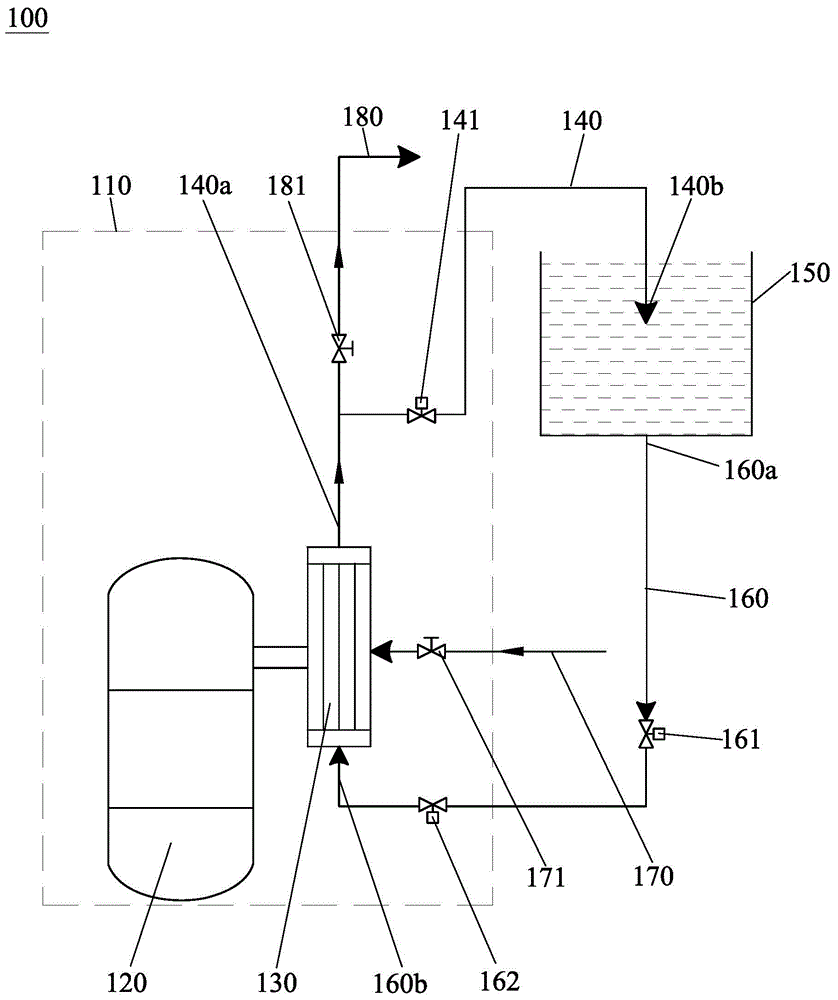
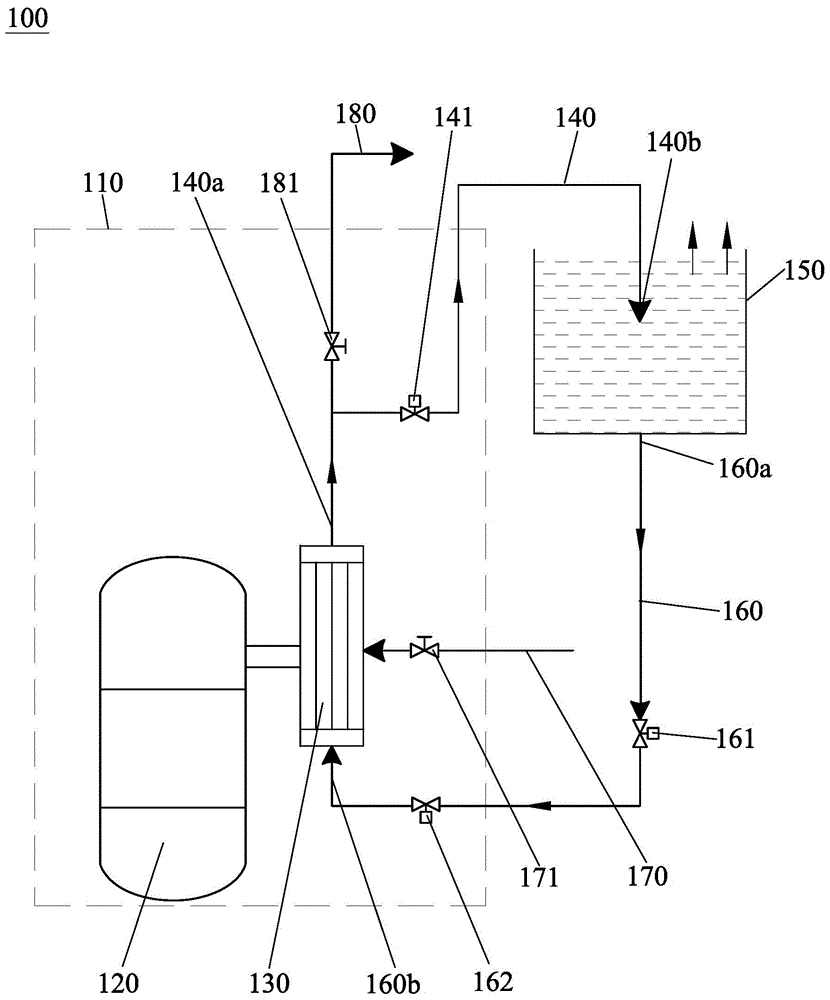
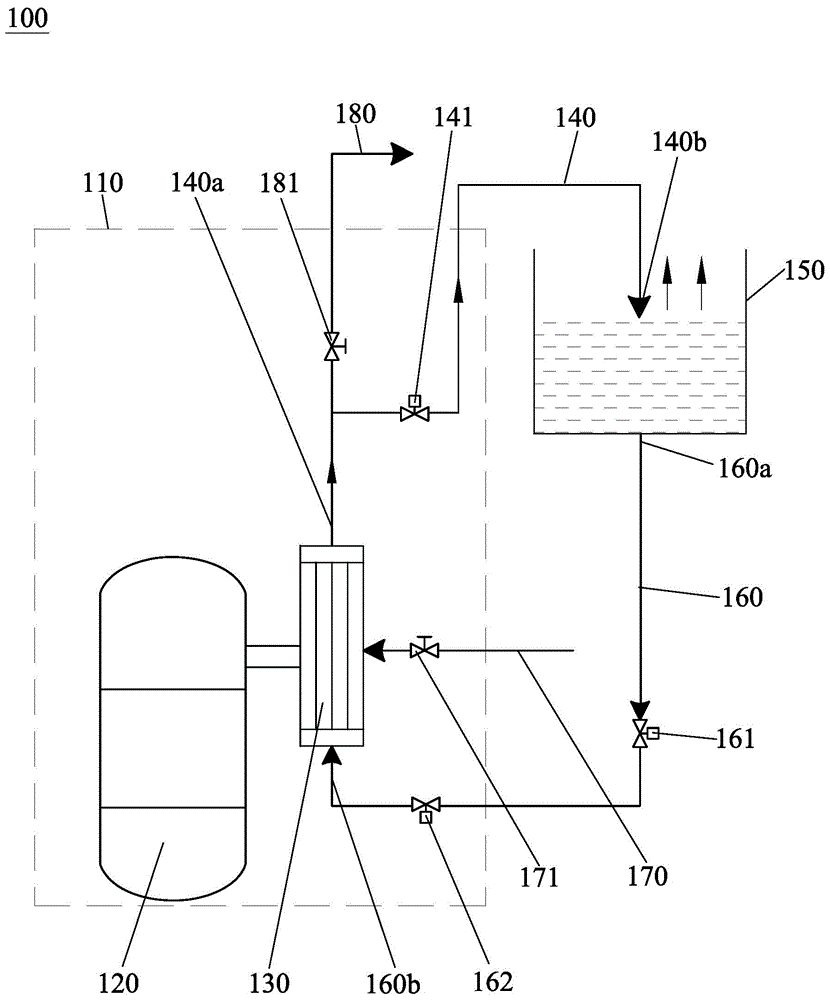
Patents
Literature
135 results about "Decay heat" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
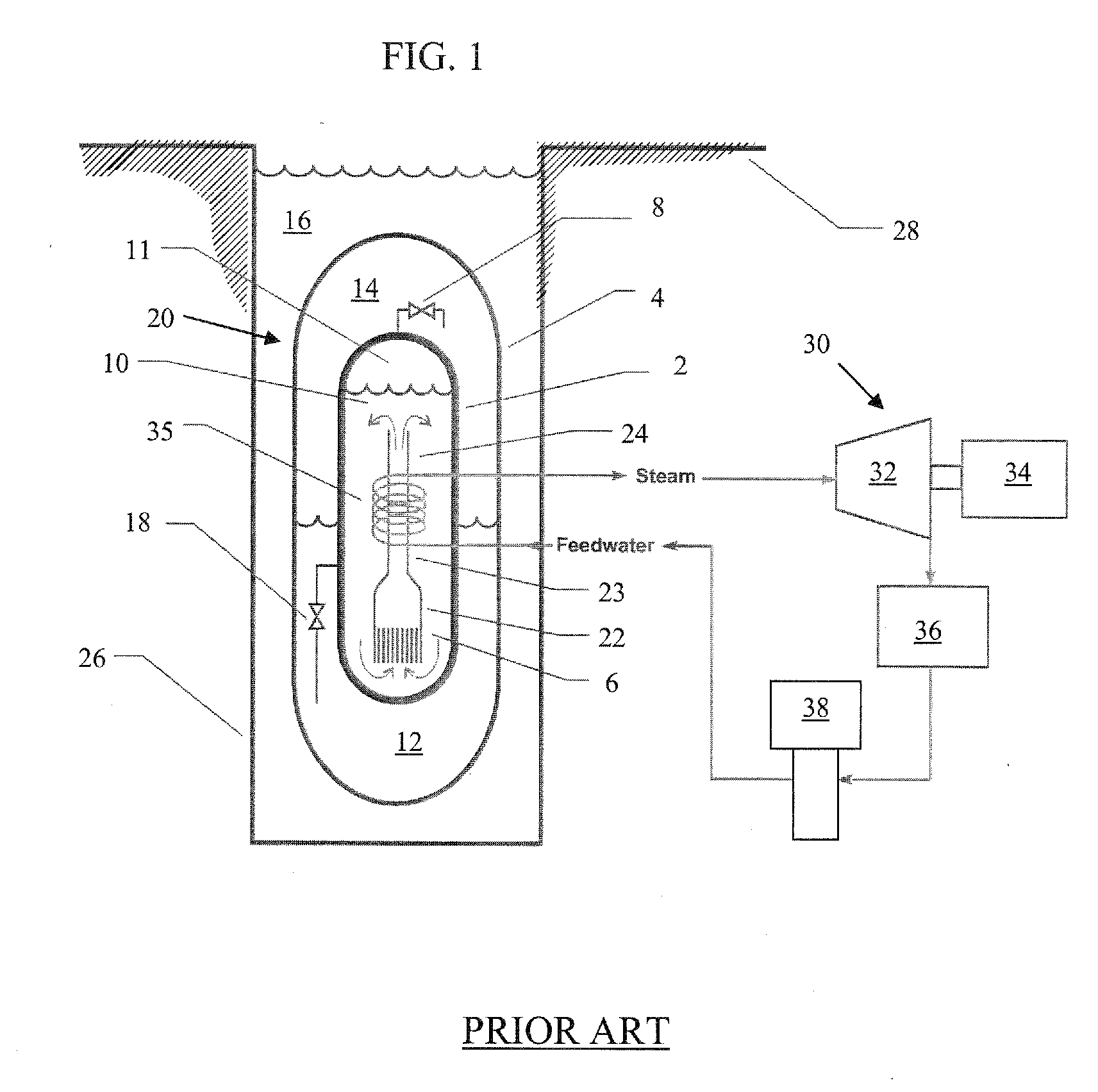
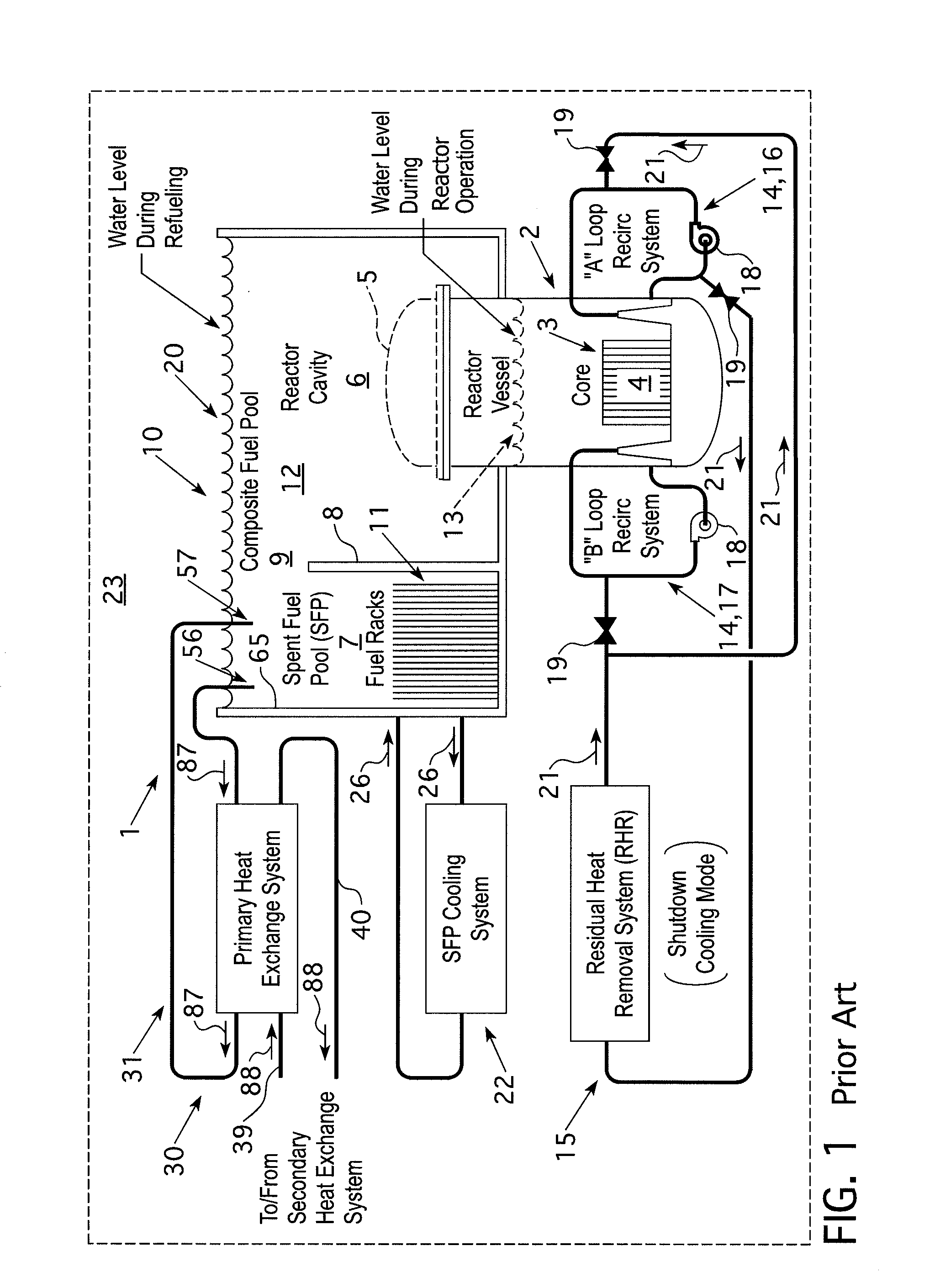
Decay heat is the heat released as a result of radioactive decay. This heat is produced as an effect of radiation on materials: the energy of the alpha, beta or gamma radiation is converted into the thermal movement of atoms.
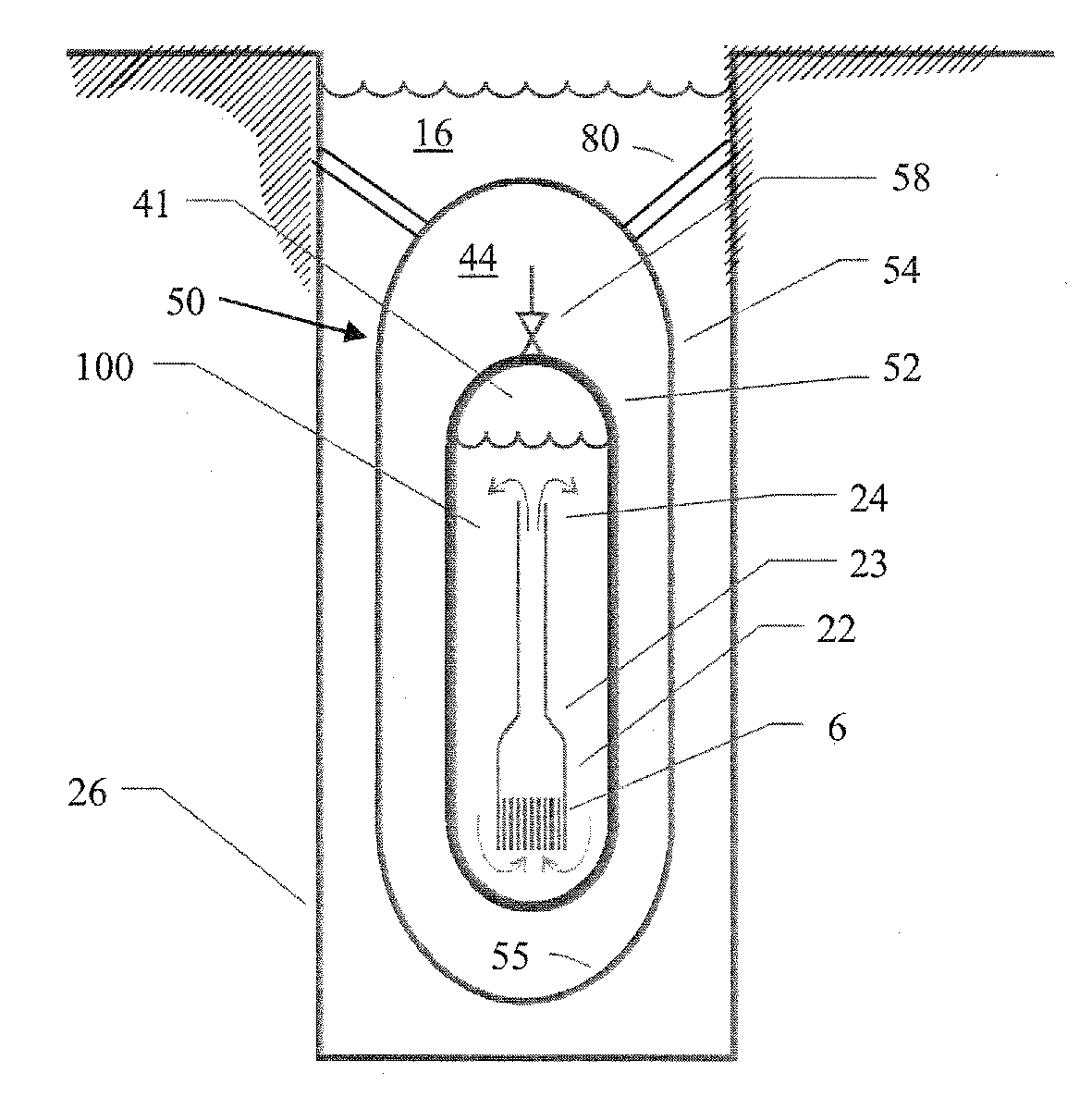
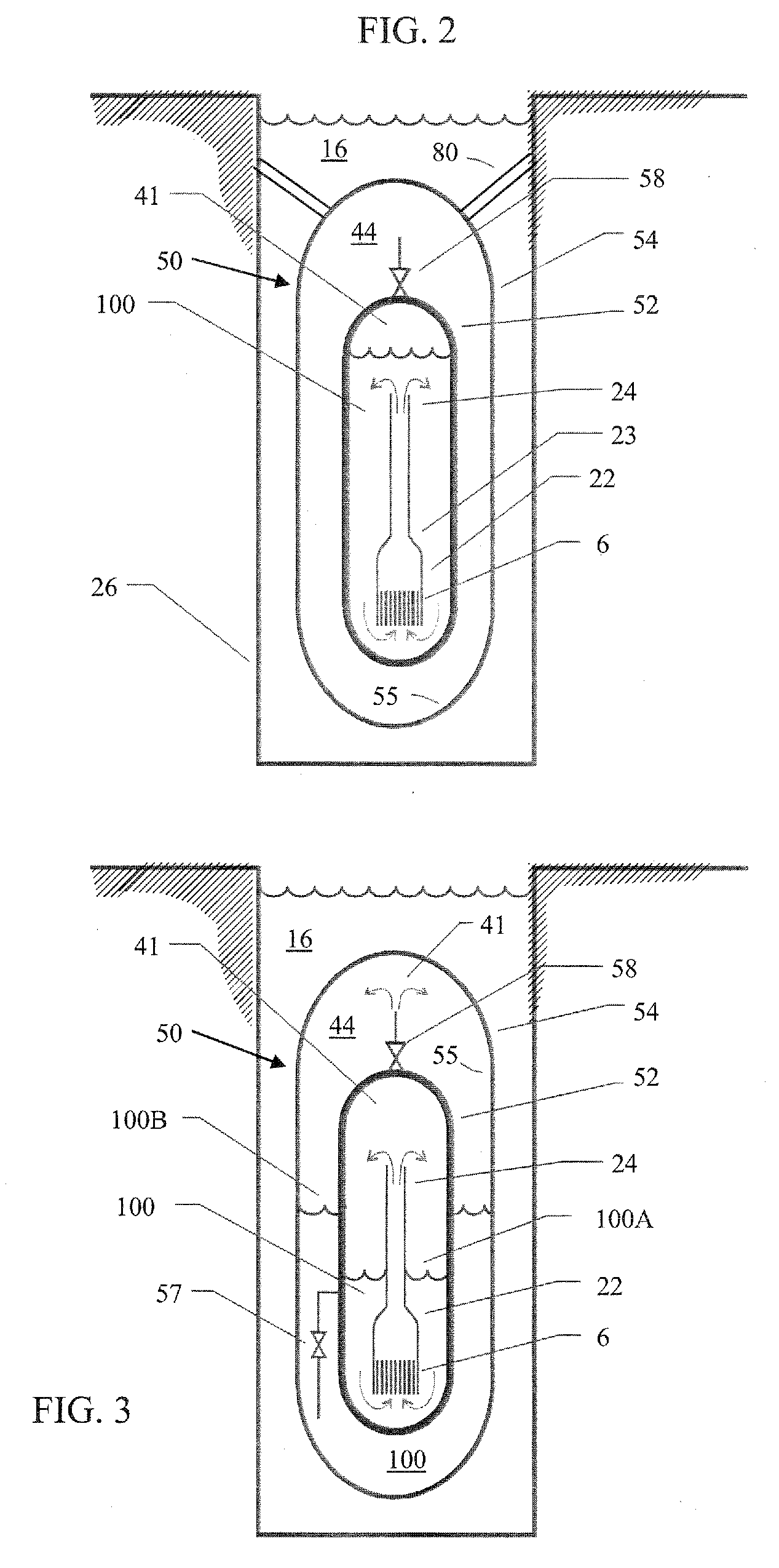
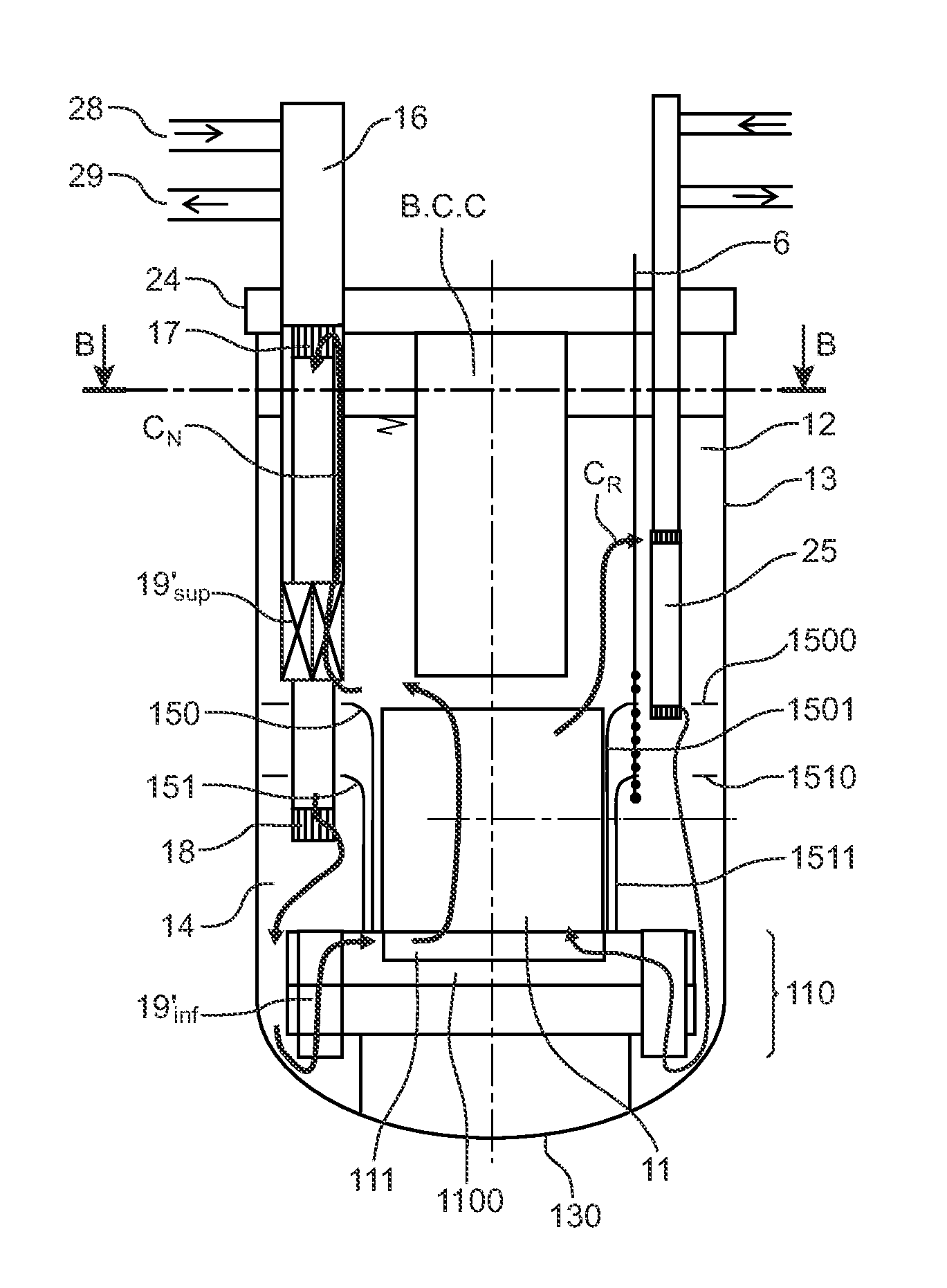
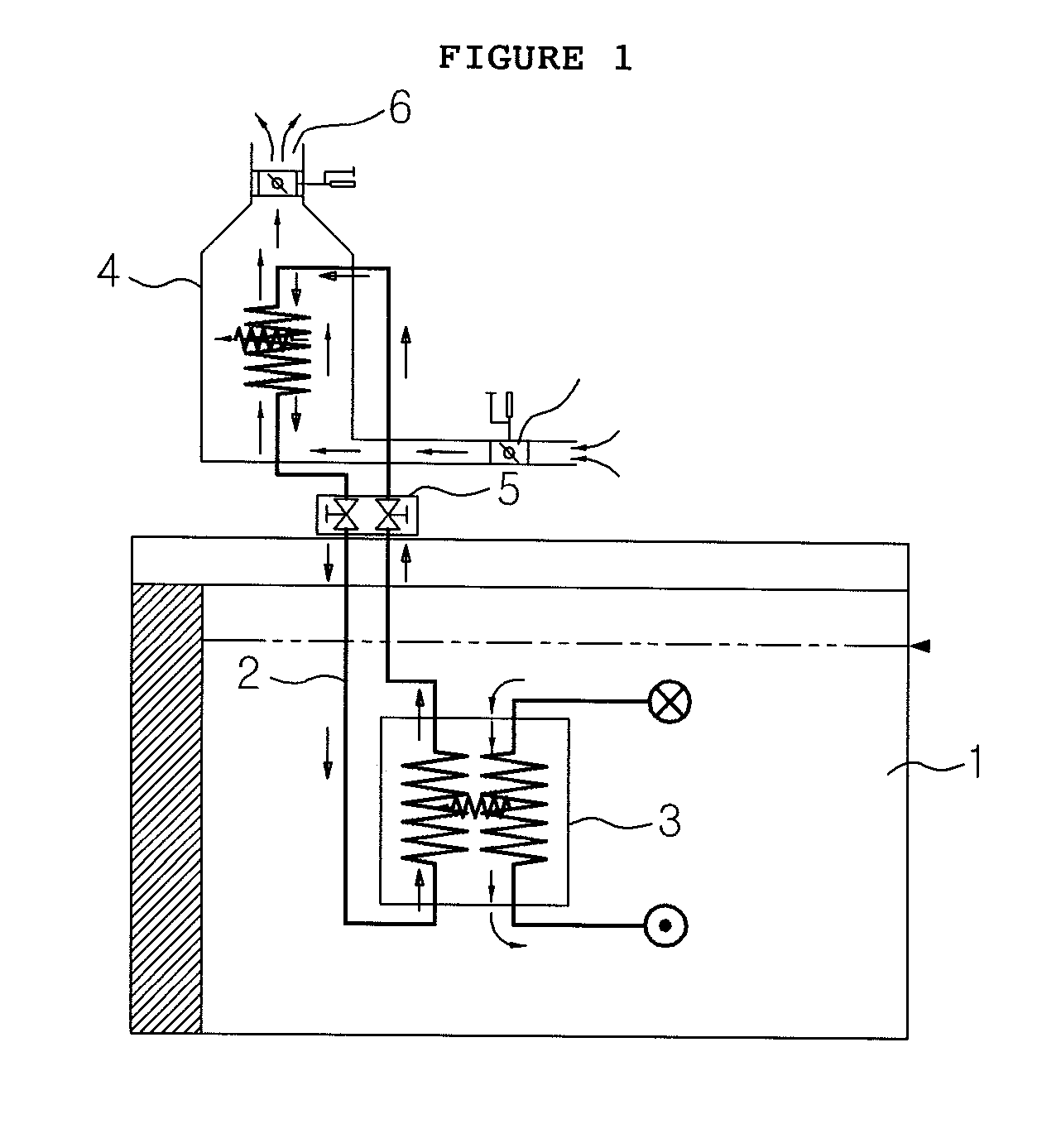
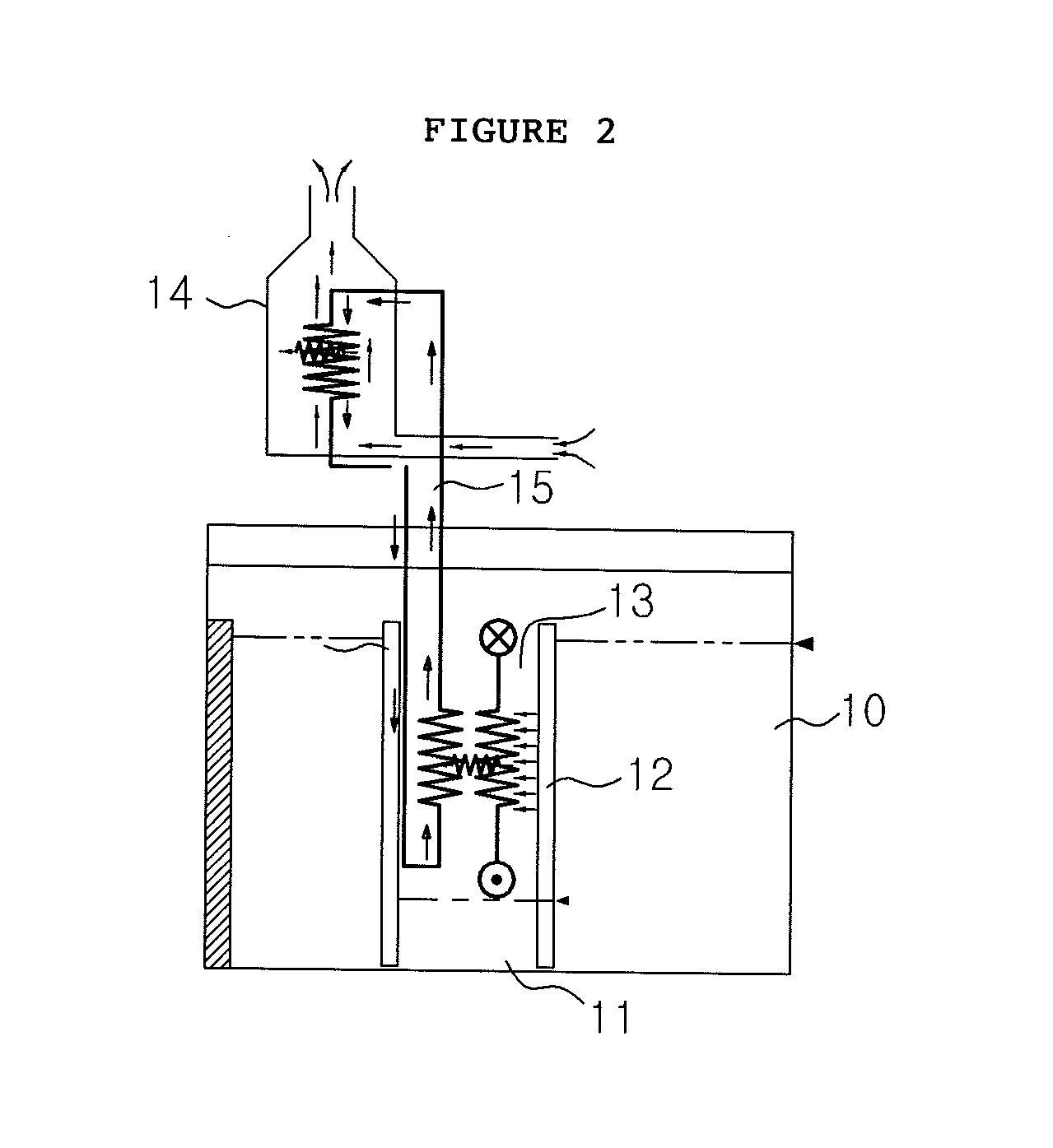
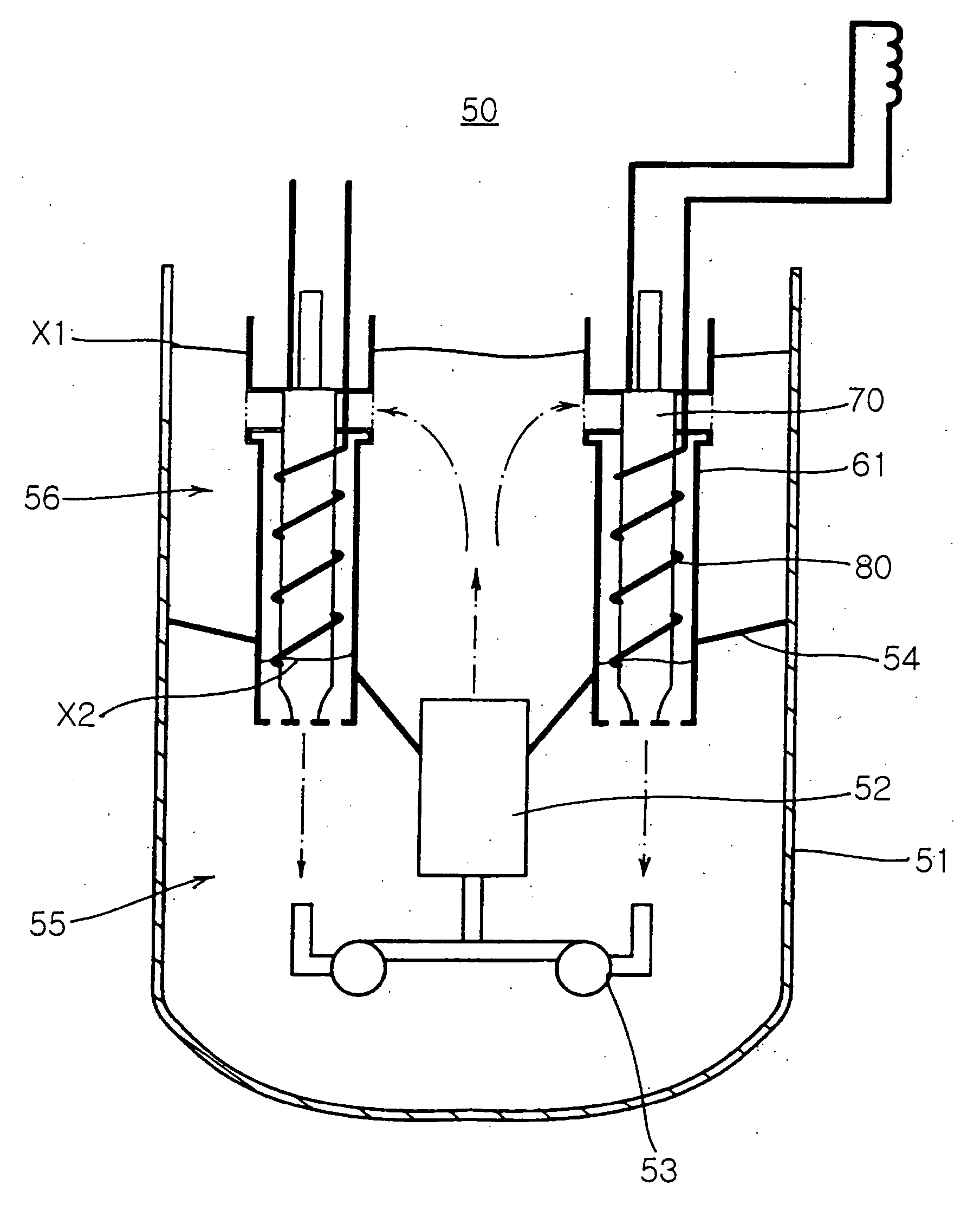
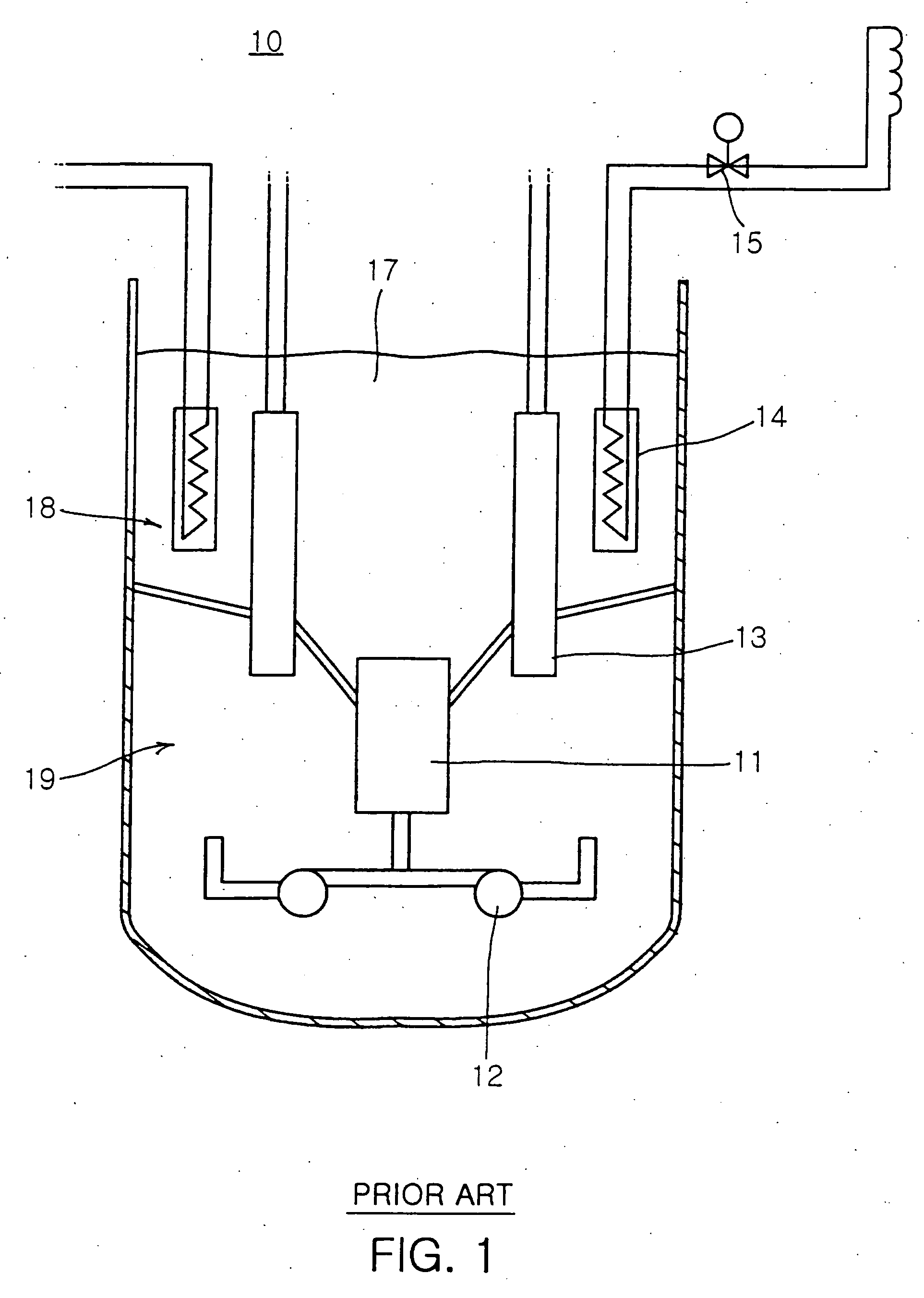
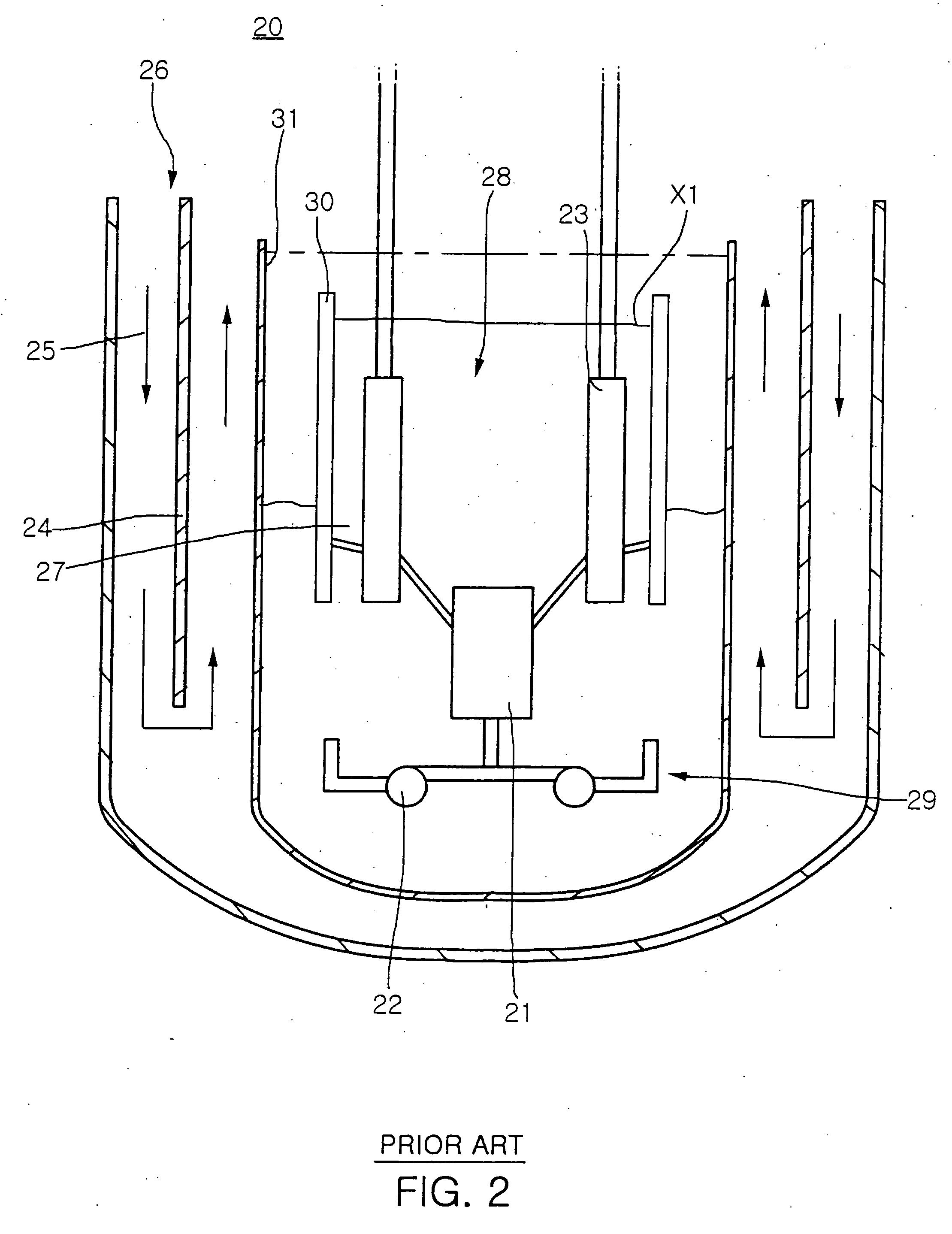
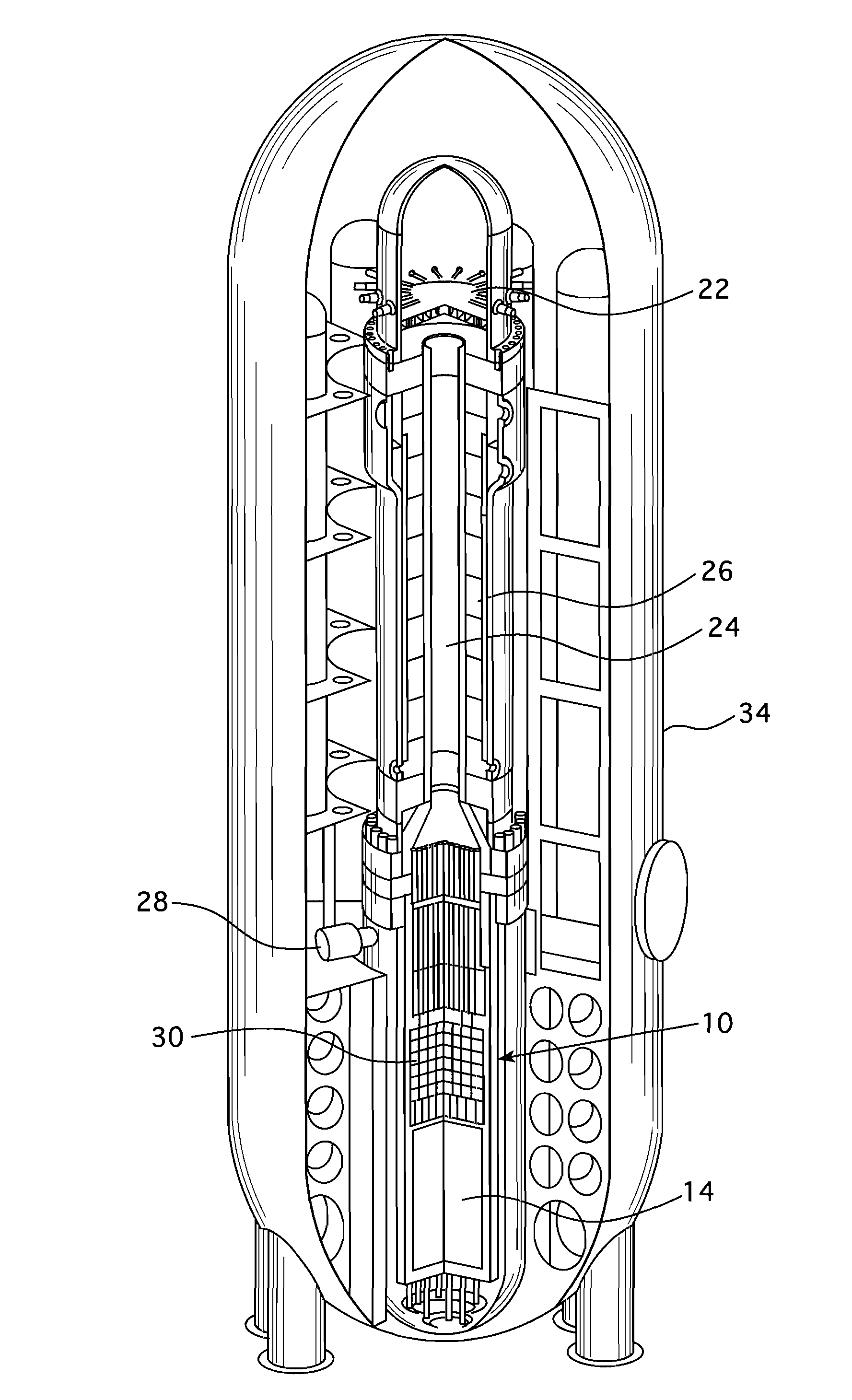
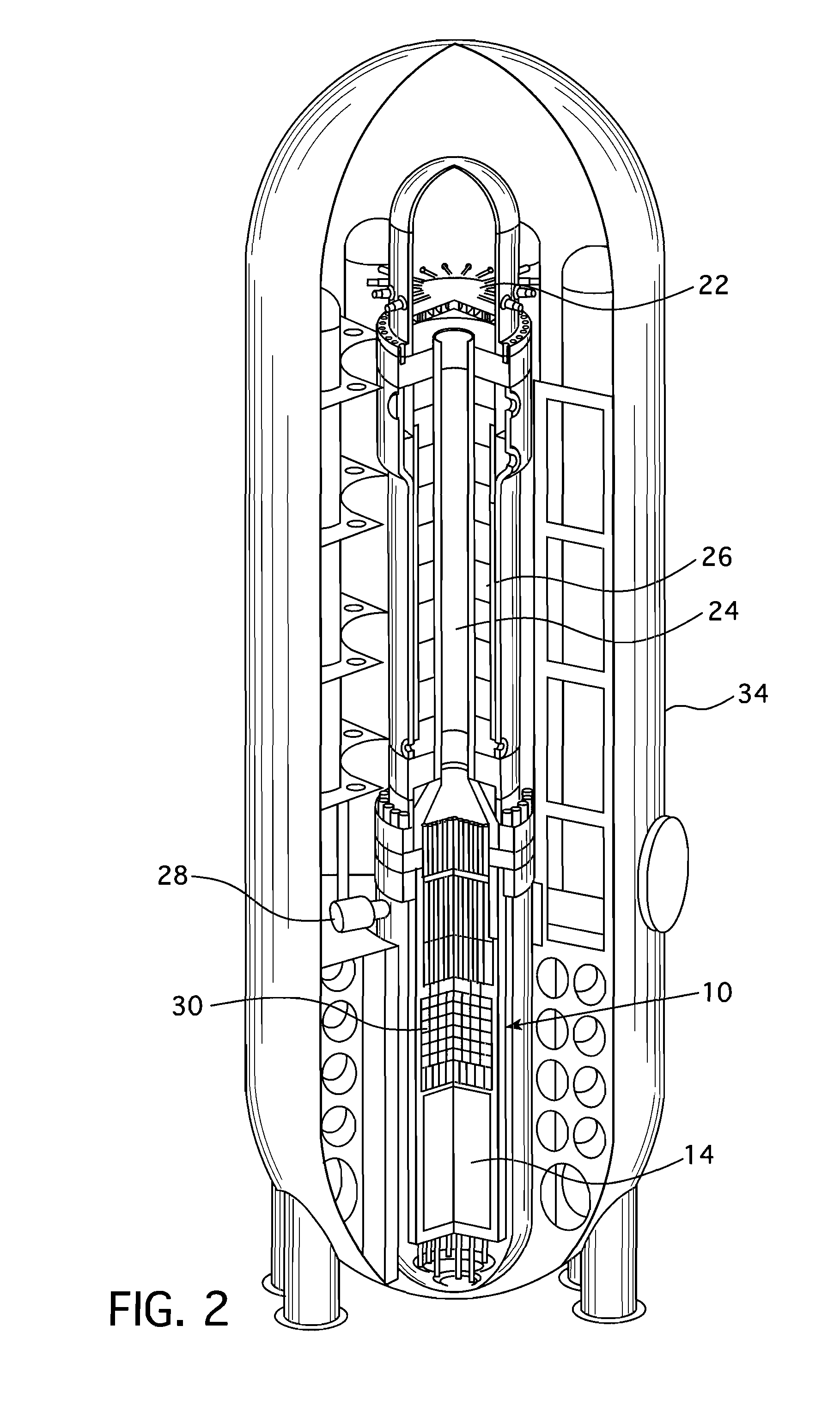
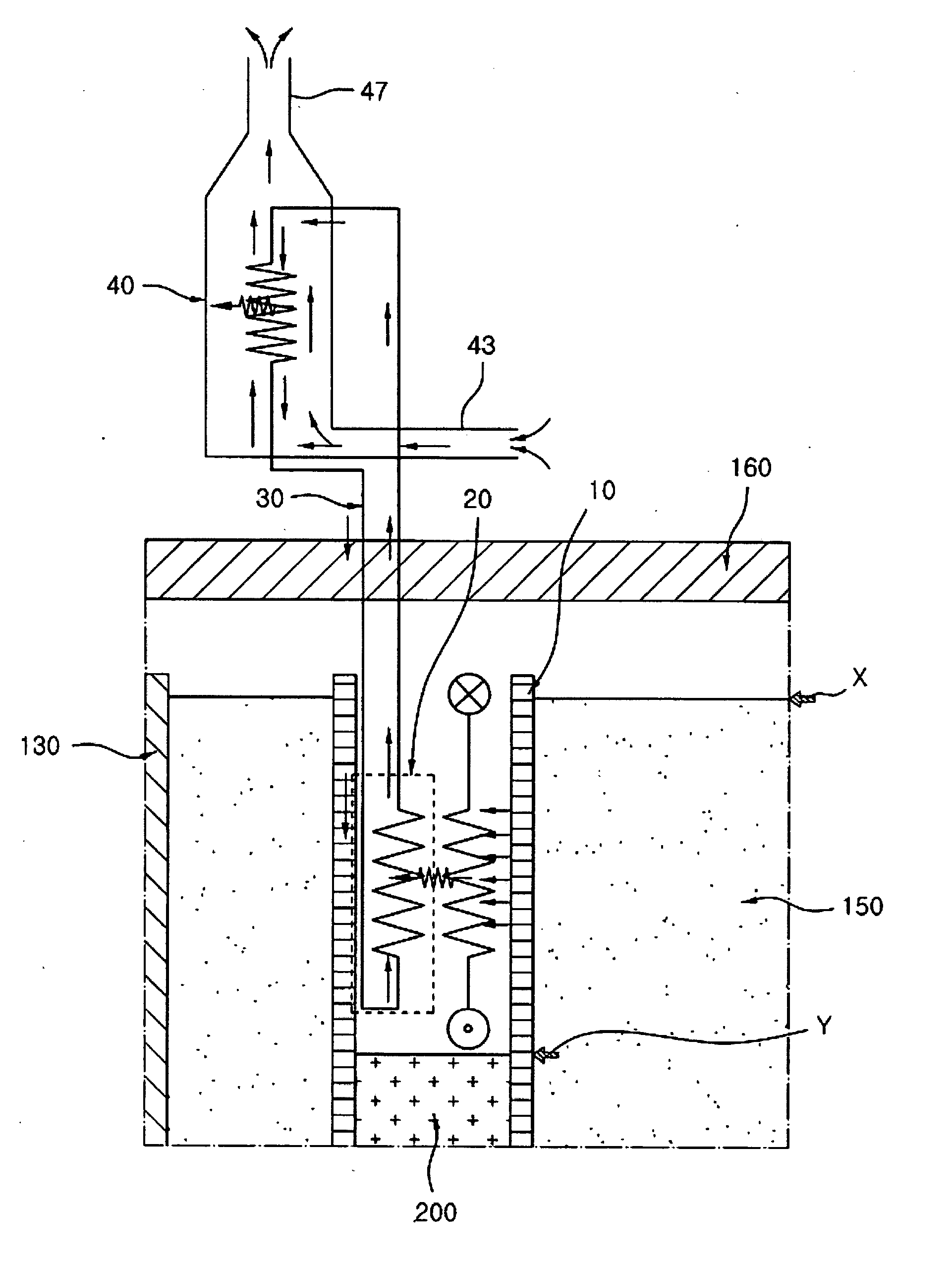
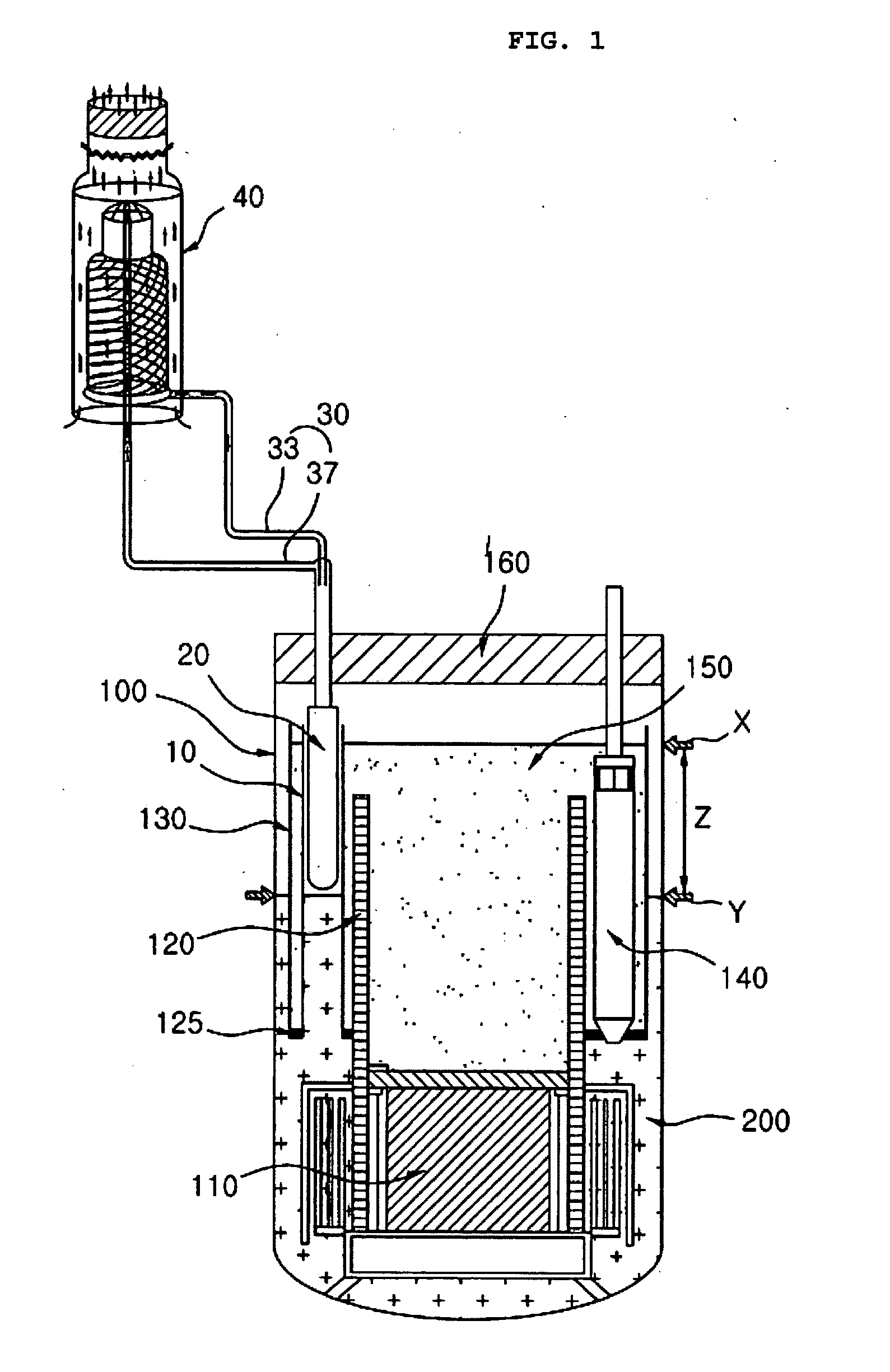
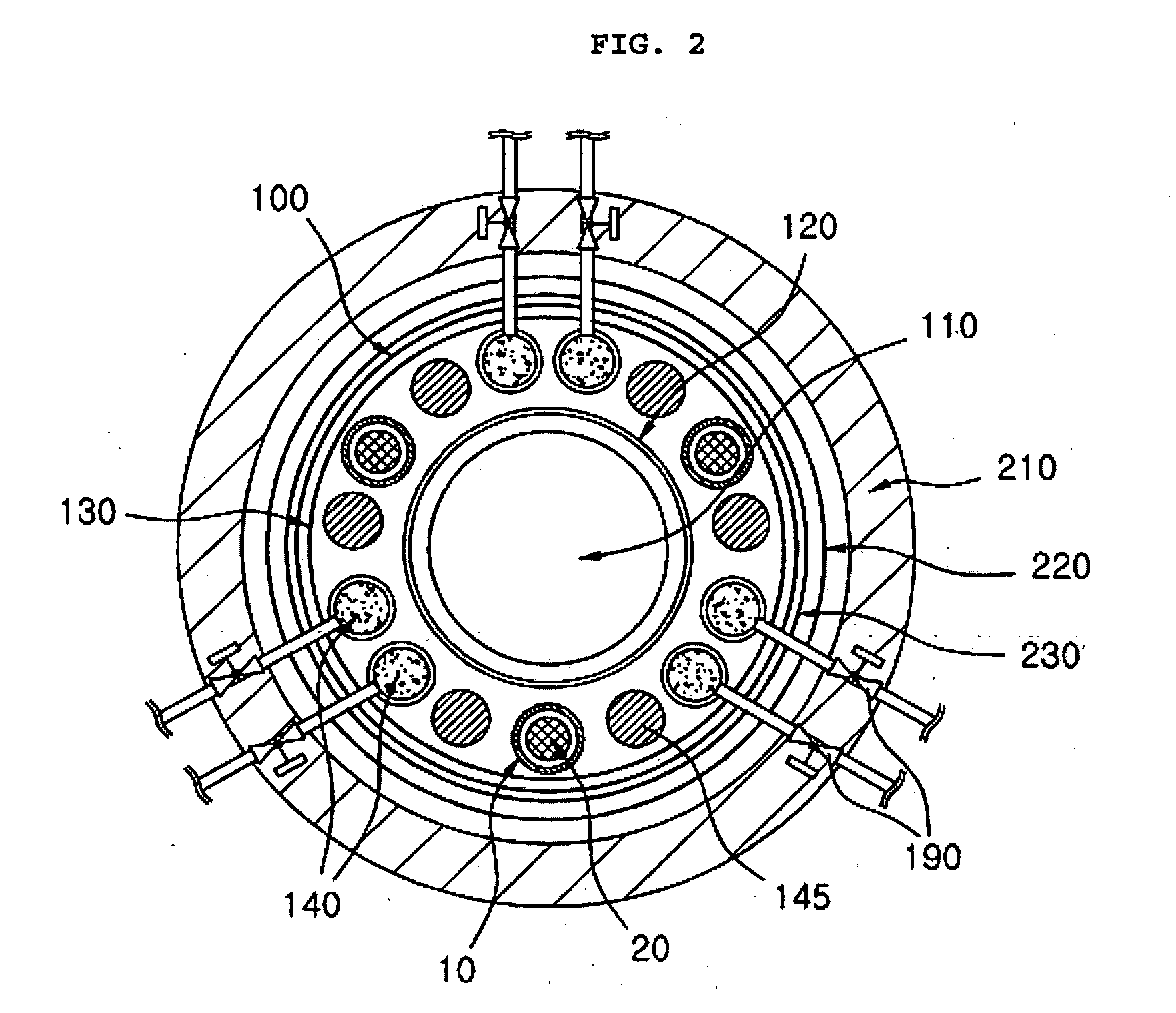
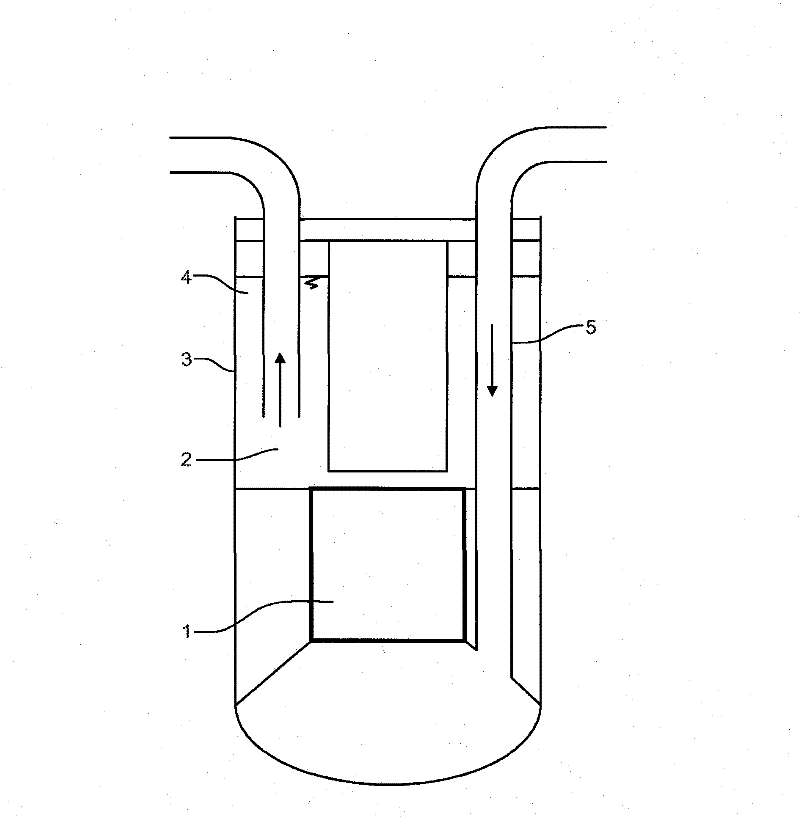
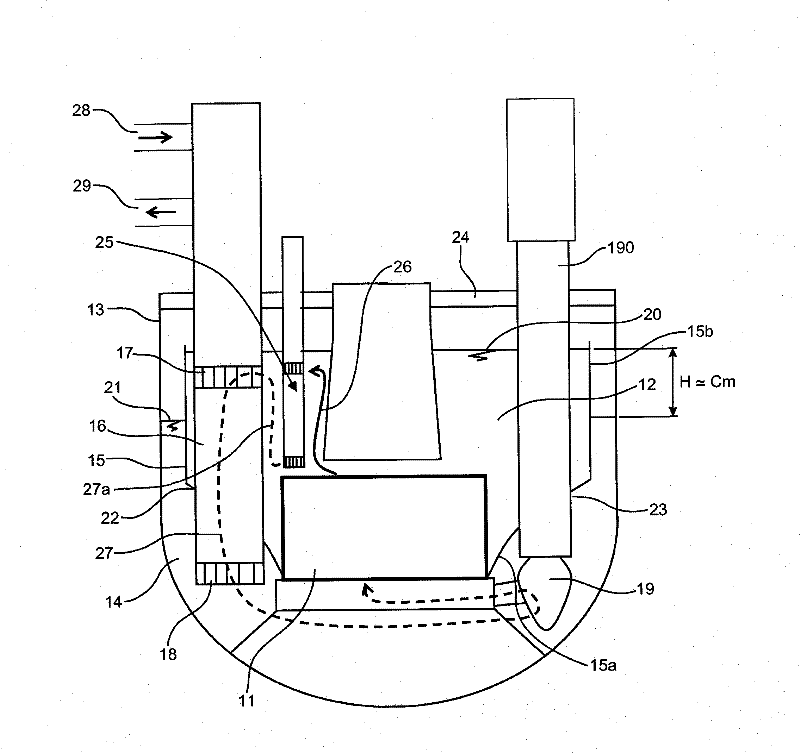
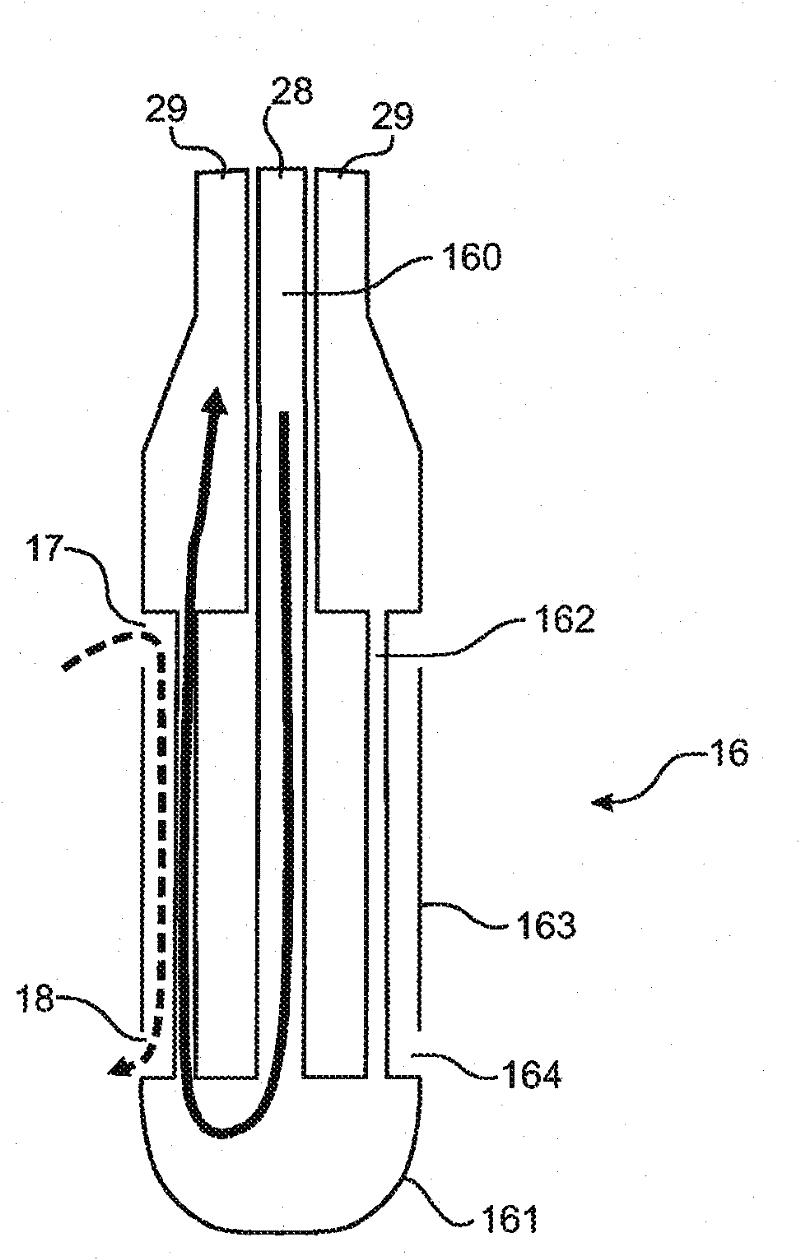
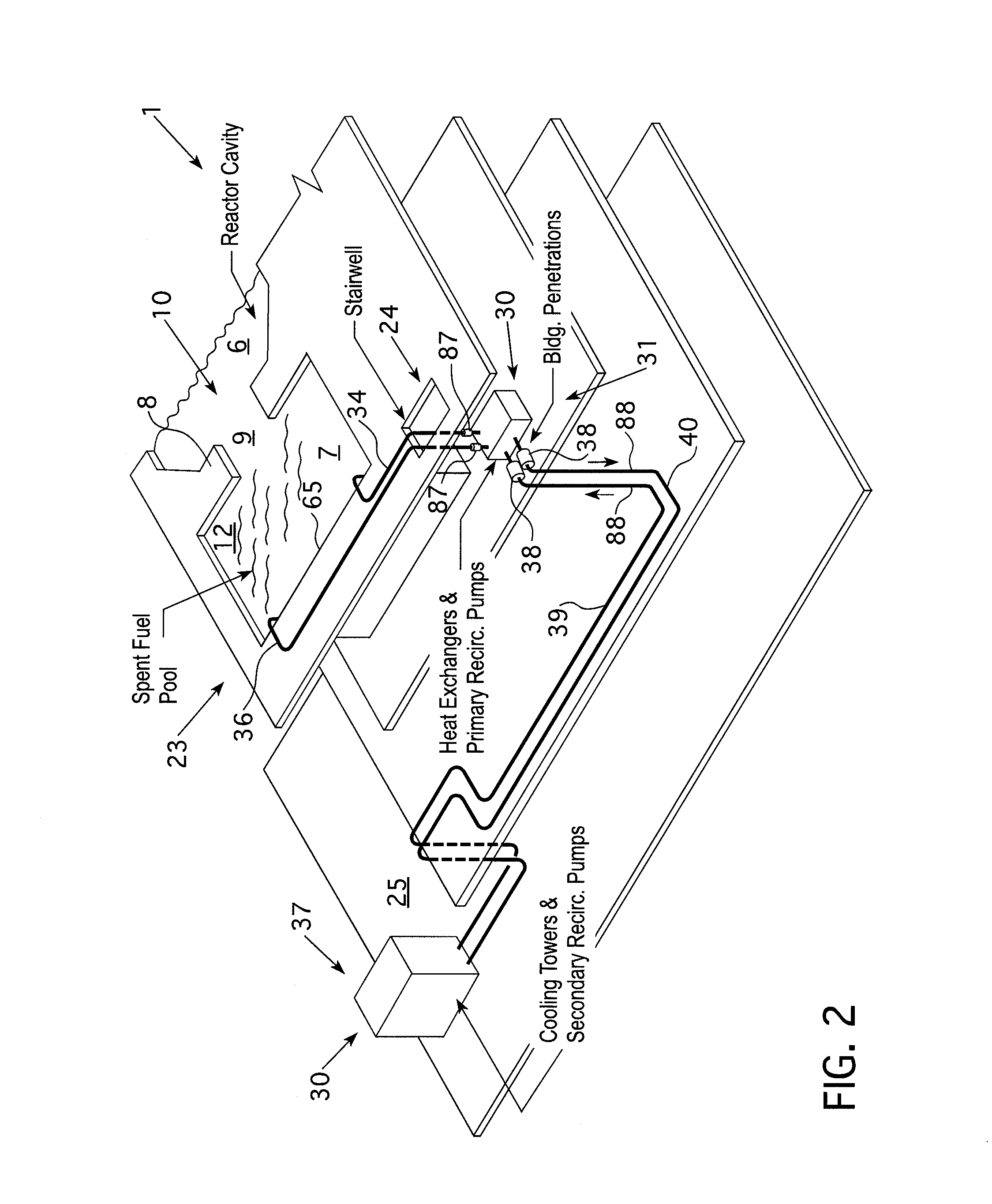
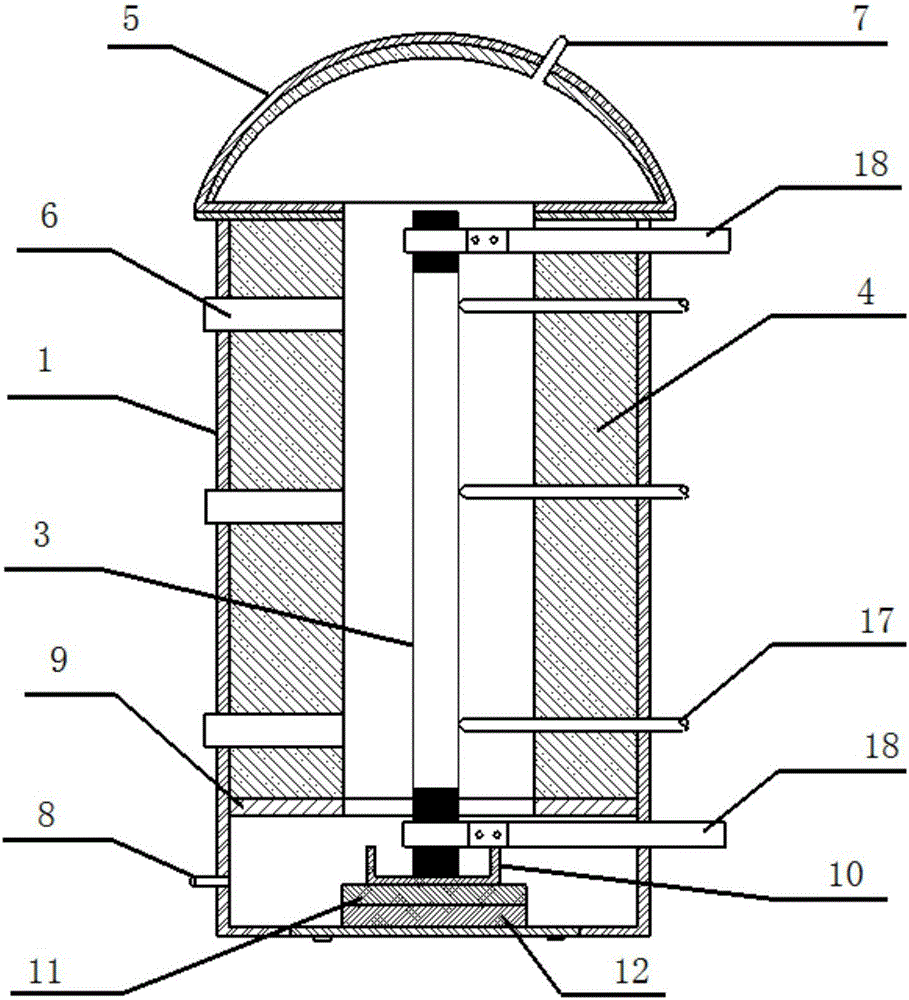
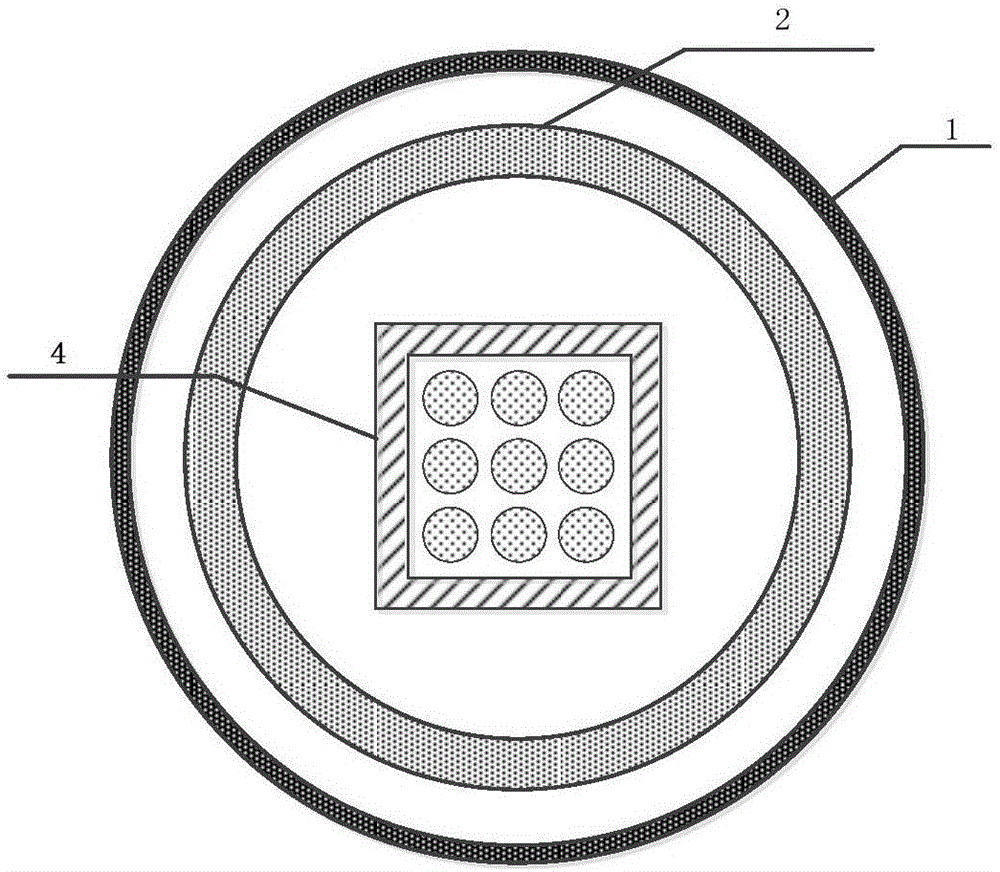
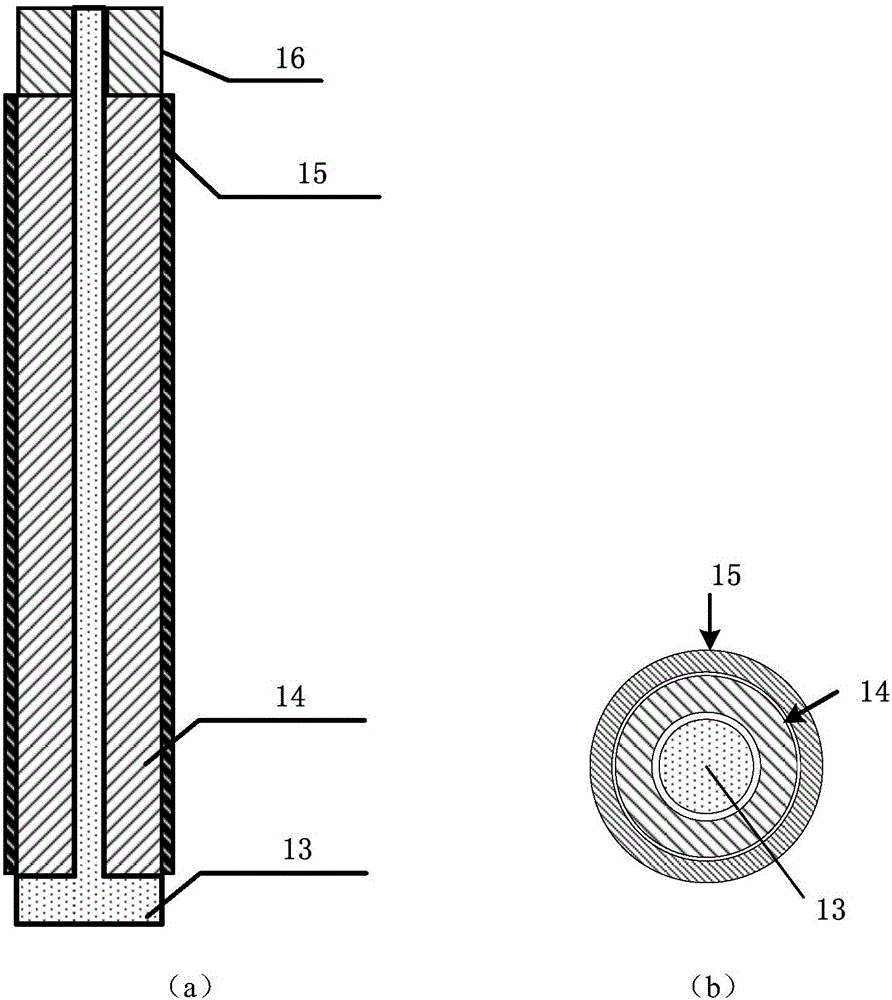
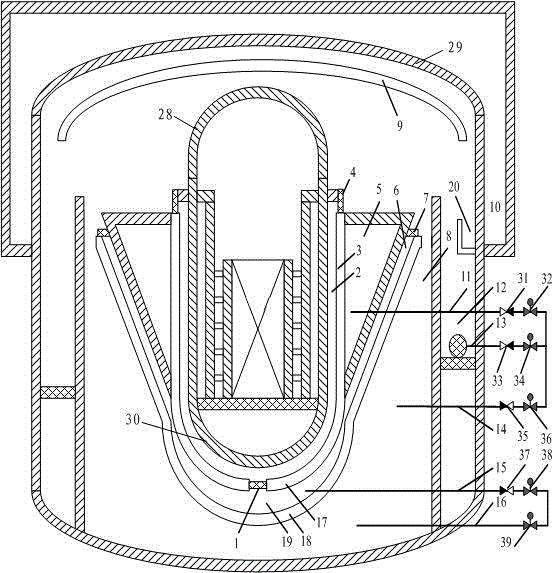
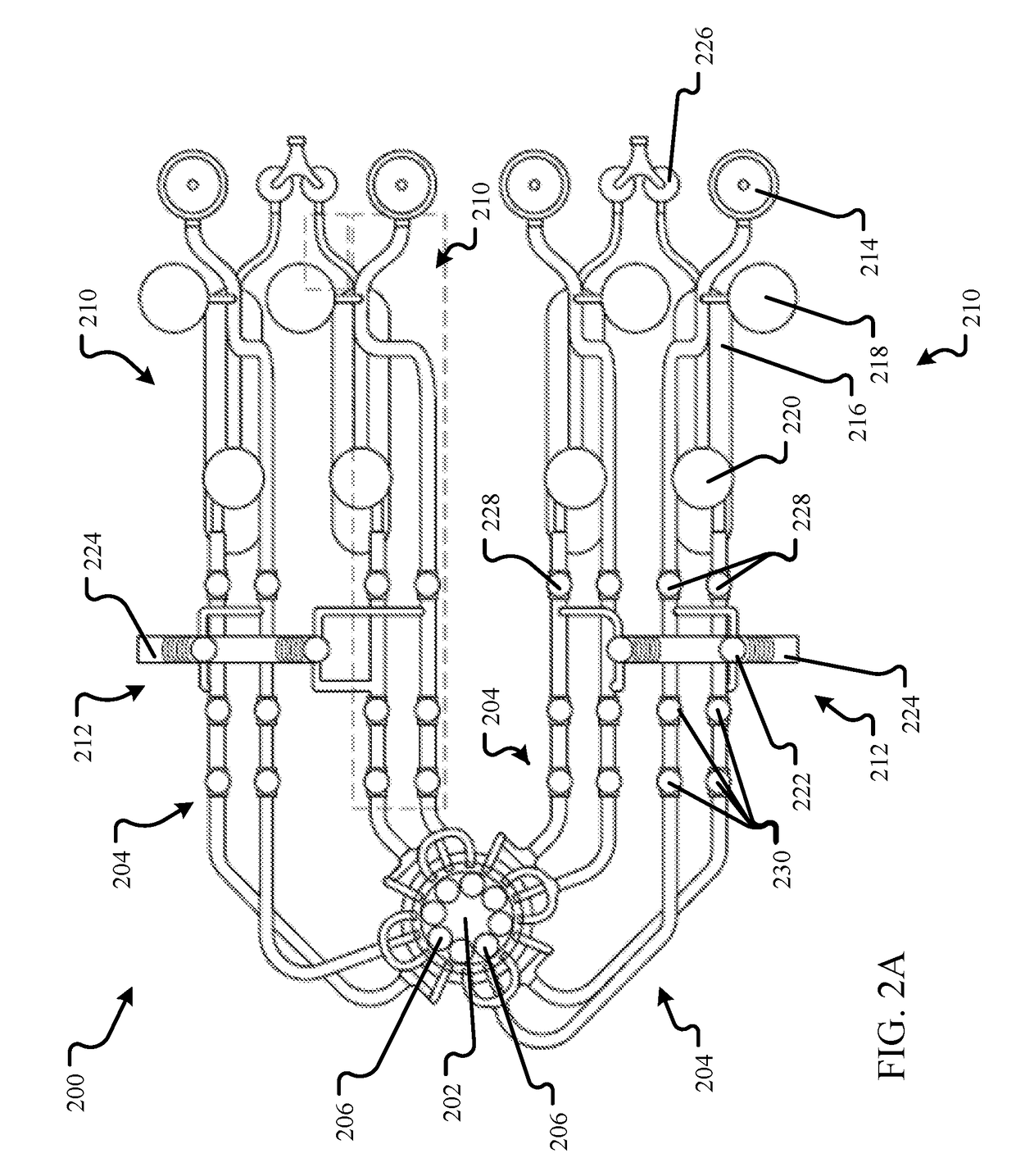
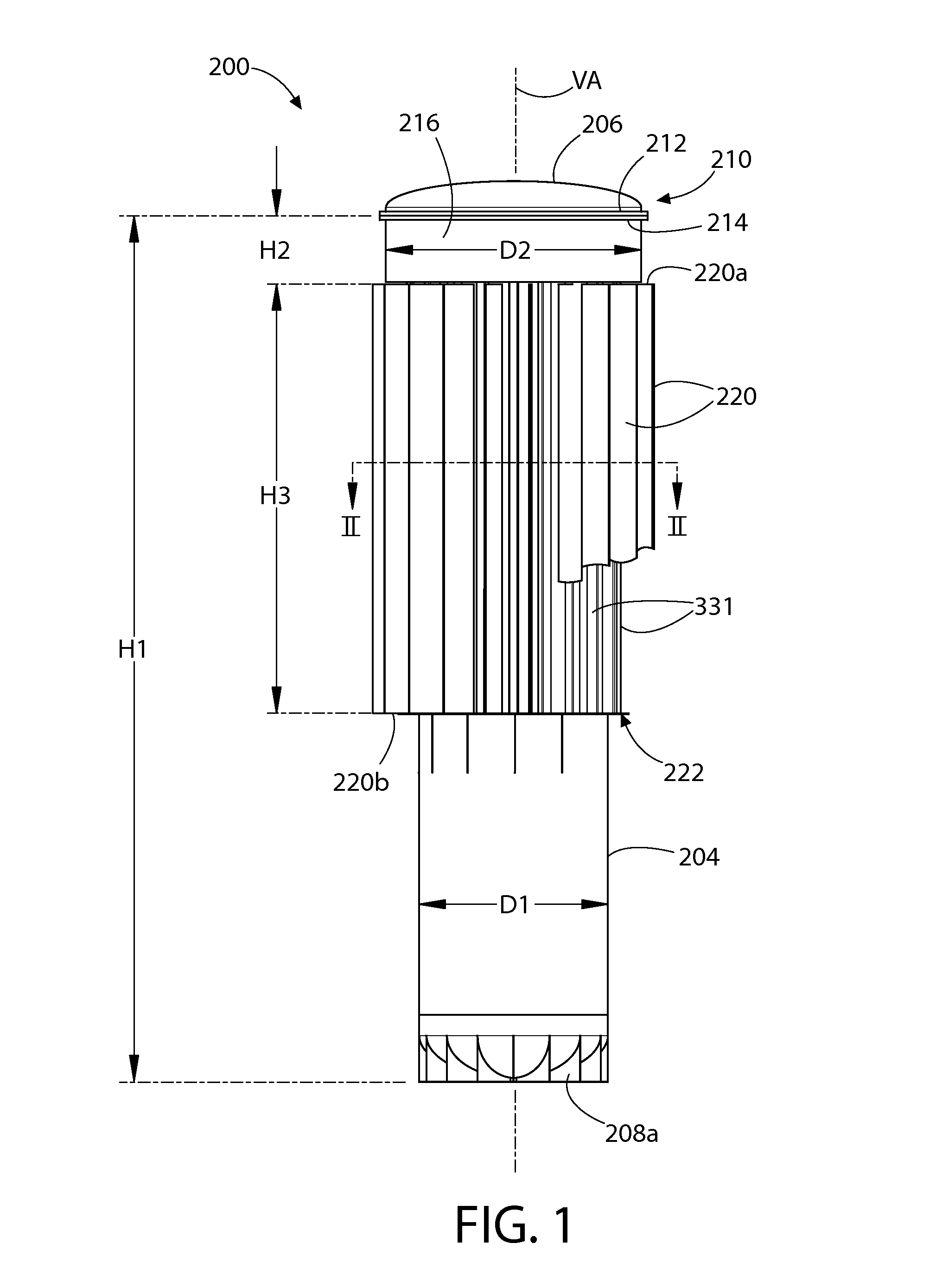
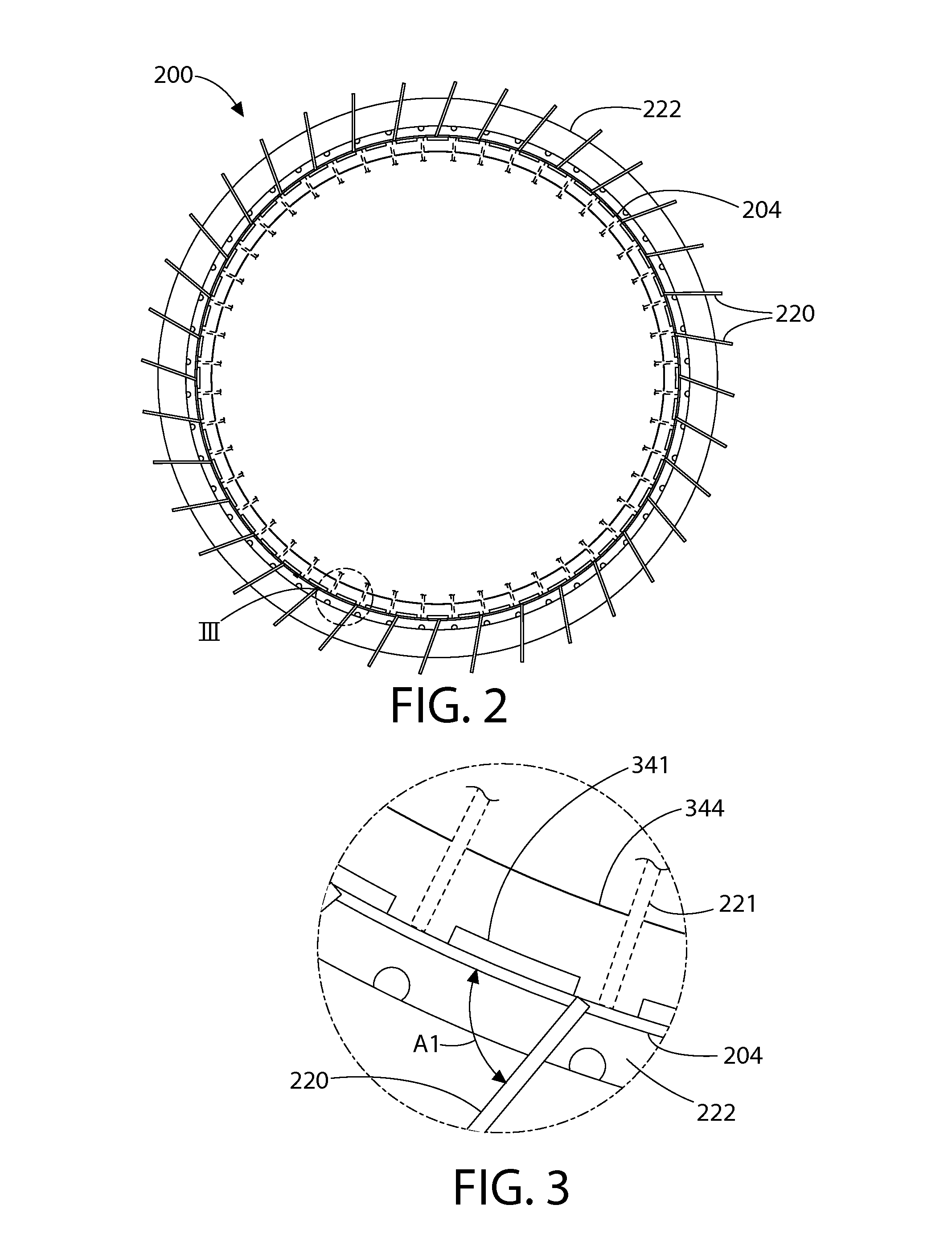
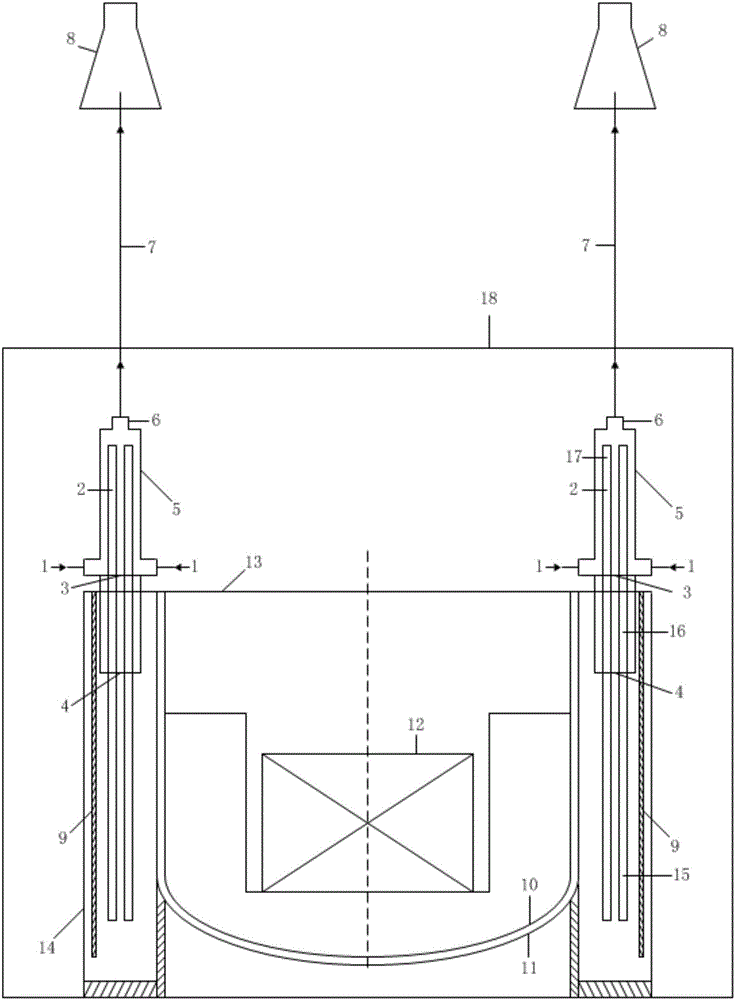
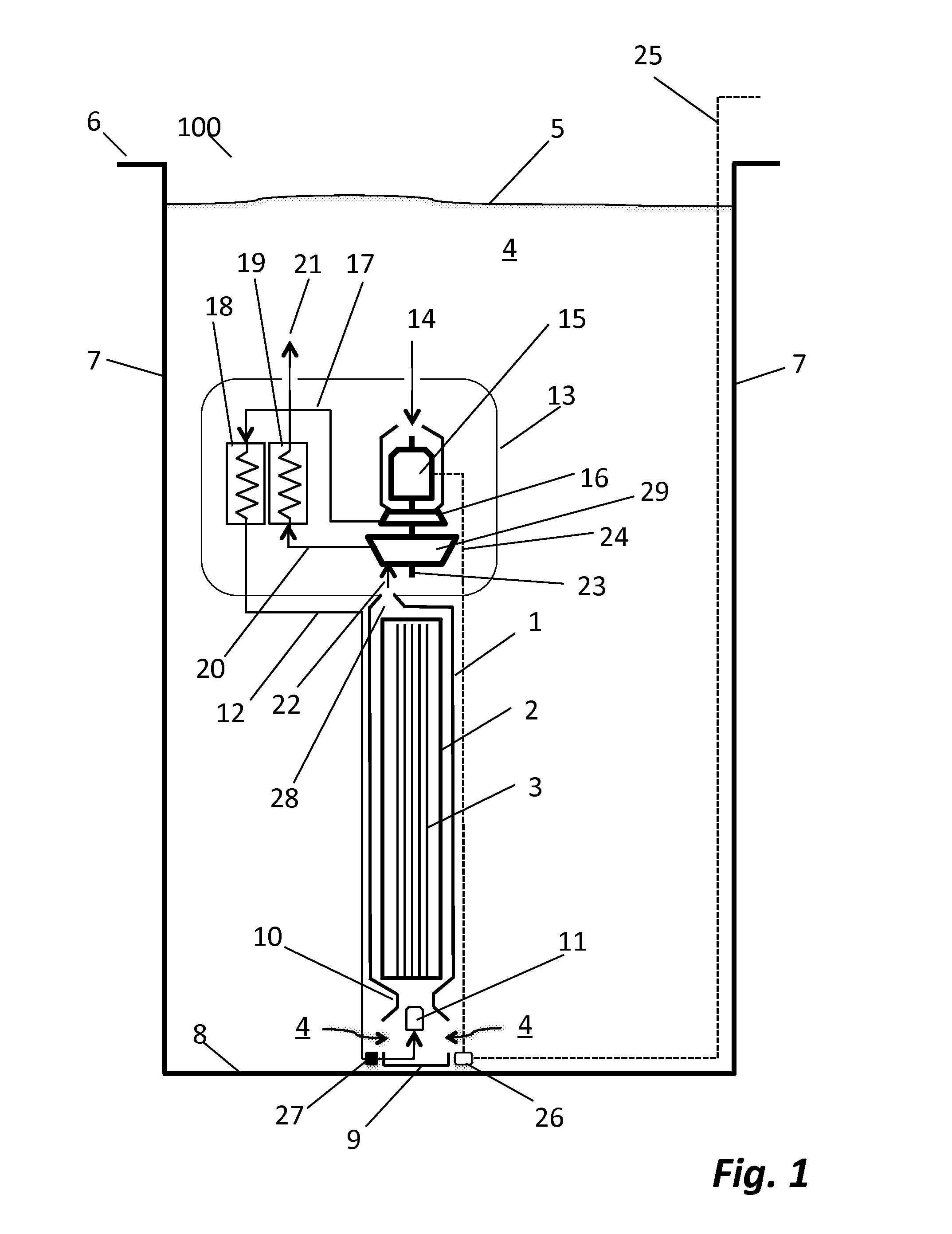
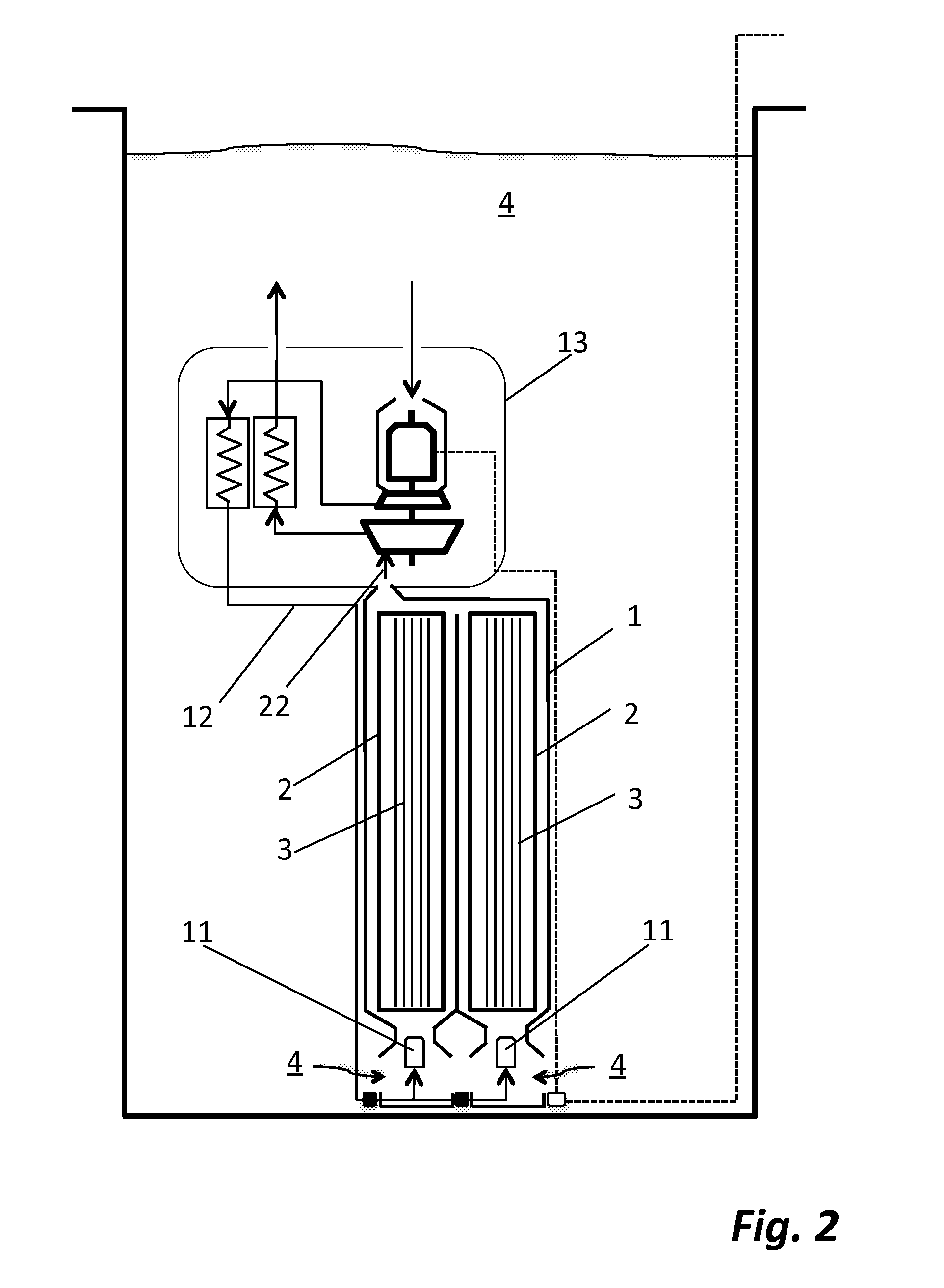
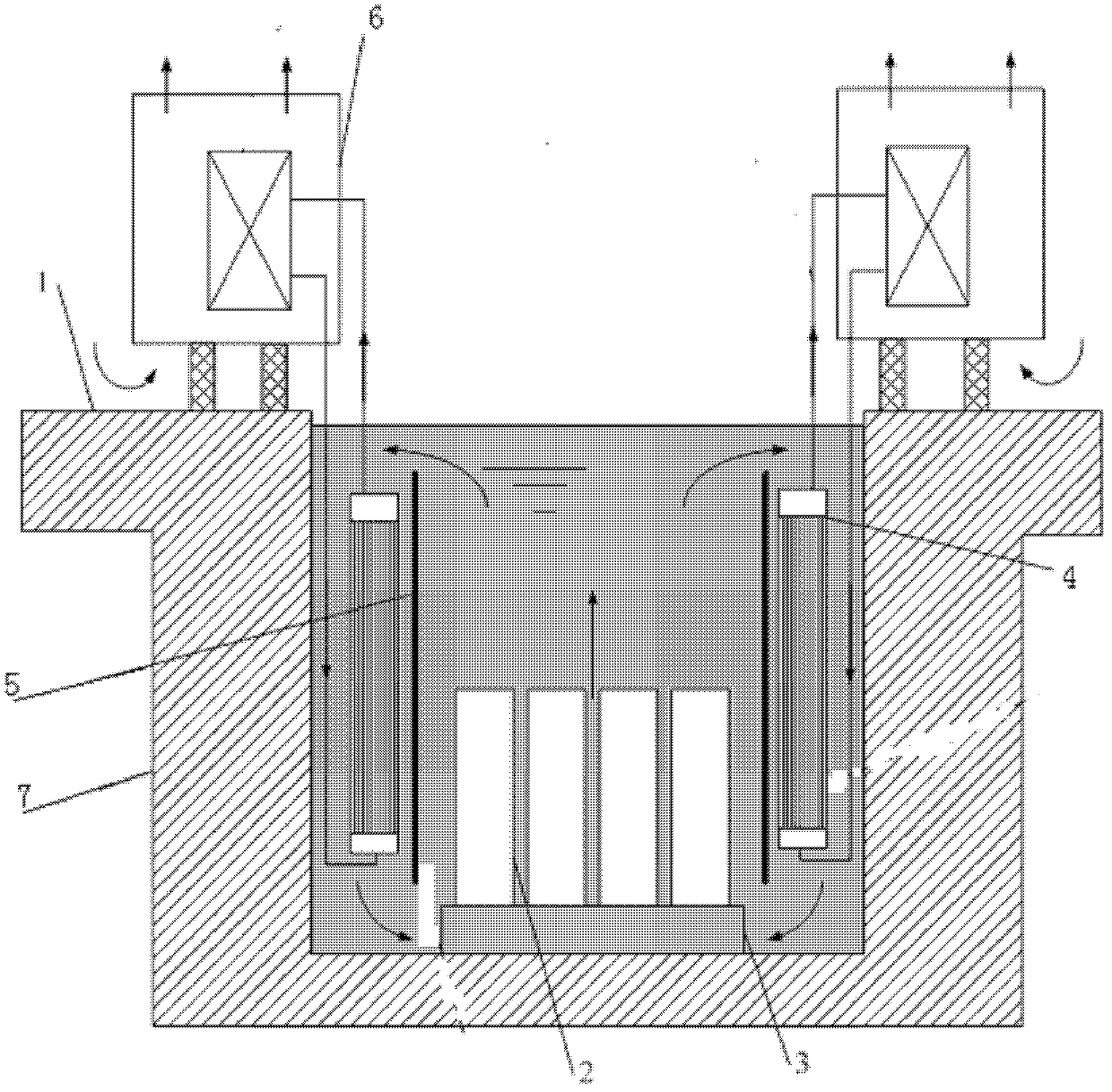
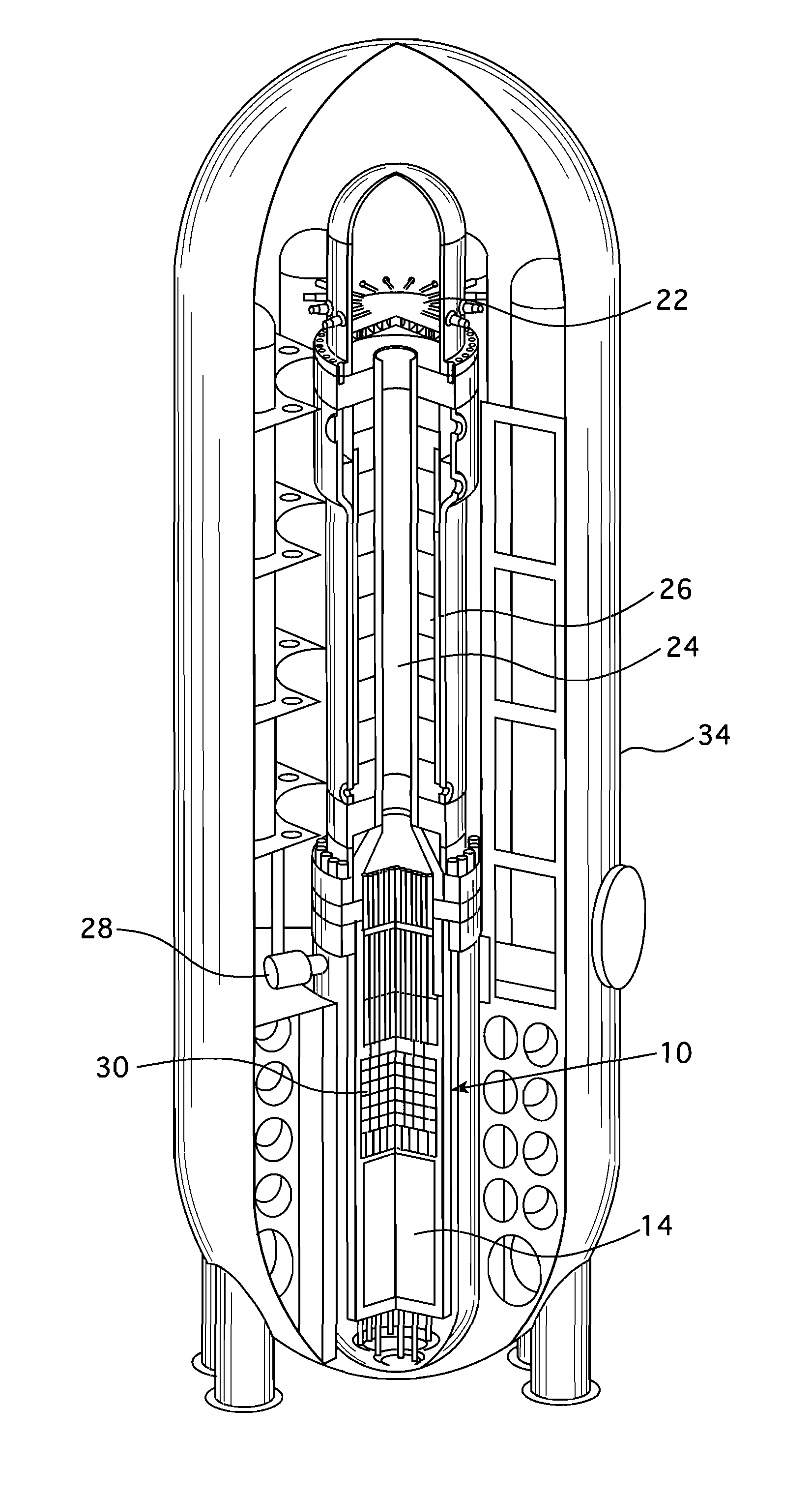
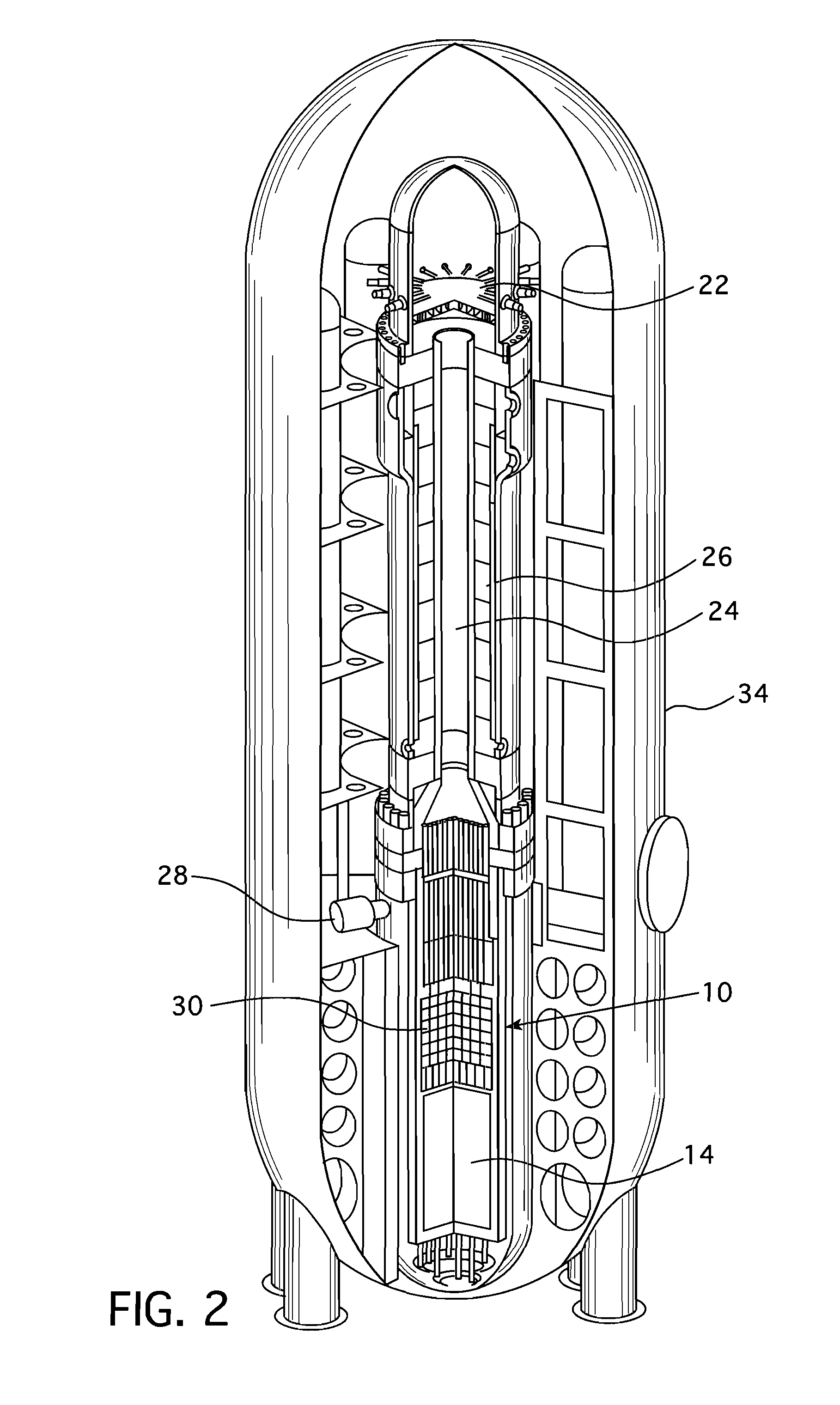
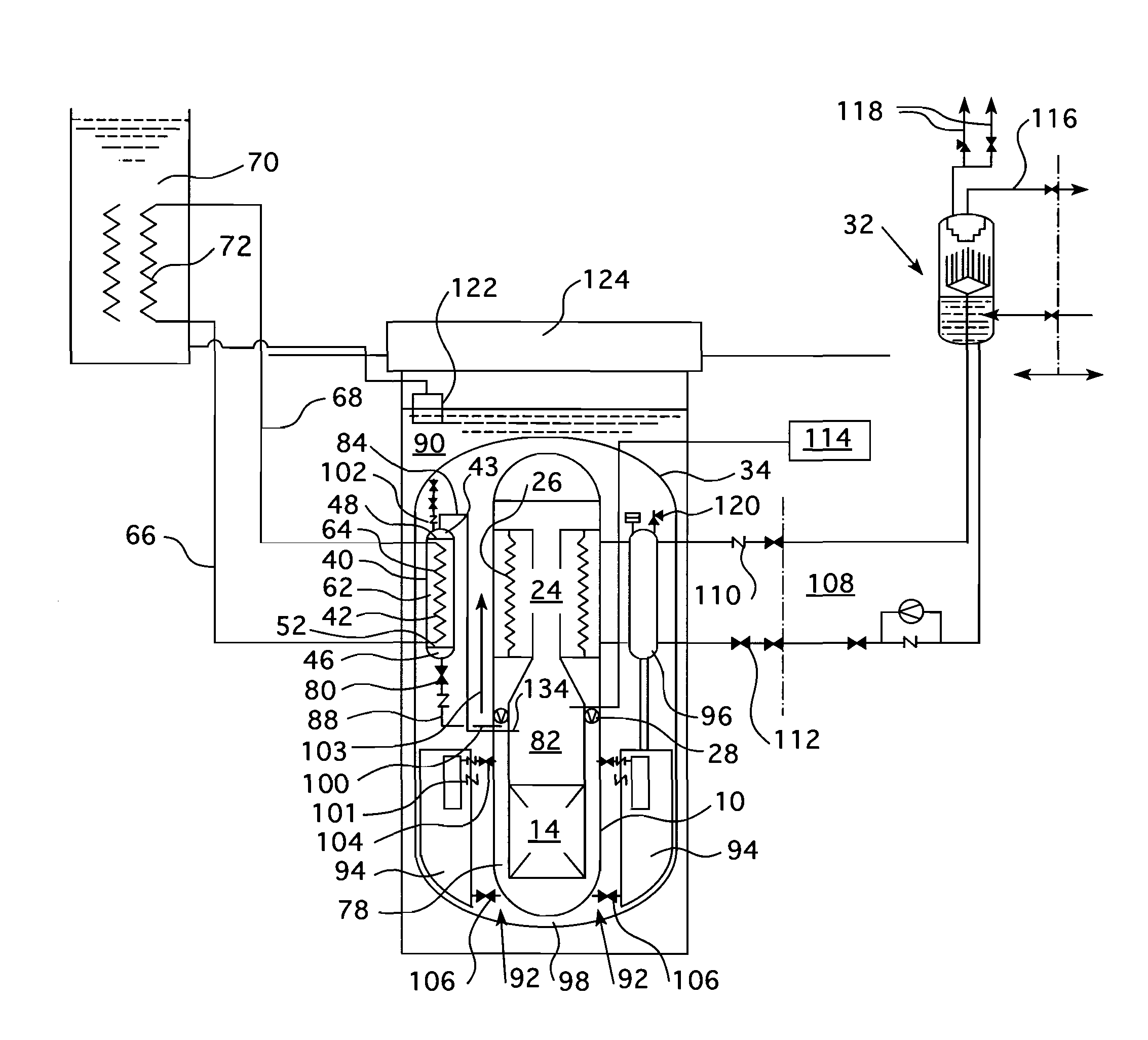
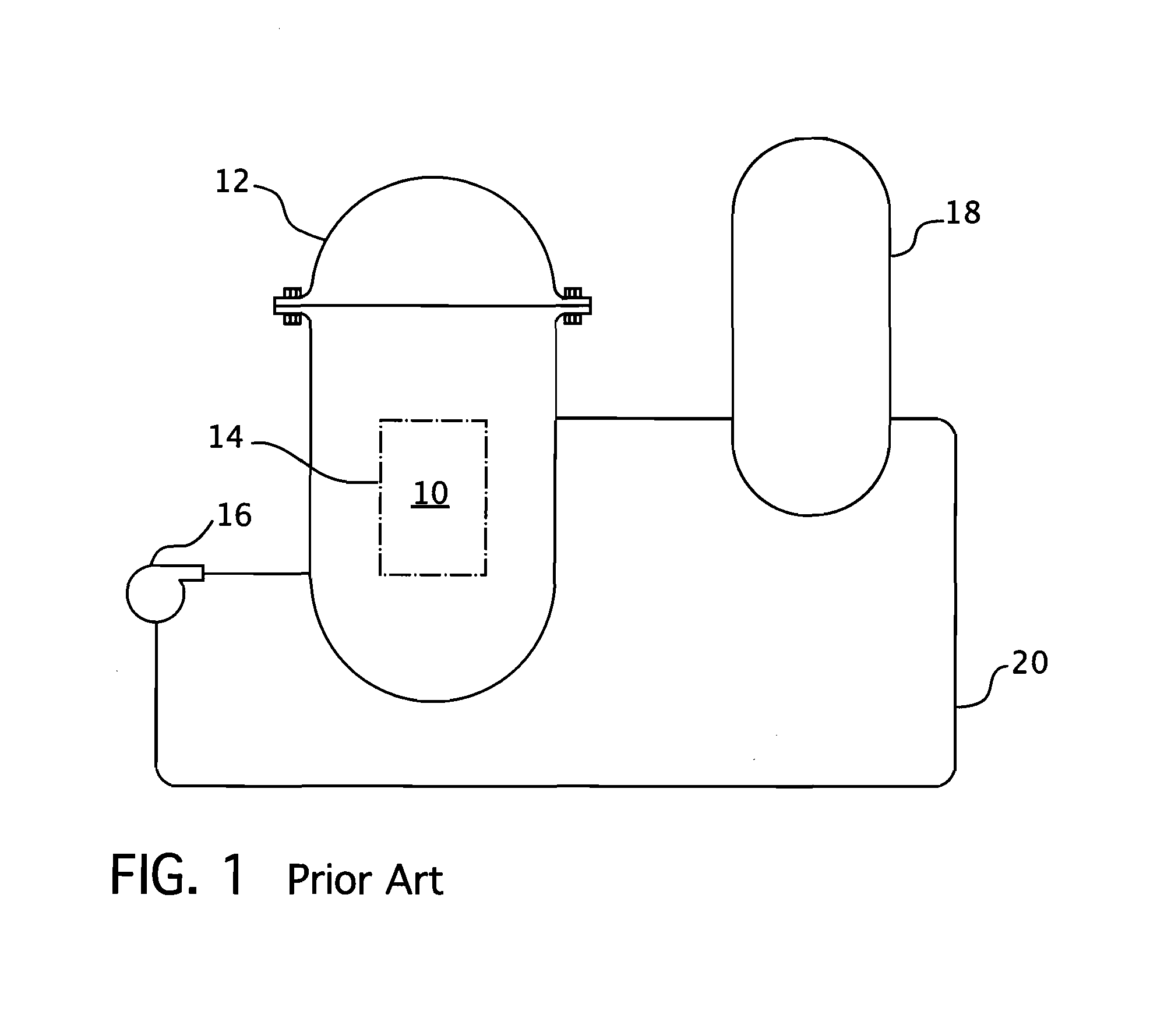
Submerged containment vessel for a nuclear reactor
A power module assembly includes a reactor core immersed in a coolant and a reactor vessel housing the coolant and the reactor core. An internal dry containment vessel submerged in liquid substantially surrounds the reactor vessel in a gaseous environment. During an over-pressurization event the reactor vessel is configured to release the coolant into the containment vessel and remove a decay heat of the reactor core through condensation of the coolant on an inner surface of the containment vessel.
Owner:NUSCALE
Passive heat removal device for dealing with station blackout accident
InactiveCN102867550AIntegrity guaranteedNo action requiredNuclear energy generationCooling arrangementRadioactive agentReactor design
The invention relates to reactor design technology, in particular to a passive heat removal device for dealing with a station blackout accident. The passive heat removal device structurally comprises a secondary side passive residual heat removal system and a passive containment heat export system, and the secondary side passive residual heat removal system is used for exporting residual heat of a reactor core and sensible heat of various devices of a reactor coolant system, so that a reactor is maintained to be in a safe shutdown state. The passive containment heat export system is used for exporting heat in a containment released by the reactor core so as to maintain integrity of the containment. The secondary side passive residual heat removal system and the passive containment heat export system share a hot water tank. The passive heat removal device for dealing with the station blackout accident is capable of exporting decay heat of the reactor core and heat in containment space released by the reactor core under the working condition of the station blackout accident, and melting probability of the reactor core and probability of radioactive substances released to the environment are evidently lowered.
Owner:CHINA NUCLEAR POWER ENG CO LTD
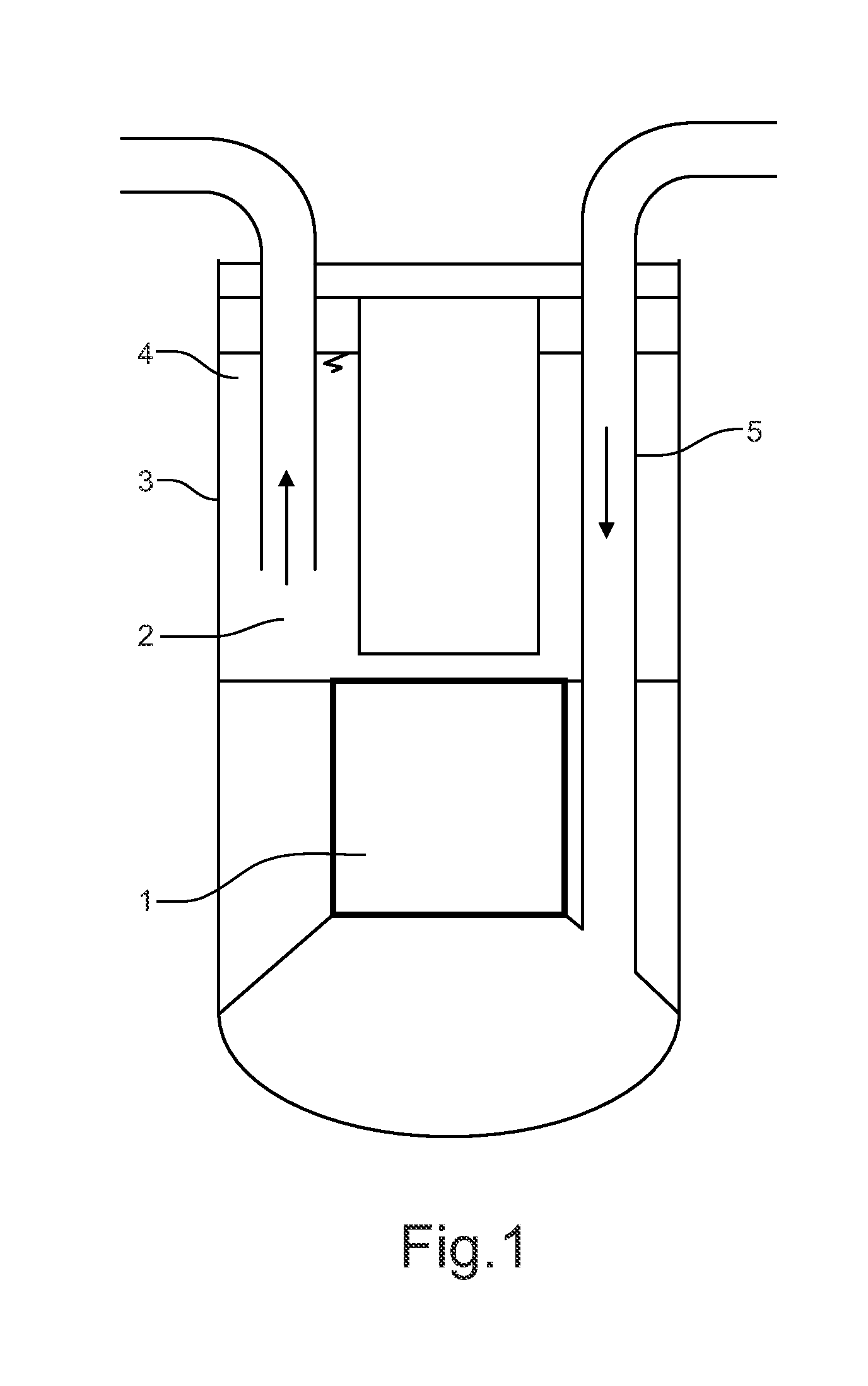
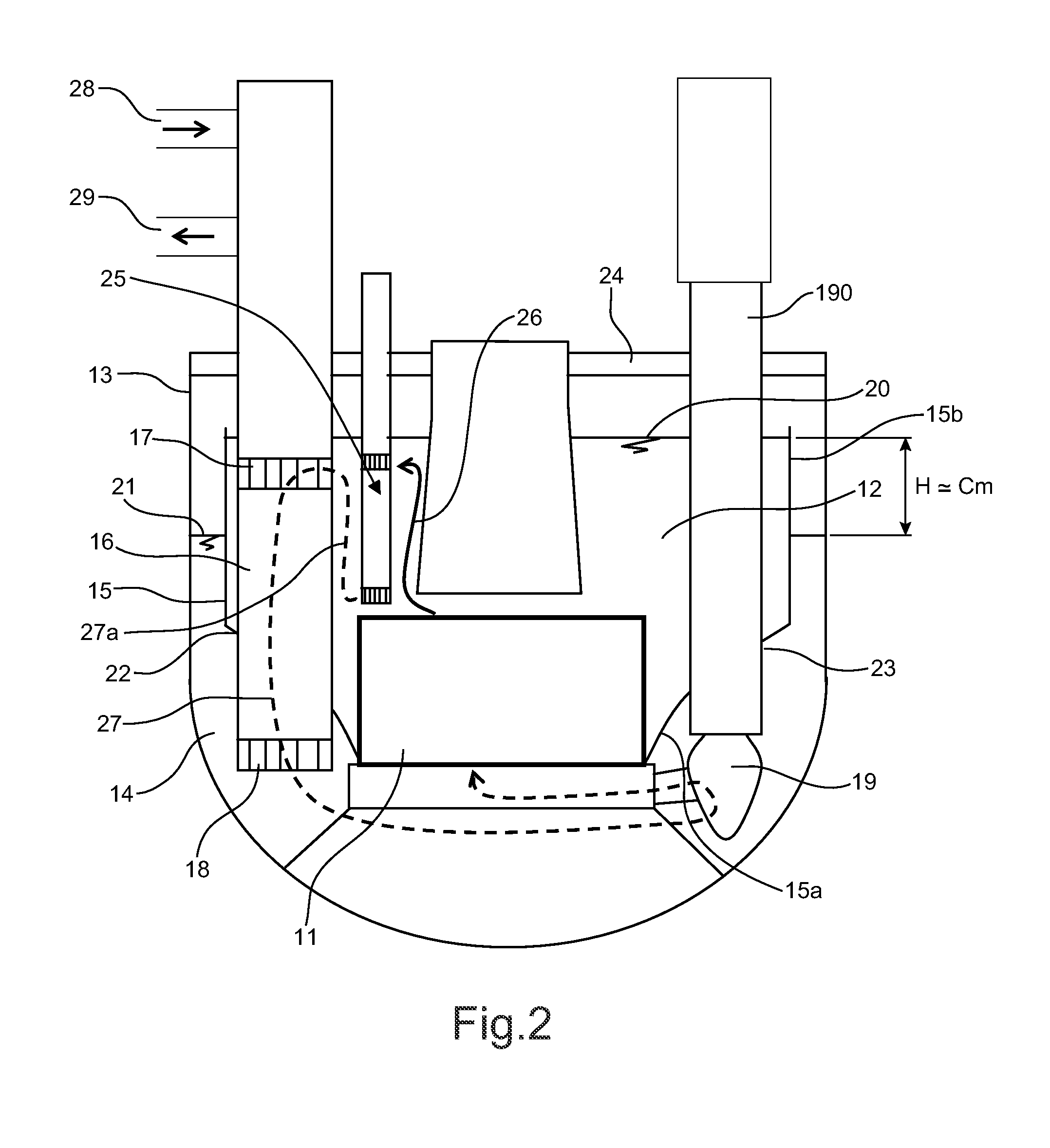
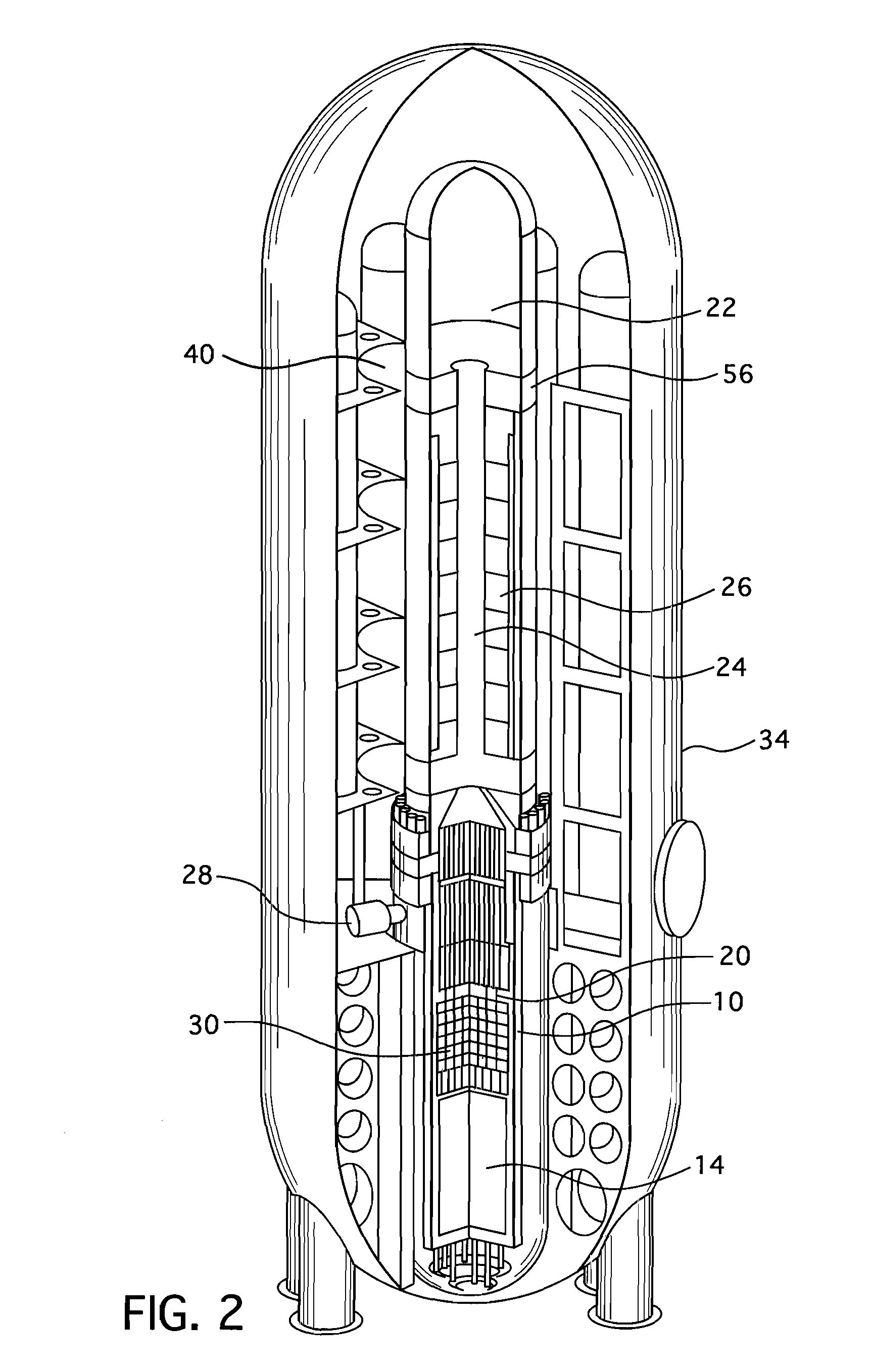
Sfr nuclear reactor of the integrated type with improved compactness and convection
The invention relates to a novel architecture for a nuclear reactor of the integrated type.The invention comprises:realising the hot area and cold area separation device for the primary sodium flow in the form of two walls with cuts,providing two pumping groups hydraulically in series, one for the flow of sodium from the hot area to the cold area through the intermediate exchangers and the other in the cold area;providing outlet windows of the intermediate exchangers below the lower wall;providing outlet windows of the removal exchangers of the decay heat above the cold area, wherein all of clearances between the walls with cuts and the heat removal exchangers and the height between the two walls with cuts are previously determined so as to, during normal operation, take up differential movements between the walls, exchangers and vessel and to make it possible to establish during normal operation a thermal stratification of the primary sodium in the space defined between the horizontal portions of the two walls and so as to reduce, in case of an unexpected stop of a single pumping group, the mechanical stress applied to the walls and due to the portion of the primary sodium flow passing between said clearances.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Fully passive decay heat removal system for sodium-cooled fast reactors that utilizes partially immersed decay heat exchanger
ActiveUS20100177860A1Reduced operational reliabilityImprove business performanceNuclear energy generationFast fission reactorsIntermediate heat exchangerSodium-cooled fast reactor
Disclosed herein is a fully passive decay heat removal system utilizing a partially immersed heat exchanger, the system comprising: a hot pool; an intermediate heat exchanger which heat-exchanges with the sodium of the hot pool; a cold pool; a support barrel extending vertically through the boundary between the hot pool and the cold pool; a sodium-sodium decay heat exchanger received in the support barrel; a sodium-air heat exchanger provided at a position higher than the sodium-sodium decay heat exchanger; an intermediate sodium loop connecting the sodium-sodium decay heat exchanger with the sodium-air heat exchanger; and a primary pump, wherein a portion of the effective heat transfer tube of the sodium-sodium decay heat exchanger is immersed in the cold pool, particularly in a normal operating state, and the surface of the lower end of a shroud for the sodium-sodium decay heat exchanger, the lower end being immersed in the sodium of the cold pool, has perforated holes.
Owner:KOREA ATOMIC ENERGY RES INST +1
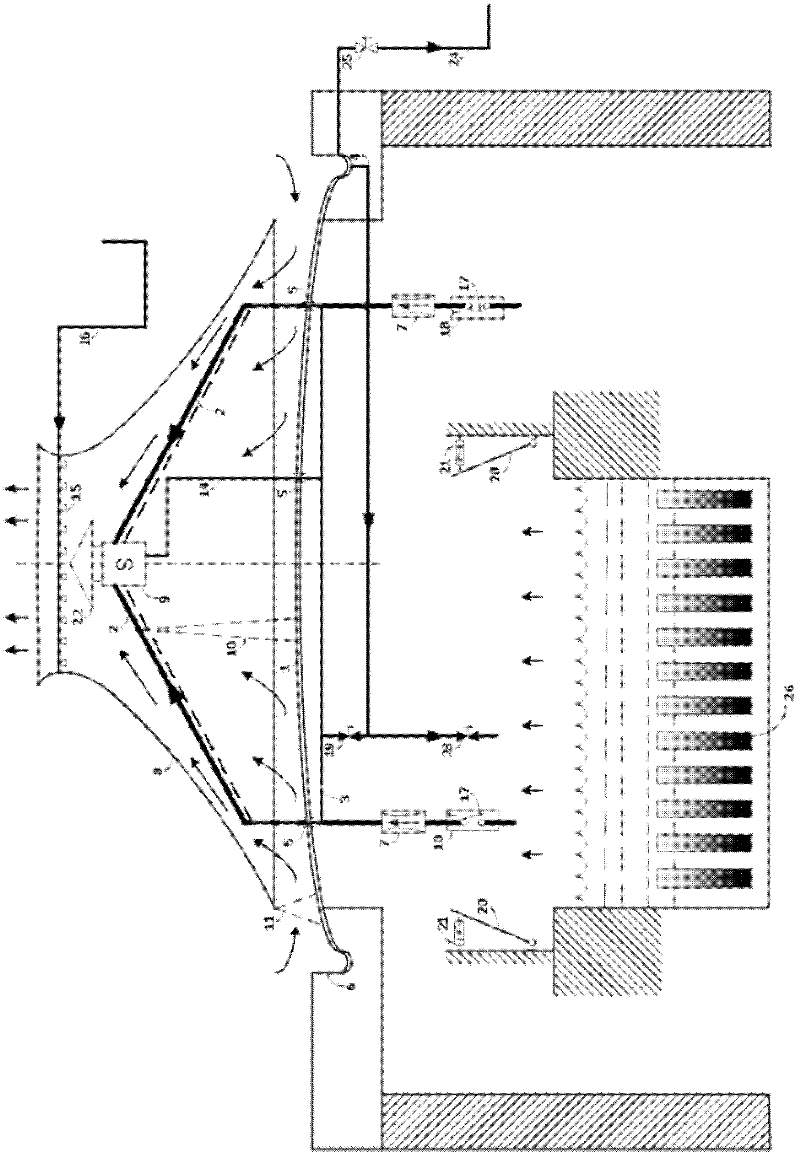
Stable and passive decay heat removal system for liquid metal reactor
InactiveUS20070253520A1Eliminate heat decayNuclear energy generationFast fission reactorsNuclear plantIntermediate heat exchanger
A decay heat removal system for a liquid metal reactor, in which a decay heat exchanger (DHX) is installed concentrically with an intermediate heat-exchanger (IHX) in the same cylinder which separates the DHX and IHX from the reactor pool fluid, and serves to remove the reactor core decay heat. The cylinder surrounds the IHX and the DHX, and has an opened top portion protruded out of the level of the fluid in a hot pool, a bottom portion connected to a cold pool and a guide pipe for allowing the passage of the fluid from the hot pool into the IHX. The decay heat removal system can remove decay heat immediately after occurrence of an accident, thereby improves the safety of a nuclear plant.
Owner:KOREA ATOMIC ENERGY RES INST
Pressurized water reactor compact steam generator
ActiveUS20130336442A1Facilitate natural recirculation of recirculatingBoiler drums/headersIntegral reactorsPressurized water reactorSteam drum
A steam generator system for a pressurized water reactor which employs an external to containment steam drum and recirculation loop piping. The steam generator system changes the arrangement of a typical pressurized water reactor recirculation steam generator by relocating the functions of steam separation and feedwater preheating outside of the reactor coolant system. The steam generator system and thermal hydraulic conditions are selected in order to minimize the size of the steam generator heat exchanger component volume inside of the containment. The external steam drum component can be isolated in accident conditions when desired and is used as a source of secondary fluid inventory for improved decay heat removal capability and tolerance for loss of feedwater events. Thus, the steam generator component volume inside of the containment is reduced and the amount of maintenance required for the reactor coolant system components are similarly reduced.
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE ELECTRIC CORP
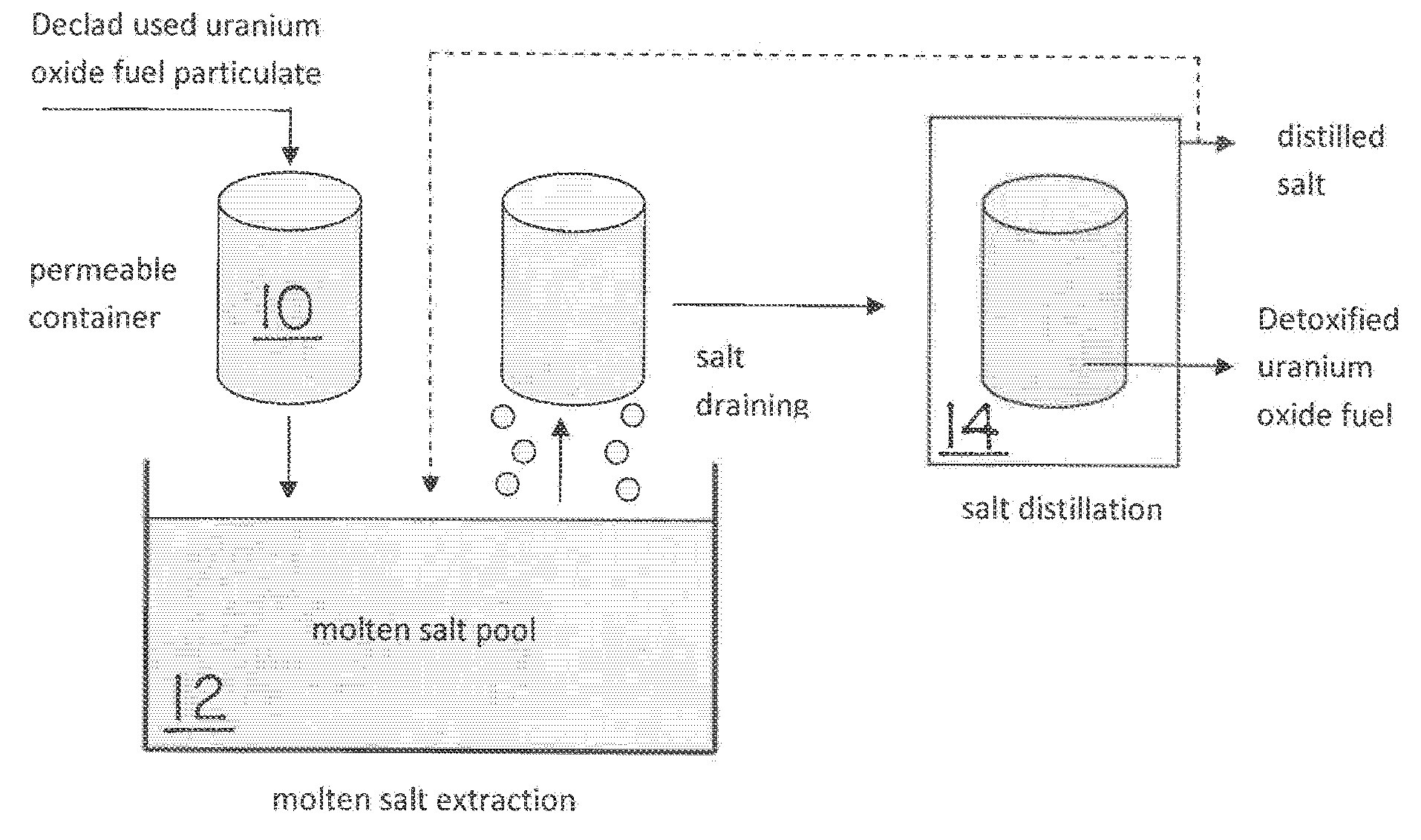
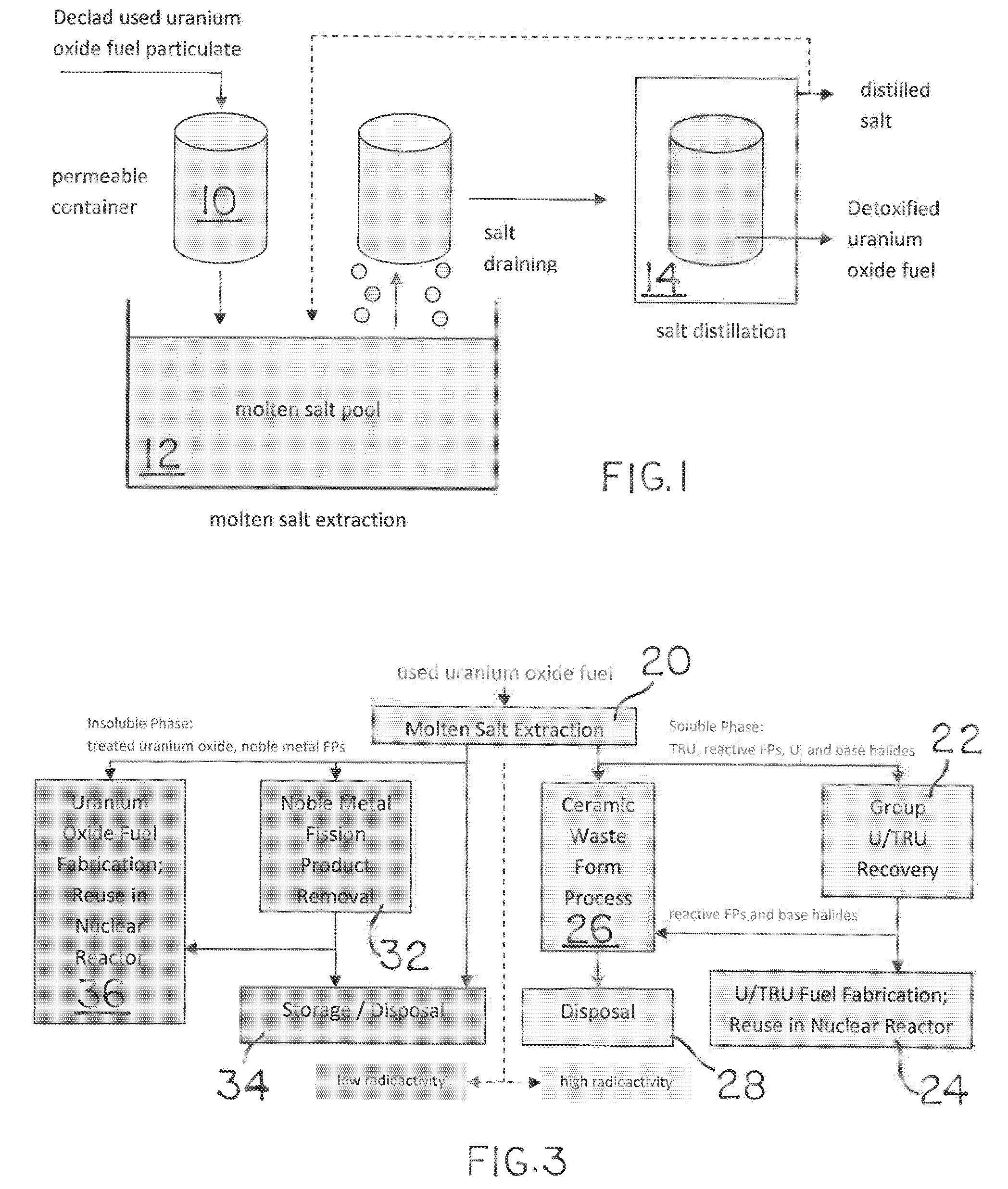
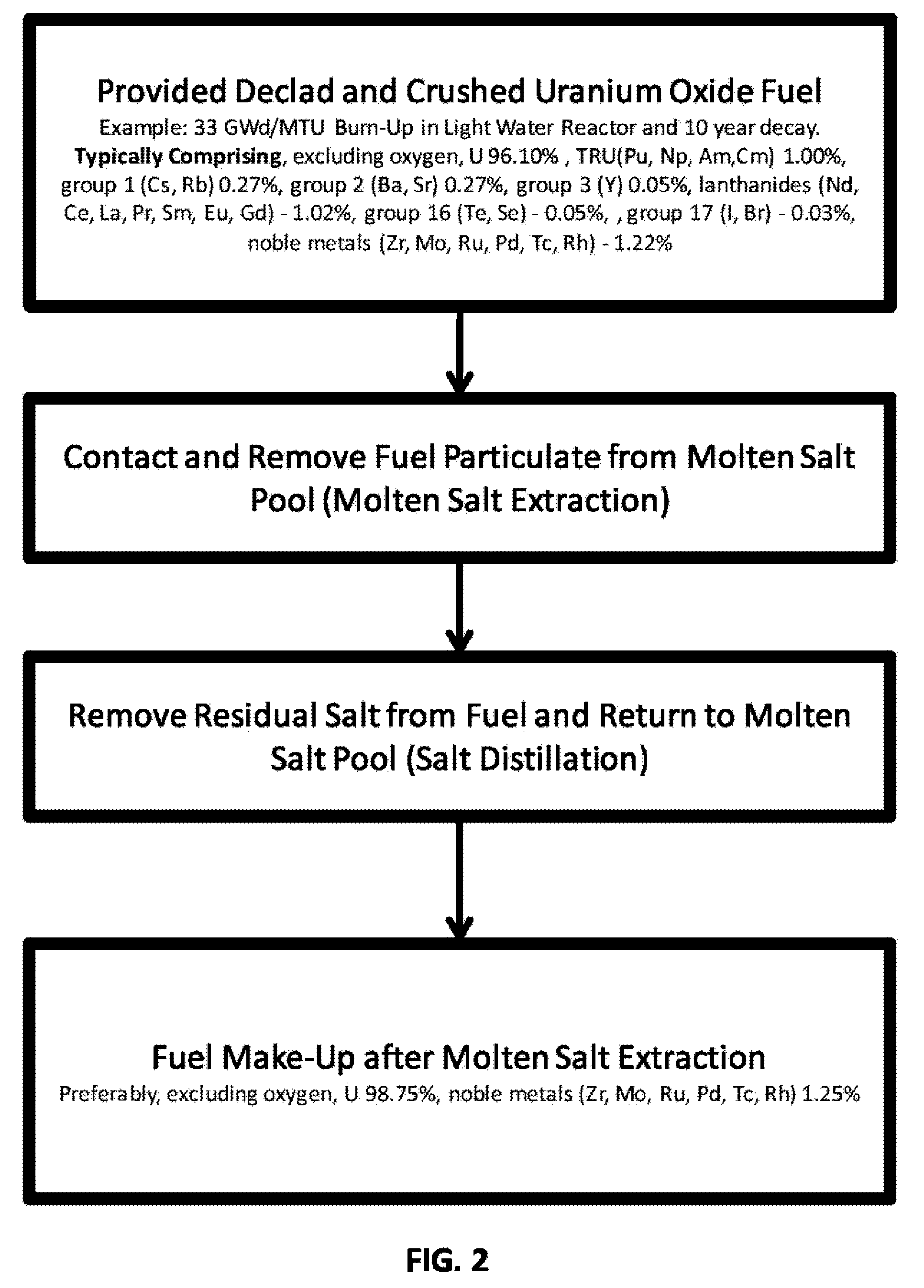
Molten salt extraction of transuranic and reactive fission products from used uranium oxide fuel
Used uranium oxide fuel is detoxified by extracting transuranic and reactive fission products into molten salt. By contacting declad and crushed used uranium oxide fuel with a molten halide salt containing a minor fraction of the respective uranium trihalide, transuranic and reactive fission products partition from the fuel to the molten salt phase, while uranium oxide and non-reactive, or noble metal, fission products remain in an insoluble solid phase. The salt is then separated from the fuel via draining and distillation. By this method, the bulk of the decay heat, fission poisoning capacity, and radiotoxicity are removed from the used fuel. The remaining radioactivity from the noble metal fission products in the detoxified fuel is primarily limited to soft beta emitters. The extracted transuranic and reactive fission products are amenable to existing technologies for group uranium / transuranic product recovery and fission product immobilization in engineered waste forms.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY
Passive residual heat exhausting system of pressurized water reactor nuclear power plant
InactiveCN103617815ASatisfy coolingFulfil requirementsNuclear energy generationCooling arrangementPlate heat exchangerPressurized water reactor
The invention provides a passive residual heat exhausting system of a pressurized water reactor nuclear power plant. The passive residual heat exhausting system comprises a passive residual heat removal system and a passive emergency water tank cooling system, wherein the passive residual heat removal system comprises a steam pipe, a passive residual heat exhausting heat exchanger and a condensed water pipe; the passive residual heat exhausting heat exchanger is positioned at the lower part of an emergency cooling water tank of the passive residual heat removal system; the passive emergency water tank cooling system comprises the emergency cooling water tank, a cooling coiled pipe, an ascending pipe, an air cooling heat exchanger and a descending pipe; the cooling coiled pipe is located at the upper part of the emergency cooling water tank. When residual heat removal needs to be carried out under an accident condition or normal shutdown, decay heat of a reactor core is removed by condensing steam at a secondary side so that the safety of a reactor is guaranteed and the possibility of releasing radioactive substances to the environment is reduced. The emergency cooling water tank is used as middle buffering equipment so as to meet the requirements of rapid cooling at the initial stage of an accident and long-time cooling at the later period of the accident.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
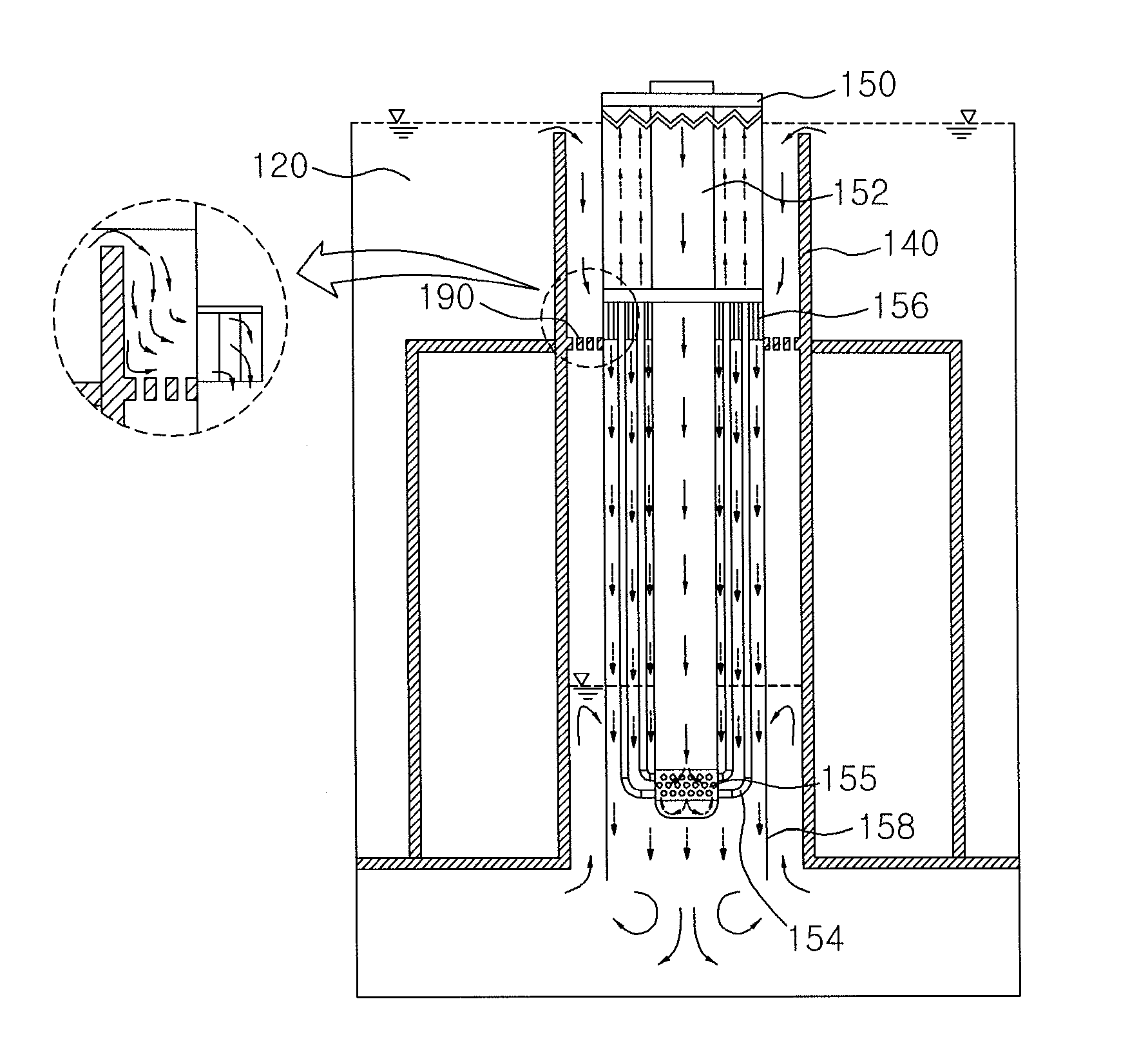
Passive safety-grade decay-heat removal method and decay-heat removal system for LMR with pool direct heat cooling process
InactiveUS20050135544A1Large heat removal capacityReduce heat lossNuclear energy generationFast fission reactorsVertical tubeLiquid metal
Dis0closed herein is a direct pool cooling type passive safety grade decay heat removal method and system for removing core decay heat in a pool type liquid metal reactor when a normal heat removal system breaks down. In the liquid metal reactor comprising a reactor vessel, the interior of which is partitioned into a hot pool above a core and a cold pool around the core so that liquid level difference between the hot pool and the cold pool is maintained by a primary pumping head under normal steady-state conditions, is disposed at least one circular vertical tube in such a manner that the sodium in the circular vertical tube is maintained with the same liquid level as the liquid level of the sodium in the cold pool. In the circular vertical tube is disposed a sodium-sodium heat exchanger, which is connected to a sodium-air heat exchanger mounted above a reactor building via a heat removing sodium loop, in such a manner that it is placed at the position higher than a liquid level of the sodium in the cold pool under the normal steady-state conditions. Under transient conditions, for example, when the normal heat removal system breaks down, the primary pump is automatically tripped, and accordingly the liquid level of the cold pool rises with the result that the liquid level difference between the hot pool and the cold pool is eliminated. Consequently, the sodium-sodium heat exchanger makes direct contact with the hot sodium so that core decay heat is discharged into a final heat sink, for example, the atmosphere. In this way, the decay heat removal system of the present invention is operated on the basis of a completely passive concept with improved operational reliability. Heat loss incurred by the decay heat removal system is minimized under normal steady-state conditions, whereby economical efficiency is maximized. The decay heat removal system of the present invention can effectively remove core decay heat under transient conditions. Moreover, the decay heat removal system of the present invention provides an additional heat removal capacity obtained by the passive vessel cooling system, whereby the decay heat removal system of the present invention can be easily applied to a large thermal rated liquid metal reactor.
Owner:KOREA ATOMIC ENERGY RES INST +1
Integrated sfr nuclear reactor with enhanced convective operation
InactiveCN102282625ASuitable for operationSmall diameterIntegral reactorsNuclear energy generationNuclear reactorHot zone
The invention relates to a novel architecture for a nuclear reactor of the integrated type. The invention comprises: realising the hot area and cold area separation device for the primary sodium flow in the form of two walls with cuts, providing two pumping groups hydraulically in series, one for the flow of sodium from the hot area to the cold area through the intermediate exchangers and the other in the cold area; providing outlet windows of the intermediate exchangers below the lower wall; providing outlet windows of the removal exchangers of the decay heat above the cold area, wherein all of clearances between the walls with cuts and the heat removal exchangers and the height between the two walls with cuts are previously determined so as to, during normal operation, take up differential movements between the walls, exchangers and vessel and to make it possible to establish during normal operation a thermal stratification of the primary sodium in the space defined between the horizontal portions of the two walls and so as to reduce, in case of an unexpected stop of a single pumping group, the mechanical stress applied to the walls and due to the portion of the primary sodium flow passing between said clearances.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT À L ÉNERGIE ATOMIQUE & AUX ÉNERGIES ALTERNATIVES FR
Semi-portable emergency cooling system for removing decay heat from a nuclear reactor
ActiveUS20130121454A1Power plant safety arrangementNuclear energy generationNuclear reactor coreNuclear reactor
An emergency temporary spent fuel pool cooling system for a nuclear power generating facility that has a permanently installed primary loop within the nuclear containment and a mobile temporary secondary loop. The secondary loop is housed in transport vehicles that can be stored off site and is connectable in heat exchange relationship with the primary loop through quick disconnect couplings that are accessible on the outside of the reactor containment. The transport vehicles also include self-contained power and compressed air sources for powering and controlling the entire emergency cooling system. The system also has a make-up water injection capability for refueling the spent fuel pool and secondary loop.
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE ELECTRIC CORP
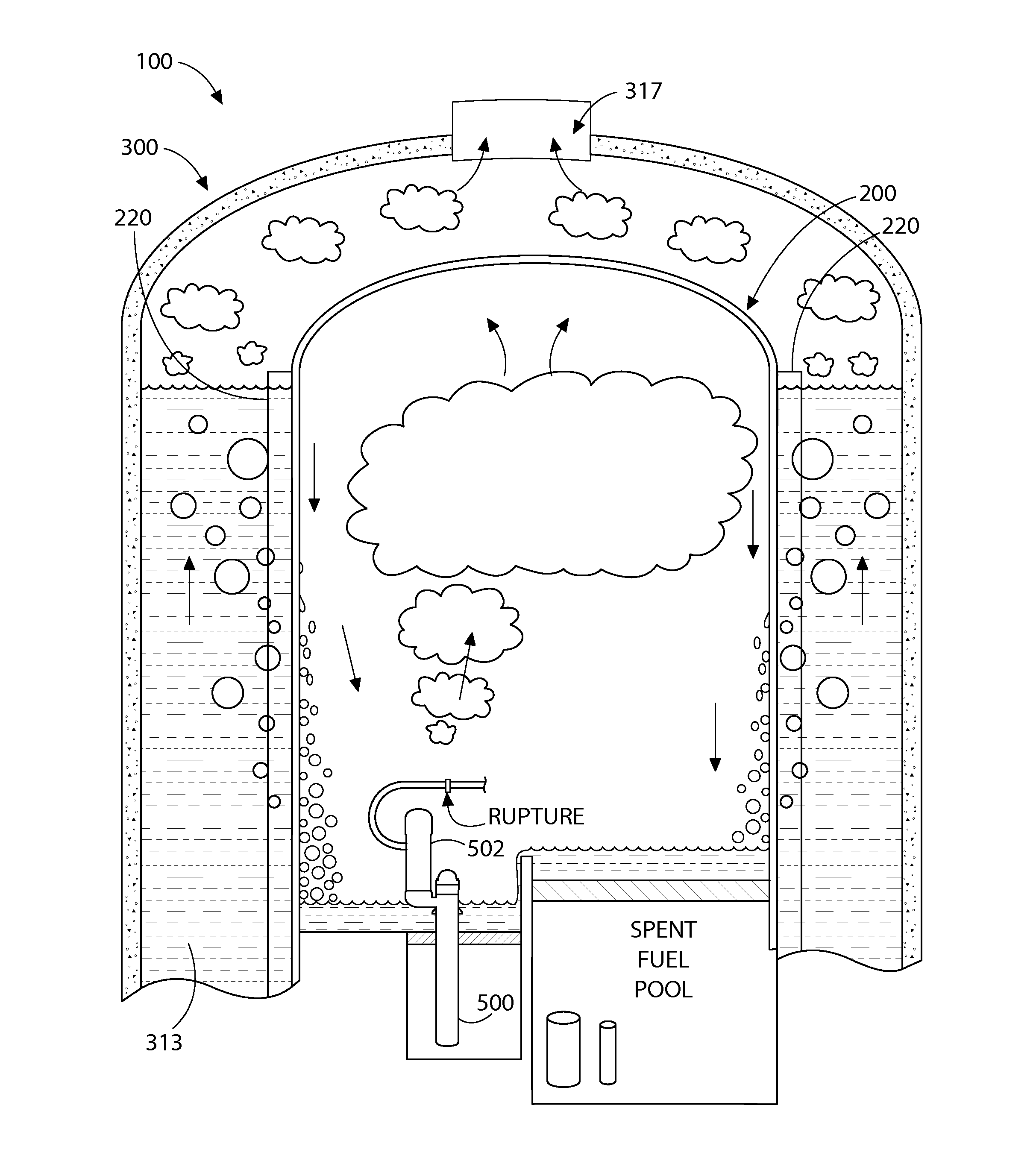
Spent fuel water tank natural ventilation and water recovery system responding to serious accident
ActiveCN102644996AExtended submersion timeAvoid overall overheatingLighting and heating apparatusNuclear energy generationNatural ventilationHydrogen
The invention belongs to design of a fuel building ventilating system for a nuclear power station and in particular relates to a spent fuel water tank natural ventilation and water recovery system responding to a serious accident. The structure of the system comprises a metal dome which is taken as one part of roof of a fuel building, wherein the metal dome is provided with a plurality of ventilation channels in circumferential direction; a natural ventilation chimney is arranged above the ventilation channels; the inlet of each ventilation channel is arranged above a spent fuel water tank; and the outlet of each ventilation channel is connected with a water receiver. According to the invention, the natural ventilation on a building in which the spent fuel water tank is located under the serious accident condition and discharge of decay heat of partial spent fuel are realized by multiple ventilation channels on the roof of the fuel building, thus the fuel building is prevented from being overheated and overpressured and hydrogen is prevented from gathering; and isolating, triggering and main functions of the spent fuel water tank natural ventilation and water recovery system disclosed by the invention are not dependent on exterior power input, thus the spent fuel water tank natural ventilation and water recovery system disclosed by the invention has non-active characteristic and high reliability.
Owner:CHINA NUCLEAR POWER ENG CO LTD
Device and method for high temperature melt growth choking experiment
ActiveCN106525895ARealistic simulation of meltingRealistic simulation of migration congestion characteristicsInvestigating phase/state changeRheniumInsulation layer
The invention provides a device and method for a high temperature melt growth choking experiment. The device comprises a heating oven which comprises an oven body made of zirconia with a cylindrical structure. A ring of a high temperature heat insulation layer is placed in the oven body around the inner wall. The side wall of the oven body is provided with several transparent windows in which thermal couples are installed. Several test bars are placed vertically at the center of the oven body. Each test bar comprises a tungsten rhenium heating bar located in the center. The outer side of the tungsten rhenium heating bar is an alumina layer. The outer side of the alumina layer is a zirconium 4 alloy layer. A transformer is mounted below the heating oven, and is connected with the tungsten rhenium heating bars. Through the implementation of electrical heating to the tungsten rhenium heating bars, the fuel rod decay heat can be simulated. The maximum heating temperature during experiment can reach 2000 DEG C, therefore, the faithful simulation of the melting of core material and the migration and choking characteristics of the high temperature melts of over 2000 DEG C are achieved. The arrangement of several visualization transparent windows at the side of the oven body can dynamically expound the behavioral mechanism of the melting of core material and the migration of melt.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Passive cooling system for retention of melts in serious accident state of reactor
ActiveCN105047236AAchieve coolingAchieve retentionNuclear energy generationCooling arrangementCrucibleEngineering
The invention provides a passive cooling system for the retention of melts in the serious accident state of a reactor. The passive cooling system comprises a pressure vessel ring cavity between a pressure vessel wall surface and a ring cavity wall surface, wherein steam discharging holes are formed in the top of the ring cavity, and a water inlet is formed in the bottom of the ring cavity; a ring cavity water tank surrounds the ring cavity wall surface, a crucible is arranged at the part, which is not encircled by the ring cavity water tank, of the ring cavity wall surface of the water tank to encircle the part so as to form a crucible cavity, the crucible extends upwards to form a water tank ring cavity, and the top of the water tank ring cavity is provided with gas discharging holes so as to be communicated with the crucible chamber; a crucible cooling water tank is arranged at the periphery of the crucible, an opening is formed in the top of the crucible cooling water tank, a steel safety shell is arranged at the periphery of the crucible cooling water tank, and an upper water tank surrounds the upper half part of the steel safety shell; the ring cavity water tank is communicated with the crucible cooling water tank through a pipeline; a re-circulation pit is arranged inside the steel safety shell, and is communicated with the crucible cooling water tank through a pipeline; the crucible cavity is communicated with the crucible cooling water tank through a pipeline. According to the technical scheme, three stages of cooling and retention of the melts of a reactor core can be realized according to different decay heat energies in accident sequences.
Owner:NUCLEAR POWER INSTITUTE OF CHINA
Molten fuel reactor cooling and pump configurations
ActiveUS20170316841A1Improve power densitySave on fuel costsIntegral reactorsFuel elementsDecay heatMolten salt reactor
Configurations of molten fuel salt reactors are described that include an auxiliary cooling system which shared part of the primary coolant loop but allows for passive cooling of decay heat from the reactor. Furthermore, different pump configurations for circulating molten fuel through the reactor core and one or more in vessel heat exchangers are described.
Owner:TERRAPOWER
Loss-of-coolant accident reactor cooling system
ActiveUS20140321597A1Avoid warpingNuclear energy generationEmergency protection arrangementsNuclear reactorWater storage tank
A nuclear reactor cooling system with passive cooling capabilities operable during a loss-of-coolant accident (LOCA) without available electric power. The system includes a reactor vessel with nuclear fuel core located in a reactor well. An in-containment water storage tank is fluidly coupled to the reactor well and holds an inventory of cooling water. During a LOCA event, the tank floods the reactor well with water. Eventually, the water heated by decay heat from the reactor vaporizes producing steam. The steam flows to an in-containment heat exchanger and condenses. The condensate is returned to the reactor well in a closed flow loop system in which flow may circulate solely via gravity from changes in phase and density of the water. In one embodiment, the heat exchanger may be an array of heat dissipater ducts mounted on the wall of the inner containment vessel surrounded by a heat sink.
Owner:SMR INVENTEC +1
Passive decay heat removal system for liquid metal cooling pool type reactor
ActiveCN106653107AImprove shielding effectWon't escapeNuclear energy generationCooling arrangementThermal isolationRadioactive agent
The invention discloses a passive decay heat removal system for a liquid metal cooling pool type reactor. The passive decay heat removal system is composed of a coolant inlet, a gravity-type heat pipe, an upper partition plate, a lower partition plate, a box body, a coolant outlet, a gas riser pipe, an exhaust stack, a thermal isolation layer, pipelines connected between devices, and valves. According to the invention, when a reactor is under accident states like station blackout, water supply interruption of a main heat exchanger or earthquake, a ventilation door of the exhaust stack is opened; cold air from the interior of a reactor containment enters into the box body through the coolant inlet, cools the condensing section of the gravity-type heat pipe and enters the gas riser pipe from the coolant outlet; hot air flows out of the reactor containment through the gas riser pipe; thus, the process has passive characteristic. The passive decay heat removal system provided by the invention has simple structure, is convenient to start, can simultaneously remove core decay heat and prevent radioactive substances in a reactor pit from escaping, and has passiveness, independence and high reliability.
Owner:NANHUA UNIV
Decay heat conversion to electricity and related methods
ActiveUS20120328068A1Reduce heat loadImprove securityNuclear energy generationEmergency protection arrangementsElectricityAlternator
Various embodiments of a decay heat conversion to electricity system and related methods are disclosed. According to one exemplary embodiment, a decay heat conversion to electricity system may include a spent fuel rack configured to pressurize spent fuel bundles to obtain superheated vapor to drive a turbine-driven pump and fast alternator all submerged with the spent fuel rack and positioned at the bottom of the spent fuel pool for conversion of electricity distributed outside of the spent fuel pool via cables without impairing spent fuel pool operations.
Owner:CARBON FREE HLDG LLC
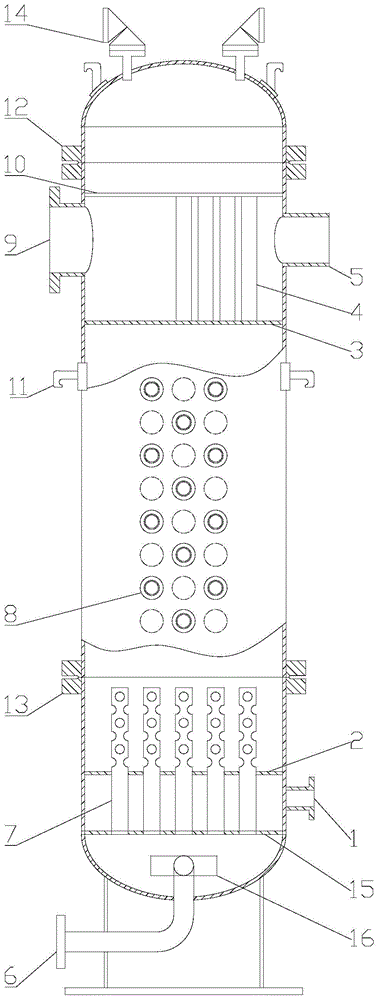
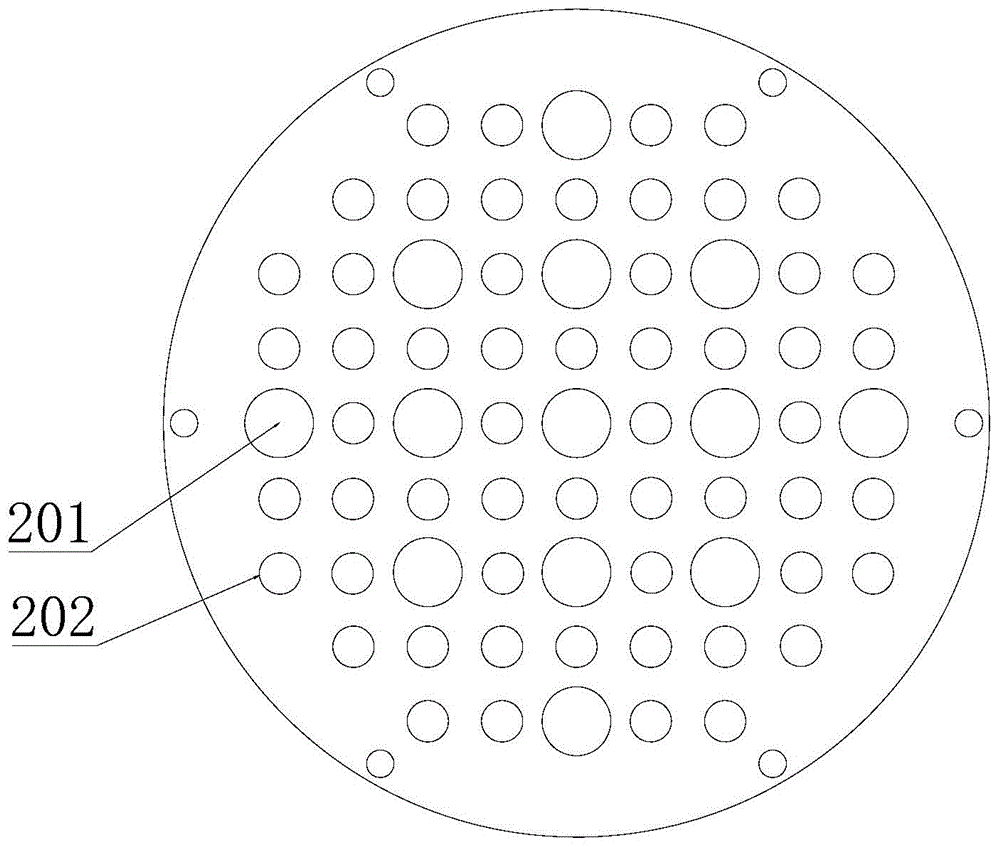
Pressure vessel and method for simulating upper chamber droplet entrainment of nuclear reactor
InactiveCN103606384AImprove experiment safetyFree installation and disassemblyNuclear energy generationReactors manufactureNuclear reactor coreNuclear reactor
The invention discloses a pressure vessel and a method for simulating upper chamber droplet entrainment of nuclear reactor. The pressure vessel is mainly composed of a water inlet, a gas inlet, a heating area, an experimental area and an air water outlet. The pressure vessel can carry out experiments in two working media, air-water and steam-water, can use heating rods to simulate core decay heat and realize physical simulation of the upper chamber entrainment phenomenon; and reactor internals and core upper plate contained in the pressure vessel can realize real reflection of simulation of upper chamber entrainment deposition phenomenon; in addition, the experimental device has the advantages of experimental process visualization, high safety and easiness for installation and maintenance, etc.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Accident decay heat discharge system for non-symmetric distribution of large pool type sodium-cooled fast reactors
ActiveCN104575635AEnsure safetyMitigating the Incident ProcessNuclear energy generationCooling arrangementNon symmetricEngineering
The invention relates to an accident decay heat discharge system for non-symmetric distribution of large pool type sodium-cooled fast reactors. The accident decay heat discharge system comprises an independent heat exchanger, and a through heat exchanger, wherein the independent heat exchanger is arranged in a heat sodium pool, the through heat exchanger is arranged between a cold sodium pool and the hot sodium pool, the independent heat exchanger, and the through heat exchanger are respectively connected with a sodium-air heat exchanger through a pipeline, the sodium-air heat exchanger is arranged outside the reactors, and the position of the sodium-air heat exchanger is higher than the independent heat exchanger and the through heat exchanger; when an accident happens, inlet baffles of the independent heat exchanger and the through heat exchanger are opened, hot sodium enters the independent heat exchanger and the through heat exchanger, sodium flowing through the independent heat exchanger sinks in clearances of a fuel assembly in the hot sodium pool, to form inter-box flow; the sodium flowing through the through heat exchanger forms a channel in a fuel assembly box to form an intra-box flow. The discharge of reactor decay heat can be realized by adopting a passive working principle.
Owner:CHINA INSTITUTE OF ATOMIC ENERGY
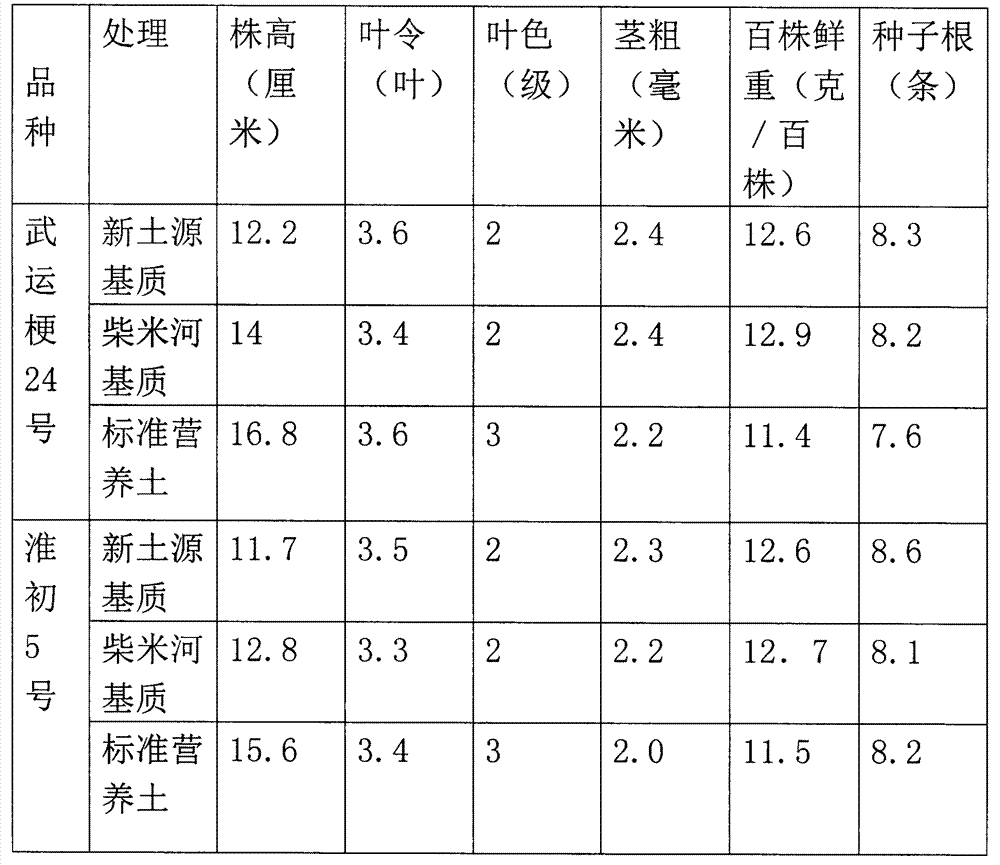
Mechanical transplanting rice seedling substrate and growth method thereof
ActiveCN104774100AImprove water retentionImprove fat retention capacityBio-organic fraction processingOrganic fertiliser preparationSludgeMoisture
The invention discloses a mechanical transplanting rice seedling substrate and a growth method thereof. The formula of the mechanical transplanting rice seedling substrate comprises the following components in percentage by mass: 60-80% of brewing industrial sludge, 15-25% of straw carbon, 5-10% of special clay and 0.8-5% of a seedling strengthening agent. The production of the substrate comprises the following steps: (1) fermentation drying; and (2) blending and crushing. The mechanical transplanting rice seedling substrate disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the fermentation drying cycle is short, the utilization ratio of a fermentation workshop is high, a small space is occupied, the production batch is large, the energy consumption is low, the labor is less, the cost is low, the material decaying heat degree is high, the raw materials used for the seedling substrate are stable in quality, the phenomena of secondary fermentation and root injuring bacterium burning are avoided, the moisture and fertilizer retention capabilities of the seedling substrate are improved, and two bottleneck problems of green withered seedlings and later-stage limb force senesced yellowing of a general seedling substrate are solved.
Owner:XINGHUA NEW SOIL SOURCE BASE FERTILIZER CO LTD
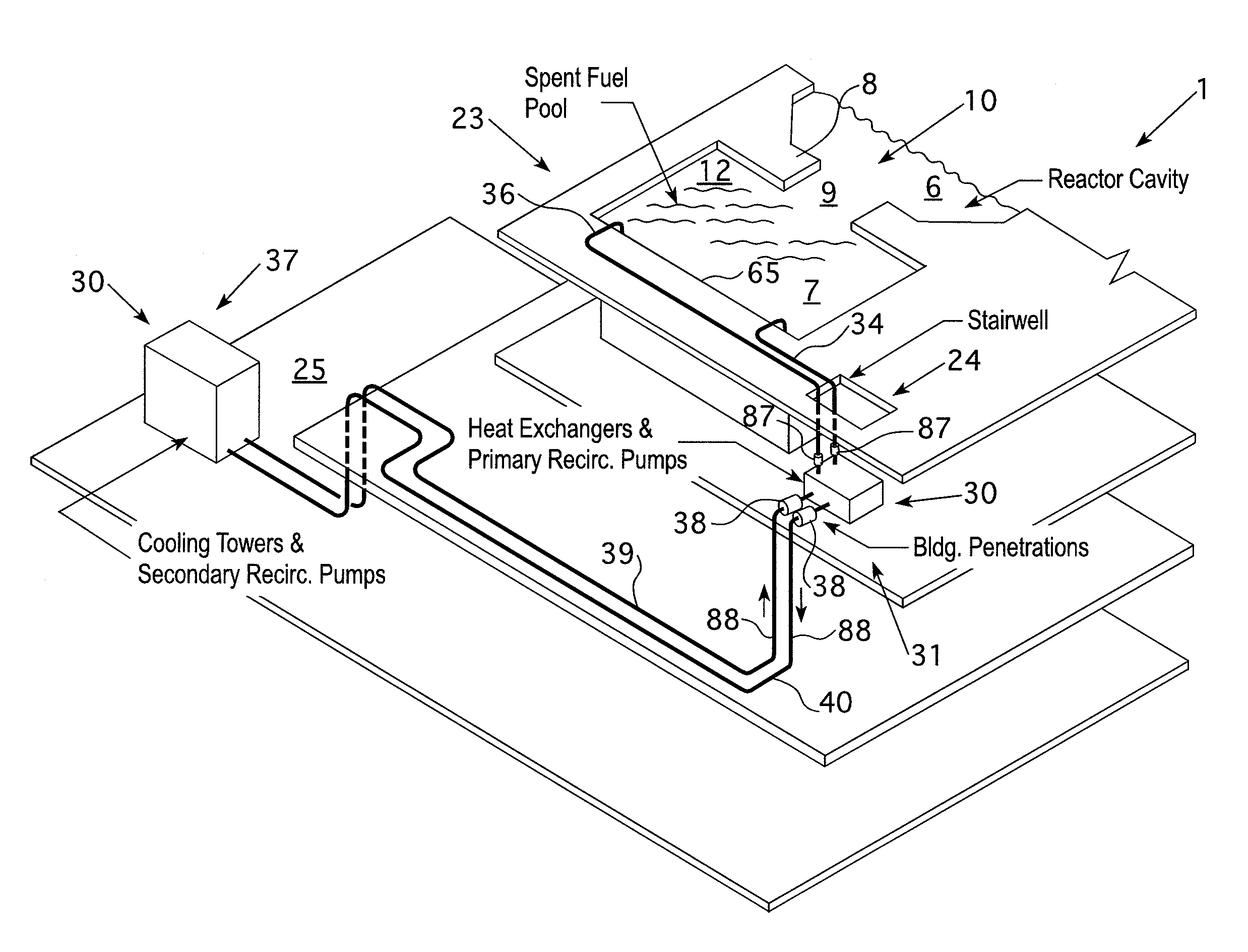
Wet-type spent fuel storage system
ActiveCN103377737AAchieve long-term storageAchieve natural circulationNuclear energy generationReactor fuel elementsCooling towerNuclear power
The invention relates to a wet-type spent fuel storage system, belonging to the field of nuclear power station spent fuel storage. The invention implements long-time storage of spent fuel by adopting a non-kinetic mode. A spent fuel storage grid is arranged on the bottom of a spent fuel storage pool which contains a coolant; a sealed container carrying a spent fuel assembly is arranged on the spent fuel storage grid; an air cooling tower is arranged on the upper part of the spent fuel storage pool; one end of a heat-tube cooling unit is arranged in the air cooling tower; and the other end of the heat-tube cooling unit is immersed in the coolant of the spent fuel storage pool. By utilizing the decay heat generated by the spent fuel to drive the separate cooling unit without external driving force, the invention implements natural circulation of the coolant in the spent fuel storage pool; the invention implements the long-time storage of the spent fuel in a non-kinetic mode, and has the advantage of reliable operation.
Owner:SHANGHAI NUCLEAR ENG RES & DESIGN INST CO LTD
Reactor core molten debris grouping retention and cooling system
ActiveCN105513649AIncrease the heat exchange areaIncrease decay heat export powerNuclear energy generationEmergency protection arrangementsIrradiationDecay heat
The invention relates to a reactor core molten debris grouping retention and cooling system which comprises a grouping retention system and a cooling system. The grouping retention system comprises a molten debris retention vessel loading shaft arranged at the bottom of a reactor cavity and multiple molten debris retention vessels arranged in the molten debris retention vessel loading shaft, the molten debris retention vessels are connected with the reactor cavity through multistage molten debris transport channels, molten debris retention vessel transfer devices are arranged on the molten debris retention vessel loading shaft in a penetrating mode, and the molten debris retention vessel transfer devices are connected with the cooling system; the cooling system comprises a molten debris cooling water tank and a cooling circuit of the molten debris cooling water tank. The reactor core molten debris grouping retention and cooling system aims at achieving grouping retention and cooling on reactor core molten debris by means of an independent packaging container on the working condition that serious accidents occur; improvement of molten debris decay heat exporting power is facilitated, and an irradiation dose to a worker is reduced; the structure is compact, and the occupied space is small.
Owner:CHINA NUCLEAR POWER ENG CO LTD
Experimental system for forming characteristic of sodium-cooled fast reactor debris bed
ActiveCN106409349AApplicable to a wide range of researchThe results of the study are comprehensiveNuclear energy generationEmergency protection arrangementsData acquisitionSodium-cooled fast reactor
The invention provides an experimental system for the forming characteristic of a sodium-cooled fast reactor debris bed. The experimental system comprises an experimental support, a particle container, a particle conduit, a visual experiment container, a particle release controller, a visual data acquisition module, an environmental parameter detection module and a decay heat simulating generator, wherein the particle container and the particle conduit support multiple release apertures and release heights, an experimental particle system comprises various debris particles with different materials, shapes and sizes, visual experimental containers with different sizes are designed for two-dimensional and three-dimensional experiments, and the particle release controller and the visual data acquisition module can acquire and store images synchronously in the whole experimental process. The experimental system can be applied to researching and analyzing the forming mechanism of the fuel particle debris bed in the sodium-cooled fast reactor core disassembly accident process. The experimental system has the advantages that the experimental process is visual, qualitative analysis is combined with quantitative analysis, multiple controllable experimental variables exist, the operation principle is simple, the system is easy to expand, stable and safe and the like.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
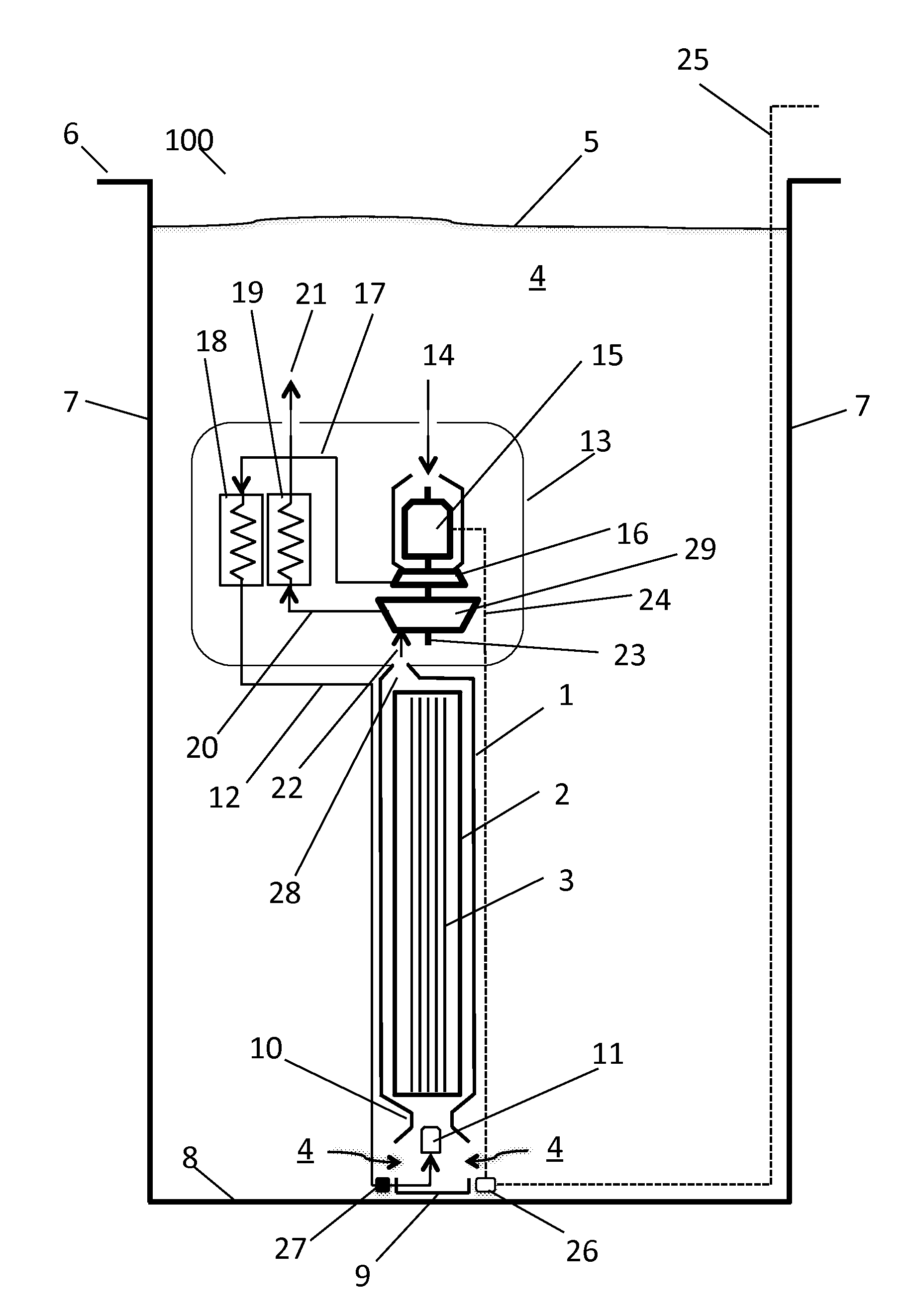
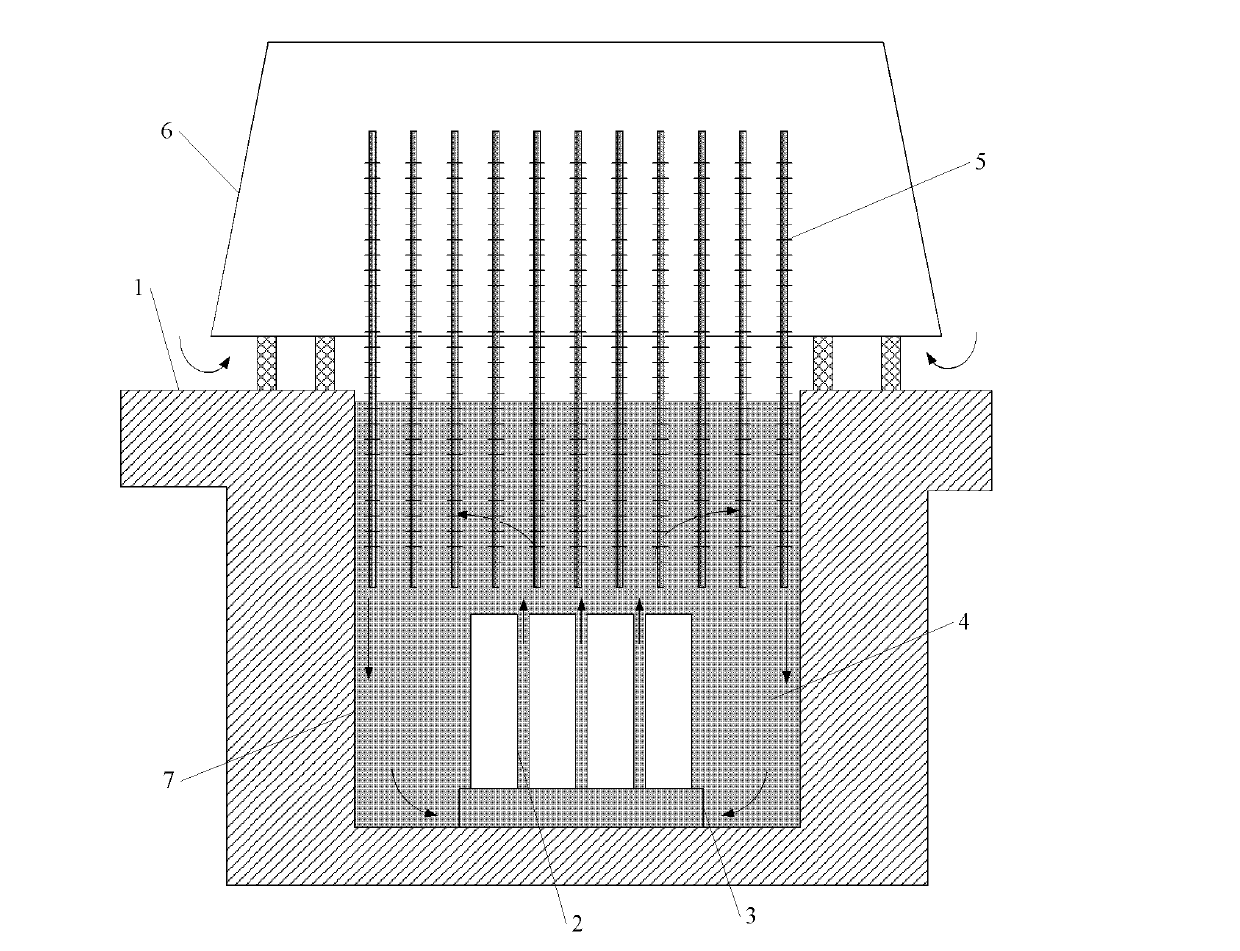
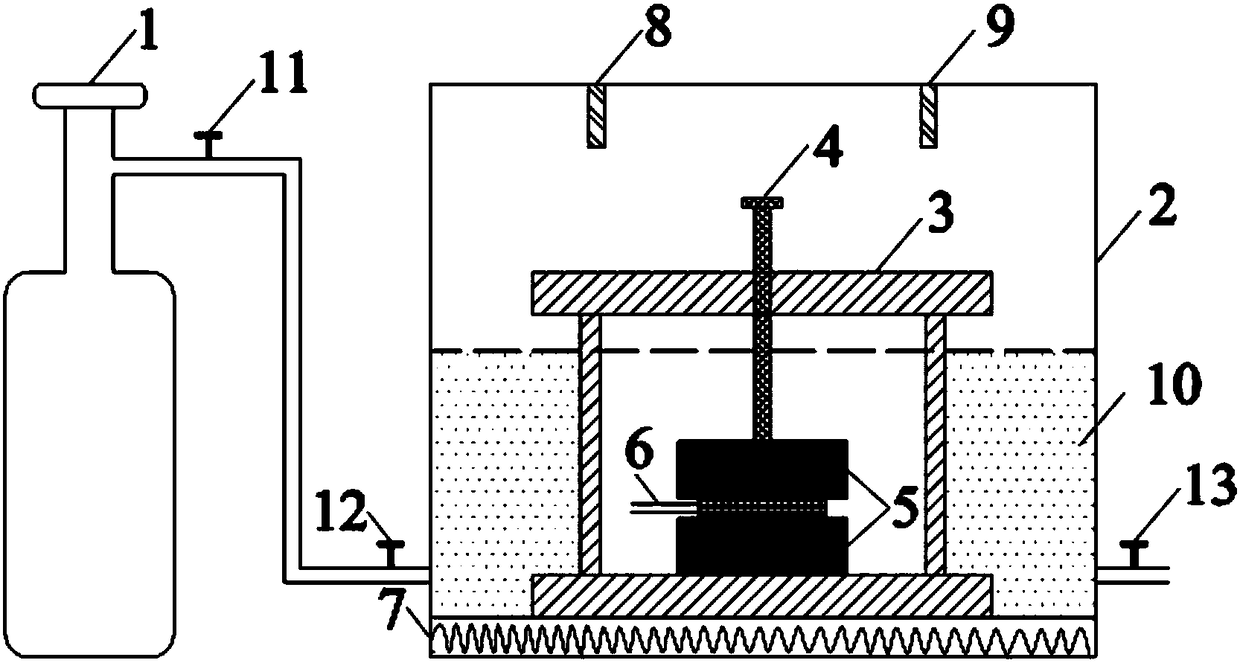
Device and method for measuring heat conductivity coefficient of buffer/backfill material
ActiveCN108693209ARapid determinationAccurate measurementMaterial heat developmentThermal energyDeep geological repository
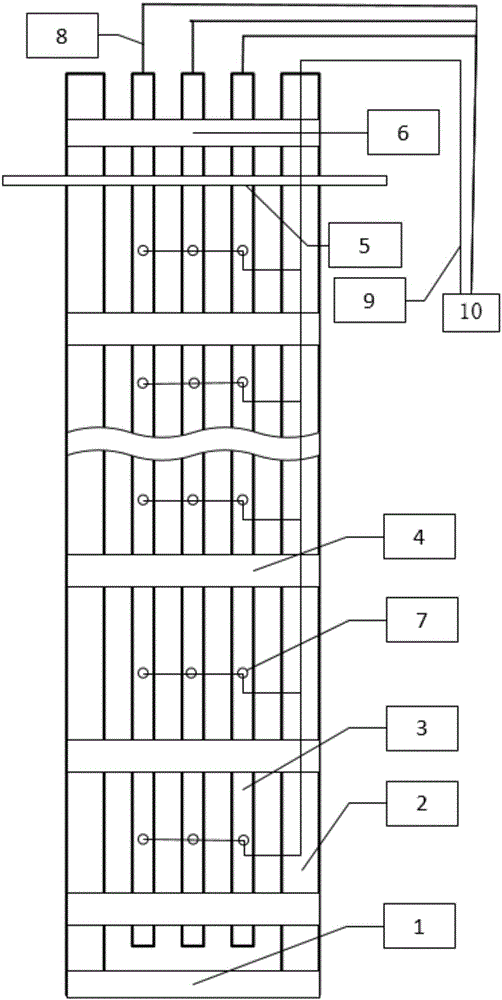
The invention specifically relates to a device and method for measuring the heat conductivity coefficient of a buffer / backfill material, belonging to the field of testing of the thermal conductivity of buffer / backfill materials applied to geological disposal of high-level waste. The objective of the invention is to provide the measuring device and method capable of acquiring the thermal conductivity of the buffer / backfill material, controlling effective transmission of decay heat produced in a high-level waste tank and providing bases for engineering design of deep geological disposal repositories of high-level waste so as to overcome disadvantages in the prior art. The device comprises a gas loading device (1), a testing box (2), a sample holder (3), a screw (4), a sample (5), a test probe (6), a heater (7), a temperature sensor (8), a gas monitoring probe (9), a liquid (10), a valve A (11), a valve B (12) and a valve C (13).
Owner:BEIJING RES INST OF URANIUM GEOLOGY
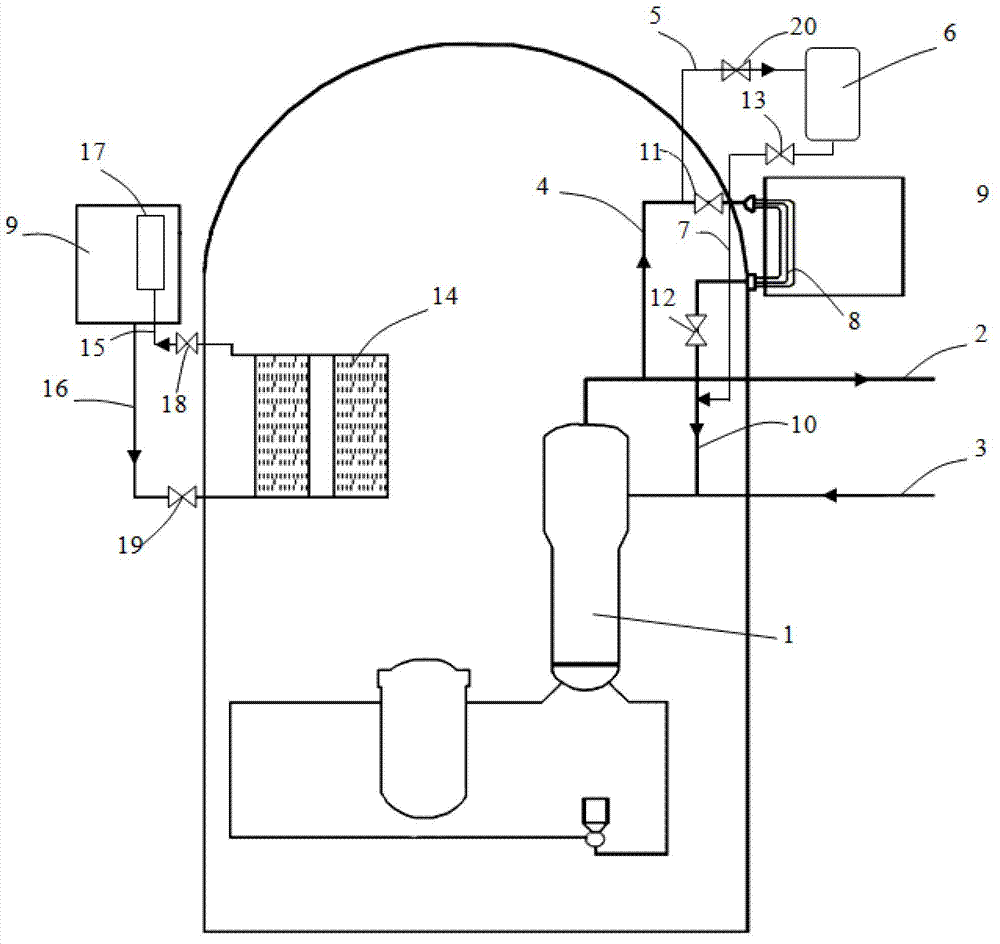
Secondary side passive waste heat removal system
InactiveCN104361913AAvoid drying outAvoid the situationNuclear energy generationEmergency protection arrangementsEngineeringDecay heat
The invention discloses a secondary side passive waste heat removal system which comprises a steam pipeline and a water feeding pipeline, wherein the steam pipeline hermetically penetrates through a containment and is connected with the outlet of a steam generator in the containment as well as a cooling water tank which is arranged outside the containment; the water feeding pipeline hermetically penetrates through the containment and is connected with the cooling water tank and the inlet of the steam generator; the steam pipeline, the feeding water pipeline and the cooling water tank form a circulating channel so as to remove decay heat in the containment out of the containment. The steam pipeline and the feeding water pipeline are directly connected with the steam generator on the secondary side so as to prevent the steam generator from being burned and a coolant from being leaking. The cooling water tank is arranged outside the containment, so that available space of the containment is saved. Moreover, by using an open circuit, a heat exchanger which is required by the conventional passive waste heat removal system in the cooling water tank is not arranged, and no emergency equipment is required, so that the expenditure of design and construction of the system is lowered.
Owner:CHINA NUCLEAR POWER TECH RES INST CO LTD +2
Liquid-immersed spent fuel storage system
InactiveCN103377738AEfficient heat exchange and coolingEliminate dependenciesNuclear energy generationReactor fuel elementsCooling towerNuclear power
Owner:SHANGHAI NUCLEAR ENG RES & DESIGN INST CO LTD
Heating device
InactiveCN106229018AImprove safe storageImprove securityNuclear energy generationHeater elementsDecay heatPower control
The invention relates to a heating device which comprises a framework and an electrical heating rod bundle arranged on the framework. The electrical heating rod bundle comprises multiple electrical heating rods, the upper ends of all the electrical heating rods are connected with a power control and data recording system through corresponding electrical heating wires, and the power control and data recording system is used for controlling and setting electrical heating powder in the electrical heating rods; temperature measuring devices are arranged at different heights of the outer walls of all the electrical heating rods respectively, and all the temperature measuring devices are connected with the data control and data recording system through corresponding measuring wires. The heating device can simulate the processes of evaporation to dryness and heating after dryness of spent fuel elements which are different in decay heat under different working conditions after the cooling function is lost and the spray cooling process for relieving accident consequences, the heating device is used for spent fuel element storage, process simulation validation, spent fuel pool accident analysis and design of a spray cooling system, and the purposes of improving safety storage of the spent fuel elements and safety of a spent fuel pool are achieved.
Owner:CHINA NUCLEAR POWER ENG CO LTD
Pressurized water reactor compact steam generator
A steam generator system for a pressurized water reactor which employs an external to containment steam drum and recirculation loop piping. The steam generator system changes the arrangement of a typical pressurized water reactor recirculation steam generator by relocating the functions of steam separation and feedwater preheating outside of the reactor coolant system. The steam generator system and thermal hydraulic conditions are selected in order to minimize the size of the steam generator heat exchanger component volume inside of the containment. The external steam drum component can be isolated in accident conditions when desired and is used as a source of secondary fluid inventory for improved decay heat removal capability and tolerance for loss of feedwater events. Thus, the steam generator component volume inside of the containment is reduced and the amount of maintenance required for the reactor coolant system components are similarly reduced.
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE ELECTRIC CORP
Pressurized water reactor depressurization system
InactiveUS20140241484A1Reduce pressureReduce openingIntegral reactorsNuclear energy generationPressurized water reactorDecay heat
A passive cooling system of a pressurized water reactor that relies on a depressurization system to reduce the pressure in the reactor vessel in the event of a loss of coolant accident and vent the steam generated by the decay heat of the reactor core in a post loss of coolant accident stage. The depressurization results in a low pressure difference between the reactor vessel and the containment and enables gravity driven cooling system injection into the reactor vessel. The depressurization system includes a flow restrictor within an orifice in the reactor vessel wall that connects to a vent pipe which forms a flow path between the interior of the reactor vessel and the containment atmosphere when a valve within the vent pipe is in an open position. Preferably, the flow restrictor is a venturi that has a gradual contraction and a gradual expansion in the flow path area.
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE ELECTRIC CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com