Ferritic oxide dispersion strengthened alloy with enhanced room temperature and high temperature strength and manufacturing method thereof
A technology of dispersion strengthening and high-temperature strength, which is applied in the field of ferrite oxide dispersion-strengthening alloys and its manufacturing, can solve the problems of small enhancement of high-temperature strength characteristics and achieve good tensile properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0045] Example 1. Manufacture of Ferritic Oxide Dispersion Strengthened Alloy
[0046] Ferritic oxide dispersion strengthened alloys having the compositions listed in Table 1 below were produced.
[0047] [Table 1]
[0048]
Fe
Cr
W
Mo
Ti
Zr
Y 2 o 3
Reference Alloy 1
Bal.
15
2
0.25
0.35
Reference Alloy 2
Bal.
15.5
1
1.8
0.25
0.35
new alloy 1
Bal.
15.5
1
1.8
0.1
0.2
0.35
New Alloy 2
Bal.
15.5
2
1
0.1
0.2
0.35
New Alloy 3
Bal.
14
0.2
1
0.1
0.25
0.35
[0049] (unit weight%)
[0050] That is, high-purity raw material powder (Fe, W, Cr, Mo, Ti, Zr, particle size below 200 mesh, purity above 99%) and Y 2 o 3 Powders (below 50nm, purity 99.9%) are mixed by weight, and the alloy powder is produced by mechanical alloying method using a horizontal ball mil...
Embodiment 2
[0051] Embodiment 2. Comparison experiment of normal temperature and high temperature strength characteristics
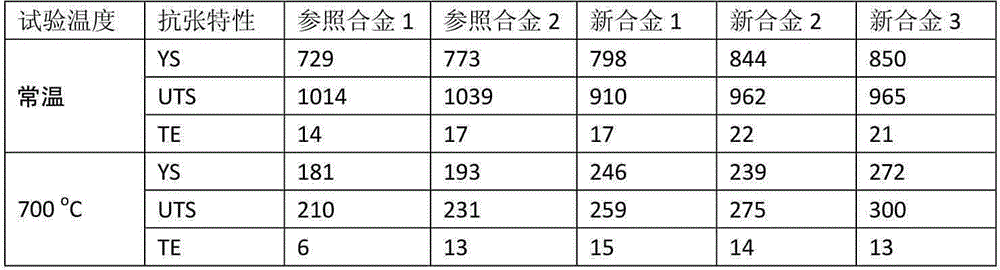
[0052] Measure its YS (yield strength), UTS (ultimate tensile strength) and TE (total elongation) under normal temperature and 700 ℃ conditions for 5 kinds of ferritic oxide dispersion strengthened alloys manufactured in embodiment 1, and The result is shown in the figure 1 middle.
[0053] refer to figure 1 It can be seen that the yield strength of reference alloy 1 without zirconium (Zr) and molybdenum (Mo) is 729 MPa at room temperature and 181 MPa at 700°C. The yield strength of Reference Alloy 2 not containing zirconium (Zr) was 773 MPa at room temperature and 193 MPa at 700°C. In contrast, for the new alloys 1, 2 and 3 of the present invention that add molybdenum (Mo) as a solid solution strengthening element and add trace alloy elements such as titanium (Ti) and zirconium (Zr), at room temperature The yield strength is 798-850MPa, and it is 239-272MPa a...
Embodiment 3
[0055] Embodiment 3. Comparative experiment of high temperature creep characteristics
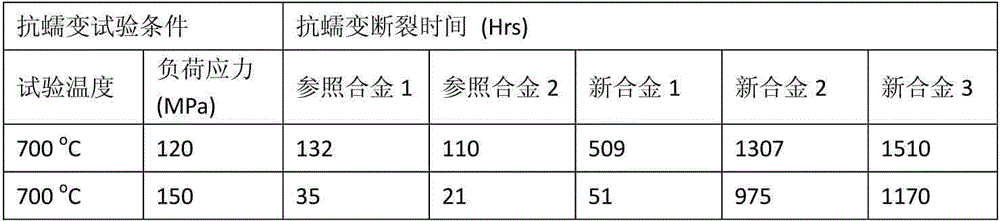
[0056] Creep (Creep) tests were carried out at 700°C for the five ferritic oxide dispersion-strengthened alloys manufactured in Example 1, and the results are shown in figure 2 middle.
[0057] refer to figure 2 It can be seen that under the stress of 120, 150 MPa, compared with the reference alloy 1 and the reference alloy 2, the creep rupture time of the alloys of the present invention (new alloys 1 to 3) is significantly increased.
[0058] The above results show that the ferritic oxide dispersion strengthened alloy according to the present invention has better high temperature creep properties than the existing ferrite oxide dispersion strengthened alloy.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com