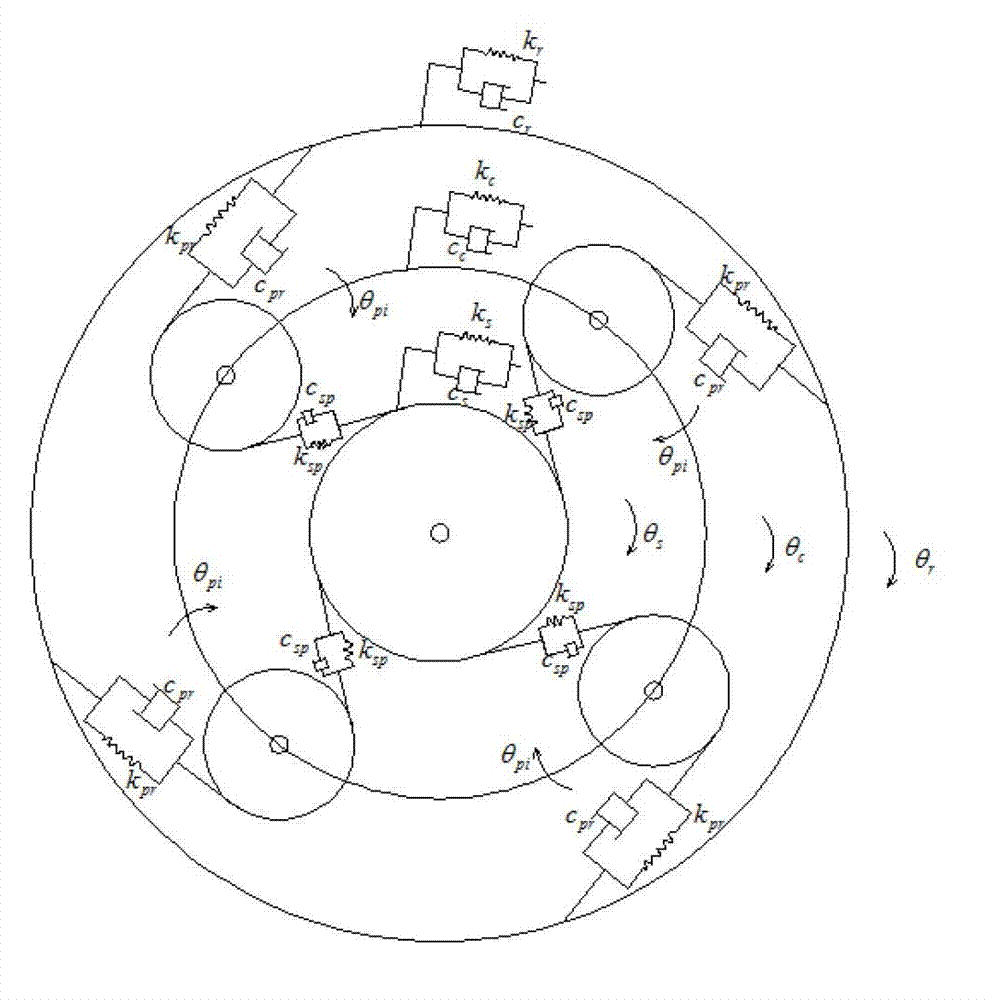
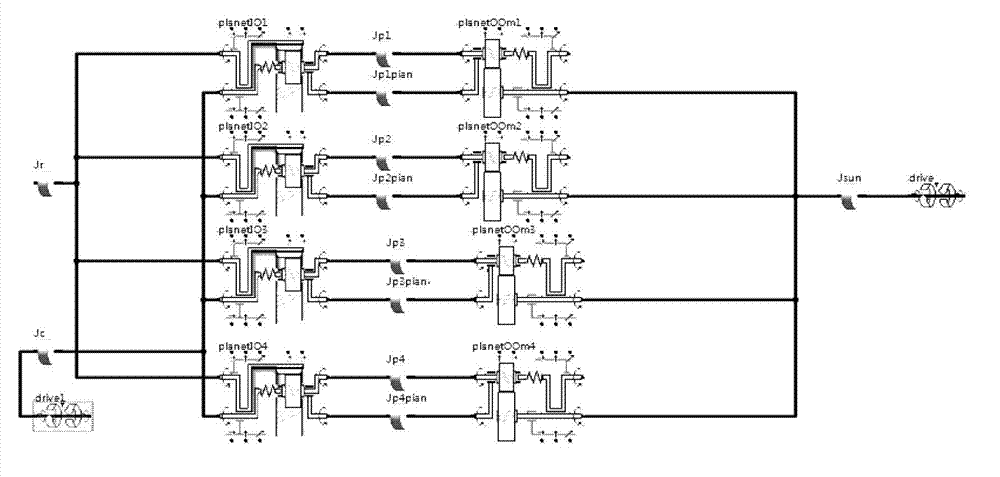
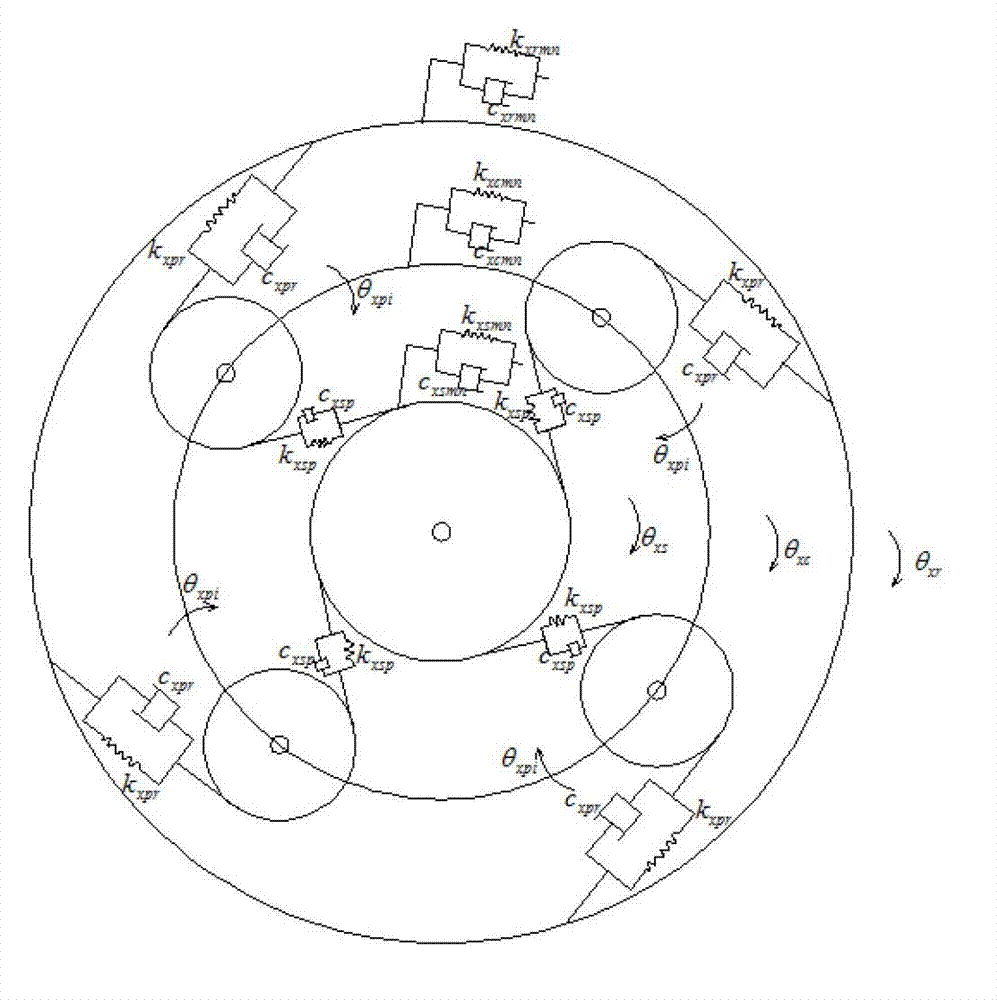
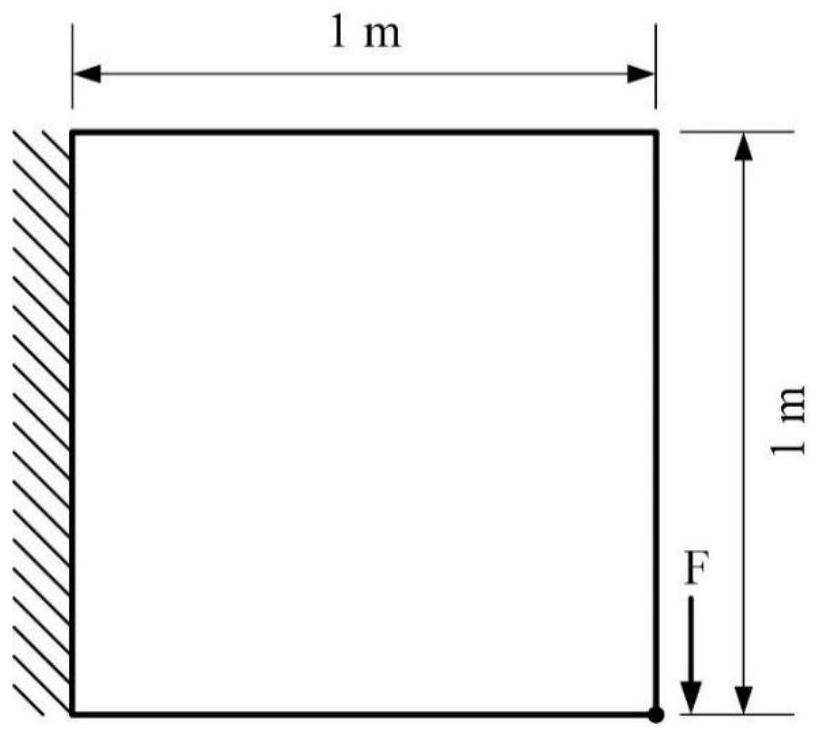
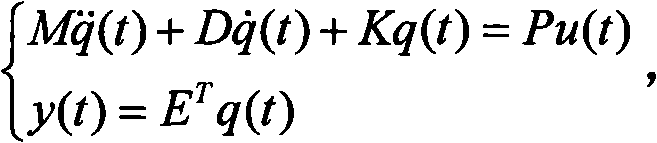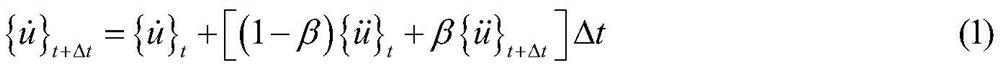Patents
Literature
193 results about "Rigidity matrix" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The rigidity of a matrix A for a target rank r is the minimum number of entries of A that must be changed to ensure the altered matrix has rank at most r. The notion of matrix rigidity was introduced by Valiant (1977) as a means to proving lower bounds on the arithmetic complexity of linear transformations.
Pneumatic elastic mechanical characteristic analytical method of hypersonic speed aircraft in thermal environment
ActiveCN104133933AGuaranteed continuitySustainable transportationSpecial data processing applicationsElement modelEngineering
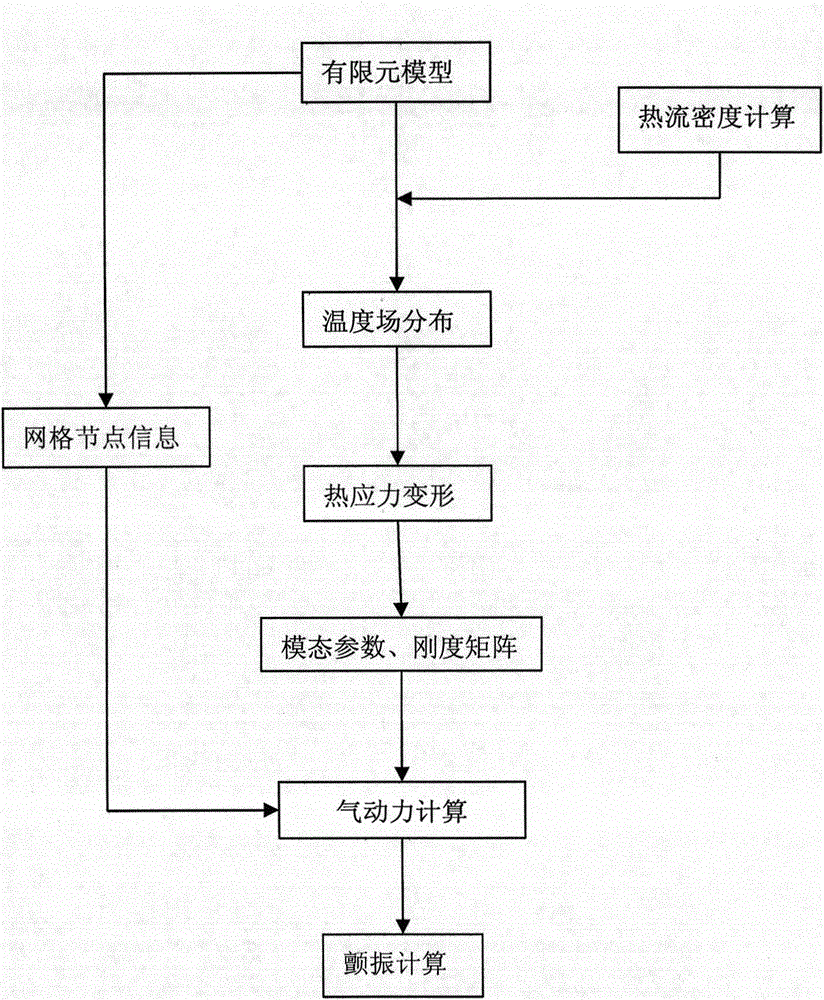
The invention relates to a pneumatic elastic analytical method, and provides a pneumatic elastic mechanical characteristic analytical method of a hypersonic speed aircraft in thermal environment. According to the method, the piston theory is used for carrying out frequency domain nonsteady aerodynamic calculation on a full-aircraft finite element model of the hypersonic speed aircraft; on the basis, the pneumatic thermal effect on the model in the hypersonic speed thermal environment is considered; the weak coupling effect of pneumatic thermal input in aerodynamic input and elastic force input is ignored; only the structure temperature steady-state characteristics under the pneumatic thermal load effect are considered; after the steady aerodynamic calculation, the thermal flux density on the surface of the aircraft is obtained by adopting a reference enthalpy method; further, the steady temperature distribution on the surface of the aircraft is calculated; the practical equivalent rigidity matrix of the structure at the moment is obtained; and the critical flutter speed is calculated by an engineering method. The pneumatic elastic mechanical characteristic analytical method has the advantages that the pneumatic elastic analytical problem of the hypersonic speed aircraft in the pneumatic thermal environment is solved, and the pneumatic elastic performance of the hypersonic speed aircraft is improved through flutter speed analysis.
Owner:ANHUI JINSANHUAN METAL SCI & TECH
Five-axis side milling machining cutter path smoothing method
ActiveCN105425727AAddressing drastic changesConsider geometric accuracy requirementsProgramme controlComputer controlFree formCutter location
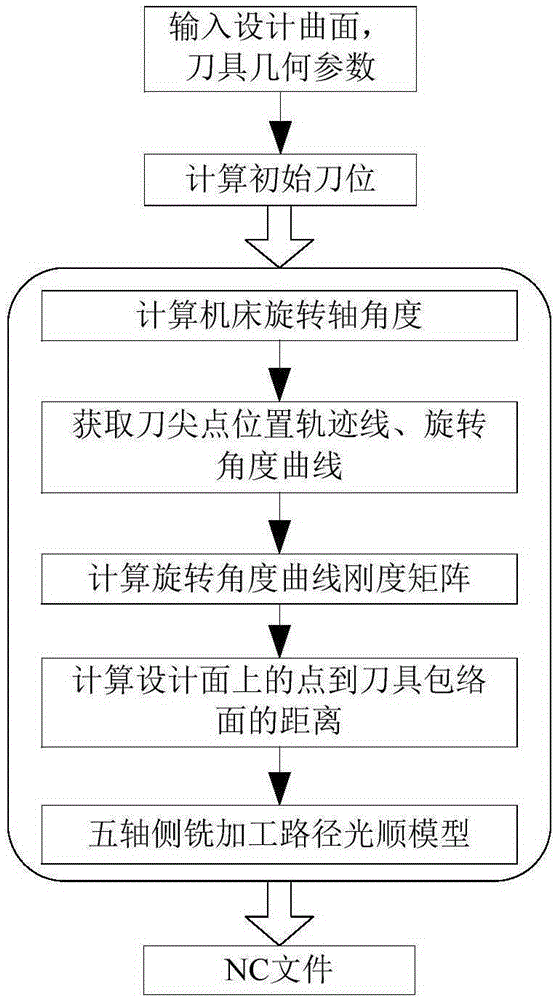
The invention provides a five-axis side milling machining cutter path smoothing method. The method comprises calculating the initial cutter location, and calculating the machine tool turning axle angle corresponding to the direction of a cutter axis through a dynamitic model of a specific machine tool; performing interpolation for the machine tool turning axle angle of the initial cutter location and the cutter nose point location, and obtaining a cutter nose point location trajectory and a machine tool rotation angle change curve; according to the cutter nose point location trajectory and the cutter axis vector, showing a side milling machining cutter path; calculating the rigidity matrix, corresponding to the cutter path, of the machine tool rotation angle curve; according to a differential evolution algorithm, calculating the point that the distance between the point to the cutter enveloping surface is shortest among the points on the design surface; and according to a weighted least square method, establishing a five-axis side milling machining cutter path smoothing model, and obtaining an optimized the initial cutter location and the cutter nose point location curve and a smooth machine tool rotation angle curve after solution. The five-axis side milling machining cutter path smoothing method solves the problem about smoothing and geometric deviation control of the five-axis side milling machining cutter path, and is suitable for five-axis side milling machining on a free form surface, a ruled surface or a curved surface similar to the ruled surface.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
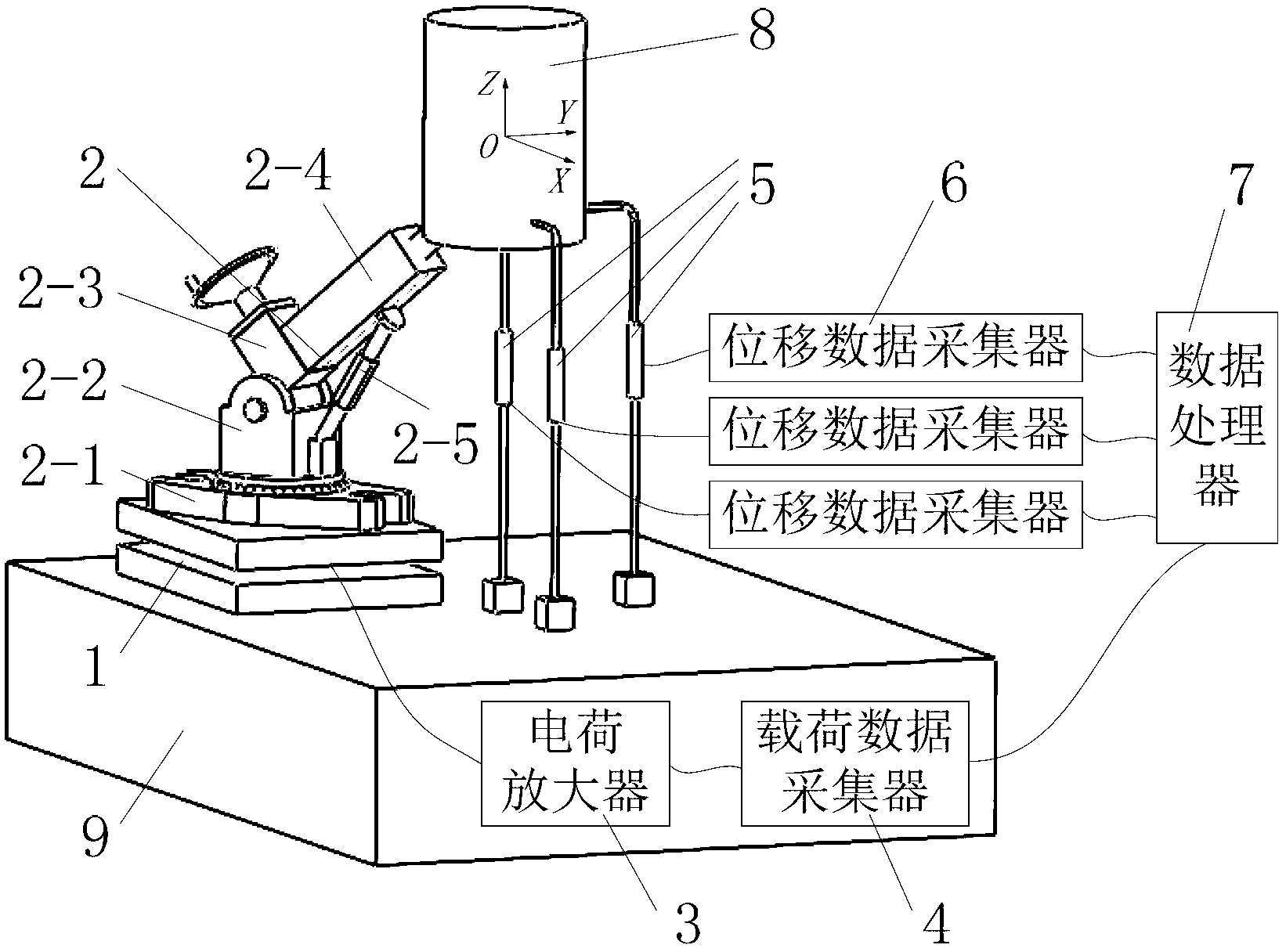
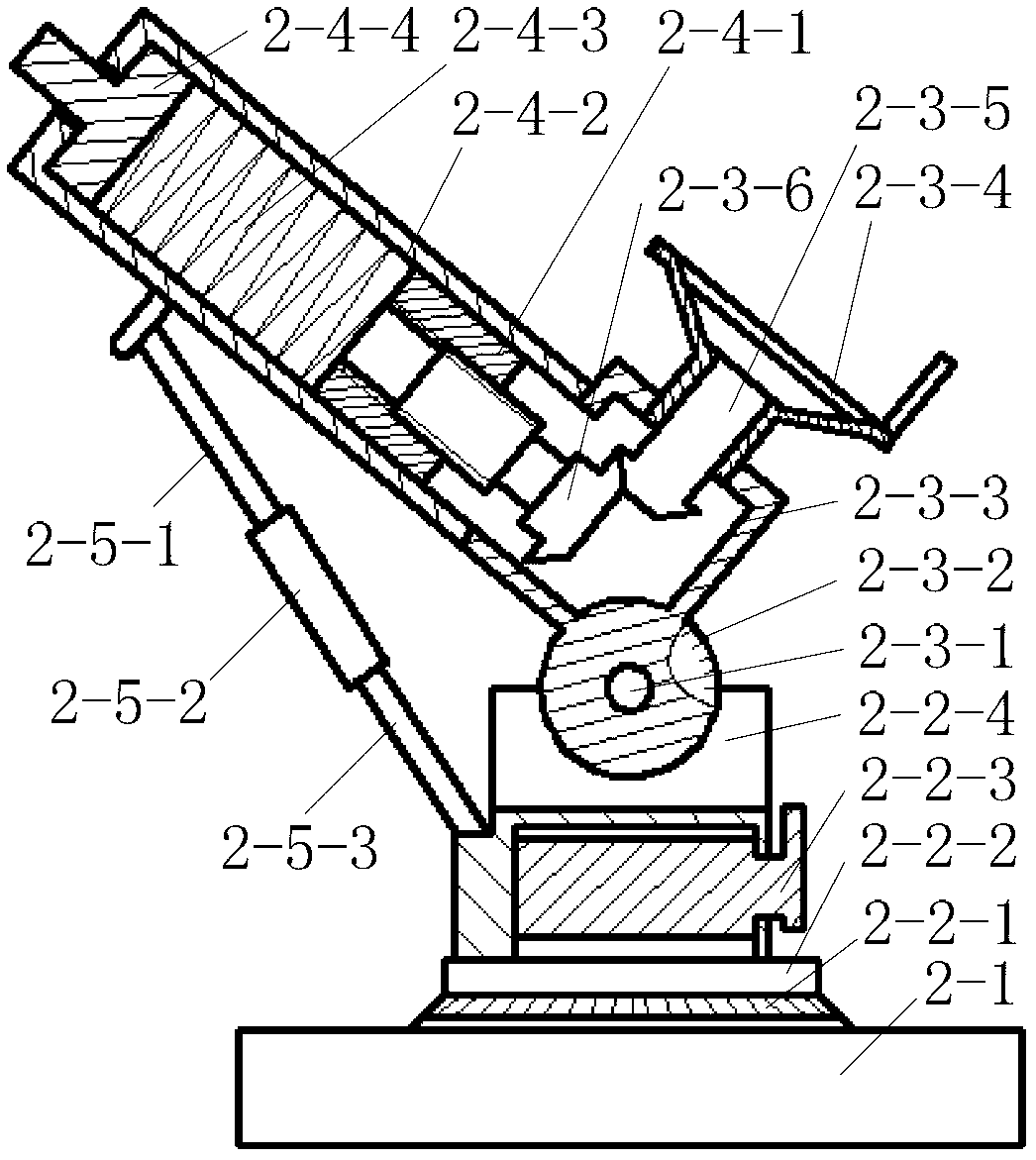
Three-directional static rigidity synchronous testing system for machine tool
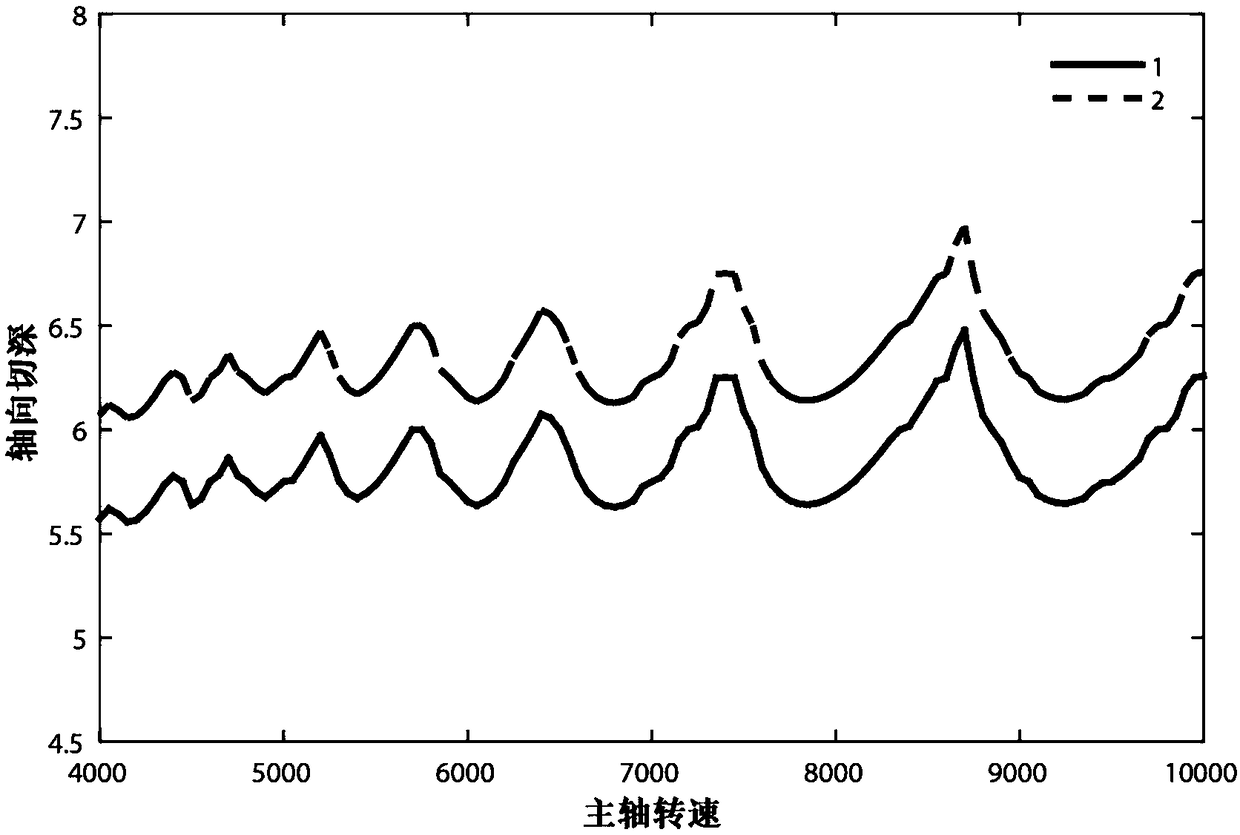
InactiveCN103257050AImprove test efficiencyAccurately reflect static stiffness characteristicsStructural/machines measurementEngineeringRigidity matrix
The invention relates to a three-directional static rigidity synchronous testing system for a machine tool, and belongs to the technical field of static rigidity detection of the machine tool. The system comprises a load measuring subsystem, a three-directional stressing device, a displacement measuring subsystem and a data processor. The input end of the three-directional stressing device and the input end of the displacement measuring subsystem are connected with a main shaft of the machine tool, the output end of the three-directional stressing device is connected with the input end of the load measuring subsystem, and the output end of the displacement measuring subsystem and the output end of the load measuring subsystem are connected with the input end of the data processor. The testing system can apply load which is at certain angles with the X-axis, the Y-axis and the Z-axis of a machine tool coordinate system, and can measure continuously changing data of the load and deformation of the machine tool along three directions at the same time. After the data are processed by data processing programs, a continuously changing curve of nine Kig components in a 3*3 order static rigidity matrix can be obtained.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Method for identifying variable boundary cable force of medium or long cable
InactiveCN101900620AImproved frequency methodBreak through the blind zone of frequency testTension measurementSpecial data processing applicationsIdentifying VariableEngineering
The invention discloses a method for identifying a variable boundary cable force of a medium or long cable. The method comprises the following steps of: performing unit discreteness on the cable, dividing the cable into n units (n is in a range of 40 to 400), and calculating a unit rigidity matrix [K]e and a mass matrix [M]e of each unit according to formulas (1) to (2); then arranging rubber cushion blocks on the cable to form external restraint, wherein the number of the rubber cushion blocks is 2 to 6 and the mounting number of the rubber cushion blocks is determined according to the length of the tested cable; and after the total rigidity matrix [K] and the total mass matrix [M] are determined, solving a characteristic value equation l[K]-omega2[M]l=0 of natural vibration frequency of a cable structure by adopting an iteration method to obtain the cable force T. Under the condition that the cable force is not changed, if the boundary condition of the cable is changed, the frequency of the cable is changed, and the equation of the frequency of the cable and the cable force is changed along with the change of the boundary condition of the cable, so the condition that the frequency of the cable cannot be tested under complex environments is solved, and meanwhile the frequency of the cable is in an interval capable of being tested by the conventional instrument by regulating the boundary condition.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
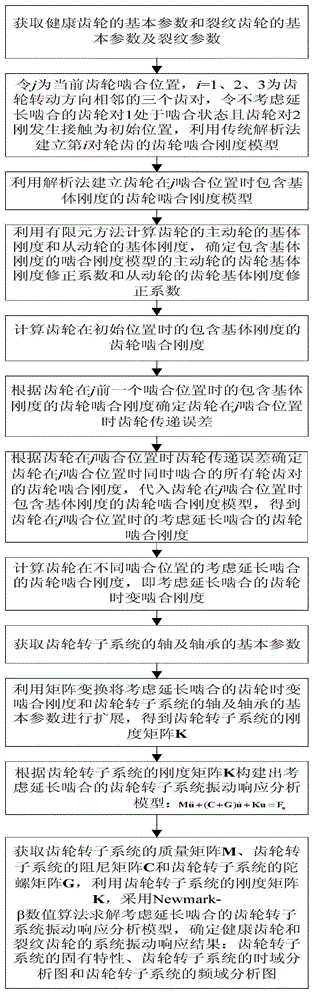
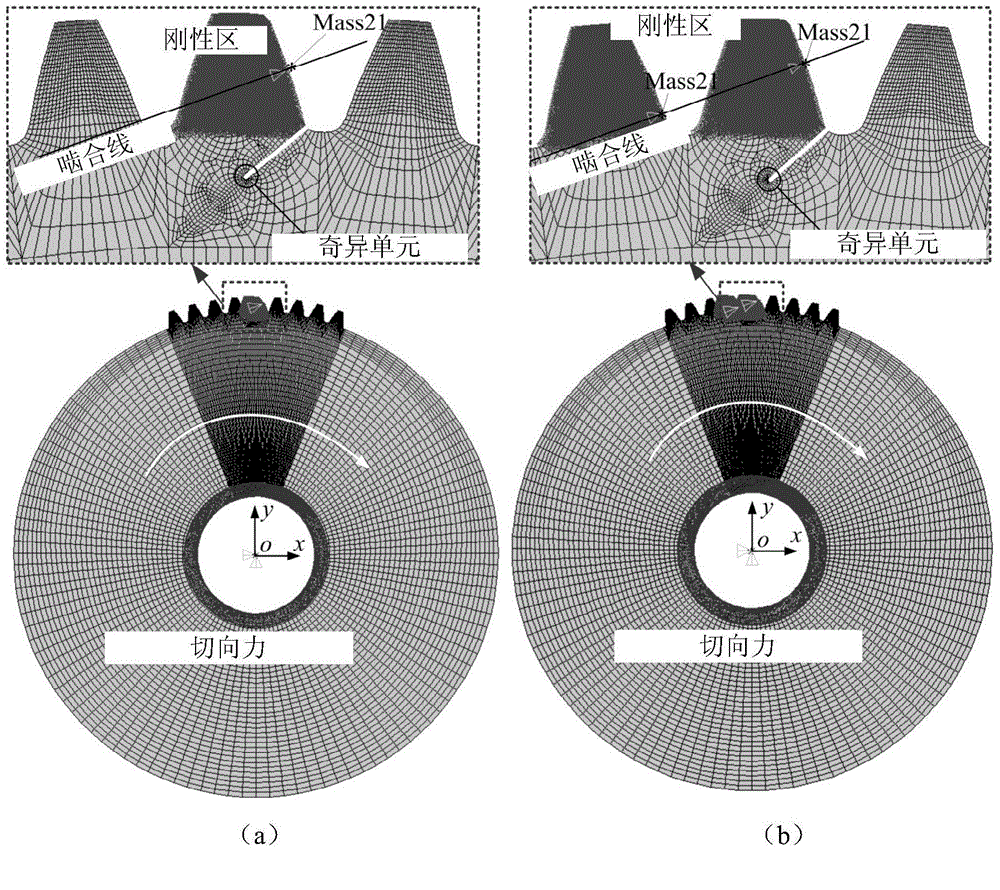
Kinetic parameter determination method of extended tooth contact considered crack gear rotor system
ActiveCN104820756AFix the problem of repeated calculation of stiffnessCalculation method is simpleSpecial data processing applicationsDrive wheelEngineering
The invention relates to a kinetic parameter determination method of an extended tooth contact considered crack gear rotor system. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining a basic parameter of a healthy gear and a basic parameter and a crack parameter of a crack gear; establishing a gear meshing rigidity model, which comprises matrix rigidity, of the gear; calculating the matrix rigidity of a driving wheel of the gear and the matrix rigidity of a driven wheel of the gear by a finite element method; determining a gear matrix rigidity correction coefficient of the meshing rigidity model which comprises the matrix rigidity; determining the gear tooth deformation of the gear by a method that a gear transferring error is solved to obtain extended tooth contact considered gear time varying meshing rigidity; obtaining the basic parameters of a shaft and a bearing of a gear rotor system; obtaining a rigidity matrix K of the gear rotor system; and according to the rigidity matrix K of the gear rotor system, constructing an extended tooth contact considered rotor system vibration response analysis model, and determining a system vibration response result of the healthy gear and the crack gear.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
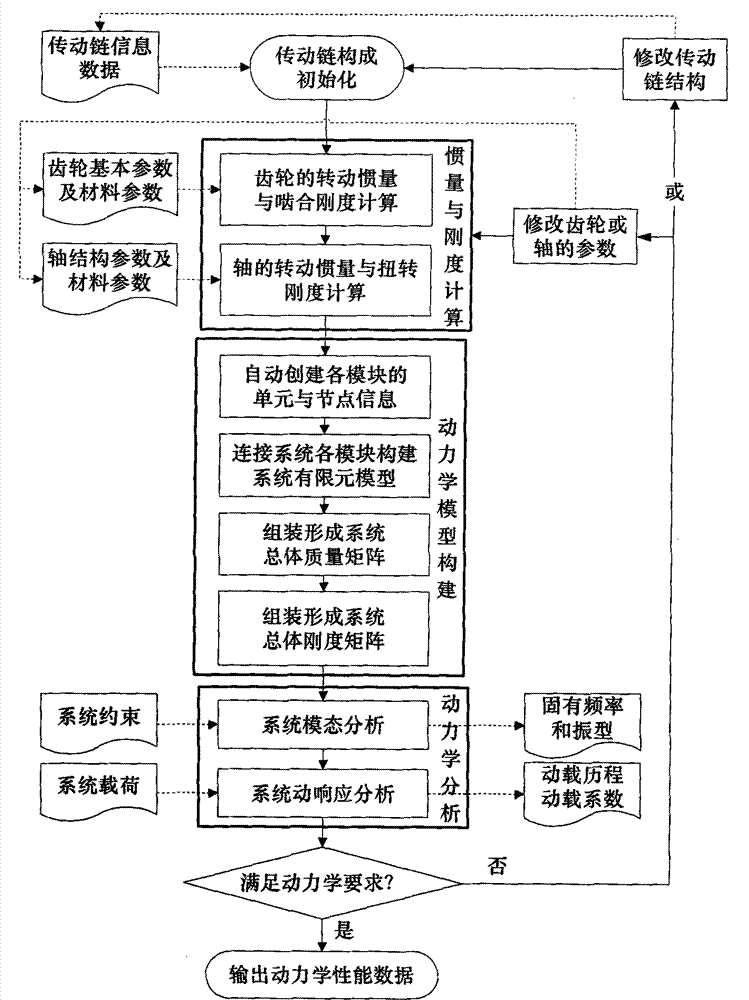
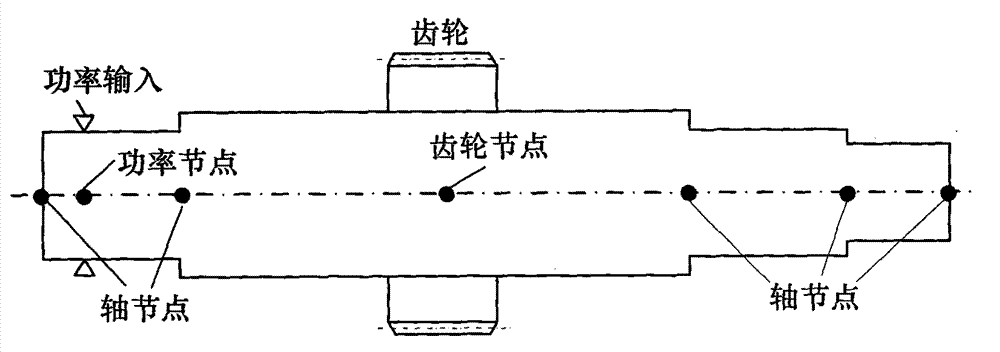
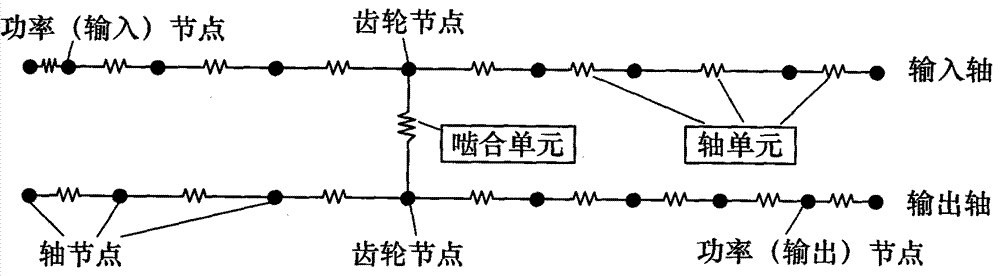
Dynamic analysis modular-modeling method for gear transmission system
InactiveCN103870630AImprove modeling efficiencyImprove accuracySpecial data processing applicationsModularitySystem configuration
The invention discloses a dynamic analysis modular-modeling method for a gear transmission system. Parts of the gear transmission system are modularly processed to form three modules with specific input and output interfaces, i.e. a shaft module, a gear pair module and a planetary gear module, according to the dynamic rapid evaluation requirements of a gear transmission system configuration design scheme; an overall mass matrix and an overall rigidity matrix of the gear transmission system can be rapidly generated only by using transmission part connecting relationship information, gear basic parameters and shaft structure basic parameters are in the gear transmission system configuration design scheme as input data, so that a dynamic analysis model of the gear transmission system is established, and the dynamic analysis efficiency of the gear transmission system can be greatly improved. In addition, a shaft with a complex structure is discretized into a plurality of shaft sections to form a plurality of shaft units, so that the accuracy of a dynamic calculation result can be improved.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Cubic spline multi-scale finite element method for simulating two-dimension flow movement
InactiveCN105354362AGuaranteed continuityHigh precisionDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsNODALMatrix method
The present invention discloses a cubic spline multi-scale finite element method for simulating two-dimension flow movement. The method comprises: firstly converting a problem that needs resolution into a variational version; determining a boundary condition of a research area, setting a coarse grid cell dimension h, dissecting the research area to obtain a coarse grid cell, and dissecting the coarse grid cell into a fine grid cell; resolving a degradation elliptic problem on each coarse grid cell to construct a basis function; resolving a total rigidity matrix and a right-hand side simultaneous equations system by using an effective calculation matrix method; obtaining a water head of each node (the coarse dimension) on the research area; obtaining a coarse dimension water head derivative by using the cubic spline technique, and obtaining Darcy flow velocity of the coarse dimension according to Darcy's Law; obtaining a water head of each node (the fine dimension) by using the basis function and an interpolation formula; and obtaining a fine dimension water head derivative by using the cubic spline technique, and obtaining Darcy flow velocity of the fine dimension according to the Darcy's Law. Compared to the prior art, the method disclosed by the present invention has similar precision, but has higher calculation efficiency.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Fiber-reinforced-plastic composite material R region ultrasonic inspection model establishing method
ActiveCN105158333ATruly reflect the communication behaviorAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesComplex mathematical operationsRigidity matrixCross-Sectional Anatomy
A fiber-reinforced-plastic (FRP) composite material R region ultrasonic inspection model establishing method is disclosed and belongs to the technical field of composite material ultrasonic inspection. The method comprises the following steps: measuring the geometrical dimension and the density of an FRP composite material R region sample; dissecting and polishing the R region sample cross section and observing the microstructure, concretely observing the unidirectional ply thickness, ply sum and fiber paving sequence; measuring the acoustic velocity of the FRP composite material unidirectional plate sample and performing inversion calculation on the elasticity rigidity matrix; calculating the corresponding Bond transformation matrix of an optimal position in the R region, and performing rotation transformation on the elasticity rigidity matrix; and setting ultrasonic inspection probe parameters and coupling medium material characteristics, so as to finish model establishment. The method gives consideration to the FRP composite material anisotropy, and also realizes quantitative description on the multilayer structure and the curved-surface shape elasticity characteristic. The model can be utilized for performing simulation calculation on FRP composite material R region ultrasonic inspection, and support is provided for researching sonic propagation law and improving inspection quality.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Method for analyzing torsional vibration inherent characteristic of planet gear transmission system
ActiveCN102968537AAccurate calculationVersatilitySpecial data processing applicationsSystem matrixEngineering
A method for analyzing a torsional vibration inherent characteristic of a planet gear transmission system comprises the following four steps: (1) carrying out mathematical modeling on pure torsional vibration of a single planet row with damping by using an Lagrangian equation; (2) analyzing the inherent characteristic of the transmission system; (3) verifying the influence of the damping on a fixed frequency through multigroup calculation; and (4) establishing a general matrix for the planet gear transmission system and carrying out modeling simulation verification through instance value calculation and simulation X. Through the adoption of the invention, an obtained damped natural vibration differential equation in the form of a parameterized matrix (a rigidity matrix, a damping matrix and a connecting matrix) in the planet transmission system is general; corresponding matrix forms are directly selected for corresponding parts according to different connecting structures and planet gear system parameters to construct an integral system matrix; and after parameters are brought in, the inherent characteristic of the transmission system is rapidly and accurately analyzed.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Power transmission tower pole stress calculation method based on finite element analysis
ActiveCN104281739AThe analysis result is accurateForce analysis is simpleGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationElement analysisMechanical models
The invention discloses a power transmission tower pole stress calculation method based on finite element analysis. The power transmission tower pole stress calculation method comprises the following steps: establishing a finite element mechanical model of a tower structure by utilizing a finite element method, and carrying out discretization of an integral structure according to the composition of the tower structure; generating an element rigidity matrix for each element, and overlapping the element rigidity matrixes to generate an integral rigidity matrix in combination with a space angle relationship and a connection relationship among various poles in the tower structure; then, generating a load array according to a load borne by the tower, and constituting a matrix equation by a node displacement array as an unknown quantity, the integral rigidity matrix and the load array; finally, acquiring a node strain by solving the matrix equation, and finally acquiring the stress of each pole in the tower structure. According to the power transmission tower pole stress calculation method, the power transmission tower pole stress is accurately solved directly by a mathematical method, and a scientific basis is provided for safety evaluation of the tower structure.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +2
Order reduction modeling method of micro electro-mechanical system containing considerable input ports
InactiveCN101315649AImprove design efficiencyDegrees of freedom scale downSpecial data processing applicationsOrder reductionSimulation based
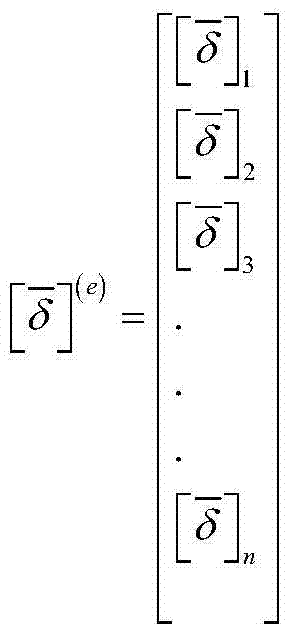
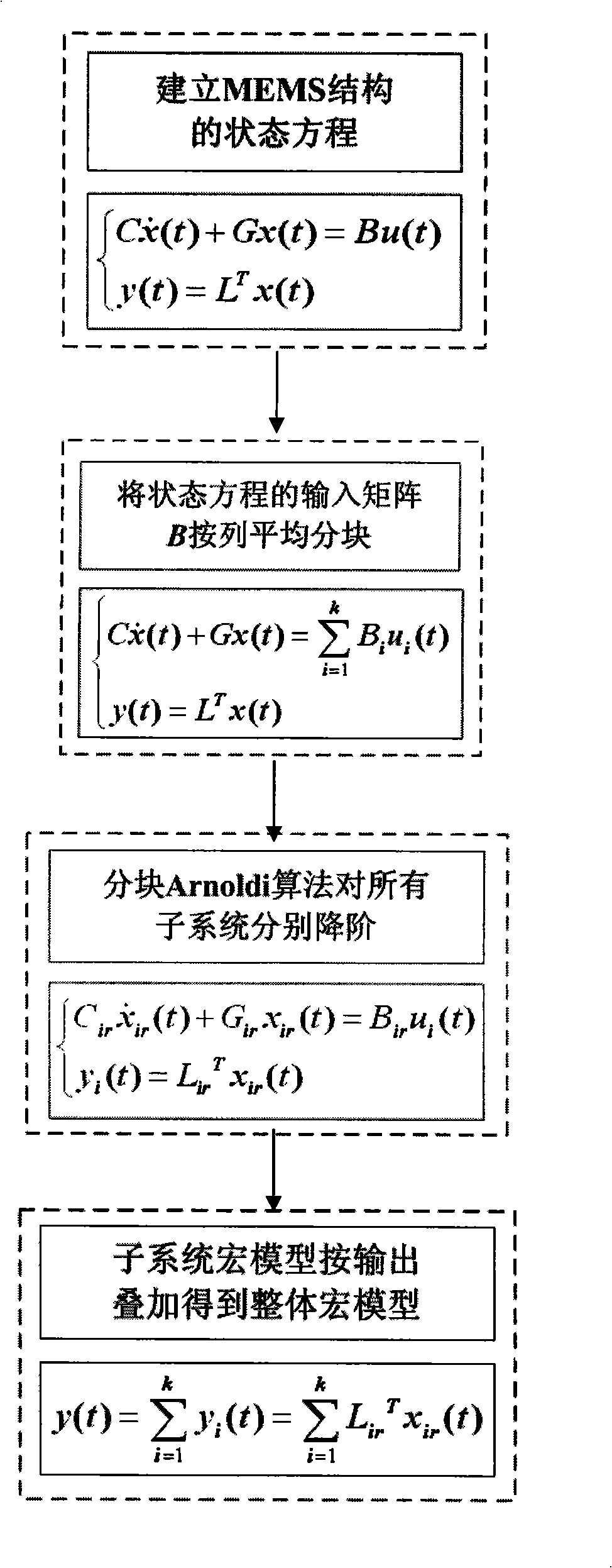
The invention discloses a deflation modeling method of a micro-electronic-mechanical-system (MEMS) which contains a plurality of input ports. A three-dimension solid model of the structure is established according to the parameters of structure design, modal analysis is carried out by using a finite element method, the quality and the rigidity matrix of the structure is extracted from analysis results, and a second order dynamics action equation of the structure is converted into a first order state equation after being established; an input matrix B is uniformly splitted into k blocks by rows to obtain the state equation of the structure after splitting; deflation is carried out to the application subblock of the (i)th sub-system to obtain the macro model state equation of the (i)th sub-system; the integral macro model of the original system can be obtained after the macro models of all the sub-systems are superposed according to output. The method speeds up the MEMS system level modeling and simulation based on the macro models, thus improving the design efficiency of the MEMS.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
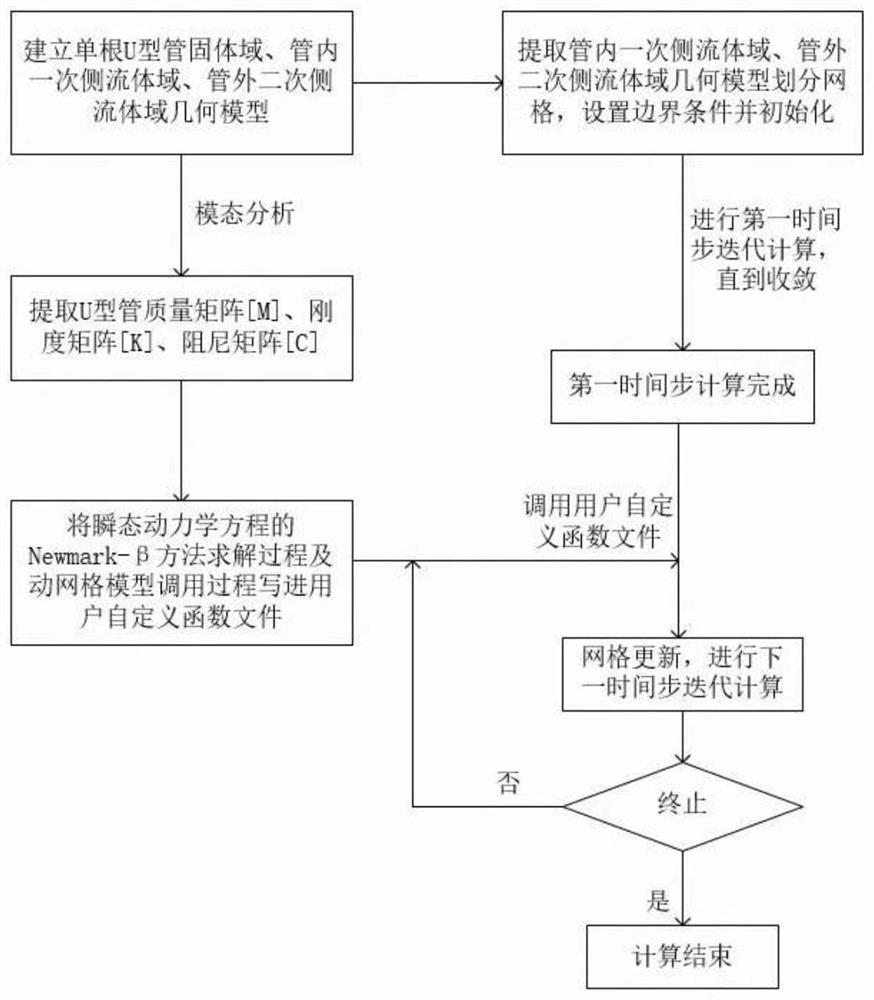
Flow-induced vibration calculation method for nuclear reactor steam generator
ActiveCN111859752AReduce dependenceAvoid complexityDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsNuclear reactorComputational model
The invention discloses a flow-induced vibration calculation method for a nuclear reactor steam generator, and the method comprises the following steps: 1, building a steam generator heat transfer tube wet modal analysis model, carrying out the wet modal analysis, and extracting a mass matrix [M], a rigidity matrix [K] and a damping matrix [C] of a heat transfer tube; 2, writing a Newmark-beta method for solving a transient kinetic equation and a dynamic grid model into a user-defined function file; 3, establishing fluid dynamic calculation models of primary and secondary side fluid domains inside and outside the heat transfer tube, and carrying out first time step iterative calculation; 4, calling and executing the user-defined function file in the step 2, updating the fluid domain grid,and performing iterative computation of the next time step on the fluid domain after the grid is updated; and 5, circularly executing the step 4 until the set calculation termination time is calculated, and stopping the calculation. The flow-induced vibration characteristics of the nuclear reactor steam generator are obtained through calculation, and the method has important significance in designand safety analysis of the nuclear reactor steam generator.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Method for predicting effective stress relaxation coefficient of polymer matrix composite
InactiveCN105787167ATightnessExact strengthComputer aided designSpecial data processing applicationsStress relaxationRigidity matrix
The invention provides a method for predicting the effective stress relaxation coefficient of a polymer matrix composite.The method includes the steps that firstly, a linear viscoelatic material constitutive equation in a time intra-domain integral form is established based on the Boltzmann superposition principle; then the effective stress relaxation rigidity of the polymer matrix composite formed by periodic unit cells is defined; then a mesomechanics model for solving an effective stress relaxation rigidity matrix of the polymer matrix composite is established based on the variation asymptotic homogenization theory; finally the effective stress relaxation rigidity of the polymer matrix composite is predicted based on the established mesomechanics model.According to the method, attributes of different materials in different directions can be obtained in the one-time solving process, and compared with a method in which rerunning is conducted under different loading conditions, the method is simpler, more convenient, more efficient and rapider.The calculated effective stress relaxation coefficient is consistent with the precision of a wave function, no more approximation relations need to be introduced, calculation precision is higher, and the strength and service life of the polymer matrix composite are predicted more accurately.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
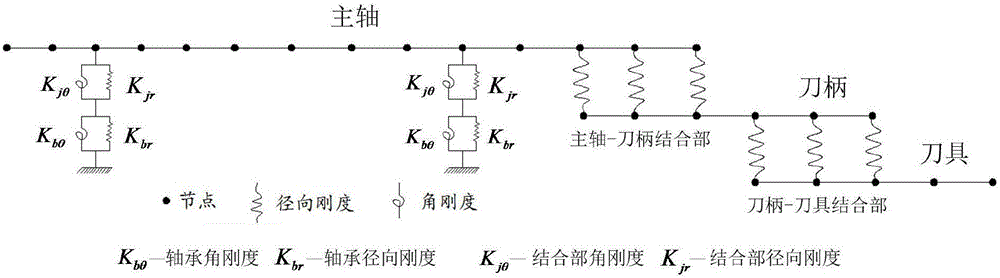
Electric main shaft system modeling method taking features of combination portions into consideration
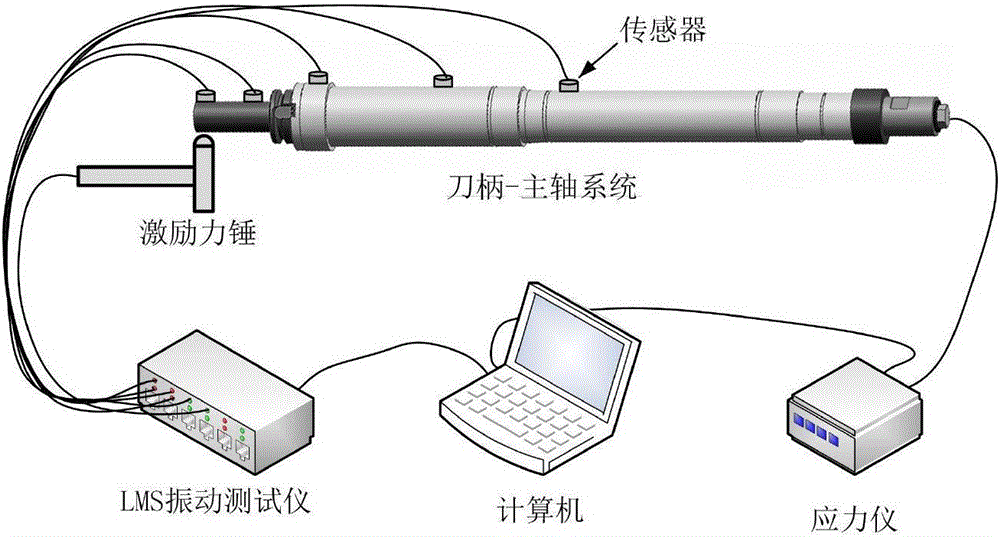
The invention discloses an electric main shaft system modeling method taking features of combination portions into consideration. According to the method, first of all, based on a frequency response function method, the rigidity of the combination portion of an electric main shaft system is identified by use of a hammering experiment, then a finite element model of a main shaft-handle-cutter system is established through the mode of adding and deleting a transition unit at the tail end of a main shaft and a handle, and finally, bearing rigidity, and a rigidity matrix of a main shaft-bearing combination portion and a rigidity matrix of a main shaft-handle-cutter combination portion which are obtained through identification are added to the rigidity matrix of the electric main shaft system so that a complete electric main shaft system kinetic equation is obtained. According to the invention, the rigidity of the combination portions are identified by use of an experiment method, and a theoretical model of the electric main shaft system is established with the influences of the combination portions are taken into consideration, so that the influence rules of the rotating speed, the bearing rigidity, the rigidity of each combination portion and the like for the dynamic features of the electric main shaft system can be simultaneously analyzed. The method can provide guidance for design and application of an electric main shaft and also provides a theoretical basis for prediction of the cutting stability of the electric main shaft system.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Orthotropic dielectric fluid factor and fracture parameter inversion method.
The invention provides an orthotropic dielectric fluid factor and fracture parameter inversion method. The method comprises the following steps: deducing a rigidity matrix of an ortho-symmetric anisotropic fracture medium by using a vertical transverse isotropic medium under a dry rock background according to fracture weakness; with utilization of hypotheses of weak anisotropy and small fracture weakness, deducing a new expression of weak anisotropy approximate rigidity of a saturated fluid rock in an orthogonal medium by combining an anisotropy Gassmann equation; acquiring a PP wave linearized reflection coefficient for fluid and fracture parameter decoupling in the orthogonally symmetrical weak anisotropic medium by combining stiffness disturbance and scattering theories; and with logging information as prior information, realizing elastic impedance pre-stack inversion changing with offset and azimuth angle by using a partial incident angle stacked by azimuth seismic data under Bayesian framework. According to the invention, Reliable results can be provided for fluid identification and fracture characterization; and technical supports are provided for seismic wave propagation research, oil and gas development and seismic disaster prevention.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method for detecting scouring depths of soil body around marine pile foundation
ActiveCN109610528AOvercome the Difficulty of Underwater Scour Depth MeasurementConstraint simulationFoundation testingCross modelEngineering
The invention discloses a method for detecting scouring depths of a soil body around a marine pile foundation. The method comprises the steps: (1) a pile-soil system is built; (2) the pile foundationis divided into n joints through a concentrated mass method to be numbered, the joints are connected through massless elastic rods with the length being d, each joint and a lower connecting rod serveas a unit, and the rod length d serves as the unit thickness; (3) the soil body around the foundation is layered, the thickness of each layer is the same as the unit thickness, namely d, the soil bodyaround the foundation is simplified to be massless spring constraint around the joints, and the elastic coefficient is determined; (4) an overall rigidity matrix and a mass matrix under the pile-soilsystem are built; (5) the inherent frequency and vibration modes of all orders of the pile foundation under the different scouring depths are detected; and (6) the rigidity correction coefficient isobtained through a cross-model and cross-mode method (CMCM method), the joints, namely damaged units, corresponding to mutation positions of the correction coefficient are found, the number of the units between the damaged units and pile foundation units on the mud surface is determined, and the range of the scouring depths is determined by multiplying the number of the units and the unit thickness.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
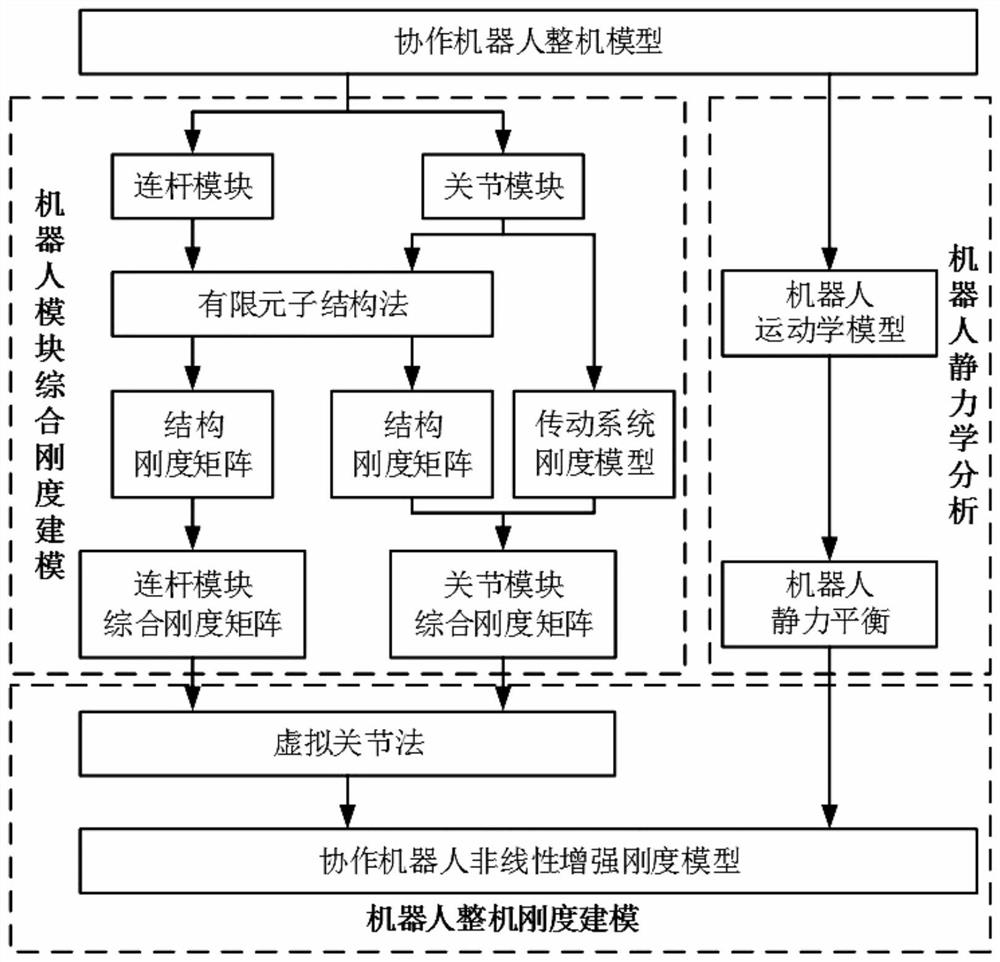
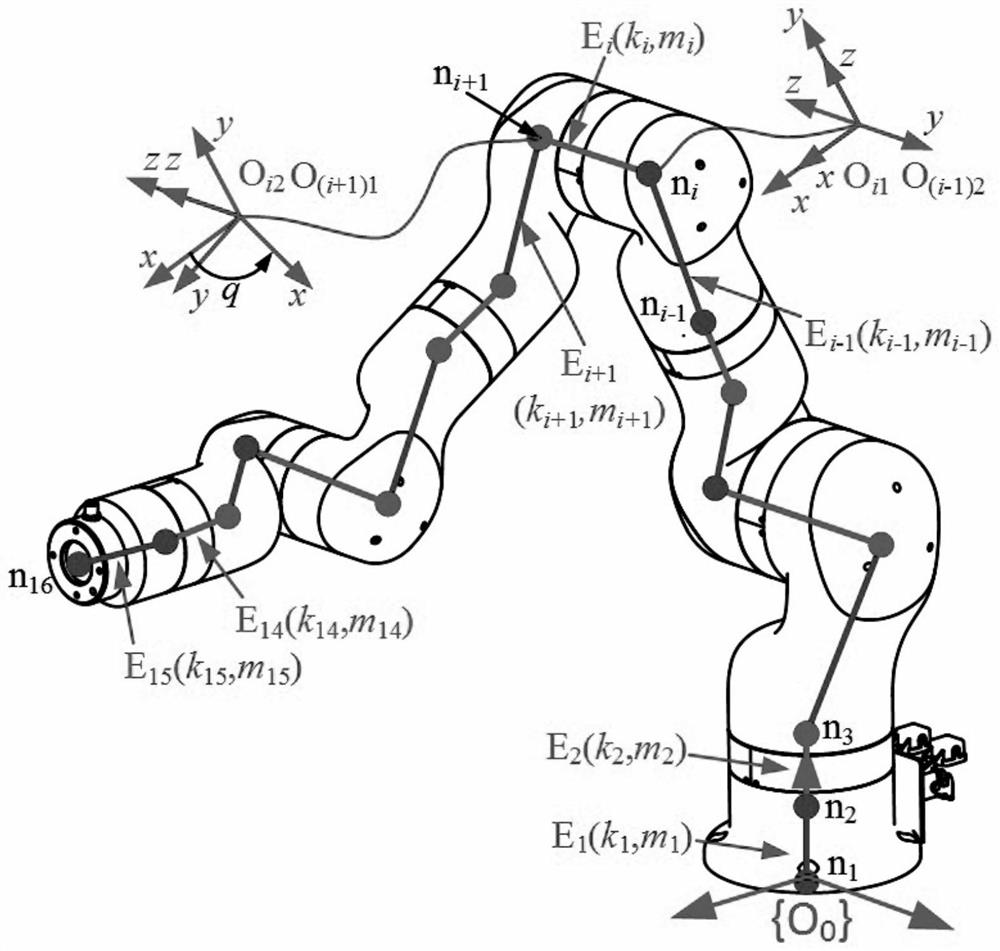
Collaborative robot nonlinear stiffness modeling method
PendingCN112949103AAchieve stiffnessIncrease stiffnessGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationSimulationRigidity matrix
The invention relates to the field of collaborative robots, in particular to a nonlinear stiffness modeling method for a collaborative robot, which comprises the following steps: step 1, robot module comprehensive stiffness modeling: splitting a robot into a plurality of modules, obtaining a structural stiffness matrix of each module, and then carrying out nonlinear modeling on a robot transmission system, the overall comprehensive rigidity of the robot is the sum of the comprehensive rigidity of all the modules, a connecting rod module comprehensive rigidity matrix is a structural rigidity matrix, and a joint module rigidity matrix is synthesized by the structural rigidity matrix and the nonlinear rigidity of the robot transmission system; step 2, robot static balance modeling: flexible deformation of each module is represented by adding virtual joints, and a robot static balance model under load and self-weight conditions is established; and step 3, robot nonlinear stiffness modeling. According to the method, finite element and virtual joint stiffness modeling methods are combined, and the overall stiffness and positioning precision of the robot can be improved.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF AUTOMATION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Rapid acquisition method of workpiece dynamics parameters in milling process
ActiveCN108732995AReduce dimensionalitySave storage spaceProgramme controlComputer controlNonlinear dimensionality reductionMaterial removal
For acquisition of workpiece dynamics parameters and rapid prediction of milling chatter stability considering material removal and cutting tool position variation causing the variation of the workpiece dynamics parameters in the thin-walled workpiece milling process, the invention provides a method for acquiring time-varying dynamics parameters of a workpiece through degree-of-freedom reduction and matrix dimensionality reduction. The method comprises the steps of: utilizing a finite element to obtain quality and stiffness matrixes of the workpiece; reducing the dimensionality of the qualityand stiffness matrixes of the workpiece through carrying out degree-of-freedom reduction and matrix dimensionality reduction; and finally, acquiring dynamics parameters of the workpiece at different tool position points rapidly by adopting a numerical calculation method, and performing stability prediction.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Heterogeneous hierarchical structure topological optimization method containing variable-size unit cells
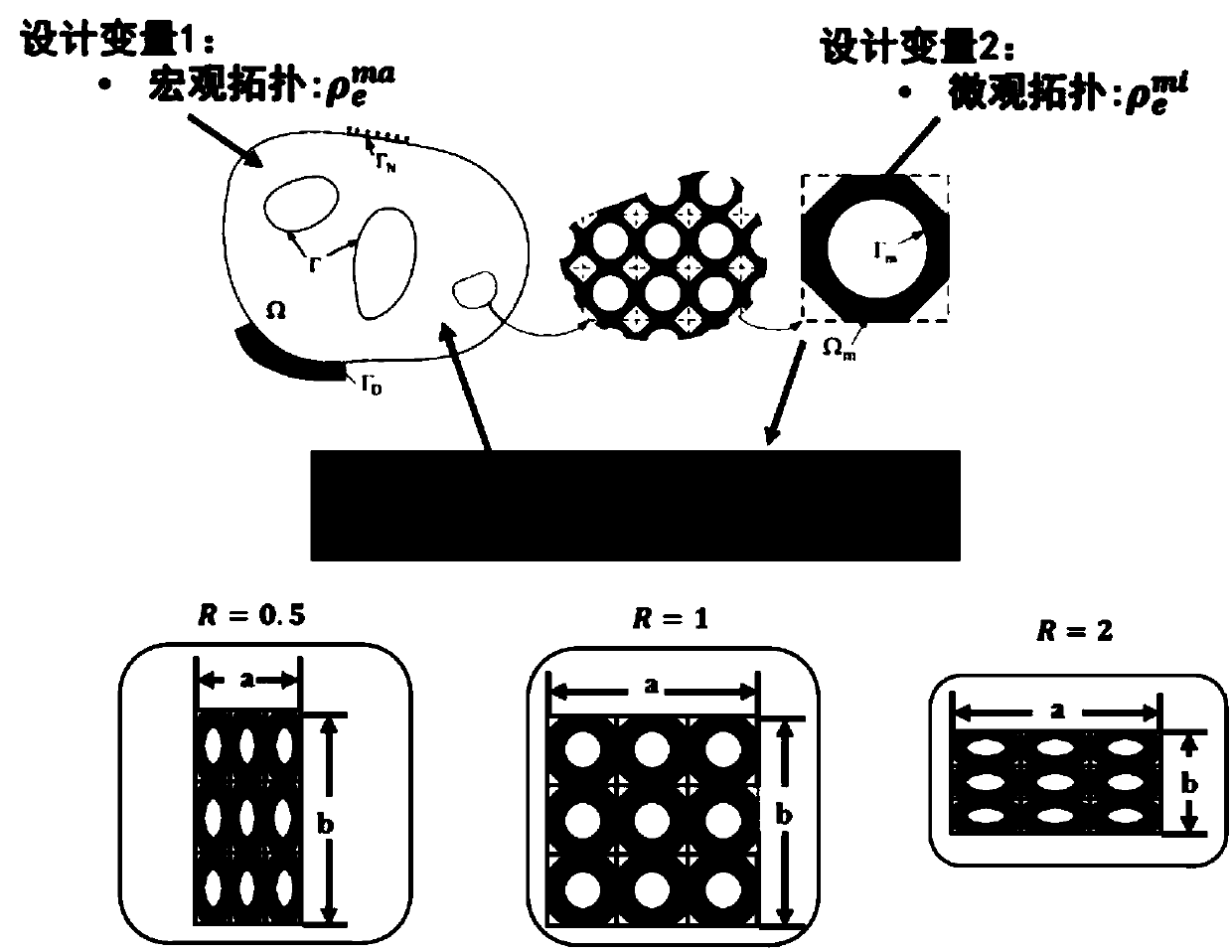
ActiveCN109657378ARealize space transformationIncrease stiffnessDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsElastic tensorAlgorithm
The invention belongs to the technical field of structural topological optimization, and particularly relates to a heterogeneous hierarchical structure topological optimization method containing variable-size unit cells. The method comprises the following steps: 1) defining a topological optimized microscopic design domain, and dividing a microscopic grid, a macro design domain and the like in thedomain; 2) establishing a design domain model; 3) selecting a size variable interpolation point; 4) fitting a function relationship between the dimension variable interpolation point and the equivalent elastic tensor thereof; 5) calculating a unit stiffness matrix and a macroscopic displacement field according to the size variable interpolation point; 6) calculating the interpolation point sensitivity of the flexibility function of the structure to the macroscopic design variable, the micro-unit cell size variable and the size variable, and completing the collaborative optimization design; According to the method, macro-micro collaborative optimization is achieved through the structure with the variable unit cell size, the problems that in the prior art, the unit cell length-width ratio is constant, and the performance potential of a microstructure is limited can be well solved, and spatial transformation of material attributes can be achieved by adjusting the distribution of the length-width ratio in space.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
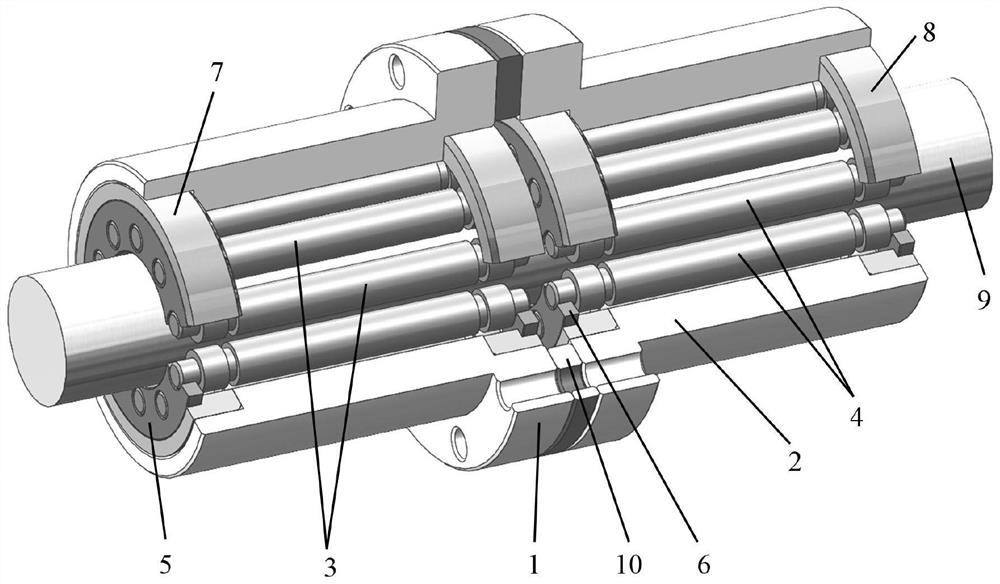
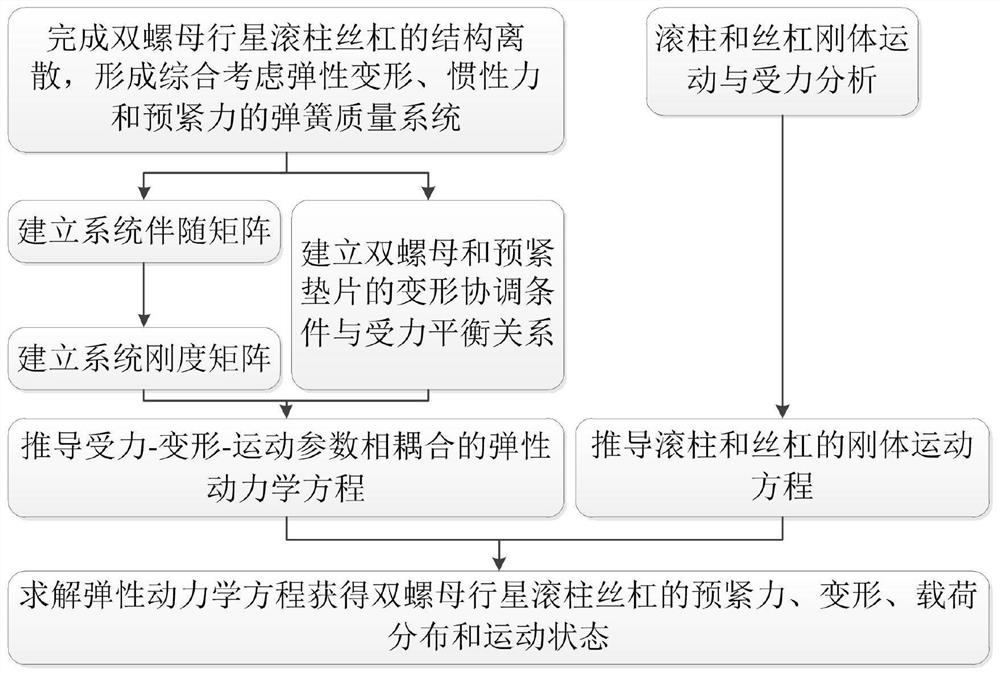
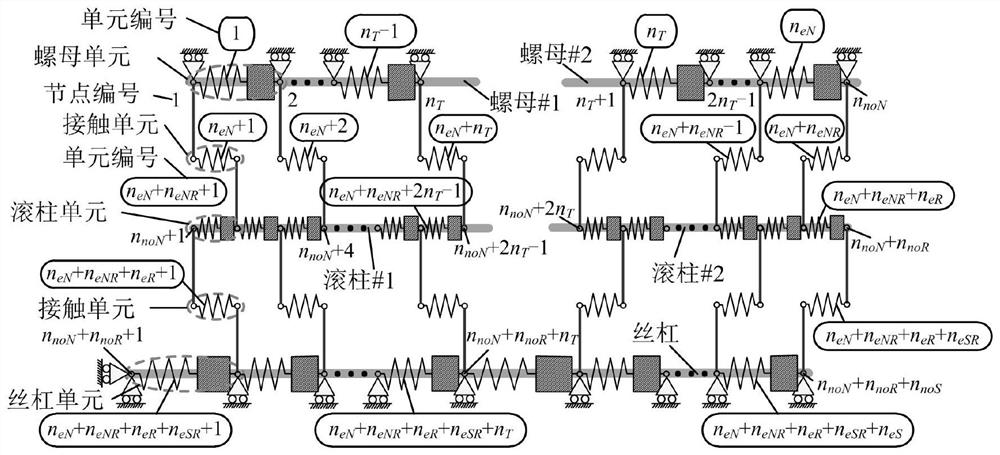
Double-nut planetary roller screw dynamics research method based on elastic deformation
The invention discloses a double-nut planetary roller screw dynamics research method based on elastic deformation. The method comprises the following steps: S1, building a double-nut planetary rollerscrew spring quality system which comprehensively considers the elastic deformation, inertia force and pre-tightening force according to the structural features of a double-nut planetary roller screw;s2, calculating an adjoint matrix and a rigidity matrix of the spring mass system; s3, establishing a stress-deformation-motion parameter coupled double-nut planetary roller screw elastic kinetic equation; s4, establishing a rigid body motion equation of the lead screw and the pin roller; and S5, solving the elastic kinetic equation in the step S3 in combination with the rigid body motion equation of the lead screw and the pin roller in the step S4. According to the research method, a stress-deformation-motion parameter coupled double-nut planetary roller screw elastic kinetic equation is provided, and the pre-tightening force, deformation, load distribution and motion state of the mechanism under different use working conditions are obtained by solving the equation.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Temperature parameterized reduced-order modeling method for micro-electromechanical system
InactiveCN101567018AImprove computing efficiencyImprove calculation accuracySemi-permeable membranesPiezoelectric/electrostrictive/magnetostrictive devicesTemperature stressHat matrix
The invention discloses a temperature parameterized reduced-order modeling method for a micro-electromechanical system, and belongs to the field of micro-electromechanical system design and model order reduction. The method comprises the following steps: extracting quality, rigidity and temperature stress rigidity matrixes, and establishing a two-order dynamical equation related to temperature; constructing an orthogonal mapping matrix V; and projecting the primary two-order dynamical equation to a subspace in which the orthogonal mapping matrix V is positioned so as to acquire a temperature parameterized low-order model. The reduced-order method can greatly reduce the freedom scale of the primary model through an order reduction algorithm so as to improve the system-level modeling and simulating speed based on the reduced-order model. Simultaneously, by adopting the matrix matching principle, transfer functions of the reduced-order model and the primary model can be approximate better so as to have higher precision. During order reduction, a projection matrix irrelative with parameters can be generated, and finally, a temperature parameter in the primary system is reserved in the low-order model.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
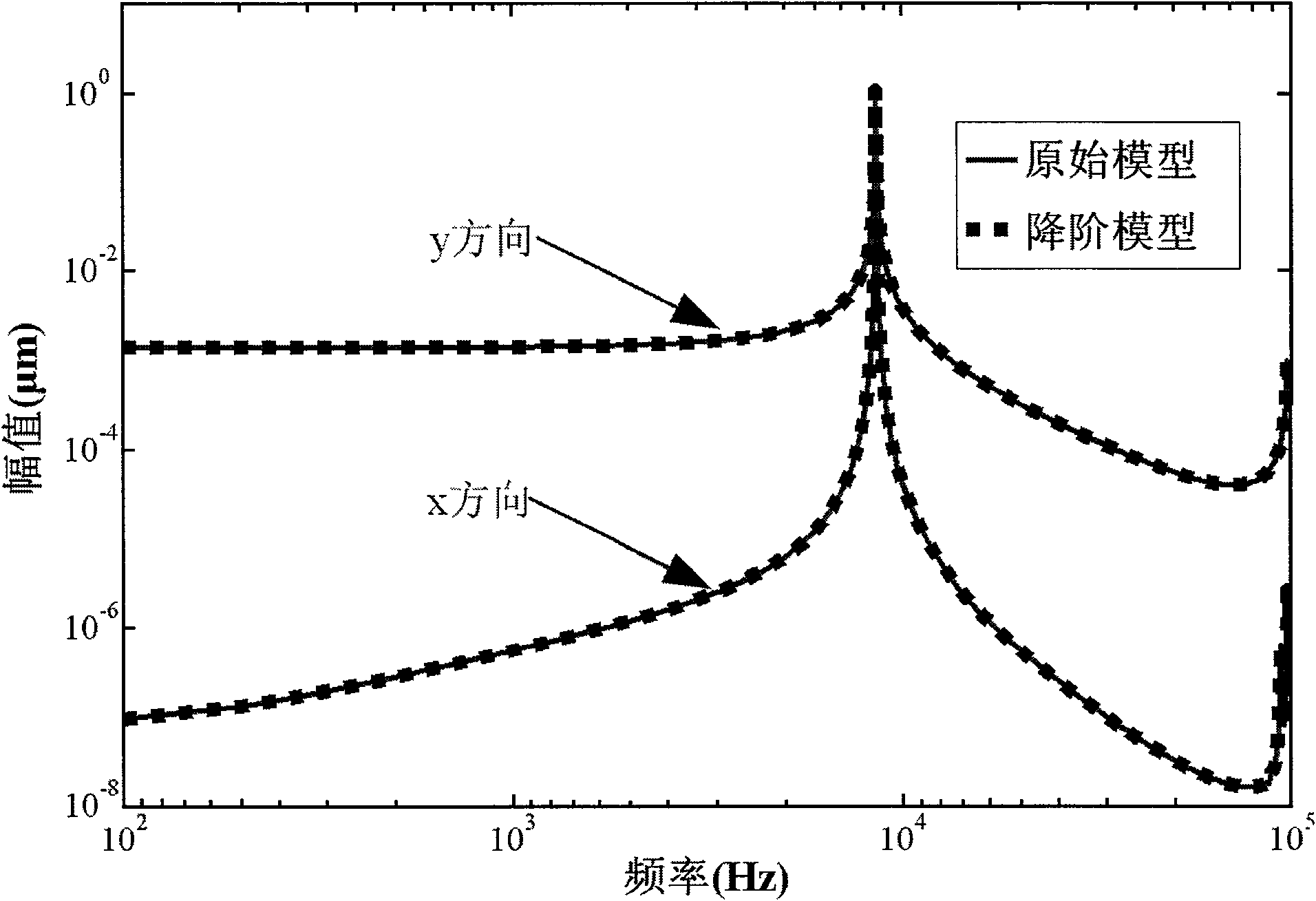
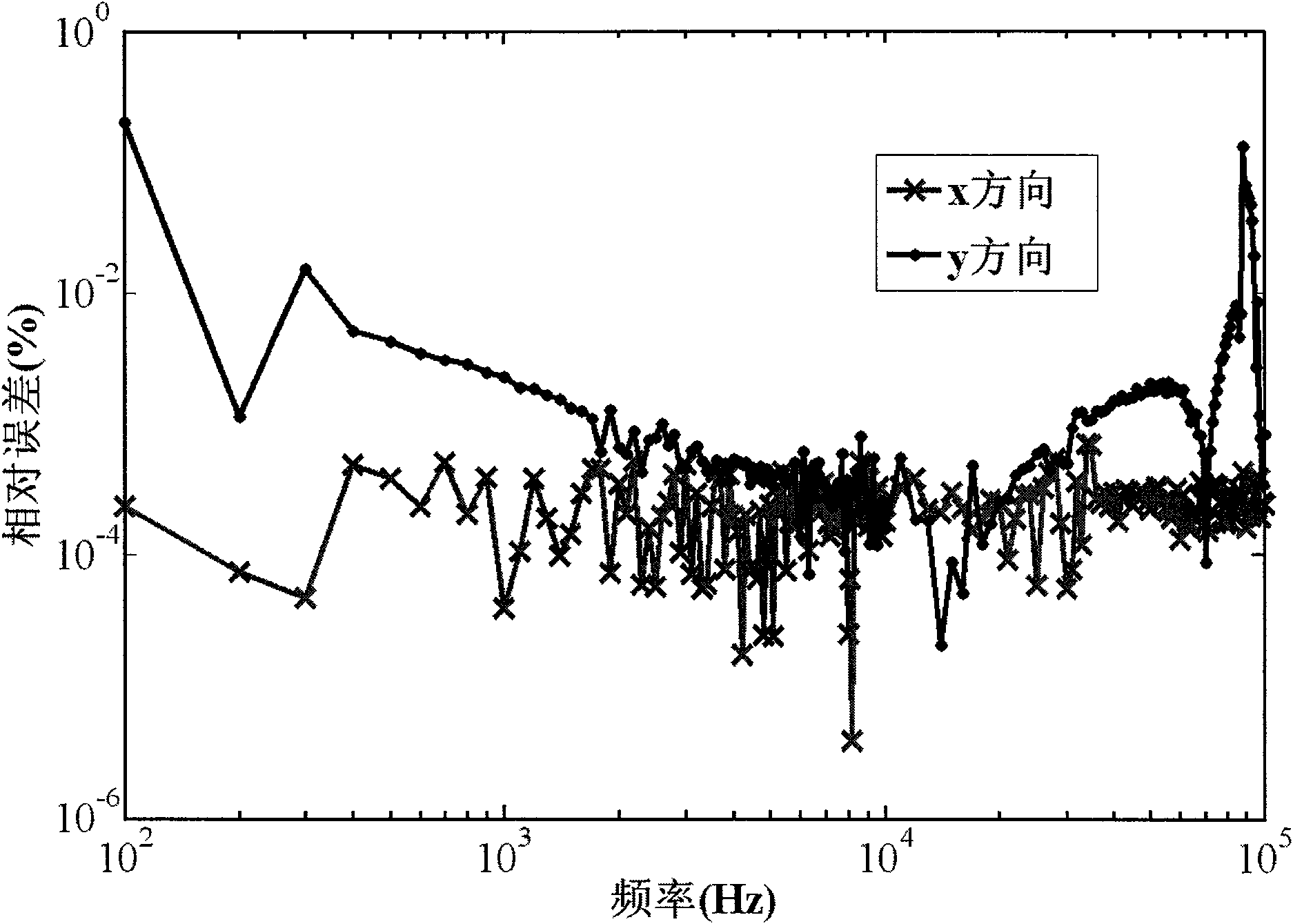
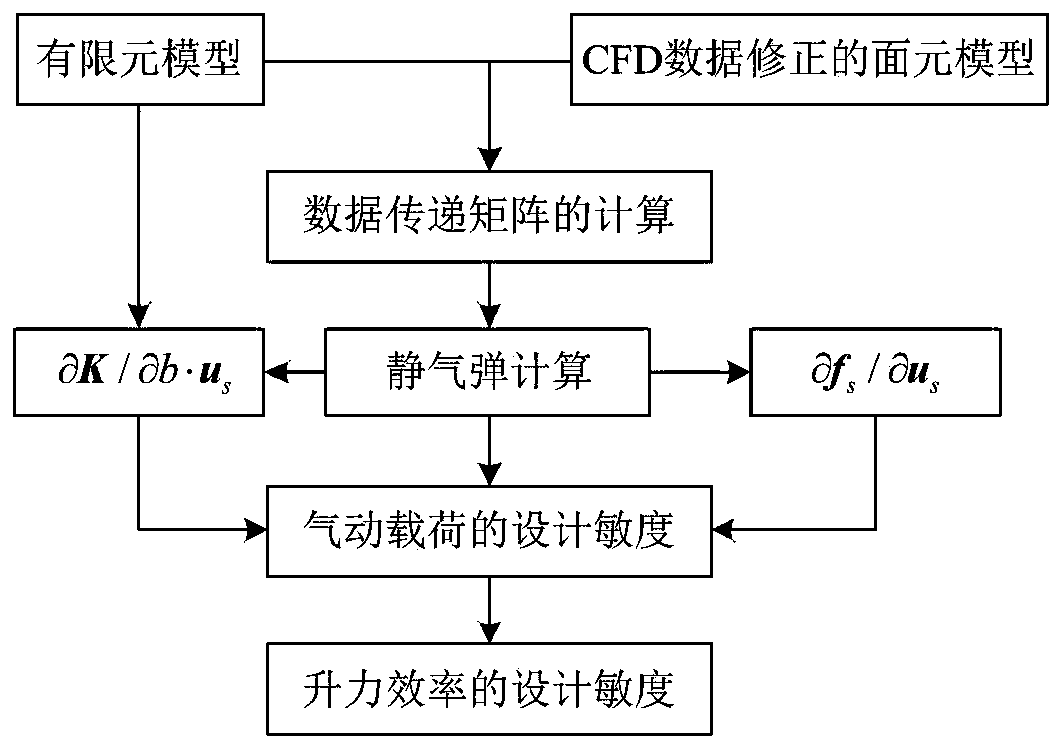
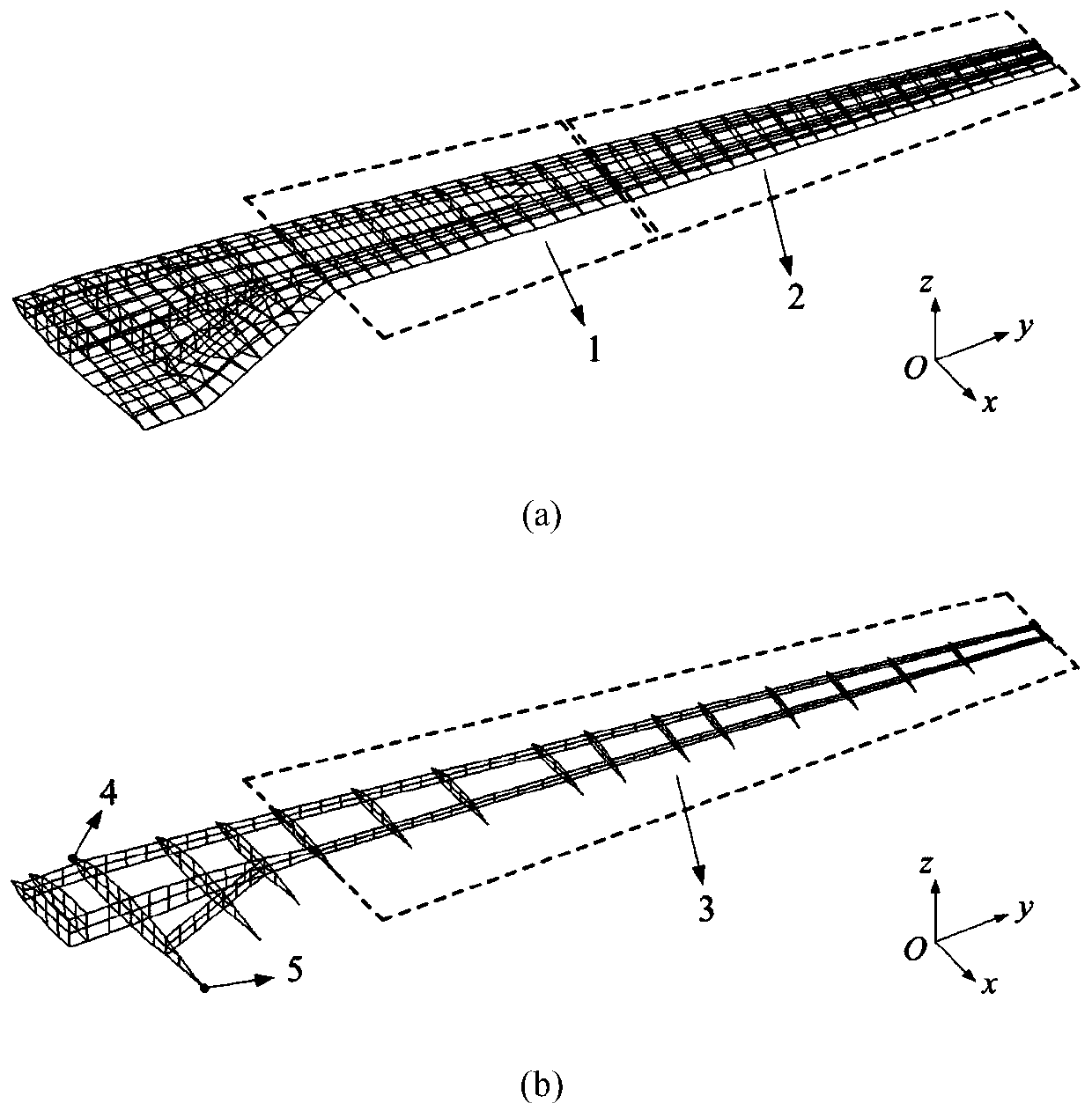
Method for analyzing design sensitivity of aerostatic elastic energy of wing with high aspect ratio
ActiveCN110704953ASolving Volatility Issues on Deformed SurfacesAvoid destructionGeometric CADAerodynamic loadClassical mechanics
According to the method, the least square fitting surface function is established by utilizing the linear function and the consistent tight support radial basis function, so that the simulation of theelastic deformation of the wing is realized, and the problem of deformation surface volatility during displacement transmission of a traditional interpolation method is solved. On the basis of staticaeroelastic calculation, a model analysis solving method for aerodynamic load design sensitivity based on an iteration mode is provided and comprises a direct method and an accompanying method, the algorithm avoids damage to an original rigidity matrix, meanwhile, calculation efficiency is high, and the requirement of engineering practice is met.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
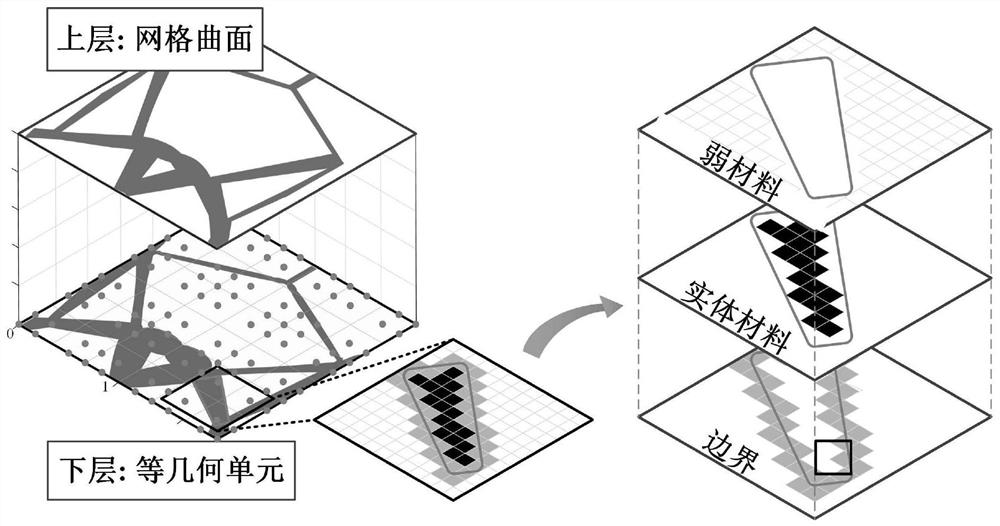
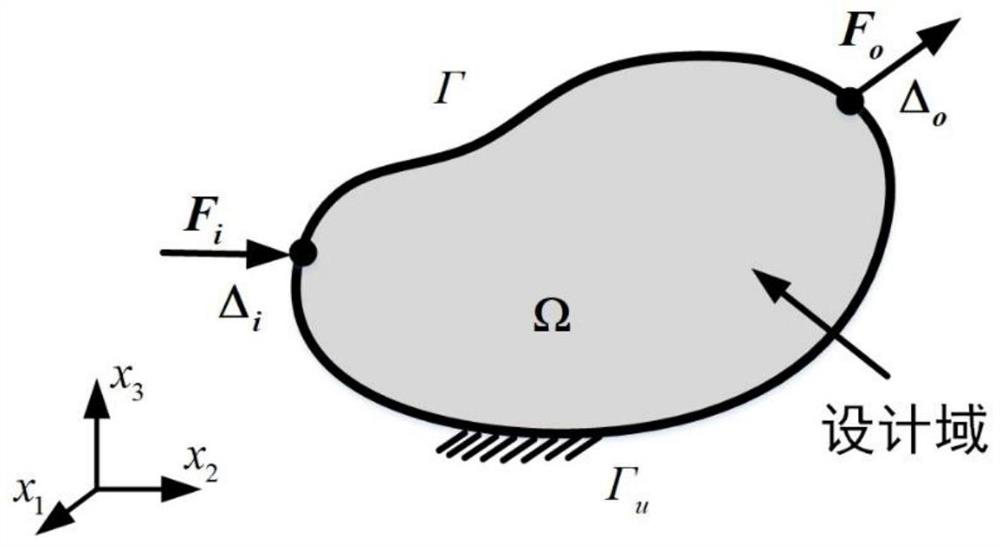
Compliant mechanism generation method based on zero-depletion grid curved surface continuous deformation
ActiveCN111709097ASolve the problem that the initial layout has a heavy dependencyImprove continuityGeometric CADConstraint-based CADTopology mappingAlgorithm
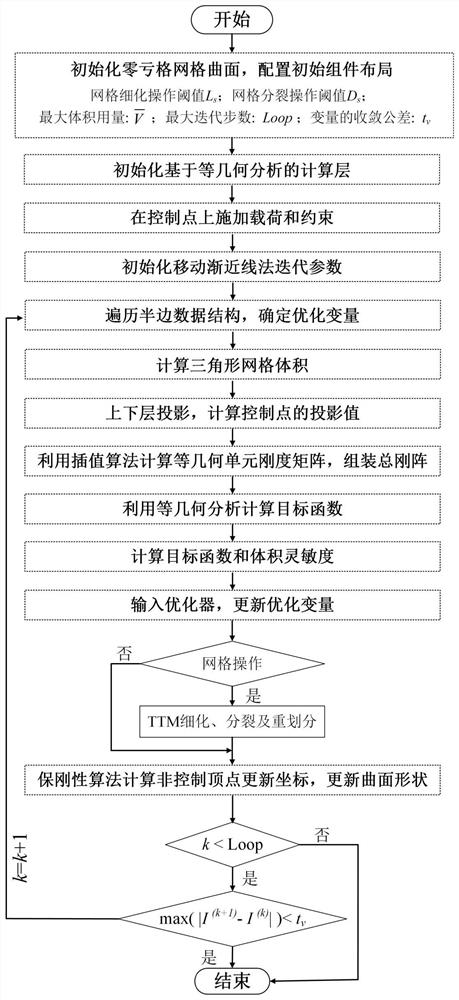
The invention discloses a compliant mechanism generation method based on zero depletion grid surface continuous deformation. The compliant mechanism generation method comprises the following steps: firstly, configuring initial component layout, initializing a calculation layer based on isogeometric analysis, applying load and constraint on isogeometric unit control points of the calculation layer,initializing iterative parameters of a moving asymptotic method, and optimizing iteration; calculating the volume of the triangular mesh, mapping the topology described by the upper triangular mesh to a lower calculation layer, calculating the projection value of a control point, and assembling an overall rigidity matrix; calculating a target function value of the structure response, solving thesensitivity of the volume, and inputting the sensitivity into an optimizer to obtain an updated coordinate value; judging triggering conditions of grid refinement, grid splitting and grid re-divisionoperation according to the updated vertex coordinate value, completing grid re-update, calculating non-control vertex update coordinates, updating the triangular grid curved surface shape, and completing one iteration; repeating iteration until convergence conditions are met. According to the method, structural response calculation and sensitivity analysis in the topological optimization process are reliably realized.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
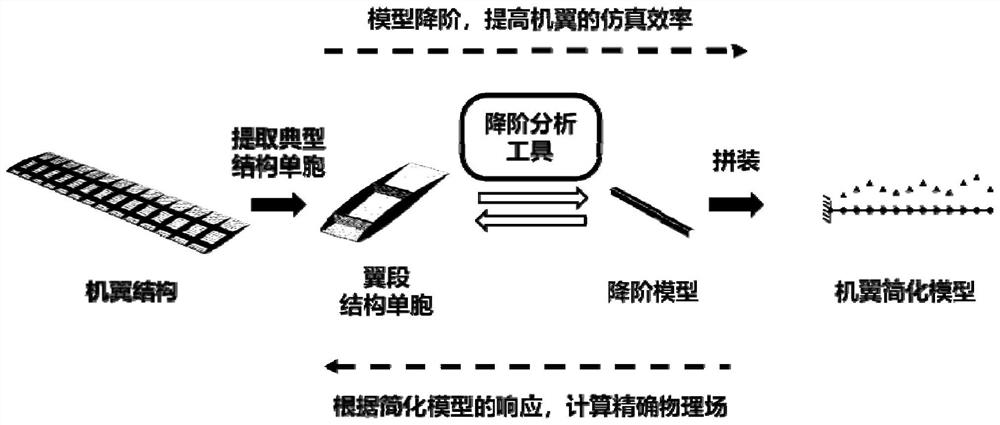
Wing structural mechanics high-fidelity order reduction simulation method, electronic equipment and storage medium
ActiveCN112560167ASolve problems that are no longer cyclicalWell formedGeometric CADSustainable transportationElement analysisFinite elemente analyse
The invention provides a wing structure mechanics high-fidelity order reduction simulation method. The method comprises the steps of finite element grid node pairing and rigid body constraint application, non-shear load loading analysis, shear load loading analysis and equivalent section attribute calculation. The invention relates to electronic equipment and a storage medium, which are used for the method. According to the method, the problem that the internal force of the structure does not have periodicity when the slender structure is under the action of the shearing force is well solved,the shearing force condition is corrected by utilizing the mechanical response of the structure unit cells under the action of the bending load, the disturbance displacement field and the surface force are restrained, the form is simple and clear, and the embeddability is good. According to the method, the equivalent section stiffness matrix of the equivalent reduced-order model can be calculatedby simulating deformation of the wing structure unit cells under different loads, so that a reduced-order model unit is provided for finite element analysis of the aircraft wing, and the analysis efficiency of the aircraft wing model is improved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
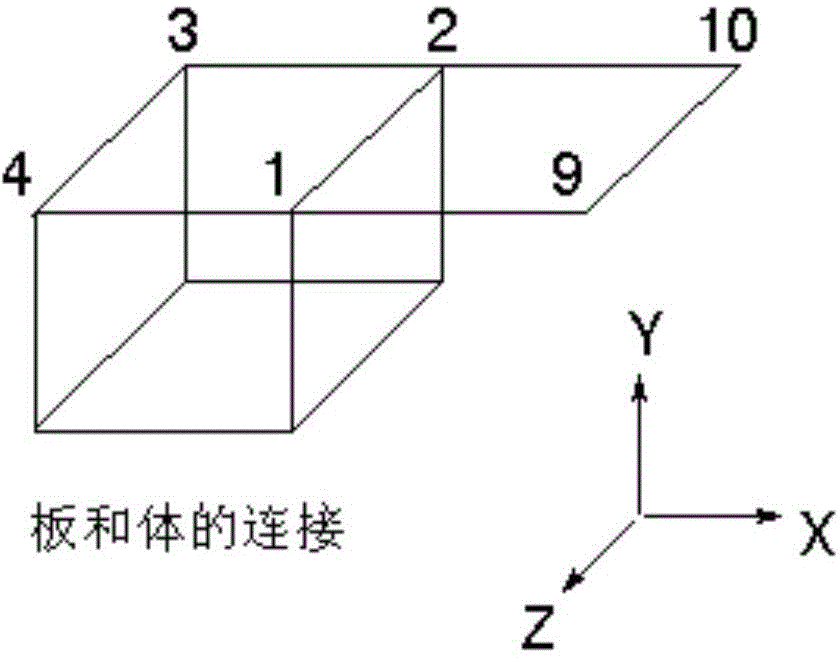
Numerical analysis method for connection between three-dimensional and two-dimensional finite element units
InactiveCN104699872AImprove analysis timeRaise the cost of analysisSpecial data processing applications3D modellingStress distributionTime efficient
The invention provides a numerical analysis method for the connection between three-dimensional and two-dimensional finite element units, and aims to save time and reduce analysis cost by replacing part of a test result with numerical simulation. The numerical analysis method is characterized by comprising the following steps: (1) constructing a three-dimensional unit and a two-dimensional unit at actual structure positions respectively, endowing the three-dimensional unit with a simulated rotating freedom degree at the connection between the three-dimensional unit and the two-dimensional unit, and establishing a connection relationship between the two-dimensional unit and a new three-dimensional unit by virtue of a rigid body element; (2) creating a card required by structure analysis according to a connection form and a constraint relationship of the rigid body element; (3) creating a unit rigidity matrix according to the card required by analysis, assembling the unit rigidity matrix with other unit rigidity matrixes of the structure to form an overall rigidity matrix, and creating structure deformation and unit stress distribution according to a structure load and a boundary condition.
Owner:CHINA AIRPLANT STRENGTH RES INST
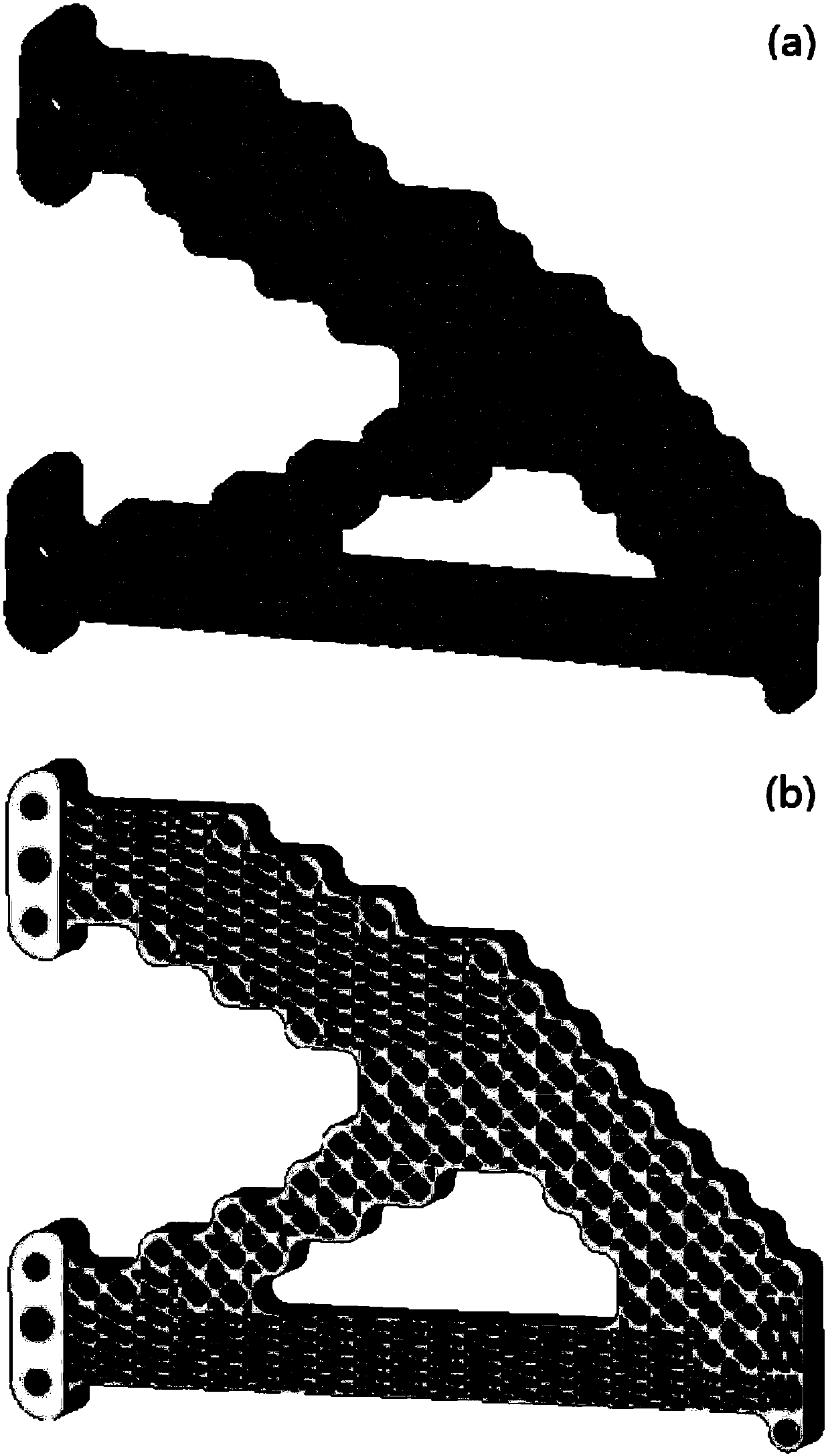
Parameterization static state ultra-unit structuring method
ActiveCN101276381AEasy to modelLow number of nodesSpecial data processing applicationsAlgorithmRigidity matrix
The invention discloses a parameterized static super-unit construction method. The unit reduces the model freedom by the substructure method, then parameterizing various sizes of the structure; fits rigidity matrix K and strain matrix B to construct the super-unit that has a small number of nodes, so that considerable computing time is saved for easy optimization and the guaranteed accuracy of calculations. Based on the construction method for the super-unit, various super-units with computational complexity greatly reduced are constructed.
Owner:深圳网蓝通用科技有限公司
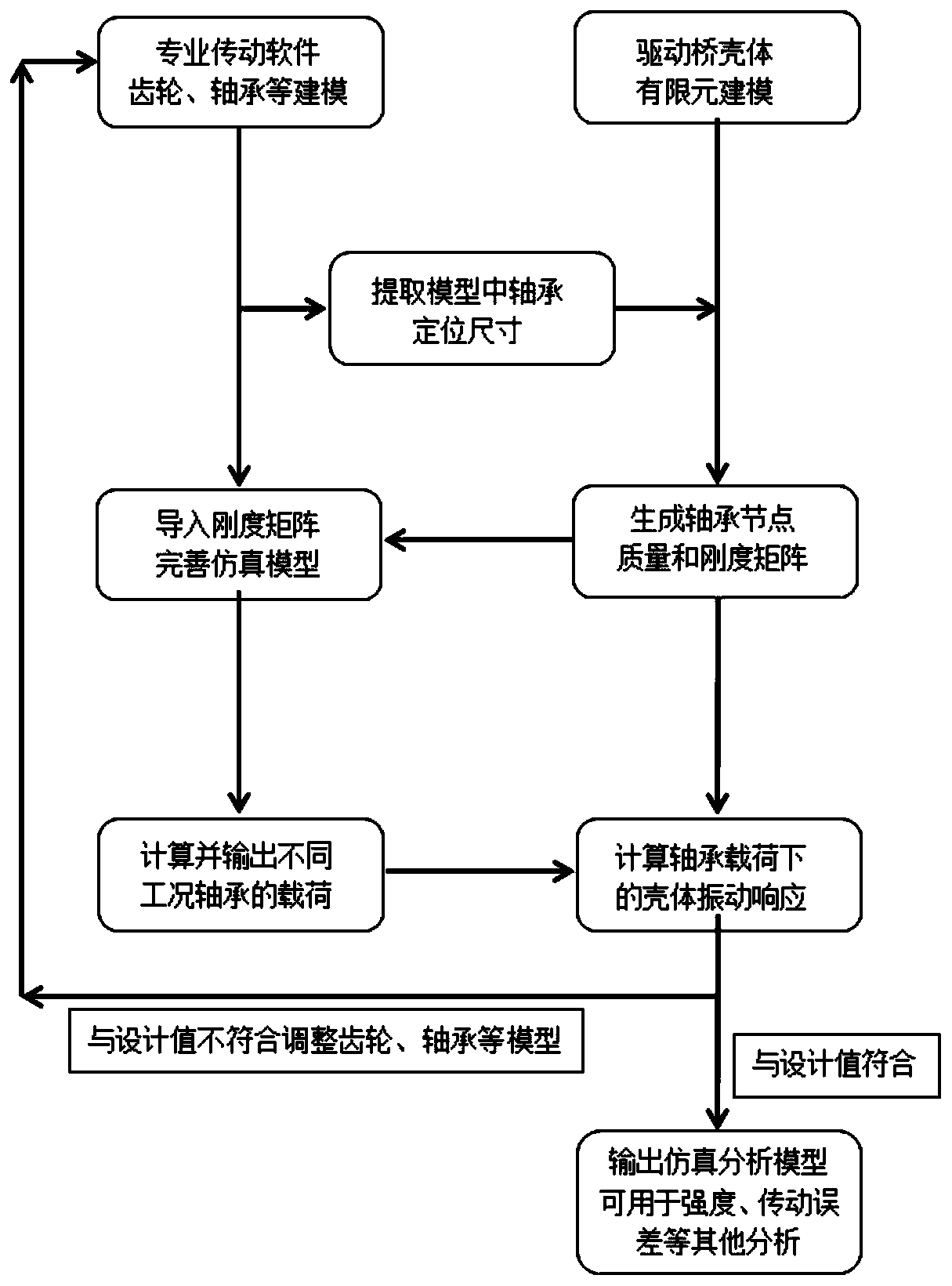
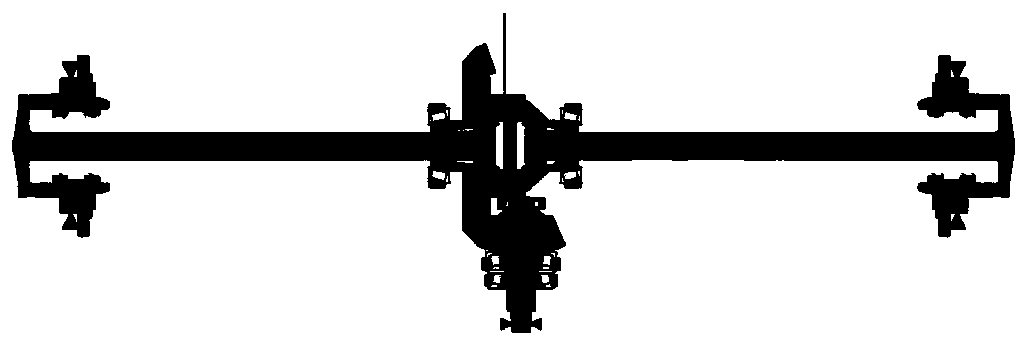
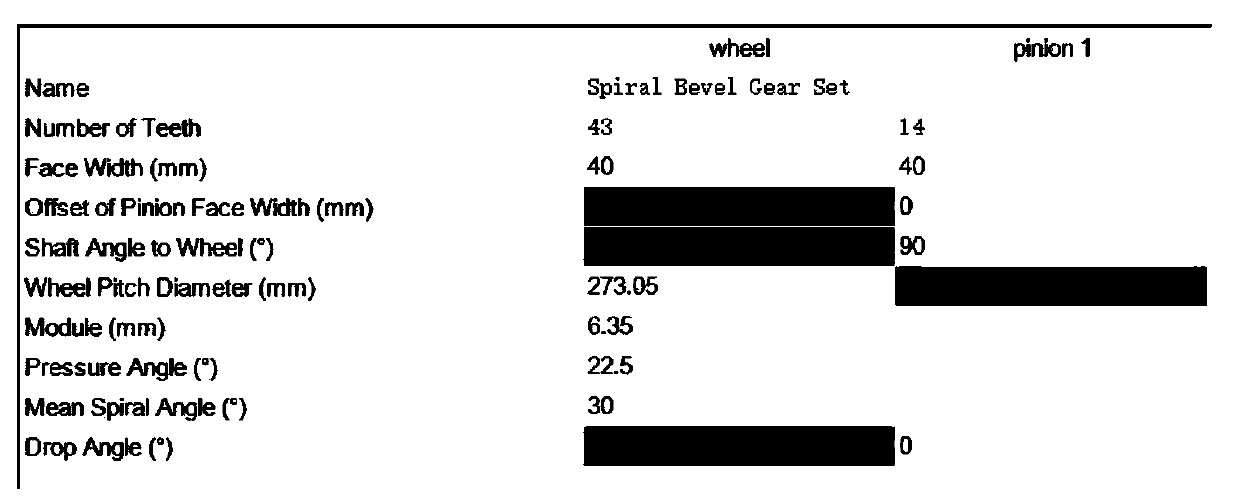
Automobile drive axle vibration simulation analysis method
ActiveCN111090952AReduce manufacturing costReduce test volumeGeometric CADSustainable transportationElement modelModel extraction
The invention provides an automobile drive axle vibration simulation analysis method. The method comprises the following steps: 1) establishing a main speed reducer transmission model of an automobiledrive axle through transmission analysis software; 2) extracting positioning size information of a bearing center point of a main speed reducer; 3) establishing a shell finite element model of a drive axle shell through finite element software; 4) generating a mass and rigidity matrix of a bearing center point; 5) importing the mass and rigidity matrix of the central point of a bearing into transmission analysis software; 6) outputting dynamic displacement information of the bearing center point under different working conditions; 7) calculating the shell vibration response under the bearingload. Finite element software and professional transmission analysis software are combined, the test amount is reduced, the test period is shortened, a simulation model is used for optimizing and improving the drive axle, the improvement effect is checked before formal improvement and implementation, and the production cost of enterprises is saved.
Owner:CATARC AUTOMOTIVE TEST CENT TIANJIN CO LTD +1
Method for calculating load distribution of composite bolt connection by considering clearance and friction influence
ActiveCN106295024AImprove computing efficiencyImprove modeling efficiencyDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsModel modificationUnit model
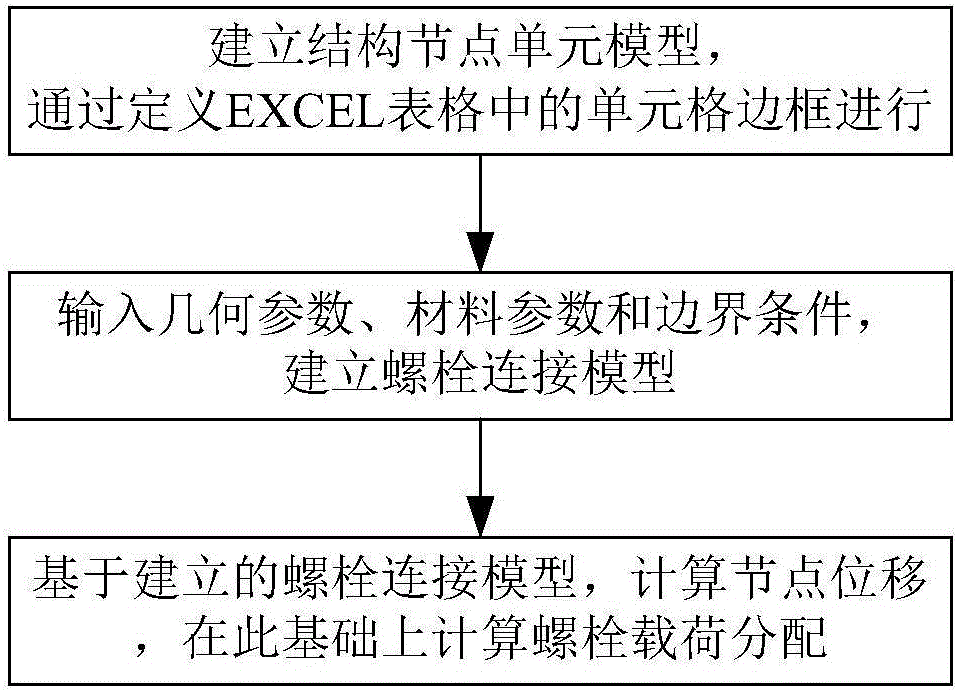
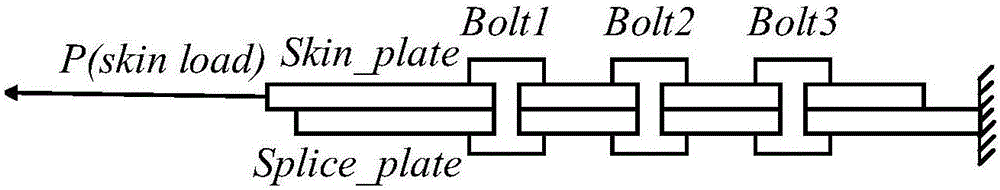
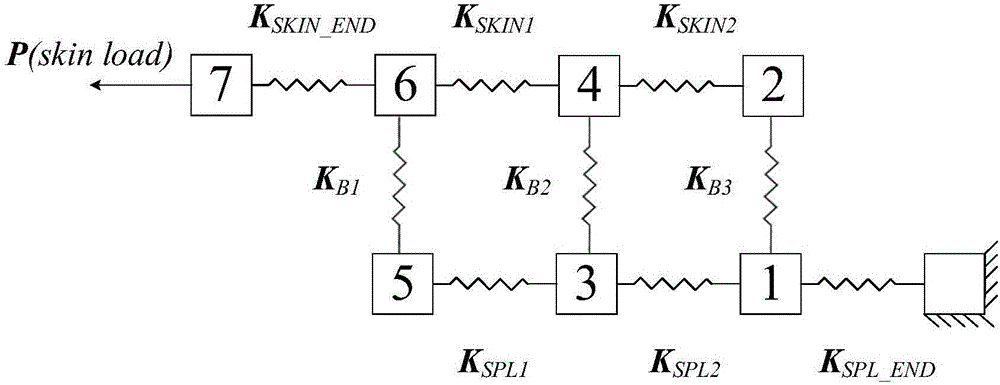
The invention provides a method for calculating load distribution of composite bolt connection by considering clearance and friction influence and relates to a composite bolt connection technique. The method comprises the following steps: constructing a structure node unit model; inputting a geometrical parameter, a material parameter and a boundary condition to complete the construction of a bolt connecting model; calculating node displacement on the basis of the constructed bolt connecting model; accordingly calculating the bolt load distribution. According to the method, a bolt connecting model structure is generated on the basis of an EXCEL frame; the following three conditions are considered for the unit stiffness matrix and the corresponding equivalent load vector of the bolt: the influence caused by clearance and friction is not considered, the influence caused by clearance is considered and the influence caused by clearance and friction is considered; the method has the advantages of high calculation efficiency of spring model and high modeling efficiency of finite element method; the problems of low calculation efficiency and complex modeling on the basis of consideration for the influence caused by clearance and friction of the traditional finite element method can be avoided; compared with the traditional spring model, the method is higher in modeling efficiency and is short in model modification time.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Level set method for optimal design of fiber curve laying variable stiffness structure
ActiveCN111723457AAngular Layout OptimizationImprove structural rigidityGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationFiberAlgorithm
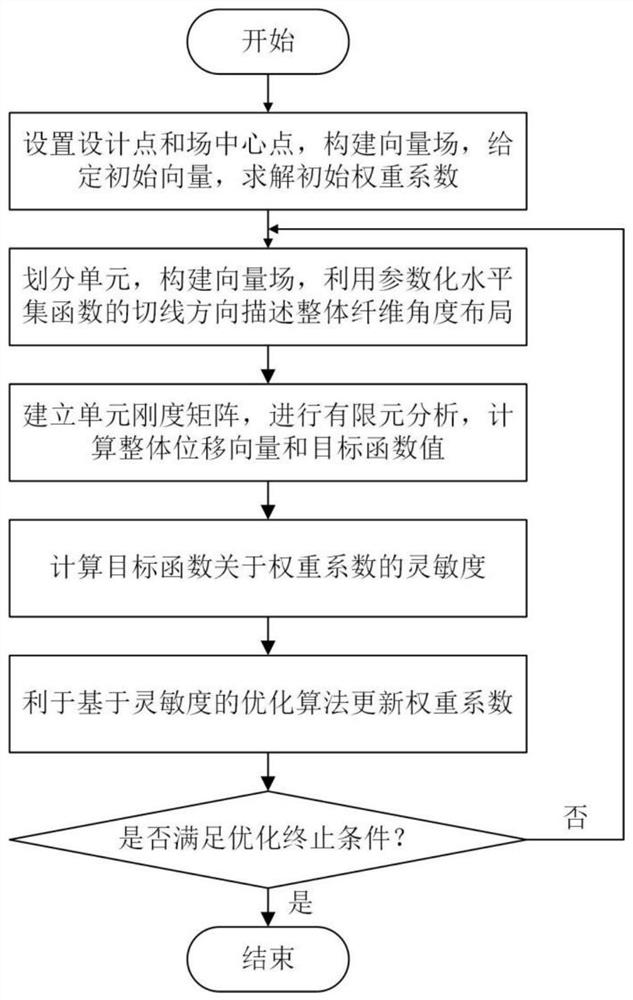
The invention belongs to the related technical field of structural optimization design, and discloses a level set method for optimal design of a fiber curve laying variable stiffness structure, whichcomprises the following steps of: firstly, setting a series of design points and field center points in a structural design domain, constructing a vector field, and further solving an initial weight coefficient at each field center point; secondly, dividing a structural design domain into limited units, constructing a vector field according to the central points of the units and the central pointof the field, and describing the overall fiber angle layout by utilizing the tangential direction of a parameterized level set function; thirdly, establishing a unit stiffness matrix to solve an overall displacement vector and a target function value, and calculating the sensitivity of a target function about a design variable by taking a weight coefficient as the design variable and minimizing the flexibility as a design target; and secondly, repeatedly iterating after updating the design variable until an optimization termination condition is met. According to the method, the fibers can be parallel to each other, and the situation of fiber overlapping or gaps in the manufacturing process of the optimal structure is avoided.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
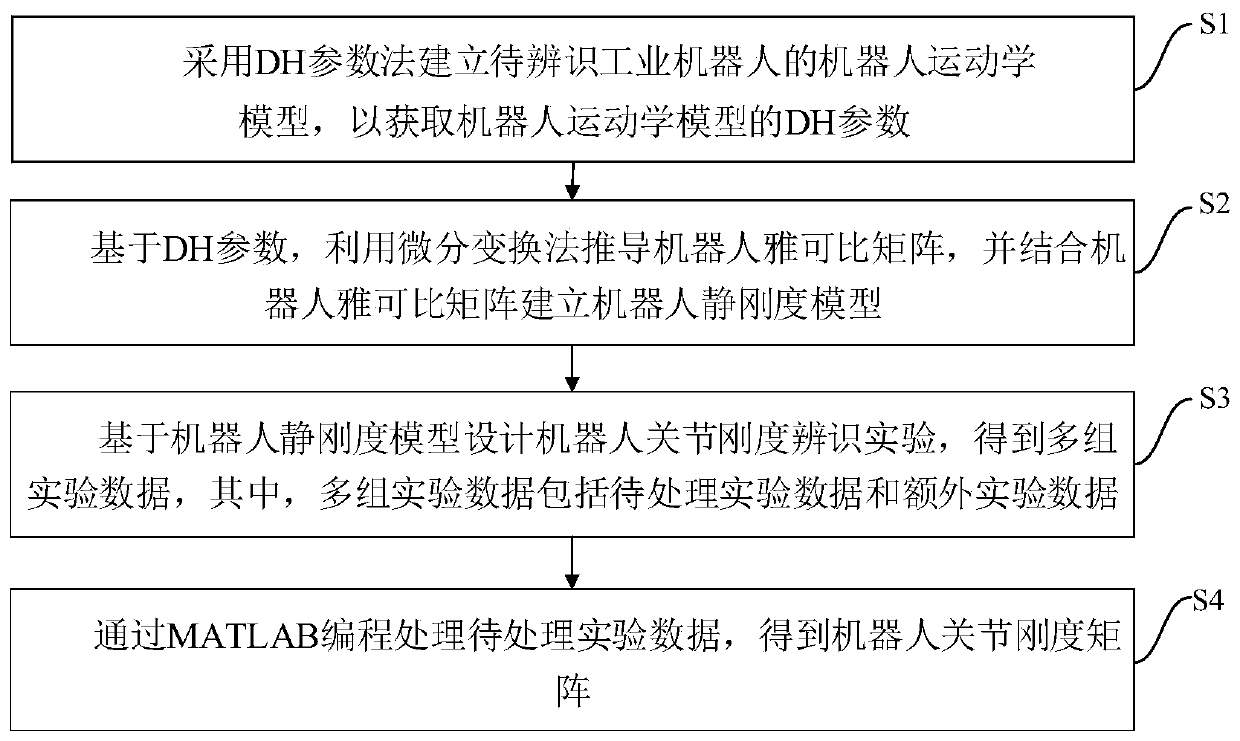
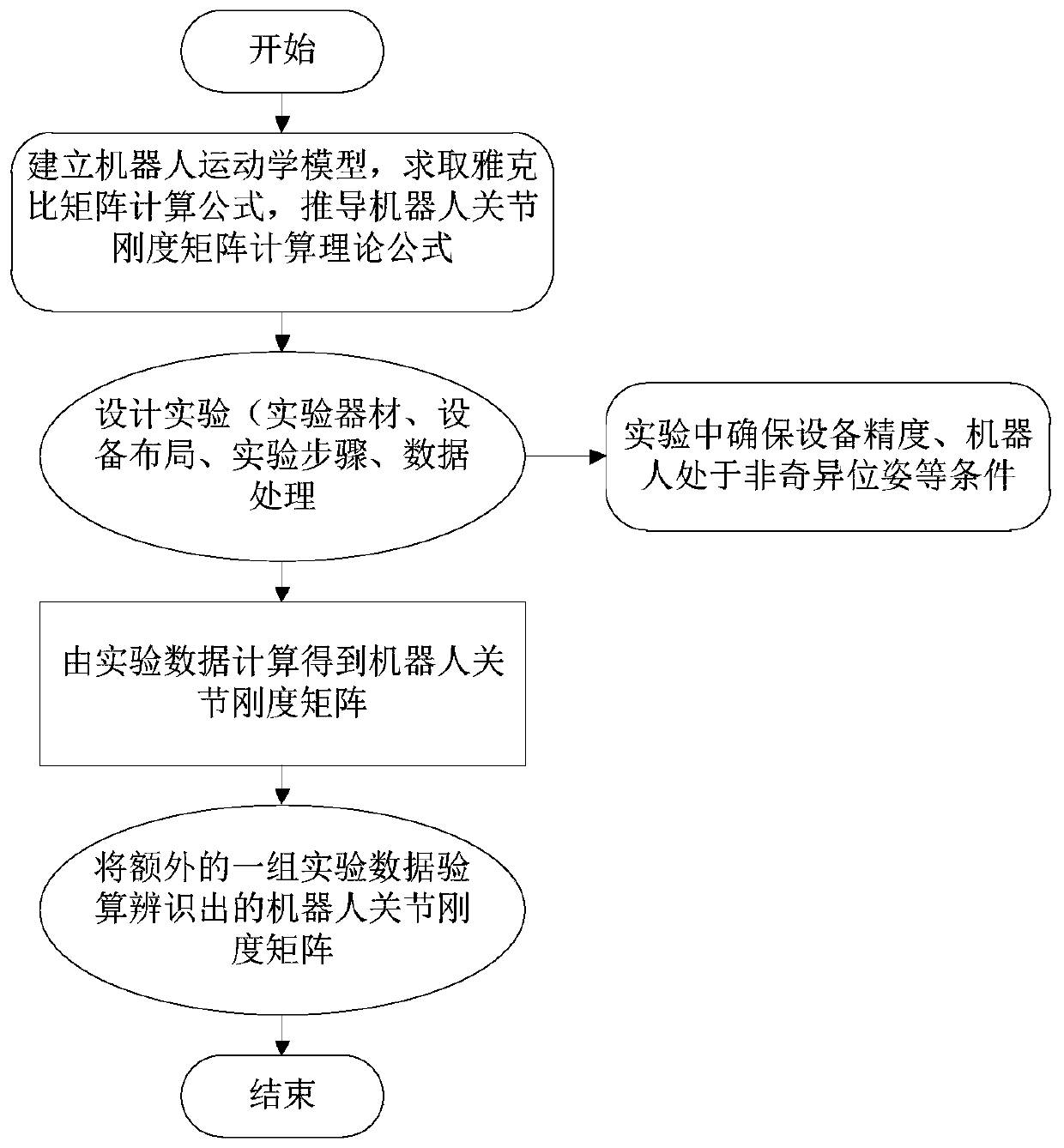
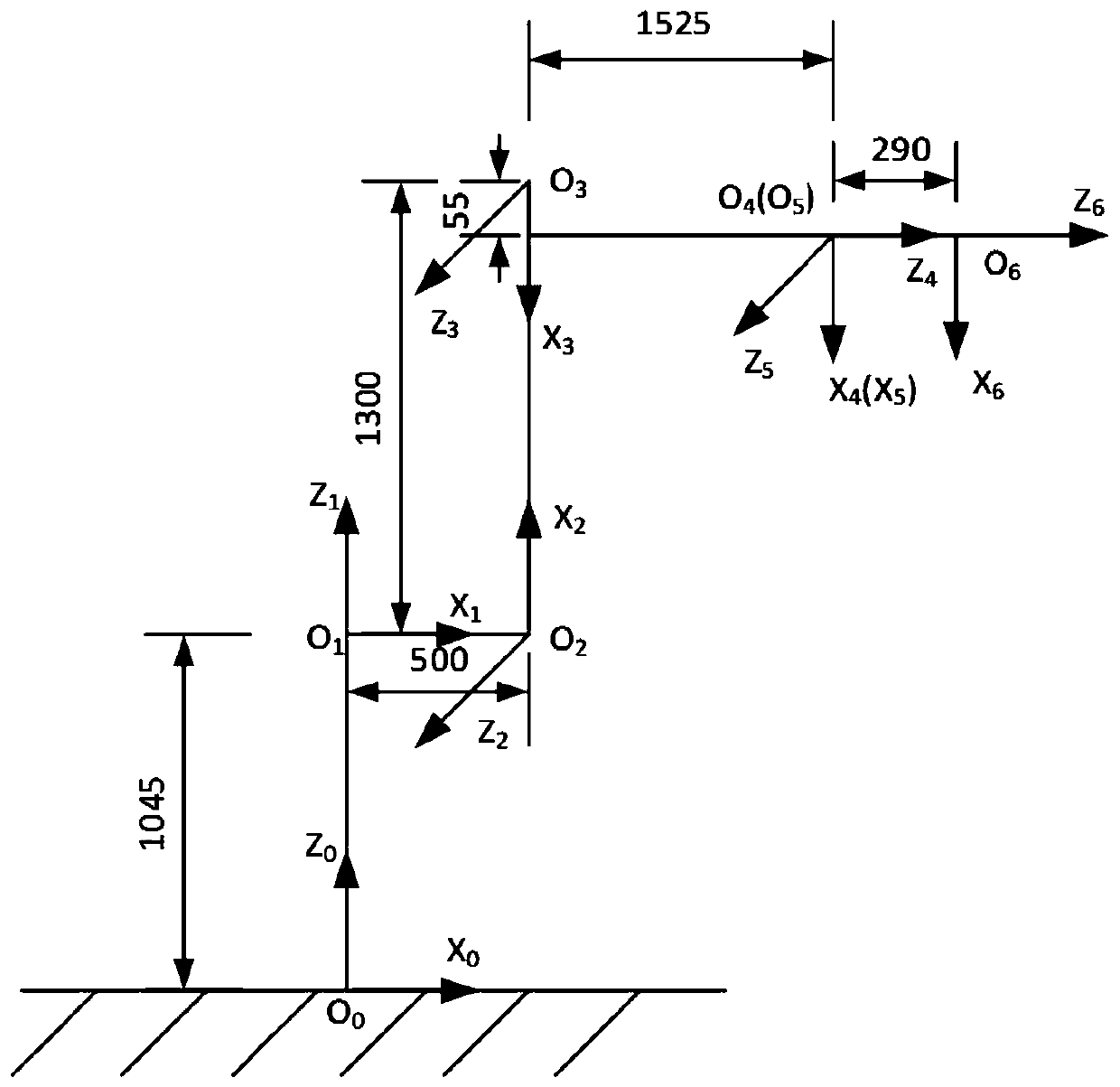
Identification method and system for rigidity of joint of six-degree-of-freedom industrial serial robot
The invention discloses an identification method and system for the rigidity of a joint of a six-degree-of-freedom industrial serial robot. The method comprises the following steps that a DH parametermethod is adopted for establishing a robot kinematics model of the to-be-identified industrial robot so as to acquire a DH parameter of the robot kinematics model; based on the DH parameter, a differential transformation method is used for deducing a Jacobi matrix of the robot, and in combination with the Jacobi matrix of the robot, a robot static rigidity model is established; and based on the robot static rigidity model, a robot joint rigidity identification experiment is designed to obtain multiple sets of experiment data, wherein the experiment data comprises to-be-processed experiment data and additional experiment data. The to-be-processed experiment data is processed through MATLAB programming to obtain a robot joint rigidity matrix. According to the method, the operability of theidentification process is lowered, the identification accuracy is improved, and the foundation is laid for looking for the optimal rigidity pose of the robot and performing deformation compensation, flutter analysis and other research on the robot.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com