Washing machine
A technology for washing machines and washing tanks, applied in the field of washing machines, which can solve problems such as difficulty in performing stable movements and inability to reduce the vibration of the washing tank, and achieve the effect of reducing vibration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
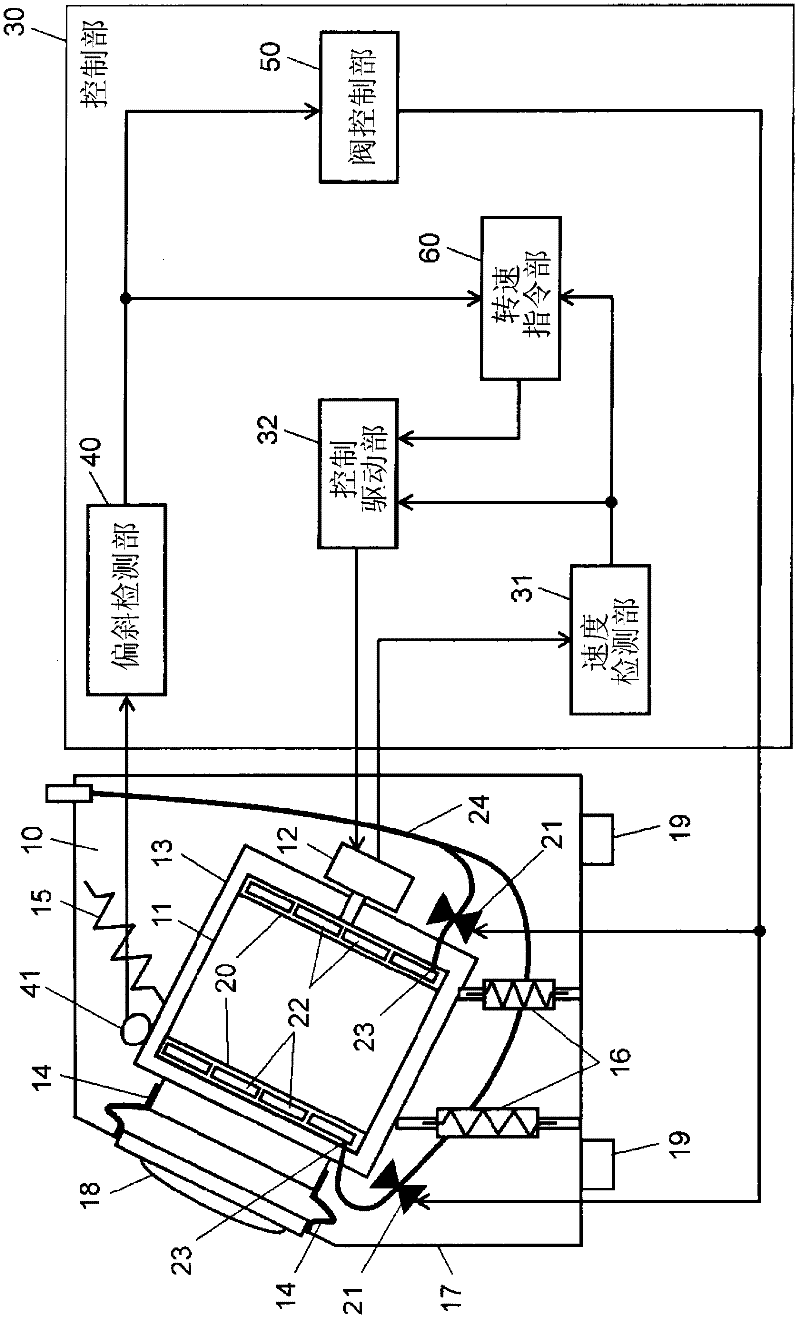
[0024] figure 1 It is a block diagram of the washing machine according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention. exist figure 1 Among them, the casing cover 17 of the washing machine has an inlet 18 for taking out / putting in laundry and anti-vibration rubber 19 as legs when the washing machine is installed on the floor. In the inside of the housing cover 17, as the mechanism part 10 of the washing machine, it is provided with: a support cylinder 13 injected with water; a washing tank 11, which is arranged on the inside of the support cylinder 13, and accommodates laundry; and a motor 12, which is provided On the outside of the support drum 13, the washing tub 11 is rotated while controlling the speed of the washing tub 11. The motor 12 is constituted by a brushless motor. The surroundings of the inlet 18 of the case cover 17 and the opening of the support cylinder 13 are connected by a seal 14 so that there is no gap therebetween.
[0025] The support cylinder 13 supports ...
Embodiment approach 2
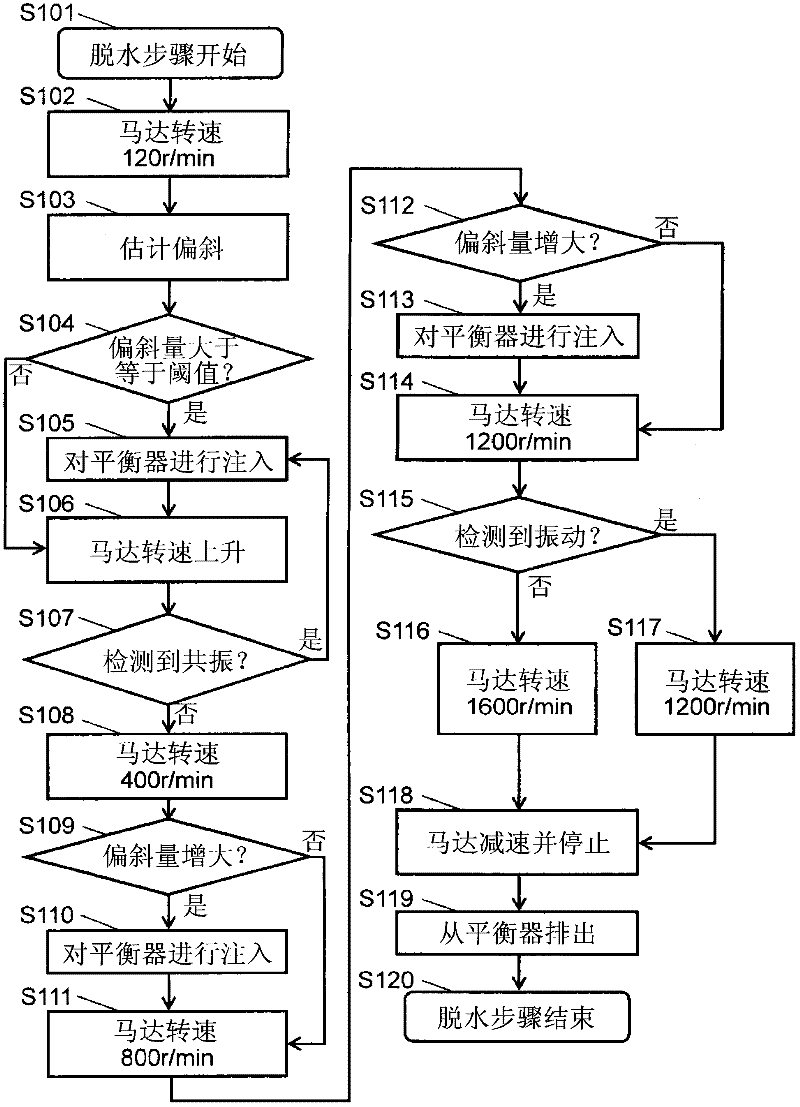
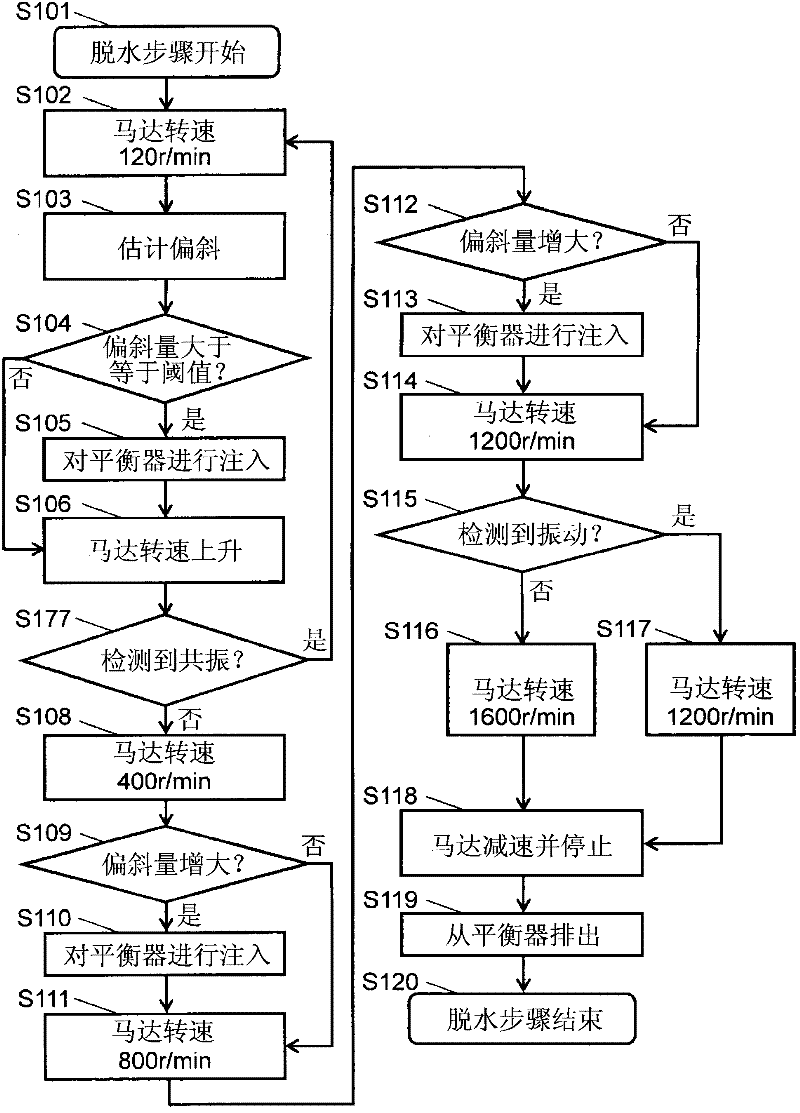
[0045] image 3 It is a flowchart of the spin-drying process of the front-loading-type washing machine in Embodiment 2 of this invention. Additionally, for figure 2 The same steps as those in Embodiment 1 shown will be described using the same reference numerals. The difference from Embodiment 1 is that, as image 3 As shown, in the resonance detection in step S177, when resonance is detected (YES in step S177), the process returns to step S102.
[0046] Step S101 to step S106 in the dehydration step of the present embodiment are the same steps as those in the first embodiment. Here, when the rotational speed of the motor 12 increases from 120 r / min (step S106 ), if resonance is detected (YES in step S177 ), the process returns to step S102 . As a result, the rotational speed of the motor 12 is reduced to 120 r / min, thereby returning to the initial state of dehydration. After that, the fluid balancer 20 is injected again (step S105). In addition, when the rotation speed...
Embodiment approach 3
[0049] Figure 4 It is a flowchart of the spin-drying process of the front-loading-type washing machine in Embodiment 3 of this invention. Additionally, for figure 2 The same steps as those in Embodiment 1 shown will be described using the same reference numerals. First of all, the difference from Embodiment 1 is that, if Figure 4 As shown, even if the rotation speed is rising (step S106), when the vibration is detected by the vibration detection part 41 (step S171), and the amount of deflection increases ("Yes" in step S172), switch to the following control (step S173 ): Stop increasing the speed and make the speed fixed. In addition, the difference from Embodiment 1 is that when the amount of deflection increases when the motor 12 is rotated at 800 r / min (step S111) (YES in step S182), it switches to the following: Control (step S183): stop increasing the rotation speed, and make the rotation speed constant.
[0050] Step S101 to step S106 in the dehydration step of t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com