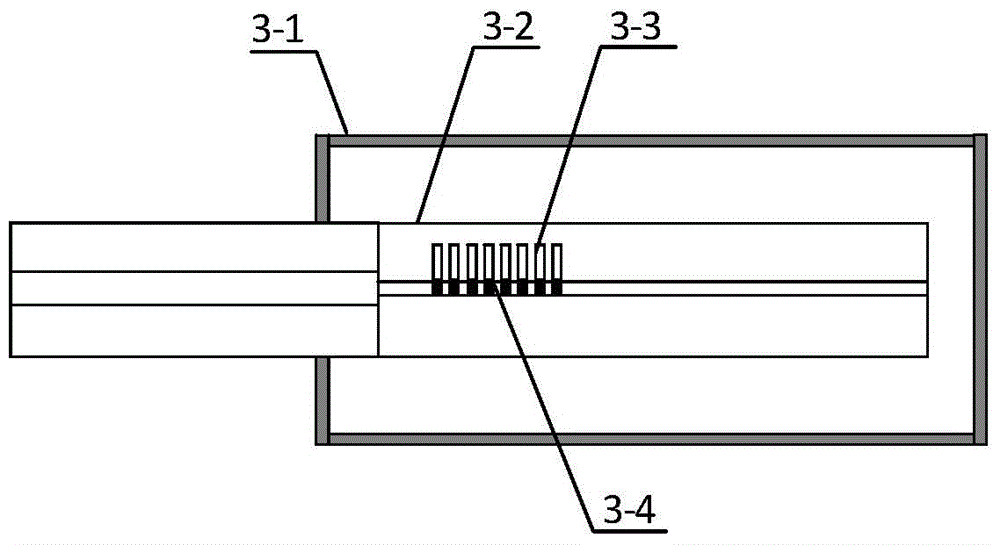
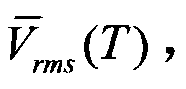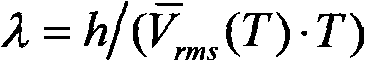Patents
Literature
161 results about "Seismic wave propagation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
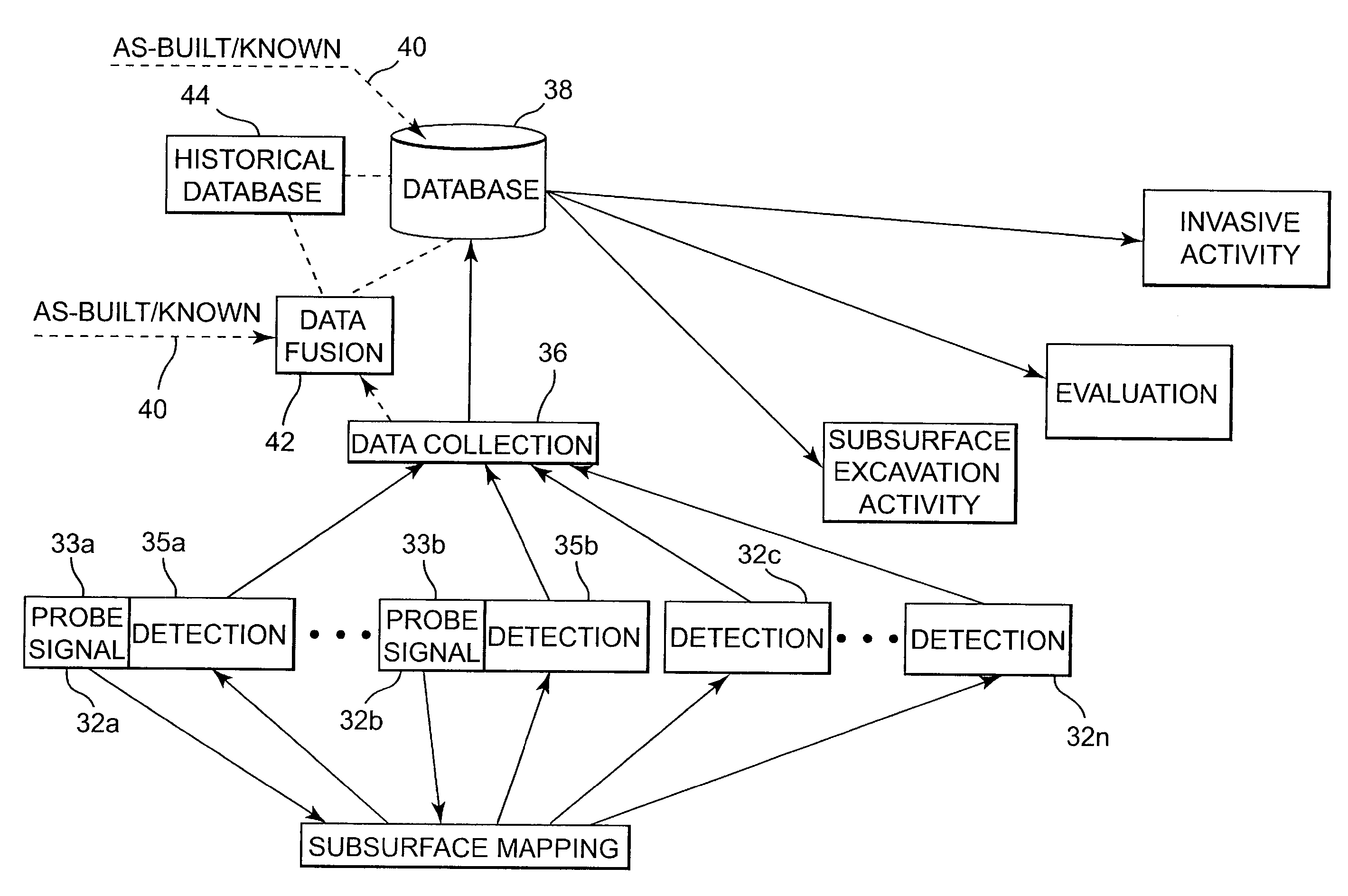
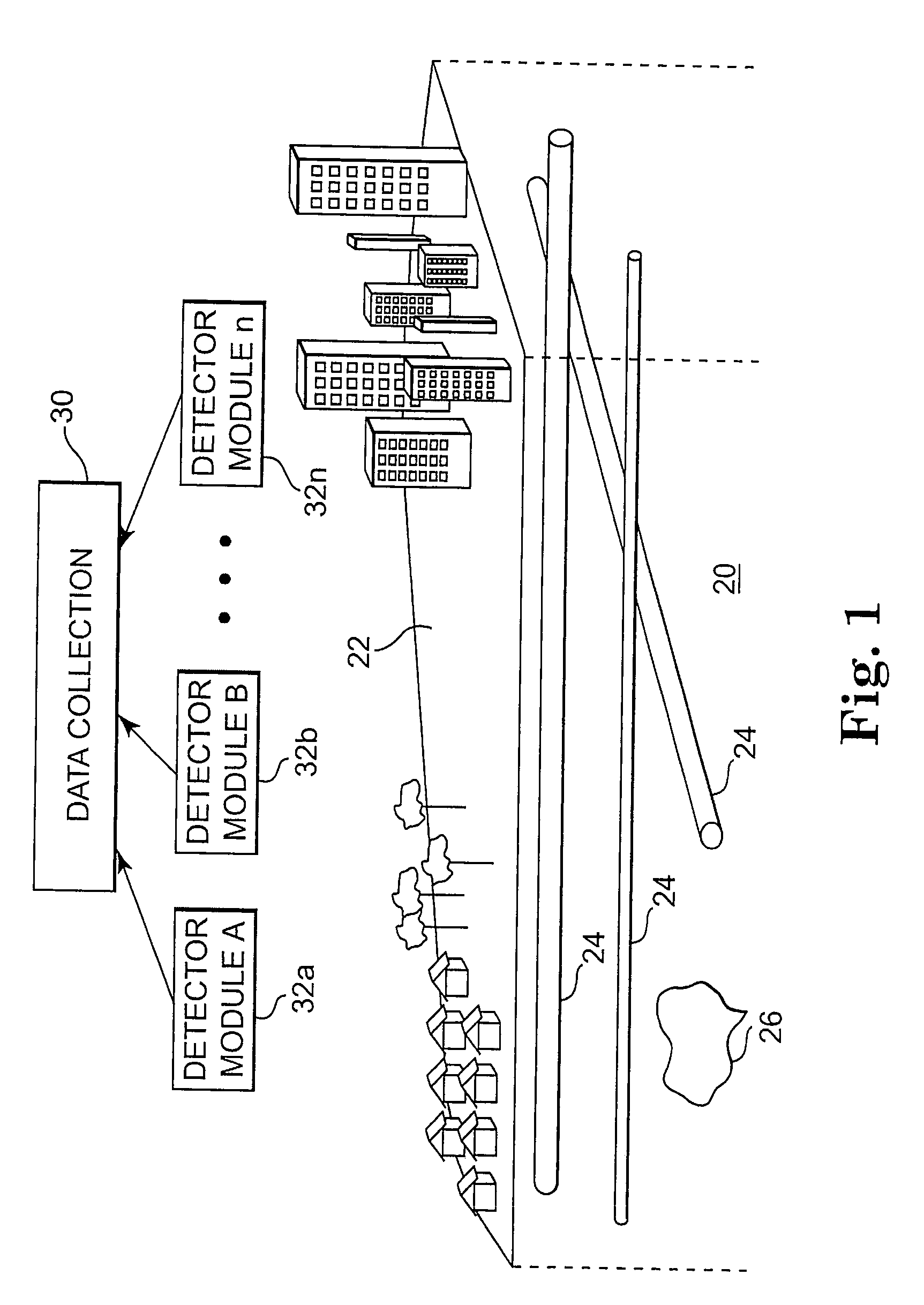
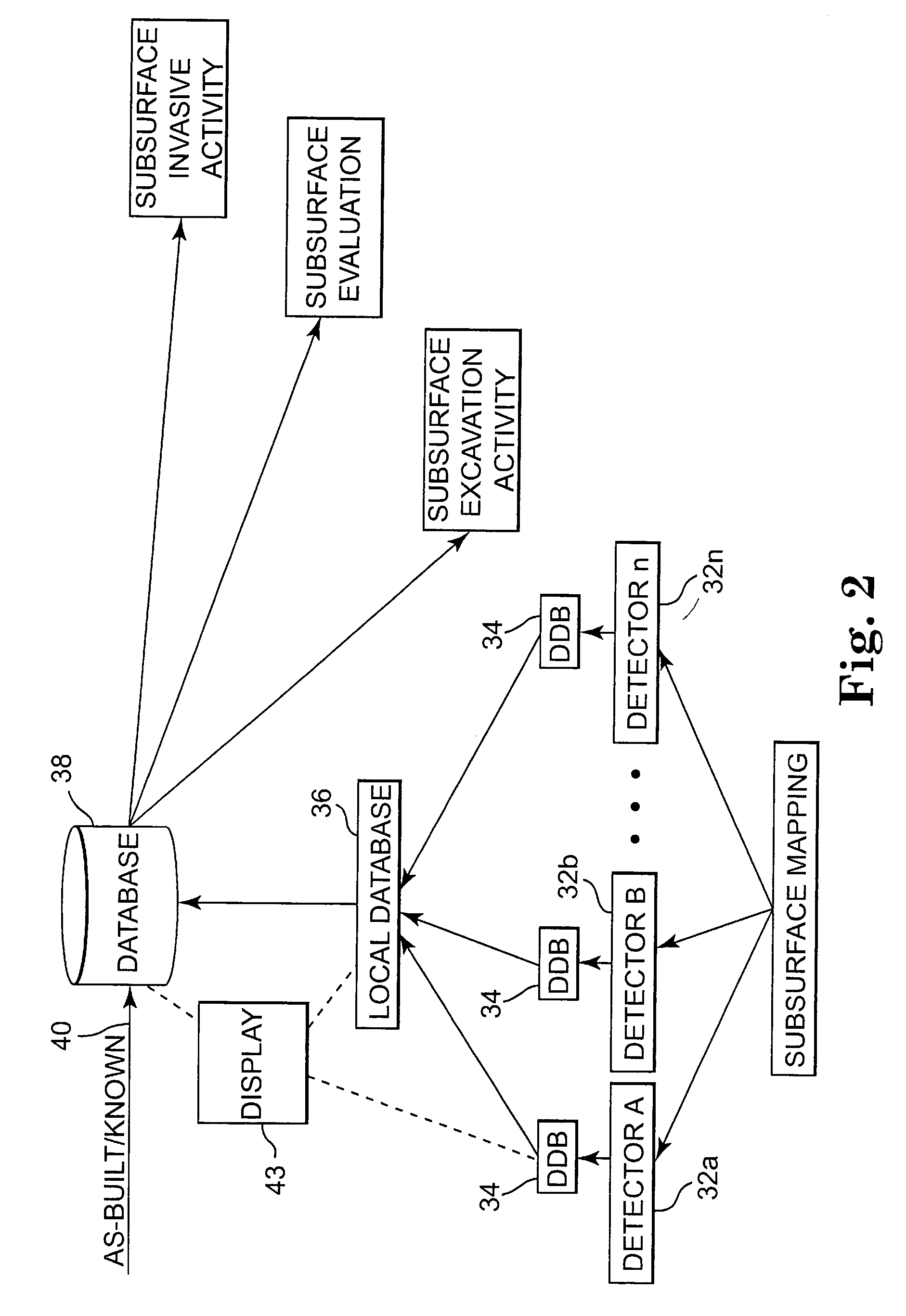
Underground utility detection system and method
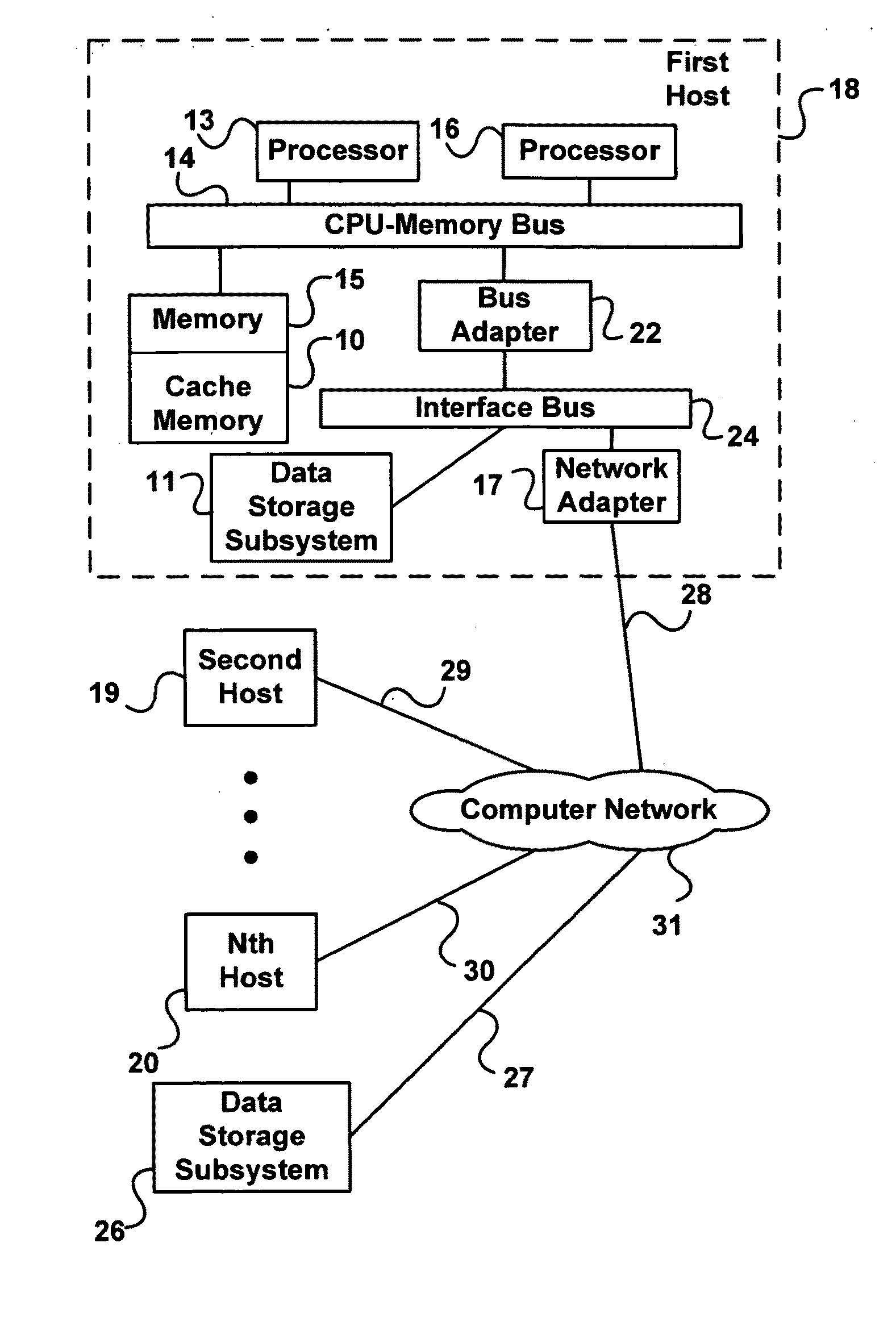
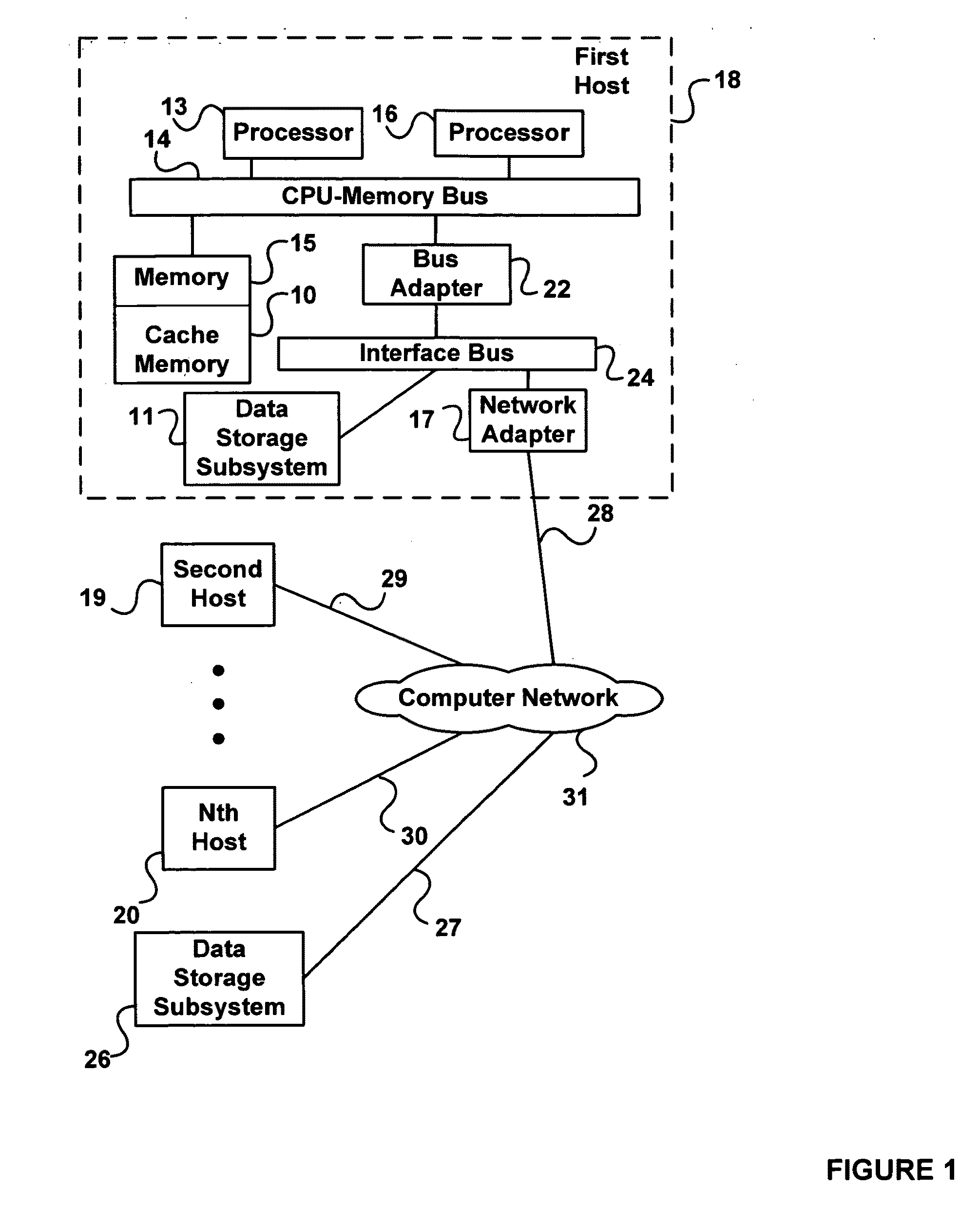
Systems and methods provide for detection of one or more underground utilities. Radar waves and seismic waves of about the same wavelength are generated and communicated into a subsurface. Radar and seismic response signals resulting from communication of the radar and seismic waves into the subsurface are concurrently received. Data associated with the received radar and seismic response signals are stored. One or more underground utilities within the subsurface is / are detected using the stored data. The underground utilities may include metallic and non-metallic utilities.
Owner:VERMEER MFG CO
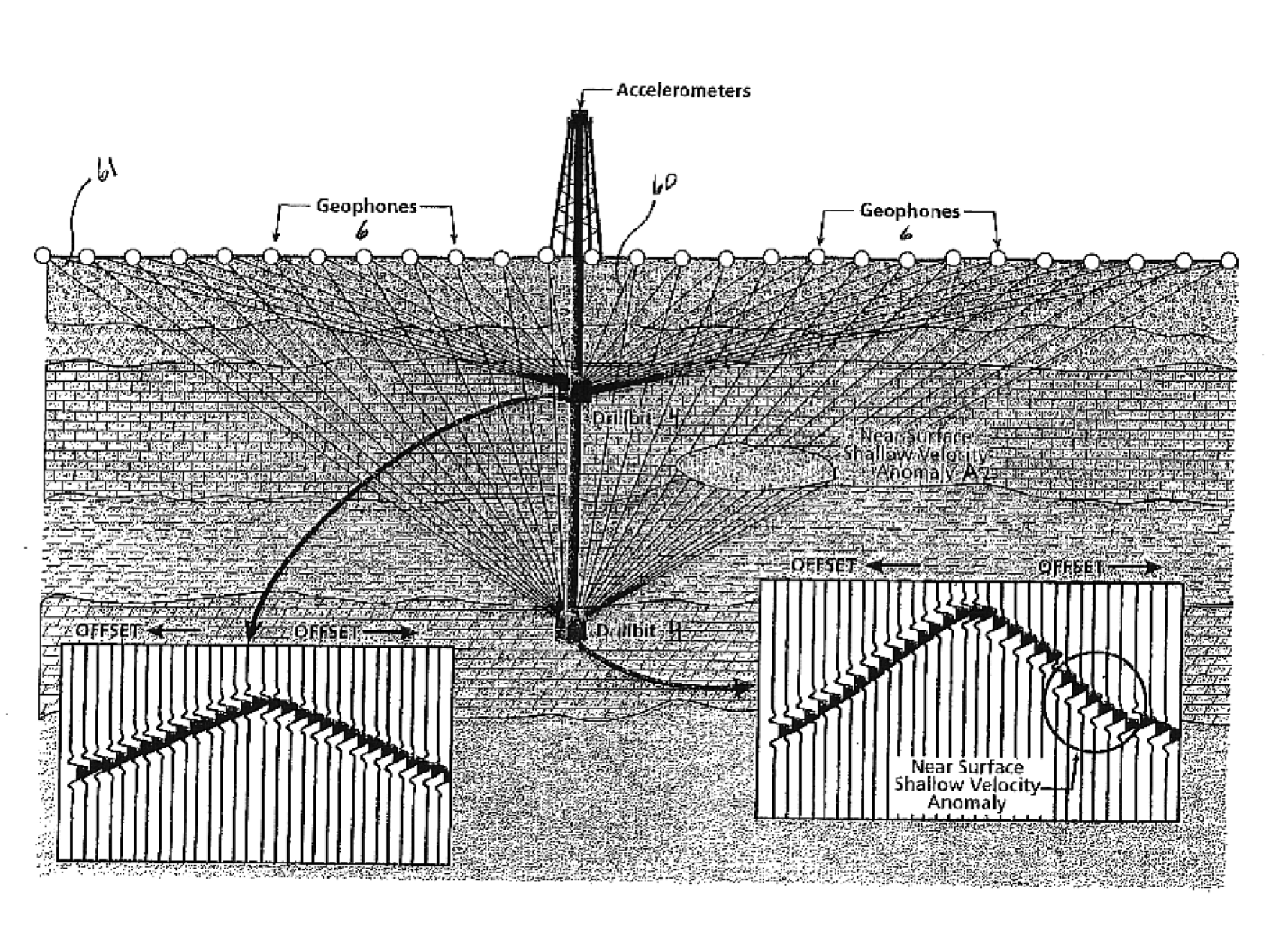
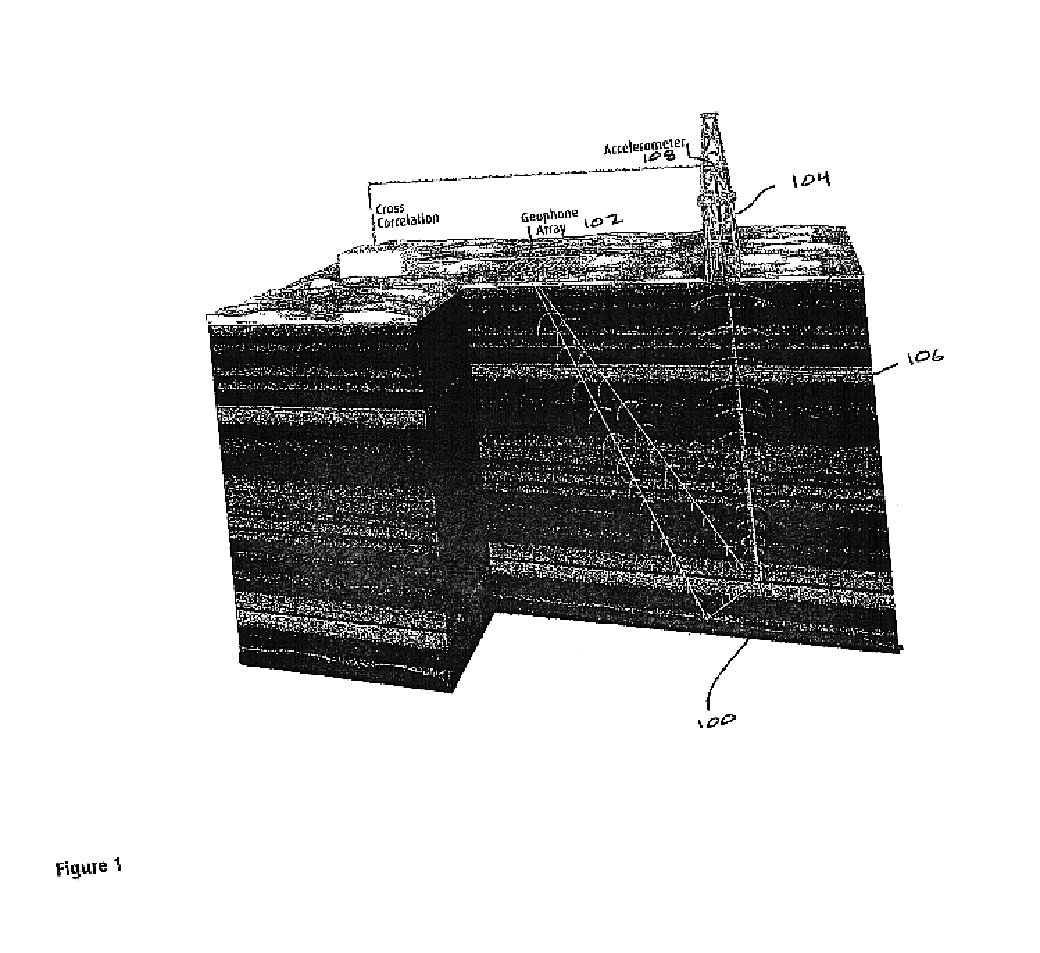
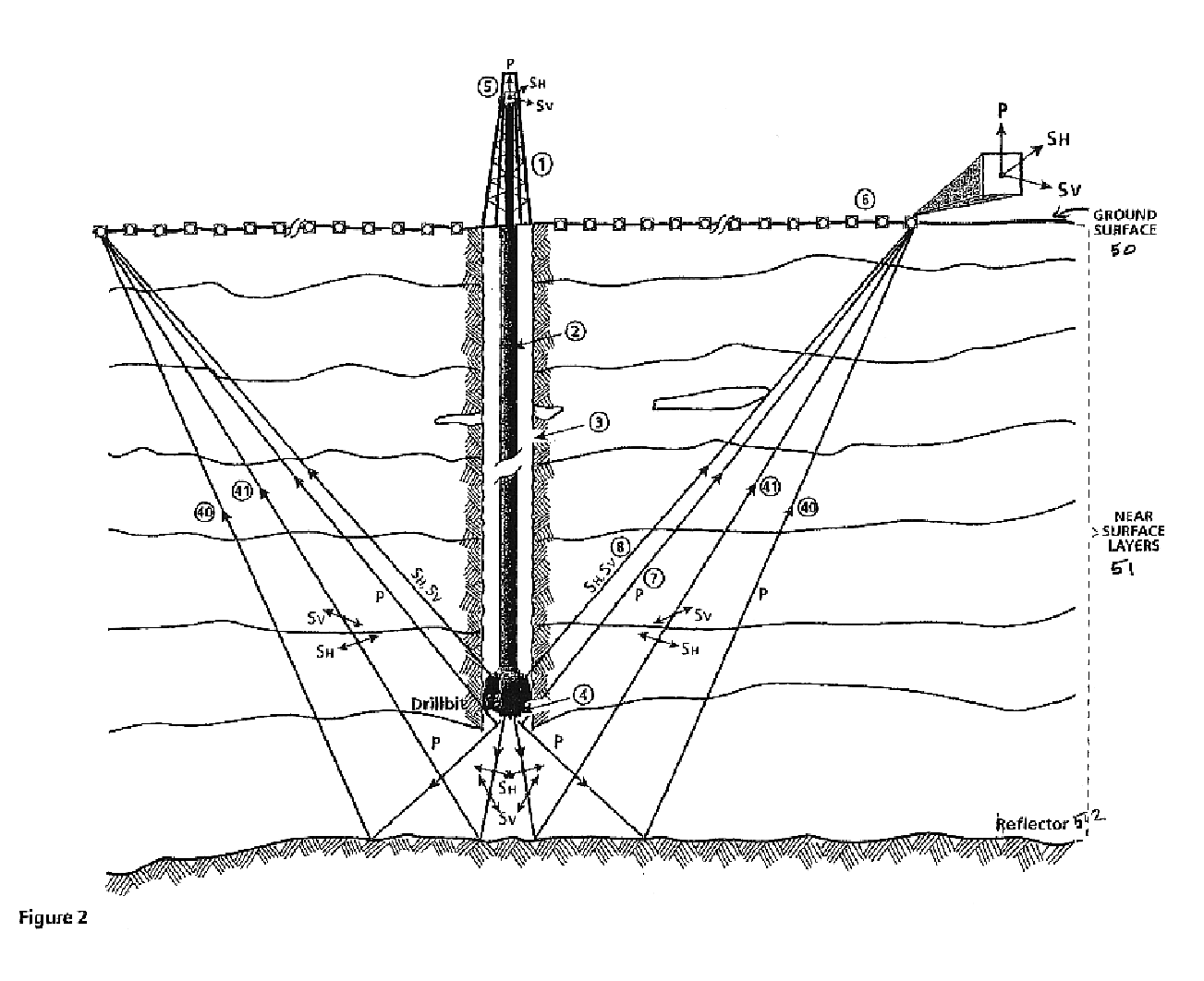
Use of drill bit energy for tomographic modeling of near surface layers
InactiveUS6868037B2Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSeismic signal processingSurface layerWell drilling
A method for tomographic modeling of seismic wave travel times from well drilling records generated by drill string vibrations during drilling and identifying in the recorded vibration at least one of direct, reflected, refracted, converted and diving waves so as to measure wave velocity in near surface layers.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
Estimation of propagation angles of seismic waves in geology with application to determination of propagation velocity and angle-domain imaging
InactiveUS20100114494A1Accurate measurementAccurate imagingSeismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsPeak valueDomain imaging
The invention relates to methods and computer-readable medium to implement computing the propagation velocity of seismic waves in the earth. The invention computes the true propagation velocity of seismic waves in the earth, which is a condition of obtaining an accurate image of subsurface geology that can be used to prospect for oil and gas deposits. In an embodiment, the method of computing the propagation velocity of seismic waves in earth, includes providing an estimate of the propagation velocity, generating a time shift gather using a depth migration at a plurality of locations of the earth, converting each of the time shift gathers to a semblance gather, transforming each semblance gather into a velocity gather whose energy peaks represent a root-mean-square average of the propagation velocity along the forward and backward path between earth's surface and a point of the subsurface geology, and converting the energy peaks to the propagation velocity.
Owner:SEIMAX TECH LP
Method and device for analyzing dispersion and attenuation of unsaturated double-porosity medium earthquake waves
ActiveCN102508296AGood physical achievabilitySeismic signal processingSeismology for water-loggingPorositySeismic wave propagation
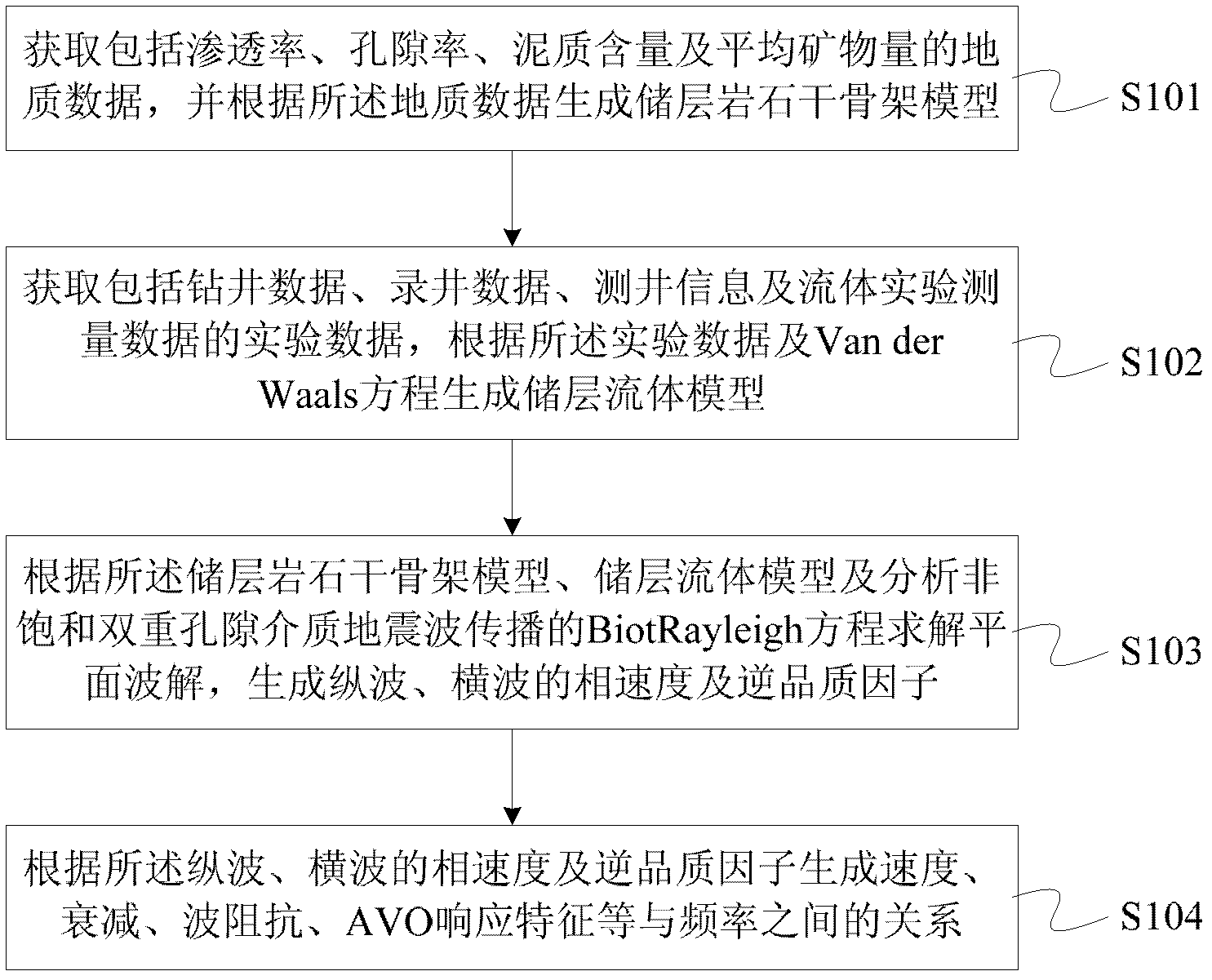
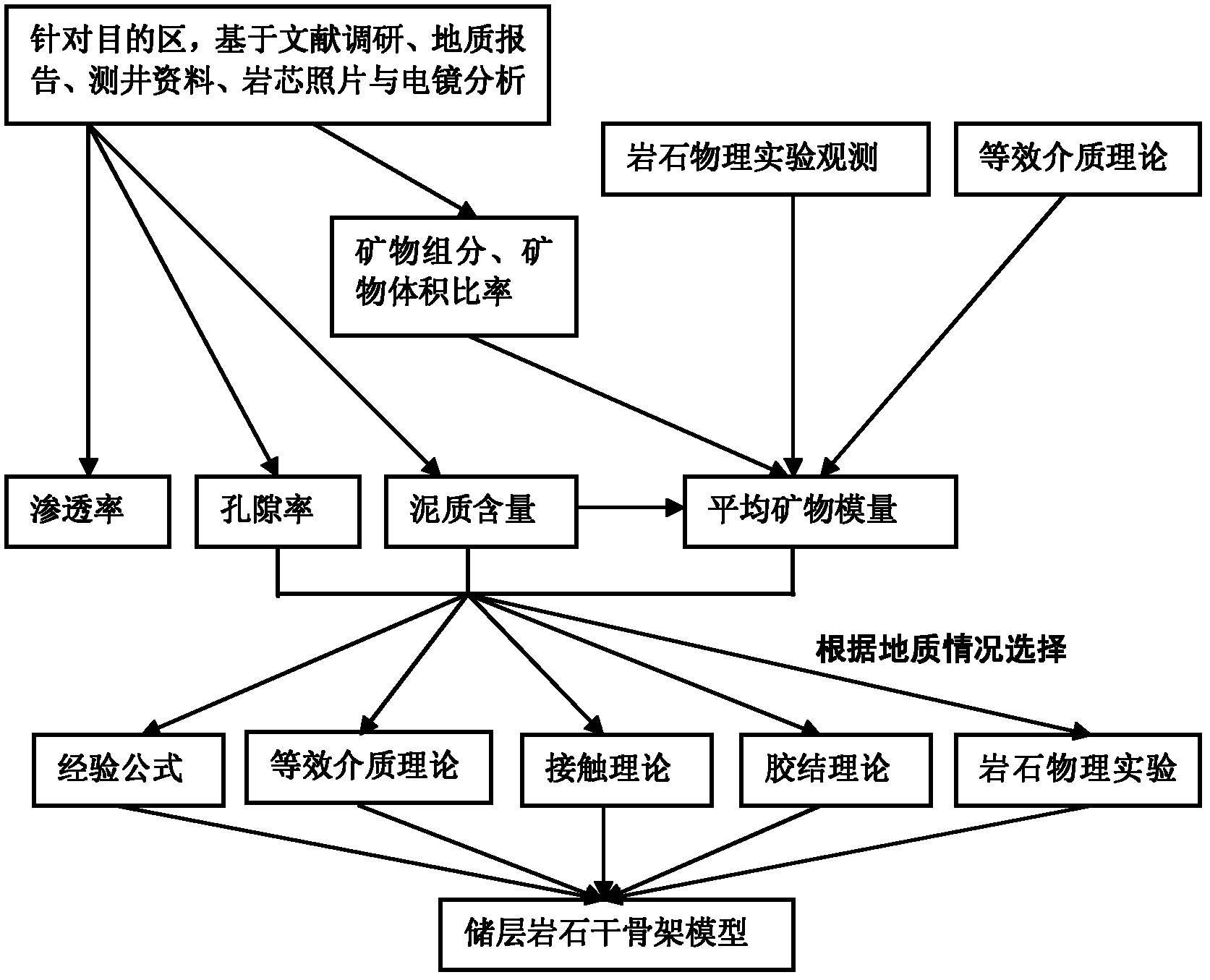
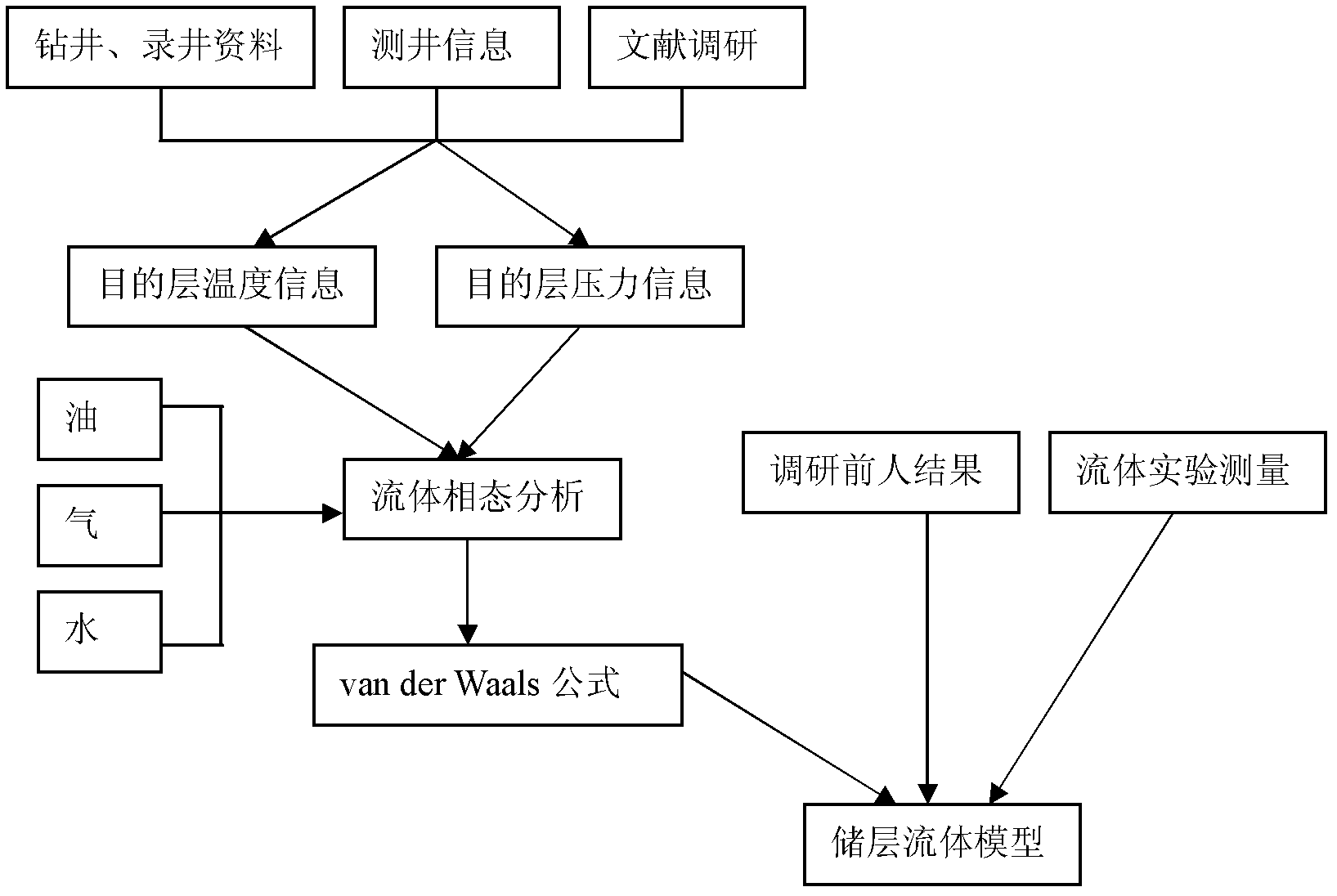
The invention discloses a method and a device for analyzing the dispersion and attenuation of unsaturated double-porosity medium earthquake waves. The method comprises the following steps of: 1, acquiring geological data including penetration rate, porosity, shale content and mineral components and generating a reservoir rock dry framework model according to the geological data; 2, acquiring measured data including drilling data, logging data, logging information and fluid experiment measured data and generating a reservoir fluid model according to the measured data and a Van derWaals equation; 3, solving plane waves according to the reservoir rock dry framework model, the reservoir fluid model and a Biot-Rayleigh equation for describing the spread of the unsaturated double-porosity medium earthquake waves, and generating phase speed and inverse quality factors of longitudinal waves and horizontal waves; and 4, generating relationships between frequency and each of speed, attenuation,wave impedance, AVO (Amplitude Versus Offset) response characteristic and the like according to the phase speed and inverse quality factors of the longitudinal waves and the horizontal waves.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Anisotropic three-dimensional prestack time migration method
InactiveCN102141633AImprove imaging effectAccurate homing and margin protectionSeismic signal processingMineral SourcesData acquisition
The invention provides an anisotropic three-dimensional prestack time migration method which is applied to processing reflection seismic data in seismic exploration and relates to a prestack time migration method aiming at three-dimensional seismic data acquisition. The method takes into account the effect of the velocity anisotropy of an earth medium on the travel time and the amplitude value propagated by a seismic wave and can independently determine the migration velocity and the anisotropic parameters during the migration process, therefore, a migration image which is accurately homed and is preserved in amplitude is obtained. The method determines the three-dimensional time-varying migration aperture in an anisotropic medium according to an underground structure time-varying inclination angle and can simultaneously press the migration noise during the migration process. With the adoption of the method, the efficient and parallel calculation is realized through reasonable distribution of the seismic data among compute nodes of a cluster computer. The method has the key point that the travel time, the amplitude value and the imaging weight coefficients of the seismic wave and an incident angle in the anisotropic medium are solved with the application of a one-way wave operator with deep migration and the steady phase point principle; and has the important application value for oil-gas and mineral resource exploration.
Owner:INST OF GEOLOGY & GEOPHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
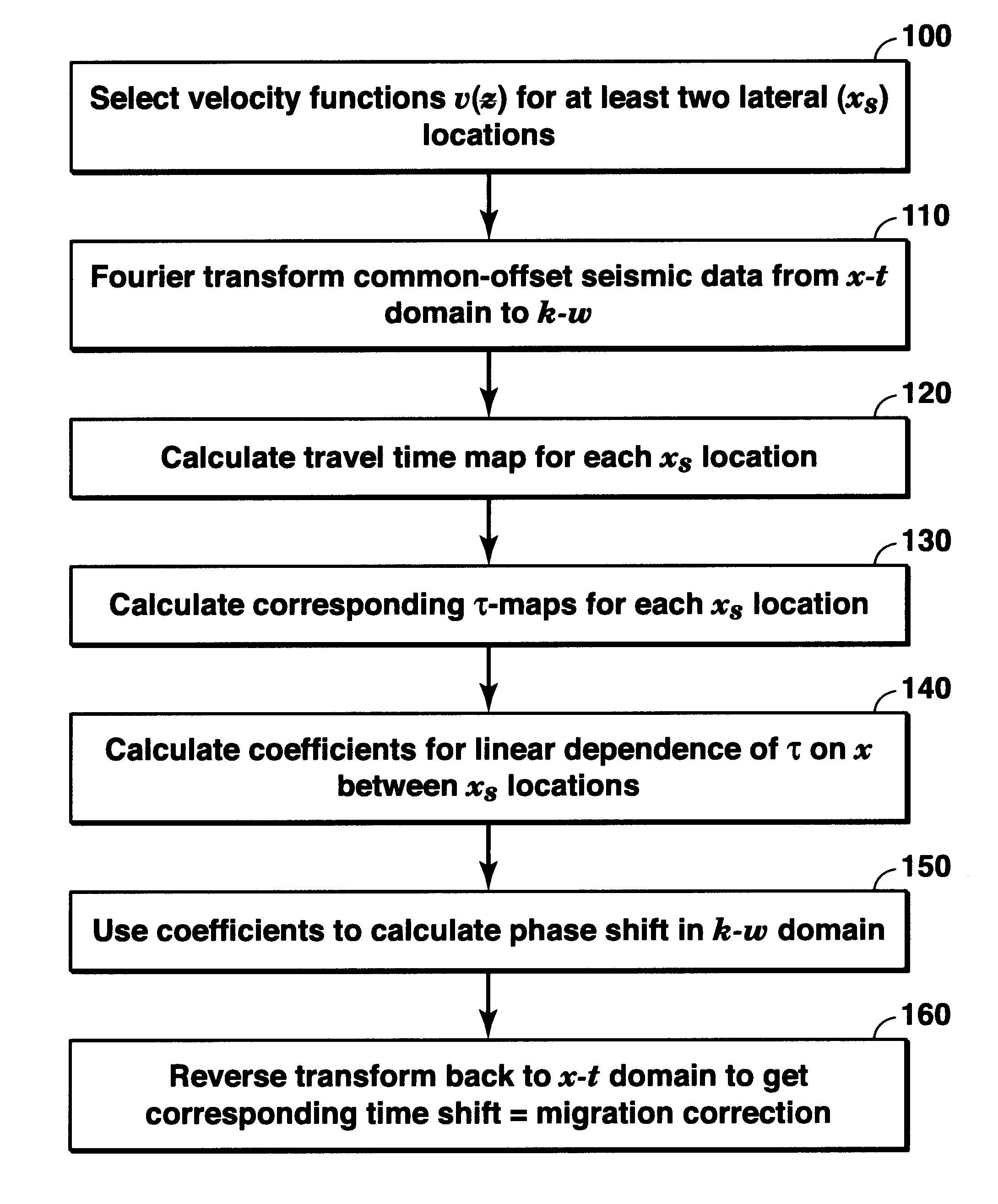
Method for compensating mild lateral velocity variations in pre-stack time migration in the frequency-wave number domain
InactiveUS6865489B2Seismic signal processingPermeability/surface area analysisFrequency wavePhase shifted
A method for performing pre-stack time migration of seismic data in a region where the subsurface seismic wave propagation velocity varies in both the vertical direction and a horizontal direction. The migration is performed in the wave number—frequency domain and involves using travel time maps to find a linear fitting of the migration phase shift for a given ray parameter and at a given vertical depth versus horizontal position. The slope and intercept parameters from the linear fit are used to adjust a known pre-stack time migration equation, with the accuracy of the linear approximation requiring mild horizontal velocity variation.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
Direct prestack time migration method for three-dimensional seismic data acquired from irregular surfaces
InactiveCN102193109AAvoid difficultiesReduce processing linksSeismic signal processingLand acquisitionSurface velocity
The invention discloses a direct prestack time migration method for three-dimensional seismic data acquired from irregular surfaces, and the method is applied to the processing on reflected seismic information in seismic exploration. The method can be used for directly carrying out three-dimensional seismic data migration imaging (at different elevations) on shot points and geophone points acquired from irregular surfaces without statically correcting a processing process. In the method, no vertical emergence and incidence assumption is performed on nearsurface seismic wave propagation, therefore, the method can adapt to the situations which have no obvious low velocity region and velocity-reduction region such as high-velocity rock outcropping, and the like. In the method, the seismic wave propagation in near surfaces or stratums is described by using two equivalent speed parameters; and the two equivalent speed parameters can be determined according to the straightness of lineups inmigrated gathers, thereby avoiding the difficulties in near-surface velocity modeling. By using the method disclosed by the invention, the gathers subjected to migration can be subjected to remainingstatic correction, thereby effectively compensating the inherent errors existing in a land acquisition technology. The method has important application value in oil, gas and mineral resource exploration in complex surface areas.
Owner:INST OF GEOLOGY & GEOPHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
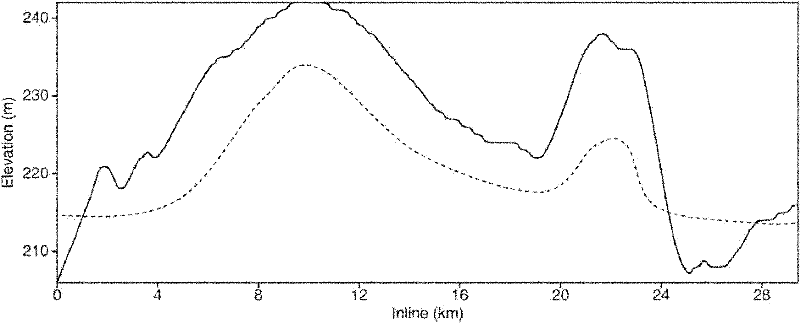
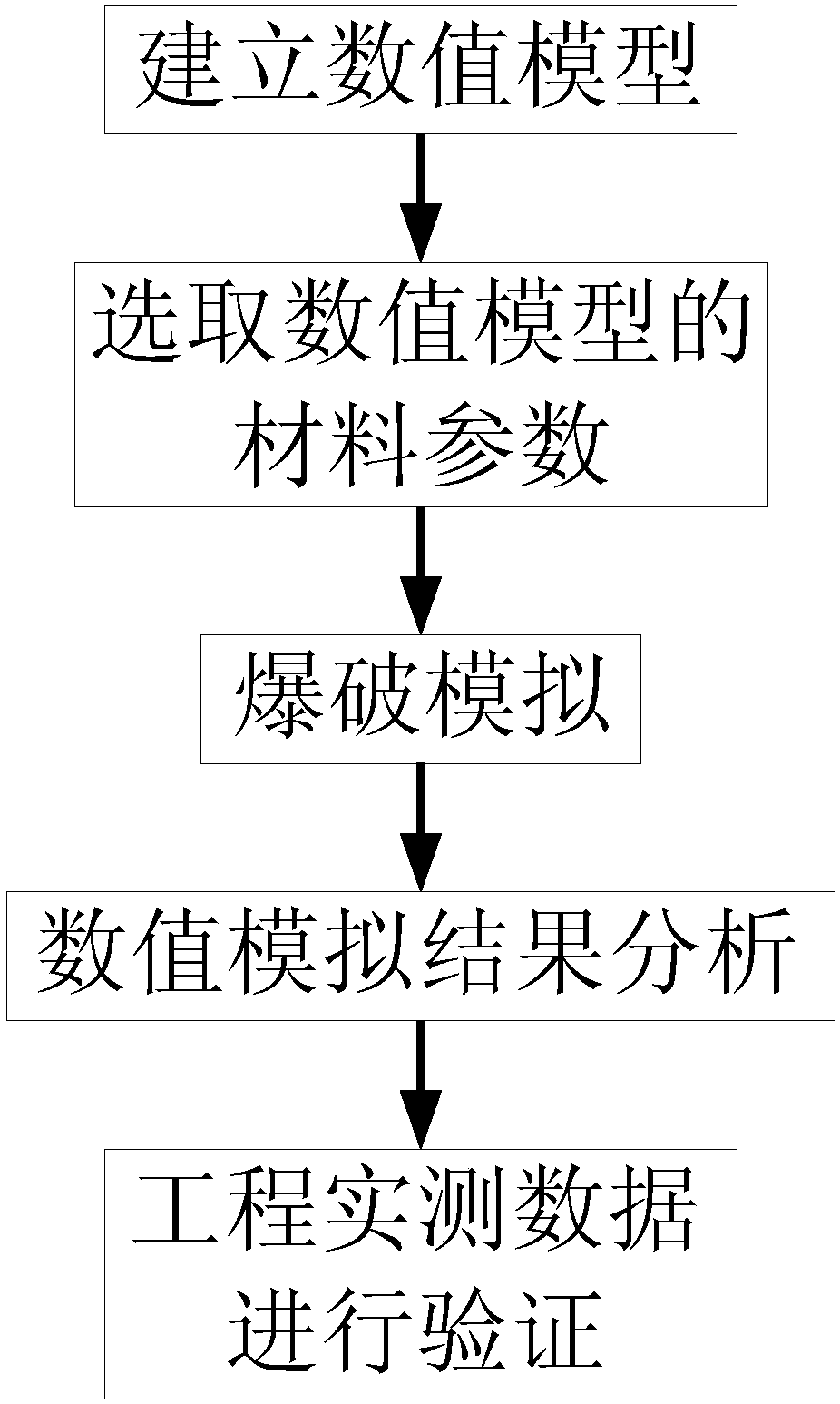
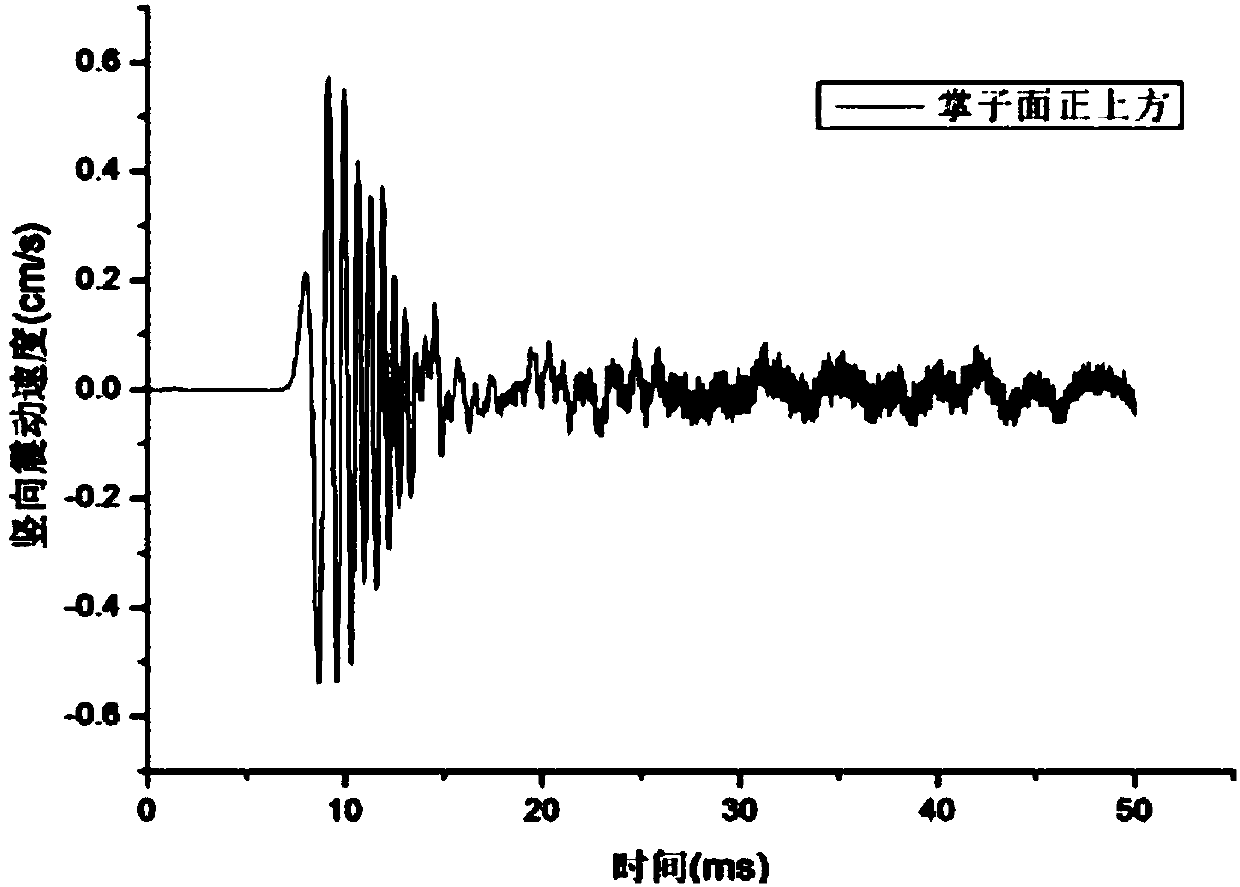
Blast construction method of shallow-buried railway tunnel in underneath pass of civil house weak segments
The invention discloses a blast construction method of a shallow-buried railway tunnel in underneath pass of civil house weak segments. The method includes the following steps that a, according to characteristics of the shallow-buried railway tunnel in underneath pass of the civil house weak segments, a numerical value model is established; b, material parameters corresponding to the numerical value model of the shallow-buried railway tunnel in underneath pass of the civil house weak segments are selected; c, blasting simulation of the shallow-buried railway tunnel in underneath pass of the civil house weak segments is performed; d, numerical value simulation results of different cutting blasting modes are analyzed; e, in combination with engineering measured data of blasting constructionfor the shallow-buried railway tunnel in underneath pass of the civil house weak segments, verification is performed so that the demands of blasting safety vibration control standards can be met. By the utilization of a power finite element method, numerical value simulation analysis is performed to research the rule of a blasting seism, verification is performed in combination with the engineering measured data, and therefore blasting vibration is reflected accurately to a certain degree. The blasting vibration reduction effect of a vibration reduction technical scheme is researched, bases are provided for making a vibration reduction blasting scheme for the tunnel in underneath pass of dense civil houses, and influences on the rule of seismic wave propagation by excavation of the tunnelare researched.
Owner:ZHONGJIAN SUIDAO CONSTR CO LTD
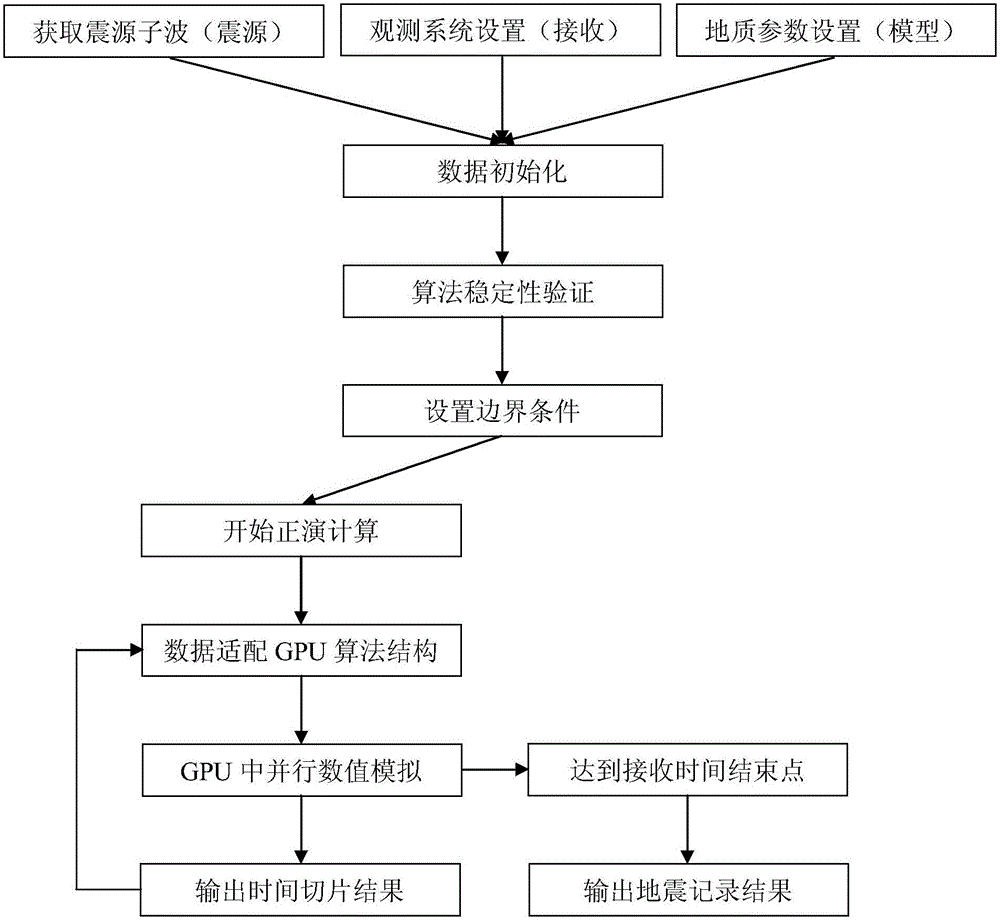
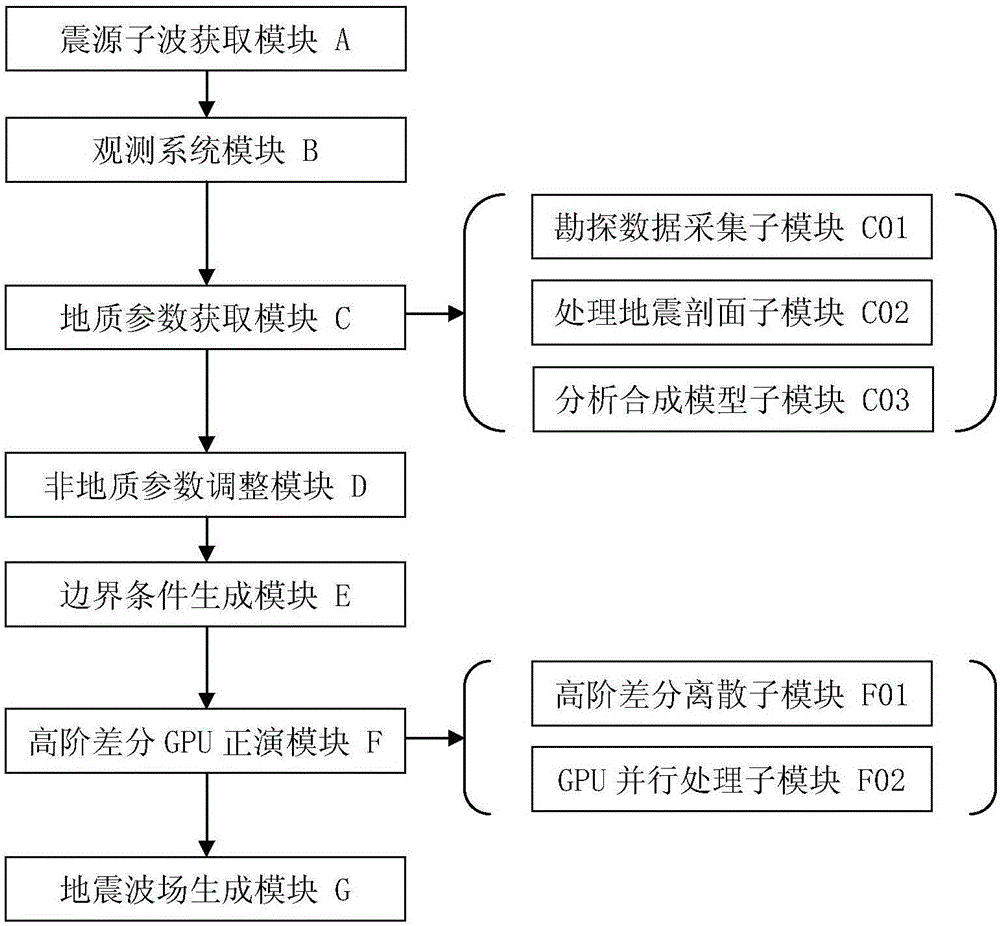
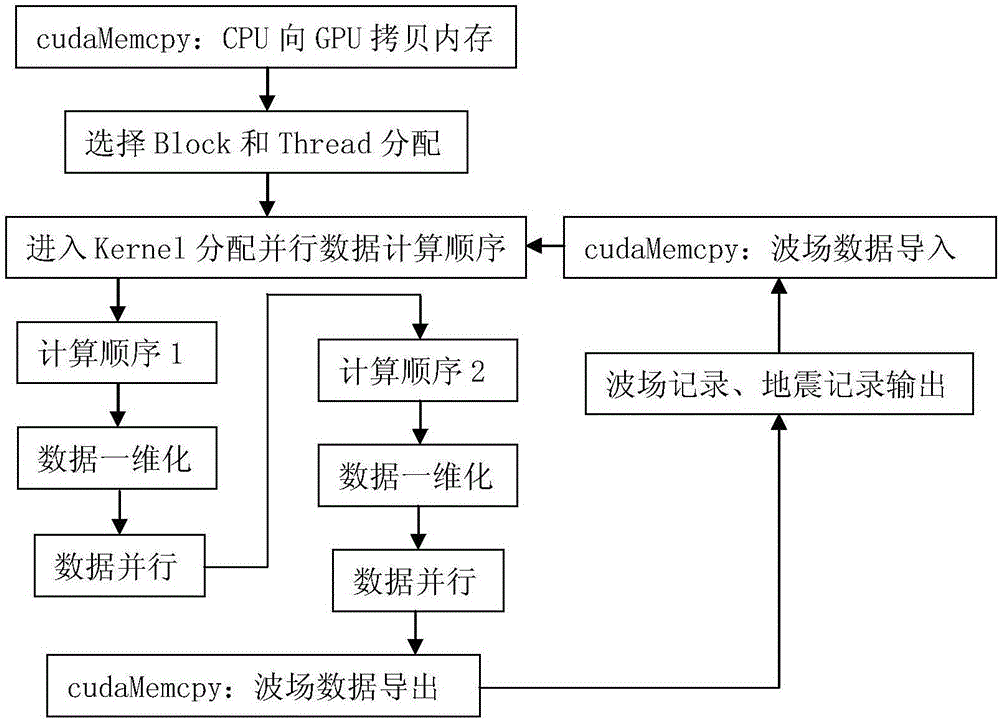
GPU parallel three-dimensional seismic wave field generating method and system
ActiveCN106842320AHigh precisionImprove efficiencySeismic signal processingWave equationPerformance computing
The invention discloses a forward simulation method and system of a three-dimensional seismic wave field based on GPU parallel acceleration and belongs to the technical field of numerical simulation and high-performance computing. According to the method, high-order finite difference is conducted on a seismic wave propagation equation, high-precision explored seismic wave propagation data is obtained through numerical simulation calculation, acceleration processing is conducted on a GPU, and ground seismic recorded data and wave field section results are efficiently generated in a high-precision mode. By adopting the forward simulation method and system, the three-dimensional seismic wave equation can be calculated in a high-precision and high-efficiency mode, the computational efficiency is greatly improved, and the computational accuracy is effectively improved.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
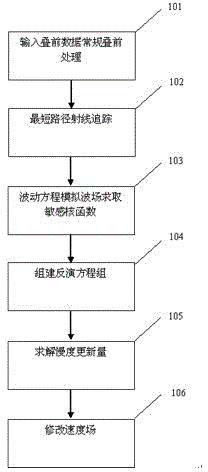
Near-surface tomographic velocity analysis method
InactiveCN104570106ASolve the problem of solving instabilityTrue portrayalSeismic signal processingWave equationClassical mechanics
The invention discloses a near-surface tomographic velocity analysis method. The near-surface tomographic velocity analysis method comprises the following steps: picking up travel time of first arrival by aiming at pre-stack data, and obtaining an initial model reflecting underground medium velocity distribution by pre-stack processing; performing a shortest path ray tracing method on the model to obtain simulated travel time; performing wave field simulation on the model by utilizing a frequency domain wave equation to obtain a sensitive kernel function reflecting disturbance of a medium to the travel time; establishing a corresponding inversion equation and solving to obtain a slowness updating amount. According to the tomographic velocity analysis based on the Fresnel zone, the problem that the solution of a large-scale sparse matrix is instable during the traditional temographic velocity analysis based on the ray theory is solved, and the seismic wave propagation rule is more truly portrayed; the near-surface tomographic velocity analysis method has the advantages that the physical geography significance is obvious, the stability is strong, the efficiency is high, and calculation results are more real and reliable.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Methods and computer-readable medium to implement computing the propagation velocity of seismic waves
InactiveUS20100030479A1Accurate imagingSeismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsPeak valueSubsurface geology
The invention relates to methods and computer-readable medium to implement computing the propagation velocity of seismic waves in the earth. The invention computes the true propagation velocity of seismic waves in the earth, which is a condition of obtaining an accurate image of subsurface geology that can be used to prospect for oil and gas deposits. In an embodiment, the method of computing the propagation velocity of seismic waves in earth, includes providing an estimate of the propagation velocity, generating a time shift gather using a depth migration at a plurality of locations of the earth, converting each of the time shift gathers to a semblance gather, transforming each semblance gather into a velocity gather whose energy peaks represent a root-mean-square average of the propagation velocity along the forward and backward path between earth's surface and a point of the subsurface geology, and converting the energy peaks to the propagation velocity.
Owner:SEIMAX TECH LP
Seismic wave attenuation and speed dispersion prediction method in complex heterogeneous reservoir medium
The invention provides a seismic wave attenuation and speed dispersion prediction method in a complex heterogeneous reservoir medium and belongs to the hydrocarbon fossil energy exploration and development field. The method comprises the following steps of (1) according to lithology, a fluid containing property, a fluid saturation Sg of the heterogeneous reservoir medium, carrying out two-dimensional rock physical modeling on a reservoir rock unit; (2) implementing a conventional two-dimensional seismic wave propagation simulation numerical experiment on a physical modeling acquired from the step (1), through applying a single source, realizing propagation of an elastic wave in the reservoir medium, acquiring a stress field and a speed field of each time layer and calculating a strain field of any one point in a space; (3) when the conventional two-dimensional seismic wave propagation simulation numerical experiment is completed, recording time records of the stress field and the strain field; (4) based on a macro average principle, calculating an average stress and a strain field of an REV unit, wherein psi belongs to {tauxx, tauzz, epsilonxx and epsilonzz}.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +2
Initiation Control Method for Reducing Blasting Vibration Effect
InactiveCN102269553AEnsure safetyReduce the impact of blasting vibrationBlastingDetonatorVibration control
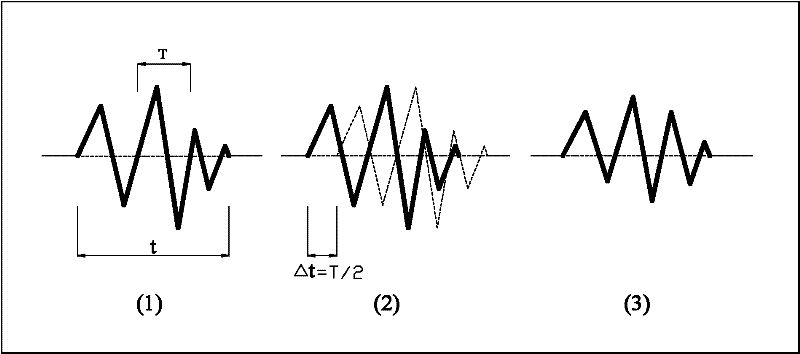
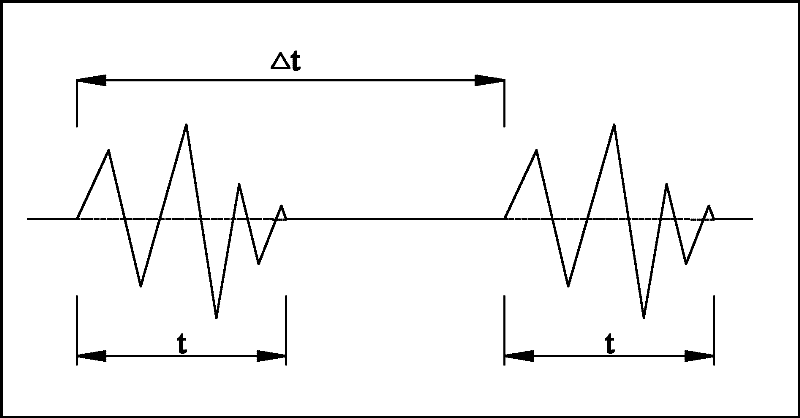
The invention discloses a detonation control method for reducing blasting vibration effect, which uses digital electronic detonators to reduce blasting vibration effects by controlling the number of each detonator section. One is: the selection of the number of detonator segments adopts the principle of mutual interference between blasting vibration peaks and troughs to reduce vibration, specifically: the delay time between the holes of each row of blast holes adjacent to the detonator detonator ΔTi = T / 2-1000*a / c, where T is the main vibration period of the blasting vibration, in milliseconds; ΔTi is the delay time between adjacent blastholes for sequential detonation, in milliseconds; a is the distance between blastholes, in meters; c is the propagation velocity of seismic waves in rocks, The unit is m / s; the inter-row delay between adjacent rows: ΔTj=nΔTi, ΔTj is the inter-row delay time, and the unit is millisecond; n is the number of adjacent front row detonator segments. The second method is: the selection of the number of each detonator section adopts the principle that the blasting vibration waves are independent of each other and vibration does not superimpose, that is, the inter-hole delay ΔTi=(1.0~1.5)t of sequentially detonating adjacent detonators.
Owner:CHANGJIANG RIVER SCI RES INST CHANGJIANG WATER RESOURCES COMMISSION
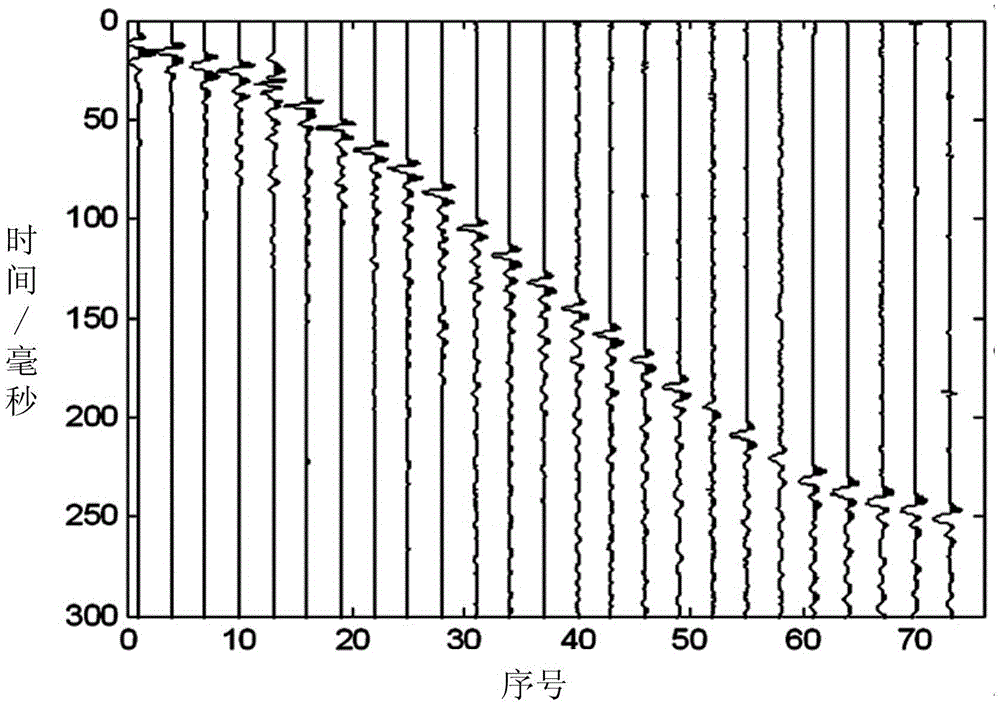
Dispersion curve extracting method for mine channel wave double-component seismic signal
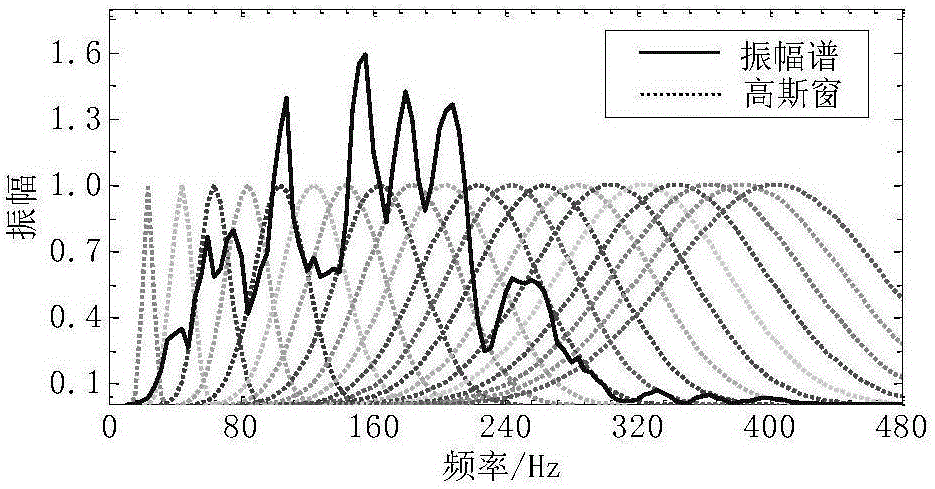
ActiveCN105785440AAccurate dispersion characteristicsHigh precisionSeismic signal processingVibration amplitudeDispersion curve
The invention relates to a dispersion curve extracting method for a mine channel wave double-component seismic signal. The dispersion curve extracting method comprises the steps of firstly acquiring a Love channel wave signal from the mine channel wave double-component seismic signal; performing generalized S transformation on the acquired Love channel groove signal for obtaining a relationship diaphragm between group speed and frequency of the Love channel wave; drawing a line between maximal vibration amplitudes in the relationship diaphragm between the group speed and the frequency, and utilizing the obtained curve as the dispersion curve. According to the dispersion curve extracting method, the width of a Gauss window in S transformation is changed by means of a linearly changed adjusting parameter, thereby improving precision of a channel wave signal dispersion curve. Furthermore, according to the method, before generalized S transformation, propagation direction and polarization angle of the seismic wave are determined through calculation according to an energy distribution criterion of a longitudinal wave in the acquired signal in a double-component detector. Coordinate rotation is performed for obtaining the Love channel wave signal which horizontally vibrates in the propagation direction of the vertical wave. Then dispersion calculation is performed on the signal. The dispersion characteristic of the obtained dispersion curve is more accurate.
Owner:HENAN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
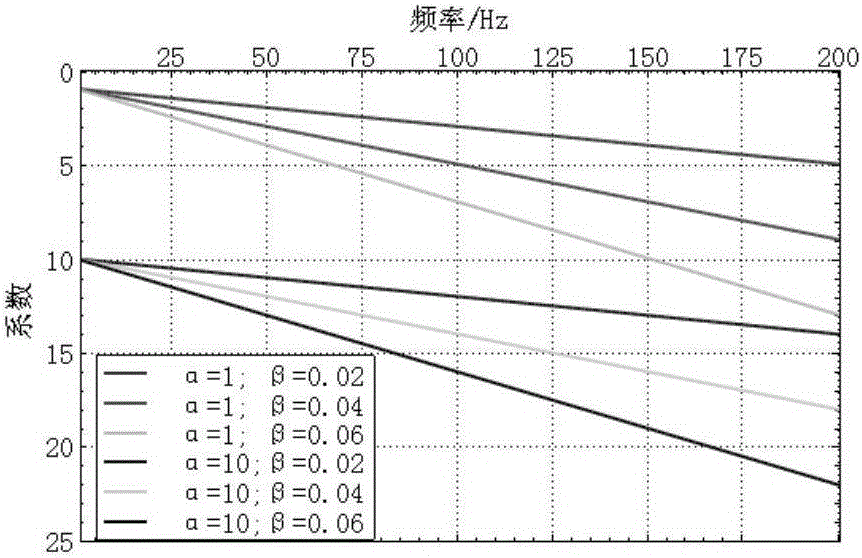
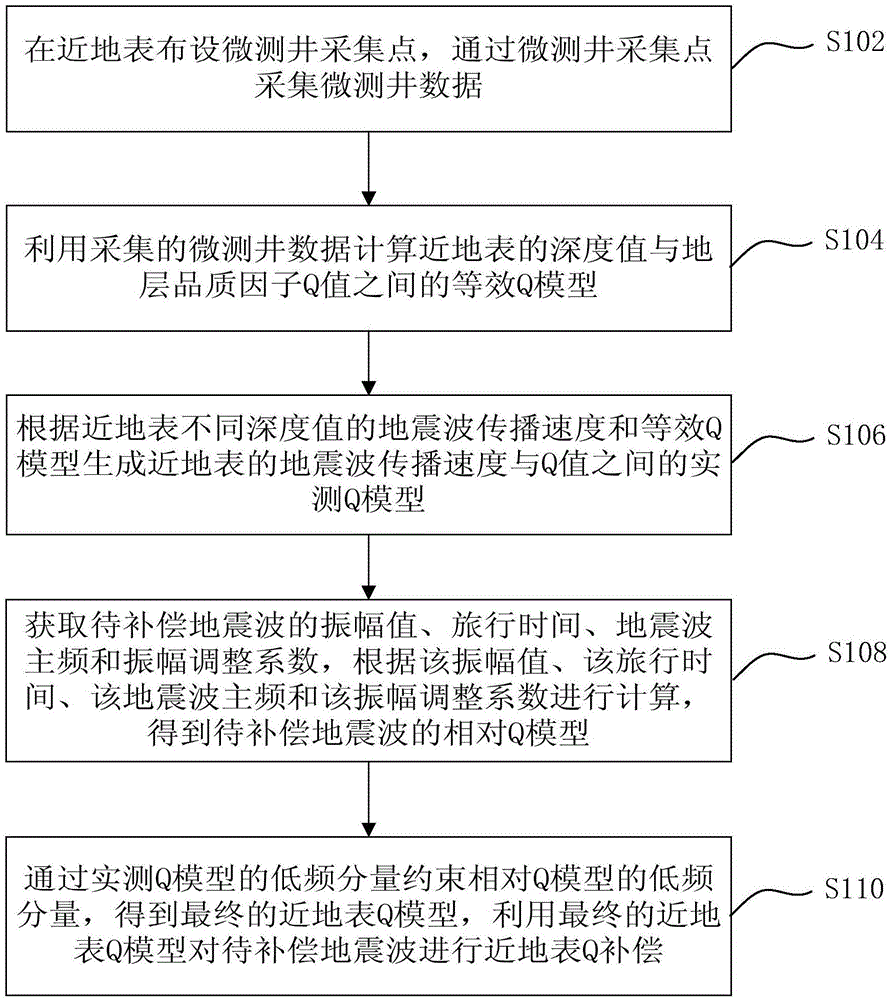
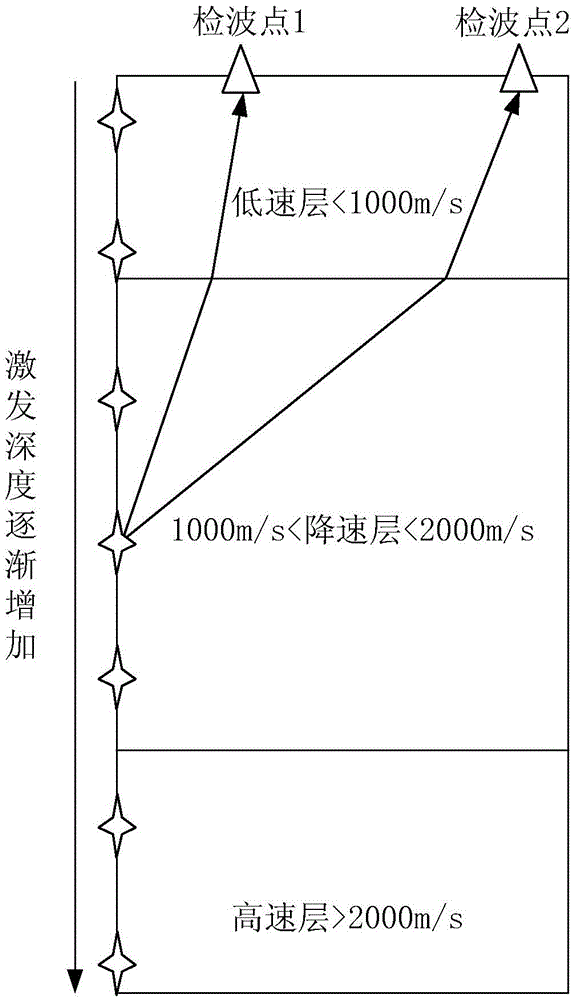
Seismic-wave near-surface stratum quality factor compensation method and device
The invention provides a seismic-wave near-surface stratum quality factor compensation method and device. The method comprises: setting micro-logging acquisition points near the earth surface and acquiring micro-logging data via the micro-logging acquisition points; calculating an equivalent Q model between a depth value near the earth surface and the stratum quality factor Q value by using the micro-logging data; generating a measured Q model between the seismic-wave propagation velocity near the earth surface and the Q value according to the seismic-wave propagation velocity at different depths near the earth surface and the equivalent Q model; calculating a relative Q model of the to-be-compensated seismic wave in accordance with the amplitude value, the travel time, the seismic-wave main frequency and the amplitude adjustment coefficient of the to-be-compensated seismic wave; and constraining the low-frequency component of the relative Q model by means of the low-frequency component of the measured Q model to obtain a final near-surface Q model, and compensating the near-surface Q for the to-be-compensated seismic wave by using the final near-surface Q model. The invention realizes compensation for the seismic wave near the earth surface and alleviates the problem that in the prior art it is impossible to compensate for the seismic wave near the earth surface.
Owner:蒋立
System and method for computational geology
ActiveUS20140278289A1Simple methodSeismic data acquisitionGeomodellingGeological processSeismic wave propagation
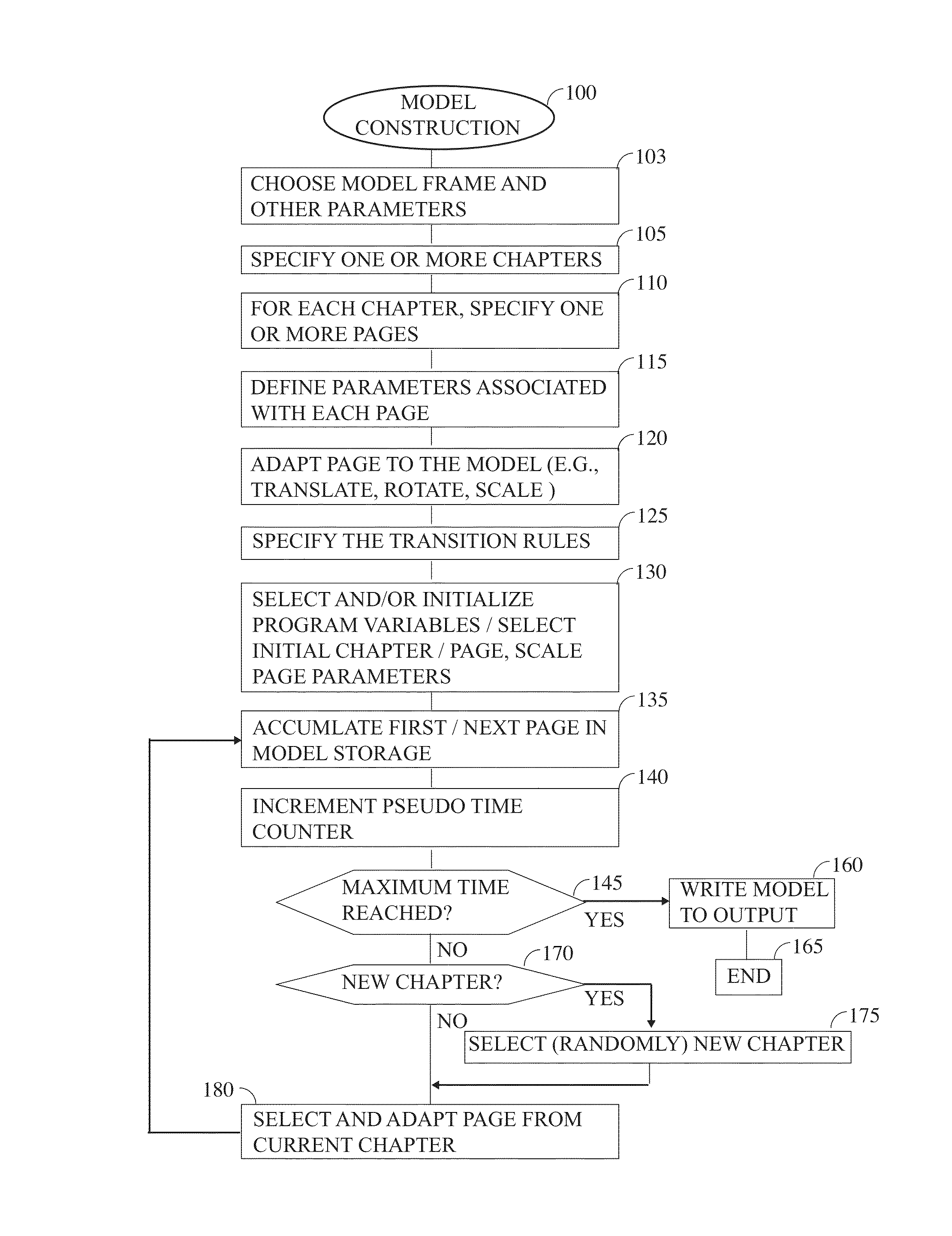
One aspect of the invention is a method for building geologic / stratigraphic models of the earth for the purposes of numerical simulations of phenomena of interest, such as seismic wave propagation, or fluid flow, reservoir simulation, etc. An embodiment of the invention uses stochastic methods to create material property models that have desired statistical properties by numerically simulating deposition of geological layers. The method can create multiple material parameter models from numerical implementations of a variety of geological processes.
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC
Cladded optical fiber grating vibration sensor
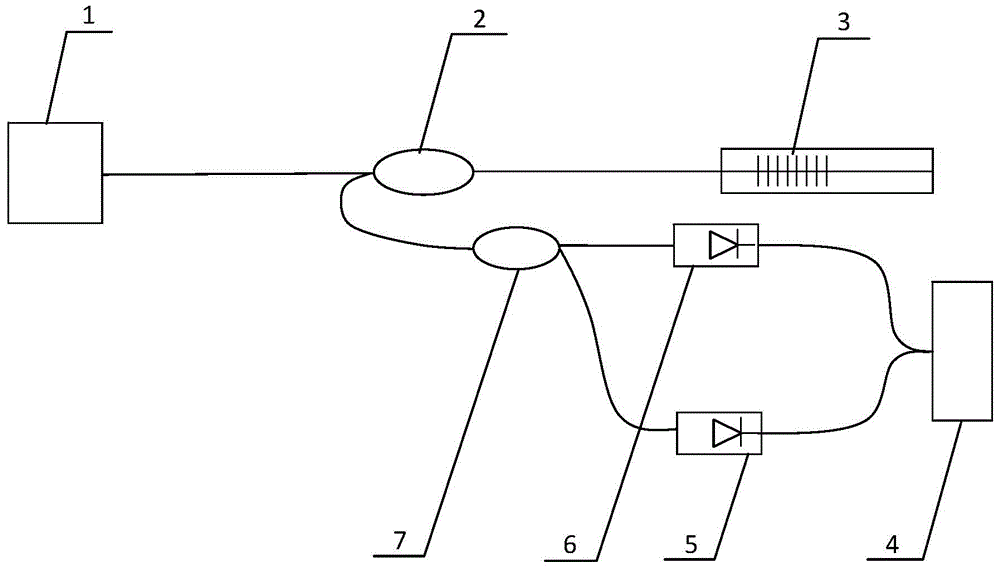
InactiveCN104390694ARealize impending earthquake predictionSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementUsing wave/particle radiation meansStructural deformationGrating
The invention discloses a cladded optical fiber grating vibration sensor. A semiconductor laser is connected with an optical fiber circulator by single-mode optical fibers; the optical fiber circulator is connected with an optical fiber grating sensor and an optical fiber wavelength division multiplexer by the single-mode optical fibers; the optical fiber wavelength division multiplexer is connected with a cladded grating photoelectric detector and a fiber core grating photoelectric detector by the single-mode optical fibers; the cladded grating photoelectric detector and the fiber core grating photoelectric detector are connected with an oscilloscope by coaxial cables; a fiber core gratings is written on thin-core optical fibers; cladded gratings are written on optical fiber claddings. During shock detection of a building, laser emitted by the semiconductor laser is transmitted to the fiber core gratings and the cladded gratings through the optical fiber circulator, vibration of a to-be-detected vibrating body leads to changes of cladding energy distribution reflected by the cladded gratings and changes the energy which enters the single-mode optical fibers in a coupled manner, so that information of vibration direction is obtained, structural deformation of civil engineering such as bridges, tunnels and dams can be detected in real time, and interior structure of earth and earthquake wave propagation characteristics can be researched in order to predict impending earthquake.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV(CN)
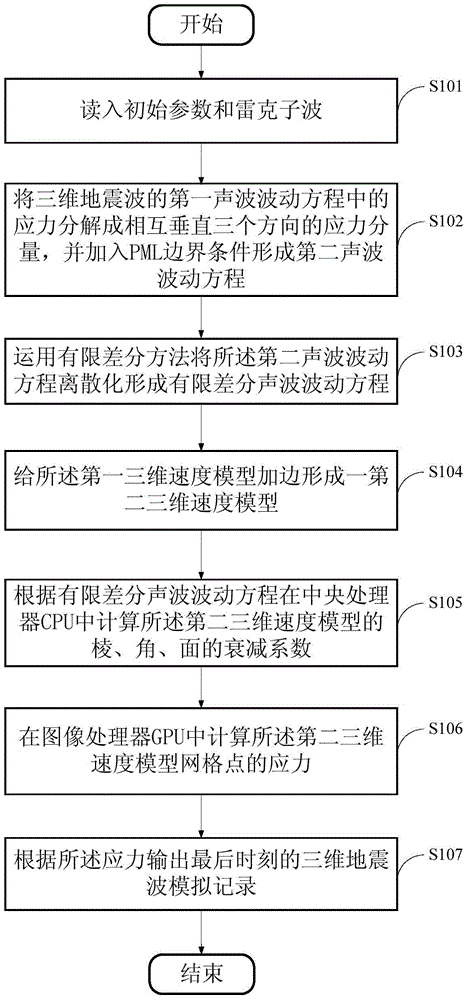
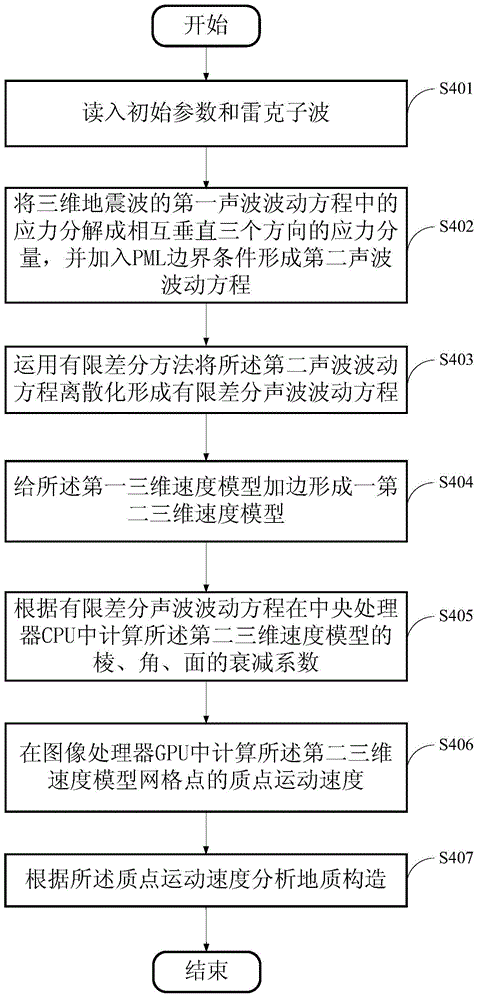
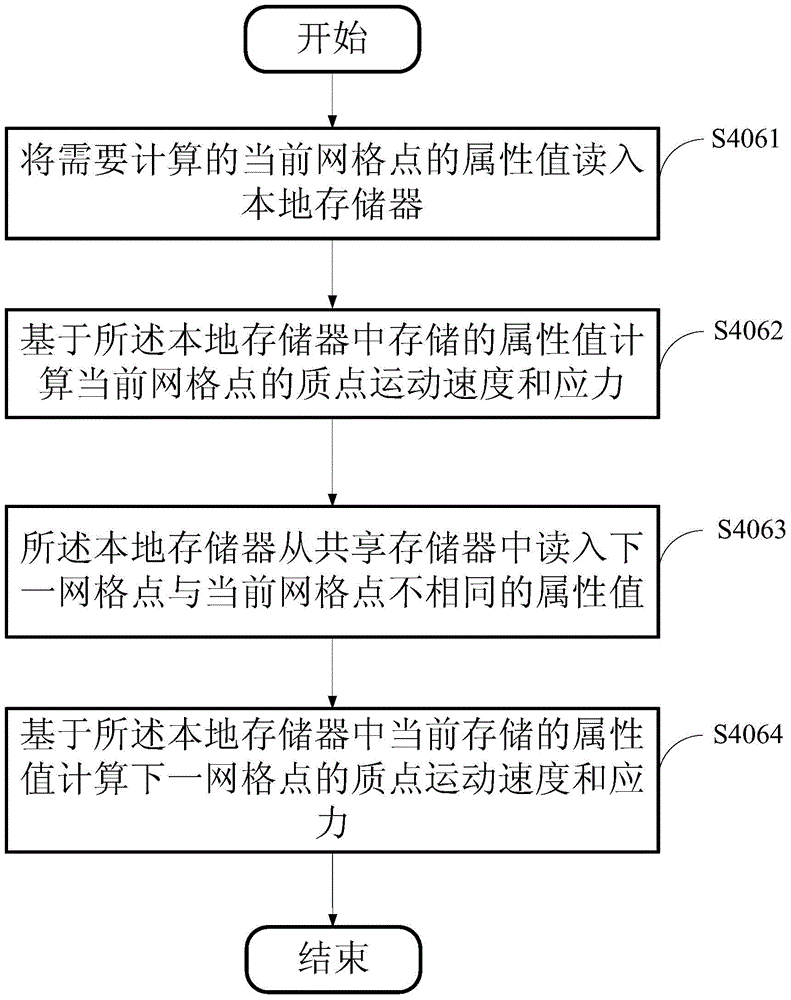
PML boundary three-dimensional seismic wave propagation simulation method utilizing CUDA
InactiveCN105005072AImprove computing efficiencyHigh speedupSeismic signal processingWave equationDiscretization
The present invention provides a PML (Perfectly Matched Layer) boundary three-dimensional seismic wave propagation simulation method utilizing CUDA (Compute Unified Device Architecture), comprising the steps of: reading in an initial parameter and a Ricker wavelet; decomposing a stress in a first acoustic wave fluctuation equation of a three-dimensional seismic wave into stress components in three directions which are mutually perpendicular, and adding a PML boundary condition to form a second acoustic wave fluctuation equation; using a finite difference method to discretize the second acoustic wave fluctuation equation, so as to form a finite difference acoustic wave fluctuation equation; bordering a first three-dimensional speed model to form a second three-dimensional speed model; calculating attenuation coefficients of edges, angles and surfaces of the second three-dimensional speed model in a CPU (Central Processing Unit) according to the finite difference acoustic wave fluctuation equation; calculating stresses of net points of the second three-dimensional speed model in a GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) according to the attenuation coefficients; and outputting a three-dimensional seismic wave simulation record at the last moment according to the stresses. The PML boundary three-dimensional seismic wave propagation simulation method of the present invention can achieve high speed-up ratio and shorten simulation time.
Owner:INST OF GEOLOGY & GEOPHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Ground microseism monitoring anisotropy speed model
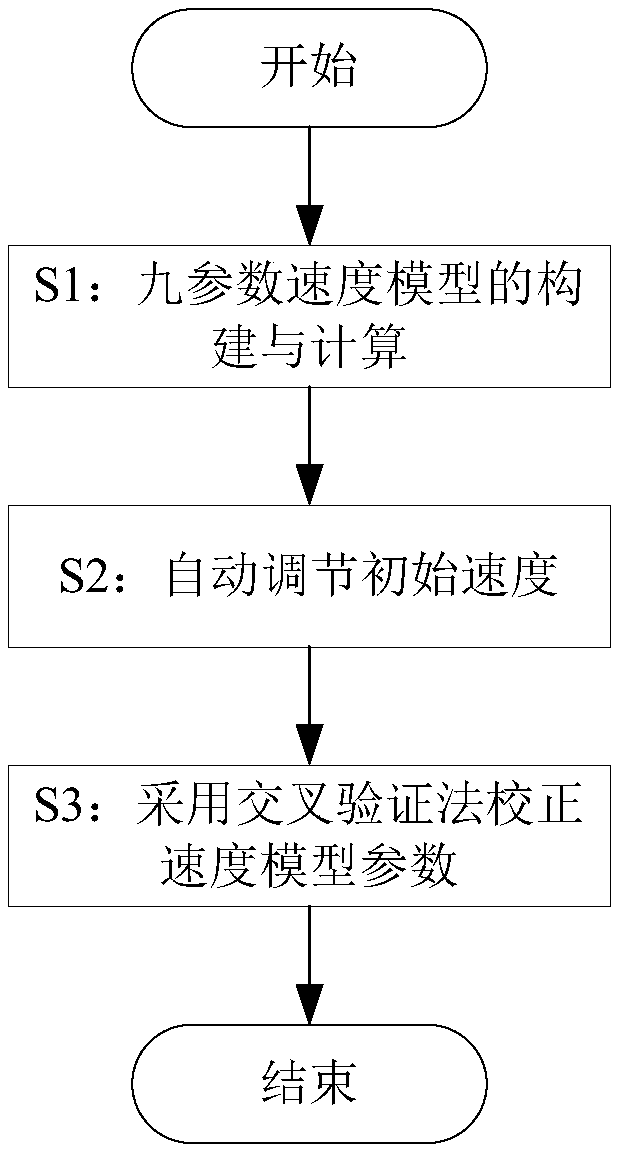
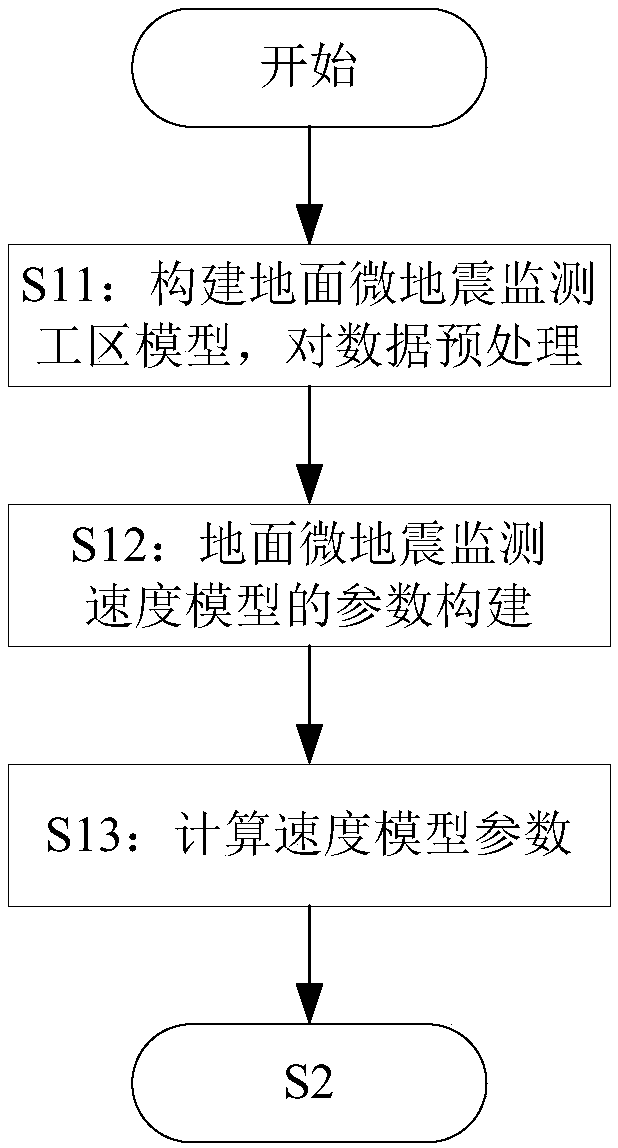
ActiveCN105116444AHigh simulationHigh positioning accuracySeismic signal processingModel parametersSeismic wave propagation
The invention provides a ground microseism monitoring anisotropy speed model and an automatic construction method thereof. The automatic construction method comprises: S1, constructing and calculating a nine-parameter speed model; S2, automatically regulating an initial speed; and S3, employing a cross validation method to calibrate speed model parameters. Compared with a traditional horizontal layer speed model, the speed model of the invention can embody the change trend of the speed with seismic wave propagation directions in a better way, and better simulate real seismic wave propagation, thereby building a more accurate speed model; through the speed model, positioning accuracy is higher; the speed model can automatically adjust an initial speed, thereby avoiding the trouble of artificially adjusting the initial speed, and determining the initial speed more efficiently; the speed model parameters are corrected by employing the cross validation method, the reciprocal value of positioning errors is used as a weight to linearly superpose speed model parameters of all sets, and corrected speed model parameters can improve positioning precision effectively.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Land-use four-component digital geophone
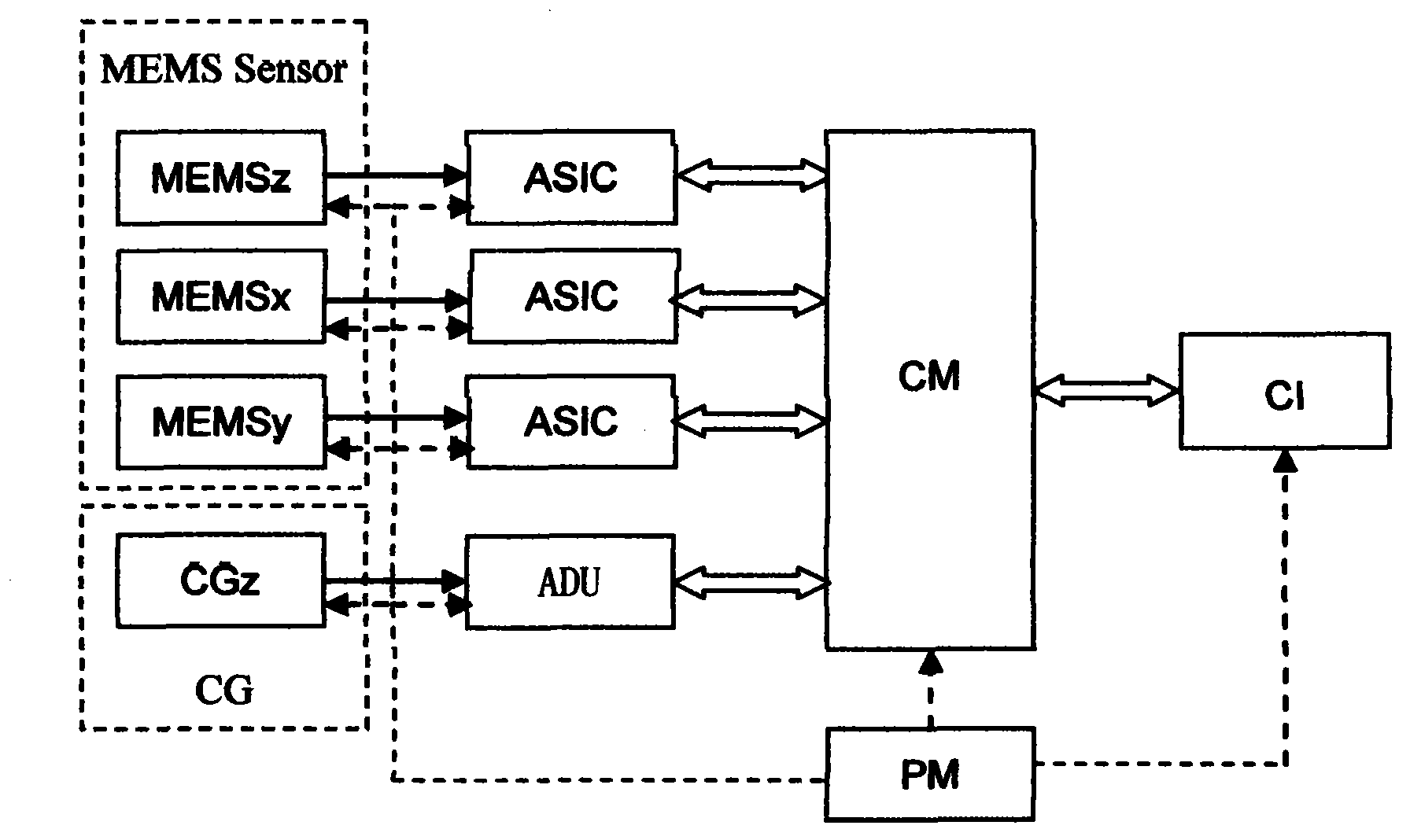
InactiveCN103513273AImprove exploration accuracyConvenient researchSeismic signal receiversGeophoneCommunication unit
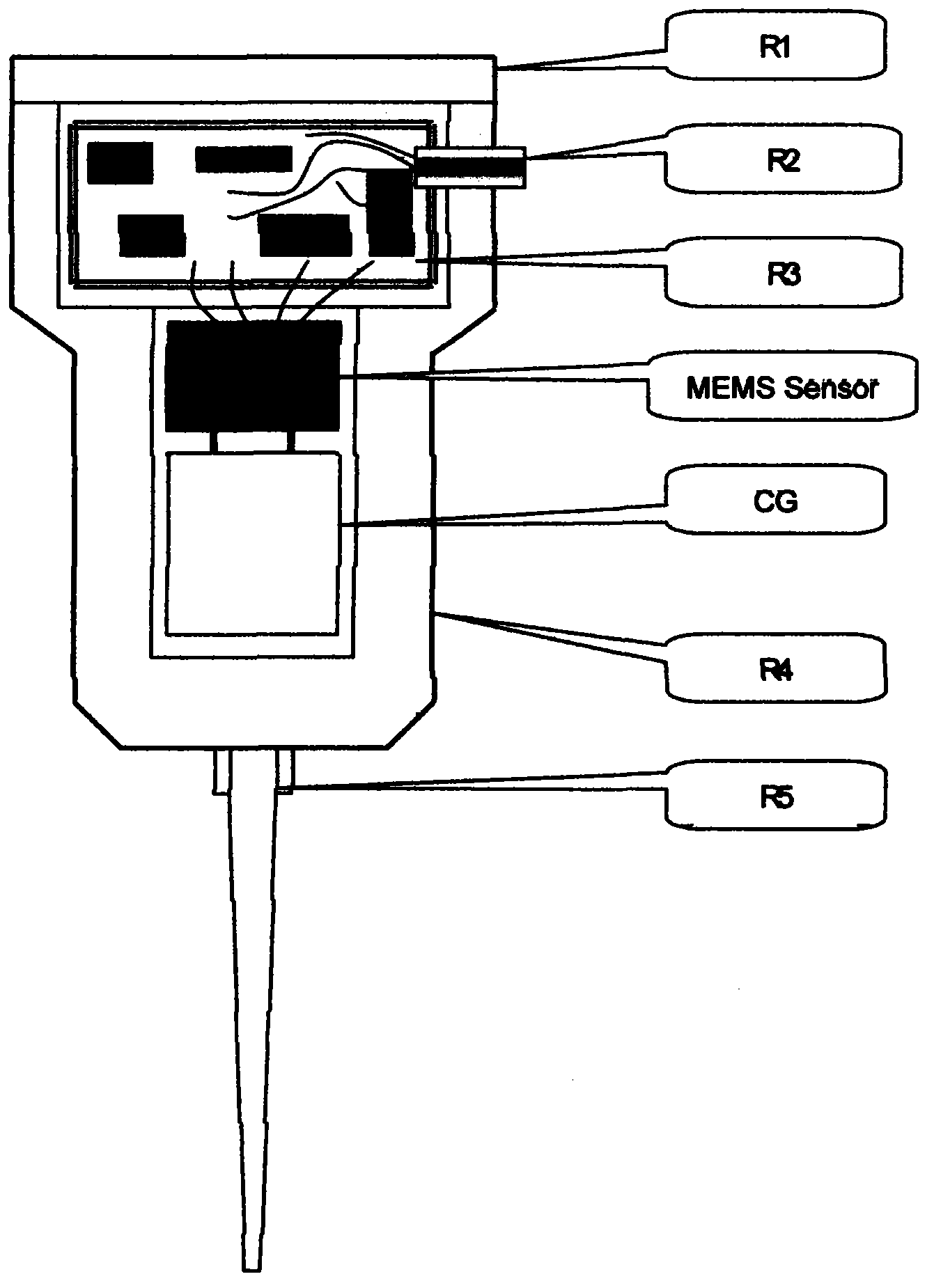
The invention relates to a land-use four-component digital geophone. In the prior art, a seismic wave propagation characteristic can not be finely researched. By using the geophone of the invention, the above problem is solved. The geophone is a four-component geophone formed by a three-component MEMS acceleration geophone and a moving-coil velocity geophone. The geophone is formed by a micro electromechanical system earthquake three component acceleration sensor, a weak signal detection and feedback circuit, a moving-coil geophone, a digital unit, a control module CM, a data communications unit and a power module PM. The micro electromechanical system earthquake three component acceleration sensor and the weak signal detection and feedback circuit are used to complete acquisition and digital functions of an acceleration parameter. The moving-coil geophone and the digital unit are used to complete the acquisition and digital functions of a velocity parameter. The geophone possesses the advantages that a signal acquisition and receiving function of the one velocity parameter and the three-component acceleration parameter can be performed on a same receiving point; the seismic wave propagation characteristic can be finely researched; exploration precision is greatly increased.
Owner:INST OF GEOLOGY & GEOPHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for calculating propagation speed of earthquake waves in mine region by utilizing microearthquake point as earthquake source
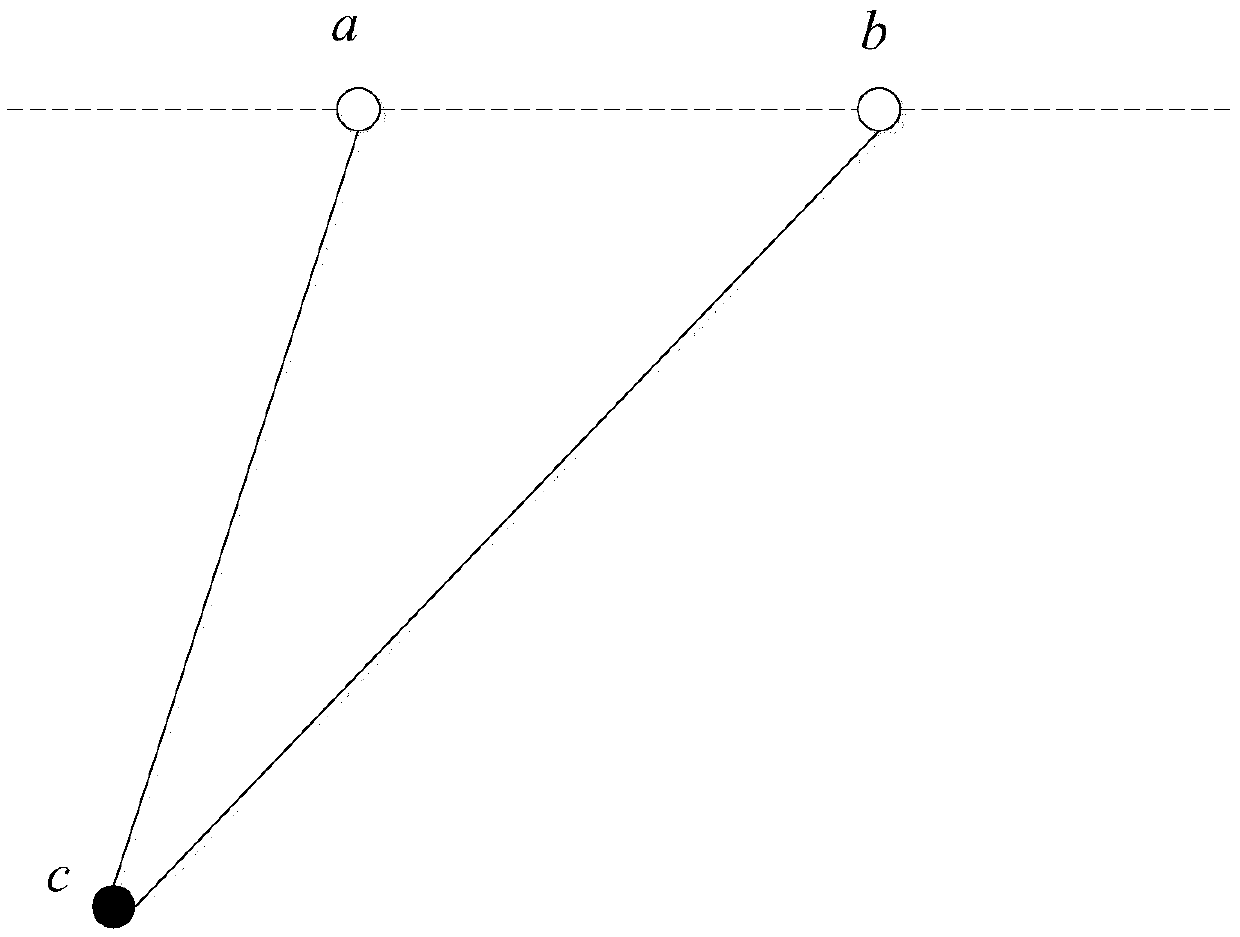
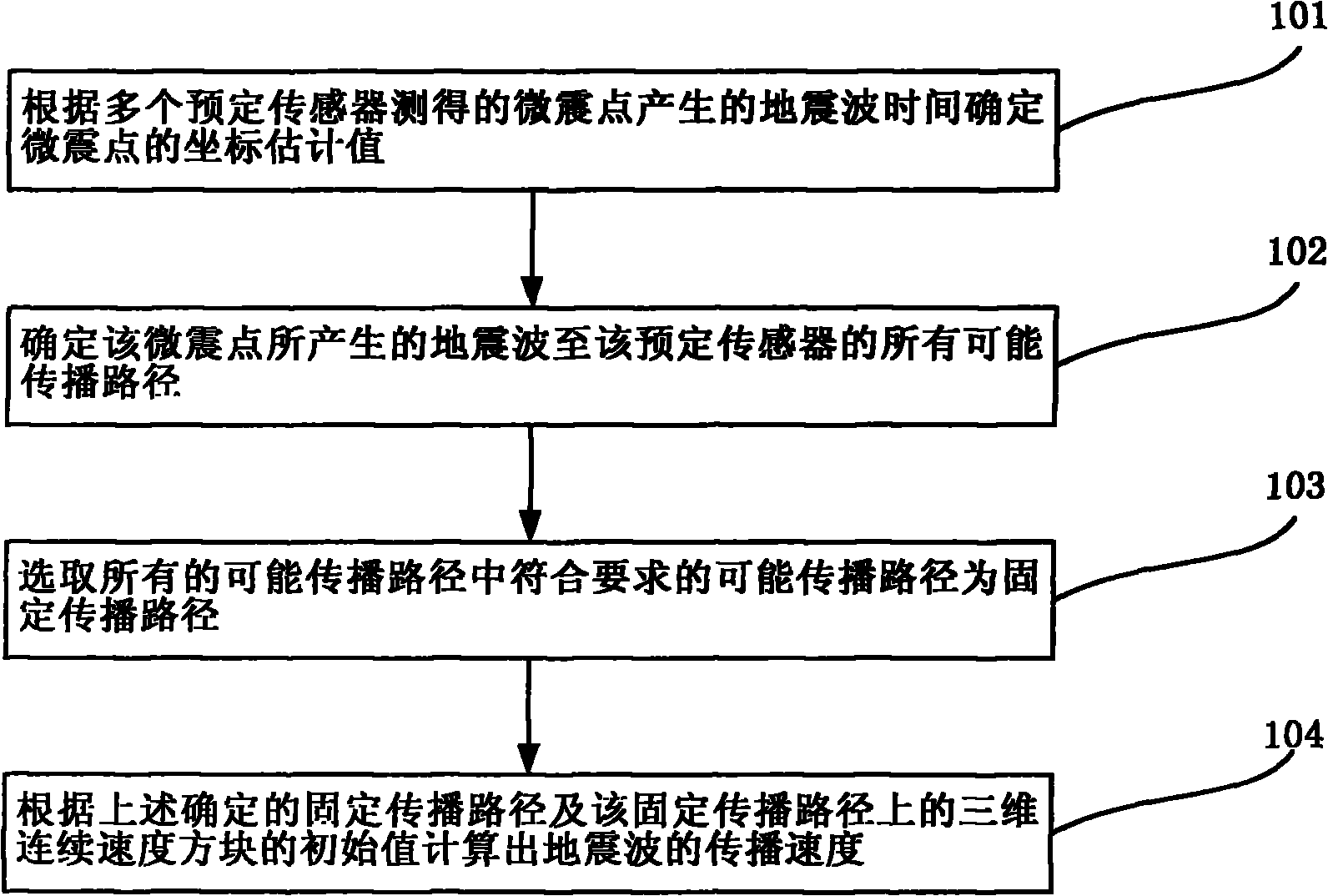
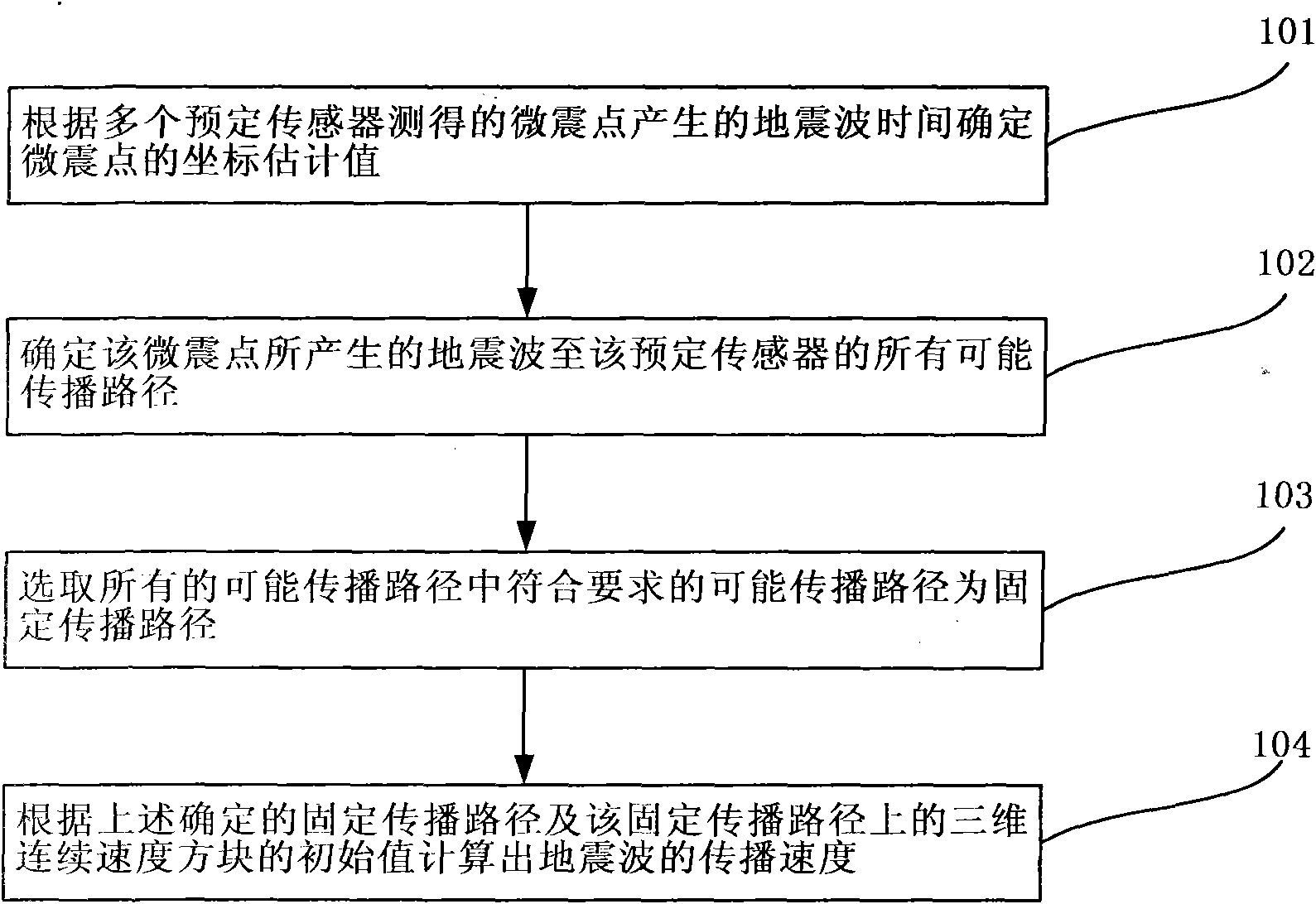
InactiveCN102096093AConvenient for mine operationsReduce manufacturing costSeismologyVelocity propogationSeismic wave propagationDiamond
The invention discloses a method for calculating the propagation speed of earthquake waves in a mine region by utilizing a microearthquake point as an earthquake source, comprising the following steps: determining the coordinate estimated value of the microearthquake point according to the earthquake wave time generated by the microearthquake point measured by multiple preset sensors; determiningall possible propagation paths of the earthquake waves generated by the microearthquake point to the preset sensors according to the coordinate estimated value of the microearthquake point and the speed layer where the preset sensors are; selecting the possible propagation path with the difference between the earthquake wave propagation time and the earthquake wave time measured by the preset sensors corresponding to a preset range from all the possible propagation paths as a fixed propagation path; and calculating the propagation speed of the earthquake waves according to the determined fixed propagation path and the initial value of a three-dimensional continuous speed diamond on the fixed propagation path.
Owner:杨本才
Normal moveout stretch cutting method for processing geophysical exploitation seismic data
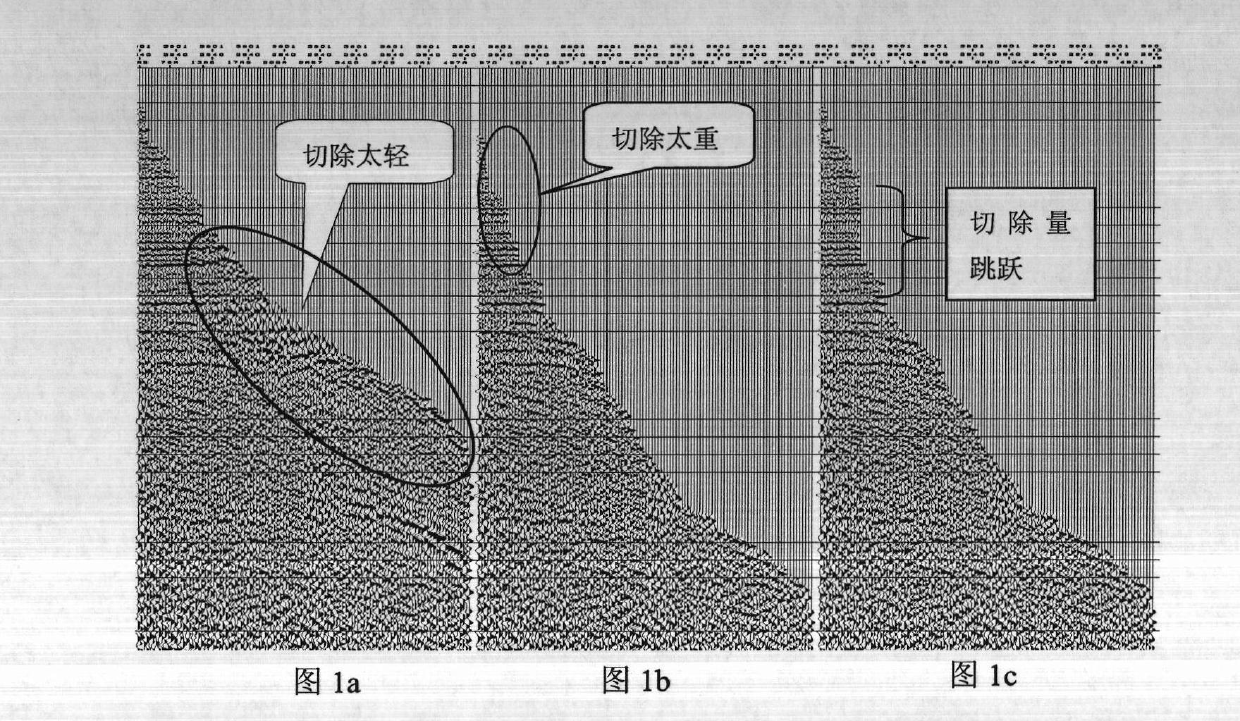
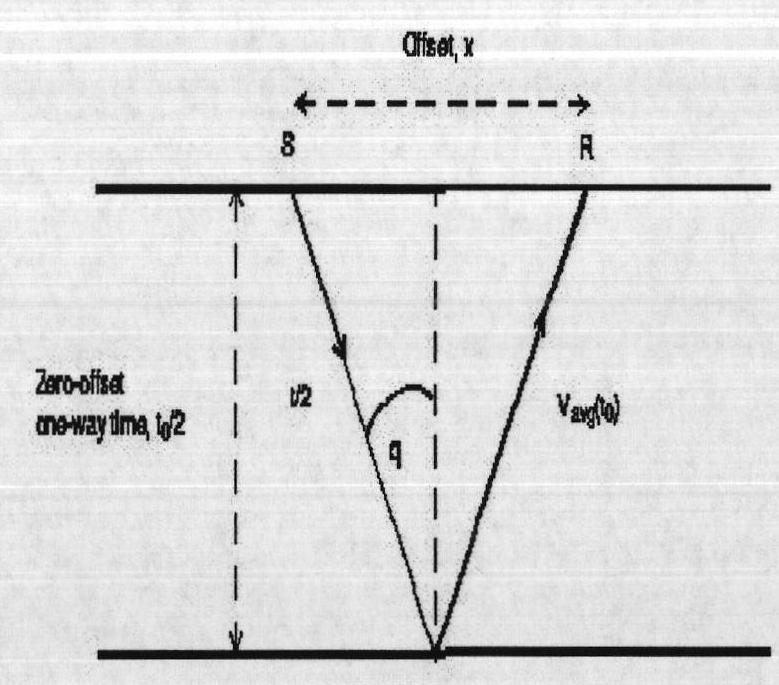
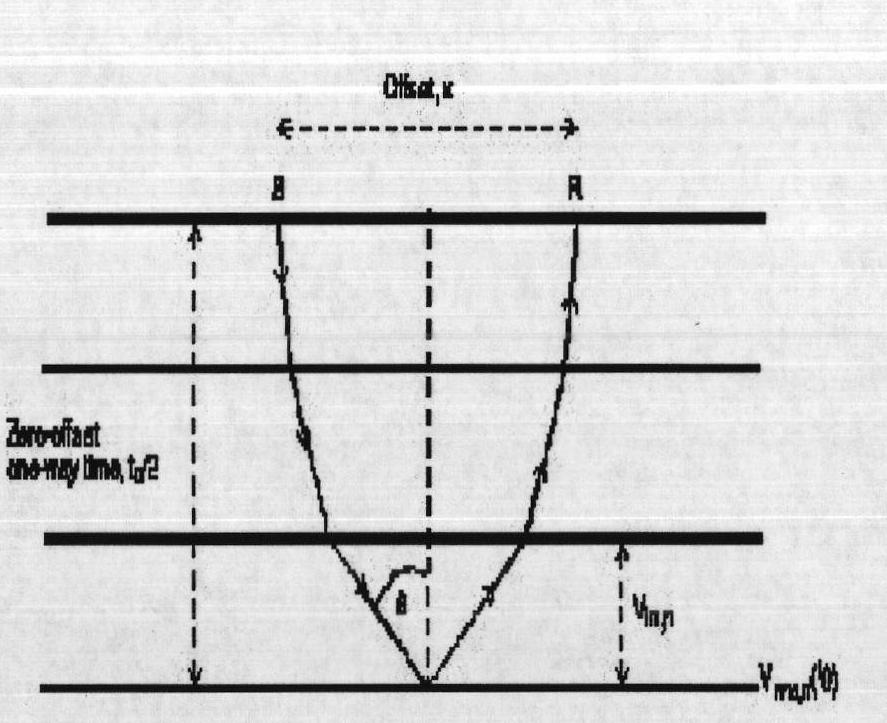
ActiveCN102636813AHigh resolutionImprove signal-to-noise ratioSeismic signal processingGeophoneNormal moveout
The invention provides a normal moveout stretch cutting method for processing geophysical exploitation seismic data. According to the method, a stacking velocity field is utilized, average speed is calculated, or interval velocity is calculated after smoothing the average speed. Further, by using the velocity and shot-geophone distance information, approximate calculation of an incident angle is performed according to the theory of ray (straight ray or curved ray) propagated by seismic wave, and a 1D or 3D space varying incident angle threshold value reference is used as a standard of measurement to determine the cut of each seismic channel. Thus, more accurate automatic cutting of the normal moveout stretch is realized, the interference caused by net normal moveout stretch can be cut, effective wave amplitude can also be protected to the greatest extent, and finally, the resolution and the signal-noise ratio of a stacked section are improved.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Static correction method and static correction device for converted wave
ActiveCN104199103AHigh precisionImprove efficiencySeismic signal processingGeophoneCorrection method
The invention relates to a static correction method and a static correction device for a converted wave. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out pretreatment on multi-wave seismic data; obtaining the correcting value of field shot points and the correcting value of geophone; correcting the seismic data; carrying out separation and speed analysis on the seismic data after correction to generate the propagation speed of the seismic data; carrying out correction and excision operation on a trace gather to generate dynamic correction trace gather data; converting the CMP trace gather data of PP wave into PS domain, overlapping the CMP trace gather data of PP wave converted into the PS domain; selecting a goal layer on the overlapped seismic data, and carrying out position pickup on the goal layer to obtain position time; presetting a reference plane, and calculating the time difference of the position time and the preset horizontal reference plane time; correcting the dynamic correction trace gather data onto the preset reference plane, and generating the PP wave dynamic correction trace gather data after construction leveling; carrying out geophone trace gather separation and trace gather overlapping on the dynamic correction trace gather data after construction leveling, and generating geophone trace gather overlapped data after construction leveling.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
Orthotropic dielectric fluid factor and fracture parameter inversion method.
The invention provides an orthotropic dielectric fluid factor and fracture parameter inversion method. The method comprises the following steps: deducing a rigidity matrix of an ortho-symmetric anisotropic fracture medium by using a vertical transverse isotropic medium under a dry rock background according to fracture weakness; with utilization of hypotheses of weak anisotropy and small fracture weakness, deducing a new expression of weak anisotropy approximate rigidity of a saturated fluid rock in an orthogonal medium by combining an anisotropy Gassmann equation; acquiring a PP wave linearized reflection coefficient for fluid and fracture parameter decoupling in the orthogonally symmetrical weak anisotropic medium by combining stiffness disturbance and scattering theories; and with logging information as prior information, realizing elastic impedance pre-stack inversion changing with offset and azimuth angle by using a partial incident angle stacked by azimuth seismic data under Bayesian framework. According to the invention, Reliable results can be provided for fluid identification and fracture characterization; and technical supports are provided for seismic wave propagation research, oil and gas development and seismic disaster prevention.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
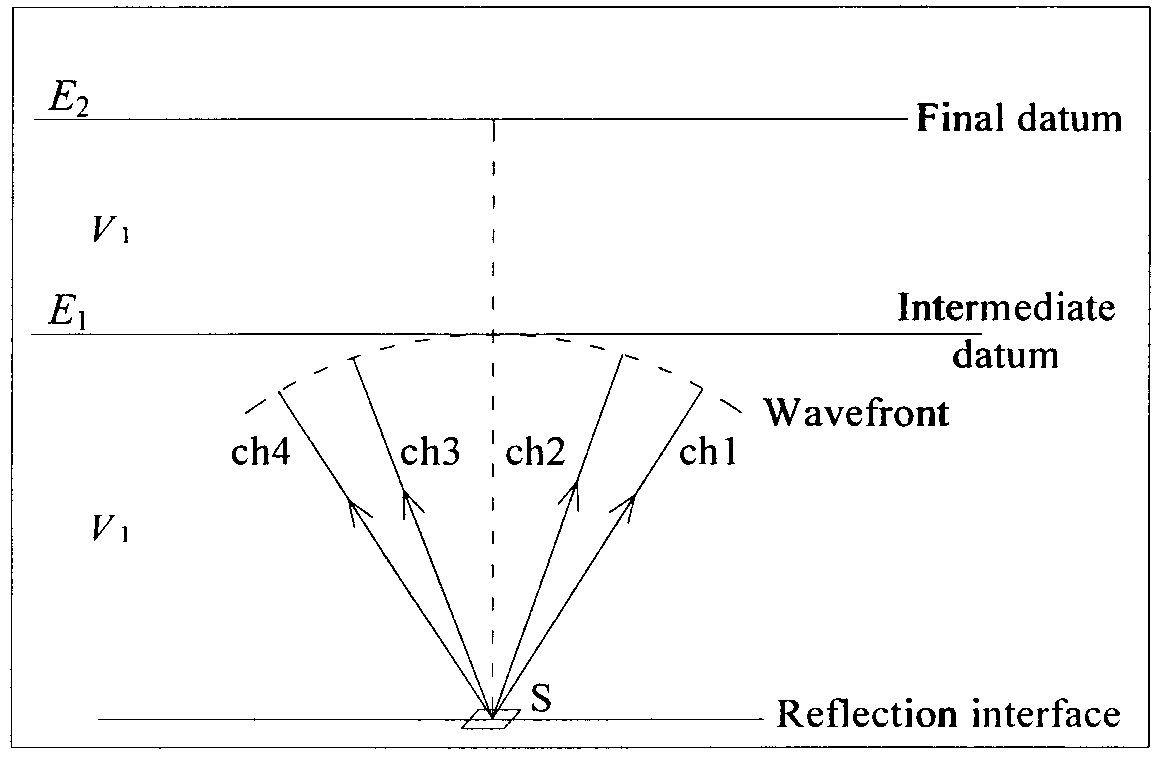
Ghost common shot point (GCSP) ray tracing dynamic and static correction method
The invention discloses a ghost common shot point (GCSP) ray tracing dynamic and static correction method, which is a non-surface consistency static correction method for solving the problem of coalfield seismic exploration static correction of a complex near-surface structure. According to the method, the deviation of rays in a near-surface layer is considered; a static correction amount is dynamic, is changed along with reflection time, offset distance and azimuth, and is in accordance with a wave field propagation law; and the influence on a reflected wave caused by near-surface abnormities can be eliminated effectively. The method comprises the following steps of: first, converting common midpoint (CMP) gathers into GCSP trace gathers, performing forward modeling by adopting a critical path method based on the GCSP trace gathers, and tracking the path and the travel time of the rays in the near-surface layer; then, correcting seismic data to the wave front surface at the time when a seismic wave is propagated to an intermediate reference plane; and finally, replacing the speed of the near-surface layer by the speed of the high-speed layer, and correcting the seismic data to a final reference plane. By the method, zero-offset distance conversion of non-zero offset CMP gathers can be further realized; and the CMP gathers can be stacked directly to form a stacked section without performing speed analysis and dynamic correction.
Owner:彭苏萍 +2
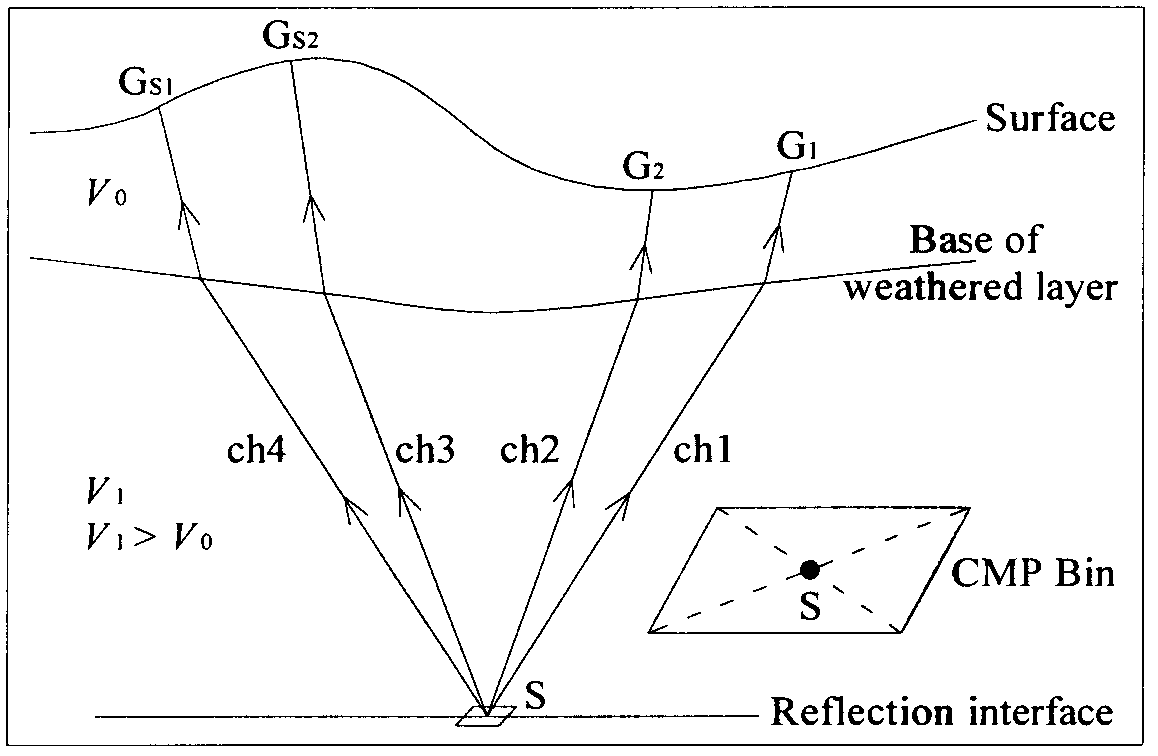
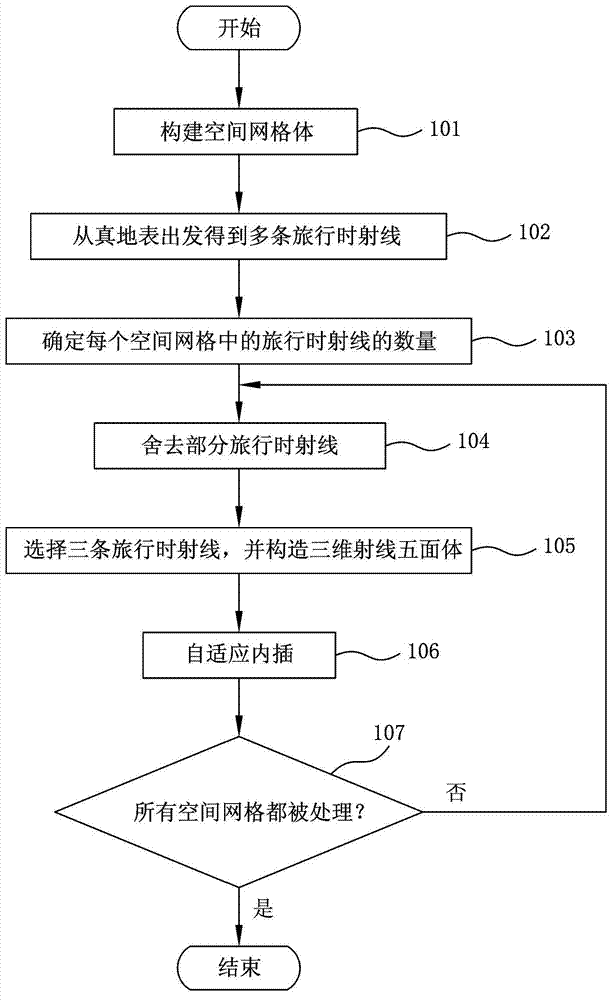
Self-adaption interpolating method for real ground-surface ray tracking
ActiveCN102830431AHigh precisionImprove efficiencySeismic signal processingSelf adaptiveComputer science
The invention provides a self-adaption interpolating method for real ground-surface ray tracking. The self-adaption interpolating method includes steps of (a), dividing a space required for travel-time ray tracking into spatial lattice bodies formed by a plurality of spatial lattices; (b) performing ray tracking computation from a real ground surface, and acquiring a plurality of travel-time rays in transmission of earthquake waves; (c) determining the number of travel-time rays penetrating through each spatial lattice; (d) selecting three travel-time rays penetrating through one or more spatial lattices adjacent to the spatial lattices with travel-time rays fewer than the preset number, and constructing a three-dimensional ray pentahedron on the basis of step length of the travel-time rays; (e) performing self-adaption interpolation via travel time of each control point at the six peaks arranged on the ray pentahedron, and accordingly, acquiring a travel-time ray penetrating through the spatial lattices; and (f), repeatedly executing the steps (d) and (e) until the number of the travel-time rays penetrating through the spatial lattices reaches the preset number.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
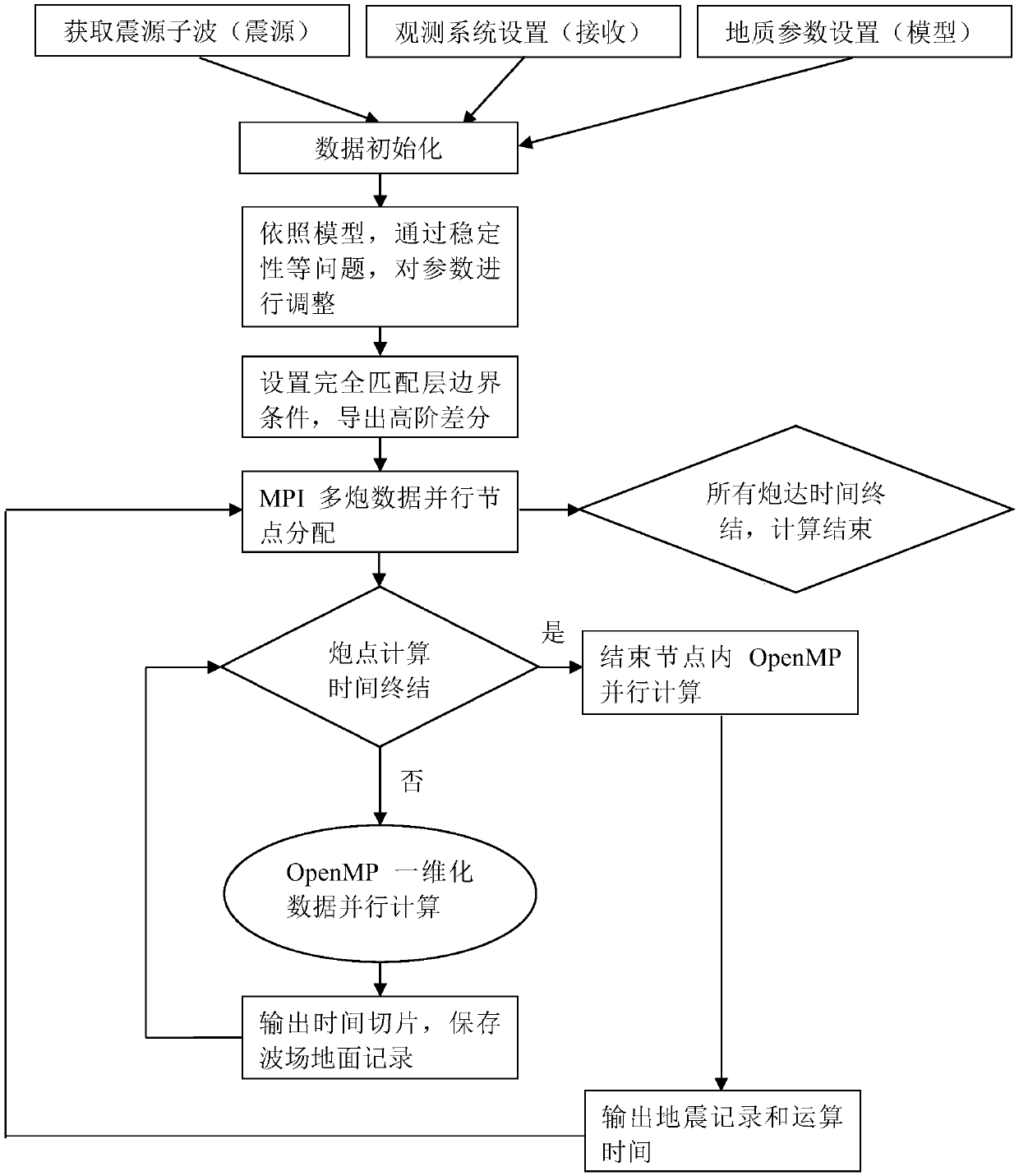
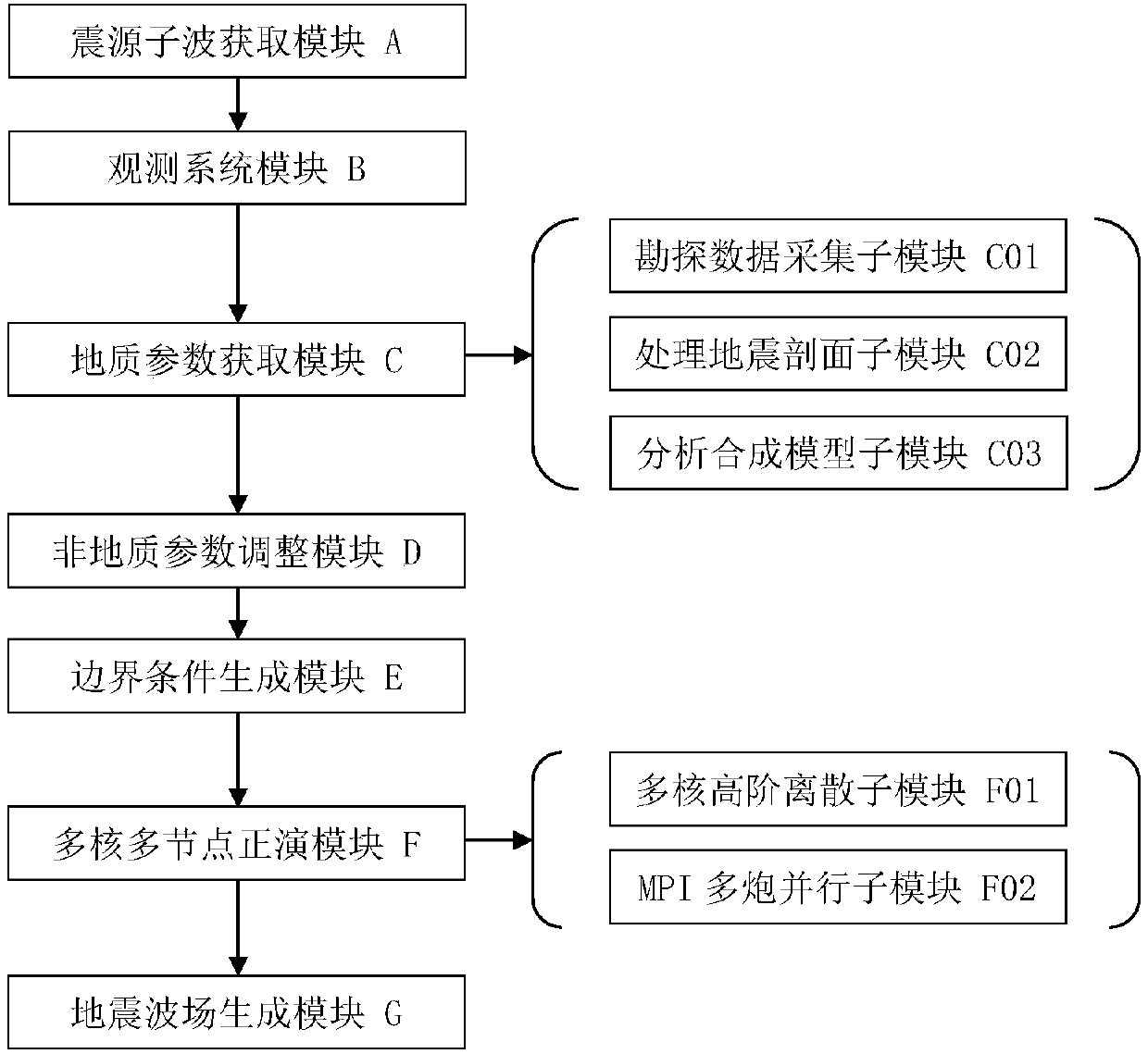
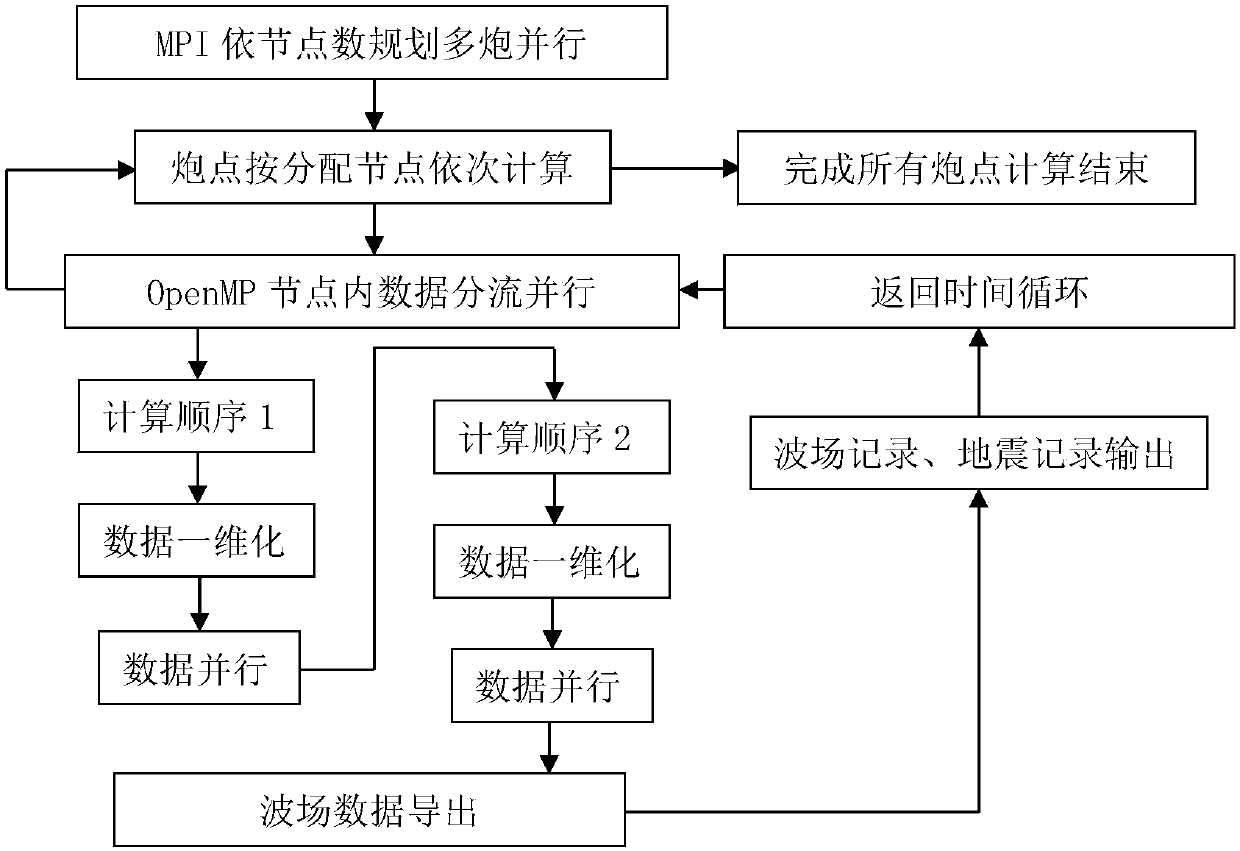
Multi-core multi-node parallel three-dimensional seismic wave field generation method and system
InactiveCN107561585AHigh precisionImprove numerical stabilitySeismic signal processingMulti core computingWave equation
The invention discloses a multi-core multi-node parallel three-dimensional seismic wave field generation method and system. High-precision and high-efficiency solving of a three-dimensional seismic wave equation can be realized based on high-order finite difference and multi-core multi-node parallel acceleration. The method comprises the steps that data information is acquired; the initial condition, the generation boundary condition and the algorithm stability condition of a seismic wave propagation three-dimensional forward simulation model are determined, and high-order finite difference and numerical simulation are performed on the seismic wave propagation equation; a hybrid multi-core multi-node parallel forward simulation algorithm structure based on MPI / OpenMP is designed through combination of the processing capacity of the MPI for multi-node parallel and OpenMP for multi-core computing; and multi-gun data cyclic parallel computing is controlled by the MPI, and the multi-gun wave field slice result and the ground seismic record data are outputted to simulate and generate the exploration seismic wave field. The computing efficiency can be greatly enhanced and the computing accuracy can be effectively enhanced so that the requirements of three-dimensional seismic wave field generation for the computing efficiency and accuracy can be met.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
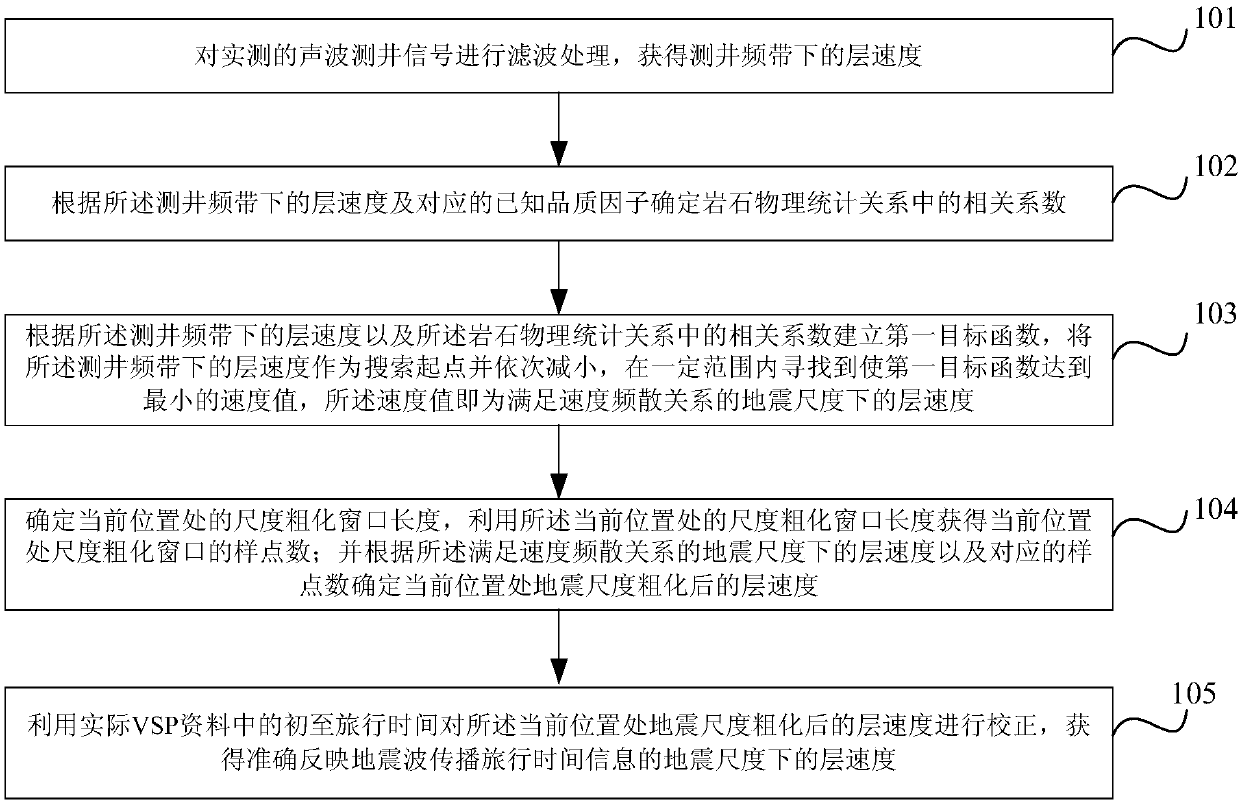
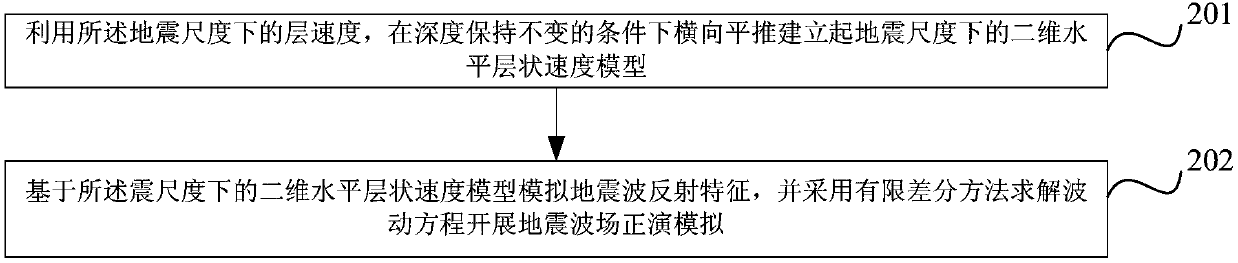
Method and apparatus for determining interval velocity under seismic scale
ActiveCN107065013ASynthetic seismic records are reliableReliable well-seismic relationshipSeismic signal processingSeismology for water-loggingTemporal informationCorrelation coefficient
The invention relates to a method and apparatus for determining an interval velocity under a seismic scale. The method includes the following steps that: an interval velocity under a logging frequency is obtained; a correlation coefficient in a rock physical statistic relation is determined according to the interval velocity under the logging frequency and a corresponding known quality factor; a first objective function is established according to the interval velocity under the logging frequency and the correlation coefficient in the rock physical statistic relation, and an interval velocity under the seismic scale, which satisfies a velocity dispersion relation, is obtained according to the first objective function; the length of a scale coarsening window at a current position is determined, the number of sampling points of the scale coarsening window at the current position is obtained through using the length of the scale coarsening window at the current position; and an interval velocity which has been subjected to seismic scale coarsening at the current position is determined according to the interval velocity under the seismic scale which satisfies the velocity dispersion relation and the number of the sampling points; and the interval velocity which has been subjected to seismic scale coarsening at the current position is corrected, so that the interval velocity under the seismic scale, which can accurately reflect the travel time information of seismic wave propagation can be obtained.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
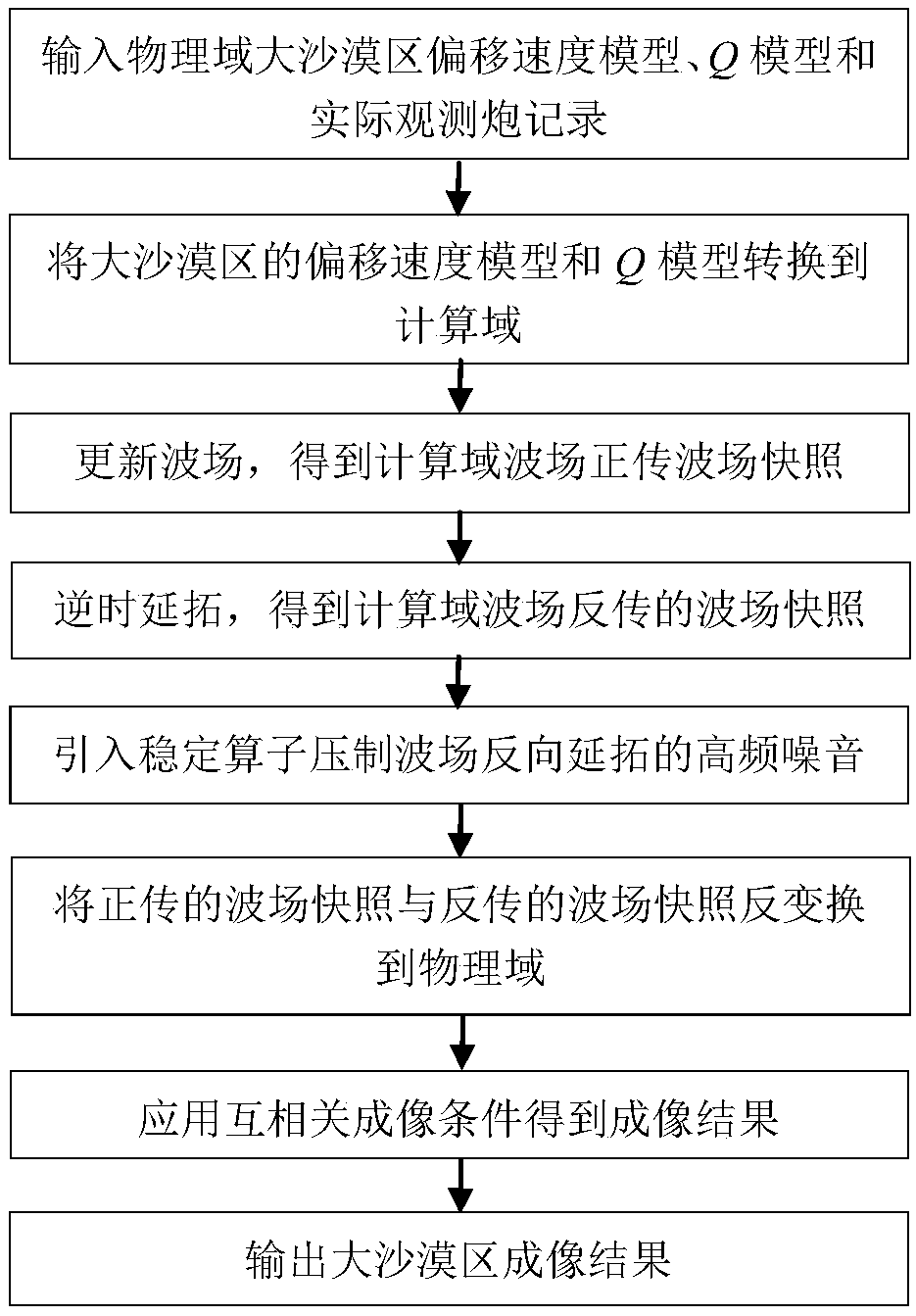
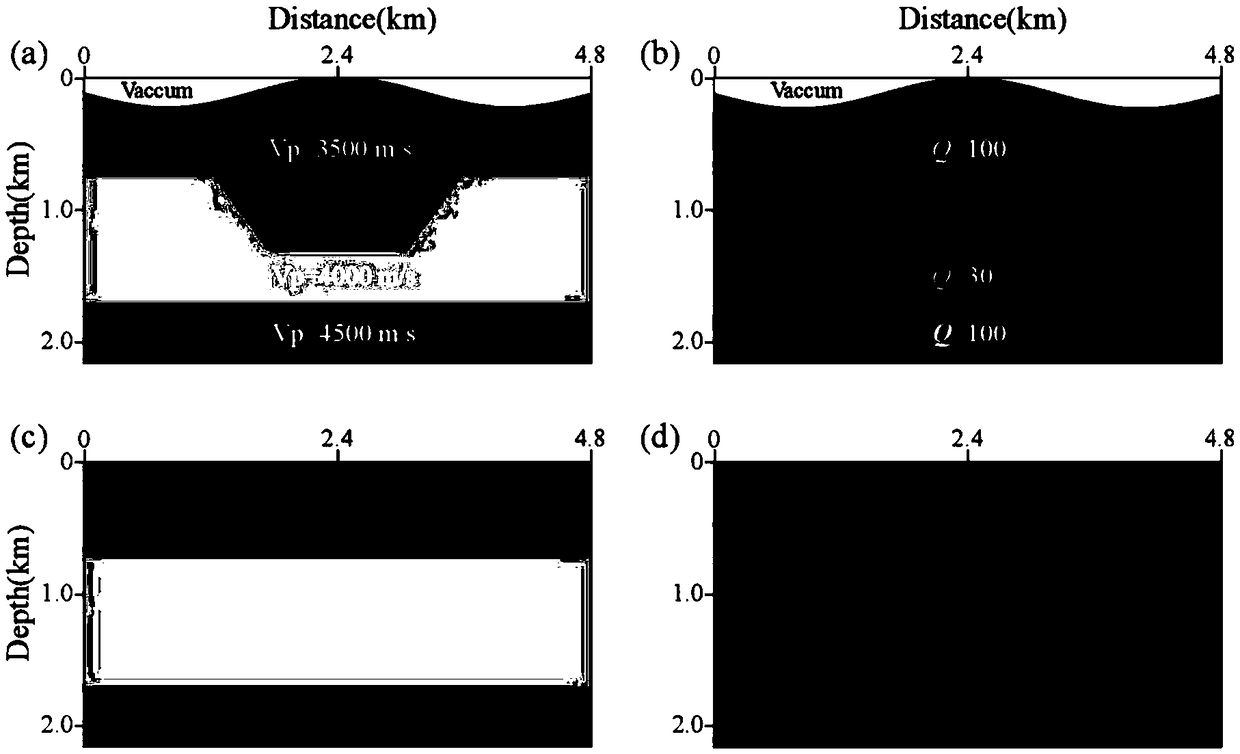
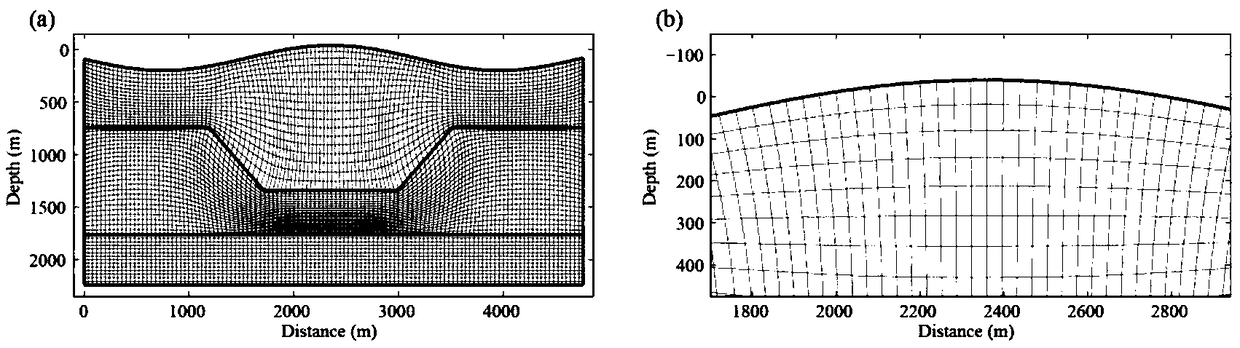
Stable attenuation compensation reverse-time migration imaging system and method in large desert area
The invention discloses a stable attenuation compensation reverse-time migration imaging system and method in a large desert area, and belongs to the field of petroleum geophysical exploration. The stable attenuation compensation reverse-time migration imaging method comprises the steps that a migration model and shot records are input; the migration model is converted into a computational domain;a forward-propagation wave field snapshot of the wave field of the computational domain is obtained through forward extension; a reverse extension equation of the sand-dune ground surface capable ofaccurately correcting amplitude attenuation and the irregular attenuation of phase frequency dispersion is obtained, and a reverse-propagation wave field snapshot of the wave field of the computational domain is obtained; a computational domain stabilization operator is introduced to suppress high-frequency noise of reverse extension; the wave field snapshots of forward extension and reverse extension are inversely transformed to a physical domain; and an imaging result is obtained by applying physical domain zero phase cross-correlation imaging conditions, and the imaging result is output. According to the stable attenuation compensation reverse-time migration imaging system and method, the influence of the irregular sand-dune ground surface on seismic wave propagation can be accurately corrected, meanwhile, attenuation of seismic recording energy and phase frequency dispersion due to the loose sand-dune ground surface can be corrected, and the high-precision imaging results of seismic collected data in the large desert area are obtained.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
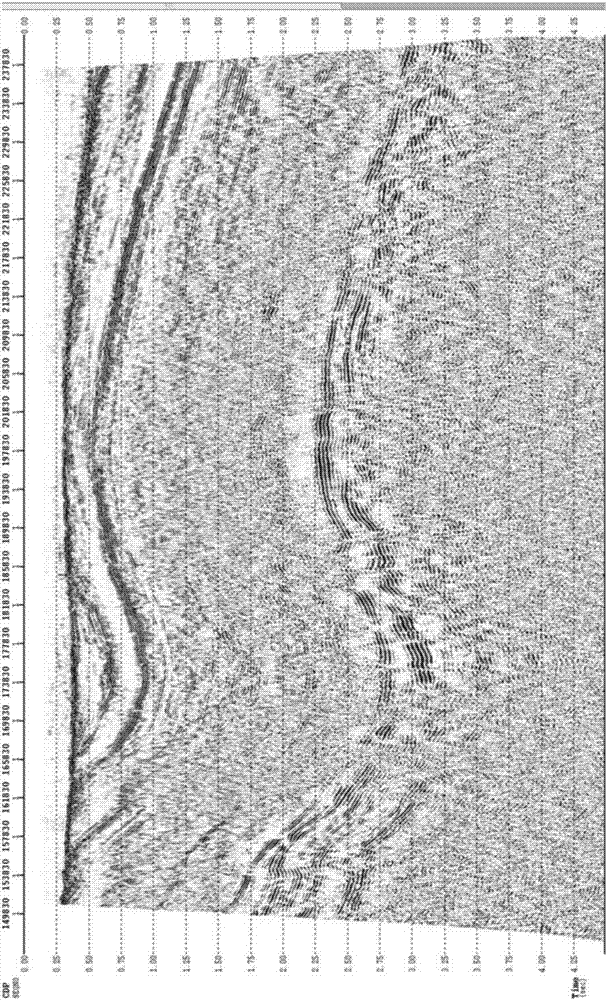
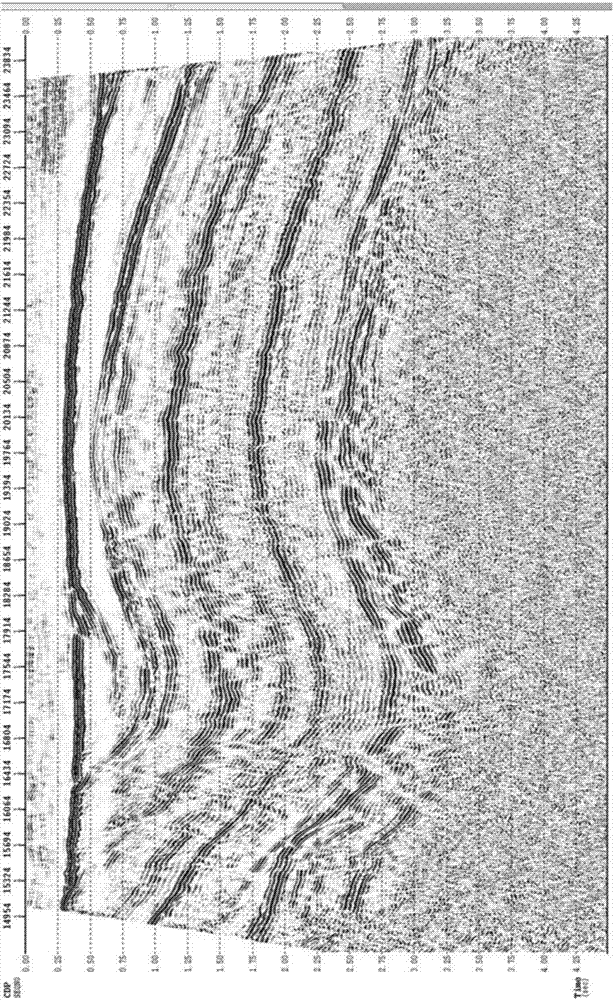
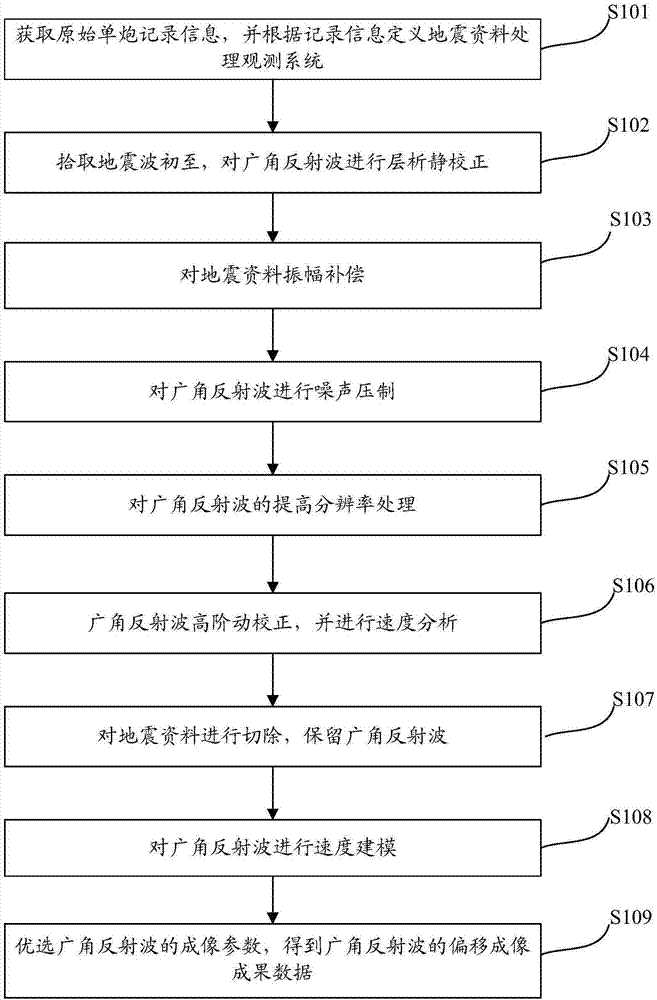
Imaging method of wide angle reflection waves of deep carbonate reservoirs in large desert region
ActiveCN107367761AHigh-resolutionQuality improvementSeismic signal processingImage resolutionWave field
The invention discloses an imaging method of wide angle reflection waves of deep carbonate reservoirs in a large desert region. The method comprises steps of acquiring original single shot record information, and defining a seismic data processing observation system according to the record information, wherein the record information comprises seismic data including the wide angle reflection waves; picking up the primary arrival of seismic waves and carrying out chromatography static correction on the wide angle reflection waves; compensating the amplitude of the seismic data; carrying out noise compression on the wide angle reflection waves; carrying out resolution increasing processing on the wide angle reflection waves; carrying out high-order dynamic correction on the wide angle reflection waves and carrying out speed analysis; cutting the seismic data and keeping the wide angle reflection waves; carrying out speed modeling on the wide angle reflection waves; and optimally selecting imaging parameters of the wide angle reflection waves so as to obtain migration imaging result data of the wide angle reflection waves. According to the invention, according to the seismic data spreading mechanism, based on the wave field analysis, the wide angle reflection waves in the single shot records can be effectively recognized; and by use of the wide angle reflection wave imaging, the quality of the deep seismic data imaging is improved.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com