Liquid-state metal electronic paste and preparation method thereof
A technology of liquid metal and electronic paste, which is applied in the field of electronics, can solve problems such as large contact resistance, high cost, and complex metal powder preparation process, and achieve the effects of improving adhesion, low paste cost, and reducing the formation of gaps
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0042] A liquid metal electronic paste, the formula of each component is shown in Table 1, and its preparation method is
[0043] 1) Weigh low-melting point alloys or elemental metals, binders, organic solvents, and functional additives according to the proportioning ratio;
[0044] 2) Add the binder and functional additives to the organic solvent in turn, stir while heating to dissolve and mix to form a uniform solution, and cool to room temperature for use; the heating temperature is kept at 60° C., and the stirring time is 1 h.
[0045] 3) Place the low-melting point alloy or elemental metal in vacuum (vacuum degree-0.1MPa) for constant temperature treatment until it changes into a liquid state; the constant temperature treatment time is 4h; the constant temperature treatment temperature is 10% higher than the melting point of the low melting point alloy. ℃;
[0046] 4) Add the homogeneous solution obtained in step 2) into the liquid metal obtained in step 3) under stirrin...
Embodiment 2-5
[0049] Liquid metal electronic paste, the formula of each component is shown in Table 1, and its preparation method is the same as that of Example 1.
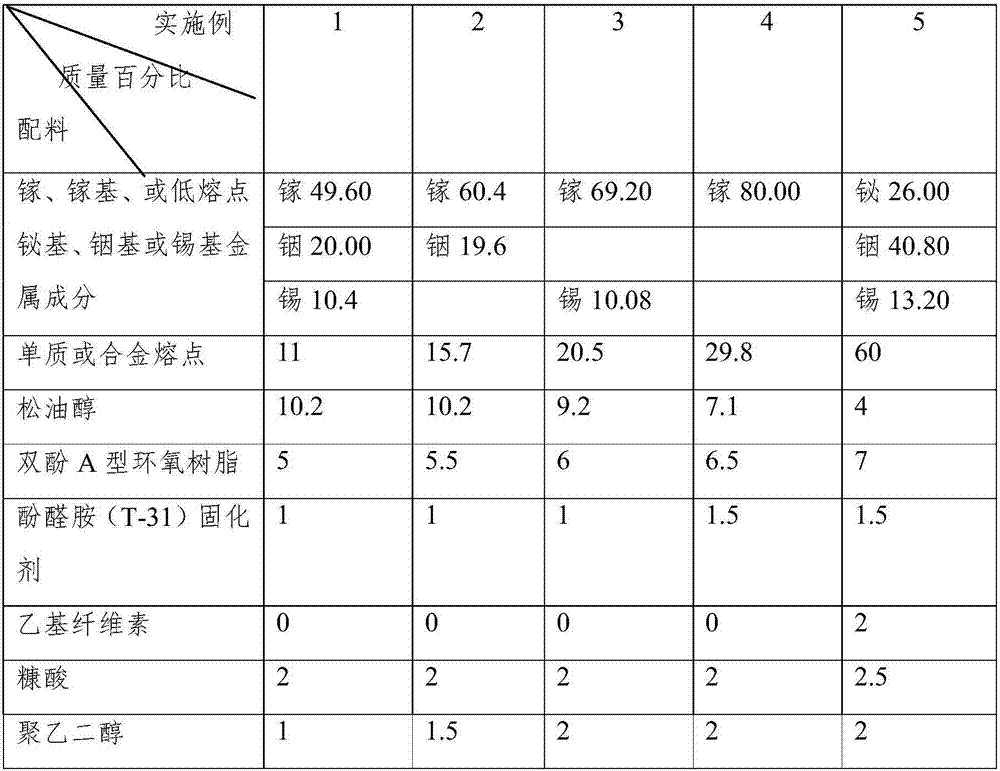
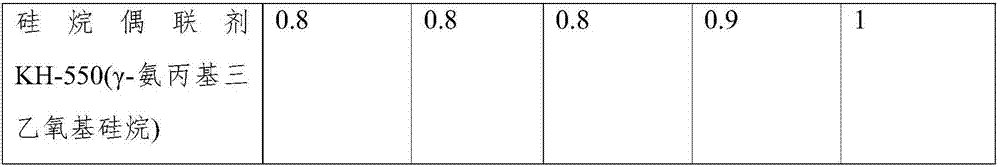
[0050] Table 1: Liquid Metal Electronic Paste Components
[0051]
[0052]
[0053] The above-mentioned embodiment is the method and formulation of direct mechanical dispersion in the organic carrier to prepare the electronic paste when the low-melting-point metal is in liquid state. From Example 1 to Example 5, the melting point of the low-melting-point metal gradually increases, and the mass ratio is 80%. It can also be based on Actual demand is adjusted between 45% and 90%. In actual production, the proportion structure of the alloy can be adjusted according to the demand to achieve the required melting point value. For example, add or replace one or more of cadmium, lead, zinc, silver, gallium, copper, etc. in the bismuth, indium, and tin metals in the embodiment, including gallium indium, gallium tin, gallium mercur...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com