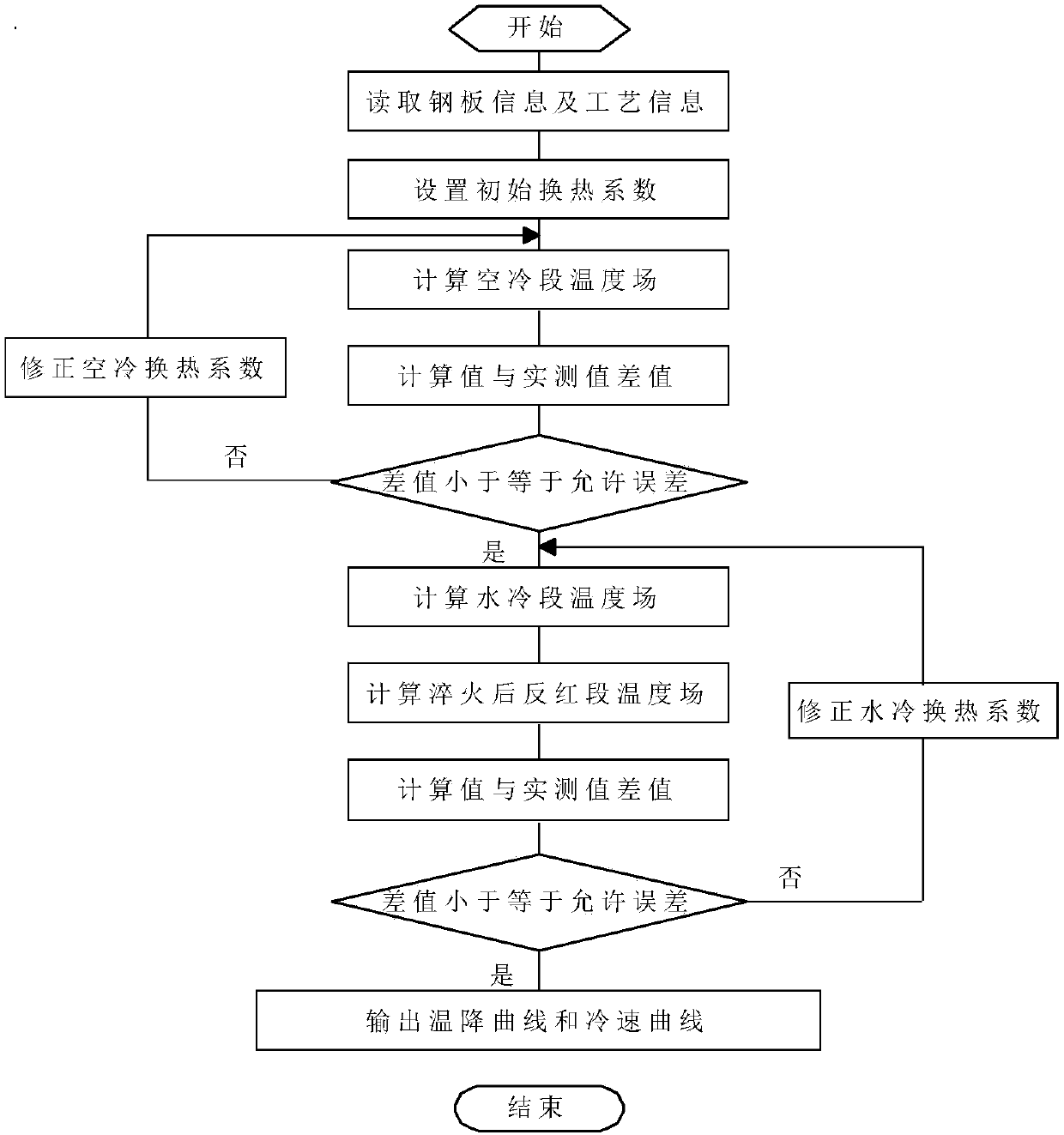
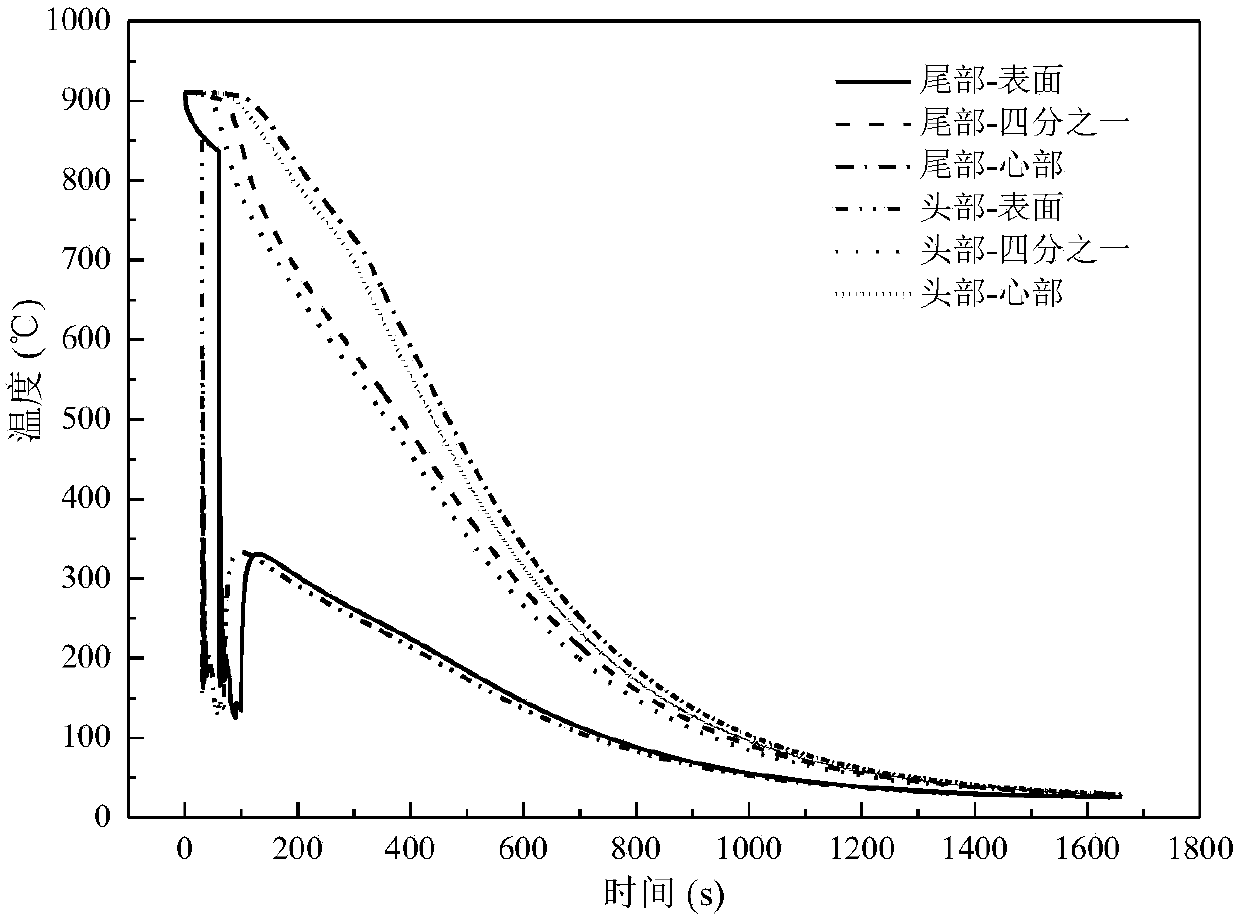
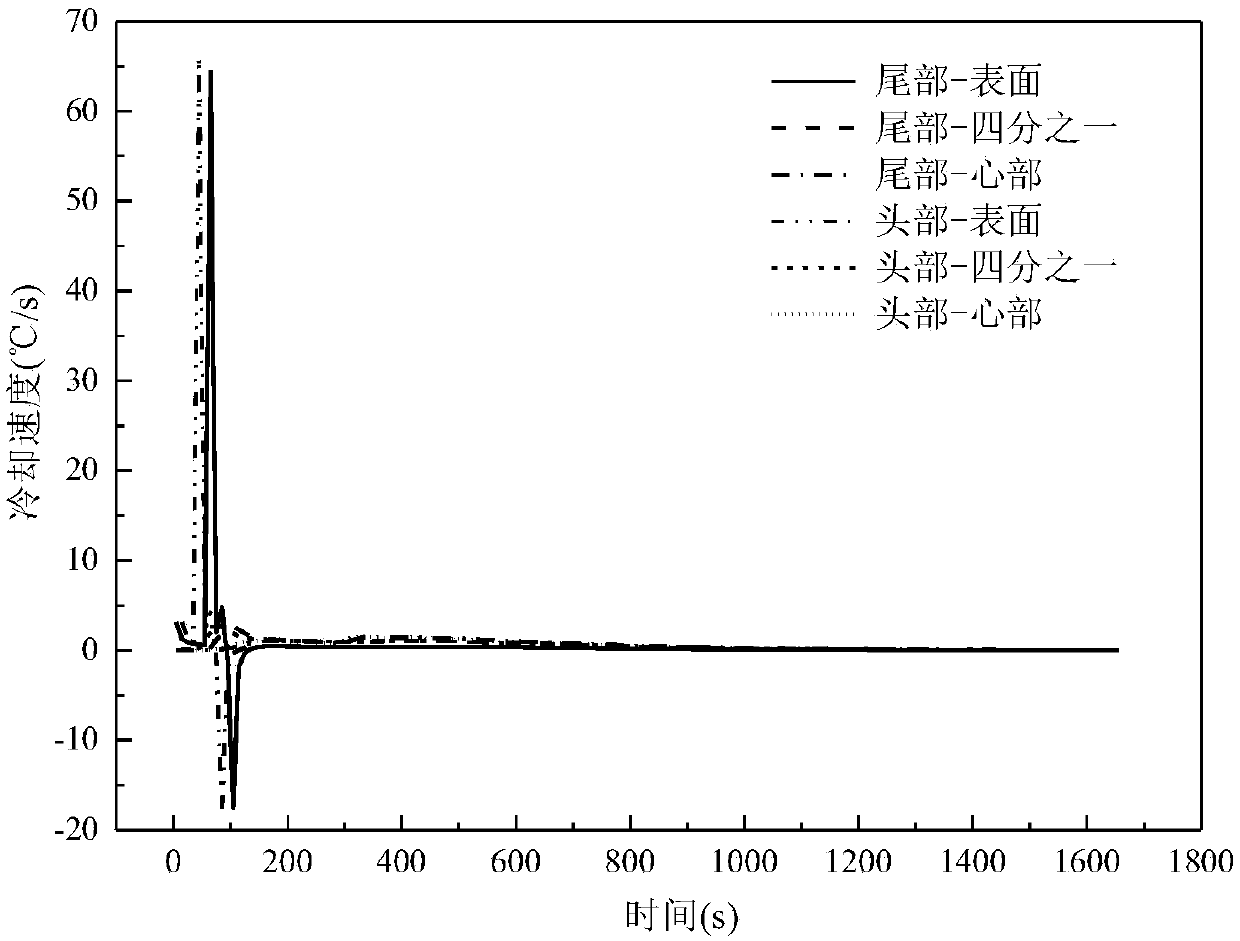
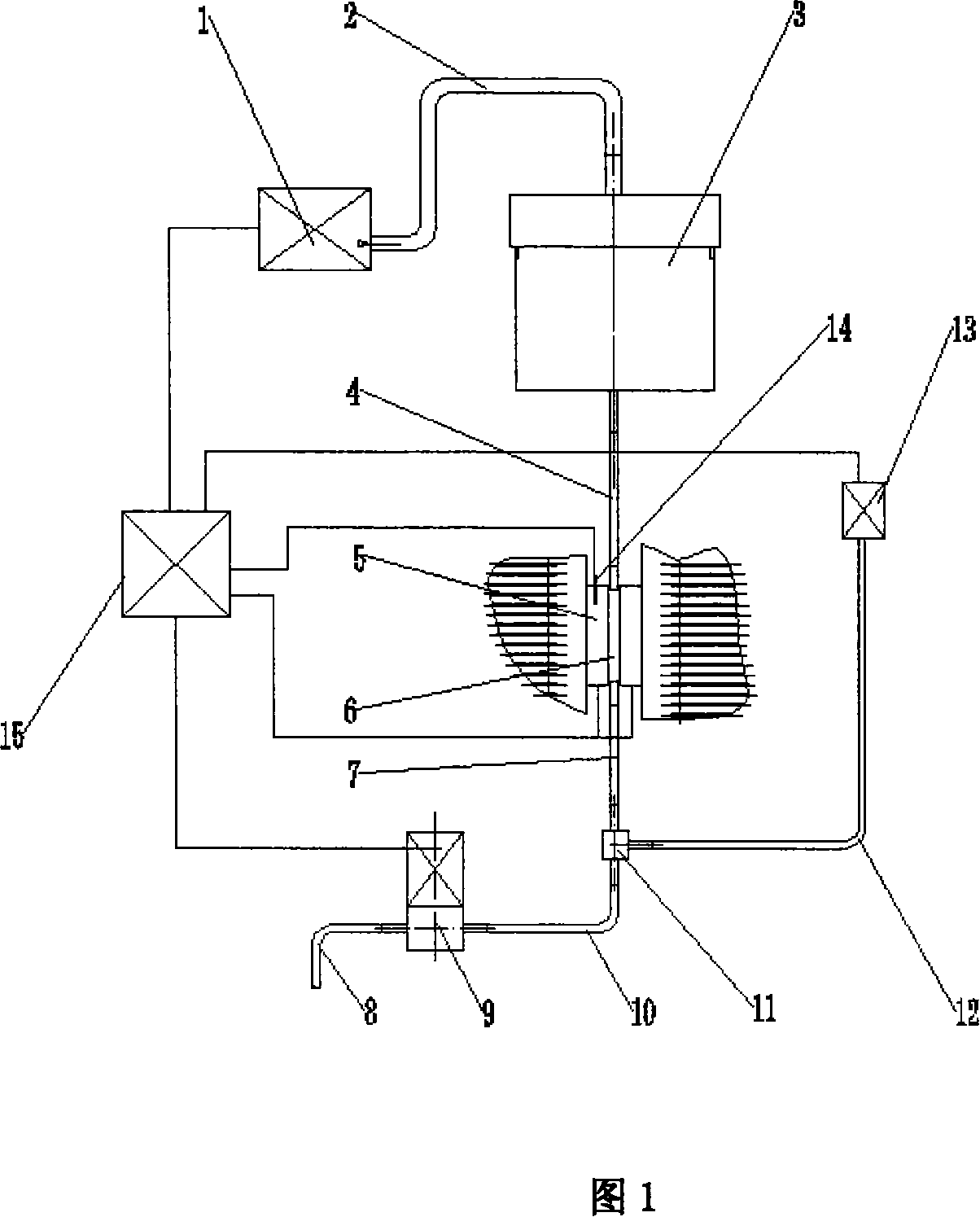
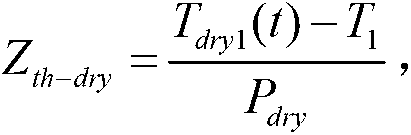Patents
Literature
265 results about "Cooling curve" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
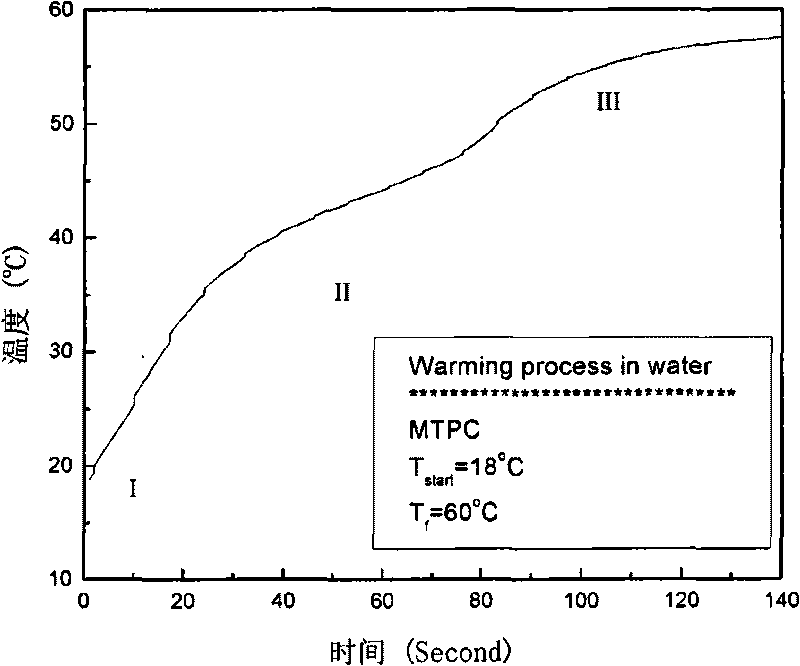
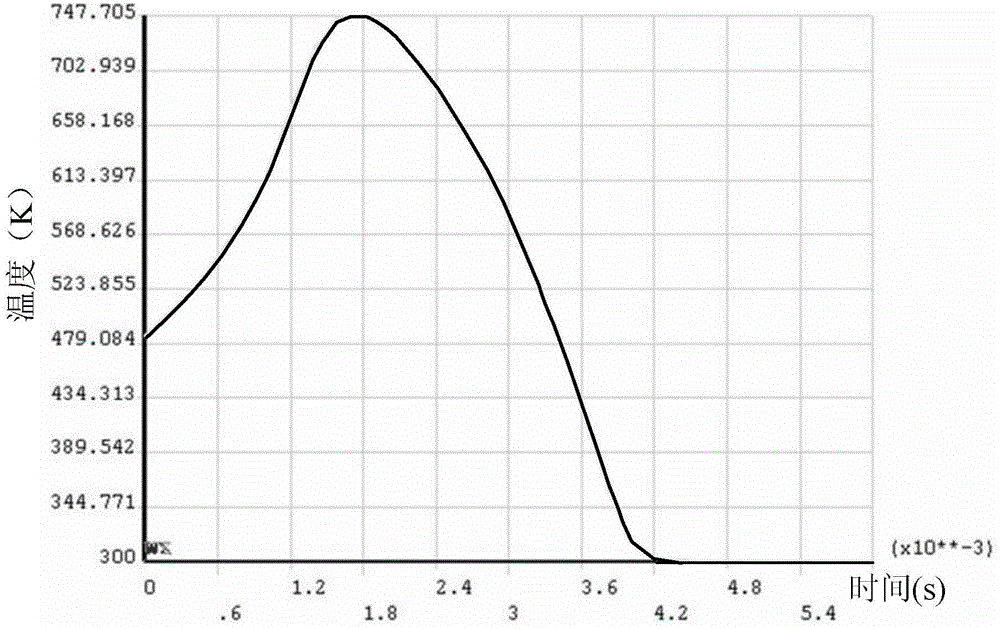
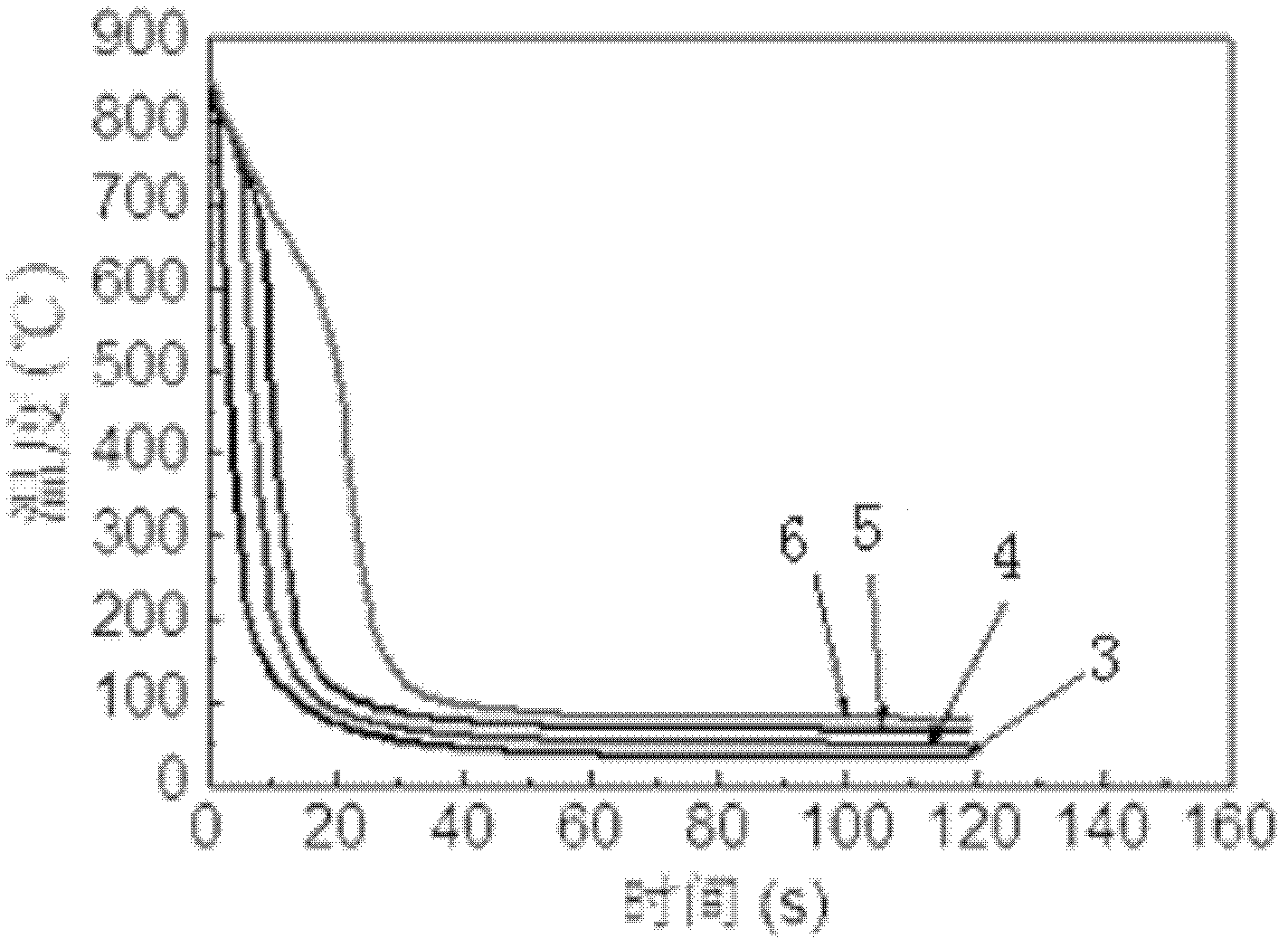
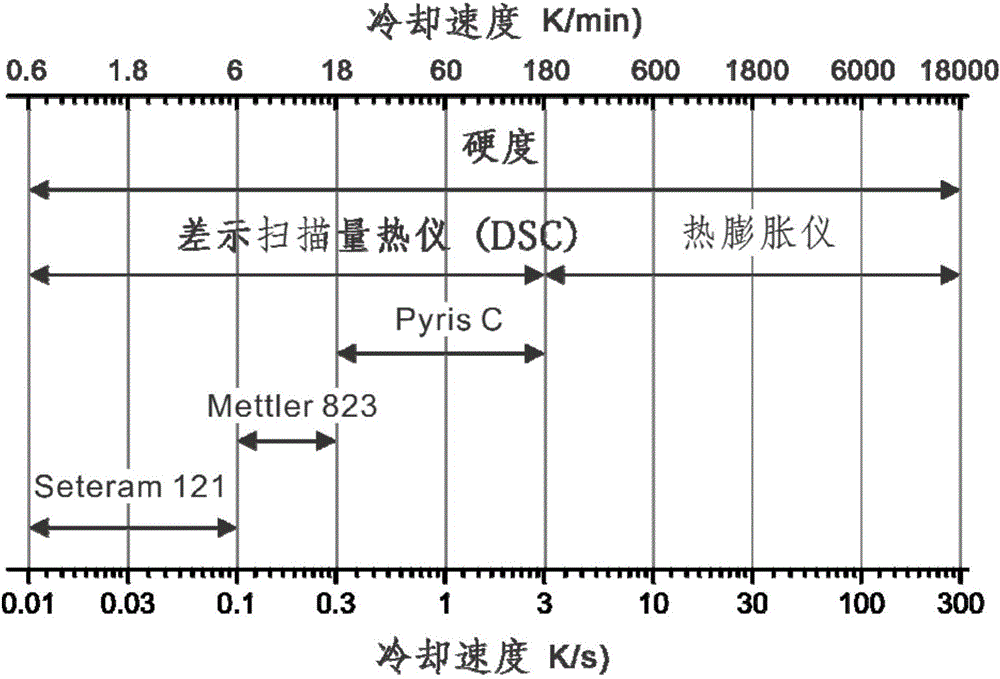
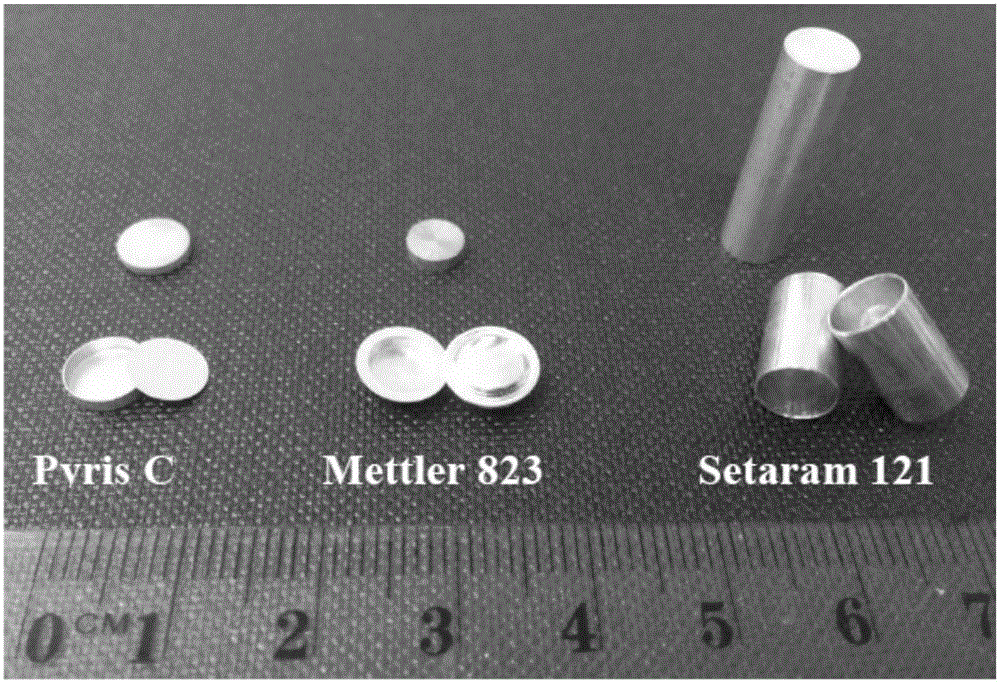
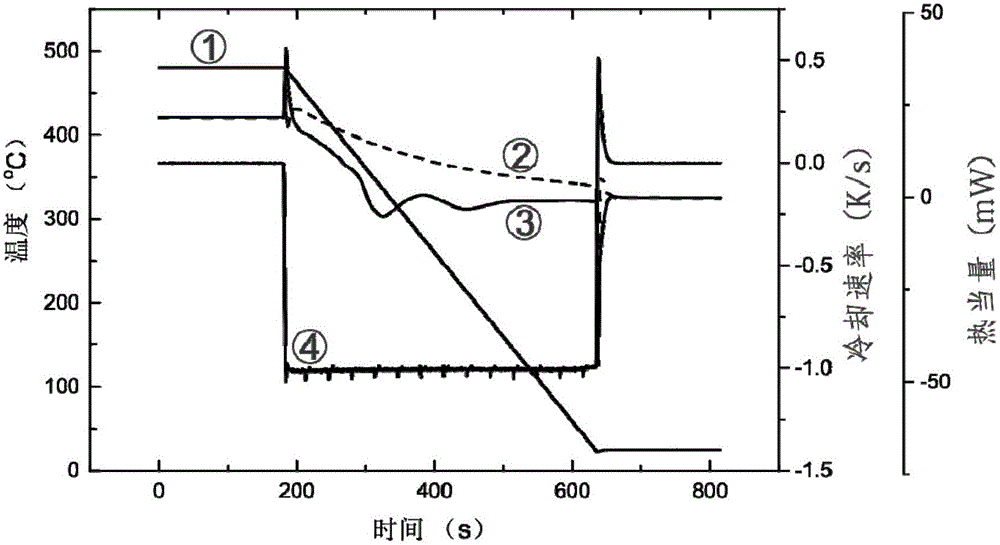
A cooling curve is a line graph that represents the change of phase of matter, typically from a gas to a solid or a liquid to a solid. The independent variable (X-axis) is time and the dependent variable (Y-axis) is temperature. Below is an example of a cooling curve used in castings.
Method and a device for thermal analysis of cast iron
InactiveUS7168852B2Improve accuracyEliminate sourceThermometer detailsWithdrawing sample devicesCooling curveComputer module
Owner:SINTERCAST
Rapid Thermal Firing IR Conveyor Furnace Having High Intensity Heating Section
InactiveUS20080012499A1Effectively doubling heating rate and furnace processing throughputIncrease productionSoldering apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNameplate capacityCooling curve
Isolation IR heat lamp module and method of firing multi-zone IR furnaces for solar cell processing comprising lamps disposed in individual parallel channels in a reflector / insulator body to provide a cooling air channel surrounding each tube; the channels are covered with IR-transmissive plate material to isolate each lamp from adjacent lamps and the process zone. Cooling air is exhausted and recycled upstream for energy conservation. Lamp spacing can be varied and power to each lamp individually controlled to provide infinite control of temperature profile in each heating zone. For a spike zone, and in combination with downstream quench control and annealing zones, steep heating and cooling curves with very short dwell (sharp) peak temperature profiles permit faster throughput due to operation of the lampsm at essentially 100% rated capacity, at a 2× or greater heating and throughput rate without compromising lamp life, while producing solar cells with improved output efficiency.
Owner:TP SOLAR OF USA
Rapid thermal firing IR conveyor furnace having high intensity heating section
InactiveUS7805064B2Effectively doubling heating rate and furnace processing throughputIncrease productionSoldering apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNameplate capacityCooling curve
Isolation IR heat lamp module and method of firing multi-zone IR furnaces for solar cell processing comprising lamps disposed in individual parallel channels in a reflector / insulator body to provide a cooling air channel surrounding each tube; the channels are covered with IR-transmissive plate material to isolate each lamp from adjacent lamps and the process zone. Cooling air is exhausted and recycled upstream for energy conservation. Lamp spacing can be varied and power to each lamp individually controlled to provide infinite control of temperature profile in each heating zone. For a spike zone, and in combination with downstream quench control and annealing zones, steep heating and cooling curves with very short dwell (sharp) peak temperature profiles permit faster throughput due to operation of the lampsm at essentially 100% rated capacity, at a 2× or greater heating and throughput rate without compromising lamp life, while producing solar cells with improved output efficiency.
Owner:TP SOLAR OF USA
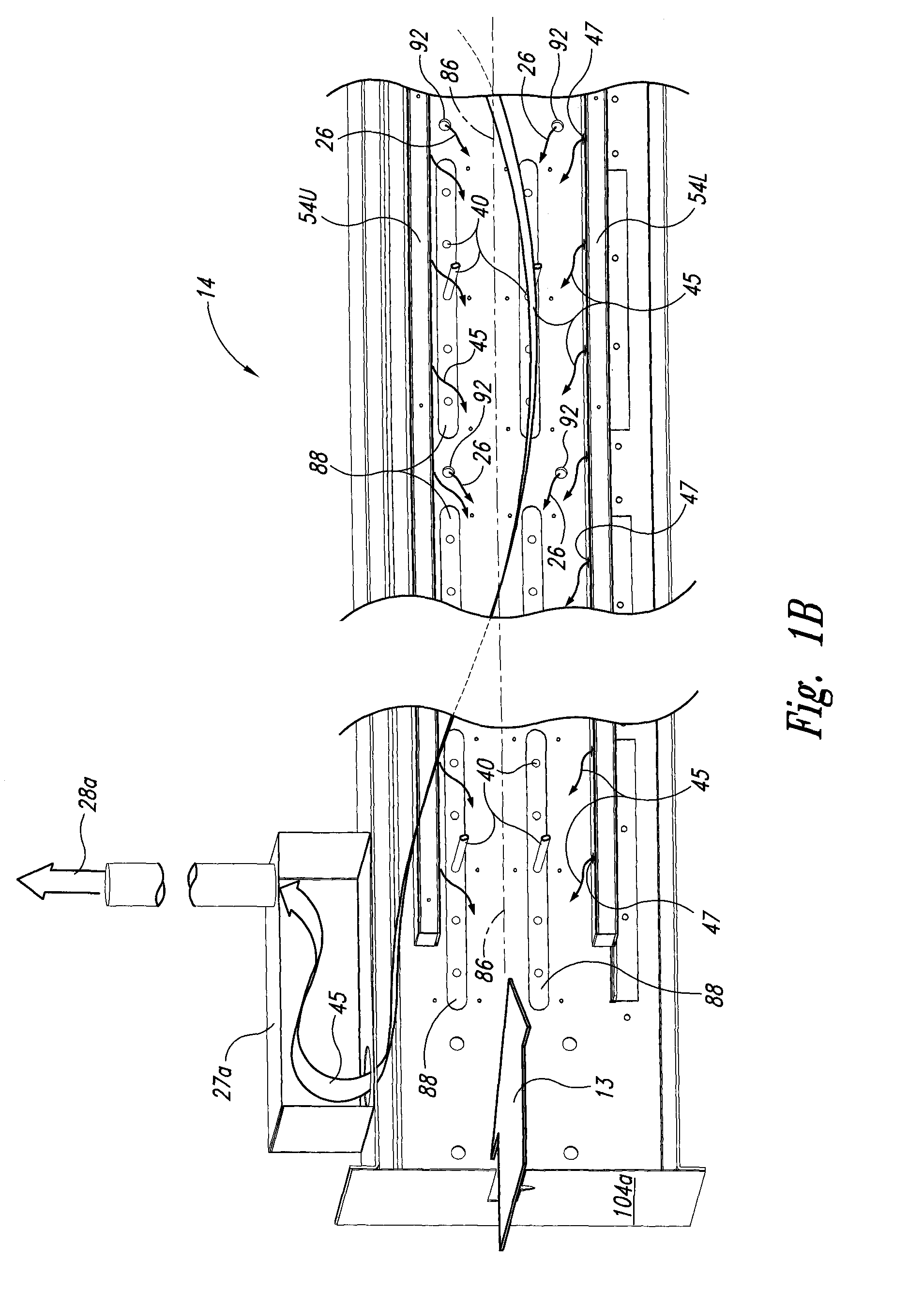
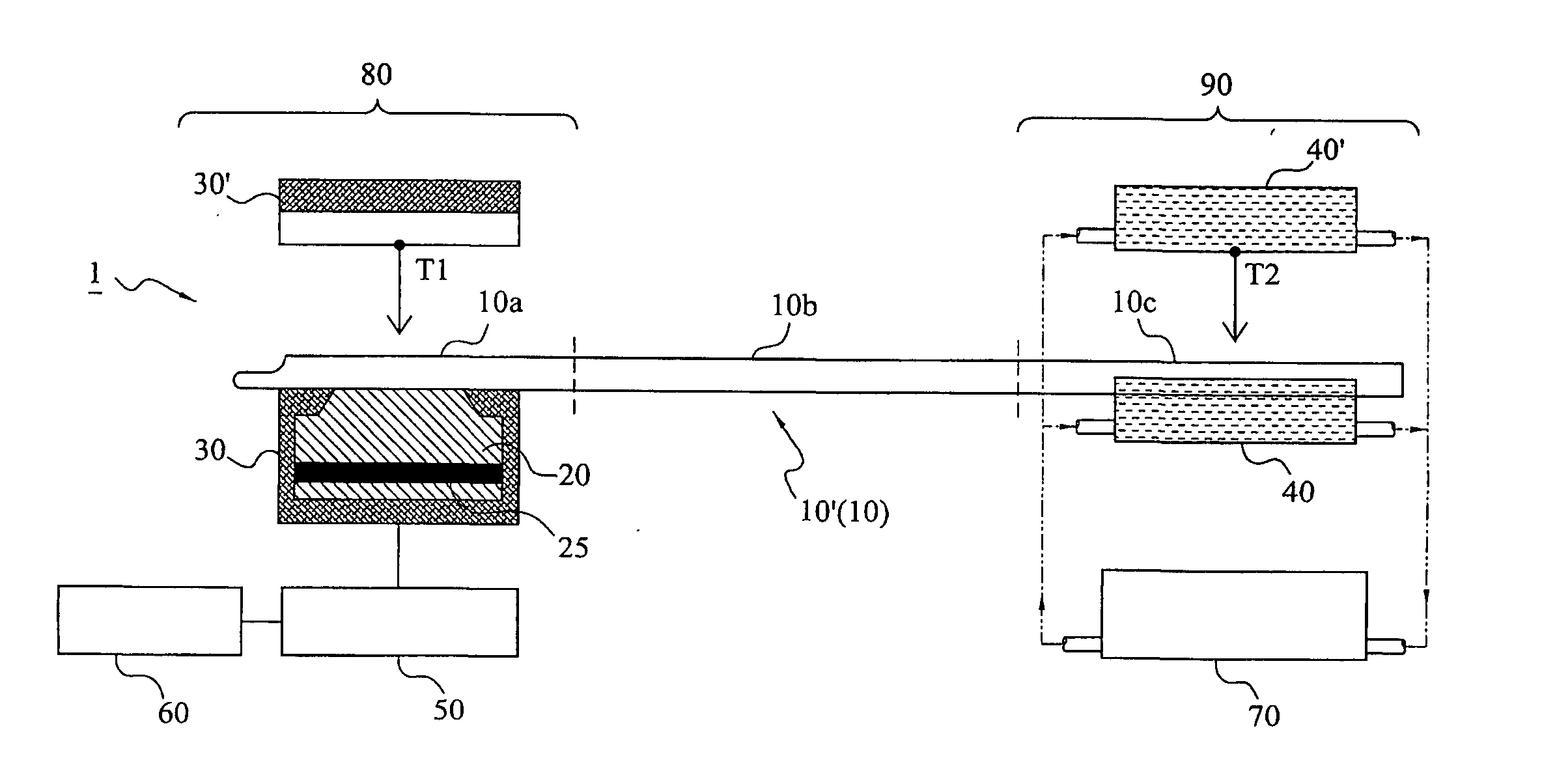
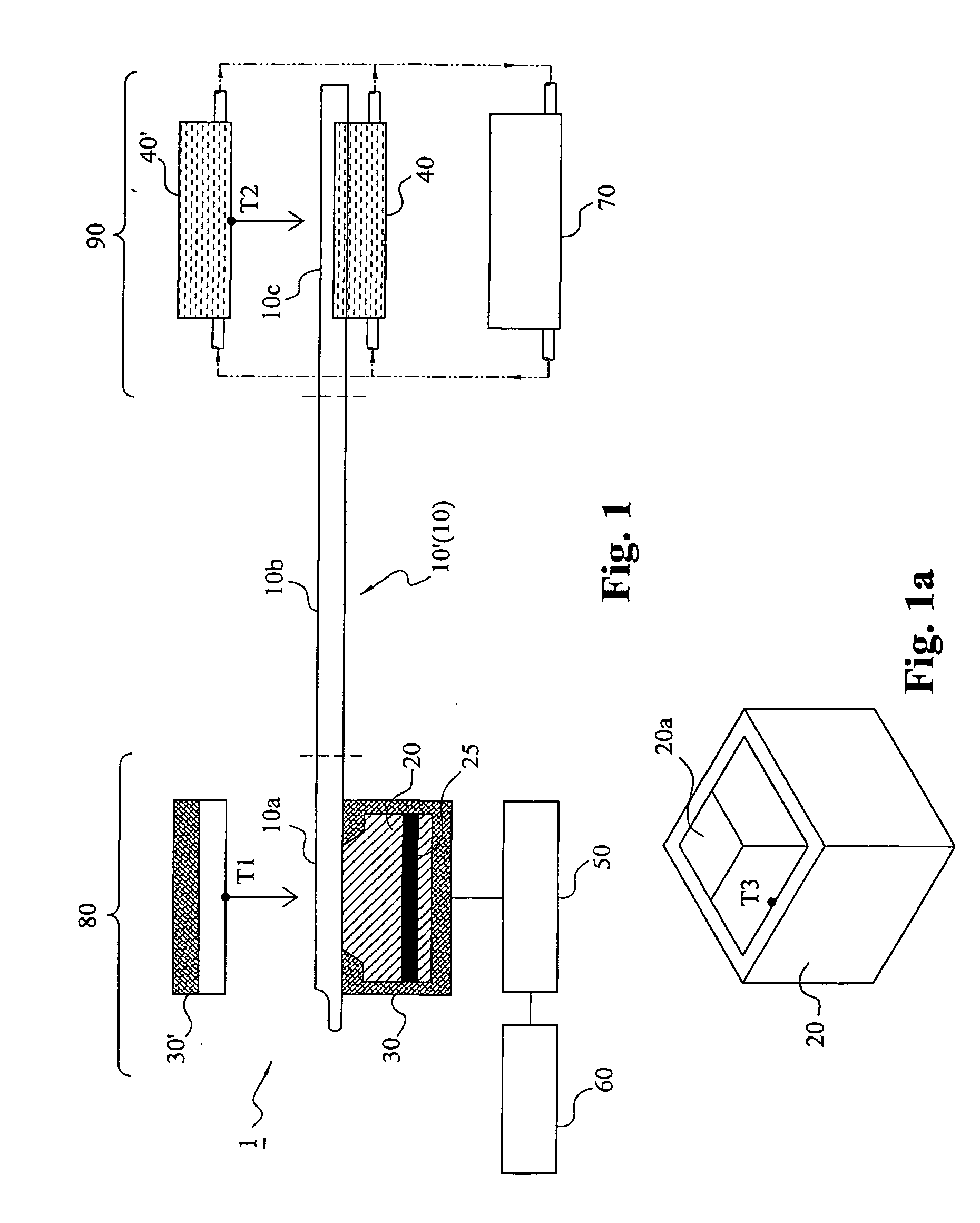
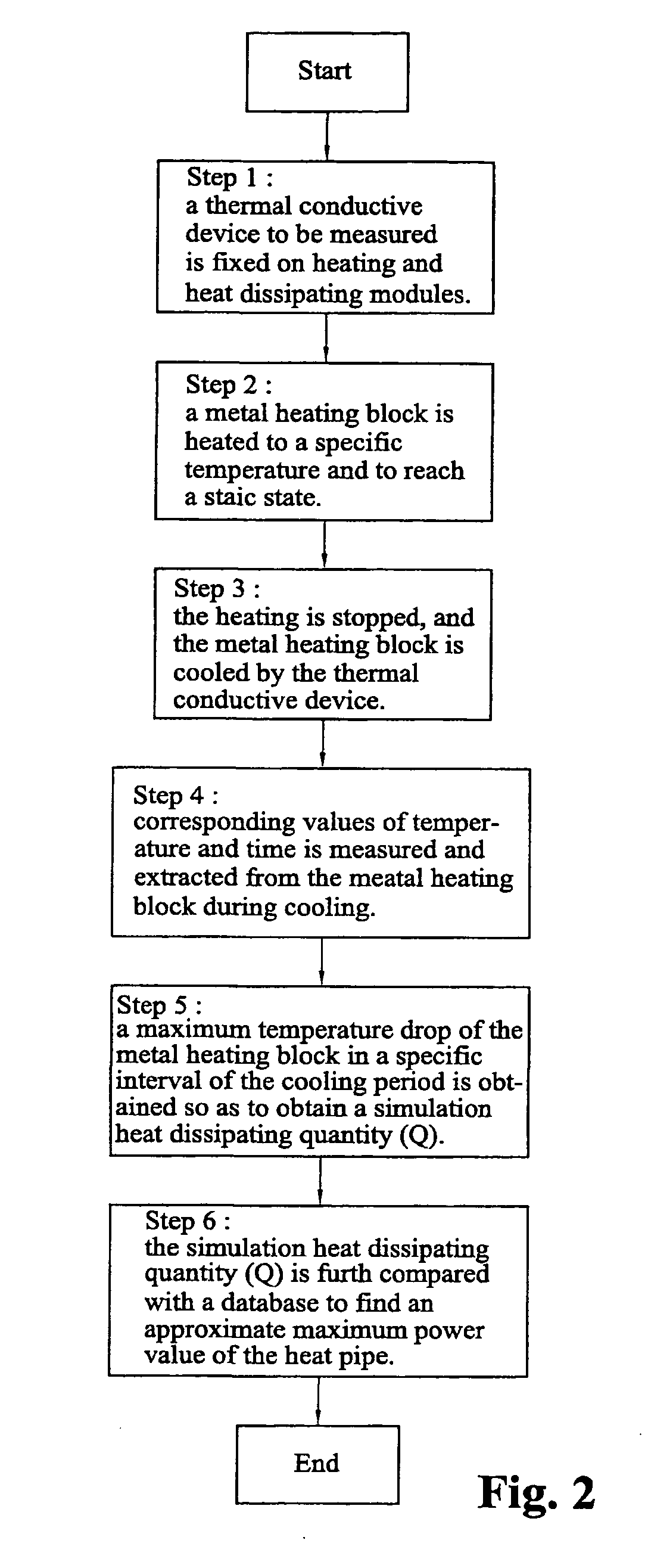
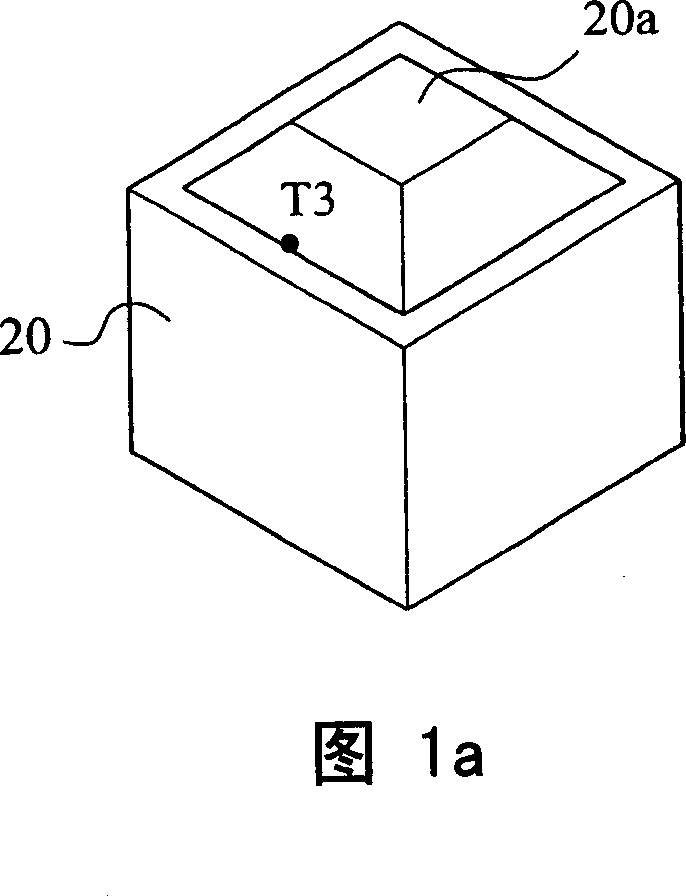
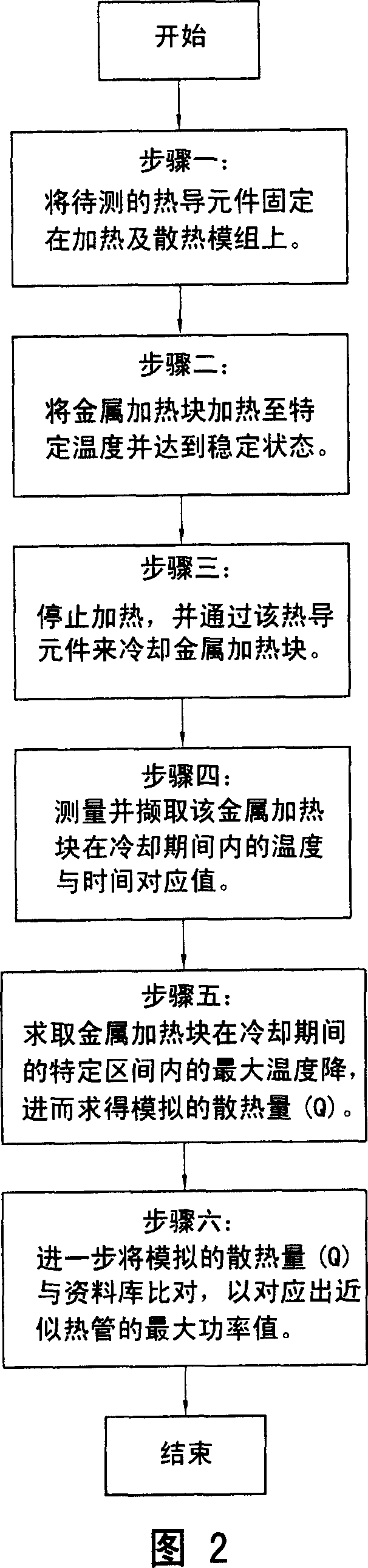
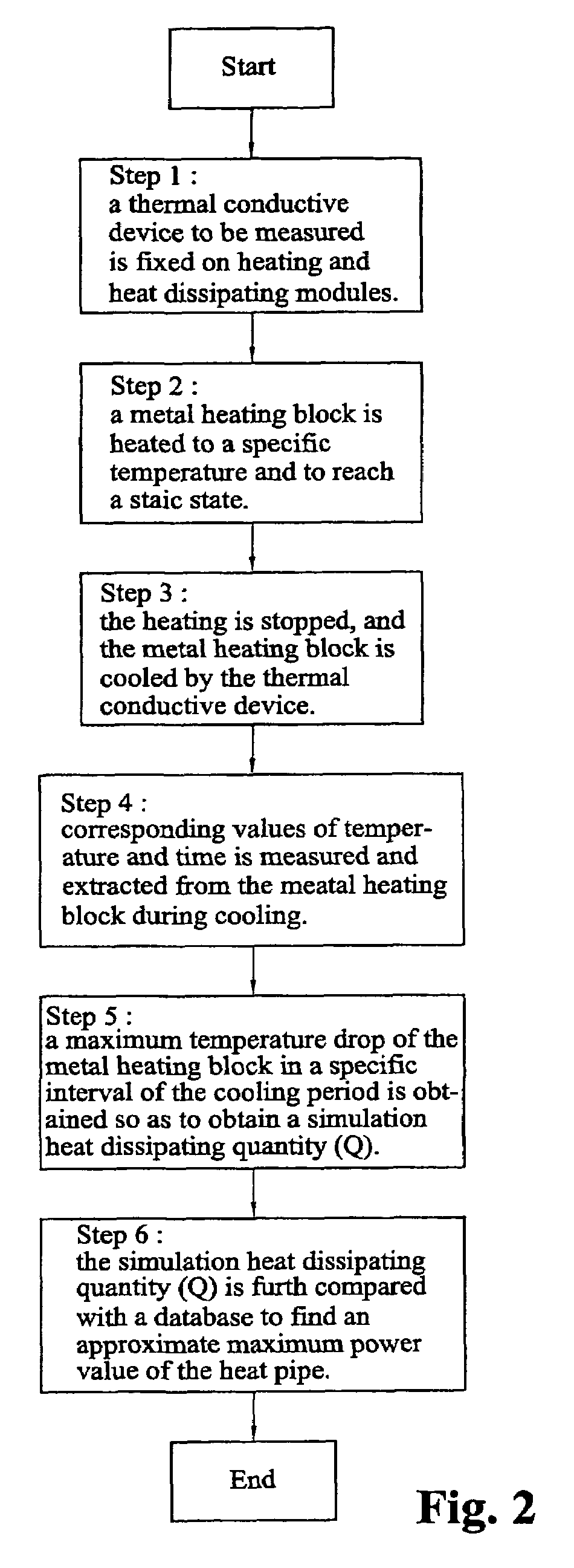
Measuring system and screening method for thermal conductive efficiencies of thermal conductive devices
ActiveUS20070047614A1Good reproducibilityStable resolutionThermometer detailsMaterial thermal conductivityCooling curveScreening method
The measuring system generates a temperature difference between a heating terminal and a terminal conductive device by setting the temperature of a metal heated block at the heating terminal and the temperature of a heat dissipating water jacket at a heat dissipating terminal, and judges the thermal conductive capability of the thermal conductive device by comparing the cooling speed of the metal heating bock to obtain a relative power value according to the variation of heat quantity of the metal heated block in practical temperature reduction process. The maximum thermal conductive quantity (Qmax value) of the thermal conductive device can be rapidly obtained by parameter conversion with respect to the maximum power value. In the case of confirming the cooling curve (cooling speed) of a standard sample, the object of screening the thermal conductive efficiencies of the thermal conductive devices can be achieved by using the cooling curve.
Owner:YEH CHIANG TECH CORP
Infrared furnace system
InactiveUS20100220983A1Minimized footprintOptimized profileDrying solid materials with heatIndirect heat exchangersCooling curveProcess engineering
An infrared furnace system provides for adjusting the amount of time a workpiece spends in a respective section of the furnace while at the same time minimizing the footprint, i.e., the amount of floor space that the furnace uses. Various embodiments allow for optimizing the required thermal duration of each section which then also optimizes the heating and / or cooling profile within each section. Transfer conveyors are provided to transfer a workpiece from one conveyor operating at a first speed to a second conveyor operating at a second speed, different from the first speed in order to prevent damage to the workpiece. Rollers are provided to support the workpiece and to maintain a proper orientation. A heating lamp support assembly provides power to the lamp and facilitates exchange and replacement of the lamp. An air delivery system provides process gas maintained at the correct temperature. An exhaust system provides air flow with improved turnover and reduced noise considerations. Infrared heating lamps are cooled by providing gas flow across the end terminals. The wavelength of light emitted by the heating lamps is adjusting by controlling parameters of the process gas being introduced into a section of the furnace.
Owner:BTU INTERNATIONAL
Method and device for thermal physical property test of high-temperature phase-change energy storage material
InactiveCN101762618AOvercoming test flawsObserve the phase transition processMaterial heat developmentData treatmentPhysical property
The invention relates to a method and a device for the thermal physical property test of a high-temperature phase-change energy storage material, belonging to the technical field of high-temperature phase-change energy storage materials. Two kinds of inorganic salts close to a eutectic point are adopted for inorganic salt mixture, are evenly mixed, are ground into powder and are contained into a nickel crucible. The nickel crucible containing the inorganic salt mixture is placed in an iron box and is put into a box-type resistance furnace till the inorganic salt mixture is fully molten. After the inorganic salt mixture is molten, the molten salt is taken out. The probe of a thermocouple is inserted right into the middle of the molten salt to enable the molten salt to be cooled under natural conditions. The nickel crucible is fixed in the iron box to test a heating curve. The heating curve is observed and the iron box is taken out after the mixed salt is fully molten and the temperature is 30 DEG C to 60 DEG C higher than the temperature of a melting platform. The cooling curve of the mixed salt is tested under room temperature. After the test is completed, data is stored and data processing is conducted. The invention provides an effective means for the thermal physical property test of the phase-change energy storage material with wide temperature change range and high melting point, overcomes the test defects of DSC and DTA, and has the advantages of small investment, low raw material cost and easily obtainable raw materials, easy operation, good repeatability and high applicability.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
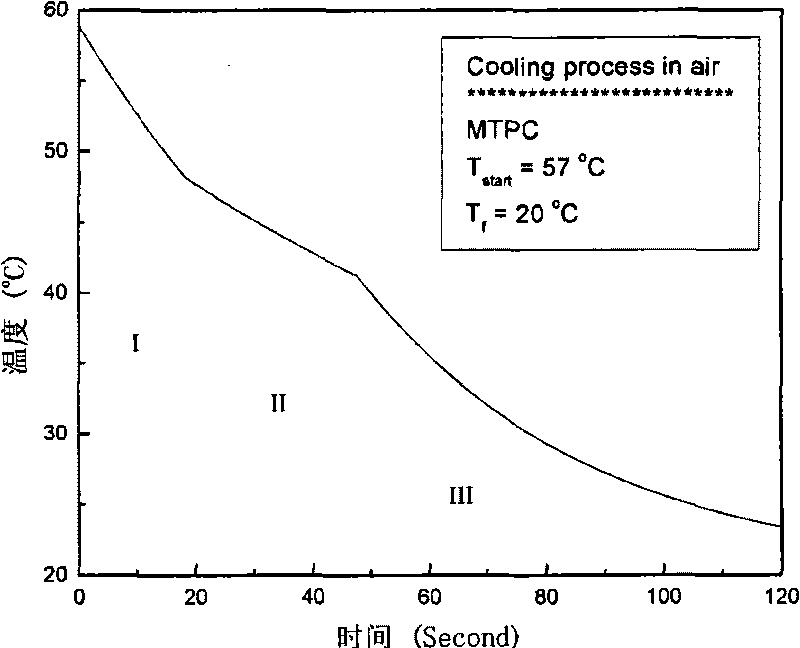
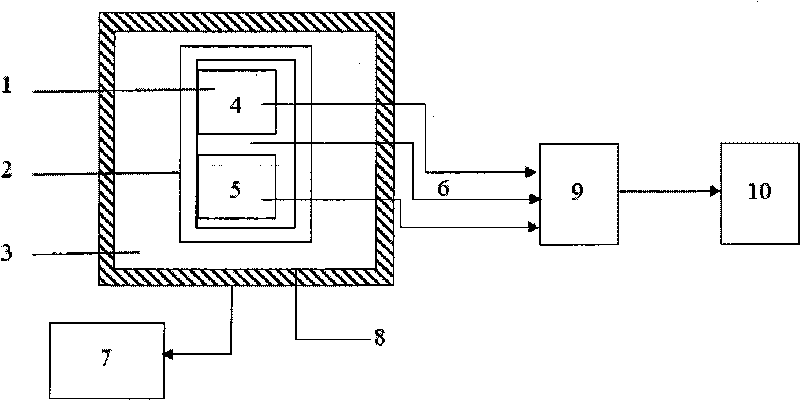
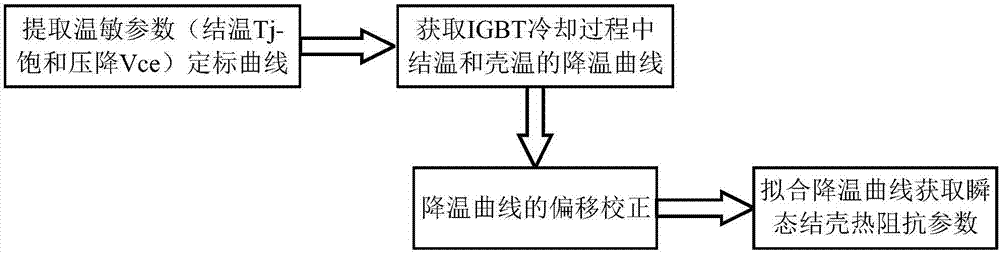
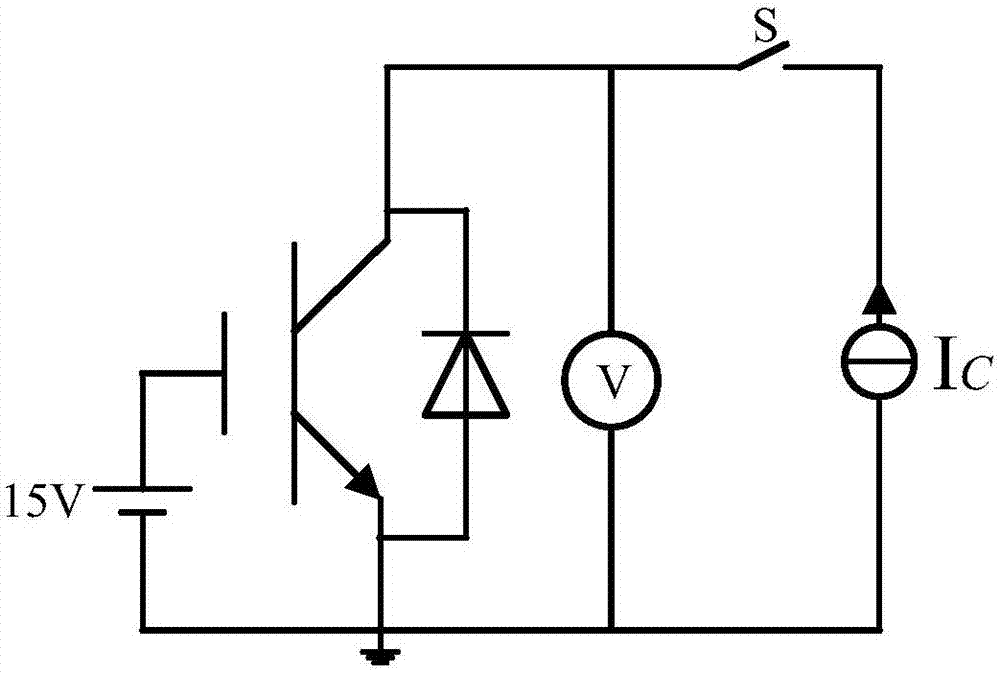
Crusting transient thermal impedance measuring method used for high power IGBT
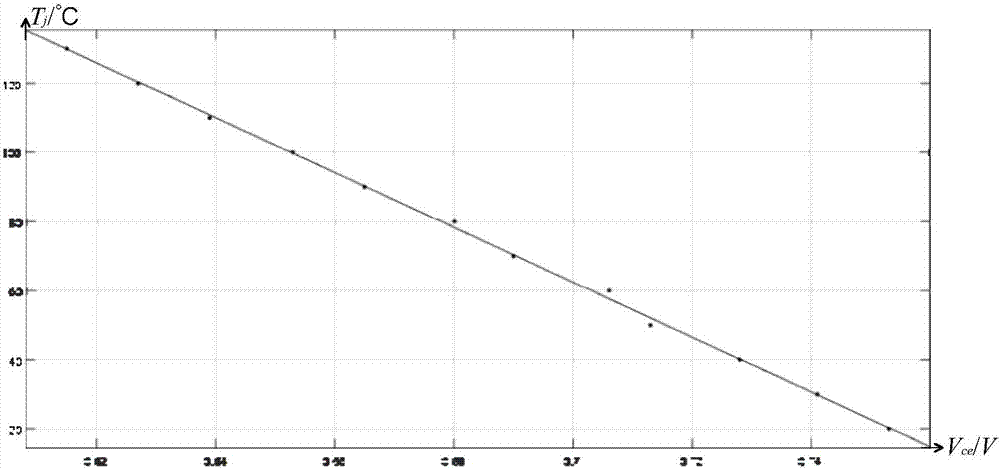
InactiveCN107192934ALow costAccurate measurementIndividual semiconductor device testingCooling curveCurve fitting
The invention discloses a crusting transient thermal impedance measuring method used for a high power IGBT. The method comprises the steps that an IGBT thermo-sensitive parameter calibration curve is acquired; junction temperature and case temperature cooling curves in an IGBT cooling process are acquired; and cooling curve deviation correcting and cooling curve fitting are carried out to acquire transient crusting thermal impedance parameters. According to the invention, a thermo-sensitive parameter method is used to measure the junction temperature cooling curve in the high power IGBT cooling process, and at the same time a thermocouple method is used to acquire the IGBT case temperature cooling curve; the IGBT transient thermal impedance parameters are acquired through curve fitting; and the method has the advantages of easy operation and wide use range, can directly and accurately acquire the transient thermal impedance parameters in the IGBT, and can be used to predict the junction temperature change trend in the actual operation of the high power IGBT for further thermal stability evaluation.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Rapid thermal firing ir conveyor furnace having high intensity heating section
InactiveCN101478882AIncrease powerIncrease heating rateDrying solid materials with heatHigh-frequency/infra-red heating bakingEngineeringSolar cell
Isolation IR heat lamp module and method of firing multi-zone IR furnaces for solar cell processing comprising lamps disposed in individual parallel channels in a reflector / insulator body to provide a cooling air channel surrounding each tube; the channels are covered with IR-transmissive plate material to isolate each lamp from adjacent lamps and the process zone. Cooling air is exhausted and recycled upstream for energy conservation. Lamp spacing can be varied and power to each lamp individually controlled to provide infinite control of temperature profile in each heating zone. For a spike zone, and in combination with downstream quench control and annealing zones, steep heating and cooling curves with very short dwell (sharp) peak temperature profiles permit faster throughput due to operation of the lamps at essentially 100 % rated capacity, at a 2X or greater heating and throughput rate without compromising lamp life, while producing solar cells with improved output efficiency.
Owner:TP SOLAR OF USA
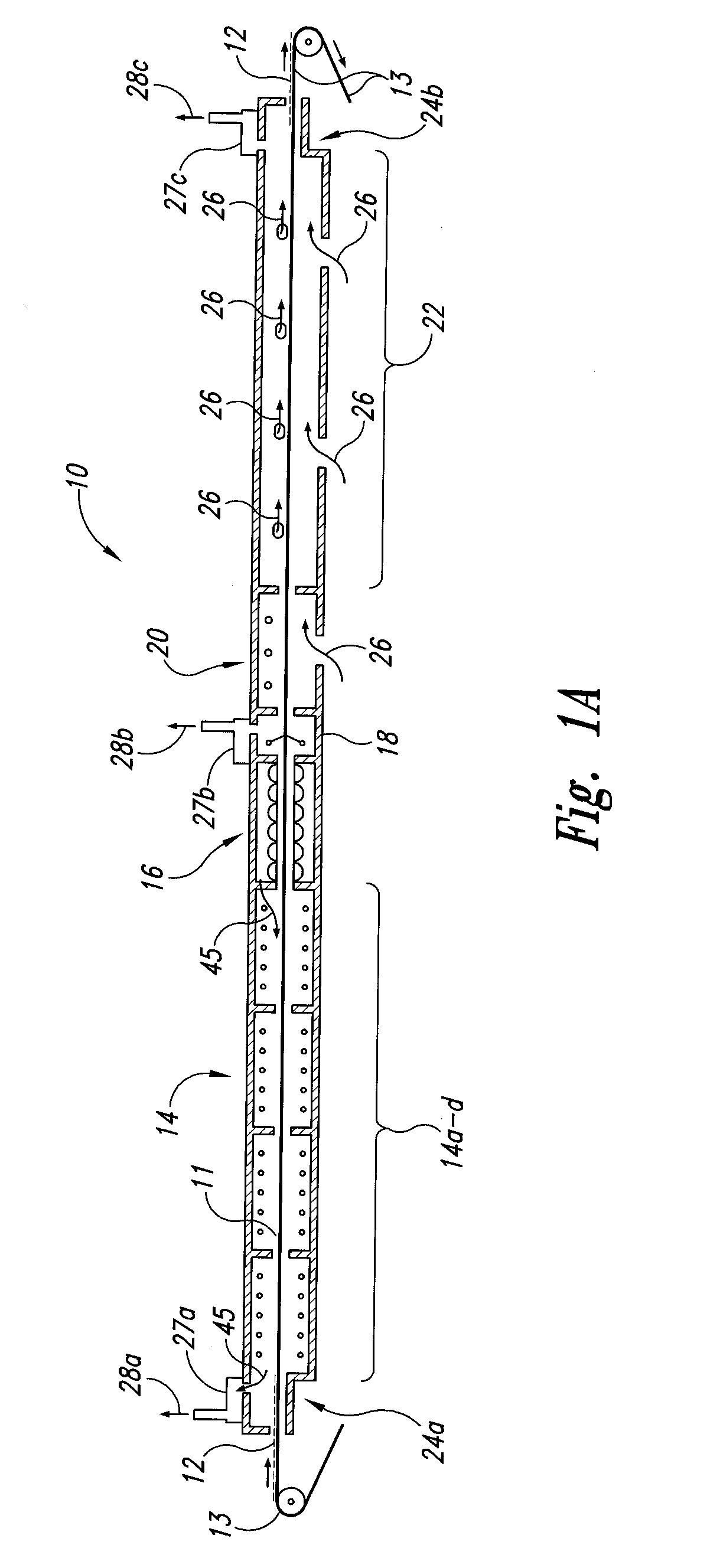
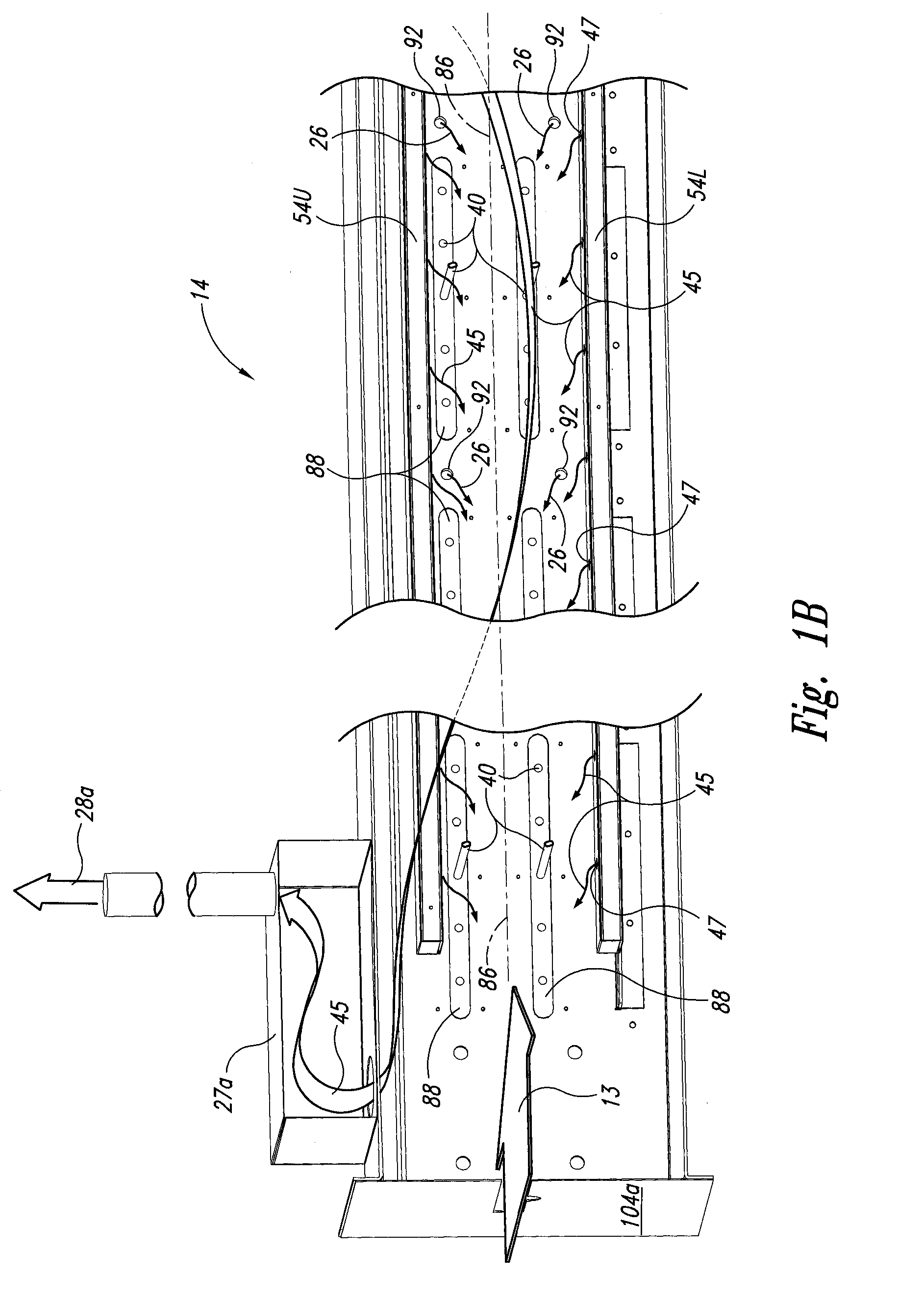
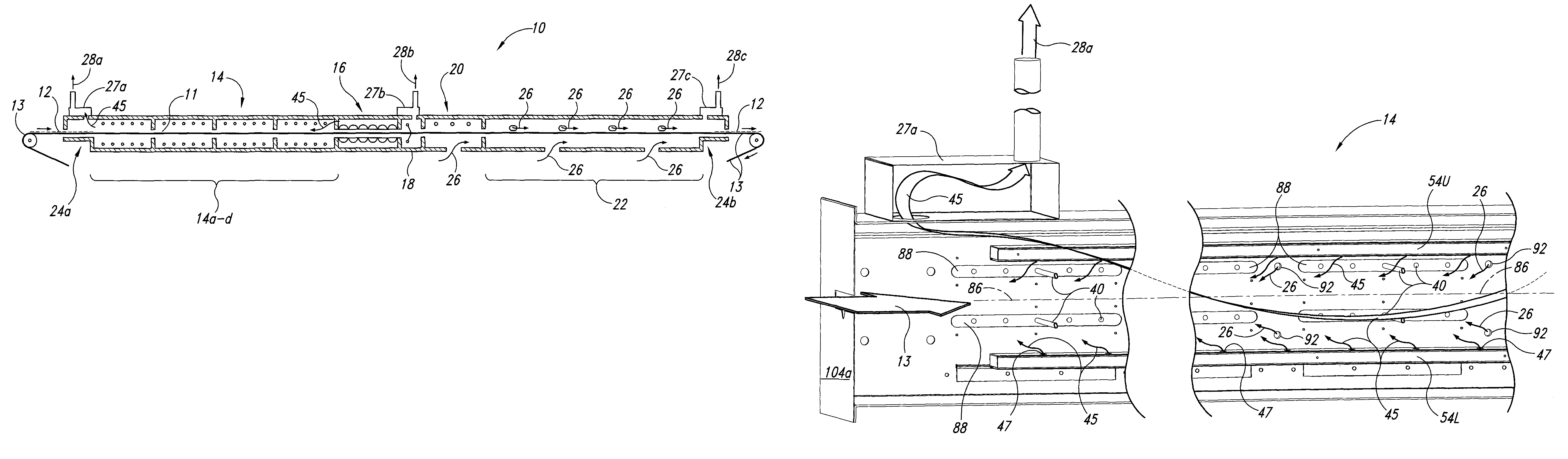
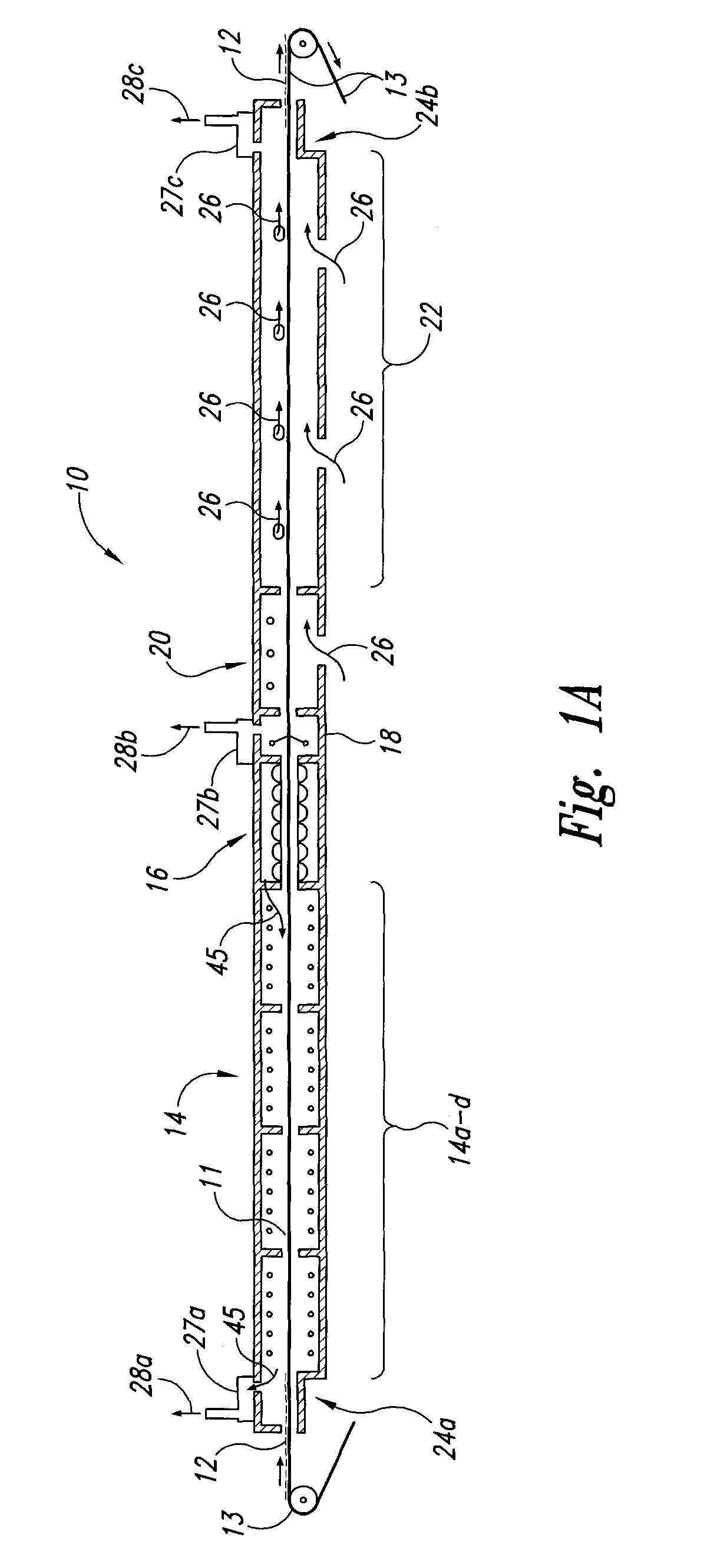
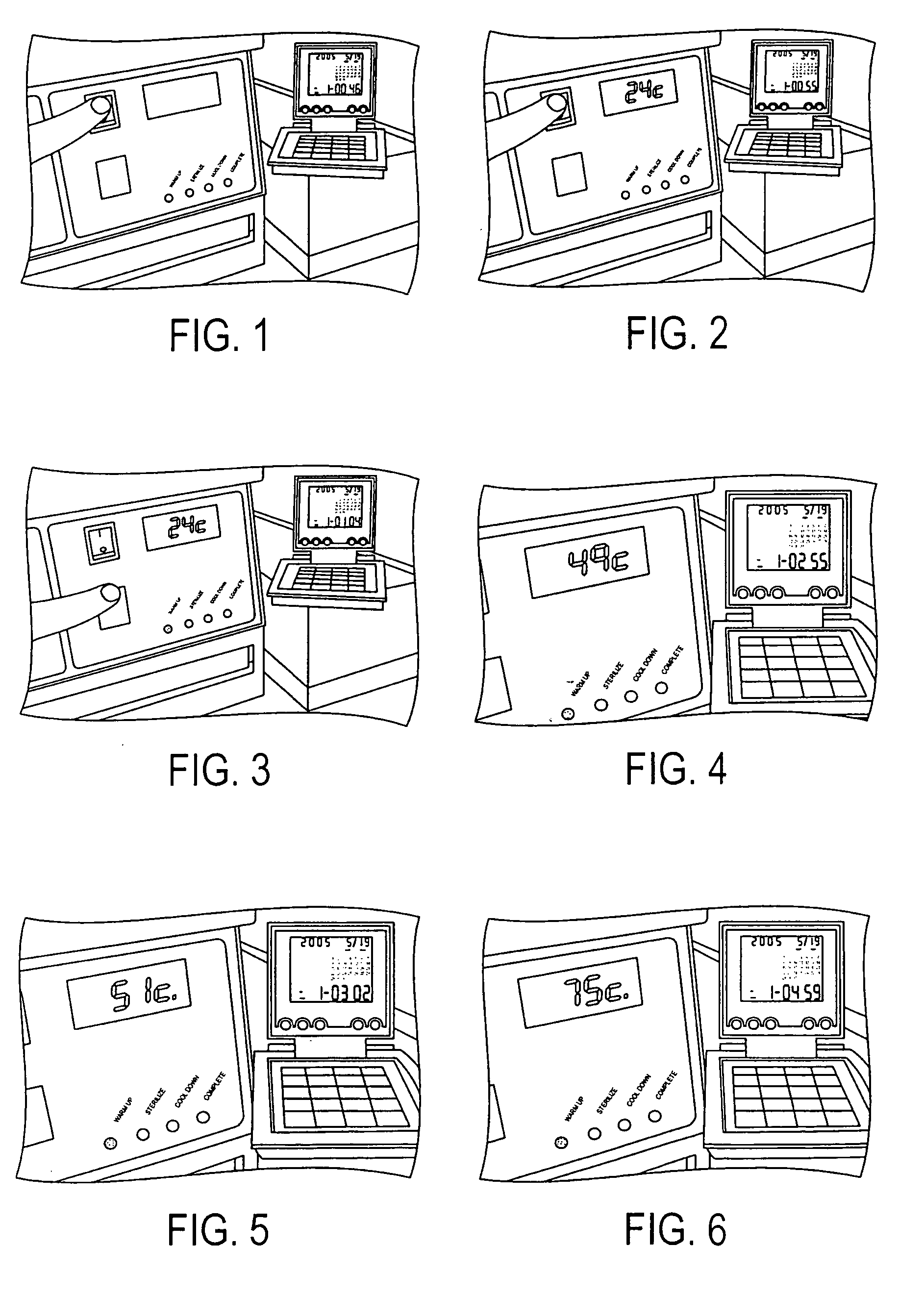
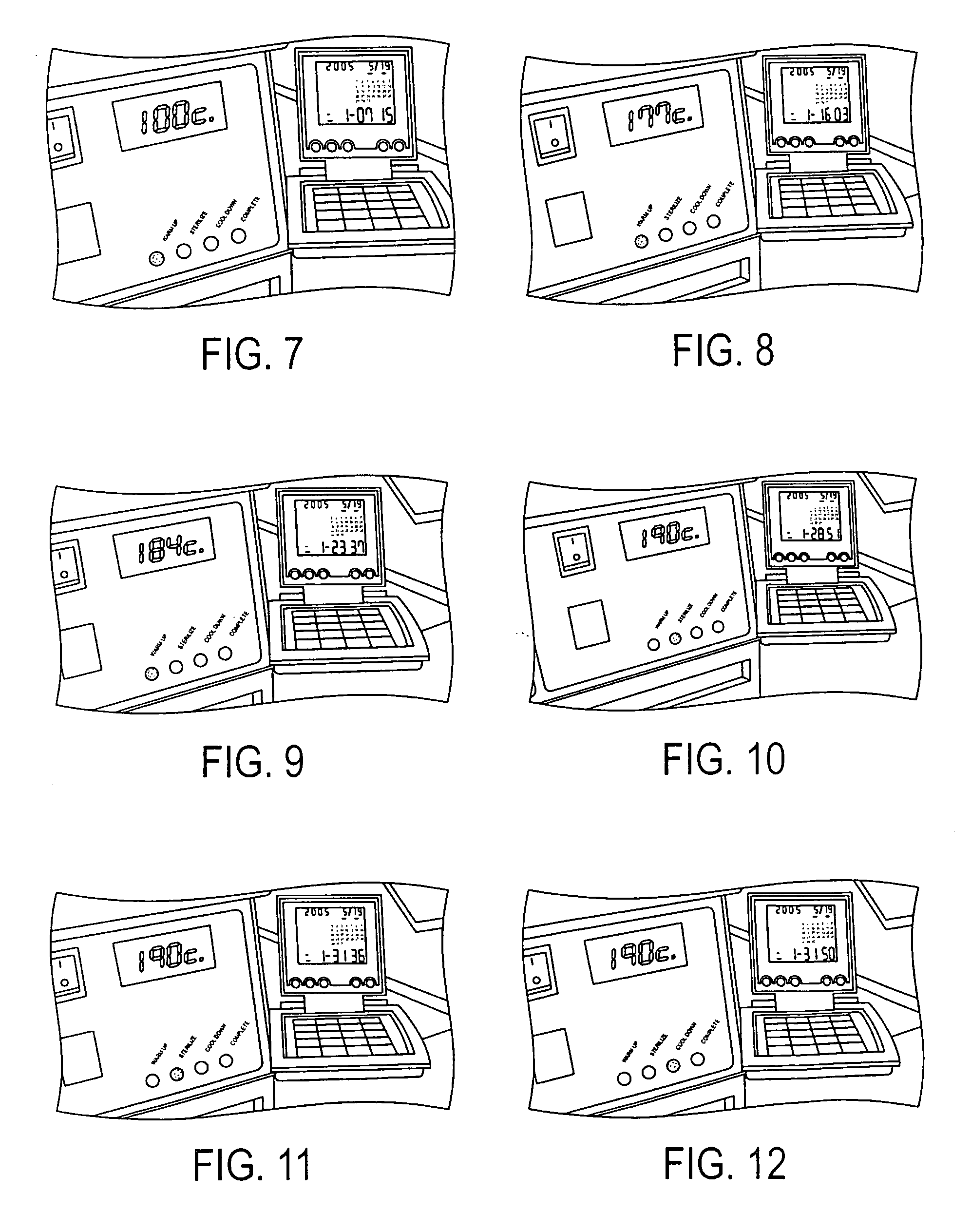
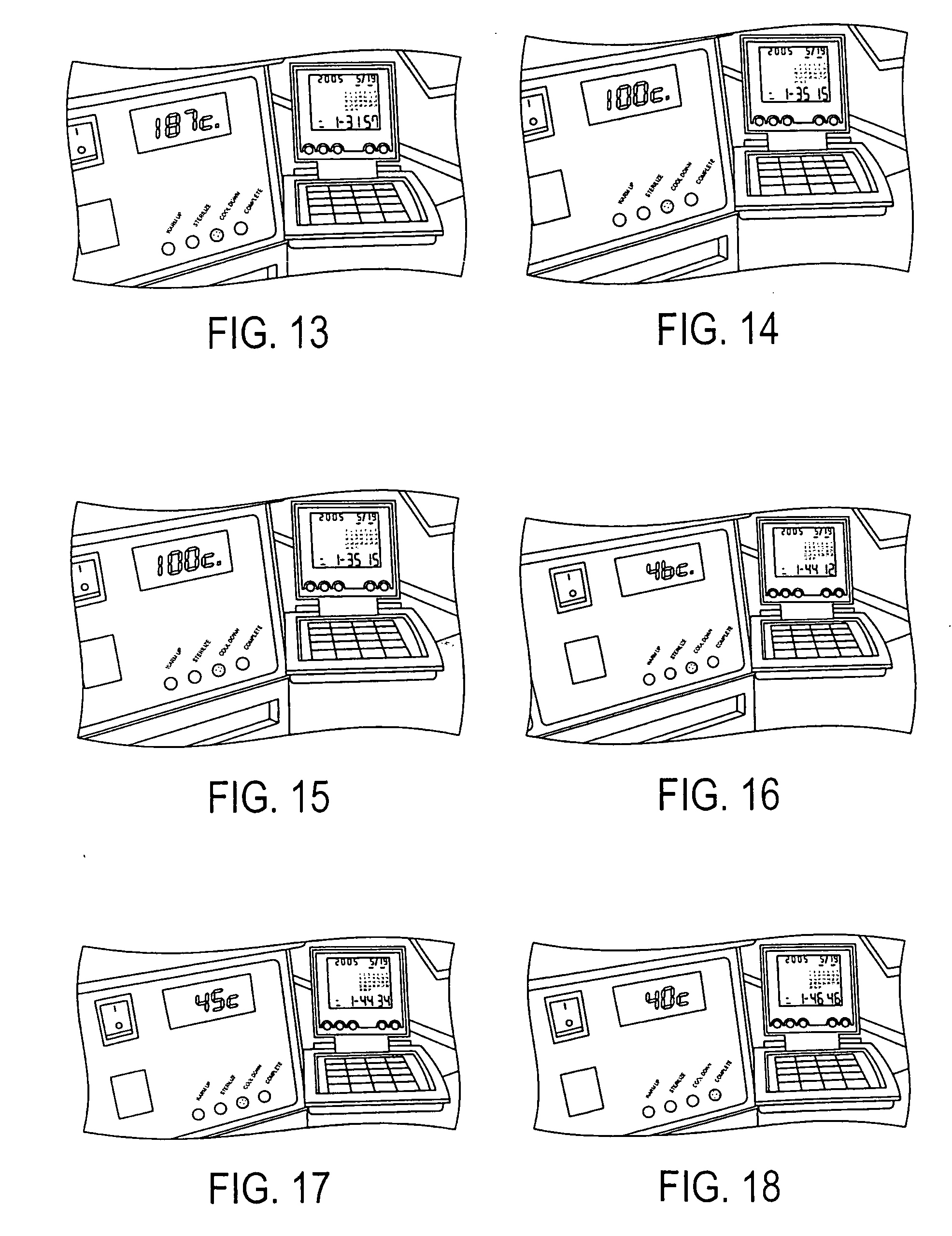
Methods and apparatus for hot air sterilization of medical instruments
Owner:COLTENE WHALEDENT INC
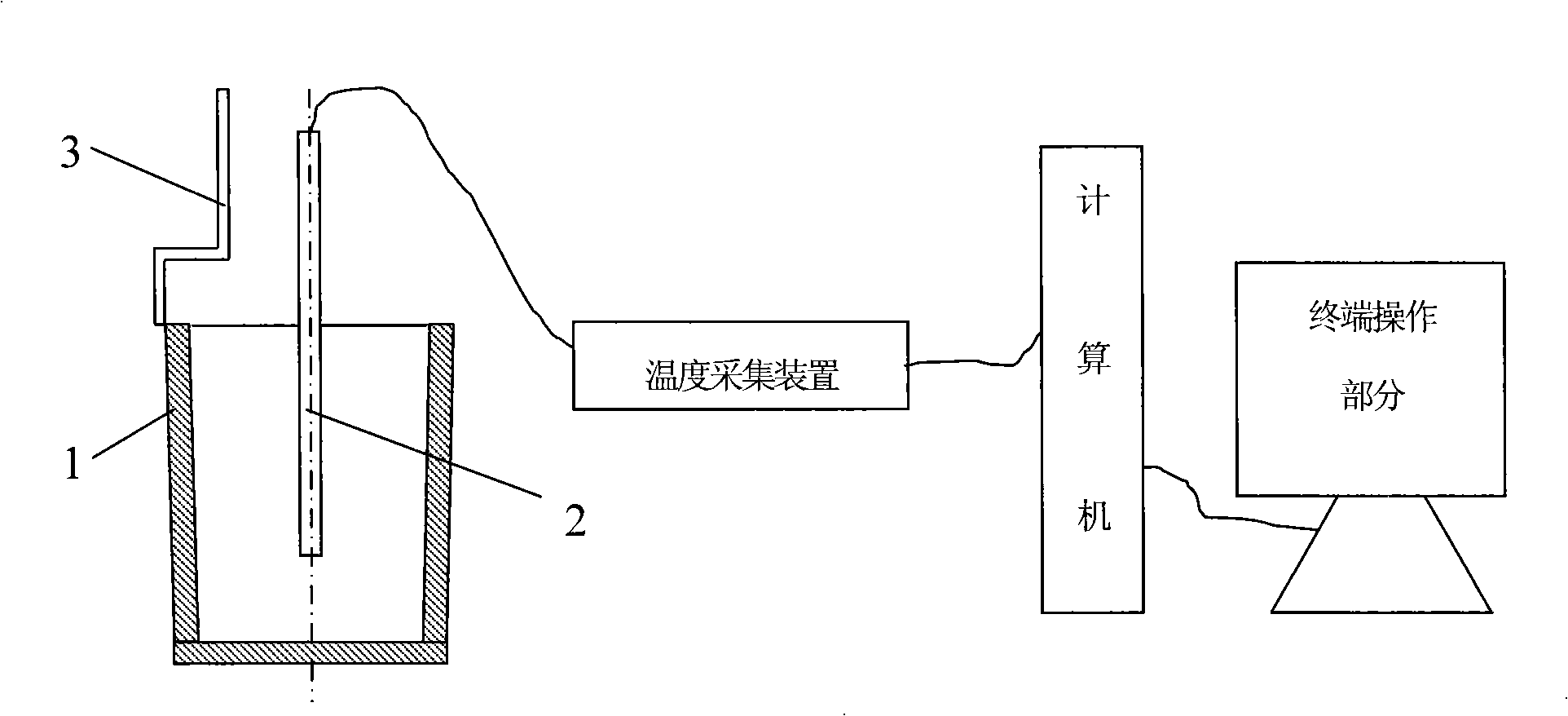
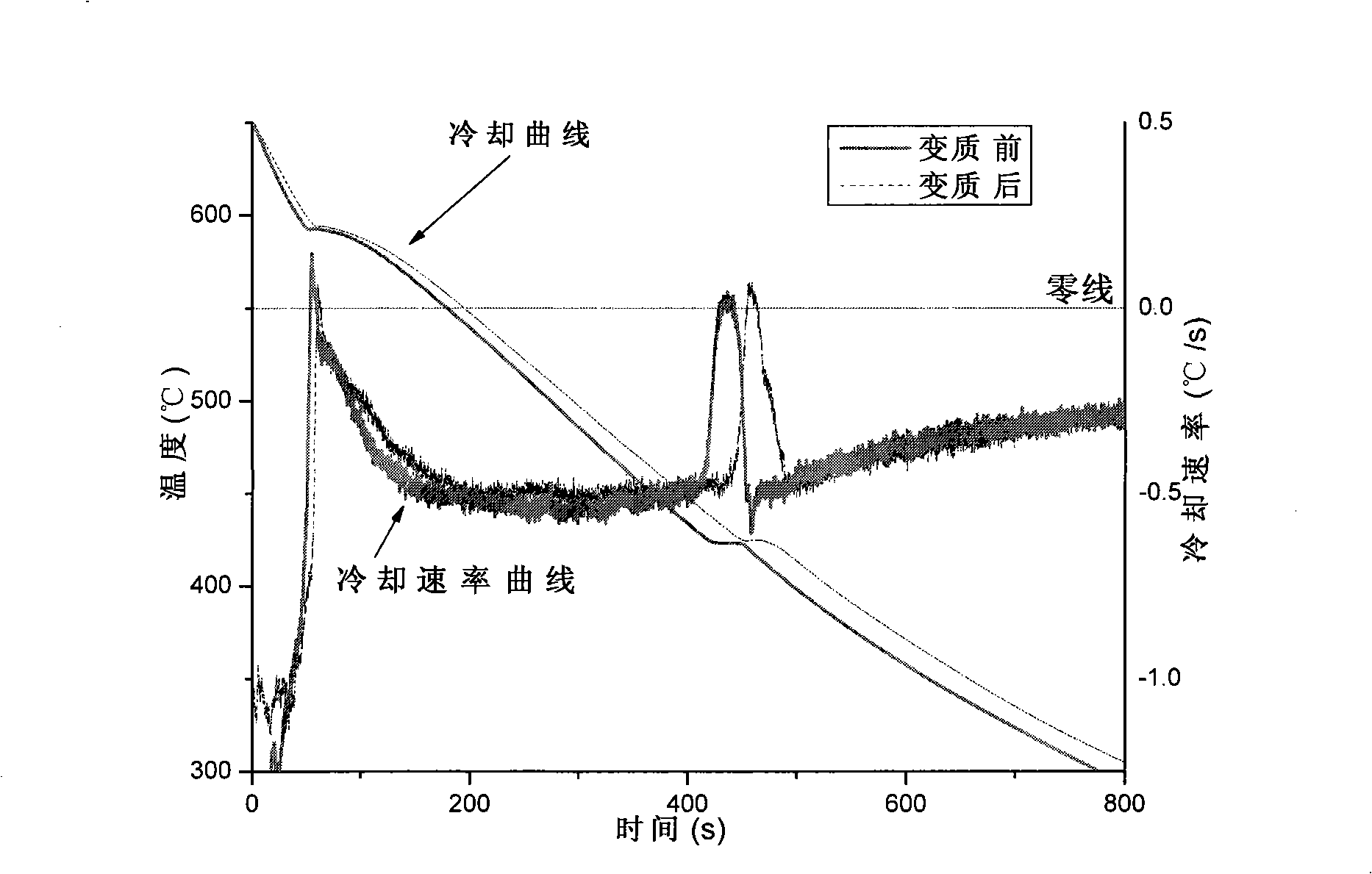
Thermal analysis test method and apparatus of magnesium and magnesium alloy deteriorative processing tissue thinning effect
InactiveCN101303319AObservation of reglow phenomenonRe-glow phenomenon recordsMaterial thermal analysisComputer-aidedComputer aid
The invention relates to a thermal analysis testing method of magnesium and magnesium alloy deteriorate process organizing thinning effect, which specifically uses the correlation between the deteriorate effect and the characteristic parameter on the cooling rate curve when a fused mass is solidified, establishes a thermal analysis testing technique, and develops a corresponding thermal analysis apparatus based on the thermal analysis testing technique. The thermal analysis testing technique of the invention has the following steps: 1, establishing a thermal analysis cooling curve (T -t); 2, derivation to the cooling curve to obtain a cooling rate curve (dT / dt -t); 3, respectively calculating the recalescence exothermic peak areas of the fused mass fore and after the deterioration; 4, defining the deterioration degree to judge the deterioration effect. The thermal analysis process includes data capture, computer analysis of the cooling curve, quantization of the exothermic peak areas, and result comparison; the process is realized by the computer and data analysis software, which are configured to a computer aided thermal analysis detecting device. The thermal analysis testing method and testing apparatus of the invention can be used in the smelting field of magnesium and magnesium alloy, as a ladle analysis approach to control and improve the metallurgy quality.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
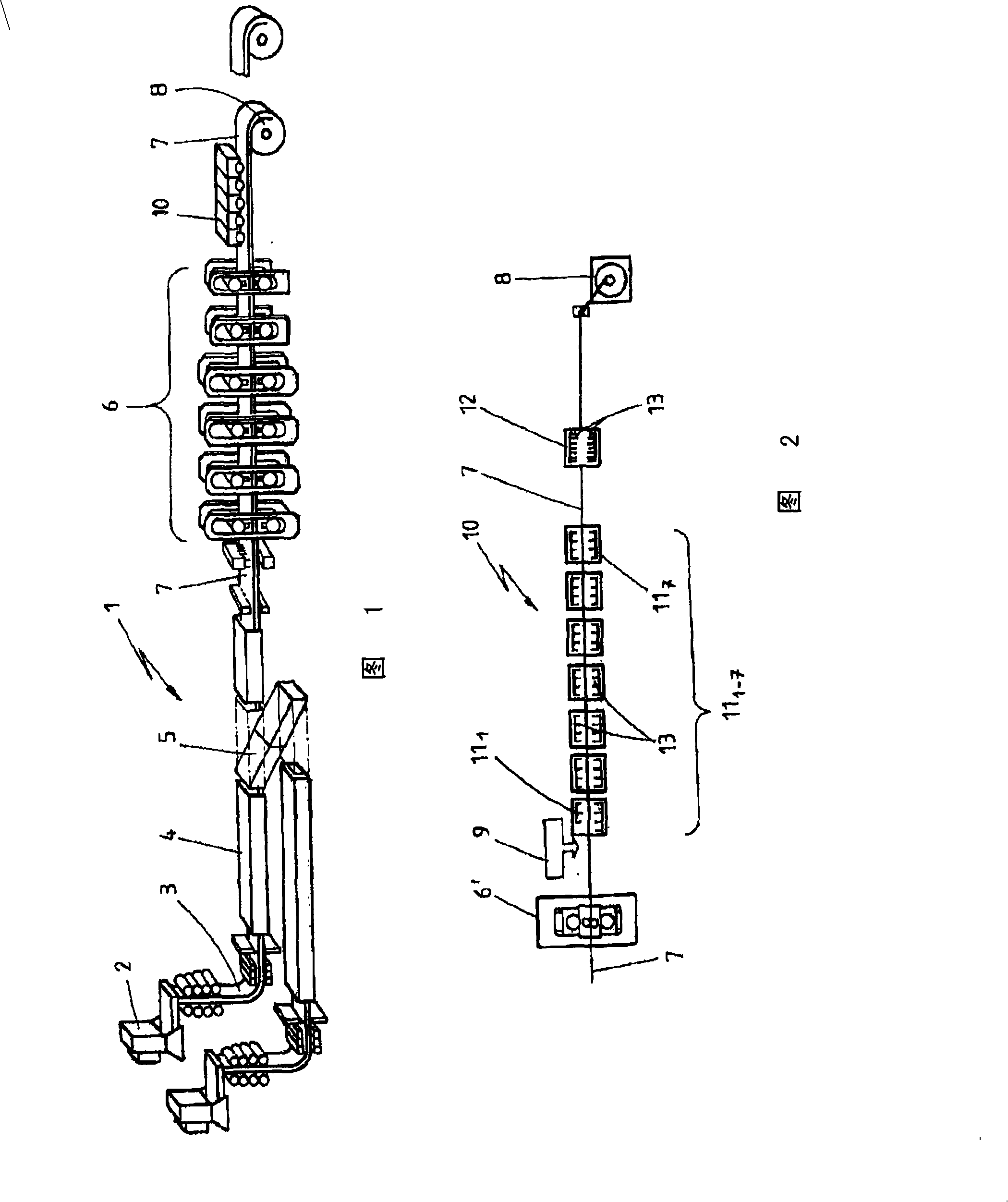
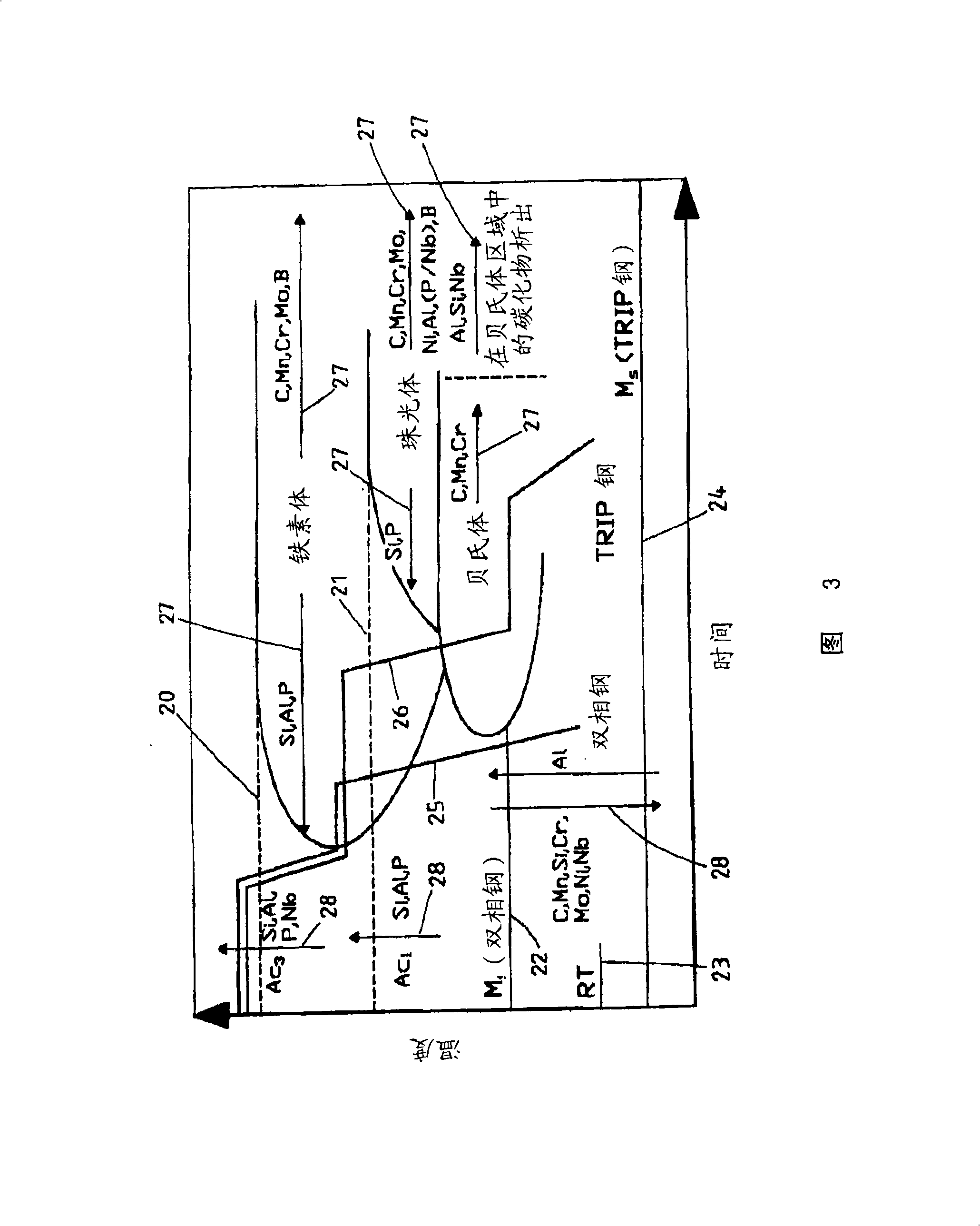
Method for producing hot strip with a multiphase structure
For the production of hot strip referred to as TRIP steel (transformation induced plasticity), with a multiphase structure and with outstandingly good deformation properties along with high strengths, from the hot-rolled state, the invention proposes a method which is carried out with a predetermined chemical composition of the steel grade used within the limits 0.12 - 0.25% C; 0.05 - 1.8% Si; 1.0 -2.0% Mn; the remainder Fe and customary accompanying elements and with a combined rolling and cooling strategy in such a way that a structure comprising 40 - 70% ferrite, 15 - 45% bainite and 5 - 20% residual austenite is obtained, wherein the finish rolling of the hot strip (7) is performed to set a very fine austenite grain (d < 8 [mu]m) in the final forming operation (6') at temperatures between 770 and 830 DEG C just above Ar3 in the region of the metastable austenite, and a controlled two-stage cooling (10, 11, 12) is carried out after the last rolling stand (6') of the hot strip (7) to a strip temperature in the range of bainite formation of 320 - 480 DEG C, with a holding time of about 650 - 730 DEG C,; the beginning of which is determined by the entry of the cooling curve into the ferrite region and the duration of which is determined by the transformation of the austenite into at least 40% ferrite.
Owner:SMS DEMAG AG
Memory alloy phase-change temperature measuring method and measuring system for implementing same
InactiveCN103499599AHigh sensitivityStrong reliabilityInvestigating phase/state changeAlloySpeed of sound
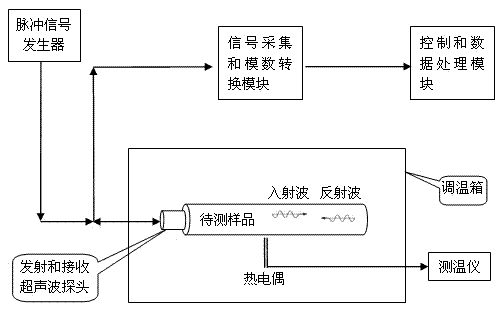
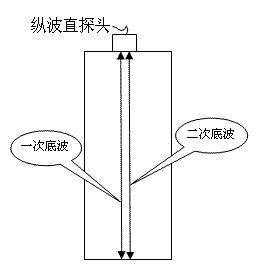
The invention discloses a memory alloy phase-change temperature measuring method. The measuring method comprises the following steps: firstly measuring a sound velocity-temperature curve in which the velocity of ultrasonic longitudinal waves in a memory alloy to be measured changes along with the temperature, wherein the sound velocity-temperature curve comprises a heating curve and a cooling curve; and determining the phase-change temperature of the memory alloy to be measured according to the sound velocity-temperature curve by using the sensitivity of the ultrasonic longitudinal velocity on the phase-change process of the memory alloy. The invention also discloses a measuring system implementing the measuring method. The measuring system comprises an ultrasonic wave emitting and receiving module, a signal collecting and analog-to-digital converting module, a sample temperature adjusting module and a control and data processing module. According to the measuring method and the measuring system, the phase-change temperature of the memory alloy is measured by using the sensitivity of the ultrasonic longitudinal wave velocity on the phase-change process of the memory alloy; compared with the prior art, the measuring method and the measuring system have the advantages of high sensitivity, strong reliability, wide application range and nondestructive measurement.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Multi-cycle quenching-partitioning-tempering (M Q-P-T) technique
ActiveCN102337385AAvoid crackingHigh strengthFurnace typesHeat treatment process controlCooling curveTempering
The invention discloses a multi-cycle quenching-partitioning-tempering (M Q-P-T) technique, belonging to the field of thermal processing technologies. The technique disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps of: dividing a workpiece with a large section into a plurality of regions from the surface to the centre part along the section, and making an MQ-P-T technique for the workpiecein combination with an isothermal cooling transformation curve of the workpiece; through alternately cooling the workpiece in a medium capable of quickly cooling and a medium capable of slowly cooling for many times, realizing a Q-P-T technique process in each alternate cooling of quick cooling and slow cooling; and gradually finishing martensitic transformation and carbon-rich retained austenitegeneration from the surface layer to the internal layer in the technique. The technique can be used for quenching and cooling processes of various types of mechanical structure members, thick plates directly quenched after rolling and various types of large-size profile steels which are made of microalloyed steels or alloy steels containing various types of components. According to the application of the technique disclosed by the invention, the purpose of obviously improving strength and toughness of large-size workpieces is achieved on the premise of avoiding cracking.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
System and method for sealing glass packaging body through laser scanning
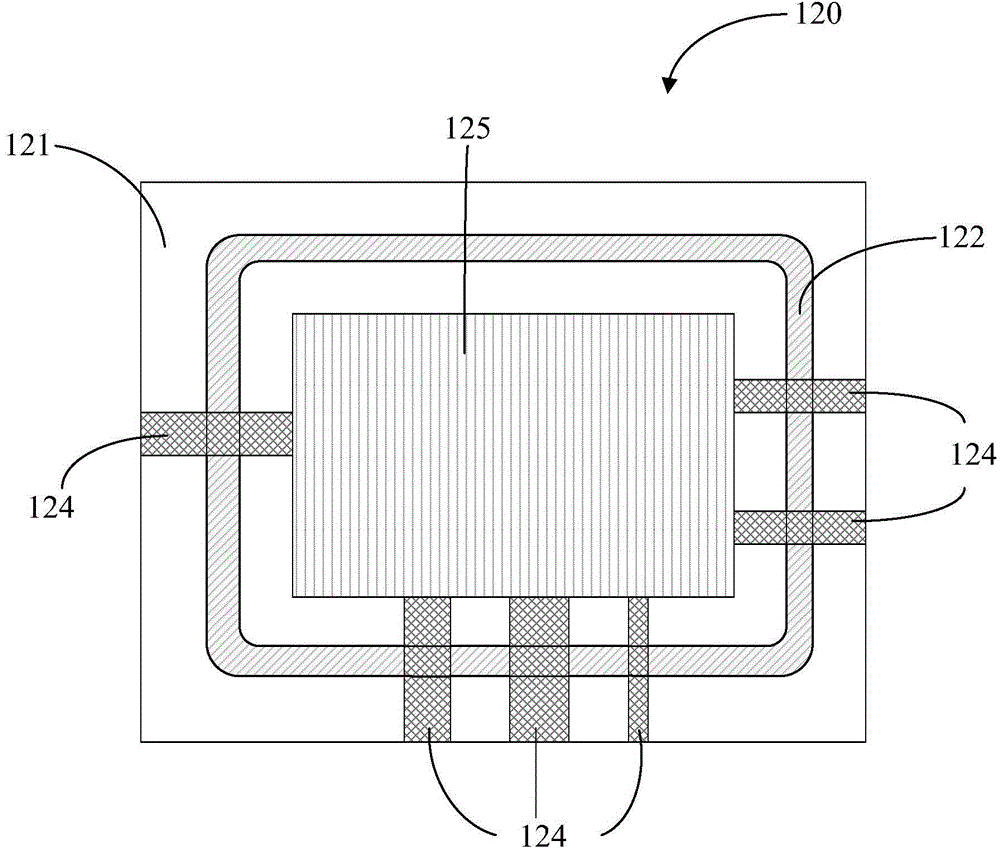
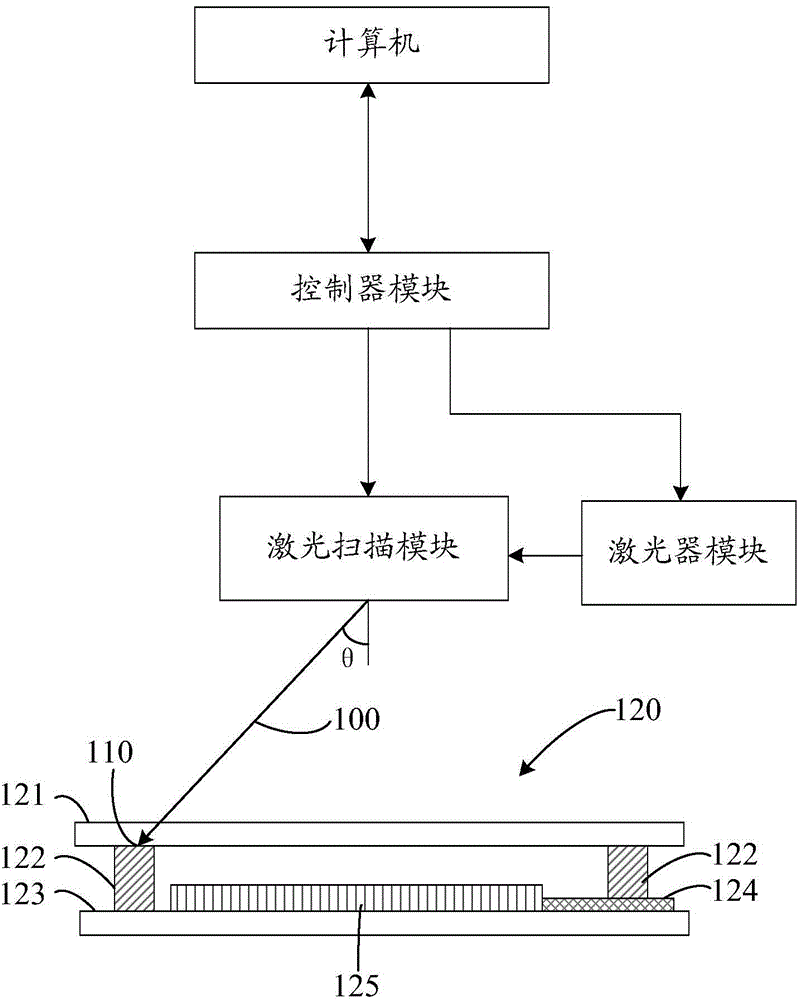
ActiveCN105336877AUniform and simultaneous heatingImprove the problem of uneven distribution of temperature fieldSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCooling curveState of art
The invention provides a system and a method for sealing a glass packaging body through laser scanning. A laser scanning module can enable laser to rapidly and periodically scan on glass frit so as to more uniformly heat the glass frit in a synchronous manner, and to solve the problem of uneven temperature field distribution in a packaging process in the prior art; according to the method for sealing the glass packaging body through laser scanning, a laser module can give out laser with a predetermined power curve, so that the heating process of the glass frit can be controlled according to the predetermined power curve; and further more, an additional temperature measurement module can measure and give feedback on real-time temperature on the surface of the glass frit, so that the glass frit can be heated or cooled based on the predetermined heating or cooling curves by adopting predetermined heating or cooling modes and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI MICRO ELECTRONICS EQUIP (GRP) CO LTD
Method and device for testing heat exchange coefficients of steel plate with different water film thickness
InactiveCN102661969AAccurate Cooling ControlAvoid errorsMaterial heat developmentCooling curveData acquisition
The invention provides a method and a device for testing heat exchange coefficients of steel plates with different water film thicknesses. A cylindrical water film cofferdam is welded on the surface of a cylindrical steel plate, the height h of a cofferdam is equal to the tested thickness of the water film; three temperature measuring points are set in a direction perpendicular to cylindrical steel plate at a distance interval x, holes are drilled on the side face of the cylindrical steel plate at positions which are x / 2, x3 / 2 and x5 / away from the upper end face of the cylindrical steel plate, thermocouples are then placed in the holes, and the cold ends of the thermocouples are connected to a multi-channel data acquisition device; during experiment, a steel sample is placed in a heating furnace, then the data acquisition device is started to acquire the temperature; when the steel plate reaches an initial cooling temperature, the steel sample is taken out and placed in a heat-insulation tank which is placed under a spray nozzle, later the spray nozzle is opened to spray water onto the water film cofferdam and thus, and a water film is covered on the surface of the steel plate; and when the steel plate reaches a final cooling temperature, the temperature acquisition is stopped, and thus, the steel plate cooling curve T (t) based on different positions at the upper end face of the cylindrical steel plate is obtained. Therefore, the method and the device can test the heat exchange coefficient of the surface of the steel plates under a condition of different thicknesses of water films.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
A device and method for heating or cooling a sample
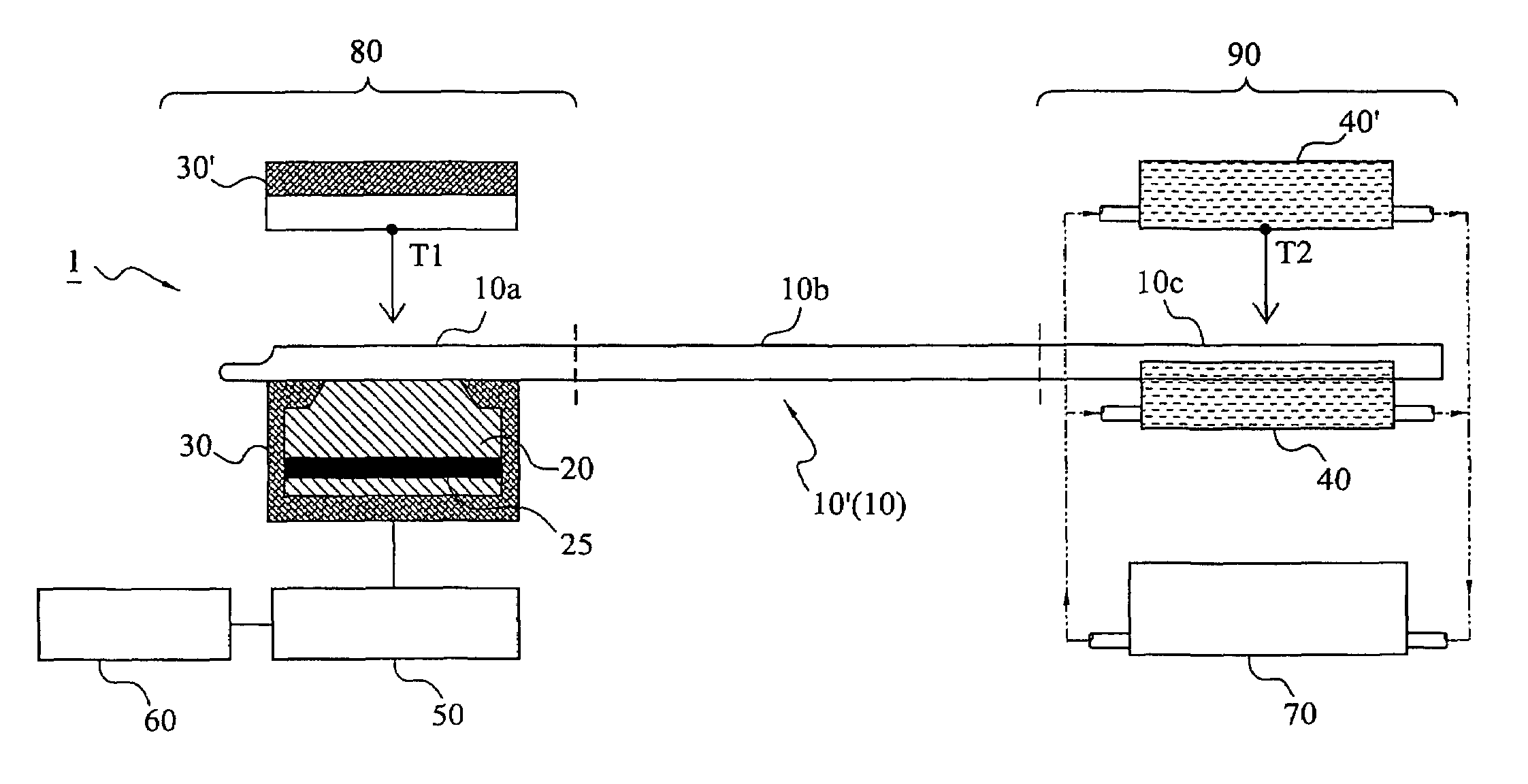
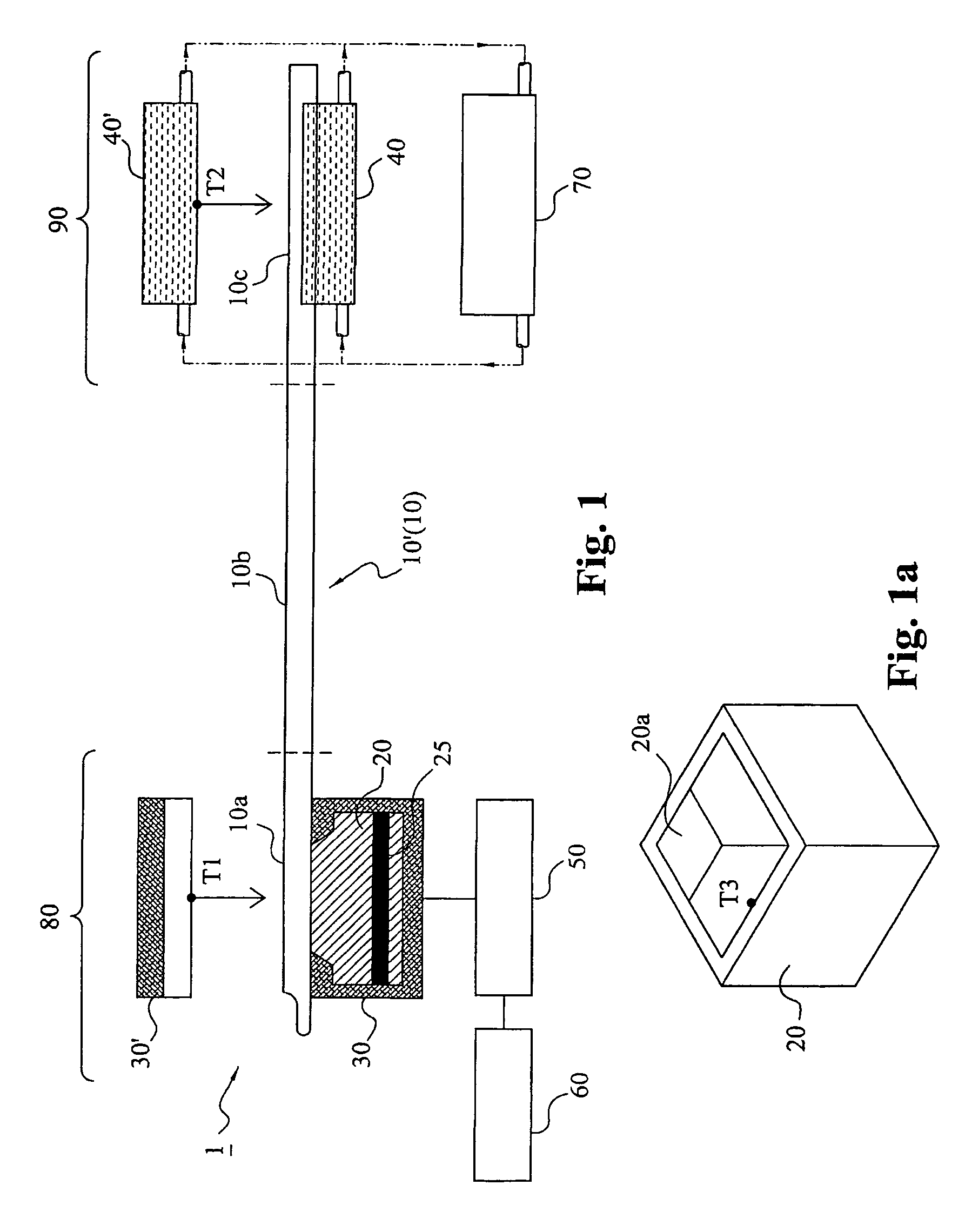
ActiveUS20190075786A1Enhanced agitationImprove the heating effectHeating or cooling apparatusBiological substance pretreatmentsThermal energyCooling curve
A sample heating / cooling device comprises a plurality of members operable in use to heat and / or cool one or more samples. Each member has a sample contact surface and is biased towards a resting position under the operation of a biasing means. The members are movable independently of one another against said bias under the application of a force on the sample contact surface and so are able to conform to the shape of a sample placed on the members to provide a uniform heating / cooling profile. The members may be mounted in a heating / cooling element and adapted to conduct thermal energy between the sample and the element. The device is particularly suitable for thawing frozen sample bags having an irregular shape. A corresponding method is also described.
Owner:CELL THERAPY CATAPULT
Development of certain mechanical cooling profiles and their use in an automated optimization method to reduce energy consumption in commercial buildings during the cooling season
ActiveUS20160195865A1Reduce thermal energyGeometric CADMechanical apparatusOperating energyEnergy consumption
The invention teaches a system and method for reducing energy consumption in commercial buildings. The invention provides development of certain mechanical cooling profiles and use of such profiles in an automated optimization method. Outputs communicate with the building management system of the commercial building, and regulate the cooling system during a season when the building activates the cooling system. Various embodiments are taught.
Owner:SHIEL PATRICK ANDREW
Method for calculating quenching medium heat exchange coefficient by combining finite element method with inverse heat conduction method
ActiveCN102521439AGuaranteed credibilityGuaranteed accuracySpecial data processing applicationsCooling curveElement model
The invention discloses a method for calculating a quenching medium heat exchange coefficient by combining a finite element method with an inverse heat conduction method, which relates to a method for calculating a quenching medium heat exchange coefficient. The method comprises the following steps of: using a probe body, testing by an experiment to obtain the cooling curve of an internal point of the body, establishing a finite element model of the probe body, simulating a temperature field, and verifying the one-dimensional property of a problem; establishing a one-dimensional heat conduction micro equation and a sensitive coefficient equation under a coordinate system, and solving the heat-flow density value of the surface of the body surface by using the inverse heat conduction method; and verifying the measured temperature of the internal point of the probe in comparison to a calculated value, namely the heat exchange coefficient of the quenching medium calculated according to the Newton heat exchange law, so that the solution accuracy is ensured. The method is used for calculating the heat exchange coefficient of quenching medium.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Automatic server fan speed adjusting method
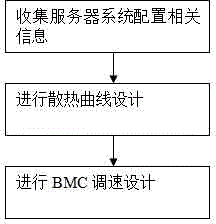
InactiveCN104314852AIncrease flexibilityEliminate workloadDigital data processing detailsPump controlCooling curveRelevant information
Disclosed is an automatic server fan speed adjusting method. The automatic server fan speed adjusting method includes the steps of S10, collecting related information of server system configuration, and specifically, collecting the information of the server system configuration in the server system startup phase by the aid of a BIOS (basic input / output system); S11, performing cooling curve design, completing the cooling curve design according to the various collected information of the server system configuration and forming a corresponding form of the server system configuration and cooling curves; S12, performing BMC speed adjusting design and loading different cooling curves according to the information of the server system configuration to have rotating speed of a fan automatically adjusted. The corresponding form of the configuration and the cooling curves is completed in the design state, functional design in BMC speed adjusting is led in, the automatic speed adjusting function after modification of the configuration of the system can be realized, flexibility in operation of a server room is improved, workload for re-customizing of BMC and updating of firmware is omitted, and cost is lowered.
Owner:LANGCHAO ELECTRONIC INFORMATION IND CO LTD
Measuring system and screening method for thermal conductivity assembly heat conductivity
ActiveCN1932494AReduced measurement timeShorten the timeMaterial heat developmentSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsCooling curveFast measurement
A measuring system for the temperature conductivity of the thermal conducting module is to set the heated metal mass temperature of the heating end and the radiating water cover temperature of the radiating end. So it can generate the temperature difference between the heating end and the thermal conducting module to compare the cooling speed of the heating metal mass to determine the temperature conductivity. In addition, it can get the relative performance number by the heat changing in the cooling process to get the Qmax value by conversing with the biggest performance number. Also the invention provides a method to select the temperature conductivity of the thermal conducting module by defining the cooling curve of the standard sample.
Owner:YEH CHIANG TECH CORP
Automatic cooling method and equipment in process of heating large forgings
ActiveCN102108435APrecision coolingMeet the requirements of the cooling curveFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesCooling curveAutomatic control
The invention discloses an automatic cooling method and automatic cooling equipment in the process of heating large forgings. The automatic cooling equipment in the process of heating the large forgings mainly cools the large forgings through blast blowers aiming at the heat treatment of forgings such as large spindles and the like; and by measuring the temperature of the large forgings, the number and rotating speed of the blast blowers participating the cooling work are automatically controlled, and when preset time (temperature) is achieved, an automatic control system stops the work of the blast blowers and the cooling process is finished. Through the invention, the large forgings can be cooled according to a cooling curve, no deviation is ensured, and the cooling process is accurately controlled. The invention can be applied to the heat treatment cooling process of large spindle forgings, and also can be applied to the field of machining requiring accurate control of the cooling process.
Owner:JIANGSU JINYUAN FORGE
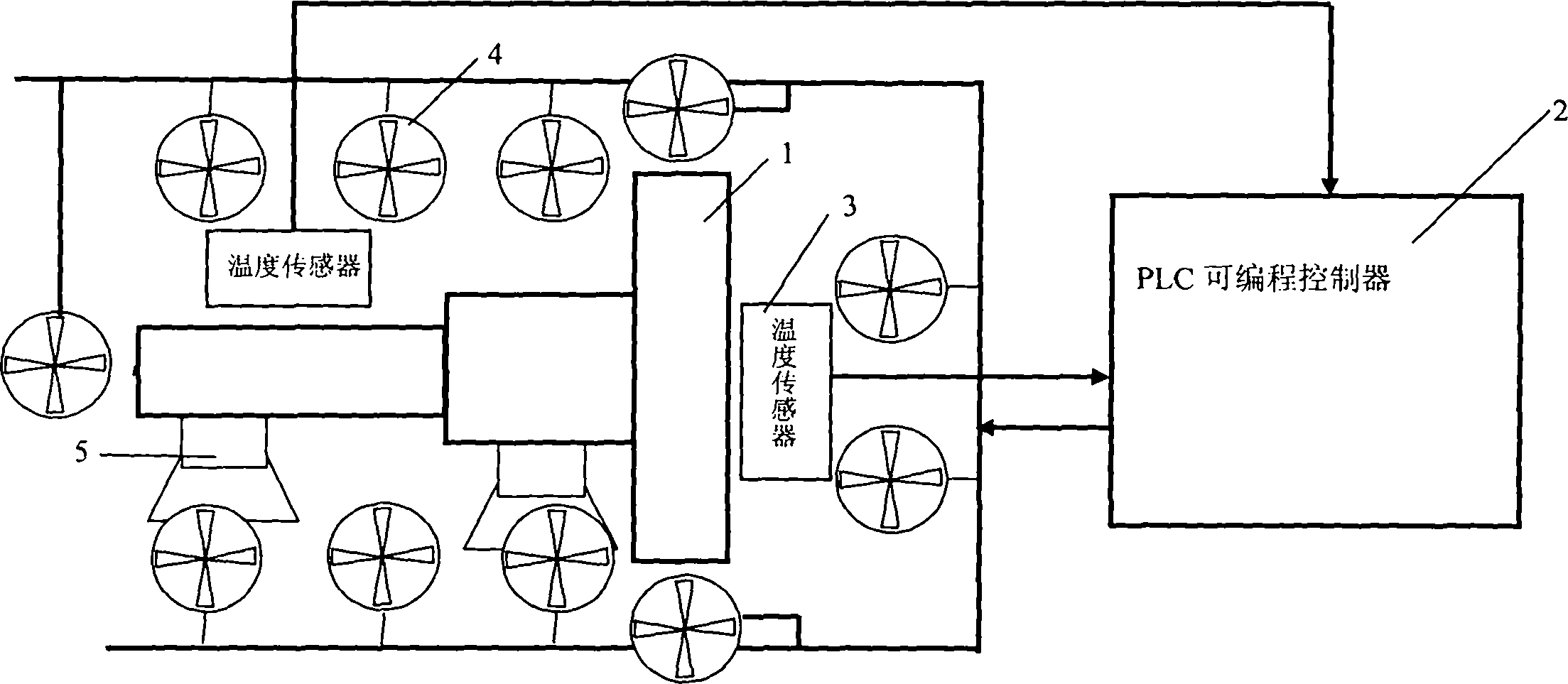
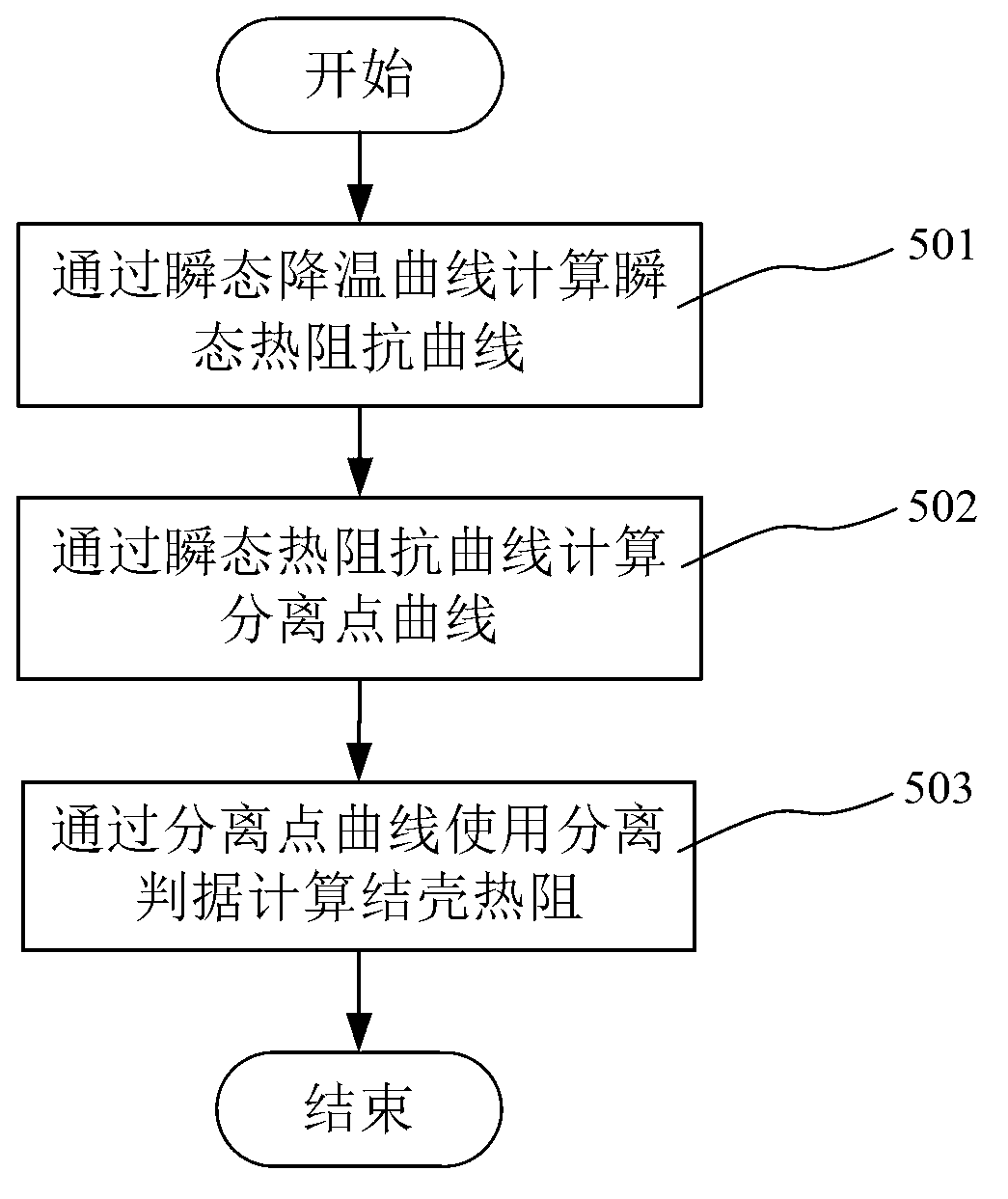
Junction-to-case thermal resistance testing method
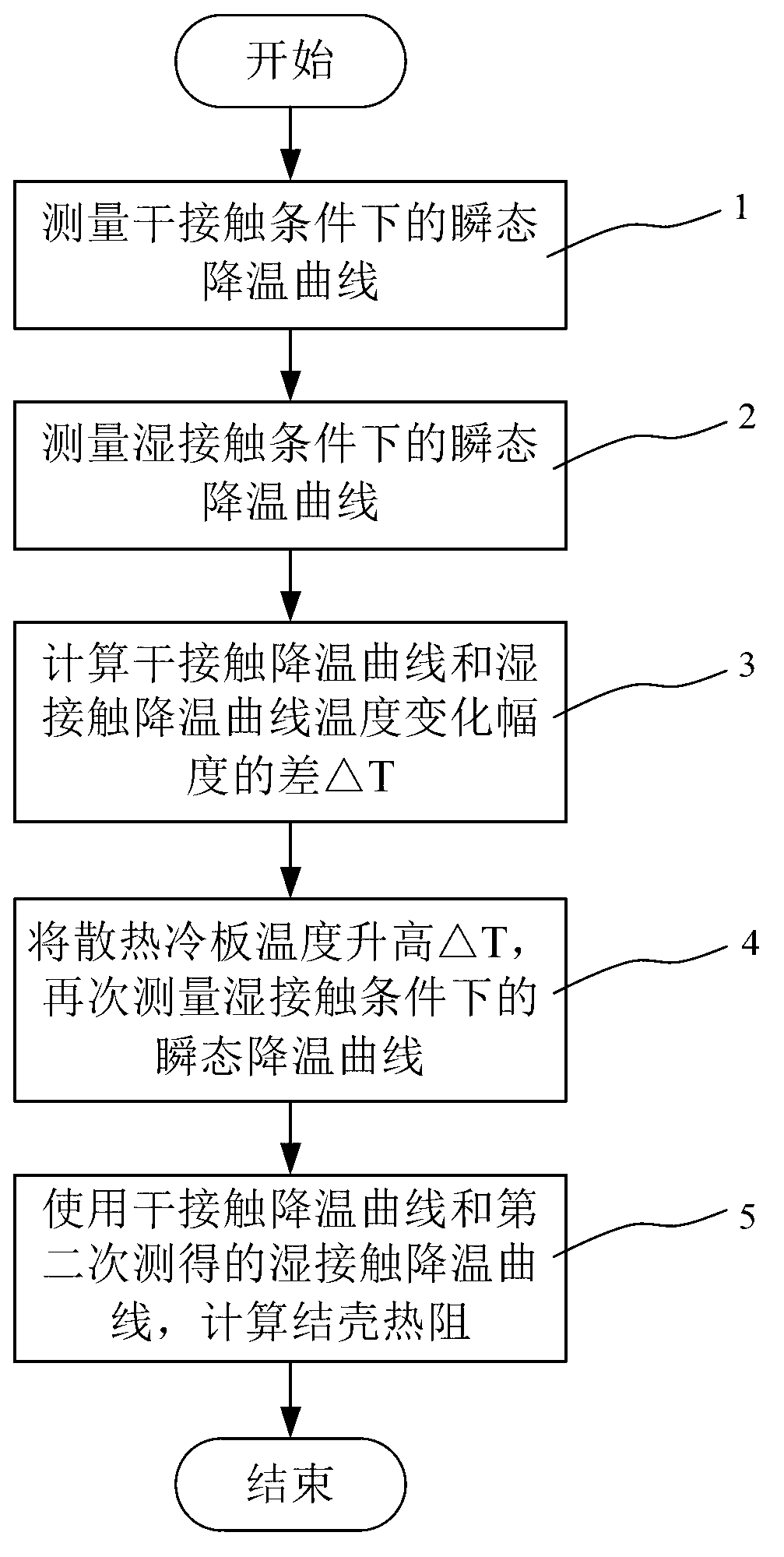
ActiveCN103175861AAvoid early separationUniform temperature distributionMaterial thermal conductivityMaterial heat developmentCooling curveEngineering
The invention discloses a junction-to-case thermal resistance testing method, comprising the following steps of: (1) measuring a transient cooling curve of a to-be-tested device under a dry contact condition; (2) measuring a transient cooling curve of the to-be-tested device under a wet contact condition; (3) calculating difference Delta T between temperature variation amplitudes of the transient cooling curve under the dry contact condition and the transient cooling curve under the wet contact condition; (4) warming up a constant-temperature heat dissipation cold plate in the tested equipment by Delta T, and measuring the transient cooling curve under the wet contact condition again; (5) calculating the junction-to-case thermal resistance according to the dry-contact transient cooling curve measured in the step (1) and the wet-contact transient cooling curve measured in the step (4).
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Control method for roller-type quenching process of large-single-weight large-section super-thick steel plate
ActiveCN107760830AThe actual cooling curve is close toReduce consumptionFurnace typesHeat treatment process controlCooling curveQuenching
The invention provides a control method for a roller-type quenching process of a large-single-weight large-section super-thick steel plate. According to the control method, a specific heat model, a heat conduction coefficient model, a temperature field model and a correction model are involved. An implementation process of the control method comprises the following steps: inputting various parameters such as steel plate parameters, technological regulations and actually measured parameters at first, wherein the steel plate parameters comprise the thickness, the length and the carbon content, the technological regulations comprise the roller bed speed, the acceleration and the like, and the actually measured parameters comprise the tapping temperature, the temperature after air cooling, thetemperature after self-tempering and the like; calculating temperature fields in an air cooling section, a water cooling section and a self-tempering temperature section in sequence by utilizing thetemperature field mode as well as by invoking the specific heat model and the heat conduction coefficient model; correcting the temperature fields through the correction model; and acquiring a simulation result, that is, acquiring a group of cooling curves and cooling rate curves at different thicknesses. The control method has the advantages of being combined with the actual production situationso as to acquire the actual cooling curves and cooling rate curves; part of an actual debugging process can be substituted with model calculation; the control method can be utilized for guiding the adjustment of the technological regulations; the production cost can be reduced; and besides, a product in a good plate shape can be acquired.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Petroleum product condensation point metering device
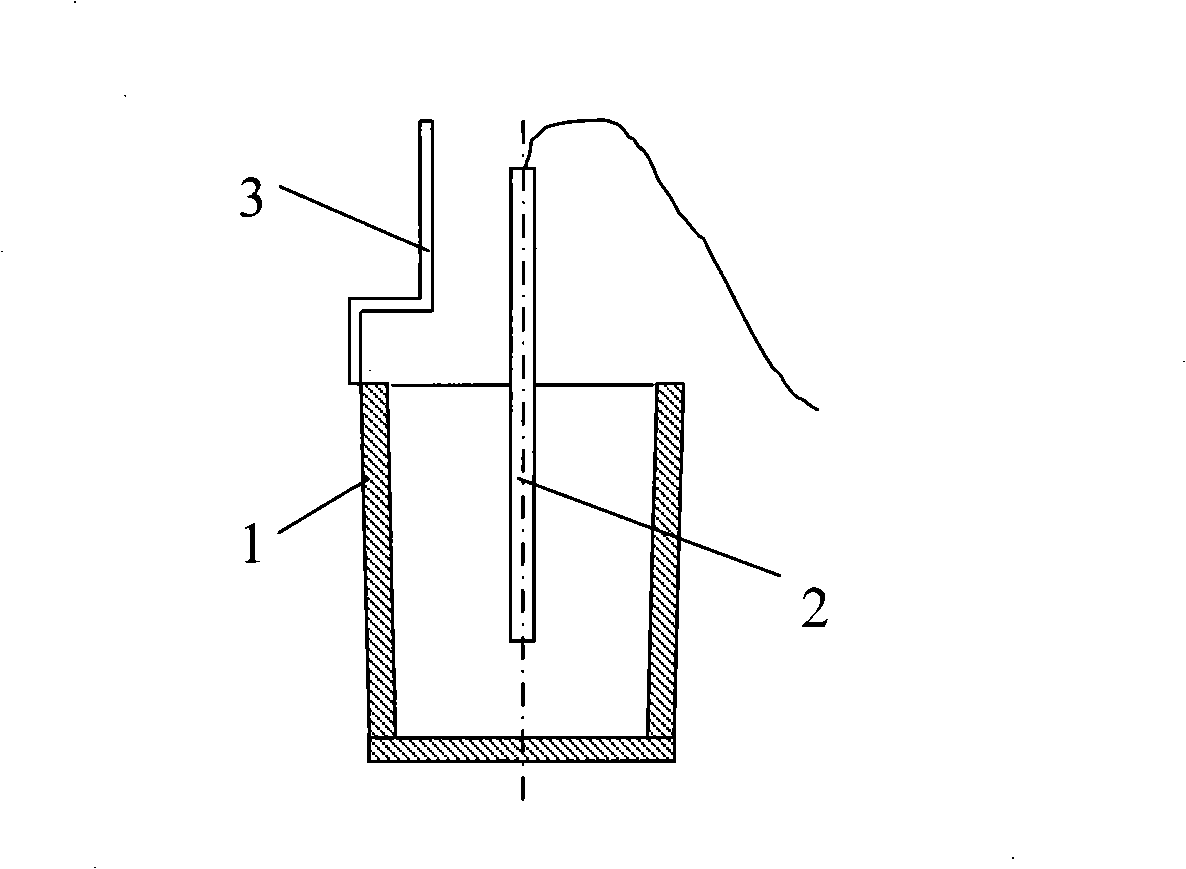
InactiveCN101101270ASimple structureReduce volumeMaterial testing goodsInvestigating phase/state changeCooling curveLine tubing
A metering system of petroleum products solidification point, it is made up of control device, pressure device, oil bottle, measurement transducer, solenoid valve, pressure transducer, temperature transducer and refrigerating plant, of which pressure transducer, oil bottle, measurement transducer and solenoid valve are connected with pipeline compliably, temperature transducer is set in the measurement transducer, control device is connected apart with pressure device, refrigerating plant, solenoid valve, pressure transducer and temperature transducer, in term of the testing process of cooling curve under national standard defined experiment condition. The invention is under anticipative temperature spot of experiment, compressing to oil bottle by pressure device, driving the flow of sample in the pipeline, and confirming the freezing point of sample by testing the change of line pressure, providing the new method of testing petroleum products' freezing point.
Owner:冯俊博
Testing method for thermal conductivity of phase change energy storage material
ActiveCN108717067AAvoid makingGuarantee stabilityMaterial thermal conductivityMaterial heat developmentCooling curveHeat flow
The invention provides a testing method for the thermal conductivity of a phase change energy storage material. The testing method comprises the following steps: S1, respectively measuring the heat flows P (Sam) of a background, water and a sample to be tested in the temperature range of T1-T2 by using a scanning differential calorimeter; S2, assembling a heating / cooling curve tester, respectivelytesting heating curves or cooling curves of the water and the sample to be tested by using the rising / cooling curve tester, and according to whether the temperature T0 to be tested is equal to the phase change temperature T (Sam) as well as a heating melting process or a cooling crystallization process, calculating the thermal conductivity lambda (Sam) of the sample to be tested at the temperature T0 to be tested through an Equation 1 or 2 or 3. The testing method is a method proposed on the basis of the thermal conductivity law (Fourier's law), has no special requirement on the shape of thesample to be tested, and is applicable to thermal conductivity testing of solid-state and liquid-state samples and even a sample during phase change; especially, by the testing method, a great convenience is brought to thermal conductivity testing and enhanced thermal conductivity research of a room temperature PCM.
Owner:QINGHAI INST OF SALT LAKES OF CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Device for judging eye disease and using method thereof
InactiveCN101238972ALess susceptible to infectionReduce duplicationThermometers using physical/chemical changesEye diagnosticsPatient needCooling temperature
The invention discloses a device for judging the eye disease (including xerophthalma) and method thereof of application. The image at the front surface of the eyeball of patient suffered from eye disease is shot by a infra-red thermograph and the precise temperature variation of cornea special position is traced in unit time, and the K value of cooling curve and cooling temperature difference delta T are obtained according to temperature difference in time sequence, the curve of K value and delta T value is maximized to help the doctor judge the diseases of the eye. The said device and method has features of non-invasion, high repeatability and low mutation, the patient needs not induce the fear resulted from the filter paper or stain into eyes and uncomfortable feeling and danger of infecting the bacteria because of direct contact, so that the invention provides convenience and high accuracy.
Owner:UNITED INTEGRATED SERVICES
Method for measuring aluminum alloy continuous cooling transformation curve
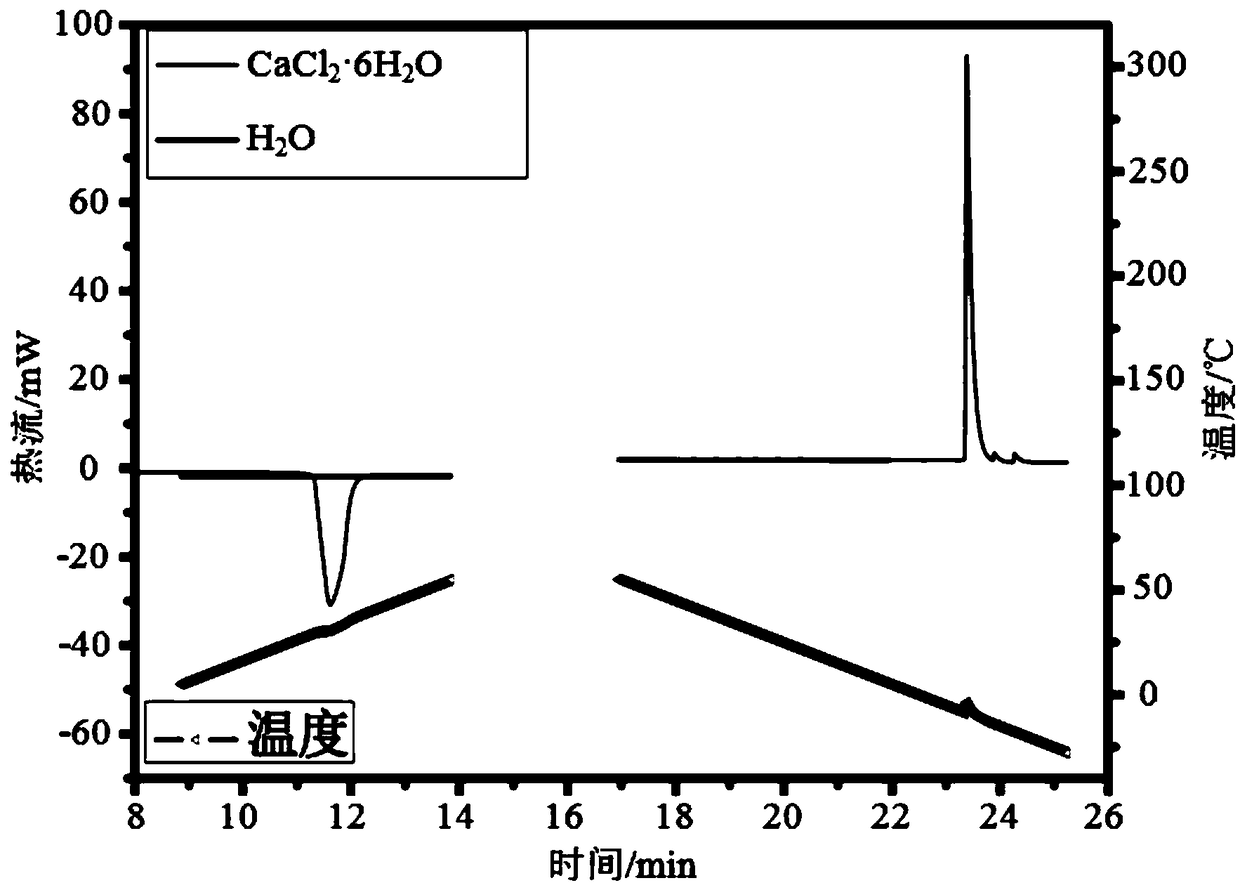
The invention relates to a method for measuring an aluminum alloy continuous cooling transformation curve, and belongs to the technical field of non-ferrous metal material preparation. According to the method provided by the invention, by recording the change of thermal equivalents in different temperature intervals, precipitation temperature intervals of quenching reaction in a quenching process are distinguished based on the change of the thermal equivalents. The method provided by the invention measures exothermic reaction of aluminum alloy in the quenching process by applying a differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), and combines with microstructure analysis and mechanical property testing, so as to obtain the aluminum alloy continuous cooling transformation curve. Compared with other methods, the method provided by the invention can distinguish initial and final temperatures of different quenching-induced precipitated phases based on accurate cooling curves in certain cooling intervals. The continuous cooling transformation curve obtained by the method provided by the invention has the advantages of high precision, great guiding significance and the like.
Owner:深圳卓聚新材料有限责任公司
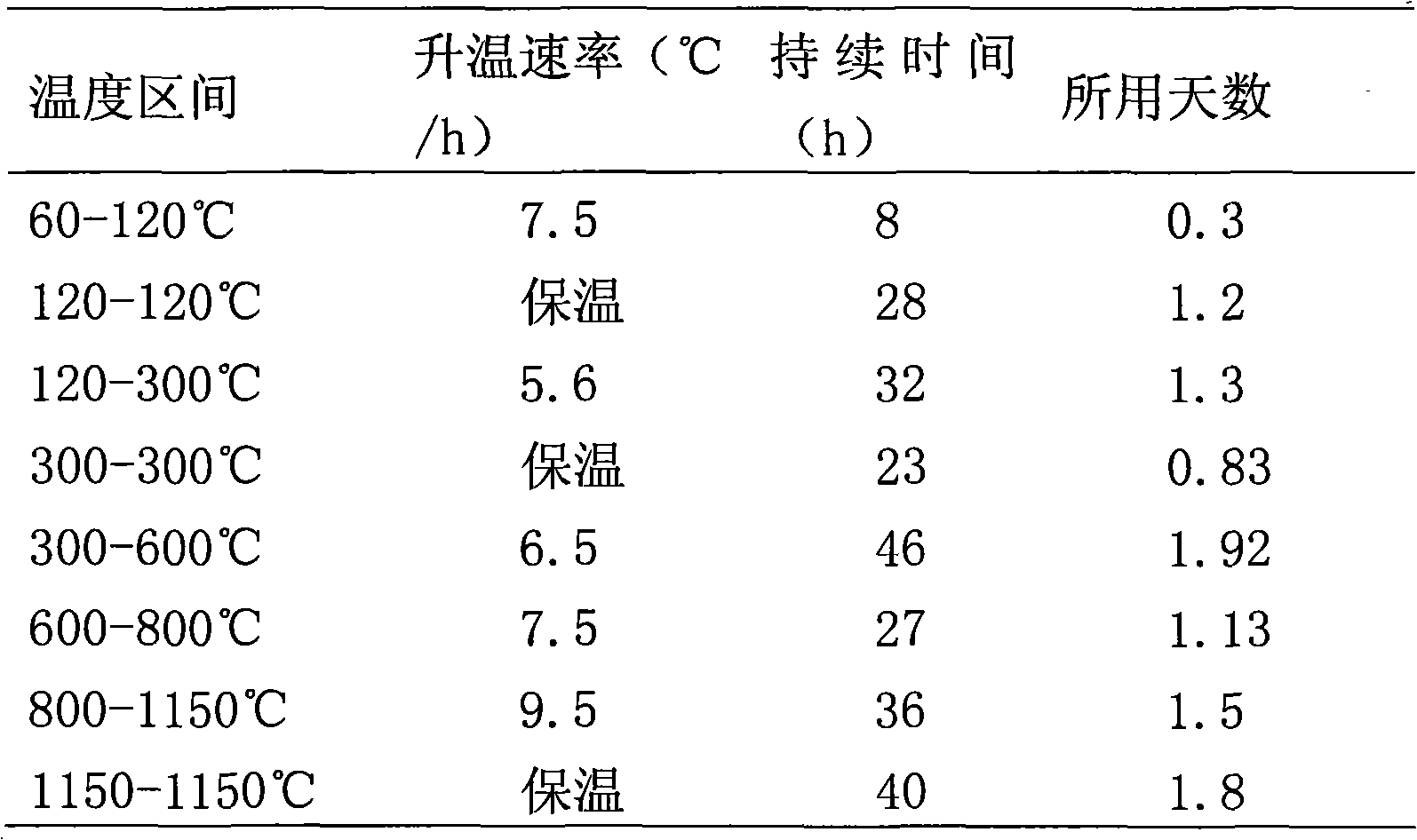
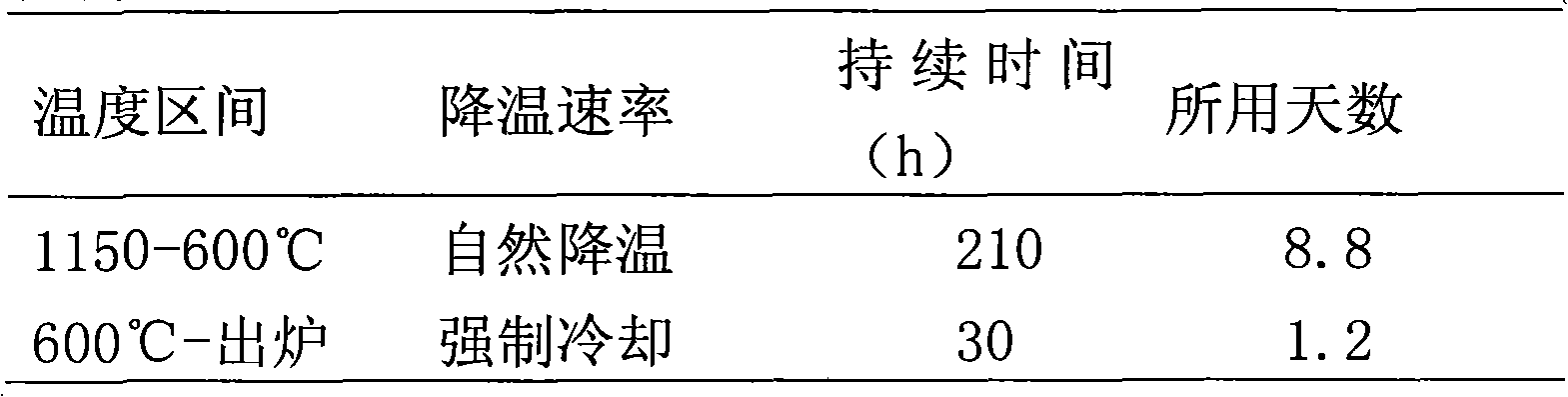
Method for drying carbon anode roasting furnace
The invention discloses a method for drying an annular open roasting furnace, which is characterized in that: (1), a 240-hour heating curve and a 240-hour cooling curve are adopted in a roasting process; and (2), combustion racks are placed in observation holes 2 and 4 of a No.2 furnace chamber and a No.22 furnace chamber, smoke exhaust racks are placed in a No.4 furnace chamber and a No.23 furnace chamber, ignition is started from the observation holes 2 in the No.2 furnace chamber and the No.22 furnace chamber, a fourth furnace chamber is added by moving the smoke exhaust racks after three flame travel periods, ignition in the observation hole 4 is determined according to the following condition of the temperature rise to the temperature curve of the drying furnace, and after each flame travel period, the smoke exhaust rack is continuously moved and a combustion rack is added till each system has three combustion racks and forms 8-chamber operation, wherein a system travel period is 30 hours. In the method for drying the carbon anode roasting furnace, the carbon anode roasting furnace is a 38-chamber annular open roasting furnace, the technical parameters are optimized effectively, the furnace drying time is shortened, the process for converting a roasting drying furnace curve into a normal roasting production curve after the furnace drying is finished is simplified, and the furnace drying cost is reduced.
Owner:SUNSTONE DEV
Detection method of semiconductor laser degradation mechanism
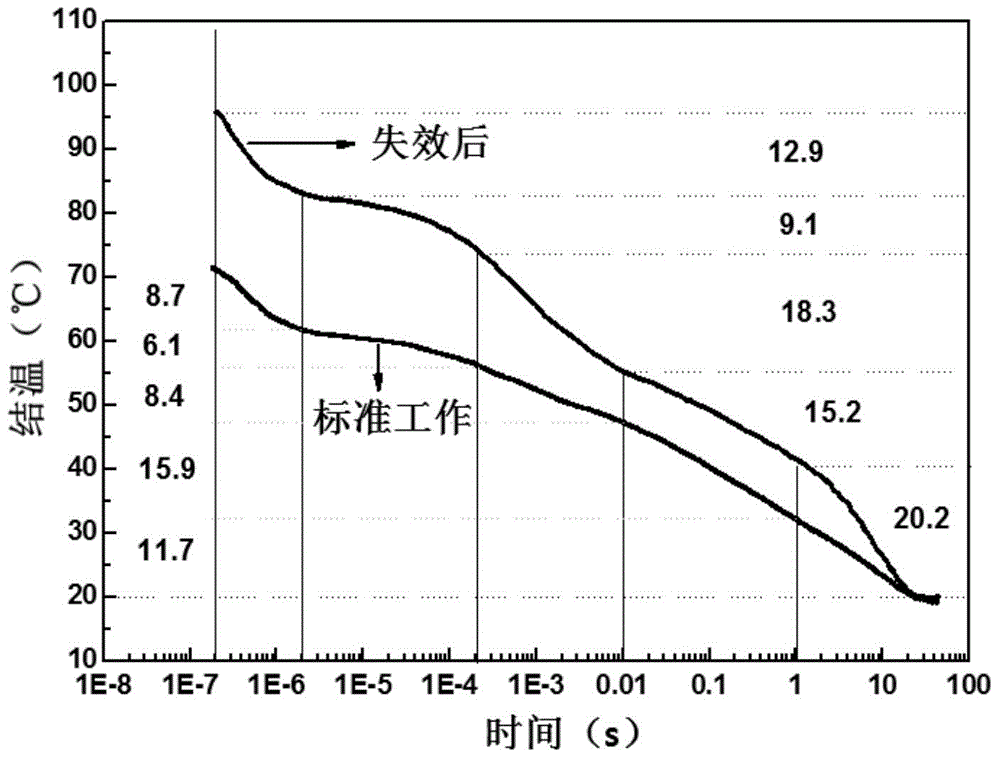
InactiveCN105807197AExtend working lifeIndividual semiconductor device testingCooling curveJunction temperature
The present invention discloses a detection method of a semiconductor laser degradation mechanism. The method comprises the steps of measuring the transient cooling curve of a failed semiconductor laser and the transient cooling curve of a normally working semiconductor laser in a same condition, comparing the two transient cooling curves, and obtaining the degradation mechanism of the failed semiconductor laser. According to the method, the transient heat transfer characteristics of the semiconductor laser is utilized, the transient cooling curve of the laser is obtained through a forward voltage junction temperature measurement method or other methods, then the degradation position of the laser is found through comparing the difference between the transient cooling curve of the failed laser and the transient cooling curve of the normally working laser, the possible failure mechanism of the laser is preliminarily determined according to the magnitude of change, thus the failure reason of the laser is rapidly determined and a solution is rapidly found, and finally the service life of the laser is prolonged.
Owner:杭州增益光电科技有限公司
Measuring system and screening method for thermal conductive efficiencies of thermal conductive devices
ActiveUS7581878B2Reduced measurement timeLow costThermometer detailsMaterial thermal conductivityCooling curveScreening method
The measuring system generates a temperature difference between a heating terminal and a terminal conductive device by setting the temperature of a metal heated block at the heating terminal and the temperature of a heat dissipating water jacket at a heat dissipating terminal, and judges the thermal conductive capability of the thermal conductive device by comparing the cooling speed of the metal heating bock to obtain a relative power value according to the variation of heat quantity of the metal heated block in practical temperature reduction process. The maximum thermal conductive quantity (Qmax value) of the thermal conductive device can be rapidly obtained by parameter conversion with respect to the maximum power value. In the case of confirming the cooling curve (cooling speed) of a standard sample, the object of screening the thermal conductive efficiencies of the thermal conductive devices can be achieved by using the cooling curve.
Owner:YEH CHIANG TECH CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com