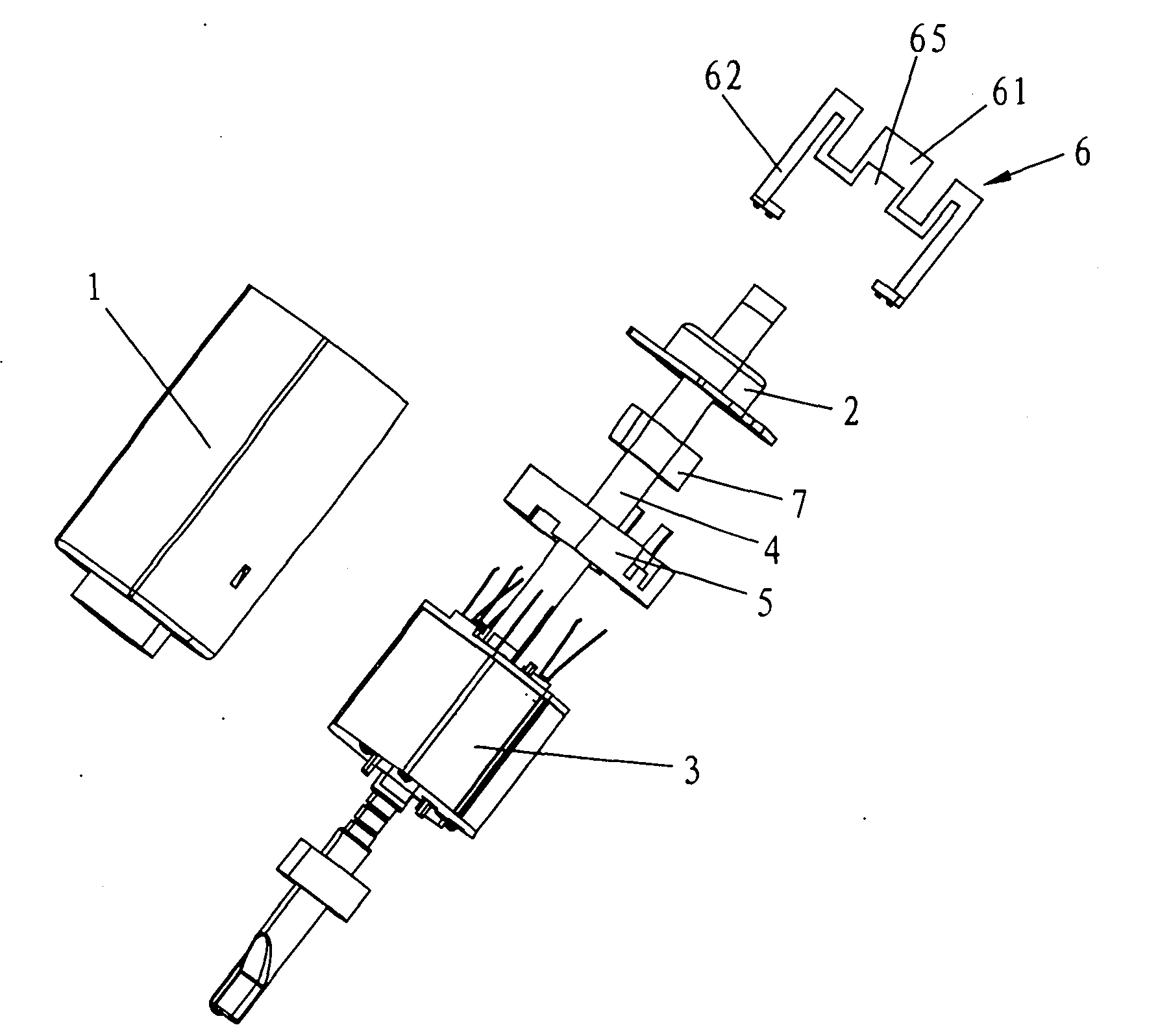
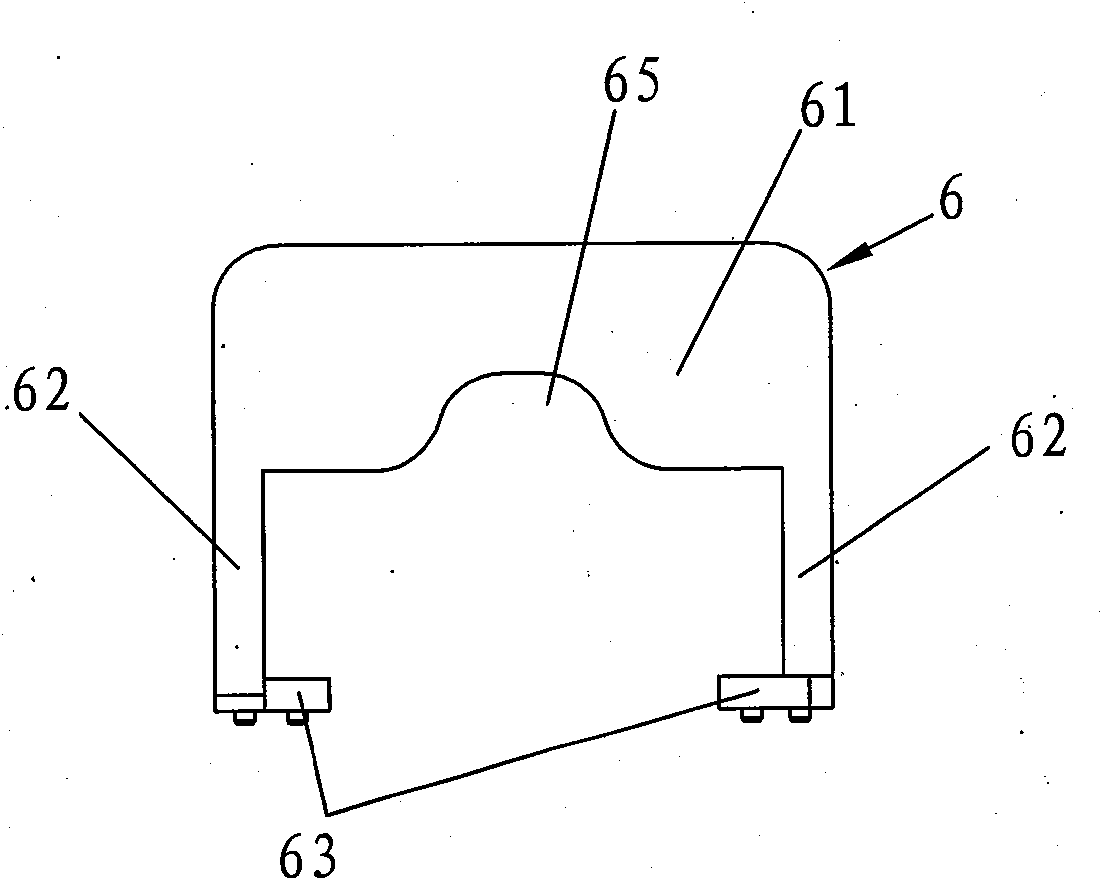
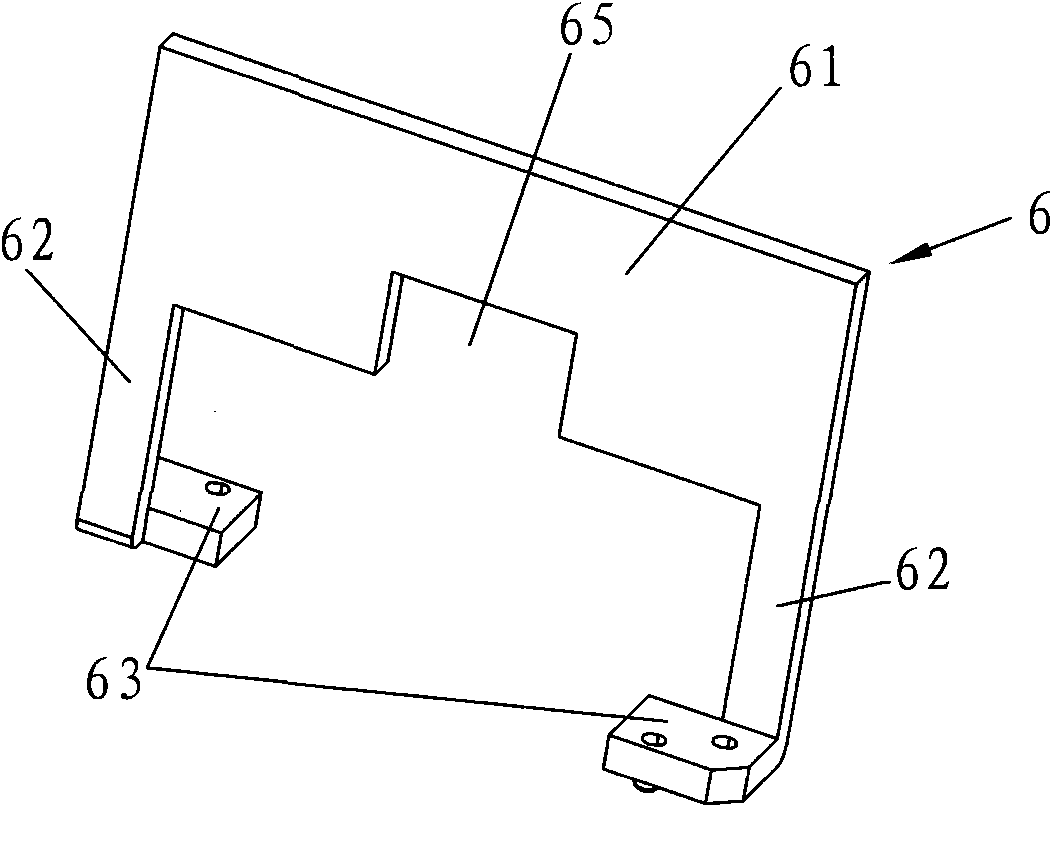
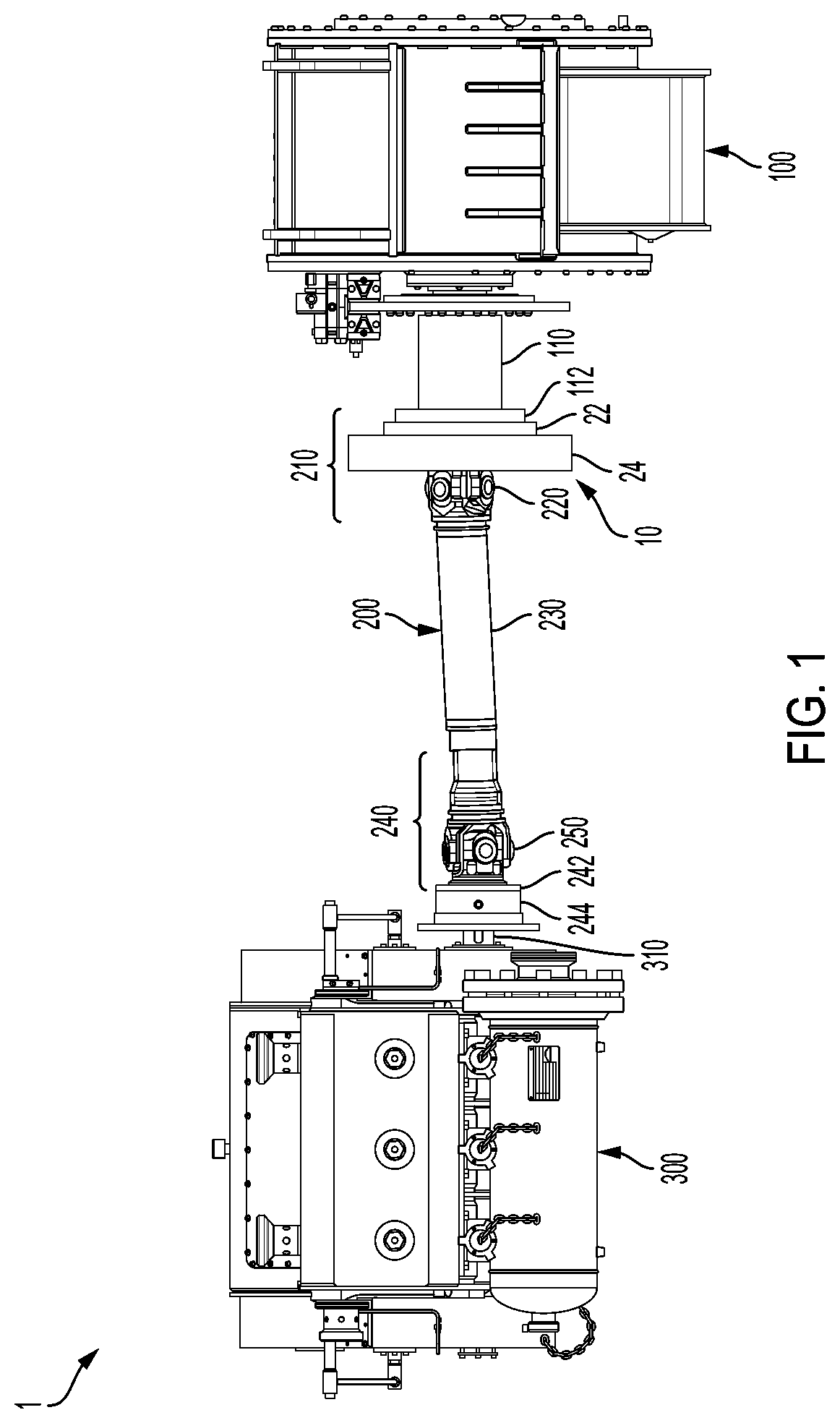
Patents
Literature
2447 results about "Torsional vibration" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Torsional vibration is angular vibration of an object—commonly a shaft along its axis of rotation. Torsional vibration is often a concern in power transmission systems using rotating shafts or couplings where it can cause failures if not controlled. A second effect of torsional vibrations applies to passenger cars. Torsional vibrations can lead to seat vibrations or noise at certain speeds. Both reduce the comfort.
Ultrasonic calculus treatment apparatus
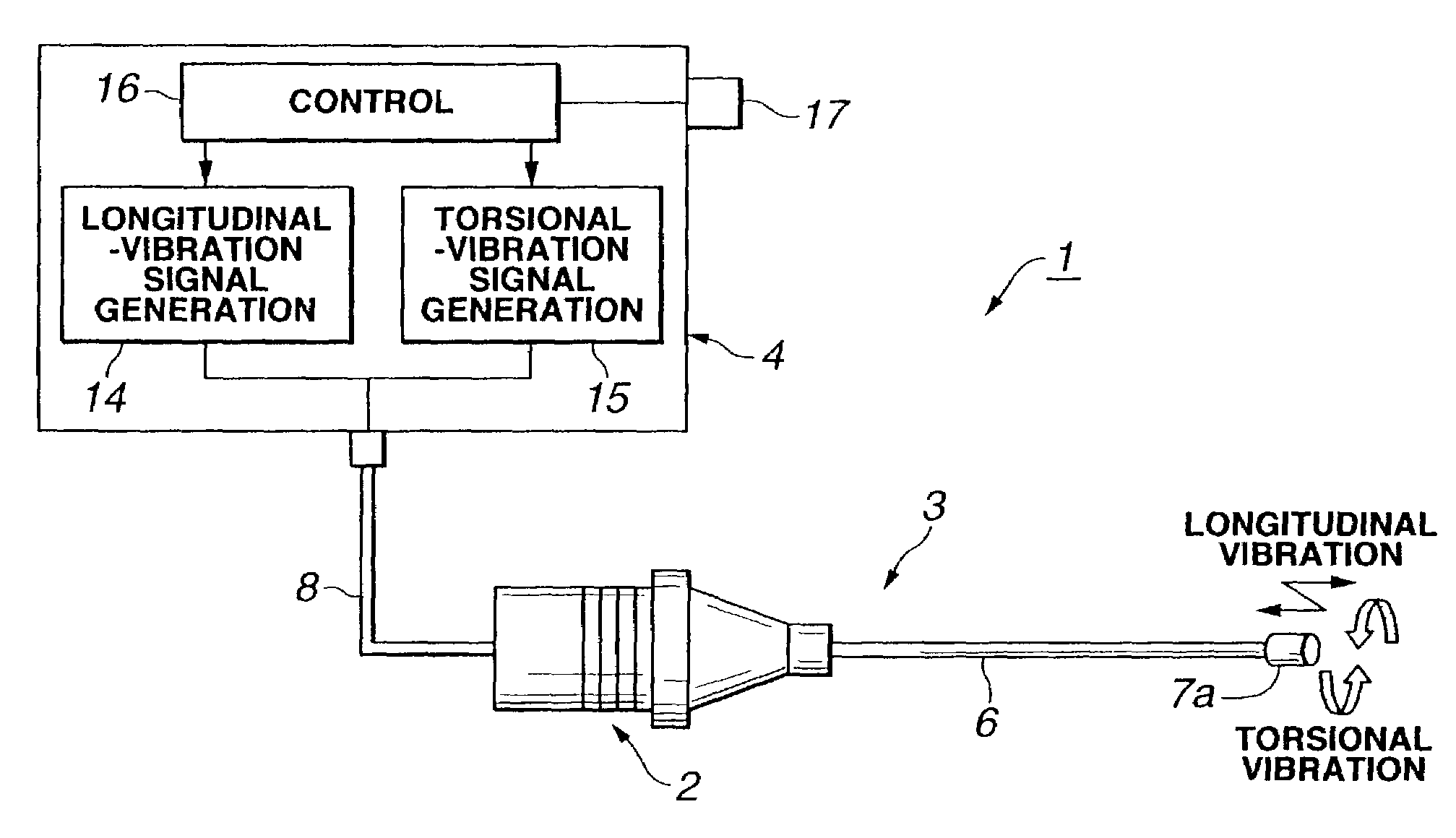
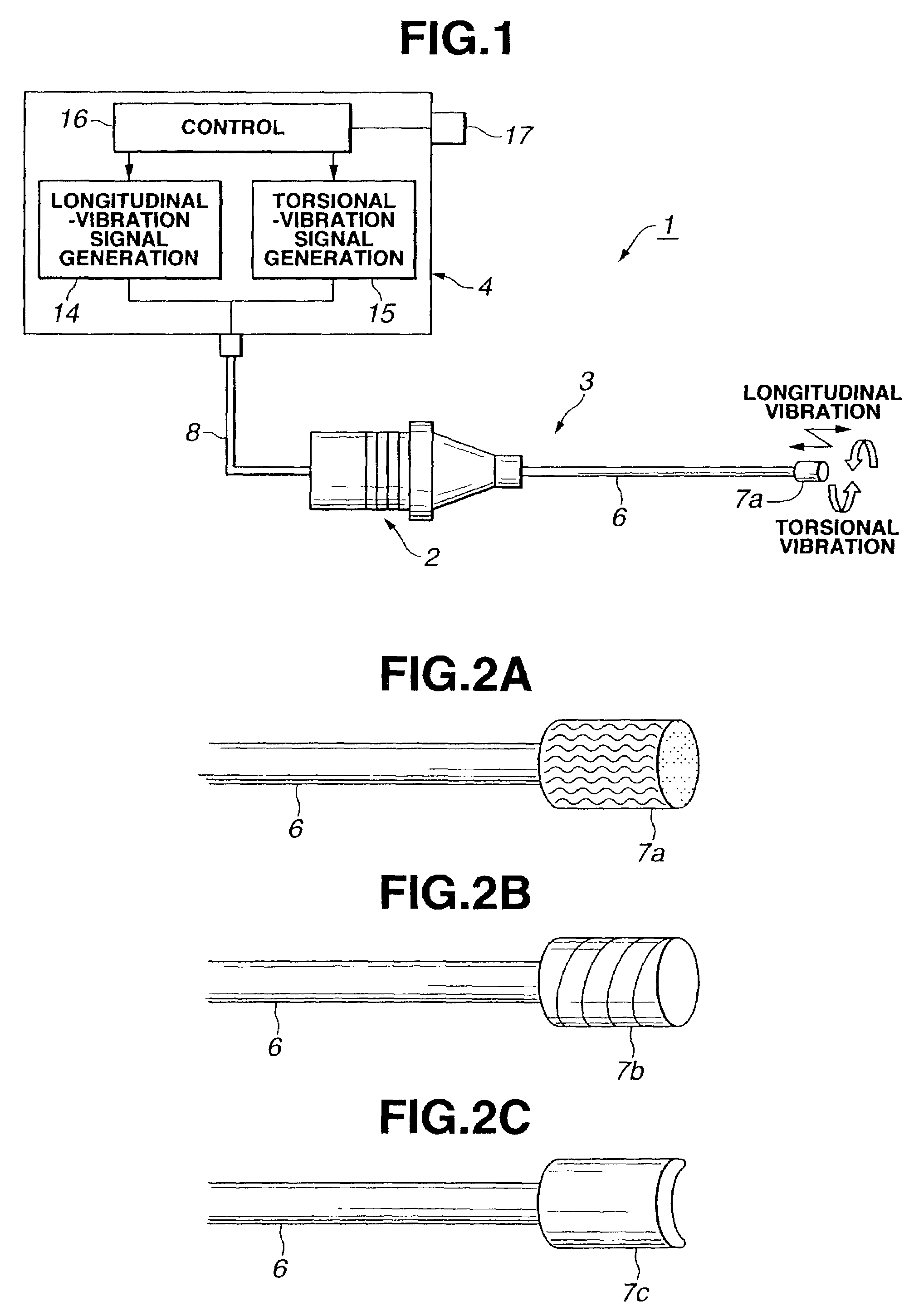
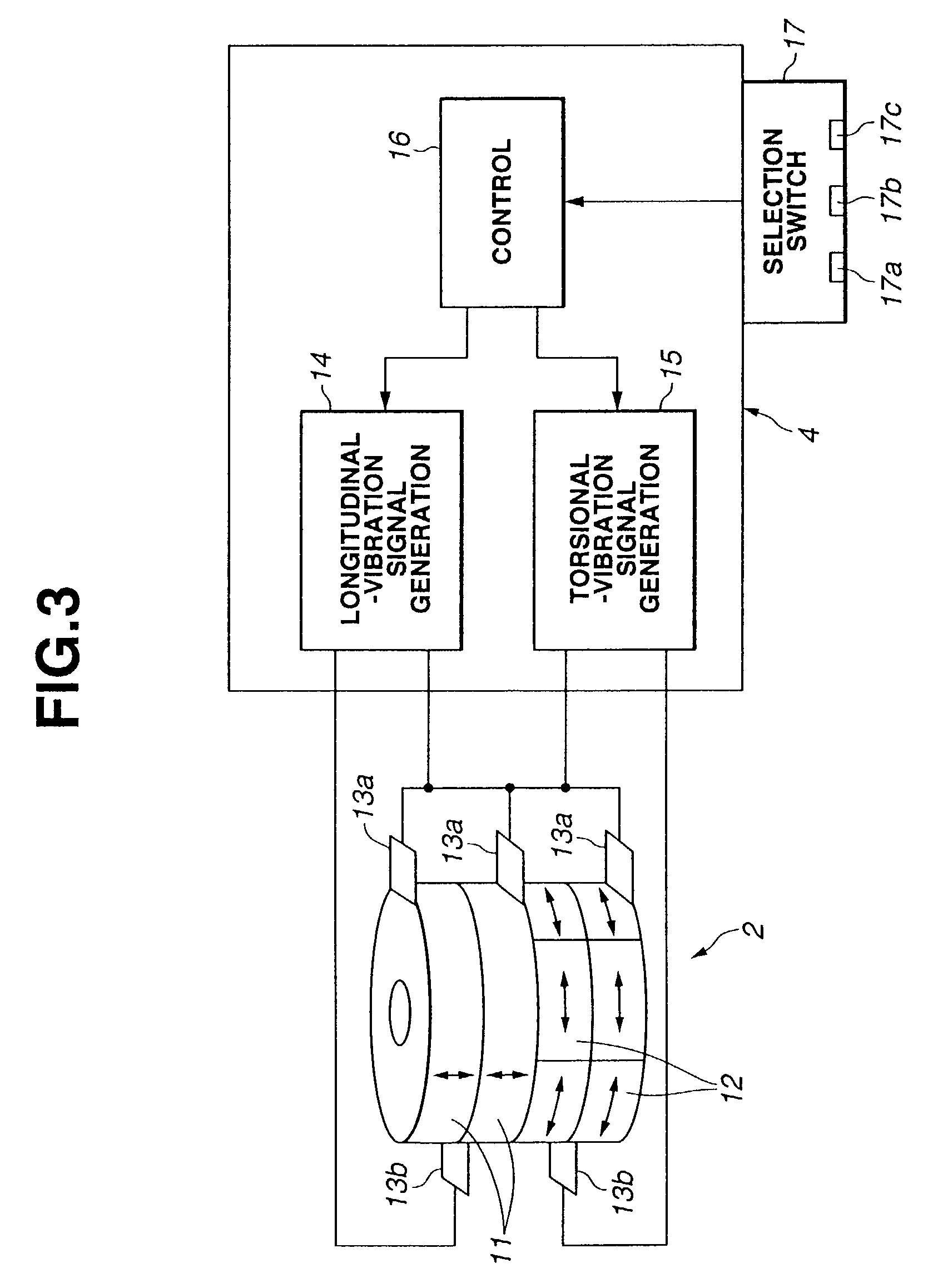
An ultrasonic calculus treatment apparatus includes a longitudinal-vibration piezoelectric oscillator for vibrating in the axial direction of an ultrasonic transmitting member and a torsional-vibration piezoelectric oscillator for vibrating about the axial direction, and further includes driving circuits for driving the piezoelectric oscillators at respective resonance frequencies and a mode selection switch for permitting the oscillators to vibrate independently or in combination, so that lithotripsy can be performed effectively in accordance with the size of a calculus or a function of an operating tool.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Vibratory transducer
InactiveUS6840109B2Simple and robust mannerSimplifies isolationVibration measurement in solidsMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesTransducerEngineering
To conduct a fluid, the transducer has a flow tube which in operation vibrated by an excitation assembly. Inlet-side and outlet-side vibrations of the flow tube are sensed by means of a sensor arrangement. To produce shear forces in the fluid, the flow tube is at least intermittently excited into torsional vibrations about a longitudinal flow-tube axis. An internal portion of the transducer, formed at least by the flow tube, an antivibrator, the sensor arrangement, and the excitation assembly and mounted at least on the inlet and outlet tube sections, has a centroid which is located inside the flow tube. The transducer is suitable for use in viscometers or Coriolis mass flowmeter-viscometers. In spite of using only a single straight flow tube, it is dynamically well balanced in operation, and the development of bending moments by the torsionally vibrating flow tube is largely prevented. This also effectively prevents the transducer case or the connected pipe from being excited into sympathetic vibration. Measurement signals representative of mass flow rate are readily distinguishable from measurement signals representative of viscosity, particularly if the sensors used for the viscosity measurement are also used for the mass flow measurement.
Owner:ENDRESS HAUSER FLOWTEC AG
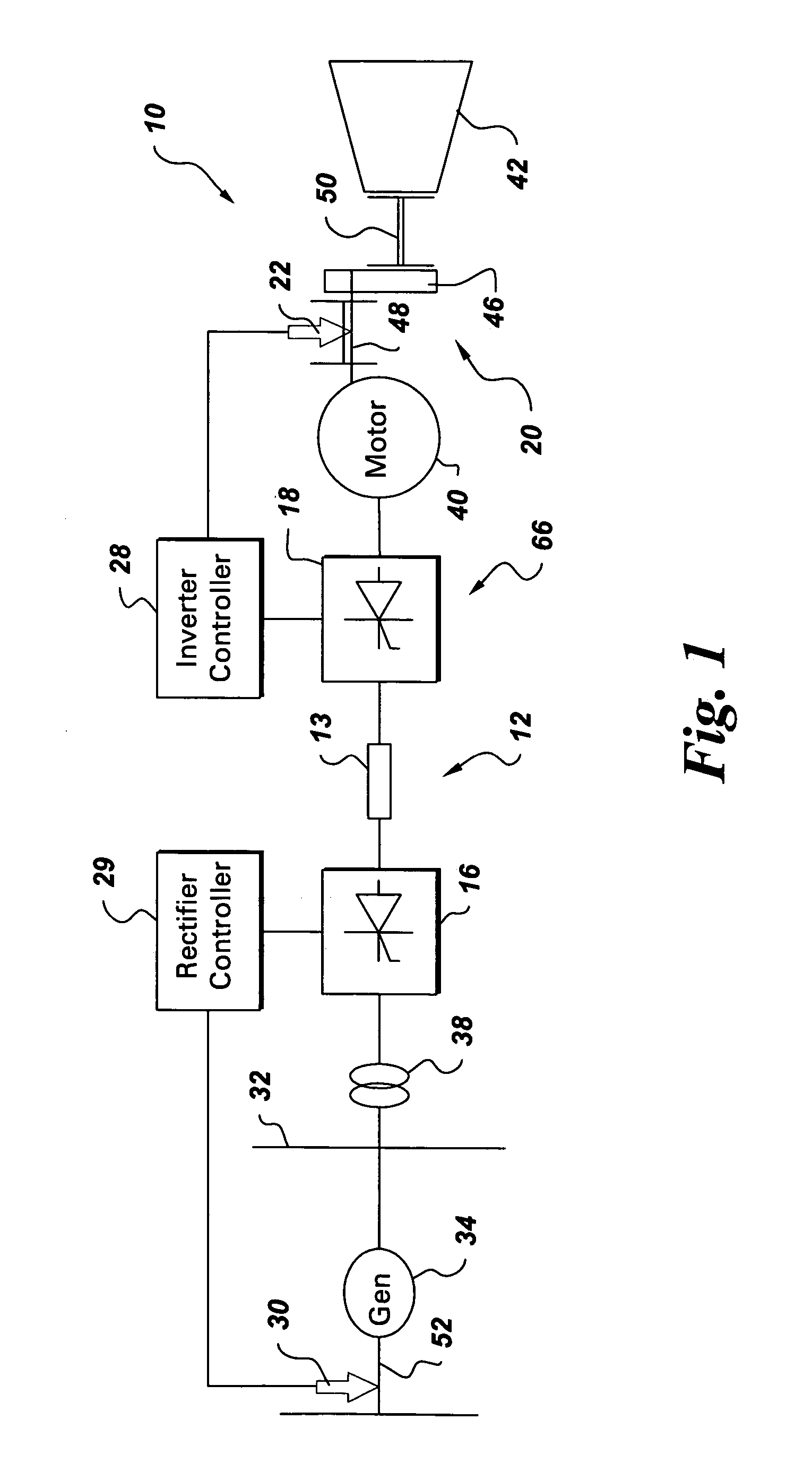
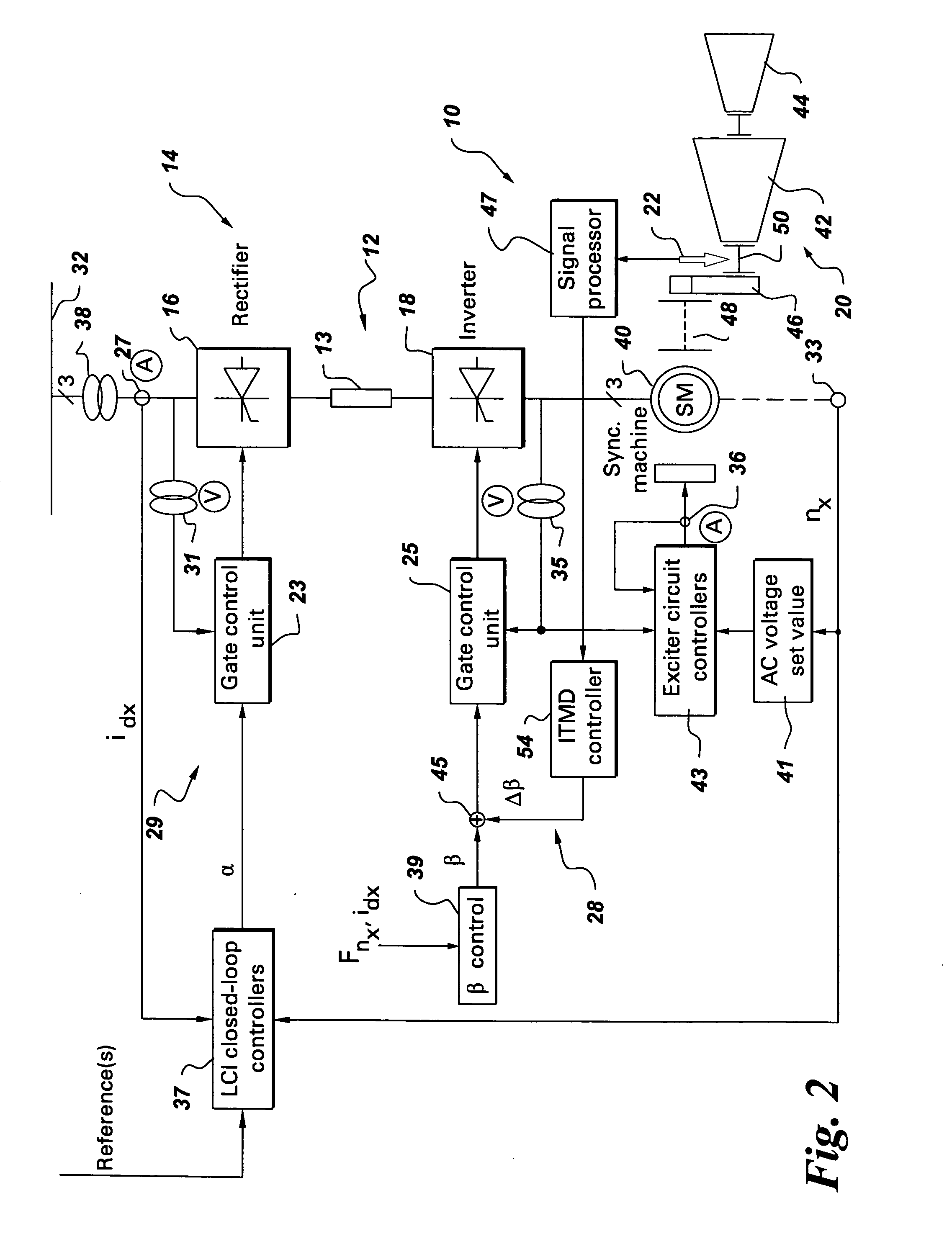
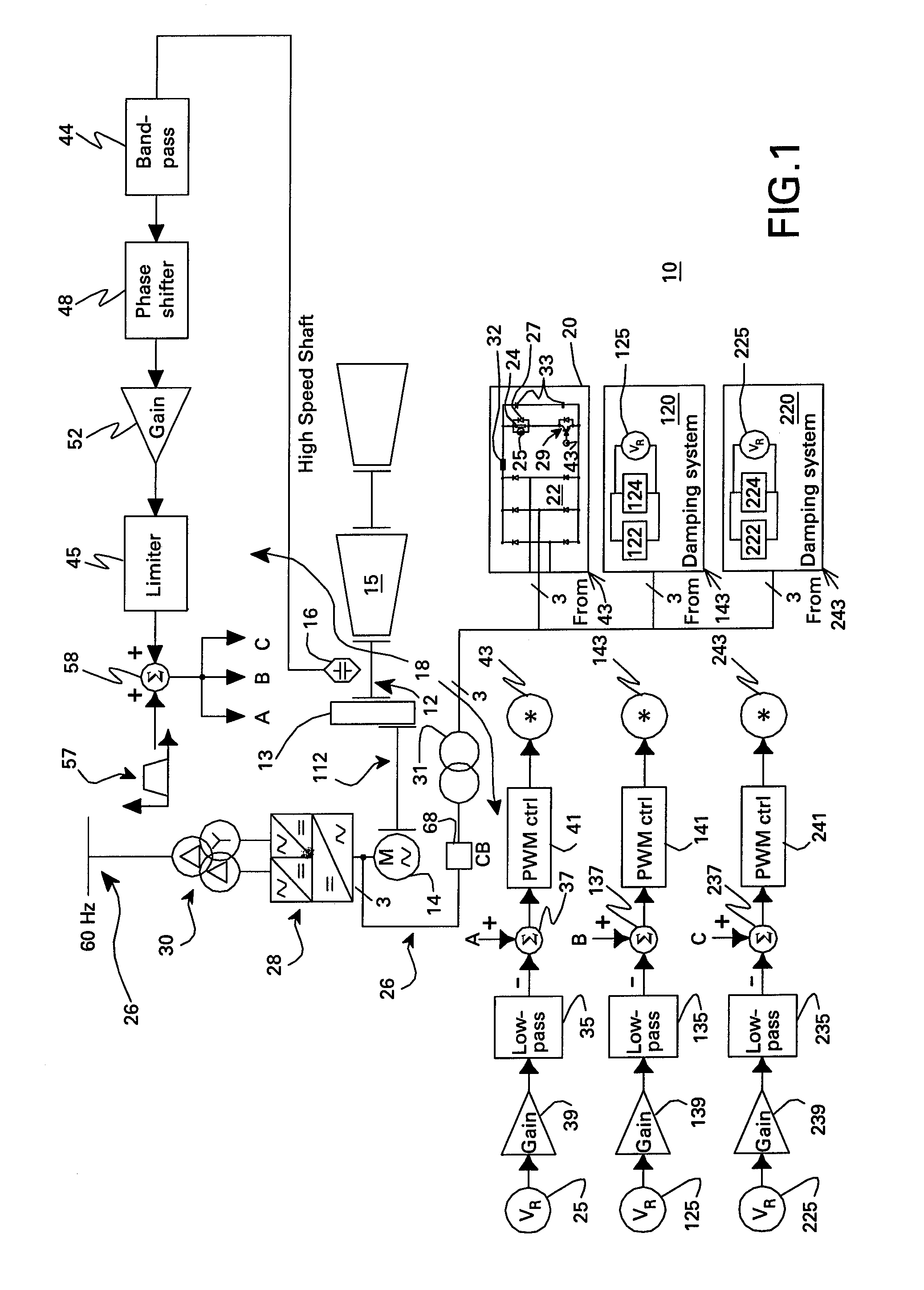
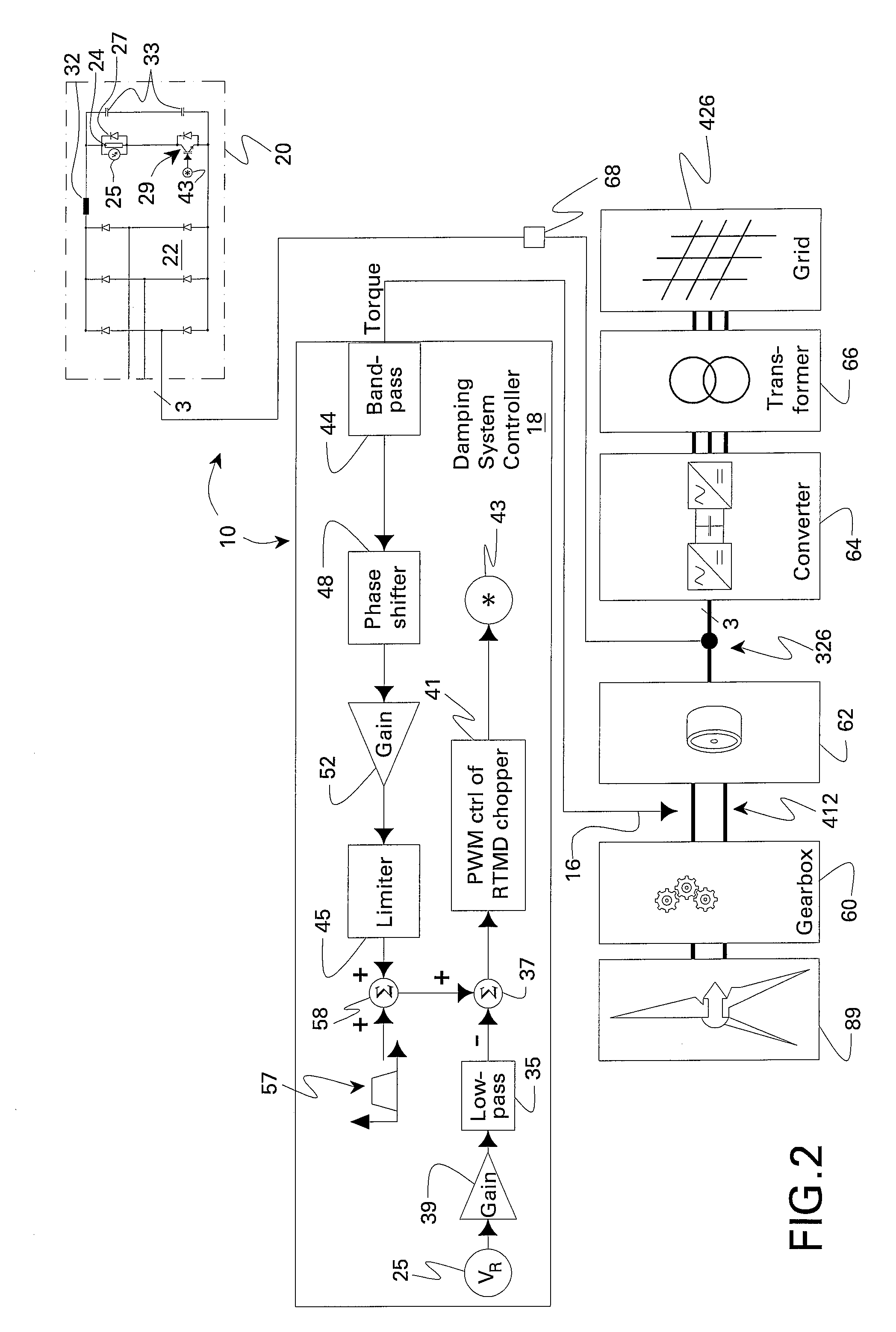
Integrated torsional mode damping system and method
InactiveUS7173399B2DC motor speed/torque controlEmergency protective circuit arrangementsInductorTorsional vibration
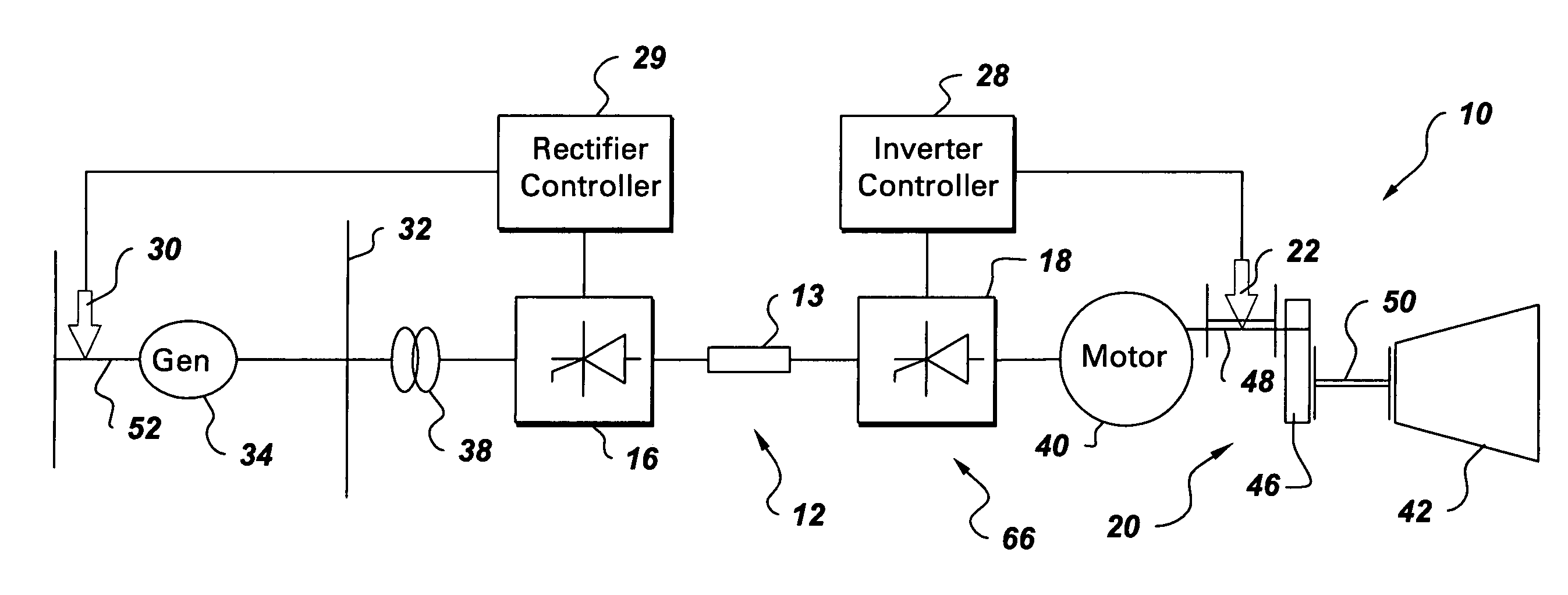
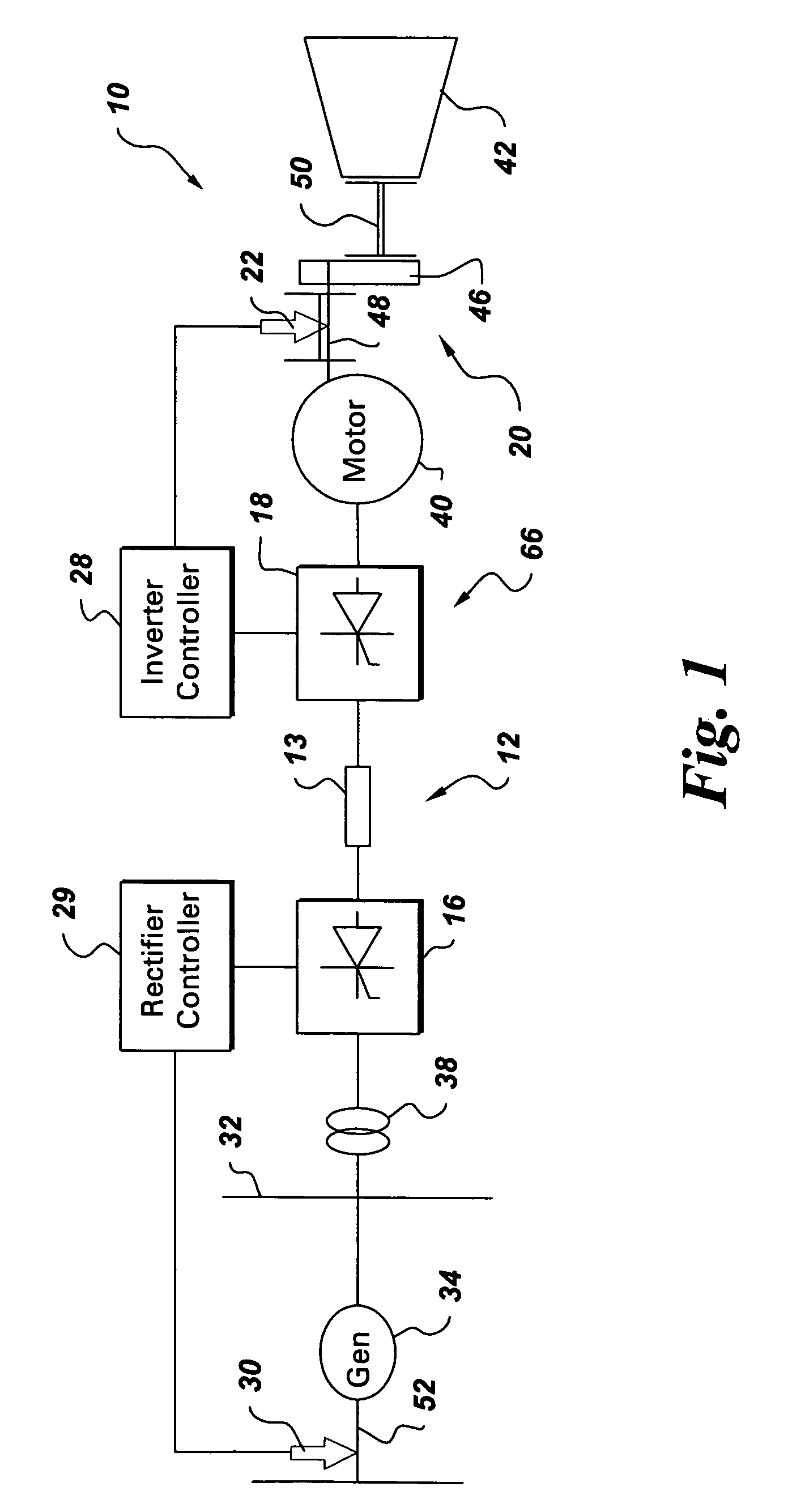
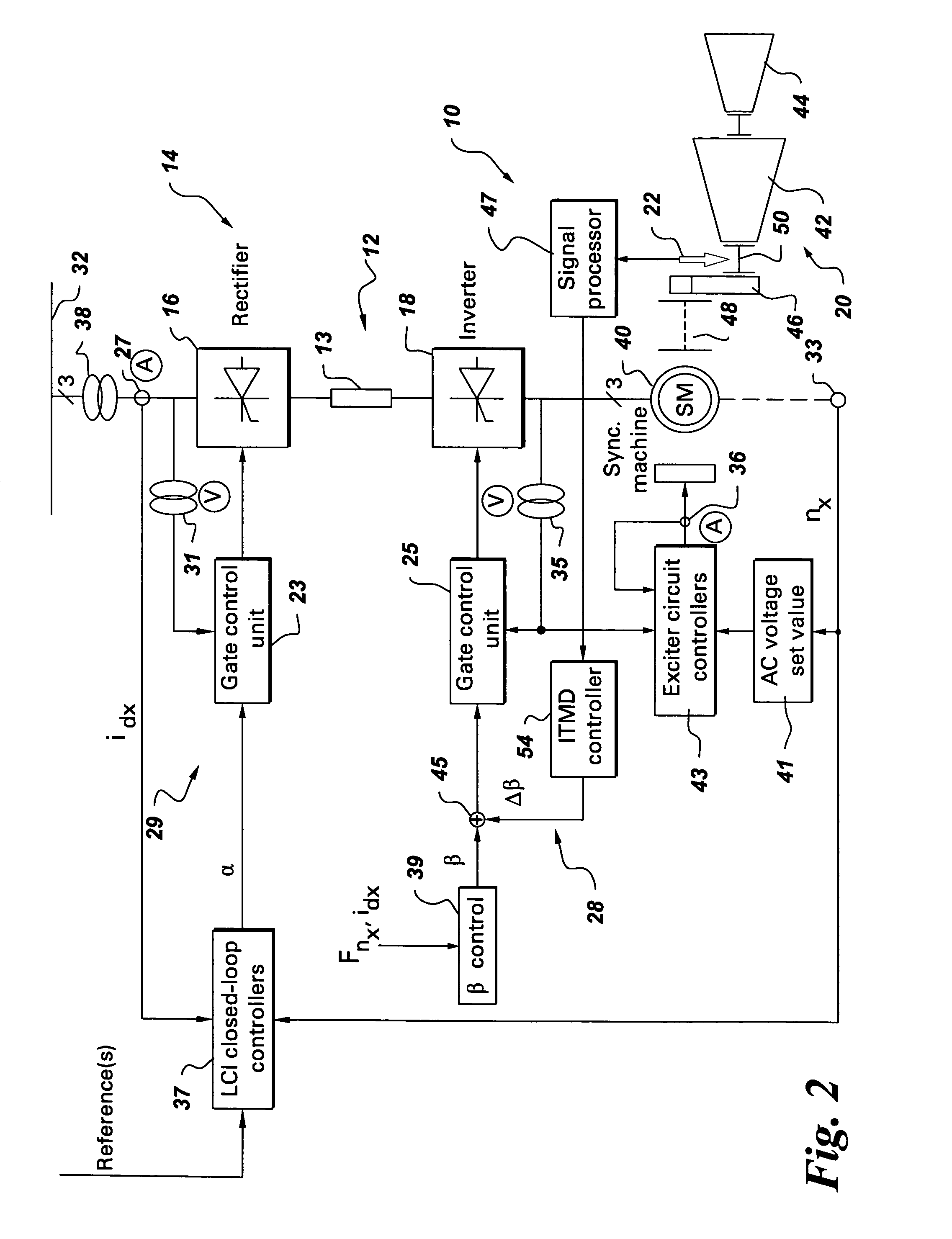
An integrated torsional mode damping method for a current source converter, including a rectifier, an inverter, and a DC link inductor coupled between the rectifier and the inverter, includes sensing a signal representative of torque on a shaft coupled to the inverter or rectifier; using the sensed signal for detecting a presence of a torsional vibration on the shaft; and damping the torsional vibration by modulating active power through the respective inverter or rectifier.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
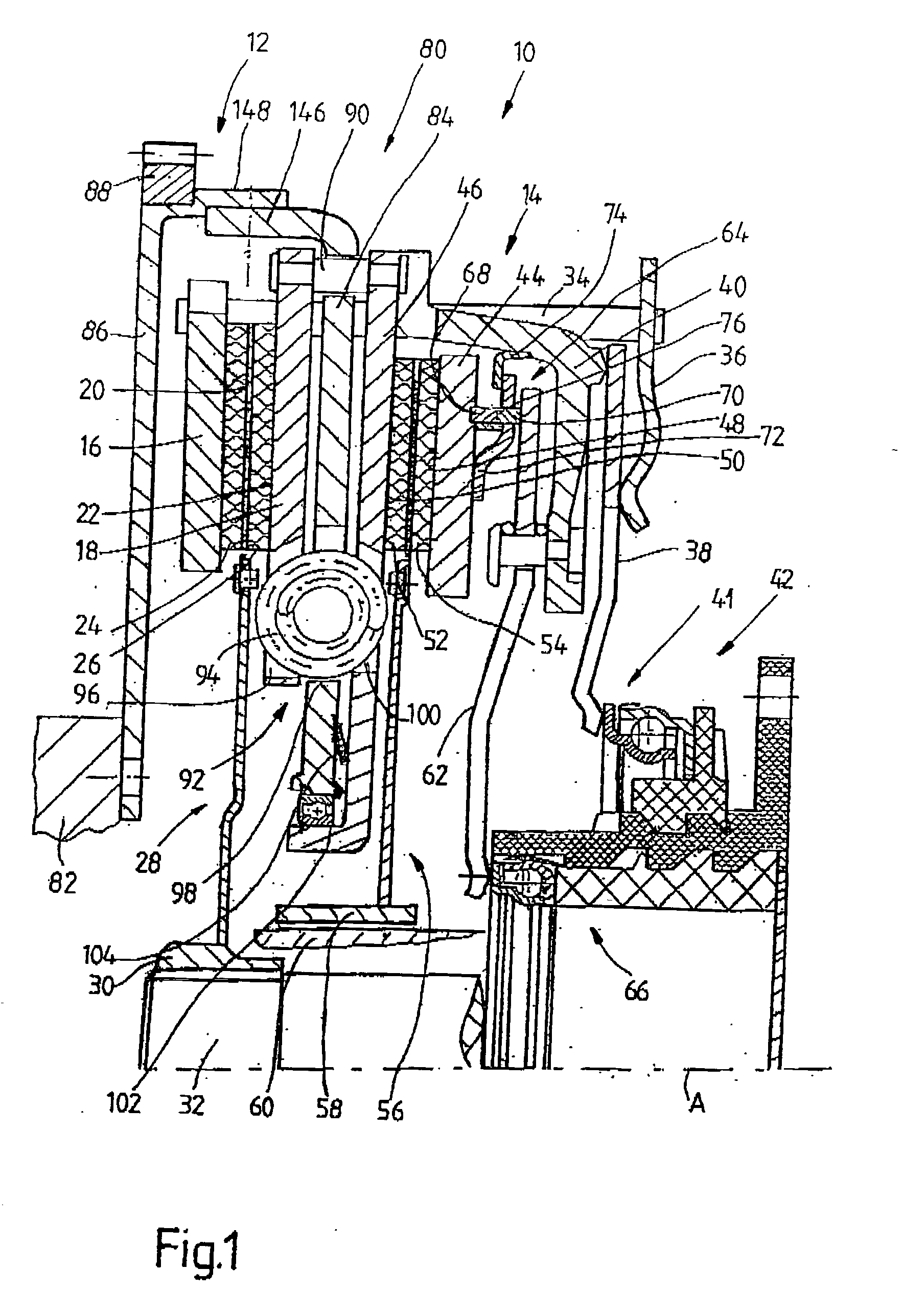
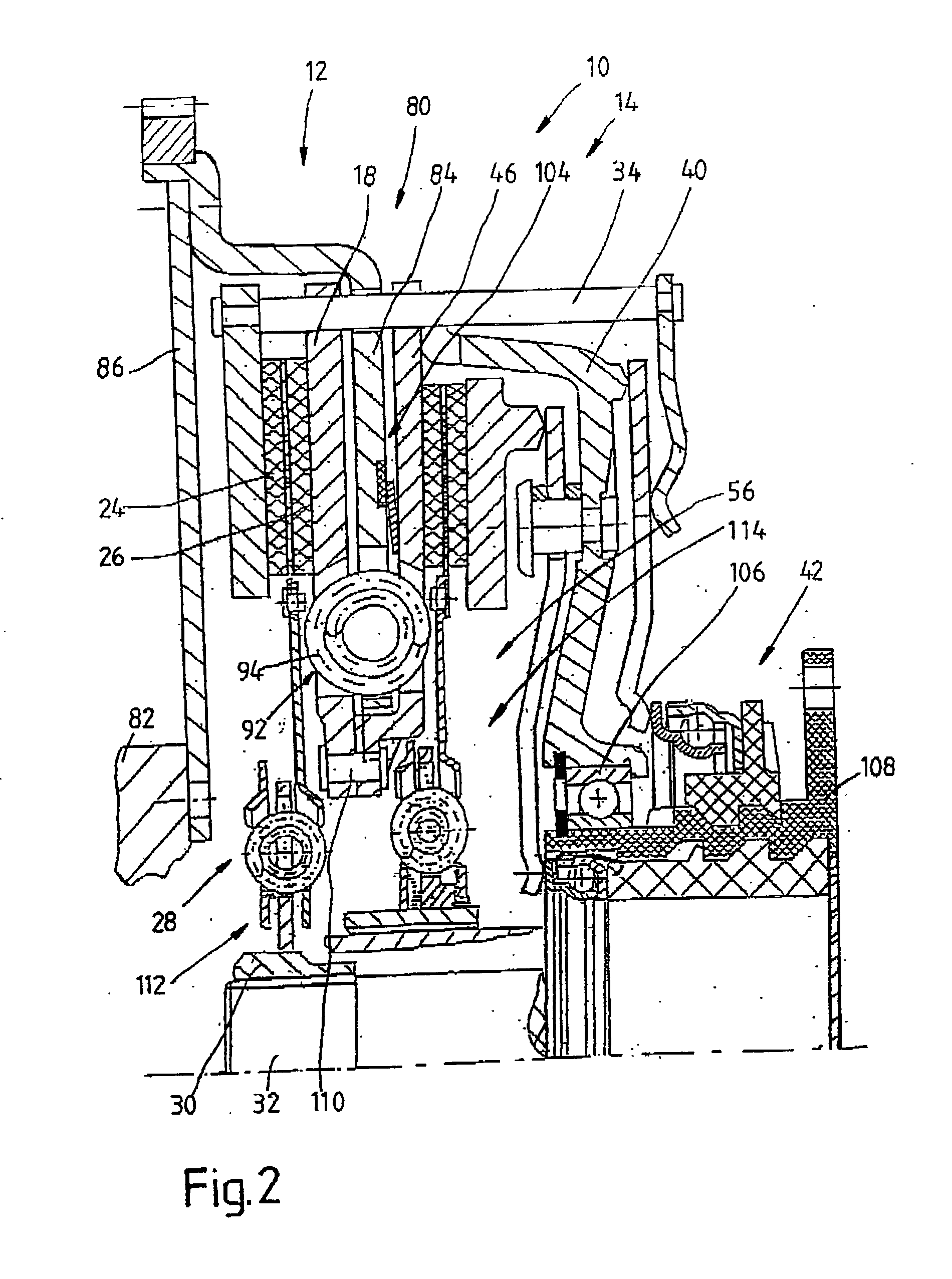
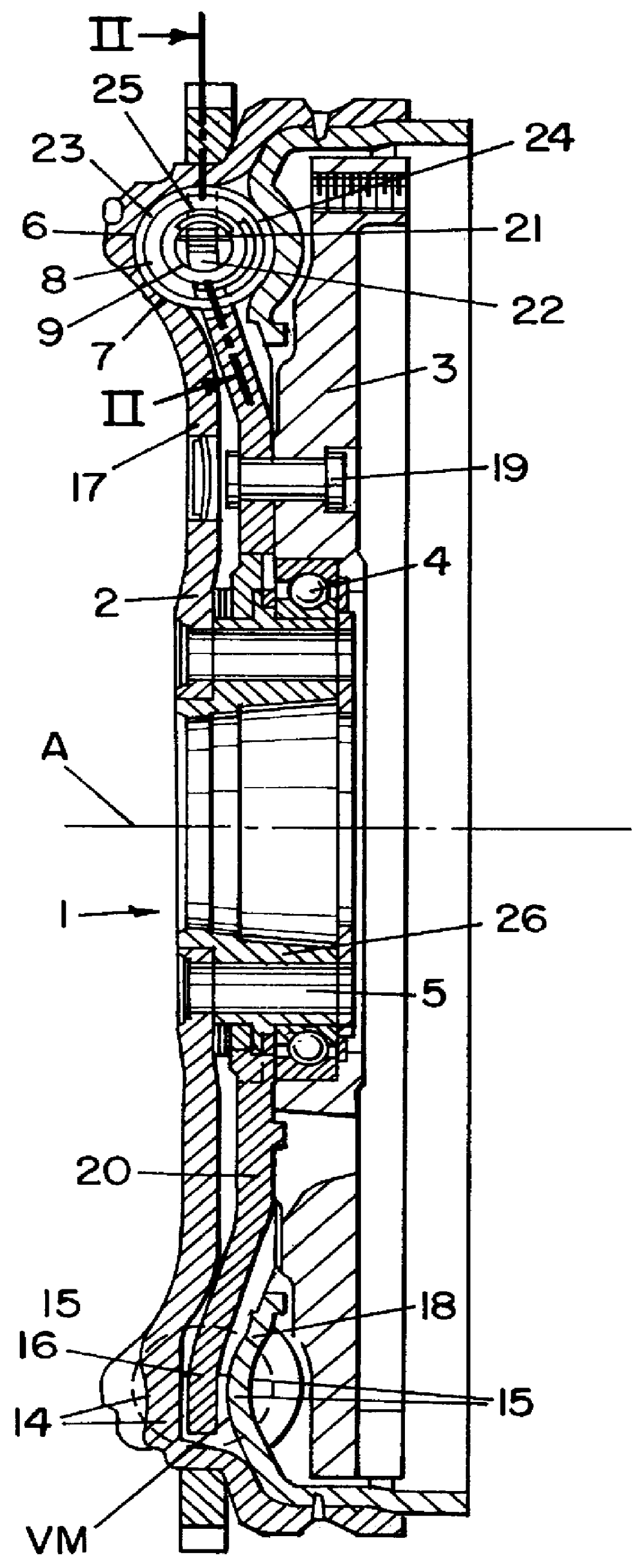
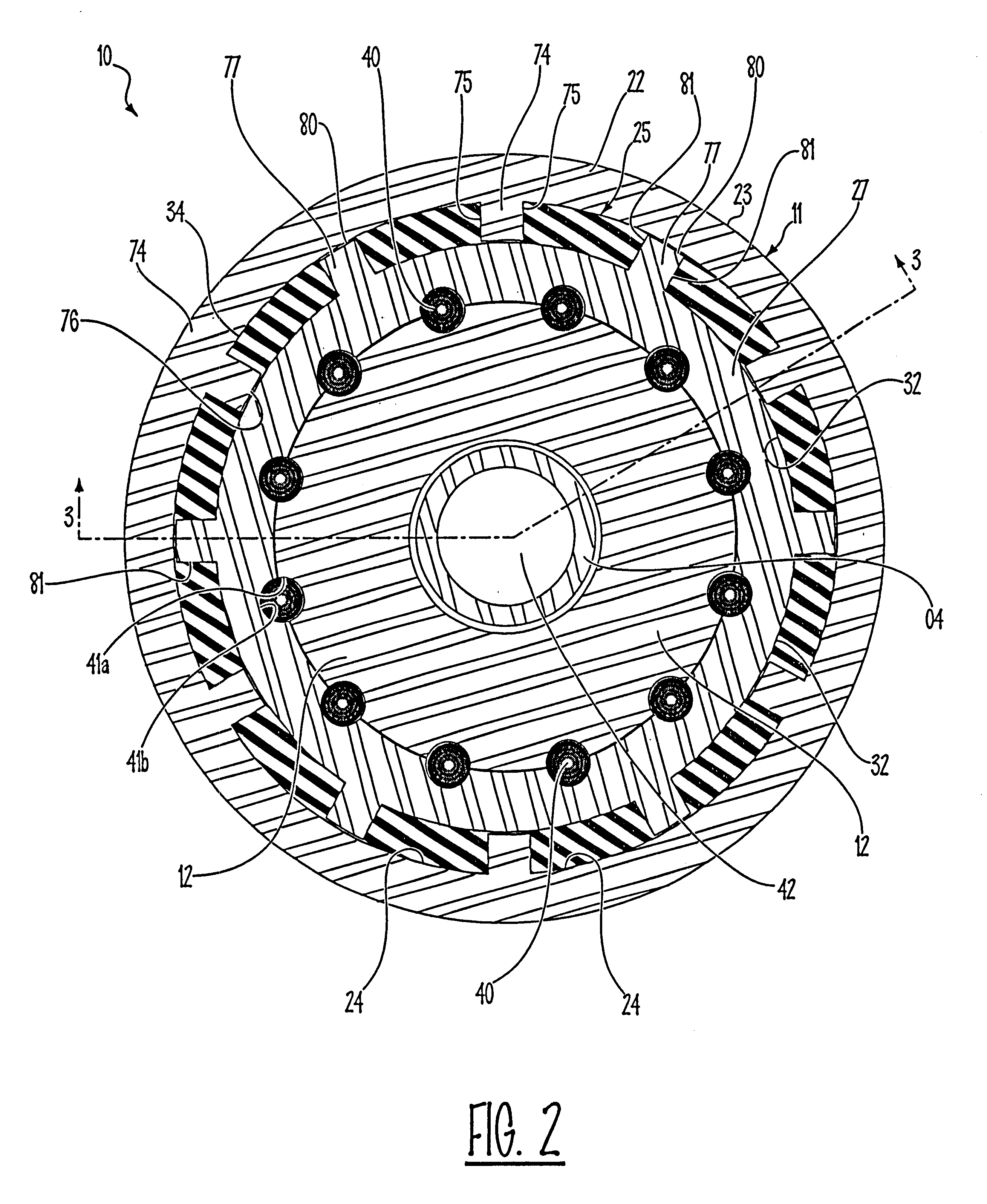
Lockup clutch with a compensation flywheel mass at the torsional vibration damper
A lockup clutch at a hydrodynamic torque converter is constructed with a torsional vibration damper which has a drive-side transmission element and a driven-side transmission element which is rotatable relative to the latter. Both of the transmission elements are provided with driving devices for driving elastic elements of a damping device. A carrier for a compensation flywheel mass is associated with the driven-side transmission element, wherein the carrier is connected with the turbine wheel on the one hand and with the driven-side driving device of the elastic elements on the other hand so as to be fixed with respect to rotation relative thereto and is provided at least with a cutout for receiving the compensation flywheel mass. The cutout has a guide path at least in its area of contact with the compensation flywheel mass, which guide path allows a movement of the compensation flywheel mass with at least one component perpendicular to the radial direction at the carrier.
Owner:ZF FRIEDRICHSHAFEN AG
Torsional vibration damper
A torsional vibration damper having a hub carrying a radially projecting flange and an annular inertia mass defining an annular channel encompassing the radially projecting flange and an elastomeric member. An annular compression ring is attached to the opening of the annular channel to axially compress and extrude the elastomeric member to fill the annular channel around the radial flange within the inertia ring. Projections defining an intermittent annular inner rim of the inertia mass extend through openings between the spokes of the hub and cooperate with an annular outer rim of the inertia mass to retain the compression ring.
Owner:DAYCO IP HLDG +1
Hybrid vehicle drive for a motor vehicle
InactiveUS6102144AReducing and eliminating vibrationExcessive vibrationSuspensionsRotating vibration suppressionFrequency spectrumLoad torque
A hybrid vehicle drive for a motor vehicle includes an internal combustion engine and an electric machine which is selectively coupled with the internal combustion engine. The electric machine can be operated as a generator and as a motor. Regulation device which responds to a reference signal predetermined by a reference signal preset device are provided for the active damping of vibrations, especially torsional vibrations in the torque transmission path between the internal combustion engine and wheels of the motor vehicle driven by the latter. The regulation device also respond to sensing device which deliver an actual-value vibration signal containing vibration information about a rotating structural component of the motor vehicle and control the load torque exerted on the internal combustion engine by the electric machine for reducing or eliminating the vibrations of the structural component. An analysis device for determining a frequency spectrum of the actual-value vibration signal is associated with the regulation device. The reference signal preset device establishes a reference signal with predetermined frequency spectrum. The regulation device control the frequency spectrum of the load torque exerted on the internal combustion engine by the electric machine such that excessive spectral vibrations of the actual-value vibration signal are reduced or eliminated.
Owner:ZF FRIEDRICHSHAFEN AG
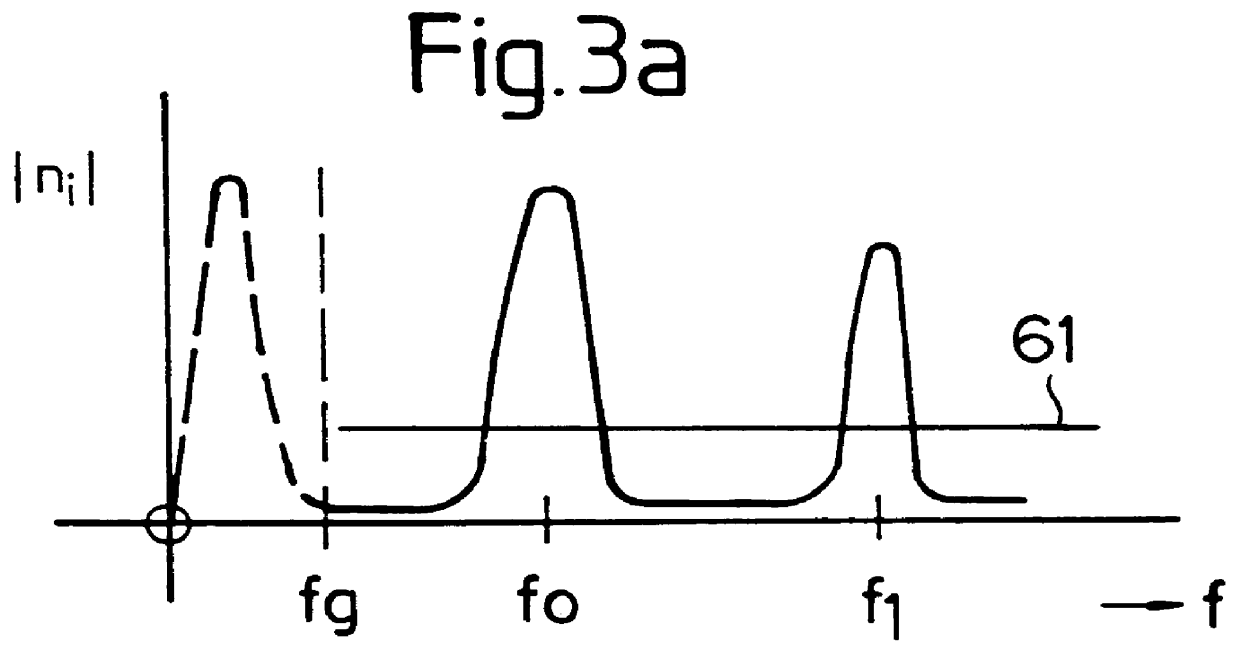
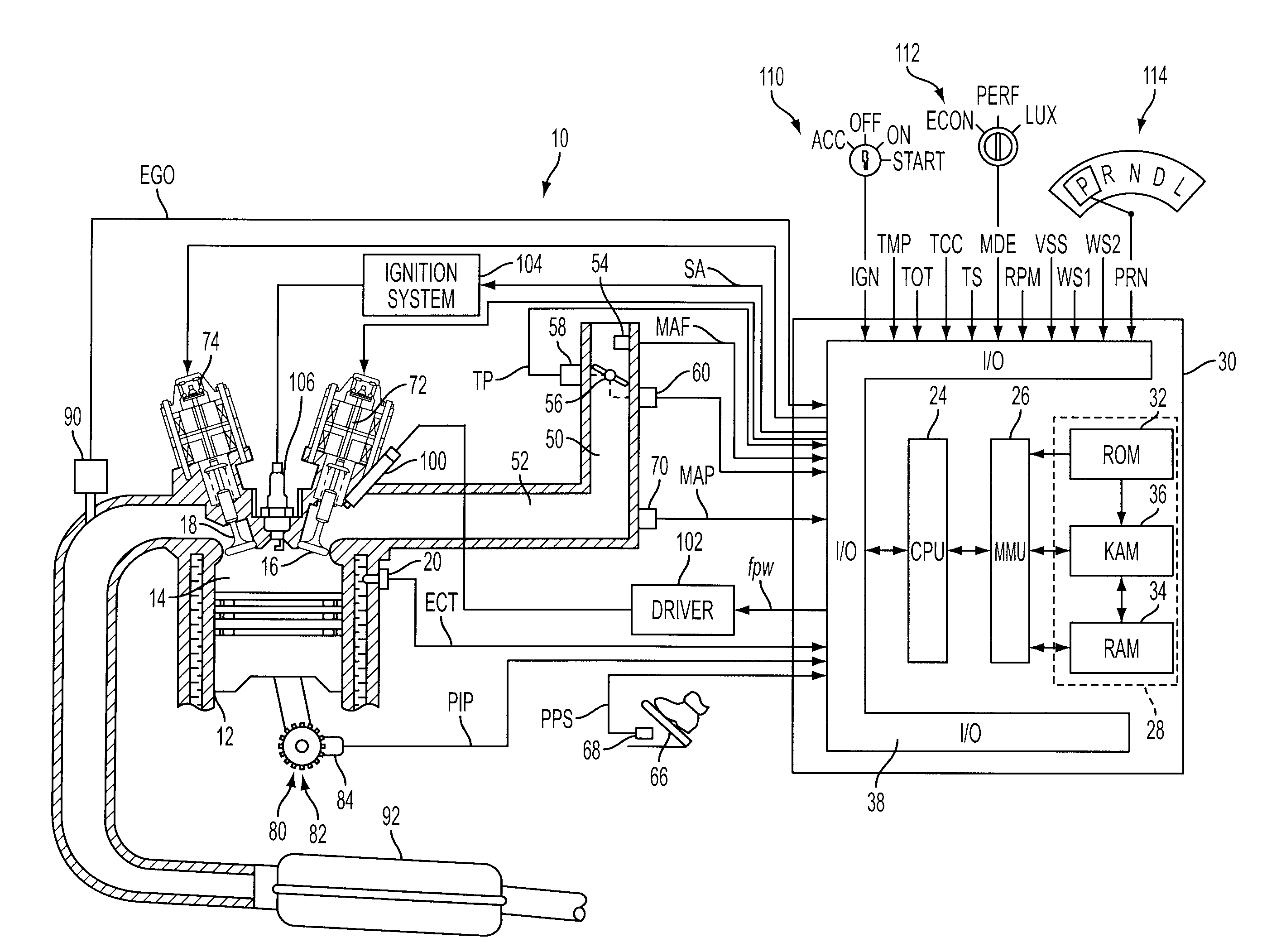
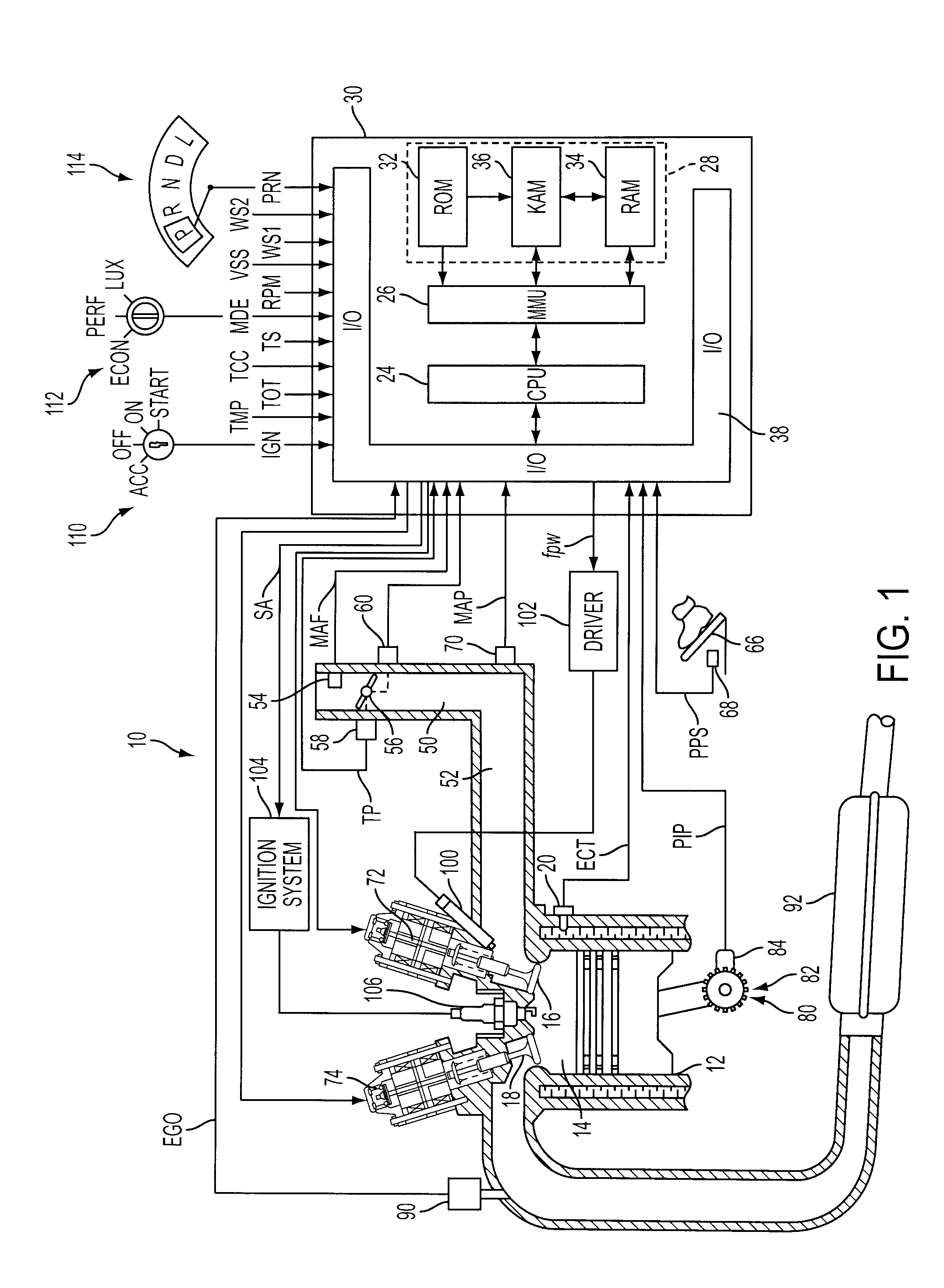
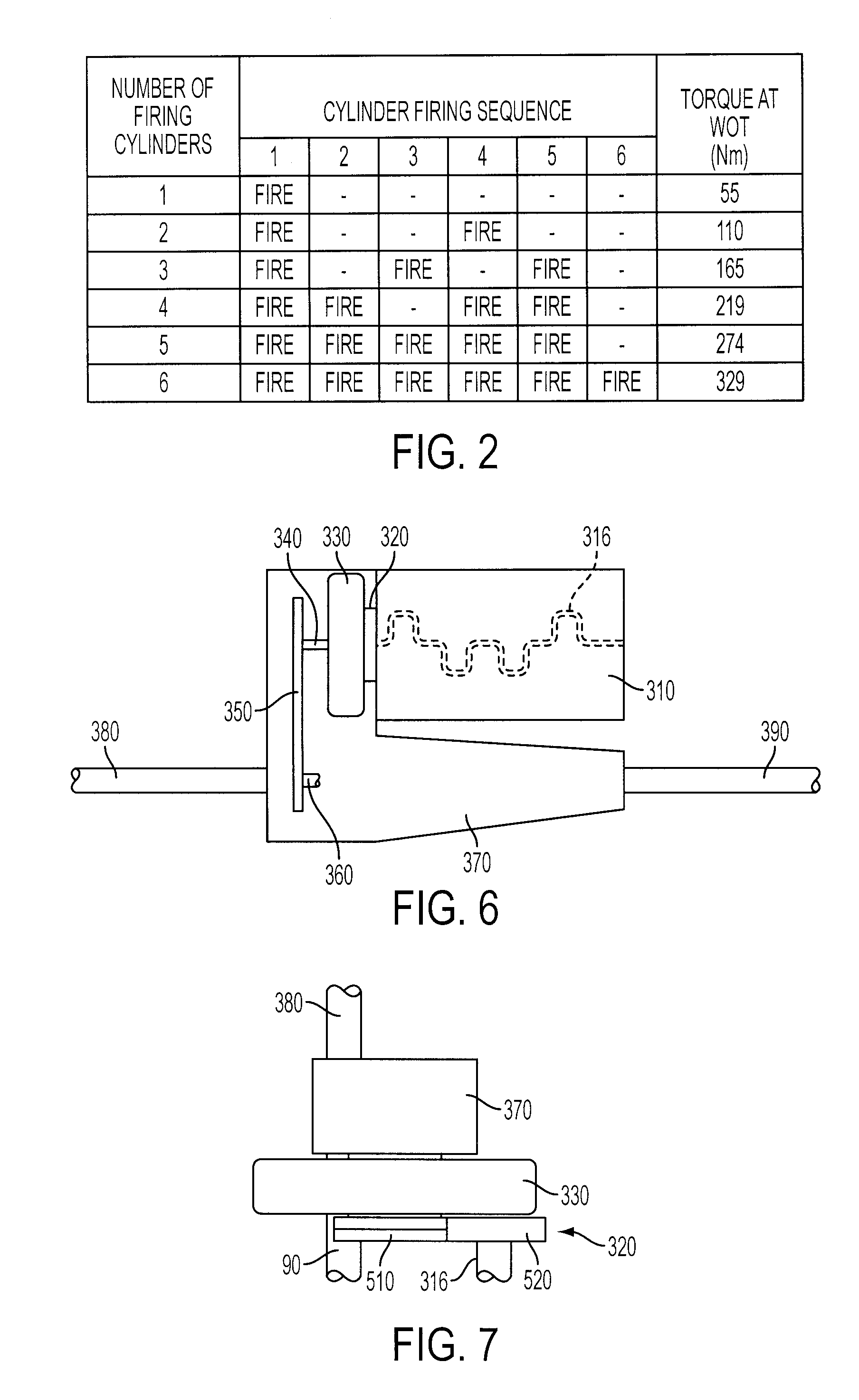
Variable Displacement Engine Operation With NVH Management
InactiveUS20080154468A1Reduce and eliminate torque reactionNo backlashAnalogue computers for vehiclesDigital data processing detailsClose couplingDrivetrain
A system and method for controlling an internal combustion engine operable with a first cylinder firing frequency and a second cylinder firing frequency to reduce or eliminate transmission of torsional vibrations associated with the second cylinder firing frequency to reduce or eliminate constraints on reduced displacement mode operation using a closely coupled drive train component rotating in an opposite direction relative to rotating components of the engine. A close coupling device allows the inertia of the counter-rotating elements to reduce or eliminate the torque reaction of the drivetrain associated with acceleration and deceleration of the engine crankshaft in response to the second cylinder firing frequency in the reduced displacement mode.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Apparatus and method for an ultrasonic medical device operating in torsional and transverse modes
InactiveUS20050187513A1Effective timeSimple, user-friendlySurgeryChiropractic devicesCavitationTransducer
The present invention provides an apparatus and a method for an ultrasonic medical device operating in a torsional mode and a transverse mode. An ultrasonic probe of the ultrasonic medical device is placed in communication with a biological material. An ultrasonic energy source is activated to produce an electrical signal that drives a transducer to produce a torsional vibration of the ultrasonic probe. The torsional vibration produces a component of force in a transverse direction relative to a longitudinal axis of the ultrasonic probe, thereby exciting a transverse vibration along the longitudinal axis causing the ultrasonic probe to undergo both a torsional vibration and a transverse vibration. The torsional vibration and the transverse vibration cause cavitation in a medium surrounding the ultrasonic probe to ablate the biological material.
Owner:CYBERSONICS
Integrated torsional mode damping system and method
InactiveUS20060232250A1Damp torsional vibrationDC motor speed/torque controlEmergency protective circuit arrangementsInductorTorsional vibration
An integrated torsional mode damping method for a current source converter, including a rectifier, an inverter, and a DC link inductor coupled between the rectifier and the inverter, includes sensing a signal representative of torque on a shaft coupled to the inverter or rectifier; using the sensed signal for detecting a presence of a torsional vibration on the shaft; and damping the torsional vibration by modulating active power through the respective inverter or rectifier.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Apparatus And Method For Damping Vibration In A Drill String
ActiveUS20120228028A1Reducing drill string torsional vibrationLimiting maximum angular velocityDrilling rodsDirectional drillingMagnetorheological fluidAngular velocity
An apparatus and method for damping vibration, especially torsional vibration due to stick-slip, in a drill string, Sensors measure the instantaneous angular velocity of the drill string at one or more locations along the length of the drill string. One or more vibration damping modules are also spaced along the length of the drill string. When torsional vibration above a threshold is detected, the damping module imposes a reverse torque on the drill that dampens the torsional vibration. The reverse torque can be created by imparting a frictional resistance to the rotation of the drill string. The frictional resistance can be created externally, by extending friction pads from the damping module so that they contact the bore hole wall and drag along the bore hole as the drill string rotates, or internally by anchoring a housing mounted on the drill string to the wall of the bore hole and then imposing frictional resistance on a fluid, such as a magnetorheological fluid, flowing within the drill string.
Owner:APS TECH
Method and apparatus for applying vibrations during borehole operations
A method of conducting borehole operations using a system including an elongate tubular conveyance that is moved through the borehole, the method comprising imposing a torsional vibration at a predetermined frequency on the tubular conveyance as it is moved through the borehole:wherein the predetermined frequency is obtained by determining the frequency-dependent mobility of the system based on the relationship between rotational velocity and torque for the system; and imposing torsional vibrations at a frequency where the relationship is optimised.
Owner:MISC
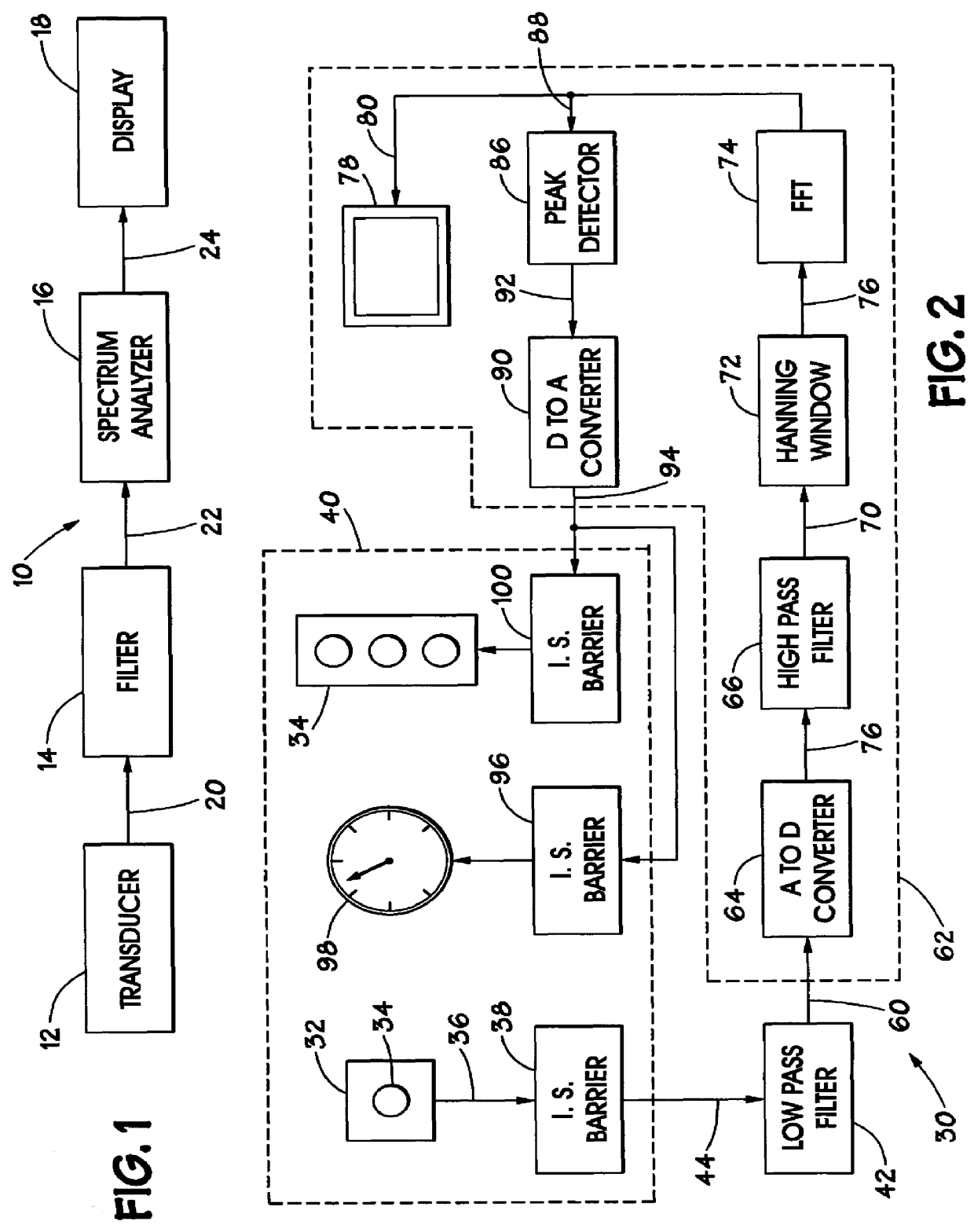
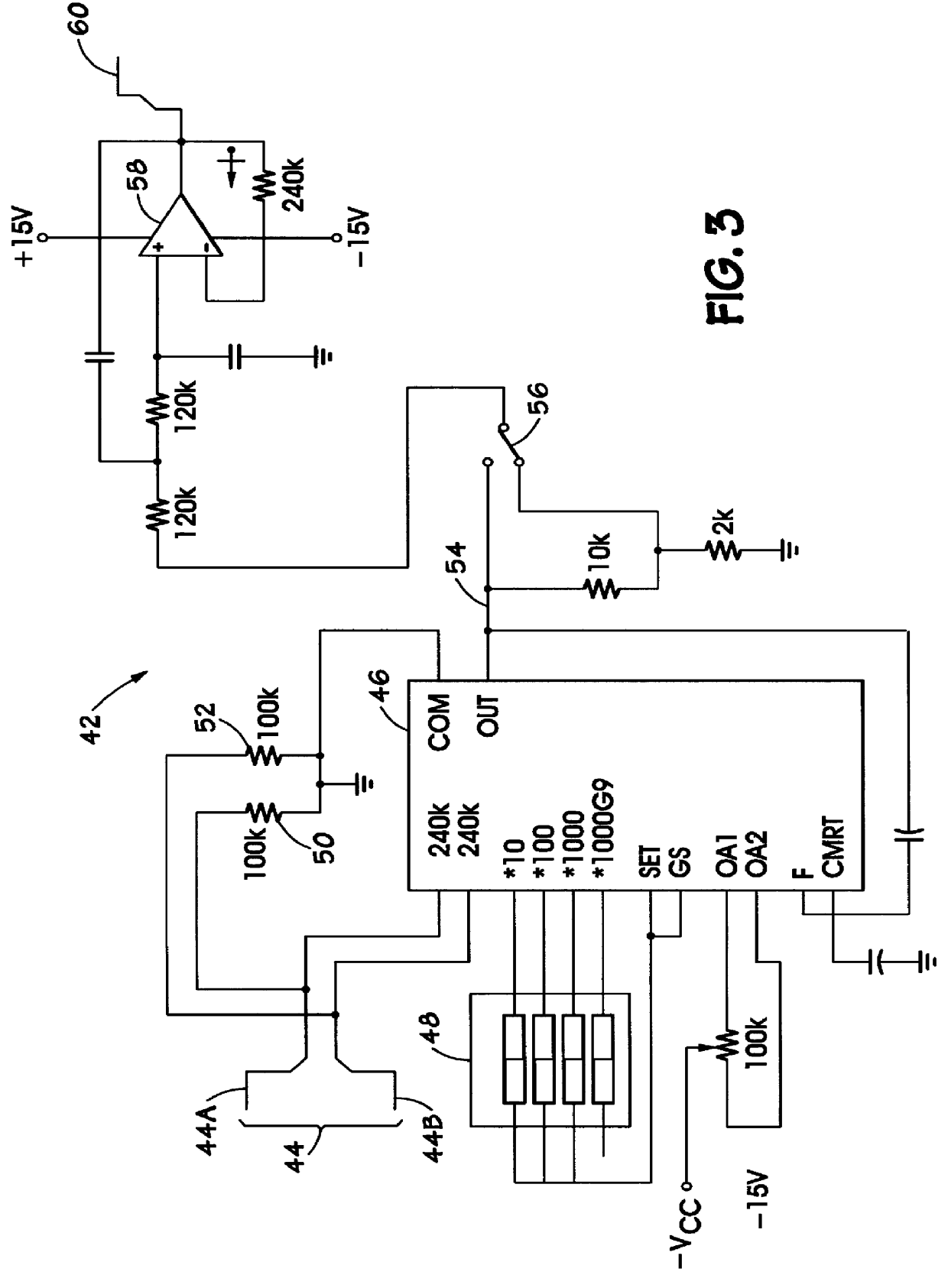
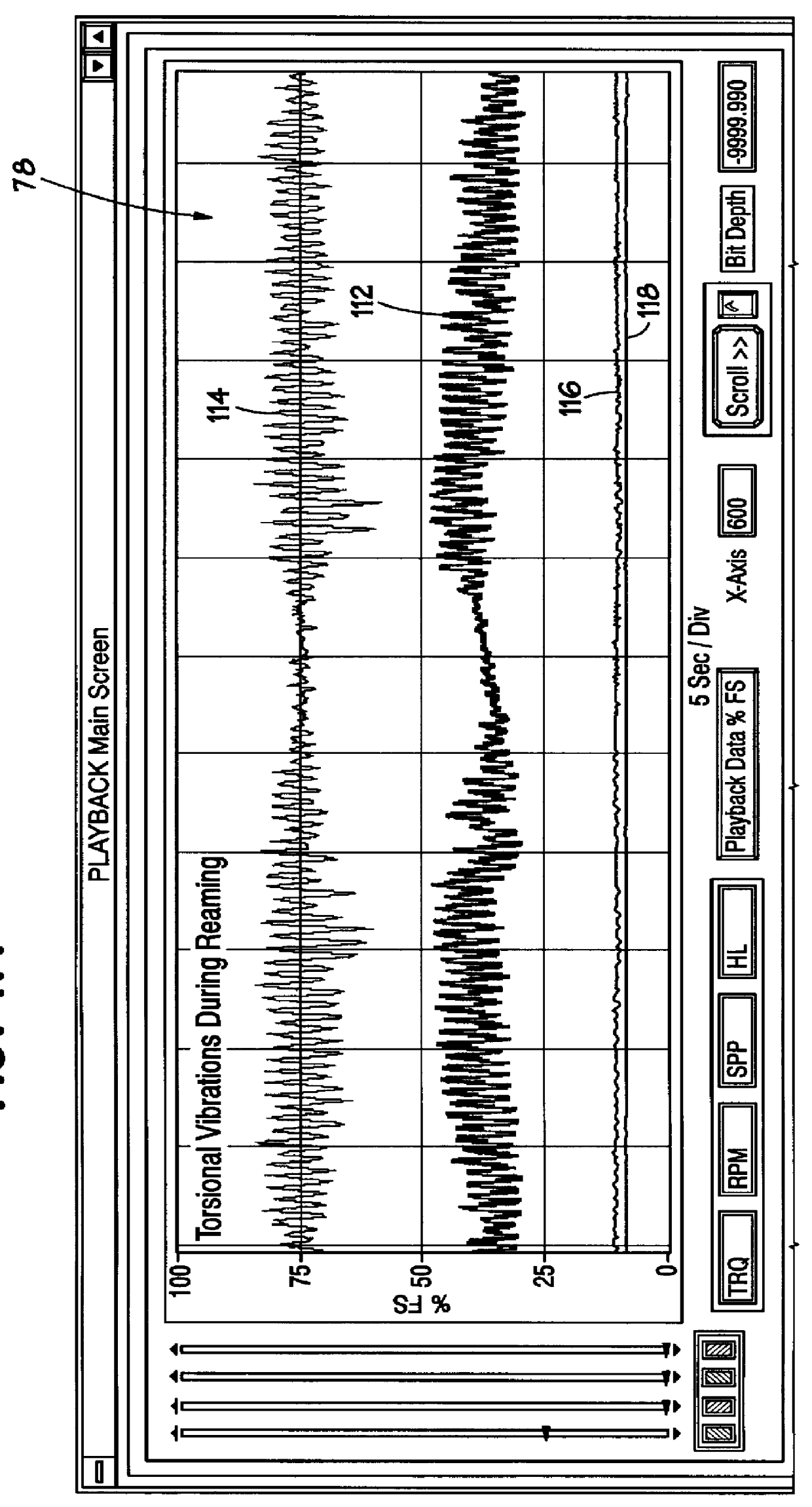
Method and apparatus for sensing and displaying torsional vibration
A method and apparatus for sensing and displaying the magnitude of torsional vibrations. A transducer provides a signal indicative of the torsional vibrations being experienced by a rotating member. The magnitude of the frequency components of the signal are determined and displayed to an operator who may take corrective action.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Coupling vibration ultrasonic hand piece
ActiveUS6955680B2Shorten speedReduce vibrationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgical instrument detailsRotation velocityLongitudinal vibration
Problems to be SolvedSurgical operation or others excellent in operability, safety, operation efficiency and precision are realized by outputting a vertical-torsional composite vibration through conversion processing of the longitudinal vibration from an ultrasonic oscillation mechanism and reducing the displacement speed of the non-working plane in a female portion less than the speed of the working plane.Means to Solve the ProblemA configuration, comprising an ultrasonic oscillation mechanism composed of a longitudinal vibration element, a backing plate and a front plate for generating an ultrasonic vibration, a horn coupled with the ultrasonic oscillation mechanism for amplifying the vibration transmitted from said ultrasonic oscillation mechanism, a vibration conversion mechanism for converting the vibration transmitted from said ultrasonic oscillation mechanism into a composite vibration composed of a longitudinal vibration in the horn central axial direction and a torsional vibration having the horn central axis as fulcrum, and a female portion provided with a working plane and disposed at said horn tip, wherein said ultrasonic oscillation mechanism is composed of one or more groove portions formed on the circumferential surface of the horn or said backing plate, and a speed variation mechanism of torsional vibration in said composite vibration is formed in the female portion, in order to reduce the reciprocating rotation speed of the non-working plane less than the speed of the working plane.
Owner:STRYKER CORP
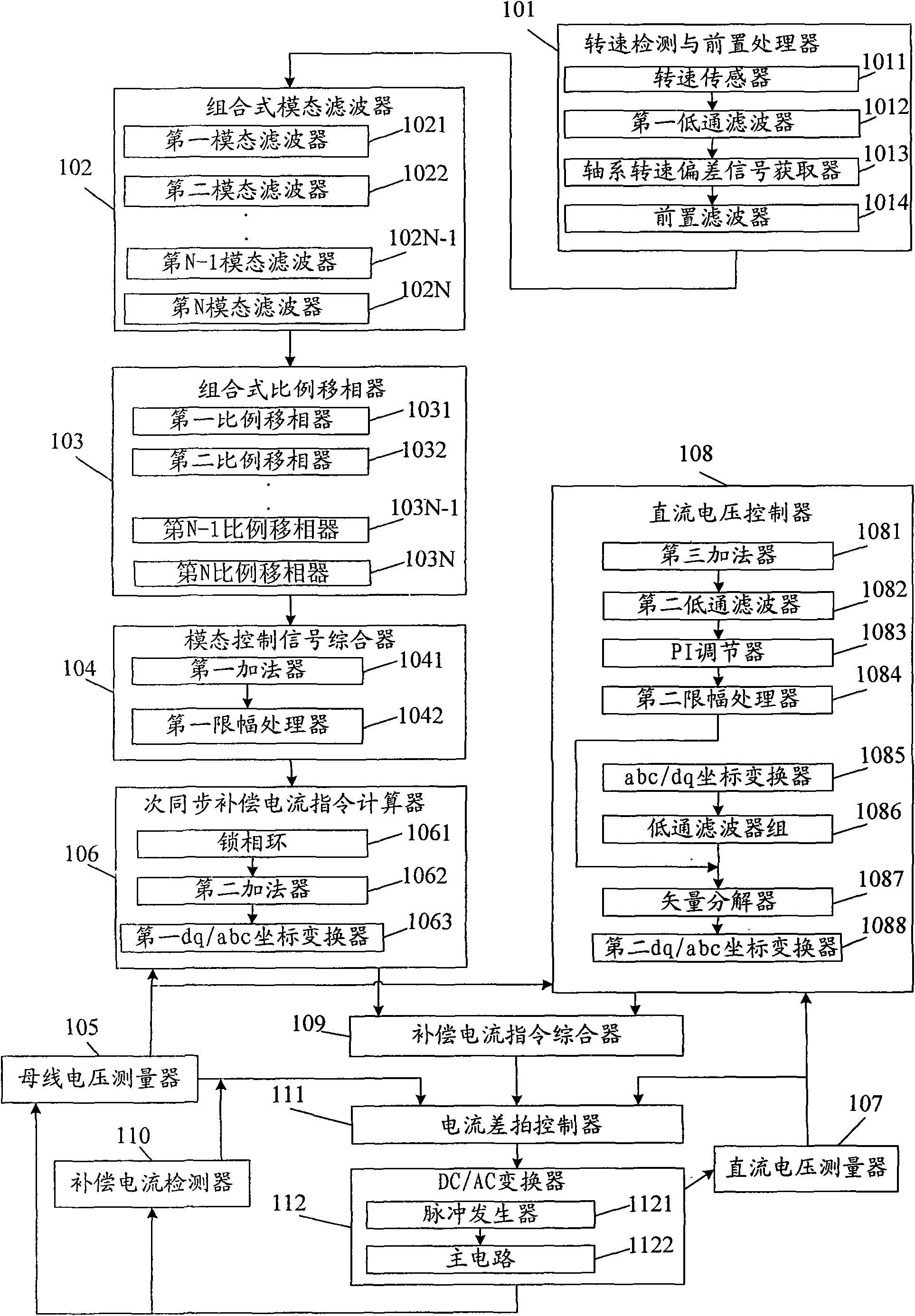
Subsynchronous damping control system for effectively inhibiting subsynchronous resonance and oscillation
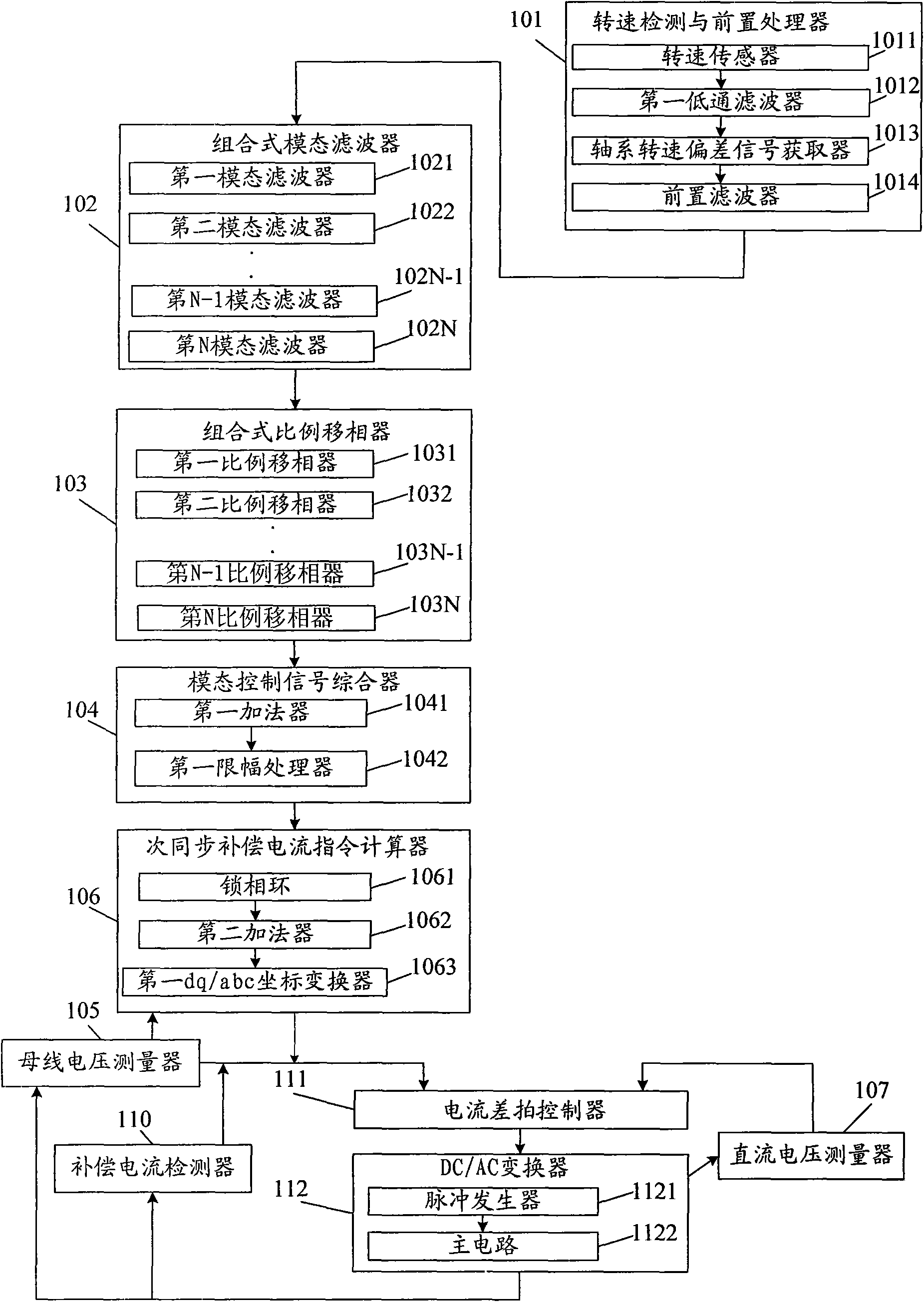
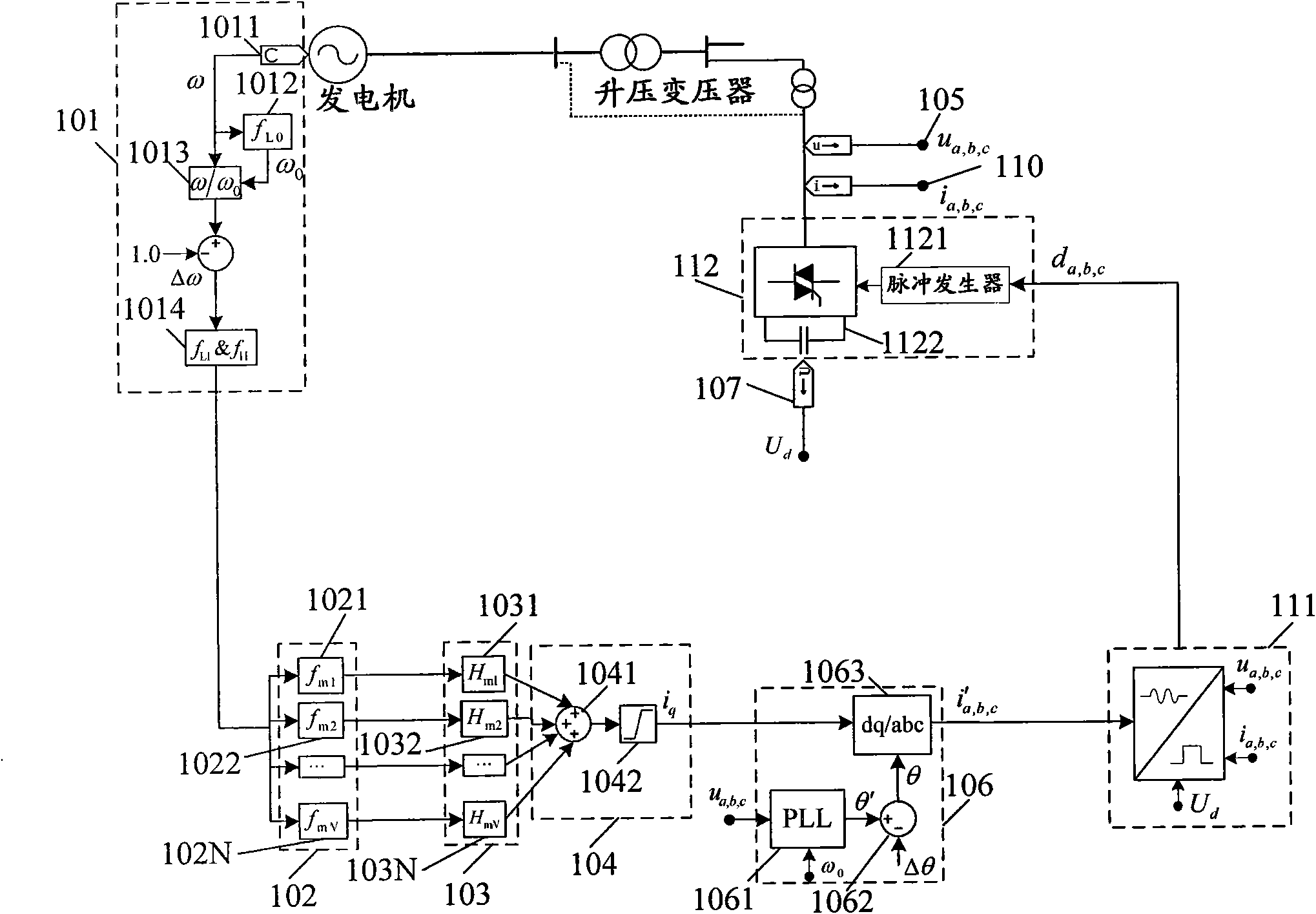
InactiveCN101615791AReduce torsional vibration fatigue lossSolve Oscillation ProblemsReactive power adjustment/elimination/compensationElectric generator controlModal filterMode control
The invention discloses a subsynchronous damping control system for effectively inhibiting subsynchronous resonance and oscillation, belonging to the technical field of stableness and control of the electrical power systems. The system comprises a rotary speed checking pre-processor, a combined mode filter, a combined proportion phase shifter, a mode control signal synthesizer, a subsynchronous compensating current command calculator, a current beat controller and a DC / AC convertor. The invention inhibits shafting torsional vibration by injecting subsynchronous / supersynchronous current complementary with machine set shafting modal frequency, and can simultaneously inhibit multiple torsional vibration modals, so that the invention has comprehensive function, can solve the multi-modal subsynchronous resonance and oscillation problems of the electrical power system, improves the supersynchronous stability of the system and lowers shafting torsional vibration fatigue loss of a high-rating generator.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method for manufacturing a micromechanical device
InactiveUS6369931B1Slight frictionIncrease electrostatic forceDecorative surface effectsSolid-state devicesEngineeringTorsional vibration
A method for manufacturing a micromechanical device, in particular a micromechanical vibrating-mirror device, having the following steps: making available a three-layer structure having a first layer, a second layer and a third layer, the second layer lying between the first and the third layers; etching through the first layer up to the second layer to produce an island region, lying on the second layer, which is joined to region of the first layer surrounding the island region by way of one or more connecting webs, and etching through a region of the third layer up to the second layer and removing a region of the second layer below the island region in such a way that the island region can perform movements, preferably torsional vibrations, about the one or more connecting webs, the torsional vibrations having such an amplitude that a part of the island region extends into the etched-through region of the third layer.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
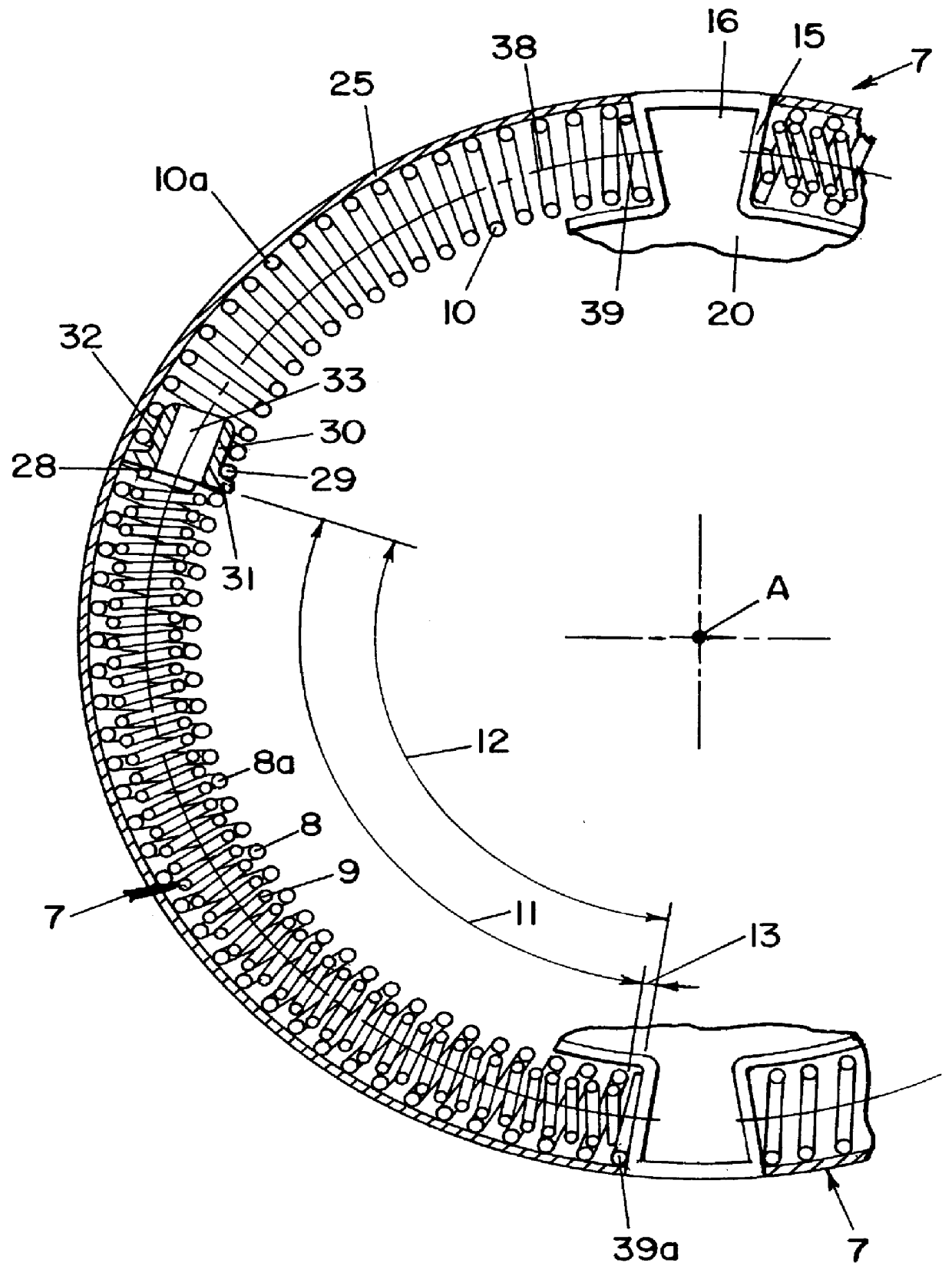
Torsional vibration damper
A torsional vibration damper on the bridging clutch of a hydrodynamic clutch arrangement has a first connecting device, which can be brought into working connection with the clutch housing and with a drive-side transmission element. The drive-side transmission element is connected via first energy-storage devices to an intermediate transmission element. The torsional vibration damper also has a second connecting device for establishing a working connection via second energy-storage devices between the intermediate transmission element and a takeoff-side transmission element, which is connected to a takeoff-side component of the hydrodynamic clutch arrangement. The intermediate transmission element accepts a mass element, located operatively between the two connecting devices.
Owner:ZF FRIEDRICHSHAFEN AG
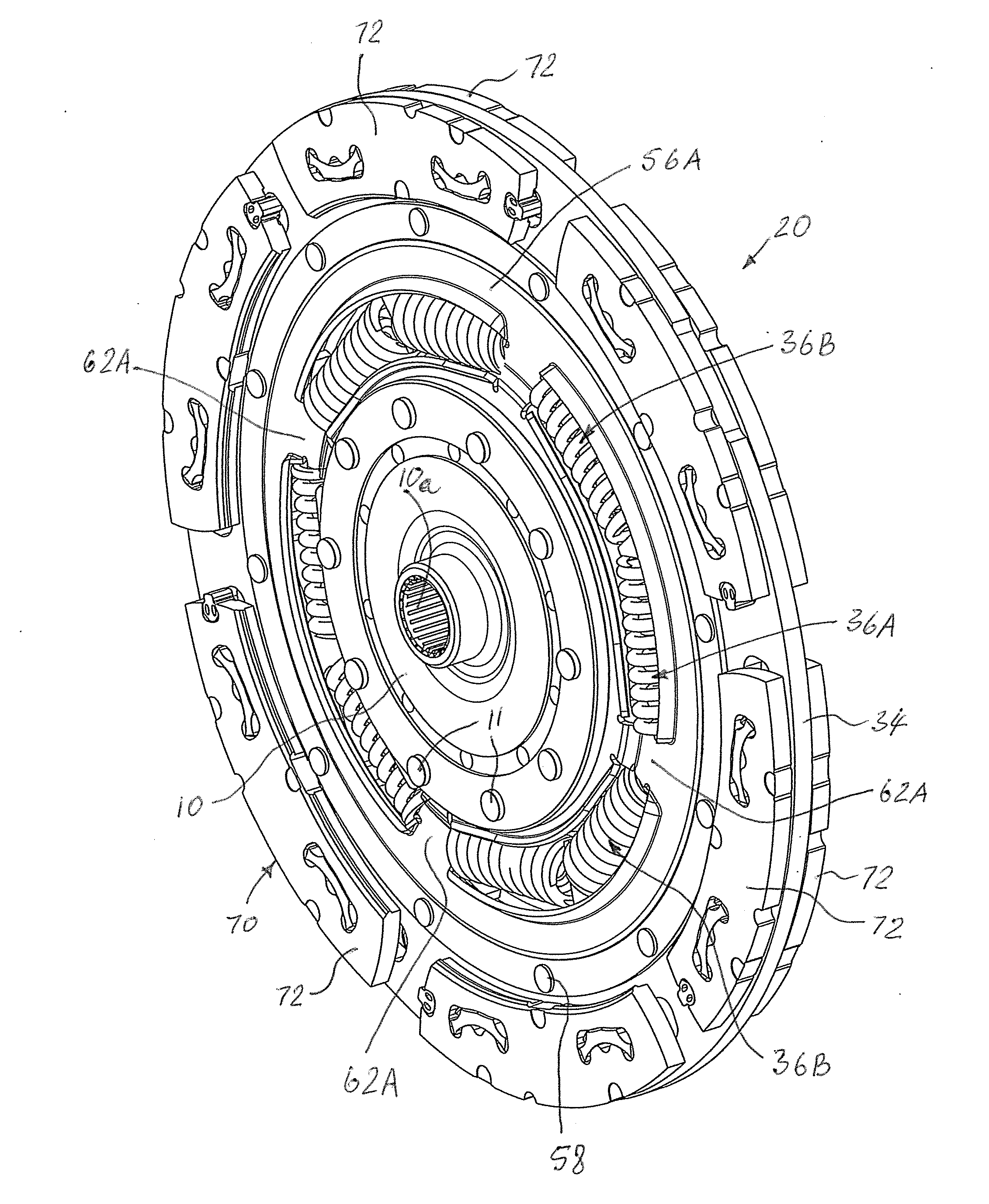
Multi-clutch arrangement
InactiveUS20030079953A1Large amount of space is occupiedIncrease in driving comfortYielding couplingFriction clutchesMobile vehicleEngineering
A multi-clutch arrangement, especially a dual clutch for motor vehicles, comprising a first clutch area with a first pressure plate arrangement, with a first opposing support arrangement, and with a first clutch disk arrangement , which can be clamped between the first pressure plate arrangement and the first opposing support arrangement to transmit torque via the first clutch area; and a second clutch area with a second pressure plate arrangement, with a second opposing support arrangement, and with a second clutch disk arrangement, which can be clamped between the second pressure plate arrangement and the second opposing support arrangement to transmit torque via the second clutch area. A torsional vibration damper arrangement is assigned to at least one of the clutch areas, and where-relative to an axis of rotation (A)-the torsional vibration damper arrangement is arranged at least partially in the axial area of the first clutch area and / or of the second clutch area.
Owner:ZF SACHS AG
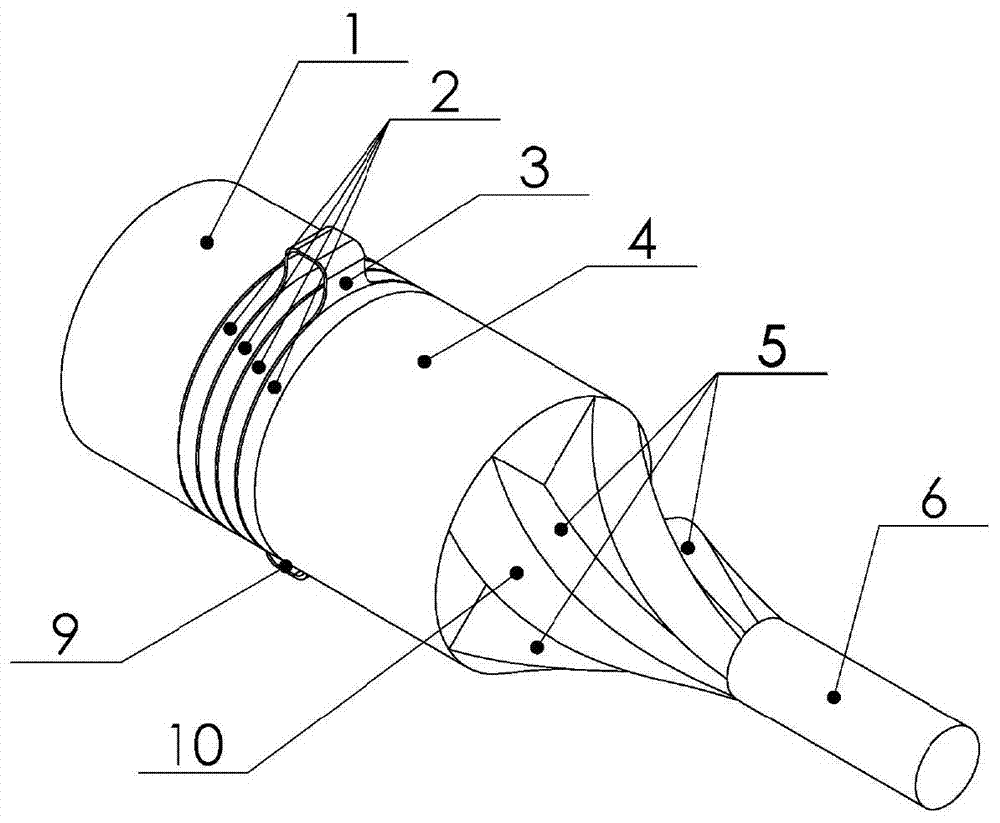
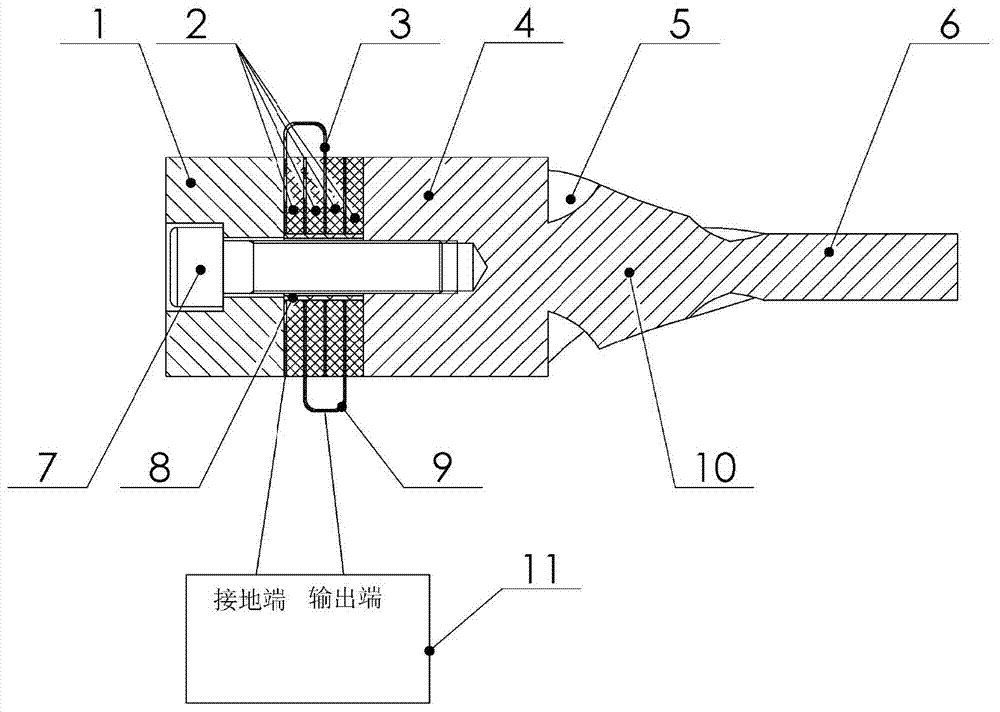
Longitudinal torsion composite supersonic vibration machining device
ActiveCN103920635ASimplify machining complexityLow costMechanical vibrations separationTransformerEngineering
The invention discloses a longitudinal torsion composite supersonic vibration machining device. The longitudinal torsion composite supersonic vibration machining device comprises a longitudinal supersonic vibration energy converter and an ultrasonic amplitude transformer arranged at the front end of the longitudinal supersonic vibration energy converter and integrally connected with the longitudinal supersonic vibration energy converter. The longitudinal supersonic vibration energy converter comprises a back cover plate, a piezoelectric ceramic piece, an electrode plate, a front cover plate, an insulating sleeve and a pre-tightening bolt for connecting the back cover plate, the piezoelectric ceramic piece, the electrode plate, the front cover plate and the insulating sleeve. The ultrasonic amplitude transformer comprises an amplitude transformer index section and an amplitude transformer cylindrical section, the amplitude transformer index section and the front cover plate are designed into a whole, the amplitude transformer cylindrical section is used for being connected with a machining tool, the surface of the amplitude transformer index section is provided with four same spiral grooves, part of longitudinal vibration generated by the longitudinal supersonic vibration energy converter can be converted into torsion vibration through the spiral grooves, and therefore the longitudinal torsion composite supersonic vibration can be generated one the end face of the amplitude transformer cylindrical section. The longitudinal torsion composite supersonic vibration machining device has the advantages of being simple in structure, large in torsion component, high in converting efficiency and the like.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Parallel hybrid vehicle
InactiveUS6840341B2Easy to have torsional vibrationSuppress torsional vibrationElectrical controlToothed gearingsDrive wheelDrive shaft
In a parallel hybrid vehicle, a controlling section controls an engine and a motor / generator, a torque from the engine and the motor / generator being transmitted to driven wheels via a transmission and a drive shaft. The controlling section comprises: an engine torque calculating section that calculates an engine torque and a torsional vibration suppression torque calculating section that calculates a torsional vibration suppression torque to suppress a torsional vibration developed on the drive shaft according to the engine torque calculated by the engine torque calculating section, the torsional vibration suppression torque calculated by the torsional vibration suppression torque calculating section being outputted from the motor / generator.
Owner:JATCO LTD
Torsional vibration excitation device and test bed of vehicle drive system
InactiveCN101865778AChange frequencyLarge amount of adjustmentVehicle testingMachine gearing/transmission testingElectric machineryDrive motor
The invention relates to a torsional vibration excitation device and a test bed of a vehicle drive system, comprising a torsional vibration excitation device, a wheel loading device, an inertia flywheel and a testing system. The torsional vibration excitation device is used for providing a torsional vibration excitation torque for the torsional vibration research of the drive system and providing power for the drive system. The wheel loading device is used for supporting wheels and simulating a carload acting on the wheels, pressing the wheels towards the inertia flywheel through a mechanical loading mode and locking the positions of the wheels. The testing system is used for collecting pull and pressure signals as well as rotate speed signals output by a sensor and analyzing the pull and pressure signals as well as the rotate speed signals. The torsional vibration excitation device comprises a driving motor, a driving gear shaft, an excitation gear shaft and an excitation motor, wherein the driving motor drives the driving gear shaft to rotate through the belt of the driving motor, the excitation motor drives the excitation gear shaft to rotate through the belt of the excitation motor, and the excitation gear shaft is coaxial with the driving gear shaft.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Resistive torsional mode damping system and method
InactiveUS7423411B2Emergency protective circuit arrangementsDynamo-electric converter controlElectrical resistance and conductanceControl signal
A resistive torsional mode damping system for a shaft of a machine includes: a sensor configured for sensing a signal representative of torque on the shaft; a controller configured for using the sensed signal for detecting a presence of a torsional vibration on the shaft corresponding to a natural frequency of the shaft and for generating control signals for damping the torsional vibration; and a damper including a damping converter and resistor coupled to a DC output of the damping converter, the damping converter being coupled to the machine through a power bus and having a power rating on the order of less than or equal to about five percent of a nominal power of the machine.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Rotating machine active balancer and method of dynamically balancing a rotating machine shaft with torsional vibrations
InactiveUS20060005623A1Rotating vibration suppressionRotating bodies balancingEngineeringTorsional vibration
An active balancer for dynamically balancing a rotating machine is provided. The active balancer has a balancer body which rotates with the rotating machine and at least one controllable position counter weight having a real-time adjustable position relative to the balancer body and the rotating machine inorder to produce an actively adjustable controllable counter weight balance force for dynamically balancing the rotating machine. The active balancer includes a spring with the balancer body mounted to the rotating machine through the spring wherein the balancer body mass resonates on the spring with a torsional vibration canceling frequency which cancels a torsional vibration of the rotating machine.
Owner:LORD CORP
Apparatus and method for an ultrasonic medical device operating in a torsional mode
InactiveUS20050187514A1Effective timeSimple, user-friendlySurgical instrument detailsCavitationTransducer
The present invention provides an apparatus and a method for an ultrasonic medical device operating in a torsional mode to treat a biological material. An ultrasonic probe of the ultrasonic medical device is placed in communication with the biological material. An ultrasonic energy source is activated to produce an electrical signal that drives a transducer to produce a torsional vibration of the ultrasonic probe. The torsional vibration produces a rotation and a counterrotation along the longitudinal axis of the ultrasonic probe that creates a plurality of torsional nodes and a plurality of torsional anti-nodes along a portion of the longitudinal axis of the ultrasonic probe resulting in cavitation along a portion of the longitudinal axis of the ultrasonic probe comprising a radially asymmetric cross section that ablates the biological material.
Owner:CYBERSONICS
Torsional vibration damper
InactiveUS6131487ASatisfactory supportEasy to manufactureRotating vibration suppressionYielding couplingCoil springAbutment
A composite flywheel has primary and secondary masses rotatable relative to each other against the resistance of a damper having arcuate coil springs and an abutment between neighboring end portions of such springs. The abutment can move in the circumferential direction of the masses and is preferably form-lockingly connected against loss to at least one of the springs. To this end, a portion of the abutment extends into the adjacent convolutions of the at least one spring and is engaged by such convolutions with a force which suffices to prevent unintentional separation of the at least one spring from the abutment in the axial direction of the at least one spring.
Owner:LUK LAMELLEN & KUPPLUNGSBAU BETEILIGUNGS KG
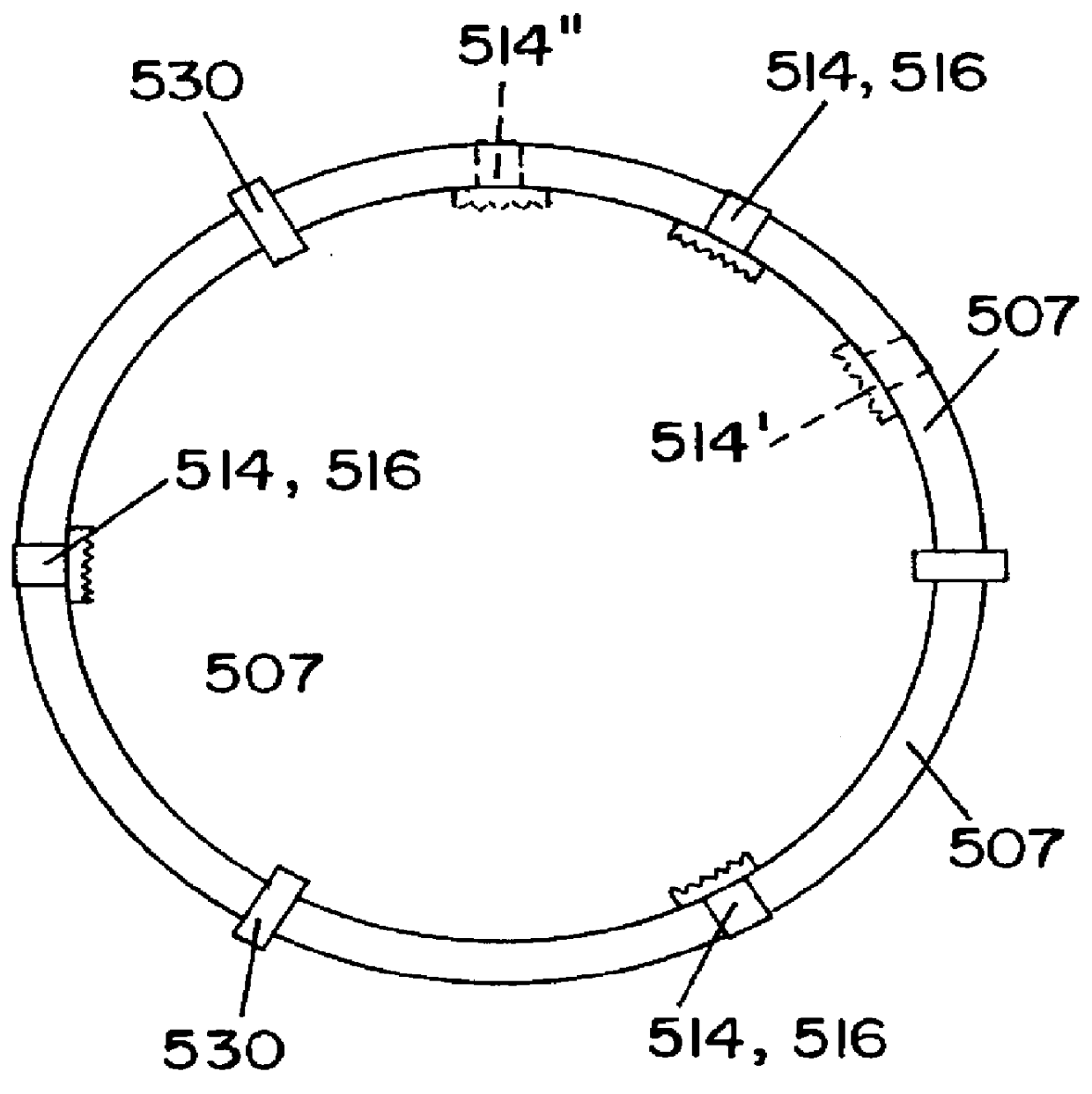
Torsional vibration damper for hydrokinetic torque coupling device
A torsional vibration damper of a hydrokinetic torque coupling device, comprises a driven plate rotatable about a rotation axis, an intermediate plate rotatably mounted about the driven plate coaxially with the rotation axis, a back plate rotatably mounted about the intermediate plate coaxially with the rotation axis, a plurality of circumferentially acting elastic members interposed between the driven plate and the intermediate plate, and a damper retainer plate non-moveably secured to the back plate coaxially with the rotation axis. The damper retainer plate is operatively connected to the elastic members. The driven plate, the intermediate plate and the back plate are aligned with each other along a radial axis perpendicular to said rotation axis.
Owner:VALEO EMBRAYAGES SAS
Drilling string torsional energy control assembly and method
InactiveUS20040238219A1Fast penetrationProlong lifeDrilling rodsDirectional drillingEnergy controlBrief periods
The present invention provides a torsional energy control assembly and method for eliminating slip-stick and / or drill bit oscillations comprising axial and / or rotational oscillations. In one preferred embodiment, the assembly permits slippage between an upper portion of the drilling string and a lower portion of a drill string. The rotational control assembly may be installed at any desired position in the drill string. The rotational control assembly could also be utilized as a component of other drilling mechanisms such as a downhole drilling motor. The rotational control permits slippage while drilling for a selected time or selected rotational distance or other criteria to thereby release torsional energy in the drilling string which otherwise may produce damaging slip-stick torsional oscillations such as slip-stick. The rotational control assembly may, in one embodiment, comprise an on-off clutch whereby torque is either substantially completely transmitted or substantially not transmitted through the assembly for brief periods.
Owner:STRATALOC TECH PROD +1
Torsional vibration damper
InactiveUS6875113B2Without inflicting significant mechanical damageReliable mechanical interconnectionRotating vibration suppressionYielding couplingRotational axisSnubber
A torsional vibration damper mountable to a rotatable shaft. The torsional vibration damper is a composite structure including a body formed of a polymer, such as a glass-reinforced polyamide, that surrounds an insert formed of a structurally-rigid material, such as a metal. The insert includes one or more support flanges that extend radially outward into the polymer body. When the torsional vibration damper is removed from the rotatable shaft, axial forces applied to the damper are transferred by the support flanges to the insert such that the polymer body remains substantially stress-free. In addition to, or instead of, the support flanges, the insert may include torque-locking structure that locks the polymer annular body with the insert to prevent relative rotation therebetween.
Owner:DAYCO IP HLDG
High-frequency vibration motor for electric toothbrush
ActiveCN102111032AReduce in quantityReasonable structureMechanical energy handlingTooth cleaningVibration amplitudeReciprocating motion
The invention relates to the technical field of electric toothbrushes, in particular to a high-frequency vibration motor for an electric toothbrush. The high-frequency vibration motor for the electric toothbrush comprises a shell and a rear cover, wherein a stator, a rotating shaft and an adjusting pad are arranged in the shell; the output end of the rotating shaft is connected with the rear cover through a spring piece; the spring piece comprises a spring piece main body and an elastic arm; the motor generates power to drive the rotating shaft to rotate reciprocally so as to drive the springpiece connected with the rotating shaft to twist to generate torsional deformation; when the frequency of the motor generating reciprocating movement is close to or reaches the torsional resonant frequency of the spring piece, the torsional vibration amplitude of the spring piece reaches the maximum so that the swinging amplitude of the motor reaches the maximum; because of the influence of the reluctance force of the motor per se, the vibration amplitude of an overall system reaches a balanced state, and the spring piece and the motor generate movement under the balanced condition. The high-frequency vibration motor for the electric toothbrush is easy to manufacture and position, along with reasonable structure, less elements, simple machining process, low cost and long service life.
Owner:DONGGUAN LEBOND ELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
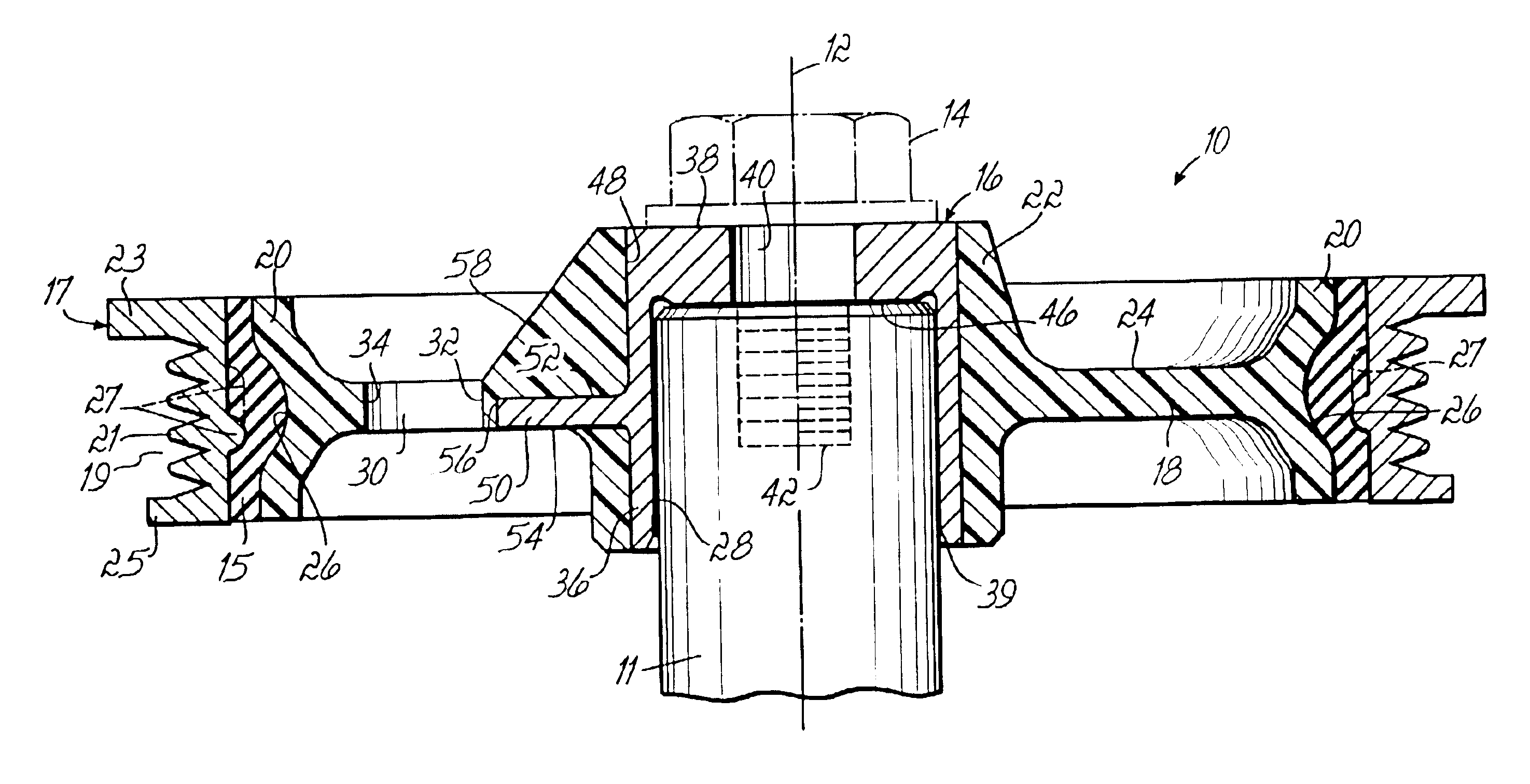
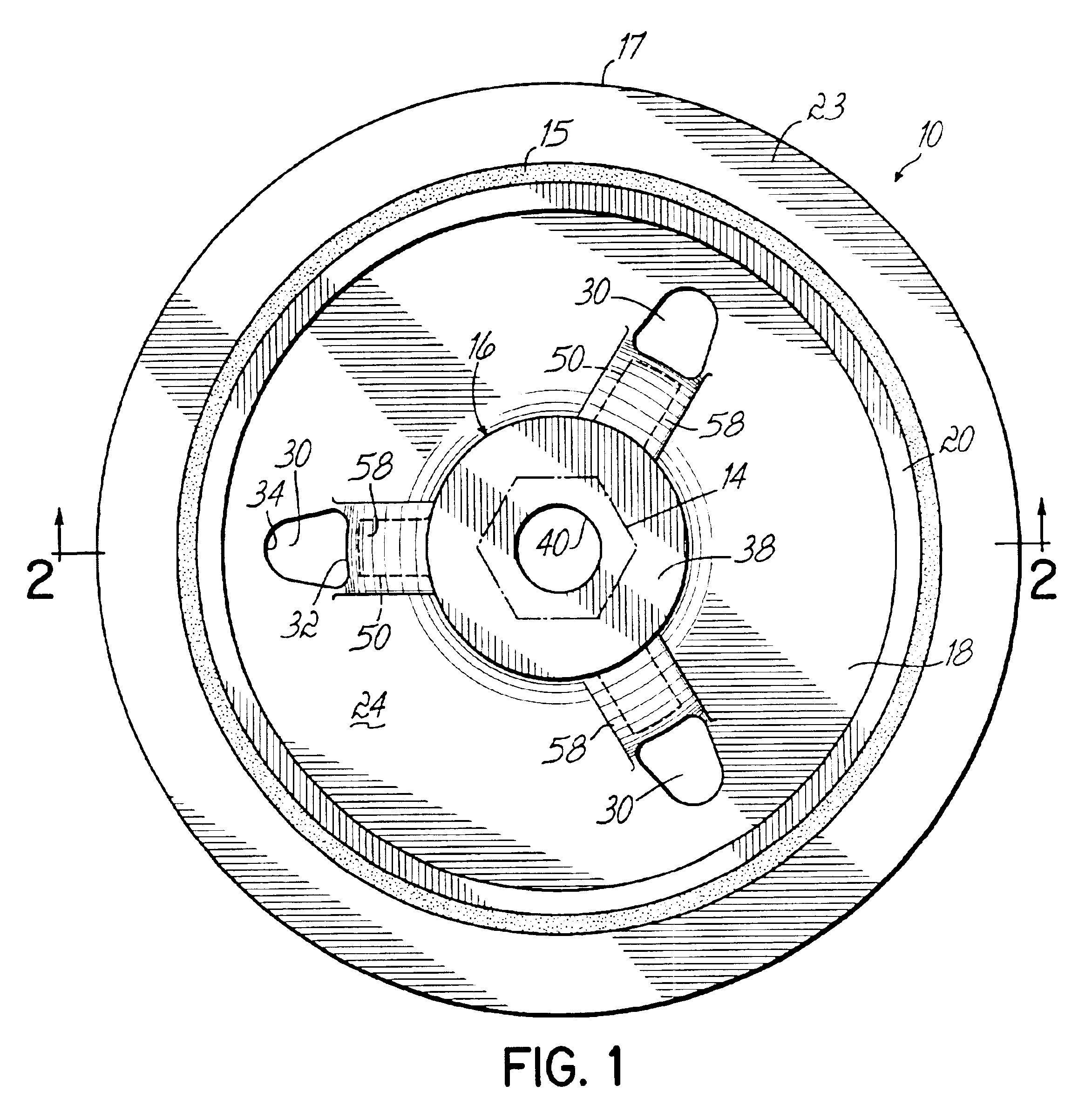
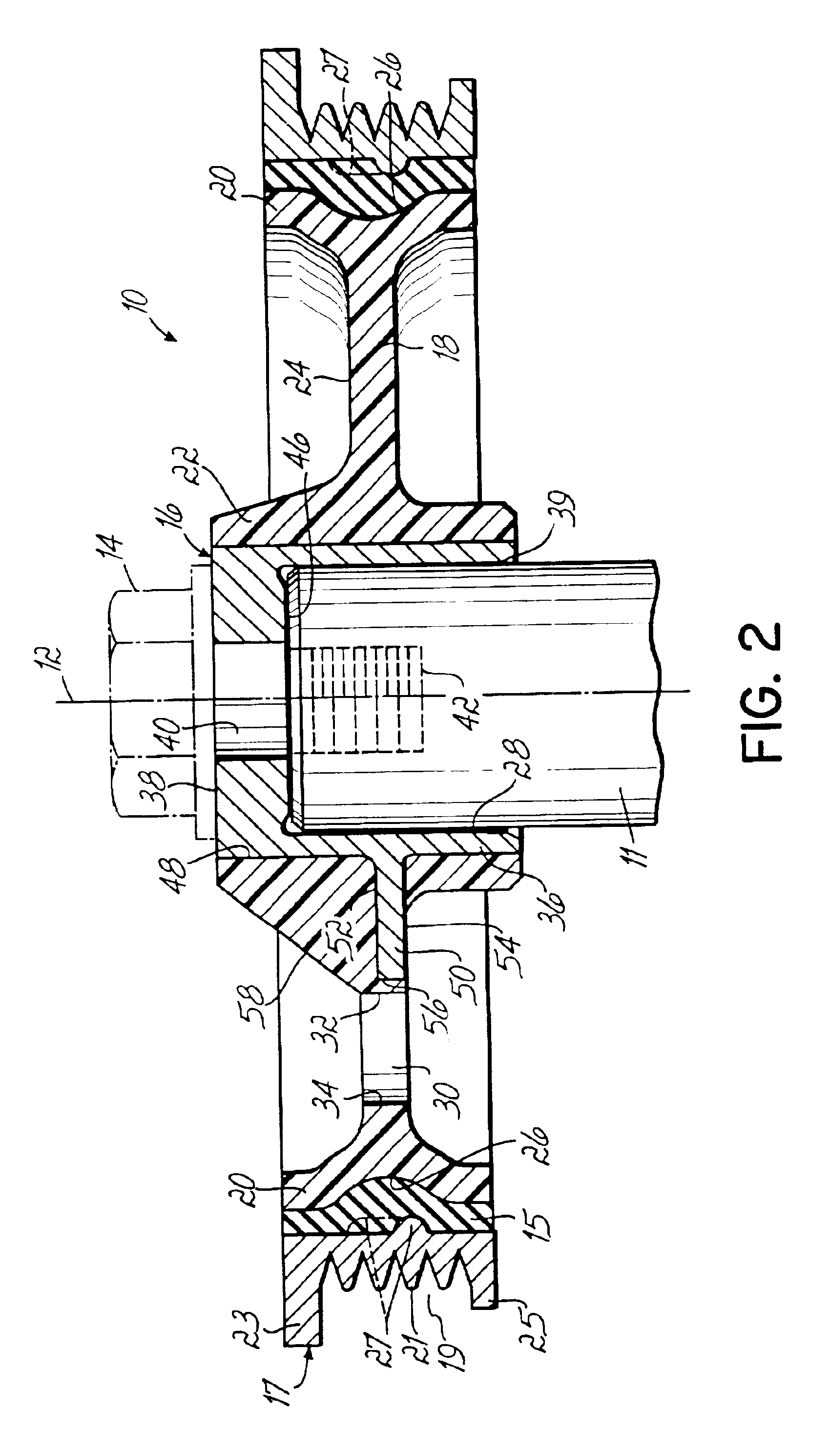
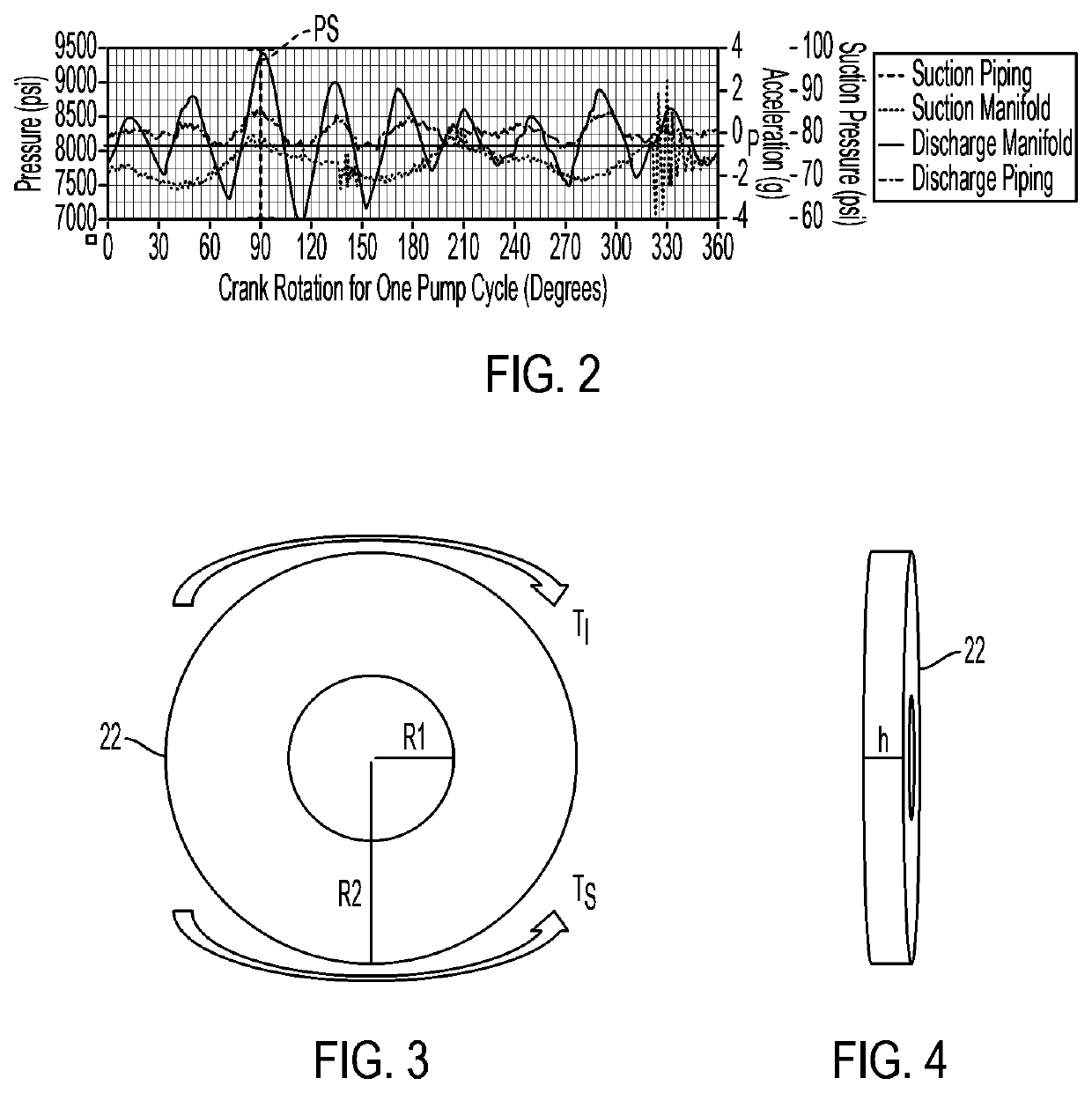
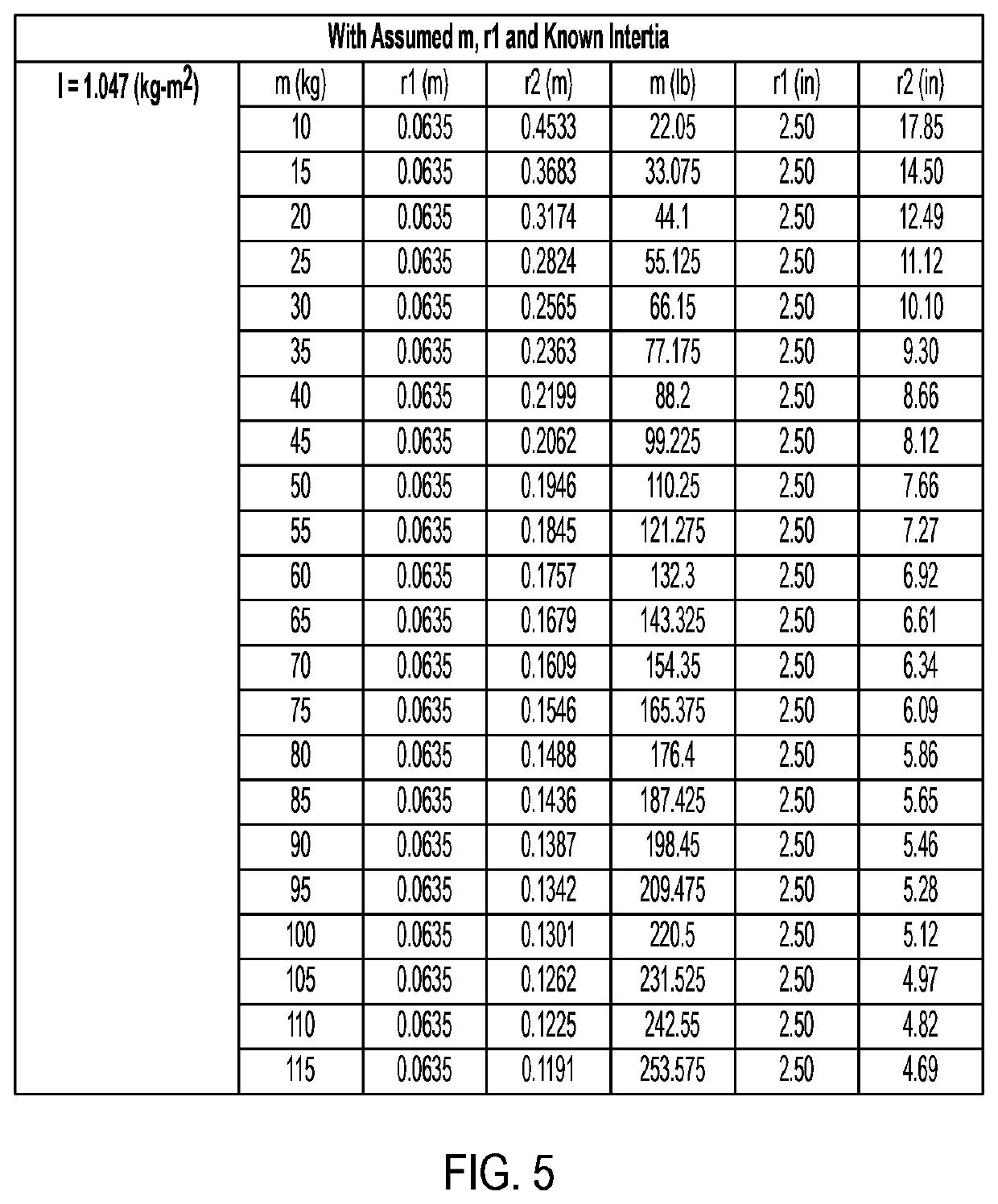
Systems and method for use of single mass flywheel alongside torsional vibration damper assembly for single acting reciprocating pump
ActiveUS11015594B2Reduce and eliminate shock loadingDampen torsional resonanceRotating vibration suppressionSpringsRotary pumpClassical mechanics
A pump system may include a pump, a driveshaft, driving equipment, and a vibration dampening assembly configured to reduce pump-imposed high frequency / low amplitude and low frequency / high amplitude torsional vibrations. The pump may have an input shaft connected to the driveshaft. The driving equipment may include an output shaft having an output flange connected to the driveshaft. The driving equipment may be configured to rotate the driveshaft to rotate the input shaft of the pump therewith. The vibration dampening assembly may include one or more flywheels operably connected to the input shaft and configured to rotate therewith.
Owner:BJ ENERGY SOLUTIONS LLC
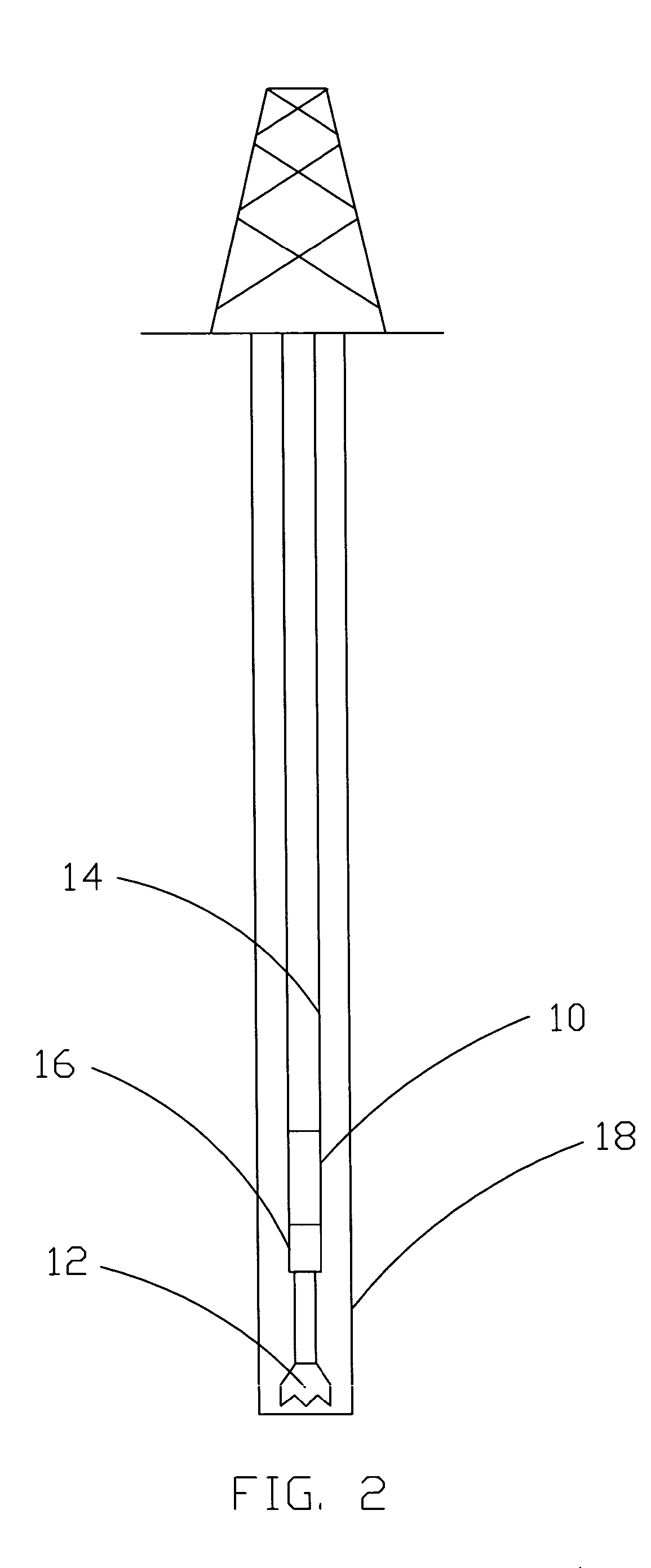
Floating cushion sub
InactiveUS6332841B1Easy to handleEffective absorptionYielding couplingDrilling rodsTorsional vibrationAxial vibration
A cushion sub for absorbing both axial and torsional vibration in a drill string and including an outer casing connectable at one end to a section of a drill string, and an inner piston reciprocally mounted in a cylinder within the casing, the piston having a shaft projecting from the other end of the casing connectable to another section of the drill string. The cylinder includes a first cushion device at opposite ends thereof for engagement by the piston to absorb axial vibrations. A spline type connection prevents relative rotation between the piston and the cylinder. The cylinder is mounted for arcuate turning in a chamber within the casing, but the cylinder has vanes which are interposed between vanes fixed to the casing, and elastomeric material between the vanes of the cylinder and the vanes of the casing absorbs torsional vibrations being transmitted between the cylinder and the casing. The elastomeric material is preferably formed in situ as an integral mass in the chamber of the casing by pouring the elastomeric material in a fluid state into the chamber.
Owner:FOREMOST INDS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com