Patents
Literature
965results about "Suspensions" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
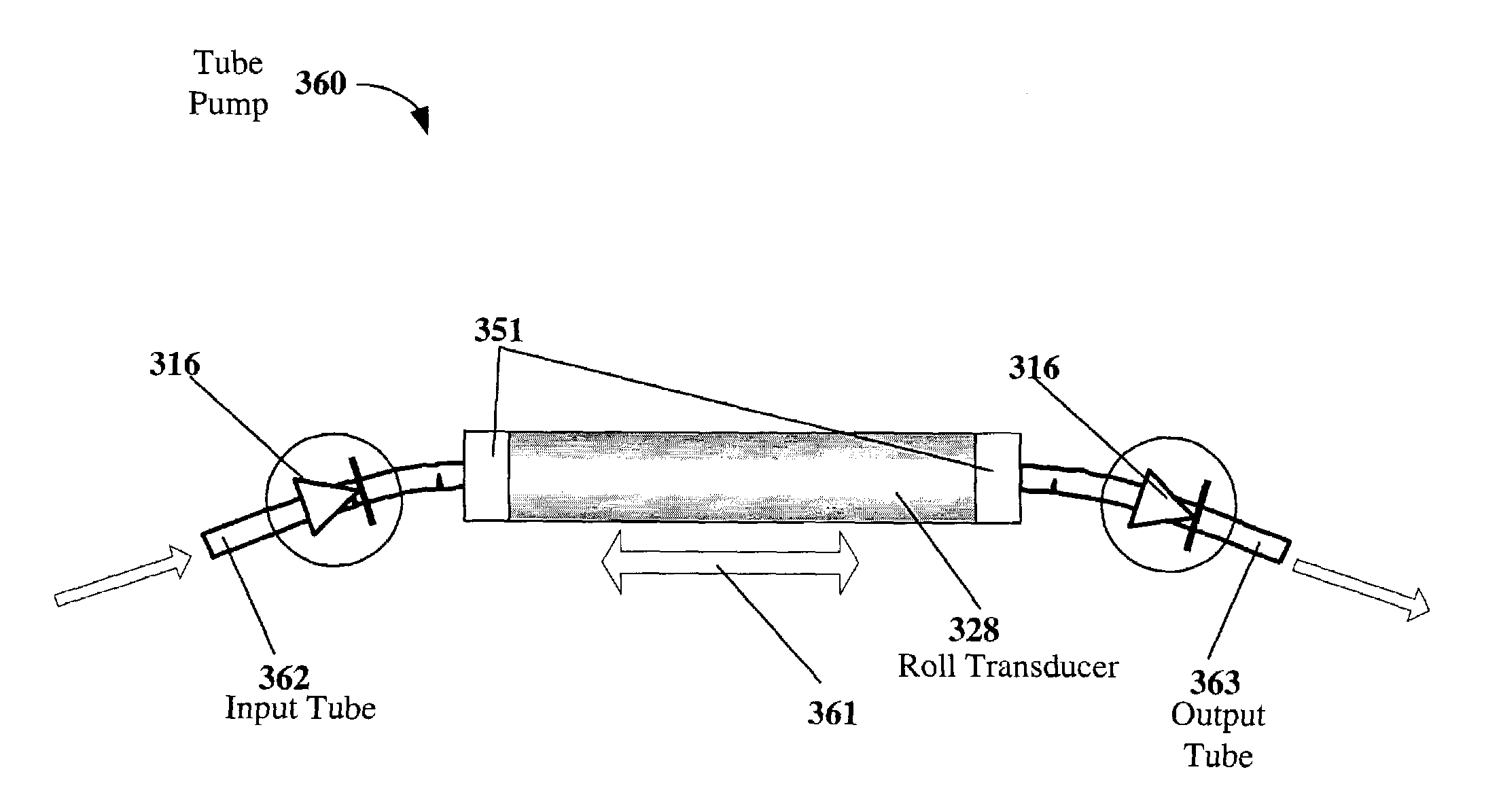
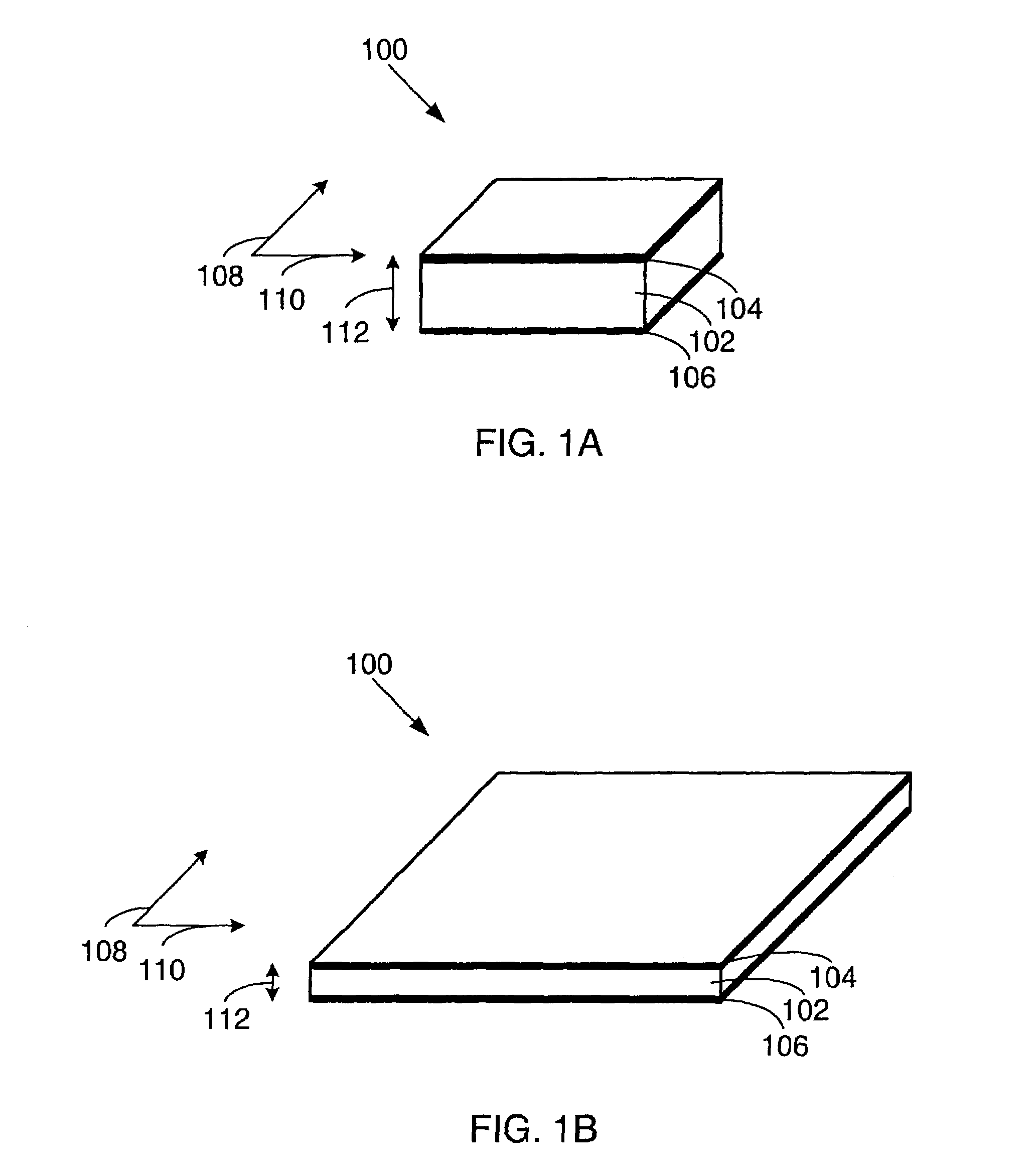
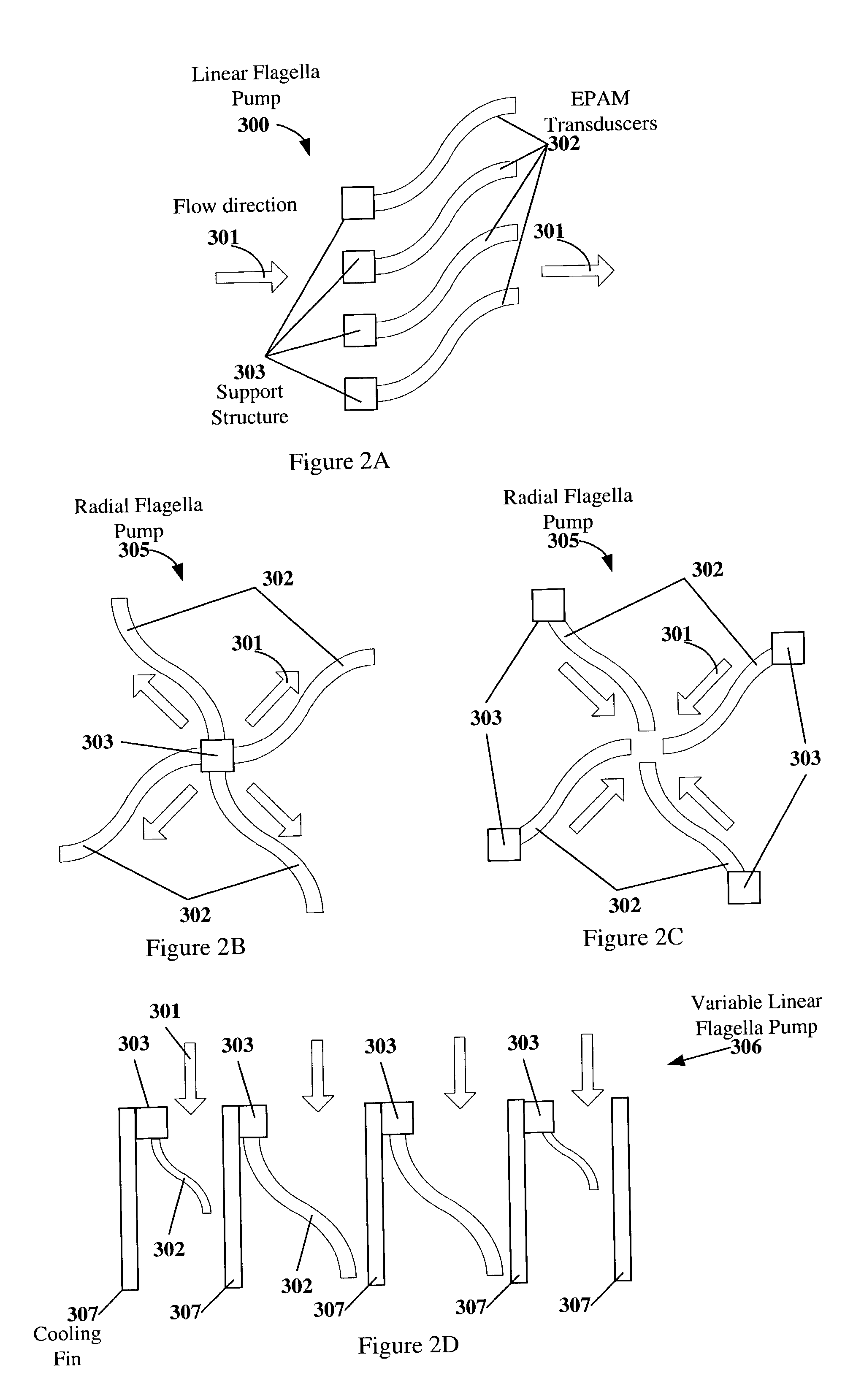
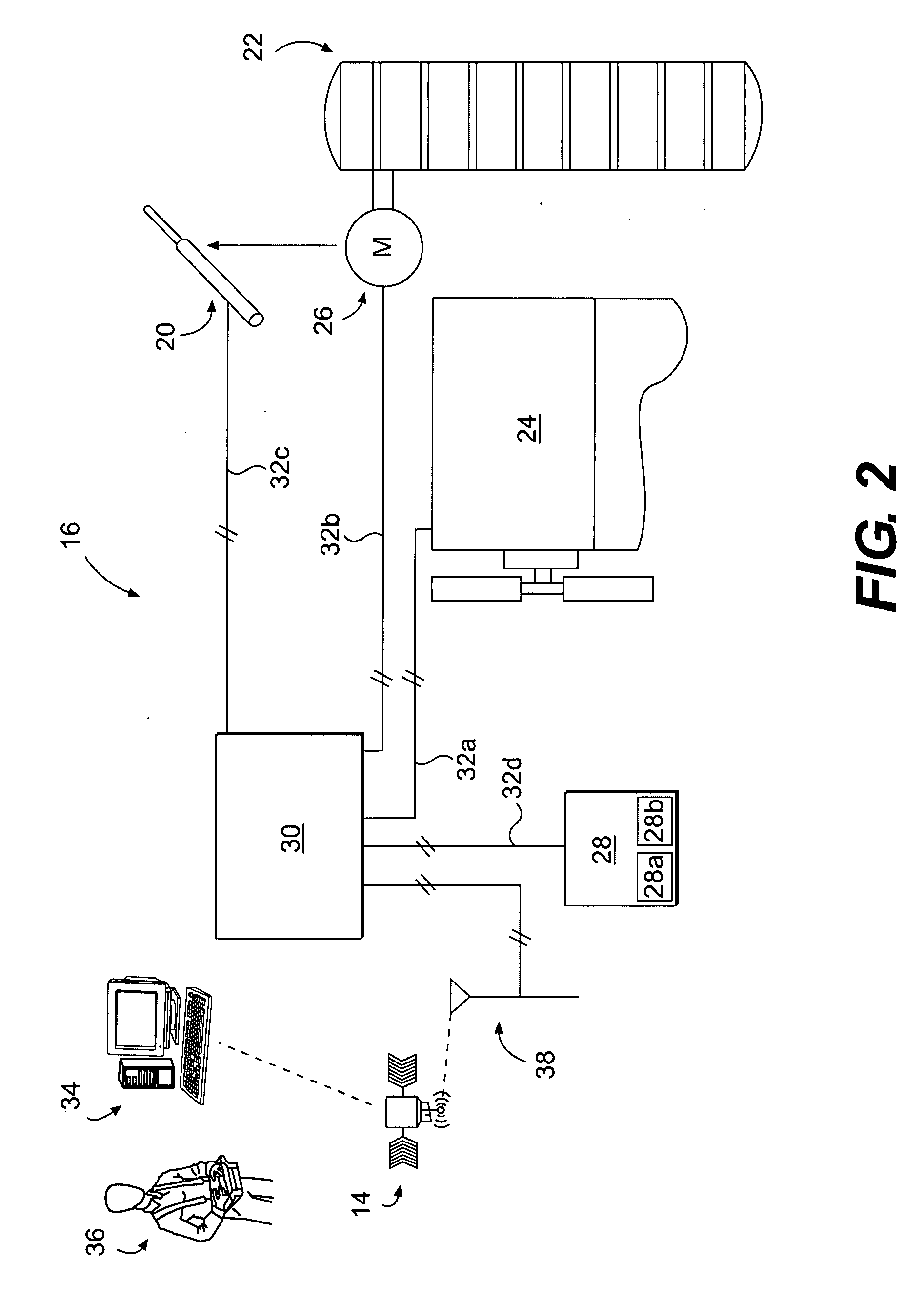
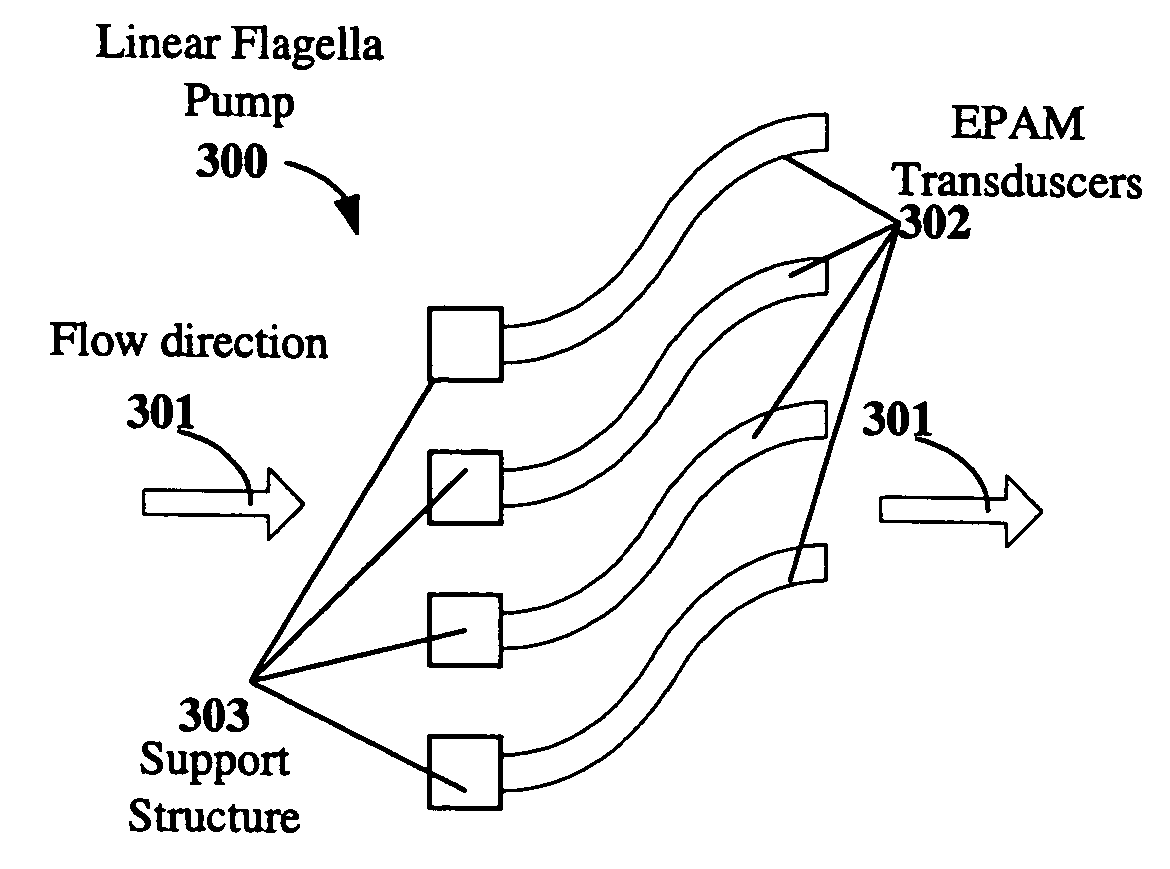
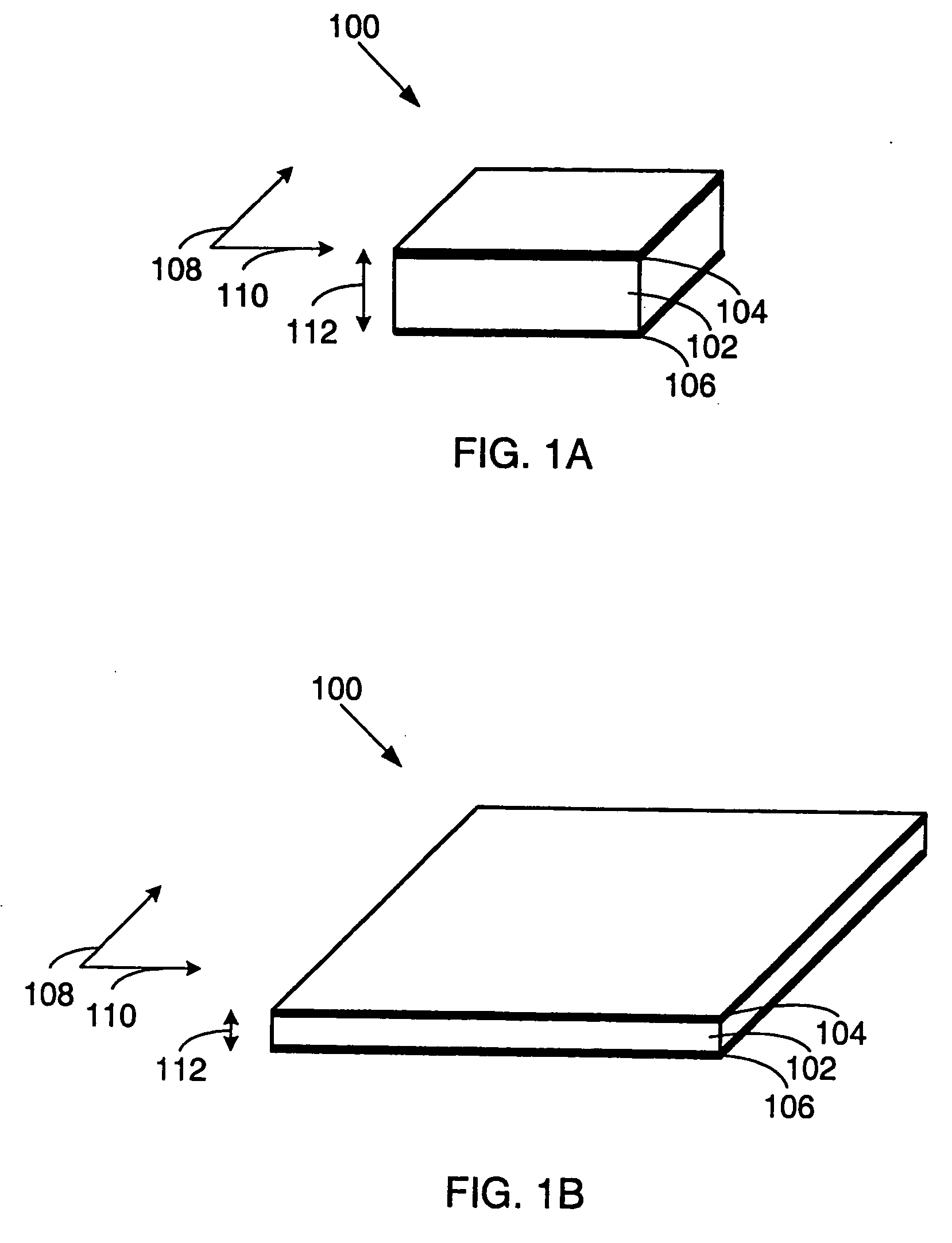
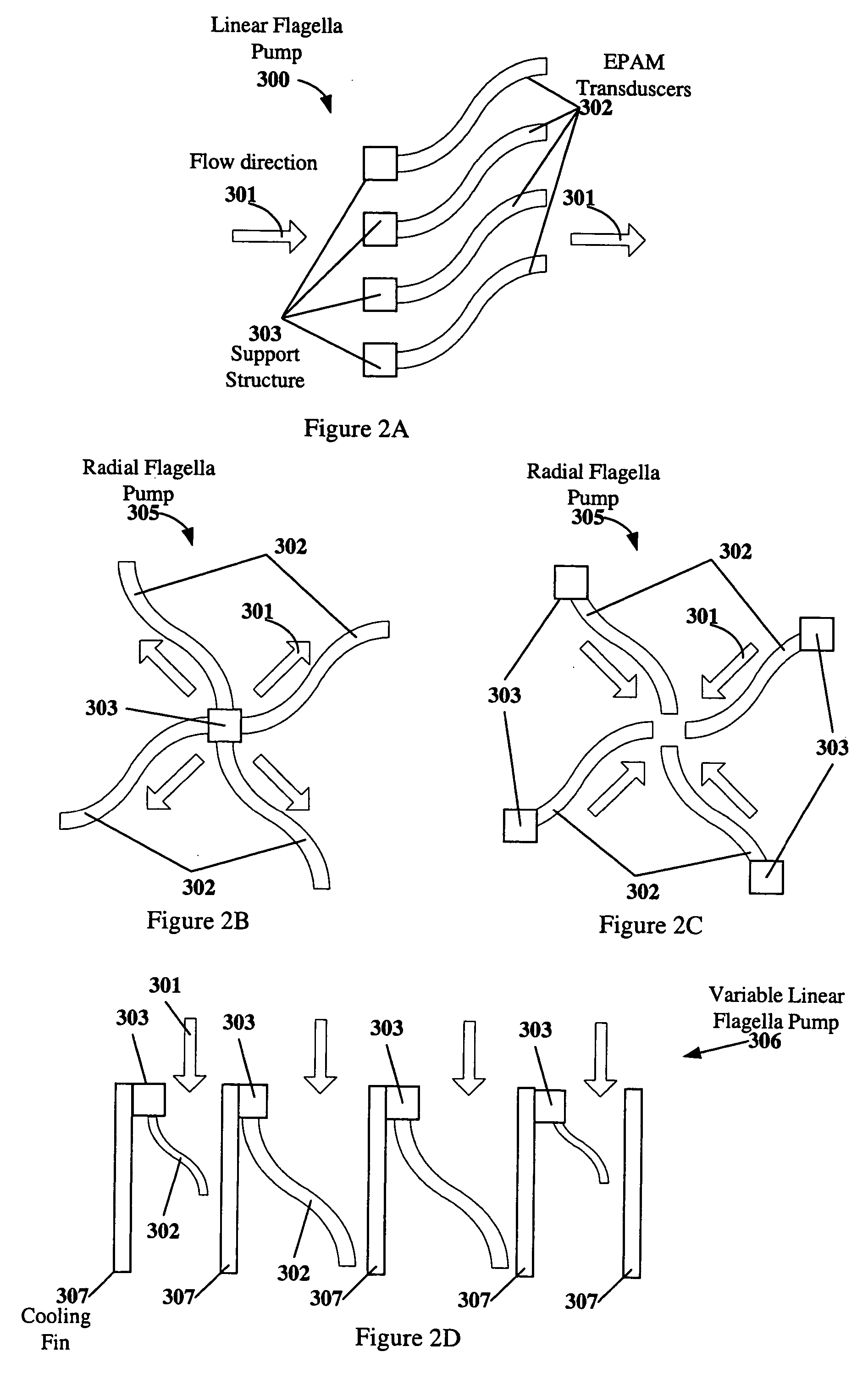
Electroactive polymer devices for moving fluid
InactiveUS7064472B2Improve mechanical responseImprove responseTransducer detailsFlexible member pumpsHearing rangeThermal force
The invention describes devices for performing thermodynamic work on a fluid, such as pumps, compressors and fans. The thermodynamic work may be used to provide a driving force for moving the fluid. Work performed on the fluid may be transmitted to other devices, such as a piston in a hydraulic actuation device. The devices may include one or more electroactive polymer transducers with an electroactive polymer that deflects in response to an application of an electric field. The electroactive polymer may be in contact with a fluid where the deflection of the electroactive polymer may be used to perform thermodynamic work on the fluid. The devices may be designed to efficiently operate at a plurality of operating conditions, such as operating conditions that produce an acoustic signal above or below the human hearing range. The devices may be used in thermal control systems, such as refrigeration system, cooling systems and heating systems.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
Hybrid vehicle drive for a motor vehicle
InactiveUS6102144AReducing and eliminating vibrationExcessive vibrationSuspensionsRotating vibration suppressionFrequency spectrumLoad torque
A hybrid vehicle drive for a motor vehicle includes an internal combustion engine and an electric machine which is selectively coupled with the internal combustion engine. The electric machine can be operated as a generator and as a motor. Regulation device which responds to a reference signal predetermined by a reference signal preset device are provided for the active damping of vibrations, especially torsional vibrations in the torque transmission path between the internal combustion engine and wheels of the motor vehicle driven by the latter. The regulation device also respond to sensing device which deliver an actual-value vibration signal containing vibration information about a rotating structural component of the motor vehicle and control the load torque exerted on the internal combustion engine by the electric machine for reducing or eliminating the vibrations of the structural component. An analysis device for determining a frequency spectrum of the actual-value vibration signal is associated with the regulation device. The reference signal preset device establishes a reference signal with predetermined frequency spectrum. The regulation device control the frequency spectrum of the load torque exerted on the internal combustion engine by the electric machine such that excessive spectral vibrations of the actual-value vibration signal are reduced or eliminated.
Owner:ZF FRIEDRICHSHAFEN AG
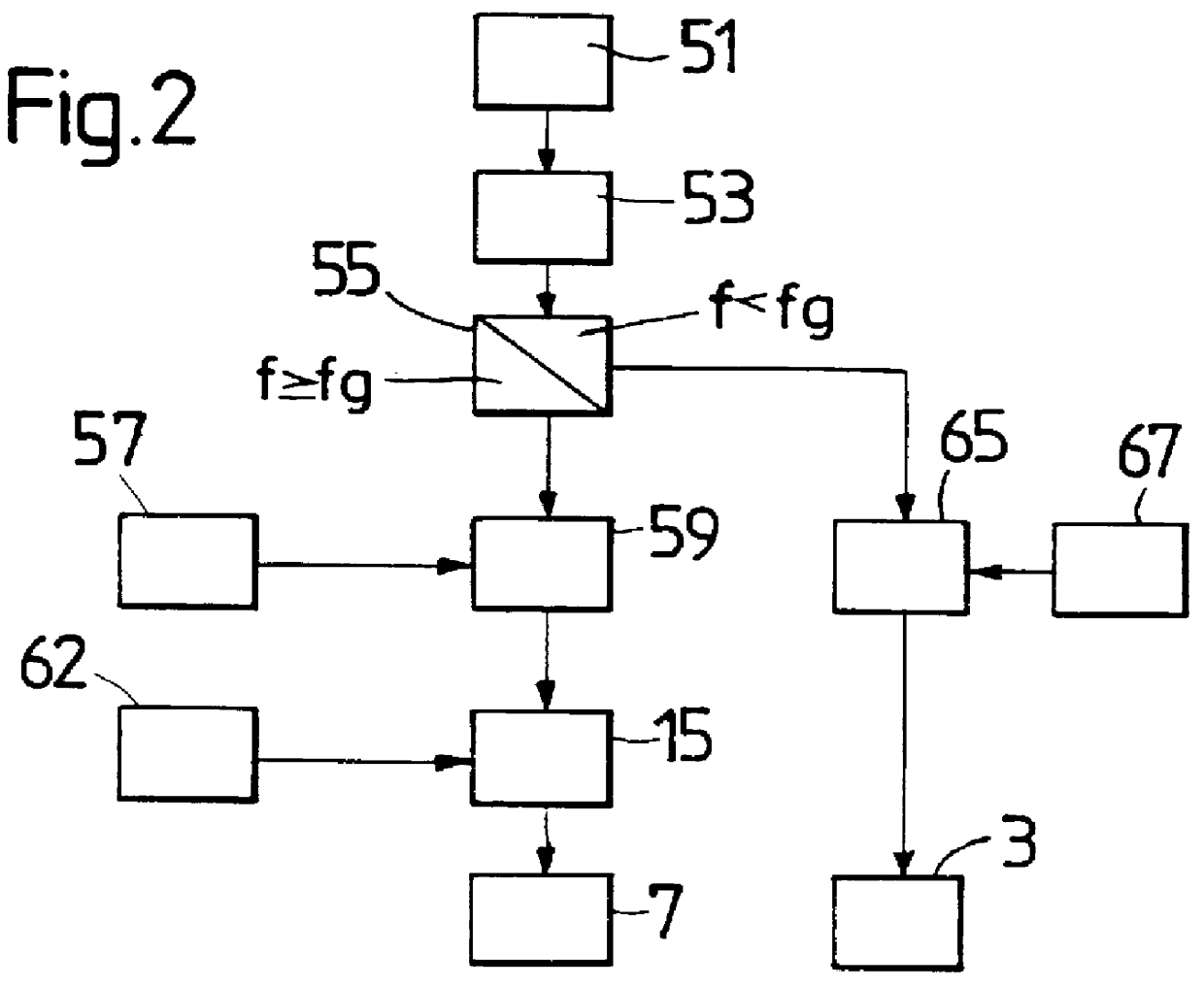
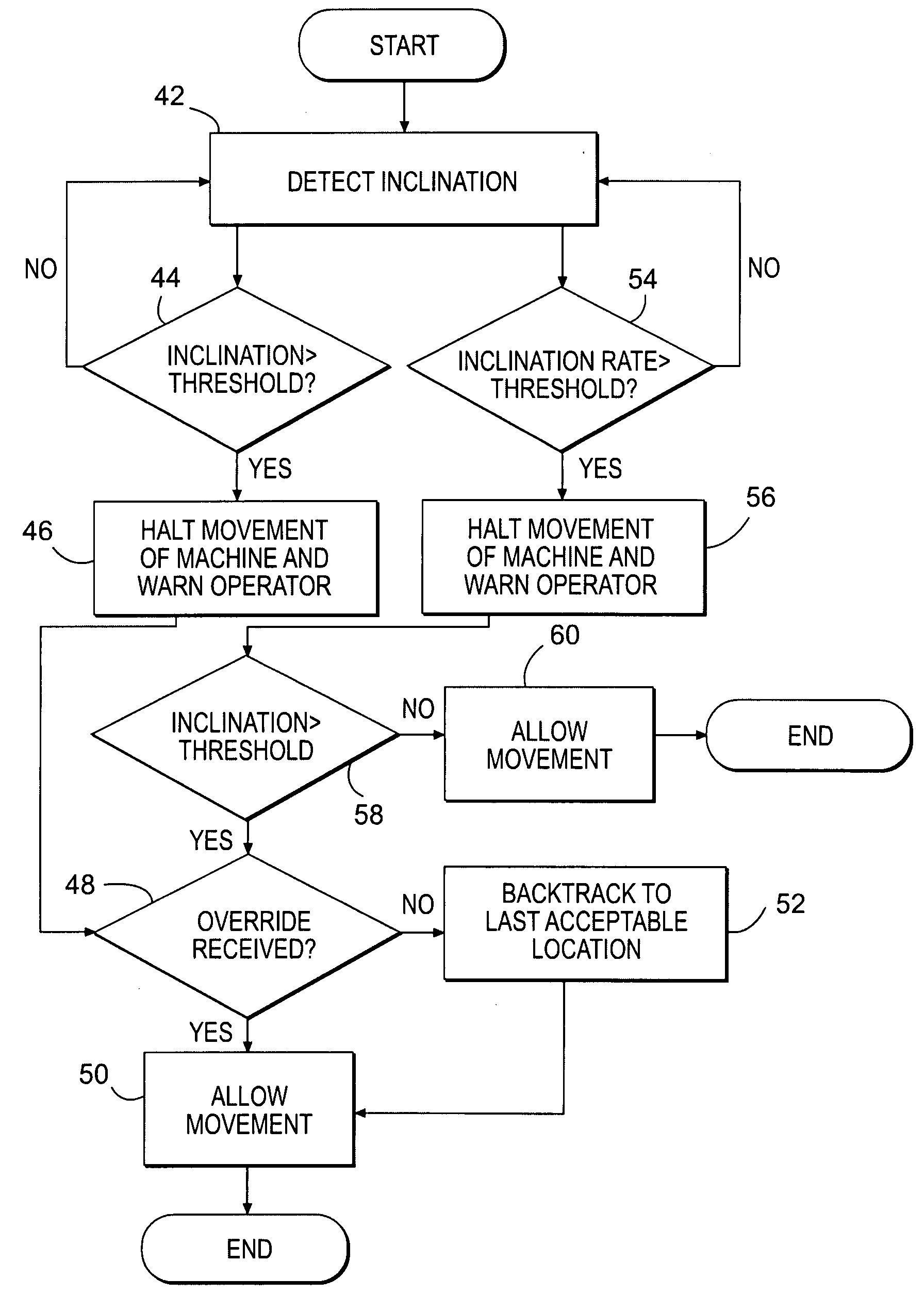
Automated rollover prevention system
ActiveUS20080208416A1Preventing machine rolloverVehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesRolloverControl system
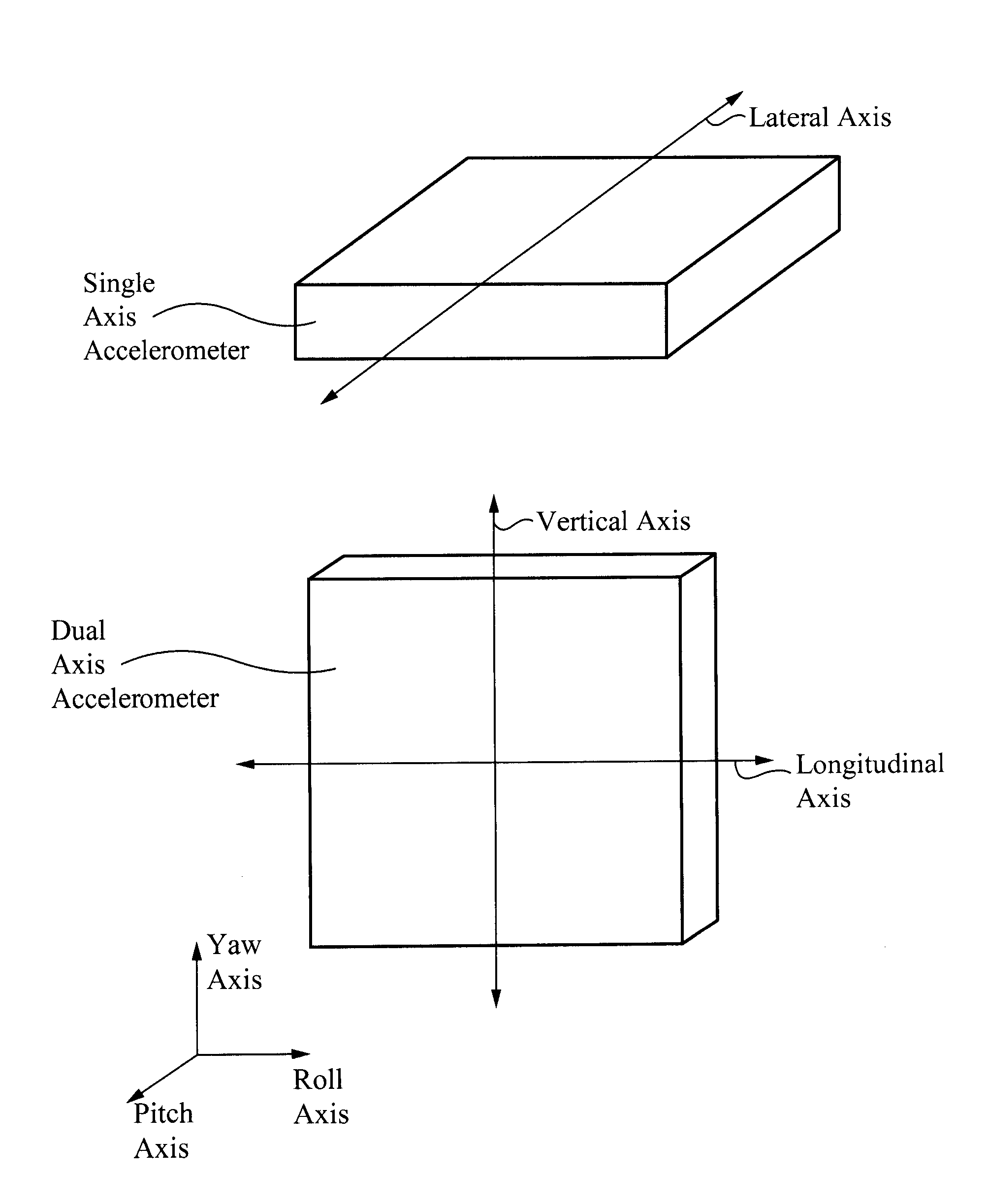
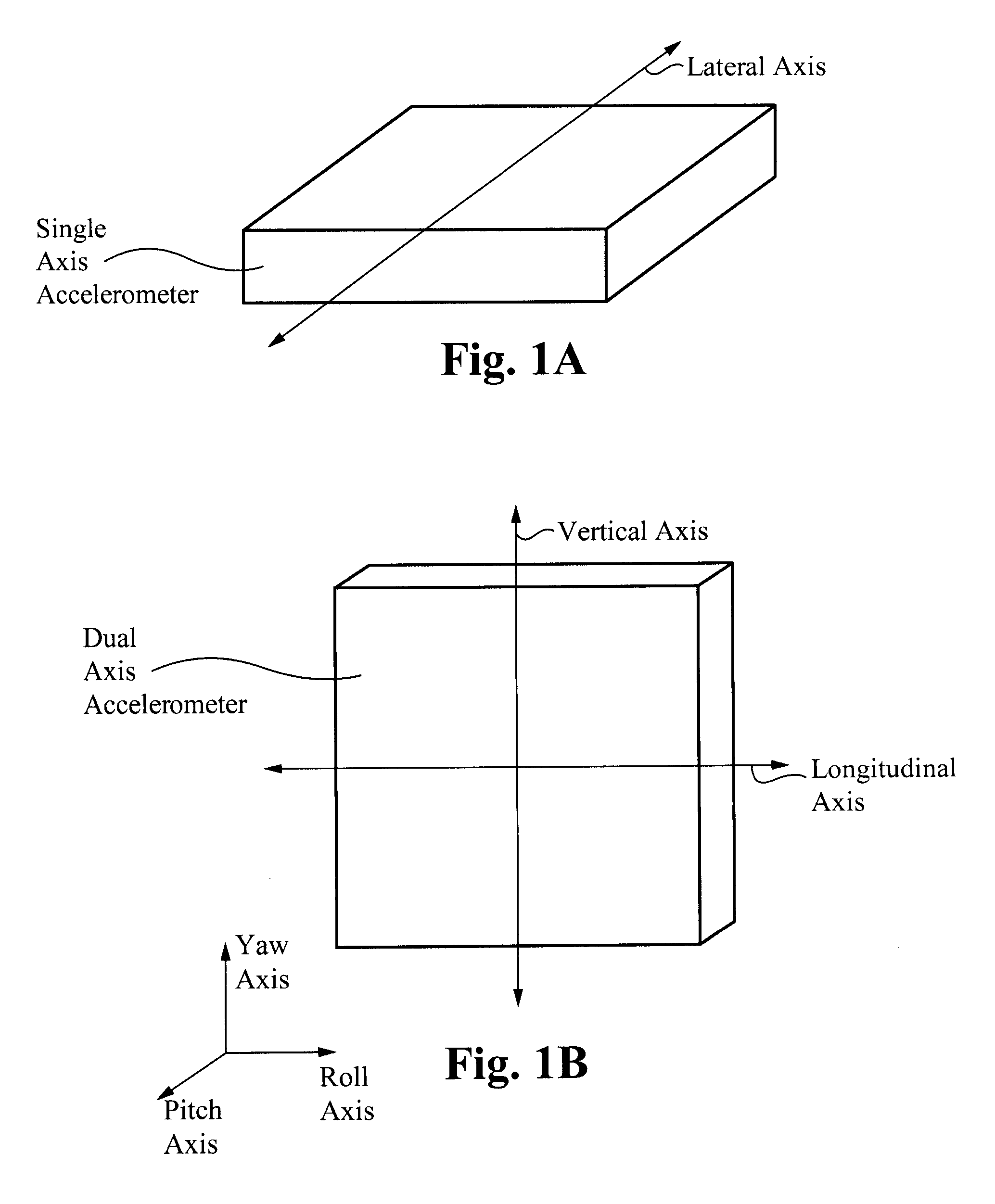
A control system for a machine is disclosed. The control system may have at least one sensor configured to generate a signal indicative of an inclination of the machine. The control system may also have a controller in communication with the at least one sensor. The controller may be configured to stop operation of the machine in response to the signal.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
Electroactive polymer devices for moving fluid
InactiveUS20060158065A1Improve responseTransducer detailsFlexible member pumpsHearing rangeThermal force
The invention describes devices for performing thermodynamic work on a fluid, such as pumps, compressors and fans. The thermodynamic work may be used to provide a driving force for moving the fluid. Work performed on the fluid may be transmitted to other devices, such as a piston in a hydraulic actuation device. The devices may include one or more electroactive polymer transducers with an electroactive polymer that deflects in response to an application of an electric field. The electroactive polymer may be in contact with a fluid where the deflection of the electroactive polymer may be used to perform thermodynamic work on the fluid. The devices may be designed to efficiently operate at a plurality of operating conditions, such as operating conditions that produce an acoustic signal above or below the human hearing range. The devices may be used in thermal control systems, such as refrigeration system, cooling systems and heating systems.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
System and method for controlling a safety system of a vehicle in response to conditions sensed by tire sensors related applications
InactiveUS20050033486A1Low costDigital data processing detailsAnimal undercarriagesControl systemForce sensor
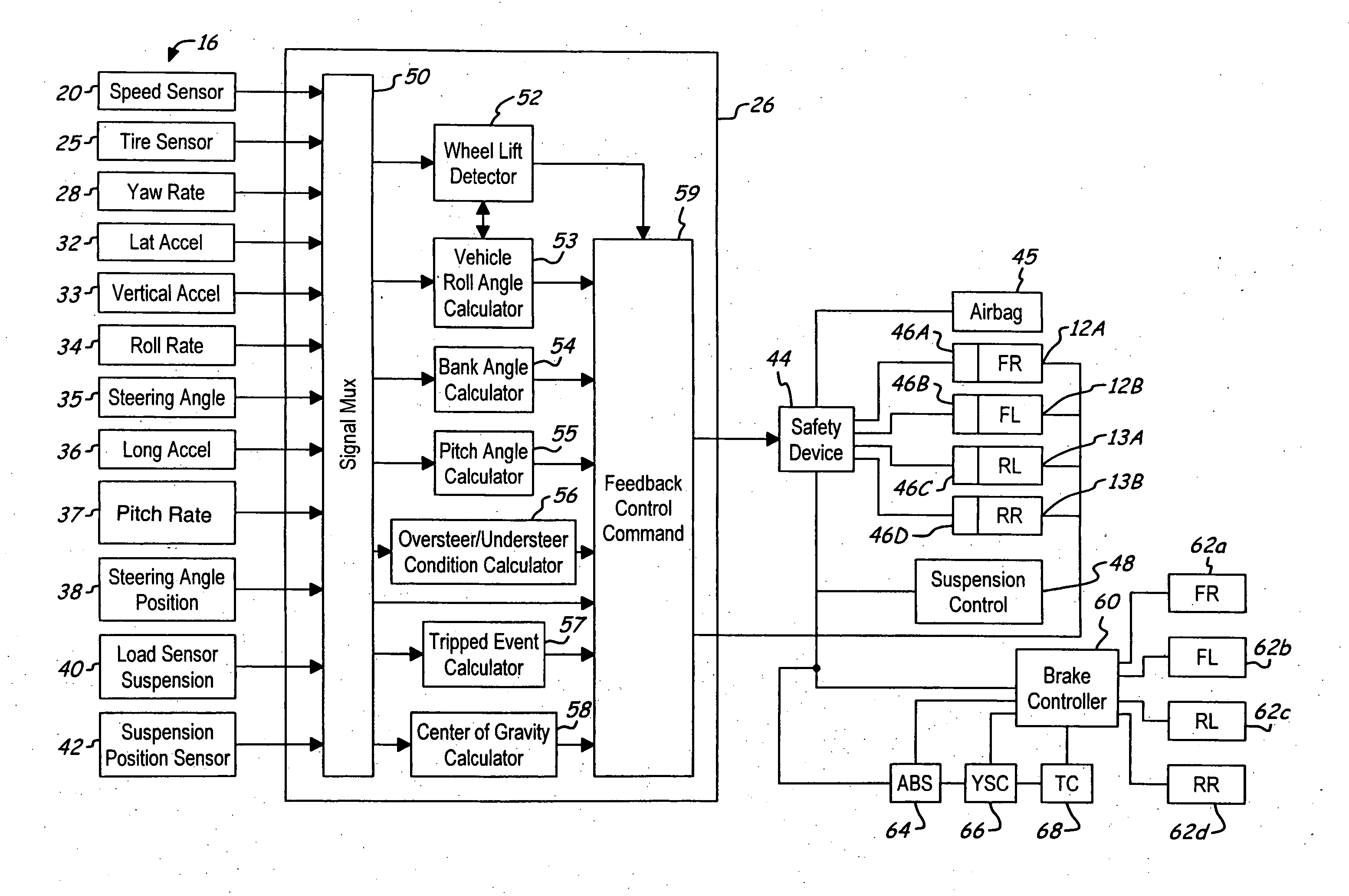
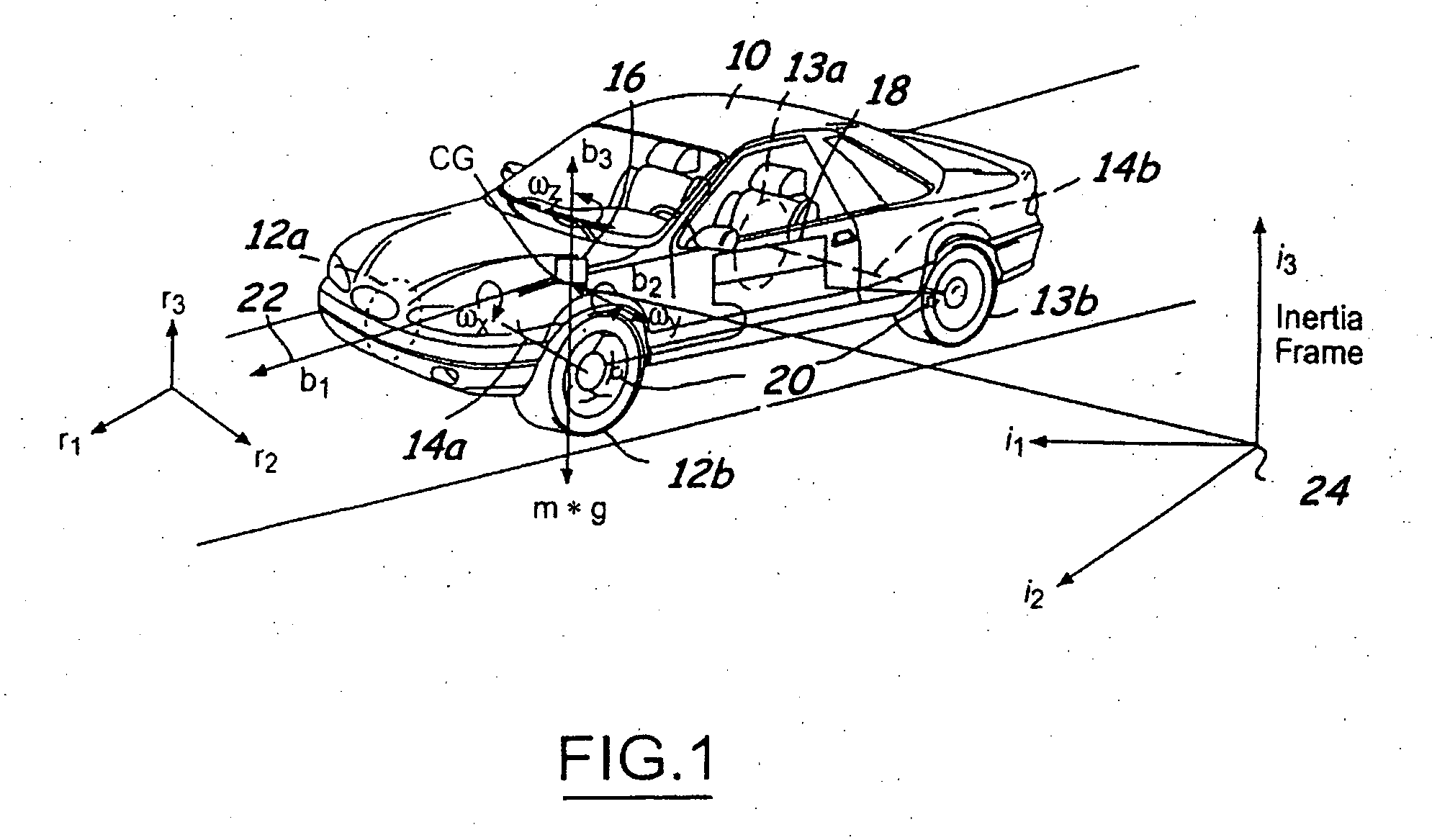
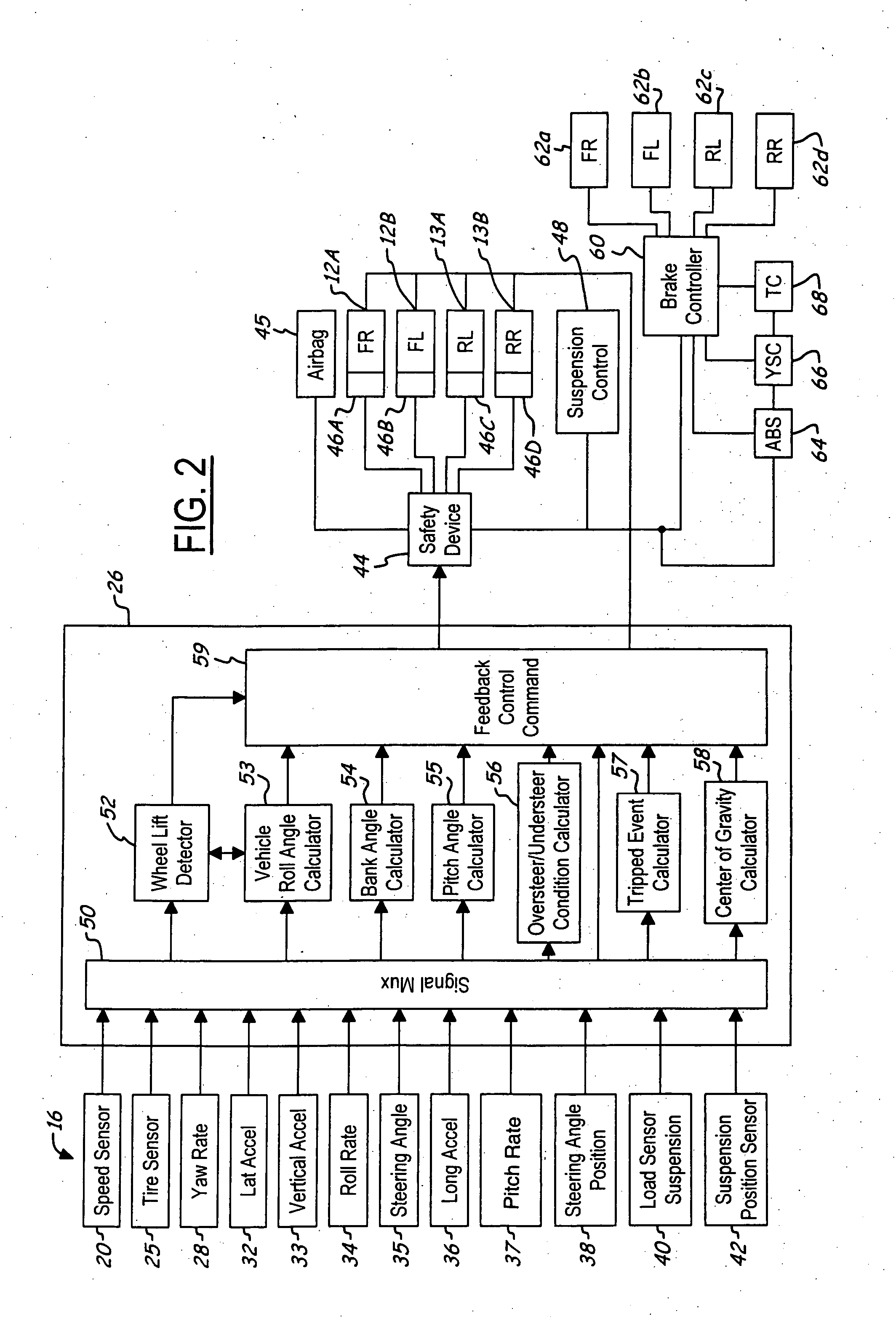
A control system for a vehicle (10) is described for use in conjunction with the safety system (44) of the vehicle (10). A tire sensor or plurality of tire sensors generates tire force signals. The tire force signals may include lateral tire forces, longitudinal (or torque) tire forces, and normal tire forces. Based upon the tire force signals, a safety system (44) may be activated. The tire force sensors may be used to monitor various conditions including but not limited to sensing a roll condition, wheel lift detection, a trip event, oversteering and understeering conditions, pitch angle, bank angle, roll angle, and the position of the center of gravity of the vehicle.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
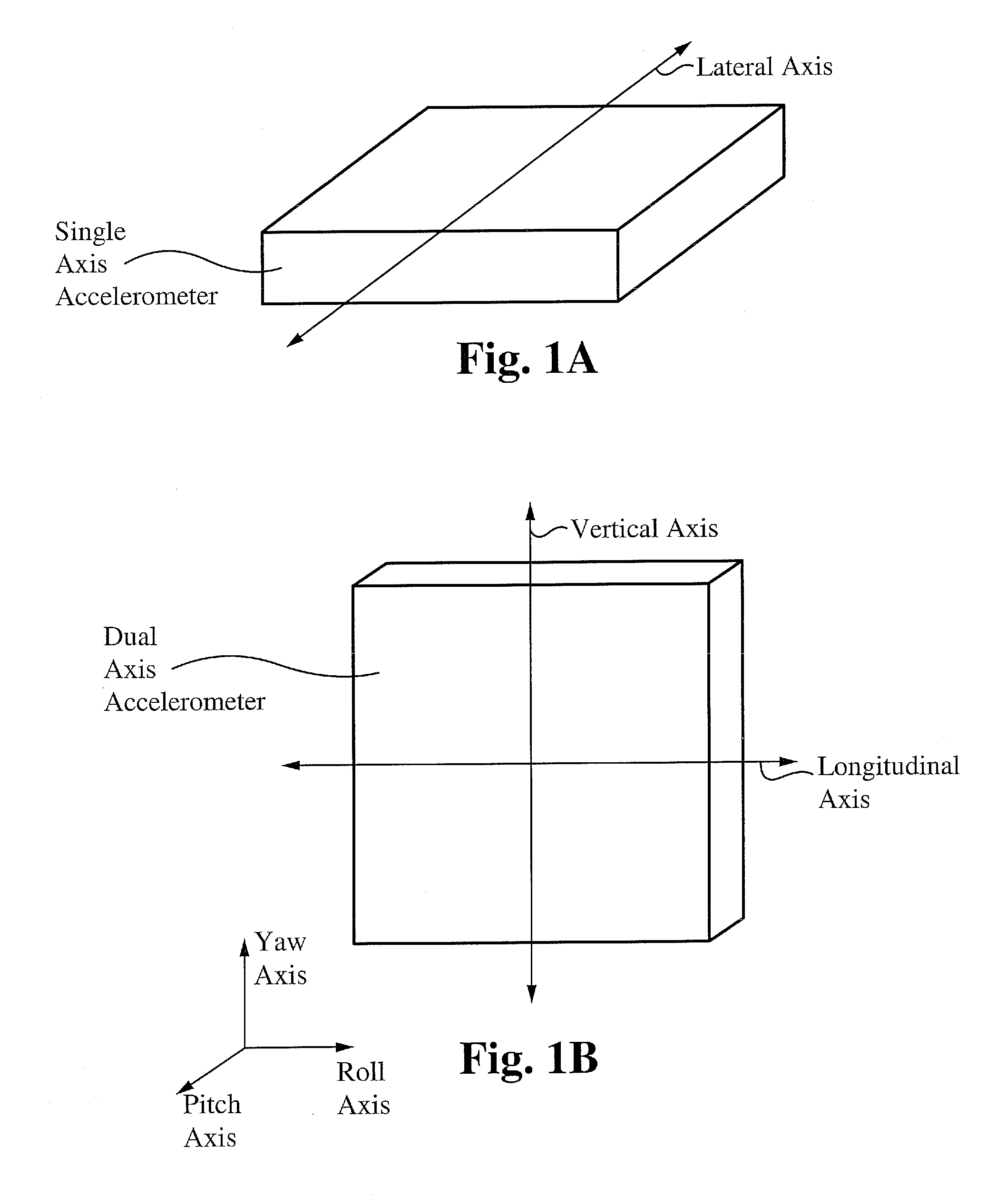
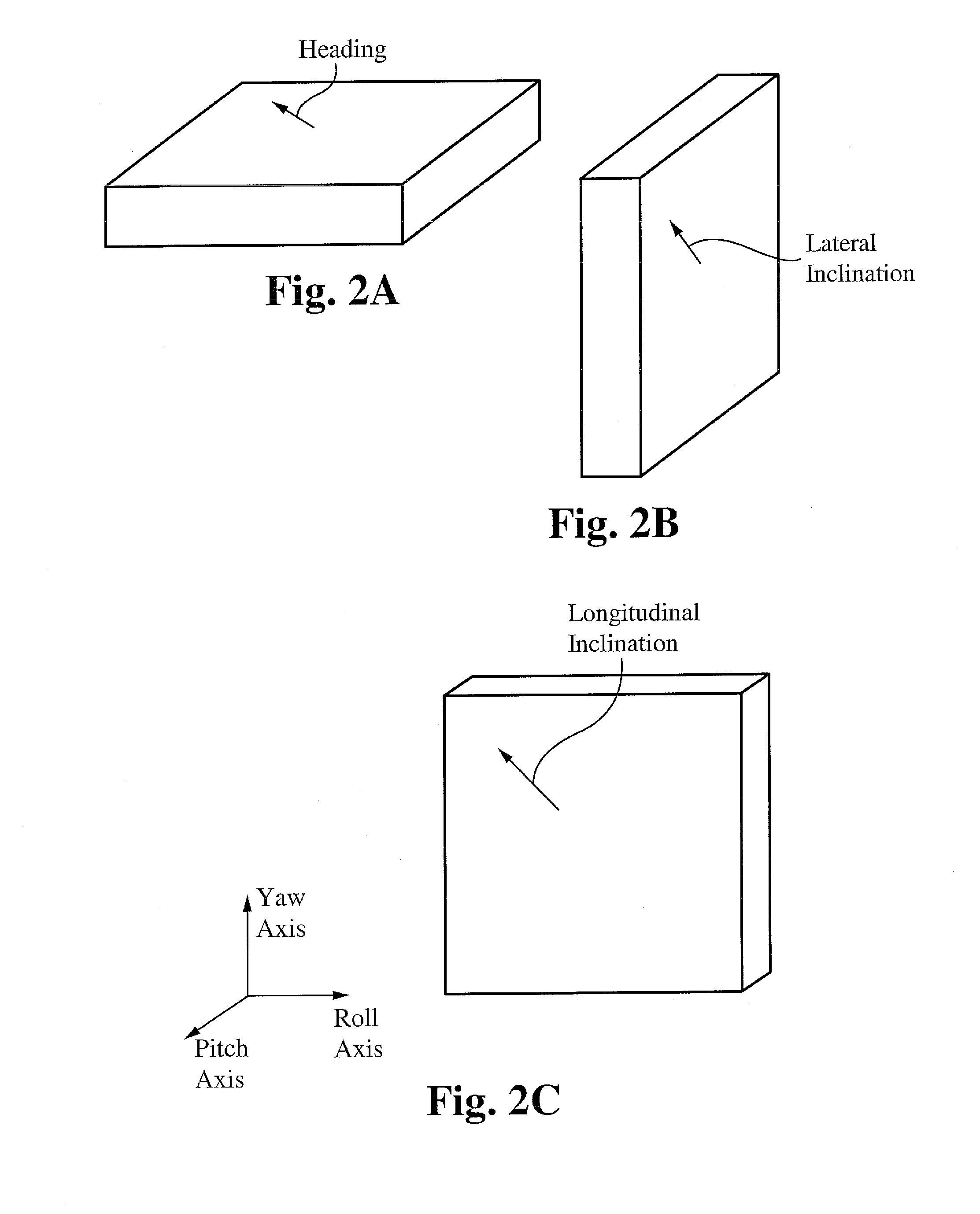
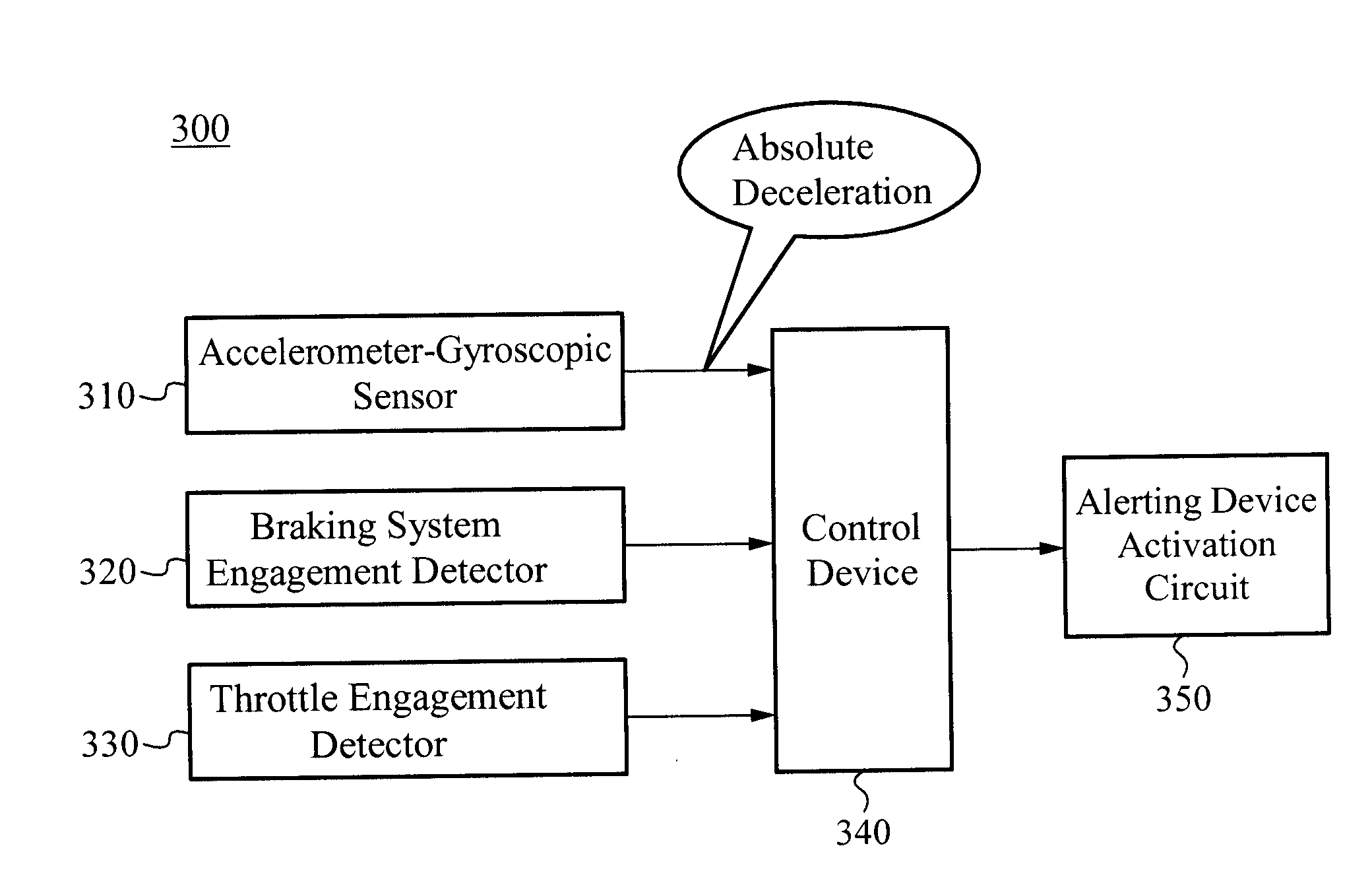
Absolute acceleration sensor for use within moving vehicles
InactiveUS20100332101A1Quick responseSuspensionsArrangements for variable traffic instructionsMobile vehicleCommunications system
A communication system for a vehicle comprises a receiver to receive a signal corresponding to a traveling speed of a lead vehicle, a response device that generates an alert to warn of a change in the traveling speed of the lead vehicle, and a control device coupled to the receiver and the response device, wherein the receiver sends a signal to the control device corresponding to the traveling speed of the lead vehicle and the control device operates the response device in a manner dependent on the traveling speed of the lead vehicle. In some embodiments, the signal comprises one or more of infrared, radio frequency, wireless, WiFi, and Bluetooth®. In some embodiments, the communication system further comprises a speed control system coupled to the control device, wherein the control device operates the speed control system in a manner dependent on the traveling speed of the lead vehicle.
Owner:VISION WORKS IP CORP
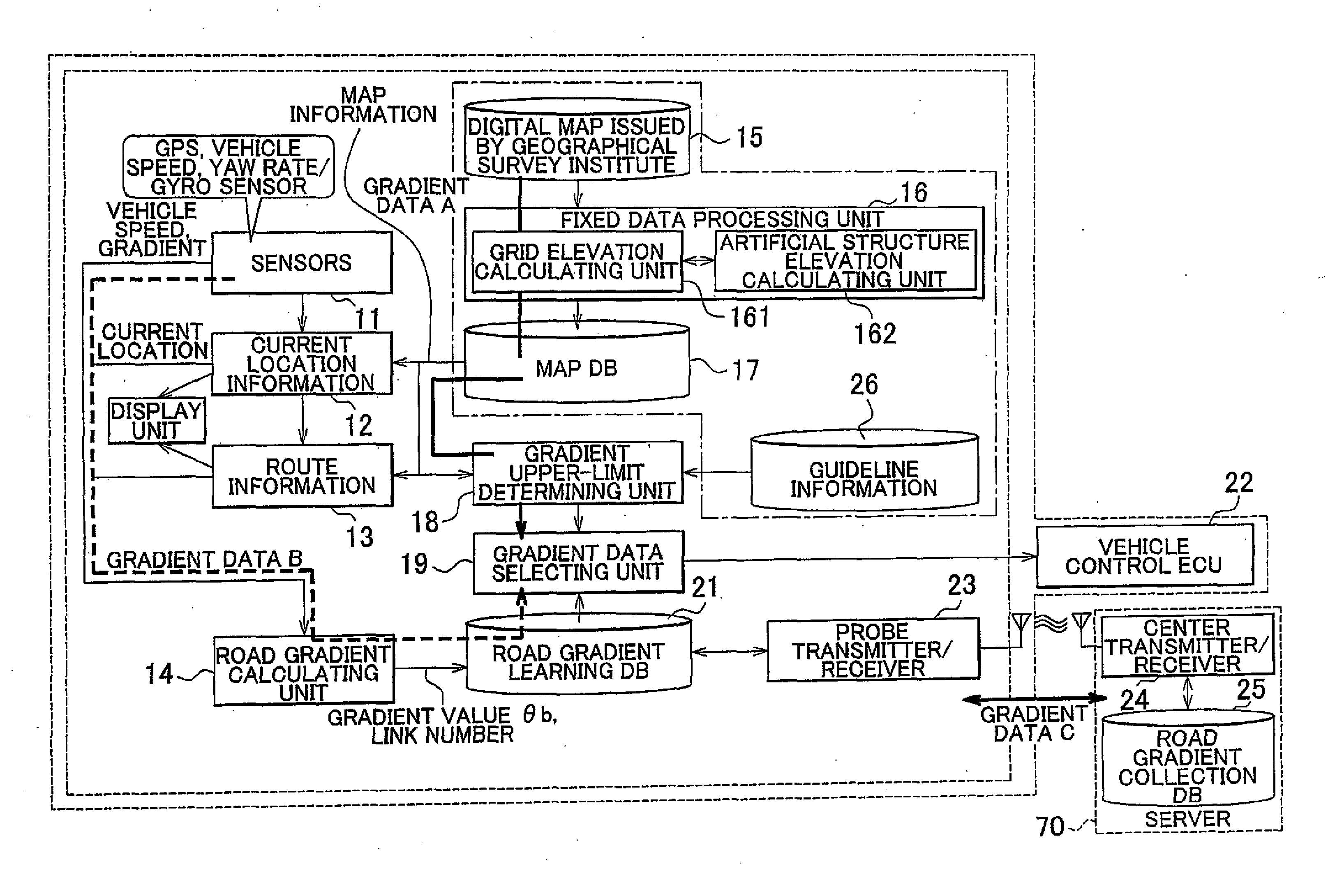
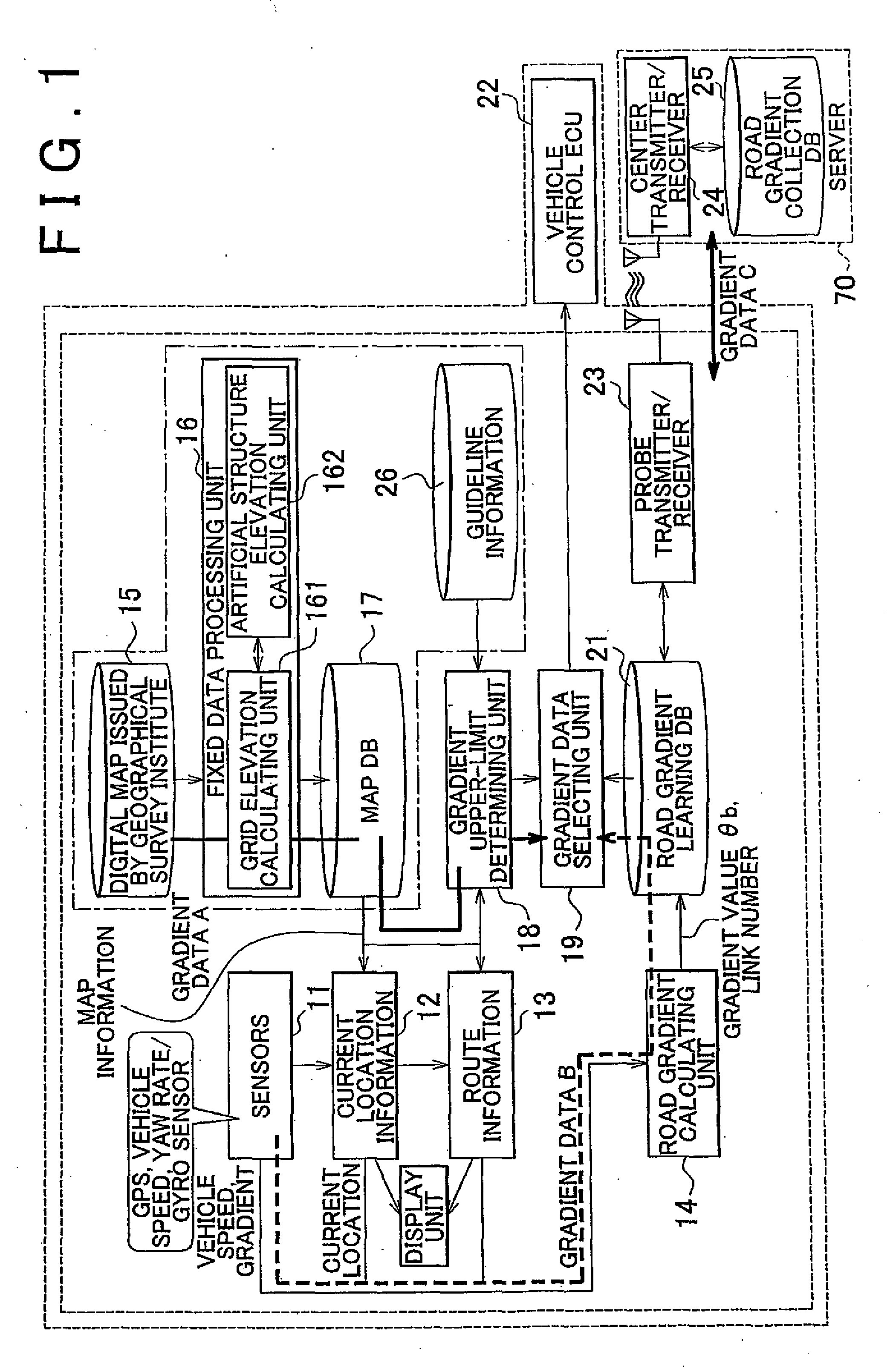
Gradient information calculating system, vehicle running control system, navigation system, and gradient information calculating method
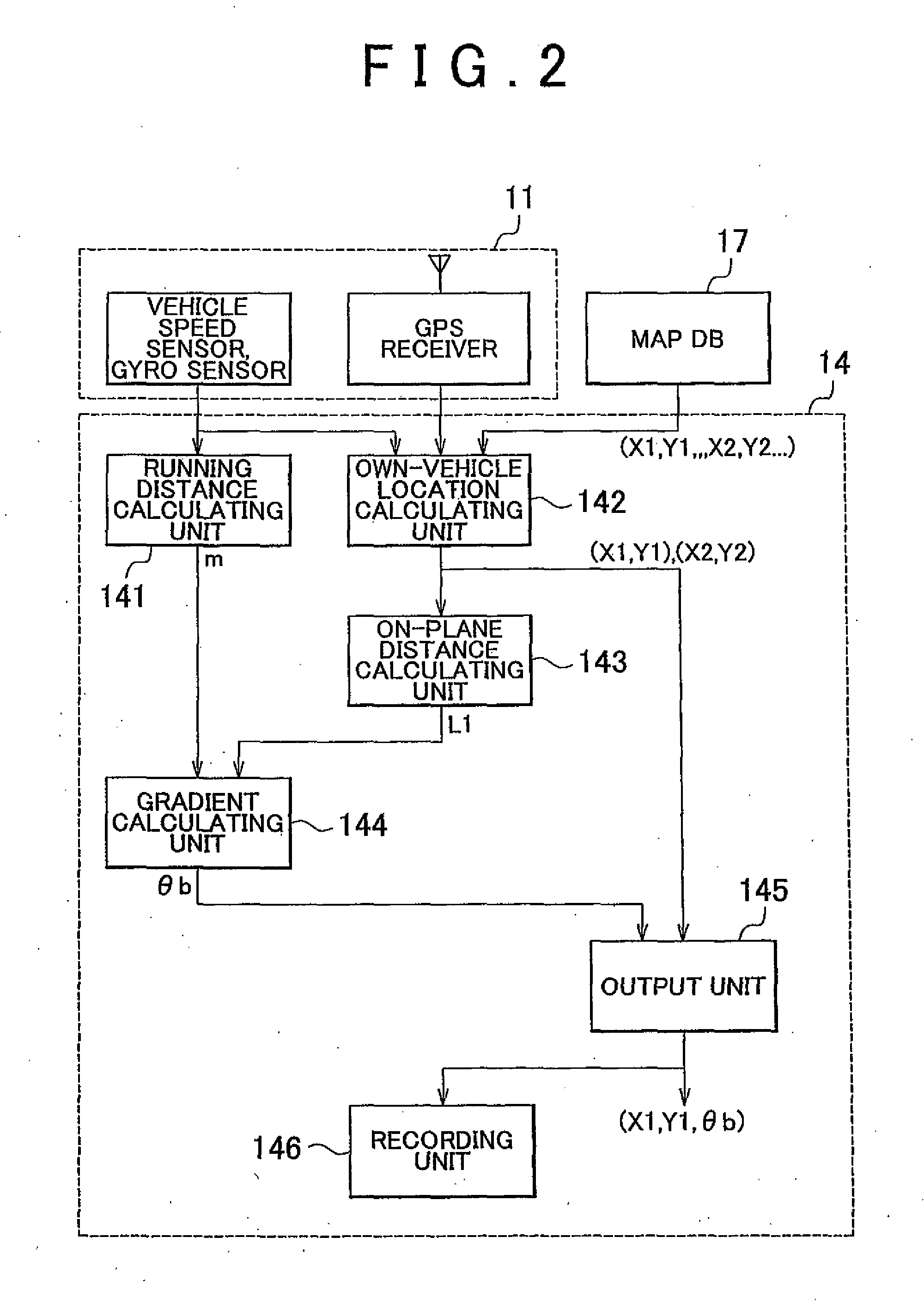
ActiveUS20100324752A1High densityInstruments for road network navigationDigital data processing detailsControl systemData selection
A gradient information calculating system includes a first calculating unit (14) that detects three-dimensional location information through autonomous navigation, and calculates a first gradient value (θb, B), based on a distance (m) traveled, and an on-plane distance (L1) obtained by projecting the distance (m) traveled on a horizontal plane, a road map information storing unit (17) that stores road map information that represents each road by nodes of which the location information is known, and a link that connects the nodes, a second calculating unit (16) that estimates elevations of the nodes from previously measured elevation data, and calculates a second gradient value (A), based on a difference in elevation between the nodes and the length of the link, and a gradient data selecting unit (19) that selects one of the first and second gradient values to be adopted as a gradient value of the link, according to a difference between the first and the second gradient values.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Automatic following guidance system for motor vehicles
InactiveUS6370471B1Reduce the burden onVehicle fittingsDigital data processing detailsGuidance systemLevel iv
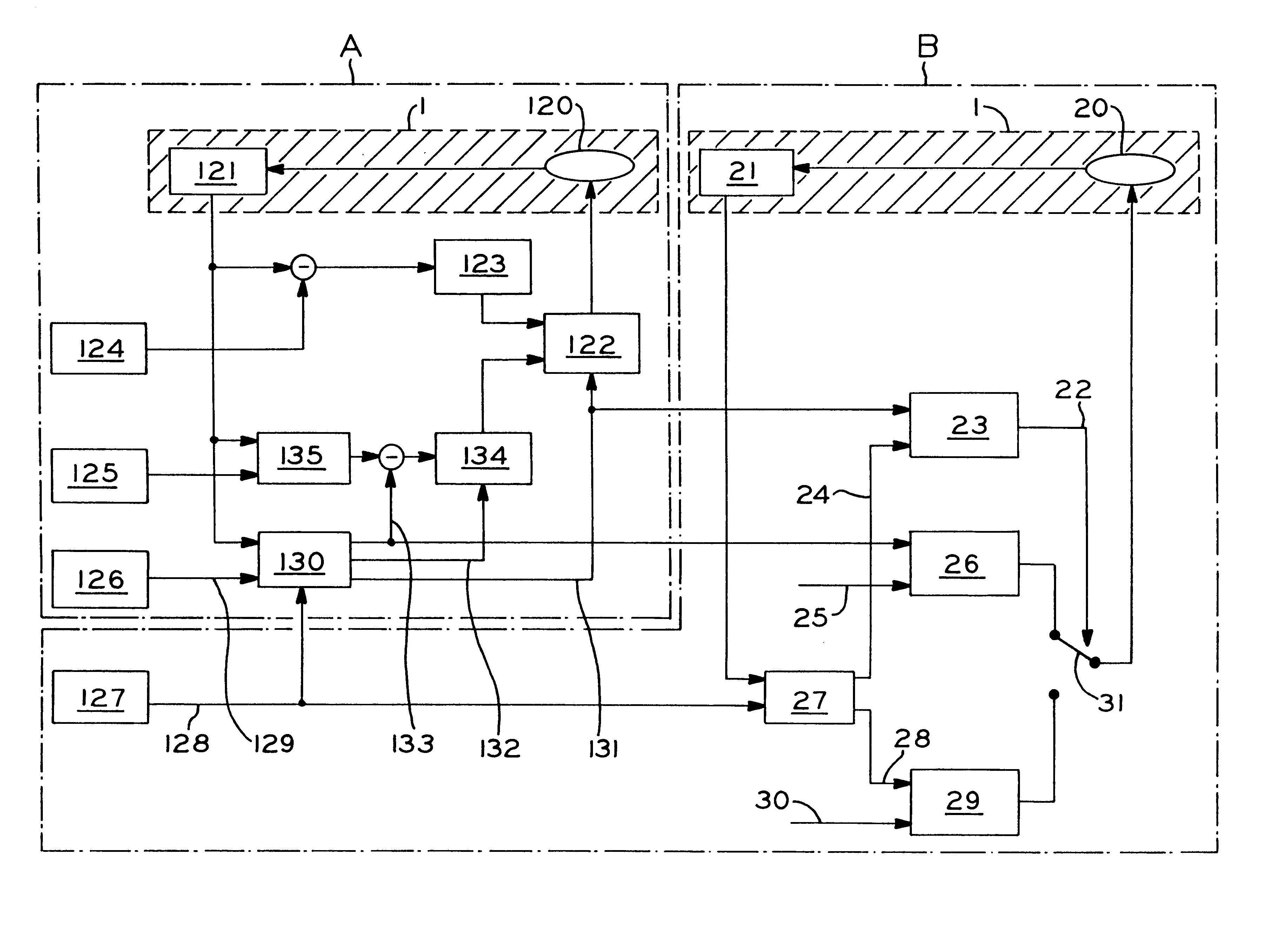
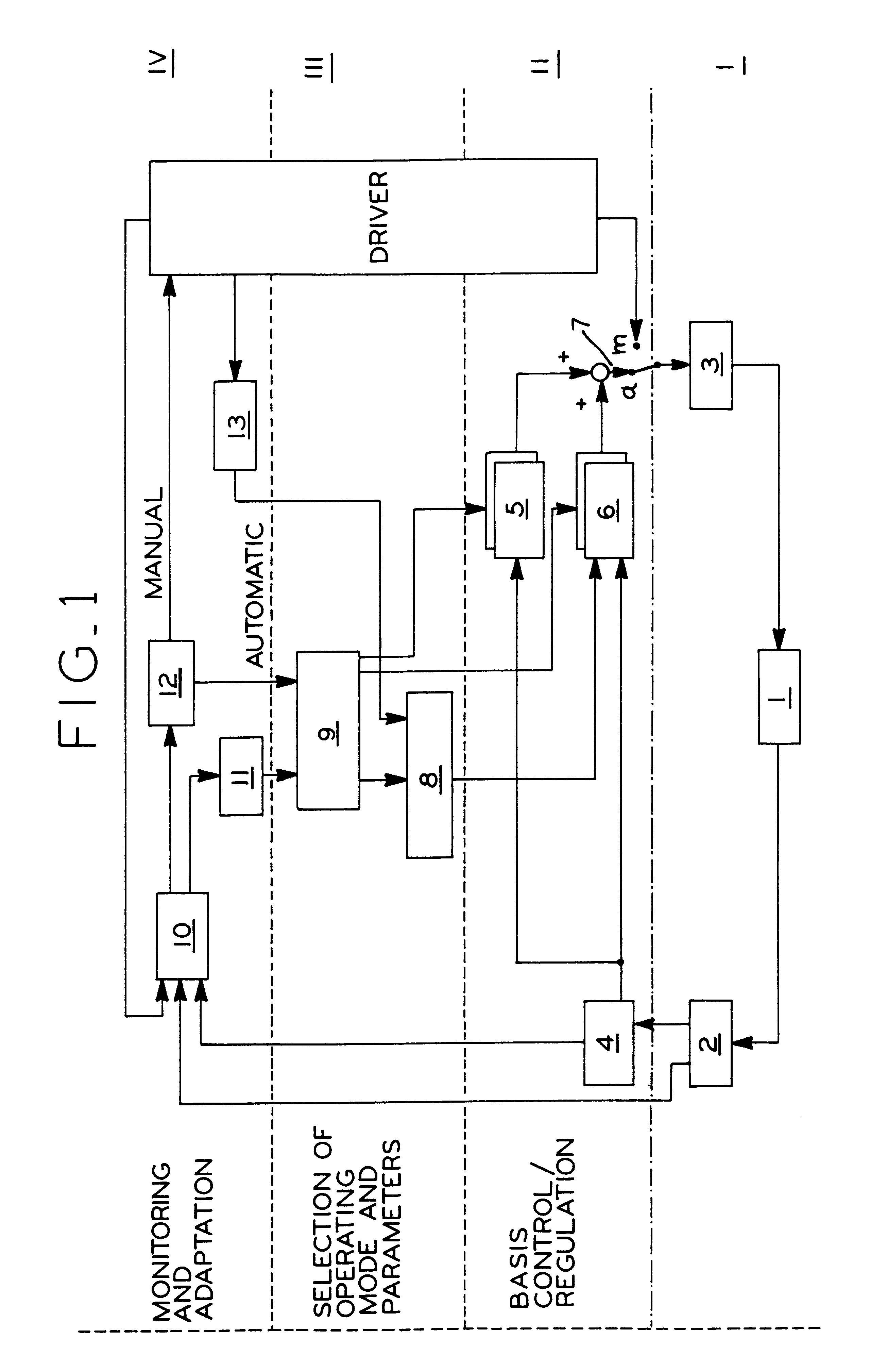
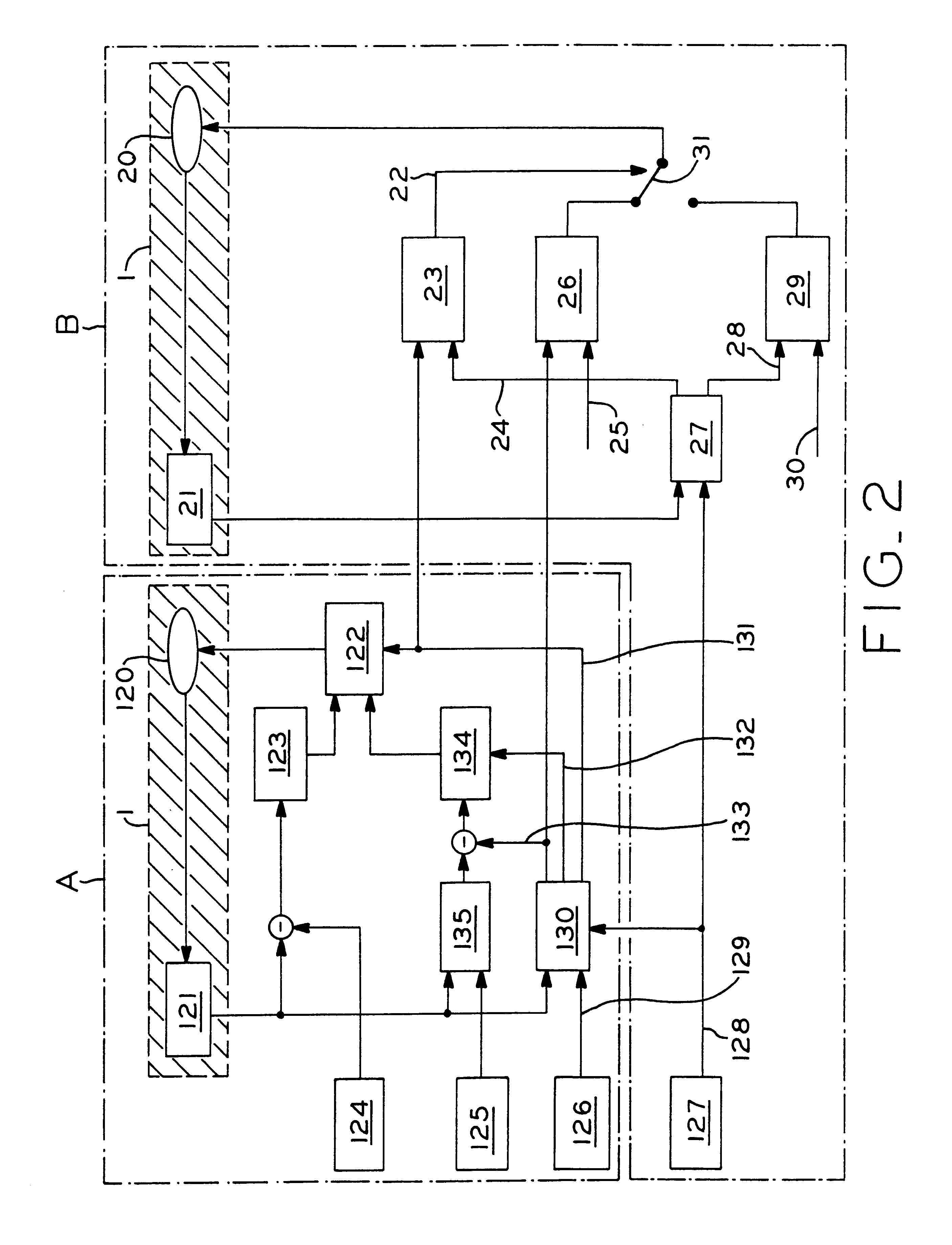
The invention concerns a system for automatic following guidance, particularly for heavy-traffic automatic following guidance, of a motor vehicle (1), designed to ease the burden on the driver in heavy-traffic situations both by taking over lateral guidance by means of an automatic steering regulation system and by maintaining a set distance from a leading vehicle. The latter function requires an adaptive cruise and braking regulation system with "stop" and "go" function. According to the invention, selection and decision means (5, 6, 7, 8, 9) are provided that select both the regulating parameters and the types of controllers [sic], e.g., following guidance of the motor vehicle (1) on the basis of lane markings recognized by means of a video camera or on the basis of a recognized leading vehicle. The system is divided into hierarchical levels I-IV, the driver always being in the monitoring and adaptation loop assigned to the top level IV of the hierarchy, so that he has the highest priority and can override the system at any time.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
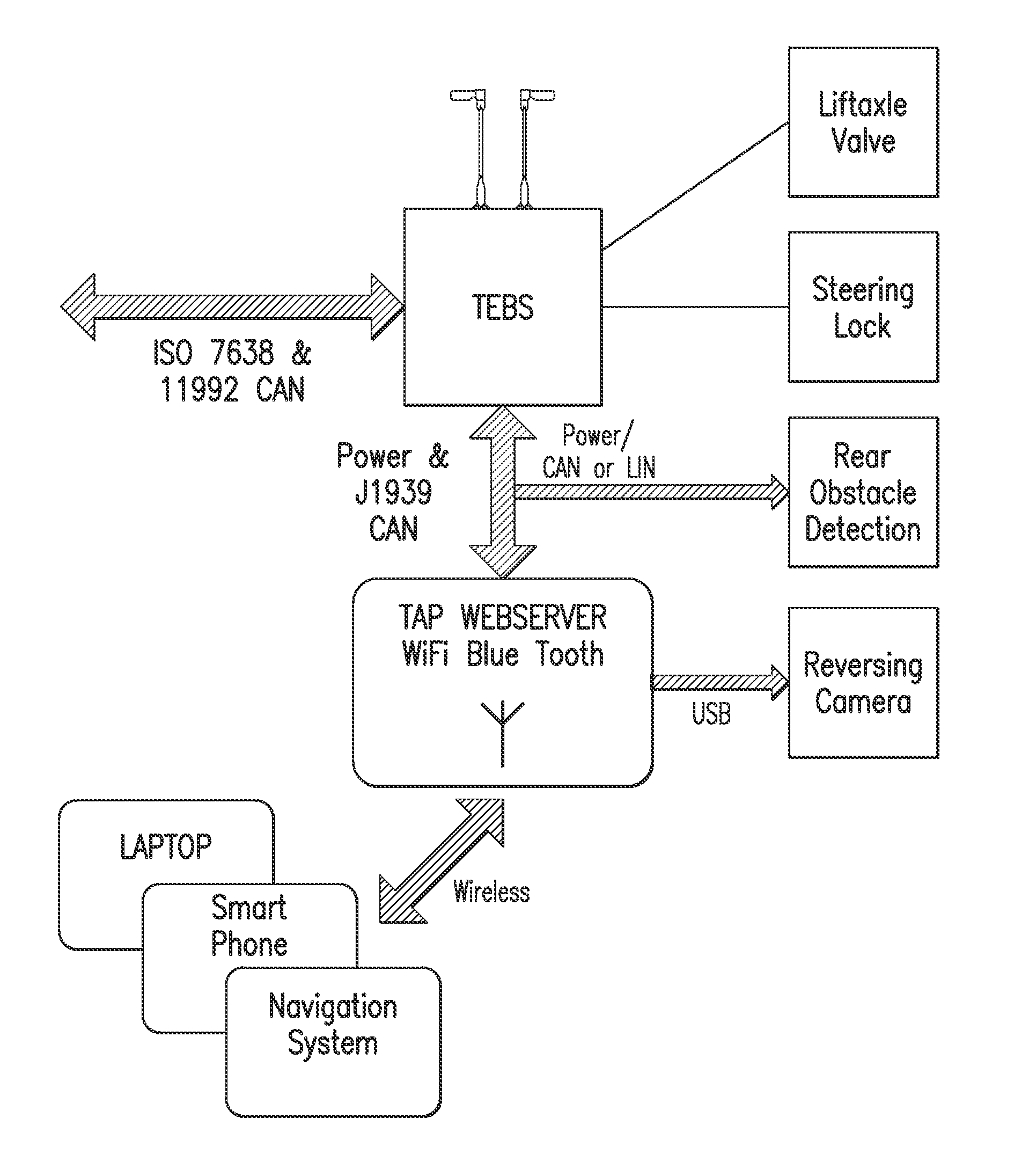
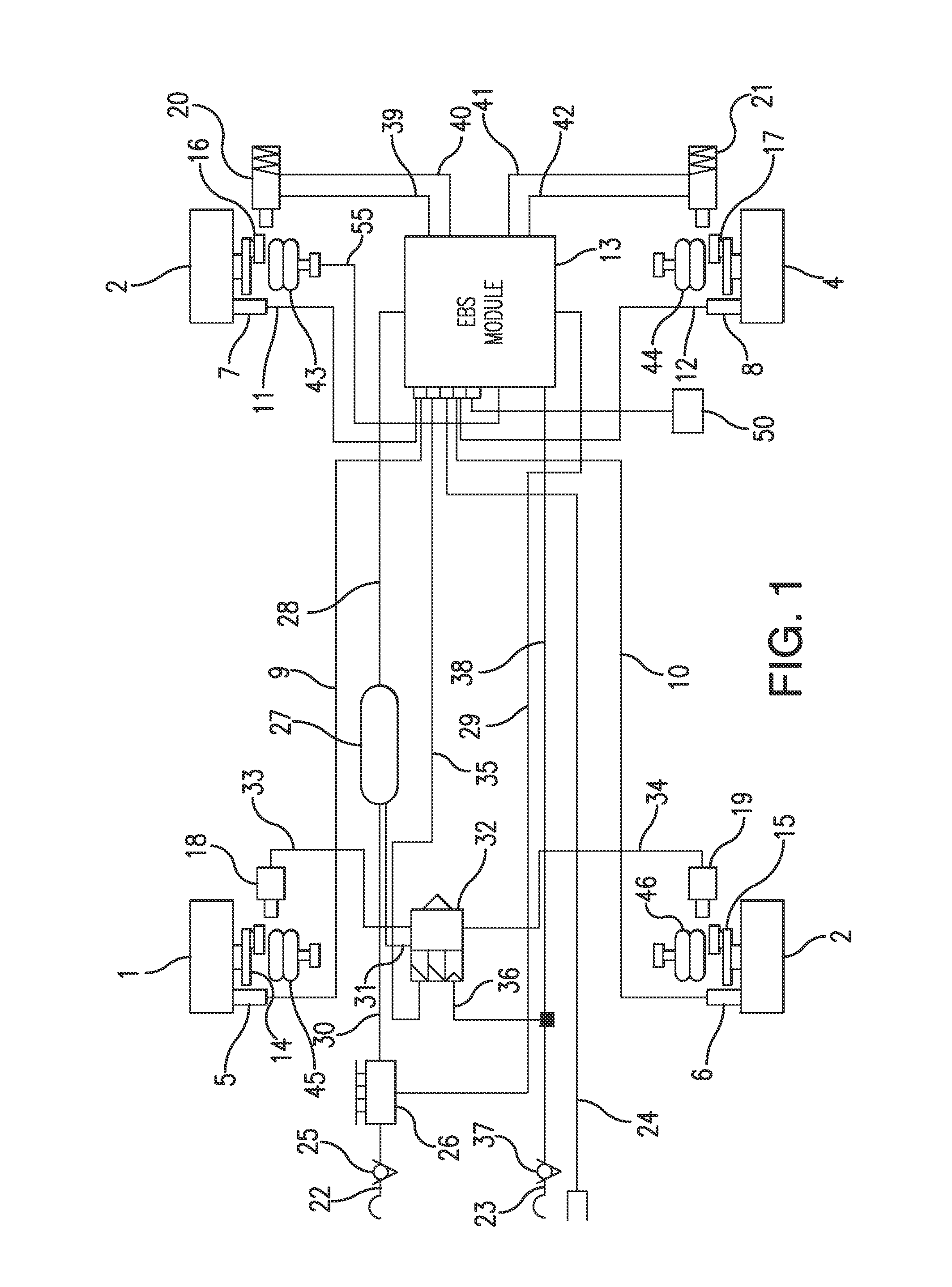
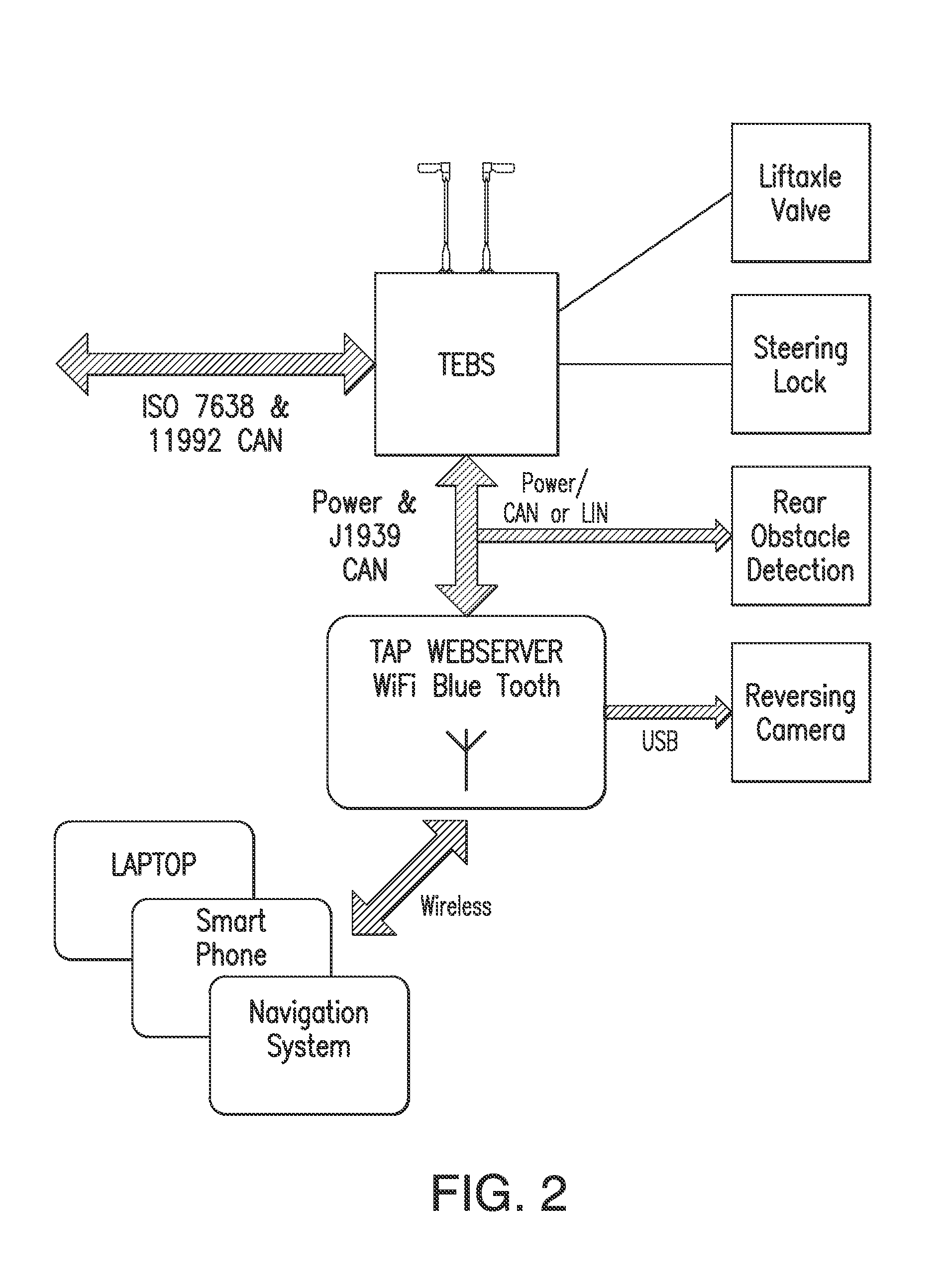
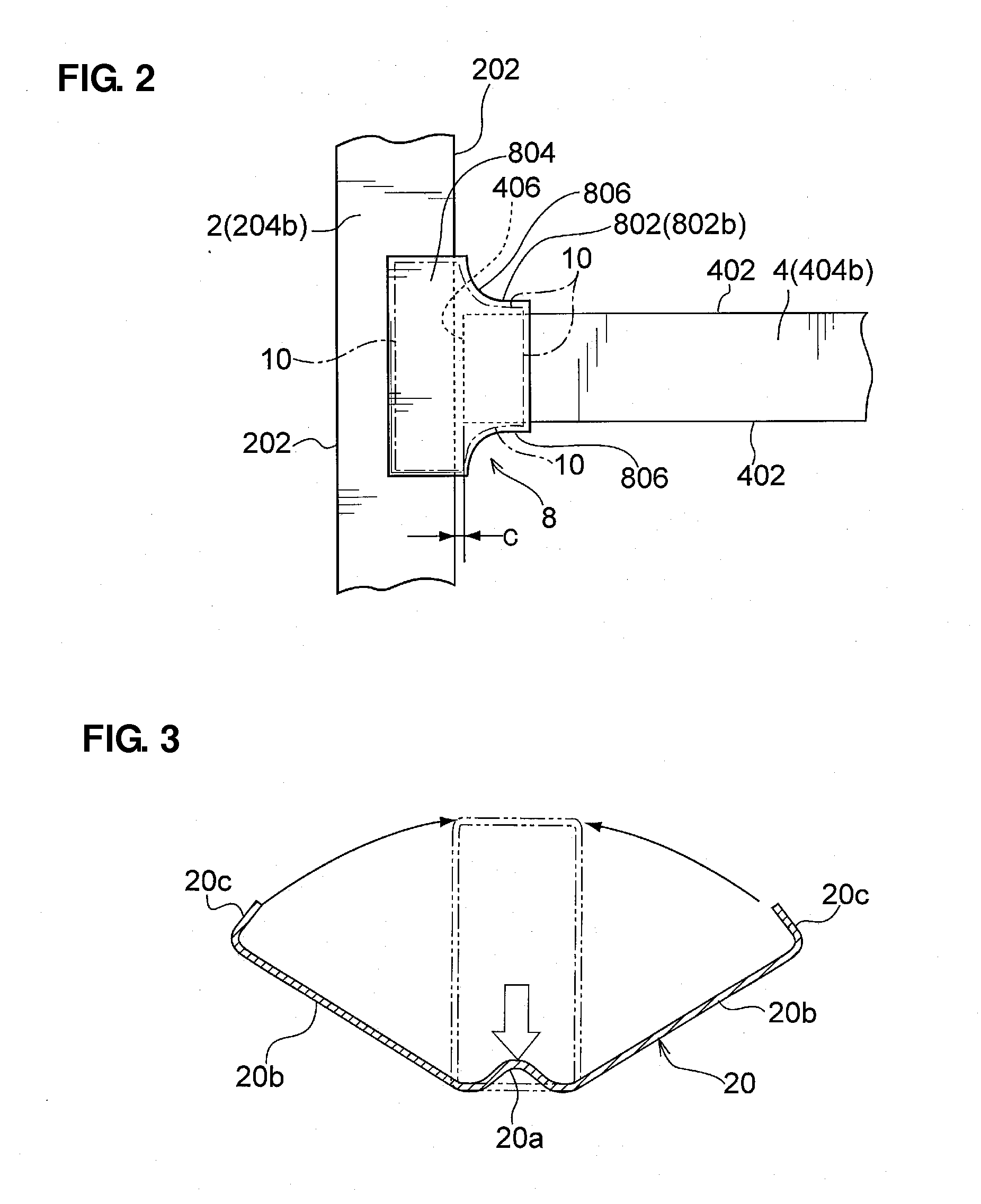
Trailer access point pairing
A trailer electronic braking system comprising a braking device capable of generating a braking force on a wheel on the trailer. The braking force is applied to the brake cylinders and is controllable by a braking ECU, which braking ECU is connected to a standards compliant communication bus on the trailer. The ECU is adapted to receive data inputs from sensors on the trailer. The system further includes an arrangement to interface to trailer electronics and a communications interface. In use, the arrangement transmits a request to the device for a driver to apply a predetermined condition to the trailer to enable control functions to be actuated from a remote device.
Owner:KNORR BREMSE SYST FOR COMML VEHICLES
Absolute acceleration sensor for use within moving vehicles
A communication system for a vehicle includes a vehicle speed sensor configured to emit a periodic function with a parameter correlated to the speed of the vehicle, an acceleration monitoring system, a braking system engagement detector to detect a braking status of the vehicle, an alerting device capable of signaling other drivers of a deceleration condition of the vehicle, and a control device. The acceleration monitoring system is configured to compute the acceleration of the vehicle from variations in the parameter of the periodic function of the vehicle speed sensor and to output a deceleration status of the vehicle. The control device is coupled to the acceleration monitoring system, the braking system engagement detector, and the alerting device, wherein the acceleration monitoring system sends signals to the control device and the control device operates the alerting device in a manner dependent on the deceleration status of the vehicle.
Owner:VISION WORKS IP CORP
Communication system and method, and distributed control system and method
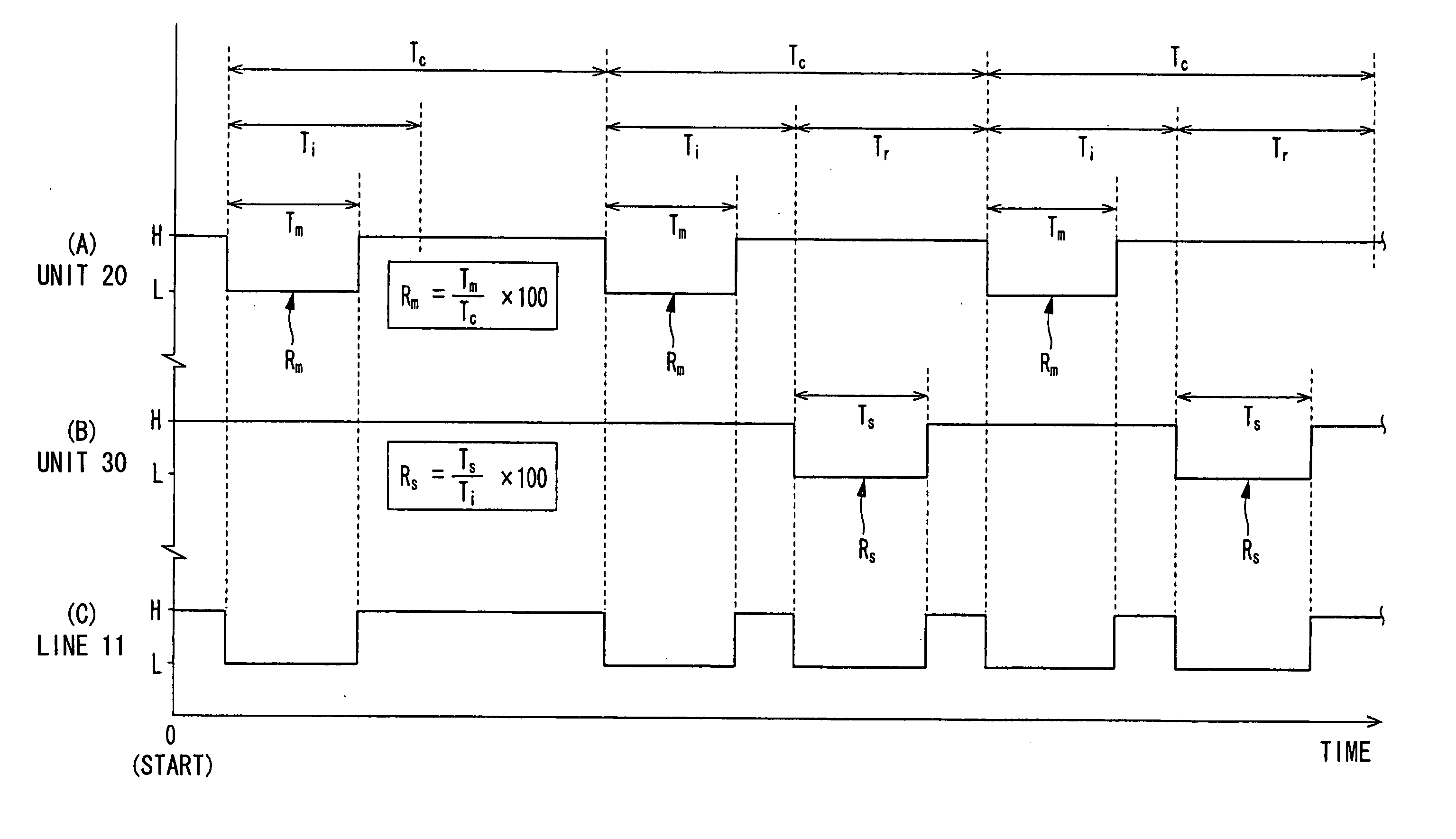
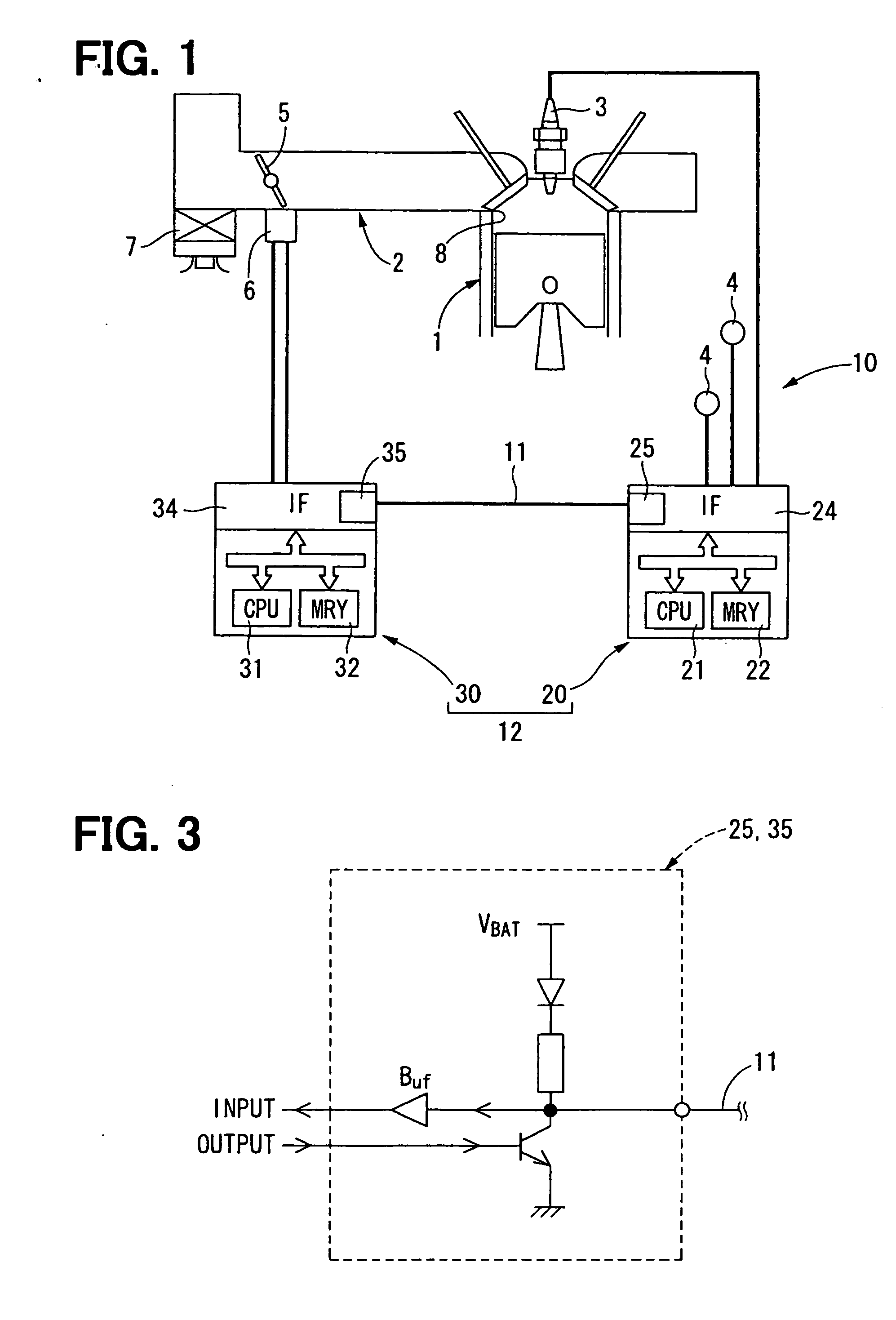
InactiveUS20070088883A1Low costAccurate communicationSuspensionsElectrical controlCommunications systemTime segment
A communication system performs bidirectional communication through a same communication path every communication cycle period between a master station and a slave station. From the start of the communication cycle period until an interval period shorter than the communication cycle period elapses, the master station transmits master data represented at a first ratio of first pulse width to the communication cycle period to the slave station. In a remaining period after the interval period in the communication cycle period, the slave station transmits slave data represented at a second ratio of second pulse width to the interval period to the master station.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Sensor-equipped axle unit having a built-in motor of in-wheel type
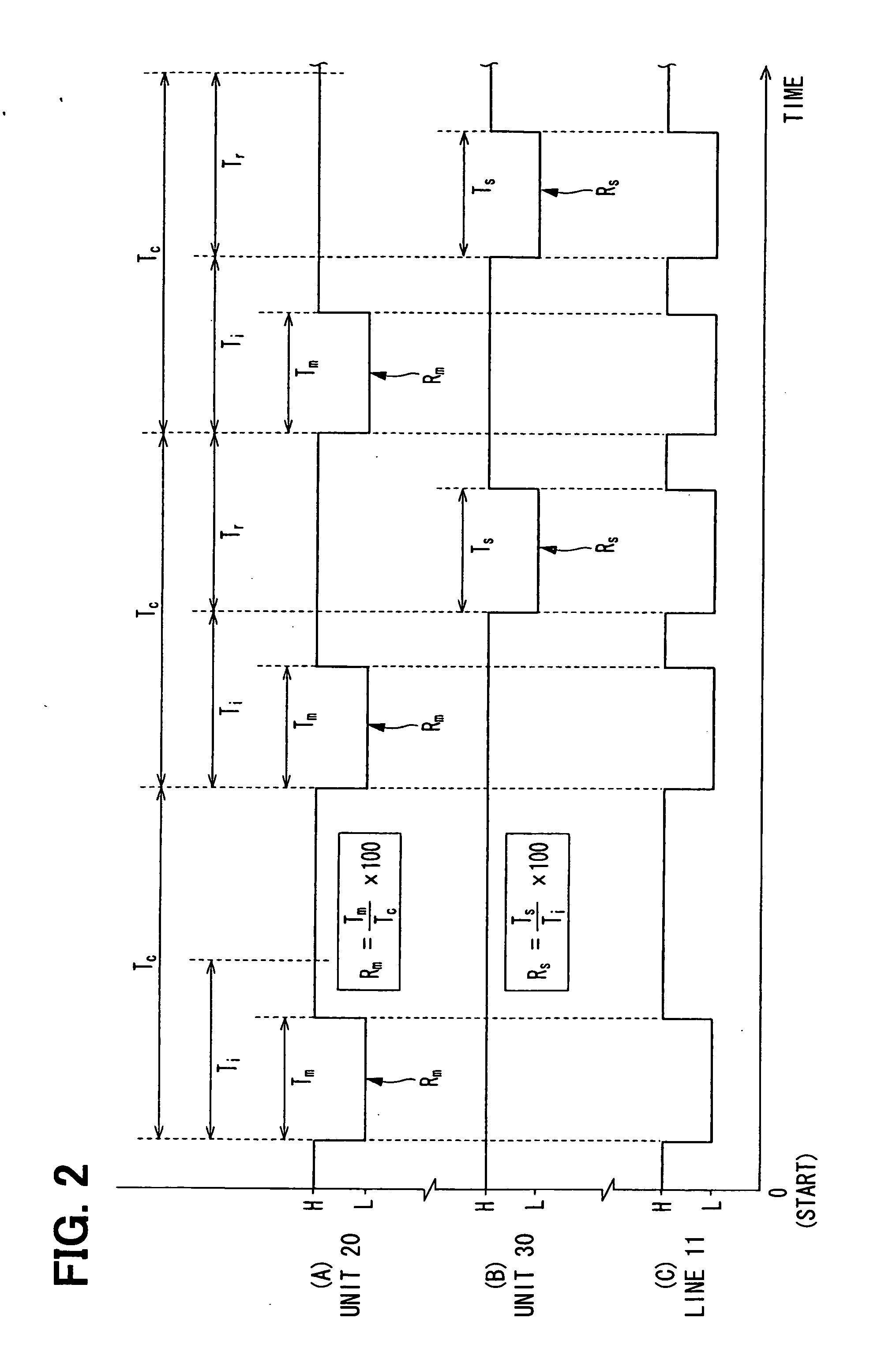
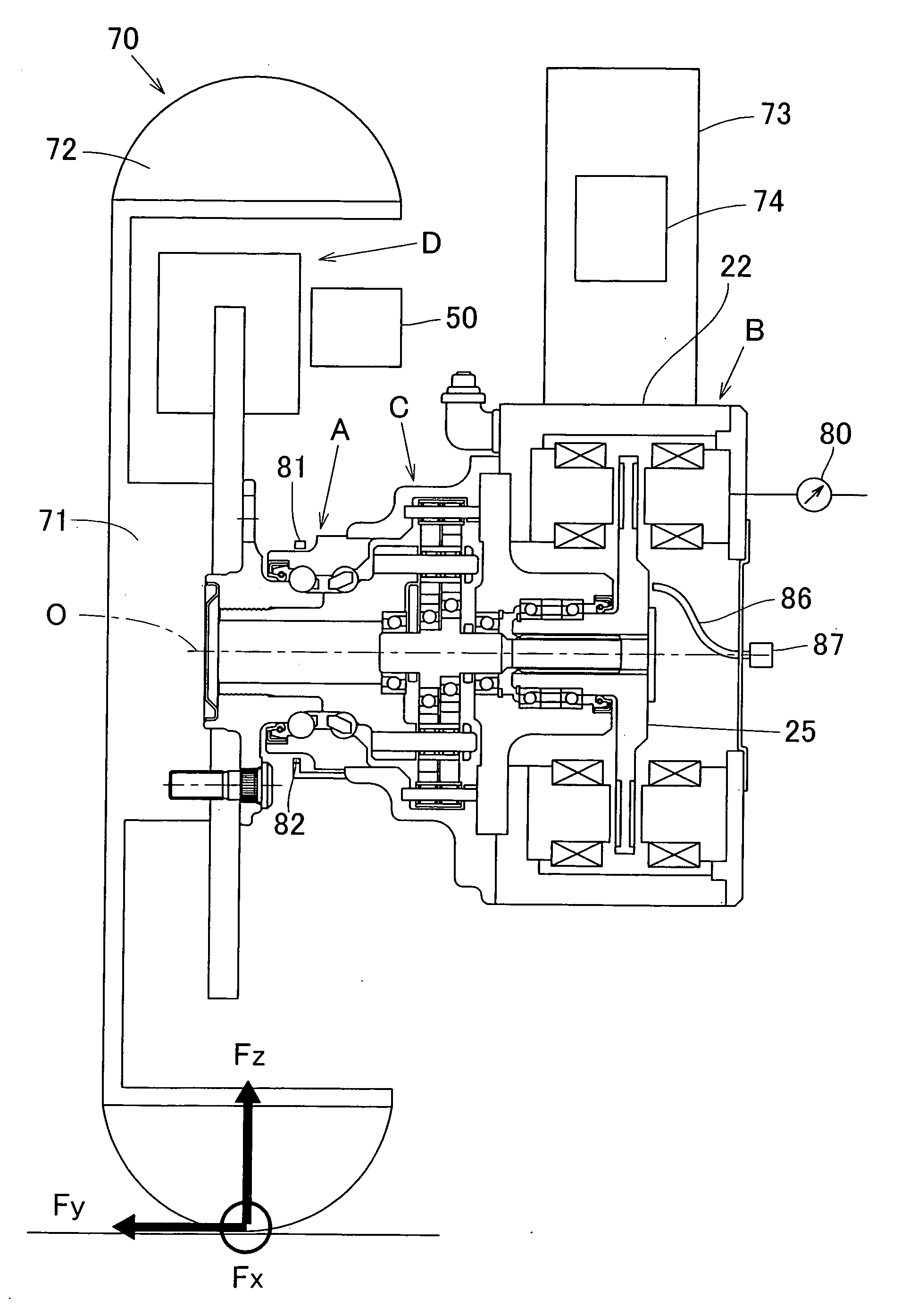
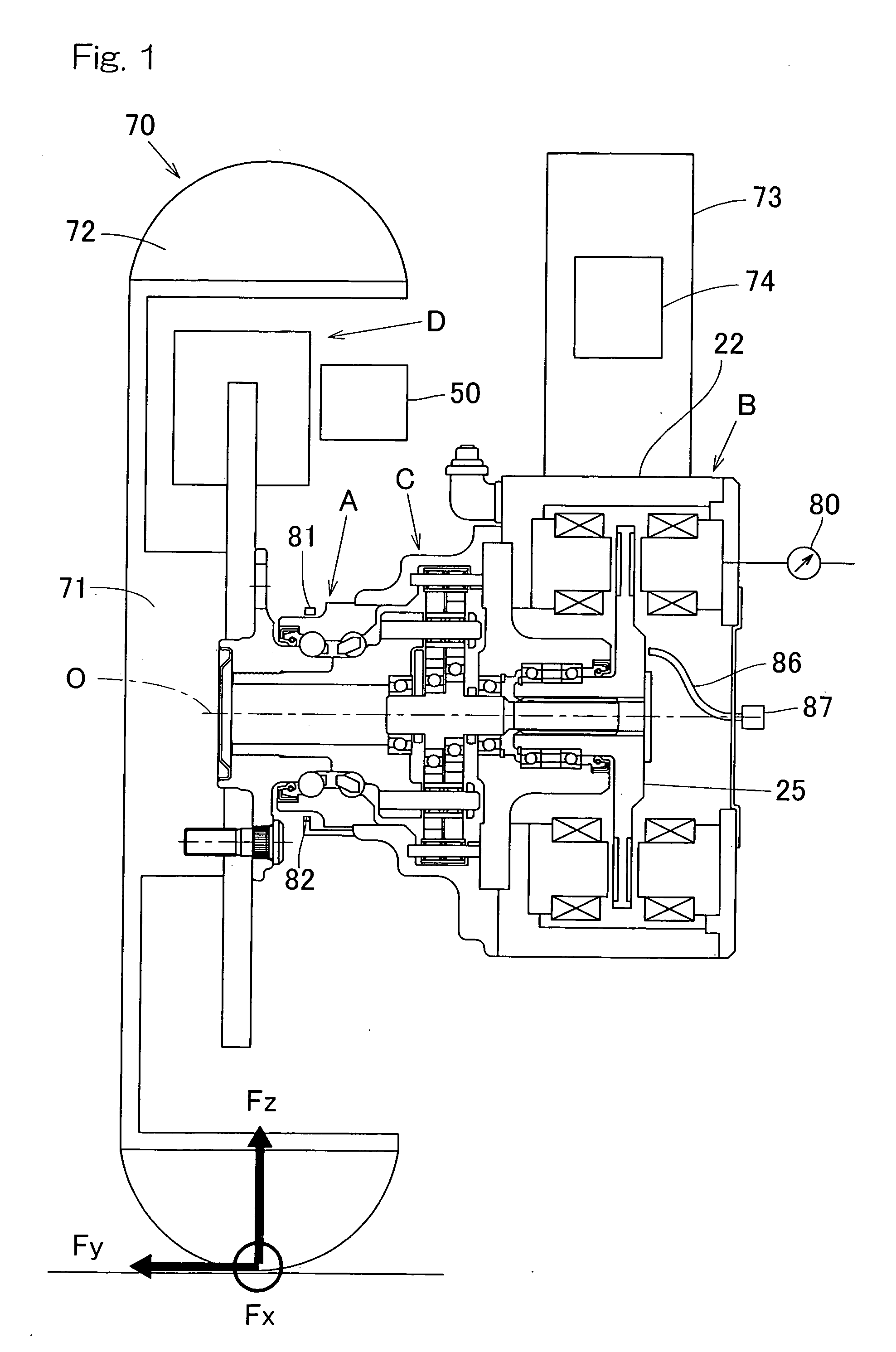
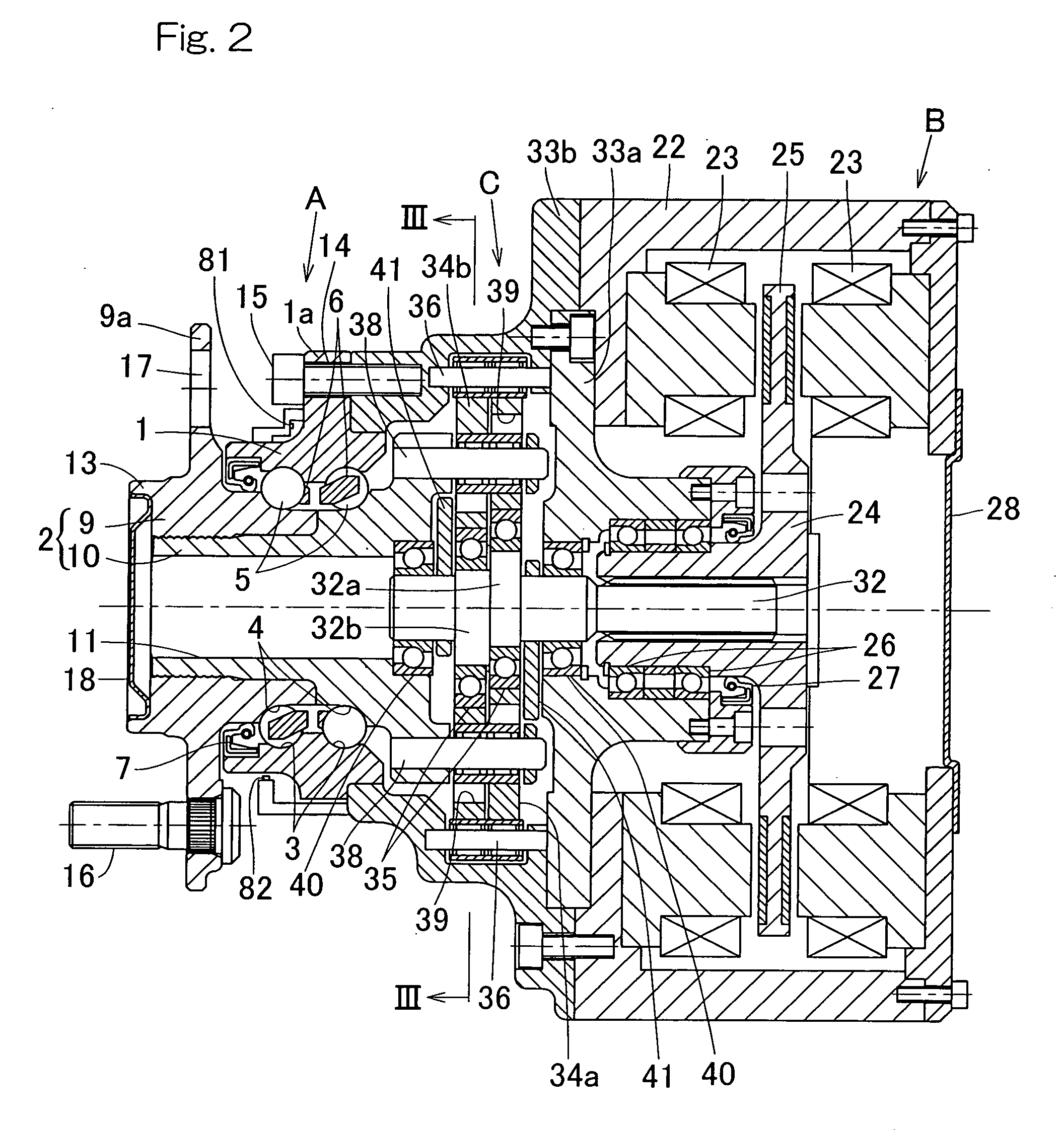
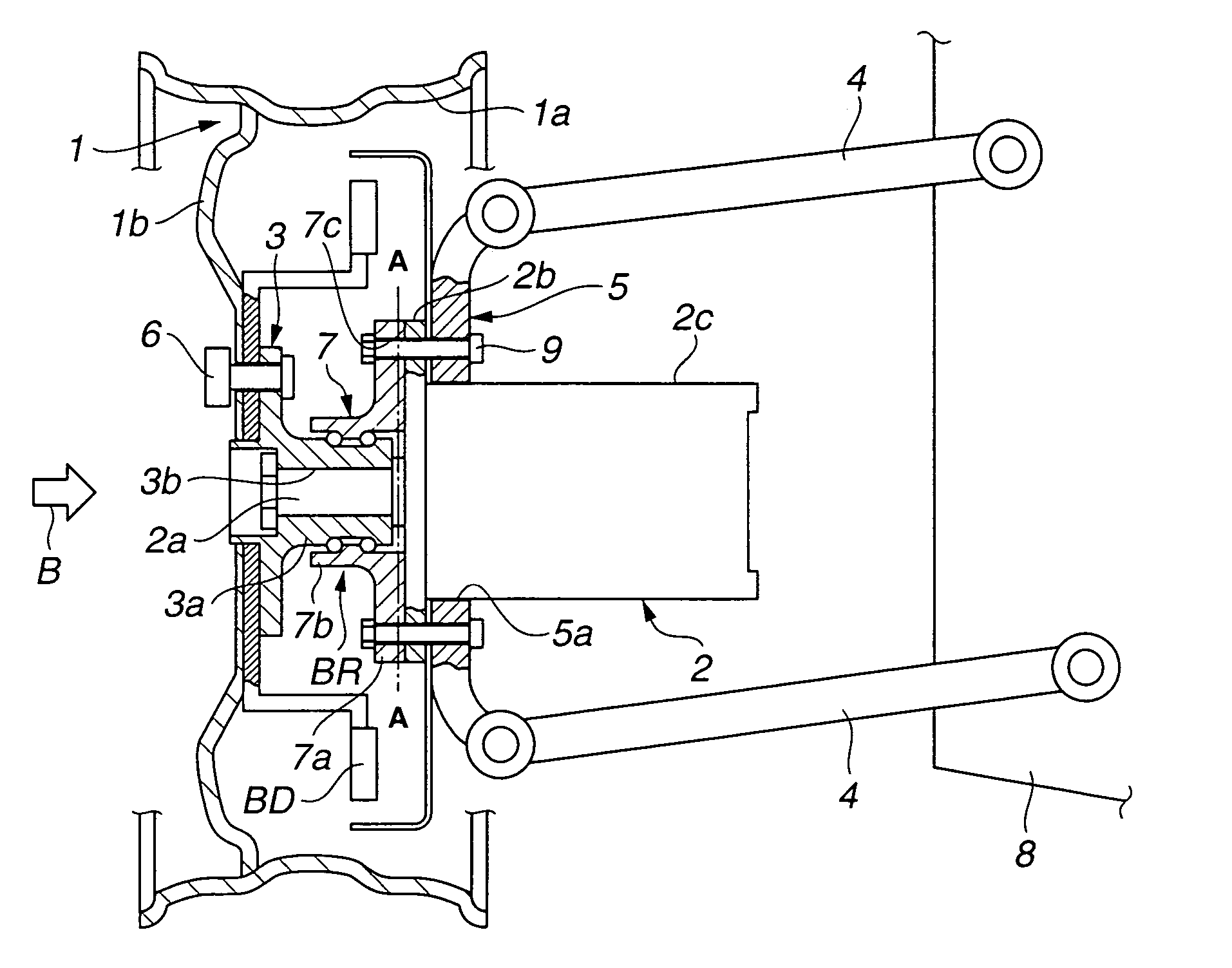
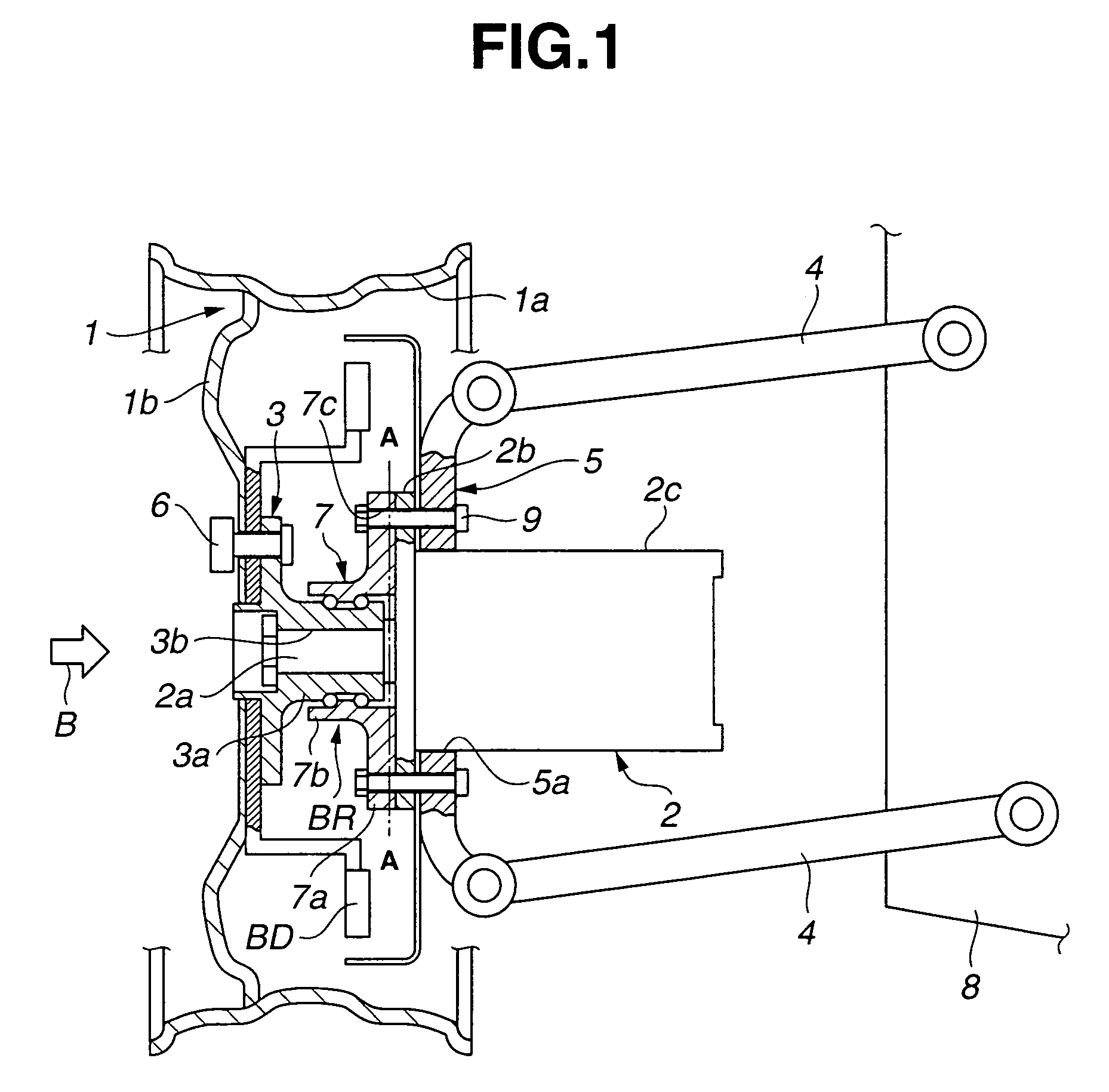
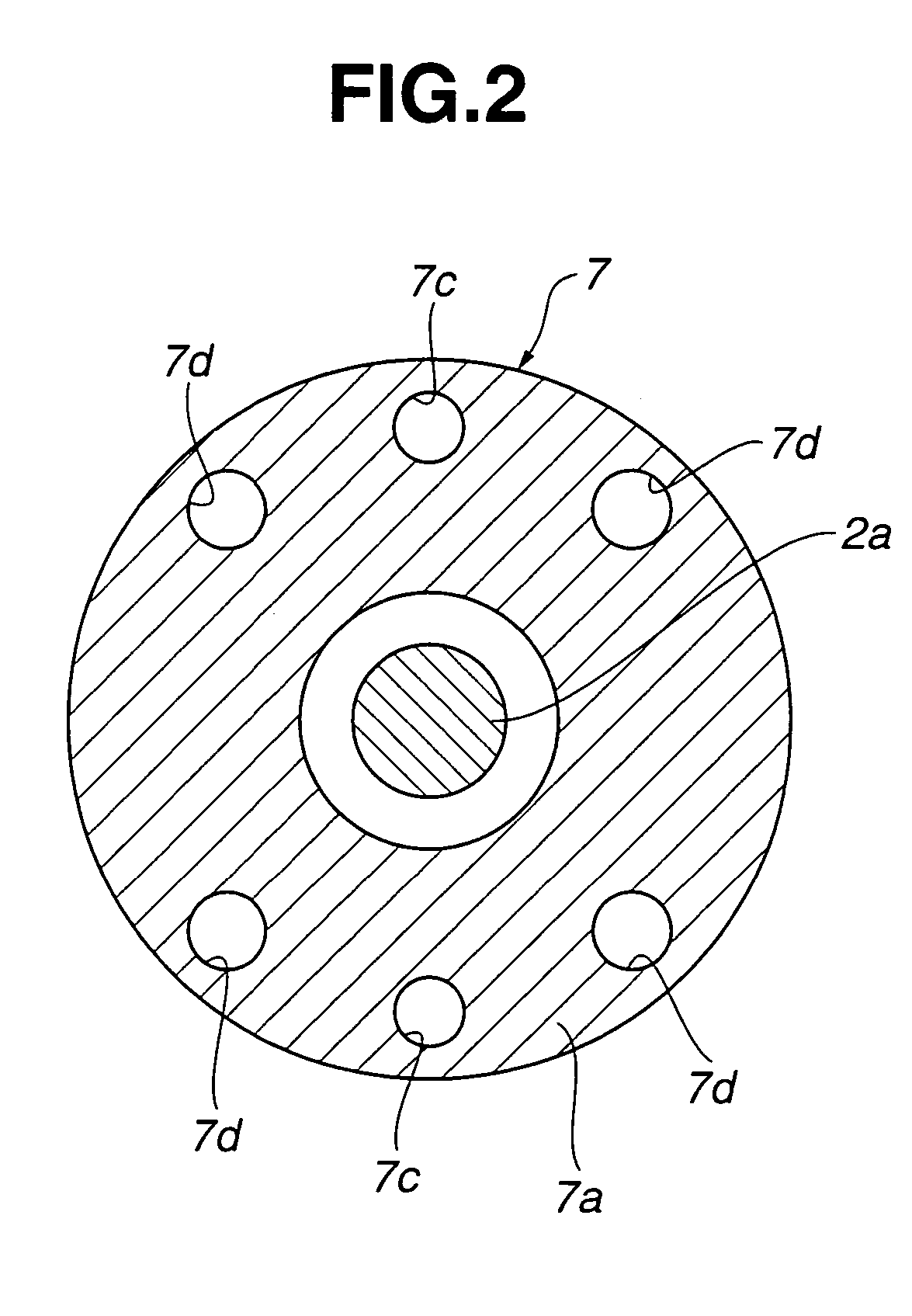
ActiveUS20090236157A1Improve accuracyHigh sensitivityHybrid vehiclesMotor depositionDrive wheelElectric machine
A sensor equipped axle unit having an in-wheel type motor built therein, in which a hub bearing assembly (A), an electric motor (B), a reduction gear unit (C) and a brake assembly (D) are arranged coaxially on a center axis of a vehicle drive wheel. Sensors (80, 81 and 82) are provided for measuring forces Fx, Fy and Fz acting at a point of contact of the vehicle drive wheel (70) and a road surface in three axis directions perpendicular to each other, respectively, from the status of at least one of the hub bearing assembly (A), the electric motor (B), the reduction gear unit (C) and the brake assembly (D). Results of such measurement are utilized for a suspension control, an ABS control and any other control.
Owner:NTN CORP
System, tire, wheel, vehicle, and method for determining the behavior of a tire in motion
InactiveUS6959593B2Uniform structureAvoid physical contactSuspensionsSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementElectricityMobile vehicle
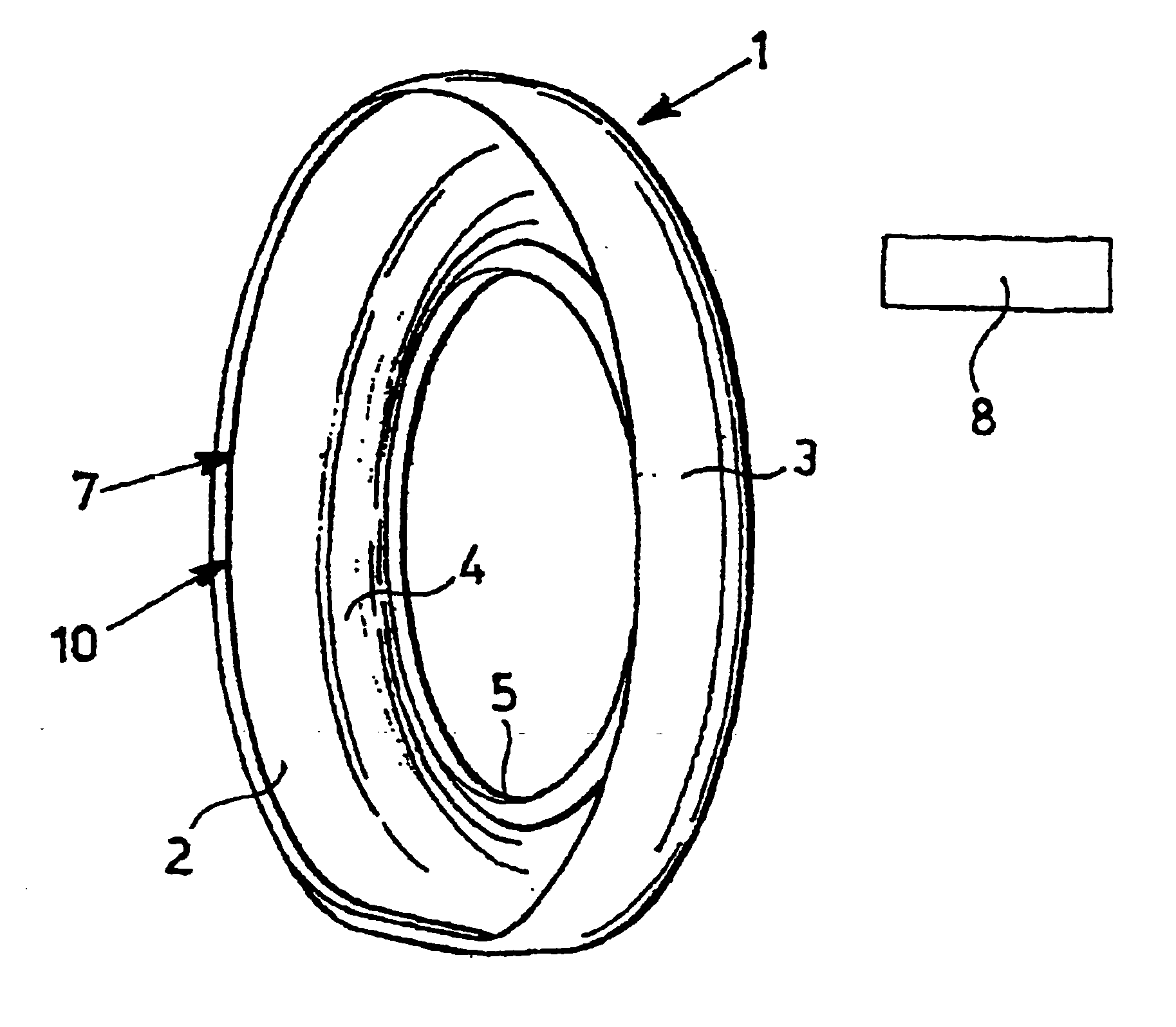
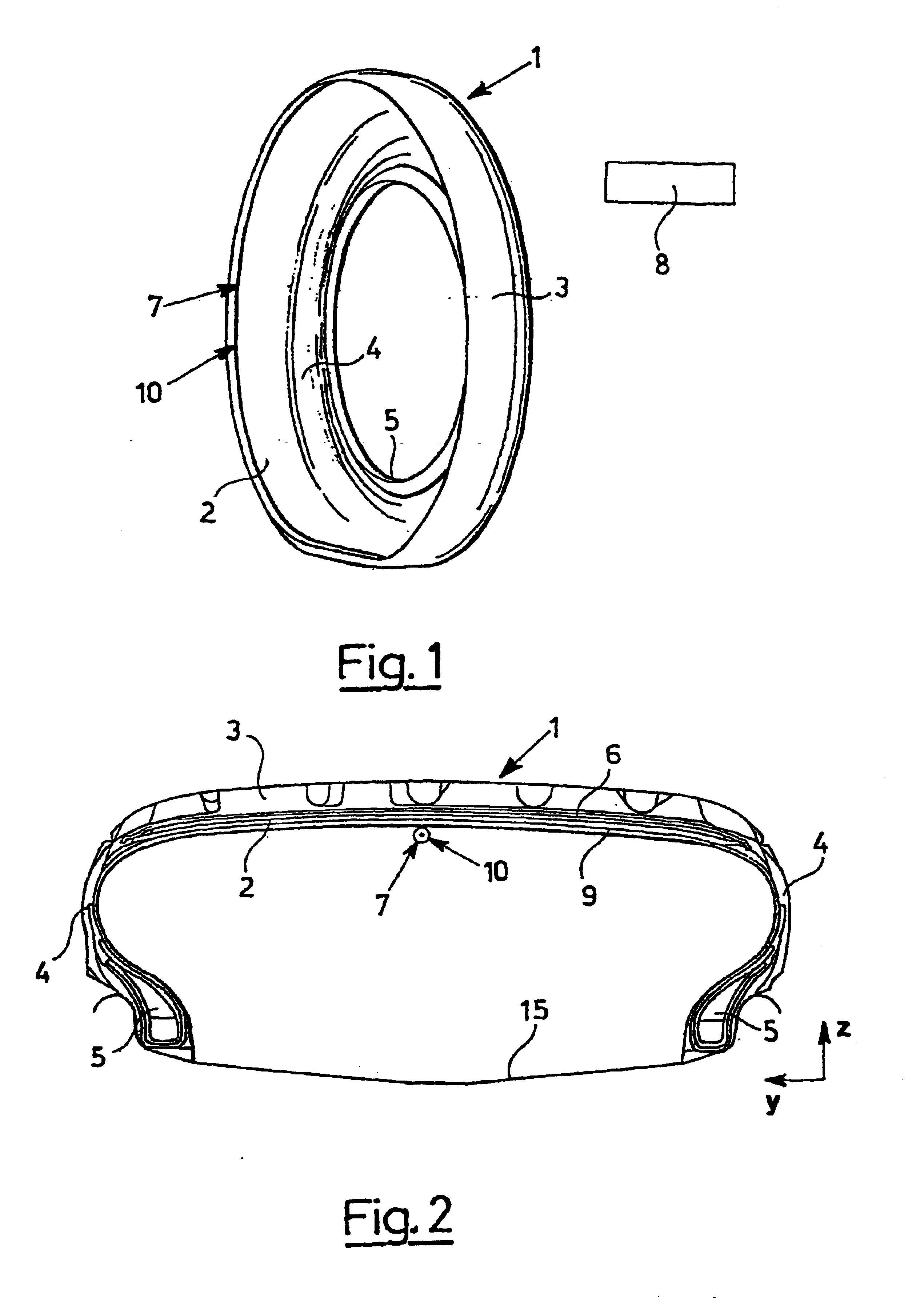
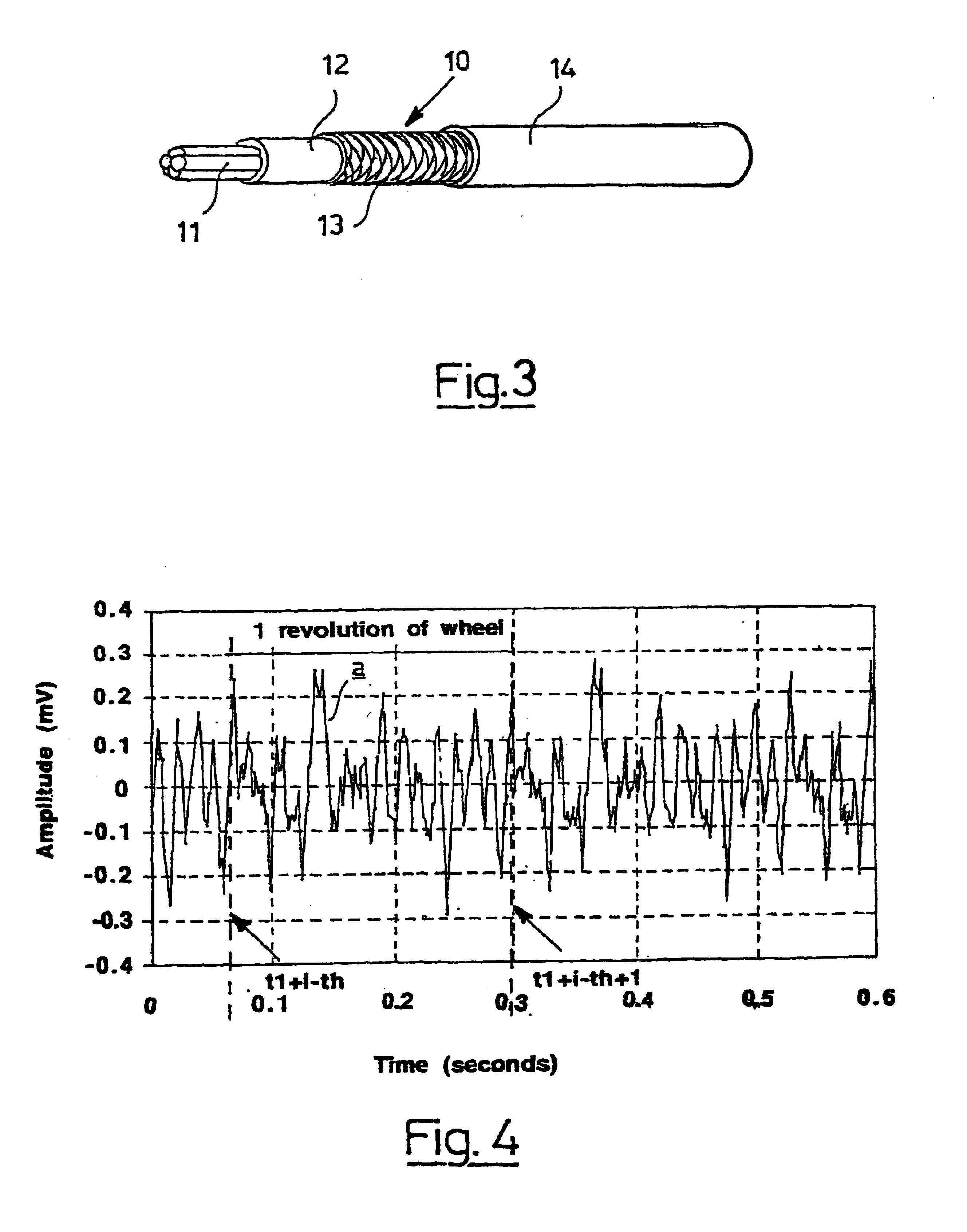
A system for determining interaction between a tire and a contact surface during movement of a motor vehicle includes at least one first sensor and processing means. The at least one first sensor includes one or more first elongated piezoelectric elements which extend along at least a first portion of the tire. The at least one first sensor supplies a first signal to the processing means. The first signal is generated by rotation of the tire and is generated cyclically with each revolution of the tire. The processing means detects variations in time intervals between distinctive elements of the first signal. A tire including the system, a kit for detecting behavior of a tire moving with respect to a contact surface, a method for monitoring events correlated with interactions between tires of a moving vehicle and a contact surface, and related systems, tires, methods, and vehicles are also disclosed.
Owner:PIRELLI TYRE SPA
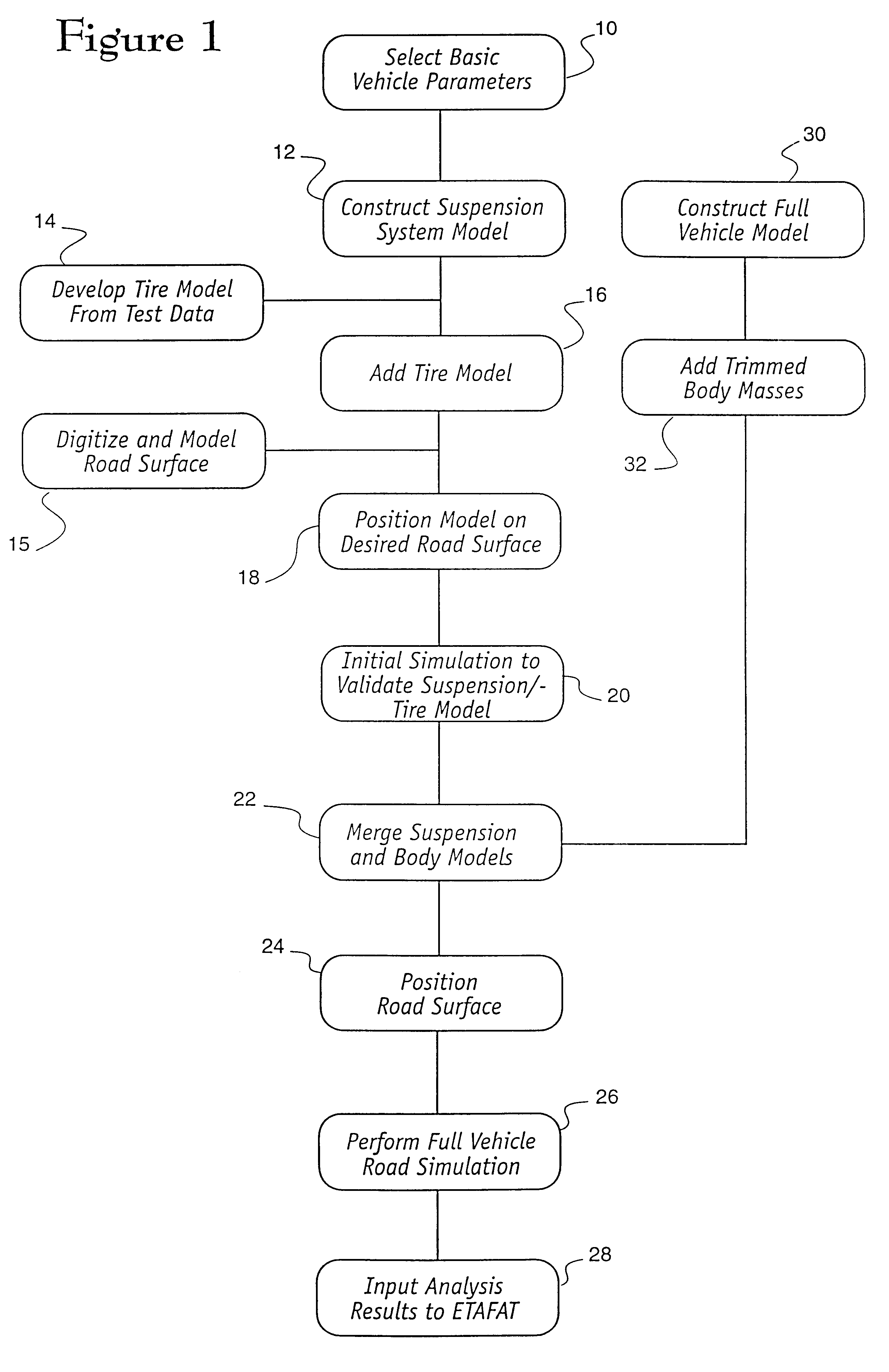
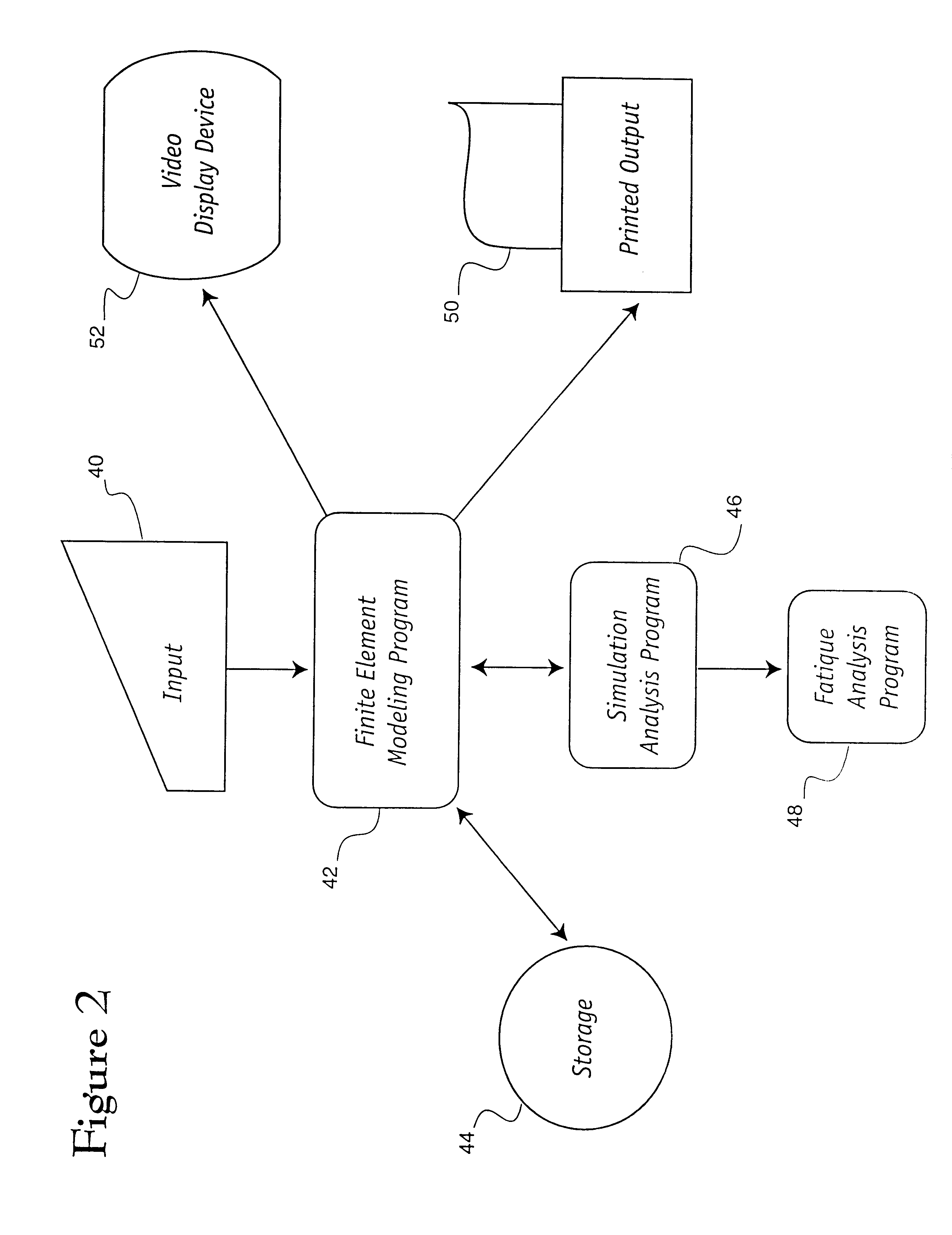
Method and system for simulating vehicle and roadway interaction
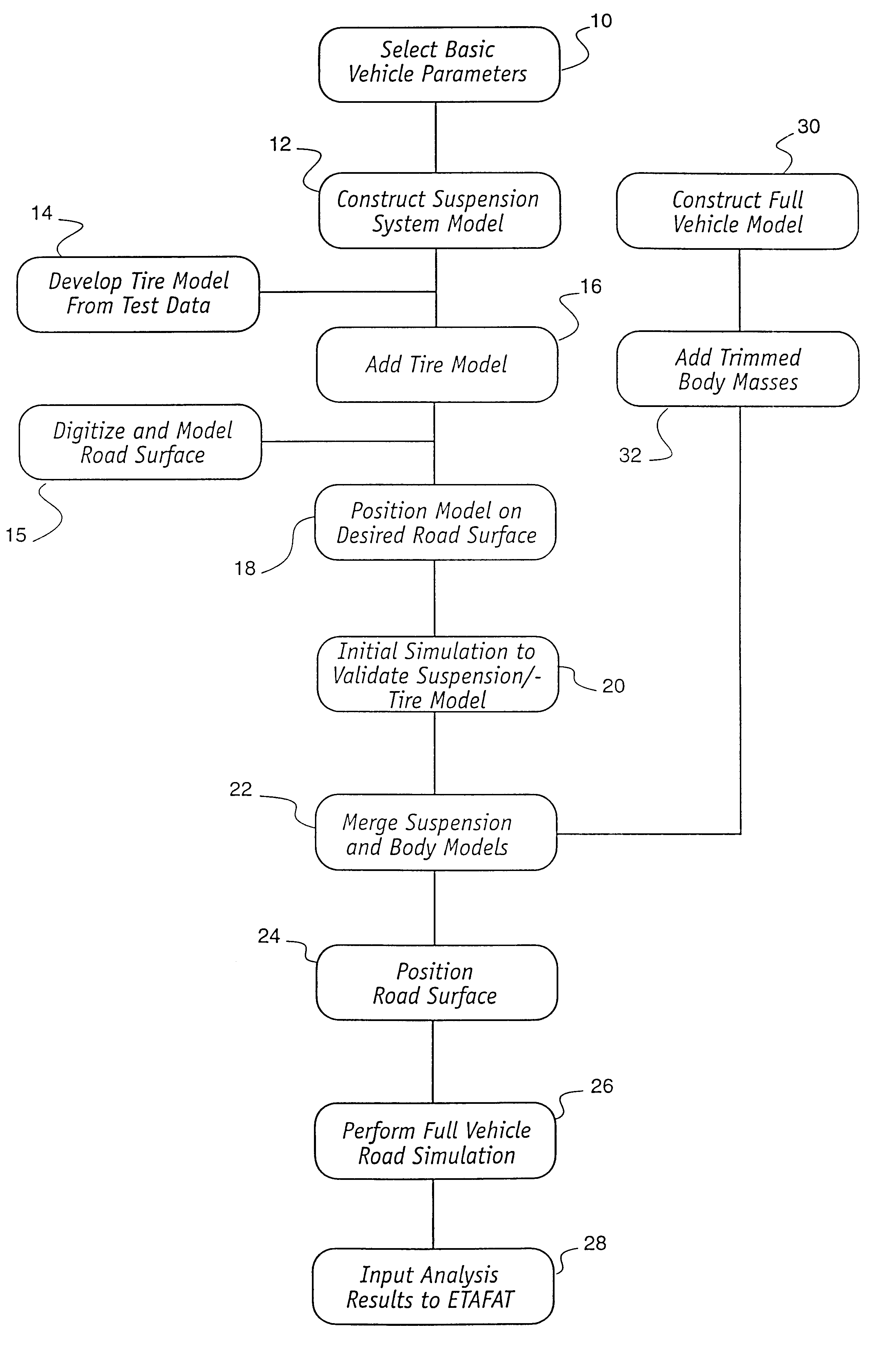
The present invention is directed to a system and method for simulating the interaction of a simulated vehicle with one or more simulated road surfaces. A computer modelling program is used to create a computer-based road surface model and a computer-based vehicle model. The computer-based vehicle model may include a body model, a chassis model, a suspension model, a wheel model and a tire model. A computer simulation engine program is operative with the computer-based road surface and vehicle models to selectively simulate the interaction therebetween and provide simulation data relative thereto. The simulation data may be used to identify high stress areas or low durability areas of the vehicle or to compute vehicle suspension parameters.
Owner:ENG TECH ASSOC
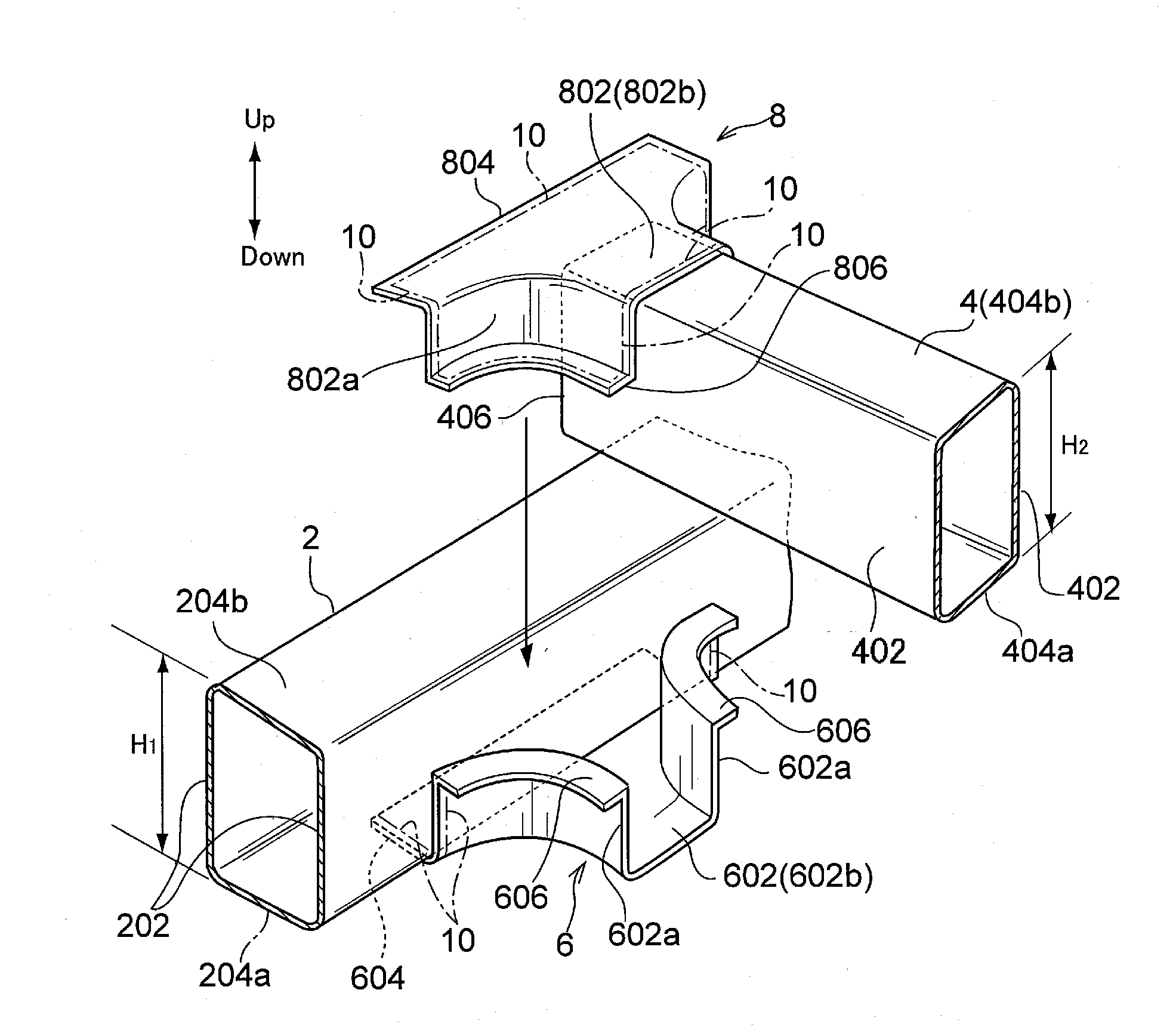
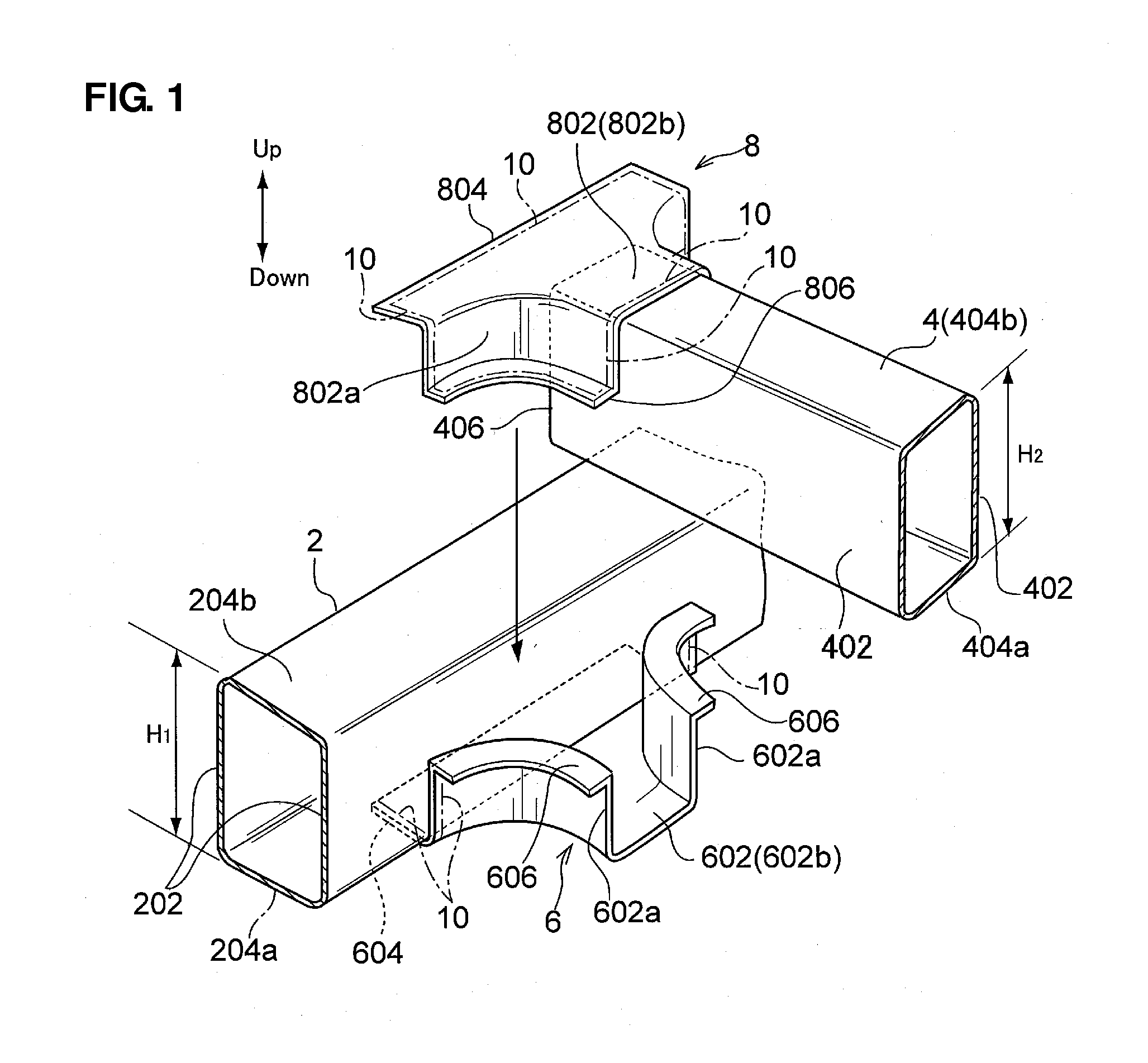
Connection structure and assembly method of tube-shaped frames
InactiveUS20100244497A1Accurate connectionEnsures rigiditySuspensionsVehicle seatsEngineeringSpot welding
A first split-bracket is joined to a first tube-shaped frame by lazar welding. A second split-bracket is joined to an end portion of a second tube-shaped frame by the lazar wielding. The second tube-shaped frame equipped with the second split-bracket is assembled to the first tube-shaped frame equipped with the first split-bracket. A second flange of the first split-bracket and a second flange of the second split-bracket are joined temporarily by spot welding. The second flange of the first split-bracket and the second flange of the second split-bracket are joined by continuous welding with lazar welding. Accordingly, the tube-shaped frames can be connected properly without forming any hole at a wall of the tube-shaped frame, ensuring the rigidity of the connection portion of the tube-shaped frames.
Owner:MAZDA MOTOR CORP
Absolute acceleration sensor for use within moving vehicles
ActiveUS20100217507A1Quick responseSuspensionsAnalogue computers for vehiclesMobile vehicleDriver/operator
A vehicle monitoring system for turning off an idling engine comprises a vehicle speed sensor configured to detect a lack of motion, or “stationary status” of a vehicle and emit a parameter correlated to the motion status of the vehicle, a transmission status detector configured to detect a transmission status of the vehicle, an alerting device capable of warning other drivers of a stationary status of the vehicle and a control device. The control device is coupled to the vehicle speed sensor, the transmission status detector and the alerting device, wherein the vehicle speed sensor and the transmission status detector send a signal to the control device and the control device operates in a manner dependent on the motion status of the vehicle and the transmission status of the vehicle.
Owner:VISION WORKS IP CORP
Systems and methods for active vibration damping
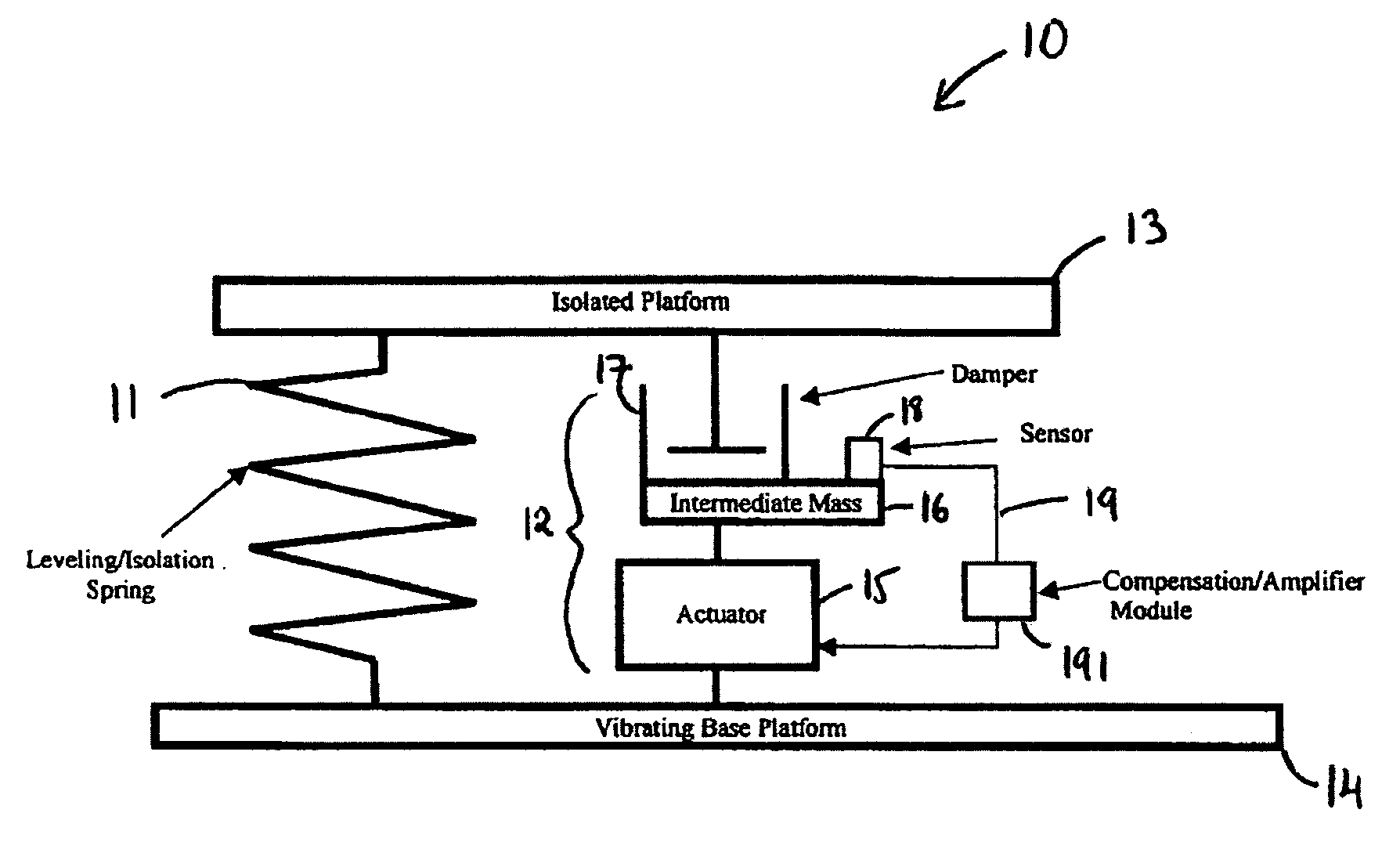
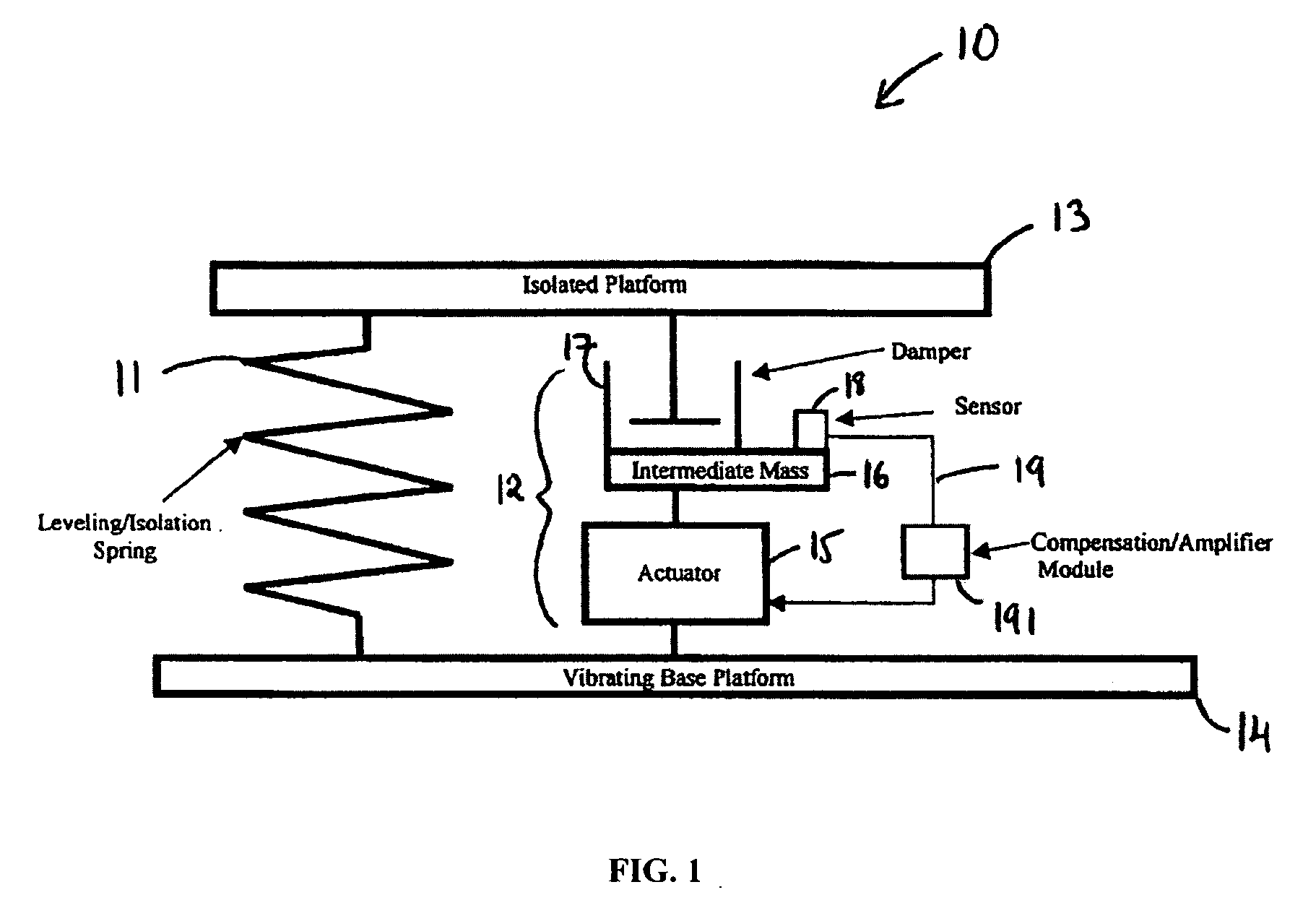
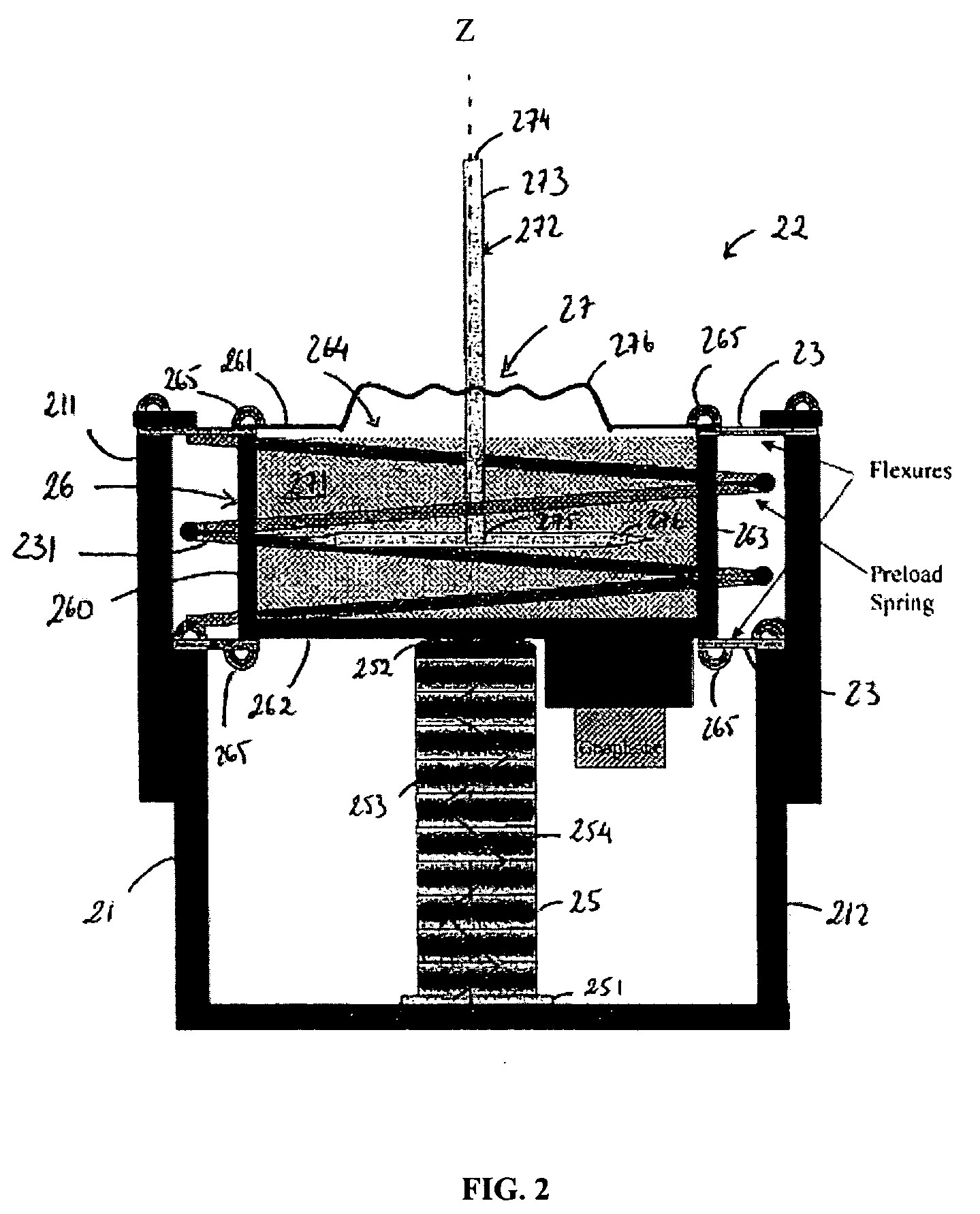
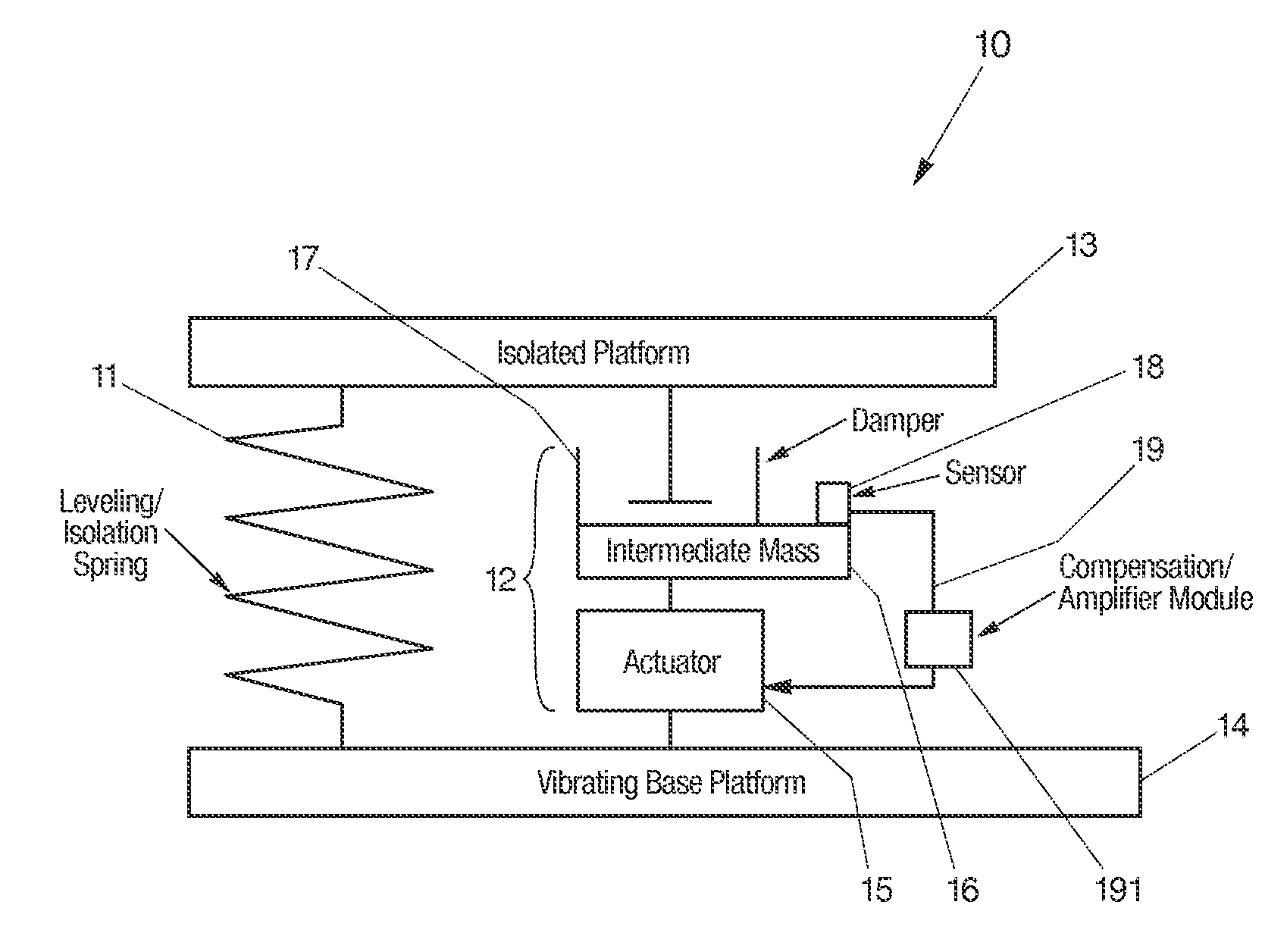
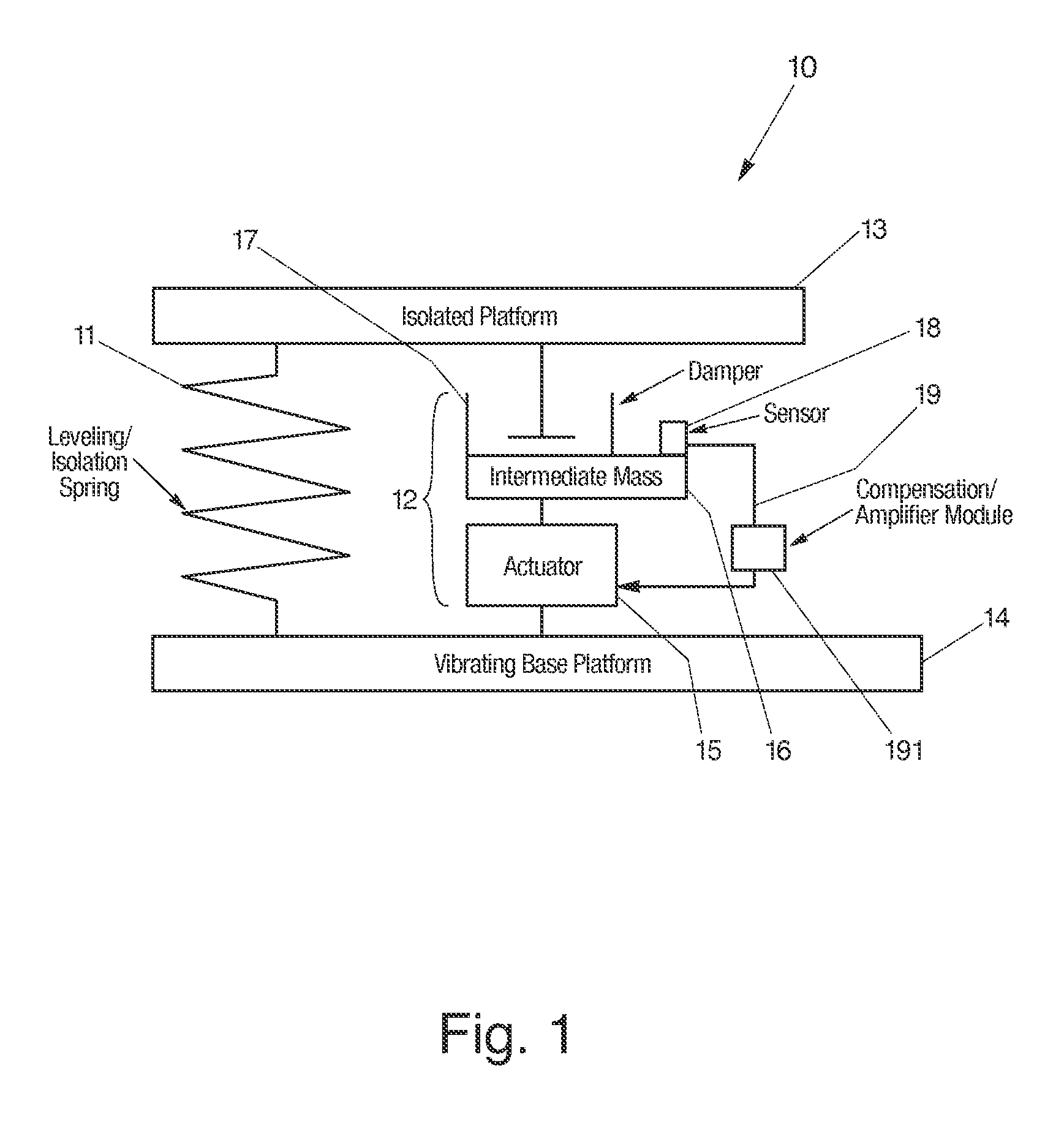
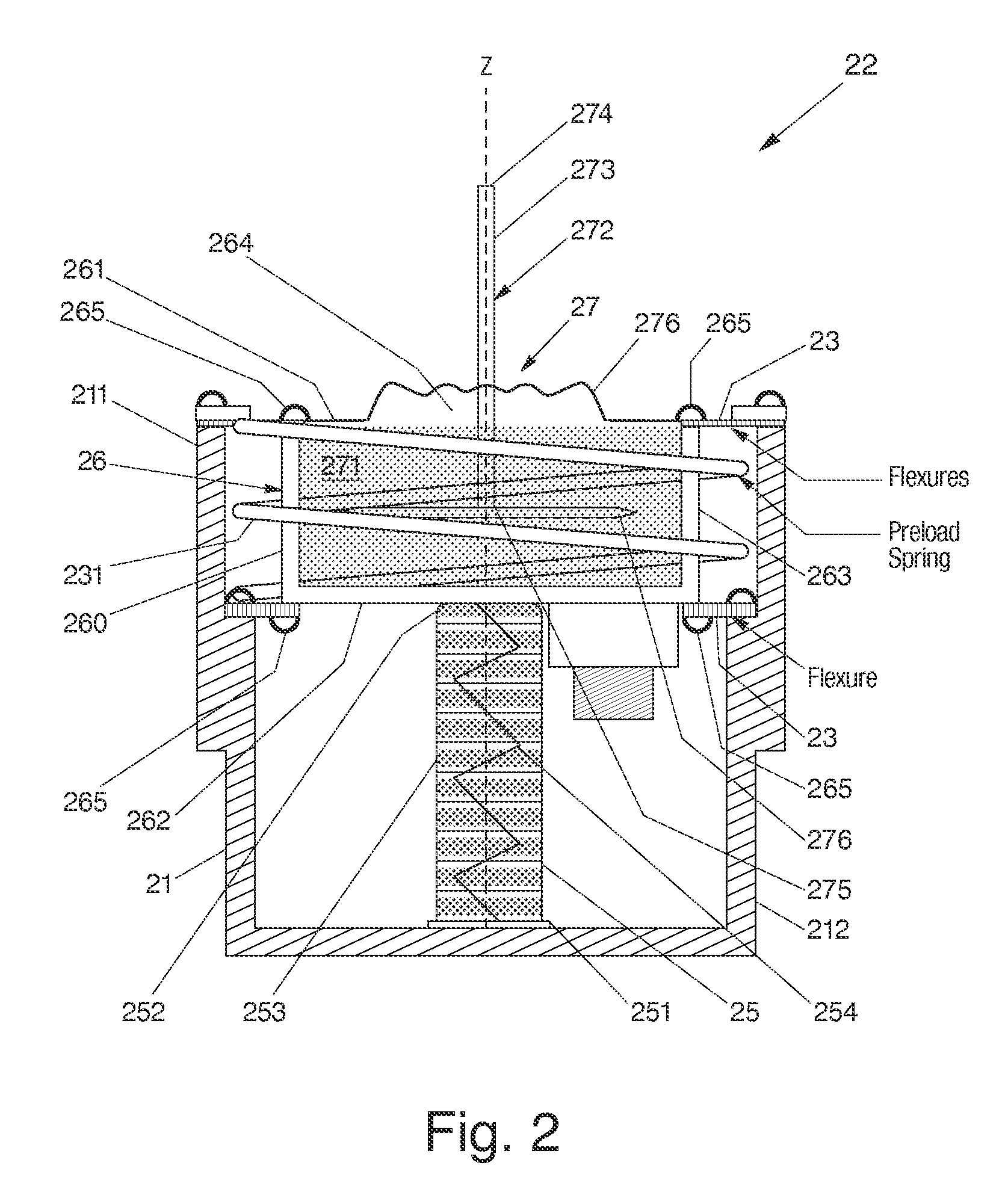
InactiveUS20060272910A1Improve isolationIncrease stiffnessSuspensionsPortable framesAudio power amplifierActuator
An active vibration damping system having a supporting spring for addressing a static force from a payload, and an independent actively isolated damper positioned in parallel between a payload and a source of vibration for damping dynamic force from the payload to an actively isolated point. The actively isolated damper includes a small intermediate mass, distinct and decoupled from the payload mass, and a passive isolator element for dynamic coupling of the isolated platform to the small intermediate mass. The small intermediate mass provides a point to which dynamic forces from the payload may be dampened. The active damper also includes at least one actuator coupled at one surface to the small intermediate mass and coupled at a second surface to the vibrating base platform. A motion sensor may also be provided on the small intermediate mass so as to generate a feedback signal as a function of the movement of the small intermediate mass. The motion sensor together with a compensation / amplifier module and the actuator act as part of a feedback compensation loop for minimizing vibration.
Owner:TECHN MFG
Systems and methods for active vibration damping
InactiveUS7726452B2Improve isolationIncrease stiffnessSuspensionsPortable framesAudio power amplifierEngineering
An active vibration damping system having a supporting spring for addressing a static force from a payload, and an independent actively isolated damper positioned in parallel between a payload and a source of vibration for damping dynamic force from the payload to an actively isolated point. The actively isolated damper includes a small intermediate mass, distinct and decoupled from the payload mass, and a passive isolator element for dynamic coupling of the isolated platform to the small intermediate mass. The small intermediate mass provides a point to which dynamic forces from the payload may be dampened. The active damper also includes at least one actuator coupled at one surface to the small intermediate mass and coupled at a second surface to the vibrating base platform. A motion sensor may also be provided on the small intermediate mass so as to generate a feedback signal as a function of the movement of the small intermediate mass. The motion sensor together with a compensation / amplifier module and the actuator act as part of a feedback compensation loop for minimizing vibration.
Owner:TECHN MFG
Electrically operated power unit, electric vehicle and electric motorcycle
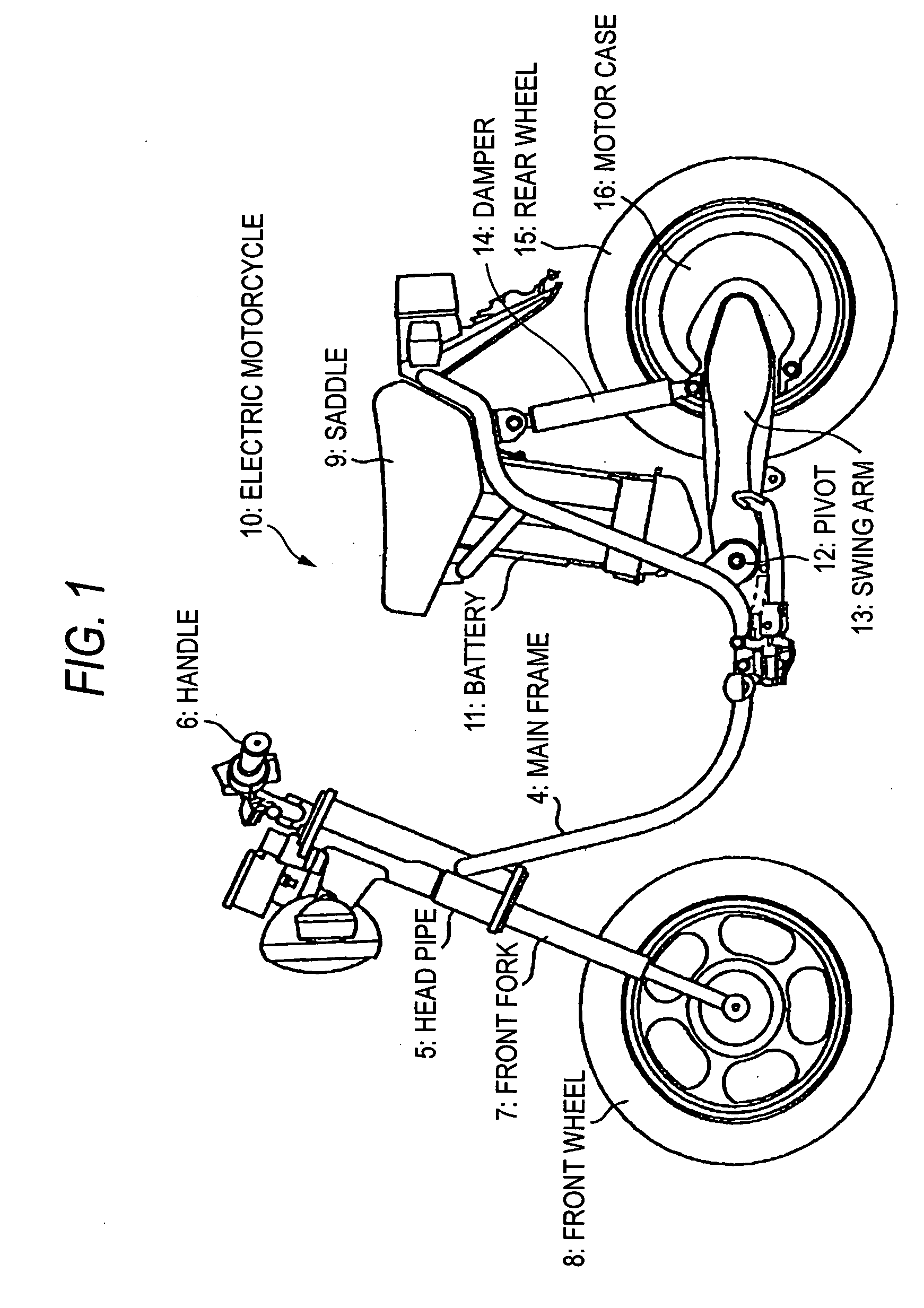
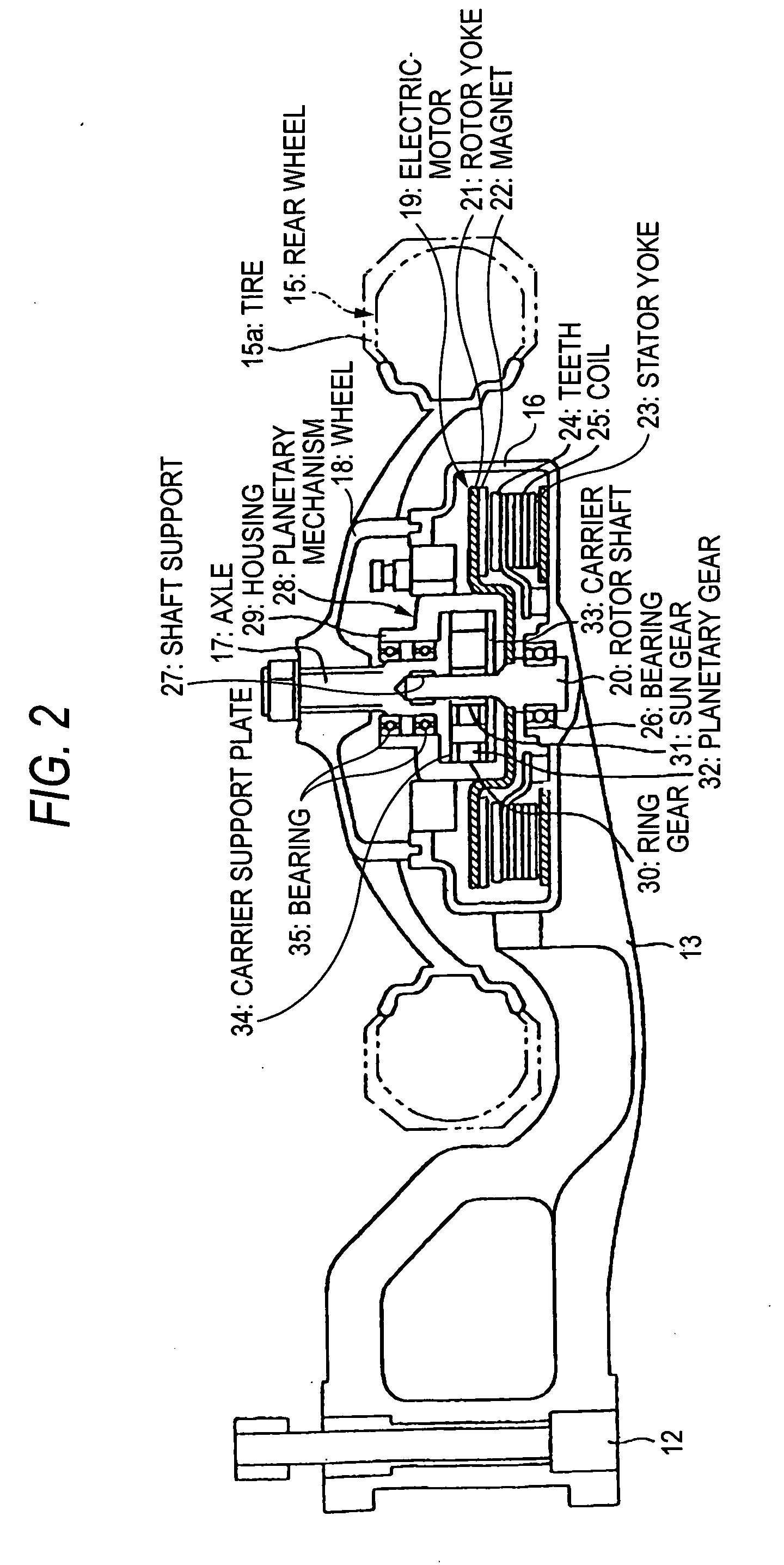
InactiveUS7017694B2Avoid long connectionsMinimal damageSuspensionsWheel based transmissionElectric machineBattery electric vehicle
An electronically controlled compact motor and planetary transmission system including a compact control unit and wiring for an electrical vehicle or electric motorcycle. The compact motor and integrated transmission system enables the operator to enjoy a powerful, conveniently sized, lightweight vehicle.
Owner:YAMAHA MOTOR CO LTD
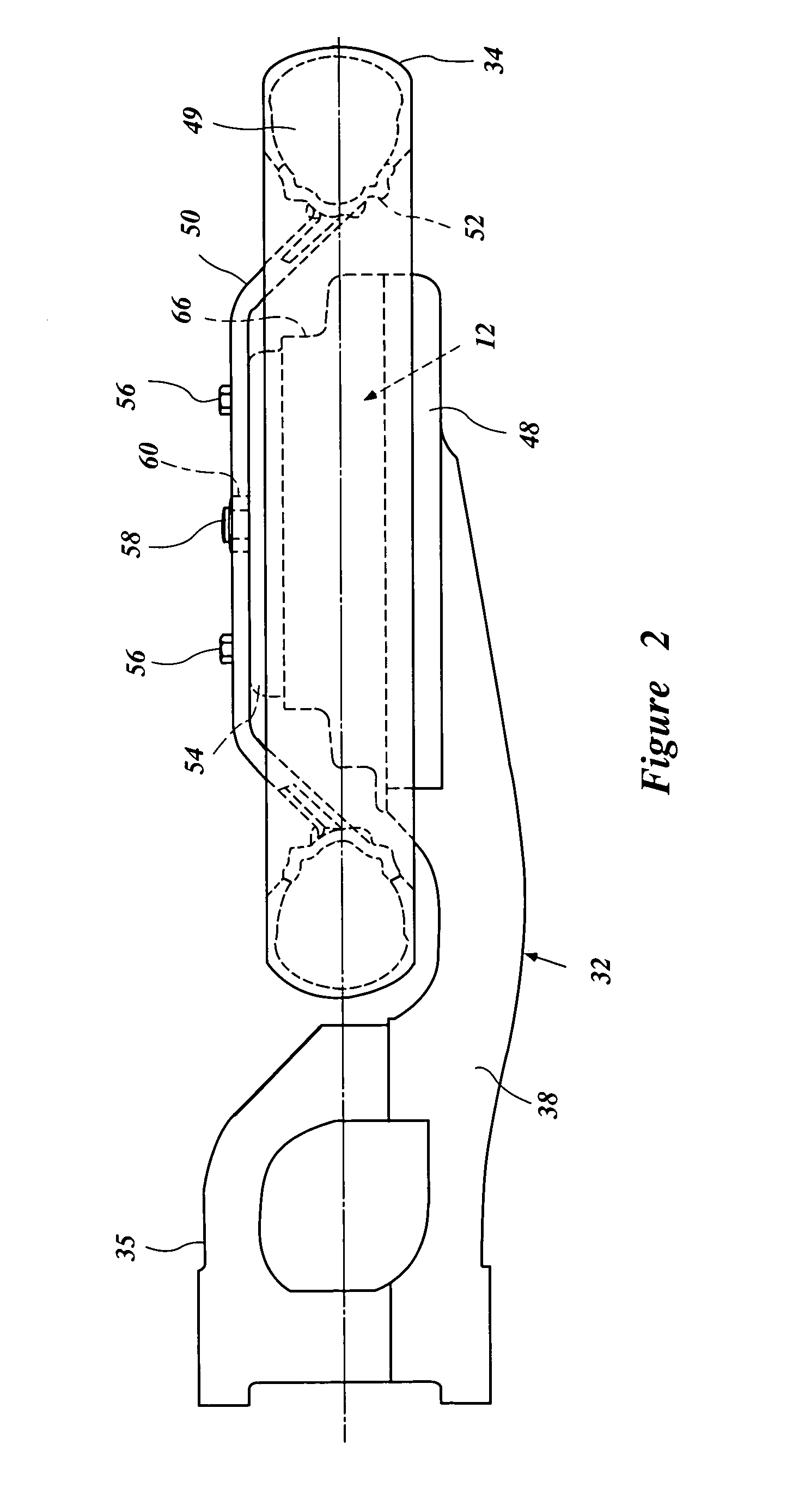
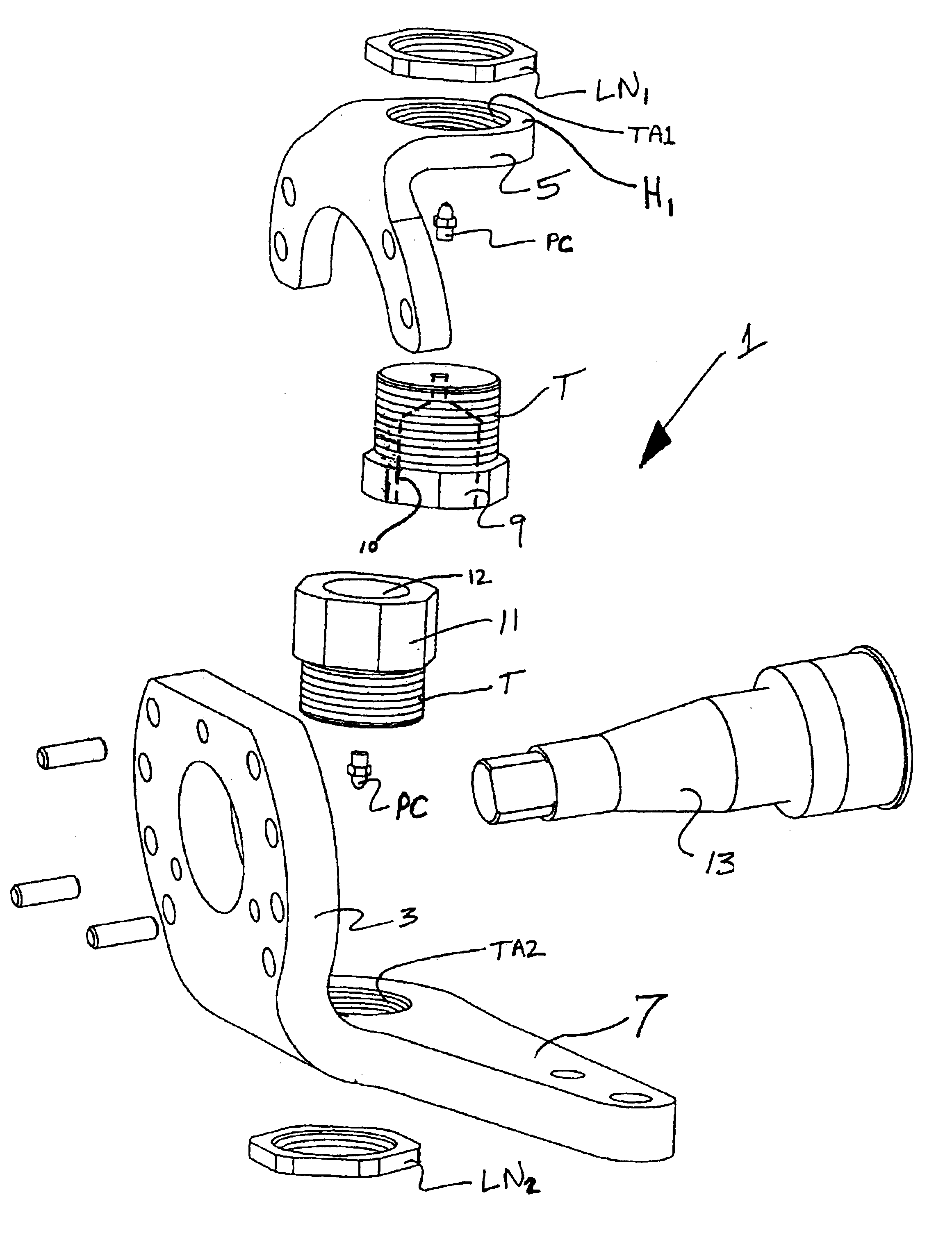
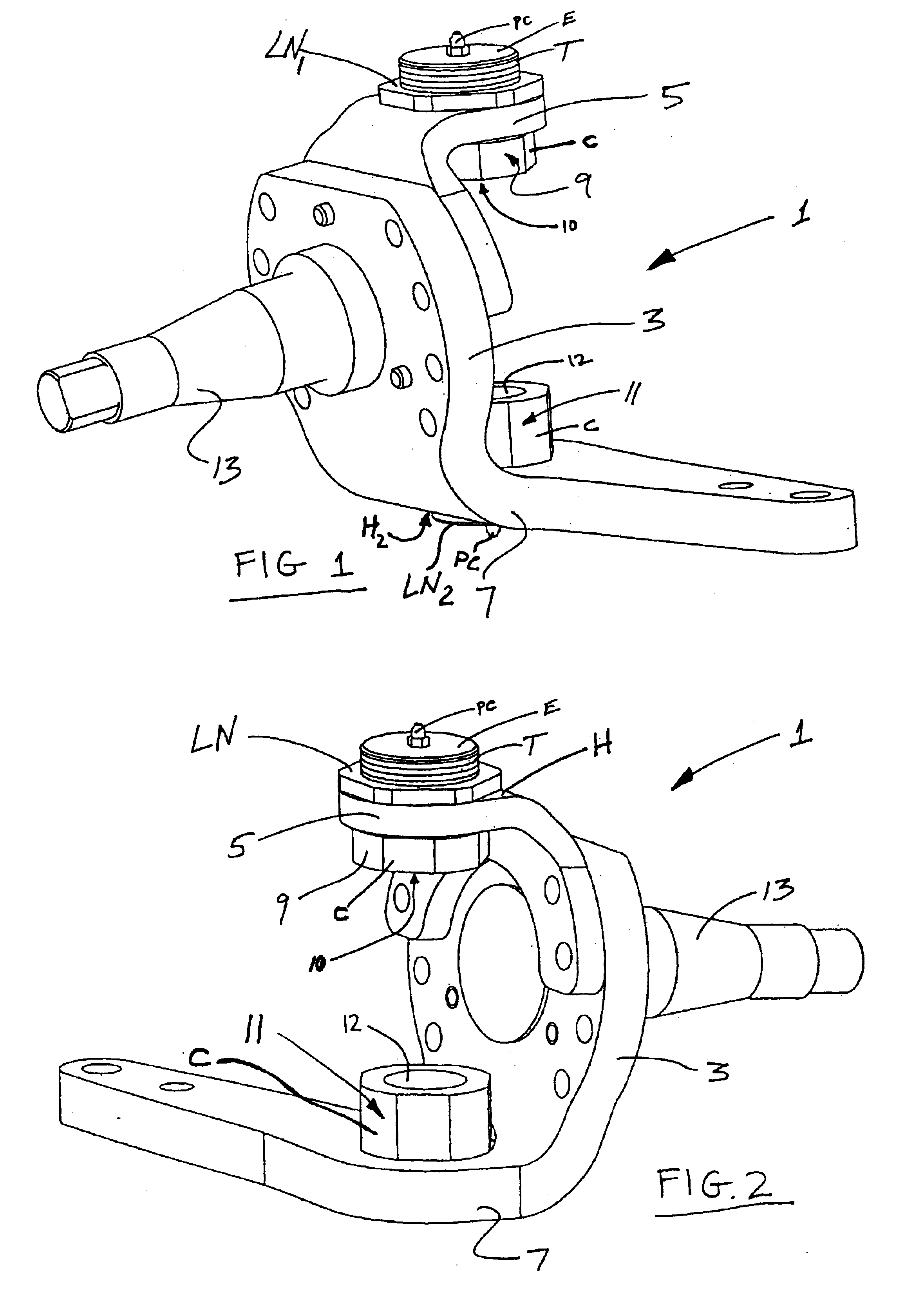
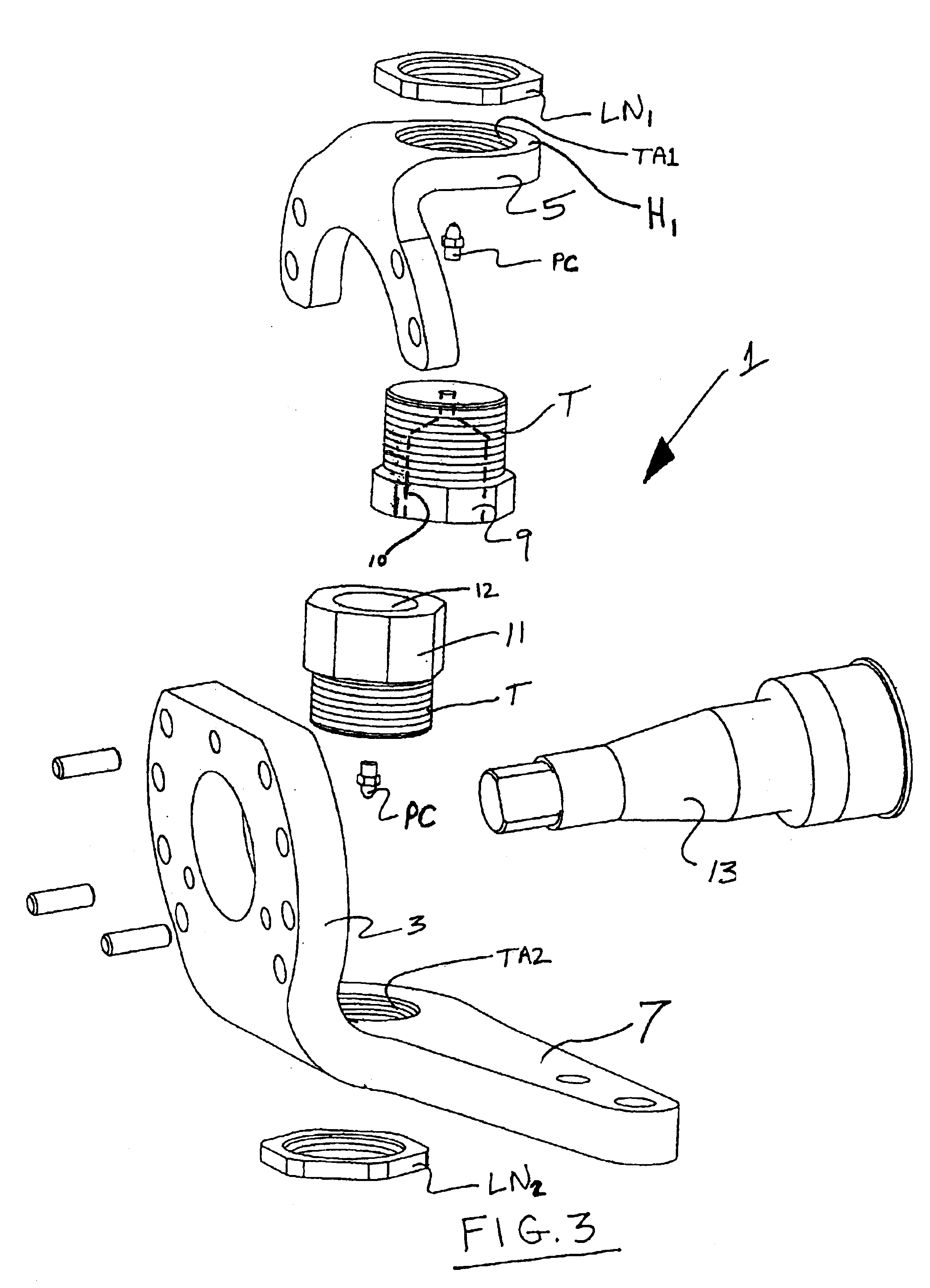
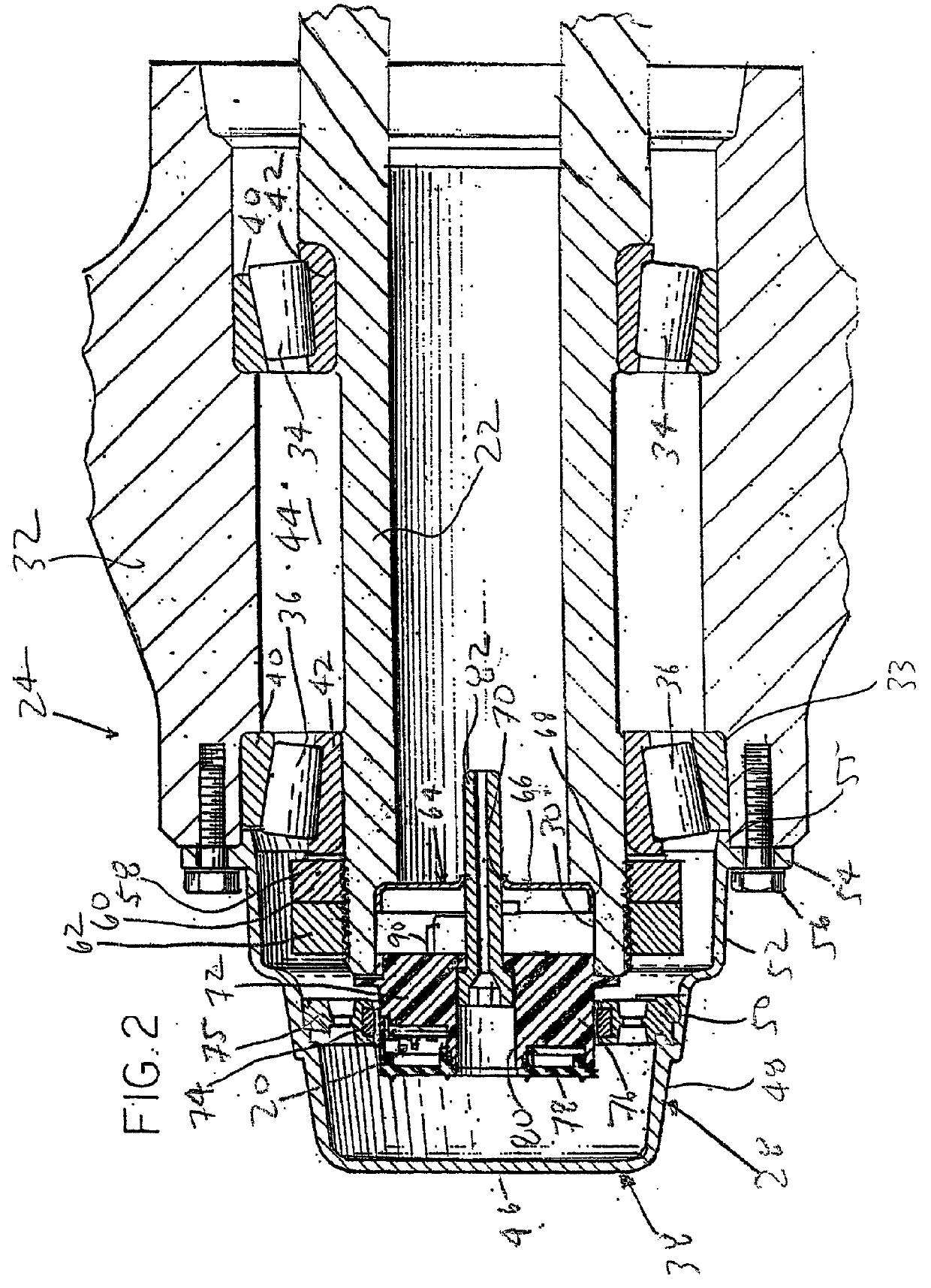
Steering knuckle and adjustable boss
Owner:THE BOLER
Absolute acceleration sensor for use within moving vehicles
A vehicle monitoring system for turning off an idling engine comprises a vehicle speed sensor configured to detect a lack of motion, or “stationary status” of a vehicle and emit a parameter correlated to the motion status of the vehicle, a transmission status detector configured to detect a transmission status of the vehicle, an alerting device capable of warning other drivers of a stationary status of the vehicle and a control device. The control device is coupled to the vehicle speed sensor, the transmission status detector and the alerting device, wherein the vehicle speed sensor and the transmission status detector send a signal to the control device and the control device operates in a manner dependent on the motion status of the vehicle and the transmission status of the vehicle.
Owner:VISION WORKS IP CORP
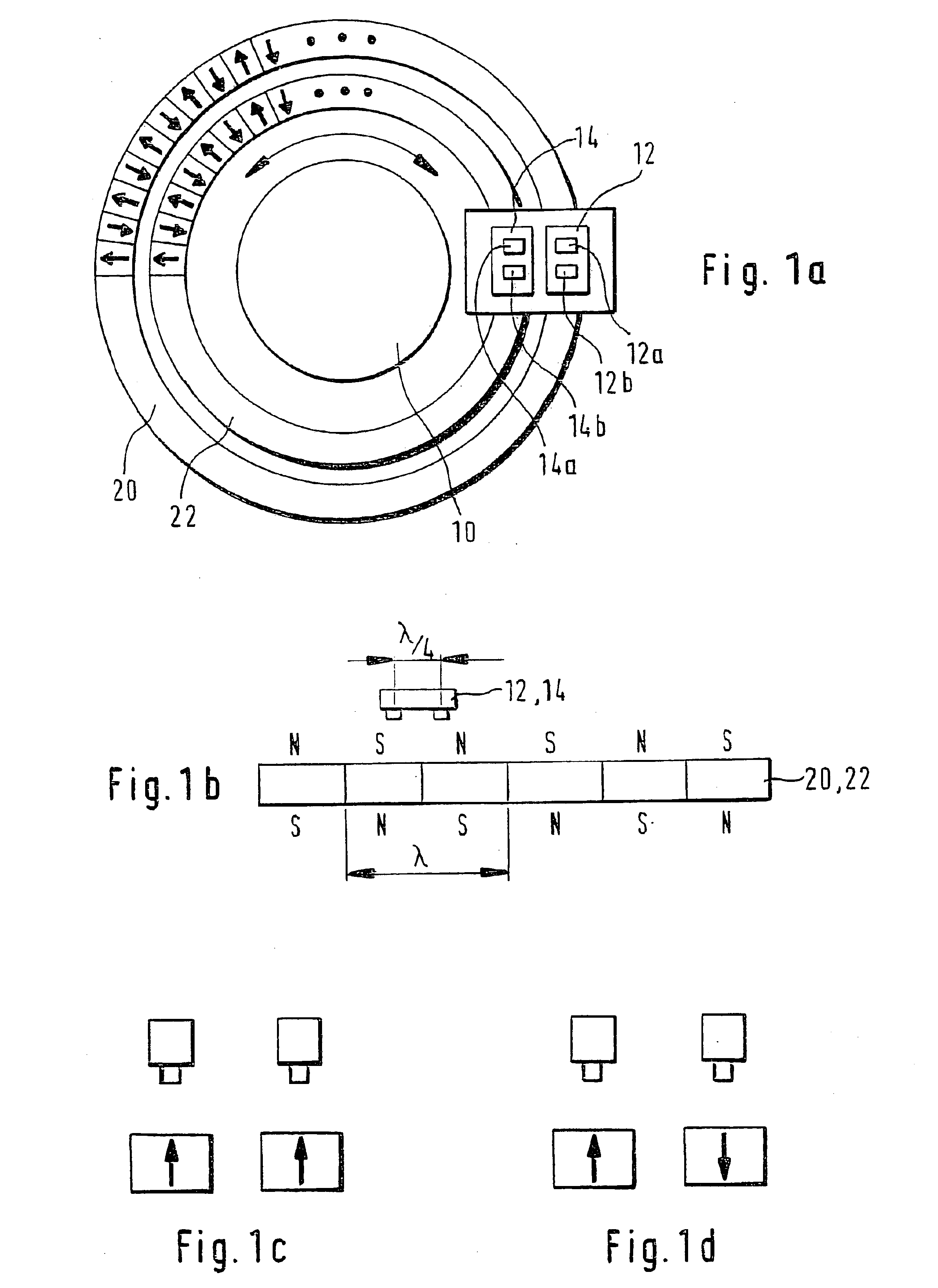
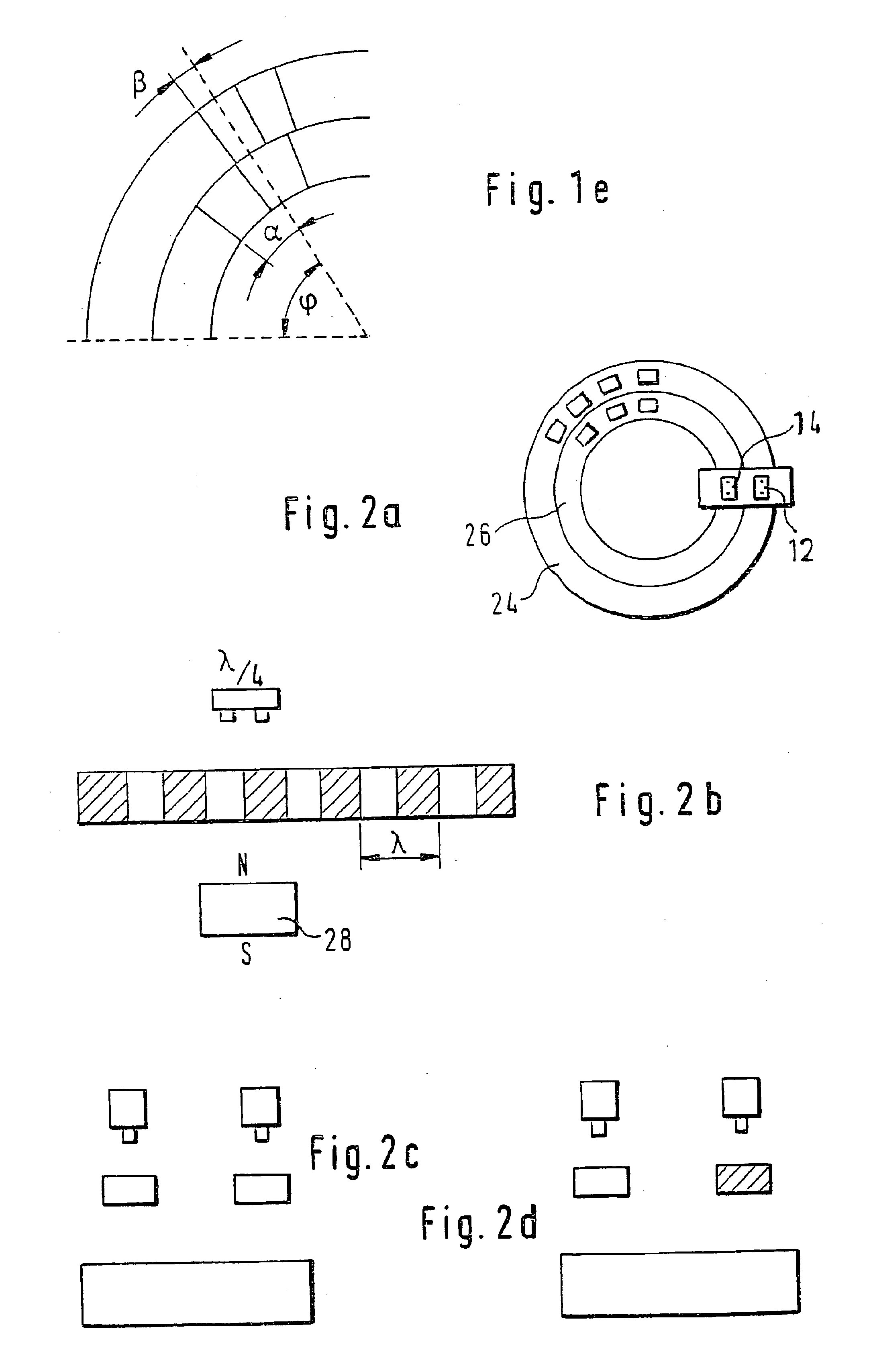
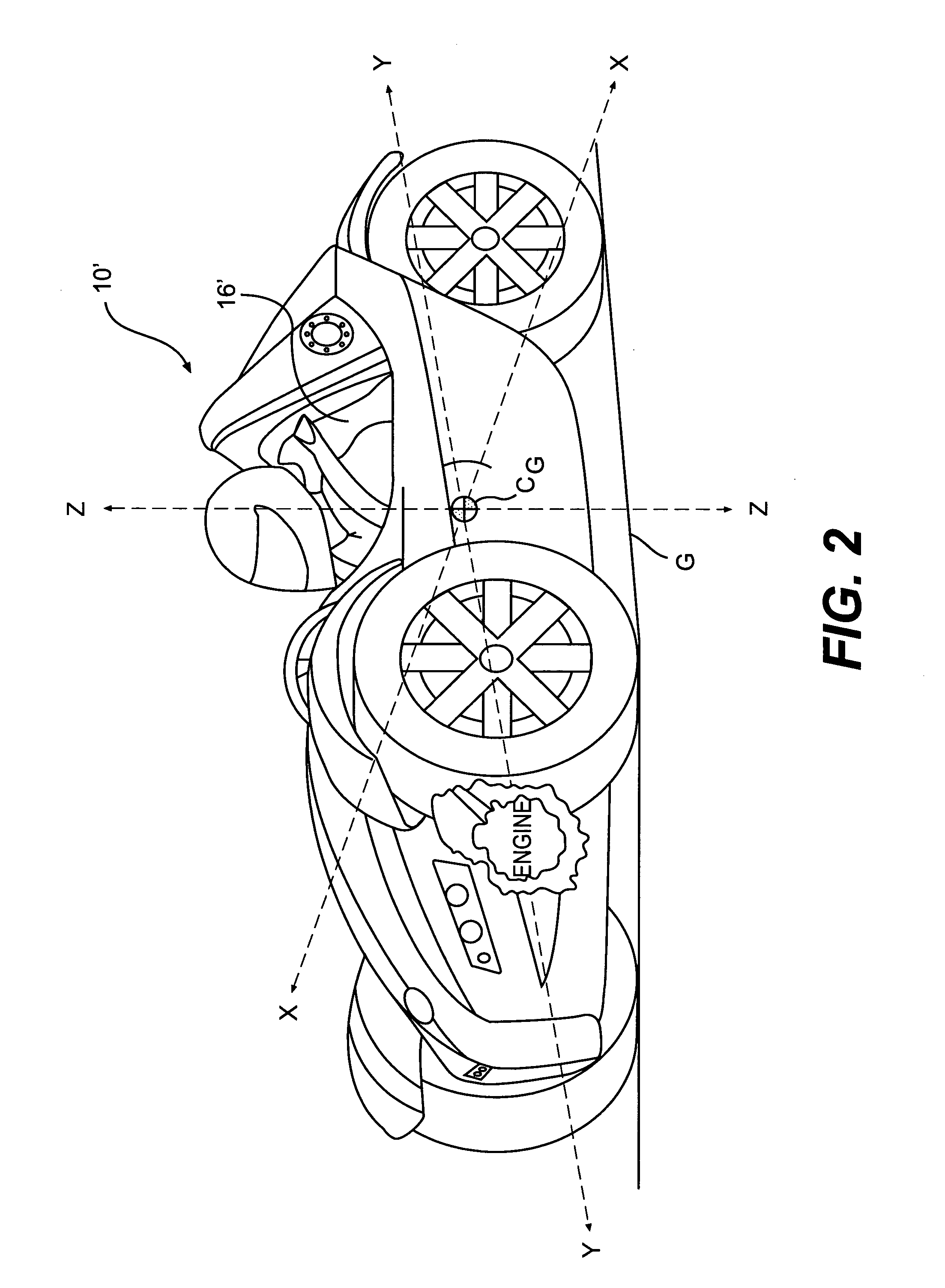
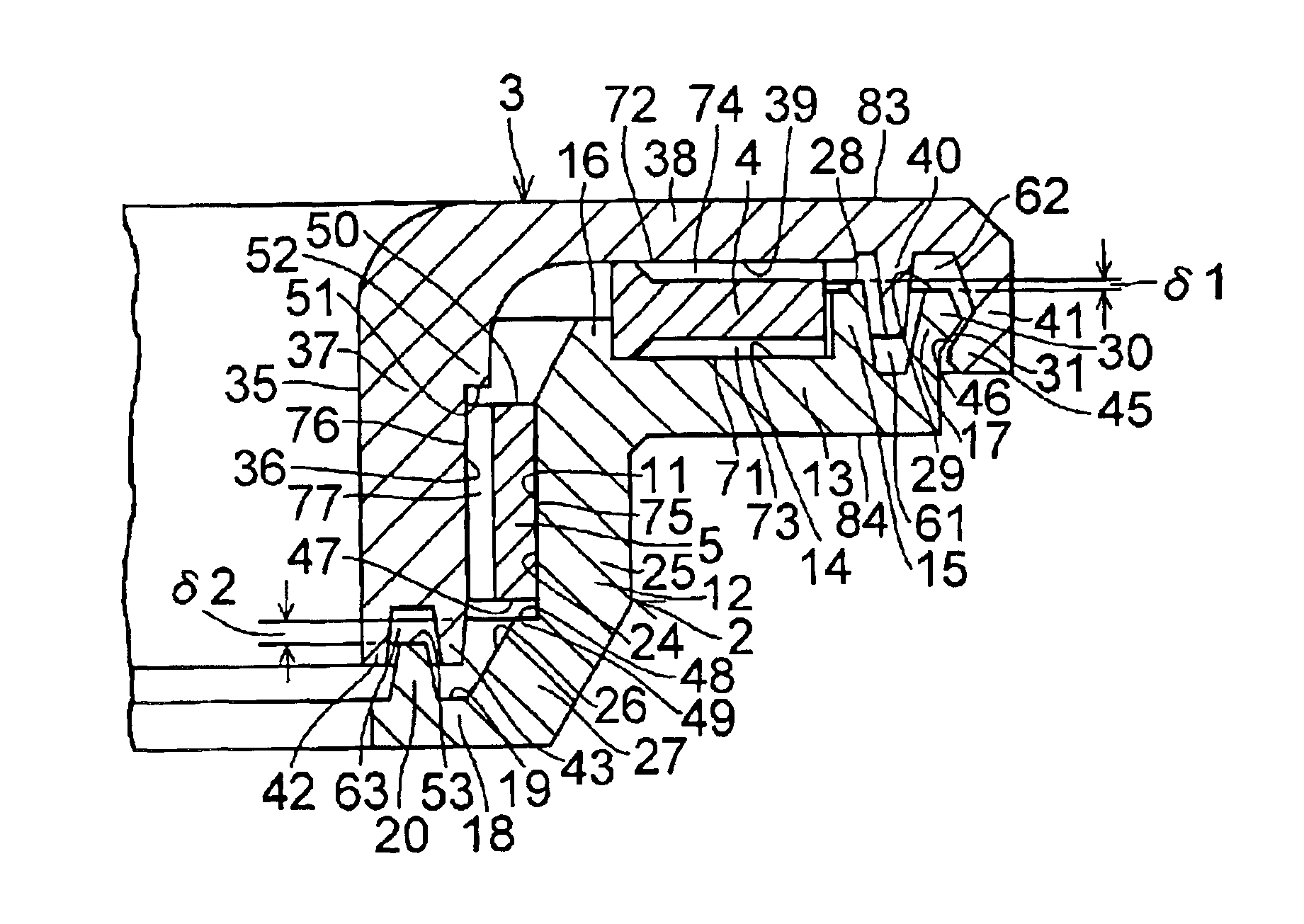
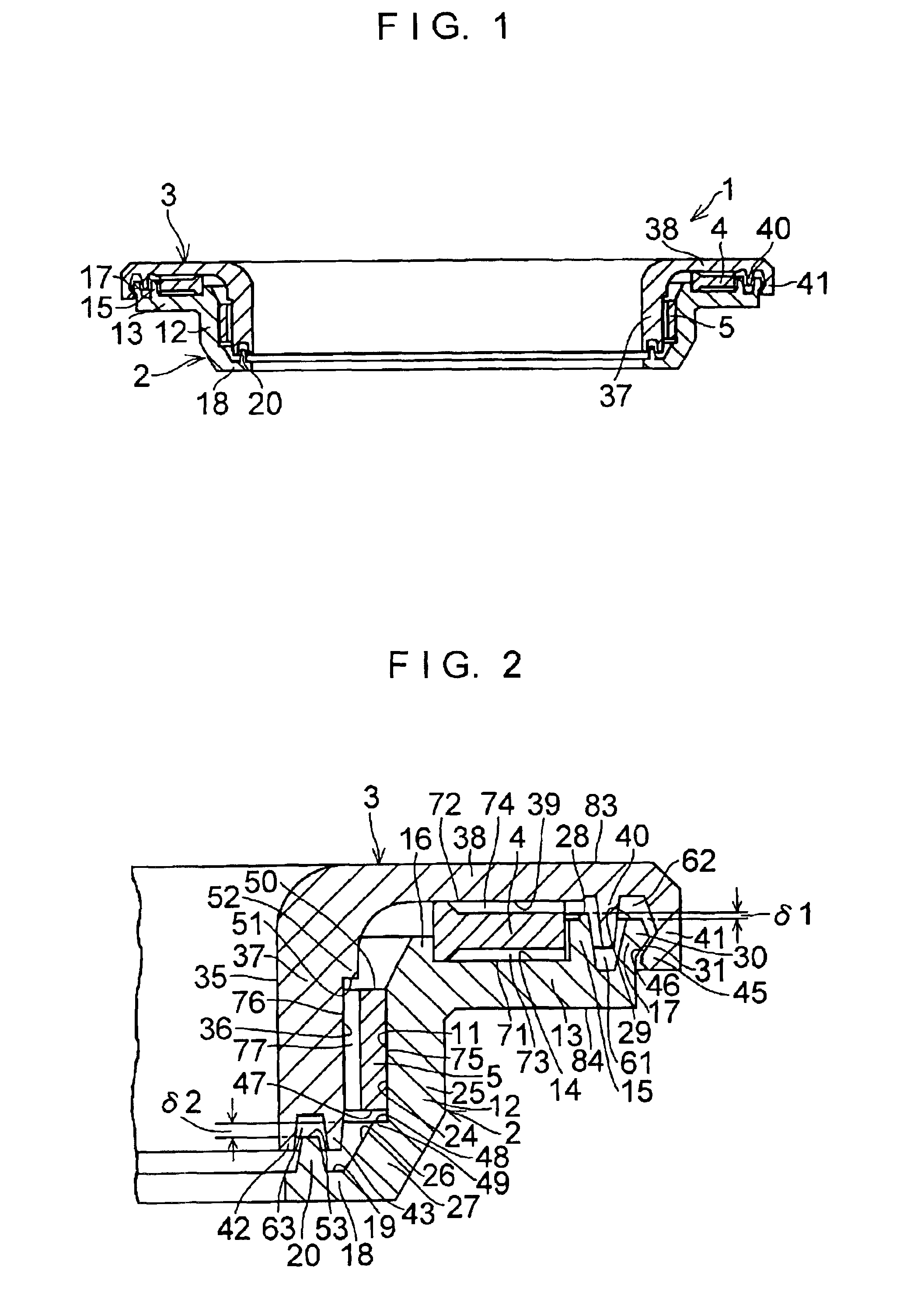
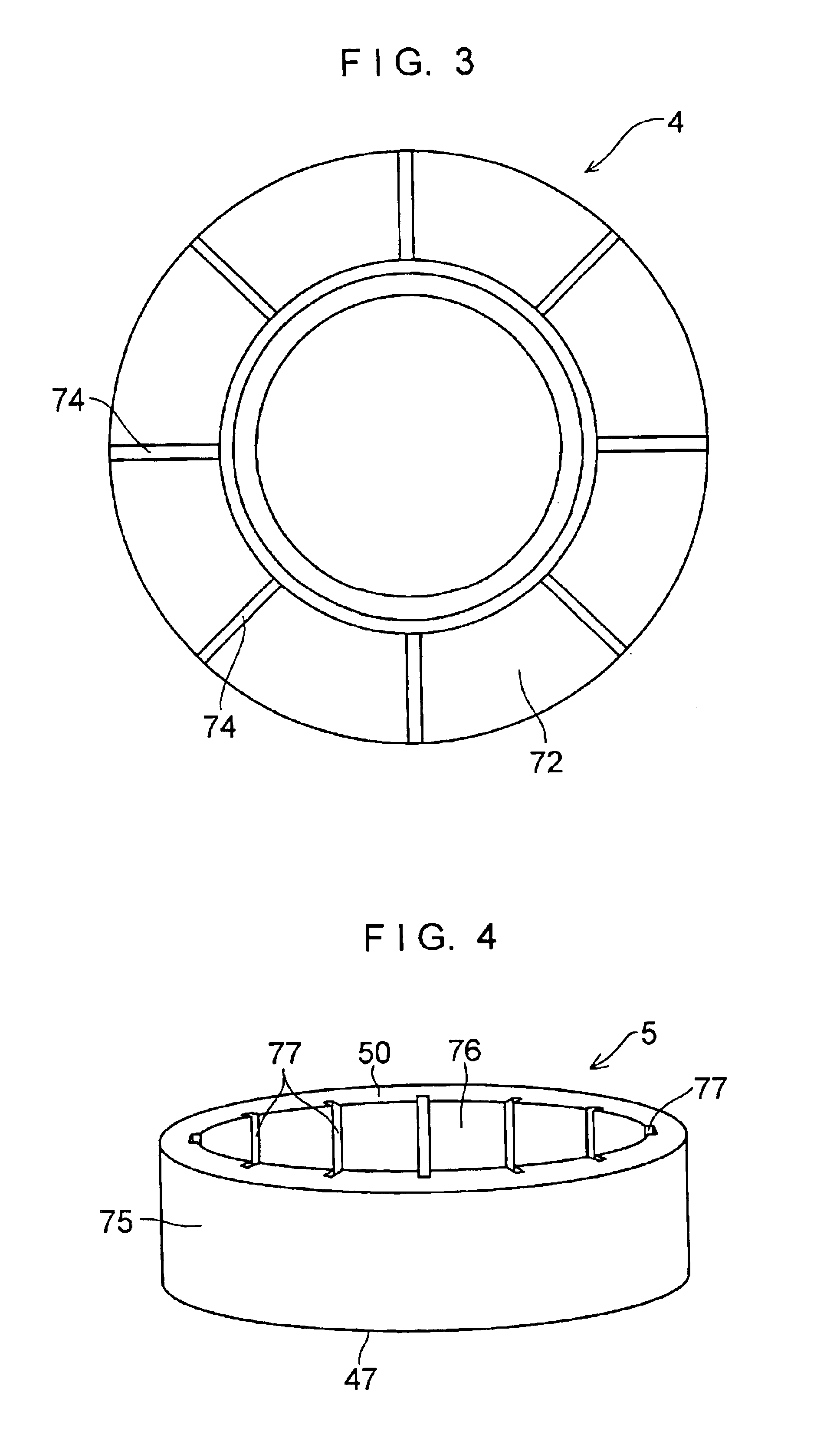
Device for measuring the angle and/or the angular velocity of a rotatable body and/or the torque acting upon said body
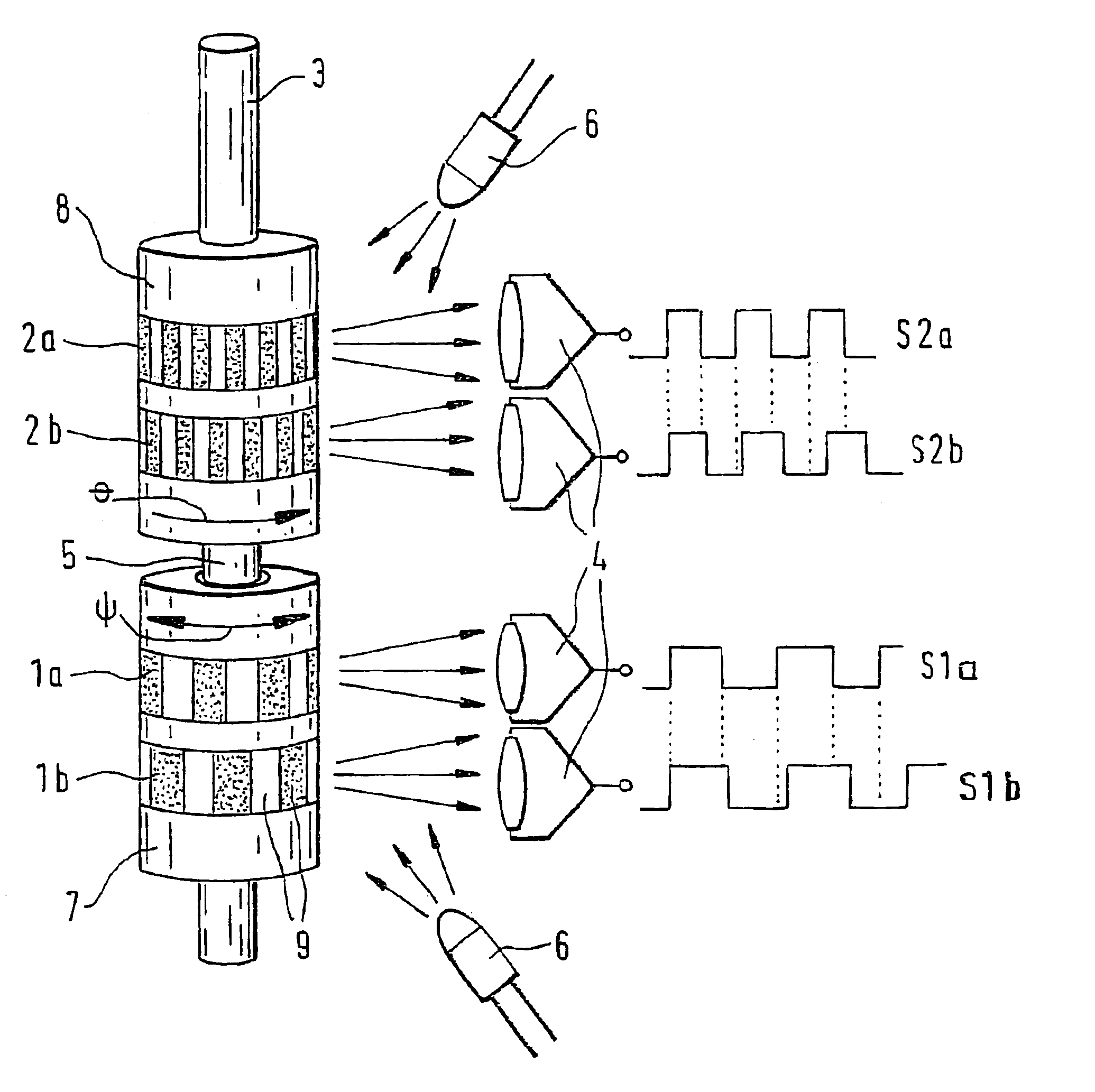
InactiveUS6935193B2High measurement accuracyExpand the measurement rangeSuspensionsDetection of fluid at leakage pointAngular velocityTorsion element
A device for measuring an angle and / or the torque acting on a rotatable body is proposed according to the invention, whereby the rotational angle is detected by means of magnetic or optical sensors. In particular, in a preferred exemplary embodiment, two devices (7, 8) are proposed, each of which comprises two optically readable code tracks. The two code tracks (1a, 1b or 2a, 2b) on one device (7 or 8) are similar in design and are offset in relation to each other, so that associated sensors (4) output a digital signal. The rotational angle is calculated based on the lag between the two digital signals. In a further embodiment it is provided that a torsion element (5) having a known torsional stiffness is situated between the two devices (7, 8). Torque transferred by the rotatable body (3) can also be calculated therefore from the angular difference of the two devices 7, 8. The device is used preferably in the steering axle of a motor vehicle.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
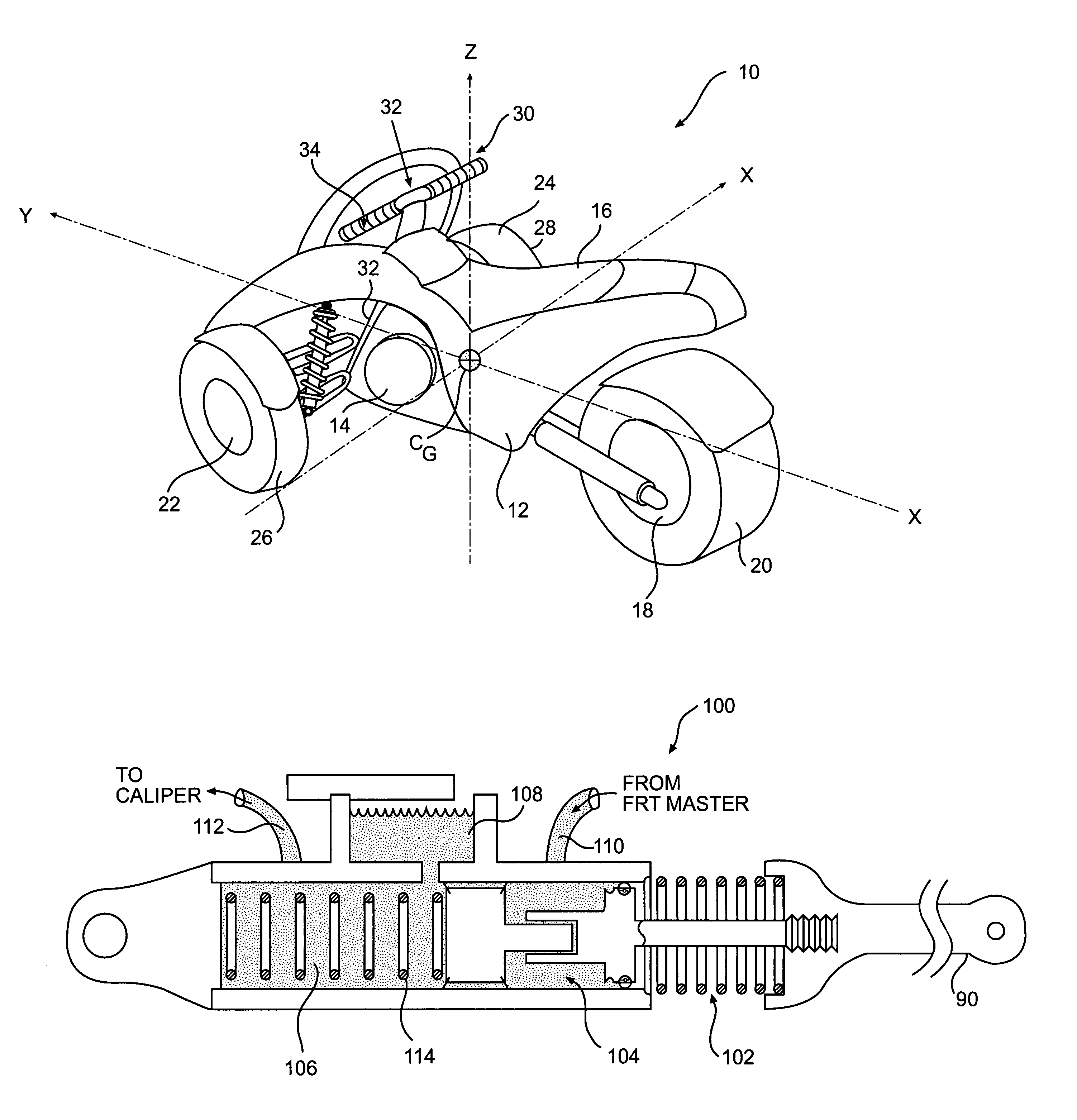
Roll-related reactive system
A three-wheeled vehicle having a pair of front wheels and a single rear wheel is provided with a roll-related reactive system. The roll-related reactive system provides braking of at least one of the front wheels independent of braking initiated by an operator of the vehicle.
Owner:BOMBARDIER RECREATIONAL PROD INC
Synthetic resin-made sliding bearing
InactiveUS6918701B2Avoid enteringReduced characteristicsSuspensionsSpringsEngineeringSynthetic resin
Owner:OILES CORP
Vehicle traveling control device
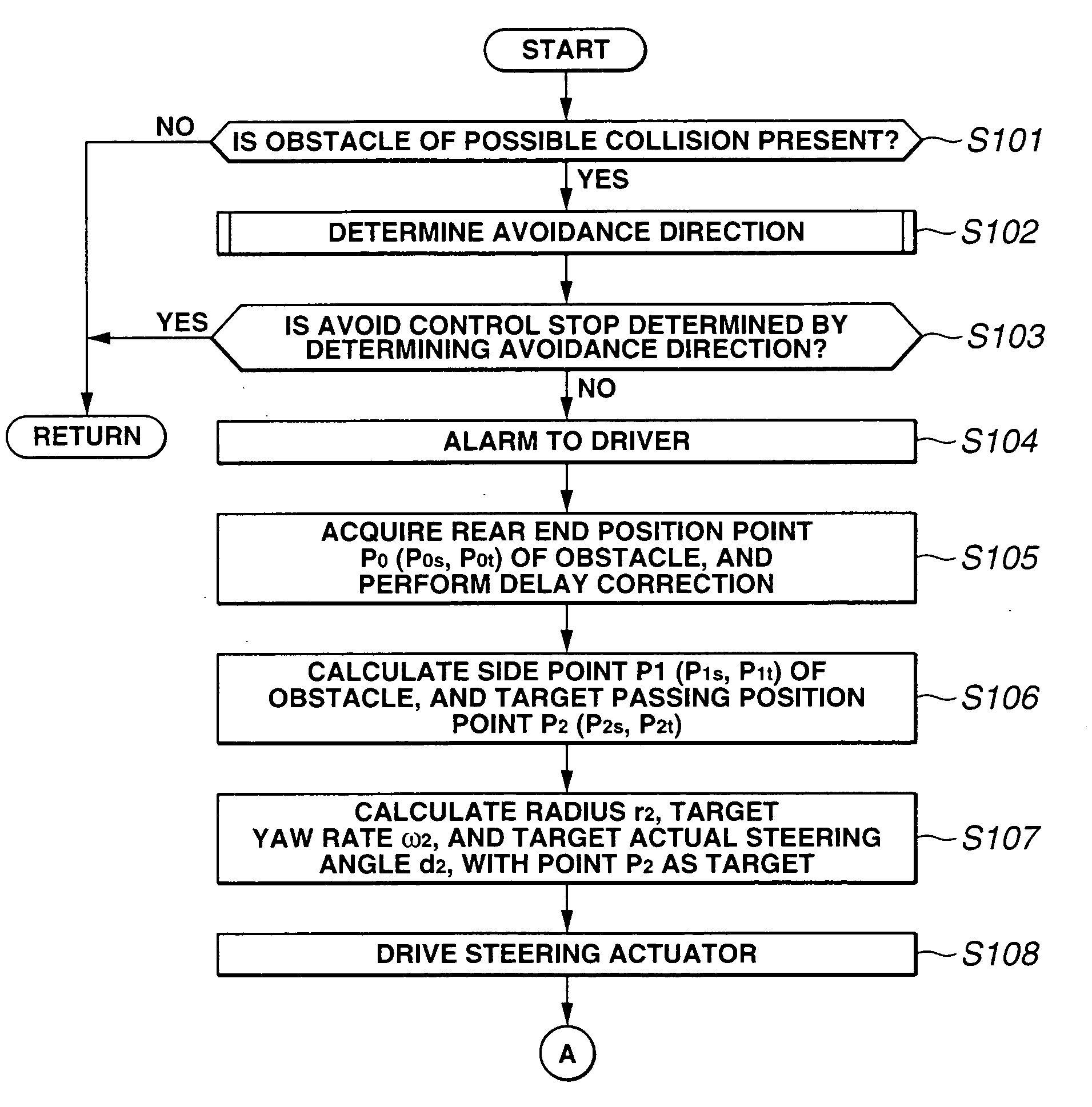
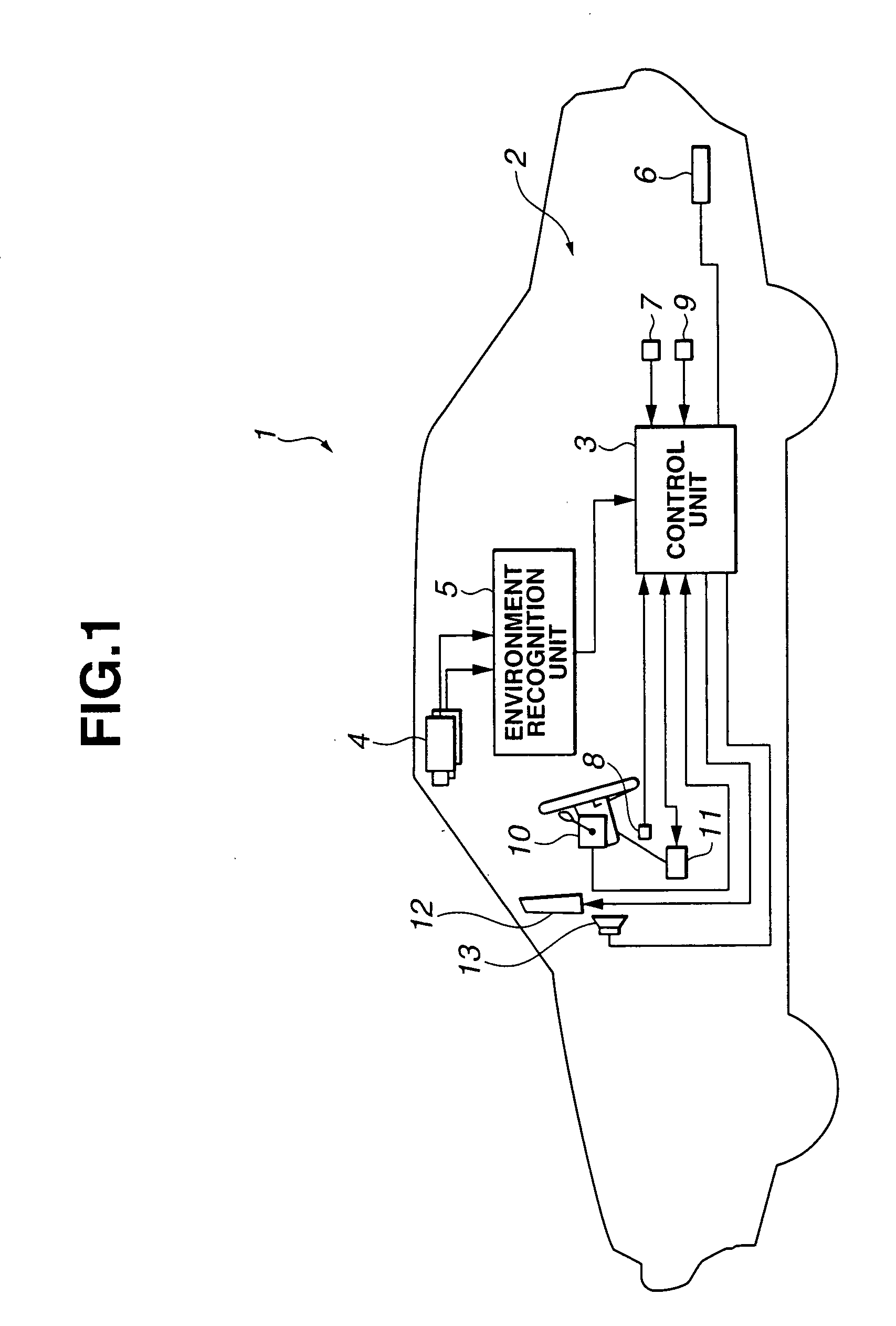
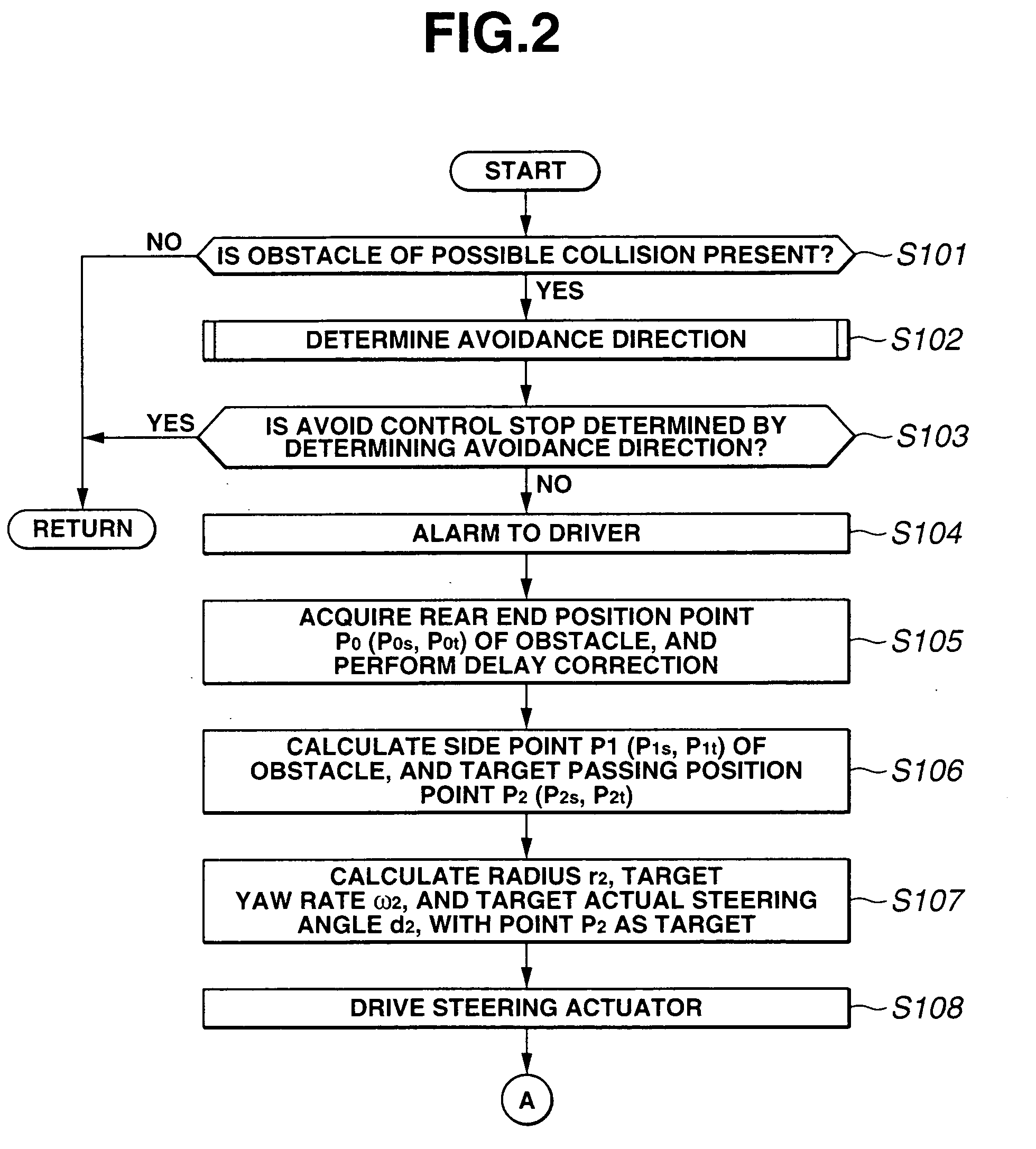
InactiveUS20050125155A1Increase the number ofSmoothly and efficiently and stably avoidingBrake system interactionsDigital data processing detailsElectric power steeringStereo camera
A control device sets avoidance traveling reaching points, avoidance traveling target points, and a final avoidance target point of an obstacle to be avoided based on the position of the obstacle to be avoided and the position of the vehicle for the target passing position based on obstacle information recognized by a stereo camera, and an environment recognition unit, inputs the target actual steering angle as a vehicle motion parameter obtained according to a vehicle motion model to an electric power steering control device with these target passing positions as a target, and guides the avoidance traveling. The increase of the number of operations is controlled thereby to a minimum, and the obstacle is smoothly, efficiently and stably avoided based on actual behavior of the vehicle.
Owner:SUBARU CORP
Installation structure for electric rotating machine in motor vehicle
InactiveUS7121367B2Strengthen restrictionsReduce designSuspensionsElectric propulsion mountingEngineeringFlange
An installation structure for an electric rotating machine such as an electric motor to a wheel of a motor vehicle. The installation structure comprises a wheel hub fixed to and rotatable with the wheel. A bearing through which the wheel hub is rotatably supported is provided. A suspension is installed between a vehicle body of the motor vehicle and the wheel. A bearing support member is connected to a wheel-side section of the suspension and supports the bearing. In the above installation structure, the electric rotating machine includes a power output shaft which is in fit with the wheel hub, and a flange for location of the electric rotating machine in a direction of axis of the power output shaft, the flange being brought into contact with a wheel-side section of the bearing support member.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
Vehicle comprising a crawler track assembly
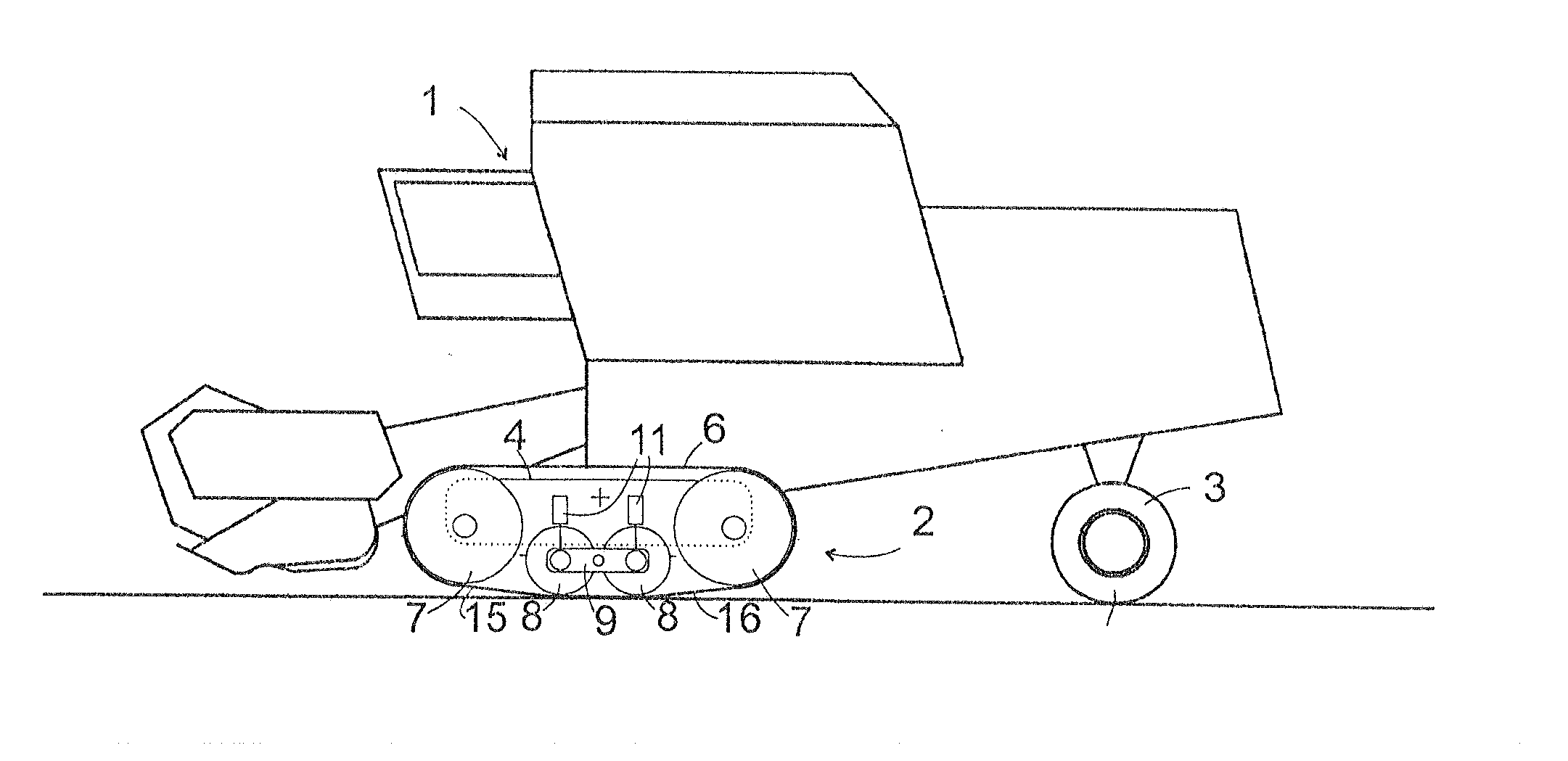
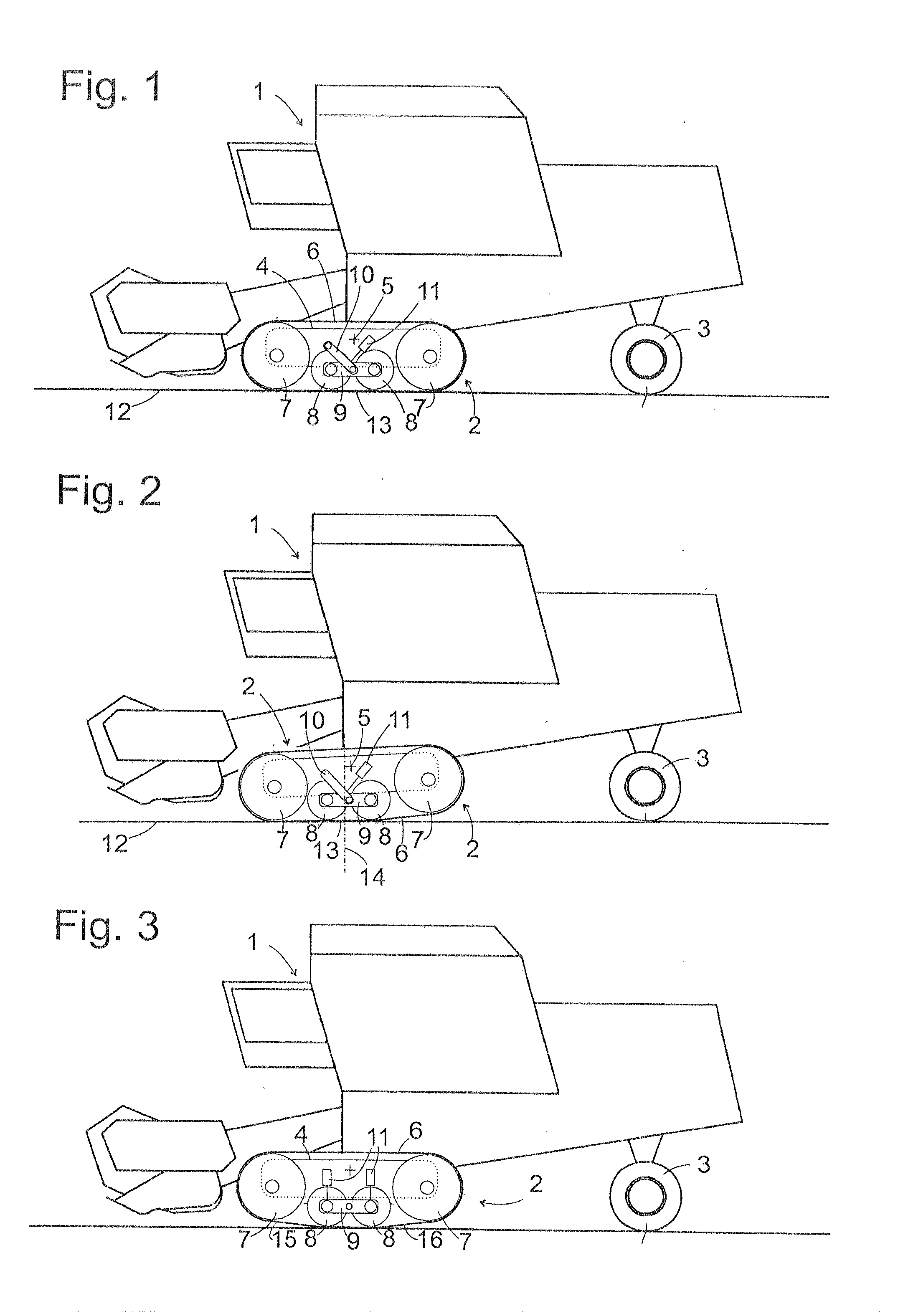
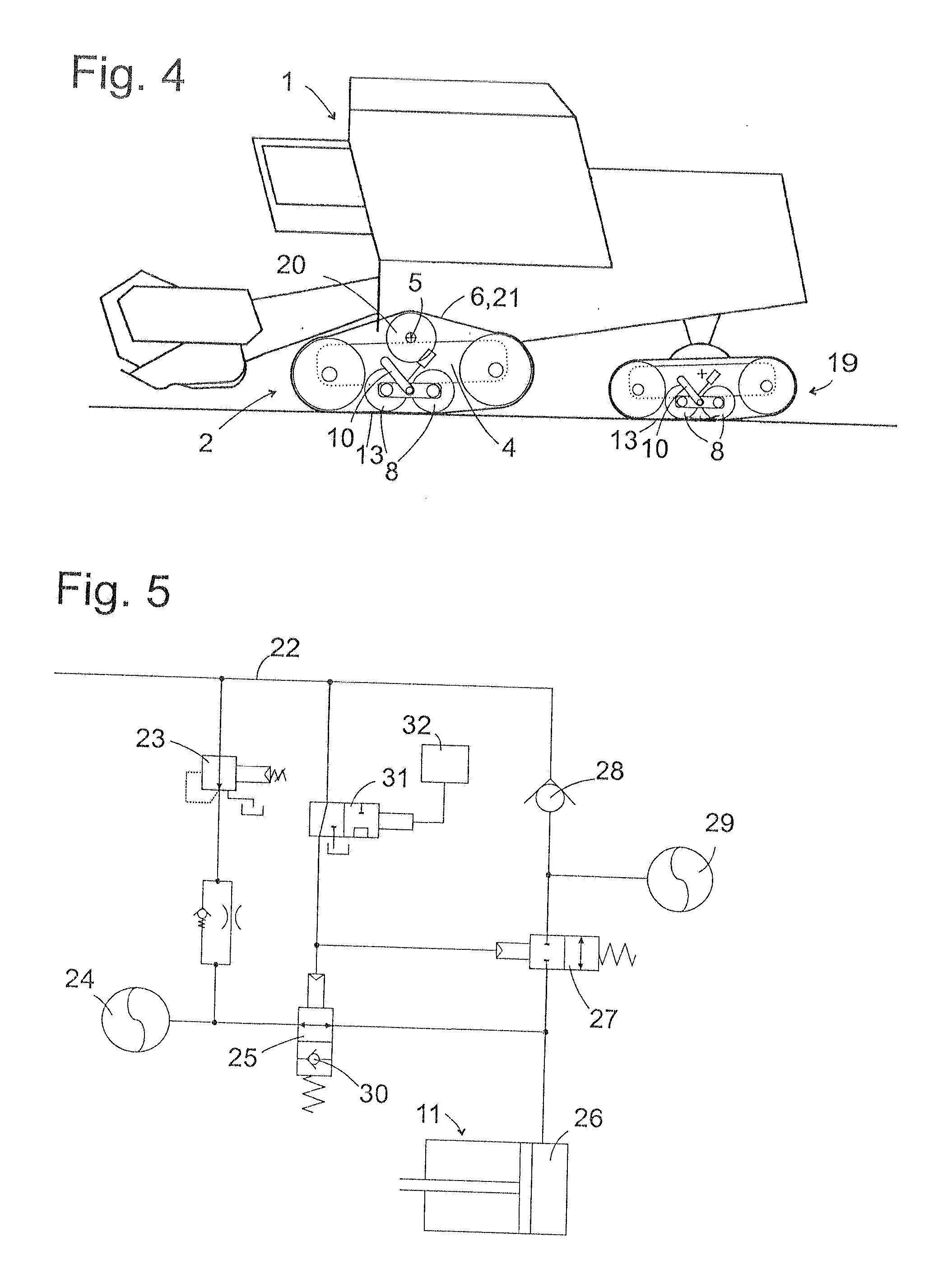
InactiveUS20130154345A1Improve vehicle tractionGreat tractionSuspensionsEndless track vehiclesActuatorControl theory
An agricultural vehicle includes comprises a crawler track assembly having a plurality of supporting rollers arranged one behind the other in the direction of travel of the vehicle and around which a belt is wrapped. The rollers are adjusted by way of an actuator between a first configuration, in which all supporting rollers are loaded, and a second configuration, in which at least one outer roller of the supporting rollers is relieved. An energy accumulator is charged by a drive energy source and connected to the actuator in order to provide the actuator with the drive energy required to adjust the configuration.
Owner:CLAAS SELBSTFAHRENDE ERNTEMASCHINEN GMBH
Axial gap type dynamo-electric machine
InactiveUS20050073213A1Total current dropImprove electrical resistanceSuspensionsMagnetic circuit rotating partsElectric machineHigh torque
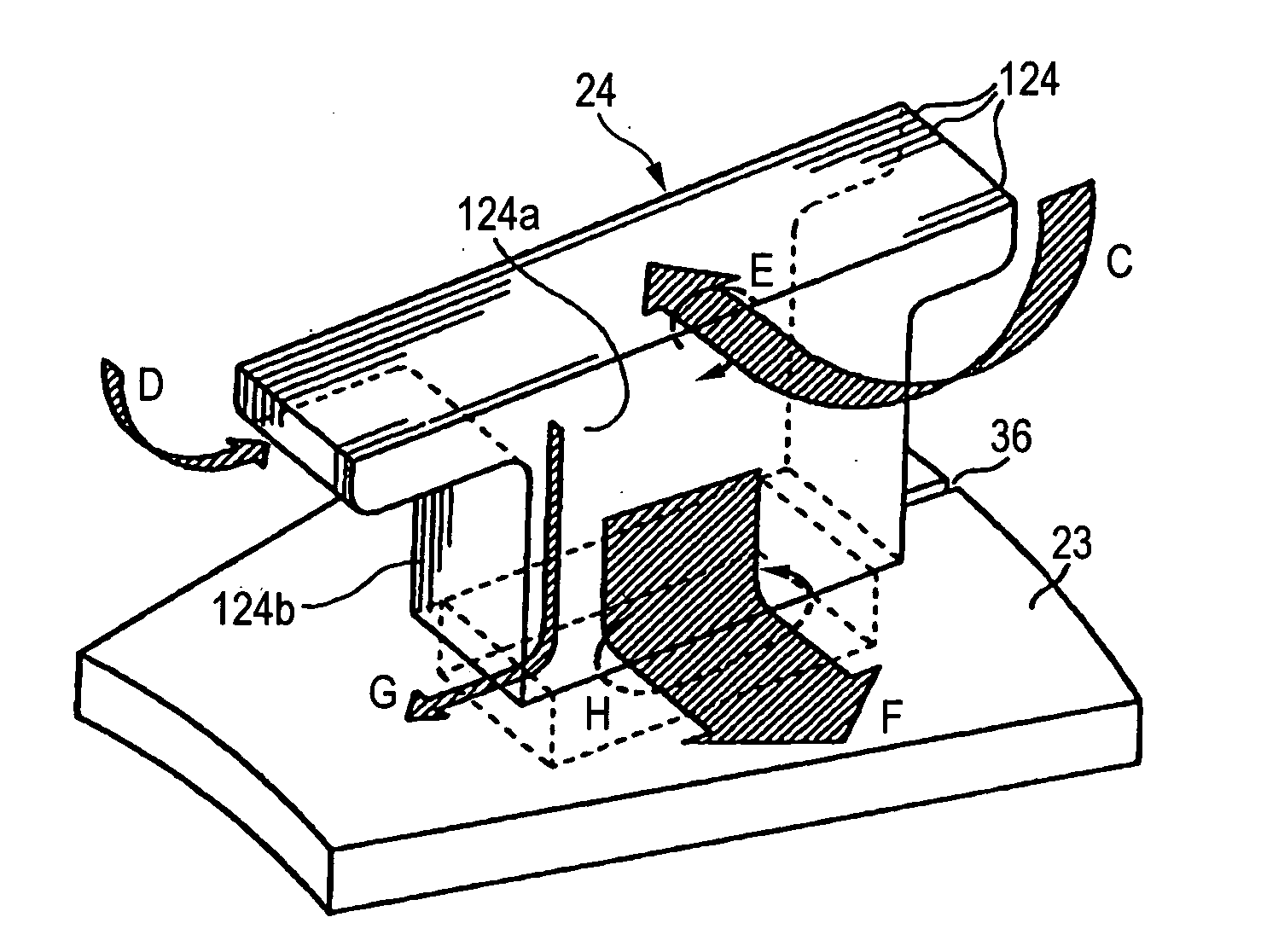
There is provided an axial gap type rotating electric machine which is small-sized and achieves a high motor efficiency as a drive source having a high torque using, for example, a strong magnet by reducing an energy loss by an induced current. An axial gap type rotating electric machine having a yoke on a side of a rotor in a circular plate shape fixed to a rotating shaft, a yoke 23 on a side of a stator in a circular plate shape opposed to the yoke on the side of the rotor, a magnet fixed to a side of an opposed face of either one of the yokes on the side of the rotor or the side of the stator, a plurality of teeth 24 arranged on a side of an opposed face of other yoke on the side of the rotor or the side of the stator radially and opposedly to the magnet and fixed to the yoke 23, and a coil wound around each of the plurality of teeth, in which the teeth 24 has a laminated member of plate members 124 for the teeth and faces 124a to be superposed of the plate members 124 for the teeth are arranged in a circumferential direction.
Owner:YAMAHA MOTOR CO LTD
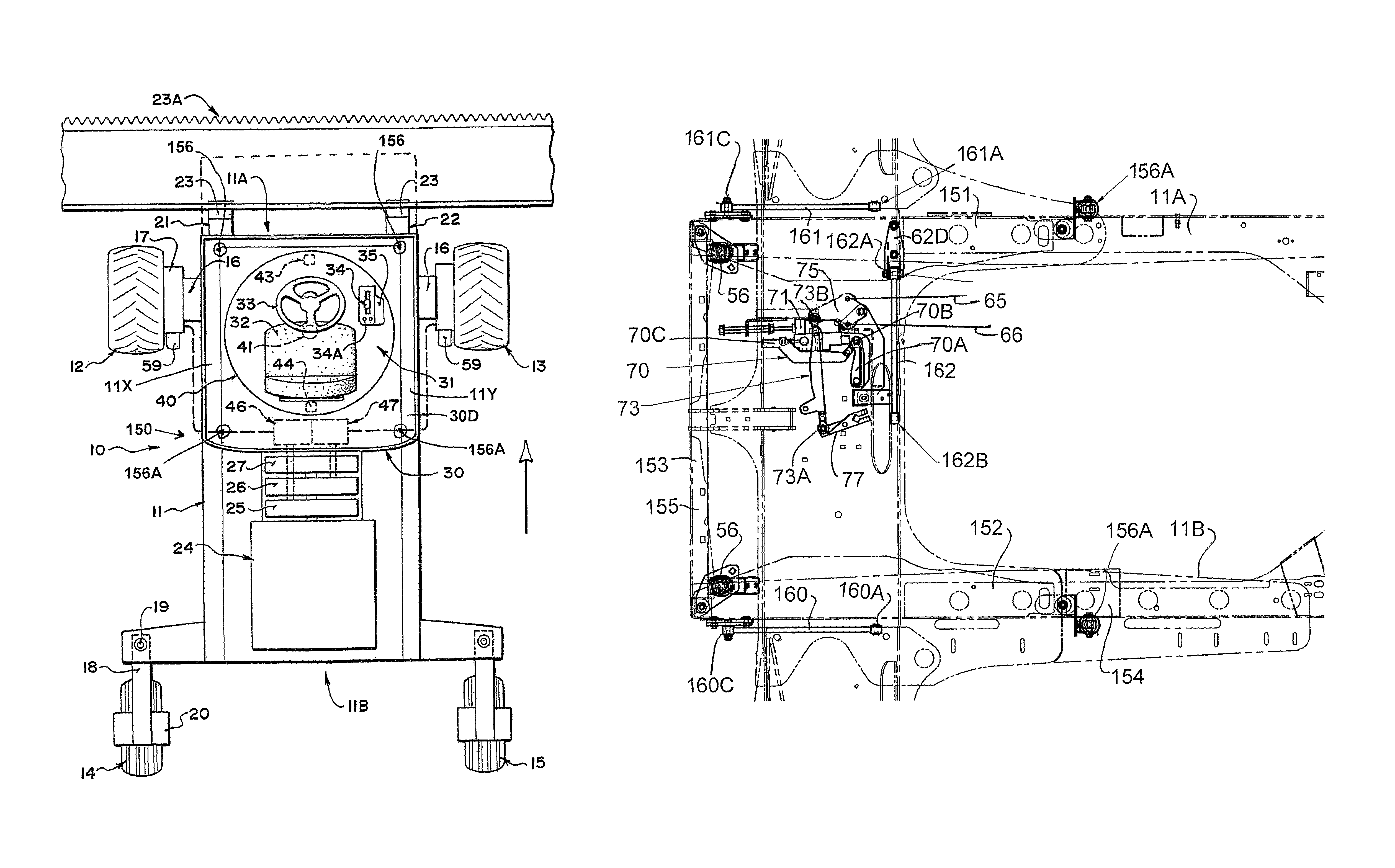
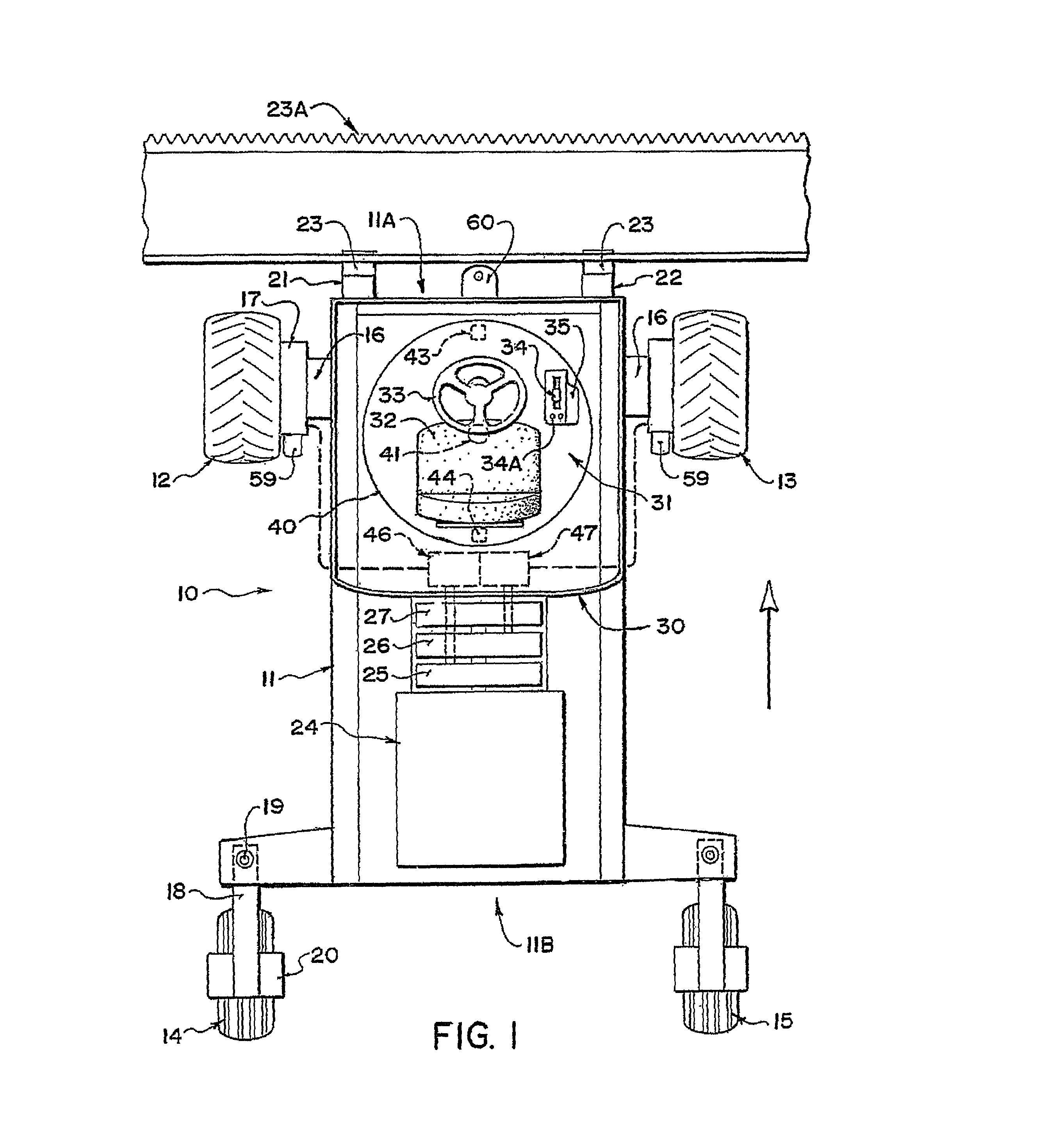
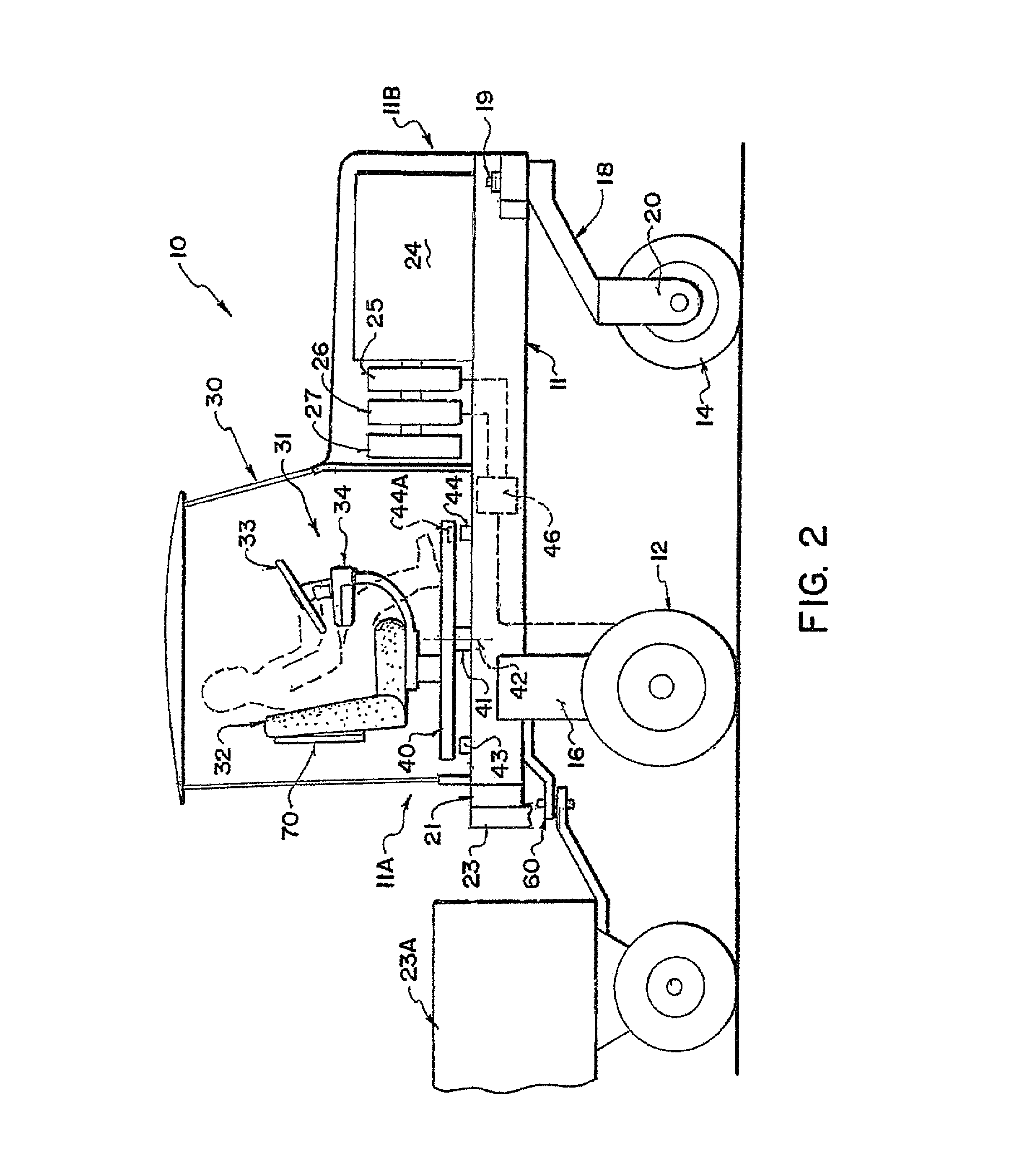
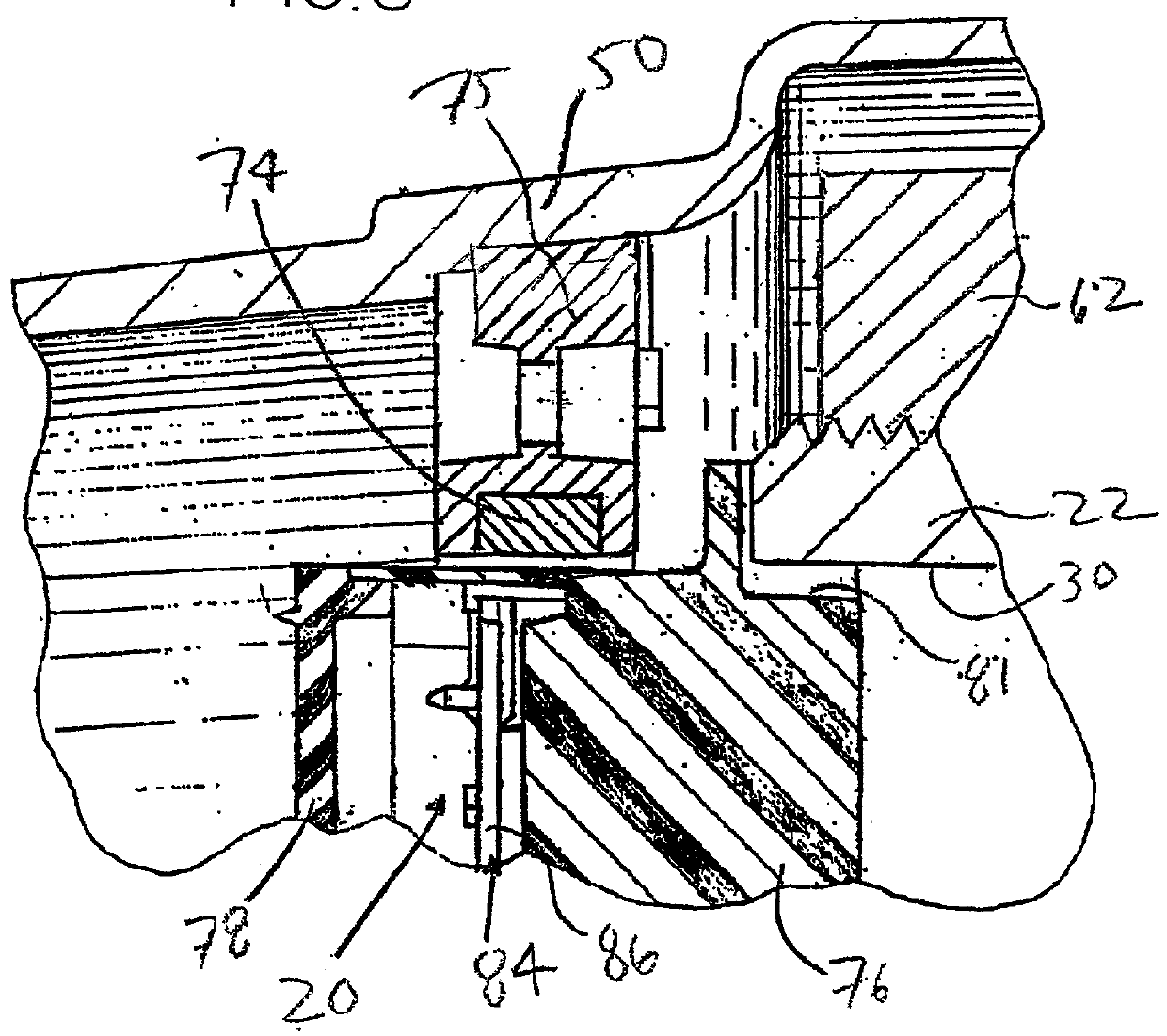
Cab suspension
ActiveUS8225903B2Prevent movementSuperior in pointAgricultural vehiclesSuspensionsSteering controlEngineering
A suspension for a cab base on the frame of a swather tractor includes four dampened springs at the four corners with three links each pivoted on one end of the frame and the other end on the base. The links include two parallel links in the fore and aft direction parallel to the mechanical speed control link arm and one side to side link which constrain movement of the base against fore and aft movement and side to side movement parallel to the mechanical steering control link arm. This arrangement restricts movement of the base while allowing roll and pitch movements of the cab structure with the links arranged such that steering and ground speed are substantially unaffected when the cab moves on the suspension.
Owner:MACDON INDS
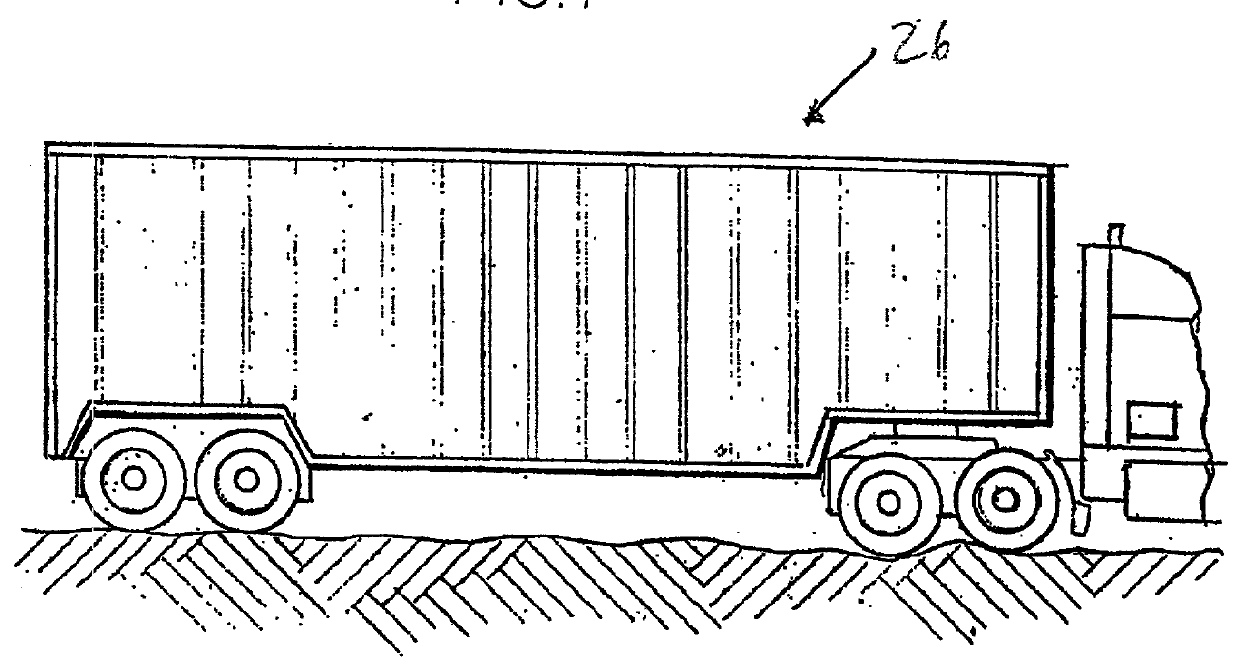
Axle end wheel sensor for a vehicle, such as a truck or a trailer
InactiveUS20010052258A1Precise positioningAxially engaging brakesMachine bearings testingEngineeringTruck
Owner:WABASH NATIONAL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com