Patents
Literature
2790results about "Rotating vibration suppression" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
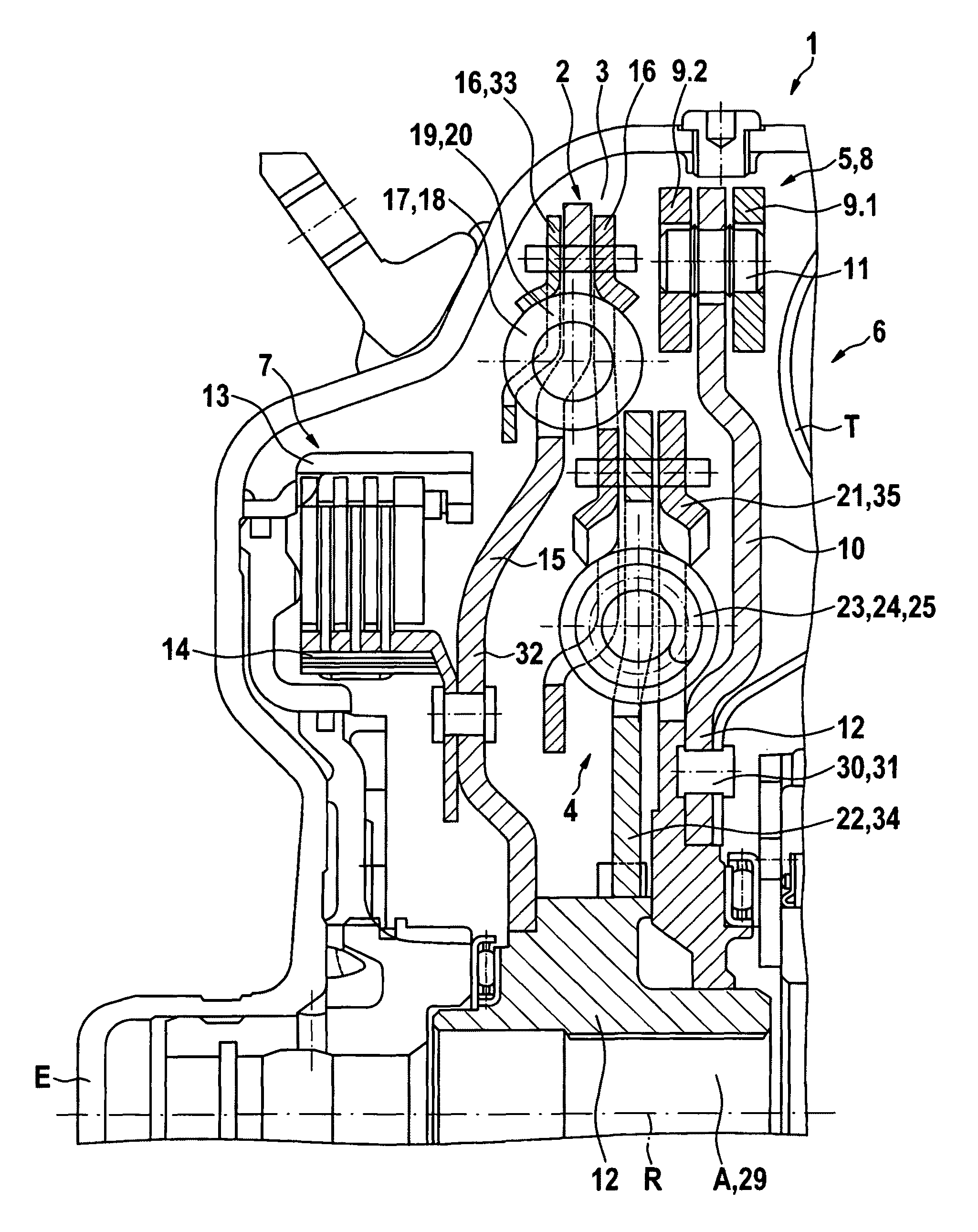
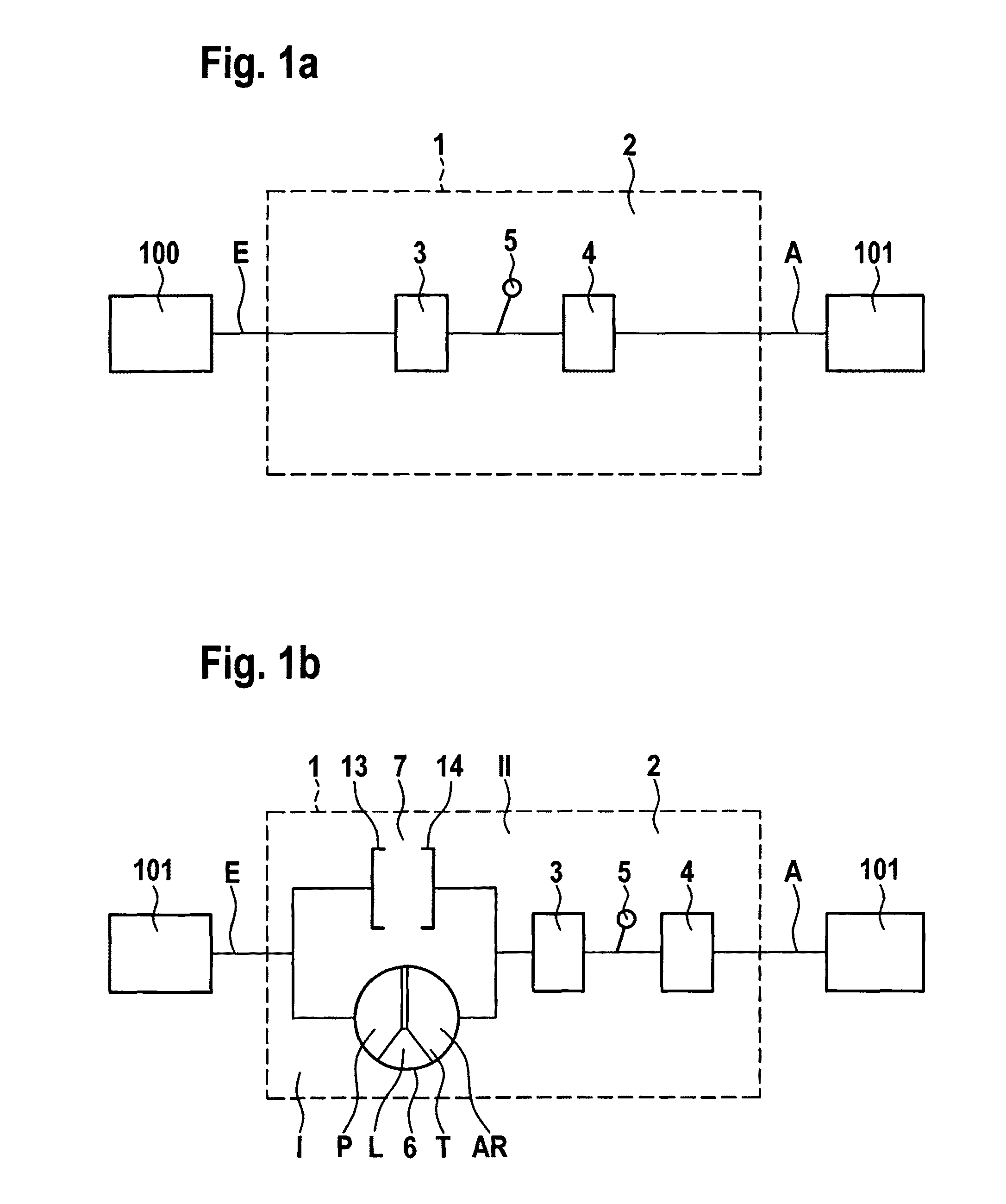
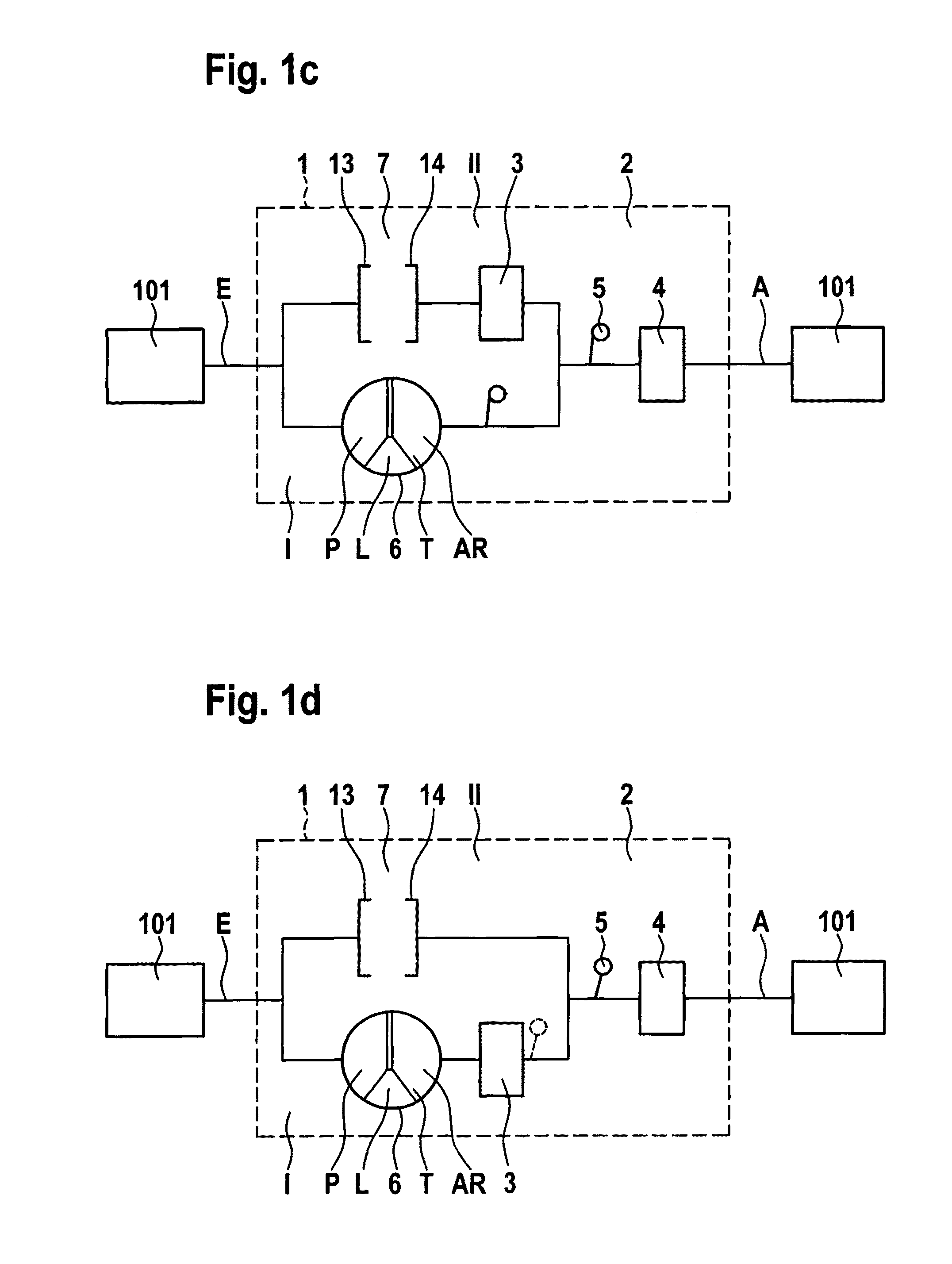
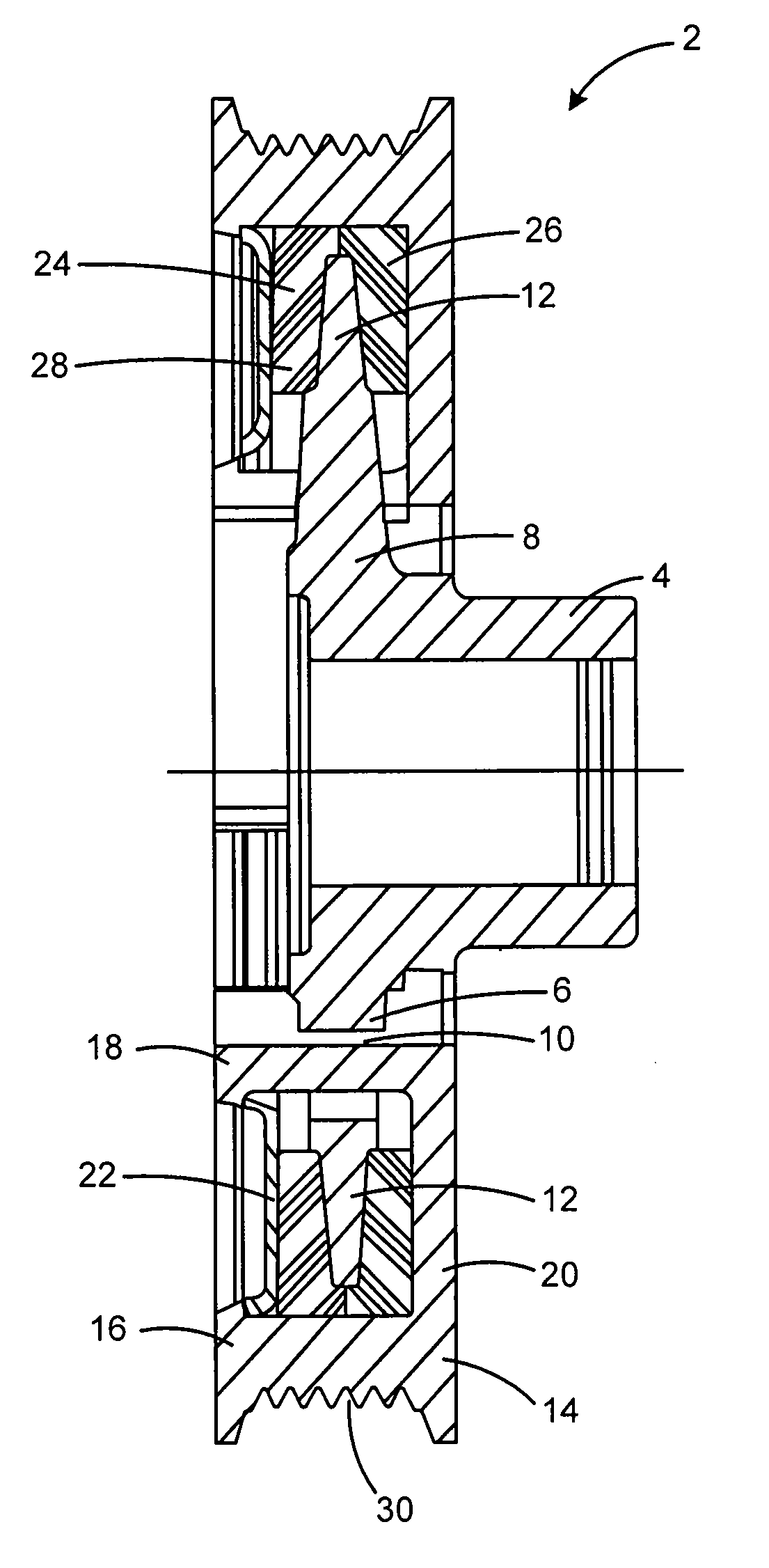
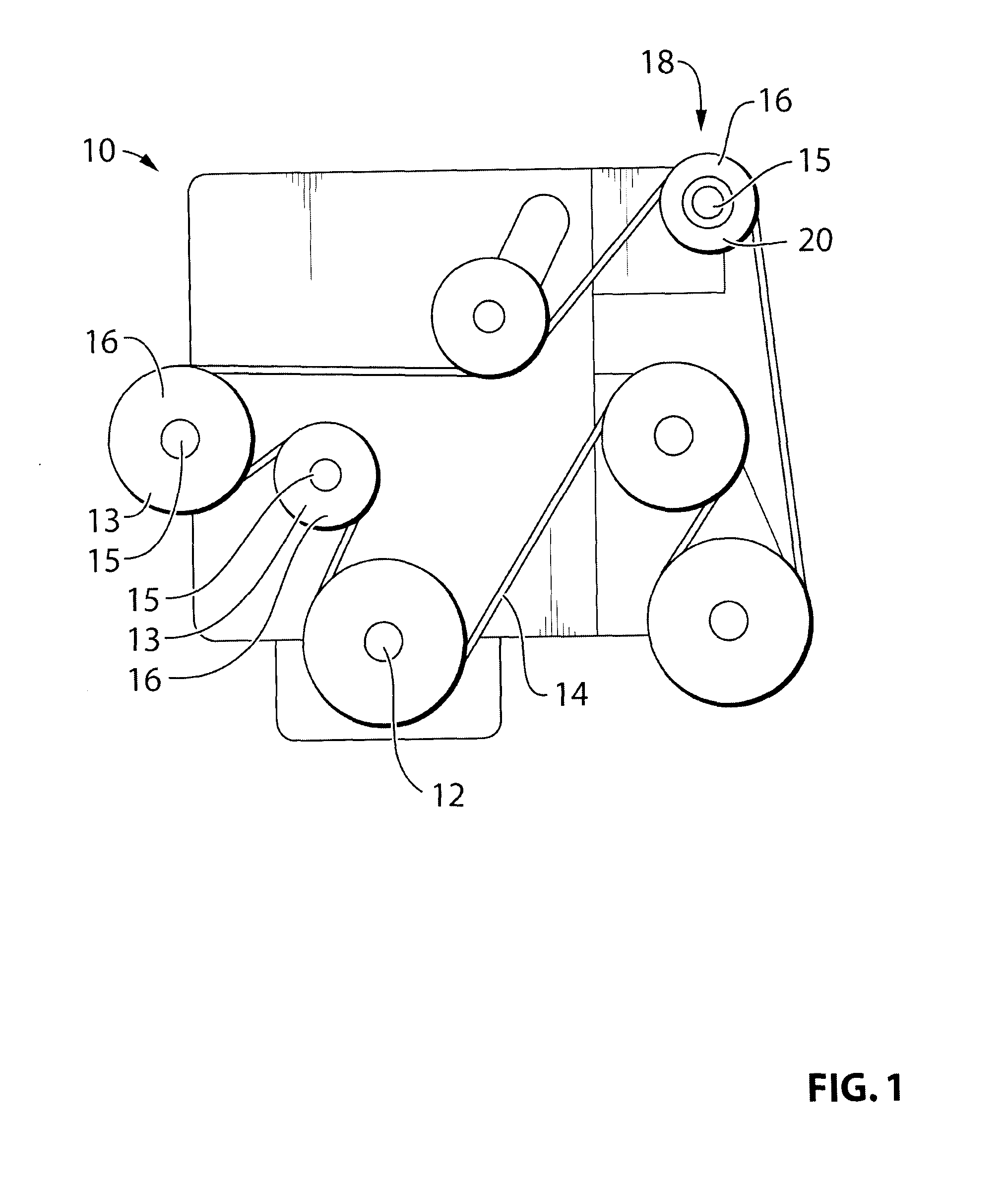
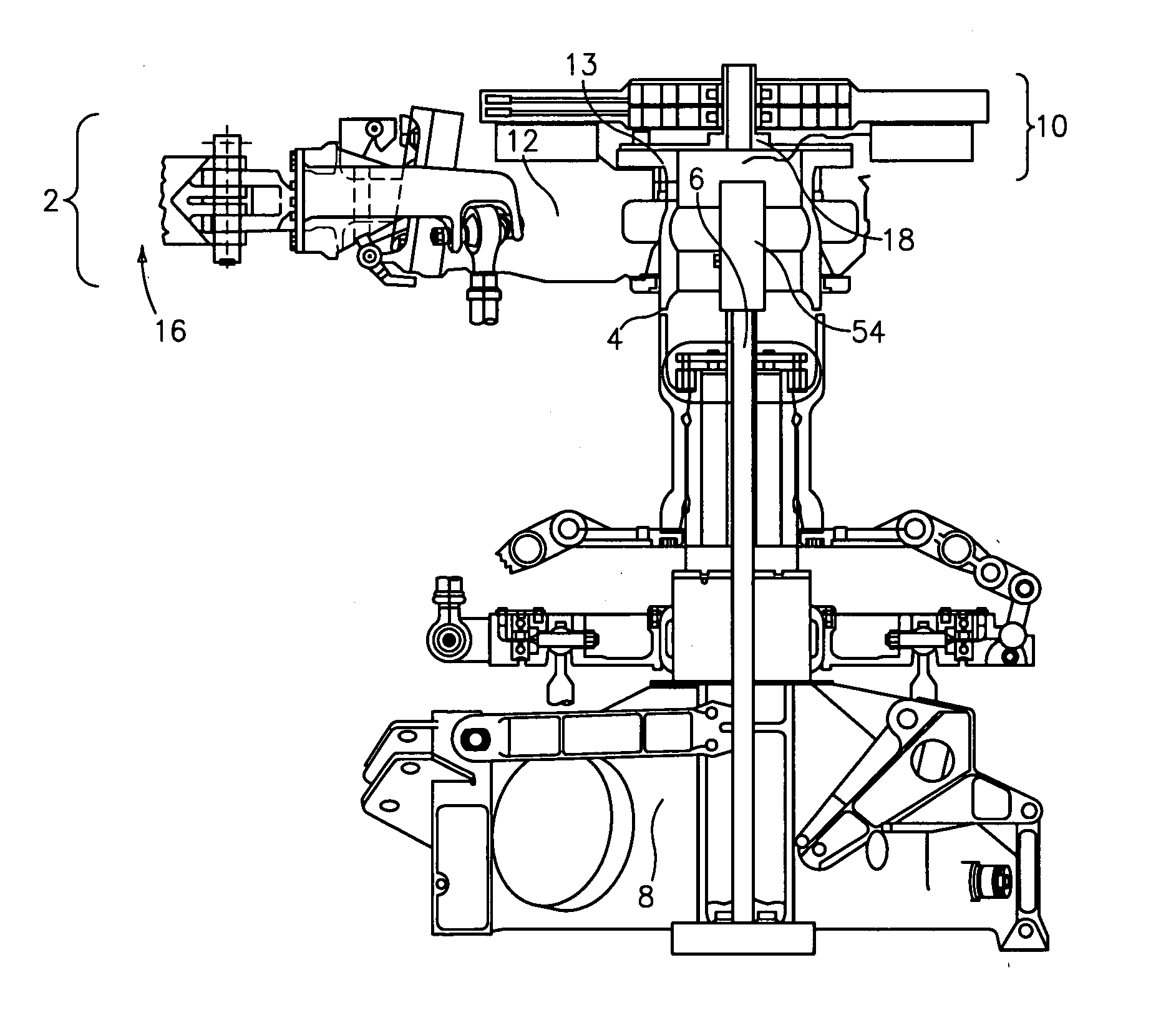
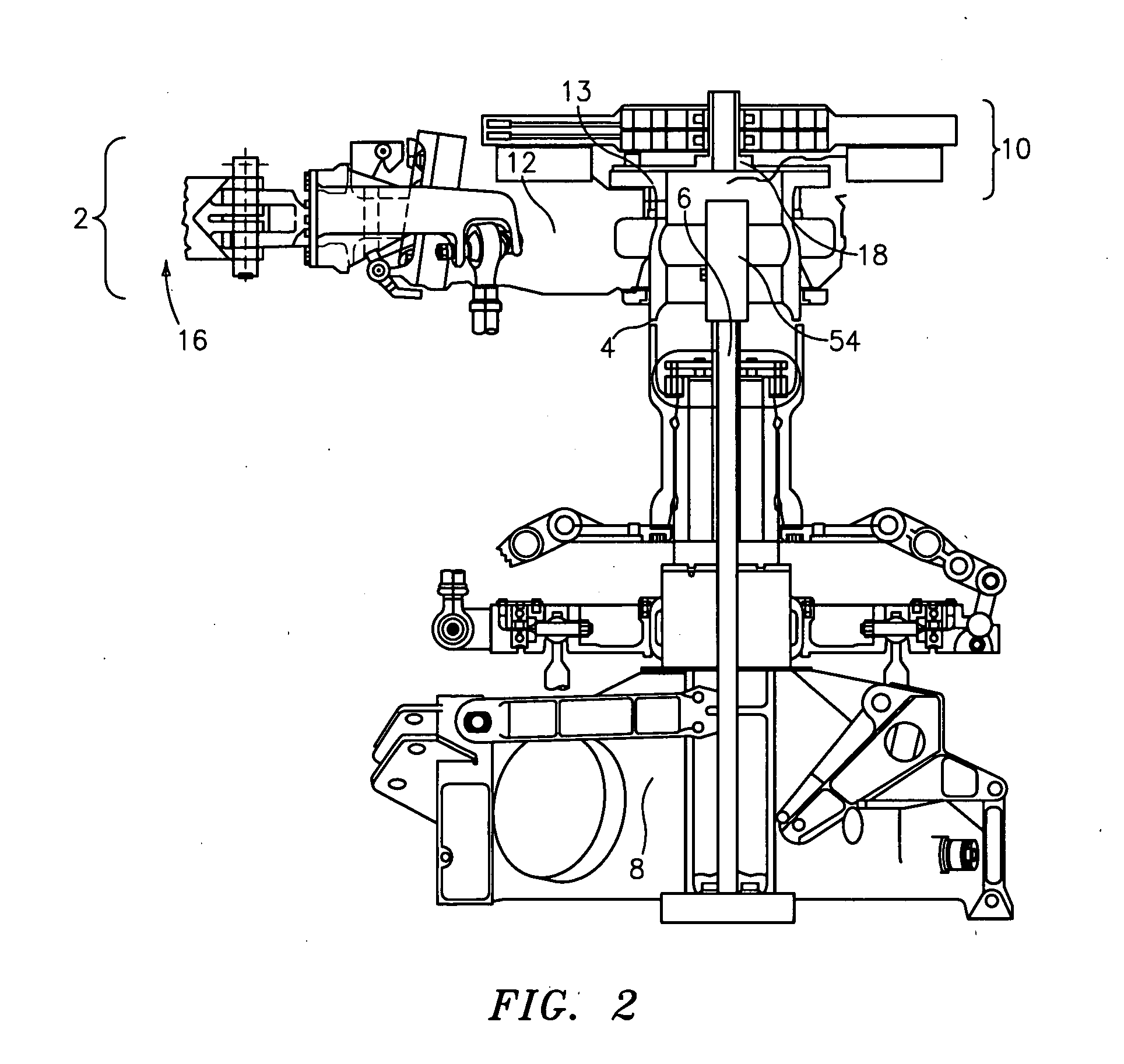
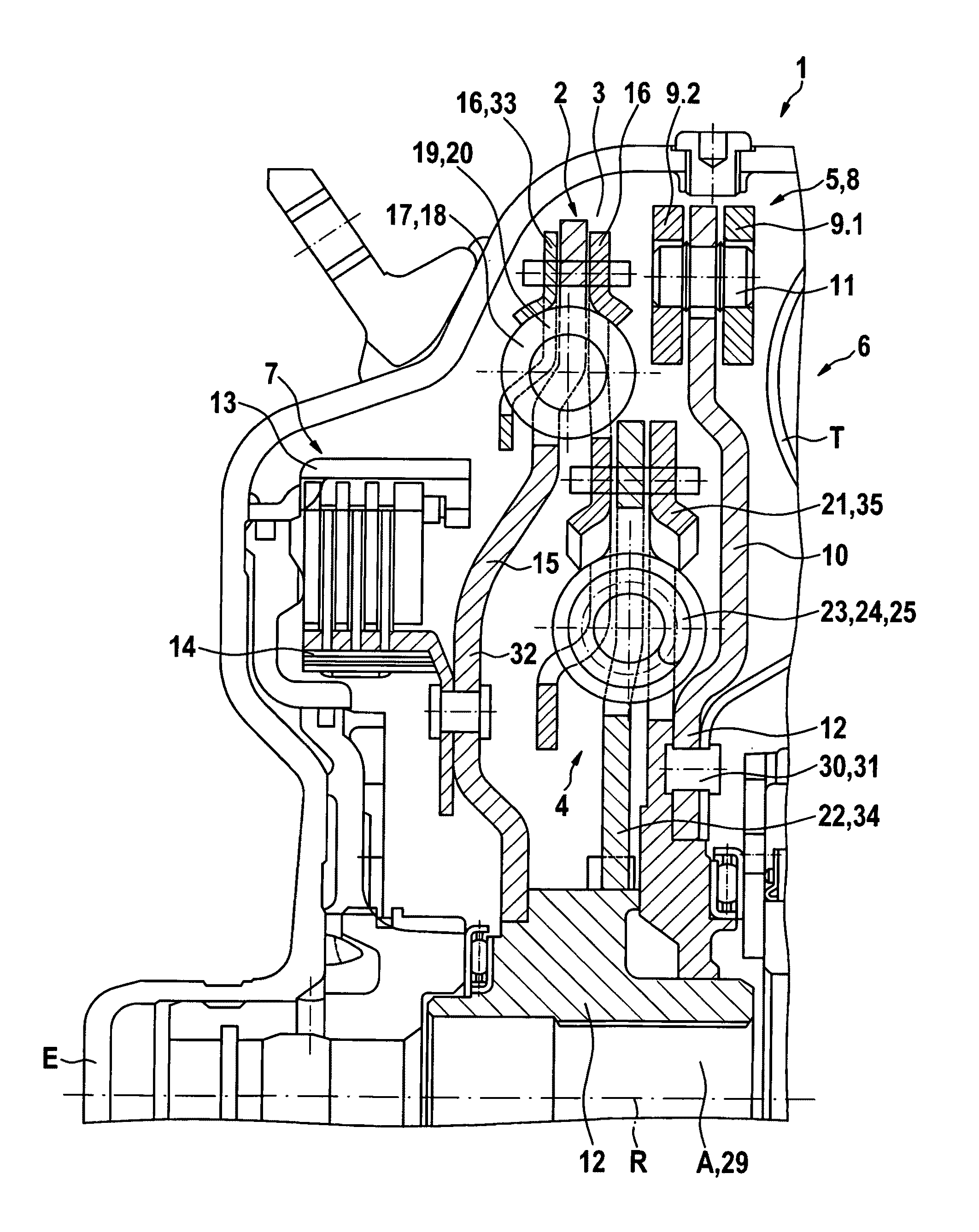
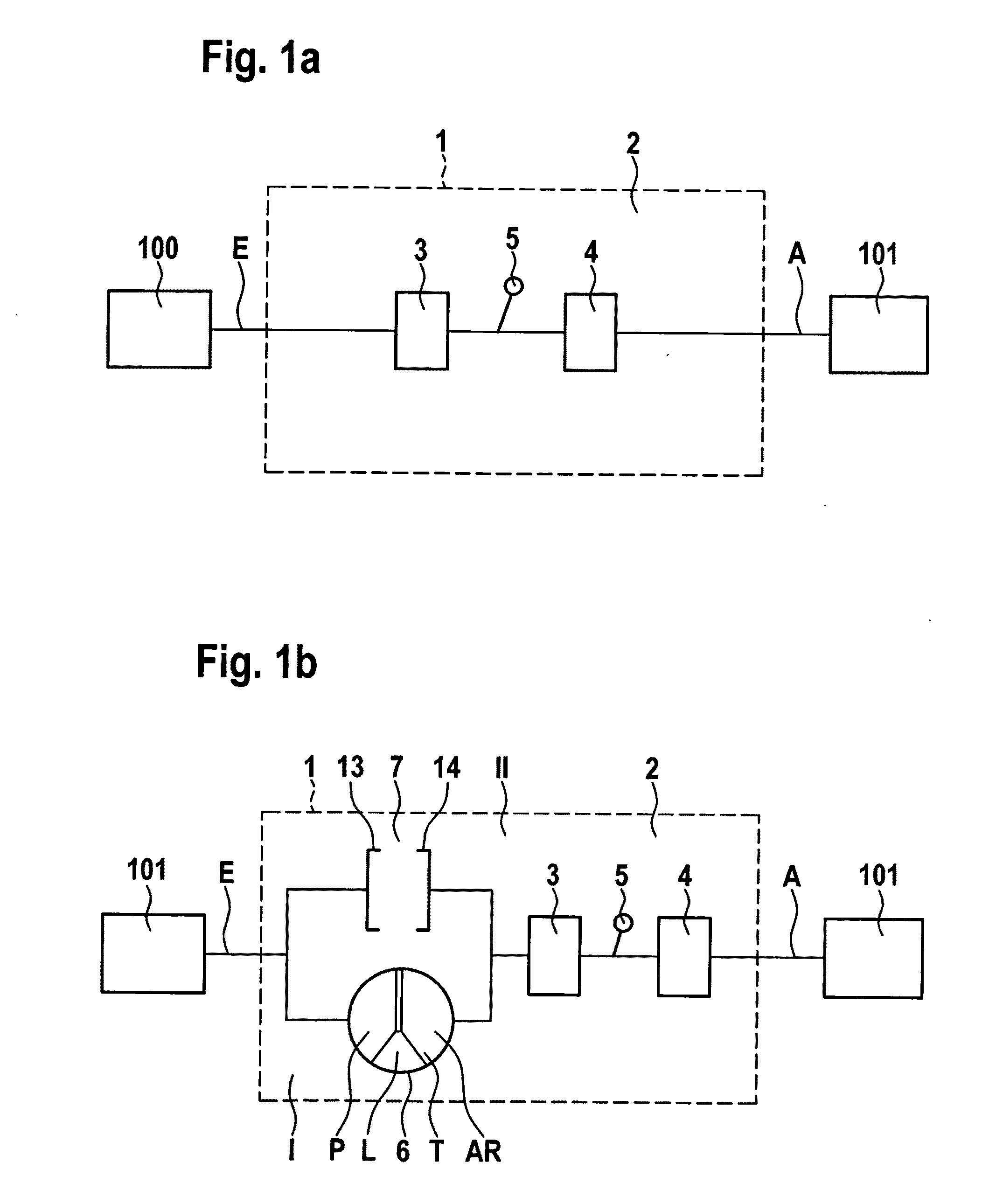
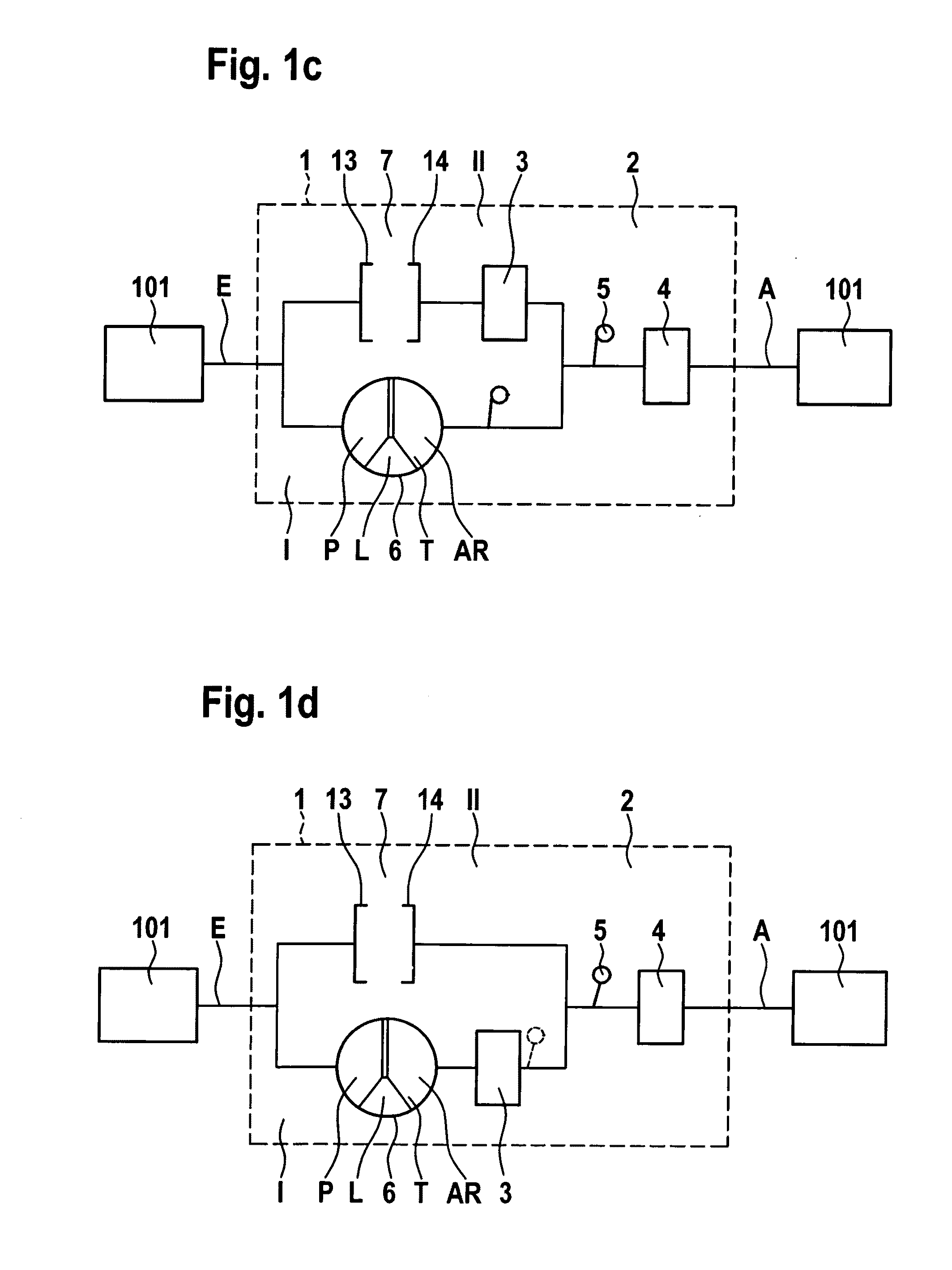
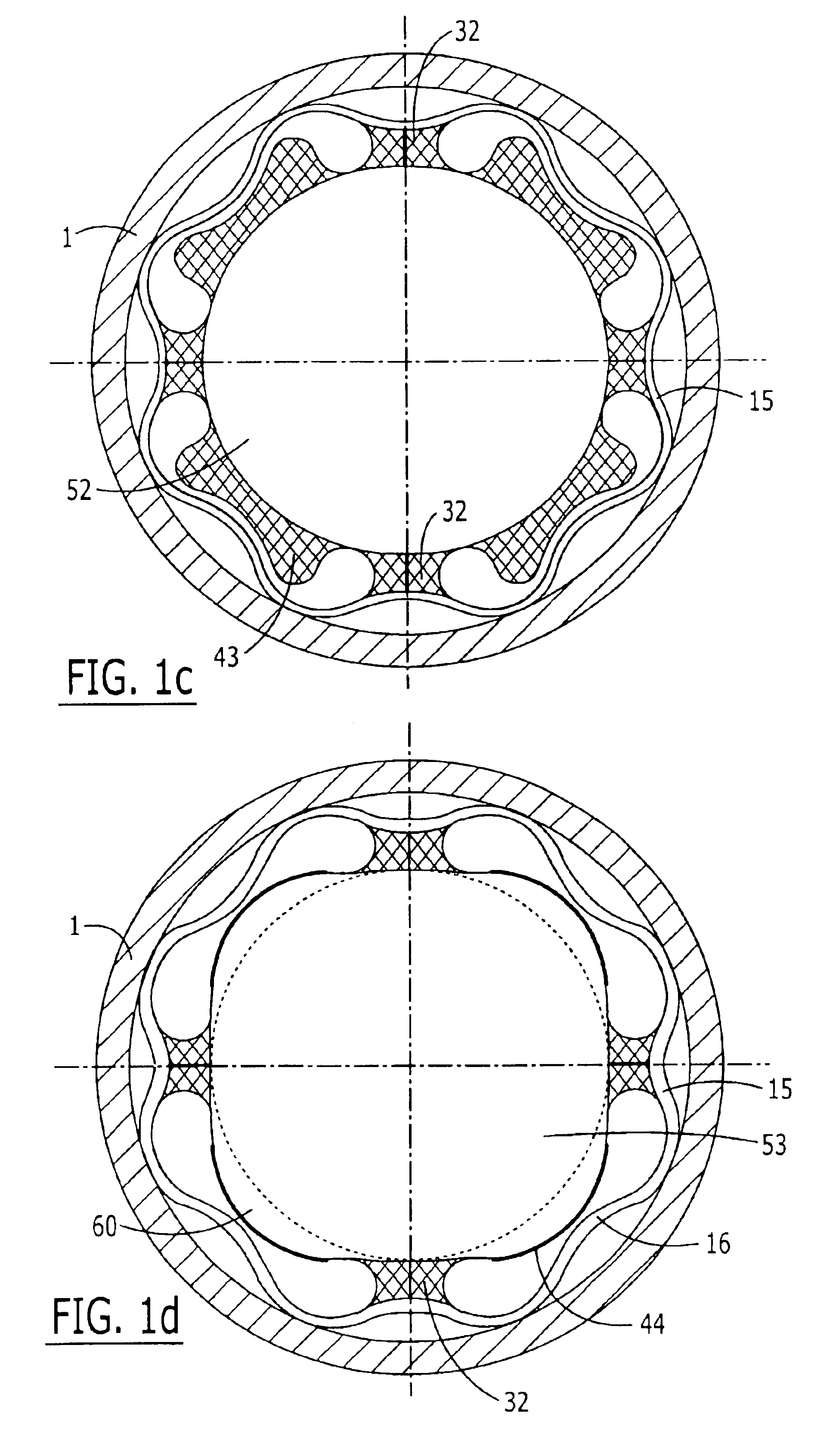
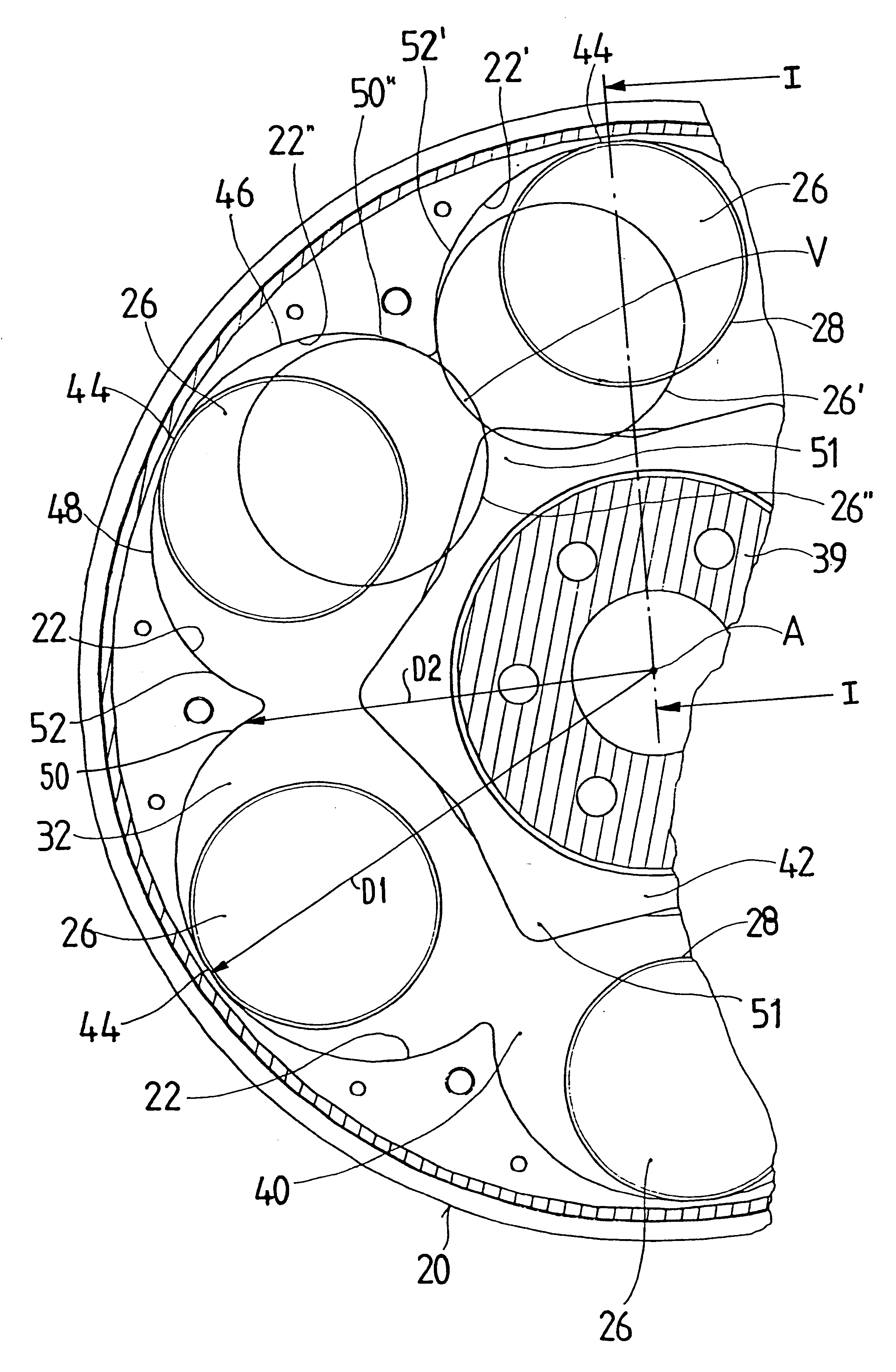
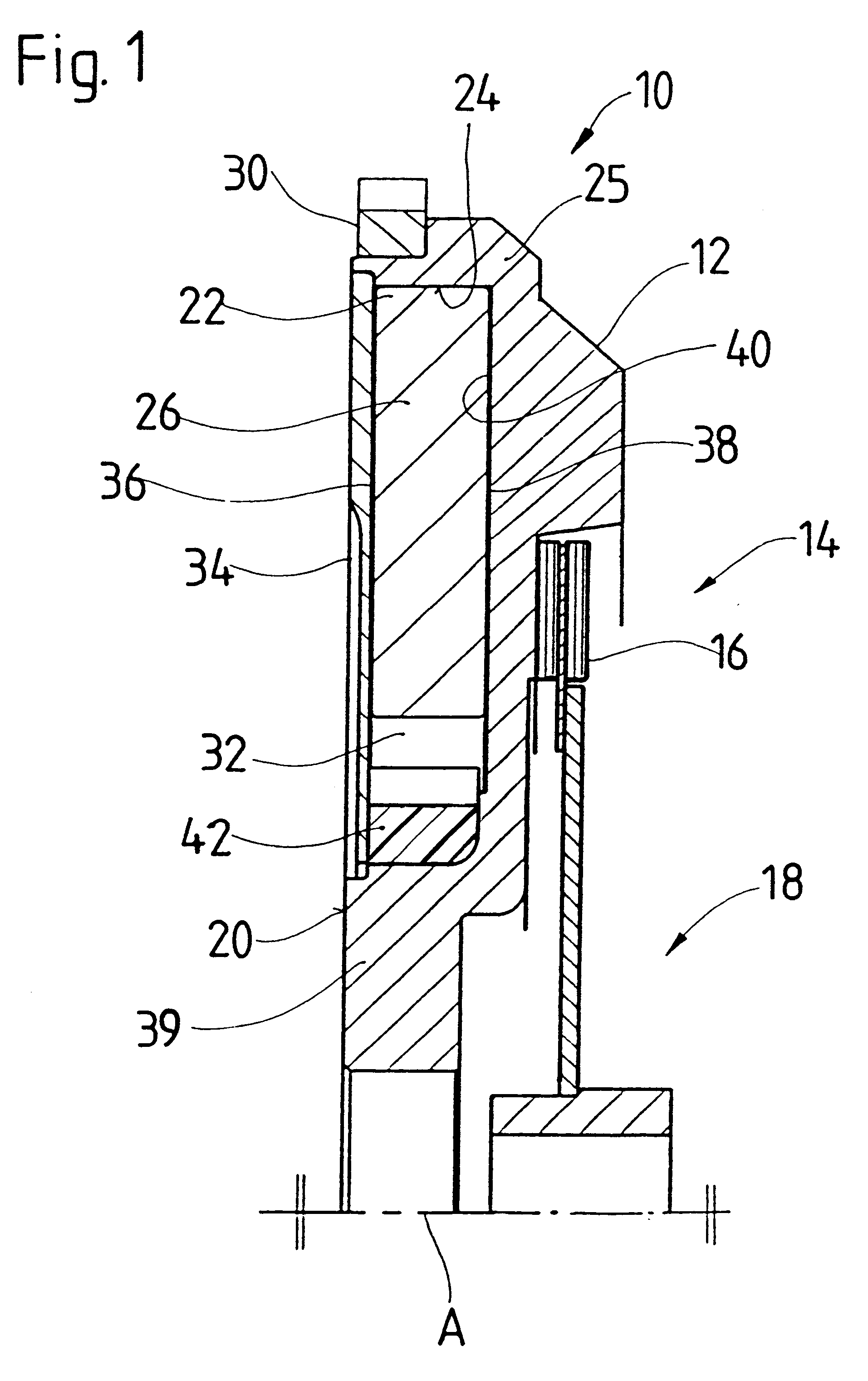
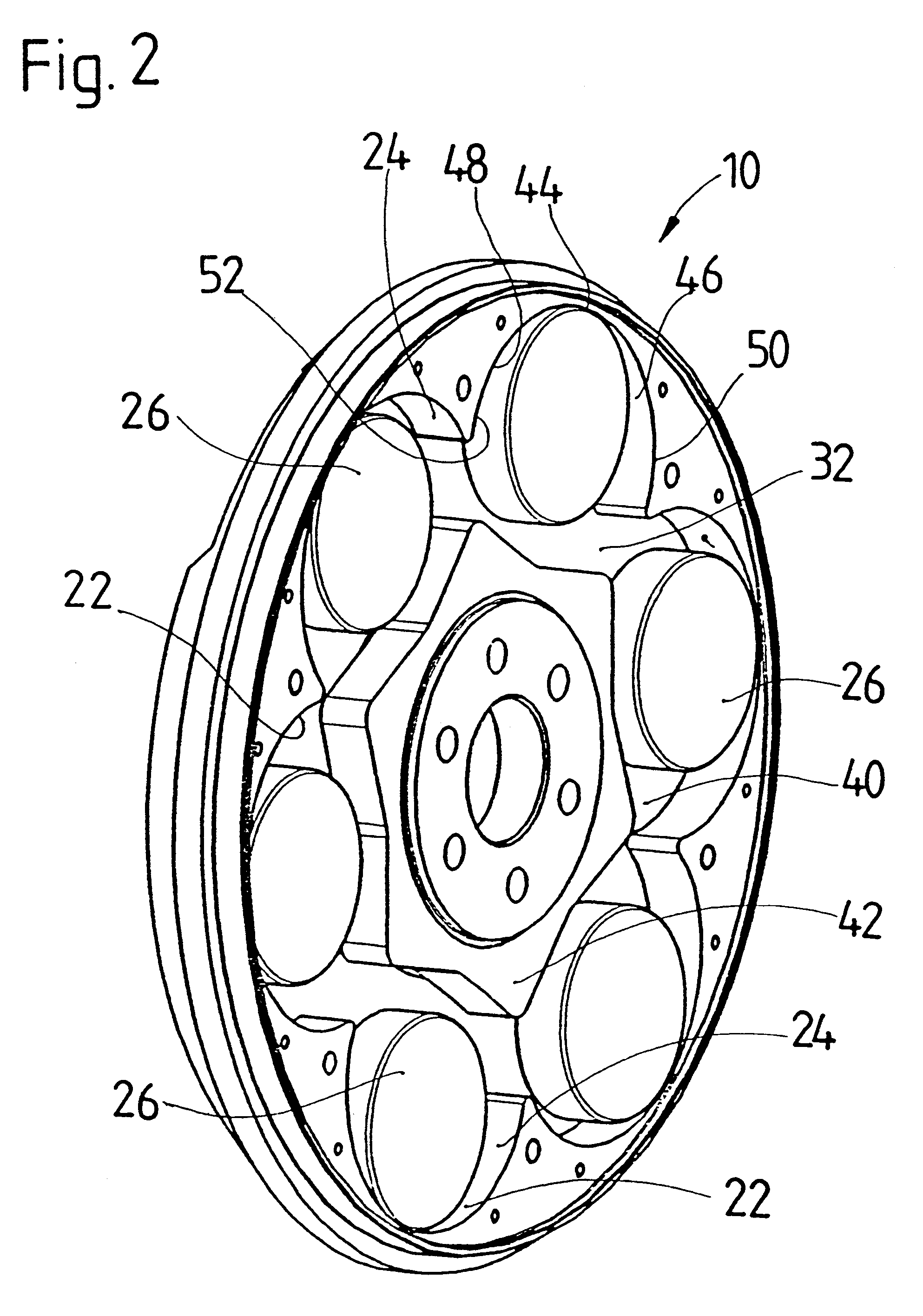
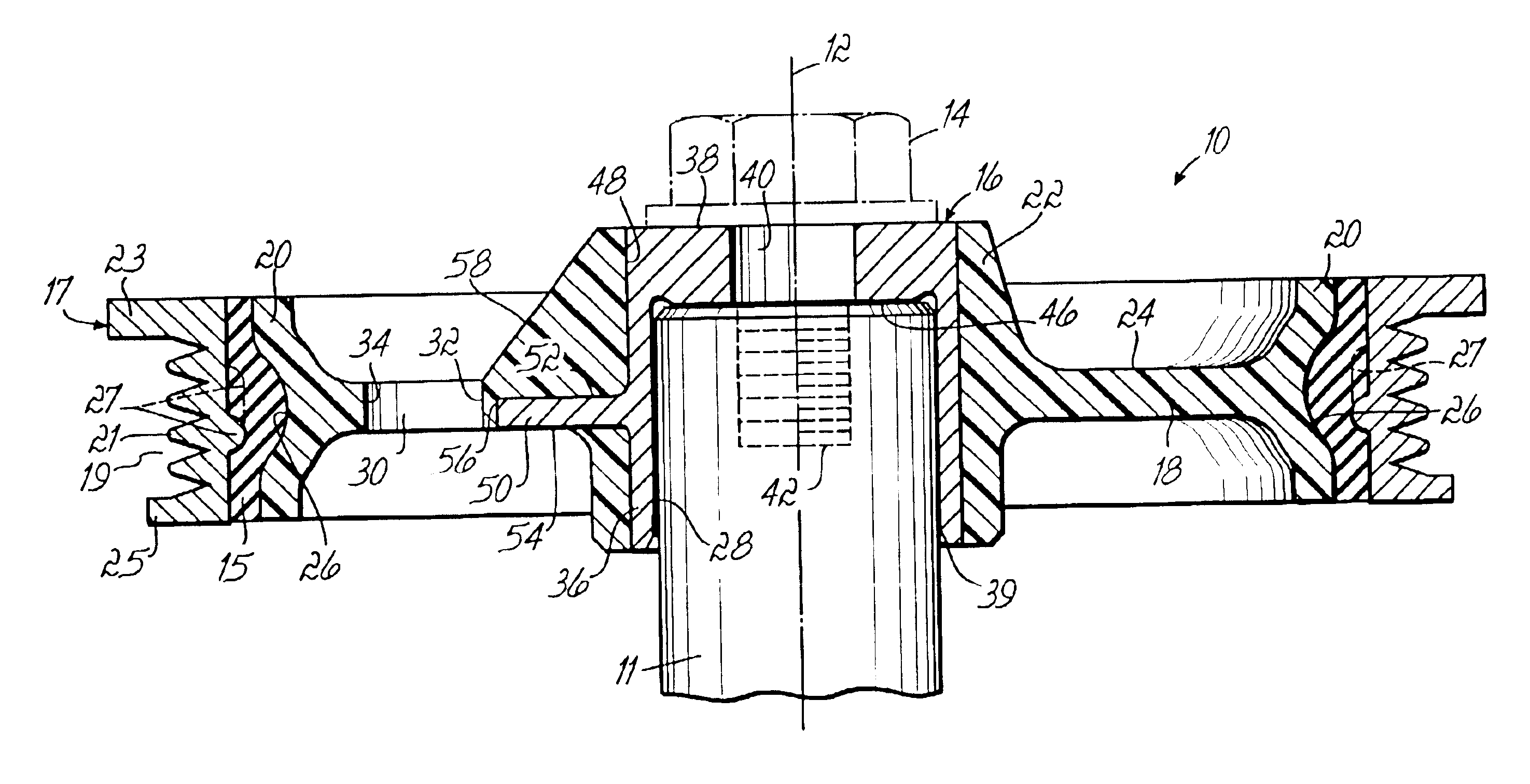
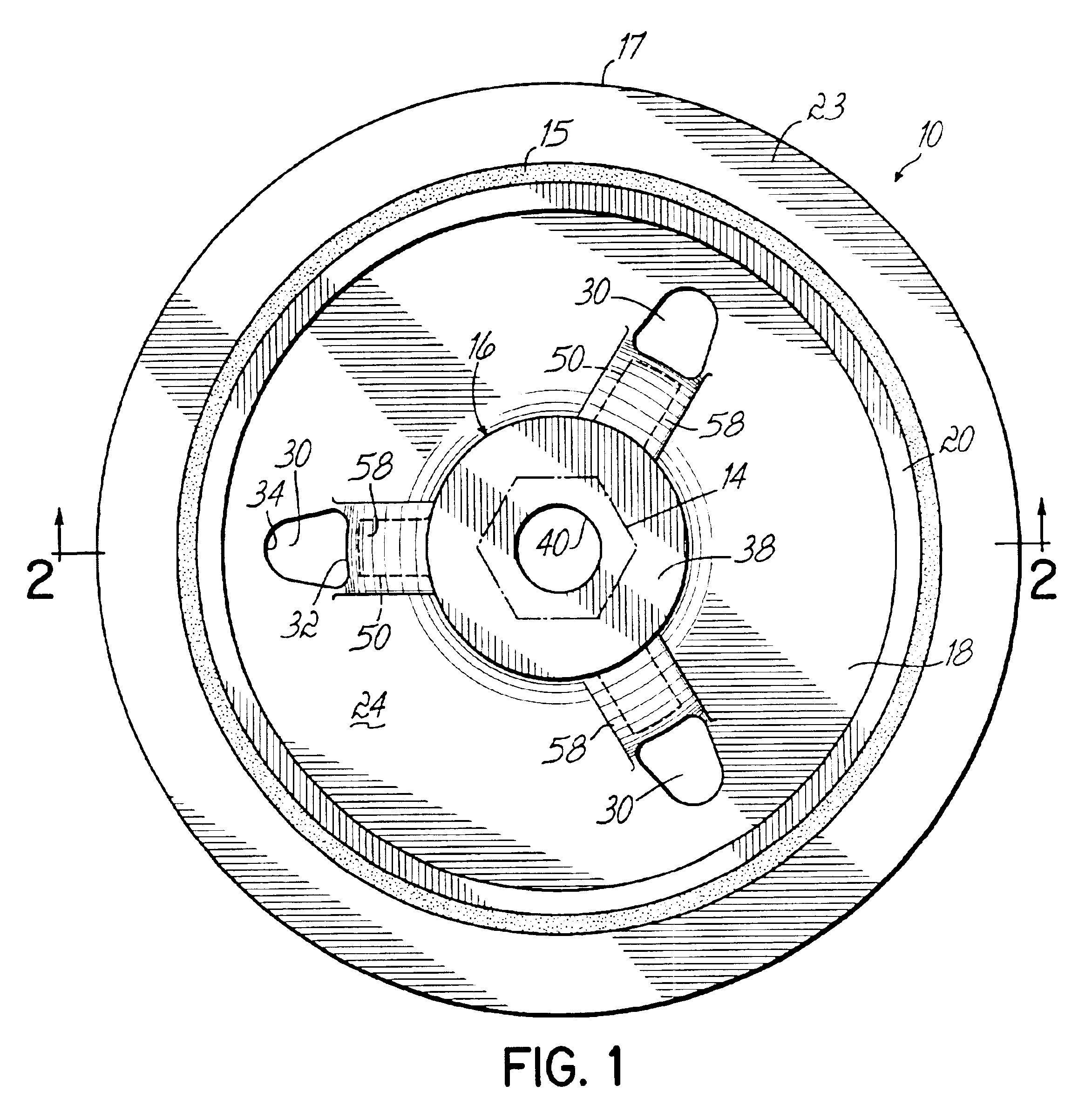
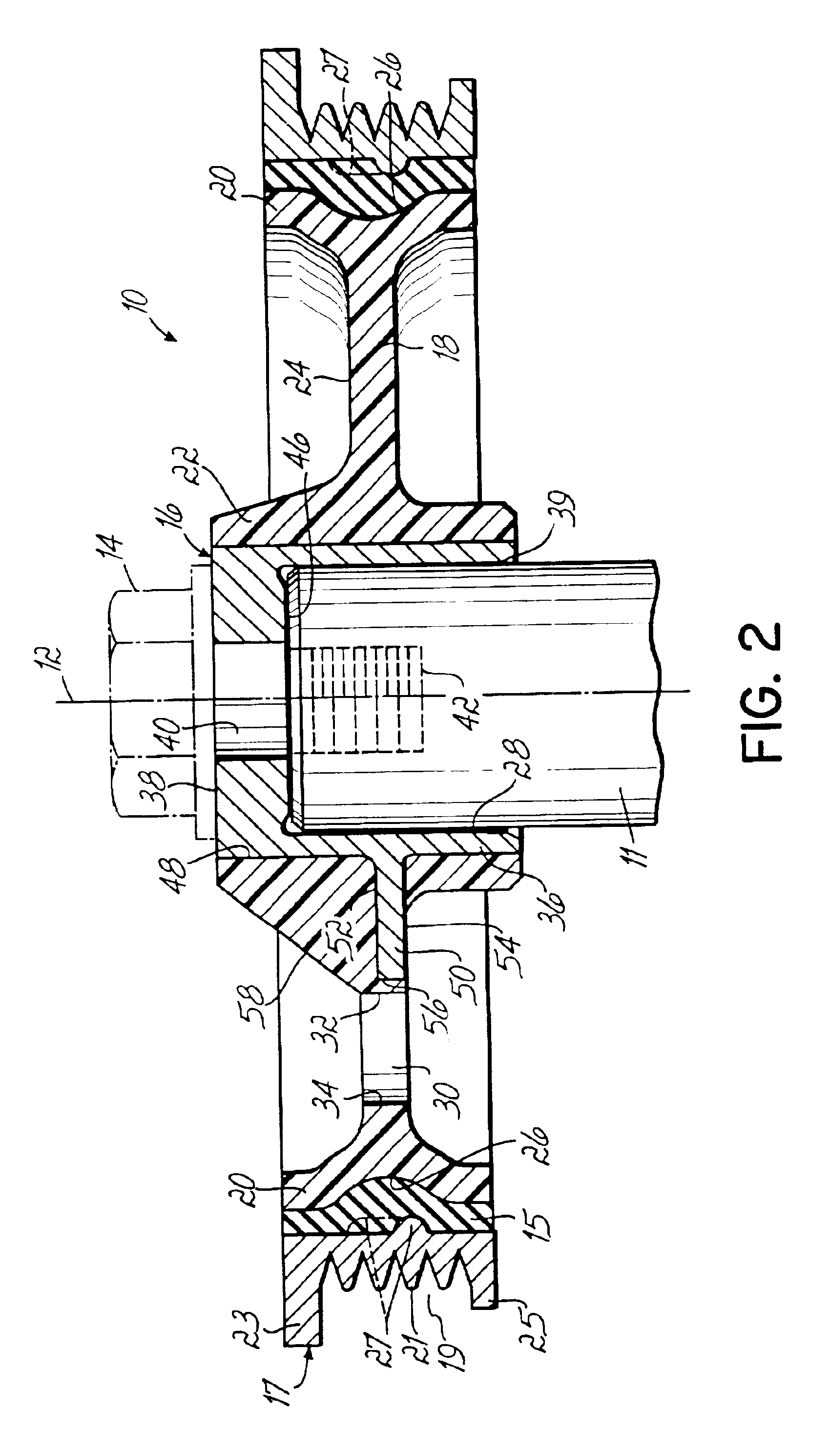
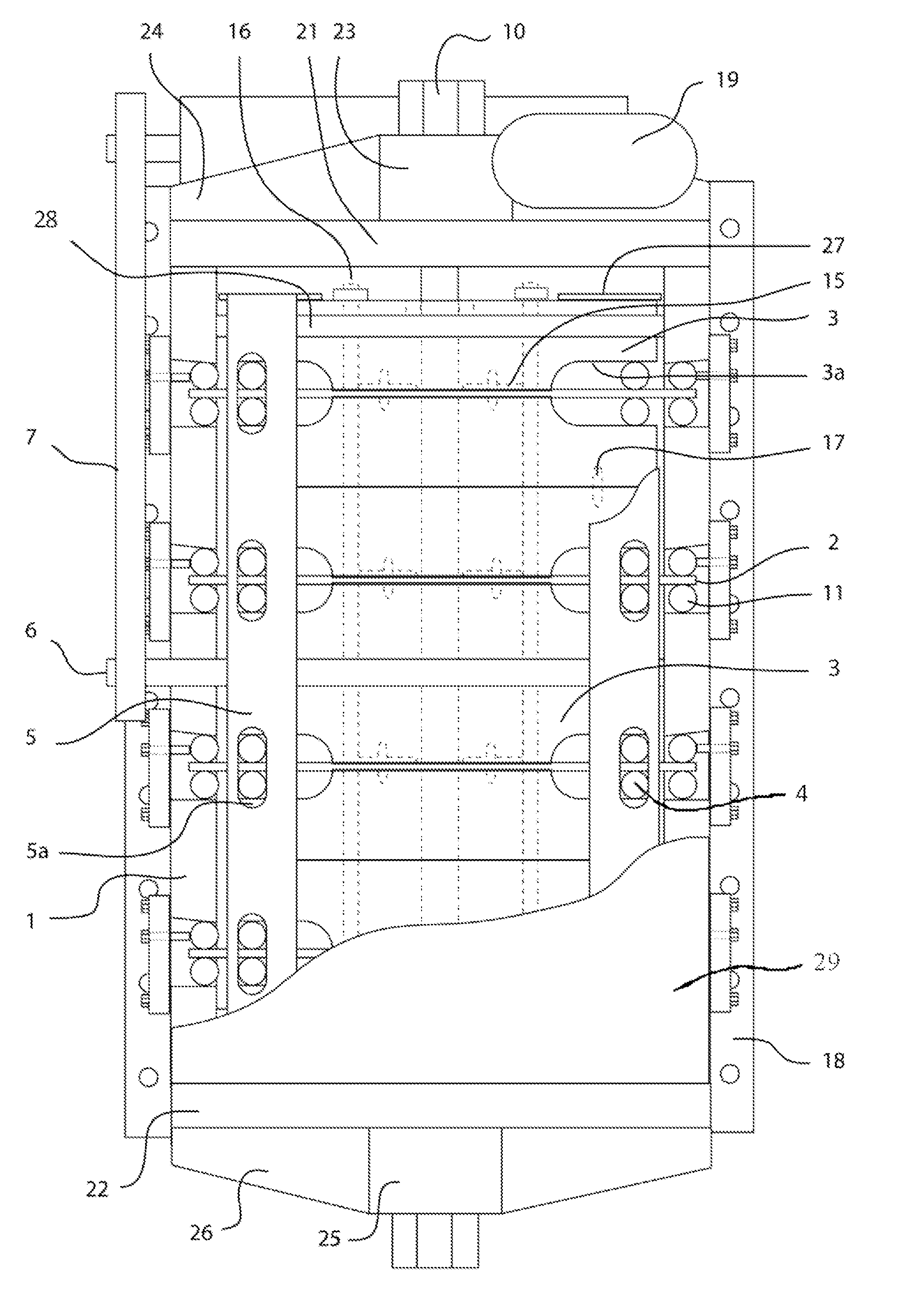
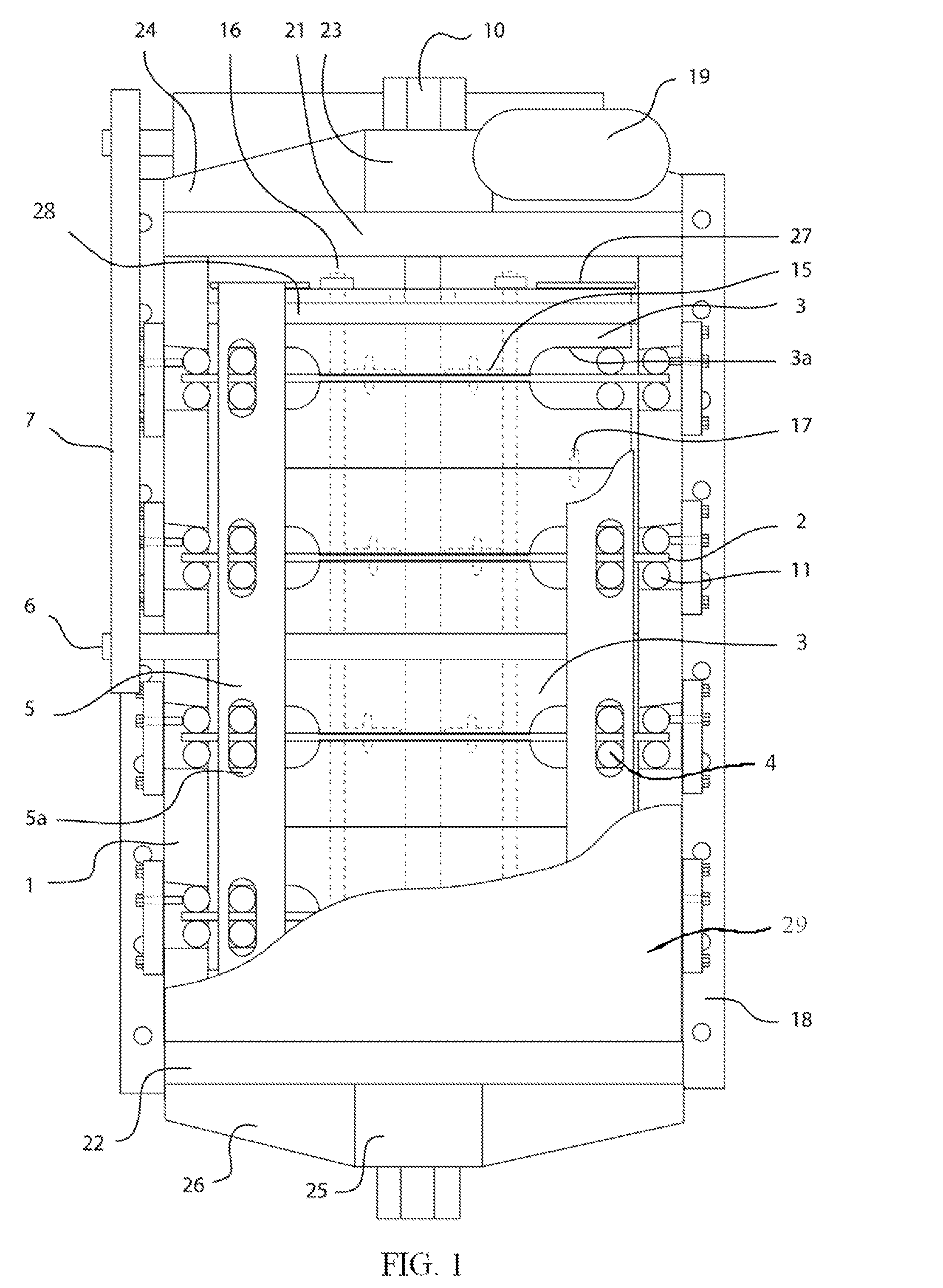
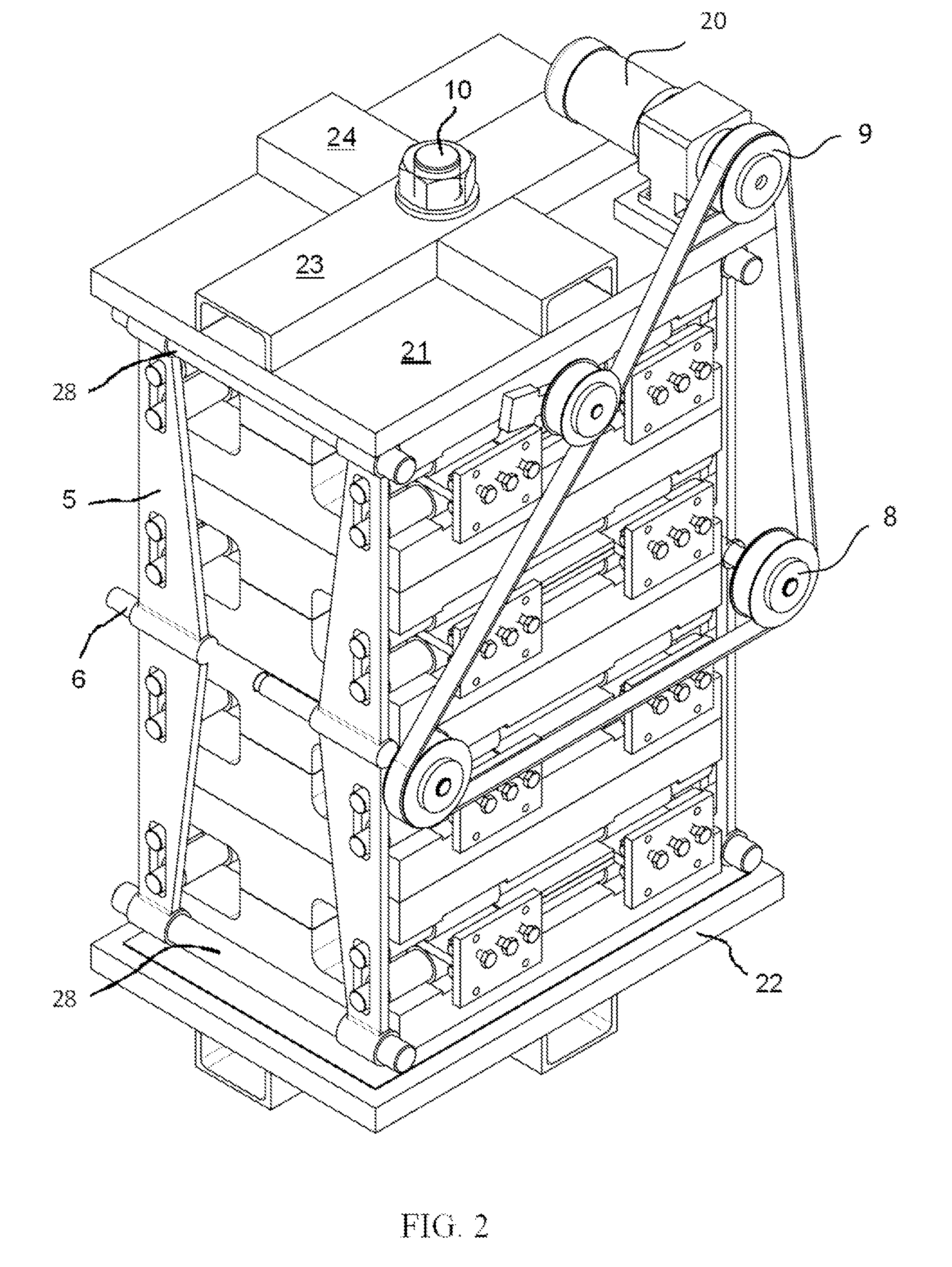
Force transmission device in particular for power transmission between a drive engine and an output
ActiveUS8161739B2Reduce variationEliminate variationRotating vibration suppressionYielding couplingTuned mass damperSelf adaptive
A force transmission device, in particular or power transmission between a drive engine and an output, comprising a damper assembly with at least two dampers, which can be connected in series, and a rotational speed adaptive absorber, wherein the rotational speed adaptive tuned mass damper is disposed between the dampers at least in one force flow direction through the force transmission device.
Owner:SCHAEFFLER TECH AG & CO KG
Torsional vibration damper
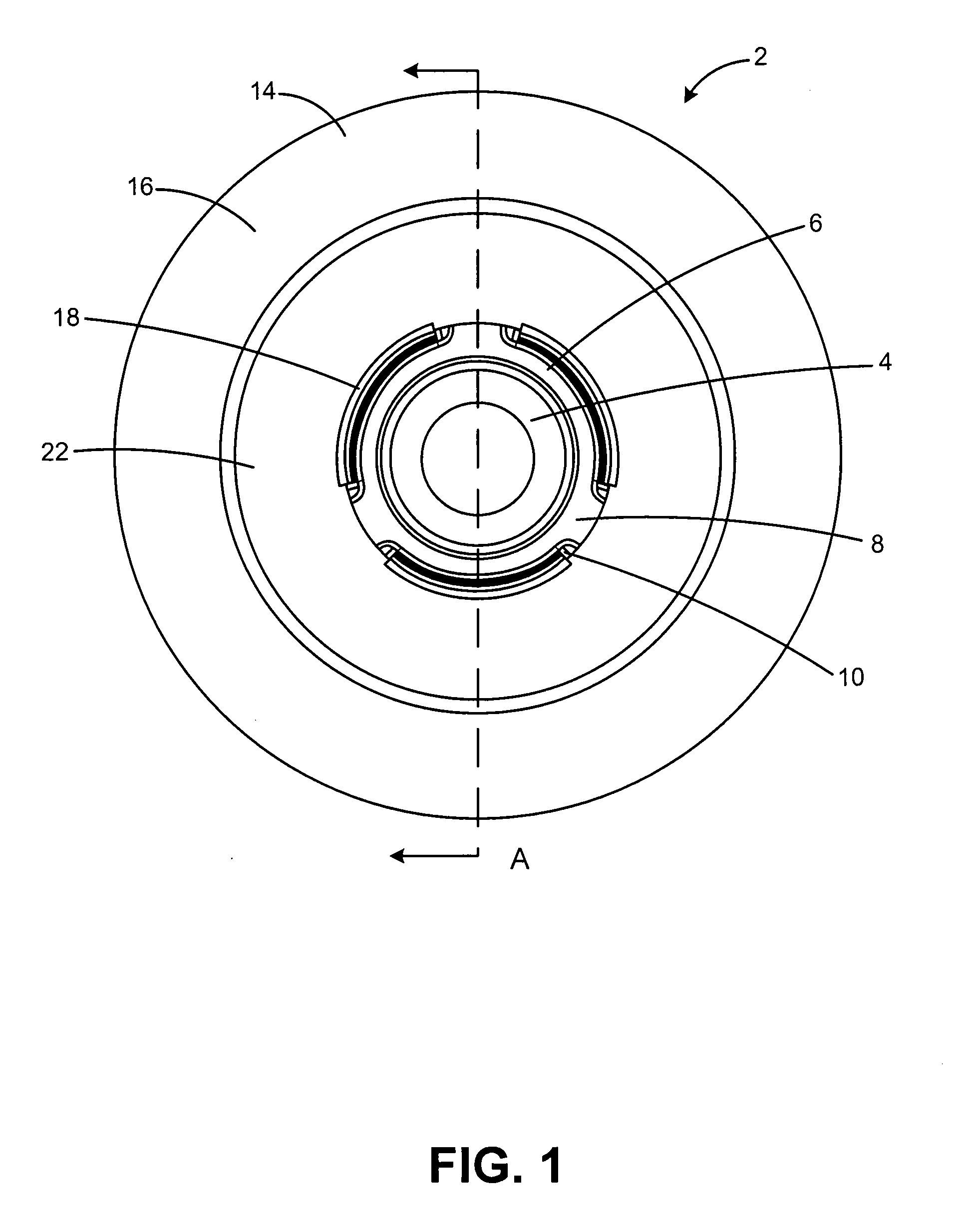
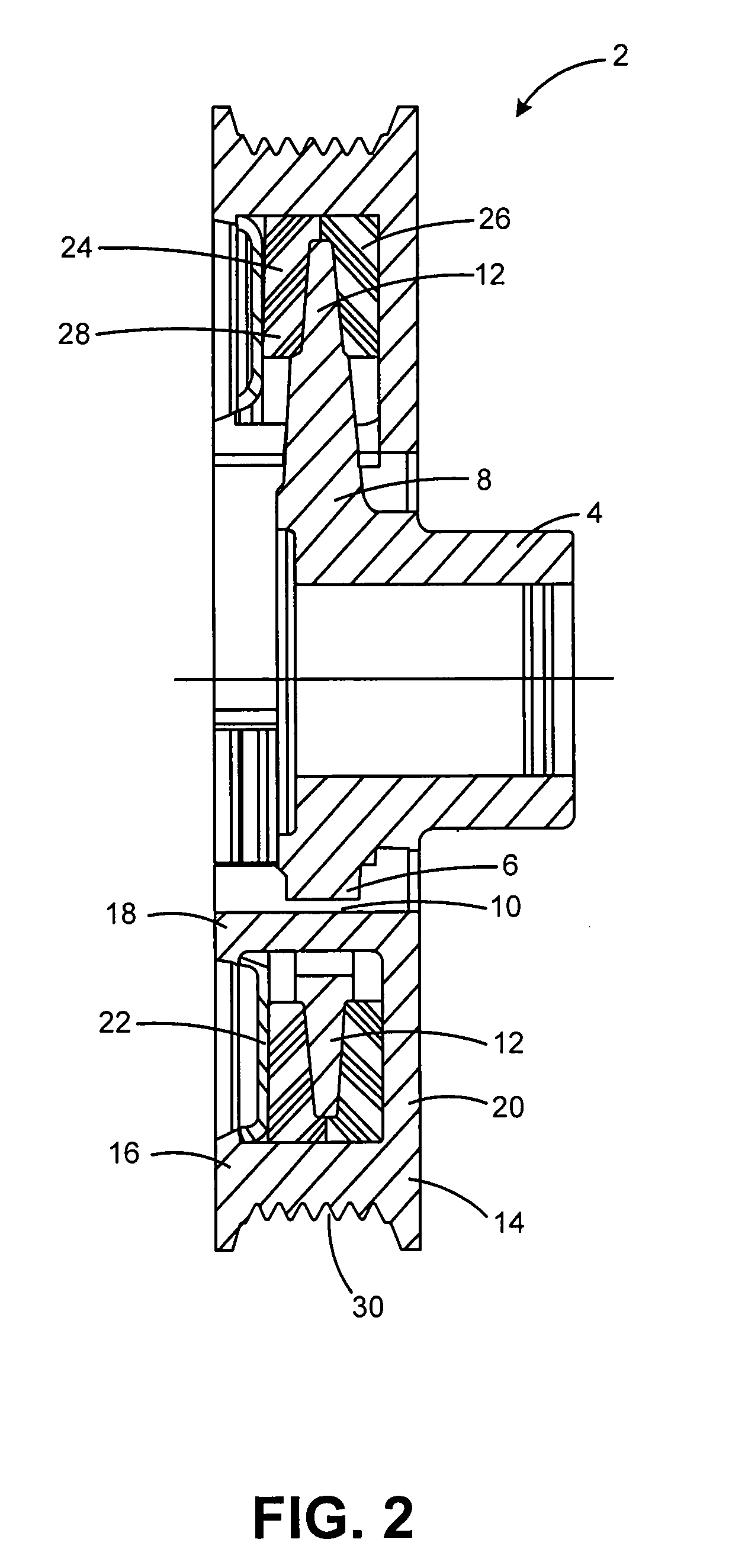
A torsional vibration damper having a hub carrying a radially projecting flange and an annular inertia mass defining an annular channel encompassing the radially projecting flange and an elastomeric member. An annular compression ring is attached to the opening of the annular channel to axially compress and extrude the elastomeric member to fill the annular channel around the radial flange within the inertia ring. Projections defining an intermittent annular inner rim of the inertia mass extend through openings between the spokes of the hub and cooperate with an annular outer rim of the inertia mass to retain the compression ring.
Owner:DAYCO IP HLDG +1
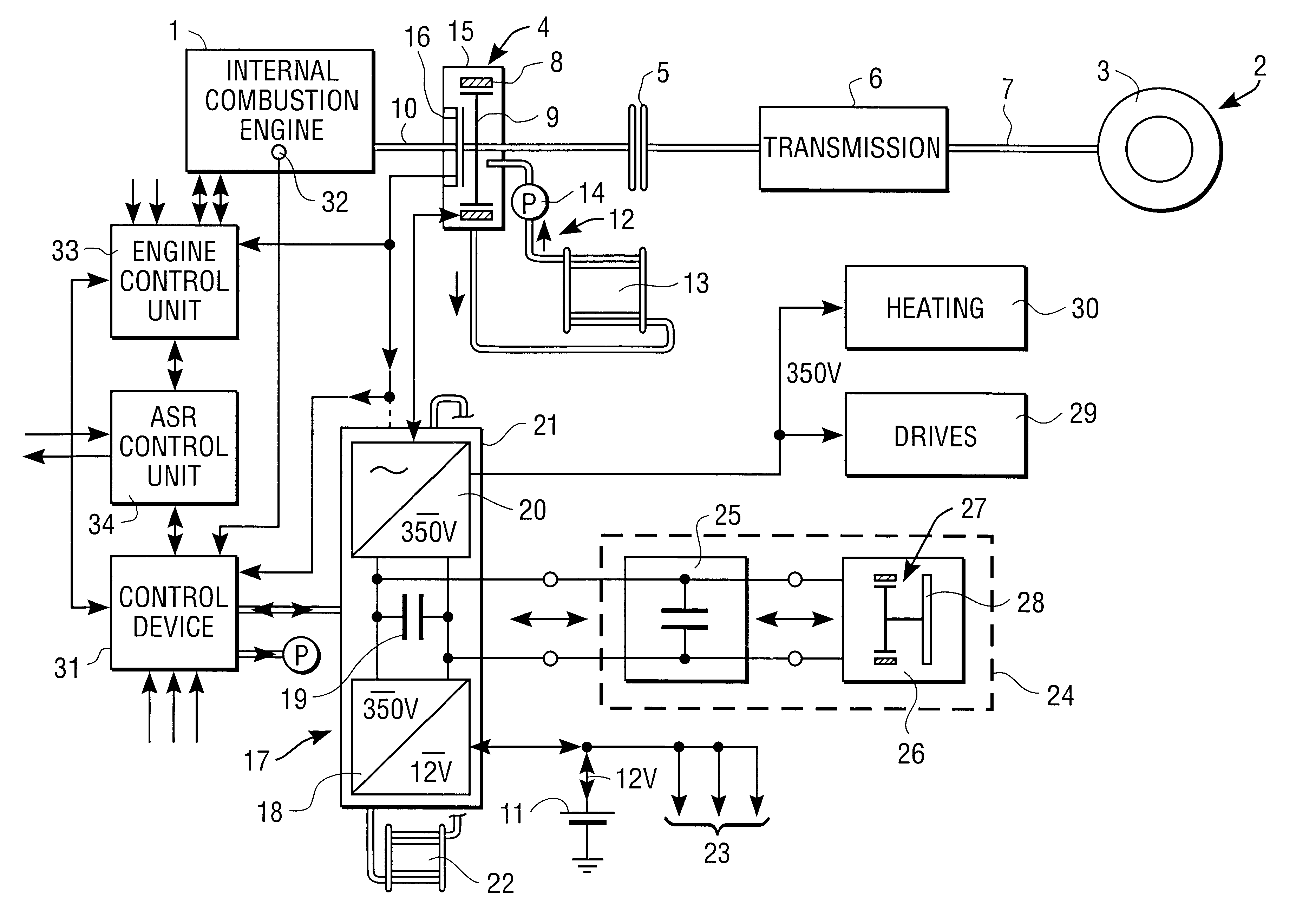
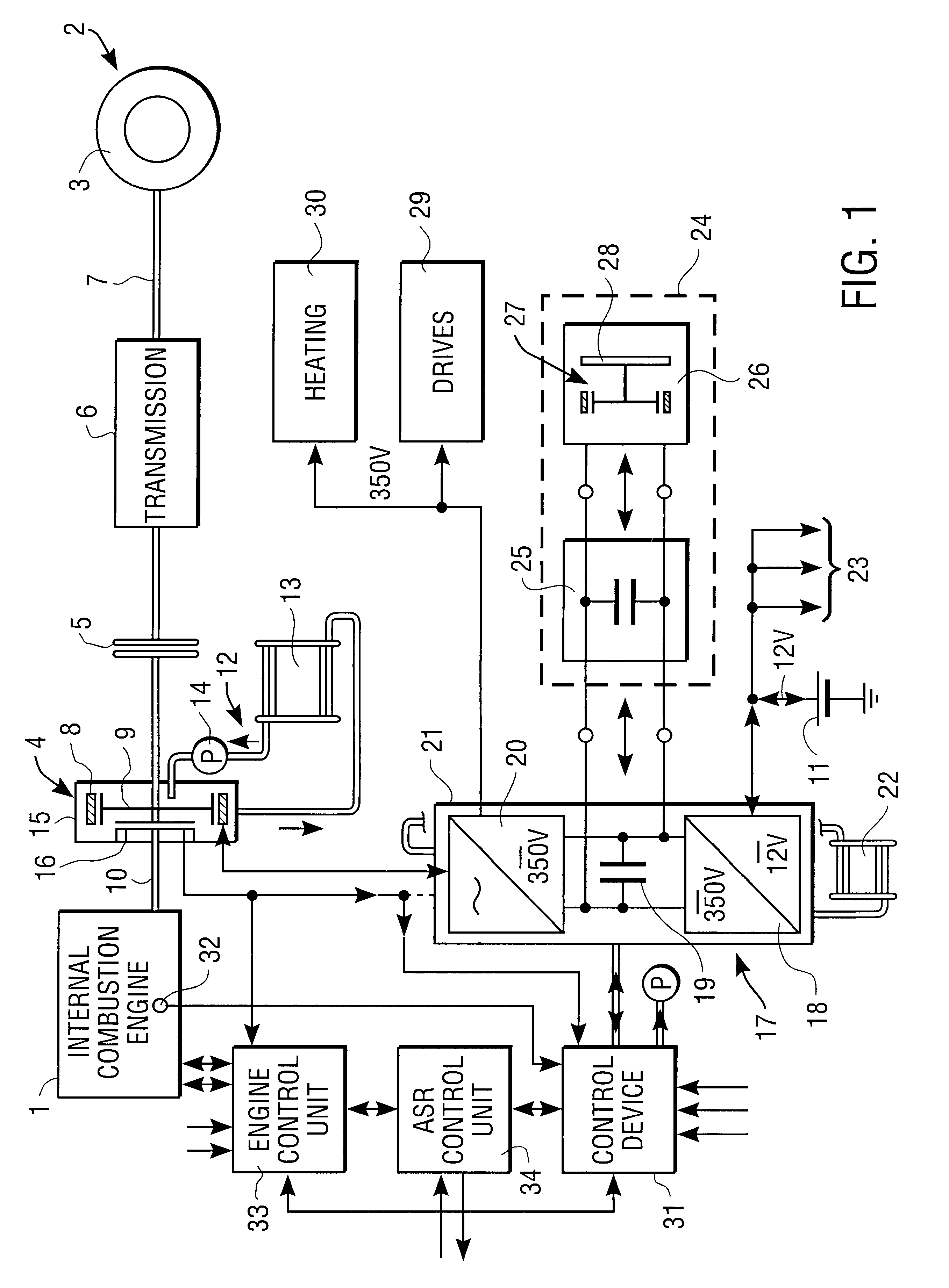
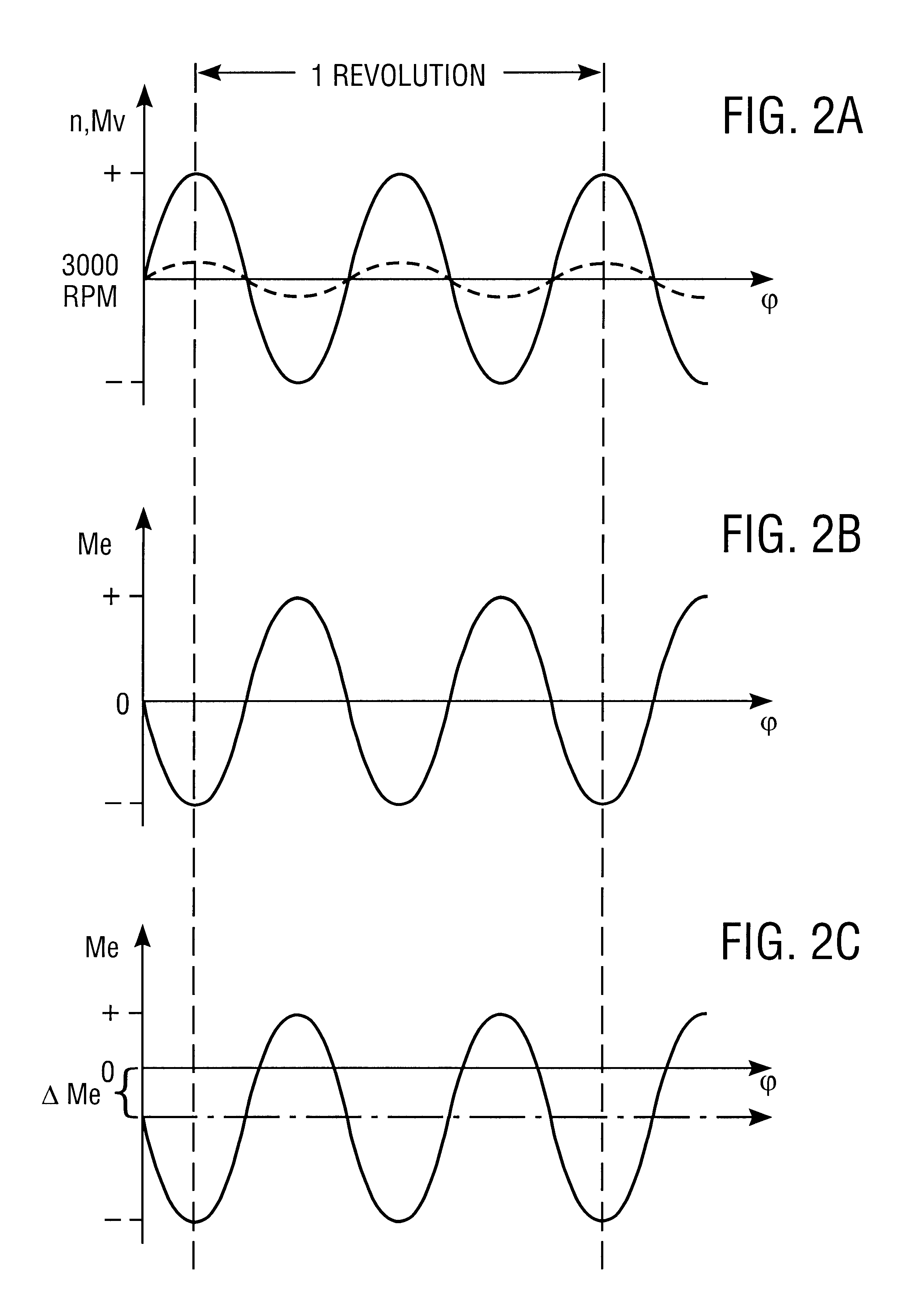
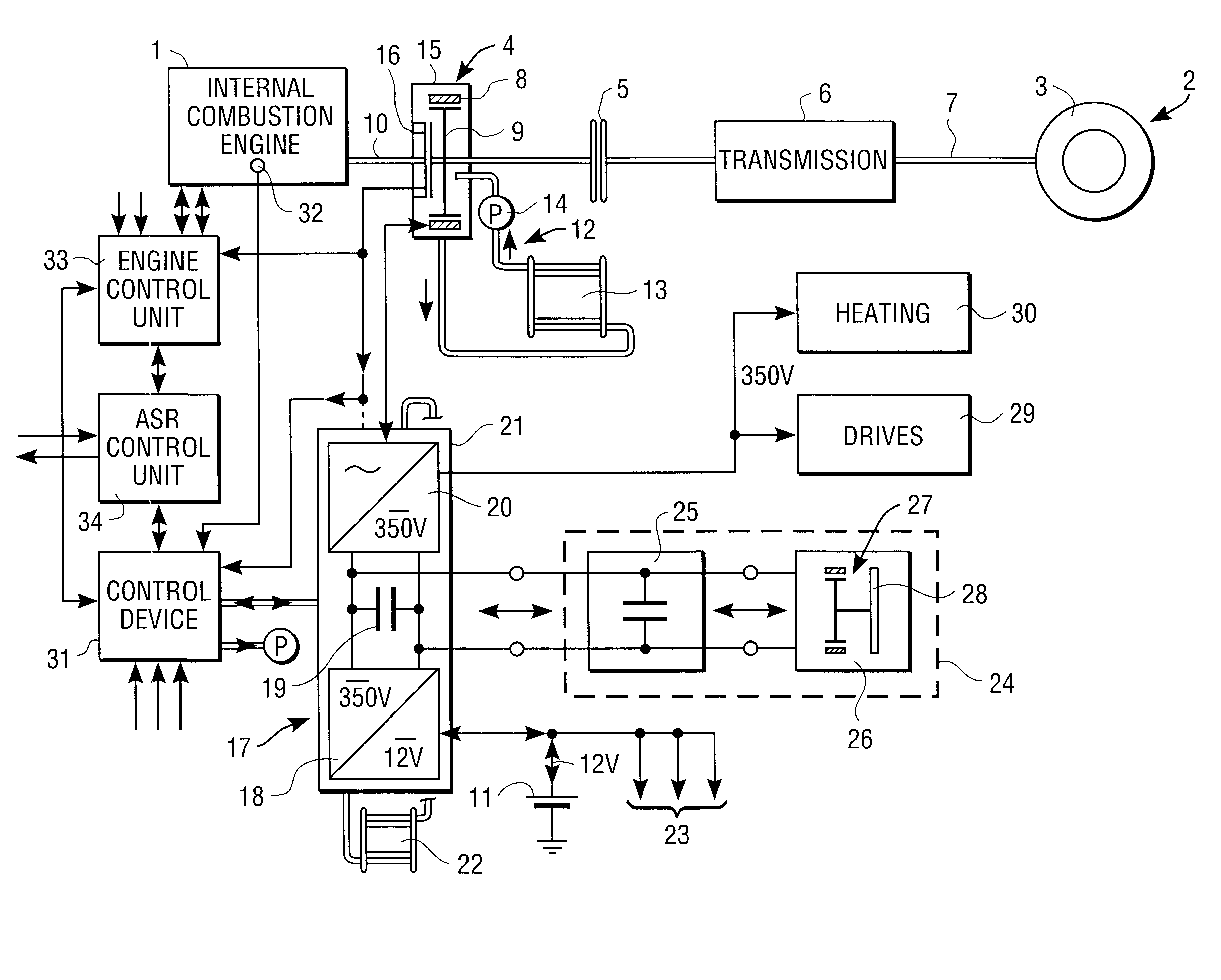
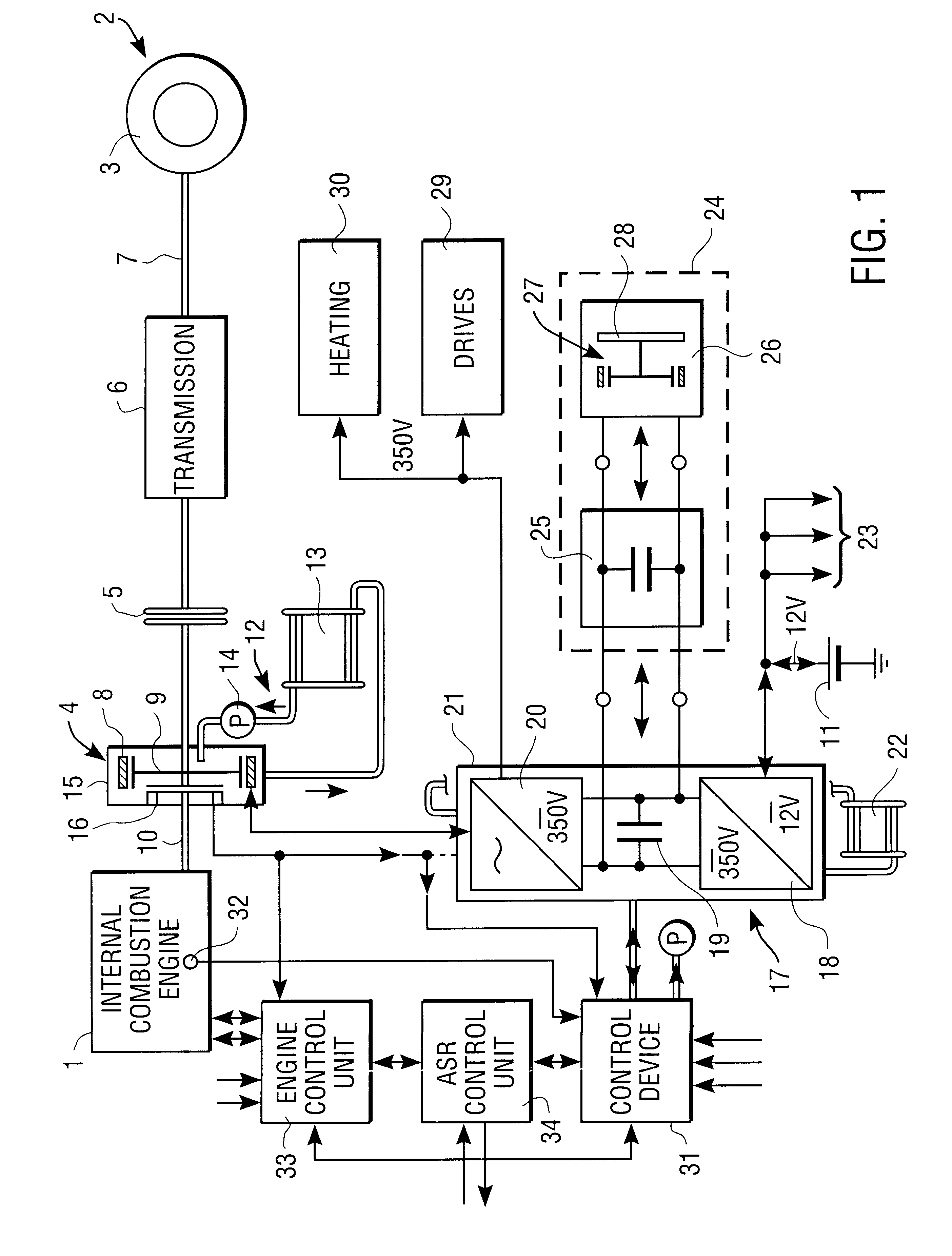
Hybrid vehicle drive for a motor vehicle
InactiveUS6102144AReducing and eliminating vibrationExcessive vibrationSuspensionsRotating vibration suppressionFrequency spectrumLoad torque
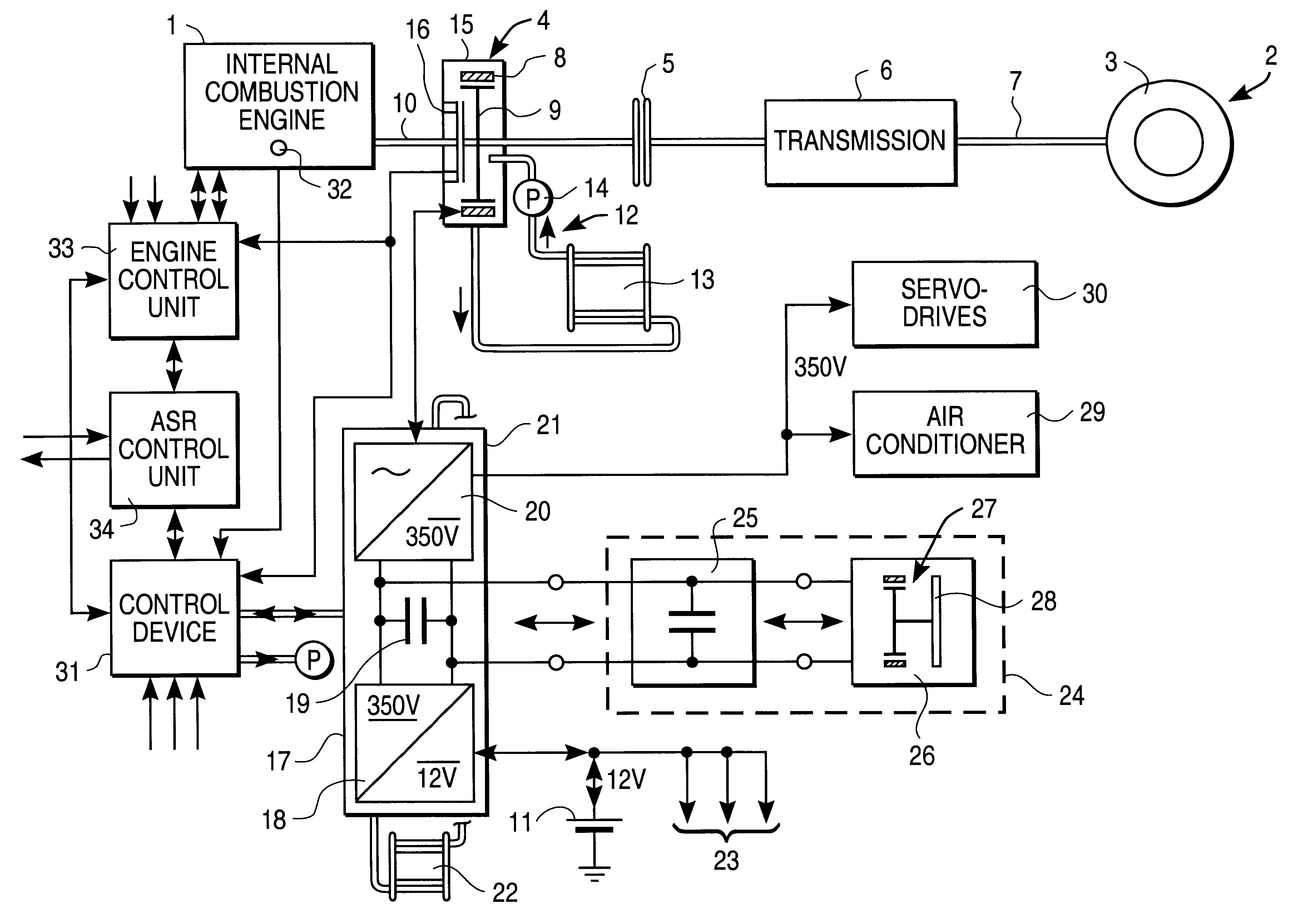
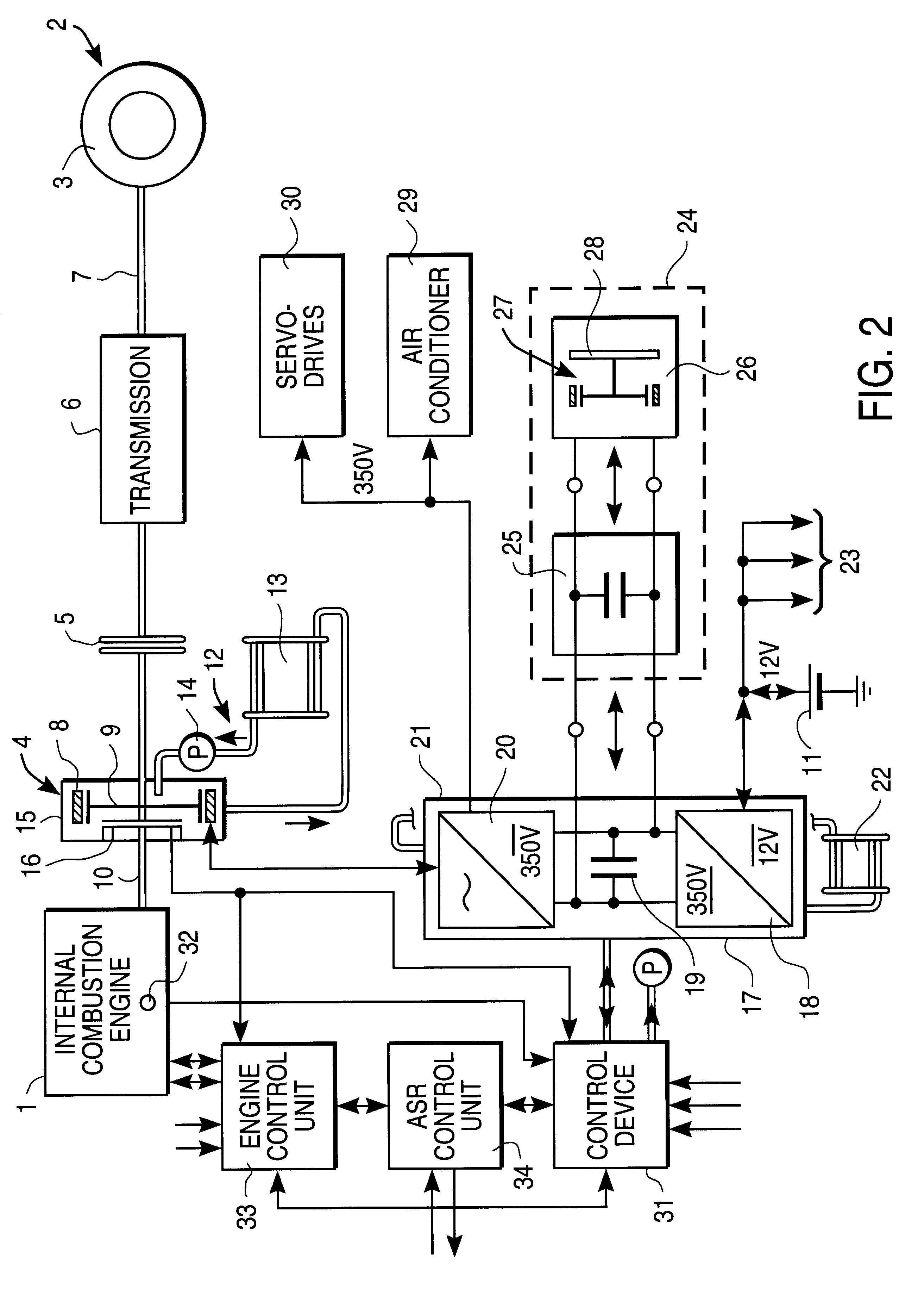
A hybrid vehicle drive for a motor vehicle includes an internal combustion engine and an electric machine which is selectively coupled with the internal combustion engine. The electric machine can be operated as a generator and as a motor. Regulation device which responds to a reference signal predetermined by a reference signal preset device are provided for the active damping of vibrations, especially torsional vibrations in the torque transmission path between the internal combustion engine and wheels of the motor vehicle driven by the latter. The regulation device also respond to sensing device which deliver an actual-value vibration signal containing vibration information about a rotating structural component of the motor vehicle and control the load torque exerted on the internal combustion engine by the electric machine for reducing or eliminating the vibrations of the structural component. An analysis device for determining a frequency spectrum of the actual-value vibration signal is associated with the regulation device. The reference signal preset device establishes a reference signal with predetermined frequency spectrum. The regulation device control the frequency spectrum of the load torque exerted on the internal combustion engine by the electric machine such that excessive spectral vibrations of the actual-value vibration signal are reduced or eliminated.
Owner:ZF FRIEDRICHSHAFEN AG
Starter/generator for an internal combustion engine, especially an engine of a motor vehicle
InactiveUS6365983B1Improve overall utilizationReduce the overall diameterRotating vibration suppressionBraking element arrangementsExternal combustion engineElectric machine
The invention concerns a starter / generator for an internal combustion engine (1), especially that of a motor vehicle, with an electric rotary-field machine (4), which exercises the starter and generator function; and at least one invertor (17) for generating the voltages and / or currents of variable frequency, amplitude and / or phase required for the magnetic fields of the electric machine (4); wherein the electric machine (4) starts the internal combustion engine (1) by merging in from standstill.
Owner:GRUNDL ANDREAS +2
Overrunning coupling assembly having improved shift feel and/or noise reduction
ActiveUS7275628B2Improved shift feel and noise reductionReduce axial forceRotating vibration suppressionFluid actuated clutchesWave shapeCoupling
An overrunning coupling assembly having improved shift feel and / or noise reduction is provided. The assembly includes planar first and second members rotatable about a first axis. In a locked position, torque transfer is permitted between the first and second members in a first direction about the first axis. In a disengaged position, the first and second members are permitted to free-wheel relative to each other in a second direction opposite the first direction. A compliant retaining device retains the first and second members together and absorbs axial impact loads. The retaining device is less compliant in the locked position than in the disengaged position to decrease axial force at time of axial impact and improve shift feel and / or noise reduction. In a first embodiment, the retaining device includes a wave spring. In a second embodiment, the retaining device includes a stepped weir plate.
Owner:MEANS IND INC
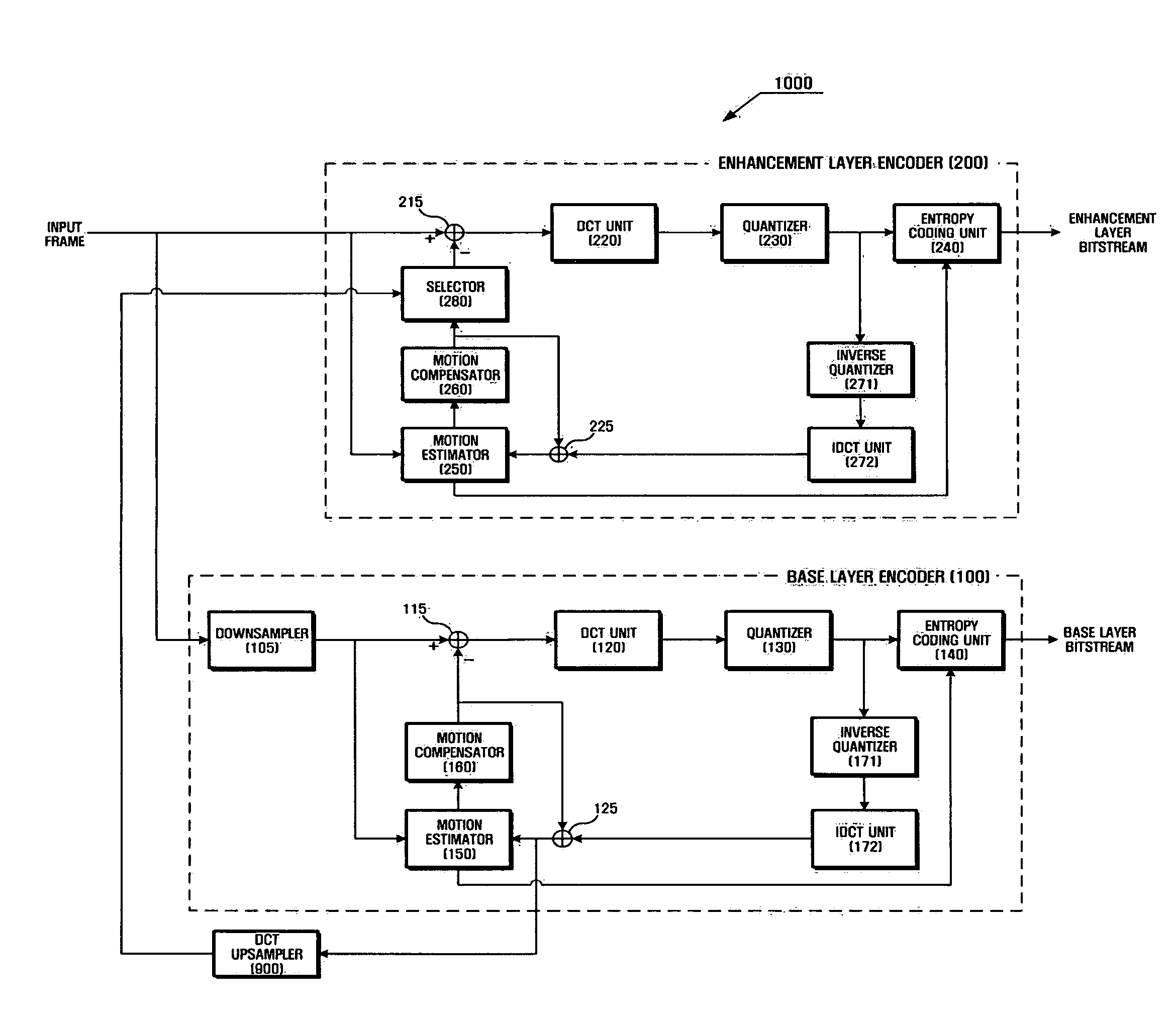
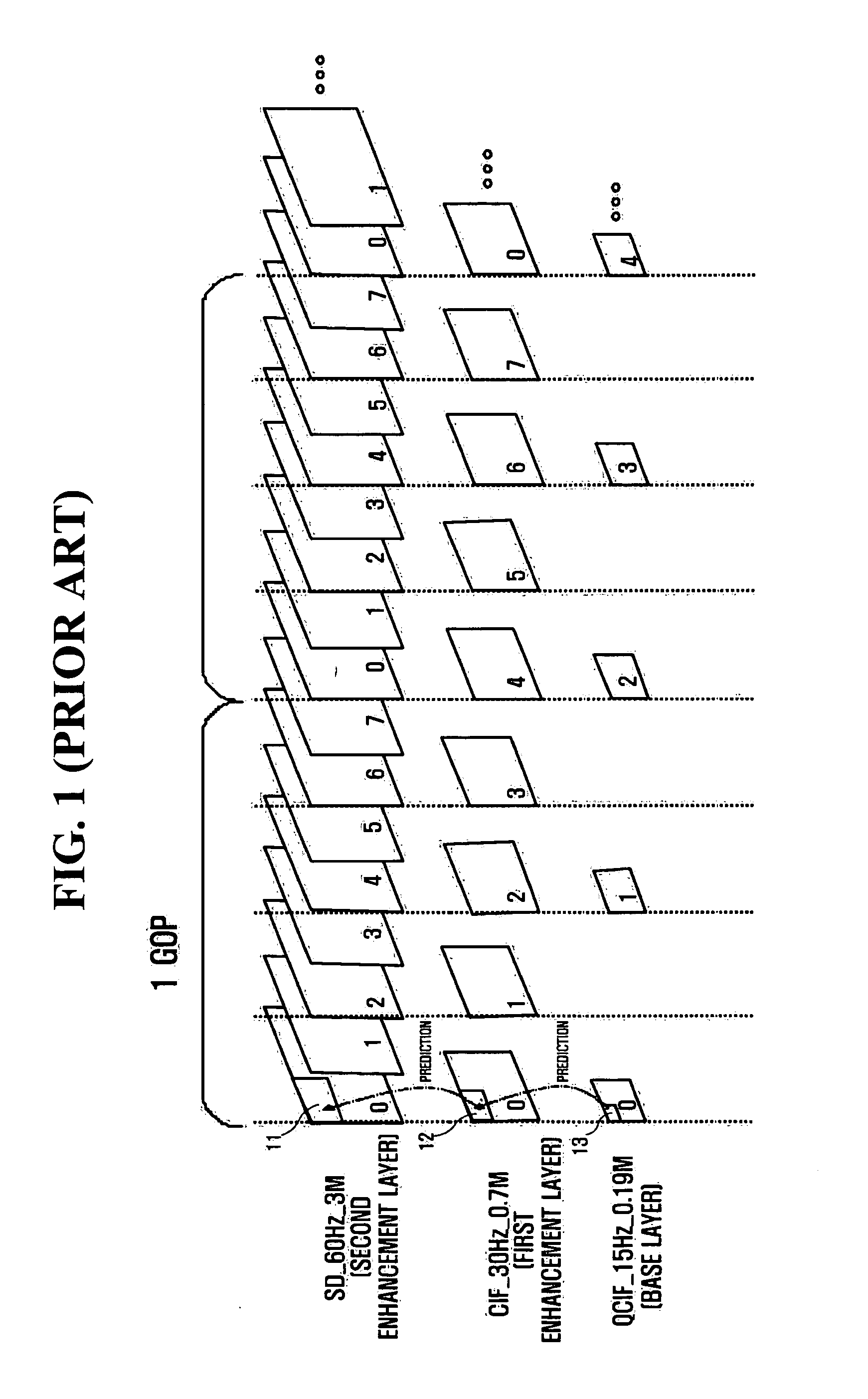
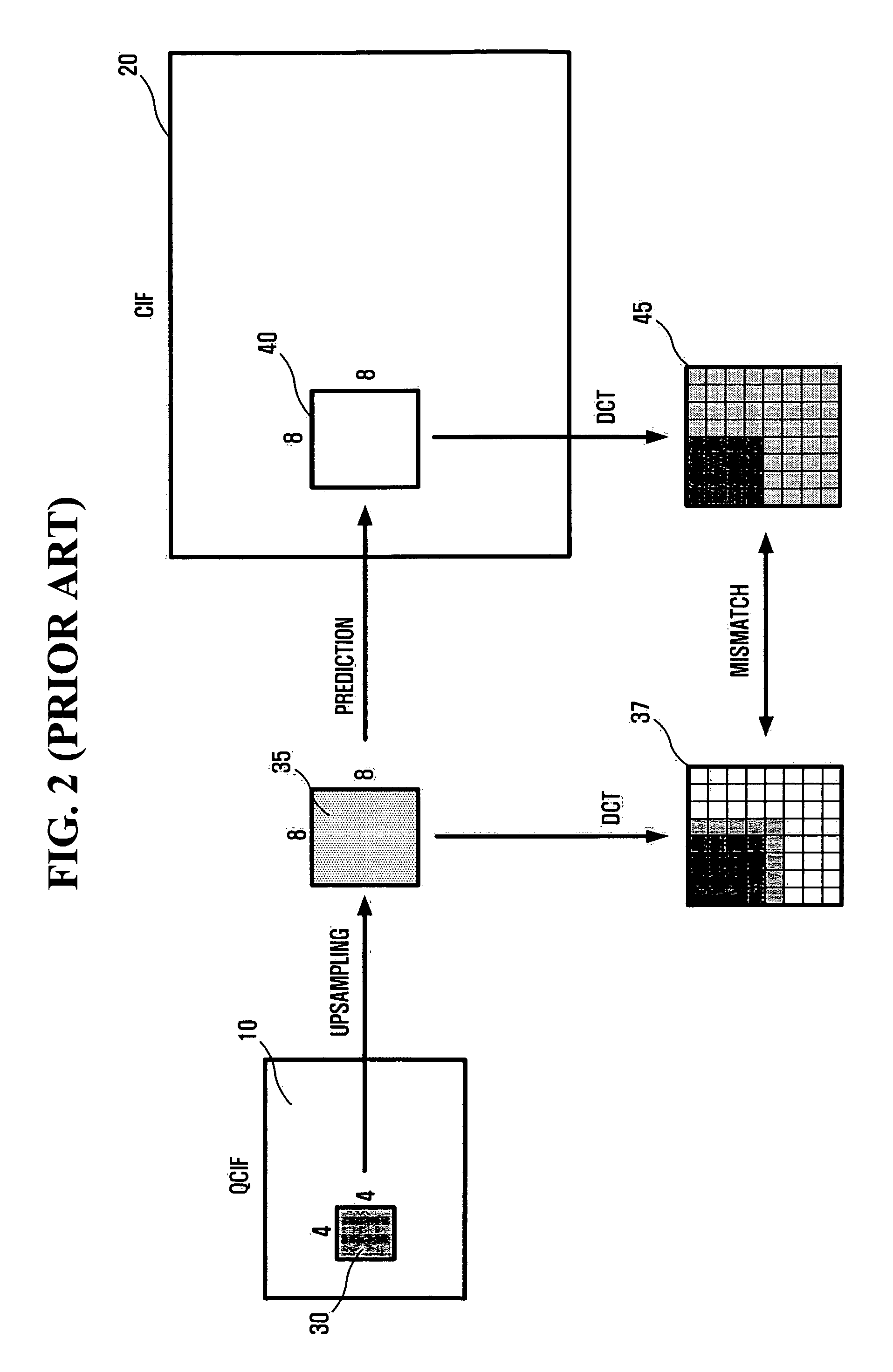
Method and apparatus for encoding/decoding multi-layer video using DCT upsampling
InactiveUS20060120448A1Reduce mismatchRotating vibration suppressionPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesCoding decodingDiscrete cosine transform
A method and apparatus for more efficiently upsampling a base layer to perform interlayer prediction during multi-layer video coding are provided. The method includes encoding and reconstructing a base layer frame, performing discrete cosine transform (DCT) upsampling on a second block of a predetermined size in the reconstructed frame corresponding to a first block in an enhancement layer frame, calculating a difference between the first block and a third block generated by the DCT upsampling, and encoding the difference.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
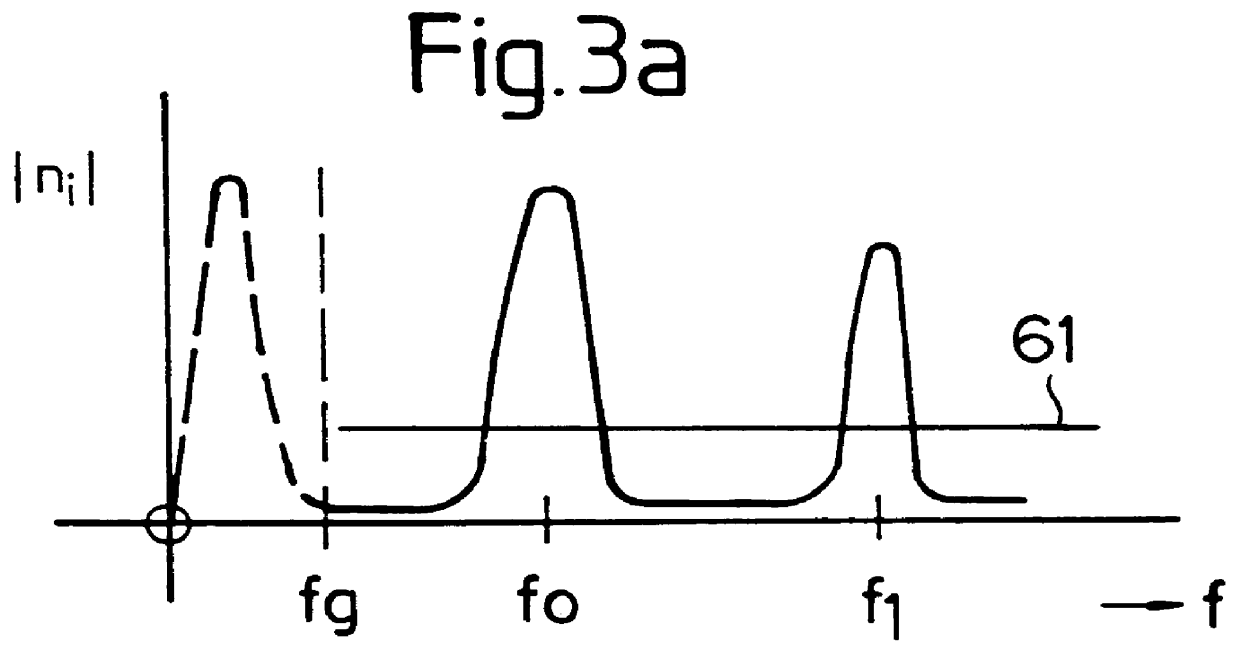
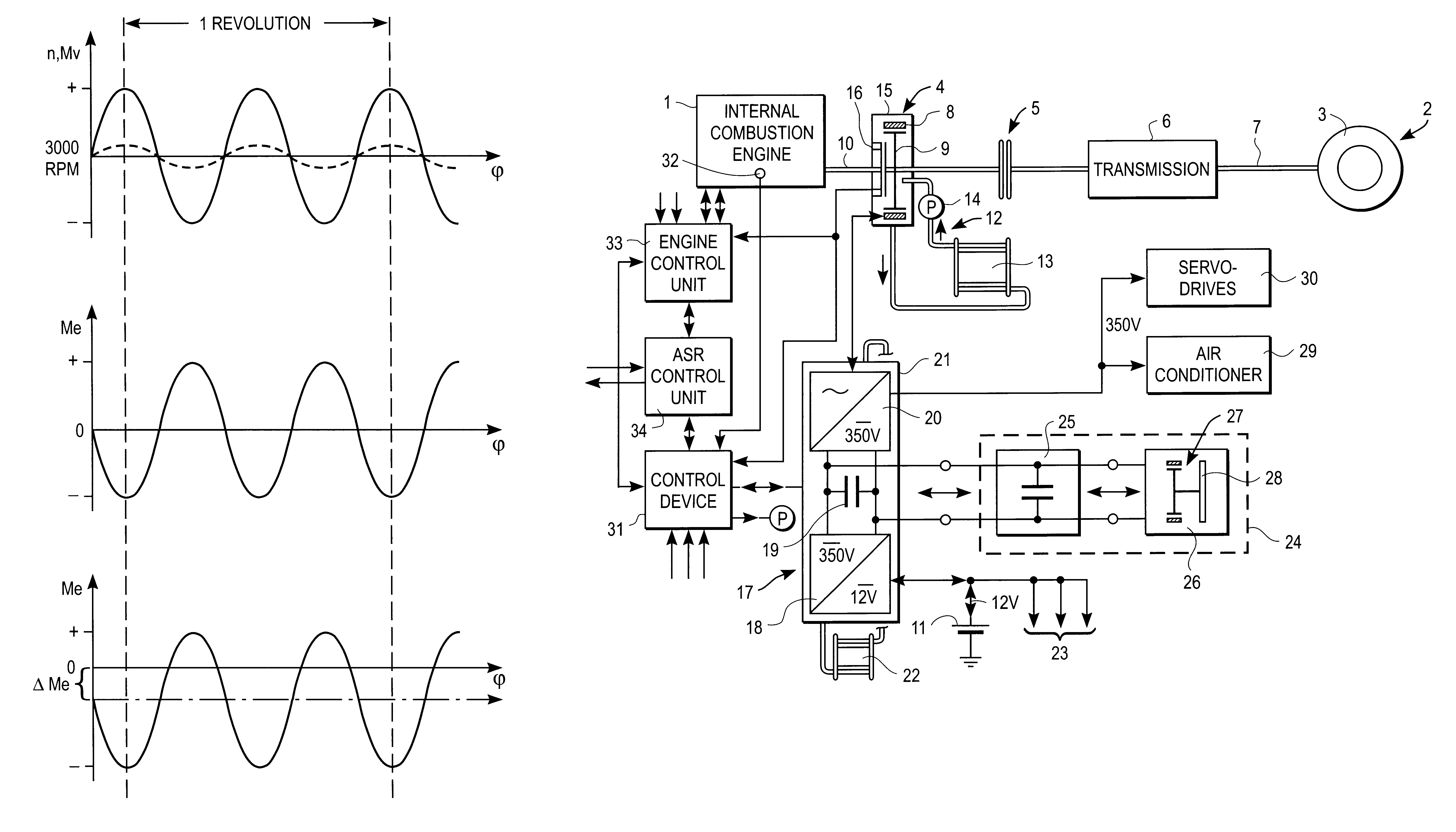
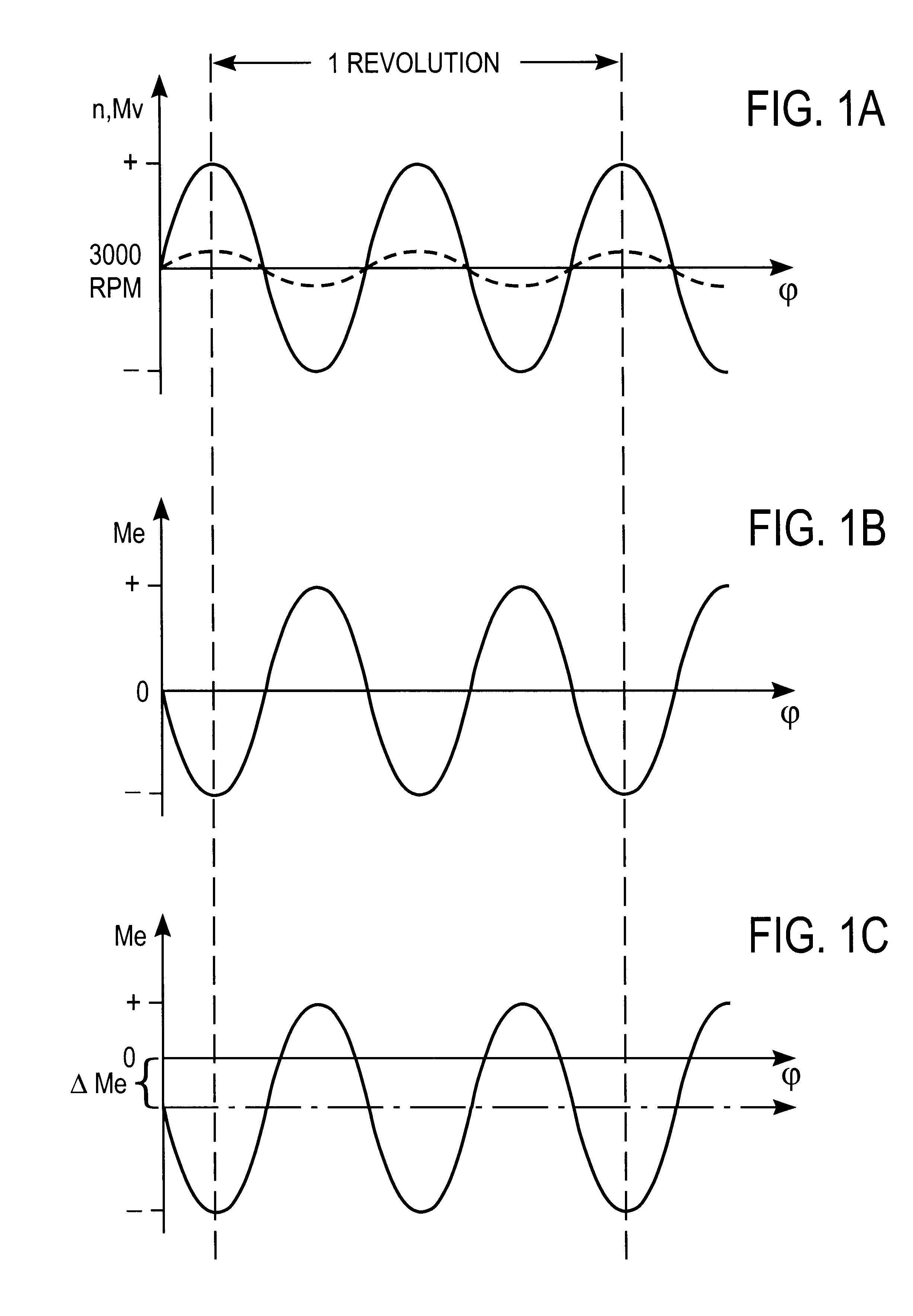
System for actively reducing rotational nonuniformity of a shaft, in particular, the drive shaft of an internal combustion engine, and method for this
InactiveUS6405701B1Rotating vibration suppressionDC motor speed/torque controlExternal combustion engineDrive shaft
The invention concerns a system for active reduction of rotational nonuniformities of a shaft, especially the drive shaft (10) of an internal combustion engine or a shaft that is coupled or can be coupled to it, with at least one electric machine (4), which is coupled or can be coupled to the shaft, wherein the electric machine (4) is controlled such that it generates a rapidly varying torque, to reduce the rotational nonuniformities, and it superimposes on this torque a positive or negative torque in order to further achieve a driving action or braking or generator type action. The invention is also oriented to a corresponding method for active reduction of rotational nonuniformities.
Owner:CONTINENTAL ISAD ELECTRONICS SYST GMBH & CO KG
Active shock module prosthesis
InactiveUS6887279B2Provide resistanceSmooth responseBelleville-type springsRotating vibration suppressionProsthesisEngineering
An impact-absorbing shock module comprises two pylons telescopingly engaged to permit axial and rotational motion therebetween. A resilient element, such as a spring-fluid combination, a plurality of interconnected disks, or a Belleville spring, provides axial shock absorption. A tubular torque-resisting cuff provides rotational resistance, or torsion-resistance. A fluid valve is optionally provided so that the fluid pressure may be varied to adjust the torsion resistance.
Owner:OSSUR HF +1
Starter/generator for an internal combustion engine, especially an engine of a motor vehicle
InactiveUS6177734B1Improve overall utilizationReduce the overall diameterRotating vibration suppressionBraking element arrangementsElectric machineExternal combustion engine
The invention concerns a starter / generator for an internal combustion engine (1), especially that of a motor vehicle, with an electric rotary-field machine (4), which exercises the starter and generator function; and at least one invertor (17) for generating the voltages and / or currents of variable frequency, amplitude and / or phase required for the magnetic fields of the electric machine (4); wherein the electric machine (4) starts the internal combustion engine (1) by merging in from standstill.
Owner:GRUNDL ANDREAS +2
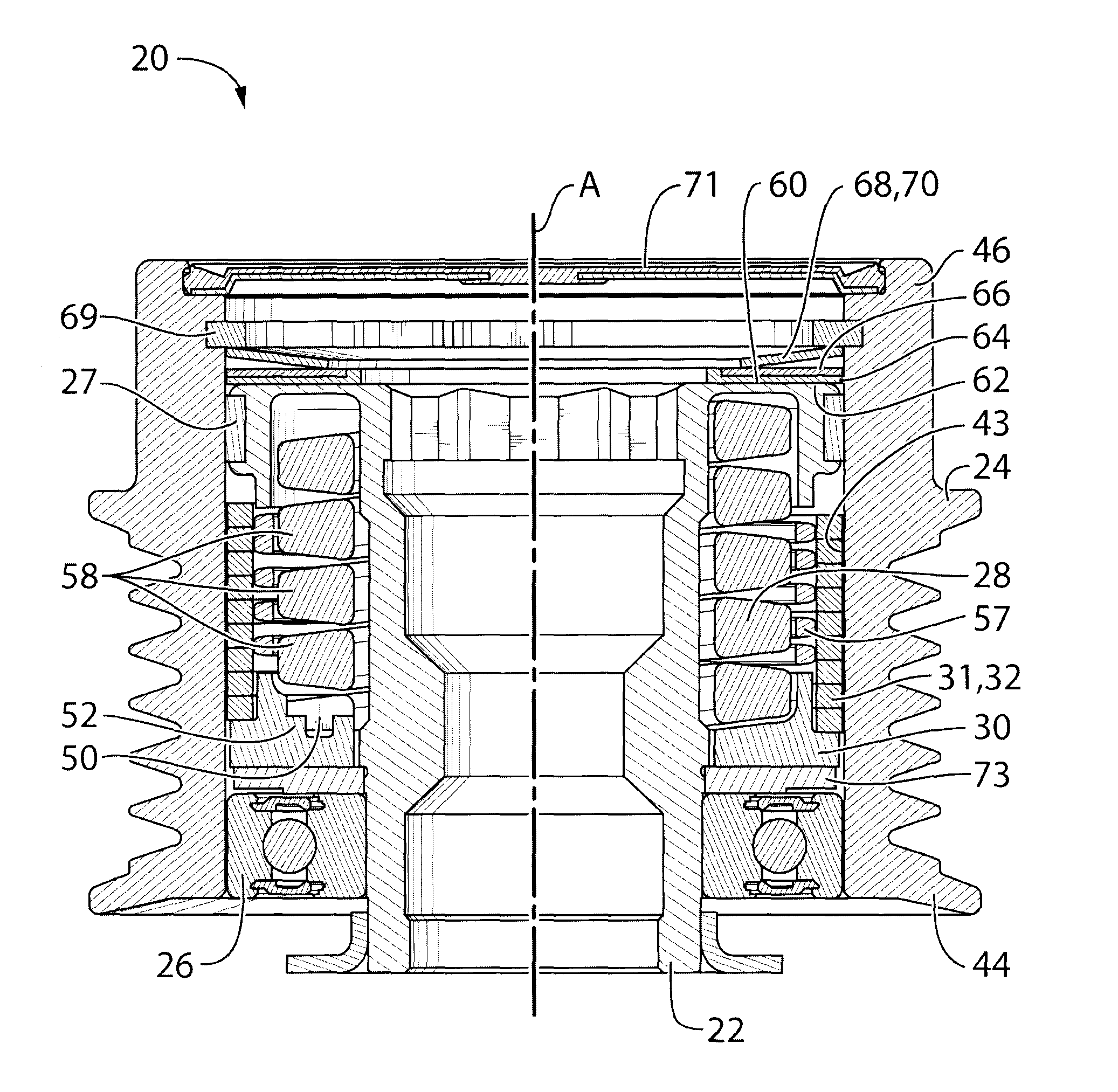
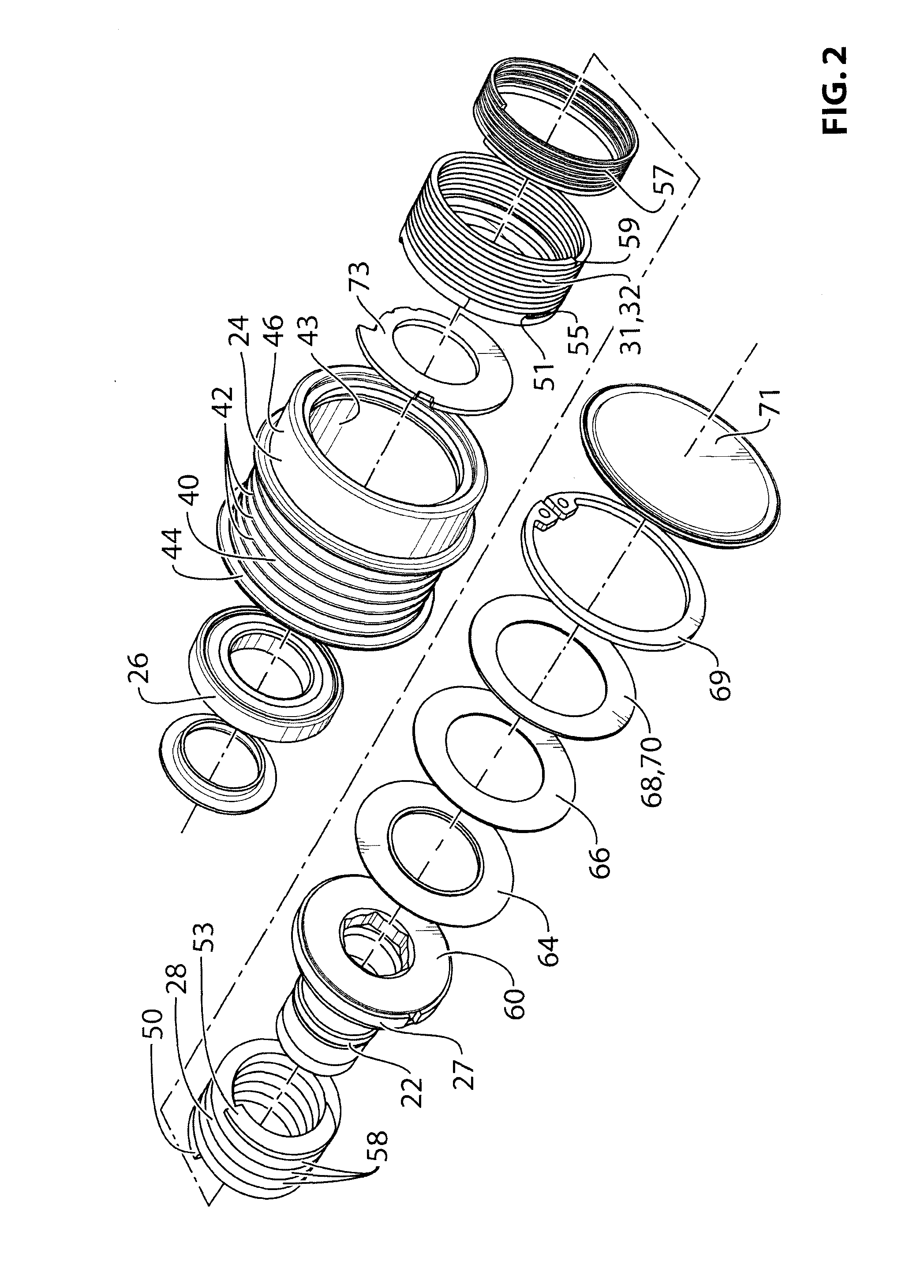
Decoupler with tuned damping and methods associated therewith
ActiveUS20130217524A1Reduce torsional vibrationImprove fatigue lifeAuxillary drivesRotating vibration suppressionEngineeringDamping torque
In an aspect, the invention relates to a decoupler that is positionable between a shaft (eg. for an alternator) and an endless power transmitting element (eg. a belt) on an engine. The decoupler includes a hub that mounts to the shaft, and a pulley that engages the endless power transmitting element, an isolation spring between the hub and the shaft. The decoupler provides at least a selected damping torque between the hub and the pulley.
Owner:LITENS AUTOMOTIVE INC
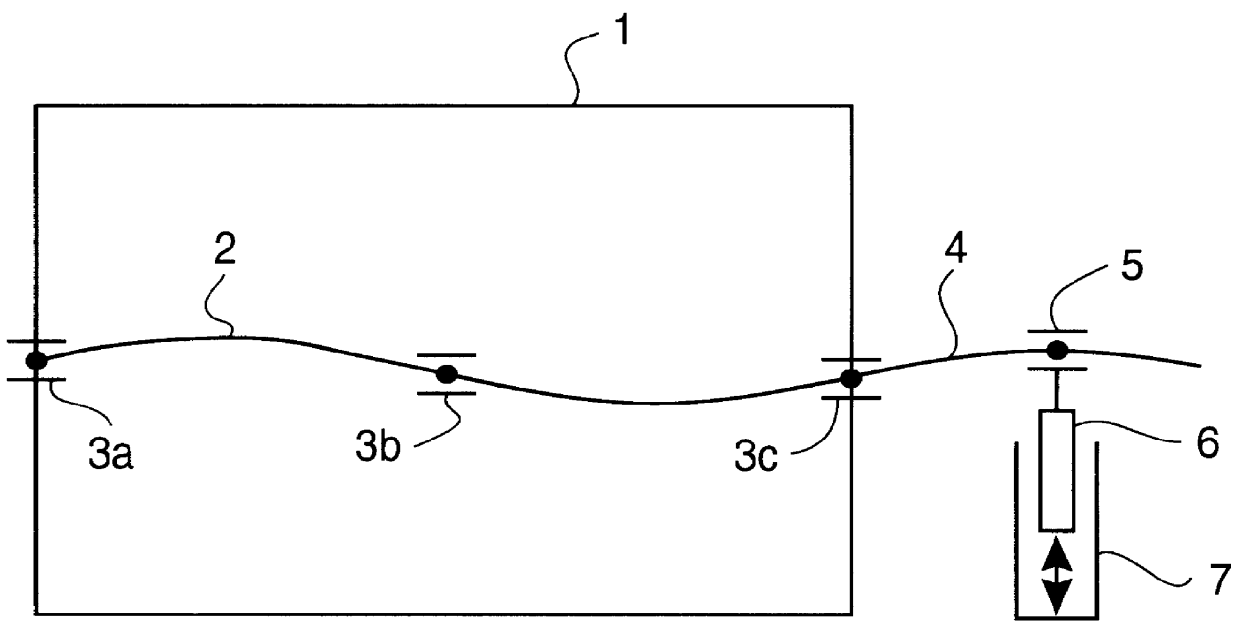
System for actively reducing radial vibrations in a rotating shaft, and method of operating the system to achieve this
InactiveUS6138629AReduce vibrationReduce unevennessRotating vibration suppressionBraking element arrangementsDrive shaftEngineering
PCT No. PCT / DE96 / 01665 Sec. 371 Date Jul. 23, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Jul. 23, 1998 PCT Filed Aug. 31, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 08477 PCT Pub. Date Mar. 6, 1997The invention concerns a system for active reduction of radial vibrations of a rotating shaft (4), especially the drive shaft of an internal combustion engine (1), with at least one active electromagnetic device (7; 10; 15, 16), which is configured and controlled such that it applies radial forces to the shaft (4), which counteract the radial vibrations of the shaft (4).
Owner:CONTINENTAL ISAD ELECTRONICS SYST GMBH & CO KG
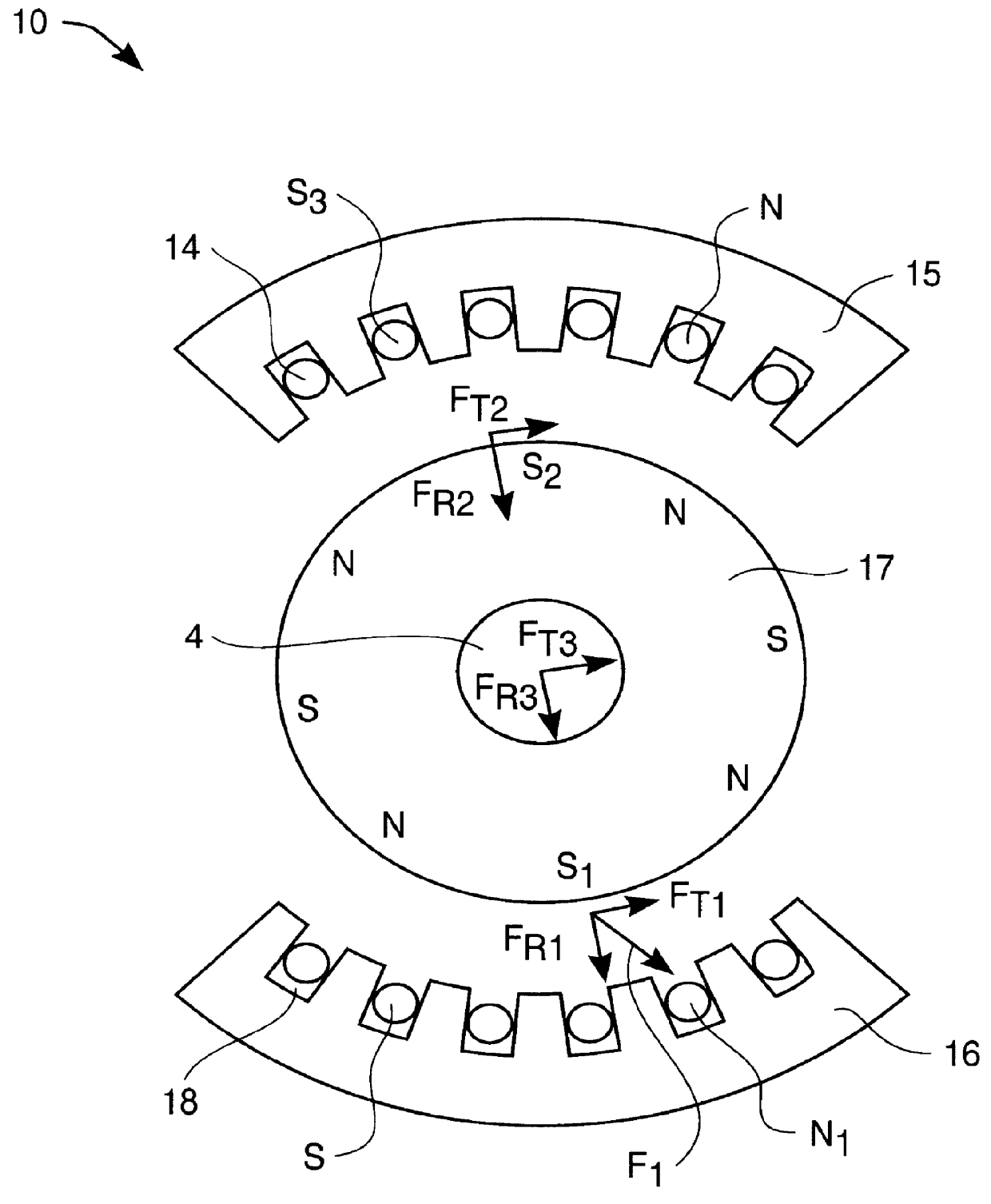
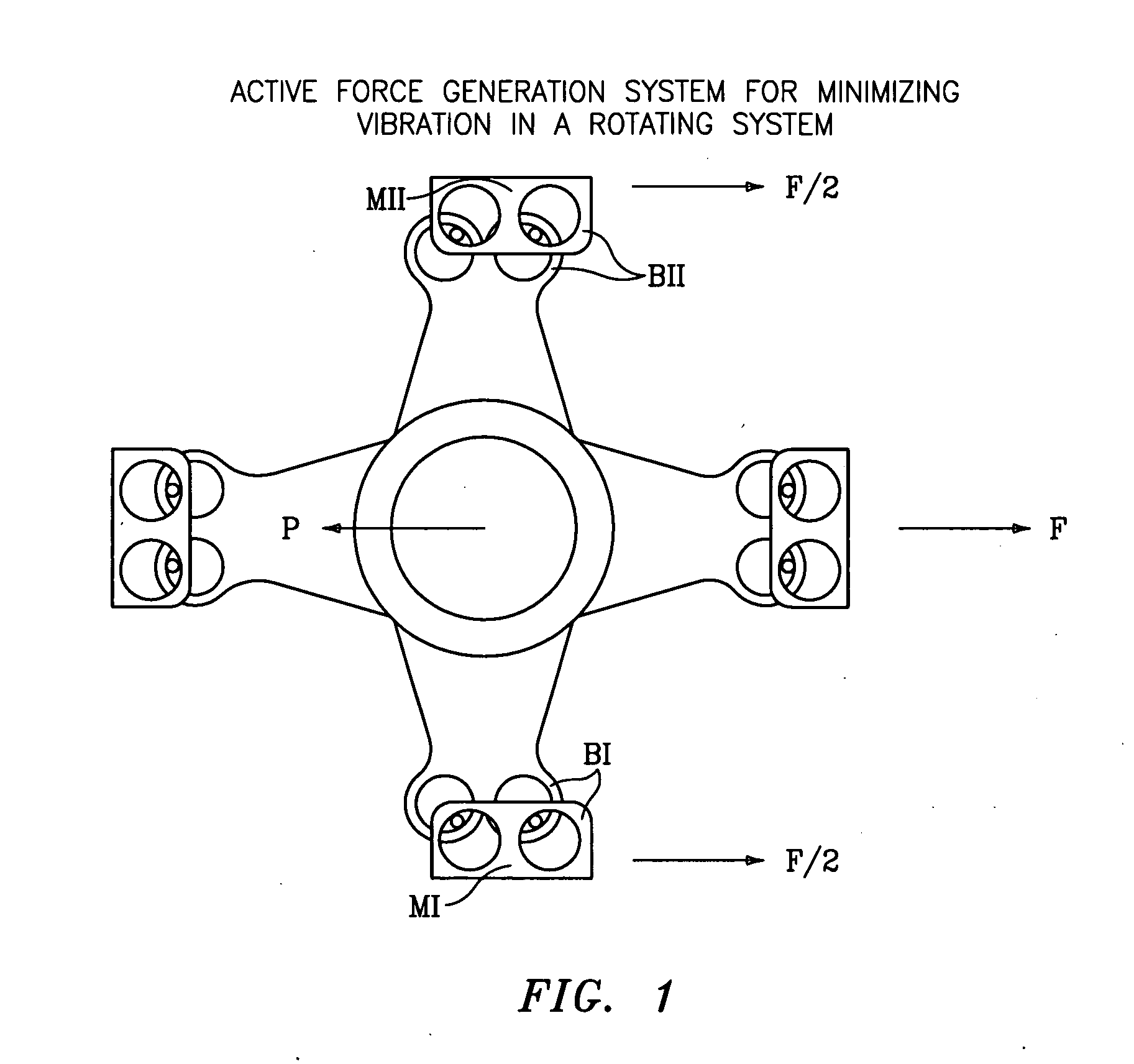
Active force generation system for minimizing vibration in a rotating system
ActiveUS20050079056A1Minimizing system weightReduce manufacturing costRotating vibration suppressionPropellersControl signalAngular velocity
A method and device for reducing vibratory noise in a system with an integral rotating member includes independently operable drive means for controlling the angular velocity of at least two masses. Control signals manipulate the drive means to allow each mass to rotate at optimal speed, direction and phase for reducing the noise induced in the system by the rotating member.
Owner:SIKORSKY AIRCRAFT CORP
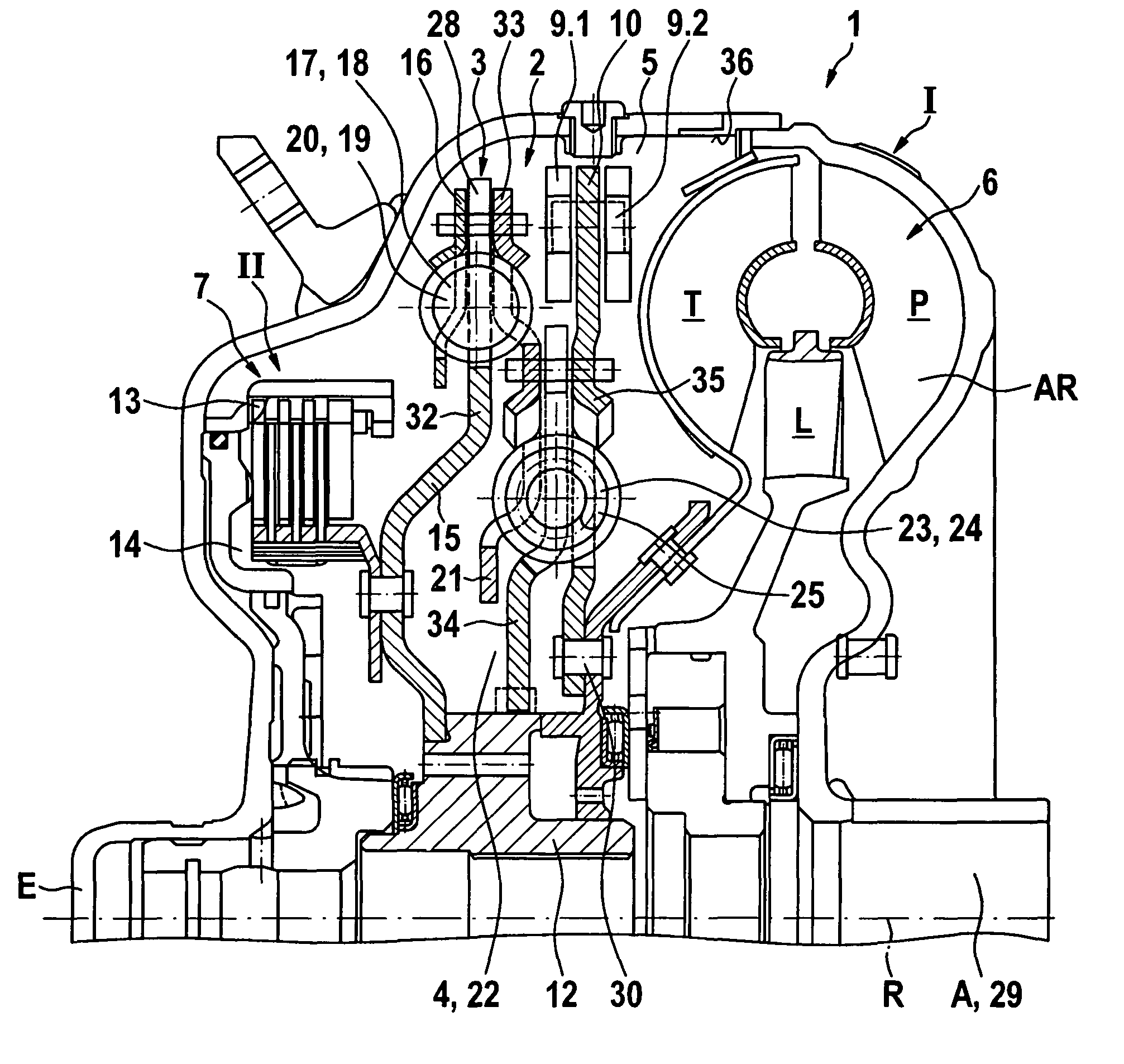
Force transmission device in particular for power transmission between a drive engine and an output
ActiveUS20100236228A1Reduce variationEliminate variationRotating vibration suppressionYielding couplingSelf adaptiveTuned mass damper
A force transmission device, in particular or power transmission between a drive engine and an output, comprising a damper assembly with at least two dampers, which can be connected in series, and a rotational speed adaptive absorber, wherein the rotational speed adaptive tuned mass damper is disposed between the dampers at least in one force flow direction through the force transmission device.
Owner:SCHAEFFLER TECH AG & CO KG
Force transmission device with a rotational speed adaptive damper and method for improving the damping properties
ActiveUS8161740B2Improve drivabilityRotating vibration suppressionMechanical actuated clutchesControl theorySelf adaptive
The invention relates to a force transmission device for power transmission between an input and an output, comprising at least an input and an output, and a vibration damping device disposed in a cavity that can be filled at least partially with an operating medium, in particular oil, the vibration damping device coupled with a rotational speed adaptive absorber, wherein the rotational speed adaptive absorber is tuned as a function of an oil influence to an effective order qeff, which is greater by an order shift value qF than an order q of an exciting vibration of a drive system.
Owner:SCHAEFFLER TECH AG & CO KG
Vibration damper for a tubular drive shaft
InactiveUS6837345B1Improve imbalanceLittle effortRotating vibration suppressionShaftsDrive shaftPropeller
A vibration damper for a tubular propeller shaft in the drive train of a motor vehicle having a mass body mounted concentrically, in the propeller shaft or in a sleeve attached in the propeller shaft, by way of at least one rubber spring element. Metal and / or flexible rubber stop elements that limit the vibration travel of the mass body at least in the radial direction are arranged between the mass body and the sleeve. Alternatively, the mass body and / or the sleeve are configured at least locally, in mutually opposite regions, as stop elements that limit the vibration travel of the mass body at least in the radial direction.
Owner:DAIMLER AG
Vibration damping device
InactiveUS6382050B1Avoid knockingEasy constructionRotating vibration suppressionControlling membersMobile vehicleRotational axis
A vibration damping device for a drive system of a motor vehicle includes a base body arranged for rotating about an axis of rotation and a deflection mass arrangement arranged in said base body and having at least one deflection mass and a deflection path associated with the at least one deflection mass and along which the deflection mass is movable during rotation of the base body about the axis of rotation. The deflection path has a vertex area at a position furthest from the axis of rotation and deflection areas on both sides of the vertex area extending from the vertex area to ends areas. The deflection areas have a decreasing distance from the axis of rotation (A) proceeding from the vertex area toward their end areas. A braking arrangement acts in the end areas of the deflection areas for gradually slowing the approach of the at least one deflection mass to a respective end area of the deflection path.
Owner:ZF FRIEDRICHSHAFEN AG
Rotating machine active balancer and method of dynamically balancing a rotating machine shaft with torsional vibrations
InactiveUS20060005623A1Rotating vibration suppressionRotating bodies balancingEngineeringTorsional vibration
An active balancer for dynamically balancing a rotating machine is provided. The active balancer has a balancer body which rotates with the rotating machine and at least one controllable position counter weight having a real-time adjustable position relative to the balancer body and the rotating machine inorder to produce an actively adjustable controllable counter weight balance force for dynamically balancing the rotating machine. The active balancer includes a spring with the balancer body mounted to the rotating machine through the spring wherein the balancer body mass resonates on the spring with a torsional vibration canceling frequency which cancels a torsional vibration of the rotating machine.
Owner:LORD CORP
Torsional vibration damper
InactiveUS6131487ASatisfactory supportEasy to manufactureRotating vibration suppressionYielding couplingCoil springAbutment
A composite flywheel has primary and secondary masses rotatable relative to each other against the resistance of a damper having arcuate coil springs and an abutment between neighboring end portions of such springs. The abutment can move in the circumferential direction of the masses and is preferably form-lockingly connected against loss to at least one of the springs. To this end, a portion of the abutment extends into the adjacent convolutions of the at least one spring and is engaged by such convolutions with a force which suffices to prevent unintentional separation of the at least one spring from the abutment in the axial direction of the at least one spring.
Owner:LUK LAMELLEN & KUPPLUNGSBAU BETEILIGUNGS KG
Rear wheel hub, in particular for bicycles
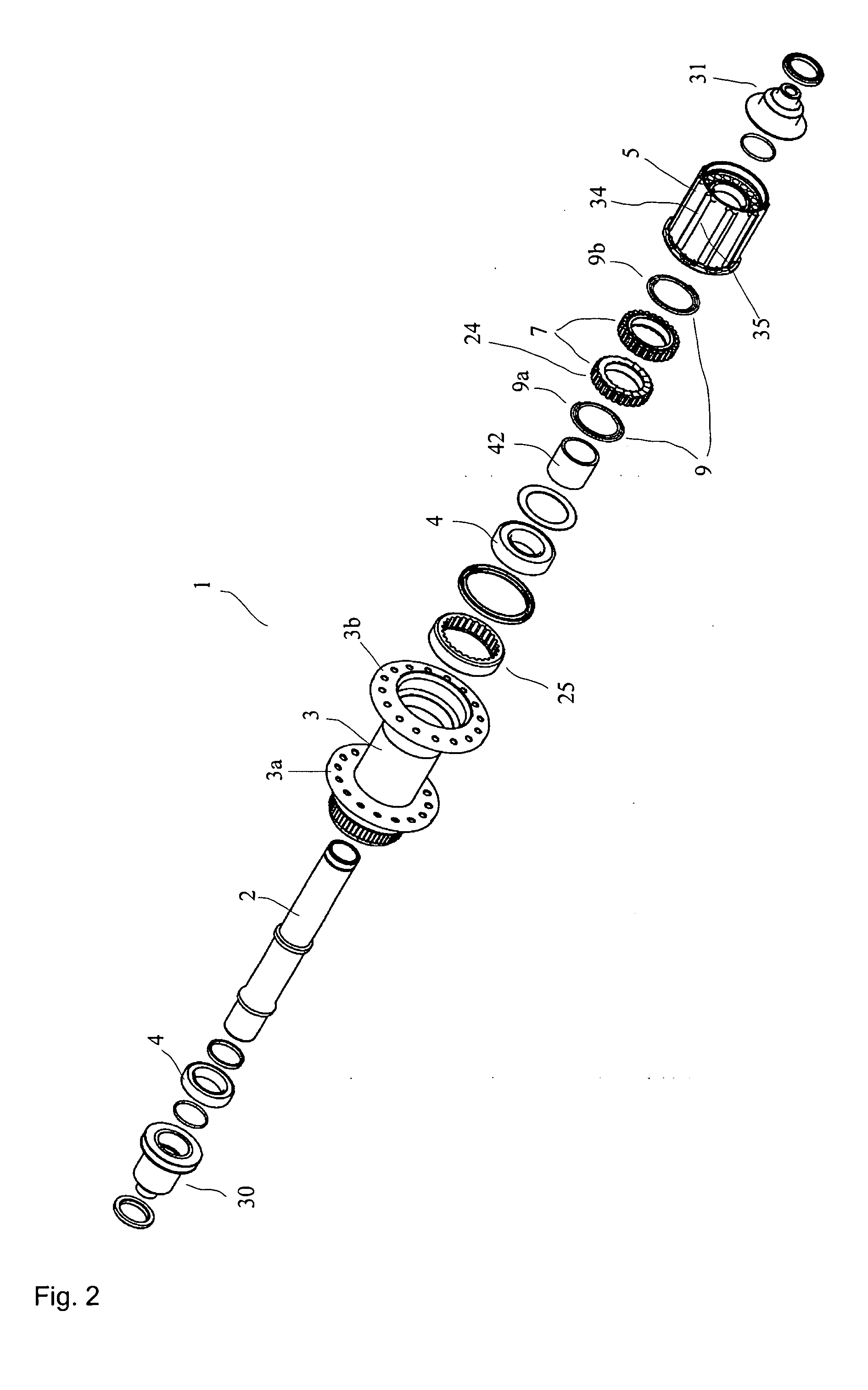
ActiveUS20080006500A1Increased stressabilityMore materialRotating vibration suppressionHubsFreewheelSprocket
A hub for bicycles, having an axle and a shell, two bearing units arranged substantially between the hub axle and the hub shell, and a rotor rotatably supported relative to the hub axle for receiving a sprocket the rotor, and a freewheel having two toothed disc units with biased tooth faces for transmitting the drive torque from the rotor to the hub shell. The two toothed disc units are disposed around the hub axle upon assembly, they are, at idle, disposed transverse to the hub axle. At least one toothed disc unit includes a toothed disc having a hole, a radial wall and an axial toothed wall, wherein an inner diameter of the hole is smaller at the axial wall than an inner dimension in the radial wall to form a receiving space at the toothed disc between the clear inner diameter of the axial wall and the radial wall.
Owner:SWISS
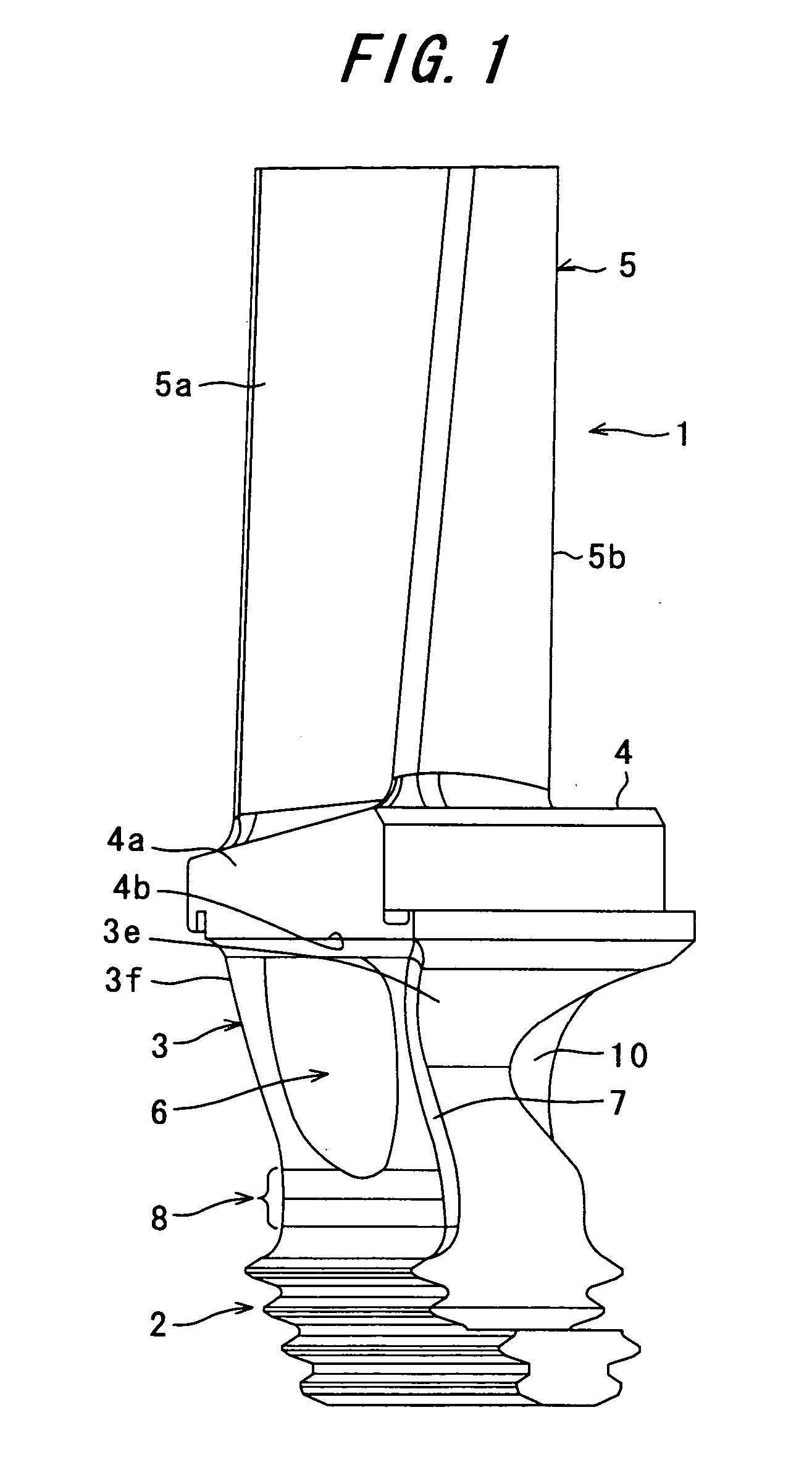
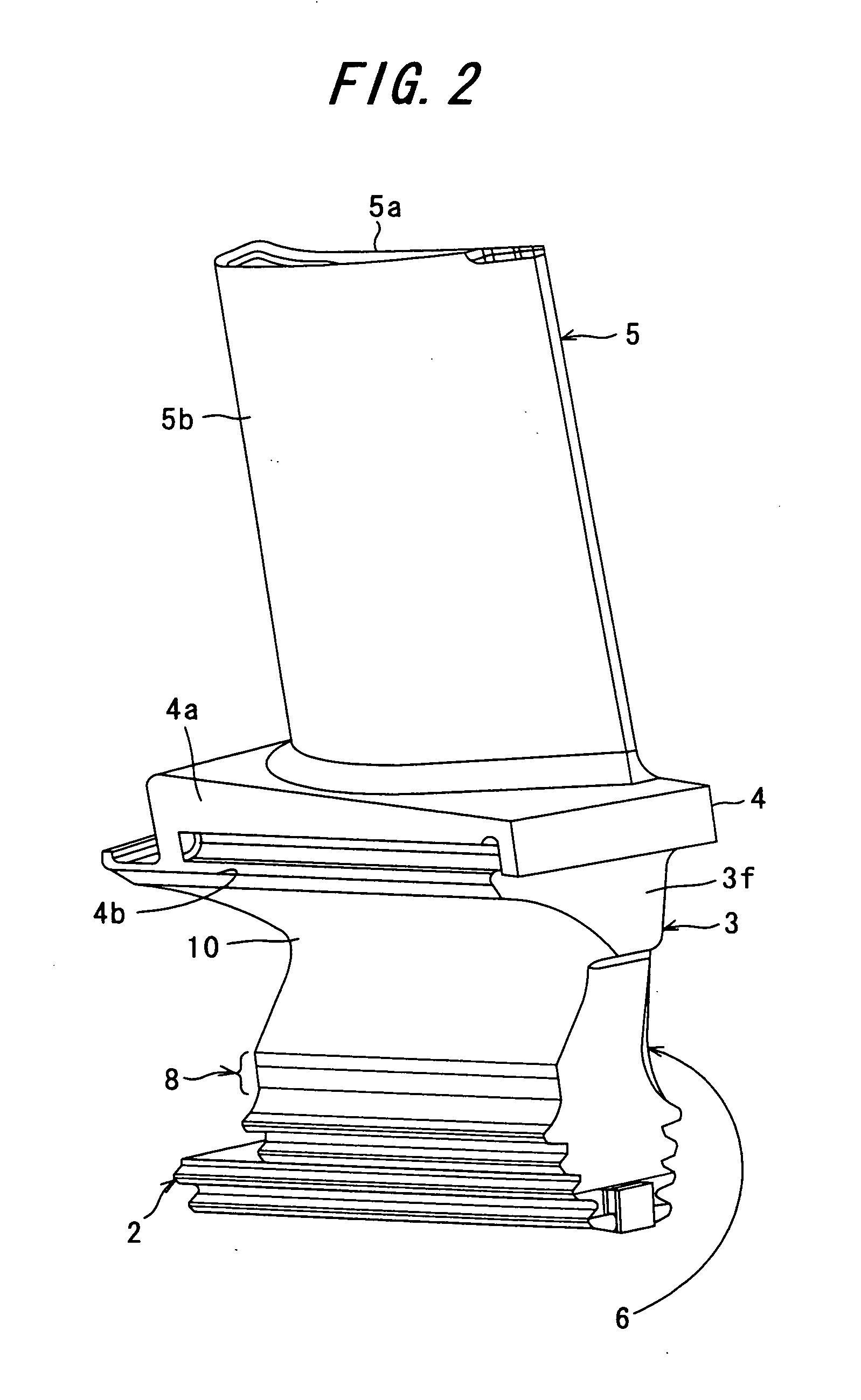
Torsional vibration damper
InactiveUS6875113B2Without inflicting significant mechanical damageReliable mechanical interconnectionRotating vibration suppressionYielding couplingRotational axisSnubber
A torsional vibration damper mountable to a rotatable shaft. The torsional vibration damper is a composite structure including a body formed of a polymer, such as a glass-reinforced polyamide, that surrounds an insert formed of a structurally-rigid material, such as a metal. The insert includes one or more support flanges that extend radially outward into the polymer body. When the torsional vibration damper is removed from the rotatable shaft, axial forces applied to the damper are transferred by the support flanges to the insert such that the polymer body remains substantially stress-free. In addition to, or instead of, the support flanges, the insert may include torque-locking structure that locks the polymer annular body with the insert to prevent relative rotation therebetween.
Owner:DAYCO IP HLDG
Drive System
InactiveUS20020062713A1Small sizeSimple designRotating vibration suppressionYielding couplingRotational axisDrive shaft
A drive system that includes a drive shaft, which is or can be brought into torque-transmitting connection with a drive train, a secondary drive system for transmitting torque between the drive shaft and at least one auxiliary unit, and at least one vibration-damping device including a deflection mass carrier with freedom to rotate around a rotational axis and at least one deflection mass, which can shift position relative to the deflection mass carrier in at least one deflection plane. Upon deflection of the at least one deflection mass from the home position relative to the deflection mass carrier, the radial position of the deflection mass changes relative to the rotational axis. At least part of the vibration-damping device can be integrated into part of the secondary drive system.
Owner:ZF FRIEDRICHSHAFEN AG
Moving blade and gas turbine using the same
ActiveUS20050186074A1Avoid stress concentrationUniform intensity distributionRotating vibration suppressionRotary propellersGas turbinesSpring system
In a gas turbine having a plurality of moving blades provided on a rotary shaft in a circumferentially adjoining condition, a seal pin is provided in a spacing between the shanks of the adjacent moving blades for preventing leakage of cooling air from a blade root portion side to an airfoil side; an arcuately depressed portion is formed on the shank of each of the moving blades; and vibration of each of the moving blades is suppressed in such a manner that the seal pin serves as a spring system while the airfoil portion, the platform, the shank, and the blade root portion serve as a mass system.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND LTD
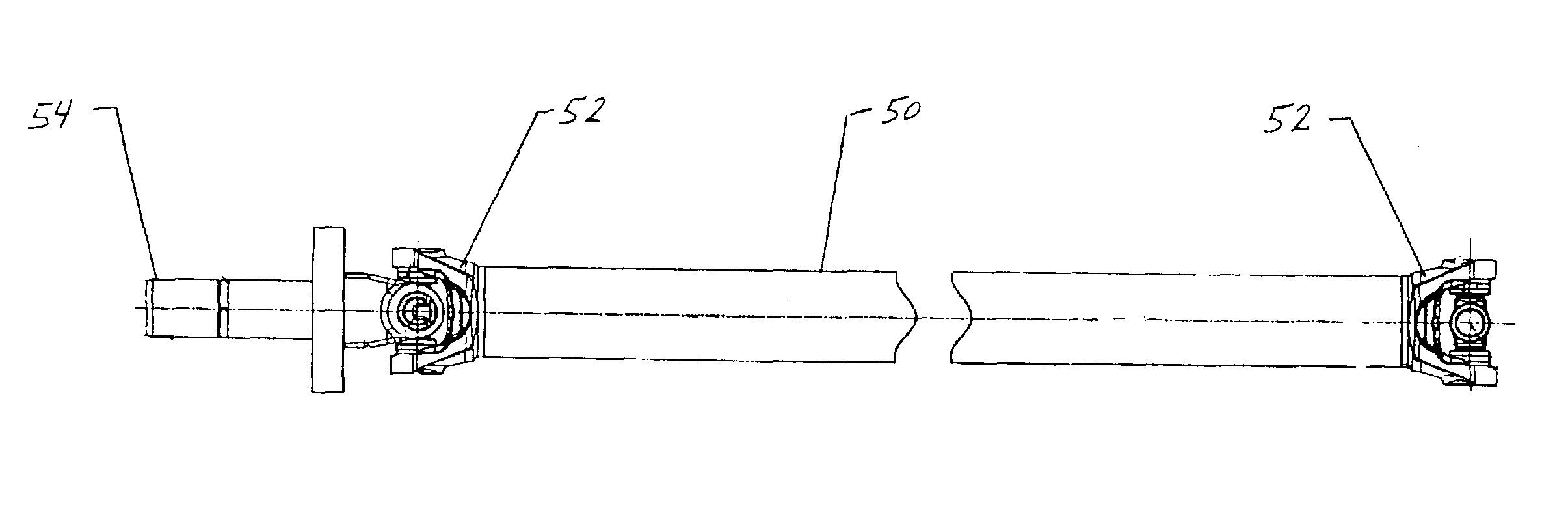
System and method for balancing a driveline system
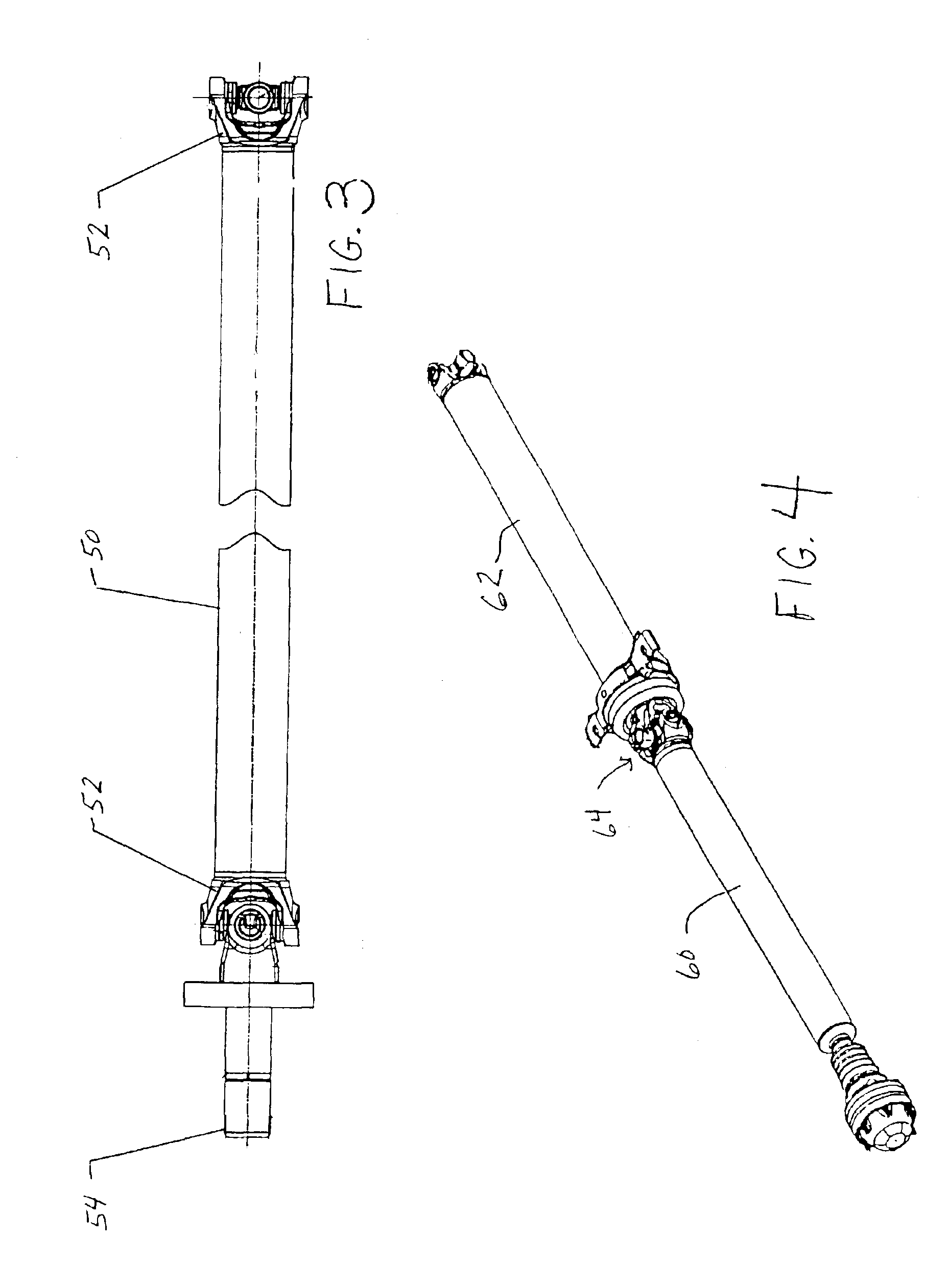
InactiveUS6923058B2Reduce errorsReduce vibrationRotating vibration suppressionRotating bodies balancingDrive shaftUniversal joint
A process for balancing a vehicular driveline including a propeller shaft and an input shaft of a vehicle axle interconnected by a universal joint. First, the vehicle propeller shaft is balanced to a predetermined residual imbalance having an imbalance vector angle of 0° or 180° which lies inline with open set of cardan joint trunnions. The corrected residual imbalance is then visually marked. Next, the input shaft is balanced to a predetermined residual imbalance having an imbalance vector angle of 0° or 180° which lies inline with cross-holes in yoke ears. Again, the corrected residual imbalance on the input shaft is then visually marked. During the assembly of the vehicle, the assembly line operator couples the propeller shaft to the input shaft through a cardan joint cross by aligning the marks on the propeller shaft and the input shaft so that the marks are located opposite to each other.
Owner:TORQUE TRACTION TECH INC
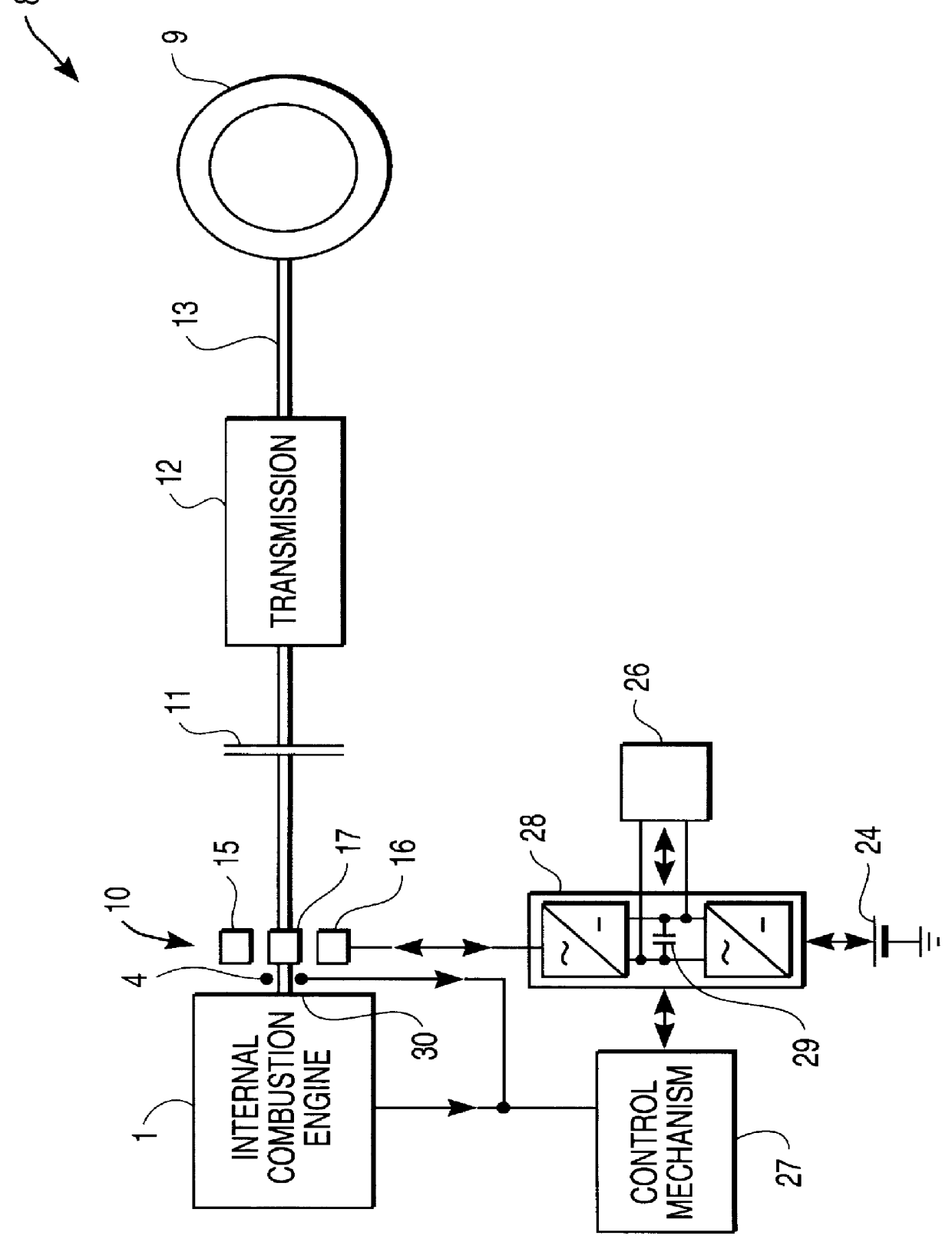
Drive system, especially for a motor vehicle, and method of operating same
InactiveUS6199650B1Reduction of the drive slip is ideally controllableImprove traffic safetyRotating vibration suppressionBraking element arrangementsMobile vehicleCoupling
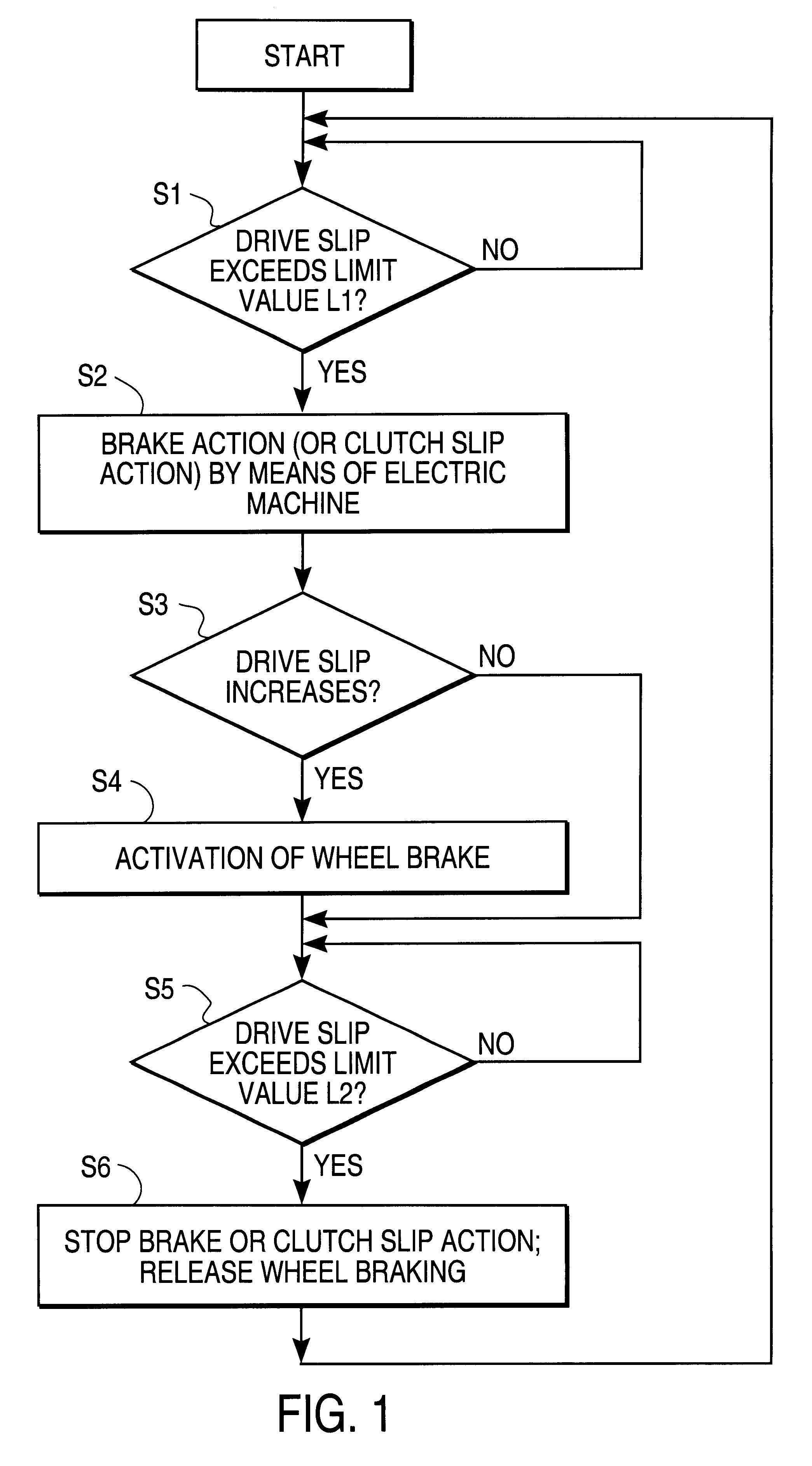
Drive system, especially for a motor vehicle, with a drive assembly, especially an internal combustion engine (1), an electric machine (4) and an antislip control, in which the (one) electric machine (4) is designed such that it can produce a reduction of drive slip, in particular by braking action and / or-when the electric machine (4) is acting as a coupling-by clutch slip action.
Owner:CONTINENTAL ISAD ELECTRONICS SYST GMBH & CO KG +1
Mass damper
ActiveUS20140008163A1Reduce tensionSmall sizeRotating vibration suppressionNon-rotating vibration suppressionEngineeringTuned mass damper
A tuned mass damper comprising a frame, at least one bendable spring element being connected from its ends to the frame, and at least one mass element being connected to the spring element at a distance from the ends of the spring element, at least one movable spring support element for adjusting the tuning frequency of the damper, and means for moving the spring support element.
Owner:WARTSILA FINLAND OY
Systems and method for use of single mass flywheel alongside torsional vibration damper assembly for single acting reciprocating pump
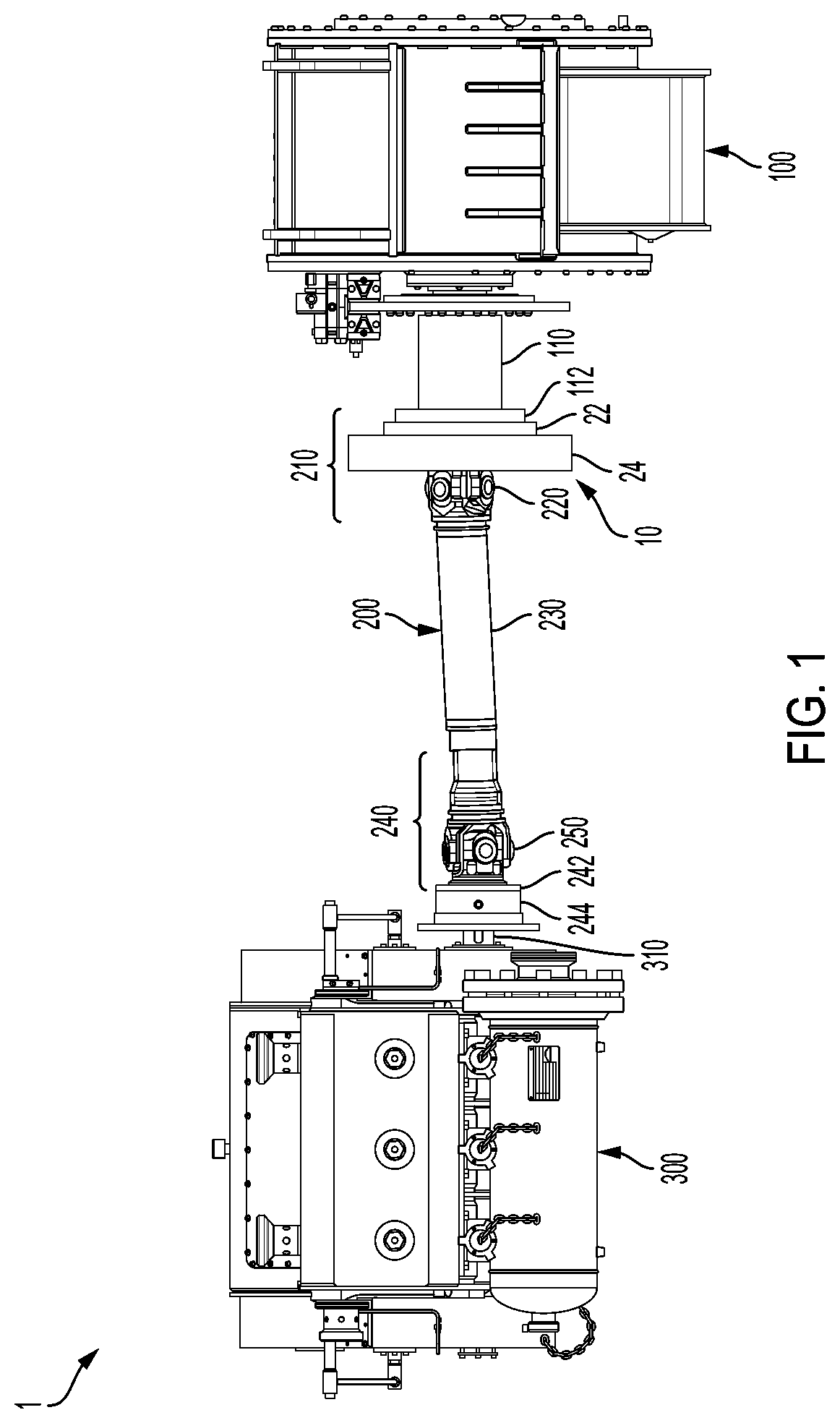
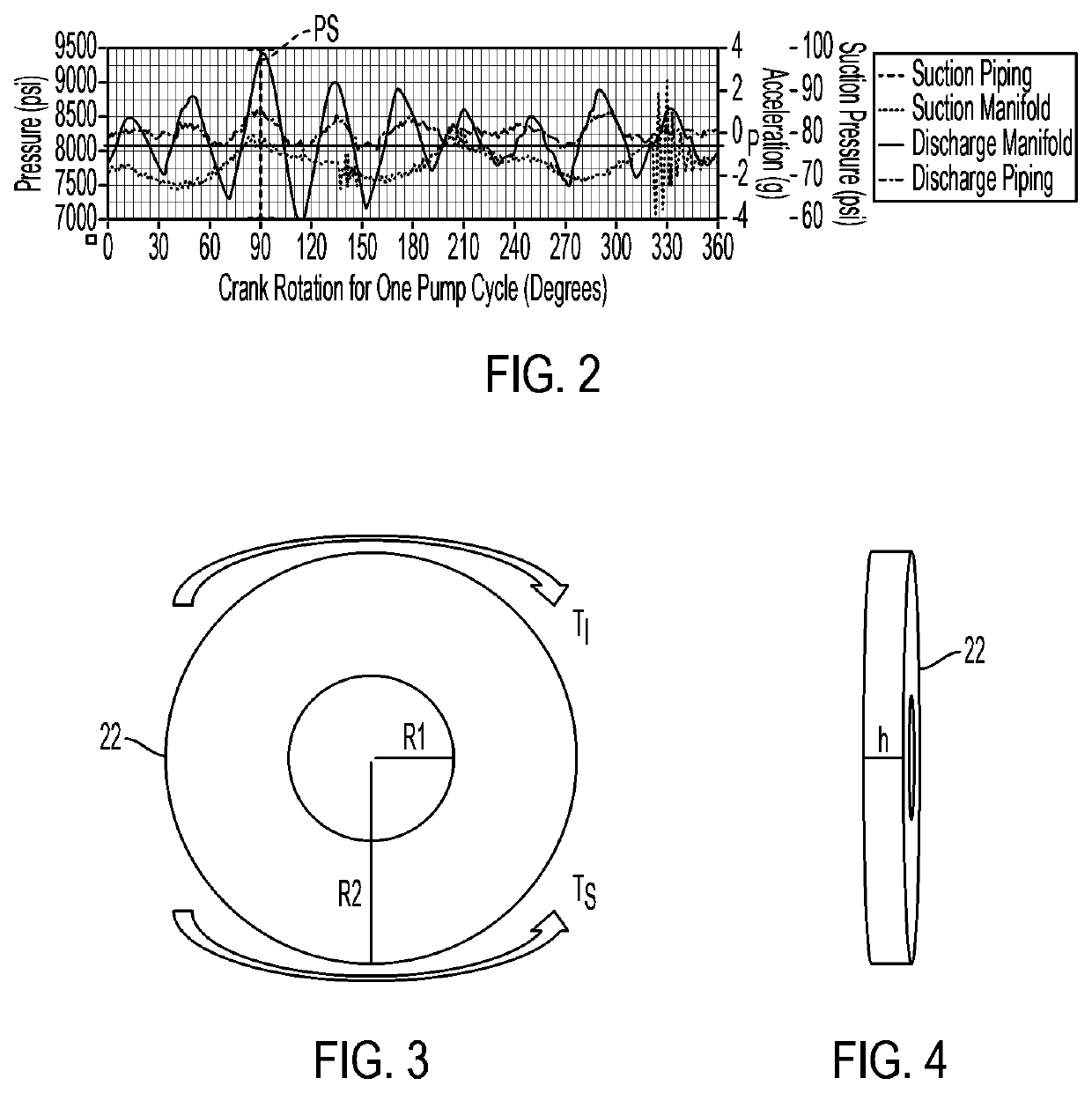
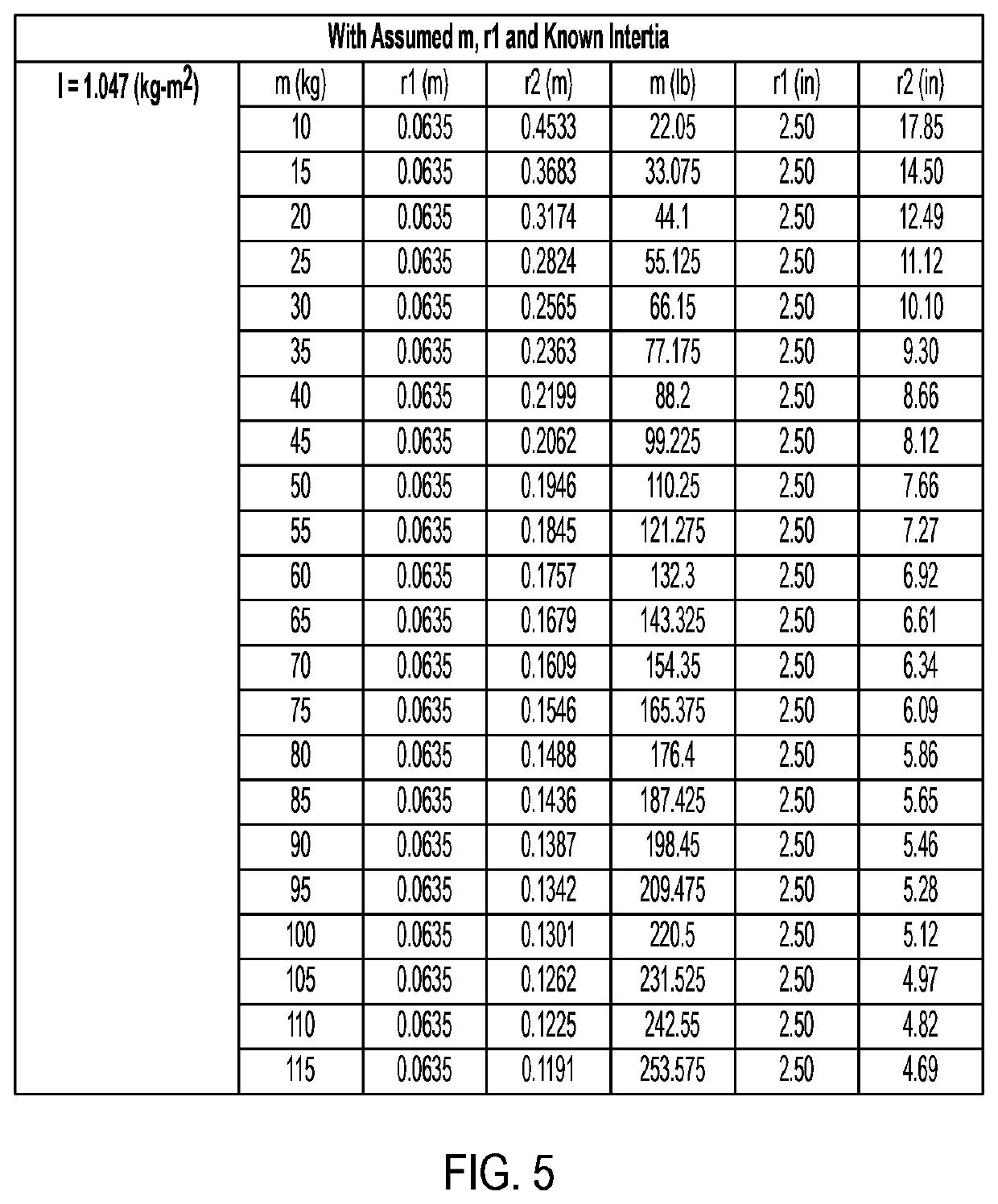
ActiveUS11015594B2Reduce and eliminate shock loadingDampen torsional resonanceRotating vibration suppressionSpringsRotary pumpClassical mechanics
A pump system may include a pump, a driveshaft, driving equipment, and a vibration dampening assembly configured to reduce pump-imposed high frequency / low amplitude and low frequency / high amplitude torsional vibrations. The pump may have an input shaft connected to the driveshaft. The driving equipment may include an output shaft having an output flange connected to the driveshaft. The driving equipment may be configured to rotate the driveshaft to rotate the input shaft of the pump therewith. The vibration dampening assembly may include one or more flywheels operably connected to the input shaft and configured to rotate therewith.
Owner:BJ ENERGY SOLUTIONS LLC
Washing machine and control method thereof
ActiveUS20120278996A1Improve performanceRotating vibration suppressionRotating bodies balancingEngineeringLaundry
A washing machine which improves performance of balancers, and a control method thereof. The washing machine includes a drum accommodating laundry and rotated by rotary force transmitted from a drive source, balancer housings mounted on the drum, each of the balancer housings including a disc-shaped channel formed therein, balancing modules movably disposed in the channels of the balancer housings, vibration sensors to sense unbalance applied to the drum during rotation of the drum, position sensors to sense the positions of the balancing modules, and a controller controlling movement of the balancing modules to positions to compensate for the unbalance sensed by the vibration sensors.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Apparatus and Method for Regulating Active Driveline Damping in Hybrid Vehicle Powertrain
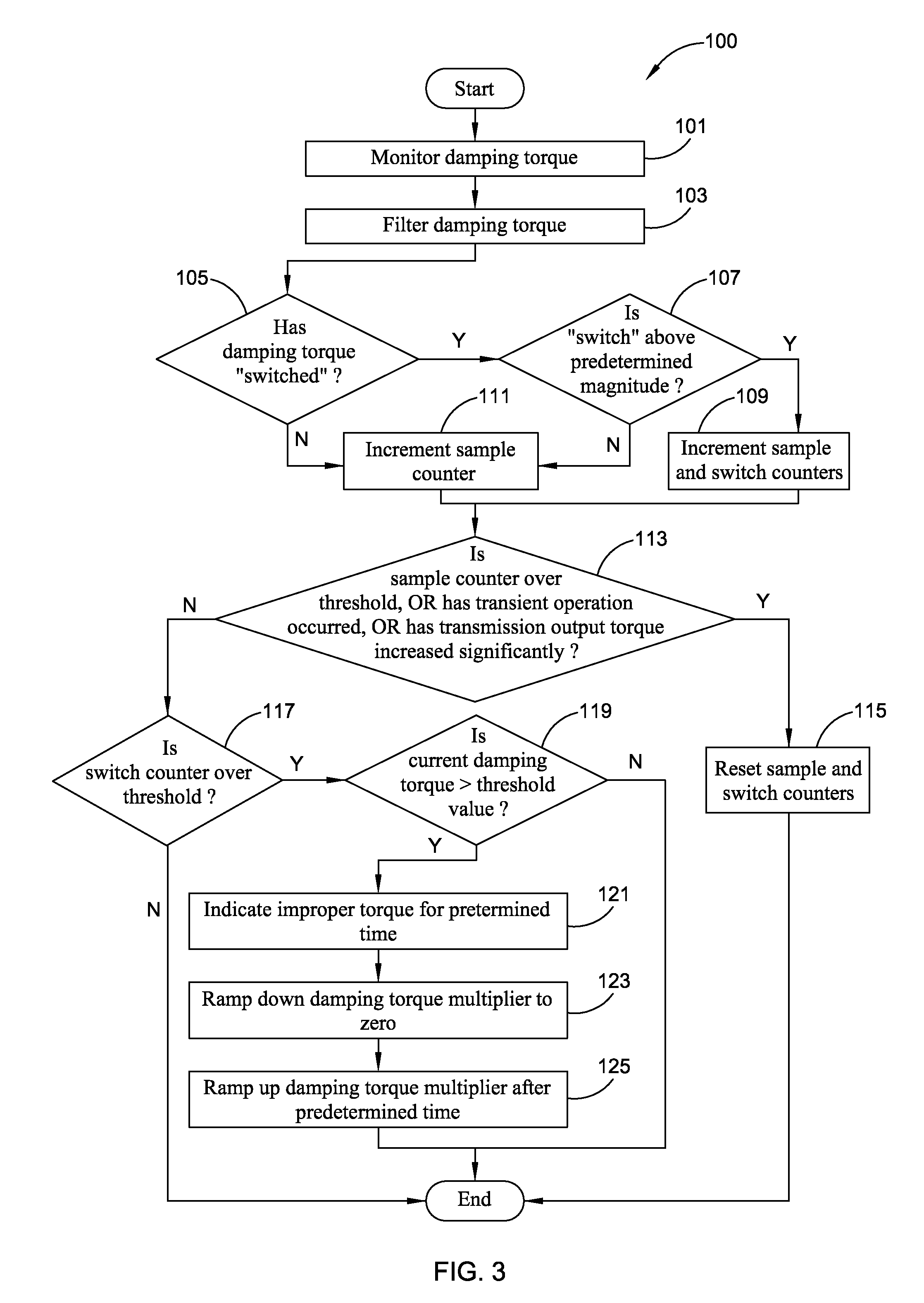
ActiveUS20100087996A1Avoid problemsHybrid vehiclesAnalogue computers for vehiclesDamping torqueEngineering
The present invention provides an improved method and apparatus for regulating active damping in a hybrid vehicle powertrain. The method includes: monitoring the damping command sent to the active damping system; determining a mean reference point, which may be a filtered value of the damping torque command; determining if the unfiltered damping torque command value switches from one side to the other of the mean reference point; if a switch is detected, determining if the size of the switch exceeds a predetermined minimum; if it does, then increasing a total number of switches; determining if the total number of switches exceeds a switch threshold; if the total number of switches exceeds the switch threshold, determining if the current damping torque exceeds a damping torque threshold; and decreasing the damping torque if the total number of switches exceeds the switch threshold and the current damping torque exceeds the damping torque threshold.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
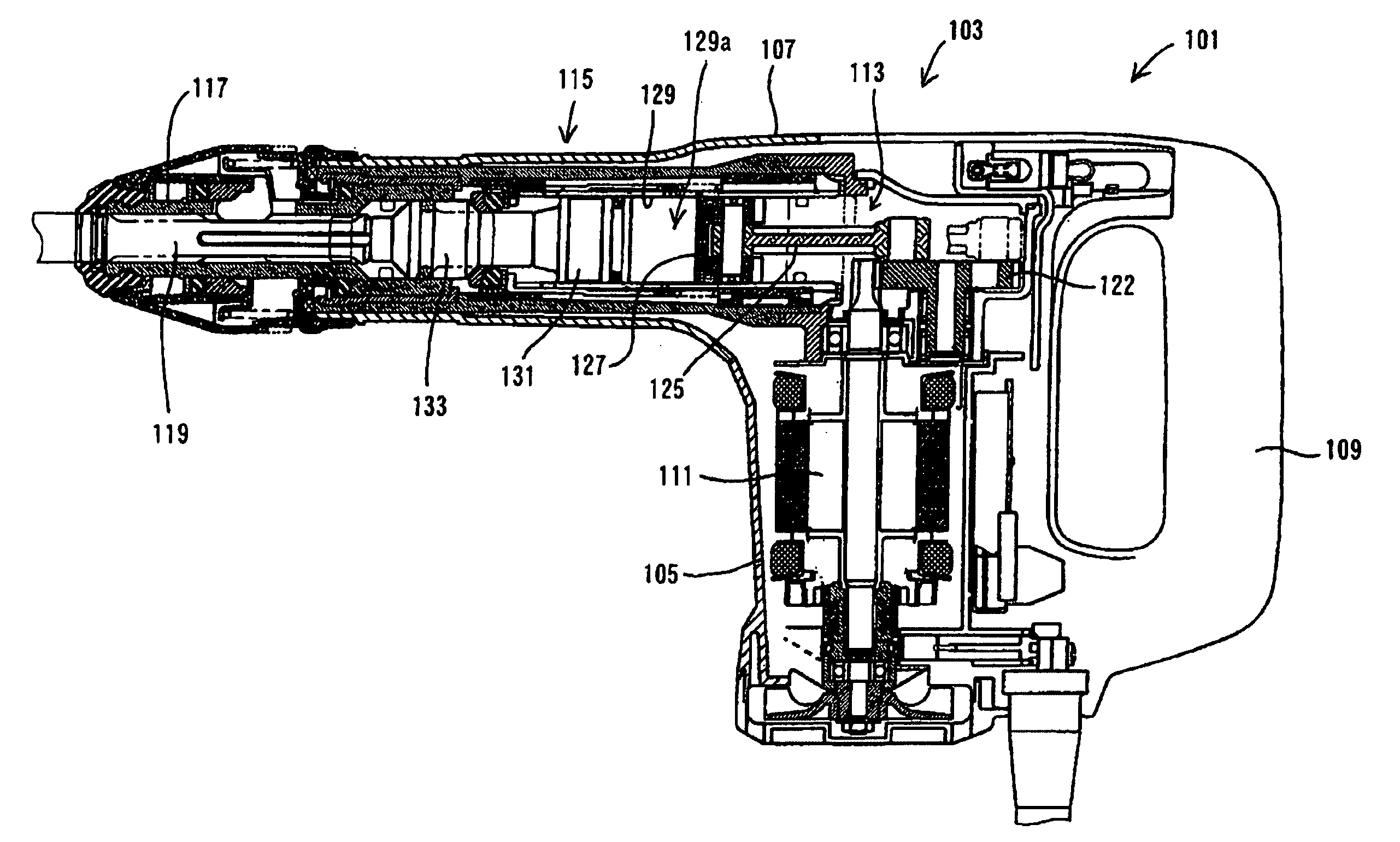
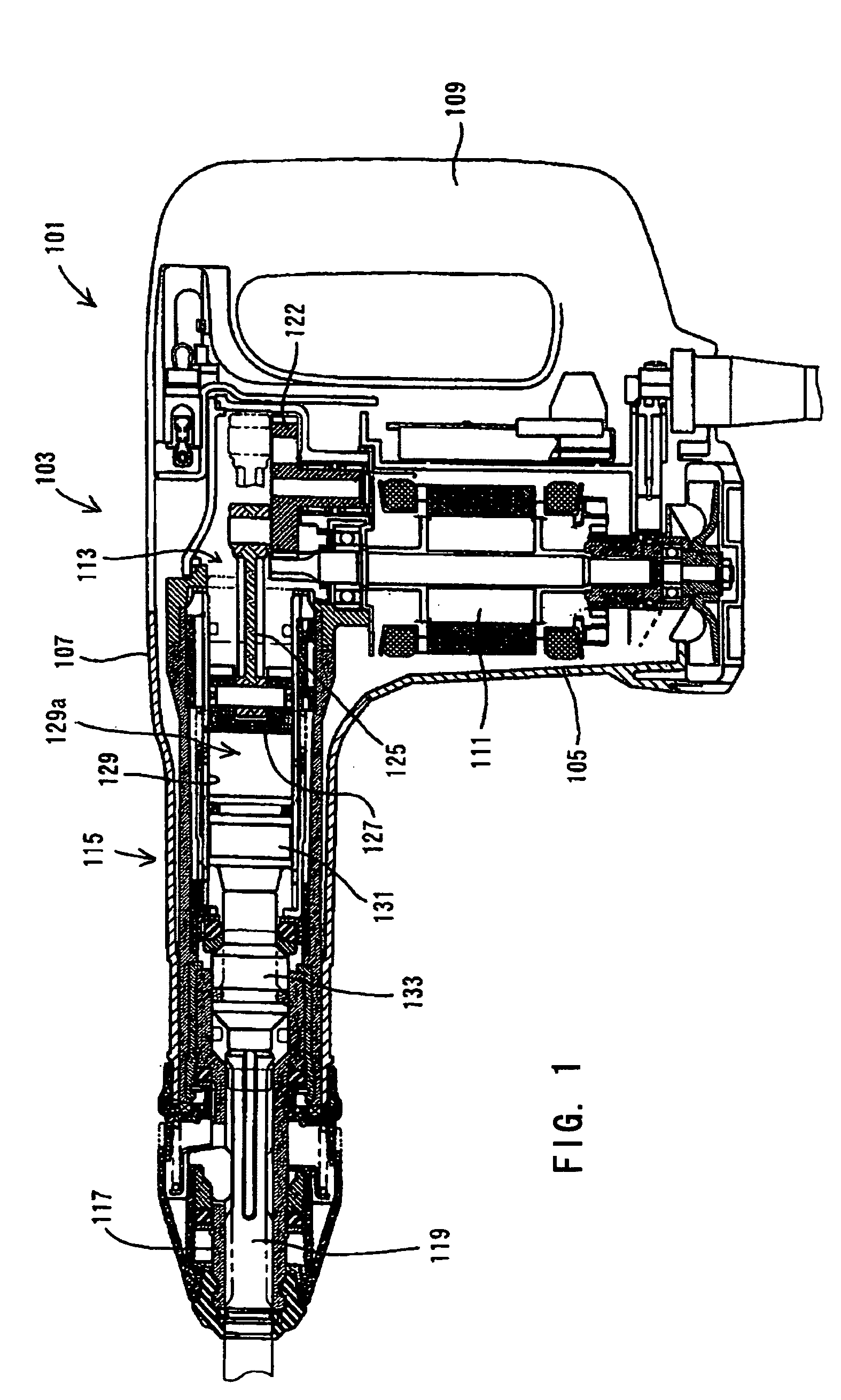
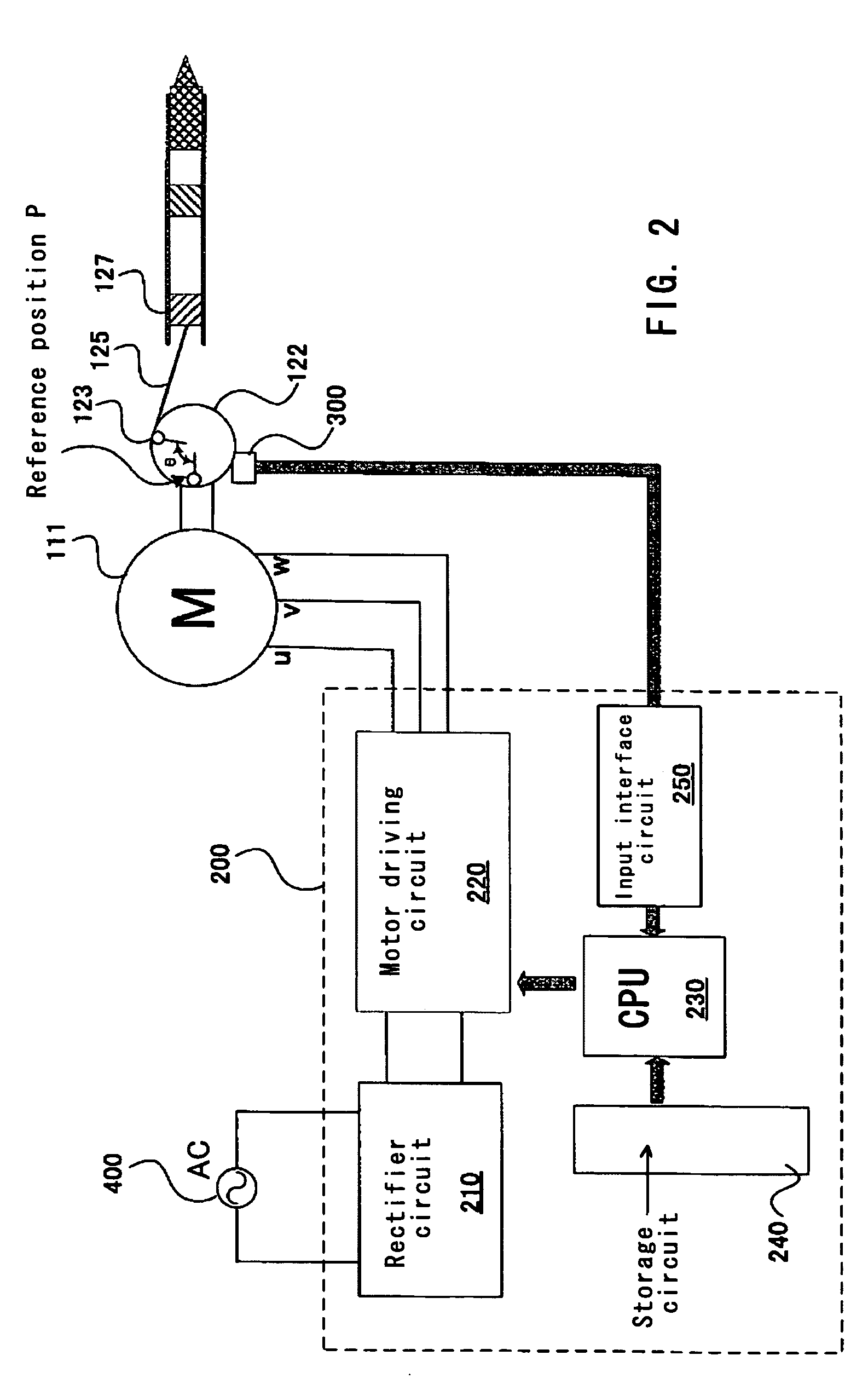
Power tool having pneumatic vibration dampening
It is an object of the present invention to provide a vibration reducing technique caused by air pressure fluctuations within a power tool. According to the present invention, a representative power tool may comprise a driving motor, a driver and a tool bit. The driving motor drives the driver to cyclically reciprocate. The tool bit is linearly driven by utilizing the pressure of air within the power tool. The air may be compressed by the reciprocating movement of the driver. The power tool changes the rotational speed of the driving motor in the cycle of the reciprocating movement of the driver so that vibration caused in the power tool can be alleviated.
Owner:MAKITA CORP
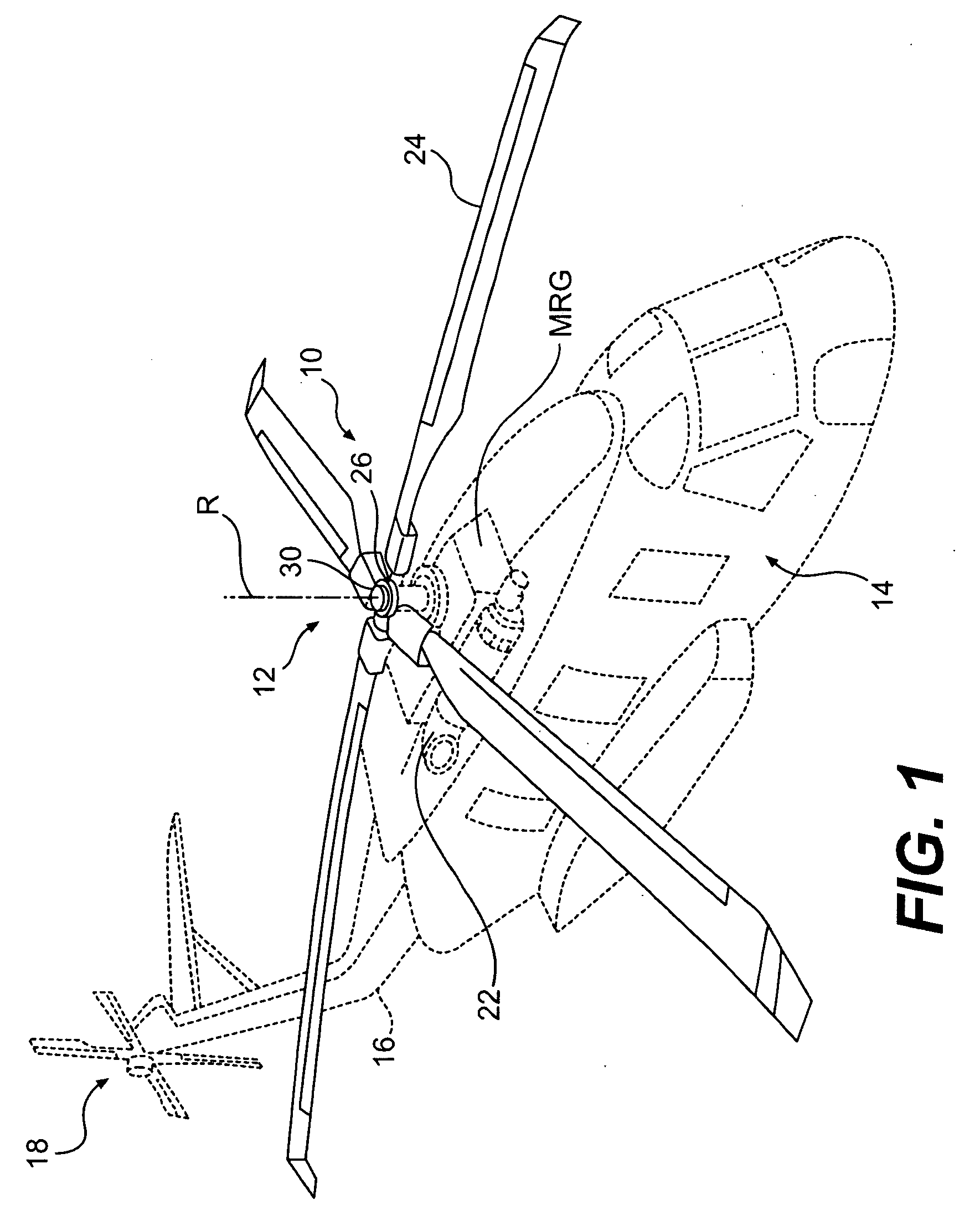
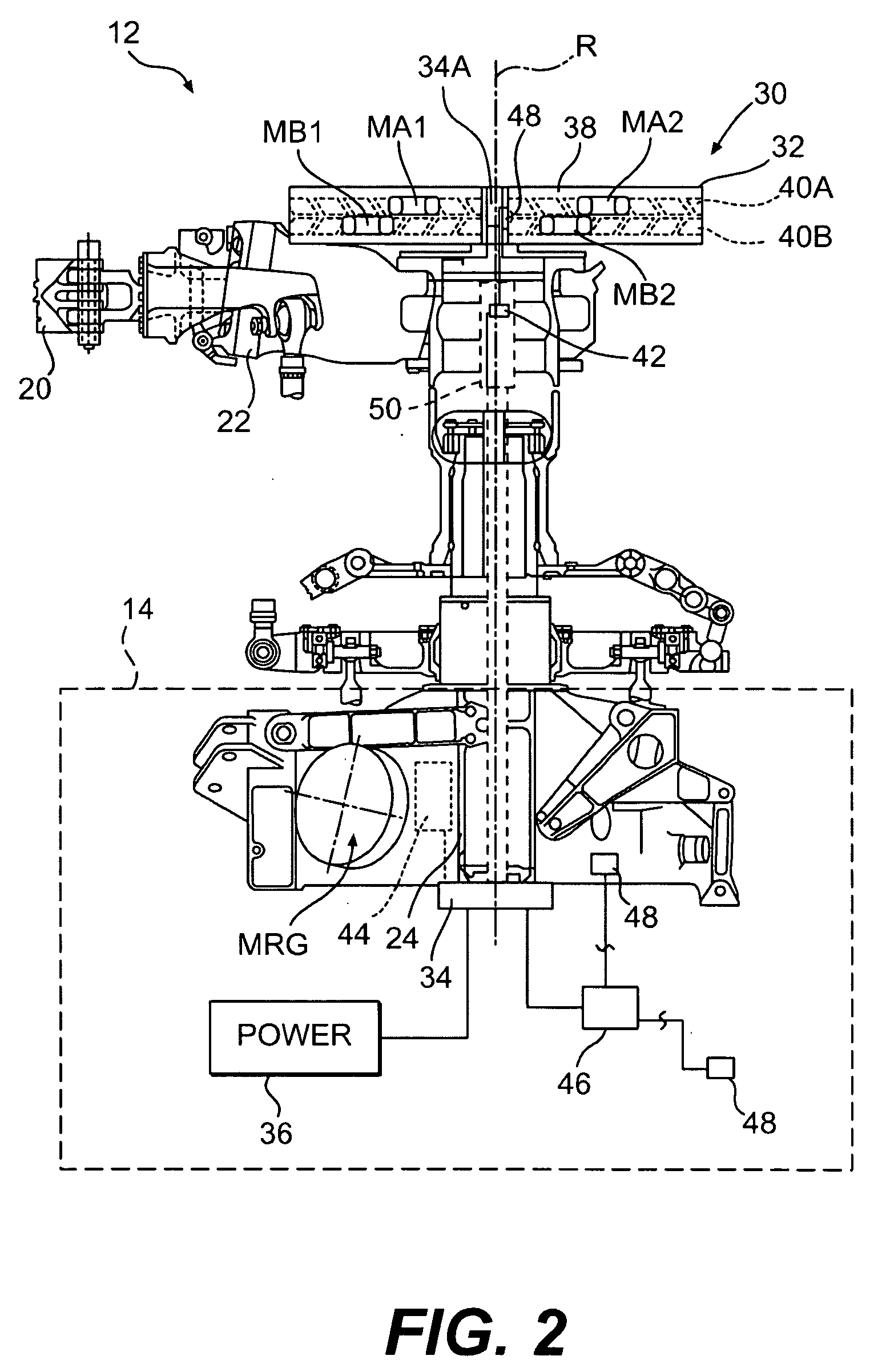
Dual frequency hub mounted vibration suppressor system
ActiveUS20090236468A1Reduce in-plane vibrationReduce NP vibrationRotating vibration suppressionTemperatue controlIn planeDual frequency
A vibration suppressor system includes an annular electric motor system which independently controls rotation of at least two masses about the axis of rotation to reduce in-plane vibration of the rotating system. A method of reducing vibrations in a rotary-wing aircraft includes independently controlling a relative angular position of a multiple of independently rotatable masses to reduce vibrations of a main rotor system.
Owner:SIKORSKY AIRCRAFT CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com