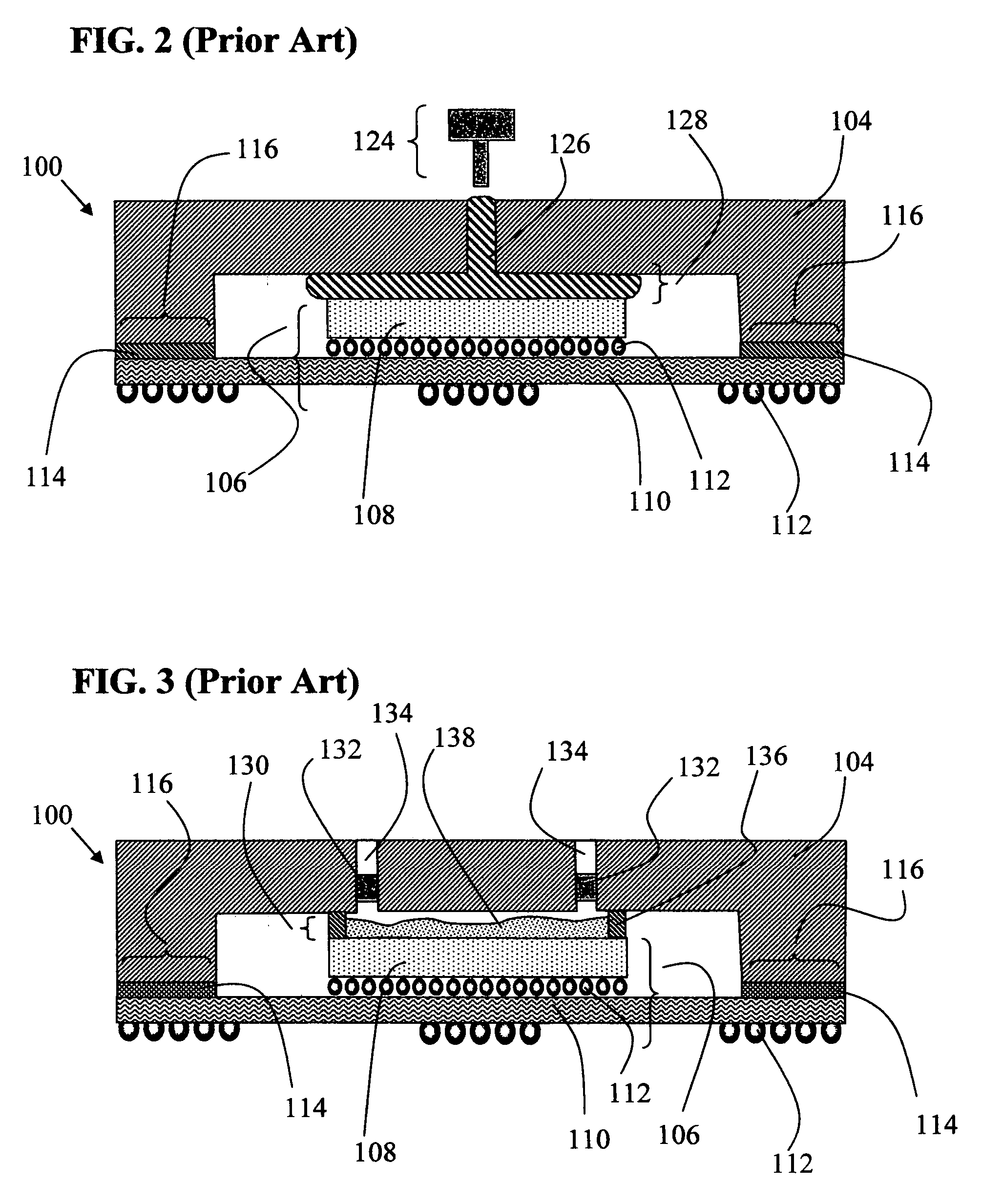
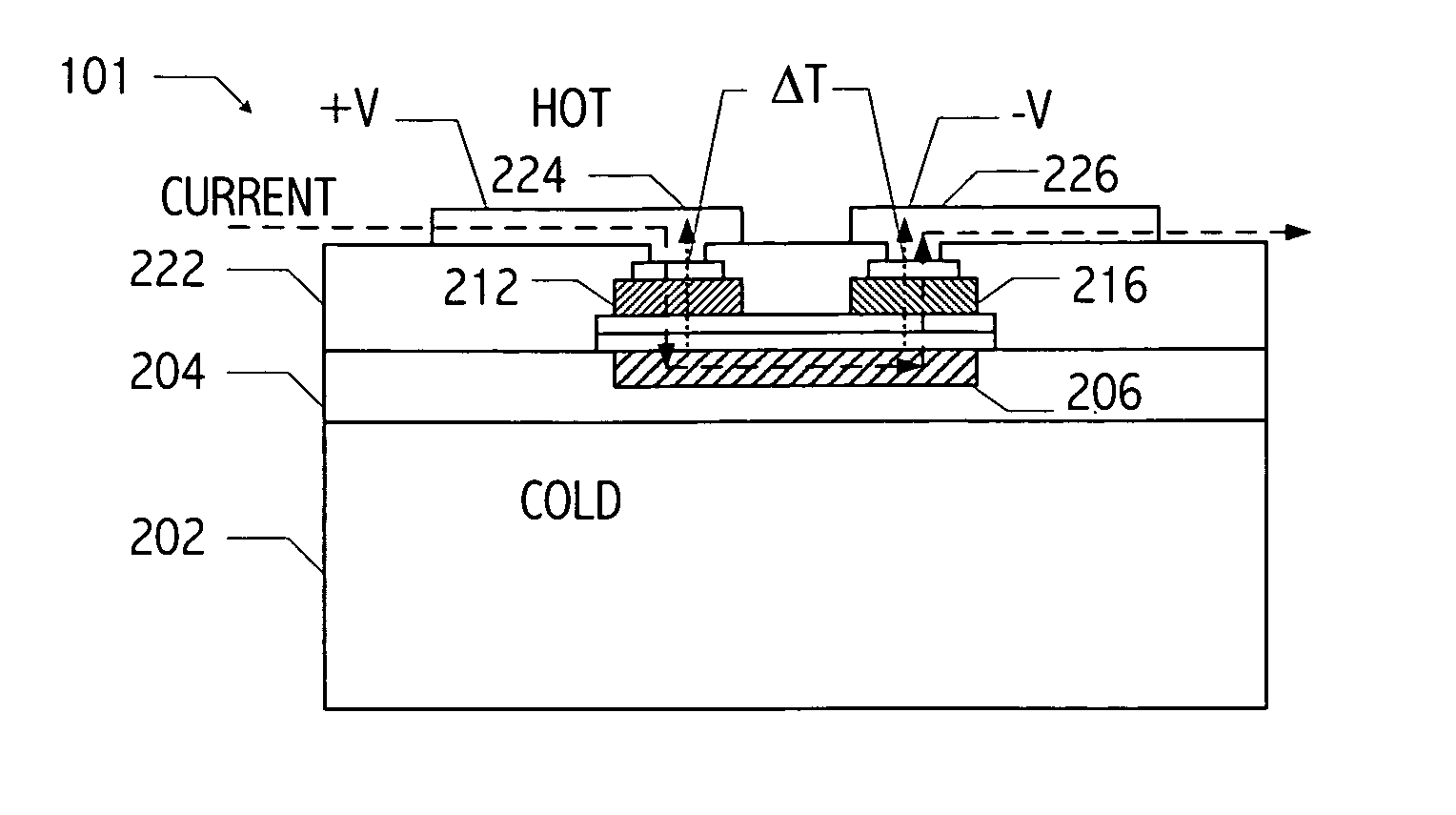
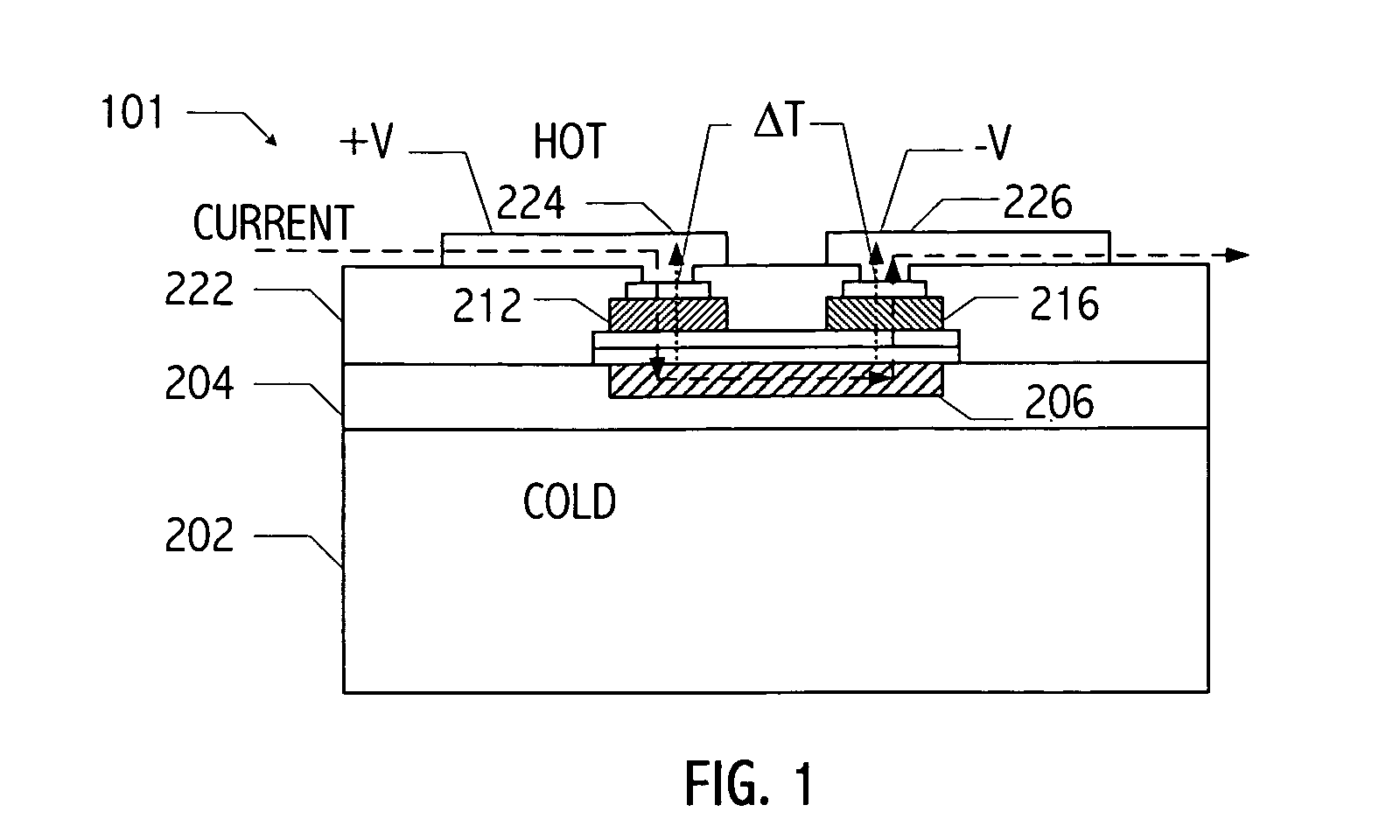
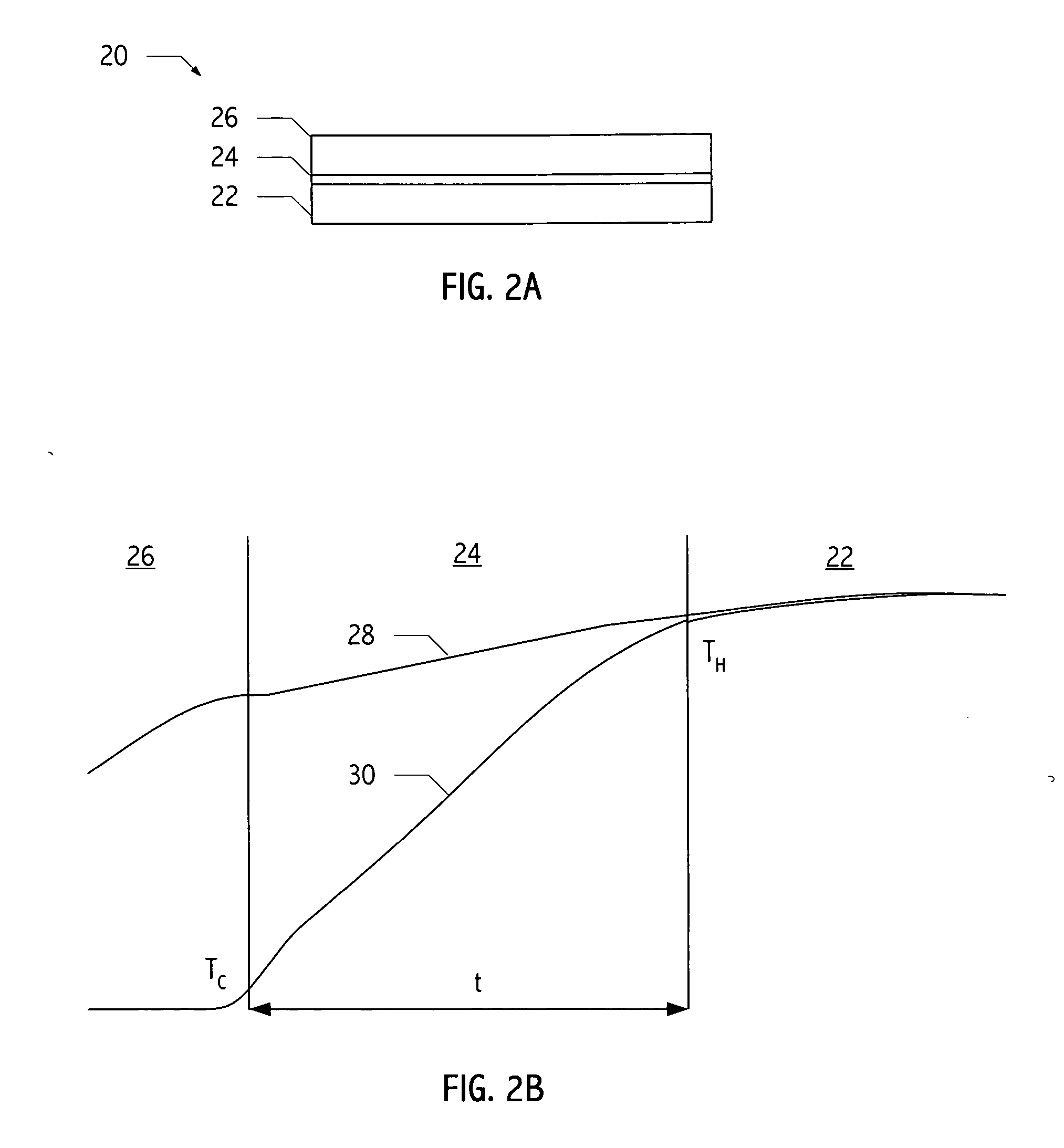
Patents
Literature
5559 results about "Liquid metal" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Liquid metal consists of alloys with very low melting points which form a eutectic that is liquid at room temperature. The standard metal used to be mercury, but gallium-based alloys, which are lower both in their vapor pressure at room temperature and toxicity, are being used as a replacement in various applications.
Method and apparatus for germanium tin alloy formation by thermal CVD
InactiveUS20130280891A1Polycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSelective depositionLiquid metal
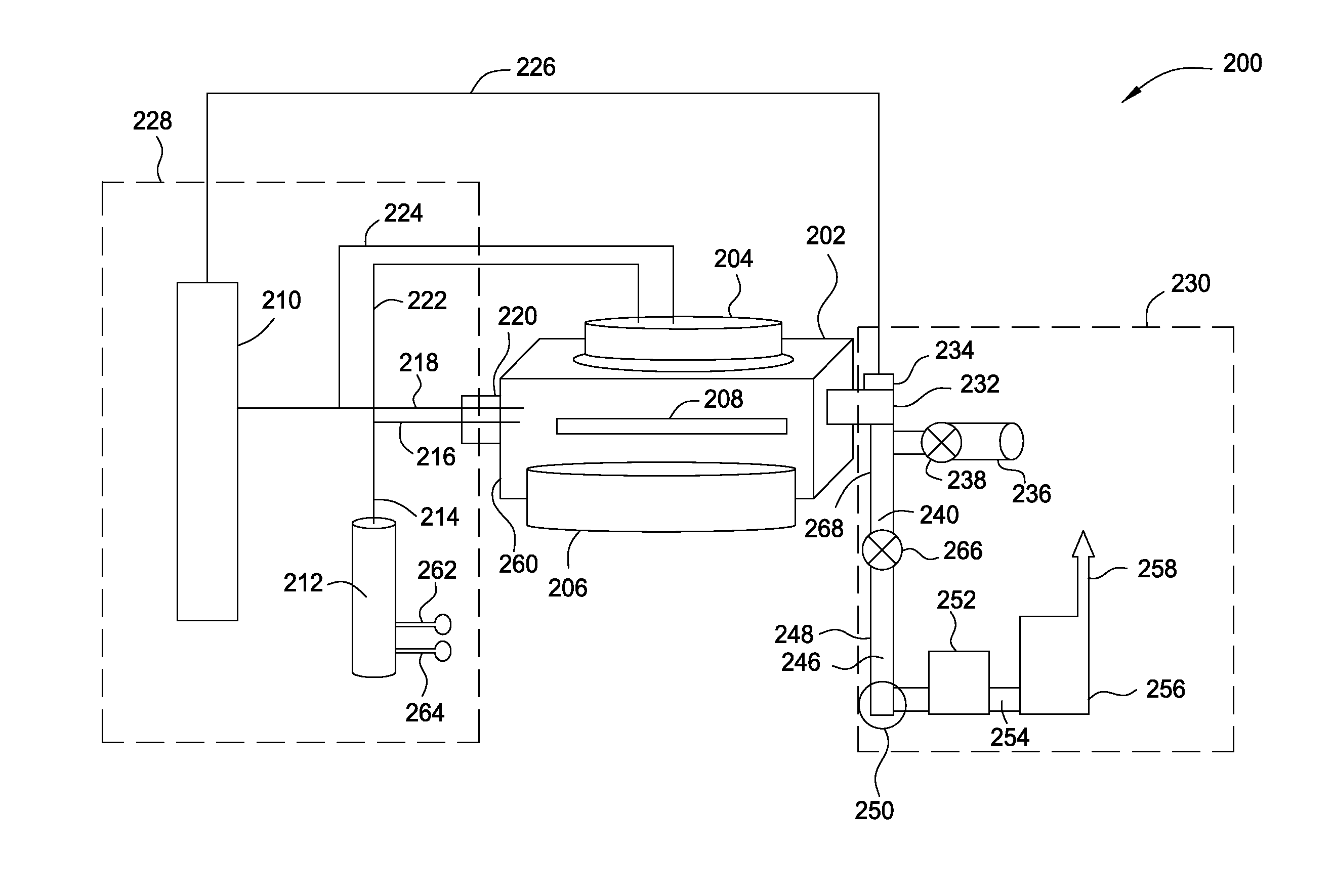
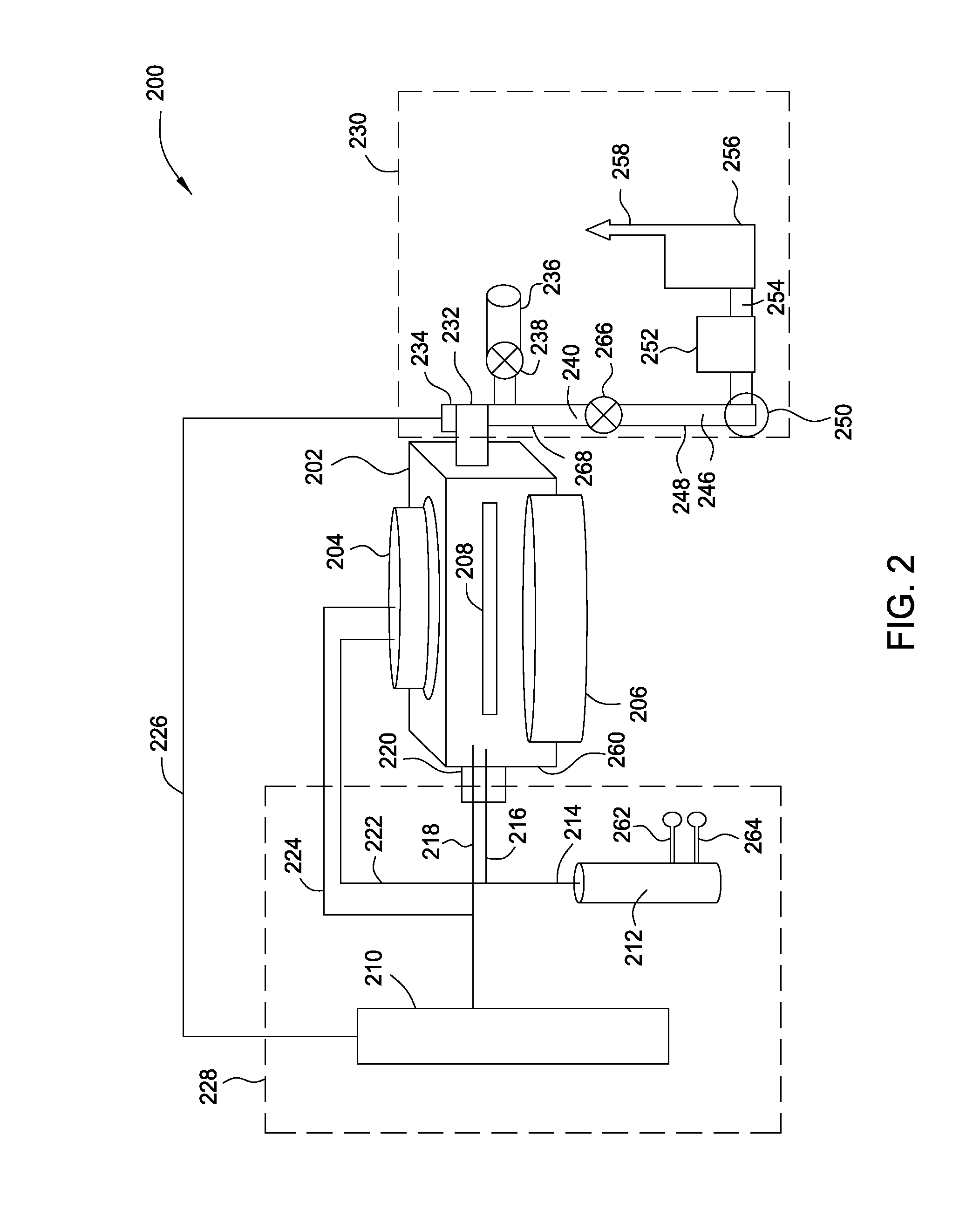
A method and apparatus for forming semiconductive semiconductor-metal alloy layers is described. A germanium precursor and a metal precursor are provided to a chamber, and an epitaxial layer of germanium-metal alloy, optionally including silicon, is formed on the substrate. The metal precursor is typically a metal halide, which may be provided by evaporating a liquid metal halide, subliming a solid metal halide, or by contacting a pure metal with a halogen gas. A group IV halide deposition control agent is used to provide selective deposition on semiconductive regions of the substrate relative to dielectric regions. The semiconductive semiconductor-metal alloy layers may be doped, for example with boron, phosphorus, and / or arsenic. The precursors may be provided through a showerhead or through a side entry point, and an exhaust system coupled to the chamber may be separately heated to manage condensation of exhaust components.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Thermally conductive compositions and methods of making thereof
InactiveUS20050228097A1Material nanotechnologySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsLiquid metalMetal
A composition comprising at least one liquid metal; at least one electrically insulating solid filler comprising thermally conducting materials; at least one curable resin; is provided. The composition is thermally conducting and electrically insulating. A method of making and using such a composition is also provided.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
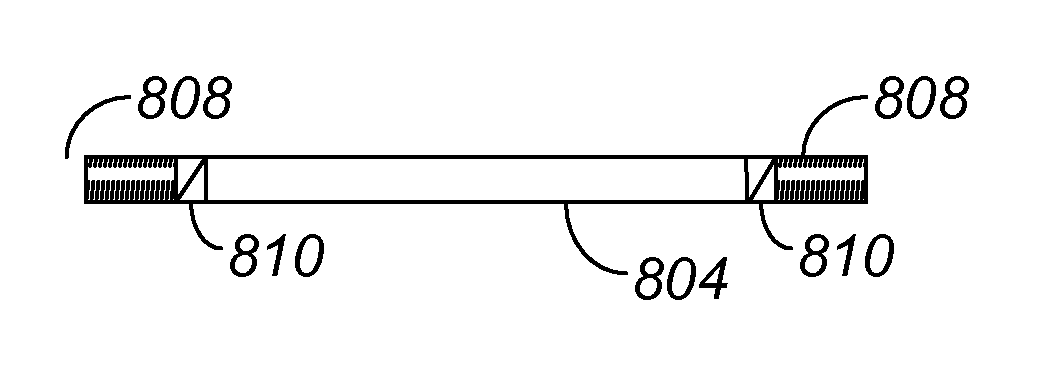
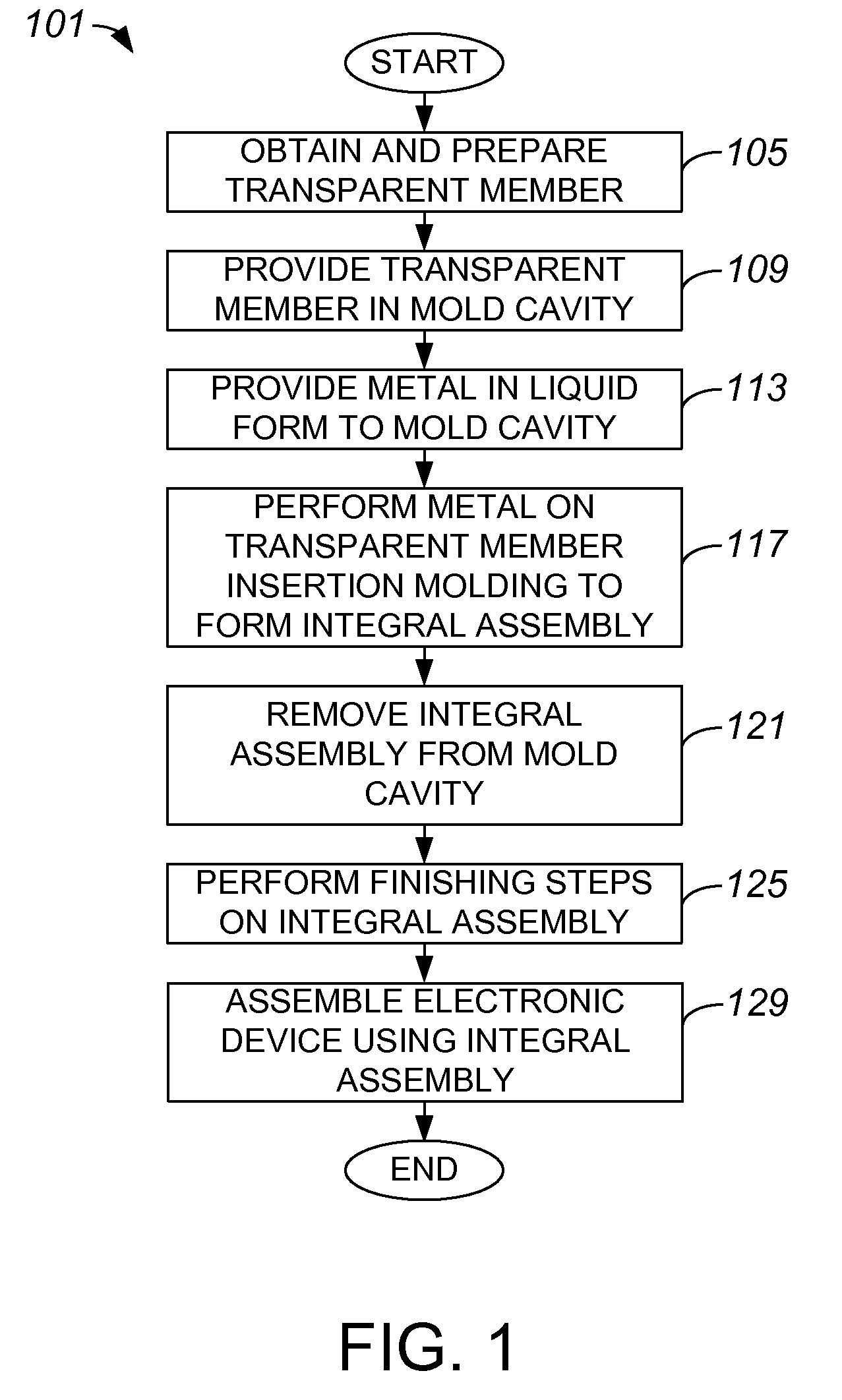
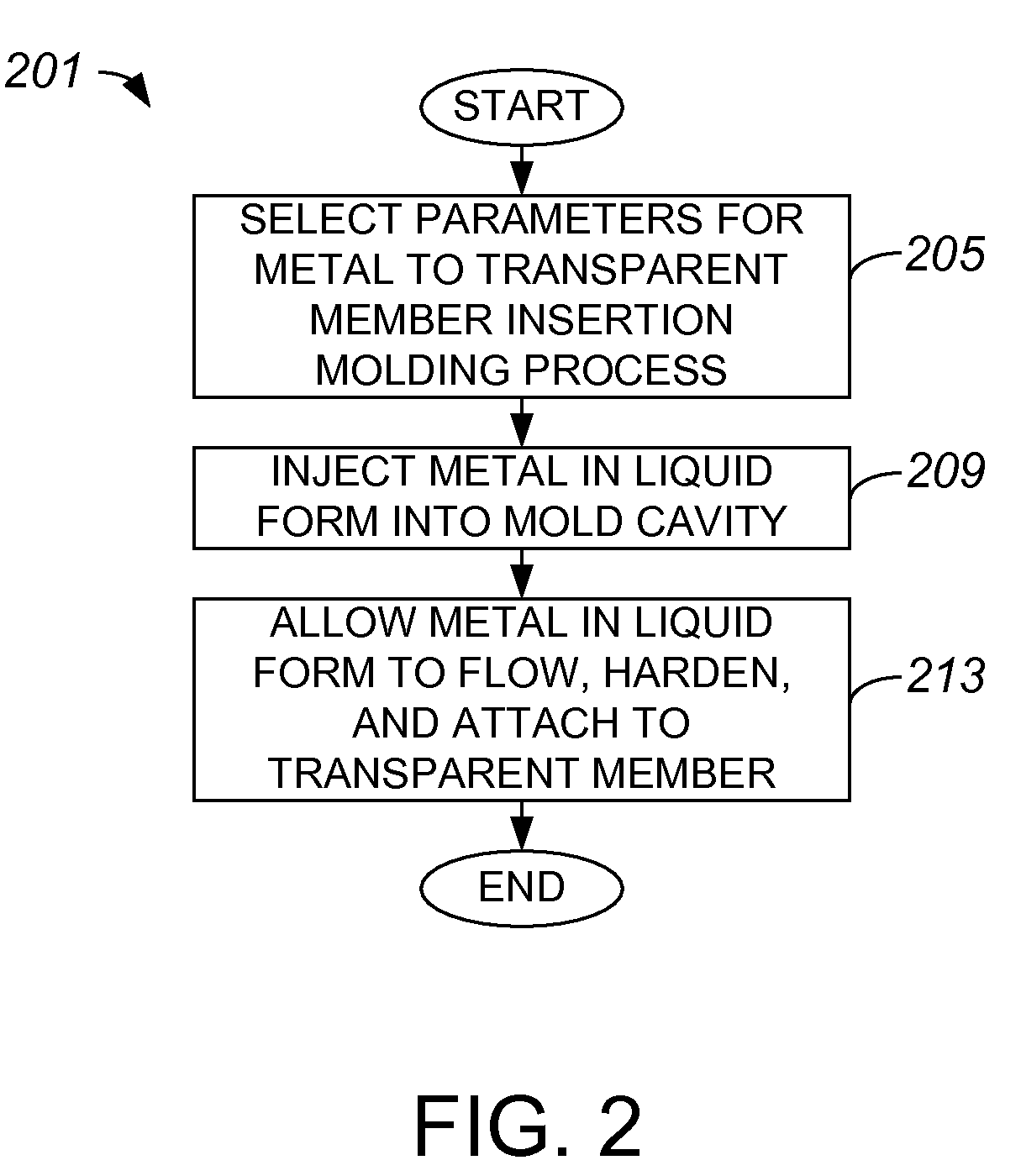
Methods and Systems for Integrally Trapping a Glass Insert in a Metal Bezel
ActiveUS20090017263A1Digital data processing detailsCircuit arrangements on support structuresLiquid metalMetal
Methods and apparatus for creating an overall assembly formed from a transparent member and a metal member are disclosed. According to one aspect of the present invention, a method includes positioning a transparent member in a mold configured for insertion molding, and providing a liquid metal into the mold. The method also includes hardening the liquid metal in the mold. Hardening the liquid metal includes binding the metal to the transparent member to create the integral assembly.
Owner:APPLE INC
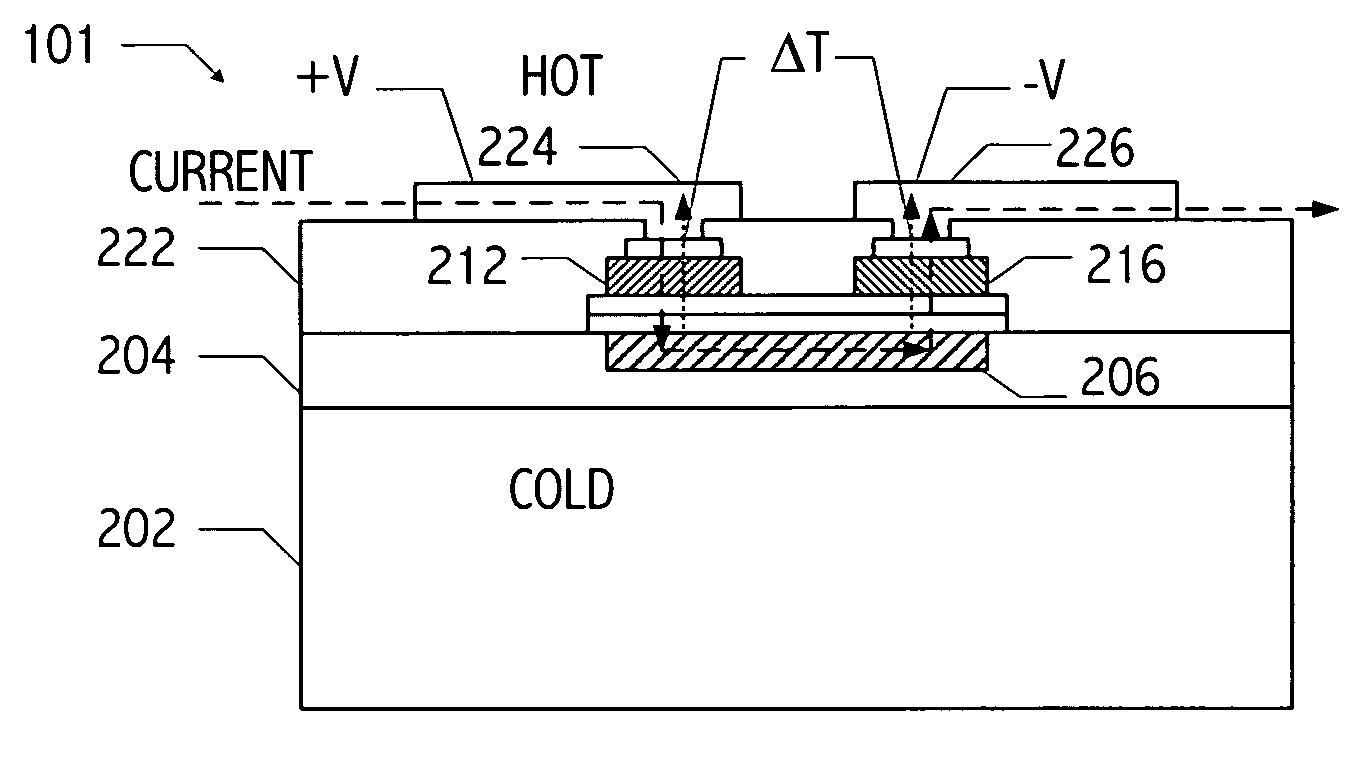
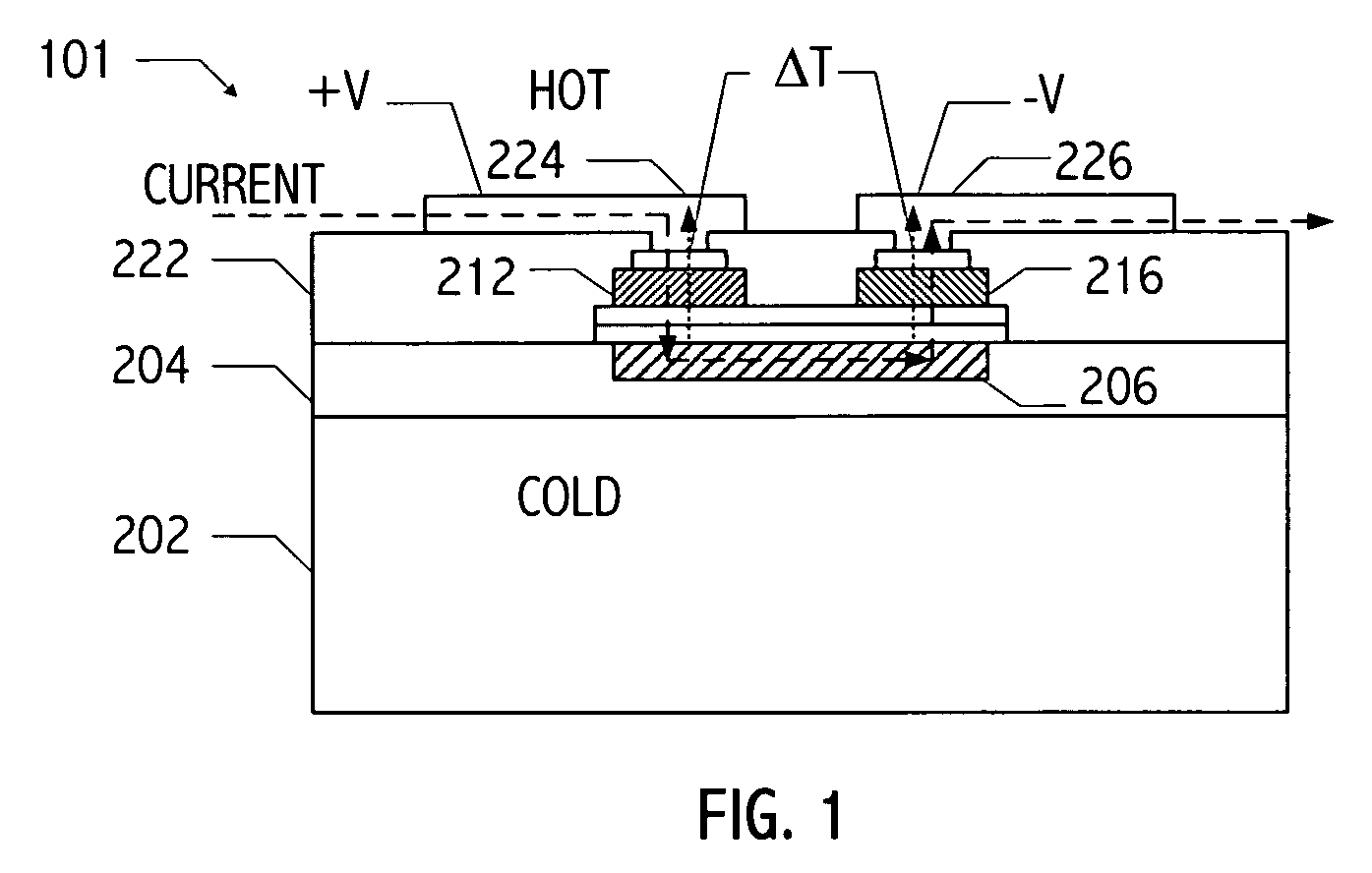
Method for forming a thin-film thermoelectric device including a phonon-blocking thermal conductor
InactiveUS20050150535A1Reduce needReduction in electron thermal conductivityThermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectThermoelectric device manufacture/treatmentElectrical conductorLiquid metal
A vertical, monolithic, thin-film thermoelectric device is described. Thermoelectric elements of opposing conductivity types may be coupled electrically in series and thermally in parallel by associated electrodes on a single substrate, reducing the need for mechanisms to attach multiple substrates or components. Phonon transport may be separated from electron transport in a thermoelectric element. A thermoelectric element may have a thickness less than an associated thermalization length. An insulating film between an electrode having a first temperature and an electrode having a second temperature may be a low-thermal conductivity material, a low-k, or ultra-low-k dielectric. Phonon thermal conductivity between a thermoelectric element and an electrode may be reduced without a significant reduction in electron thermal conductivity, as compared to other thermoelectric devices. A phonon conduction impeding material may be included in regions coupling an electrode to an associated thermoelectric element (e.g., a liquid metal).
Owner:NANOCOOLERS
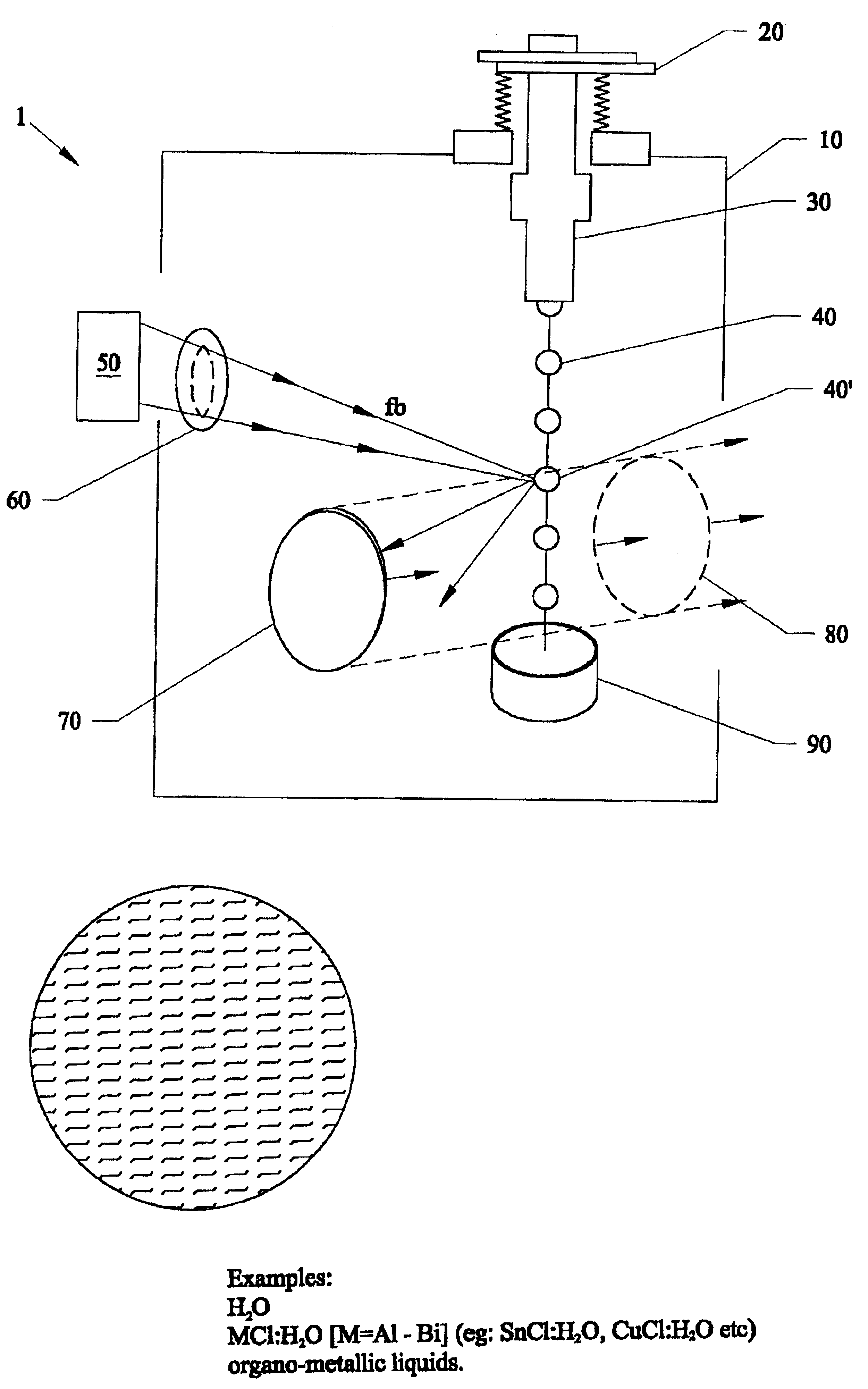
EUV, XUV, and X-ray wavelength sources created from laser plasma produced from liquid metal solutions, and nano-size particles in solutions
InactiveUS6865255B2Efficient and inexpensiveEliminate damageX-ray tube electrodesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHigh power lasersUltraviolet
Special liquid droplet targets that are irradiated by a high power laser and are plasmarized to form a point source EUV, XUV and x-ray source. Various types of liquid droplet targets include metallic solutions, and nano-sized particles in solutions having a melting temperature lower than the melting temperature of some or all of the constituent metals, used a laser point source target droplets. The solutions have no damaging debris and can produce plasma emissions in the X-rays, XUV, and EUV(extreme ultra violet) spectral ranges of approximately 0.1 nm to approximately 100 nm, approximately 11.7 nm and 13 nm, approximately 0.5 nm to approximately 1.5 nm, and approximately 2.3 nm to approximately 4.5 nm. The second type of target consists of various types of liquids which contain as a miscible fluid various nano-size particles of different types of metals and non-metal materials.
Owner:CENT FLORIDA UNIV OF
Multi-structure metal matrix composite armor and method of making the same
InactiveUS6895851B1Improve efficiencyWelding/cutting media/materialsArmour platesPorosityLiquid state
A lightweight armor system may comprise multiple reinforcement materials layered within a single metal matrix casting. These reinforcement materials may comprise ceramics, metals, or other composites with microstructures that may be porous, dense, fibrous or particulate. Various geometries of flat plates, and combinations of reinforcement materials may be utilized. These reinforcement materials are infiltrated with liquid metal, the liquid metal solidifies within the material layers of open porosity forming a dense hermetic metal matrix composite armor in the desired product shape geometry. The metal infiltration process allows for metal to penetrate throughout the overall structure extending from one layer to the next, thereby binding the layers together and integrating the structure.
Owner:CERAMICS PROCESS SYST
Thermal cycling system
InactiveCN101522909ARapid productionReduce production processMicrobiological testing/measurementEngineeringLiquid metal
This invention provides a system for performing PCR, and real time PCR in particular, with great speed and specificity. The system employs a heat block containing a liquid composition to rapidly transfer heat to and from reaction vessels. The system makes use of the reflective properties of the liquid metal to reflect signal from the PCR into the vessel and out the top. In this way, the signal can be measured by an optical assembly in real time without removing the vessels from the heat block.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Prefabricated part of composite abrasion-resistant part and method for manufacturing abrasion-resistant part with same
The invention relates to a prefabricated part of a composite abrasion-resistant part and a method for manufacturing the abrasion-resistant part with the same. The prefabricated part is formed by mixing metal powder with carbide ceramic particles or particles by crushing a hard alloy and sintering the mixture at a high temperature and can be made into special shapes of columns, strips, blocks, honeycombs, and the like. The method comprises the following steps of: regularly arranging prefabricated parts on the end surface of a cast form; casting liquid metal by adopting a common or negative pressure cast method; impregnating the liquid metal into the prefabricated parts to form an abrasion-resistant part of a composite material, wherein the surface layer of the abrasion-resistant part comprises a matrix metal and a composite material. The abrasion-resistant part of the composite material, which is made by using the method, ensures the wear-resistant performance of the abrasion-resistant part and has high anti-impact capability.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV +1
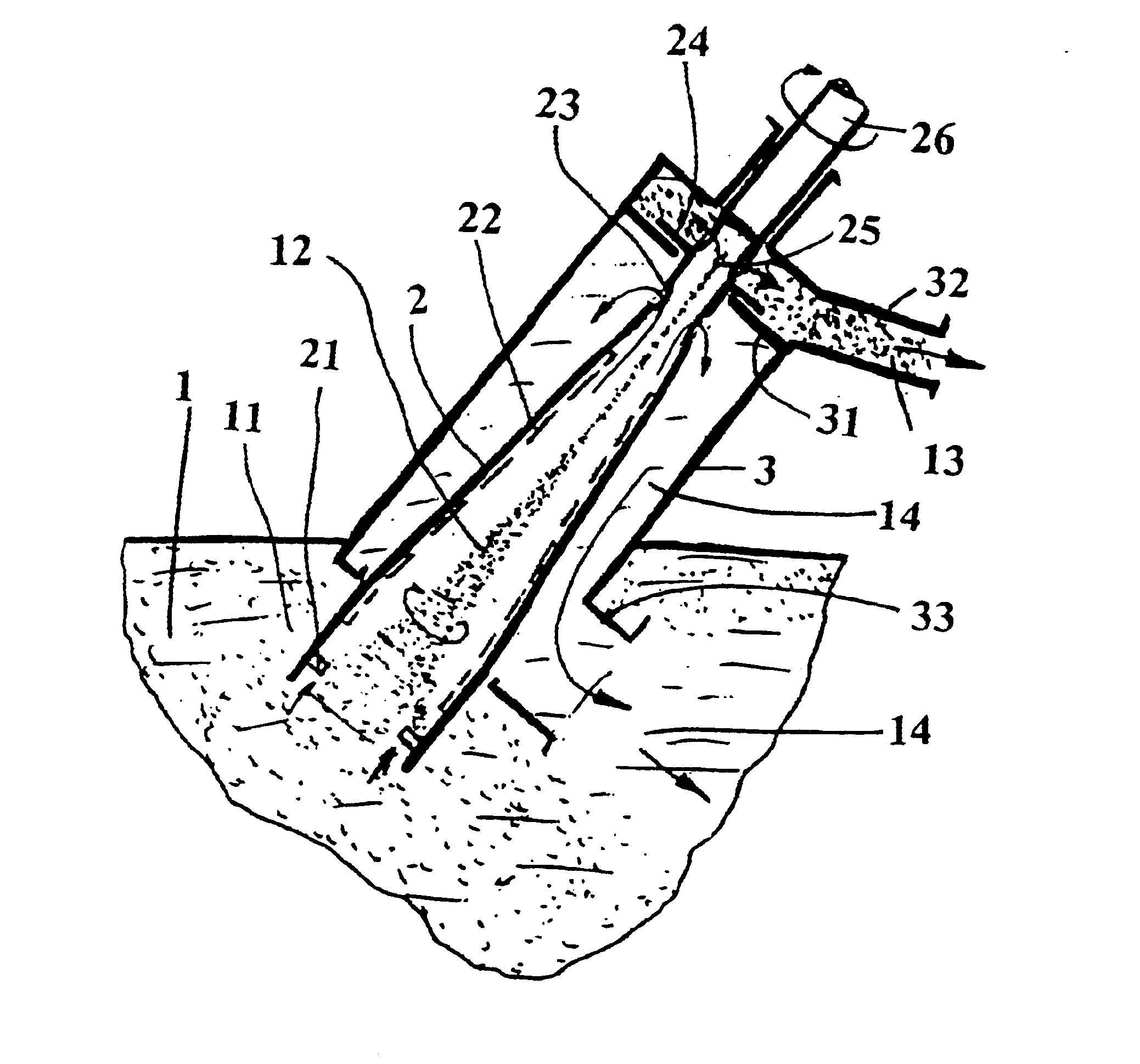
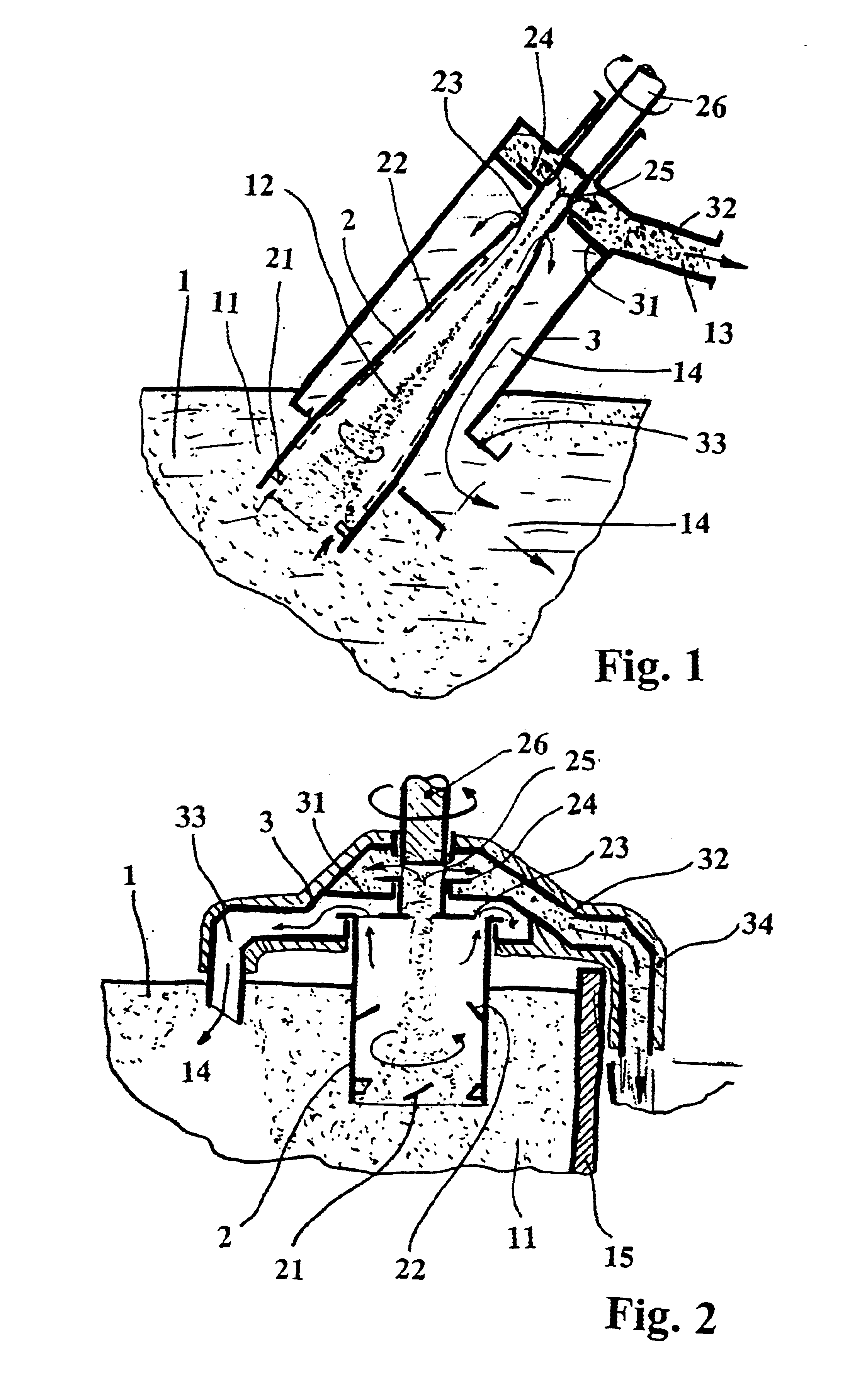
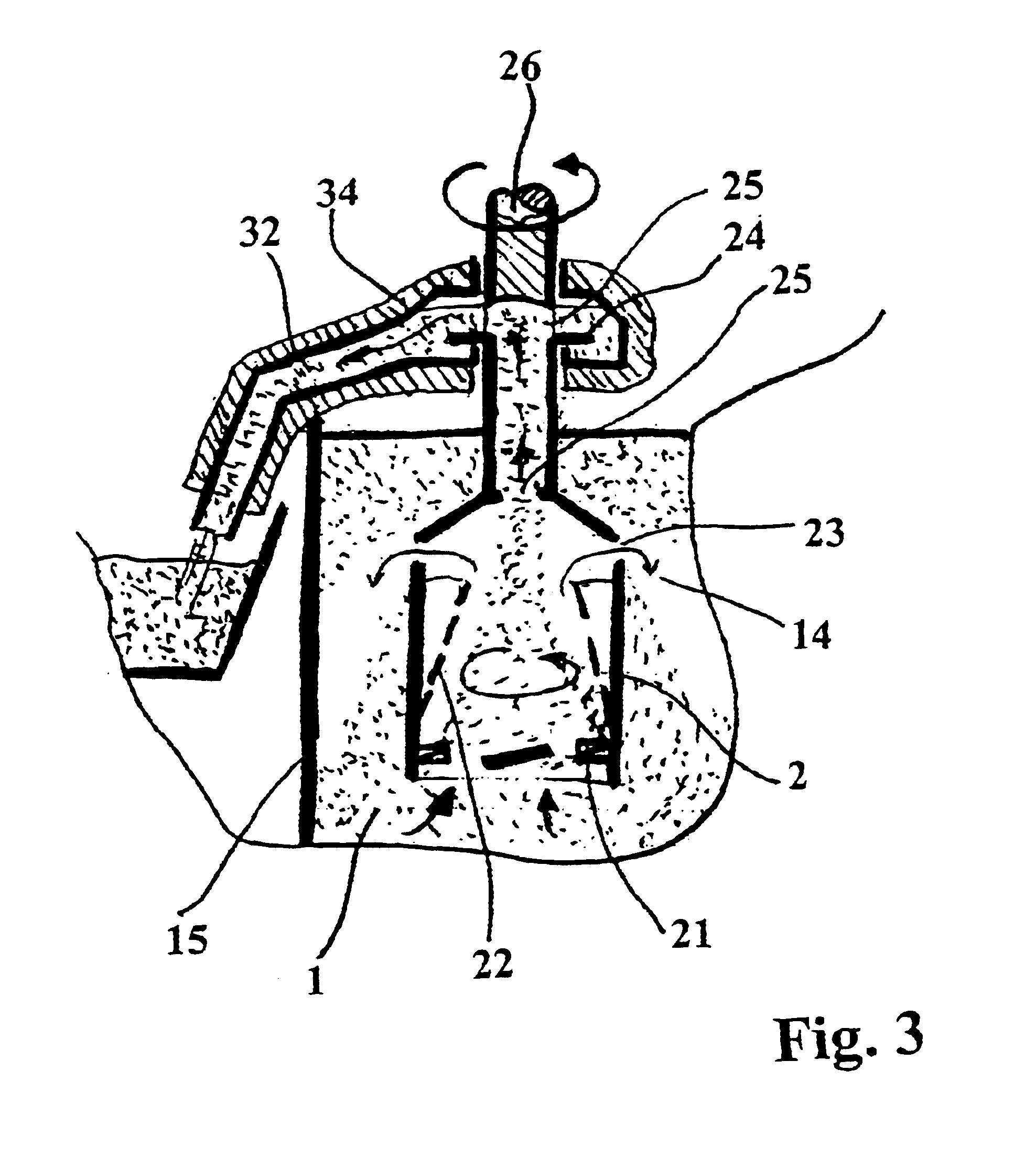
Process for precipitating compounds from zinc metal baths by means of a hollow rotary body that can be driven about an axis and is dipped into the molten zinc
InactiveUS6364930B1High acceleration of the metalRapid and highly effective separationHot-dipping/immersion processesSpecific fluid pumpsZinc metalLiquid metal
A process and device are disclosed for precipitating solid compounds from the liquid zinc or liquid zinc-based alloys of a metal bath. According to the disclosed process, partial amounts of the metal phase containing the compound(s) are exposed to an acceleration higher than the acceleration due to gravity and at least partially dissociated thereby into fractions containing heavier and / or lighter components. The molten mass depleted of solid compounds is returned to the metal bath and the part of the molten mass enriched with the desired compounds is discharged. The disclosed device is substantially characterized in that a hollow rotary body (2) is introduced into the molten mass (1). The hollow rotary body (2) can be driven about an axis and is fitted in the submerged or lower area with conveyor means (21) which project into the cavity. In its discharge or upper area, the hollow rotary body (2) is provided with at least one discharge opening (23) for the depleted molten mass (14) eccentrically arranged in its wall and with at least one further discharge opening (25) for the liquid metal enriched with the desired compounds centrally arranged and / or eccentrically arranged on the discharge side. At least one of the upper molten mass discharge openings (23, 24) in the rotary body (2) opens into a discharge area of a housing (3) which at least partially surrounds the rotary body (2).
Owner:ANDRITZ PATENTVERW GES
Process and device for precipitating compounds from zinc metal baths by means of a hollow rotary body that can be driven about an axis and is dipped into the molten zinc
InactiveUS6656415B2High acceleration of the metalRapid and highly effective separationHot-dipping/immersion processesSpecific fluid pumpsLiquid stateZinc metal
Process and device for precipitating solid compounds from zinc metal baths. Partial amounts of the metal phase containing these compounds are exposed to an acceleration higher than gravity and dissociated into fractions containing heavier or lighter components. The molten mass depleted of solid compounds is returned to the metal bath. The device has a hollow rotary body for introduction into the molten mass and provided with a discharge opening for the depleted molten mass and a discharge opening for the liquid metal enriched with the solid compounds.
Owner:ANDRITZ PATENTVERW GES
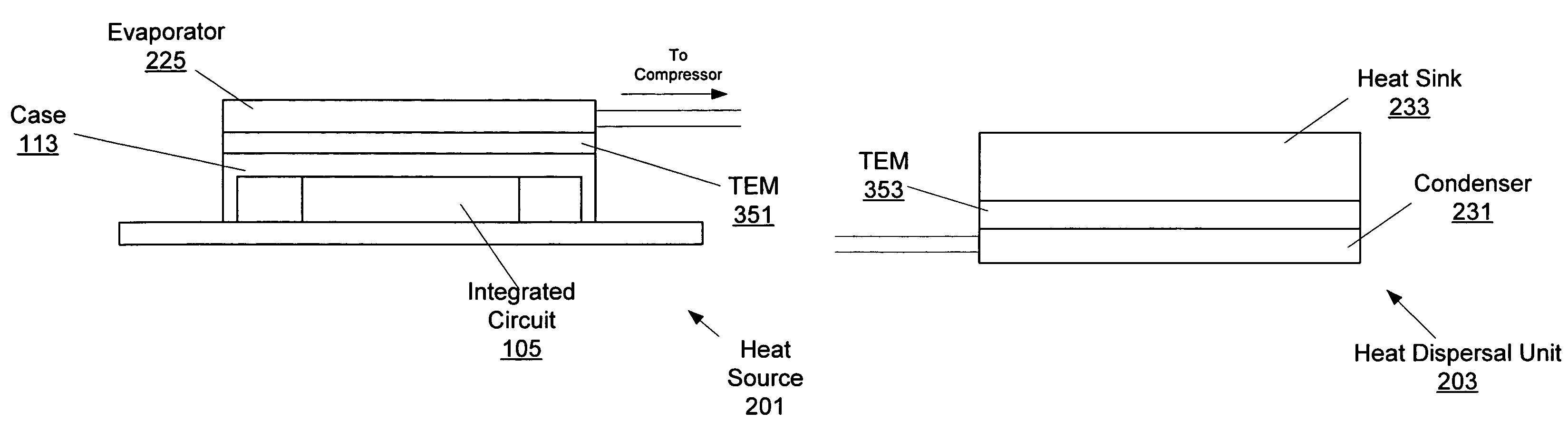
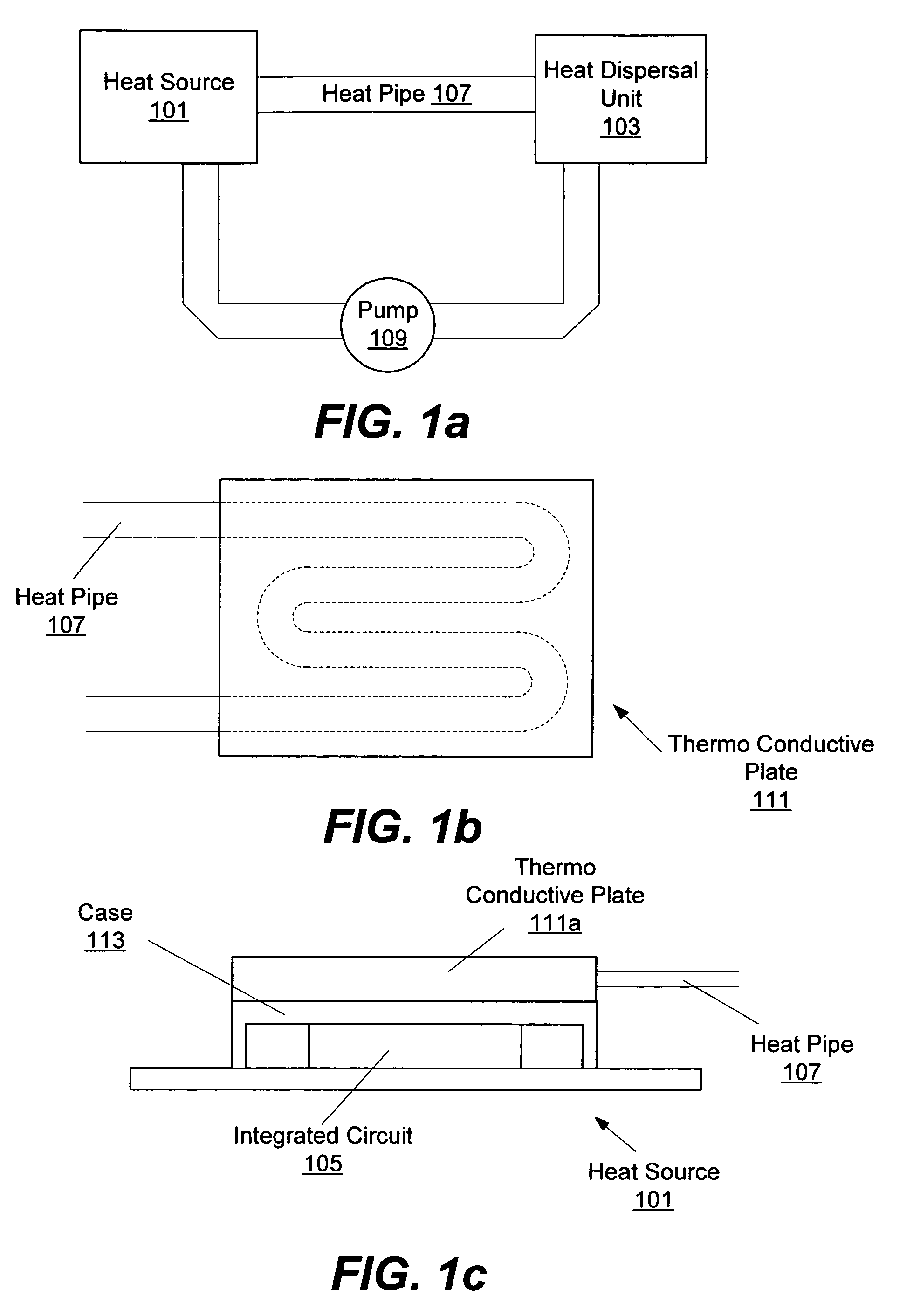
Integrated circuit cooling apparatus and method
ActiveUS7342787B1Digital data processing detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsLiquid metalEngineering
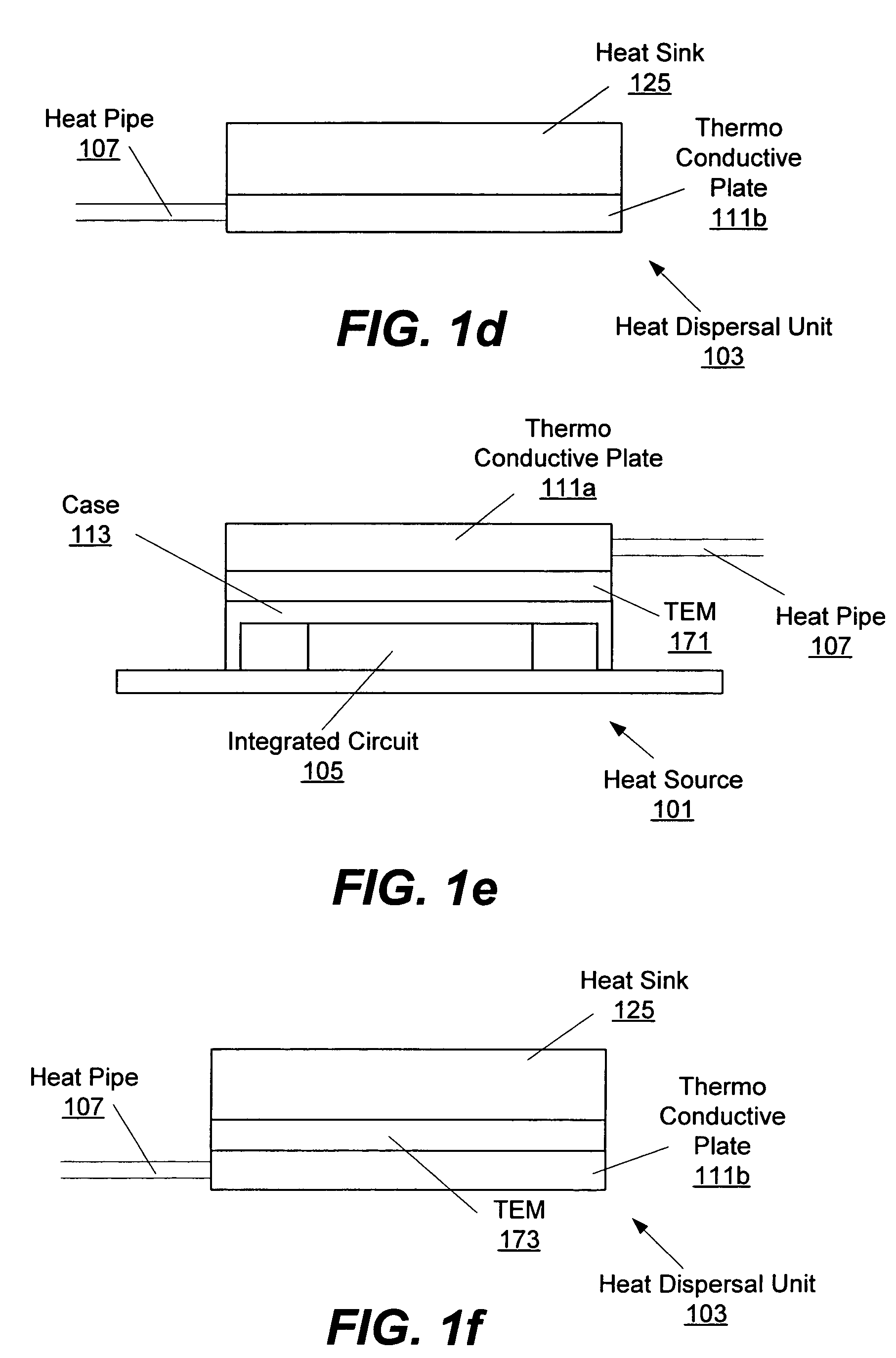
In various embodiments, heat from a computer component may be absorbed into a medium, moved to a remote heat dispersal unit and dissipated into the surrounding air. In some embodiments, the heat dispersal unit may include a heat sink. In some embodiments, the medium may include a liquid metal. In various embodiments, a vapor compression system may include an evaporator, a compressor, a condenser, and an expansion valve. In some embodiments a separate heat pipe may be placed between the computer component and the evaporator. In various embodiments, a thermo conductive plate may be used to thermally couple the heat pipe to various components including the computer component, evaporator, condenser, and / or heat sink. In some embodiments, a thermo electric module (TEM) may be coupled to various parts of the system.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Preparation method of composite lithium metal anode
InactiveCN108365200AReduce chalkingImprove cycle stabilityCell electrodesLi-accumulatorsLiquid metalLithium-ion battery
The invention discloses a preparation method of a composite lithium metal anode and belongs to the technical field of lithium metal batteries. The preparation method of the composite lithium metal anode comprises steps as follows: firstly, the surface of a framework material is modified, the framework material with the lithiophilic surface is prepared, the framework material is contacted with liquid metal lithium, so that the liquid metal lithium is injected into the framework material with the lithiophilic surface, and the composite lithium metal anode is prepared after cooling. The lithiophilic surface can be obtained through modification of various framework materials (including a conductive framework material and an insulated framework material), the framework materials are efficientlycomposited with the liquid metal lithium, and the composite lithium metal anode material is obtained. When the obtained composite lithium metal anode material is assembled in a total battery, growthof lithium dendrites can be effectively inhibited, the volume expansion effect of the anode is relieved, the pulverization phenomenon of the lithium metal anode is reduced, and the cycling stability and the safety of the lithium metal battery are substantially improved, and the cycle life of the lithium metal battery is substantially prolonged.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Systems and methods for compressing plasma
ActiveUS20110026657A1Sufficient reactionIncrease plasma densityNuclear energy generationLow temperature fusion reactorLiquid metalBreaking point
Embodiments of systems and methods for compressing plasma are described in which plasma pressures above the breaking point of solid material can be achieved by injecting a plasma into a funnel of liquid metal in which the plasma is compressed and / or heated.
Owner:GENERAL FUSION INC
Fabrication of conductive pathways, microcircuits and microstructures in microfluidic networks
ActiveUS20110045577A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsThermal energyElectricity
Disclosed herein are a variety of microfluidic devices and solid, typically electrically conductive devices that can be formed using such devices as molds. In certain embodiments, the devices that are formed comprise conductive pathways formed by solidifying a liquid metal present in one or more microfluidic channels (such devices hereinafter referred to as “microsolidic” devices). In certain such devices, in which electrical connections can be formed and / or reformed between regions in a microfluidic structure; in some cases, the devices / circuits formed may be flexible and / or involve flexible electrical components. In certain embodiments, the solid metal wires / conductive pathways formed in microfluidic channel(s) may remain contained within the microfluidic structure. In certain such embodiments, the conductive pathways formed may be located in proximity to other microfluidic channel(s) of the structure that carry flowing fluid, such that the conductive pathway can create energy (e.g. electromagnetic and / or thermal energy) that interacts withy and / or affects the flowing fluid and / or a component contained therein or carried thereby. In other embodiments, a microsolidic structure may be removed from a microfluidic mold to form a stand-alone structure. In certain embodiments, the solid metal structures formed may interact with light energy incident upon a structure or may be used to fabricate a light-weight electrode. Another aspect of the invention relates to the formation of self-assembled structures that may comprise these electrically conductive pathways / connections.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Method and apparatus for removing heat
A device includes a liquid metal and a ferrofluid contained in a closed tube. Many electrode groups are connected to the closed tube. A feedback device is connected to the electrode groups. The feedback device switches power to each electrode group in series to circulate the liquid metal and move the ferrofluid in the closed tube.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Reversible hydride thermal energy storage cell optimized for solar applications
InactiveUS20110100356A1Low costGood benefitFrom solar energySolar heat devicesThermal energyThermal energy storage
A solar energy collection and storage system and a method of collecting and storing solar energy. The system includes a device for focusing solar energy onto a reaction chamber for the conversion of metal hydride to liquid metal and hydrogen, a metal / metal hydride chamber containing a metal / metal hydride mixture, a hydrogen storage system using hydrides and a thermo-cline for recovering the thermal energy from the hydrogen when it is cooled from 2000 F to ambient conditions for storage.
Owner:BLIESNER WAYNE THOMAS
Multi-die semiconductor package with heat spreader
ActiveUS20100230805A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor packageLiquid metal
A semiconductor device includes first and second stacked semiconductor dies on a substrate. A lid having a plurality of fins extending downwardly into the cavity is mounted on the substrate to encapsulate the semiconductor dies. At least some of the fins are longer than other ones of said fins. The lid is attached to the substrate, with the longer fins extending downwardly above a region of the substrate not occupied by the first die. The shorter fins extend downwardly above a region of said first die not covered by said second die. A thermal interface material fills the remainder of the cavity and is in thermal communication with both dies, the substrate and the fins. The lid may be molded from metal. The lid may be bonded to the topmost die, using a thermal bonding material that may be liquid metal, or the like.
Owner:ATI TECH INC
Composite phase-change thermal storage material
ActiveCN104140786AHigh freeze-thaw rateHigh thermal conductivityHeat-exchange elementsLiquid metalVolumetric Mass Density
The invention provides a composite phase-change thermal storage material. A porous material with high thermal conductivity is used as a supporting framework, and low-melting-point metal or low-melting-point metal with nano-particles is distributed in pores of the porous material, wherein melting point or solidus temperature of the low-melting-point metal is less than or equal to 80 DEG C; and thermal conductivity of the porous material is within 40-400 W / (m.K). The material provided by the invention has high equivalent thermal conductivity and high storage energy density; there is a large contact area between the liquid metal and the porous material; and the material has a wide application temperature range, has good fixability, stable physico-chemical property and good reversibility; and the problem of decreasing heat storage efficiency after multiple times of heat adsorption and release cycles is avoided.
Owner:TECHNICAL INST OF PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Liquid metal thermal interface material system
InactiveUS20060118925A1Efficiently transferring thermal energyEnergy efficiencySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesLiquid stateMetal alloy
A metal thermal interface structure for dissipating heat from electronic components comprised a heat spreader lid, metal alloy that is liquid over the operating temperature range of the electronic component, and design features to promote long-term reliability and high thermal performance.
Owner:MACRIS CHRIS +2
Monolithic thin-film thermoelectric device including complementary thermoelectric materials
InactiveUS20050150539A1Reduce needReduction in electron thermal conductivityThermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectThermoelectric device manufacture/treatmentLiquid metalThermoelectric element
A vertical, monolithic, thin-film thermoelectric device is described. Thermoelectric elements of opposing conductivity types may be coupled electrically in series and thermally in parallel by associated electrodes on a single substrate, reducing the need for mechanisms to attach multiple substrates or components. Phonon transport may be separated from electron transport in a thermoelectric element. A thermoelectric element may have a thickness less than an associated thermalization length. An insulating film between an electrode having a first temperature and an electrode having a second temperature may be a low-thermal conductivity material, a low-k, or ultra-low-k dielectric. Phonon thermal conductivity between a thermoelectric element and an electrode may be reduced without a significant reduction in electron thermal conductivity, as compared to other thermoelectric devices. A phonon conduction impeding material may be included in regions coupling an electrode to an associated thermoelectric element (e.g., a liquid metal).
Owner:NANOCOOLERS
Means and method for a liquid metal evaporation source with integral level sensor and external reservoir
InactiveUS20050229856A1Long operating timeReduce hydrostatic pressureVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingEvaporation (deposition)Engineering
A liquid metal evaporation source for use in Molecular Beam Epitaxy and related metal vacuum deposition techniques. An evaporator is maintained at a high temperature to evaporate a liquid metal, a reservoir for holding the liquid metal source is maintained at a temperature above the melting point of the metal but below the temperature in the evaporator, and a hollow transport tube connecting the evaporator and reservoir is maintained at a temperature between these temperatures. The reservoir is in the shape of a hollow cylinder with a close-fitting cylindrical piston which is used to force the liquid metal through the hollow transport tube into the evaporator. The liquid metal will not flow past the piston seal if a suitably small gap is formed between the piston and the reservoir walls wherein the surface tension of the liquid metal will exceed its hydrostatic pressure against the piston thus forming a leak-tight seal.
Owner:RJM SEMICON
Method for preparing metal liquid mixed with granule having high heat-transfer performance
ActiveCN101418210AReduce thermal resistanceImprove thermal conductivityHeat-exchange elementsLiquid metalSolvent
The invention relates to a method for preparing a metal liquid mixed with particles which has high heat transferring performance. The method comprises the following steps: a. particles as a solute and liquid metal as a solvent are mixed to form the liquid metal mixed with the particles; the ratio of mass portions of the particles to the liquid metal is between 1 to 0.1 and 1 to 99; and b. the liquid metal mixed with the particles is subjected to mechanical stirring and ultrasonic dispersion in order that the particles in the liquid metal are evenly dispersed, thereby obtaining the metal liquid mixed with the particles. Through the method, the prepared metal liquid mixed with the particles has high thermal conductivity.
Owner:TECHNICAL INST OF PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
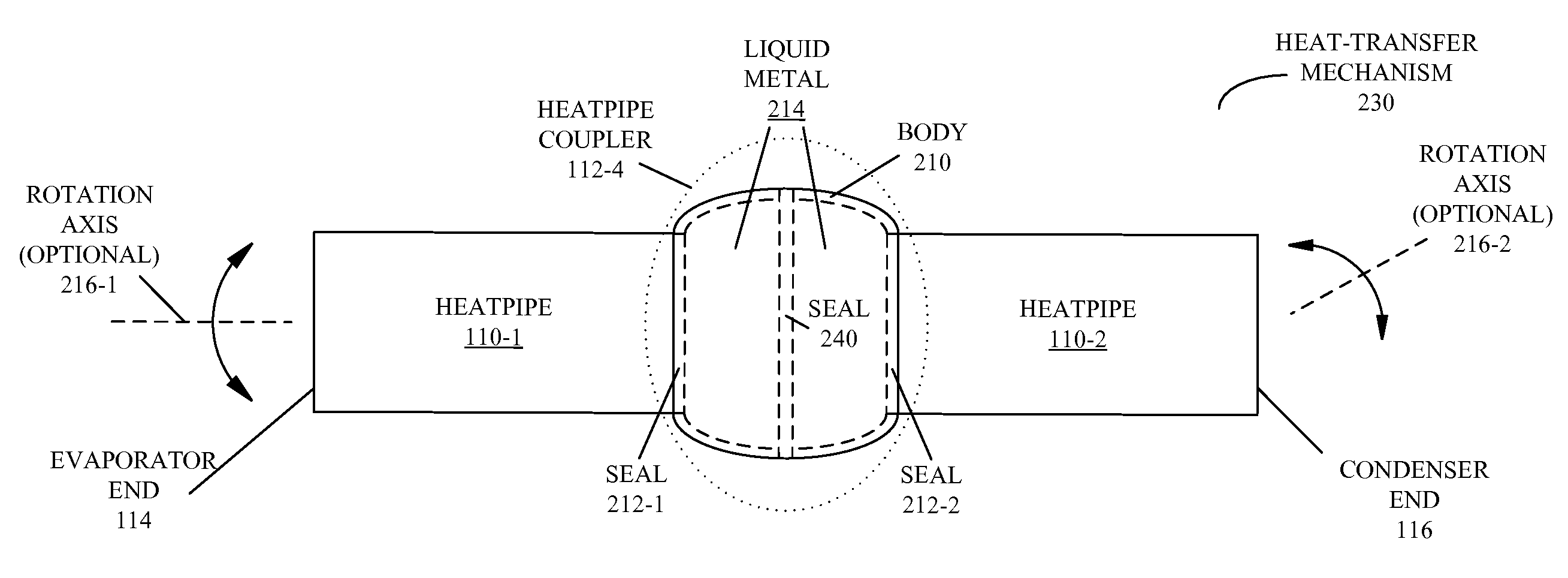
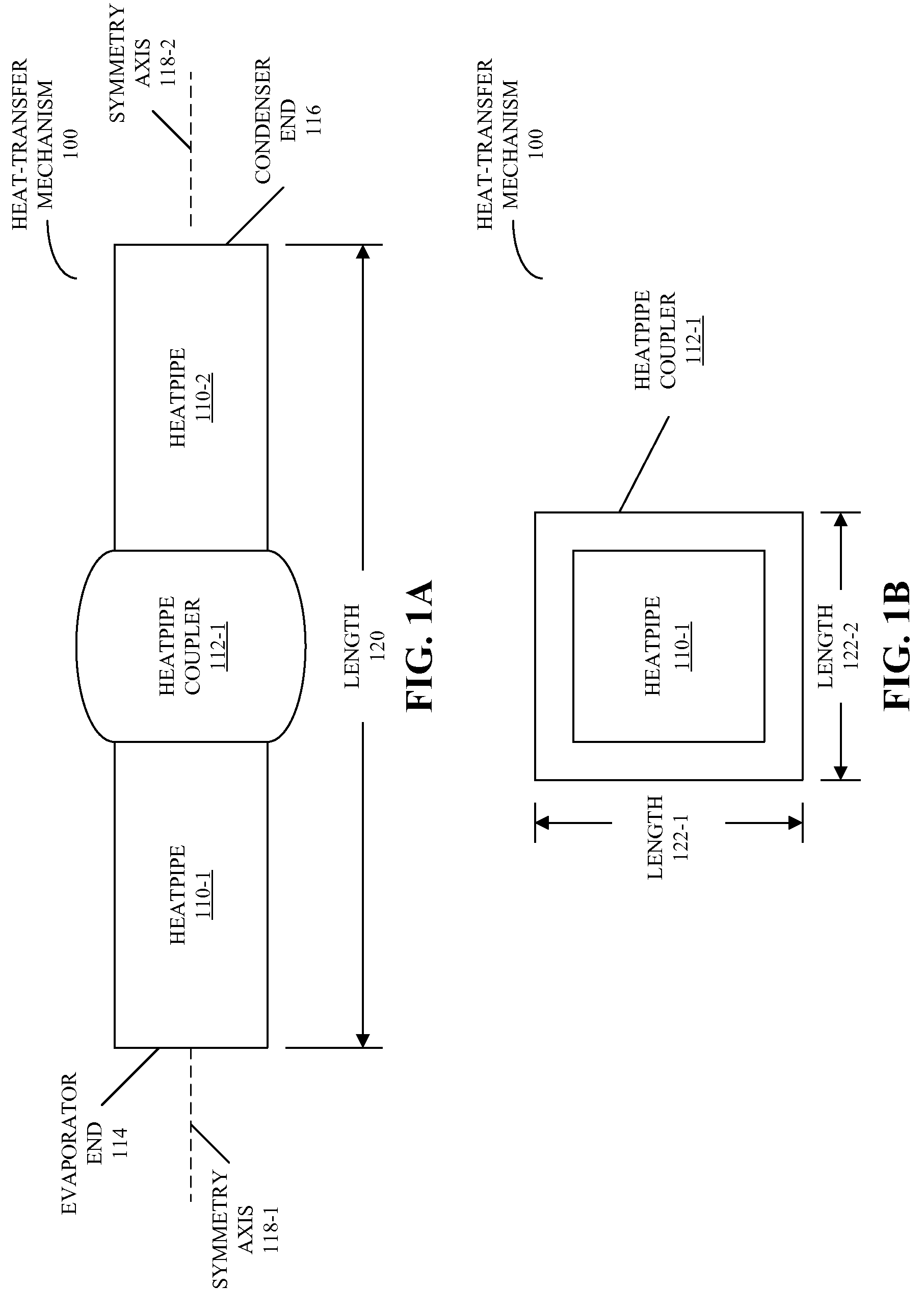
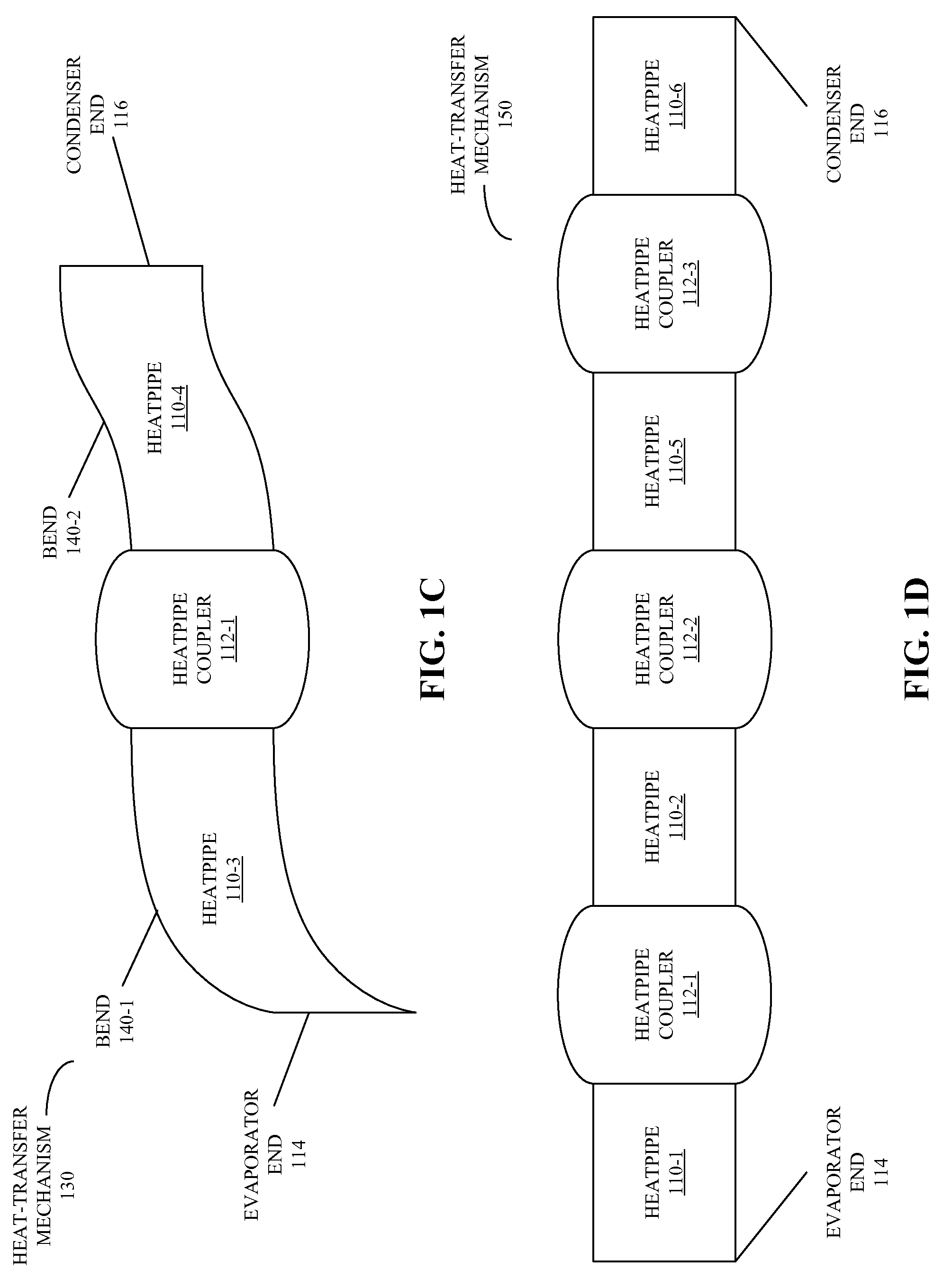
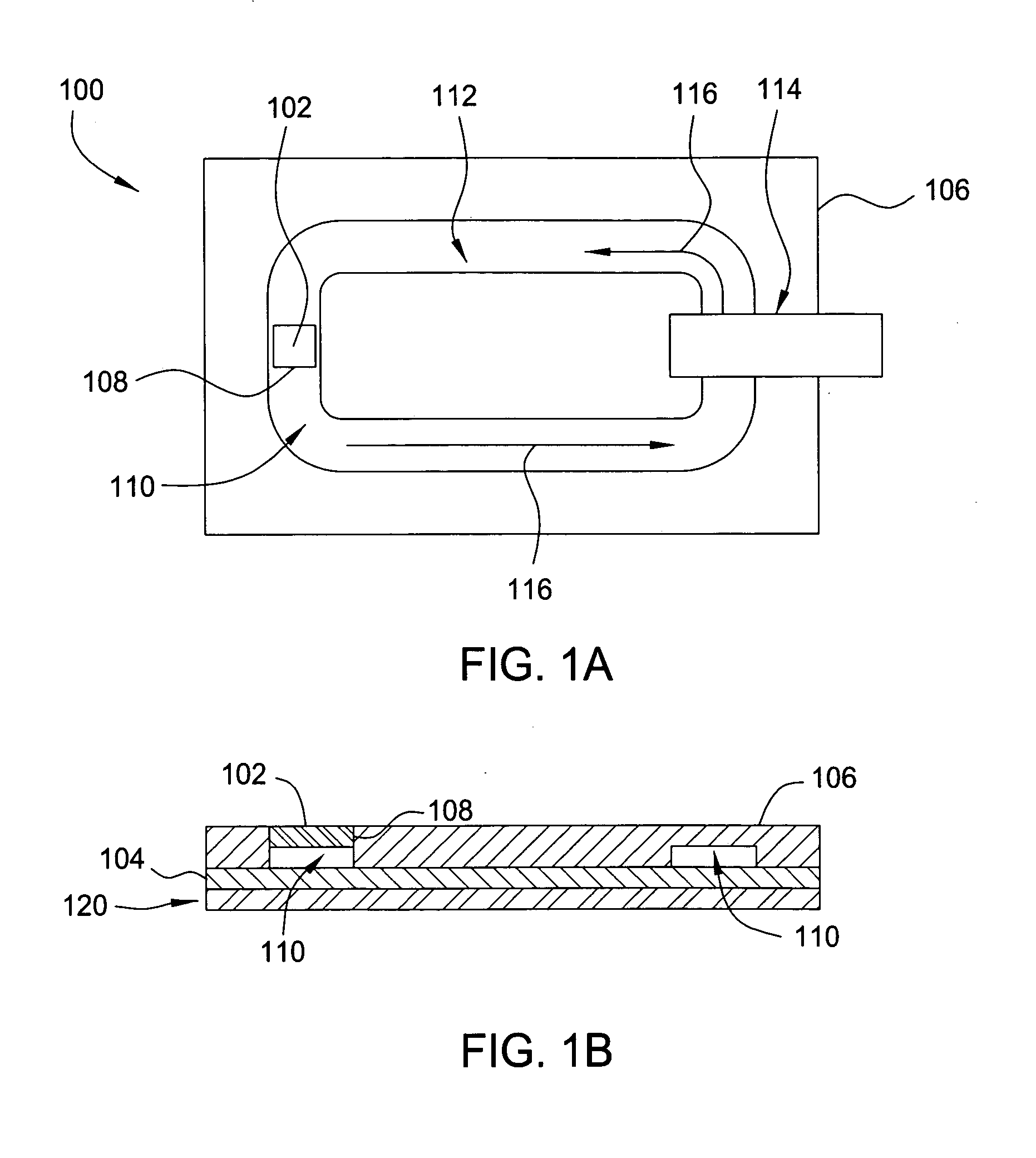
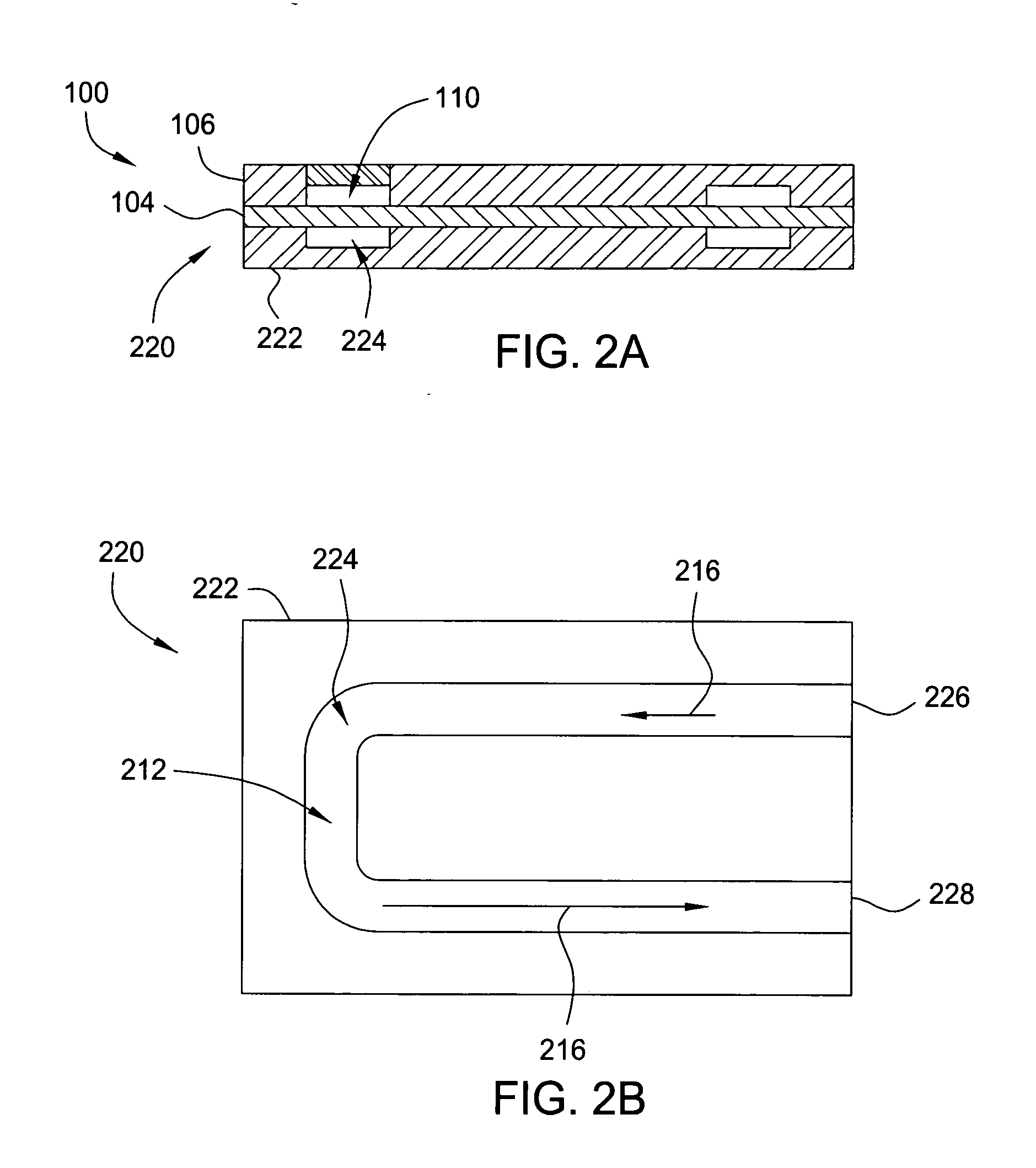
Heat-transfer mechanism including a liquid-metal thermal coupling
Embodiments of a heat-transfer mechanism are described. This heat-transfer mechanism includes a first heatpipe having a first end and a second end, and a second heatpipe having a third end and a fourth end. Moreover, a heatpipe coupler is thermally coupled to the second end of the first heatpipe and the third end of the second heatpipe. This heatpipe coupler includes a housing surrounding a cavity and a liquid metal contained within the cavity, thereby providing a thermal path from the first end of the first heatpipe, which is configured to couple to a condenser, to the fourth end of the second heatpipe, which is configured to couple to an evaporator.
Owner:APPLE INC
Heterogeneous thermal interface for cooling
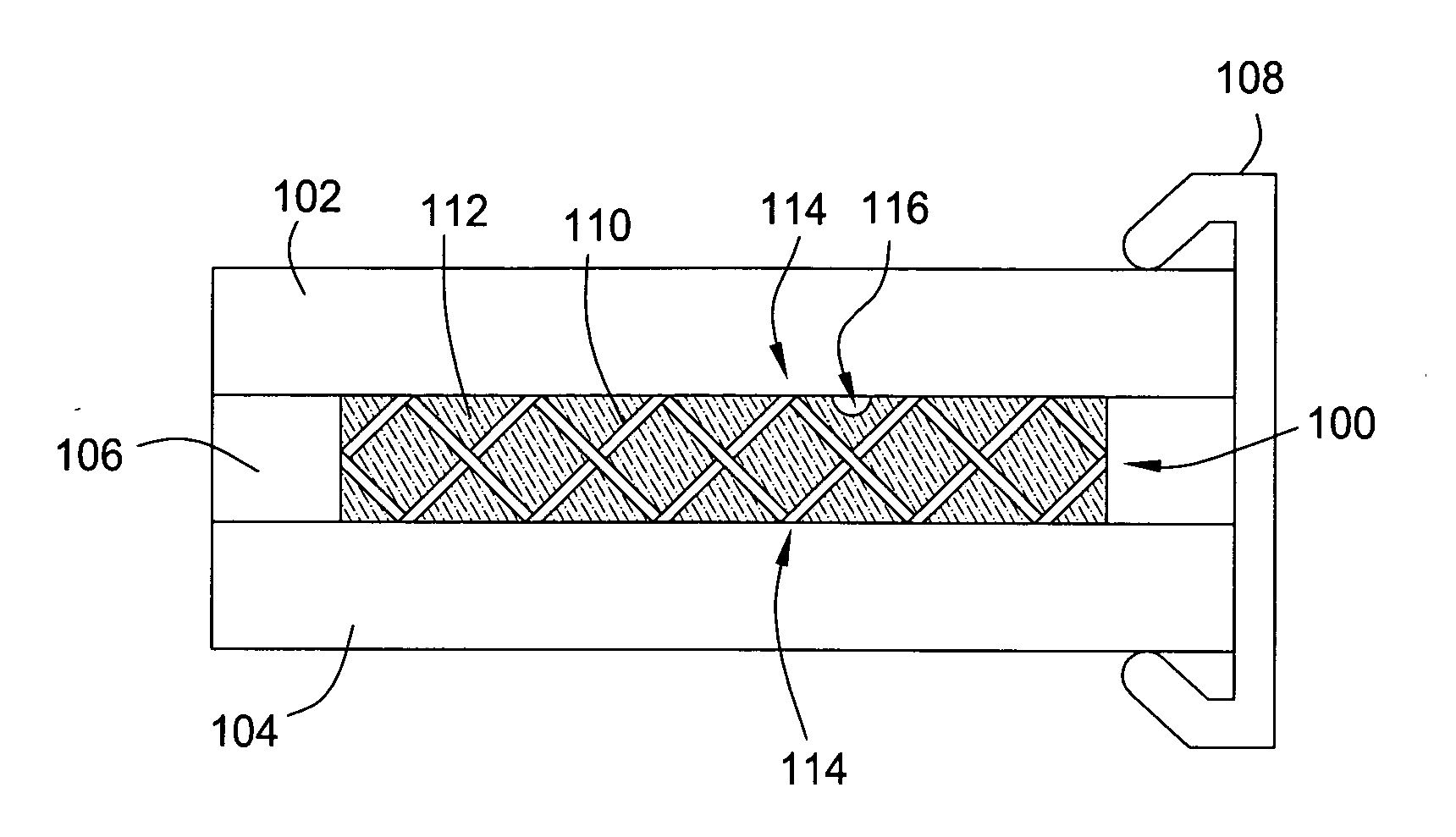
The present invention is a thermal interface for coupling a heat source to a heat sink. One embodiment of the invention comprises a mesh and a liquid, e.g., a thermally conductive liquid, disposed in the mesh. The mesh and the thermally conductive liquid are adapted to contact both the heat source and the heat sink when disposed therebetween. In one embodiment, the mesh may comprise a metal or organic material compatible with the liquid. In one embodiment, the liquid may comprise liquid metal. For example, the liquid may comprise a gallium indium tin alloy. A gasket may optionally be used to seal the mesh and the liquid between the heat source and the heat sink. In one embodiment, the heat source is an integrated circuit chip.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Liquid metal ink-jet printing equipment and printing method
InactiveCN104108248ANo consumptionReduce ineffective lossOther printing apparatusElectrical controlIntegrated circuit layout
The invention provides a liquid metal ink-jet printing equipment. The liquid metal ink-jet printing equipment comprises a control circuit used for carrying integral control on the printing equipment, a liquid metal printing mechanism used for bearing an ink box and an electrical control nozzle and printing liquid metal oil ink on a base, a carriage mechanism which is used for bearing the liquid metal printing mechanism and moves according to an instruction of the control circuit, a paper conveying mechanism used for conveying a printing base of the printing equipment, and a state sensor used for detecting a work state of the printing equipment. According to the liquid metal ink-jet printing equipment and the printing method, problems of complex manufacturing process, large material and energy consumption and relatively serious environment pollution existing in an integrated circuit or an electronic device in the prior art are solved, and the relatively good technology effect is acquired.
Owner:TECHNICAL INST OF PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
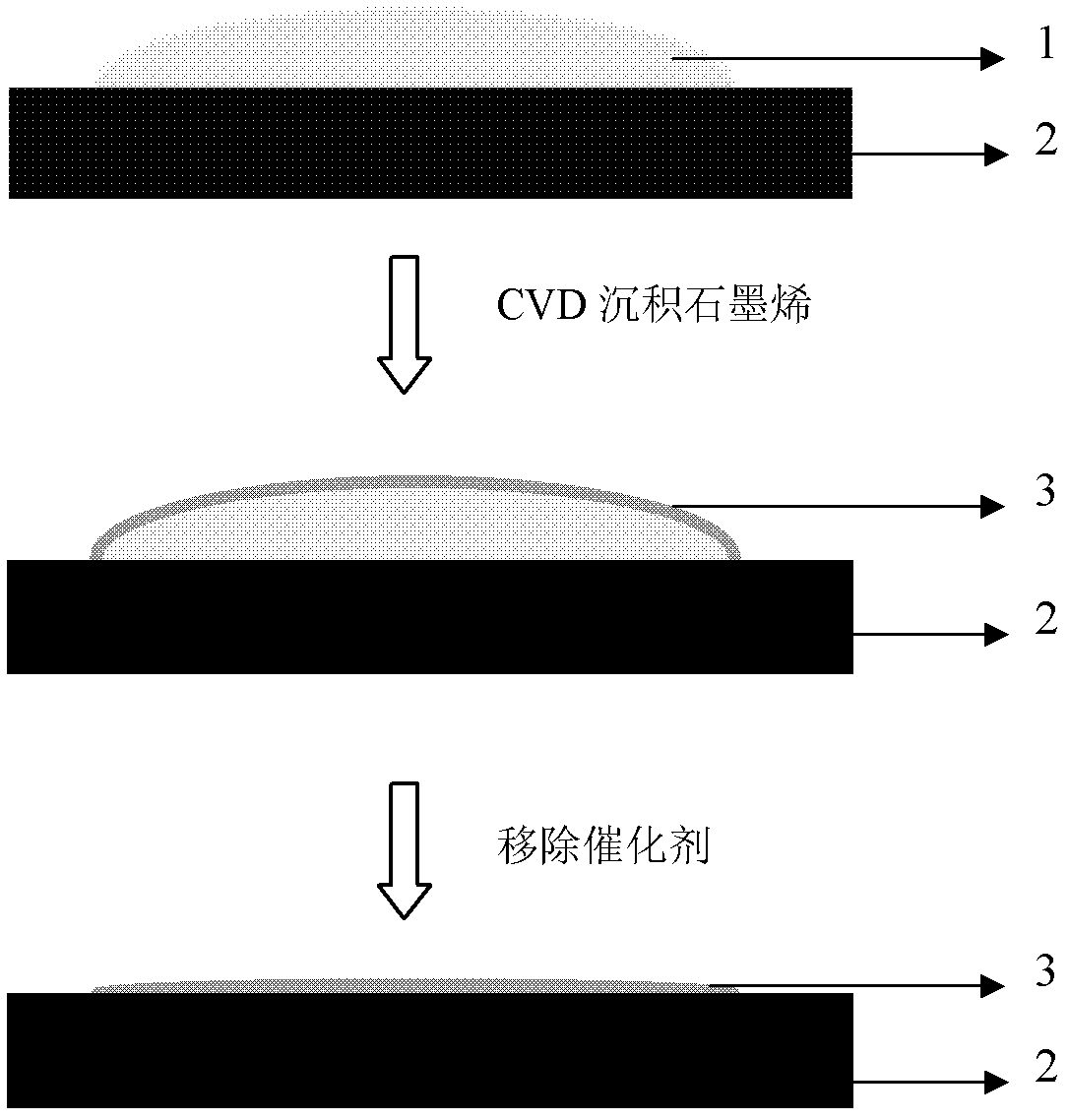
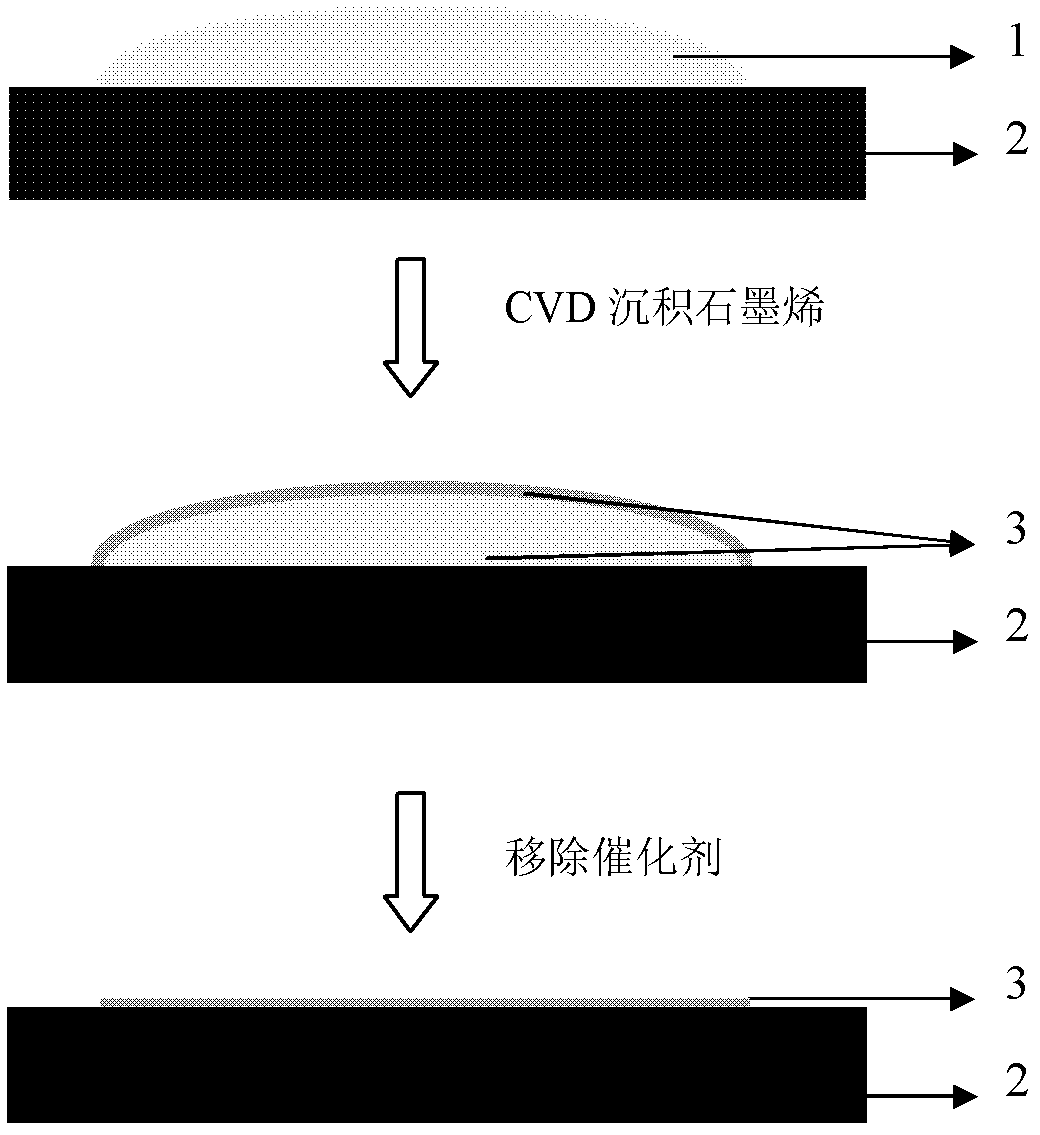
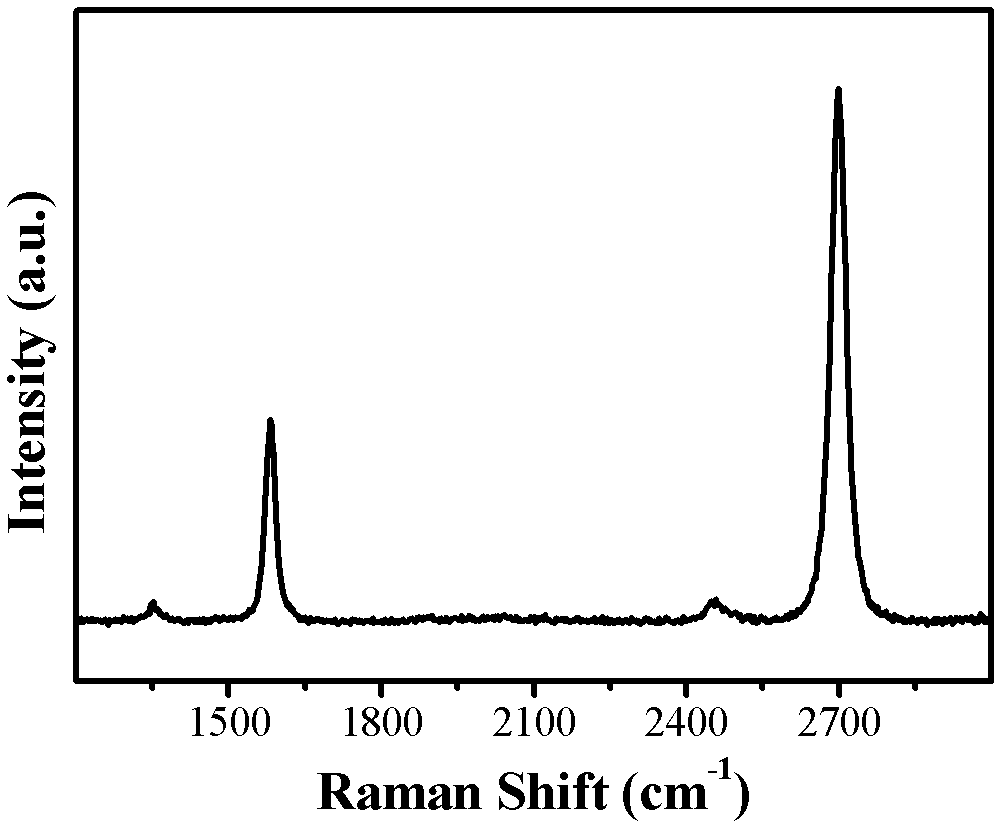
Method for preparing graphene by adopting liquid catalyst aided chemical vapor deposition
ActiveCN102583359ARealize layer controlMolecular activityMaterial nanotechnologyGrapheneIndiumLiquid metal
The invention discloses a method for preparing a graphene film by using a liquid metal or alloy as a catalyst and adopting chemical vapor deposition. The metal with low melting point comprises typical gallium, tin, indium and the like; and the alloy with low melting point comprises gallium-copper, gallium-nickel, indium-copper, indium-nickel, tin-copper, tin-nickel, copper-silver-tin and the like. The chemical vapor deposition is performed above the melting point of the metal or alloy catalyst, so that the continuous graphene film is formed on the surface of the catalyst and the interface of the catalyst and a substrate. Compared with the graphene grown on the surface of a solid catalyst such as copper and nickel, the invention has the advantages that the prepared graphene is controllable in layer number, low in requirement for the micro morphology of the surface of the substrate and suitable for multiple substrate materials, and the catalyst is very easy to remove. The obtained graphene positioned on the surface of the liquid has unique application value.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Fast reactor having reflector control system and neutron reflector thereof
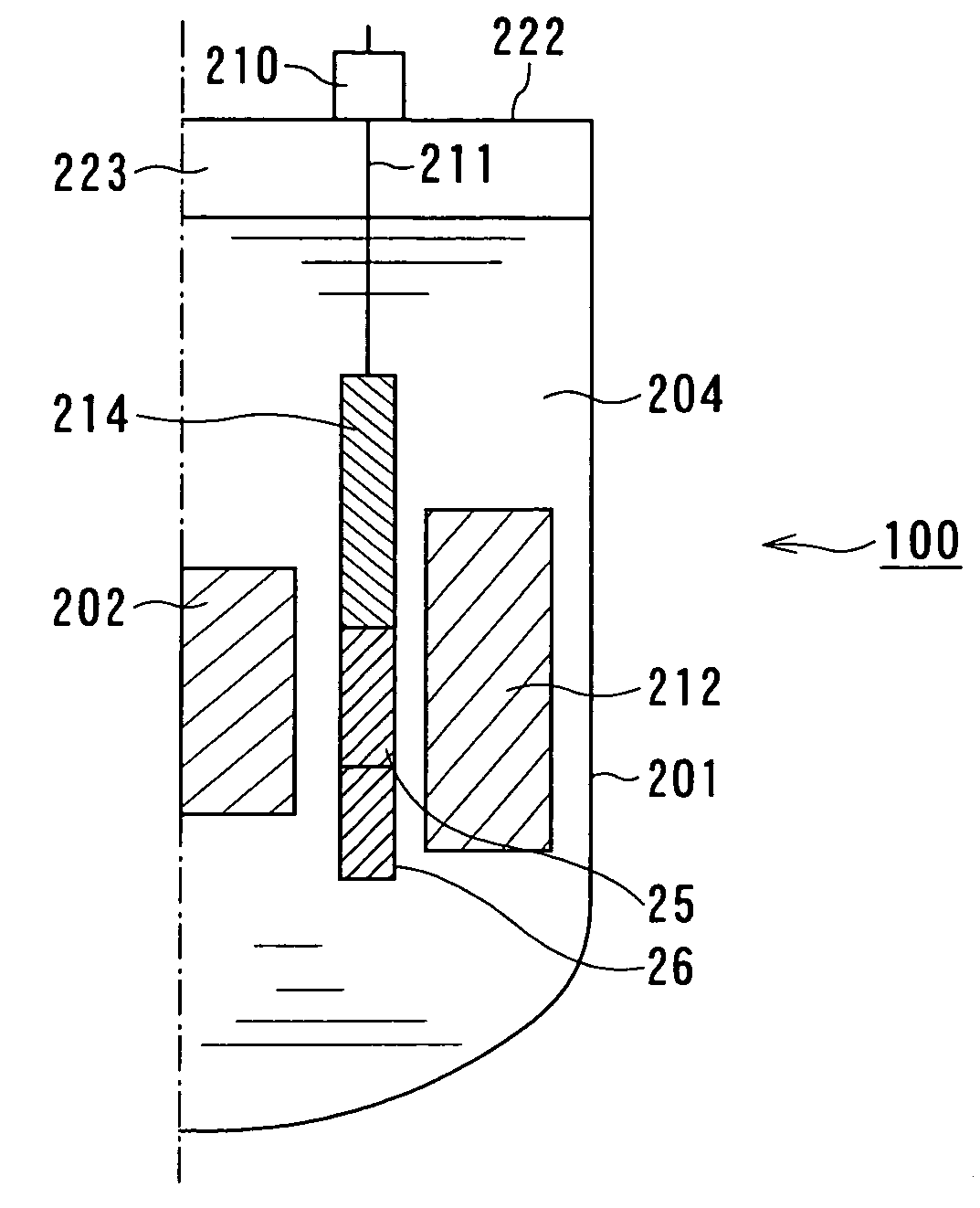
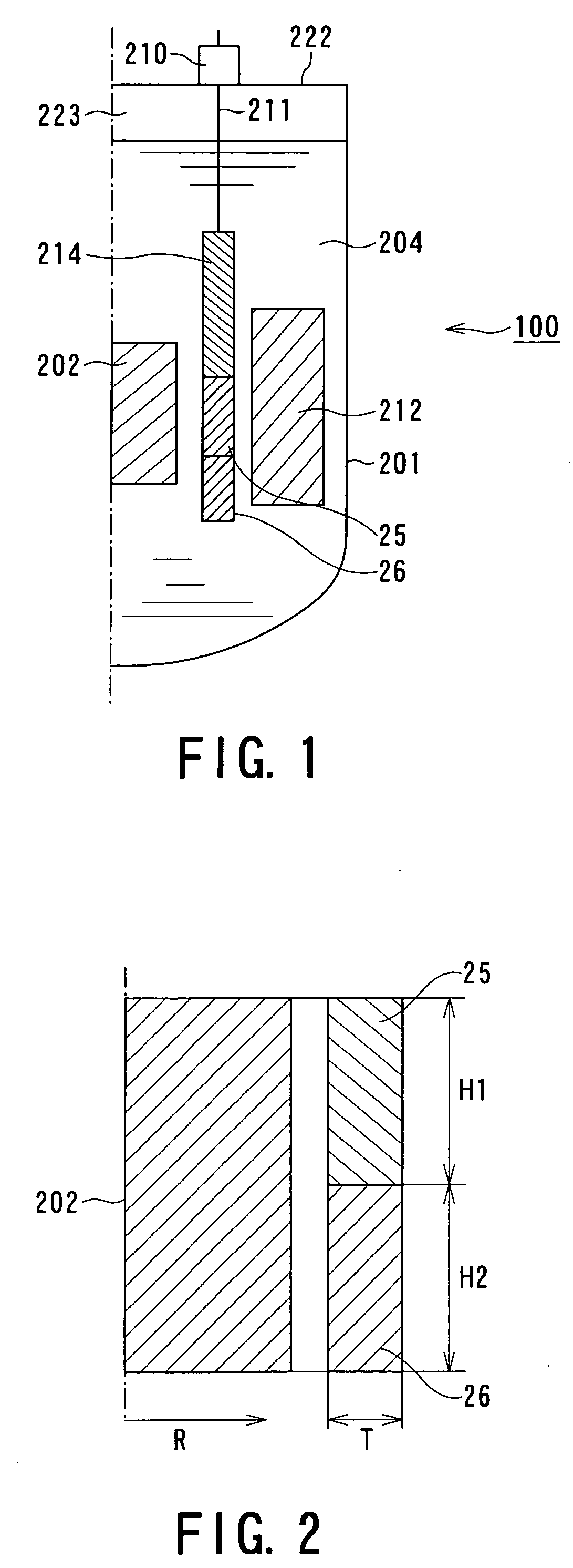
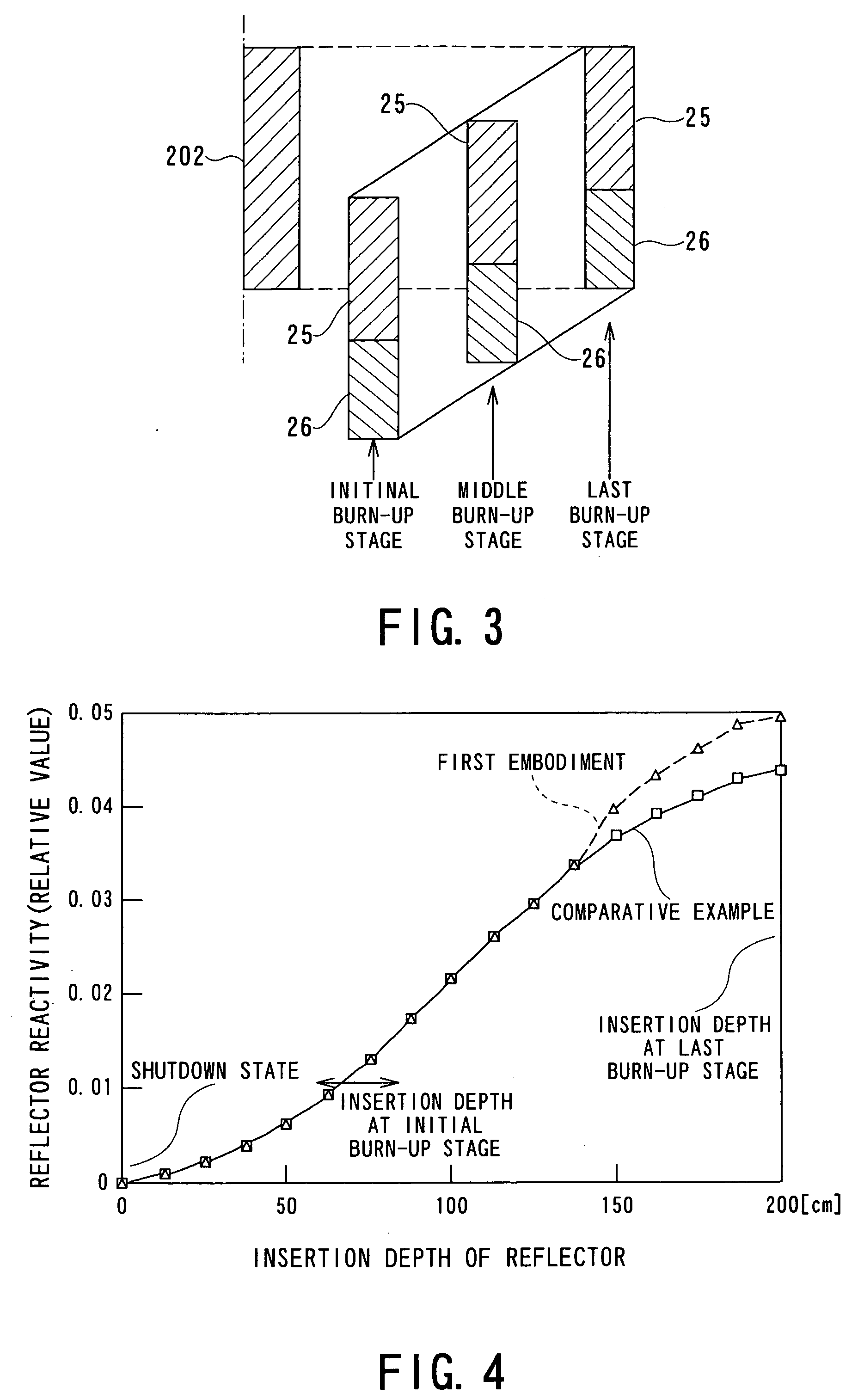
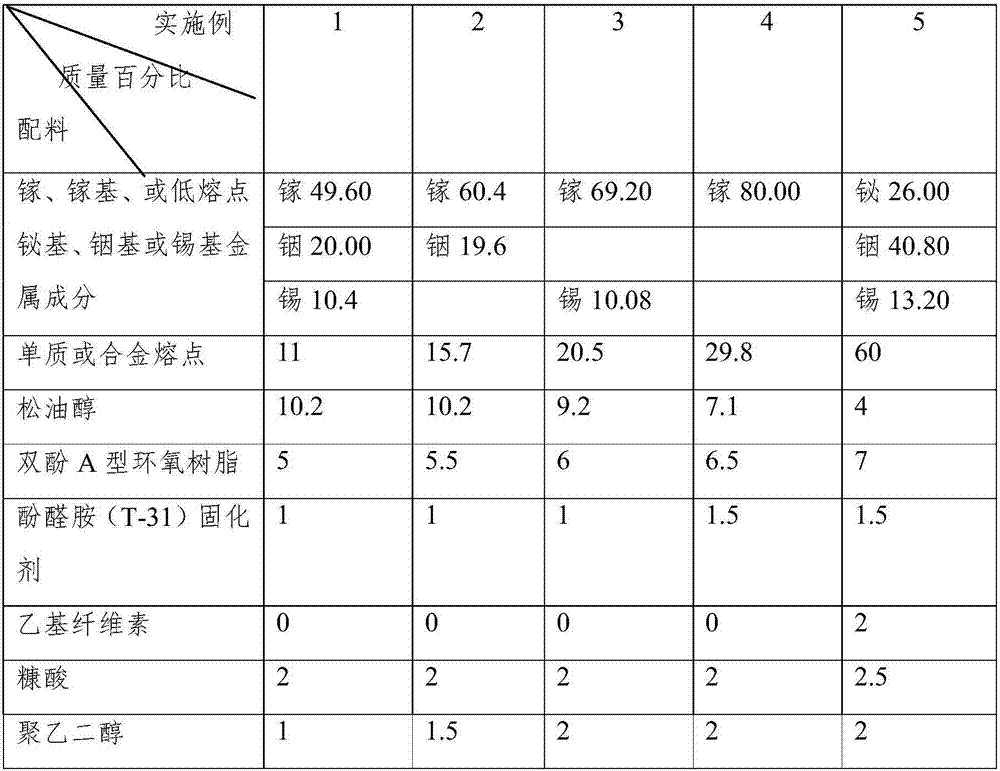
InactiveUS20050220251A1Operation efficiency is highSlow changeNuclear energy generationNuclear engineering problemsNuclear engineeringControl system
A fast reactor having a reflector control system is provided which decreases the change in reactivity of the reactor core with time without performing control of a reflector lifting speed and that of a water flow rate. The above fast reactor has a liquid metal coolant, a reactor core immersed therein, and a neutron reflector which is provided outside the reactor core and which is moved in a vertical direction for adjusting leakage of neutrons therefrom for controlling the reactivity of the reactor core. The neutron reflector described above is gradually moved in an upward direction with the change in reactivity caused by fuel burn-up, and at least a part of a lower region of the neutron reflector is a high reflection region having a high neutron reflection ability as compared to that of the other region. The high reflection region is located from the bottom to a place between one fourth and one half of the height of the neutron reflector from the bottom end thereof.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Liquid-state metal electronic paste and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107452436ALow costReduce surface tensionNon-conductive material with dispersed conductive materialCable/conductor manufactureOrganic solventLiquid state
The invention proposes liquid-state metal electronic paste. The liquid-state metal electronic paste comprises an organic carrier and liquid-state metal, wherein the liquid-state metal is dispersed in the organic carrier, the organic carrier comprises an organic solvent, a binding agent and a functional additive, and the liquid-state metal is elemental metal or alloy with a melting point being (-78.2)-232 DEG C. The invention also provides a preparation method of the liquid-state metal electronic paste. In the electronic paste proposed by the invention, the liquid-state elemental metal or alloy with a low melting point, the organic carrier and the binding agent form a uniform phase, alloy particle is not needed to be prepared, and the paste is low in cost; an activating agent, a thixotropic agent, resin and the like are added into the organic carrier, the surface tension of the liquid-state metal is reduced, and the adhesion between the paste and a substrate is improved; and after sintering and curing, the organic solvent is volatilized after being heated, the elemental metal or alloy with the low melting point is heated and molten, particles are contacted and pasted to form lines, gaps among the particles are reduced, and the conductivity of the paste is improved.
Owner:YUNNAN KEWEI LIQUID METAL VALLEY R & D CO LTD
Liquid-metal printed circuit board and preparation method thereof
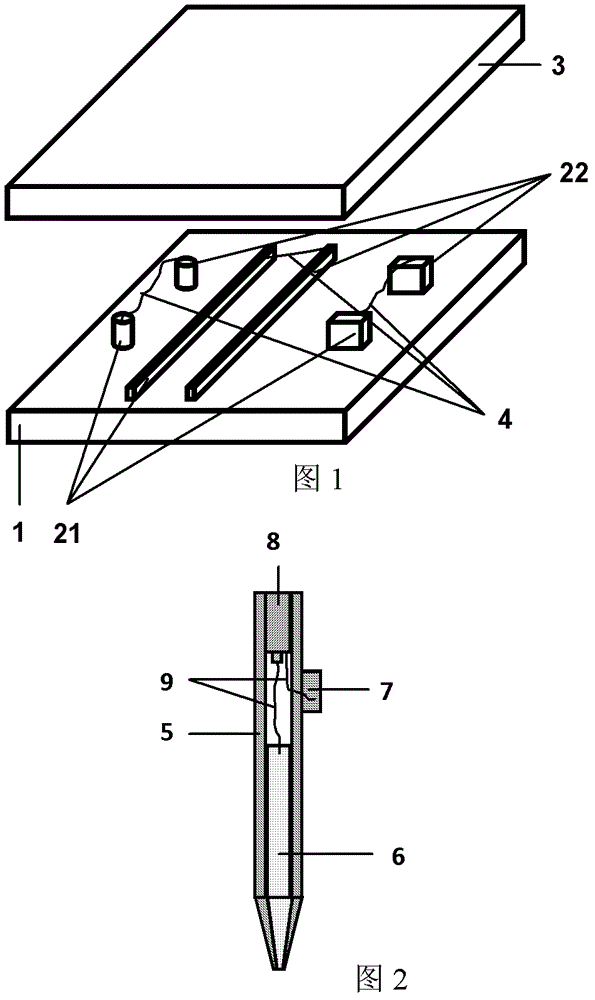
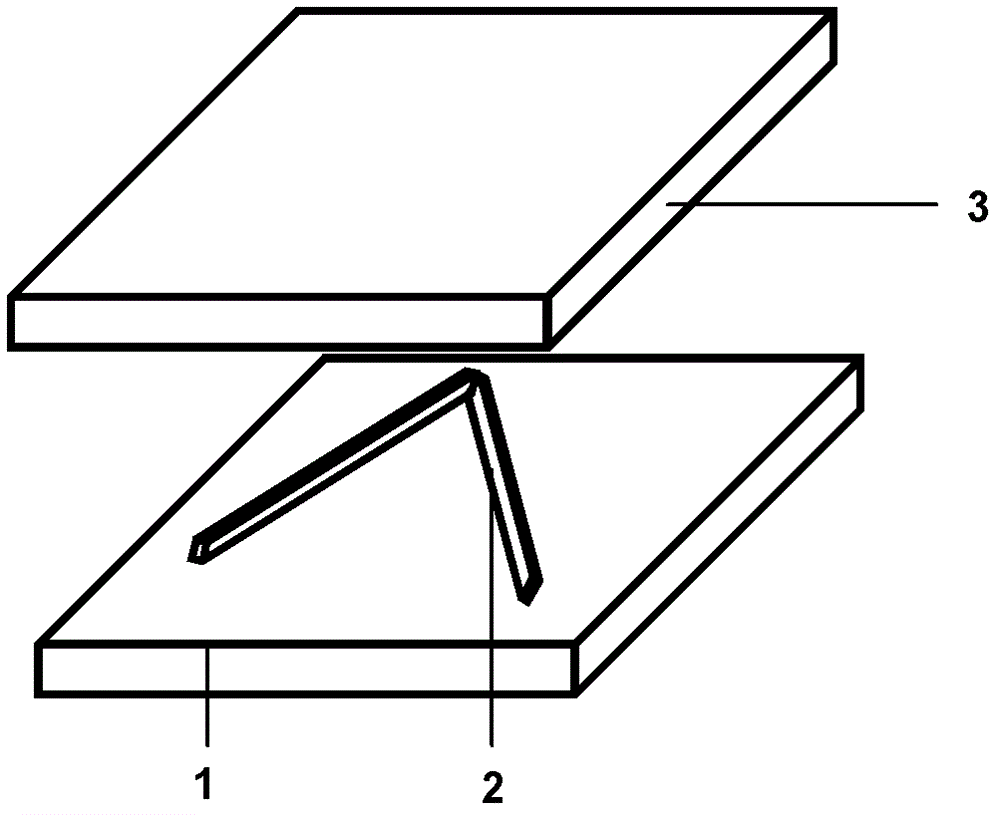
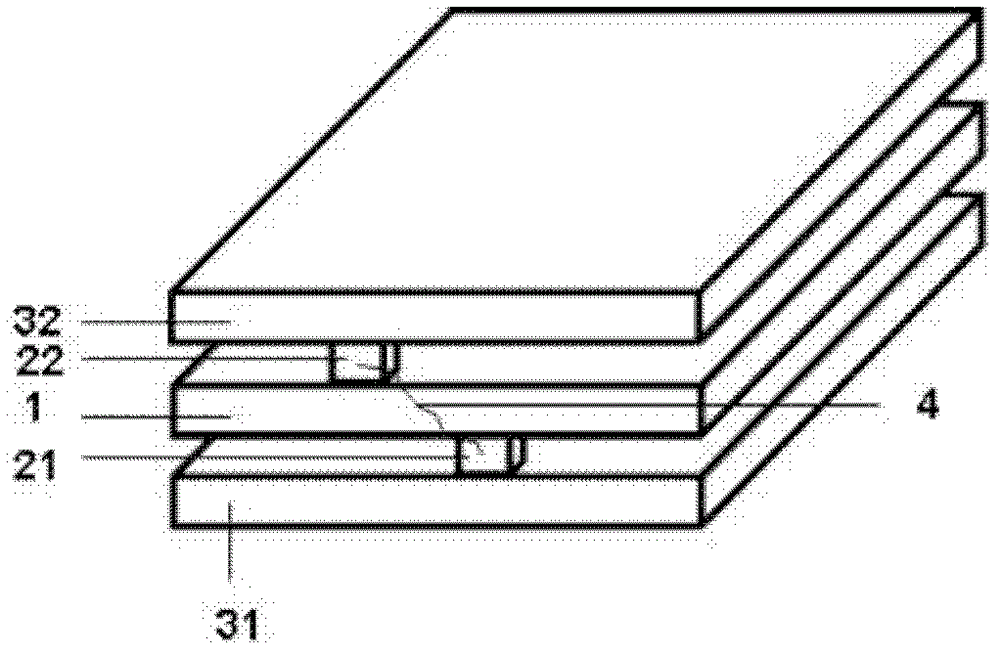
ActiveCN102802346AEasing production constraintsEase constraintsConductive pattern formationCircuit susbtrate materialsFlexible circuitsLiquid metal
The invention relates to a liquid-metal printed circuit board, and in particular relates to a flexible printed circuit board and a preparation method thereof. The liquid-metal printed circuit board comprises a substrate, metal electrodes printed on the substrate and an anti-oxidation insulated membranous layer which is used as a cover plate. The preparation method comprises the following steps: a), providing the substrate; b), respectively drawing the first electrode and the second electrode on the surface of the substrate by using a pen type device filled with liquid-metal ink, according to a preset shape to form the metal electrodes, wherein the first electrode and the second electrode are connected through a lead wire or an electronic component; and c), covering the electrodes with the insulated membranous layer to finish the preparation of the circuit board. The preparation method for constructing various circuit boards, especially the flexible circuit boards, has the advantages that the process is simple, the environment is friendly, the operation can be performed under normal temperature, the production cost of the circuit board can be effectively reduced, the production efficiency can be greatly improved, and very high application value is provided.
Owner:TECHNICAL INST OF PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Active liquid metal thermal spreader
InactiveUS20060158849A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesLiquid stateEngineering
The present invention is a method and apparatus for cooling a semiconductor heat source. In one embodiment a thermal spreader is provided and includes a substrate for supporting the semiconductor heat source and a heat sink coupled to the substrate. A channel is disposed between the heat sink and substrate. The channel has at least one wall defined by the heat sink. The surface area of the channel wall defined by the heat sink is about 10 to about 100 times the surface area of a bottom surface of the semiconductor heat source. A coolant, for example liquid metal, circulates within the channel.
Owner:IBM CORP
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com