and the neutron data, non-fluid influencing factors, such as lithology, borehole conditions, mud invasion and the like are removed, therefore, influence features of different fluids to the density and the neutron data can be truly reflected, and the coincidence rate for judging the reservoir fluid type can be enhanced to above 90 percent from the existing 70 percent.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
Self-controlled inflow control device
ActiveUS20130068467A1Reduce reservoir fluid flowSolution to short lifeFluid removalWell/borehole valve arrangementsEngineeringReservoir fluid
An inflow control device controls the rate of fluid flow from a subsurface fluid reservoir into a production tubing string. The inflow control device includes a particulate screen to remove particulate matter from the reservoir fluid, and at least two flow restrictors. The flow restrictors are positioned on circumferentially opposite sides of the inflow control device and are connected by an isolated fluid passage. The flow restrictors limit the flowrate of reservoir fluid when the reservoir fluid has a high water or gas-to-oil ratio. The inflow control device also includes at least one pressure drop device that generates a pressure drop for the reservoir fluid in response to fluid pressure in the reservoir. The inflow control device also includes a choking apparatus that allows the flow of reservoir fluid to be shut off and the particulate screen cleaned while the inflow control device is in place in hole.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
Fluid control in reservior fluid sampling tools
ActiveUS20120018152A1Easy to controlIncrease pumping speedSurveyFluid removalFluid controlReservoir fluid
A pumping system comprising: a probe to suction a fluid from a fluid reservoir; a pump in fluid communication with said probe; a sensor for detecting phase changes in said pumping system, said sensor in fluid communication with said probe or pump, said sensor generating a sensor signal; a fluid exit from said pumping system, said fluid exit being in fluid communication with said pump; and a variable force check valve located between said probe and said fluid exit.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
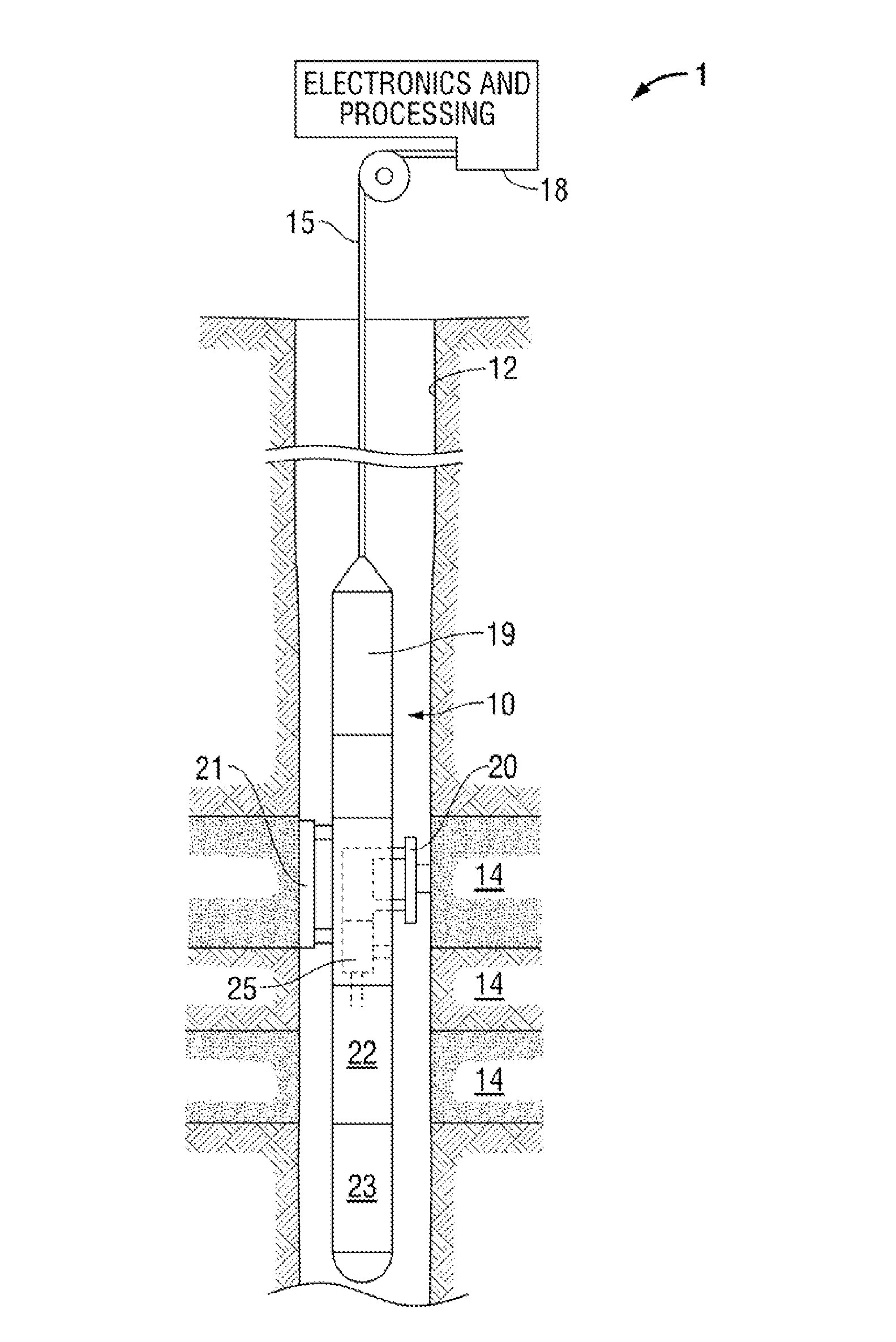
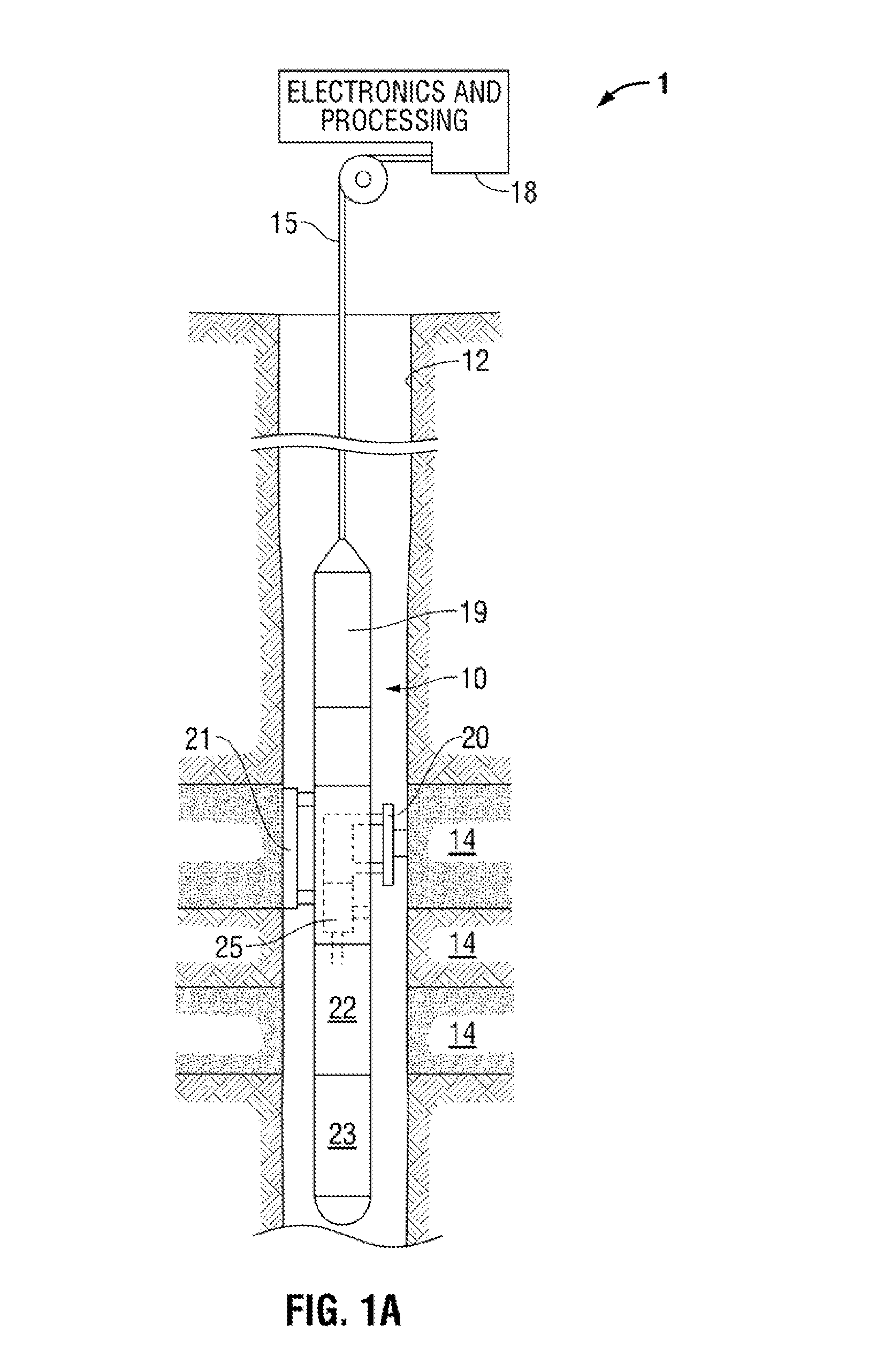
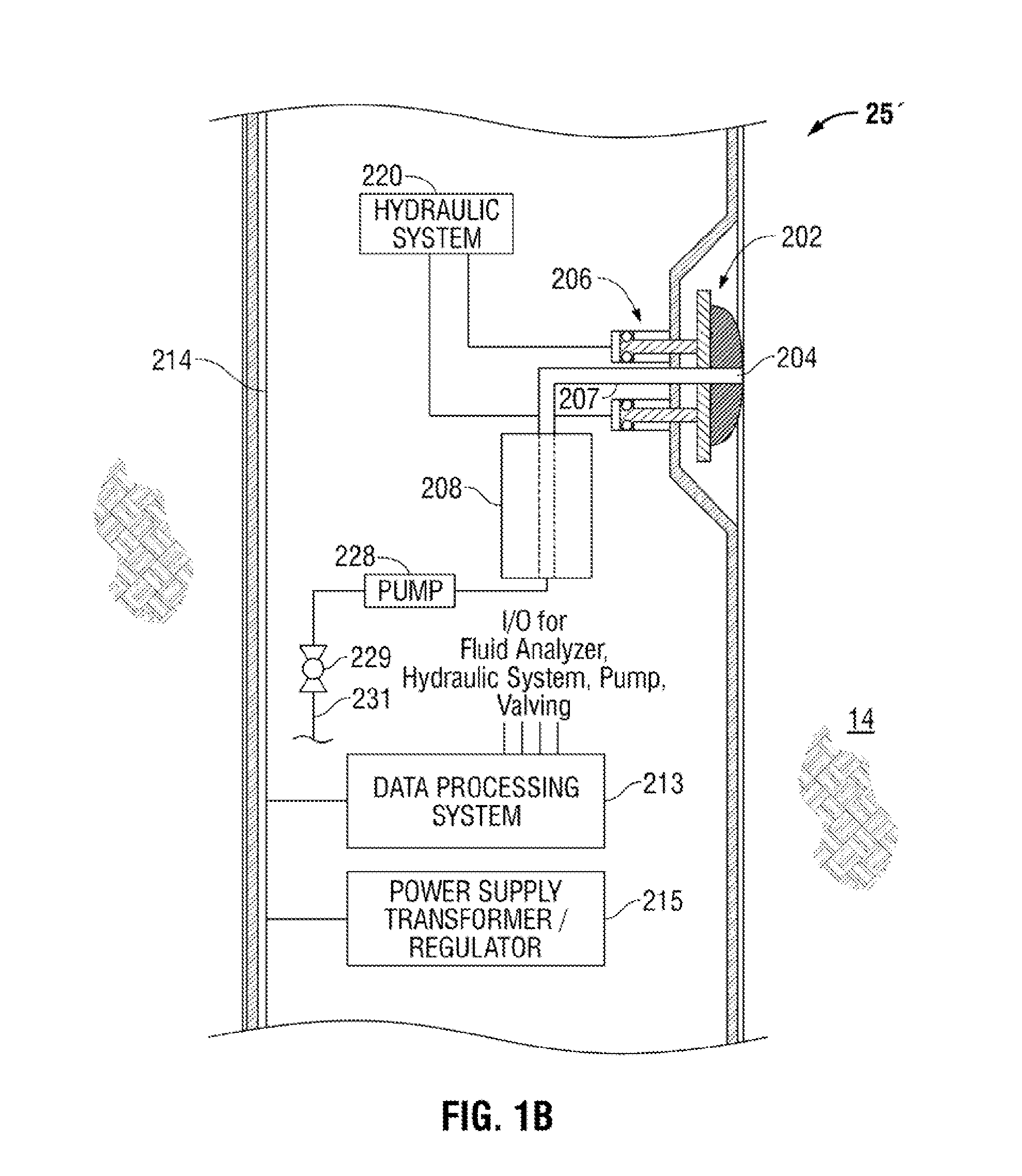
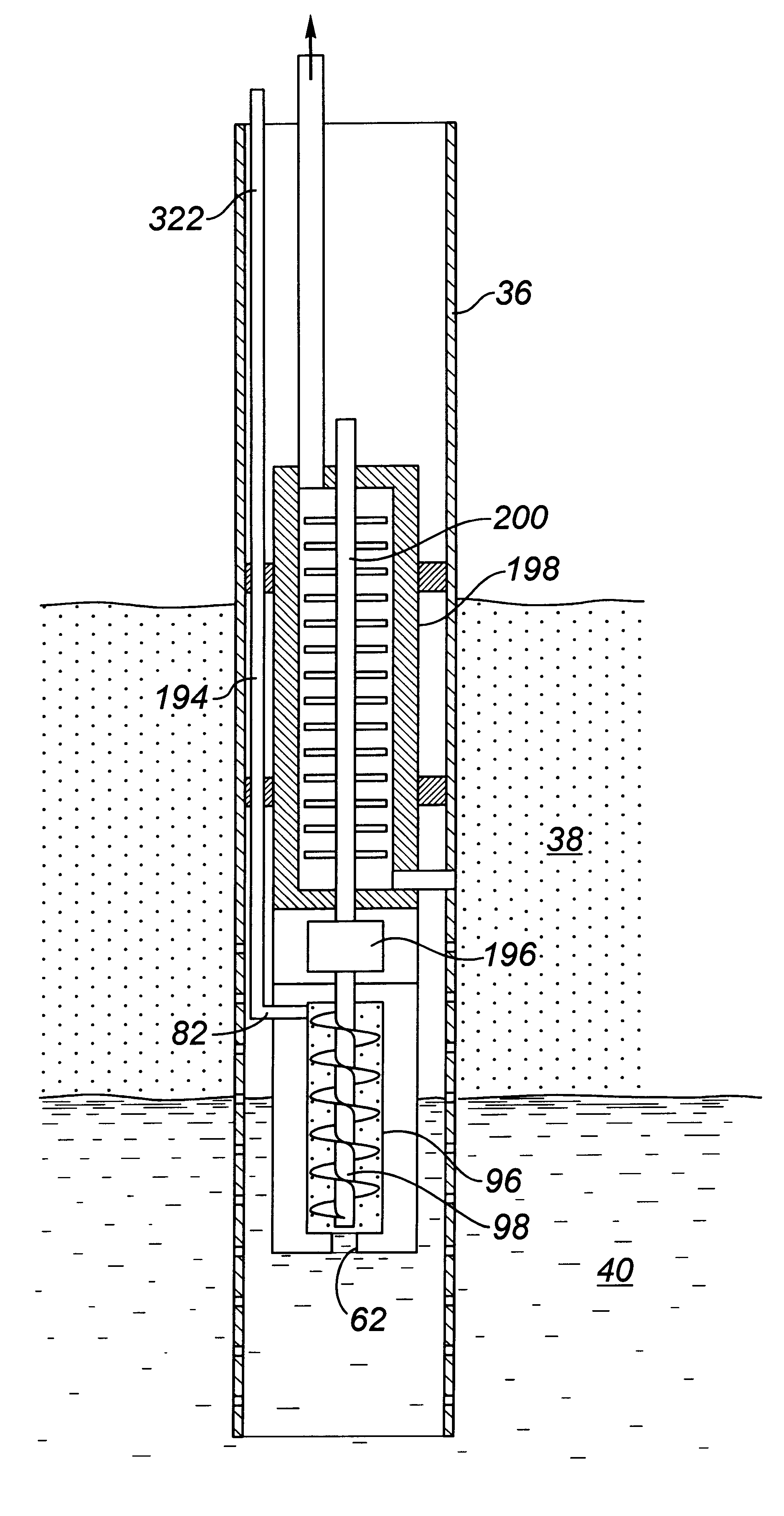
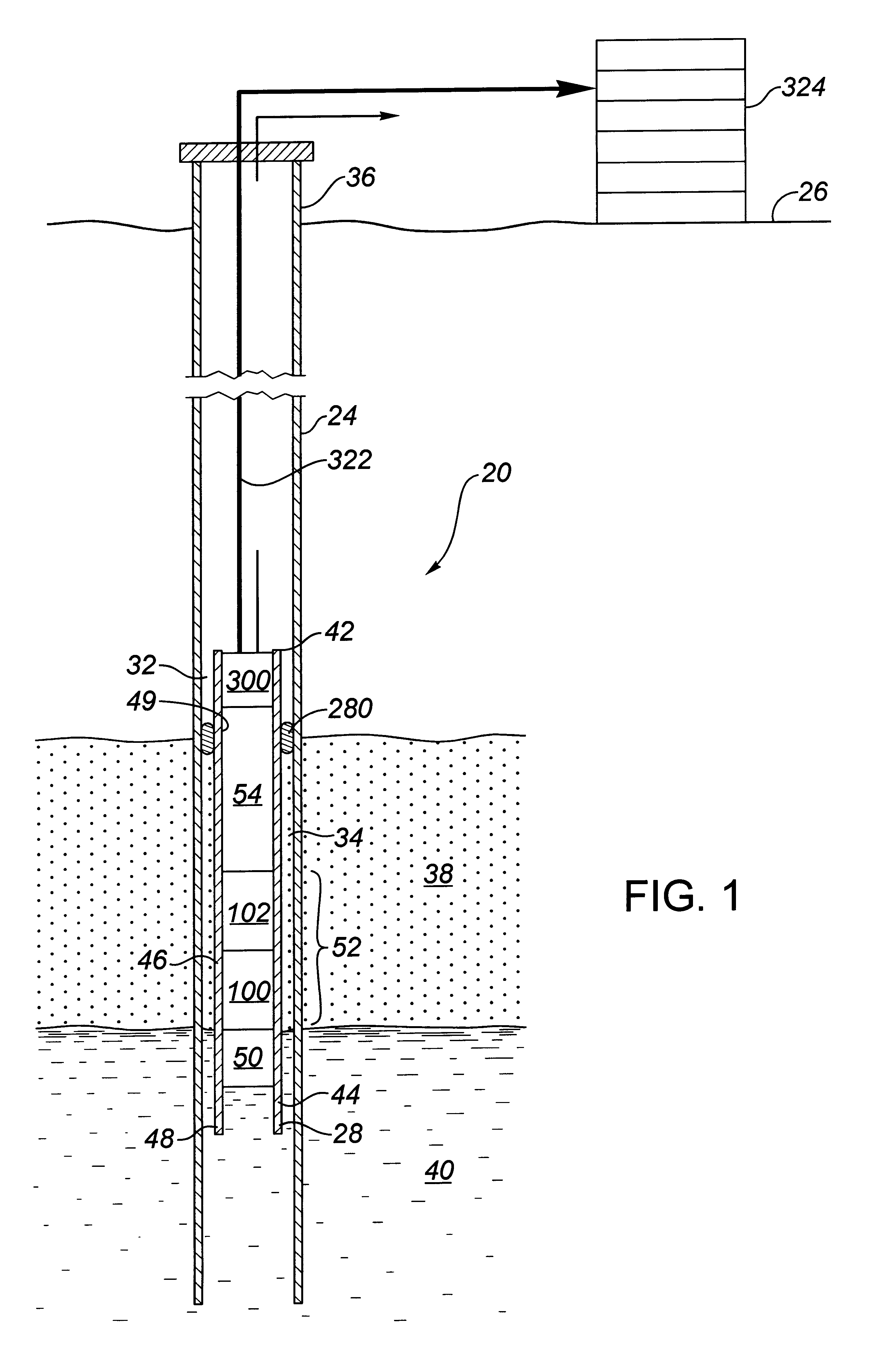
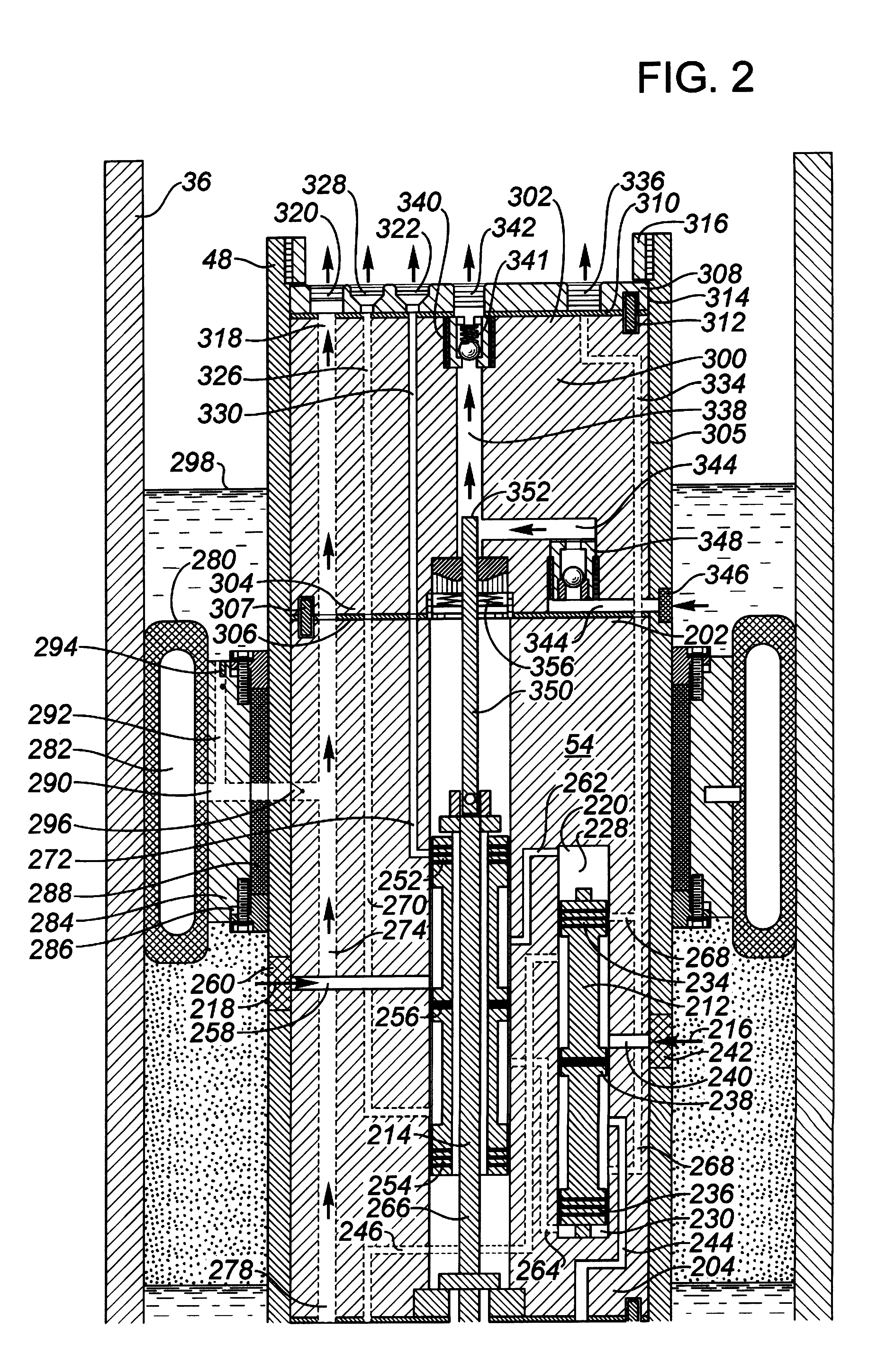
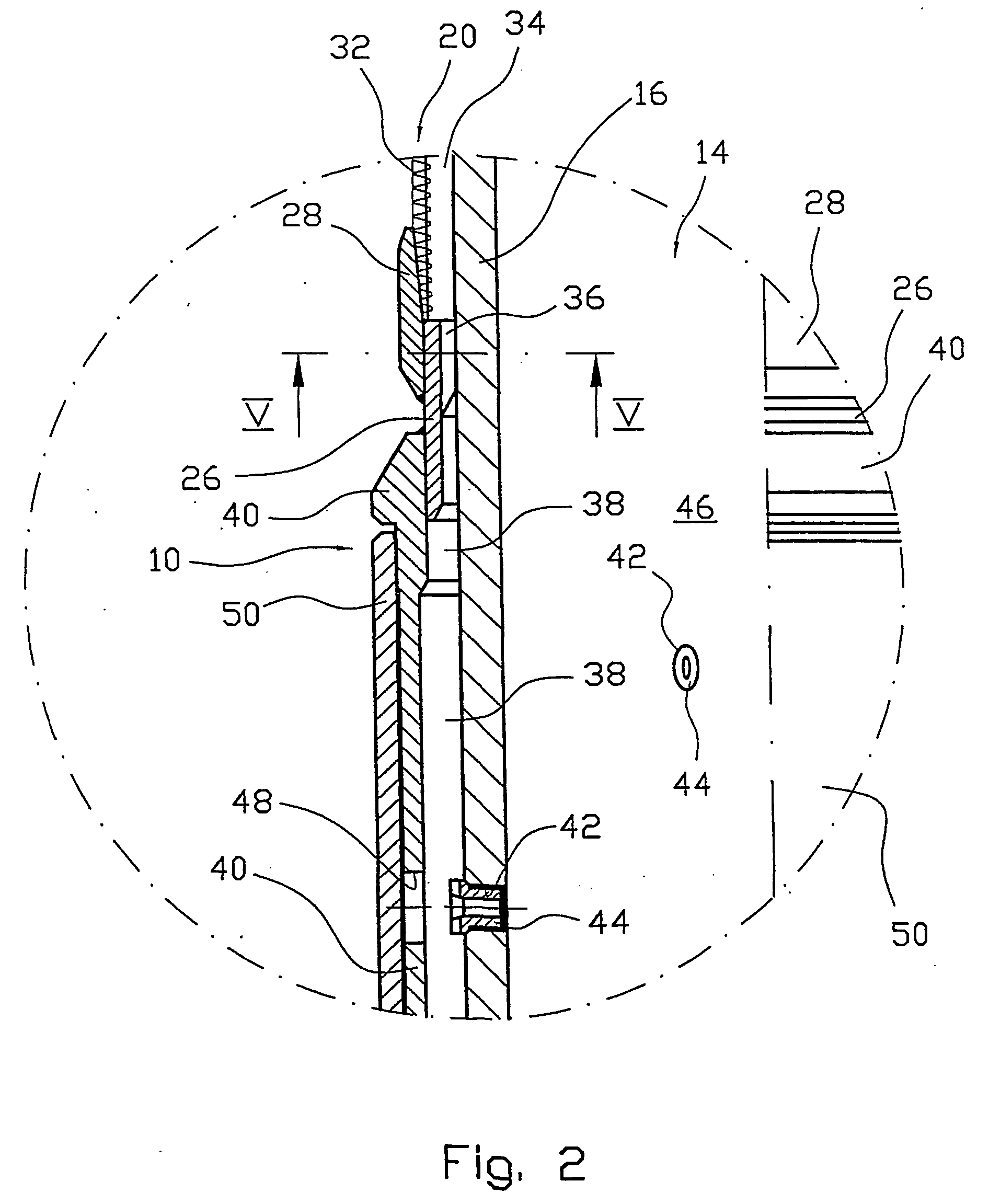
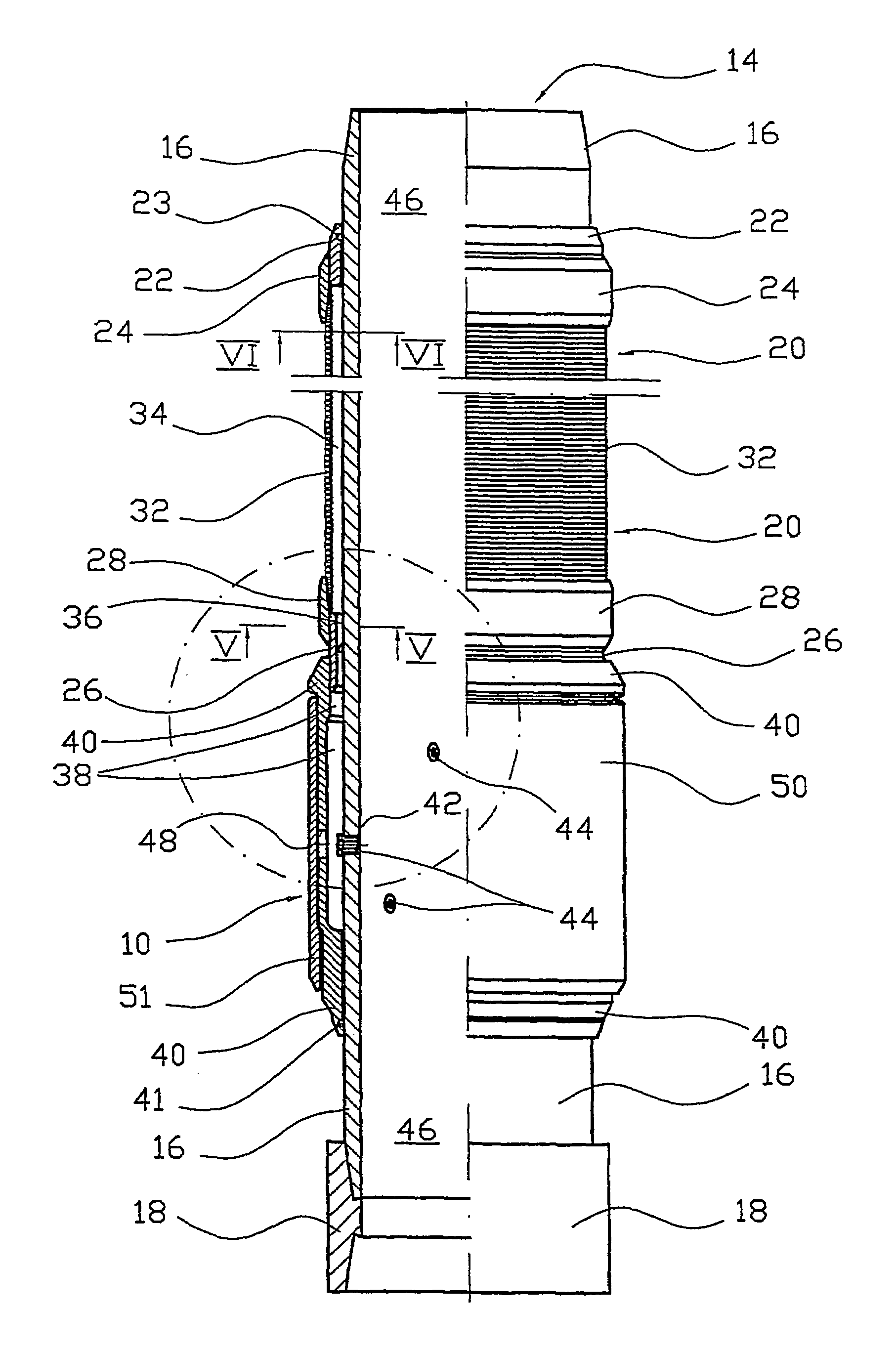
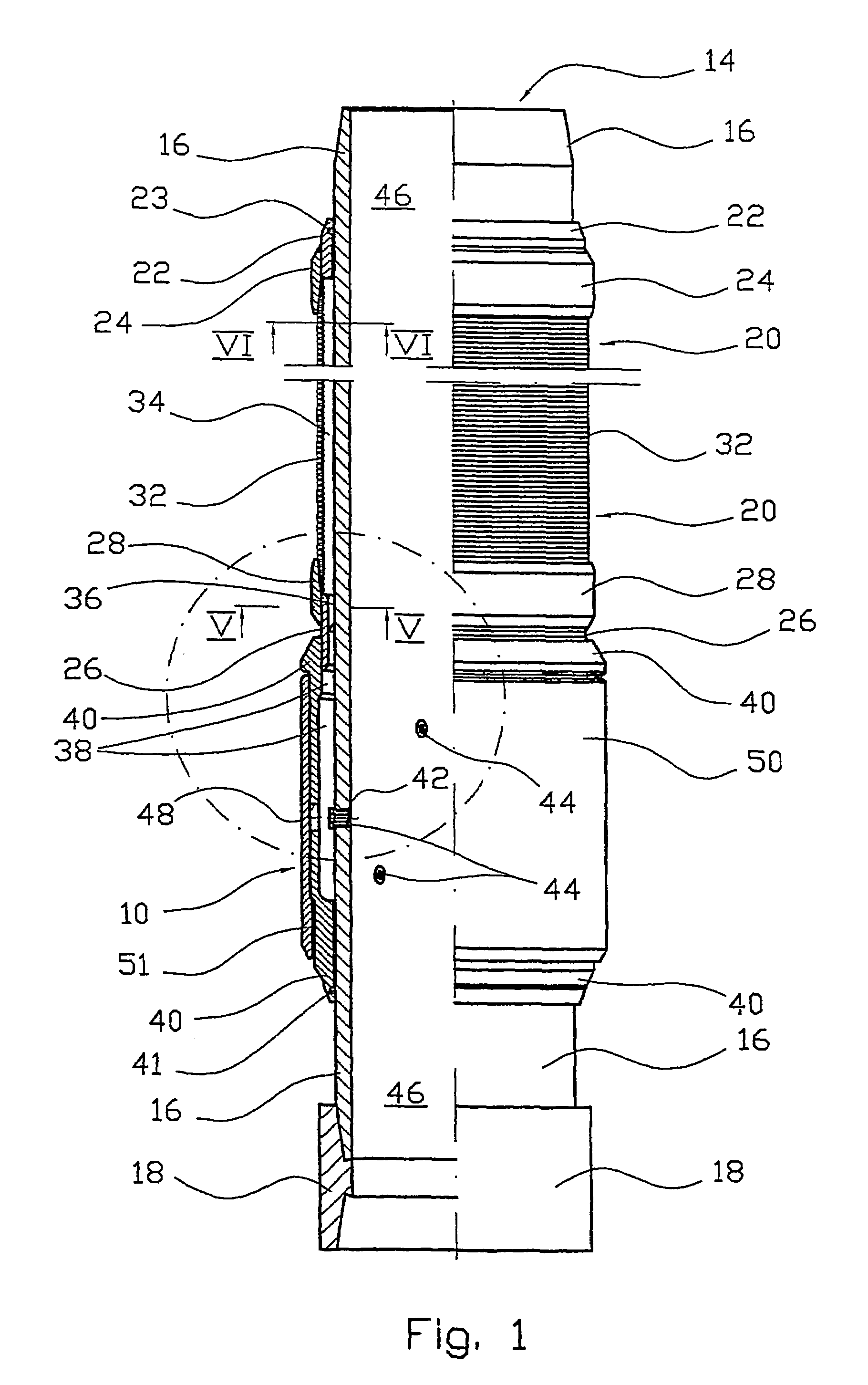
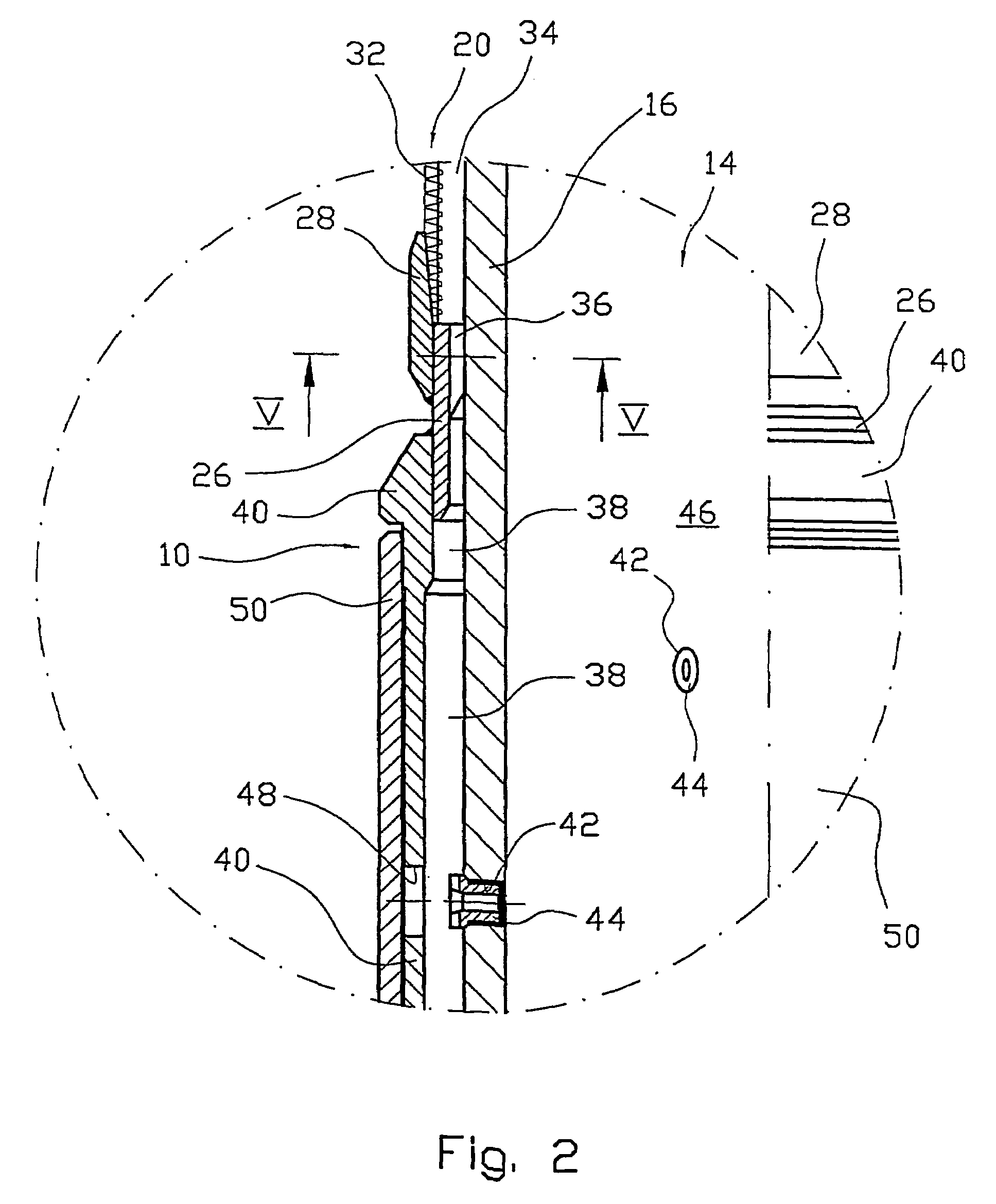
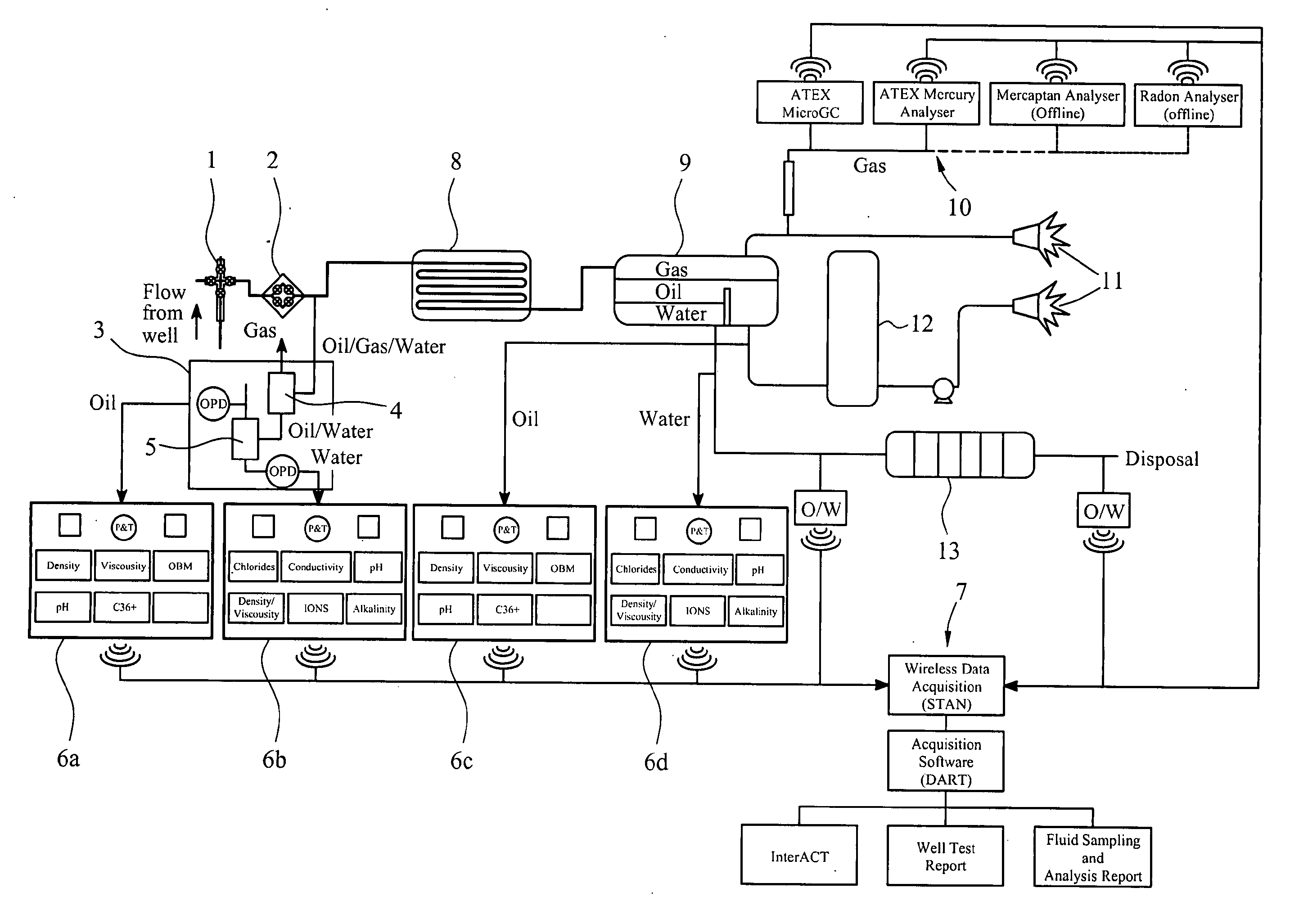
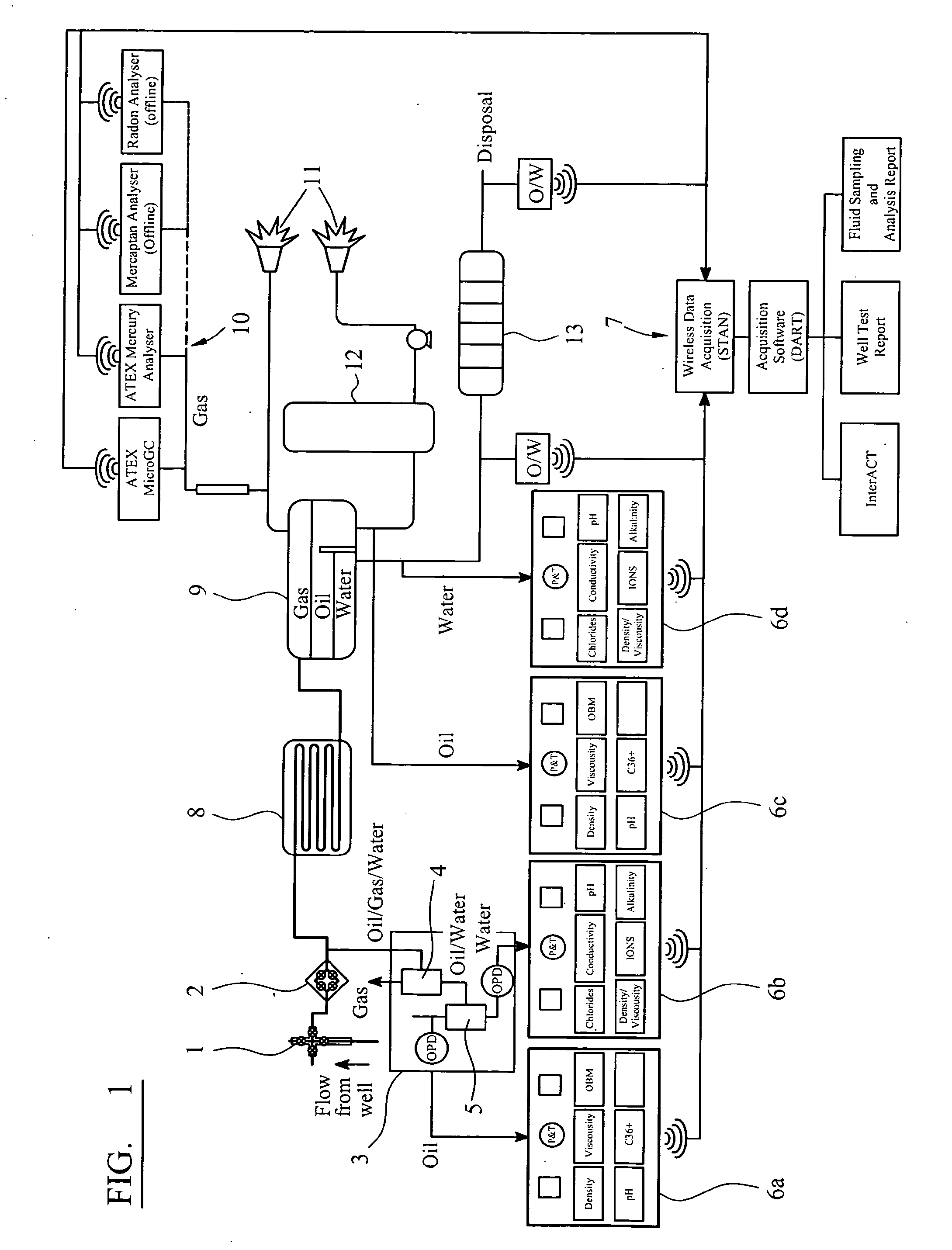
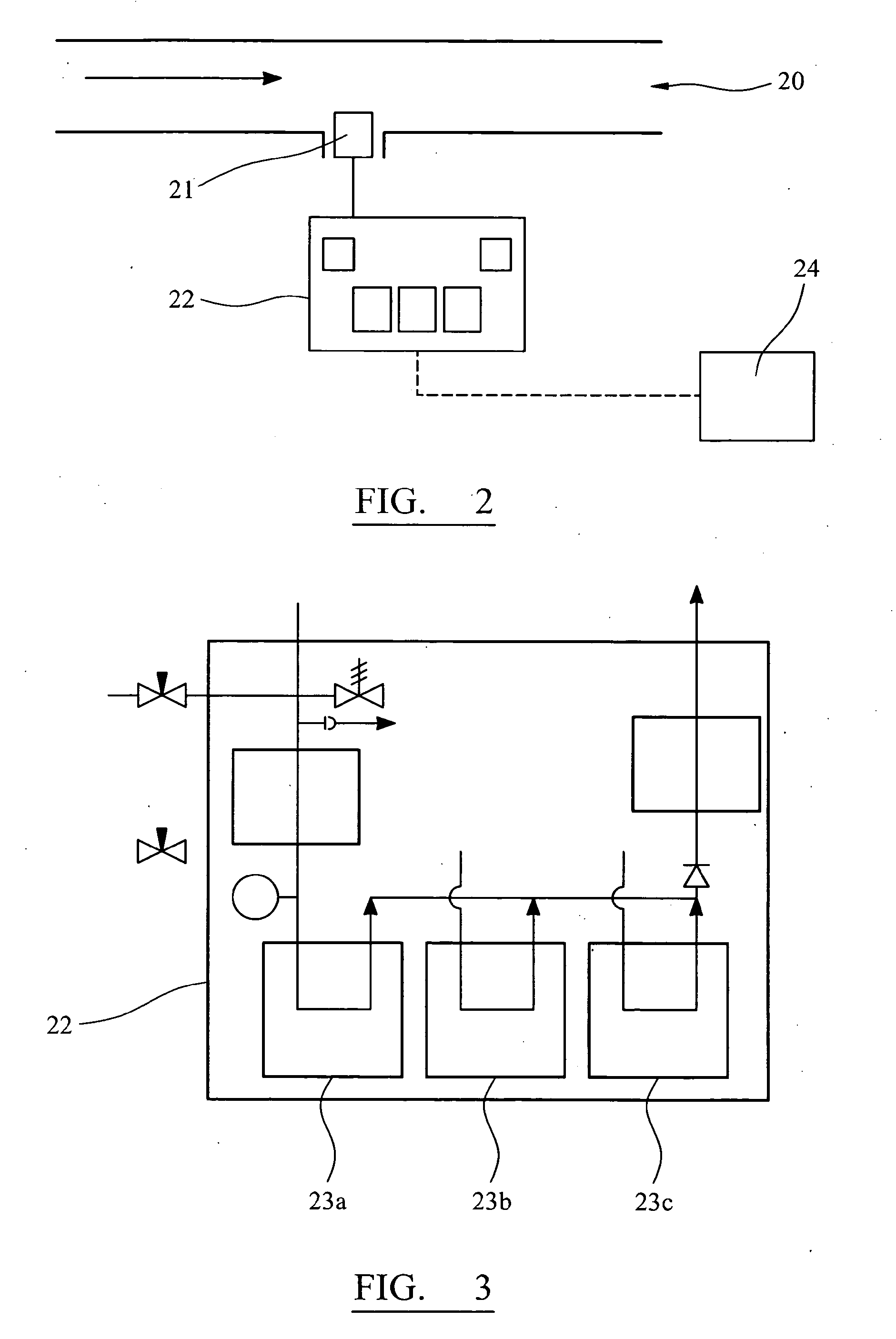
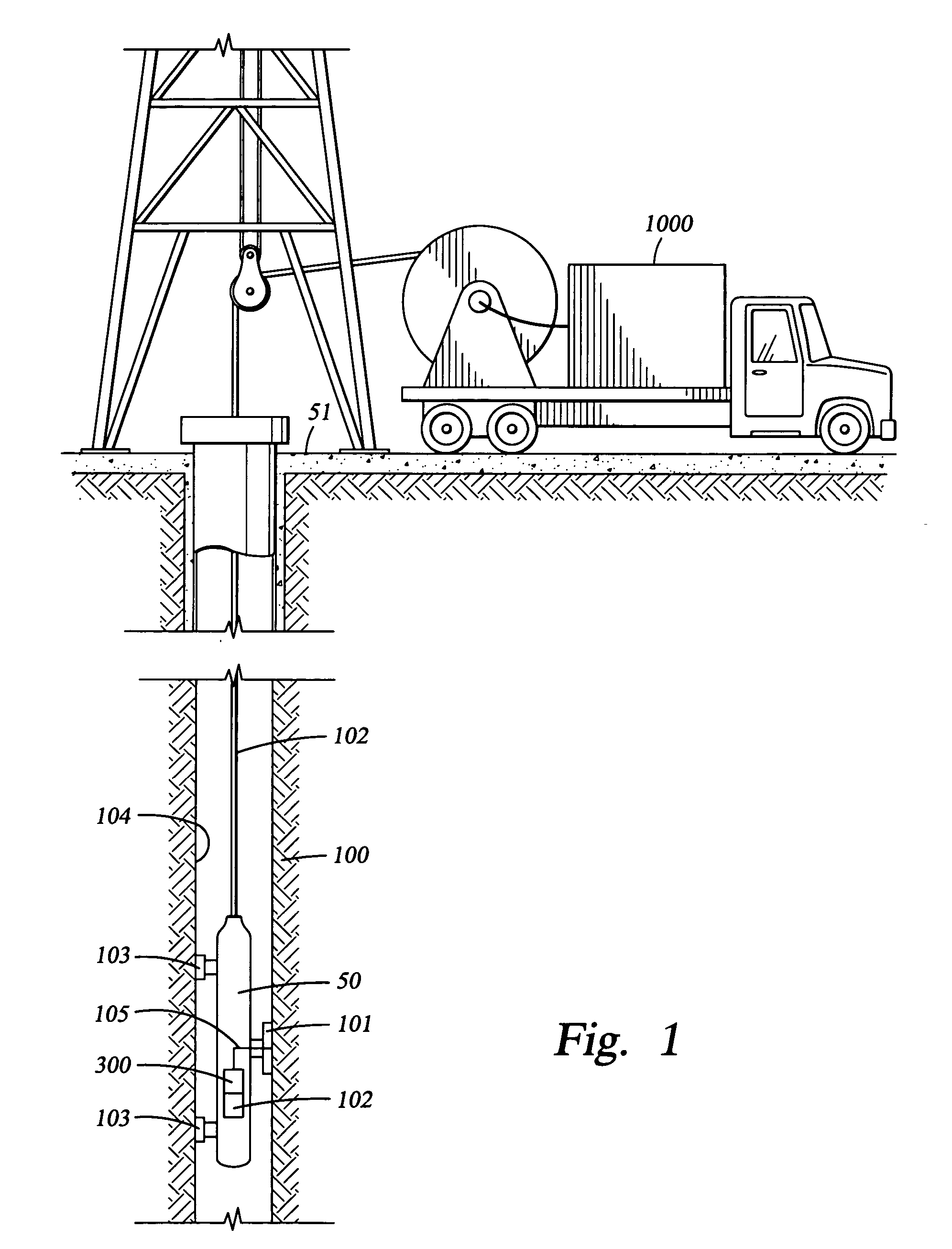
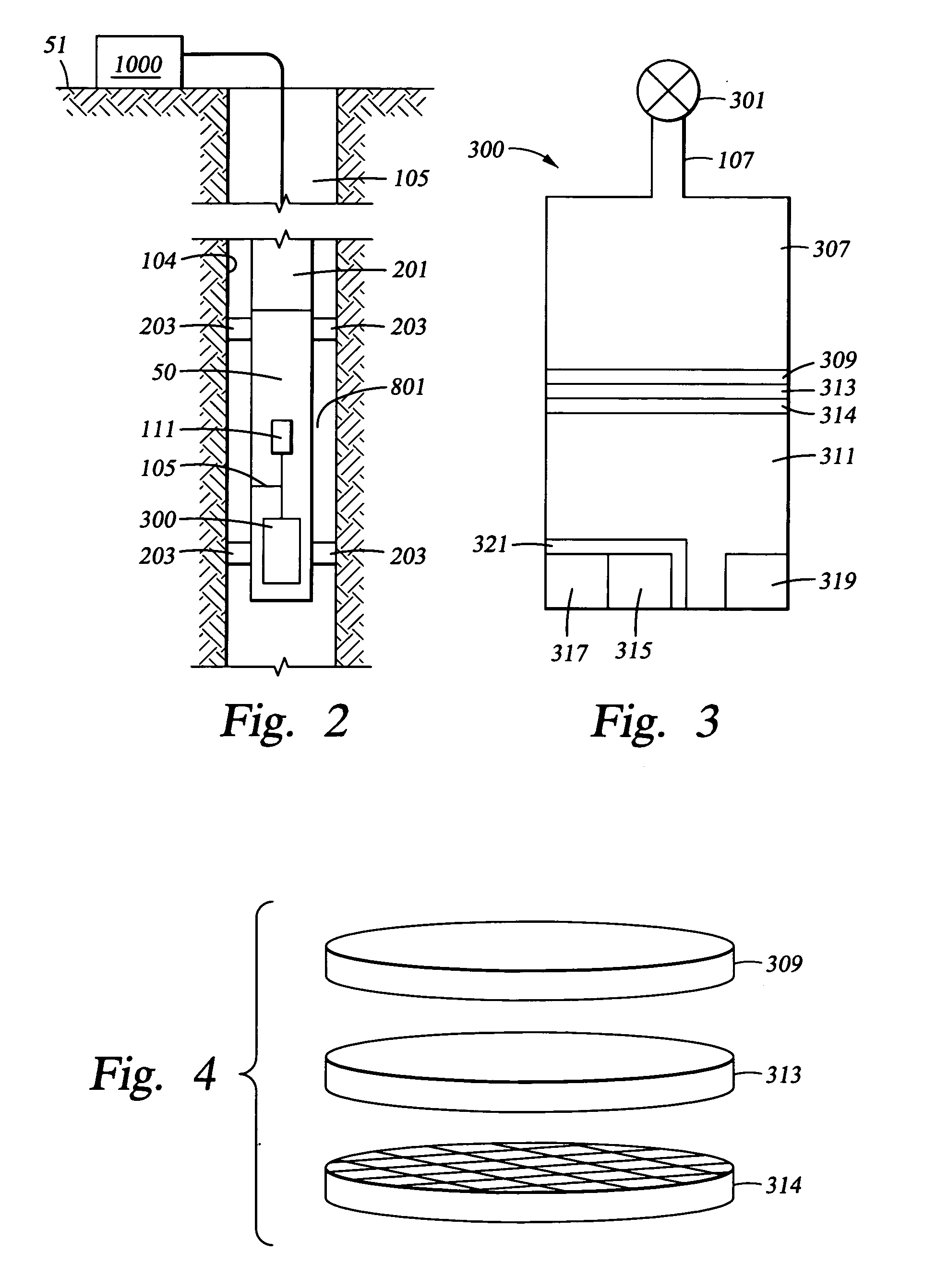
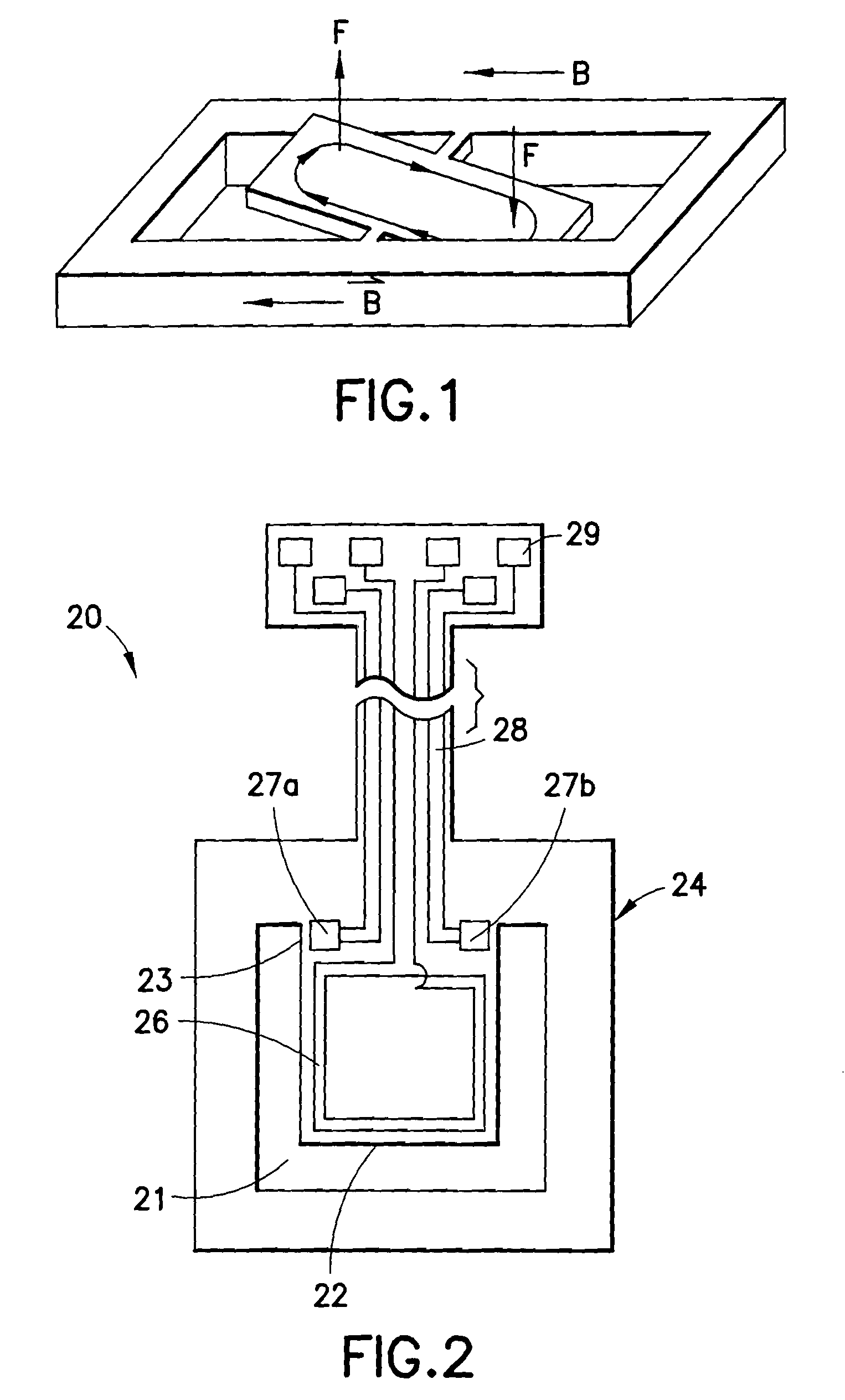
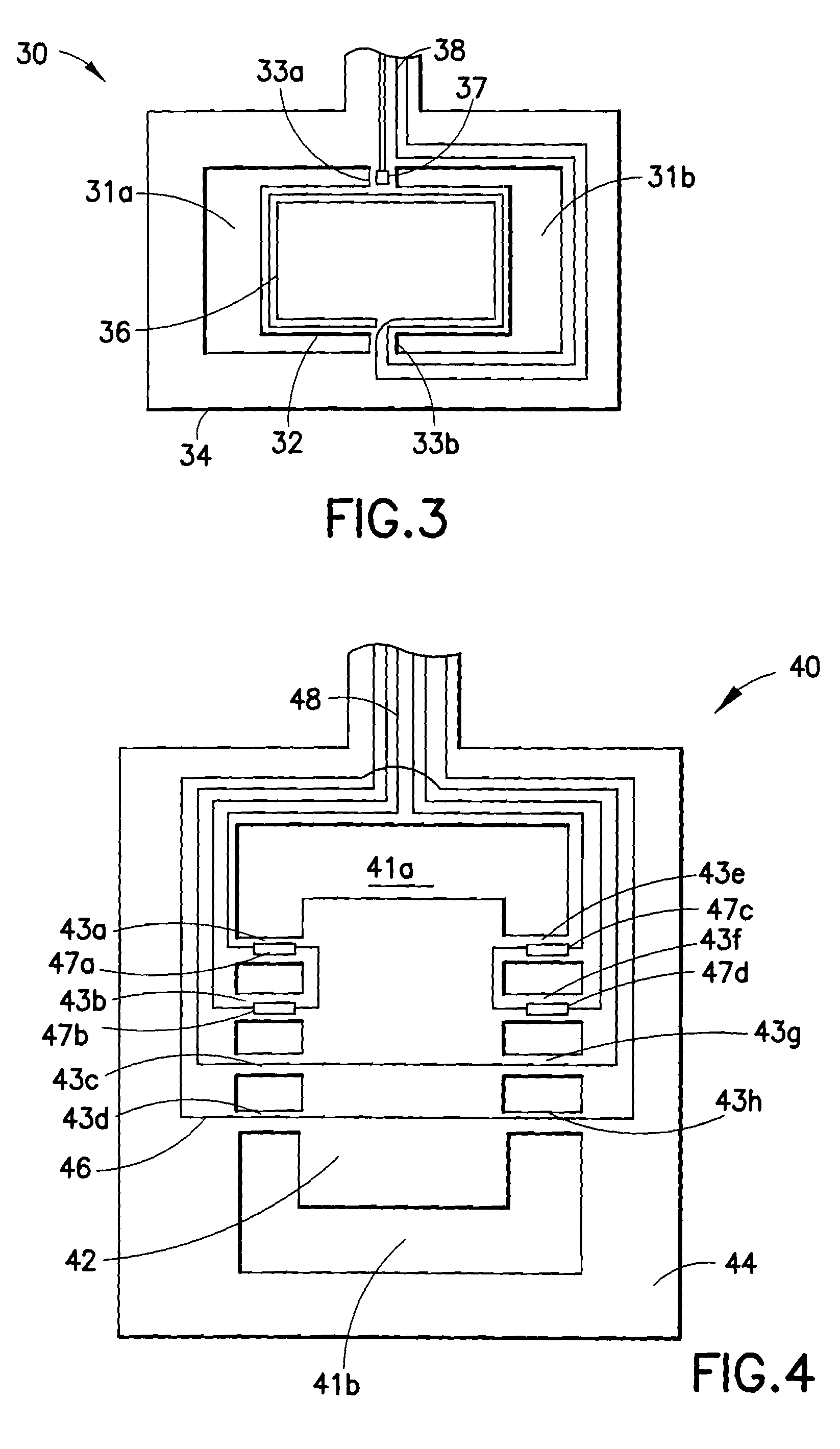
[real-time monitoring and control of reservoir fluid sample capture]
InactiveUS20050150287A1Withdrawing sample devicesBorehole/well accessoriesLine tubingMonitoring and control
A method of sampling reservoir fluid includes establishing communication between a reservoir and an entry port of a flow line disposed in a borehole penetrating the reservoir. The method includes separating fluid received in the entry port into individual fluid components and sequentially flowing slugs of each individual fluid component along the flow line, observing the slugs as they move along the flow line in order to determine the composition of the slugs, estimating when a desired slug containing a desired fluid component would be in the vicinity of a sample chamber in the flow line, and opening the sample chamber to capture the desired slug when the desired slug is in the vicinity of the sample chamber. The method also includes checking that the sample chambers open and close successfully. Finally, the method further includes creating an accurate record of events, which can then be used to audit the sampling process.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Method and apparatus for reservoir fluid characterization in nuclear magnetic resonance logging
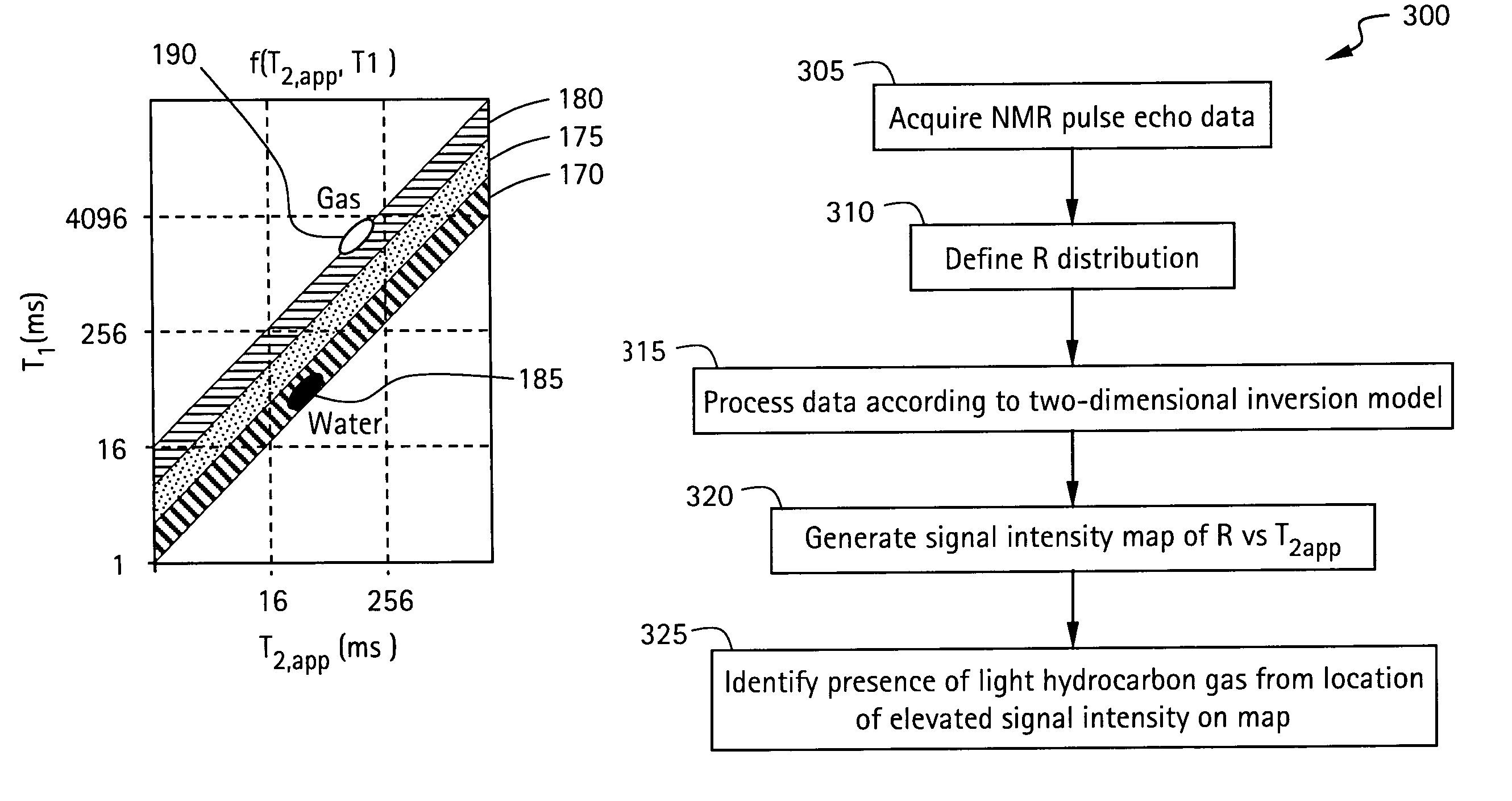
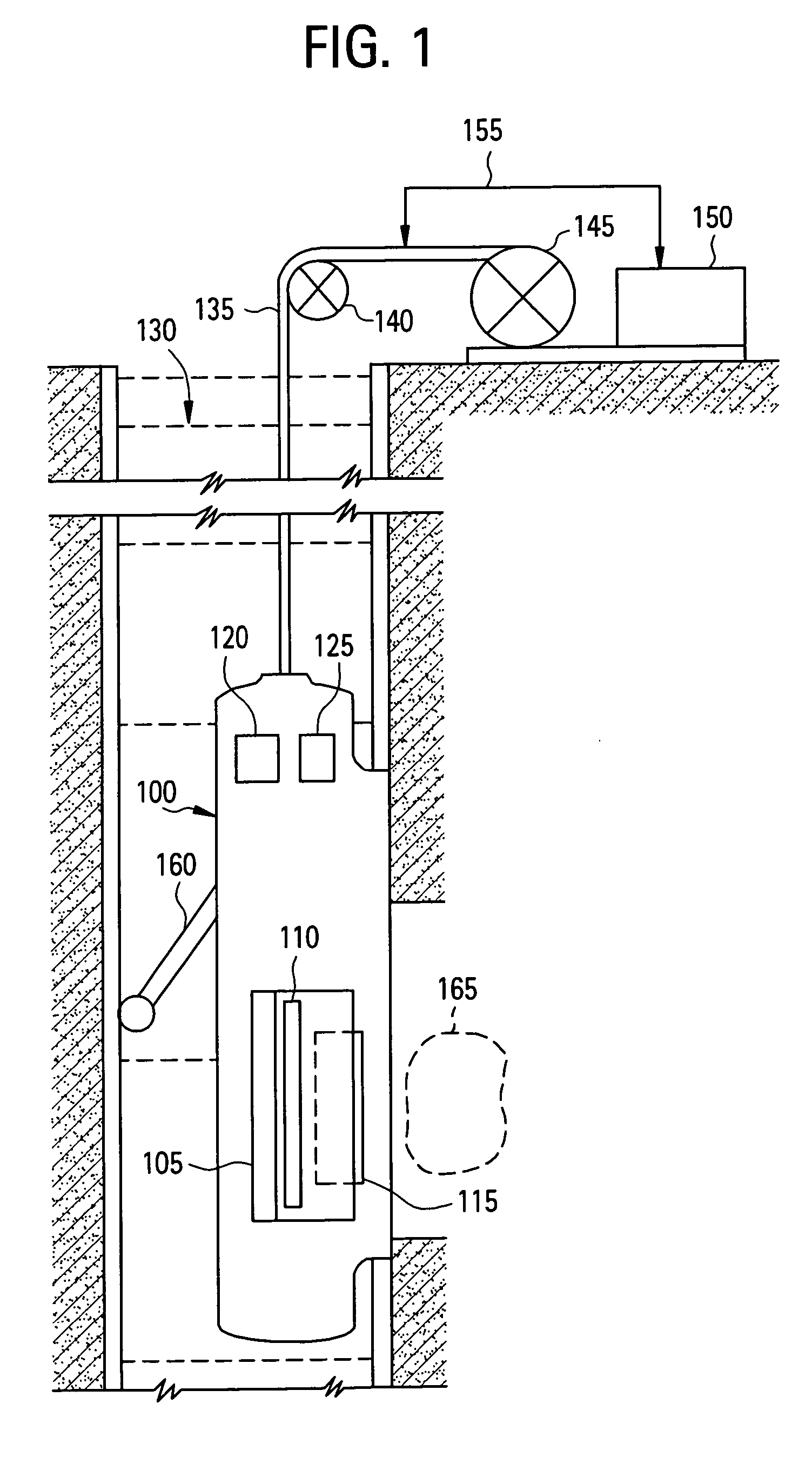
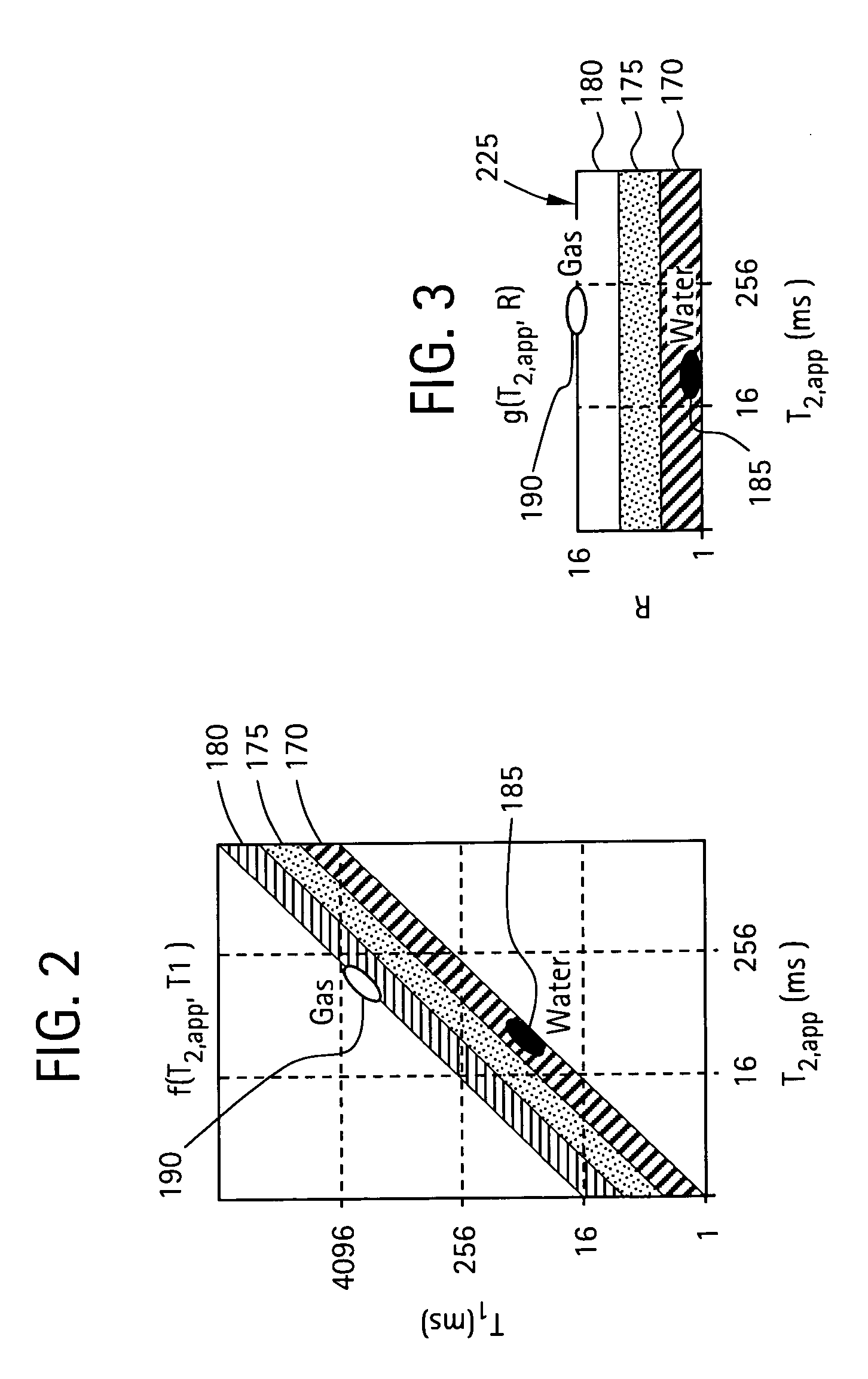
ActiveUS20060290350A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceWell logging
A method and apparatus for obtaining a parameter of interest relating to a region proximate a nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) logging tool suitable for subterranean well logging is disclosed. The nuclei of the region are subjected to a pulsed NMR technique and are productive of NMR logging data, the nuclei of the region characteristically having a longitudinal relaxation time T1 distribution and an apparent transverse relaxation time T2app distribution. In response to the NMR logging data, an R distribution is defined as R=T1 / T2app, the T2app and R distributions are processed as separate bins, along with the NMR logging data, according to a two-dimensional inversion model, and a signal intensity map of R versus T2app is provided that is representative of the parameter of interest relating to the region. In response to a high-intensity signal on the map being within a first range of T2app values and a first range of R values, the presence of a light hydrocarbon within the region is identified.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
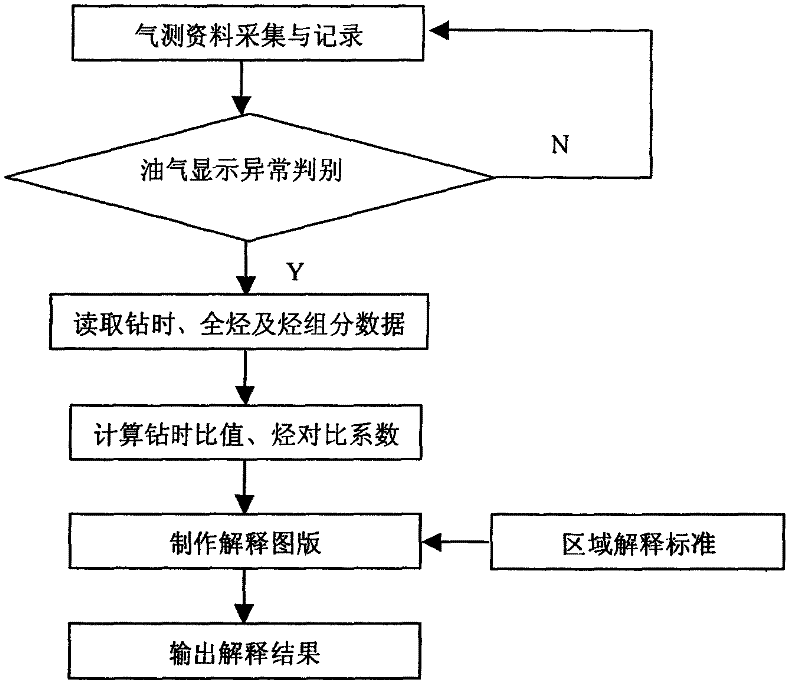
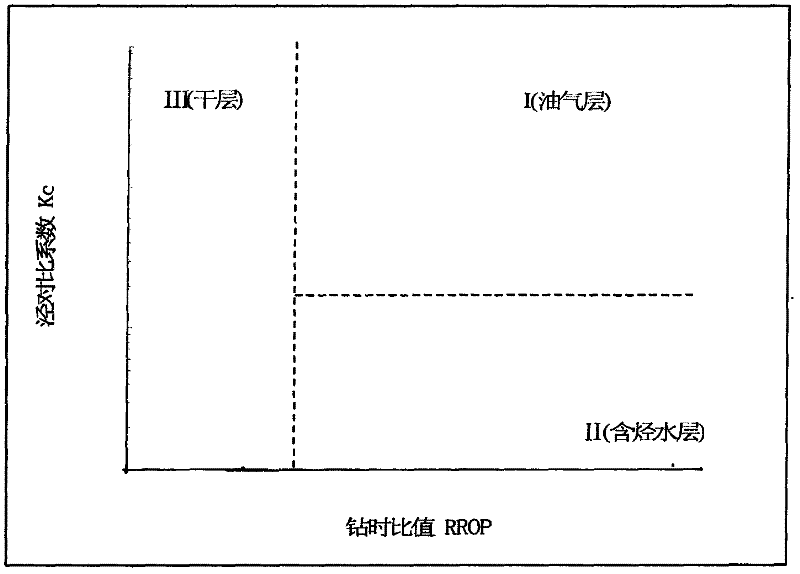
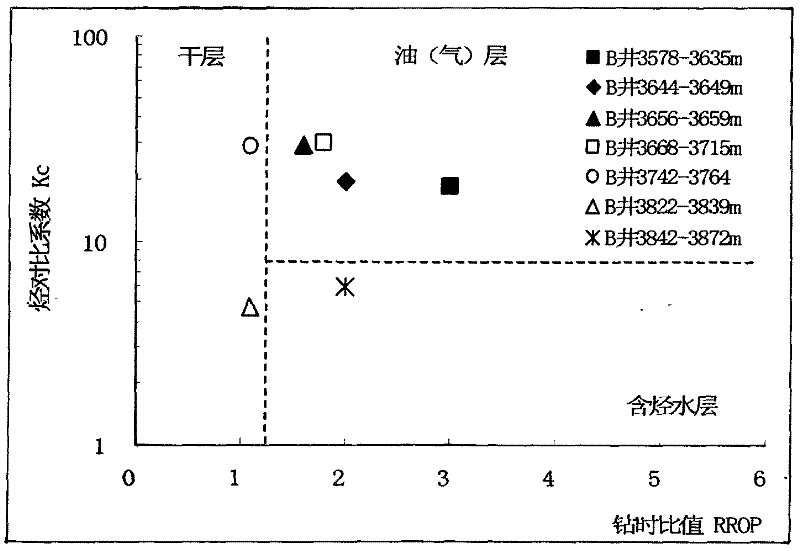
Method capable of fast explaining and evaluating reservoir fluid properties
The invention relates to a method capable of fast explaining and evaluating reservoir fluid properties. The logging drilling time and the total hydrocarbon and hydrocarbon components are collected and recorded through a drilling time instrument, a gas logging instrument, an integral logging instrument and other logging devices. The total hydrocarbon value Ct (percent) of the maximum effective value of a reservoir is obtained, and the total hydrocarbon average value, i.e. the basic value Cb (percent) of a cover layer of 5m to 20m above the reservoir is selected. The drilling time specific value RROP of the reservoir is calculated by the cover layer drilling time ROPn and the reservoir drilling time ROPs. The hydrocarbon contrast coefficient Kc is calculated by the total hydrocarbon value Ct (percent) and the basic value Cb (percent). RROP-Kc patterns are drawn through data points of an oil gas layer, a hydrocarbon-containing water layer and a dry layer after oil test verification according to region statistics, boundary lines AB and CD and three regions of the oil gas layer, the hydrocarbon-containing layer and the dry layer are determined according to the data statistics principle, regions of the data points in the RROP-Kc patterns are corresponding fluid explaining and evaluating results. The method is applied to more than two thousand wells in Jianghan oil regions, and the regional coincidence rate is higher than 85 percent. The method is applied in low-resistance oil gas layers, fractured oil gas layers and shale gas layers, particularly weak oil gas display and single component display layers.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Methods for Characterizing Asphaltene Instability in Reservoir Fluids
ActiveUS20130112406A1Efficient identificationOptimization and efficiency in developmentSurveyConstructionsFlocculationStability study
A methodology for reservoir understanding that performs investigation of asphaltene instability as a function of location in a reservoir of interest. In the preferred embodiment, results derived as part of the investigation of asphaltene instability are used as a workflow decision point for selectively performing additional analysis of reservoir fluids. The additional analysis of reservoir fluids can verify the presence of asphaltene flocculation onset conditions and / or determine the presence and location of phase-separated bitumen in the reservoir of interest.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
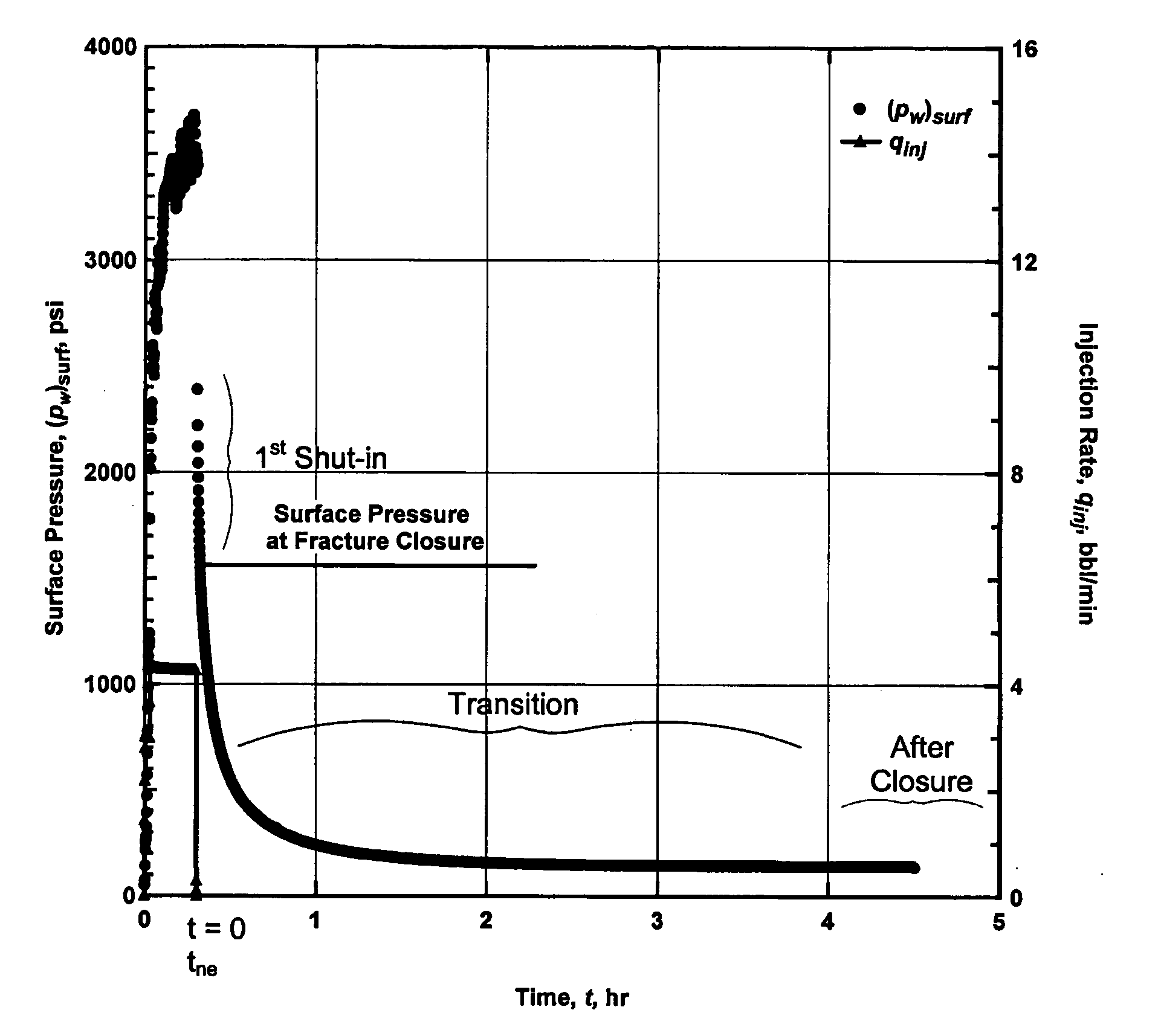
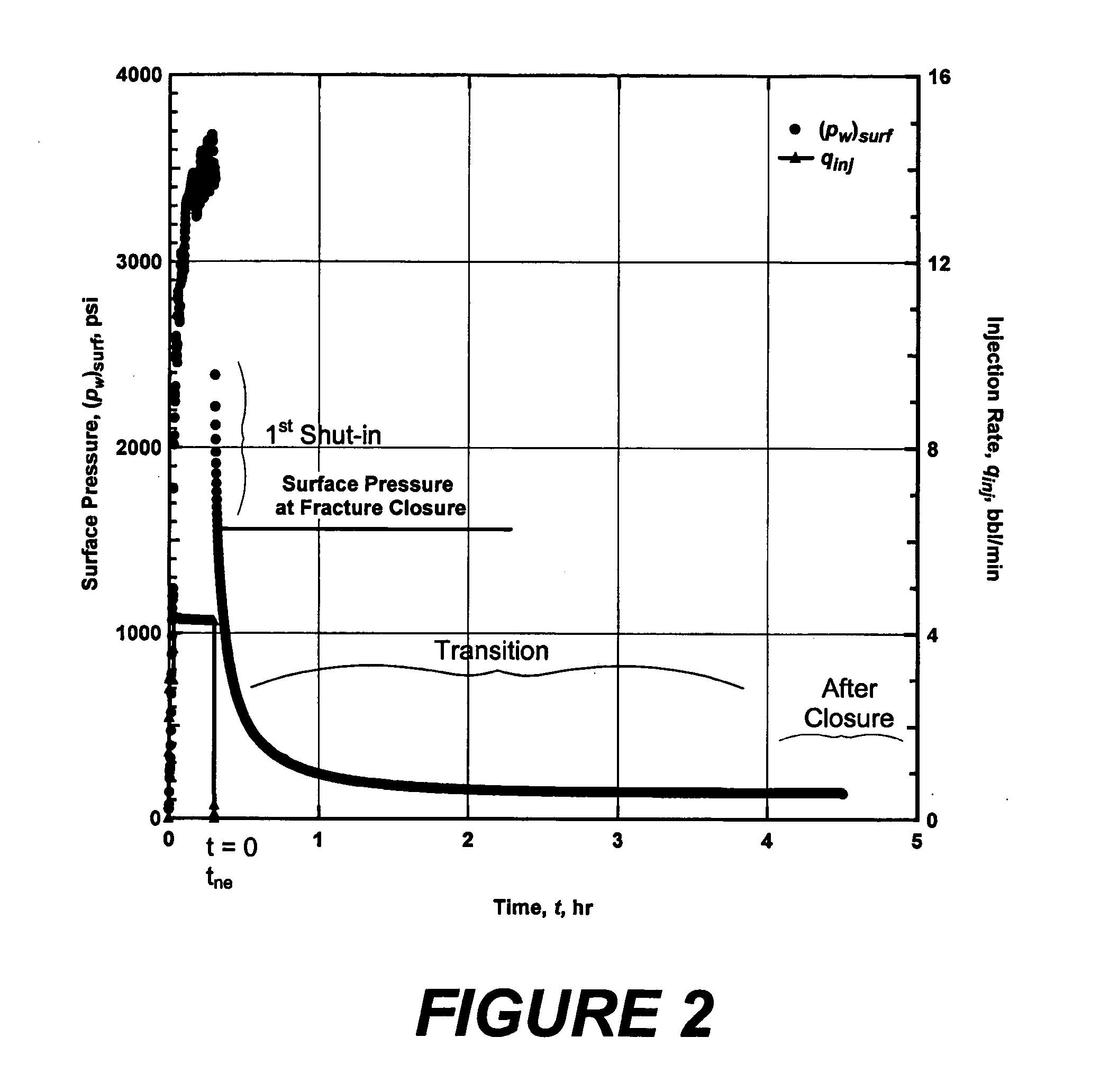
Method and an apparatus for detecting fracture with significant residual width from previous treatments
ActiveUS20050222852A1Rapid determinationElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyDual unitMedicine
A refracture-candidate diagnostic test is an injection of compressible or slightly compressible fluid such as liquid, gas, or combination at pressures in excess of minimum in-situ stress and formation fracture pressure with pressure decline following injection test recorded to detect a fracture retaining residual width from previous stimulation treatments. The diagnostic consists of small volume injections with injection time being a small fraction of time required for compressible or slightly compressible reservoir fluid to exhibit pseudoradial flow. The fracture-injection portion of a test can be considered as occurring instantaneously, and the results obtained in an open infinite-conductivity hydraulic fracture with pressures above fracture closure stress during before-closure portion of pressure falloff and with pressures less than fracture closure stress during after-closure portion of pressure falloff. Data measurements are transformed into a constant rate equivalent pressure transformation to obtain adjusted pressures or adjusted pseudovariables which are analyzed to identify dual unit-slope before and after closure periods confirming a residual retaining width.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Method and device for analyzing dispersion and attenuation of unsaturated double-porosity medium earthquake waves
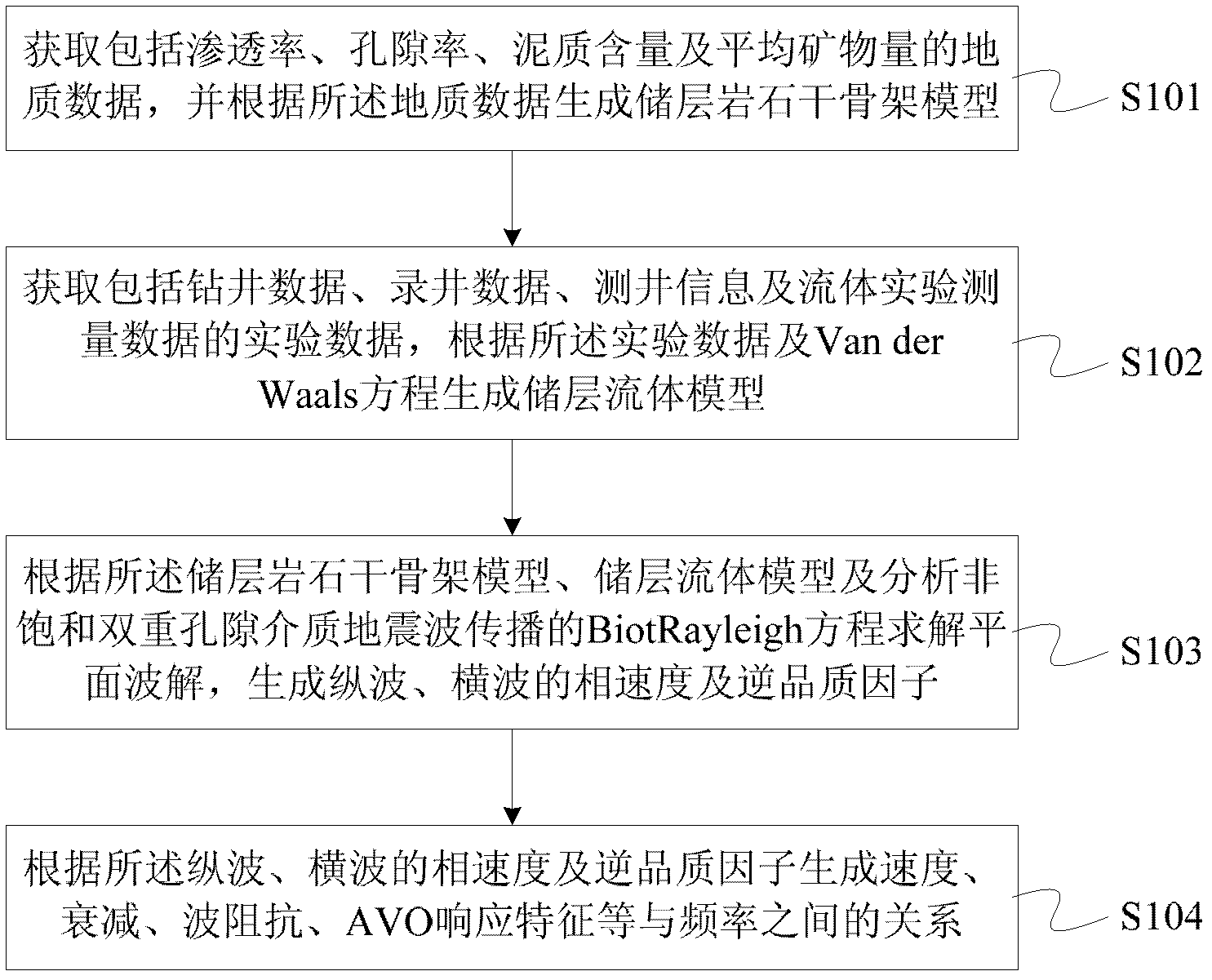
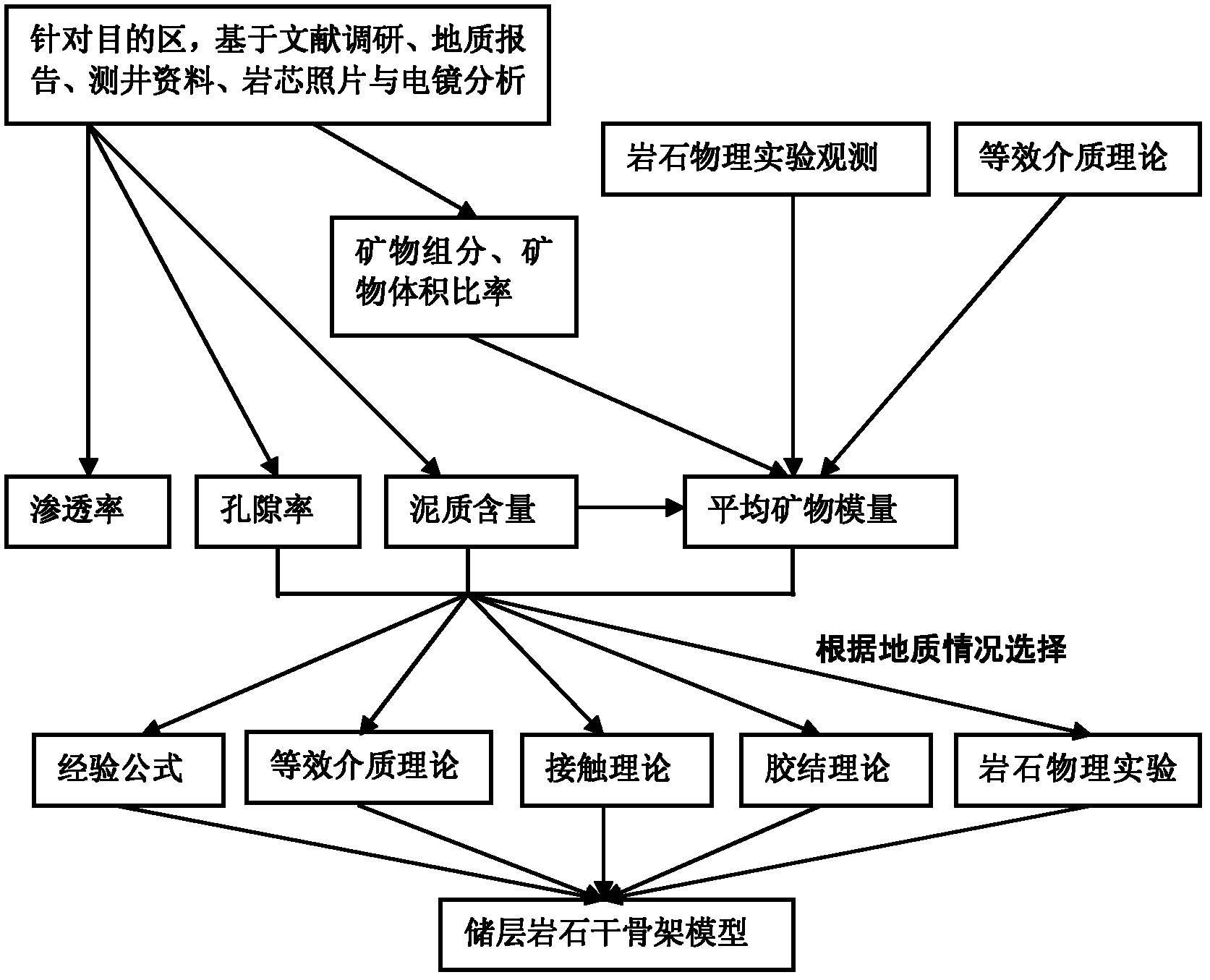
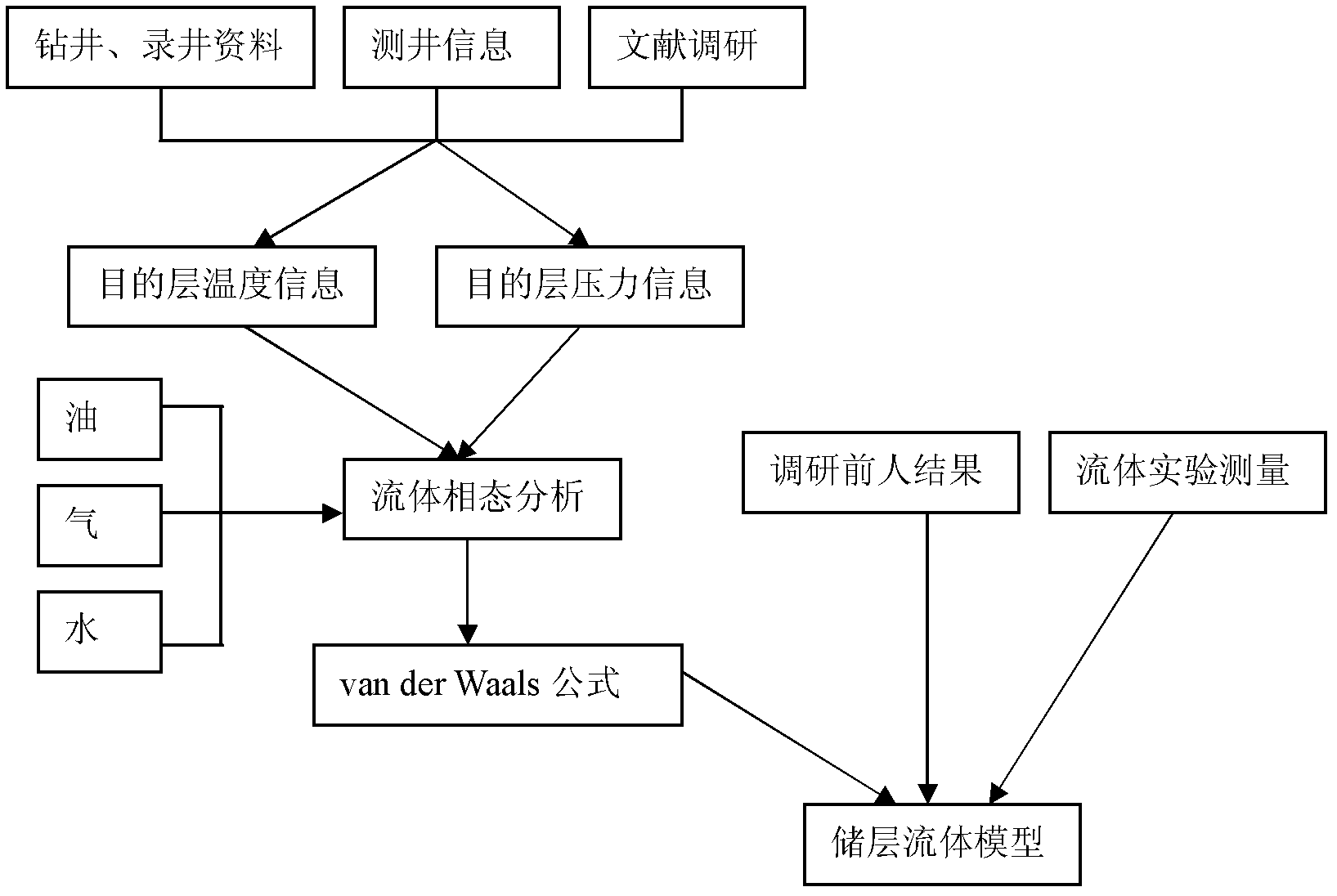
ActiveCN102508296AGood physical achievabilitySeismic signal processingSeismology for water-loggingPorositySeismic wave propagation
The invention discloses a method and a device for analyzing the dispersion and attenuation of unsaturated double-porosity medium earthquake waves. The method comprises the following steps of: 1, acquiring geological data including penetration rate, porosity, shale content and mineral components and generating a reservoir rock dry framework model according to the geological data; 2, acquiring measured data including drilling data, logging data, logging information and fluid experiment measured data and generating a reservoir fluid model according to the measured data and a Van derWaals equation; 3, solving plane waves according to the reservoir rock dry framework model, the reservoir fluid model and a Biot-Rayleigh equation for describing the spread of the unsaturated double-porosity medium earthquake waves, and generating phase speed and inverse quality factors of longitudinal waves and horizontal waves; and 4, generating relationships between frequency and each of speed, attenuation,wave impedance, AVO (Amplitude Versus Offset) response characteristic and the like according to the phase speed and inverse quality factors of the longitudinal waves and the horizontal waves.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Reservoir fluids production apparatus and method
The invention is an apparatus for moving reservoir fluids from an underground reservoir using a wellbore extending from the surface to an end beneath the surface, wherein the wellbore communicates with the reservoir such that reservoir fluids enter the wellbore and separate into a liquid phase and a gas phase at a gas pressure. The apparatus includes a first pump, for containing within the wellbore in communication with the liquid, for pumping the liquid phase. The apparatus further includes a pump drive, for containing within the wellbore, operably connected to the first pump for driving the first pump. The pump drive is powered using the gas pressure of the gas phase in the wellbore. An intake communicates with the gas phase in the wellbore and directs the gas phase to the pump drive in order to power the pump drive, while an exhaust directs the gas phase from the pump drive. Further, the invention is a method for moving reservoir fluids from an underground reservoir using a wellbore. The method includes the steps of intaking the gas phase from the wellbore into the pump drive, powering the pump drive using the gas pressure of the gas phase in the wellbore, pumping the liquid phase from the wellbore by the first pump and exhausting the gas phase from the pump drive.
Owner:ALBERTA INNOVATES TECH FUTURES
Method for judging fluid type of reservoir through acoustic porosity-neutron porosity differential
ActiveCN101787884AHigh compliance rateMastering the Influence CharacteristicsPermeability/surface area analysisBorehole/well accessoriesLithologyNeutron porosity
The invention discloses a method for judging the fluid type of a reservoir through an acoustic porosity-neutron porosity differential, which relates to the technical field of oil and gas logging, geology and core test analysis. The method comprises the following steps: 1) accurately calculating shale content, rock compositions, acoustic porosity and neutron porosity of the reservoir through core data calibration logging and logging data environment correction; 2) excluding the influence of factors such as lithology, borehole diameter and mud invasion on an acoustic transit time and neutron data; and 3) establishing a standard for judging the fluid type of the reservoir by comparing the magnitude of the acoustic porosity and the neutron porosity and using the response difference of the acoustic transit time and the neutron data to the gas and formation water. In the method, non-fluid influence factors such as the lithology, borehole conditions, mud invasion and the like are excluded when the fluid type of the reservoir is judged, so the characteristics of the influence of different fluids on the acoustic transit time and the neutron data can be grasped truly, and the coincidence rate of judging the fluid type of the reservoir is improved from 70 percent currently to over 90 percent.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
Fracturing fluid for subterranean formations
A method of fracturing a reservoir comprising the steps of pumping a geopolymer precursor fluid through a wellbore into the reservoir at a fracture pressure, the geopolymer precursor fluid at the fracture pressure generates fractures in the reservoir, wherein the geopolymer precursor fluid is comprised of an amount of aluminosilicate, an amount of alkaline reagent, and a permeability enhancer, allowing the geopolymer precursor fluid to fill the fractures in the reservoir, shutting-in the wellbore at a wellbore pressure, the wellbore pressure maintains the geopolymer precursor fluid in the fractures, allowing the geopolymer precursor fluid to harden for a hardening time to form a geopolymer in the fractures, the geopolymer has a geopolymer matrix, the geopolymer matrix has a permeability, the geopolymer has a compressive strength, and reducing the wellbore pressure allows a reservoir fluid to flow from the reservoir through the geopolymer matrix of the geopolymer to the wellbore.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com
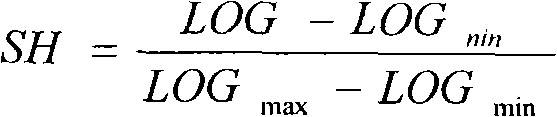
![[real-time monitoring and control of reservoir fluid sample capture] [real-time monitoring and control of reservoir fluid sample capture]](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/8c758555-6731-4fc4-9b44-e969453d0ecb/US20050150287A1-20050714-D00000.png)
![[real-time monitoring and control of reservoir fluid sample capture] [real-time monitoring and control of reservoir fluid sample capture]](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/8c758555-6731-4fc4-9b44-e969453d0ecb/US20050150287A1-20050714-D00001.png)
![[real-time monitoring and control of reservoir fluid sample capture] [real-time monitoring and control of reservoir fluid sample capture]](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/8c758555-6731-4fc4-9b44-e969453d0ecb/US20050150287A1-20050714-D00002.png)