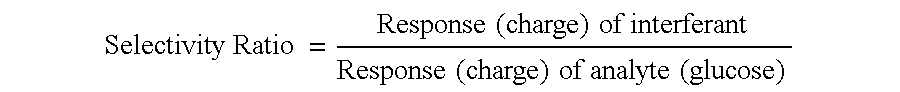Patents
Literature
36726results about "Withdrawing sample devices" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
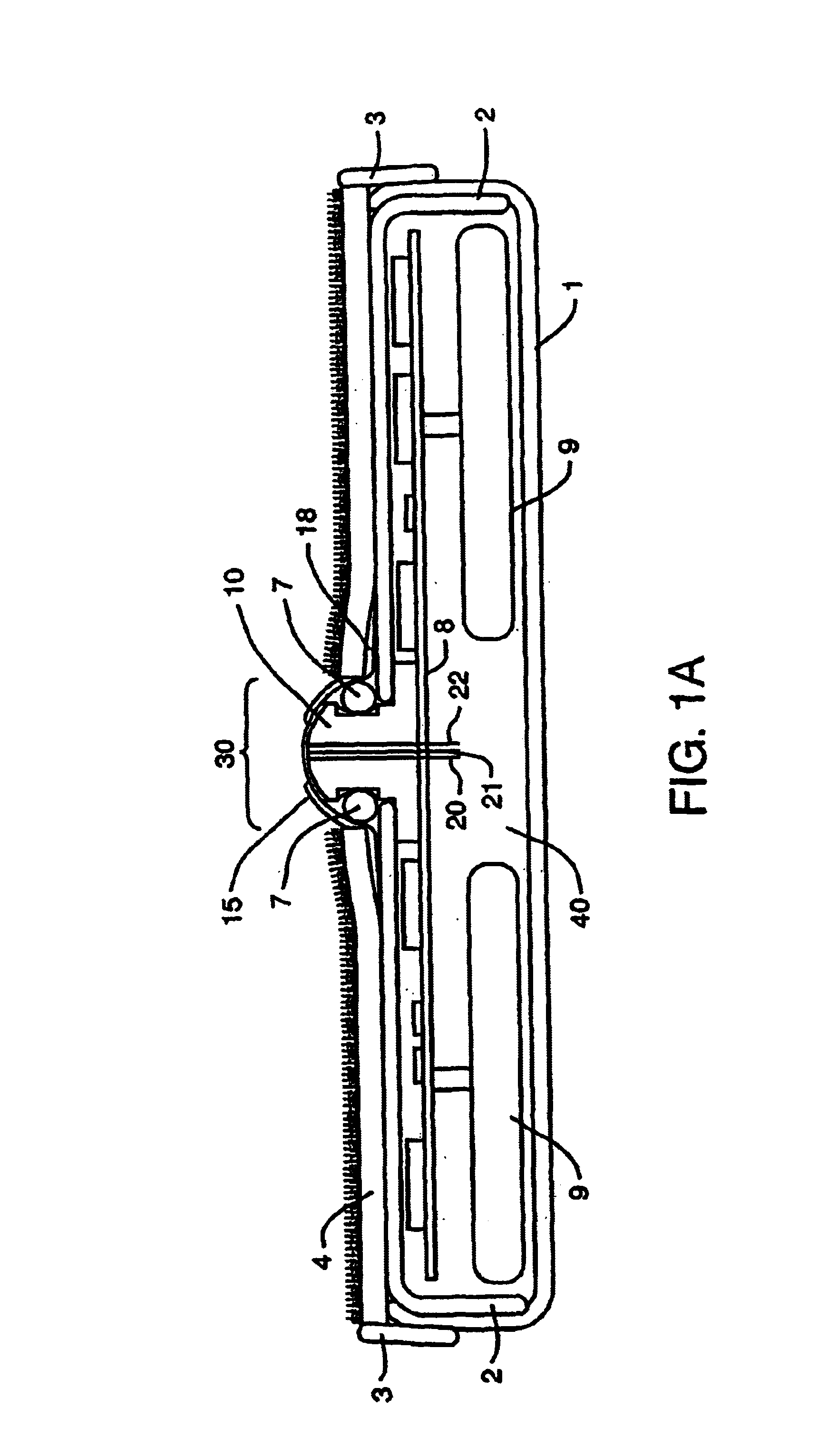
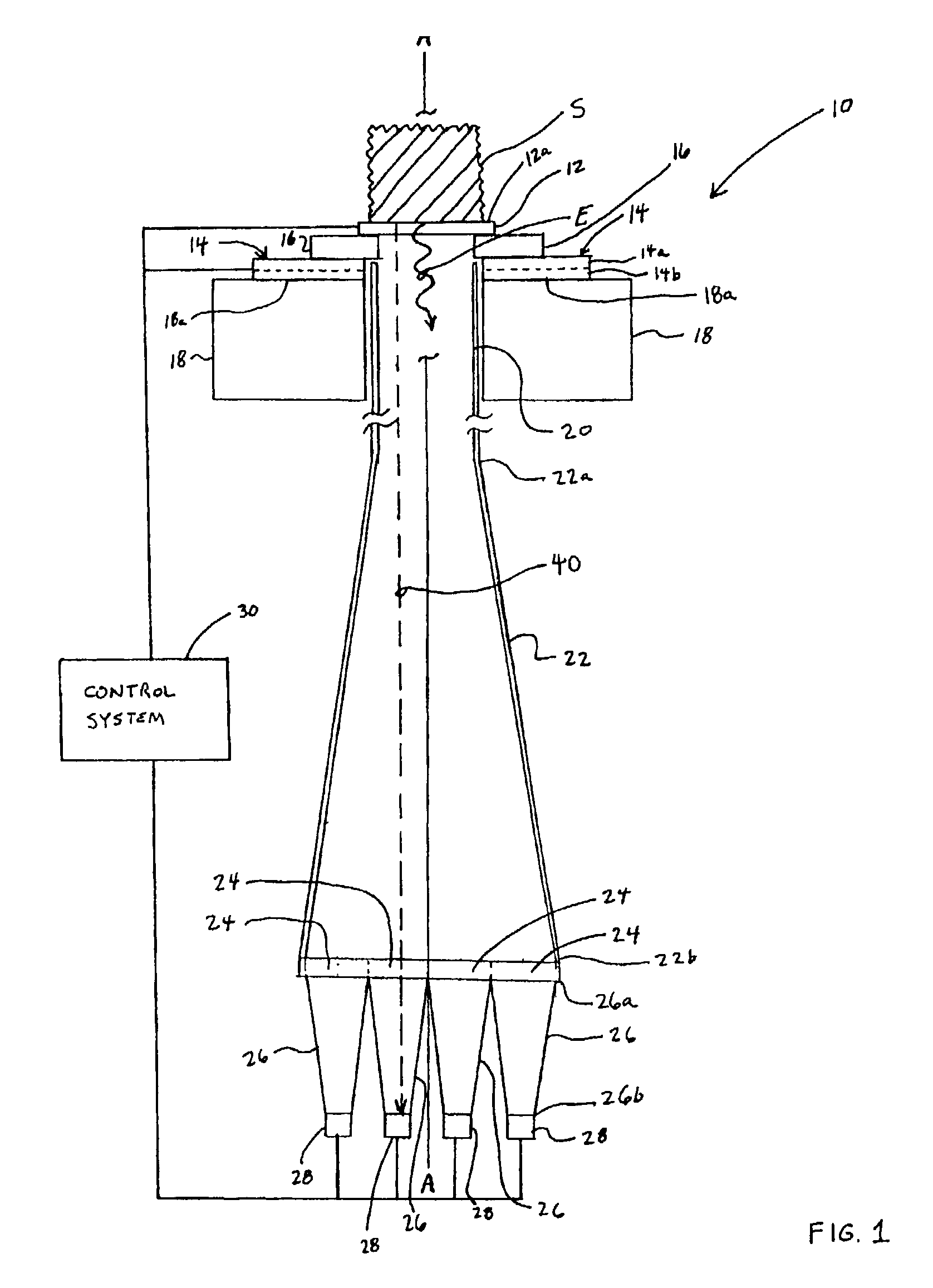
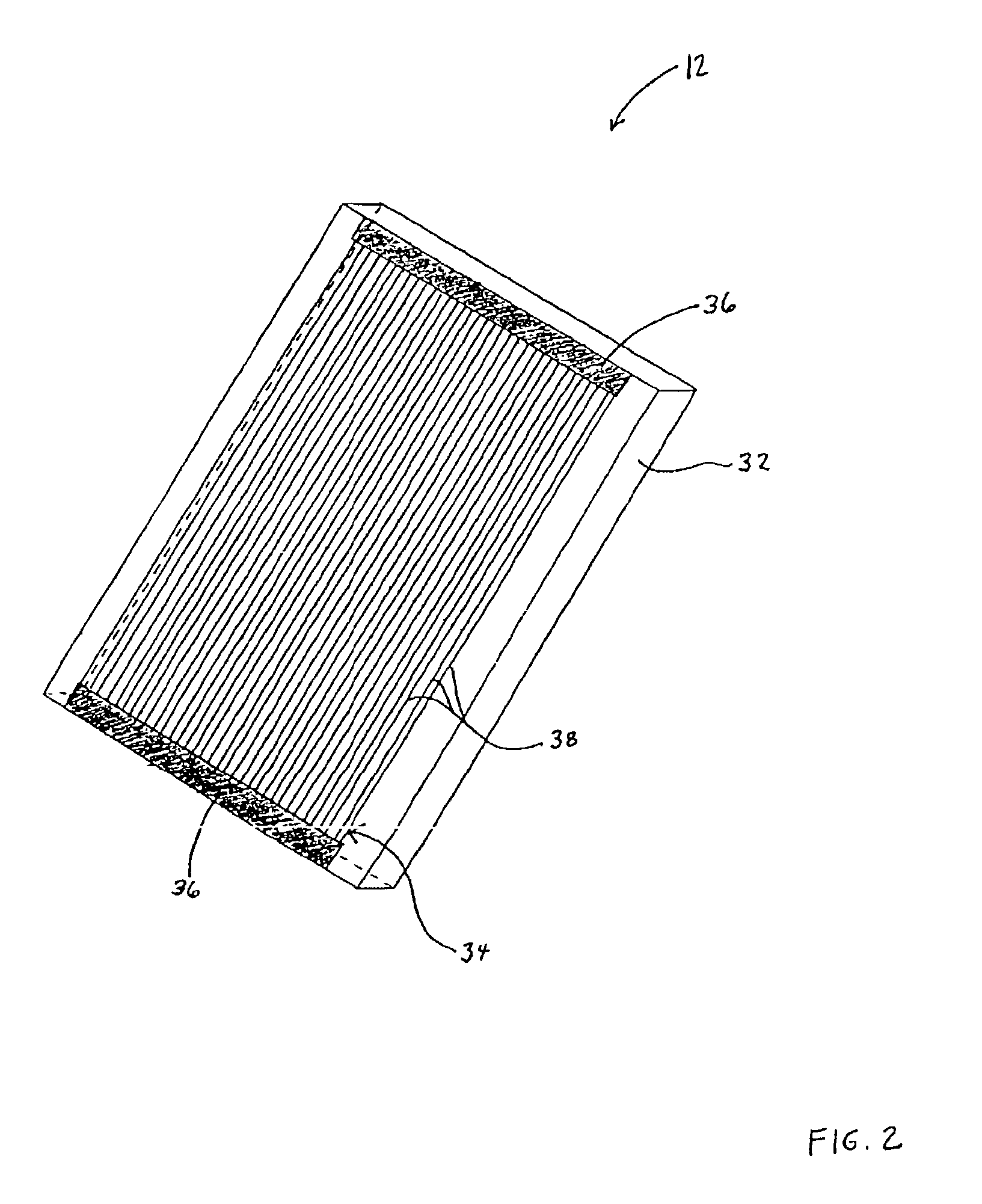
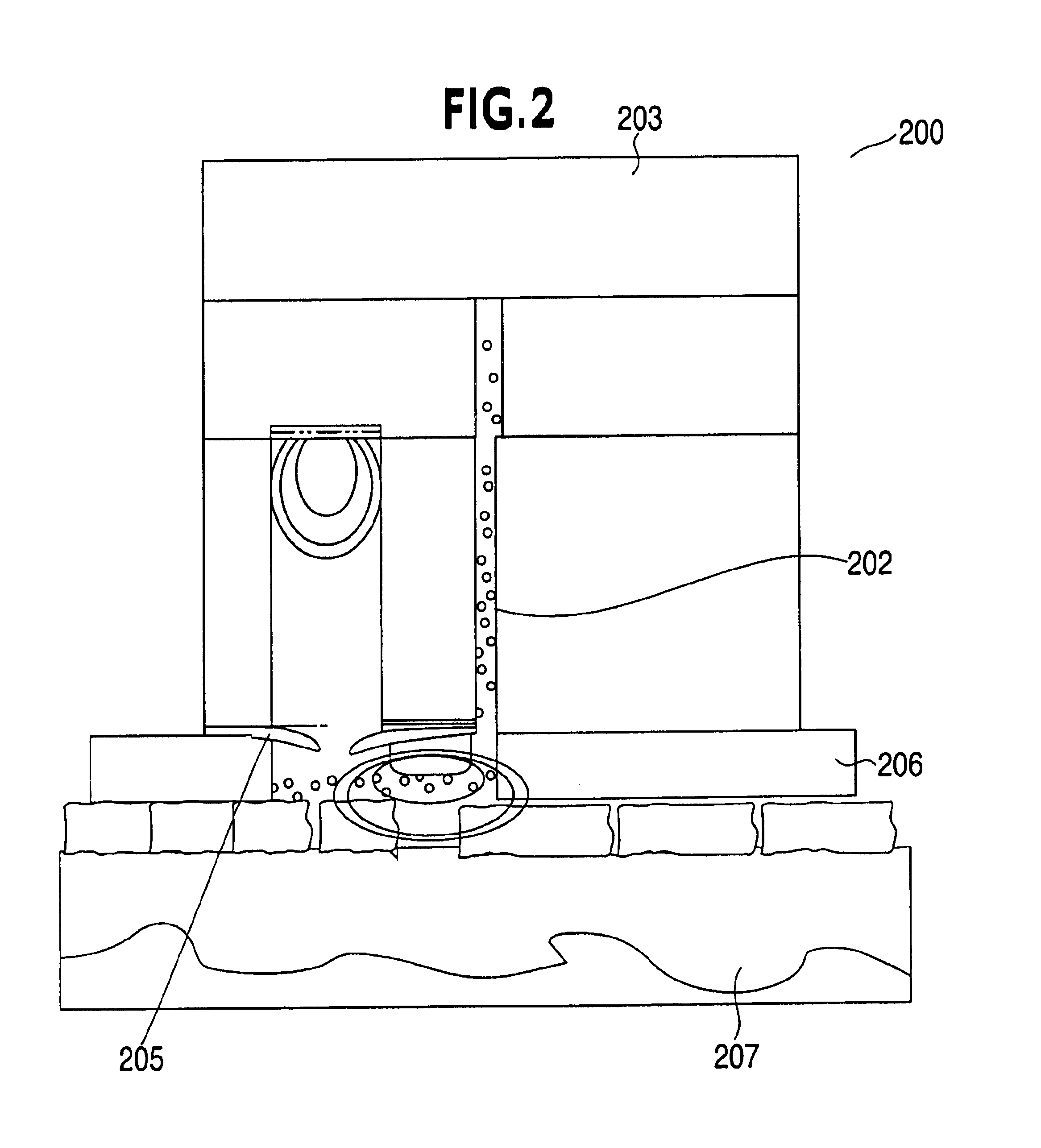
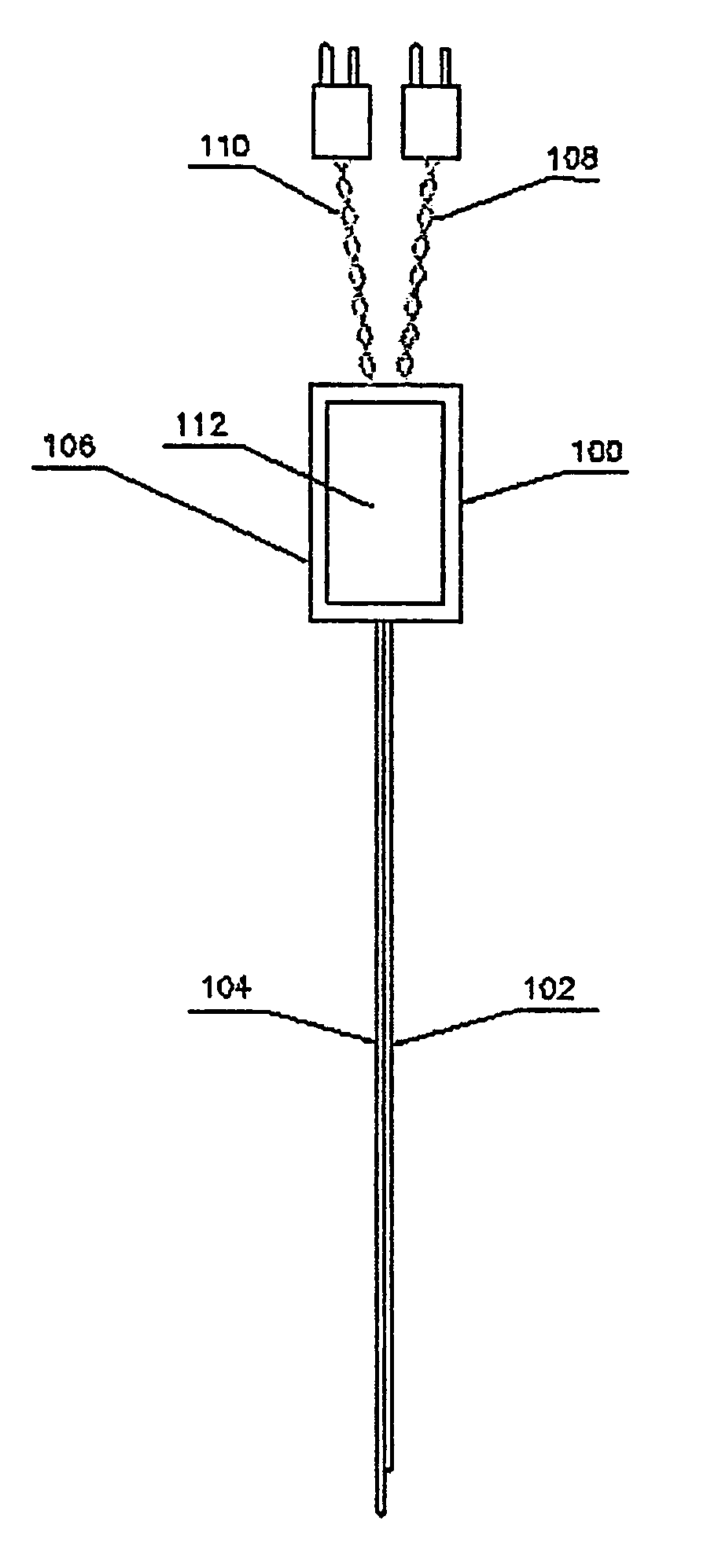
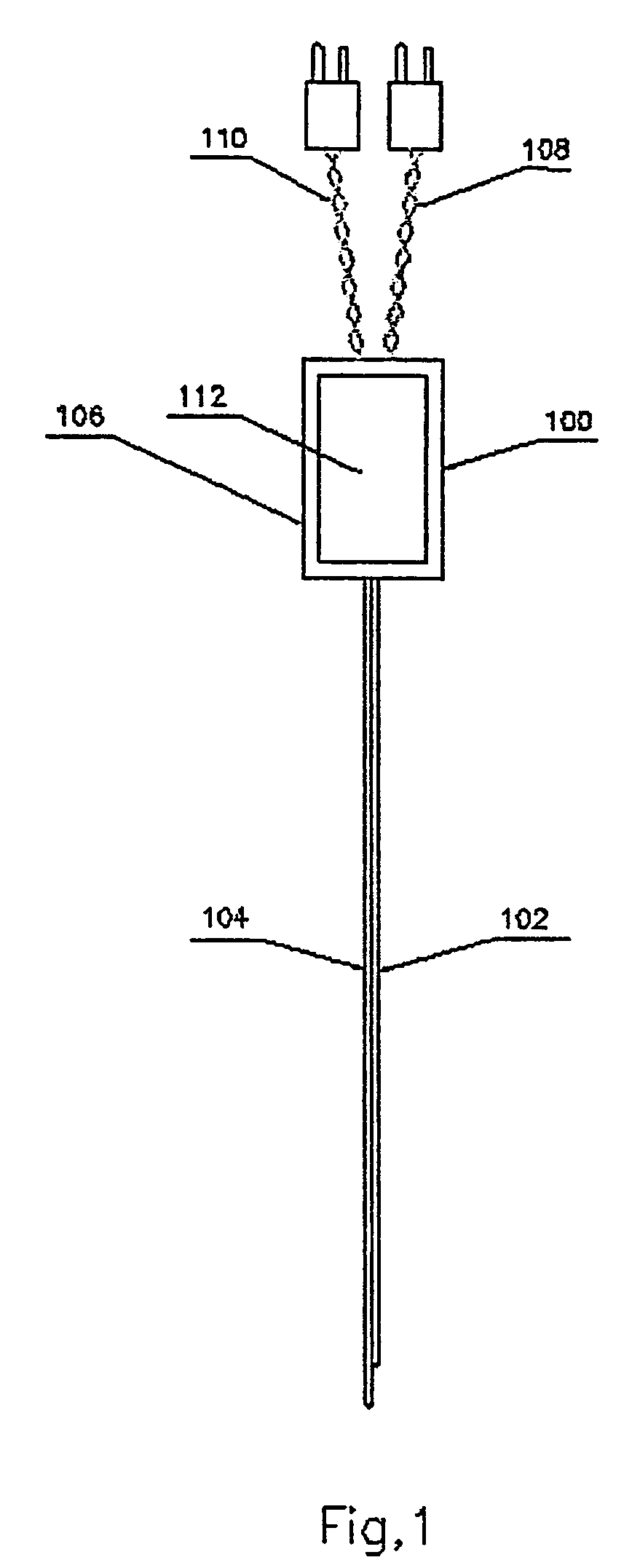
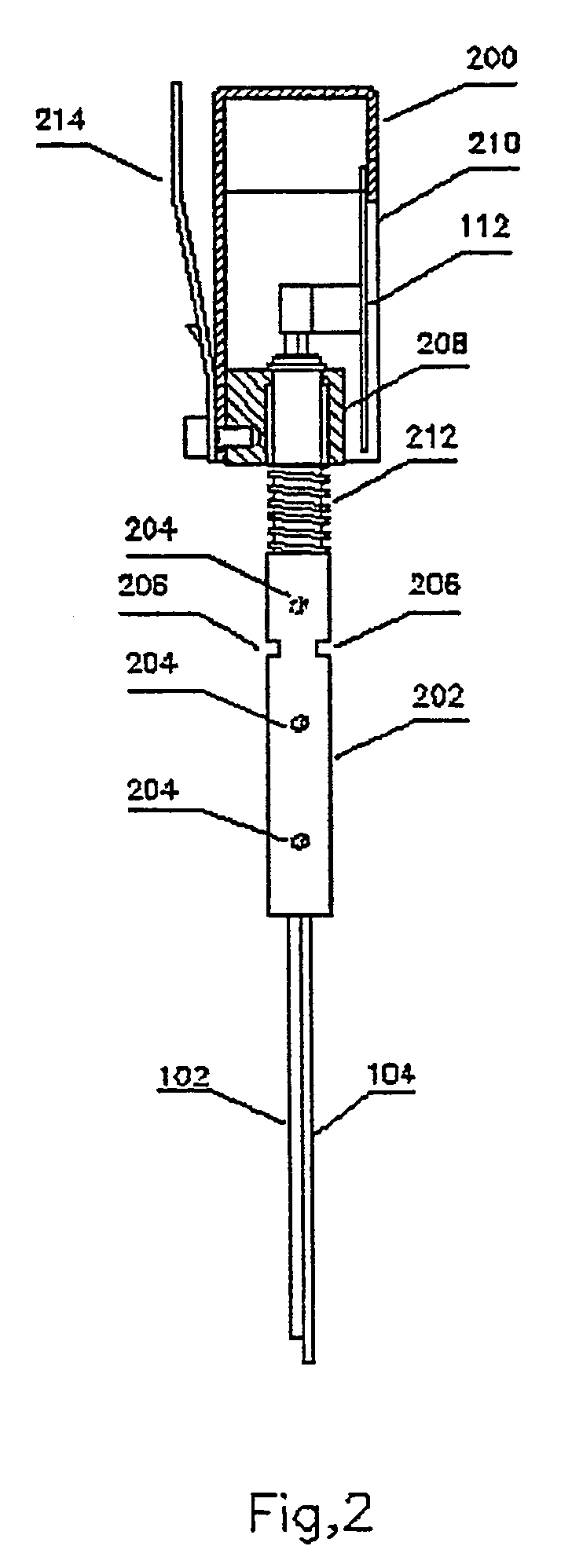
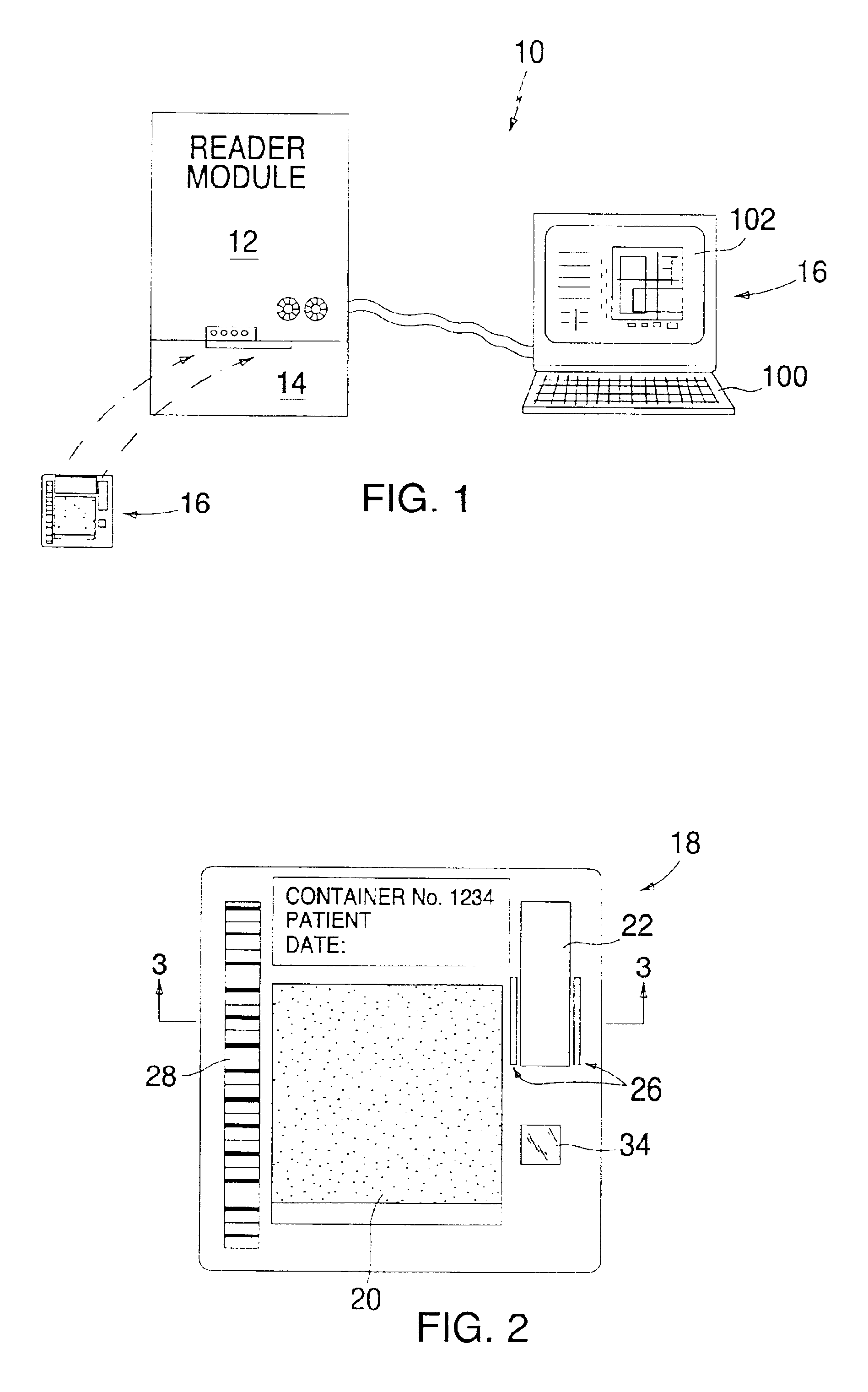
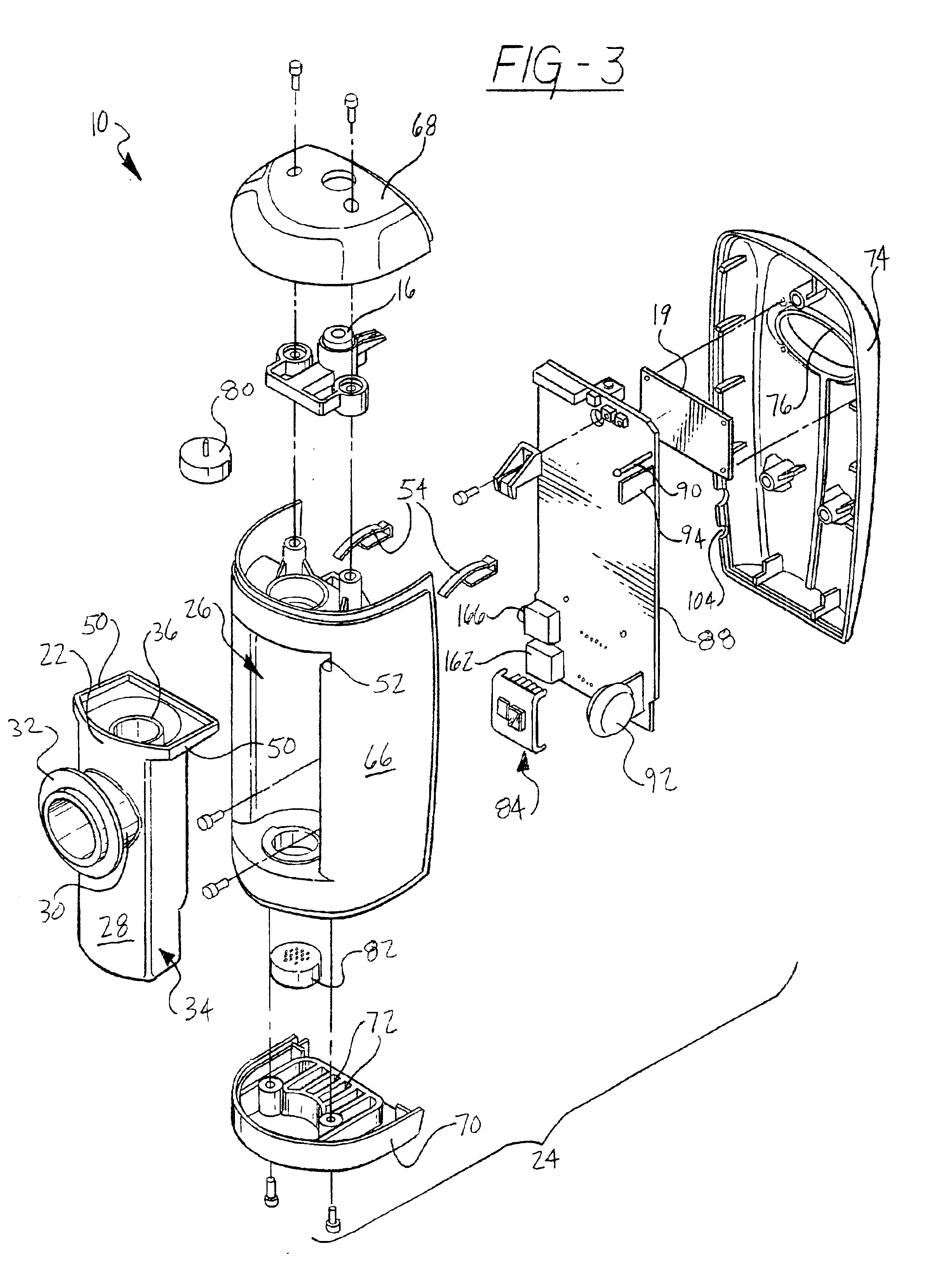
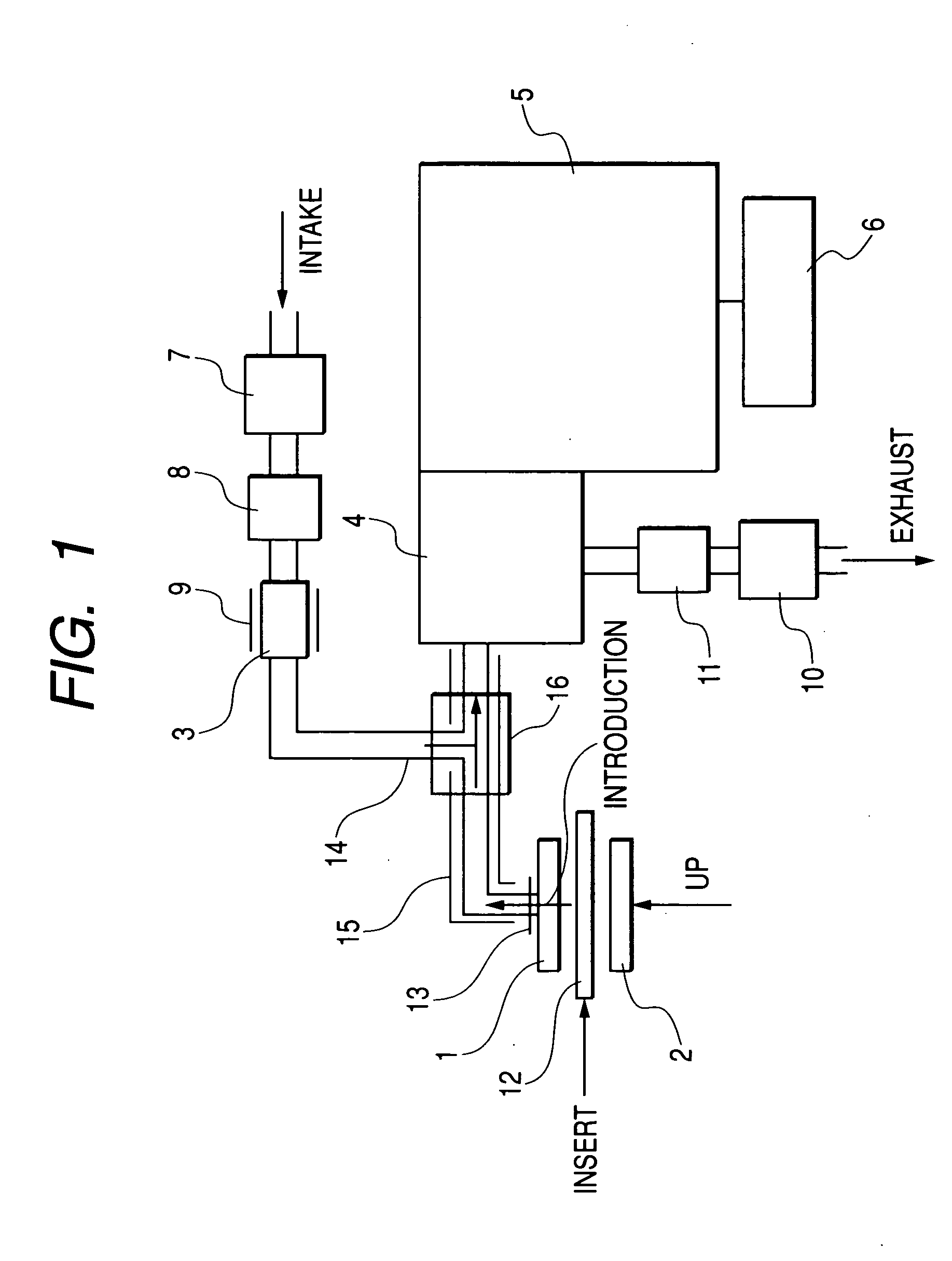
Device and method for determining analyte levels
InactiveUS7110803B2Reducing and eliminating phenomenonEliminate and significantly delay environmental stress crackingMicrobiological testing/measurementWithdrawing sample devicesAnalyteImplanted device
Owner:DEXCOM
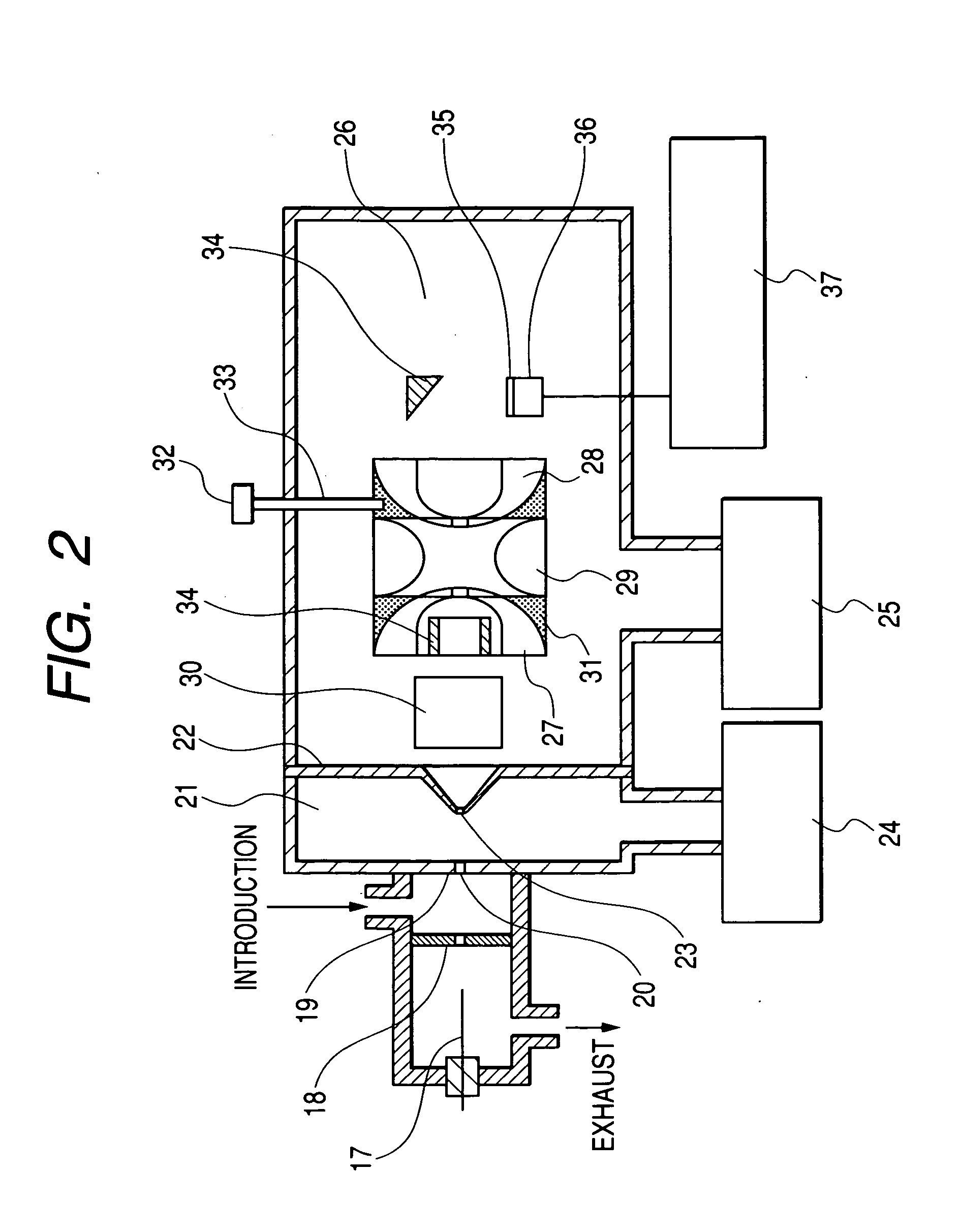
Robust system for screening mail for biological agents
InactiveUS6887710B2Lower the thresholdReduce riskAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesLiquid dispersion analysisParticulatesEngineering
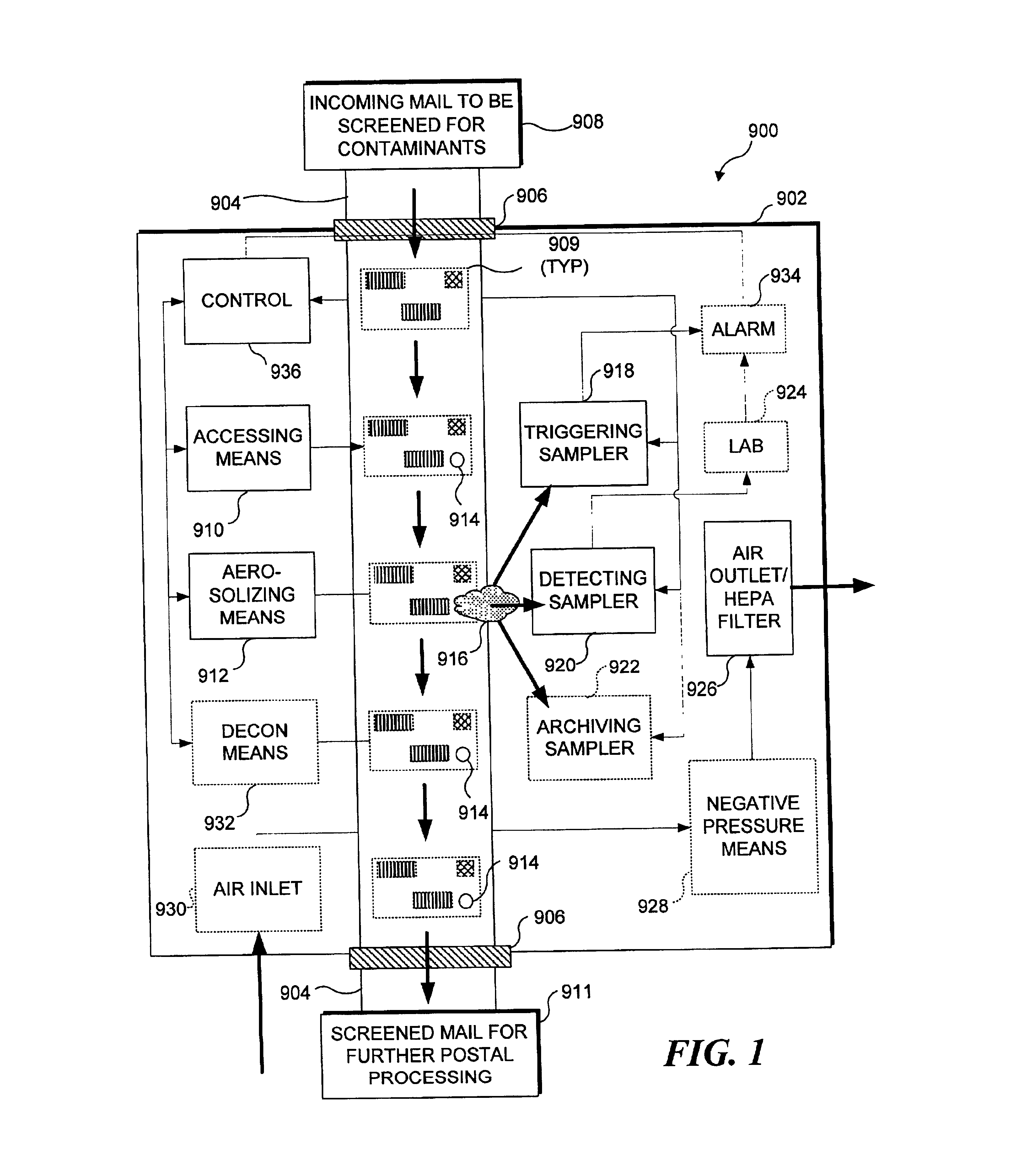
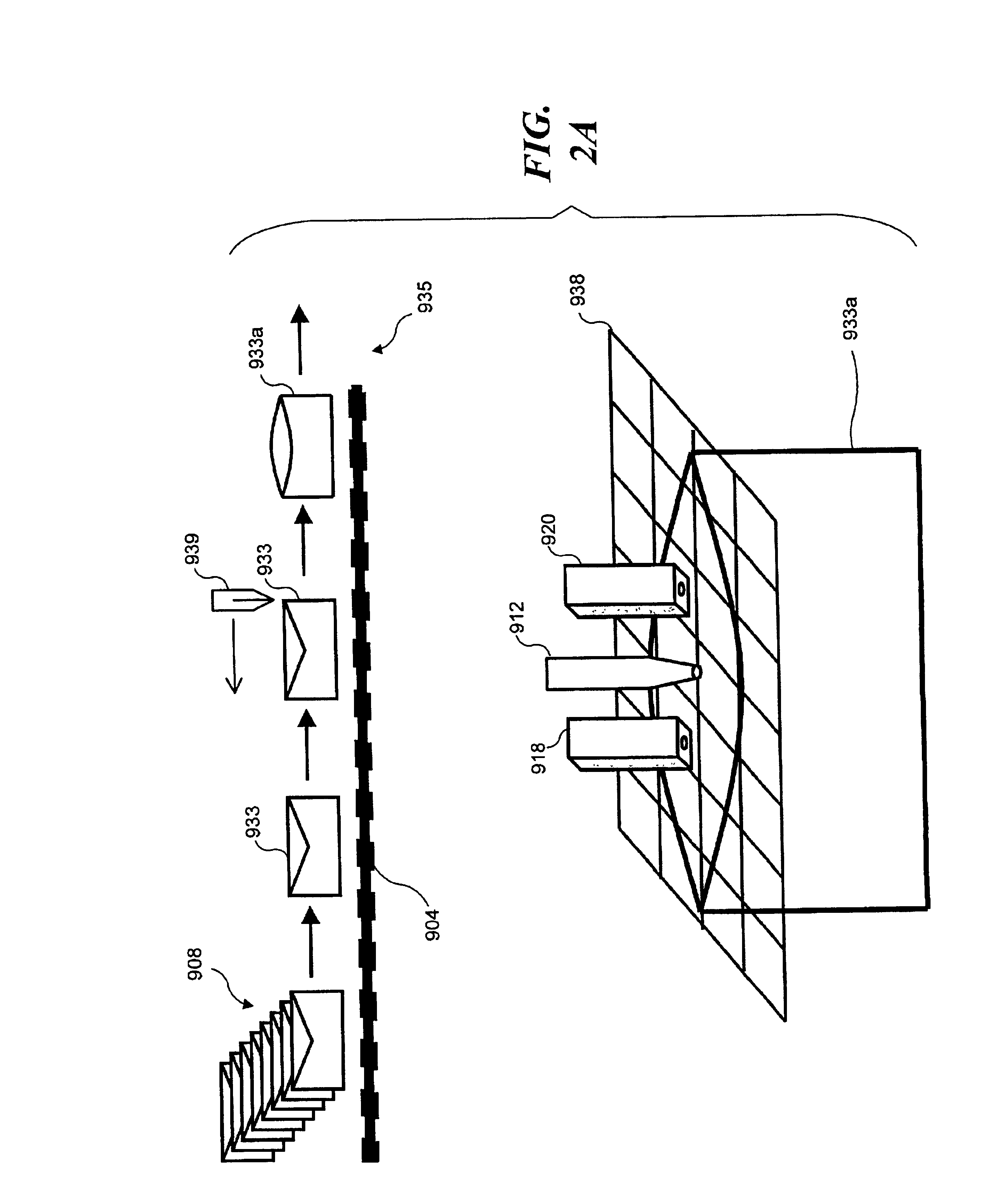
Items of mail are rapidly processed in a mail sampling system to determine if the mail is contaminated with a chemical or biological agent. The mail sampling system maintains a negative pressure in a containment chamber and includes a triggering sampler that makes a threshold determination regarding possible contamination, and a detecting sampler that obtains a sample for more detailed analysis in response to a signal from the triggering sampler. A sample of particulates collected from an item of mail is either removed for analysis or analyzed in the system to identify a contaminating agent. Optionally, the system includes an archiving sampler, which archives samples for subsequent processing and analysis, and a decontamination system, which is activated to decontaminate the mail if needed.
Owner:FLIR DETECTION
Method and apparatus for fluid dispersion
Owner:THE GOVERNINIG COUNCIL OF THE UNIV OF TORANTO +1
Assay plates, reader systems and methods for luminescence test measurements
ActiveUS20040022677A1Improve collection efficiencyIncrease assayBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsTest measurementBiology
Luminescence test measurements are conducted using an assay module having integrated electrodes with a reader apparatus adapted to receive assay modules, induce luminescence, preferably electrode induced luminescence, in the wells or assay regions of the assay modules and measure the induced luminescence.
Owner:MESO SCALE TECH LLC
Method and apparatus for fluid dispersion
Owner:THE GOVERNING COUNCIL OF THE UNIV OF TORONTO +1
Device and method for in vitro determination of analyte concentrations within body fluids
InactiveUS6989891B2Withdrawing sample devicesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsSpectral bandsCell wall
A reagentless whole-blood analyte detection system that is capable of being deployed near a patient has a source capable of emitting a beam of radiation that includes a spectral band. The whole-blood system also has a detector in an optical path of the beam. The whole-blood system also has a housing that is configured to house the source and the detector. The whole-blood system also has a sample element that is situated in the optical path of the beam. The sample element has a sample cell and a sample cell wall that does not eliminate transmittance of the beam of radiation in the spectral band.
Owner:OPTISCAN BIOMEDICAL
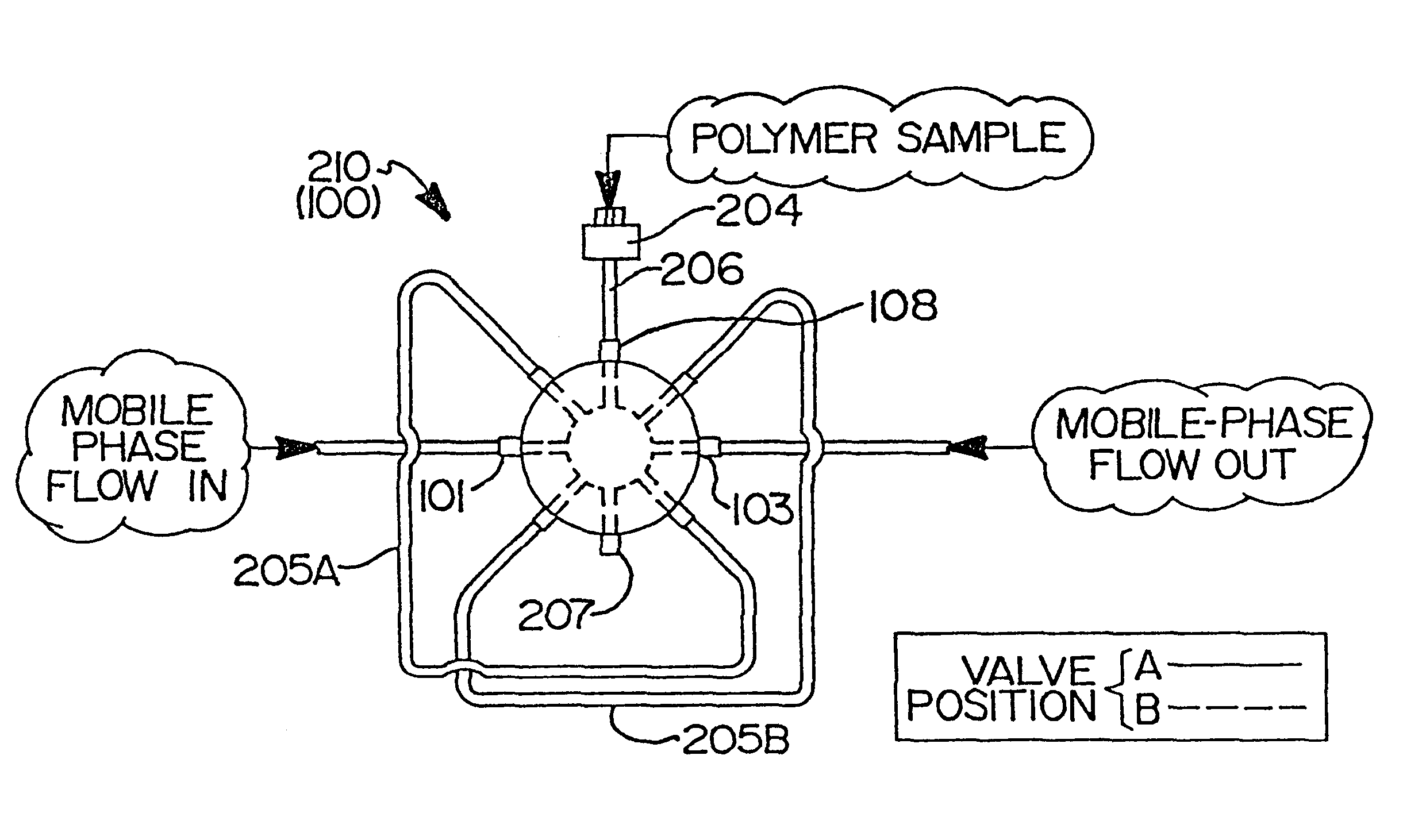
High-temperature characterization of polymers
InactiveUS6260407B1Avoid backlogImprove throughputSequential/parallel process reactionsComponent separationElutionChromatography column
Rapid characterization and screening of polymer samples to determine average molecular weight, molecular weight distribution and other properties is disclosed. Rapid flow characterization systems and methods, including liquid chromatography and flow-injection analysis systems and methods are preferably employed. High throughput, automated sampling systems and methods, high-temperature characterization systems and methods, and rapid, indirect calibration compositions and methods are also disclosed. In preferred high-temperature embodiments, the polymer sample is maintained at a temperature of not less than about 75° C. during sample preparation, loading into a liquid chromatography or flow-injection analysis system, injection into a mobile phase of a liquid chromatography or flow-injection analysis system, and / or elution from chromatographic column. The described methods, systems, and device have primary applications in combinatorial polymer research and in industrial process control.
Owner:INTERMOLECULAR
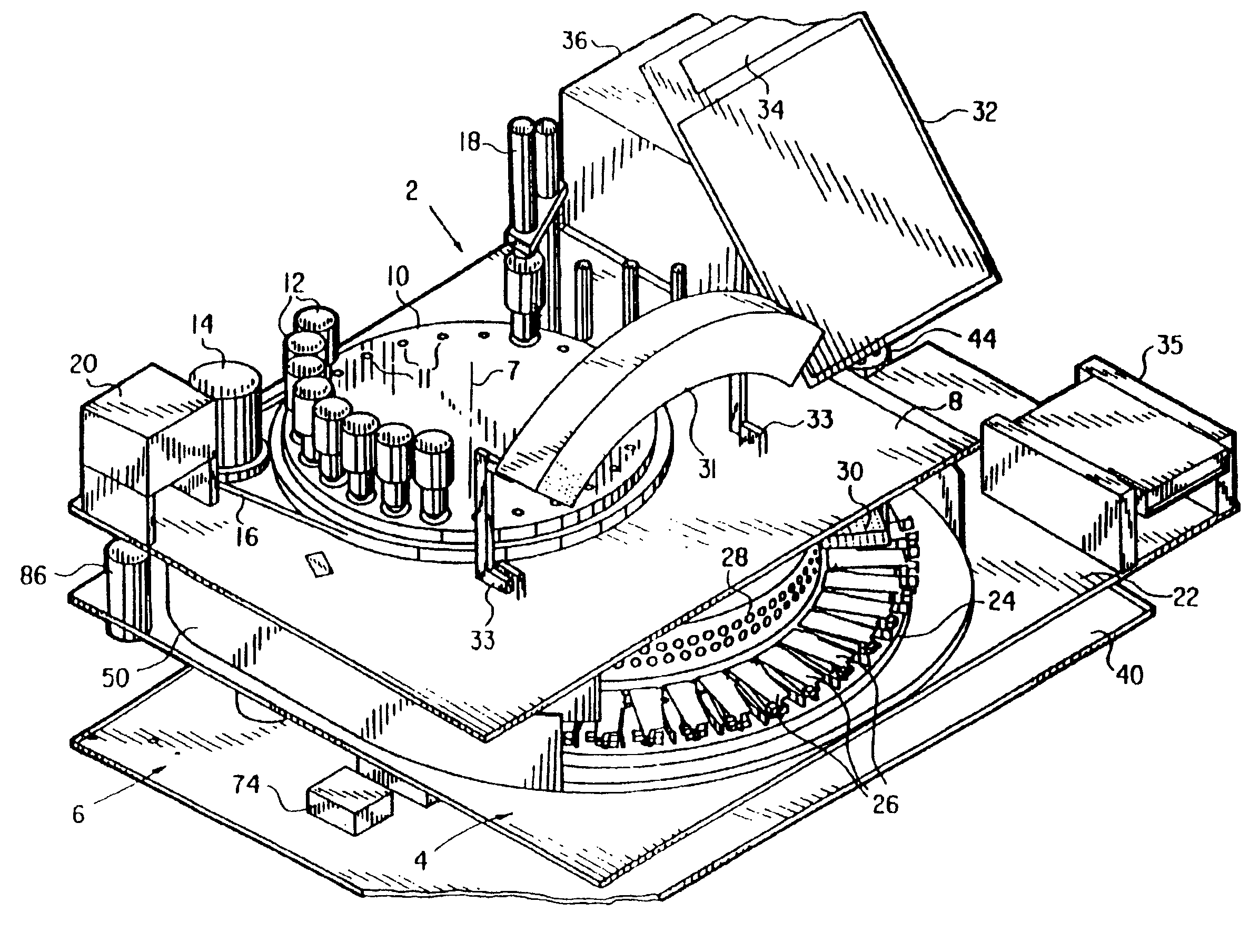
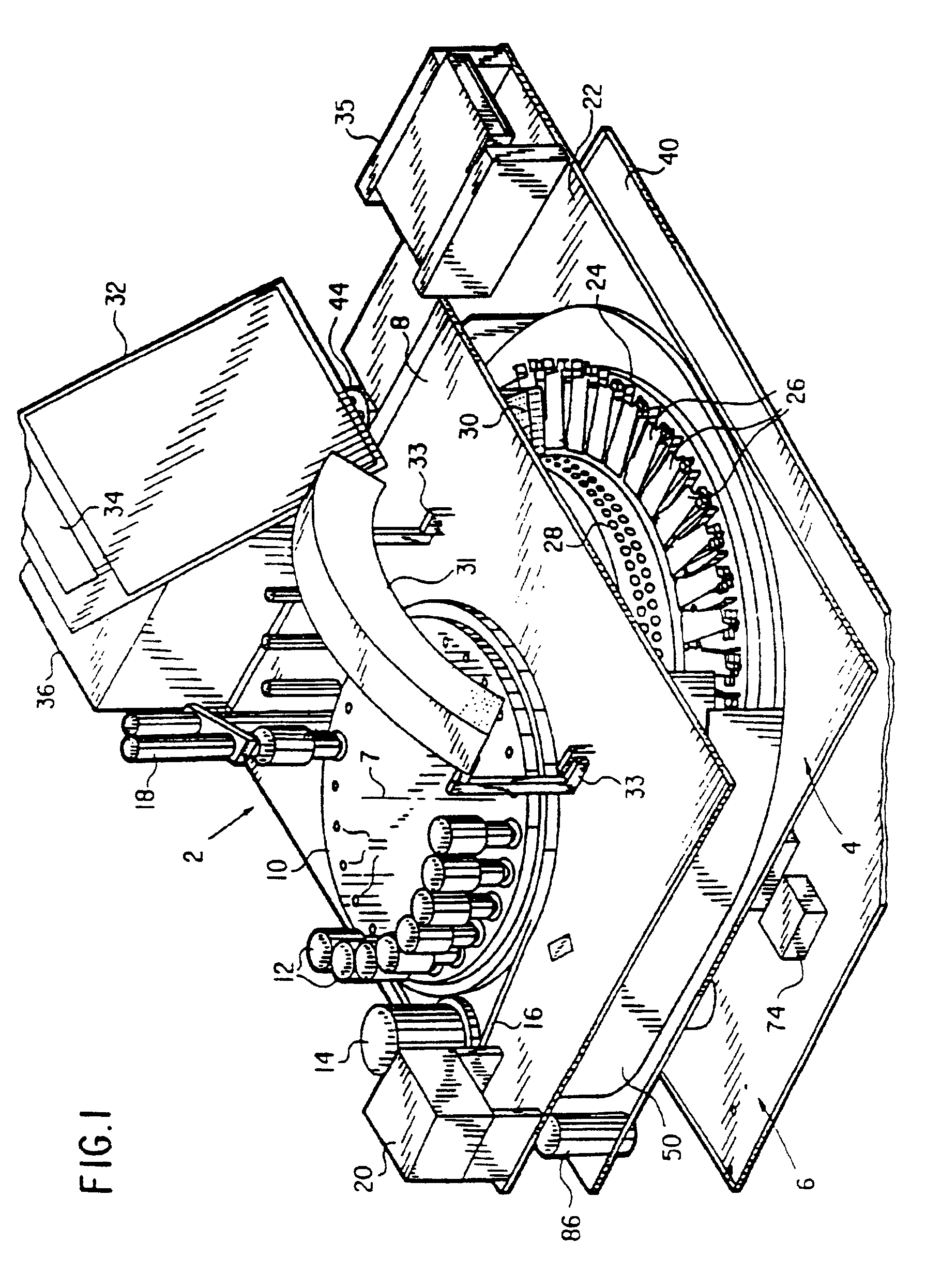
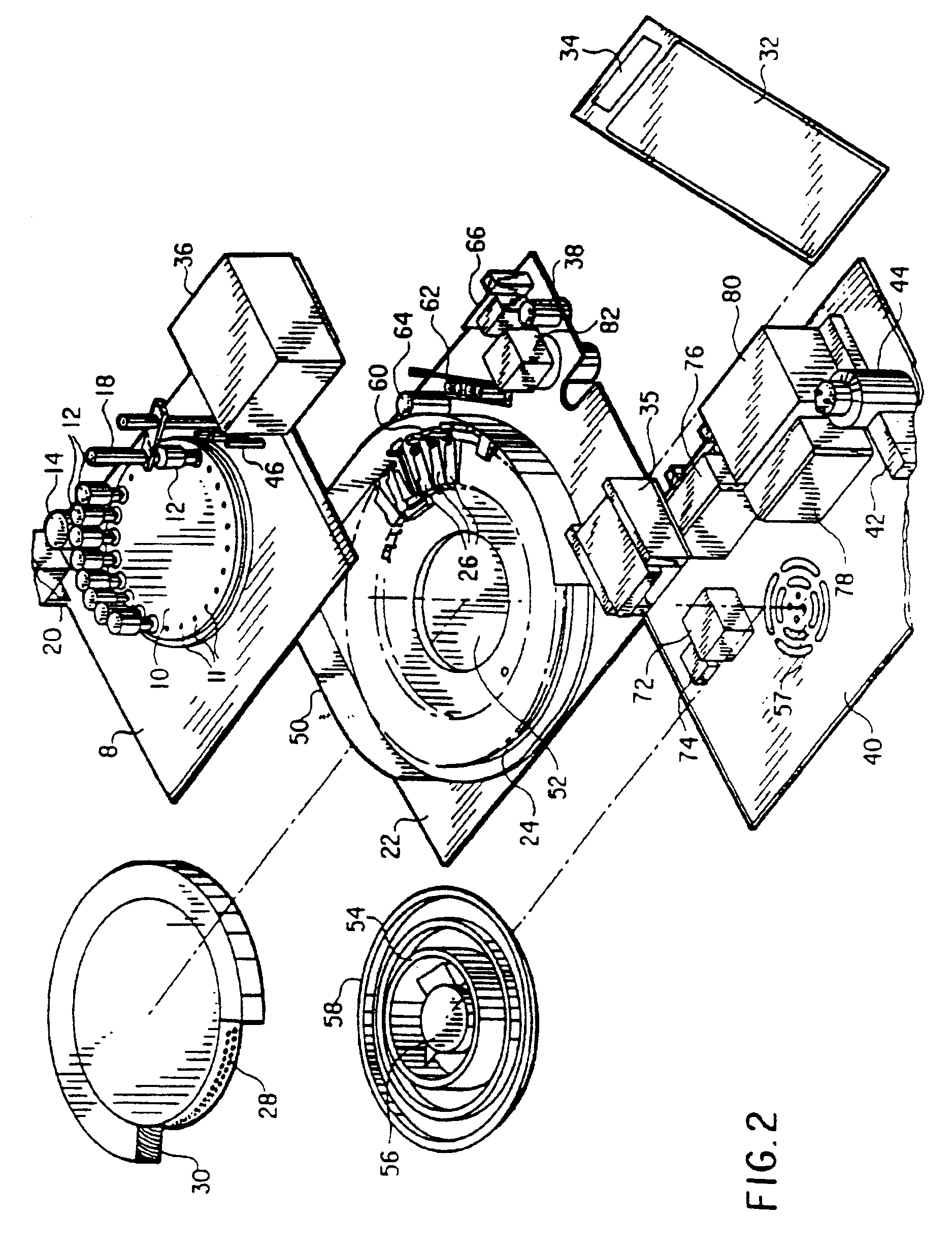
Automated biological reaction apparatus
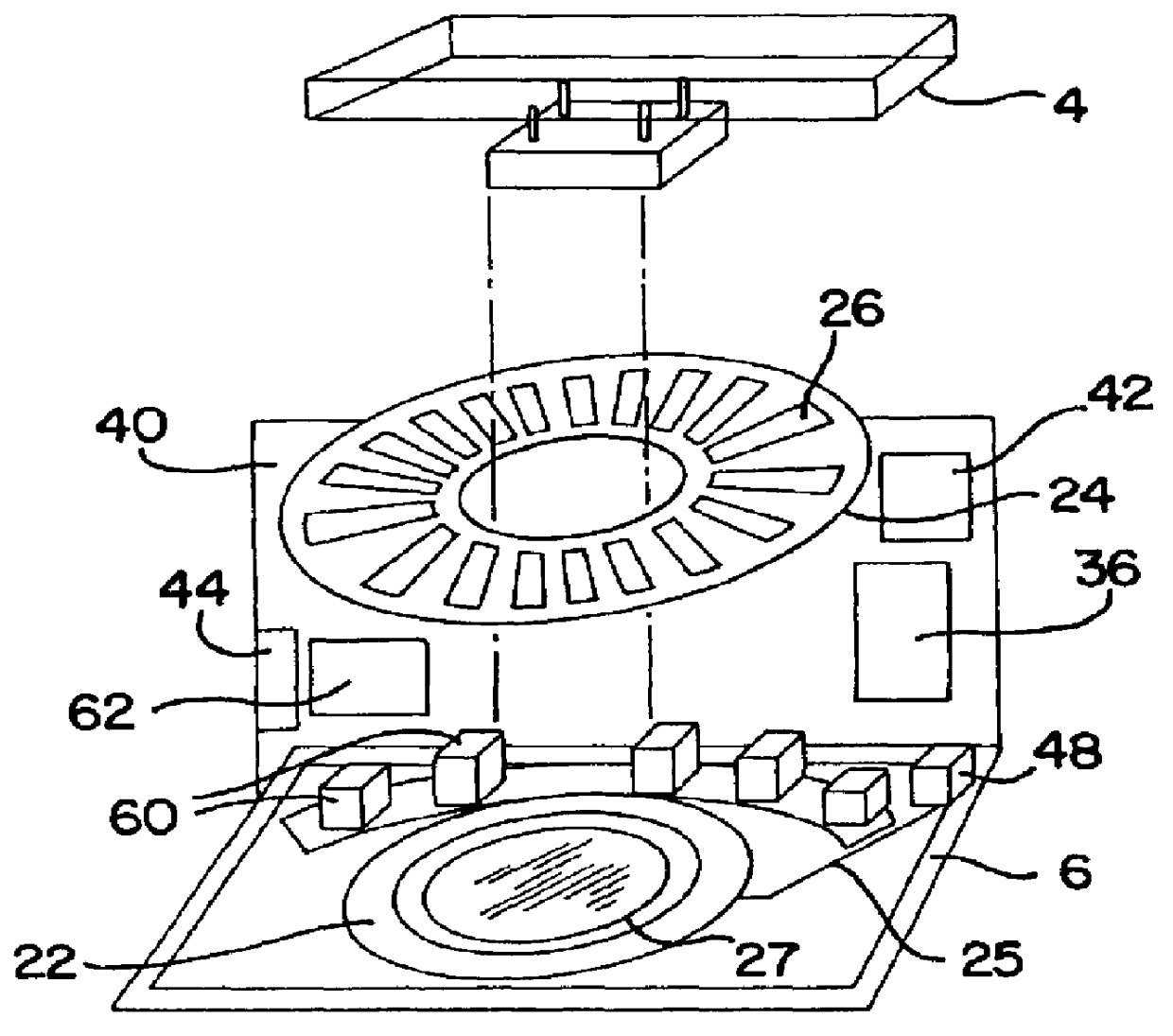
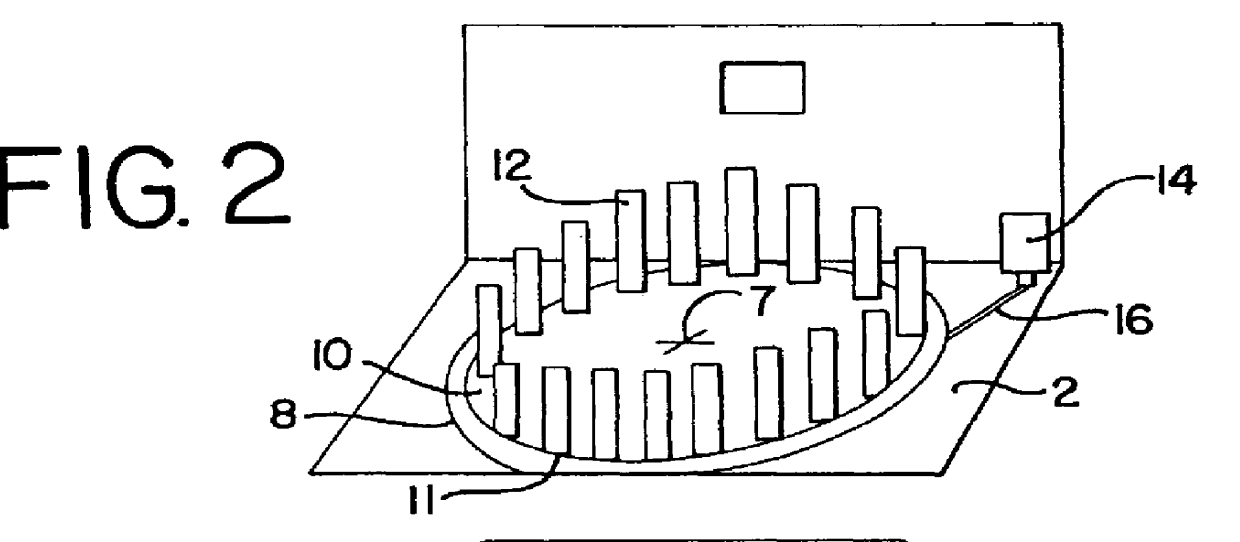
An automated immunostaining apparatus having a reagent application zone and a reagent supply zone. The apparatus has a carousel slide support supporting a plurality of slide supports thereon, and drive means engaging the carousel slide support for consecutively positioning each of a plurality of slide supports in the reagent application zone. The apparatus also has a carousel reagent support having a plurality of reagent container supports thereon, and drive means engaging the carousel for rotating the carousel and positioning a preselected reagent container support in the reagent supply zone. The apparatus also has a reagent delivery actuator means positioned for engaging a reagent container positioned on a container support in the reagent delivery zone and initiating reagent delivery from the reagent container to a slide supported on a slide support in the reagent receiving zone.
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
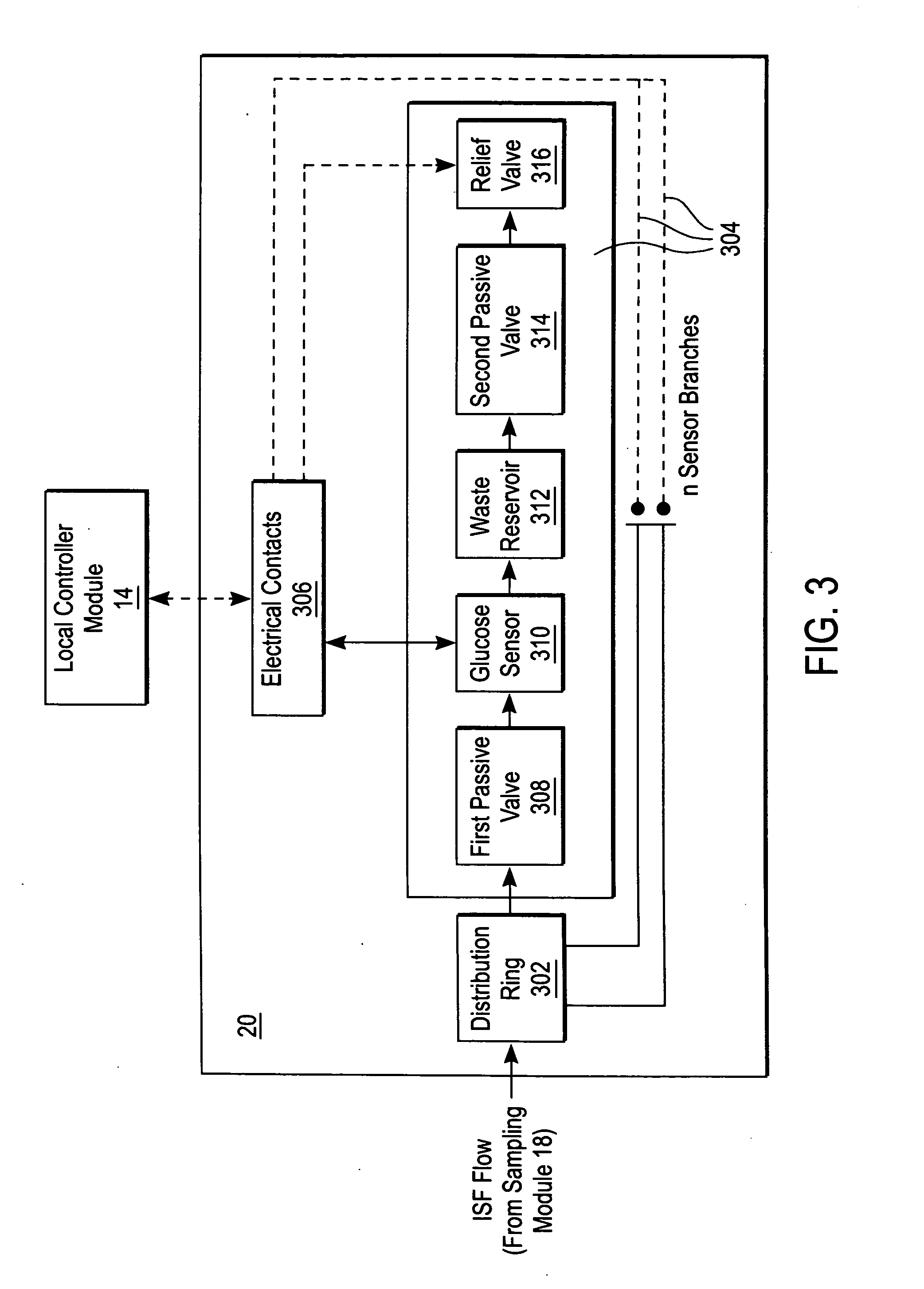
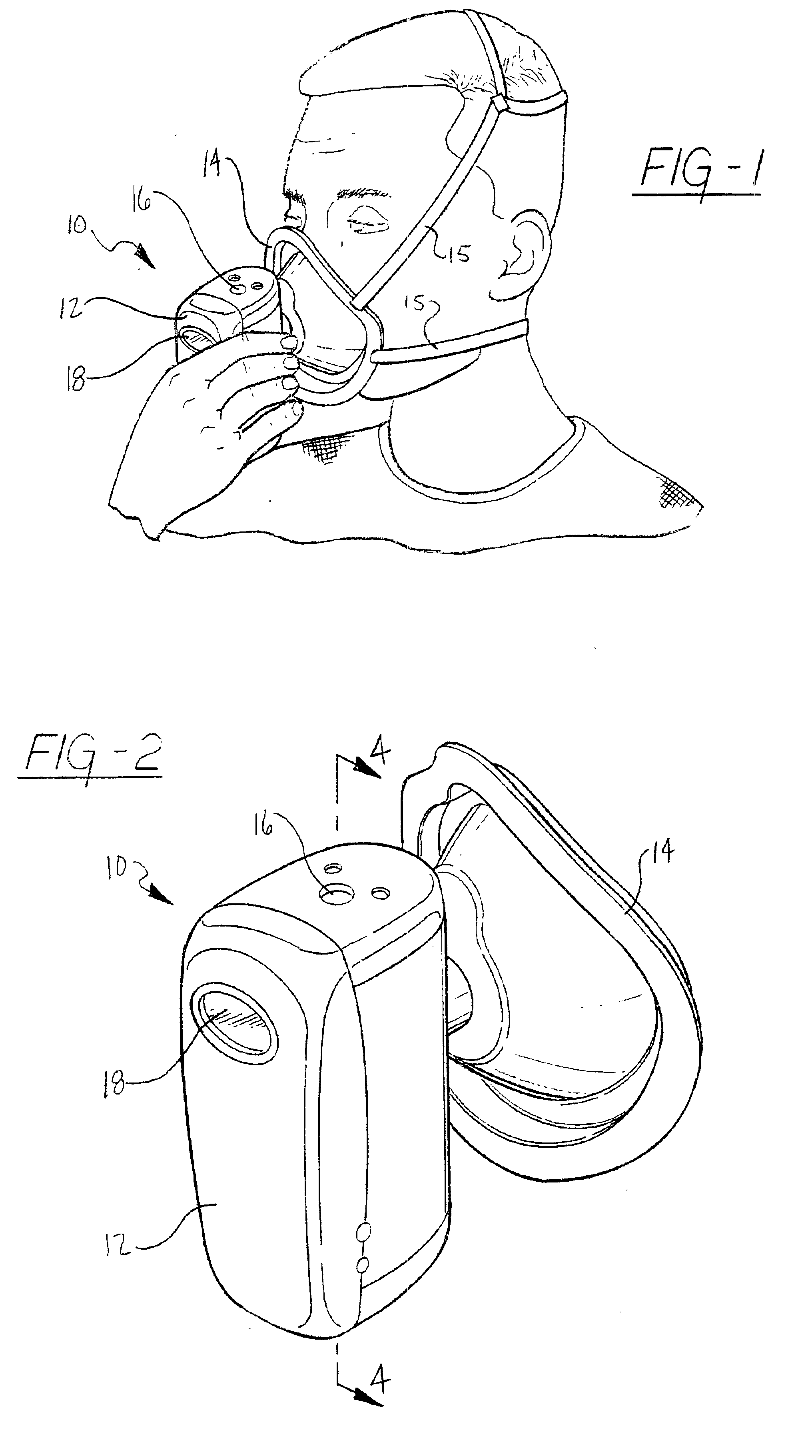
Devices, systems and methods for extracting bodily fluid and monitoring an analyte therein
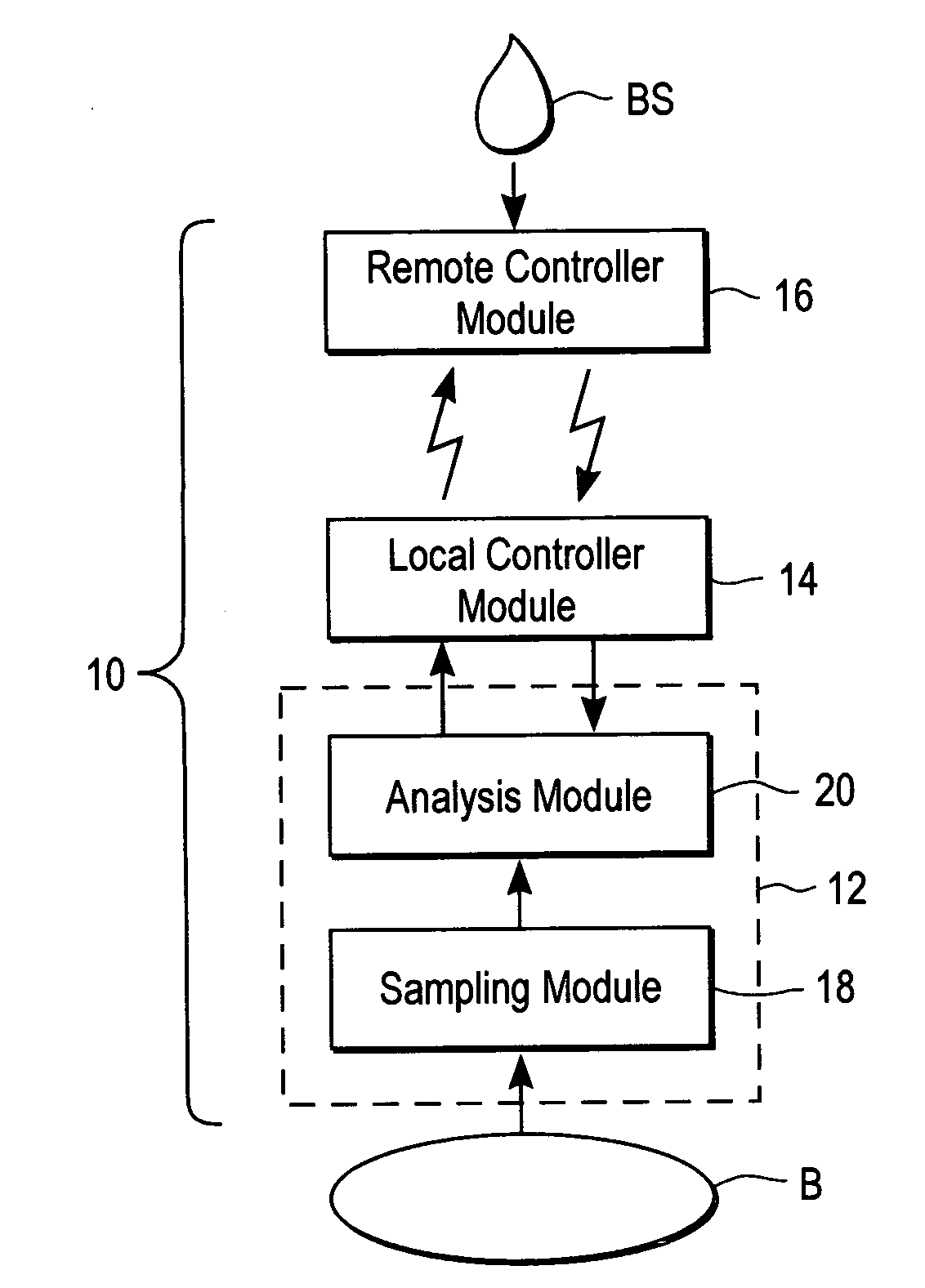
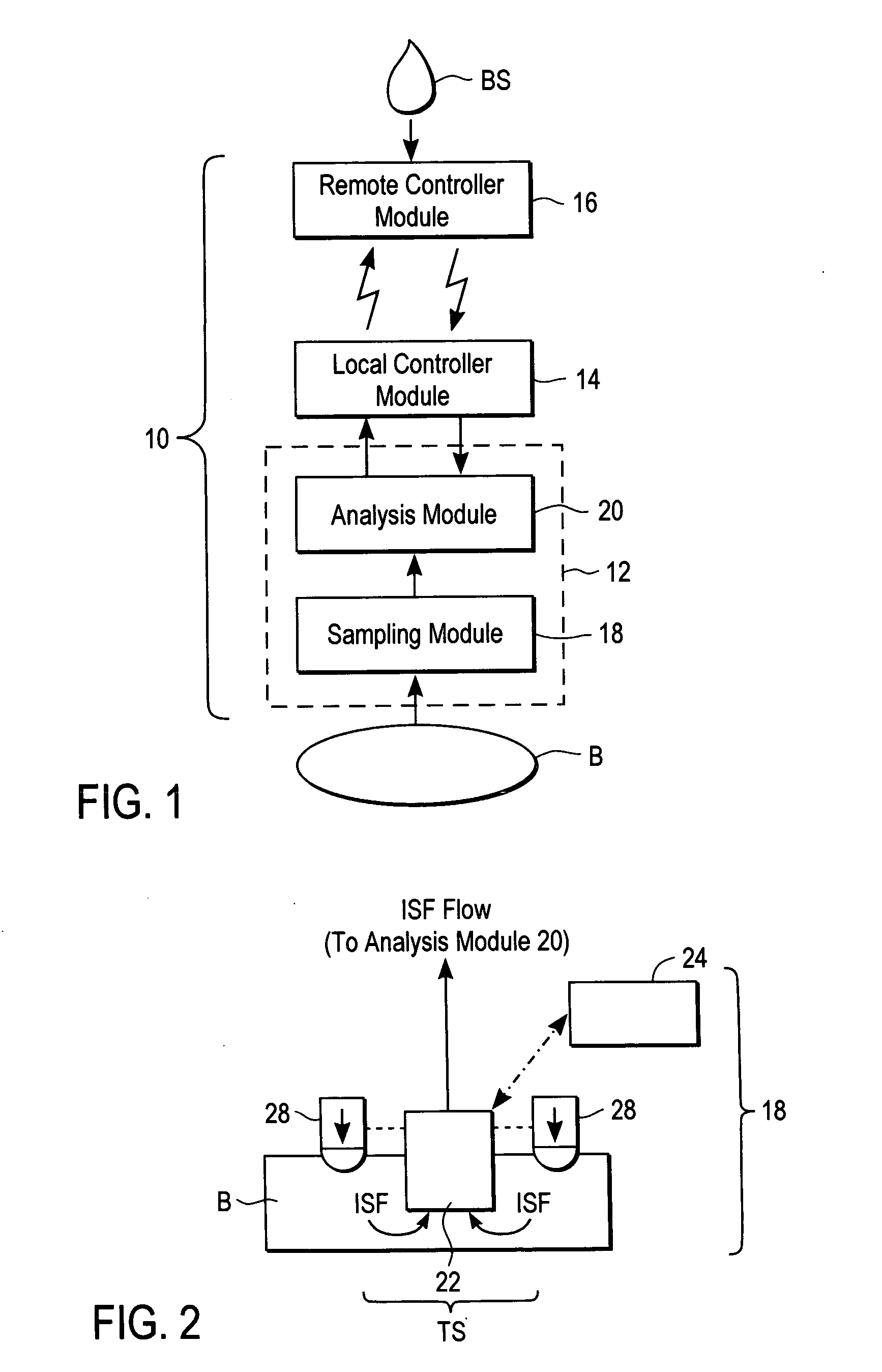
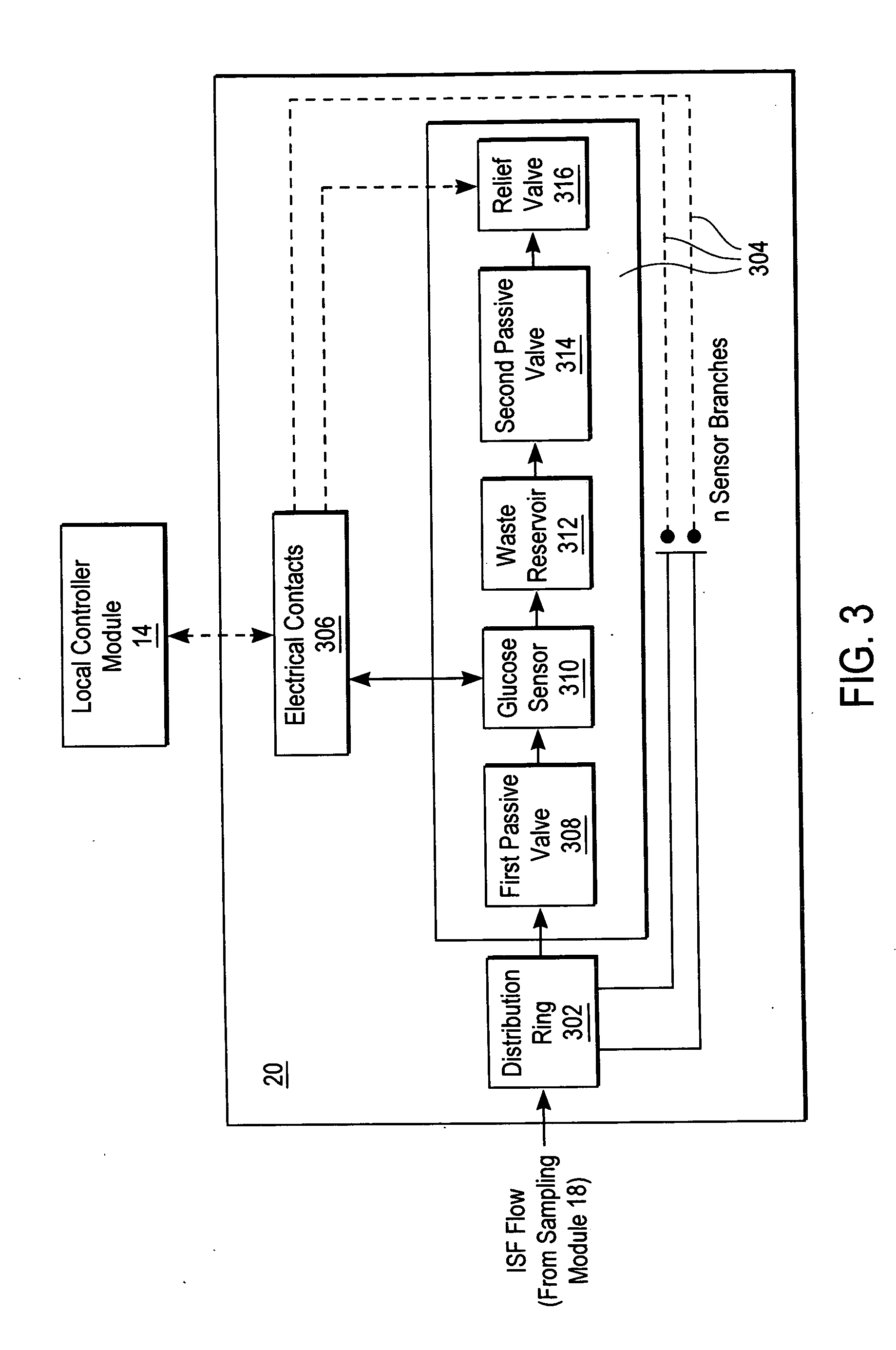
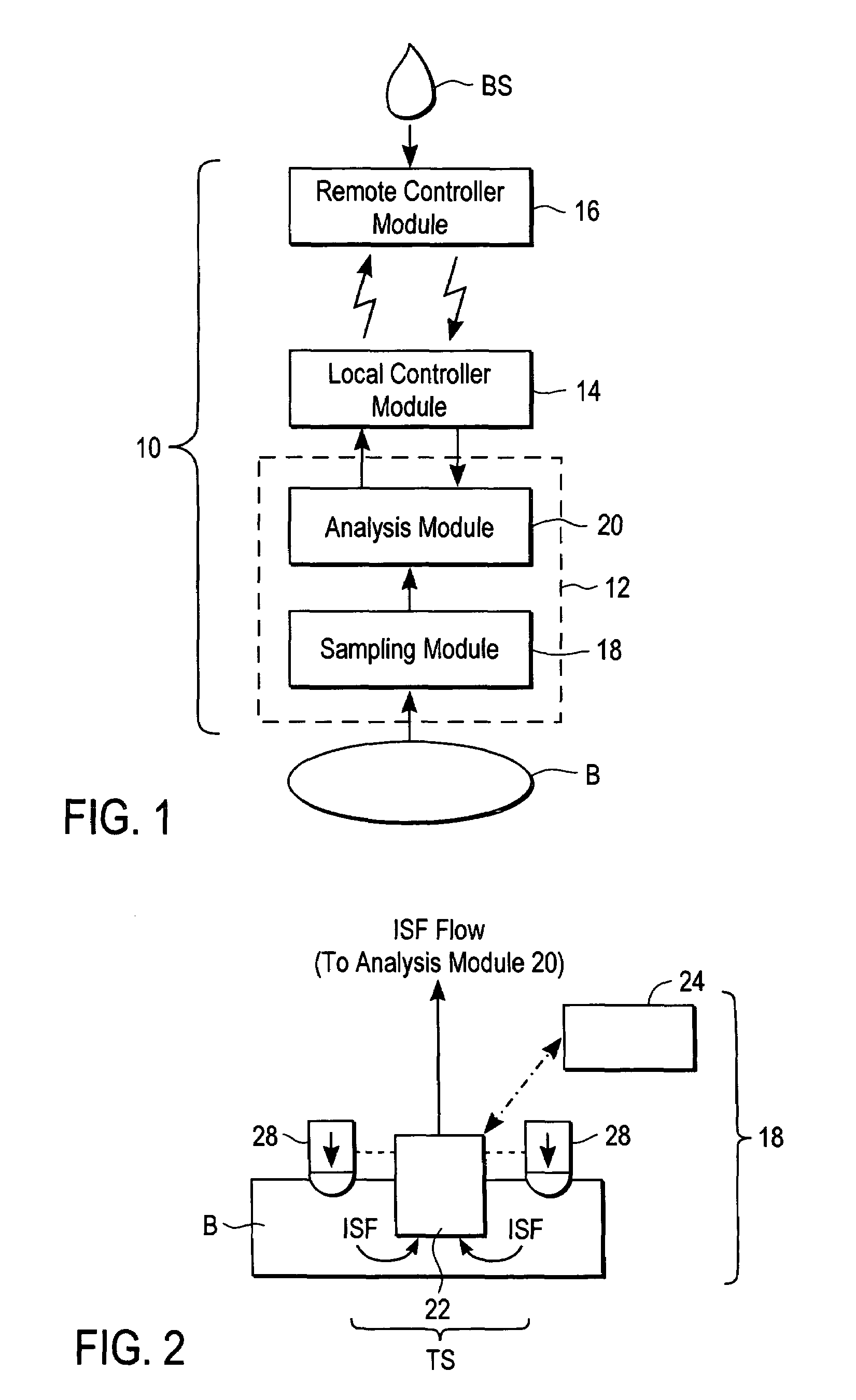
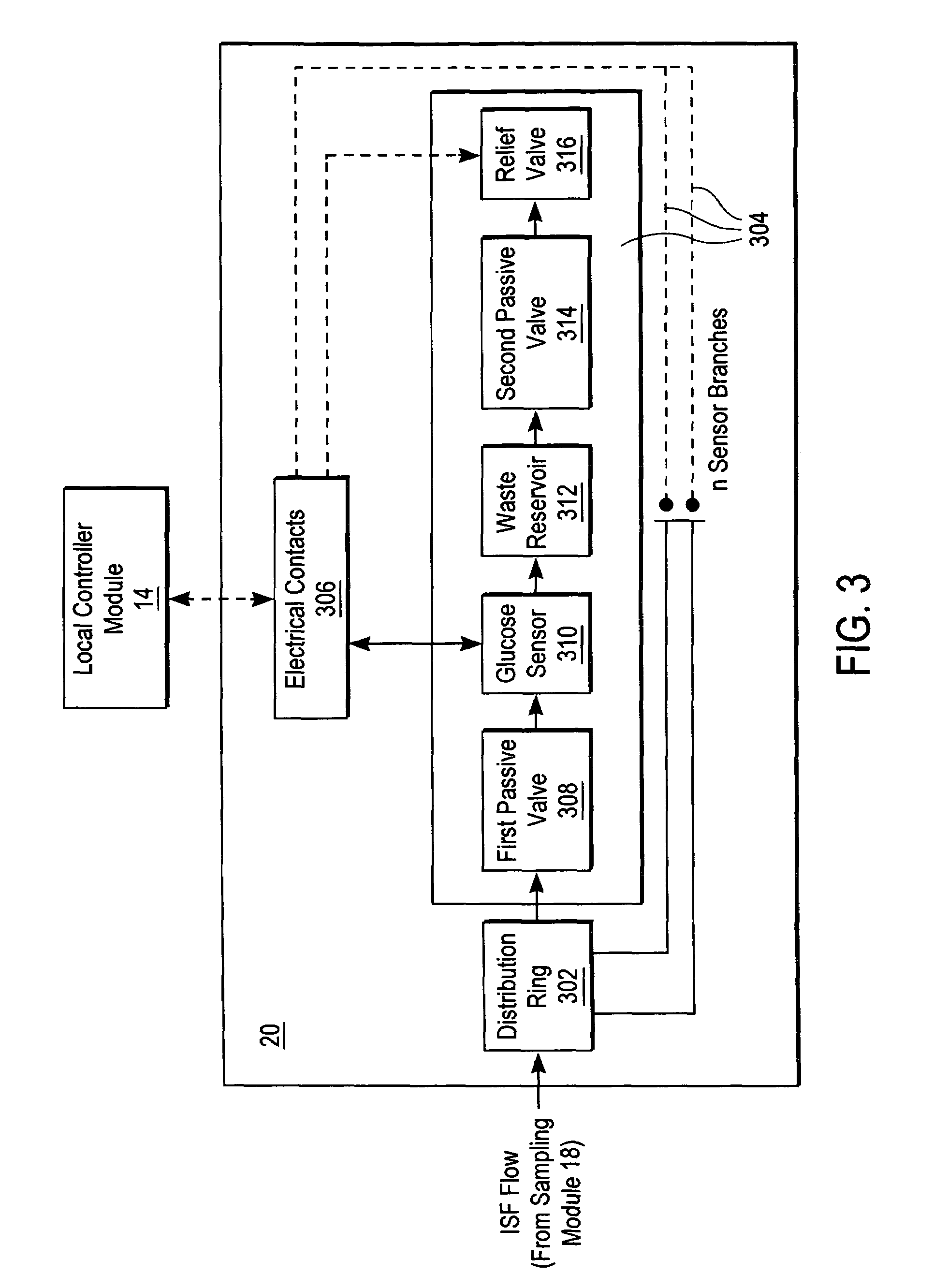
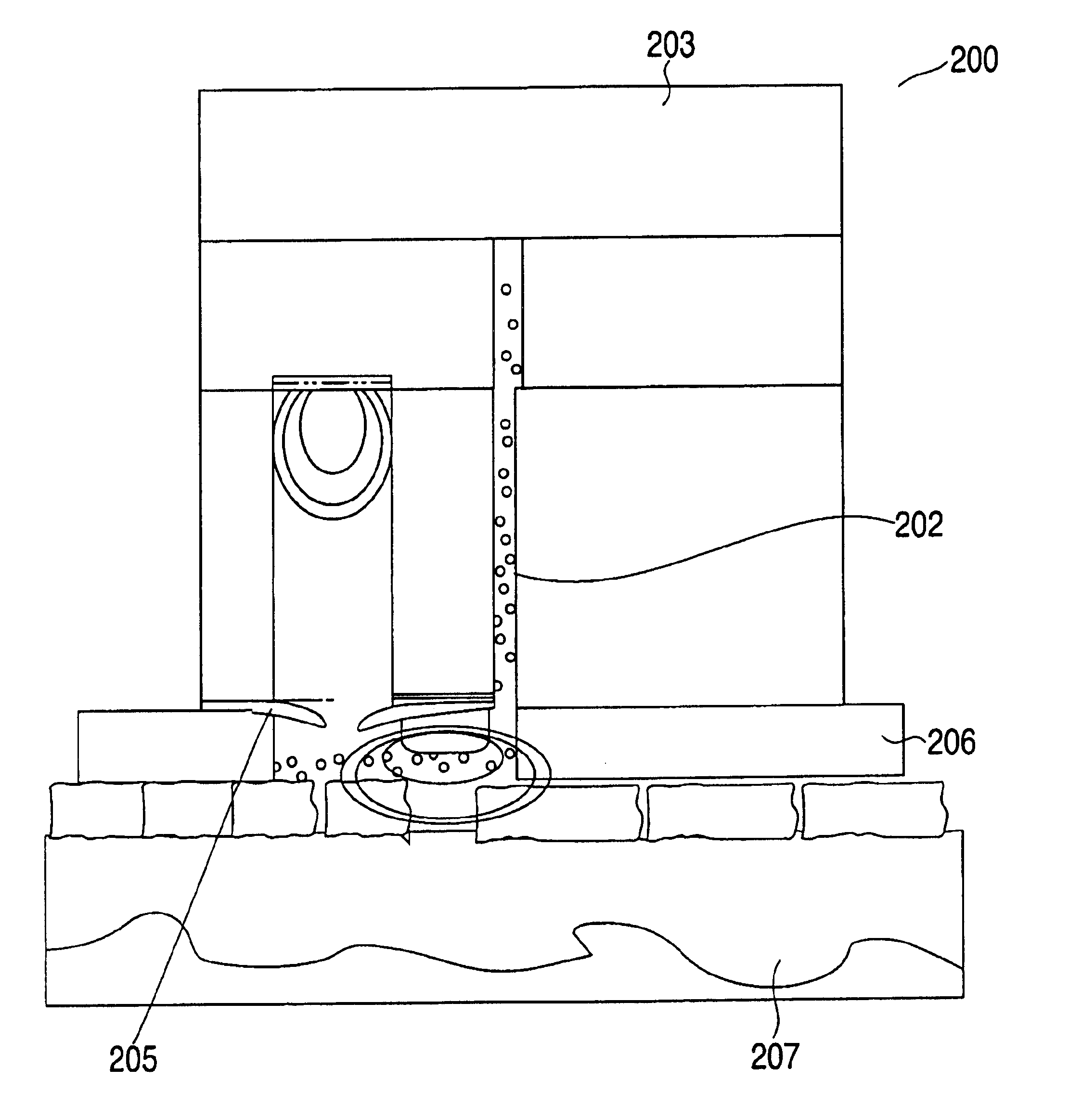
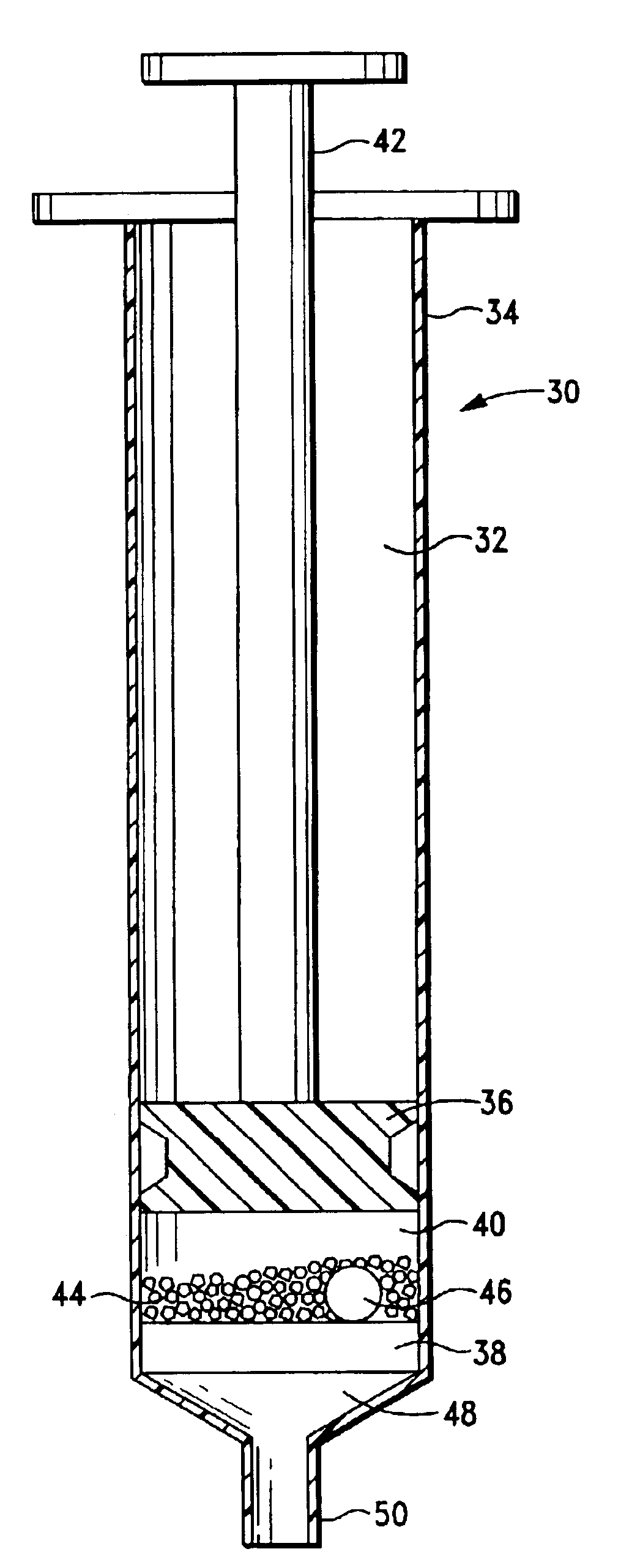
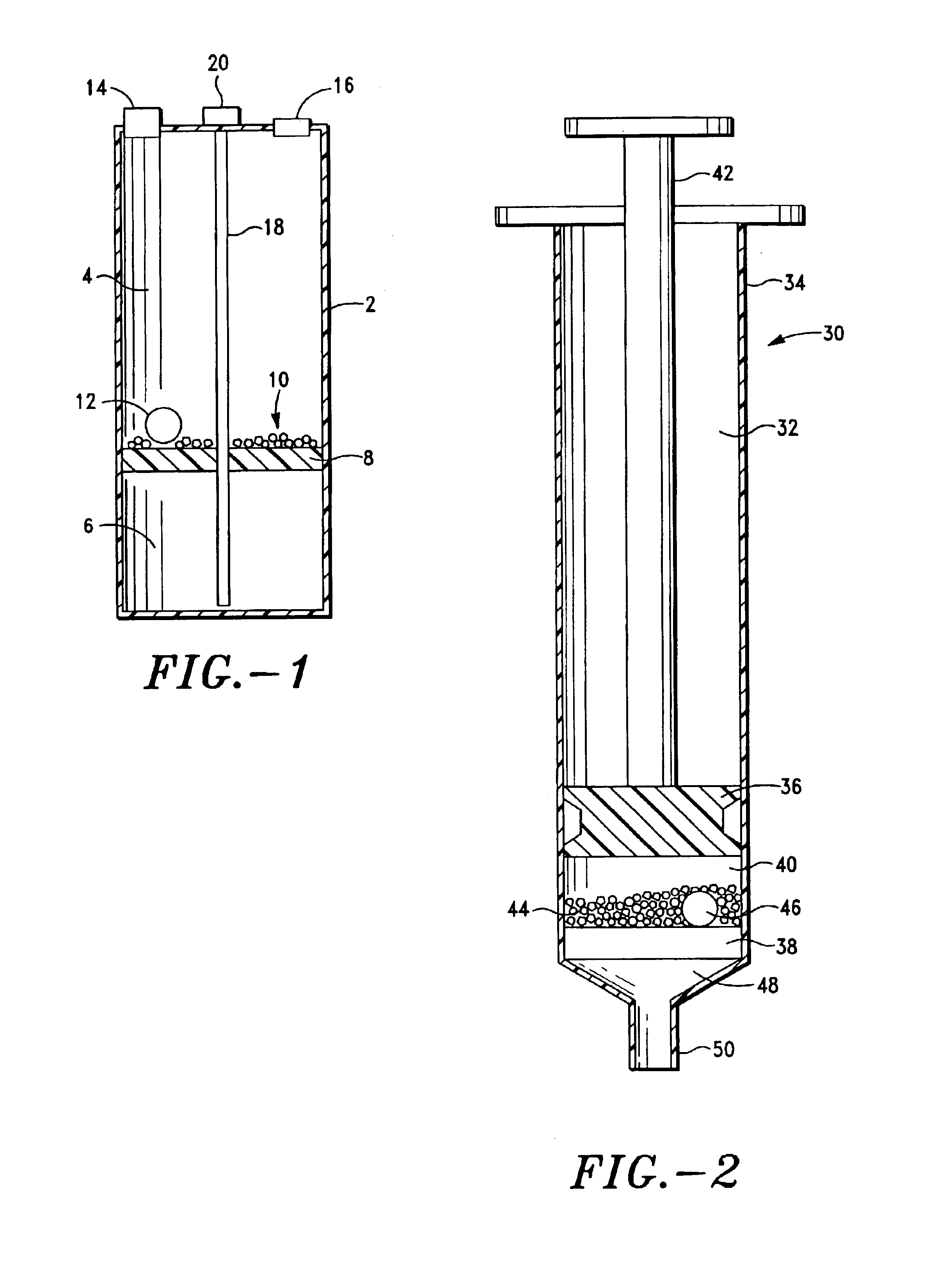
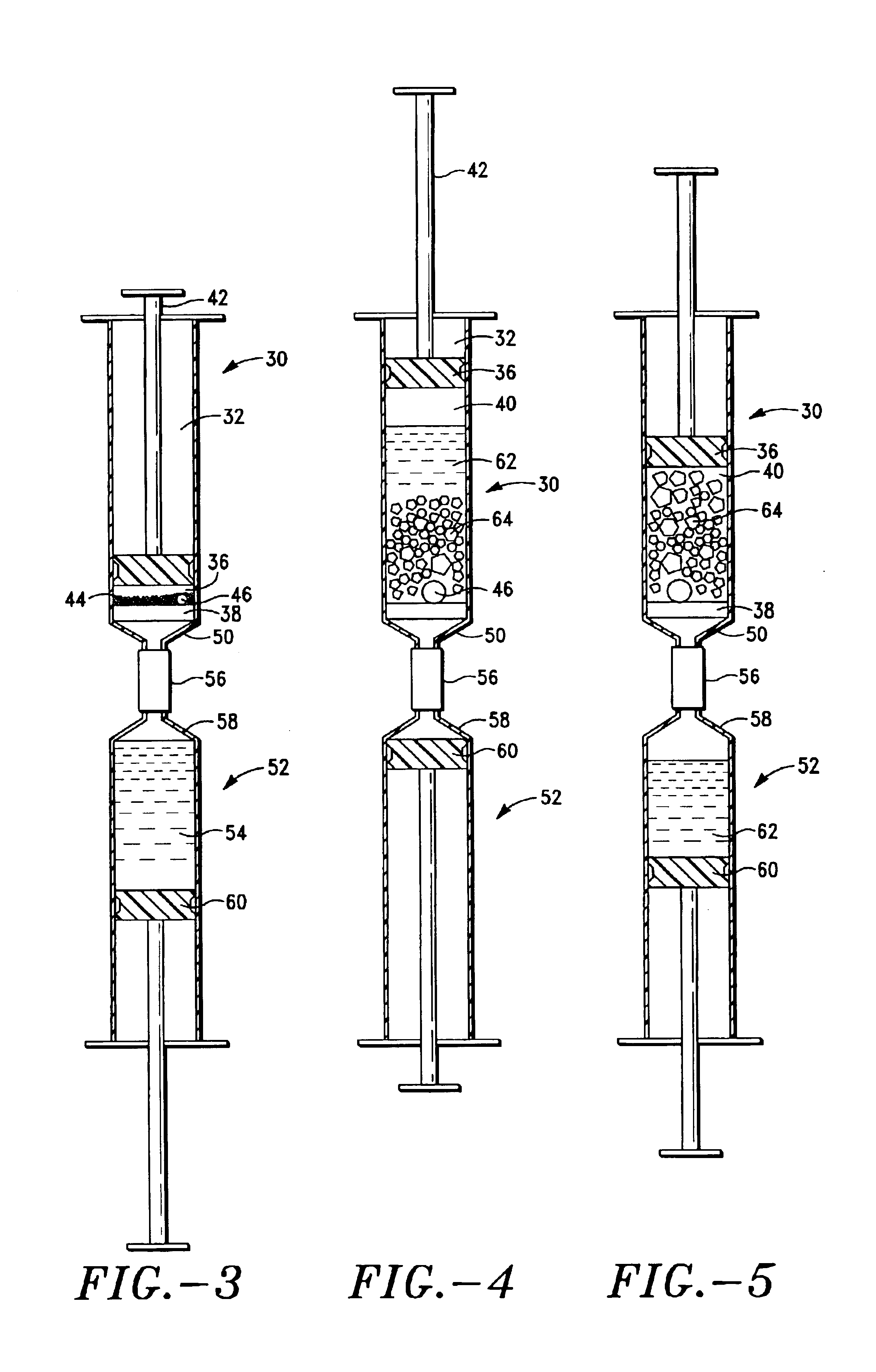
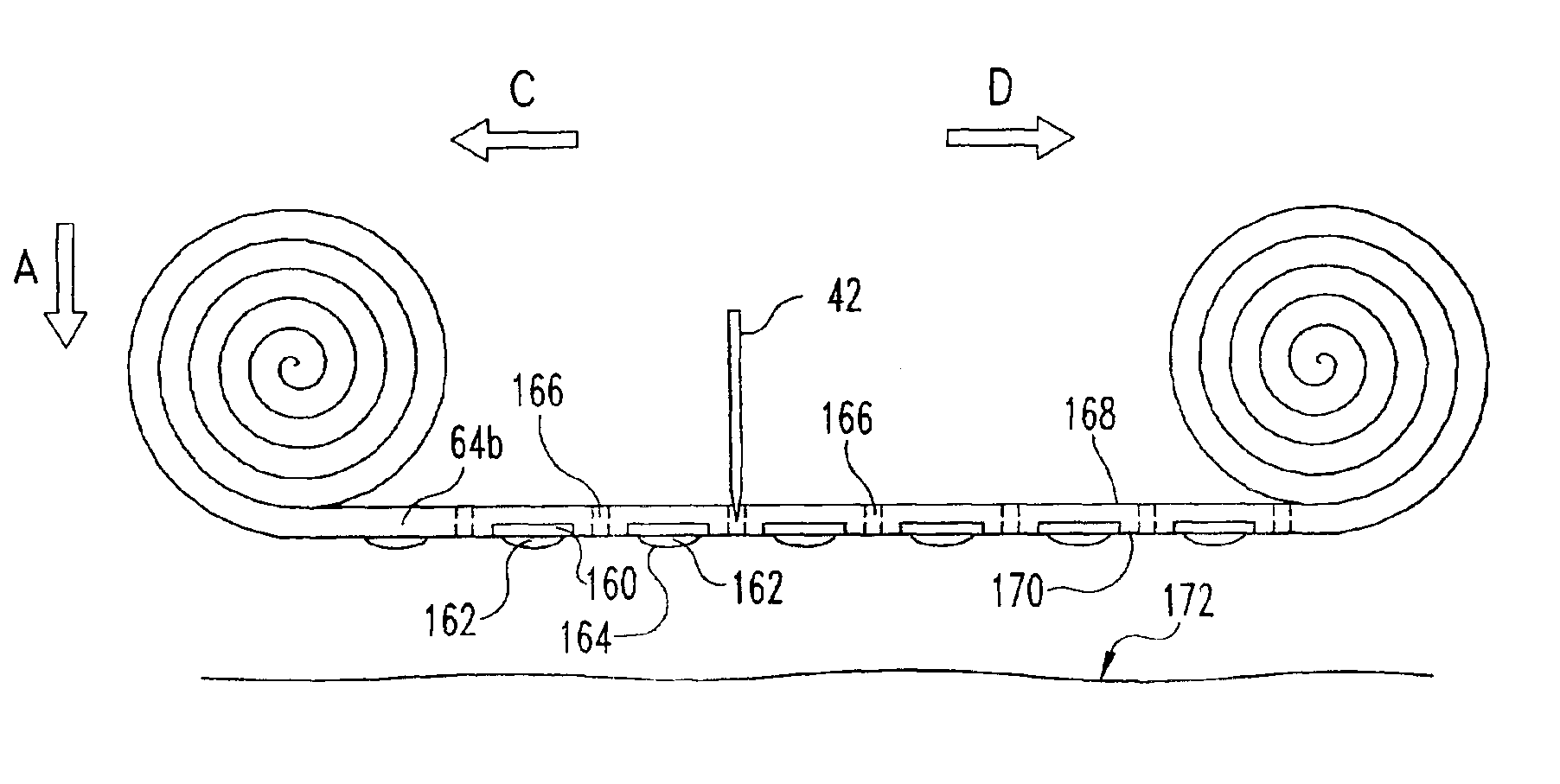
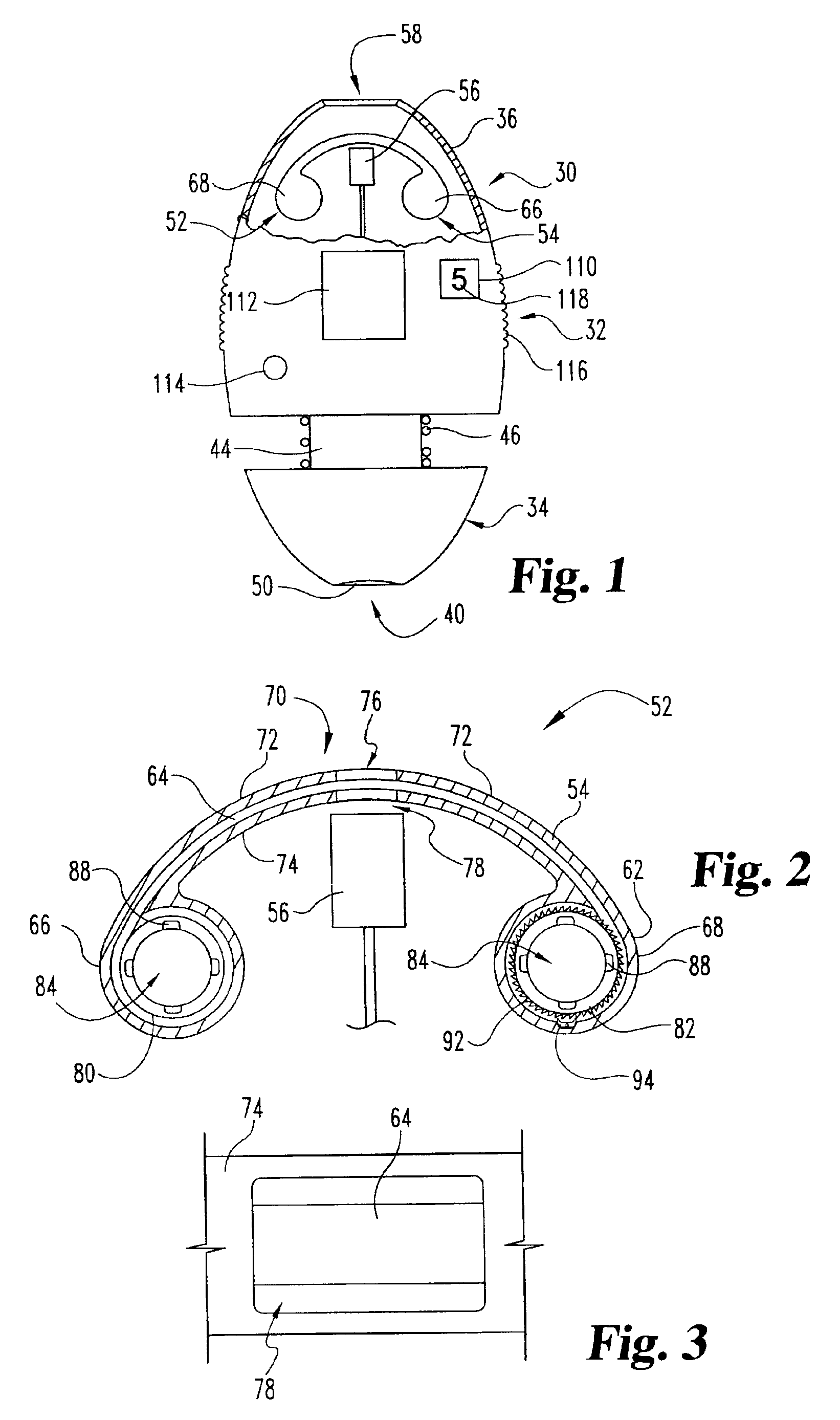
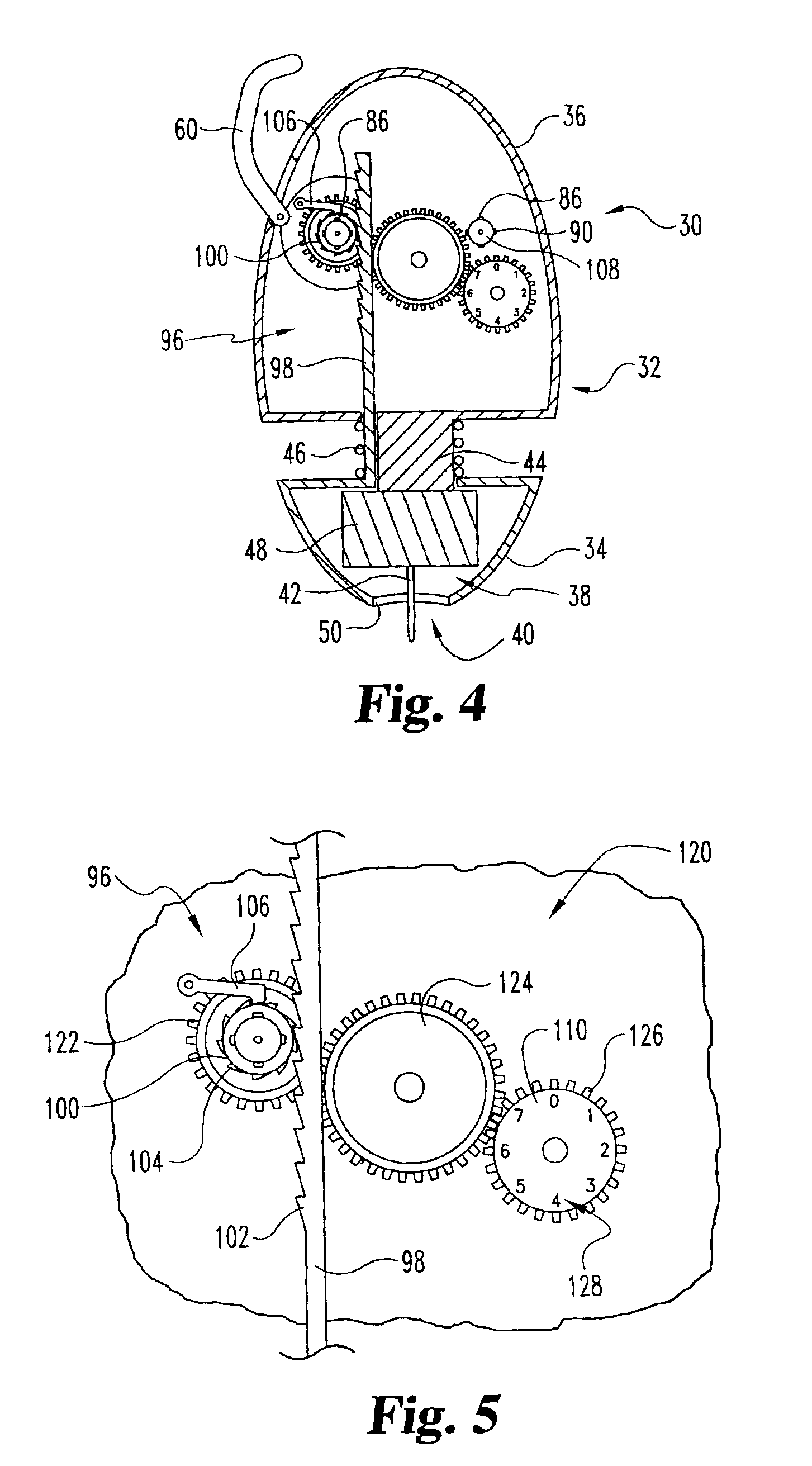
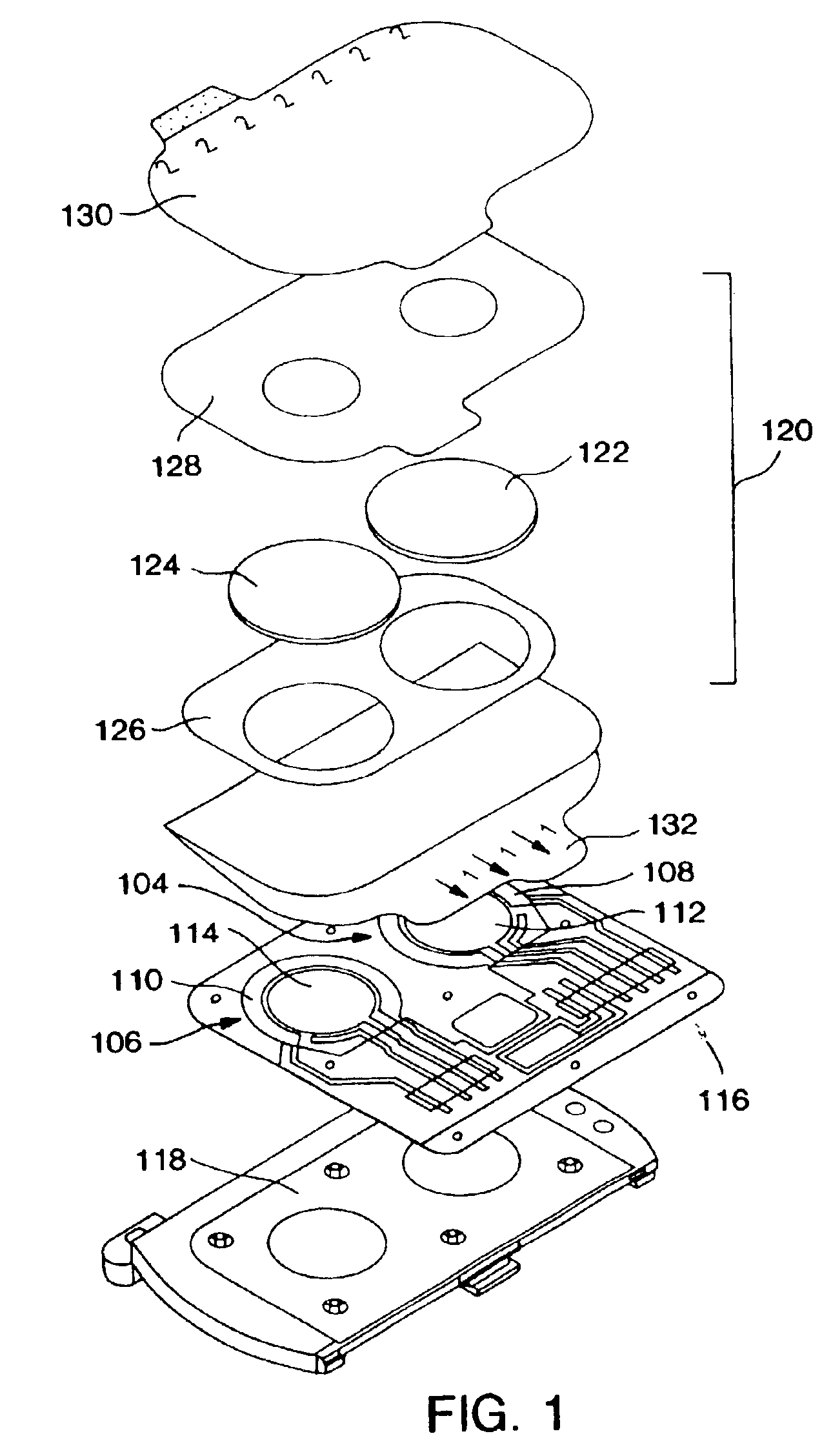
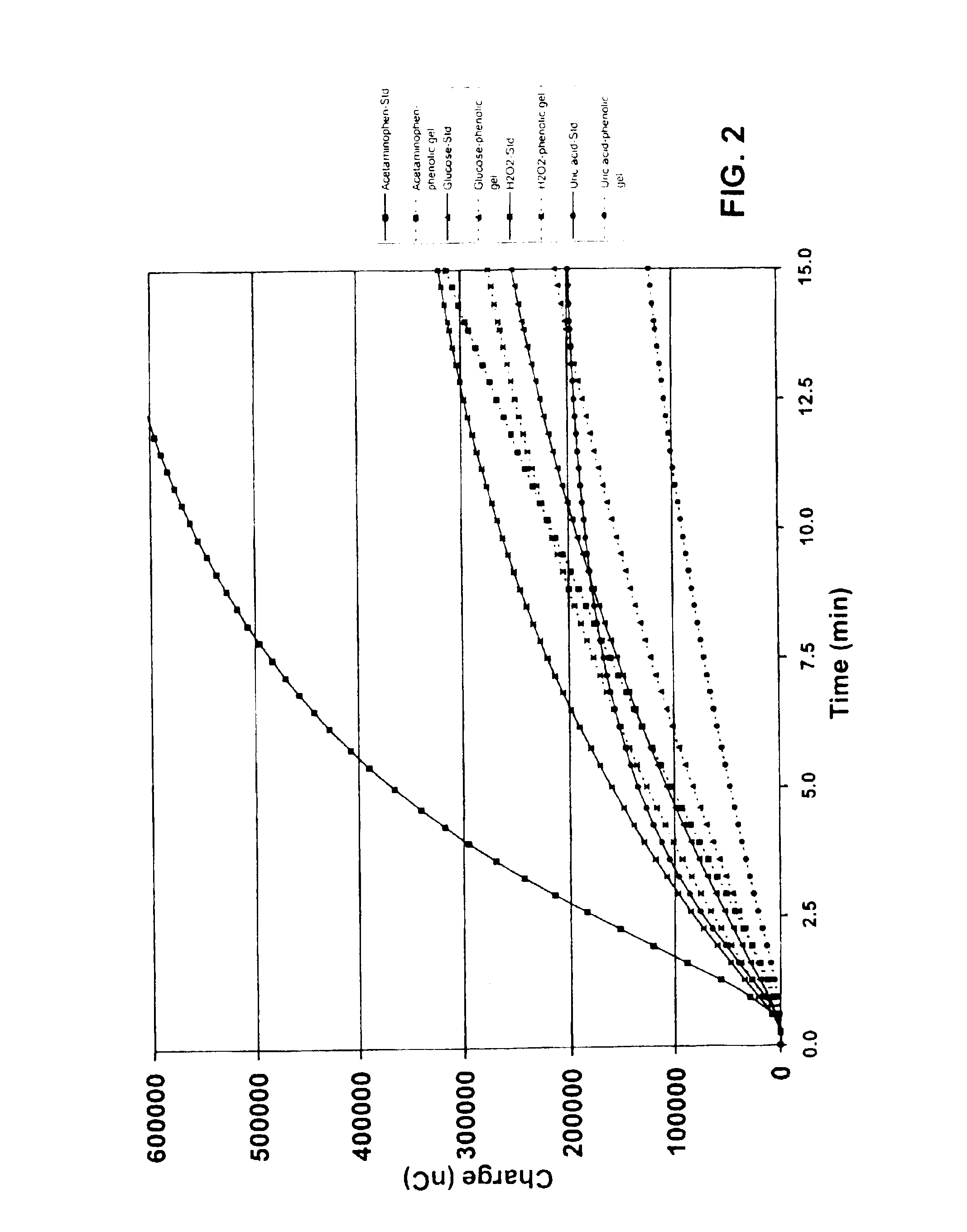
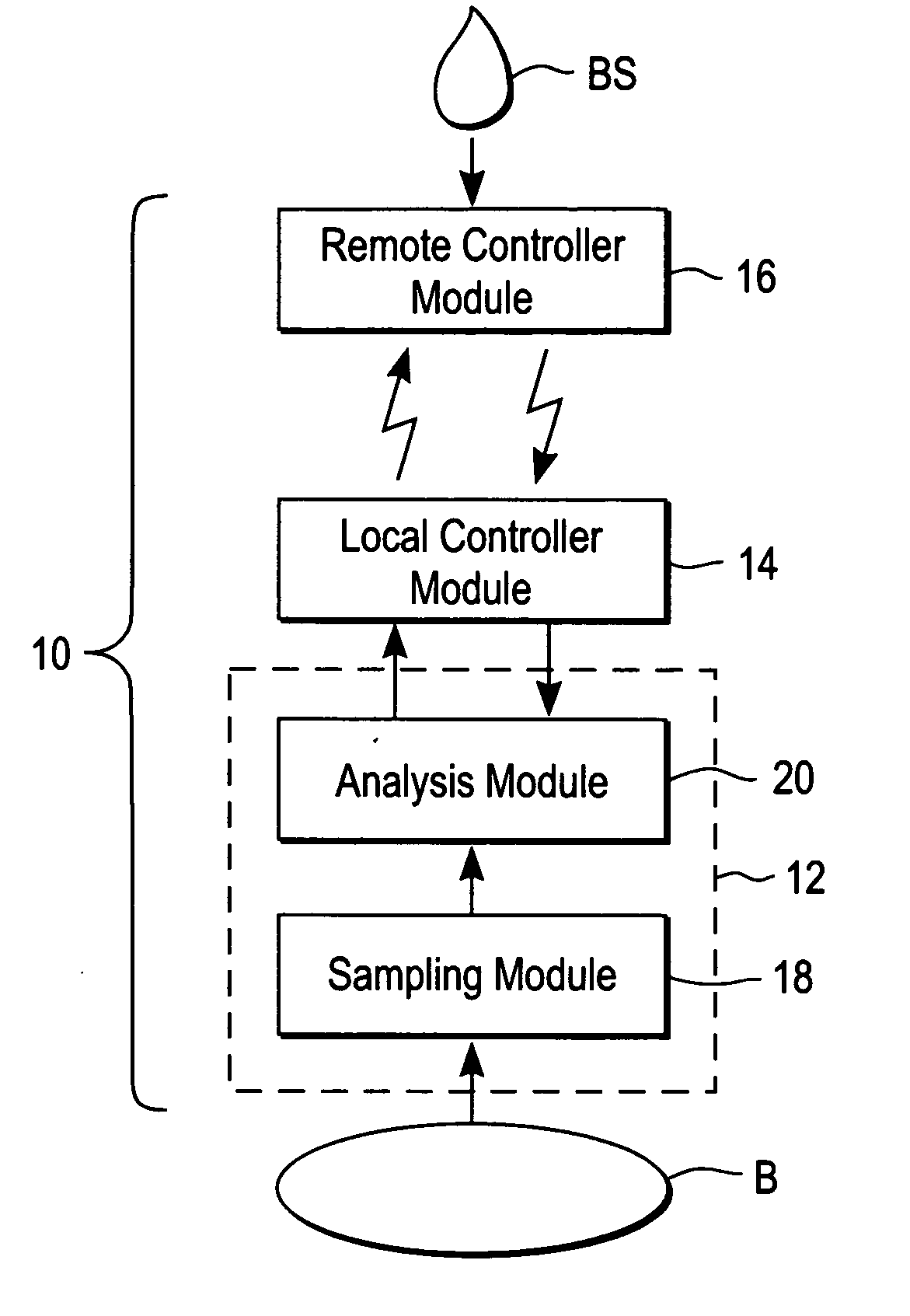
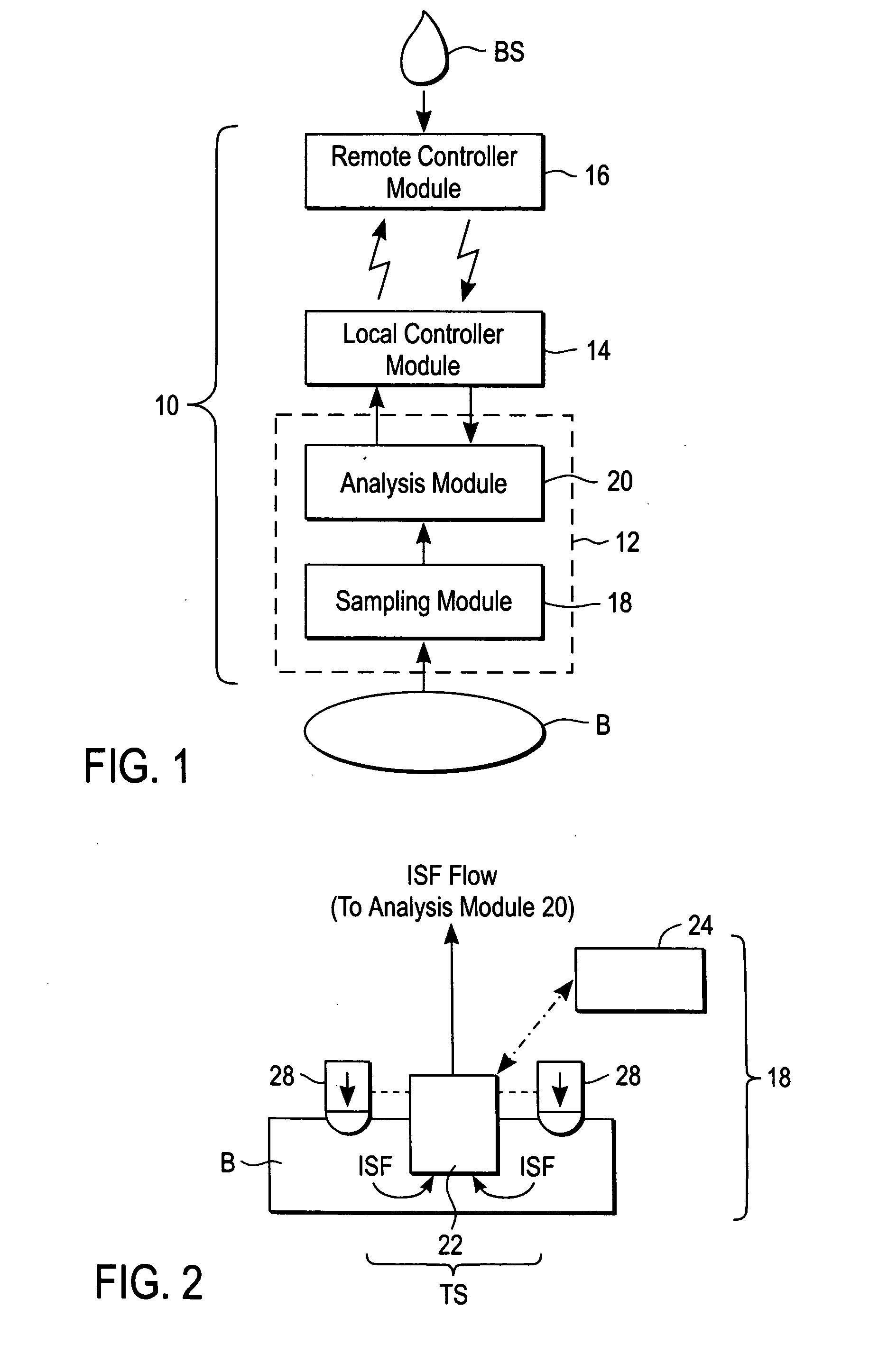
ActiveUS20040249253A1Easy to useLittle painWithdrawing sample devicesEvaluation of blood vesselsAnalyteElectronic communication
A system for extracting a bodily fluid sample (e.g., an interstitial fluid [ISF] sample) and monitoring an analyte therein includes a disposable cartridge and a local controller module. The disposable cartridge includes a sampling module adapted to extract a bodily fluid sample and an analysis module adapted to measure an analyte (e.g., glucose) in the bodily fluid sample. The local controller module is in electronic communication with the disposable cartridge and is adapted to receive and store measurement data from the analysis module. An ISF extraction device includes a penetration member configured for penetrating and residing in a target site of a user's skin layer and, subsequently, extracting an ISF sample therefrom. The device also includes a pressure ring(s) adapted for applying pressure to the user's skin layer in the vicinity of the target site. The device is configured such that the pressure ring(s) is capable of applying pressure in an oscillating manner whereby an ISF glucose lag of the ISF sample extracted by the penetration member is mitigated. A method for extracting ISF includes providing an ISF fluid extraction device with a penetration member and a pressure ring(s). Next, a user's skin layer is contacted by the pressure ring(s) and penetrated by the penetration member. An ISF sample is then extracted from the user's skin layer while pressure is being applied in an oscillating manner by the pressure ring(s). The oscillating pressure mitigates an ISF glucose lag of the extracted ISF sample extracted.
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC
Devices, systems and methods for extracting bodily fluid and monitoring an analyte therein
ActiveUS7258673B2Little painSlight discomfortWithdrawing sample devicesEvaluation of blood vesselsAnalyteD-Glucose
An interstitial fluid (ISF) extraction device includes a penetration member configured for penetrating a target site of a user's skin layer and, subsequently, residing in the user's skin layer and extracting an ISF sample therefrom and at least three concentrically-arranged pressure rings, each adapted for applying pressure to the user's skin layer in the vicinity of the target site while the penetration member is residing in the user's skin layer. In addition, the ISF extraction device is configured such that (i) the pressure rings apply pressure in an oscillating manner with asymmetric deployment and retraction cycles and (ii) only one of the at least three concentrically-arranged pressure rings is deployed at a time, thereby mitigating an ISF glucose lag of the ISF sample extracted by the penetration member.
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC
Systems and methods for monitoring health and delivering drugs transdermally
The present invention pertains to a system and method for transdermal sampling, comprising: at least one sampler for retrieving and transferring at least one analyte obtained transdermally from the skin of a subject; at least one detector system for identifying and quantifying said at least one analyte; and at least one logic module for (i) receiving and storing input data from said at least one detector, (ii) relating the input data to other data obtained from the subject, (iii) displaying output information, (iv) transmitting the output information to another system, and (v) controlling the operation of said at least one sampler and at least one detector.
Owner:DERMAL SYST INT +2
Analytical system and method
InactiveUS6071478AImprove standardizationSimple interfaceWithdrawing sample devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansBiomedical engineering
An analytical or preparatory system comprised as a base unit, an adapter, and a substrate. The adapter is attached to an attachment region on the base unit, and the substrate is attached to an attachment region on the adapter. The adapter permits the base unit to be interfaced with a wide variety of different substrates to perform chemical and biological analytical analyses and preparatory procedures.
Owner:CALIPER TECH
Method and a device for thermal analysis of cast iron
InactiveUS7168852B2Improve accuracyEliminate sourceThermometer detailsWithdrawing sample devicesCooling curveComputer module
Owner:SINTERCAST
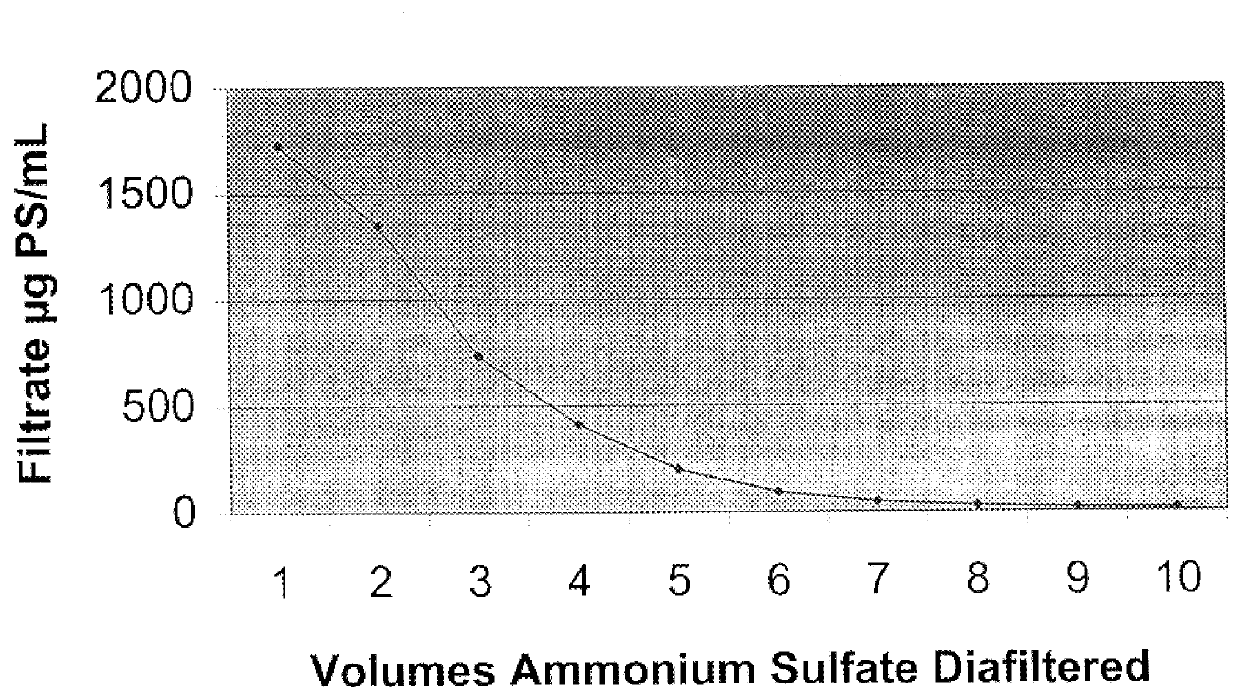
Purification of polysaccharide-protein conjugate vaccines by ultrafiltration with ammonium sulfate solutions
InactiveUS6146902AImprove scalabilityLevel of purityAntibacterial agentsSugar derivativesConjugate vaccineUltrafiltration
Disclosed and claimed are a method for the purification of polysaccharide-protein conjugate vaccines by ultrafiltration in a saturated solution of ammonium sulfate. The ultrafiltration method of the present invention provides an efficient, readily scalable method for removal of unbound polysaccharides from polysaccharide-protein vaccines, thereby improving the purity and consistency of the polysaccharide-protein vaccines.
Owner:AVENTIS PASTUER LTD
Plasma concentrate apparatus and method
ActiveUS6905612B2Effective absorptionPromote absorptionMixing methodsDead animal preservationRed blood cellAbsorption of water
A plasma concentrator for producing plasma concentrate from a plasma from which erythrocytes have been substantially removed. The device comprises a concentrating chamber having an inlet port and an concentrate outlet, the concentrating chamber containing hydrogel beads and at least one inert agitator; and a concentrate chamber having an inlet communicating with the concentrator outlet through a filter, and having an plasma concentrate outlet port. A process for producing plasma concentrate from plasma from which erythrocytes have been substantially removed, comprising the steps of a) moving the plasma into a concentrating chamber containing hydrogel beads and an agitator to form a hydrogel bead-plasma mixture; b) causing the agitator to stir the hydrogel bead-plasma mixture, facilitating absorption of water by the beads from the plasma, until a hydrogel bead-plasma concentrate is formed; and c) separating the plasma concentrate from the hydrogel beads by passing the plasma concentrate through a filter. The concentrator can be one or more syringe devices coupled for multiple concentrations.
Owner:HANUMAN
Automated analyzer
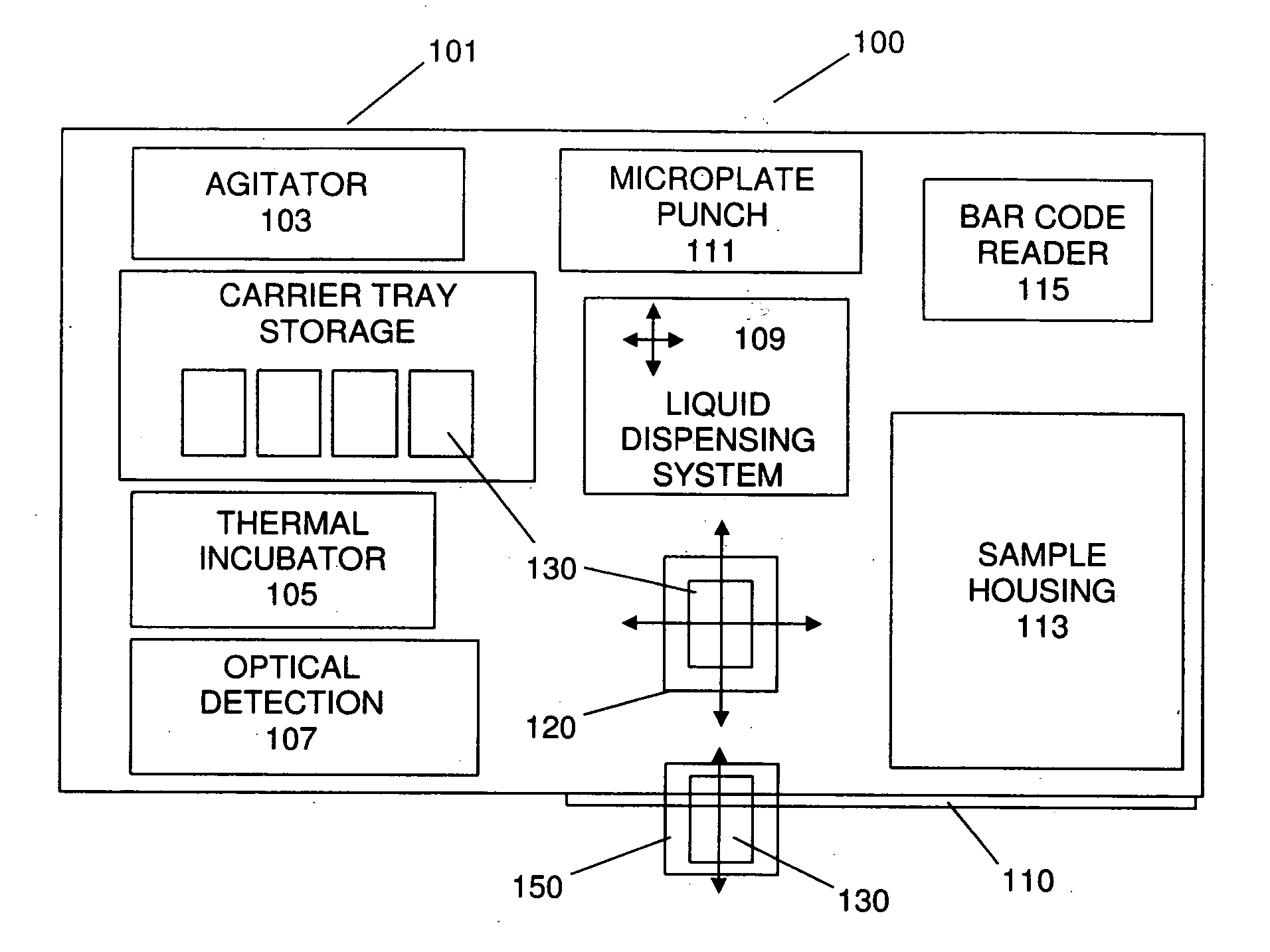
InactiveUS20060210435A1Minimal operator involvementEasy loadingBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsLiquid-crystal displayBarcode
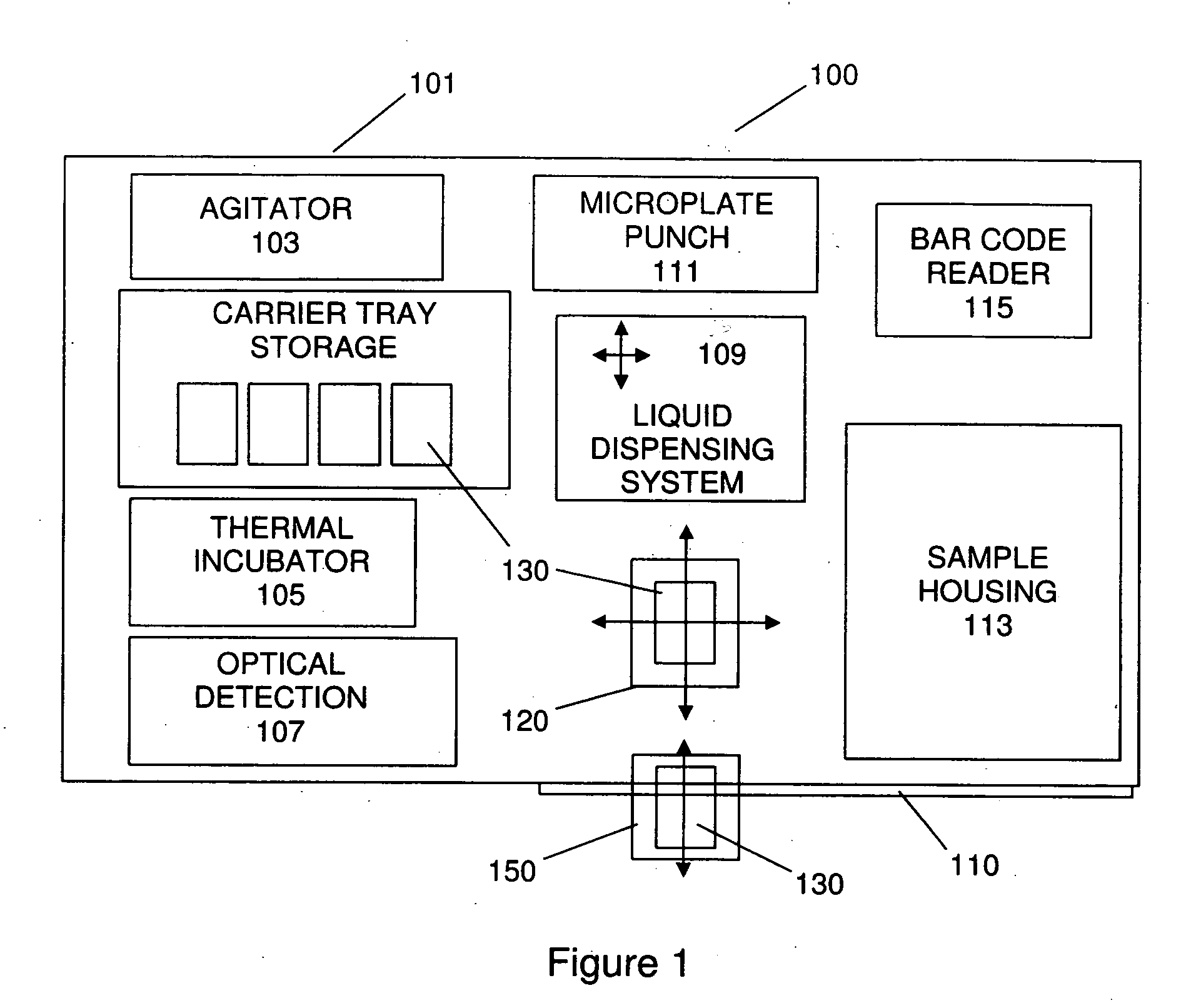
The present invention provides a bar-code driven, completely automated, microplate-based analyzer system for performing chemical, biochemical or biological assays. The analyzer is a modular, bench-top instrument that compactly integrates subsystems for sample dispensing, liquid handling, microplate transport, thermal incubation, vortexing, solid phase separation and optical reading. An internal processor is included for automating the instrument, and a user interface to facilitate communication with the operator via a touch-sensitive liquid-crystal display (LCD), and communicating with a remote network via multiple protocols. The analyzer includes firmware resident within the processing system and the user interface allows the operator to select pre-defined assay batch protocols and the user interface is configured in such as way so as to restrict an operator from programming the firmware.
Owner:NOVX SYST CANADA
Systems and methods for optical actuation of microfluidics based on opto-electrowetting
InactiveUS6958132B2Improve performanceSludge treatmentMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansElectricityMicrofluidics
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method and device for withdrawing biological samples
InactiveUS6659338B1Eliminate disadvantagesExtensive automationWithdrawing sample devicesSurgeryWork cycleBiomedical engineering
The invention relates to a method and device for withdrawing biological samples. The device has a receptacle which can receive one or several covers for sample containers, another receptacle which can receive one or several sample containers, and a mechanism. Said mechanism joins the covers and containers together during a working cycle in which the biological sample is withdrawn either through the cover or the sample container to a test capsule.
Owner:CAISLEY INT
Test media cassette for bodily fluid testing device
A bodily fluid sampling device includes a piercing device and a sensor enclosed in a housing. A cassette, which contains test media, is positioned proximal to the sensor so that the sensor is able to analyze a bodily fluid sample collected on the test media. The cassette includes a supply portion from which unused test media is supplied and a storage portion in which contaminated test media is stored after exposure to the bodily fluid. The cassette is adapted to collect a series of bodily fluid samples without requiring disposal of the test media.
Owner:ROCHE DIABETES CARE INC
Glucose measuring assembly with a hydrogel
InactiveUS6902905B2Reduce presenceIncrease percentagePowder deliveryElectrotherapyIontophoresis therapyAnalyte
This invention relates to methods for reducing the presence of a compound in an ionically conductive material, e.g., for use in iontophoretic devices, wherein the presence of the compound interferes with detecting a selected analyte. Removal of the compound can typically take place either during or after the manufacture of the ionically conductive material or an assembly comprising this material. Also disclosed are methods for generating selectively permeable barriers on the reactive faces of electrodes. Further, this invention relates to hydrogels comprising one or more biocides, as well as assemblies containing such hydrogels.
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC +1
Devices, systems and methods for extracting bodily fluid and monitoring an analyte therein
InactiveUS20040249254A1Easy to useLittle painWithdrawing sample devicesEvaluation of blood vesselsAnalyteElectronic communication
A system for extracting a bodily fluid sample (e.g., an interstitial fluid [ISF] sample) and monitoring an analyte therein includes a disposable cartridge and a local controller module. The disposable cartridge includes a sampling module adapted to extract a bodily fluid sample and an analysis module adapted to measure an analyte (e.g., glucose) in the bodily fluid sample. The local controller module is in electronic communication with the disposable cartridge and is adapted to receive and store measurement data from the analysis module. An ISF extraction device includes a penetration member configured for penetrating and residing in a target site of a user's skin layer and, subsequently, extracting an ISF sample therefrom. The device also includes a pressure ring(s) adapted for applying pressure to the user's skin layer in the vicinity of the target site. The device is configured such that the pressure ring(s) is capable of applying pressure in an oscillating manner whereby an ISF glucose lag of the ISF sample extracted by the penetration member is mitigated. A method for extracting ISF includes providing an ISF fluid extraction device with a penetration member and a pressure ring(s). Next, a user's skin layer is contacted by the pressure ring(s) and penetrated by the penetration member. An ISF sample is then extracted from the user's skin layer while pressure is being applied in an oscillating manner by the pressure ring(s). The oscillating pressure mitigates an ISF glucose lag of the extracted ISF sample.
Owner:LIFESCAN INC
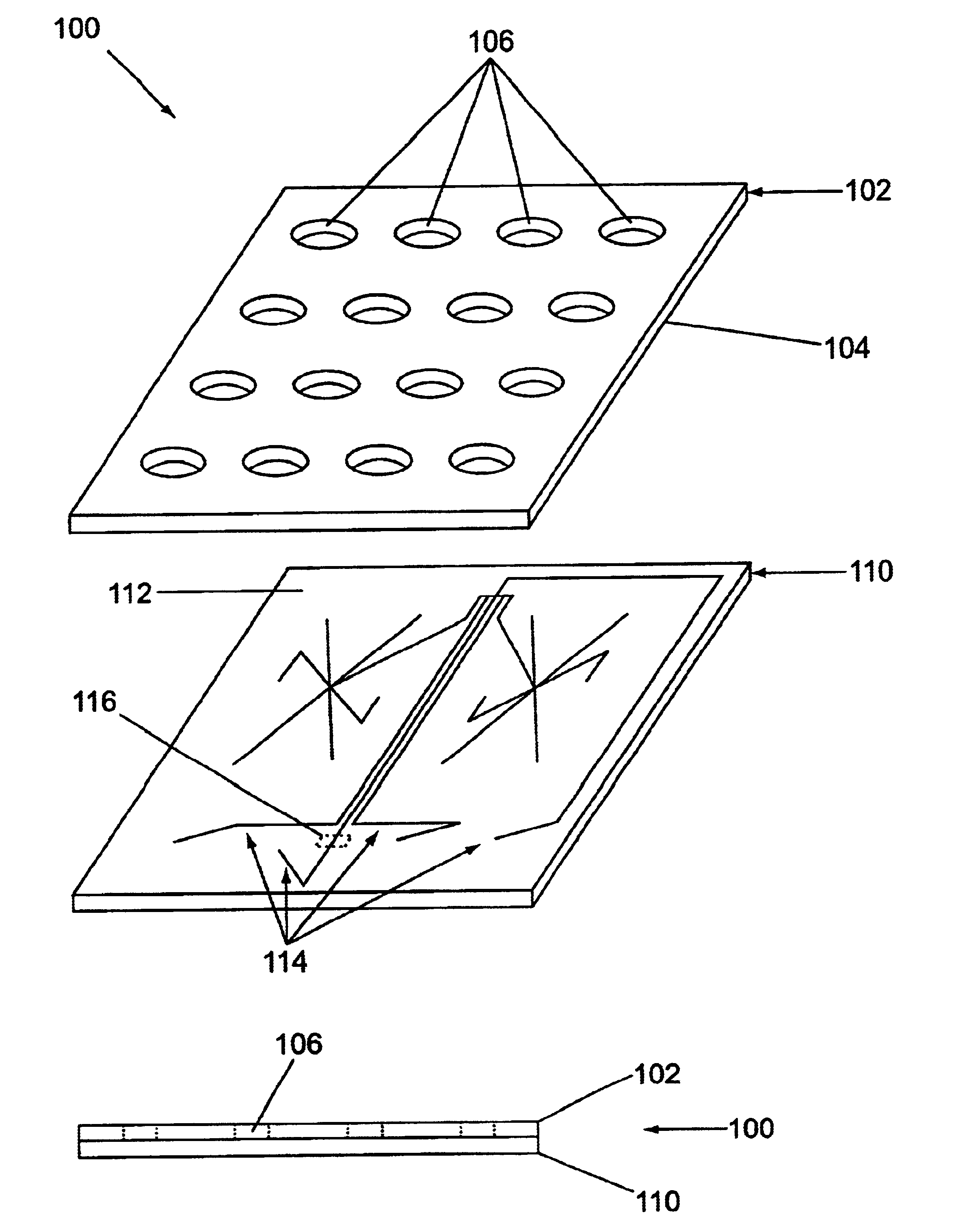
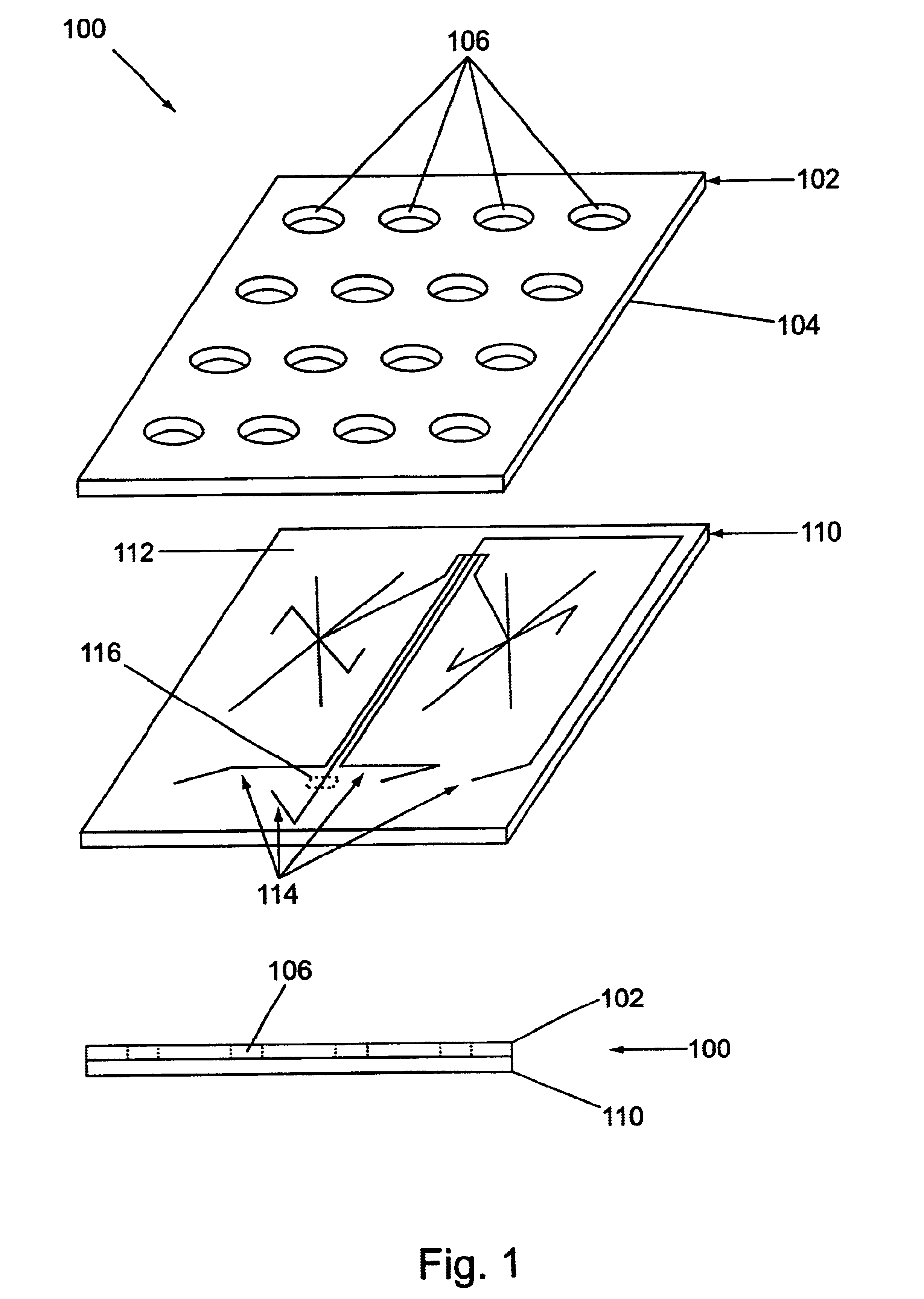
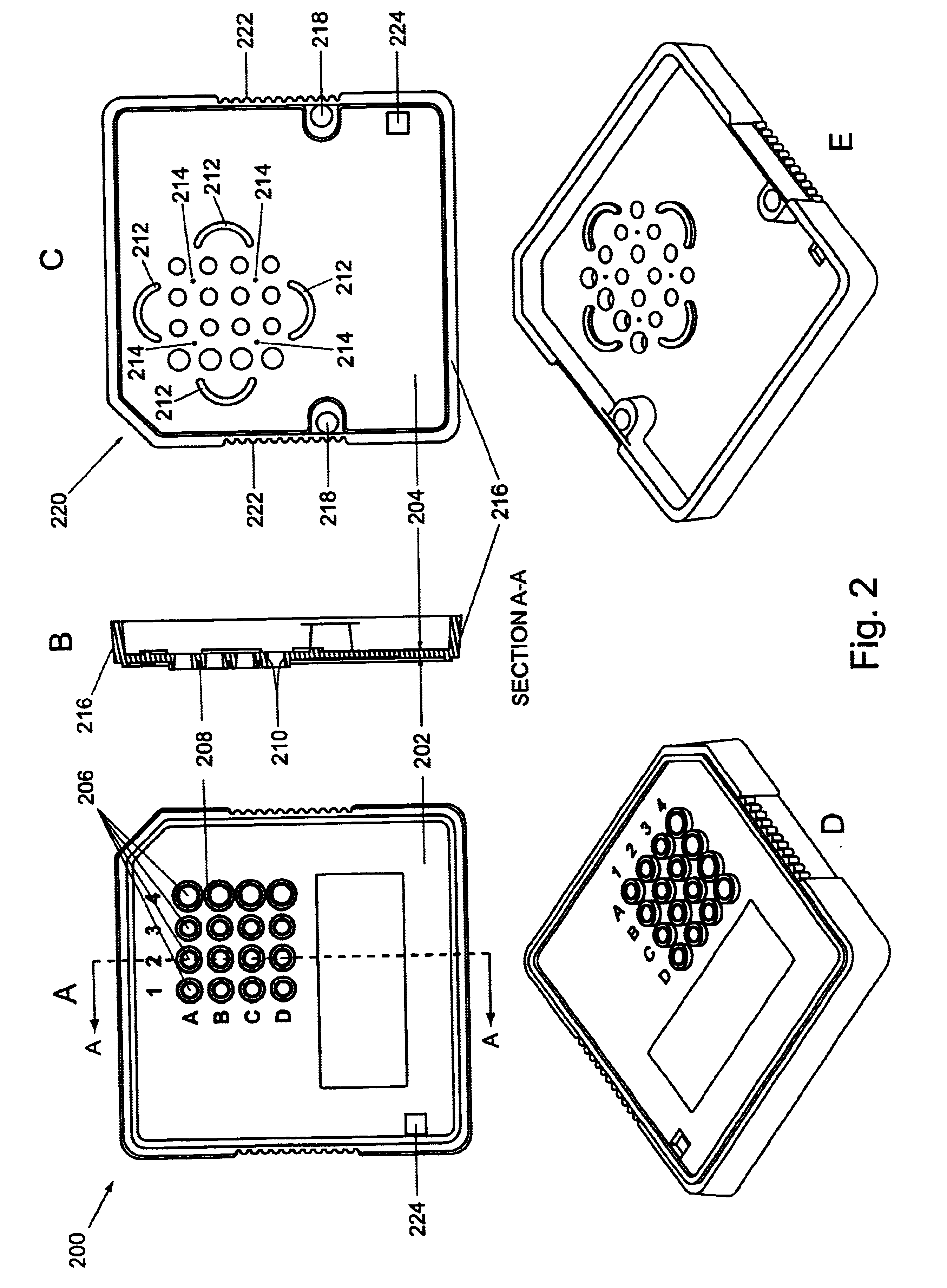
Microfluidic devices and systems incorporating cover layers
InactiveUS6756019B1Improved material handling characteristicReduce manufacturing costWithdrawing sample devicesMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansChannel networkConductive coating
The present invention provides microfluidic devices that comprise a body structure comprising at least a first microscale channel network disposed therein. The body structure has a plurality of ports disposed in the body structure, where each port is in fluid communication with one or more channels in the first channel network. The devices also include a cover layer comprising a plurality of apertures disposed through the cover layer. The cover layer is mated with the body structure whereby each of the apertures is aligned with a separate one of the plurality of ports. Rings are optionally disposed between the cover layer and the body structure and circumferentially around pairs of aligned apertures and ports. The devices also optionally include conductive coatings and membranes. The invention additionally provides methods of controlling the delivery of a composition of material into a microfluidic device.
Owner:CAPLIPER LIFE SCI INC
Microfluidic particle-analysis systems
ActiveUS7312085B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsReady to useMixed group
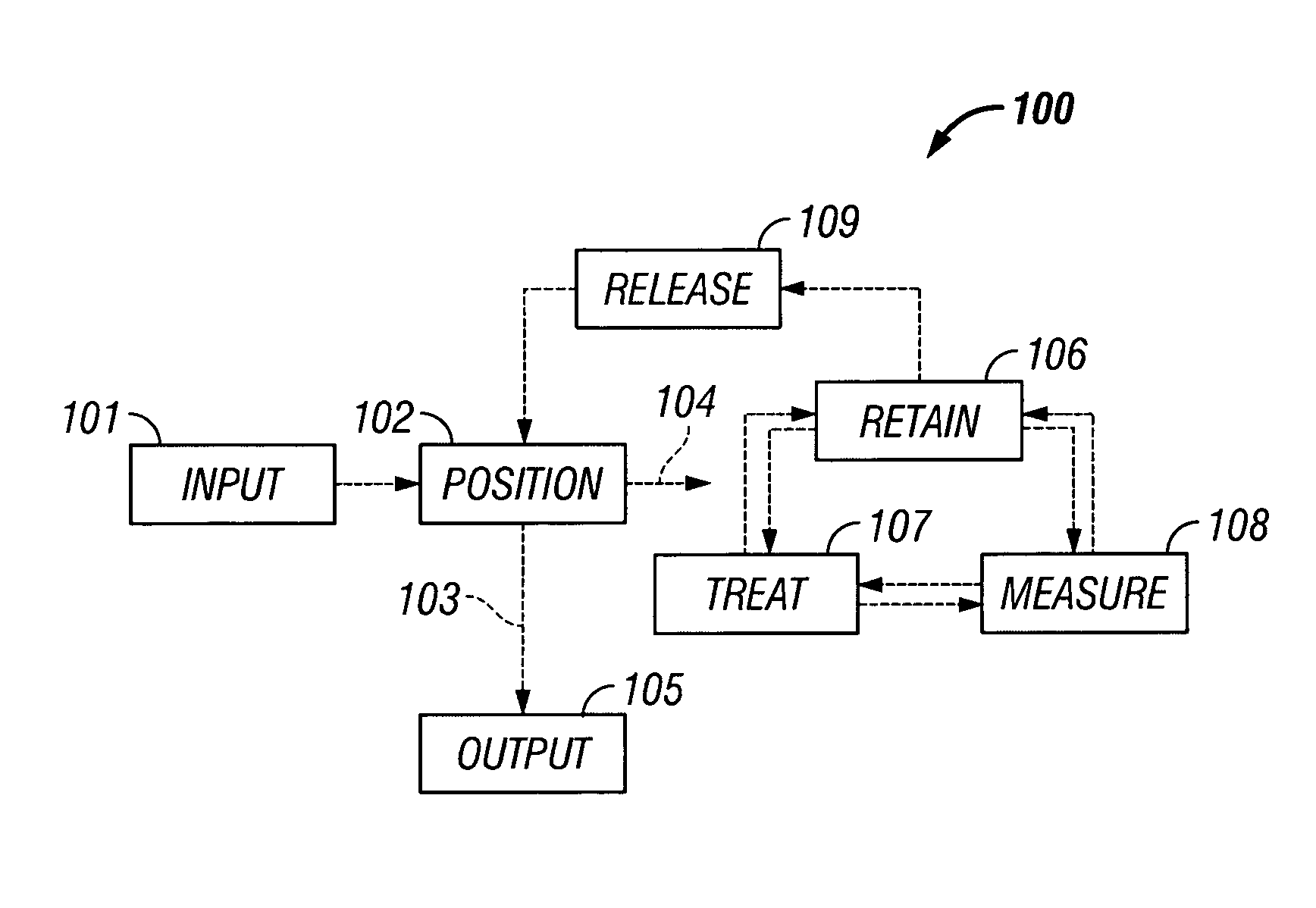
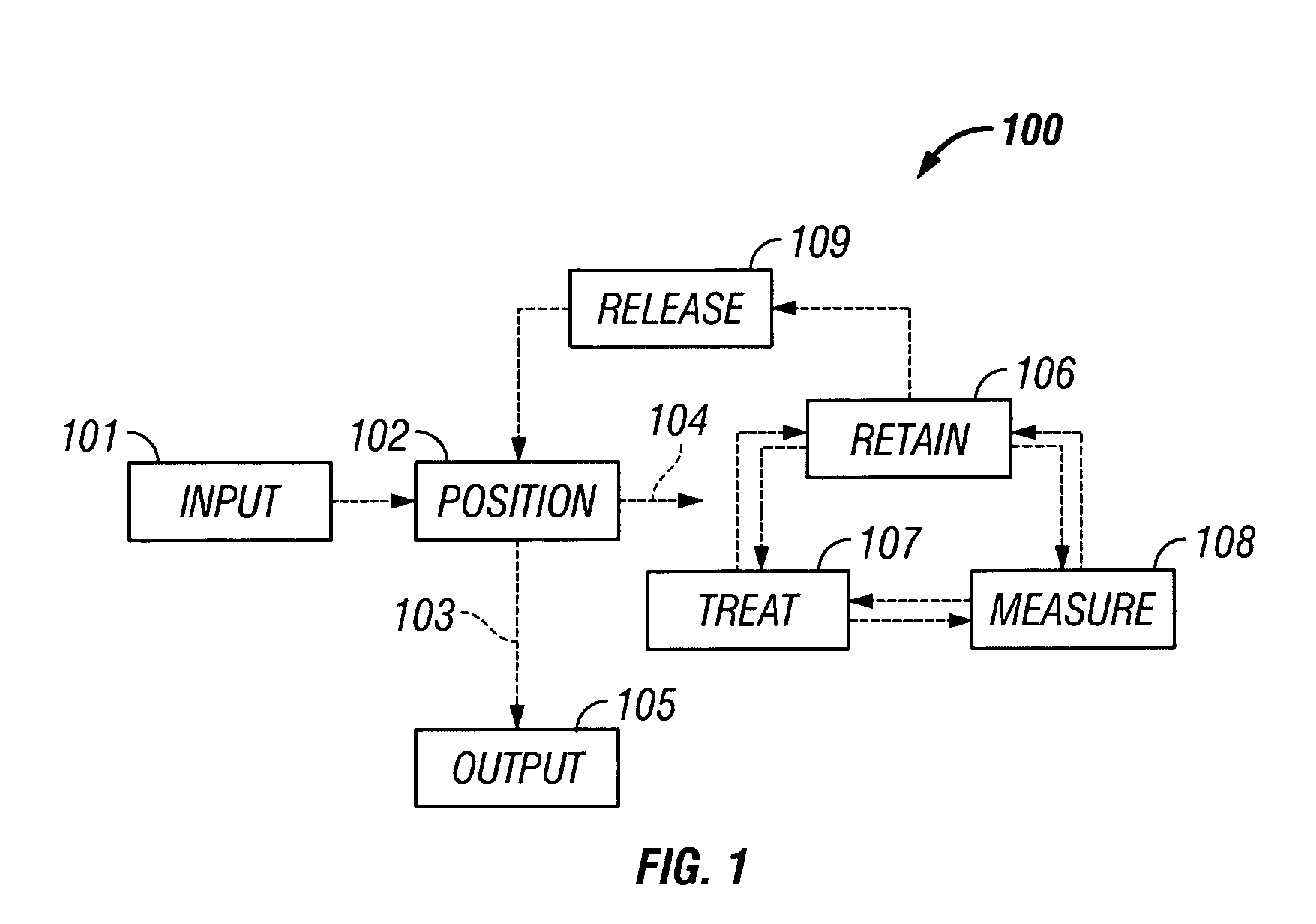
The invention provides systems, including apparatus, methods, and kits, for the microfluidic manipulation and / or detection of particles, such as cells and / or beads. The invention provides systems, including apparatus, methods, and kits, for the microfluidic manipulation and / or analysis of particles, such as cells, viruses, organelles, beads, and / or vesicles. The invention also provides microfluidic mechanisms for carrying out these manipulations and analyses. These mechanisms may enable controlled input, movement / positioning, retention / localization, treatment, measurement, release, and / or output of particles. Furthermore, these mechanisms may be combined in any suitable order and / or employed for any suitable number of times within a system. Accordingly, these combinations may allow particles to be sorted, cultured, mixed, treated, and / or assayed, among others, as single particles, mixed groups of particles, arrays of particles, heterogeneous particle sets, and / or homogeneous particle sets, among others, in series and / or in parallel. In addition, these combinations may enable microfluidic systems to be reused. Furthermore, these combinations may allow the response of particles to treatment to be measured on a shorter time scale than was previously possible. Therefore, systems of the invention may allow a broad range of cell and particle assays, such as drug screens, cell characterizations, research studies, and / or clinical analyses, among others, to be scaled down to microfluidic size. Such scaled-down assays may use less sample and reagent, may be less labor intensive, and / or may be more informative than comparable macrofluidic assays.
Owner:STANDARD BIOTOOLS INC
Apparatus for analyzing biologic fluids
InactiveUS6866823B2Low costReduce spacingMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceImage dissectorImage conversion
An apparatus for analyzing a sample of biologic fluid quiescently residing within a chamber is provided. The apparatus includes a light source, a positioner, a mechanism for determining the volume of a sample field, and an image dissector. The light source is operable to illuminate a sample field of known, or ascertainable, area. The positioner is operable to selectively change the position of one of the chamber or the light source relative to the other, thereby permitting selective illumination of all regions of the sample. The mechanism for determining the volume of a sample field can determine the volume of a sample field illuminated by the light source. The image dissector is operable to convert an image of light passing through or emanating from the sample field into an electronic data format.
Owner:WARDLAW PARTNERS +2
Metabolic calorimeter employing respiratory gas analysis
An indirect calorimeter for measuring the metabolic rate of a subject includes a disposable portion and a reusable portion. The disposable portion includes a respiratory connector configured to be supported in contact with the subject so as to pass inhaled and exhaled gases as the subject breathes. The disposable portion also includes a flow pathway operable to receive and pass inhaled and exhaled gases, having a first end in fluid communication with the respiratory connector and a second end in fluid communication with a source and sink for respiratory gases. The disposable portion is disposed within the reusable portion, which includes a flow meter, a component gas concentration sensor, and a computation unit. The flow meter generates a signal as a function of the instantaneous flow volume of respiratory gases passing through the flow pathway and the component gas concentration sensor generates a signal as a function of the instantaneous fraction of a predetermined component gas in the exhaled gases. The computation unit receives the electrical signals from the flow meter and the concentration sensor and calculates at least one respiratory parameter for the subject as the subject breathes through the calorimeter.
Owner:MICROLIFE MEDICAL HOME SOLUTIONS
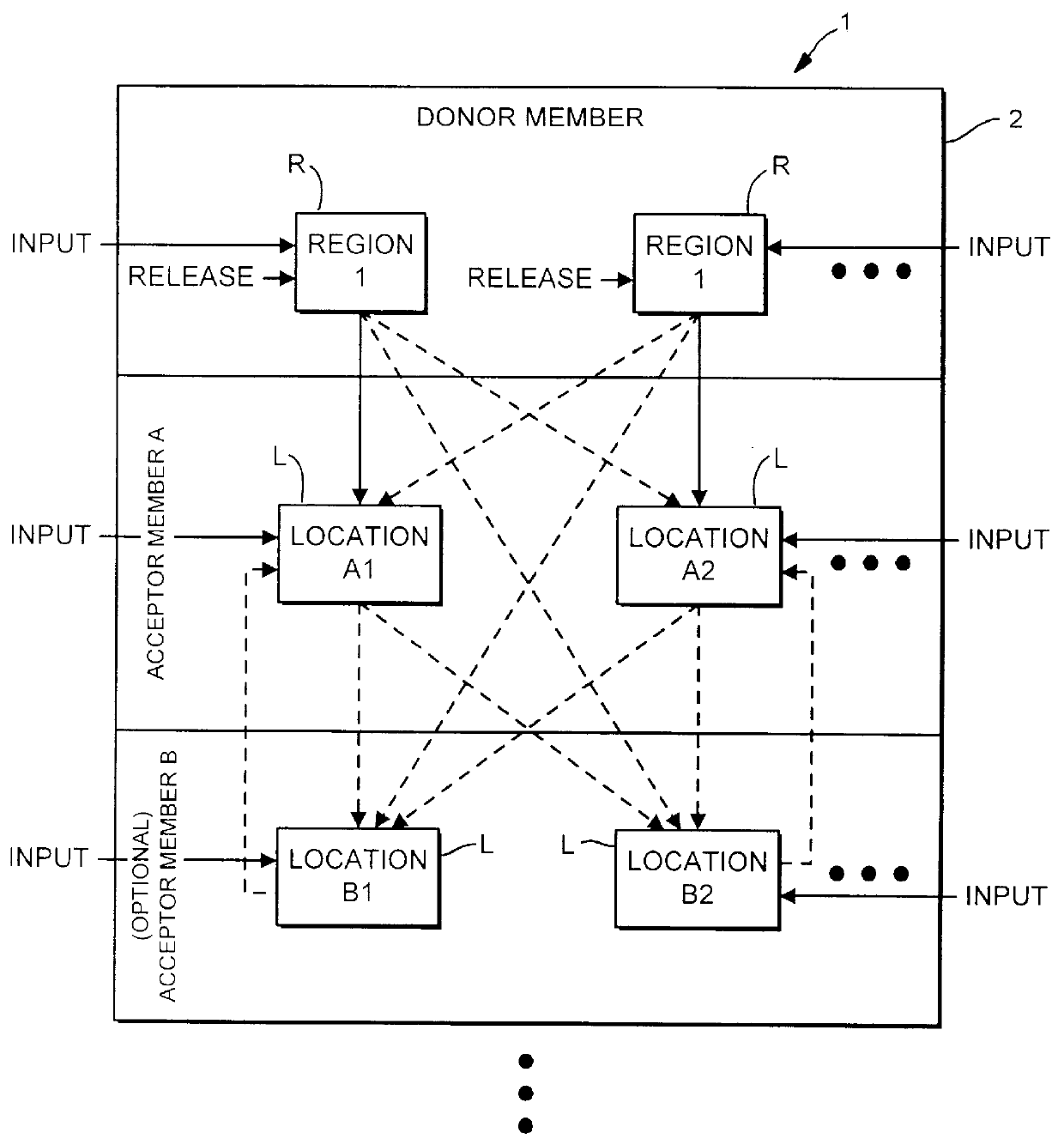
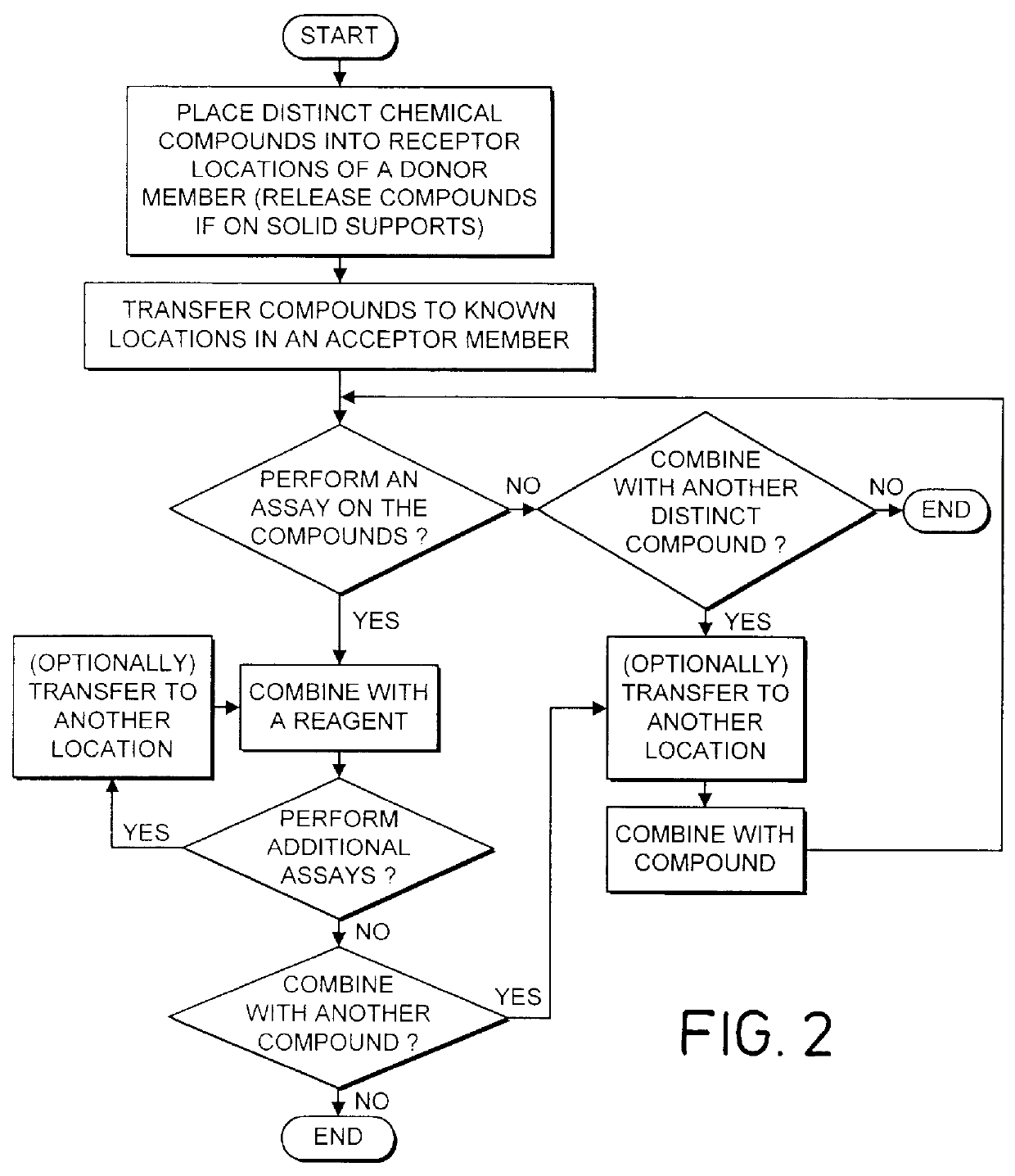
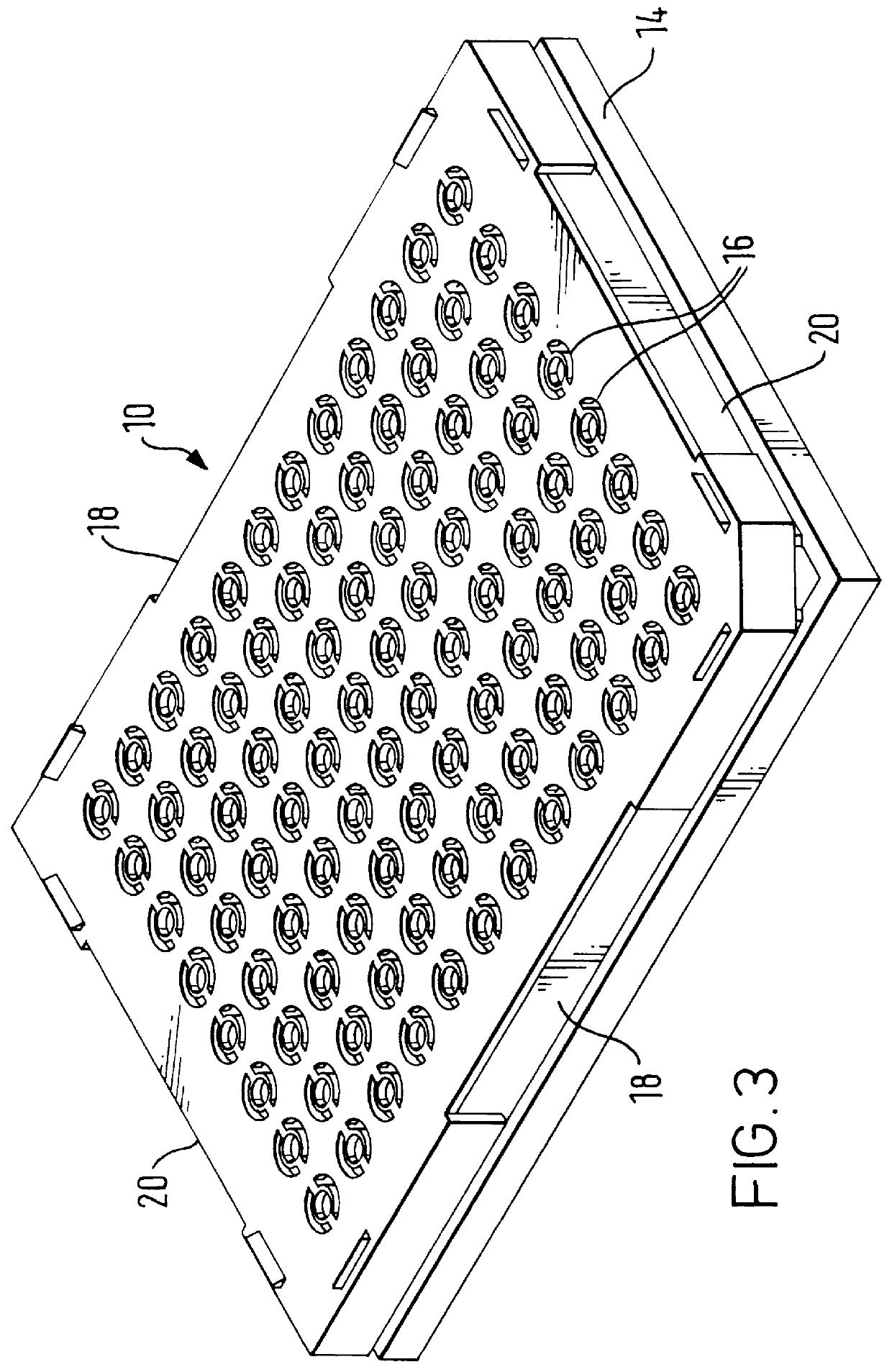
Method and apparatus for transferring and combining reagents
InactiveUS6083761AEasy to carryEfficient transferSequential/parallel process reactionsWithdrawing sample devicesChemical compositionCentrifugation
The invention provides exemplary systems, methods, and apparatus for distinctly allocating liquids containing chemical compositions or compounds to known locations in an organized manner so that assays may be performed on the compositions, or so that the chemical compositions may be combined with other distinct chemical compositions or reagents prior to evaluation. In an exemplary embodiment, the invention includes a multiwell plate for handling articles such as resin beads suspended in a liquid. The plate comprises a plurality of wells. The wells in turn have a capillary hole that is adapted to (i) retain articles in the well, and (ii) retain liquid in the well while the liquid is not subjected to extrinsic forces, such as centrifugation or vacuum.
Owner:SMITHKLINE BECKMAN CORP +1
Apparatus and method for harvesting and handling tissue samples for biopsy analysis
InactiveUS7156814B1Exemption stepsReduce the numberBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsTissue biopsyTissue fluid
A sectional cassette (10) for use in a process for harvesting and handling tissue samples for biopsy analysis is disclosed. In the procedure, a tissue biopsy sample is placed on a tissue trapping supporting material (A′) that can withstand tissue preparation procedures, and which can be cut with a microtome. The tissue is immobilized on the material, and the material and the tissue are held in the cassette (10) subjected to a process for replacing tissue fluids with wax. The tissue and supporting material are sliced for mounting on slides using a microtome. Harvesting devices and containers (200) using the filter material (202) are disclosed. An automated process is also disclosed.
Owner:BIOPATH AUTOMATION
Apparatus for detecting chemical substances and method therefor
ActiveUS20050061964A1High detection sensitivityPrevent false detectionStability-of-path spectrometersAnalysis using chemical indicatorsNon detectionData treatment
An apparatus for detecting chemical substances which is high in sensitivity and selectivity is provided. An organic acid or an organic acid salt is used to generate an organic acid gas from an organic acid gas generator 3 to be mixed with a sample gas for introduction into an ion source 4 for ionization, thereby obtaining a mass spectrum by a mass analysis region 5. A data processor 6 determines the detection or non-detection of a specific m / z of an organic acid adduct ion obtained by adding a molecule generated from the organic acid to a molecule with specific m / z generated from a target chemical substance to be detected based on the obtained mass spectrum. When there is an ion peak with the m / z of the organic acid adduct ion, the presence of the target chemical substance to be detected is determined, and an alarm is sounded. False detection can be prevented.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Methods and apparatus for sorting cells using an optical switch in a microfluidic channel network
InactiveUS20050207940A1Harm viabilityChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceSurgeryEngineeringMicrofluidic channel
Apparatus and Methods are provided for a microfabricated fluorescence activated cell sorter based on an optical switch for rapid, active control of cell routing through a microfluidic channel network. This sorter enables low-stress, highly efficient sorting of populations of small numbers of cells (i.e., 1000-100,000 cells). The invention includes packaging of the microfluidic channel network in a self-contained plastic cartridge that enables microfluidic channel network to macro-scale instrument interconnect, in a sterile, disposable format.
Owner:PROGENITY INC
Method and apparatus for rinsing a microscope slide
InactiveUS6093574AEfficient and reliableEasy to manufactureWithdrawing sample devicesPreparing sample for investigationMicroscope slideModularity
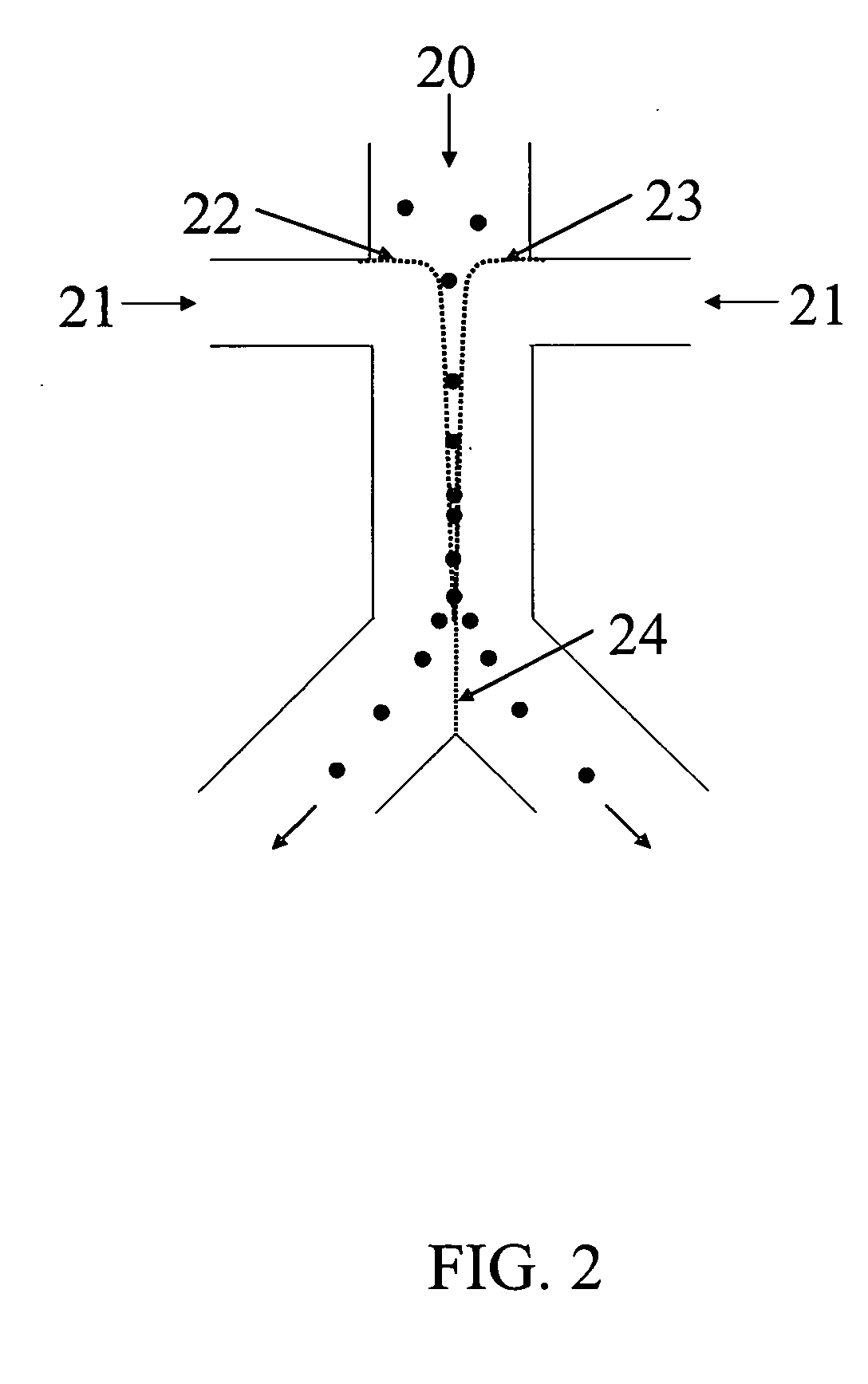
A method and apparatus for an automated biological reaction system is provided. In the processing of a biological reaction system, there is a need for consistently placing an amount of liquid on a slide. In order to accomplish this, several methods are used including a consistency pulse and a volume adjust means. Moreover, in order to reliably operate an automated biological reaction system, the dispenser must be reliable, easy to assemble and accurate. Among other things, in order to accomplish this, the dispense chamber is substantially in line with the reservoir chamber, the reservoir chamber piston is removed, and the flow of liquid through the dispenser is simplified. Further, in order to operate the automated biological reaction system more reliably, the system is designed in modular pieces with higher functions performed by a host device and the execution of the staining operations performed by remote devices. Also, to reliably catalog data which is used by the automated biological reaction system, data is loaded to a memory device, which in turn is used by the operator to update the operator's databases. The generation of the sequence of steps for the automated biological reaction device based on data loaded by the operator, including checks to determine the ability to complete the run, is provided.
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com