Patents
Literature
16135results about "Heat-exchange elements" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Compositions comprising a fluoroolefin
The present invention relates to compositions for use in refrigeration, air-conditioning, and heat pump systems wherein the composition comprises a fluoroolefin and at least one other component. The compositions of the present invention are useful in processes for producing cooling or heat, as heat transfer fluids, foam blowing agents, aerosol propellants, and fire suppression and fire extinguishing agents.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
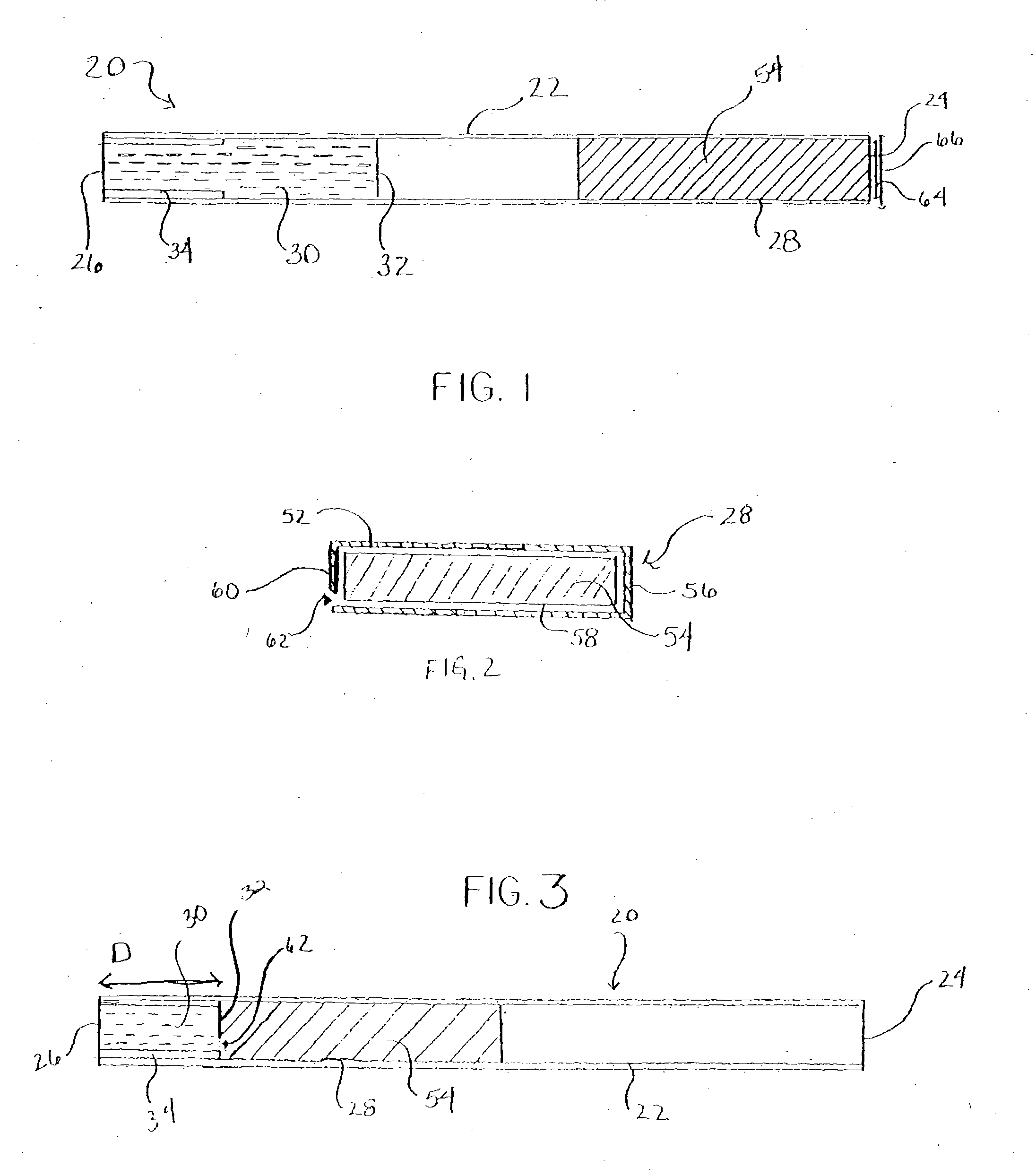
Chemical heat source for use in smoking articles
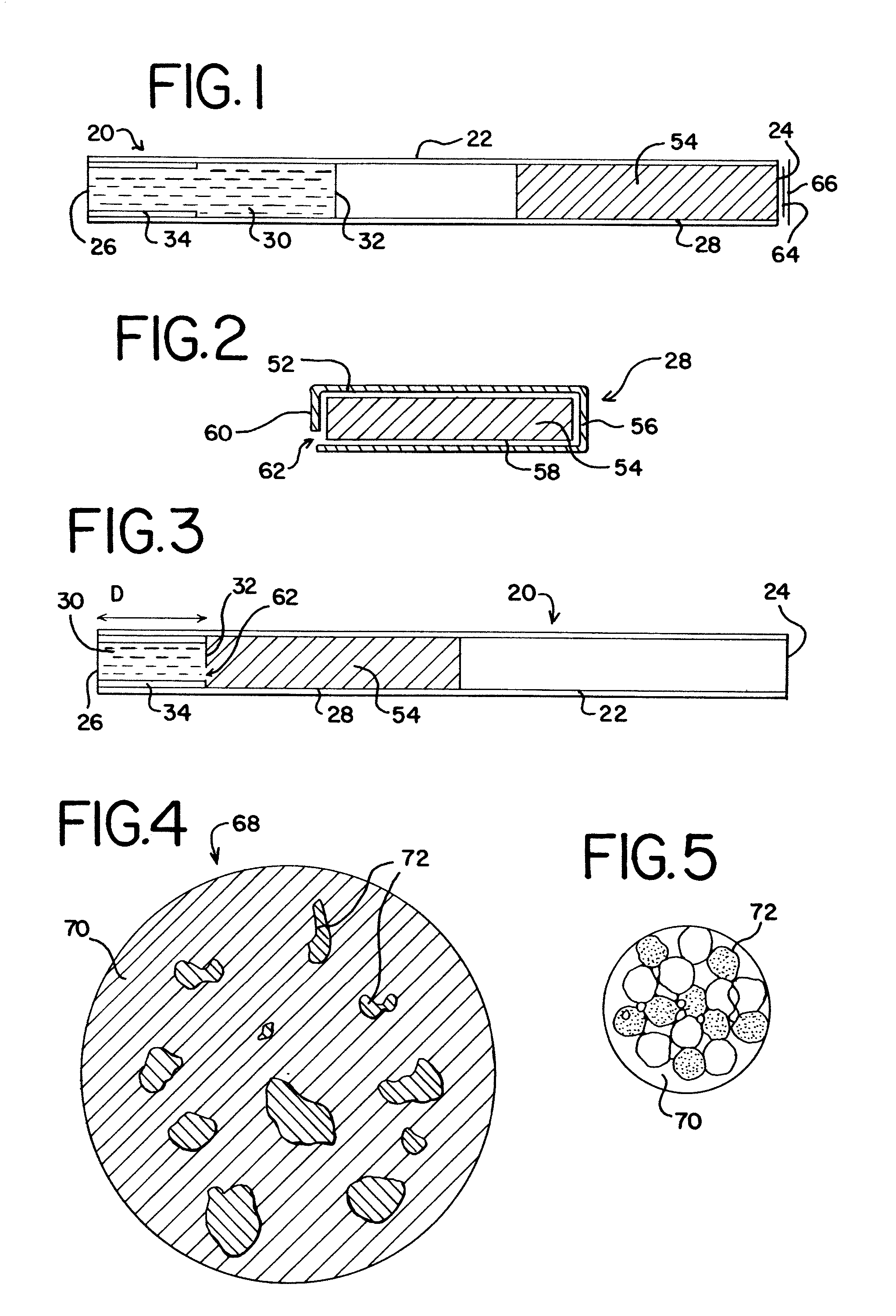
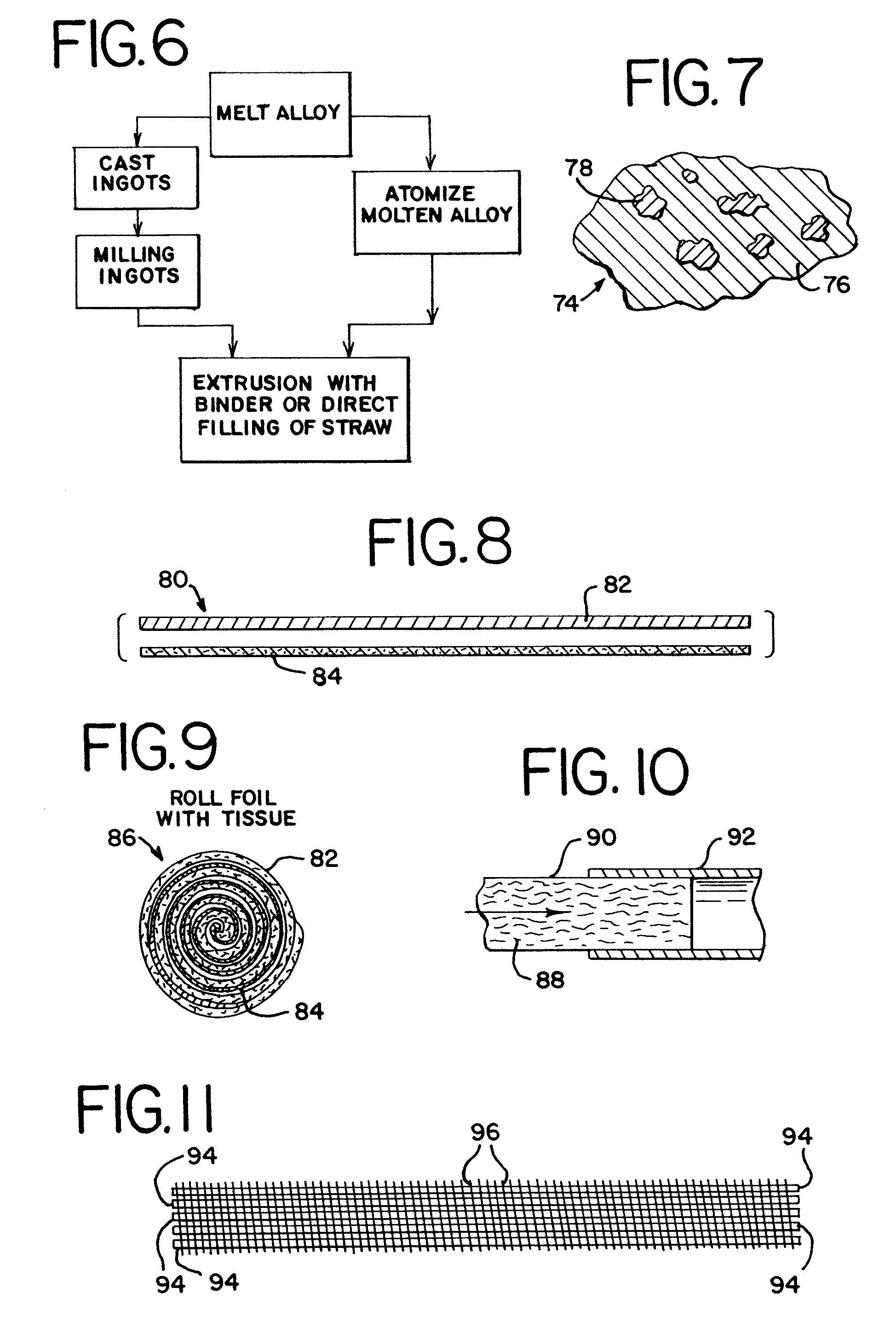
A non-combustion, chemical heat source includes a heat chamber having a closed end and an open end. The heat chamber includes an apertured heat cartridge disposed at the open end of the chamber, an abutment disposed at the closed end of the chamber, an activating solution, a frangible seal separating the activating solution and the heat cartridge. The heat cartridge includes metallic agents that may come in a variety of configurations. The heat source is activated when the heat cartridge is pushed through and breaks the frangible seal allowing contact between the metallic agents and the activating solution. The heat cartridge includes an aperture in the bottom of the cartridge and absorbent paper surrounding the metallic agents, both of which control the transfer of the activating solution into the metallic agents to cause the chemical reaction. The heat sources may be incorporated into smoking articles and may also be used to heat foods or beverages, in hand warmers, and to heat equipment or materials.
Owner:R J REYNOLDS TOBACCO COMPANY
Processes for production and purification of hydrofluoroolefins
ActiveUS20060106263A1High selectivityPreparation by hydrogen halide split-offHydrogen fluorideHydrogen fluoridePurification methods
Owner:THE CHEMOURS CO FC LLC
Chemical heat source for use in smoking articles
A non-combustion, chemical heat source includes a heat chamber having a closed end and an open end. The heat chamber includes an apertured heat cartridge disposed at the open end of the chamber, an abutment disposed at the closed end of the chamber, an activating solution, a frangible seal separating the activating solution and the heat cartridge. The heat cartridge includes metallic agents that may come in a variety of configurations. The heat source is activated when the heat cartridge is pushed through and breaks the frangible seal allowing contact between the metallic agents and the activating solution. The heat cartridge includes an aperture in the bottom of the cartridge and absorbent paper surrounding the metallic agents, both of which control the transfer of the activating solution into the metallic agents to cause the chemical reaction. The heat sources may be incorporated into smoking articles and may also be used to heat foods or beverages, in hand warmers, and to heat equipment or materials.
Owner:R J REYNOLDS TOBACCO COMPANY
Compositions comprising fluoroolefins and uses thereof
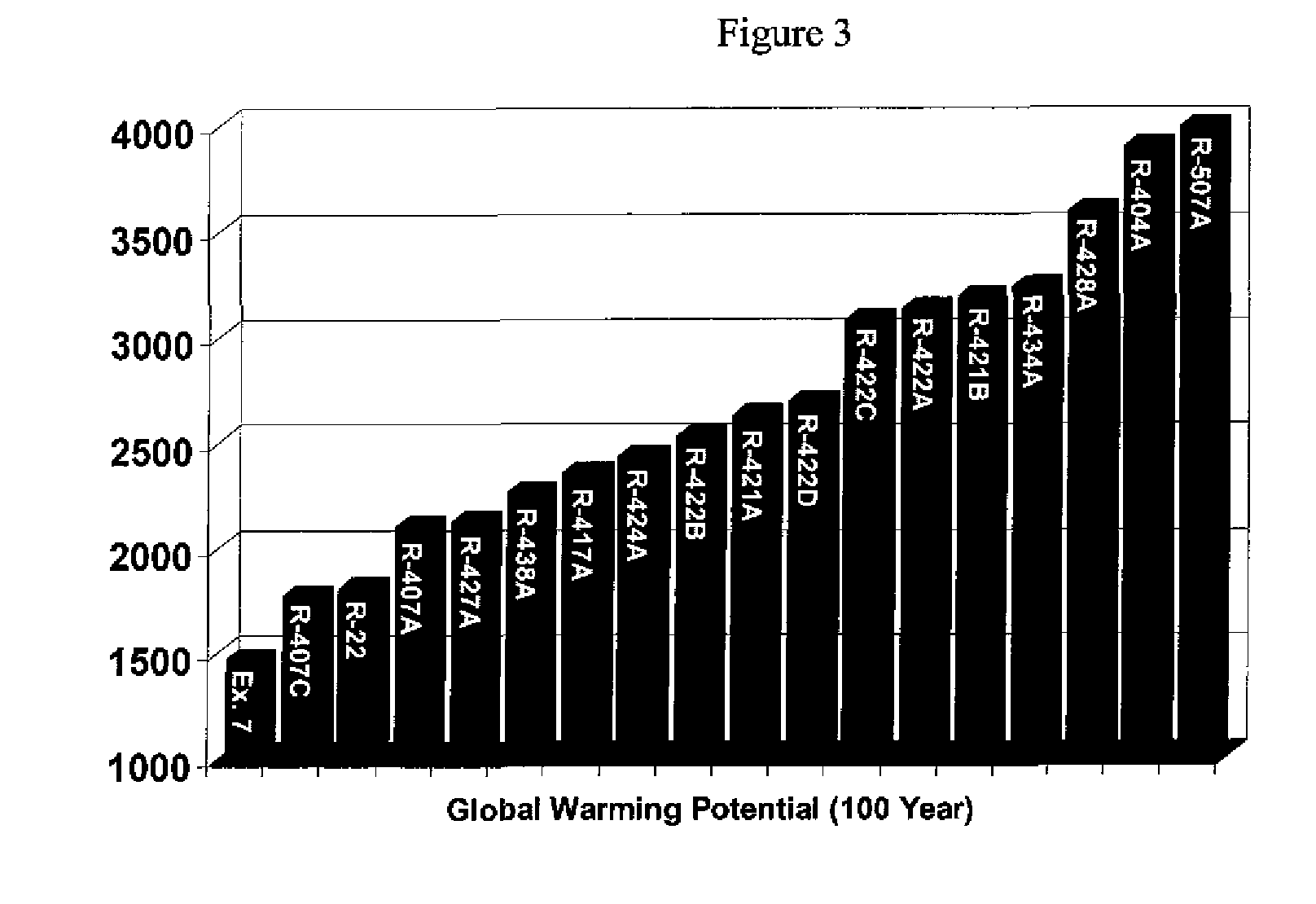
The present invention relates to fluoroolefin compositions. The fluoroolefin compositions of the present invention are useful as refrigerants or heat transfer fluids and in processes for producing cooling or heat. Additionally, the fluoroolefin compositions of the present invention may be used to replace currently used refrigerant or heat transfer fluid compositions that have higher global warming potential.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Compositions comprising a fluoroolefin
ActiveUS20080230738A1Reduce flammabilityOrganic chemistryOther chemical processesAir conditioningHeat transfer fluid
The present invention relates to compositions for use in refrigeration, air-conditioning, and heat pump systems wherein the composition comprises a fluoroolefin and at least one other component. The compositions of the present invention are useful in processes for producing cooling or heat, as heat transfer fluids, foam blowing agents, aerosol propellants, and fire suppression and fire extinguishing agents.
Owner:THE CHEMOURS CO FC LLC
Nano-composite materials for thermal management applications
InactiveUS20050116336A1Improve thermal efficiencyImprove the heating effectSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsNanoinformaticsHeat sinkNanostructure
Nano-composite materials with enhanced thermal performance that can be used for thermal management in a wide range of applications, including heat sinks, device packaging, semiconductor device layers, printed circuit boards and other components of electronic, optical and / or mechanical systems. One type of nano-composite material has a base material and nanostructures (e.g., nanotubes) dispersed in the base material. Another type of nano-composite material has layers of a base material with nanotube films disposed thereon.
Owner:KOILA
Conformal thermal interface material for electronic components
InactiveUS6054198AOptimize allocationReadily apparentSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesRoom temperatureConductive materials
A thermally-conductive interface for conductively cooling a heat-generating electronic component having an associated thermal dissipation member such as a heat sink. The interface is formed as a self-supporting layer of a thermally-conductive material which is form-stable at normal room temperature in a first phase and substantially conformable in a second phase to the interface surfaces of the electronic component and thermal dissipation member. The material has a transition temperature from the first phase to the second phase which is within the operating temperature range of the electronic component.
Owner:PARKER INTANGIBLES LLC
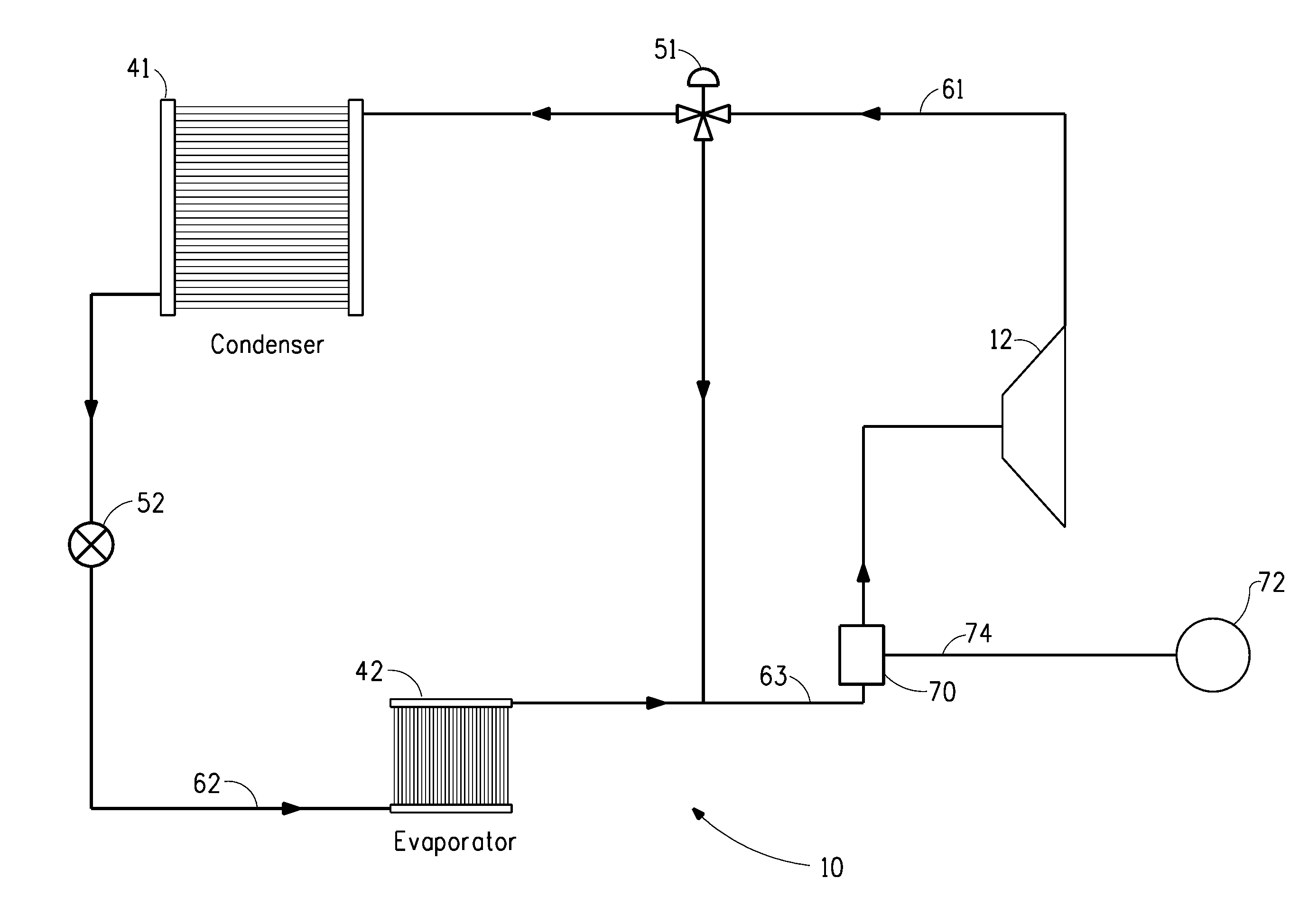
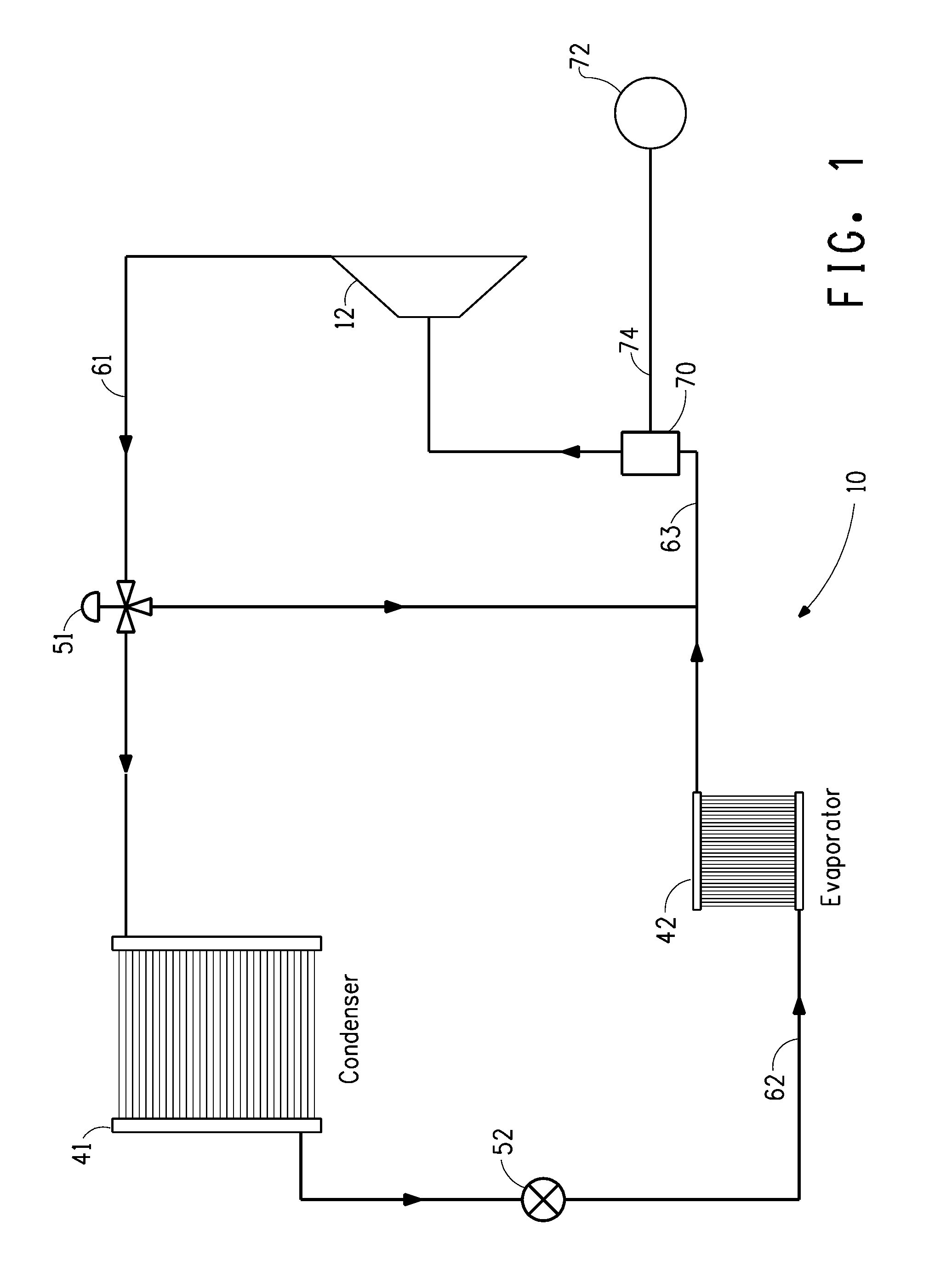
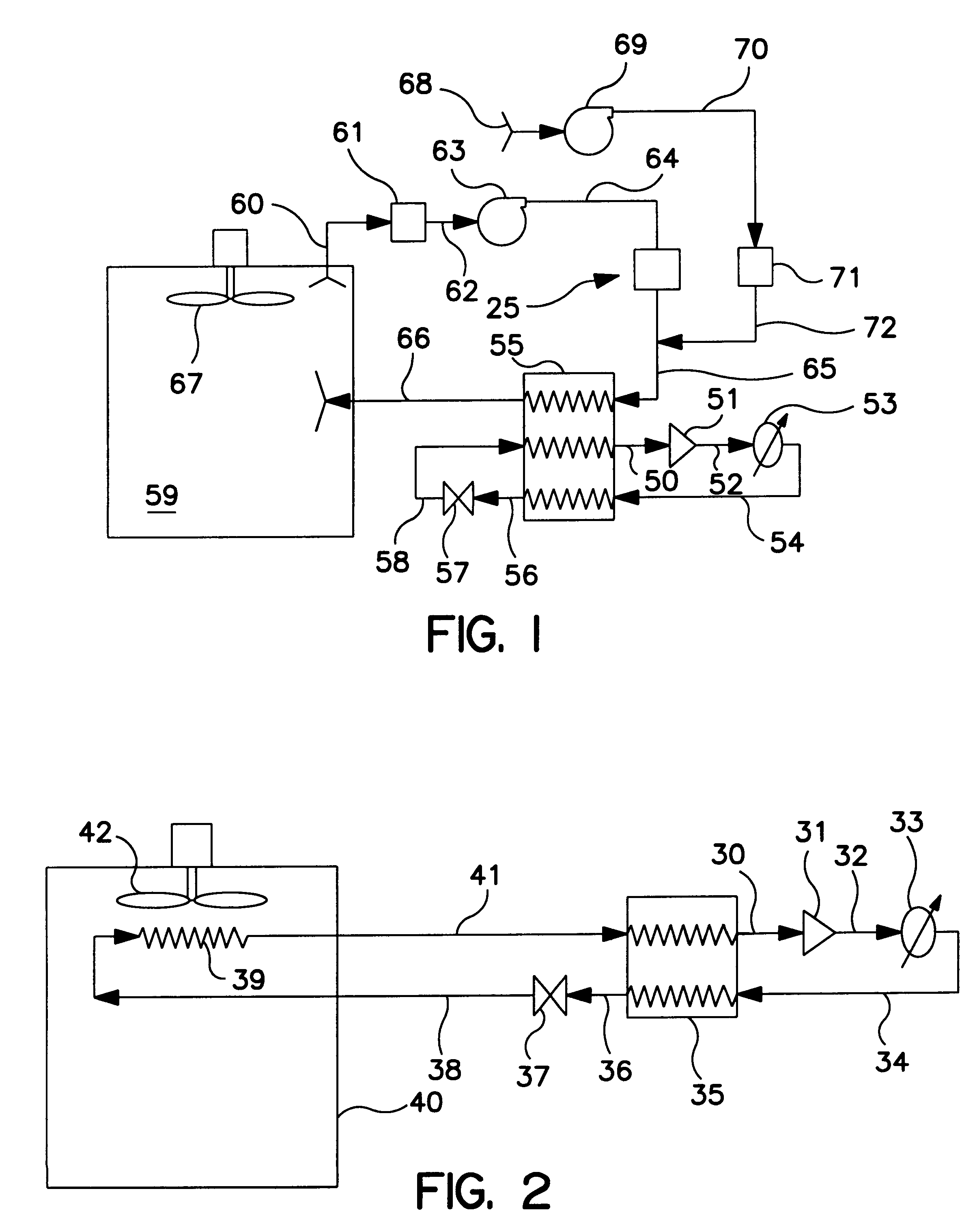
Method for leak detection in heat transfer systems
InactiveUS20080314073A1Low vapor pressureMeasurement of fluid loss/gain rateCompression machines with non-reversible cycleTransfer systemSystem pressure
Disclosed is a method for detecting a leak in a closed loop heat transfer system comprising monitoring the pressure of the heat transfer composition inside said heat transfer system, wherein a drop in pressure indicates a leak. Also disclosed is a heat transfer system comprising an evaporator, a compressor, a condenser, an expander and a device for measuring internal system pressure. The system pressure measuring device is disposed inside the closed loop heat system. The internal system pressure measuring means may be located either between the evaporator and the condenser, between the expander and the evaporator, between the compressor and the condenser, or between the condenser and the expander.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
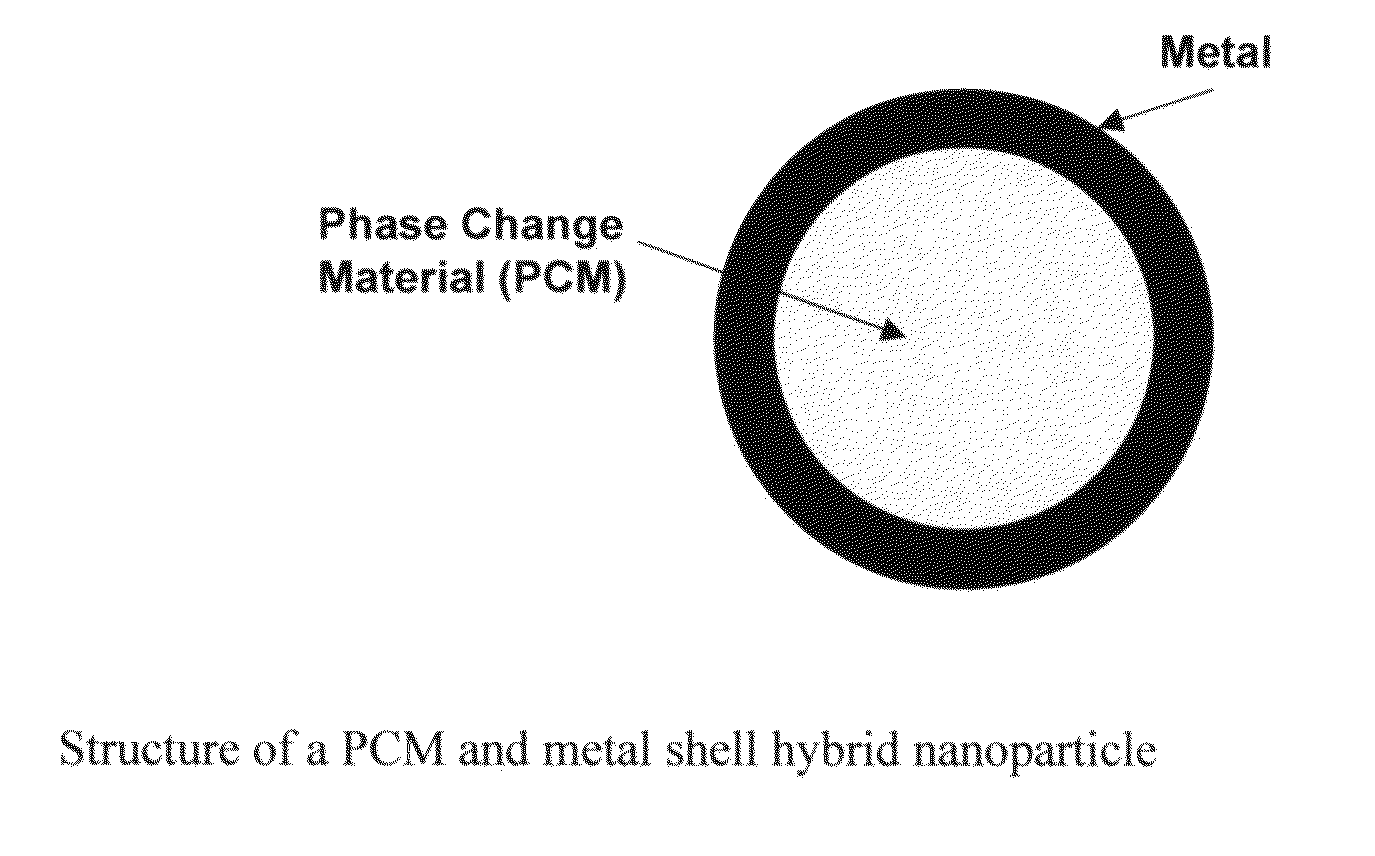
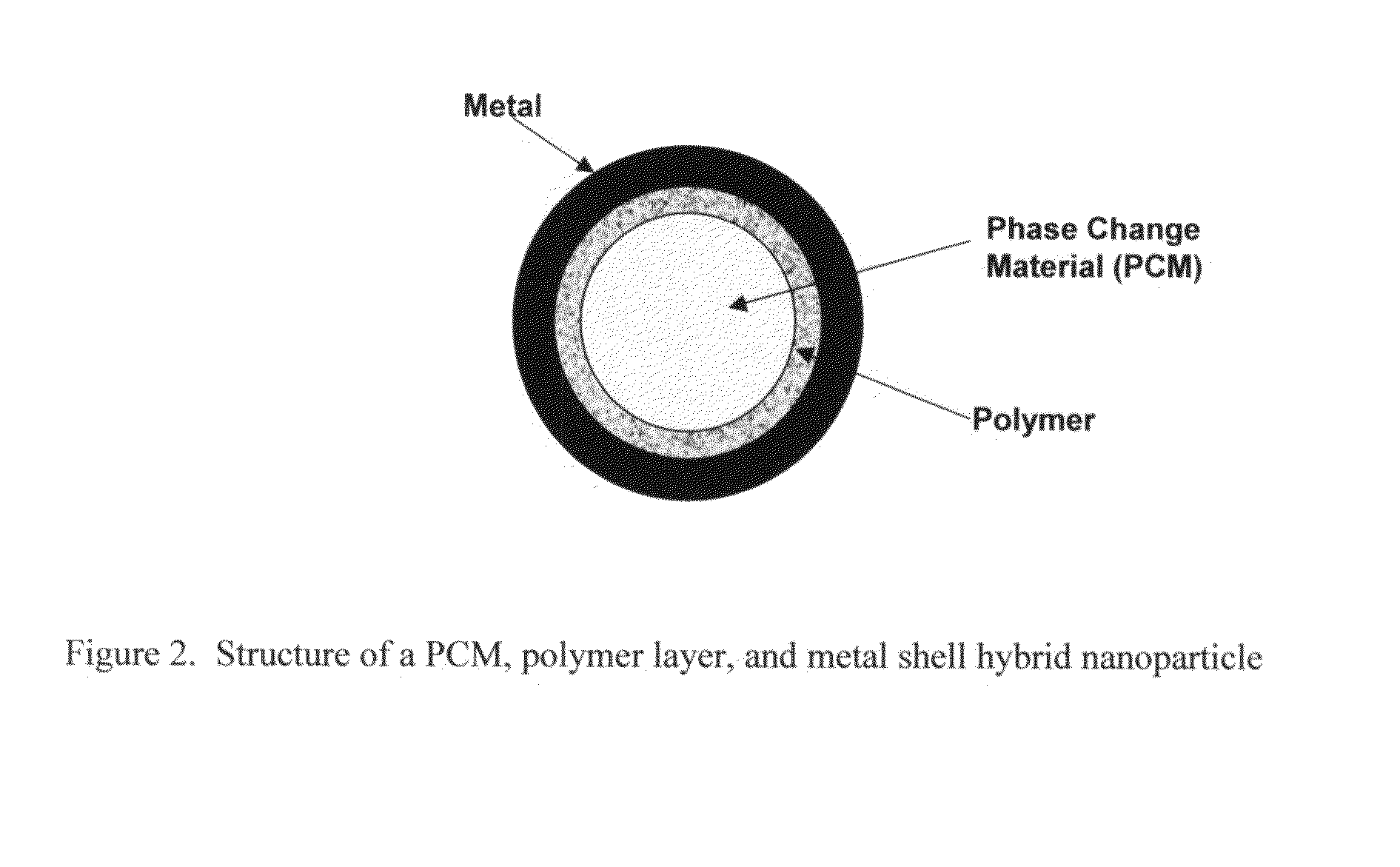
Hybrid nanoparticles
A method and composition for making hybrid nanoparticles and use of such nanoparticles are disclosed herein. In one embodiment of the invention, the hybrid nanoparticles comprise a phase change material (PCM) and a metal layer encapsulating the phase change material. In another embodiment of the invention, the hybrid nanoparticles comprise a phase change material, a polymer layer encapsulating the phase change material, and an outer metal layer encapsulating the polymer layer. In another embodiment of the invention, the hybrid nanoparticles comprise an inner core of a PCM encapsulated by a polymer shell containing embedded nanoparticles that have a high thermal conductivity.
Owner:MOHAPATRA SATISH C +6
Preparation method of polymer/graphene composite material through in situ reduction
ActiveCN101864098AEvenly dispersedQuality improvementSpecial tyresNon-conductive material with dispersed conductive materialElectrical conductorVulcanization
The invention relates to a preparation method of a polymer / graphene composite material through in situ reduction, which is characterized by comprising the following steps: adopting ultrasonic wave or grinding to evenly disperse the graphite oxide prepared by a Hummers method into polymer dispersion; introducing reducing agent into the polymer dispersion for in situ reduction, enabling the graphite oxide to be reduced into the grapheme so as to obtain stable polymer / graphene composite emulsion; carrying out demulsification, agglomeration and drying to obtain the composite polymer / grapheme composite master batch; adding the dried polymer / grapheme composite master batch and various assistants into the polymeric matrix according to a certain ratio; and carrying out double-roller mixing, vulcanization, melt extrusion or injection molding to obtain the polymer / graphene composite material with excellent physical and mechanical properties.
Owner:成都创威新材料有限公司
Tetrafluoropropene compositions and uses thereof
InactiveUS20100122545A1Lower global warming potentialCompressorHeat pumpsAir conditioningHeat transfer fluid
The present invention relates to compositions for use in refrigeration, air-conditioning, and heat pump systems wherein the composition comprises a tetrafluoropropene and at least one other component. The compositions of the present invention are useful in processes for producing cooling or heat, as heat transfer fluids, foam blowing agents, aerosol propellants, and fire suppression and fire extinguishing agents.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
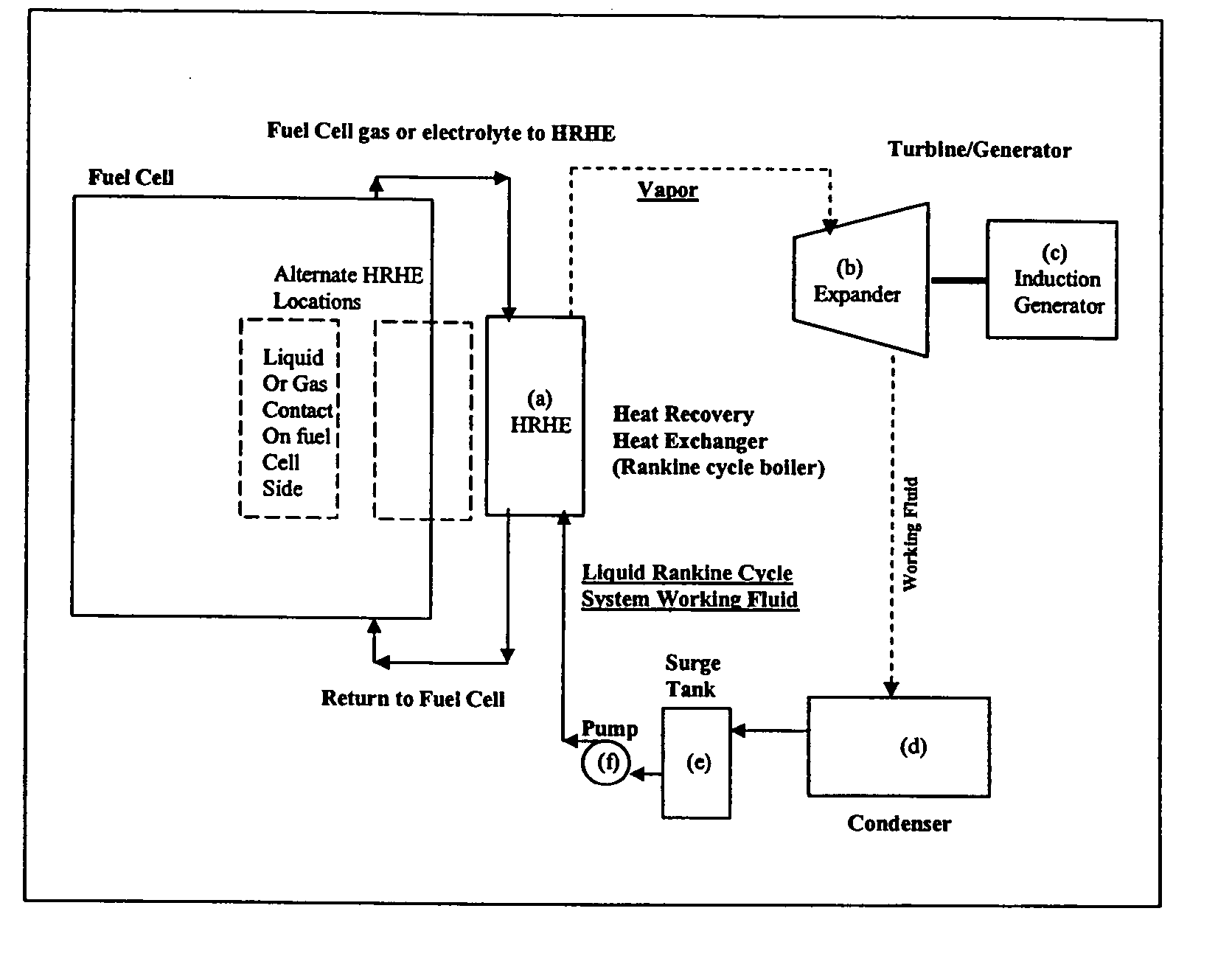
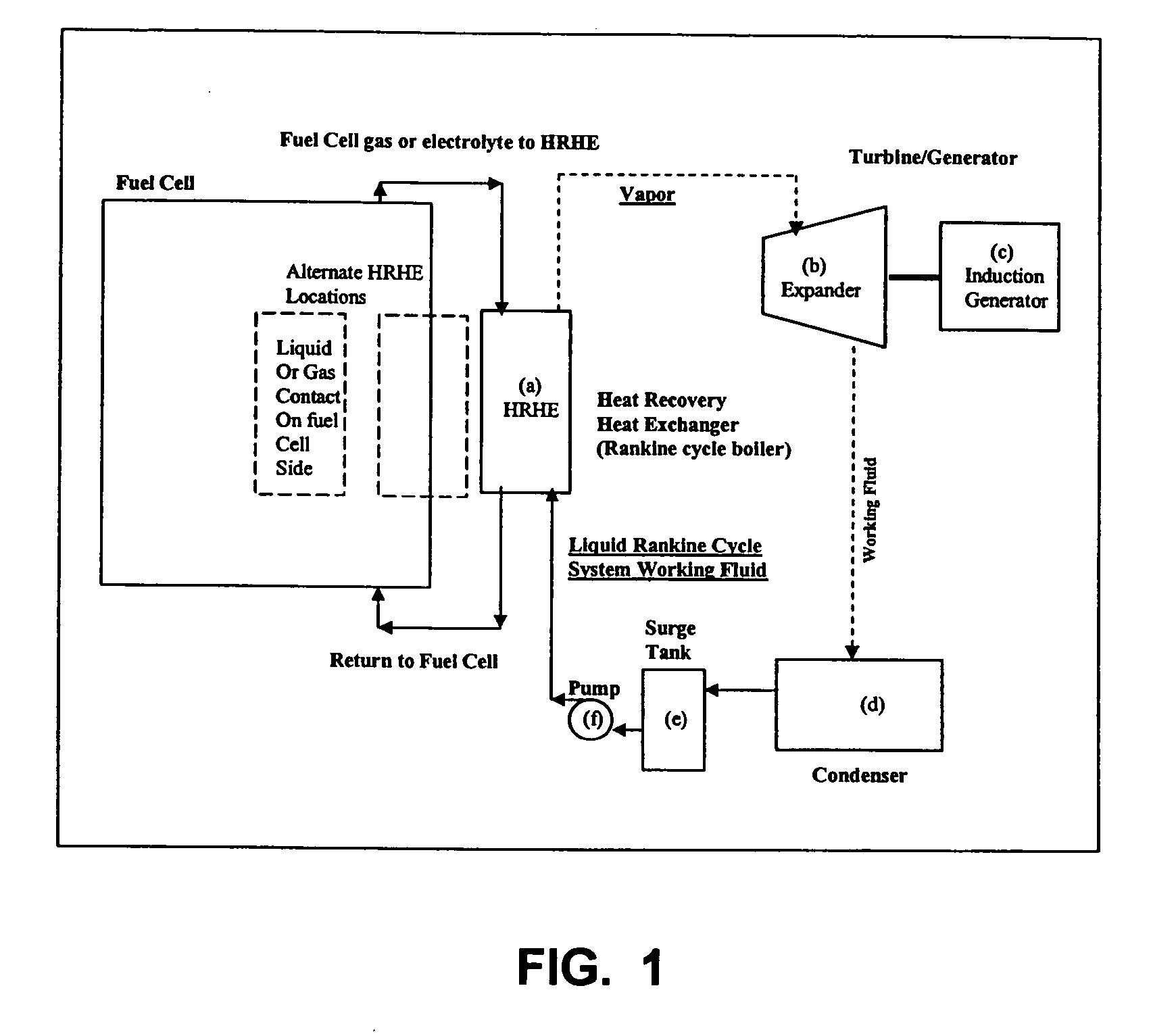
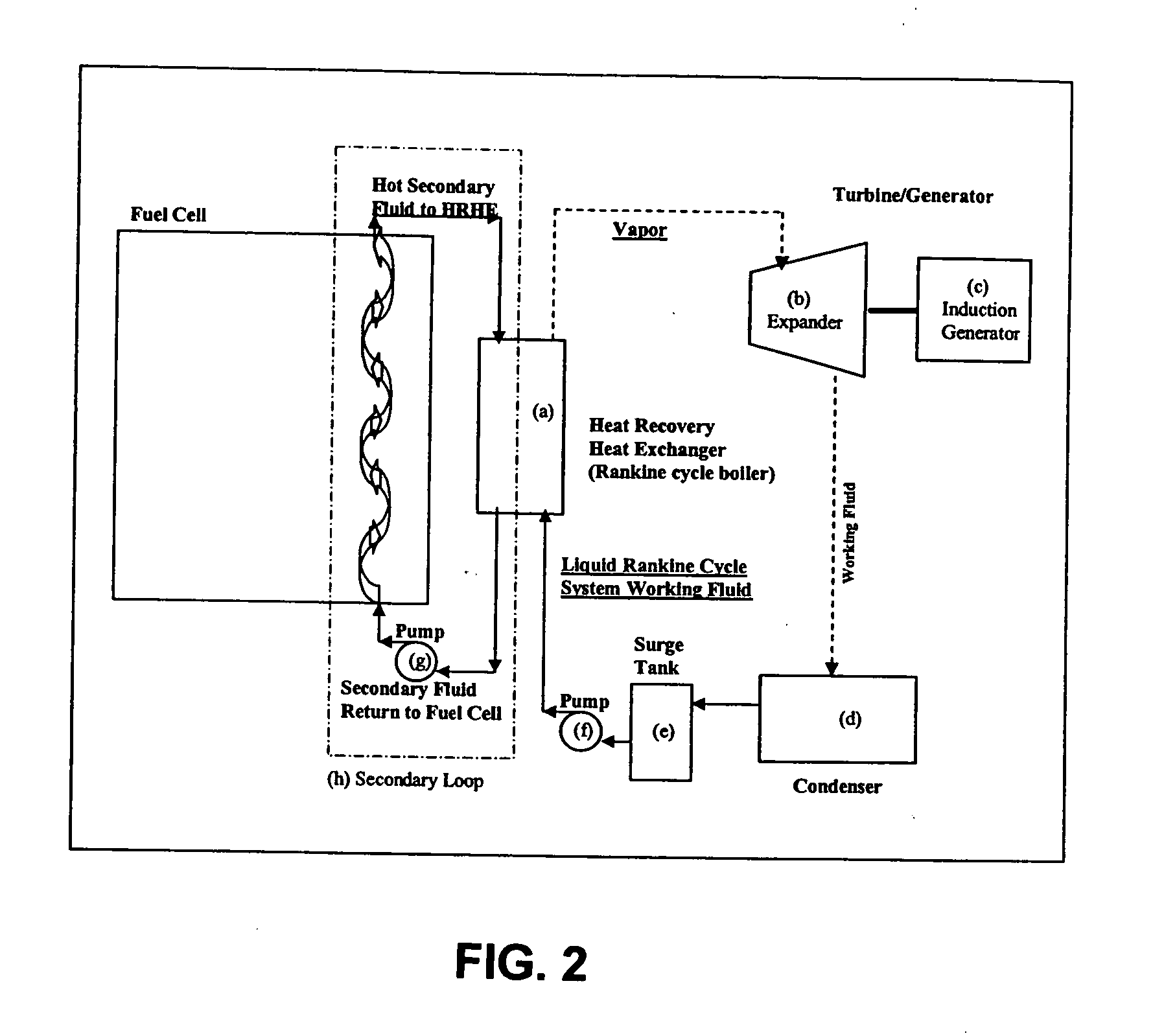
Working fluids for thermal energy conversion of waste heat from fuel cells using rankine cycle systems
A process for recovering waste heat which comprises: (a) passing a liquid phase working fluid through a heat exchanger in communication with a process which produces the waste heat; (b) removing a vapor phase working fluid from the heat exchanger; (c) passing the vapor phase working fluid to an expander, wherein the waste heat is converted into mechanical energy; and (d) passing the vapor phase working fluid from the expander to a condenser, wherein the vapor phase working fluid is condensed to the liquid phase working fluid. The preferred working fluid is an organic Rankine cycle system working fluid comprising compounds having the following general structure: where x, y, z, and m are each selected from the group consisting of: fluorine, hydrogen, Rf, and R, wherein R and Rf are each an alkyl, aryl, or alkylaryl of 1 to 6 carbon atoms, and wherein Rf is partially or fully fluorinated.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Fabric coating containing energy absorbing phase change material and method of manufacturing same
InactiveUS6514362B1Evenly dispersedEqually distributedDecorative surface effectsHeat storage plantsMicrosphereEnergy absorption
A coating composition for fabrics includes wetted microspheres containing a phase change material dispersed throughout a polymer binder, a surfactant, a dispersant, an antifoam agent and a thickener. Preferred phase change materials include paraffinic hydrocarbons. The microspheres may be microencapsulated. To prepare the coating composition, microspheres containing phase change material are wetted and dispersed in a dispersion in a water solution containing a surfactant, a dispersant, an antifoam agent and a polymer mixture. The coating is then applied to a fabric. In an alternative embodiment, an extensible fabric is coated with an extensible binder containing microencapsulated phase change material to form an extensible, coated fabric. The coated fabric is optionally flocked. The coated fabrics are manufactured using transfer techniques.
Owner:OUTLAST TECH LLC
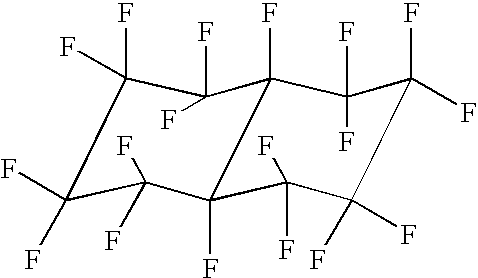
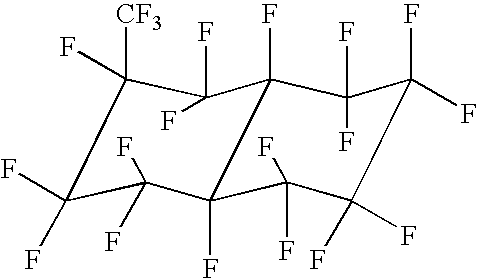
Pentafluoropropene-based compositions
ActiveUS6858571B2Reduce flammabilityMaximize effectivenessBiocideOrganic chemistry1,1-Difluoroethane1,3,3,3-Tetrafluoropropene
Provided are azeotrope-like compositions comprising pentafluoropropene (HFO-1225) and a fluid selected from the group consisting of 3,3,3-trifluoropropene (“HFO-1243zf”), 1,1-difluoroethane (“HFC-152a”), trans-1,3,3,3-tetrafluoropropene (“HFO-1234ze”), and combinations of two or more thereof. Also provided are uses thereof including as refrigerants, blowing agents, sprayable compositions, flame suppressant, and the like.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Stabilized Iodocarbon Compositions
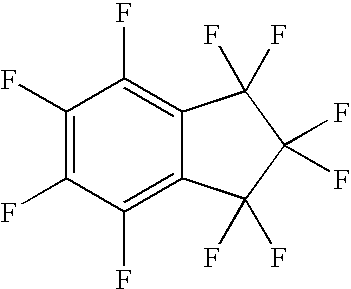
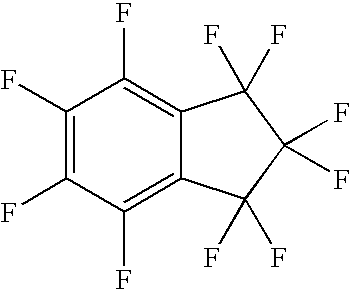
InactiveUS20080157022A1Reduce environmental damageLow propertyHalogenated hydrocarbon separation/purificationHeat-exchange elementsStabilizing AgentsSolvent composition
Disclosed are compositions comprising at least one iodocarbon compound and preferably at least one stabilization agent comprising a diene-based compound. These compositions are generally useful as refrigerants for heating and cooling, as blowing agents, as aerosol propellants, as solvent composition, and as fire extinguishing and suppressing agents.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
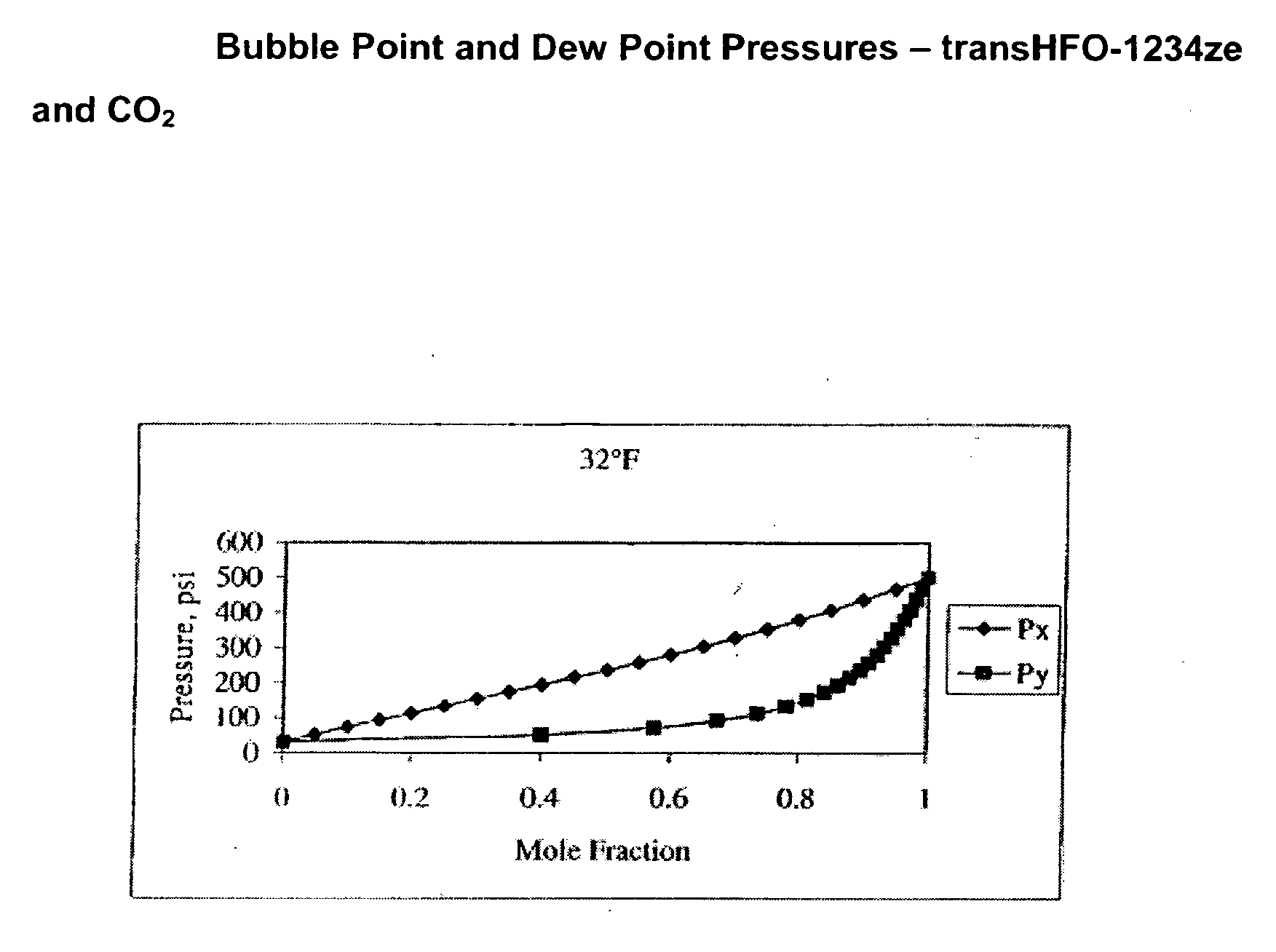
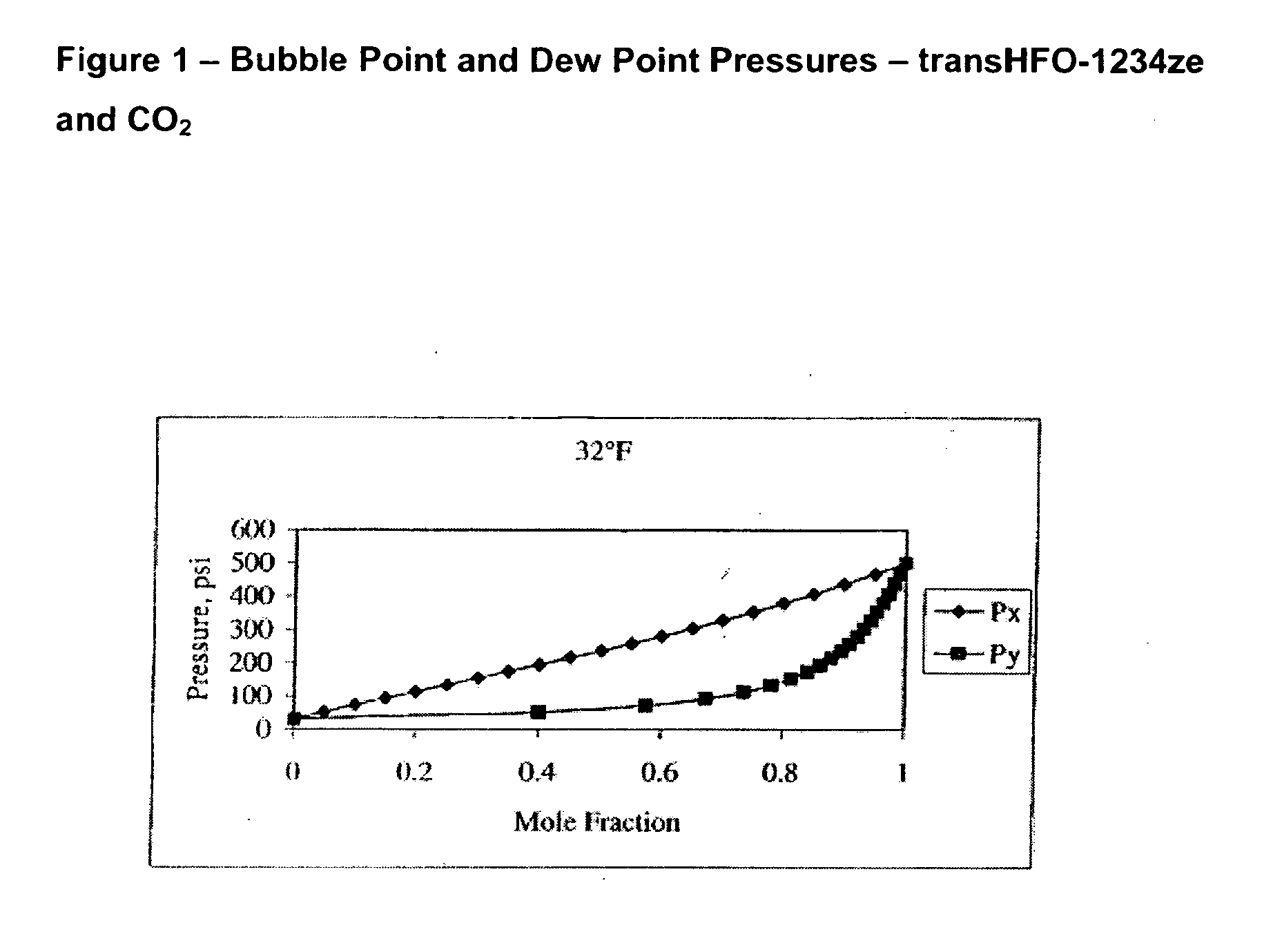
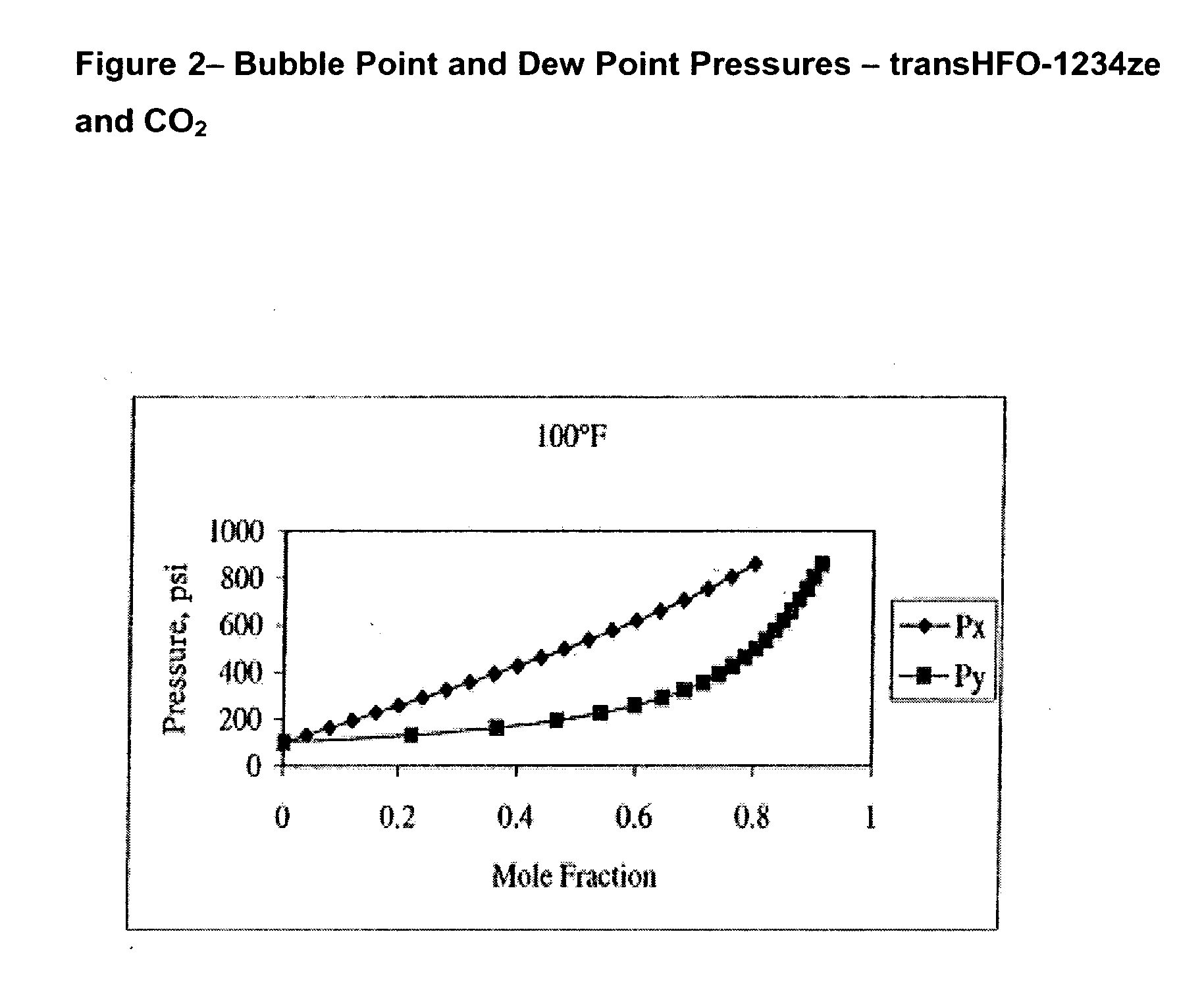
Compositions comprising tetrafluoeopropene & carbon dioxide
ActiveUS20060043331A1Maintain good propertiesReducing and eliminating deleterious ozone depletion potentialHeat-exchange elementsLiquid soapsHeat transfer fluidPhotochemistry
Disclosed are compositions useful in a wide variety of applications, including heat transfer fluids which possess a highly desirable and unexpectedly superior combination of properties, and heat transfer systems and methods based on these fluids. The preferred heat transfer fluid comprises from about 1 to about 40 percent, on a weight basis, of carbon dioxide (CO2) and from about 99 to about 60 percent, on a weight basis, of a compound having the Formula I XCFzR3-z (I), where X is a C2 or a C3 unsaturated, substituted or unsubstituted, alkyl radical, each R is independently Cl, F, Br, I or H, and z is 1 to 3. A preferred compound of Formula I is tetrafluoropropene, particularly 1,1,1,3-tetrafluoropropene and / or 1,1,1,3-tetrafluoropropene.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Compositions containing fluorine substituted olefins
The use to e of tetrafluoropropenes, particularly (HFO-1234) in a variety of applications, including refrigeration equipment, is disclosed. These materials are generally useful as refrigerants for heating and cooling, as blowing agents, as aerosol propellants, as solvent composition, and as fire extinguishing and suppressing agents.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
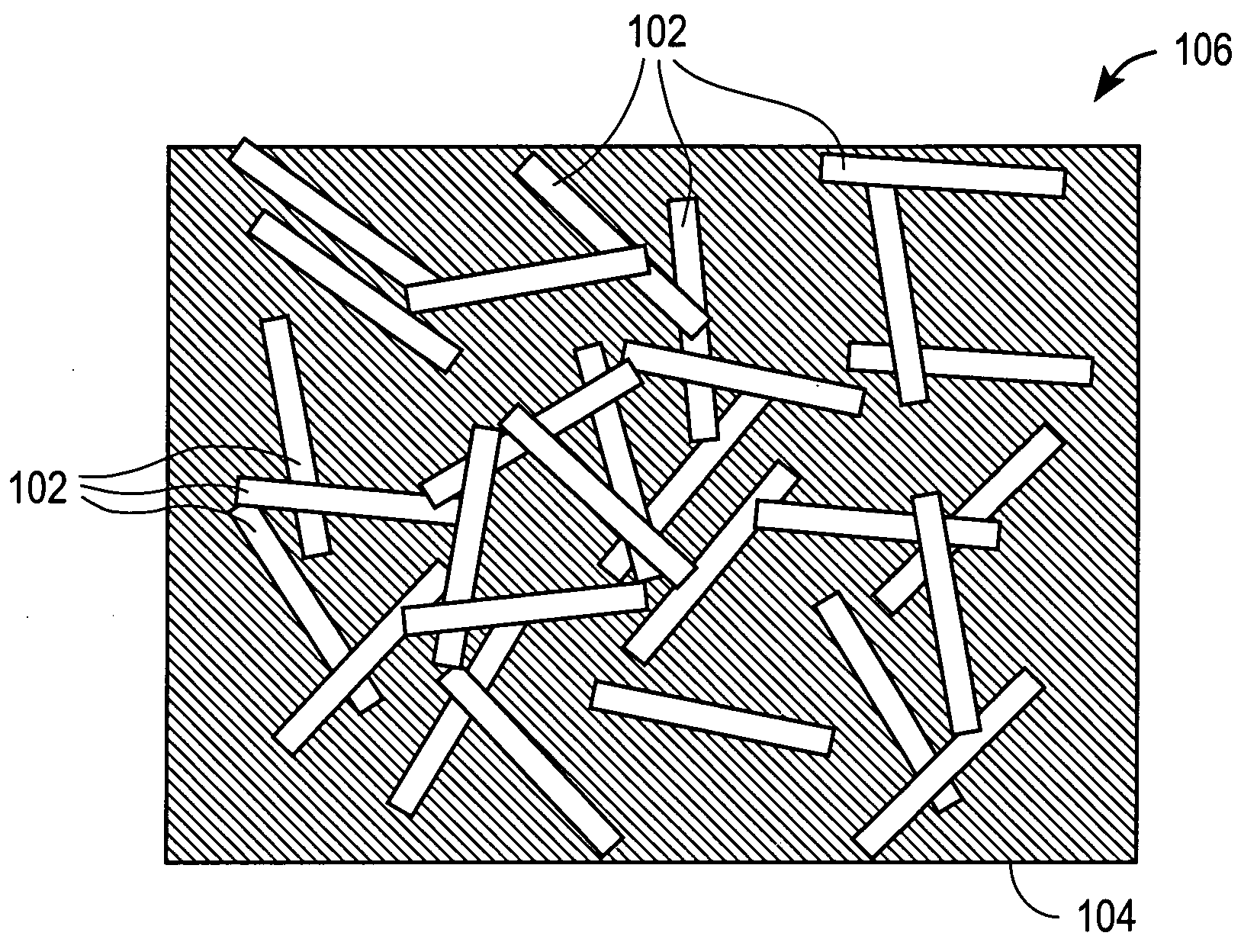
Nano carbon materials for enhancing thermal transfer in fluids
InactiveUS6695974B2Improve thermal conductivityImprove heat transfer performanceMaterial nanotechnologyNanostructure manufactureOrganic groupElectrical polarity
A novel fluid heat transfer agent suitable for use in a closed heat transfer system, for example, wherein energy is transferred between an evaporator and a condenser in heat exchange relationship with the heat transfer agent that is caused to flow from one to the other. The novel heat transfer agent is a complex comprising a body of heat transfer fluid, for example, ethylene glycol or water, having suspended therein carbon nanoparticles in a quantity sufficient to enhance the thermal conductivity of the body of heat transfers fluid, per se. The carbon nanoparticles are selected from carbon in the form of sp<2 >type and sp<3 >type bonding and preferably comprise nanotubes or fullerenes and may have a coupling agent bonded thereto or enclosed therein when the nanotube or fullerene forms a hollow capsule. The coupling agent may be a polar organic group covalently bonded to the carbon nanoparticles and miscible in the fluid medium.
Owner:MATERIALS & ELECTROCHEM RES
Method for providing refrigeration
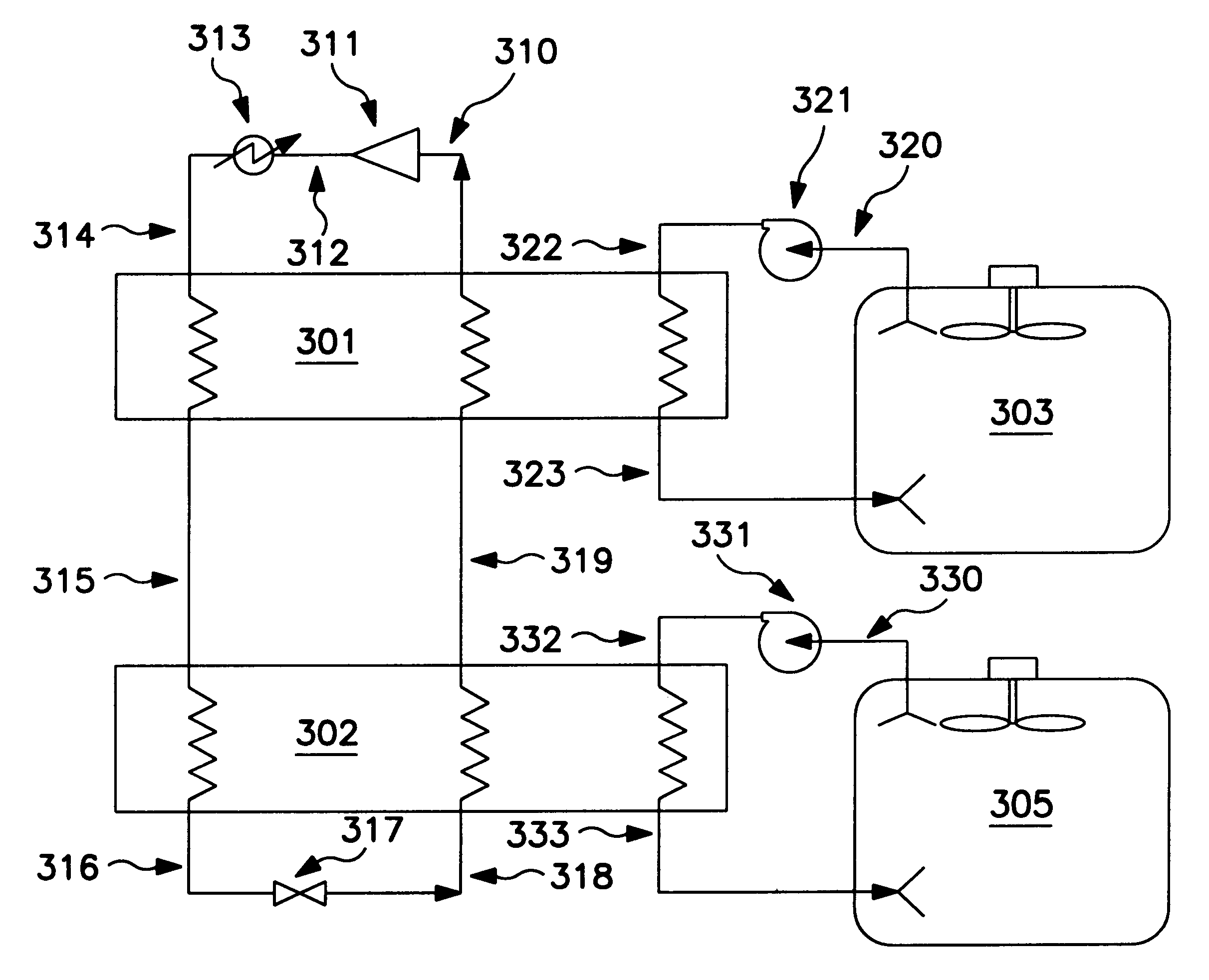
A method for providing refrigeration such as to an insulated enclosure wherein a defined multicomponent refrigerant fluid undergoes a phase change coupled with Joule-Thomson expansion to generate refrigeration over a wide temperature range which may comprise from ambient to low temperatures.
Owner:EDWARDS VACUUM LLC
Heat transfer compositions of hydrofluorocarbons and a hydrofluoroolefin
The present invention relates to heat transfer compositions comprising 2,3,3,3-tetrafluoropropene, difluoromethane, pentafluoroethane, and 1,1,1,2-tetrafluoroethane for use in refrigeration, air-conditioning, heat pump systems, and other heat transfer applications. The inventive heat transfer compositions can possess reduced global warming potential while providing good capacity and performance.
Owner:ARKEMA INC
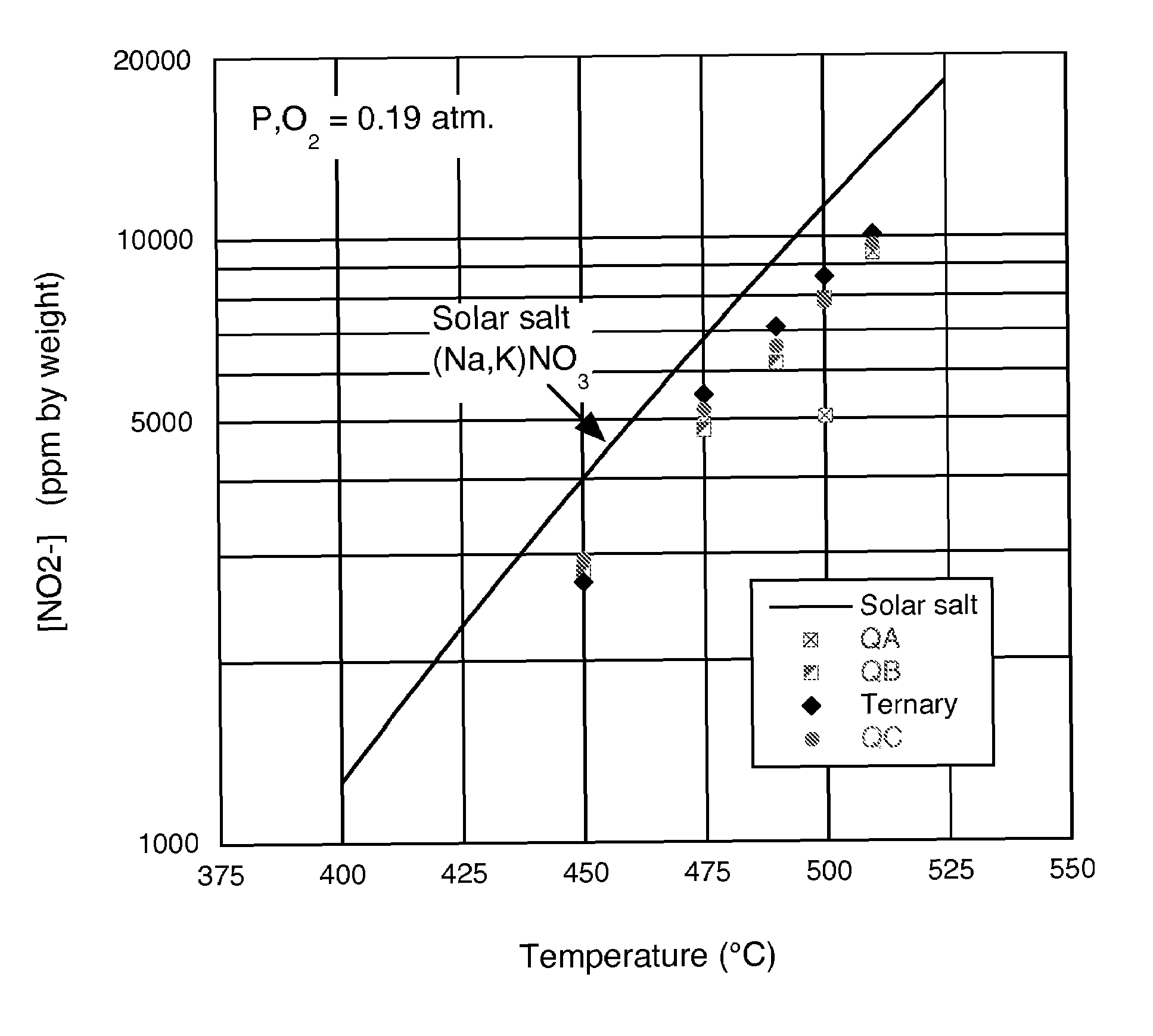
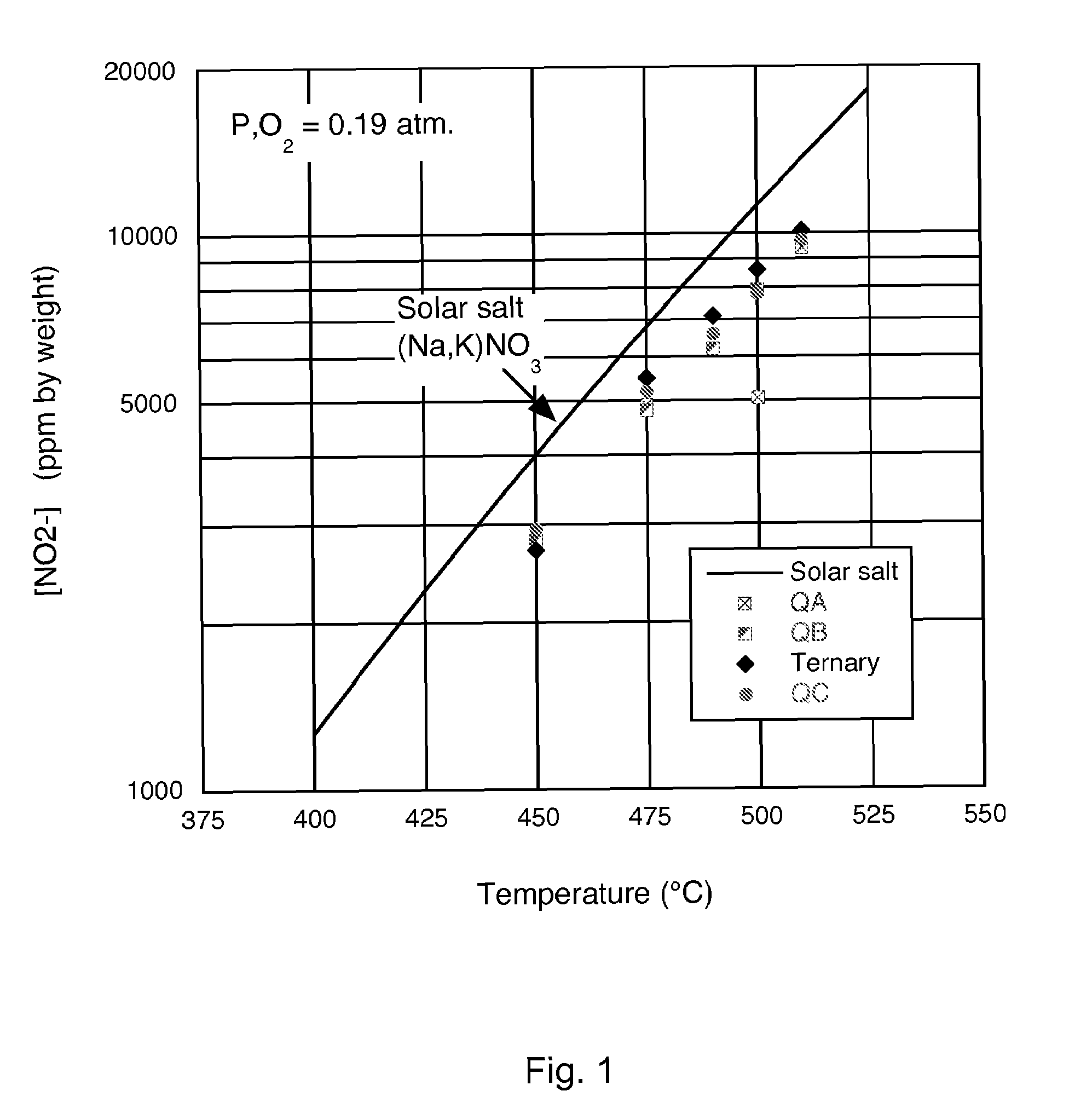
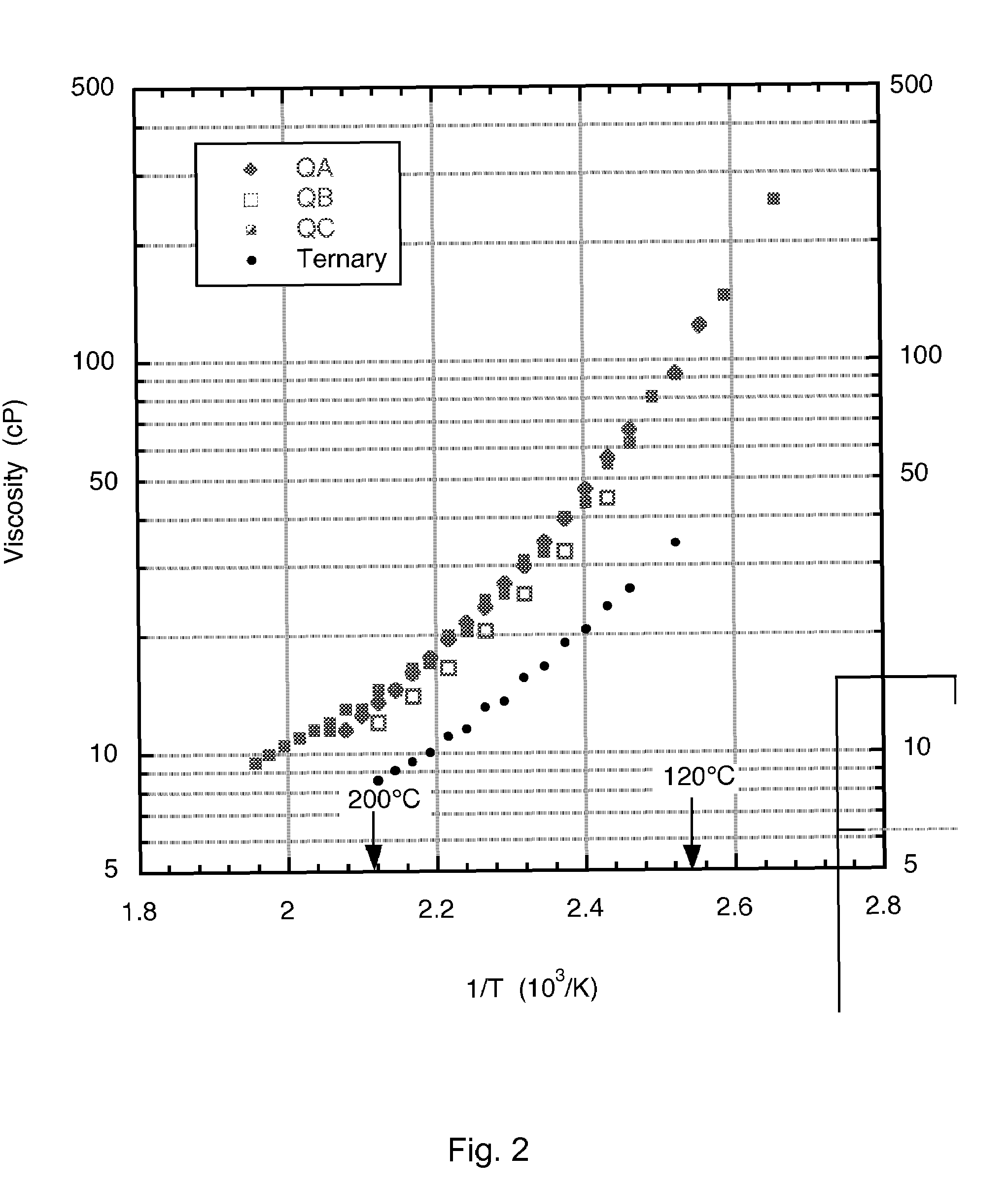
Low-melting point inorganic nitrate salt heat transfer fluid
A low-melting point, heat transfer fluid made of a mixture of four inorganic nitrate salts: 9-18 wt % NaNO3, 40-52 wt % KNO3, 13-21 wt % LiNO3, and 20-27 wt % Ca(NO3)2. These compositions can have liquidus temperatures less than 100 C; thermal stability limits greater than 500 C; and viscosity in the range of 5-6 cP at 300 C; and 2-3 cP at 400 C.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
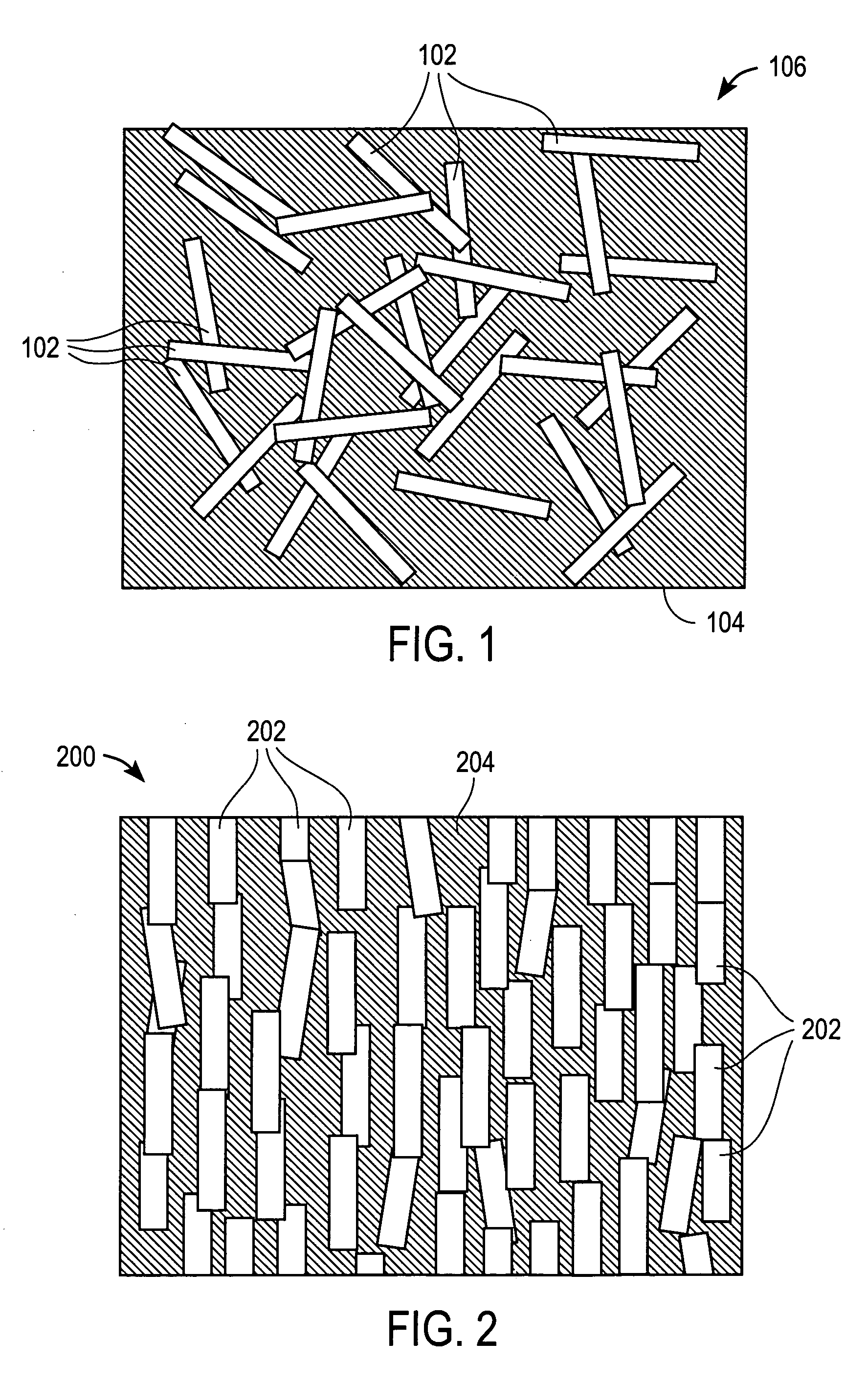
Thermal interface material and method for manufacturing same
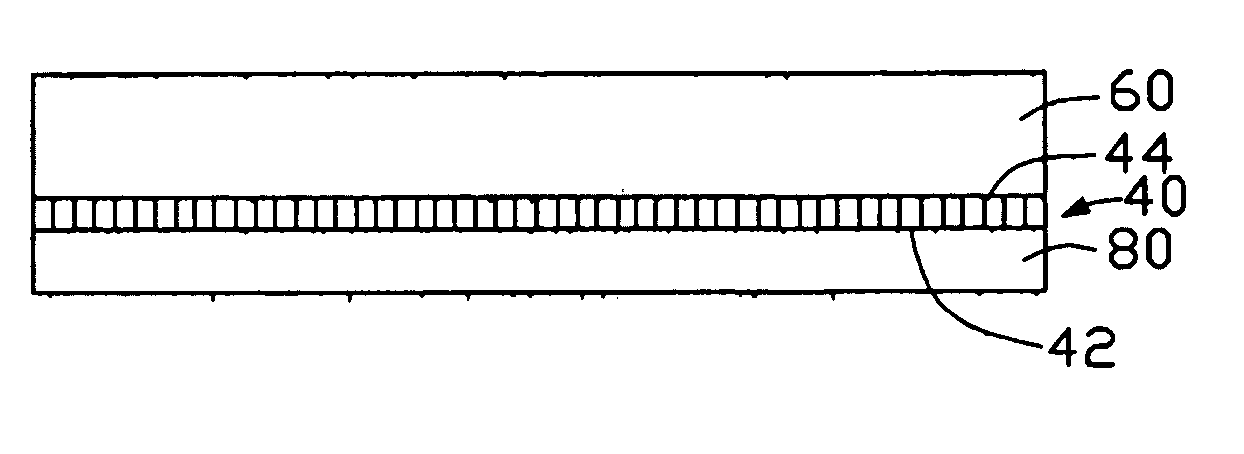
ActiveUS20050167647A1Reduce thicknessSmall resistanceMaterial nanotechnologySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsLiquid stateCarbon nanotube
A thermal interface material (40) includes a macromolecular material (32), and a plurality of carbon nanotubes (22) embedded in the macromolecular material uniformly. The thermal interface material includes a first surface (42) and an opposite second surface (44). Each carbon nanotube is open at both ends thereof, and extends from the first surface to the second surface of the thermal interface material. A method for manufacturing the thermal interface material includes the steps of: (a) forming an array of carbon nanotubes on a substrate; (b) submerging the carbon nanotubes in a liquid macromolecular material; (c) solidifying the liquid macromolecular material; and (d) cutting the solidified liquid macromolecular material to obtain the thermal interface material with the carbon nanotubes secured therein.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Thermal conductive material utilizing electrically conductive nanoparticles
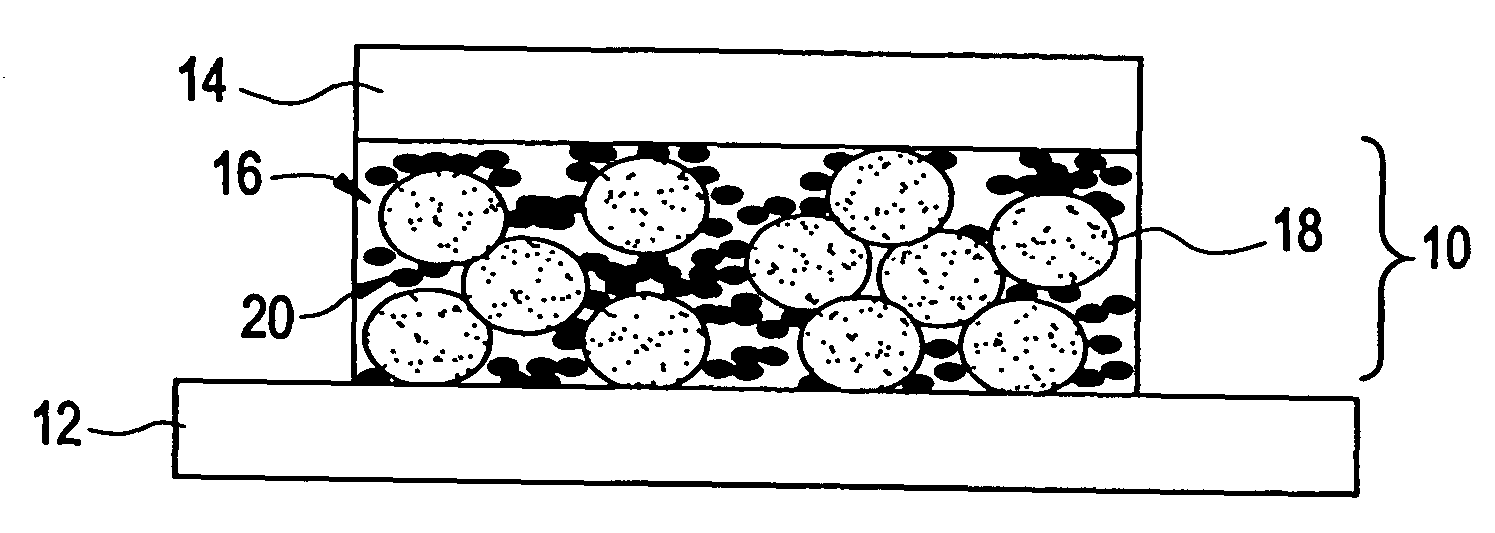
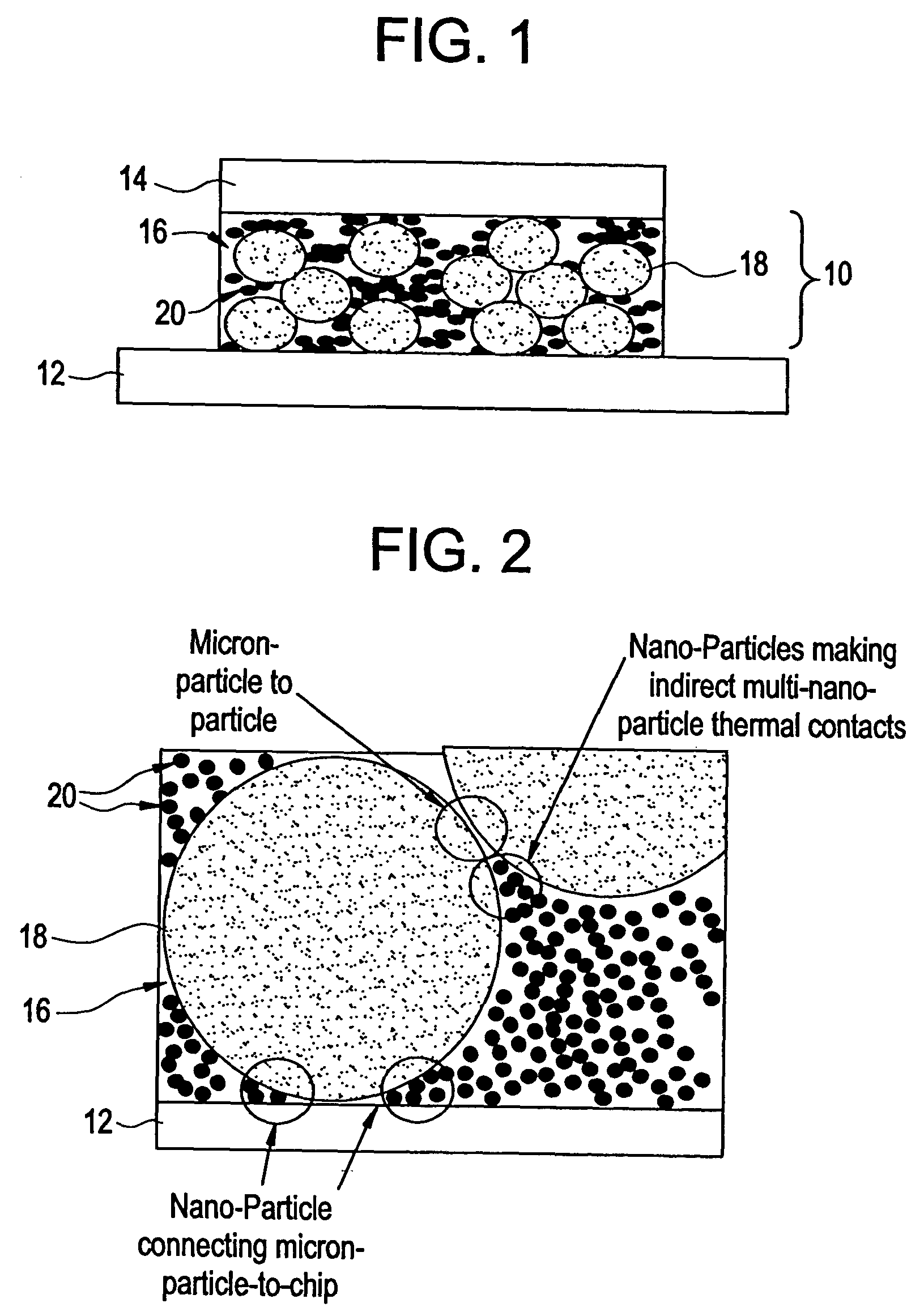
ActiveUS20050045855A1Improve heat transfer efficiencySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsConductive materialNanoparticleInterfacial resistance
Thermal interface compositions contain both non-electrically conductive micron-sized fillers and electrically conductive nanoparticles blended with a polymer matrix. Such compositions increase the bulk thermal conductivity of the polymer composites as well as decrease thermal interfacial resistances that exist between thermal interface materials and the corresponding mating surfaces. Such compositions are electrically non-conductive. Formulations containing nanoparticles also show less phase separation of micron-sized particles than formulations without nanoparticles.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Heat conductive silicone grease composition
ActiveCN102634212AImprove thermal conductivityExtended service lifeHeat-exchange elementsCarbon nanotubeGraphite
The invention discloses a heat conductive silicone grease composition which mainly contains a carbon nano tube, graphite, phase-change capsule particles and silicone oil, wherein the carbon nano tube can speed up the conduction of heat further; the phase-change capsule particles are used for improving the initial temperature absorption velocity of a heat end; the phase-change capsule particles, the carbon nano tube and graphite in a fluid form full-three-dimensional network distribution of particles (phase-change capsule), a line ( the carbon nano tube) and a plane (graphite) in the fluid finally. The heat conductive silicone grease composition provided by the invention has high heat conduction rate and low heat resistivity, the heat radiation efficiency of the heat conductive silicone grease is improved greatly, the service life of the heat conductive silicone grease is prolonged greatly, and the heat conductive silicone grease composition has high practical value.
Owner:HUZHOU MINGSHUO OPTOELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
Compositions comprising e-1,2-difluoroethylene and uses thereof
InactiveUS20110253927A1Lower global warming potentialHeat recovery systemsOther chemical processesWorking fluidPower cycle
The present invention relates to compositions for use in refrigeration, air-conditioning, and heat pump systems wherein the composition comprises E-1,2-difluoroethylene. The compositions of the present invention are useful in processes for producing cooling or heat, as heat transfer fluids, foam blowing agents, aerosol propellants, and power cycle working fluids.
Owner:THE CHEMOURS CO FC LLC
Solvent compositions containing chlorofluoroolefins or fluoroolefins
Compositions and methods based on the use of fluoroalkene containing from 3 to 4 carbon atoms and at least one carbon-carbon double bond, such as HFO-1214, HFO-HFO-1233, or HFO-1354, having properties highly beneficial in solvent cleaning applications.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Working medium and heat cycle system
ActiveUS20140070132A1Promote decompositionLess influenceOrganic chemistryCompression machinesTransport systemOzone layer
To provide a working medium for heat cycle, of which combustibility is suppressed, which has less influence over the ozone layer, which has less influence over global warming and which provides a heat cycle system excellent in the cycle performance (capacity), and a heat cycle system, of which the safety is secured, and which is excellent in the cycle performance (capacity).A working medium for heat cycle comprising 1,1,2-trifluoroethylene is employed for a heat cycle system (such as a Rankine cycle system, a heat pump cycle system, a refrigerating cycle system 10 or a heat transport system).
Owner:ASAHI GLASS CO LTD
Fireproof insulating cementitious foam comprising phase change materials
ActiveUS8070876B1Improve fire resistanceImprove high temperature resistanceSolid waste managementSynthetic resin layered productsThermal energyThermal energy storage
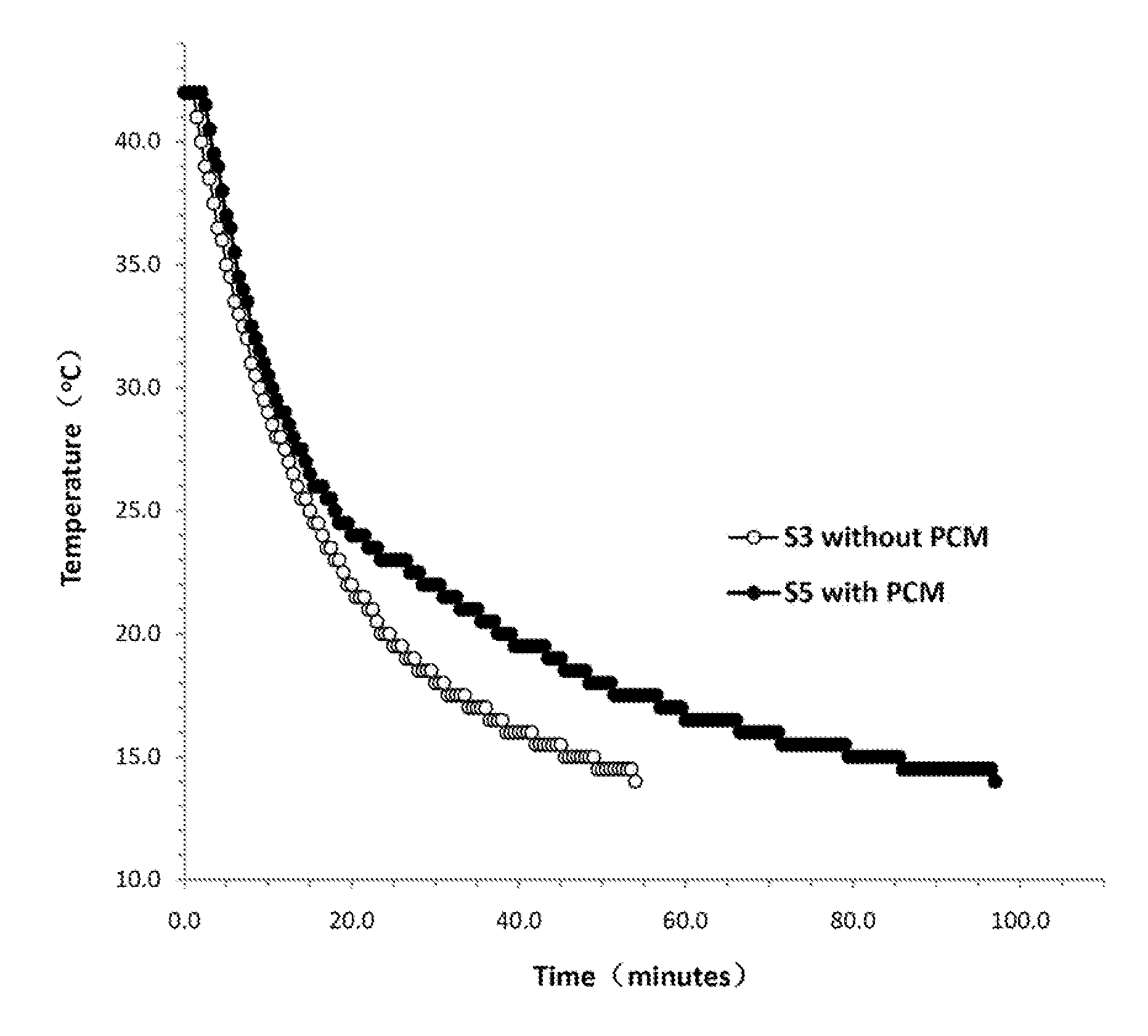
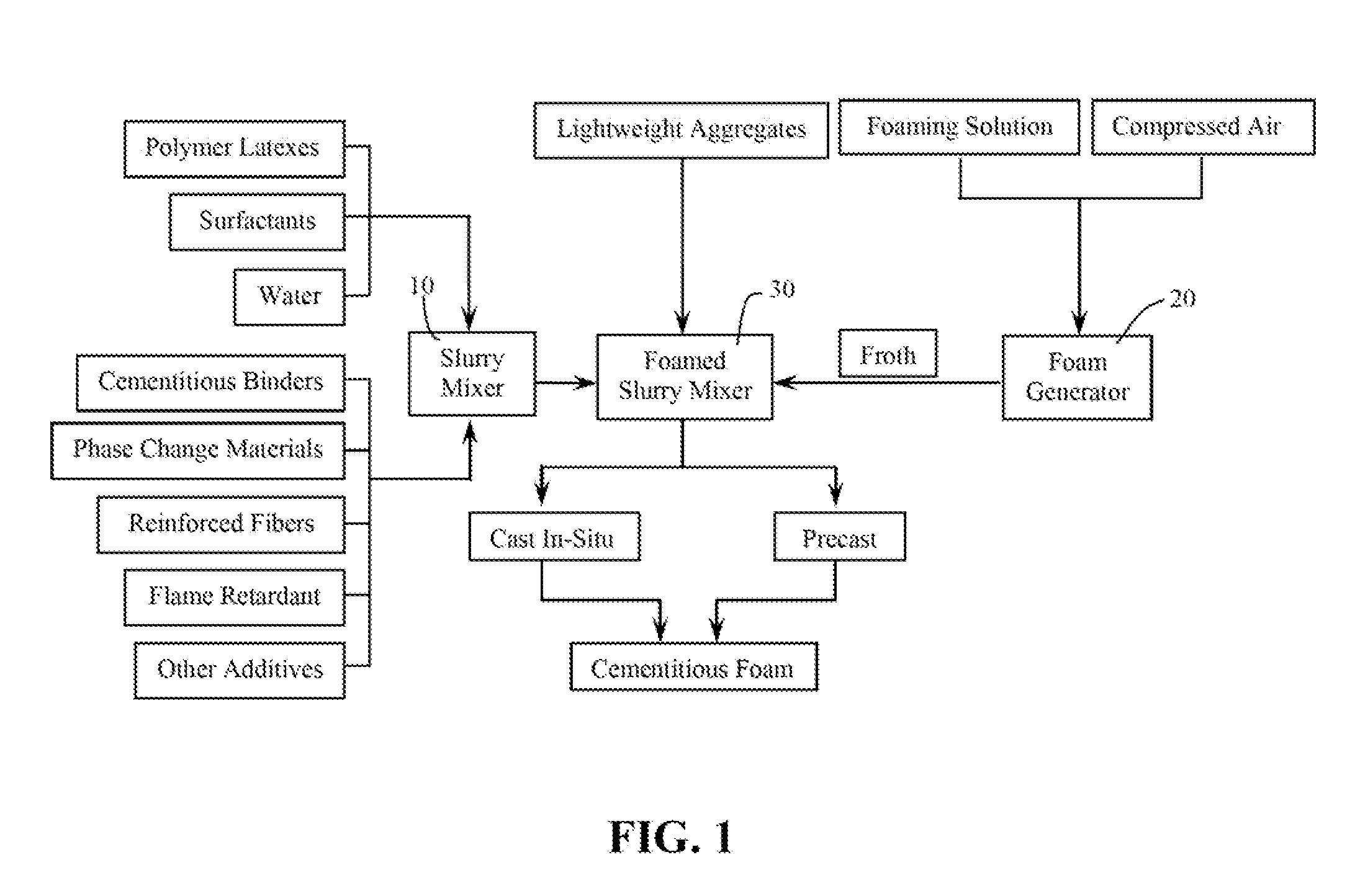
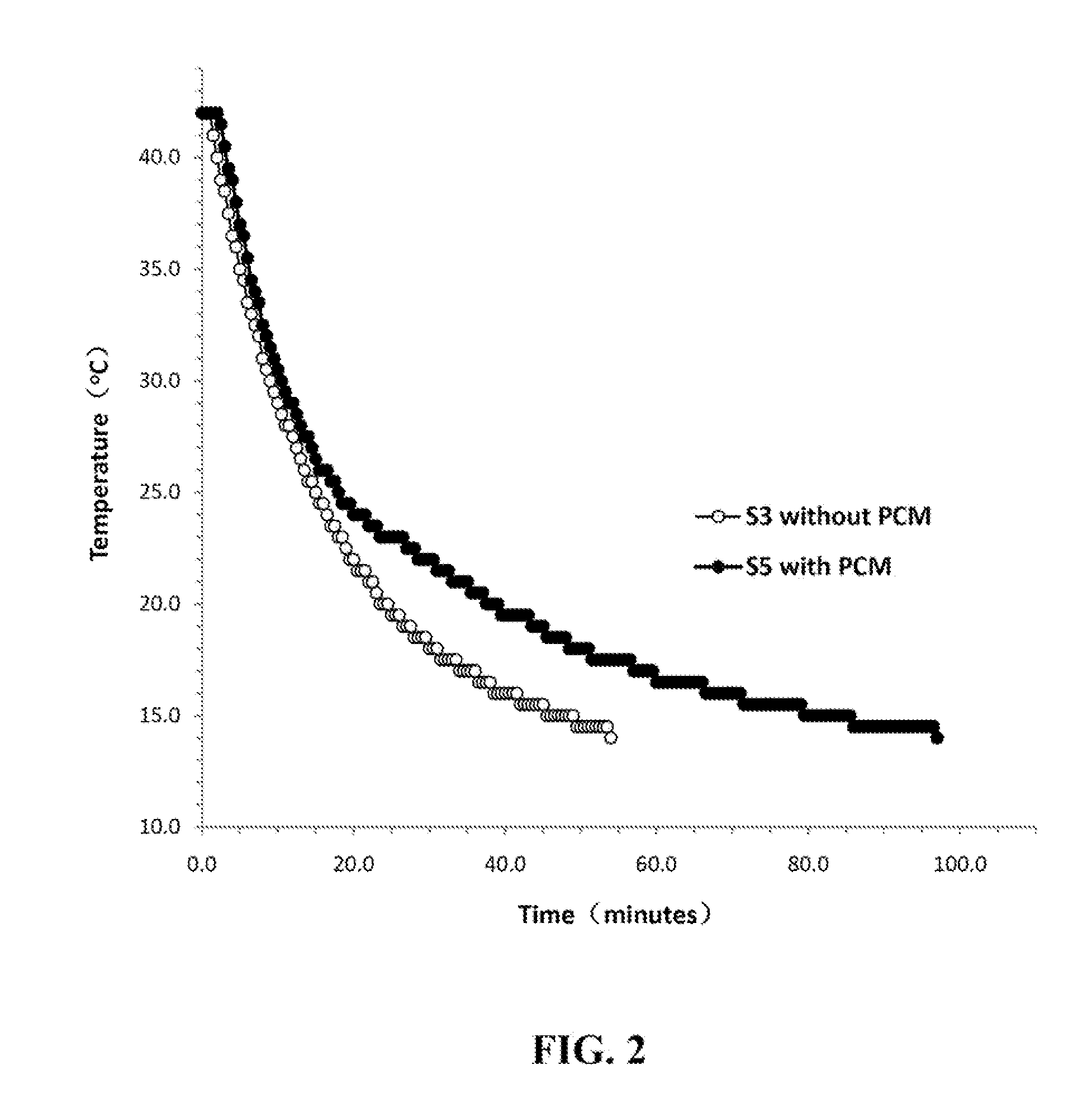
A fireproof insulating foamed cementitious composition with thermal energy storage capacity is provided for use in producing wall insulation boards, fireproof claddings for steel structures, inner cores of fire resistant wall or door panels, and the like. The composition demonstrates improved energy efficiency in which phase change materials, such as microencapsulates, are used in conjunction with a cementitious mixture of calcined gypsum and hydraulic cement, lightweight aggregates, a polymer latex, and a foaming solution to create stable air bubbles inside the cementitious matrix. The calcined gypsum and the hydraulic cement are present in a weight ratio range from about 1:3 to about 3:1. The composition may further include reinforced fibers, surfactants, inorganic flame retardants, and other additives. The presence of the phase change material not only increases energy efficiency of the cured cementitious foam material, but also improves compatibility between calcined gypsum and cement during slurry mixing and hardening.
Owner:JIANG HAIHONG
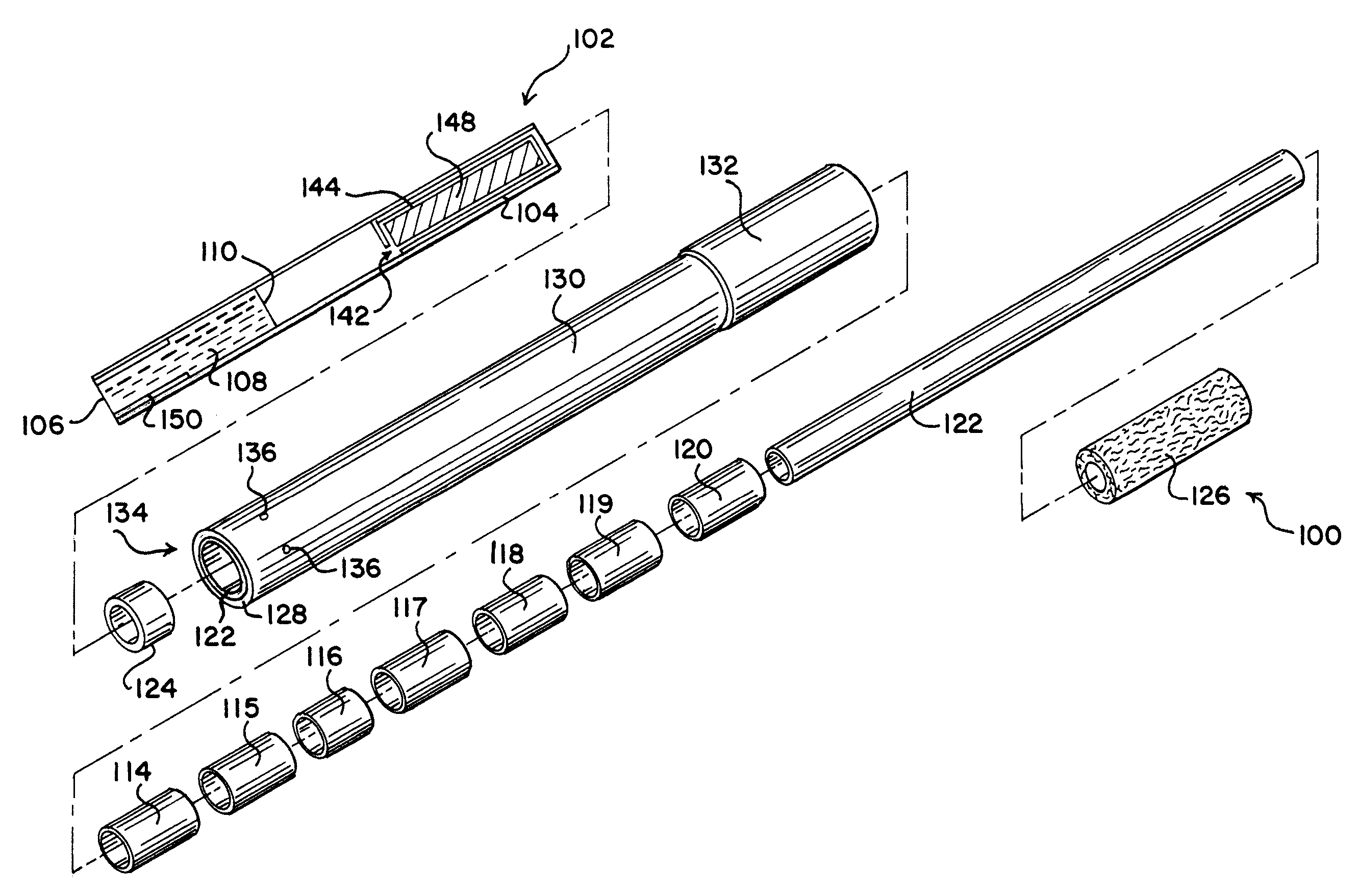
Portable heat source
InactiveUS6248257B1Excursion can be restrictedPromotes even distributionExothermal chemical reaction heat productionOther chemical processesAqueous solutionAcid anhydride
A portable heat source that may be used to warm food, beverage or other supplies. The heater contains a heat-producing composition that is a solid that may be stored for long periods of time, and activated by addition of water or an aqueous solution. Heat-producing compositions contain an acidic anhydride, an acidic salt, a basic anhydride or a basic salt. Preferred heat-producing compositions contain a mixture of an acidic anhydride or salt together with a basic anhydride or salt, such that addition of water to both acidic and basic anhydrides produces heat as well as acid and base respectively; subsequent reaction of the acid and base produces additional heat, as well as a safe, neutral product that is easily disposed. The invention further consists of means and methods for regulating the rate of heat production in heaters by the addition of inert additives to heat-producing compositions and the application of processing methods that regulate access of water to heat-producing compounds. Addition of inert materials and shaping, agglomerating, pelleting and like processing of heat-producing materials are applied to produced heat at a rate compatible with the rate at which the food or other materials can absorb the heat. The invention further consists of devices incorporating the materials to be heated in an advantageous arrangement with the heater composition.
Owner:TDA RES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com