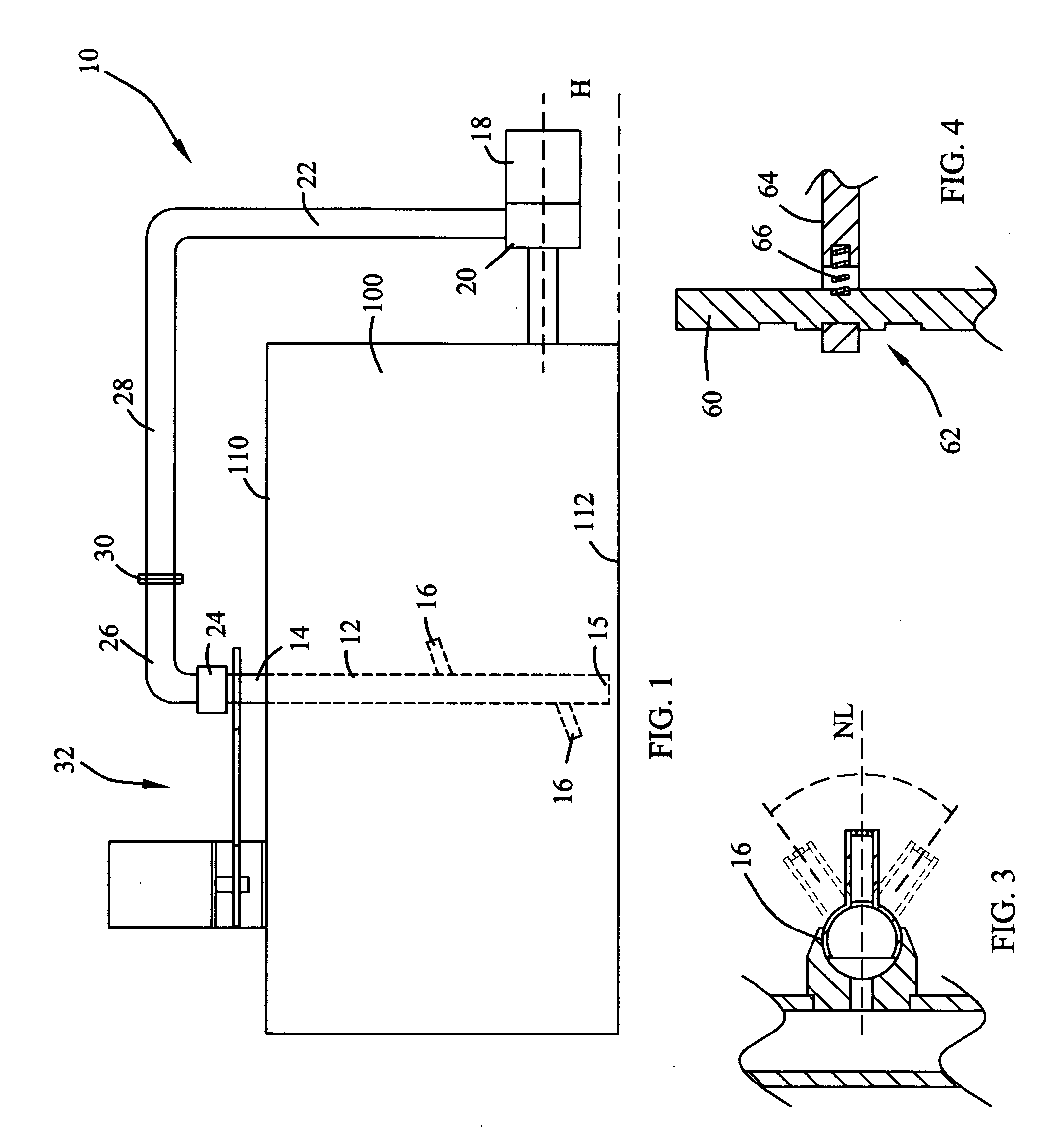
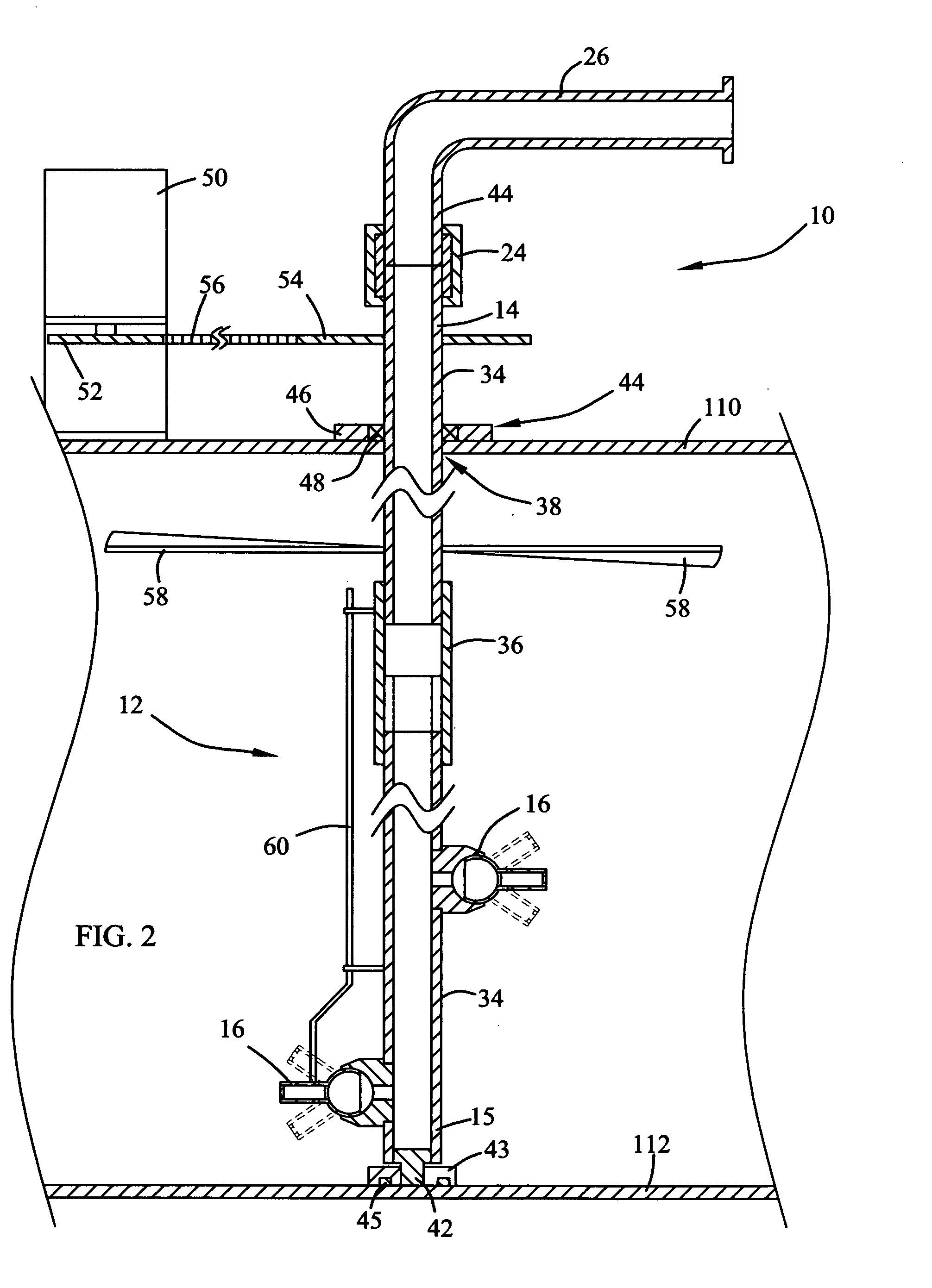
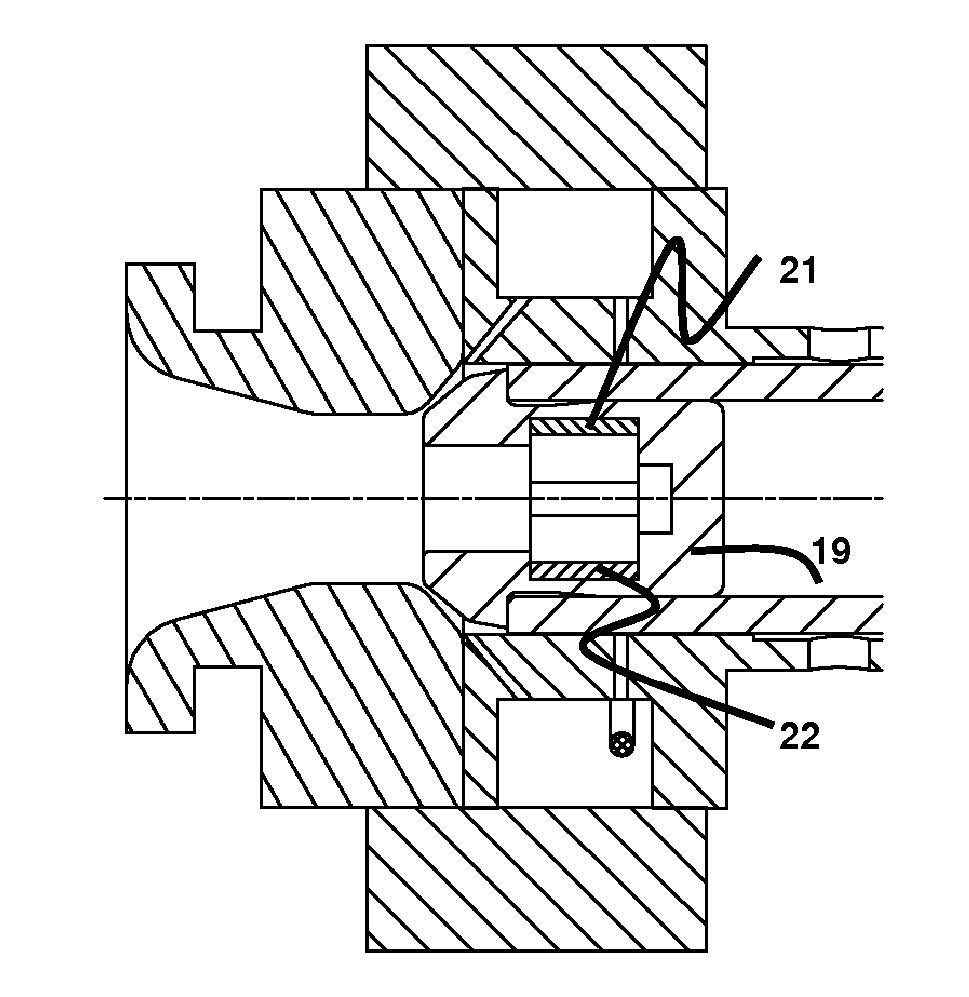
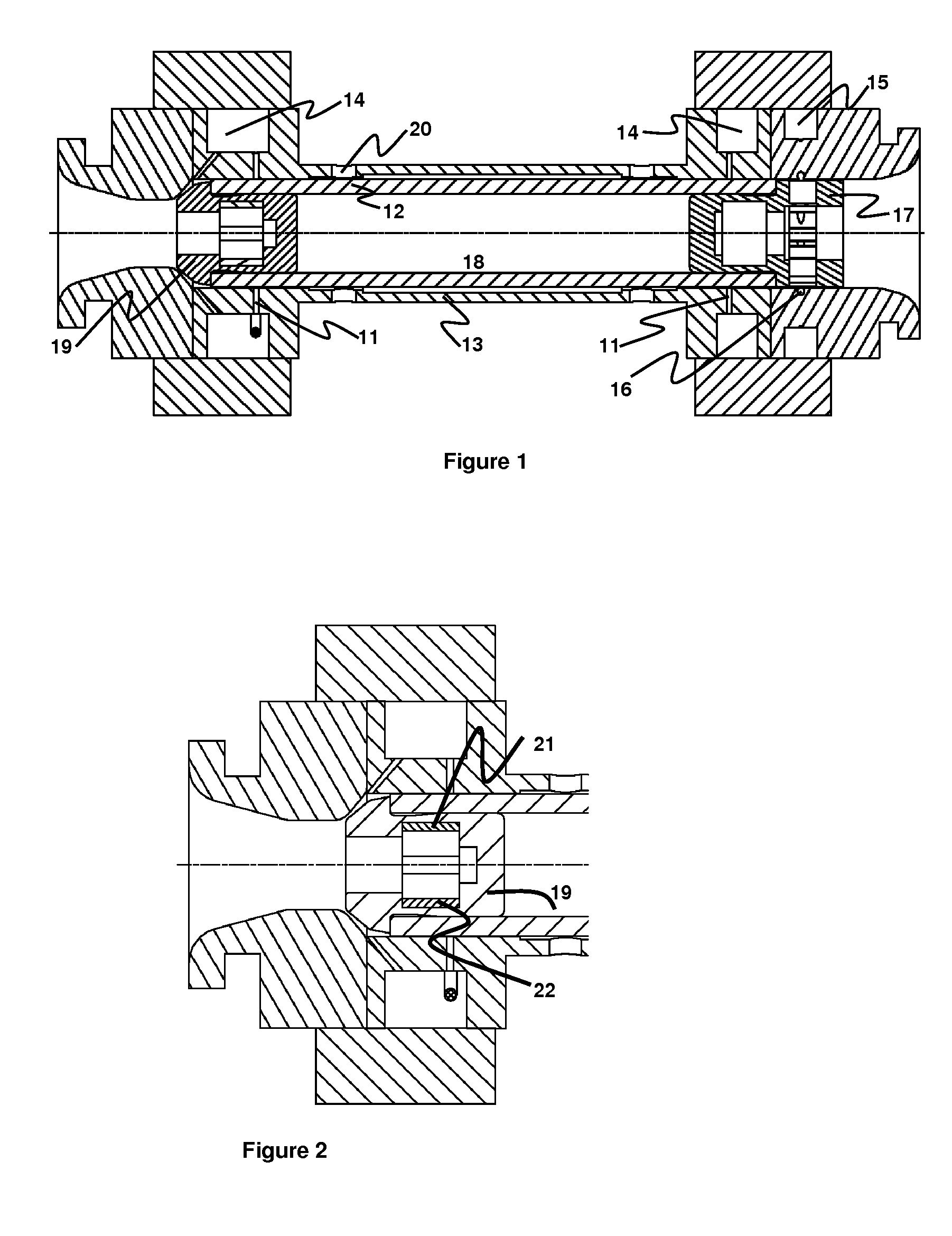
Patents
Literature
657 results about "Rotational frequency" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
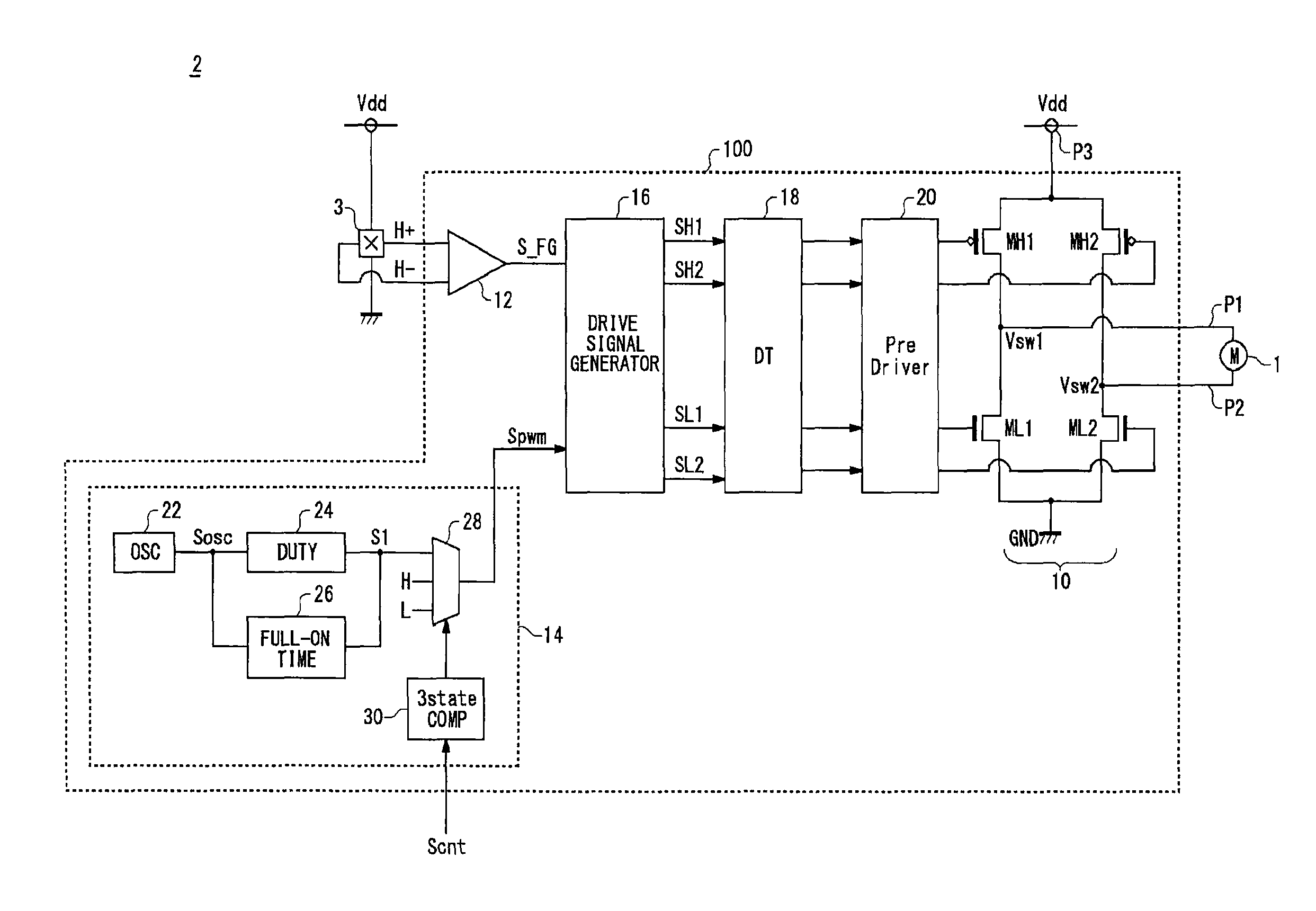
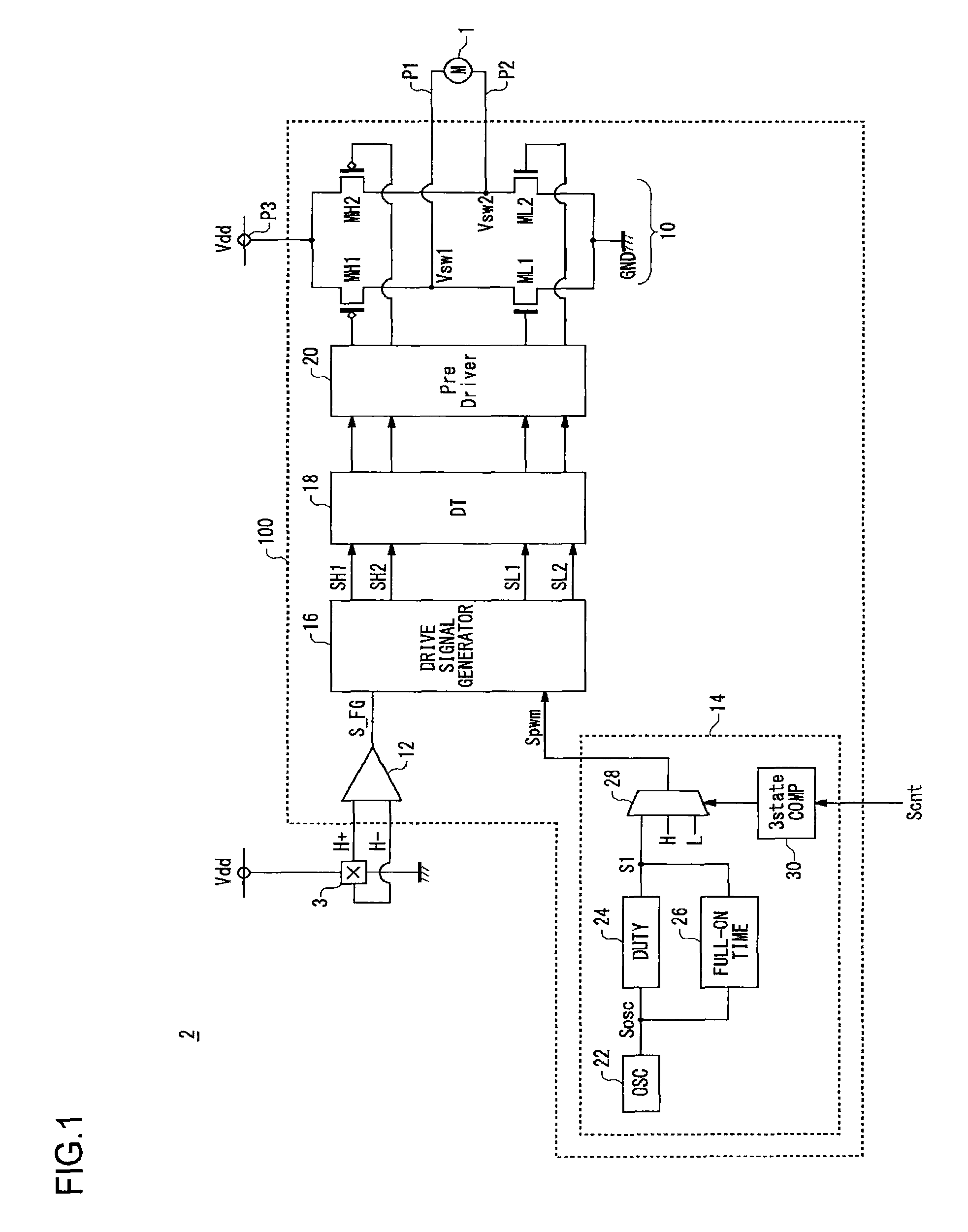
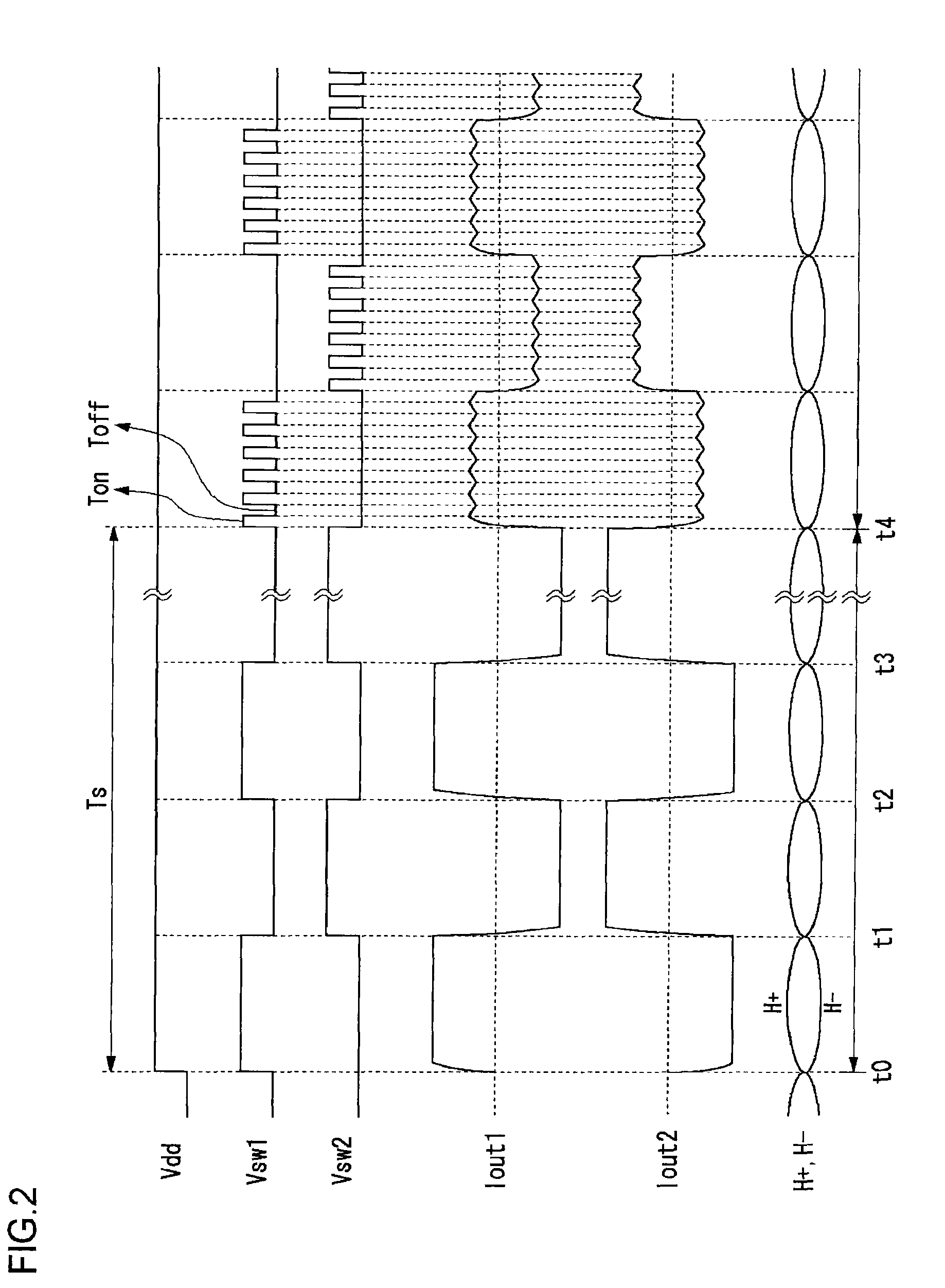
Motor drive circuit with short startup time
An H-bridge circuit is connected to a coil of the vibration motor that is to be driven. A comparator receives Hall signals indicating position information of a rotor of the vibration motor, and converts to an FG signal. A pulse width modulator generates a pulse-modulated pulse signal specifying energization time of the coil of the vibration motor. The pulse width modulator, in a first mode, after commencing start-up of the vibration motor, sets a duty ratio of the pulse signal to 100%, and after that, switches the duty ratio to a predetermined value in accordance with rotational frequency of the motor. In a second mode, the duty ratio of the pulse signal continues to be set to 100%. In a third mode, frequency and the duty ratio of the pulse signal are set based on a control signal of a pulse form inputted from outside. The control signal is used also in switching mode.
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
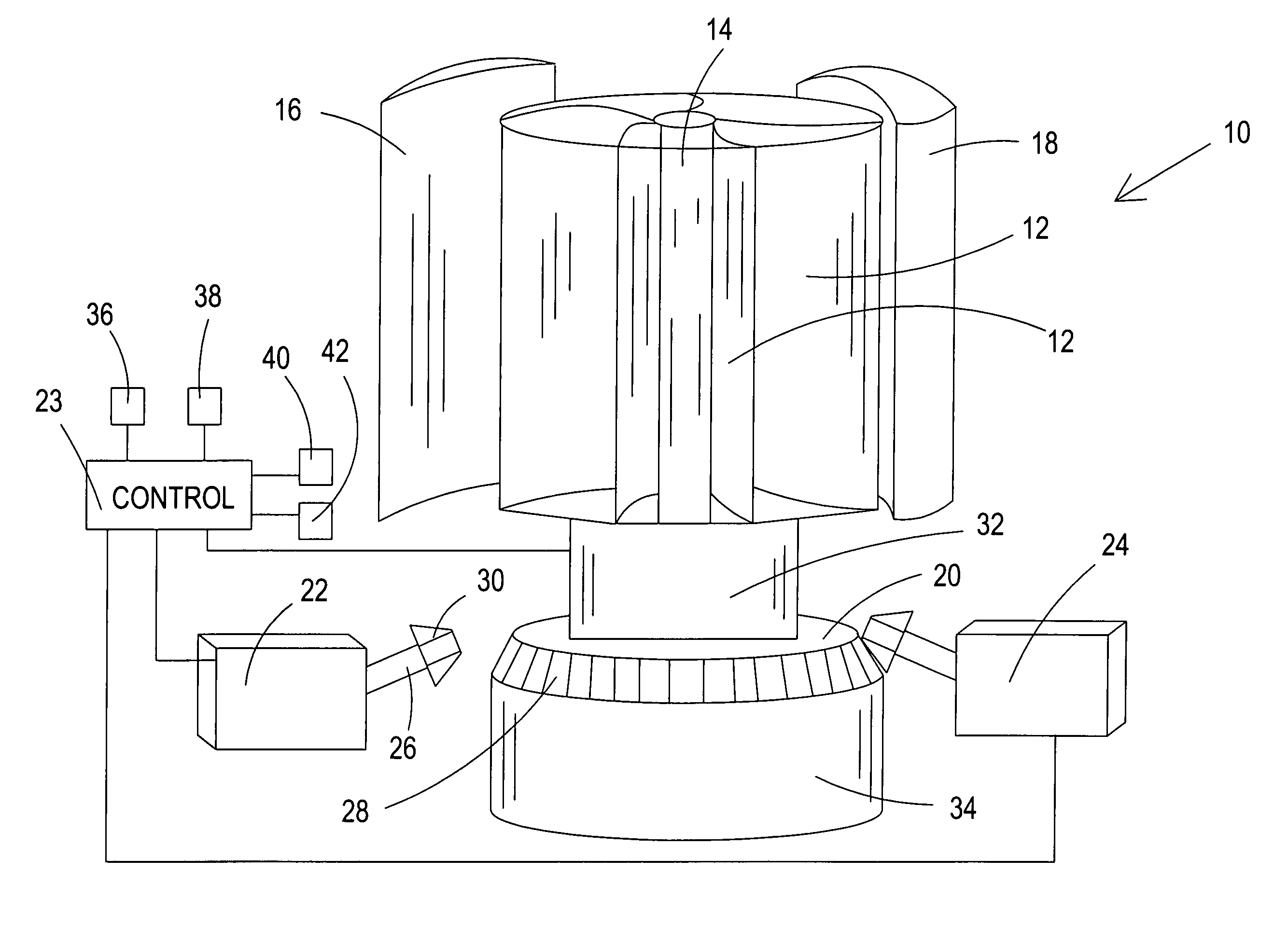
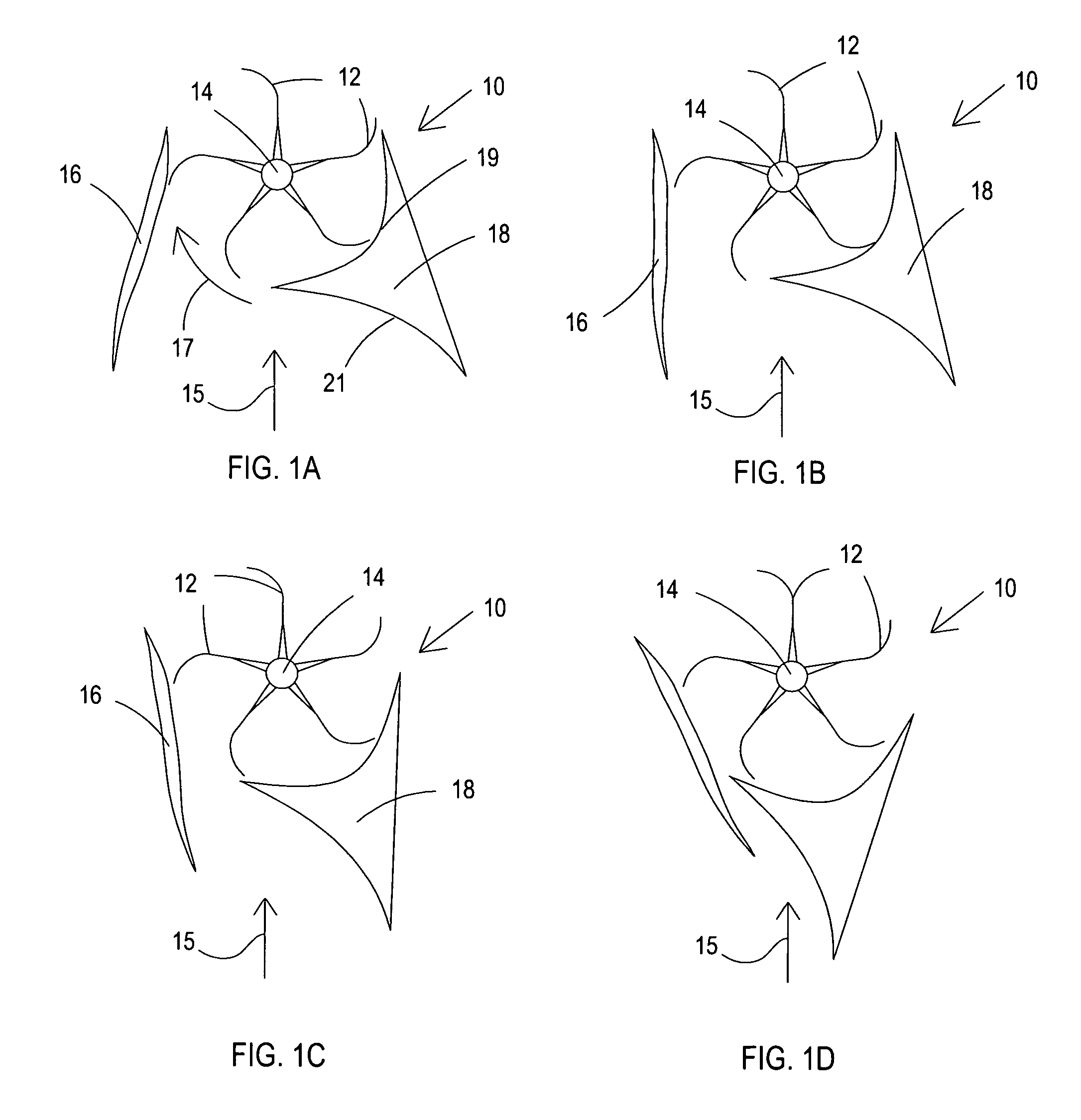
Wind dam electric generator and method
InactiveUS6984899B1Constant windmill shaft rotational speedWind motor controlEngine fuctionsAir volumeEngineering
A vertical axis windmill is provided wherein the amount of wind directed to blades in the power producing part of rotation and the mechanical load of multiple generators is controlled by a feedback control to maintain a relatively constant rotational frequency of the shaft of the windmill. In a preferred embodiment, two wind foils extend radially outwardly from the blades to thereby provide a scoop capable of pulling in more air than would normally be received by the blades. The wind foils then direct the wind flow to the power producing part of rotation of the blades for maximum power output, when necessary. The wind foils can close to control the wind flow to the blades. The generating capacity of a plurality of generators is also controlled in response to shaft rotation to maintain substantially constant shaft rotation.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
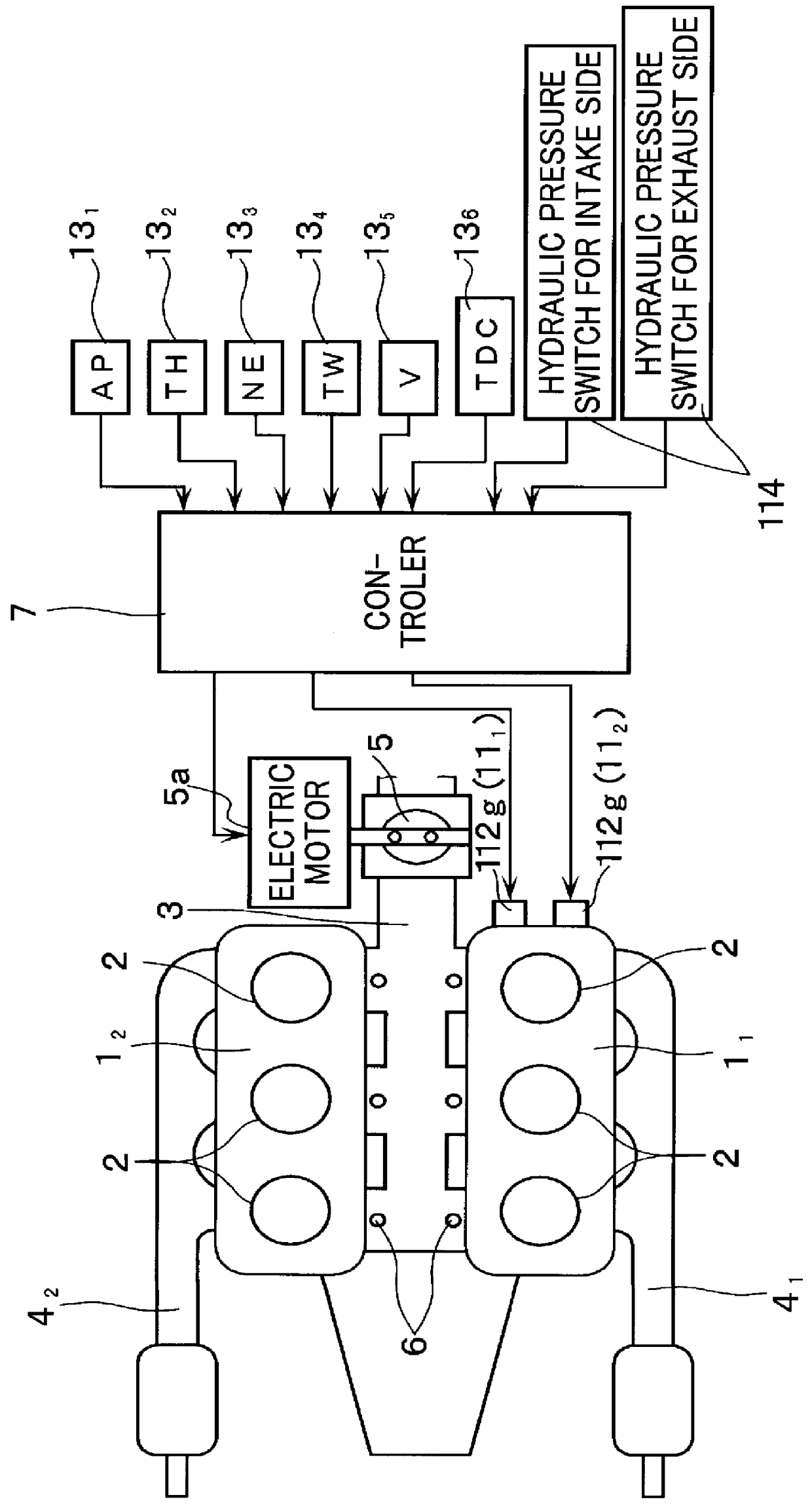
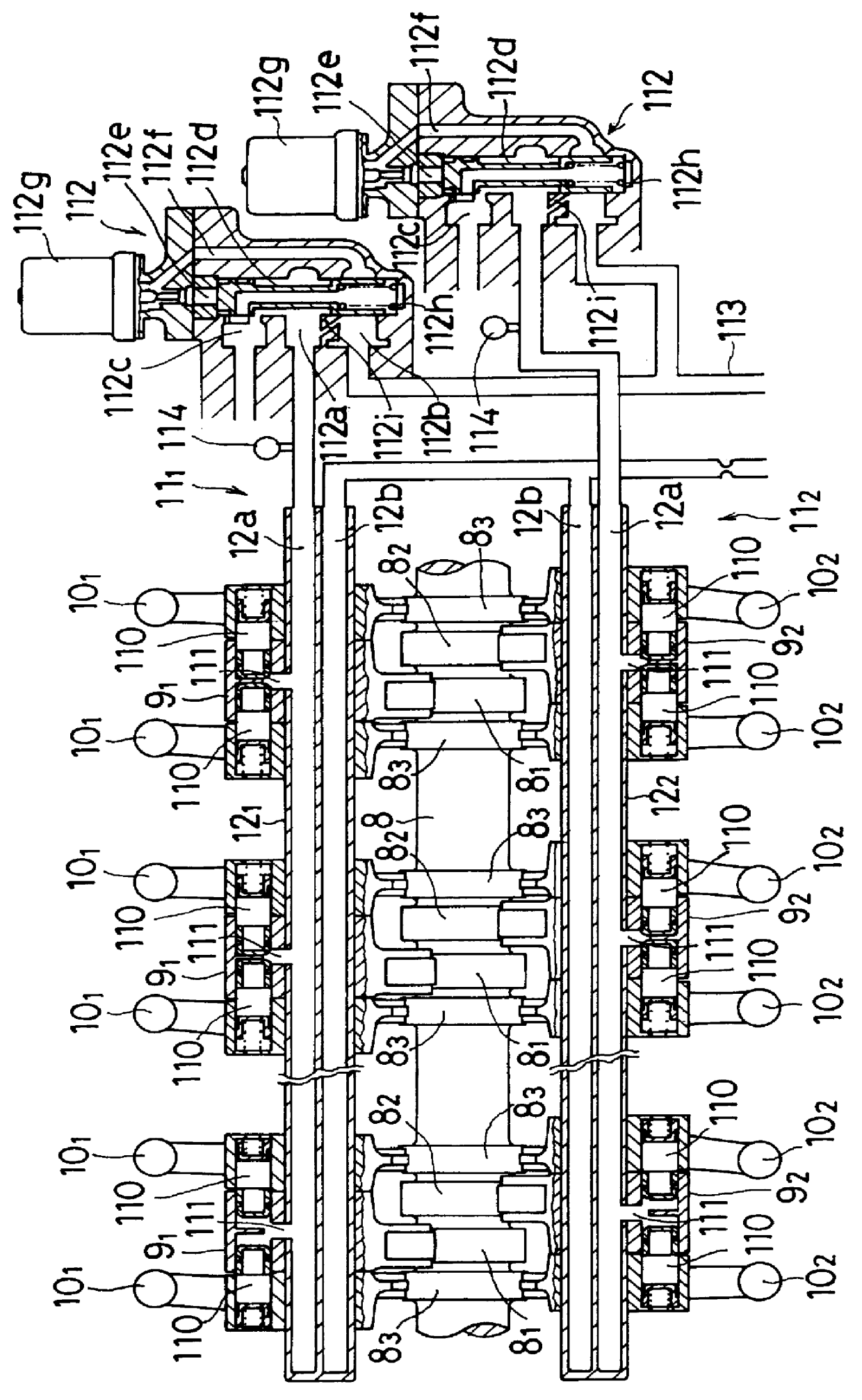
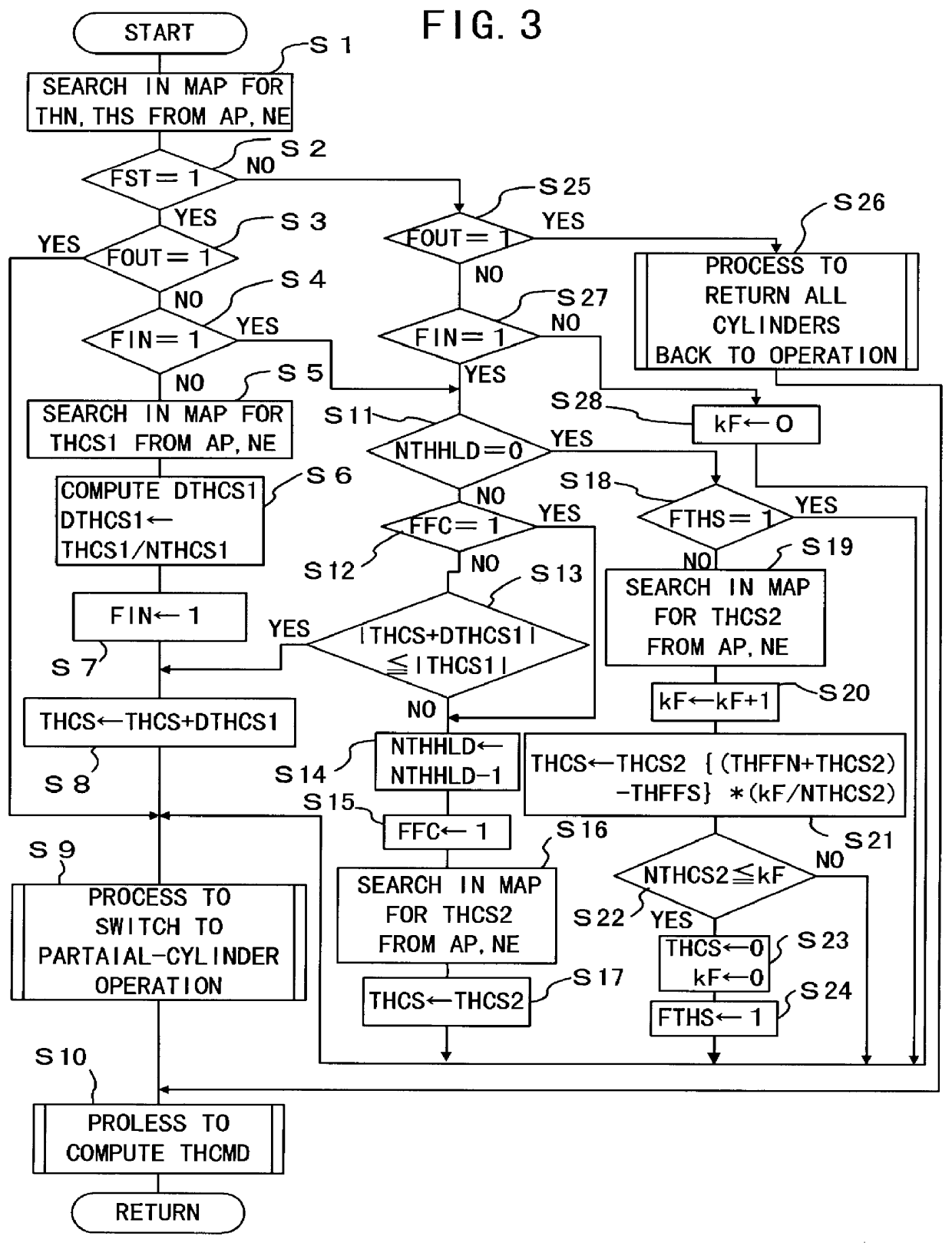
Apparatus for controlling multi-cylinder internal combustion engine with partial cylinder switching-off mechanism
In an apparatus for controlling a multi-cylinder internal combustion engine with partial cylinder switch-off mechanism which is switchable between an all-cylinder operation mode in which all cylinders are operated and a partial-cylinder operation mode in which operation of partial cylinders is suspended, the operation of intake valves and exhaust valves is suspended or resumed in a predetermined order with respect to all of the suspended cylinders irrespective of a rotational frequency of the engine. There are provided a solenoid valve on an intake side and a solenoid valve on an exhaust side for switching input hydraulic pressures for hydraulically operated switching devices respectively on the intake side and on the exhaust side between the driving state and the drive-free state. At the time of switching the operation, one of the solenoid valves on the intake side and the exhaust side is driven in advance. The subsequent number of rotations of a crankshaft is counted. When the number of this counting has reached a predetermined value, the solenoid valve on the other side is driven.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Device and method for measuring a rotational frequency of a movable game device
InactiveUS20070059675A1Low-cost and efficientEasy to useCosmonautic condition simulationsHollow inflatable ballsLow frequency modulationRadio signal
For measuring the rotational frequency of a movable game device, one resorts to an existing radio signal in the form of a broadcast signal or mobile communication signal within the framework of an open system, or to a radio signal of an evaluation unit within the framework of a closed system, so as to obtain, by means of an antenna having a directivity characteristic, a time-varying radio antenna receive signal which has a low-frequency modulation portion, the frequency of which corresponding to the rotational frequency of the movable game device.
Owner:CAIROS TECH
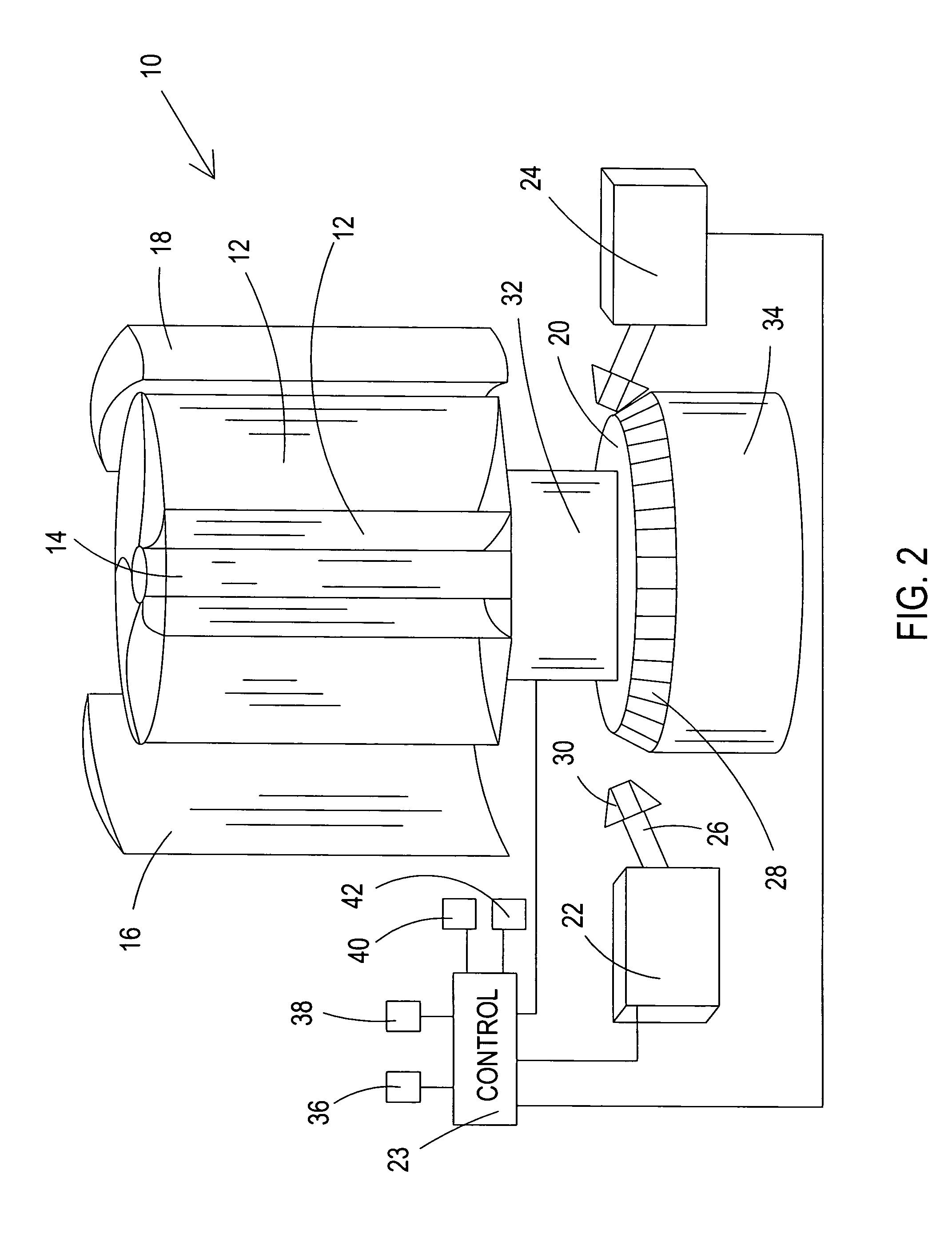
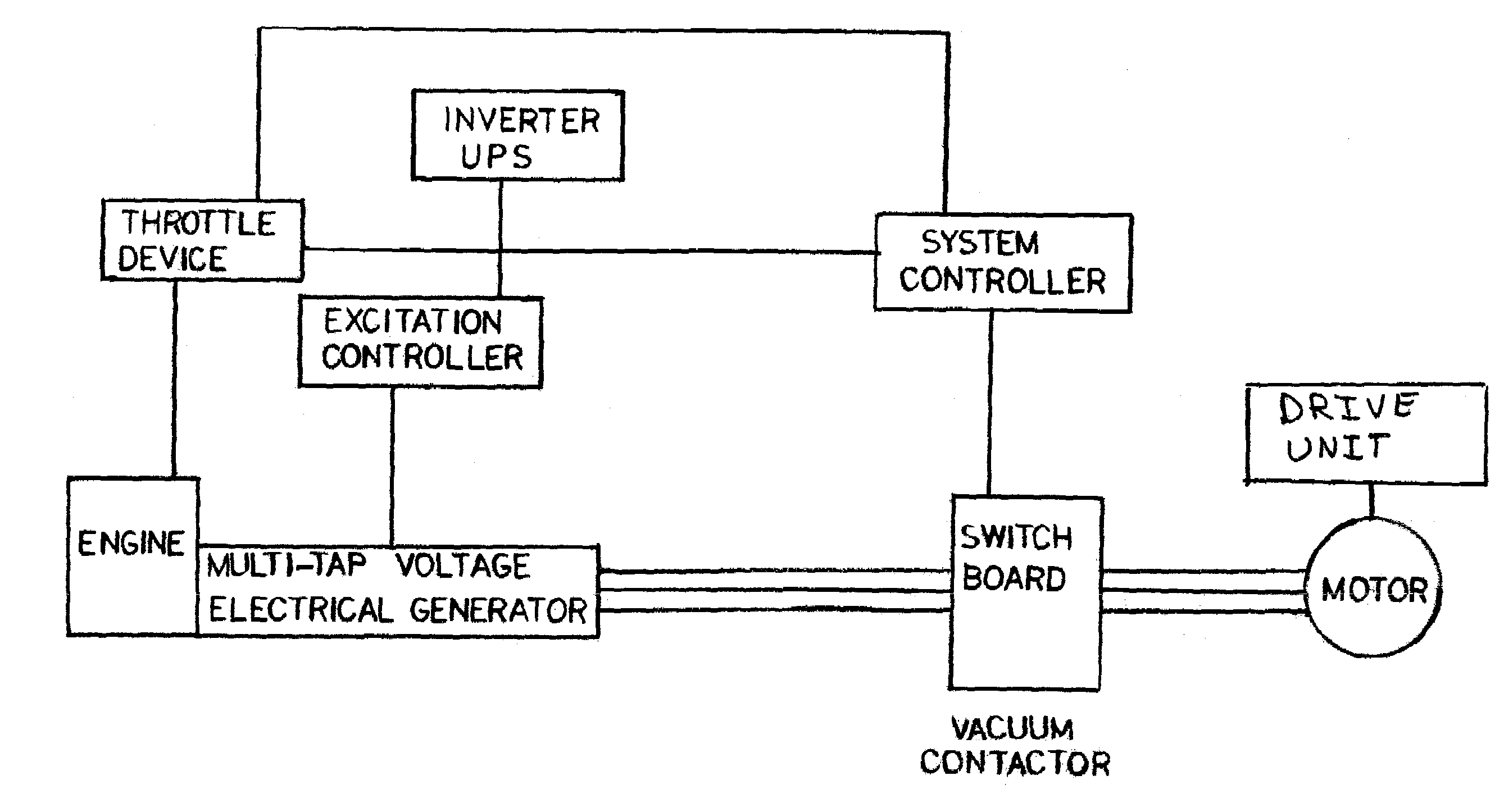
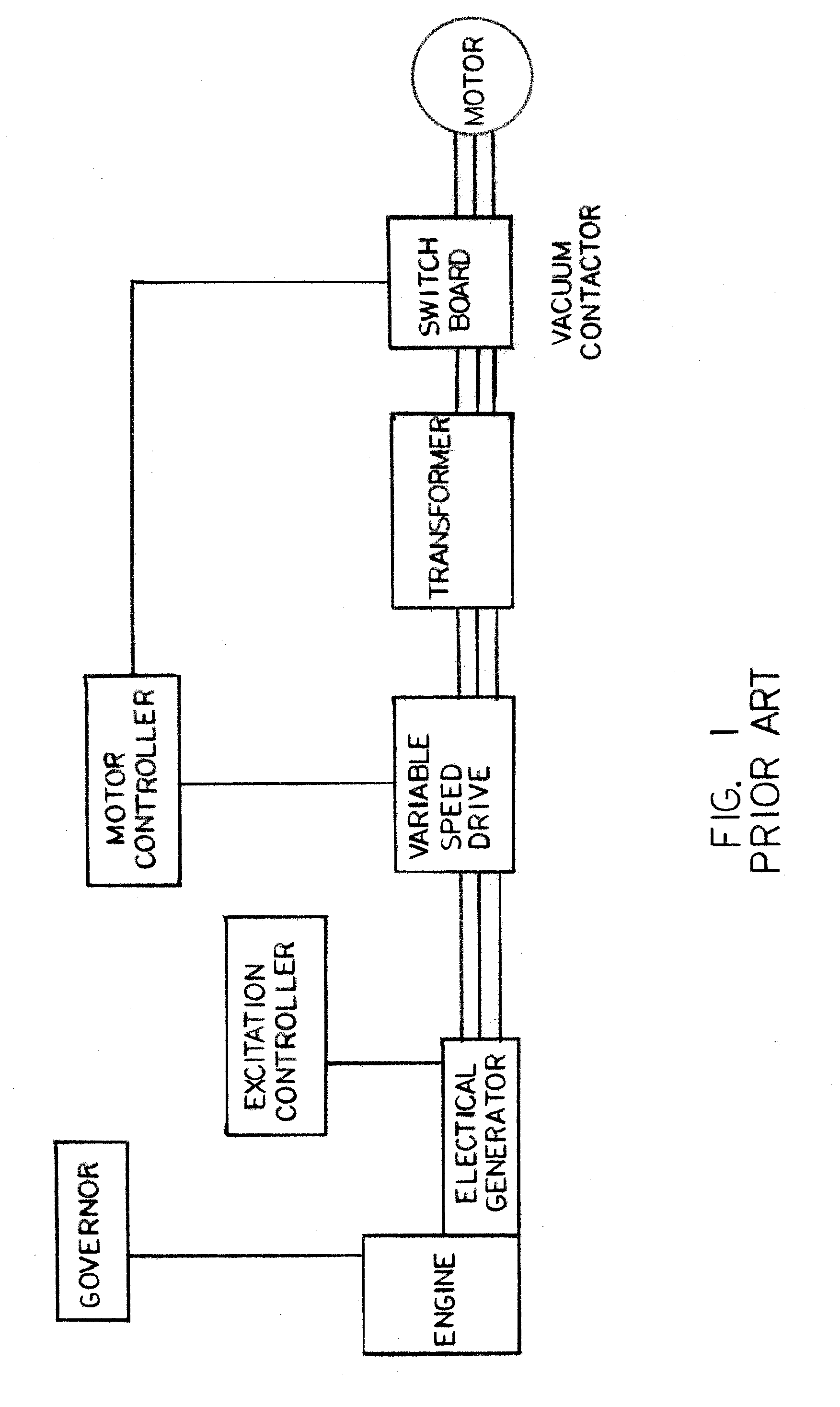
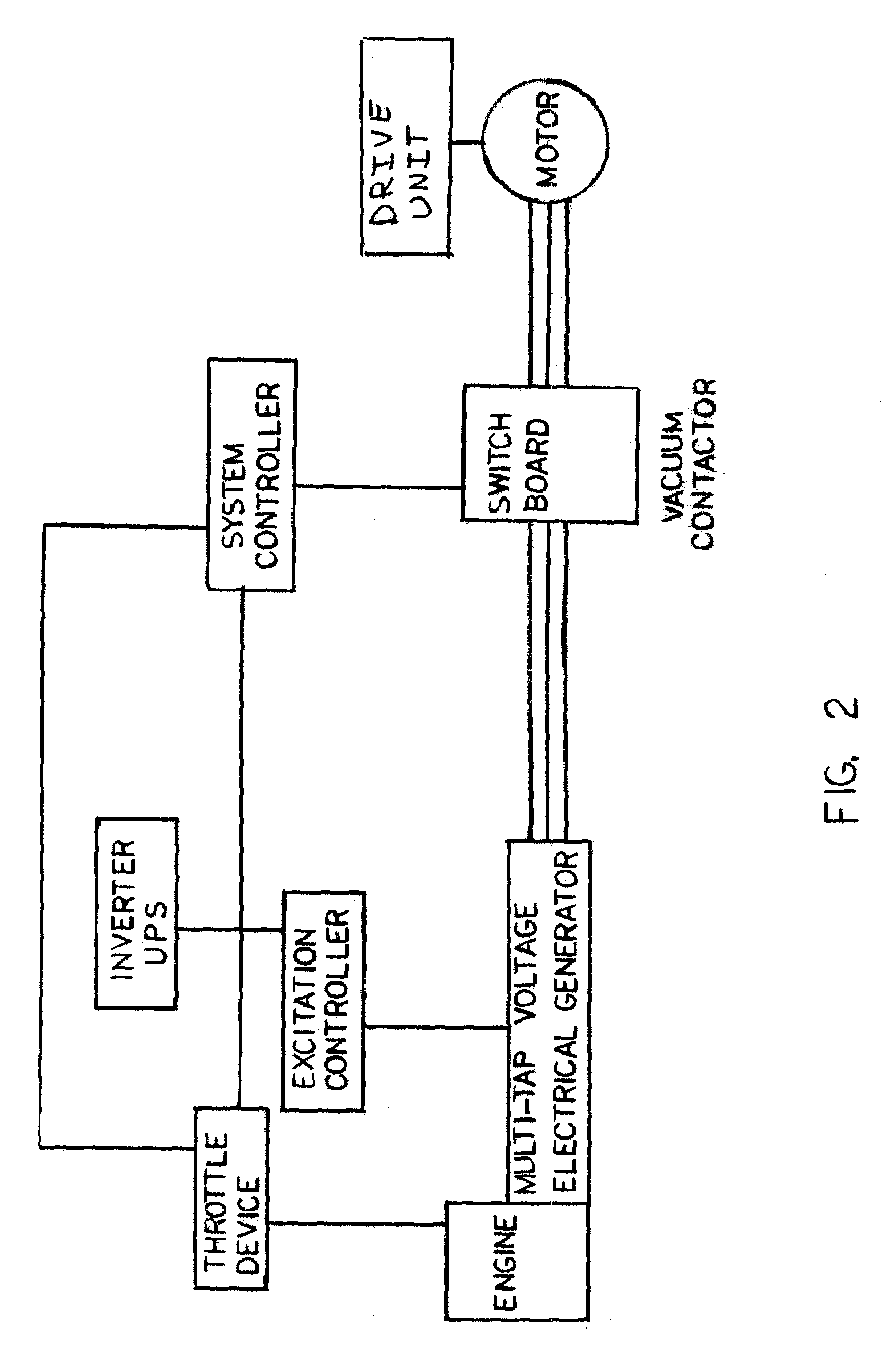
Variable frequency power system and method of use
A variable frequency power system with a power source having a rotating output and a speed control to regulate rotational speed of the rotating output. A generator coupled to and driven by the rotating output of the power source, whereby the speed control of the power source directly controls output power frequency of the generator due to control of rotational frequency of the rotating output. A voltage regulator connected between the generator and the motor regulates output voltage from the generator to the electrical motor load. A system controller controls output power frequency of the generator. The system controller interfaces with the speed control of the power source and configured to monitor generator output and operational conditions of the electrical motor load. The system controller adjusts the speed control based on generator output and operational conditions of the electrical motor load.
Owner:FOUND ENTERPRISES
Automatic power-driven toothbrushes
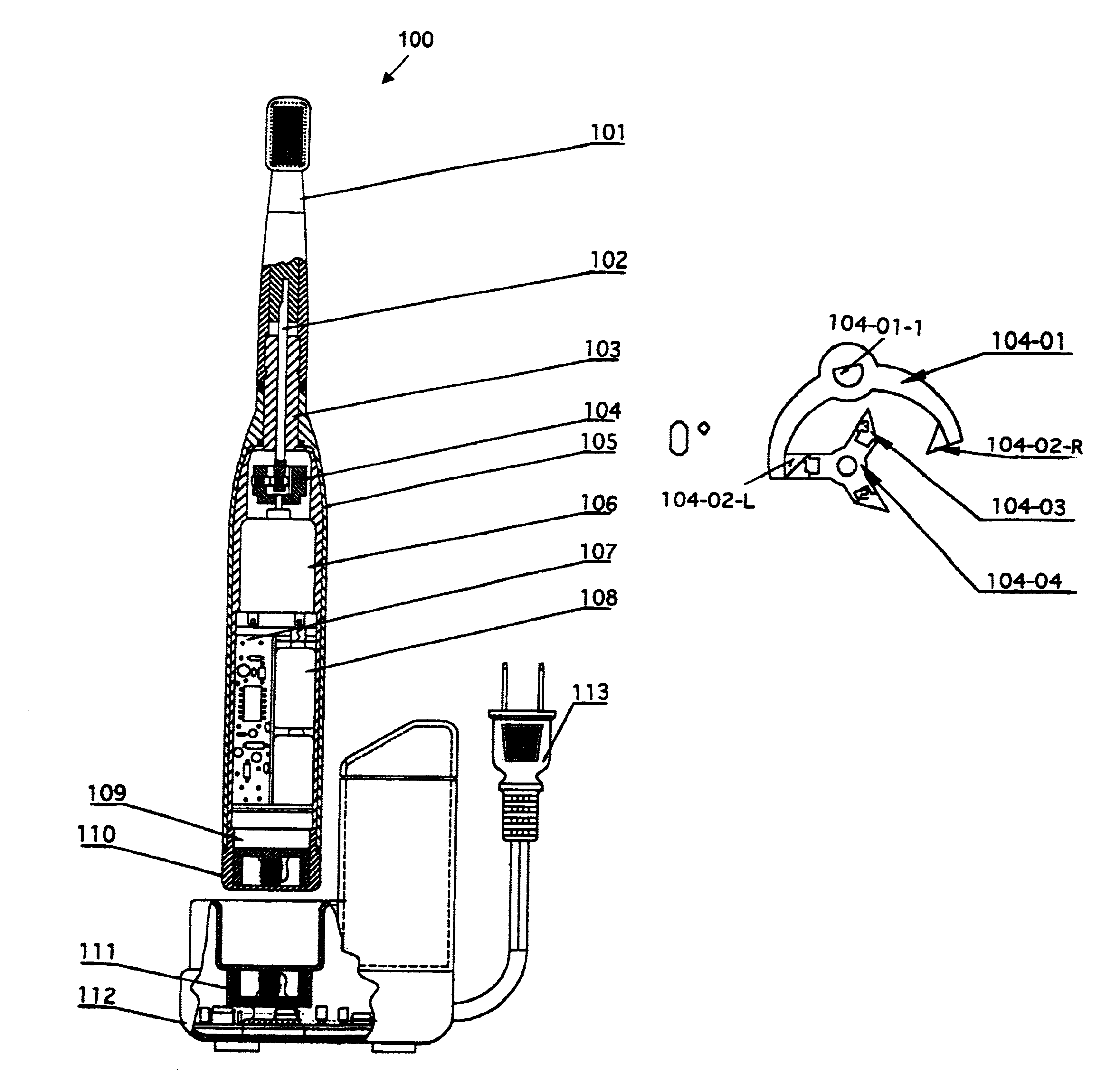
InactiveUS6845537B2Improve charging capacityDirect and efficient utilizationBowling gamesCarpet cleanersBristleEngineering
The present invention discloses the present invention discloses a power toothbrush that includes a body portion 105. An elongated level arm 102 extends from one end of the body portion to a toothbrush head 101 disposed at a distal end of the toothbrush. The toothbrush head includes a plurality of brush bristles. The elongated lever arm 102 is mounted on a vibrating pivot 104 driven by rotational DC motor engaging and pushing a set of permanent magnets attached to a two-arm fork rotating along the lever arm 102. In a preferred embodiment, the DC motor drives a three-leg permanent magnets each disposed at a 120-degree phase from each other for driving the two-arm fork for generating a vibration that three-times the frequency of the DC motor's rotational frequency.
Owner:WONG MAN KWAN
Active sound effect generating apparatus
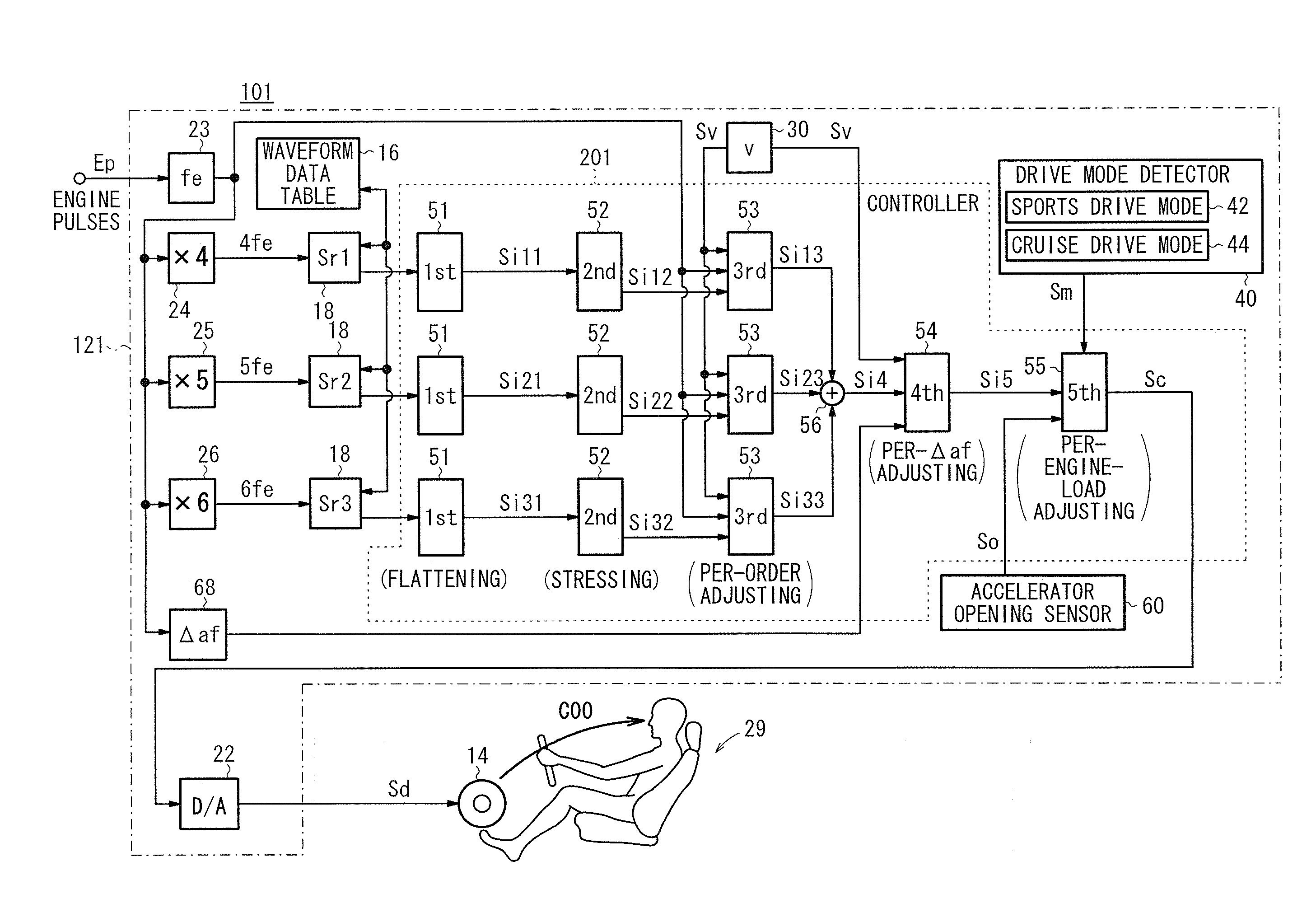
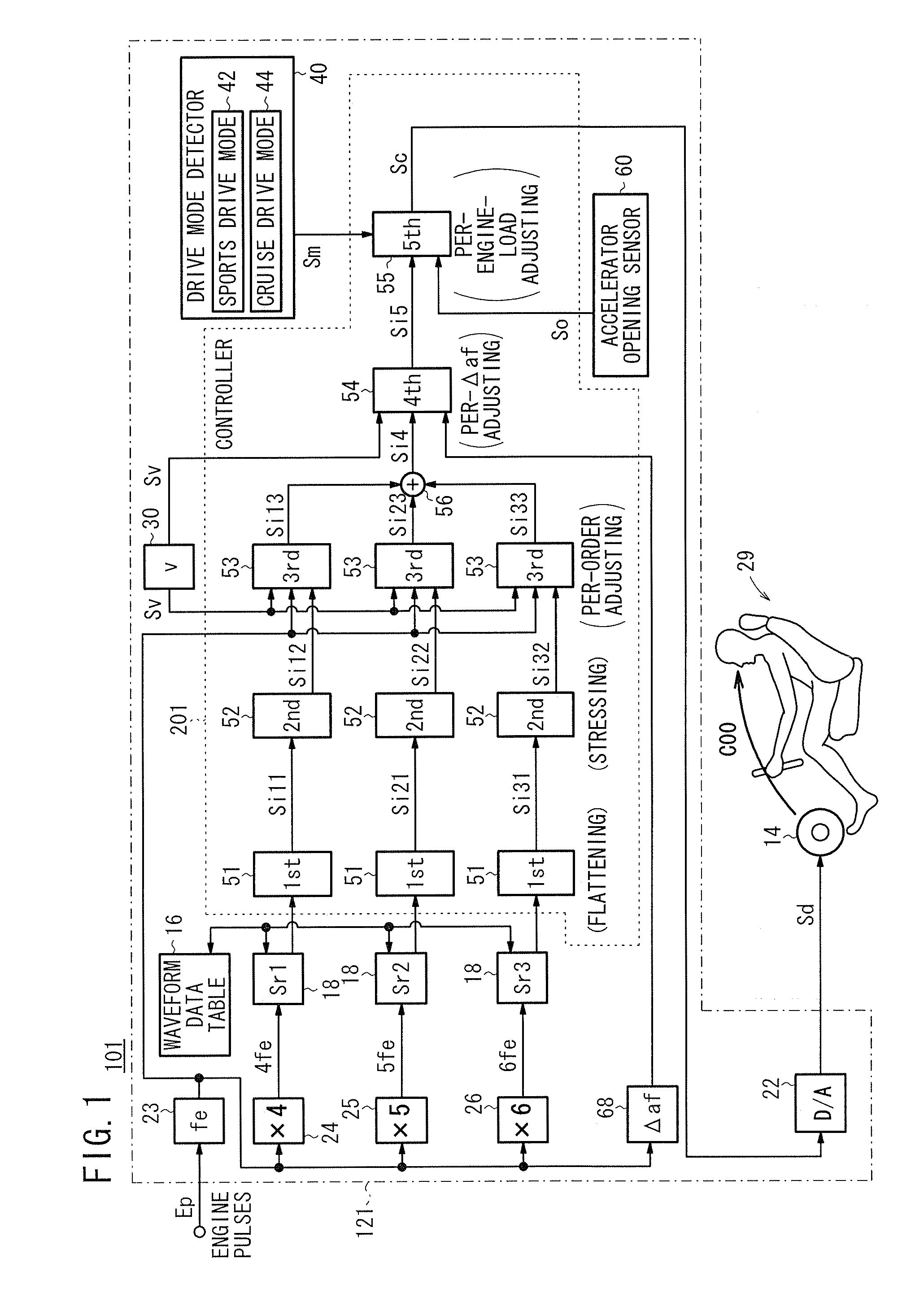
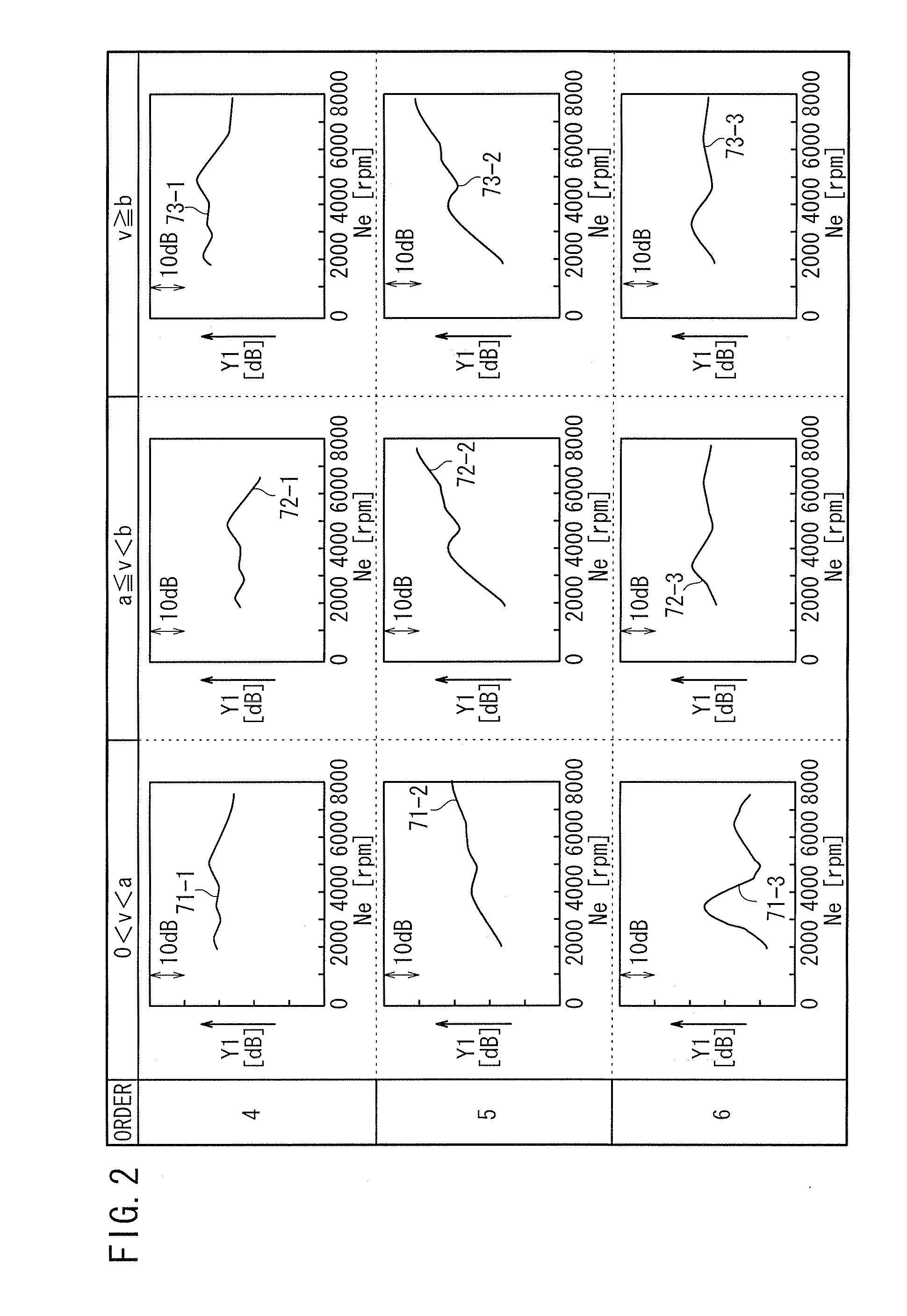
An active sound effect generating apparatus includes a controller (a fourth acoustic adjuster and a fifth acoustic adjuster) which determines the amplitude of a control signal by adjusting the amplitudes of reference signals (intermediate signals) depending on an engine rotational frequency change [Hz / second] calculated by an engine rotational frequency change calculator and an accelerator opening [%] detected by an accelerator opening sensor.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
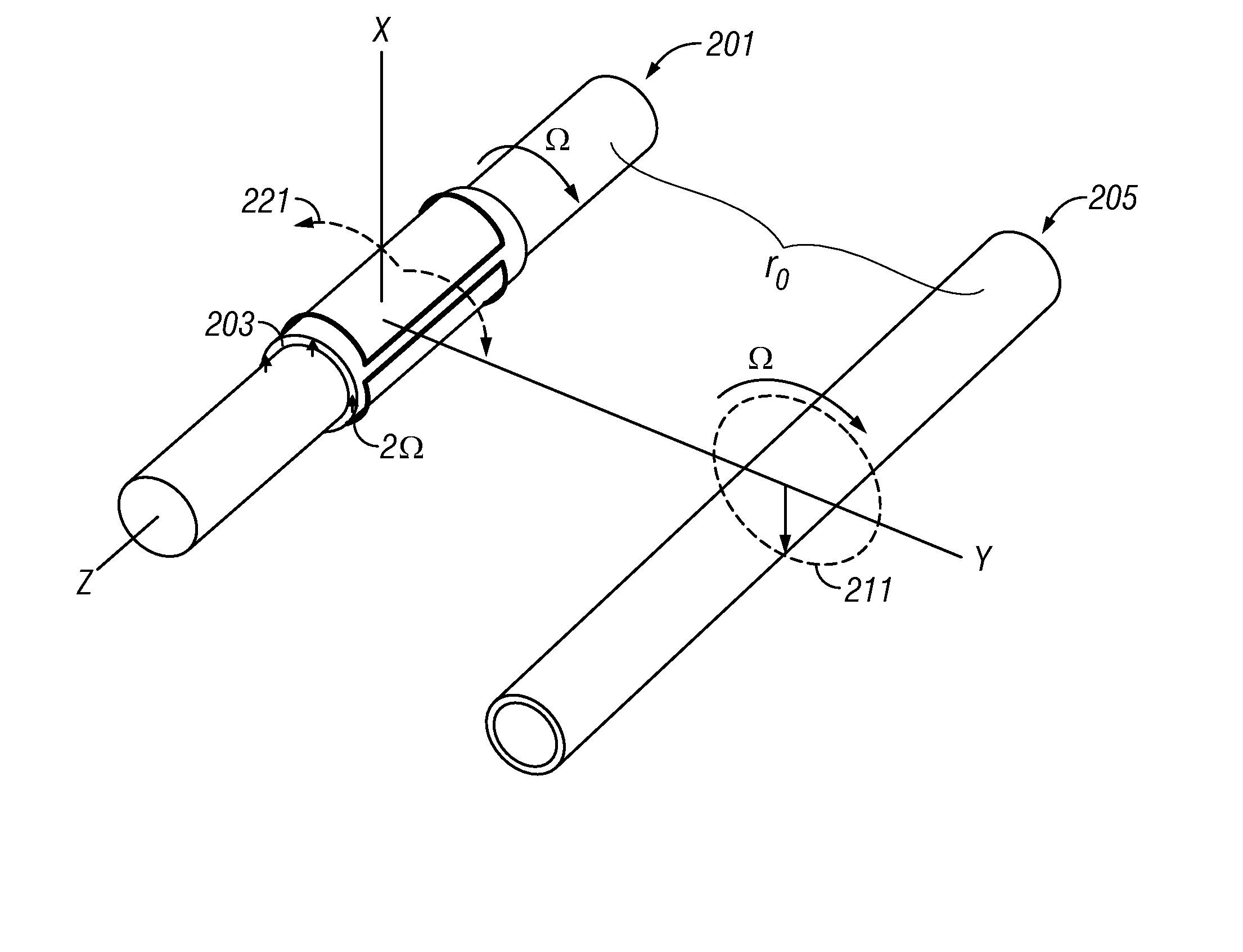
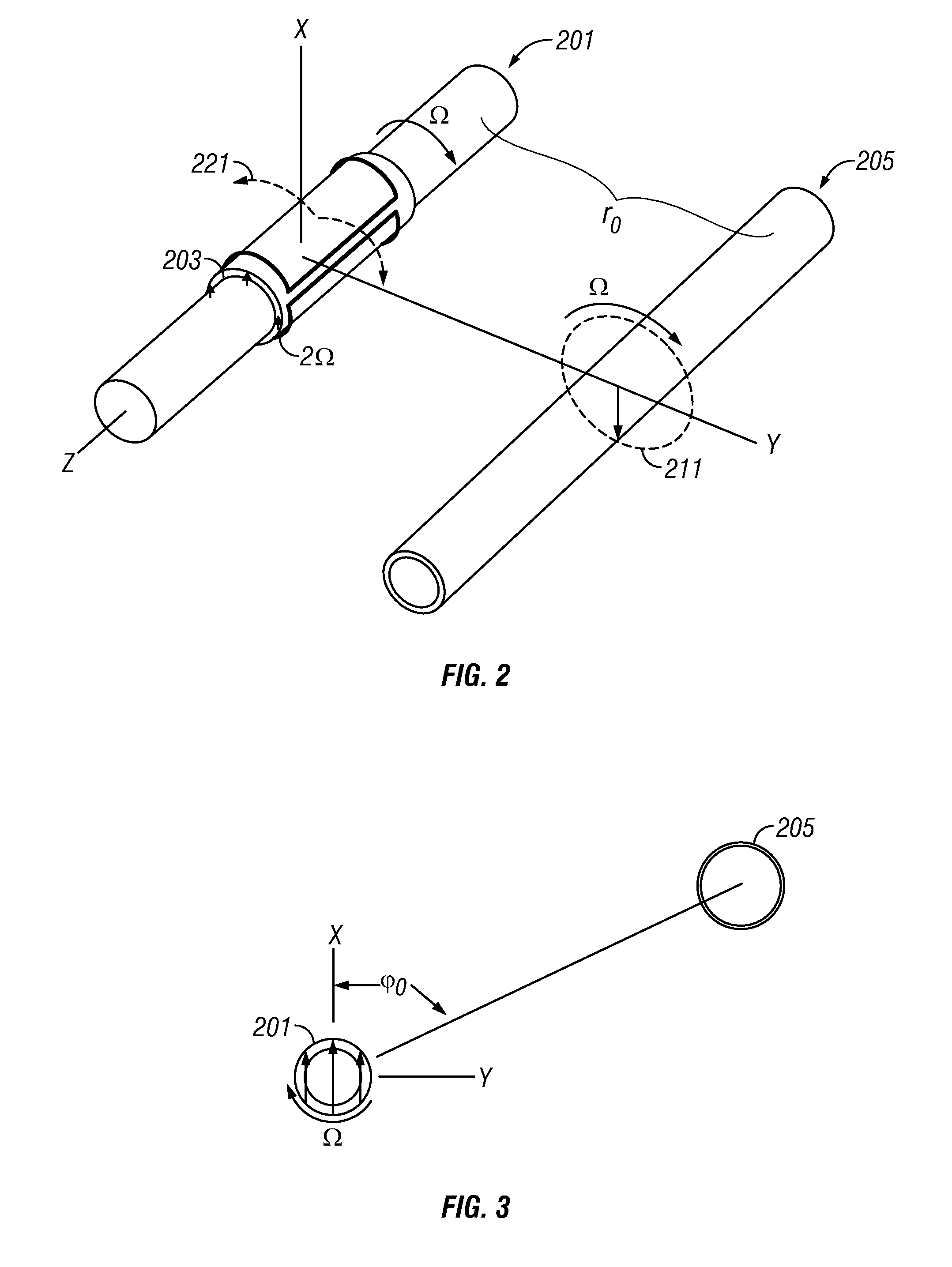
Method and Apparatus for Well-bore Proximity Measurement While Drilling
ActiveUS20080018334A1Eliminate the effects ofElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyMagnetizationClassical mechanics
A rotating, transversely magnetized, magnet on a drill collar induces magnetization in a casing of a preexisting well. A coil rotating synchronously with the magnet produces a current at twice the frequency of rotation and having an amplitude that depends upon the distance from the magnet to the preexisting well. Alternatively, a variable magnetic field is produced in the casing using a switchable magnet. It is emphasized that this abstract is provided to comply with the rules requiring an abstract which will allow a searcher or other reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the technical disclosure. It is submitted with the understanding that it will not be used to interpret or limit the scope or meaning of the claims.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
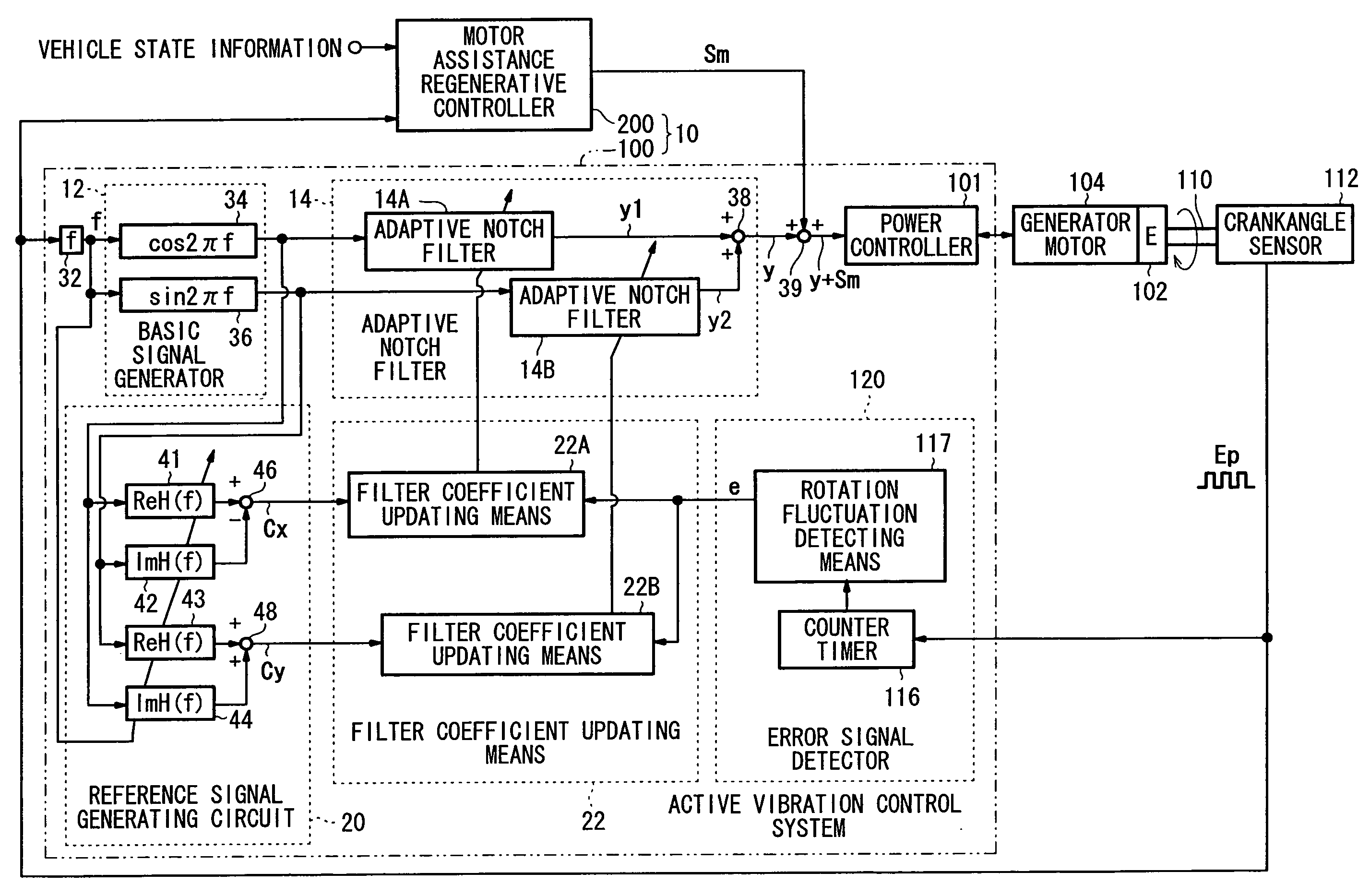
Active vibration control system for hybrid vehicle
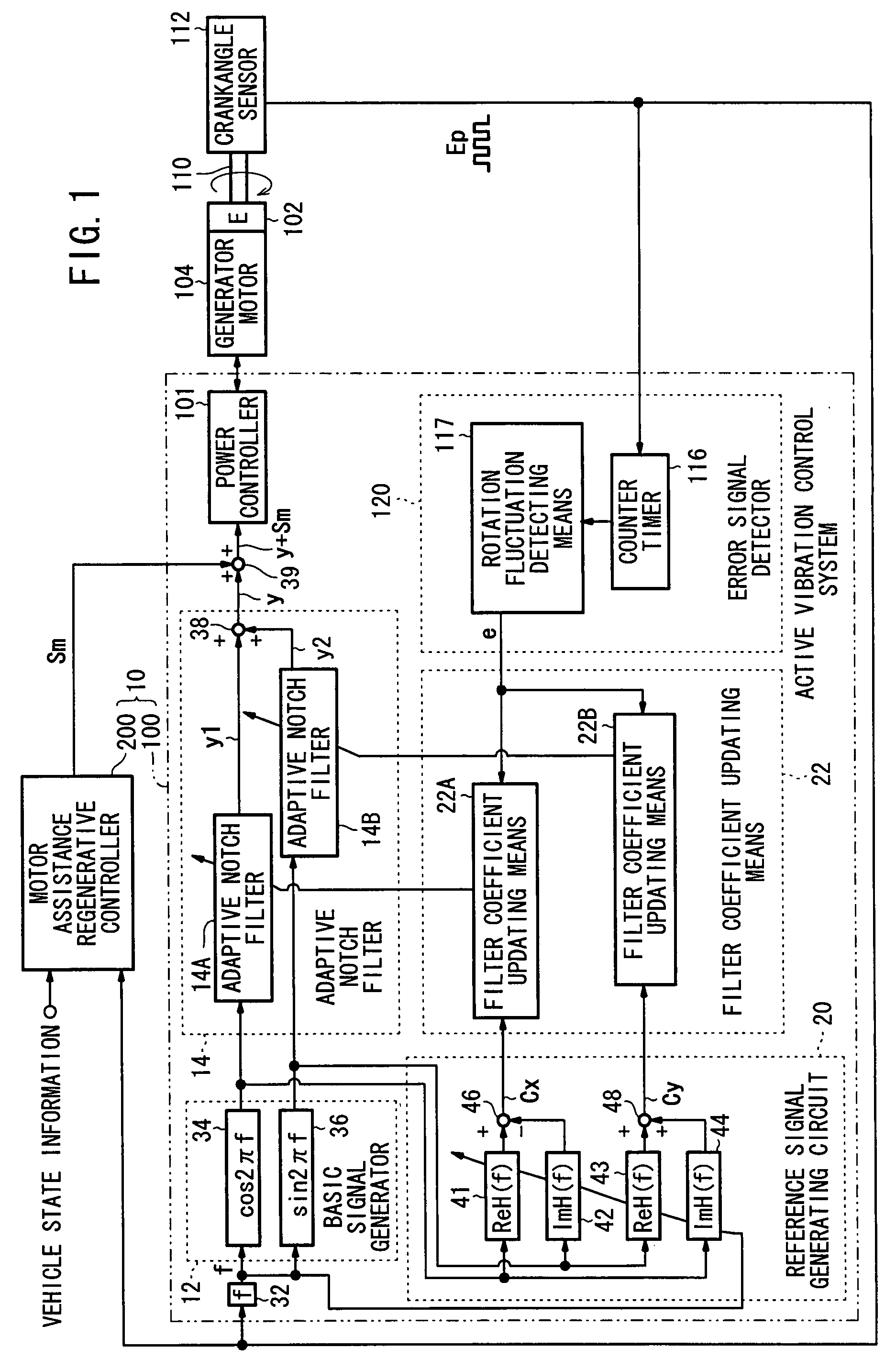
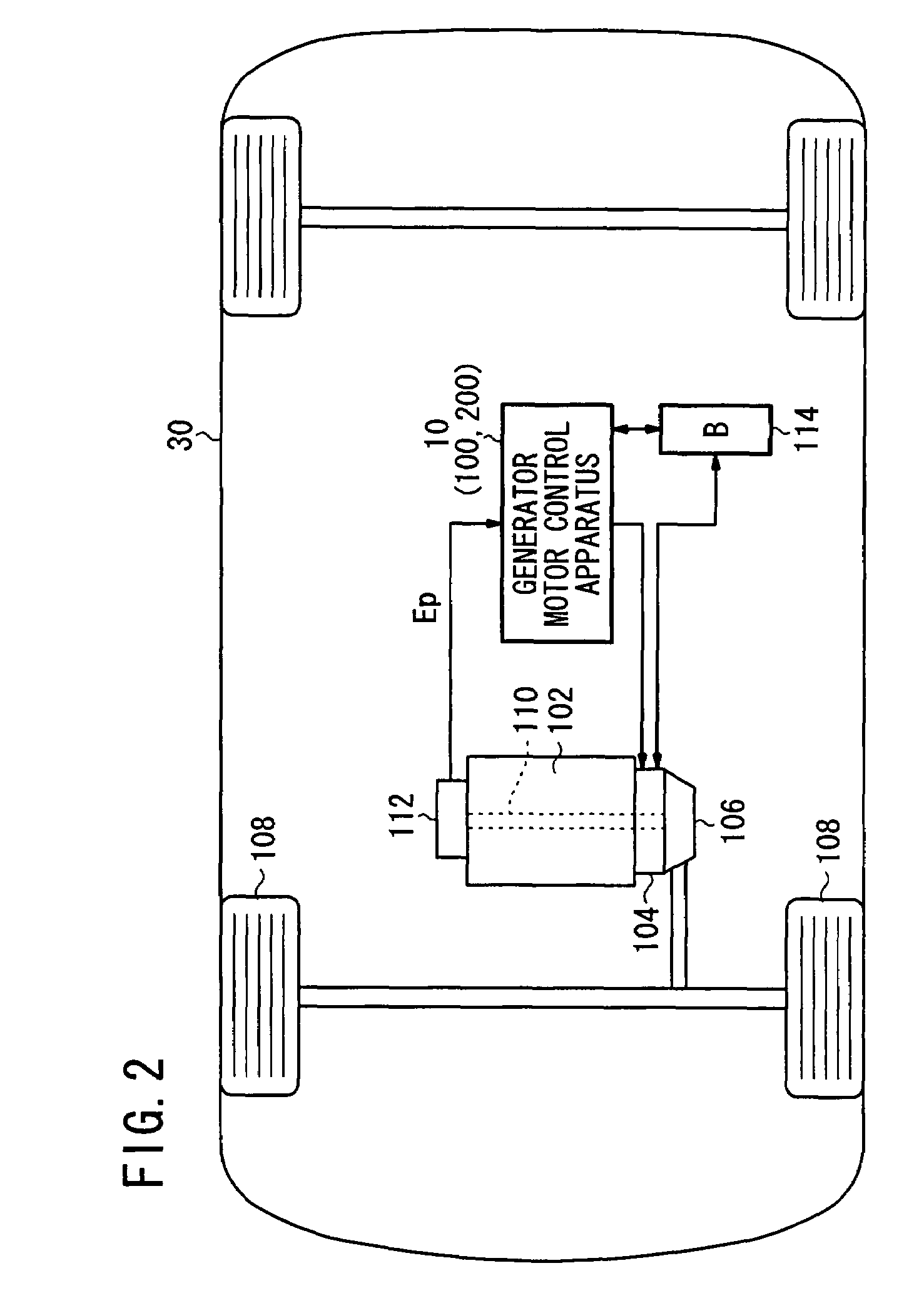
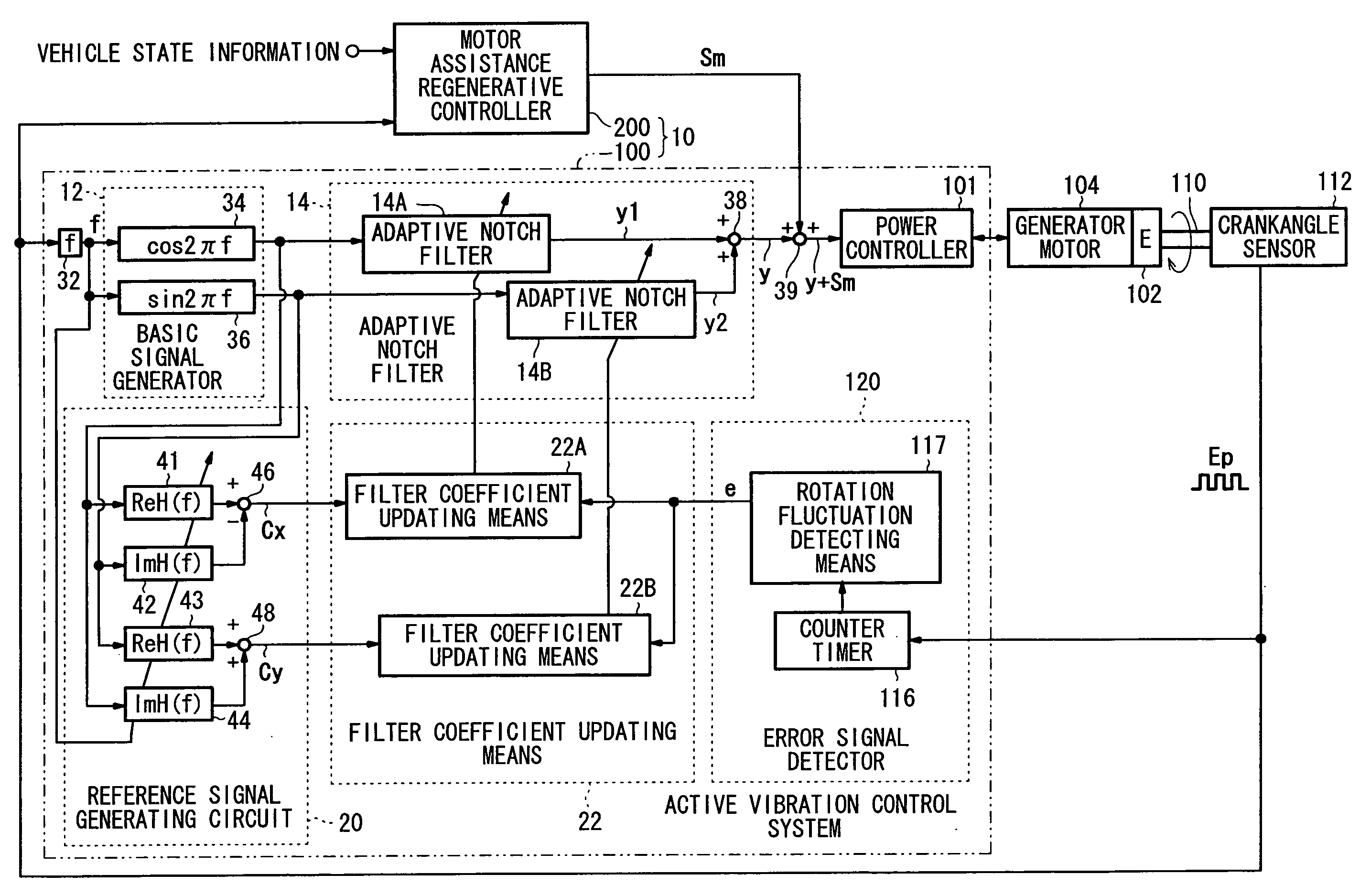
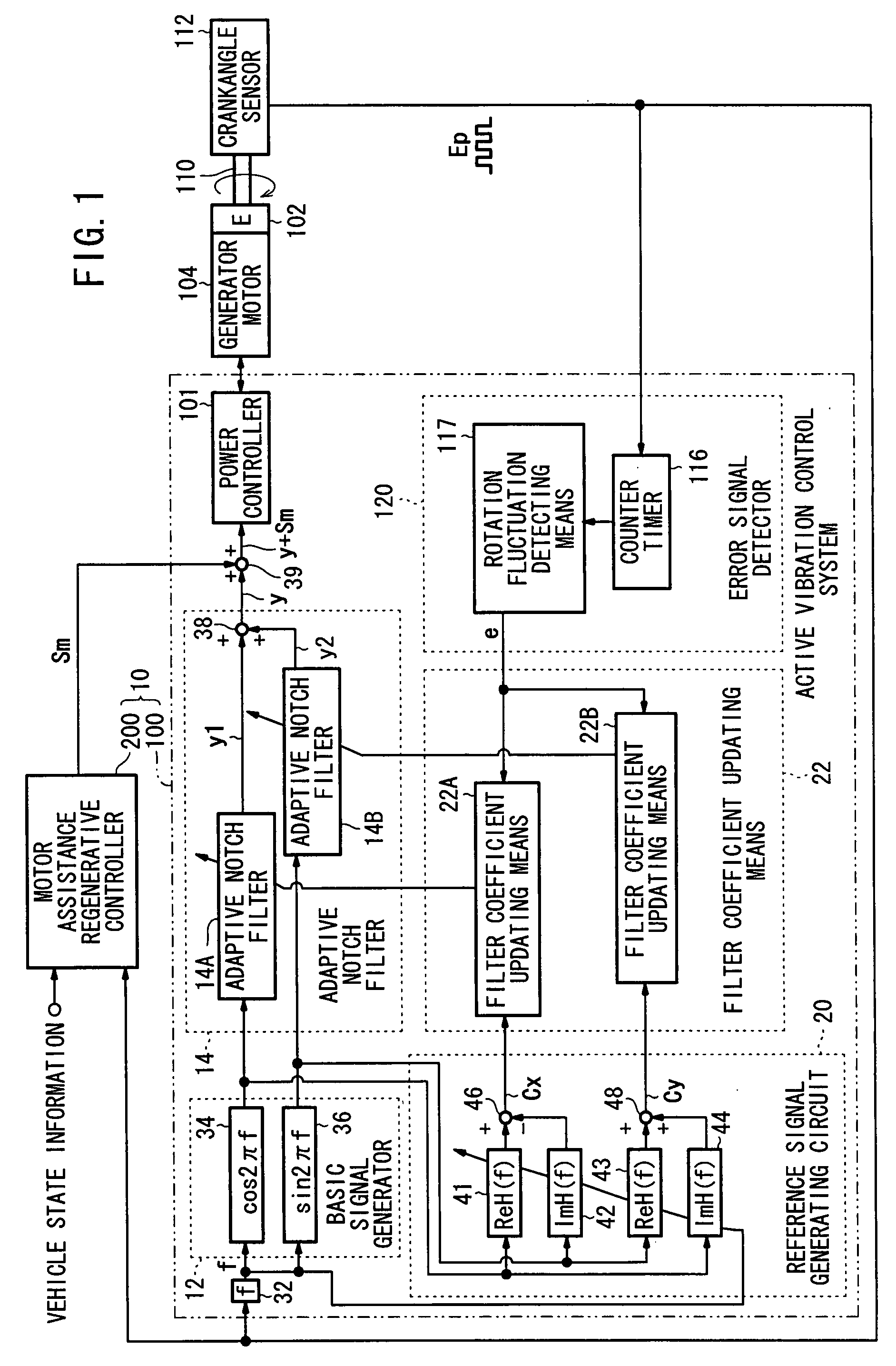
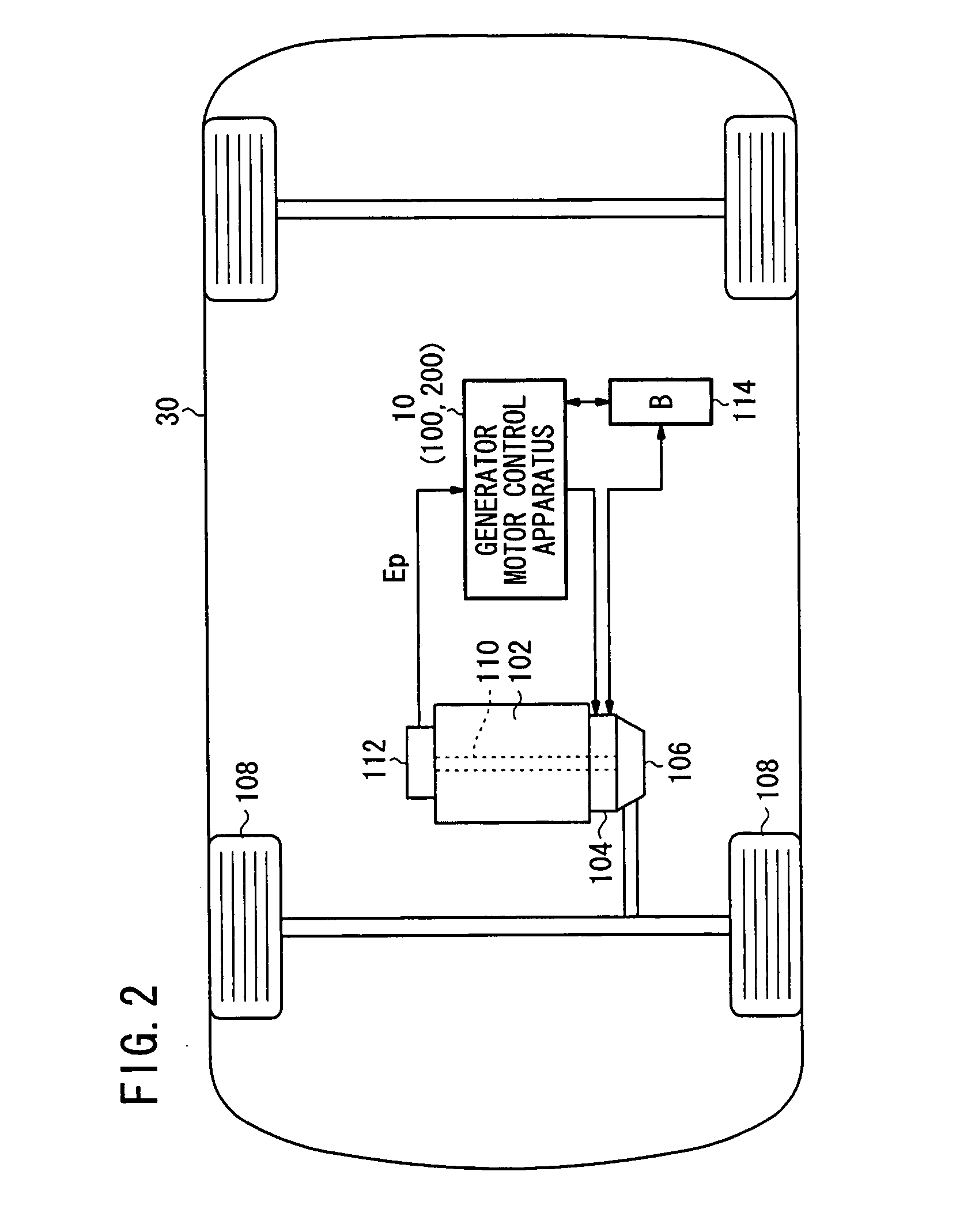
ActiveUS7633257B2Suppresses torque fluctuationsRapid responseHybrid vehiclesMechanical oscillations controlAdaptive filterControl signal
In a motor-assisted hybrid vehicle, an active vibration control system suppresses torque fluctuations of an engine without detriment to the response of a static torque. An adaptive notch filter outputs a control signal depending on a harmonic basic signal generated by a basic signal generator from a rotational frequency of a crankshaft. A combiner combines the control signal with a drive signal for the generator motor and supplies the combined signal through a power controller to the generator motor. The basic signal is supplied to corrective filters having the transfer function of the generator motor to output a reference signal. The filter coefficient of an adaptive notch filter is successively updated so that an error signal representative of a rotational speed fluctuation of the crankshaft will be minimized.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
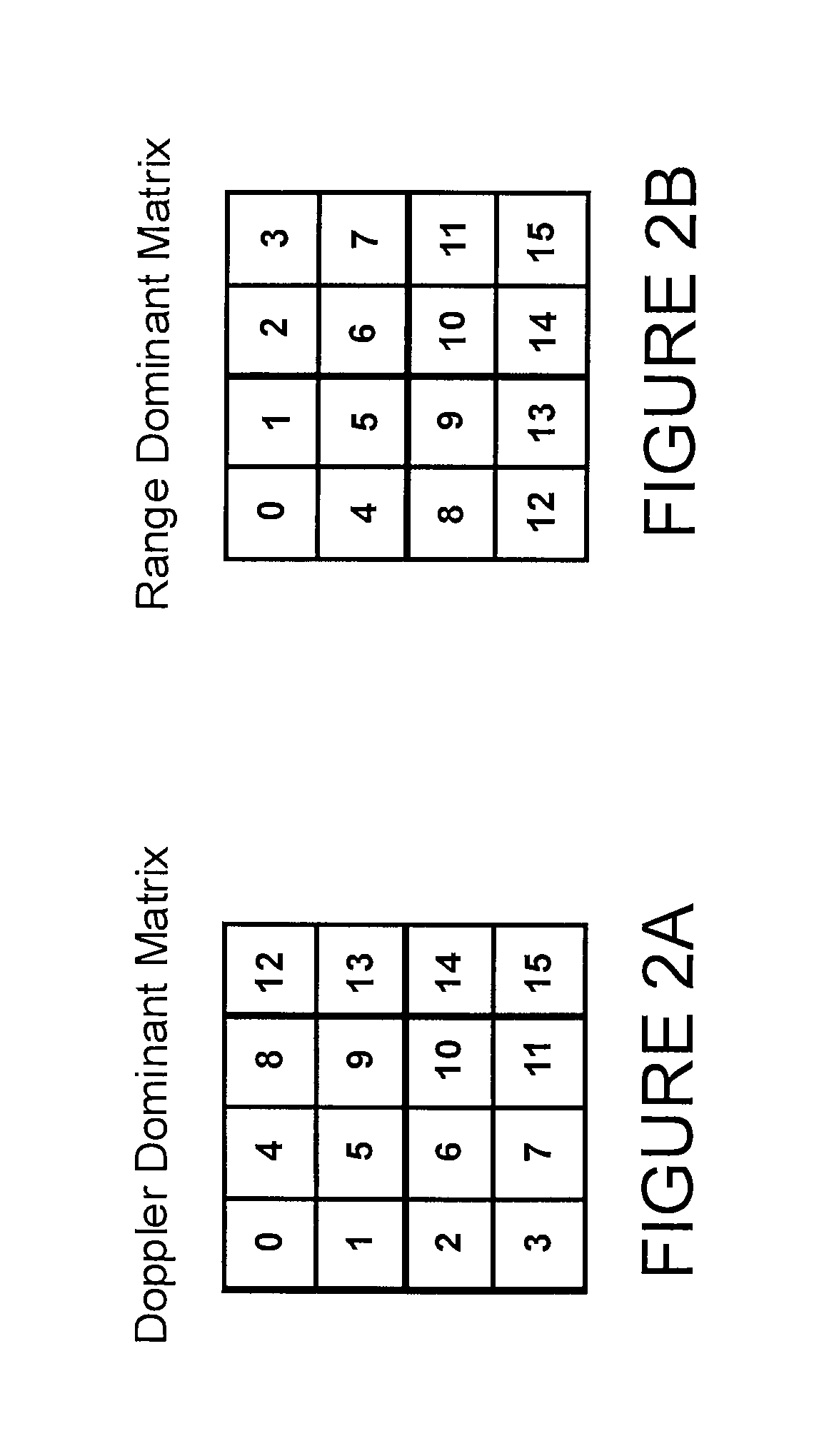
Method and apparatus for radar signal processing
A radar apparatus and method for determining the range to and velocity of at least one object comprising, transmitting a plurality of RF signals, each comprising a particular frequency and being transmitted during a particular unique finite period, the plurality of signals collectively comprising at least one first subset of signals having the same frequency and at least one second subset of signals having different frequencies, receiving the plurality of signals after reflection from an object, determining a phase difference between each of the signals and the corresponding reflected signal, each piece of phase difference information herein termed a sample, organizing the samples in two-dimensions wherein, in a first dimension, all samples have the same frequency and, in a second dimension, all consecutive samples are separated from each other by a fixed time interval; processing the samples in the first dimension to determine a phase rotation frequency corresponding to the samples in the first dimension, the phase rotation frequency comprising a Doppler frequency for the at least one object, processing the samples in the second dimension to determine a second phase rotation frequency corresponding to the samples in the second dimension; the phase rotation frequency comprising Doppler frequency and range frequency for the at least one object; comparing the first phase rotation frequency to the second phase rotation frequency to distinguish range frequency from Doppler frequency of the at least one object; and converting the Doppler frequency to a velocity of the object and converting the range frequency to a range of the object.
Owner:VEONEER US LLC
Vehicular active vibratory noise control apparatus
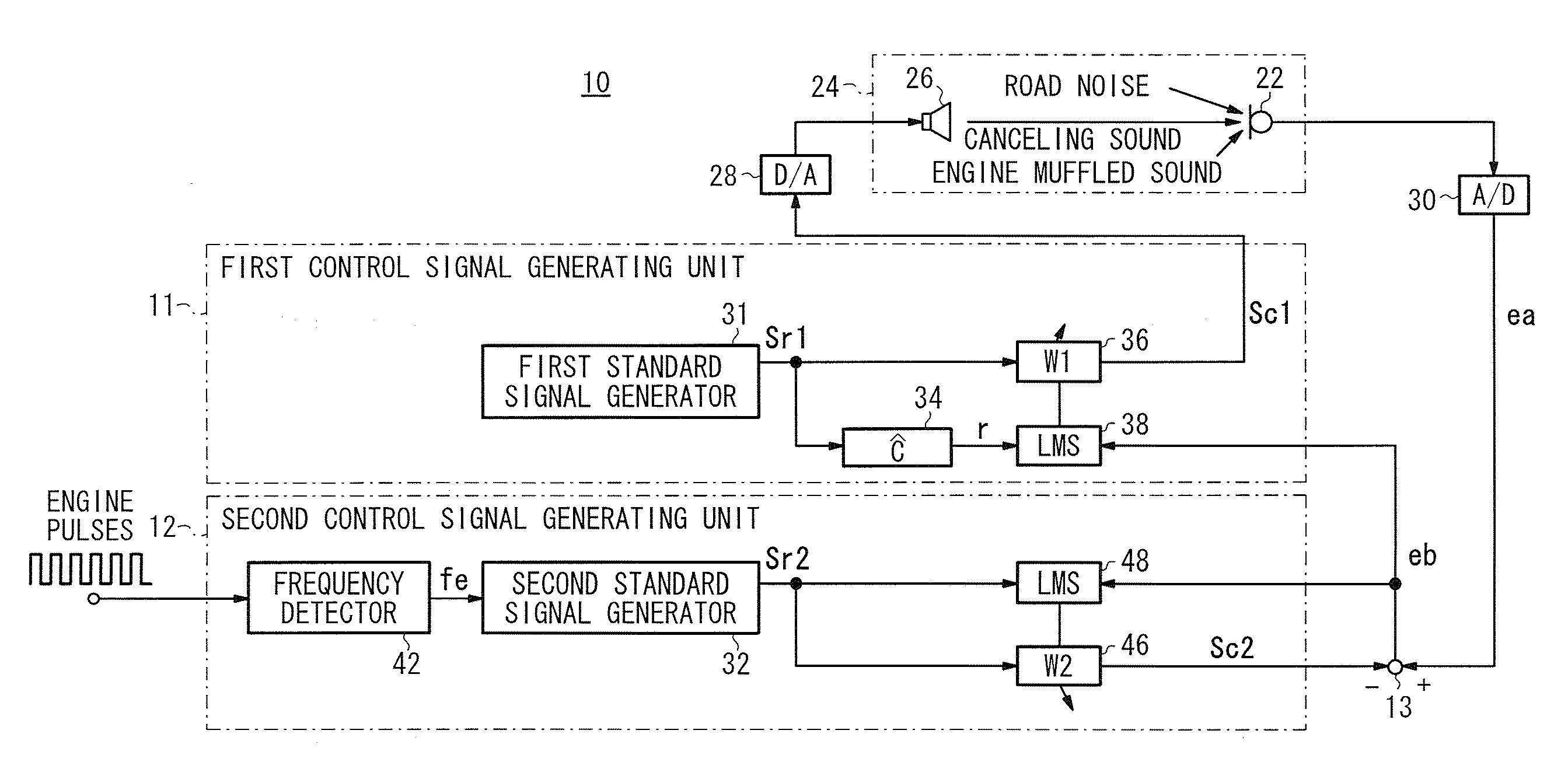
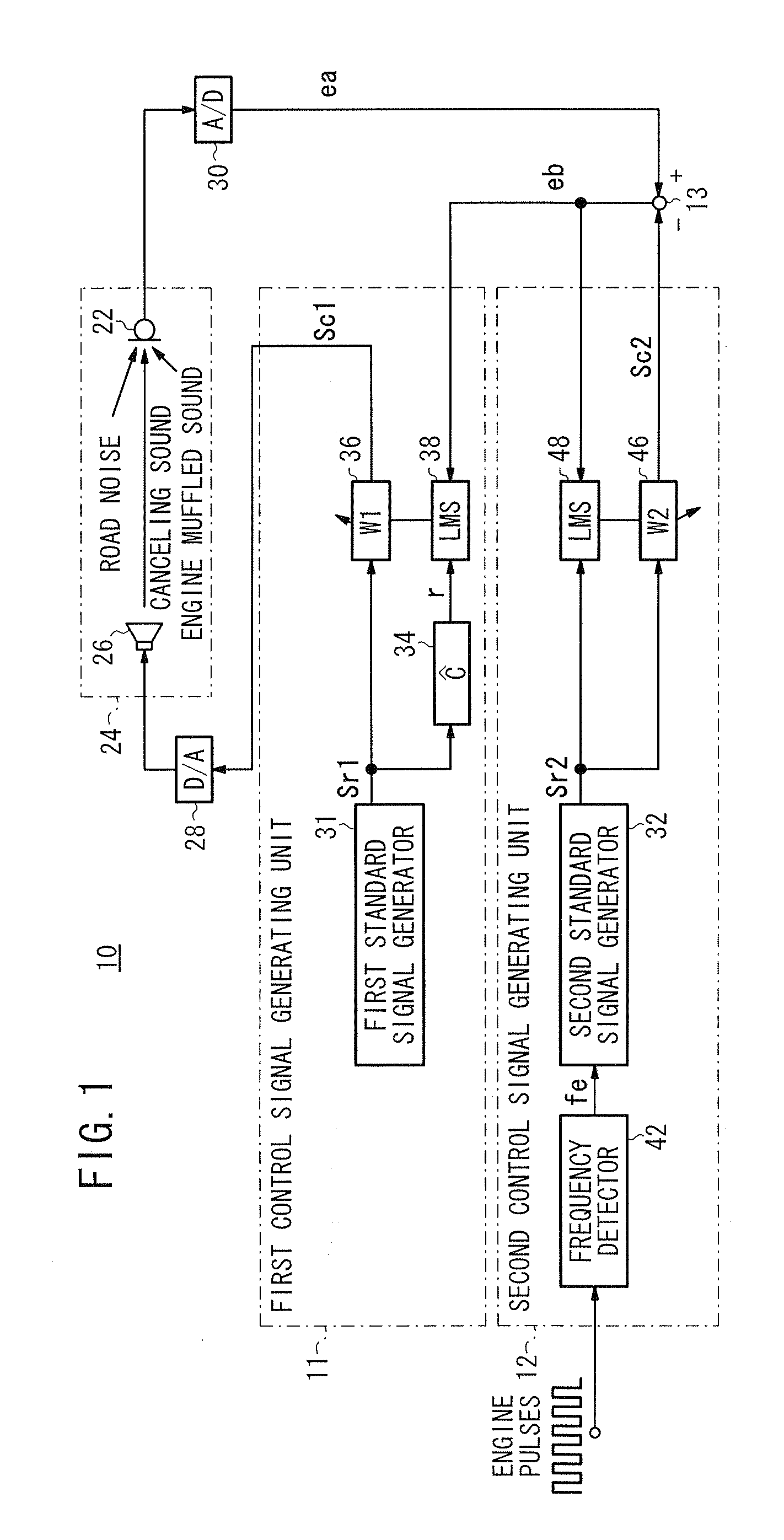
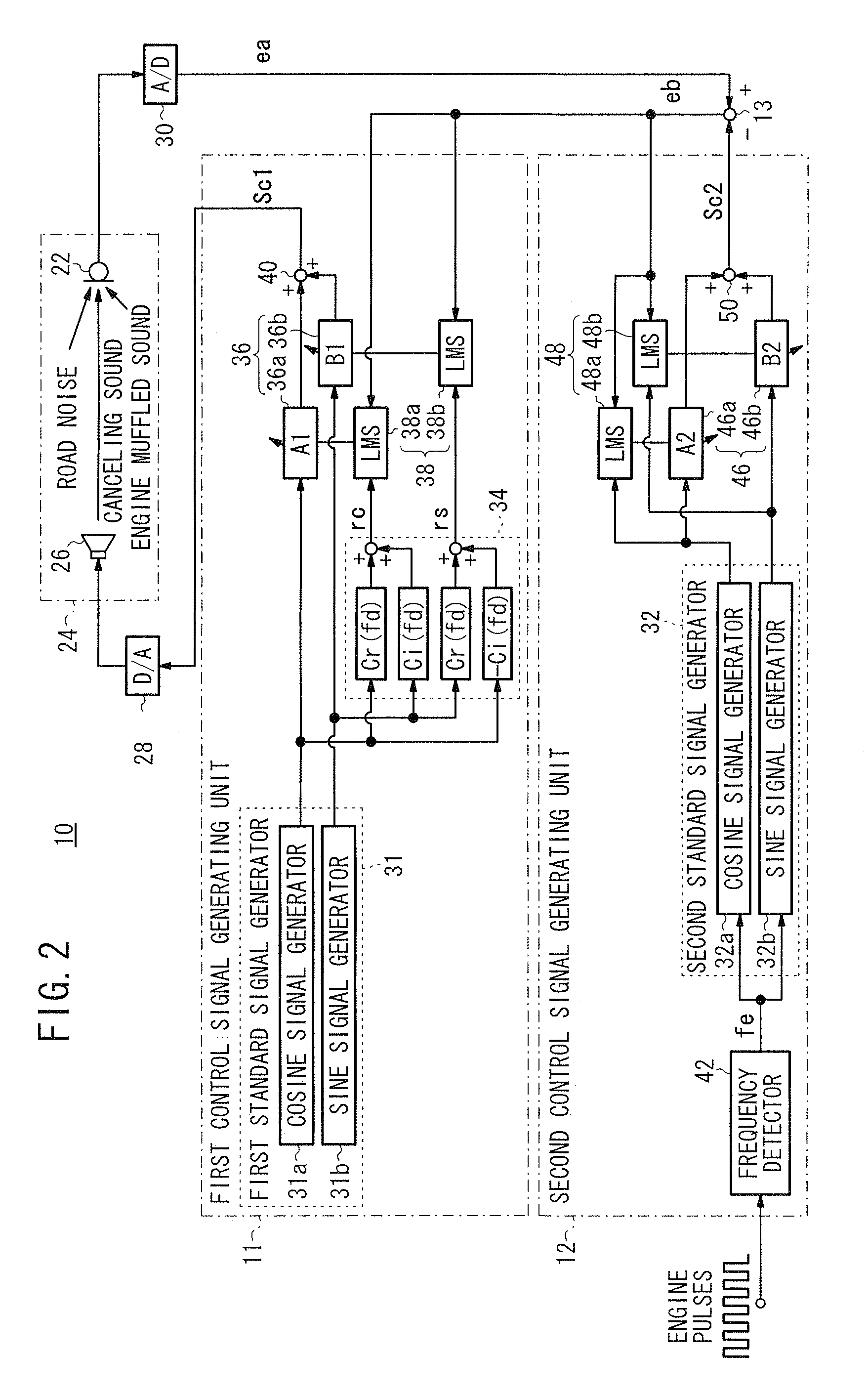
ActiveUS20090060217A1Reduce the overall heightReduce componentsEar treatmentNoise generationMuffled voiceAdaptive filter
A vehicular active vibratory noise control apparatus includes an adaptive notch filter (second control signal generating unit) for generating a corrected error signal representative of a road noise only by removing the component of a rotational frequency (the component of an engine muffled sound) from an error signal, generates a first control signal from the corrected error signal and a reference signal, and reduces the component of the rotational frequency (engine muffled sound) at a position where a microphone is located (evaluating point).
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Water supply
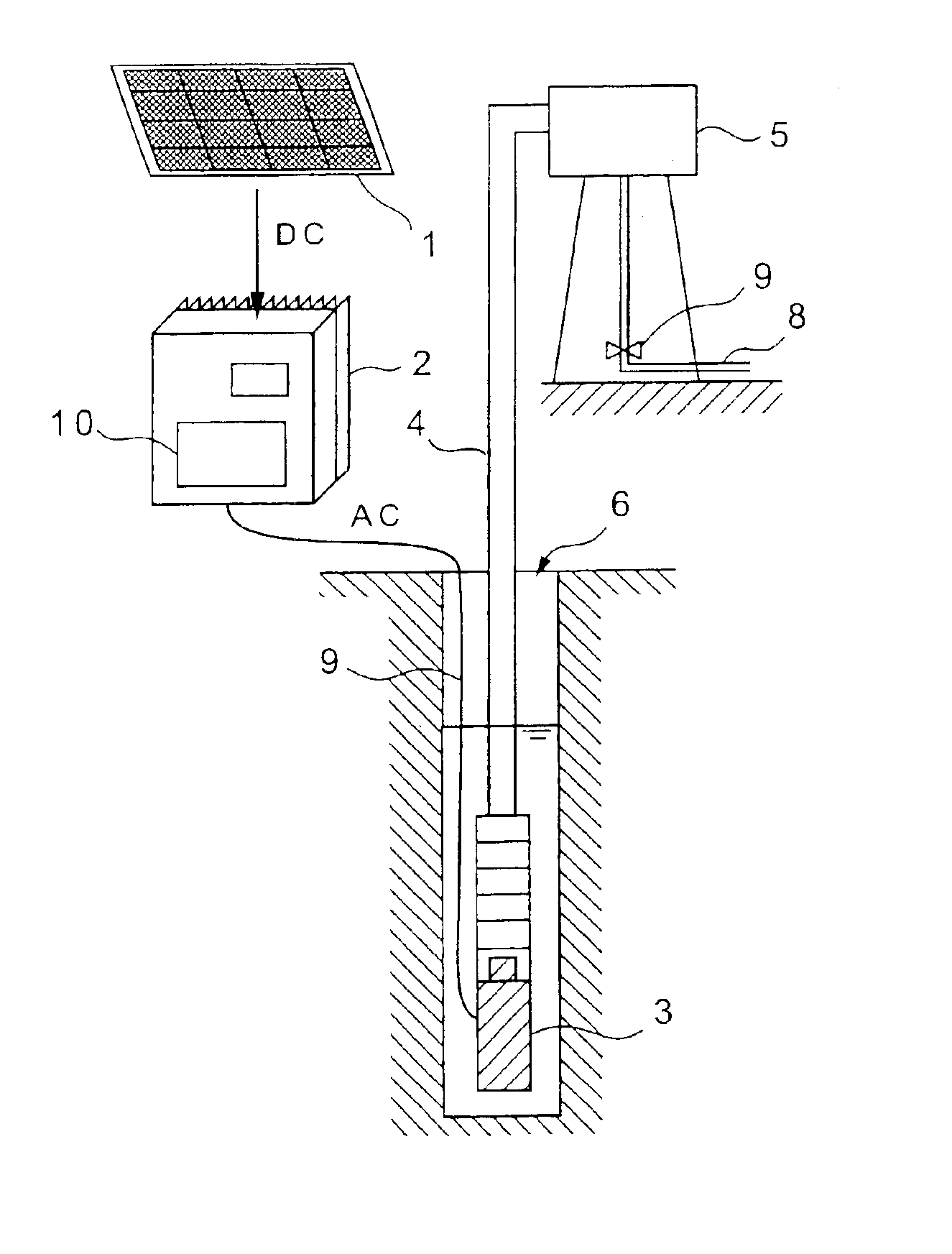
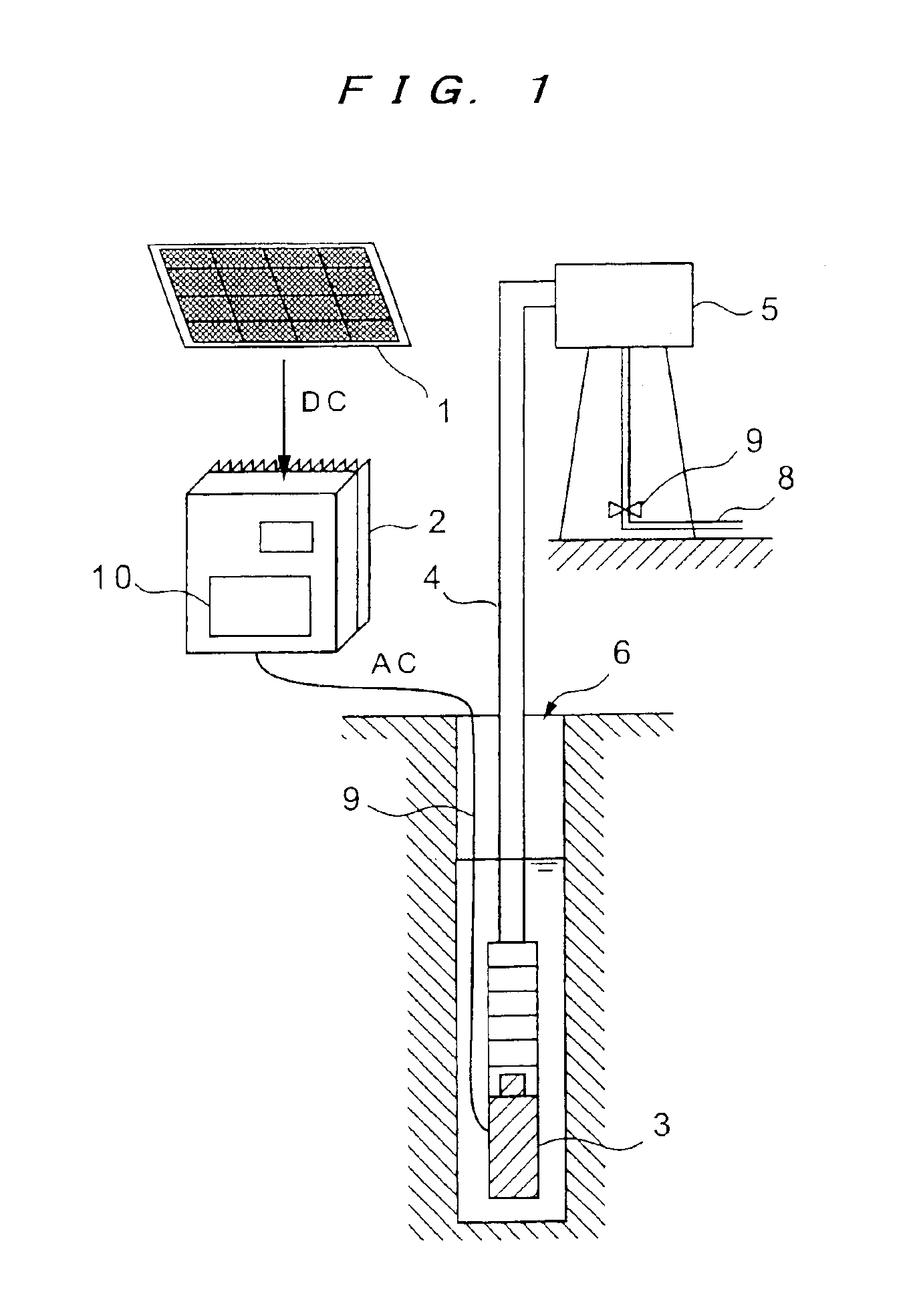
InactiveUS6922348B2Less troubleReduce maintenanceAC motor controlDC motor speed/torque controlBrushless motorsFrequency changer
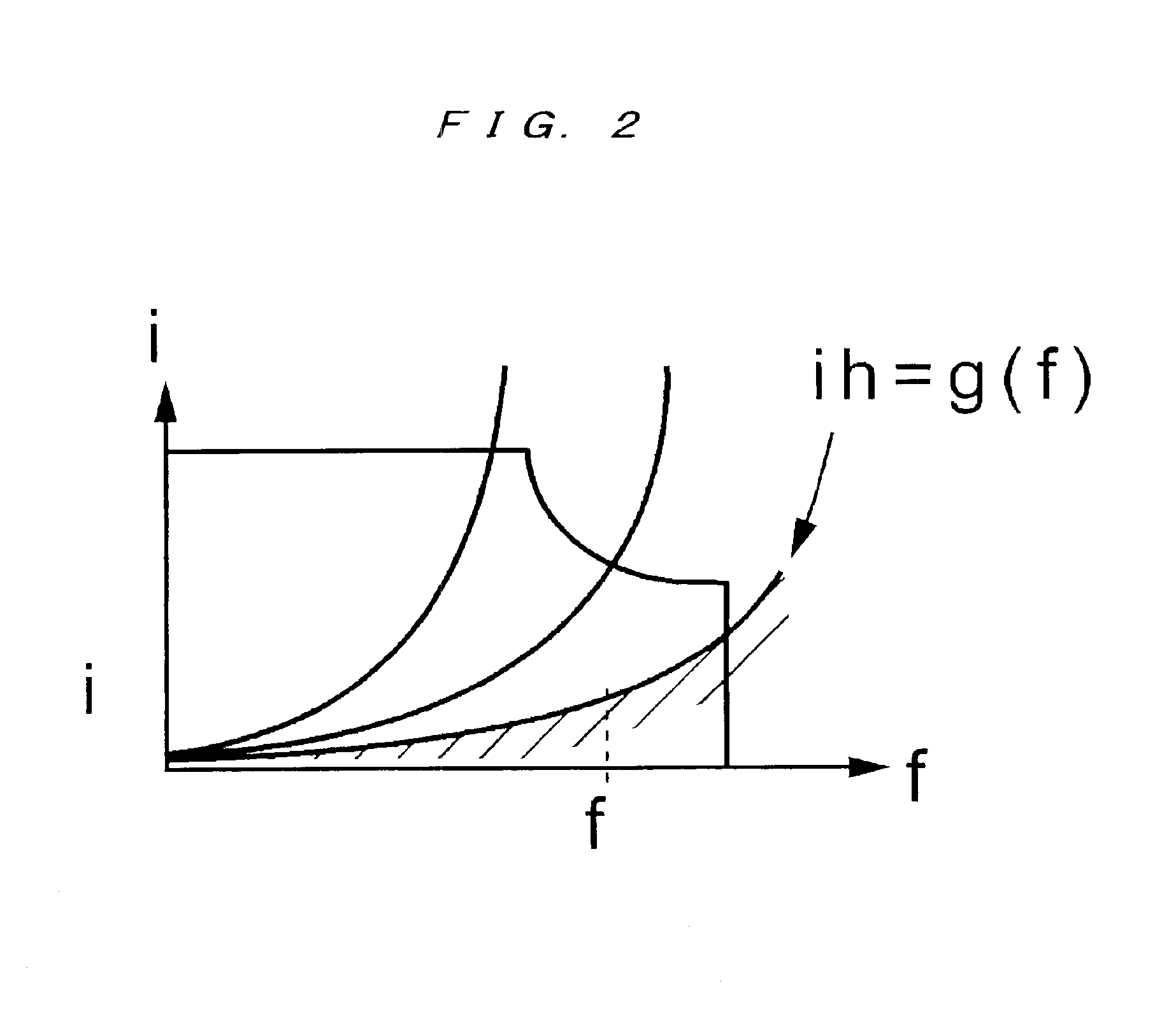
According to the present invention, in a water supply apparatus which converts output power of a solar cell with an inverter to drive a motor pump for pumping up water, a DC brushless motor having no sensor for detecting a position of a rotatable shaft is used as a motor for driving the pump. Further, the water supply apparatus, having a pump and a frequency converter for supplying electric power to the pump and controlling a rotational speed of the pump, includes a standard current value table in which rotational frequencies of the pump and standard current values as criteria for shutoff operation at the rotational frequencies are associated with each other, a rotational frequency detecting device for detecting a rotational frequency of the pump, a standard current value acquiring device for acquiring a standard current value corresponding to the rotational frequency detected by the rotational frequency detecting device with reference to the standard current value table, a current detecting device for detecting a current value supplied to the pump, and a comparing device for comparing the current value detected by the current detecting device with the standard current value acquired by the standard current value acquiring device.
Owner:EBARA CORP
Apparatus and methods for adjusting the rotational frequency of a scanning device
The present invention provides methods and apparatus for adjusting the resonant frequency, scan velocity or other parameters of a pivotally functional surface such as an oscillating mirror used as the scanning engine of a laser printer or projection display. The selected parameter is adjusted by the application of tensional or compression stress to the torsional hinges of the mirror. According to one embodiment, the appropriate stress is generated by a slice of piezoelectric material bonded to the mirror device itself or to other portions of the support structure of the scanning engine.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
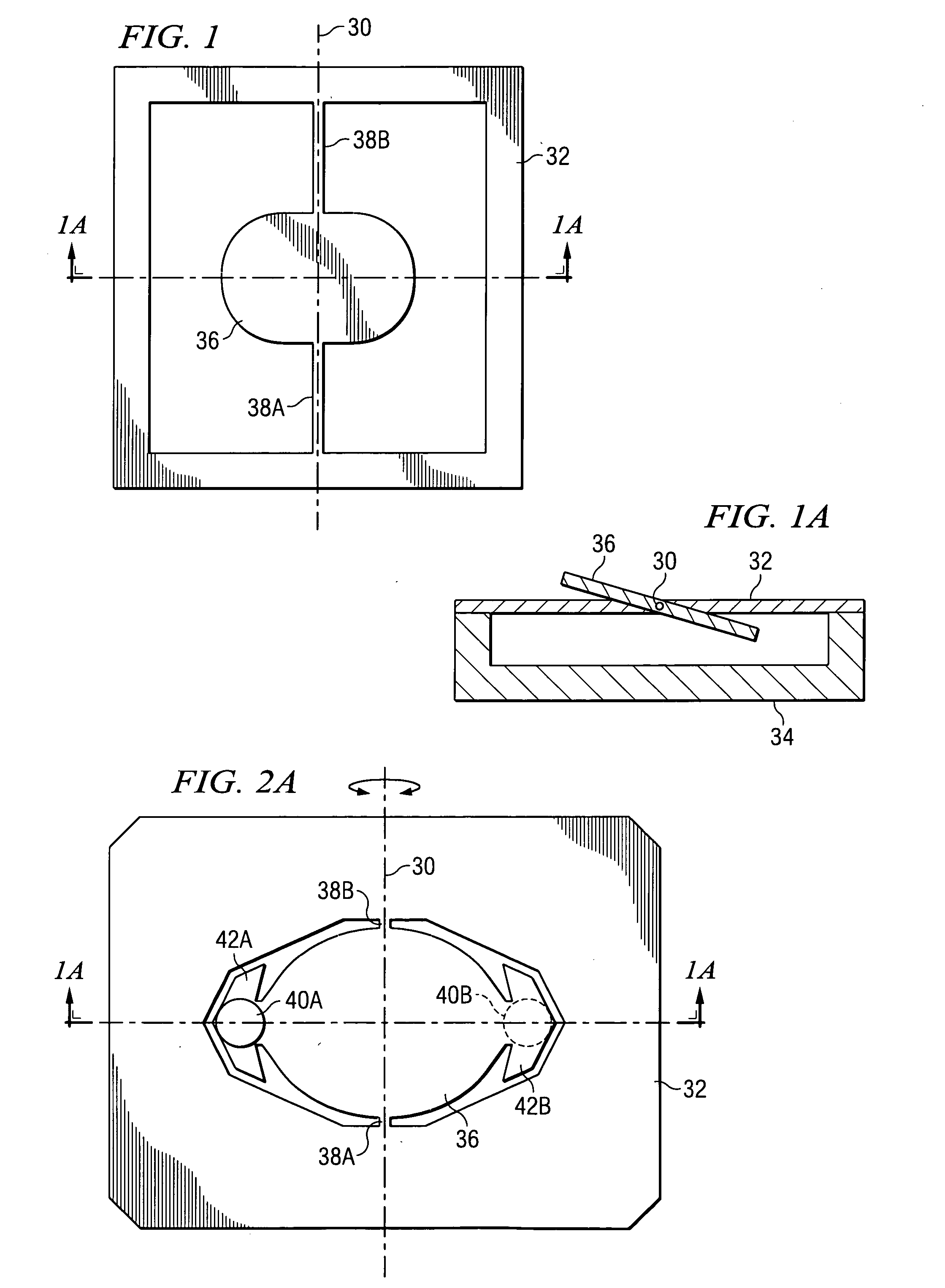
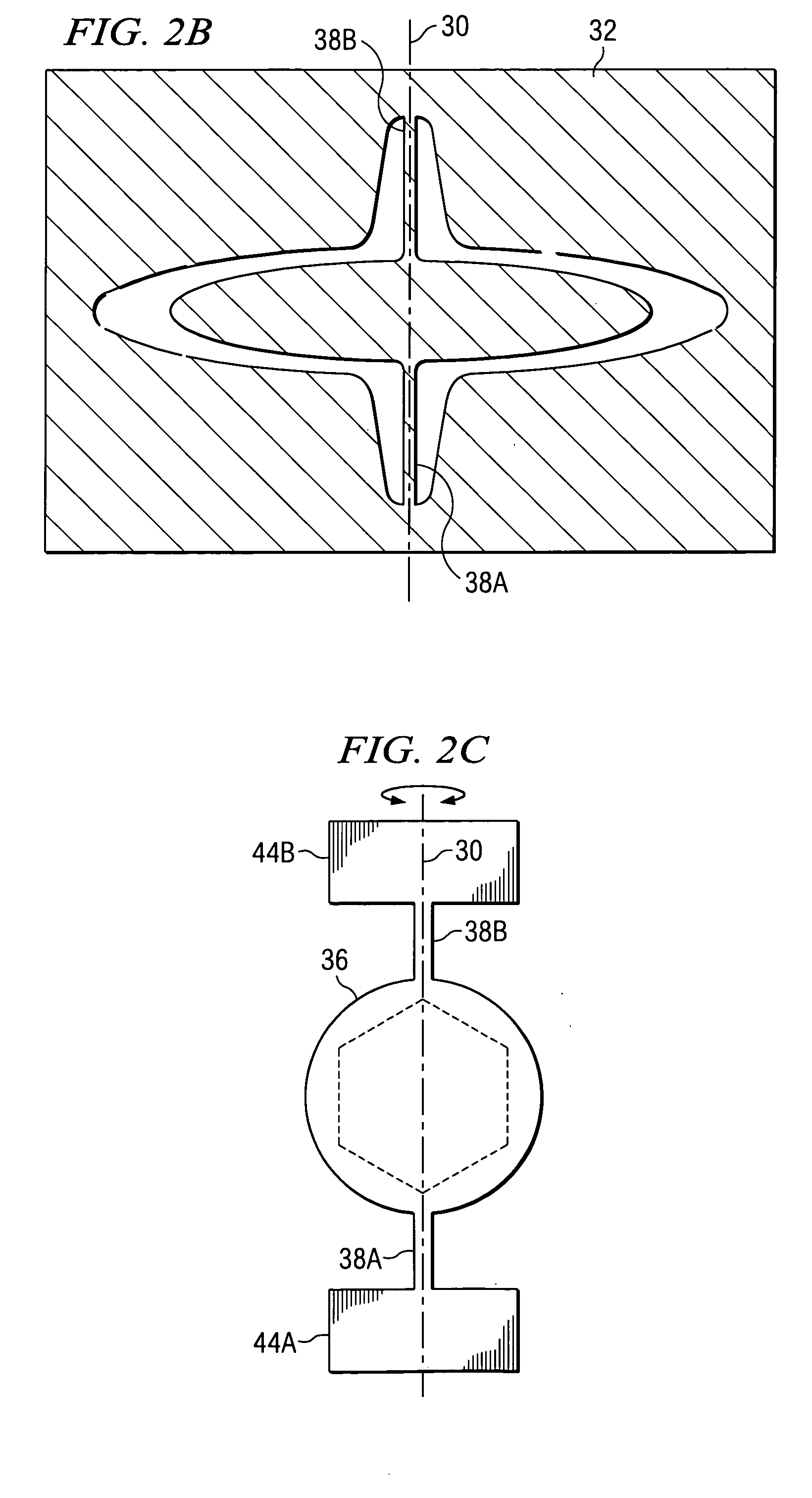
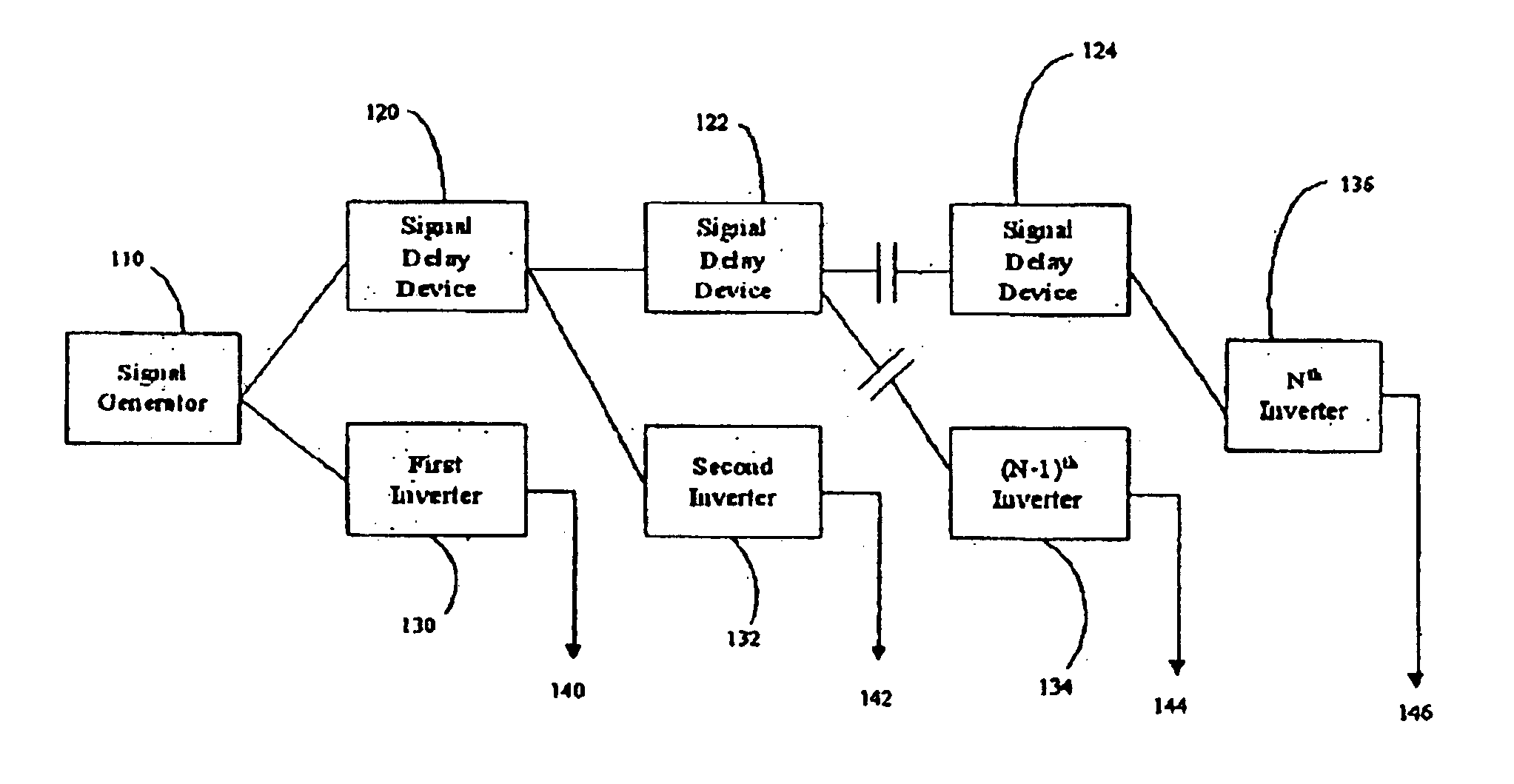
Rotating induction apparatus
InactiveUS6922037B2Reduce decreaseImprove performanceAC motor controlDC motor speed/torque controlWave shapeThird harmonic
An electrical rotating apparatus comprises an inverter system that outputs more than three phases. The apparatus further includes a stator electrically coupled to the inverter system, and a rotor electromagnetically coupled to a magnetic field generated by the stator. A signal generator generates a pulse modulated drive waveform signal, that has a frequency synchronized with the rotational frequency of the rotor, and the pulse modulated drive waveform signal drives the inverter system. The pulse modulated drive waveform signal has a pulsing frequency. Additionally, the inverter system may be fed by a pulse modulated drive waveform signal that is fed through at least one signal delay device. Alternatively, the system may also be fed selected harmonic components, such as the third harmonic, up until the number of phases in the apparatus.
Owner:BOREALIS TECH LTD
Method for ascertaining a rotational direction of a rotating body, and wheel sensor module
ActiveUS20110082663A1Good precisionImprove reliabilityDigital computer detailsAcceleration measurementEngineeringMechanical engineering
In a method for ascertaining a rotational direction of a rotating body, one rotational direction and one rotational speed value which indicates the rotational frequency of the rotating body are ascertained in each of multiple measurements. The rotational speed values of the multiple measurements are compared to each other, and a rotational direction of the rotating body is ascertained from the measured rotational directions and the comparison of the rotational speed values.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Active vibration control system for hybrid vehicle
ActiveUS20070222407A1Suppresses torque fluctuationsReduce vibrationHybrid vehiclesMechanical oscillations controlAdaptive filterControl signal
In a motor-assisted hybrid vehicle, an active vibration control system suppresses torque fluctuations of an engine without detriment to the response of a static torque. An adaptive notch filter outputs a control signal depending on a harmonic basic signal generated by a basic signal generator from a rotational frequency of a crankshaft. A combiner combines the control signal with a drive signal for the generator motor and supplies the combined signal through a power controller to the generator motor. The basic signal is supplied to corrective filters having the transfer function of the generator motor to output a reference signal. The filter coefficient of an adaptive notch filter is successively updated so that an error signal representative of a rotational speed fluctuation of the crankshaft will be minimized.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
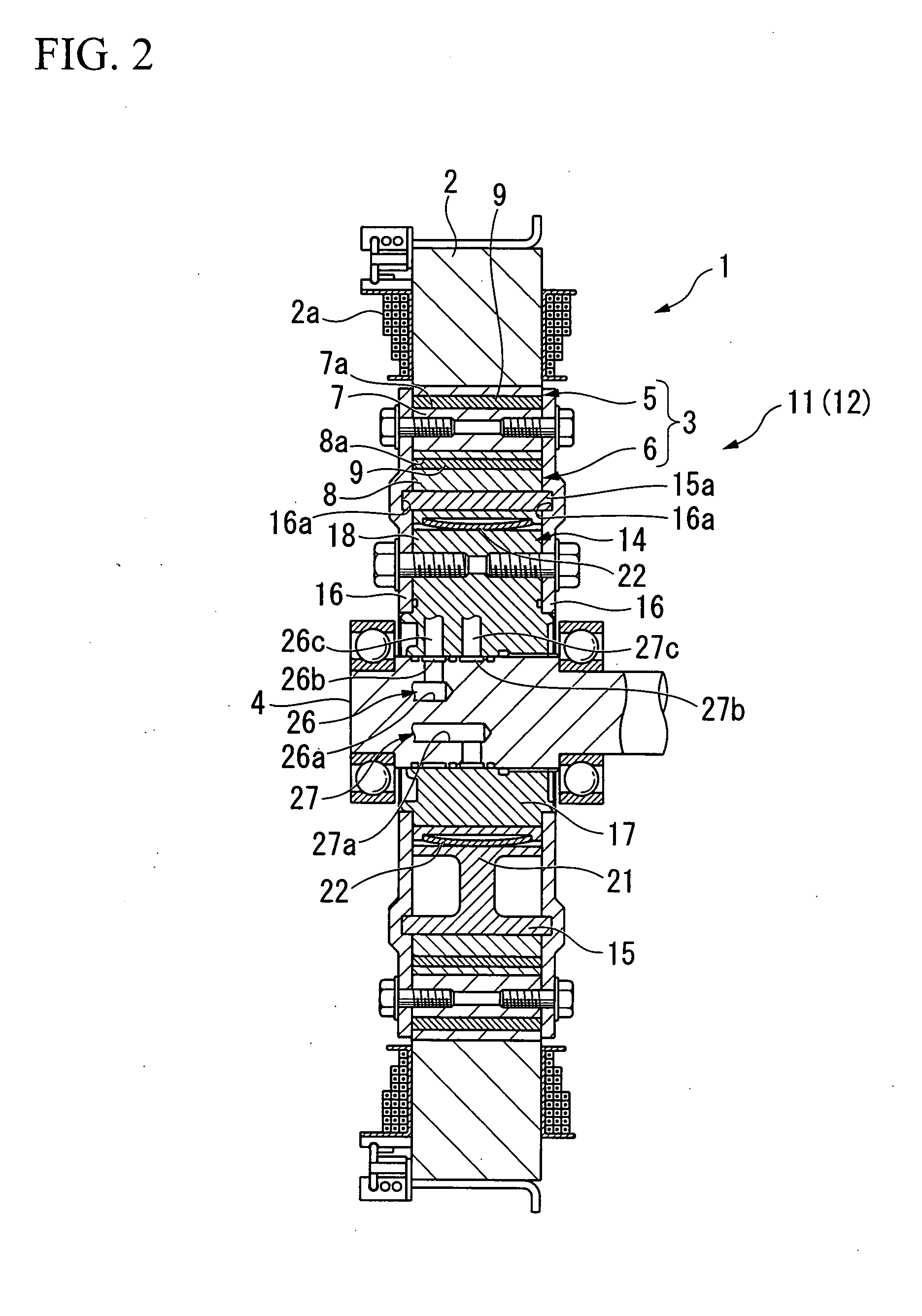
Dynamic pressure pneumatic bearing structure and method of manufacturing the same
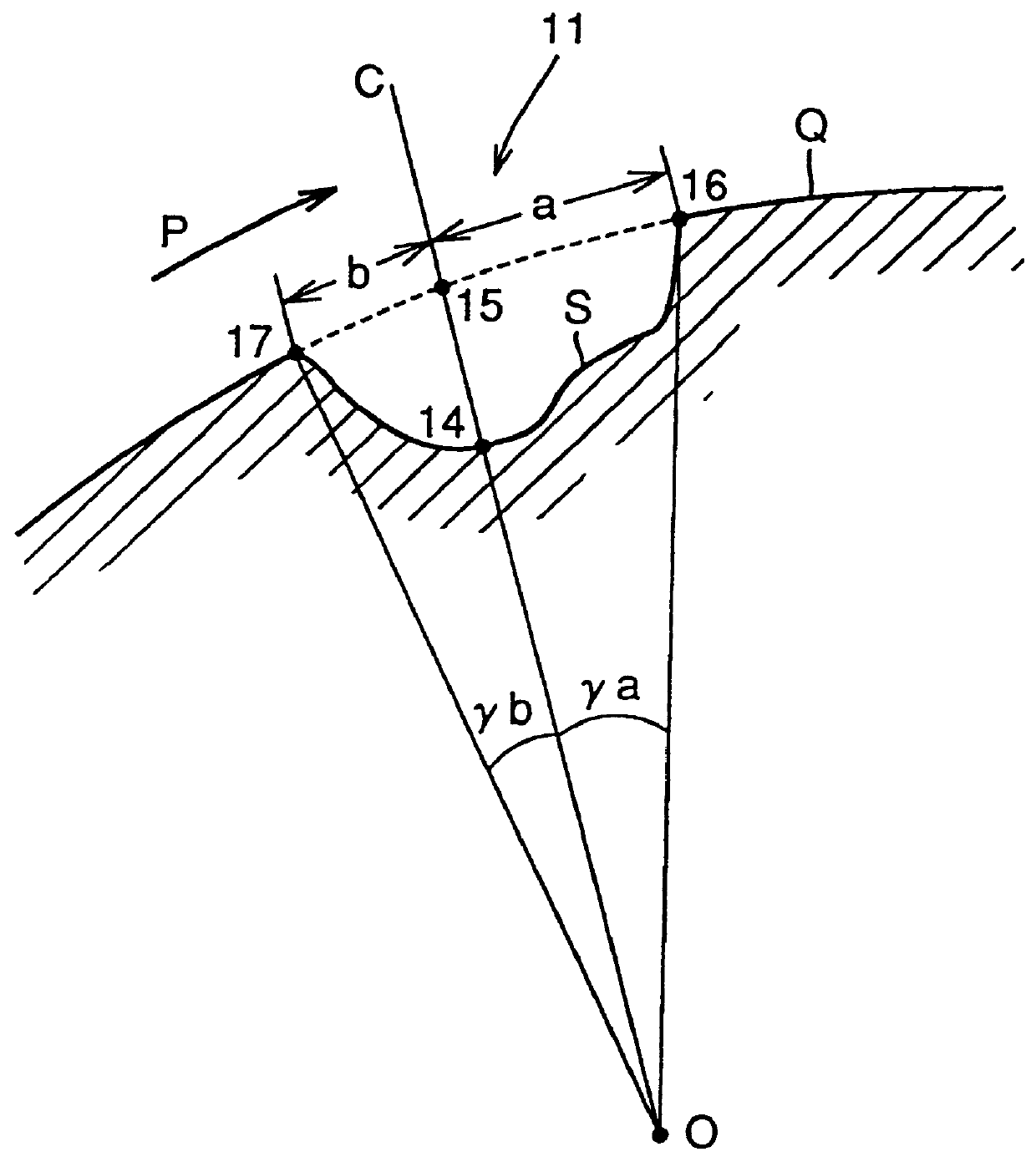
PCT No. PCT / JP98 / 00739 Sec. 371 Date Oct. 28, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Oct. 28, 1998 PCT Filed Feb. 23, 1998 PCT Pub. No. WO98 / 38433 PCT Pub. Date Sep. 3, 1998Provided is a hydrodynamic gas bearing structure which can prevent occurrence of whirl not only in high-speed rotation but also in low-speed rotation, reduces such frequency that a floating rotational frequency in starting or stoppage of rotation increases, and is capable of shifting the floating rotational frequency to a low rotational frequency side. The hydrodynamic gas bearing structure comprises a shaft body (1) and a bearing body (2). A groove (11) is formed on the outer peripheral surface of the shaft body (1). The groove (11) consists of at least two concave parts, whose depths substantially differ from each other, which are formed serially in the circumferential direction, and has a circumferentially asymmetrical shape in a cross section perpendicular to the axis. The circumferential distance a between the intersection point (15) of a line (C) connecting the deepest point (14) of the groove (11) and the center (O) of the shaft body (1) and the outer peripheral line (Q) of the shaft body (1) and one edge (16) of the groove (11) positioned downward an air current (P) generated in rotation in relation to the intersection point (15) is larger than the circumferential distance b between the intersection point (15) and the other edge (17) of the groove (11) positioned upstream the air current (P) in relation to the intersection point (15). The ratio (d2 / d1) of the mean depth d2 of a relatively shallow part of the groove (11) to the mean depth d1 of a relatively deep part of the groove (11) is less than 0.3. The hydrodynamic gas bearing structure is suitable for employment for a rotation driving part of a magnetic recording apparatus or a laser beam printer.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
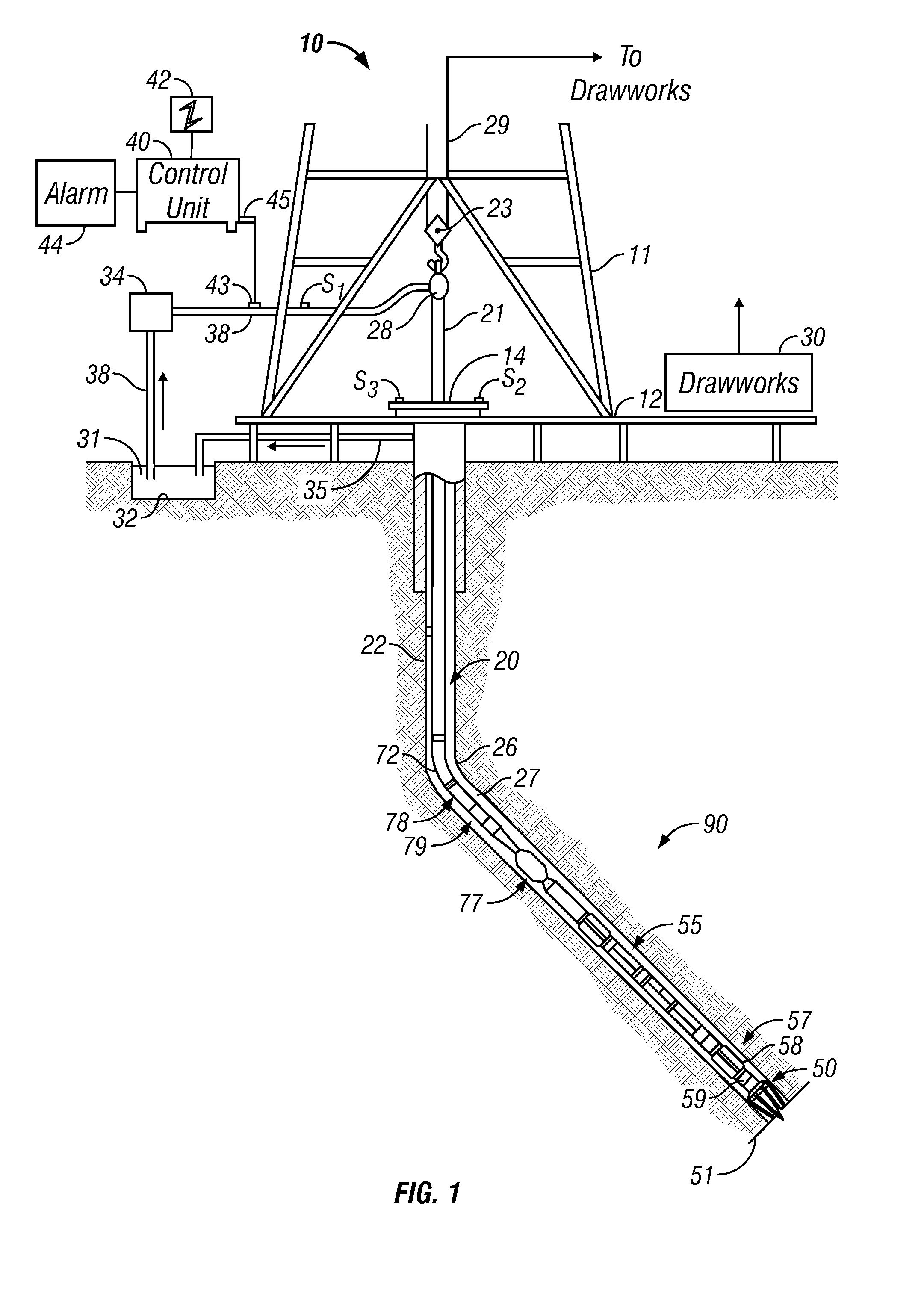
Drilling apparatus and method
A drilling apparatus including a drill bit and a nutation device. The drilling apparatus is configured to enable the drill bit to be rotated at a rotation frequency while the nutation device simultaneously nutates the drill bit at a nutation frequency. The nutation device may include a vibrating device for imposing vibrations upon the drilling apparatus at a vibration frequency, thereby causing nutation of the drill bit at the nutation frequency. The drilling apparatus may include a tuning mechanism for tuning the vibration frequency of the vibrating device. A method including rotating a drill bit at a rotation frequency and simultaneously nutating the drill bit at a nutation frequency.
Owner:DRILFORMANCE TECH
Friction wear testing machine
ActiveCN101344470AHigh simulationSimple production processUsing mechanical meansInvestigating abrasion/wear resistanceWear testingElectric machinery
The invention discloses a friction wear testing machine and comprises an abrading agent slot, a grinding steel wheel that is suspended in the abrading agent slot, a boosting lever that has a vertical arm suspended between the grinding steel wheel and a lateral wall of the abrading agent slot, a servo sand slot that has a sand discharging mouth and a transmission pipe, a servo spring loading mechanism that is connected with a horizontal arm of the boosting lever, a load sensor that is serially connected between the servo spring loading mechanism and the boosting lever and a temperature sensor that is arranged on the back of a sample. A main shaft of the grinding steel wheel is arranged on a bearing holder, connected with a torque sensor through a flexible coupler and connected with a frequency-varied speed-regulating drive motor, and a computer adjusts and detects the sand discharge amount of the sand slot, the rotating speed and the torque of the frequency-varied speed-regulating drive motor, and the loading capacity of the servo spring loading mechanism in real time, and can detect and record the rotational frequency of the grinding steel wheel and sample temperature in real time. The friction wear testing machine can detect and analyze the abrasion resistance and the frictional behaviour of hard alloy products under the conditions close to real working conditions.
Owner:株洲长江硬质合金工具有限公司
Control circuit of brush-less motor, control circuit of sensor-less brush-less motor, brush-less motor apparatus, sensor-less brush-less motor apparatus and vacuum pump apparatus
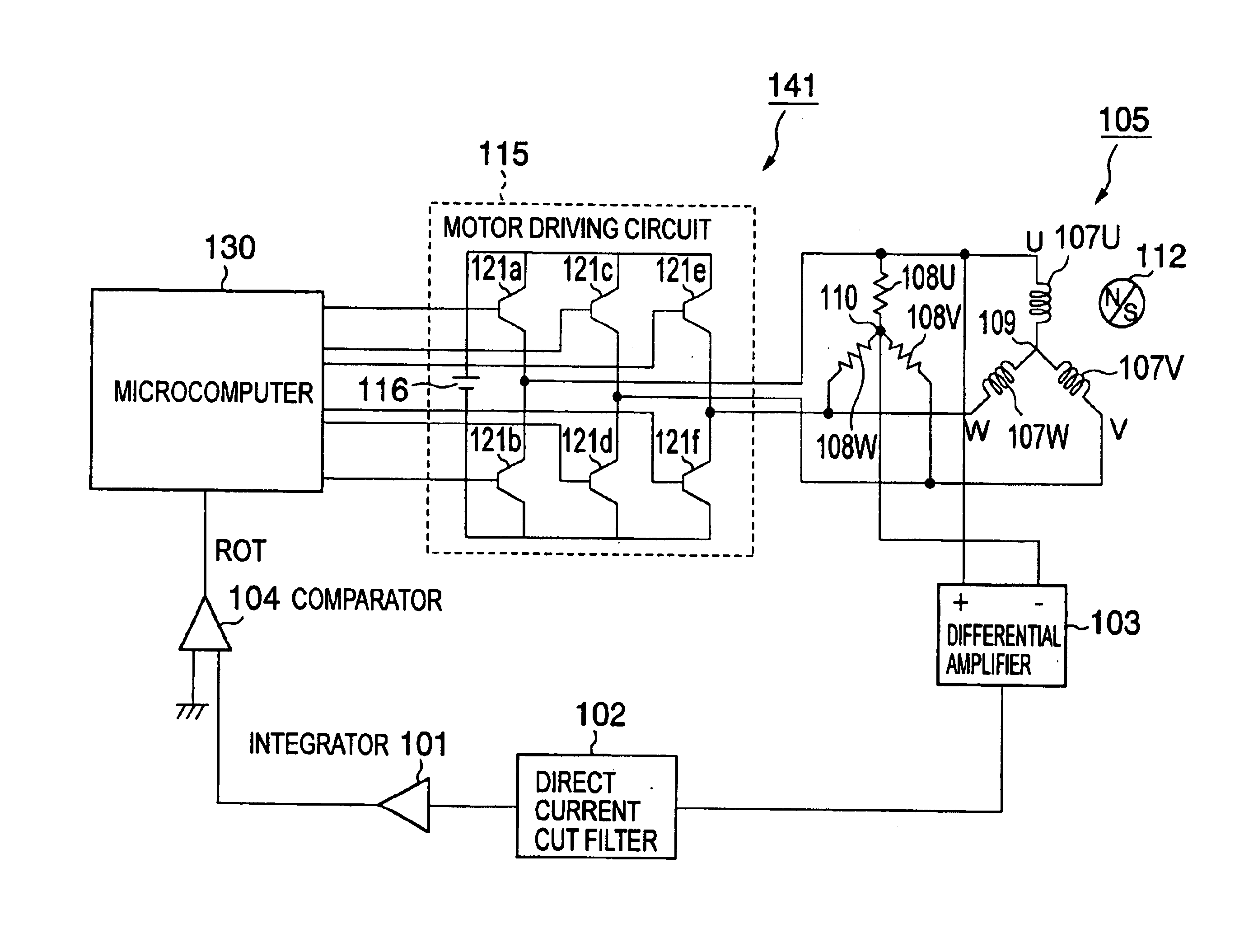
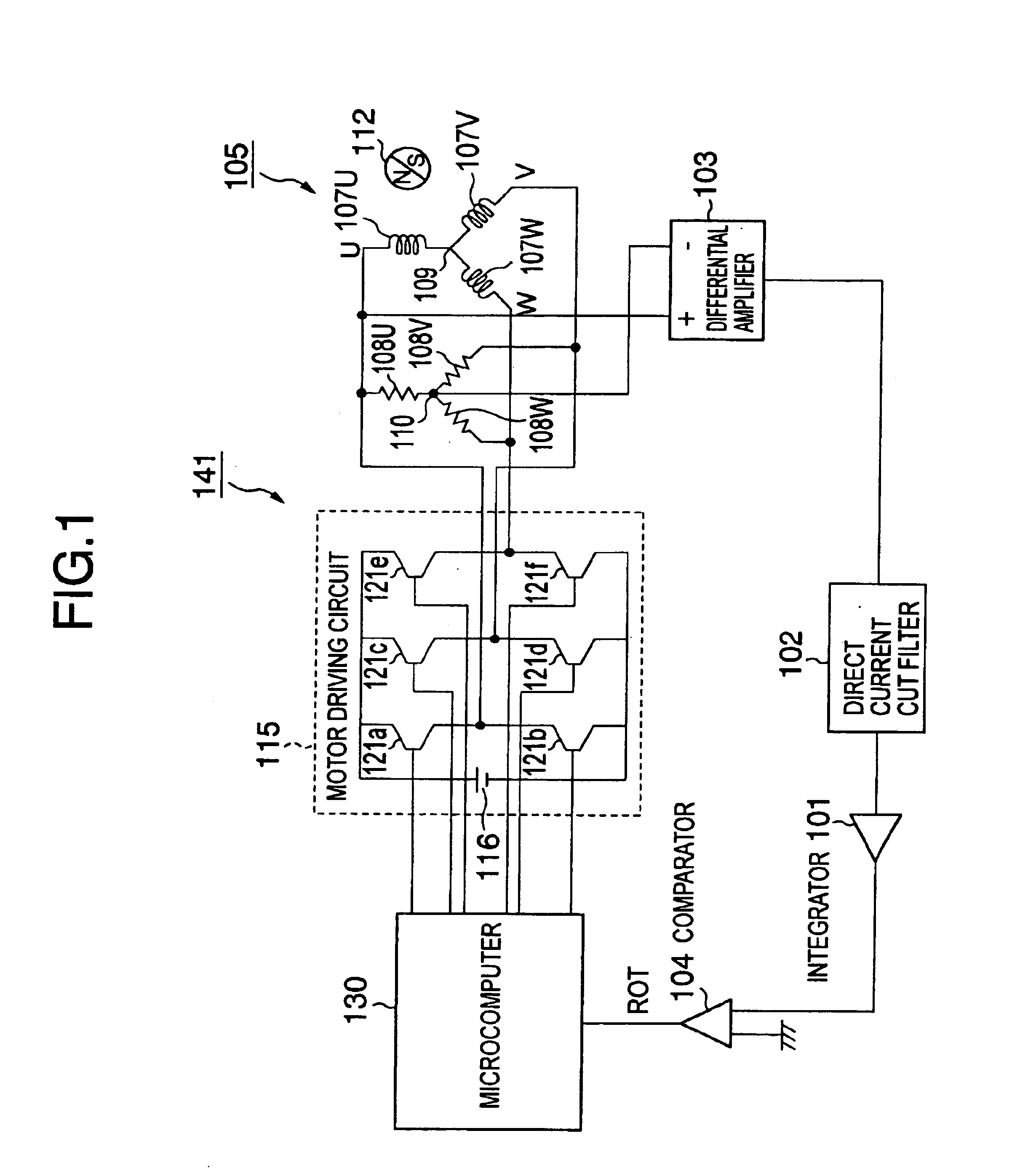
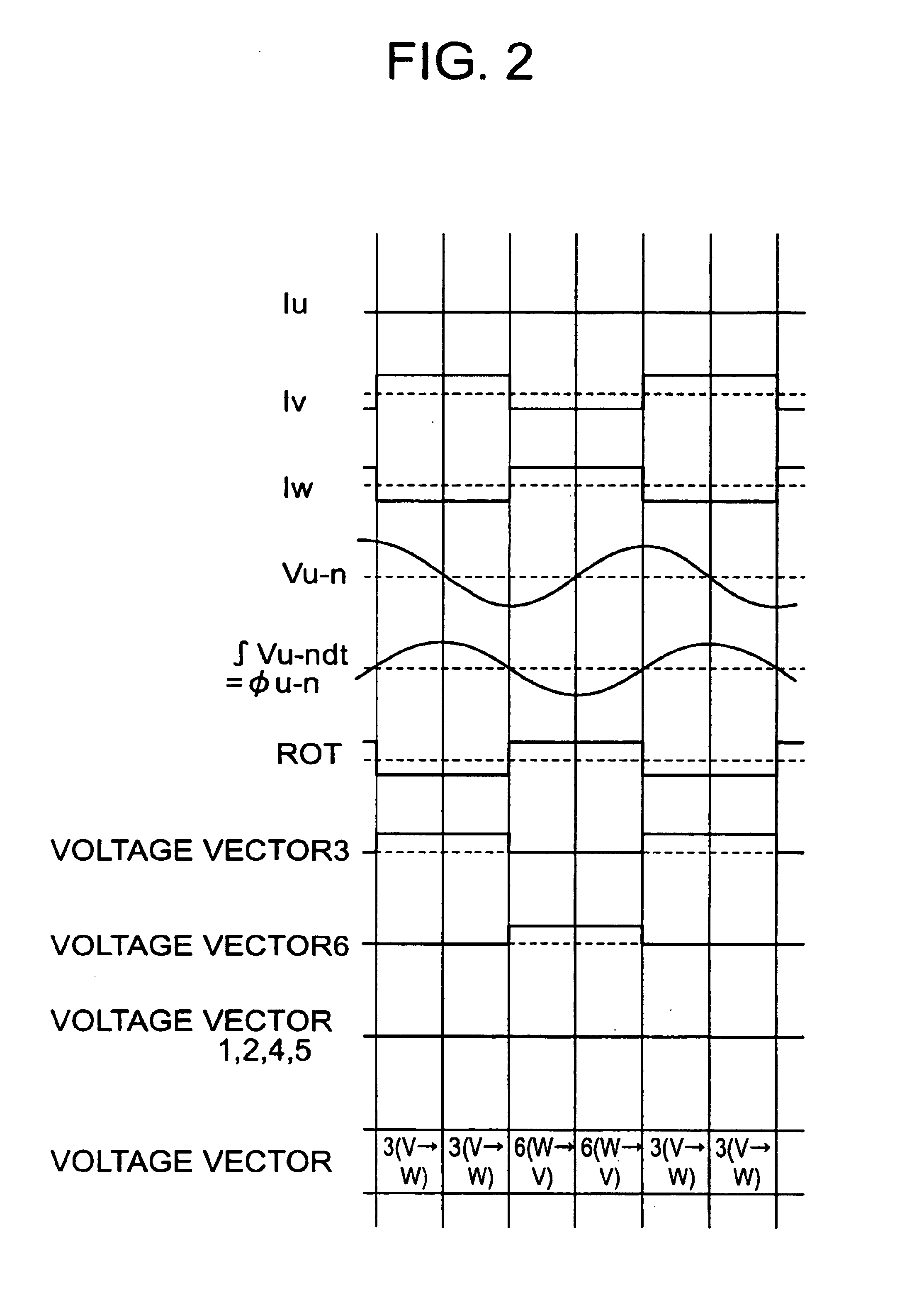
InactiveUS6759827B2Single-phase induction motor startersMotor/generator/converter stoppersVoltage vectorMagnetic poles
To provide a control circuit or the like of a brush-less motor capable of properly controlling current of motor windings by detecting positions of magnetic poles of a rotor at a rotational frequency of the rotor from low rotation which cannot lock a PLL circuit to steady-state rotation for rotating at high speed. Positions of magnetic poles are detected by a change in a magnetic flux (magnetic flux signal) of motor windings caused by rotating a rotor having the magnetic poles, thereby, a synchronizing signal (ROT signal) in synchronism with rotation of the rotor is generated. When the rotor is rotated at a low rotational frequency which cannot lock a PLL circuit, the rotor is driven by using predetermined two driving voltage vectors among outputable driving voltage vectors and when a rotational frequency capable of locking the PLL circuit is reached, the rotor is driven by successively outputting the outputable driving voltage vectors in synchronism with the positions of the magnetic poles detecting the outputable driving voltage vectors. Further, the magnetic flux signal is provided by using voltage between two phases at which phases and magnitudes of voltage drop caused by inductances of motor windings are equal to each other.
Owner:EDWARDS JAPAN
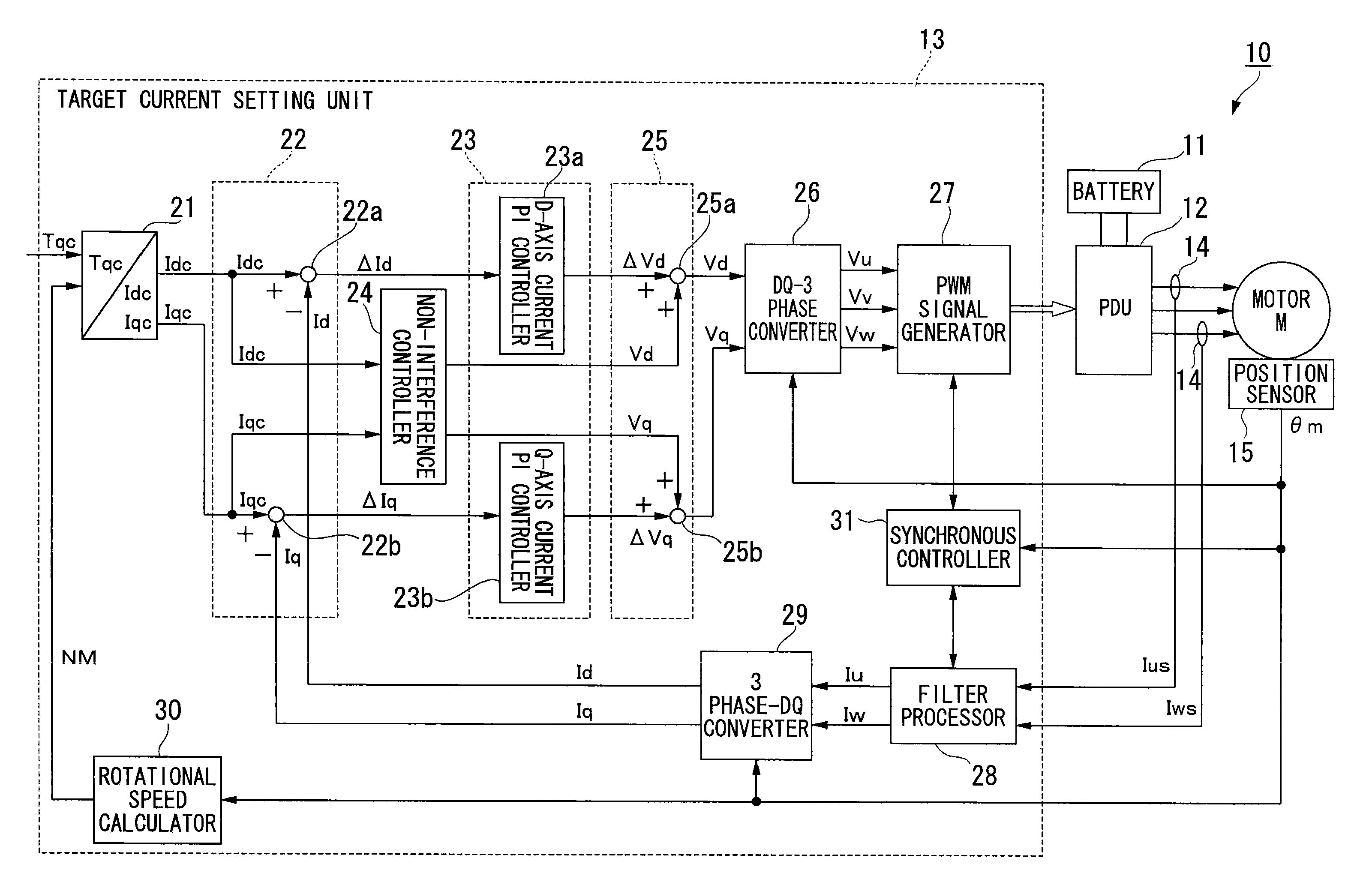
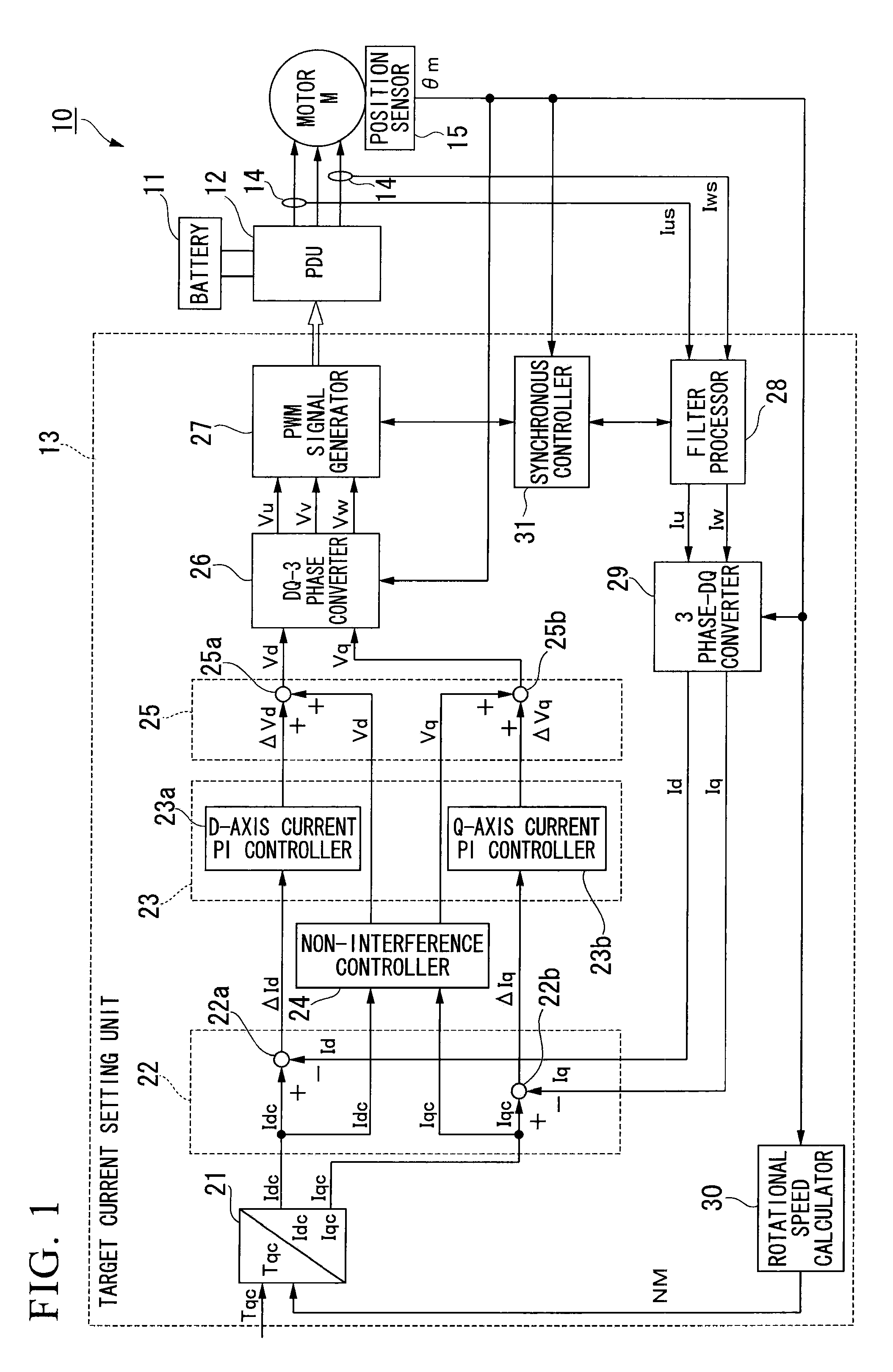
[a variable frequency power system and method of use]
ActiveUS20050146221A1Batteries circuit arrangementsAC motor controlElectric power systemVoltage regulation
A variable frequency power system with a power source having a rotating output and a speed control to regulate rotational speed of the rotating output. A generator coupled to and driven by the rotating output of the power source, whereby the speed control of the power source directly controls output power frequency of the generator due to control of rotational frequency of the rotating output. A voltage regulator connected between the generator and the motor regulates output voltage from the generator to the electrical motor load. A system controller controls output power frequency of the generator. The system controller interfaces with the speed control of the power source and configured to monitor generator output and operational conditions of the electrical motor load. The system controller adjusts the speed control based on generator output and operational conditions of the electrical motor load.
Owner:FOUND ENTERPRISES
Rotor balancing method
ActiveUS20130340521A1Reducing of methodShorten the timePump componentsBlade accessoriesEngineeringDeposition process
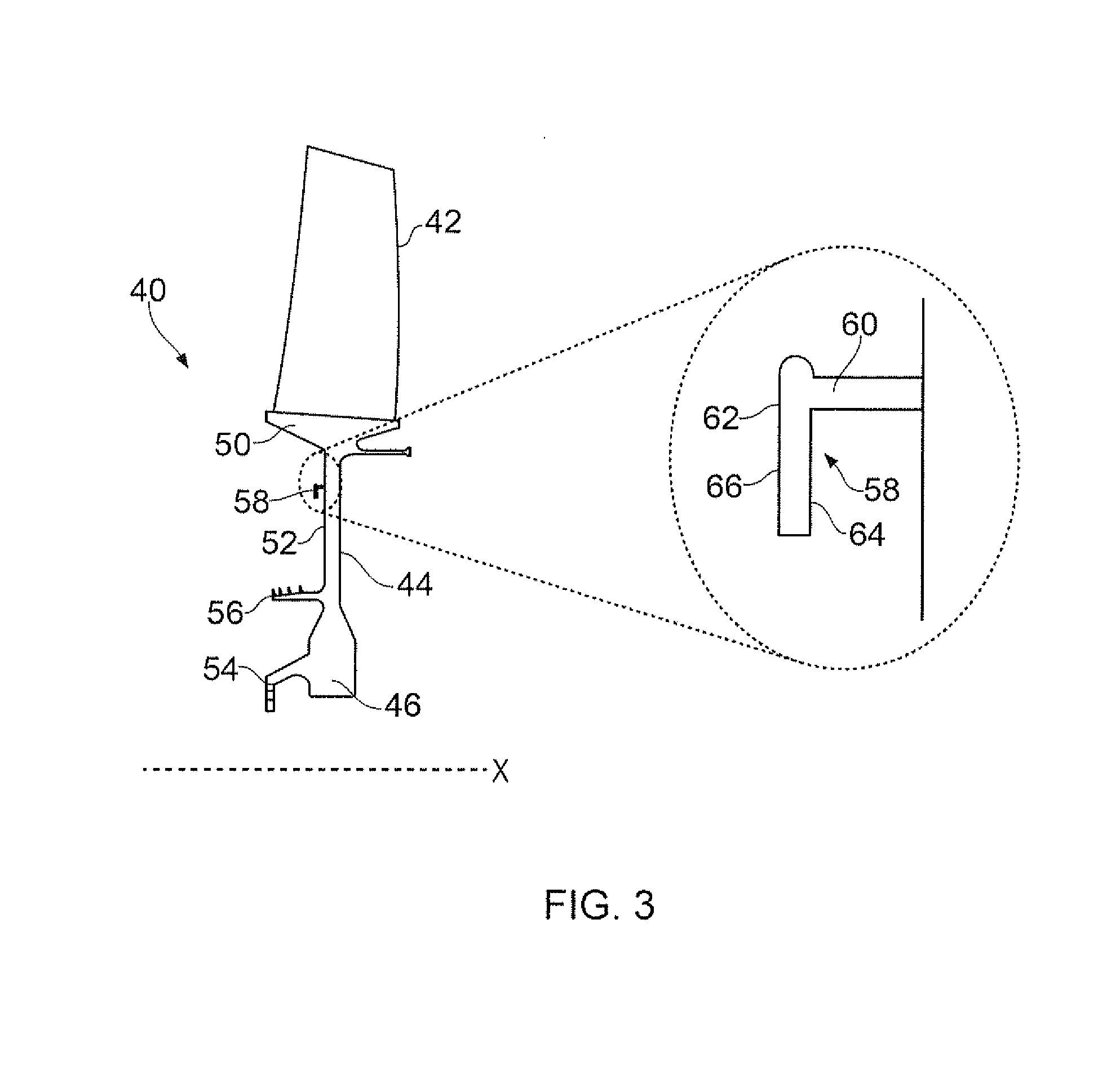
A method of balancing a physical rotor includes: determining a first balance state of the physical rotor at one or more rotational frequencies; identifying one or more balance zones on a surface of the rotor; providing a computerised simulation of the rotor having the first balance state; providing a first test mass in a first test location within one of the balance zones on the rotor simulation; determining a second balance state of the rotor simulation; providing at least one subsequent test mass in at least one subsequent test location within a balance zone on the rotor simulation and determining at least one subsequent balance state of the rotor simulation; selecting a mass and location from one of the first and subsequent test masses and test locations; and performing a material deposition process to add the selected mass of material to the selected location on the physical rotor.
Owner:ROLLS ROYCE PLC
Torsional vibration error monitoring method for shaft system of steam turbine generator unit, monitor and system
ActiveCN108716989AWon't breakWill not affect normal operationMachine gearing/transmission testingFrequency spectrumVibration acceleration
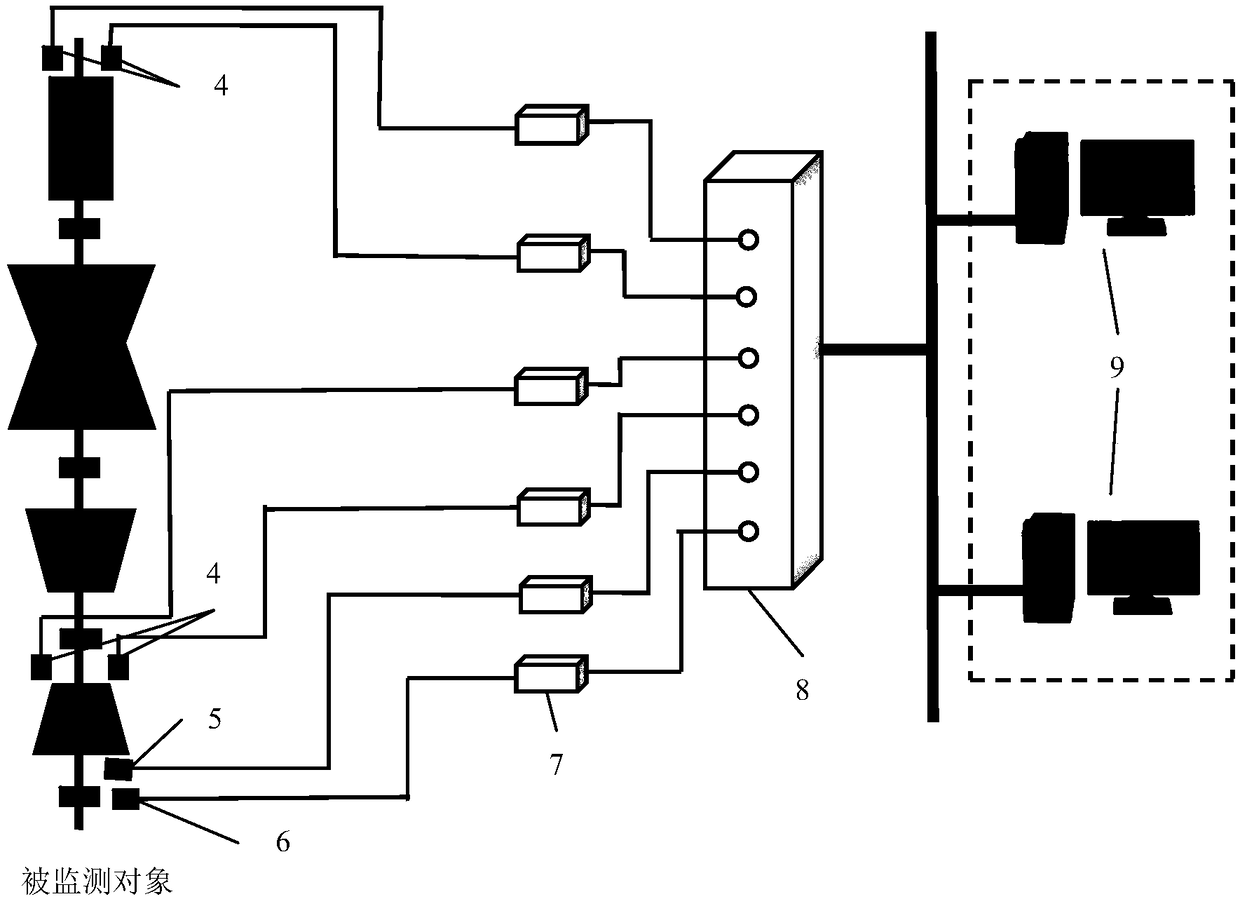
The invention discloses a torsional vibration error monitoring method for a shaft system of a steam turbine generator unit, a monitor and a system. The method includes the steps of S1, collecting output signals of rotation speed sensors, key phase sensors and bearing base vibration acceleration sensors on the steam turbine generator unit; S2, conducting Fourier transform on the collected output signal of each bearing base vibration acceleration sensor to obtain vibration spectrum signals; S3, extracting an amplitude value in the vibration spectrum signal of each bearing base vibration acceleration sensor under the corresponding rotation frequency; S4, obtaining the types of to-be-detected frequencies and separately extracting the corresponding amplitude value and phase under each type of to-be-detected frequency from the vibration spectrum signal of each bearing base vibration acceleration sensor to serve as feature parameters; S5, on the basis of a judgment principle and the extractedfeature parameters, judging whether or not torsional vibration errors of the shaft system occur in the steam turbine generator unit. By means of the method, real-time online monitoring of the torsional vibration errors of the shaft system is achieved.
Owner:CHANGSHA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
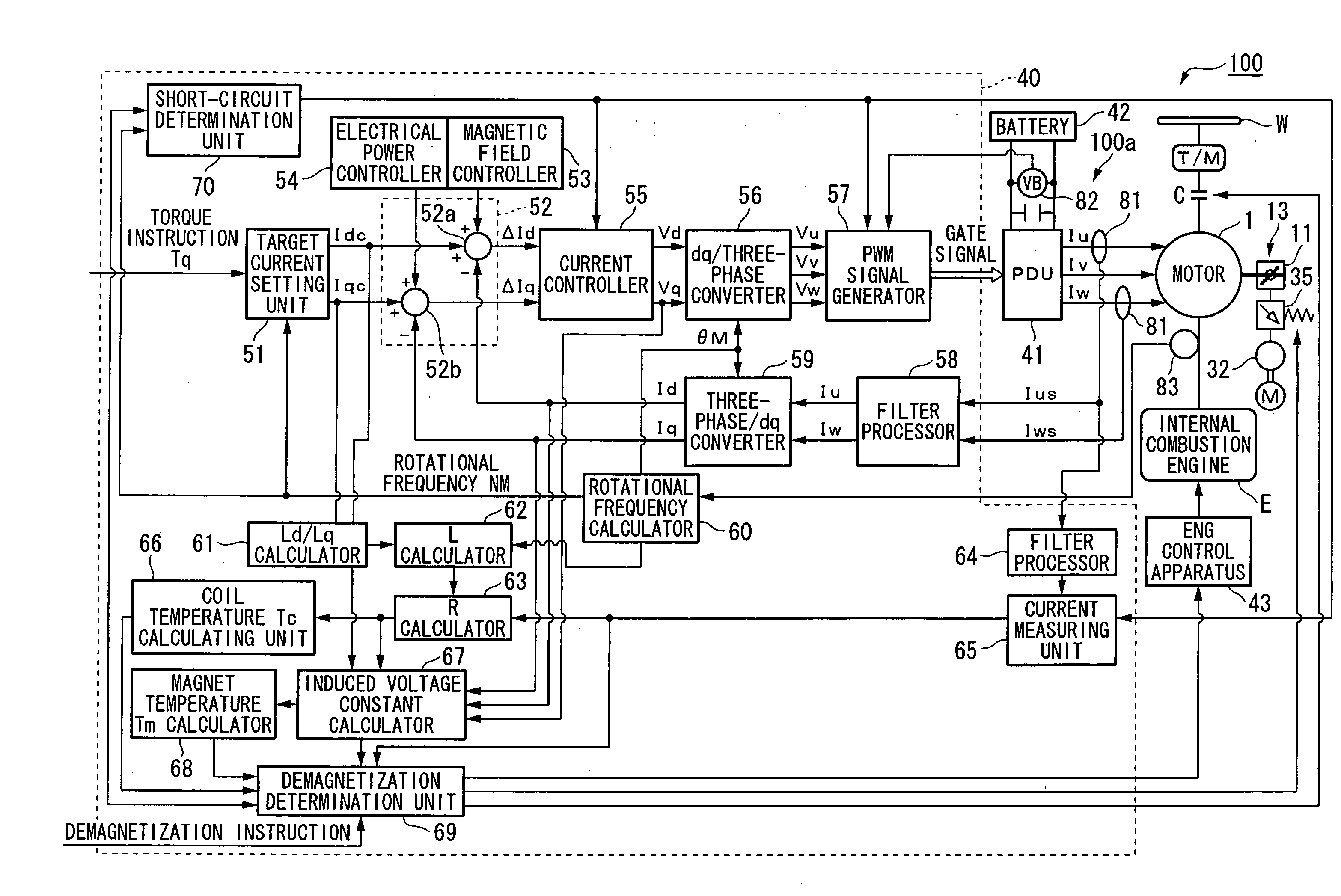
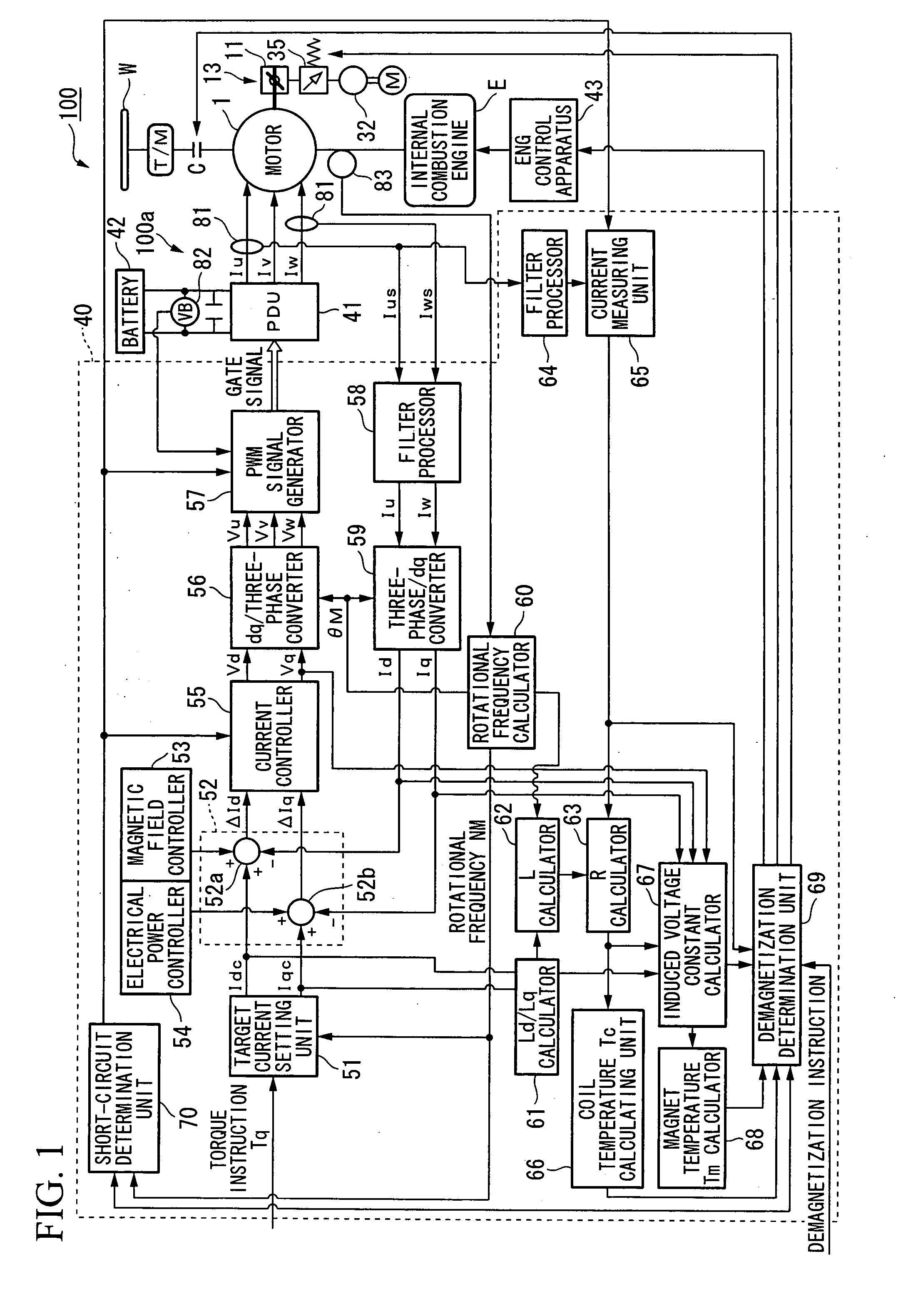
Motor control apparatus
InactiveUS20080265831A1Excessive execution of processingAvoid oscillationAC motor controlVector control systemsPhase differenceCarrier signal
A motor control apparatus provided with an inverter for successively commutating the current to a motor using a PWM signal; a PWM signal generating device for generating the PWM signal using a carrier signal; a rotational state quantity sensor for detecting a rotational state quantity; a phase difference detecting device for detecting the phase difference between the carrier signal and the rotational period based on the rotational state quantity; a frequency setting device for setting a frequency of the carrier signal to a value in accordance with a multiplier for one period in terms of electrical angle of the rotational period of the motor, when the rotational frequency is equal to or greater than a specified frequency and the phase difference is equal to or less than a specified value; and a synchronizing device for synchronizing a control period of the carrier signal to the rotational period.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Motor control method and motor control apparatus
InactiveUS20080129237A1Increase armature magnetic fluxEffectively demagnetizedHybrid vehiclesAC motor controlMotor controlRotational frequency
A motor control method that includes the steps of: rotationally driving a motor that is provided with a rotor having permanent magnet pieces, and a stator; and short circuiting a plurality of phases of the motor when the rotational frequency of the motor is equal to or greater than a predetermined rotational frequency.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
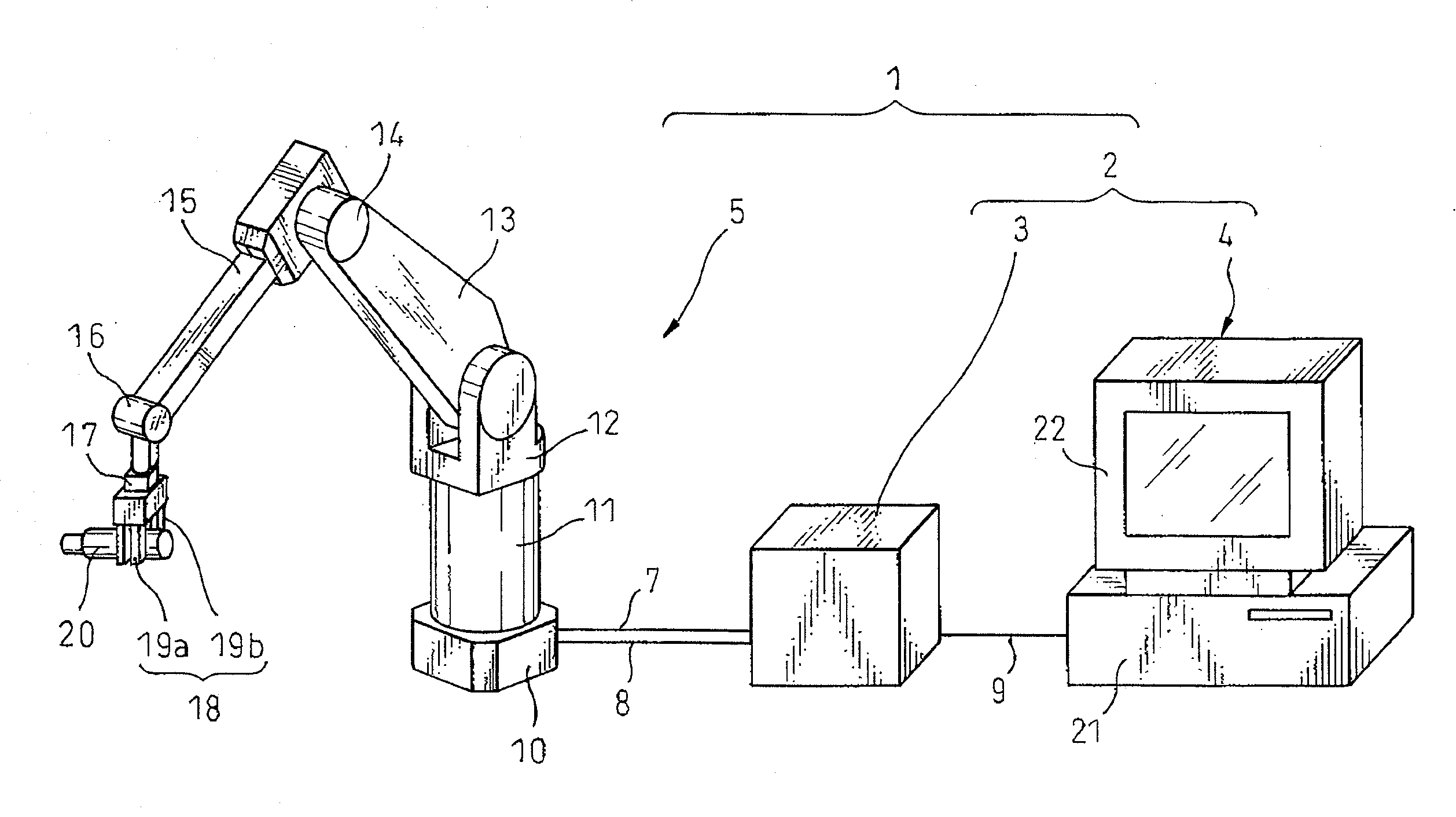
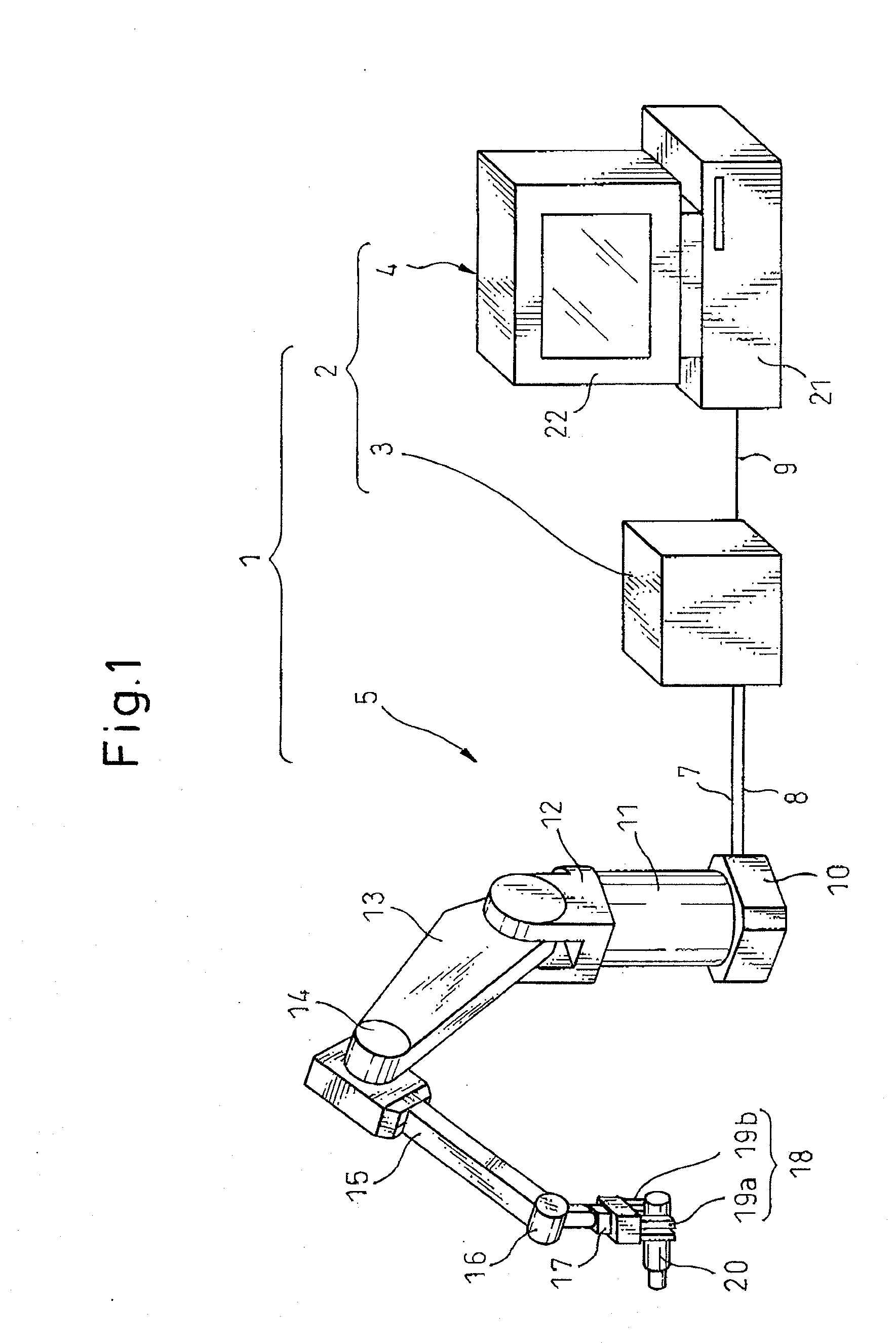
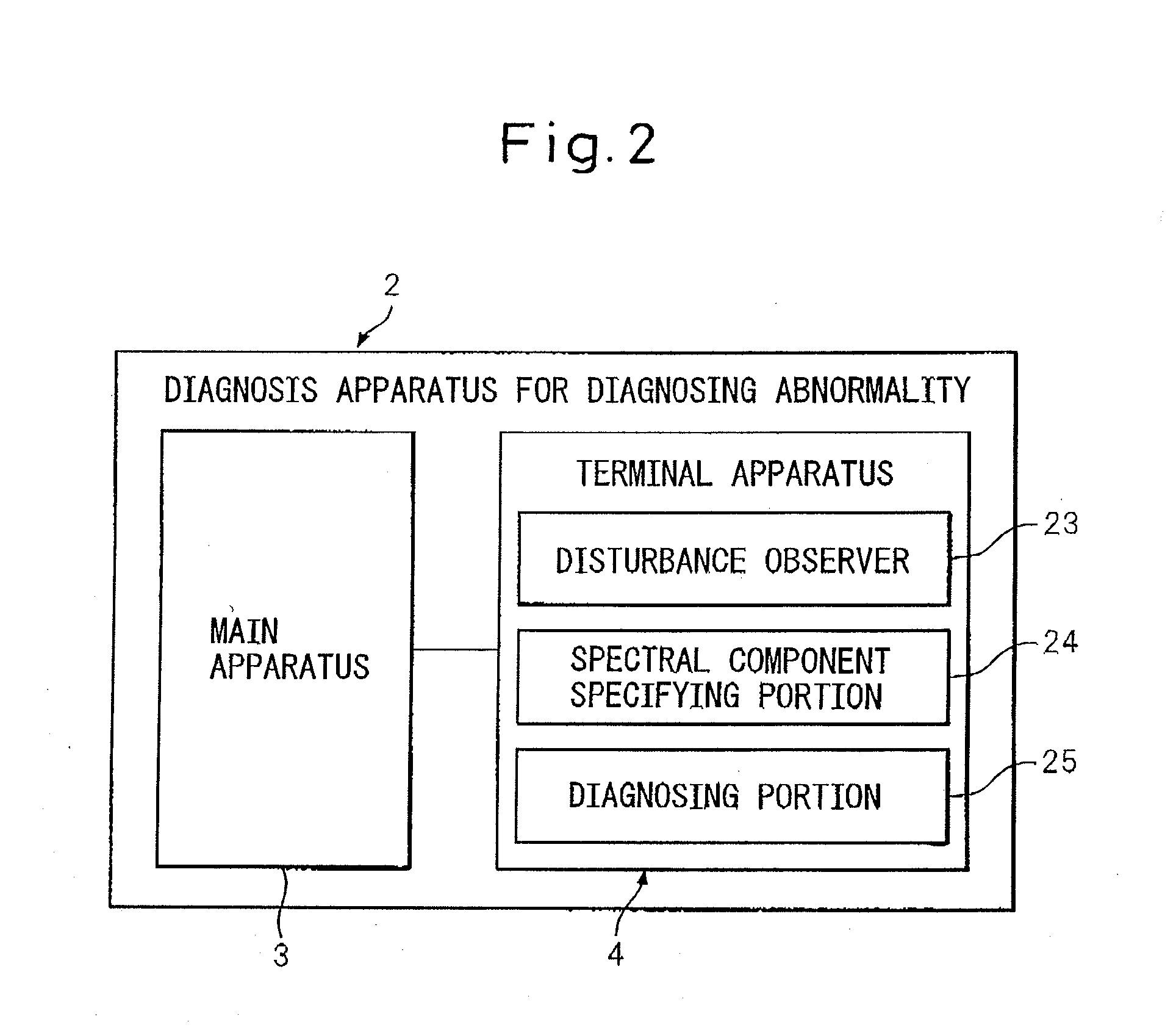
Method of diagnosing abnormality of reduction gear and apparatus for carry out the method
InactiveUS20080215292A1Improve usabilityIncrease productivityMachine part testingNuclear monitoringFrequency spectrumMedial axis
An apparatus for carry out a method of diagnosing abnormality of a reduction gear, the reduction gear including an intermediate shaft element disposed between an input shaft and an output shaft and rotating in proportion to a rotation of the input shaft to transmit the rotation to the output shaft, the apparatus has: a disturbance observer that obtains an estimated disturbance value regarding the reduction gear, based on a torque instruction and a velocity feedback-value acquired when a pair of driven members which rotate relative to each other with a motor as a driving source are in relative rotation at a constant velocity; a specific spectral component specifying portion for extracting a specific spectral component corresponding to a constant multiple of a rotational frequency of the intermediate shaft element from a frequency components of the estimated disturbance value obtained by frequency analysis; and a diagnosing portion, which compares an amplitude of the specific spectral component specified by the specific spectral component specifying portion with a threshold value, and diagnoses an abnormality in a case where the amplitude of the specific spectral component exceeds the threshold value, or a normality in a case where the amplitude of the specific spectral component is equal to or less than the threshold value.
Owner:FANUC LTD
Rotary fluid agitator
InactiveUS20050281131A1Improve actionFlow mixersTransportation and packagingParticulatesSolid particle
A rotary fluid agitator is provided. The rotary fluid agitator essentially comprises a fluid conduit that is positioned vertically within a storage tank holding a quantity of fluid, such as a drilling fluid. At least one nozzle is attached to the fluid conduit for jetting a stream of fluid into to the fluid contained within the tank. A drive means is connected to the fluid conduit and rotates the conduit to sweep the nozzle through a 360-degree arcuate path at a predetermined rotational frequency. A fluid pump is attached in fluid communication with the interior volume of the tank and pumps a quantity of drilling fluid through a fluid circulation line and through the fluid conduit to be jetted out of the nozzle. As the nozzle is swept through the arcuate path a conically shaped fluid flow path is created in the fluid contained within the tank causing the jetted fluid to tangentially act upon the fluid thereby keeping all solid particulates mixed with the fluid in suspension.
Owner:YUNGBLUT JOHN DAVID
NMR MAS electret spin rate detection
InactiveUS7196521B2High sensitivityImprove stabilityMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionHigh resistivityCharge generation
A material having a permanent external diametrical electric field is included within an NMR MAS spinner. Such materials include ferroelectret porous films, in which the electric polarization arises from opposite mono-polar charges on separated surfaces within a structured material containing voids. Rotation of electrically polarized material produces a time-dependent electric field, modulated at the rotational frequency, so that a simple antenna achieves high sensitivity and phase stability in spin rate detection. The electrically polarized material is also of sufficiently high resistivity that modulation of the external NMR polarizing magnetic field B0 is negligible.
Owner:DOTY SCI
Device for drilling and for removing material using a laser beam
ActiveUS7842901B2Lift restrictionsEasy constructionLaser beam welding apparatusOptical elementsRotational axisClassical mechanics
A device for drilling and for removing material using a laser beam comprises: a rotating image rotator (2); a beam manipulator (1) which, when viewed in the beam direction, is arranged in front of the image rotator and which serves to adjust the angle and position of the beam relative to the rotation axis of the image rotator; and a focusing device (3) located on the output side of the image rotator. A compensating device (3, 13, 14, 15) is placed between the image rotator and the focusing device and rotates with the image rotator in the same direction of rotation and with the same rotational frequency. The compensating device has a parallel displacement unit (15) and an angle changing unit (13, 14), and the compensating device, in a basic setting, is adjustable in its rotating position relative to the image rotator.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
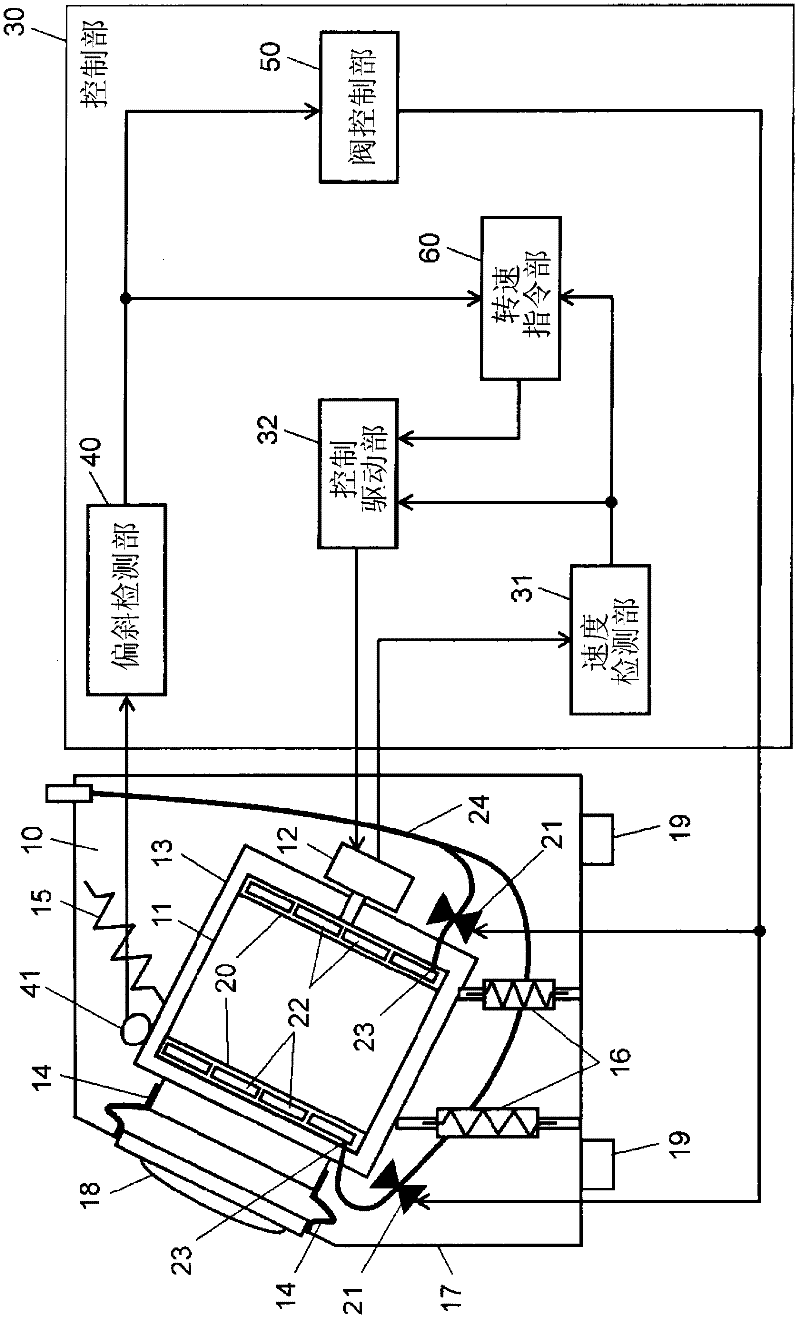
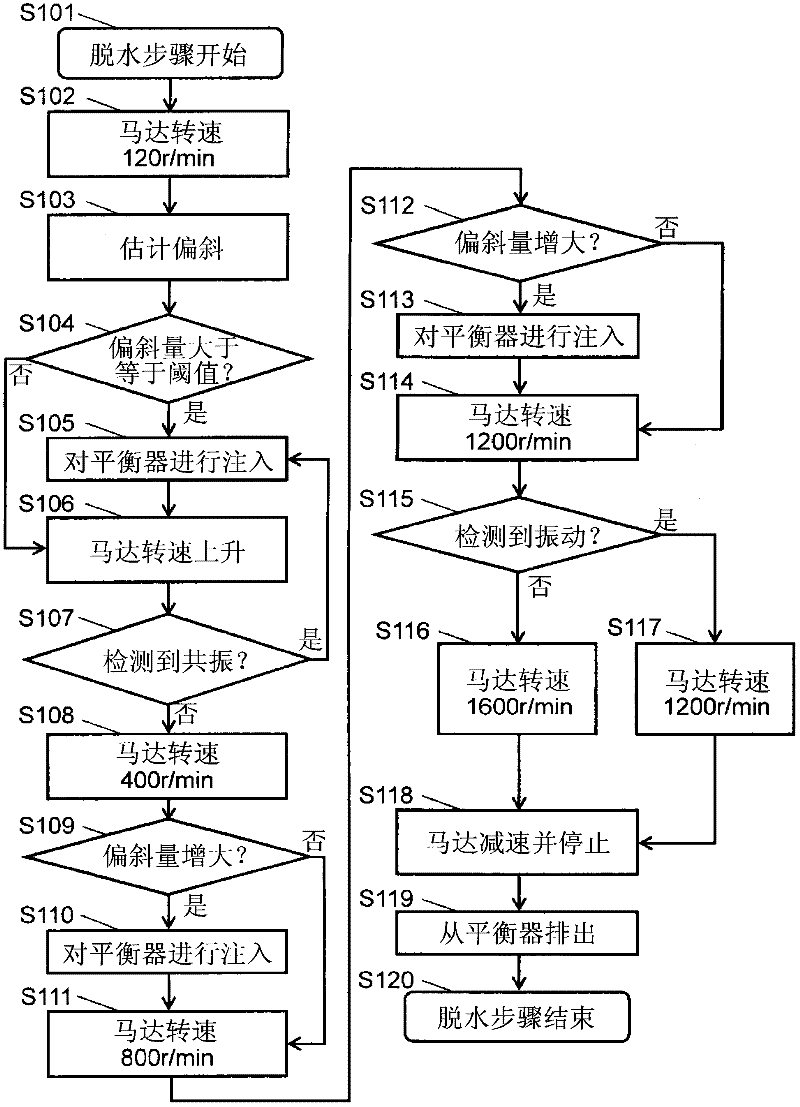
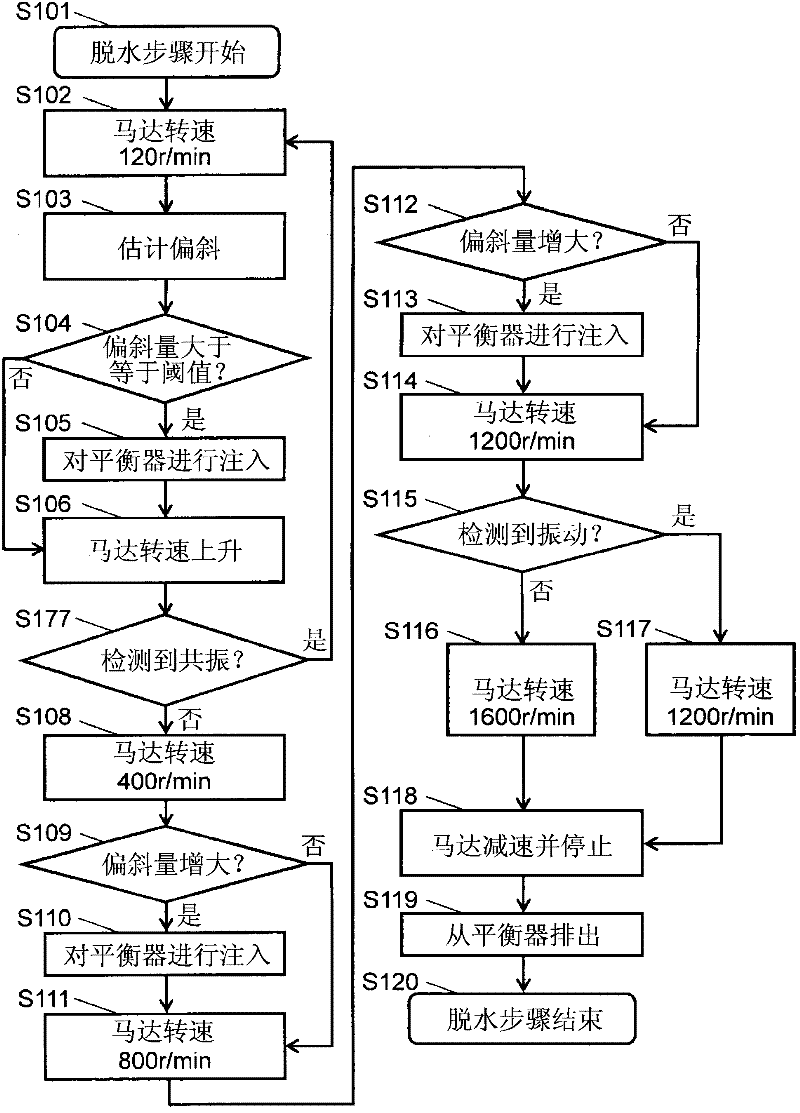
Washing machine
InactiveCN102341539AReduce vibrationOther washing machinesControl devices for washing apparatusEngineeringLaundry
A washing tub (11) is provided with a fluid balancer (20) having containing chambers (22) for containing fluid poured therein from the outside. A control section (30) controls the pouring of the fluid into the containing chambers (22) according to the output of a vibration detection section (41) for detecting the vibration of a receiving tube (13) and determines, according to the rotational frequency of a motor (12) and to the output of the vibration detection section (41), the rotational frequency of the motor (12) when the fluid is poured into the containing chambers (22). Thus, the fluid is poured into the containing chambers (22) according to the vibration and rotational frequency to reduce vibration caused by the eccentric distribution of laundry.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com
![[a variable frequency power system and method of use] [a variable frequency power system and method of use]](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/7eeeb950-4930-4bcd-b744-7891651dd015/US20050146221A1-20050707-D00000.png)
![[a variable frequency power system and method of use] [a variable frequency power system and method of use]](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/7eeeb950-4930-4bcd-b744-7891651dd015/US20050146221A1-20050707-D00001.png)
![[a variable frequency power system and method of use] [a variable frequency power system and method of use]](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/7eeeb950-4930-4bcd-b744-7891651dd015/US20050146221A1-20050707-D00002.png)