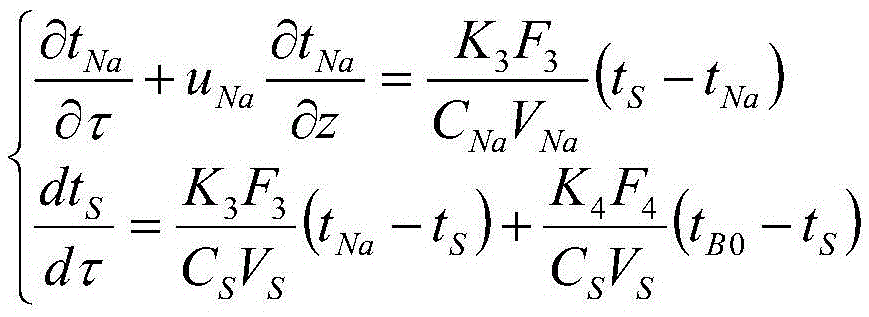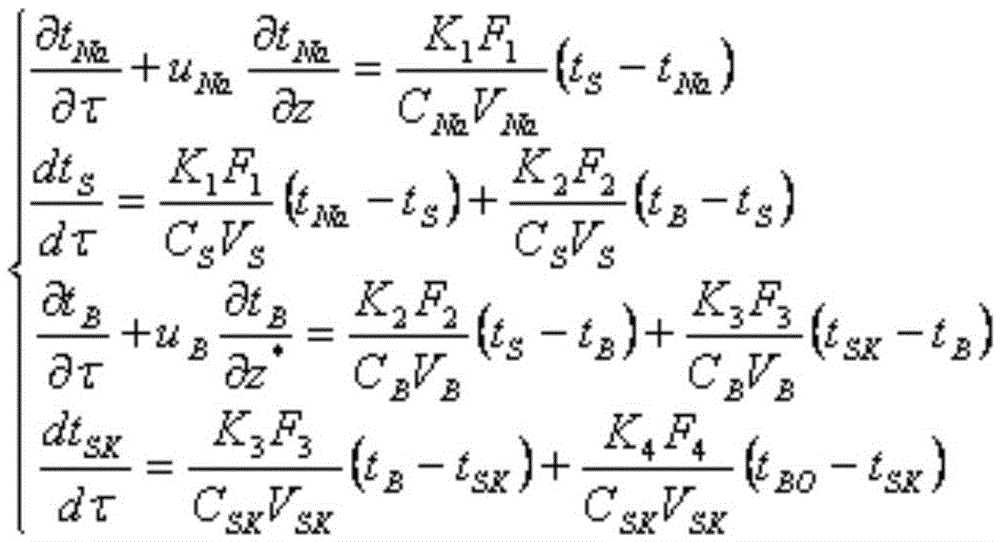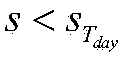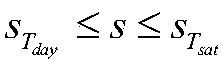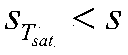Patents
Literature
90 results about "Sodium-cooled fast reactor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A sodium-cooled fast reactor is a fast neutron reactor cooled by liquid sodium. The acronym SFR particularly refers to two Generation IV reactor proposals, one based on existing LMFR technology using MOX fuel, the other based on the metal-fueled integral fast reactor.
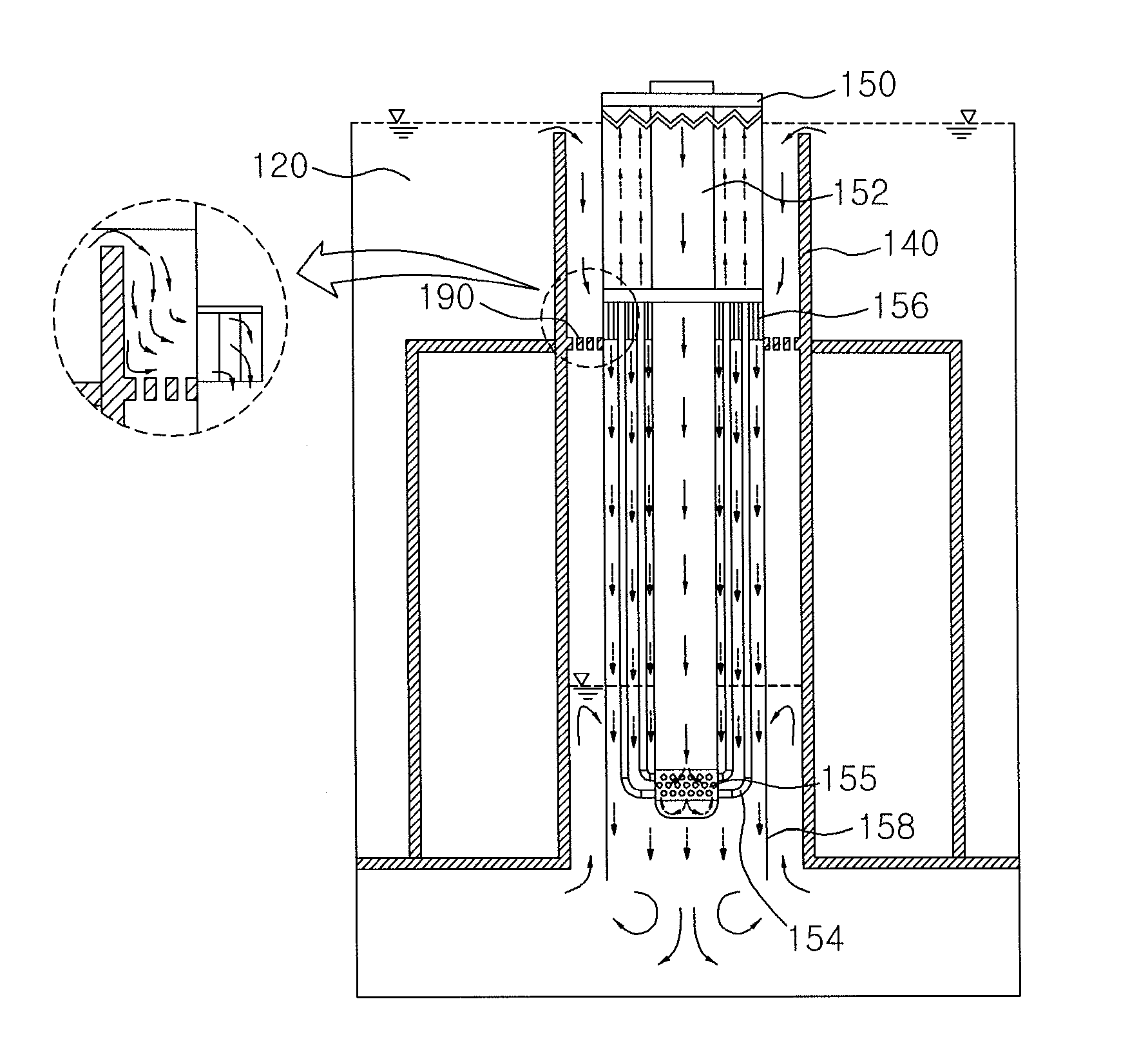
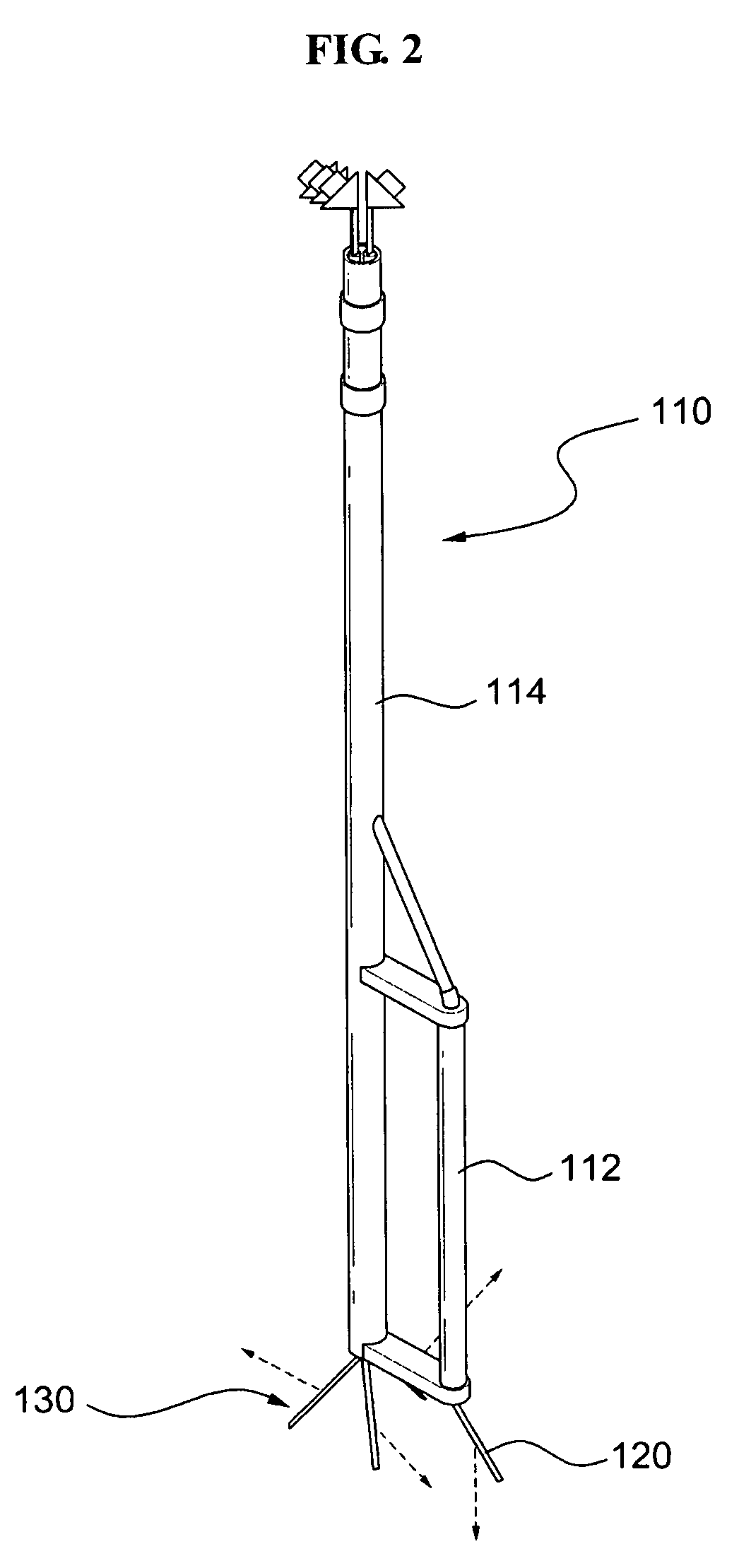
Fully passive decay heat removal system for sodium-cooled fast reactors that utilizes partially immersed decay heat exchanger
ActiveUS20100177860A1Reduced operational reliabilityImprove business performanceNuclear energy generationFast fission reactorsIntermediate heat exchangerSodium-cooled fast reactor
Disclosed herein is a fully passive decay heat removal system utilizing a partially immersed heat exchanger, the system comprising: a hot pool; an intermediate heat exchanger which heat-exchanges with the sodium of the hot pool; a cold pool; a support barrel extending vertically through the boundary between the hot pool and the cold pool; a sodium-sodium decay heat exchanger received in the support barrel; a sodium-air heat exchanger provided at a position higher than the sodium-sodium decay heat exchanger; an intermediate sodium loop connecting the sodium-sodium decay heat exchanger with the sodium-air heat exchanger; and a primary pump, wherein a portion of the effective heat transfer tube of the sodium-sodium decay heat exchanger is immersed in the cold pool, particularly in a normal operating state, and the surface of the lower end of a shroud for the sodium-sodium decay heat exchanger, the lower end being immersed in the sodium of the cold pool, has perforated holes.
Owner:KOREA ATOMIC ENERGY RES INST +1
Composite structural material and process for manufacturing pipeline component using same
ActiveCN102336038ASolving Corrosion ProblemsIncrease profitMetal layered productsNeutron irradiationAlloy
The invention belongs to the field of composite material, and in particular relates to a composite structural material and a process for manufacturing a pipeline component using the same. The composite structural material is characterized by adopting a double-layer structure, wherein one layer is made of vanadium alloy material, and the other layer is made of low-activity martensite steel material. In practical application, the side in contact with liquid alkali metal is made of vanadium alloy, and the side in contact with the environment gas or other cooling agents is made of low-activity martensite steel. In the composite structural material provided by the invention, respective advantages of the vanadium alloy and low-activity martensite steel in the application to the sodium cooled fast reactor and fusion reactor liquid metal are sufficiently used, and the problems of neutron irradiation resistance and liquid metal corrosion resistance can be effectively solved. Through the manufacturing process provided by the invention, the utilization rate of material can be obviously improved, and the processing cycle can be remarkably shortened.
Owner:SOUTHWESTERN INST OF PHYSICS
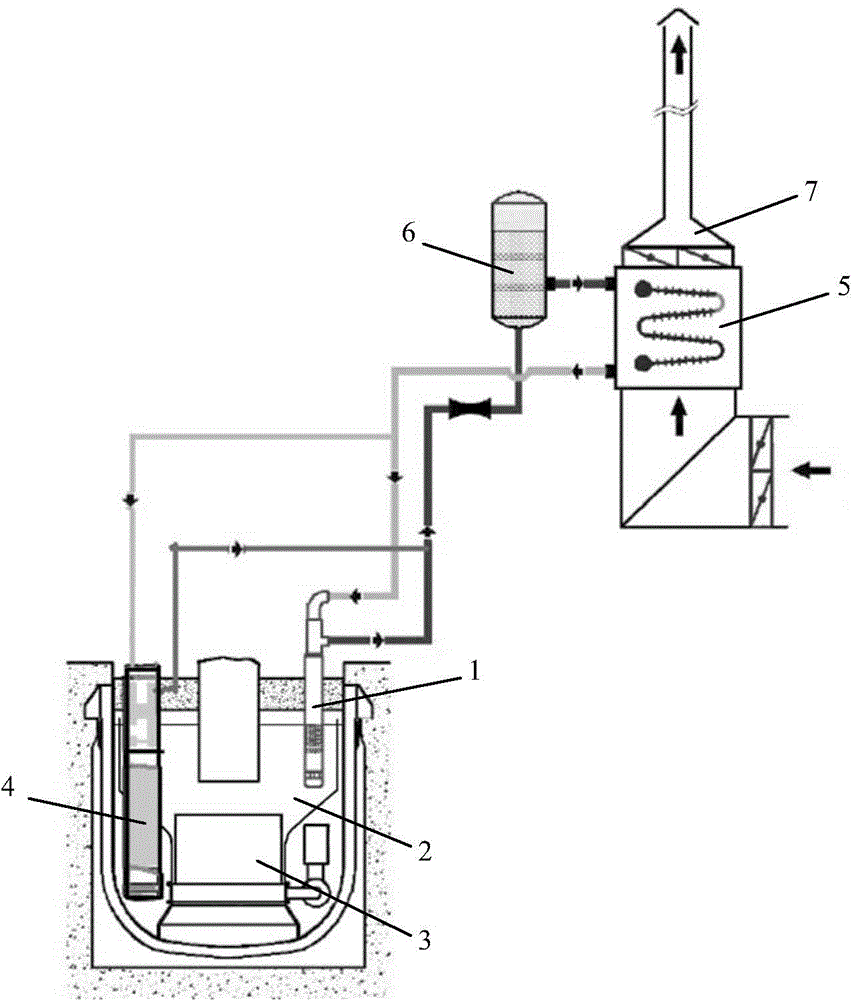
Pool type sodium cooled fast reactor accident afterheat exhausting system
InactiveCN101221823APassive WarrantyNuclear energy generationCooling arrangementEngineeringSodium-cooled fast reactor
The invention discloses an accidental afterheat discharge system of a pool type SFR. The afterheat discharge system is an independent heat-transfer system and is formed by an independent heat exchanger and an air heat exchanger which are connected in series, wherein, the lower part of the independent heat exchanger is immersed into a sodium pool of an active zone, the air heat exchanger is connected with a down-draught chimney outside. The accidental afterheat discharge system provided by the invention has independence and nonmotility. In the accidental condition, the invention can effectively discharge the remaining releasing heat of the active zone.
Owner:CHINA INSTITUTE OF ATOMIC ENERGY
Austenitic stainless steel clad tube and technique of preparing the same
ActiveCN101333631AMeet chemical composition requirementsGuaranteed to dissolveFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesRare-earth elementHydrogen
The invention discloses an austenitic stainless steel cladding tube used for a sodium-cooled fast reactor as well as a method for the production thereof. The stainless steel cladding tube has components, in weight proportion: 0.04 percent to 0.08 percent of C; less than or equal to 0.75 percent of Si; less than or equal to 0.02 percent of P; less than or equal to 0.02 percent of S; 1.5 percent to 2.0 percent of Mn; 11.0 percent to 14.0 percent of Ni; 16.0 percent to 18.0 percent of Cr; 2.0 percent to 3.0 percent of Mo; 0.3 percent to 0.5 percent of Ti; less than or equal to 0.1 percent of Co; less than or equal to 0.002 percent of B; less than or equal to 0.035 percent of N; balance Fe. The double-smelting is adopted when in smelting, and the adding of rare earth elements is prohibited; the hydrogen protection or vacuum bright annealing treatment is adopted when in hot working; and a drawing process of empty sinking is banned in the cold working process, and the polishing treatment to surfaces of finished pipes by mechanical method is prohibited. The stainless steel cladding tube made by the process can meet the requirements of the sodium-cooled fast reactor core subassembly.
Owner:CHINA INSTITUTE OF ATOMIC ENERGY
Accident decay heat discharge system for non-symmetric distribution of large pool type sodium-cooled fast reactors
ActiveCN104575635AEnsure safetyMitigating the Incident ProcessNuclear energy generationCooling arrangementNon symmetricEngineering
The invention relates to an accident decay heat discharge system for non-symmetric distribution of large pool type sodium-cooled fast reactors. The accident decay heat discharge system comprises an independent heat exchanger, and a through heat exchanger, wherein the independent heat exchanger is arranged in a heat sodium pool, the through heat exchanger is arranged between a cold sodium pool and the hot sodium pool, the independent heat exchanger, and the through heat exchanger are respectively connected with a sodium-air heat exchanger through a pipeline, the sodium-air heat exchanger is arranged outside the reactors, and the position of the sodium-air heat exchanger is higher than the independent heat exchanger and the through heat exchanger; when an accident happens, inlet baffles of the independent heat exchanger and the through heat exchanger are opened, hot sodium enters the independent heat exchanger and the through heat exchanger, sodium flowing through the independent heat exchanger sinks in clearances of a fuel assembly in the hot sodium pool, to form inter-box flow; the sodium flowing through the through heat exchanger forms a channel in a fuel assembly box to form an intra-box flow. The discharge of reactor decay heat can be realized by adopting a passive working principle.
Owner:CHINA INSTITUTE OF ATOMIC ENERGY
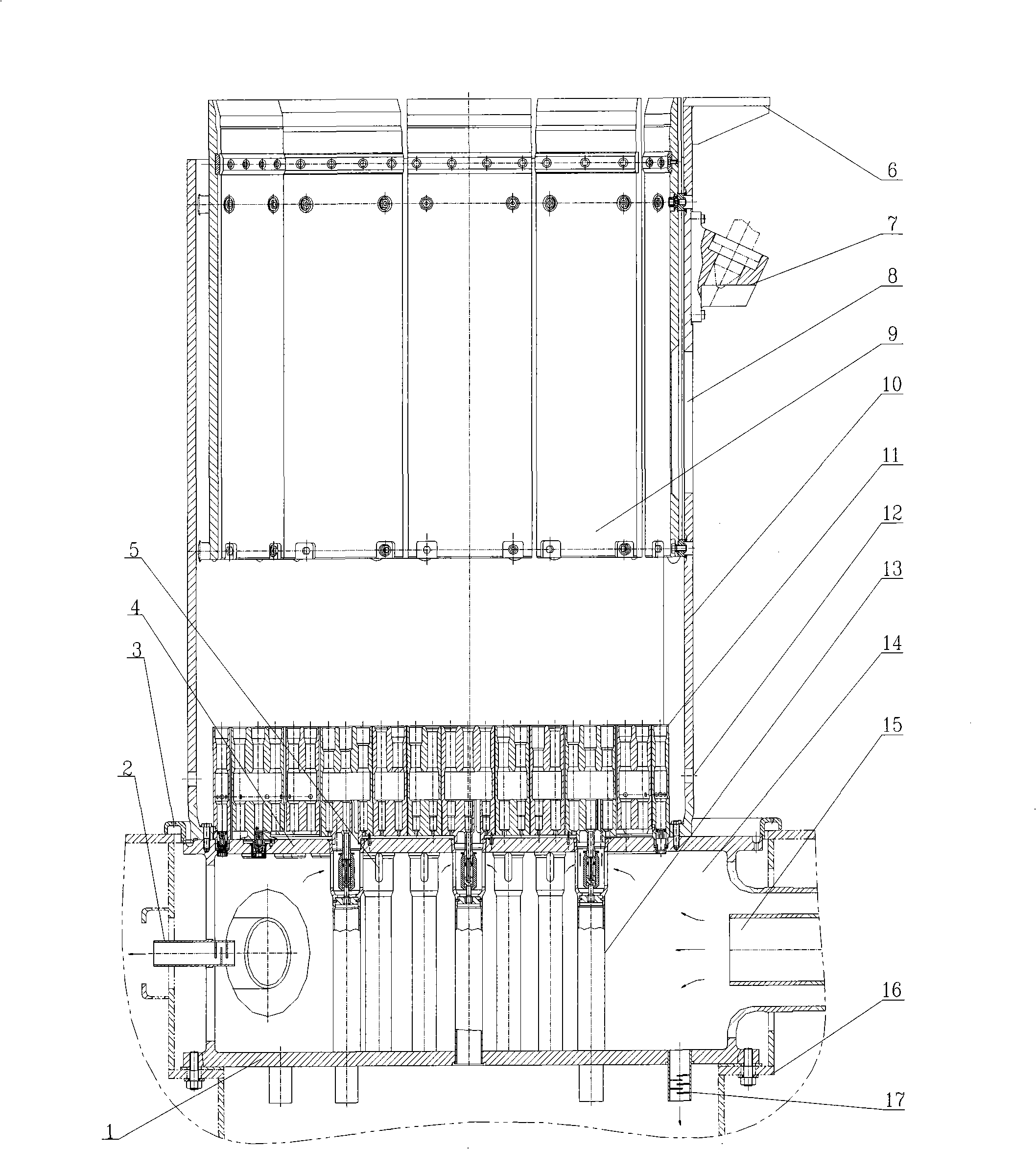
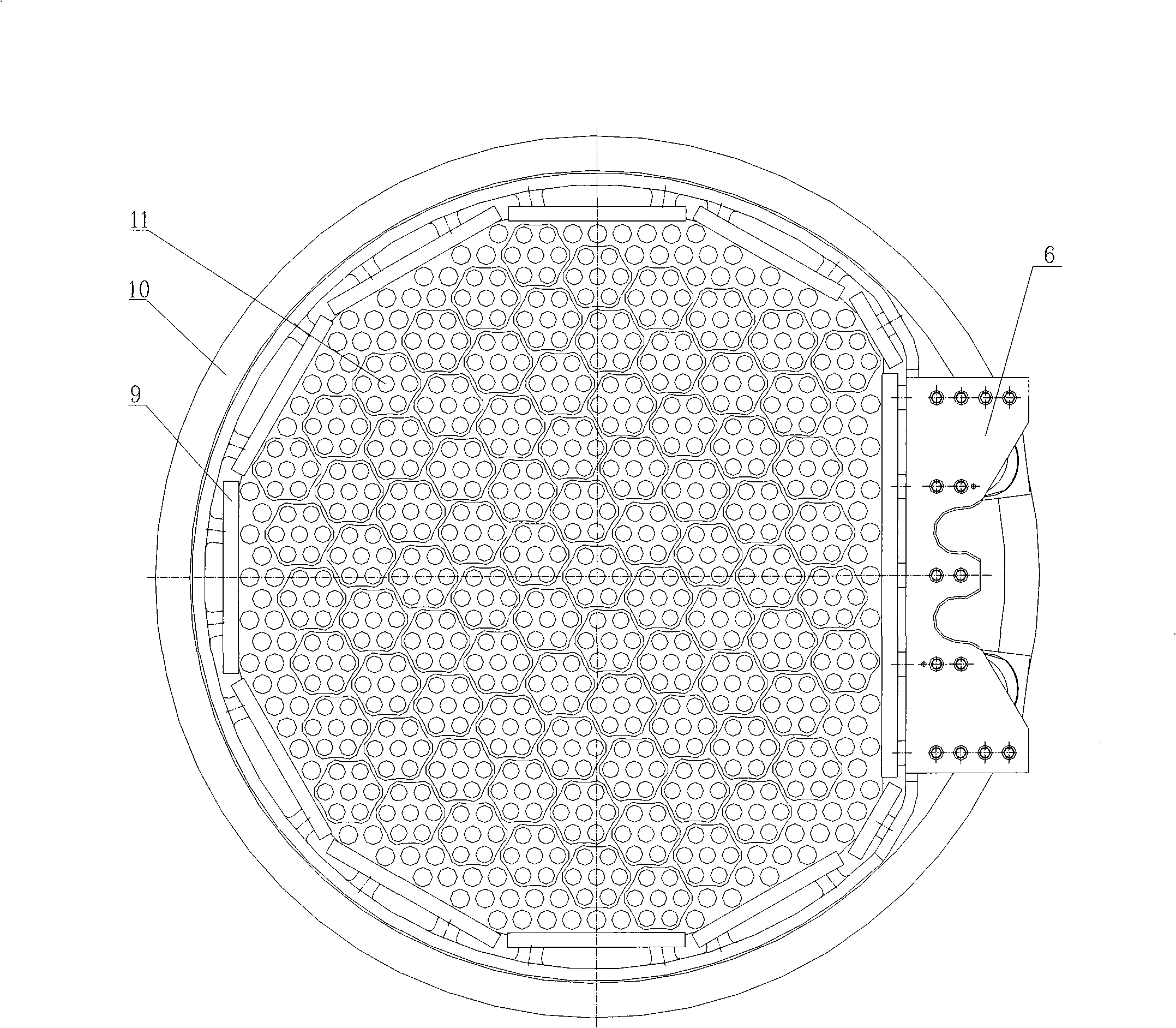
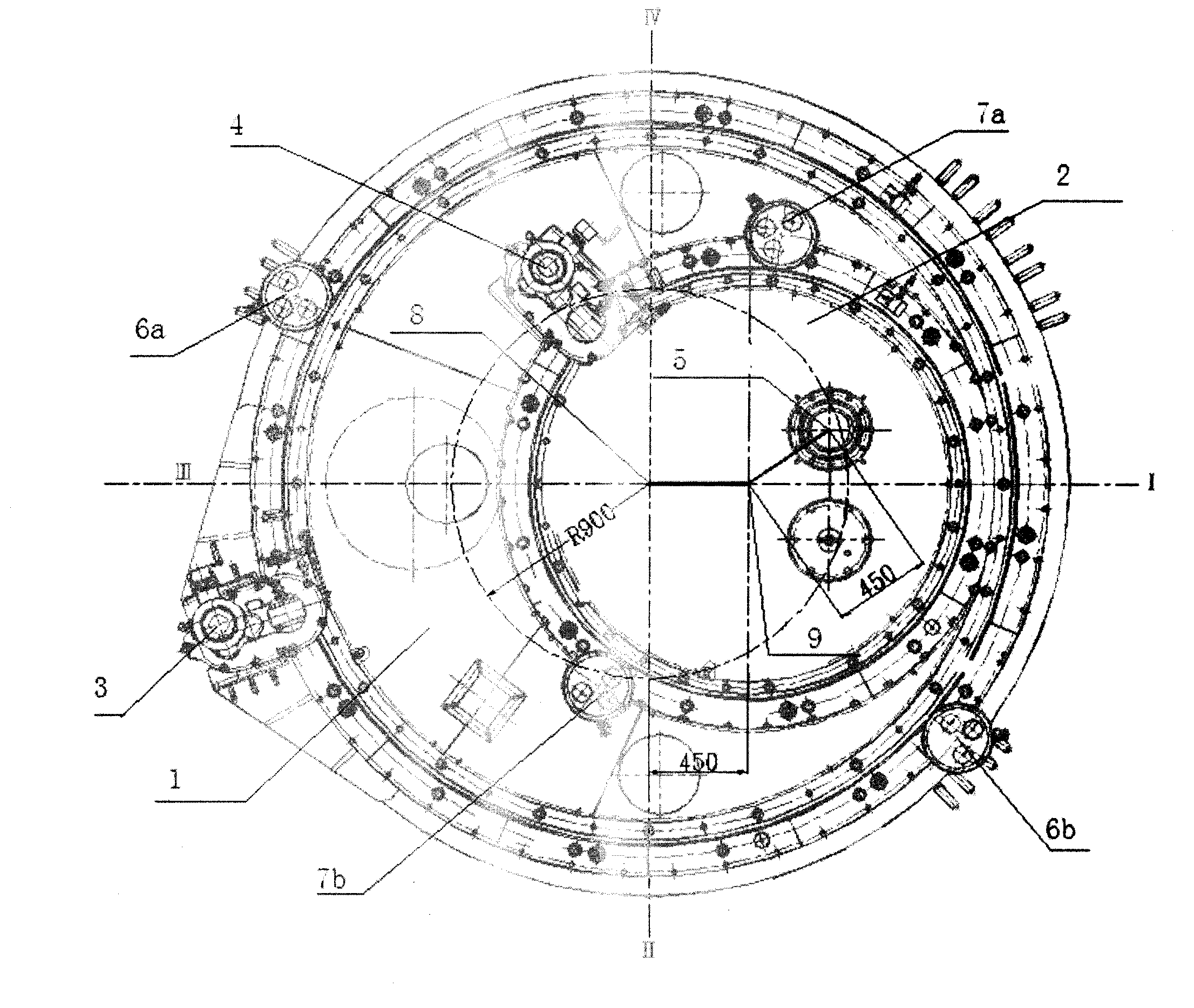
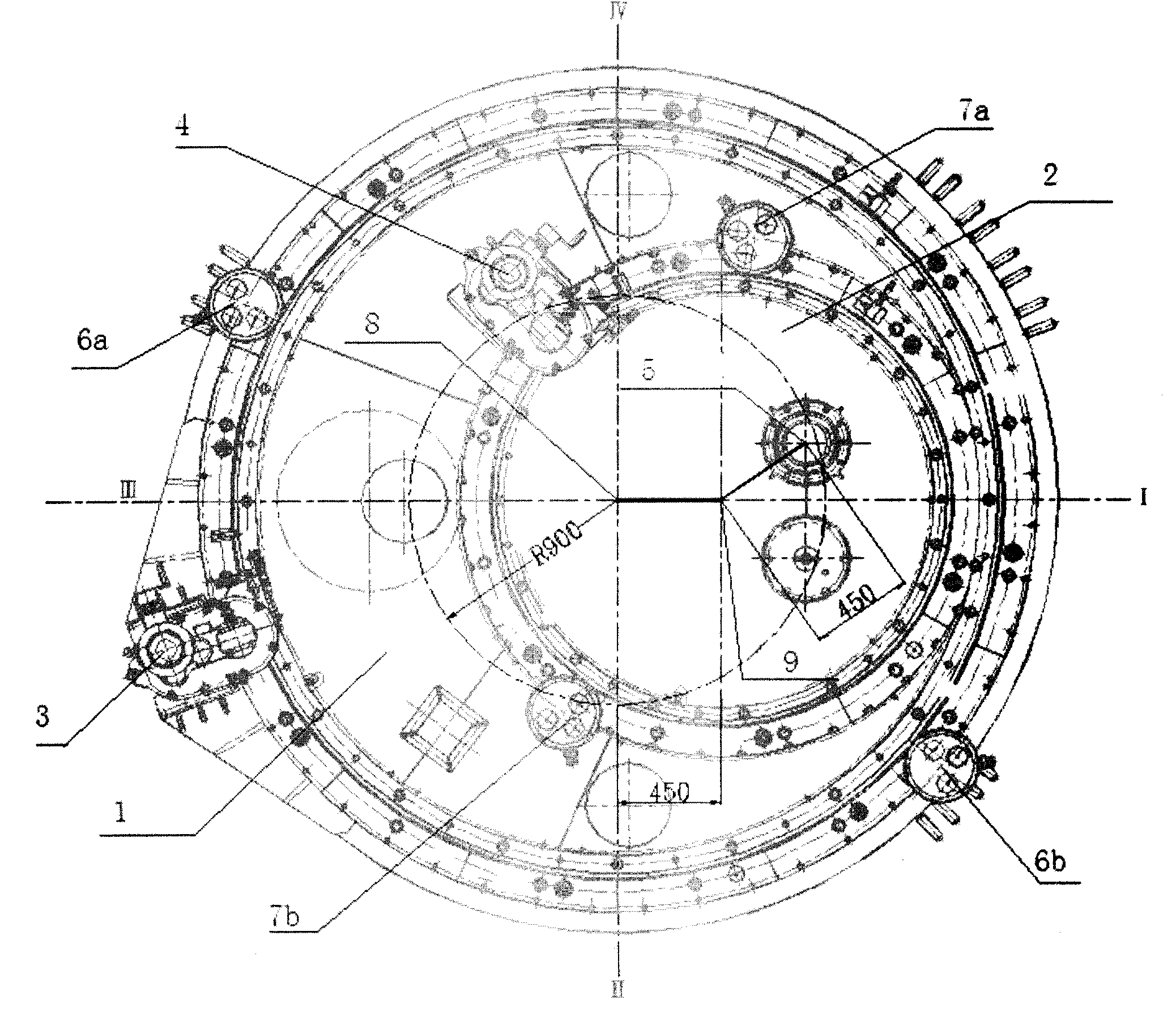
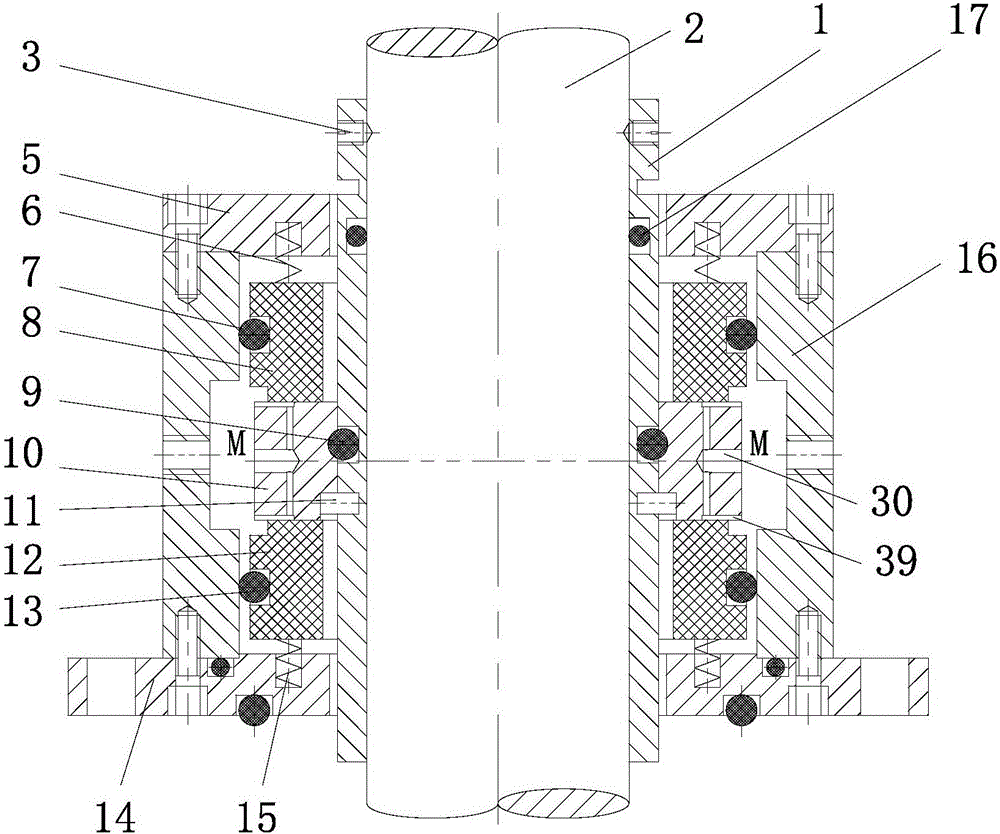
Reactor core support construction of pool type sodium-cooled fast reactor
InactiveCN101335056AReduce the number of openingsReduce structural difficultyNuclear energy generationFast fission reactorsNuclear engineeringCore component
The invention discloses a reactor core supporting structure of a pool-typed sodium-cooled fast reactor. The reactor core supporting structure of the invention comprises a large grid-plate header, a small grid-plate header and a reactor core support barrel, which results in that the number of opening of the large grid-plate header and the structural complexity of the large grid-plate header are both greatly reduced and the entire rigidity of the reactor core supporting structure is also improved. In addition, the small grid-plate header which is split can more easily achieve the distribution of the flow required by different reactor core components.
Owner:CHINA INSTITUTE OF ATOMIC ENERGY
Rotary positioning device for sodium-cooled fast-reactor reloading
InactiveCN101783190APositioning is safe and reliablePrecise positioningNuclear energy generationReactor fuel elementsBreeder reactorStopcock
The invention belongs to the technical field of fast breeder reactors, and particularly relates to a rotary positioning device for sodium-cooled fast-reactor reloading, which consists of a large cock and a pet cock. The large cock is arranged at the top of a reactor vessel; the pet cock is arranged on the large cock; the large cock and the pet cock can do rotary motion around respective axis; the large cock is driven by a large cock driving mechanism arranged at the top of the reactor vessel; and the pet cock is driven by a pet cock driving mechanism arranged on the large cock. The rotary positioning device is characterized in that: the pet cock is eccentrically arranged on the large cock; a reloading machine is eccentrically arranged on the pet cock; and the reloading machine can be guided to be aligned with any reactor core component through the rotary motion of the large cock and the pet cock by adjusting the eccentricity of the pet cock and the large cock and the eccentricity of the reloading machine and the pet cock. The rotary positioning device for the sodium-cooled fast-reactor reloading can safely, conveniently, and precisely realize the positioning mode that the reloading machine is aligned with the reactor core component in a totally closed state.
Owner:CHINA INSTITUTE OF ATOMIC ENERGY
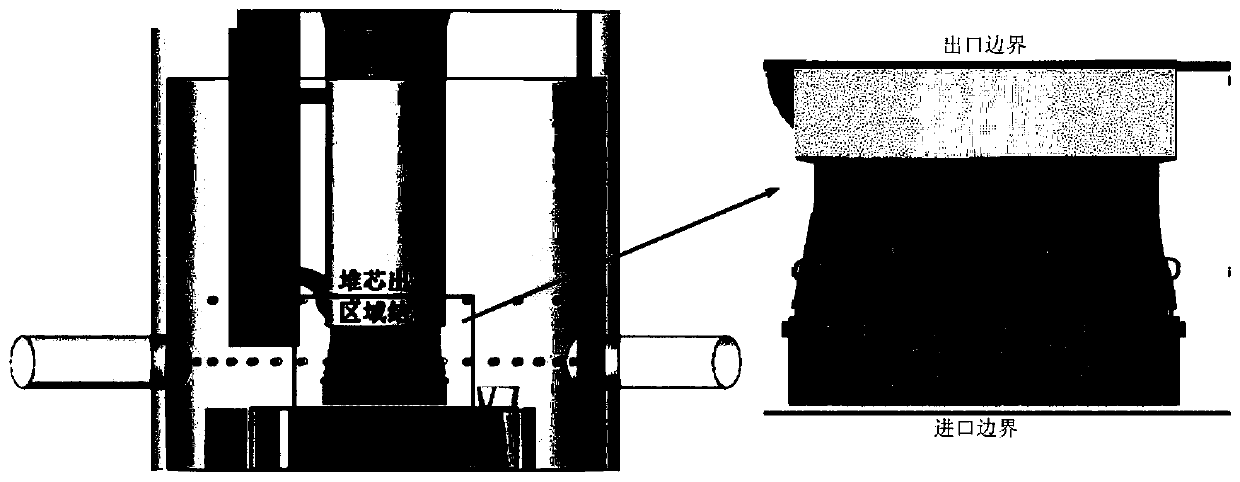
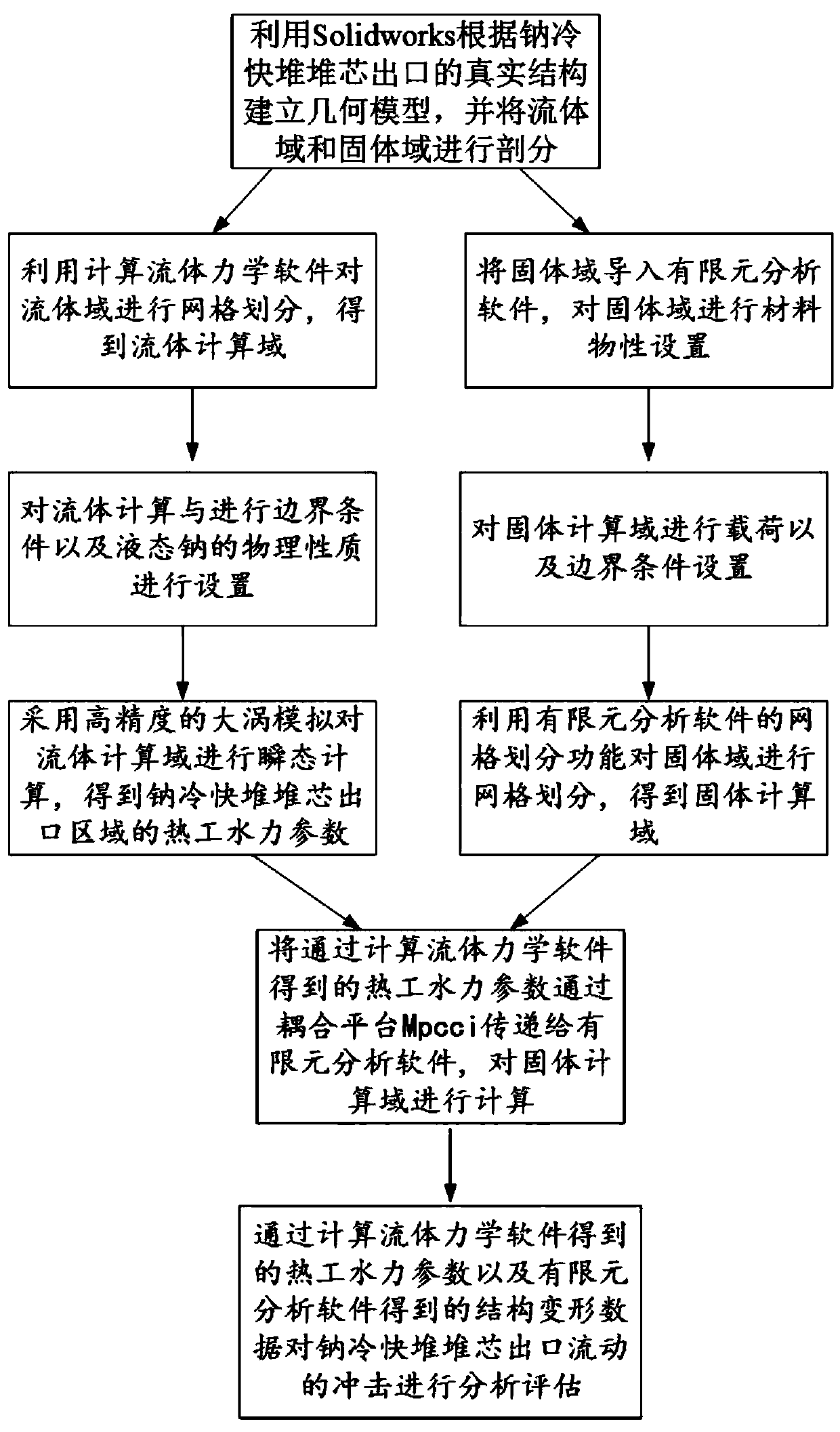
Method for evaluating flow impact at reactor core outlet of sodium-cooled fast reactor
ActiveCN110633520AReduce calculation errorsAccurate assessmentSpecial data processing applications3D modellingPhysical fieldLiquid metal
The invention discloses a method for evaluating flow impact of a reactor core outlet of a sodium-cooled fast reactor, which comprises the following steps of: carrying out geometric modeling by using Solidworks according to an actual structure of the reactor core outlet of the sodium-cooled fast reactor, and carrying out fluid domain and solid domain subdivision; performing grid division on a fluiddomain in a grid division function of computational fluid mechanics software, setting physical properties and boundary conditions of liquid metal sodium in a fluid computational domain, and performing transient flow field calculation by adopting a high-precision large eddy simulation method; performing condition setting and mesh generation on the solid domain in finite element analysis software;using a multi-physical field coupling platform MpCCI for transmitting flow field parameters obtained through computational fluid mechanics software to finite element analysis software, and making solid structure mechanics calculation in the finite element analysis software; and finally, evaluating the flow impact influence of the reactor core outlet of the sodium-cooled fast reactor through mechanical analysis of a flow field and a solid structure.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
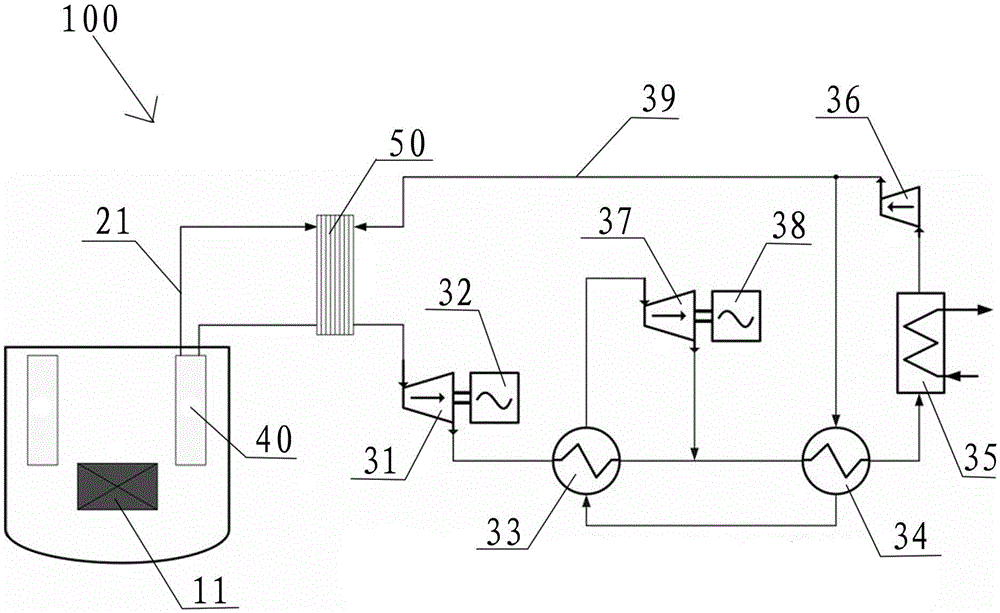
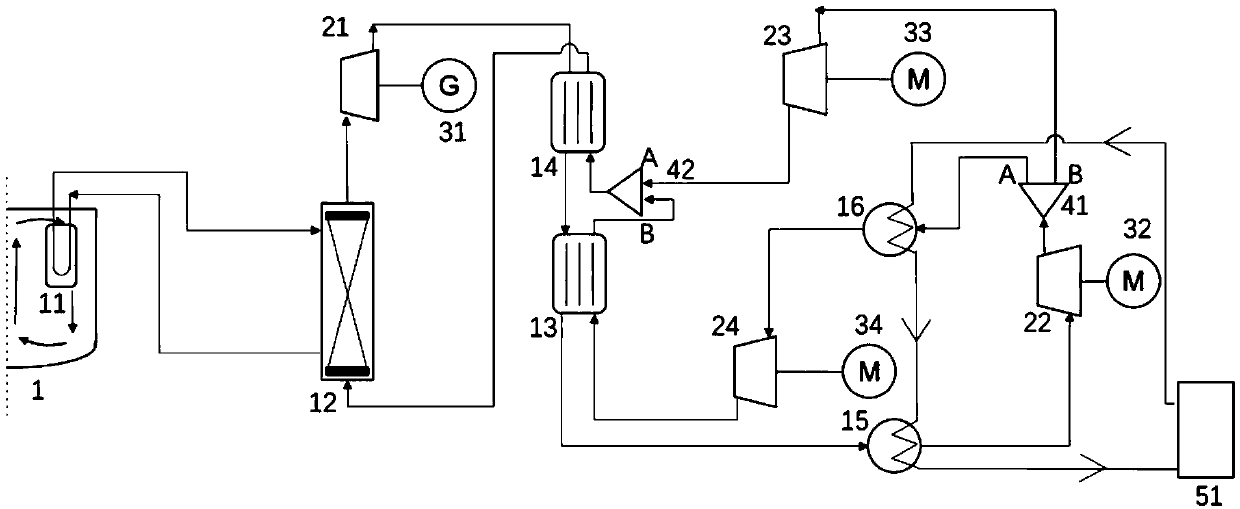
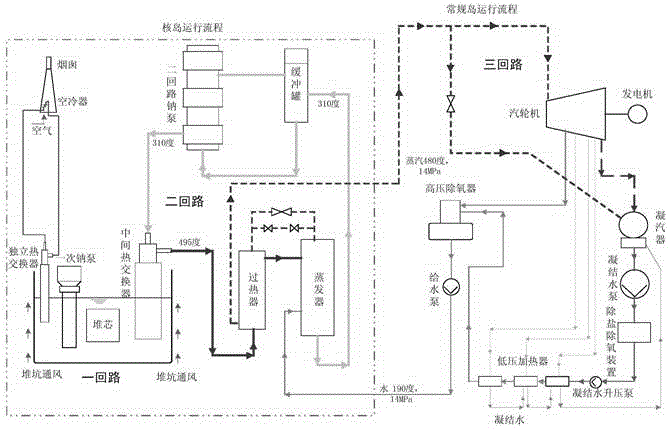
Sodium cooled fast reactor power generation system using supercritical carbon dioxide working medium
InactiveCN105261404AMatch the inlet and outlet temperature parametersImprove economic competitivenessNuclear energy generationSteam engine plantsNuclear engineeringGas compressor
The invention discloses a sodium cooled fast reactor power generation system using a supercritical carbon dioxide working medium. The sodium cooled fast reactor power system comprises a sodium cooled fast reactor for providing a heat source and a third loop of the supercritical carbon dioxide working medium, wherein the third loop converts heat energy into electric energy; the third loop comprises a third pipeline communicated with a second heat exchanger; the third pipeline is provided with a first generator, a first turbine which drives the first generator to generate power, a first regenerator, a second regenerator, a cooler, a gas compressor, a second generator and a second turbine which drives the second generator; the secondary-side outlet of the second heat exchanger passes through the first turbine, the high-temperature side of the first regenerator, the high-temperature side of the second regenerator and the cooler and then is communicated with the gas compressor; the outlet of the gas compressor is communicated with the secondary-side inlet of the second heat exchange and the low-temperature side of the second regenerator respectively; and the low-temperature side of the second regenerator passes through the low-temperature of the first regenerator and the second turbine, and then is communicated with the high-temperature side of the second regenerator. The third loop in the power generation system can realize the optimization of power generation efficiency.
Owner:NUCLEAR POWER INSTITUTE OF CHINA
Experimental system for forming characteristic of sodium-cooled fast reactor debris bed
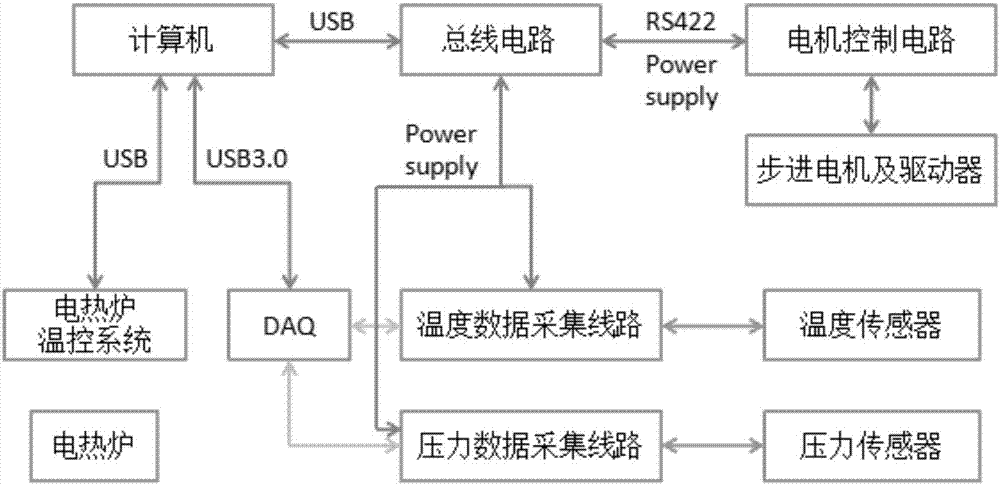
ActiveCN106409349AApplicable to a wide range of researchThe results of the study are comprehensiveNuclear energy generationEmergency protection arrangementsData acquisitionSodium-cooled fast reactor
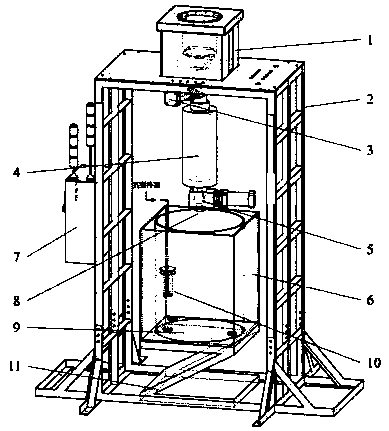
The invention provides an experimental system for the forming characteristic of a sodium-cooled fast reactor debris bed. The experimental system comprises an experimental support, a particle container, a particle conduit, a visual experiment container, a particle release controller, a visual data acquisition module, an environmental parameter detection module and a decay heat simulating generator, wherein the particle container and the particle conduit support multiple release apertures and release heights, an experimental particle system comprises various debris particles with different materials, shapes and sizes, visual experimental containers with different sizes are designed for two-dimensional and three-dimensional experiments, and the particle release controller and the visual data acquisition module can acquire and store images synchronously in the whole experimental process. The experimental system can be applied to researching and analyzing the forming mechanism of the fuel particle debris bed in the sodium-cooled fast reactor core disassembly accident process. The experimental system has the advantages that the experimental process is visual, qualitative analysis is combined with quantitative analysis, multiple controllable experimental variables exist, the operation principle is simple, the system is easy to expand, stable and safe and the like.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
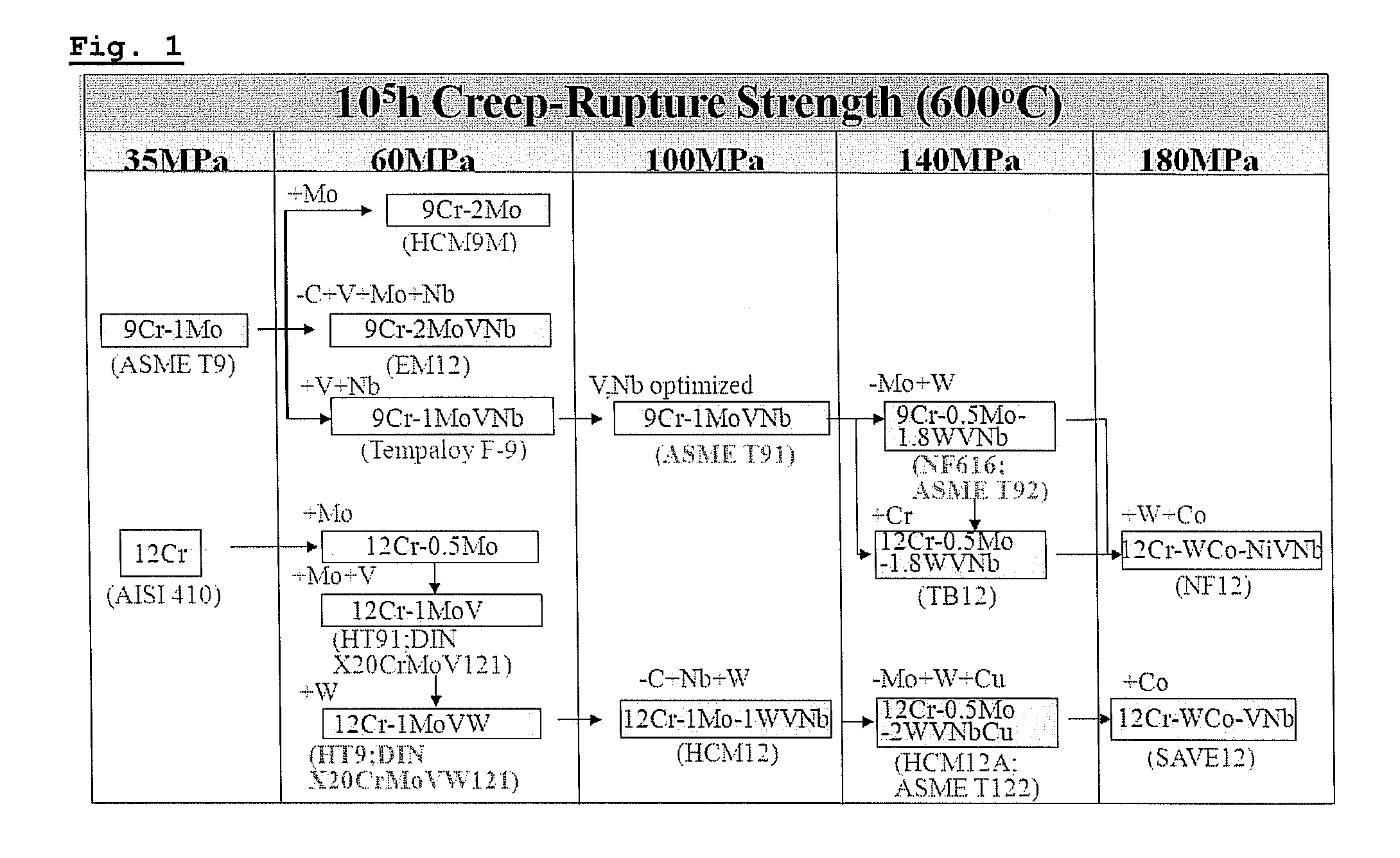
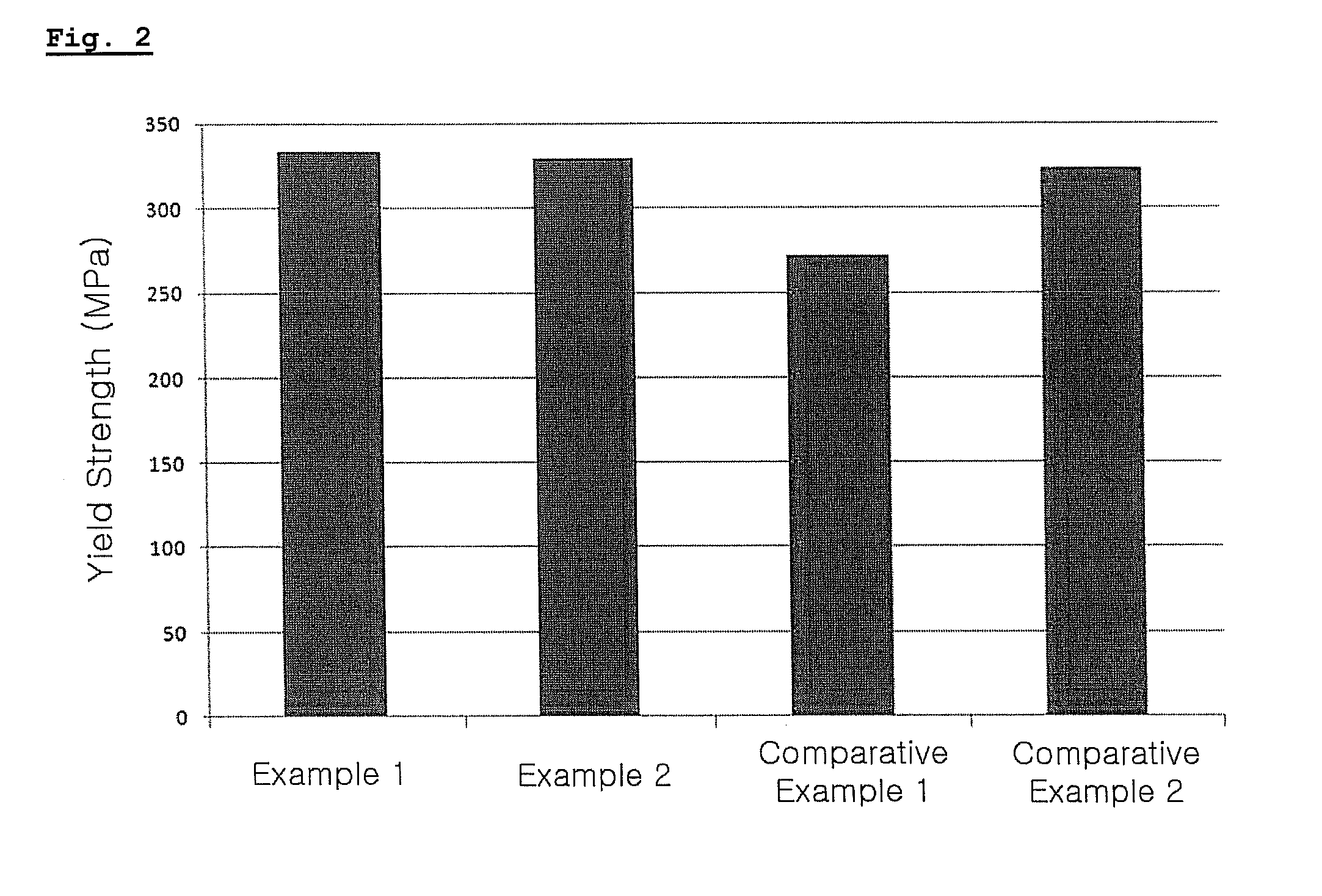
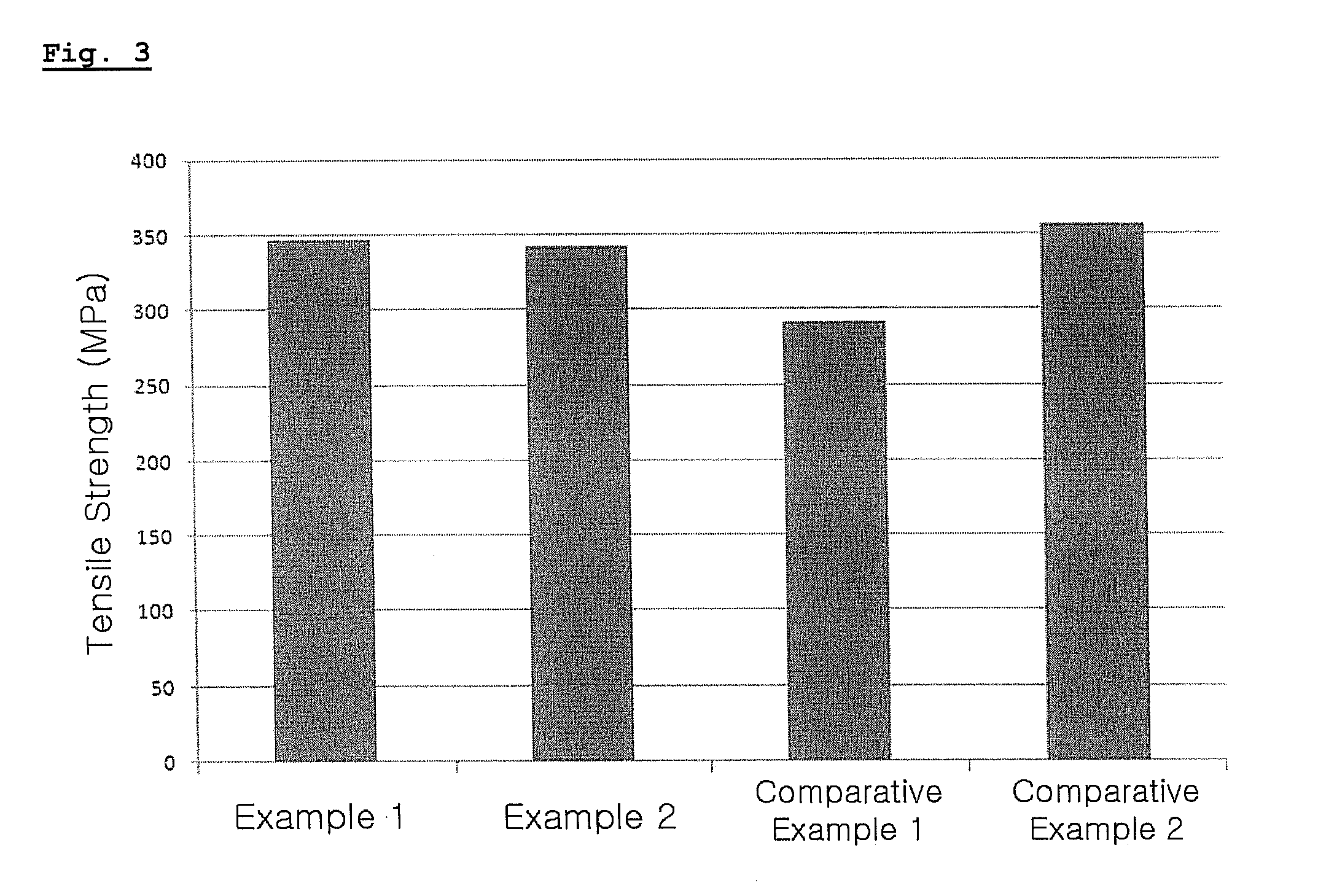
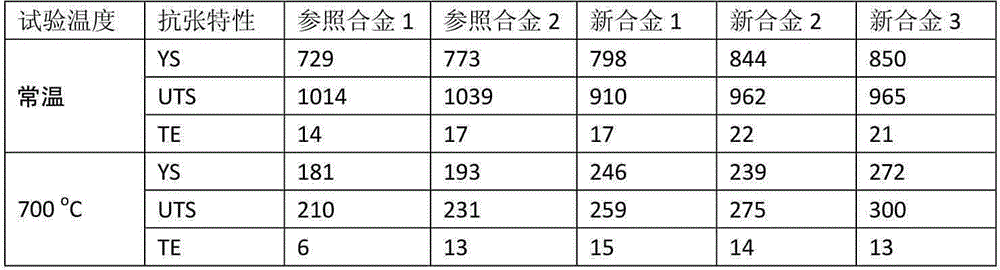
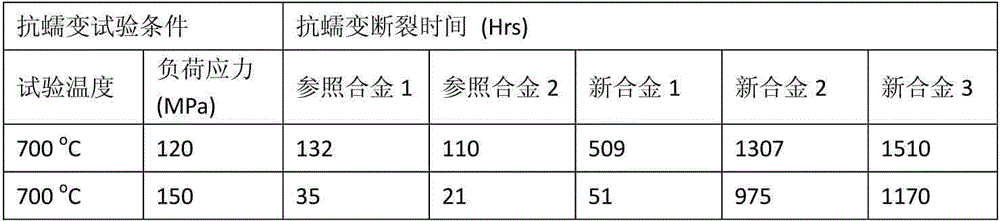
HIGH Cr FERRITIC/MARTENSITIC STEELS HAVING AN IMPROVED CREEP RESISTANCE FOR IN-CORE COMPONENT MATERIALS IN NUCLEAR REACTOR, AND PREPARATION METHOD THEREOF
ActiveUS20120106693A1Improve creep resistanceHigh CRFast fission reactorsReactor fuel elementsNiobiumManganese
Disclosed herein is a high Cr Ferritic / Martensitic steel comprising 0.04 to 0.13% by weight of carbon, 0.03 to 0.07% by weight of silicon, 0.40 to 0.50% by weight of manganese, 0.40 to 0.50% by weight of nickel, 8.5 to 9.5% by weight of chromium, 0.45 to 0.55% by weight of molybdenum, 0.10 to 0.25% by weight of vanadium, 0.02 to 0.10% by weight of tantalum, 0.21 to 0.25% by weight of niobium, 1.5 to 3.0% by weight of tungsten, 0.015 to 0.025% by weight of nitrogen, 0.01 to 0.02% by weight of boron and iron balance. By regulating the contents of alloying elements such as nitrogen, born, the high Cr Ferritic / Martensitic steel with to superior tensile strength and creep resistance is provided, and can be effectively used as an in-core component material for sodium-cooled fast reactor (SFR).
Owner:KOREA ATOMIC ENERGY RES INST +1
Circulating heat and power cogeneration system for stair type heat supplying supercritical carbon dioxide used for sodium-cooled fast reactor
PendingCN109616229AAchieve cycle efficiencyAdjustable powerNuclear energy generationCooling arrangementGeneration processNuclear engineering
The invention discloses a circulating heat and power cogeneration system for stair type heat supplying supercritical carbon dioxide used for a sodium-cooled fast reactor, and belongs to the technicalfield of efficient utilization of clean energy. The system aims at solving the problems that a traditional heat and power cogeneration system is lower in thermal circulating efficiency and cannot achieve stair type heat supplying, and hidden safety danger exists in sodium-water actuating medium heat conduction. A first loop absorbs heat of a heat source through a sodium-sodium heat exchanger, theheat is exchanged to a second loop through a sodium-carbon dioxide heat exchanger, and a second loop low-temperature heat regenerator achieves switching between a simple circulating form and a partialcooling circulating form, thereby utilizing heat for power generation or achieving stair type heat supplying in the power generation process. The circulating heat and power cogeneration system for stair type heat supplying supercritical carbon dioxide used for the sodium-cooled fast reactor adopts a novel circulating actuating medium for replacing a water-steam actuating medium used by an existing experiment reactor, the efficiency of an original system is reached or exceeded, switchable nuclear piling heat and power cogeneration is achieved, the sodium piling characteristics are reasonably utilized, running parameters of the actuating medium are combined, and the safety of a nuclear piling system is significantly improved.
Owner:HARBIN ELECTRIC CO LTD
Sodium-cooled-fast-reactor-structure-based material irradiation capsule
InactiveCN104240787AEasy to operateReasonable structural designMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationIrradiation devicesNuclear radiationSodium-cooled fast reactor
The utility model relates to a measurement apparatus using nuclear radiation inside a reactor to measure a material irradiation performance. In order to solve a problem of lack of convenient and applicable sodium-cooled-fast-reactor-structure-based material irradiation capsule, the invention provides a sodium-cooled-fast-reactor-structure-based material irradiation capsule comprising an outer cylinder body, an inner cylinder body, and a central tube; and the central tube is arranged at the center inside the inner cylinder body. A sample placing region is arranged between the central tube and the inner cylinder body. A joint is arranged at the opening end of the inner cylinder body. The outer cylinder body is arranged outside the integrated structure; and an outer end cover is arranged at the top end. The inside of the inner cylinder body is filled with liquid sodium; and space between the inner cylinder body and the outer cylinder body is filled with helium. The connecting way is realized by welding. With the sodium-cooled-fast-reactor-structure-based material irradiation capsule, the problem of lack of convenient and applicable sodium-cooled-fast-reactor-structure-based material irradiation capsule in the prior art can be solved. The minimum sample number required by the standard testing requirement can be met by one-time test. Moreover, the structure is design reasonably; and the capsule can be used conveniently and has the non-on-line test parameter monitoring function.
Owner:CHINA INSTITUTE OF ATOMIC ENERGY
Low-power operation method of pool type sodium-cooled fast reactor needless of conventional island investment
ActiveCN105551551AImprove utilization efficiencyImprove the level ofPower plant safety arrangementPlant parameters regulationProcess engineeringSodium-cooled fast reactor
The invention relates to a low-power operation method of a pool type sodium-cooled fast reactor needless of conventional island investment, and belongs to the technology of pool type sodium-cooled fast reactor design. According to the method, the total normal heat radiation quantity of main and auxiliary systems of first and second loops is determined without investment of a third loop, and thus, the maximal power for long-term operation in a balanced state is determined. According to the total sodium loaded amount of the first and second loops and the initial starting temperature, the maximal power level and corresponding time relation of the reactor can be determined under highest temperature limit. Besides physical thermal calculation, control protection related setting values are modified correspondingly to satisfy the requirement for the safety allowance. On the premise that the safety allowance is ensured, the economical, reliable and flexible performances of the reactor are improved, the utilization rate of the reactor is effectively and fully improved, and corresponding scientific research level is improved.
Owner:CHINA INSTITUTE OF ATOMIC ENERGY
Austenitic stainless steel bare welding wire for sodium cooled fast reactor and application of austenitic stainless steel bare welding wire
ActiveCN107553004ASuitable for weldingReduce splashArc welding apparatusWelding/cutting media/materialsSodium-cooled fast reactorAustenite
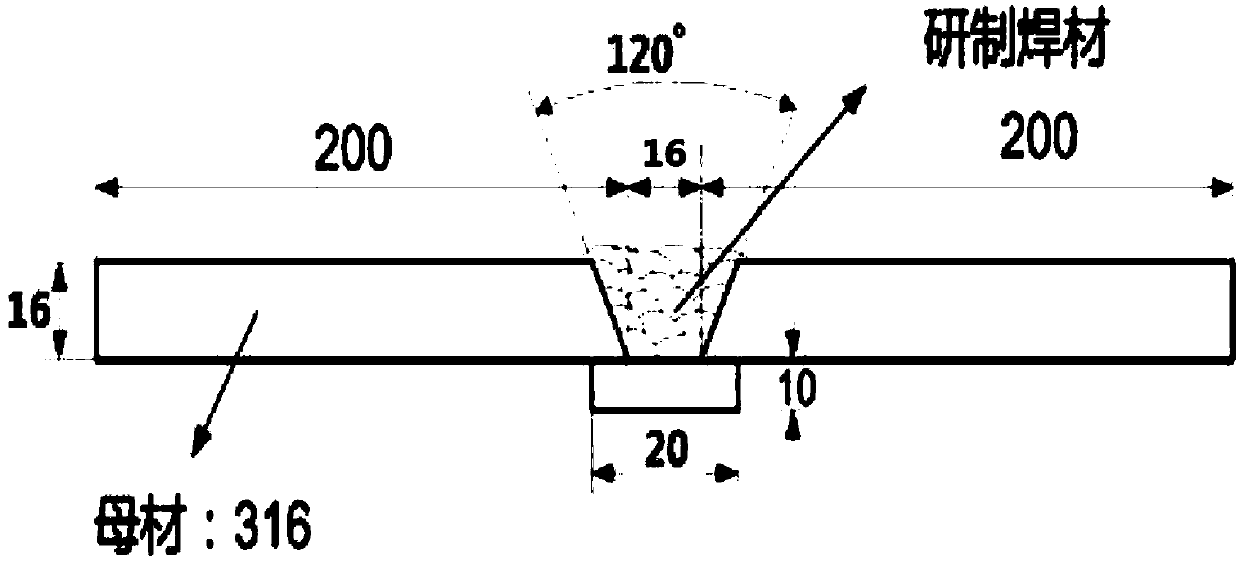
The invention discloses an austenitic stainless steel bare welding wire for a sodium cooled fast reactor and application of the austenitic stainless steel bare welding wire, and belongs to the technical field of welding materials. The chemical components of the welding wire include, by weight, 0.03-0.08% of C, 18.0-20.0% of Cr, 11.5-13.5% of Ni, 2.00-2.60% of Mo, 0.04-0.08% of N, 1.40-2.40% of Mn,0.30-0.70% of Si and the balance iron and unavoidable impurities. The welding wire is suitable for welding of the sodium cooled fast reactor, and is small in splashing, stable in process and good intechnological property when welding is conducted. By adopting the stainless steel welding wire, a welding joint conforming to required properties can be obtained, and the stainless steel welding wirecan replace an imported welding wire.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
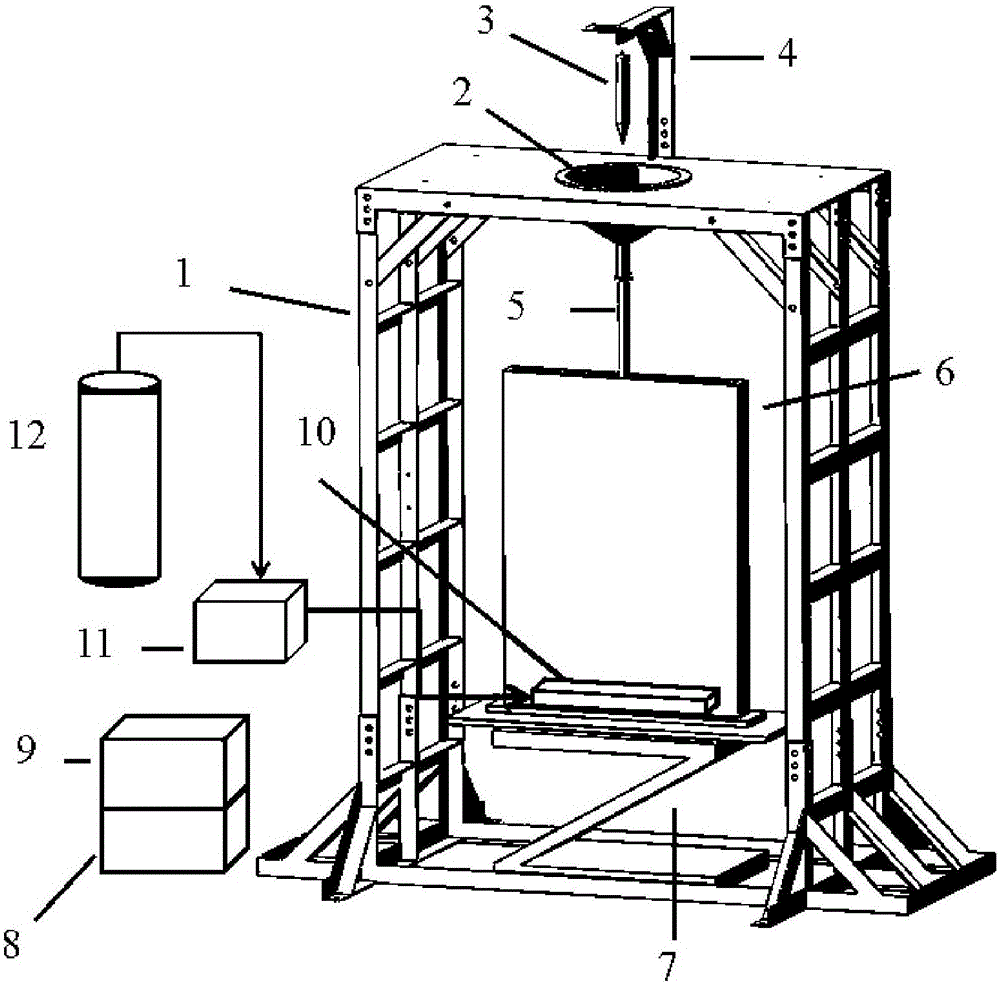
Visual experimental system for fragmentation behaviors of reactor core melts in severe accidents of sodium cooled fast reactors
ActiveCN109087718AReduce Refraction BiasComprehensive research parametersNuclear energy generationNuclear monitoringEngineeringSodium-cooled fast reactor
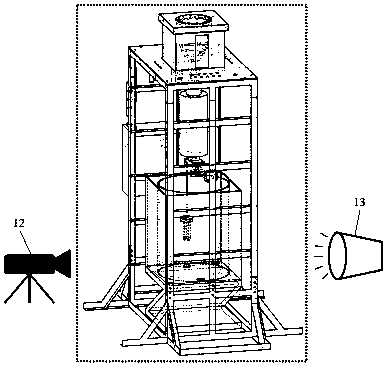
The invention relates to a visual experimental system for fragmentation behaviors of reactor core melts in severe accidents of sodium cooled fast reactors. The visual experimental system comprises a support, a temperature-controllable annular resistance wire heating furnace, a first high-temperature melt pneumatic valve, a pressurized heat supplementing pipe, a second high-temperature melt pneumatic valve, a visual experimental container and a fragmented-product collector. The temperature-controllable annular resistance wire heating furnace is arranged on the support, the top of the first high-temperature melt pneumatic valve is connected with the bottom of the temperature-controllable annular resistance wire heating furnace, the top of the pressurized heat supplementing pipe is connectedwith the bottom of the first high-temperature melt pneumatic valve, the top of the second high-temperature melt pneumatic valve is connected with the bottom of the pressurized heat supplementing pipe,the visual experimental container is arranged below the second high-temperature melt pneumatic valve, and the fragmented-product collector is arranged in the visual experimental container made of a transparent material.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
High-temperature-resistant corrosion-resistant anti-crystallization pressure and differential pressure transmitter isolation module
InactiveCN105352651AAvoid cloggingTemperature additional error compensation function improvedFluid pressure measurement using capacitance variationDifferential pressureLiquid state
The invention relates to a high-temperature-resistant corrosion-resistant anti-crystallization pressure and differential pressure transmitter isolation module. The isolation module comprises a ripple diaphragm, a ripple flange, a capillary tube and a filling liquid. The ripple diaphragm is welded at the bottom of the ripple flange, the capillary tube goes deep into the ripple flange from the upper portion of the ripple flange, a communicating channel is arranged between the capillary tube and the ripple diaphragm, and the filling liquid fills the capillary tube and the communicating channel. A transmitter applying the module can realize measurement of high-temperature liquid-state sodium pressure and provides a pressure measurement means for sodium-cooled fast reactor and a test loop, and the structure of the pressure and differential pressure transmitter isolation module realizes high temperature and corrosion isolation; a heating apparatus realizes prevention of sodium crystallization obstruction; and a temperature additional error compensation function is realized, and the measurement precision is improved.
Owner:CHINA INSTITUTE OF ATOMIC ENERGY
Multi-dimensional scanning temperature measuring device of sodium-cooled fast reactor assembly test piece and method
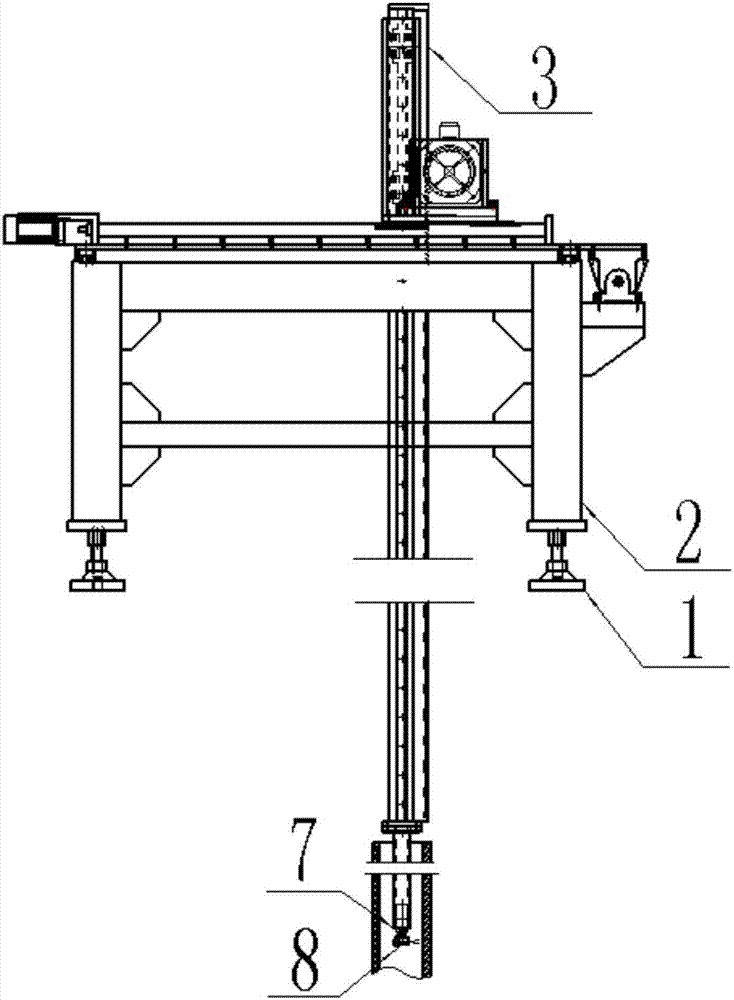
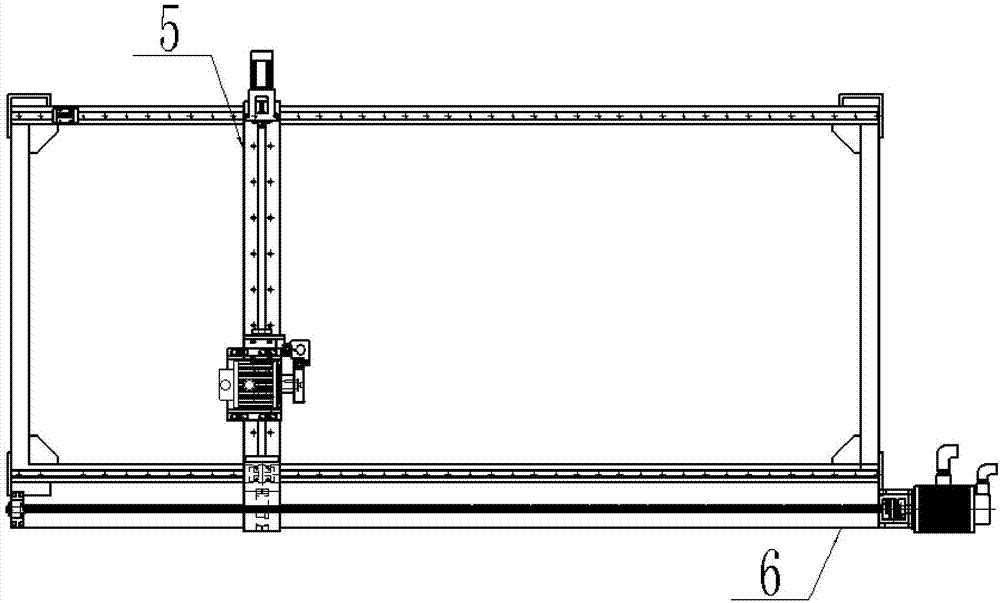
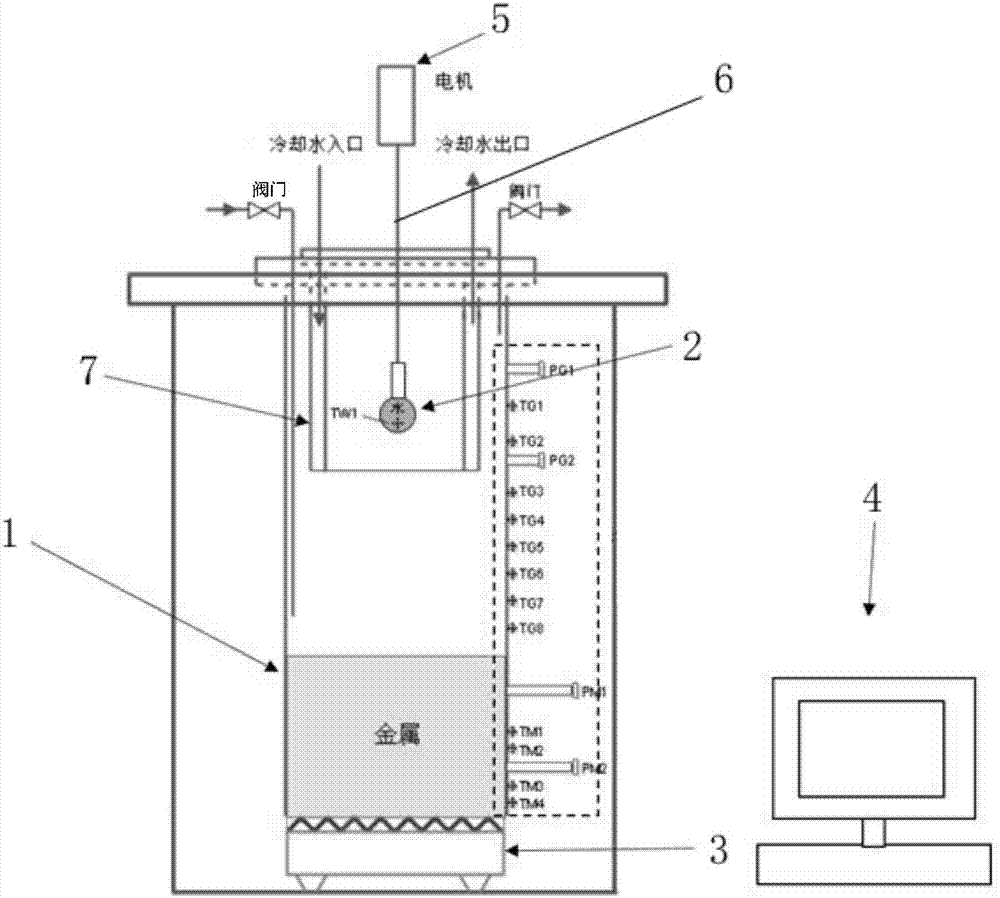
The invention relates to a multi-dimensional scanning temperature measuring device of a sodium-cooled fast reactor assembly test piece and a method. The device comprises an adjustment base, a portal frame, a Z-axis assembly, a Z-axis supporting seat, a Y-axis assembly, an X-axis assembly, a temperature measuring probe rotation mechanism and a micro temperature measuring probe; the portal frame is connected with the adjustment base through a high-strength bolt; the Z-axis assembly mainly comprises a fixed guide rail and a telescopic rod and carries the linear motion of a non-contact temperature measuring probe along a Z axis; the Z-axis supporting seat rigidly supports the Z axis; the Y-axis assembly realizes the linear motion of the Z-axis assembly and the Z-axis supporting seat along a Y axis; the X-axis assembly realizes the linear motion of the Z-axis assembly, the Z-axis supporting seat and the Y-axis assembly along the sliding guide rails of the X-axis assembly; the temperature measuring probe rotation mechanism realizes the rotation of the micro temperature measuring probe in an XY plane according to a specified angle; and the micro temperature measuring probe receives the infrared radiation of the inner wall surface of a hexagonal casing of the fast reactor assembly test piece and feeds backs the temperature signals of the inner wall surface to a computer processing unit. The invention also discloses a temperature measuring method of the device. The device can satisfy measurement requirements of an assembly test piece temperature field in an ex-reactor experiment process.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Double-end-face fluid dynamic and static pressure mechanical seal for sodium cooling fast reactor nuclear main pump
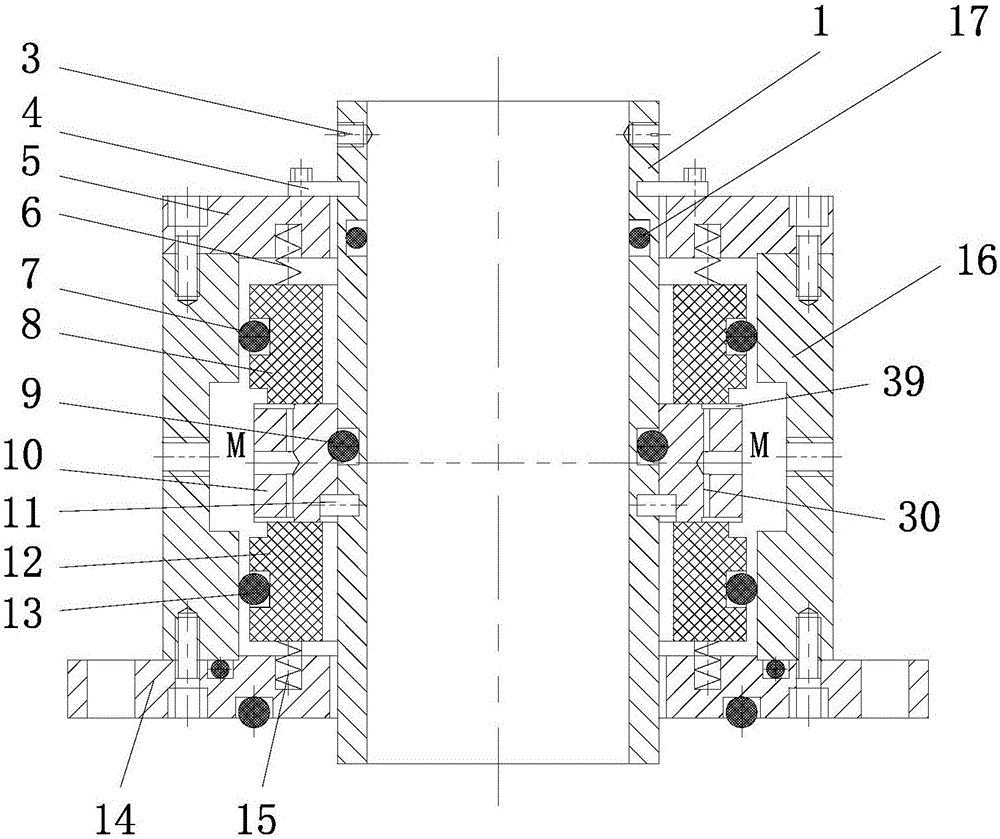
ActiveCN106640740APrevent leakageImprove sealingPump componentsPumpsDifferential pressureEngineering
The invention provides a double-end-face fluid dynamic and static pressure mechanical seal for a sodium cooling fast reactor nuclear main pump. The double-end-face fluid dynamic and static pressure mechanical seal aims at solving the problems that a circulating working medium in an existing sodium pump leaks, and blocking fluid lubricating oil probably leaks into the pump to contaminate the working medium, and guaranteeing safe, stable and long-term operation of a fast reactor. The mechanical seal is composed of a dynamic ring, static rings, a spring, a sealing shell and the like, wherein a self-pumping fluid sealing structure is formed by the static rings and the two ends of the dynamic ring. The dynamic ring is matched with a pin on a shaft sleeve, and it is achieved that the dynamic ring is circumferentially and axially positioned; a set screw is arranged on the shaft sleeve; a limiting stopper is detachably arranged between the sealing shell or spring bases and the shaft sleeve to limit axial relative positions of the shaft sleeve and the spring bases, the elasticity of springs is changed, and pressure between the dynamic ring and the two static rings is identical; and when the dynamic ring rotates, blocking fluid inflated into an outer sealing space defined by the dynamic ring, the sealing shell and the like flows into a backwards-bent type fluid groove formed in the end face of the dynamic ring through an axial and radial combined pore canal under the effect of differential pressure, and self-pumping circulation is formed over and over again.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV +1
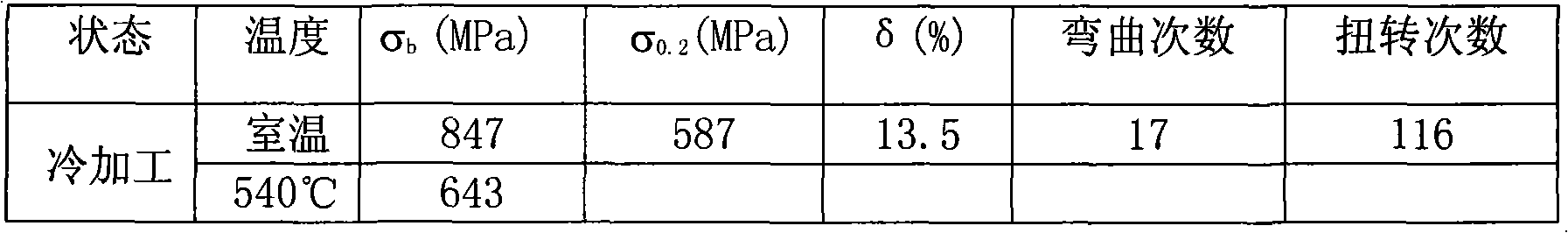
Ferritic oxide dispersion strengthened alloy with enhanced room temperature and high temperature strength and manufacturing method thereof
The invention relates to a ferritic oxide dispersion strengthened alloy with enhanced room temperature and high temperature strength containing Cr in a range of from 12 to 20wt%, Y2O3 in a range of from 0.1 to 0.5wt%, W 0.1 to4wt%, Mo 0.5 to 2 wt%, Ti 0.1 to 0.3 wt%, and Zr 0.02 to 0.3 wt%, and Fe, and a manufacturing method thereof. The ferritic oxide dispersion strengthened alloy is advantageous in that under the 700-degree temperature condition, the anti-tensioning performance is good, the alloy can be used for the supercritical steam generator part (rotor wings, and shafts) used for the thermal power, airplane engine part (circular discs, and effusers), and sodium-cooled fast reactor and other nuclear power system reactor core structural parts such as nuclear coating tube, conduits, conductors, and end plugs).
Owner:KOREA ATOMIC ENERGY RES INST +1
Stainless steel wrap wire for sodium cooled fast reactor core assembly and method for preparing same
InactiveCN101333632AMeet chemical composition requirementsGuaranteed to dissolveHydrogenSingle crystal
The invention discloses a stainless steel wrap wire of a sodium-cooled fast reactor core subassembly as well as a method for the production thereof. The stainless steel wrap wire has components, in weight proportion: 0.04 percent to 0.08 percent of C; less than or equal to 0.75 percent of Si; less than or equal to 0.02 percent of P; less than or equal to 0.02 percent of S; 1.5 percent to 2.0 percent of Mn; 11.0 percent to 14.0 percent of Ni; 16.0 percent to 18.0 percent of Cr; 2.0 percent to 3.0 percent of Mo; 0.3 percent to 0.5 percent of Ti; less than or equal to 0.1 percent of Co; less than or equal to 0.002 percent of B; less than or equal to 0.035 percent of N; balance Fe. The double-smelting is adopted when in smelting; the hydrogen protection or vacuum bright annealing treatment is adopted when in annealing; a single crystal silicon dioxide mold with rather high precision is adopted in the drawing process; and the degree of cold working of final delivery state is between 17 and 20 percent. The wrap wire prepared by the proposal can meet the requirements of the sodium-cooled fast reactor core subassembly.
Owner:CHINA INSTITUTE OF ATOMIC ENERGY
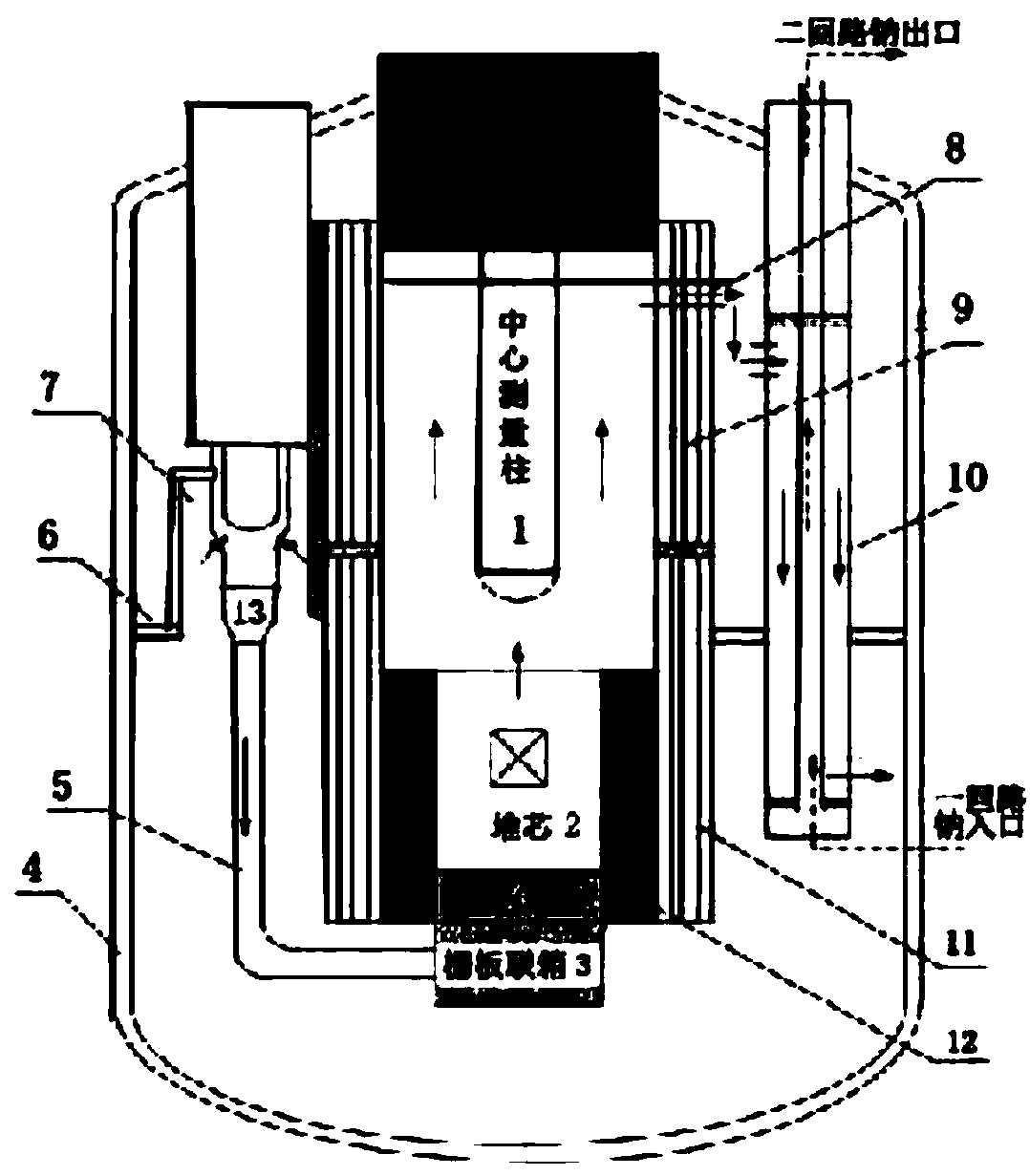
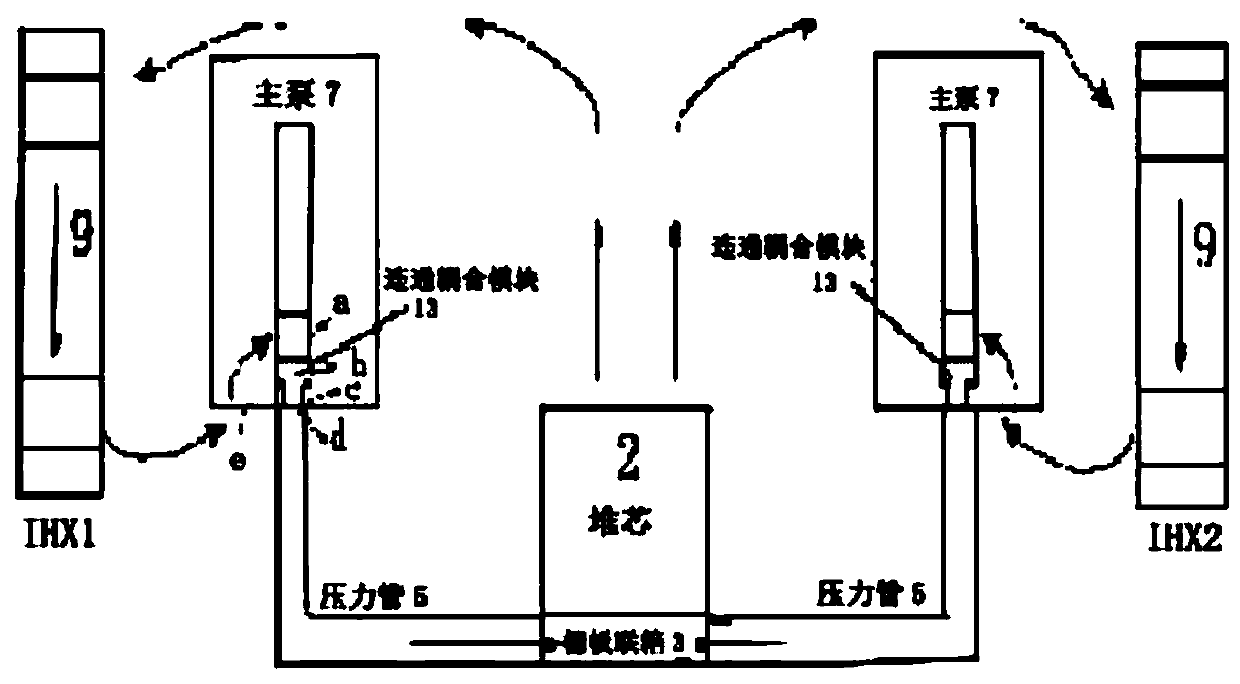
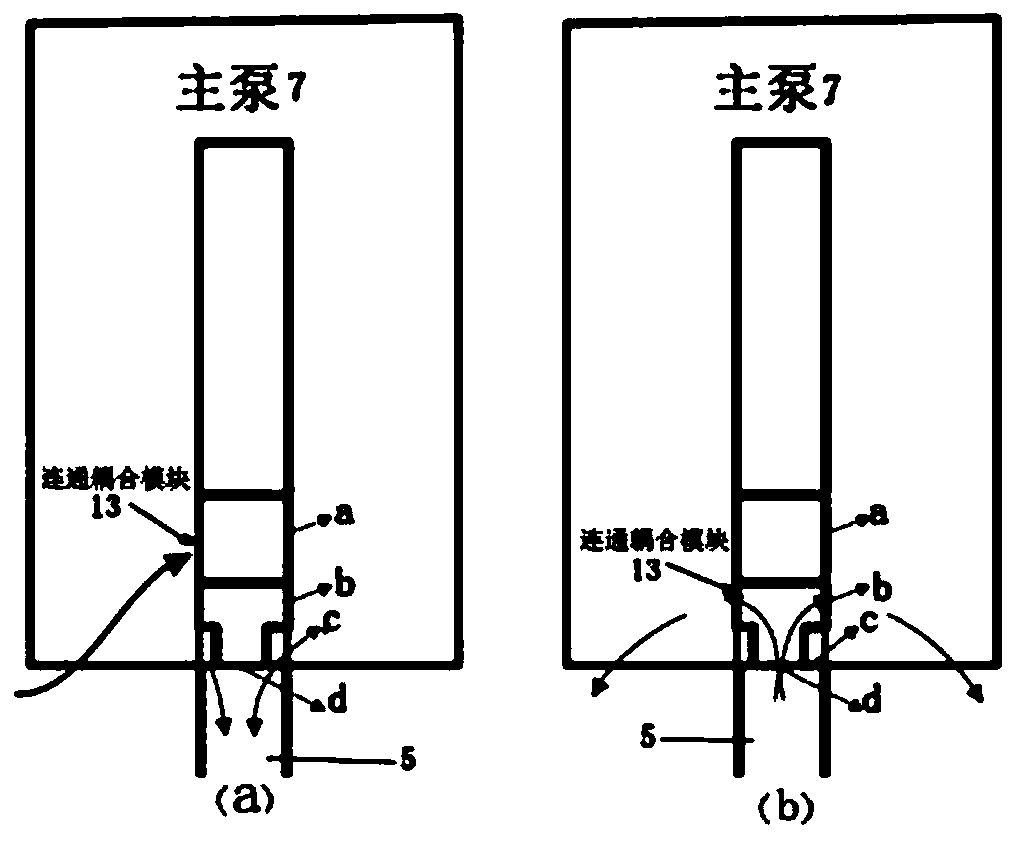
Modeling and calculation method for flow channel of main pump of fast reactor based on virtual valve
The invention discloses a modeling and calculation method for a flow channel of a main pump of a fast reactor based on a virtual valve and belongs to the technical field of three-dimensional numericalsimulation of a reactor. The method comprises the steps of based on a pool-type sodium-cooled fast reactor, reasonably simplifying a reactor vessel and reactor internals to establish a three-dimensional pool-type fast reactor model; performing three-dimensional thermo-technical fluid transient calculation under multiple working conditions by use of a model; and performing part of simple change onsurface attributes of a connection coupling module of a primary main pump by changing the attribute of each surface of the connection coupling module between the main pump and a pressure pipe. The instantaneous conditions of the in-pile flowing process can be accurately simulated, the analysis of a primary loop accident system of the fast reactor and the three-dimensional thermo-technical transient calculation are performed under various types of working conditions, including normal operation, expected operating events and accident working conditions. With the modeling and calculation methodfor the flow channel of the main pump of the fast reactor based on the virtual valve disclosed by the invention, the workload of modeling and calculation is greatly reduced; the effect that the calculation of multiple working conditions can be completed by use of a set of grid files is implemented and the support and basis are provided for design and safety analysis of the fast reactor.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
Experimental system for interaction between fuel and coolant inside sodium-cooled fast reactor molten fuel tank
InactiveCN107016913AImprove safety evaluationConvenient researchEducational modelsElectricityNuclear engineering
The present invention relates to an experimental system for the interaction between the fuel and the coolant inside a molten fuel tank during the occurrence of a severe accident in a sodium-cooled fast reactor. The experimental system comprises a reaction occurrence container, a coolant container, a driving module, a heating module, a data acquisition module and a control terminal. The heating module is used for heating the reaction occurrence container. The coolant container is arranged above the reaction occurrence container. The coolant container is connected with the driving end of the driving module. The driving module is used for downwardly delivering the coolant into the reaction occurrence container. The data acquisition module is arranged in the reaction occurrence container. The heating module, the driving module and the data acquisition module are electrically connected with the control terminal.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
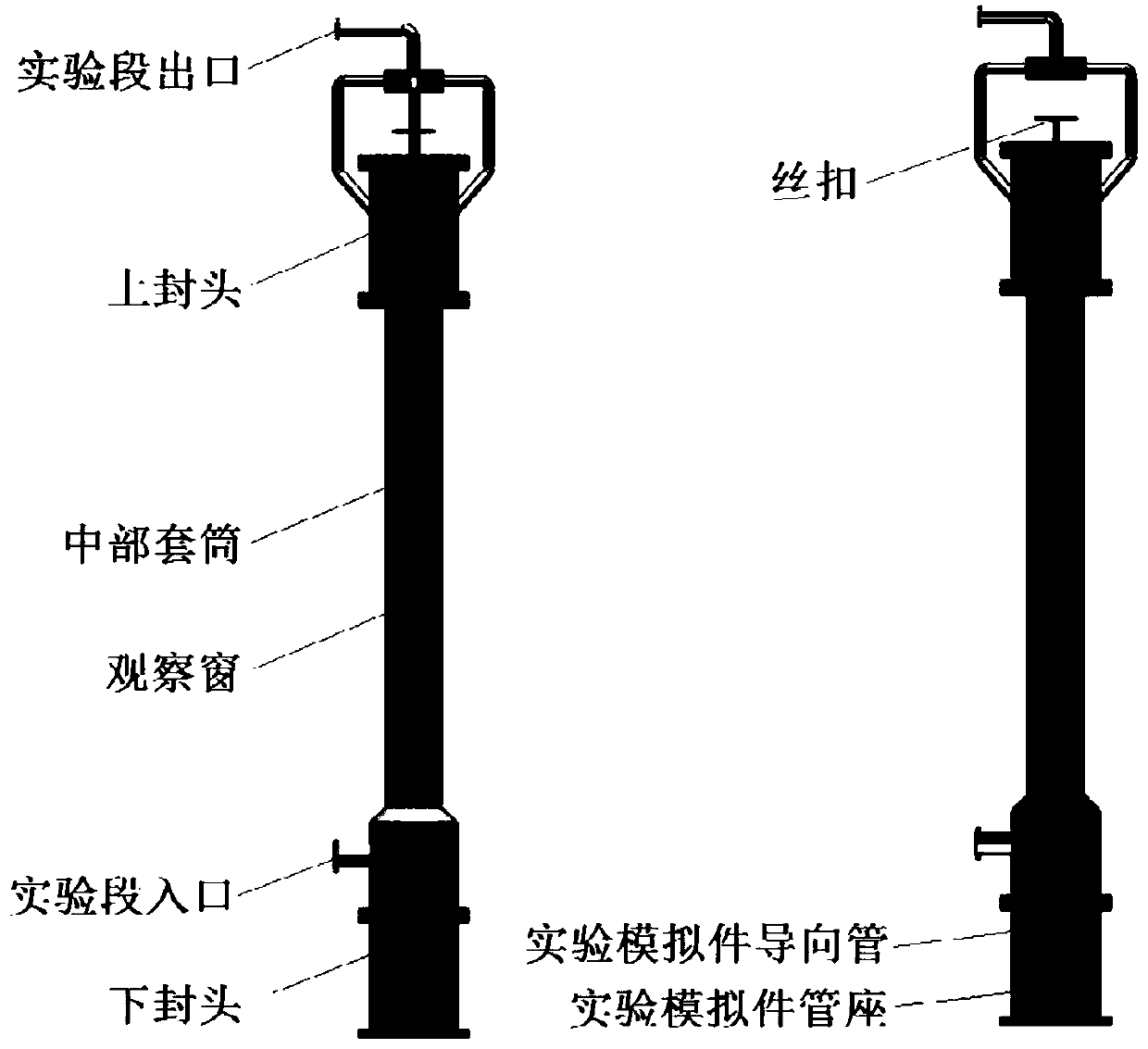
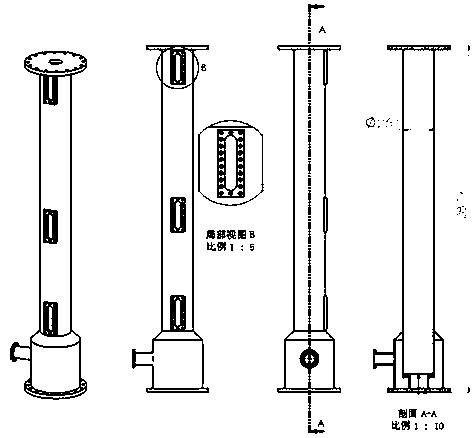
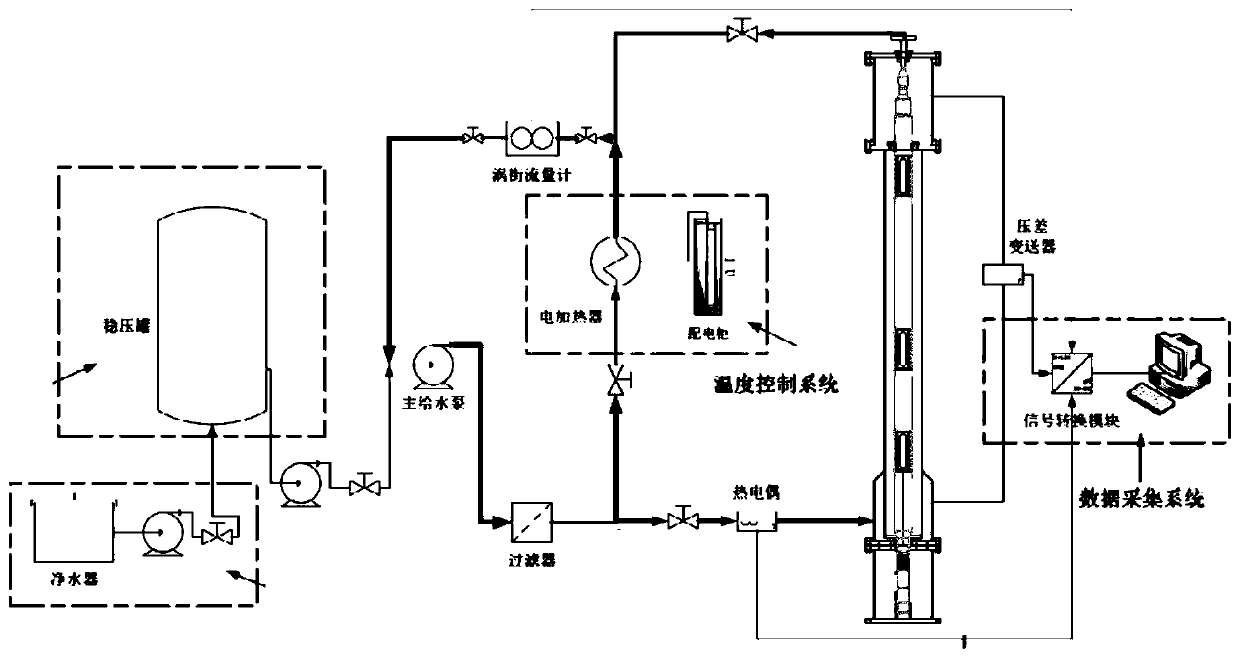
Universal sodium-cooled fast reactor assembly single-body hydraulic experiment bench and experiment method thereof
PendingCN110033872AImprove general performanceStrong scalabilityNuclear energy generationNuclear monitoringExperimental methodsEngineering
The invention belongs to the technical field of flow characteristic experiments of sodium-cooled fast reactor assemblies, and particularly relates to a universal sodium-cooled fast reactor assembly single-body hydraulic experiment bench and an experiment method thereof. The experiment bench comprises a water purification system, a pressure stabilizing system, a main circulation loop and an experiment section which are sequentially connected, wherein a heating section in the main circulation loop and the experiment section are connected in parallel; and a measured experiment simulation piece isplaced in the experiment section. The experimental method comprises the following steps: injecting deionized water into the main circulation loop and the experimental section, and discharging gas gathered in a pipeline; starting a water feeding pump of a main circulation system, and establishing stable circulation flow in an experiment loop; heating an experiment working medium to a preset temperature, and then closing a heater; and adjusting the frequency of a main water feeding pump and the opening degree of an outlet valve to achieve switching of different experiment working conditions, and collecting and recording experiment data. The flow characteristics of various assemblies and corresponding rod bundle sections of a sodium-cooled fast reactor can be studied through hydraulic experiments, and the sodium-cooled fast reactor assembly single-body hydraulic experiment bench has high universality and expansibility.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
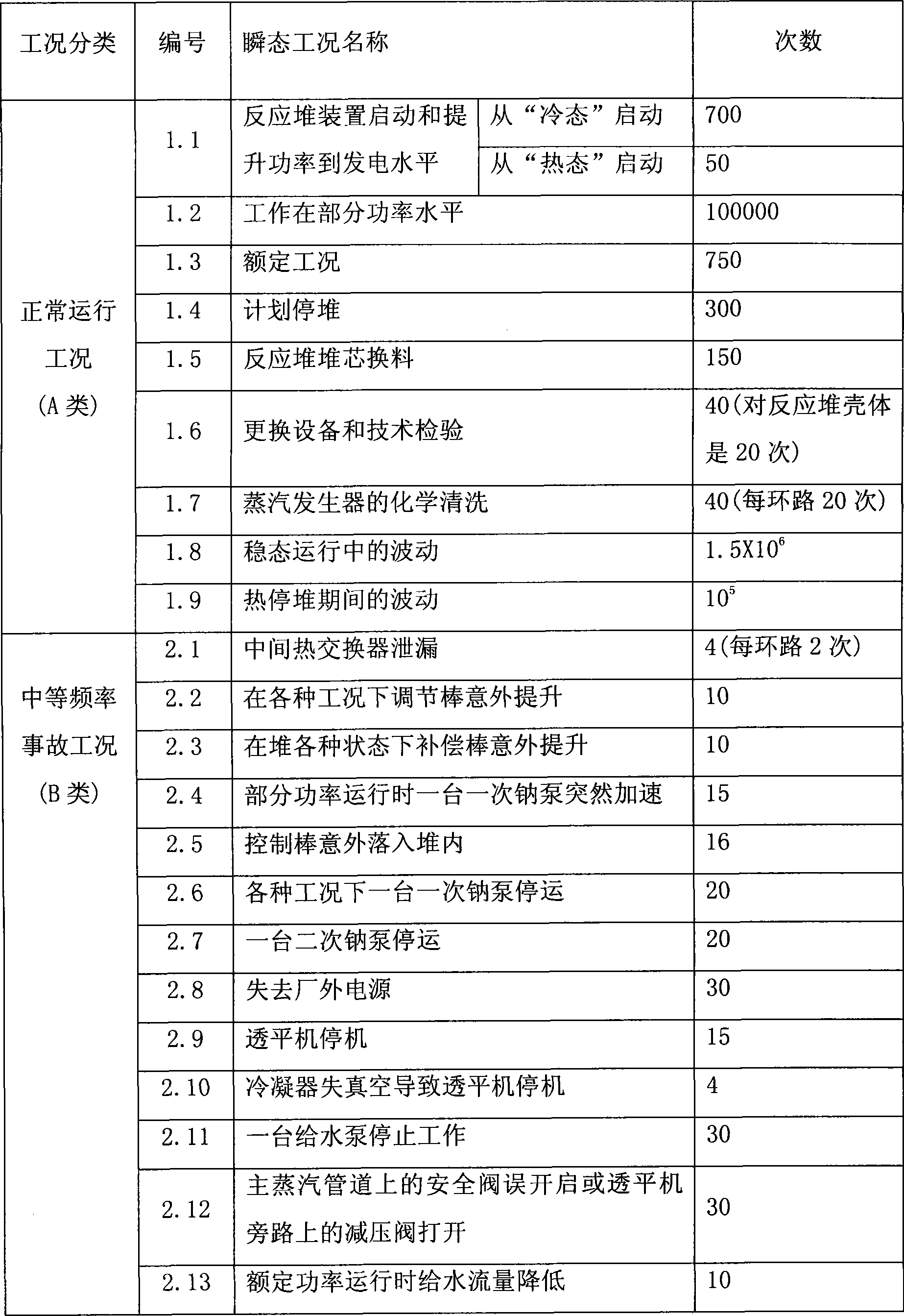
Design transient determination method for sodium-cooled fast reactor nuclear power station cooling agent system and member
The invention belongs to fast fission reactor technology field and discloses a design transient determination method for sodium-cooled fast reactor nuclear power station cooling agent system and member. The method comprises three steps: defining design standard of cooling agent system and member, determining classification rule of design transient, determining design transient status and circulation times. The invention adopts American mechanical engineering boiler and pressure container standard (simply ASME) and France RCC-M standard. The design transient status of sodium-cooled fast reactor is classified to five conditions: normal operation condition, middle frequency accident condition, sparse accident condition, limit accident condition, experiment condition. The circulation times of a condition in service life of a reactor is target value of transient impact to be experienced by cooling agent system and member in service life of a reactor. The method satisfies design demand for sodium-cooled fast reactor.
Owner:CHINA INSTITUTE OF ATOMIC ENERGY
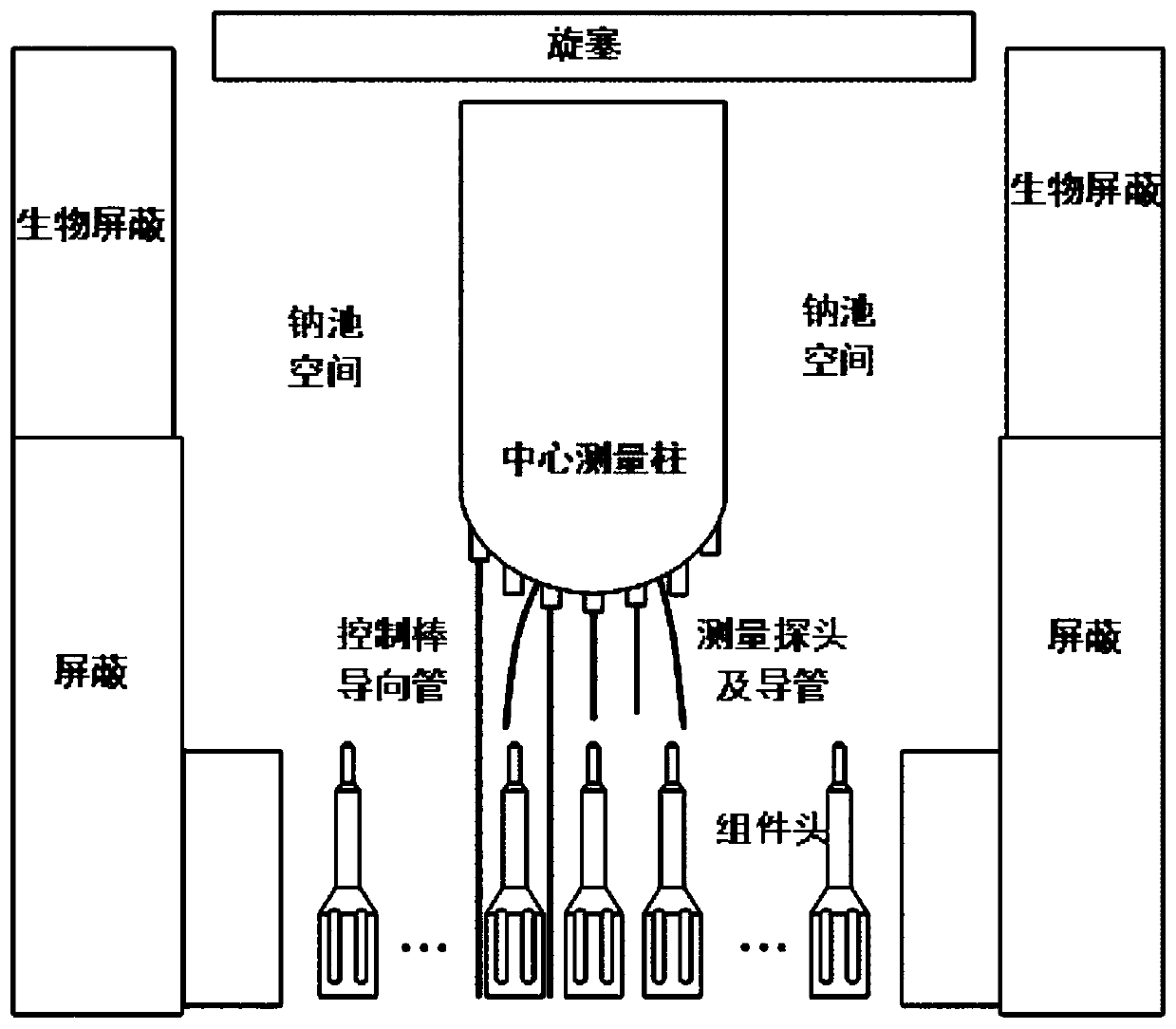
Refueling apparatus for sodium-cooled fast reactor and method for the same
ActiveUS20090129527A1Improve handlingSimple processNuclear energy generationNuclear monitoringUltrasonic sensorSodium-cooled fast reactor
A refueling apparatus for charging nuclear fuel in a reactor vessel, the refueling apparatus including: a refueling unit loading new nuclear fuel to a core or extracting spent nuclear fuel from the core; and a waveguide sensor unit including an ultrasonic wedge to form a Lamb wave, a waveguide with an end connected to the ultrasonic wedge and with another end transmitting the Lamb wave into the reactor vessel, and an ultrasonic sensor connected to the ultrasonic wedge and sensing a reflection signal reflected from an inside of the reactor vessel, the waveguide being formed in a plate shape and mounted in an end of the refueling unit. The waveguide integrally moves with the refueling unit, and the waveguide sensor unit detects a condition of the inside of the reactor vessel, while the refueling unit refuels the fuel assembly in the reactor vessel.
Owner:KOREA HYDRO & NUCLEAR POWER CO LTD +1
A method for determining the heat transfer and drying point of a debris bed after a serious accident of a sodium cooled fast reactor
ActiveCN109033529ASimple calculationDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsEngineeringSodium-cooled fast reactor
A method for determining the heat transfer and drying point of a debris bed after serious accident of sodium-cooled fast reactor features that boundary conditions of debris bed aft serious accident ofreactor are determined and grid is divided according to energy equation of temperature distribution. Then the equivalent thermal conductivity of the debris bed is calculated for the non-boiling state, boiling state and drying state respectively. Then, the equivalent thermal conductivity of the debris bed in the channel region where the debris particles are cracked by steam extrusion is calculatedwhen the debris bed is superheated locally. Finally, the initial conditions and boundary conditions are set to calculate the next time step temperature and the equivalent thermal conductivity of eachgrid, and the temperature distribution of the debris bed and the location of the drying point at each time point are finally obtained. A simple equivalent thermal conductivity model is used to calculate the complex energy transfer process in the debris bed, and the equivalent thermal conductivity of the debris bed adopts different calculation modes according to different working conditions, and finally the temperature distribution at each time in the cooling process of the debris bed of the sodium-cooled fast reactor and the position of the debris bed drying point when the cooling is insufficient are obtained.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Steam generator for sodium cooled fast reactor, heat transfer tubes thereof, and leak detection unit for heat transfer tube thereof
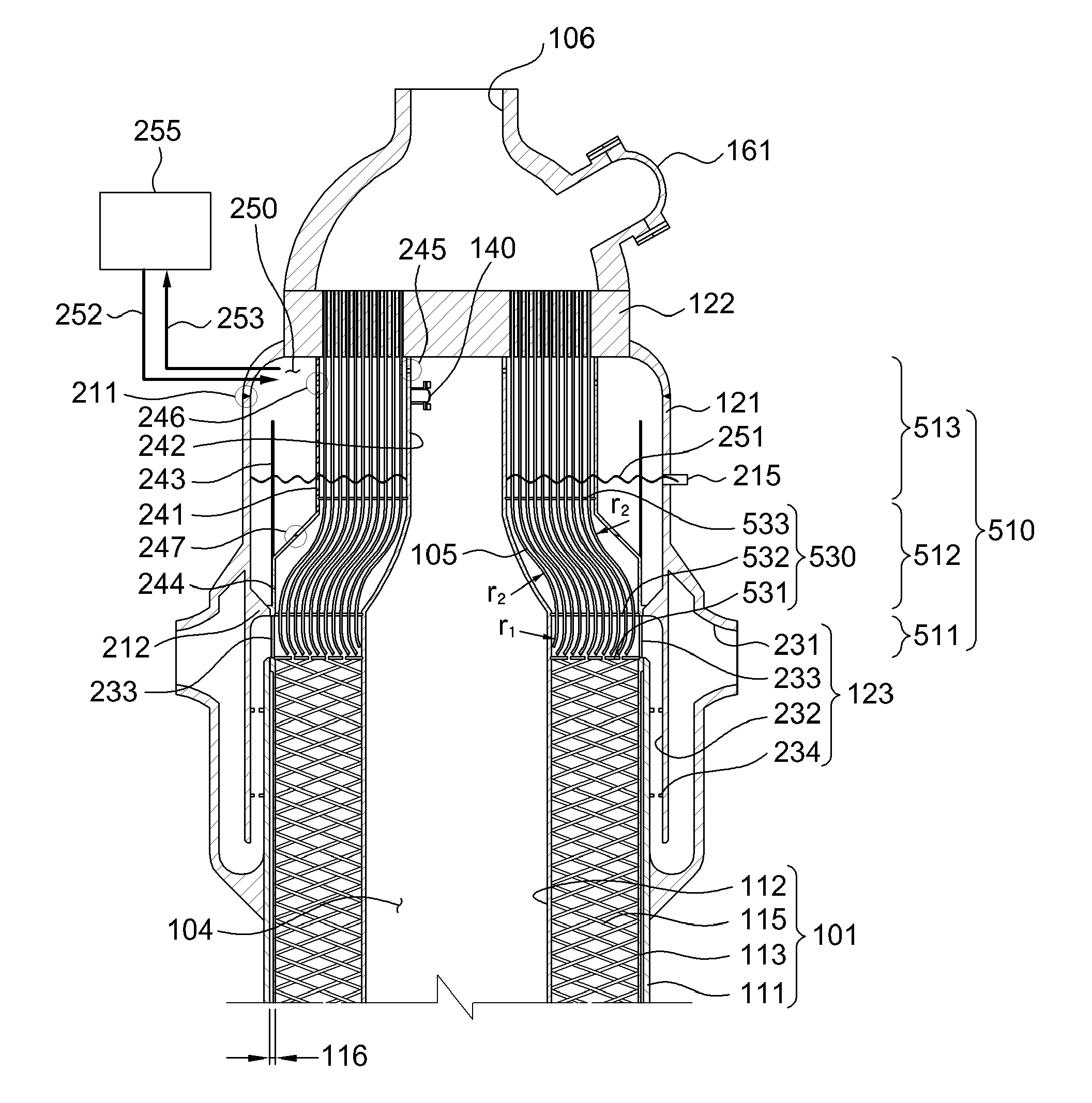
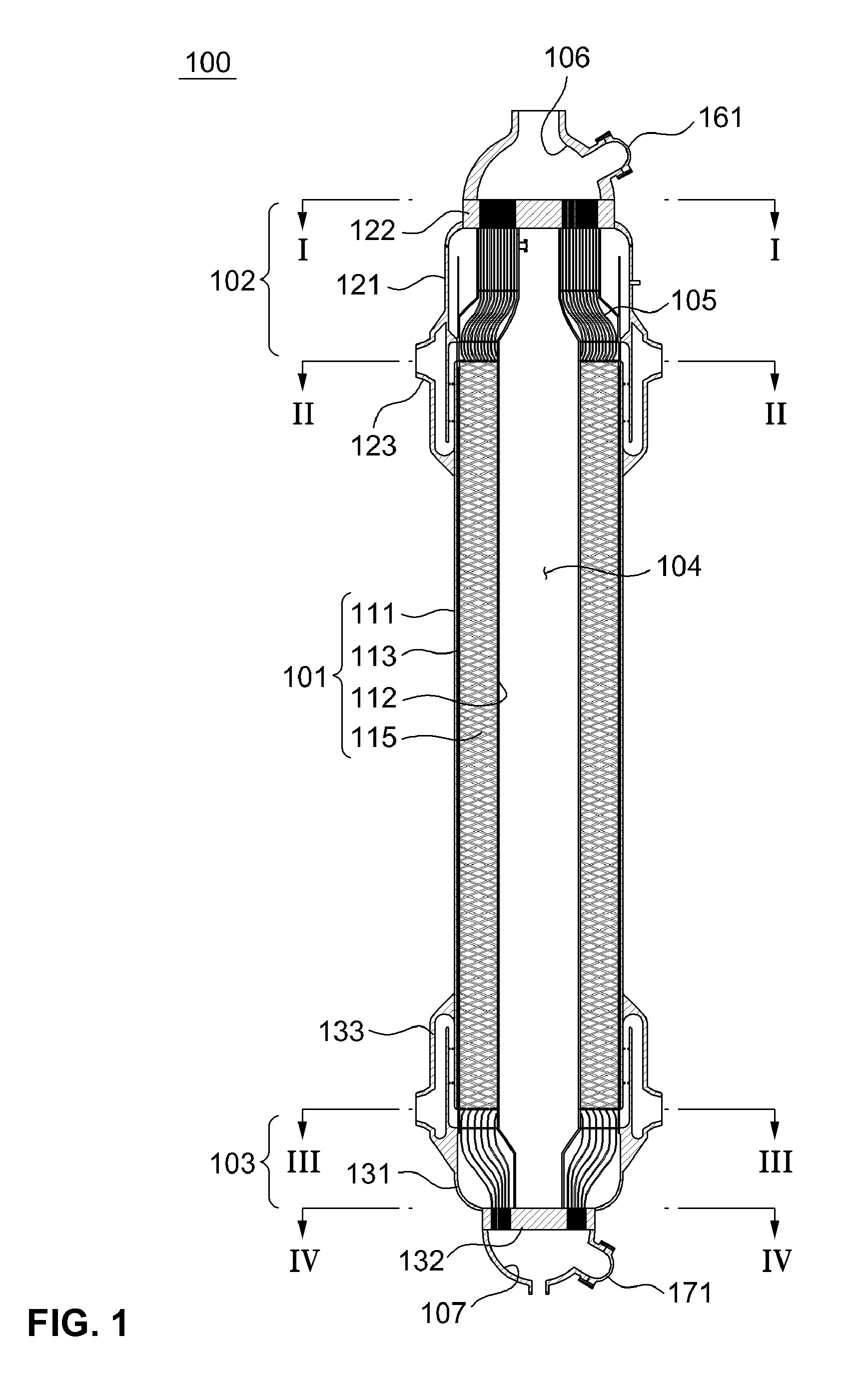
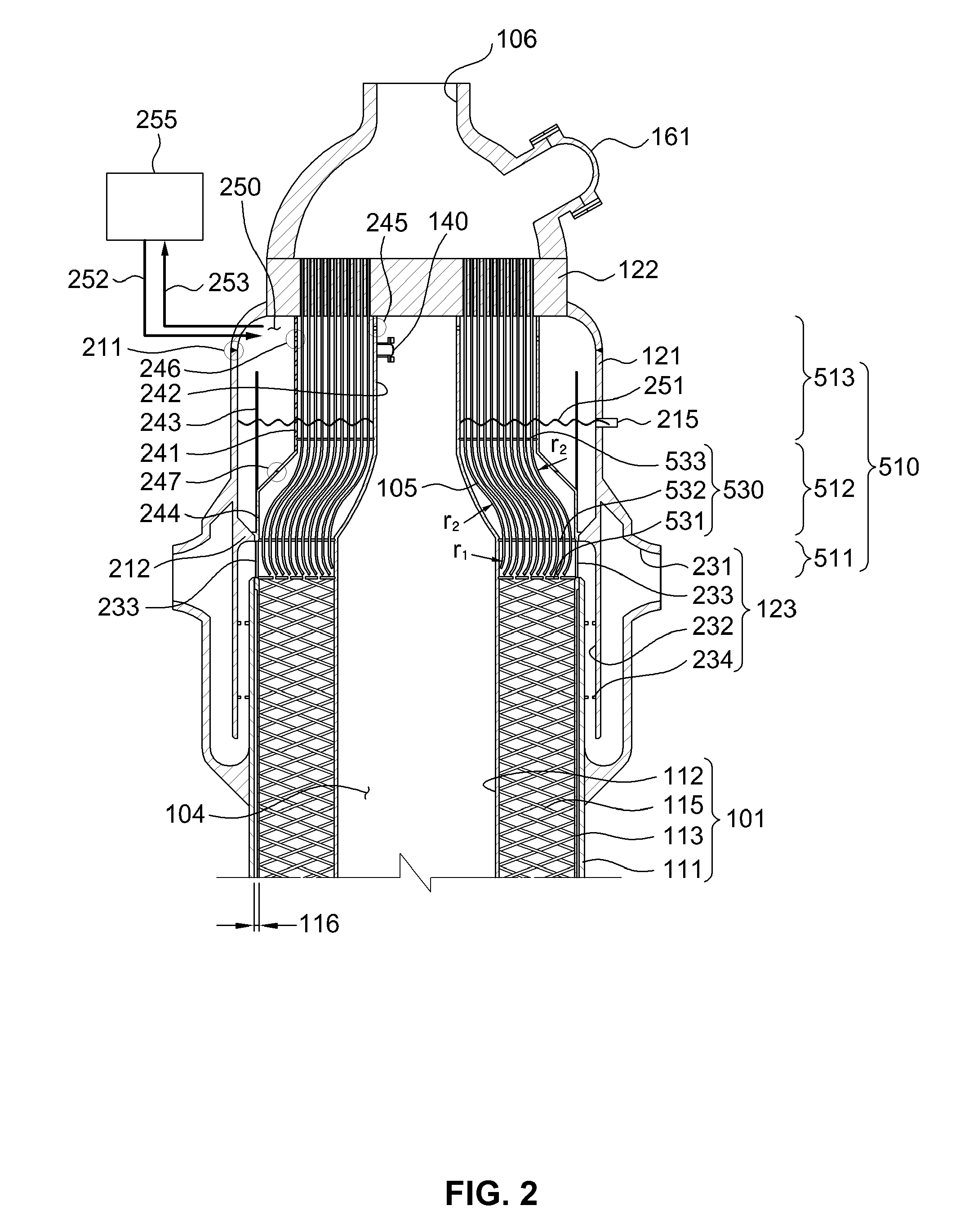
InactiveUS20100064988A1Avoid lostReduce pressure riseInternal combustion piston enginesBoiler water tubesDouble wallThermal expansion
A steam generator, used in a helical coil type steam generator for a sodium-cooled fast reactor which has heat transfer tubes of a double-wall tube structure, with high heat transfer efficiency and a heat transfer tube damage detection unit that can detect on-line in real-time whether the heat transfer tube is damaged or not. The heat transfer tube of a steam generator for a sodium-cooled fast reactor, includes an inner tube formed with a first material; an outer tube formed with a second material that is in close contact with the inner tube and which has a thermal expansion coefficient less than that of the first material; and a plurality of helium flow grooves formed between the inner tube and the outer tube along a lengthwise direction of the heat transfer tube for flowing helium gas. The inner tube and the outer tube are identically due to heat for the temperature difference generated during normal operation of the steam generator, so the degree of close contact between the inner tube and the outer tube does not decrease, and the decrease of heat transfer efficiency can be prevented.
Owner:KOREA ATOMIC ENERGY RES INST +1
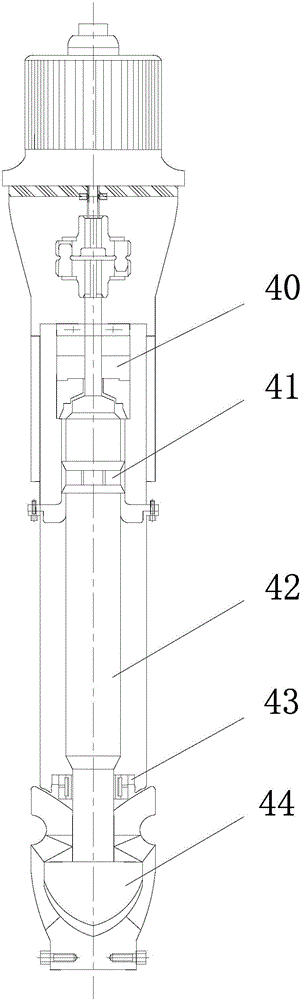
Mounting duct for sodium-cooled fast reactor inner sodium liquid level meter
ActiveCN101335057AImprove protectionAvoid shockNuclear energy generationFast fission reactorsEngineeringSodium-cooled fast reactor
The invention discloses an installation channel used for a sodium fluid level gauge in a sodium-cooled fast reactor. The channel of the invention comprises a pipeline with holes and a stop component is connected in the pipeline. In addition, the invention also provides an installation channel device which can carry out the locating and protection to the sodium fluid level gauge.
Owner:CHINA INSTITUTE OF ATOMIC ENERGY
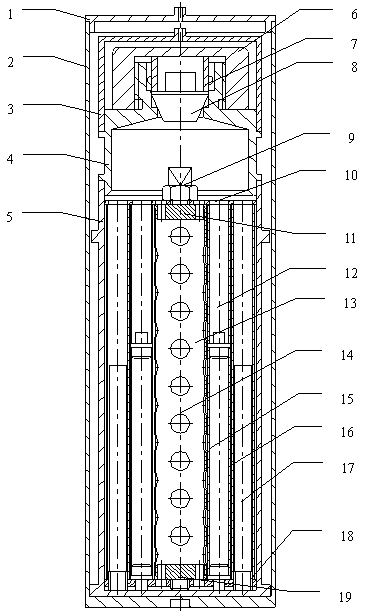
Sodium-sodium heat converter
ActiveCN101174481AEnsure safetyNuclear energy generationHeat exchanger casingsEngineeringSodium-cooled fast reactor
The invention disclose an immersion sodium-sodium heat exchanger for sodium-cooled fast reactor, comprising a safety housing, wherein, an outer tube is arranged in the safety housing; an inner tube is arranged in the outer tube; the top of the inner tube is open, while the bottom of the inner tube is communicated with the bottom of the safety housing; the lower part of the safety housing is sealed by an upper tube sheet and a lower tube sheet; a heat exchange pipe bundle is arranged between the upper tube sheet and the lower tube sheet; the inlet of the heat exchange pipe bundle is communicated with the bottom of the safety housing, while the outlet is communicated with a sodium outlet; an inlet grate is arranged at the upper part of the sealing section between the upper tube sheet and the lower tube sheet, while an outlet grate is arranged at the lower part. The invention has the advantages that heat exchange of a loop and an intermediate loop in an emergency residual heat release system by means of natural circulation, so as to release the residual heat of the reactor core in the sodium pool and ensure the safety of the reactor core.
Owner:CHINA INSTITUTE OF ATOMIC ENERGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com