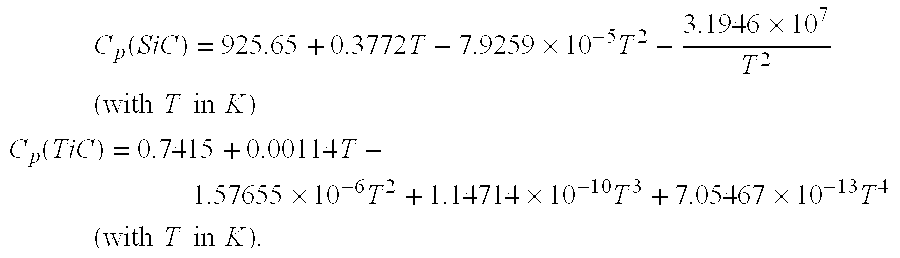Patents
Literature
350 results about "Spent nuclear fuel" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Spent nuclear fuel, occasionally called used nuclear fuel, is nuclear fuel that has been irradiated in a nuclear reactor (usually at a nuclear power plant). It is no longer useful in sustaining a nuclear reaction in an ordinary thermal reactor and depending on its point along the nuclear fuel cycle, it may have considerably different isotopic constituents.
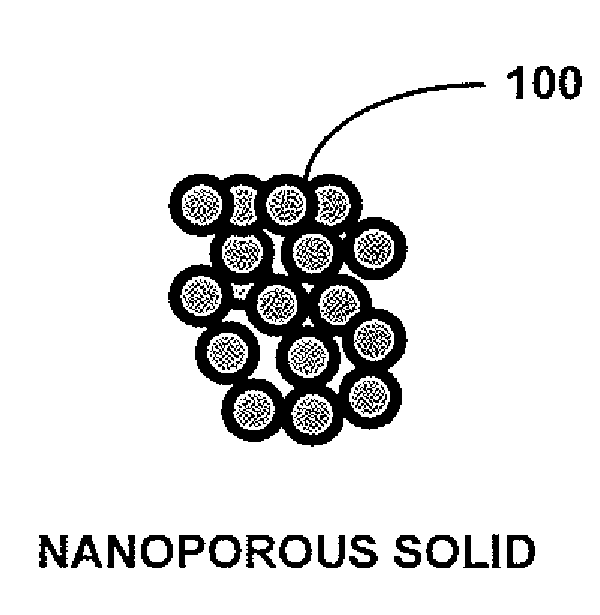
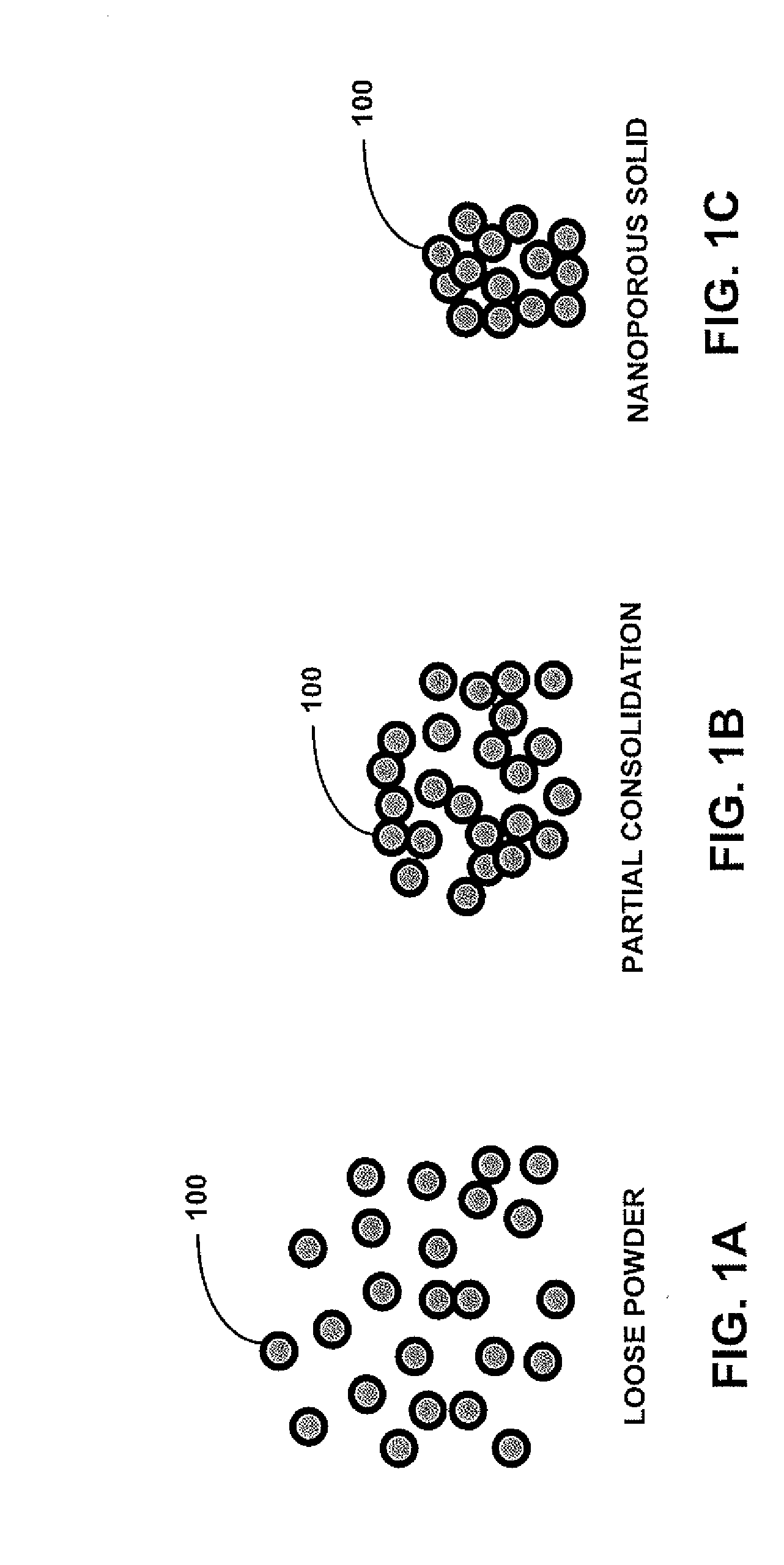
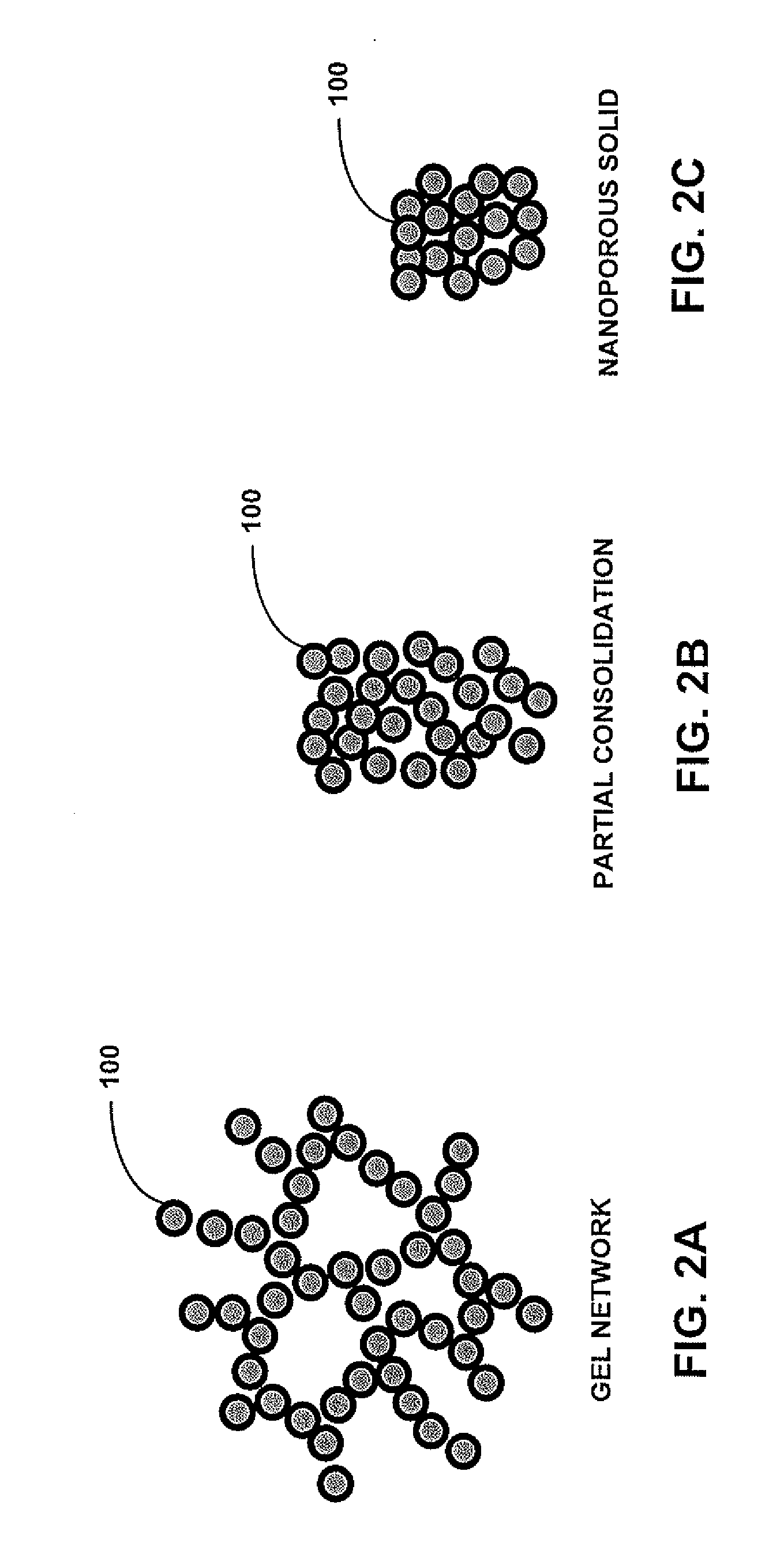
Swelling-resistant nuclear fuel
A nuclear fuel according to one embodiment includes an assembly of nuclear fuel particles; and continuous open channels defined between at least some of the nuclear fuel particles, wherein the channels are characterized as allowing fission gasses produced in an interior of the assembly to escape from the interior of the assembly to an exterior thereof without causing significant swelling of the assembly. Additional embodiments, including methods, are also presented.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
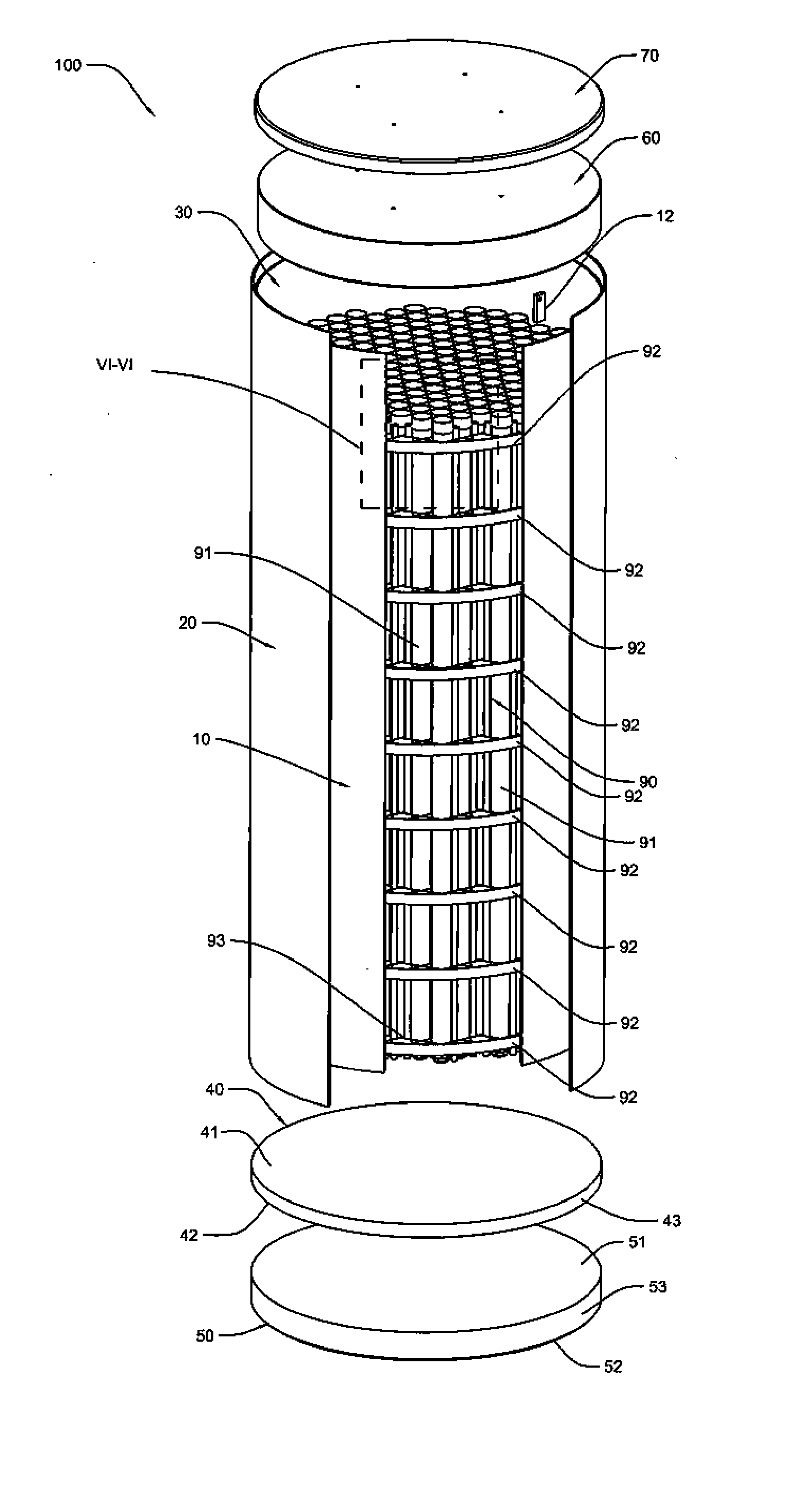
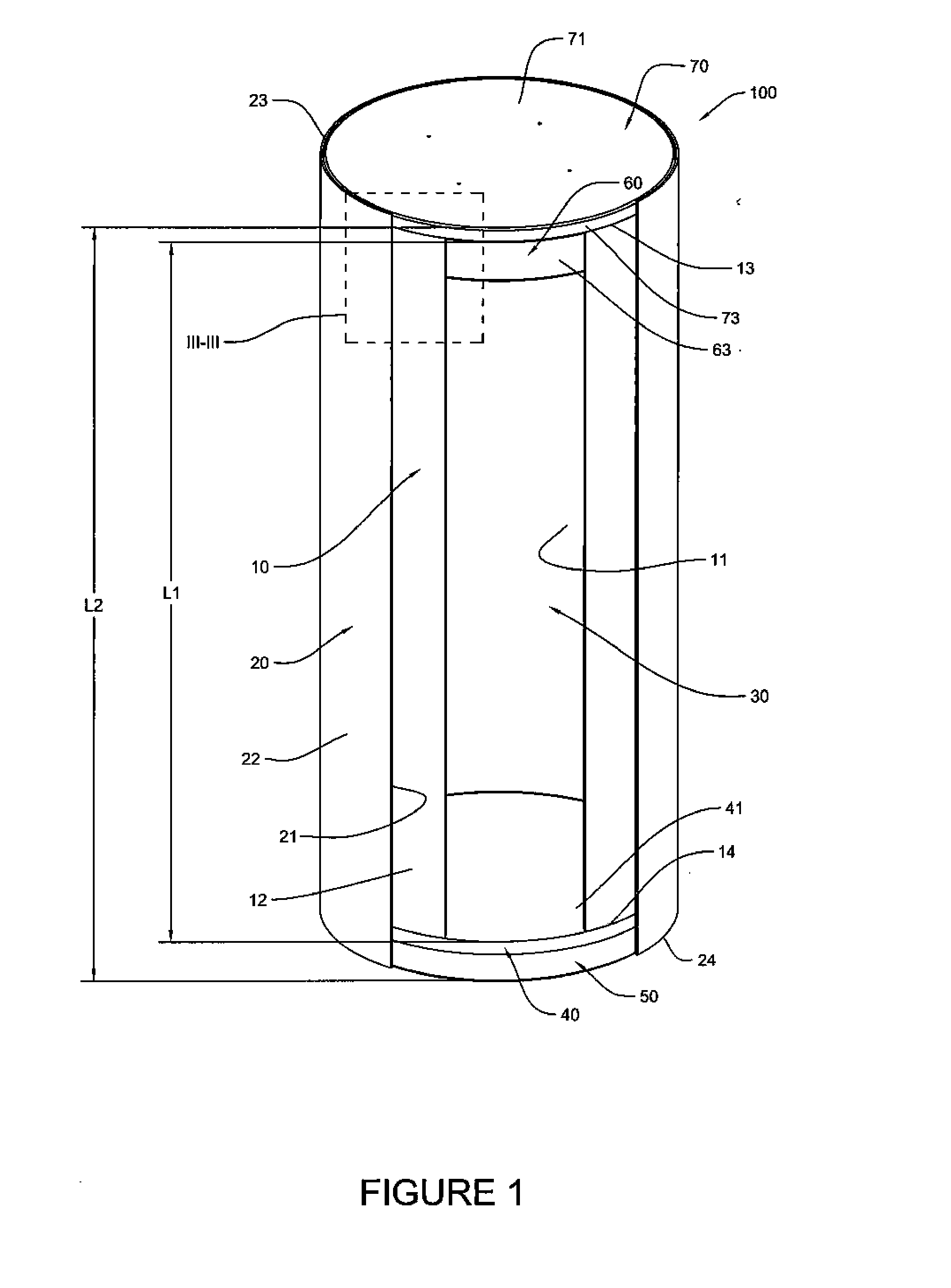
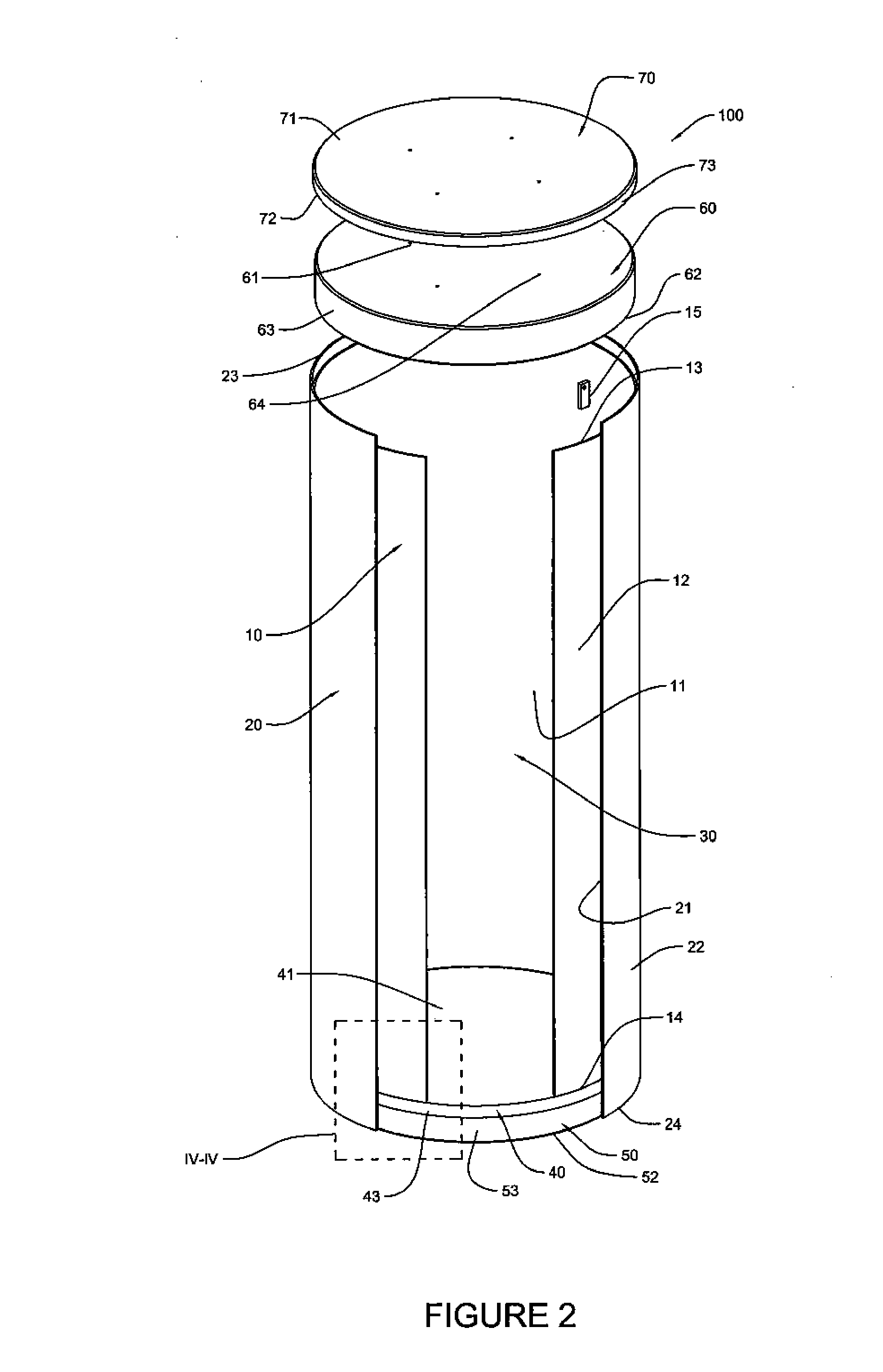
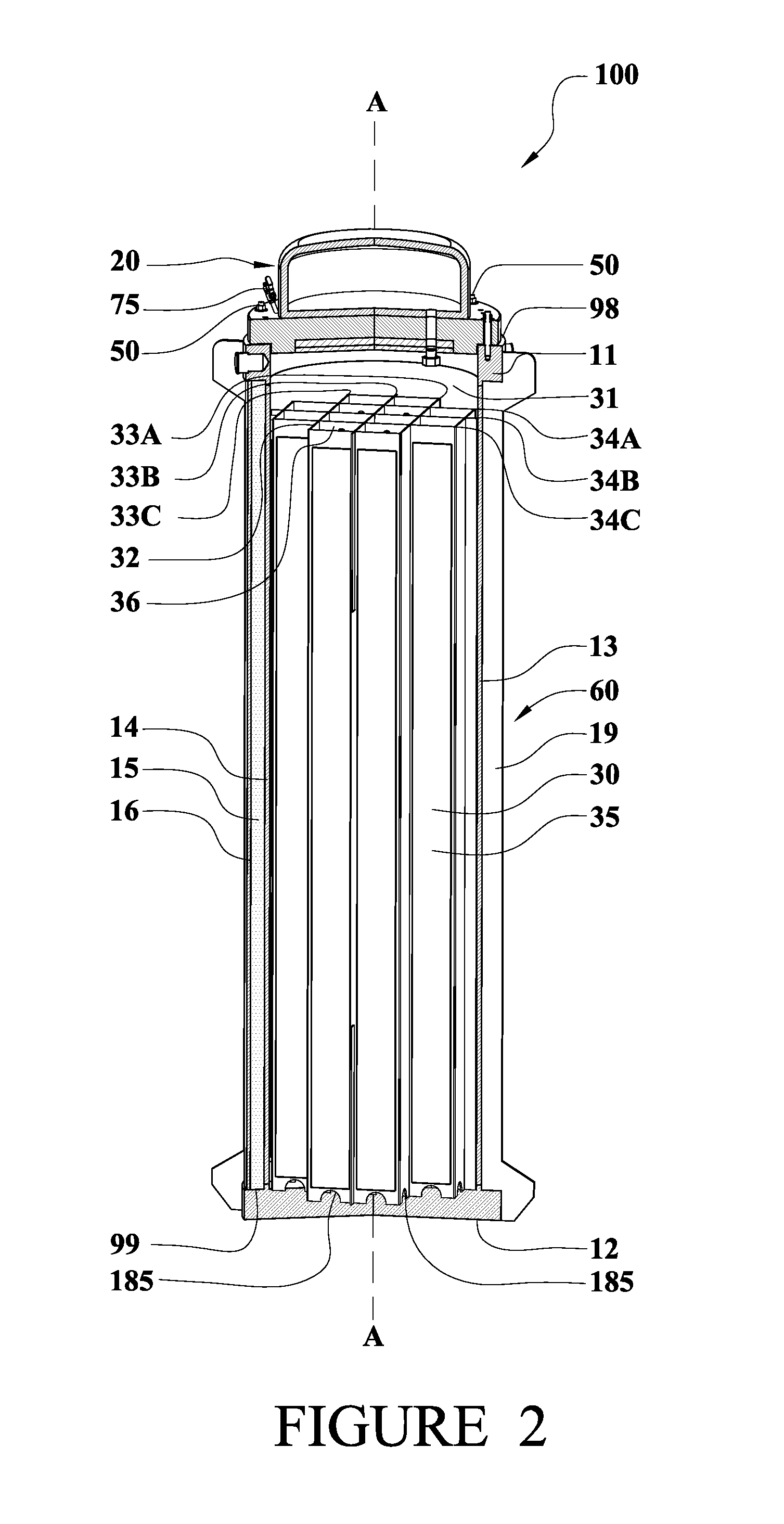
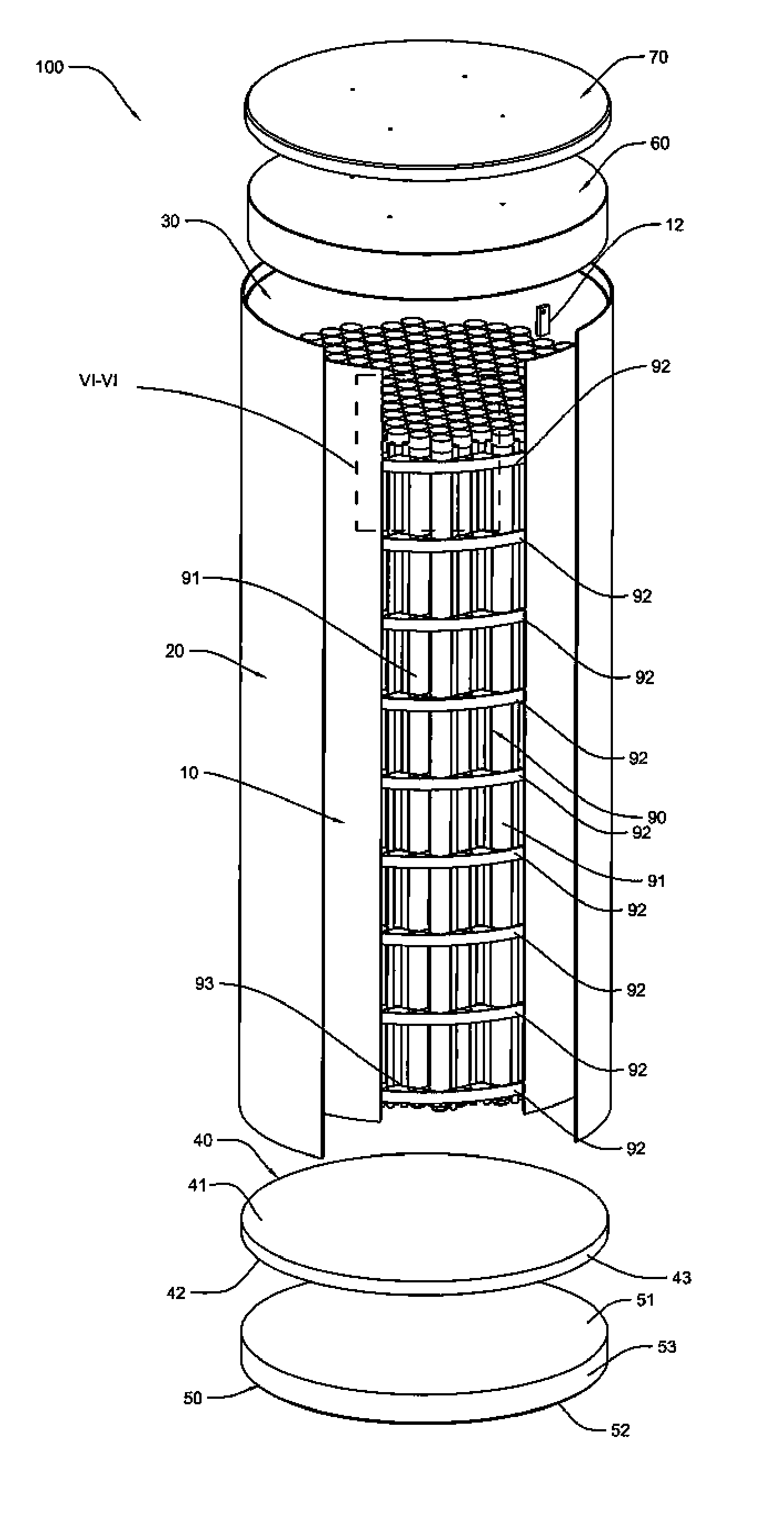
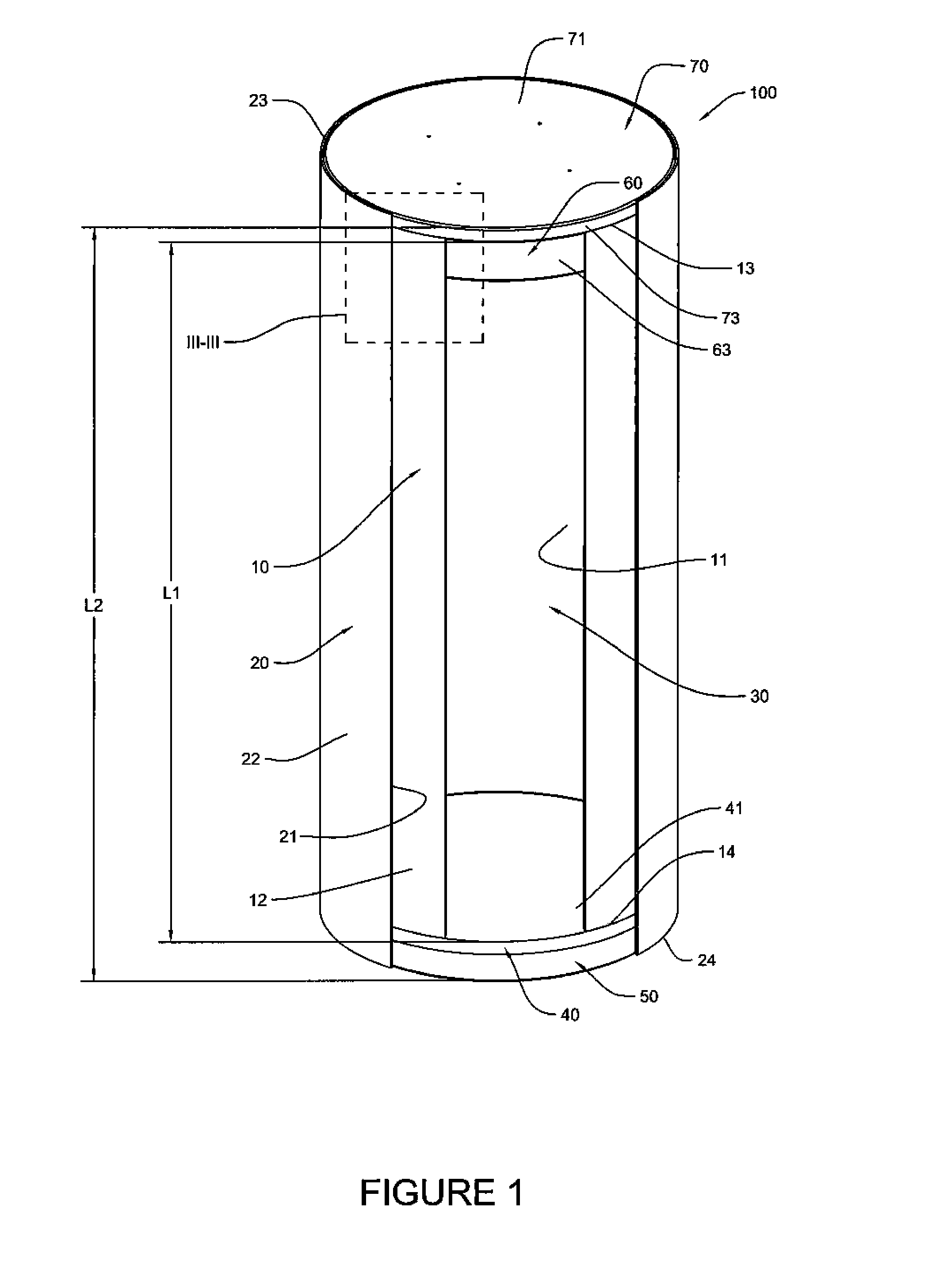
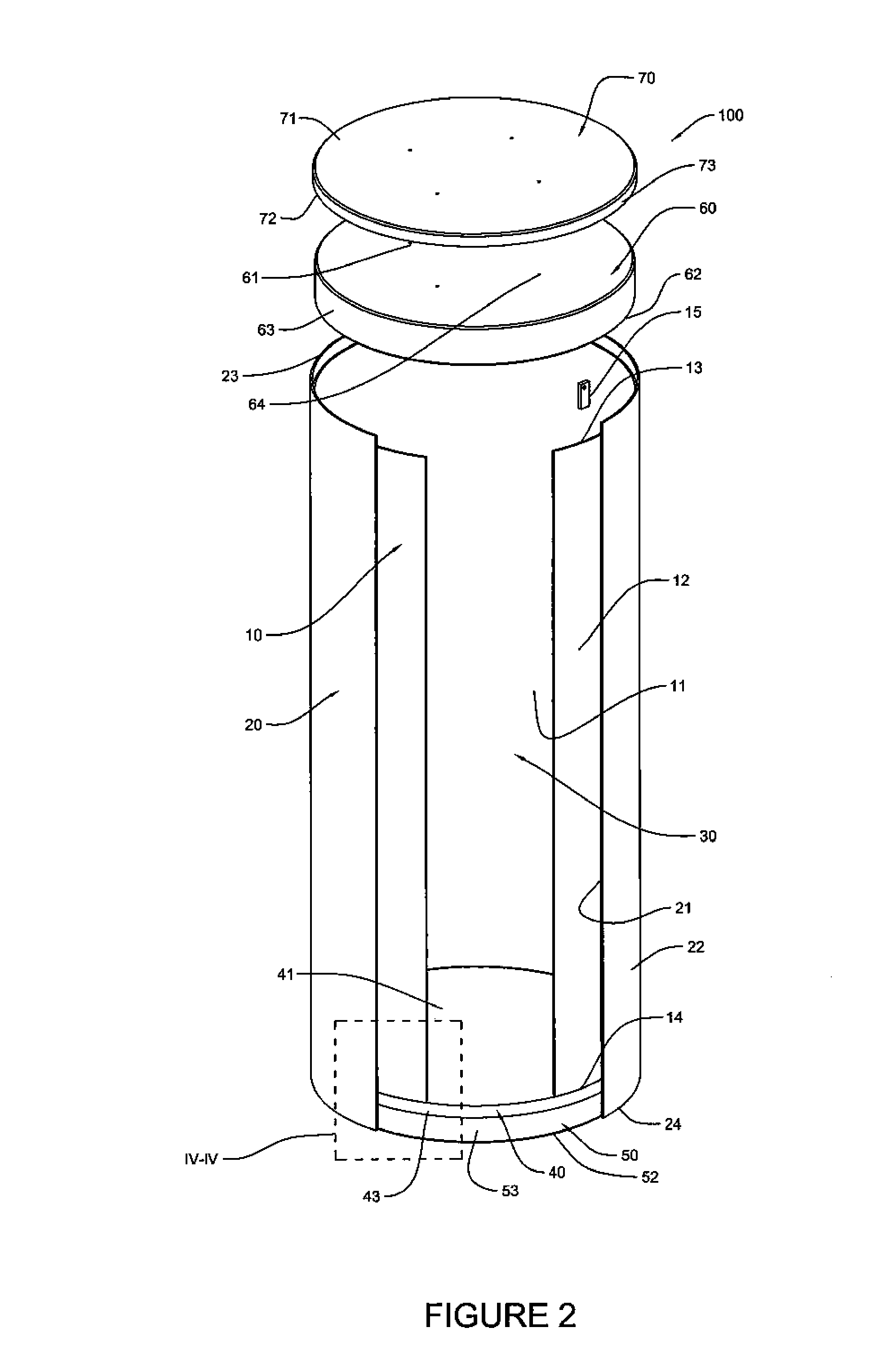
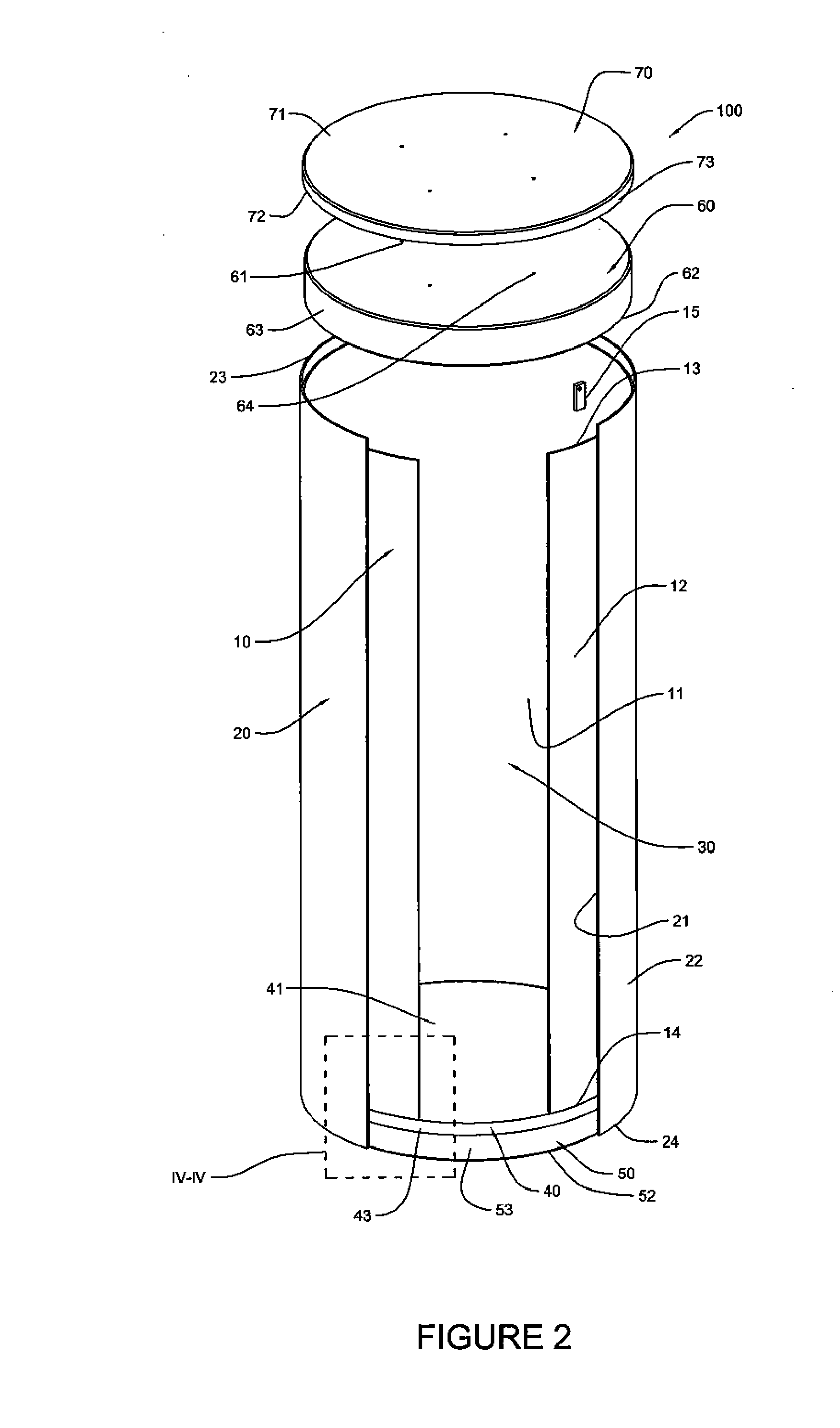
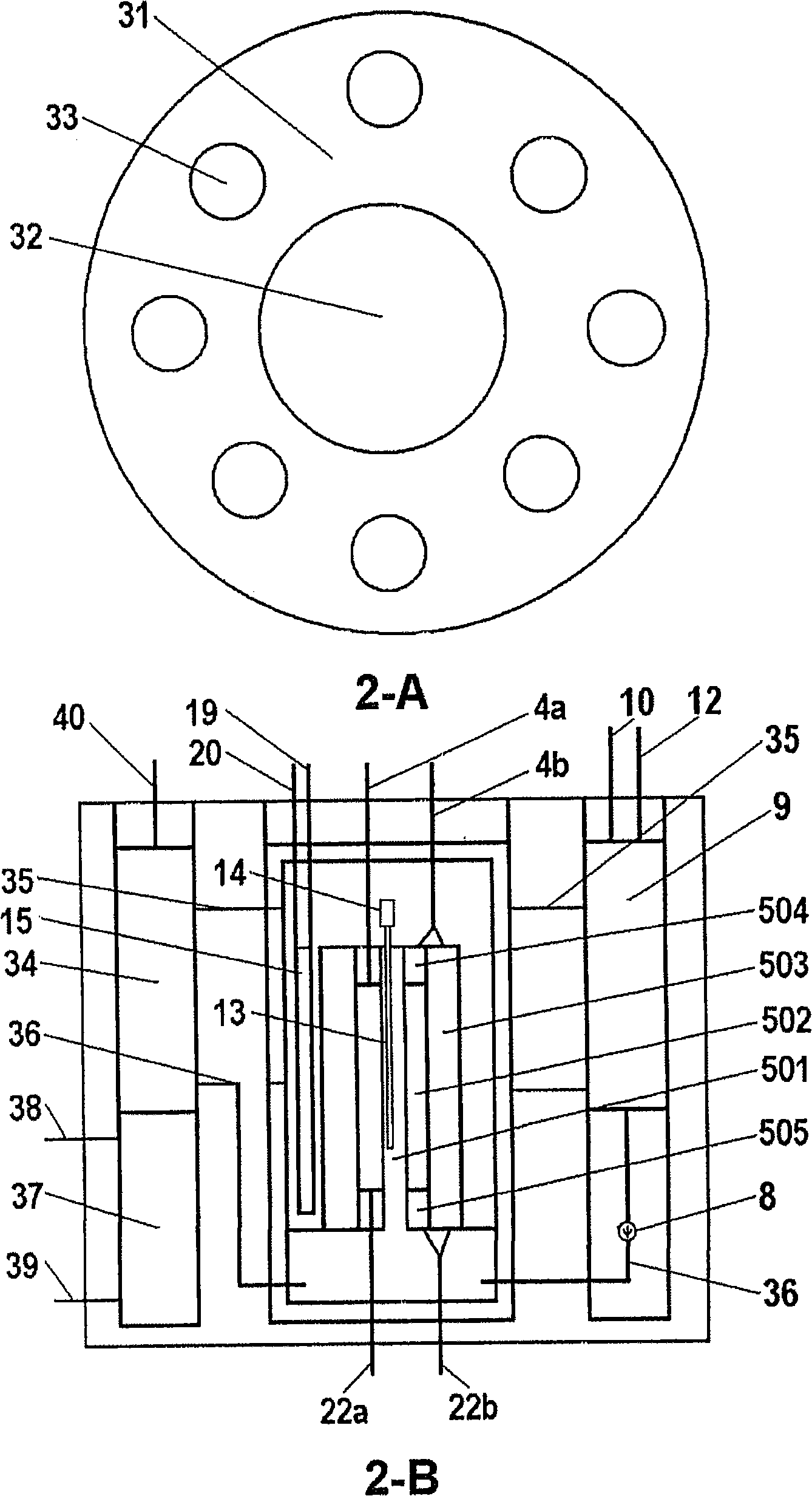
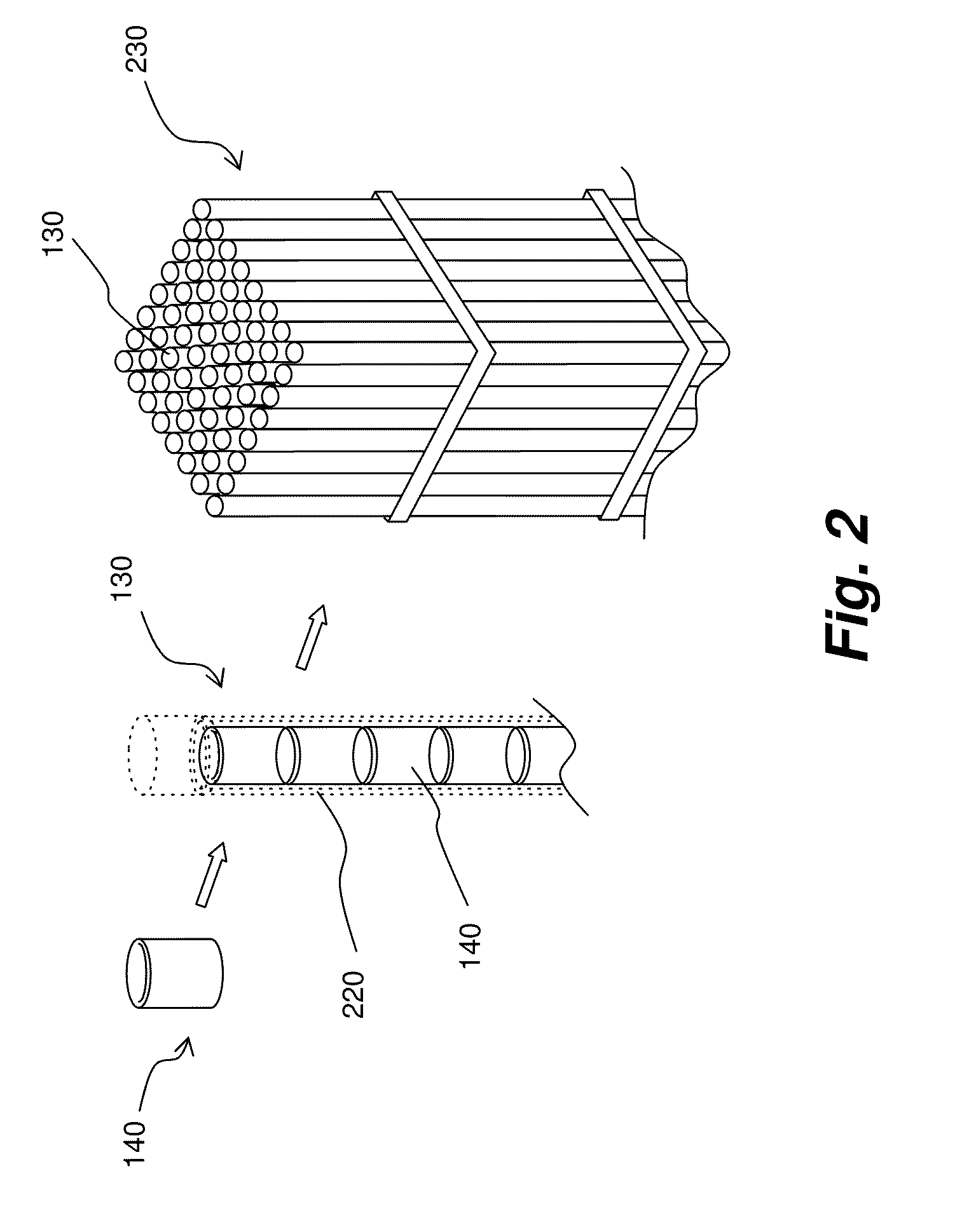
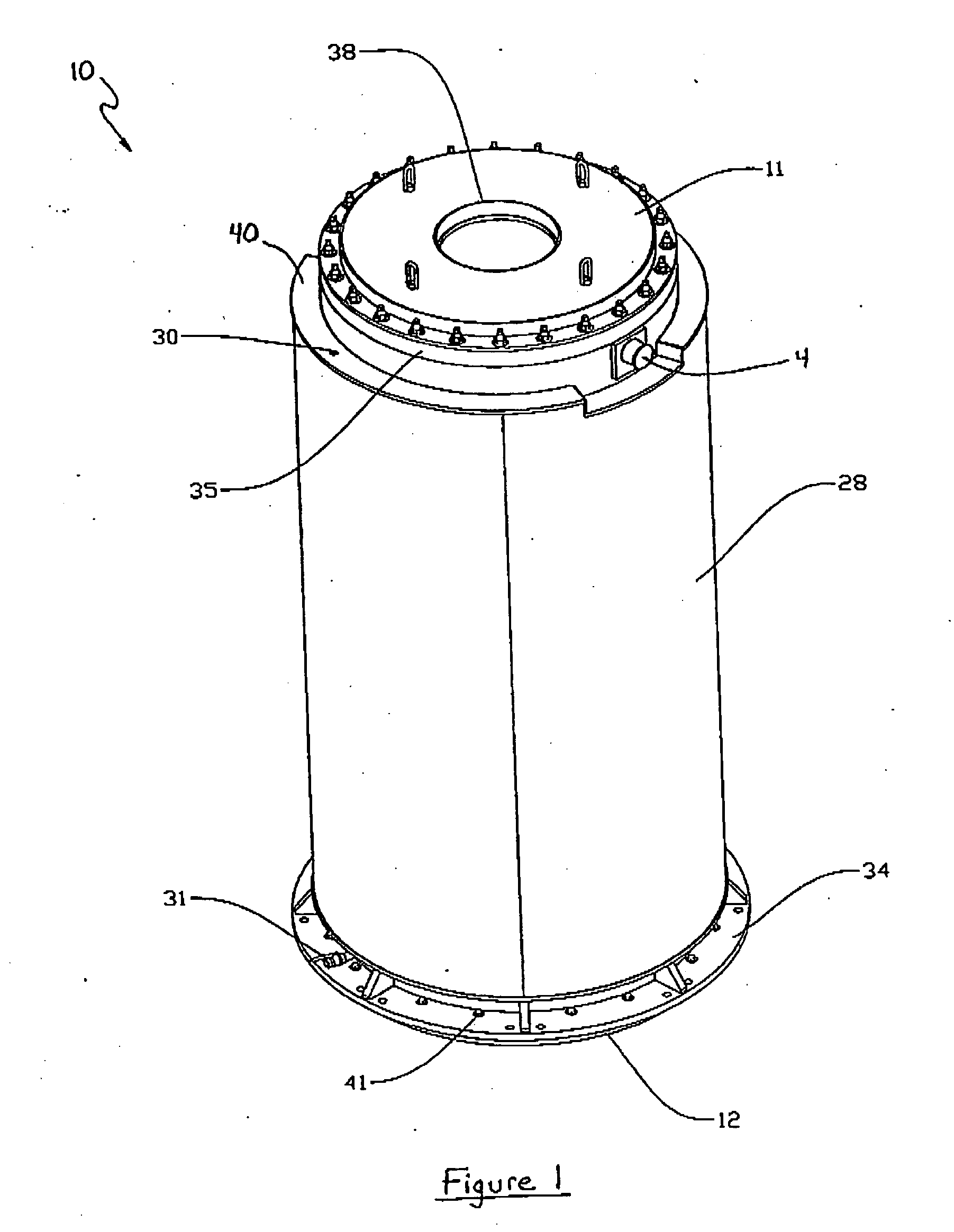
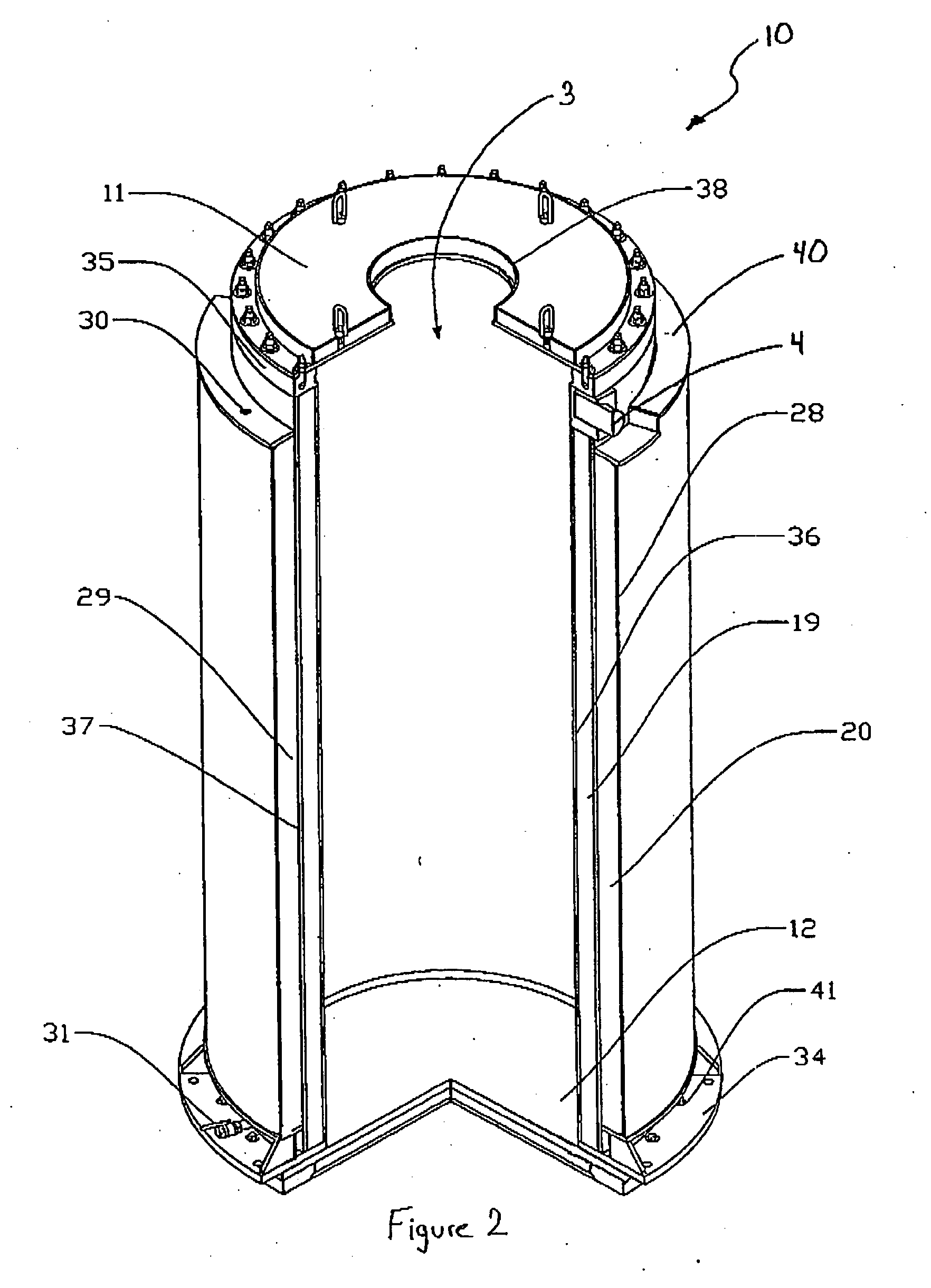
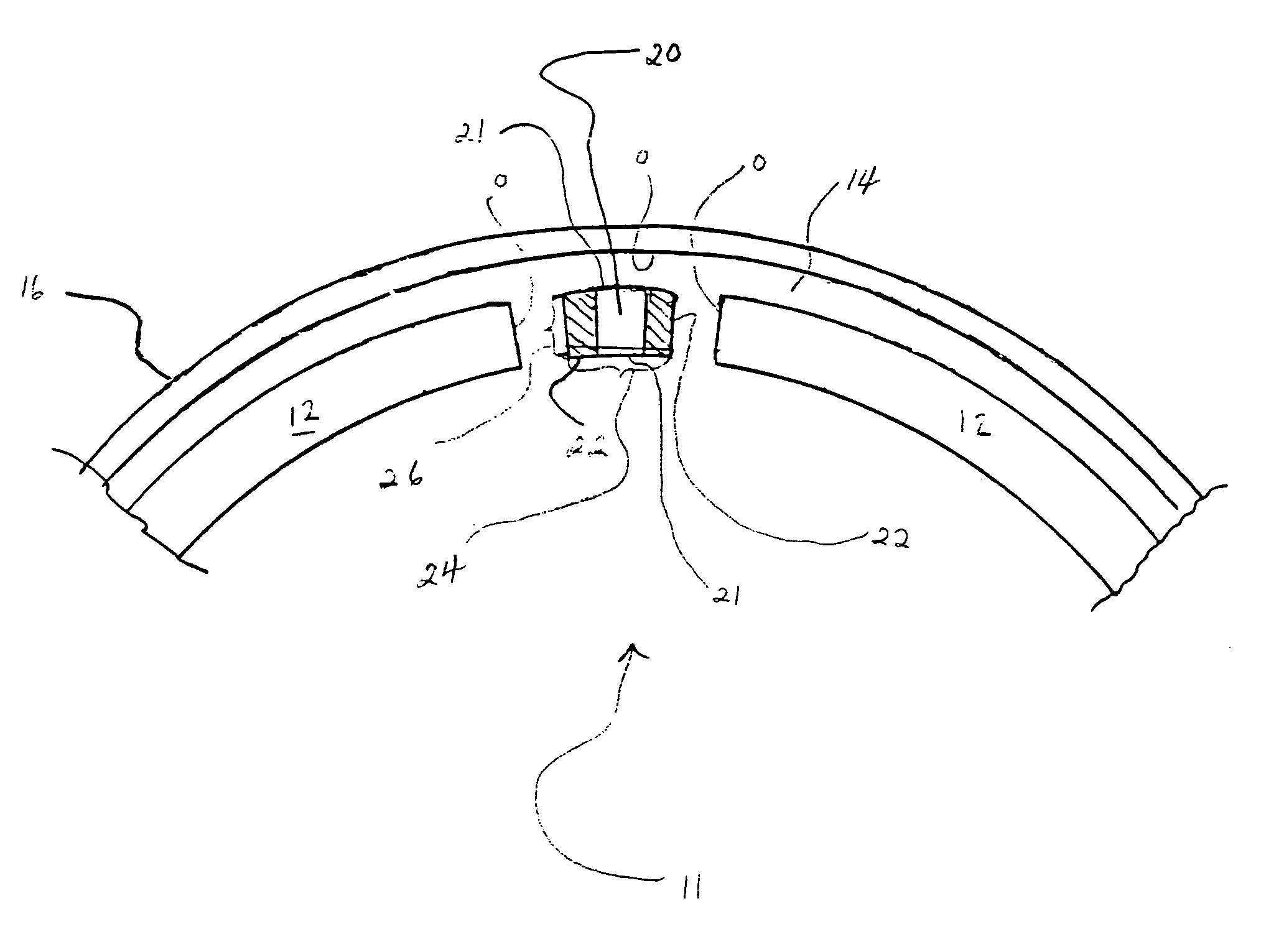
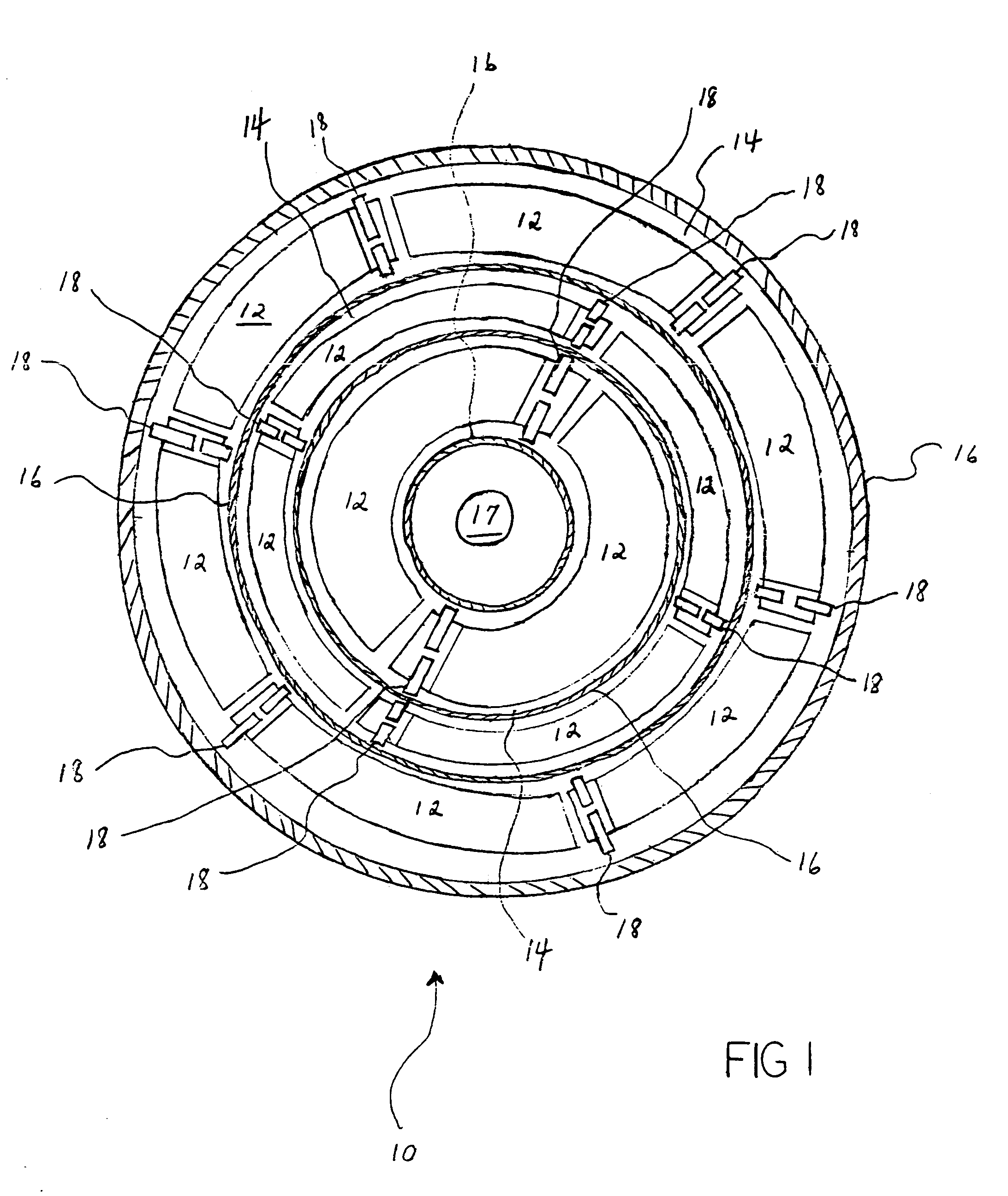
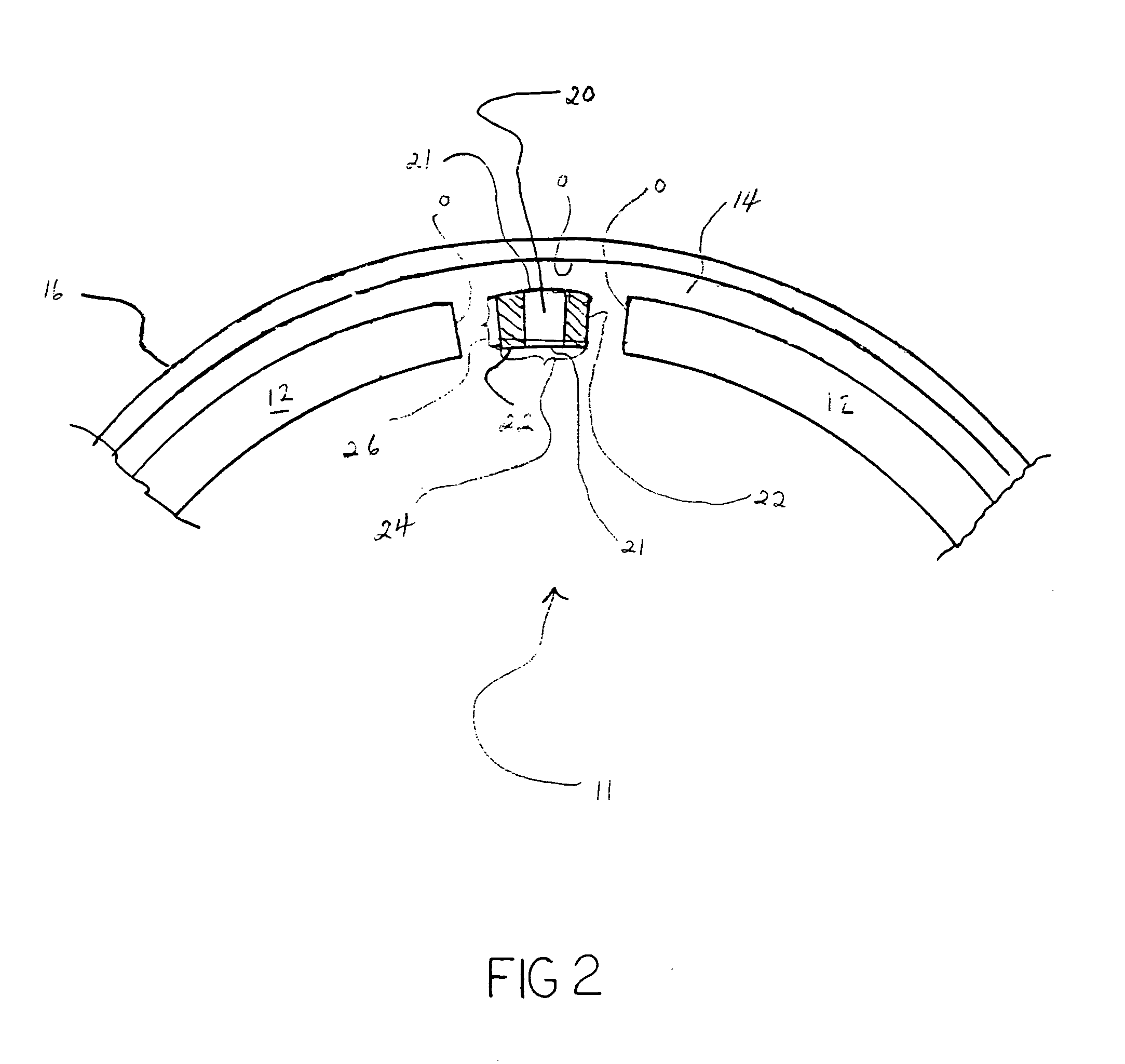
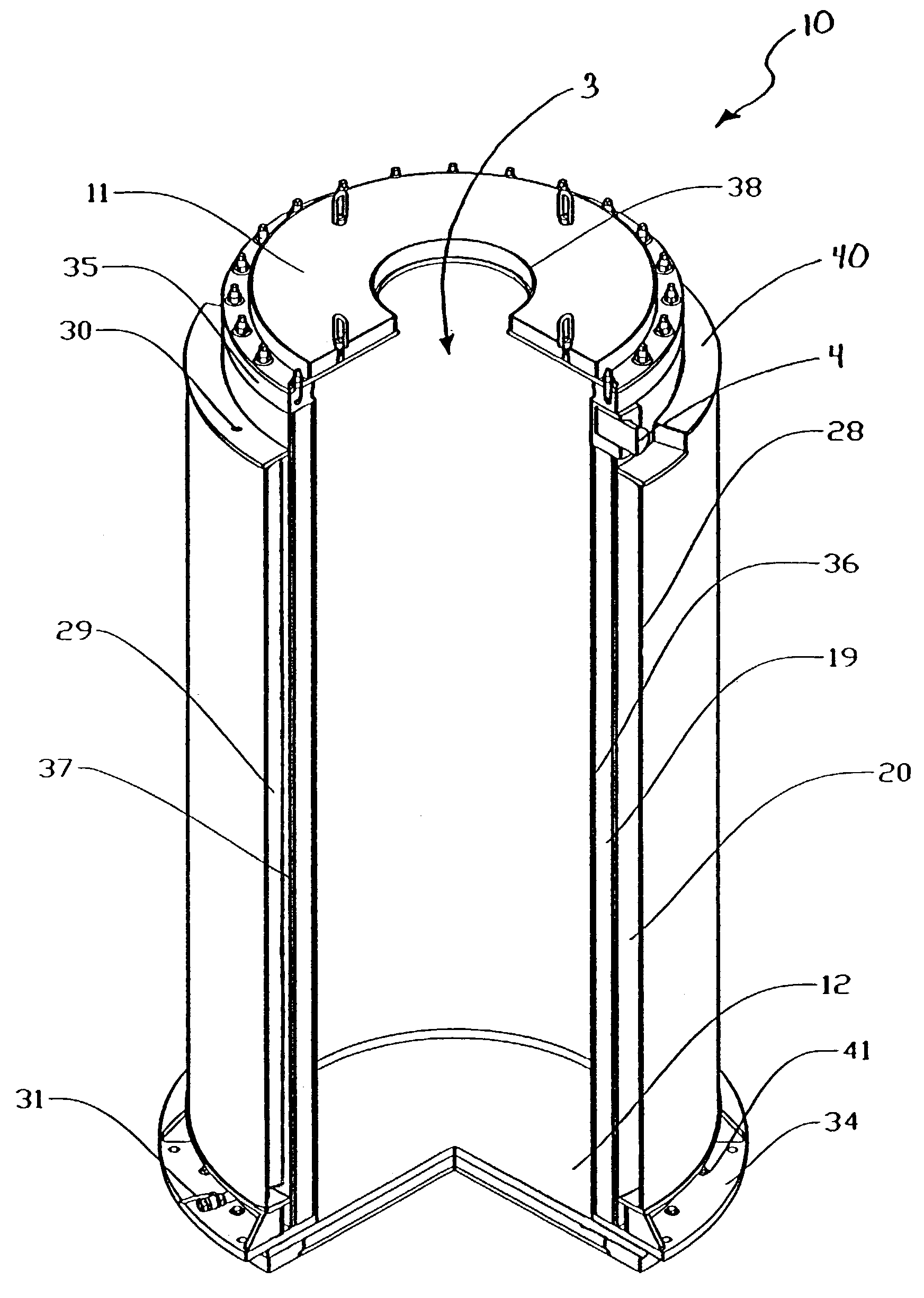
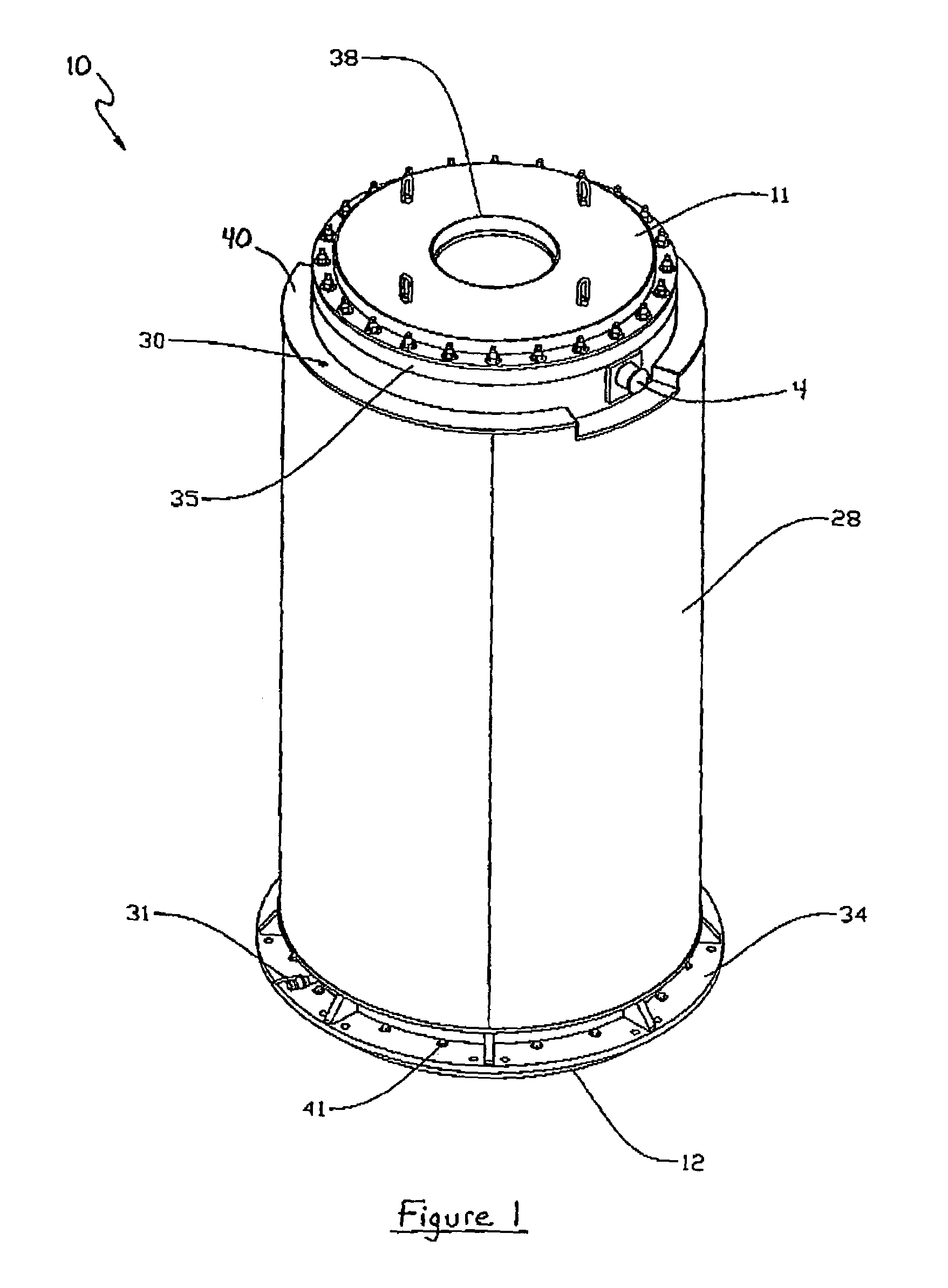
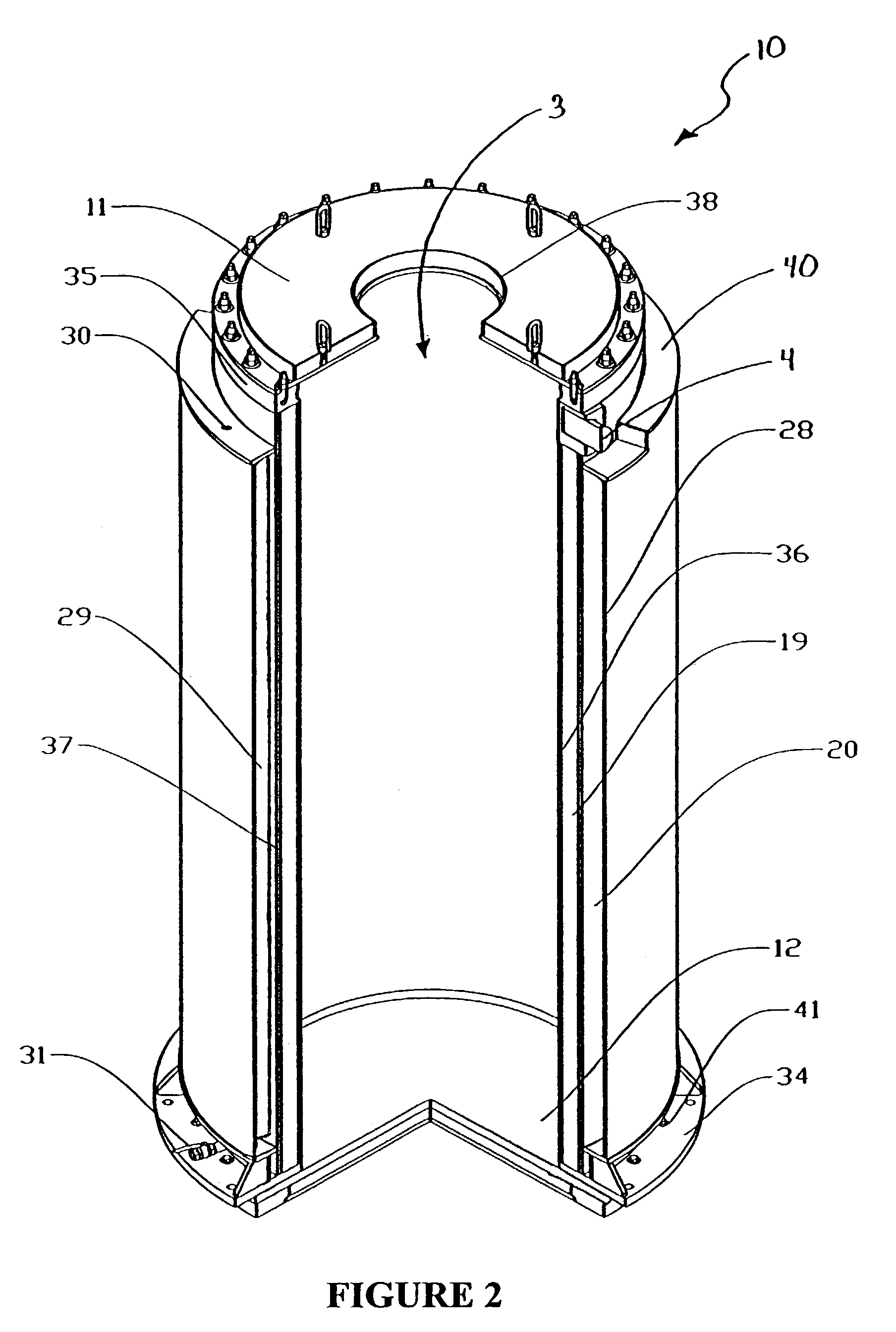
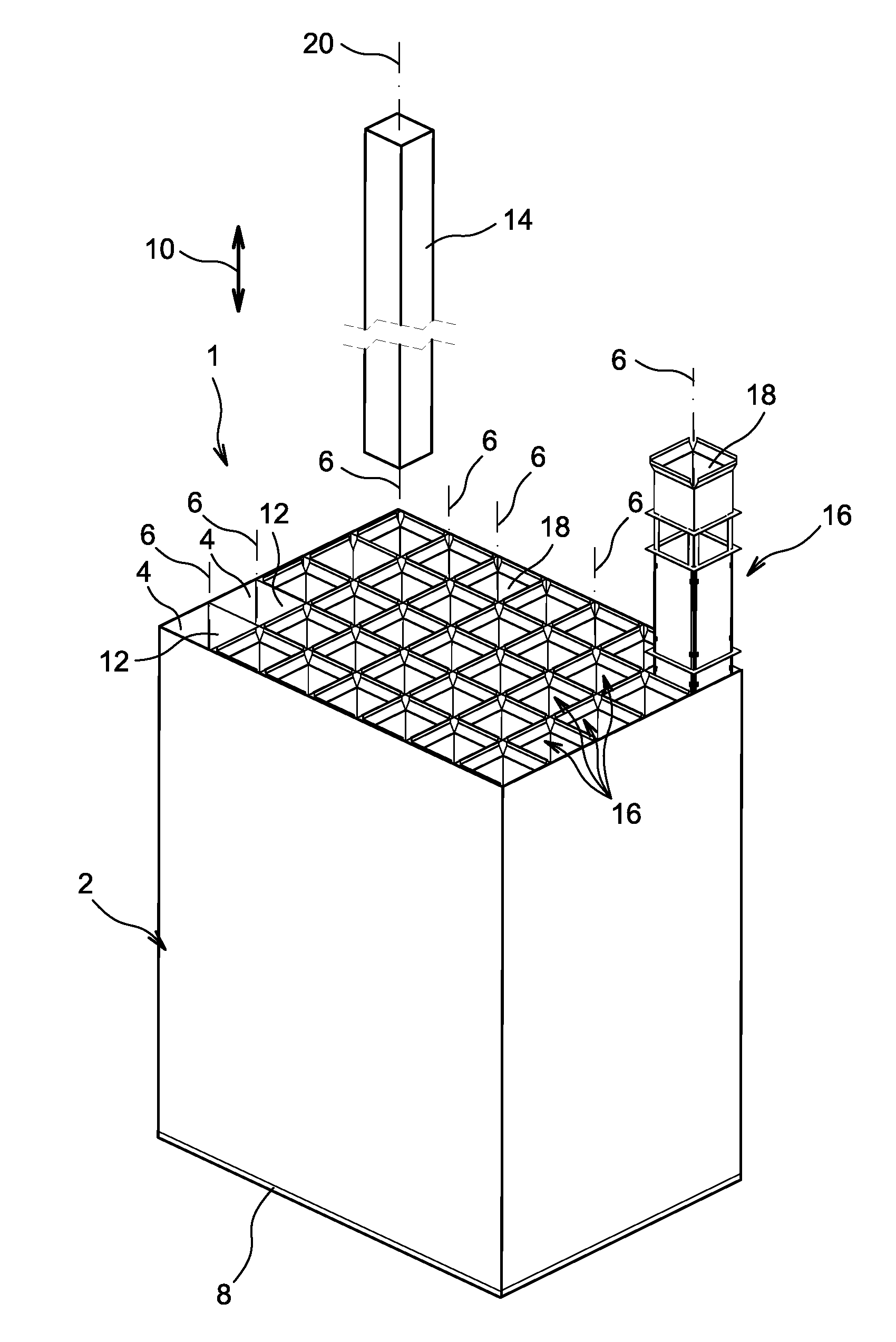
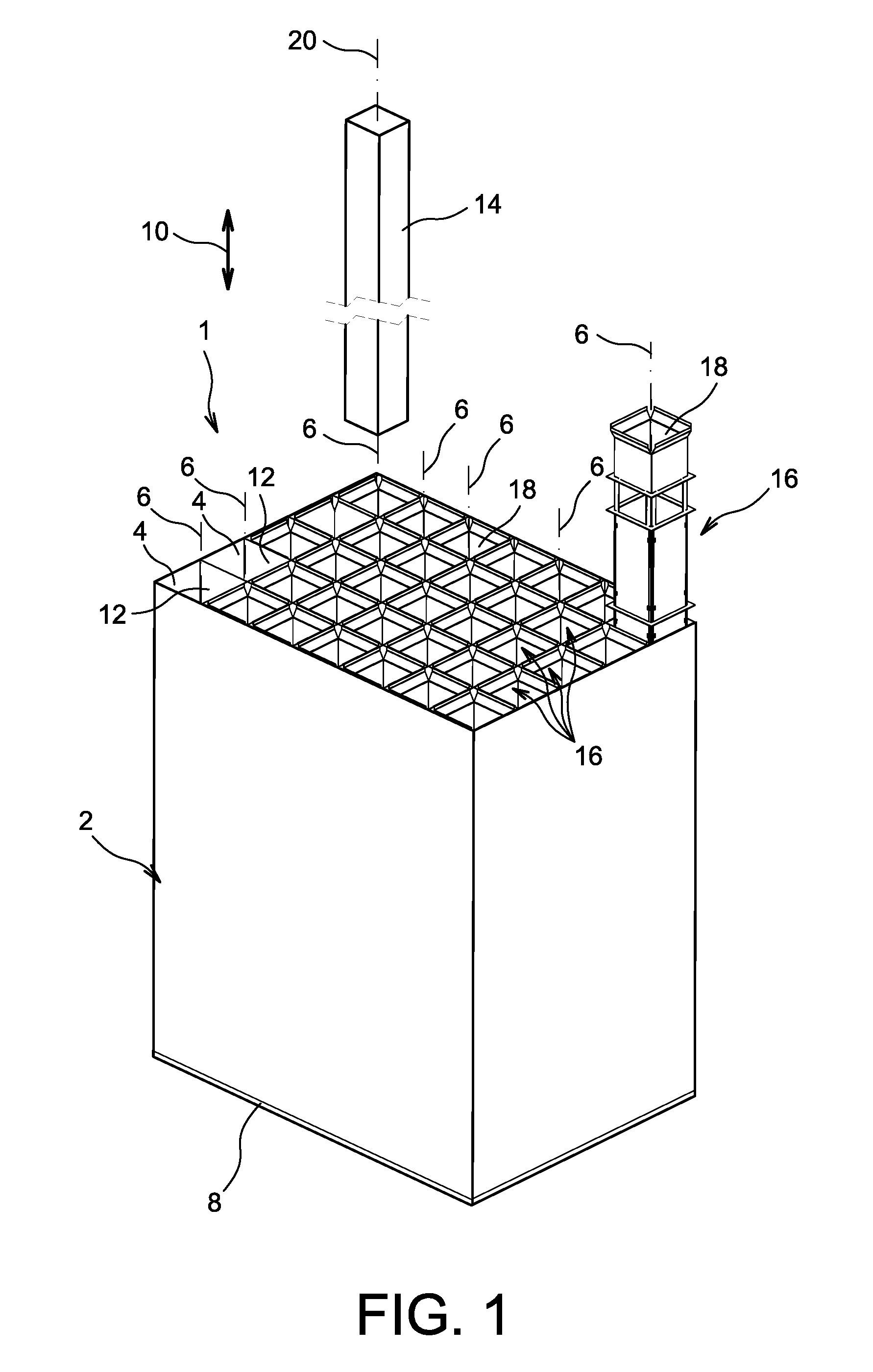
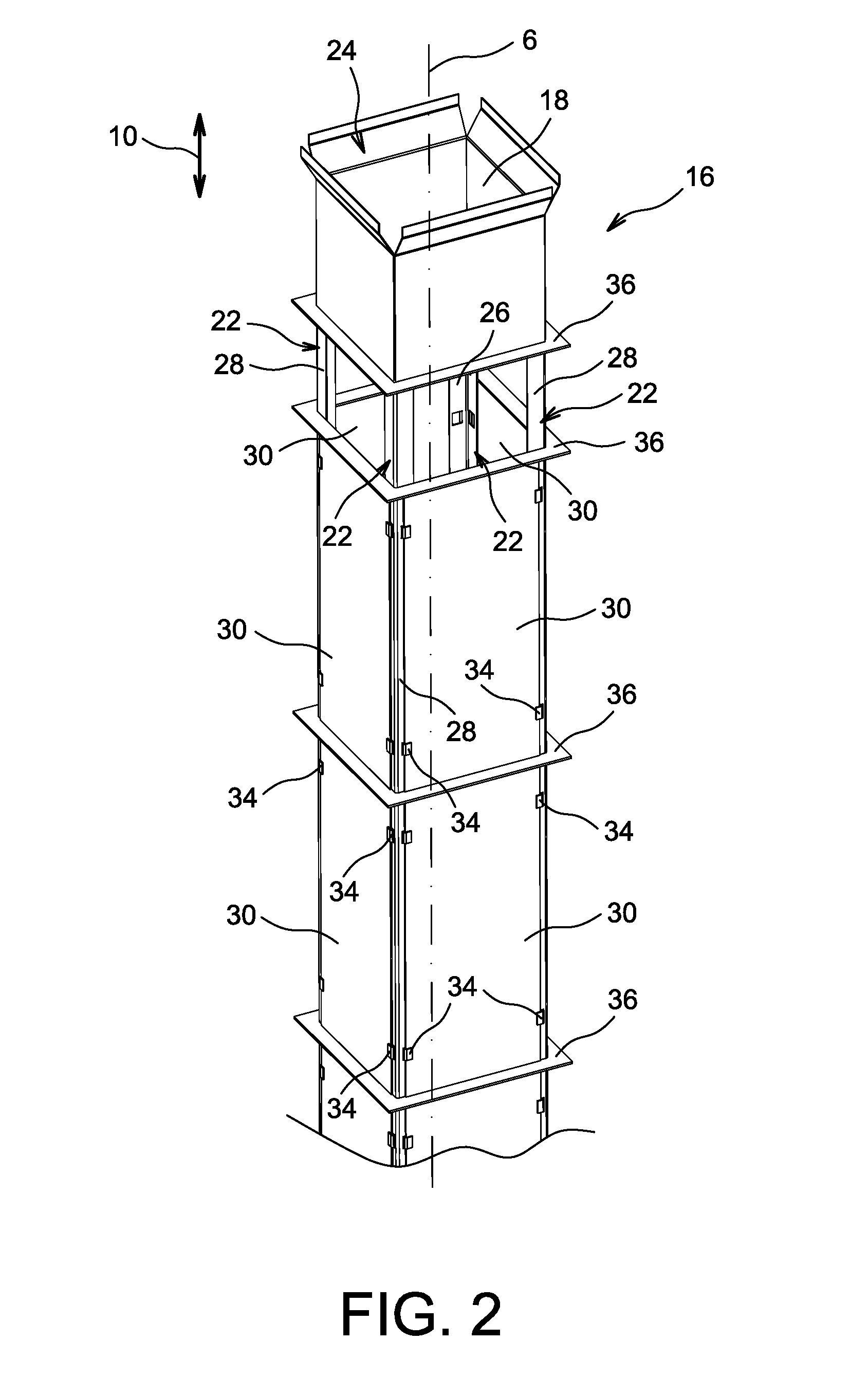
Canister apparatus and basket for transporting, storing and/or supporting spent nuclear fuel
ActiveUS20080069291A1Efficiently accommodate both poison rodEfficiently spent nuclear fuelNuclear engineering problemsNuclear engineering solutionsRadioactive wasteEngineering
A canister apparatus, basket apparatus and combinations thereof for transporting and / or storing high level radioactive waste, such as spent nuclear fuel. The canister apparatus comprises a cavity for receiving the spent nuclear fuel that is surrounded by two independent gas-tight containment boundaries. The structures that form the two independent gas-tight containment boundaries are in substantially continuous surface contact with one another, thereby facilitating sufficient heat removal from the cavity. In another aspect, the invention is a basket apparatus having a plurality of disk-like grates arranged in a stacked and spaced arrangement so that the cells of the disk-like grates are aligned. In still another aspect, the invention can be a basket apparatus having a disk-like grate having a ring-like structure encompassing a gridwork of beams specially arranged to achieve a unique cell configuration.
Owner:HOLTEC INT
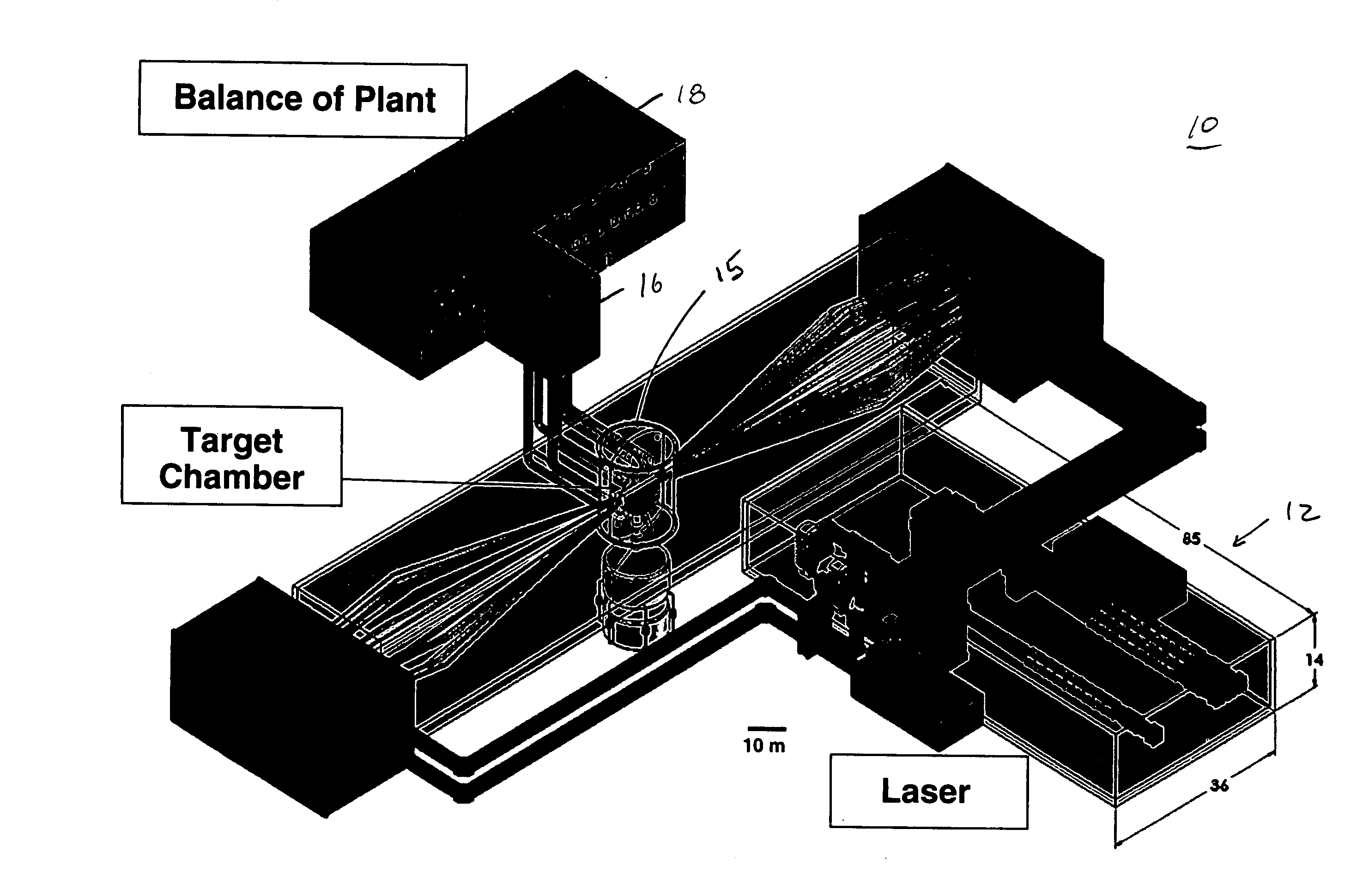
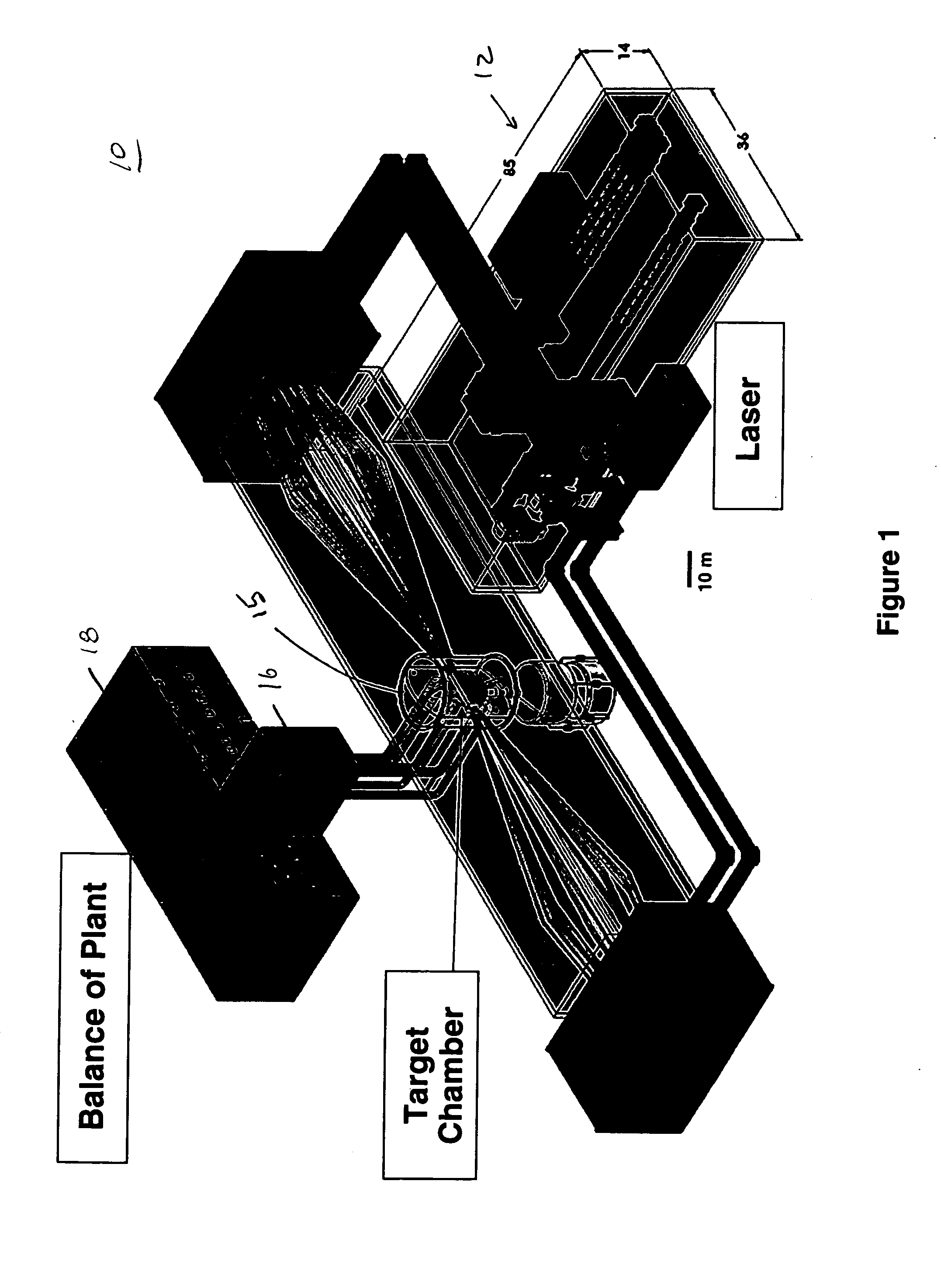
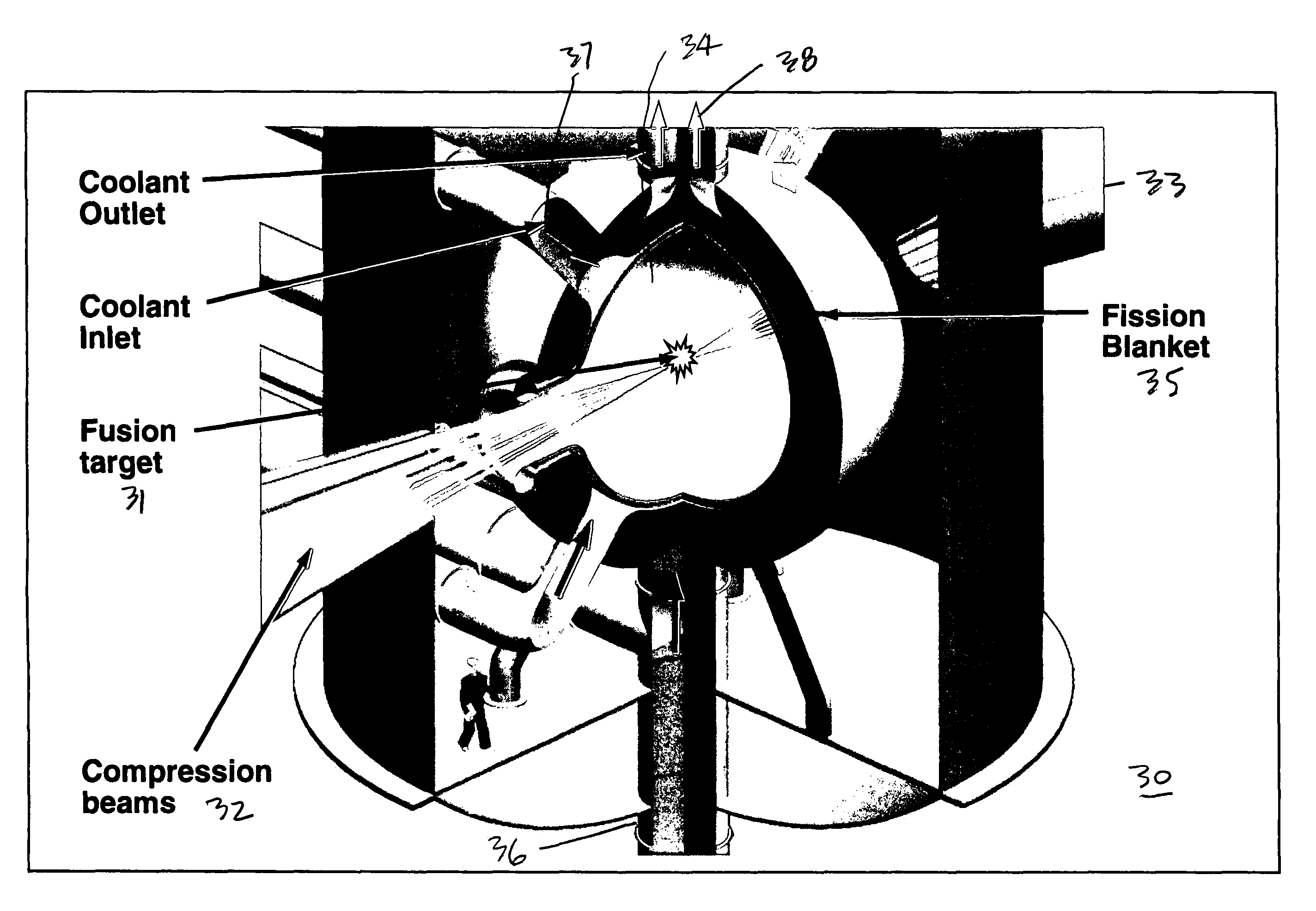
Control of a Laser Inertial Confinement Fusion-Fission Power Plant
ActiveUS20110286563A1Extended service lifeReduce spreadNuclear energy generationWaste based fuelFusion fissionEngineering
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
Nuclear fuel cladding with high heat conductivity and method for making same
ActiveUS20110170653A1Optimal transfer of thermal energyEasy transferFuel elementsNuclear energy generationThermal energyFiber
The invention relates to a nuclear fuel cladding totally or partially made of a composite material with a ceramic matrix containing silicon carbide (SiC) fibers as a matrix reinforcement and an interphase layer provided between said matrix and said fibers, the matrix including at least one carbide selected from titanium carbide (TiC), zirconium carbide (ZrC), or ternary titanium silicon carbide (Ti3SiC2).When irradiated and at temperatures of between 800° C. and 1200° C., said cladding can mechanically maintain the nuclear fuel within the cladding while enabling optimal thermal-energy transfer towards the coolant.The invention also relates to a method for making the nuclear fuel cladding.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
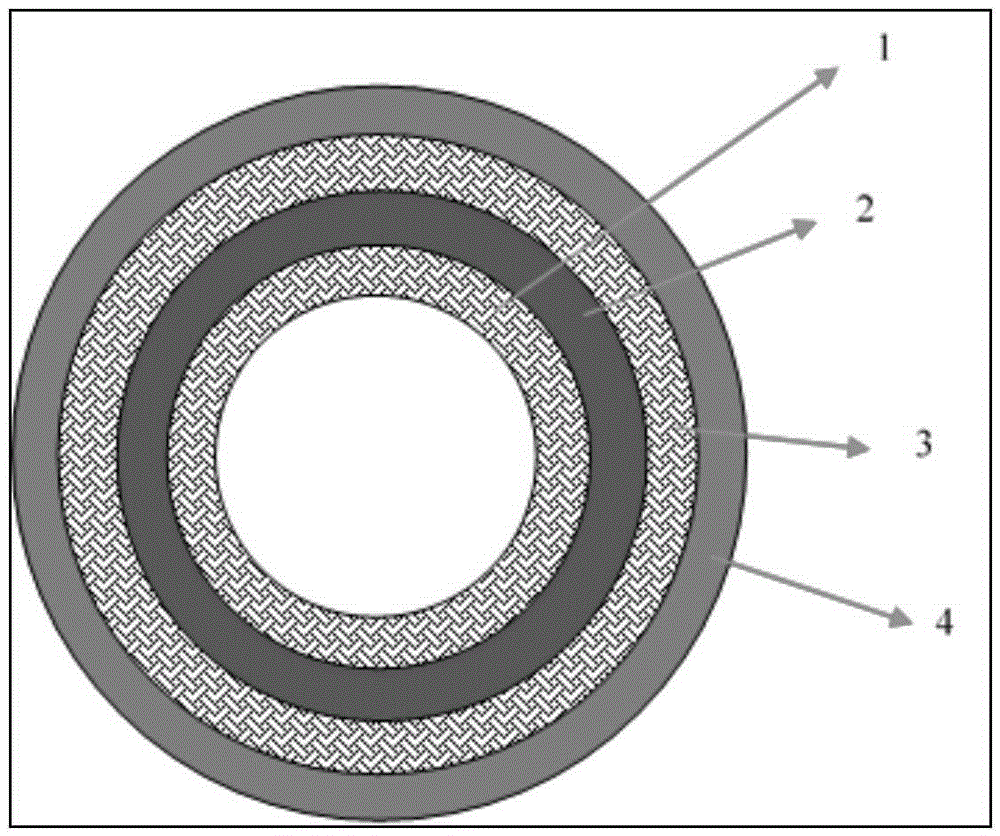
Multilayer tube in ceramic matrix composite material, resulting nuclear fuel cladding and associated manufacturing processes
ActiveUS20140153688A1Improve sealingOptical rangefindersFuel elementsMetal alloyCeramic matrix composite
The invention relates to a multilayer tubular part (1) comprising a metal layer forming a metal tubular body (3) and two layers in ceramic matrix composite material covering the metal tubular body, wherein one of the two layers in ceramic matrix composite material covers the inner surface of the metal tubular body to form an inner tubular body (4), whilst the other of the two layers in ceramic matrix composite material covers the outer surface of the metal tubular body to form an outer tubular body (2), the metal tubular body therefore being sandwiched between the inner and outer tubular bodies. The metal tubular body is in metal or metal alloy. Finally, the metal tubular body has a mean thickness smaller than the mean thicknesses of the inner and outer tubular bodies. A said part is useful in particular for producing nuclear fuel claddings.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
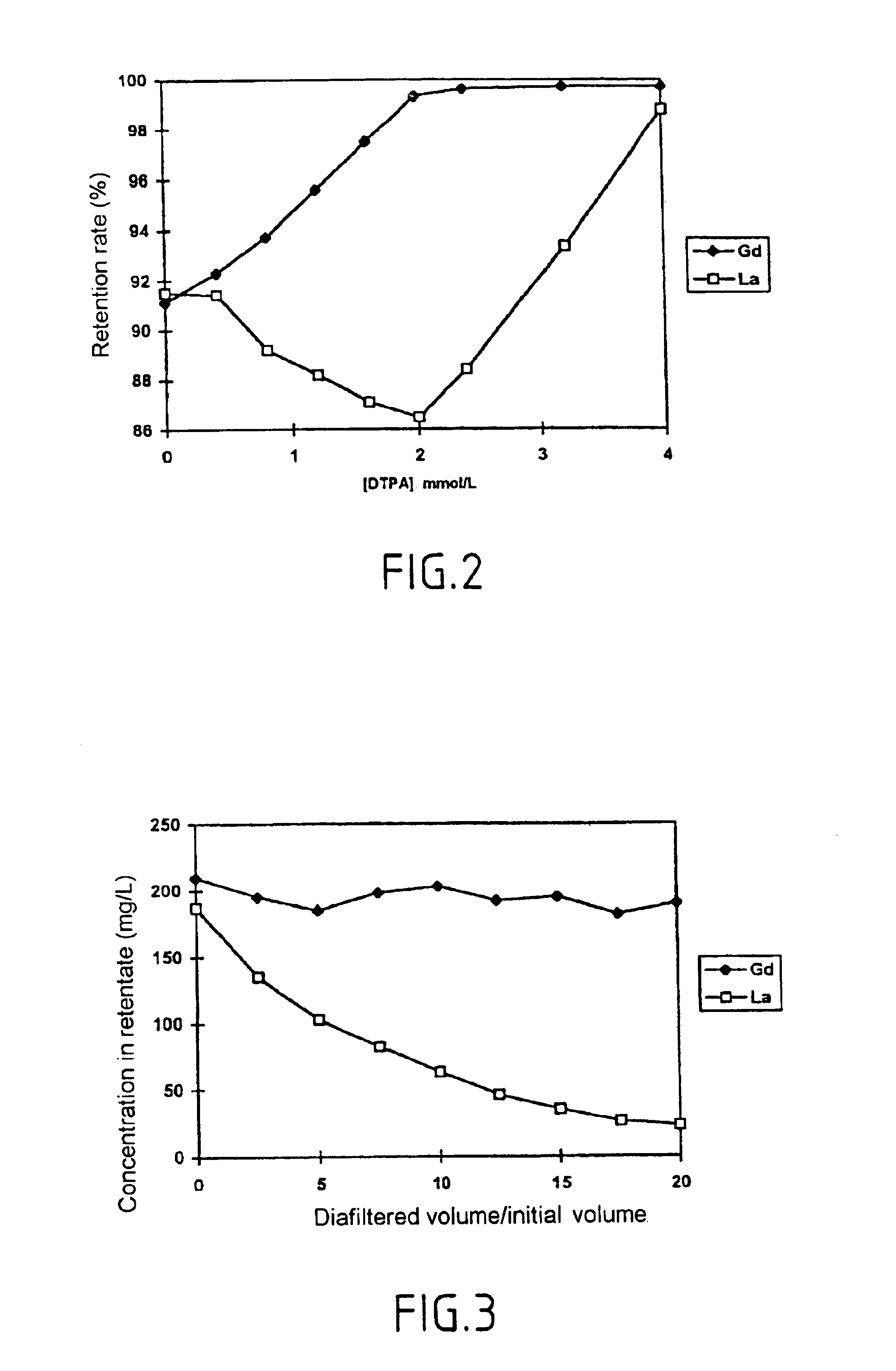
Method for separating in an aqueous medium lanthanides and/or actinides by combined complexing-nanofiltration, and novel complexing agents therefor
InactiveUS6843917B1Easy to implementEasily degradableMembranesOrganic chemistryWaste processingLanthanide
The invention relates to the separation of lanthanides and actinides by nanofiltration complexation. The object of the invention is to satisfy the existing need for a simple, efficient and economical technique for separating lanthanides and actinides. This object is achieved by a process consisting of using ligands of the polyamino acid type, such as EDTA or DTPA, for complexing lanthanides and / or actinides before separating them by nanofiltration. The invention further relates to novel polyamino acid ligands incorporating ligand structures additional to EDTA and DTPA. Application to the production of rare earths or nuclear waste processing, especially to recycling operations carried out on spent nuclear fuels is also discussed.
Owner:UNIV CLAUDE BERNARD LYON 1 +1
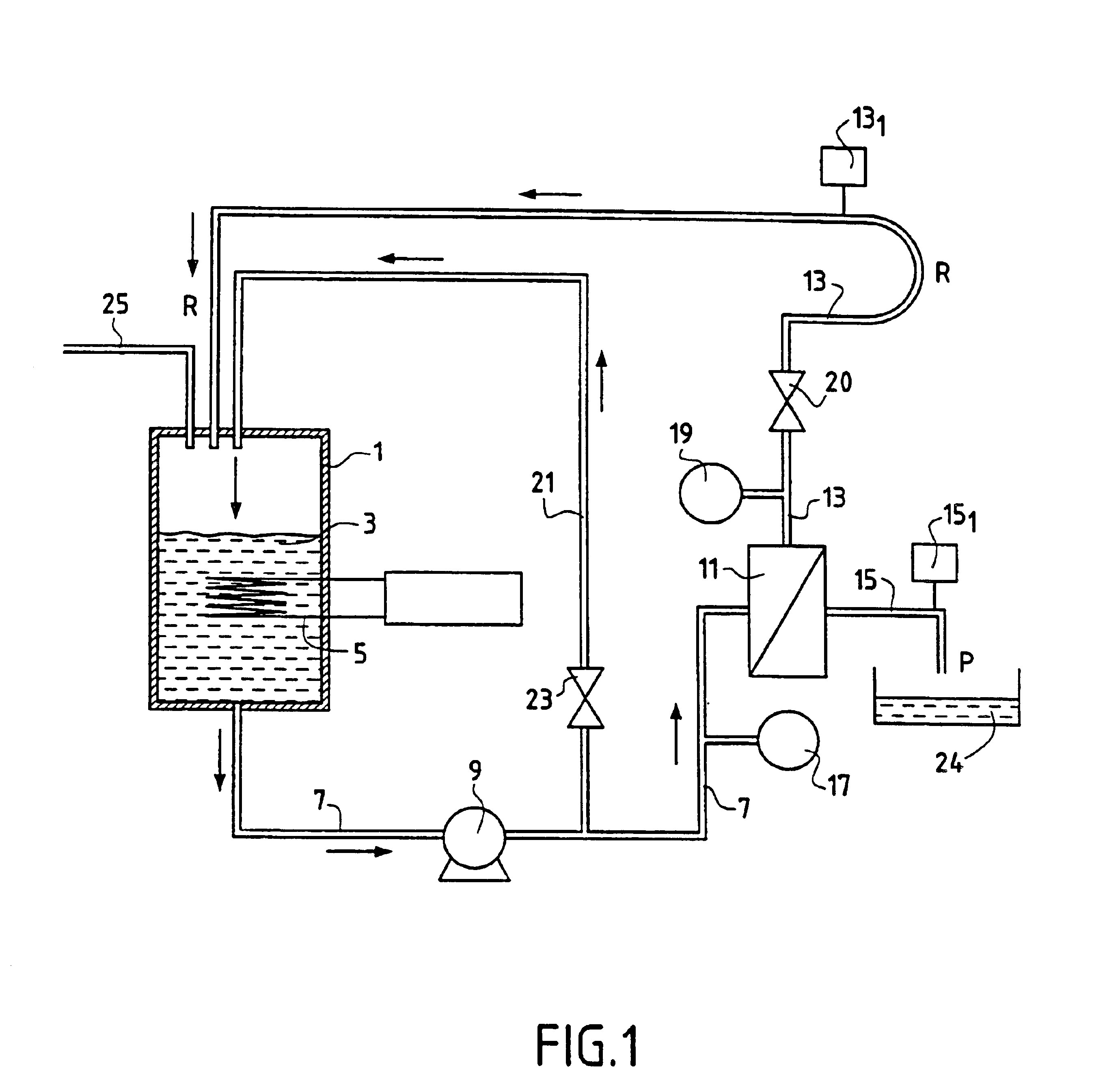
Nuclear Power Plant, Fuel Pool Water Cooling Facility and Method Thereof
InactiveUS20120294407A1Lower Level RequirementsPower plant safety arrangementNuclear energy generationNuclear plantReactor pressure vessel
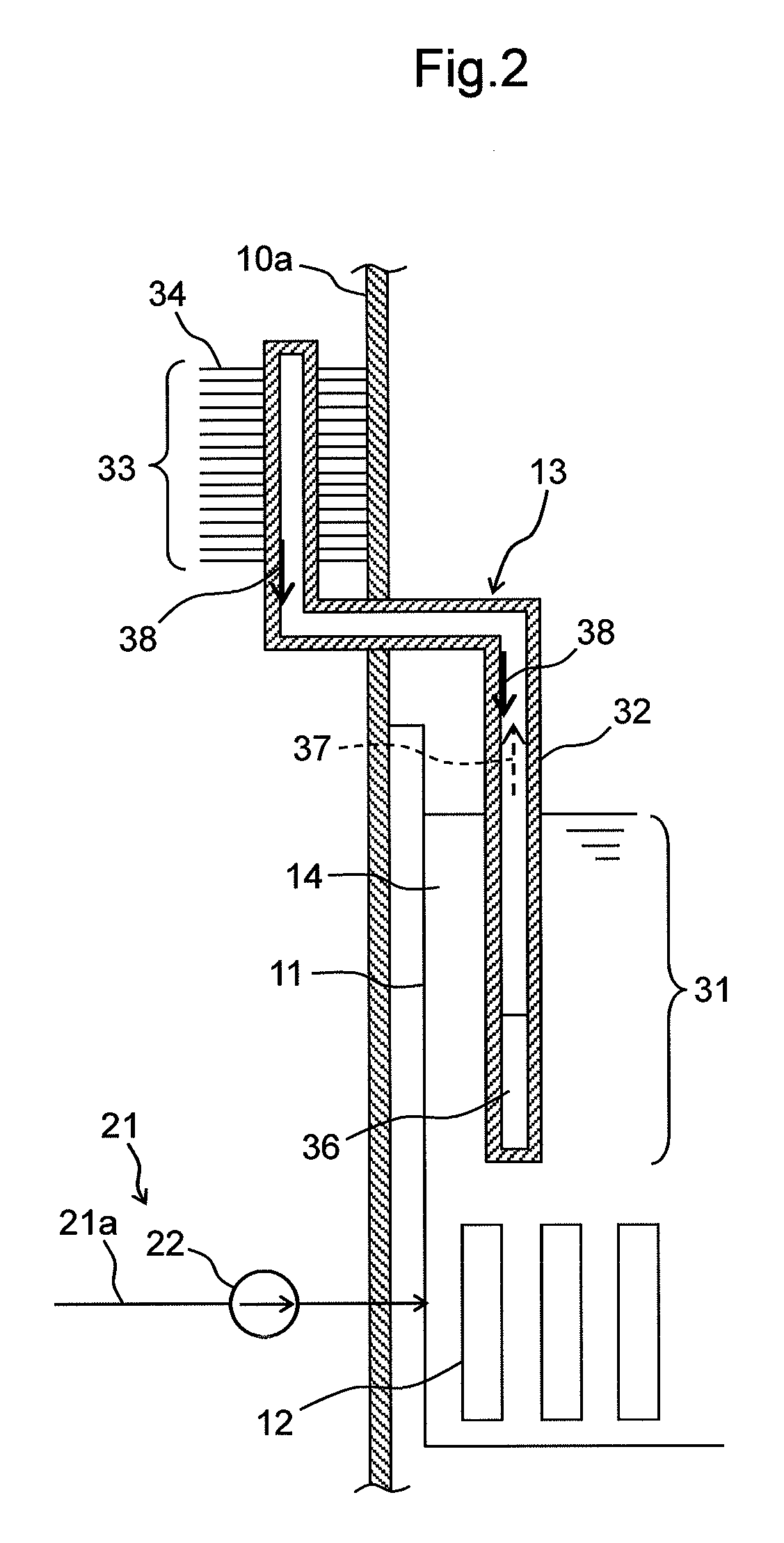
A nuclear power plant and a fuel pool water cooling facility and method are provided that can suppress the decrease of a water level in a fuel pool with no power supply at the time of malfunction of a circulating water system.The nuclear power plant includes a reactor pressure vessel 2 that encompasses a reactor 1 containing nuclear fuel; a containment vessel 3 for housing the reactor pressure vessel 2; a fuel pool 11 for storing spent fuel 12; a reactor building 10 that houses the reactor pressure vessel 2, the containment vessel 3 and the fuel pool 11; a circulating water system 21 adapted to forced-circulating-cool the fuel pool water 14 in the fuel pool 11; and at least one heat pipe 13 for transferring heat of the fuel pool water 14 in the fuel pool 11 and discharging the heat to the atmosphere.
Owner:HITACHI-GE NUCLEAR ENERGY LTD
Method of transferring high level radionactive materials, and system for the same
ActiveUS20110150164A1Minimize thermal shockNuclear energy generationPortable shielded containersRadioactive agentEnvironmental engineering
An apparatus and method for inter-unit transfer of spent nuclear fuel. In one aspect, the invention is a method of transferring high level radioactive waste comprising: a) loading high level radioactive waste into a water-filled cavity of a canister body having an open top end at a first location; b) coupling a lid to the canister body to enclose the open top end; c) removing a volume of water from the cavity so that a water level of the water within the cavity is above a top end of the high level radioactive waste and a space exists between the water level and a bottom surface of the lid; d) hermetically sealing the cavity; and e) transferring the canister to a second location, the water level remaining above the top end of the high level radioactive waste during the transfer.
Owner:HOLTEC INTONAL
Porous membrane electrochemical cell for uranium and transuranic recovery from molten salt electrolyte
InactiveUS7799185B1Eliminate the problemDiffusion slowCellsIsotope separationMaterials scienceUranium
Owner:THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY
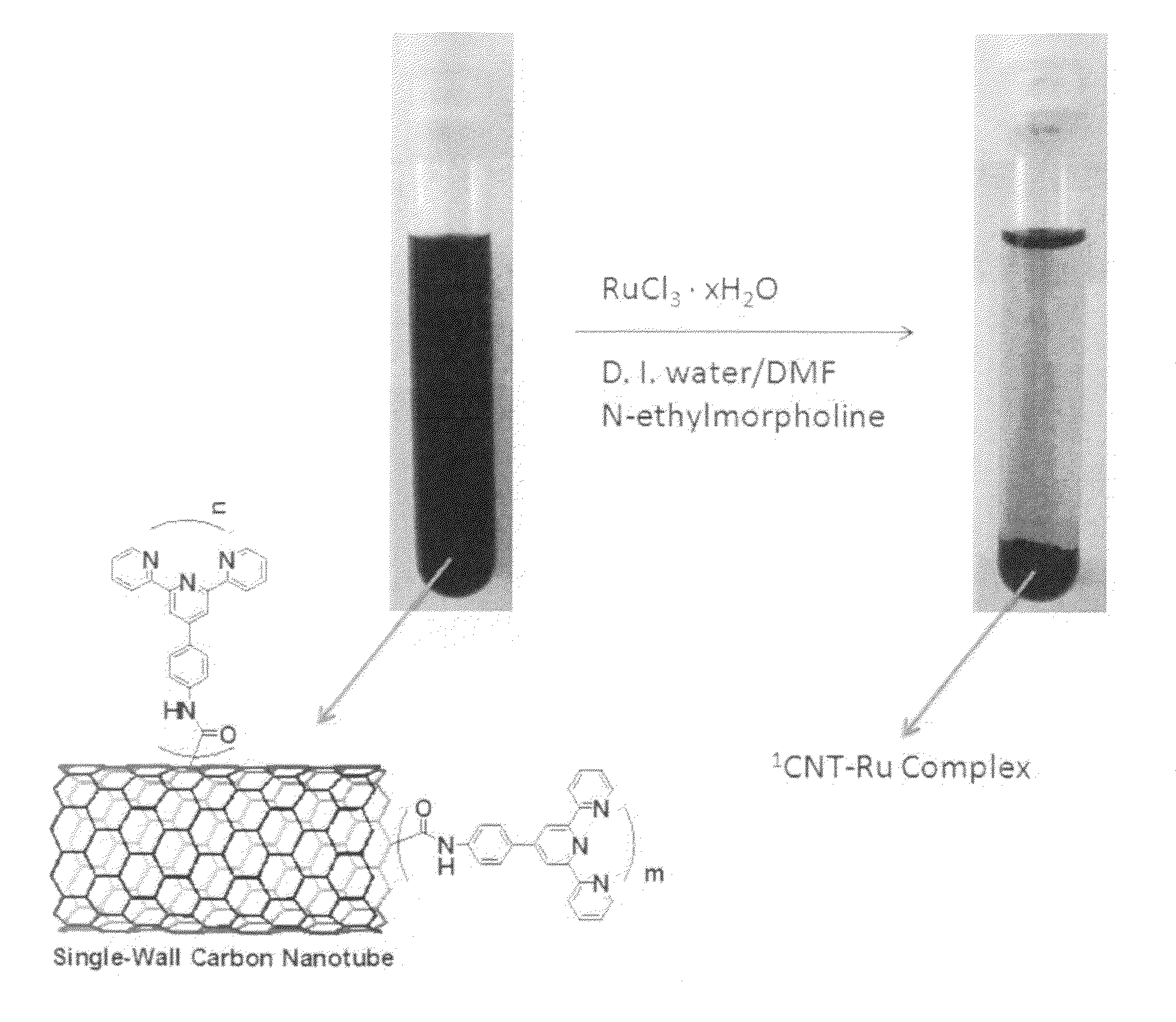
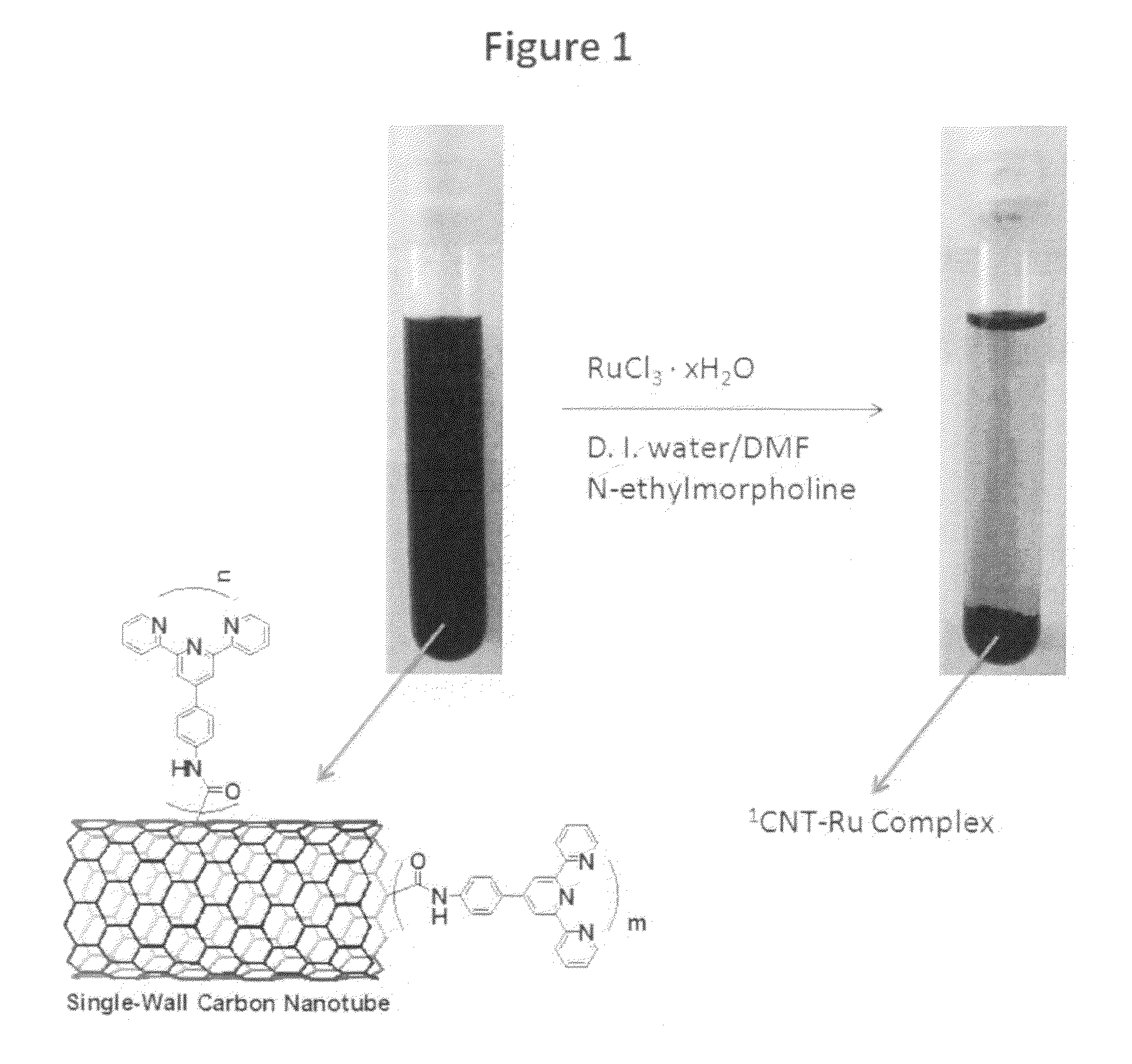
Carbon nanotubes using for recovery of radionuclides and separation of actinides and lanthanides
ActiveUS20090093664A1High mechanical strengthExcellent chemical/physical stabilityFibre chemical featuresPhosphorus organic compoundsNuclear powerPhosphate
Methods and compositions to extract radionuclides such as various actinides and lanthanides from organic and / or aqueous solutions by utilizing extractant functionalized carbon nanotubes are disclosed. More particularly, phosphorous-containing (such as phosphine oxides, phosphoric acids or phosphates) organic extractants and other predesigned extractants (such as crown ethers, calncrown derivatives, malonamide and diglycolamide derivatives, polyethylene glycol derivatives, cobalt dicarbollite derivatives, and N-donating heterocyclic ligands) can be covalently and / or non-covalently employed on the surfaces and / or ends (tips) of carbon nanotubes for the purpose of removal radionuclides such as various actinides and lanthanides from organic and / or aqueous solutions. Extractant functionalized carbon nanotubes can be used for extracting radioactive nuclides from nuclear waste or spent nuclear fuel, which are produced and / or reprocessed from the nuclear power generation or other nuclear application. The invention also relates to the solid-liquid separation process based on the contact of liquid radioactive waste by using the invention extracting agents as the solid phase.
Owner:CHEMNANO MATERIALS
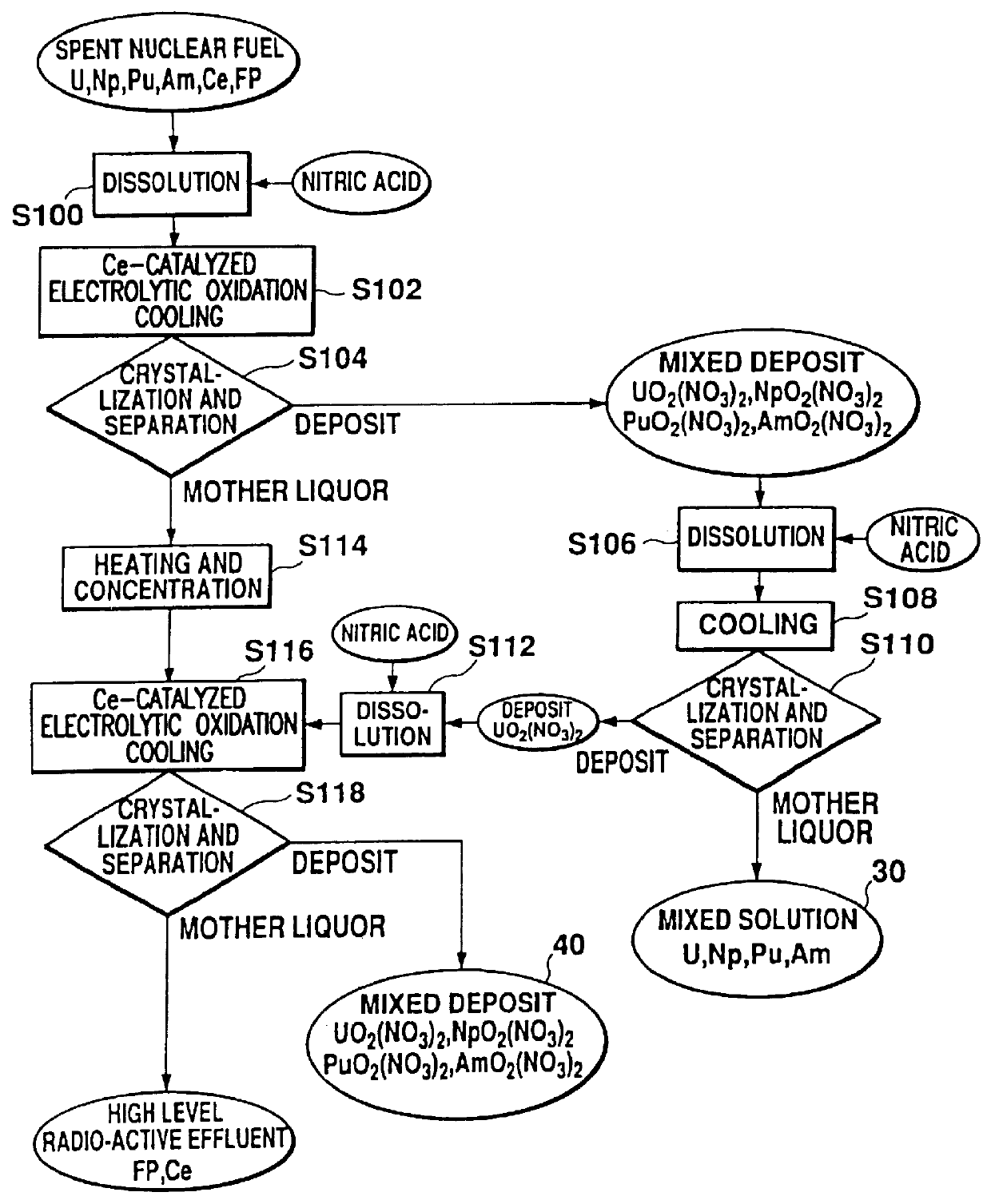
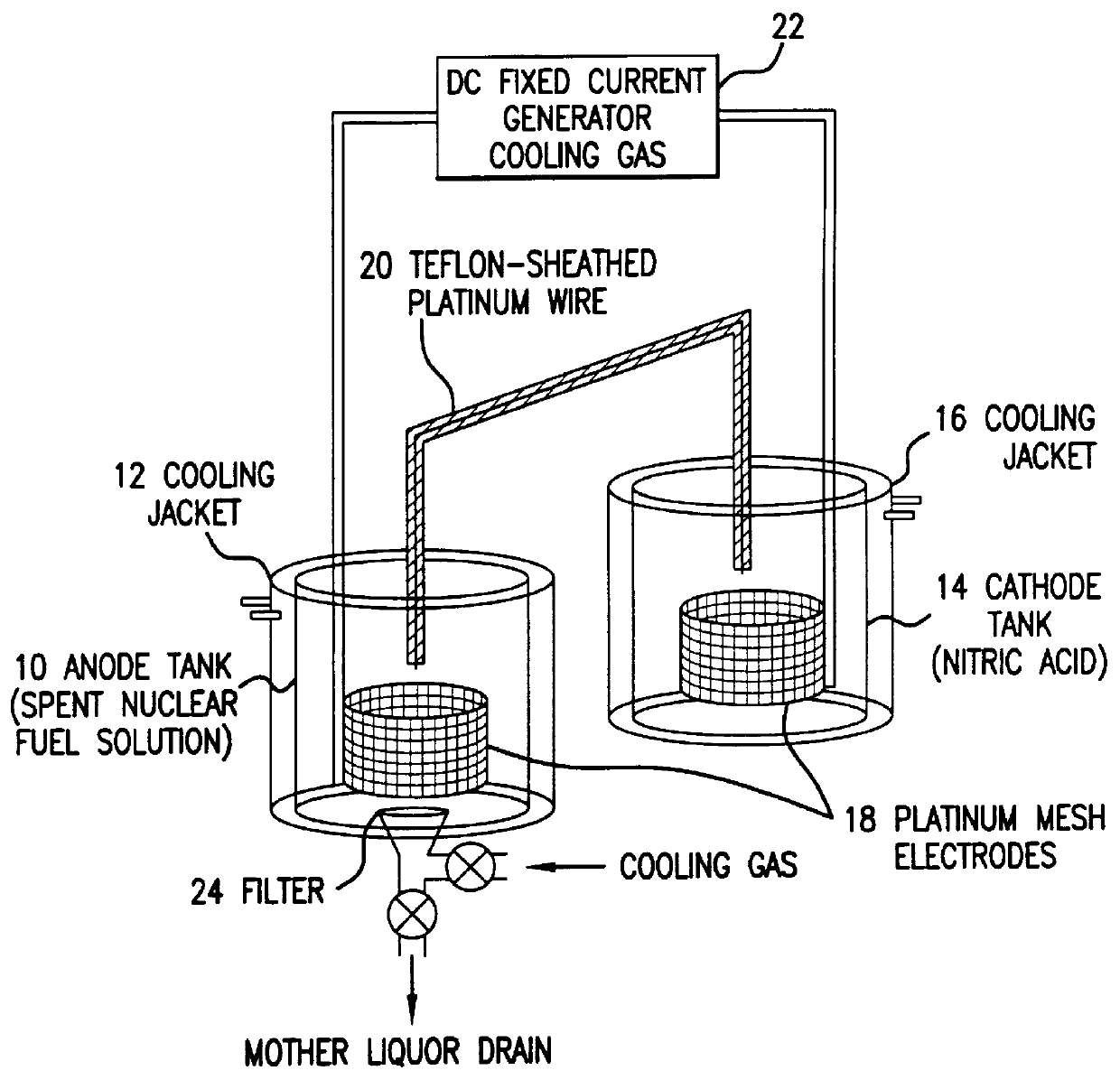
Method of recovering uranium and transuranic elements from spent nuclear fuel
InactiveUS6033636AReduce solubilityPromote recoveryElectrolysis componentsSolvent extractionSolventWaste material
The steps for recovering uranium and transuranic elements are simplified, and the generation of waste solvent and waste materials is suppressed. Spent nuclear fuel is dissolved in nitric acid (S100) and the resulting solution is subjected to electrolytic oxidation so that U, Np, Pu, Am is oxidized to VI using Ce as oxidation catalyst. The solution is cooled, and nitrates of valence VI thereby deposit as crystals and are separated from the mother liquor (S104). The mother liquor is heated and concentrated (S114). The mixed crystalline deposit is dissolved in nitric acid (S106), uranyl nitrate is deposited alone by cooling (S108), and the crystals are separated from the U, Np, Pu, Am mixed solution (S110). The uranyl nitrate is dissolved in nitric acid (S112), and the heated and concentrated mother liquor is added to it to prepare another mixed solution. This mixed solution is then subjected to electrolytic oxidation to oxidize the remaining U, Np, Pu, Am to valence VI, and the solution is cooled so that U, Np, Pu, Am are coprecipitated with uranyl nitrate as crystals, and can be separated from high level radioactive effluent (S118).
Owner:DORYOKURO KAKUNENRYO KAIHATSU JIGYODAN
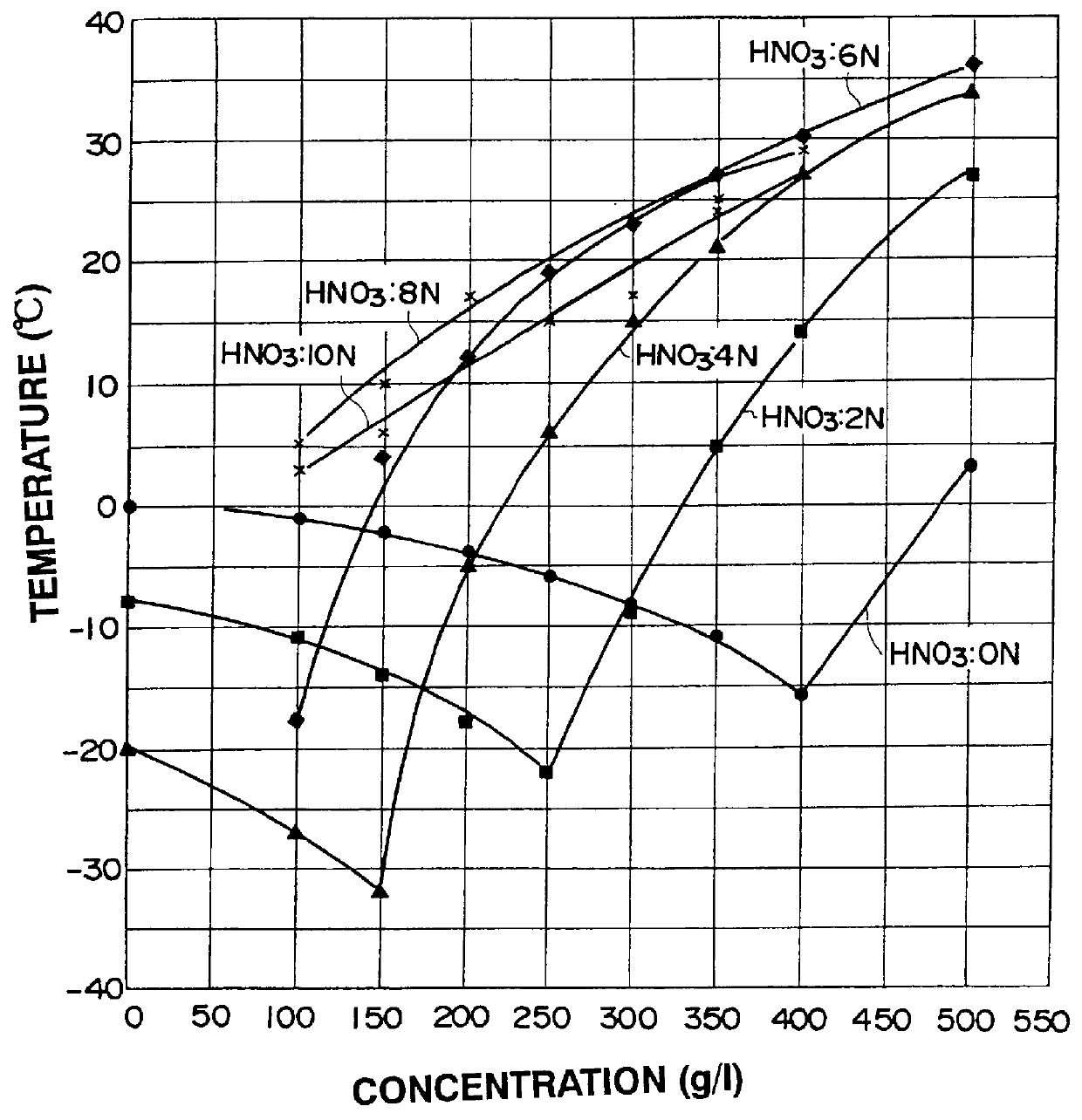
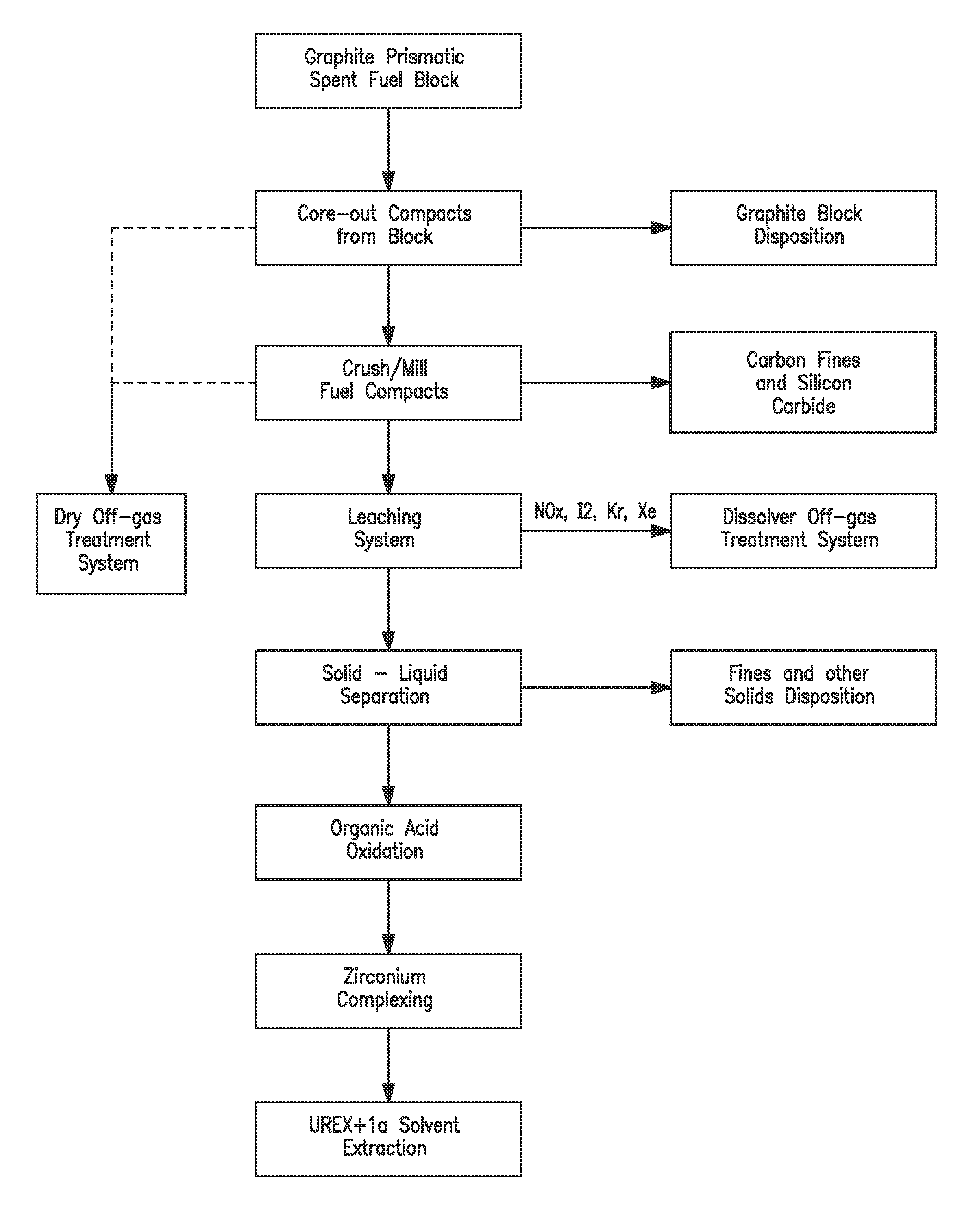
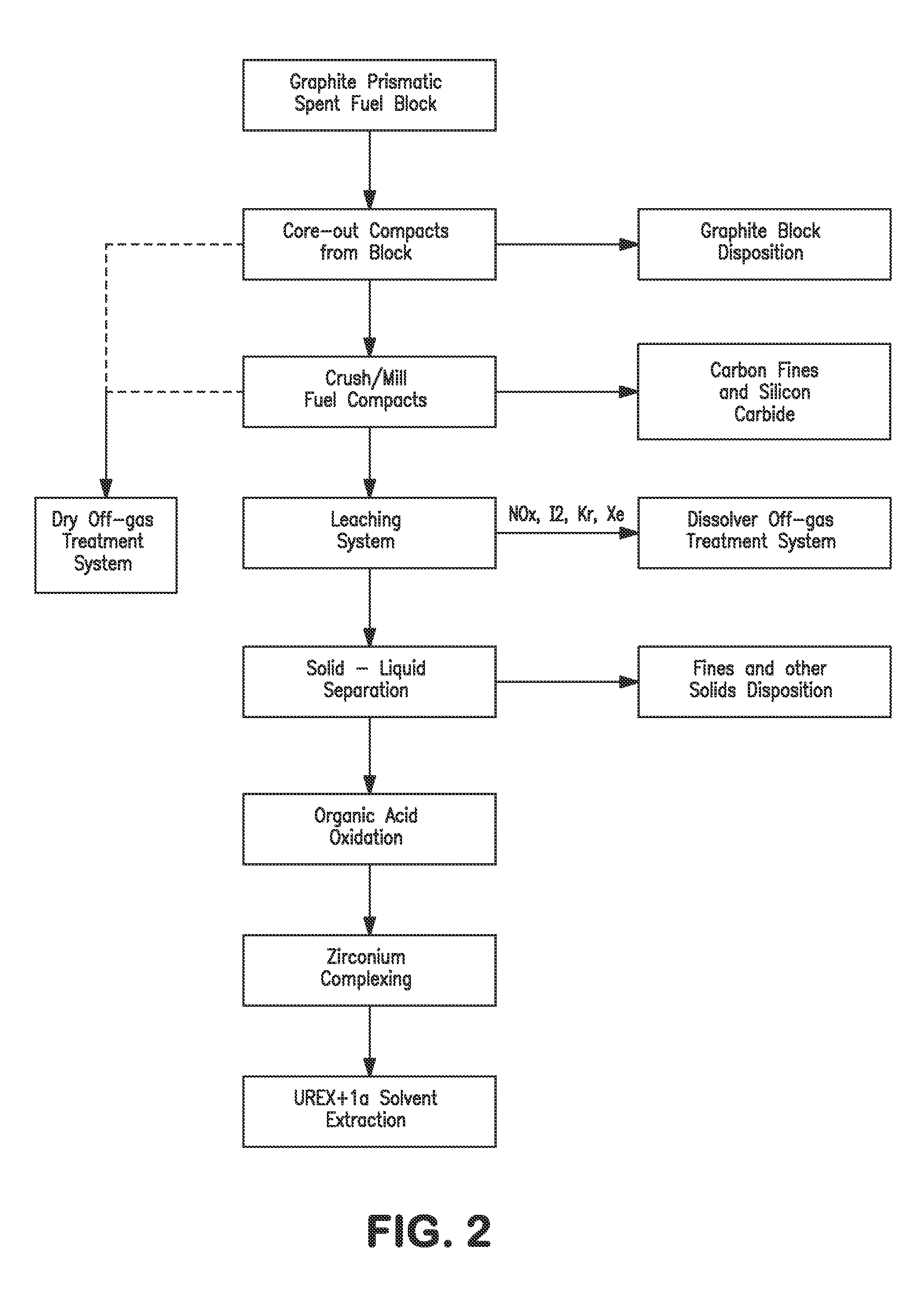
Processing fissile material mixtures containing zirconium and/or carbon
A method of processing spent TRIZO-coated nuclear fuel may include adding fluoride to complex zirconium present in a dissolved TRIZO-coated fuel. Complexing the zirconium with fluoride may reduce or eliminate the potential for zirconium to interfere with the extraction of uranium and / or transuranics from fission materials in the spent nuclear fuel.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY
Method for manufacturing a tube and a sheet of niobium-containing zirconium alloy for a high burn-up nuclear fuel
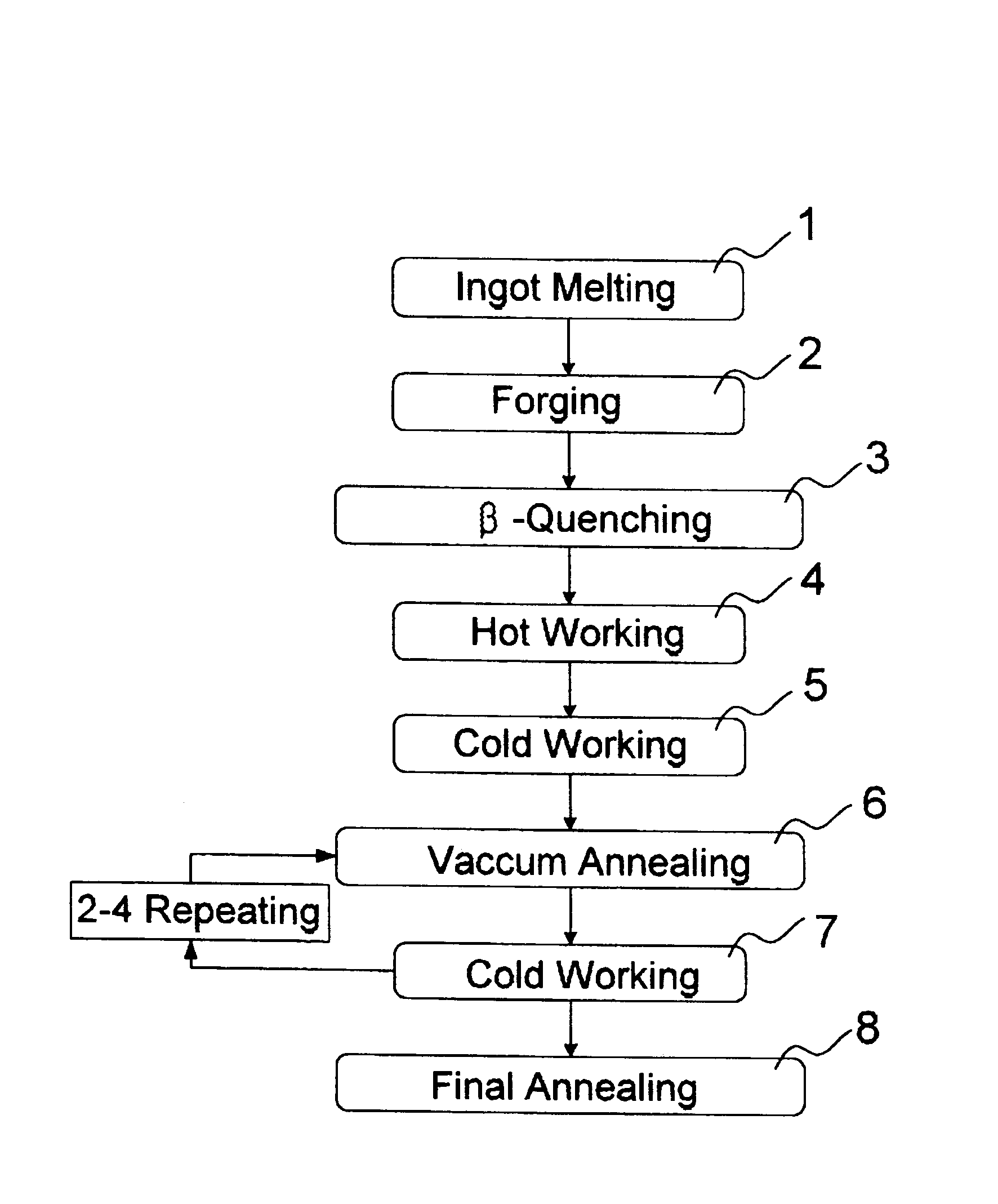
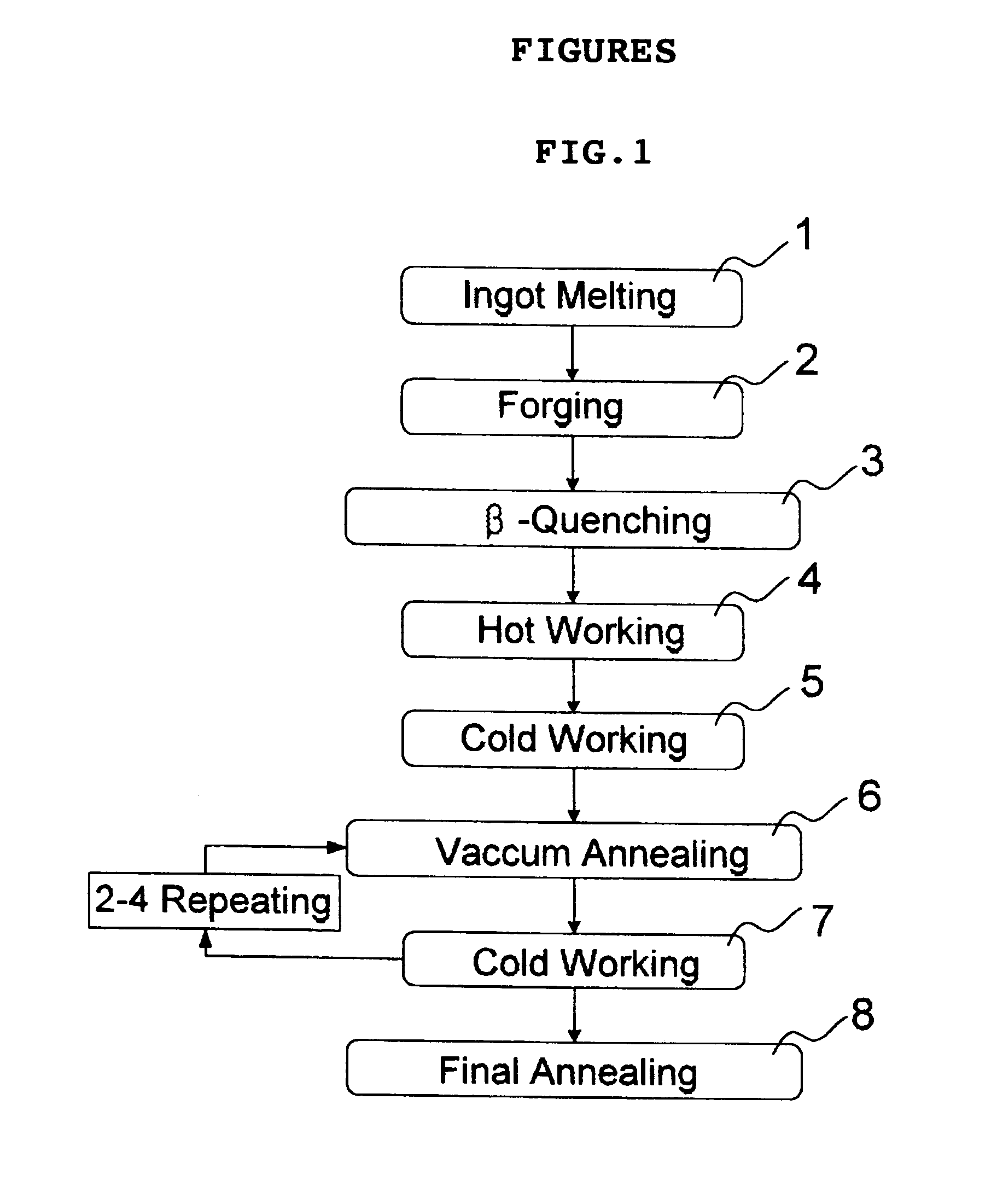
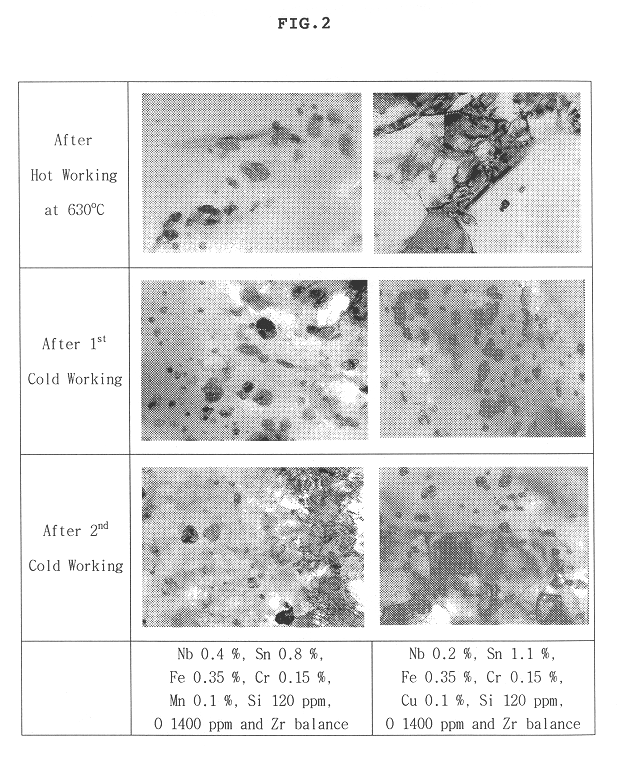
Disclosed is a method for manufacturing a tube and a sheet of niobium-containing zirconium alloys for the high burn-up nuclear fuel. The method comprises melting Nb-added zirconium alloy to ingot; forging the ingot at beta phase range; beta-quenching the forged ingot after solution heat-treatment at 1015-1075° C.; hot-working the quenched ingot at 600-650° C.; cold-working the hot-worked ingot in three to five passes, with intermediate vacuum annealing; and final vacuum annealing the cold-worked ingot at 440-600° C., wherein temperatures of intermediate vacuum annealing and final vacuum annealing after beta-quenching are changed so as to attain the condition under which precipitates in the alloy matrix are limited to an average diameter of 80 nm or smaller and the accumulated annealing parameter (SIGMA A) is limited to 1.0x10-18 hr or lower.
Owner:KEPCO NUCLEAR FUEL CO LTD +1
FeCrAl base alloy material for nuclear fuel cladding material
InactiveCN106319369AImprove antioxidant capacityExcellent fault toleranceOptical rangefindersNuclear energy generationNuclear powerPressurized water reactor
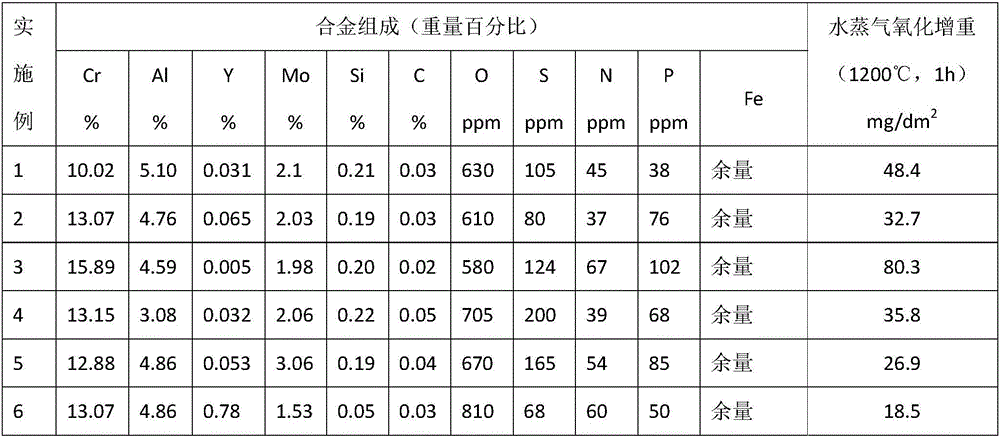
The invention relates to a FeCrAl base alloy material for a nuclear fuel cladding material. With the total weight of the FeCrAl base alloy material as a standard, the alloy material comprises 6%-16% of Cr, 3%-8% of Al, 0.001%-1% of Y, 0.1%-4% of Mo, 0.01%-0.5% of Si, 0.001%-0.5% of C, less than or equal to 500 ppm of N, less than or equal to 1000 ppm of O, less than or equal to 500 ppm of P, less than or equal to 500 ppm of S and the balance Fe. A FeCrAl base alloy shows the excellent antioxygenic property in the 1200 DEG C vapor environment, the excellent accident fault-tolerant ability is achieved and is obviously superior to that of a Zr base alloy, the machining performance is good, and the FeCrAl base alloy material can be used as core structural materials such as fuel element cladding, fuel element composite cladding, fuel cladding coatings and positioning grillage stripes in nuclear power station pressurized water reactors.
Owner:SUZHOU NUCLEAR POWER RES INST +3
Control of a laser inertial confinement fusion-fission power plant
ActiveUS9171646B2Extended service lifeNuclear energy generationWaste based fuelFusion fissionEngineering
A laser inertial-confinement fusion-fission energy power plant is described. The fusion-fission hybrid system uses inertial confinement fusion to produce neutrons from a fusion reaction of deuterium and tritium. The fusion neutrons drive a sub-critical blanket of fissile or fertile fuel. A coolant circulated through the fuel extracts heat from the fuel that is used to generate electricity. The inertial confinement fusion reaction can be implemented using central hot spot or fast ignition fusion, and direct or indirect drive. The fusion neutrons result in ultra-deep burn-up of the fuel in the fission blanket, thus enabling the burning of nuclear waste. Fuels include depleted uranium, natural uranium, enriched uranium, spent nuclear fuel, thorium, and weapons grade plutonium. LIFE engines can meet worldwide electricity needs in a safe and sustainable manner, while drastically shrinking the highly undesirable stockpiles of depleted uranium, spent nuclear fuel and excess weapons materials.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
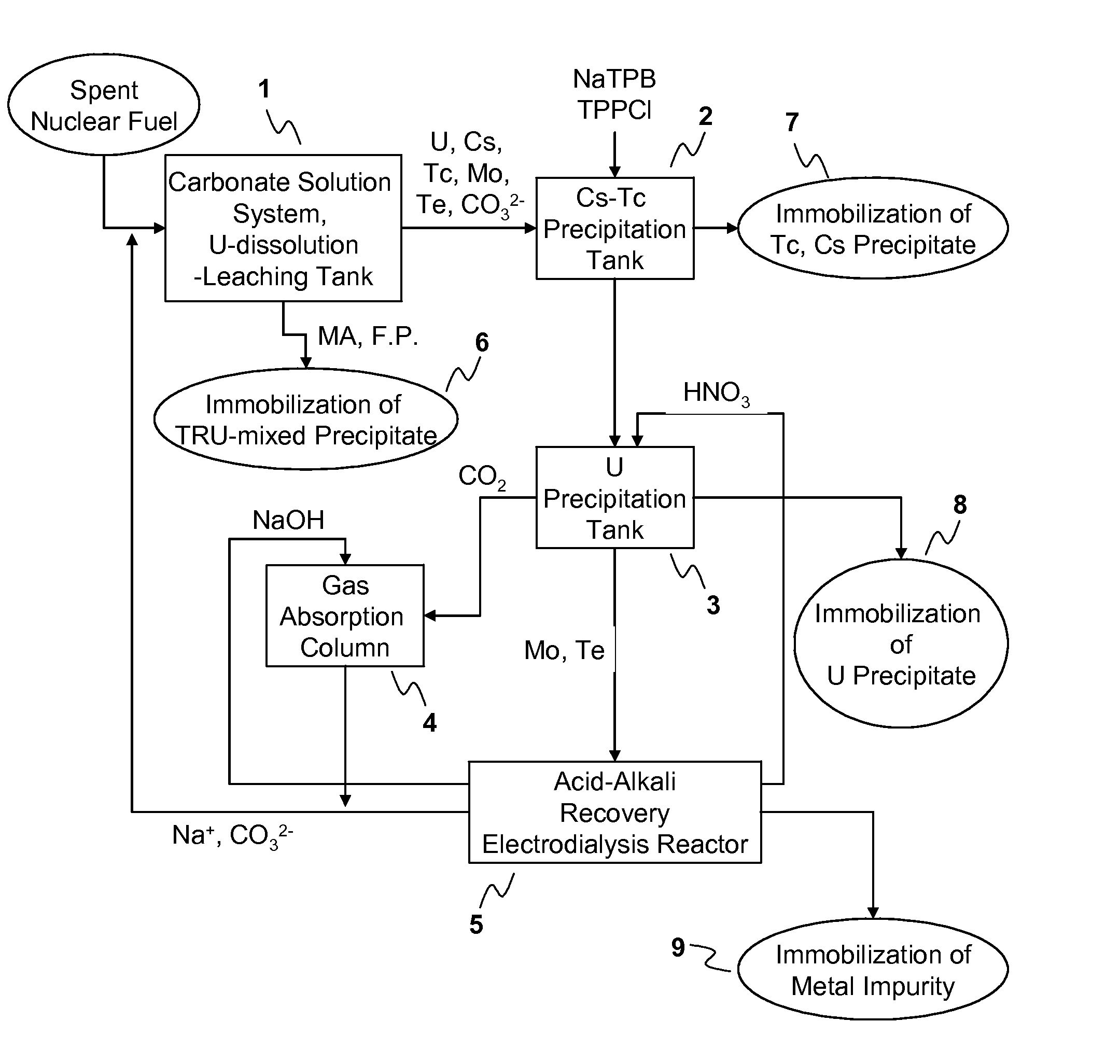
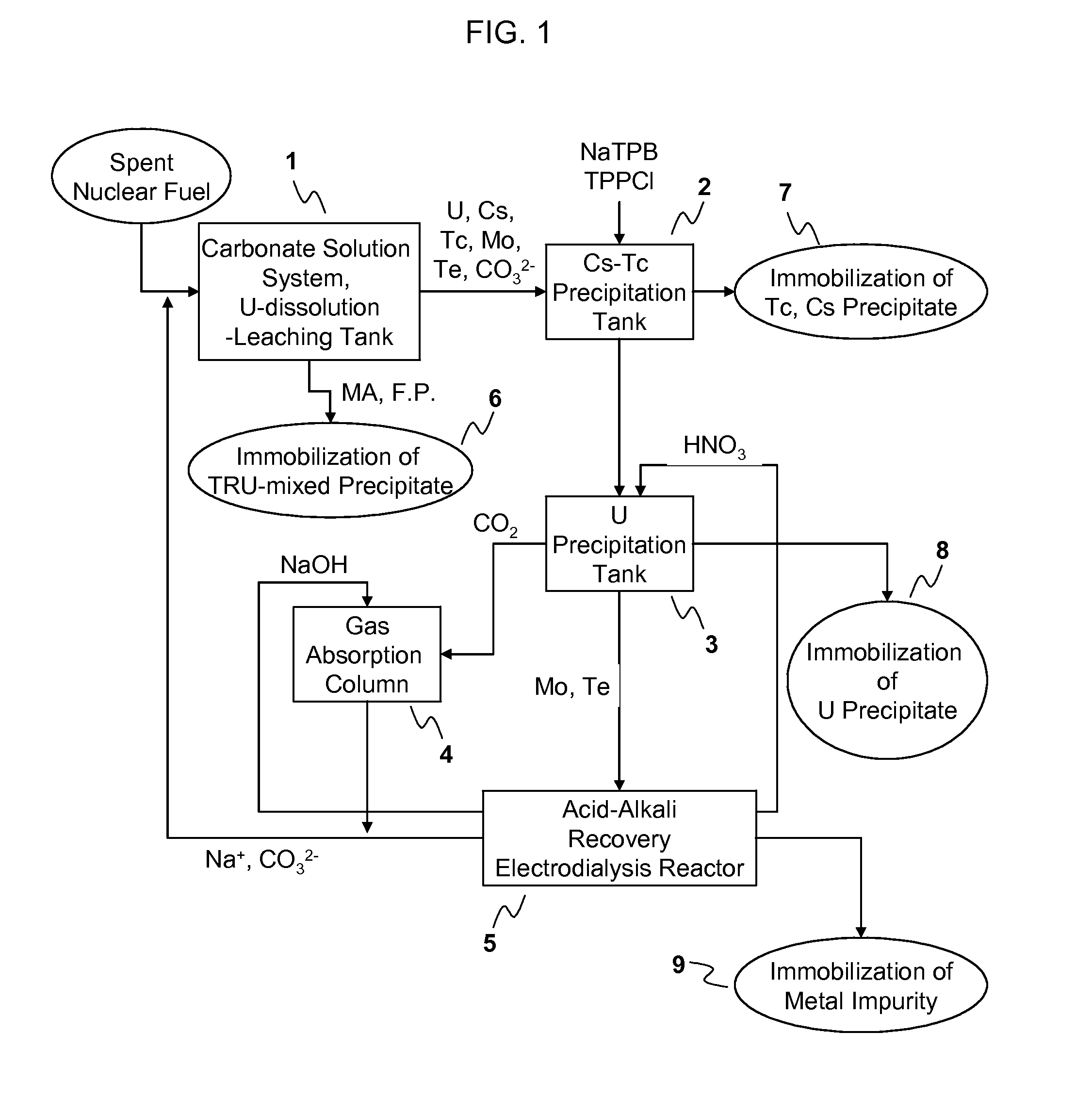
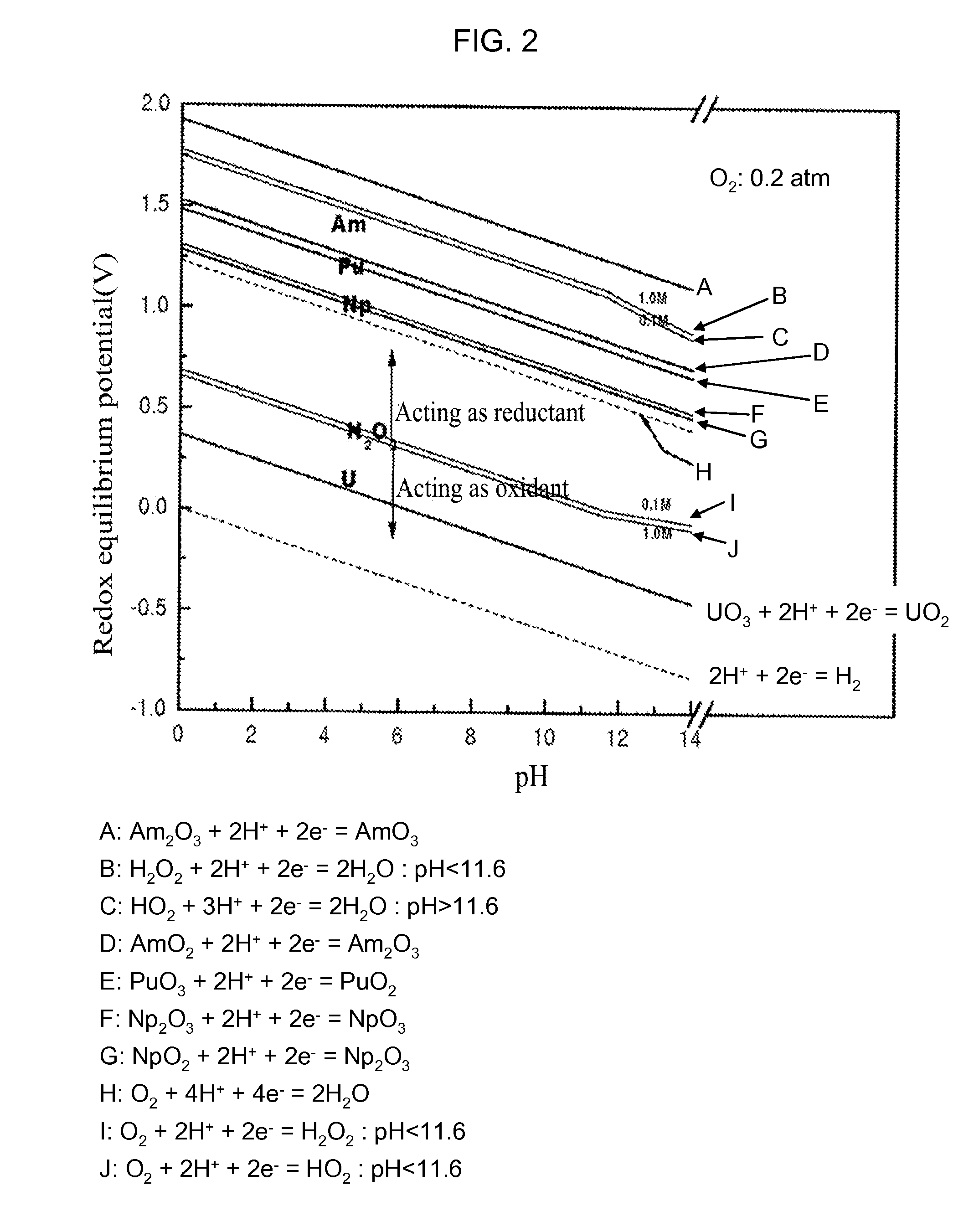
Process for Recovering Isolated Uranium From Spent Nuclear Fuel Using a Highly Alkaline Carbonate Solution
InactiveUS20090269261A1Easy to separateEnhance proliferation resistanceElectrolysis componentsPhotography auxillary processesTransuranium elementCarbonate
Disclosed is a process for recovery of uranium from a spent nuclear fuel using a carbonate solution, characterized by excellent proliferation resistance of preventing leaching of transuranium element (TRU) nuclides such as Pu, Np, Am, Cm, etc. from the spent nuclear fuel as well as environmental friendliness of minimizing waste generation, wherein a highly alkaline carbonate solution is used to separate uranium alone from the spent nuclear fuel.
Owner:KOREA ATOMIC ENERGY RES INST
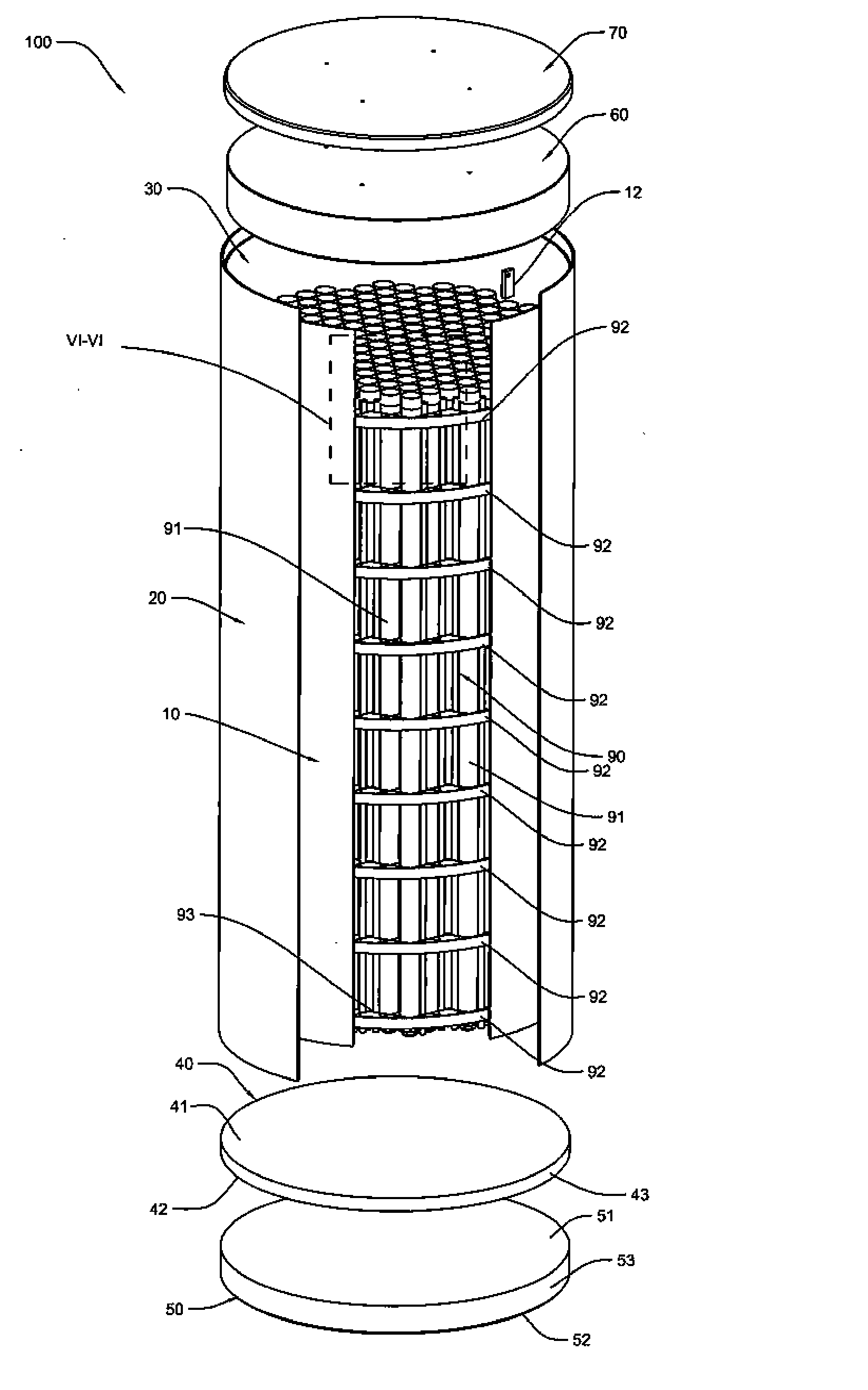
Canister apparatus and basket for transporting, storing and/or supporting spent nuclear fuel
ActiveUS8135107B2Efficiently accommodatedNuclear engineering problemsNuclear engineering solutionsEngineeringMechanical engineering
A canister apparatus, basket apparatus and combinations thereof for transporting and / or storing high level radioactive waste, such as spent nuclear fuel. The canister apparatus comprises a cavity for receiving the spent nuclear fuel that is surrounded by two independent gas-tight containment boundaries. The structures that form the two independent gas-tight containment boundaries are in substantially continuous surface contact with one another, thereby facilitating sufficient heat removal from the cavity. In another aspect, the invention is a basket apparatus having a plurality of disk-like grates arranged in a stacked and spaced arrangement so that the cells of the disk-like grates are aligned. In still another aspect, the invention can be a basket apparatus having a disk-like grate having a ring-like structure encompassing a gridwork of beams specially arranged to achieve a unique cell configuration.
Owner:HOLTEC INT
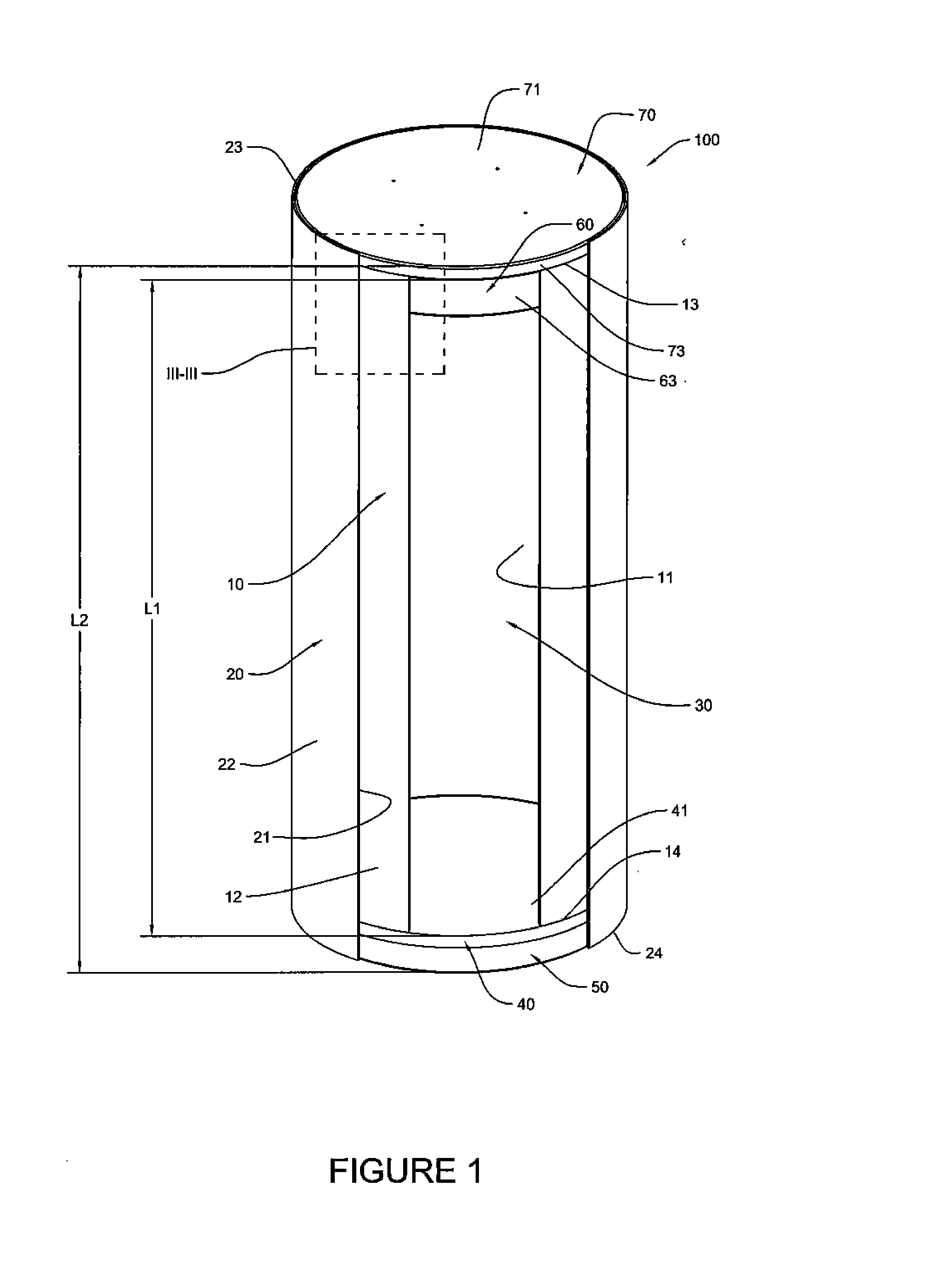
Canister apparatus and basket for transporting, storing and/or supporting spent nuclear fuel
ActiveUS20130070885A1Efficiently accommodatedNuclear engineering problemsNuclear engineering solutionsRadioactive wasteAtomic physics
A canister apparatus, basket apparatus and combinations thereof for transporting and / or storing high level radioactive waste, such as spent nuclear fuel In one embodiment, the invention can be a basket apparatus for supporting a plurality of spent nuclear fuel rods within a containment structure, the basket apparatus comprising a plurality of disk-like grates, each disk-like grate, having a plurality of ceils formed by a gridwork of beams; and means for supporting the disk-like grates in a spaced arrangement with respect to one another and so that the cells of the disk-like grates are aligned.
Owner:HOLTEC INT
Process for reprocessing a spent nuclear fuel and of preparing a mixed uranium-plutonium oxide
ActiveUS20070290178A1Risk minimizationUranium compounds preparationSolvent extractionUranium oxideDissolution
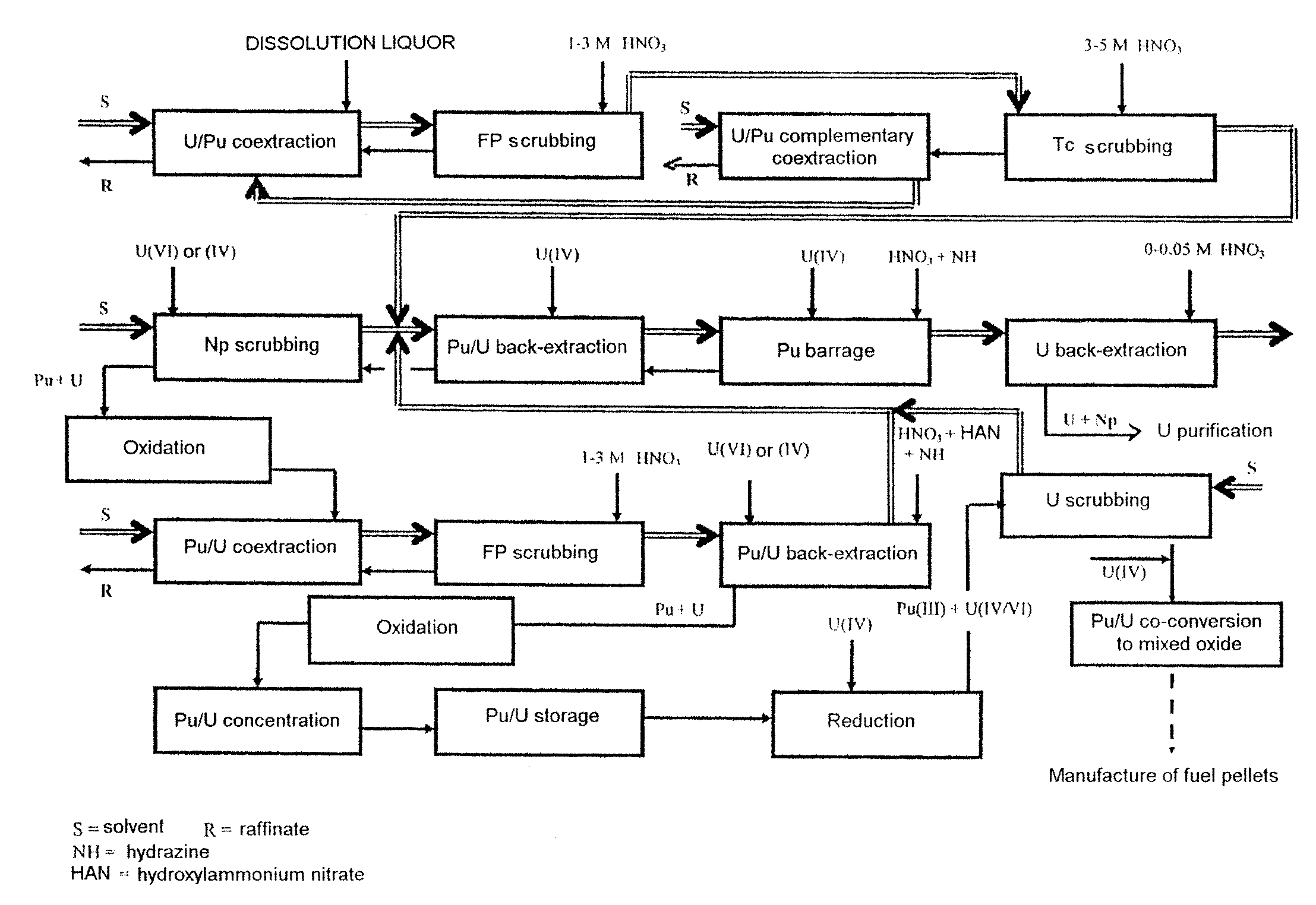
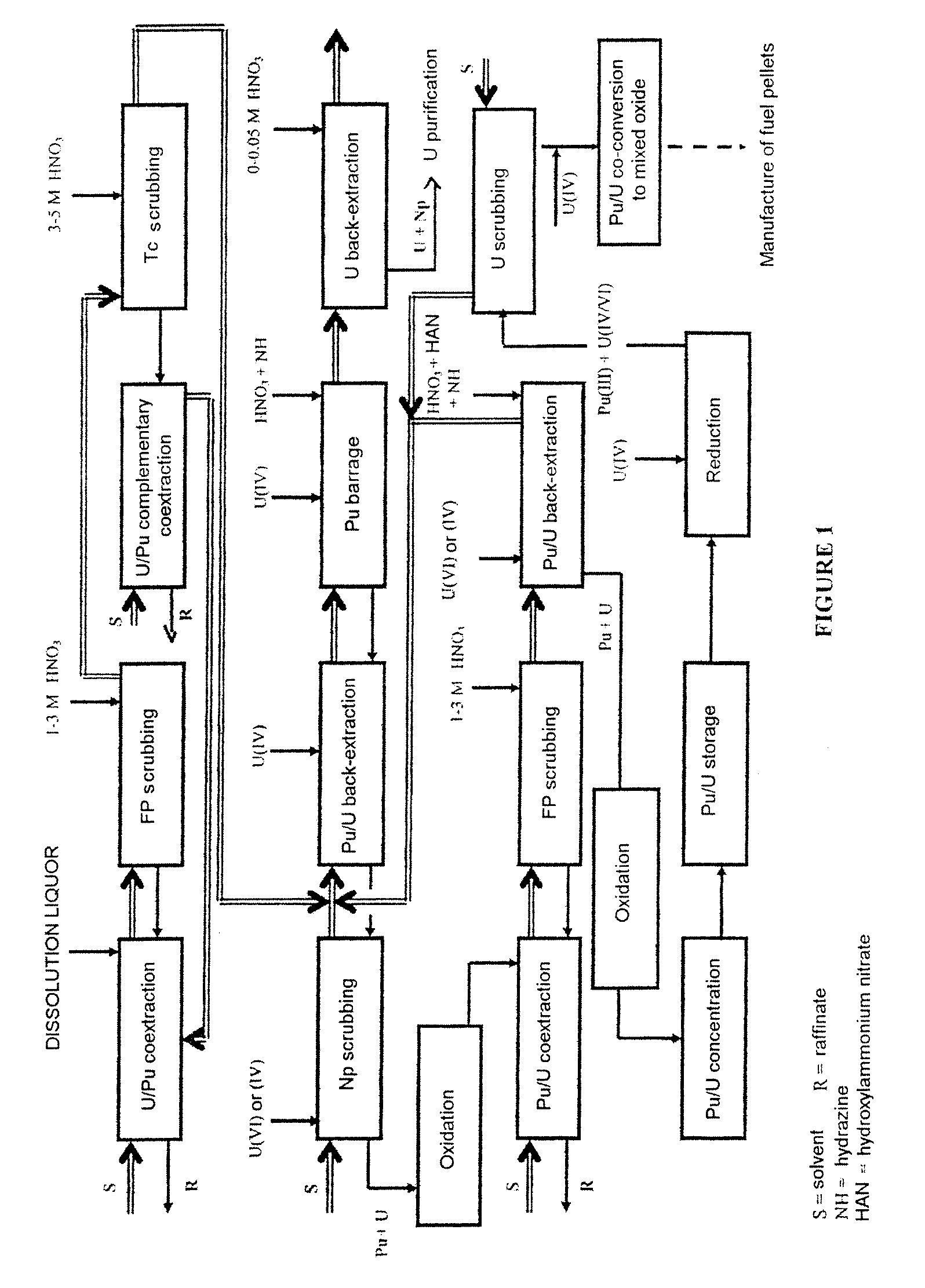
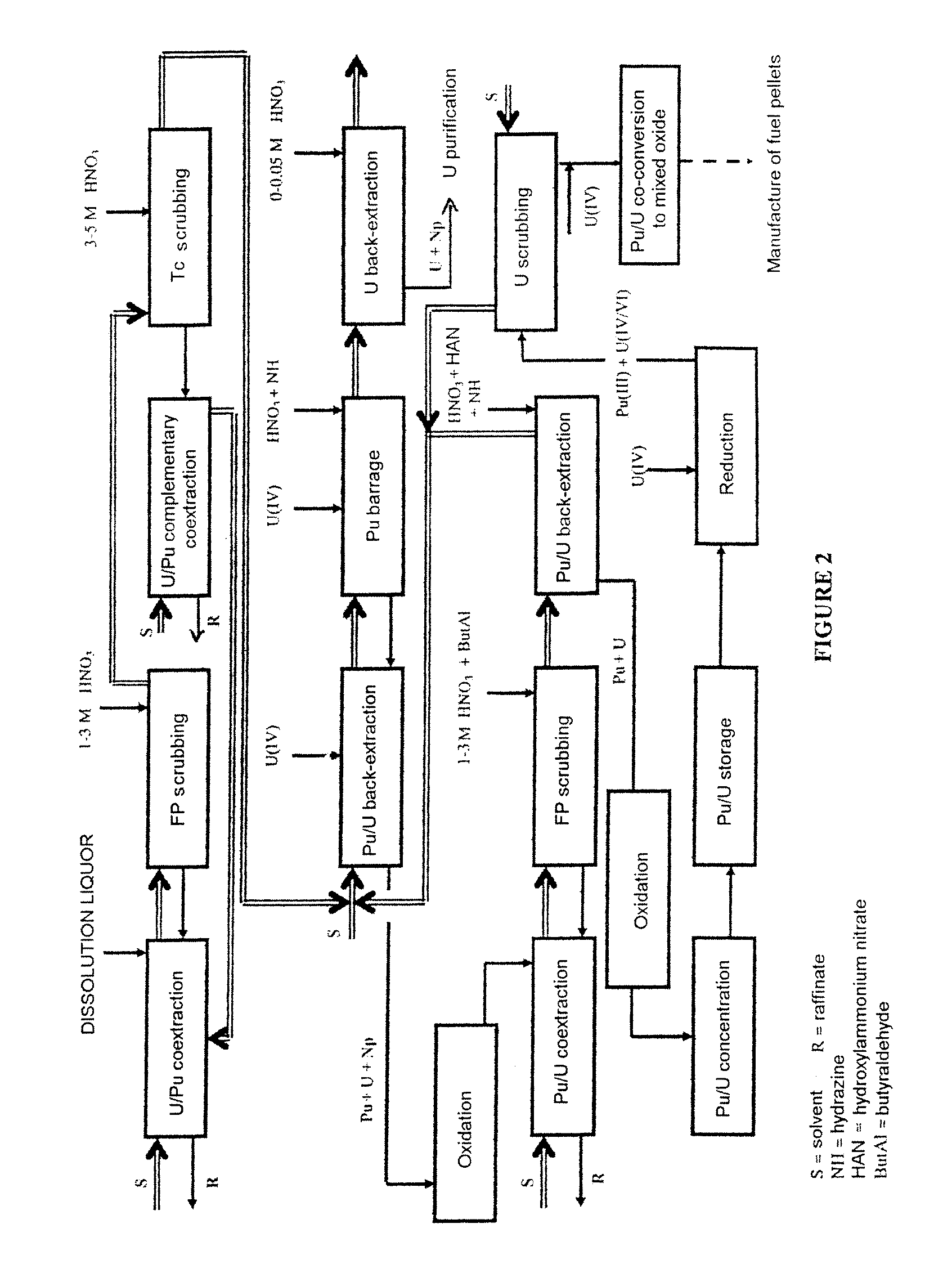
The invention relates to a process for reprocessing a spent nuclear fuel and for preparing a mixed uranium-plutonium oxide, which process comprises: a) the separation of the uranium and plutonium from the fission products, the americium and the curium that are present in an aqueous nitric solution resulting from the dissolution of the fuel in nitric acid, this step including at least one operation of coextracting the uranium and plutonium from said solution by a solvent phase; b) the partition of the coextracted uranium and plutonium to a first aqueous phase containing plutonium and uranium, and a second aqueous phase containing uranium but no plutonium; c) the purification of the plutonium and uranium that are present in the first aqueous phase; and d) a step of coconverting the plutonium and uranium to a mixed uranium / plutonium oxide. Applications: reprocessing of nuclear fuels based on uranium oxide or on mixed uranium-plutonium oxide.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES +2
Method and device for fast breeding and converting nuclear fuel
InactiveCN101315815ALow costMeet needsFuel elementsNuclear energy generationInherent safetyNuclear power
The invention discloses a method and a device for fast multiplicating and transforming nuclear fuel with high inherent security and low cost, and the method and the device adopt 'moving solid nuclear fuel' which can flow and is similar to fluid, can be applied in a fast neutron reactor, and produce more nuclear fuel with less fissile fuel initial installation quantity and lower cost in a shorter time, thus satisfying the nuclear fuel demand at the current world nuclear power big development stage. The method and the device for fast multiplicating and transforming nuclear fuel are real nuclear reactors with inherent security, and can thoroughly eliminate the serious accident of massive radioactive release caused by element melting of the nuclear fuel which still possibly occurs in the current nuclear power station.
Owner:吕应中
Nuclear fuel assembly and related methods for spent nuclear fuel reprocessing and management
InactiveUS20110317794A1Increase fuel consumptionLower the volumeFuel elementsConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsUranium dioxideNuclear fuel
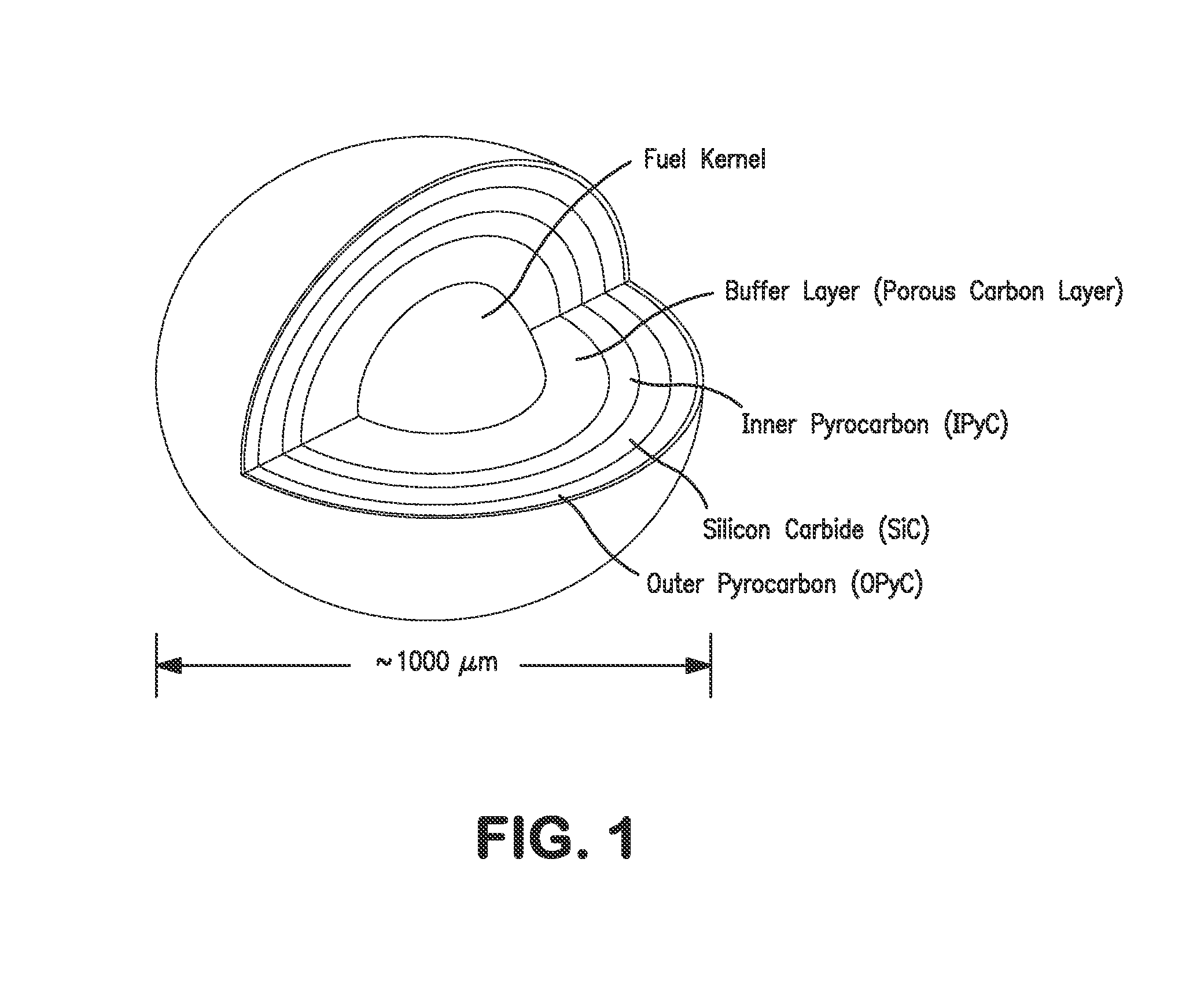
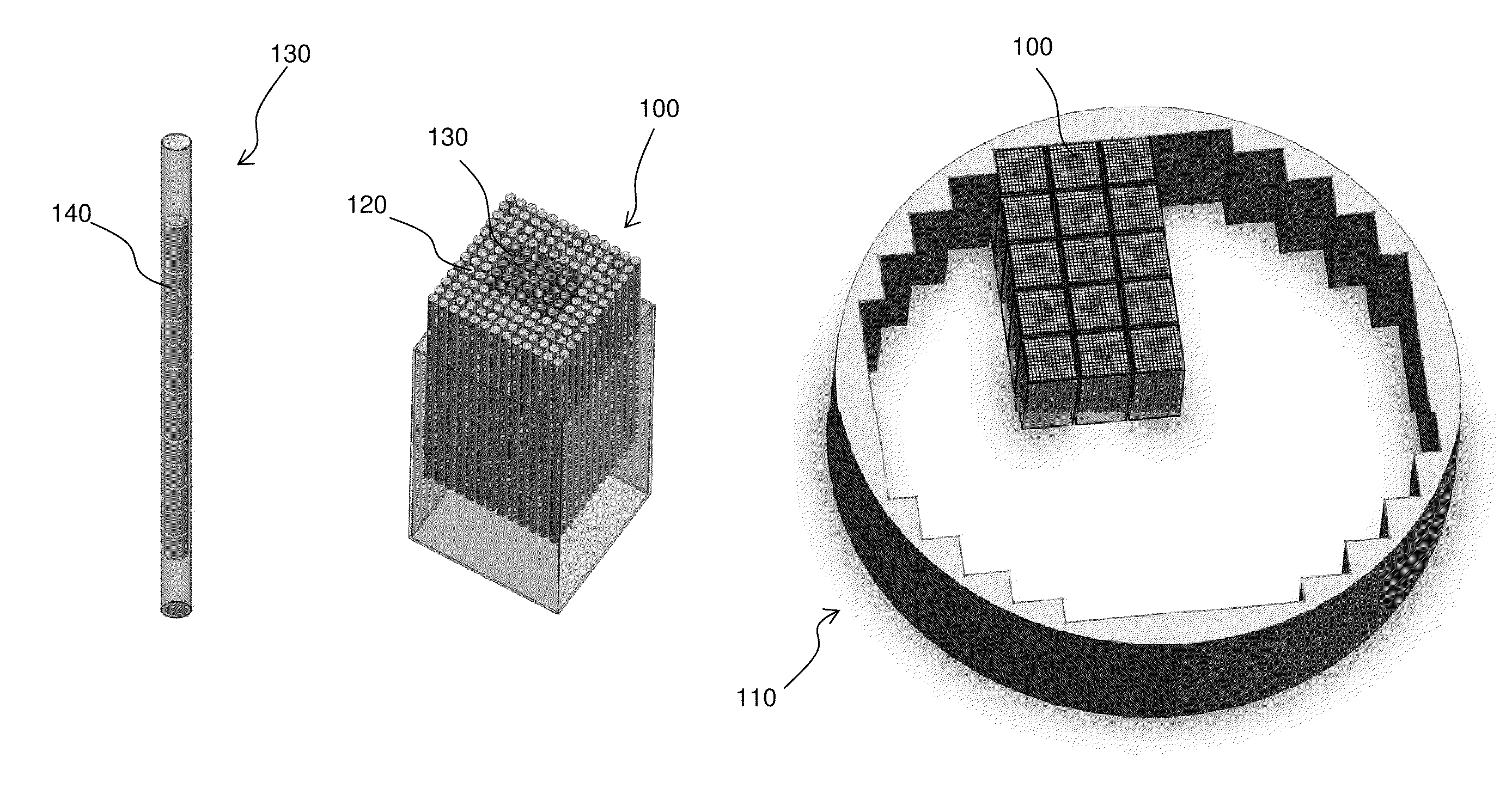
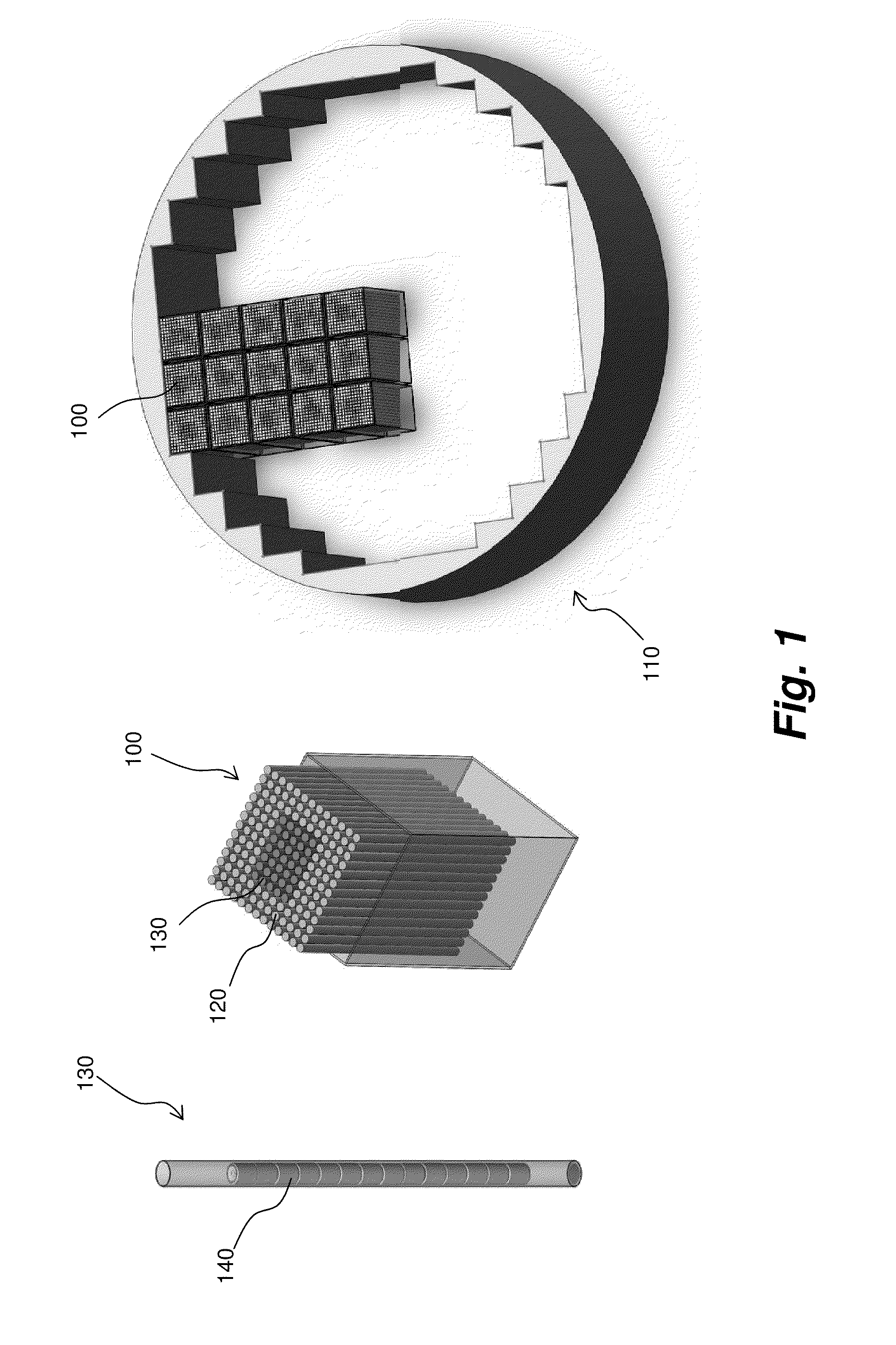
Various embodiments of a nuclear fuel assembly and related methods for processing and managing spent nuclear fuel are disclosed. According to one exemplary embodiment, a nuclear fuel may include a plurality of first fuel rods having a plurality of first fuel elements and a plurality of second fuel rods having a plurality of second fuel elements. Each of the first fuel elements may include uranium dioxide fuel, and each of the second fuel elements may include a plurality of tristructural isotropic fuel particles embedded in a silicon carbide matrix. The plurality of first fuel rods and the plurality of second fuel rods are arranged in a fuel assembly.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC +1
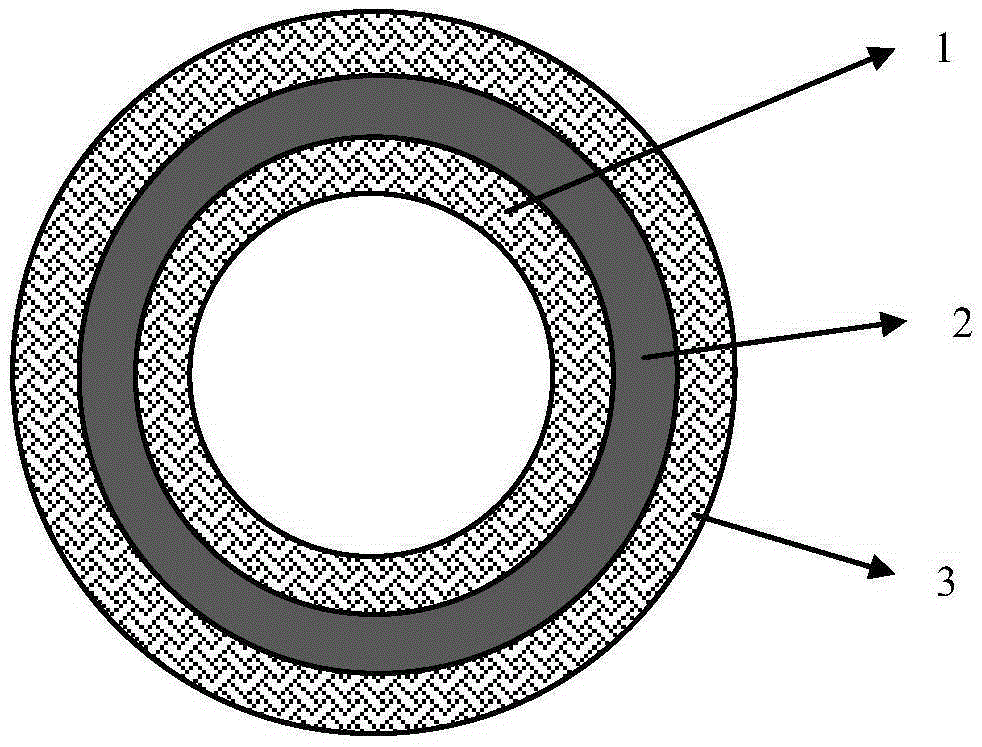
Structure and preparation method of nuclear fuel cladding tube with crack expansion resisting capability
InactiveCN105405474AAvoid crackingOptical rangefindersNuclear energy generationStructure of the EarthIrradiation
The invention relates to a structure and a preparation method of a nuclear fuel cladding tube with a crack expansion resisting capability. The structure comprises a two-layered or three-layered SiC-based nuclear fuel cladding tube, and is characterized in that an inner layer of the SiC-based nuclear fuel cladding tube is used as a secondary inner layer structure; one layer of a crack expansion resisting layer is introduced into the interior of a secondary inner layer to be used as an inner layer structure, so that a three-layered or four-layered SiC-based nuclear fuel cladding tube is formed; the modulus of the material of the introduced inner layer structure is lower than that of an anti-irradiation material with low modulus of a SiC material of the secondary inner layer. By virtue of the three-layered or four-layered SiC-based nuclear fuel cladding tube, the effect of preventing cracks from being formed on a SiC ceramic layer of the inner wall of the nuclear fuel cladding tube.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
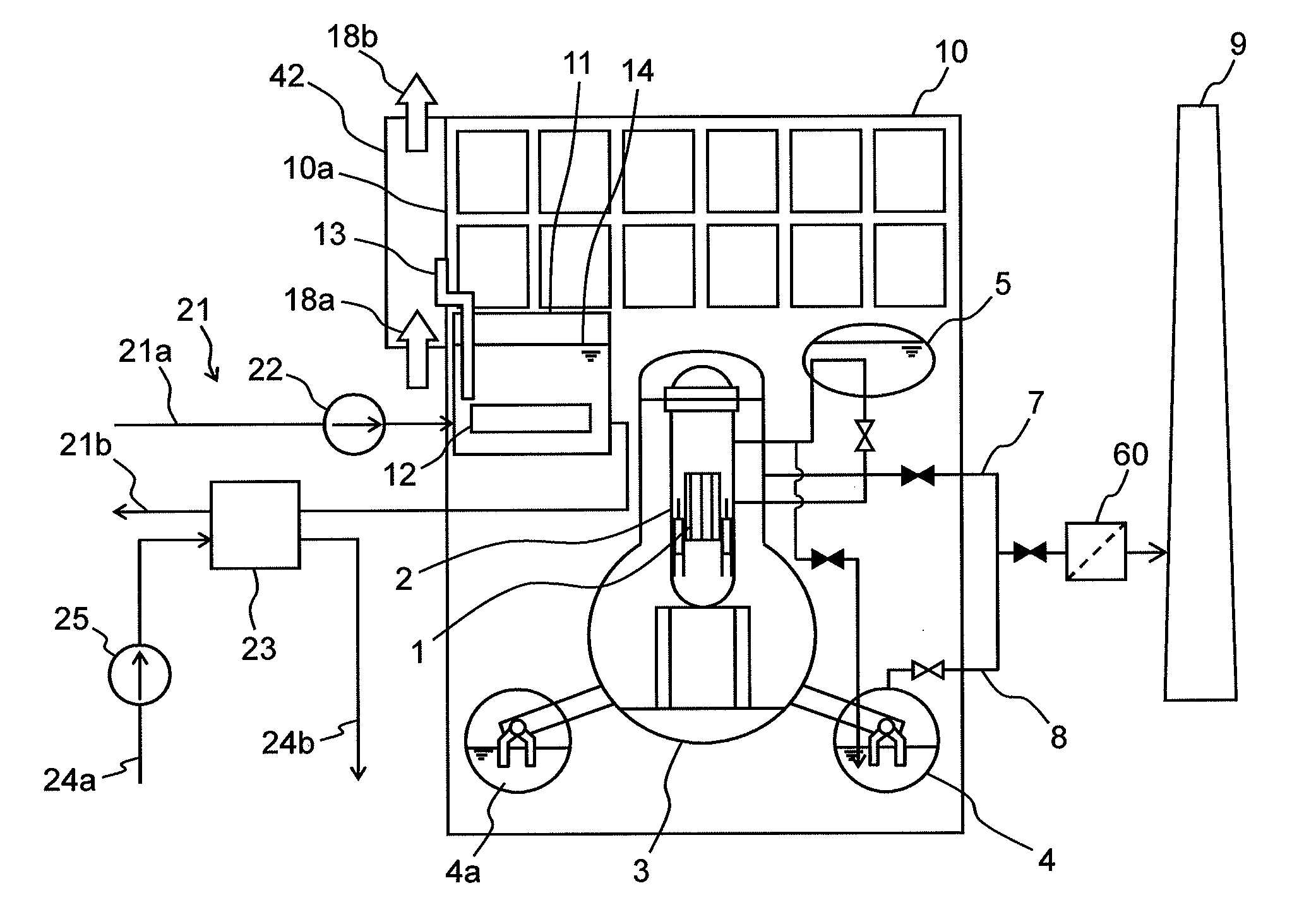
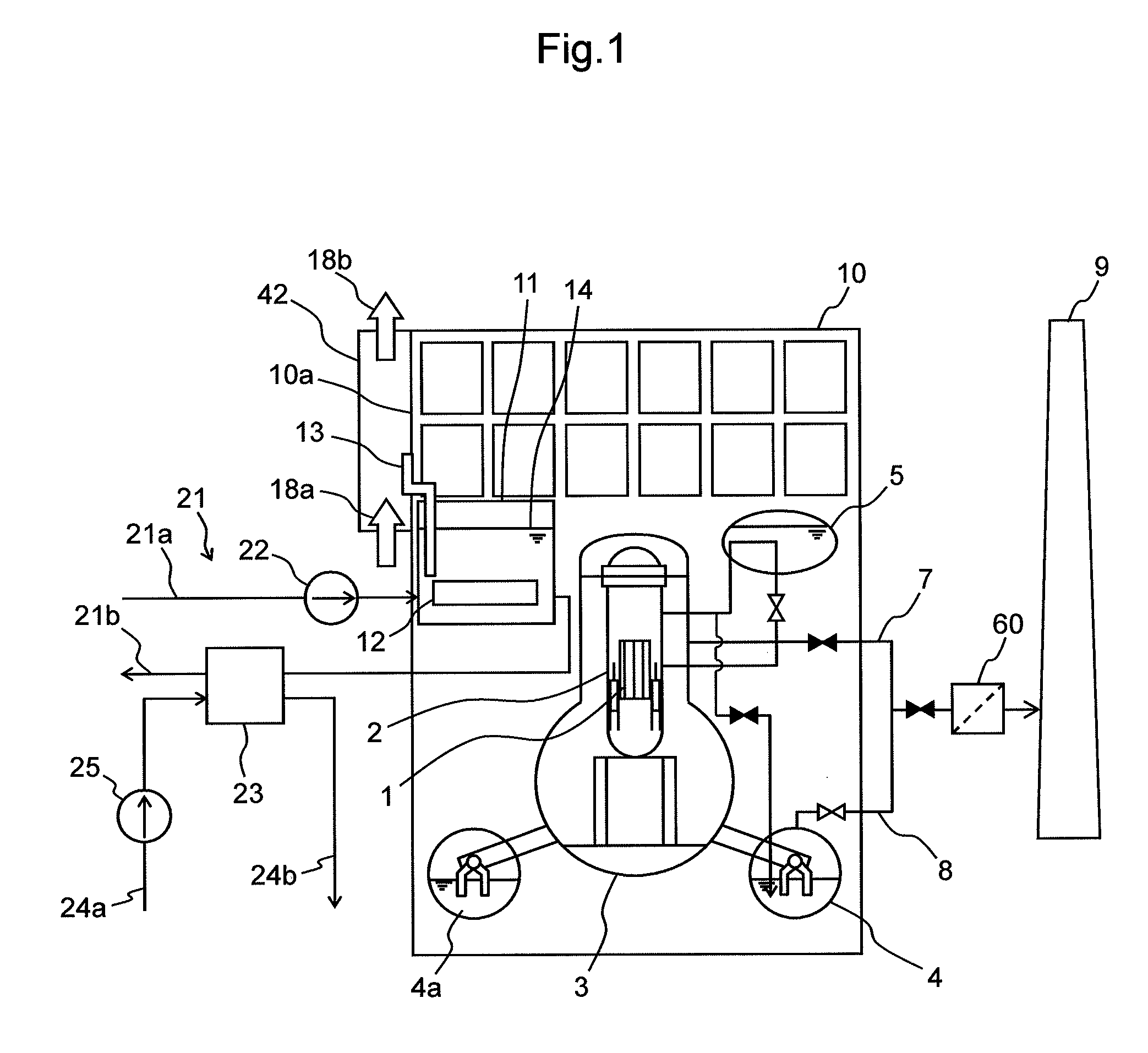
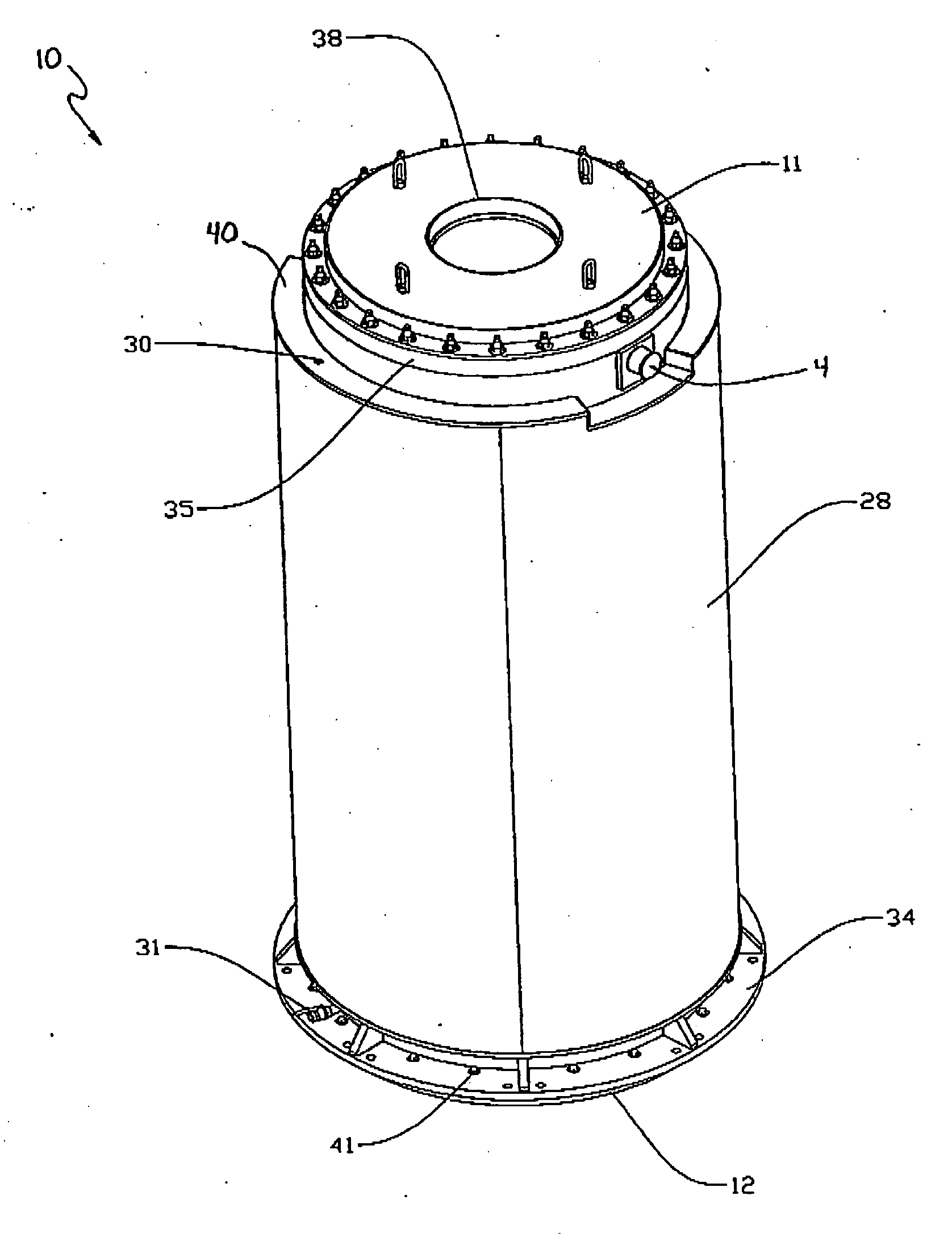
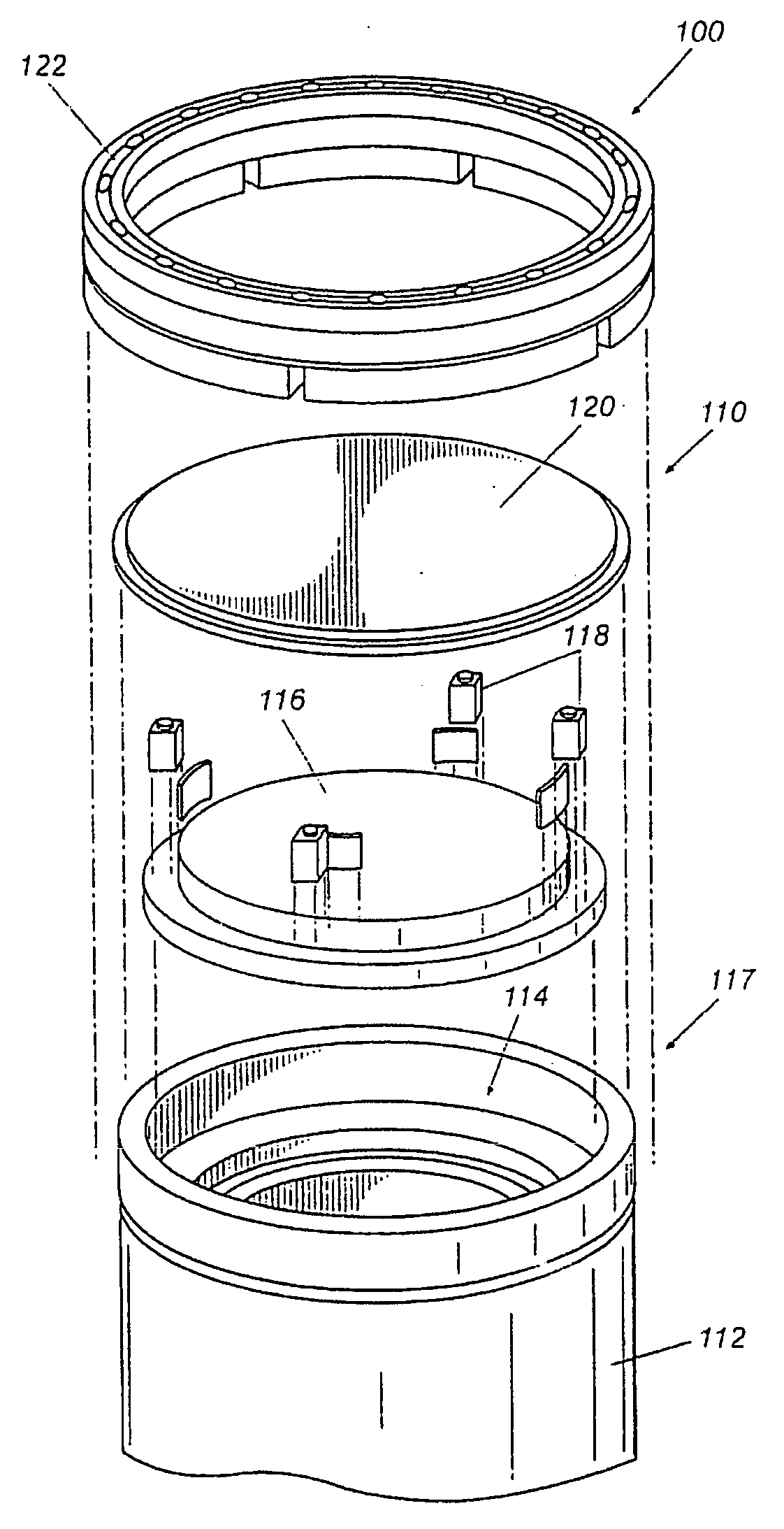
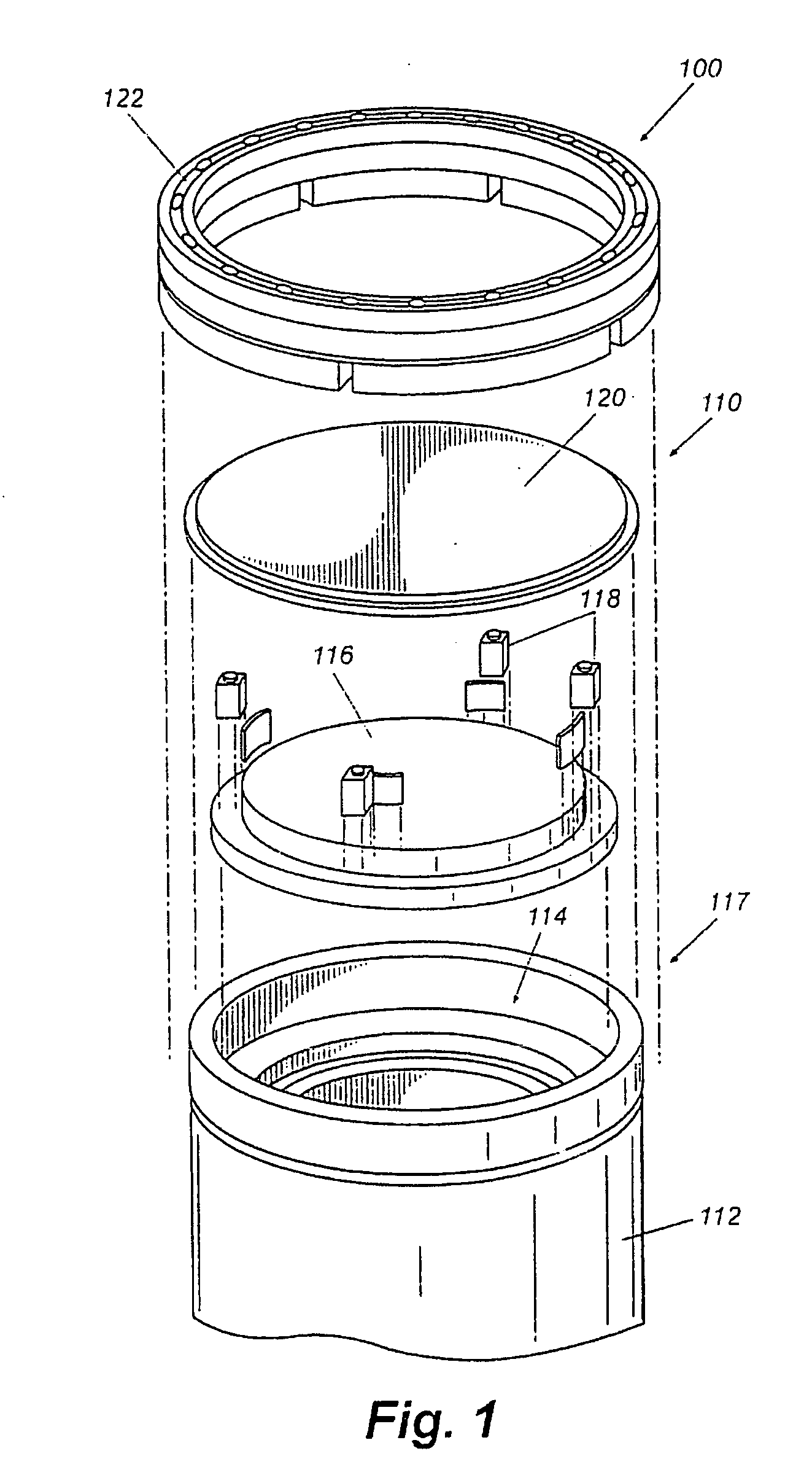
Method and apparatus for maximizing radiation shielding during cask transfer procedures
InactiveUS20070003000A1A large amountQuantity maximizationNuclear energy generationShieldingTransfer procedureEngineering
A transfer cask for maximizing the radiation shielding for spent nuclear fuel during cask transfer procedures has a cylindrical inner shell forming a cavity within which a spent nuclear fuel canister can be placed; a cylindrical outer shell concentric with and surrounding the inner shell to form an annulus with the inner shell, the annulus adapted for receiving gamma absorbing material; a jacket shell concentric with and surrounding the second shell to form a jacket for holding a neutron absorbing liquid; the jacket shell having filling and drainage systems; and a removable bottom lid so that a canister can be lowered from the cavity into a transport cask or permanent storage cask.
Owner:HOLTEC INT
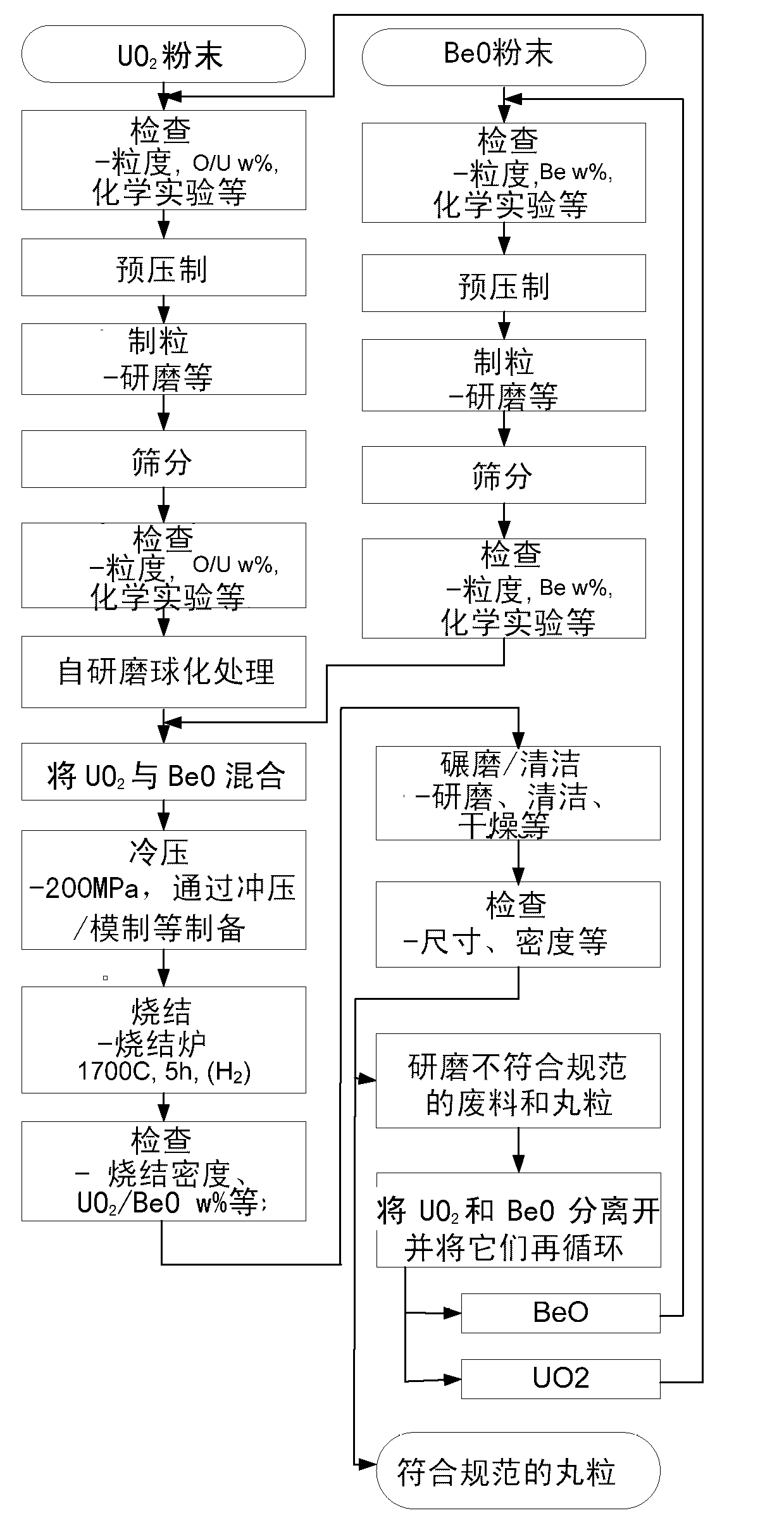
Ceramic-ceramic composites and process therefor, nuclear fuels formed thereby, and nuclear reactor systems and processes operated therewith
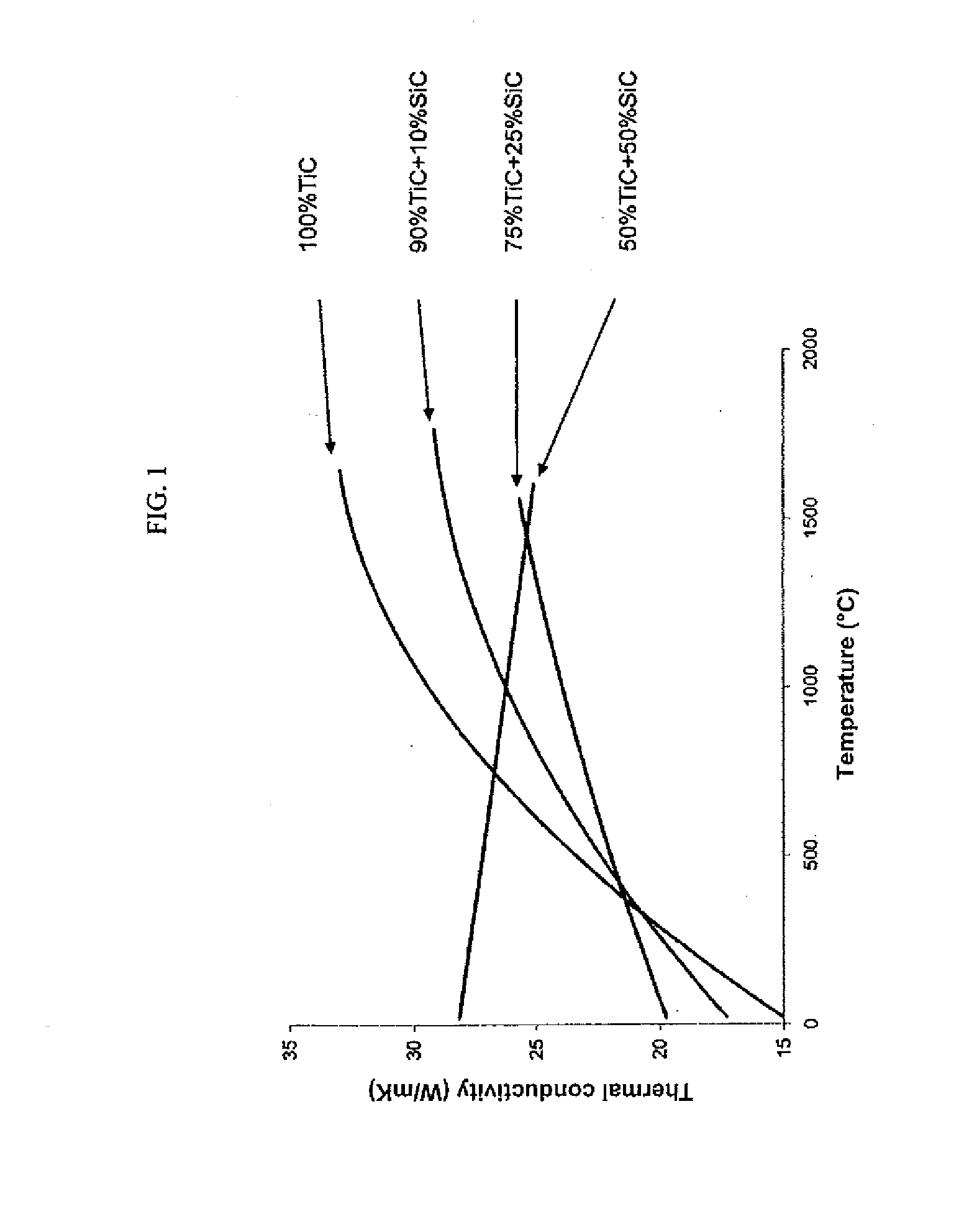
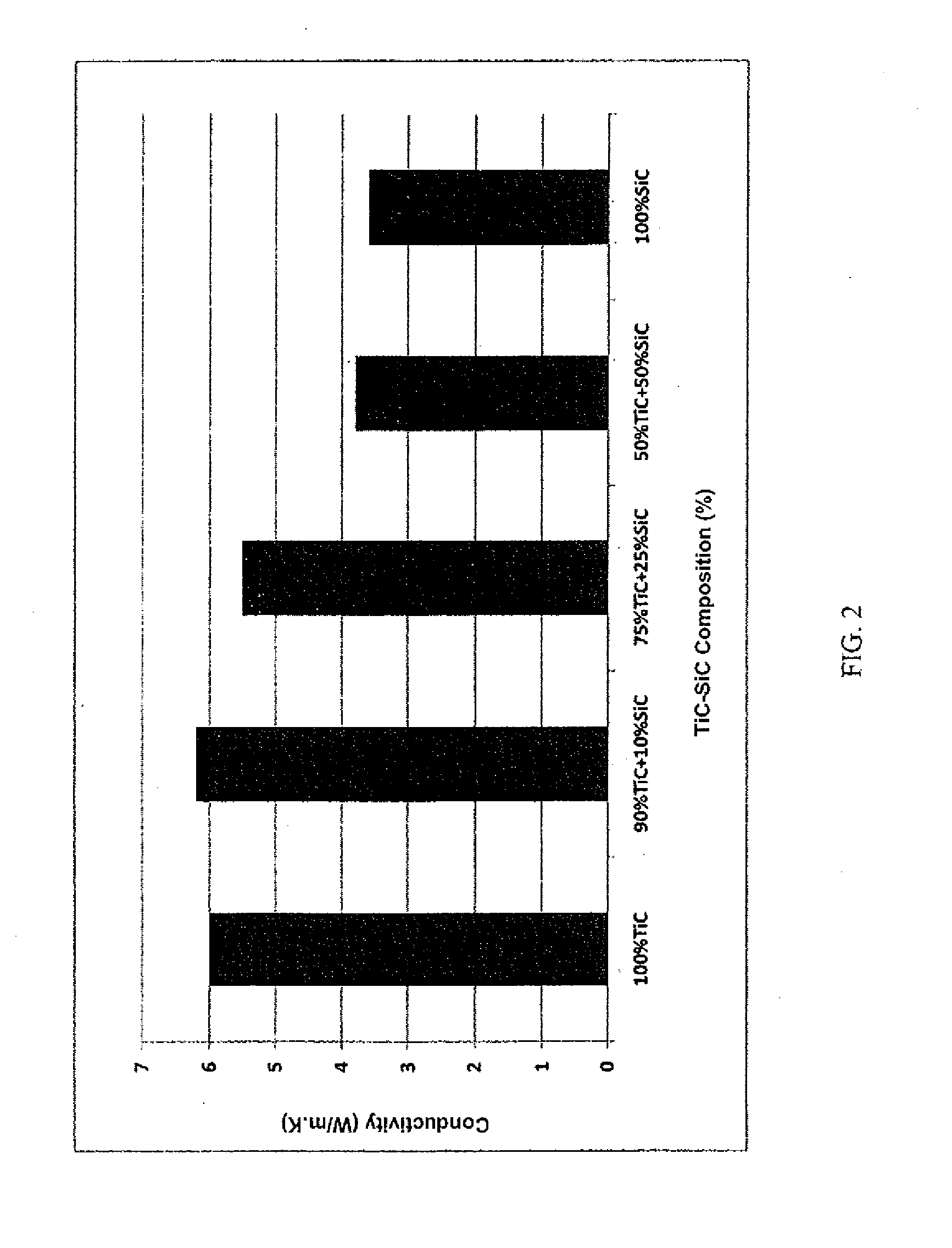
InactiveCN103299375AImprove thermal conductivityHigh thermal conductivityNuclear energy generationReactors manufactureNuclear reactorCeramic composite
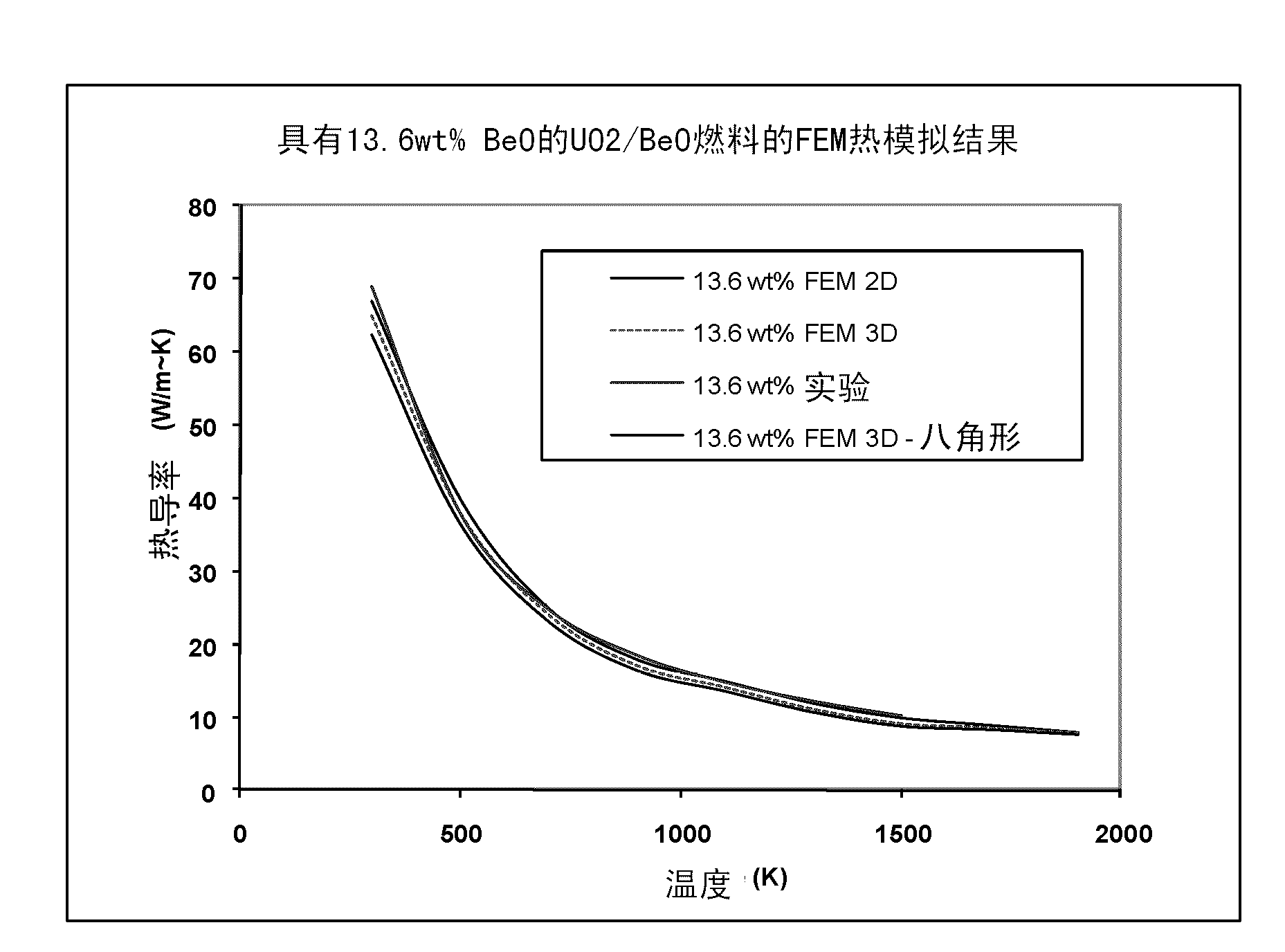
A process of producing ceramic-ceramic composites, including but not limited to nuclear fuels, and composites capable of exhibiting increased thermal conductivities. The process includes milling a first ceramic material to produce a powder of spheroidized particles of the first ceramic material, and then co-milling particles of a second ceramic material with the spheroidized particles of the first ceramic material to cause the particles of the second ceramic material to form a coating on the spheroidized particles of the first material. The spheroidized particles coated with the particles of the second ceramic material are then compacted and sintered to form the ceramic-ceramic composite, in which the second ceramic material forms a continuous phase completely surrounding the spheroidized particles of the first ceramic material.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Thermal management of molten fuel nuclear reactors
ActiveUS20180137944A1Improve power densitySave on fuel costsNuclear energy generationFast fission reactorsNuclear reactorOperating temperature
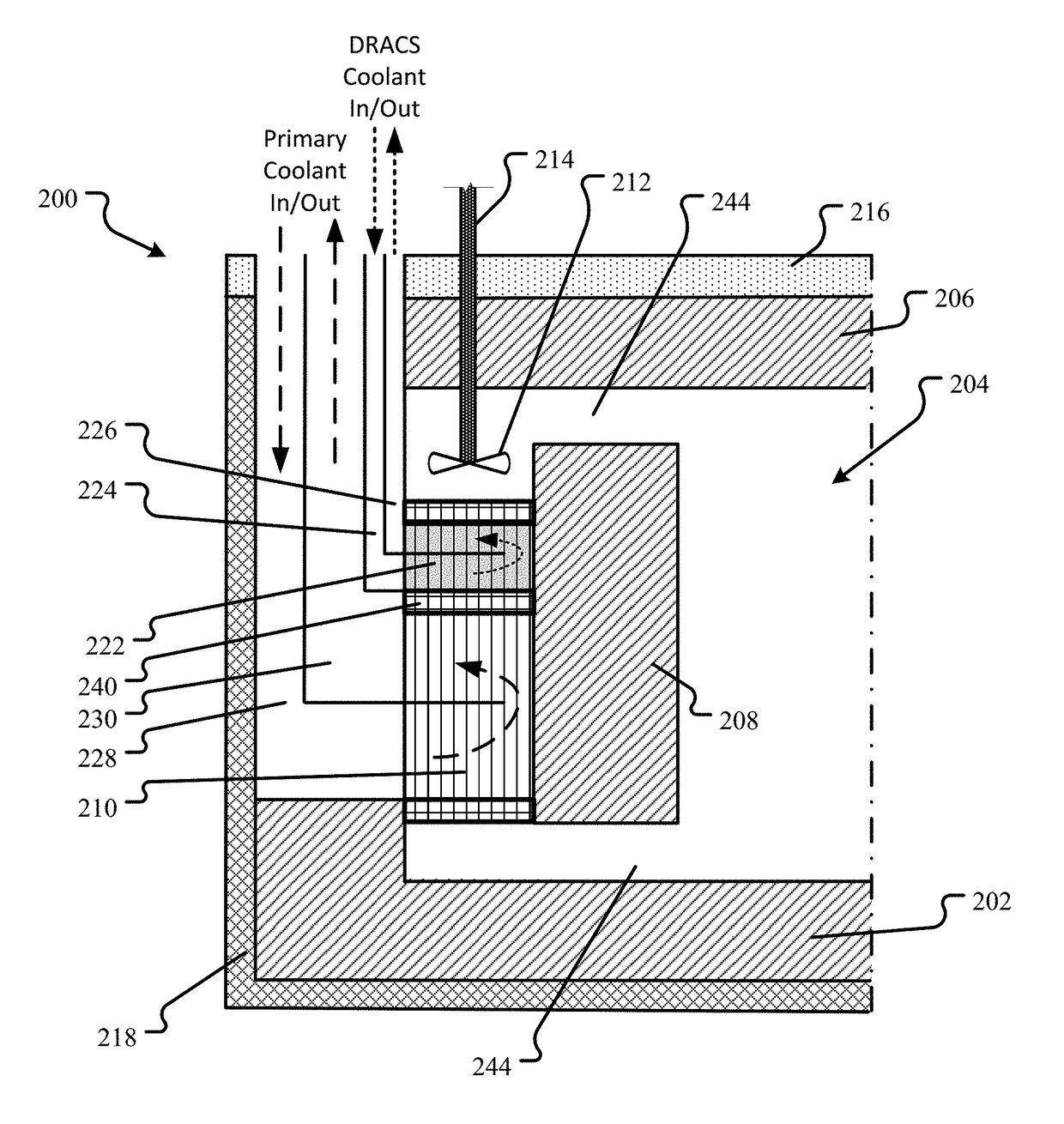
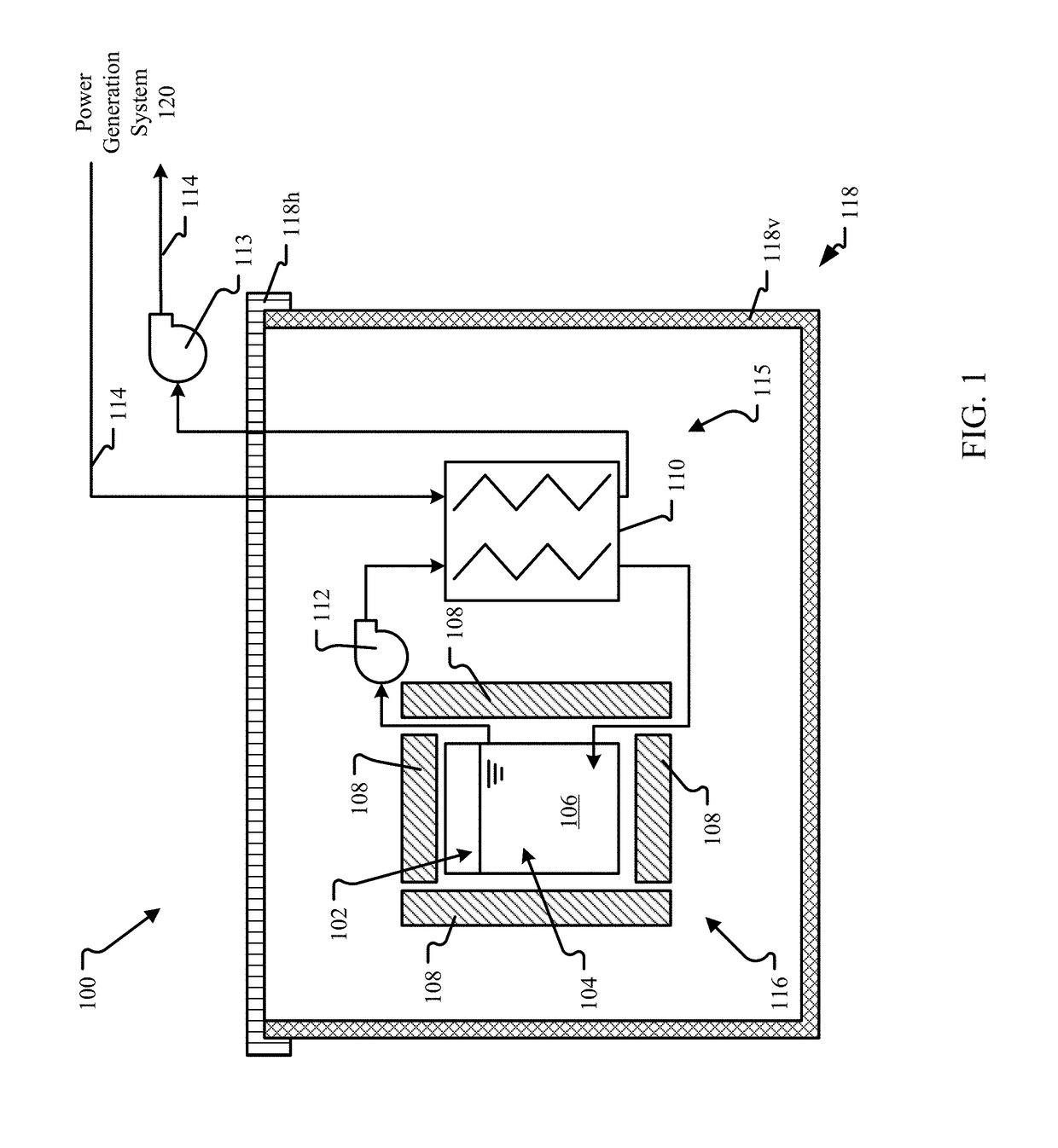
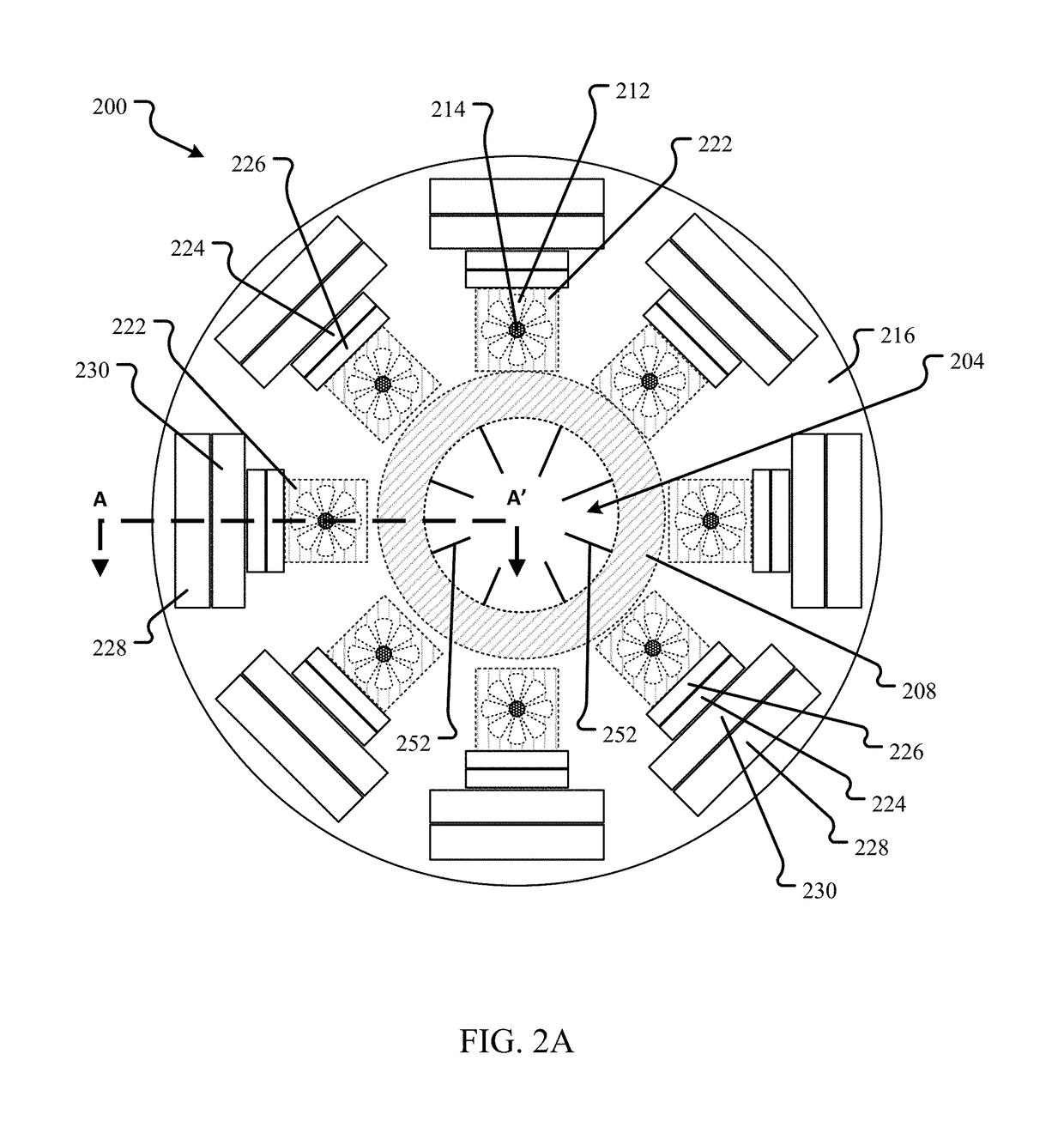
This disclosure describes various configurations and components of a molten fuel fast or thermal nuclear reactor for managing the operating temperature in the reactor core. The disclosure includes various configurations of direct reactor auxiliary cooling system (DRACS) heat exchangers and primary heat exchangers as well as descriptions of improved flow paths for nuclear fuel, primary coolant and DRACS coolant through the reactor components.
Owner:TERRAPOWER
U+4 generation in HTER
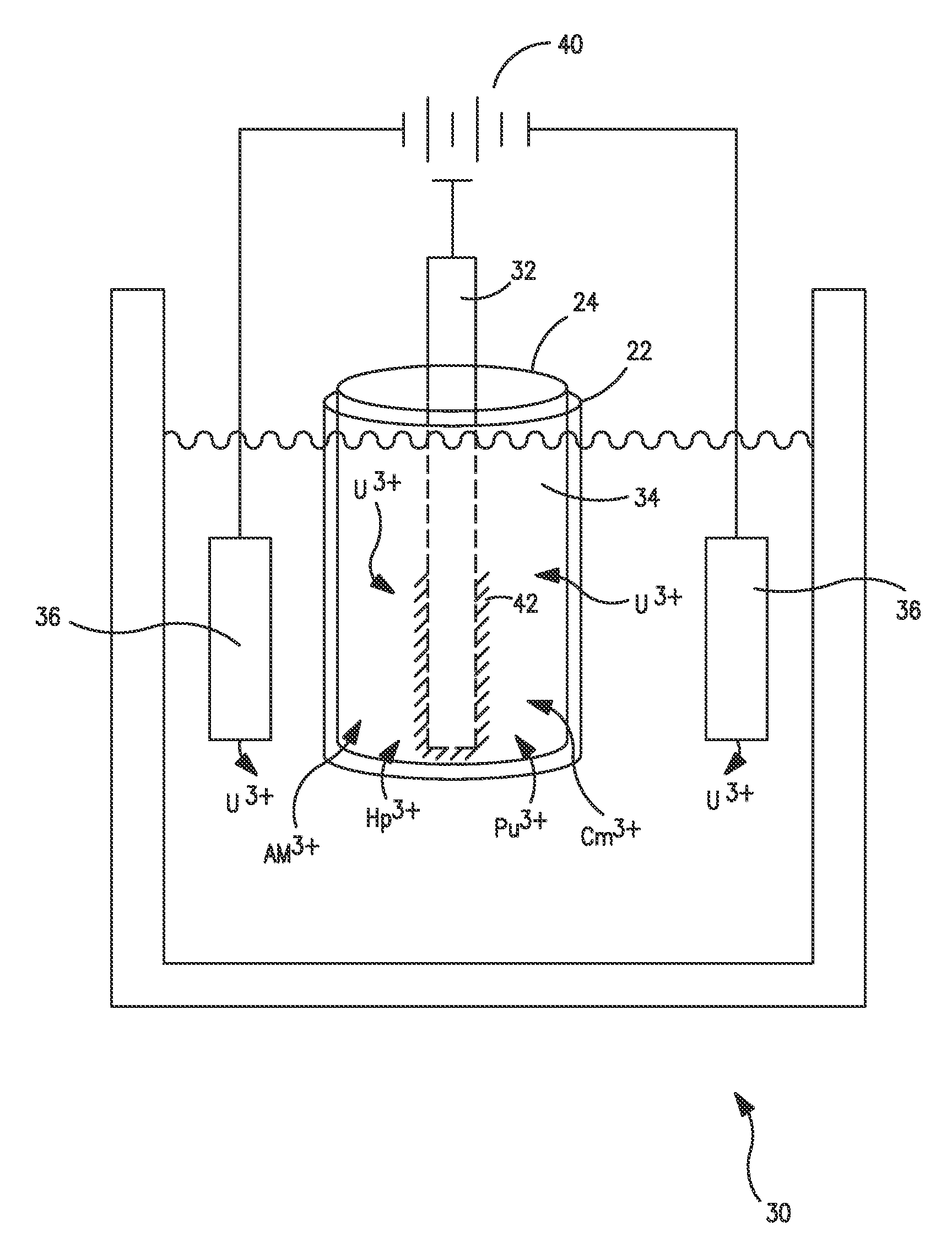
InactiveUS7011736B1More facile recoveryLess rigorous scraper technologyCellsPhotography auxillary processesElectrolysisEngineering
A improved device and process for recycling spent nuclear fuels, in particular uranium metal, that facilitates the refinement and recovery of uranium metal from spent metallic nuclear fuels. The electrorefiner device comprises two anodes in predetermined spatial relation to a cathode. The anodese have separate current and voltage controls. A much higher voltage than normal for the electrorefining process is applied to the second anode, thereby facilitating oxidization of uranium (III), U+, to uranium (IV), U+4. The current path from the second anode to the cathode is physically shorter than the similar current path from the second anode to the spent nuclear fuel contained in a first anode shaped as a basket. The resulting U+4 oxidizes and solubilizes rough uranium deposited on the surface of the cathode. A softer uranium metal surface is left on the cathode and is more readily removed by a scraper.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY
Method and apparatus for maximizing radiation shielding during cask transfer procedures
InactiveUS7330525B2A large amountQuantity maximizationNuclear energy generationShieldingTransfer procedureEngineering
A transfer cask for maximizing the radiation shielding for spent nuclear fuel during cask transfer procedures has a cylindrical inner shell forming a cavity within which a spent nuclear fuel canister can be placed; a cylindrical outer shell concentric with and surrounding the inner shell to form an annulus with the inner shell, the annulus adapted for receiving gamma absorbing material; a jacket shell concentric with and surrounding the second shell to form a jacket for holding a neutron absorbing liquid; the jacket shell having filling and drainage systems; and a removable bottom lid so that a canister can be lowered from the cavity into a transport cask or permanent storage cask.
Owner:HOLTEC INT
Methods for transporting and canistering nuclear spent fuel
InactiveUS20060188054A1Less personnel costLess time costReactor fuel elementsPortable shielded containersPower stationSpent nuclear fuel
Disclosed are methods for transporting and canistering nuclear spent fuel. In one embodiment, the method for transporting and canistering nuclear spent fuel comprises providing a canister that includes a mechanical closure for a lid on a container. The canister containing the nuclear spent fuel is loaded into a transport cask, and the transport cask is sealed at the power plant. It is preferred that the lid is not installed on the canister at the power plant. The transport cask containing the canister and nuclear spent fuel is transported to a remote facility. At the remote facility, the transport cask is opened and the lid of the canister is installed using the mechanical closure to seal the canister after the canister is transported to the remote facility. The canister containing the spent nuclear fuel is placed into an overpack, which is stored at the remote facility.
Owner:NAC INT
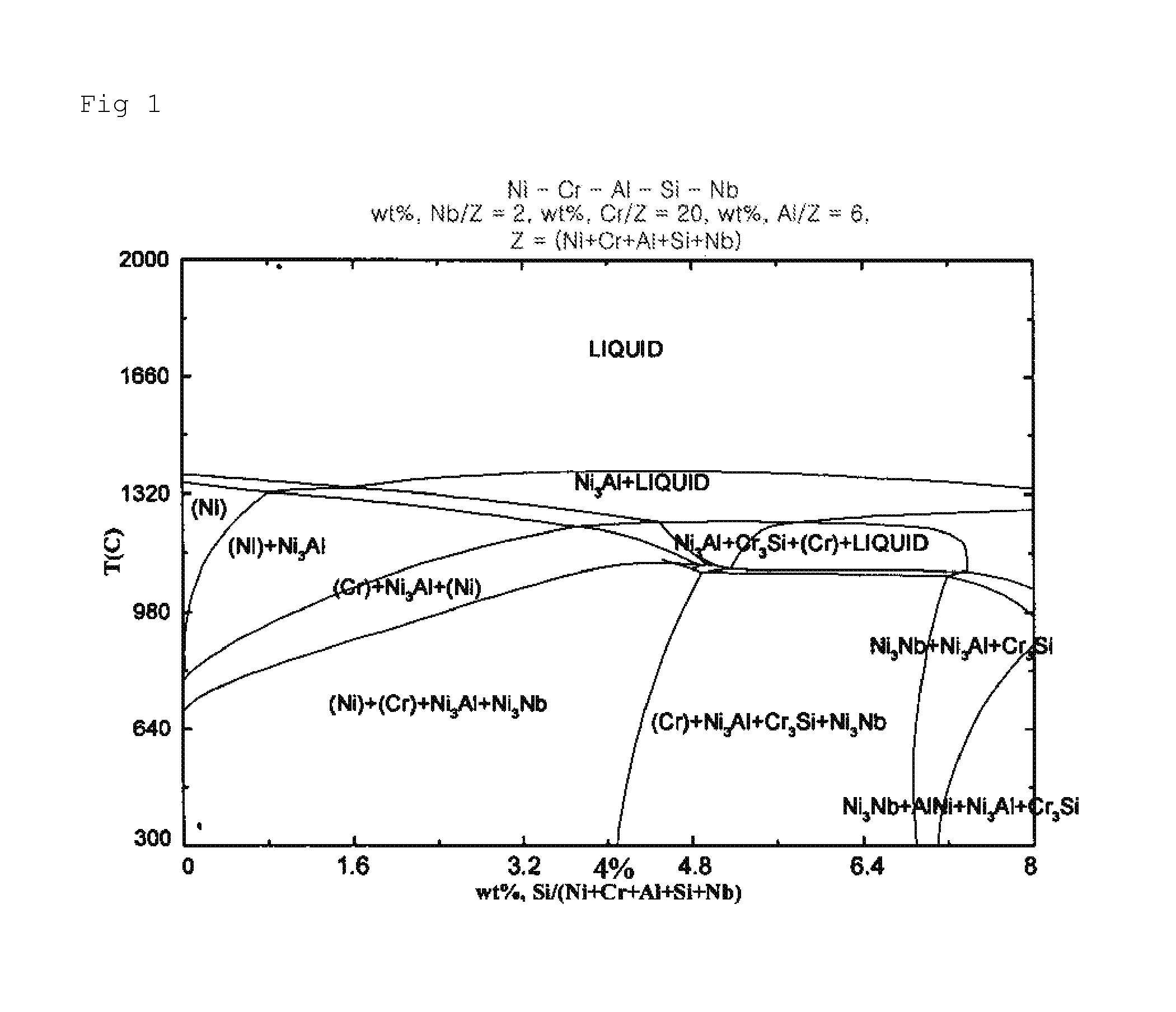
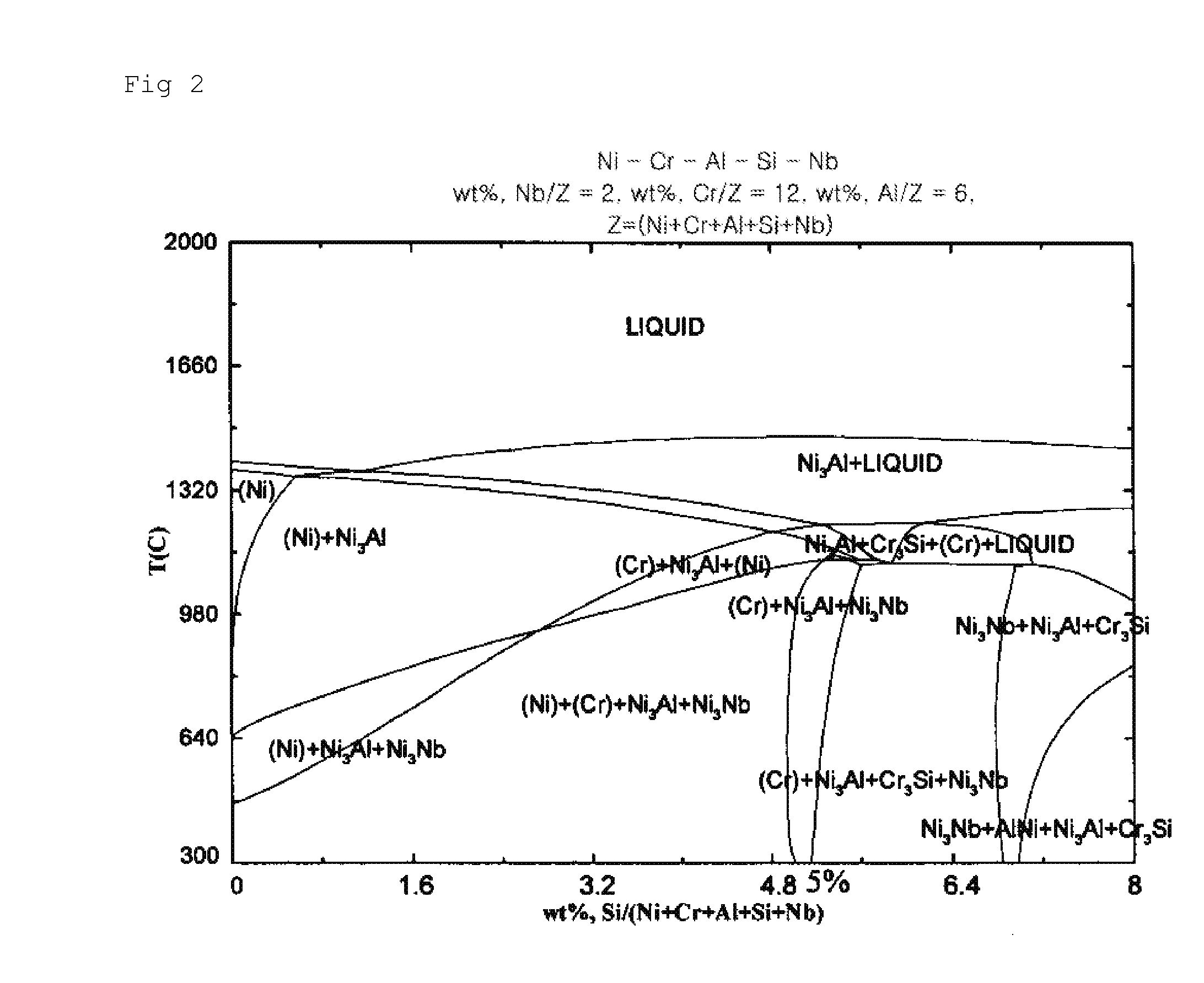
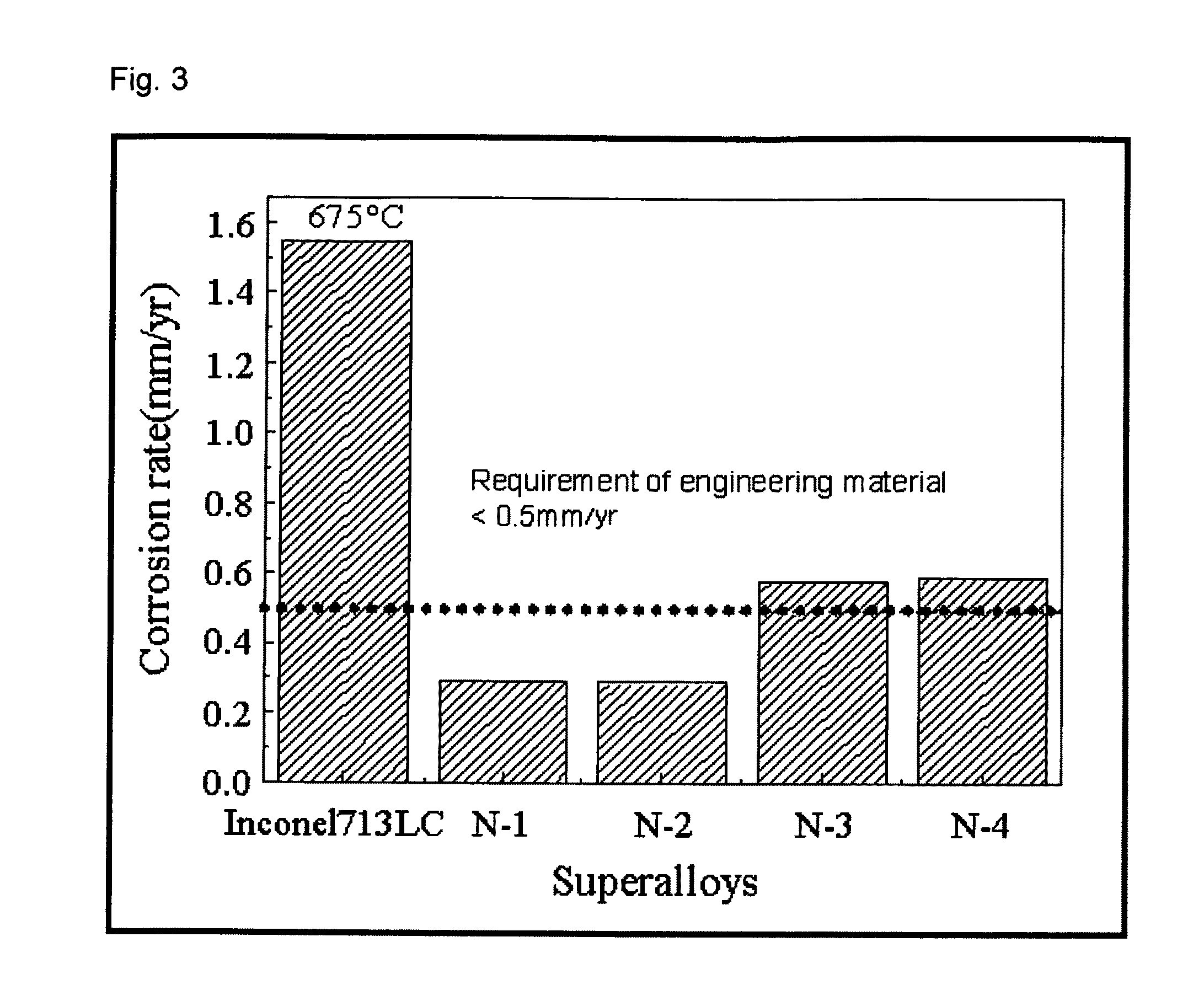
Corrosion Resistant Structural Alloy for Electrolytic Reduction Equipment for Spent Nuclear Fuel
InactiveUS20100155236A1Improve corrosion resistanceImprove reliabilityElectrodesElectrolysisMolten salt
Disclosed is a structural alloy with oxidation resistance for electrolytic reduction equipment for treatment of spent nuclear fuel. More particularly, the present invention relates to a structural alloy with oxidation resistance for electrolytic reduction equipment for treatment of spent nuclear fuel wherein Cr, Si, Al, Nb and Ti are added to a Ni-based substrate so as to form an oxide coating film which is stable in a LiCl—Li2O molten salt and, in addition, a process thereof and use of the same.
Owner:KOREA ATOMIC ENERGY RES INST
Storage rack for fresh or spent nuclear fuel assemblies
ActiveUS20110142189A1High mechanical strengthSmall massNuclear energy generationNuclear engineering problemsEngineeringRigid structure
A storage rack for nuclear fuel assemblies, comprising a rigid structure defining a plurality of adjacent cells, and comprising in each cell a sleeve defining a cavity intended to receive a nuclear fuel assembly, the sleeve having, in cross-sectional orthogonal to the longitudinal direction, a generally polygonal shape whereof the sides are produced using plates made from a neutron-absorbing material. According to the invention, the sleeve also includes: profiles each forming a corner piece, arranged on at least several angles of said generally polygonal cross-section, these profiles serving as a mounting bracket for the plates made of a neutron-absorbing material; and a means for maintaining the profiles therebetween.
Owner:TN INT (FR)
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com