Patents
Literature
473 results about "Sample temperature" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The temperature of a drug test sample must be measured during the first 4 minutes after it was received, as the sample changes depending on the ambient temperature. Acceptable range is from 90°F to 100°F (32°C - 38°C). Any sample with a temperature outside this range will immediately be suspicious.
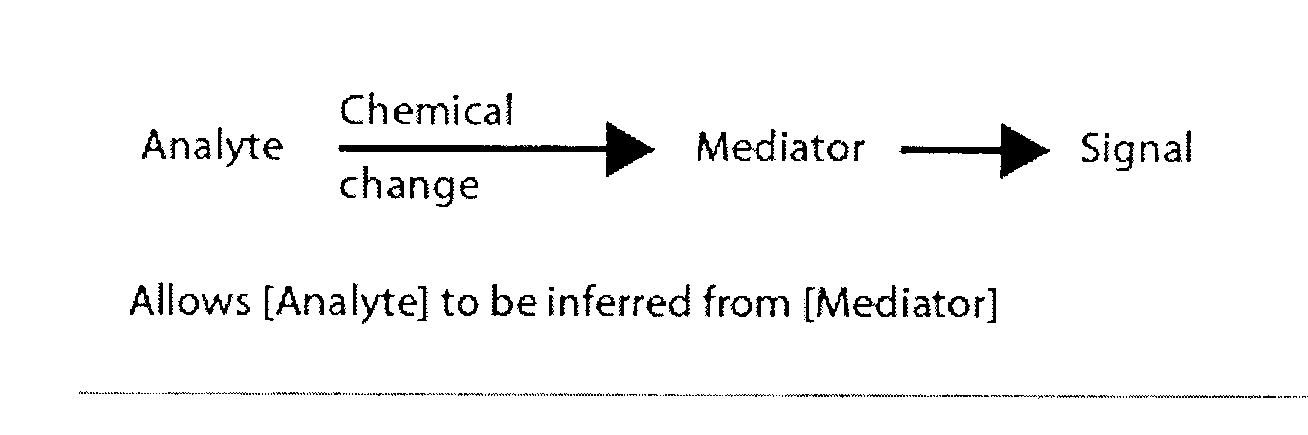
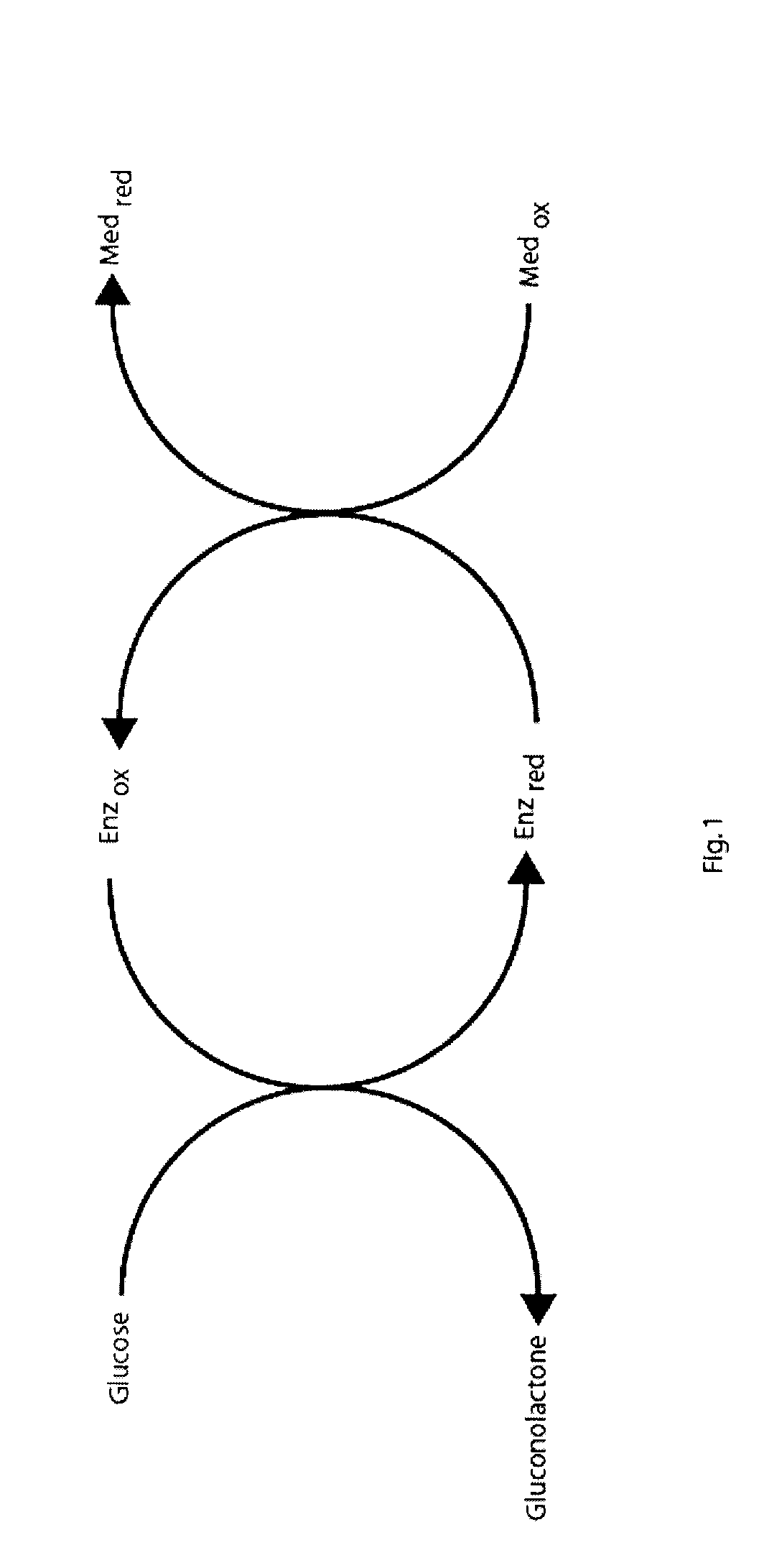
Analyte determination method and analyte meter
The presence of oxygen or red blood cells in a sample applied to an electrochemical test strip that makes use of a reduced mediator is corrected for by an additive correction factor that is determined as a function of the temperature of the sample and a measurement that reflects the oxygen carrying capacity of the sample. The measured oxygen carrying capacity can also be used to determine hematocrit and to distinguish between blood samples and control solutions applied to a test strip.
Owner:AGAMATRIX INC
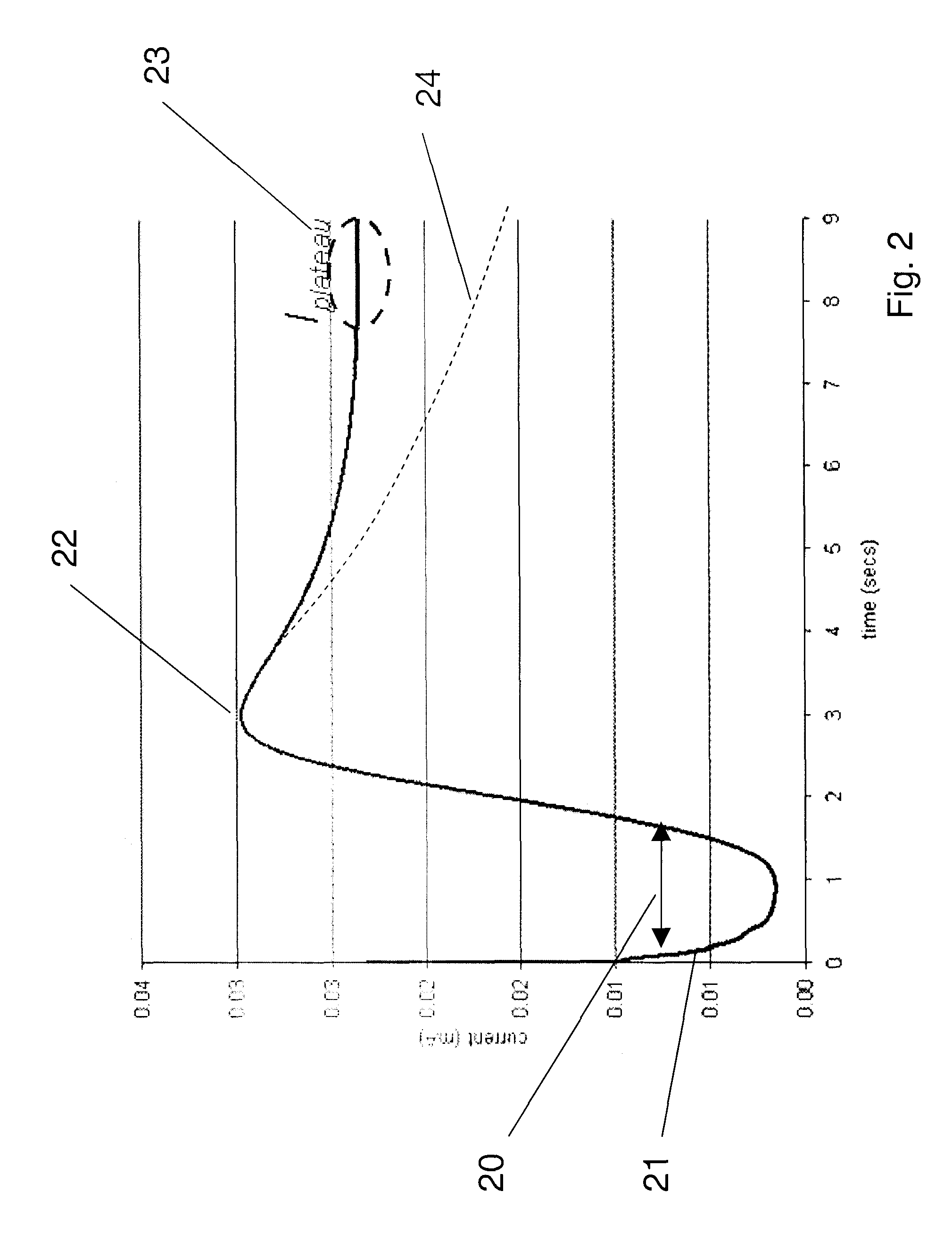
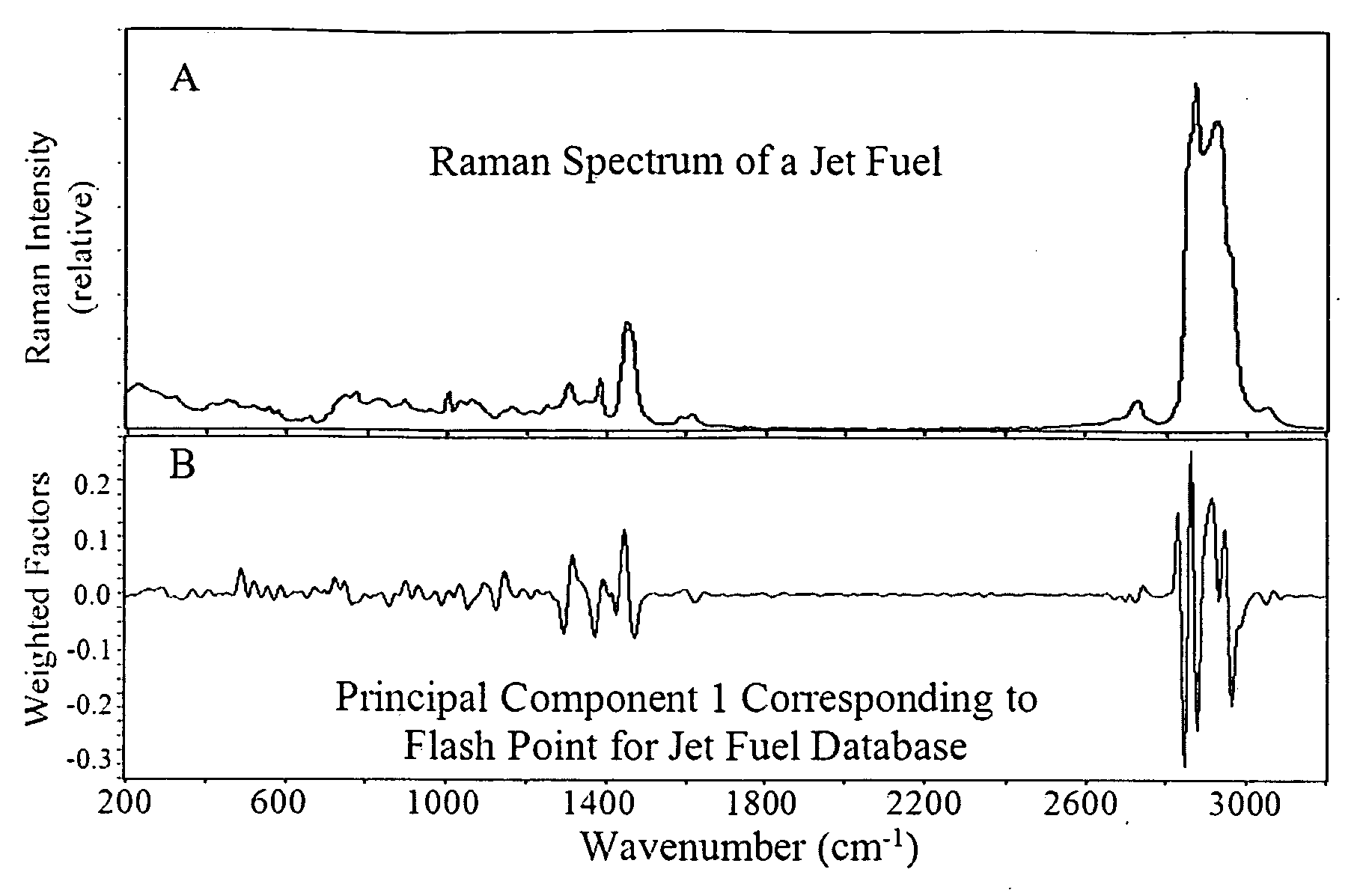
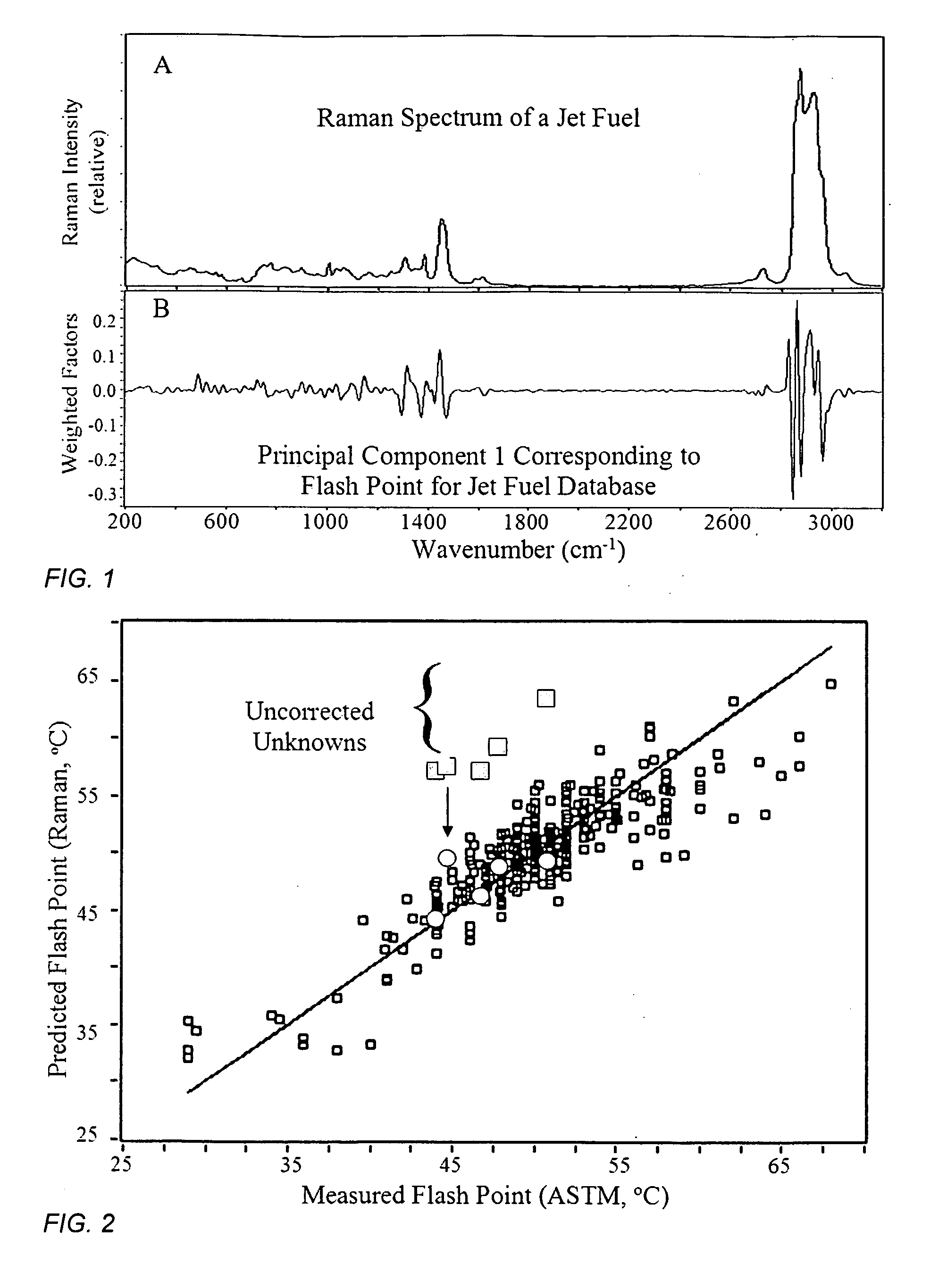
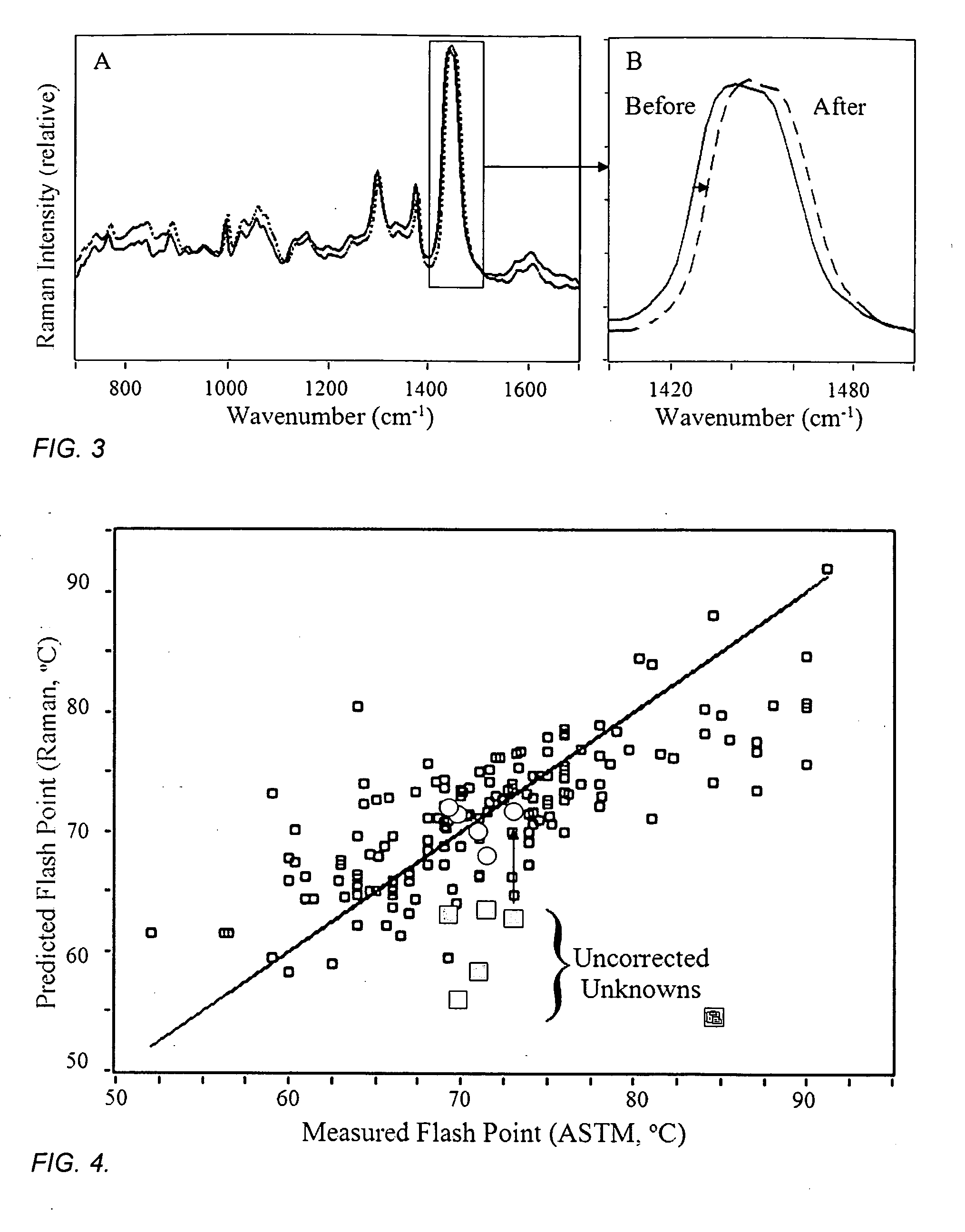
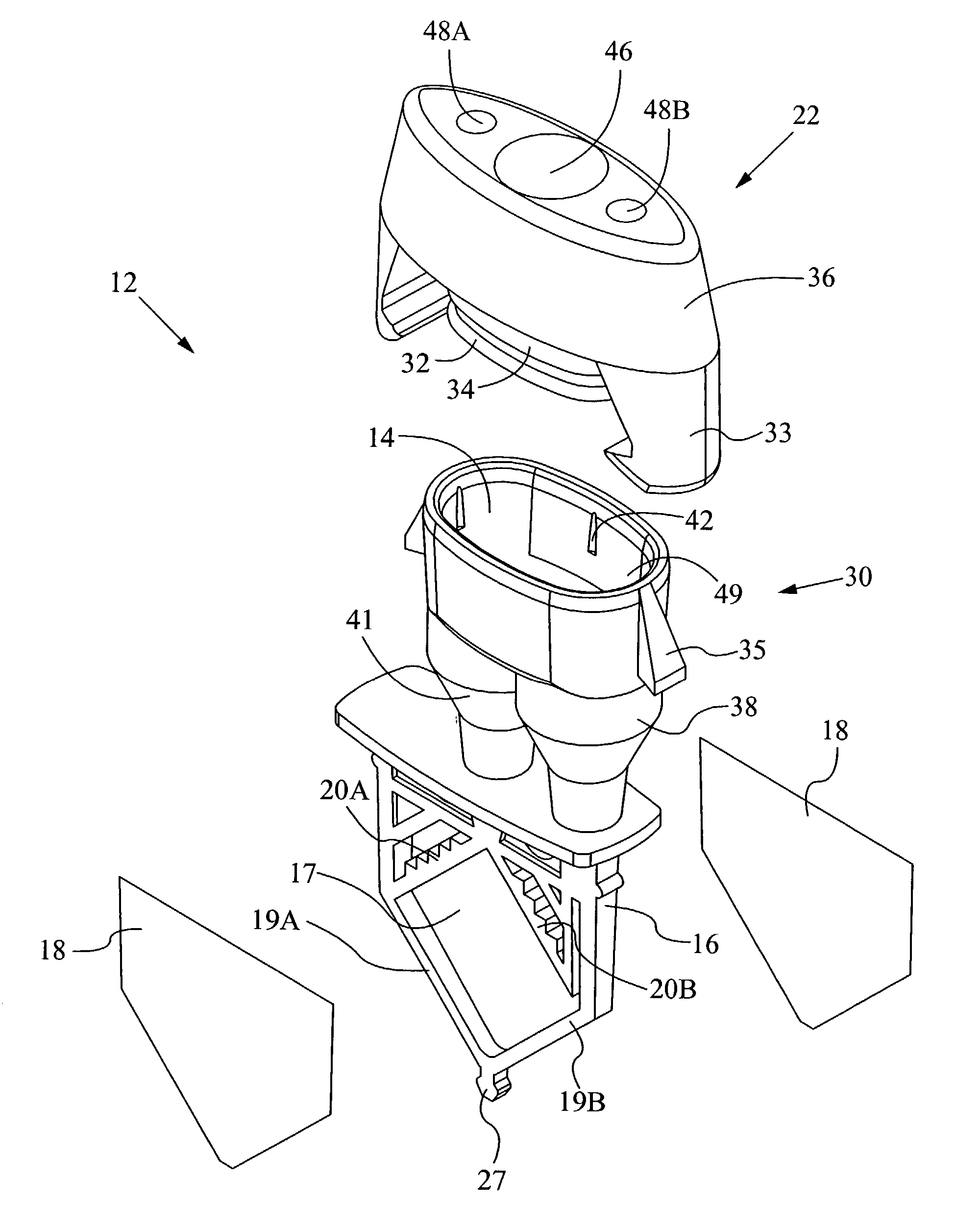
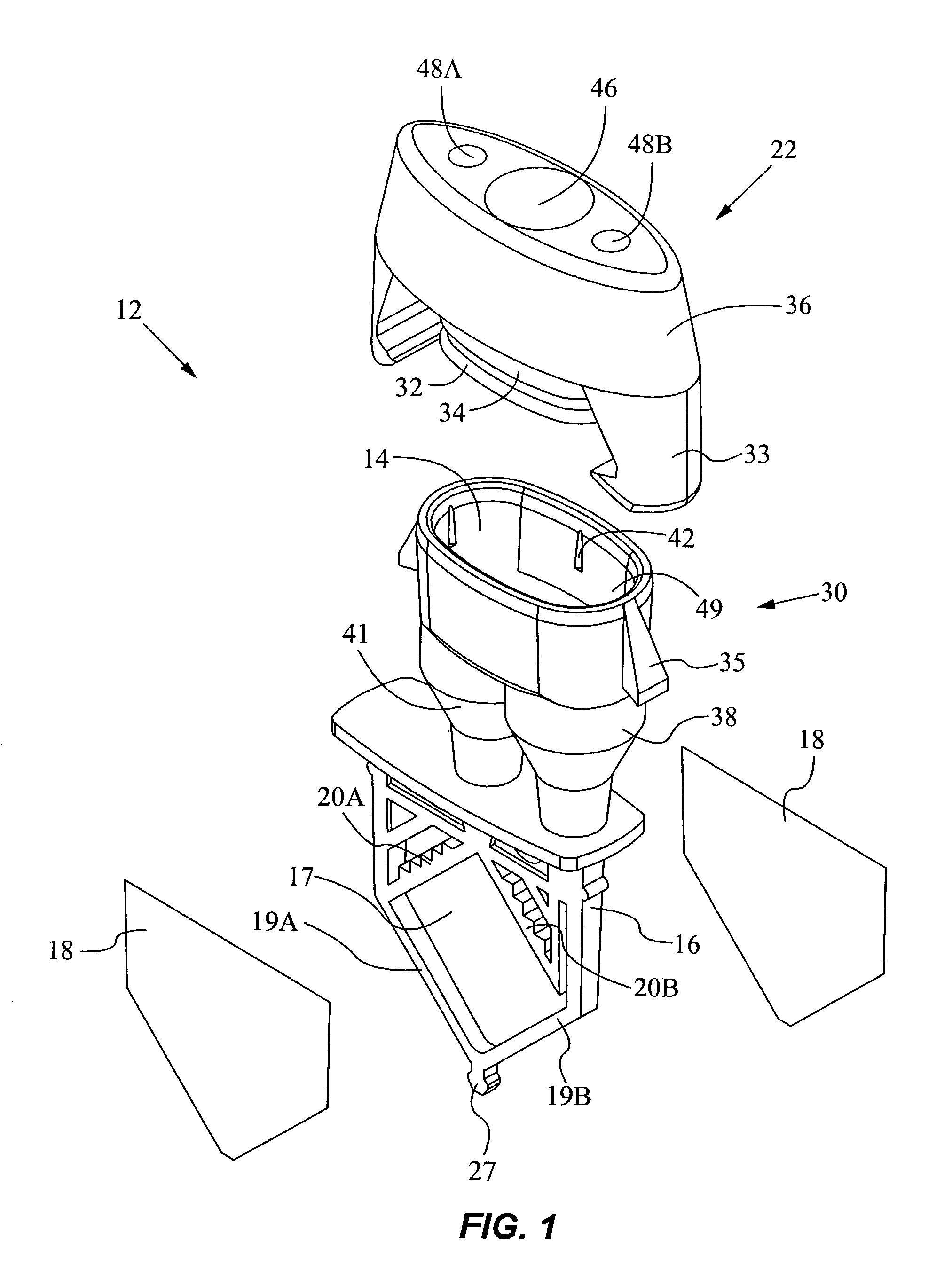
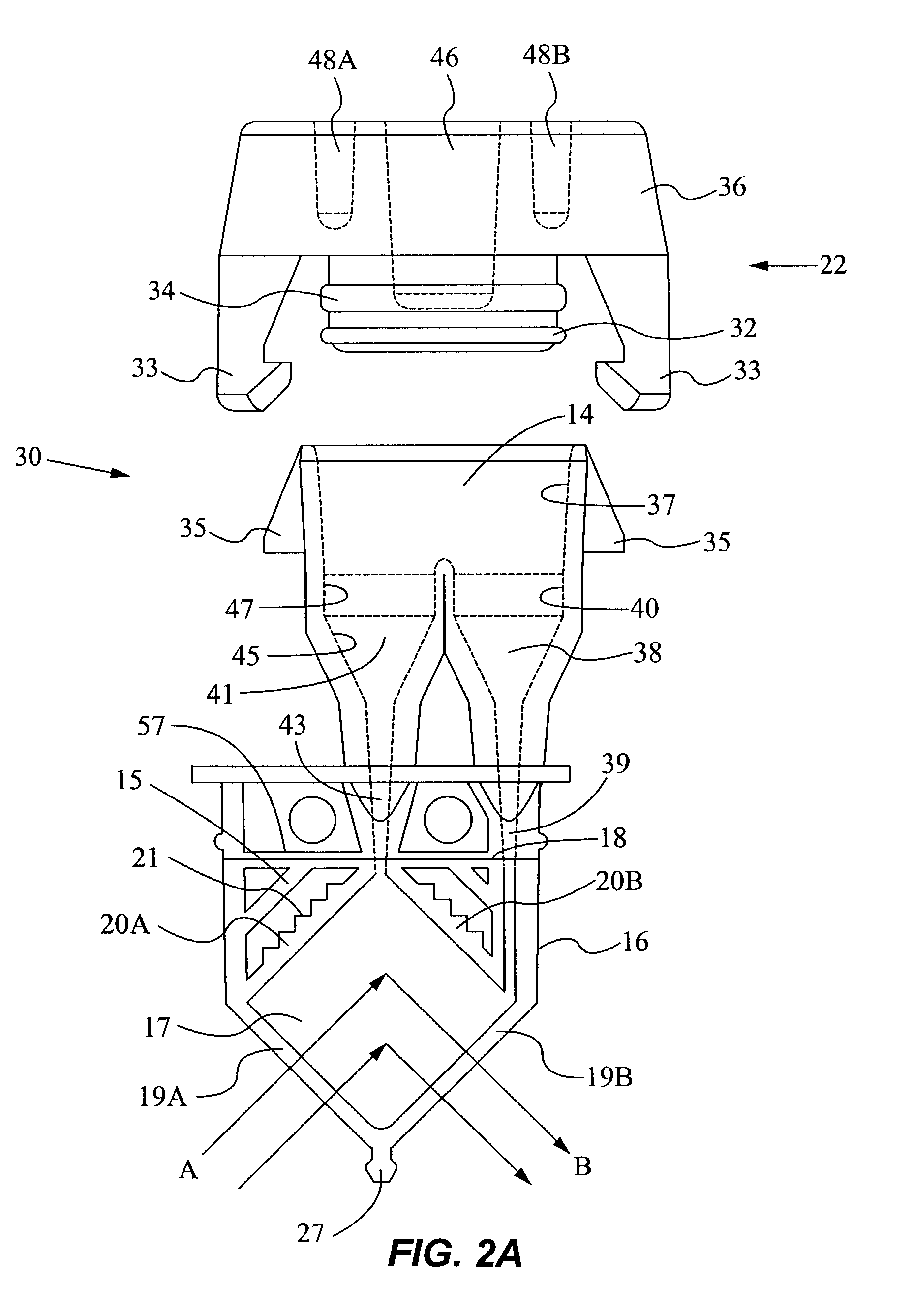
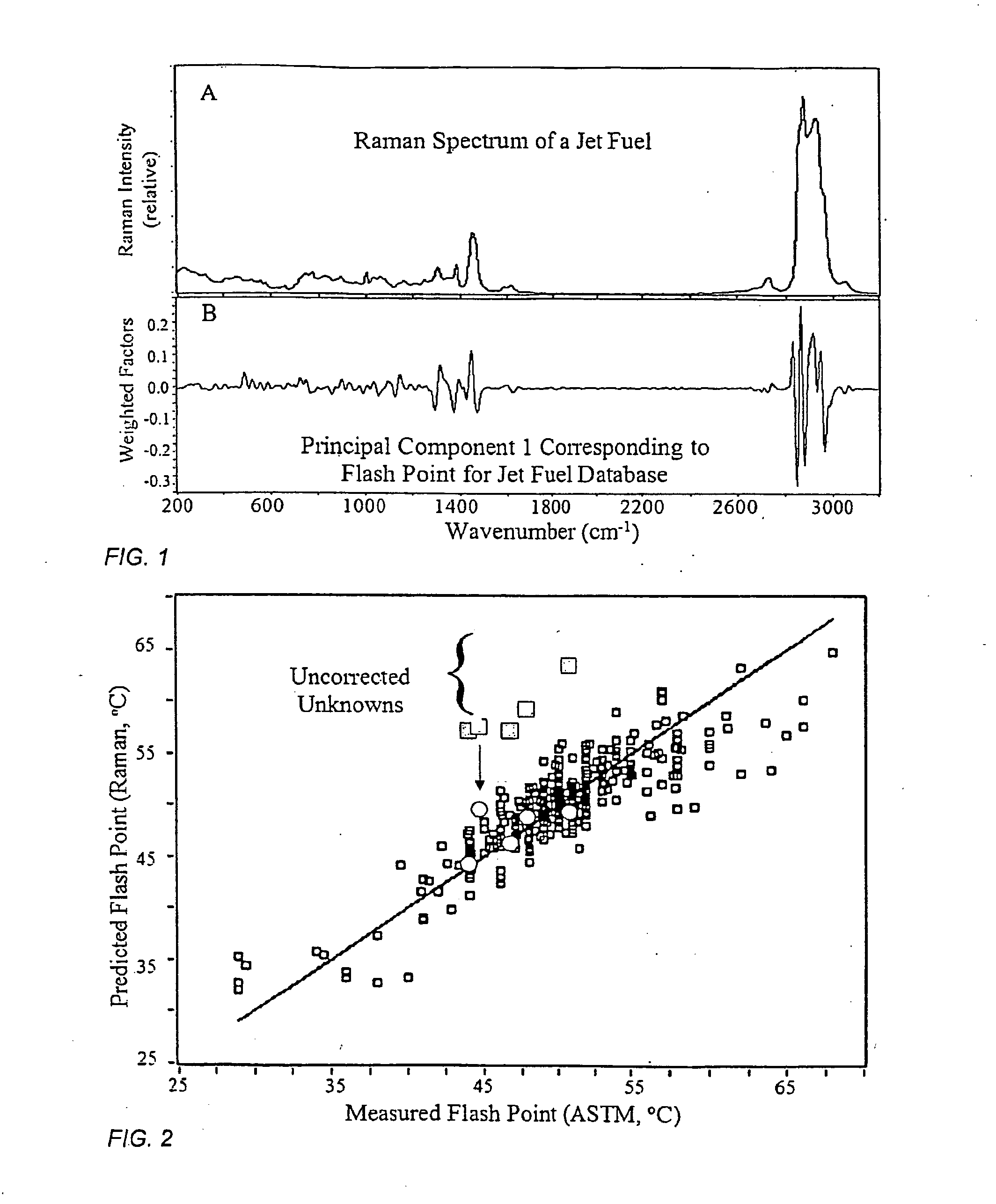
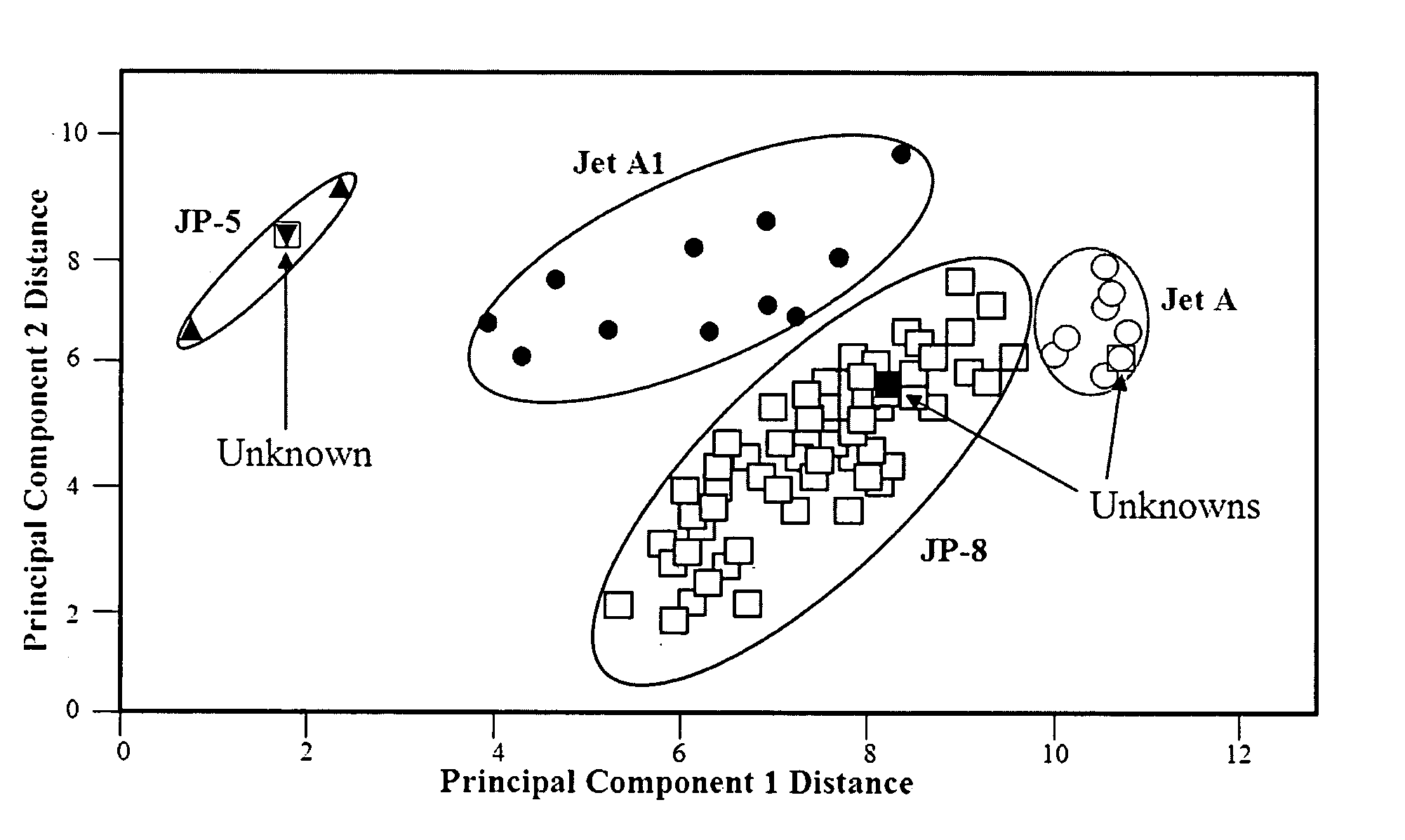
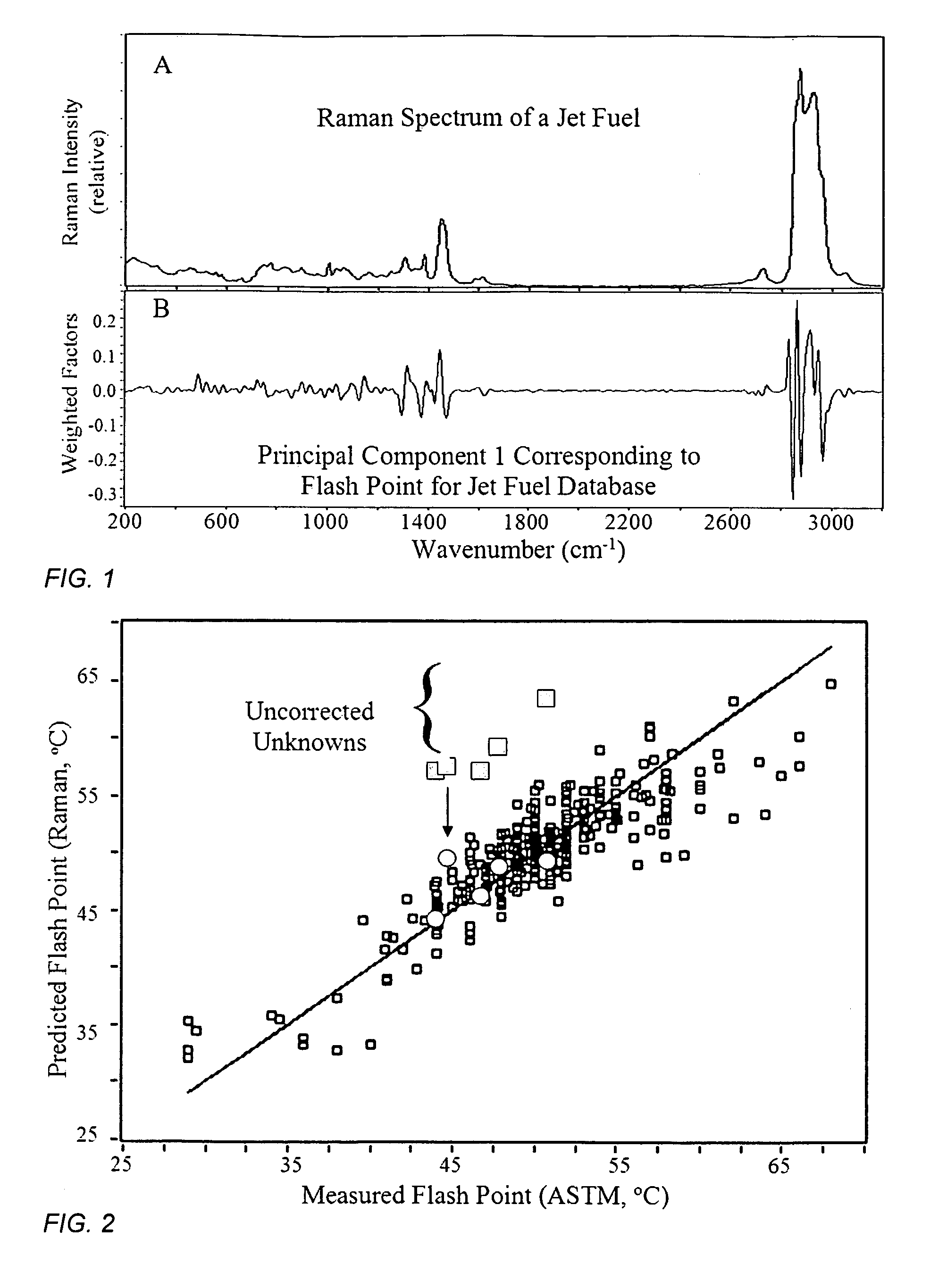
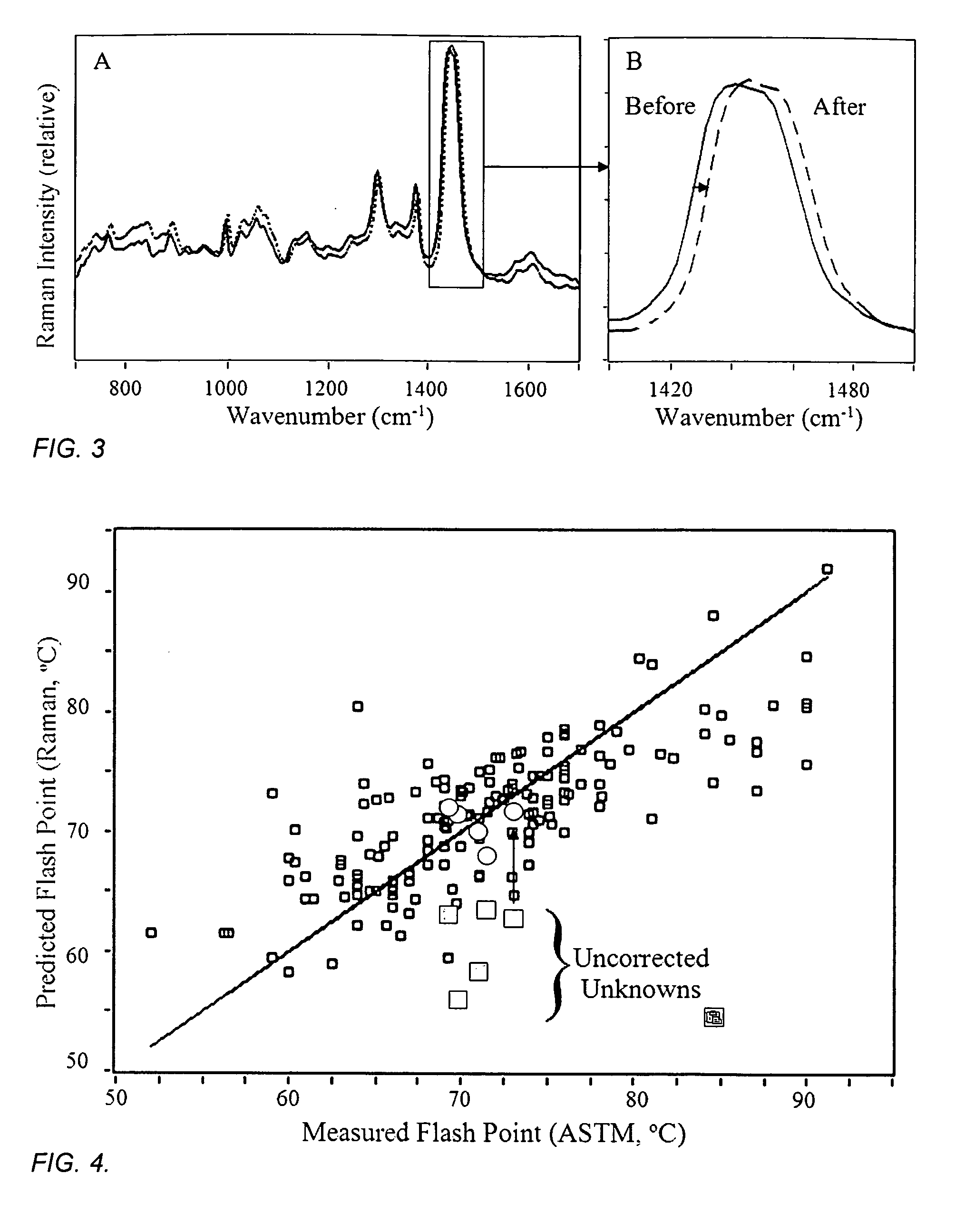
Method and apparatus for determining properties of fuels
ActiveUS20100211329A1Easy to operateRaman scatteringSpecial data processing applicationsPresent methodDistillation
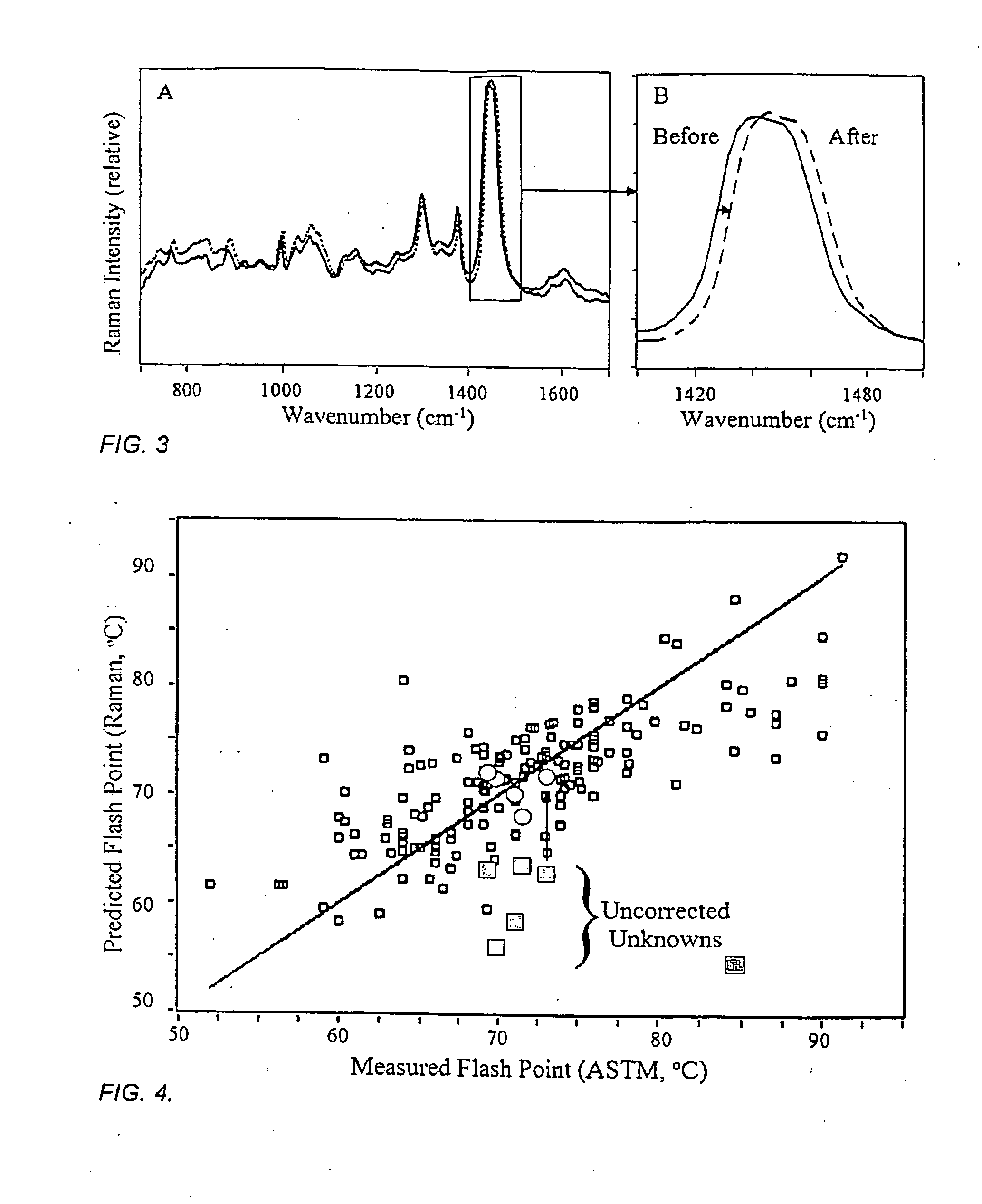
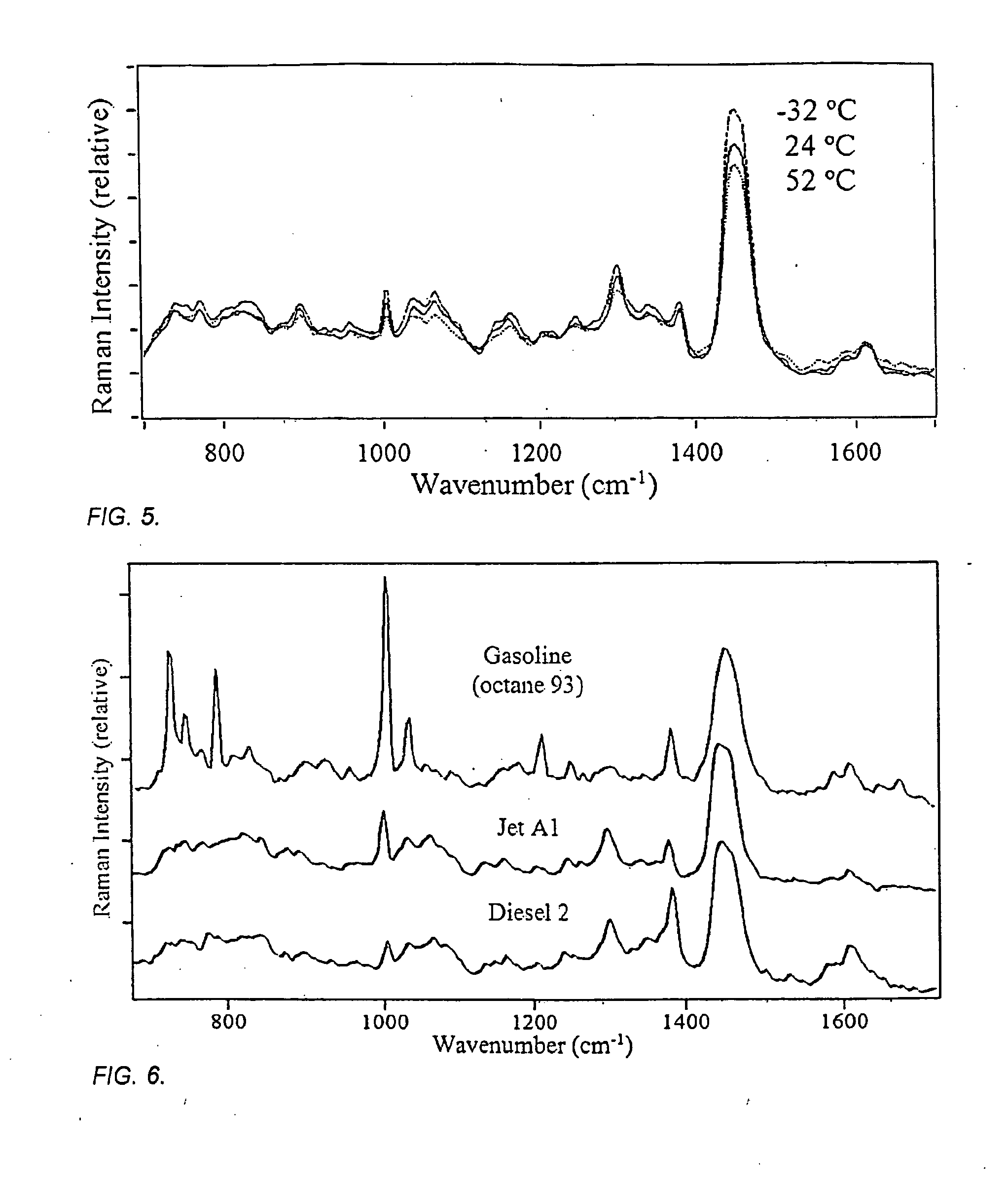
The method and apparatus are used to determine class, grade and properties of fuel samples, regardless of ambient, instrument, or sample temperature, using mathematical correlations between fuel class, grade and properties and their spectra developed from a database of samples with measured properties and spectra. The ability to measure a fuel sample using the present method and apparatus is useful in identifying unknown fuel samples, determining suitability in equipment, and monitoring and controlling fuel processes, such as blending operations, distillation, and synthesis.
Owner:REAL TIME ANALYZERS
Thermal cycler for PCR
InactiveUS20050145273A1Limit heat conductionMinimize thermal non-uniformityHeating or cooling apparatusThermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectThermal isolationThermoelectric cooling
An instrument for performing highly accurate PCR employing an assembly, a heated cover and an internal computer. The assembly is made up of a sample block, a number of Peltier thermal electric devices and heat sink, clamped together. The sample block temperature is changed exclusively by the thermoelectric devices controlled by the computer. The sample block is of low thermal mass and is constructed of silver. The Peltier devices are designed to provide fast temperature excursions over a wide range. The heat sink has a perimeter trench to minimize edge losses and is adjacent to a continuously variable fan. A perimeter heater is used to improve the thermal uniformity across the sample block to approximately ±0.2° C. A heated platen pushes down onto the tube caps to apply a minimum acceptable force for seating the tubes into the block, ensuring good thermal contact with the block. The force is applied about the periphery of the tube caps to prevent distortion of the caps during thermal cycling. The platen is heated to provided thermal isolation from ambient conditions and to prevent evaporation from the surface of the sample into the upper portion of the sample tube. A control algorithm manipulates the current supplied to the thermoelectric coolers such that the dynamic thermal performance of the block can be controlled so that pre-defined thermal profiles for the sample temperature can be executed. The sample temperature is calculated instead of measured using a design specific model and equations. The control software includes calibration diagnostics which permit variation in the performance of thermoelectric coolers from instrument to instrument to be compensated for such that all instruments perform identically. The block / heat sink assembly can be changed to another of the same or different design. The assembly carries the necessary information required to characterize its own performance in an on-board memory device, allowing the assembly to be interchangeable among instruments while retaining its precision operating characteristics. The instrument has a graphical user interface. The instrument monitors the thermoelectric devices and warns of changes in resistance that may result in failure.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
Apparatus and reaction vessel for controlling the temperature of a sample
InactiveUS7255833B2Optimal thermal transferEfficient optical viewing of chemical reactionAnalysis using chemical indicatorsHeating or cooling apparatusOptical observationReaction chamber
This invention provides an apparatus for rapidly heating and / or cooling a sample in a reaction vessel. In some embodiments, the apparatus includes optics for the efficient detection of a reaction product in the vessel. The invention also provides a reaction vessel having a reaction chamber designed for optimal thermal conductance and for efficient optical viewing of reaction products in the chamber.
Owner:CEPHEID INC
Low vibration cryocooled system for low temperature microscopy and spectroscopy applications
ActiveUS8746008B1Easy to disconnectFirmly connectedSolidificationLiquefactionLoop controlClosed loop
A vertical support rigidly mounted to a planar base positions and supports a cryocooler expander unit off axis and away from a sample to be examined. The sample support is likewise rigidly mounted to the planar base with a rigidly mounted sample housing therein. The cryocooler expander unit is suspended in the vertical support by spring dampening bearings. A pair of opposing flexible vacuum bellows connects the cryocooler expander unit to the sample housing and vertical support. This configuration isolates the sample from vibration. Flexible thermal links associated with an predictive electronic closed loop control sequence maintains sample temperature.
Owner:MONTANA INSTR
Film adhesive for sealing, film laminate for sealing and sealing method
InactiveUS20040213973A1Poor compatibilityReduce adhesionImpedence networksSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsDynamic viscoelasticityAdhesive
A film adhesive for sealing a plurality of chip-type devices on a substrate at one time, including an adhesive layer of an adhesive composition which exhibits a minimum value of a storage modulus of elasticity before curing from 1x10<3 >to 5x10<5 >Pa measured by using a dynamic visco-elasticity measuring apparatus while elevating the temperature from 80° C. to 150° C. at an elevating temperature rate of 2.4° C. / min and at a shearing rate of 6.28 rad / sec and a storage modulus of elasticity after curing from 5x10<5 >to 5x10<7 >Pa measured by using a dynamic visco-elasticity measuring apparatus at a sample temperature of 150° C. in a tensile mode at a measuring frequency of 6.28 rad / sec.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Sample Conditioning System for Low Pressure Gas
InactiveUS20150000426A1MaintenanceFacilitate pressureComponent separationWithdrawing sample devicesProduct gasEngineering
A system and method for conditioning of very low pressure gas samples extracted from a source, heating the samples, boosting the pressure to a level appropriate for analysis, regulating the gas sample temperature and pressure to prevent dew-point dropout from Joules Thompson condensation, and passing the gas sample to an a remotely located analyzer or analyzer array where the electrical power for the pressurizing pump and heated regulator is provided by heat tracing.
Owner:MUSTANG SAMPLING
Reaction vessel and temperature control system
InactiveUS7101509B2Easy loadingRapid heating and coolingAnalysis using chemical indicatorsHeating or cooling apparatusTemperature controlAnalyte
A reaction vessel has a reaction chamber, a loading reservoir connected to the reaction chamber via a first channel, and an aspiration port connected to the chamber via a second channel. To load the sample into the reaction chamber, the sample is dispensed into the loading reservoir and then drawn into the chamber by application of a vacuum to the aspiration port. A system for controlling the temperature of the sample in the reaction vessel includes one or more thermal elements for heating or cooling the sample and optionally optics for detecting one or more analytes in the sample.
Owner:CEPHEID INC
Method of monitoring and controlling activity involving a fuel composition
InactiveUS20140229010A1Easy to operateSampled-variable control systemsFuel testingPresent methodDistillation
The method and apparatus are used to determine class, grade and properties of fuel samples, regardless of ambient, instrument, or sample temperature, using mathematical correlations between fuel class, grade and properties and their spectra developed from a database of samples with measured properties and spectra. The ability to measure a fuel sample using the present method and apparatus is useful in identifying unknown fuel samples, determining suitability in equipment, and monitoring and controlling fuel processes, such as blending operations, distillation, and synthesis.
Owner:REAL TIME ANALYZERS
Biological sample temperature control system and method
InactiveUS20100087325A1Remove heatSlow responseHeating or cooling apparatusLibrary screeningTemperature controlTotal internal reflection
The present invention provides a novel approach for controlling the temperature of biological samples on a support structure. The support structure may, for instance, be a flow cell through which a reagent fluid is allowed to flow and interact with biological samples. A thermoelectric heat exchange device, such as a Peltier device, may be used to heat or cool the biological samples on the support structure. In addition, a fluid circulating heat exchange device, such as a water heating or cooling system, may be used to heat or cool the thermoelectric heat exchange device. In general, the support structure may be located on top of the thermoelectric heat exchange device which, in turn, may be located on top of the fluid circulating heat exchange device. The thermoelectric heat exchange device and fluid circulating heat exchange device may be integrated into a holder bench which may be part of a station within an imaging processing system. The holder bench may be configured to hold multiple support structures at a time. In addition, the support structures may be configured to be evaluated and imaged using both epifluorescent and total internal reflection (TIRF) excitation techniques.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
Sample temperature control method
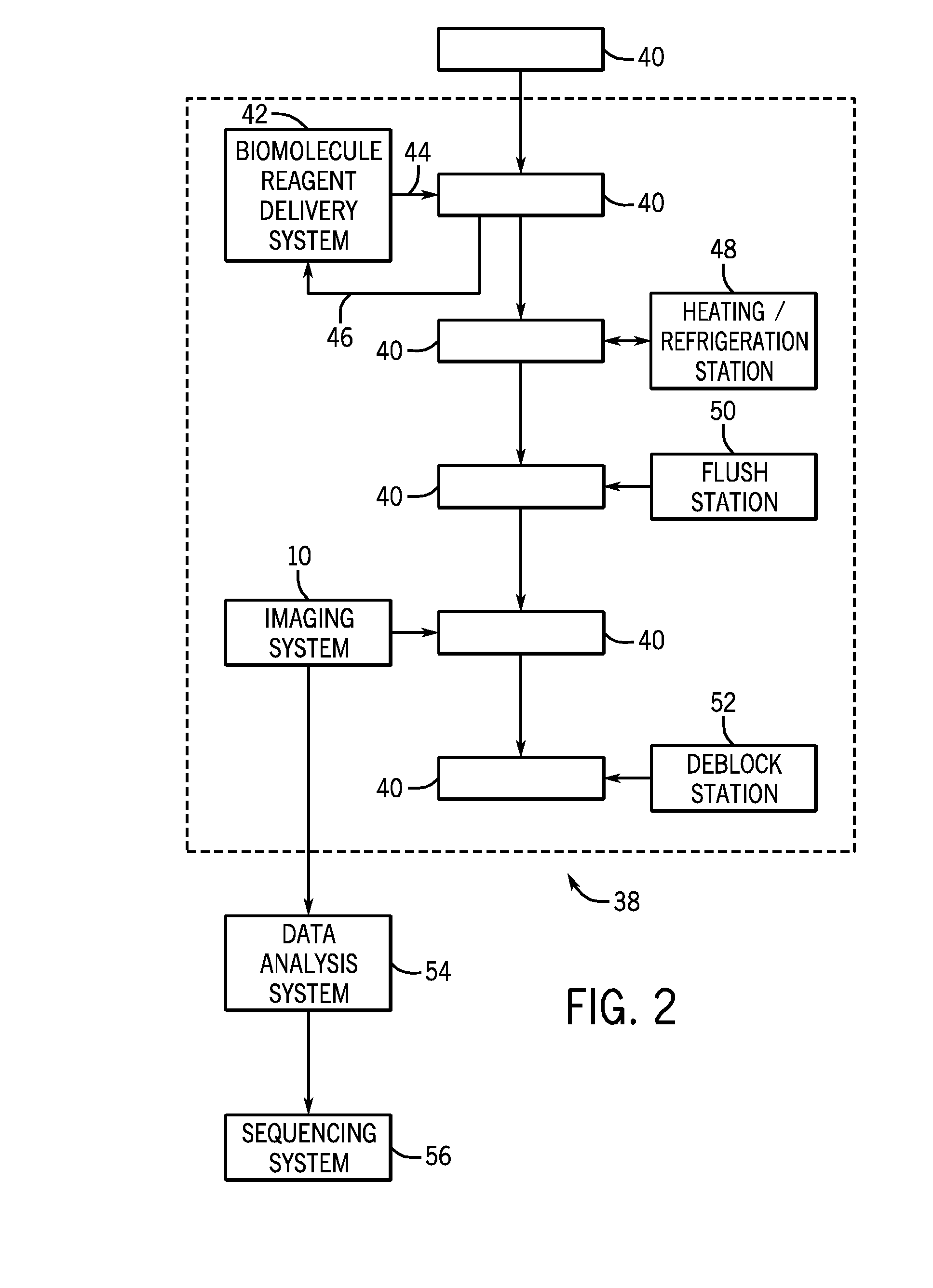
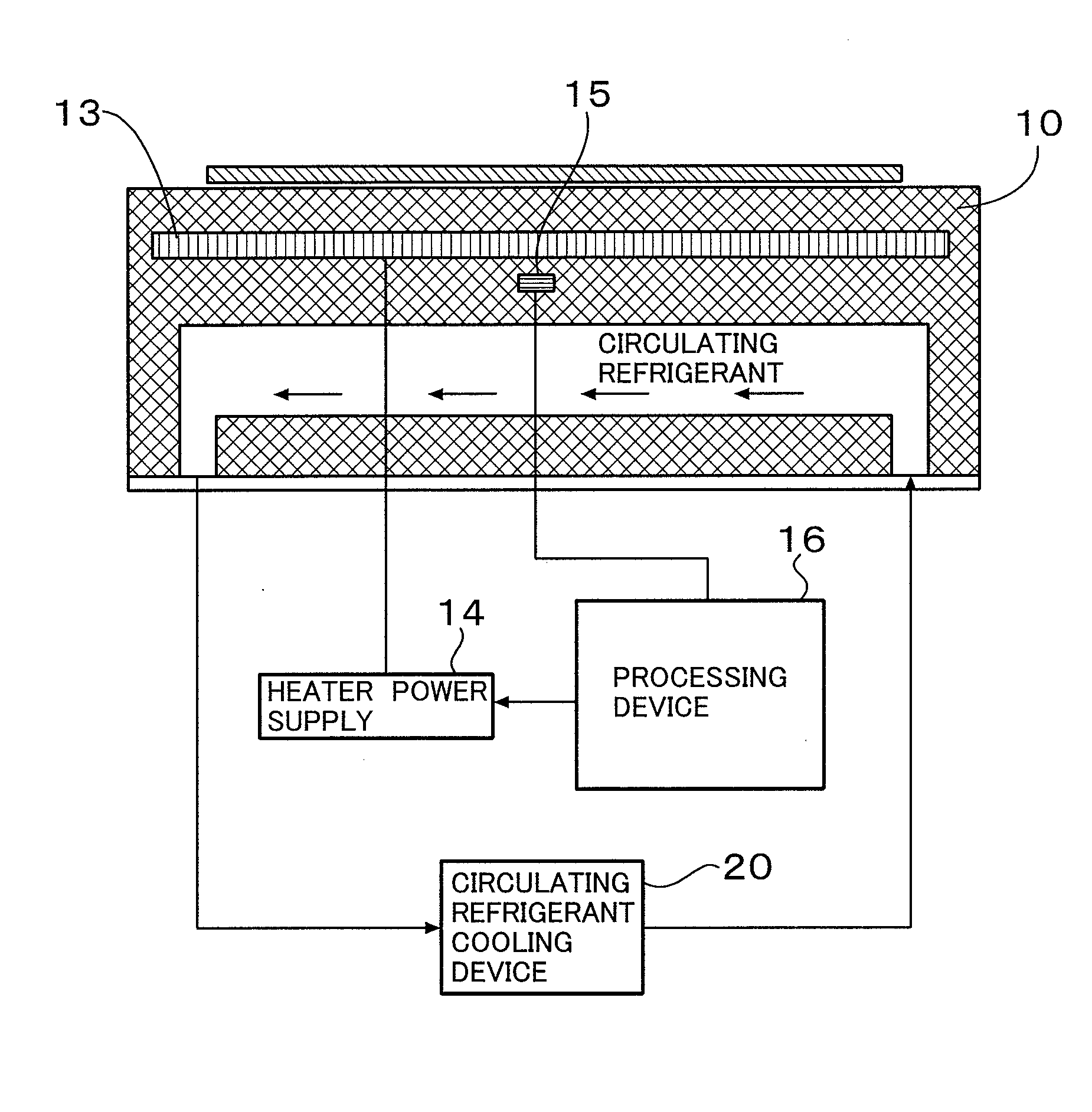
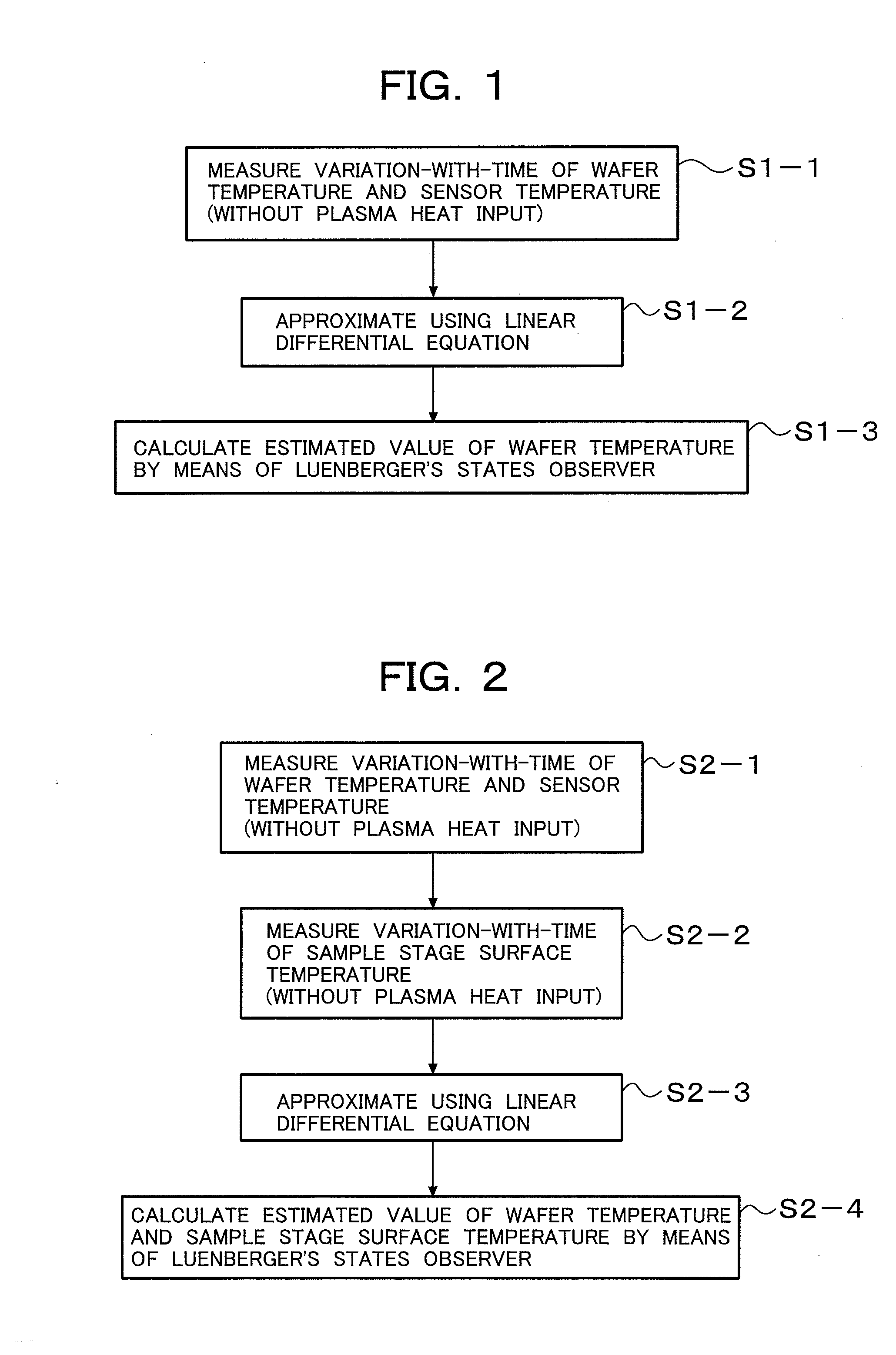
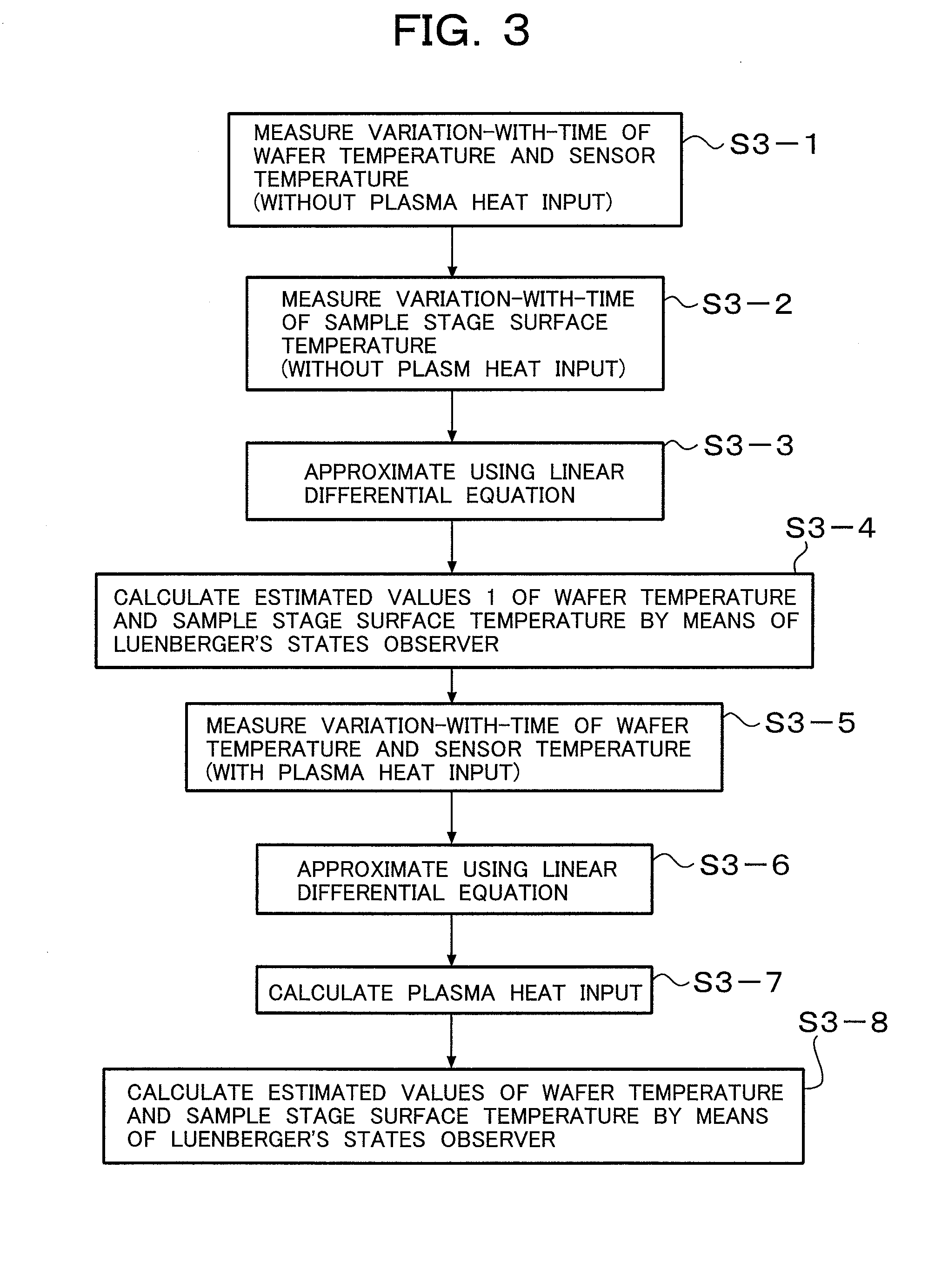
InactiveUS20090310645A1Stable controlAccurate temperatureElectric heatingDigital computer detailsTemporal changeState observer
A method of stably controlling the temperature of a sample placed on a sample stage to a desired temperature by estimating a sample temperature accurately, the sample stage including a refrigerant flow path to cool the sample stage, a heater to heat the sample stage, and a temperature sensor to measure the temperature of the sample stage. This method comprises the steps of: measuring in advance the variation-with-time of supply electric power to the heater, temperature of the sample, and temperature of the temperature sensor, without plasma processing; approximating the relation among the measured values using a simultaneous linear differential equation; estimating a sample temperature from the variation-with-time of sensor temperature y1, heater electric power u1, and plasma heat input by means of the Luenberger's states observer based on the simultaneous linear differential equation used for the approximation; and performing a feedback control of sample temperature using the estimated sample temperature.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
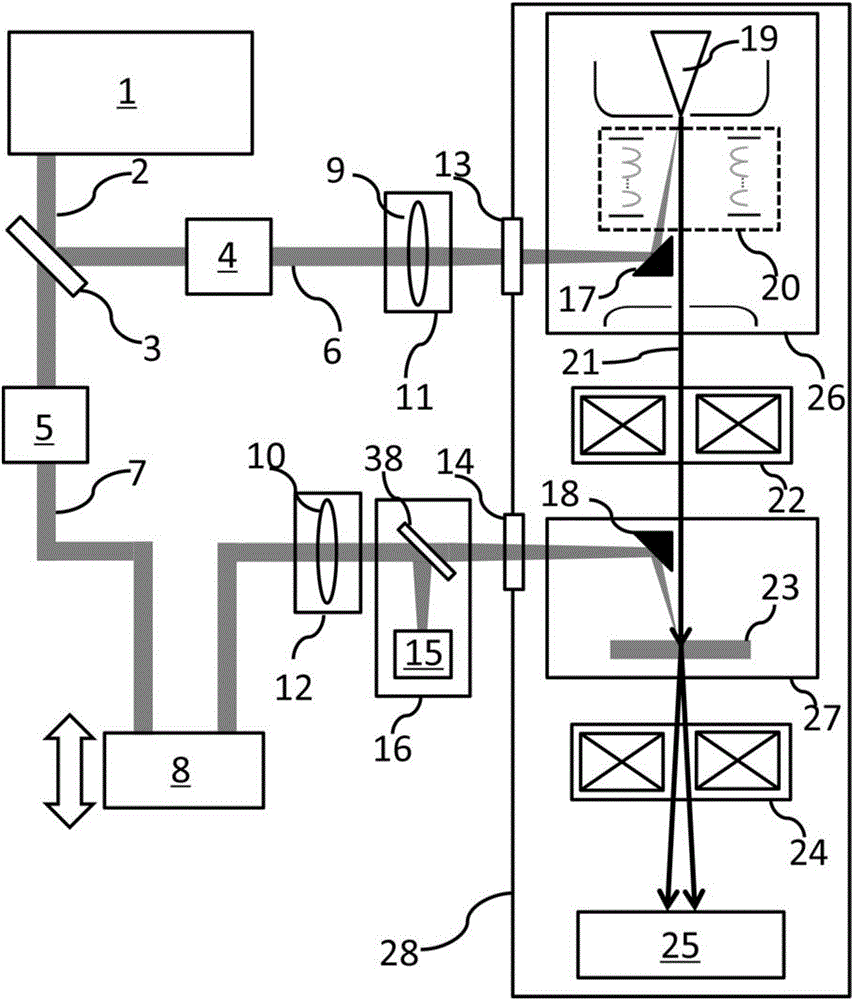
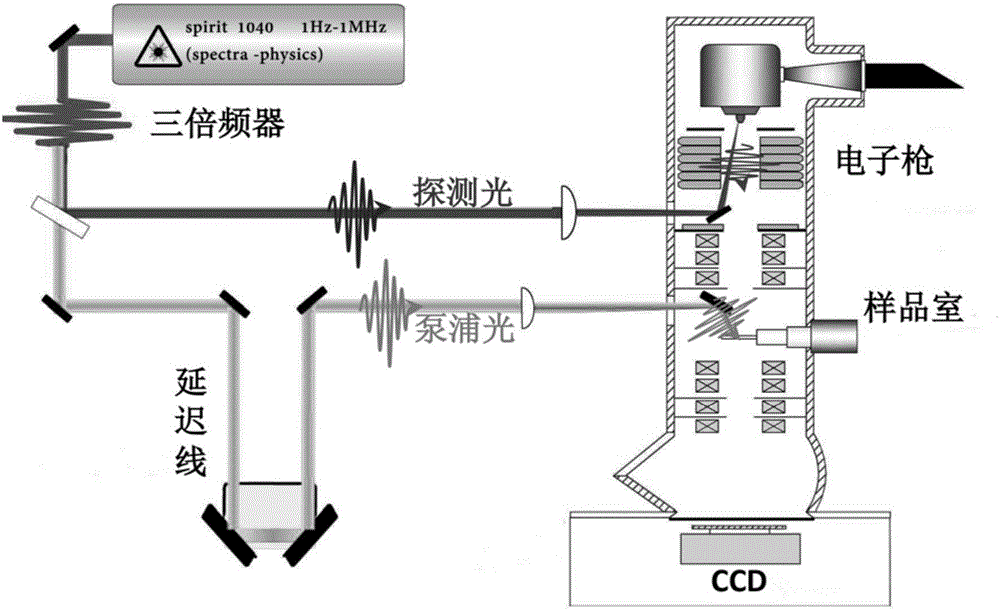
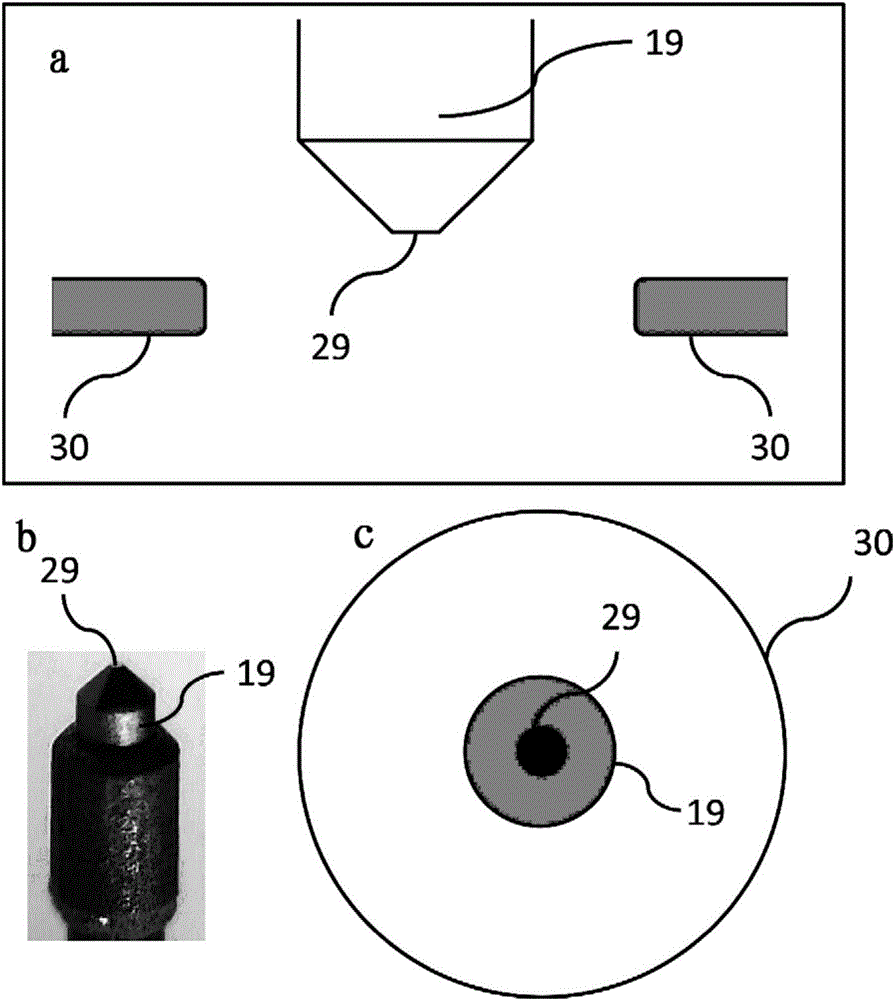
Ultra-fast transmission electron microscope system and use method thereof
ActiveCN106645236AMaterial analysis using radiation diffractionConventional transmission electron microscopeMicroscopic image
The invention provides an ultra-fast transmission electron microscope system which comprises an ultra-fast laser system, an electronic gun, an illuminating system, an imaging system, a sample chamber, a detector and a vacuum device, the ultra-fast transmission electron microscope system can particularly test ultra-fast structure change processes of samples under different laser parameters and environmental temperature, the different laser parameters include different excitation wavelengths, pulse width, laser power, repetitive frequency, sample temperature and the like, acquired signals comprise diffraction, microscopic images, energy loss spectroscopy and the like, and the ultra-fast structure change processes are analyzed by analyzing position and strength of diffraction peaks, image contrast change and the like.
Owner:INST OF PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Friction wear testing machine
ActiveCN101344470AHigh simulationSimple production processUsing mechanical meansInvestigating abrasion/wear resistanceWear testingElectric machinery
The invention discloses a friction wear testing machine and comprises an abrading agent slot, a grinding steel wheel that is suspended in the abrading agent slot, a boosting lever that has a vertical arm suspended between the grinding steel wheel and a lateral wall of the abrading agent slot, a servo sand slot that has a sand discharging mouth and a transmission pipe, a servo spring loading mechanism that is connected with a horizontal arm of the boosting lever, a load sensor that is serially connected between the servo spring loading mechanism and the boosting lever and a temperature sensor that is arranged on the back of a sample. A main shaft of the grinding steel wheel is arranged on a bearing holder, connected with a torque sensor through a flexible coupler and connected with a frequency-varied speed-regulating drive motor, and a computer adjusts and detects the sand discharge amount of the sand slot, the rotating speed and the torque of the frequency-varied speed-regulating drive motor, and the loading capacity of the servo spring loading mechanism in real time, and can detect and record the rotational frequency of the grinding steel wheel and sample temperature in real time. The friction wear testing machine can detect and analyze the abrasion resistance and the frictional behaviour of hard alloy products under the conditions close to real working conditions.
Owner:株洲长江硬质合金工具有限公司
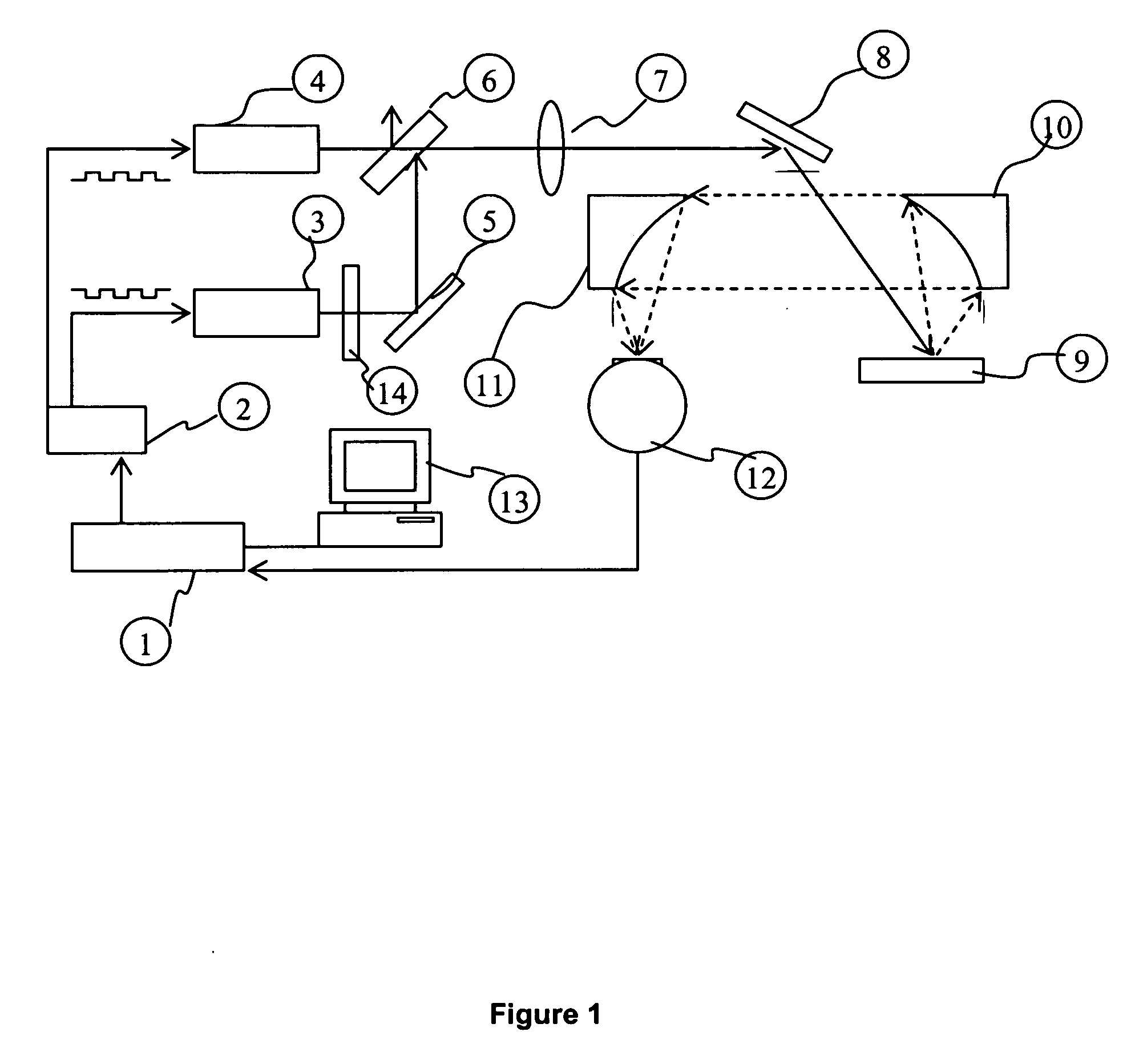
Non-invasive biothermophotonic sensor for blood glucose monitoring
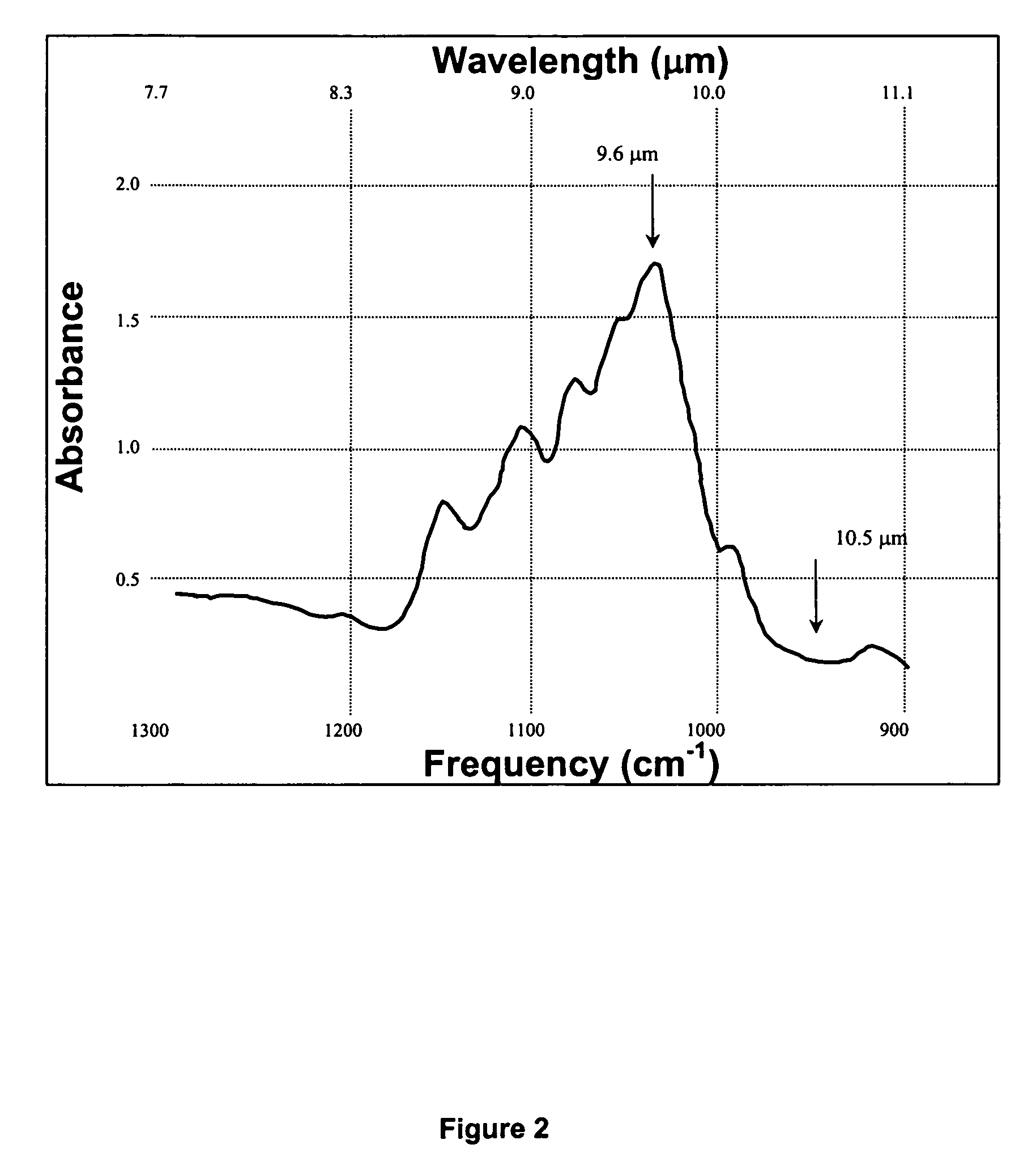
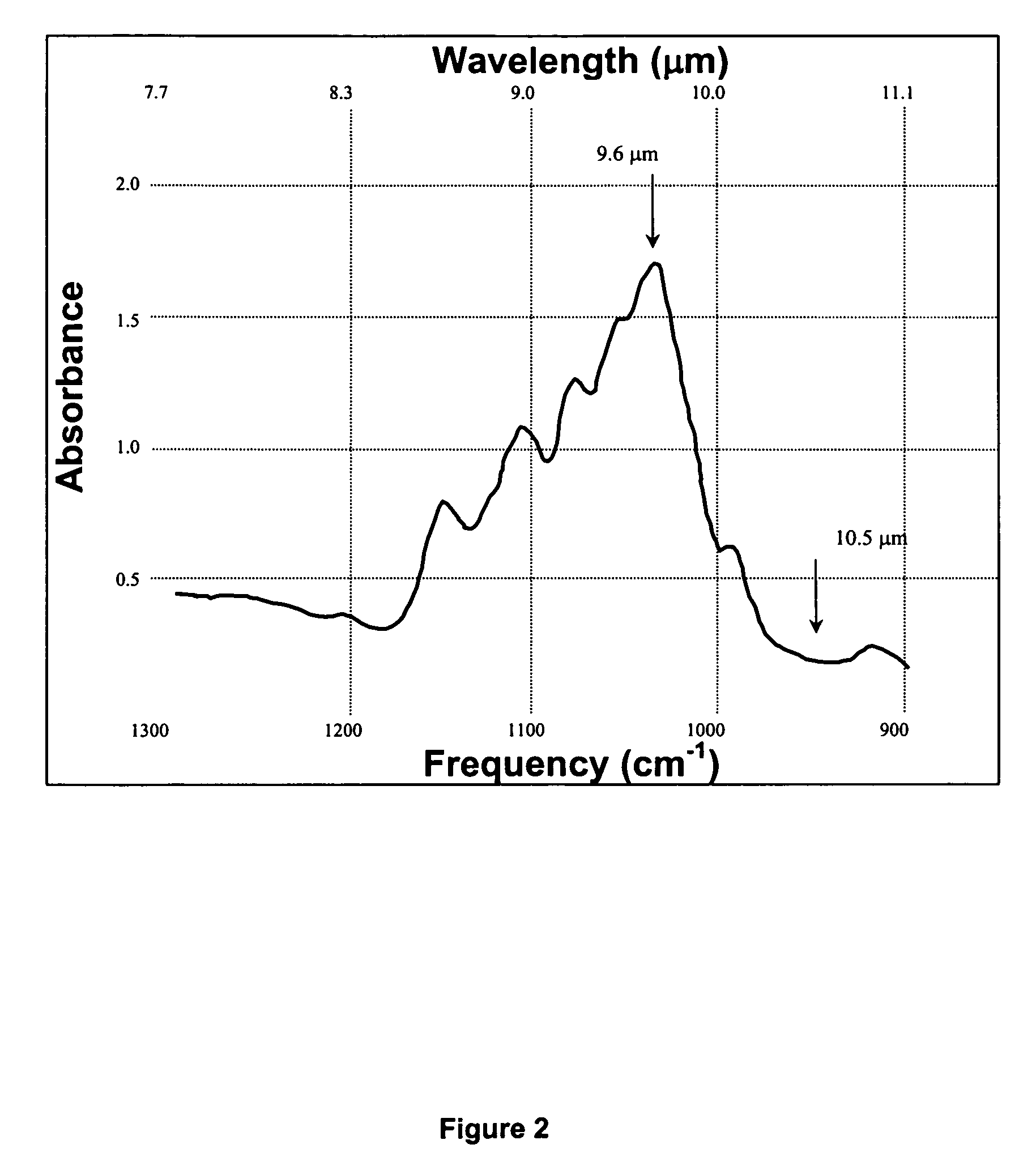
There is provided a glucose monitoring method and apparatus based on the principle of Wavelength-Modulated Differential Laser Photothermal Radiometry (WM-DPTR). Two intensity modulated laser beams operating in tandem at specific mid-infrared (IR) wavelengths and current-modulated synchronously by two electrical waveforms 180 degrees out-of-phase, are used to interrogate the tissue surface. The laser wavelengths are selected to absorb in the mid infrared range (8.5-10.5 μm) where the glucose spectrum exhibits a discrete absorption band. The differential thermal-wave signal generated by the tissue sample through modulated absorption between two specific wavelengths within the band (for example, the peak at 9.6 and the nearest baseline at 10.5 μm) lead to minute changes in sample temperature and to non-equilibrium blackbody radiation emission. This modulated emission is measured with a broadband infrared detector. The detector is coupled to a lock-in amplifier for signal demodulation. Any glucose concentration increases will be registered as differential photothermal signals above the fully suppressed signal baseline due to increased absorption at the probed peak or near-peak of the band at 9.6 μm at the selected wavelength modulation frequency. The emphasis is on the ability to monitor blood glucose levels in diabetic patients in a non-invasive, non-contacting manner with differential signal generation methods for real-time baseline corrections, a crucial feature toward precise and universal calibration (independent of person-to-person contact, skin, temperature or IR-emission variations) in order to offer accurate absolute glucose concentration readings.
Owner:MANDELIS ANDREAS +1
Method and apparatus for controlling rotation speed of fan
InactiveUS20070076372A1Automatic controlReduce noiseModifications using gaseous coolantsAutomatic controlEngineering
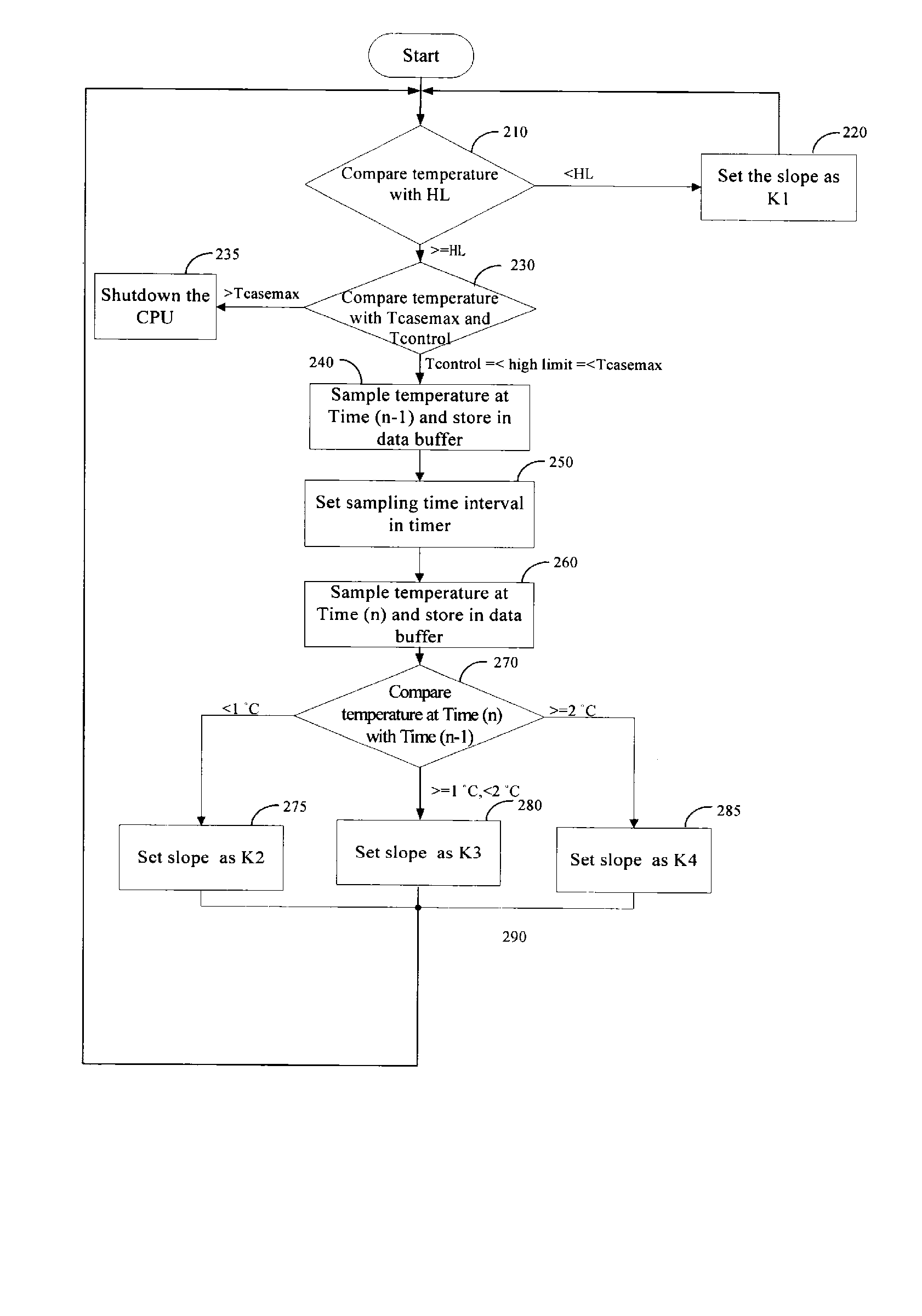
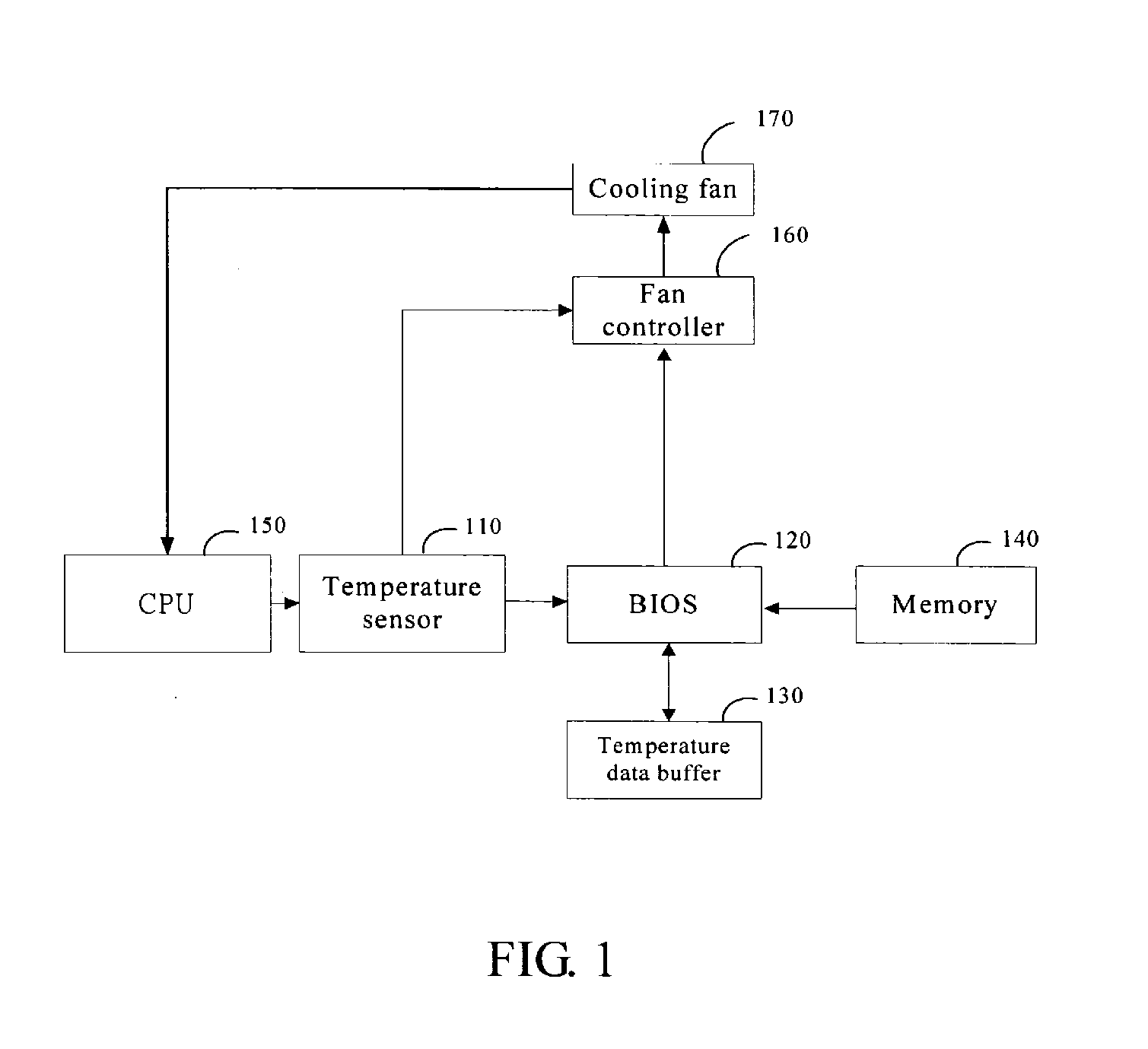
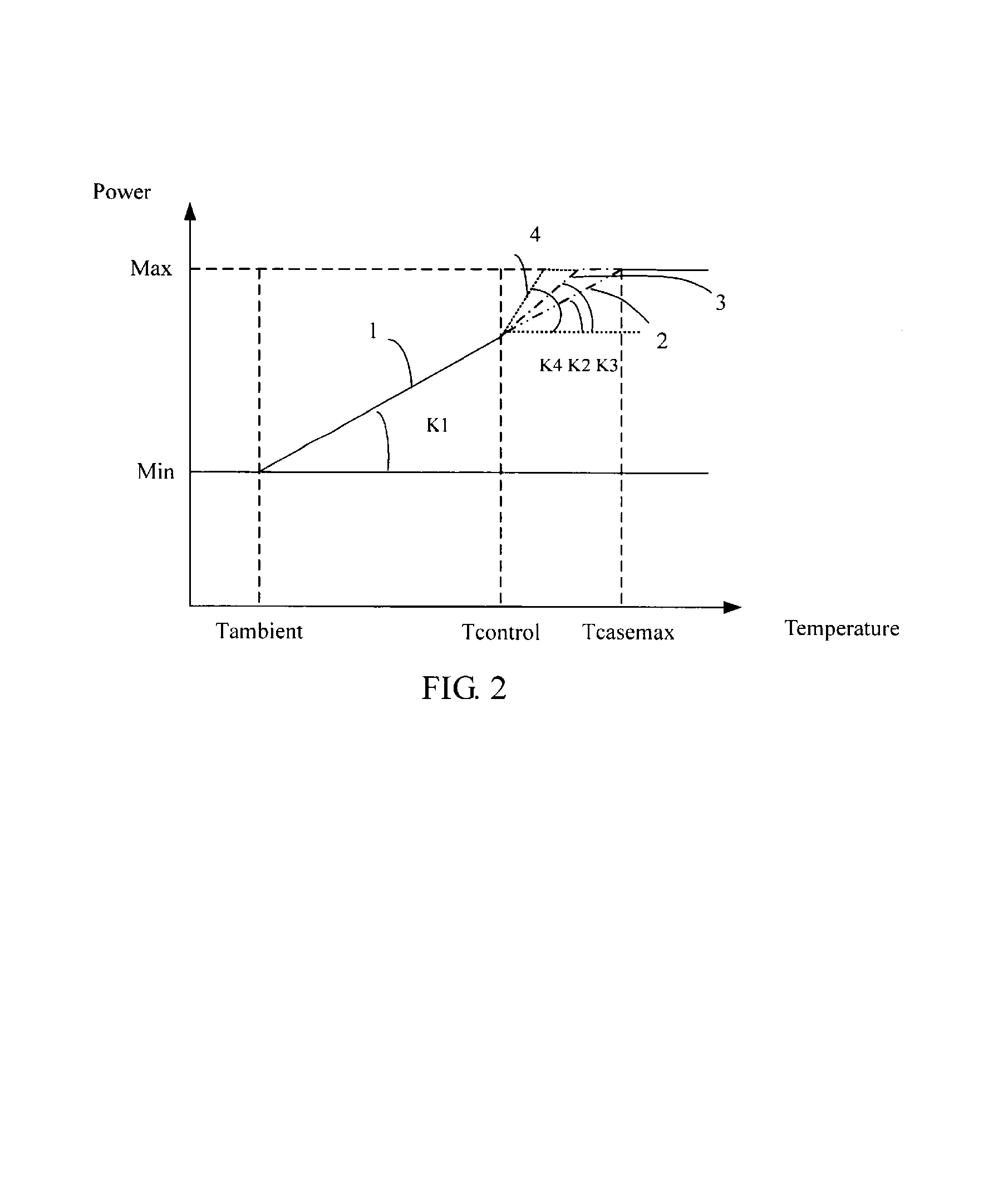
A method and an apparatus for automatically controlling rotation speed of a cooling fan are provided. The method includes the following steps: Sampling temperature values of the electronic component at Time (n−1) and at Time (n). Then storing the temperature values at Time (n−1) and at Time (n). Then comparing the temperature vale at Time (n−1) with that at Time (n). And then setting the rotation speed of the cooling fan according to the comparison result in the last step. The present invention can not only automatically control the rotation speed of a cooling fan, but also reduce the noise of the cooling fan.
Owner:HON HAI PRECISION IND CO LTD
Quick changeable temperature small-sized constant temperature sample pool
InactiveCN101281121APrecise and fast temperature controlMeet the requirements of constant temperatureMaterial analysis by optical meansWater/sand/air bathsTemperature controlMetallic materials
The invention relates to a quick variable temperature miniature thermostatic sample cell, which is made of metallic material, an opening is formed in the center of the metallic material and is used as a sample cavity, a light through hole is formed on a metallic shell along the center of the sample cavity, a transparent material is embedded in the light through hole, a Peltier temperature control element is glued on the non-light surface of the metallic material, a groove is arranged on the bottom of the metallic shell for laying aside a temperature sensor, the coat of the metal shell has a heat insulation outer frame, the center of a base connected with the bottom of the heat insulation outer frame is provided with a miniature motor, a small magnet is arranged at the edge of the leaf of a spiral leaf on the shaft of the motor, a stirring magneton is laid aside at the bottom in the sample cavity, the inner wall of the sample cavity and the outer faces of the sensor and the stirring magneton is carried on chemical inertia processing. The invention replaces the water heat conduction with the metal, and changes the system temperature with a thermo-element; the sensor directly observes the temperature of the sample, the heat conduction is speeded up by a miniature electromagnetic stirring system has accelerated; the invention is characterized in having small volume, accurate the temperature measurement, quick variable temperature, and good stability, etc, being able to be placed in analytical instrument such as spectrophotometer, etc., and realizing the quick variable temperature and the accurate thermostatic control of the temperature of the sample.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Non-invasive biothermophotonic sensor for blood glucose monitoring
There is provided a glucose monitoring method and apparatus based on the principle of Wavelength-Modulated Differential Laser Photothermal Radiometry (WM-DPTR). Two intensity modulated laser beams operating in tandem at specific mid-infrared (IR) wavelengths and current-modulated synchronously by two electrical waveforms 180 degrees out-of-phase, are used to interrogate the tissue surface. The laser wavelengths are selected to absorb in the mid infrared range (8.5-10.5 μm) where the glucose spectrum exhibits a discrete absorption band. The differential thermal-wave signal generated by the tissue sample through modulated absorption between two specific wavelengths within the band (for example, the peak at 9.6 and the nearest baseline at 10.5 μm) lead to minute changes in sample temperature and to non-equilibrium blackbody radiation emission. This modulated emission is measured with a broadband infrared detector. The detector is coupled to a lock-in amplifier for signal demodulation. Any glucose concentration increases will be registered as differential photothermal signals above the fully suppressed signal baseline due to increased absorption at the probed peak or near-peak of the band at 9.6 μm at the selected wavelength modulation frequency. The emphasis is on the ability to monitor blood glucose levels in diabetic patients in a non-invasive, non-contacting manner with differential signal generation methods for real-time baseline corrections, a crucial feature toward precise and universal calibration (independent of person-to-person contact, skin, temperature or IR-emission variations) in order to offer accurate absolute glucose concentration readings.
Owner:MANDELIS ANDREAS +1
Apparatus for crack detection during heat and load testing
InactiveUS20110249115A1Possible to viewTelevision system detailsColor television detailsTest fixtureFeedback control
Material testing under variable heat and load while continuously monitoring crack formation is provided using an apparatus that permits thermal control somewhat uniformly over a conductive sample, while permitting a controlled load to be applied to the sample in tensional or flexural modes. Thermographic imaging of a sample in situ within a standard thermo-mechanical fatigue (TMF) test rig or other heat and load test apparatus is used to detect and monitor cracks as they form. A 360° sample view is possible. Image analysis software may identify, count and / or characterize cracks. Thermographic images may be analyzed to determine a sample temperature, e.g. for temperature feedback control. Essentially passive thermography is used with an inductive heating coil that surrounds at least 60% of a length of the sample, with at least two windings, the windings having thickness and pitch so that at least half the sample is in view.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Sample processing method for automatic sample processing system
ActiveCN104101527ARealize split processingEasy to movePreparing sample for investigationBuretteFixed frame
The invention discloses a sample processing method for an automatic sample processing system. The automatic sample processing system comprises a workbench, wherein a sample preprocessing mechanism, a sample centrifuging mechanism, a sample temperature controlling mechanism, a manipulator system, a testing mechanism and a test tube stand are arranged on the platform of the workbench; the sample preprocessing mechanism comprises a support and a plurality of jacking test tube brackets; a sample smashing mechanism used for smashing solid samples and a plurality of servo-type burettes are arranged on the support; the sample smashing mechanism comprises a smashing motor and a smashing mechanism; the smashing motor is fixed on a fixing frame; the smashing mechanism is arranged on the output shaft of the smashing motor. The sample processing method comprises the following steps: sample smashing, reagent adding, liquid extracting, centrifuging, temperature controlling, eluting and detecting. According to the invention, the sample processing method has the following advantages: the samples can be smashed automatically, a reagent can be added automatically, and liquid can be extracted automatically; the accuracy of adding and extracting the liquid is high.
Owner:安徽省一一通信息科技有限公司
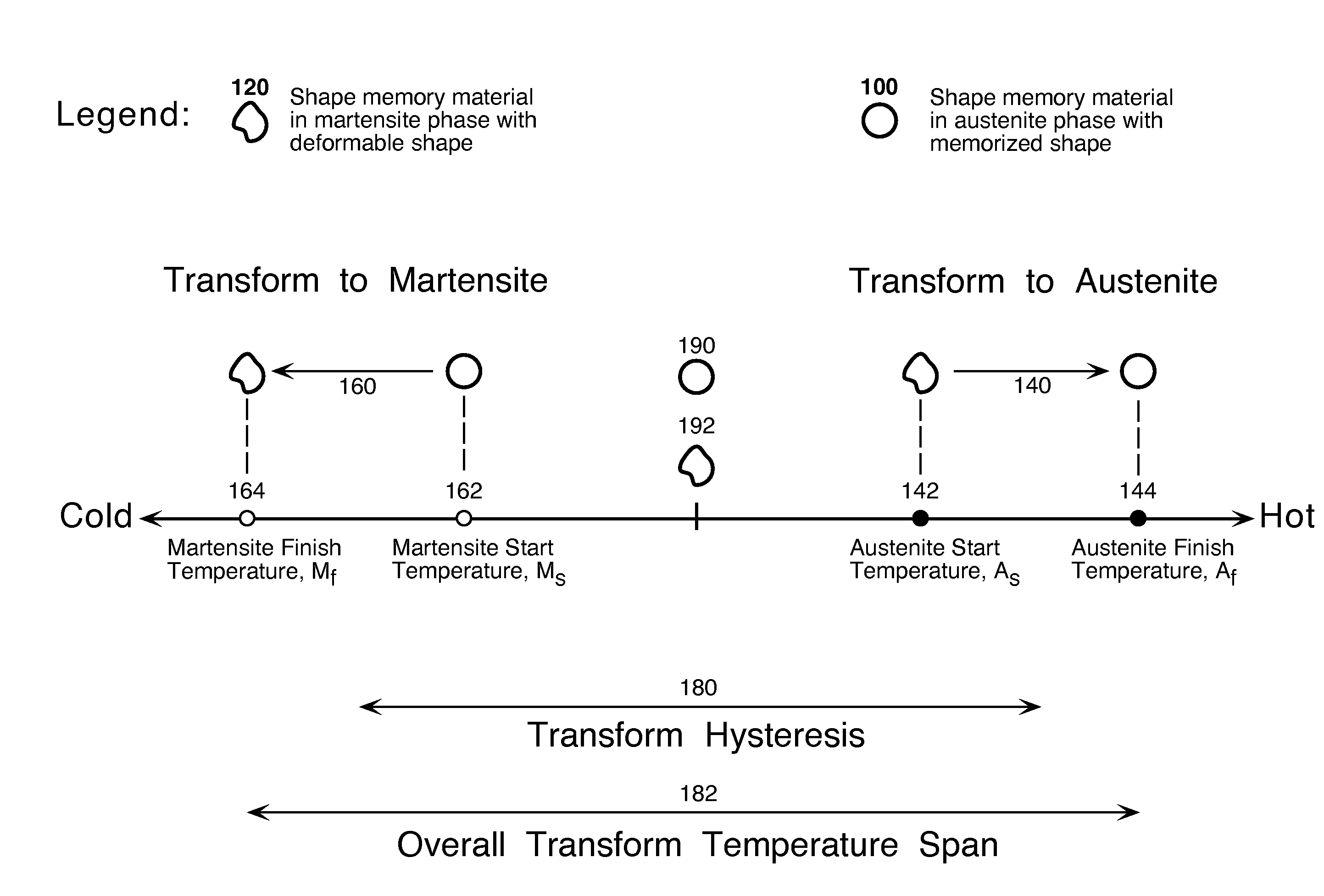
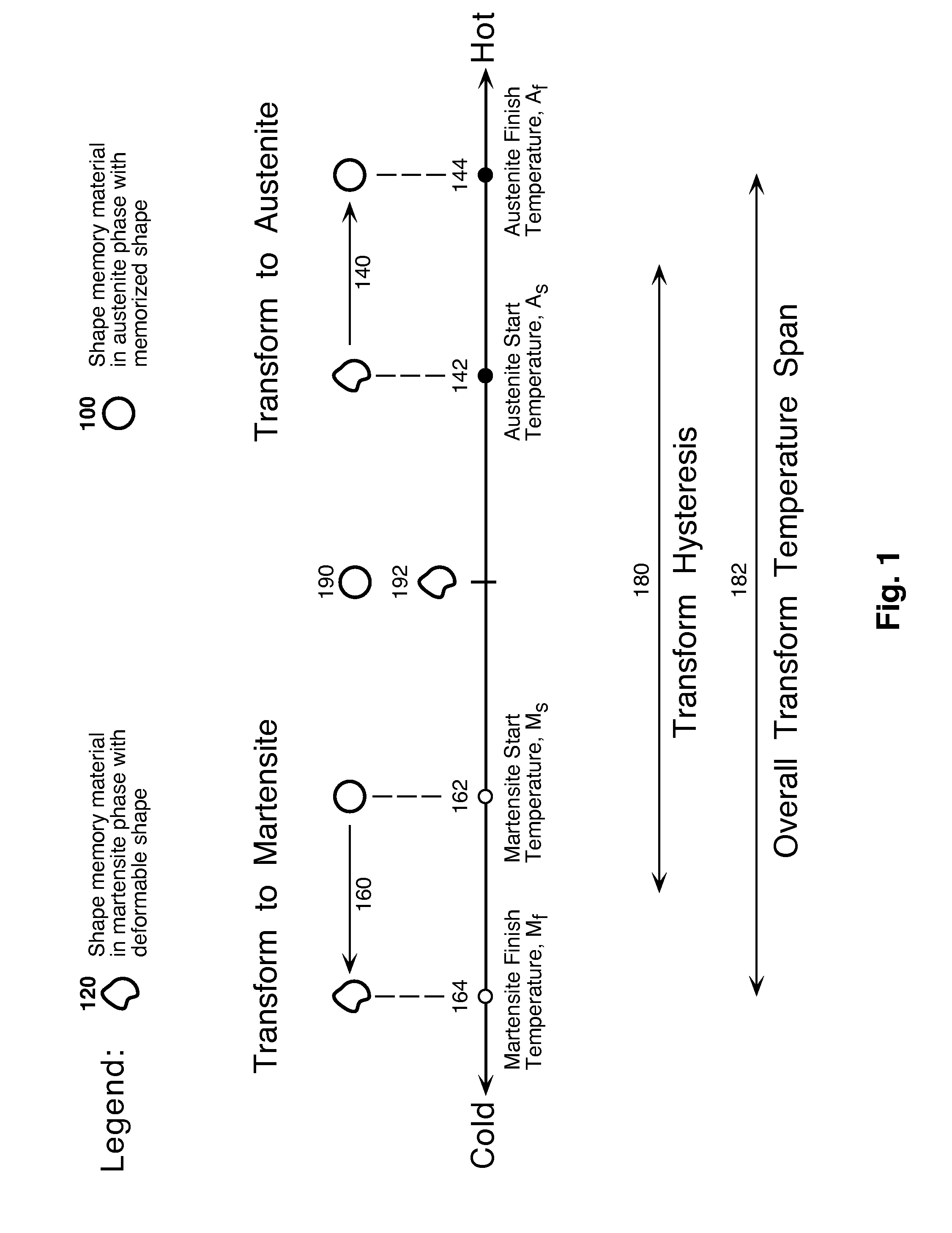
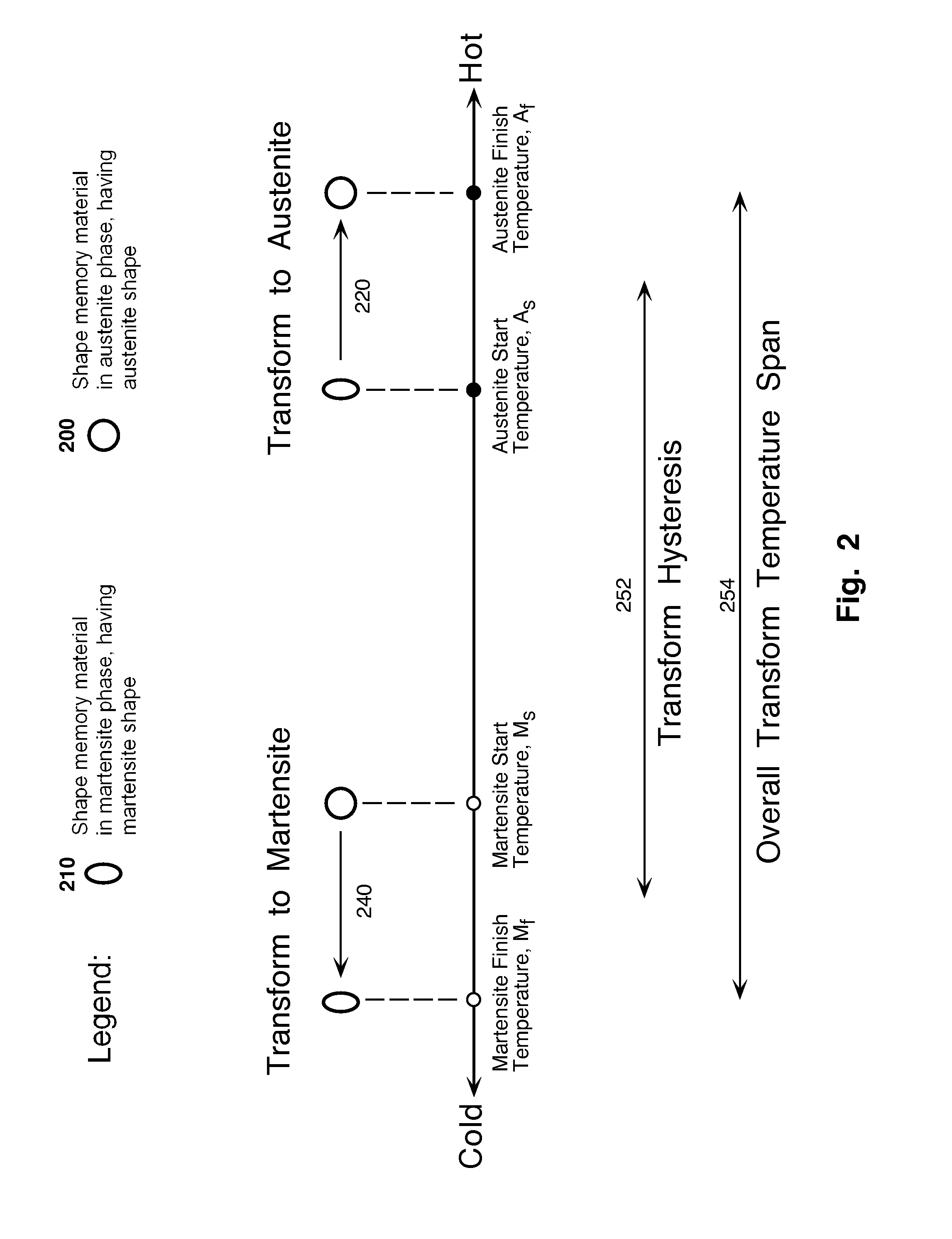
Temperature Alert Device for Cryopreservation
InactiveUS20090120106A1Container filling methodsThermometers using material expansion/contactionDevitrificationTemperature response
A temperature alert device to warn of imminent devitrification due to warming of a biological specimen that uses shape memory materials. The temperature induced phase transformation of shape memory materials causes a temperature responsive actuator to extend an alert rod upon warming as the specimen temperature approaches the devitrification temperature (e.g. −130° C.). The temperature alert device is automatically reset upon immersion in liquid nitrogen.
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC
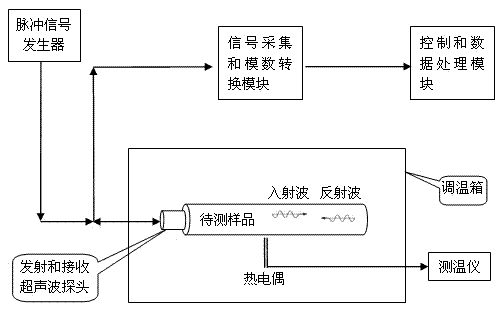
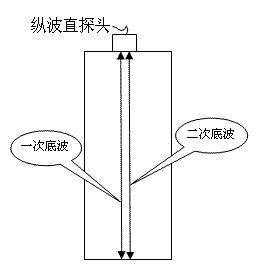
Memory alloy phase-change temperature measuring method and measuring system for implementing same
InactiveCN103499599AHigh sensitivityStrong reliabilityInvestigating phase/state changeAlloySpeed of sound
The invention discloses a memory alloy phase-change temperature measuring method. The measuring method comprises the following steps: firstly measuring a sound velocity-temperature curve in which the velocity of ultrasonic longitudinal waves in a memory alloy to be measured changes along with the temperature, wherein the sound velocity-temperature curve comprises a heating curve and a cooling curve; and determining the phase-change temperature of the memory alloy to be measured according to the sound velocity-temperature curve by using the sensitivity of the ultrasonic longitudinal velocity on the phase-change process of the memory alloy. The invention also discloses a measuring system implementing the measuring method. The measuring system comprises an ultrasonic wave emitting and receiving module, a signal collecting and analog-to-digital converting module, a sample temperature adjusting module and a control and data processing module. According to the measuring method and the measuring system, the phase-change temperature of the memory alloy is measured by using the sensitivity of the ultrasonic longitudinal wave velocity on the phase-change process of the memory alloy; compared with the prior art, the measuring method and the measuring system have the advantages of high sensitivity, strong reliability, wide application range and nondestructive measurement.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Cable conductor DC resistance on-line detection device and method thereof
InactiveCN101706530AImprove accuracyEasy to useResistance/reactance/impedencePotential clampElectrical conductor
The invention relates to a cable conductor DC resistance on-line detection device and a method thereof, aiming at solving the problems of the prior art that detection to a cable conductor needs to cut a section of the cable conductor, which brings inconvenience to operation and causes material waste; the detection is apt to be influenced by air humidity, air temperature and sample temperature and other factors; and the accuracy of detection results is low. The cable conductor DC resistance on-line detection device comprises a resistance tester, a mobile trolley, a potential clamp and a current clamp, wherein the resistance tester is arranged on the mobile trolley; a water tank for containing cables is arranged on the top end of the mobile trolley; the potential clamp and the current clamp are used for clamping cables and connected on the resistance tester through wires. The invention has the advantages of optional movement, convenient use, waster reduction and high detection structure accuracy.
Owner:浙江万马股份有限公司
Method for measuring density of Huoli Wood using near infrared spectrum
InactiveCN1936537AQuick analysisWeighing by removing componentScattering properties measurementsWater dischargeDiffuse reflection
This invention relates to a method for testing density of alive stumpage wood with near infrared spectrum including: selecting not less than 120 bug-free wood samples, controlling the temperature of the samples at 20-25deg.C, dividing them into five regions of moisture rate of 3-30%, 30-80%, 80-30%, 130-200%, 200-300% and collecting the diffuse reflection near infrared spectrums of the woods, applying a water discharge method to test the volume when the sample is full of water, applying a drying method to test the absolute weight of the sample to compute the water ratio and density of the woods, setting up a pretest model of moisture, setting up density correction models separately for five regions of water rate and utilizing the set-up models to analyze the density of unknown samples.
Owner:INST OF WOOD INDUDTRY CHINESE ACAD OF FORESTRY
Temperature-controlled circulating curing system and application
InactiveCN101803792AGood temperature-controlled marinating environmentSpeed up picklingConfectionerySweetmeatsTemperature controlLiquid storage tank
The invention belongs to the technical field of agriculture product curing, and discloses a circulating curing system. The system comprises a temperature-controlled regulation system and a curing circulation system, wherein the temperature-controlled regulation system comprises a compressor, a change valve, a condenser, a liquid storage tank, a filter and an evaporator; heat exchange is performed in the evaporator so that sample temperature-controlled circulating curing is realized in a sample reservoir. The process for the system comprises the following steps: filling a sample in the sample reservoir; adding enough curing liquid which can completely submerge the sample into the sample reservoir which is filled with the samples; and circularly and convectively submerging and curing the samples by the curing liquid at the temperature of between 0 and 50 DEG C until a cured product is mature. The curing liquid is sprayed to a porous distributed groove by using a hose from different angles, and is uniformly distributed on the cured product so that uniform curing of the sample is realized. The system not only can well control the curing environment to ensure the product is uniformly cured, and maintain the traditional food flavor, but also can speed up curing, shorten the production period, and improve the production efficiency. The curing liquid can be recycled.
Owner:WUHAN NEWSTAR FOOD
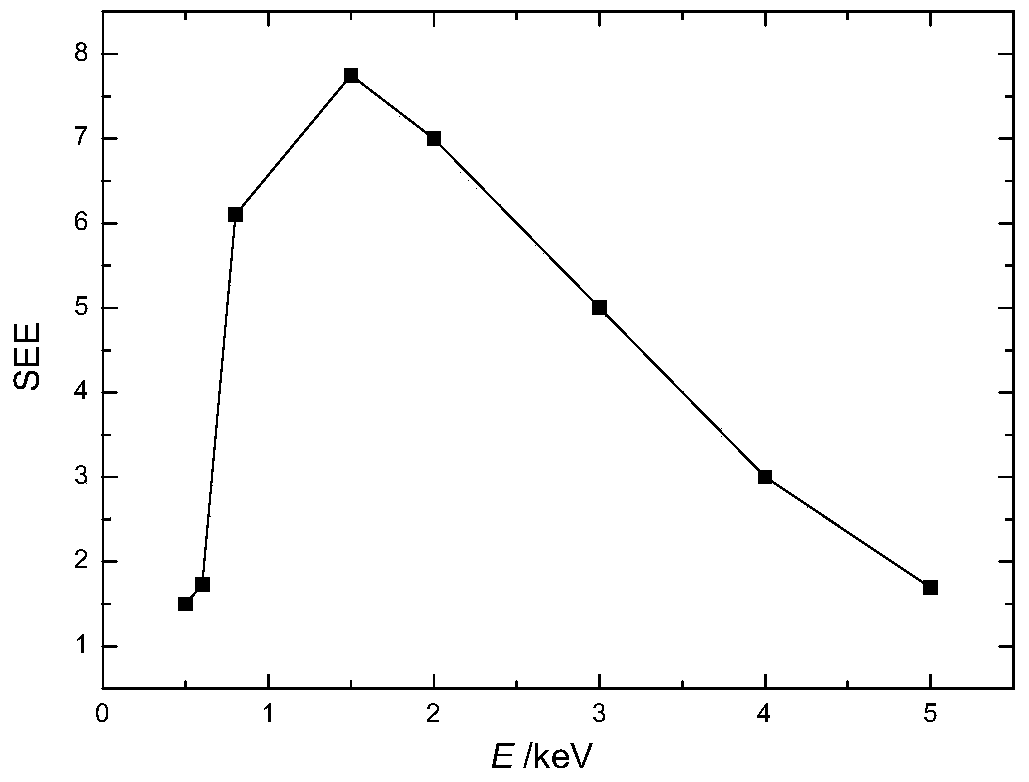
Panel type collection device and method for measuring secondary electron emission coefficient
ActiveCN103776858AEfficient collectionIntuitive and convenient adjustmentMaterial analysis by measuring secondary emissionTemperature controlMeasurement device
The invention discloses a panel type collection device and method for measuring a secondary electron emission coefficient. A measuring device mainly comprises a rotary platform, a sample table, a heating device, a Faraday cylinder, a current amplifier and a collection electrode, wherein the inner wall of the Faraday cylinder is plated with a layer of carbon, the Faraday cylinder is connected with a bias voltage device and the current amplifier and is used for measuring a primary incidence current; the collection electrode is in a panel structure, the upper surface of the collection electrode is coated with a layer of fluorescent powder so as to conveniently adjust and focus electron beam faculae, and the lower surface of the collection electrode is plated with a layer of carbon so as to inhibit electron multiplication phenomenon in a collection process; the collection electrode is connected with a bias voltage device and the current amplifier and is used for measuring secondary electron stream emitted by the surface of a material. By utilizing a rotary device, multiple samples can be simultaneously measured, so that the measuring time is saved; by utilizing the heating device and a temperature control device, the temperature of a sample can be accurately controlled in a range of 30-300 DEG C, and the heating device and a temperature control device are used for researching the influence of the temperature on the secondary electron emission coefficient; by providing the novel electron collection device for measuring the secondary electron emission coefficient, the measurement of the secondary electron emission coefficients under different temperatures is realized.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Method and apparatus for determining properties of fuels
ActiveUS8781757B2Easy to operateRaman scatteringSpecial data processing applicationsPresent methodDistillation
Owner:REAL TIME ANALYZERS
Device for rapid-heating quasi-static high-temperature Hopkinson pressure bar experiment
InactiveCN103018094AEliminate performance impactFast heatingPreparing sample for investigationStrength propertiesAudio power amplifierInduction heater
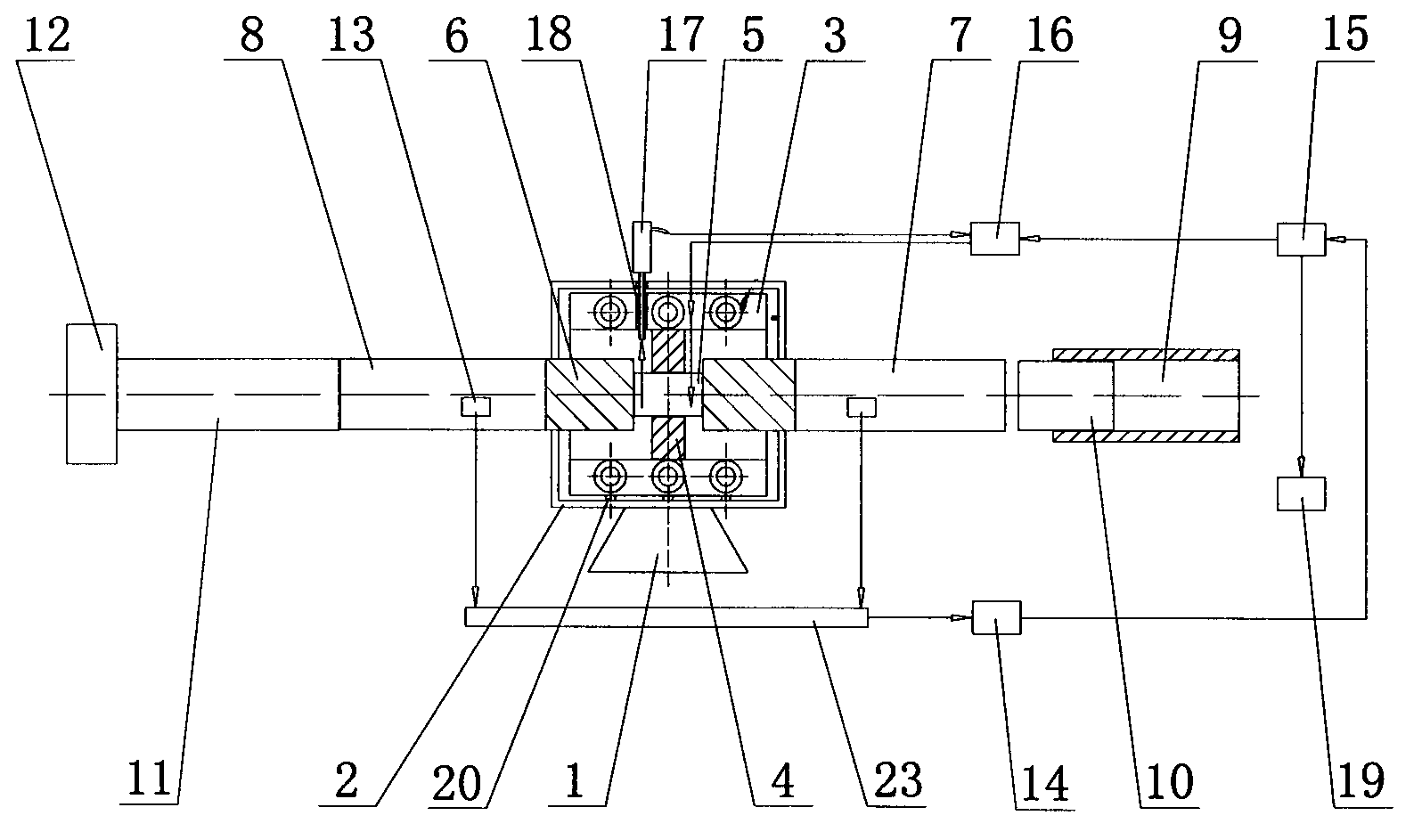
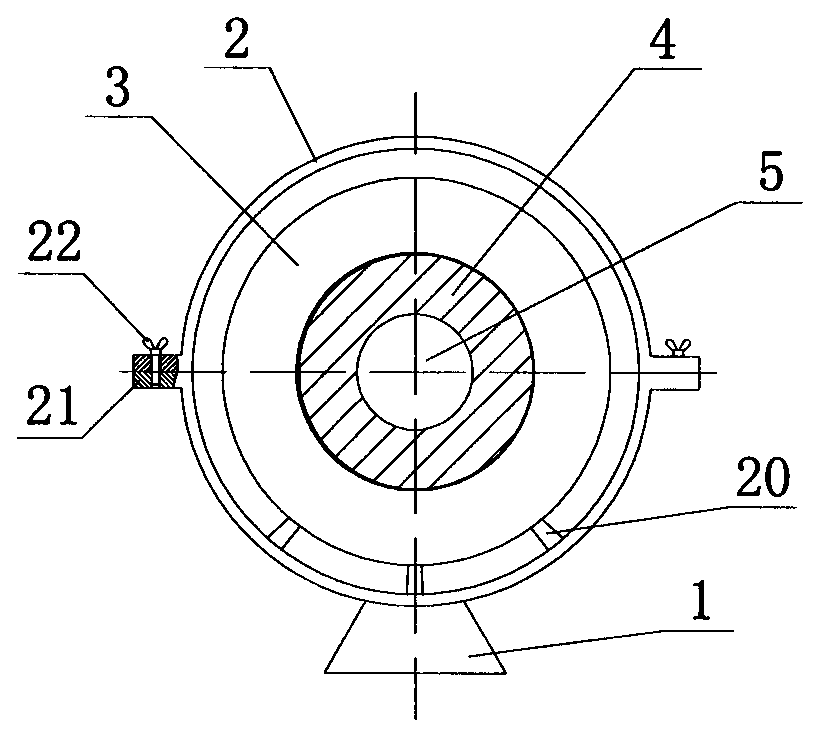
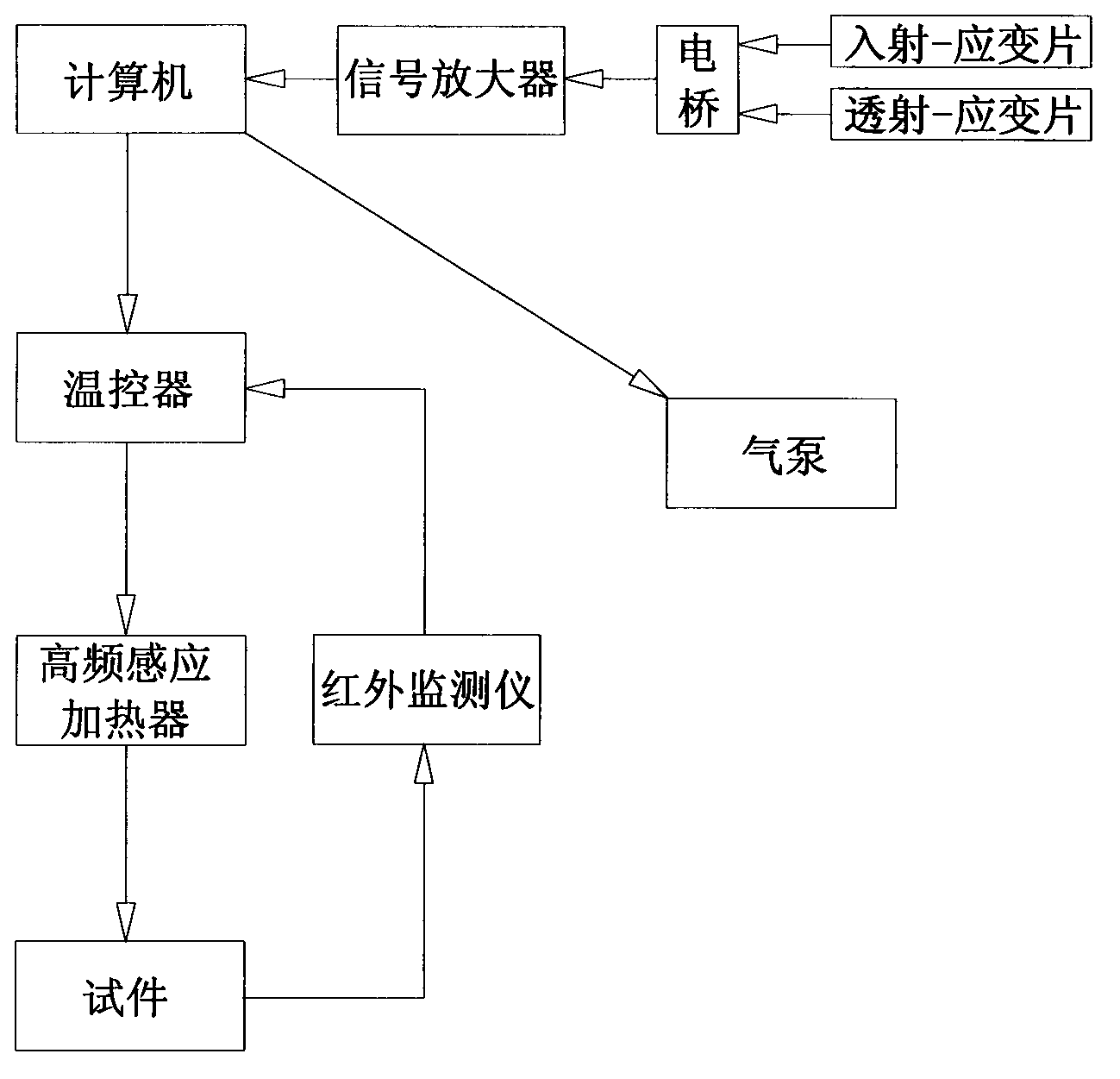
The invention discloses a device for a rapid-heating quasi-static high-temperature Hopkinson pressure bar experiment. The device adopts the technical scheme that a sample is mounted in the middle of a ceramic sleeve at the center of a high-frequency induction heater in a shielding cover; the both ends of the sample are connected with the inner ends of two short ceramic bars; the outer ends of the two short ceramic bars are connected with one end of an incidence bar and one end of a transmission bar respectively; stress wave signals of strain gages are measured from the incidence bar and the transmission bar respectively, and sent to a computer for data processing through an electric bridge and an amplifier; the computer controls the warming of the high-frequency induction heater and the sample through a temperature controller; and the sample temperature is fed back to the temperature controller by another infrared monitor. The device overcomes the defects that the available device for the split Hopkinson pressure bar experiment is complicated in structure, complicated to operate, low in working efficiency and difficult in data processing; and the quality of the experiment is influenced seriously. The device is suitable for the Hopkinson pressure bar experiments in different laboratories, in particular to the heating of the sample and the immediate processing of the information of the strain gages.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Experiment device for testing softening and dropping point of sinter
ActiveCN103713007AEasy to operateMeet testing needsInvestigating phase/state changeFurnace temperatureGas cylinder
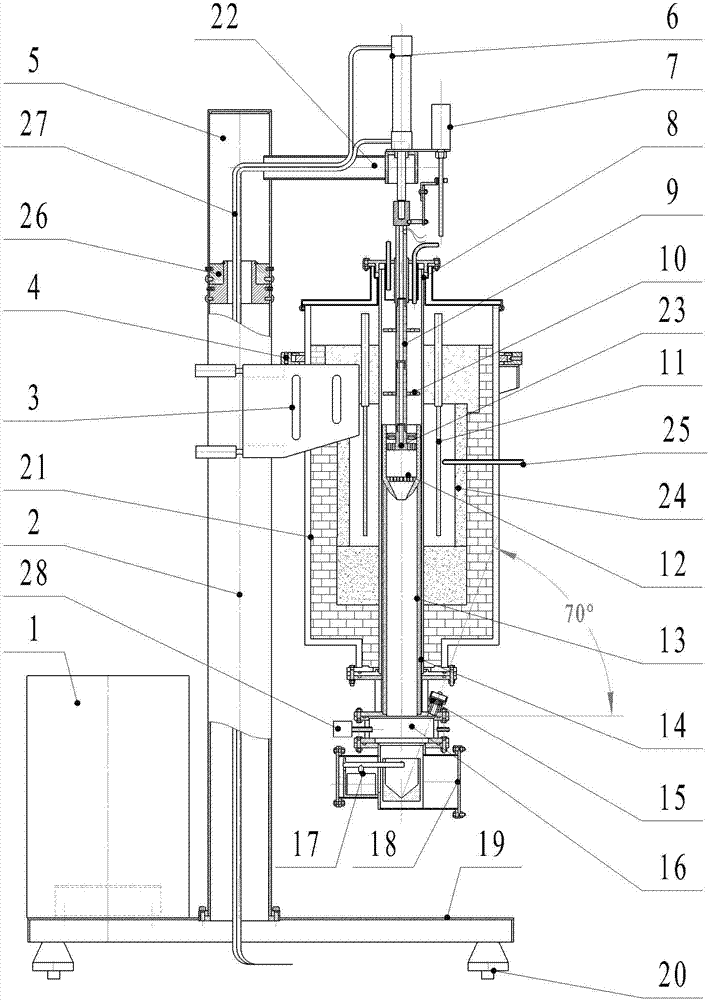
The invention relates to an experiment device for testing a softening and dropping point of a sinter. The device is composed of a large current transformer, a furnace body fixing column, a tray, a furnace body adjusting frame, a rotary column, a pressurized gas cylinder, a displacement sensor, a furnace top sealing furnace cover, a pressurized graphite compression strut, an anti-radiation graphite cover, a molybdenum disilicide heater, a graphite crucible, a high pure graphite sleeve, a sealed alundum tube, a pinhole camera, an air inlet channel fixing sleeve, a dropping crucible weighing device, a dropping crucible device, a furnace body chassis, furnace body castors, a heating furnace body, a cantilever beam, a sample temperature thermocouple, a alumina hollow ball member, a furnace temperature control thermocouple, a rotary column circular sleeve, a pressurized gas cylinder pipeline and a pressure transmitter. The large current transformer is adopted to supply power for the molybdenum disilicide heater; the pinhole camera is used to observe a dropping process of high temperature liquid slag iron; the dropping crucible weighing device is arranged; the crucible is assembled and disassembled in a manner of laterally opening the door; and the position of the heating furnace body is adjusted by the furnace body adjusting frame, so that the device is flexible, accurate and convenient for operations.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Sensor type on-line monitor of biochemical oxygen demand
InactiveCN101000341AImprove measurement stabilityOut-of-the-boxMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansInstrumentationSoftware
A BOD on-line detector of sensor type is prepared as transferring sample in filter element of sampling unit A to sample cup of measuring unit C through sampling pump, connecting microbiological membrane transducer of measuring unit C to electrode interface of controlling unit B, applying instrument software to directly calculate out BOD of sample based on measurement signals of microbiological membrane transducer through signal collector and signal amplifier.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF APPLIED CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method and system for representing numerical value of stress-strain constitutive relation of material
ActiveCN107305174AThe mechanical properties meetGuaranteed fitMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesStress–strain curveTensile testing
The invention relates to the field of materials and provides a method for representing a numerical value of a stress-strain constitutive relation of a material. The method comprises the following steps: setting a test parameter which includes sample temperature; performing tensile test on the material according to the test parameter, thereby acquiring tensile test data of the material, wherein the tensile test data include stress data and strain data; establishing a stress-strain curve according to the stress data and the strain data; and selecting a corresponding stress-strain numerical value model according to the properties of the material, fitting the stress-strain curve of the material and solving the parameters in the stress-strain numerical value model. An error between a result acquired according to the numerical value representing method and a practical value is smaller and the method is more practical. The invention also provides a system for performing the numerical value representing method and the method for acquiring the stress-strain constitutive relation of the material.
Owner:CHINA SPECIAL EQUIP INSPECTION & RES INST +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com