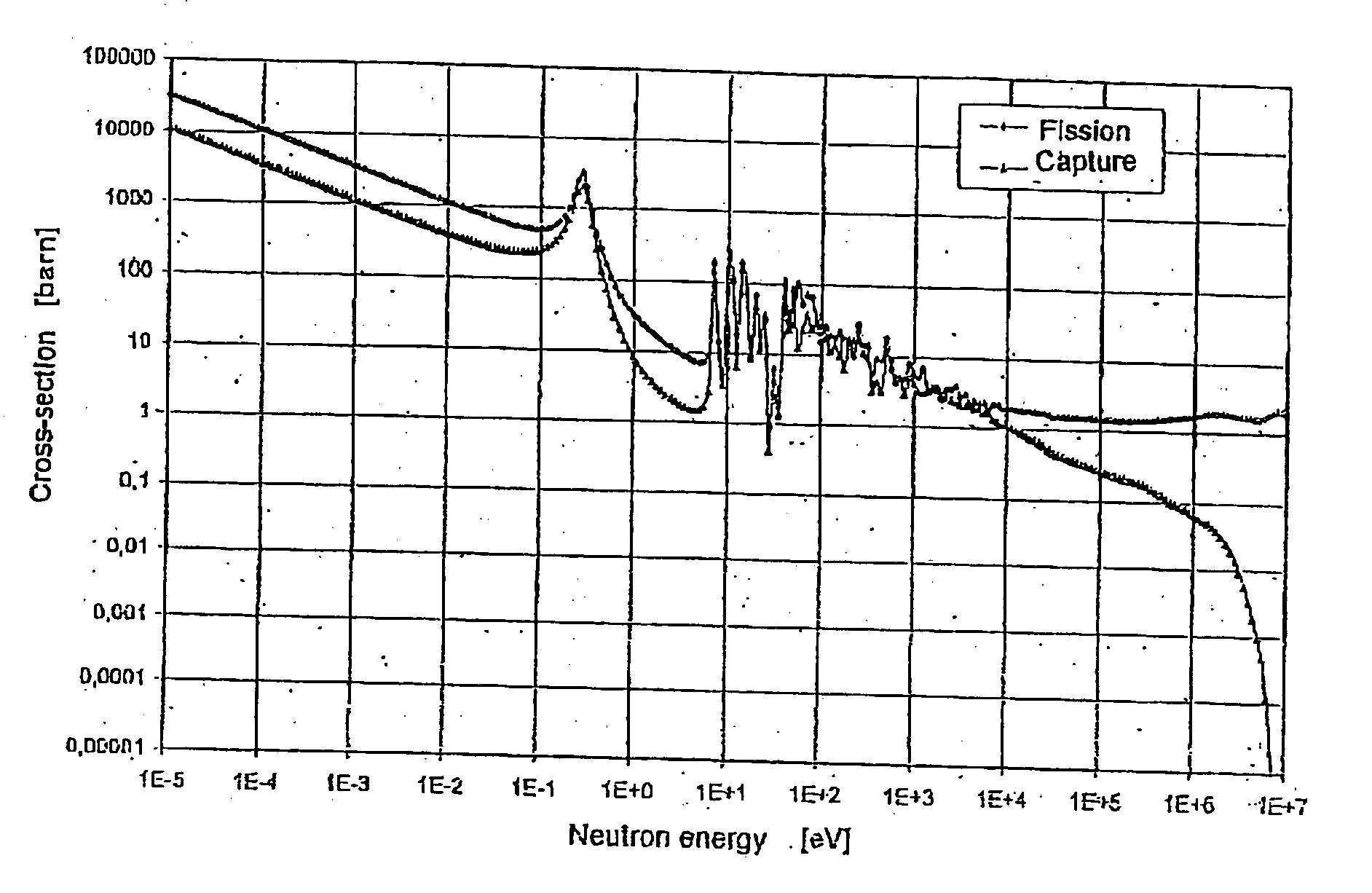
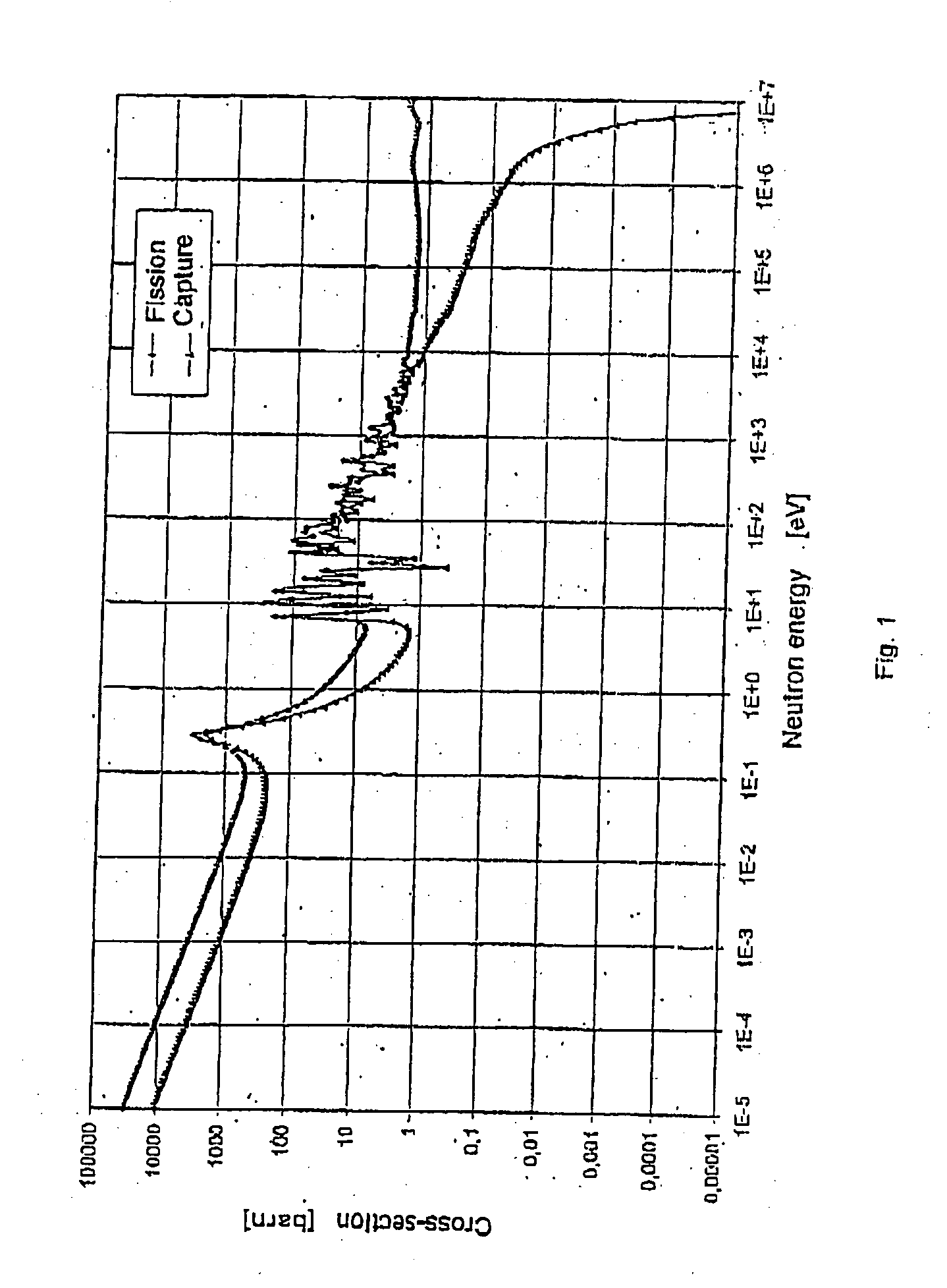
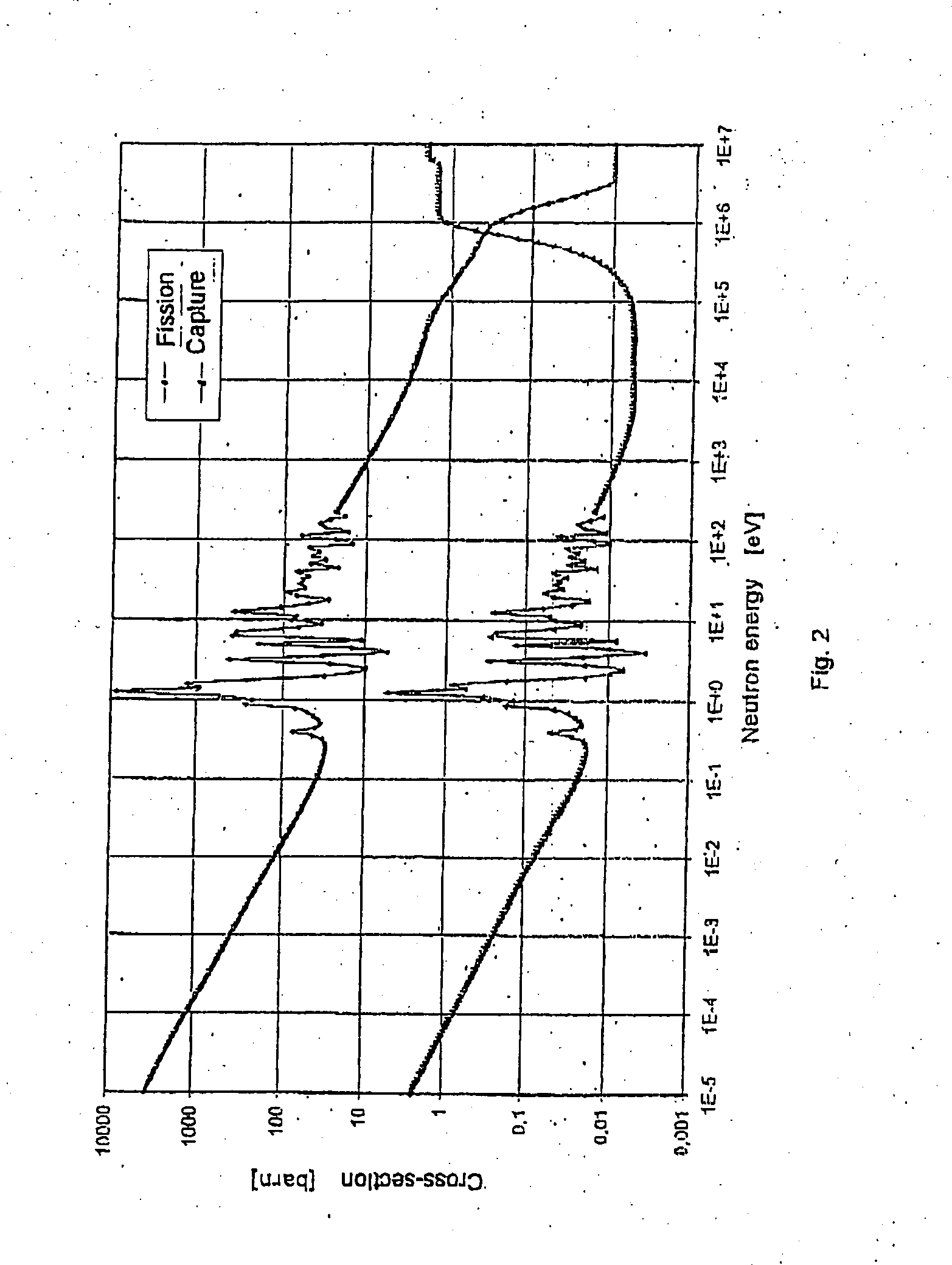
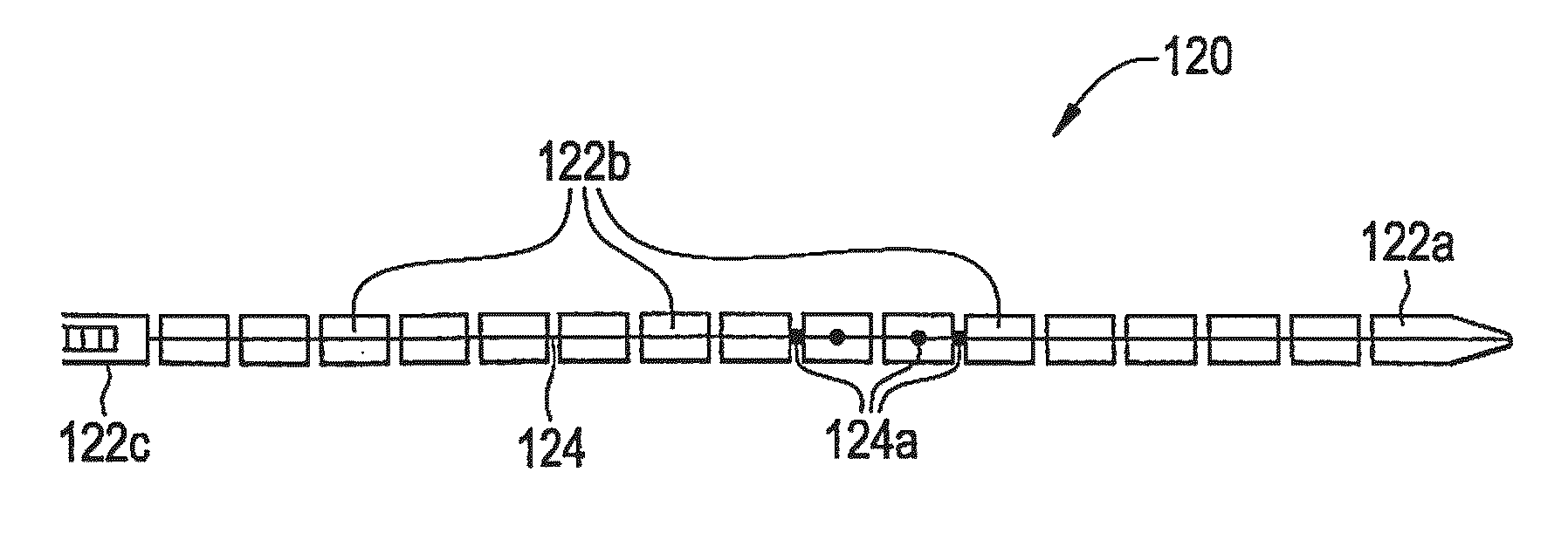
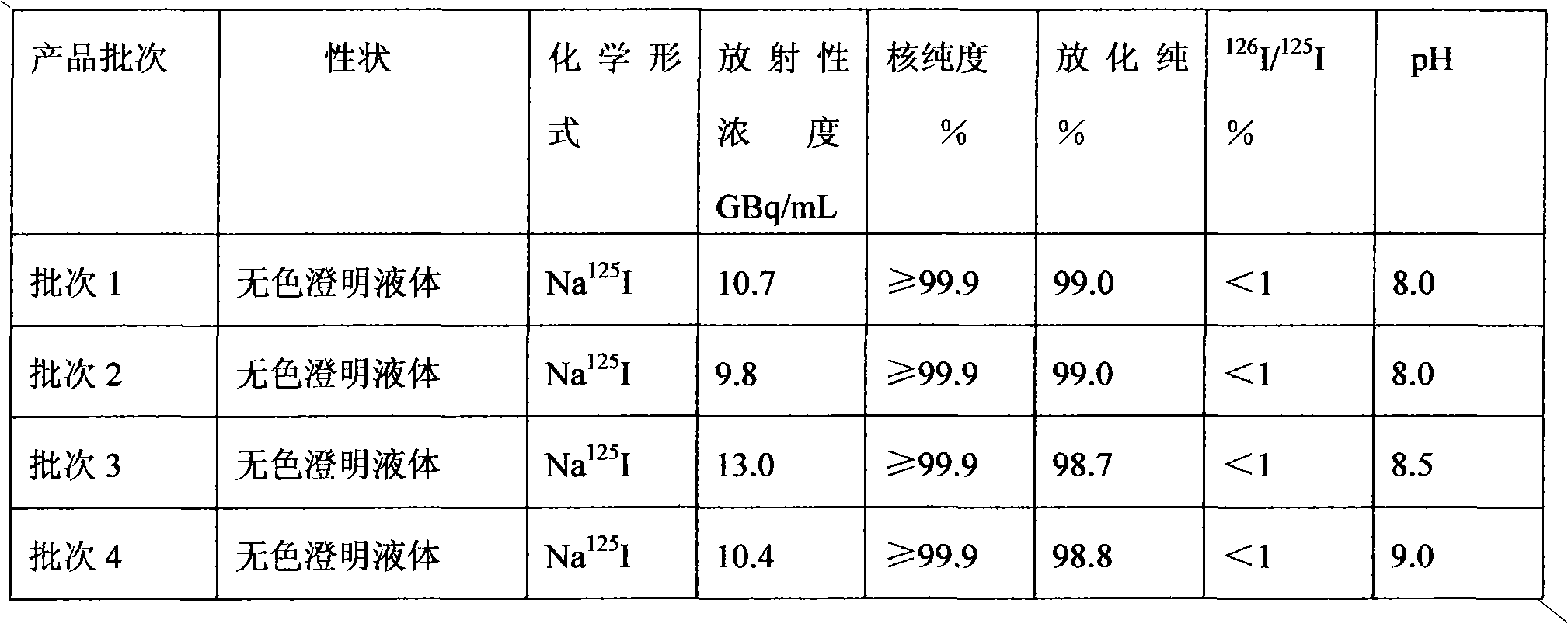
Patents
Literature
178results about "Conversion in nuclear reactor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
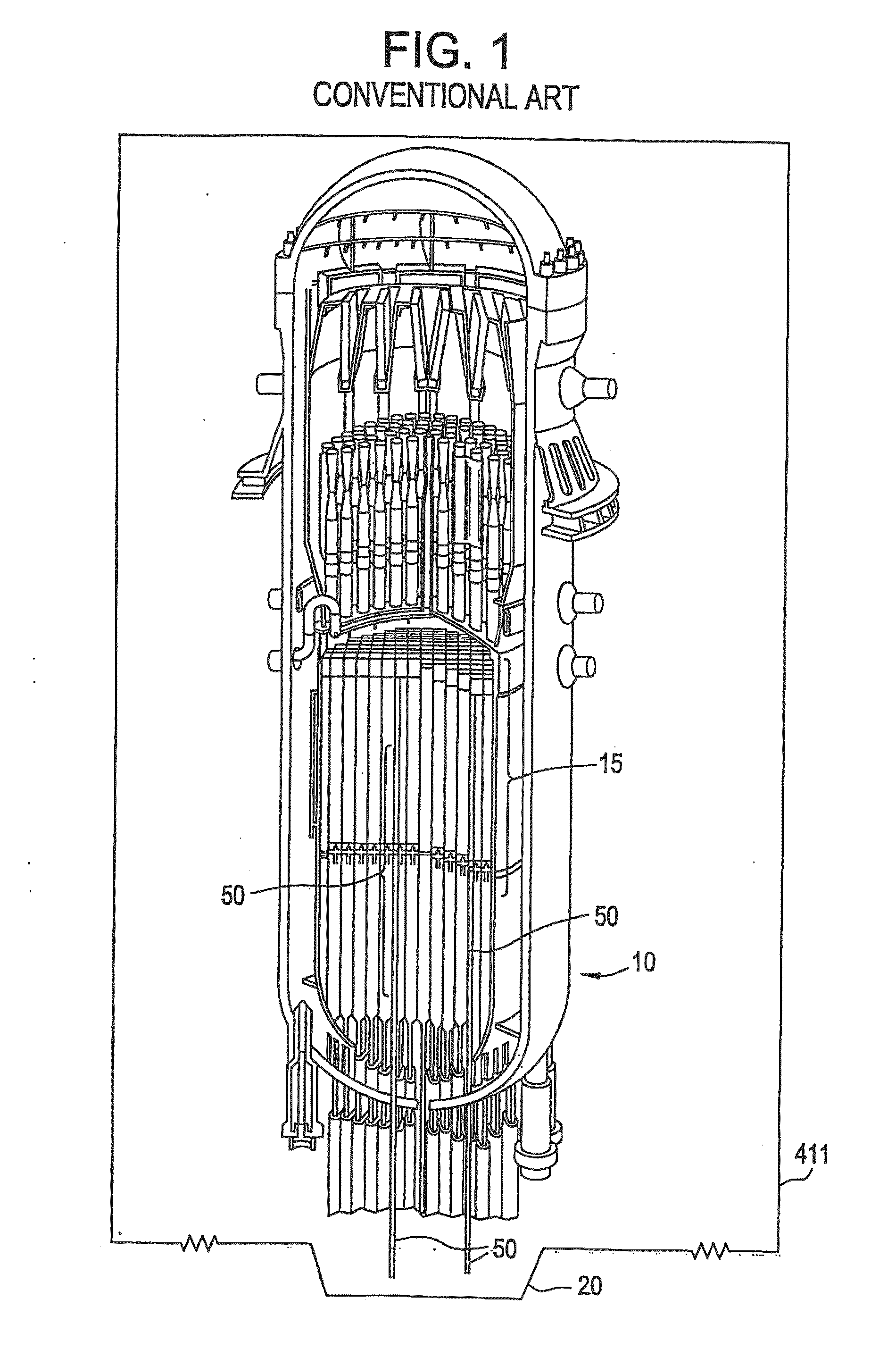
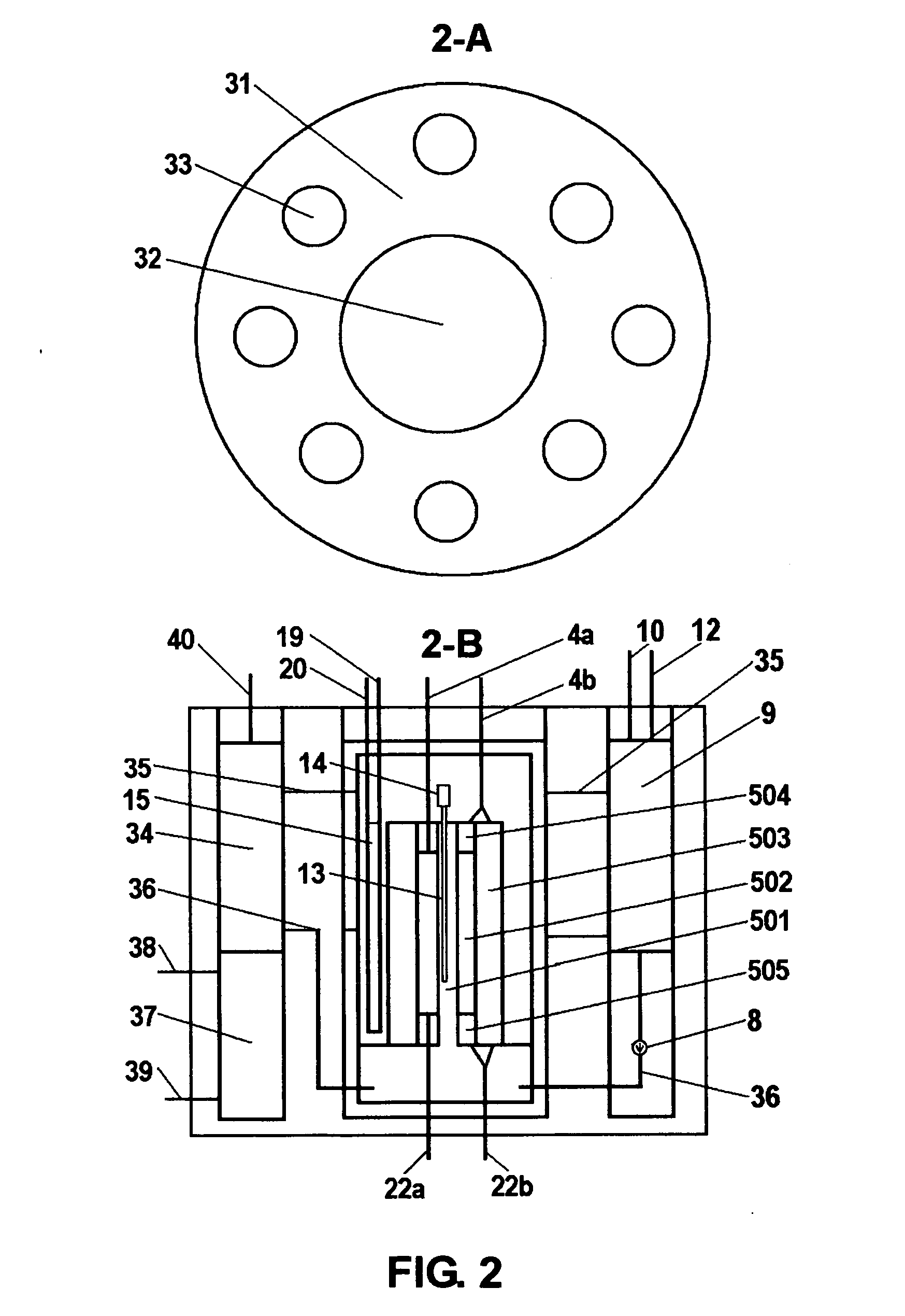
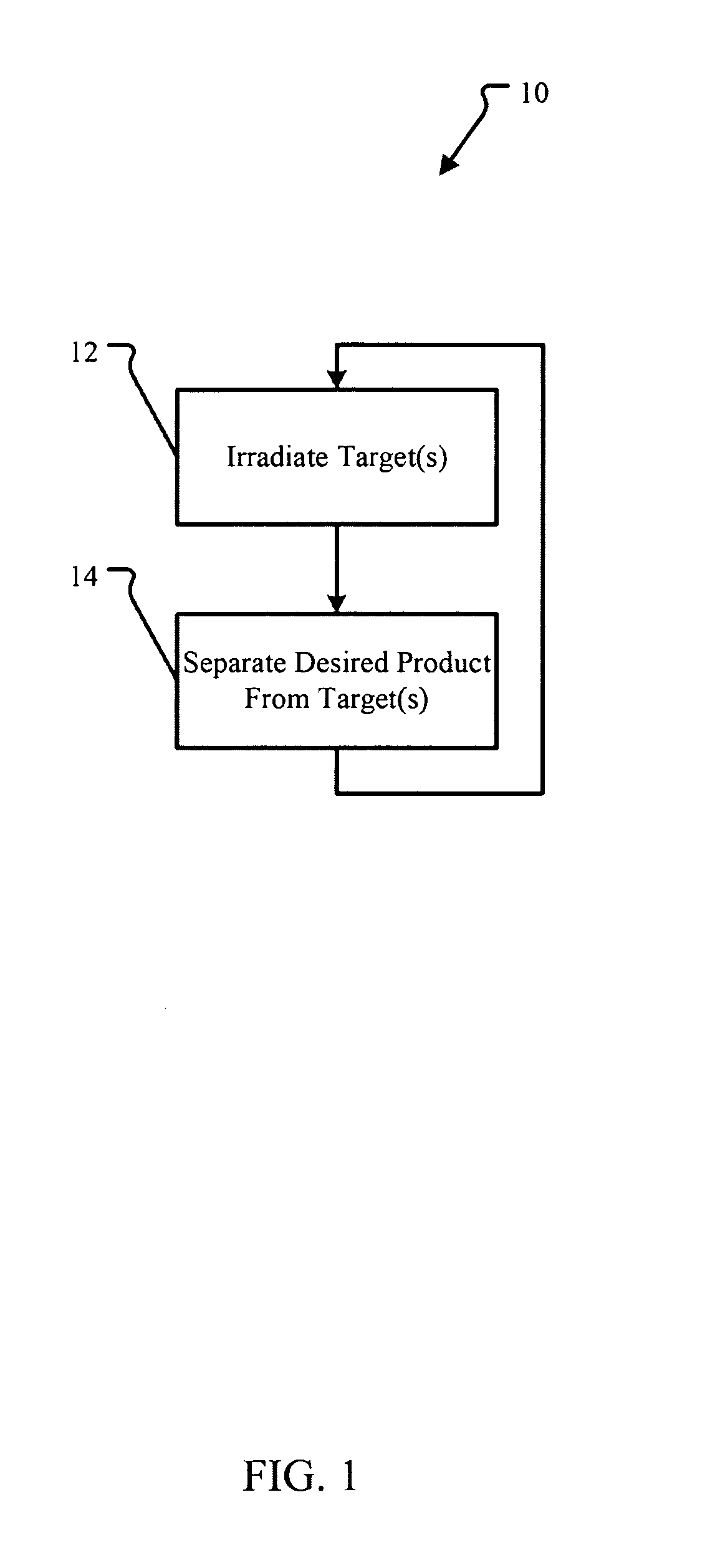
Method of producing isotopes in power nuclear reactors
ActiveUS20070133731A1Nuclear energy generationConversion in nuclear reactorNuclear reactorNeutron flux
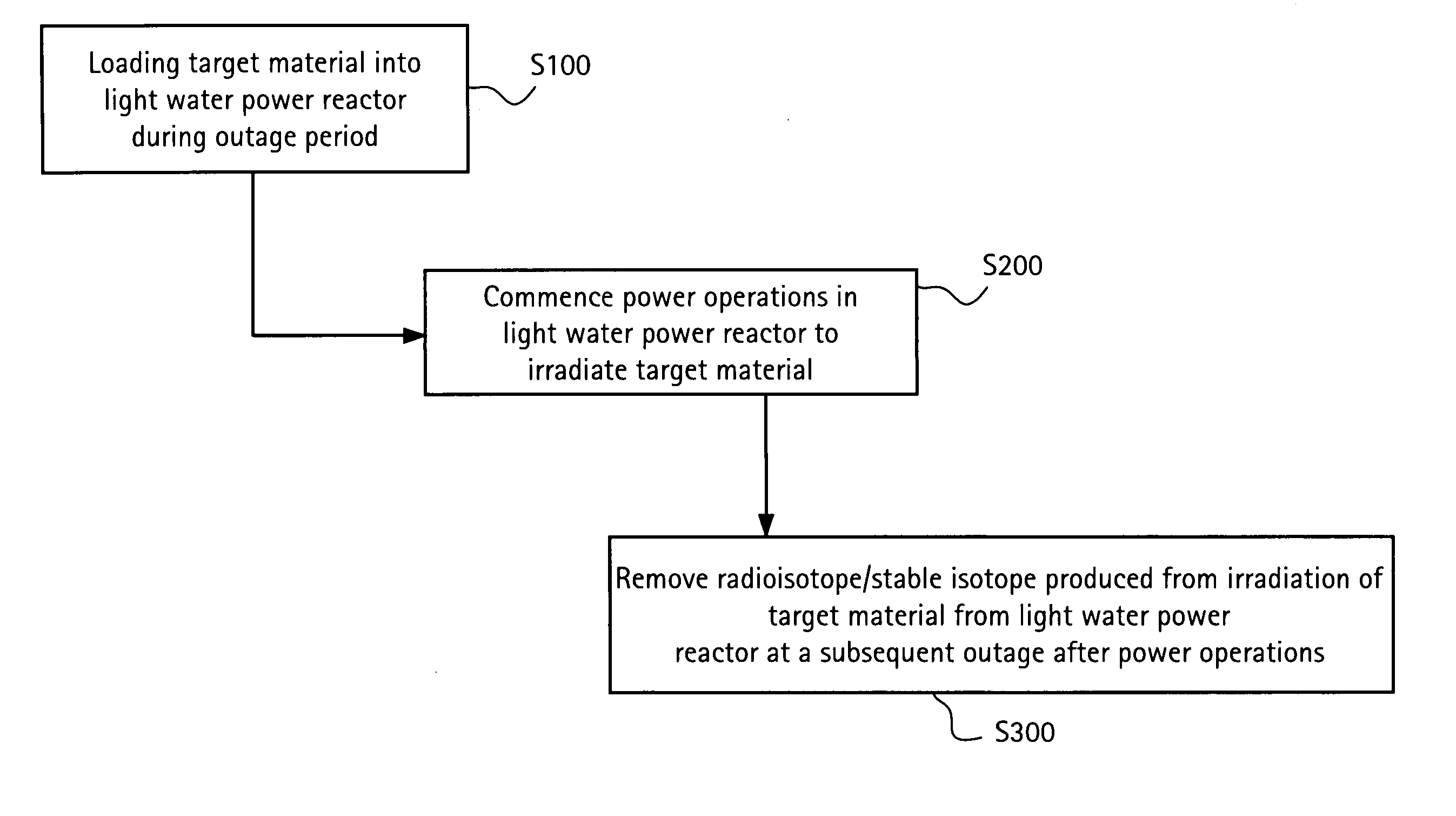
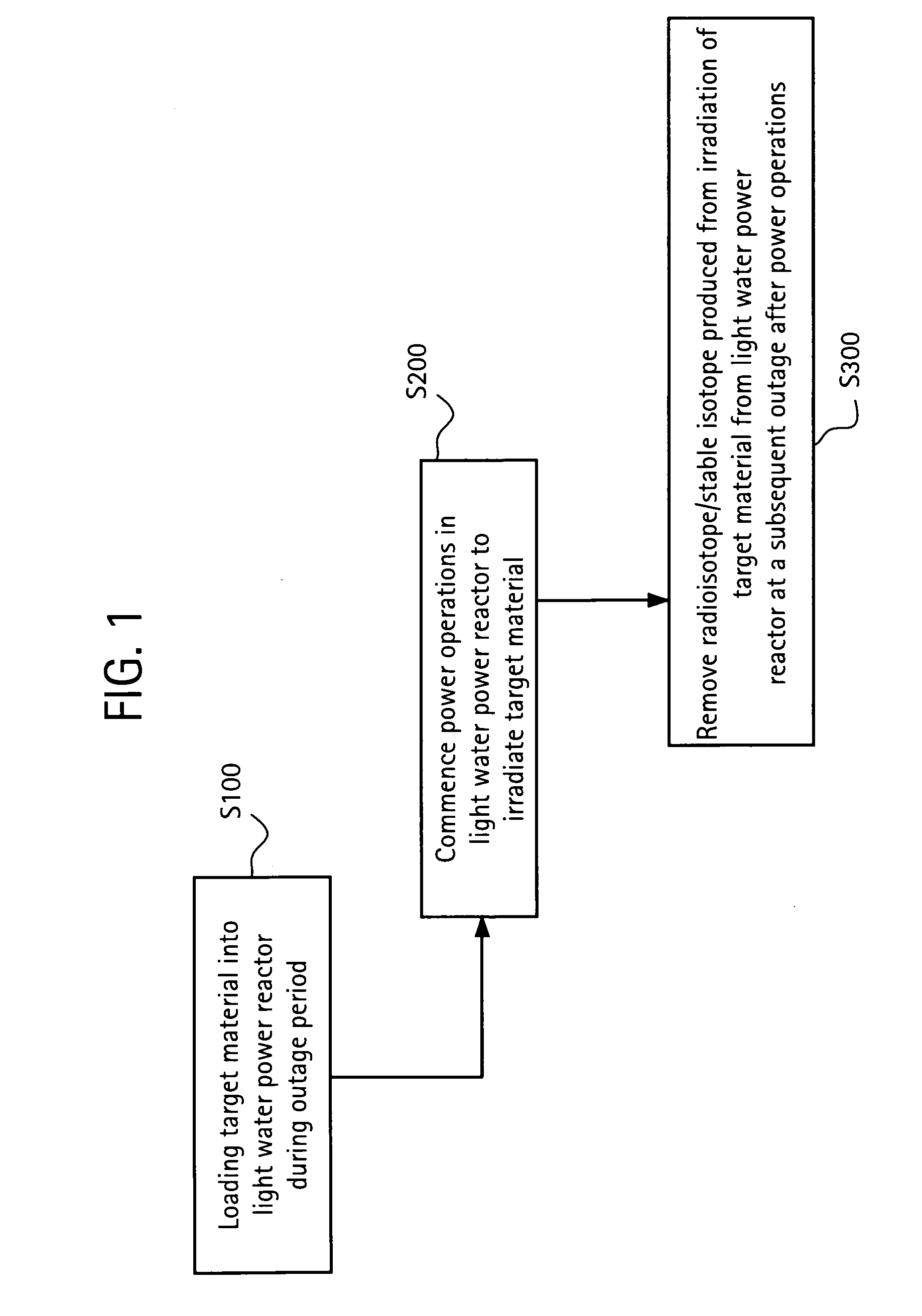
In a method of producing isotopes in a light water power reactor, one or more targets within the reactor may be irradiated under a neutron flux to produce one or more isotopes. The targets may be assembled into one or more fuel bundles that are to be loaded in a core of the reactor at a given outage. Power operations in the reactor irradiate the fuel bundles so as to generate desired isotopes, such as one or more radioisotopes at a desired specific activity or stable isotopes at a desired concentration.
Owner:NORDION (CANADA) INC
Assembly for transmutation of a long-lived radioactive material
InactiveUS6233299B1Conversion outside reactor/acceleratorsNuclear energy generationRadioactive agentTechnetium-99
A new transmutation assembly permits an efficient transmutation of a long-lived radioactive material (long-lived FP nuclides such as technetium-99 or iodine-129) which was produced in the nuclear reactor. Wire-type members of a long-lived radioactive material comprised of metals, alloys or compounds including long-lived FP nuclides are surrounded by a moderator material and installed in cladding tubes to form FP pins. The FP pins, and nothing else, are housed in a wrapper tube to form a transmutation assembly. The wire-type members can be replaced by thin ring-type members. The transmutation assemblies can be selectively and at least partly loaded into a core region, a blanket region or a shield region of a reactor core in a fast reactor. From a viewpoint of reducing the influence on the reactor core characteristics, it is optimal to load the transmutation assemblies into the blanket region.
Owner:JAPAN ATOMIC ENERGY AGENCY INDEPENDANT ADMINISTRATIVE CORP
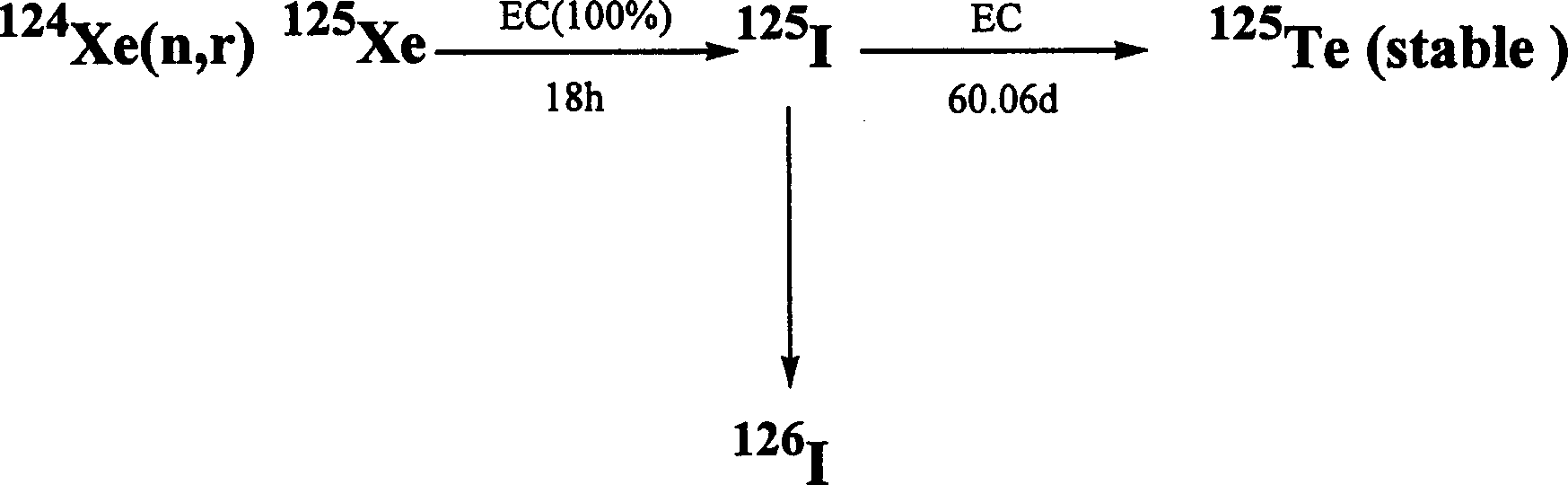
Internal circulating irradiation capsule for iodine-125 and method of producing iodine-125 using same
InactiveUS20060126774A1Reduce neutronConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsNuclear energy generationNeutron irradiationIodine
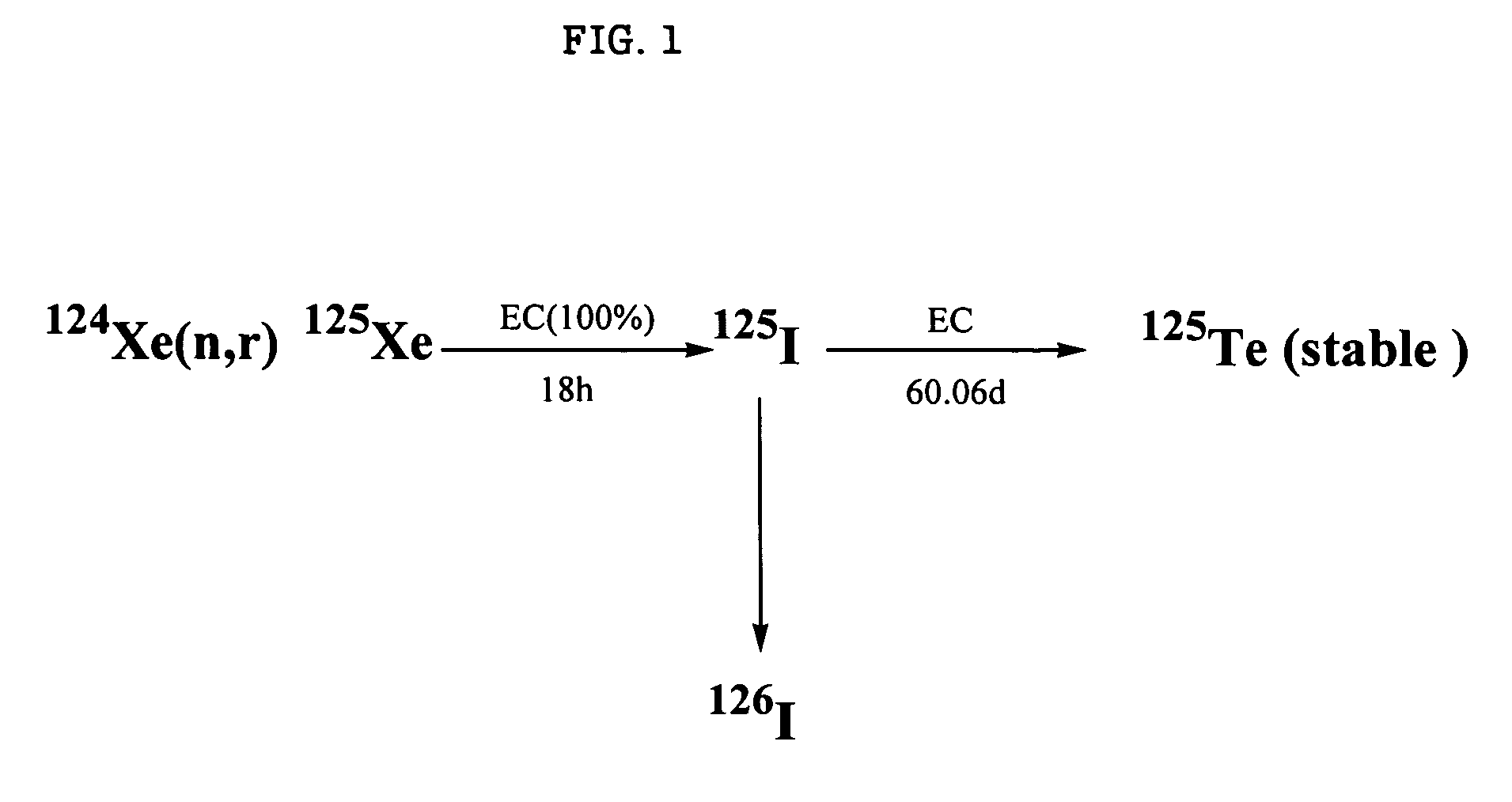
A present invention provides an internal circulating irradiation capsule available for the production of iodine-125 and a related production method. The irradiation capsule filled with xenon gas has a lower irradiation part, an upper irradiation part, and a neutron control member. The lower irradiation part is inserted into an irradiation hole of a reactor core and irradiated with a large quantity of neutron directly. When neutron is radiated to the xenon gas, iodine-125 is produced from xenon gas. The upper irradiation part protrudes from the irradiation hole, and iodine-125 is transferred to the upper irradiation part by convection and solidified in the upper part. The neutron control member reduces neutron in the upper part to produce iodine-125 of high purity and radioactivity in a large quantity.
Owner:KOREA ATOMIC ENERGY RES INST
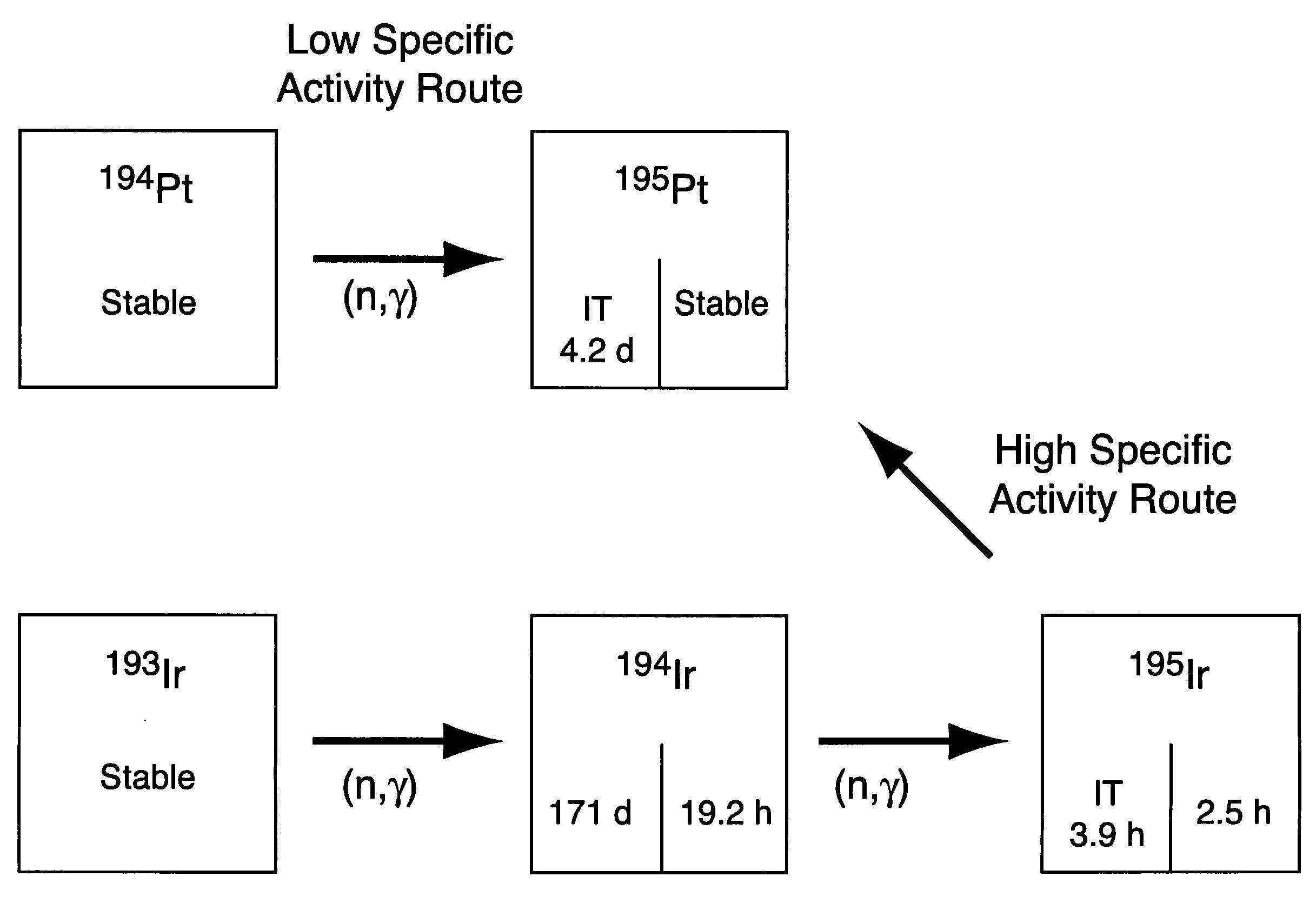
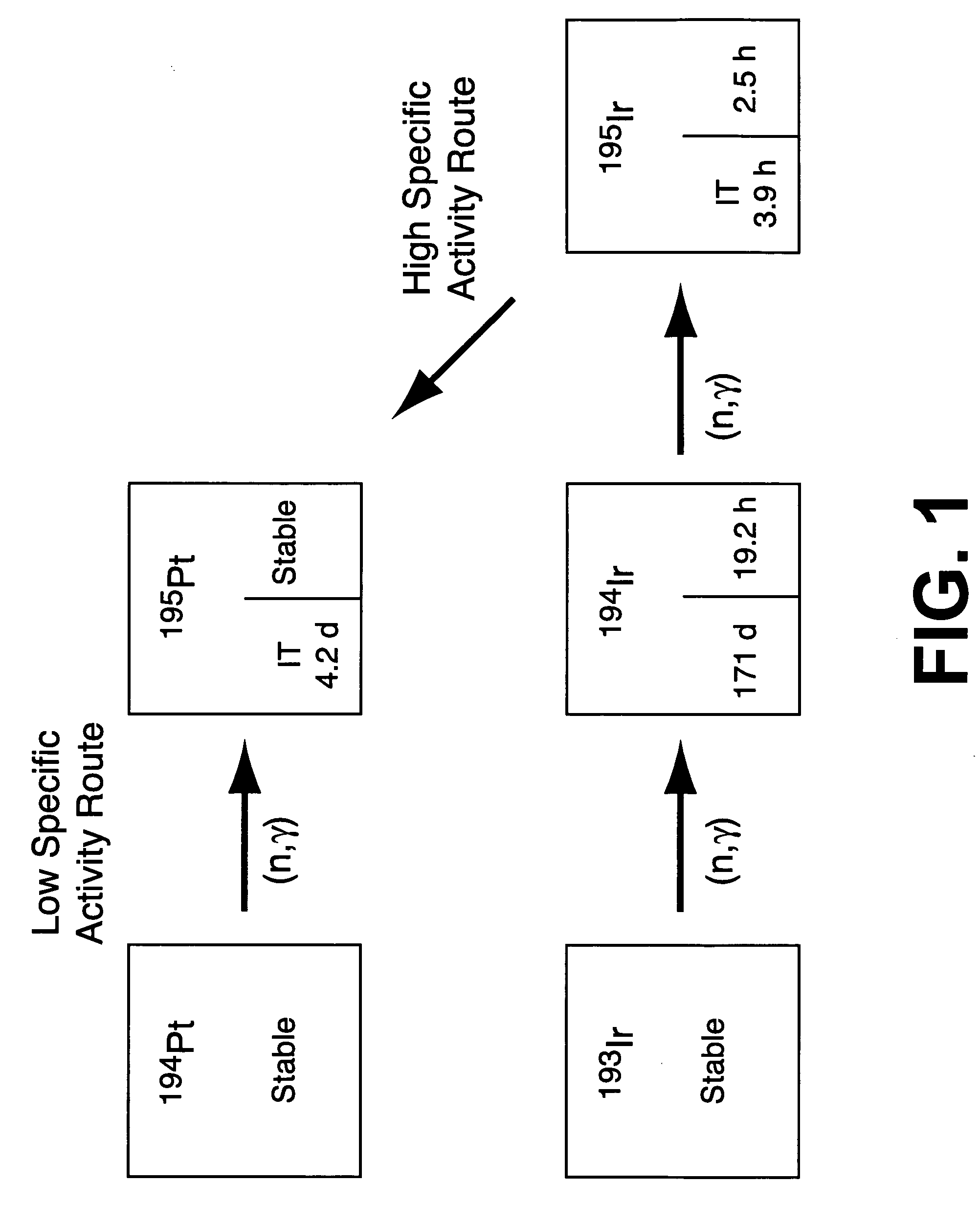
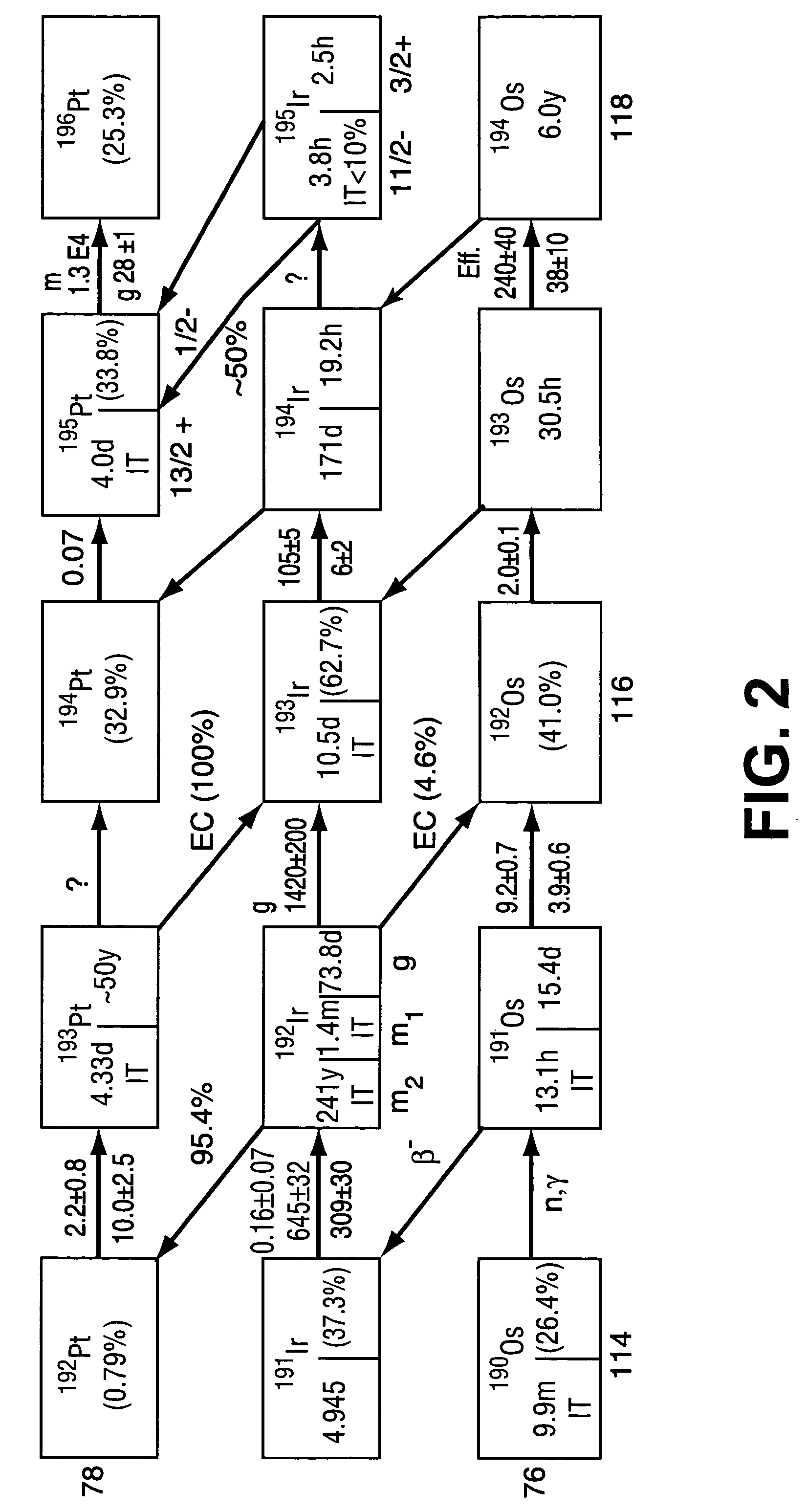
High specific activity platinum-195m
InactiveUS20040196942A1In-vivo radioactive preparationsConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsPlatinumIrradiated materials
A new composition of matter includes <195m>Pt characterized by a specific activity of at least 30 mCi / mg Pt, generally made by method that includes the steps of: exposing <193>Ir to a flux of neutrons sufficient to convert a portion of the <193>Ir to <195m>Pt to form an irradiated material; dissolving the irradiated material to form an intermediate solution comprising Ir and Pt; and separating the Pt from the Ir by cation exchange chromatography to produce <195m>Pt.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Combinatorial heterogeneous-homogeneous reactor
ActiveUS20090225923A1Reduce power densityIsotope delivery systemsConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsCorrosion resistant alloyNuclear engineering
A combinatorial heterogeneous-homogeneous reactor configuration in which an array or groups of homogeneous fuel assemblies are interlinked together in a heterogeneous lattice. The present invention removes the limitation of a homogeneous reactor by providing a reactor concept that utilizes the inherent advantages of homogeneous fuel elements but in a heterogeneous fuel lattice arrangement that limits the power density of any one homogeneous fuel element and yet forms a reactor arrangement that is capable of producing any product demand of interest. The present invention provides a method for producing medical isotopes by the use of a modular reactor core comprised of homogeneous fuel assemblies arranged in a regular rectangular or triangular pitch lattice. The aqueous fuel solution is contained within individual fuel assemblies that are right circular cylinders clad in corrosion-resistant alloys such as stainless steel, zircalloy, zircalloy alloys, or other metal alloys that are resistant to corrosive fissile environments but preserve neutron economy. The fuel assemblies are supported below by a core plate that is tied directly to the lower reactor support structure. The bottom of each assembly opens into a common plenum area which provides a hydrodynamic communication / coupling path between the individual assemblies in the lattice. The fuel assemblies are supported above by an upper plate that is welded to each assembly tube. The top of each assembly opens to a common upper plenum which provides a means of thermodynamic pressure equalization among the four assemblies in the reactor core lattice.
Owner:BABCOCK & WILCOX TECHNICALSERVICES GRP INC
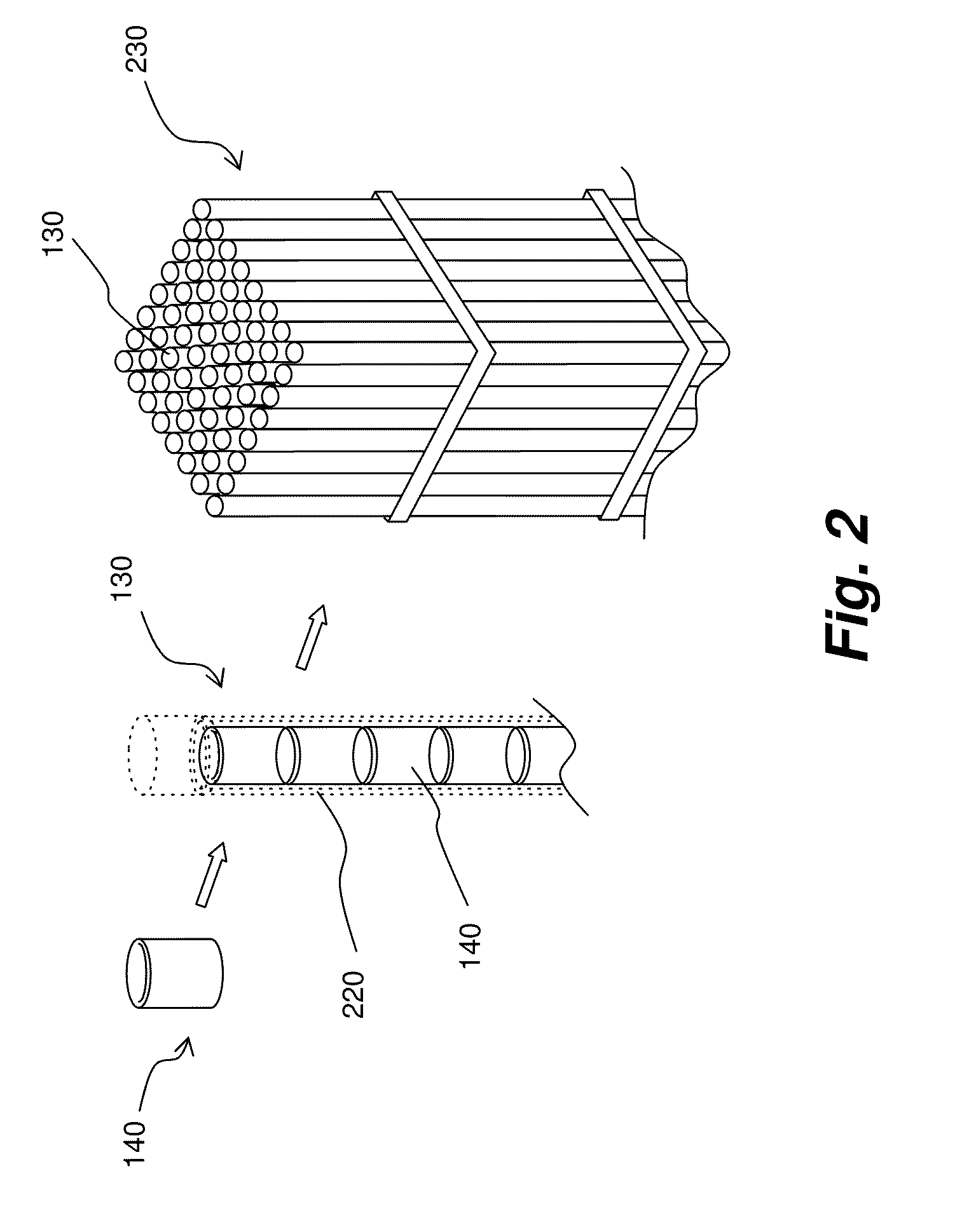
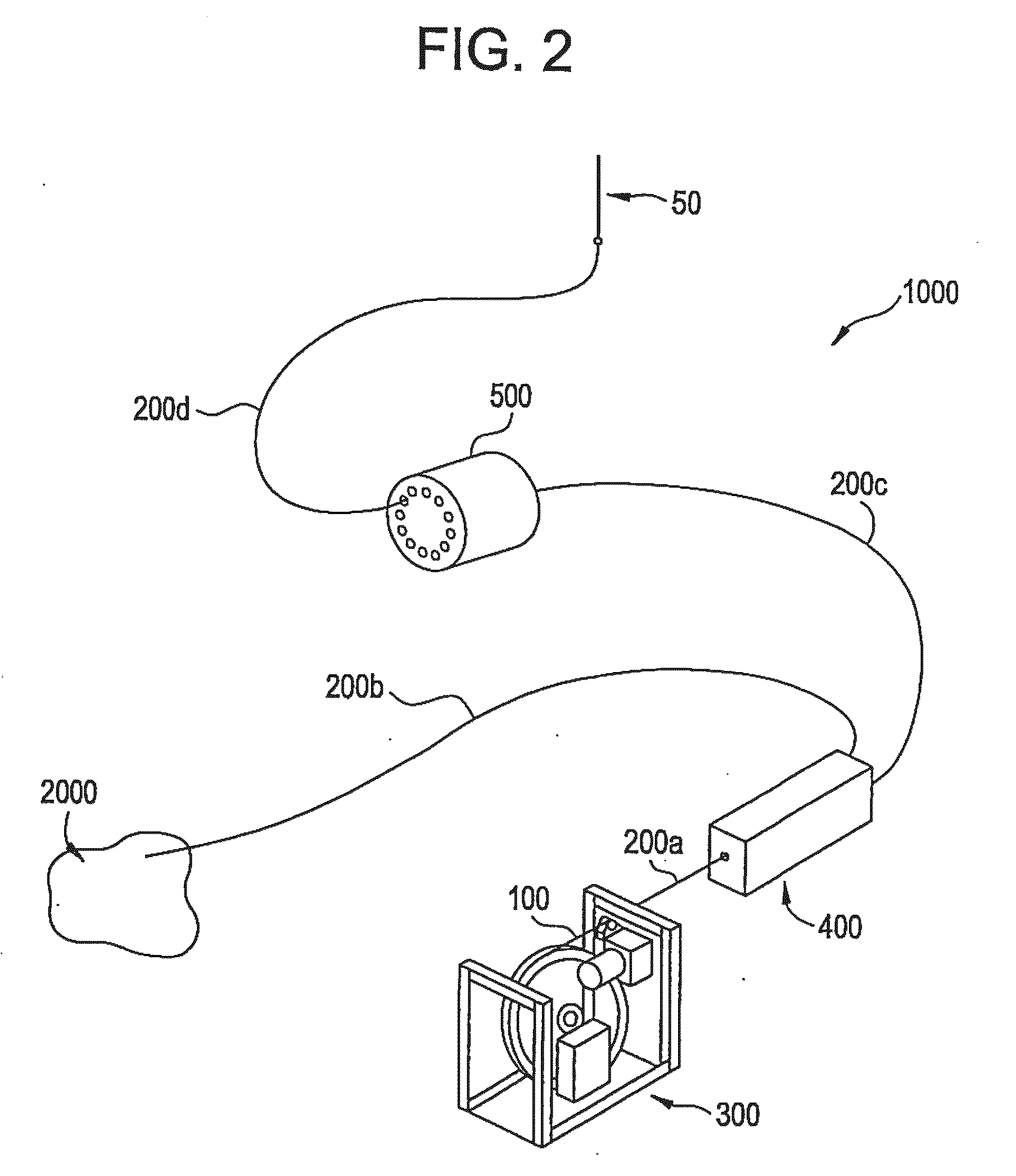
Irradiation target retention assemblies for isotope delivery systems
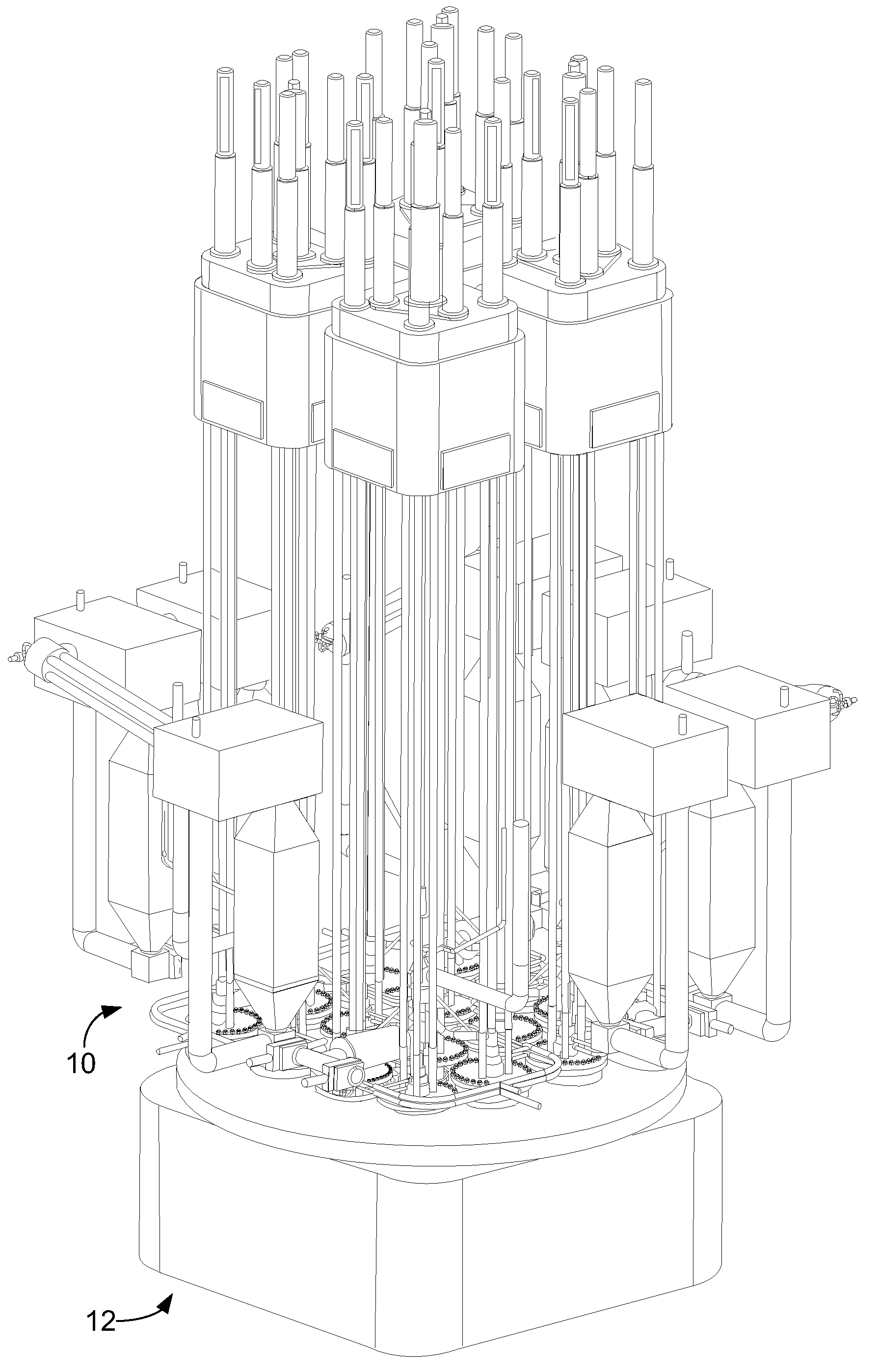
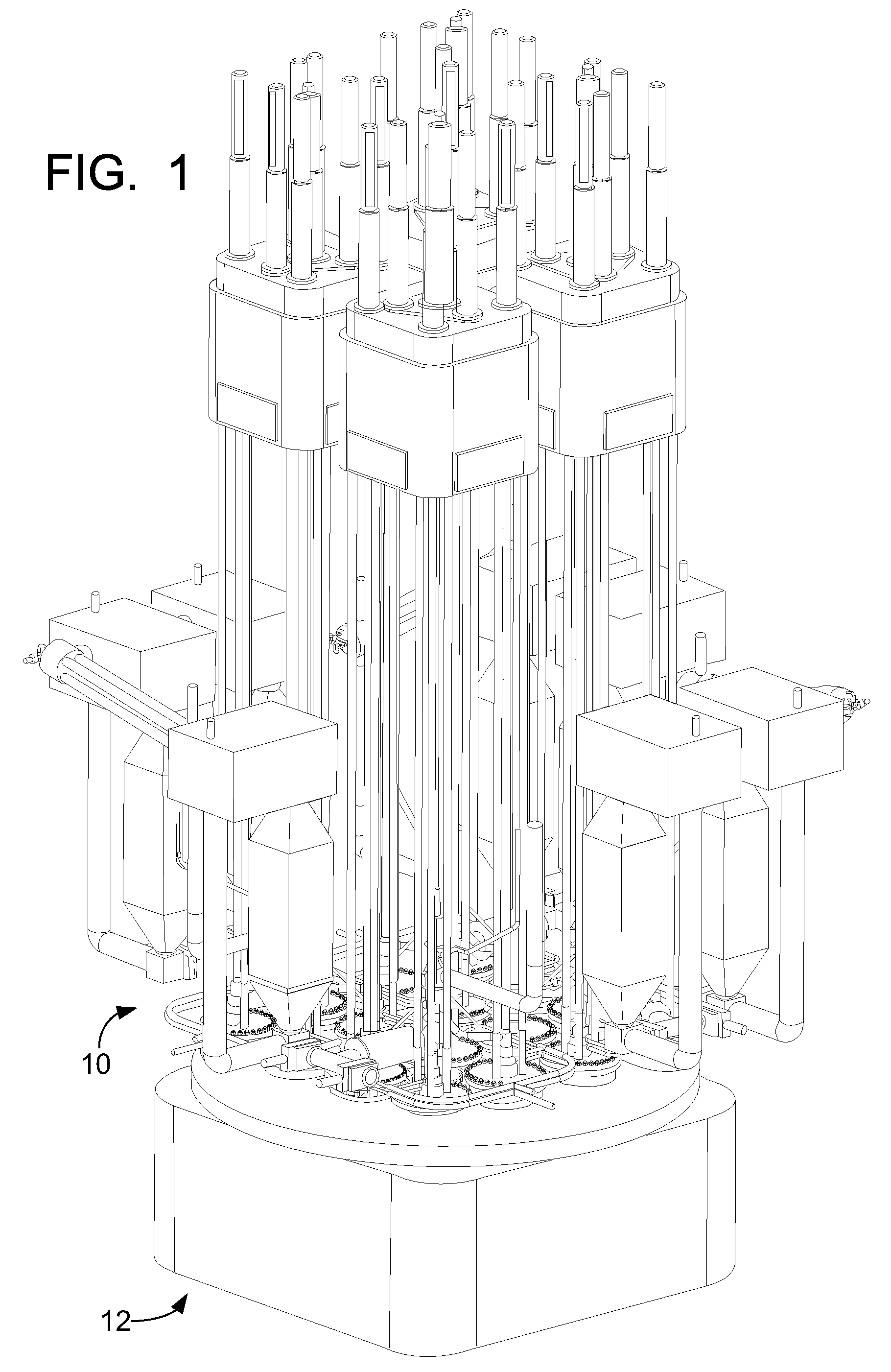
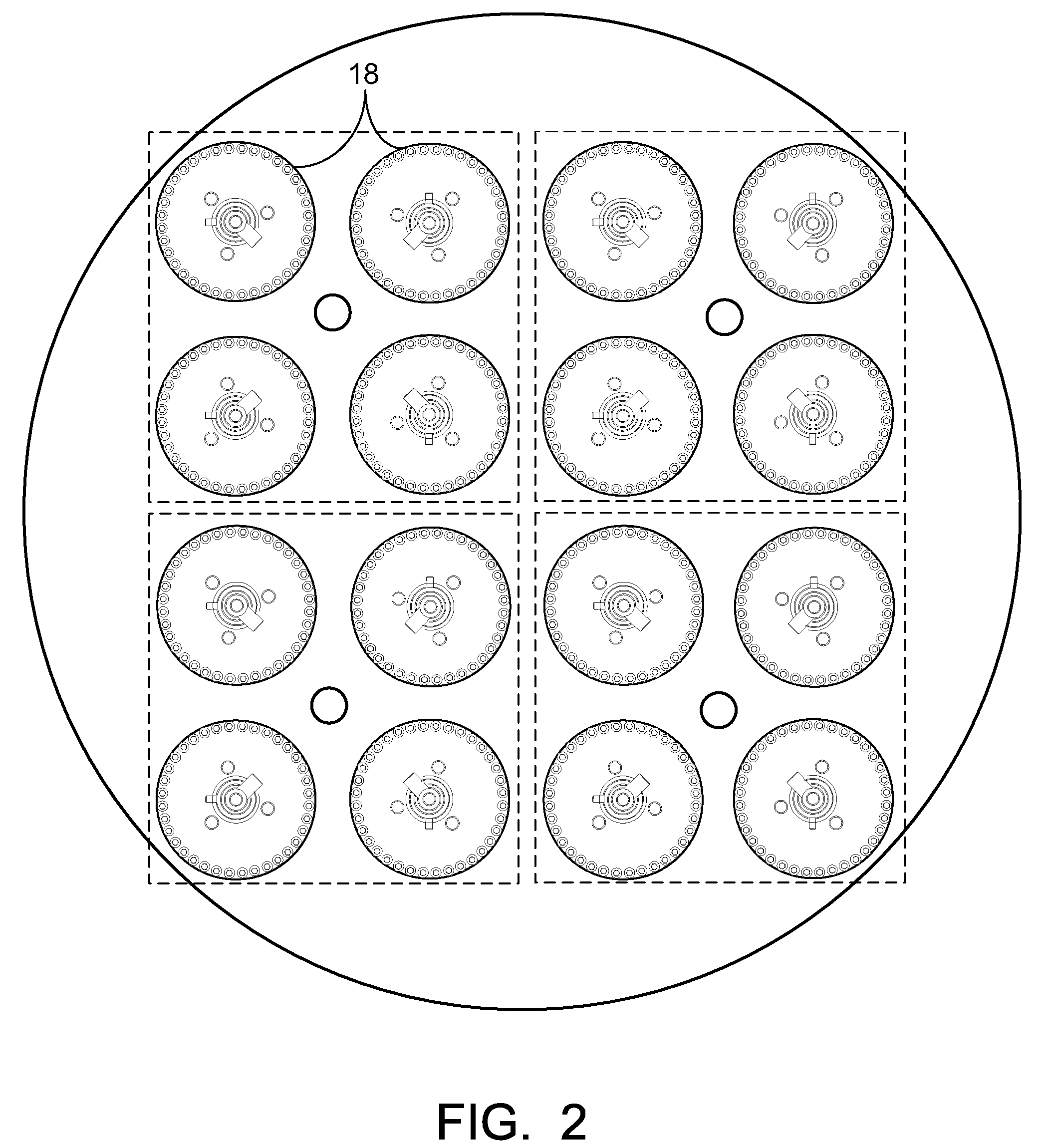
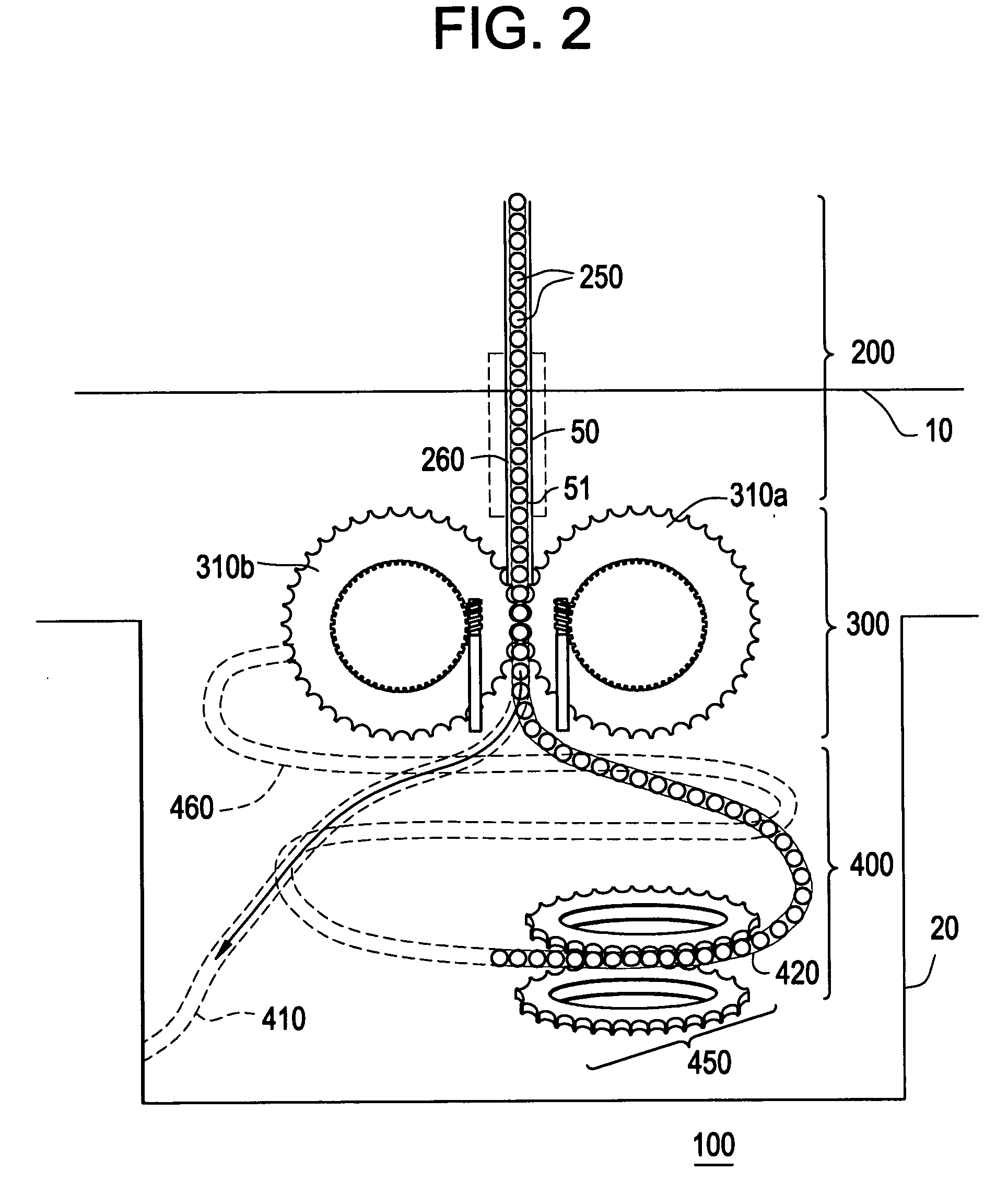
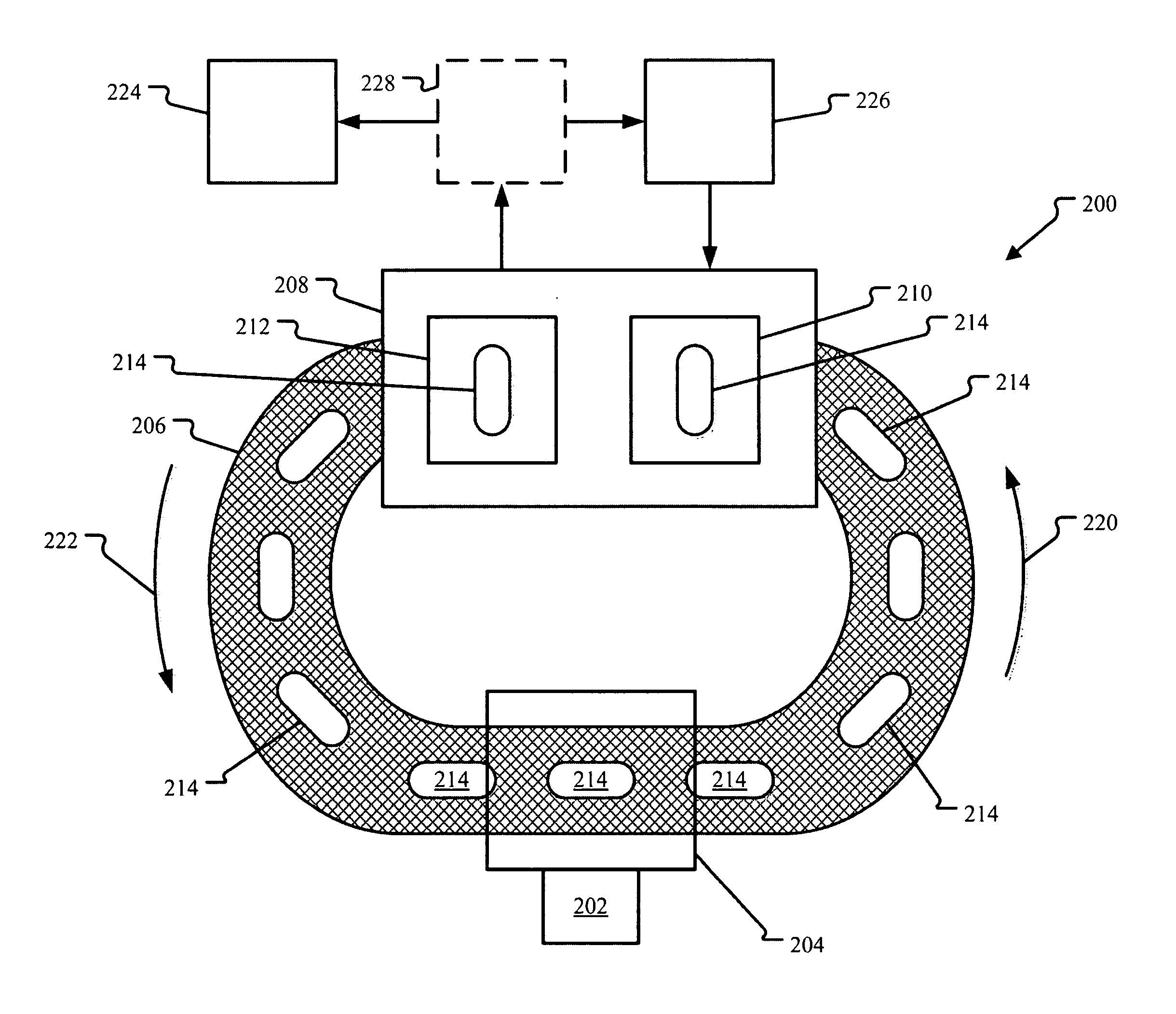
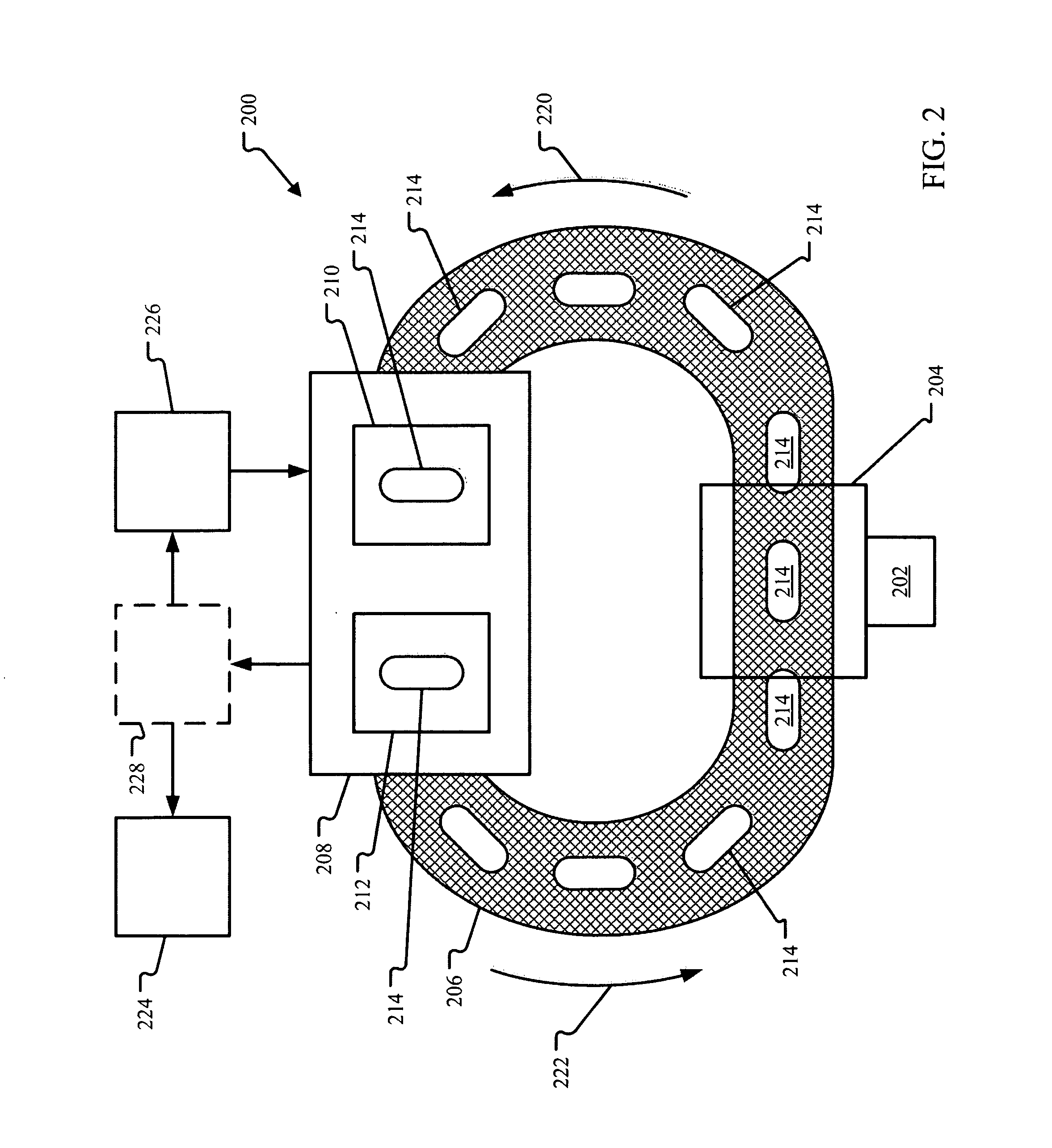
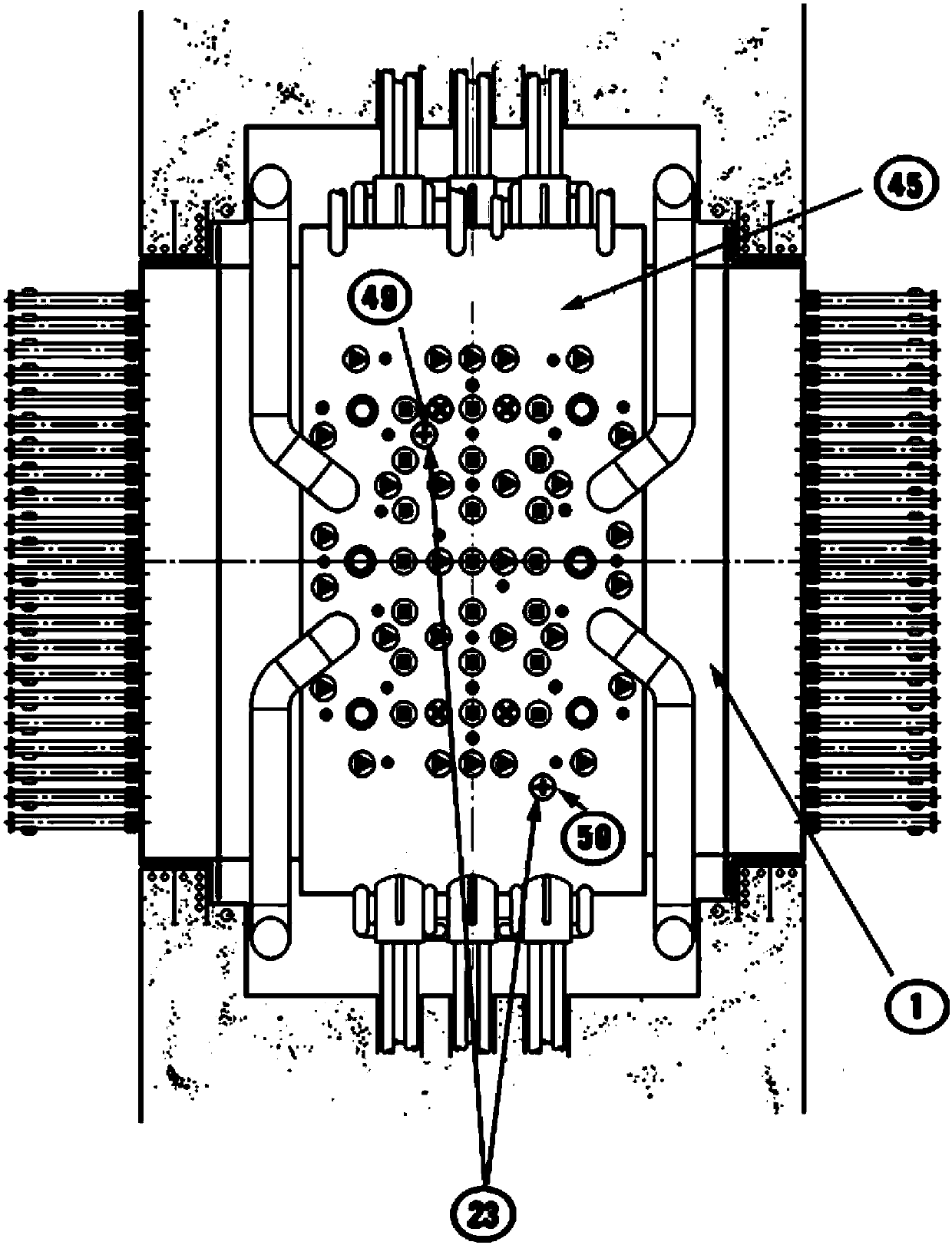
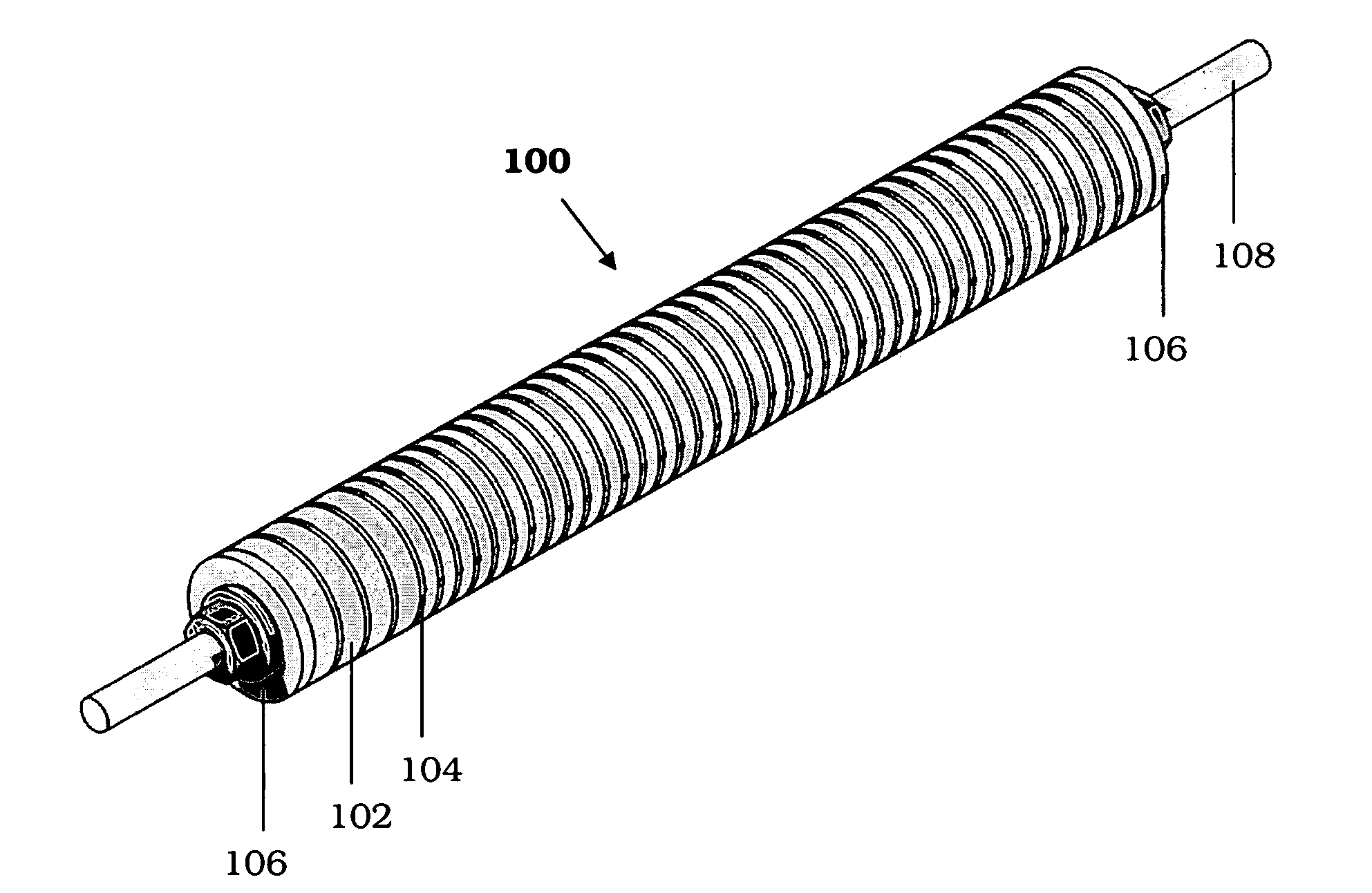
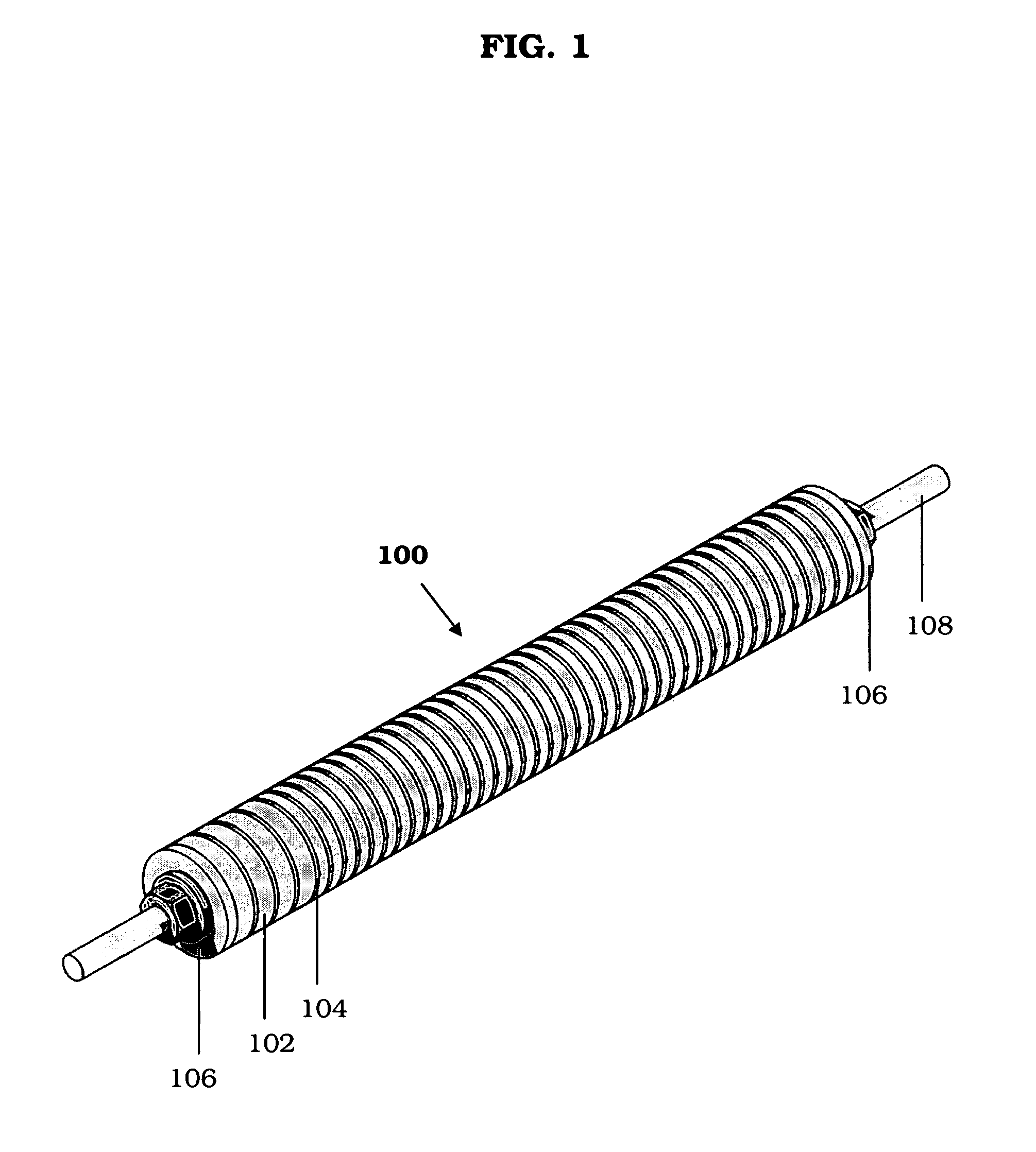
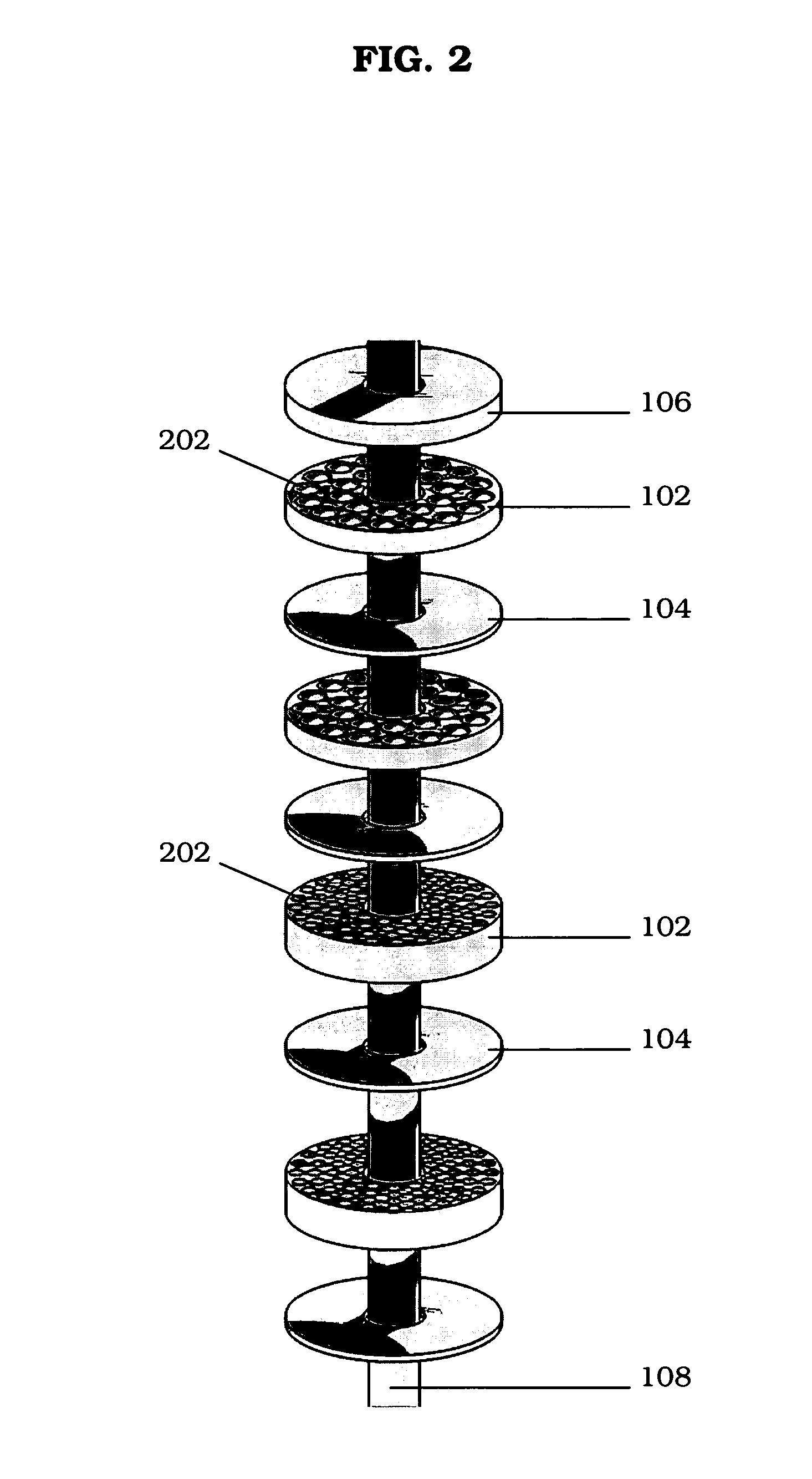
InactiveUS20110051874A1Quickly and simply harvestedIsotope delivery systemsConversion in nuclear reactorNuclear reactor coreNuclear reactor
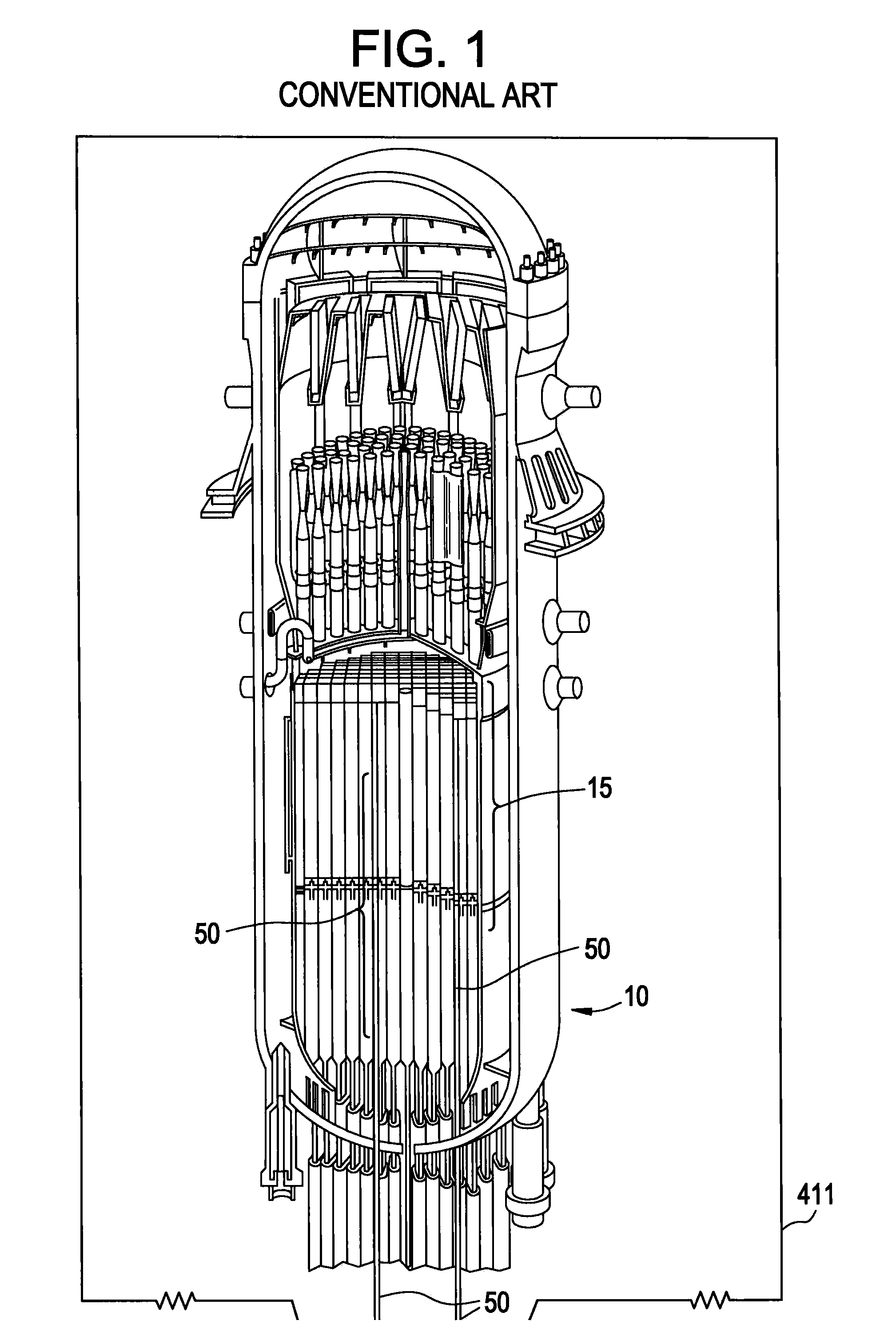
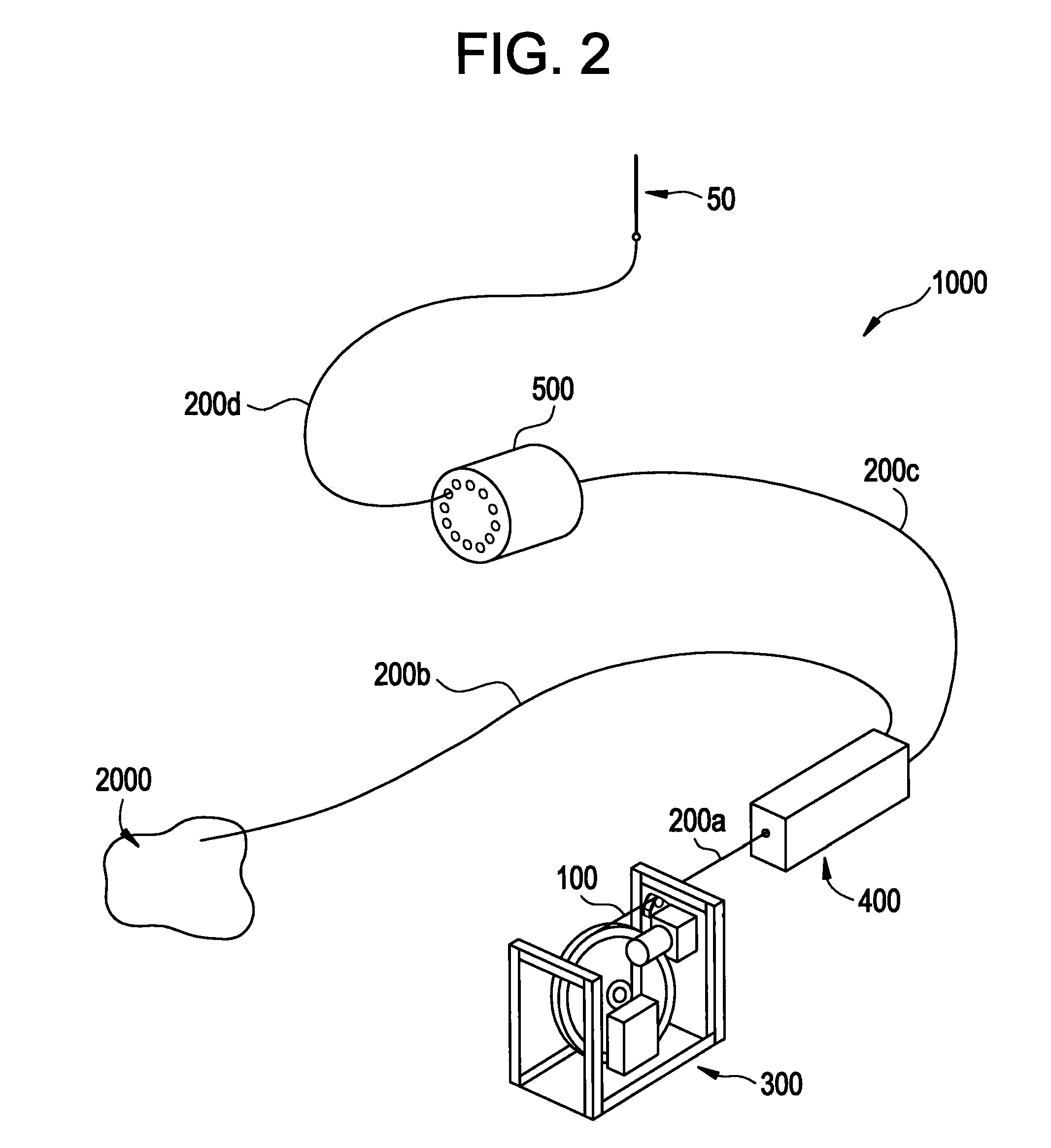
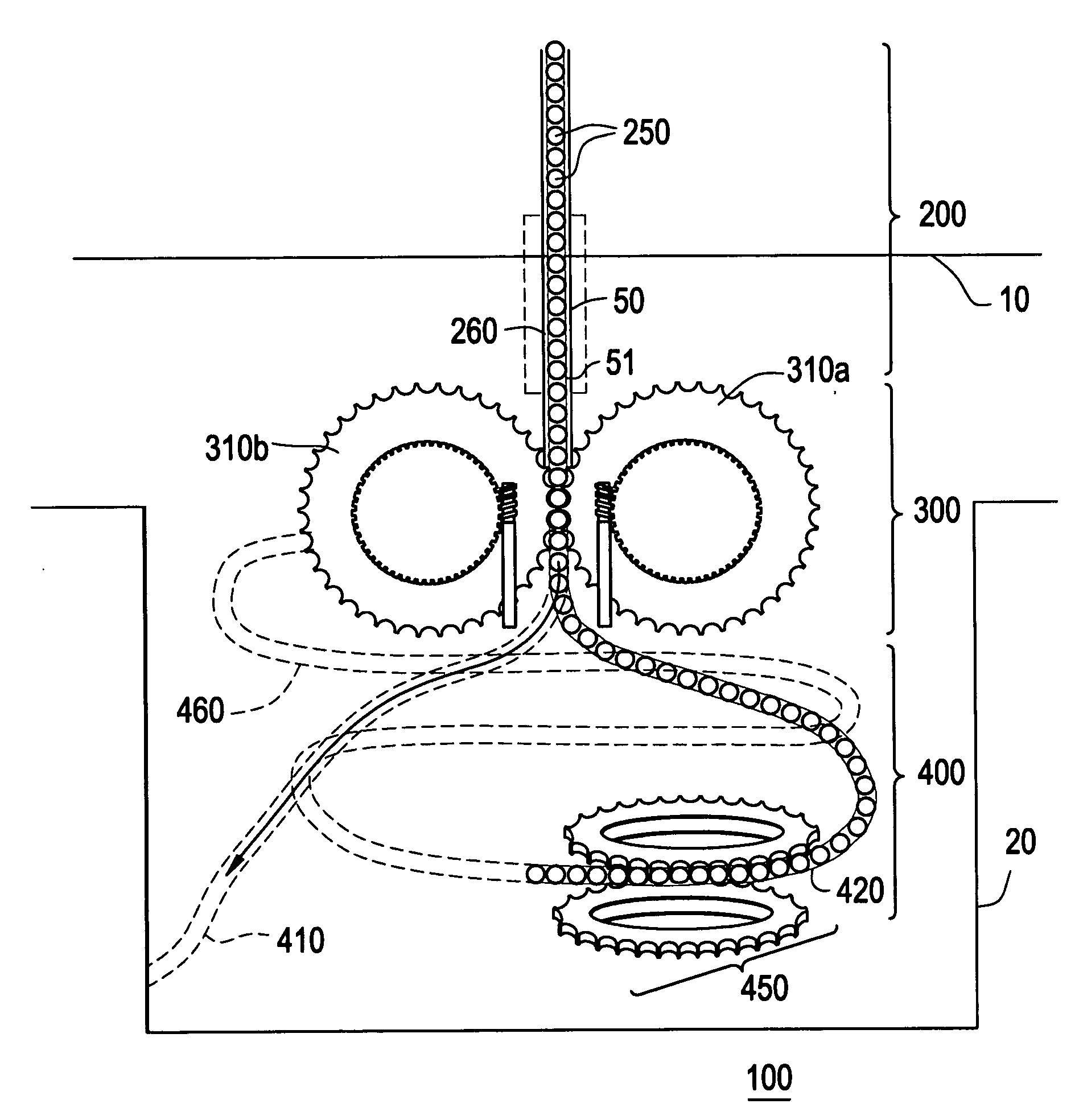
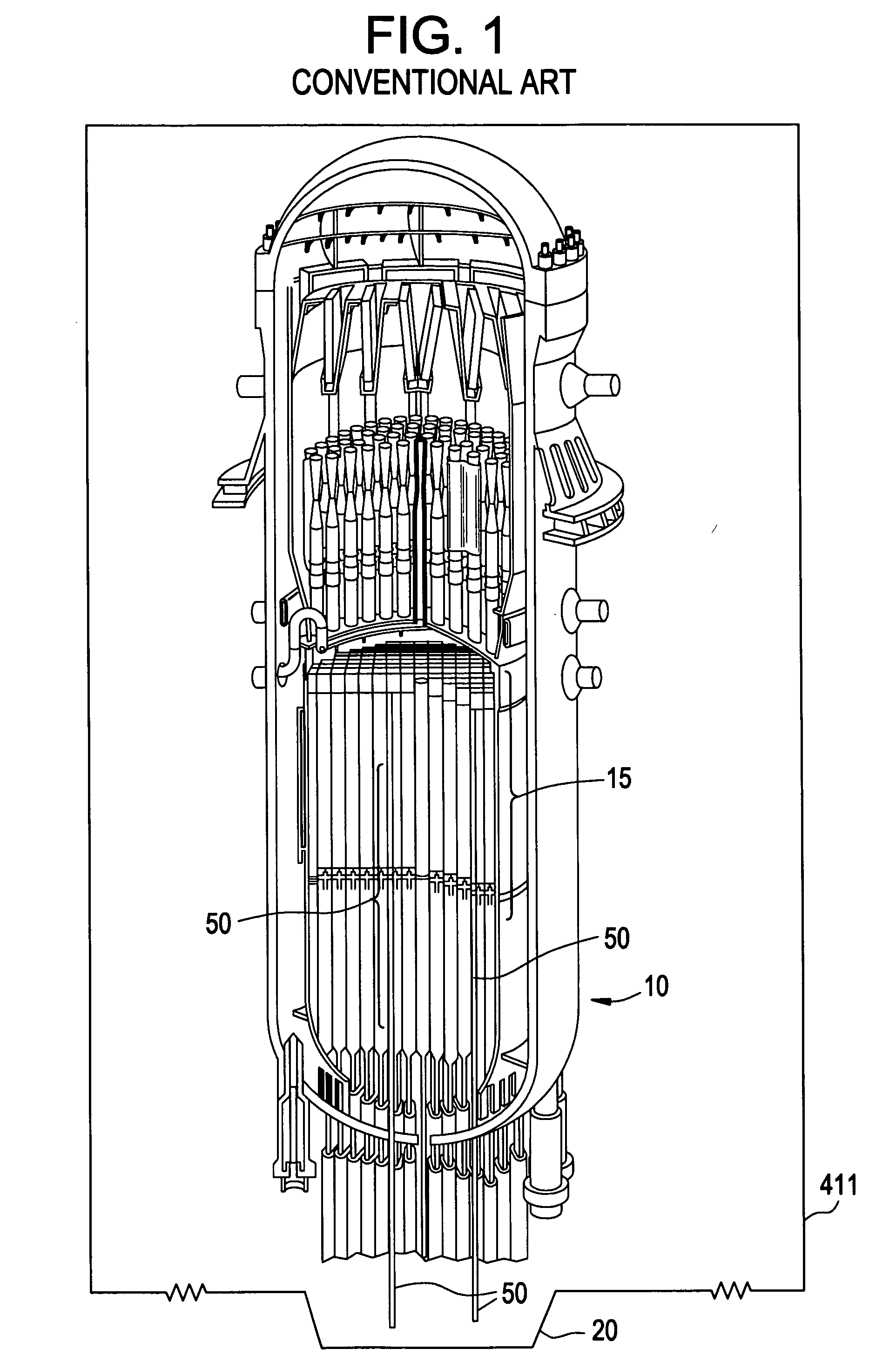
Example embodiments are directed to methods of producing desired isotopes in commercial nuclear reactors and associated apparatuses using instrumentation tubes conventionally found in nuclear reactor vessels to expose irradiation targets to neutron flux found in the operating nuclear reactor. Example embodiments include assemblies for retention and producing radioisotopes in nuclear reactors and instrumentation tubes thereof. Example embodiments include one or more retention assemblies that contain one or more irradiation targets and are useable with example delivery systems that permit delivery of irradiation targets. Example embodiments may be sized, shaped, fabricated, and otherwise configured to successfully move through example delivery systems and conventional instrumentation tubes while containing irradiation targets and desired isotopes produced therefrom.
Owner:GE HITACHI NUCLEAR ENERGY AMERICAS
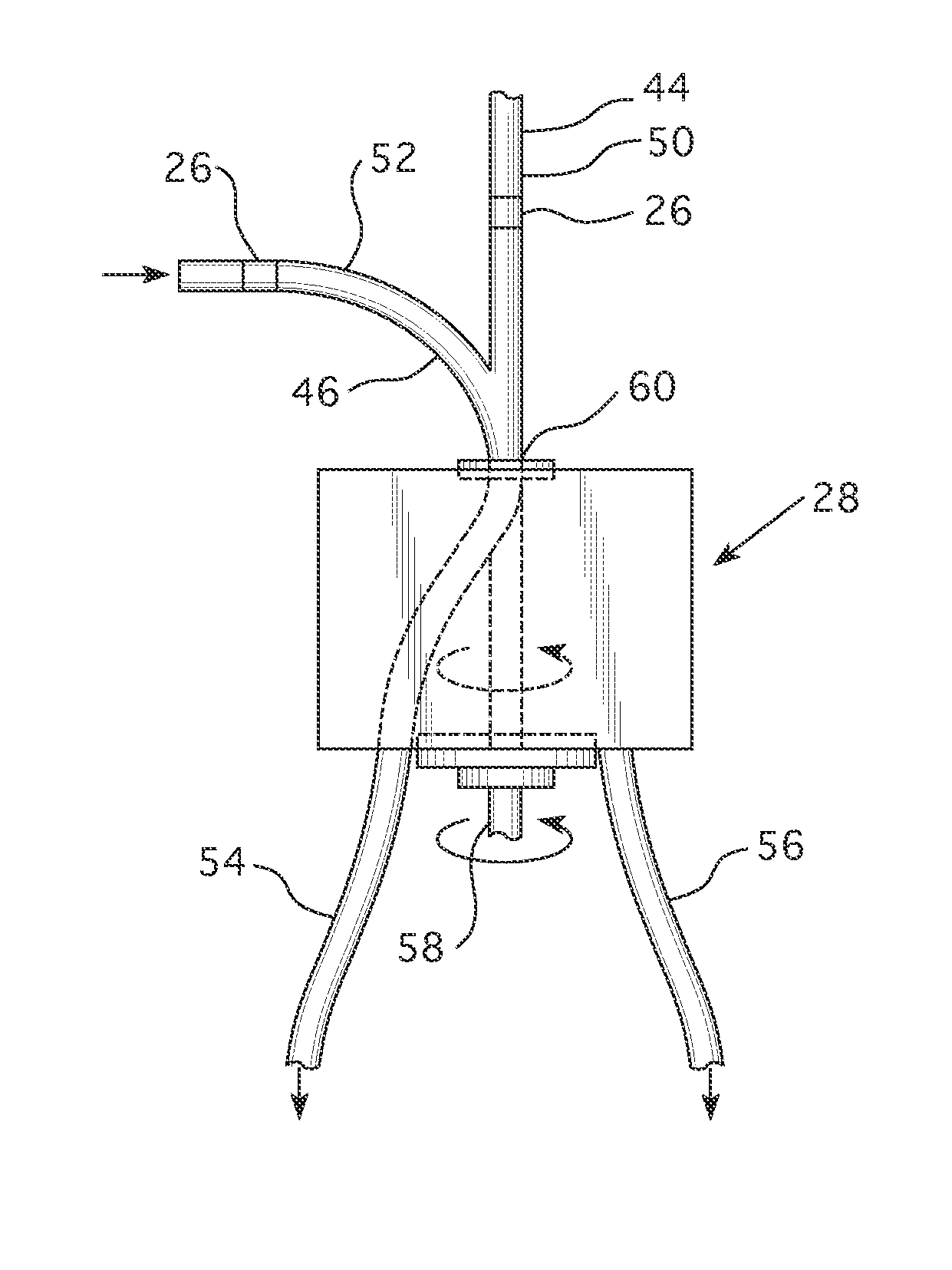
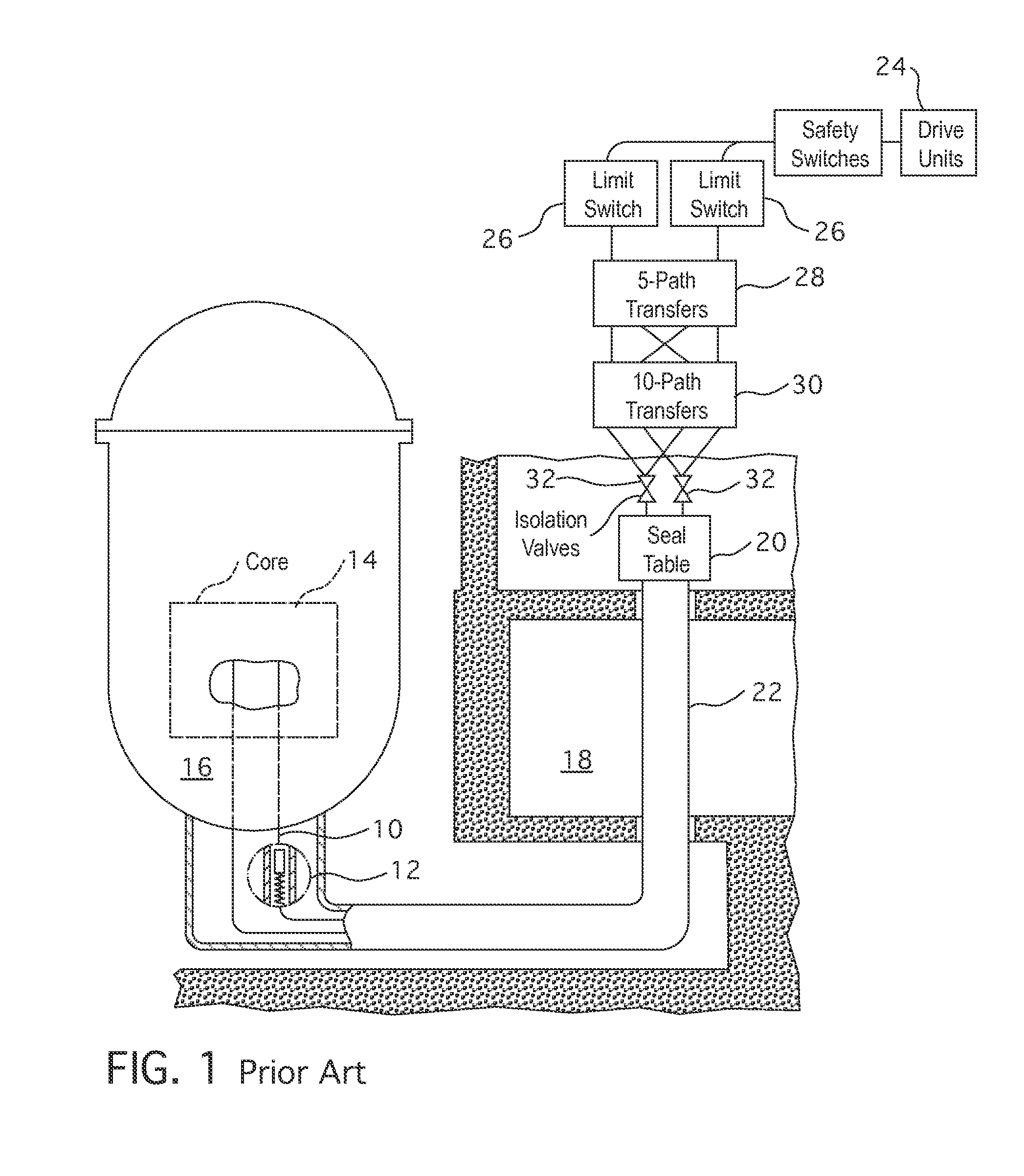
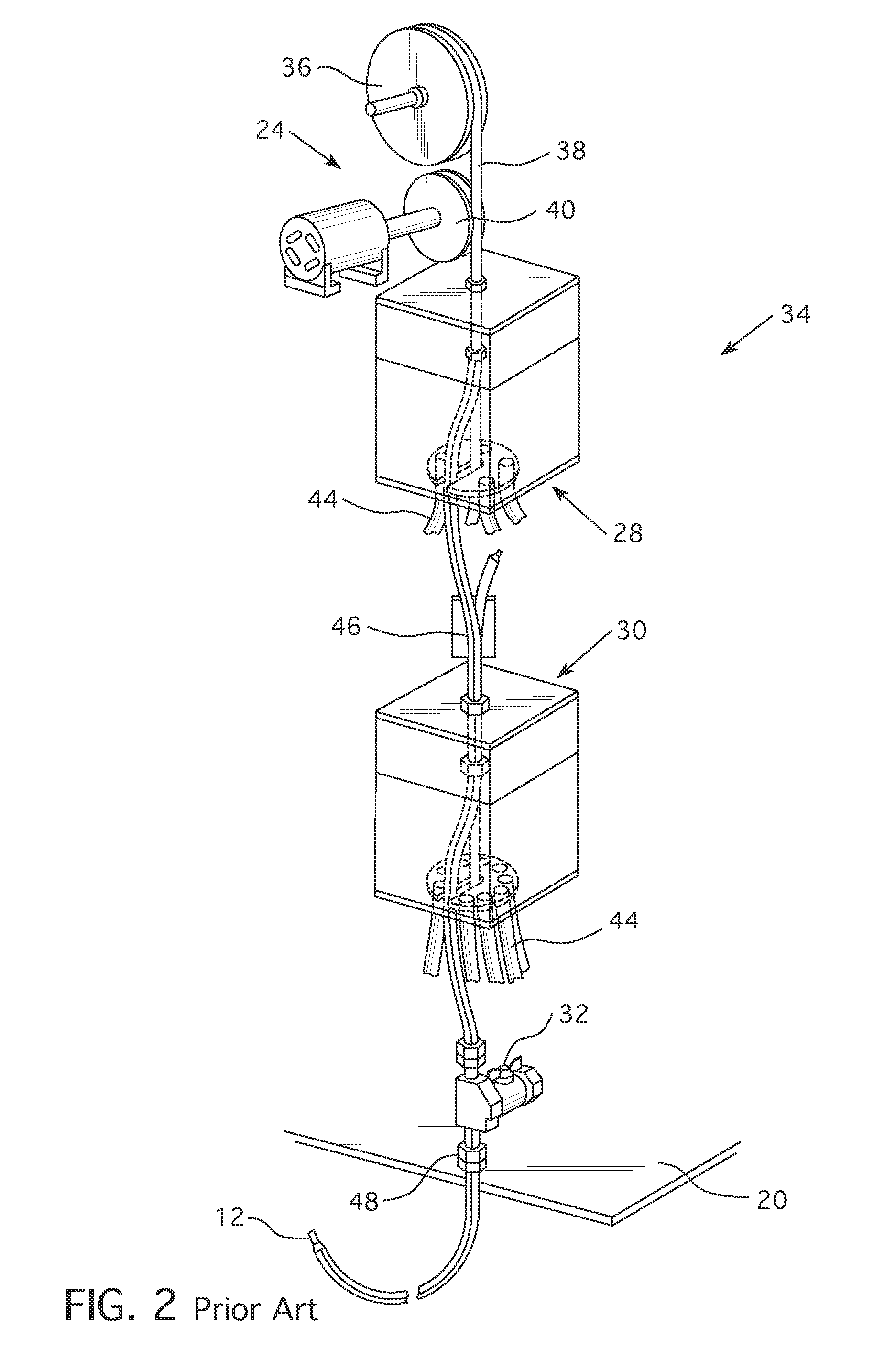
Apparatuses and methods for production of radioisotopes in nuclear reactor instrumentation tubes
ActiveUS20090213977A1Quickly and simply harvestedConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsNuclear energy generationNuclear reactorEngineering
Example embodiments are directed to apparatuses and methods for producing radioisotopes in instrumentation tubes of operating commercial nuclear reactors. Irradiation targets may be inserted and removed from instrumentation tubes during operation and converted to radioisotopes otherwise unavailable from nuclear reactors. Example apparatuses may continuously insert, remove, and store irradiation targets to be converted to useable radioisotopes.
Owner:GE HITACHI NUCLEAR ENERGY AMERICAS
Targeted Isotope Production System
A system and method for employing the in-core movable detectors of a commercial nuclear powered electric generating facility to transmute a user-specified target material into a desired isotope. The process is conducted remotely resulting in a shielded end product available for shipment for further processing.
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE ELECTRIC CORP
Brachytherapy and radiography target holding device
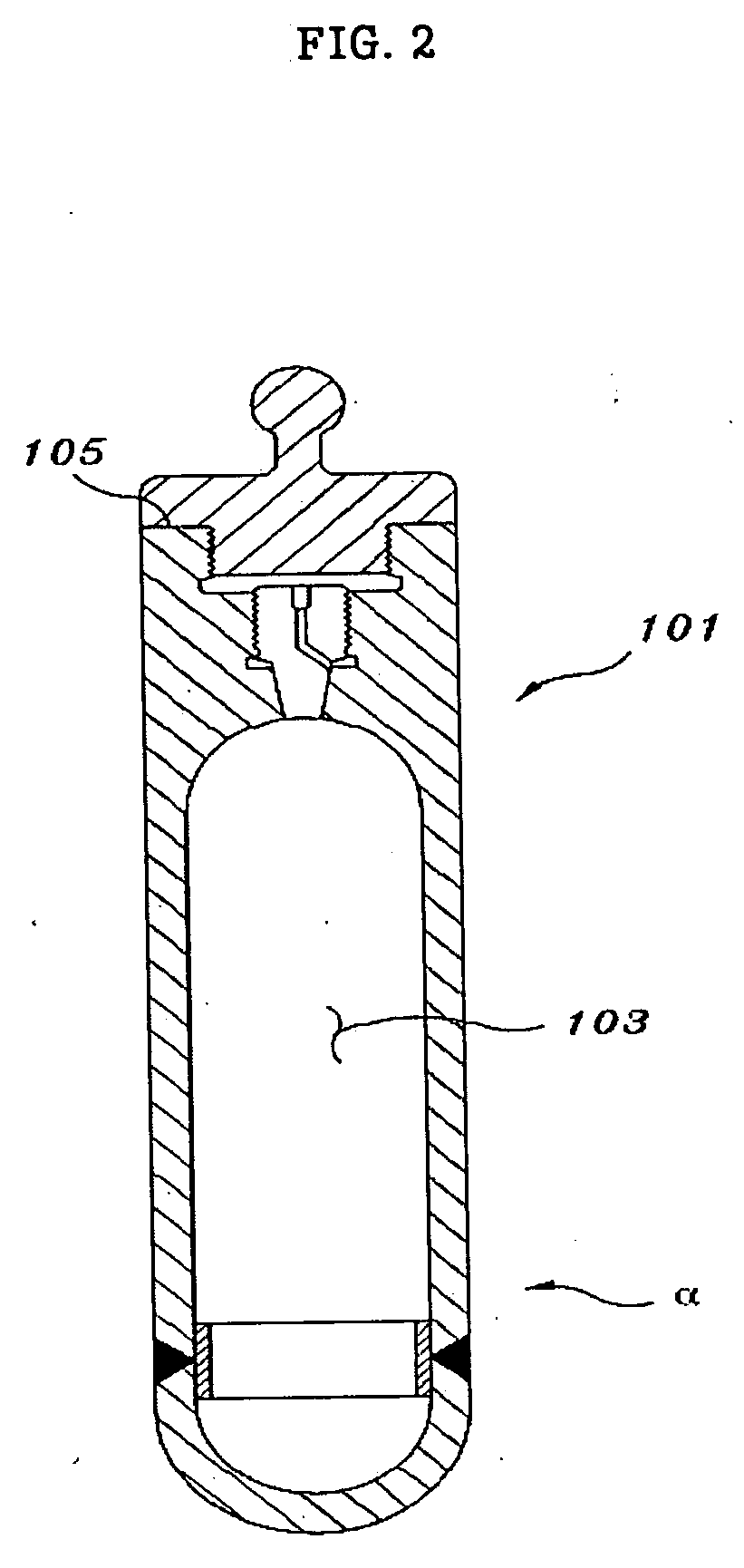
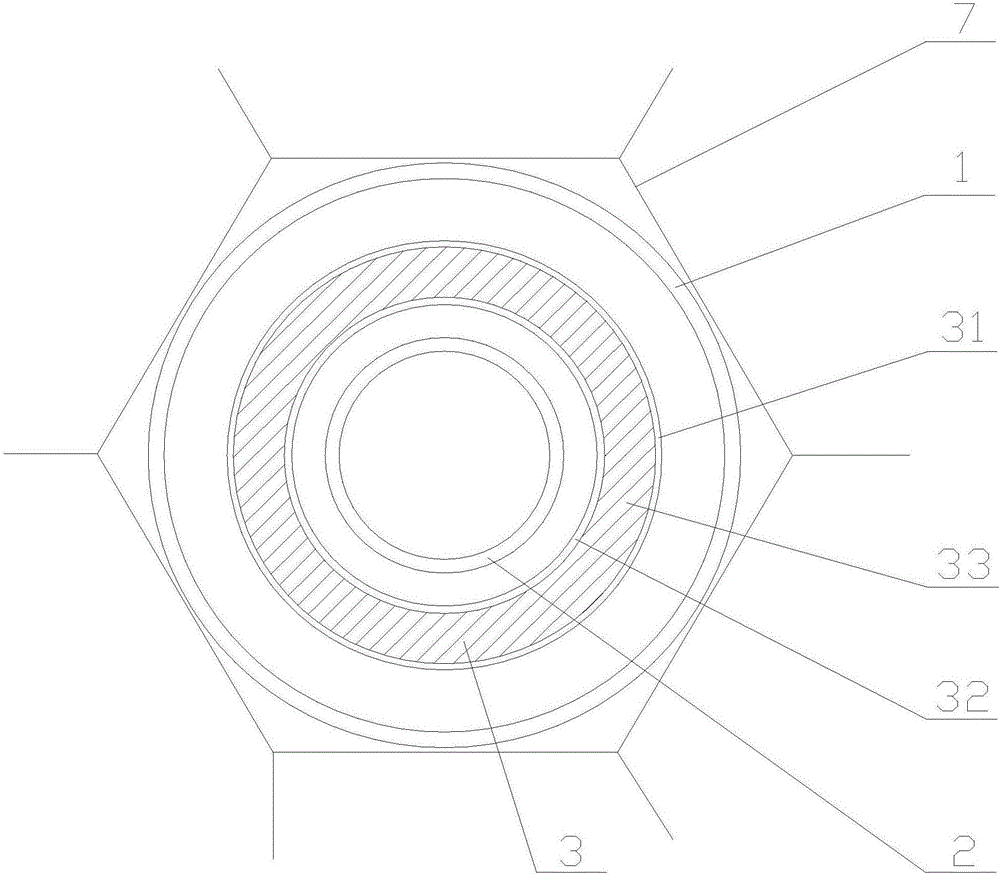
ActiveUS8366088B2Rigid enoughConvenient introductionConversion in nuclear reactorLarge fixed membersBrachytherapyEngineering
Owner:GE HITACHI NUCLEAR ENERGY AMERICAS
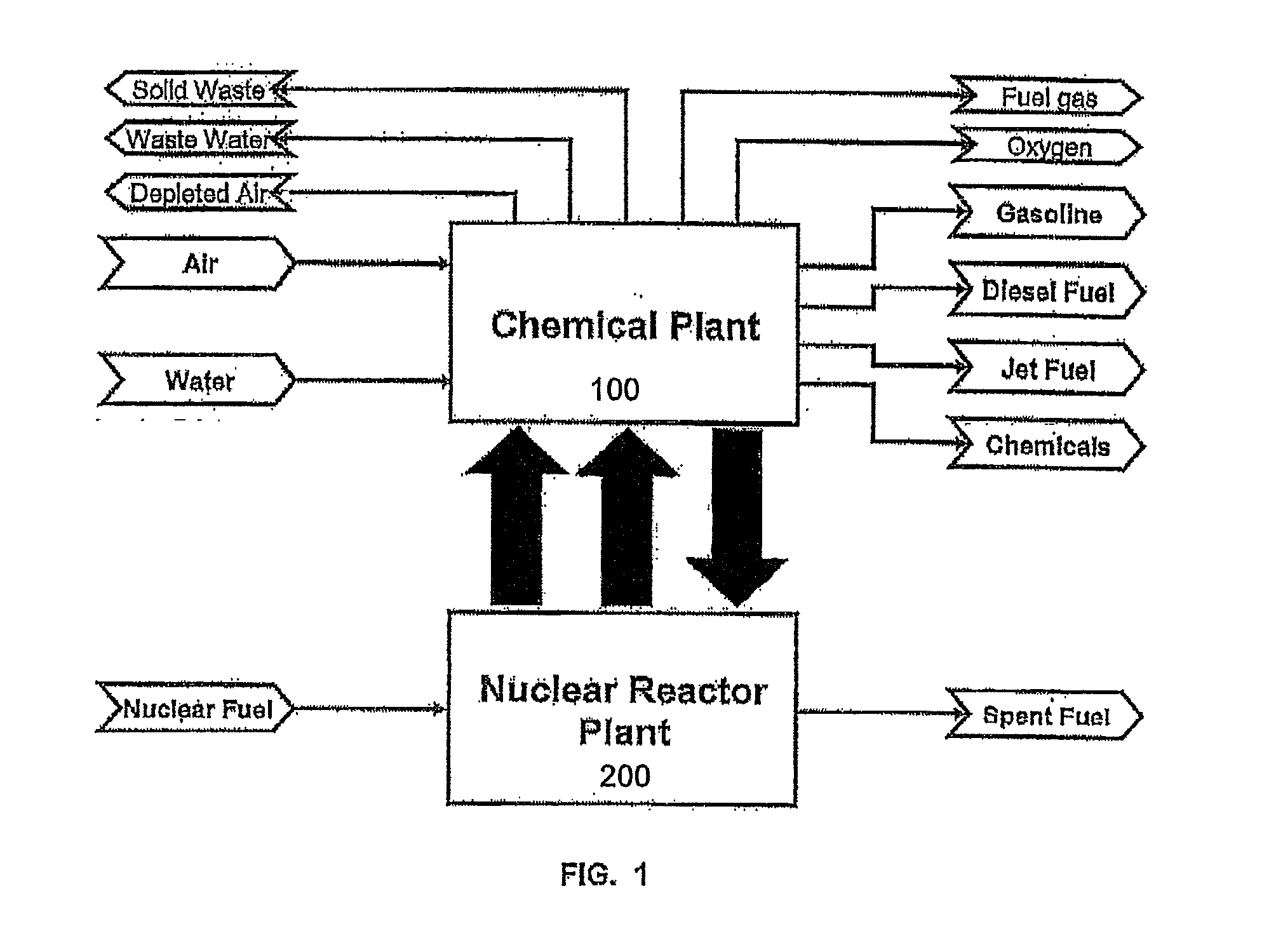
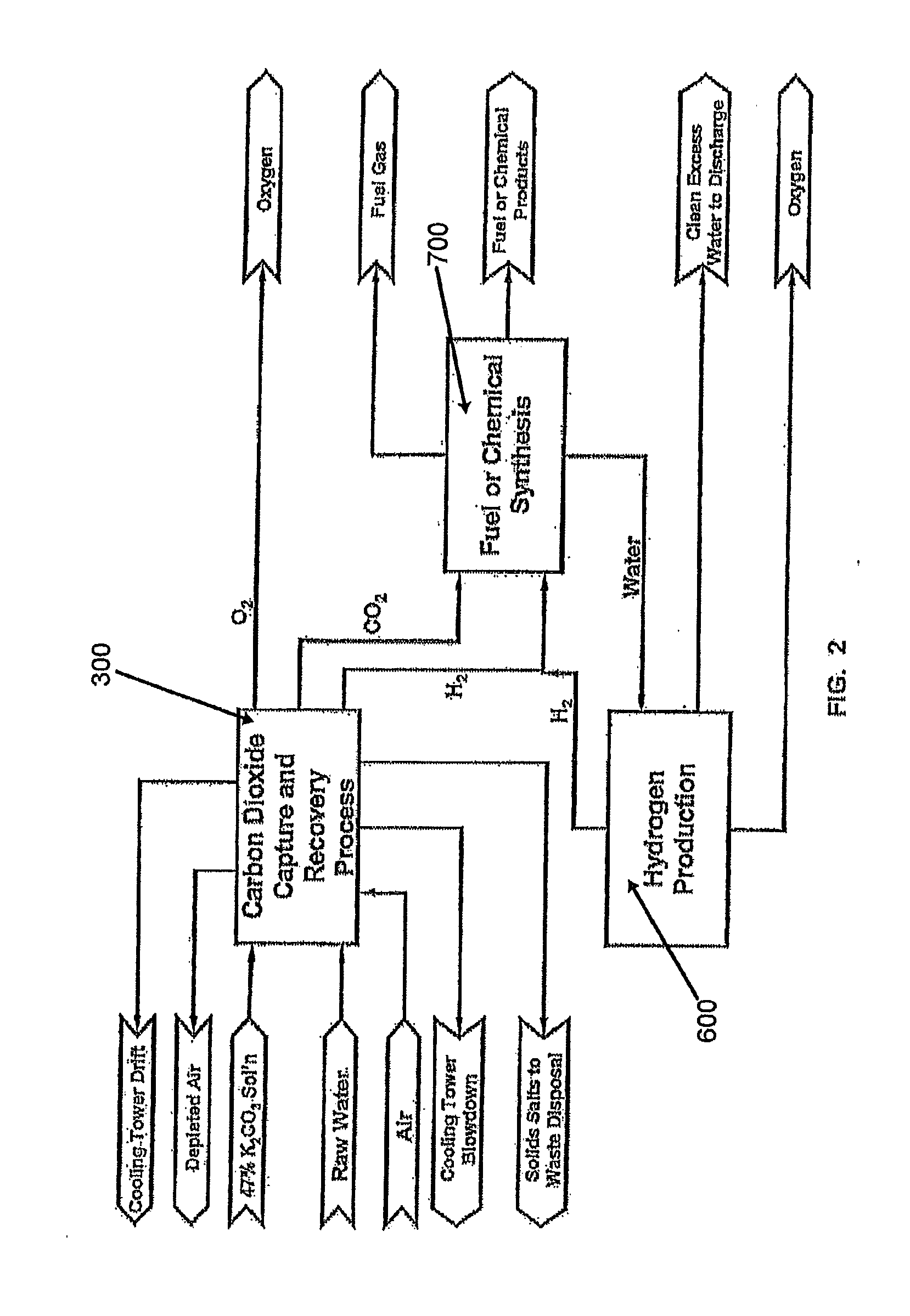
Method of producing synthetic fuels and organic chemicals from atmospheric carbon dioxide
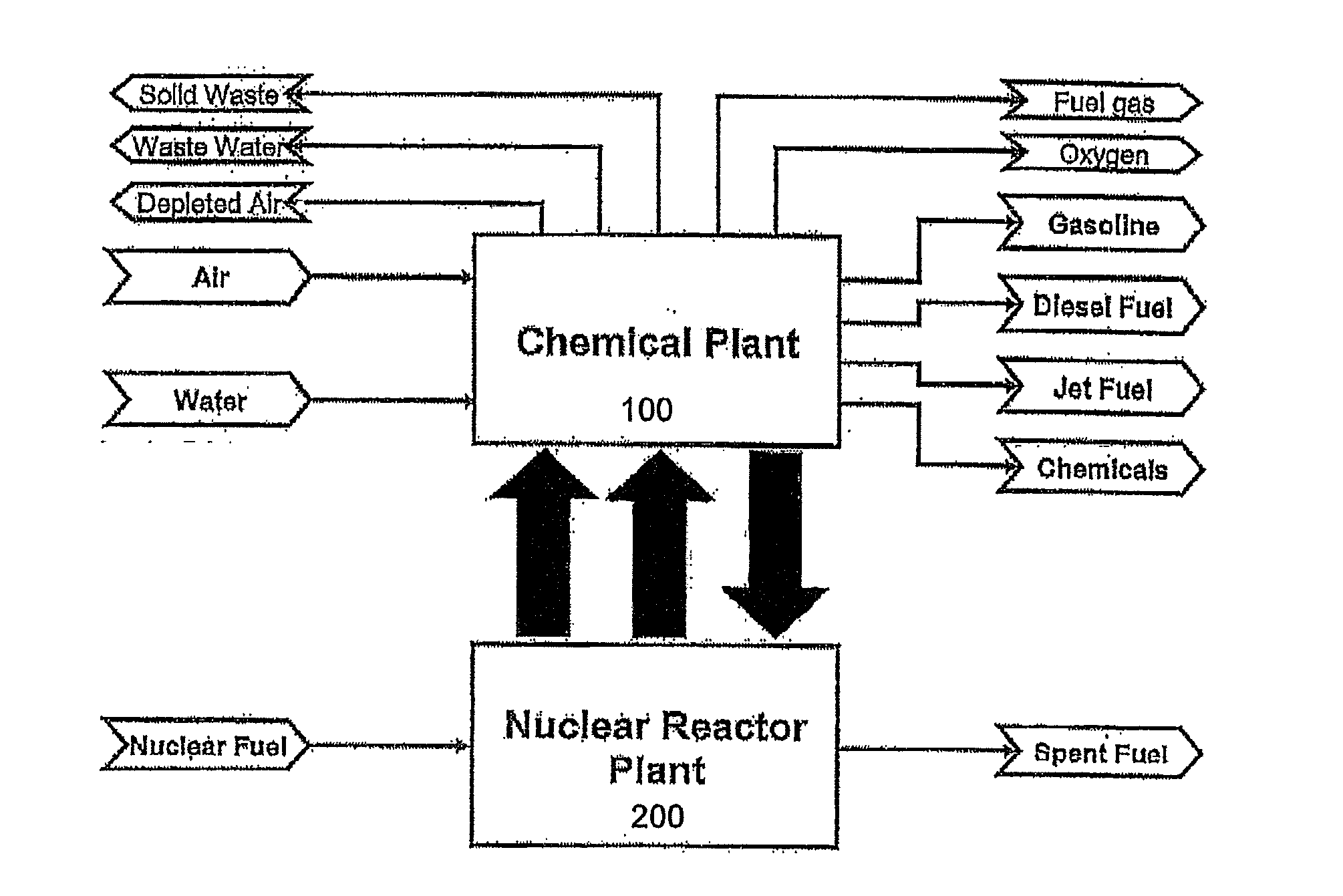
The present invention is directed to providing a method of producing synthetic fuels and organic chemicals from atmospheric carbon dioxide. Carbon dioxide gas is extracted from the atmosphere, hydrogen gas is obtained by splitting water, a mixture of the carbon dioxide gas and the hydrogen gas (synthesis gas) is generated, and the synthesis gas is converted into synthetic fuels and / or organic products. The present invention is also directed to utilizing a nuclear power reactor to provide power for the method of the present invention.
Owner:LOS ALAMOS NATIONAL SECURITY
Nuclear fuel assembly and related methods for spent nuclear fuel reprocessing and management
InactiveUS20110317794A1Increase fuel consumptionLower the volumeFuel elementsConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsUranium dioxideNuclear fuel
Various embodiments of a nuclear fuel assembly and related methods for processing and managing spent nuclear fuel are disclosed. According to one exemplary embodiment, a nuclear fuel may include a plurality of first fuel rods having a plurality of first fuel elements and a plurality of second fuel rods having a plurality of second fuel elements. Each of the first fuel elements may include uranium dioxide fuel, and each of the second fuel elements may include a plurality of tristructural isotropic fuel particles embedded in a silicon carbide matrix. The plurality of first fuel rods and the plurality of second fuel rods are arranged in a fuel assembly.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC +1
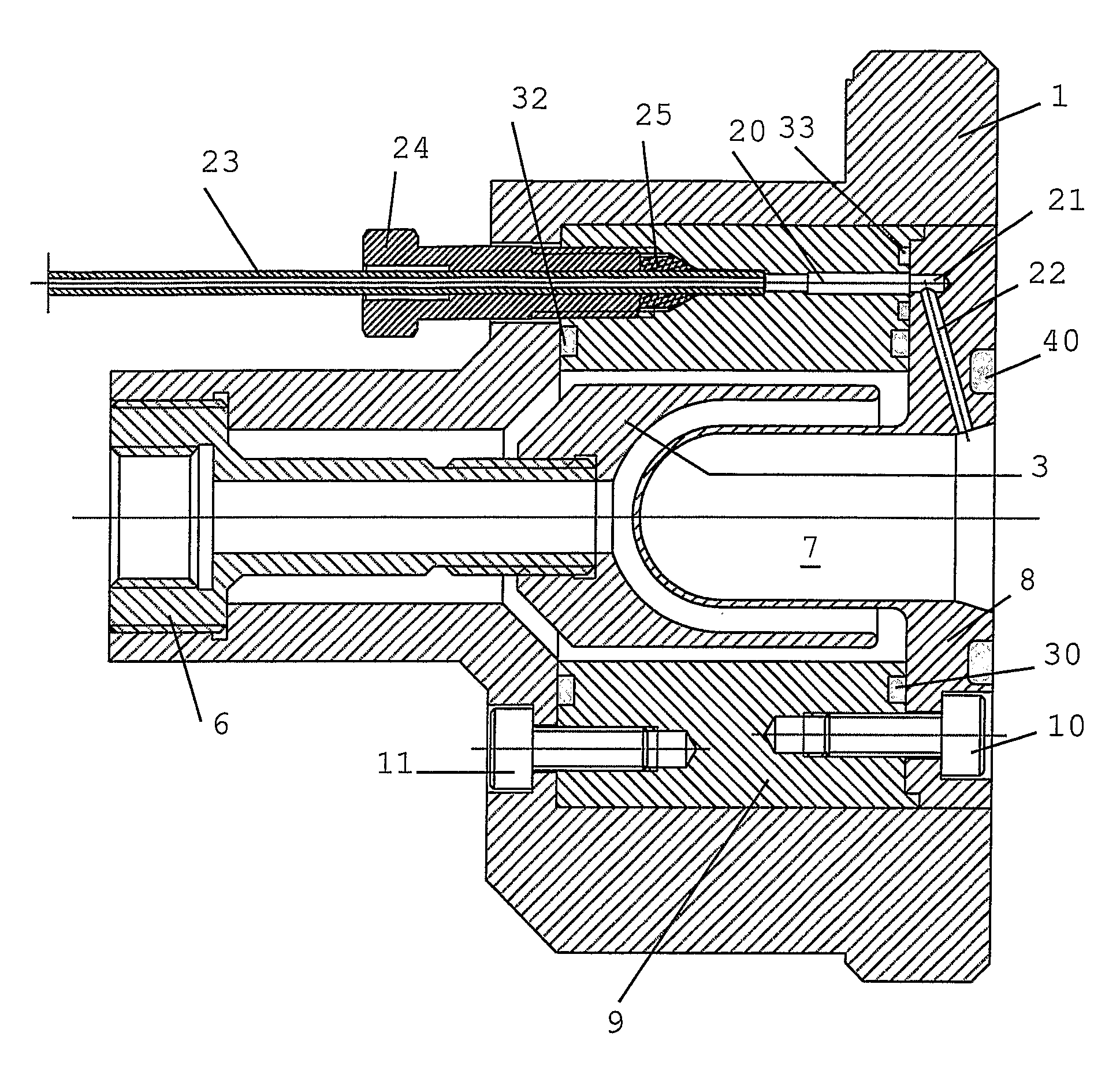
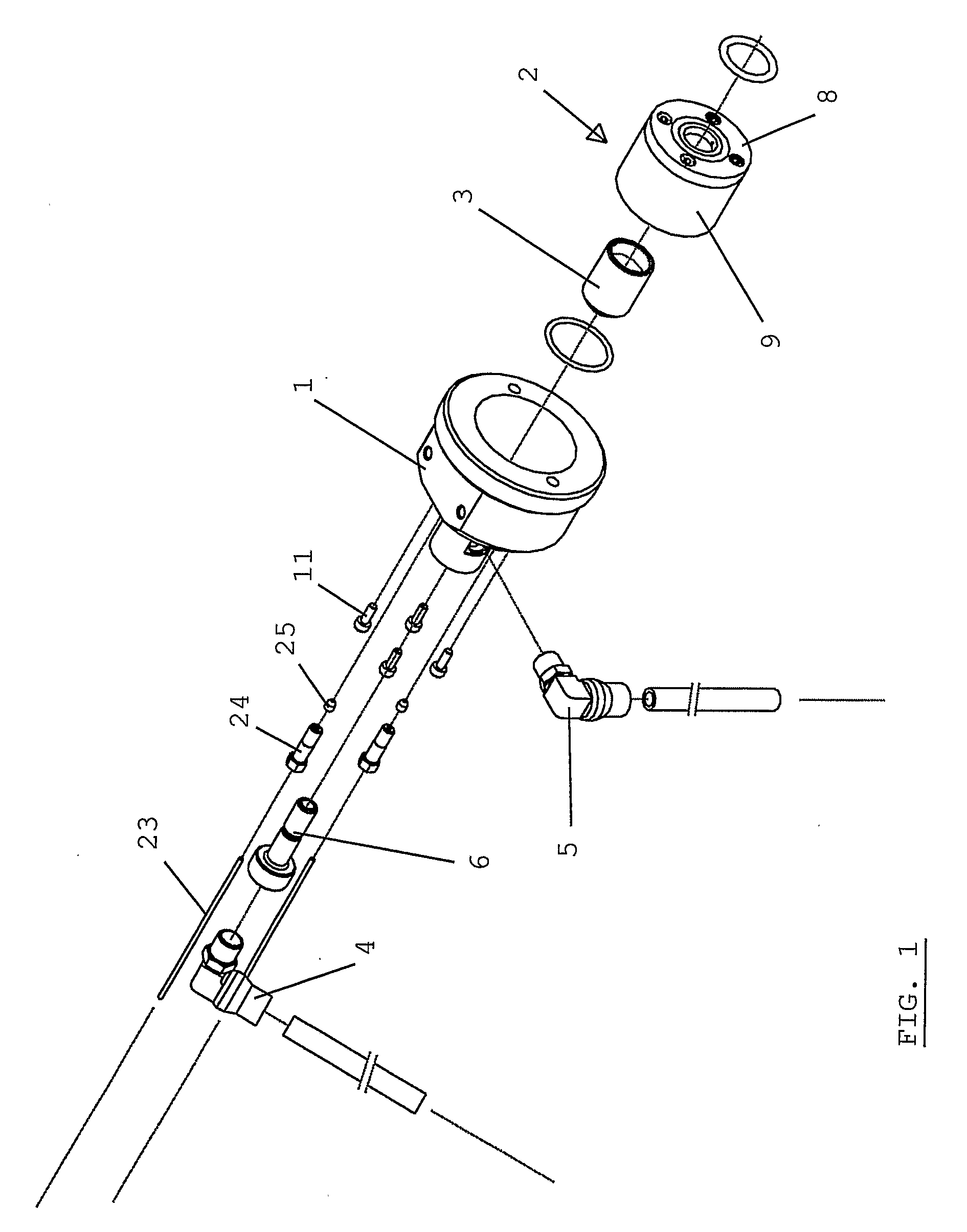
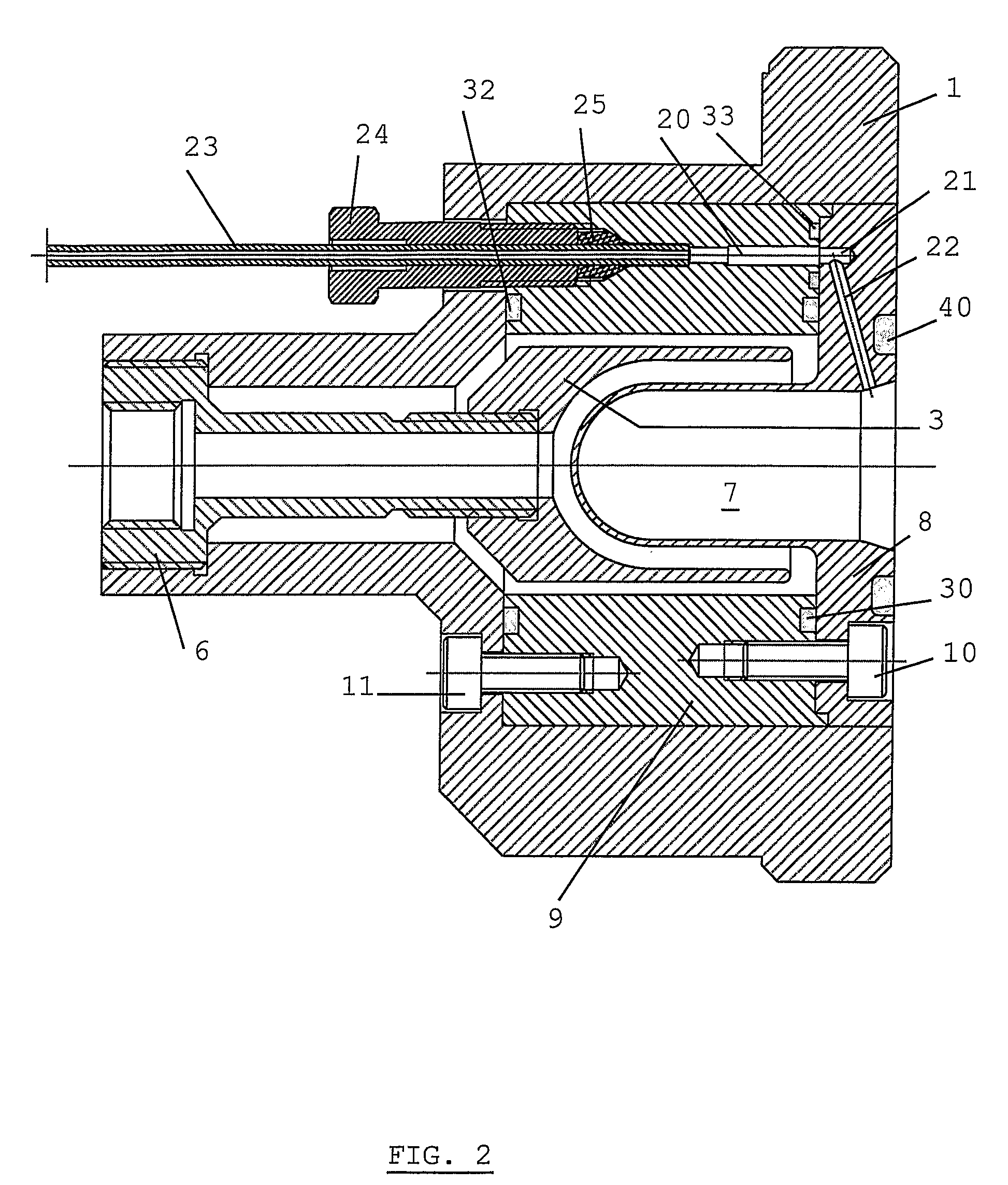
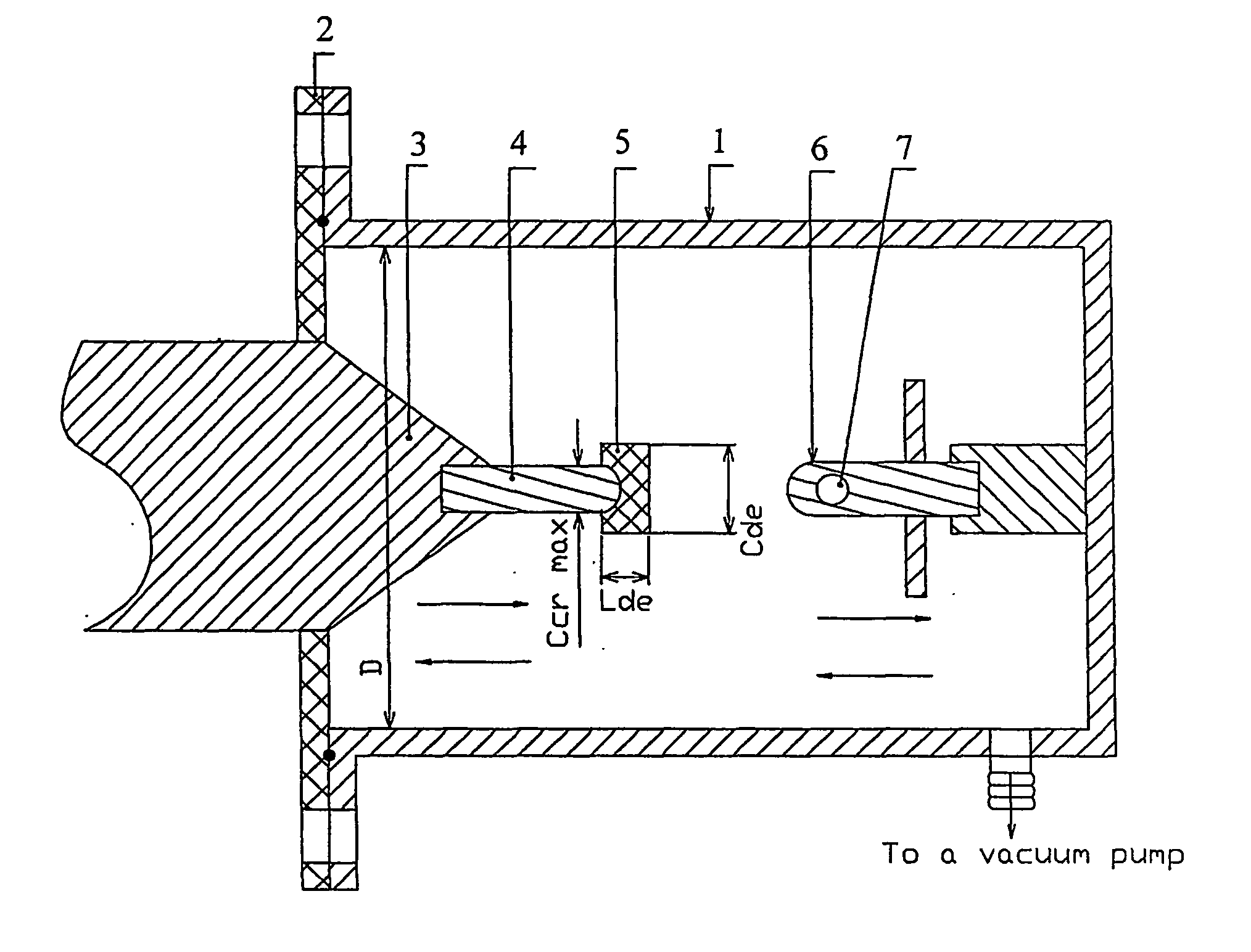
Target Device for Producing a Radioisotope
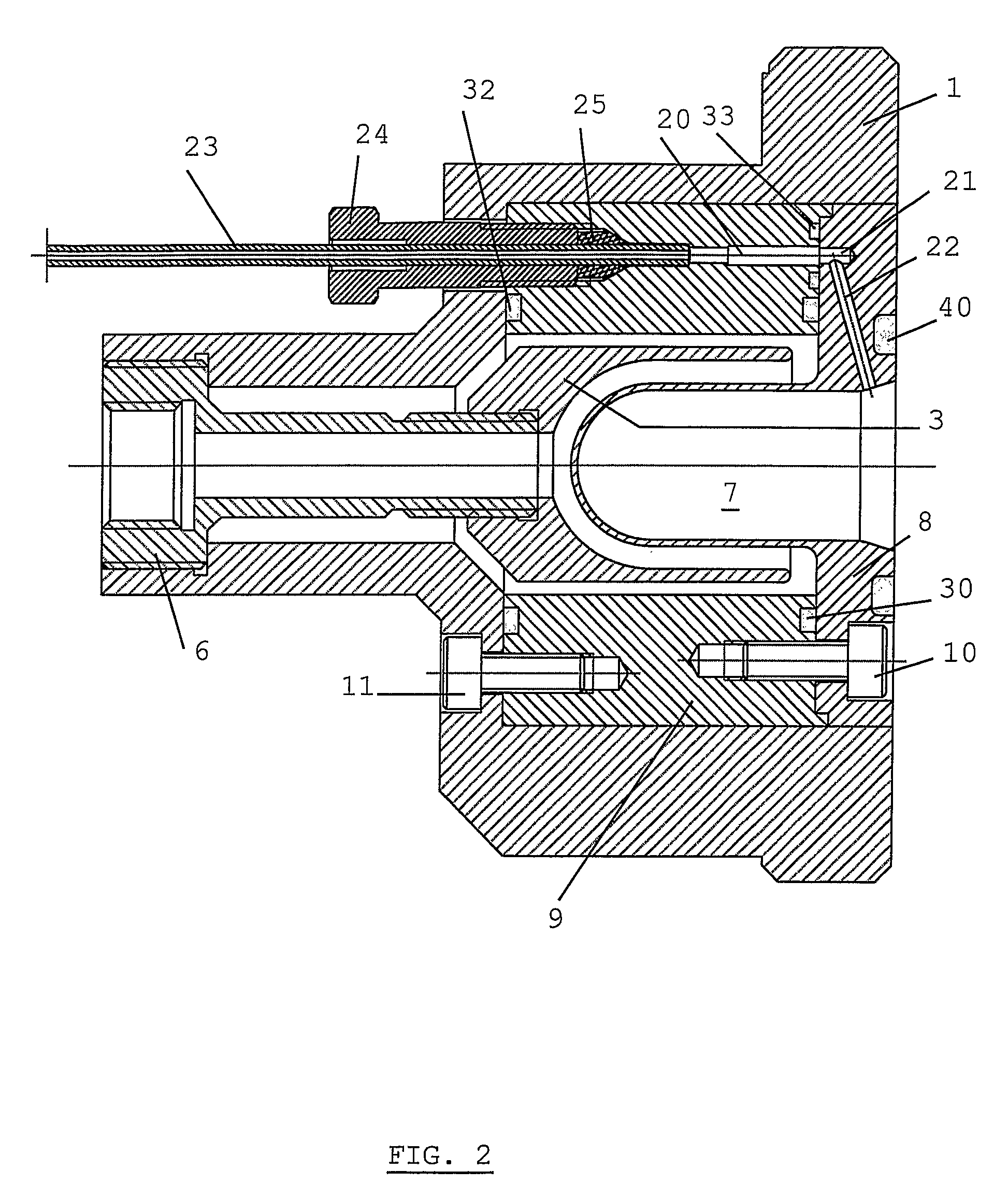
ActiveUS20080023645A1Conversion outside reactor/acceleratorsConversion in nuclear reactorParticle beamIrradiation
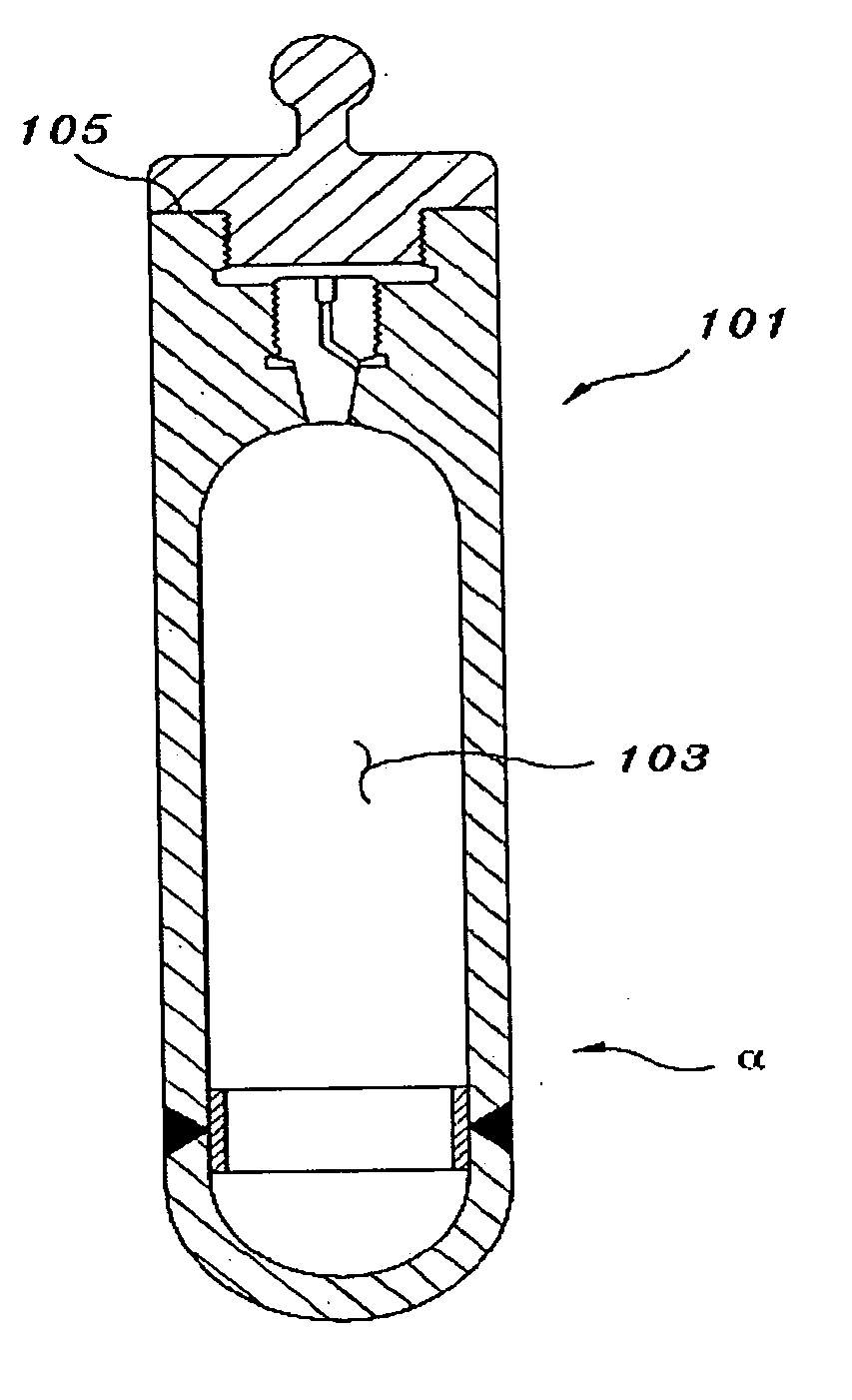
The present invention is related to an irradiation cell for producing a radioisotope of interest through the irradiation of a target material by a particle beam, comprising a metallic insert (2) forming a cavity (7) designed to house the target material and to be closed by an irradiation window, characterized in that said metallic insert (2) comprises at least two separate metallic parts (8,9) of different materials, being composed of at least a first part (8) comprising said cavity (7).
Owner:ION BEAM APPL
Method of and apparatus for transmuting radioactive waste
InactiveUS20050013397A1Improve efficiencyEasy to useConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsNuclear energy generationExpansion tankParticle accelerator
A radiocactive waste containing medium is circulated within two or more systems (1,2,3) separated from each other flowtechnically; and the circulated radioactive waste is exposed to neutron radiations of different energy spectrum in each system by operating a reactor physically united entirety of irradiated sections of the said systems as a nuclear reactor or an accelerator driven subcritical system. Each system (1,2,3) has a heat exchanger (9,10) and, in given cases, a circulating pump (10,21) and an expansion tank (5,16,27). The disclosed apparatus has two or more reactor regions (1,2,3) separated from each other by partitions (37,38) and, preferably, arranged coaxially within a reactor space encircled by a common shell structure (39). A particle beam (45) produced by a particle accelerator is preferably directed into the innermost reactor region (3).
Owner:BUDAPESTI MUSZAKI & GAZDASAGTUDOMANYL EGYETEM
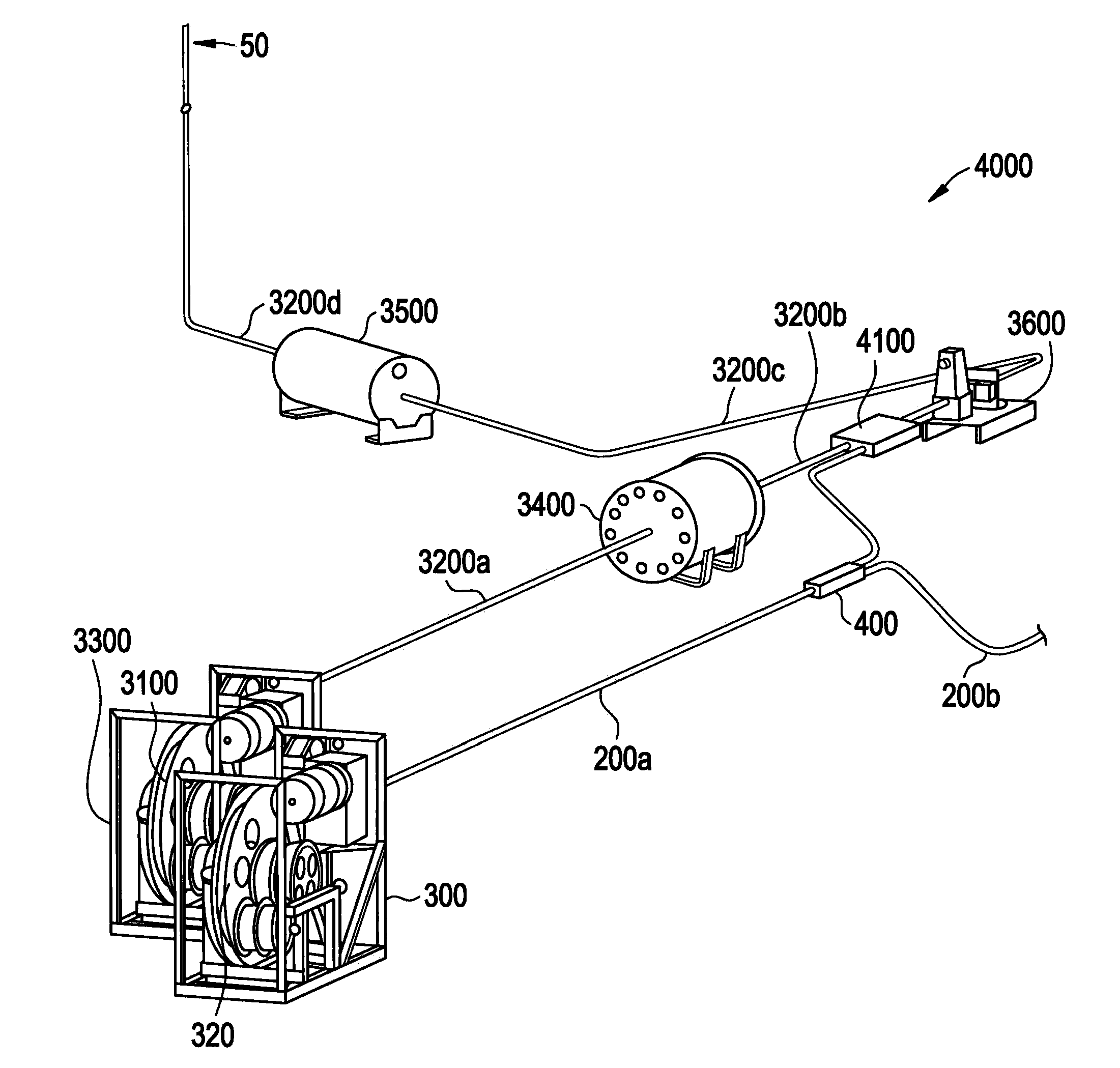
Irradiation targets for isotope delivery systems
ActiveUS20110051872A1Quickly and simply harvestedIsotope delivery systemsConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsNuclear reactor coreNuclear reactor
Example embodiments are directed to methods of producing desired isotopes in commercial nuclear reactors and associated apparatuses using instrumentation tubes conventionally found in nuclear reactor vessels to expose irradiation targets to neutron flux found in the operating nuclear reactor. Example embodiments include irradiation targets for producing radioisotopes in nuclear reactors and instrumentation tubes thereof. Example embodiments include one or more irradiation targets useable with example delivery systems that permit delivery into instrumentation tubes. Example embodiments may be sized, shaped, fabricated, and otherwise configured to successfully move through example delivery systems and conventional instrumentation tubes while producing desired isotopes.
Owner:GE HITACHI NUCLEAR ENERGY AMERICAS
Process for accelerating the breeding and conversion of fissile fuel in nuclear reactors
InactiveUS20090268860A1High specific powerHigher specific powerFuel elementsConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsNuclear reactor coreInherent safety
The present invention related to a novel process for accelerating the breeding and conversion of fissile fuel in various types of nuclear reactors. In said process a movable nuclear fuel ball bed filled with a coolant creeps through the reactor core. The said process could provide higher specific power per unit fuel volume inside the reactor core and proceed on-line refueling, thus requires much less initial fissile fuel inventory per unit power output as compared with the traditional breeding or conversion reactors. The said process has full inherent safety characteristics and could follow the external power demand with the inherent negative temperature coefficient of reactivity. The said process, therefore, is a more efficient and economic approach to meeting the enormous demand of fissile fuel for the forthcoming “second nuclear era”.
Owner:LU YINGZHONG
Device for irradiating samples in core or periphery of core of reactor
ActiveCN104795118AConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsNuclear energy generationNuclear reactorDouble wall
Device to irradiate a sample in the core or at the periphery of the core of a nuclear reactor comprising, a double wall containment (6) delimiting a chamber (7), a receptacle (4) contained in said chamber (7), said receptacle being held at a distance from an inside wall (8) of the containment, said receptacle (4) being designed to contain a coolant, a sample holder (2), a free end of which will be located in the receptacle, in which the inside of the receptacle is in fluid communication with the outside of the receptacle and in which a volume between the inside wall (8) of the containment (6) and the receptacle (4) will be filled with a gas or a mix of gases called the coolant cushion gas.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
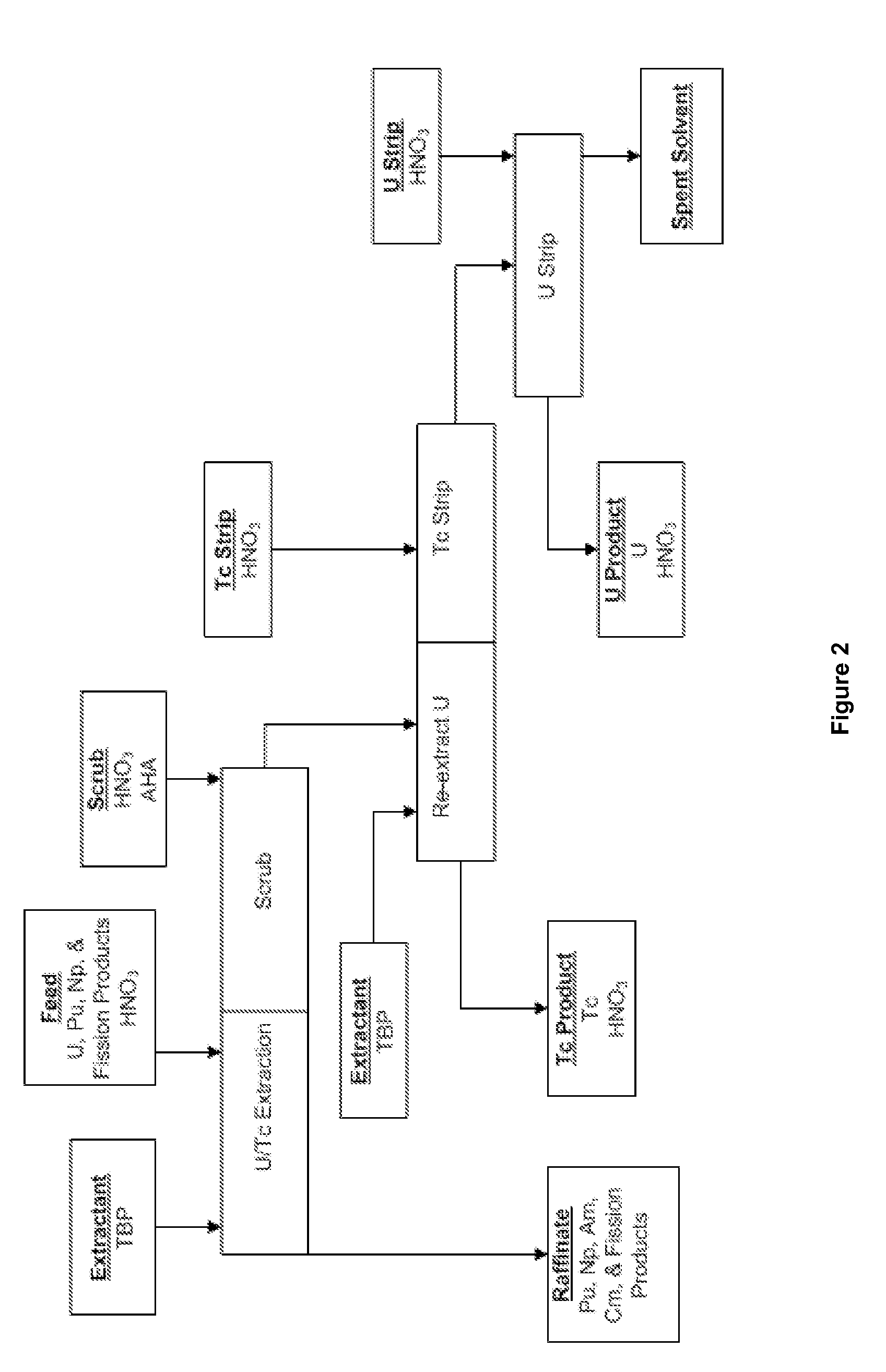
Targetry coupled separations
ActiveUS20160189816A1Minimal wasteLow costSolvent extractionConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsDissolutionEngineering
Targetry coupled separation refers to enhancing the production of a predetermined radiation product through the selection of a target (including selection of the target material and the material's physical structure) and separation chemistry in order to optimize the recovery of the predetermined radiation product. This disclosure describes systems and methods for creating (through irradiation) and removing one or more desired radioisotopes from a target and further describes systems and methods that allow the same target to undergo multiple irradiations and separation operations without damage to the target. In contrast with the prior art that requires complete dissolution or destruction of a target before recovery of any irradiation products, the repeated reuse of the same physical target allowed by targetry coupled separation represents a significant increase in efficiency and decrease in cost over the prior art.
Owner:TERRAPOWER
Method and device for compressing a substance by impact and plasma cathode thereto
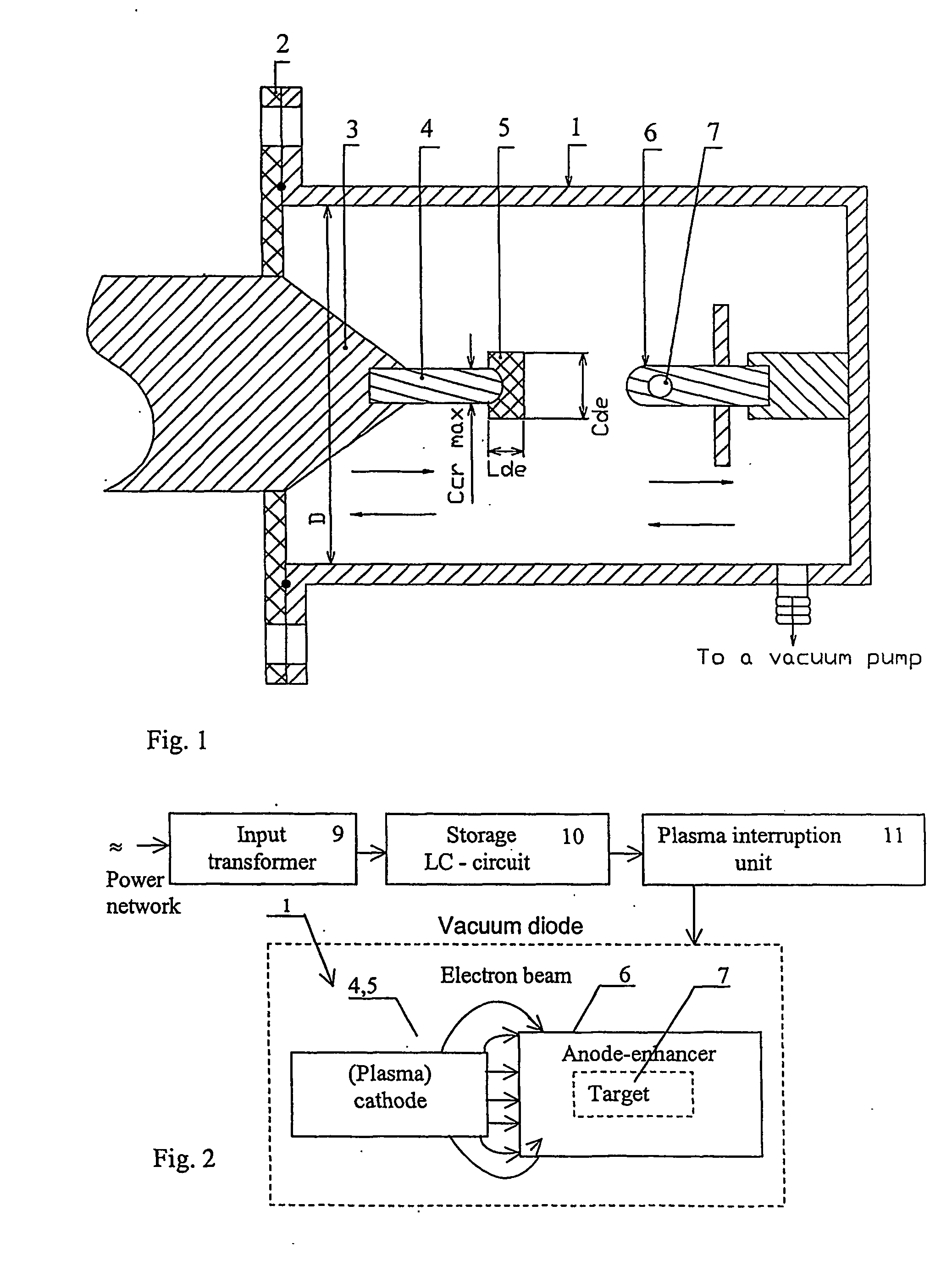
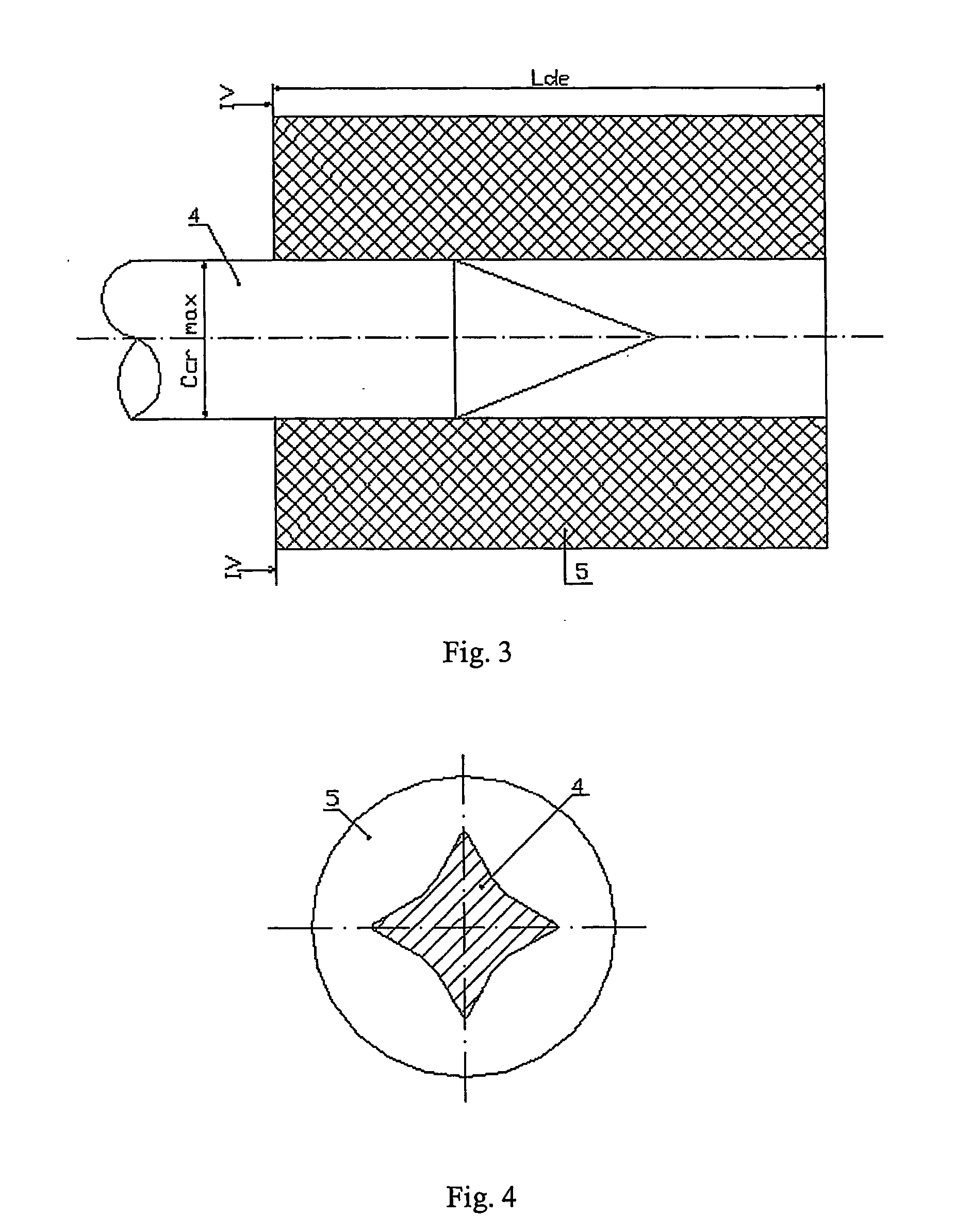
InactiveUS20050200256A1Stabilize plasma cathode operationVacuum tubesConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsAxis of symmetryVertical plane
A method of compressing a substance by impact in axisymmetric relativistic vacuum diodes (RVD) having a plasma cathode and an anode-enhancer including: producing an axisymmetric target of a condensed substance, which functions at least as a part of the anode-enhancer; axially placing said electrodes; and pulse discharge of a power source via the RVD. To compress a substantial portion of the target substance to a superdense state, a plasma cathode is used in the form of a current-conducting rod comprising a dielectric end element having the perimeter of the rear end embracing the perimeter of the rod in the plane perpendicular to the axis of symmetry with a continuous gap, and the area of the emitting surface being greater than the maximum cross-section area of the anode-enhancer; the anode-enhancer is placed towards the plasma cathode so that the center of curvature of the working surface of the anode enhancer is located inside the focal space of the collectively self focussing electron beam; and the anode-enhancer is acted upon by an electron beam with an electron energy not smaller than 0.2 MeV, current density not smaller than 106 A / cm2 and duration not greater than 100 ns.
Owner:LTD COMPANY PROTON 21
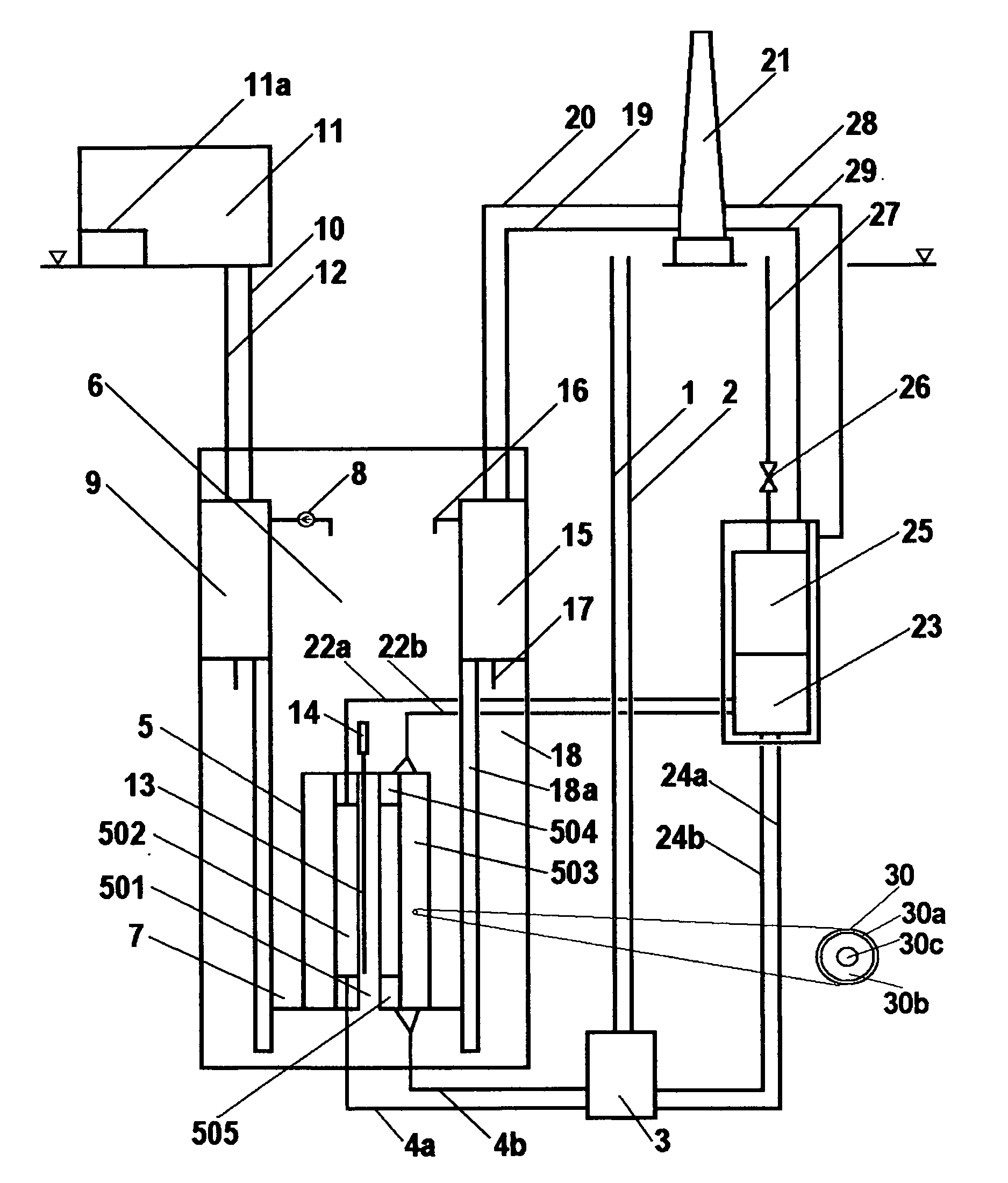
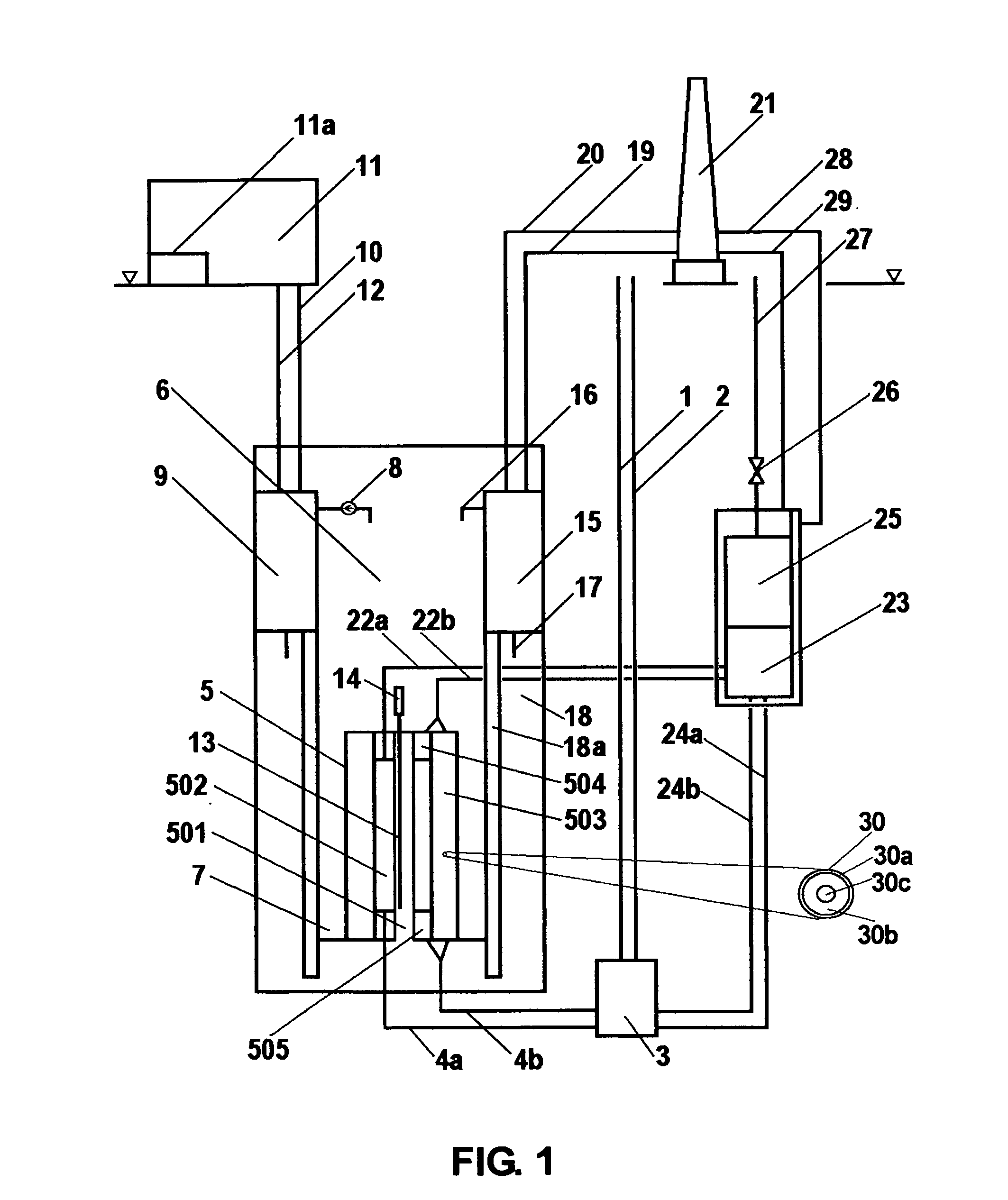
Method of producing radioisotopes using a heavy water type nuclear power plant
A method of producing radioisotopes using a heavy water type nuclear power plant is provided. The method includes inserting targets (37) into a heavy water moderator of the heavy water reactor througha guide tube (30) in a port (55) in a reactivity mechanism deck (45) of the heavy water reactor. The heavy water reactor operates to irradiate the target to convert the target into a radioisotope. The method then includes removing the radioisotope from the moderator of the heavy water reactor via the reactivity mechanism deck. A heavy water nuclear reactor is also provided.
Owner:法玛通加拿大有限公司
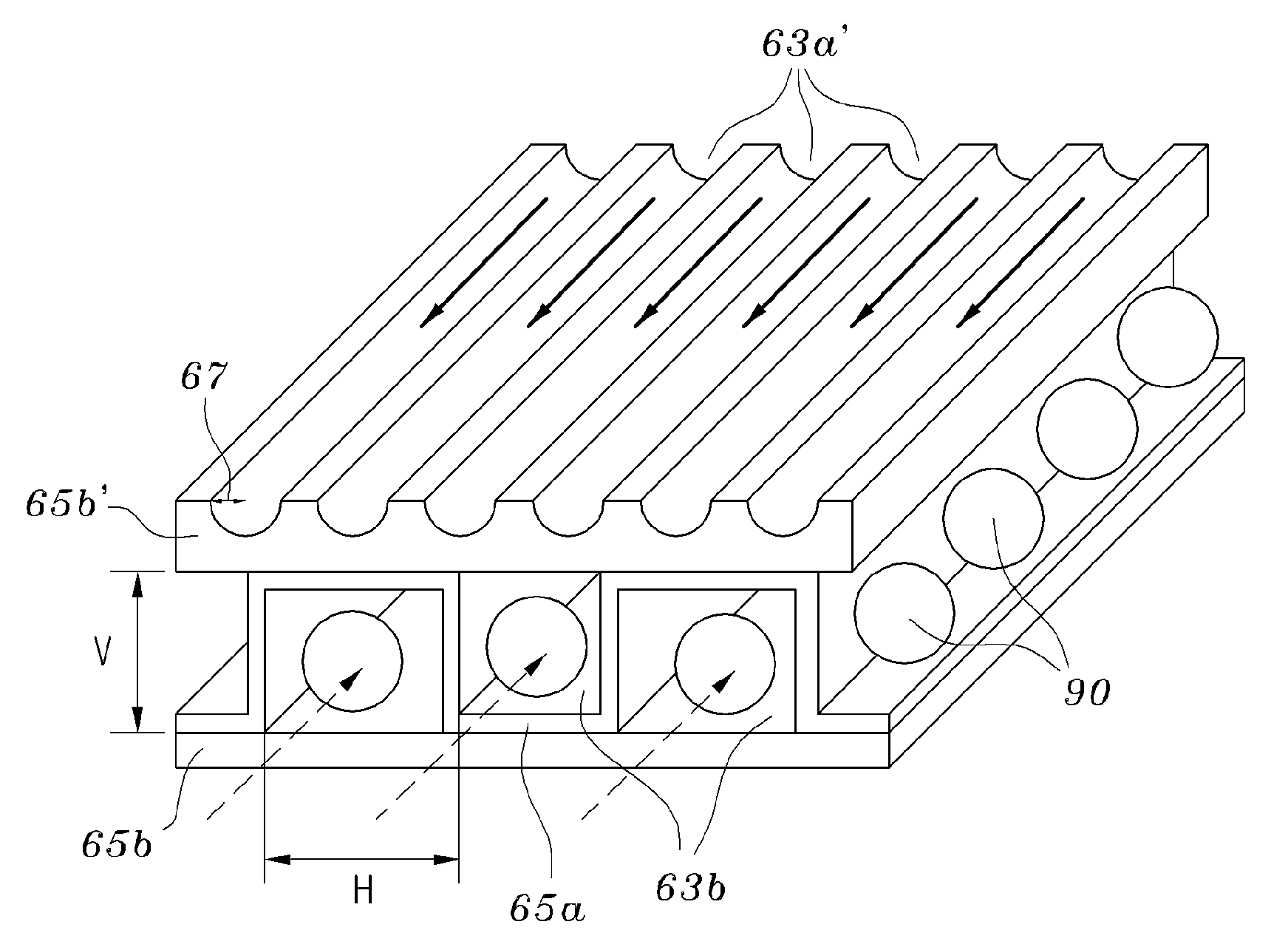
High temperature and high pressure corrosion resistant process heat exchanger for a nuclear hydrogen production system
InactiveUS20100051246A1Increase the differential pressureSecure spaceNuclear energy generationConversion in nuclear reactorDifferential pressureNuclear engineering
A high-temperature and high-pressure corrosion-resistant process heat exchanger for a nuclear hydrogen production system decomposes sulfite (SO3) using heat from a high-temperature gas-cooled reactor to thereby produce sulfide (SO2) and oxygen (O2). The process heat exchanger comprises second and third system coolant channels, each of which is defined by a heat transmission fin, which is bent in a quadrilateral shape, and heat transmission plates, and has increased corrosion resistance thanks to ion-beam coating and ion-beam mixing using a material having high corrosion resistance. The third system coolant channel includes reaction catalysts for SO3 decomposition, and is made of a super alloy. Thus, a system differential pressure between the second and third system coolant channels can be greatly maintained at a high temperature of 900° C. or higher.
Owner:YS SPECIAL STEEL
Brachytherapy and radiography target holding device
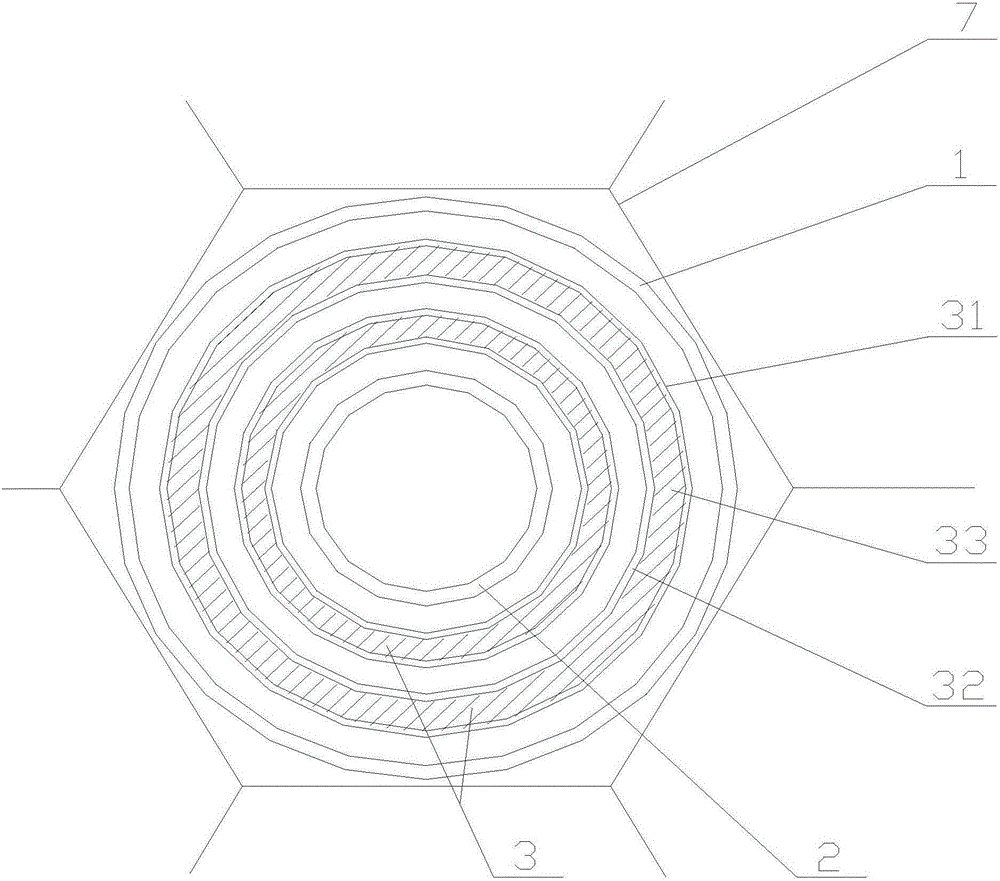
ActiveUS20110006186A1Rigid enoughConvenient introductionConversion in nuclear reactorStands/trestlesBrachytherapyEngineering
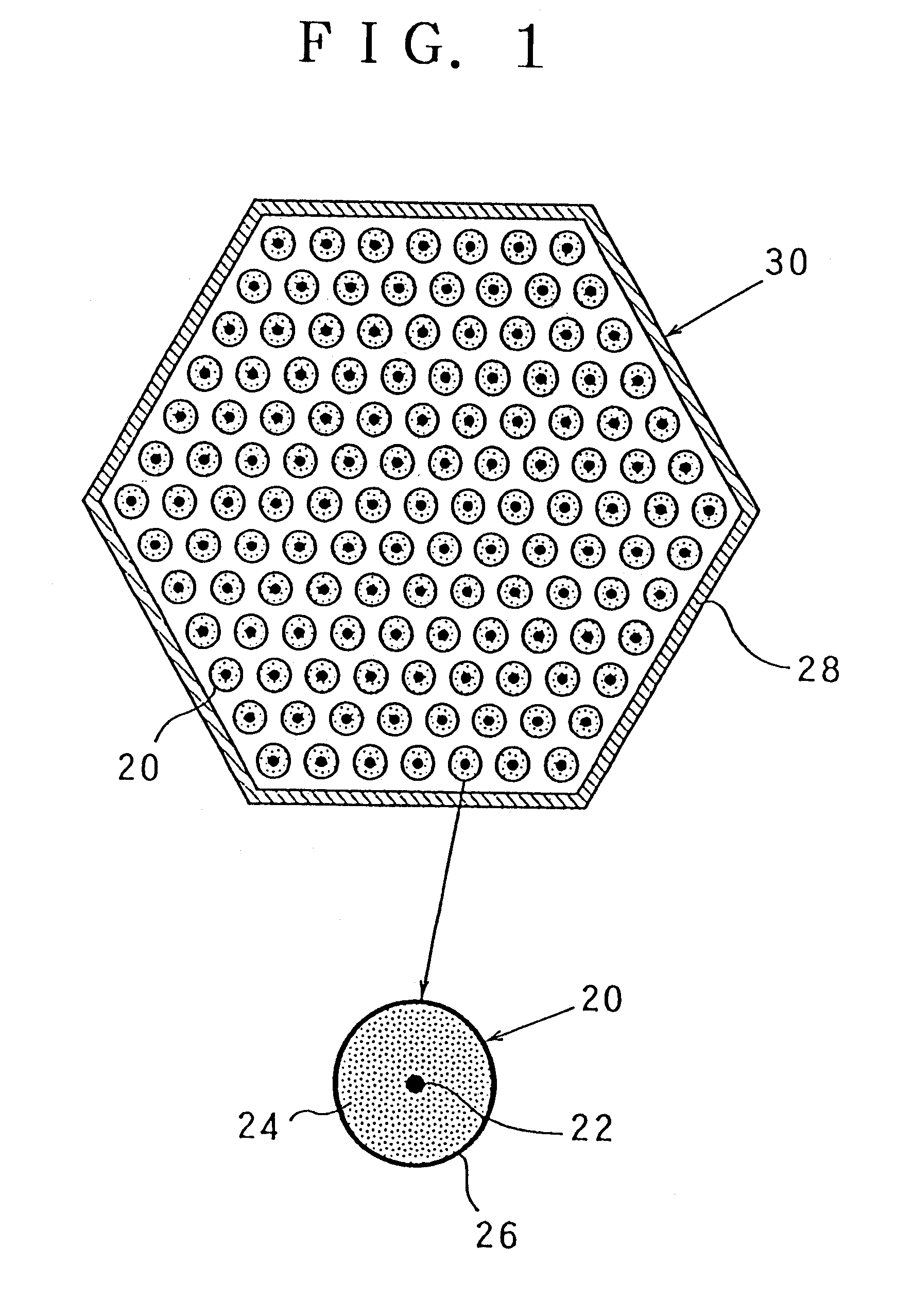
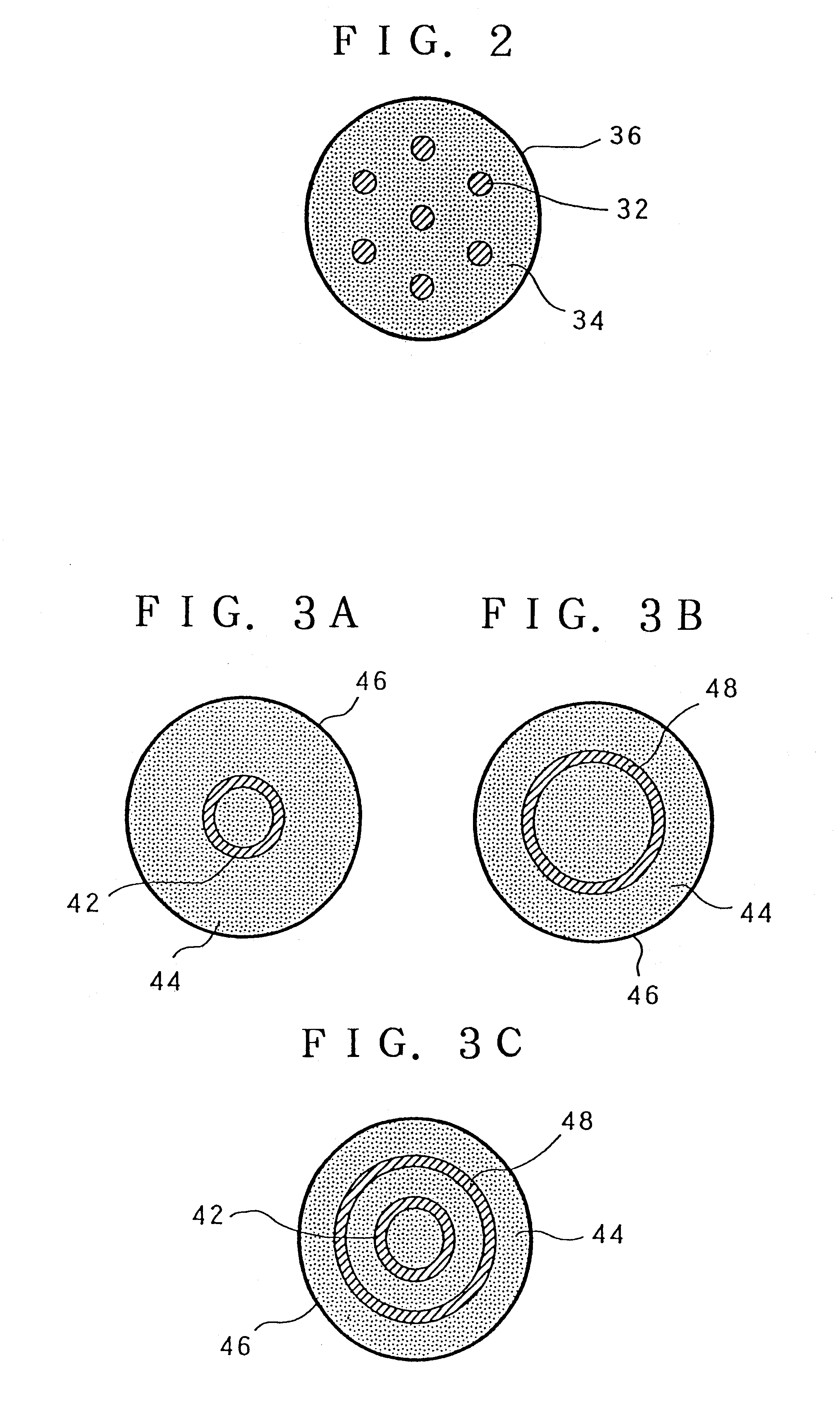
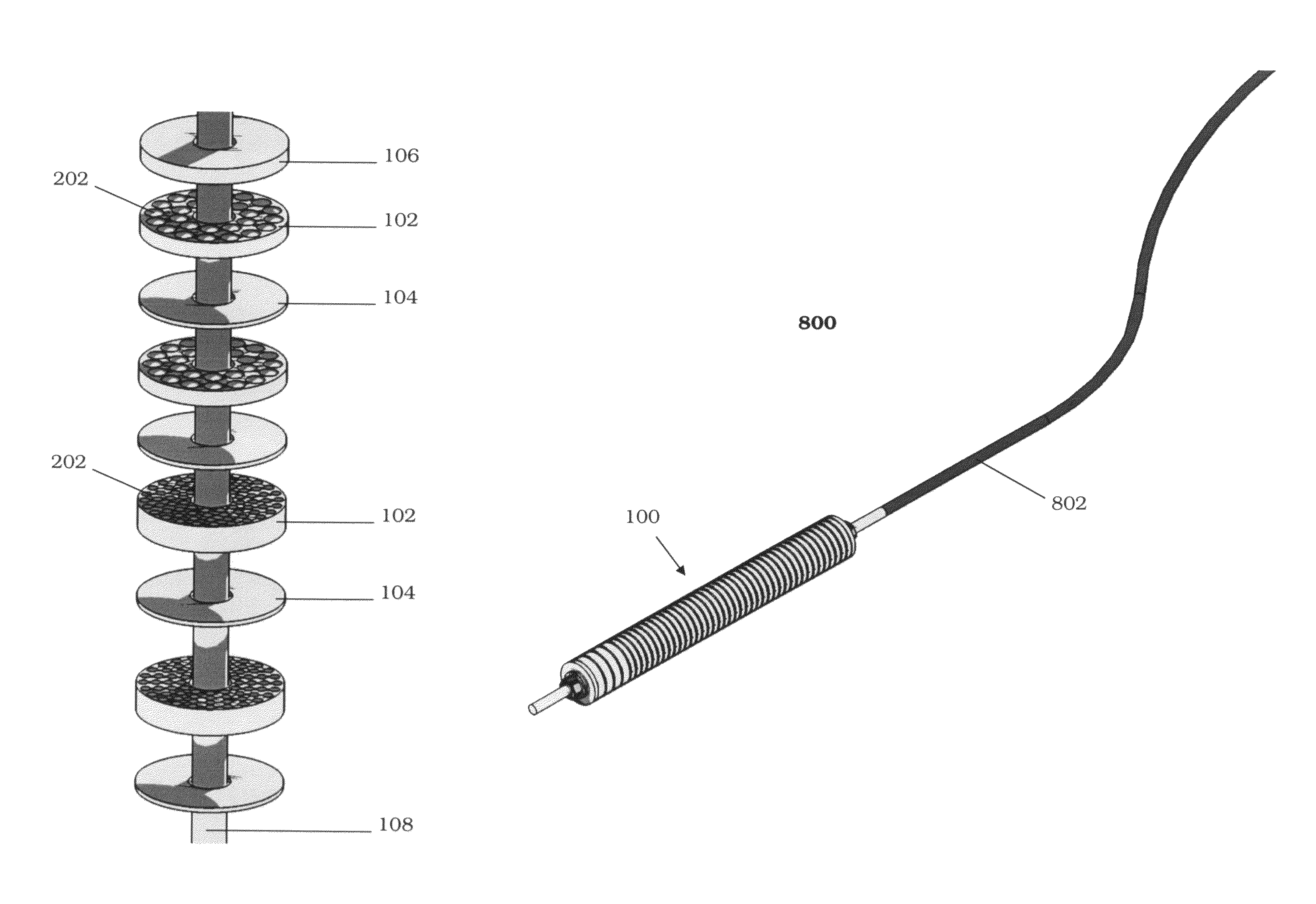
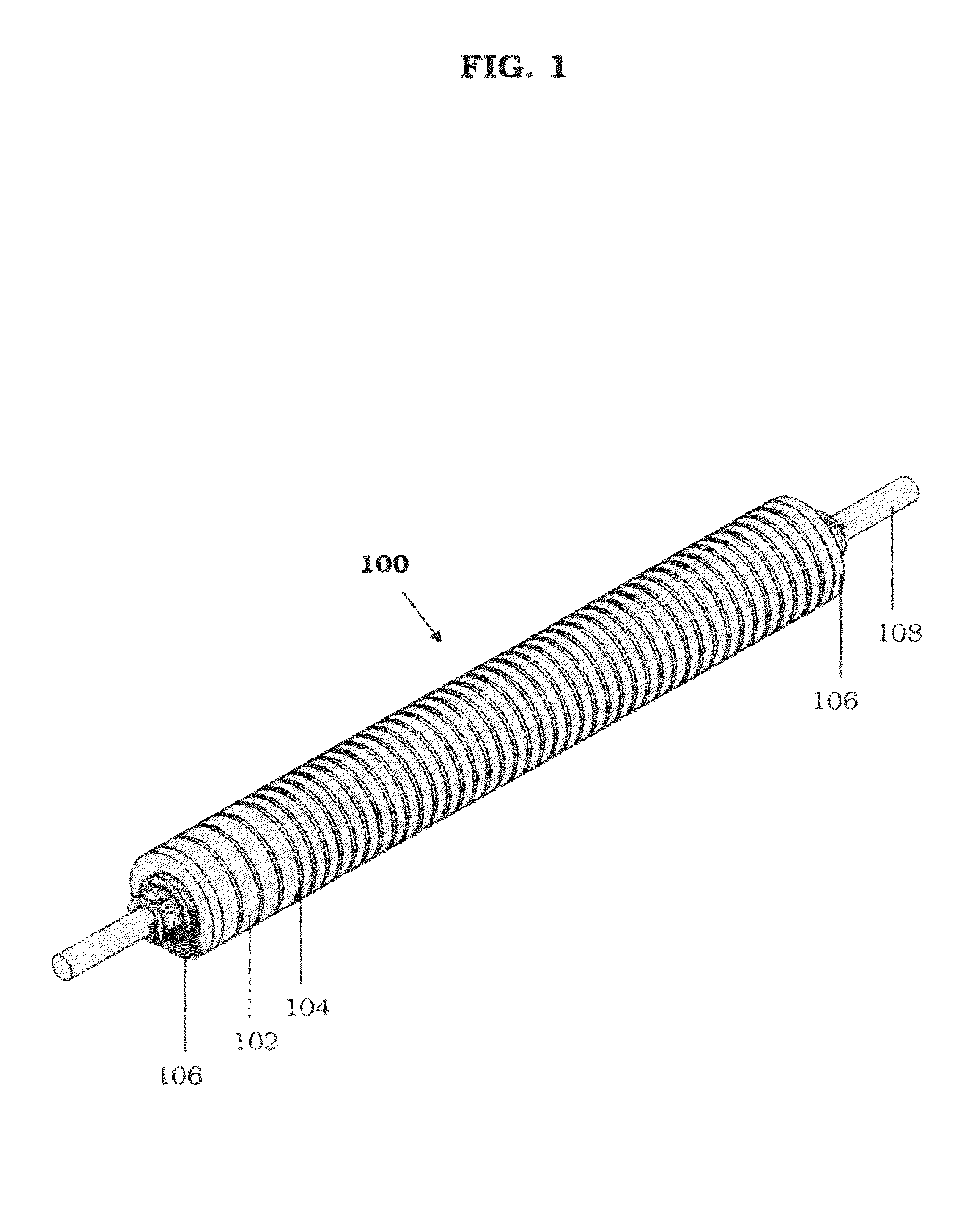
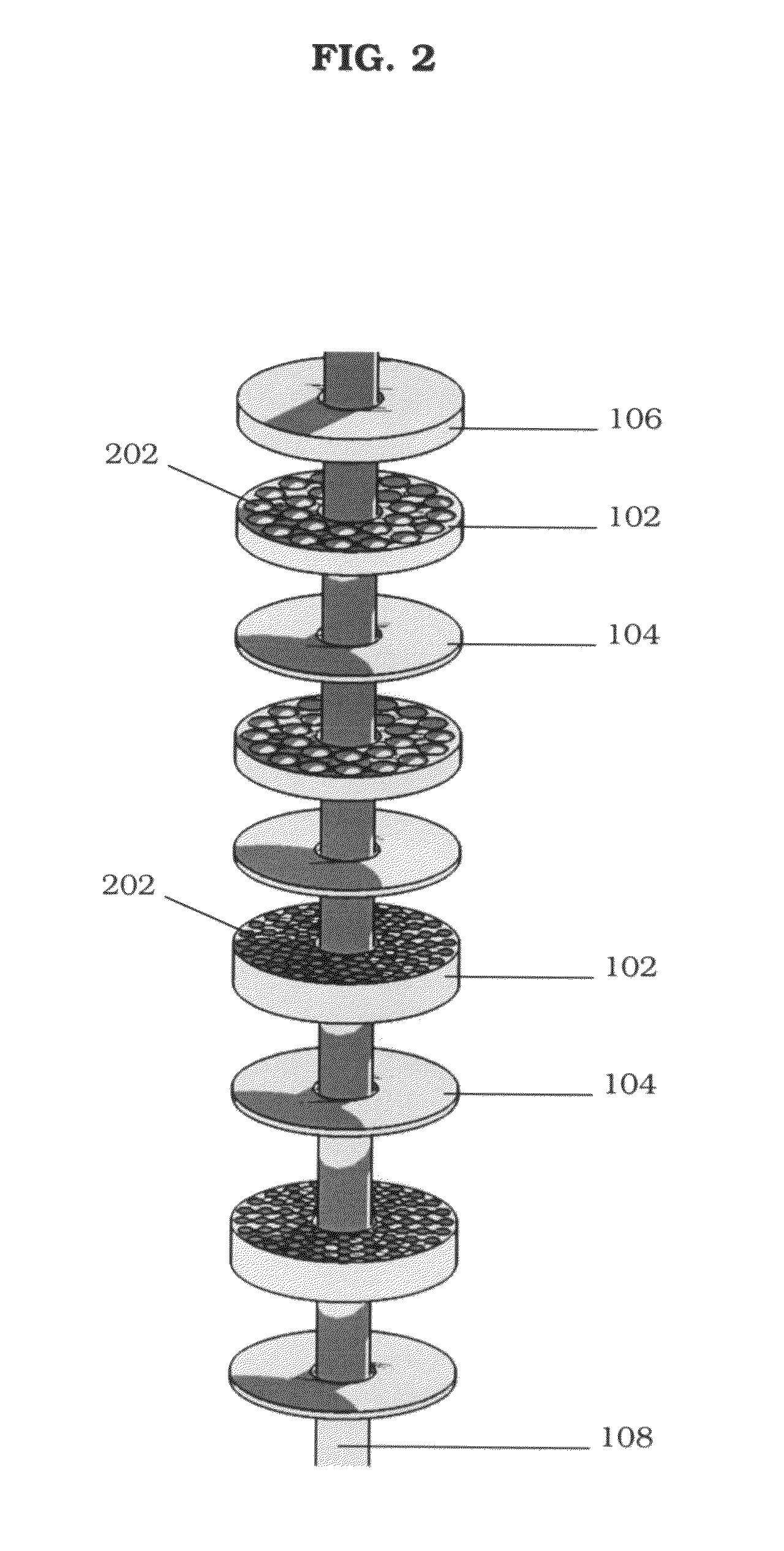
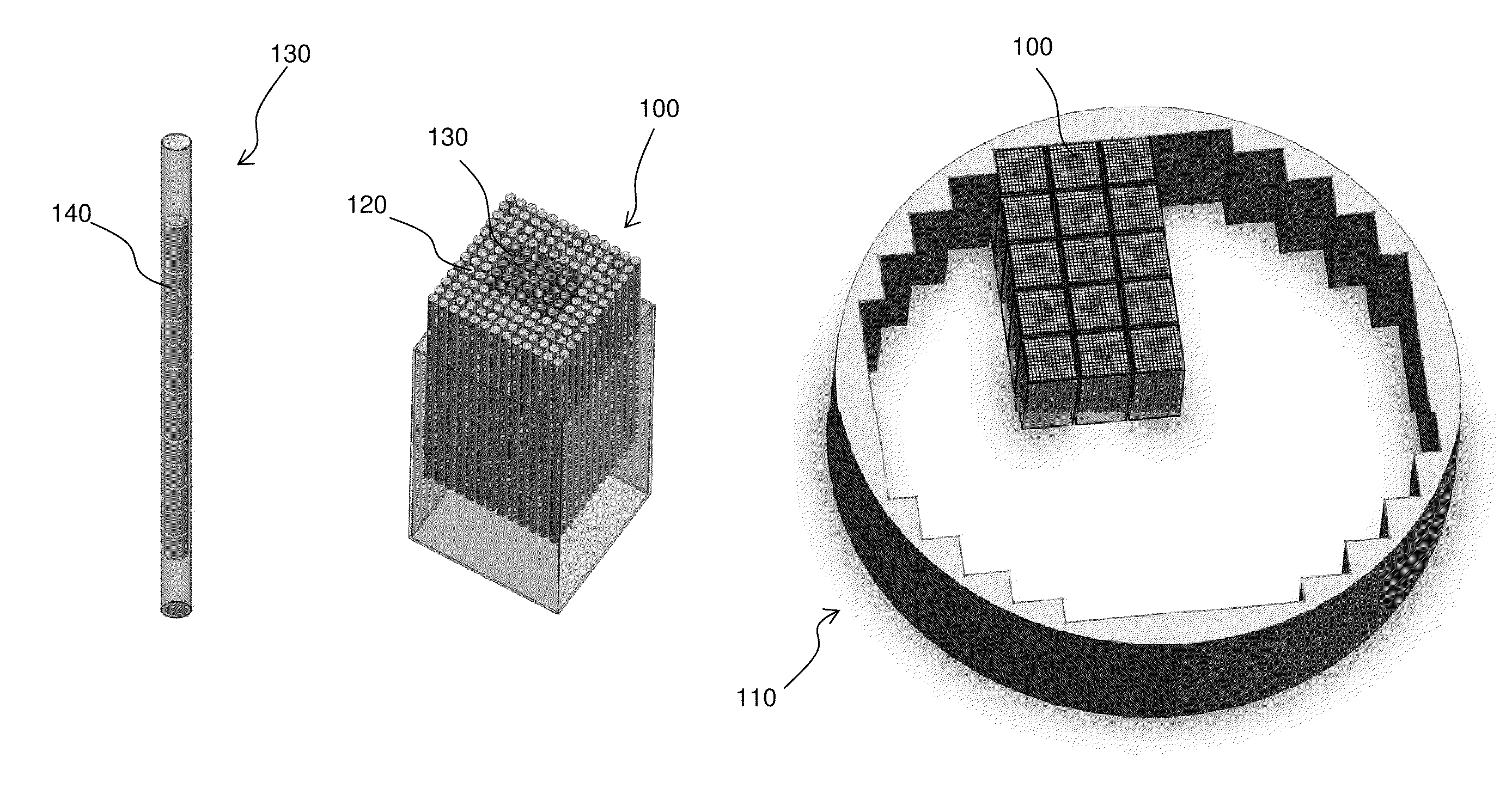
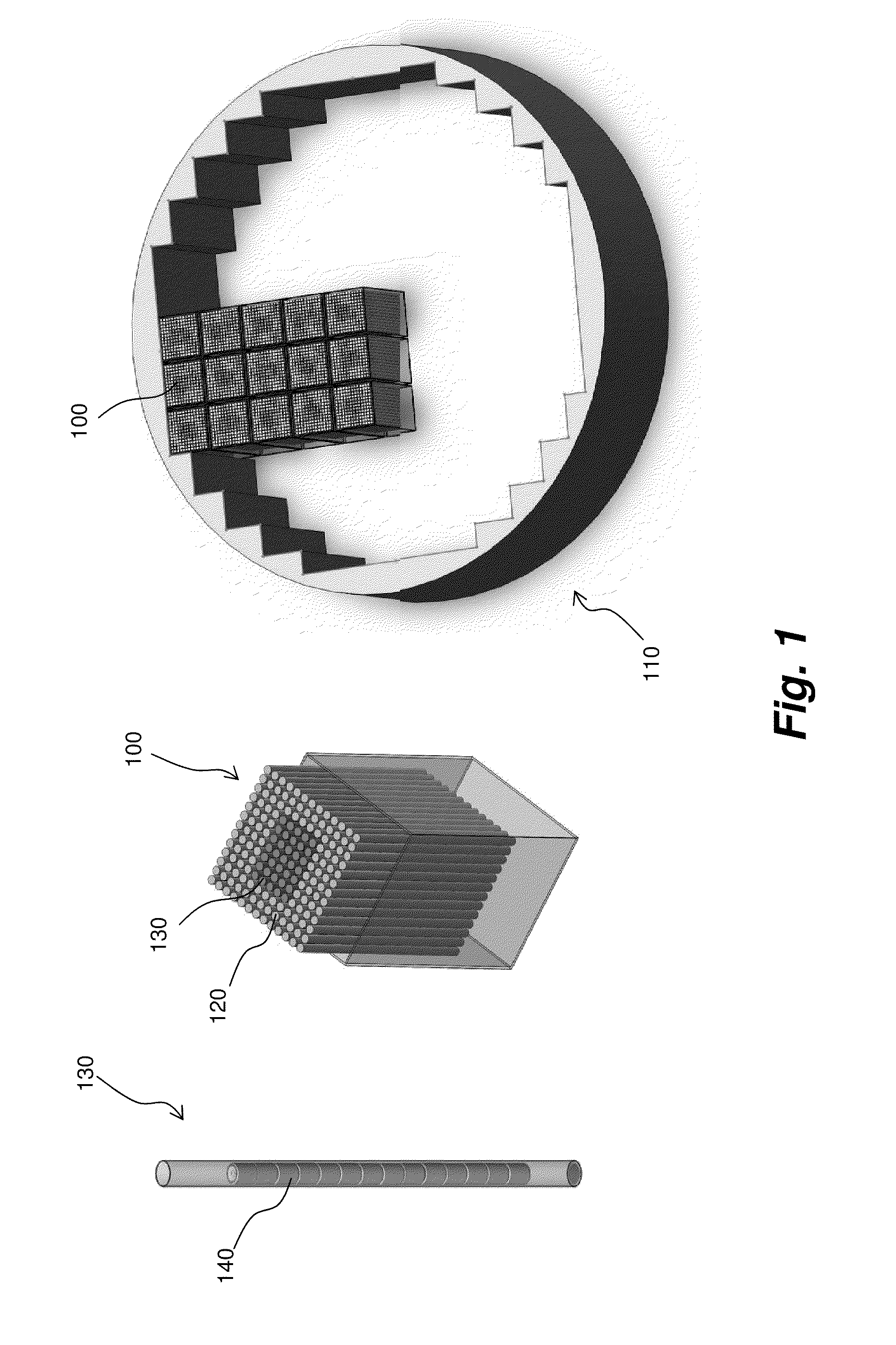
A target holding device according to an embodiment of the invention includes a plurality of target plates, each target plate having a first surface and an opposing second surface, wherein the first surface has a plurality of holes. A shaft may be used to facilitate the alignment and joinder of the target plates such that the first surface of one target plate contacts a second surface of an adjacent target plate. The target holding device may optionally include end plates arranged to sandwich the target plates therebetween and / or separator plates alternately arranged with the target plates. The target holding device may be used to produce brachytherapy and / or radiography targets (e.g., seeds, wafers) in a reactor core such that the targets have relatively uniform activity.
Owner:GE HITACHI NUCLEAR ENERGY AMERICAS
Transportable sub-critical modules for power generation and related methods
ActiveUS20180090237A1Easy to replaceLight weightIntegral reactorsFuel elementsNuclear powerElectric power
Various embodiments of a transportable nuclear power generator having a plurality of subcritical power modules are disclosed. Each of the plurality of subcritical power modules includes a fuel cartridge, a power conversion unit, and a housing substantially enclosing the fuel cartridge and the power conversion unit. The fuel cartridge contains a nuclear fuel and has a proximal end and a distal end. The power conversion unit includes a compressor turbine disposed at the proximal end of the fuel cartridge and a power turbine disposed at the distal end of the fuel cartridge. At least one of the plurality of subcritical power modules is movable with respect to the other of the plurality of subcritical power modules between a first position and a second position to control criticality of the nuclear fuel contained in the fuel cartridges of the plurality of subcritical power modules.
Owner:CARBON FREE HLDG LLC
Target device for producing a radioisotope
ActiveUS8288736B2Conversion outside reactor/acceleratorsConversion in nuclear reactorParticle beamIrradiation
The present invention is related to an irradiation cell for producing a radioisotope of interest through the irradiation of a target material by a particle beam, comprising a metallic insert forming a cavity designed to house the target material and to be closed by an irradiation window, wherein said metallic insert comprises at least two separate metallic parts of different materials, being composed of at least a first part comprising said cavity.
Owner:ION BEAM APPL
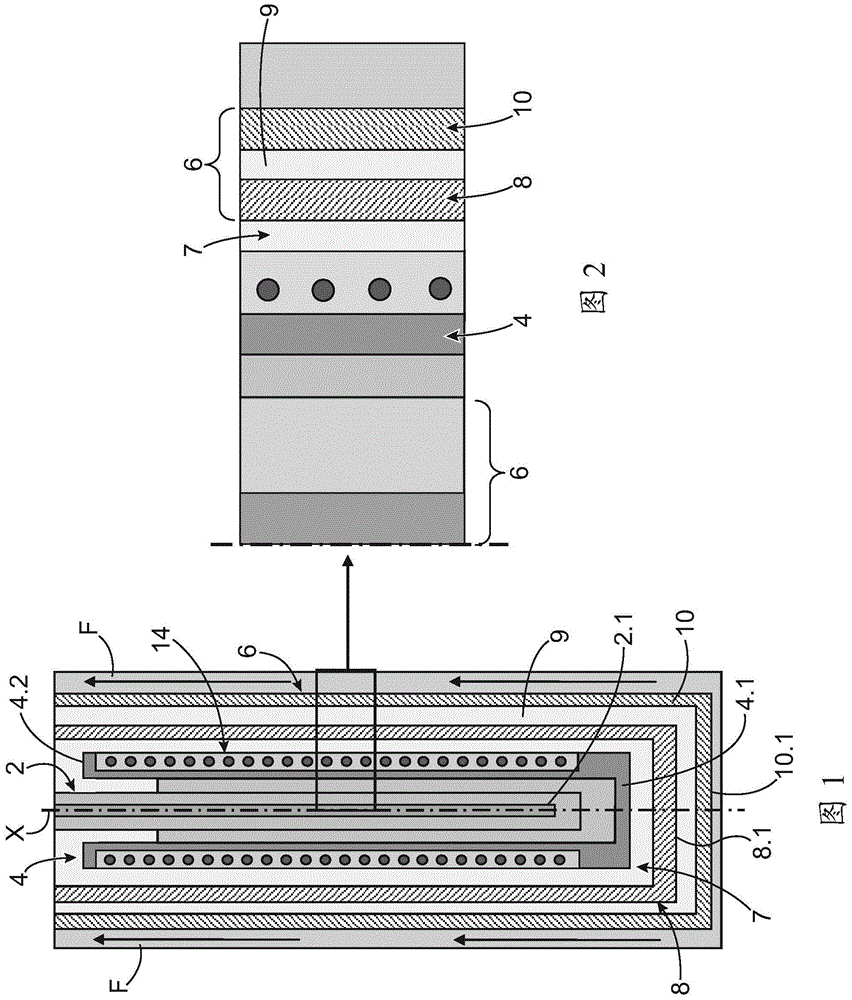
Uniform inner heat source simulator of medical isotope production solution reactor
ActiveCN101685680APrevent deviationEffective simulated flow areaConversion in nuclear reactorElectricityState of art
The invention relates to a reactor simulator, in particular to a uniform inner heat source simulator of a medical isotope production solution reactor, comprising a power simulation part and a fissiongas simulation part, wherein the power simulation part comprises a heating component and a heat exchange component, and the fission gas simulation part comprises a bubble generation device and simulation gas. The invention really reflects power distribution of fuel solution in the reactor, efficiently simulates power distribution of a prototype reactor, strictly controls occupied flow area of an electric heating element without causing great influence on natural convection heat exchange of the solution by the electric heating element, solves the problems of high simulation power and small cross section of the electric heating element in the prior art and satisfies the experimental requirements. In addition, nitrogen gas is used as the simulation gas so that the safety of an experiment is ensured.
Owner:NUCLEAR POWER INSTITUTE OF CHINA
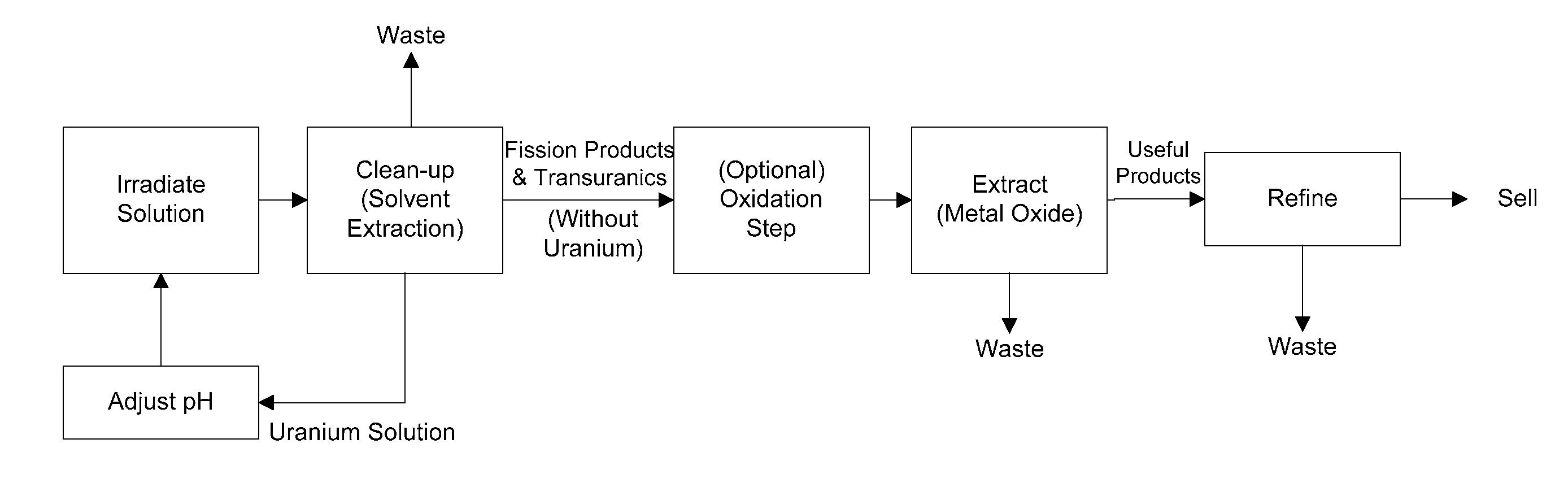
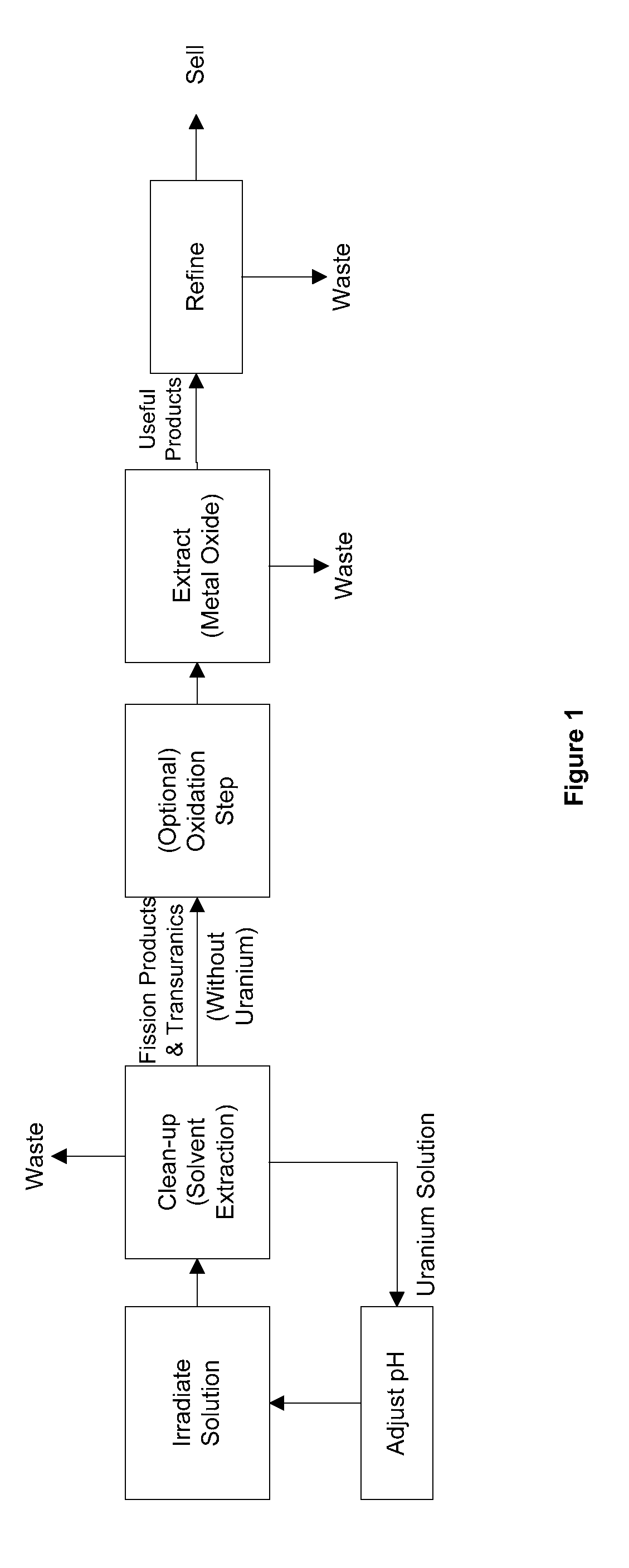
Methods of separating medical isotopes from uranium solutions
Provided are methods to separate an isotope from a first solution including uranium. The methods may include (a) cleaning the first solution to form a second solution including the uranium and a third solution including the isotope; (b) oxidizing the third solution to form an oxidized isotope; and (c) separating the oxidized isotope.
Owner:SHINE TECH LLC
Irradiated target containing Np-237 used for producing Pu-238 by means of research reactor irradiation
ActiveCN106531278AIncrease contact areaImprove cooling efficiencyConversion in nuclear reactorEngineeringCooling effect
The invention discloses an irradiated target containing Np-237 used for producing Pu-238 by means of research reactor irradiation. The irradiated target comprises a target barrel, and an upper end head and a lower end head which are arranged at both ends of the target barrel, wherein a target body to be irradiated is arranged inside the target barrel, the target body to be irradiated has high cooling performance and good cooling effect, and is suitable for producing the Pu-238 by means of research reactor irradiation. With the adoption of the irradiated target disclosed by the invention, the Pu-238 can be irradiated, the conversion rate is high and the safety is good.
Owner:NUCLEAR POWER INSTITUTE OF CHINA
Systems and methods of producing hydrogen using a nuclear reactor
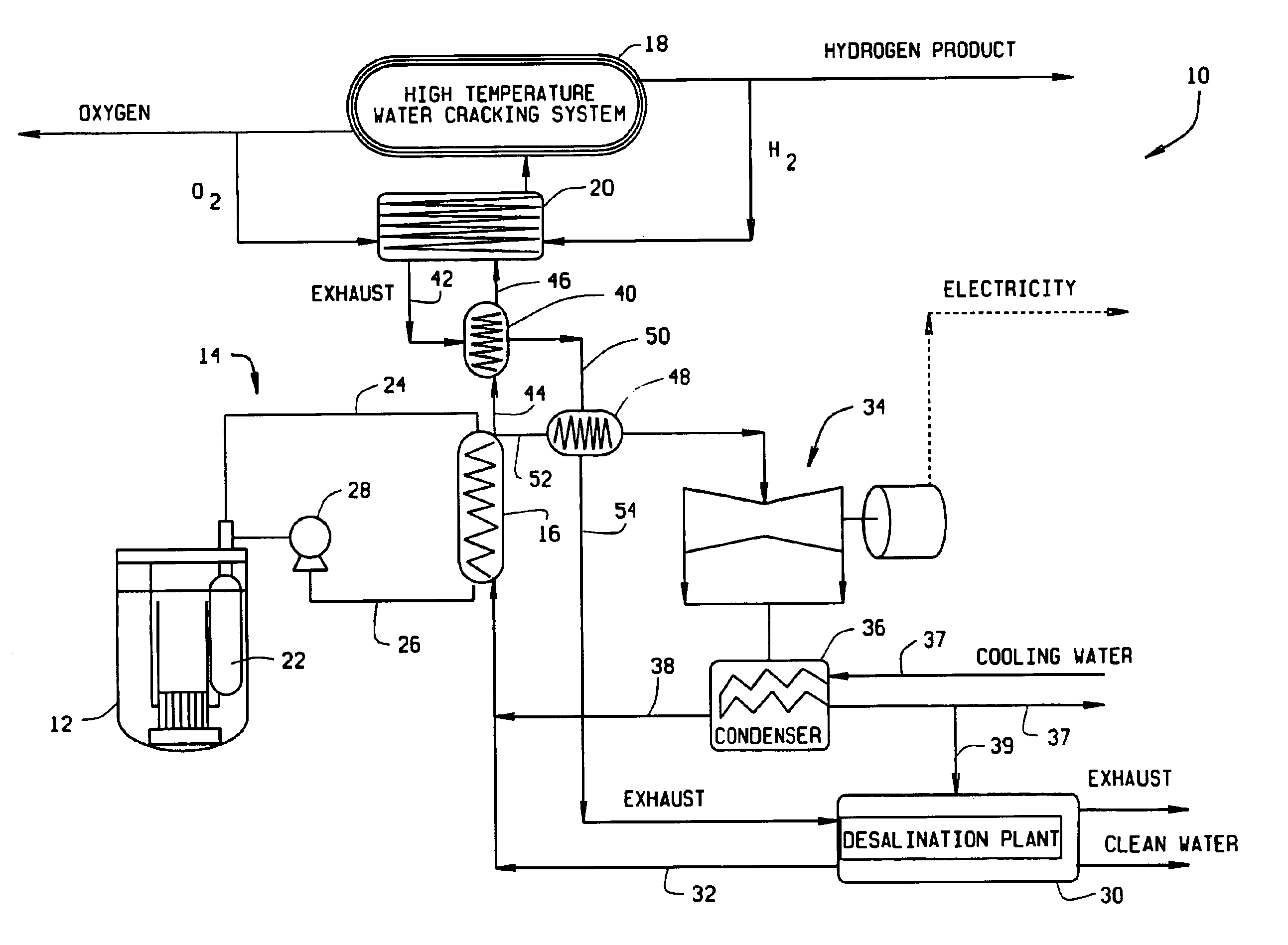
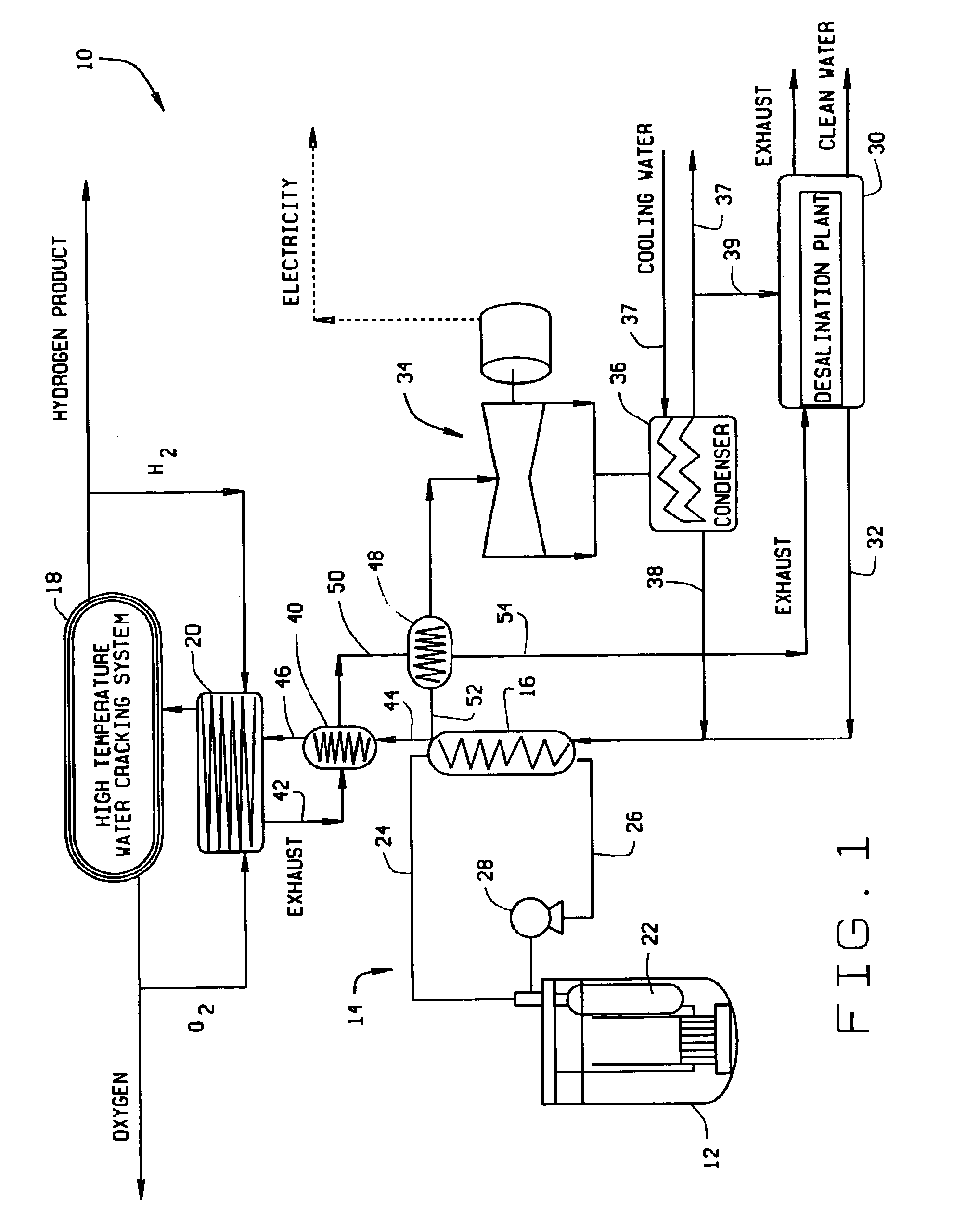
InactiveUS6862330B2Low costEfficient crackingNuclear energy generationConversion in nuclear reactorNuclear reactor coreNuclear reactor
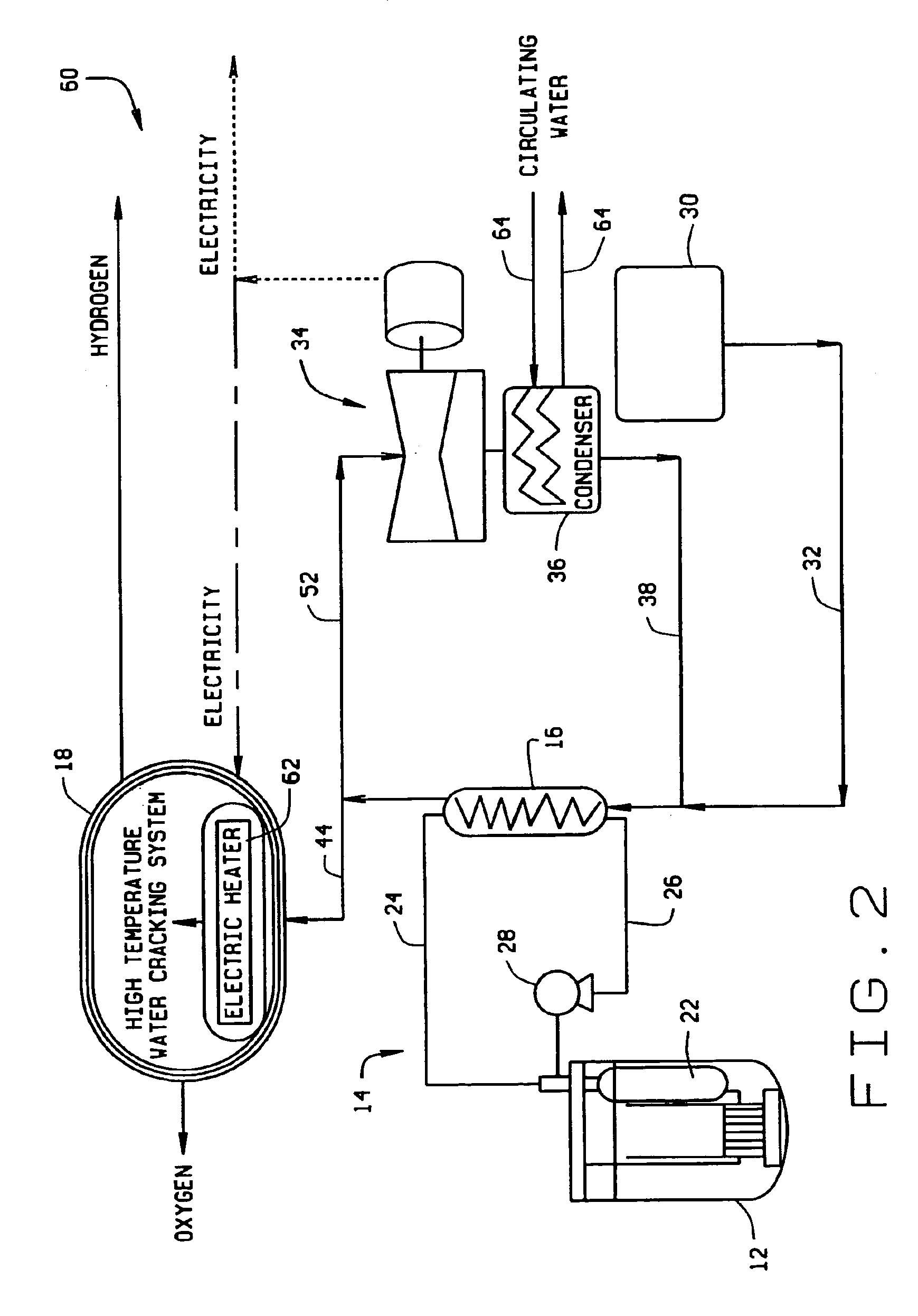
A system for generating hydrogen includes a liquid metal nuclear reactor having a non-radioactive secondary heat loop, a steam generator connected to the secondary heat loop, a high temperature water cracking system, and a topping heater. The heat produced by the nuclear reactor is used to raise the temperature of the feed water for the cracking system to between about 450° C. to about 550° C. The topping heater raises the feed water temperature from the 450° C. to 550° C. range to at least 850° C. so that the cracking system can operate efficiently to produce hydrogen and oxygen.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Charged particle acceleration device
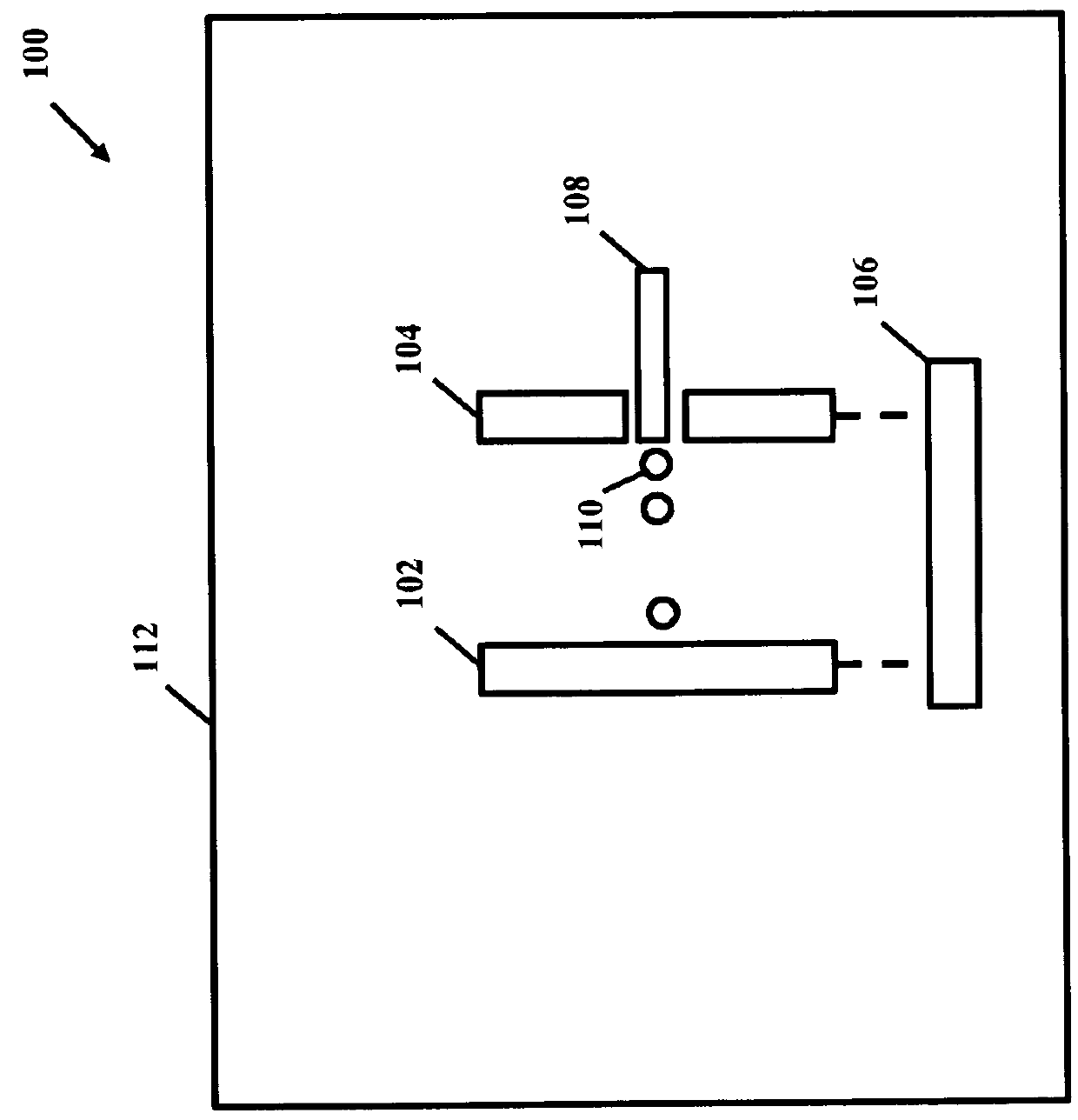
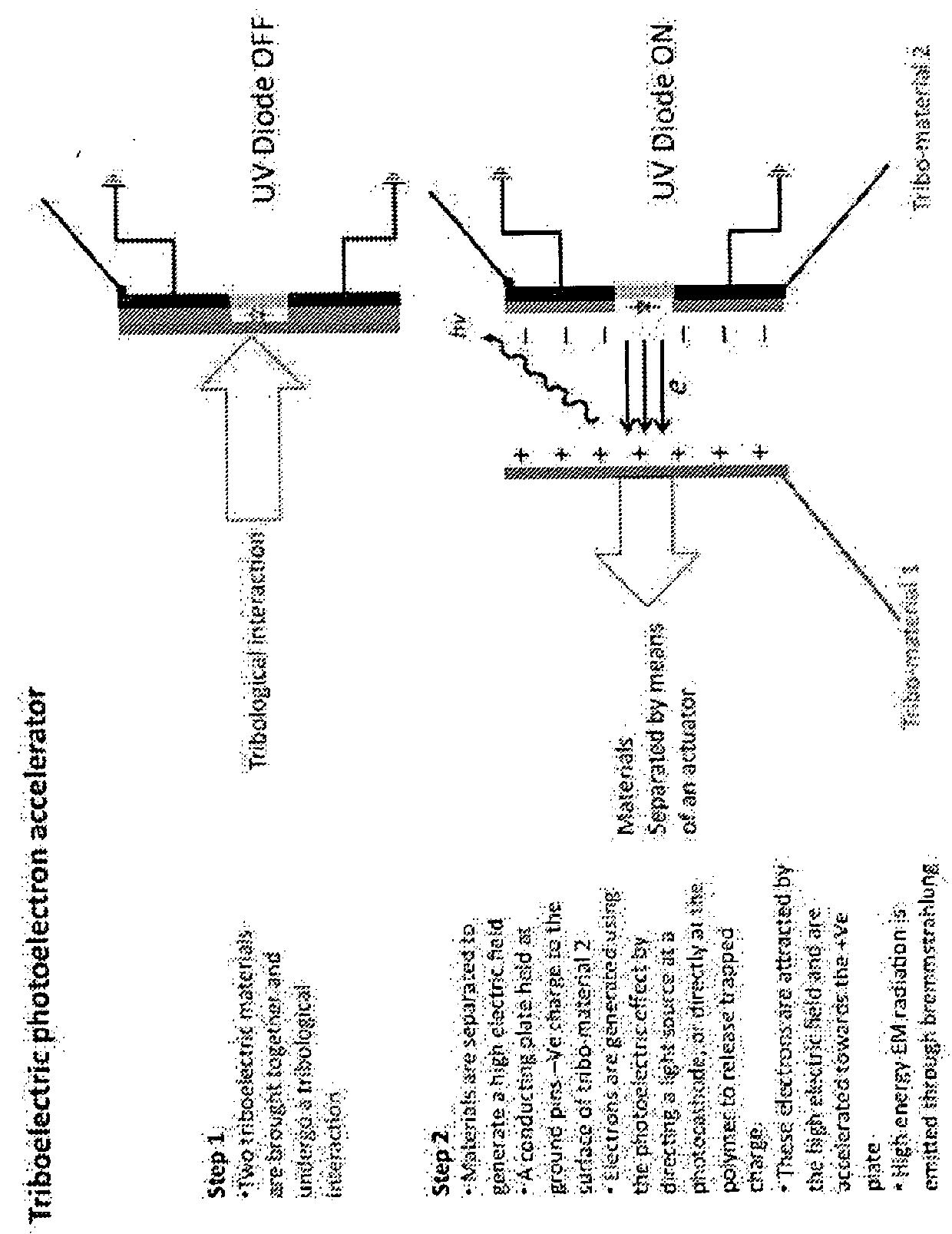
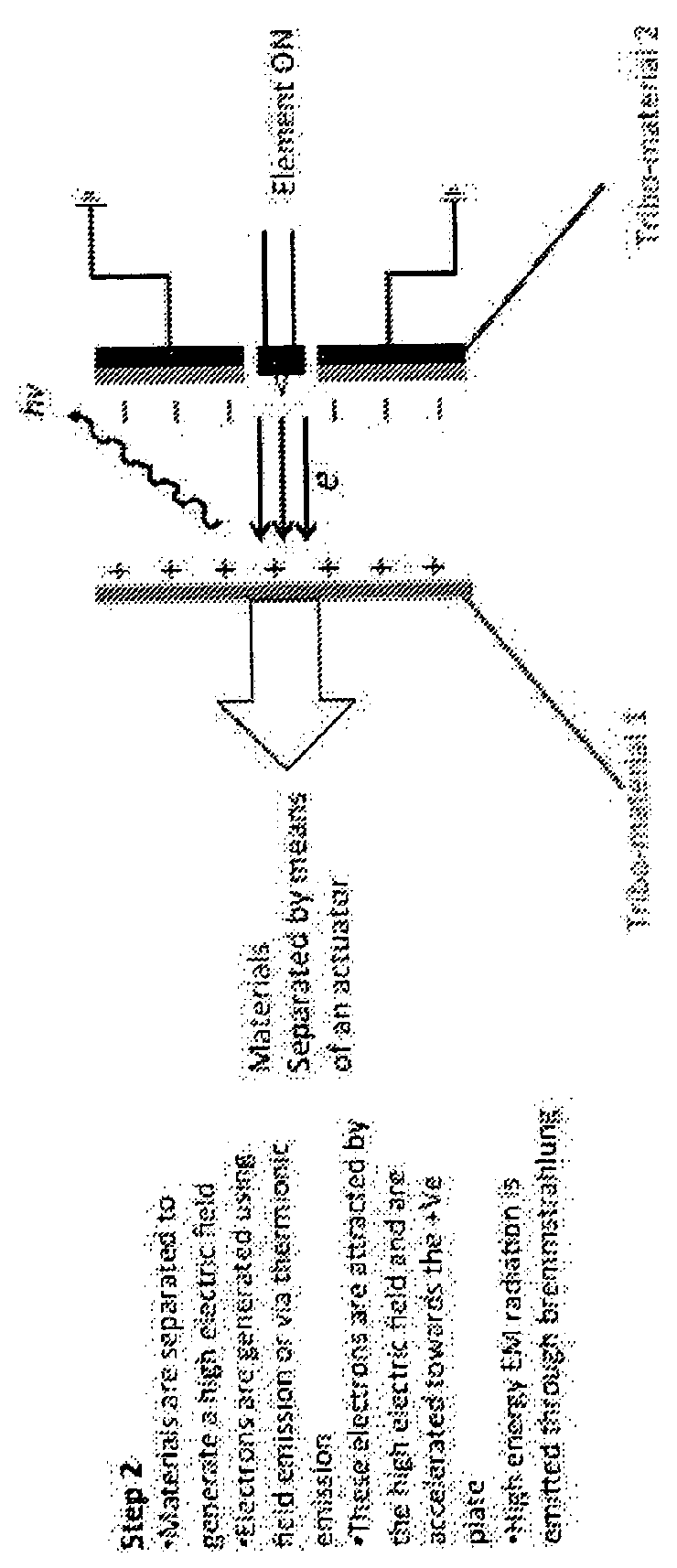
A charged particle acceleration device according to some embodiments of the current invention includes a first triboelectric element, a second tribo-electric element arranged proximate the first tribo-electric element to be brought into contact with and separated from the first triboelectric element, an actuator assembly operatively connected to at least one of the first and second triboelectric elements to bring the first and second triboelectric elements into contact with each other and to separate the first and second triboelectric elements from each other, and a charged-particle source configured to provide charged particles in a gap between the first and second triboelectric elements.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Internal circulating irradiation capsule for iodine-125 and method of producing iodine-125 using same
InactiveCN1794360AConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsNuclear energy generationIodineDirect radiation
The invention provides an inner circulation irradiation box which can be used to produce iodine-125 and a related production method. An irradiation box filled with xenon gas has a lower irradiation section and an upper irradiation section, and a neutron control member. The lower irradiation part is inserted into the irradiation hole of the reactor core and directly irradiated with a large amount of neutrons. Iodine-125 is produced from xenon gas when neutrons are irradiated to xenon gas. The upper irradiated portion protrudes from the irradiated hole, and iodine-125 is transported to the upper irradiated portion by convection and cured in the upper portion. The neutron control component reduces neutrons in the upper section to mass produce highly pure and highly radioactive iodine-125.
Owner:KOREA ATOMIC ENERGY RES INST
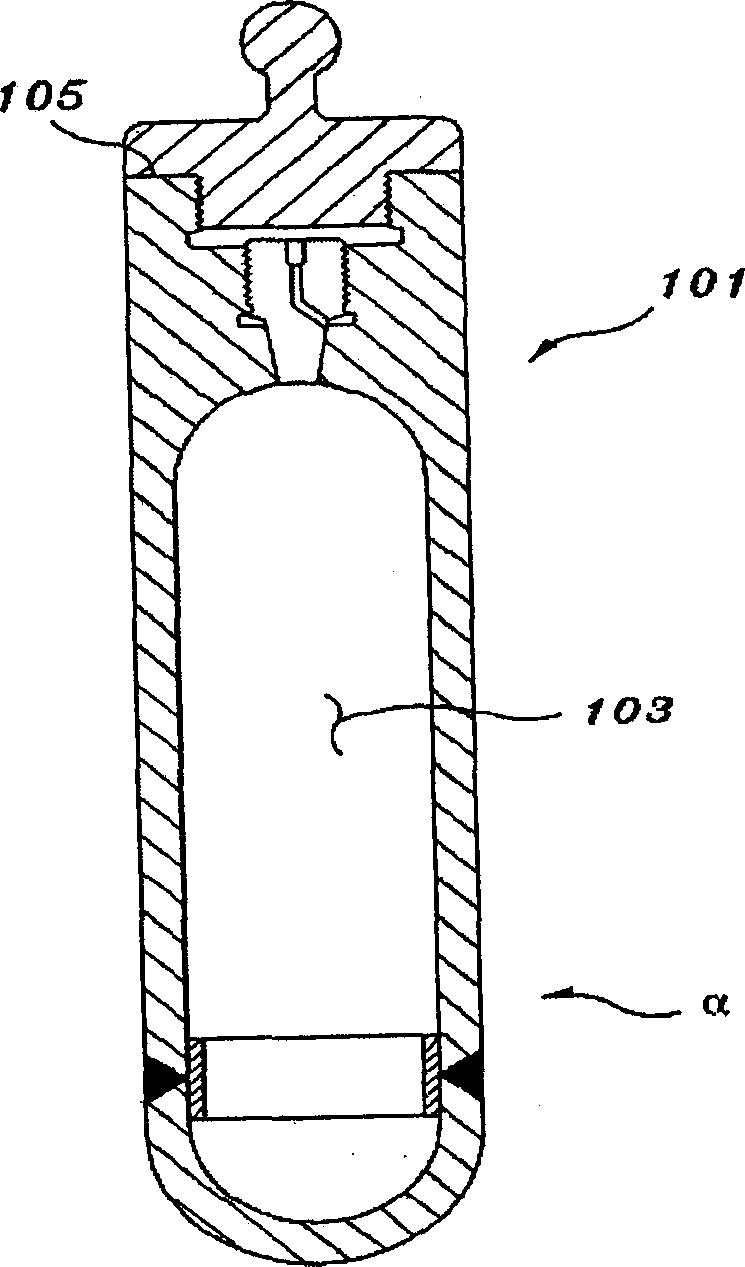
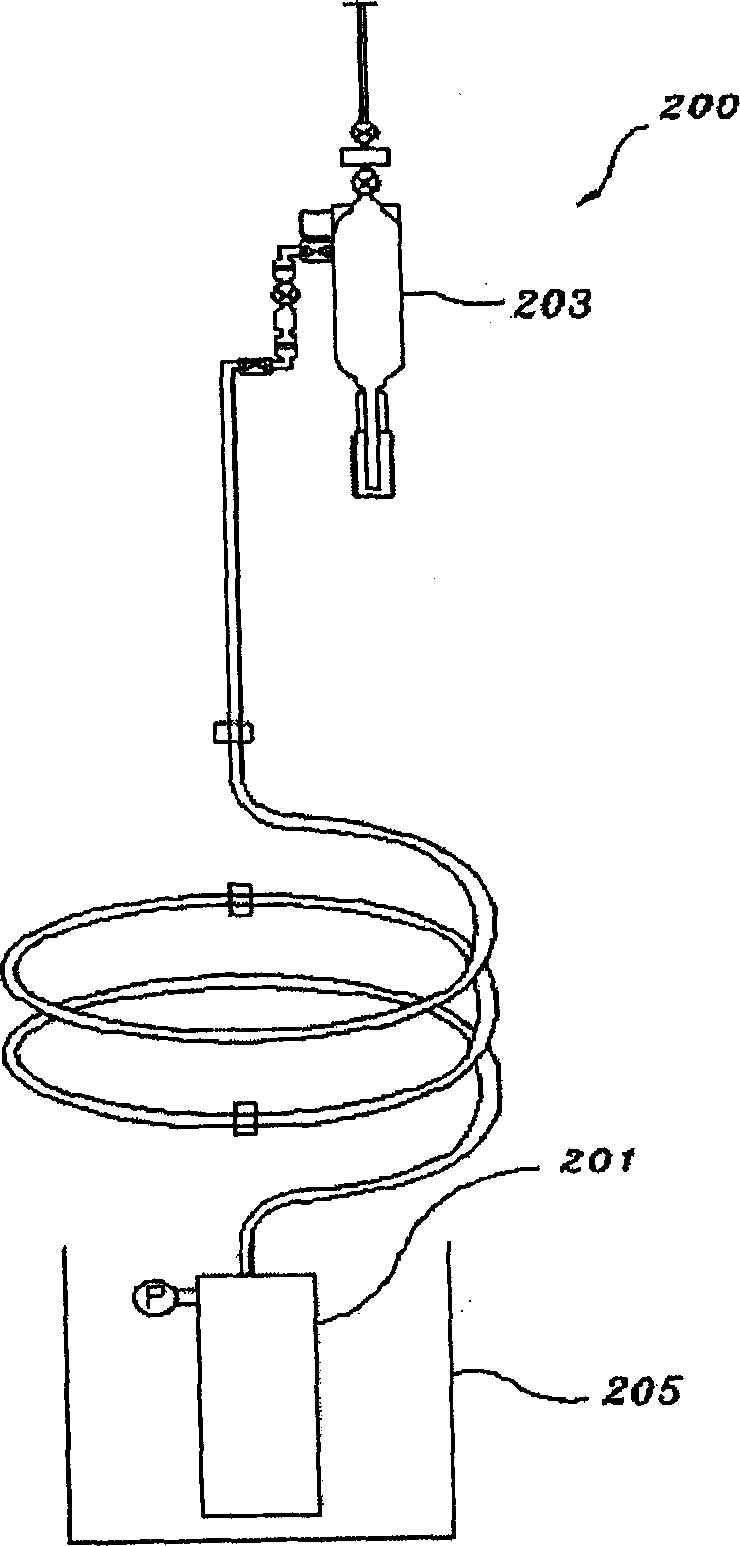
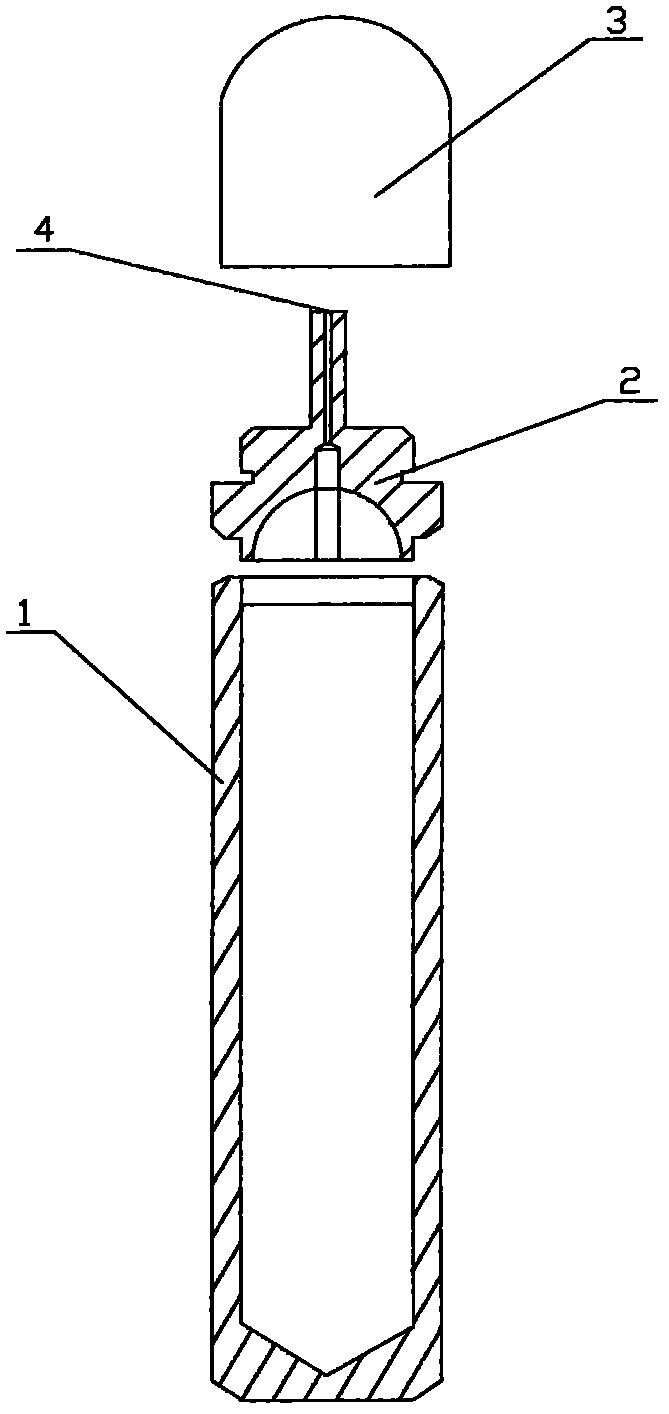
Xenon target for producing iodine-125 through reactor irradiation and preparation method thereof
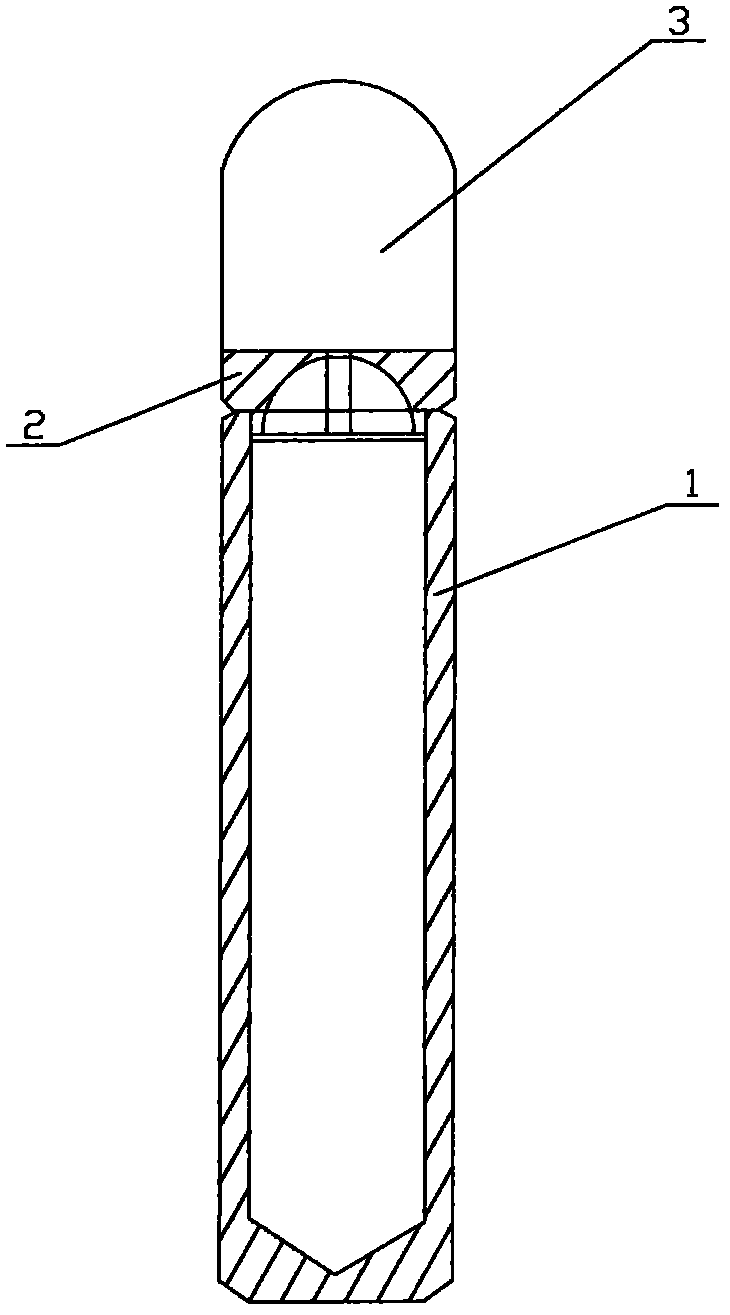
InactiveCN102137539AImprove pressure resistanceSimple and fast operationConversion in nuclear reactorDirect voltage acceleratorsIodineEngineering
The invention discloses a Xenon target for producing iodine-125 through reactor irradiation and a preparation method thereof. The Xenon target comprises a barrel body, a sealing cap and a protection cap, wherein the upper part of the barrel body and the lower end of the sealing cap are subjected to argonarc welding, an air inlet is arranged at the upper end of the sealing cap, and Xenon is injected to the barrel body through the air inlet; and the air let is subjected to cold-welding sealing, and the protection cover covers the sealing cap. The target prepared by the invention by adopting a cold welding method is simple and convenient for operation, easy to control the charge quantity of target materials, and stable and reliable in performance in the process for producing iodine-125 through reactor irradiation, and has high pressure resistance.
Owner:成都中核高通同位素股份有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com