Patents
Literature
3482 results about "Nuclear reactor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
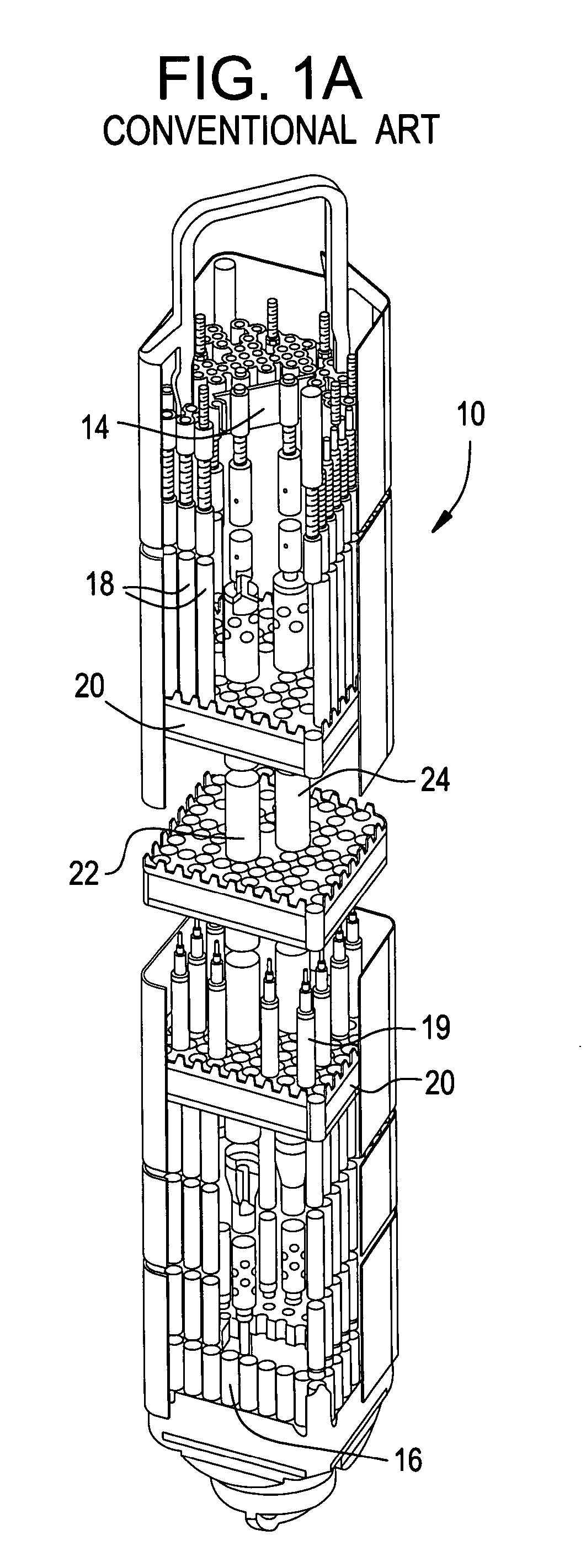
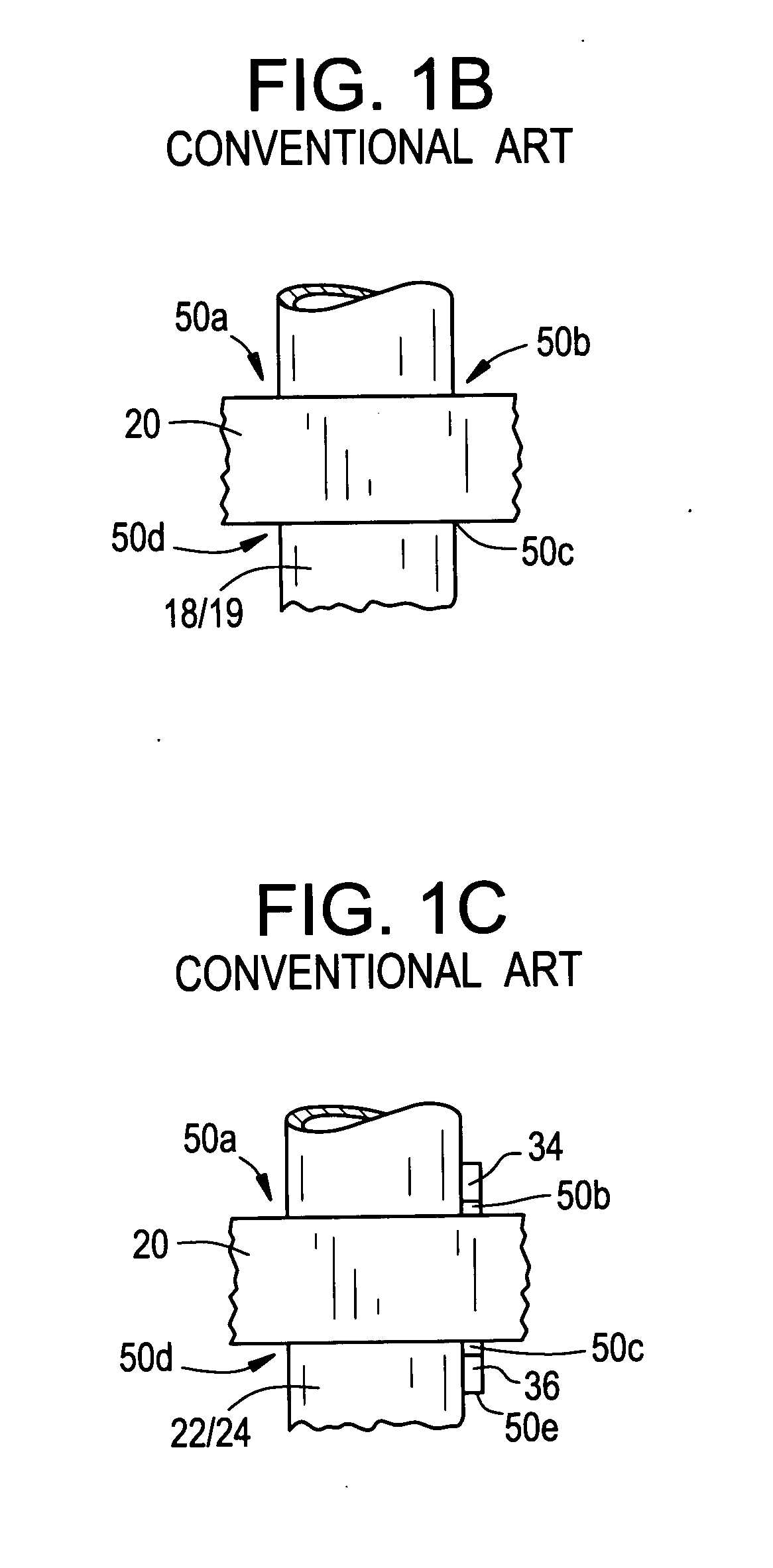
A nuclear reactor, formerly known as an atomic pile, is a device used to initiate and control a self-sustained nuclear chain reaction. Nuclear reactors are used at nuclear power plants for electricity generation and in nuclear marine propulsion. Heat from nuclear fission is passed to a working fluid (water or gas), which in turn runs through steam turbines. These either drive a ship's propellers or turn electrical generators' shafts. Nuclear generated steam in principle can be used for industrial process heat or for district heating. Some reactors are used to produce isotopes for medical and industrial use, or for production of weapons-grade plutonium. As of early 2019, the IAEA reports there are 454 nuclear power reactors and 226 nuclear research reactors in operation around the world.
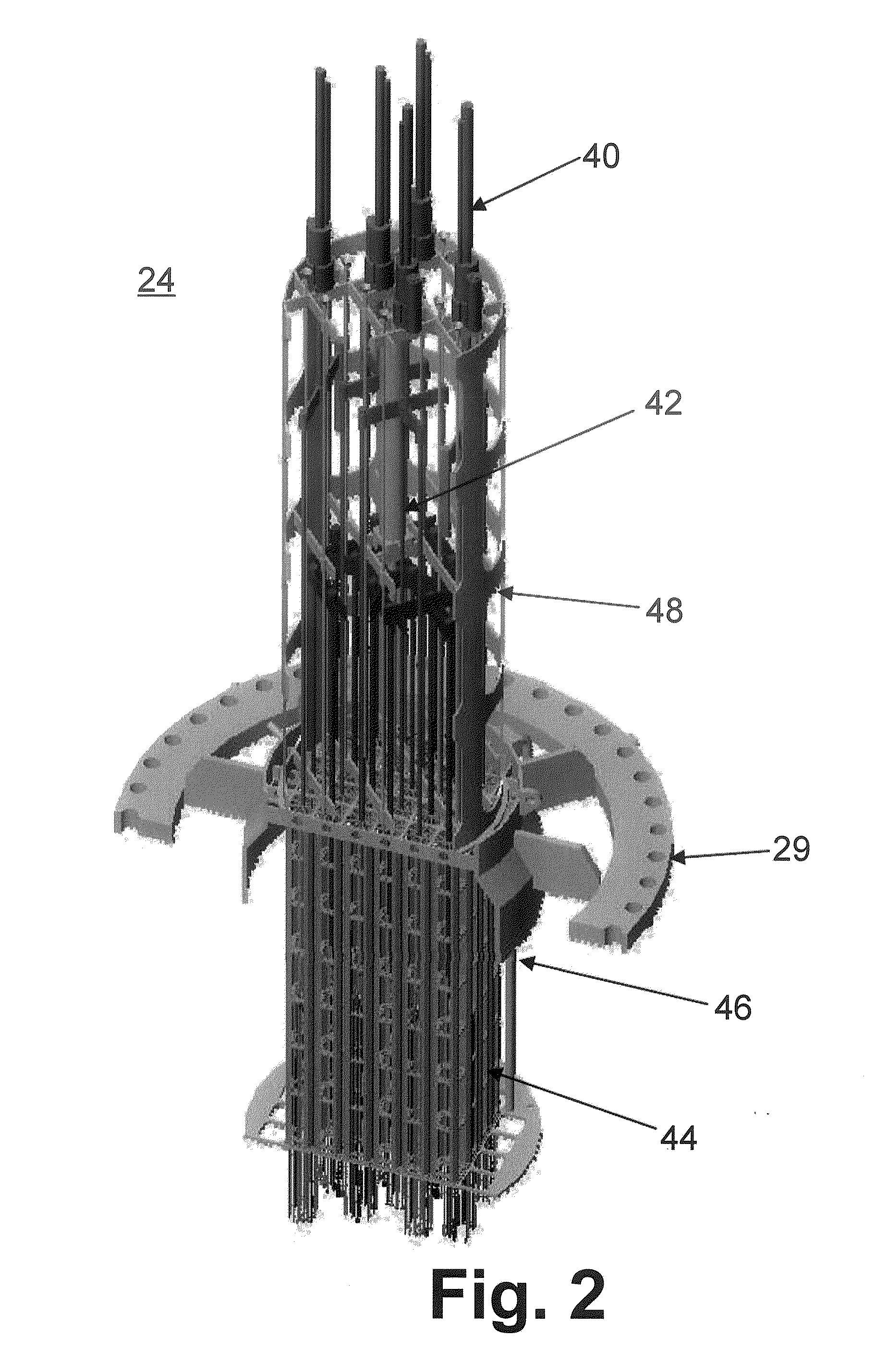
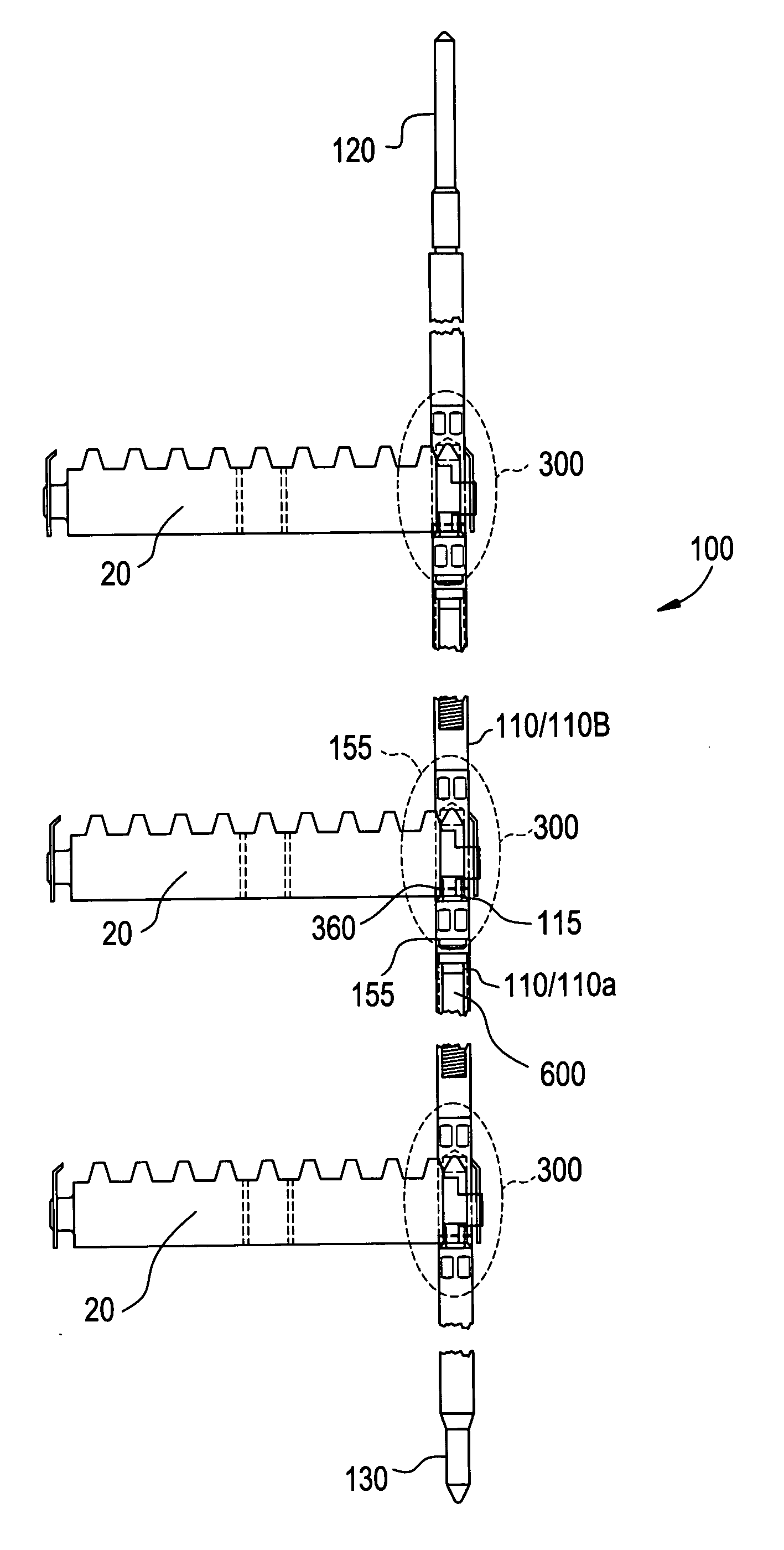
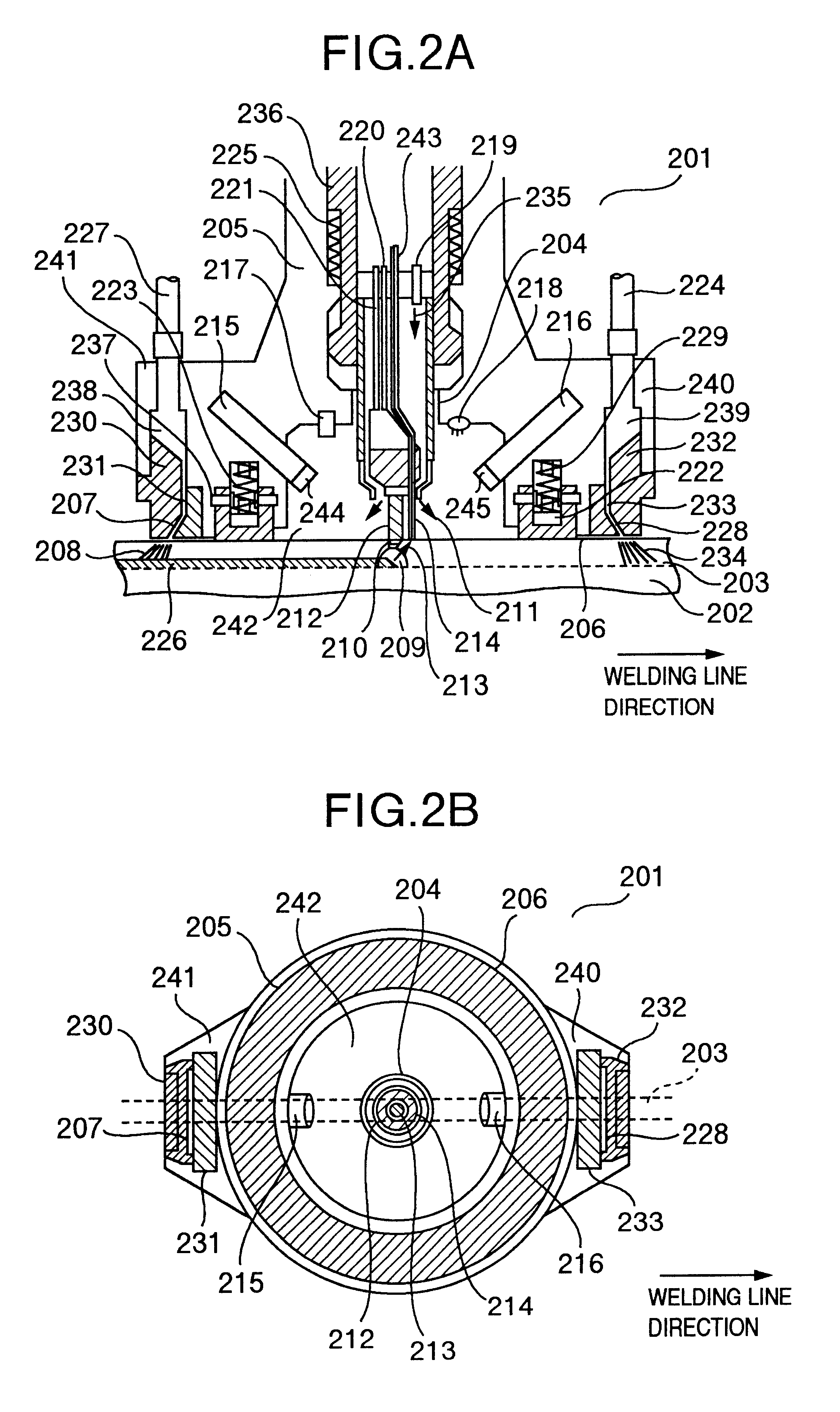
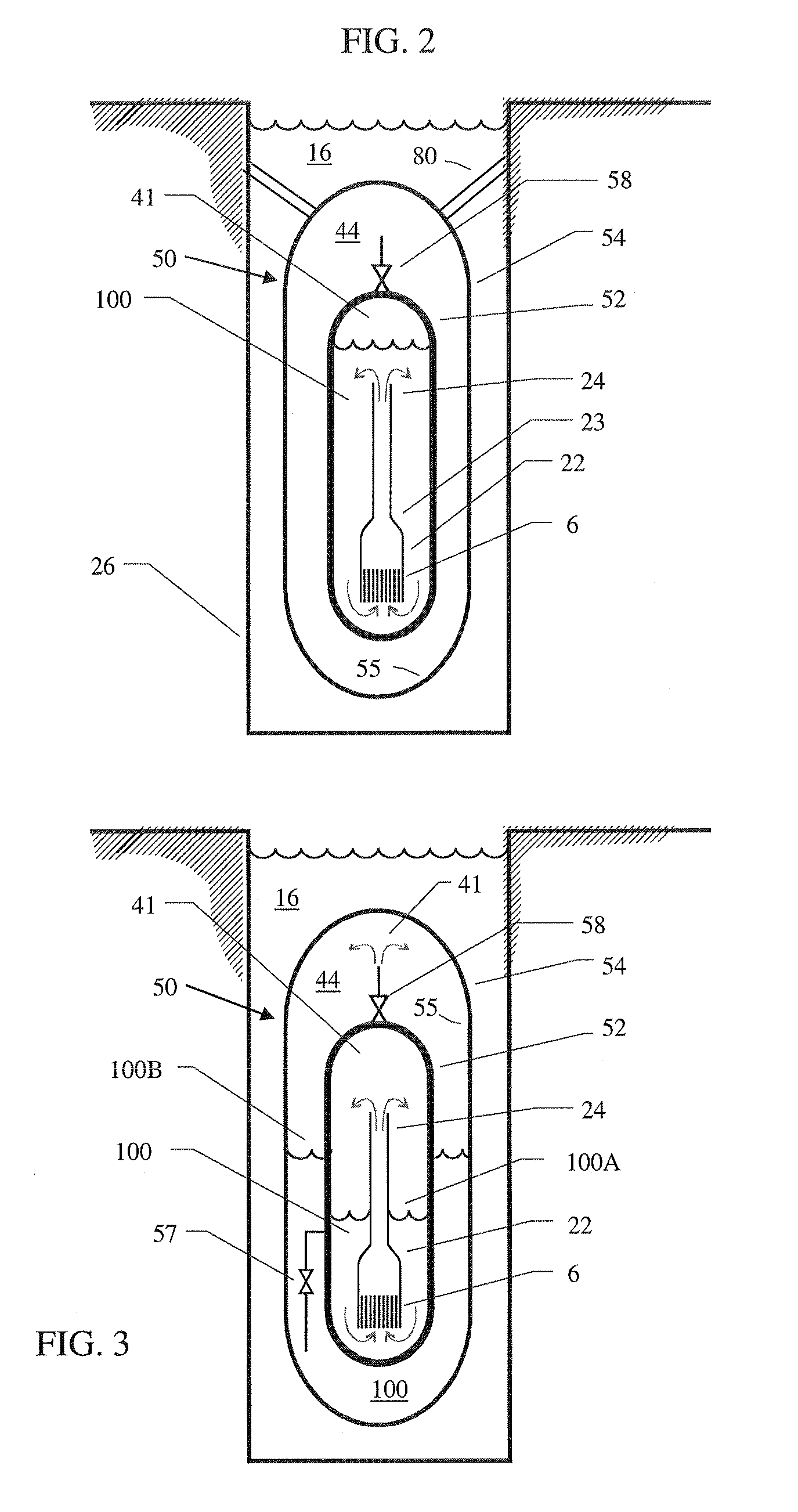
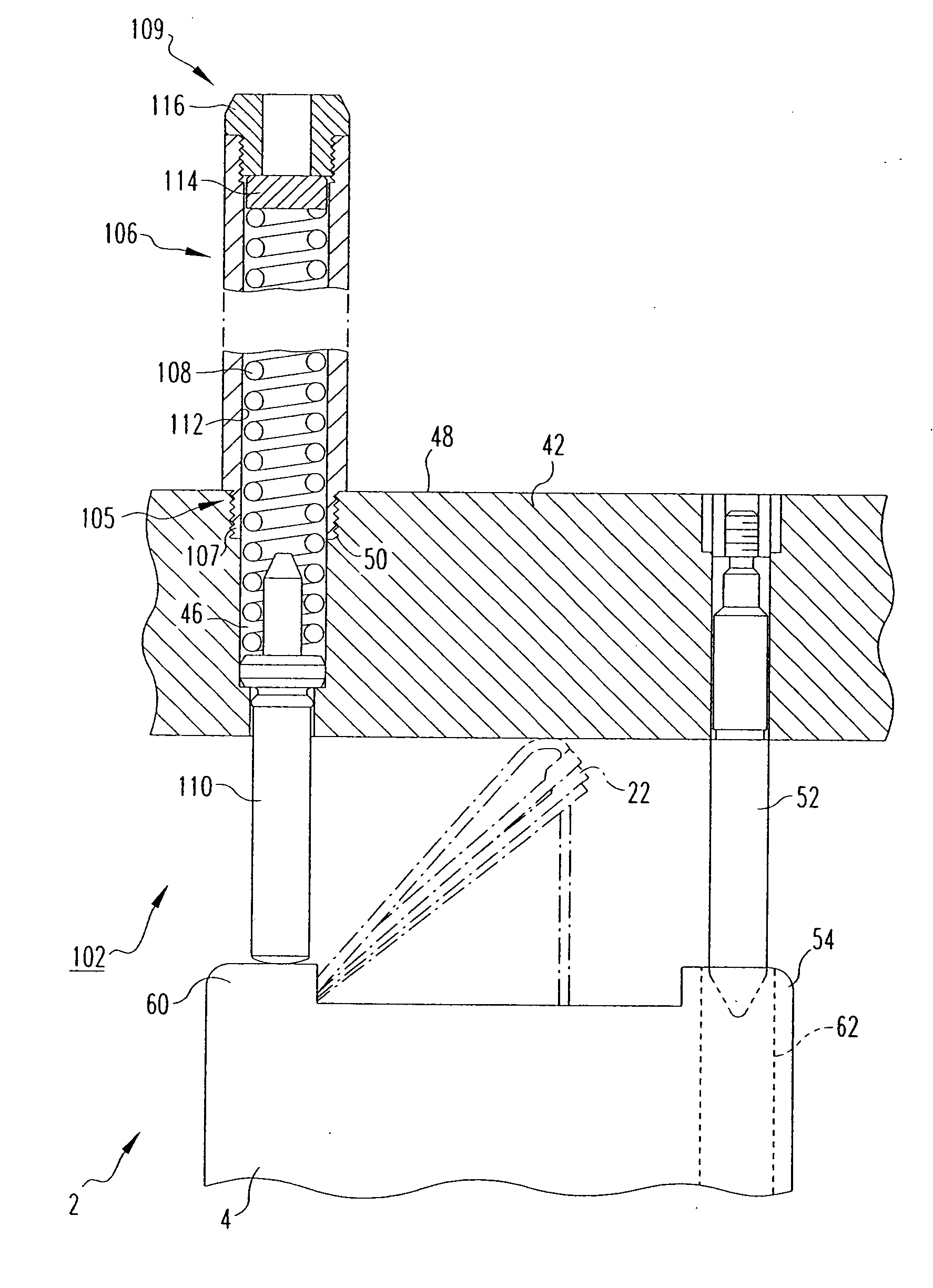
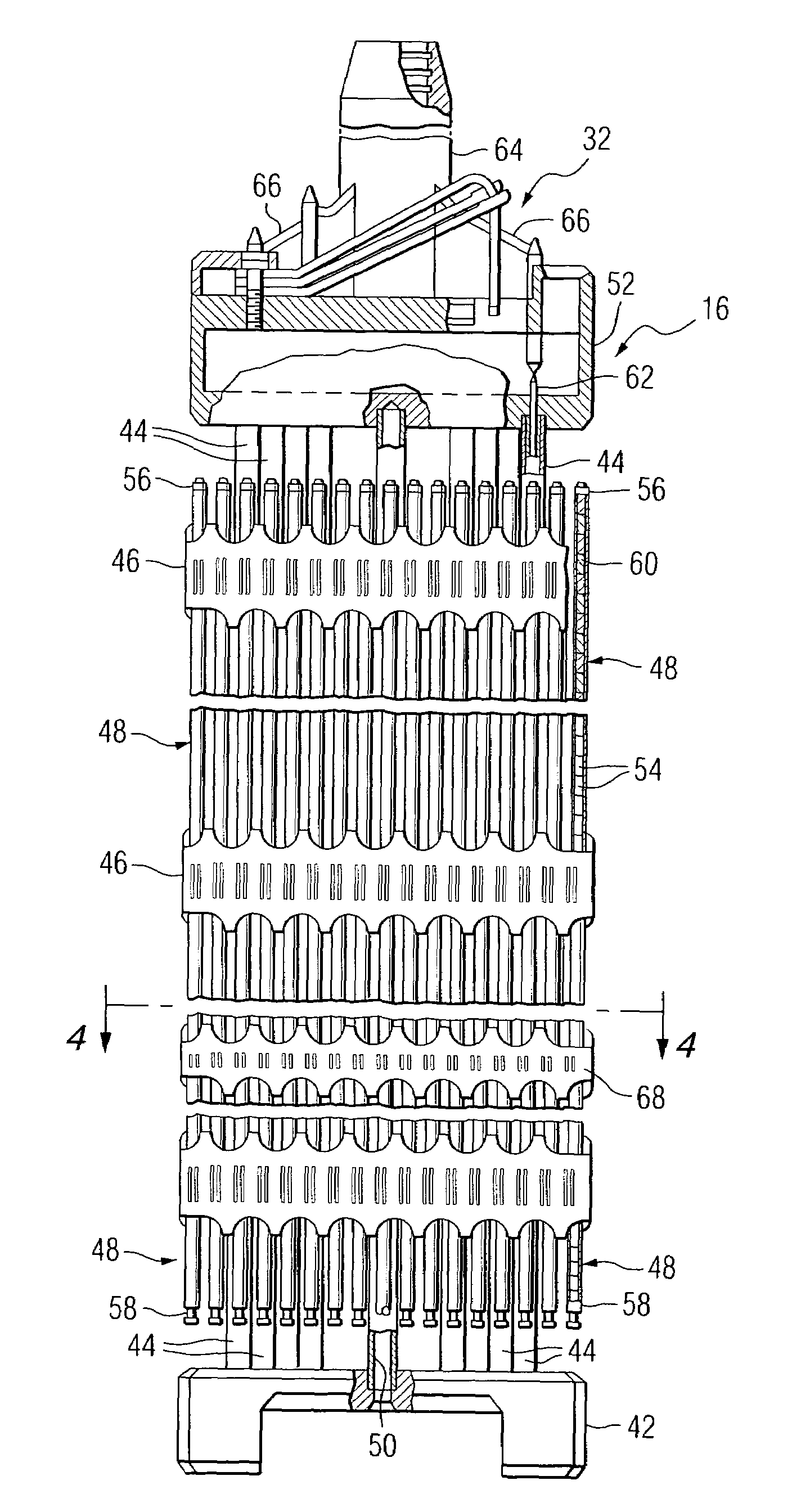
Control rod drive mechanism for nuclear reactor
ActiveUS20100316177A1Nuclear energy generationEmergency protection arrangementsNuclear reactor coreNuclear reactor
A control rod drive mechanism (CRDM) for use in a nuclear reactor, the CRDM comprising: a connecting rod connected with at least one control rod; a lead screw; a drive mechanism configured to linearly translate the lead screw; an electromagnet coil assembly; and a latching assembly that latches the connecting rod to the lead screw responsive to energizing the electromagnet coil assembly and unlatches the connecting rod from the lead screw responsive to deenergizing the electromagnet coil assembly. The latching assembly is secured with and linearly translates with the lead screw, while the electromagnet coil assembly does not move with the lead screw. The electromagnet coil assembly is at least coextensive with a linear translation stroke over which the drive mechanism is configured to linearly translate the lead screw.
Owner:BWXT NUCLEAR OPERATIONS GRP
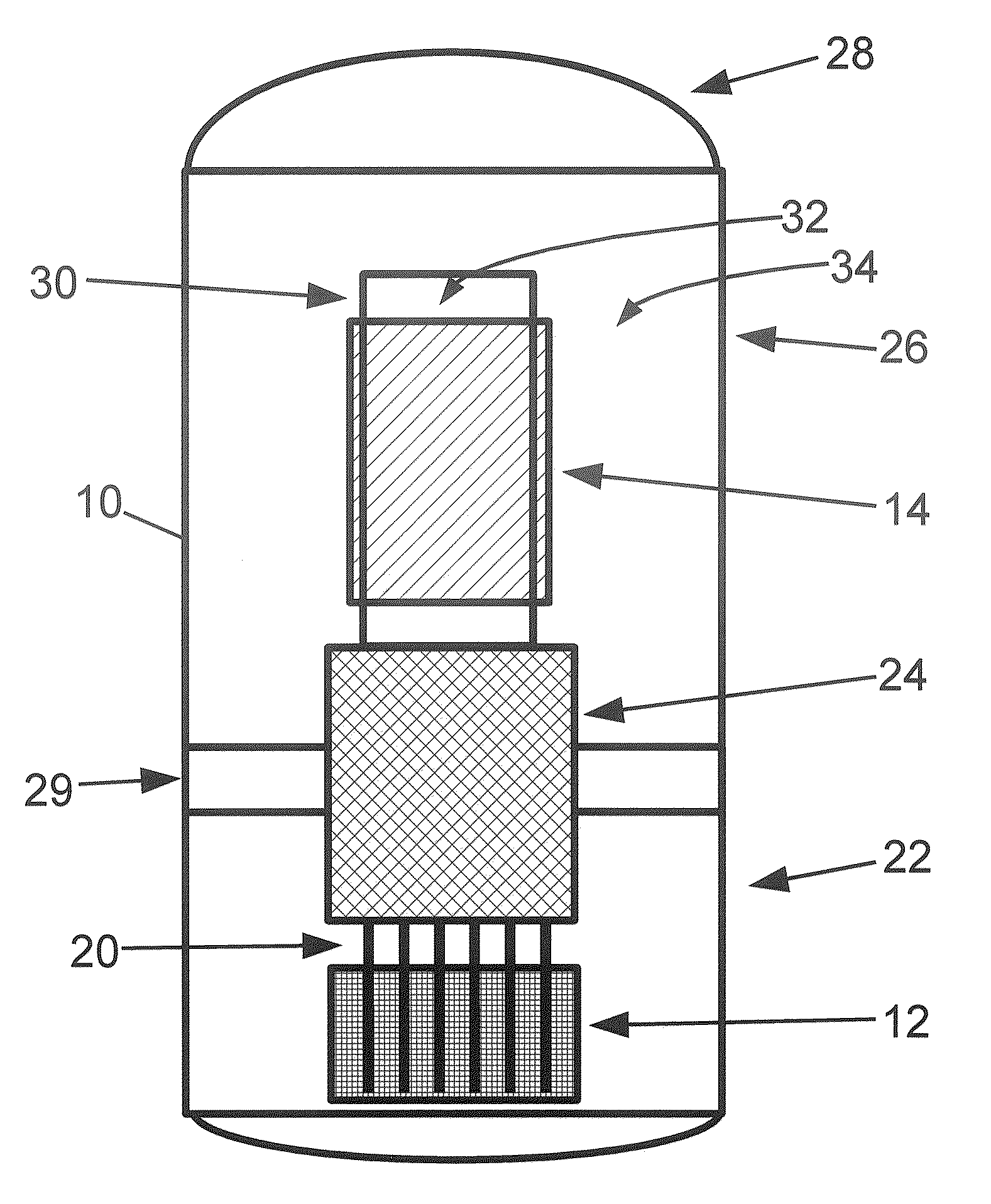
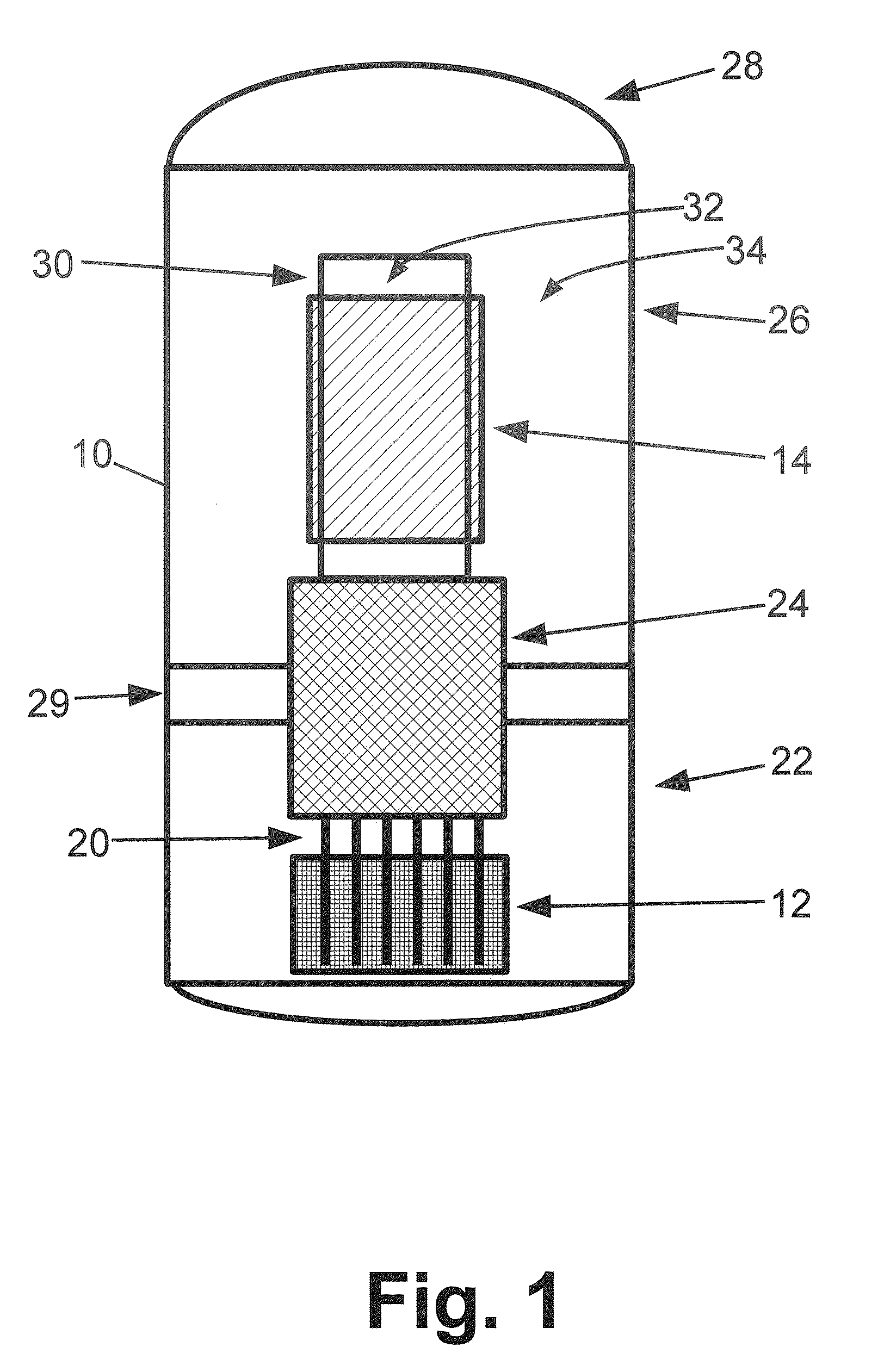
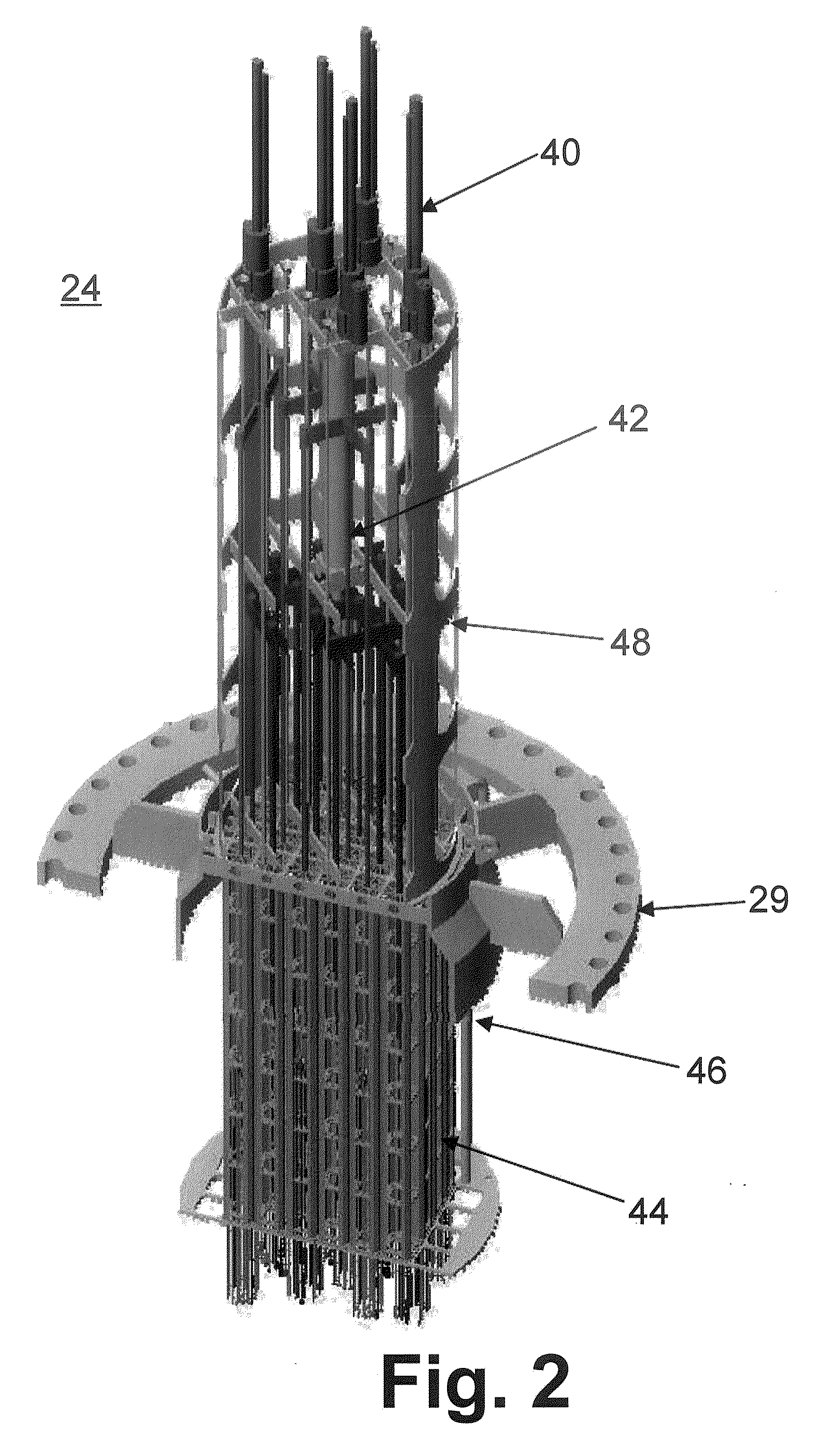
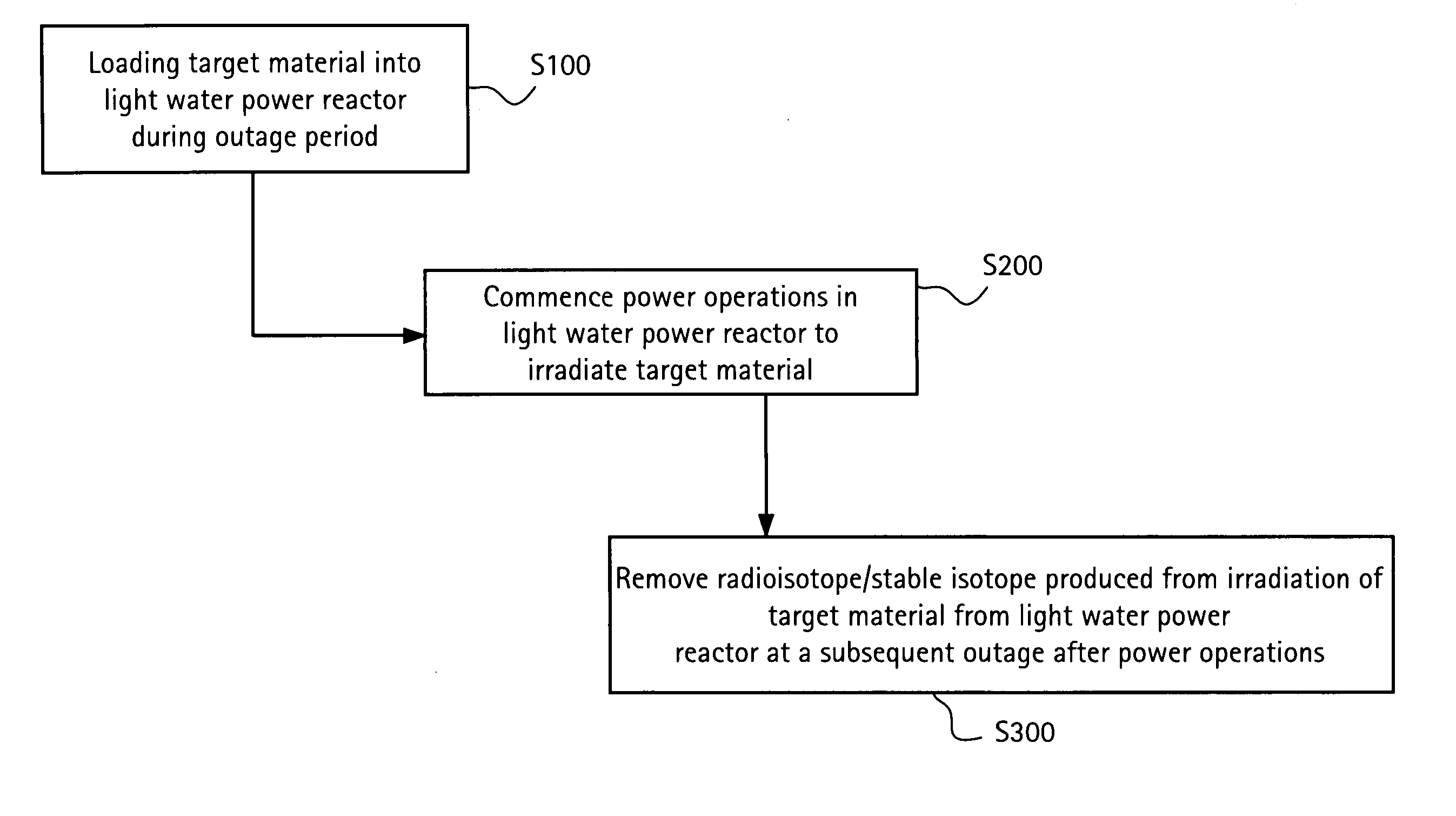
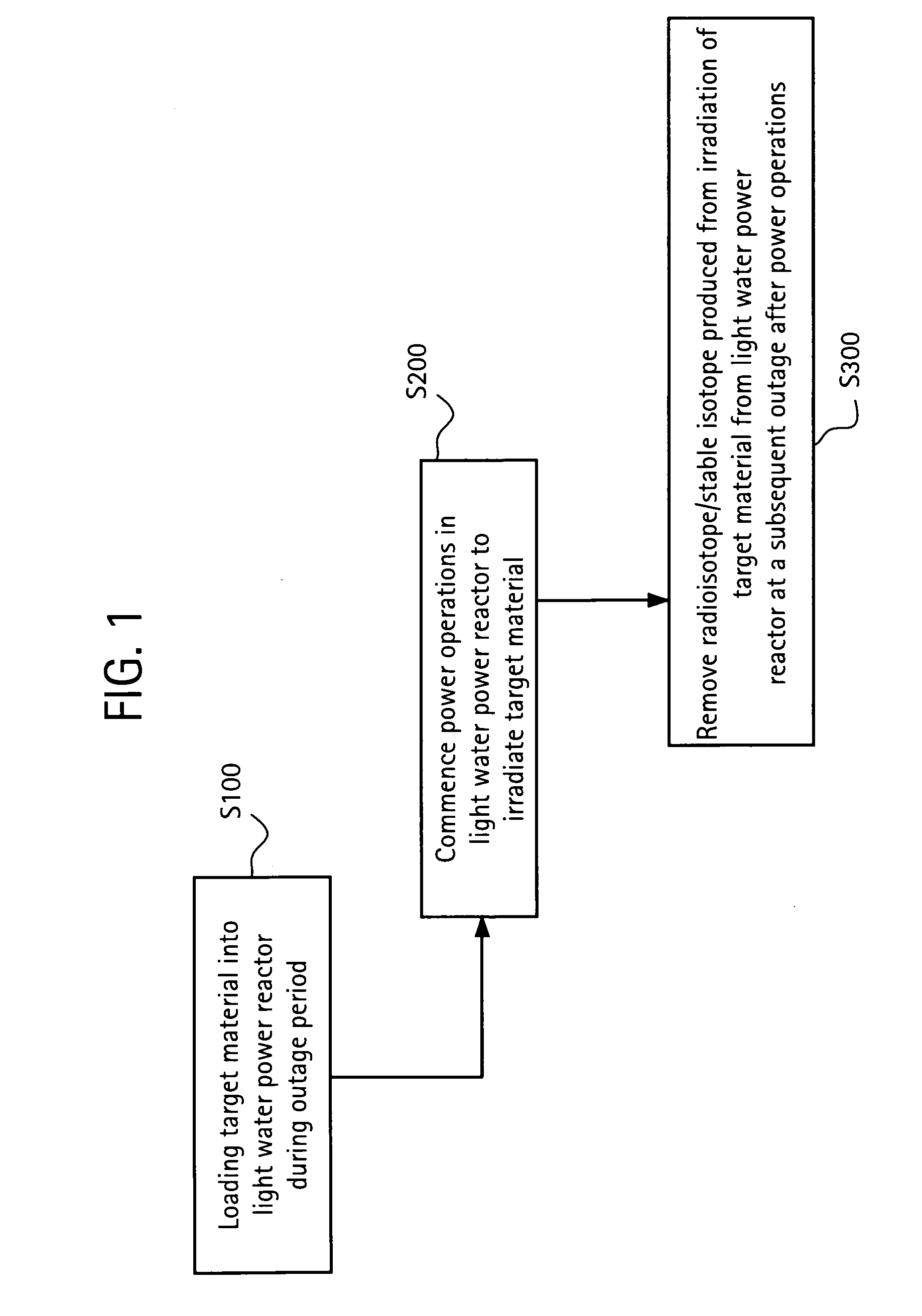
Method of producing isotopes in power nuclear reactors
ActiveUS20070133731A1Nuclear energy generationConversion in nuclear reactorNuclear reactorNeutron flux
In a method of producing isotopes in a light water power reactor, one or more targets within the reactor may be irradiated under a neutron flux to produce one or more isotopes. The targets may be assembled into one or more fuel bundles that are to be loaded in a core of the reactor at a given outage. Power operations in the reactor irradiate the fuel bundles so as to generate desired isotopes, such as one or more radioisotopes at a desired specific activity or stable isotopes at a desired concentration.
Owner:NORDION (CANADA) INC
Control rod drive mechanism for nuclear reactor
ActiveUS20110222640A1Nuclear energy generationNuclear reaction controlNuclear reactor coreNuclear reactor
A control rod drive mechanism (CRDM) comprises a lead screw, a motor threadedly coupled with the lead screw to linearly drive the lead screw in an insertion direction or an opposite withdrawal direction, a latch assembly secured with the lead screw and configured to (i) latch to a connecting rod and to (ii) unlatch from the connecting rod, the connecting rod being free to move in the insertion direction when unlatched, and a release mechanism configured to selectively unlatch the latch assembly from the connecting rod.
Owner:BWXT NUCLEAR OPERATIONS GRP
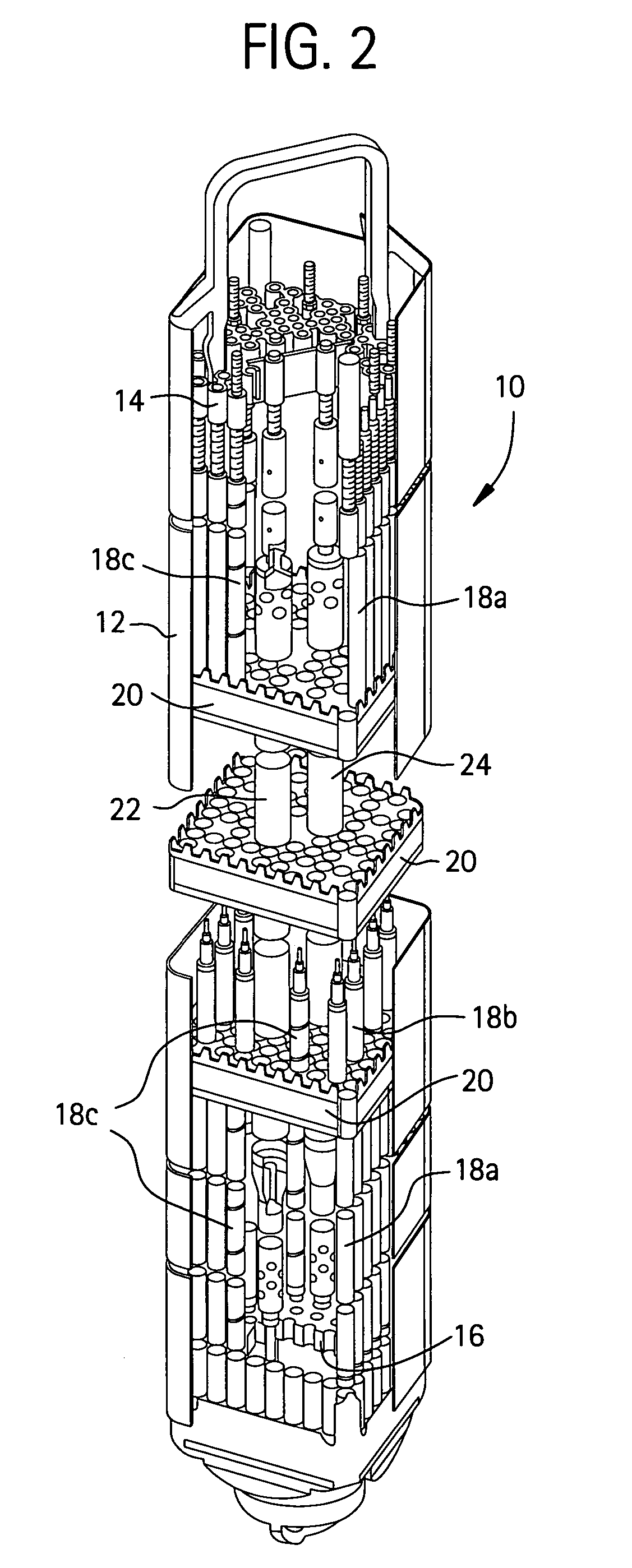
Rod assembly for nuclear reactors
A rod assembly for a fuel bundle of a nuclear reactor may include an upper end piece, lower end piece and a plurality of rod segments attached between the upper and lower end pieces and to each other so as to form an axial length of the rod assembly. The rod assembly may include an adaptor subassembly provided at given connection points for connecting adjacent rod segments or a given rod segment with one of the upper and lower end pieces. The connection points along the axial length of the rod assembly may be located where the rod assembly contacts a spacer in the fuel bundle. One (or more) of the rod segments may include an irradiation target therein for producing a desired isotope when a fuel bundle containing one (or more) rod assemblies is irradiated in a core of the reactor.
Owner:NORDION (CANADA) INC
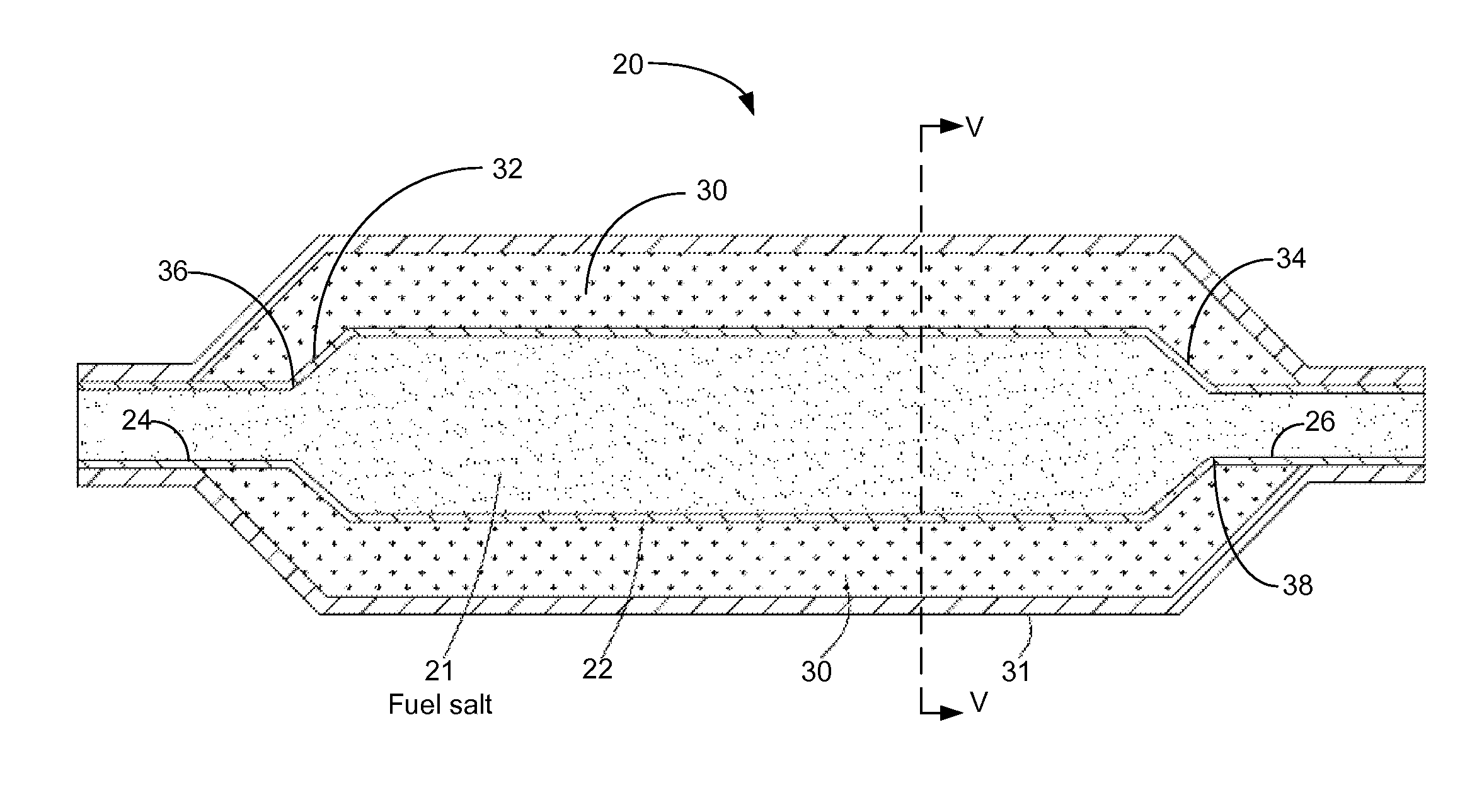
Molten salt nuclear reactor
InactiveUS20090279658A1Maximize probabilityFuel elementsNuclear energy generationBreeder reactorNuclear reactor
A molten salt breeder reactor that has fuel conduit surrounded by a fertile blanket. The fuel salt conduit has an elongated core section that allows for the generation of electrical power on a scale comparable to commercially available nuclear reactors. The geometry of the fuel conduit is such that sub-critical conditions exist near the input and output of the fuel salt conduit and the fertile blanket surrounds the input and output of the fuel salt conduit, thereby minimizing neutron losses.
Owner:OTTAWA VALLEY RES ASSOCS
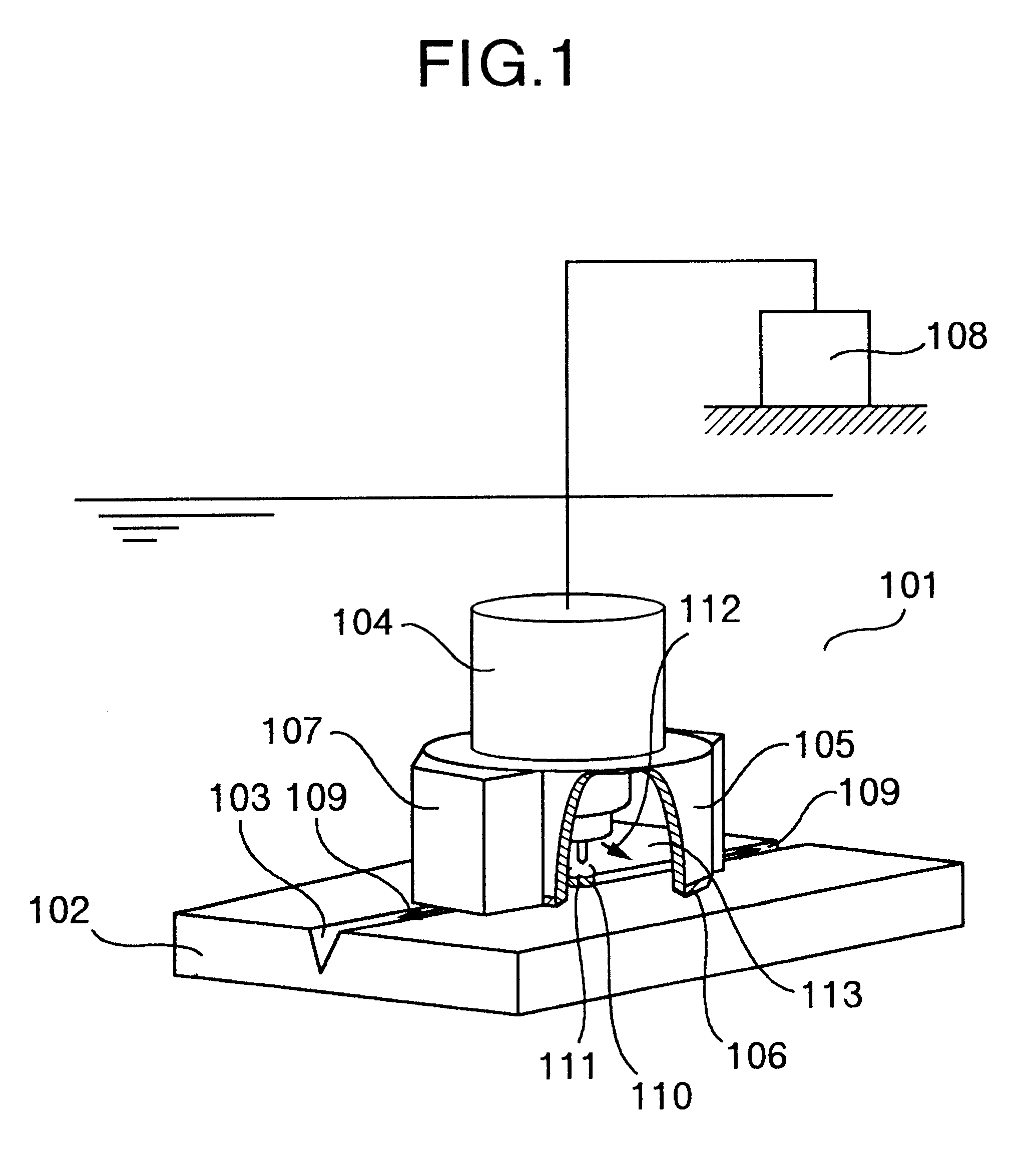
Underwater processing device and underwater processing method
InactiveUS6555779B1Reduce supplyReduce variationSupport devices with shieldingNuclear energy generationNuclear reactorEngineering
Provided are an underwater processing apparatus which can effectively prevent water from entering a shield for a workpiece having a surface ruggedness, and in which variation in a gas flow for a processing part is reduced, a processing method and an application thereof to a nuclear reactor, and the under water processing device is composed of a shield means which locally cover the processing part with the gas in order to prevent water from entering the shield member, the shield means having a solid wall formed of a member which is slidable in a part where it make contact with the workpiece, and adapted to make contact with the workpiece and to be moved up and down by a pressing force, and a water jetting means for forming a water curtain around the outer periphery of the solid wall.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
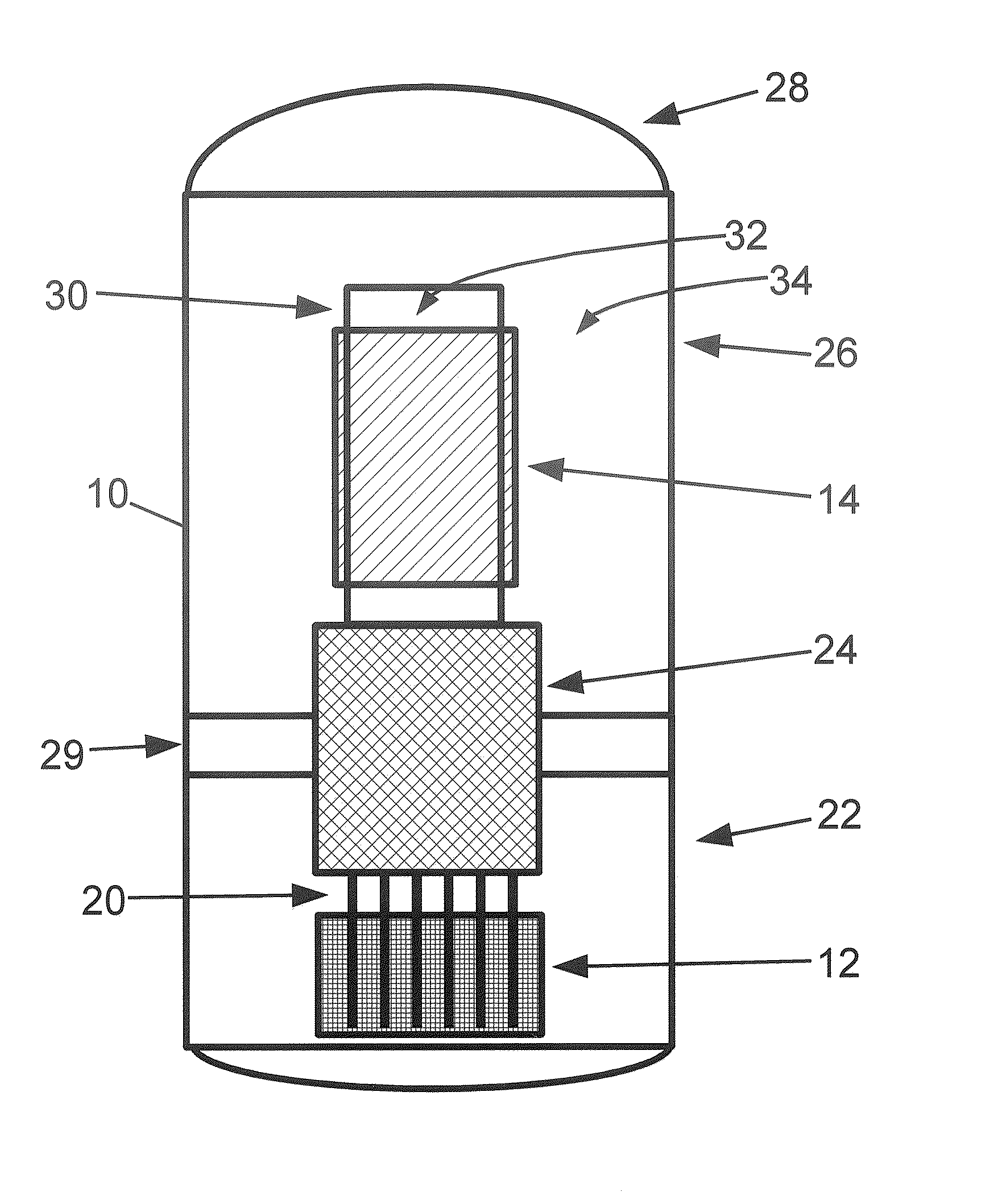
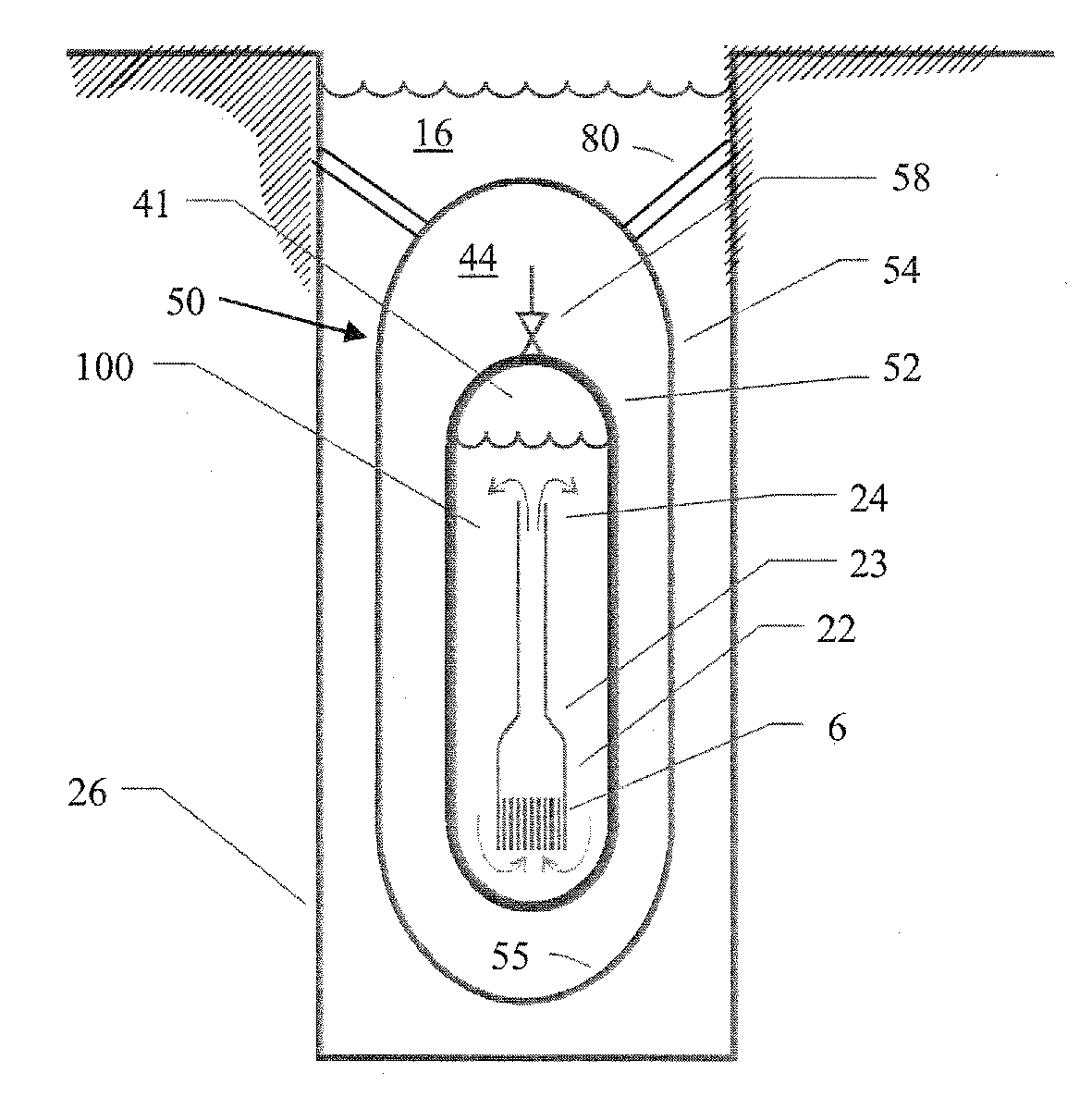
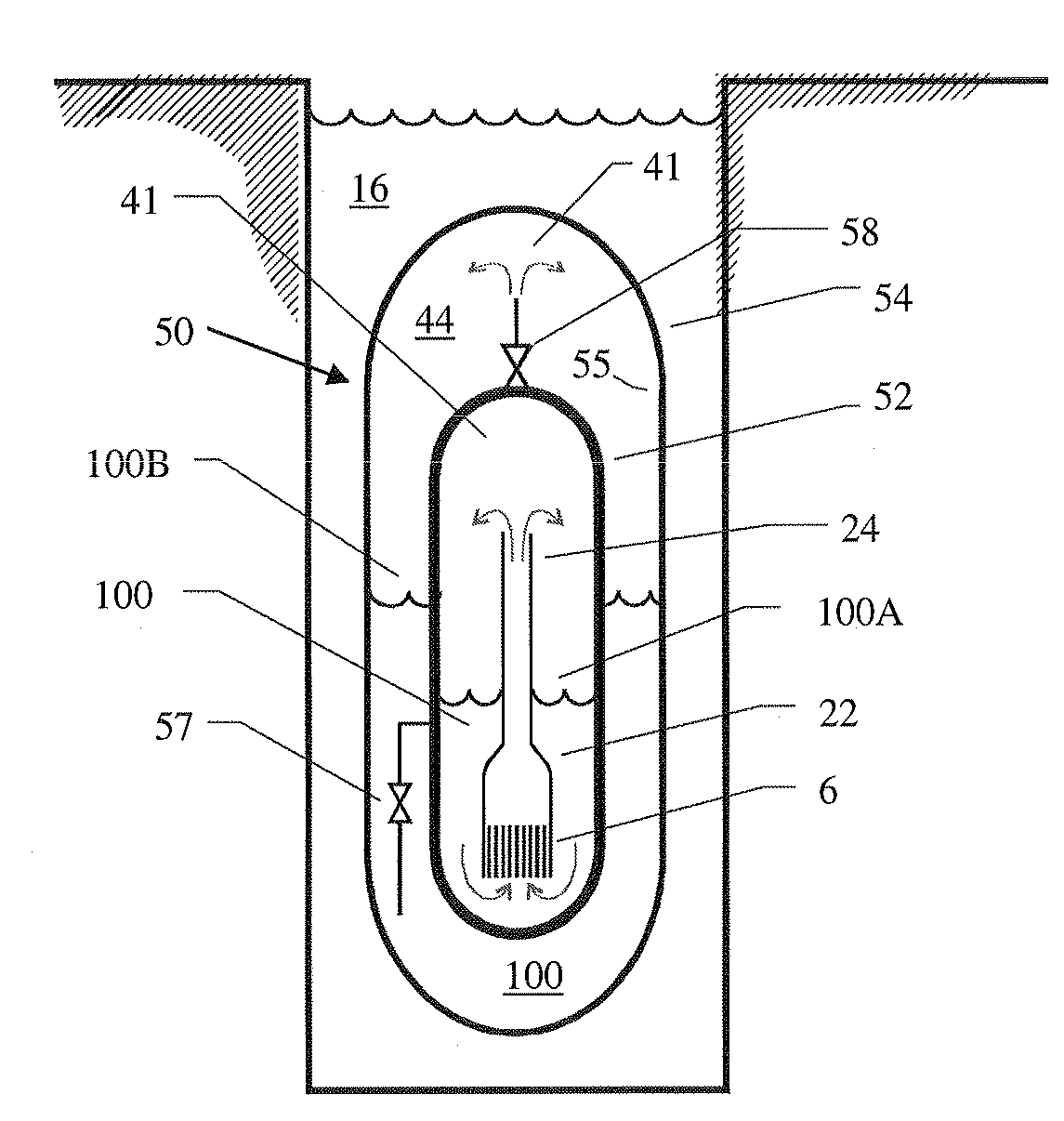
Submerged containment vessel for a nuclear reactor
A power module assembly includes a reactor core immersed in a coolant and a reactor vessel housing the coolant and the reactor core. An internal dry containment vessel submerged in liquid substantially surrounds the reactor vessel in a gaseous environment. During an over-pressurization event the reactor vessel is configured to release the coolant into the containment vessel and remove a decay heat of the reactor core through condensation of the coolant on an inner surface of the containment vessel.
Owner:NUSCALE
Process and System for producing synthetic liquid hydrocarbon fuels
ActiveUS7420004B2High volumetric and gravimetric energy densityExcellent resistance to thermal oxidation processLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionOxygen compounds purification/separationOcean thermal energy conversionElectric power
A process for producing synthetic hydrocarbons that reacts carbon dioxide, obtained from seawater of air, and hydrogen obtained from water, with a catalyst in a chemical process such as reverse water gas shift combined with Fischer Tropsch synthesis. The hydrogen is produced by nuclear reactor electricity, nuclear waste heat conversion, ocean thermal energy conversion, or any other source that is fossil fuel-free, such as wind or wave energy. The process can be either land based or sea based.
Owner:NAVY U S A AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE THE
Method For Preparing Radioactive Film
InactiveUS20080031811A1Uniform thickness distributionLow amount of residual solventOther chemical processesRadioactive preparation formsNuclear reactorNeutron irradiation
The present invention relates to a method for preparing a radioactive film for local radioactive treatment. More particularly, the present invention relates to a method for preparing a radioactive film comprising the steps of; dissolving 0.1˜14.5 weight % of a stable nuclide and 13˜32.5 weight % of a film-forming base for the total amount of a solvent in the solvent; applying a stable nuclide solution on a release paper by a coater and drying; and irradiating a stable nuclide film with neutrons in a nuclear reactor. A method for preparing a radioactive film according to the present invention provides a radioactive film having a uniform distribution of radionuclides and an even thickness. Therefore, the therapeutic efficacy of the radioactive film for selective treatment of a lesion may be maximized by attaching the radioactive film on a patient's skin or a mucous membrane and by direct radioactive radiation.
Owner:DONG WHA PHARM CO LTD +1
In orbit space transportation and recovery system
InactiveUS7216833B2Low costCosmonautic environmental control arrangementLaunch systemsNuclear reactorPropellant tank
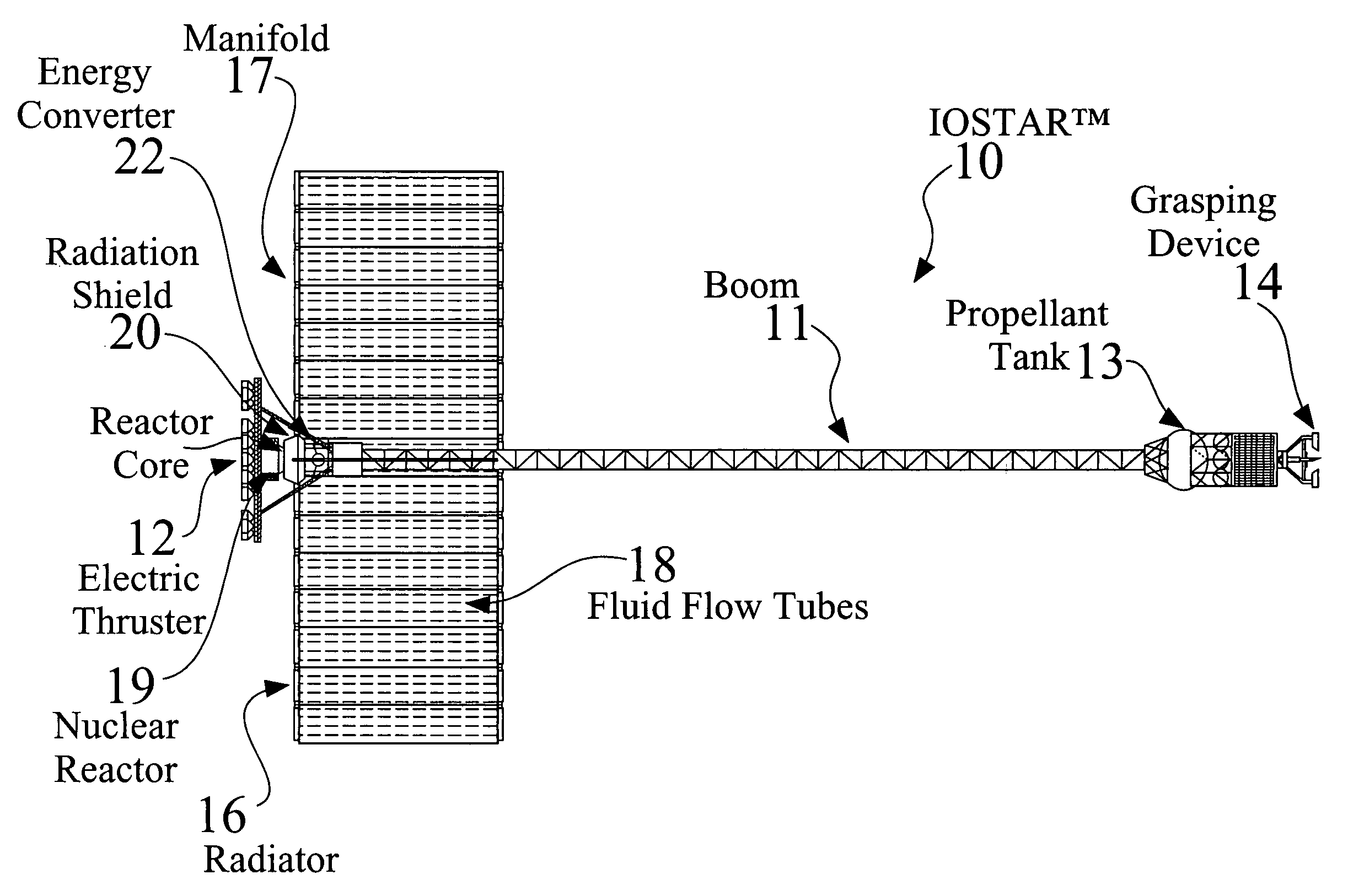
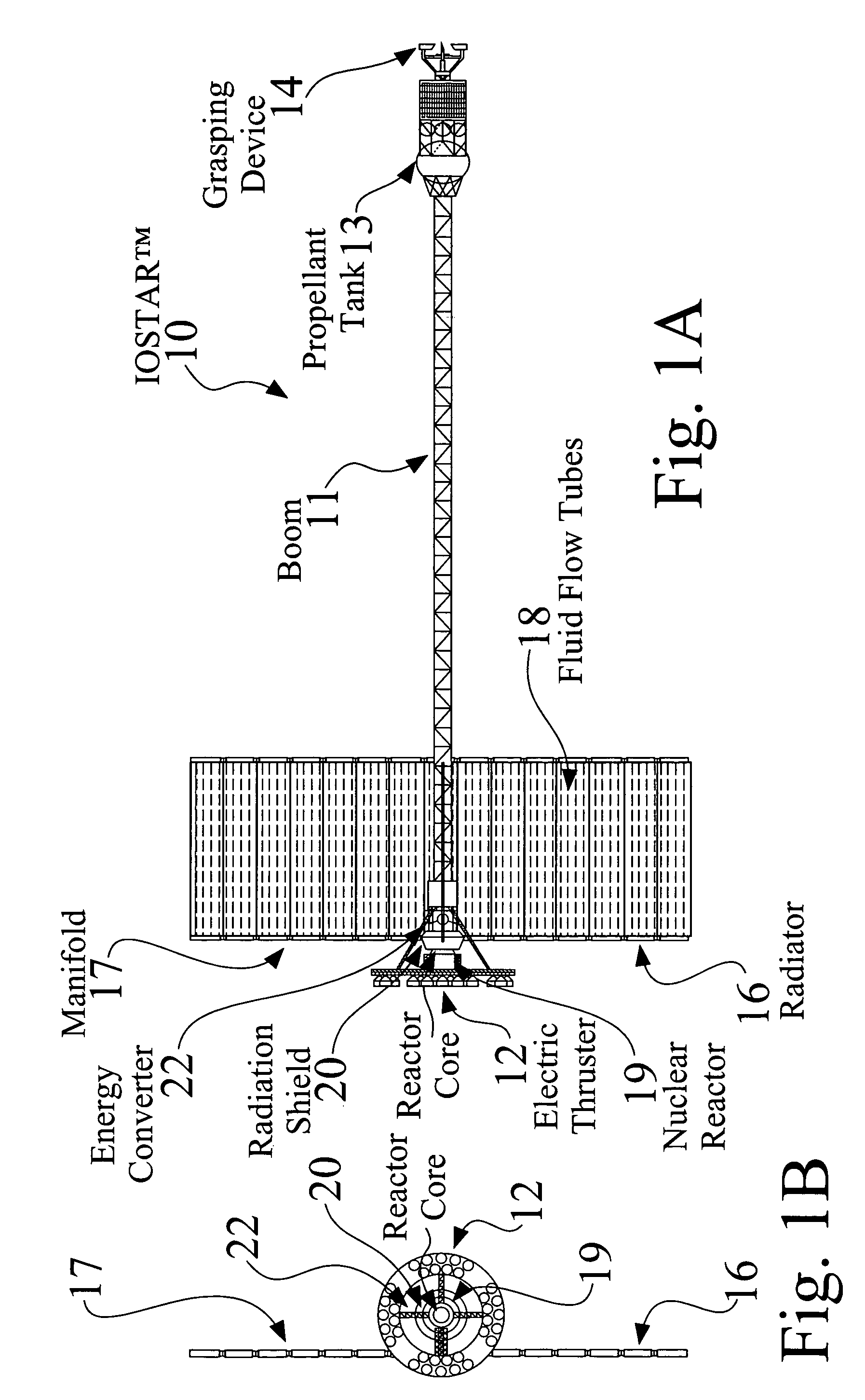
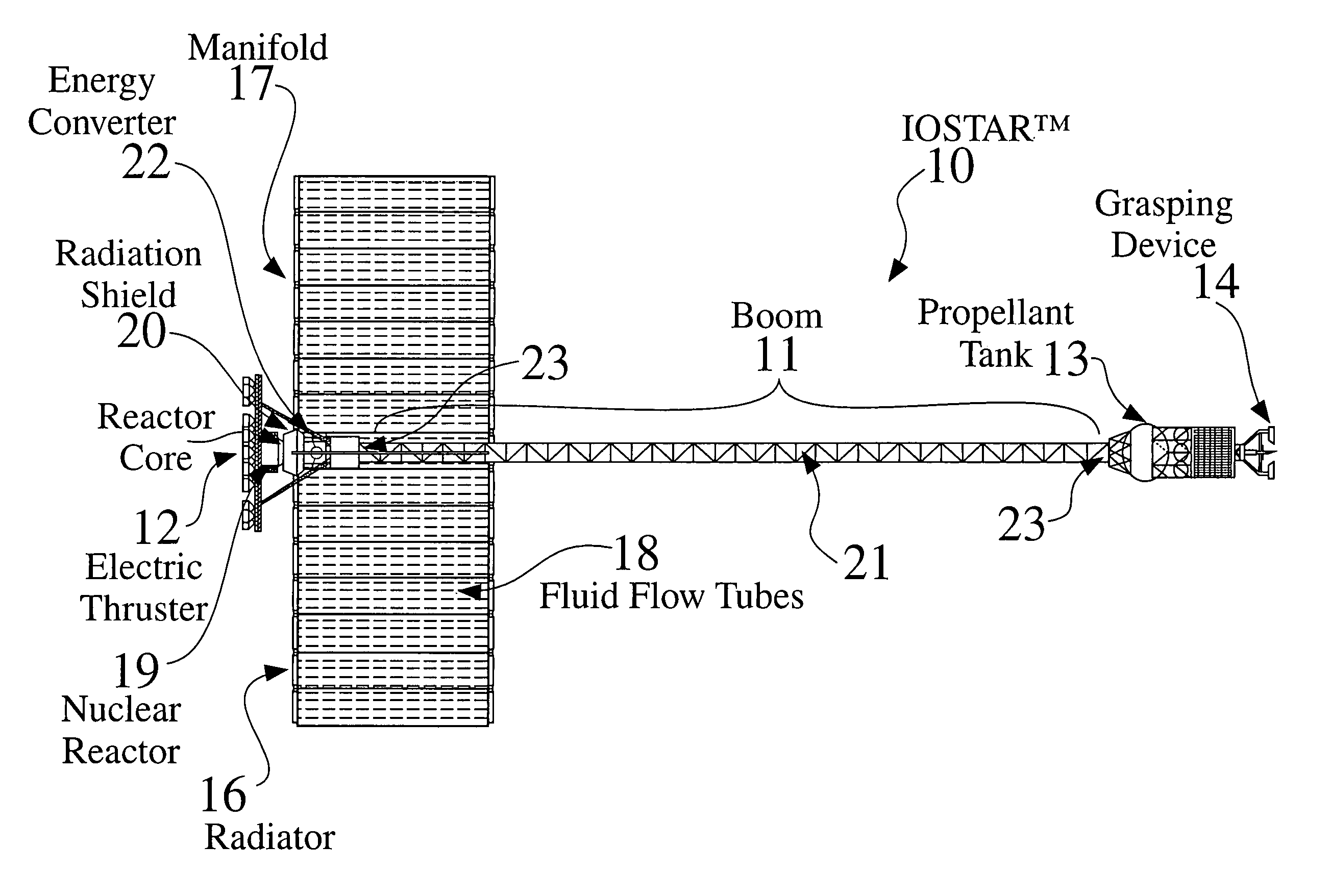
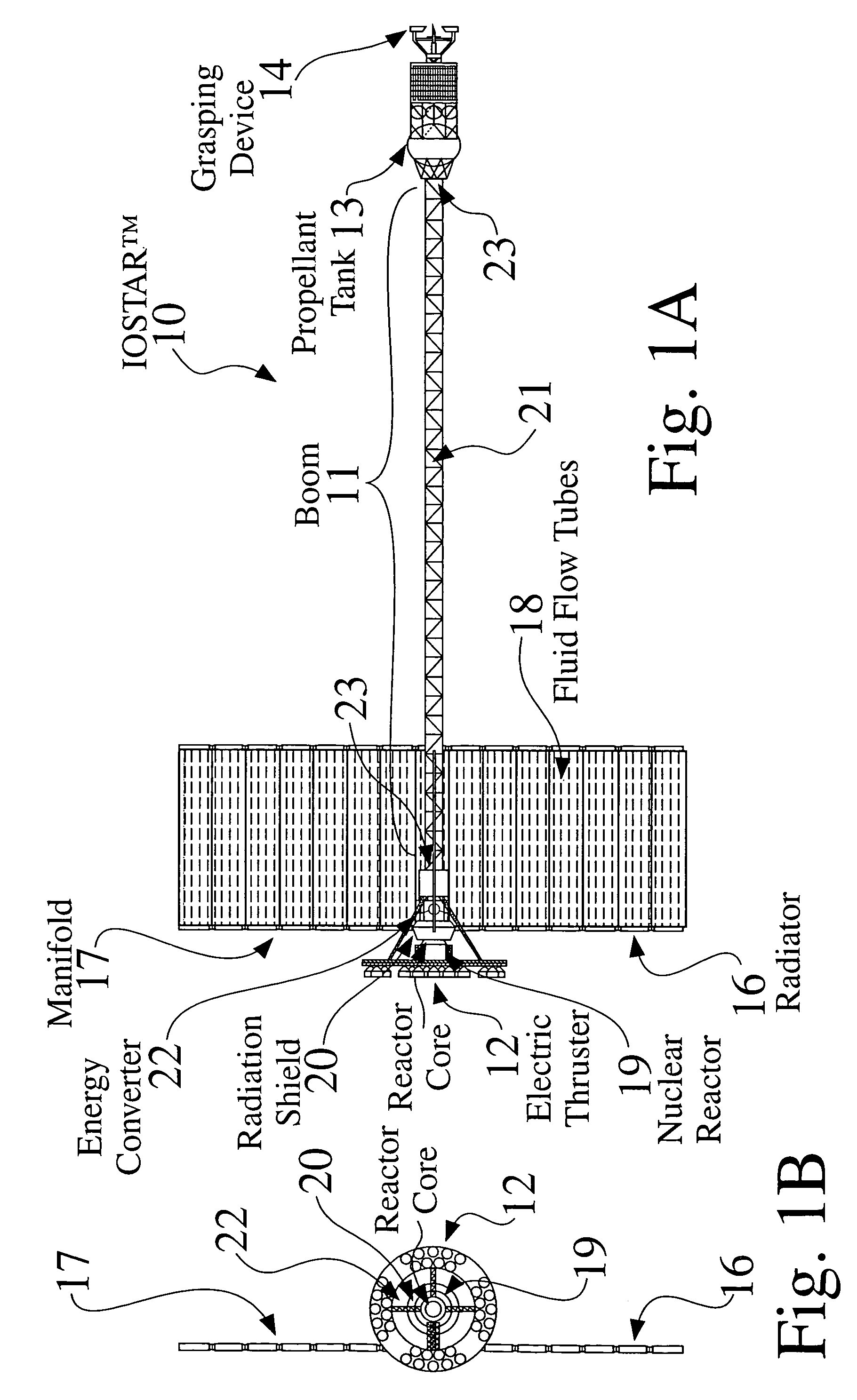
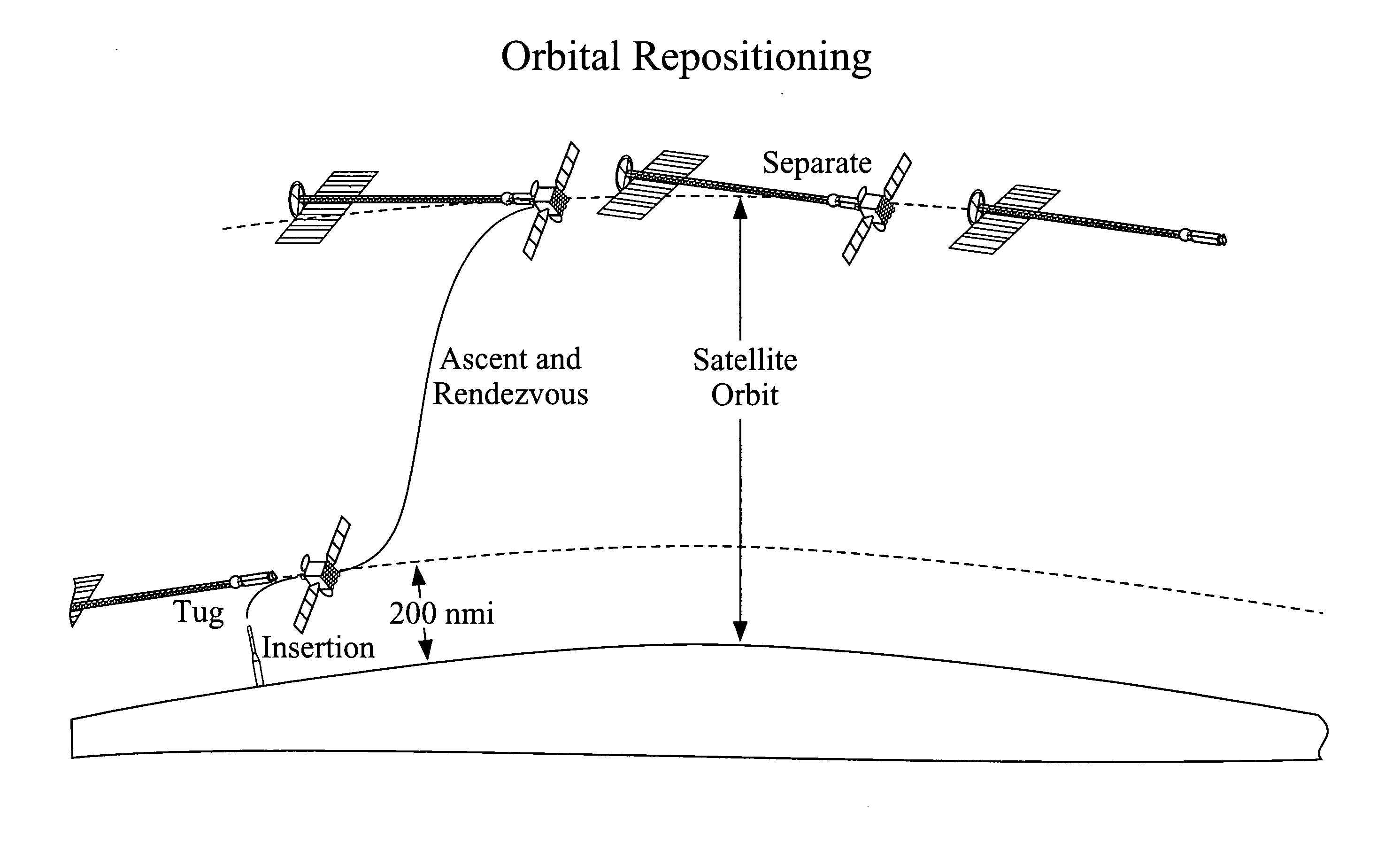
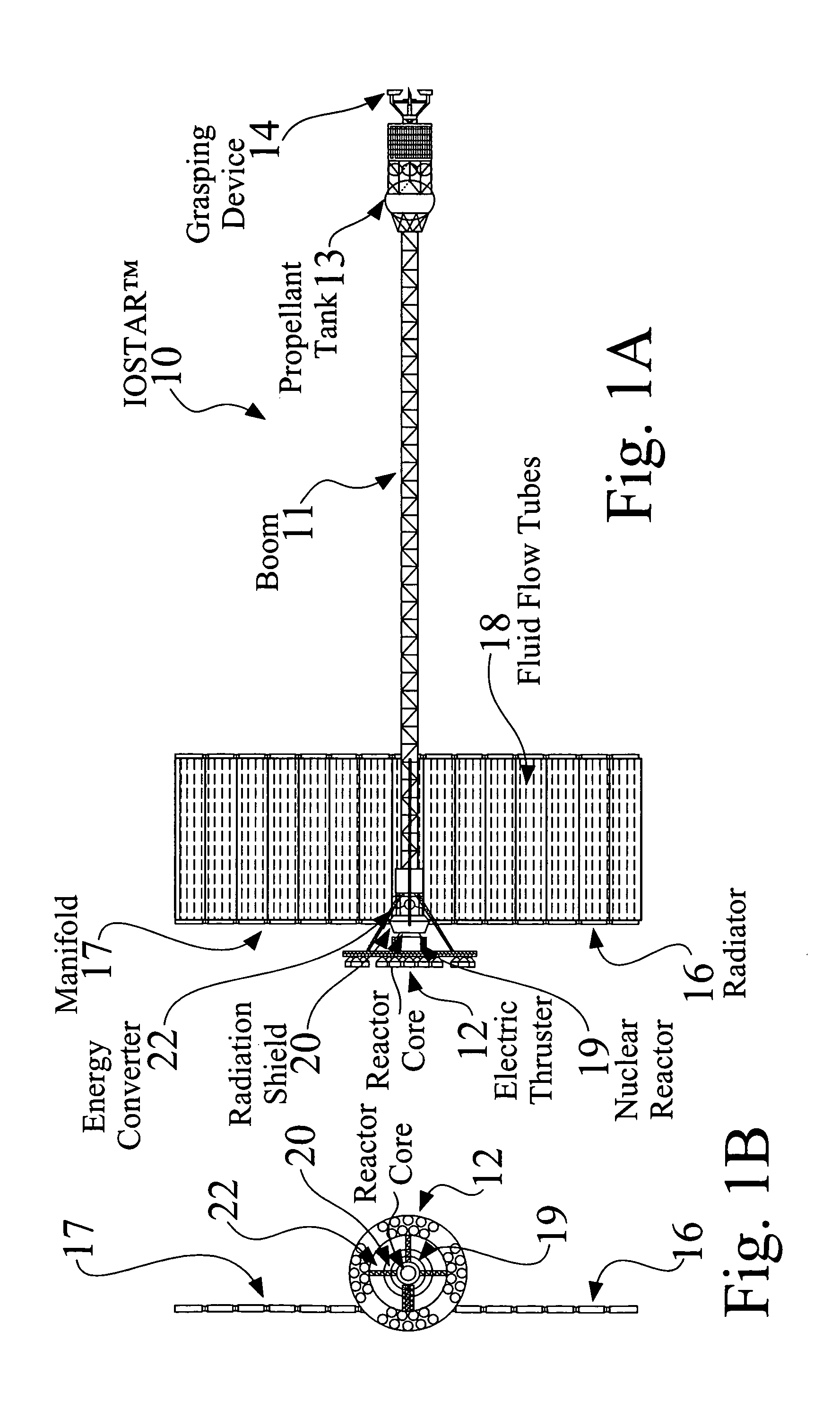
An In Orbit Transportation & Recovery System (IOSTAR™) (10). One preferred embodiment of the present invention comprises a space tug powered by a nuclear reactor (19). The IOSTAR™ includes a collapsible boom (11) connected at one end to a propellant tank (13) which stores fuel for an electric propulsion system (12). This end of the boom ( 11) is equipped with docking hardware (14) that is able to grasp and hold a satellite (15) and as a means to refill the tank (13). Radiator panels (16) mounted on the boom (11) dissipate heat from the reactor (19). A radiation shield (20) is situated next to the reactor (19) to protect the satellite payload (15) at the far end of the boom (11). The IOSTAR™ (10) will be capable of accomplishing rendezvous and docking maneuvers which will enable it to move spacecraft between a low Earth parking orbit and positions in higher orbits or to other locations in our Solar System.
Owner:IOSTAR CORP
In orbit space transportation and recovery system
InactiveUS7070151B2Low costCosmonautic radiation protectionLaunch systemsNatural satelliteNuclear reactor
An In Orbit Transportation & Recovery System (IOSTAR™) (10) One preferred embodiment of the present invention comprises a space tug powered by a nuclear reactor (19). The IOSTAR™ includes a collapsible boom (11) connected at one end to a propellant tank (13) which stores fuel for an electric propulsion system (12). This end of the boom (11) is equipped with docking hardware (14) that is able to grasp and hold a satellite (15) and as a means to refill the tank (13). Radiator panels (16) mounted on the boom (11) dissipate heat from the reactor (19). A radiation shield (20) is situated next to the reactor (19) to protect the satellite payload (15) at the far end of the boom (11). The IOSTAR™ (10) will be capable of accomplishing rendezvous and docking maneuvers which will enable it to move spacecraft between a low Earth parking orbit and positions in higher orbits or to other locations in our Solar System.
Owner:IOSTAR CORP
Process for producing synthetic liquid hydrocarbon fuels
ActiveUS20050232833A1Meet high volumeIncreased gravimetric energy densityLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionOxygen compounds purification/separationThermal energyOcean thermal energy conversion
A process for producing synthetic hydrocarbons that reacts carbon dioxide, obtained from seawater of air, and hydrogen obtained from water, with a catalyst in a chemical process such as reverse water gas shift combined with Fischer Tropsch snthesis. The hydrogen is produced by nuclear reactor electricity, nuclear waste heat conversion, ocean thermal energy conversion, or any other source that is fossil fuel-free, such as wind or wave energy. The process can be either land based or sea based.
Owner:NAVY U S A AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE THE
Software based control system for nuclear reactor standby liquid control (SLC) logic processor
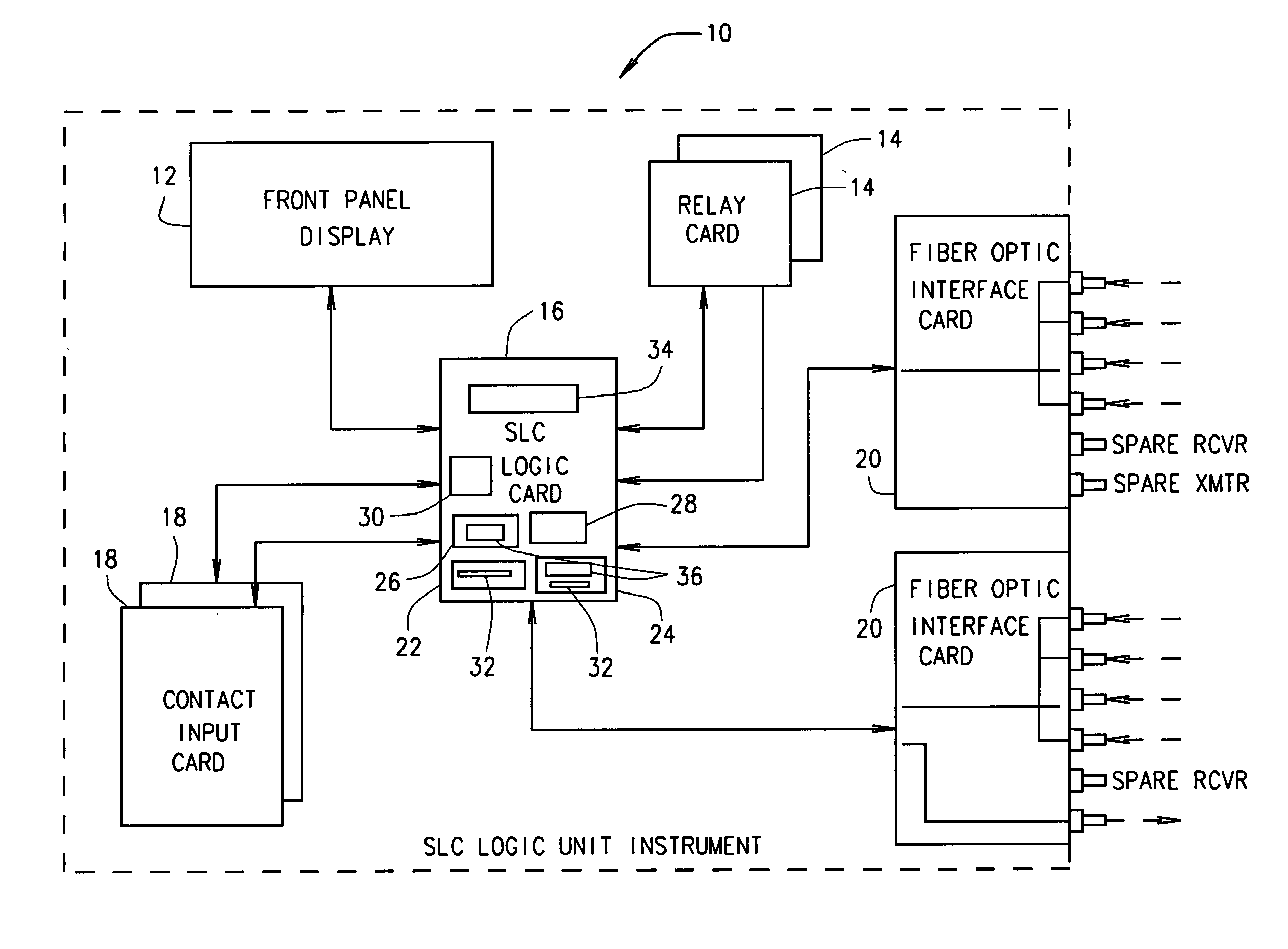
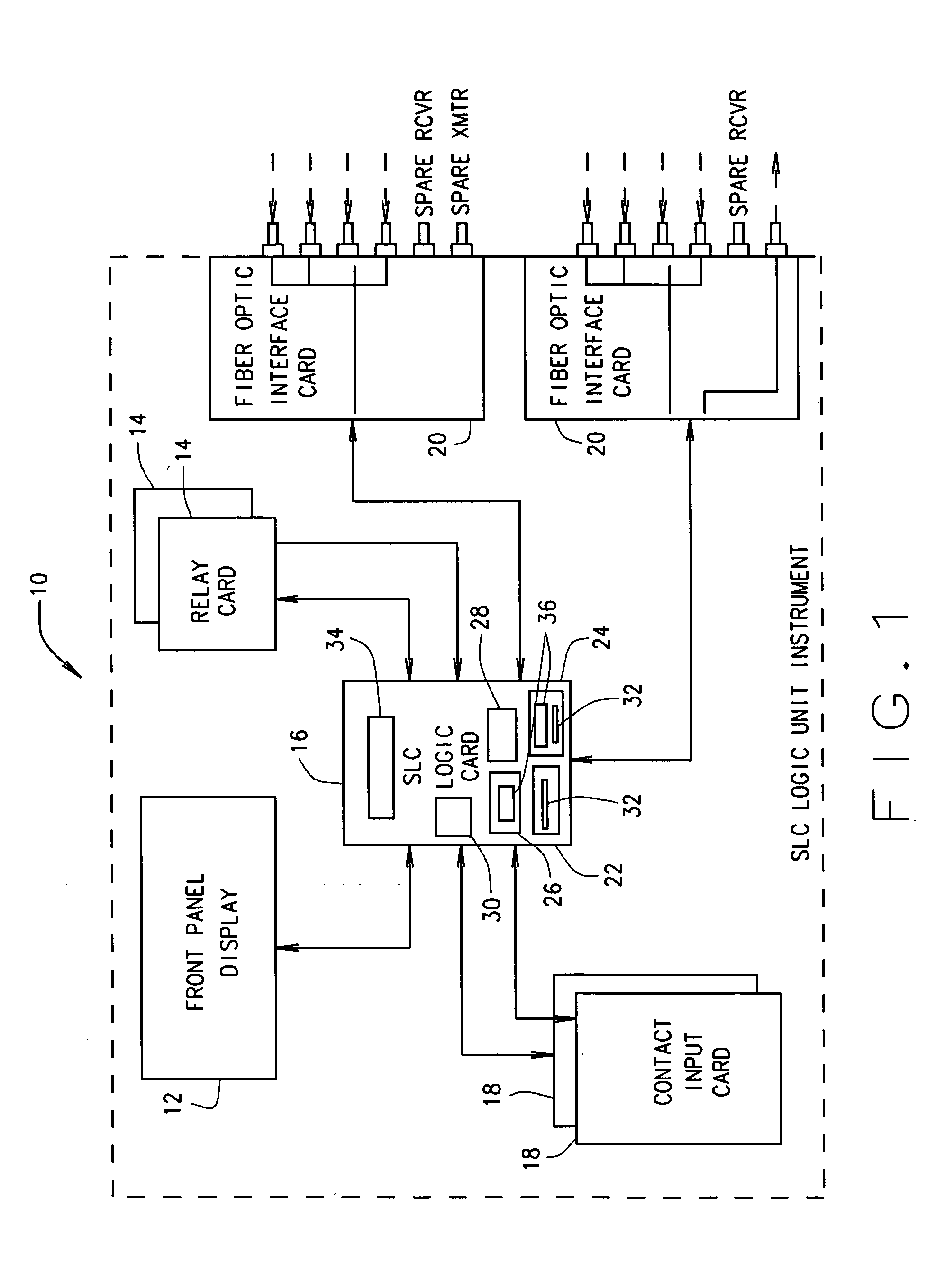
ActiveUS20050281368A1Analogue/digital conversionElectric signal transmission systemsNuclear reactorSoftware system
A method and system is provided for a nuclear reactor safety related application. The method includes executing two forms of a same application-specific logic, one of the two forms implemented as hardware logic, and the other of the two forms implemented as software instructions for execution by microprocessor-based controlling software. Each form of the application-specific logic is executed with a same set of inputs. The method compares a result produced from the execution of the hardware-implemented form to a result produced from the execution of the software-implemented form. When the compared results concur, the controlling software performs actions associated with the concurring results by executing microprocessor-based software. When the compared results fail to concur, the controlling software reports the failure of the compared results to concur to an operator by executing microprocessor-based software, and thereafter places the microprocessor-based software system into an inoperative (INOP) mode.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
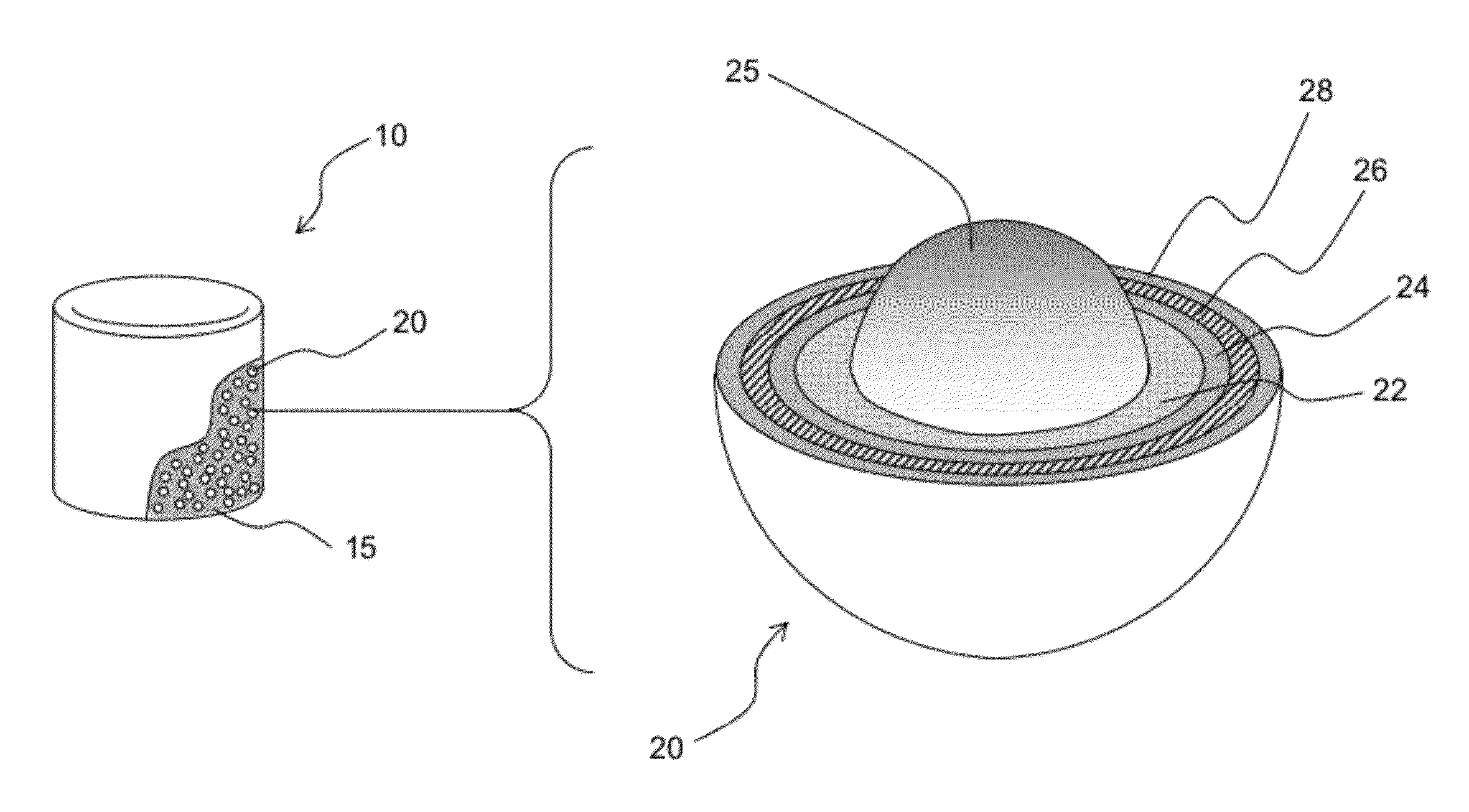
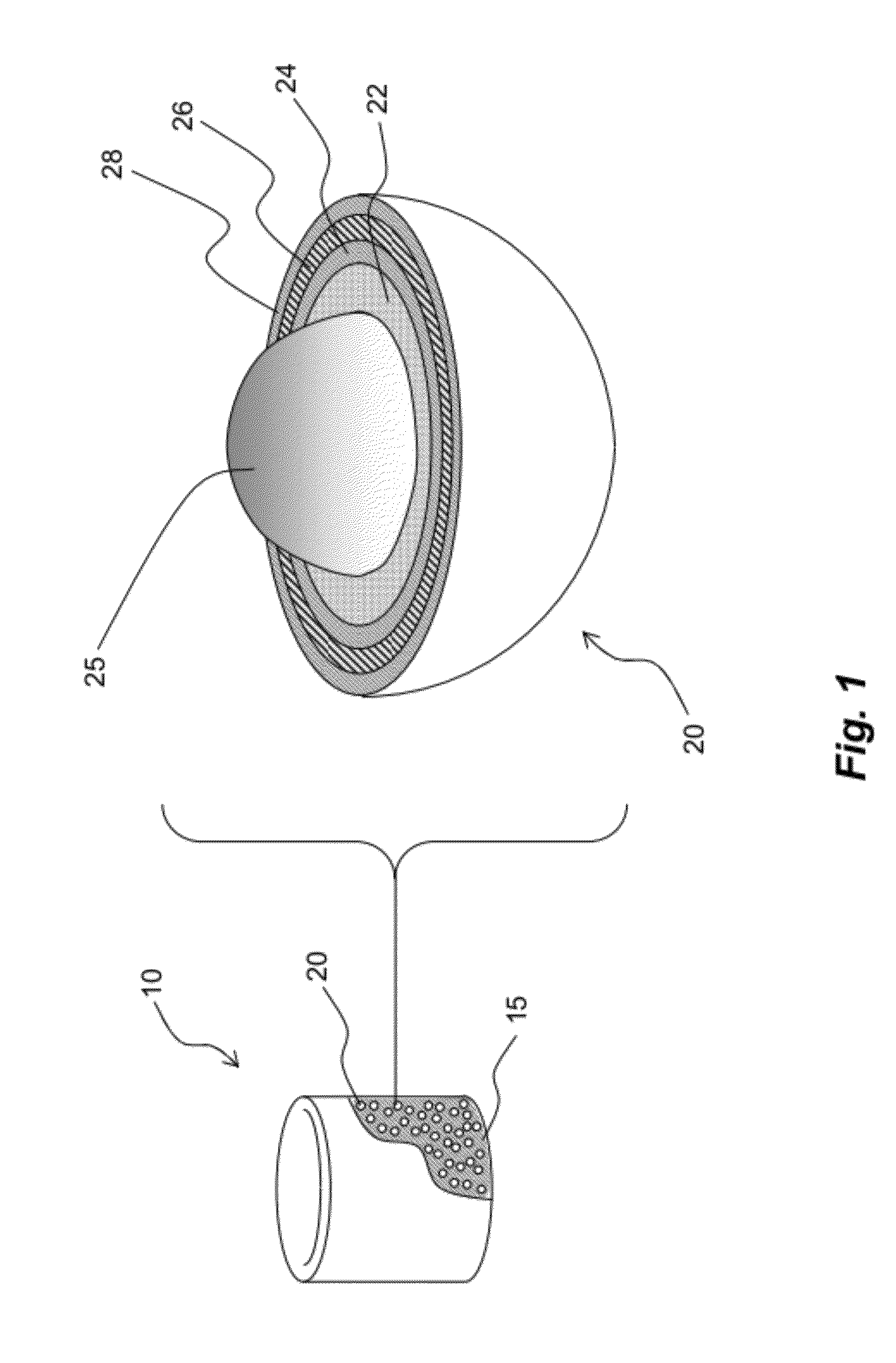
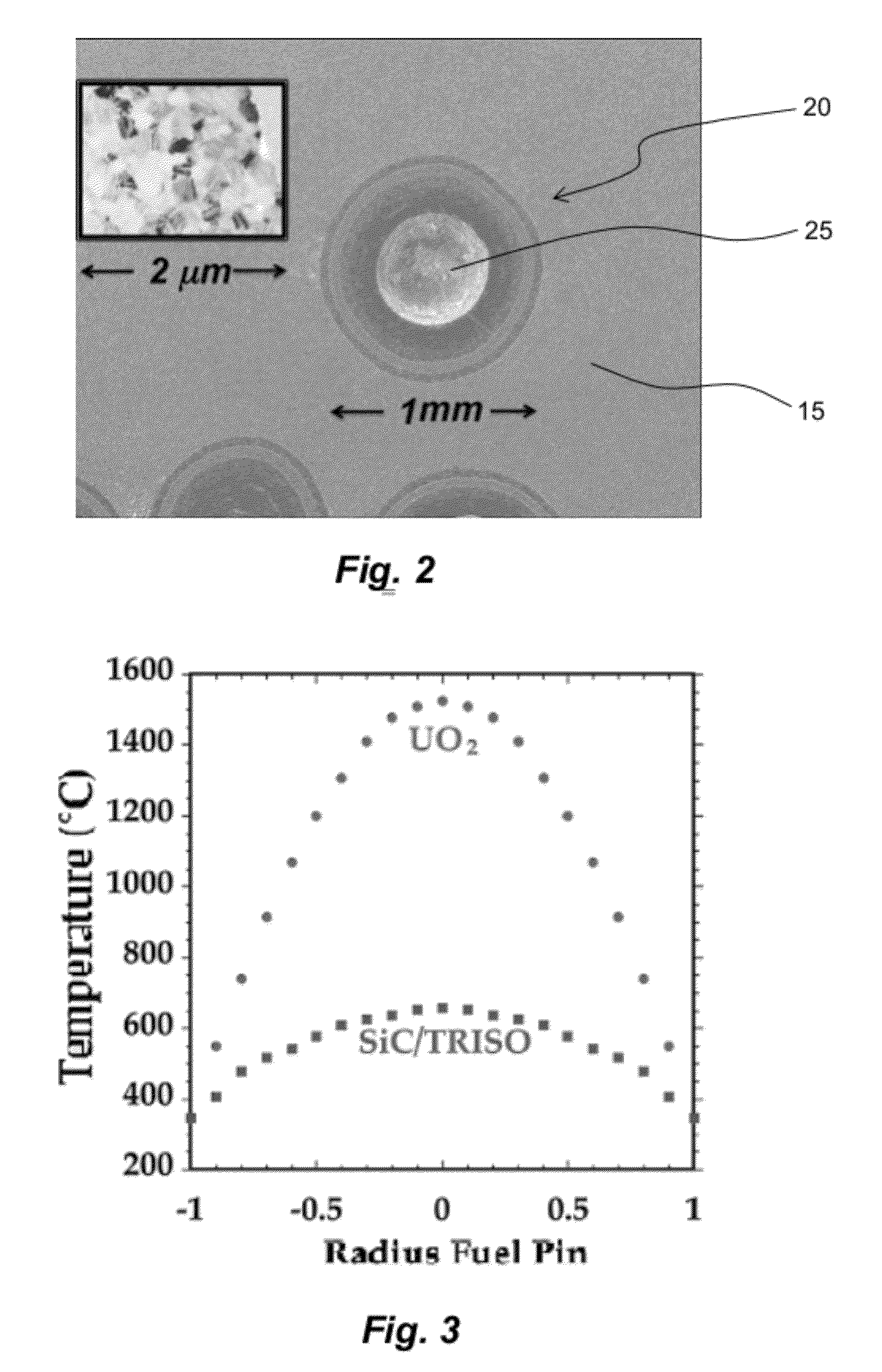
Fully ceramic nuclear fuel and related methods
Various embodiments of a nuclear fuel for use in various types of nuclear reactors and / or waste disposal systems are disclosed. One exemplary embodiment of a nuclear fuel may include a fuel element having a plurality of tristructural-isotropic fuel particles embedded in a silicon carbide matrix. An exemplary method of manufacturing a nuclear fuel is also disclosed. The method may include providing a plurality of tristructural-isotropic fuel particles, mixing the plurality of tristructural-isotropic fuel particles with silicon carbide powder to form a precursor mixture, and compacting the precursor mixture at a predetermined pressure and temperature.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC +1
Orbit space transportation and recovery system
An In Orbit Transportation & Recovery System (IOSTAR™) (10). One preferred embodiment of the present invention comprises a space tug powered by a nuclear reactor (19). The IOSTAR™ includes a collapsible boom (11) connected at one end to a propellant tank (13) which stores fuel for an electric propulsion system (12). This end of the boom (11) is equipped with docking hardware (14) that is able to grasp and hold a satellite (15) and as a means to refill the tank (13). Radiator panels (16) mounted on the boom (11) dissipate heat from the reactor (19). A radiation shield (20) is situated next to the reactor (19) to protect the satellite payload (15) at the far end of the boom (11). The IOSTAR™ (10) will be capable of accomplishing rendezvous and docking maneuvers which will enable it to move spacecraft between a low Earth parking orbit and positions in higher orbits or to other locations in our Solar System.
Owner:IOSTAR CORP
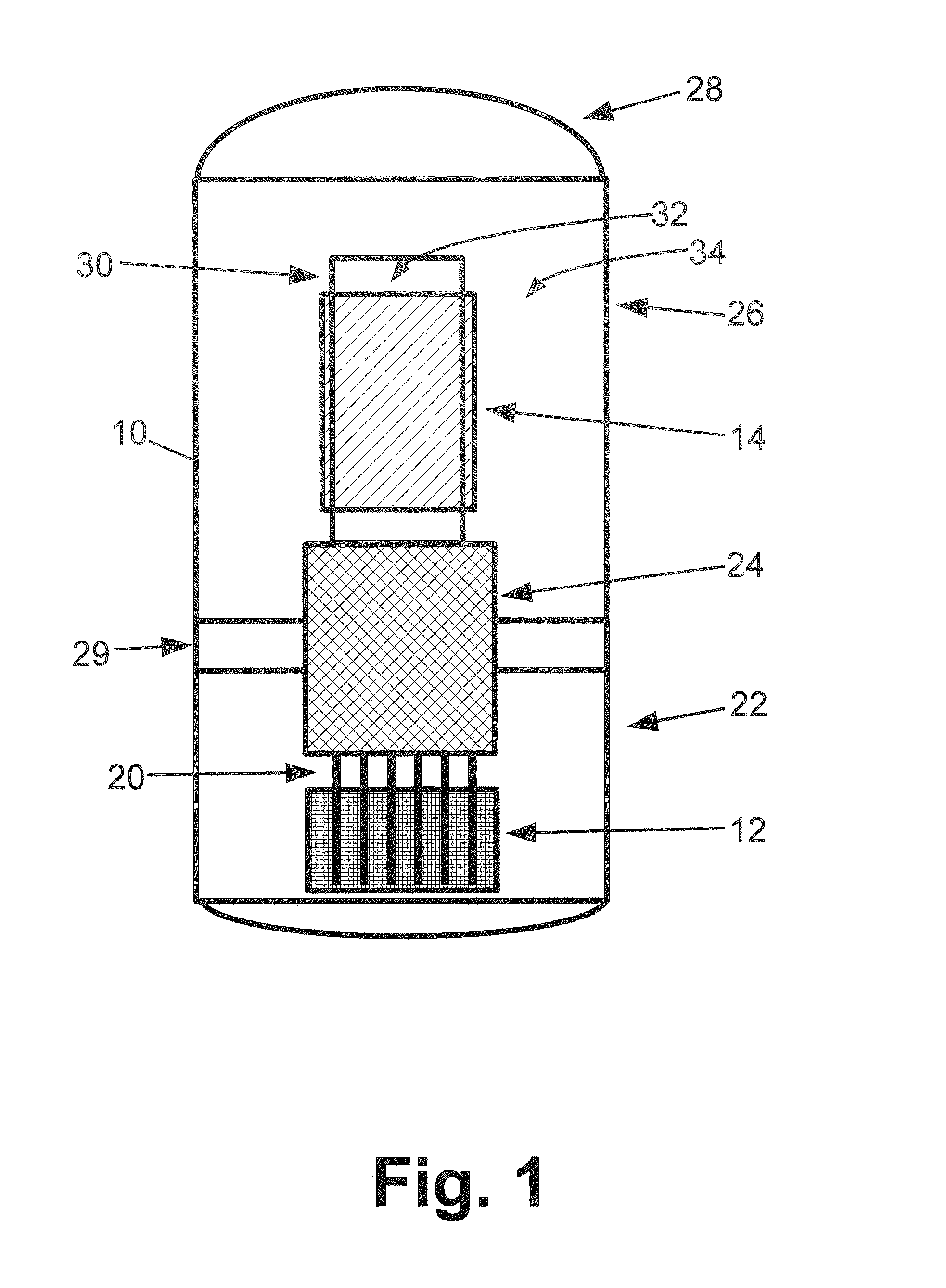
Evacuated containment vessel for a nuclear reactor
ActiveUS20090161812A1Nuclear energy generationNuclear engineering problemsNuclear reactorEngineering
A system includes a containment vessel configured to prohibit a release of a coolant, and a reactor vessel mounted inside the containment vessel. An outer surface of the reactor vessel is exposed to below atmospheric pressure, wherein substantially all gases are evacuated from within the containment vessel.
Owner:NUSCALE
In-core fuel restraint assembly
InactiveUS20060251205A1Improving resistance to liftingIncrease vibrationNuclear energy generationNuclear engineering problemsNuclear reactor coreNuclear reactor
An in-core restraint assembly is for a nuclear reactor core including an upper core plate, a lower core support plate and a plurality of fuel assemblies extending longitudinally therebetween. Each fuel assembly includes top and bottom nozzles and a plurality of elongated fuel rods extending therebetween. The in-core restraint assembly includes a first restraint element, such as a spring pack, coupled to the upper core support plate and providing a substantially axial compressive force on the top nozzle of the fuel assembly. An optional second restraint element is structured to be coupled to the lower core plate in order to engage and further restrain the fuel assembly proximate the bottom nozzle. The second restraint element includes a pin member extending from the bottom nozzle of the fuel assembly and received in a socket coupled to the lower core support plate, whereby this mating sustains a longitudinal (vertical) frictional force which must be overcome before fuel assembly lift off can occur.
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE ELECTRIC CORP
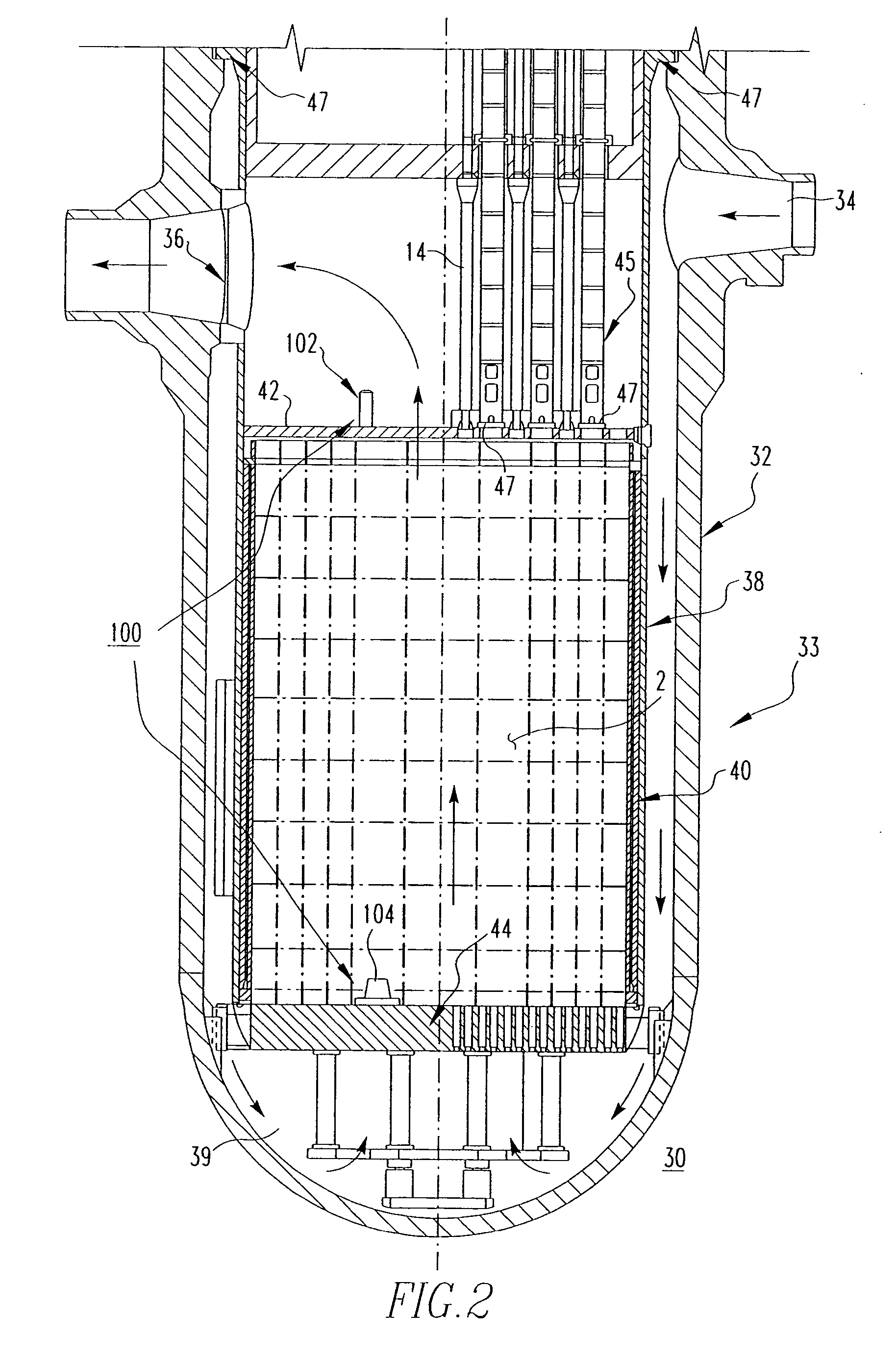
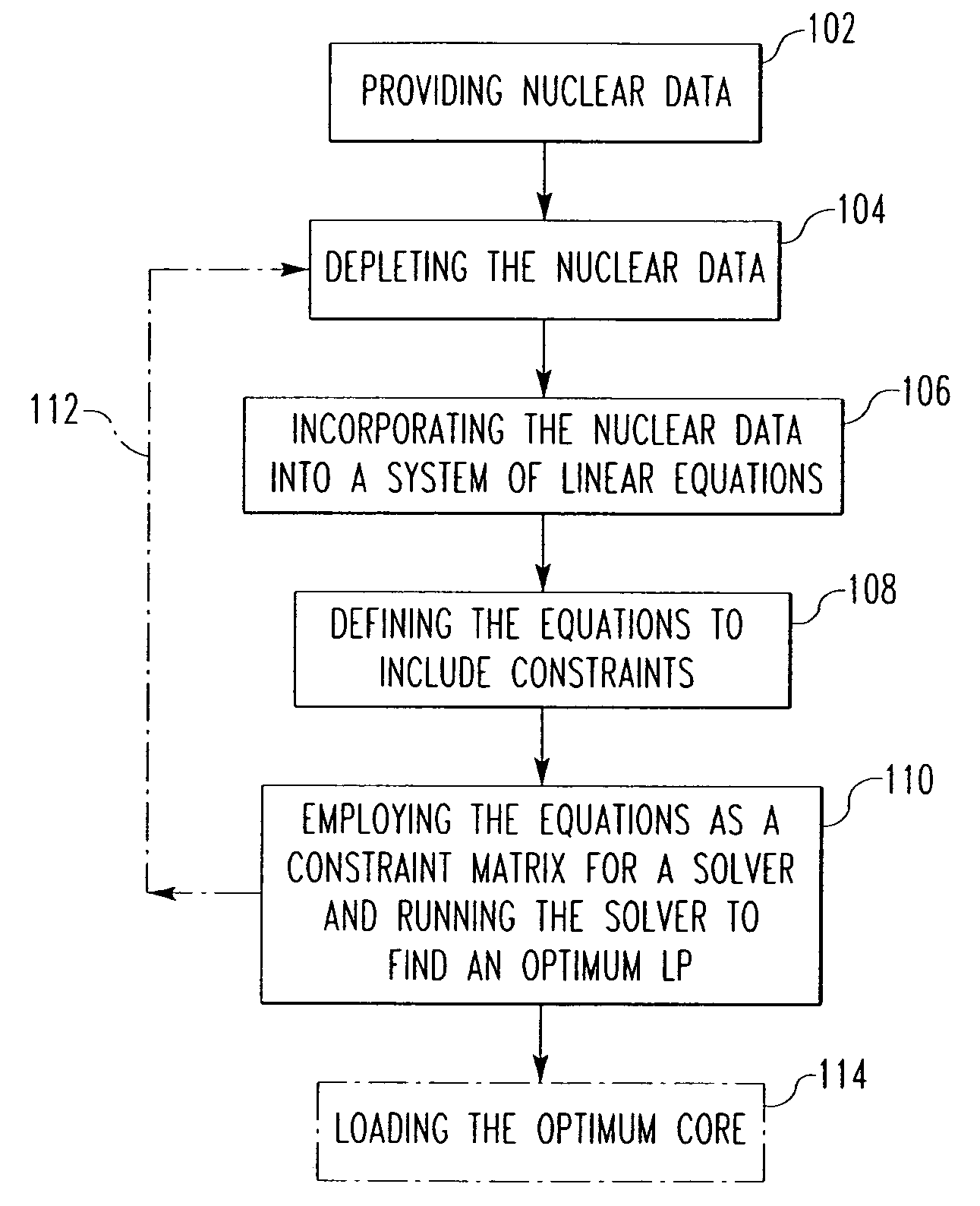
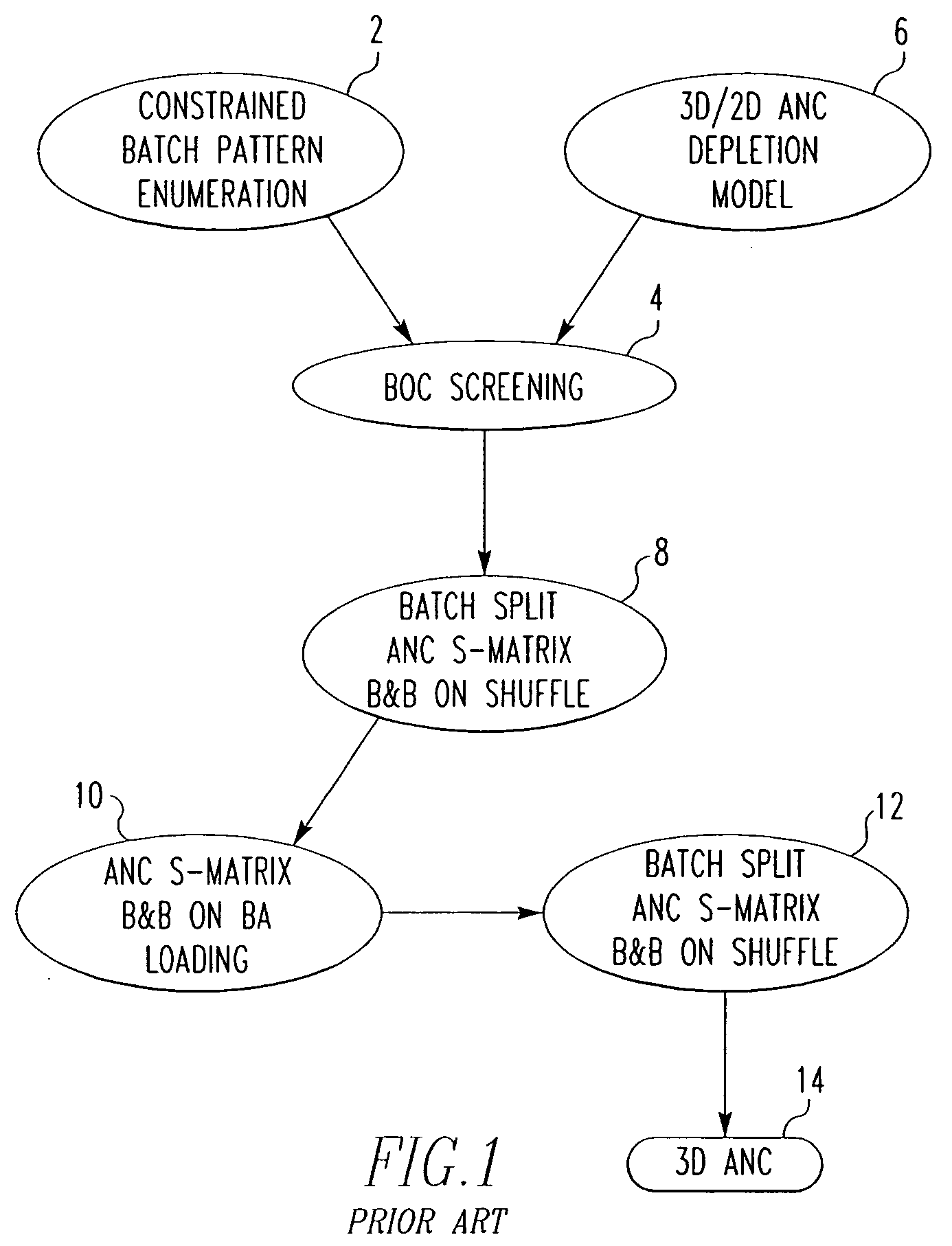
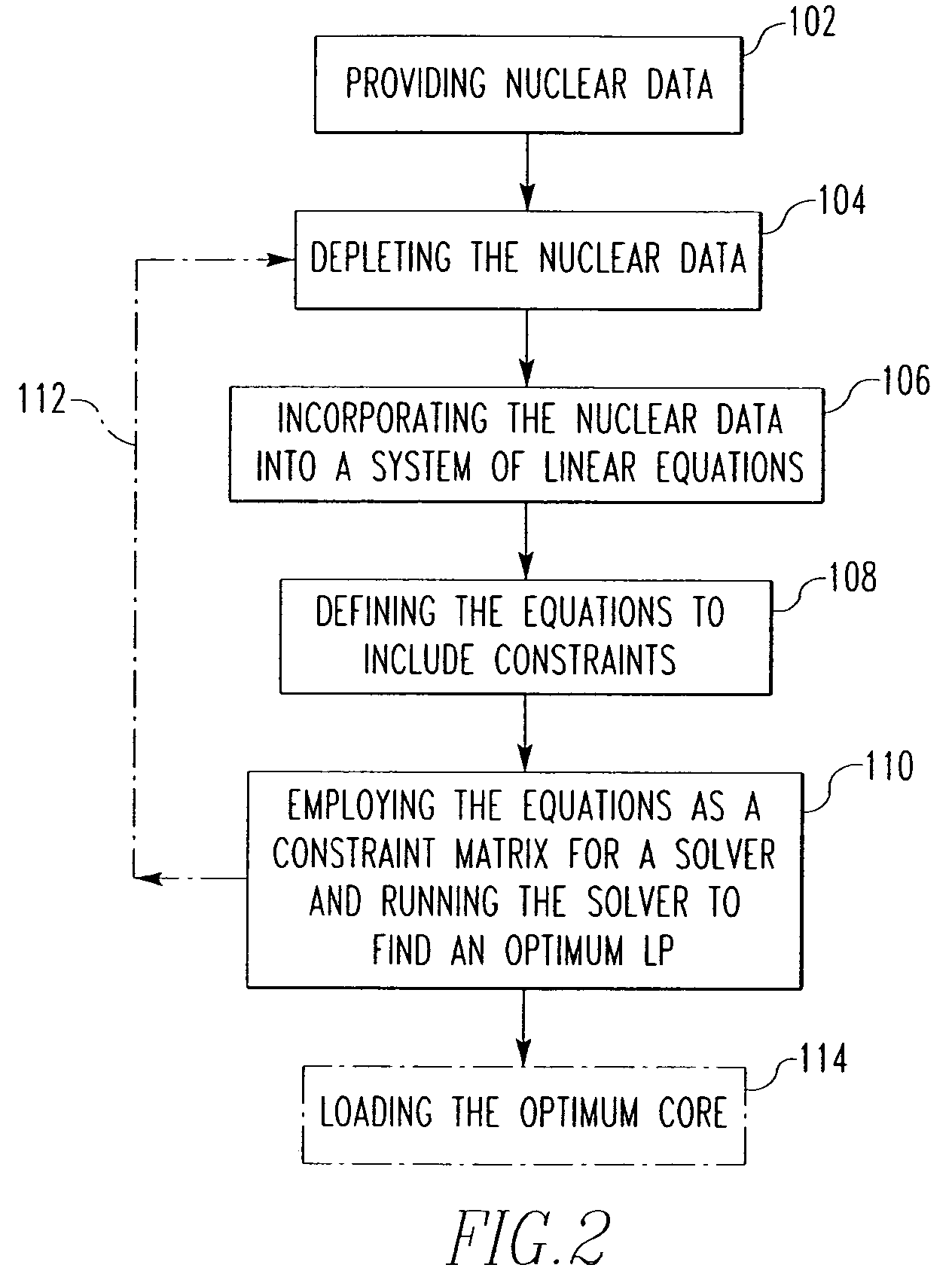
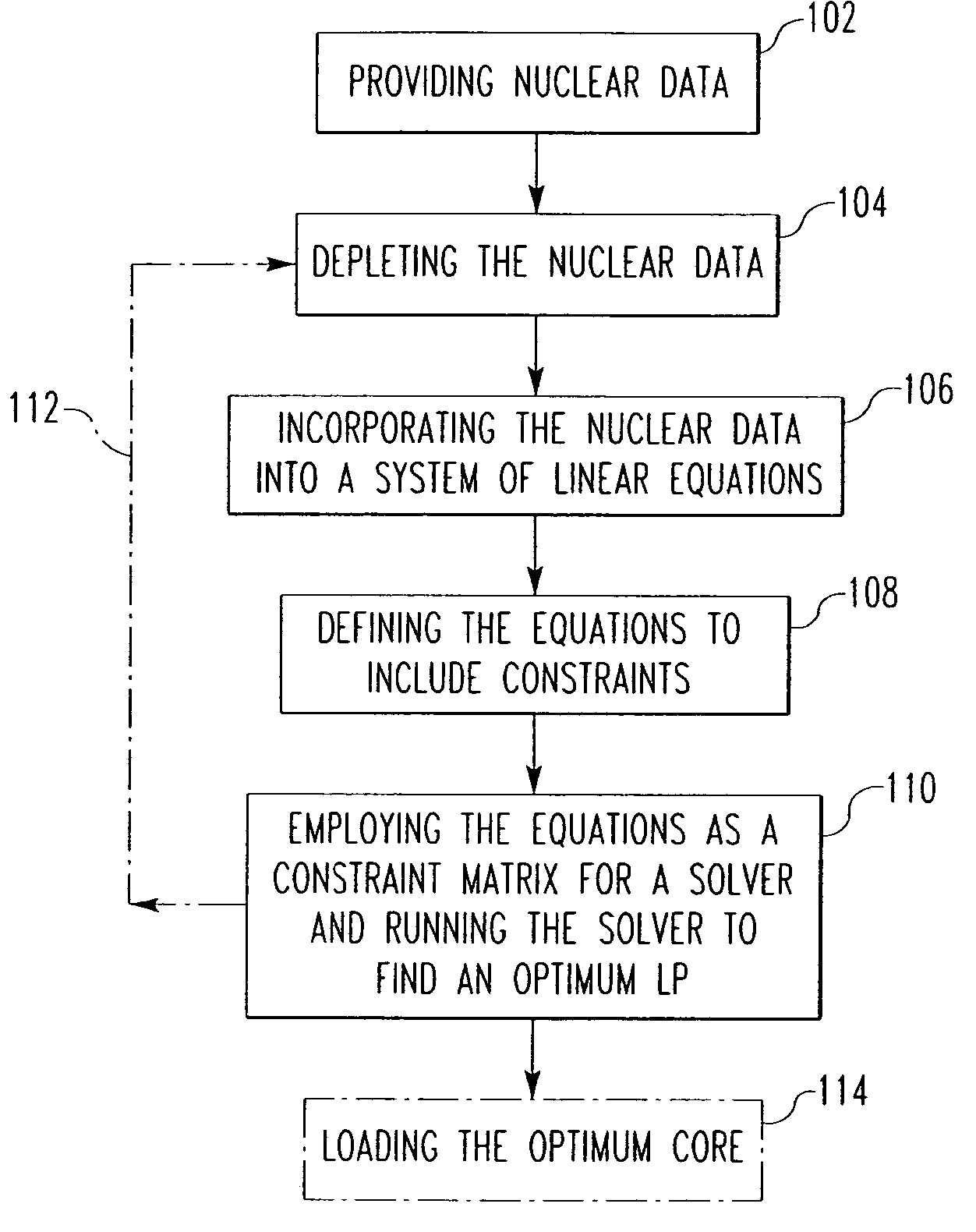
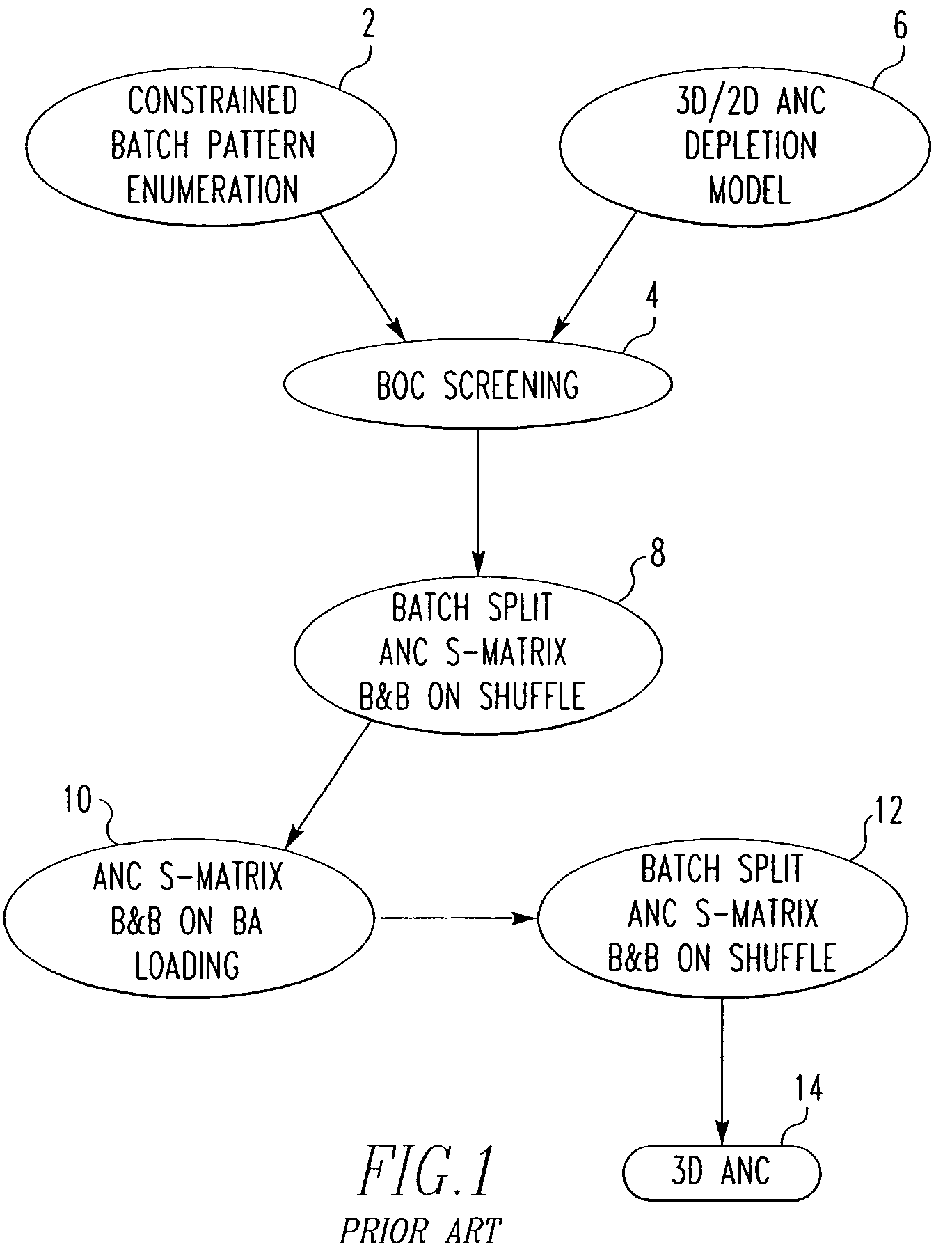
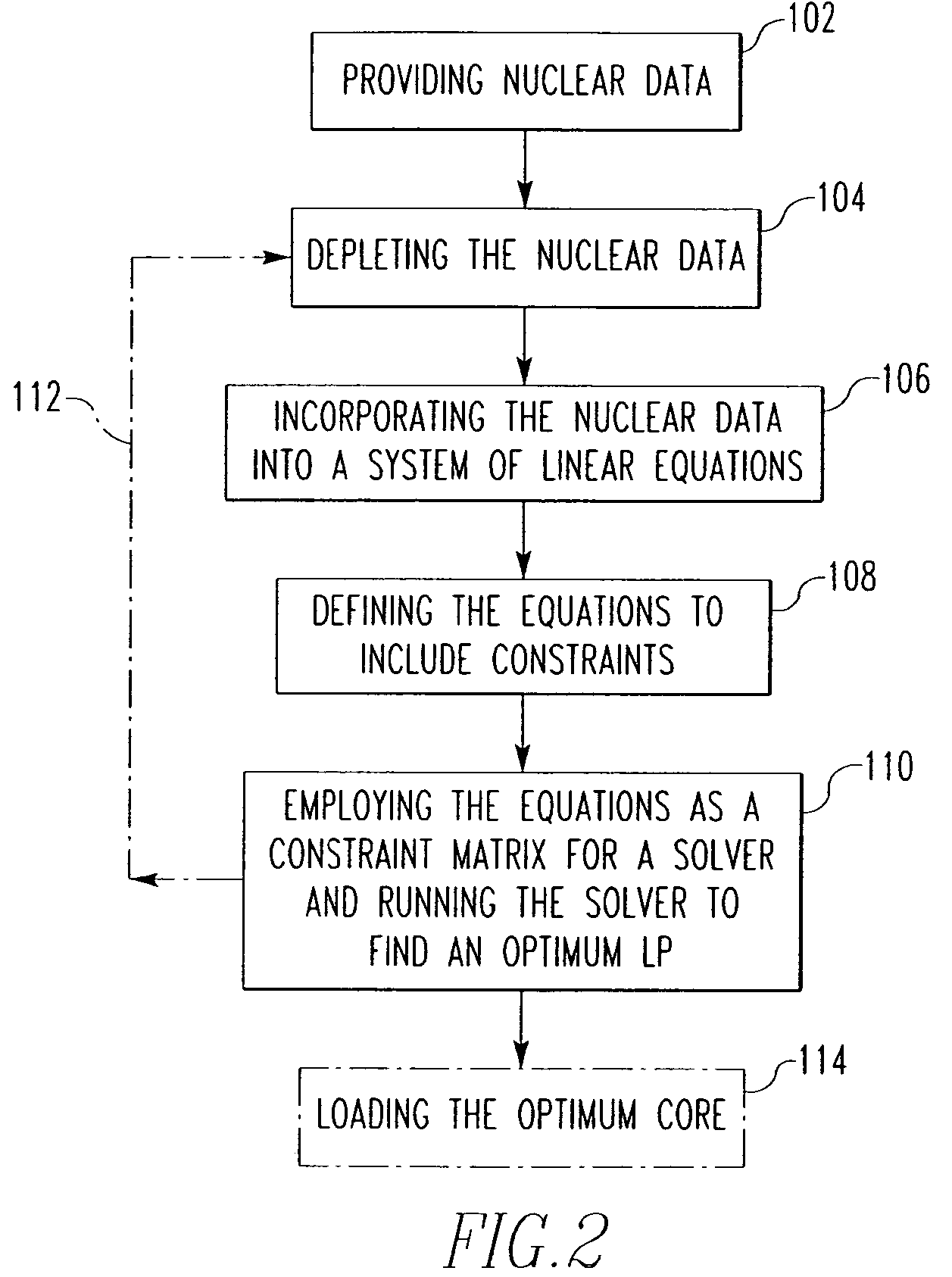
Method and algorithm for searching and optimizing nuclear reactor core loading patterns
ActiveUS20060109944A1Accurate representationSatisfies requirementCosmonautic condition simulationsNuclear energy generationNuclear reactor coreNuclear reactor
A method is for establishing a nuclear reactor core loading pattern (LP) for fuel assemblies and burnable absorbers (BAs). The method establishes an optimum LP through the steps of: a) providing nuclear data representing fuel assemblies and BAs in a nuclear reactor core; b) depleting the nuclear data to form a reference core depletion; c) incorporating the nuclear data into a system of linear equations of a nuclear design quality flux solution method; d) defining the system of linear equations to include constraints which accurately represent the neutron physics of the reactor; employing the equations as a constraint matrix for a MIP solver to find an optimum core pattern solution; f) repeating steps b) through e) updating the constraints and objective functions to satisfy specified engineering requirements and establish an optimum core loading pattern. An algorithm for deriving the system of equations is also disclosed.
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE ELECTRIC CORP
Method and algorithm for searching and optimizing nuclear reactor core loading patterns
ActiveUS7224761B2Accurate representationCosmonautic condition simulationsNuclear energy generationNuclear reactor coreNuclear reactor
A method is for establishing a nuclear reactor core loading pattern (LP) for fuel assemblies and burnable absorbers (BAs). The method establishes an optimum LP through the steps of: a) providing nuclear data representing fuel assemblies and BAs in a nuclear reactor core; b) depleting the nuclear data to form a reference core depletion; c) incorporating the nuclear data into a system of linear equations of a nuclear design quality flux solution method; d) defining the system of linear equations to include constraints which accurately represent the neutron physics of the reactor; employing the equations as a constraint matrix for a MIP solver to find an optimum core pattern solution; f) repeating steps b) through e) updating the constraints and objective functions to satisfy specified engineering requirements and establish an optimum core loading pattern. An algorithm for deriving the system of equations is also disclosed.
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE ELECTRIC CORP
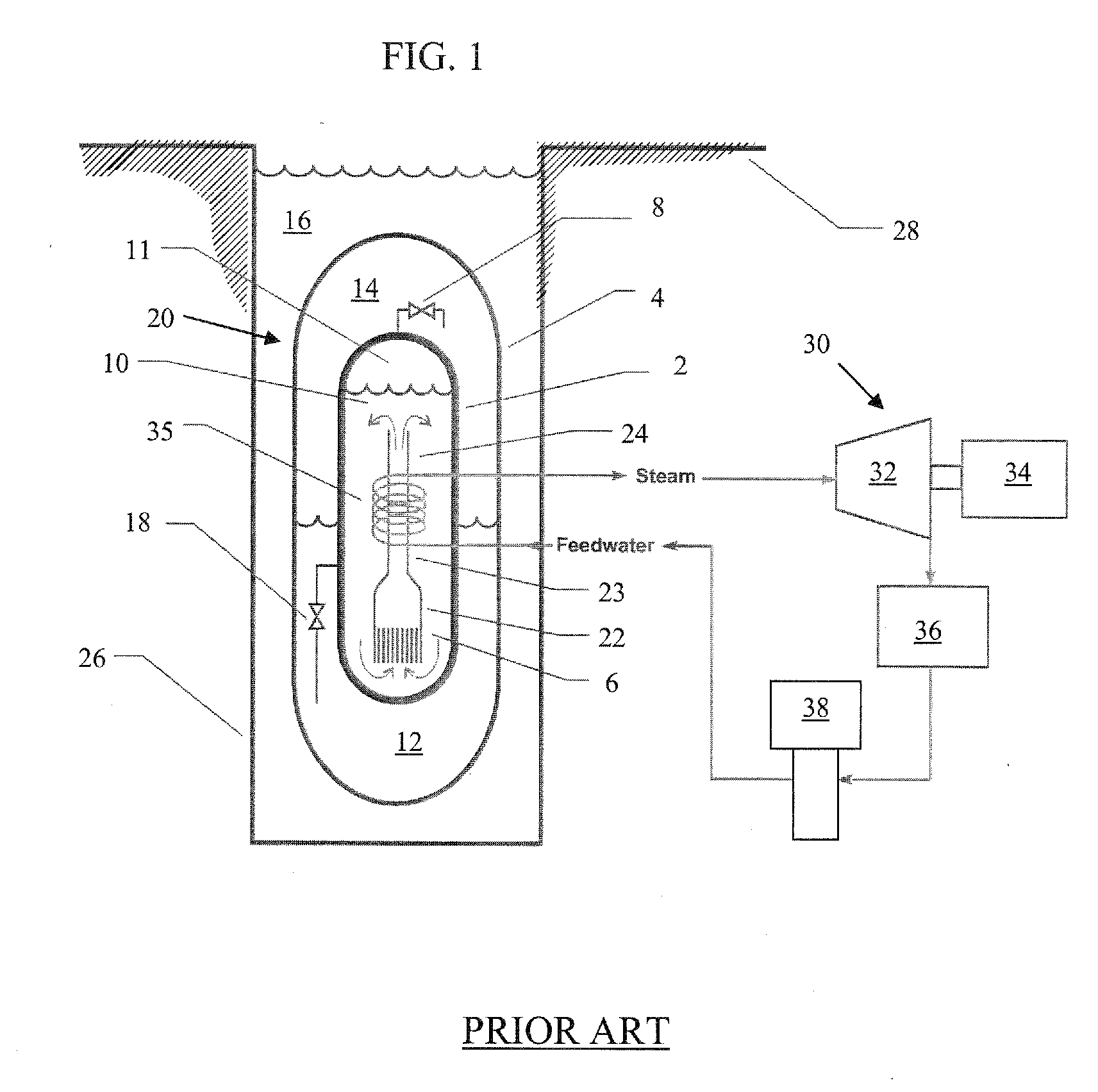
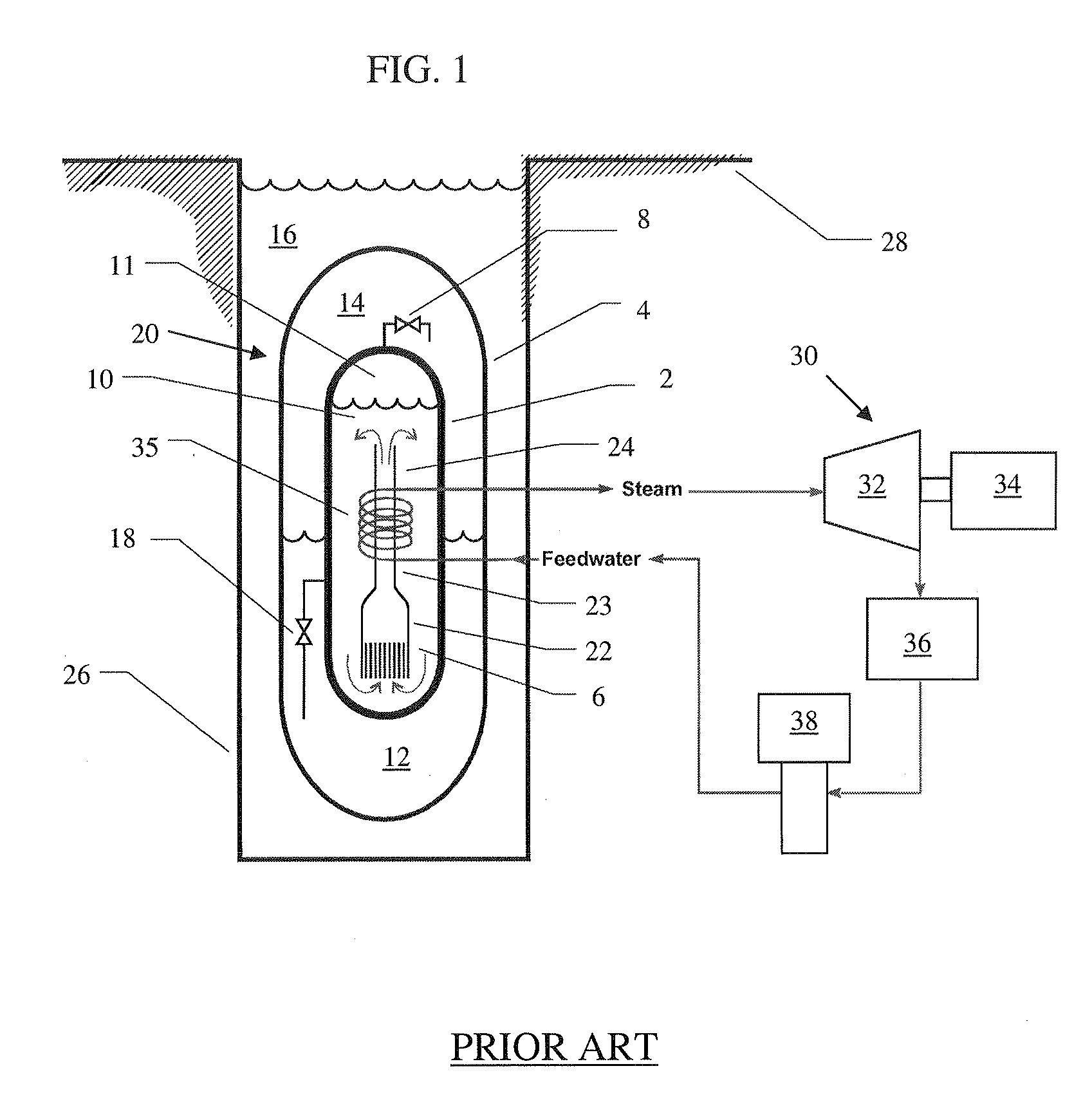
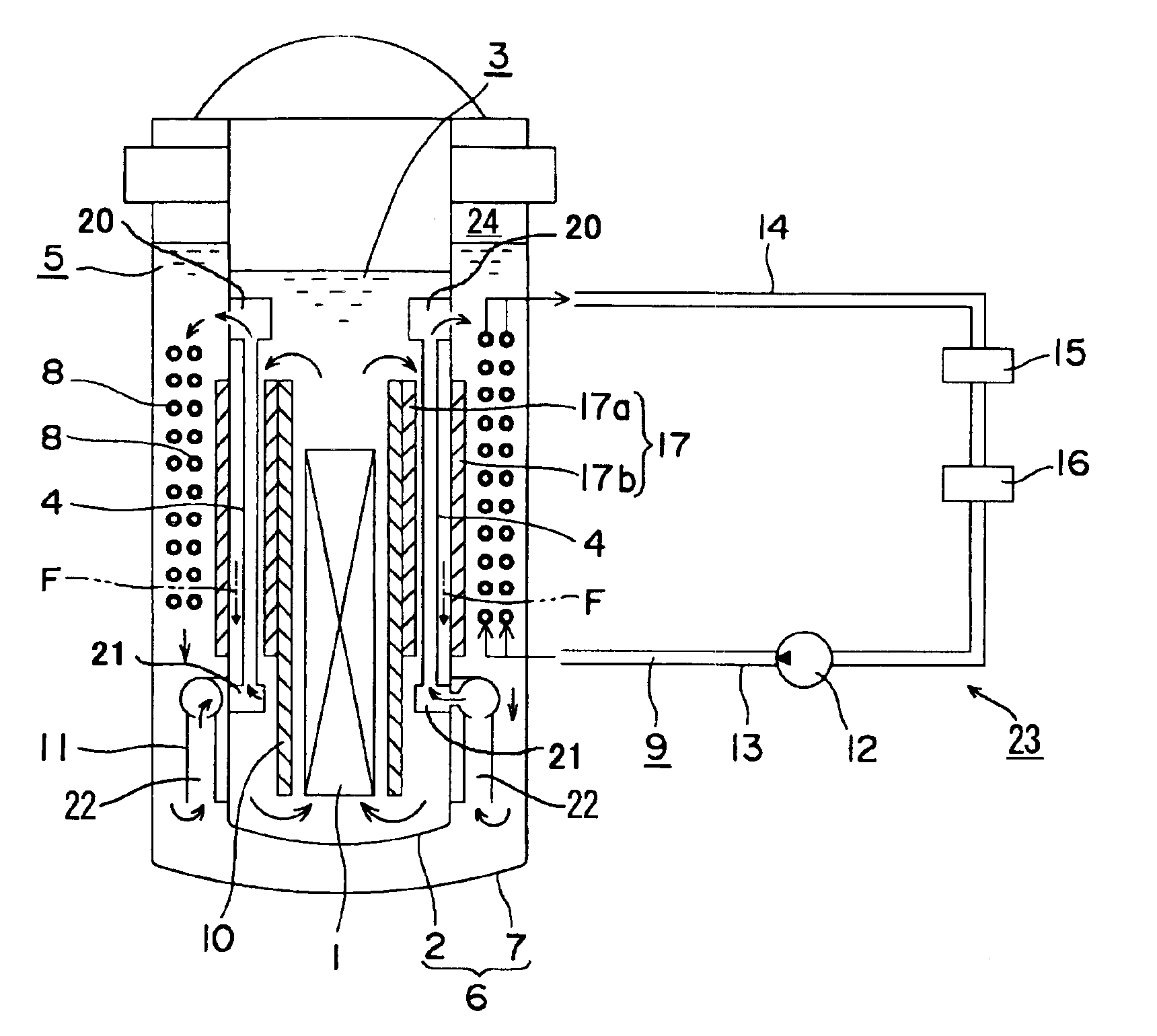
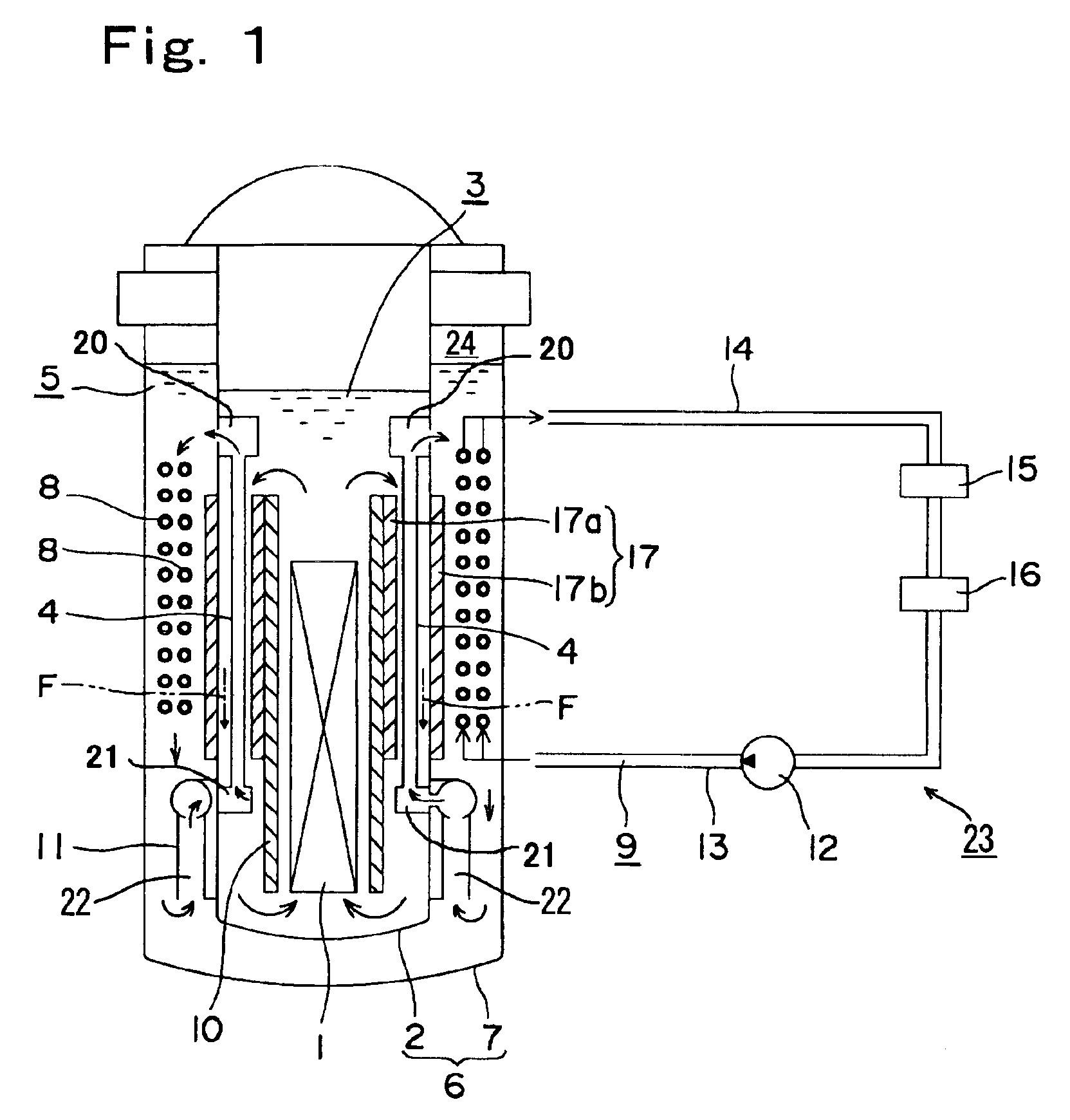
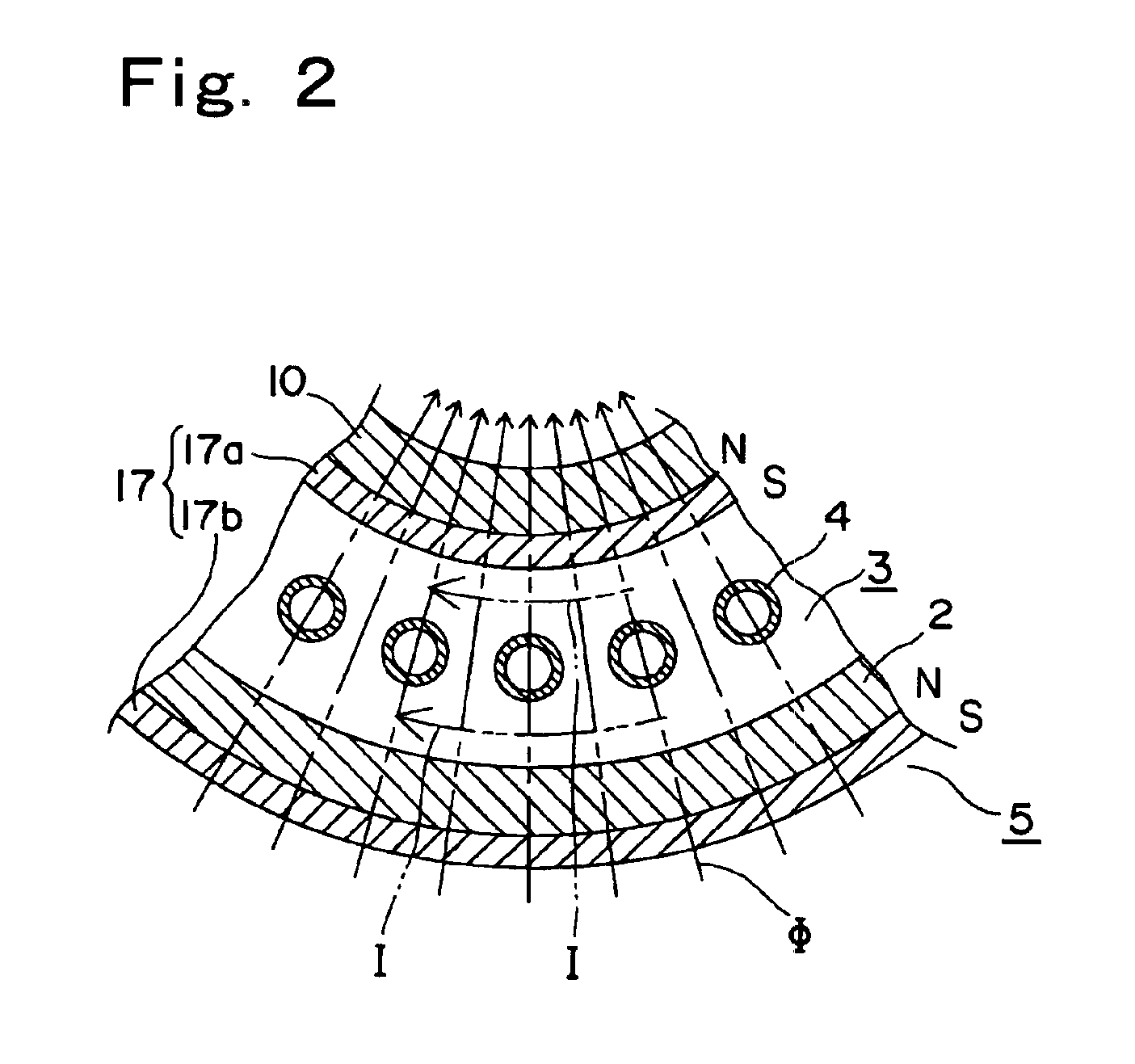
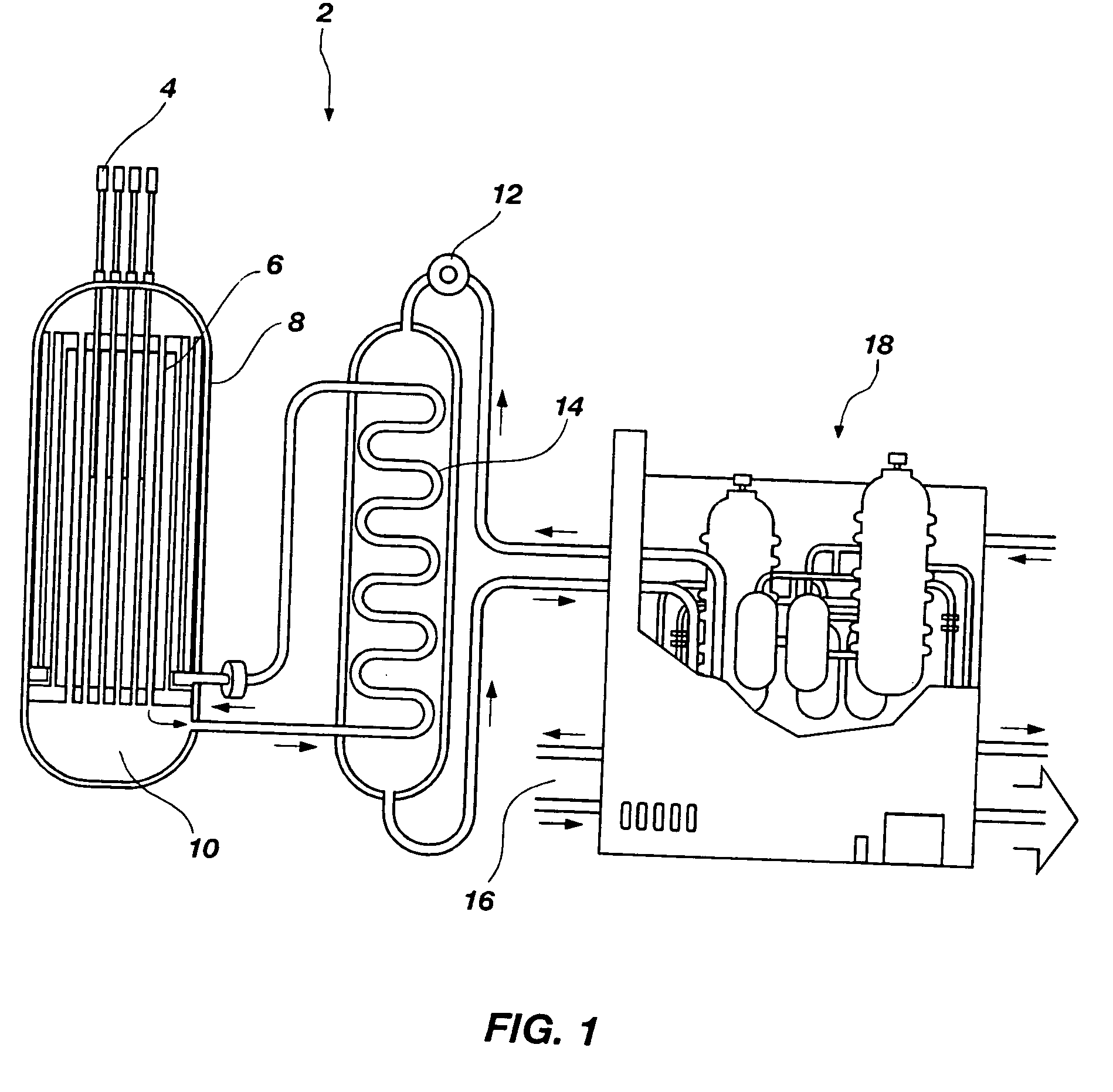
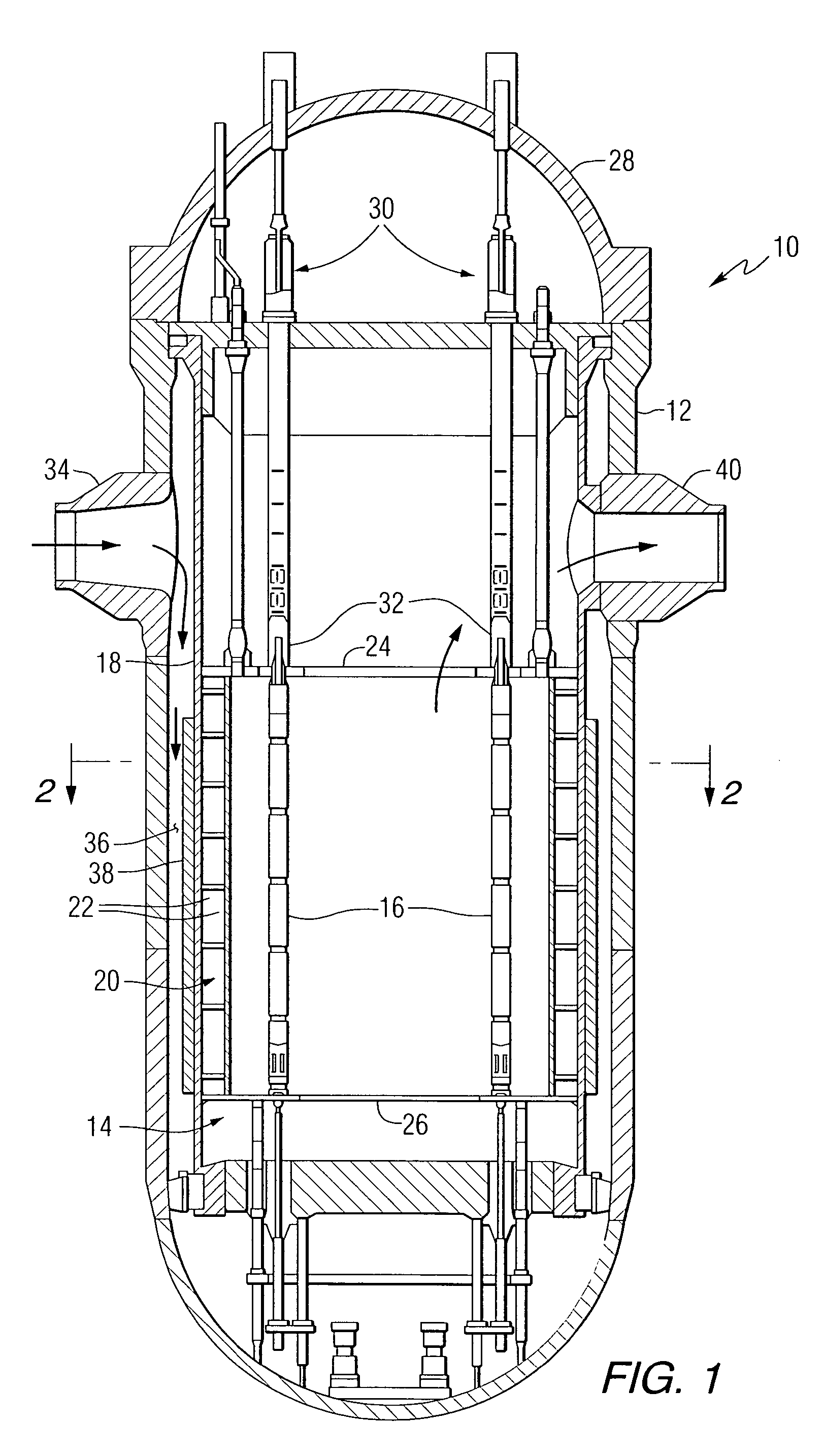
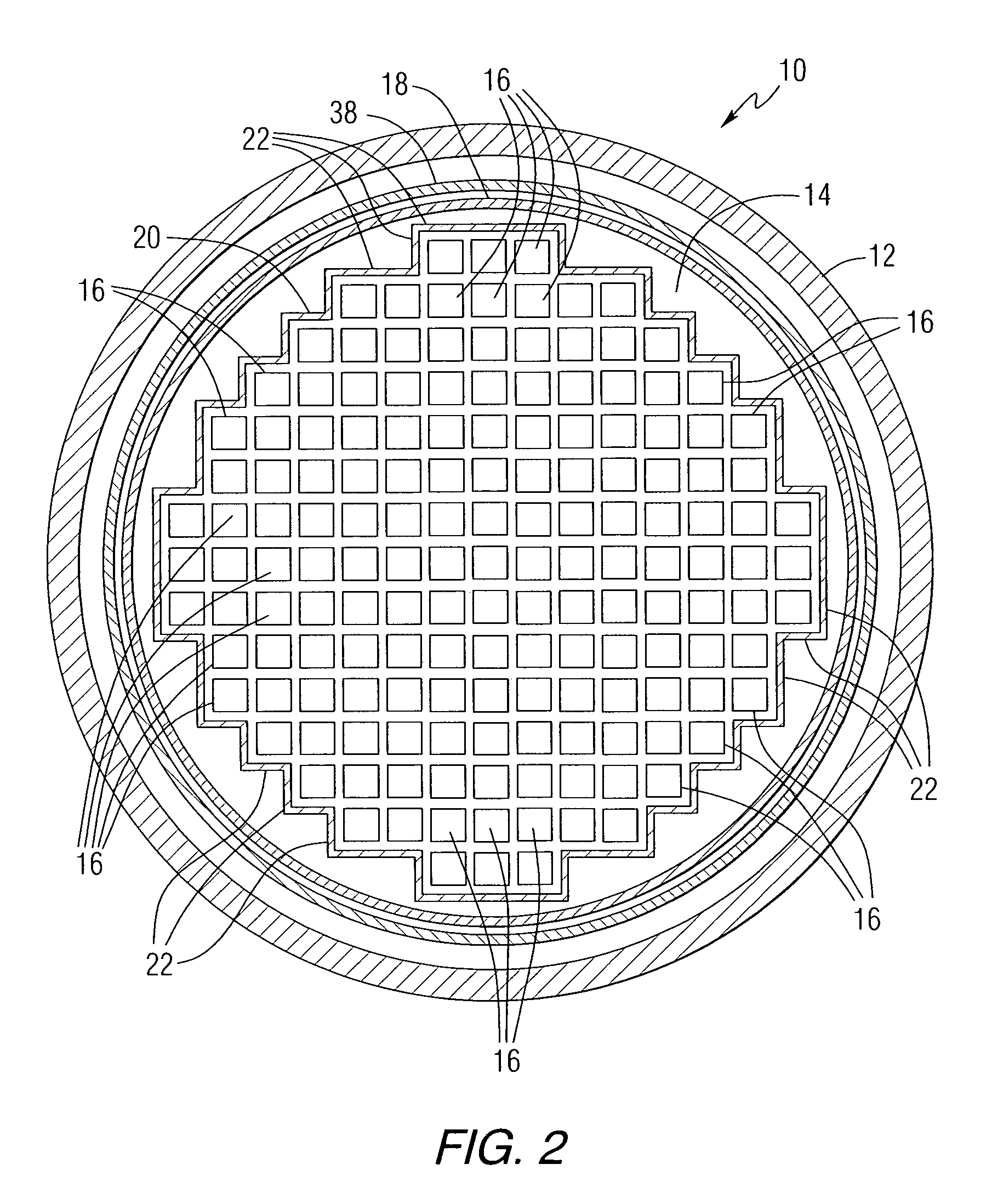
Nuclear reactor
InactiveUS6944255B2Small sizeReduce manufacturing costIntegral reactorsNuclear energy generationNuclear reactorHeat transfer tube
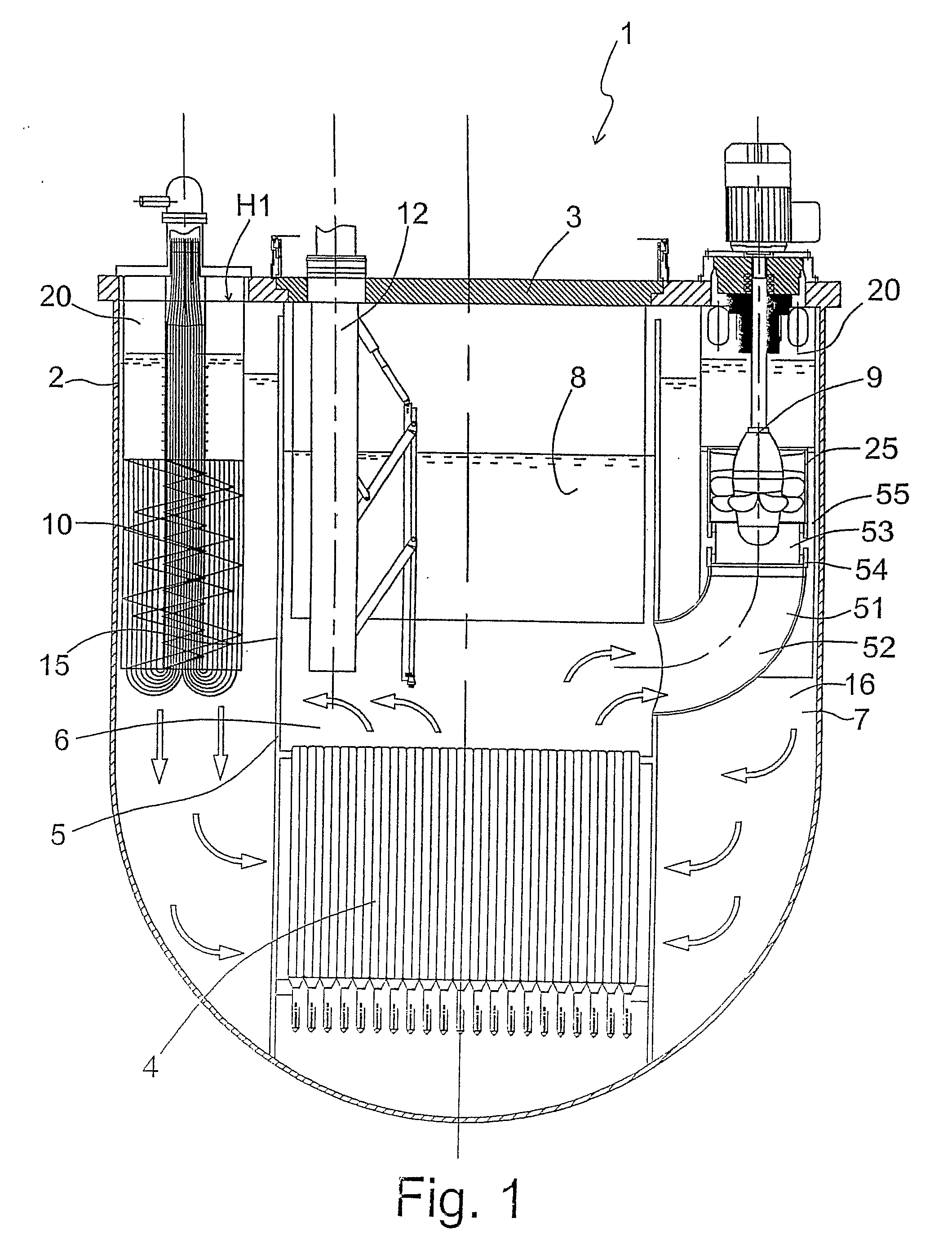
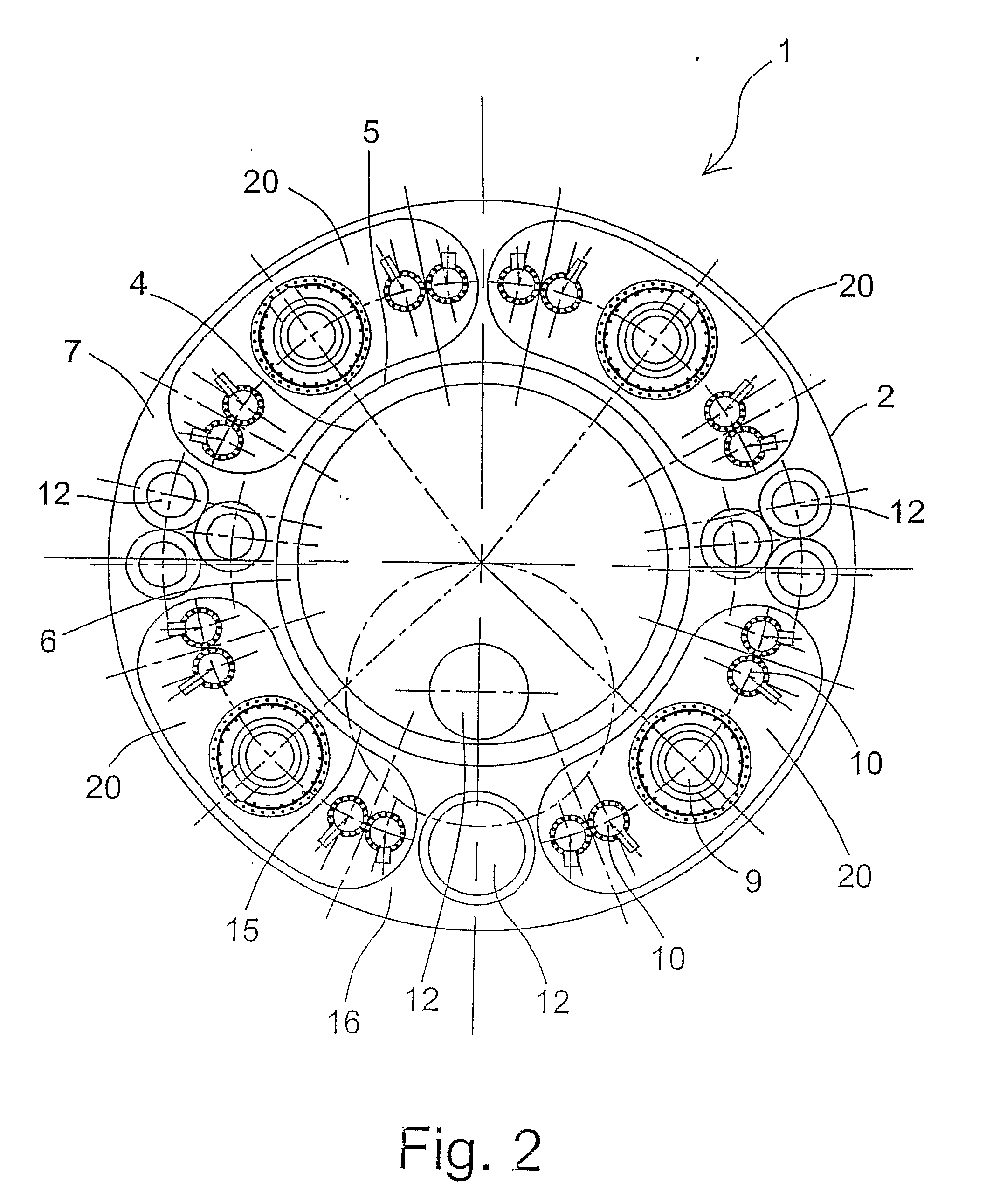
A nuclear reactor in which a secondary or tertiary coolant system of a nuclear steam supply system is simplified, comprising: a reactor vessel (2) which integrates a reactor core (1); a first coolant (3) which is stored in the reactor vessel (2) and heated by the reactor core (1) to convect; a first heat transfer tube (4) which is arranged in the reactor vessel (2) and comes into contact with the first coolant (3); and a second coolant (5) which is supplied from the outside of the reactor vessel (2) to the first heat transfer tube (4), cools the first coolant (3) and led to the outside of the reactor vessel (2).
Owner:CENTRAL RESEARCH INSTITUTE OF ELECTRIC POWER INDUSTRY
Wireless in-core neutron monitor
ActiveUS20120177166A1Avoid runningNuclear energy generationNuclear monitoringNuclear reactor coreNuclear reactor
An in-core neutron monitor that employs vacuum microelectronic devices to configure an in-core instrument thimble assembly that monitors and wirelessly transmits a number of reactor parameters directly from the core of a nuclear reactor without the use of external cabling. The in-core instrument thimble assembly is substantially wholly contained within an instrument guide tube within a nuclear fuel assembly.
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE ELECTRIC CORP
Control rod for nuclear reactor
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND LTD
Silicon carbide material for nuclear applications, precursor and method for forming same, and structures including the material
A precursor formulation of a silicon carbide material that includes a ceramic material and a boron-11 compound. The ceramic material may include silicon and carbon and, optionally, oxygen, nitrogen, titanium, zirconium, aluminum, or mixtures thereof. The boron-11 compound may be a boron-11 isotope of boron oxide, boron hydride, boron hydroxide, boron carbide, boron nitride, boron trichloride, boron trifluoride, boron metal, or mixtures thereof. A material for use in a nuclear reactor component is also disclosed, as are such components, as well as a method of producing the material.
Owner:COI CERAMICS
Nickel-base alloy for the electro-welding of nickel alloys and steels, welding wire and use
The alloy contains, by weight, less than 0.05% of carbon, from 0.015% to 0.5% of silicon, from 0.4% to 1.4% of manganese, from 28% to 31.5% of chromium, from 8% to 12% of iron, from 2% to 7% of molybdenum, from 0% to 0.75% of aluminium, from 0% to 0.8% of titanium, from 0.6% to 2% in total of niobium and tantalum, the ratio of percentages of niobium plus tantalum and of silicon being at least 4, less than 0.04% of nitrogen, from 0.0008% to 0.0120% of zirconium, from 0.0010% to 0.0100% of boron, less than 0.01% of sulphur, less than 0.020% of phosphorus, less than 0.30% of copper, less than 0.15% of cobalt and less than 0.10% of tungsten, the remainder of the alloy, with the exception of unavoidable impurities of which the total content is at most 0.5%, consisting of nickel. The alloy is used, in particular, for the production of wires for the electro-gas welding of units or components of nuclear reactors and, more particularly, of pressurised water-cooled nuclear reactors.
Owner:FRAMSTOME ANP
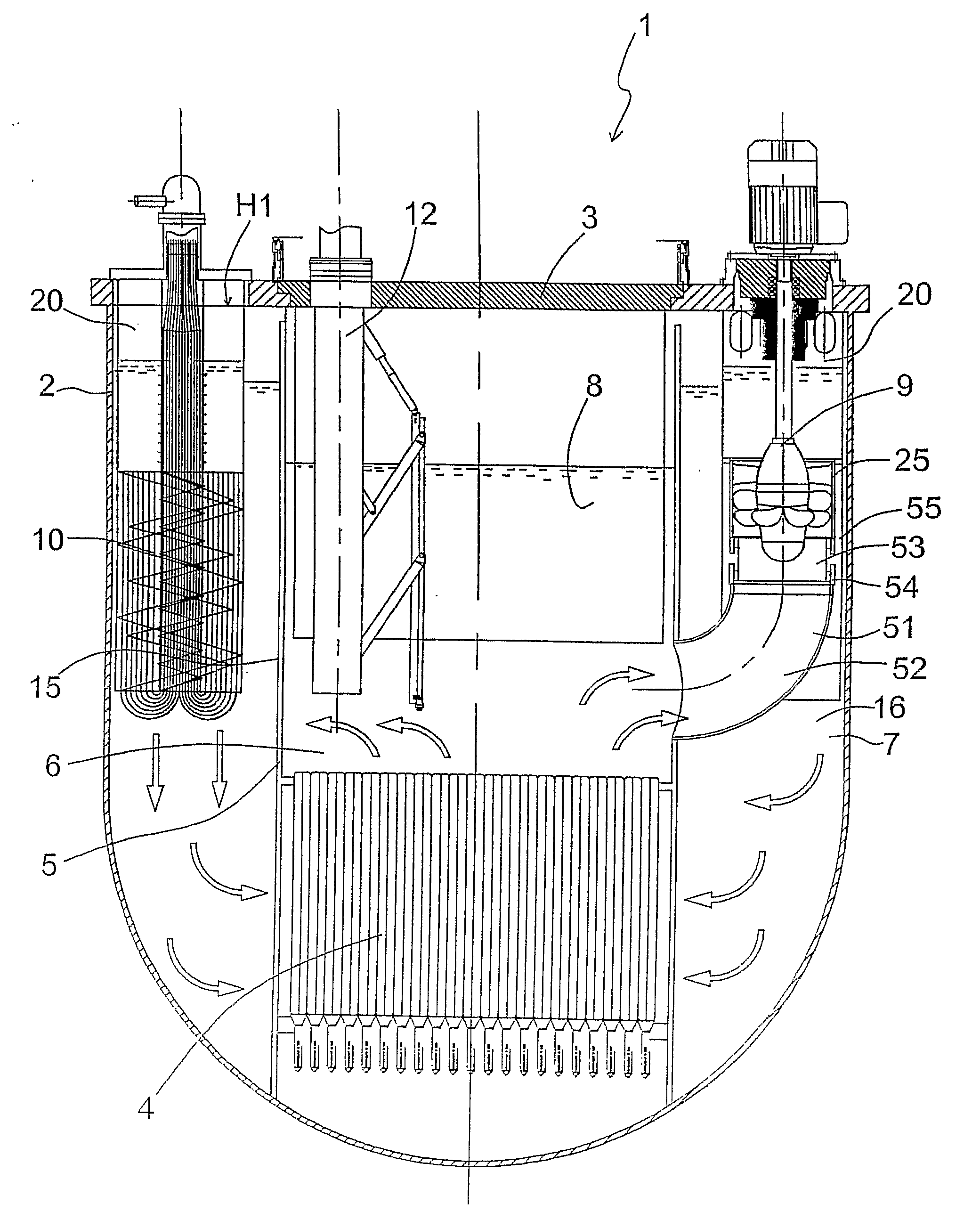
Nuclear Reactor, In Particular a Liquid-Metal-Cooled Nuclear Reactor
InactiveUS20080310575A1The overall space occupation is smallEasy to removeNuclear energy generationFast fission reactorsNuclear reactorLiquid metal
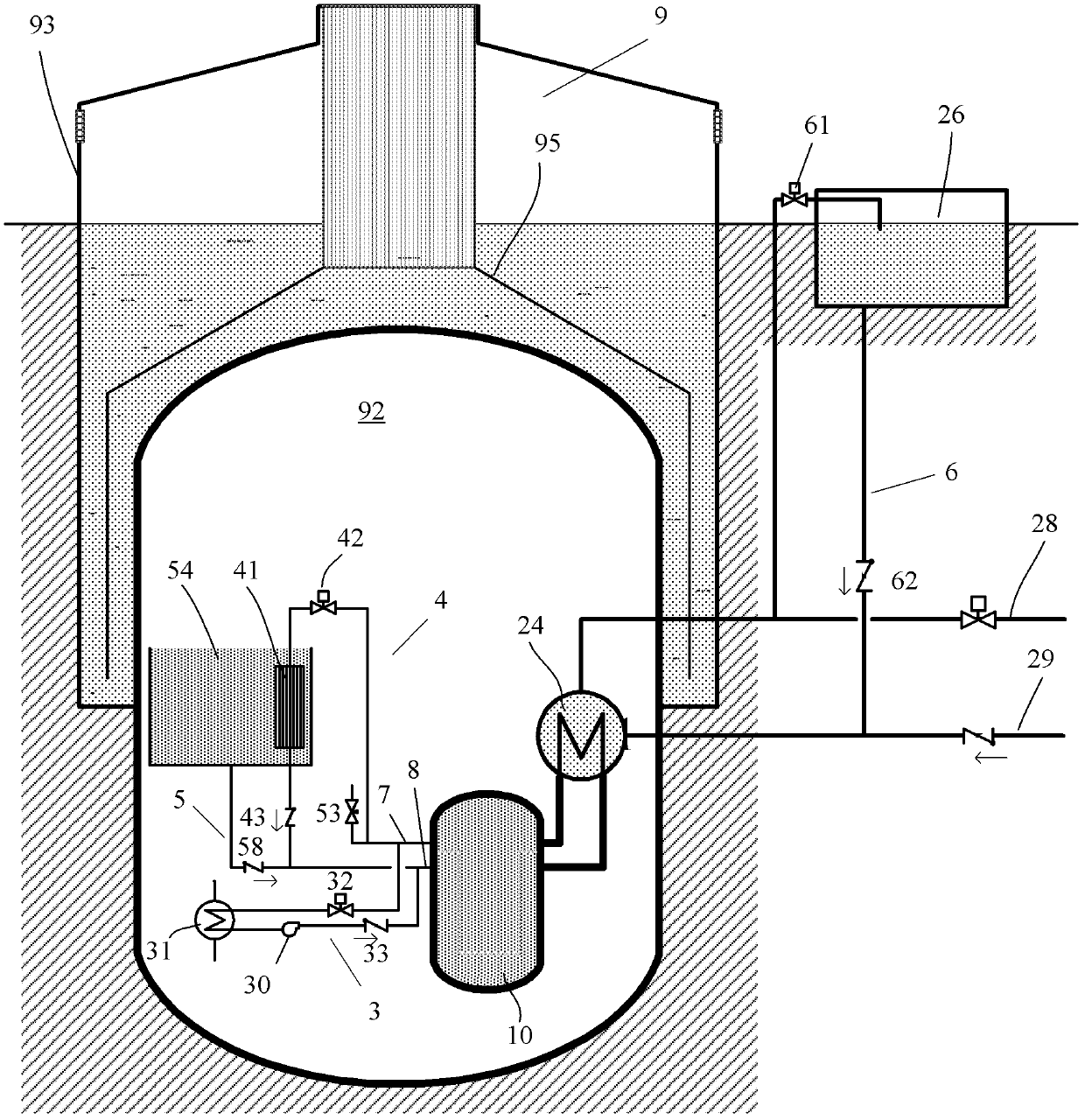
A nuclear reactor (1) is provided, in particular a nuclear reactor cooled with a liquid metal (for example, a heavy liquid metal, such as lead or lead-bismuth eutectic), of the type having a cylindrical inner vessel (15) that divides a hot collector (6) over a core (4) from a substantially annular cold collector (7) surrounding the hot collector; housed in the cold collector (7) is a plurality of integrated circulation and heat-exchange assemblies (20), each of which includes a pump (9), two heat exchangers (10) set at the sides of the pump, and a conveying structure (21) through which a primary fluid (8) for cooling the core passes from the pump to the heat exchanger, all of which are fixedly connected to one another to form a unitary structure; each integrated assembly has an inlet (26) connected to the hot collector (6) and two outlet sections (34) in the cold collector (7).
Owner:ANSALDO NUCLEARE
Diversified engineered safety system for nuclear reactor
ActiveCN103295656AGuaranteed long-term securityEasy dischargeNuclear energy generationCooling arrangementNuclear reactor coreNuclear reactor
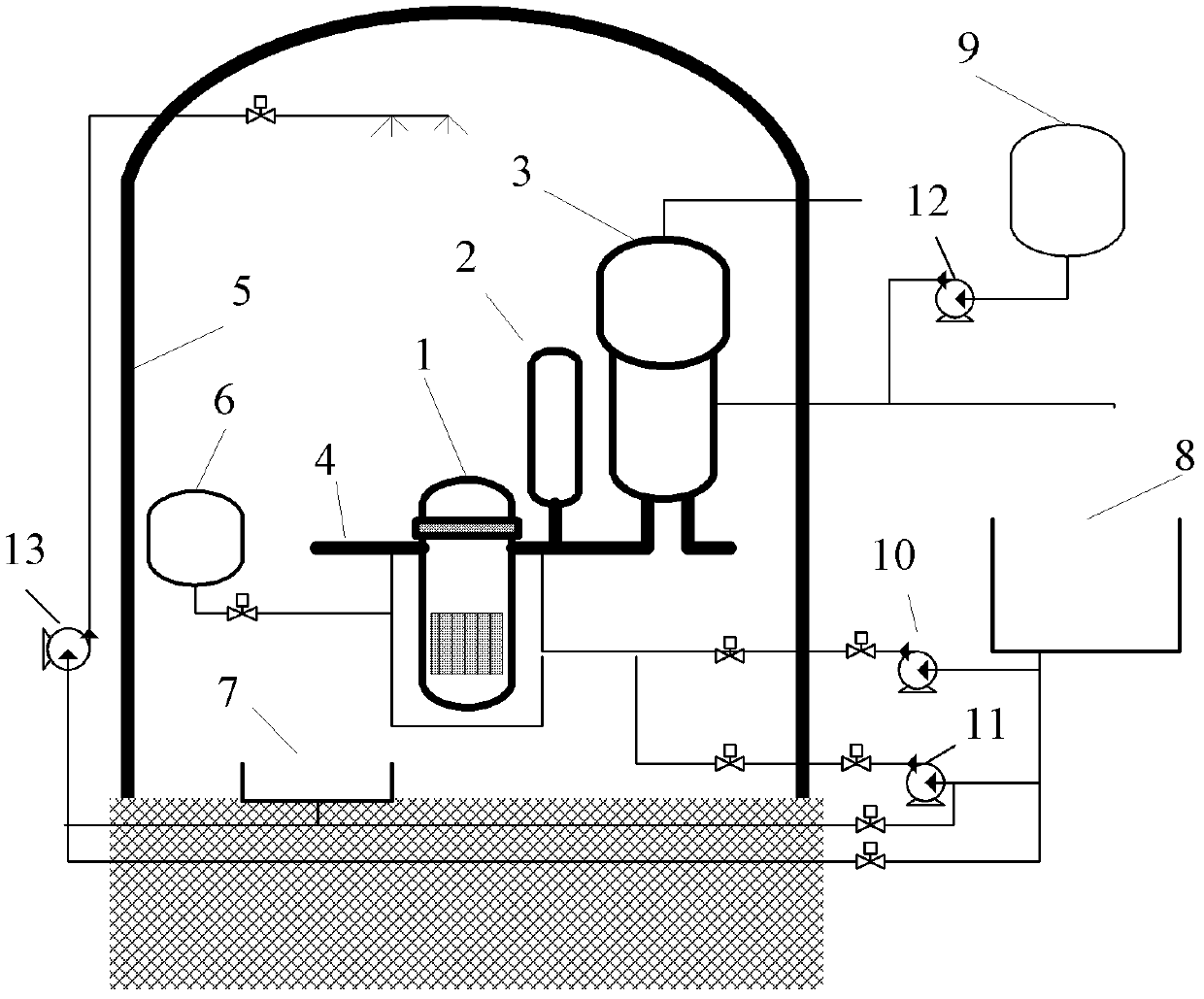
The invention aims at providing a diversified engineered safety system for a nuclear reactor. The diversified engineered safety system comprises a loop passive residual heat removal subsystem, a secondary-side passive residual heat removal subsystem of a steam generator fed with water by gravity, a total-pressure active residual heat removal subsystem, a low-pressure passive safety injection subsystem and a water-flooding and air-cooling combined passive containment cooling subsystem. All the subsystems can independently run or can be matched with one other, and parallel and redundant complete residual heat removal channels with diversified principles are built between a reactor core and an ultimate heat sink, so that a main system and the reactor core of the reactor can be quickly and efficiently cooled and the reactor can quickly enter a safety state in the initial stage of an accident. Even if one subsystem has a fault, other subsystems can still complete a complete and effective residual heat removal function for guaranteeing that the reactor is effectively cooled.
Owner:SHANGHAI NUCLEAR ENG RES & DESIGN INST CO LTD +1
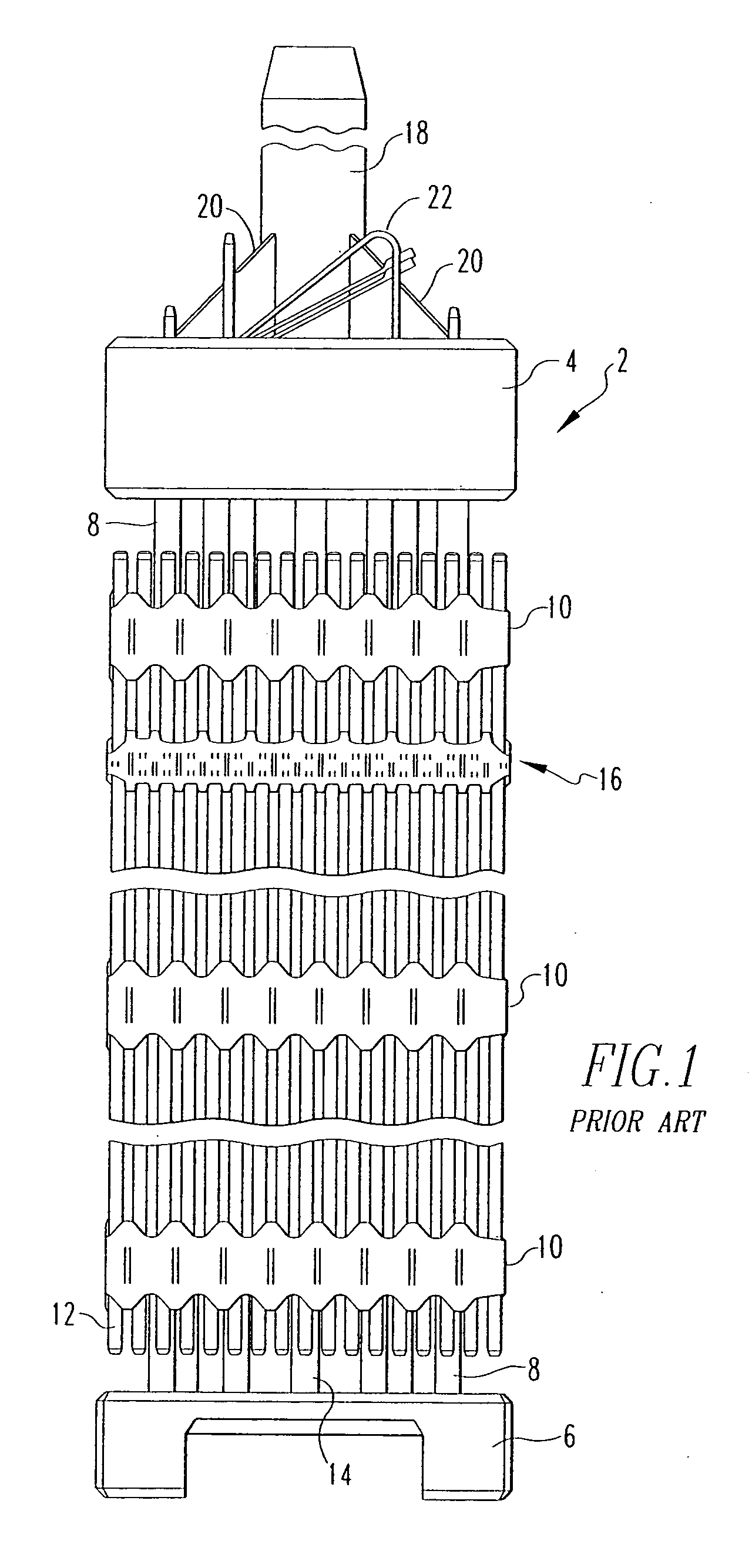
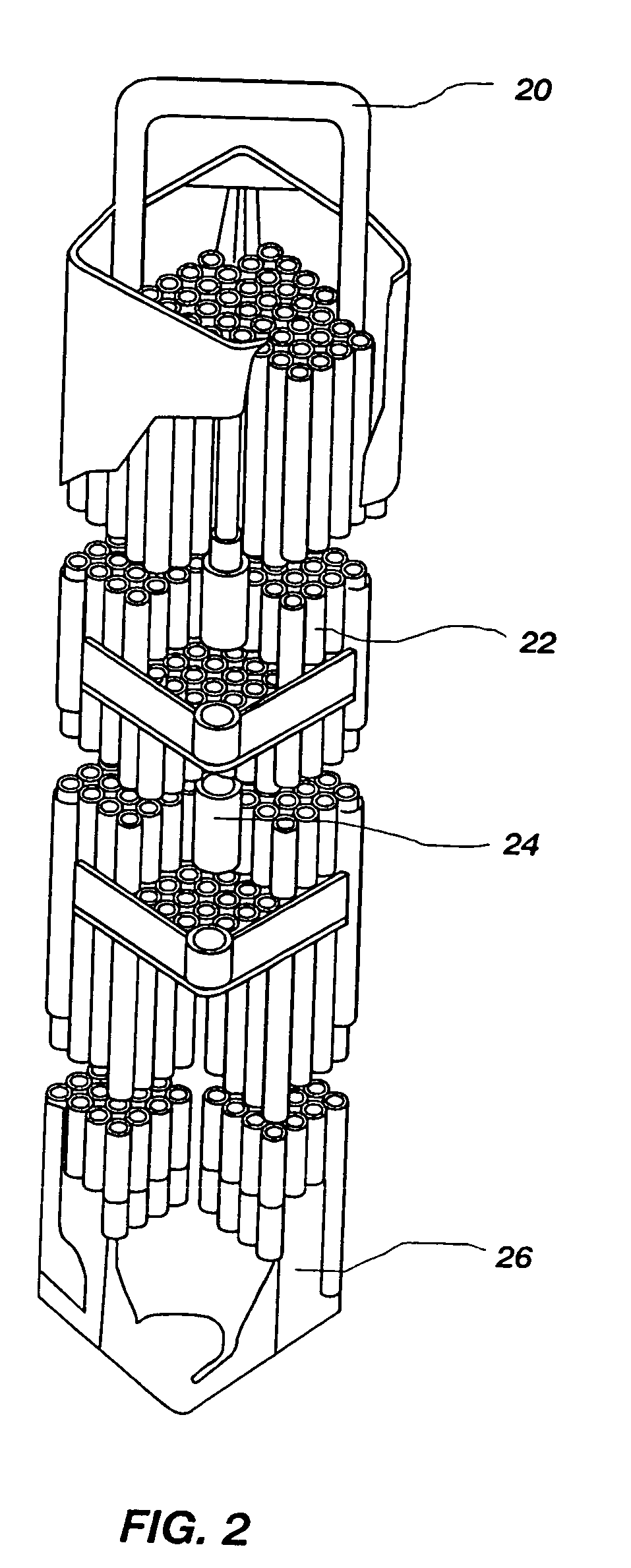
Nuclear reactor fuel assemblies
InactiveUS7085340B2Eliminate wearPrevent “hang-upsNuclear energy generationFuel element assembliesNuclear reactorParallel array
A nuclear fuel assembly having a parallel array of elongated fuel elements supported between an upper and lower nozzle. Main support grids are substantially evenly spaced along the elongated dimension of the assembly to maintain the spacing between fuel elements. A plurality of auxiliary vibration-resistant grids respectively positioned between the main support grids in the middle third elongated dimension of the fuel elements, that are smaller in height and provide a larger fuel element contact area than the main support grids.
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE ELECTRIC CORP
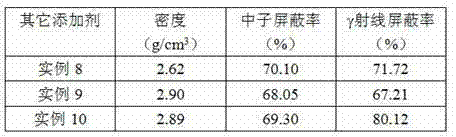
Composite shielding material and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a composite shielding material and a preparation method thereof, in particular to the composite shielding material applied to nuclear radiation places such as nuclear reactor, spent fuel assembly storage and radioactive substance storage and transportation and the like. The composite shielding material is characterized by comprising the following components in percentage by weight: 0 to 30 percent of w and compound thereof, 0 to 70 percent of B4C, 0 to 90 percent of aluminum or aluminum alloy, 0 to 8 percent of other elements and the like. The composite shielding material comprising tungsten B4C / aluminum alloy is uniform in distribution of W2B5 and B4C, high in densification degree, high in strength and toughness, and particularly applicable to the field of neutron / gamma ray shielding.
Owner:SICHUAN INST OF MATERIALS & TECH
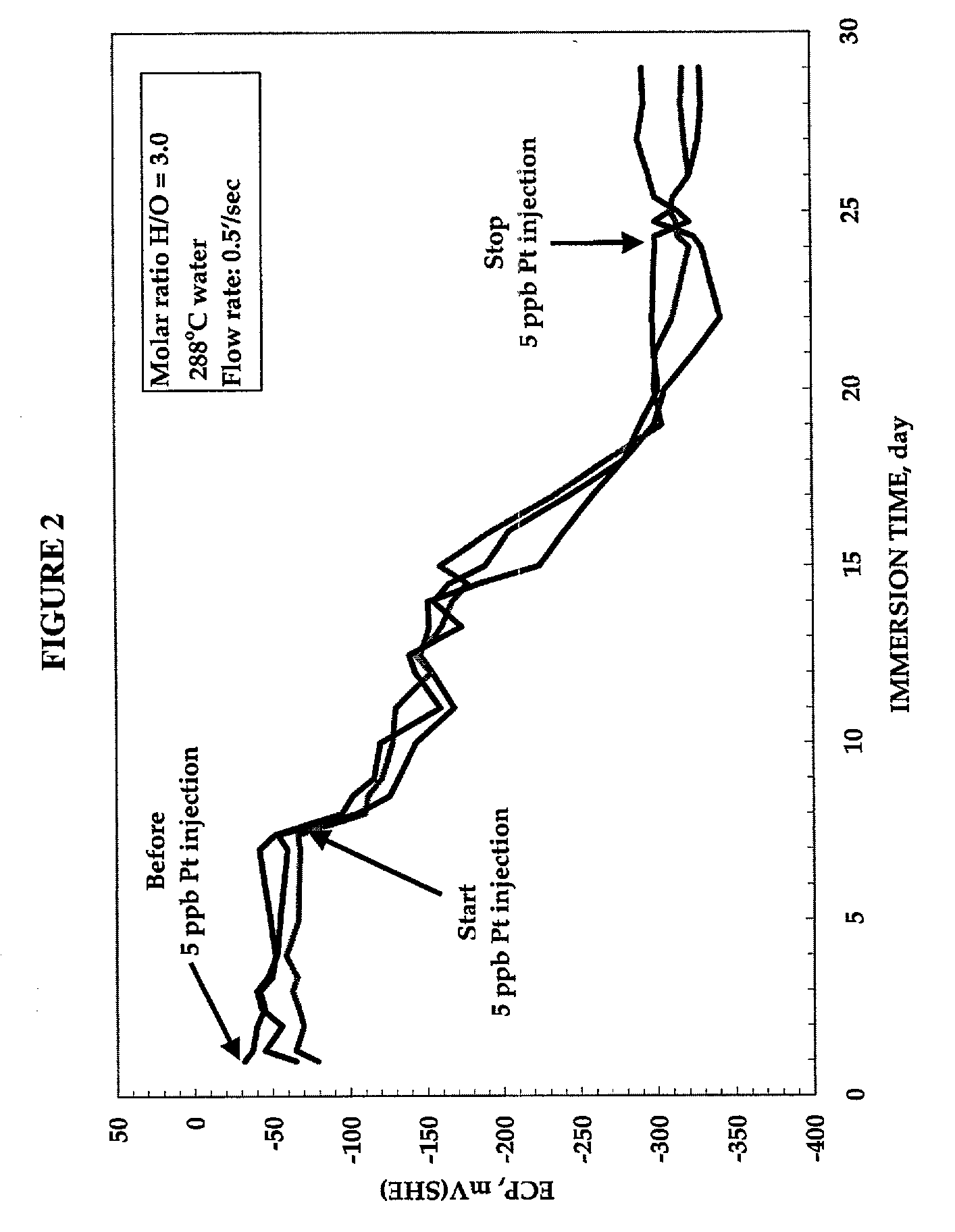
Application of catalytic nanoparticles to high temperature water systems to reduce stress corrosion cracking
InactiveUS20030012686A1Reducing electrochemical corrosion potentialReduce componentsNuclear energy generationNuclear monitoringNuclear reactorNanoparticle
A method and system for reducing stress corrosion cracking in a hot water system, such as a nuclear reactor, by reducing the electrochemical corrosion potential of components exposed to high temperature water within the structure. The method comprises the steps of: providing a reducing species to the high temperature water; and providing a plurality of noble metal nanoparticles having a mean particle size of up to about 100 nm to the high temperature water during operation of the hot water system. The catalytic nanoparticles, which may comprise at least one noble metal, form a colloidal suspension in the high temperature water and provide a catalytic surface on which a reducing species reacts with least one oxidizing species present in the high temperature water. The concentration of the oxidizing species is reduced by reaction with the reducing species on the catalytic surface, thereby reducing the electrochemical corrosion potential of the component.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
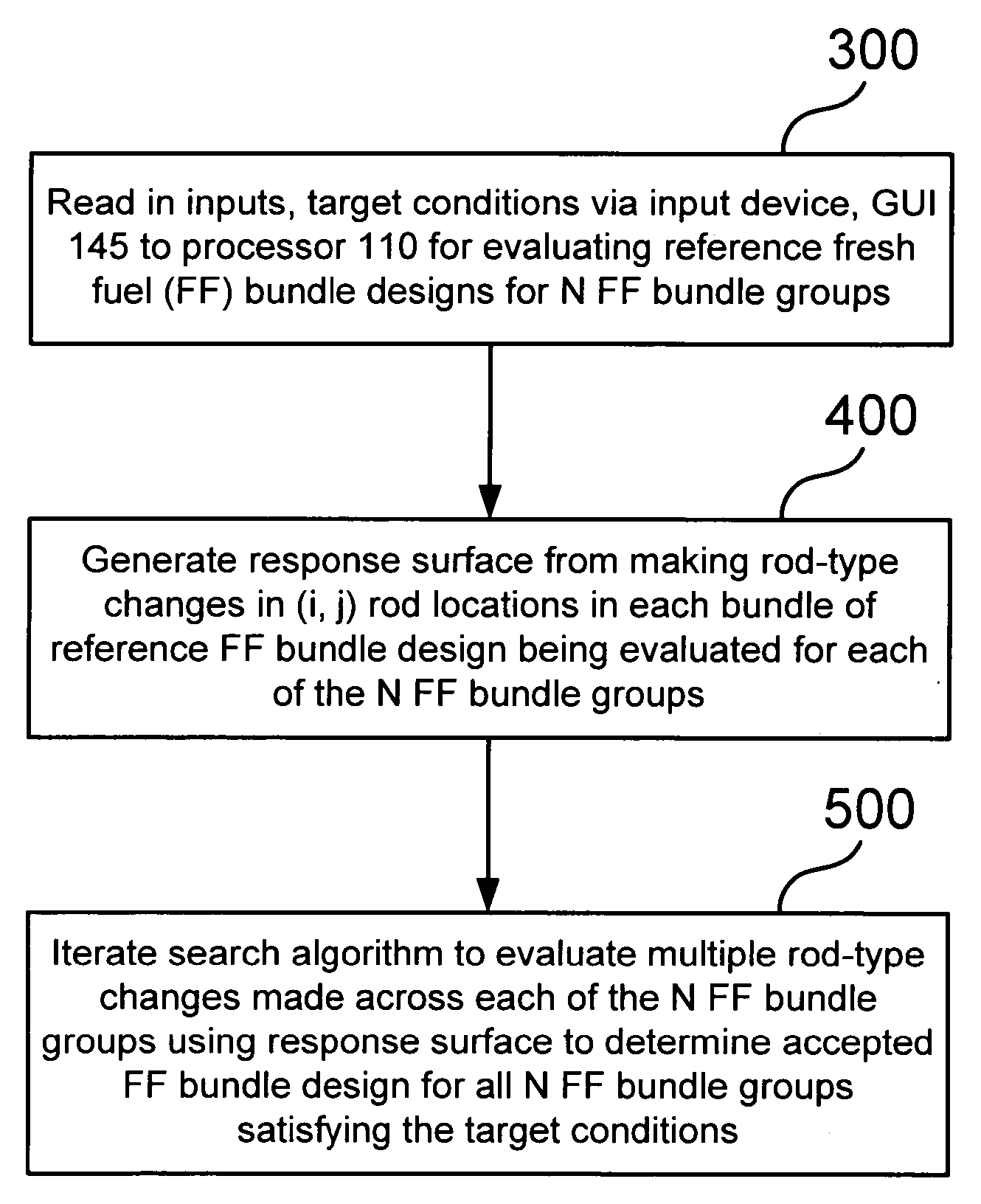
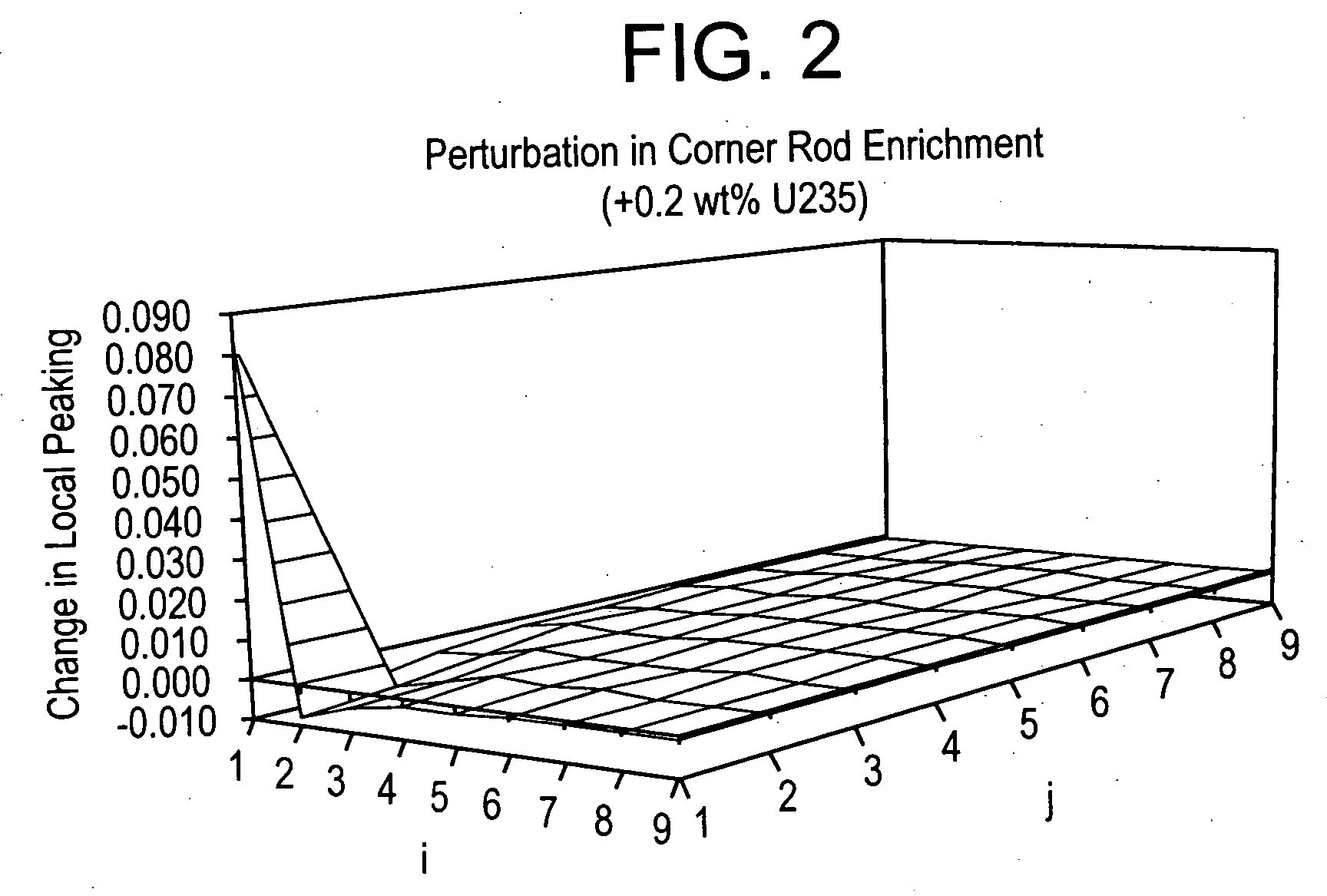
Method of determining a fresh fuel bundle design for a core of a nuclear reactor
InactiveUS20060149514A1Cosmonautic condition simulationsNuclear energy generationNuclear reactor coreNuclear reactor
A method for determining a fresh fuel bundle design for a core of a nuclear reactor may include defining a plurality of inputs including user-defined target conditions for evaluating one or more reference fresh fuel bundle designs for each of N bundle groups, and generating a response surface based on making single rod-type changes in each (i,j) rod location of each bundle of a given reference bundle design being evaluated for each of the N bundle groups. A search algorithm may be iterated to evaluate a given combination of multiple rod-type changes made simultaneously across each of the N bundle groups using the generated response surface to determine an accepted fuel bundle design for each of the N bundle groups that satisfies the user-defined target conditions.
Owner:GLOBAL NUCLEAR FUEL -- AMERICAS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com