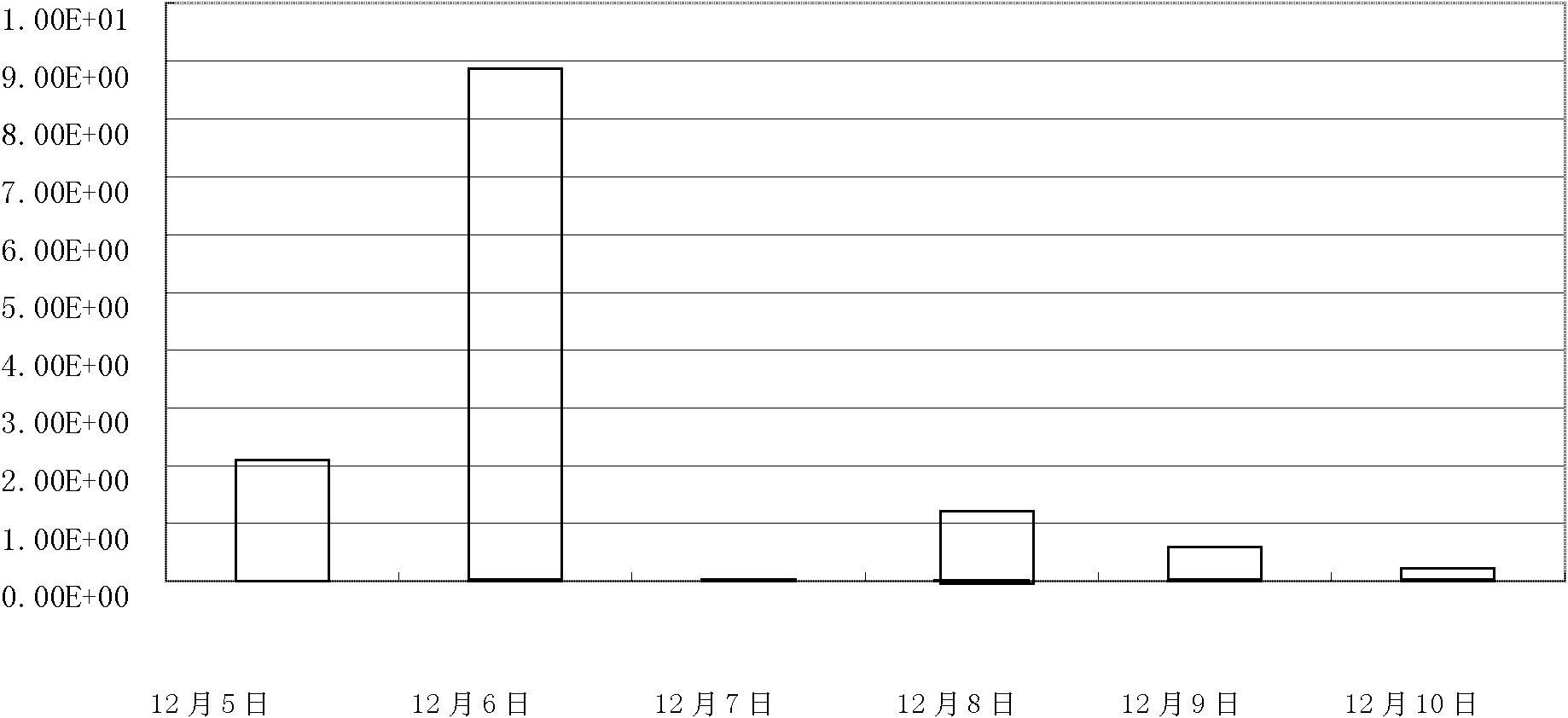
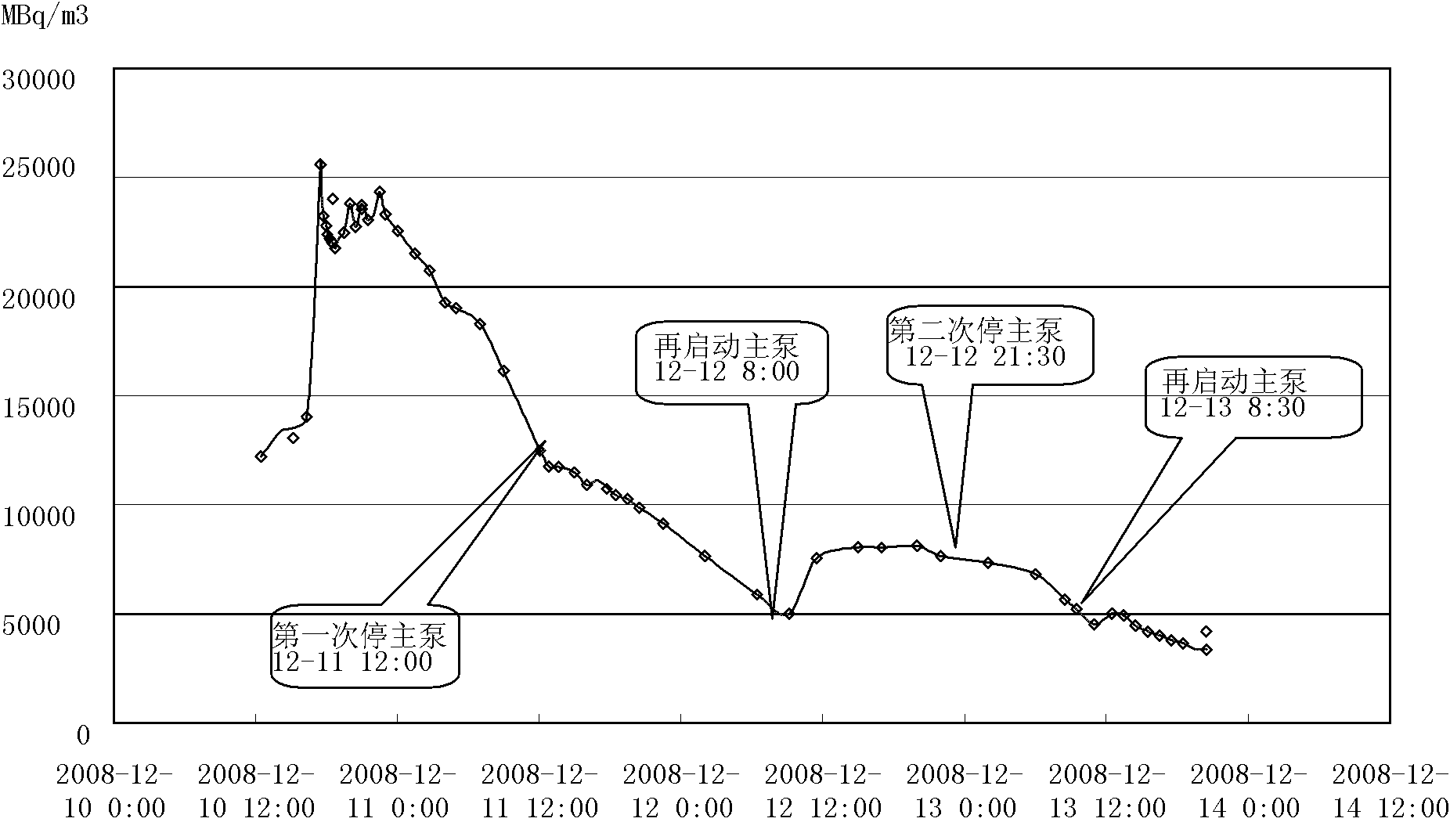
Patents
Literature
1148 results about "Pressurized water reactor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
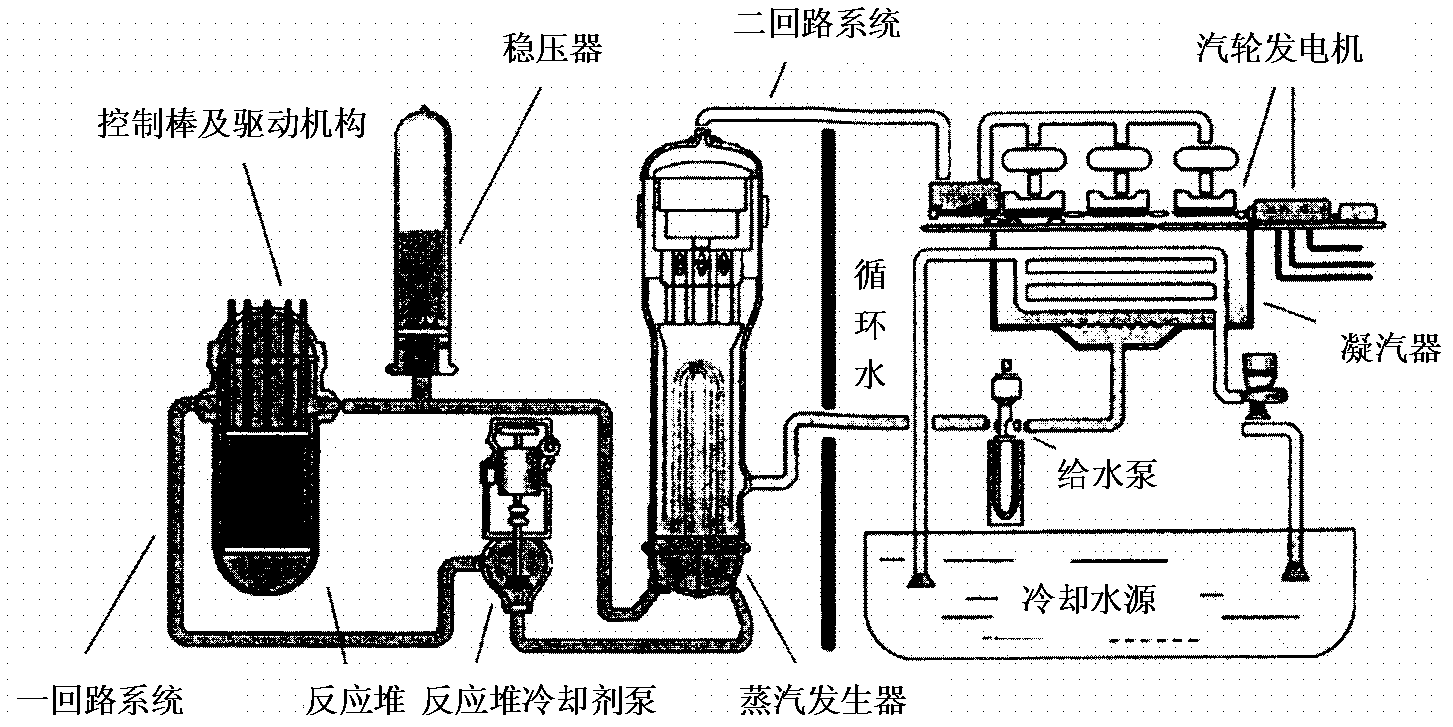
Pressurized water reactors (PWRs) constitute the large majority of the world's nuclear power plants (notable exceptions being Japan and Canada) and are one of three types of light-water reactor (LWR), the other types being boiling water reactors (BWRs) and supercritical water reactors (SCWRs). In a PWR, the primary coolant (water) is pumped under high pressure to the reactor core where it is heated by the energy released by the fission of atoms. The heated water then flows to a steam generator where it transfers its thermal energy to a secondary system where steam is generated and flows to turbines which, in turn, spin an electric generator. In contrast to a boiling water reactor, pressure in the primary coolant loop prevents the water from boiling within the reactor. All LWRs use ordinary water as both coolant and neutron moderator.
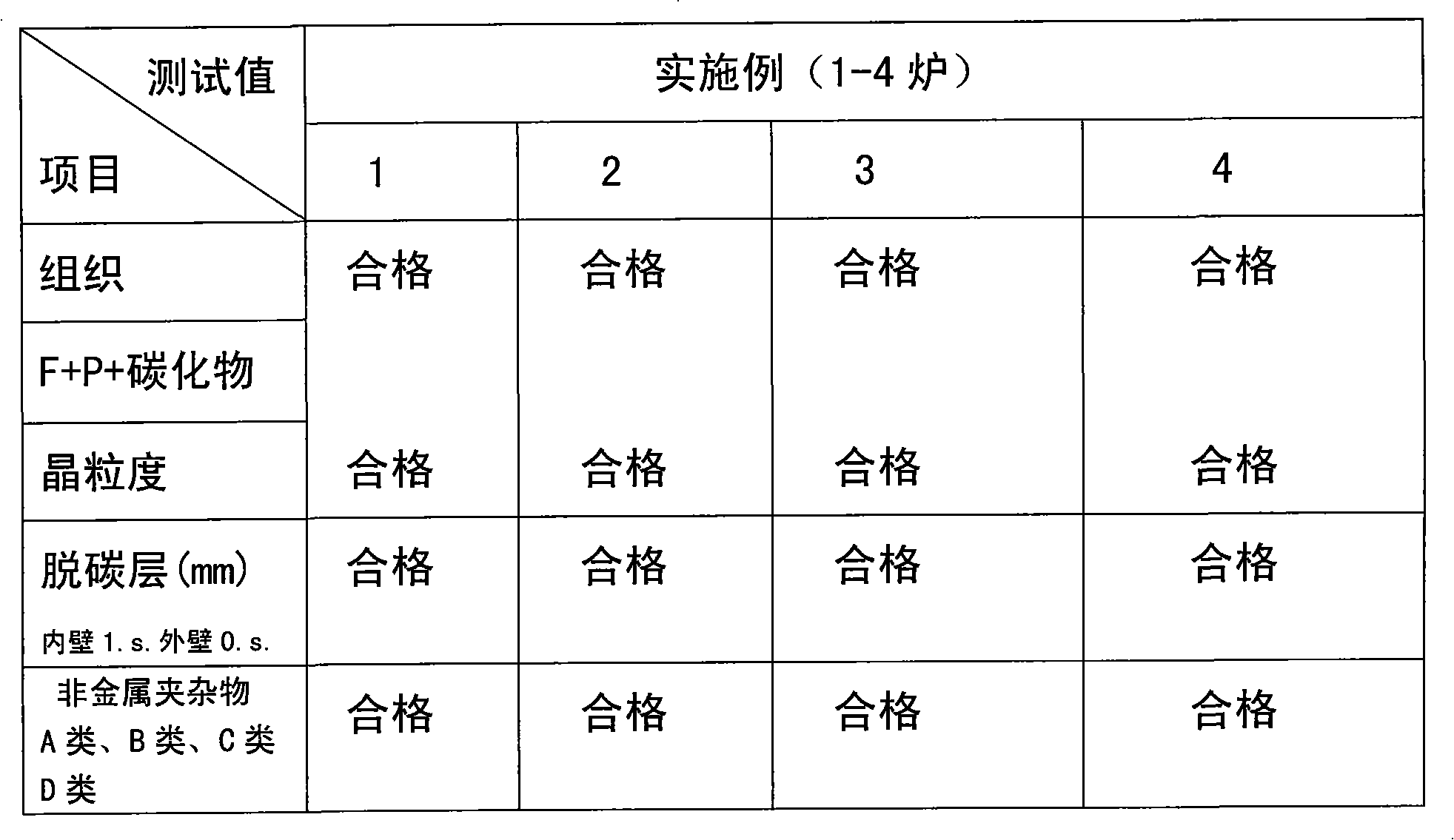
A Modeling Method for the Third Generation Pressurized Water Reactor Nuclear Power Unit
ActiveCN102279901ASolving Co-SimulationHas engineering application valueSpecial data processing applicationsInformation technology support systemNuclear engineeringPressurized water reactor
The invention discloses a modeling method for a third generation pressurized water reactor nuclear power generating unit. The modeling method comprises the following steps of: 1, decomposing a nuclear power generating unit system into a plurality of subsystem models; 2, establishing the subsystem models in the step 1 according to heat engineering and energy transfer and conversion rules; 3, combining the subsystem models obtained in the step 2 into a nuclear power generating unit full system model, and connecting the nuclear power generating unit full system model with a power system model toobtain a combined model of a nuclear power generating unit and the power system; and 4, establishing a customized model of the third generation pressurized water reactor nuclear power generating uniton the basis of the combined model of the nuclear power generating unit and the power system, and simulating the performance of the nuclear power generating unit and machine-grid interaction according to the customized model. The method effectively solves combined emulation of the nuclear power generating unit and a power unit, can be applied to machine-grid coordination analysis of a nuclear power plant and a power grid, and has high practicability.
Owner:STATE GRID HUBEI ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +1
Integrated low-temperature nuclear heat supplying pile
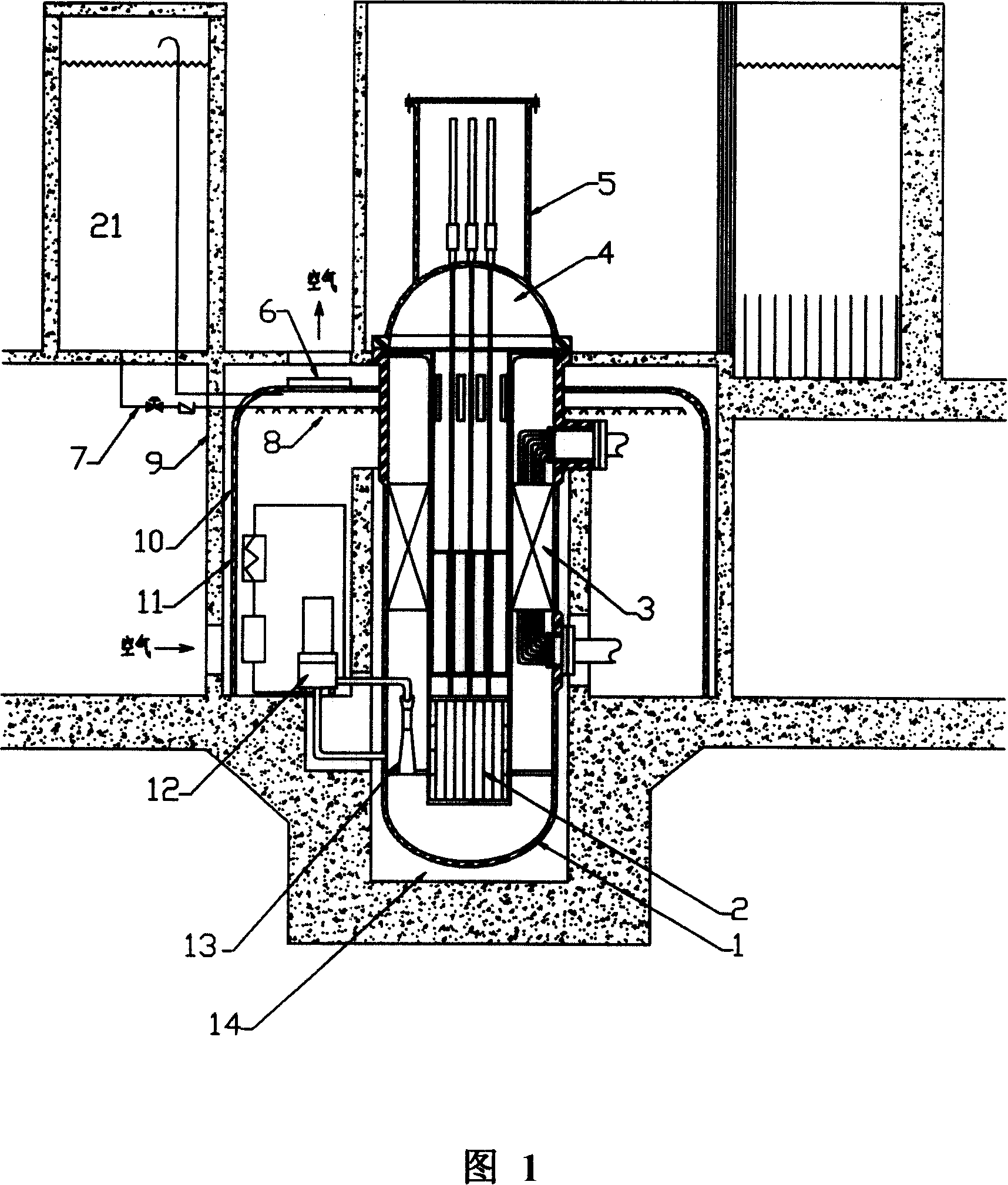
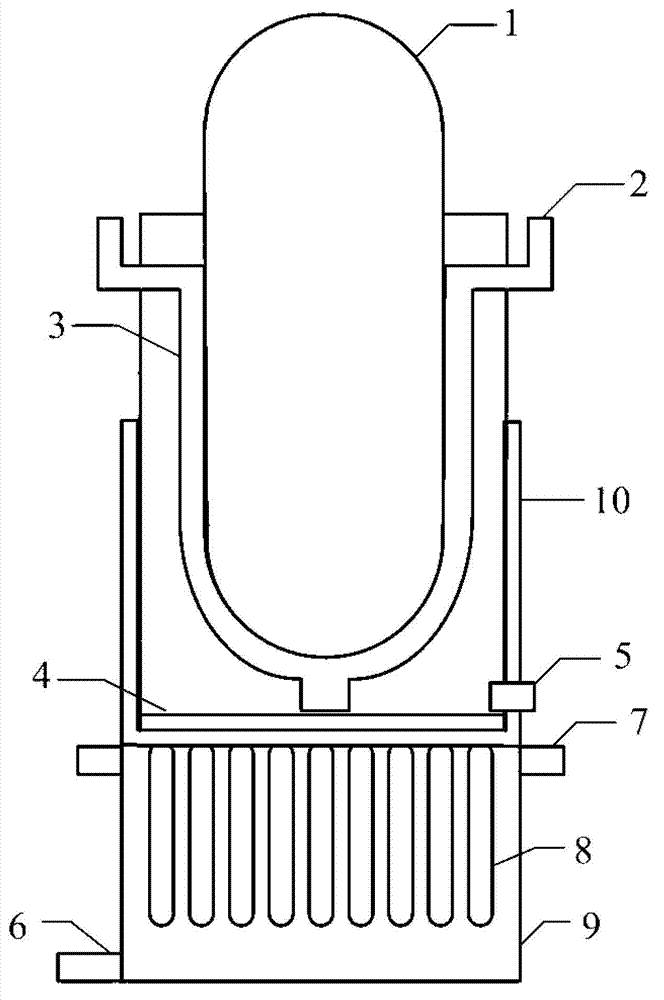
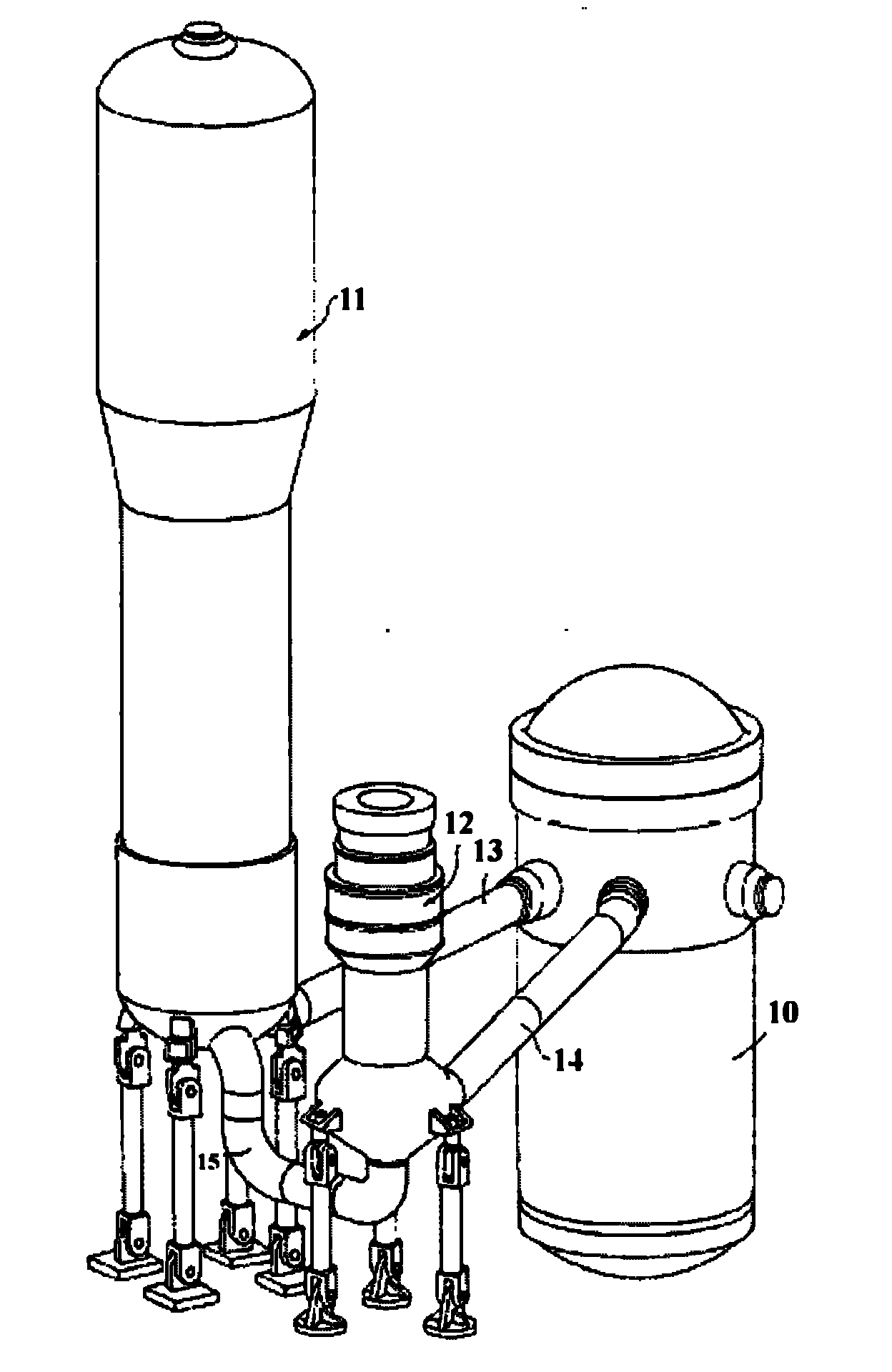
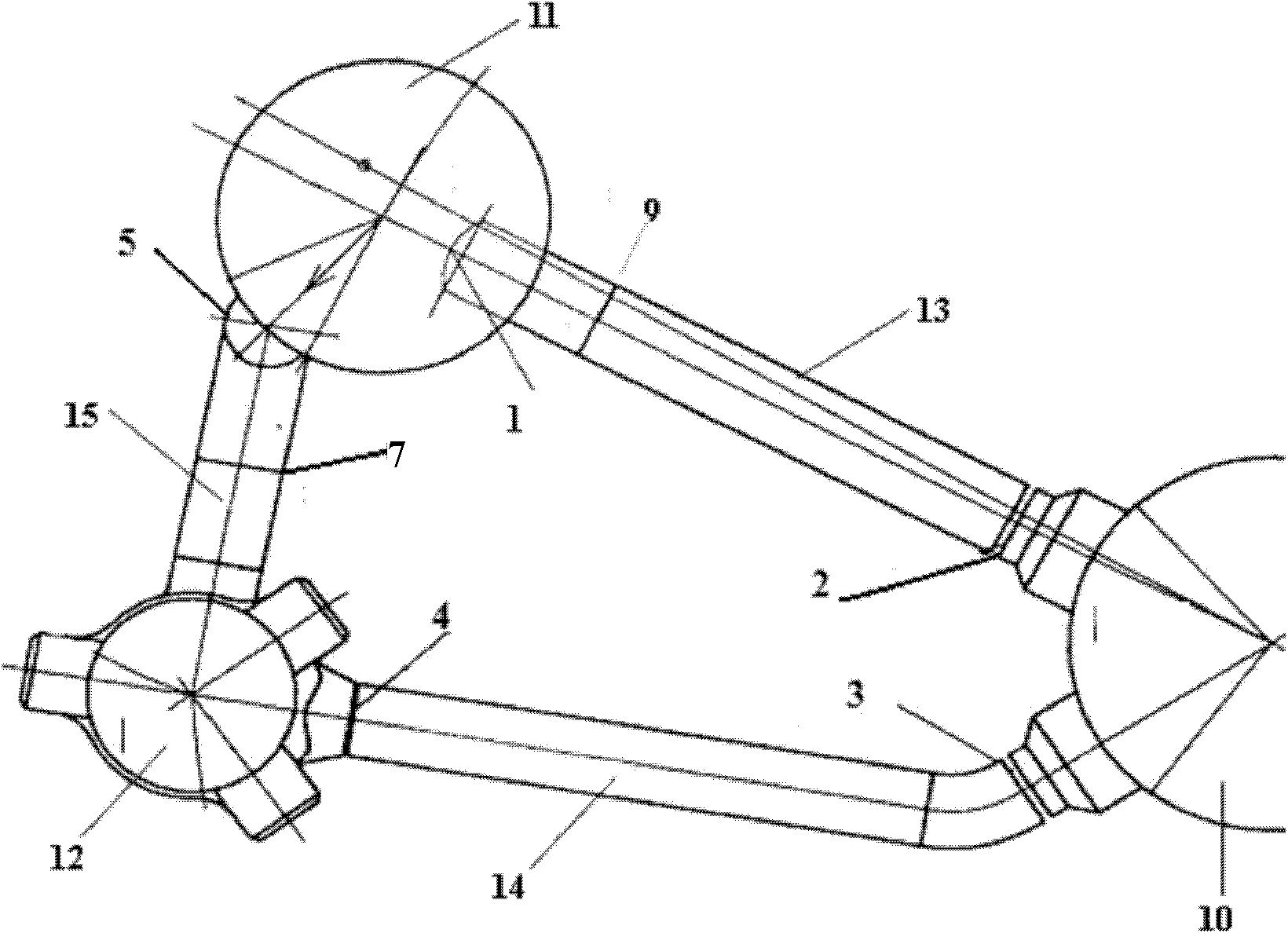
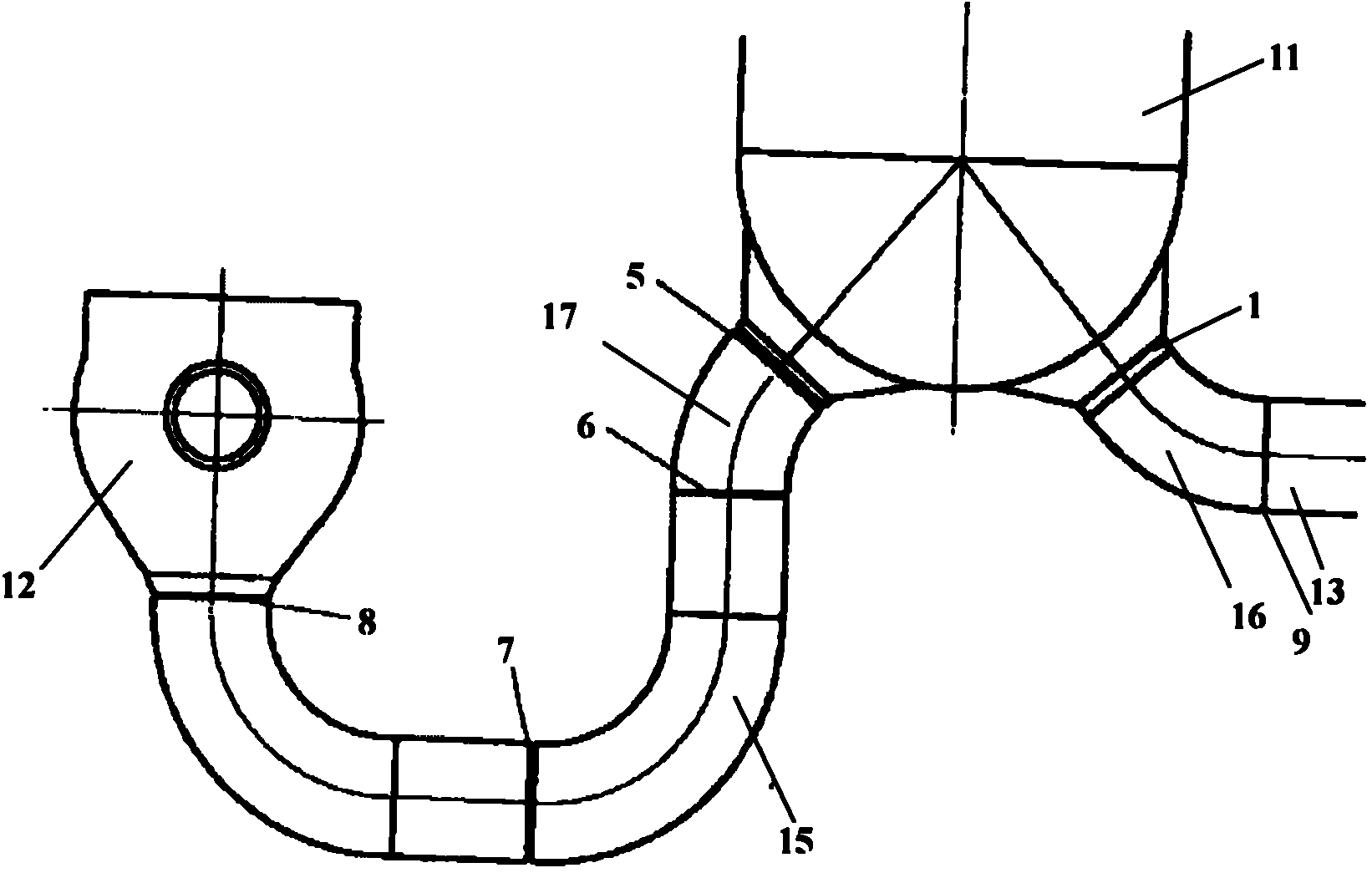
ActiveCN101154472ASmall sizeCompact layoutIntegral reactorsNuclear energy generationReactor pressure vesselPressurized water reactor
The invention discloses an integral low-temperature nuclear heat reactor with the circuit equipment adopting integral arrangement and belonging to the low- and medium-parameter pressurized-water reactor, wherein, a reactor core adopts the mature nuclear power plant fuel component and control rod component; a main heat exchanger is of integral coil type; a voltage stabilizer is a built-in nitrogen partial pressure control voltage stabilizer; coolant circulation is completed by a built-in jet apparatus and the equipment of an external drive circuit; the drive circuit and the equipment and a main circuit auxiliary system are arranged at the circumference of a reactor pressure vessel; a containment vessel consists of a reactor body containment vessel and a reactor top containment vessel; the reactor body containment vessel which is a structure combined by a reactor vault of reinforced concrete structure and a casing of steel structure is connected with a sealed refueling water storage pool through a pipe and a valve. The thermal power of the reactor can be selected between 50MW and 500MW at will and the outlet temperature of the reactor can be selected between 100 DEG C to 200 DEG C according to application, requirement and power.
Owner:NUCLEAR POWER INSTITUTE OF CHINA
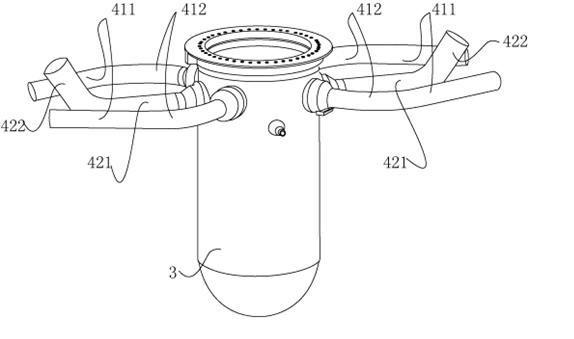
Installing method for main pipeline of coolant system of nuclear power station
ActiveCN102169736ASimple structureReduce elbowNuclear energy generationReactors manufactureNumerical controlPressurized water reactor
The invention relates to an installing method for a main pipeline of a coolant system of a nuclear power station, which is characterized in that the main pipeline of the coolant system of a reactor of the pressurized water reactor nuclear power station comprises a cool section (41) and a hot section (42), and a steam generator is directly connected with a main pump. According to the invention, the problem that the main pipeline is installed and welded by only a pressure container or steam generator in place by adopting the installing method of the main pipeline without a transition section issolved, and technical limit that the main pipeline is installed after the pressure container is in place and the steam generator or main pump is in place in the traditional main pipeline constructiontechnology is eliminated. A main pipeline groove is processed by adopting a site numerical control machining technology, the main pipeline and equipment connected with the main pipeline are subjectedto measurement, modeling and process monitoring by adopting a laser tracking measuring and 3D modeling technology, the main pipeline is regulated to meet the assembly welding requirement and is installed by using a narrow TIG (argon tungsten-arc welding) automatic welding technology, thus a feasible method is provided for shortening the construction period of the nuclear power station.
Owner:CHINA NUCLEAR IND FIFTH CONSTR CO LTD
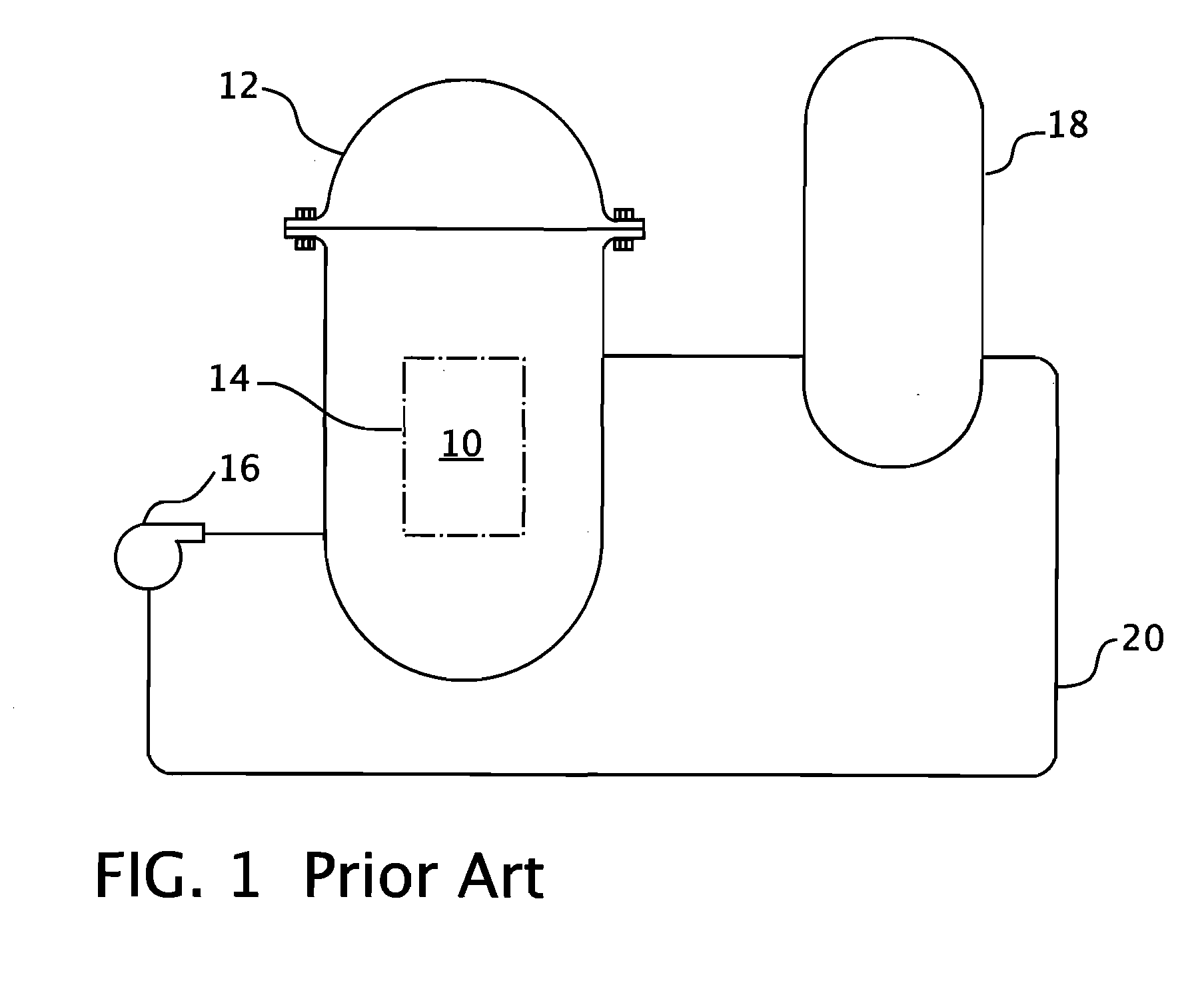
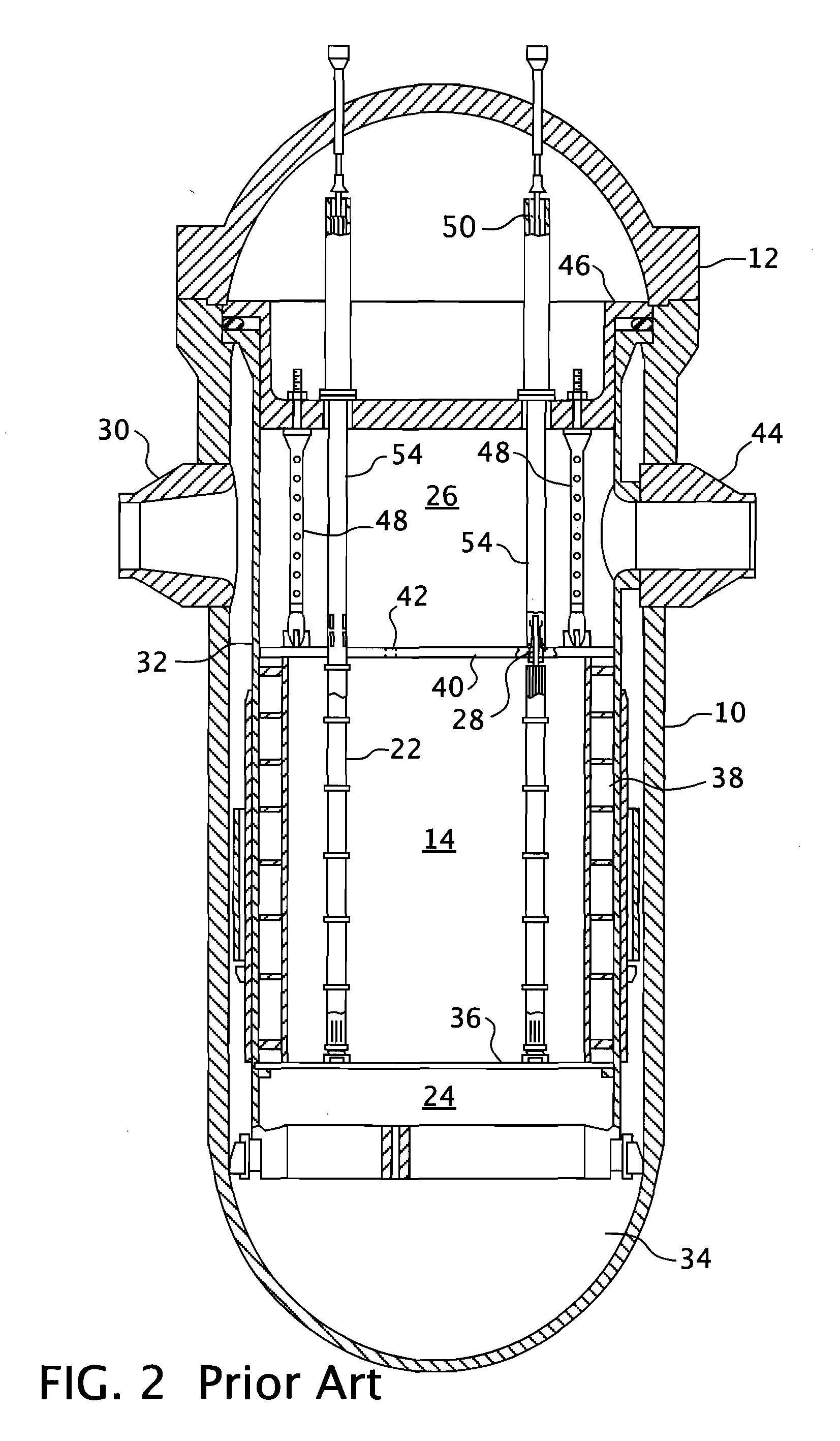
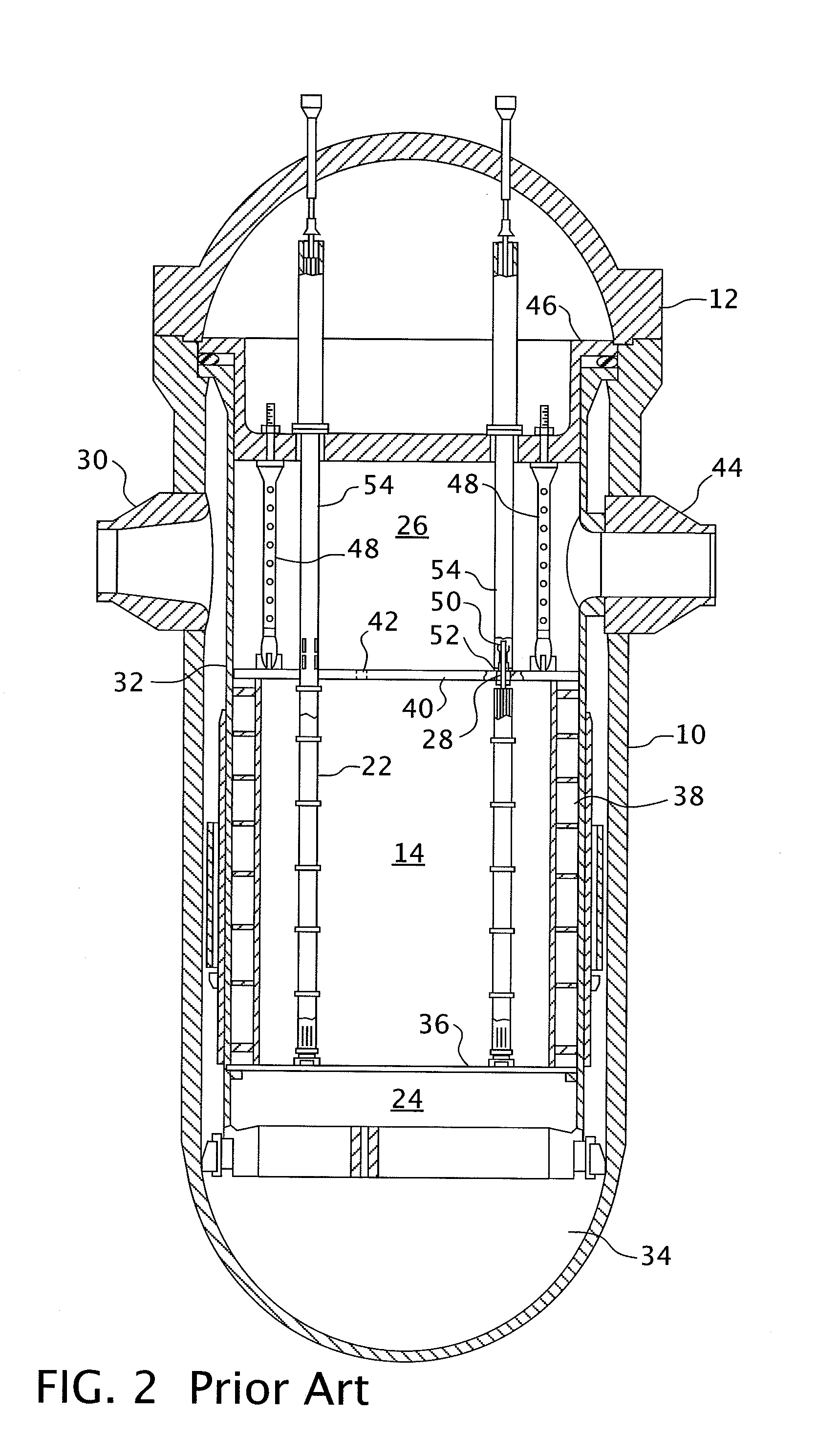
Instrumentation and control penetration flange for pressurized water reactor
A nuclear reactor having a penetration seal ring interposed between the reactor vessel flange and a mating flange on the reactor vessel head. Radial ports through the flange provide passage into the interior of the reactor vessel for utility conduits that can be used to convey signal cables, power cables or hydraulic lines to the components within the interior of the pressure vessel. A double o-ring seal is provided on both sides of the penetration flange and partial J-welds on the inside diameter of the flange between the flange and the utility conduits secure the pressure boundary.
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE ELECTRIC CORP
Large passive pressurized water reactor nuclear power plant crucible-type reactor core catcher
InactiveCN103177779AImprove securityImprove reliabilityNuclear energy generationEmergency protection arrangementsNuclear plantCore catcher
The invention discloses a large passive pressurized water reactor nuclear power plant crucible-type reactor core catcher which comprises a reactor cavity concrete bottom plate (4), a crucible cooling system water filling nozzle (6), a crucible cooling system water vapor outlet (7), a crucible component (8), a crucible cooling system cavity (9) and a melt collector (10). The reactor core catcher is organically combined with an interactive voice response (IVR) system, the safety of the nuclear power plant can be further improved, and the reliability of the system is higher due to the crucible design.
Owner:SHANGHAI NUCLEAR ENG RES & DESIGN INST CO LTD
Large-scale passive pressurized water reactor nuclear power plant reactor core catcher with melt expansion room
InactiveCN103165198AIncrease heat transfer areaImprove cooling effectNuclear energy generationEmergency protection arrangementsCore catcherPressurized water reactor
The invention provides a large-scale passive pressurized water reactor nuclear power plant reactor core catcher with a melt expansion room. The large-scale passive pressurized water reactor nuclear power plant reactor core catcher with the melt expansion room comprises a reactor cavity which coats the middle lower portion of a reactor pressure vessel, a reactor cavity concrete base plate is arranged on the lower portion of the reactor cavity, and a reactor cavity refractory layer is arranged on the lower portion of the reactor cavity concrete base plate. The upper end of a melt release passage is communicated with the reactor cavity refractory layer, and the lower end of the melt release passage is communicated with the melt expansion room. The inner wall of the melt release passage surrounds the refractory layer. An expansion room concrete base plate is arranged on the lower portion of the melt expansion room, an expansion room refractory layer is arranged on the lower portion of the expansion room concrete base plate, and an expansion room outside cooling passage is arranged on the lower portion of the expansion room refractory layer. Two ends of the expansion room outside cooling passage extend outwards and are respectively an outside cooling passage entrance and an outside cooling passage exit. The large-scale passive pressurized water reactor nuclear power plant reactor core catcher with the melt expansion room is used for successively implementing expansion, retention and cooling of the melt when the a pressure container loses efficacy and can strengthen capacity of relieving severe accidents of the large-scale passive pressurized water reactor nuclear power plant.
Owner:SHANGHAI NUCLEAR ENG RES & DESIGN INST CO LTD
Device combining in-core and out-of-core dwelling of molten material of large-scale passive nuclear power plant
InactiveCN103578580AImplementation of off-stack coolingImplement in-heap retentionNuclear energy generationEmergency protection arrangementsCore catcherPressurized water reactor
The invention provides a device combining in-core and out-of-core dwelling of a molten material of a large-scale passive nuclear power plant. The device comprises a concrete sacrificial layer (4), a core catcher chamber (7), a core catcher refractory layer (8), a cooling channel inlet (9), a cooling channel outlet (10) and a core catcher bottom cooling channel (11). The invention provides a set of device organically combining molten material out-of-core cooling with an IVR (interactive voice response) system, when IVR succeeds, in-core dwelling of the molten material can be realized; and after the IVR fails, out-of-core dwelling of the molten material is realized by passive cooling of the core catcher bottom cooling channel, and the capability of mitigating severe accidents of the large-scale passive pressurized water reactor nuclear power plant is further enhanced.
Owner:SHANGHAI NUCLEAR ENG RES & DESIGN INST CO LTD
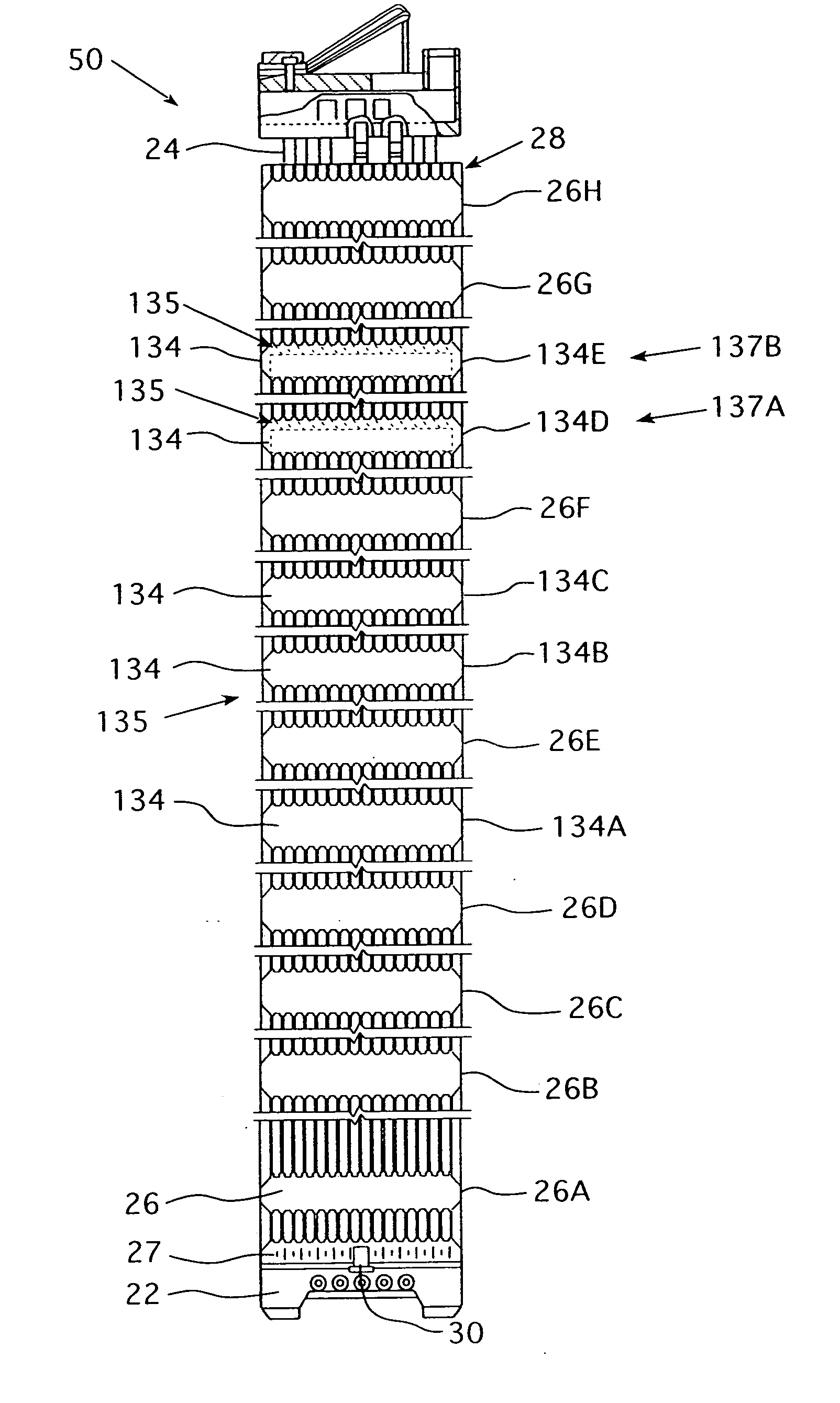
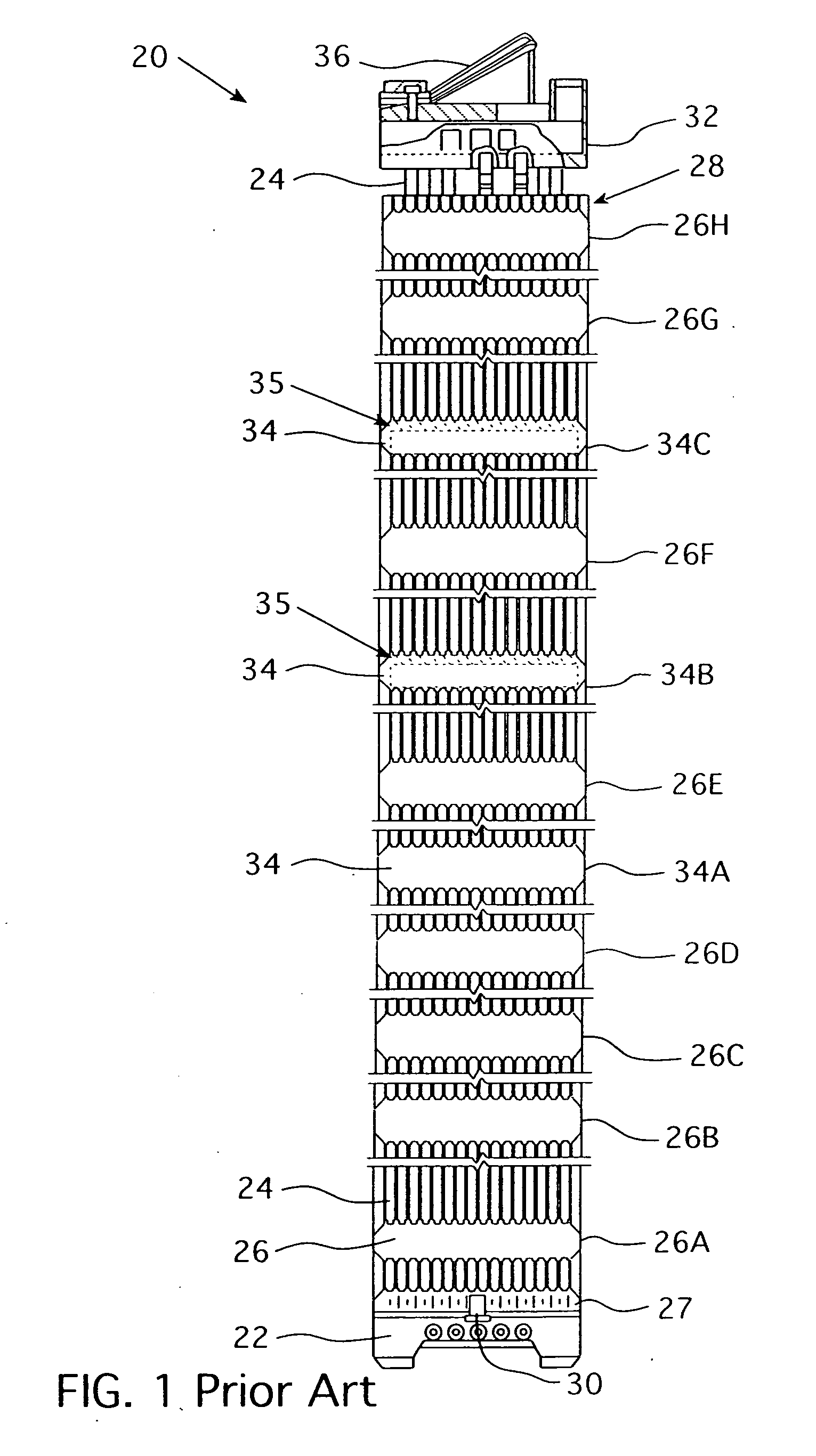
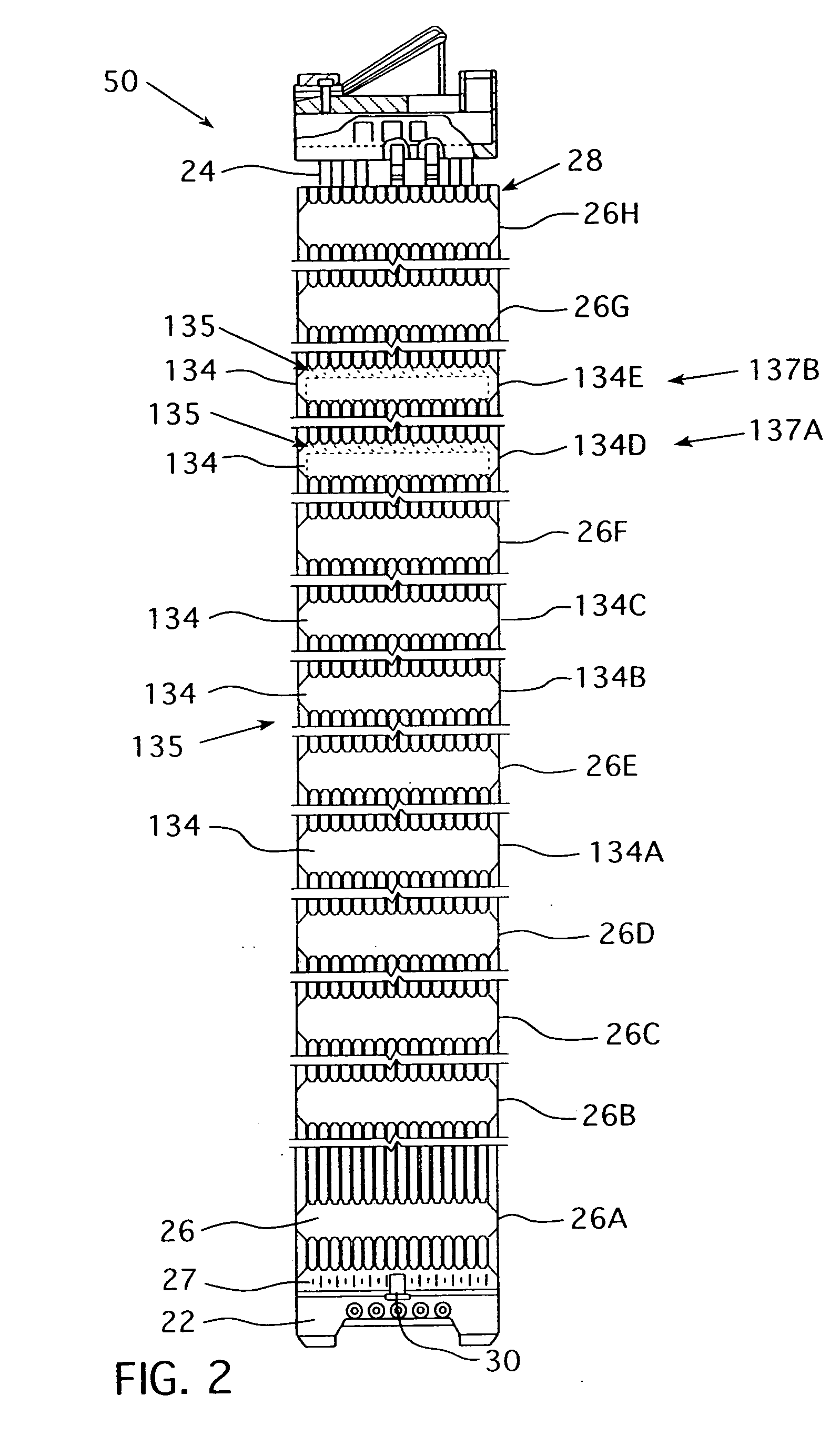
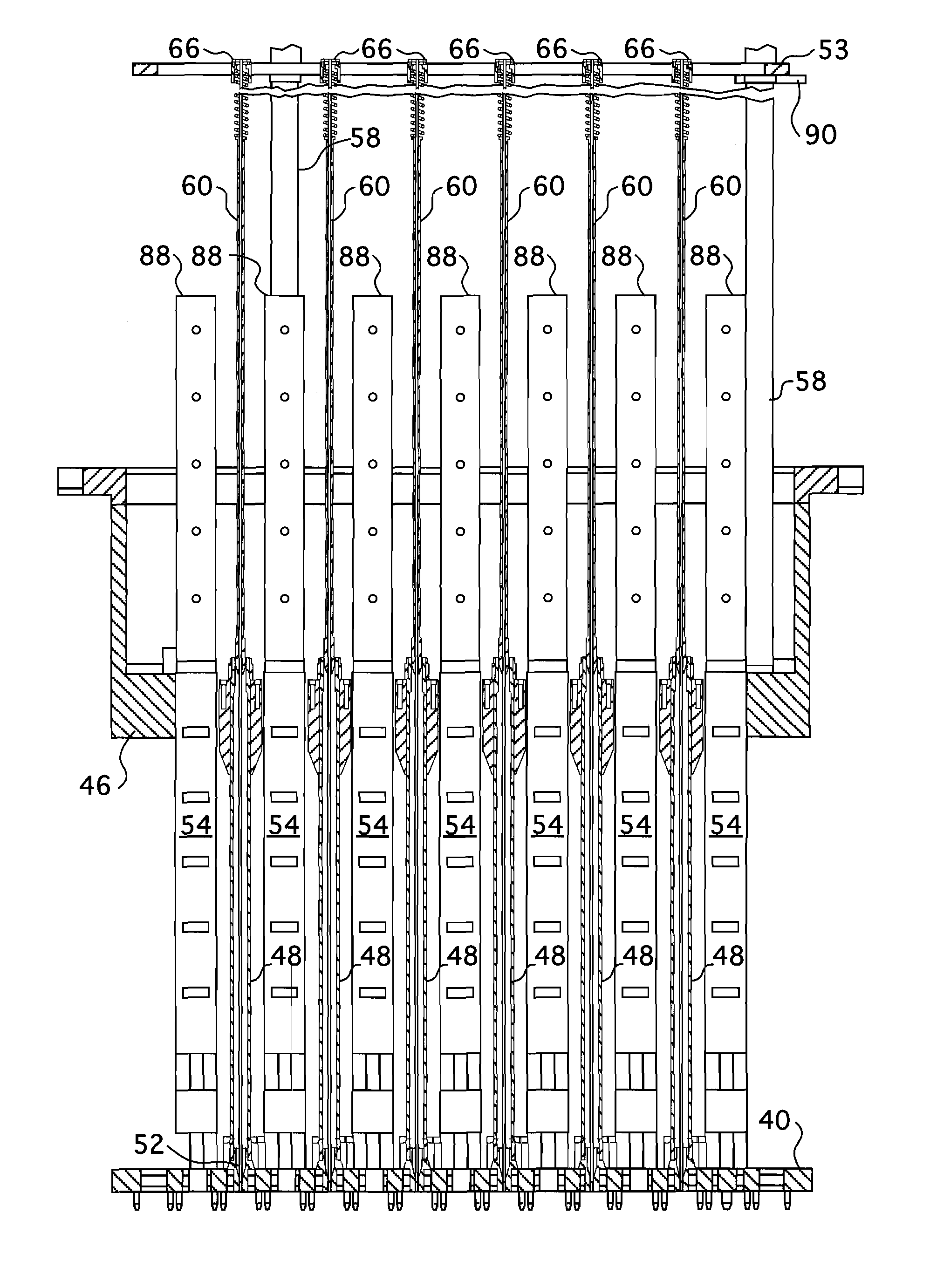
Multiple and variably-spaced intermediate flow mixing vane grids for fuel assembly
InactiveUS20070206717A1Improve heat transfer performanceReduce riskNuclear energy generationFuel element assembliesPressurized water reactorMesh grid
A fuel assembly for a pressurized water reactor that includes a bottom nozzle, a plurality of elongated guide thimbles projecting upwardly from the bottom nozzle, an array of fuel rods, a plurality of support grids axially spaced along the guide thimbles, and at least two Intermediate Flow Mixing grids, which may have different configurations of mixing device formations, disposed between pairs of non-uniformly spaced, adjacent support grids at selected locations.
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE ELECTRIC CORP
Containment filtering and discharging system
InactiveCN102723114AImprove filtering effectAccumulated radioactivityNuclear energy generationEmergency protection arrangementsLiquid wasteRadioactive agent
The invention relates to a containment filtering and discharging system. As a shielding plant (11) is arranged outside a containment, a discharging and filtering sub system is arranged in the shielding plant (11), a water washing filter (3) and a metal fiber filter (4) connected with each other in sequence are arranged in the discharging and filtering sub system and the water washing filter (3) is provided with a waste liquid returning pipeline (10), gases discharged by the containment are doubly filtered by the water washing filter (3) and the metal fiber filter (4), and the waste liquid accumulated in the water washing filter (3) self-flows into the containment through the waste liquid returning pipeline (10) under the effect of gravity force. Therefore, according to the invention, serious accidents occurred in pressurized-water reactor nuclear power stations are eased, overpressure failure of the containment is prevented, radioactive substances released to the environment are reduced, safeties of the surrounding environment and personnel are protected, and the safety of the nuclear power stations are greatly improved.
Owner:CHINA NUCLEAR POWER ENG CO LTD
Method and system for supplying emergency power to nuclear power plant
ActiveUS20140001863A1Improve securityReduce probabilityPower plant safety arrangementBatteries circuit arrangementsPressurized water reactorNuclear power
Method and system for supplying emergency power to nuclear power plant, wherein the method includes, providing accumulator battery system, connected to emergency bus, the accumulator battery system is monitored by online monitoring system; in case of power loss of electrical devices of the nuclear power plant, the online monitoring system starts the accumulator battery system to provide power supply to the electrical devices of the nuclear power plant via the emergency bus. The present application is adapt to the key technologies and battery management technologies of million kilowatt-class advanced pressurized water reactor nuclear power plant, facilitating to improve the safety of the nuclear power plant in case of serious natural disasters beyond design working conditions.
Owner:DAYA BAY NUCLEAR POWER OPERATIONS & MANAGEMENT +1
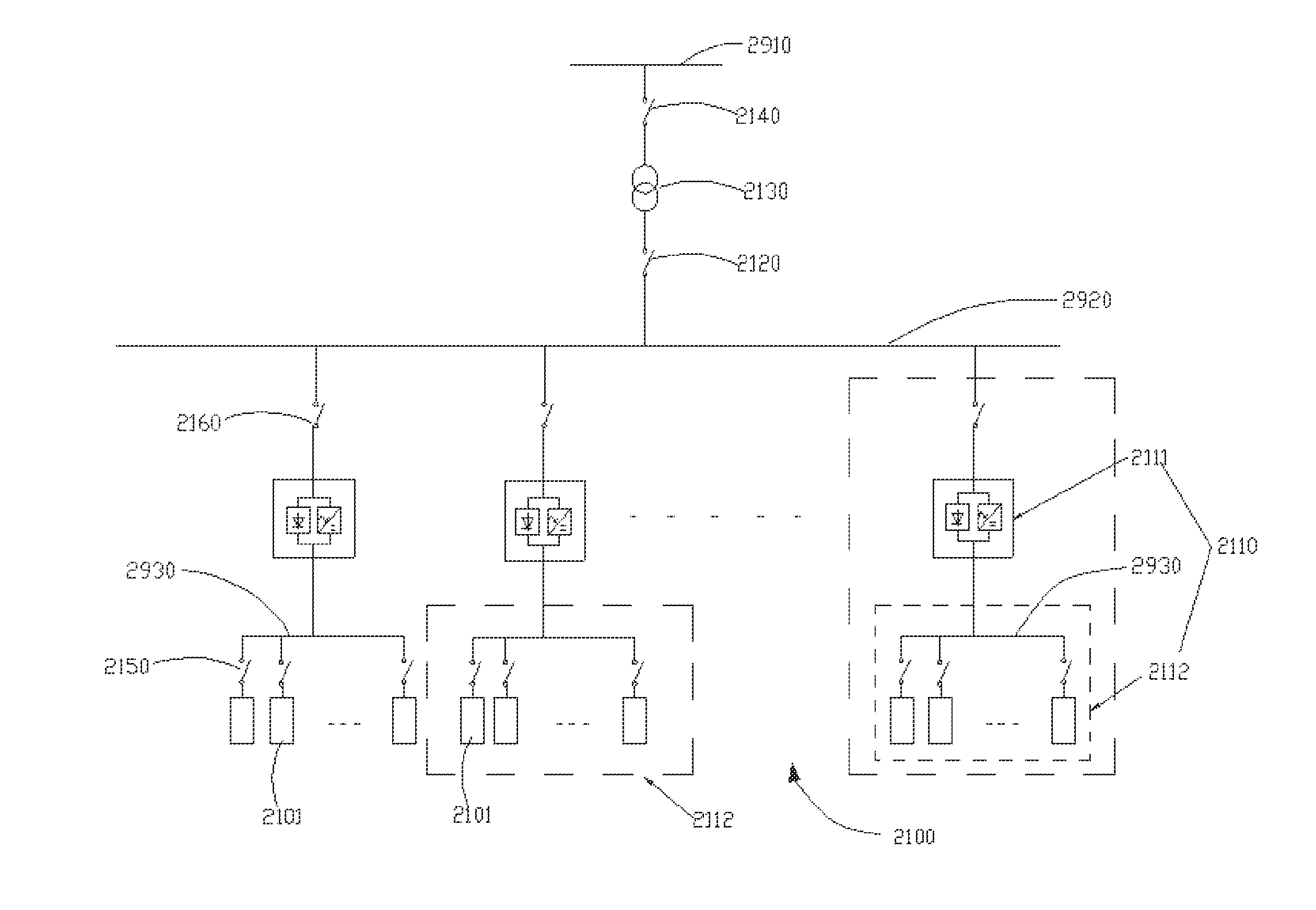
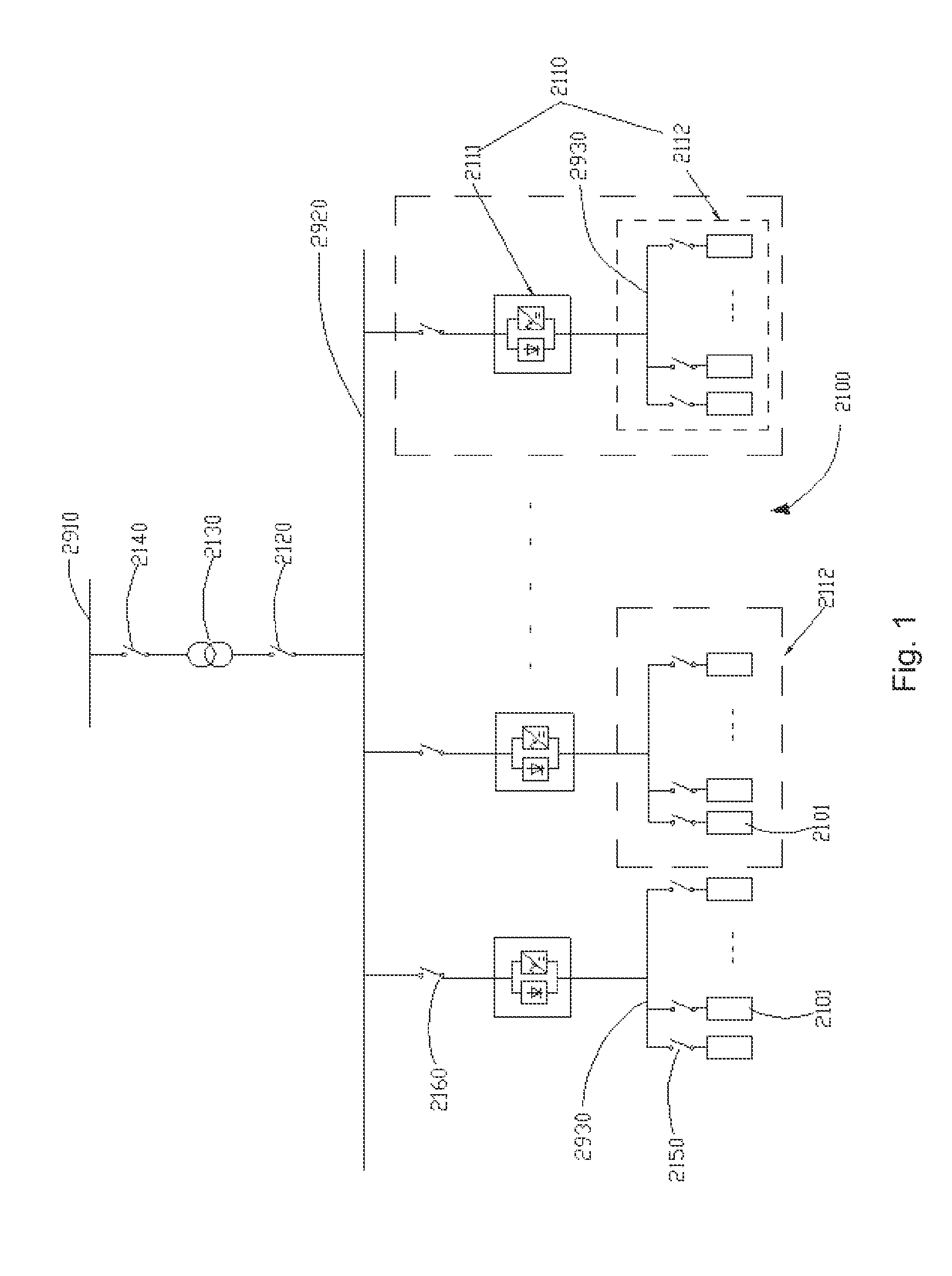
Simulation system of loading and unloading operation processes in pressurized water reactor nuclear power plants
ActiveCN102903271AMeet the process requirementsReflect vividlyCosmonautic condition simulationsSimulatorsPressurized water reactorNuclear power
The invention relates to a simulation system of loading and unloading operation processes in pressurized water reactor (PWR) nuclear power plants. The system comprises an LED (light emitting diode) display screen, a touch screen, an operation control table consisting of a component part consisting of a button, a switch, an operating rod, an indicator lamp and an alarm, an information communication and processing device consisting of a programmable logic controller PLC (programmable logic controller) and a PC graphic workstation, a display device consisting of a scene display and a camera, and an industrial personal computer. The simulation system of the loading and unloading operation processes is designed in strict accordance with functions of real loading and unloading machines, is featured with rich simulated objects, reliable simulation data and strong reality, simulates various common abnormal states or failure states, allows interactive operation, clears faults and has a component showing function; the touch screen has an interface control function; the system simplifies layout of an operation table, expands subsequent functions, effectively trains loading and unloading operators and is widely applied to nuclear power stations and related analogue simulation systems.
Owner:STATE NUCLEAR POWER PLANT SERVICE
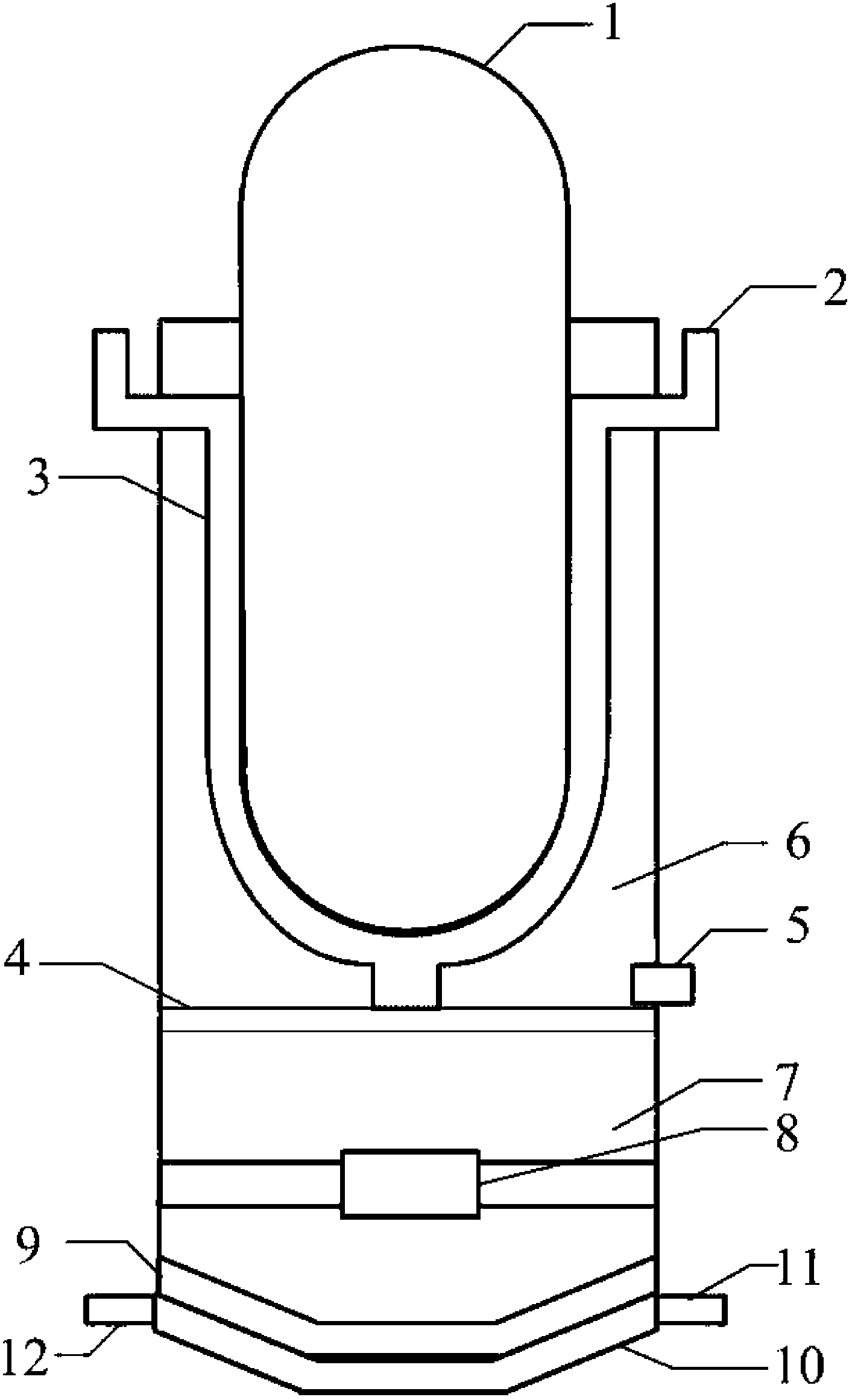
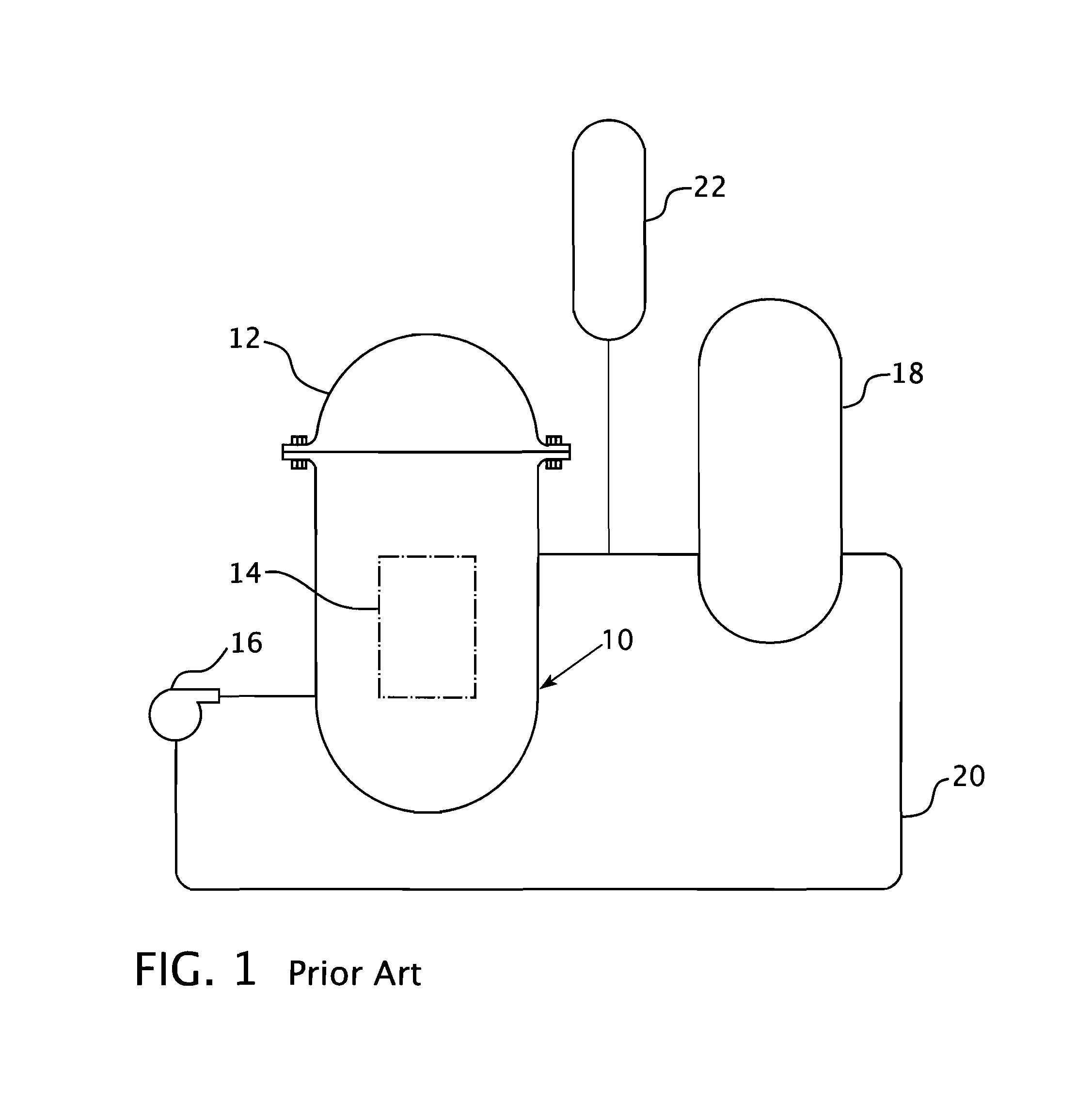
Emergency core cooling system for pressurized water reactor
ActiveUS20120243651A1Power plant safety arrangementIntegral reactorsCondensed waterPressurized water reactor
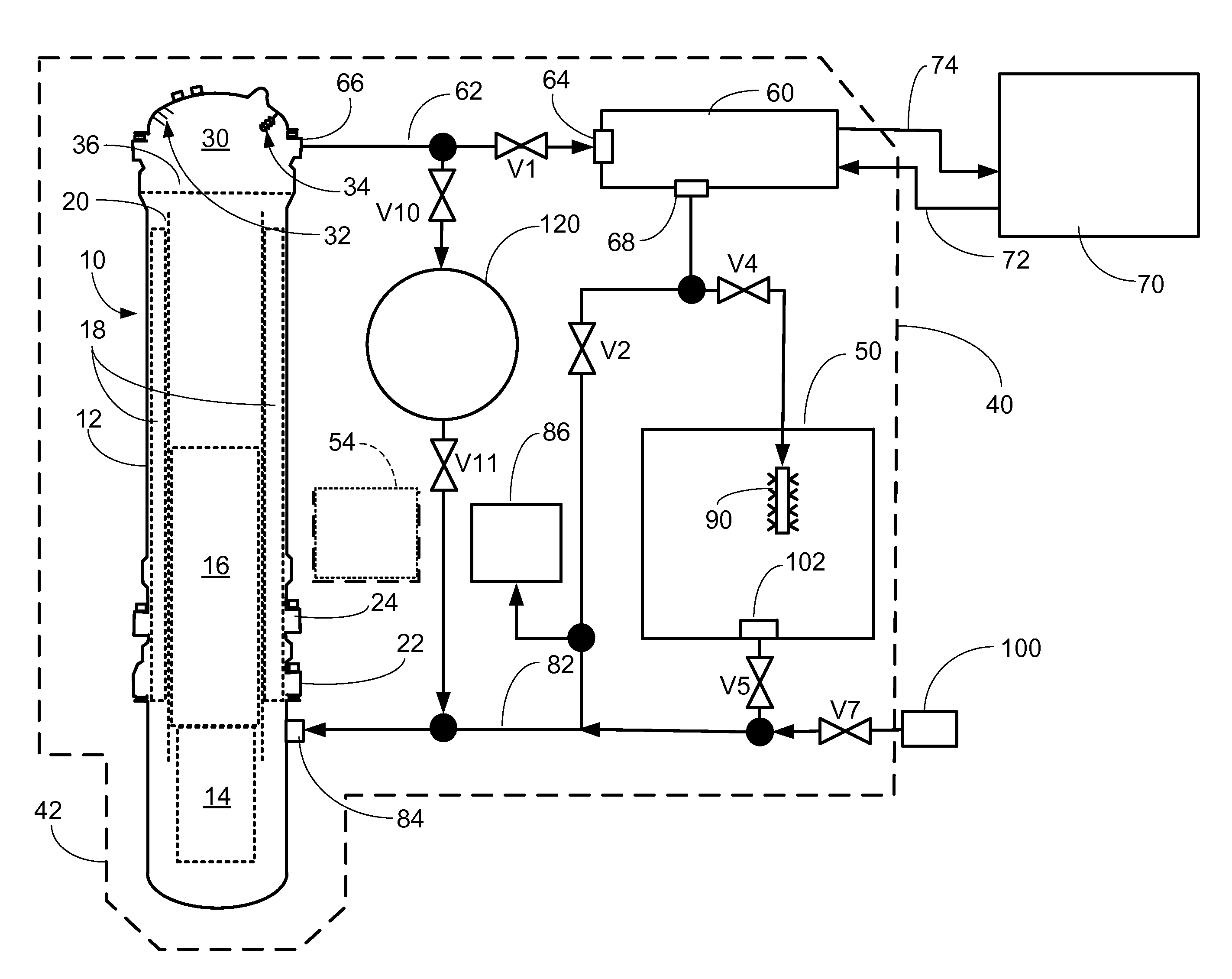
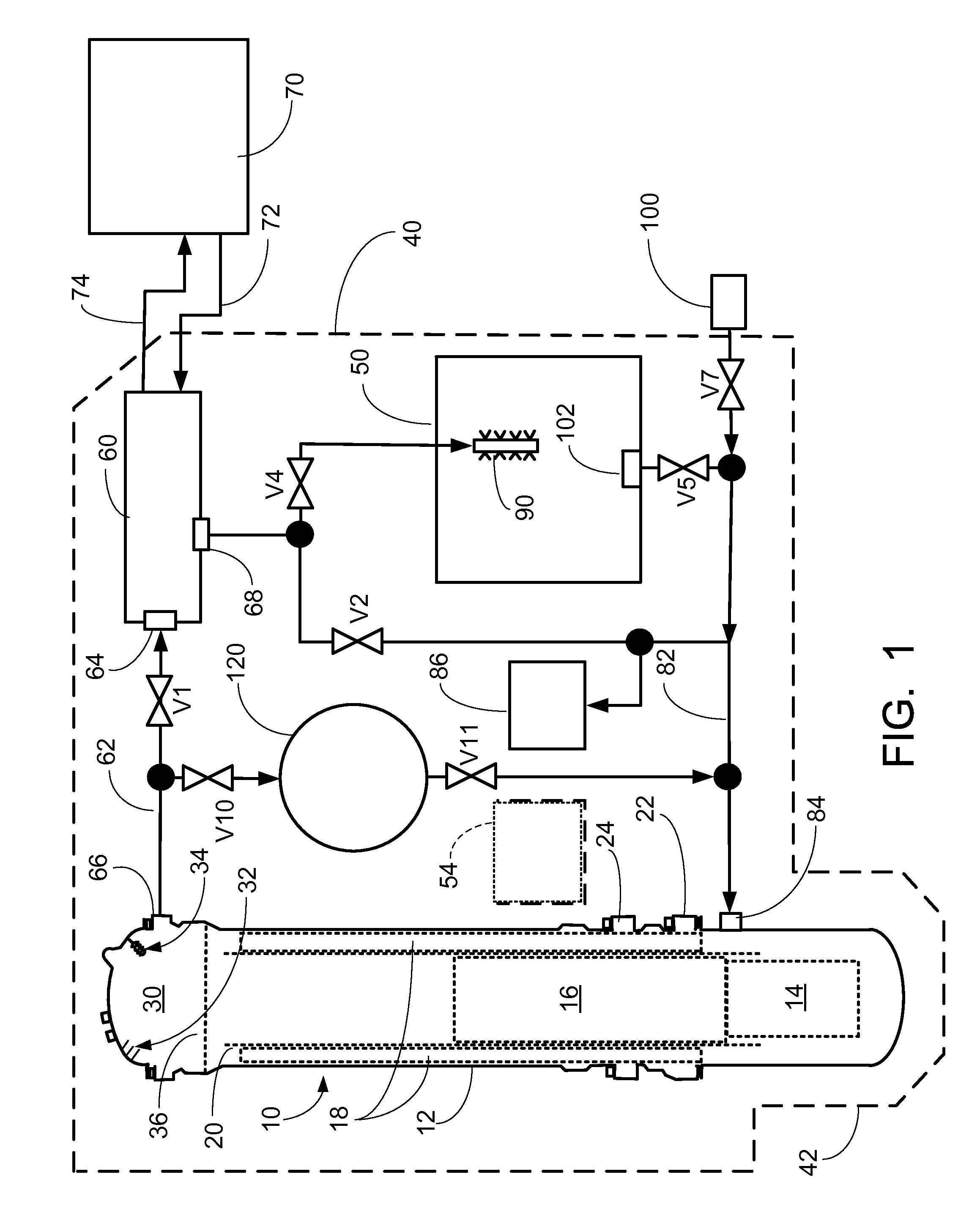
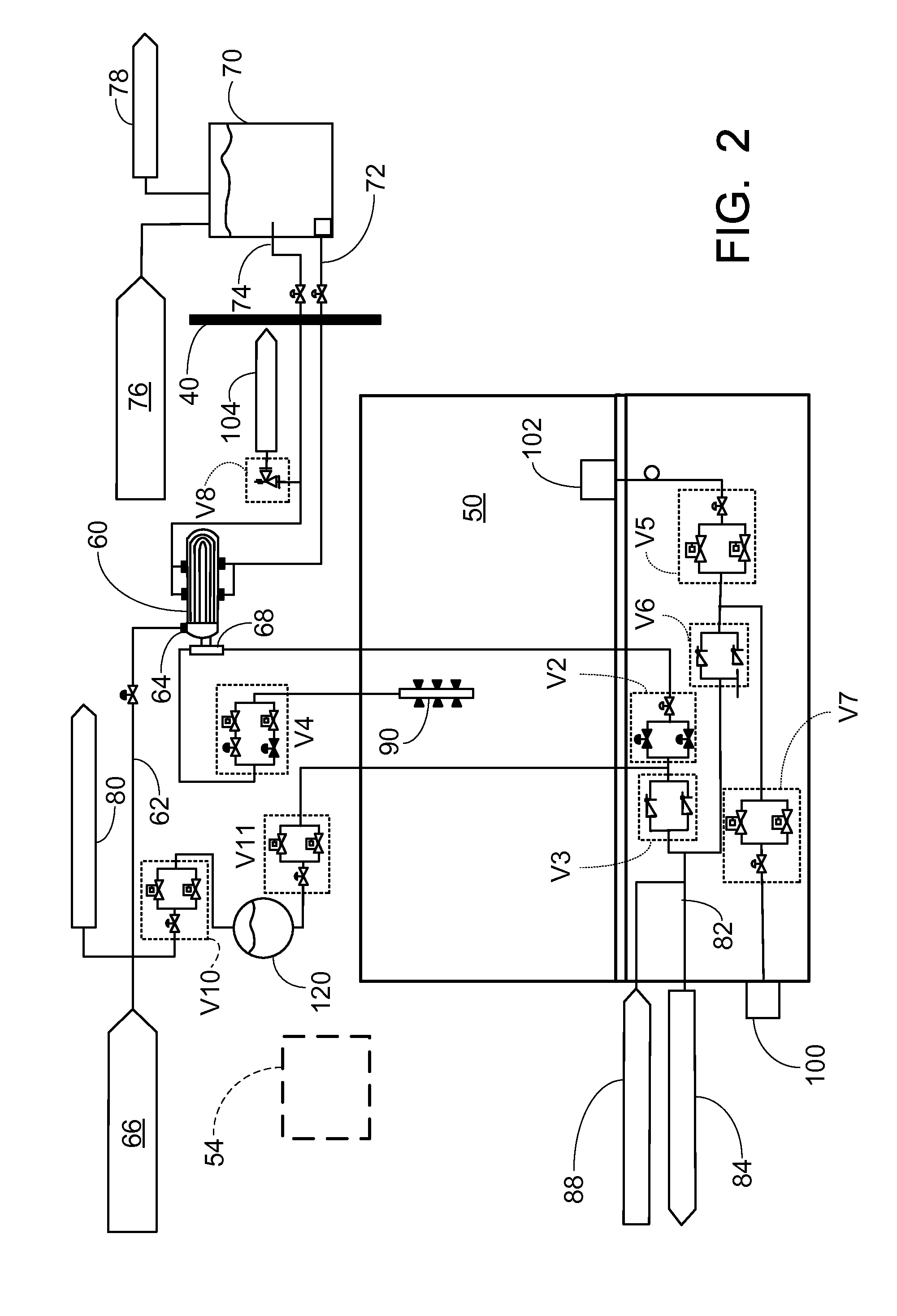
A pressurized water nuclear reactor (PWR) has an internal pressurizer volume containing a steam bubble and is surrounded by a containment structure. A condenser is disposed inside the containment structure and is operatively connected with an external heat sink disposed outside of the containment structure. A valve assembly operatively connects the PWR with the condenser responsive to an abnormal operation signal such that the condenser condenses steam from the steam bubble while rejecting heat to the external heat sink and returns the condensed water to the PWR. A quench tank contains water with dissolved neutron poison. A valved tank pressurizing path selectively connects the steam bubble to the quench tank to pressurize the quench tank, and a valved soluble poison delivery path selectively connects the quench tank to the PWR such that the quench tank under pressure from the steam bubble discharges water with dissolved neutron poison into the PWR.
Owner:BWXT MPOWER INC
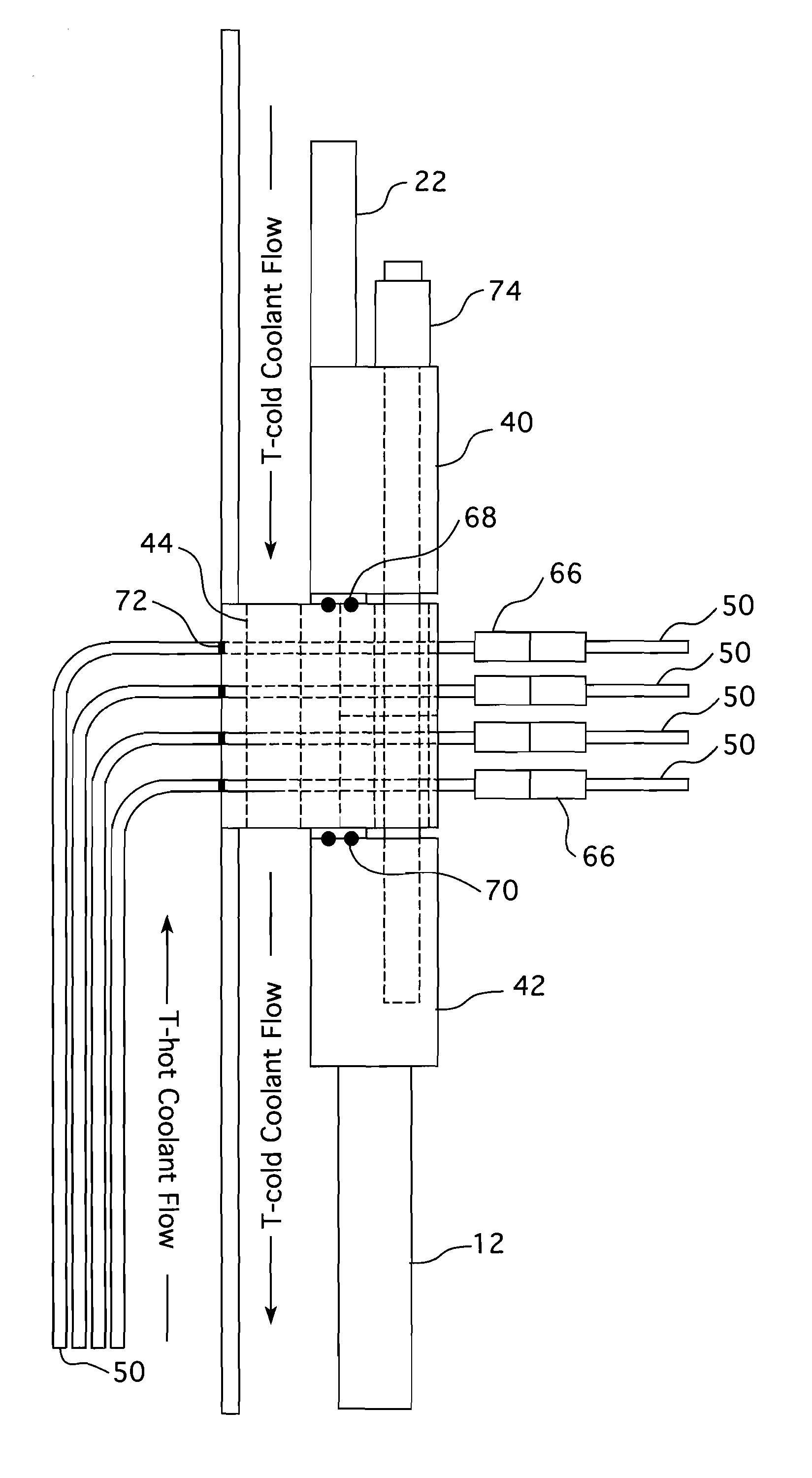
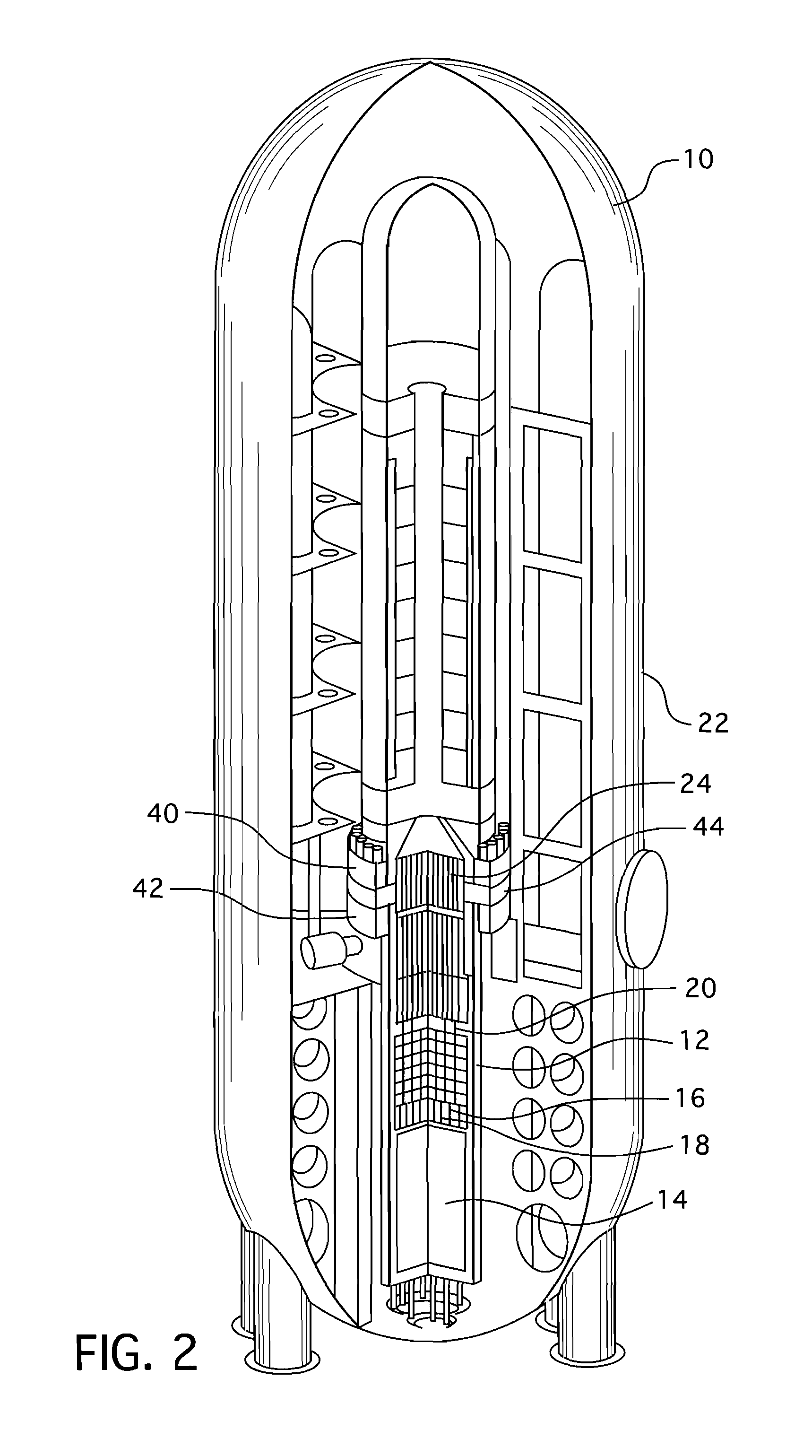
Upper internals arrangement for a pressurized water reactor
ActiveUS20100150294A1Meet growth requirementsReduce stepsNuclear energy generationNuclear monitoringPressurized water reactorEngineering
A telescoping guide for extraction and reinsertion support handling of in-core instrument thimble assemblies in the area above the upper support plate in the upper internals of a pressurized water reactor. The telescoping guides extend between the upper ends of the upper internals support columns and an axially movable instrumentation grid assembly which is operable to simultaneously raise the telescoping guides and extract the in-core instrument thimble assemblies from the reactor fuel assemblies.
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE ELECTRIC CORP
Boron-containing radioactive spent resin cement solidification method
InactiveCN101456715AImprove processing efficiencySolid waste managementPressurized water reactorPortland cement
The invention discloses a method for cement solidification of a boron-containing radioactive waste resin, which belongs to the technical field of cement solidification of the boron-containing radioactive waste resin of a pressurized water reactor nuclear power station. The method comprises the following steps: the boron-containing radioactive waste resin of the pressurized water reactor nuclear power station, ordinary Portland cement, a water reducing agent, zeolite, lime and water are taken as raw materials, the mixture ratio of the raw materials comprises that the boron-containing radioactive waste resin of the pressurized water reactor nuclear power station: the ordinary Portland cement: the water reducing agent: the zeolite: the lime: the water is equal to 300-500L: 800-1,000kg: 4-5kg: 40-50kg: 25-30kg: 90-110kg, and the raw materials are weighed; and the materials are added into a C1 solidification barrel with a volume of 1 cubic meter and are stirred evenly to obtain a cement solidification body. The adoption of each solidification drum with the volume of 1 cubic meter can solidify 300 to 500L of radioactive resin, and remarkably improve the treatment efficiency of boron-containing radioactive waste resins of pressurized water reactors.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
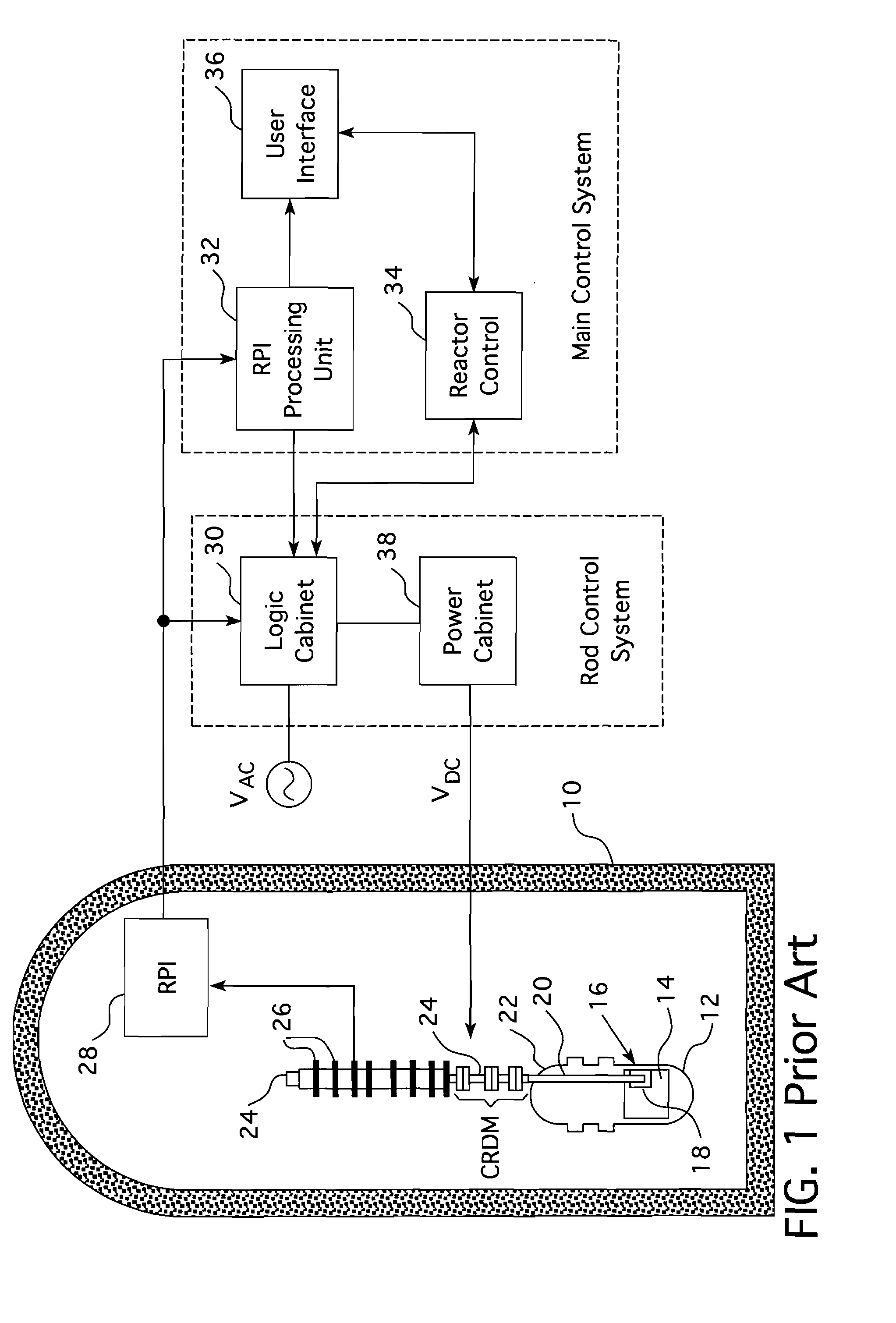
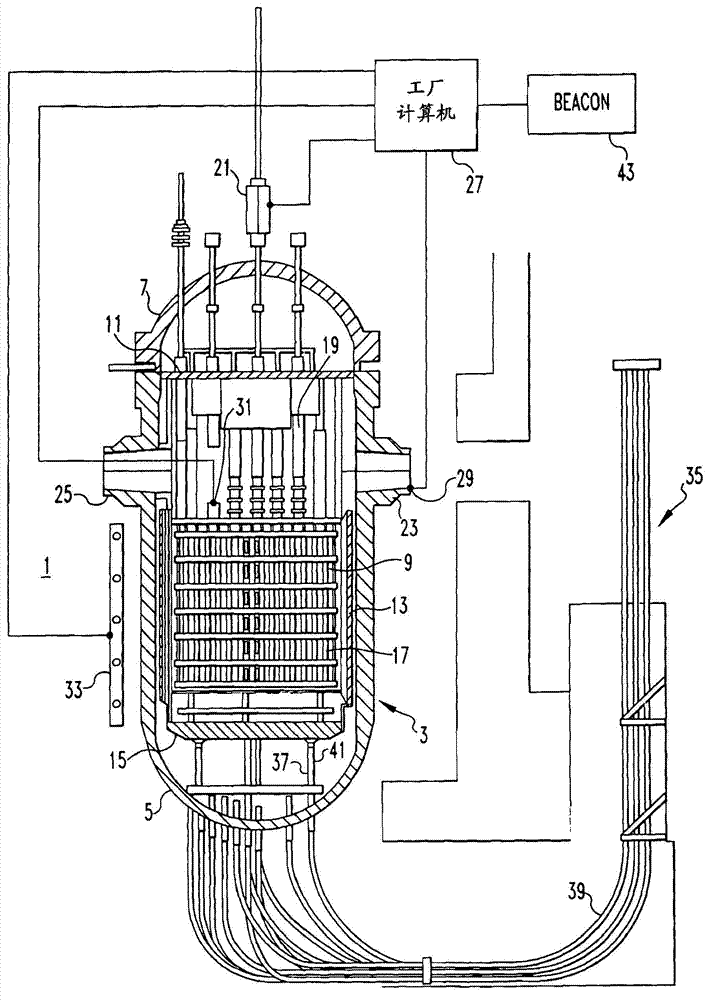
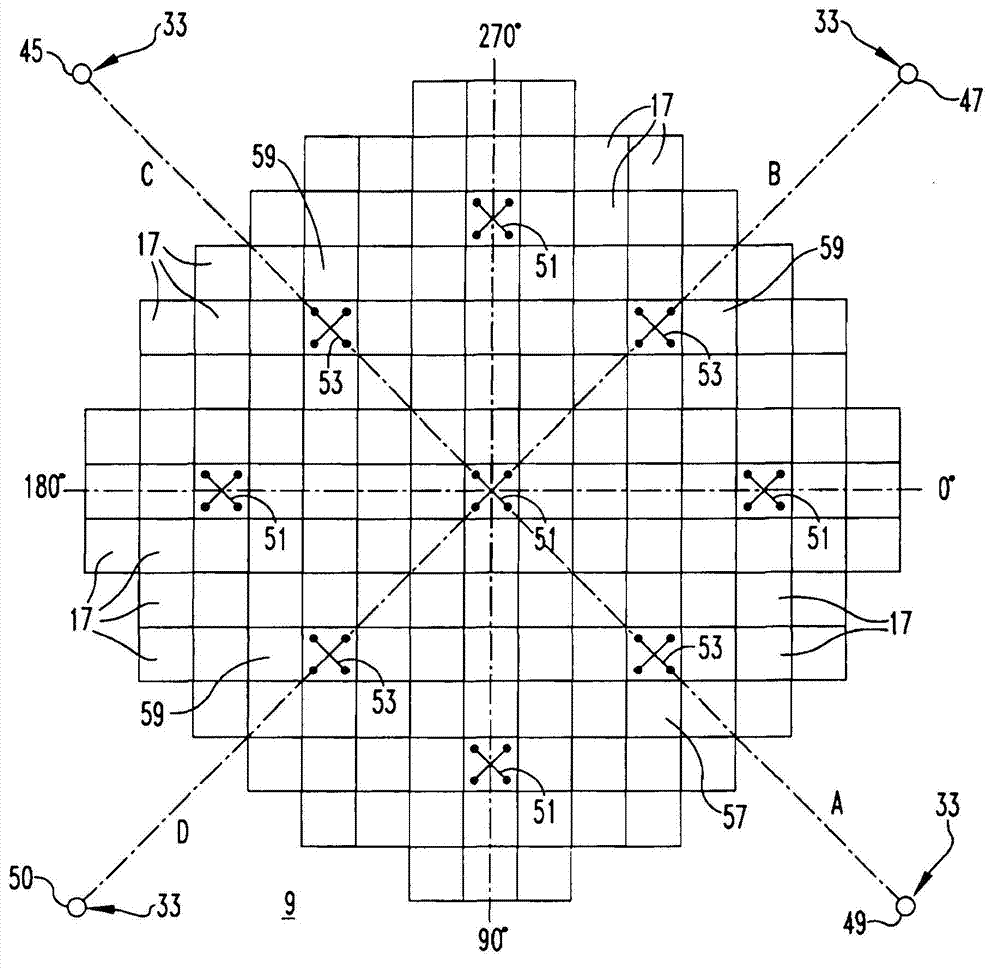
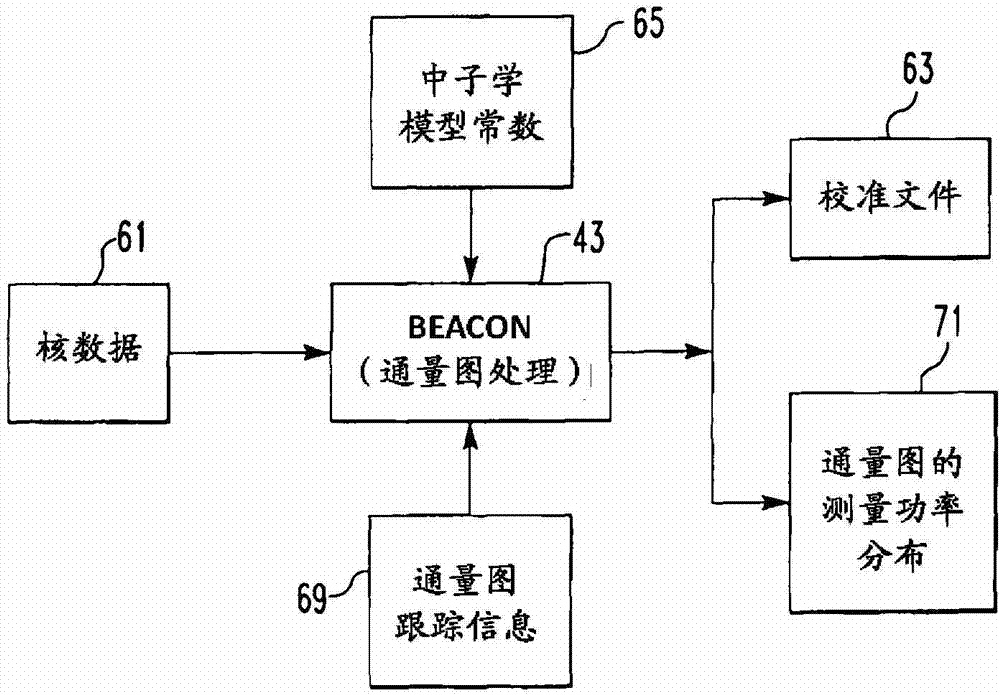
Method of calibrating excore detectors in a nuclear reactor
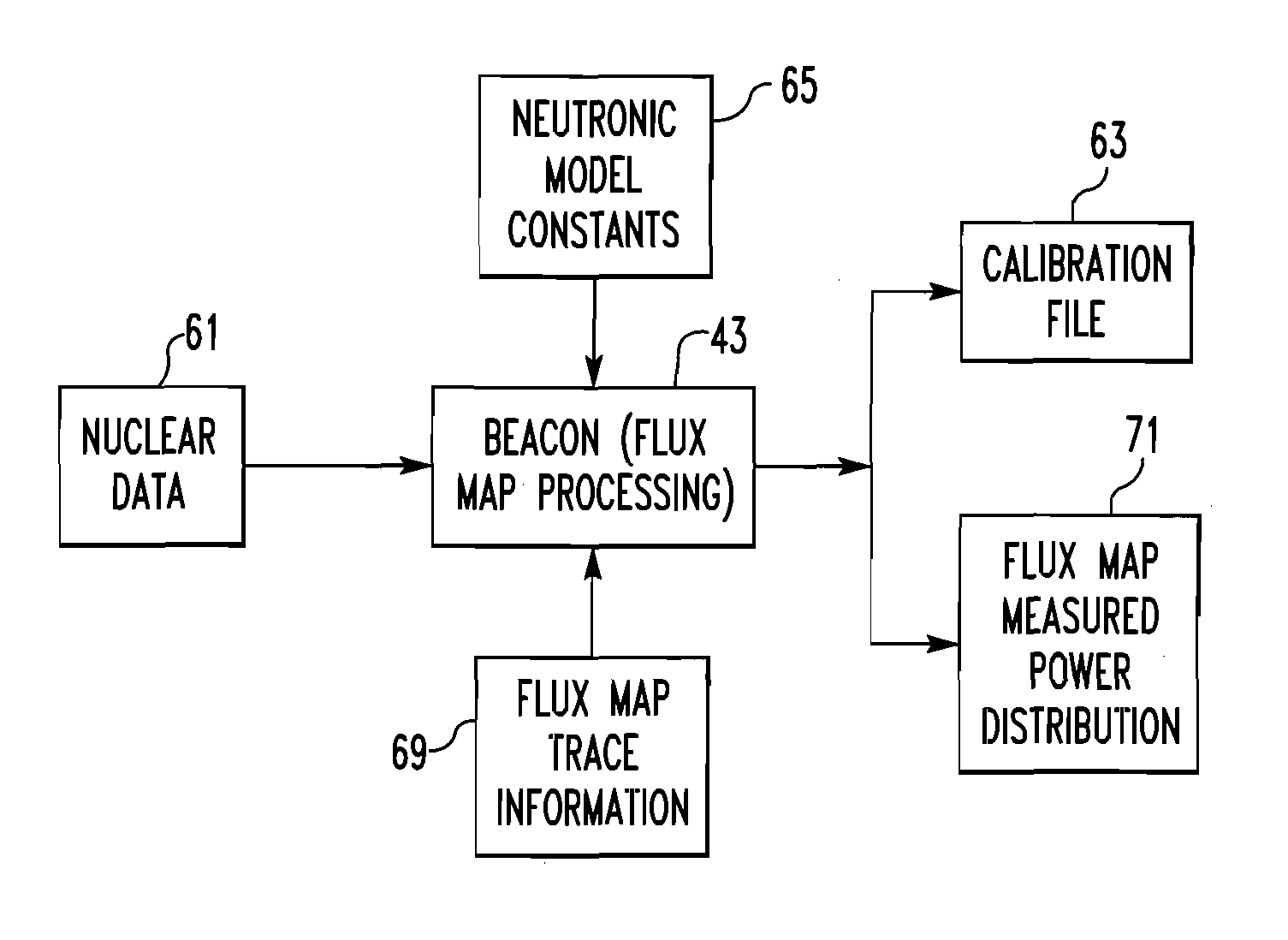
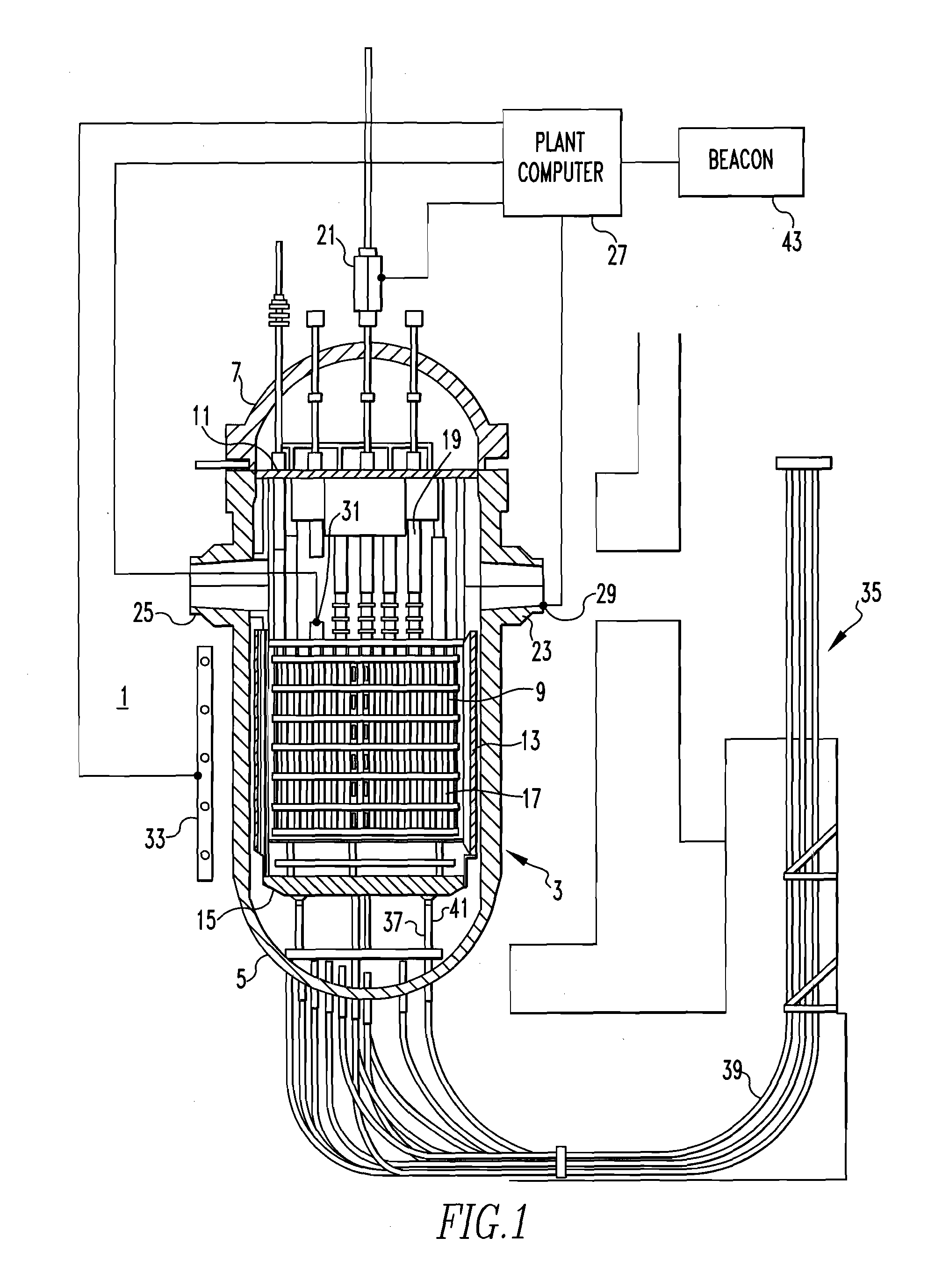
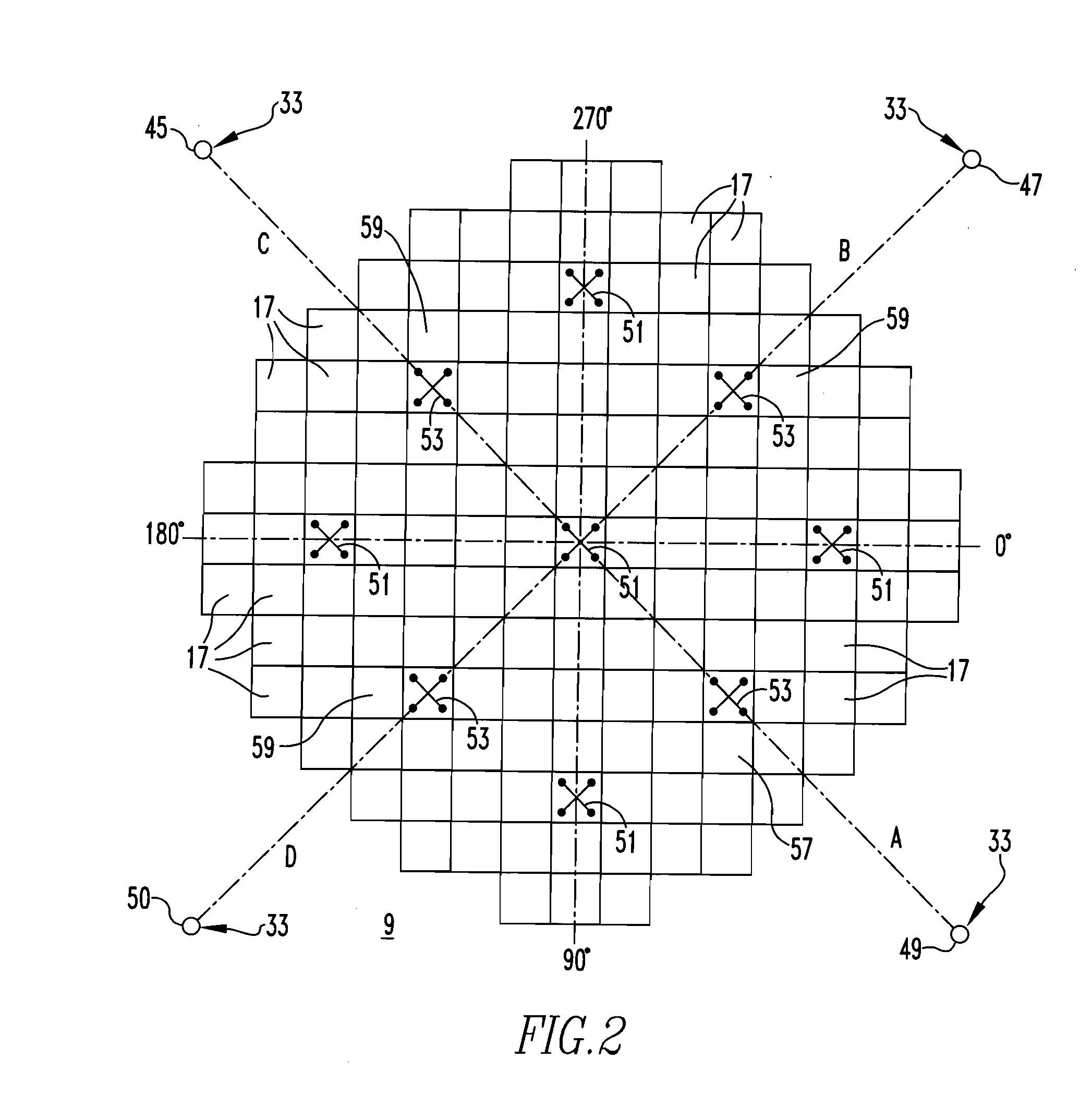
A method of calibrating excore detectors for a pressurized water reactor (PWR) (1) includes: measuring peripheral core flux signals using excore detectors (33) disposed at a plurality of locations spaced about the periphery of the core (9), and using the measured power distribution from either a core monitoring system (43) or in-core flux measurement (69). Calibration of the excore detectors (33) is broken into two parts: (1) the relation between the excore detector signal and weighted peripheral assembly axial offset, and (2) the relation between weighted peripheral assembly axial offset and core average axial offset. Relation (2) can be determined by a representative neutronics model. Accuracy of the neutronics solution is improved by applying (83) nodal calibration factors, which represent the ratio of the measured three-dimensional power distribution (75) to the nodal predicted three- dimensional power distribution and correct the neutronic results to match what would be measured if predictive scenarios were actually performed in the actual reactor core (9).
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE ELECTRIC CORP
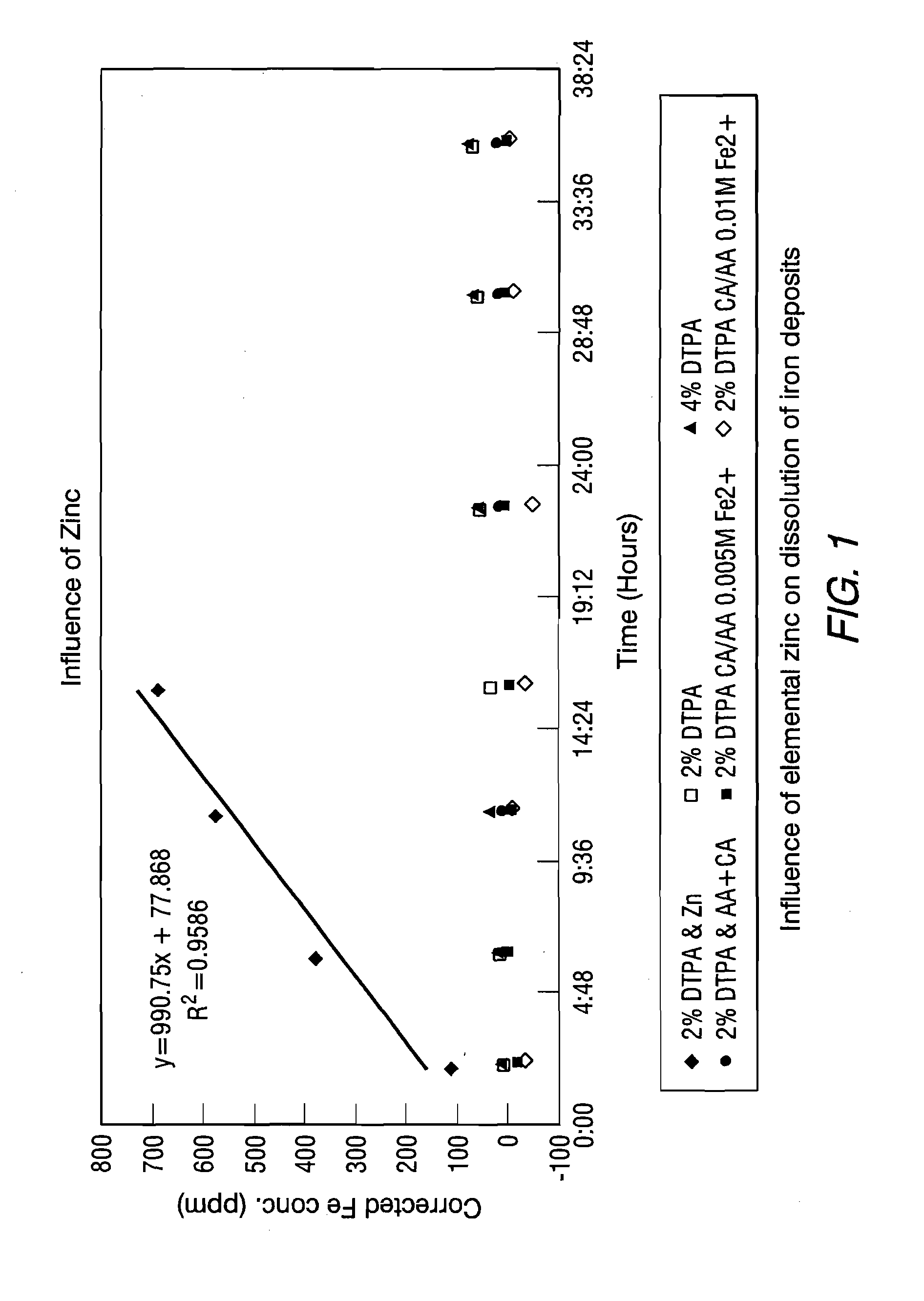
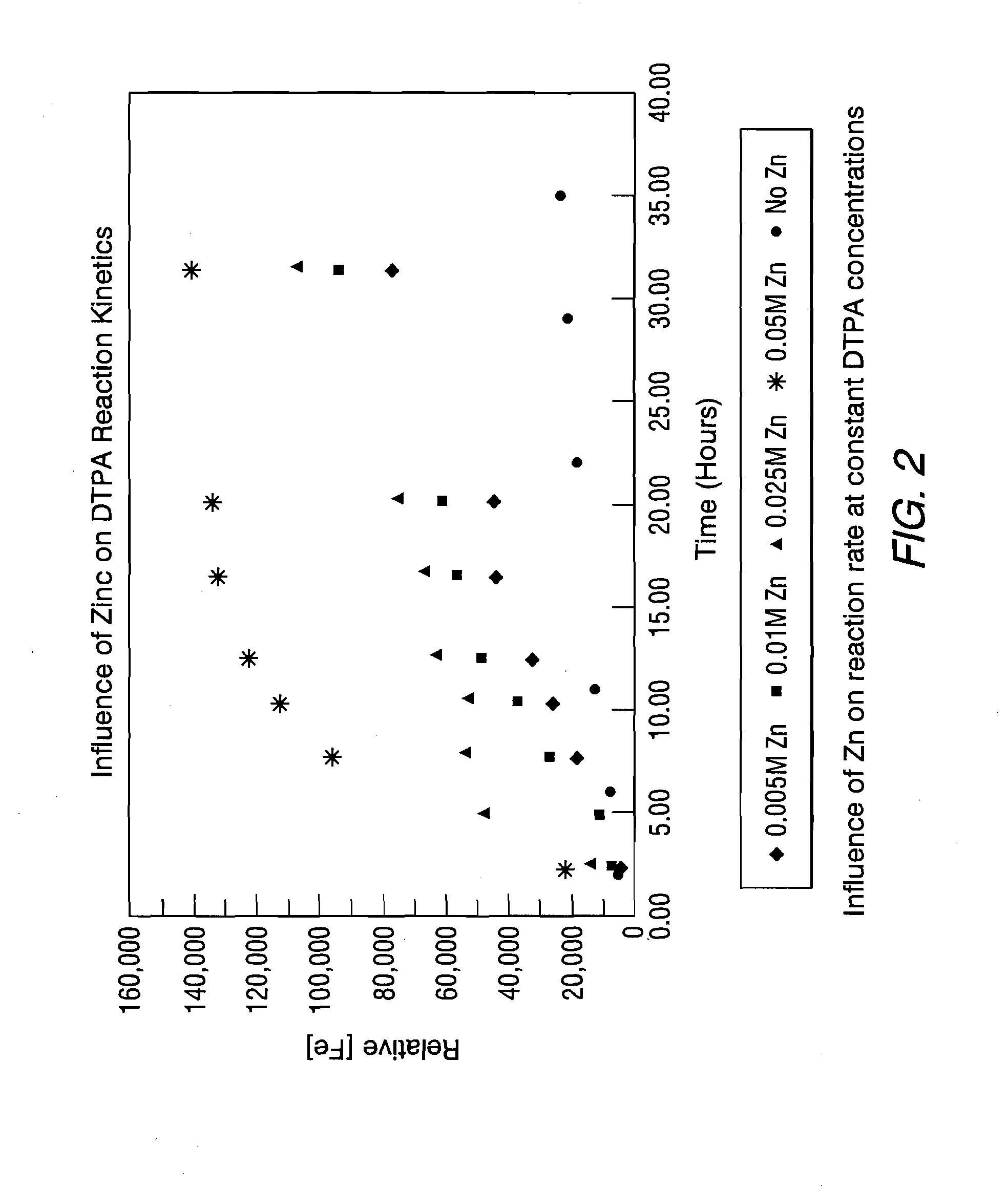
Additives for heat exchanger deposit removal in a wet layup condition
ActiveUS20130281341A1Water treatment parameter controlWater treatment compoundsPressurized water reactorDissolution
This invention relates to compositions and methods for the at least partial dissolution, disruption and / or removal of deposits, such as scale and other deposits, from heat exchanger components. The heat exchanger components can include pressurized water reactor steam generators. The pressurized water reactor steam generators can be in a wet layup condition. The compositions include elemental metal and complexing agent selected from the group consisting of sequestering agent, chelating agent, dispersant, and mixtures thereof. The methods include introducing the compositions into the heat exchanger components.
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE ELECTRIC CORP
Shockproof strip end-plate material of vapor generator of nuclear power plant and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101851714AReasonable design of ingredientsLow costPressurized water reactorVapor generator
The invention discloses a shockproof strip end-plate material of a vapor generator of a nuclear power plant and a preparation method thereof, relating to a shockproof strip end-plate material of a vapor generator of a pressurized water reactor nuclear island CPR1000. The shockproof strip end-plate material is prepared from the following components in percentage by weight: 0.003-0.08 percent of C, 0.1-0.4 percent of Si, 0.3-0.8 percent of Mn, not more than 0.015 percent of P, not more than 0.01% of S, 14-17 percent of Cr, 72-78 percent of Ni, 0.05-0.5 percent of Cu, 0.05-0.5 percent of Ti, 0.05-0.5 percent of Al, 6-10 percent of Fe, 0.01-1.0 percent of Xt and the balance of inevitable impurities. The preparation method of the shockproof strip end-plate material comprises the following steps of: preparing raw materials; smelting in a vacuum refining furnace; refining electroslag; forging; thermally rolling; normalizing; and repeating the process of drawing-annealing- drawing) many times to obtain a finished product of shockproof strip end-plate material. The designed shockproof strip end-plate material of the vapor generator of the nuclear power plant has reasonable content design, excellent resistance of corrosion, fatigue and creep properties and processing performance and has very important economic meaning to improve the production efficiency, effectively prolong the service life of the vapor generator of a nuclear power plant and decrease the production cost.
Owner:JIANGSU XINHUA ALLOY ELECTRIC
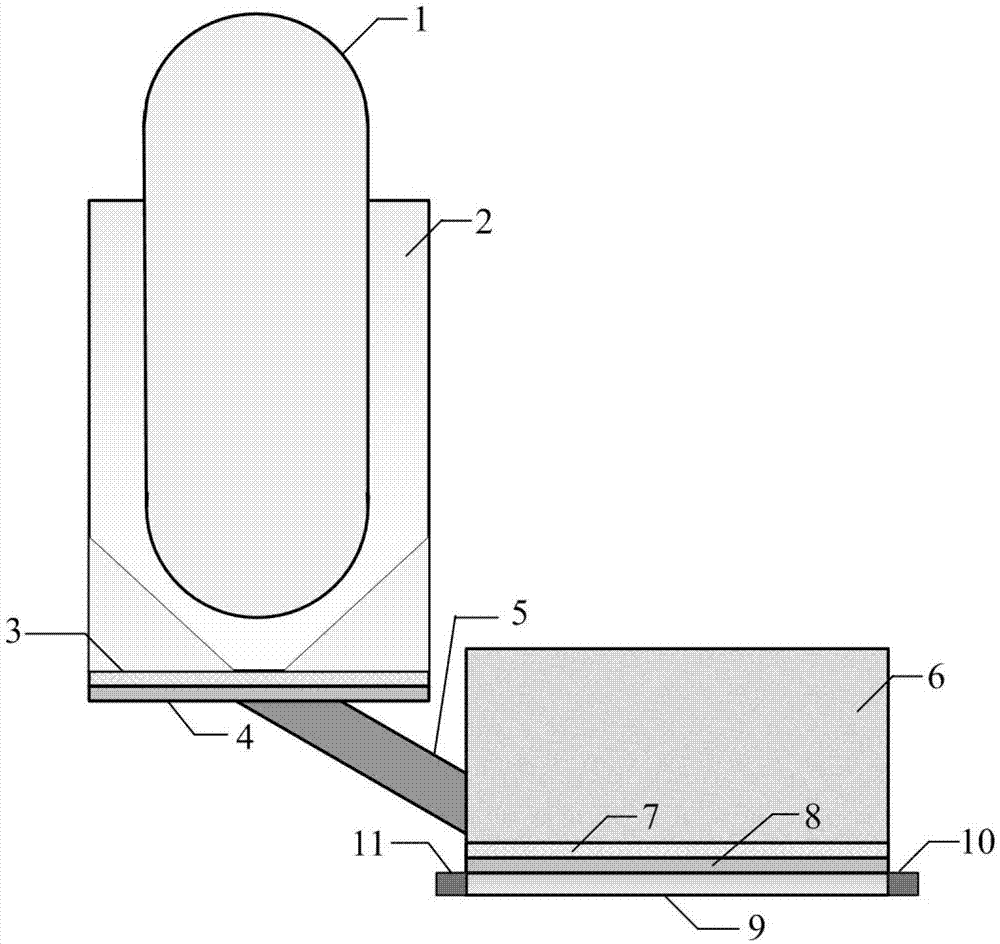
Pressurized water reactor compact steam generator
ActiveUS20130336442A1Facilitate natural recirculation of recirculatingBoiler drums/headersIntegral reactorsPressurized water reactorSteam drum
A steam generator system for a pressurized water reactor which employs an external to containment steam drum and recirculation loop piping. The steam generator system changes the arrangement of a typical pressurized water reactor recirculation steam generator by relocating the functions of steam separation and feedwater preheating outside of the reactor coolant system. The steam generator system and thermal hydraulic conditions are selected in order to minimize the size of the steam generator heat exchanger component volume inside of the containment. The external steam drum component can be isolated in accident conditions when desired and is used as a source of secondary fluid inventory for improved decay heat removal capability and tolerance for loss of feedwater events. Thus, the steam generator component volume inside of the containment is reduced and the amount of maintenance required for the reactor coolant system components are similarly reduced.
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE ELECTRIC CORP
Containment vessel and nuclear power plant therewith
InactiveUS20090323884A1Nuclear energy generationNuclear engineering problemsReactor pressure vesselGas phase
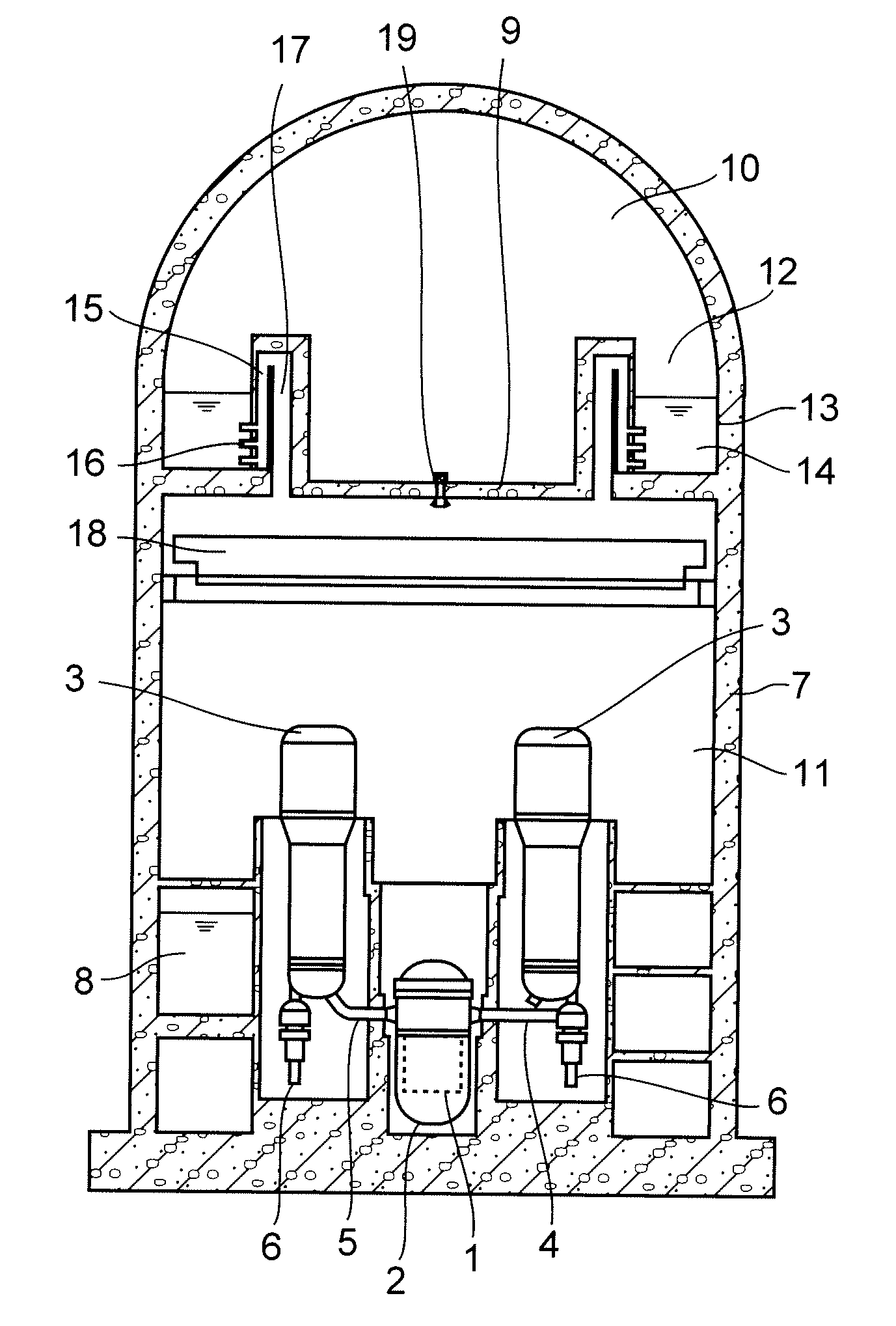
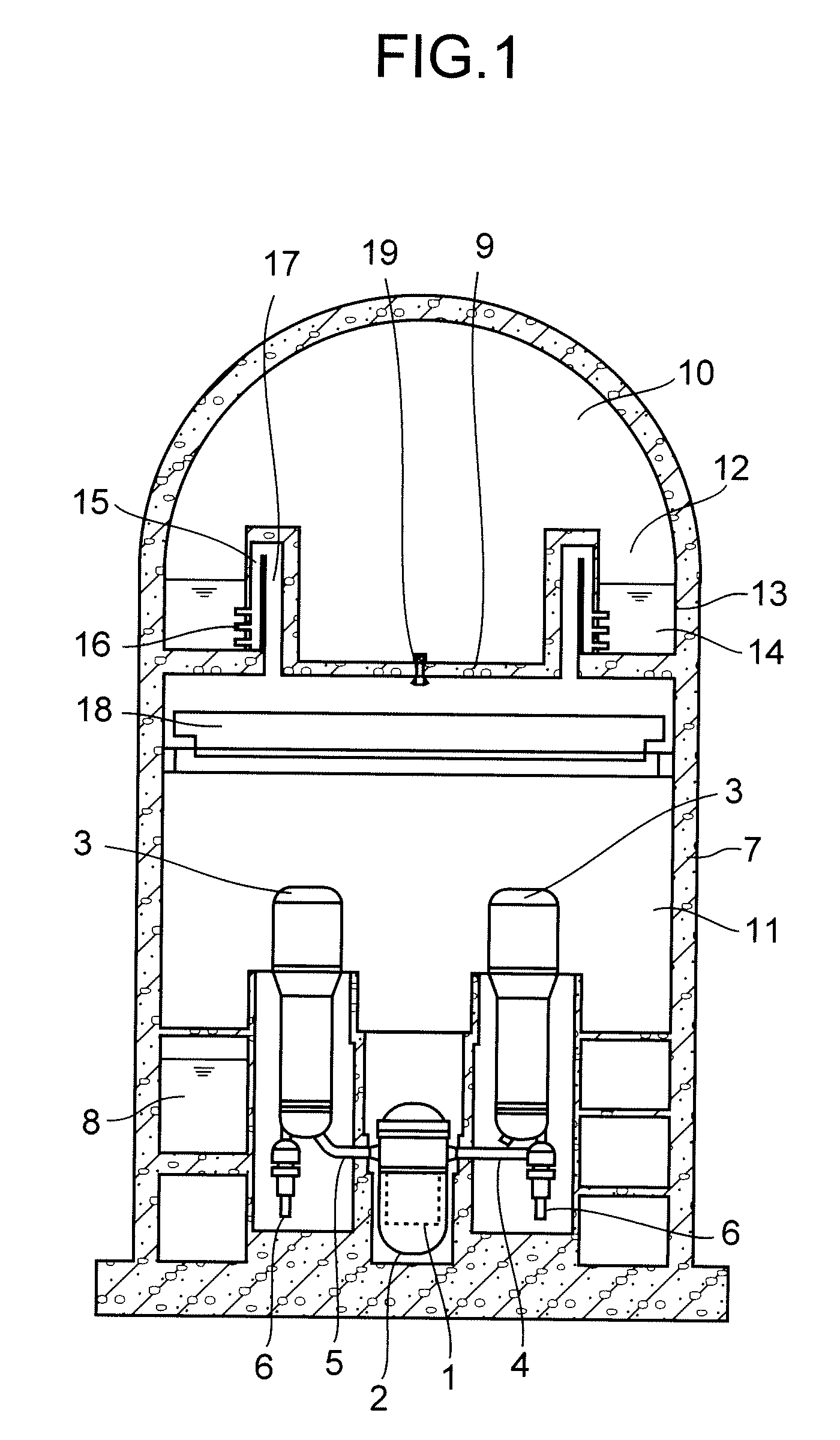
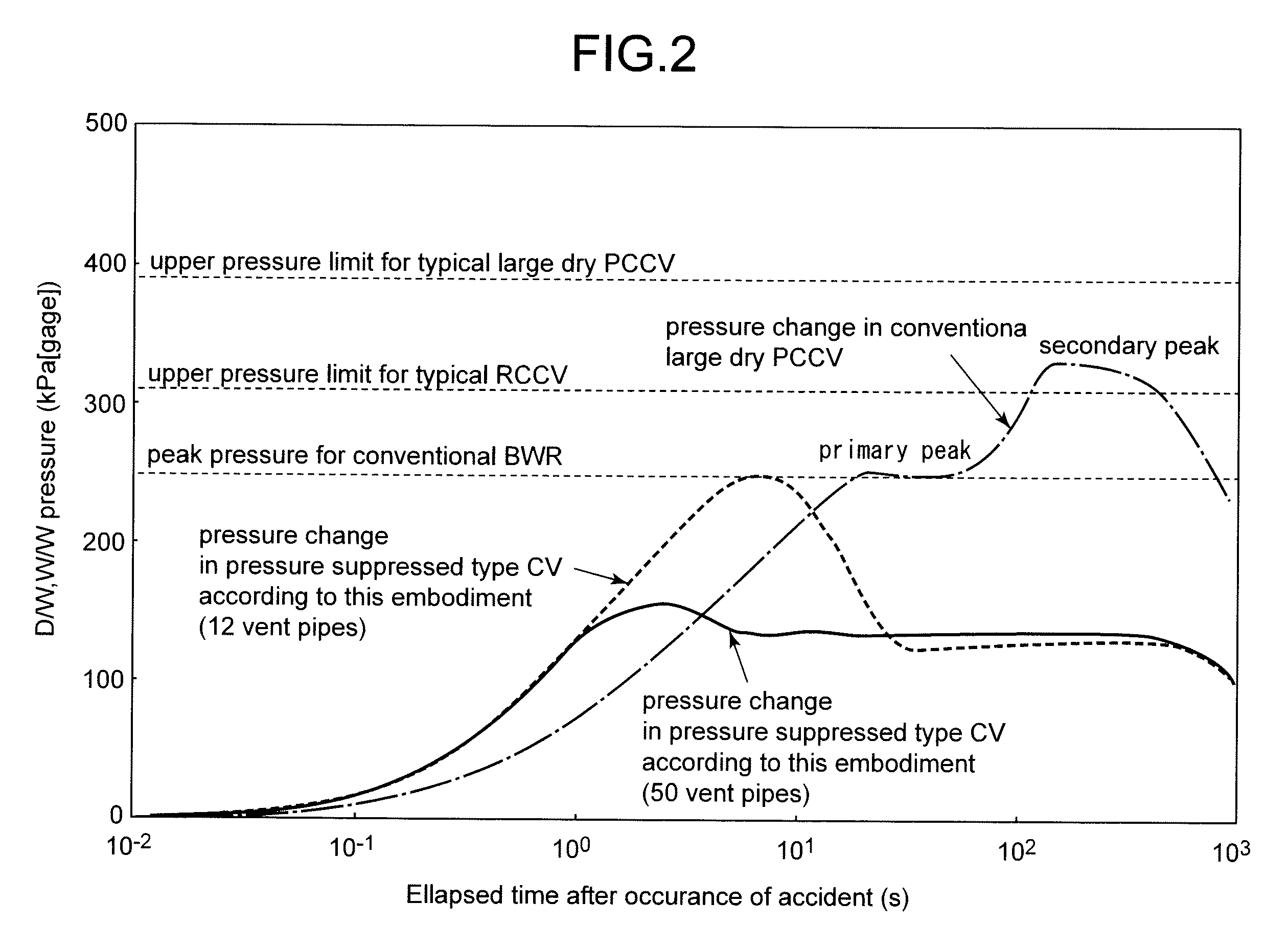
A containment vessel for containing a reactor pressure vessel and steam generators has a main containment vessel, a diaphragm, a pressure suppression chamber, LOCA vent pipes. The reactor pressure vessel contains a reactor core of a pressurized water reactor. The diaphragm partitions the main containment vessel into an upper vessel and a lower vessel. The pressure suppression chamber has a suppression pool to store water and gas phase of the pressure suppression chamber communicates with the upper vessel. The LOCA vent pipes connect the pressure suppression chamber to the lower vessel. All of the equipments and piping that constitute the reactor pressure boundary, including the reactor pressure vessel, the steam generators, a cold leg pipe and a hot leg pipe, are contained in the lower vessel.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
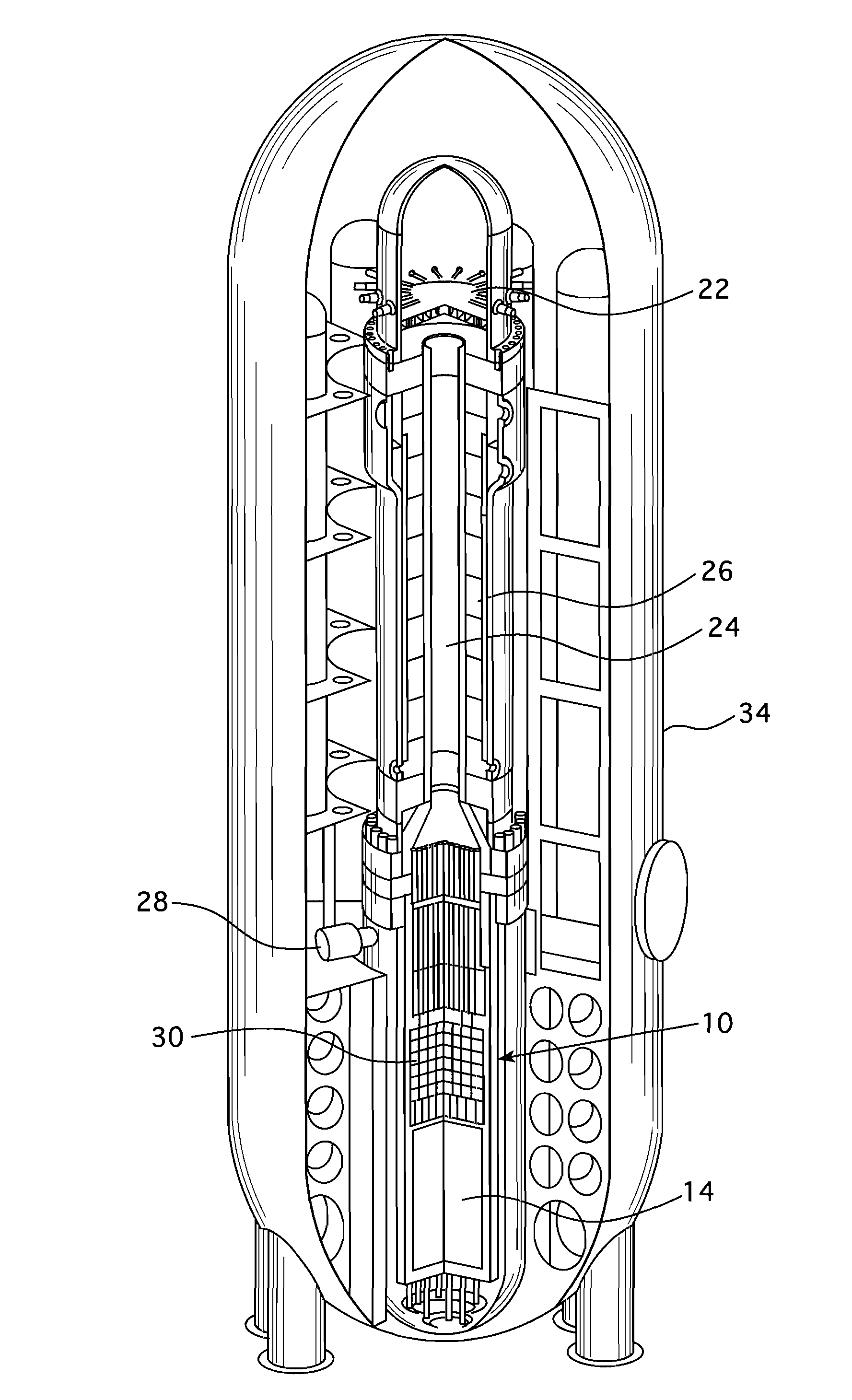
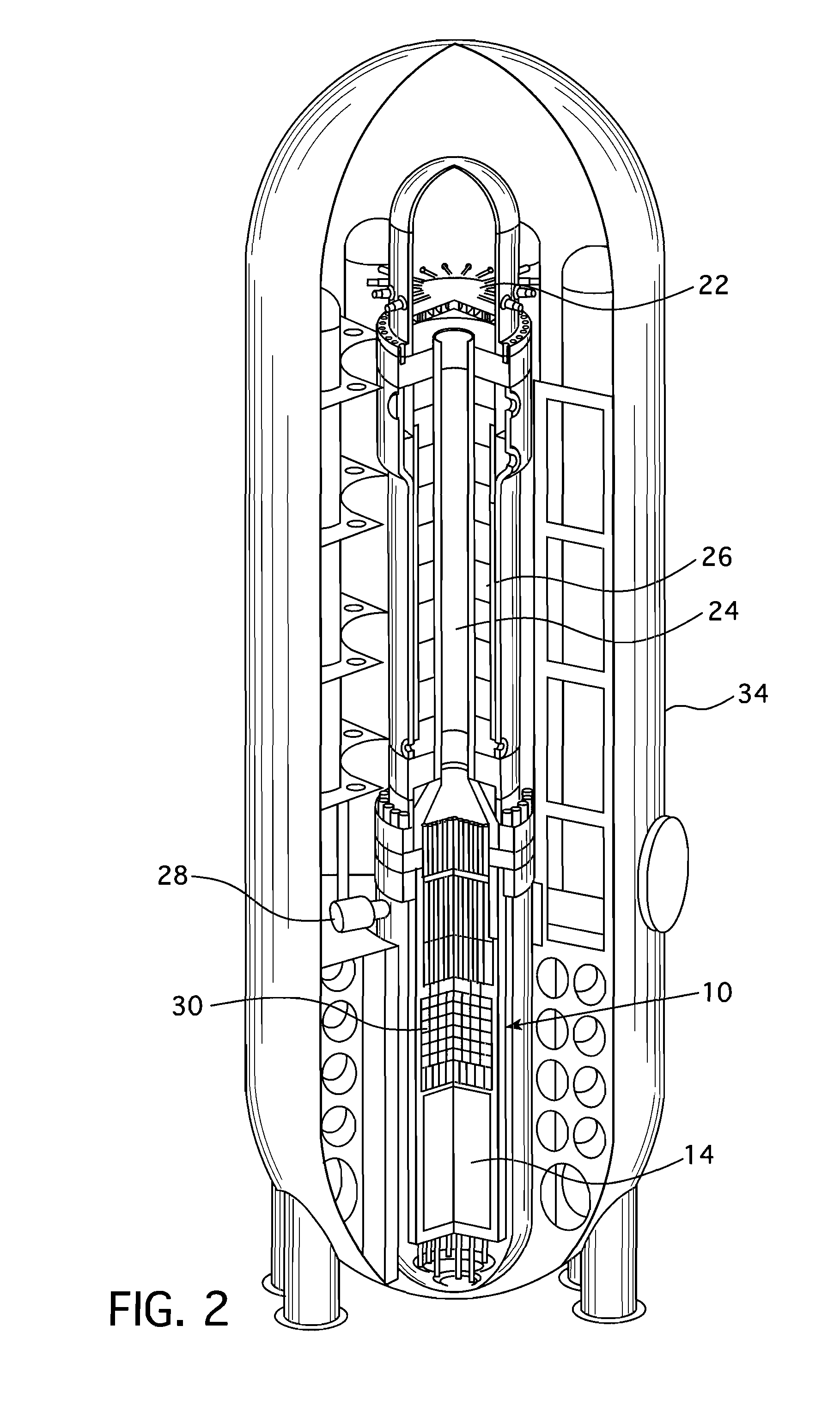
Pressurized water reactor with compact passive safety systems
ActiveUS20130051511A1Power plant safety arrangementNuclear energy generationNuclear reactor coreLine tubing
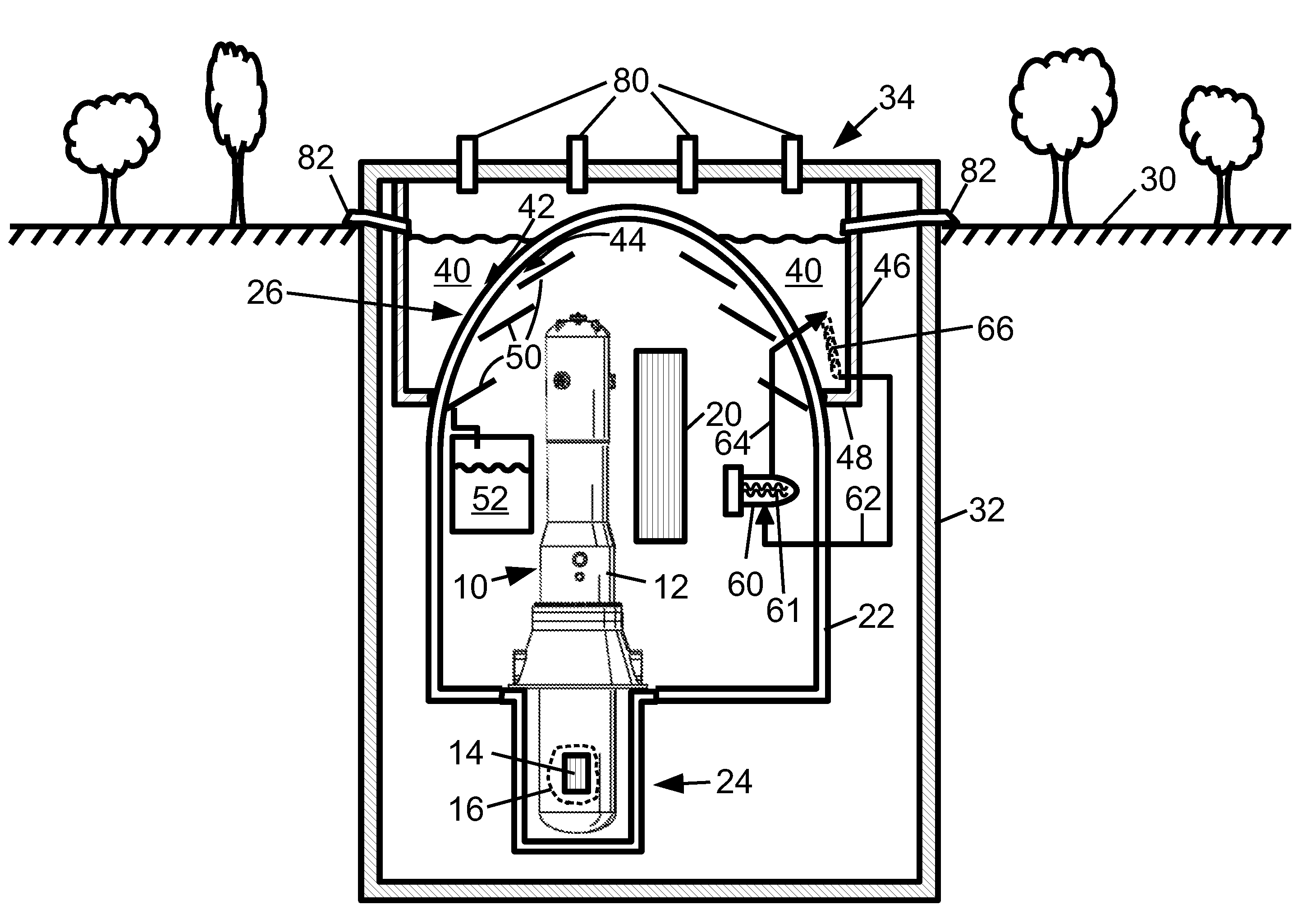
A nuclear reactor includes a pressure vessel and a nuclear reactor core disposed in the pressure vessel. A subterranean containment structure contains the nuclear reactor. An ultimate heat sink (UHS) pool is disposed at grade level, and an upper portion of the subterranean containment structure defines at least a portion of the bottom of the UHS pool. In some embodiments, the upper portion of the subterranean containment structure comprises an upper dome, which may protrude above the surface of the UHS pool to define an island surrounded by the UHS pool. In some embodiments, a condenser comprising a heat exchanger including hot and cold flow paths is disposed inside the subterranean containment structure; and cooling water lines operatively connect the condenser with the UHS pool.
Owner:BWXT MPOWER INC
Upper internals arrangement for a pressurized water reactor
ActiveUS20080253497A1Nuclear energy generationNuclear monitoringPressurized water reactorEngineering
In a pressurized water reactor with ail of the in-core instrumentation gaining access to the core through the reactor head, each fuel assembly in which the instrumentation is introduced is aligned with an upper internals instrumentation guide-way. In the elevations above the upper internals upper support assembly, the instrumentation is protected and aligned by upper mounted instrumentation columns that are part of the instrumentation guide-way and extend from the upper support assembly towards the reactor head in hue with a corresponding head penetration. The upper mounted instrumentation columns are supported laterally at one end by an upper guide tube and at the other end by the upper support plate.
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE ELECTRIC CORP
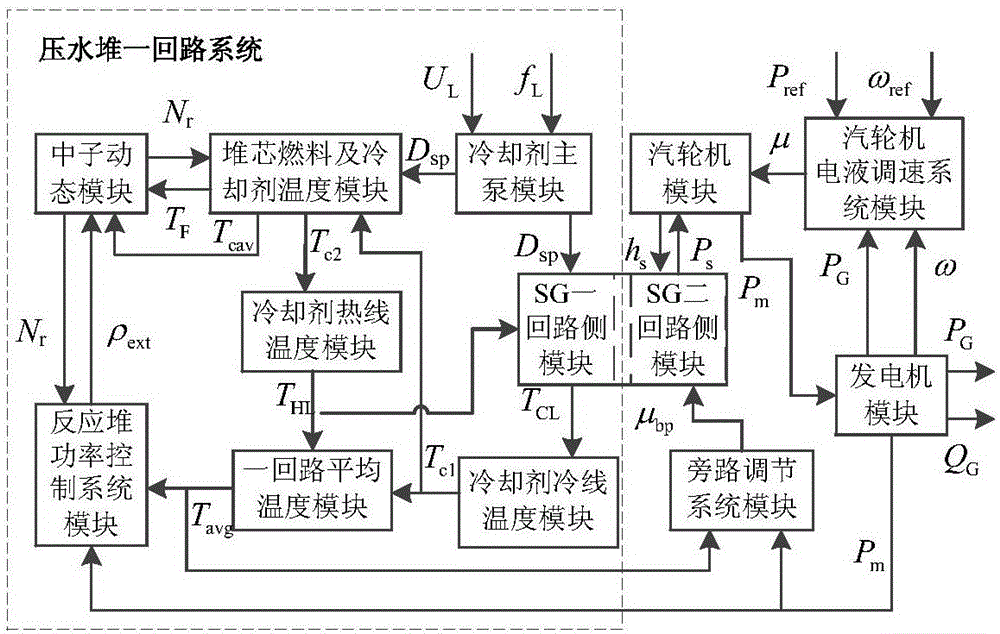
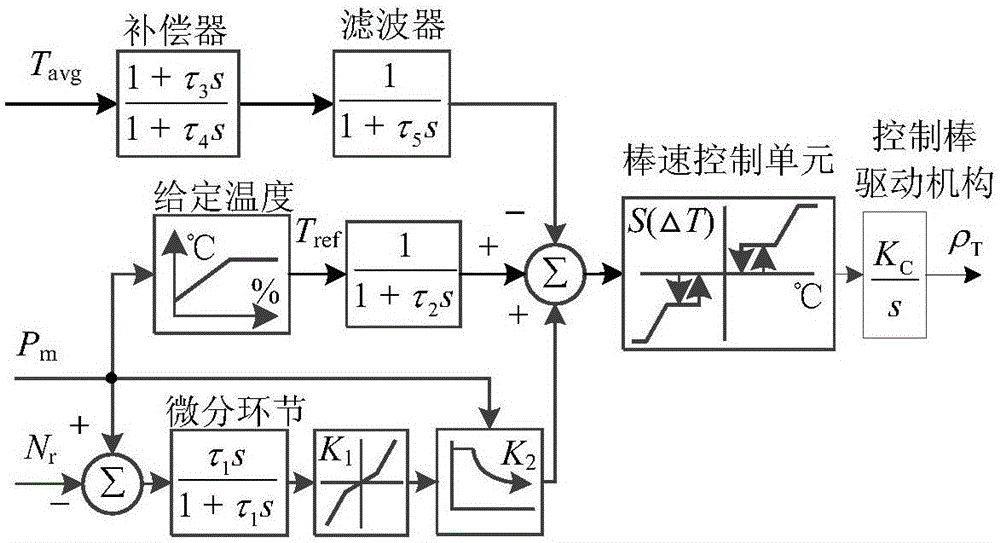
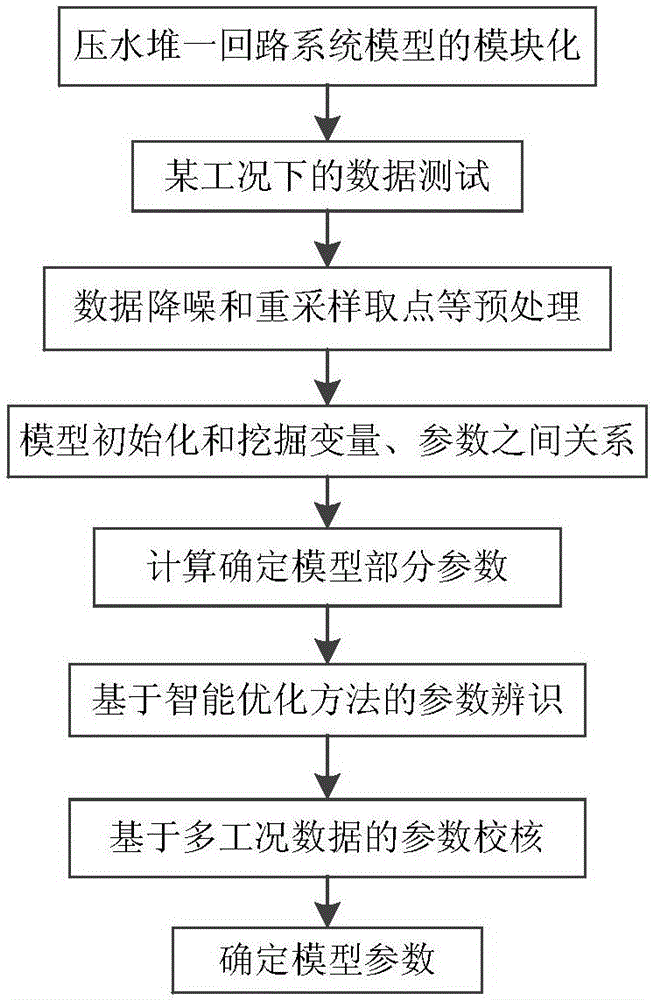
Model parameter acquisition method for primary loop system of pressurized water reactor
ActiveCN106773666AFacilitate identification workLong initial stable transition timeAdaptive controlNuclear powerElectric power system
The invention relates to a parameter acquisition method for a primary loop system of a pressurized water reactor. The model parameter acquisition method comprises the steps of combining the characteristic that the pressurized water reactor is complicated in model structure, provided with nonlinear links, long in stable transition time, great in number of model parameters and variables, mutual coupling and the like, recognizing model parameters by adopting submodules, and checking the parameters by adopting an overall model; selecting input and output variables of each module to perform testing; reducing influences imposed on a recognition effect by noise signals through preprocessing; initializing the variables based on a differential equation of each module and a program setting method, and enabling the model to be stable in initialization; recognizing parameters of each module based on a parameter perturbation theory and an intelligent optimization method; checking the parameters and the model under various conditions by combining the submodules and the overall module; and acquiring nuclear power unit system mathematic model parameters applicable to electric power system analysis. The modules are fine and clear in structure, the model parameters are definite in meaning, the variables required by recognition are easy to acquire, the parameter acquisition method is quick, efficient and accurate, and the practicability is high.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +3
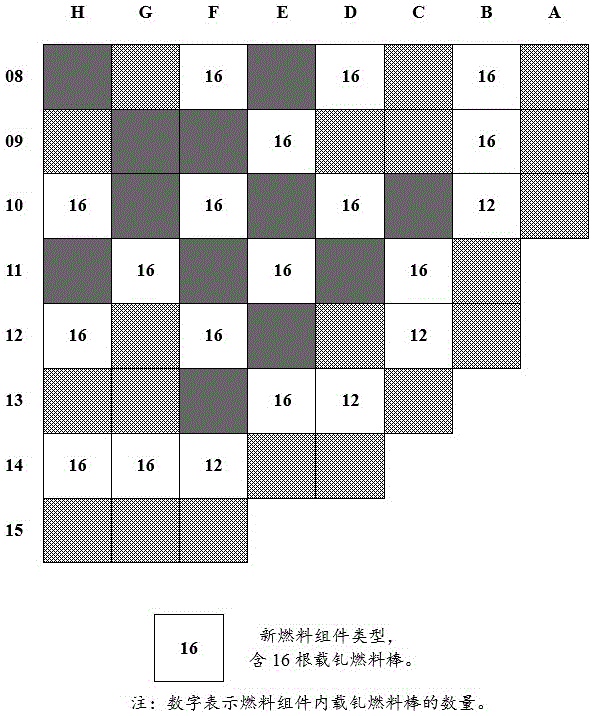
Refueling method for fuel assemblies of reactor core of PWR (pressurized water reactor) nuclear power plant
ActiveCN102332315APromote enrichmentChange layoutNuclear energy generationReactor fuel elementsPressurized water reactorNuclear power
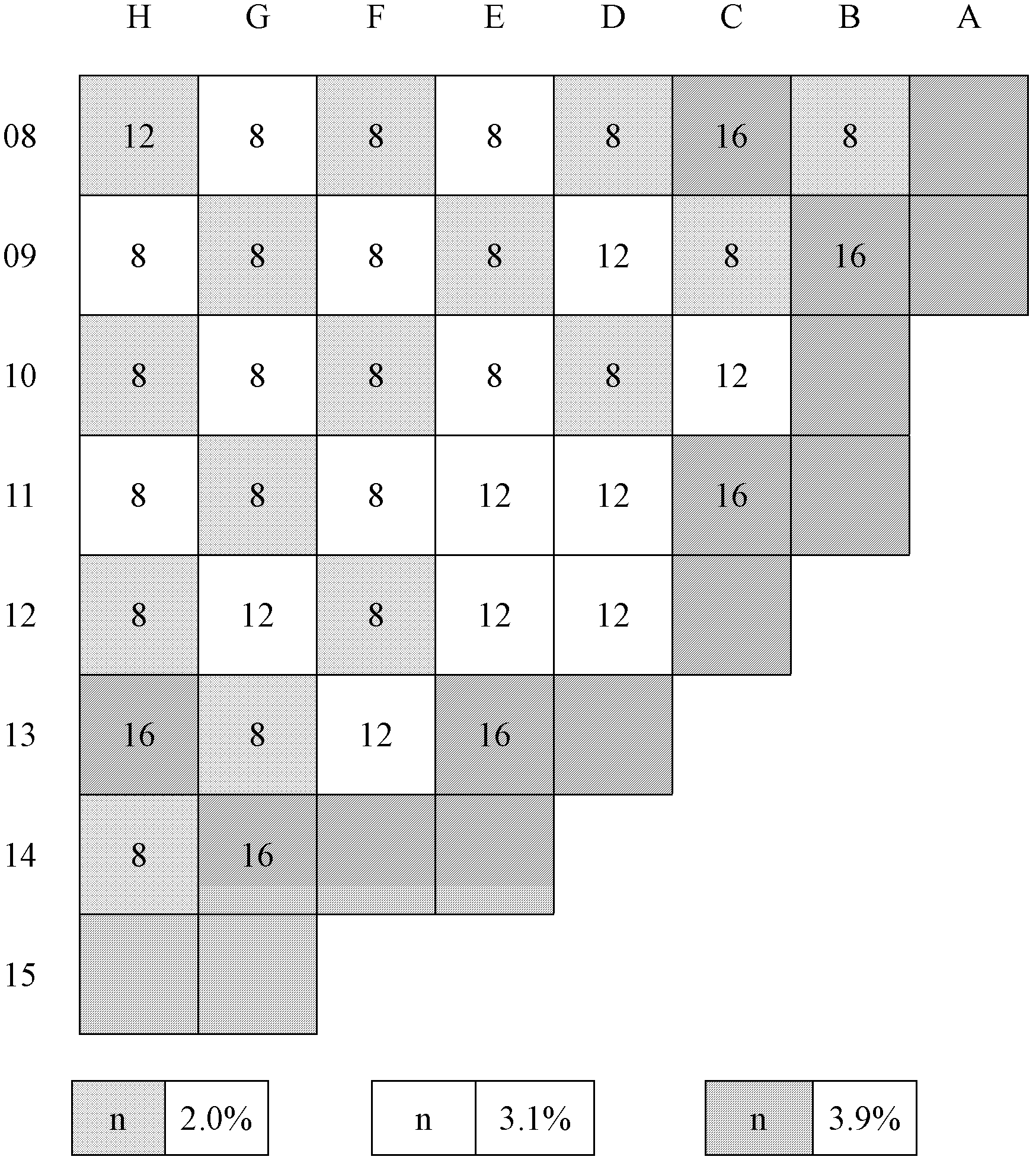
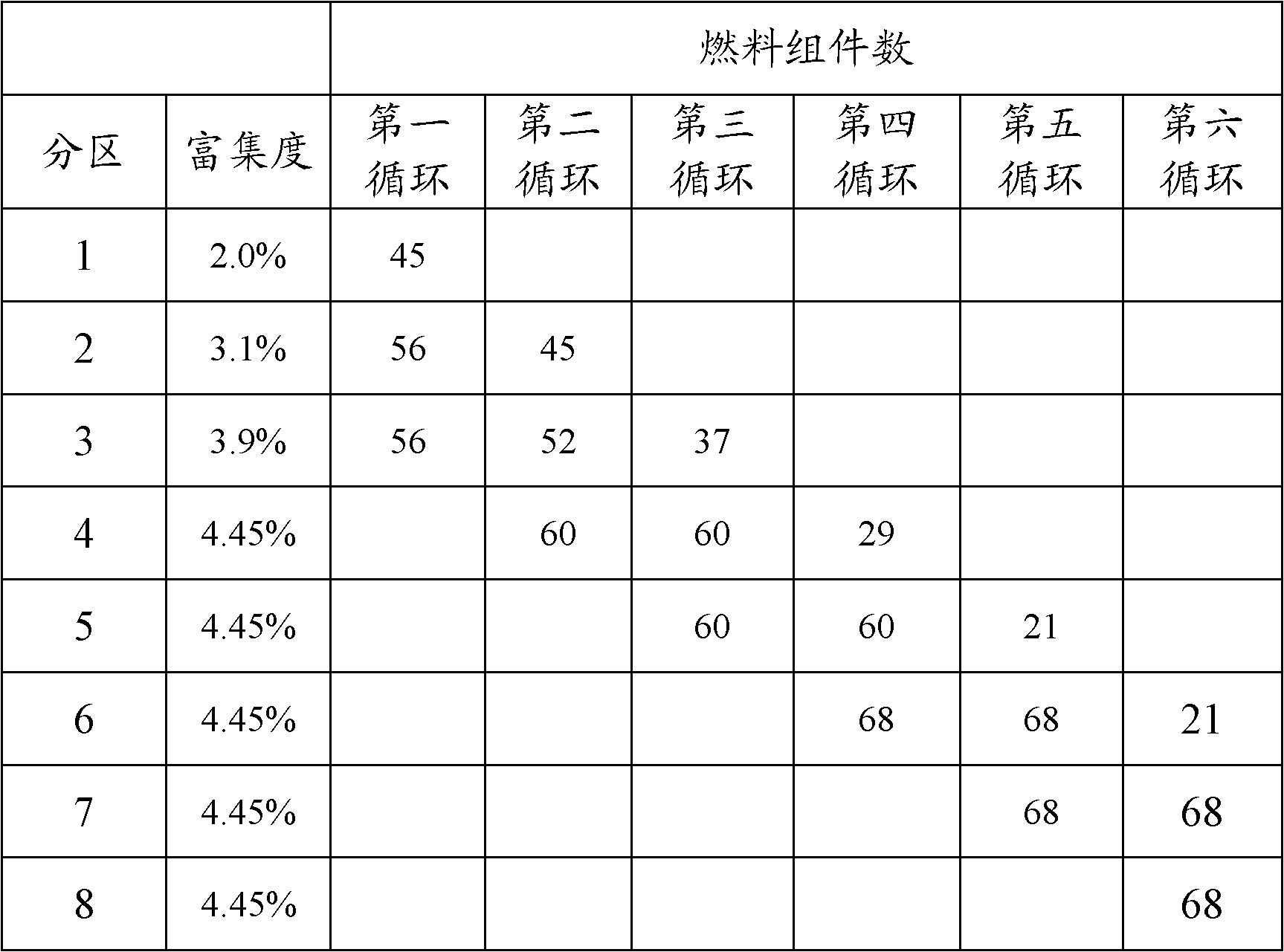
The invention is applicable to the field of fuel management on reactor cores of pressurized water reactors, and provides a refueling method for fuel assemblies of a reactor core of a PWR (pressurized water reactor) nuclear power plant. The method comprises: classifying the fuel assemblies of the reactor core into three enrichment areas according to different enrichment degrees; in an initial cycle, respectively adding 8, 12 and 16 burnable poison rods into the fuel assemblies, and according to a cycle length of 18 months, placing the fuel assemblies with high enrichment degree outside the reactor core, and placing the fuel assemblies with low enrichment degree in the reactor core, wherein the enrichment degrees of the fuel assemblies of an initial reactor core are respectively 3.9%, 3.1% and 2.0%; and in subsequent cycles, starting from a second cycle, and rapidly transitioning the subsequent cycles to an equilibrium cycle according to an enrichment degree of 4.45%, wherein a mode of 18-month refueling is adopted, and the fuel assemblies of 1 / 2-1 / 3 of the reactor core are replaced every time; meanwhile, placing the new fuel assemblies in the reactor core, and placing the fuel assemblies which are burned outside the reactor core. By using the refueling method provided by the invention, the cycle period is extended, the fuel consumption is improved, and the purpose of completely low neutron leak loading is achieved in the subsequent cycles.
Owner:GUANGDONG NUCLEAR POWER JOINT VENTURE
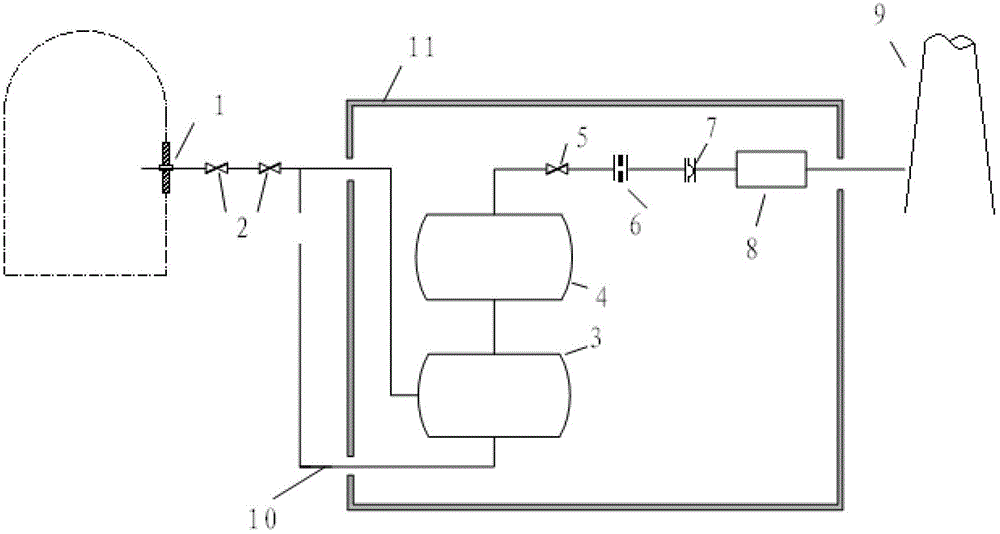
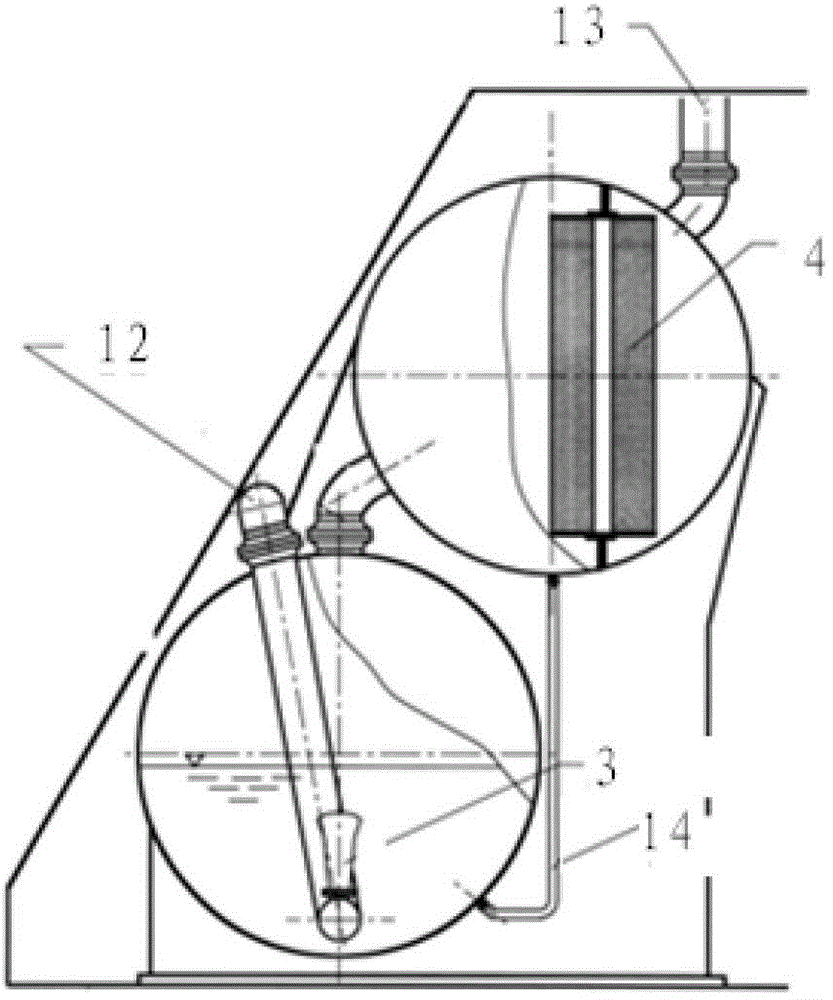
Passive residual heat exhausting system of pressurized water reactor nuclear power plant
InactiveCN103617815ASatisfy coolingFulfil requirementsNuclear energy generationCooling arrangementPlate heat exchangerPressurized water reactor
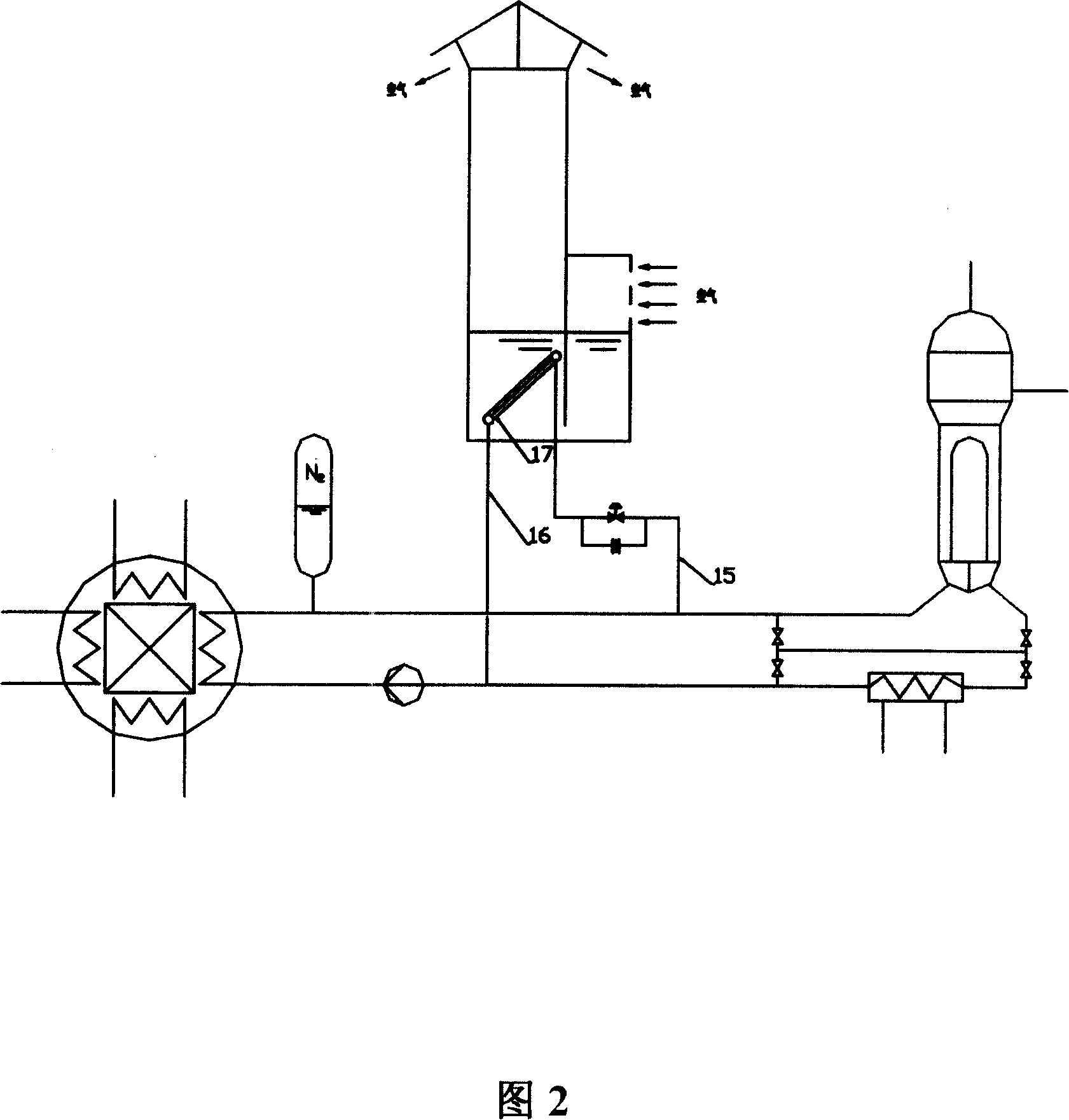
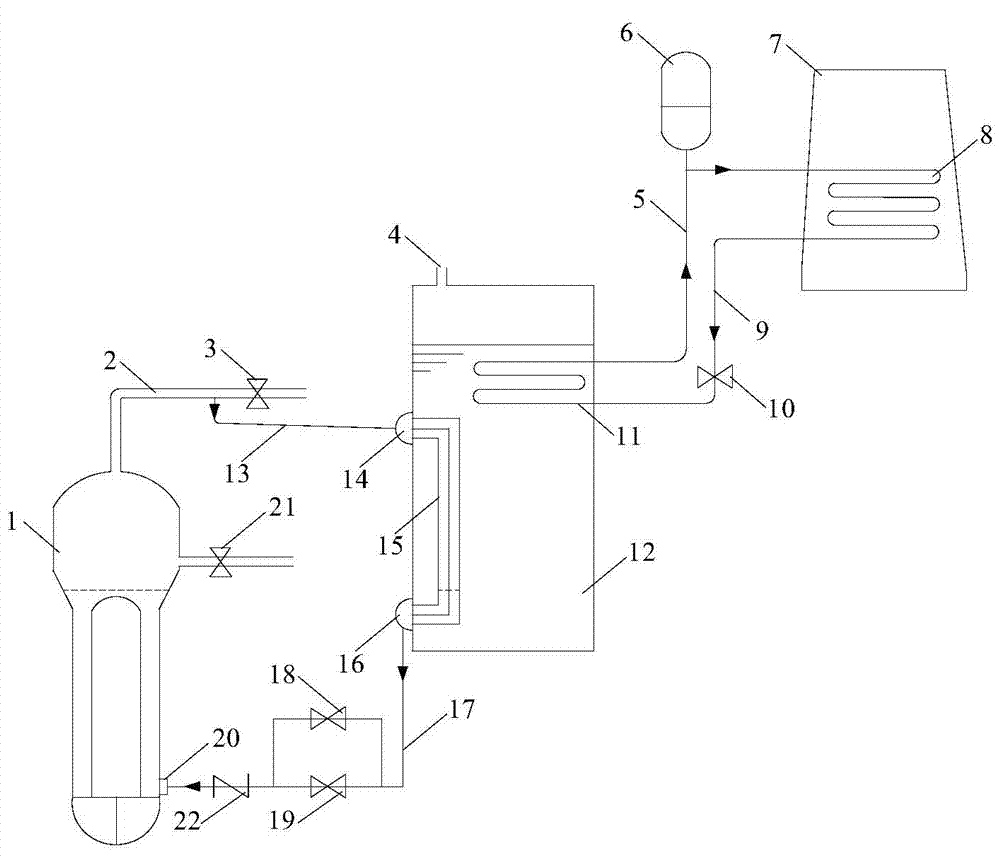
The invention provides a passive residual heat exhausting system of a pressurized water reactor nuclear power plant. The passive residual heat exhausting system comprises a passive residual heat removal system and a passive emergency water tank cooling system, wherein the passive residual heat removal system comprises a steam pipe, a passive residual heat exhausting heat exchanger and a condensed water pipe; the passive residual heat exhausting heat exchanger is positioned at the lower part of an emergency cooling water tank of the passive residual heat removal system; the passive emergency water tank cooling system comprises the emergency cooling water tank, a cooling coiled pipe, an ascending pipe, an air cooling heat exchanger and a descending pipe; the cooling coiled pipe is located at the upper part of the emergency cooling water tank. When residual heat removal needs to be carried out under an accident condition or normal shutdown, decay heat of a reactor core is removed by condensing steam at a secondary side so that the safety of a reactor is guaranteed and the possibility of releasing radioactive substances to the environment is reduced. The emergency cooling water tank is used as middle buffering equipment so as to meet the requirements of rapid cooling at the initial stage of an accident and long-time cooling at the later period of the accident.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
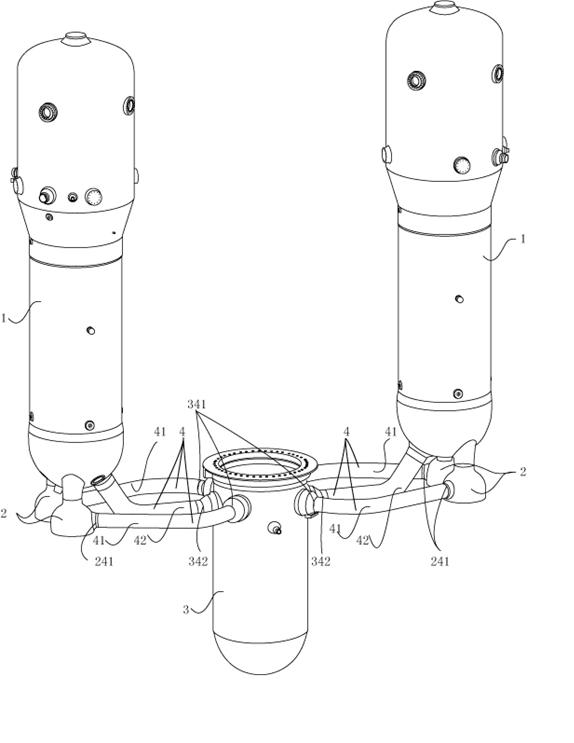
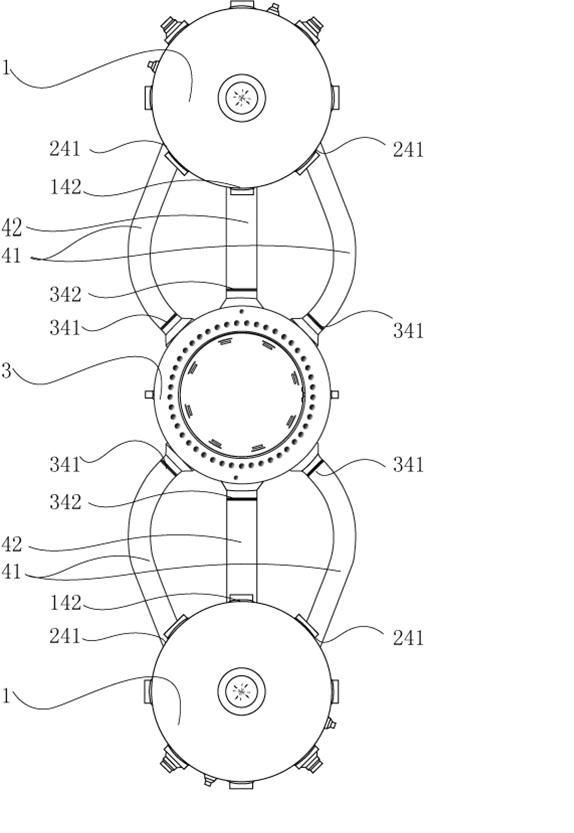
Method for mounting main pipeline and main loop of pressurized water reactor nuclear power station steam generator
ActiveCN101839467AAvoid inconvenienceEasy to controlNuclear energy generationContainmentNuclear engineeringPressurized water reactor
The invention discloses a method for mounting a main return loop of a nuclear power station pressurized water reactor coolant system, which is characterized in that: a main pipeline heat section bend (16) and a main pipeline transition section bend (17) are welded at a loop nozzle of a lower seal end of the used steam generator (1); during mounting, a welding line (9) between a main pipeline heat section (13) and the main pipeline heat section bend (16) on the lower part of the steam generator (11) and a welding line (2) between the main pipeline heat section (13) and a reactor pressure container (10) can be assembled and welded simultaneously. In addition, the working amount for a welding line (5) is reduced during mounting. The mounting method can better control and guarantee the assembling and welding quality, improve the working efficiency, reduce the mounting time, and shorten the construction period.
Owner:CHINA NUCLEAR POWER ENG CO LTD
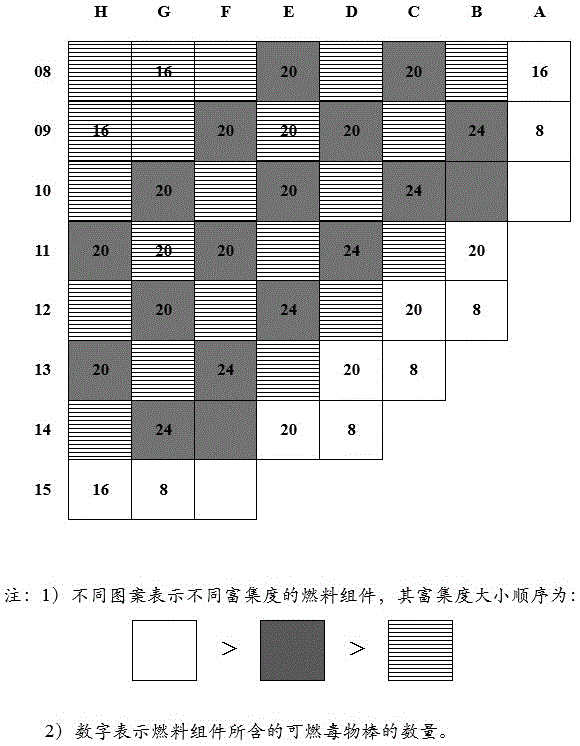
Fuel management method of pressurized water reactor core formed by 177 fuel assemblies
InactiveCN105139901AIncrease profitRaise the load factorNuclear energy generationNuclear reaction controlPressurized water reactorNuclear engineering
The invention discloses a fuel management method of a pressurized water reactor core formed by 177 fuel assemblies. The method comprises the following steps: in the first cycle, fuel assemblies with three different enrichment degrees are adopted, the fuel assemblies are arranged in a high-leakage loading mode, and the cycle length of the first cycle is designed to be annual reloading; in the second cycle, the enrichment degree of reloaded new fuel assemblies is between that of the fuel assemblies in the first cycle and that of balance cycle new fuels; the enrichment degree of the reloaded new fuel assemblies is same to or greater than that of the second cycle new fuels from the third cycle to balance cycle in order to realize 18-months long cycle reloading design; and from the second cycle, core loading adopts a low-leakage loading mode. The method smoothly realizes transition of first cycle annular reloading to balance cycle 18-months long cycle reloading, guarantees the core safety of the first cycle, fast transmits to long cycle reloading design, and improves the utilization rate and the load factor of a power plant.
Owner:NUCLEAR POWER INSTITUTE OF CHINA
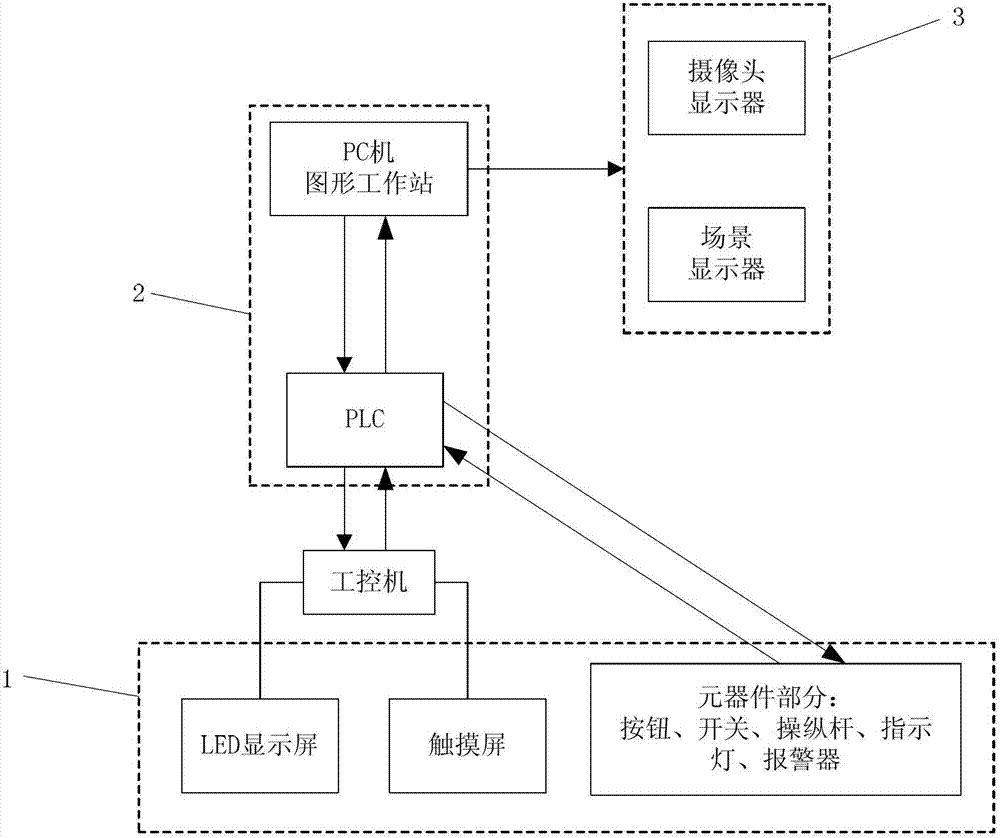
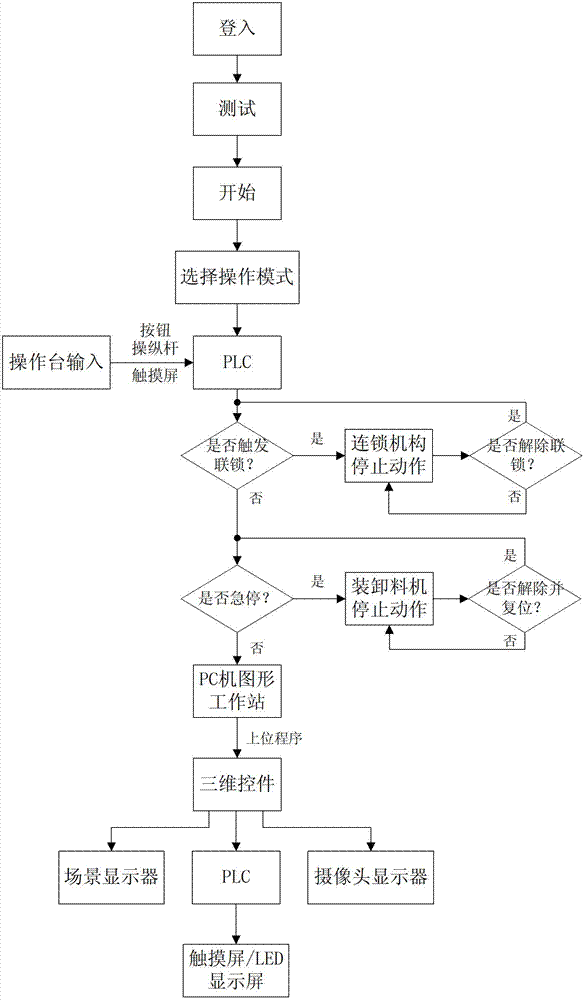
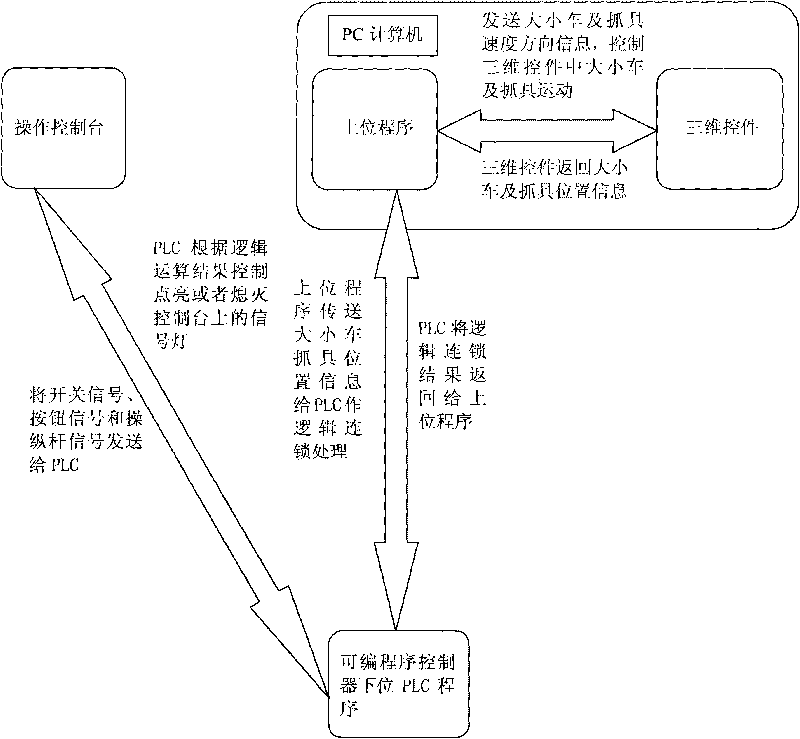
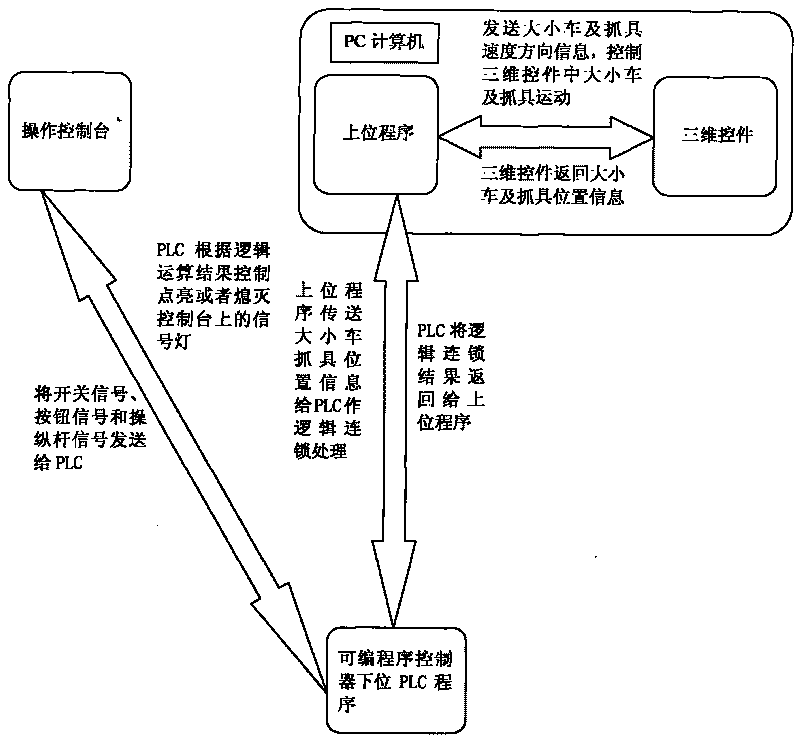
Pressurized water reactor nuclear power station material-loading/unloading simulator system
ActiveCN101763757AStrong targetingEasy to operateCosmonautic condition simulationsSimulatorsNuclear powerPressurized water reactor
The invention relates to a computer simulation and emulation system, in particular to a pressurized water reactor nuclear power station material-loading / unloading simulator system. The system consists of an operation control console, a PC computer with the configuration of a figure work station and a programmable controller PLC, wherein the operation control console is designed with the proportion of 1:1 according to a material object control console of a material-loading / unloading machine, and each operation component on the operation control console and a signal lamp display device are connected with the PLC; the PC computer is provided with an upper program unit and a three-dimensional control unit, and date interaction is performed between the PLC and the upper program unit of the PC computer; the PLC receives signals from the control console and position information of vehicles with different sizes from the upper program, sends an action instruction to the PC computer after logical operation, and controls the signal lamp on the control console; and the upper program unit in the PC computer sends information about the vehicles with the different sizes and the speed direction of a gripping apparatus to the three-dimensional control part to control the vehicles with the different sizes and the motion of the gripping apparatus in a three-dimensional control part, and the three-dimensional control unit returns the position information of the vehicles with the different sizes and the gripping apparatus back to the upper program unit.
Owner:NUCLEAR POWER QINSHAN JOINT VENTURE
Method of calibrating excore detectors in a nuclear reactor
InactiveUS20110268239A1Improve accuracyImprove excore detector calibrationPlant parameters regulationNuclear energy generationNuclear reactor coreNODAL
A method of calibrating excore detectors for a pressurized water reactor (PWR) includes: measuring peripheral core flux signals using excore detectors disposed at a plurality of locations spaced about the periphery of the core, and using the measured power distribution from either a core monitoring system or in-core flux measurement. Calibration of the excore detectors is broken into two parts: (1) the relation between the excore detector signal and weighted peripheral assembly axial offset, and (2) the relation between weighted peripheral assembly axial offset and core average axial offset. Relation (2) can be determined by a representative neutronics model. Accuracy of the neutronics solution is improved by applying nodal calibration factors, which represent the ratio of the measured three-dimensional power distribution to the nodal predicted three-dimensional power distribution and correct the neutronic results to match what would be measured if predictive scenarios were actually performed in the actual reactor core.
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE ELECTRIC CORP
Radiation protection control method for unit operation and maintenance during fuel damage of pressurized water reactor nuclear power station
ActiveCN102324257AIncrease exposureHigh control requirementsPower plant safety arrangementNuclear energy generationNuclear engineeringPressurized water reactor
The invention discloses a radiation protection control method for unit operation and maintenance during fuel damage of a pressurized water reactor nuclear power station. The radiation protection control method comprises the steps of: carrying out radiation control through scavenging and chemical operation of a main loop; monitoring relevant channel radioactivity conditions; measuring and evaluating air pollution of a production site; implementing iodine removal and scavenging on a reactor plant aiming at the radioactive contamination condition; and carrying out collective protection and personnel protection on the production site. Aiming at the defect of personal iodine internal contamination caused by poor radiation protection control after fuels of the pressurized water reactor nuclear power station are damaged in the prior art, the invention provides the radiation protection control method capable of carrying out effective control and protection without causing internal contamination to workers.
Owner:CHINA GENERAL NUCLEAR POWER CORP +1
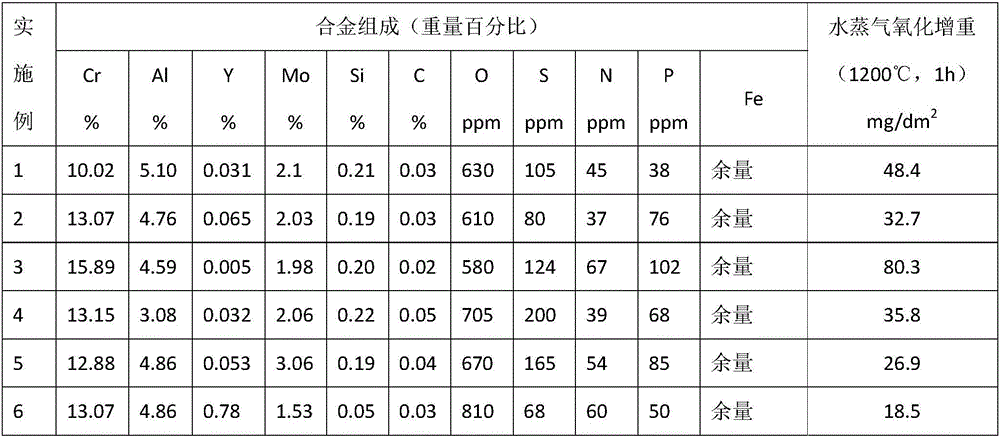
FeCrAl base alloy material for nuclear fuel cladding material
InactiveCN106319369AImprove antioxidant capacityExcellent fault toleranceOptical rangefindersNuclear energy generationNuclear powerPressurized water reactor
The invention relates to a FeCrAl base alloy material for a nuclear fuel cladding material. With the total weight of the FeCrAl base alloy material as a standard, the alloy material comprises 6%-16% of Cr, 3%-8% of Al, 0.001%-1% of Y, 0.1%-4% of Mo, 0.01%-0.5% of Si, 0.001%-0.5% of C, less than or equal to 500 ppm of N, less than or equal to 1000 ppm of O, less than or equal to 500 ppm of P, less than or equal to 500 ppm of S and the balance Fe. A FeCrAl base alloy shows the excellent antioxygenic property in the 1200 DEG C vapor environment, the excellent accident fault-tolerant ability is achieved and is obviously superior to that of a Zr base alloy, the machining performance is good, and the FeCrAl base alloy material can be used as core structural materials such as fuel element cladding, fuel element composite cladding, fuel cladding coatings and positioning grillage stripes in nuclear power station pressurized water reactors.
Owner:SUZHOU NUCLEAR POWER RES INST +3
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com