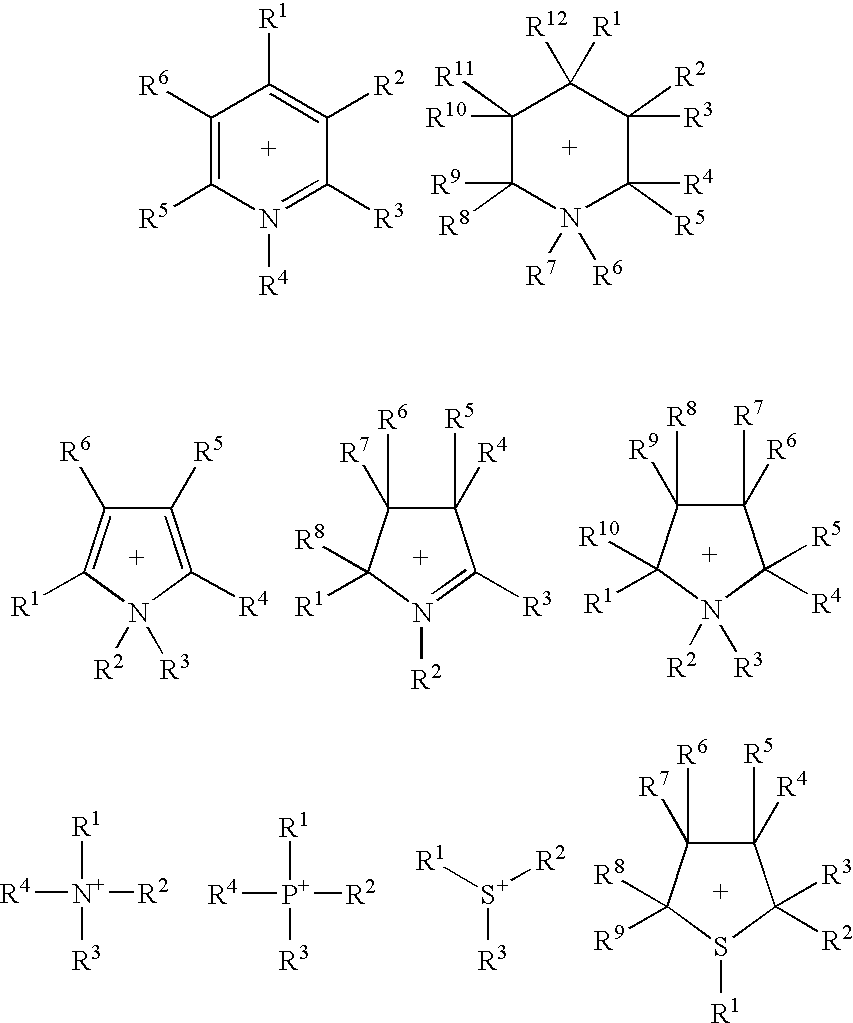
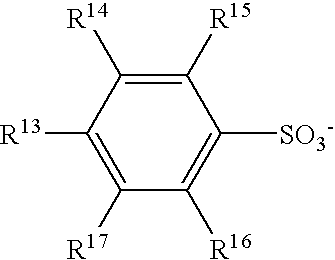
Patents
Literature
569results about How to "Low vapor pressure" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Perfume delivery systems for consumer goods
InactiveUS20070275866A1Low vapor pressureRealized benefitsCosmetic preparationsContainer decorationsEngineeringDelivery system
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Method of forming a carbon polymer film using plasma CVD
ActiveUS20070218705A1Improve featuresFunction increaseLiquid surface applicatorsPhotomechanical apparatusCapacitanceBoiling point
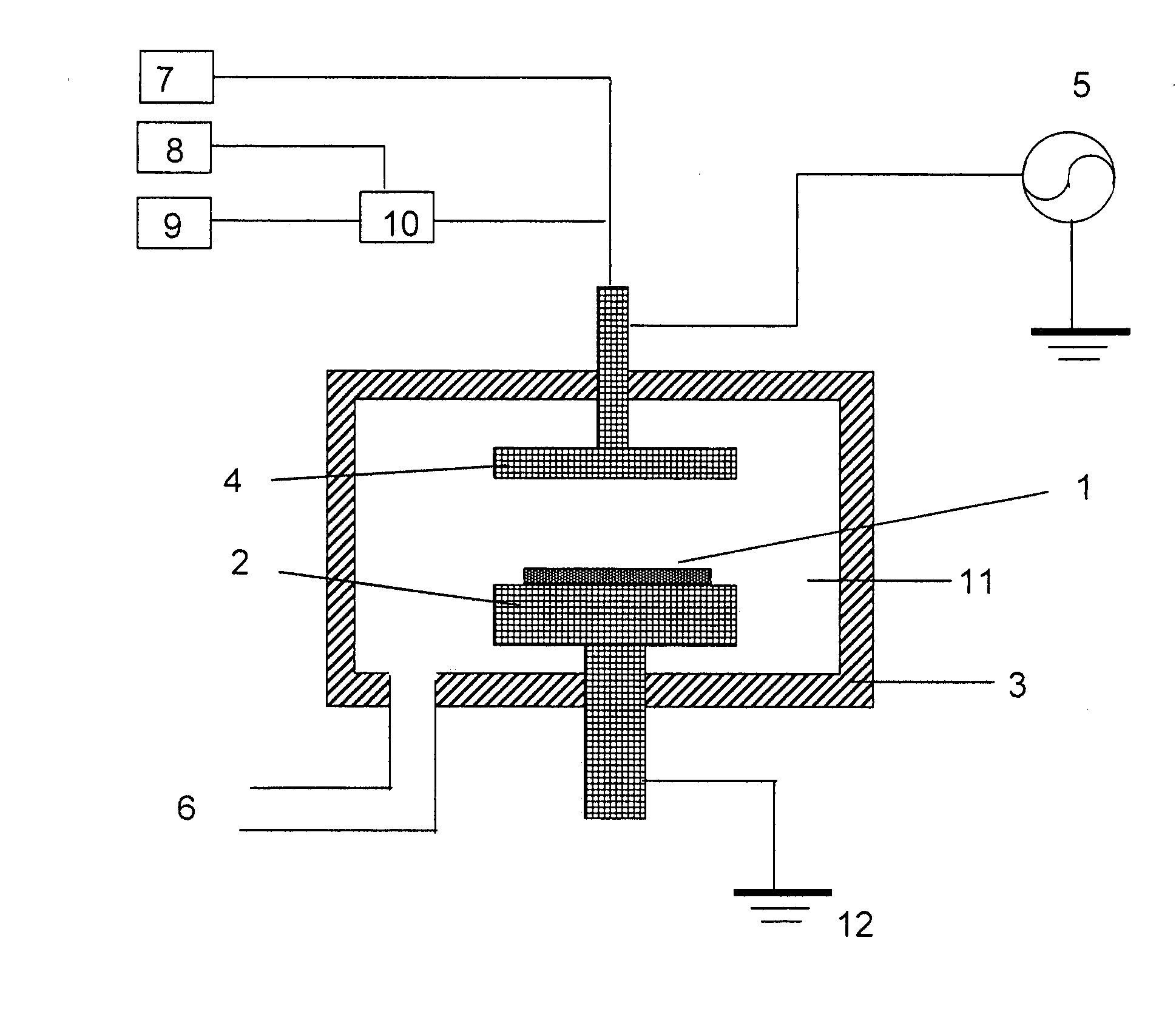
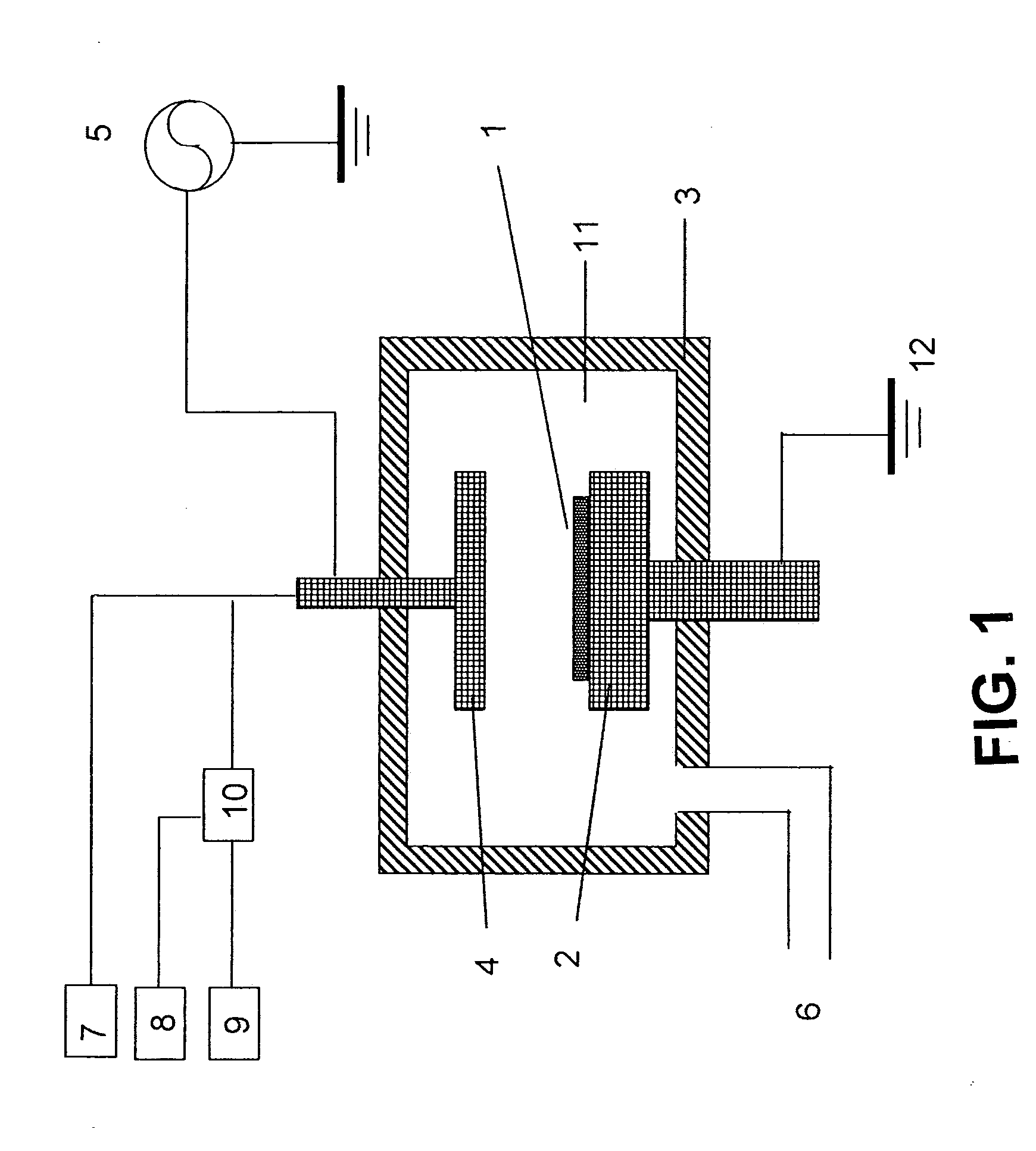
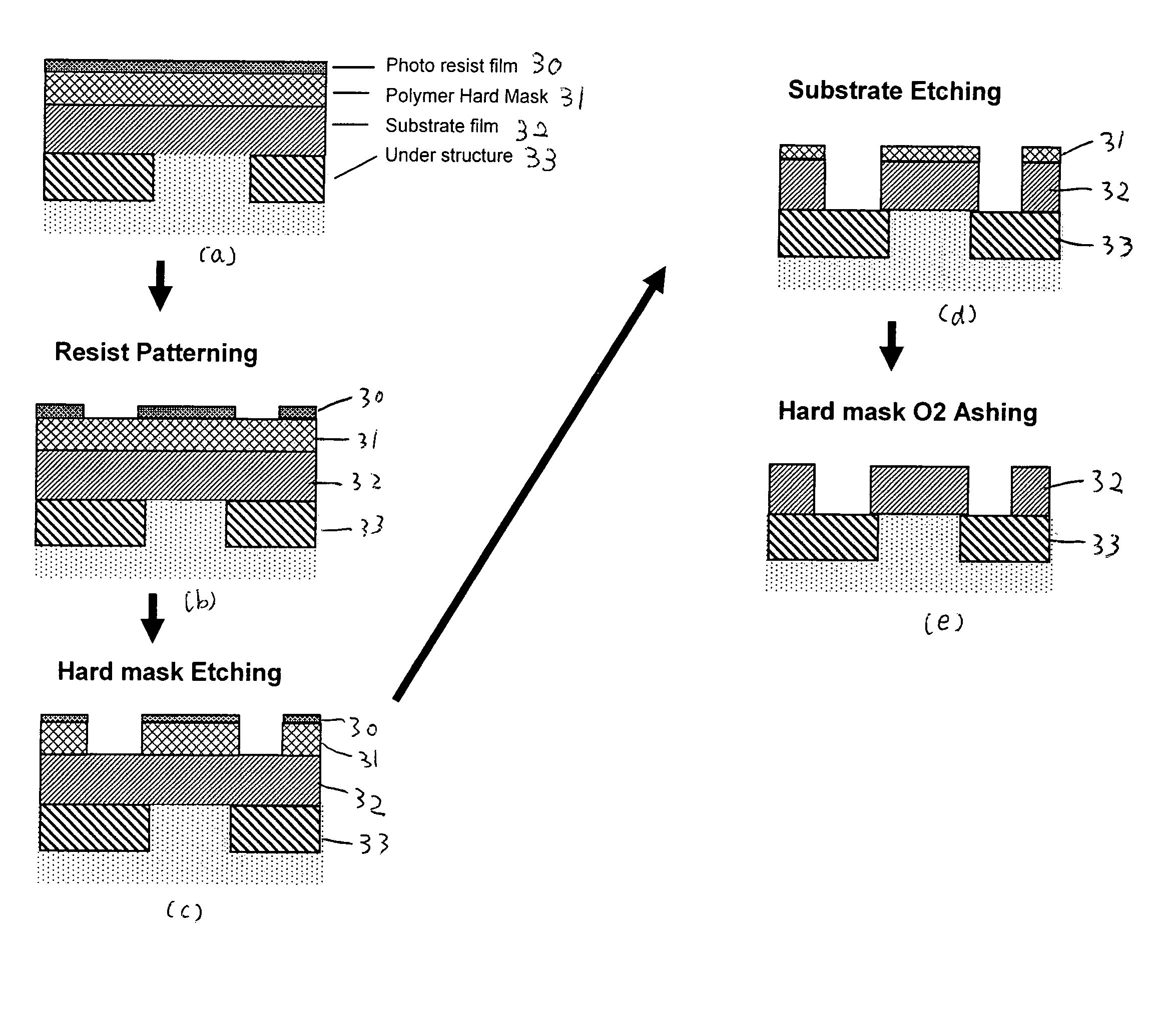
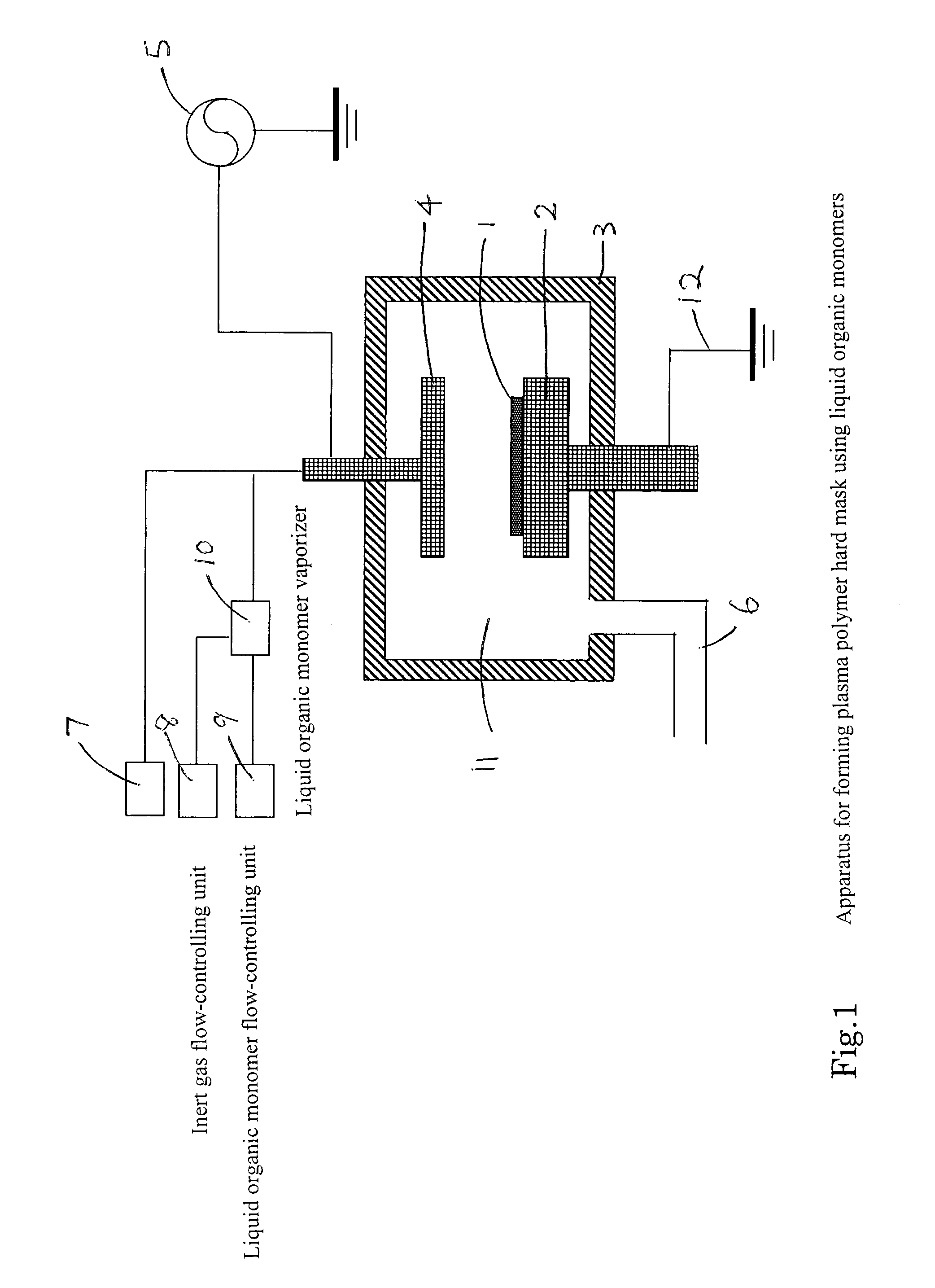
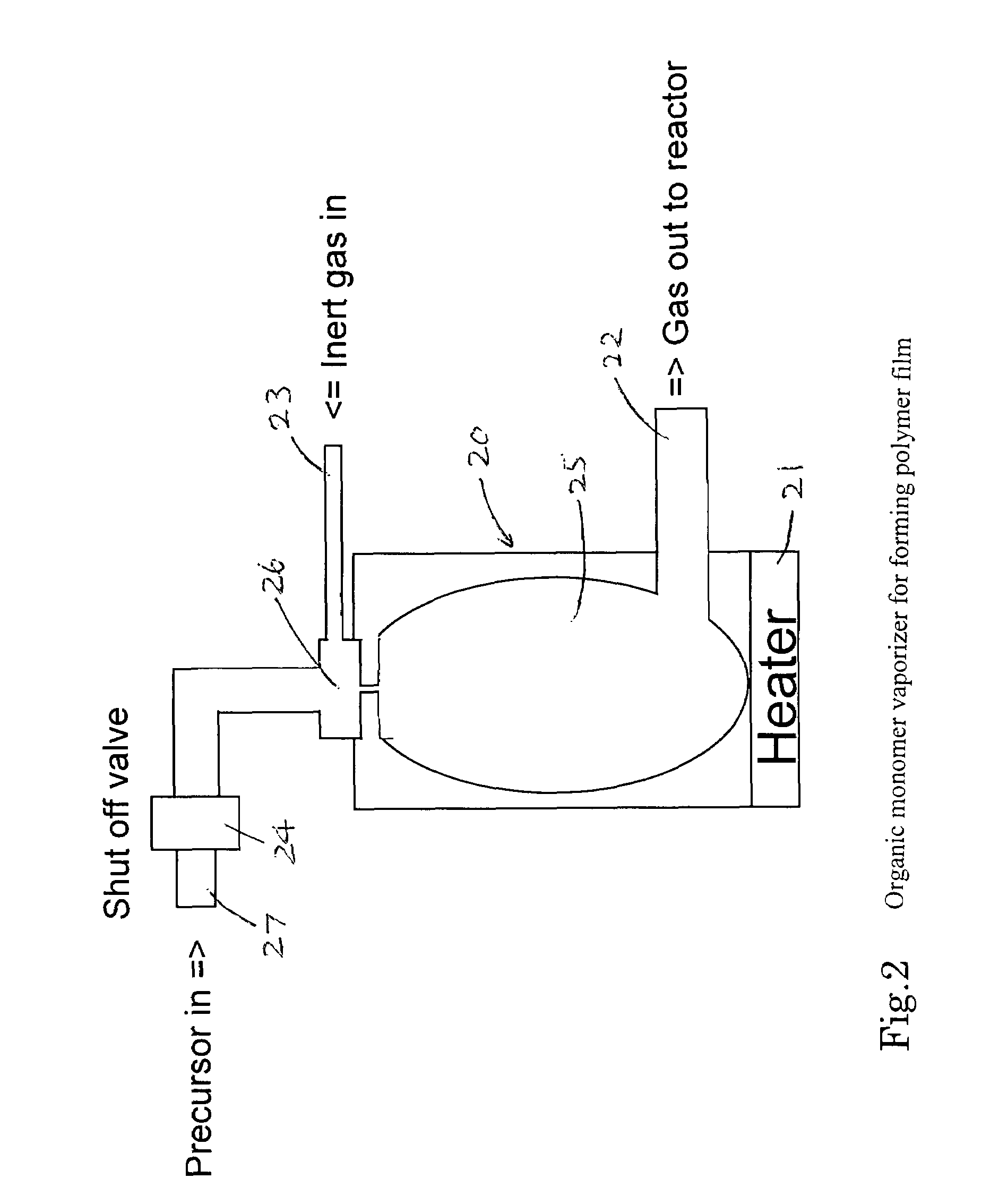
A method forms a hydrocarbon-containing polymer film on a semiconductor substrate by a capacitively-coupled plasma CVD apparatus. The method includes the steps of: vaporizing a hydrocarbon-containing liquid monomer (CαHβXγ, wherein α and β are natural numbers of 5 or more; γ is an integer including zero; X is O, N or F) having a boiling point of about 20° C. to about 350° C.; introducing the vaporized gas into a CVD reaction chamber inside which a substrate is placed; and forming a hydrocarbon-containing polymer film on the substrate by plasma polymerization of the gas.
Owner:ASM JAPAN
Method of forming a carbon polymer film using plasma CVD
ActiveUS7504344B2Improve featuresFunction increaseLiquid surface applicatorsPhotomechanical apparatusCapacitanceBoiling point
A method of forming a hydrocarbon-containing polymer film on a semiconductor substrate by a capacitively-coupled plasma CVD apparatus. The method includes the steps of: vaporizing a hydrocarbon-containing liquid monomer (CαHβXγ, wherein α and β are natural numbers of 5 or more; γ is an integer including zero; X is O, N or F) having a boiling point of about 20° C. to about 350° C. which is not substituted by a vinyl group or an acetylene group; introducing the vaporized gas into a CVD reaction chamber inside which a substrate is placed; and forming a hydrocarbon-containing polymer film on the substrate by plasma polymerization of the gas.
Owner:ASM JAPAN
Processing gas supply mechanism, film forming apparatus and method, and computer storage medium storing program for controlling same
InactiveUS20060086319A1Reduce total pressure lossPressure increase within the supply path of the processing gas can be suppressedSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingSimple Organic CompoundsProcess engineering
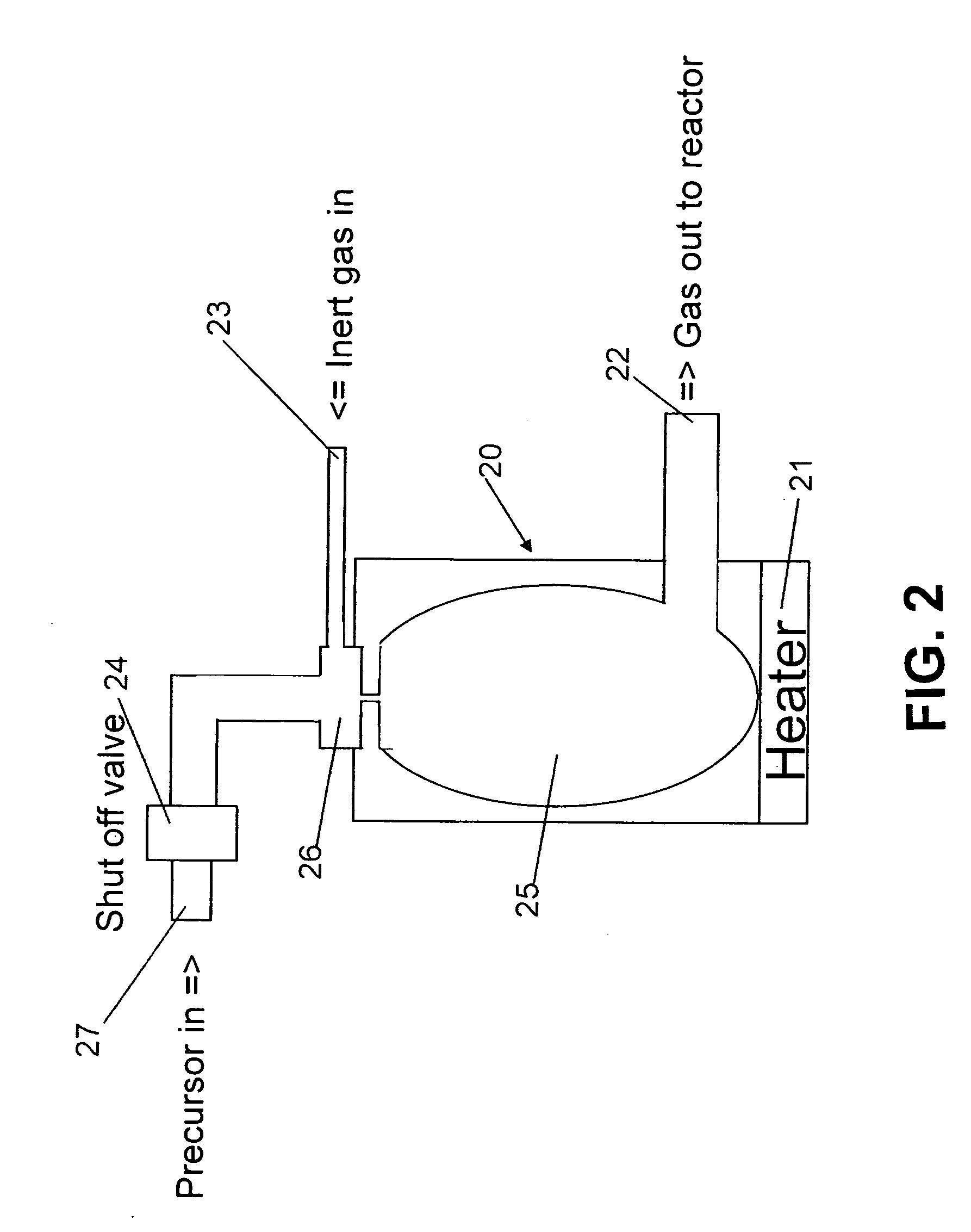
A processing gas supply mechanism installed on a processing chamber of a film forming apparatus for supplying a processing gas containing a metal organic compound onto a substrate to be processed includes a processing gas inlet opening for introducing the processing gas, a diffusion space for diffusing the processing gas introduced from the processing gas inlet opening, a processing gas supply mechanism main body for forming the processing gas diffusion space, and one or more processing gas supply holes for supplying the processing gas from the diffusion space to a processing space on the substrate in the processing chamber. Further, the processing gas supply holes are shaped to have a Peclet number of 0.5 to 2.5 when the processing gas passes therethrough.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Method for leak detection in heat transfer systems
InactiveUS20080314073A1Low vapor pressureMeasurement of fluid loss/gain rateCompression machines with non-reversible cycleTransfer systemSystem pressure
Disclosed is a method for detecting a leak in a closed loop heat transfer system comprising monitoring the pressure of the heat transfer composition inside said heat transfer system, wherein a drop in pressure indicates a leak. Also disclosed is a heat transfer system comprising an evaporator, a compressor, a condenser, an expander and a device for measuring internal system pressure. The system pressure measuring device is disposed inside the closed loop heat system. The internal system pressure measuring means may be located either between the evaporator and the condenser, between the expander and the evaporator, between the compressor and the condenser, or between the condenser and the expander.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Precursor compositions for the deposition of electrically conductive features
InactiveUS6951666B2Reduce settlementGood dispersionRadiation applicationsConductive materialElectrically conductiveCopper metal
A precursor composition for the deposition and formation of an electrical feature such as a conductive feature. The precursor composition advantageously has a viscosity of at least about 1000 centipoise and can be deposited by screen printing. The precursor composition also has a low conversion temperature, enabling the deposition and conversion to an electrical feature on low temperature substrates. A particularly preferred precursor composition includes silver and / or copper metal for the formation of highly conductive features.
Owner:CABOT CORP
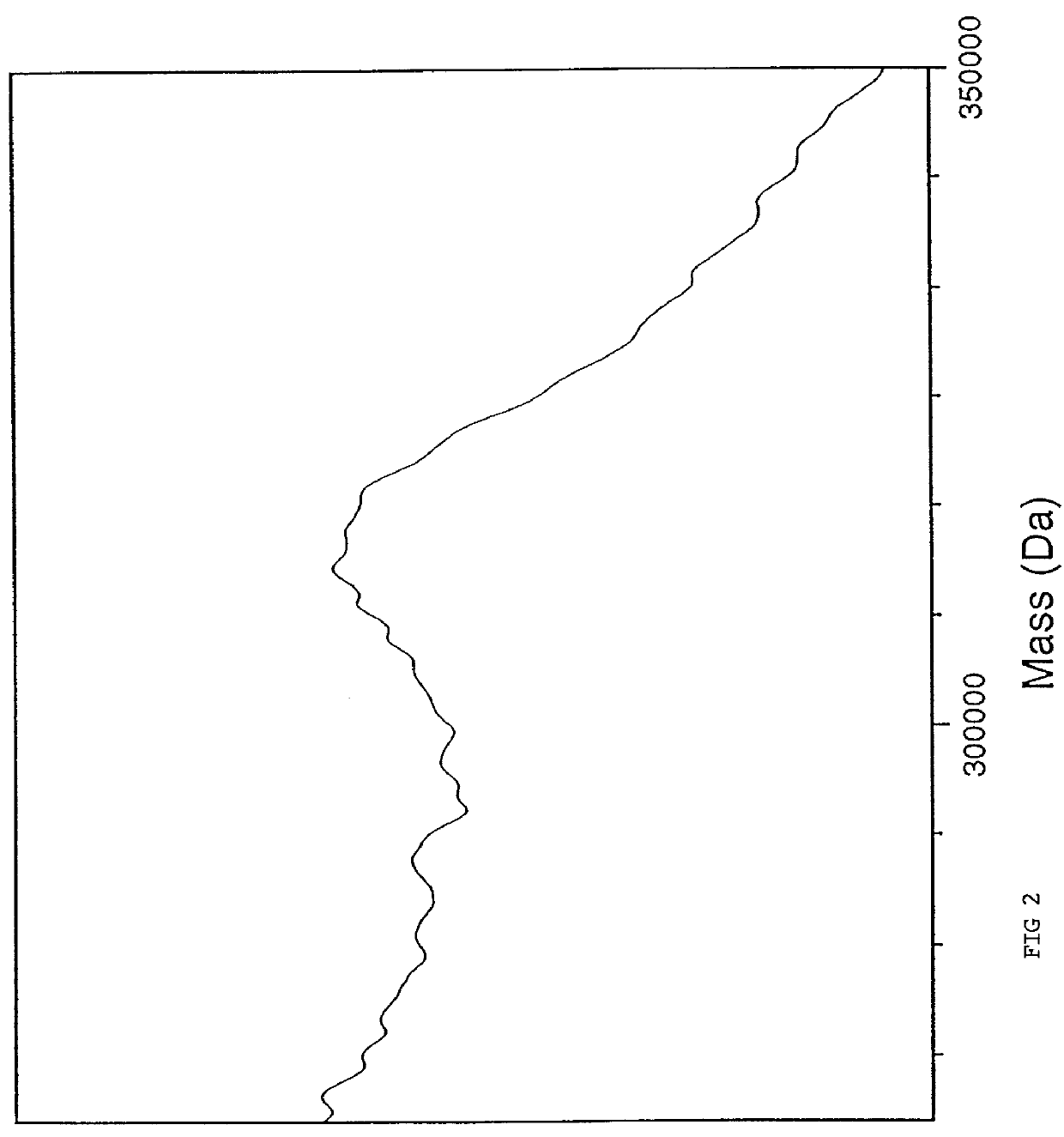
Volatile matrices for matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry
InactiveUS6104028AEasy to spreadReduce formationSamples introduction/extractionWithdrawing sample devicesThermal ionization mass spectrometryRoom temperature
A sample preparation method is disclosed for volatilization and mass spectrometric analysis of nonvolatile high molecular weight molecules. Photoabsorbing molecules having significant sublimation rates at room temperature under vacuum, and preferably containing hydroxy functionalities, are disclosed for use as matrices in matrix-assisted laser desorption / ionization mass spectrometry. The samples are typically cooled in the mass spectrometer to temperatures significantly below room temperature.
Owner:AGENA BIOSCI
Ultra Cleaning of Combustion Gas Including the Removal of Co2
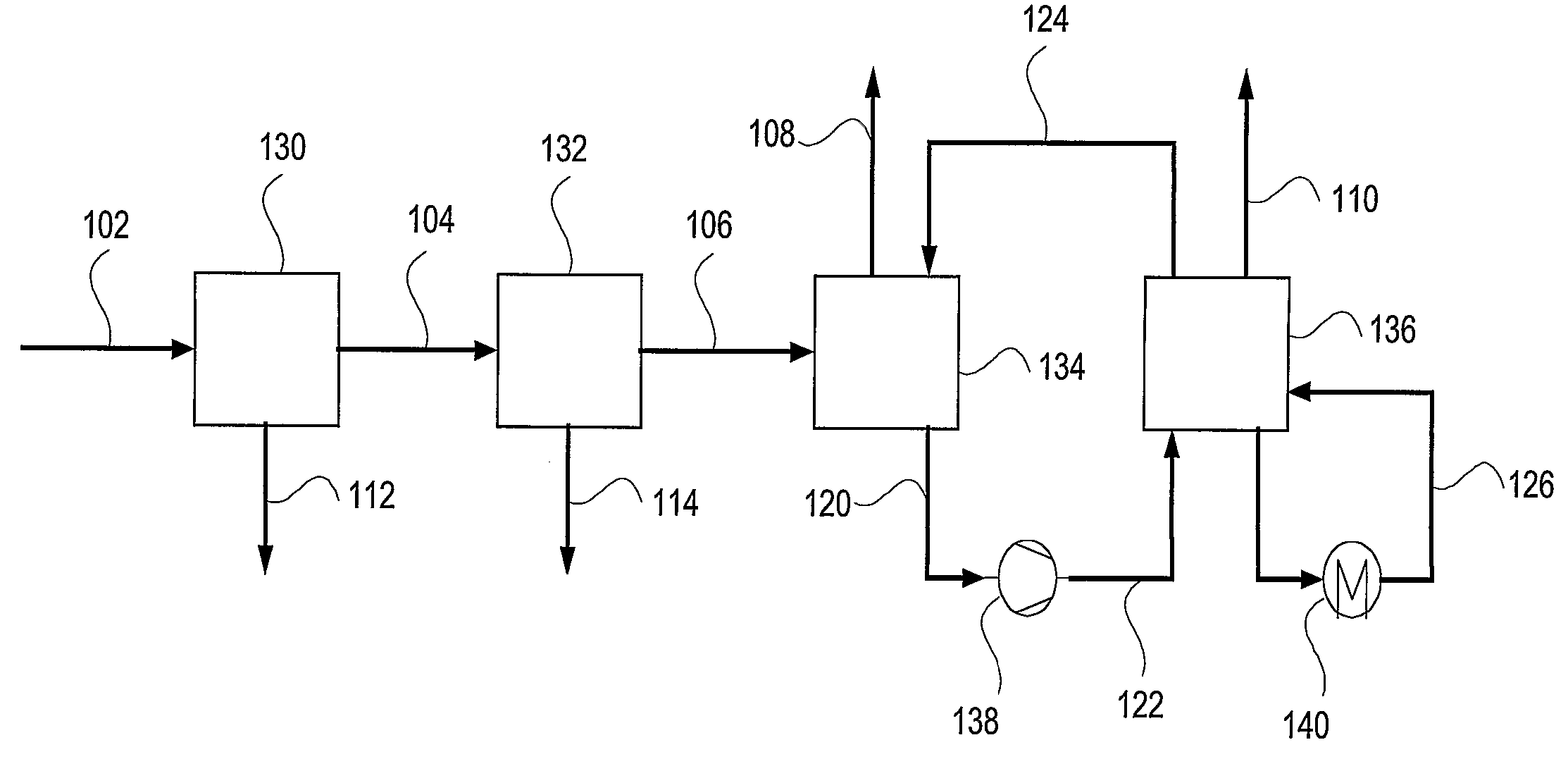
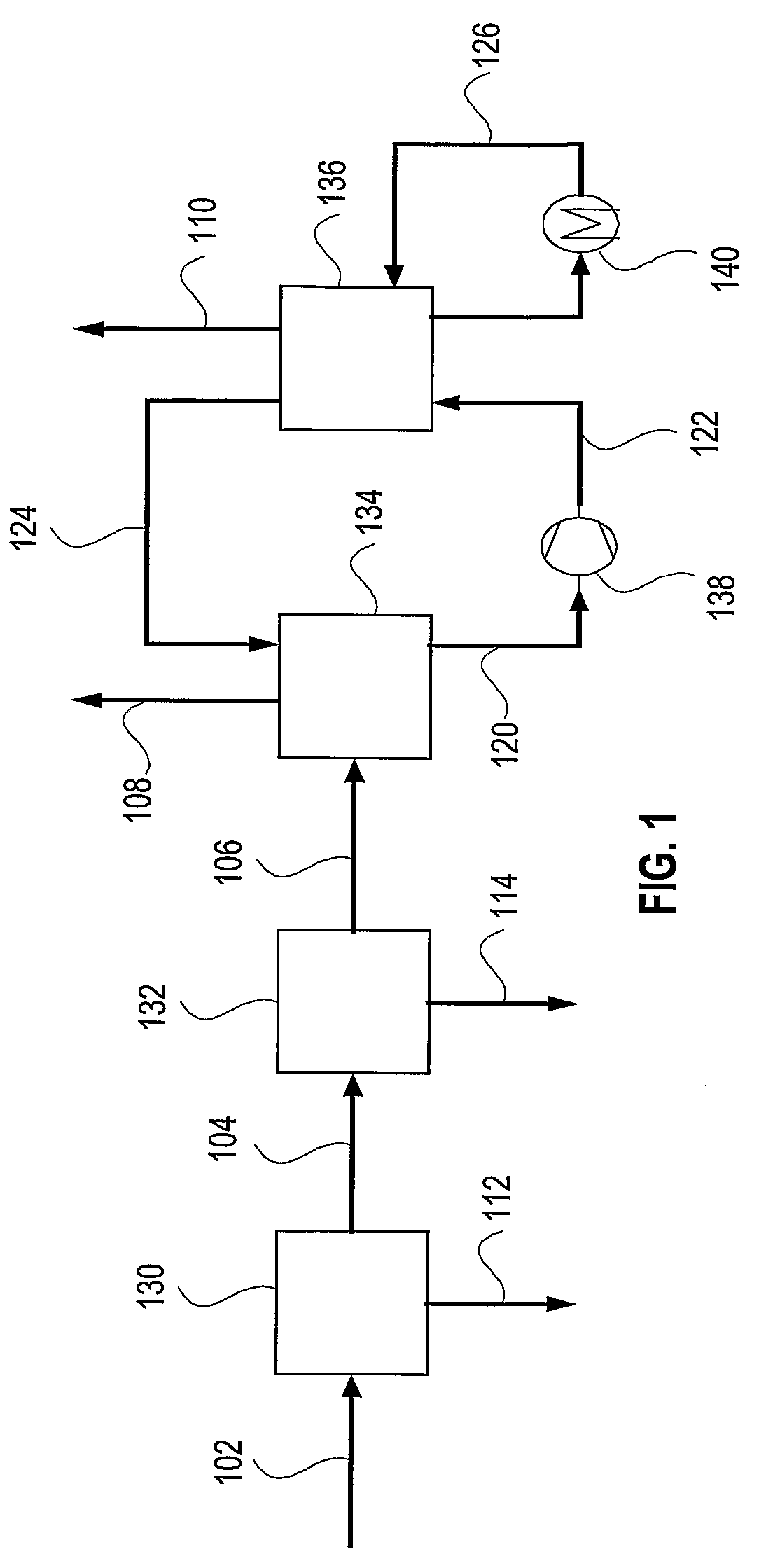
ActiveUS20080072762A1Reduce evaporationMinimize energy consumptionUsing liquid separation agentEmission preventionCo2 removalCombustion
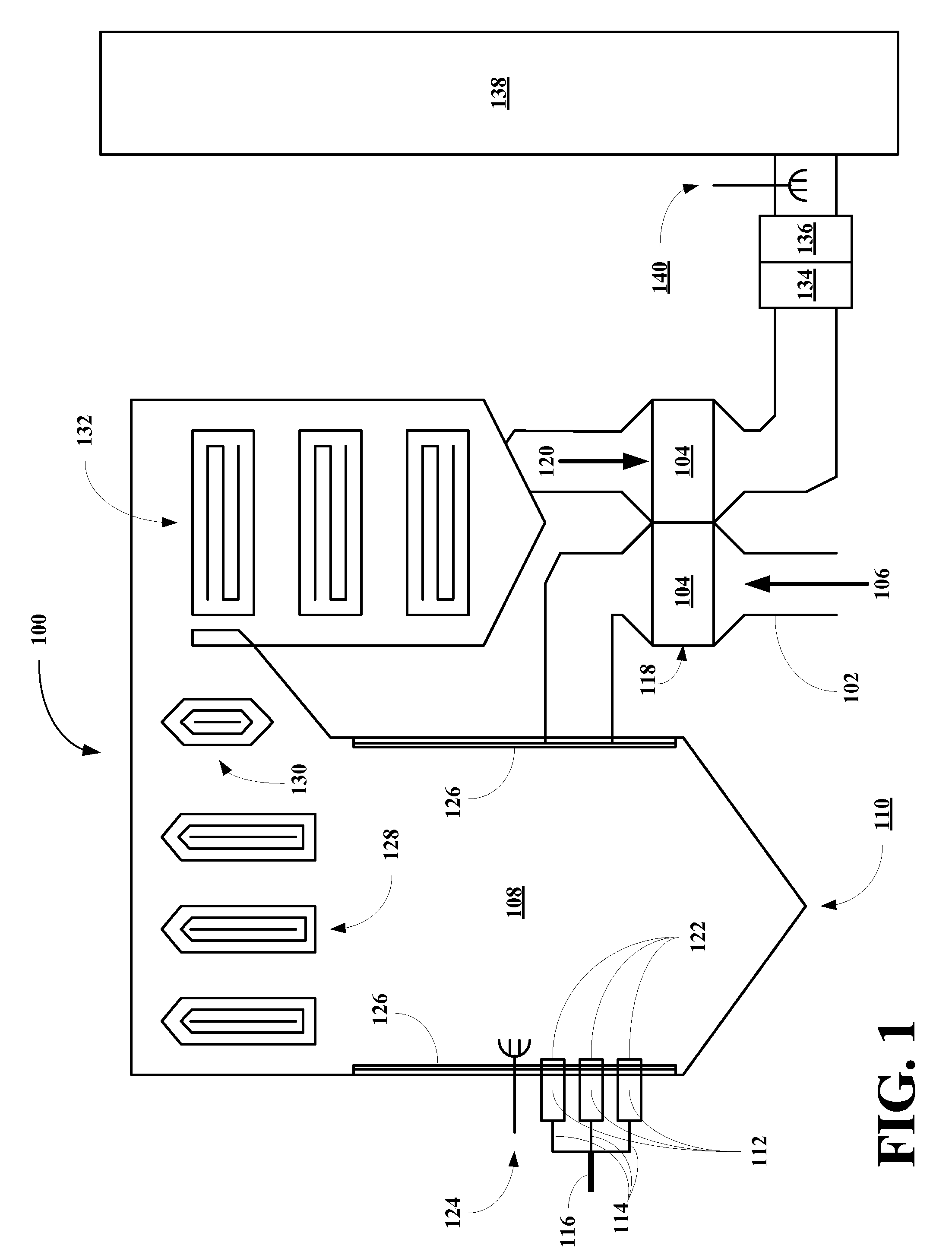
Ultra cleaning of combustion gas to near zero concentration of residual contaminants followed by the capture of CO2 is provided. The high removal efficiency of residual contaminants is accomplished by direct contact cooling and scrubbing of the gas with cold water. The temperature of the combustion gas is reduced to 0-20 degrees Celsius to achieve maximum condensation and gas cleaning effect. The CO2 is captured from the cooled and clean flue gas in a CO2 absorber (134) utilizing an ammoniated solution or slurry in the NH3—CO2H2O system. The absorber operates at 0-20 degrees Celsius. Regeneration is accomplished by elevating the pressure and temperature of the CO2-rich solution from the absorber. The CO2 vapor pressure is high and a pressurized CO2 stream, with low concentration of NH3 and water vapor is generated. The high pressure CO2 stream is cooled and washed to recover the ammonia and moisture from the gas.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC TECH GMBH
Cleaning compositions incorporating green solvents and methods for use
ActiveUS20090281012A1High flash pointLow vapor pressureOrganic detergent compounding agentsDetergent mixture composition preparationGlutaric acidActive agent
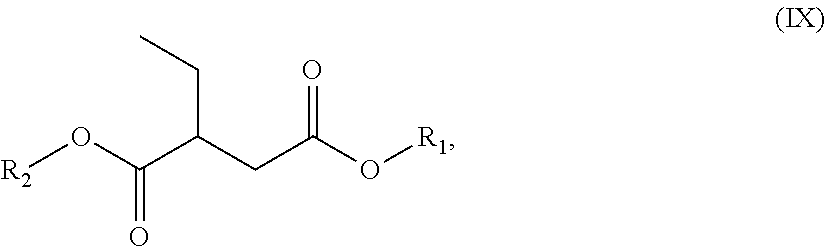
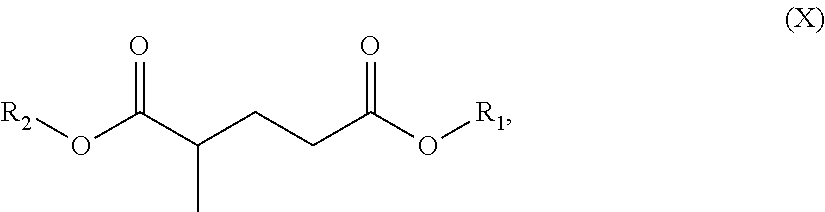
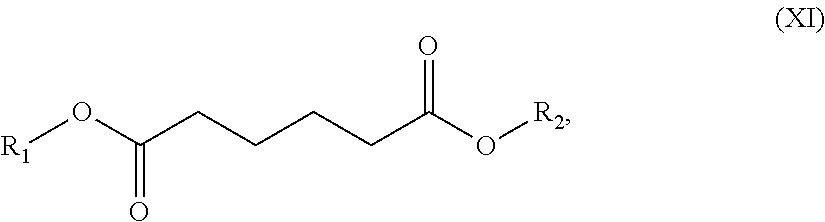
An environmentally-friendly cleaning composition for industrial and consumer applications comprising (a) a blend of dibasic esters, (b) one or more surfactants (c) and, optionally, (d) water or a solvent. The dibasic esters are be derived from a blend of adipic, glutaric, and succinic diacids, and, in one particular embodiment, the blend comprises dialkyl adipate, dialkyl methylglutarate and dialkyl ethylsuccinate, wherein the alkyl groups individually comprise a C1-C12 hydrocarbon group. The one or more surfactants are typically chosen from alcohol alkoxylate, an alkyl phenol ethoxylate, a terpene, a terpene alkoxylate or any derivates thereof. Optionally, additional components or additives including delaminates such as pinene and d-limonene, fragrances, whiteners, stabilizers, thickeners and the like can be added to the composition. The industrial or consumer application selected from the group consisting of a graffiti cleaner, a painted-substrate cleaner, an ink cleaner, a metal substrate cleaner, a plastic substrate cleaner, an environmentally friendly cleaner, a stain-spot cleaner, an industrial hand cleaner, a resin cleaner, a tar resin cleaner, a textile cleaner, a paint stripper and any combination thereof.
Owner:RHODIA OPERATIONS SAS
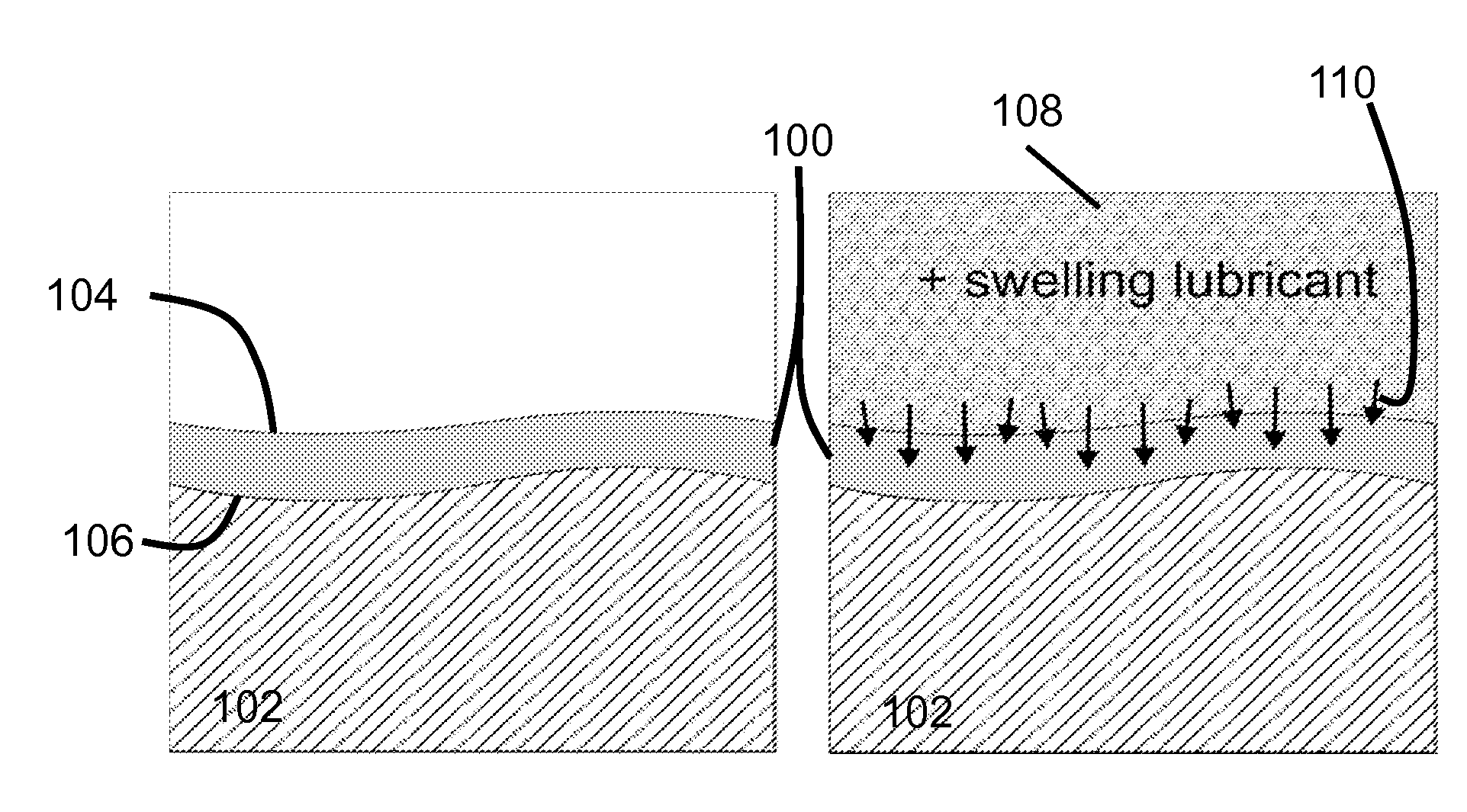
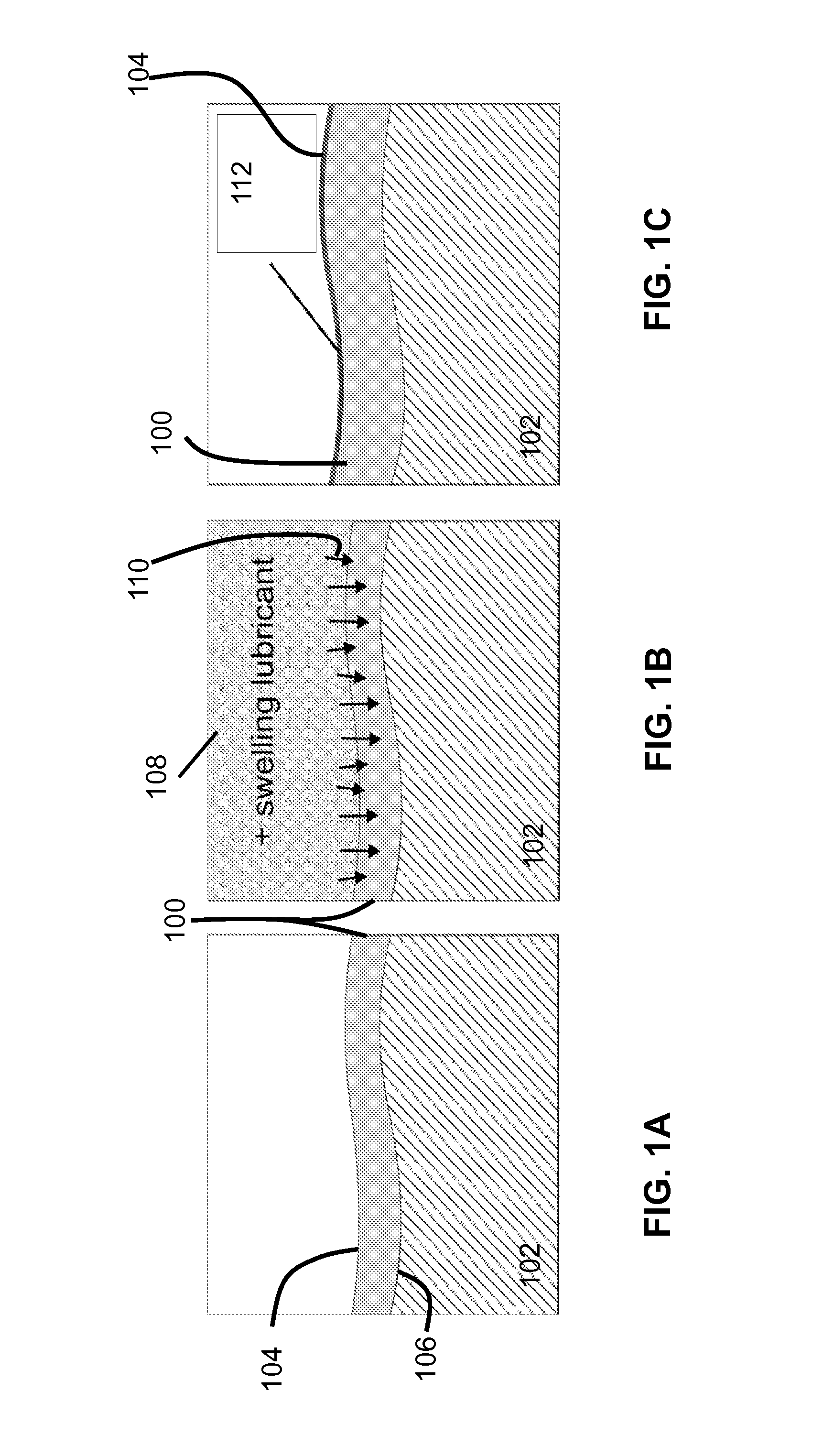
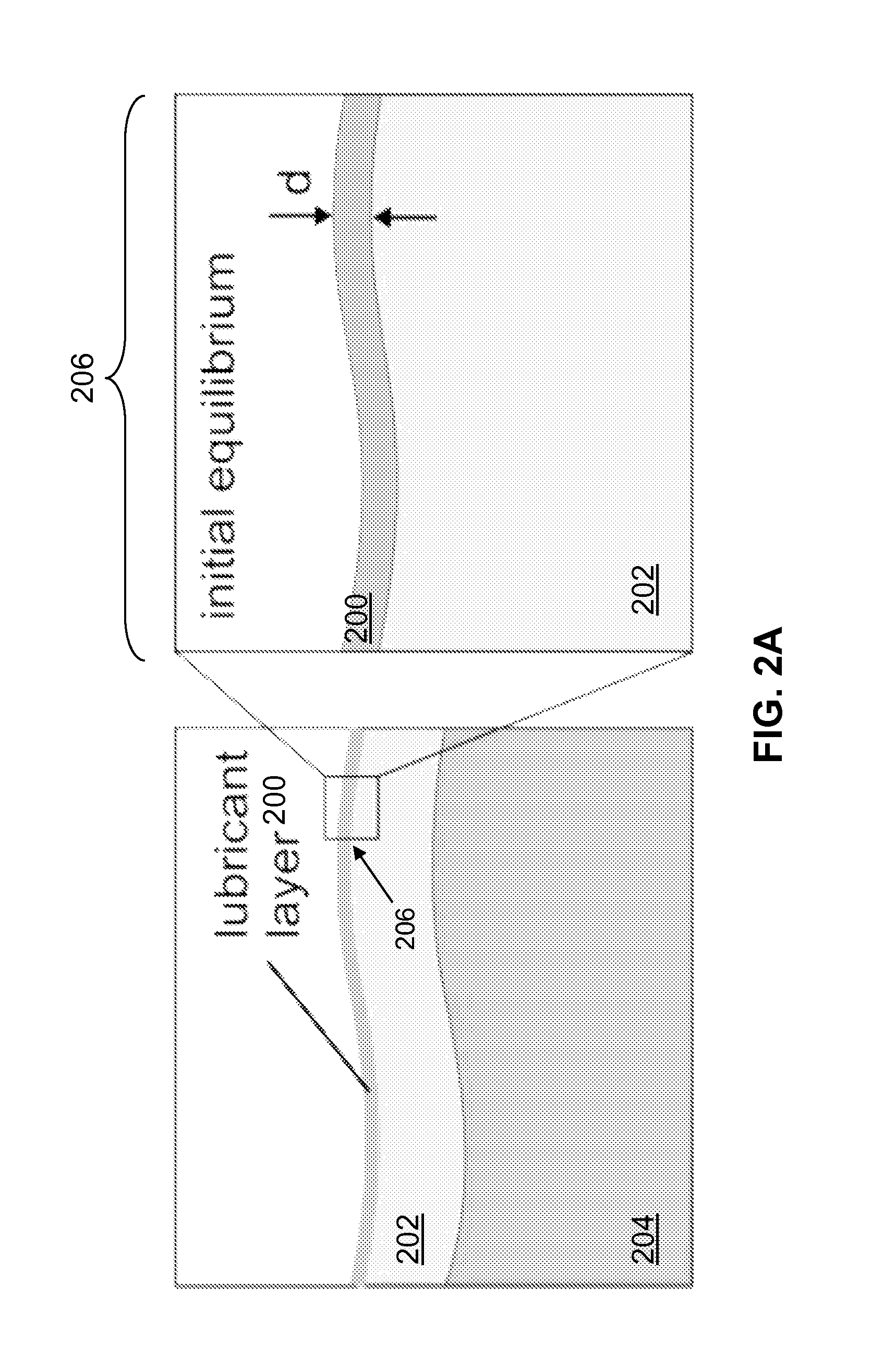
Slippery self-lubricating polymer surfaces
ActiveUS20150152270A1Enhance mechanical property and roughnessControl optical property and viscositySurgeryPretreated surfacesSelf-healingHydrocarbon
The present disclosure describes a strategy to create self-healing, slippery self-lubricating polymers. Lubricating liquids with affinities to polymers can be utilized to get absorbed within the polymer and form a lubricant layer (of the lubricating liquid) on the polymer. The lubricant layer can repel a wide range of materials, including simple and complex fluids (water, hydrocarbons, crude oil and bodily fluids), restore liquid-repellency after physical damage, and resist ice, microorganisms and insects adhesion. Some exemplary applications where self-lubricating polymers will be useful include energy-efficient, friction-reduction fluid handling and transportation, medical devices, anti-icing, optical sensing, and as self-cleaning, and anti-fouling materials operating in extreme environments.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Lubricating oil
InactiveUS20070027038A1Low vapor pressureImprove heat resistanceOrganic chemistryProtective coatings for layersHeat resistanceBase oil
The invention provides a lube oil which exhibits low vapor pressure despite having low viscosity, is non-flammable, exhibits excellent heat resistance, has tribological characteristics equivalent to those of conventional hydrocarbon-based lube oils, and can be used for a long time under very severe conditions such as high temperature and vacuum. The lube oil contains, as a base oil, an ionic liquid formed of a cation and an anion and having an ion concentration of 1 mol / dm3 or more.
Owner:IDEMITSU KOSAN CO LTD +1
Hydrogels for aqueous lithium/air battery cells
ActiveUS20090311567A1Impart conductivityHigh humidityFuel and primary cellsHybrid cell detailsHigh energyEnergy density
Li / air battery cells are configurable to achieve very high energy density. The cells include a protected a lithium metal or alloy anode and an aqueous catholyte in a cathode compartment. In addition to the aqueous catholyte, components of the cathode compartment include an air cathode (e.g., oxygen electrode) and a variety of other possible elements.
Owner:POLYPLUS BATTERY
Perfume delivery systems for consumer goods
InactiveUS20100305021A1Low vapor pressureRealized benefitsCosmetic preparationsContainer decorationsEngineeringOrganoleptic
Owner:DYKSTRA ROBERT RICHARD
Printable Composition for an Ionic Gel Separation Layer for Energy Storage Devices
InactiveUS20140017557A1Low vapor pressureHybrid capacitor separatorsHybrid capacitor electrolytesIonPolyvinylidene fluoride
Representative embodiments provide a composition for printing a liquid or gel separator utilized to separate and space apart first and second conductors or electrodes of an energy storage device, such as a battery or a supercapacitor. A representative composition comprises a plurality of particles, typically having a size (in any dimension) between about 0.5 to about 50 microns; a first, ionic liquid electrolyte; and a polymer or polymeric precursor. In another representative embodiment, the plurality of particles comprise diatoms, diatomaceous frustules, and / or diatomaceous fragments or remains. Another representative embodiment further comprises a second electrolyte different from the first electrolyte; the plurality of particles are comprised of silicate glass; the first and second electrolytes comprise zinc tetrafluoroborate salt in 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate ionic liquid; and the polymer comprises polyvinyl alcohol (“PVA”) or polyvinylidene fluoride (“PVFD”). Additional components, such as additional electrolytes and solvents, may also be included.
Owner:NTHDEGREE TECH WORLDWIDE
Cellulose oxidation by nitrogen dioxide in a perfluorinated tertiary amine solvent
ActiveUS7645874B2Efficiently oxidizedReduce usageBiocideOrganic active ingredientsAqueous alcoholNitrogen dioxide
This invention relates to a process for preparing bioabsorbable oxidized cellulose comprising combining cellulose material, with nitrogen dioxide and a nonaqueous solvent chosen from the class of perfluorinated tertiary amines. This invention also relates to a method of oxidizing cellulose material comprising introducing a solvent into the vessel, circulating the solvent through the cellulose material, adding nitrogen dioxide to said vessel containing the solvent and cellulose in the required amounts, circulating the solution for 7 to 24 hours while controlling the reaction temperature, and isolating the oxidized material. Preferably, isolation of the oxidized product is followed by first washing the oxidized cellulose material with cold water, then washing the oxidized cellulose material with an aqueous alcohol solution several times, then washing the material with 100% alcohol several times, and finally drying the oxidized material.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Ambient temperature, rechargeable cells with metal salt-based electrodes and a system of cell component materials for use therein
InactiveUS6187479B1Improve battery performanceImprove performanceLead-acid accumulatorsNon-aqueous electrolyte cellsHalogenRechargeable cell
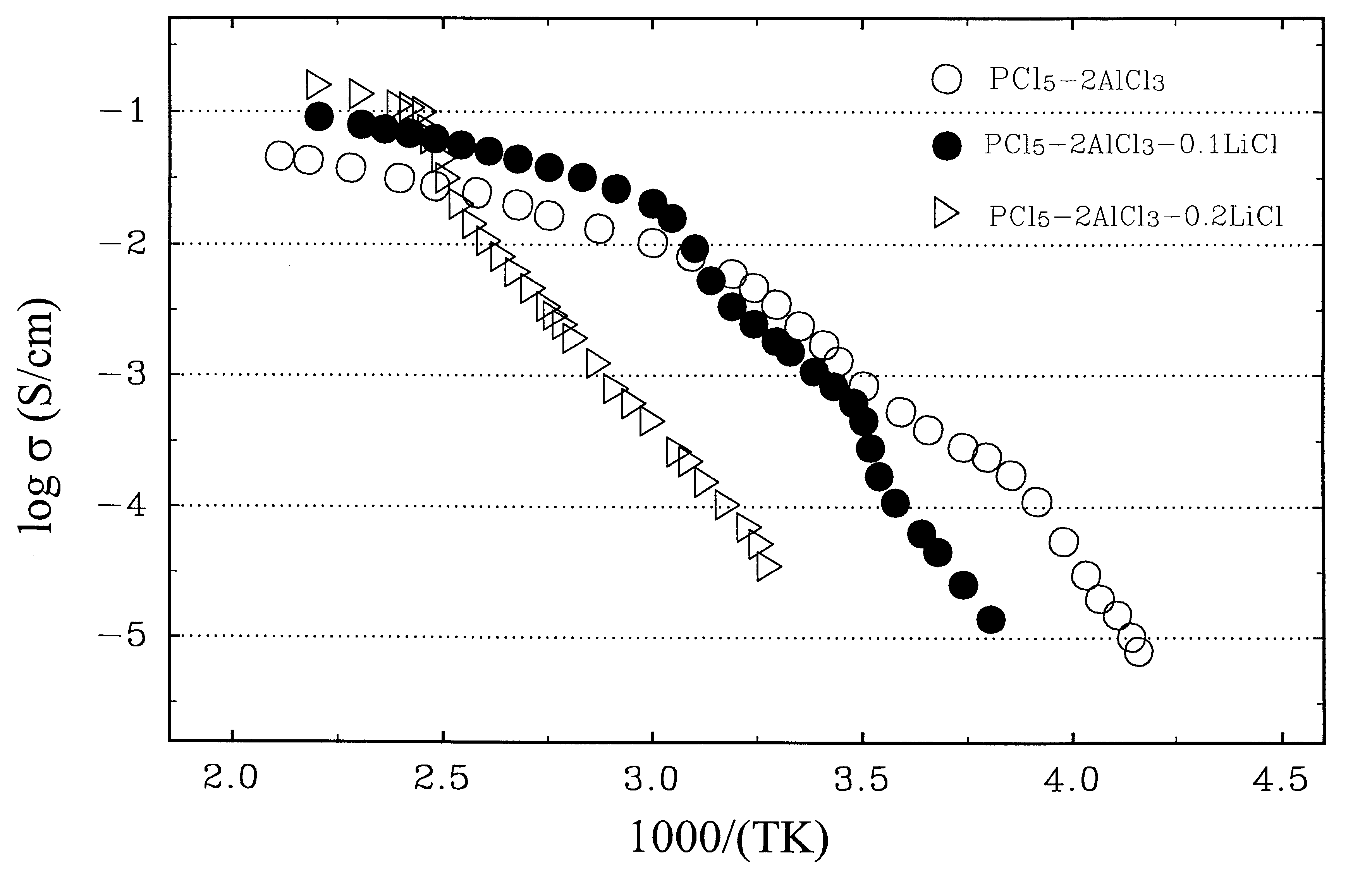
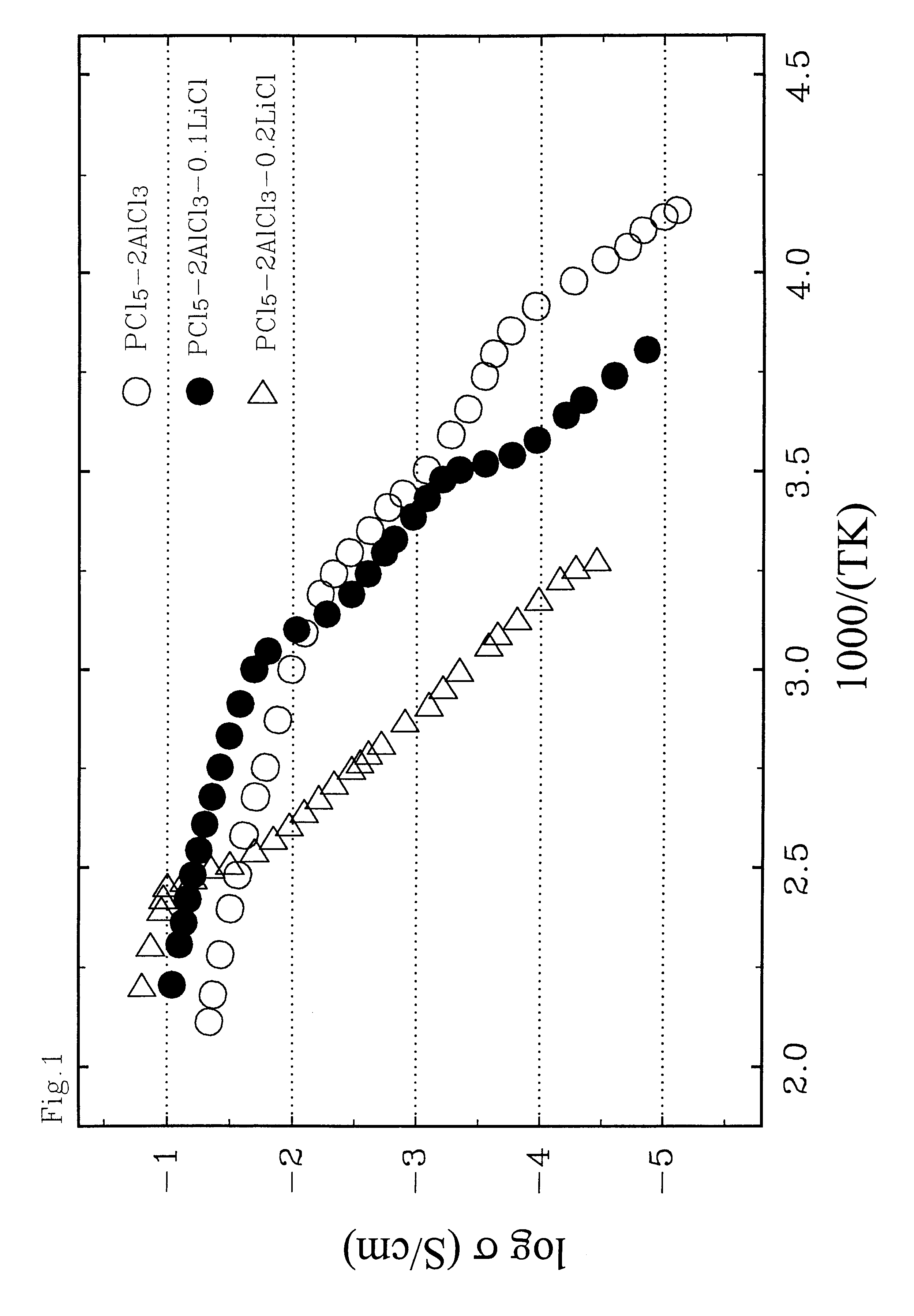
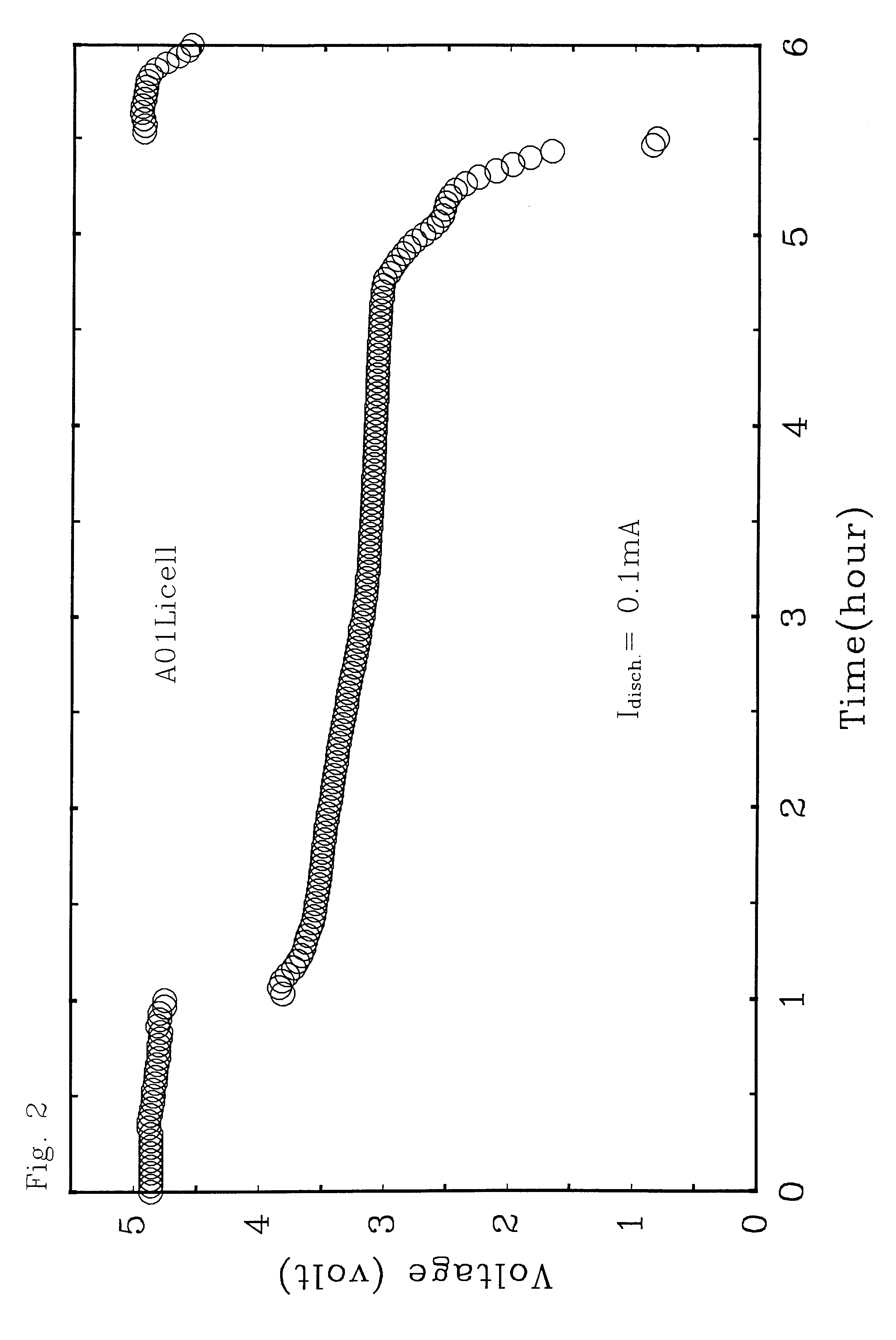
A rechargeable battery or cell is disclosed in which the electrode active material consists of at least one nonmetallic compound or salt of the electropositive species on which the cell is based, and the electrolyte or electrolyte solvent consists predominantly of a halogen-bearing or chalcogen-bearing covalent compound such as SOCl2 or SO2Cl2. Also disclosed are cell component materials which include electrodes that consist primarily of salts of the cell electropositive species and chemically compatible electrolytes. These latter electrolytes include several newly discovered ambient temperature molten salt systems based on the AlCl3-PCl5 binary and the AlCl3-PCl5-PCl3 ternaries.
Owner:LIU CHANGLE
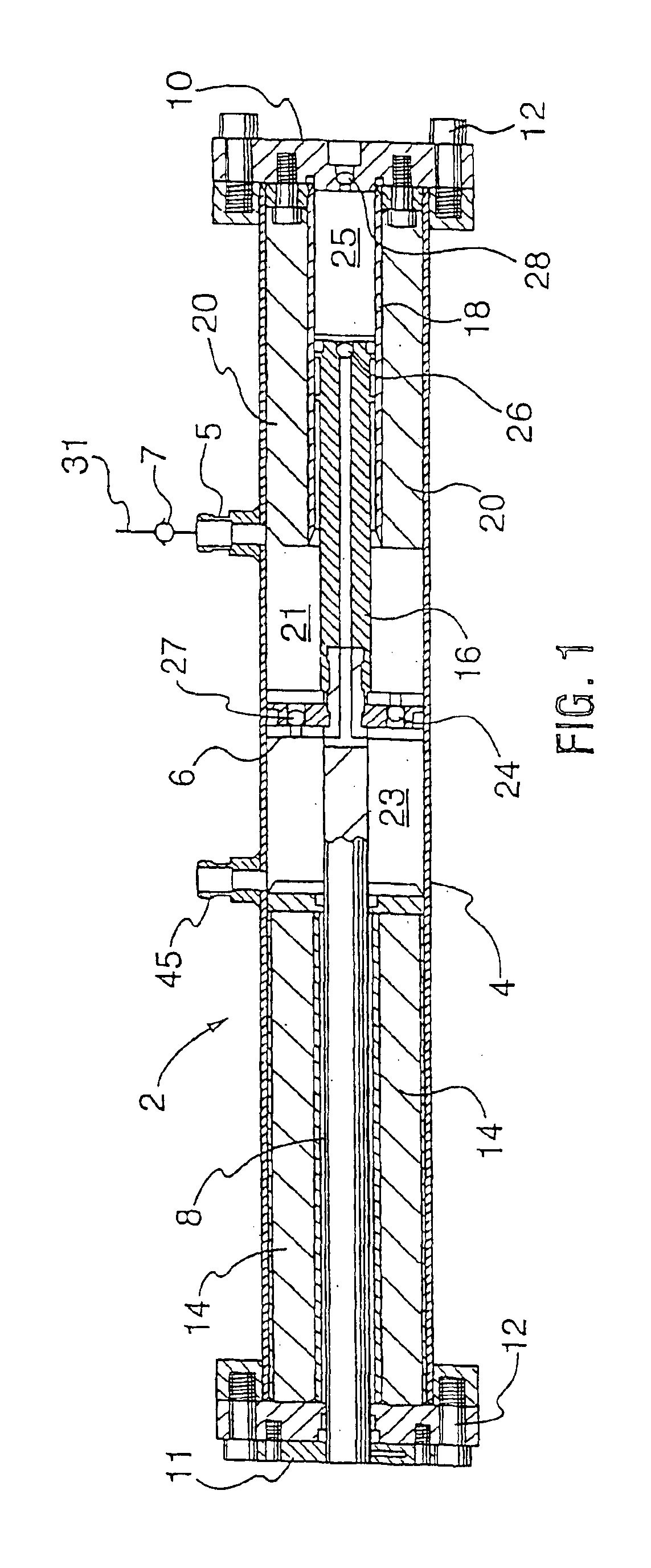
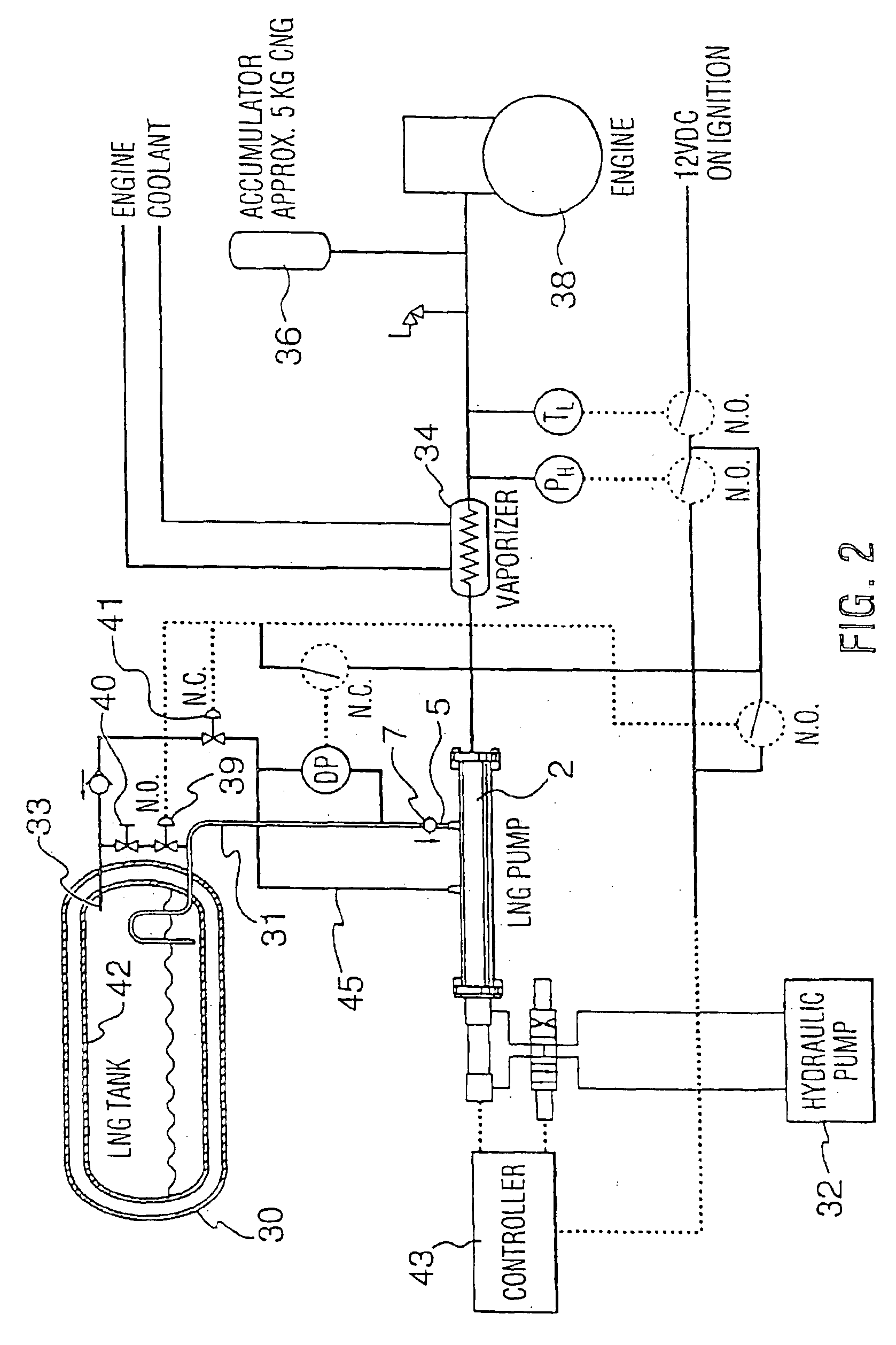
High pressure pump system for supplying a cryogenic fluid from a storage tank
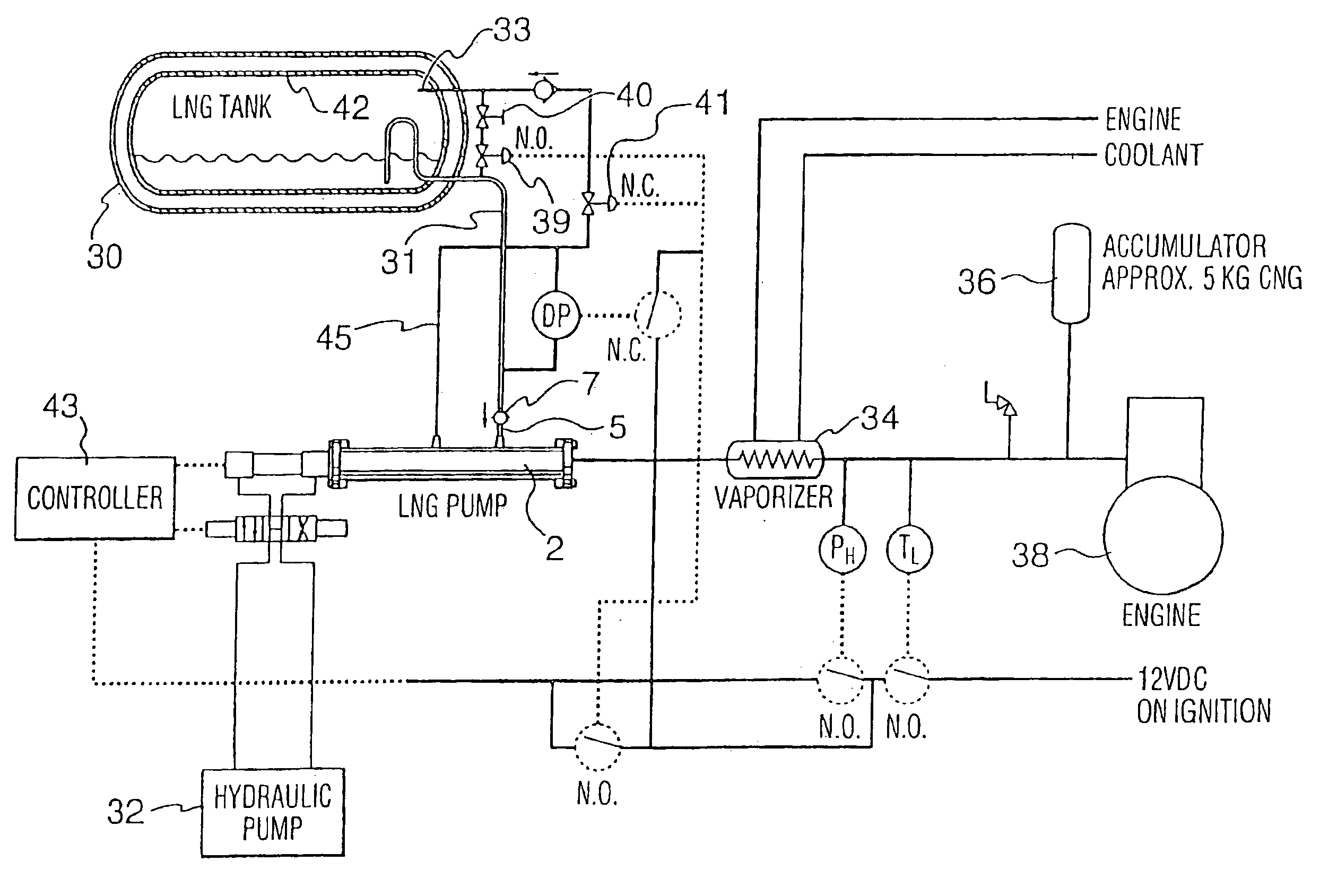
InactiveUS6898940B2Inhibit transferOptimization rangeInternal combustion piston enginesContainer filling methodsProcess engineeringInducer
A medium and high pressure pump systems supplies a cryogenic fluid from a storage tank. The system comprises a pump that is operable to pump cryogenic liquid or a mixture of cryogenic liquid and vapor. The pump preferably comprises an inducer with at least two chambers and means for recycling excess fluid within the inducer instead of returning excess fluid to the storage tank. The reciprocating pump is preferably double acting such that fluid is discharged from the pump during both extension and retraction strokes.
Owner:WESTPORT POWER
Cellulose oxidation by nitrogen dioxide in a perfluorinated tertiary amine solvent
ActiveUS20070054880A1Efficiently oxidizedReduce usageBiocideOrganic active ingredientsNitrogen dioxideAqueous alcohol
This invention relates to a process for preparing bioabsorbable oxidized cellulose comprising combining cellulose material, with nitrogen dioxide and a nonaqueous solvent chosen from the class of perfluorinated tertiary amines. This invention also relates to a method of oxidizing cellulose material comprising introducing a solvent into the vessel, circulating the solvent through the cellulose material, adding nitrogen dioxide to said vessel containing the solvent and cellulose in the required amounts, circulating the solution for 7 to 24 hours while controlling the reaction temperature, and isolating the oxidized material. Preferably, isolation of the oxidized product is followed by first washing the oxidized cellulose material with cold water, then washing the oxidized cellulose material with an aqueous alcohol solution several times, then washing the material with 100% alcohol several times, and finally drying the oxidized material.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Ultra cleaning of combustion gas including the removal of CO.sub.2
ActiveUS7641717B2Efficiently and emissionLow costUsing liquid separation agentEmission preventionCombustionCelsius Degree
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC TECH GMBH
Environmentally Friendly Solvent Systems/Surfactant Systems For Drilling Fluids
InactiveUS20140005079A1Good for healthImprove securityFlushingDrilling compositionGlutaric acidActive agent
A oil field production fluid, namely a drilling mud composition, comprising a mixture of: (a) at least one base oil component; and (b) an additive component comprising a blend of dibasic esters. The functional fluid can optionally comprise additional additive components. The blend of dibasic esters comprises two or more of dialkyl methylglutarate, dialkyl adipate, dialkyl ethylsuccinate, dialkyl succinate, dialkyl glutarate.
Owner:RHODIA OPERATIONS SAS
Method and plant for amine emission control
ActiveUS20110308389A1Eliminating substantially reducing emissionLow vapor pressureLiquid degasificationDispersed particle separationFlue gasAqueous solution
A method for eliminating or substantially reducing emission of amines (amineslip) and alkaline degradation products to the atmosphere from a plant for CO2 capture from a flue gas, where the CO2 is captured by counter-current flow to an absorbent in an absorption zone, the absorbent comprising an aqueous solution of one or more amine(s), to give a CO2 lean flue gas that is released into the surroundings, and a CO2 rich absorbent that is regenerated in a regeneration column to give a CO2 rich gas that is treated further, and regenerated absorbent that is recycled to the absorption zone, wherein the CO2 lean flue gas is washed with an acidic aqueous solution to remove or substantially reduce the amount of amine(s) and alkaline degradation products thereof in the gas, is described.
Owner:AKER CARBON CAPTURE NORWAY AS
Catholytes for aqueous lithium/air battery cells
ActiveUS20130122380A1Prevent drynessFacilitate numberFuel and primary cellsHybrid cell detailsHigh energyLithium metal
Owner:POLYPLUS BATTERY CO INC
Inspection system by charged particle beam and method of manufacturing devices using the system
InactiveUS7135676B2Improve throughputImprove reliabilityMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesLine widthIrradiation
An inspection apparatus and a semiconductor device manufacturing method using the same. The inspection apparatus is used for defect inspection, line width measurement, surface potential measurement or the like of a sample such as a wafer. In the inspection apparatus, a plurality of charged particles is delivered from a primary optical system to the sample, and secondary charged particles emitted from the sample are separated from the primary optical system and introduced through a secondary optical system to a detector. Irradiation of the charged particles is conducted while moving the sample. Irradiation spots of the charged particles are arranged by N rows along a moving direction of the sample and by M columns along a direction perpendicular thereto. Every row of the irradiation spots of the charged particles is shifted successively by a predetermined amount in a direction perpendicular to the moving direction of the sample.
Owner:EBARA CORP
Precursor compositions for the deposition of electrically conductive features
InactiveUS20060043346A1Reduce settlementGood dispersionConductive materialSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingScreen printingViscosity
A precursor composition for the deposition and formation of an electrical feature such as a conductive feature. The precursor composition advantageously has a viscosity of at least about 1000 centipoise and can be deposited by screen printing. The precursor composition also has a low conversion temperature, enabling the deposition and conversion to an electrical feature on low temperature substrates. A particularly preferred precursor composition includes silver and / or copper metal for the formation of highly conductive features.
Owner:CABOT CORP
Coloring composition for image formation and method for improving ozone resistance of color image
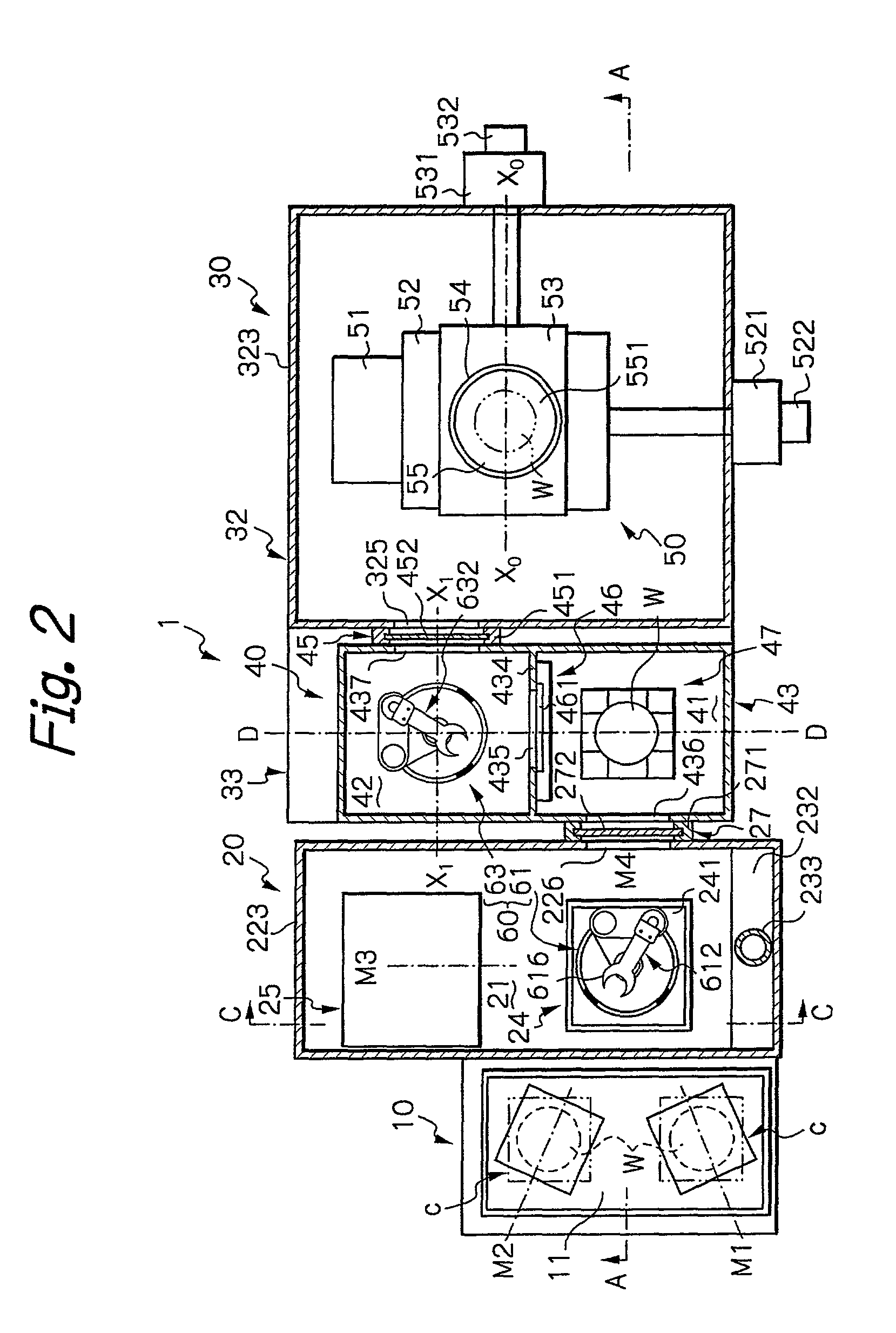
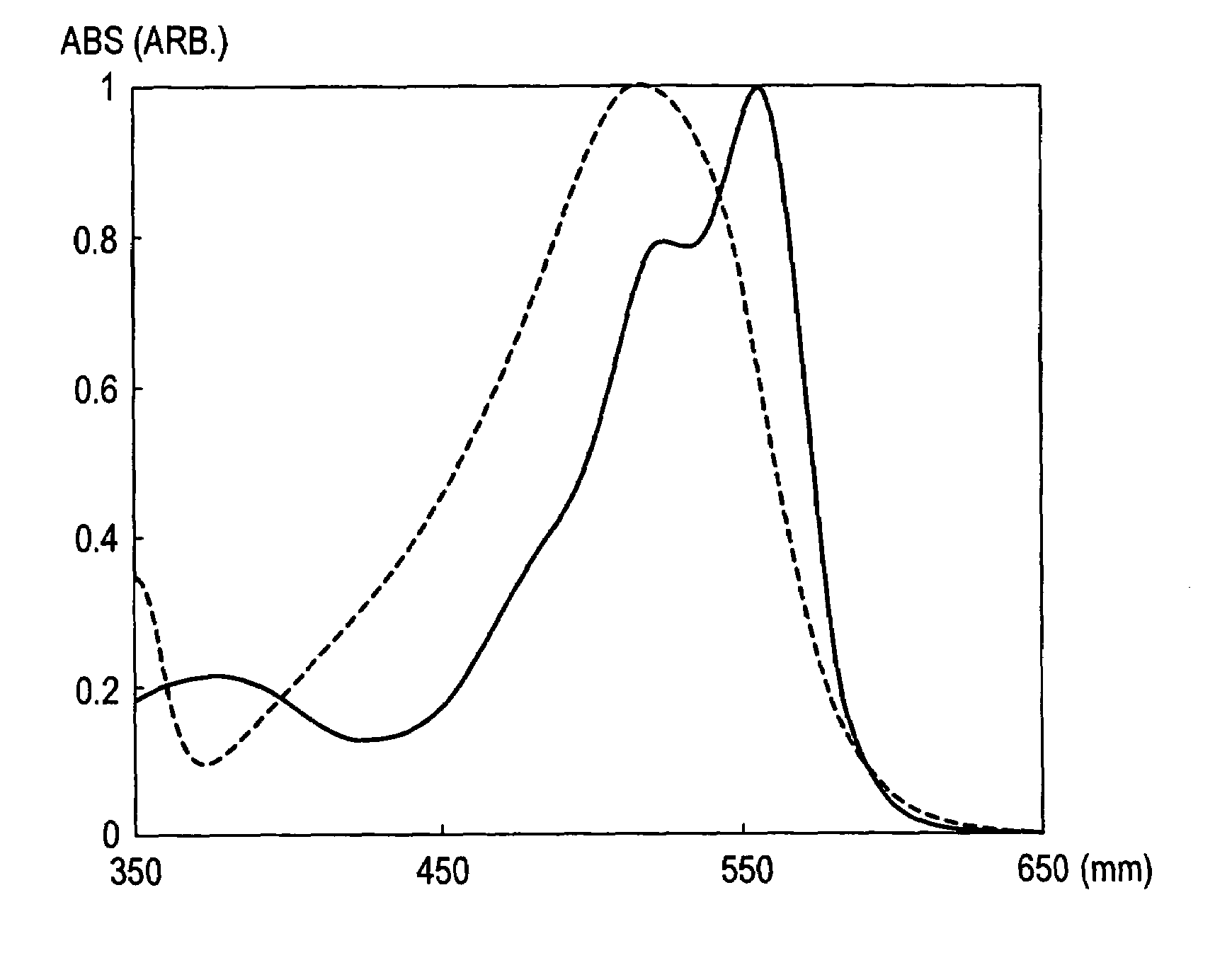
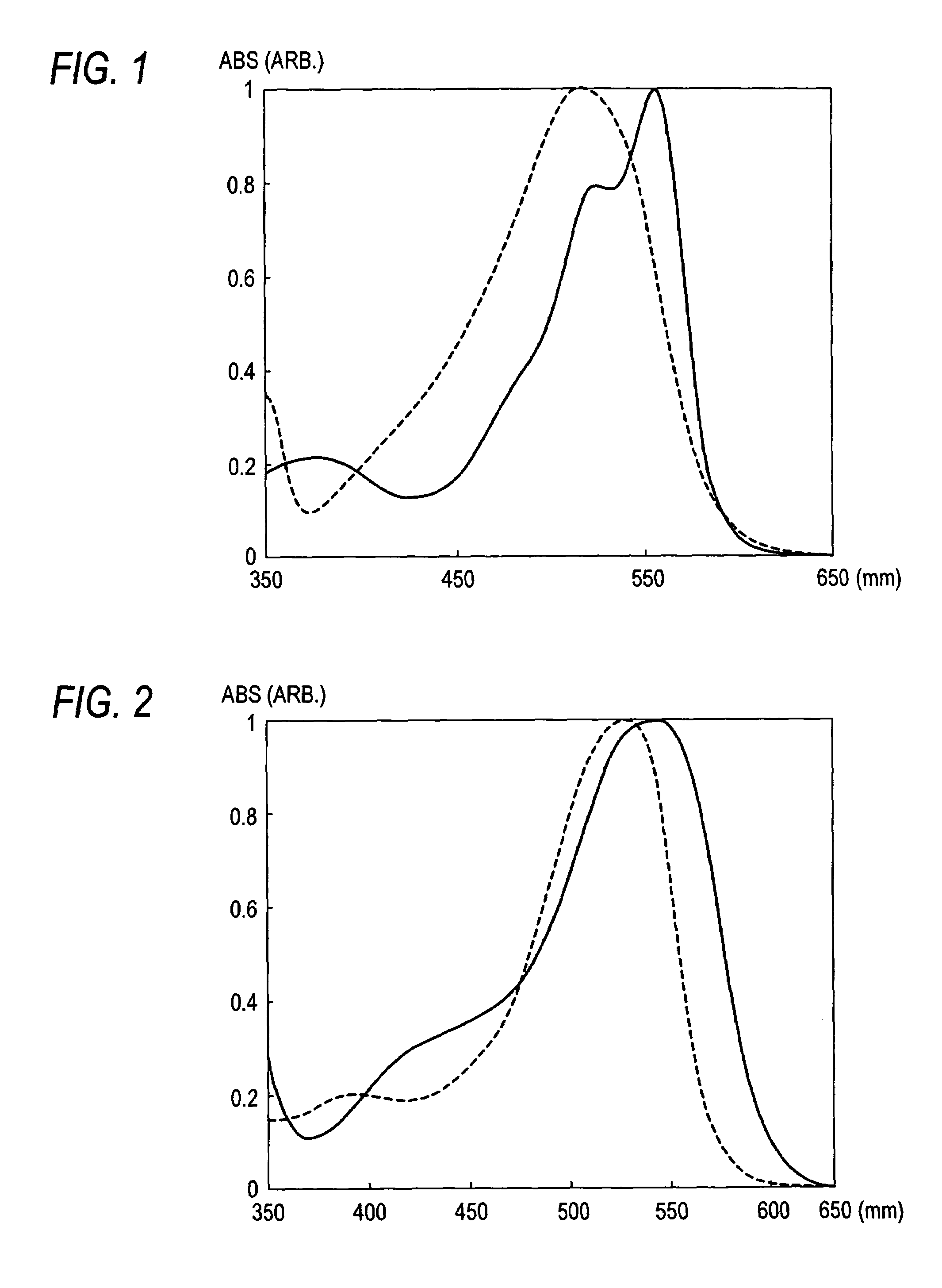
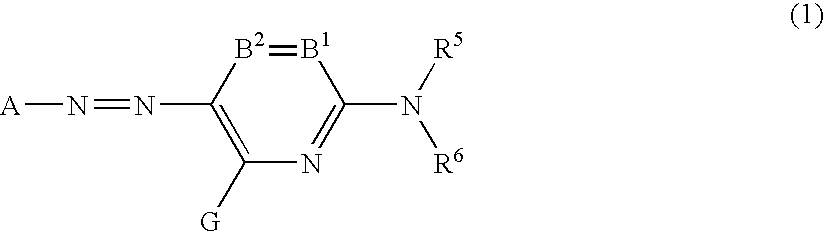
InactiveUS7108743B2Prevent nozzle cloggingLow vapor pressureMonoazo dyesDuplicating/marking methodsColor imageNitrogen
A coloring composition for image formation comprising an azo dye having an aromatic nitrogen-containing 6-membered heterocyclic ring as a coupling component, a coloring composition which comprises an azo compound having an oxidation potential nobler than 1.0 V vs. SCE and comprising at least two substituents having a pKa value of −10 to 5 in water, and a method for improving ozone resistance of a color image, the method comprising using a compound having an oxidation potential nobler than 1.0 V vs. SCE and showing a maximum absorption at a wavelength between 500 nm and 580 nm with a half-value width of 150 nm or narrower.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Acoustical sound proofing material with controlled water-vapor permeability and methods for manufacturing same
ActiveUS7883763B2Reduce sound transmissionImprove abilitiesCeilingsWallsWater vapor permeabilityMoisture
A laminated structure appropriate for use in constructing walls, floors, ceilings or doors, has a selected area and in one embodiment comprises two external layers of one or more materials such as, but not limited to, gypsum, at least one internal constraining layer having less than said selected area, and two or more internal layers of a viscoelastic glue separated by said at least one internal constraining layer, wherein each of said layers of viscoelastic glue is patterned to cover a selected percentage, but not all, of said area of said laminated structure thereby to allow moisture to pass through said structure.
Owner:SERIOUS MATERIALS +1
High flash point additives for treating carbon-based fuels
Owner:LIQUID MINERALS GRP LTD
Inkjet recording method
ActiveUS7086726B2Image quality be lowerLight fastnessMeasurement apparatus componentsDuplicating/marking methodsColoring agentsPhotochemistry
An inkjet recording method of forming an image on an inkjet recording sheet that has, on a support, a colorant-receiving layer which contains at least one inorganic mordant, by using an inkjet recording ink set that comprises, as minimum constituent elements thereof, a yellow ink which contains at least one yellow dye, a magenta ink which contains at least one magenta dye and a cyan ink which contains at least one cyan dye, wherein an oxidation potential of the magenta dye and an oxidation potential of the cyan dye are each nobler than 0.8 V (vs SCE).
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
Stabilized and Lyophilized Radiopharmaceutical Agents For Destroying Tumors
InactiveUS20070248533A1Easy to refactorReduces predictabilityPowder deliveryNervous disorderAbnormal tissue growthDiagnostic radiopharmaceuticals
A novel method is set out of preparation of radioactive diagnostic radiopharmaceutical in a stable, shippable, lyophilized form by an apparatus designed to rapidly flash freeze and dehydrate a radiopharmaceutical composition to minimize auto radiolysis. The method proposes rapid cooling and removal of ambient vapor, and then ultra cold removal when the potential of explosive liquid oxygen is eliminated. The radioactive diagnostic radiopharmaceutical requires no further cold or refrigerated storage, including with respect to shipping, subsequent to stabilization. The preferred composition can be reconstituted “on site” by the addition of a suitable diluent to bring the radiopharmaceutical complex into solution at a desired concentration.
Owner:KUPERUS JOHN H +2
Adhesion promoters for monomer-free reactive polyurethanes
InactiveUS7129312B1Low vapor pressureHigh molecular weightUrea derivatives preparationIsocyanic acid derivatives preparationSolventSealant
Polyurethane compositions are produced in a two-stage method. In a first step, a diol component with a molecular weight of less than 2000 is reacted with a monomeric diisocyanate with a molecular weight of less than 500 and the unreacted monomeric diisocyanate is removed from this reaction product. In a second step, the resulting high-molecular diisocyanate is reacted with a polyol to produce a reactive prepolymer with isocyanate and groups. The addition of polyisocyanates which are capable of migration and which have a substantially lower vapor pressure than diphenylmethanediisocyanate, improves the addition behavior of the invention polyurethane compositions. Reactive polyurethane compositions of this type are suitable for using as binding agents for reactive one or two component adhesives / sealants, which may optionally contain solvents. These compositions are also suitable for producing reactive hot melt adhesives when suitable polyols are selected. A substantial advantage of these compositions compared to known polyurethane compositions is the considerably lower proportion of monomeric diisocyanates with a molecular weight of less than 500.
Owner:HENKEL KGAA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com