Patents
Literature
2853 results about "Vibration damper" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
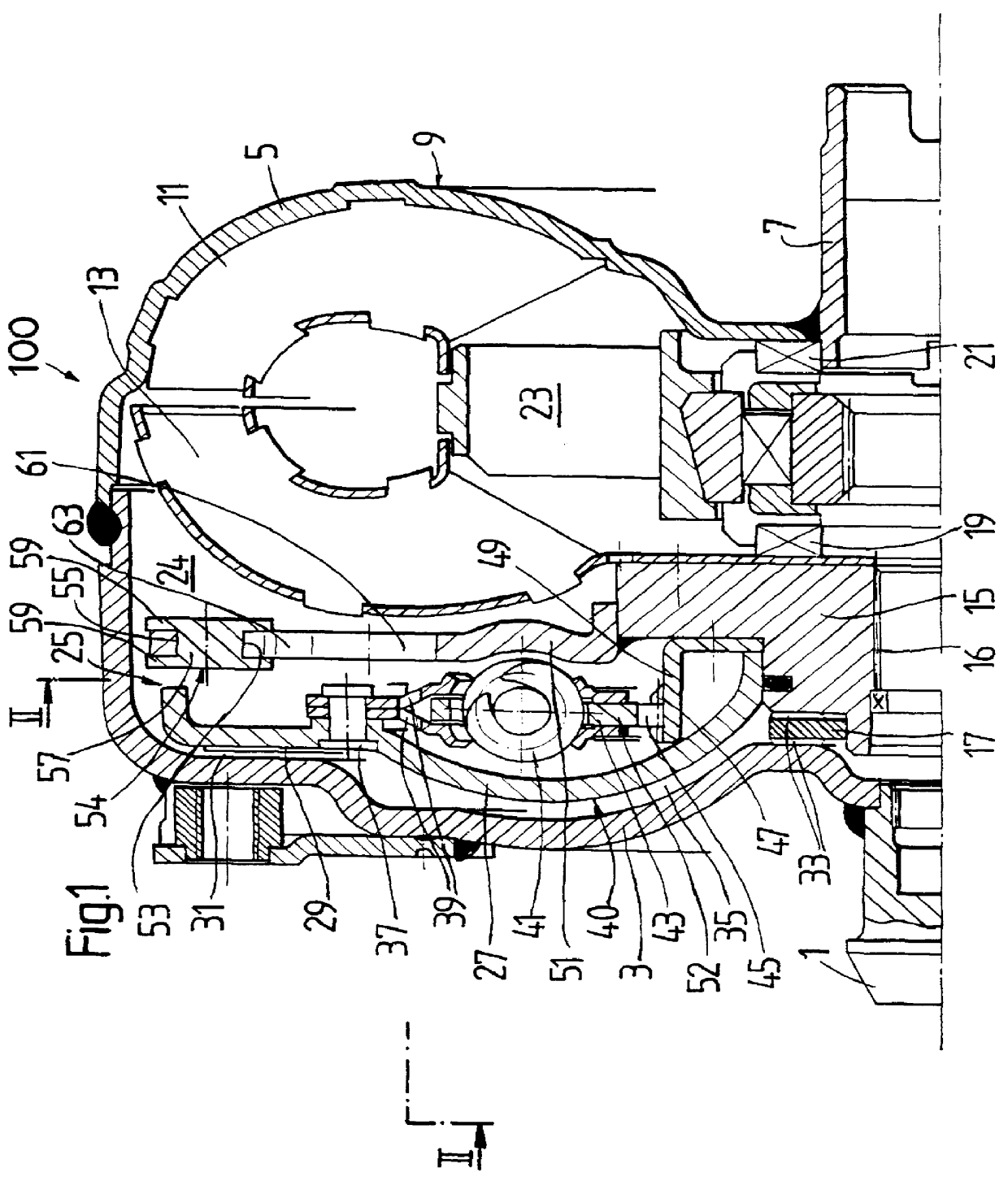
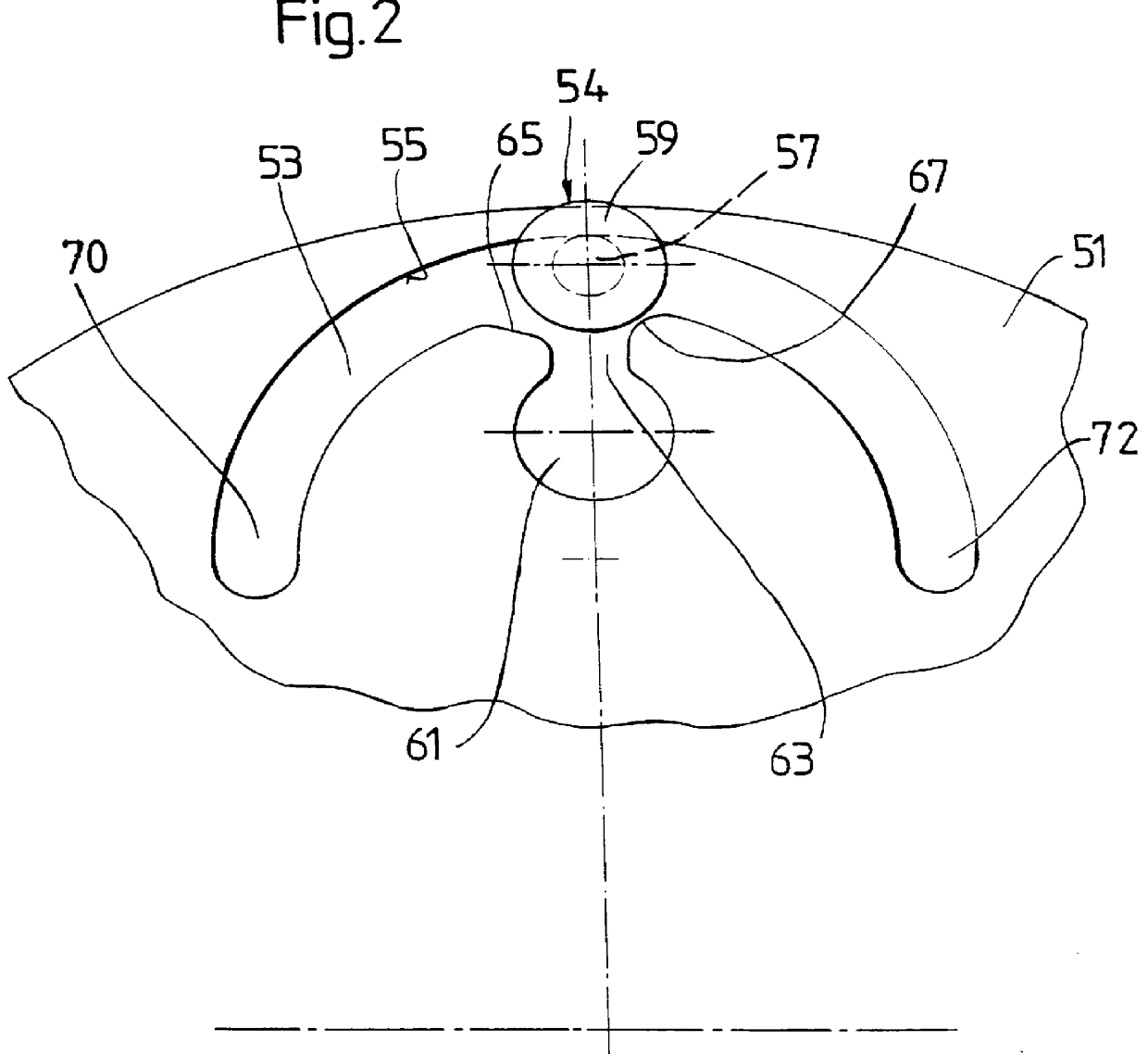
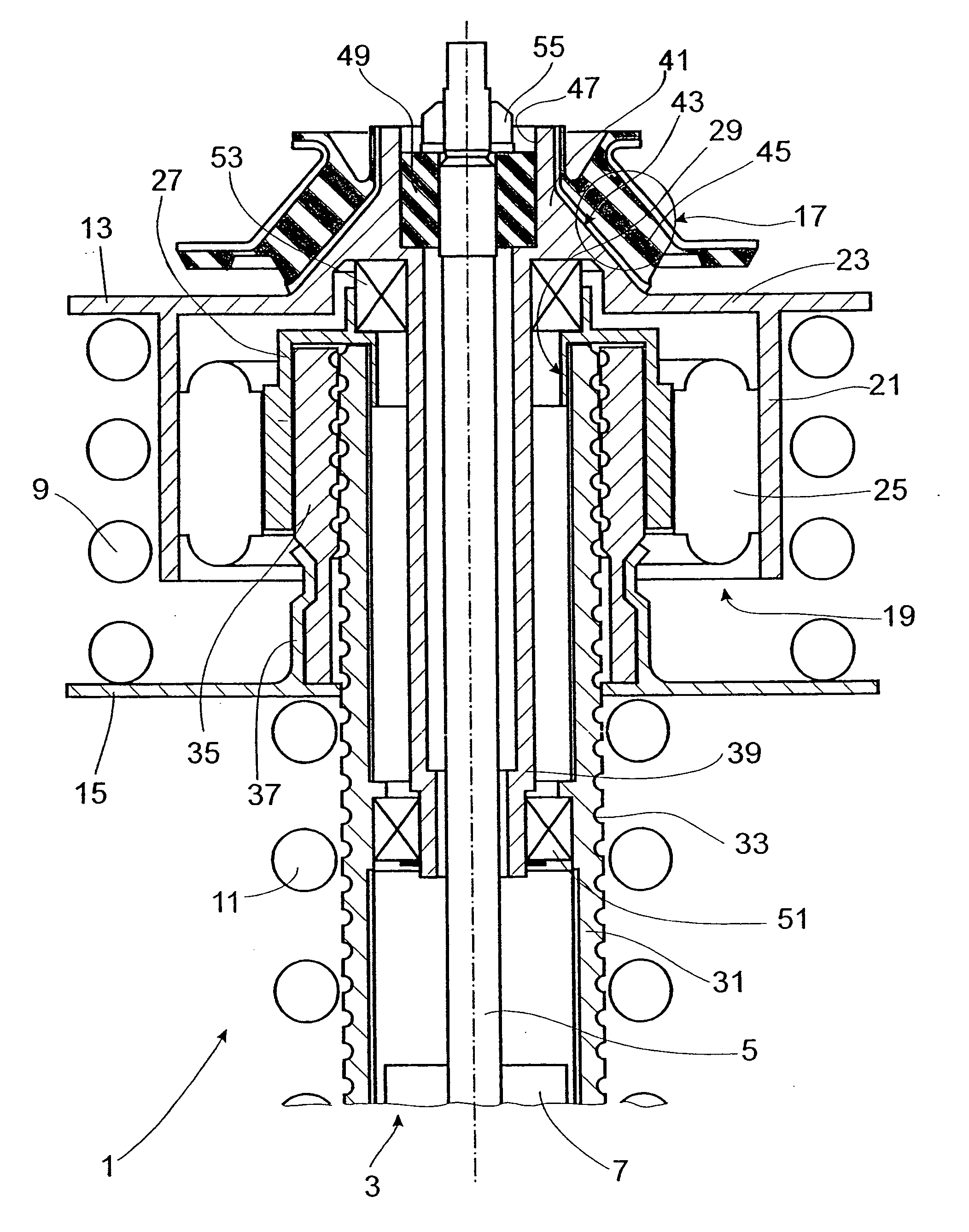
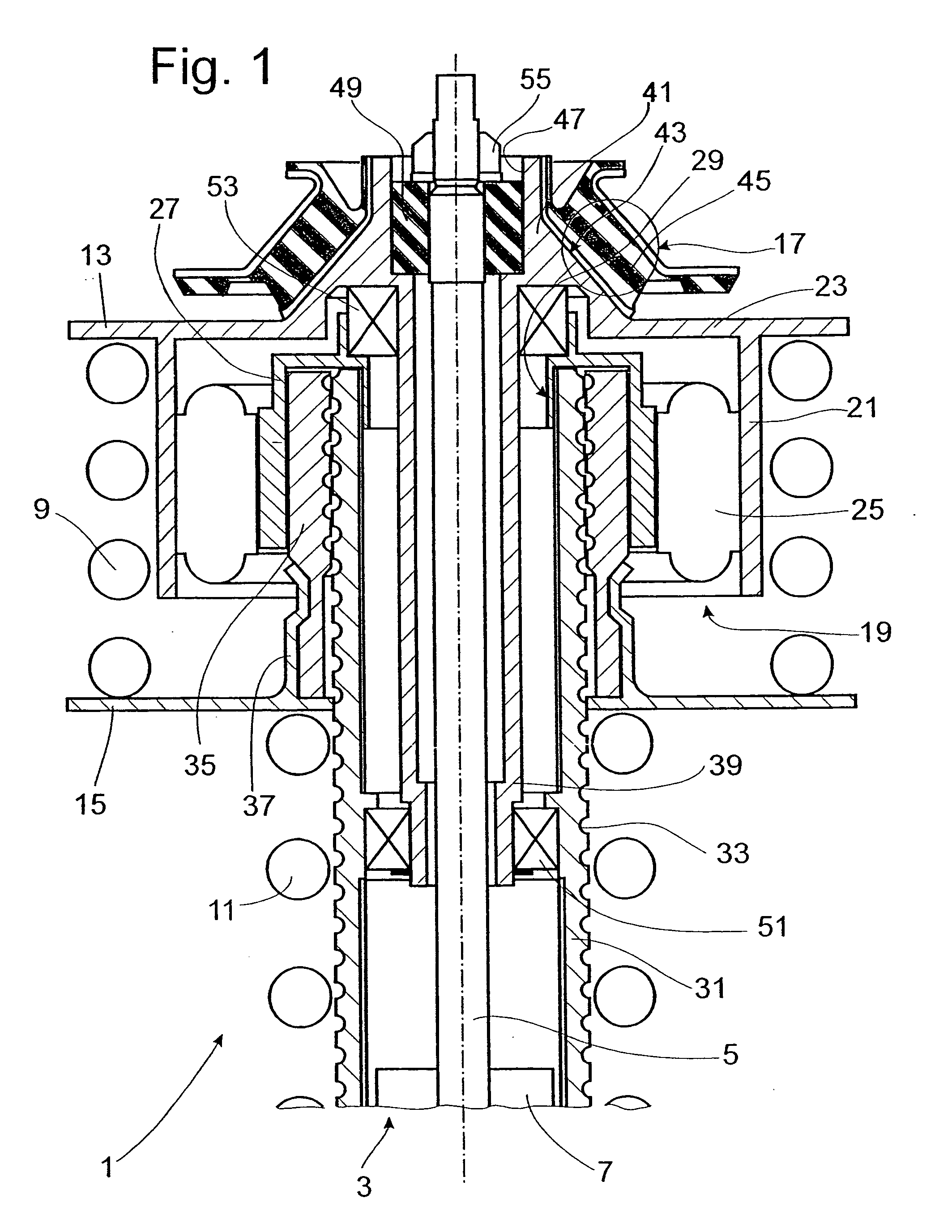
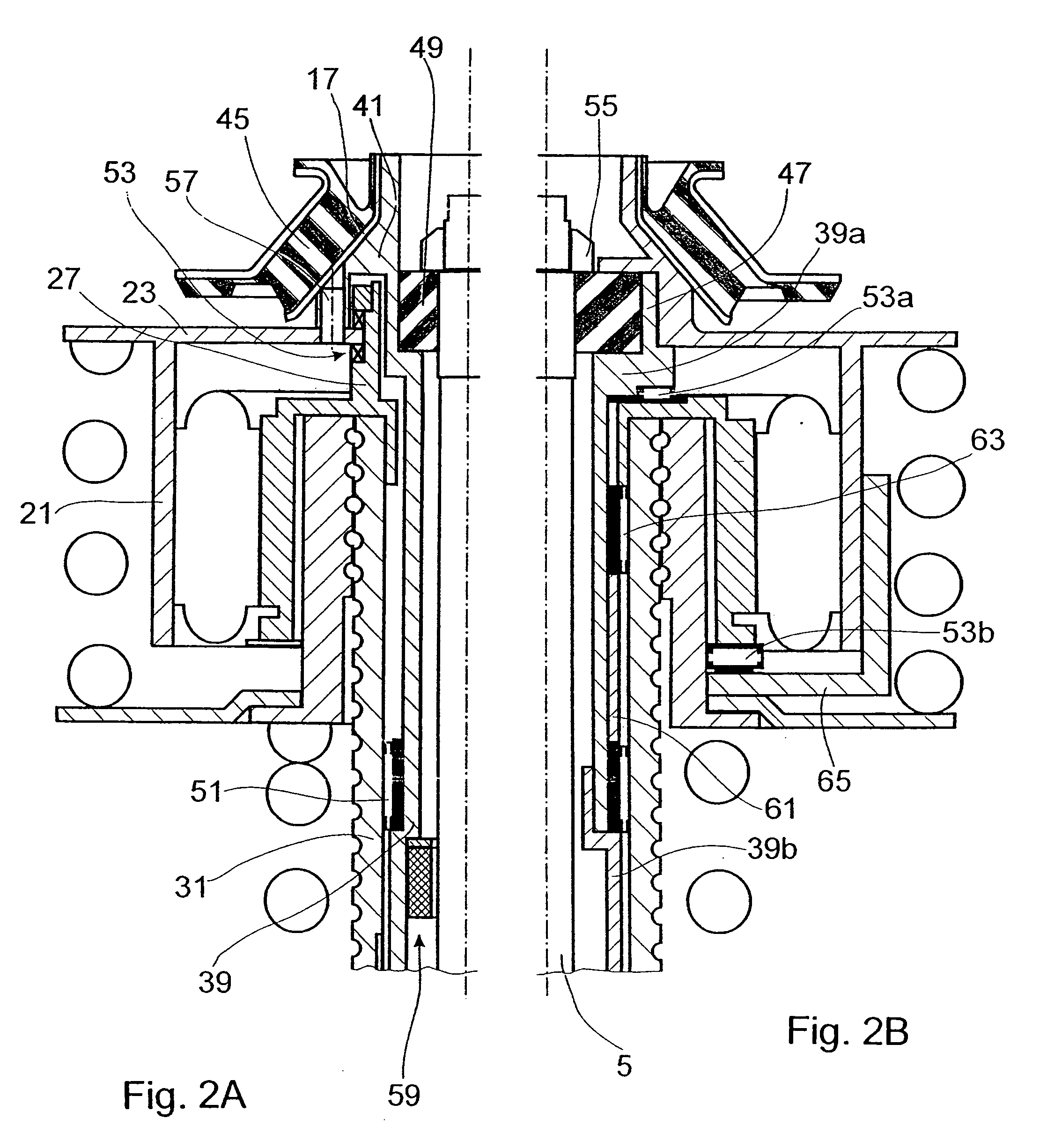
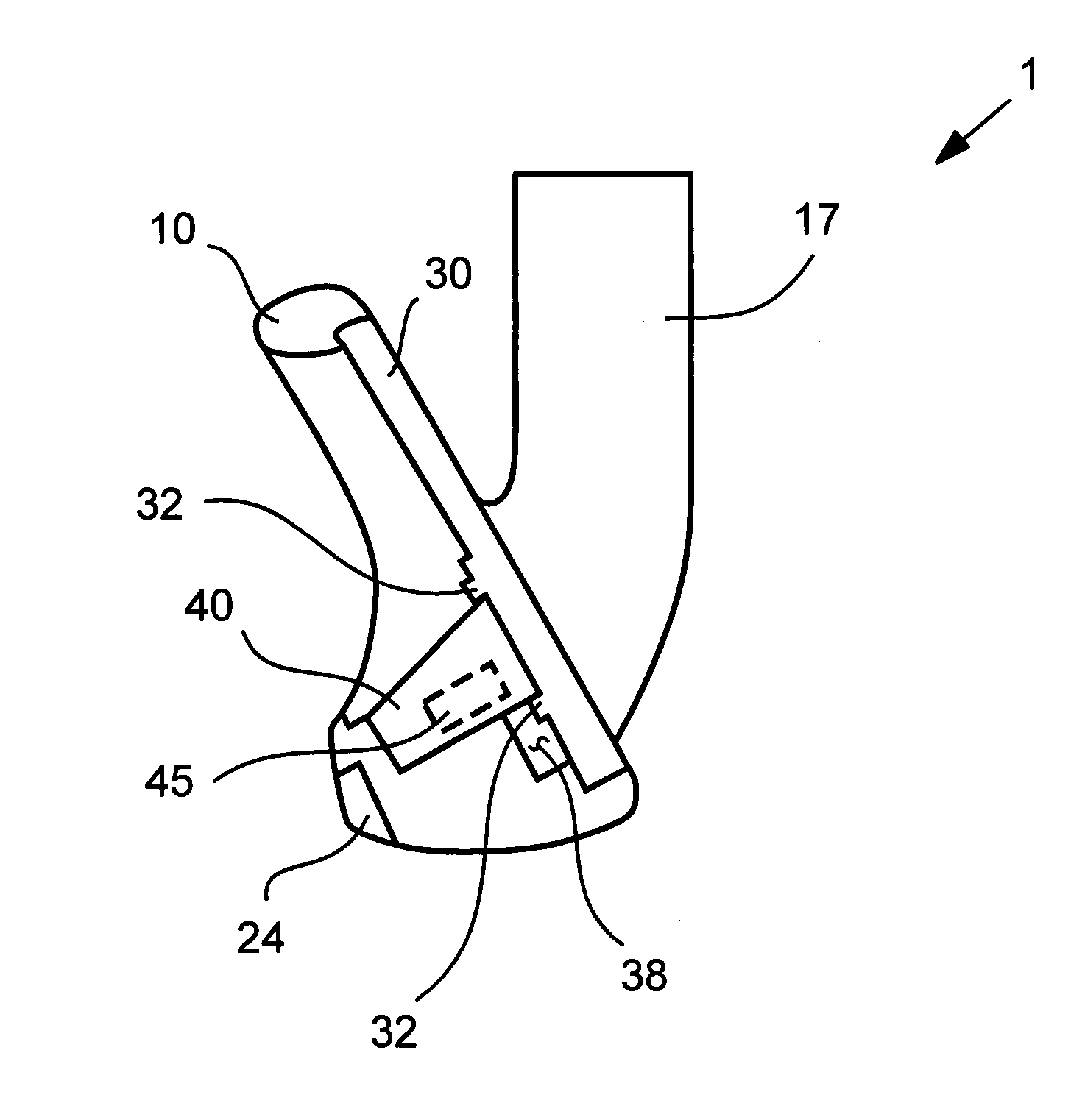
Lockup clutch with a compensation flywheel mass at the torsional vibration damper
A lockup clutch at a hydrodynamic torque converter is constructed with a torsional vibration damper which has a drive-side transmission element and a driven-side transmission element which is rotatable relative to the latter. Both of the transmission elements are provided with driving devices for driving elastic elements of a damping device. A carrier for a compensation flywheel mass is associated with the driven-side transmission element, wherein the carrier is connected with the turbine wheel on the one hand and with the driven-side driving device of the elastic elements on the other hand so as to be fixed with respect to rotation relative thereto and is provided at least with a cutout for receiving the compensation flywheel mass. The cutout has a guide path at least in its area of contact with the compensation flywheel mass, which guide path allows a movement of the compensation flywheel mass with at least one component perpendicular to the radial direction at the carrier.
Owner:ZF FRIEDRICHSHAFEN AG
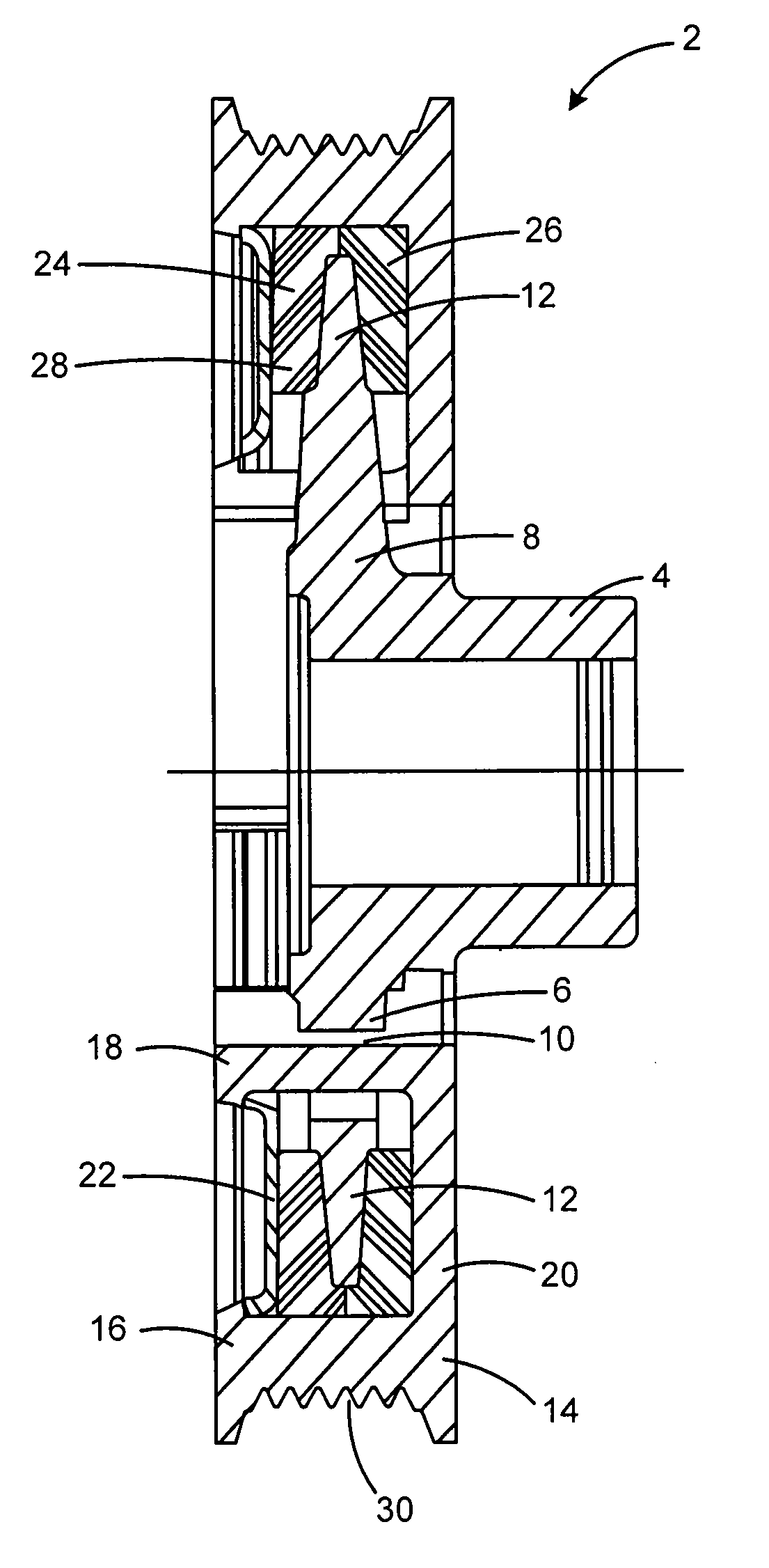
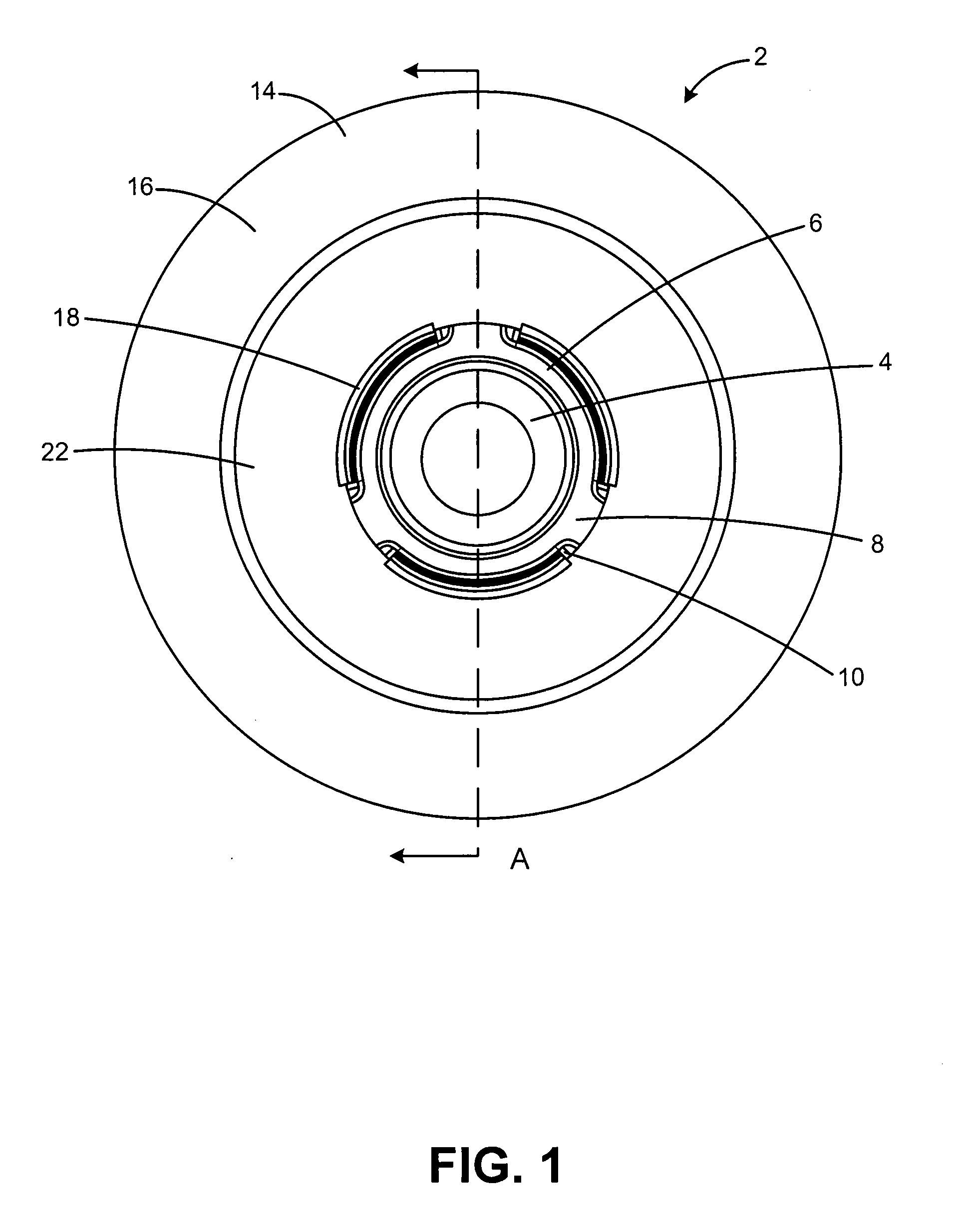
Torsional vibration damper
A torsional vibration damper having a hub carrying a radially projecting flange and an annular inertia mass defining an annular channel encompassing the radially projecting flange and an elastomeric member. An annular compression ring is attached to the opening of the annular channel to axially compress and extrude the elastomeric member to fill the annular channel around the radial flange within the inertia ring. Projections defining an intermittent annular inner rim of the inertia mass extend through openings between the spokes of the hub and cooperate with an annular outer rim of the inertia mass to retain the compression ring.
Owner:DAYCO IP HLDG +1
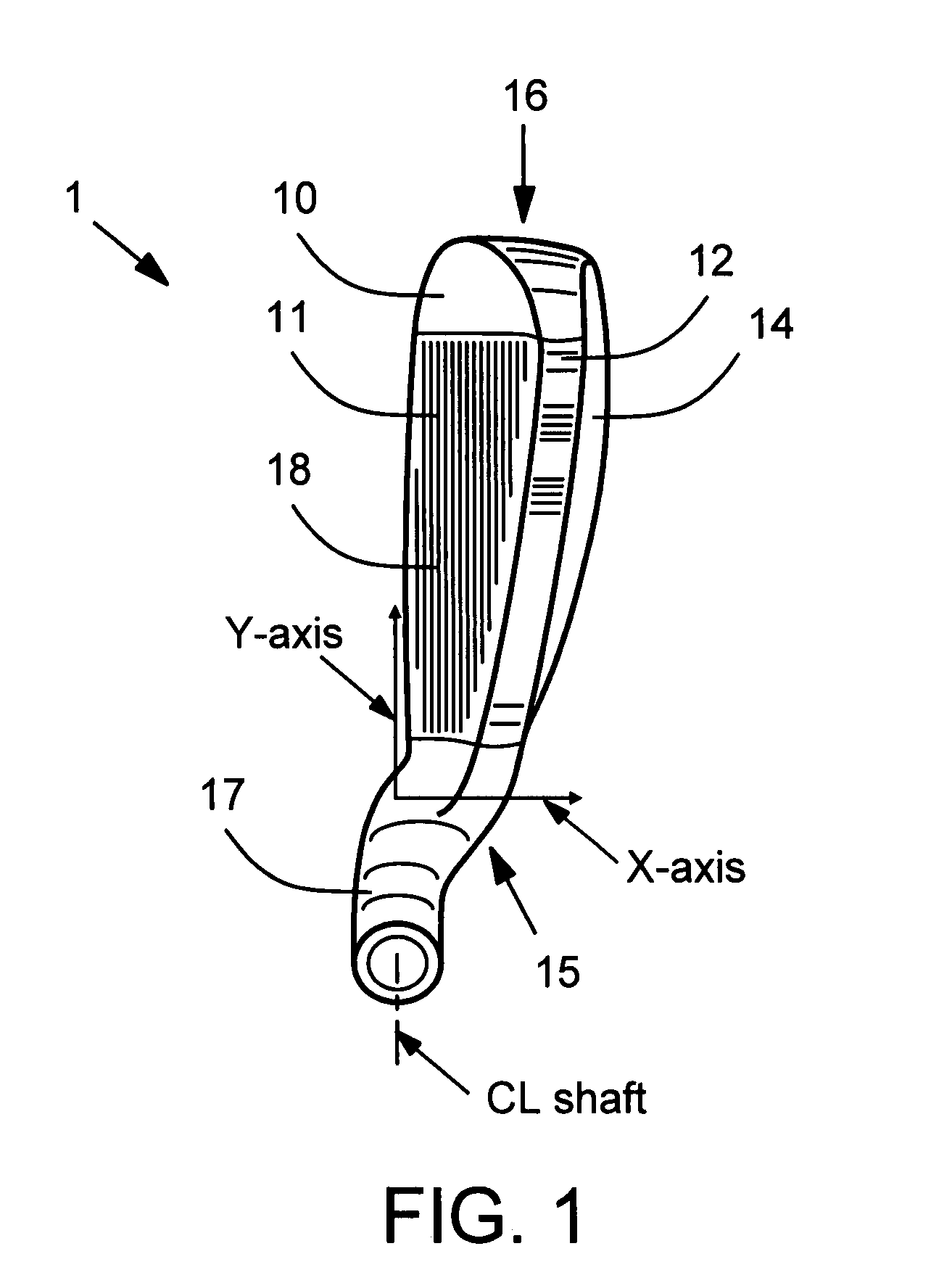
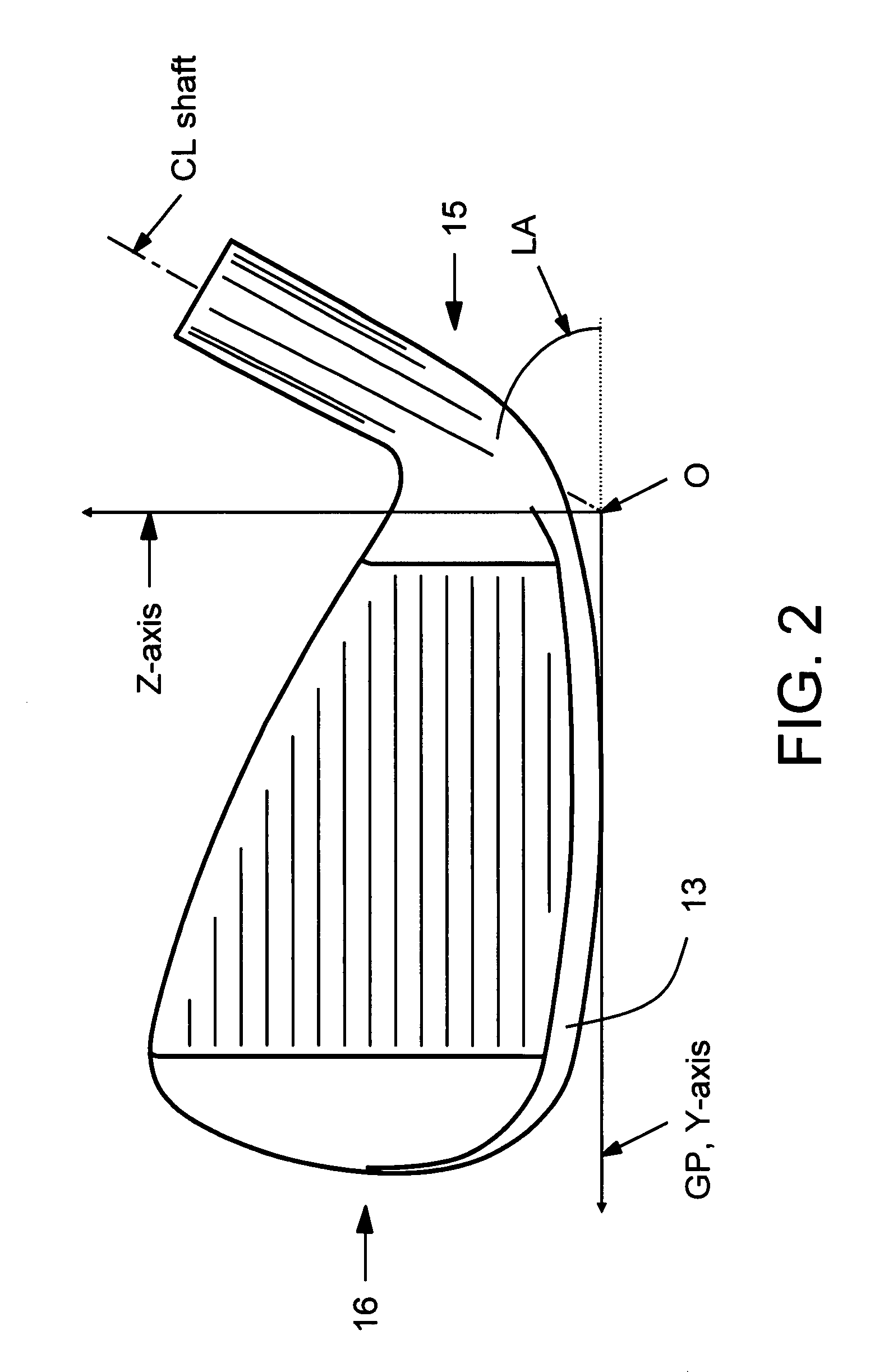
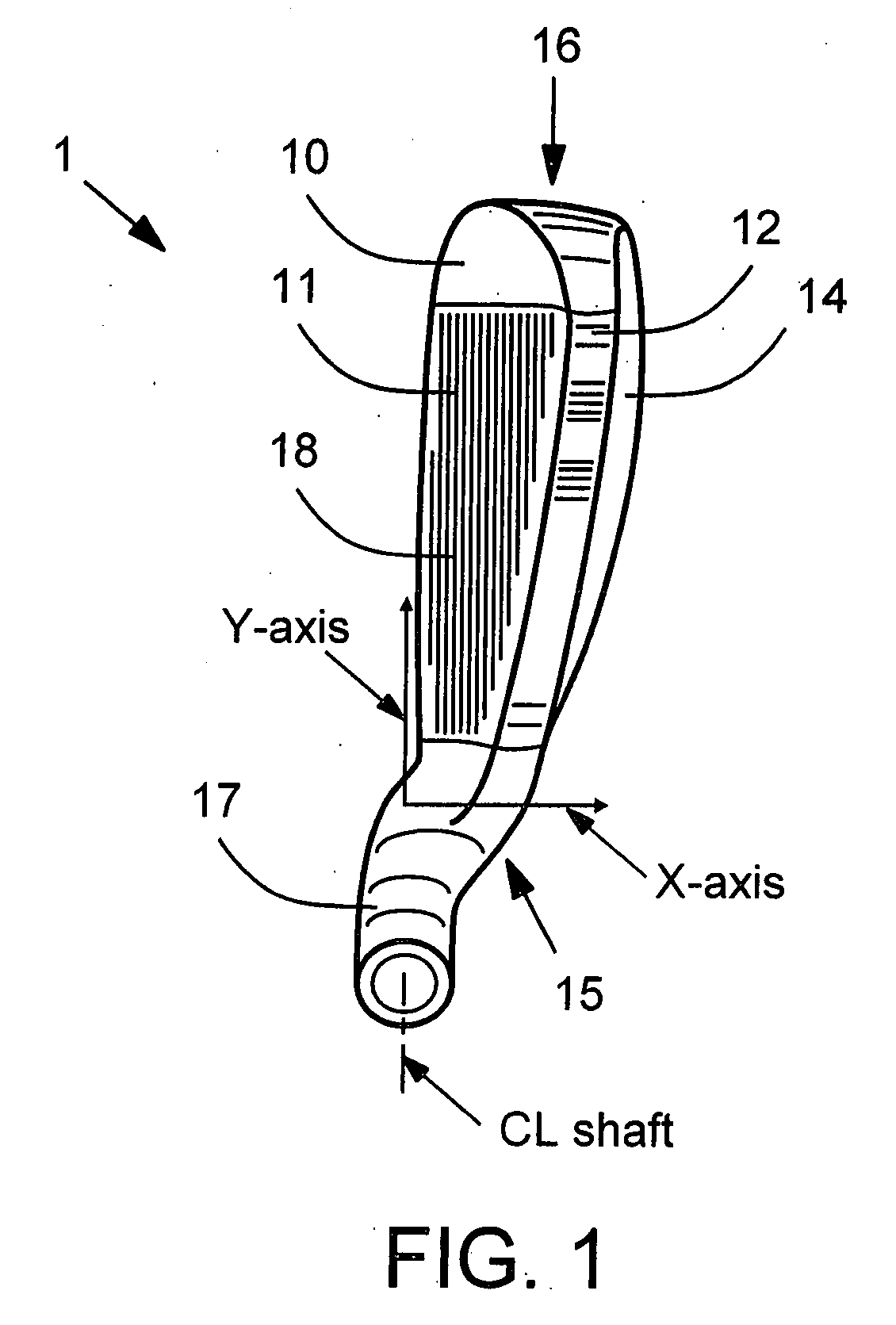
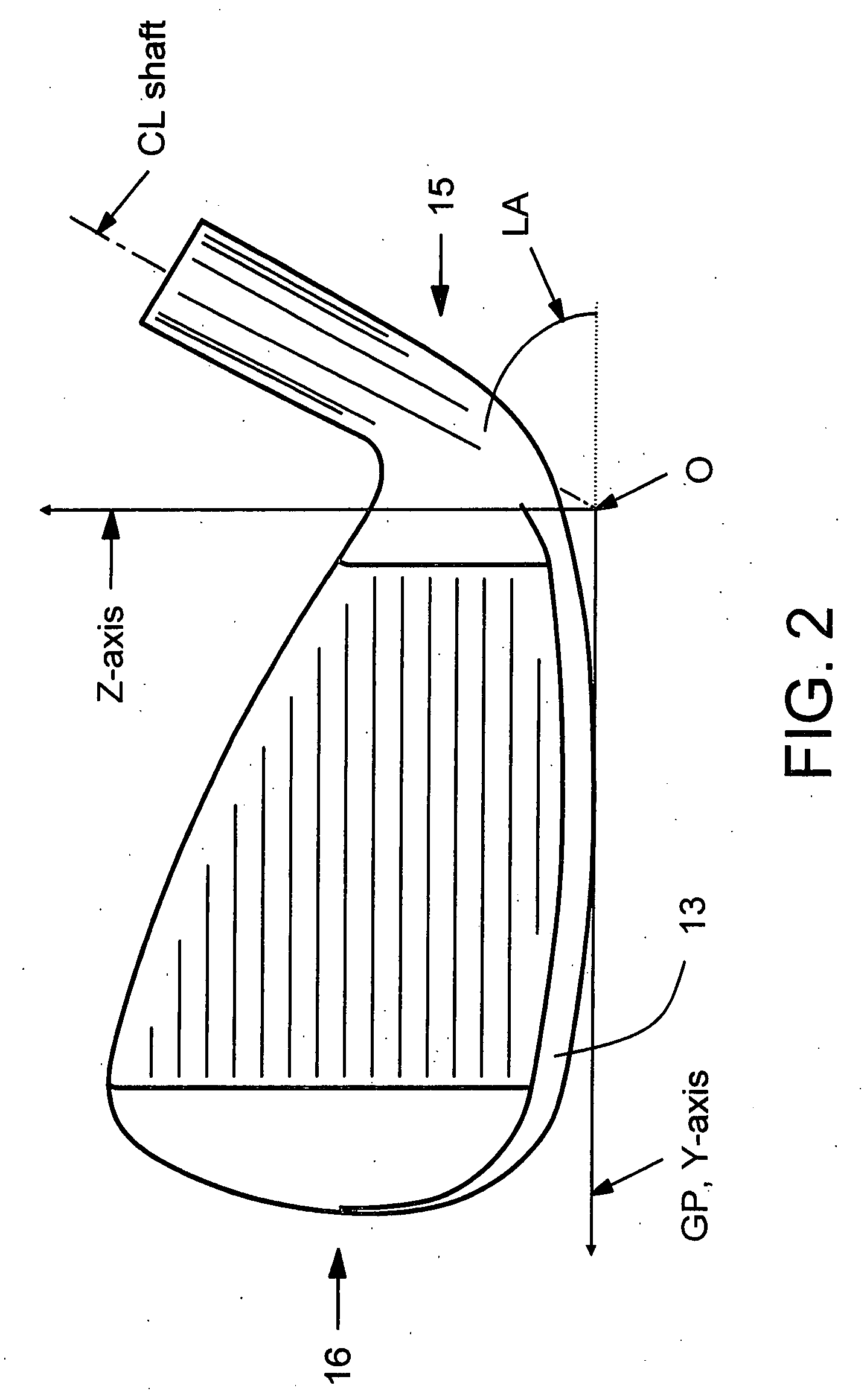
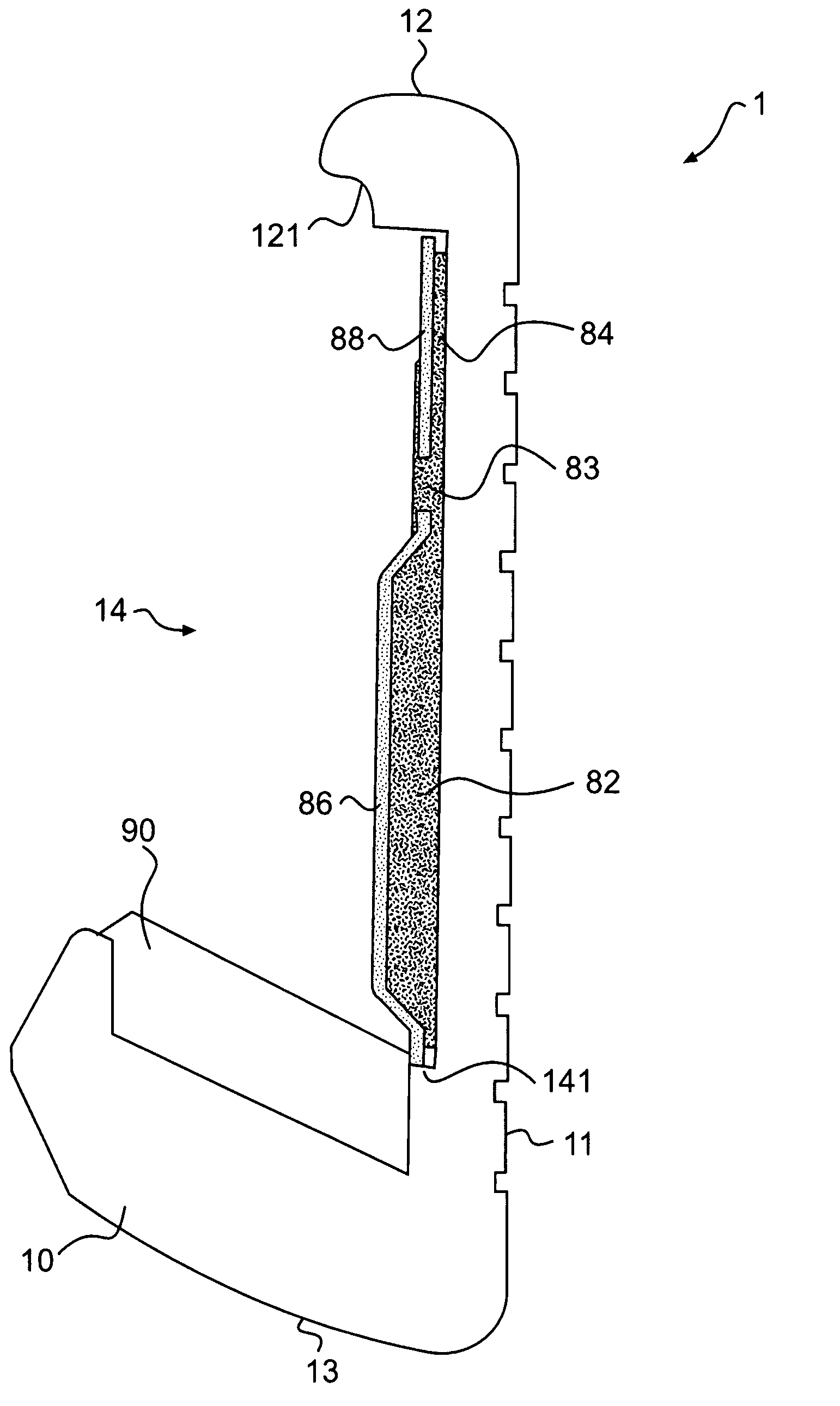
Vibration damping for hollow golf club heads
An internal vibration damper for hollow golf club heads is disclosed. Of particular concern is vibration of the club sole and crown when the face of the club impacts a golf ball. At least one column extends from the sole to the crown, approximately perpendicular to the surfaces of the sole and crown. The column construction or its mounting acts to dampen and reduce vibrations of the sole and crown toward and apart from each other upon ball impact on the face of the club head.
Owner:ORIGIN INC
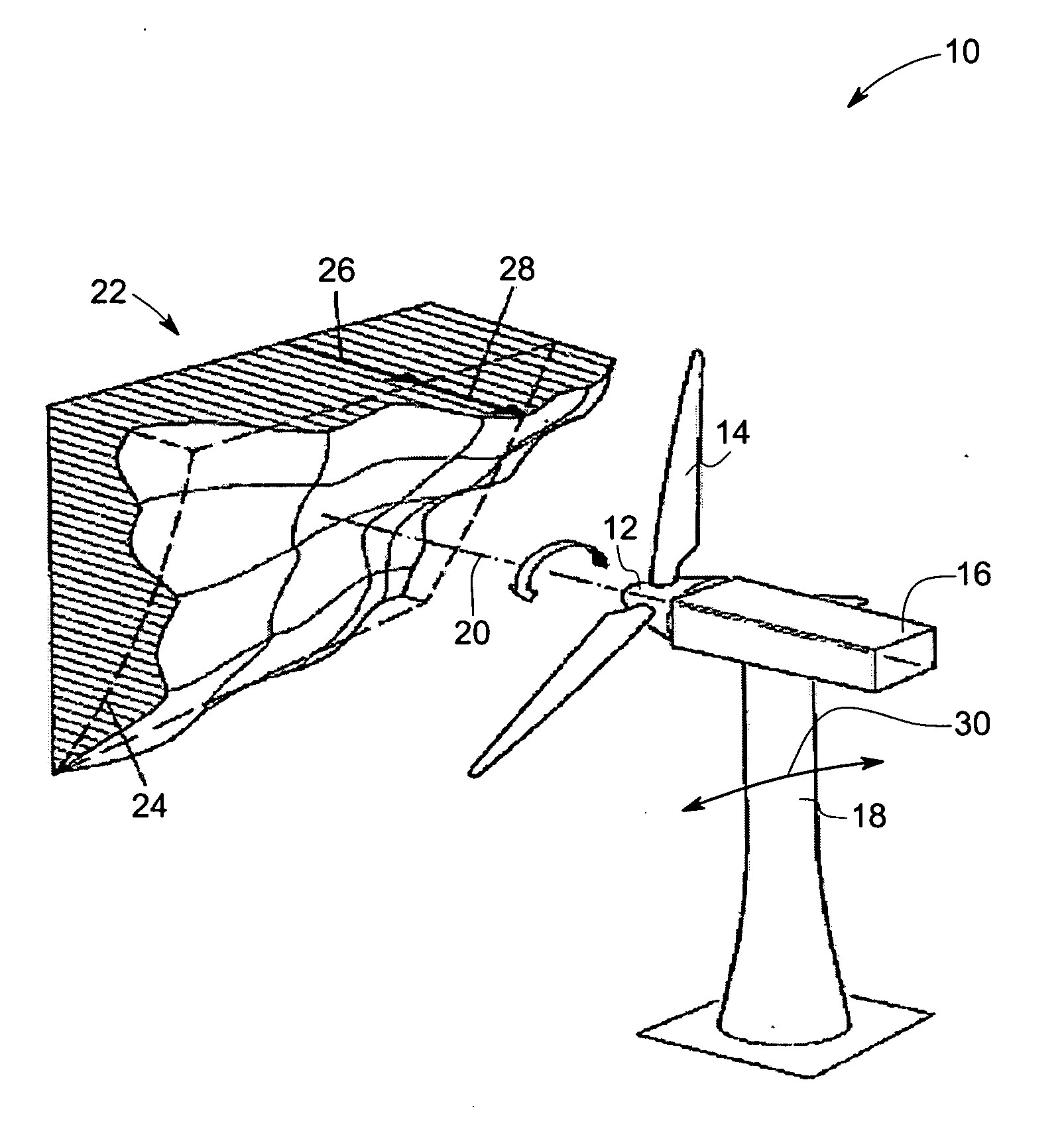
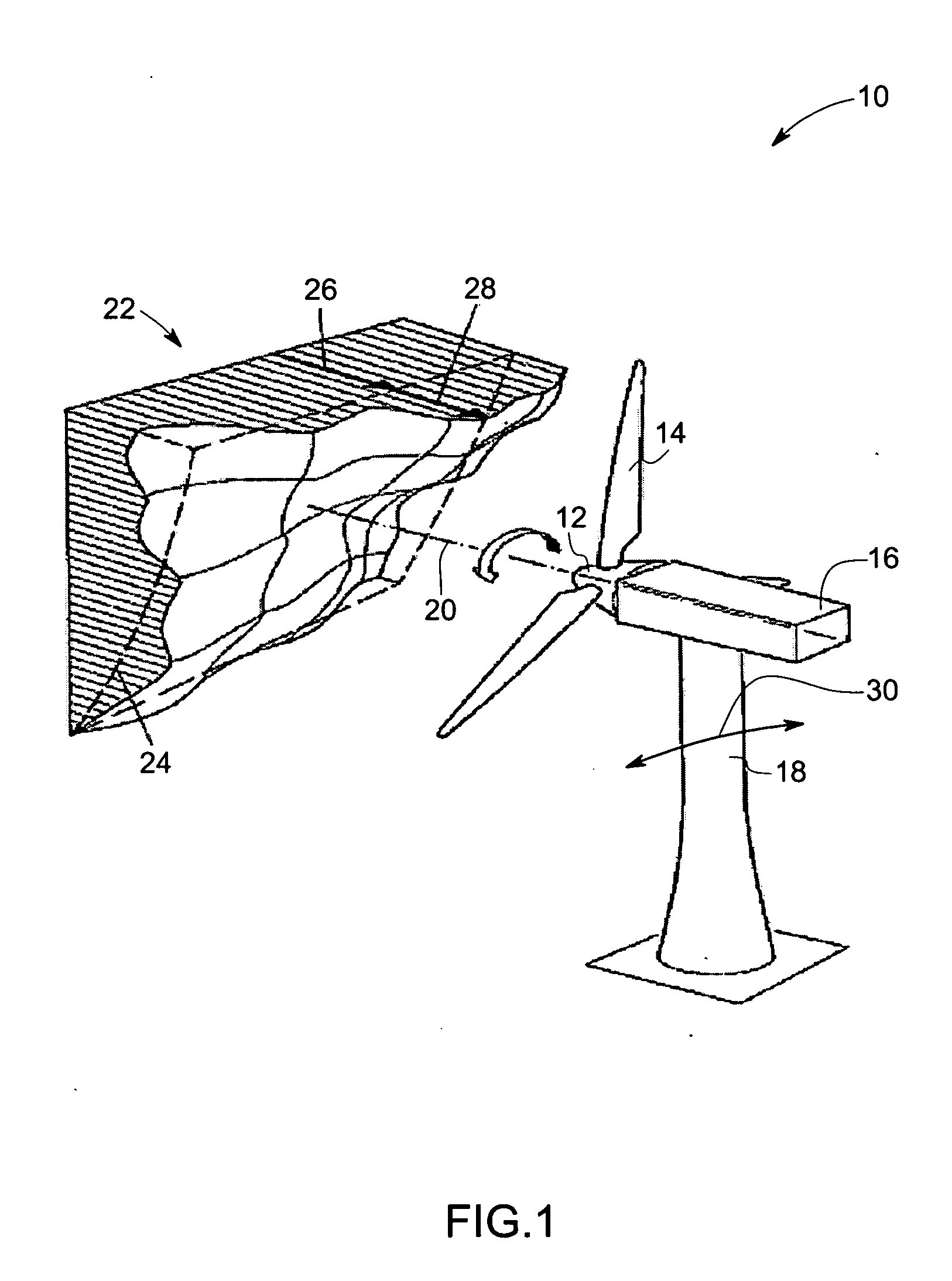
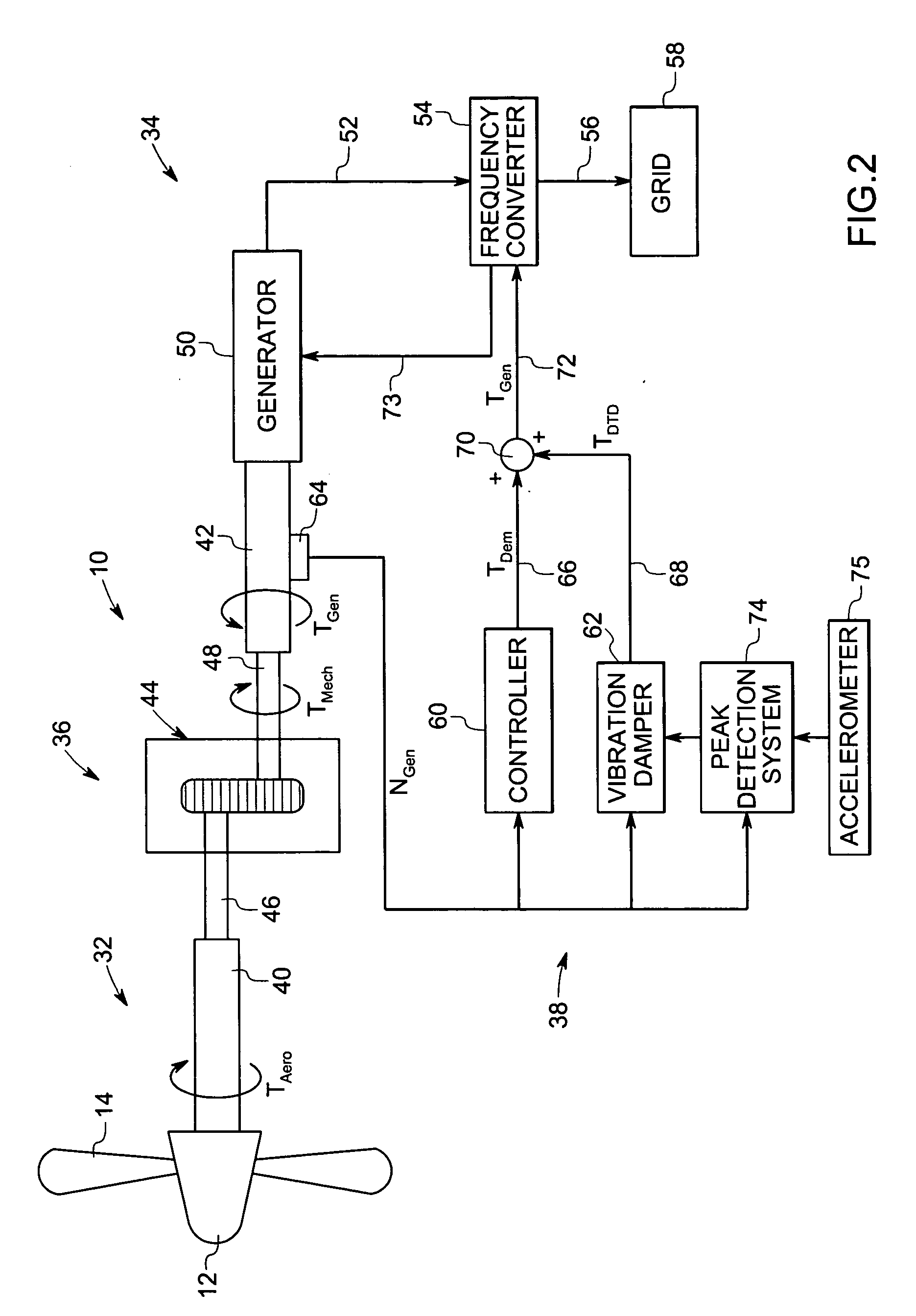
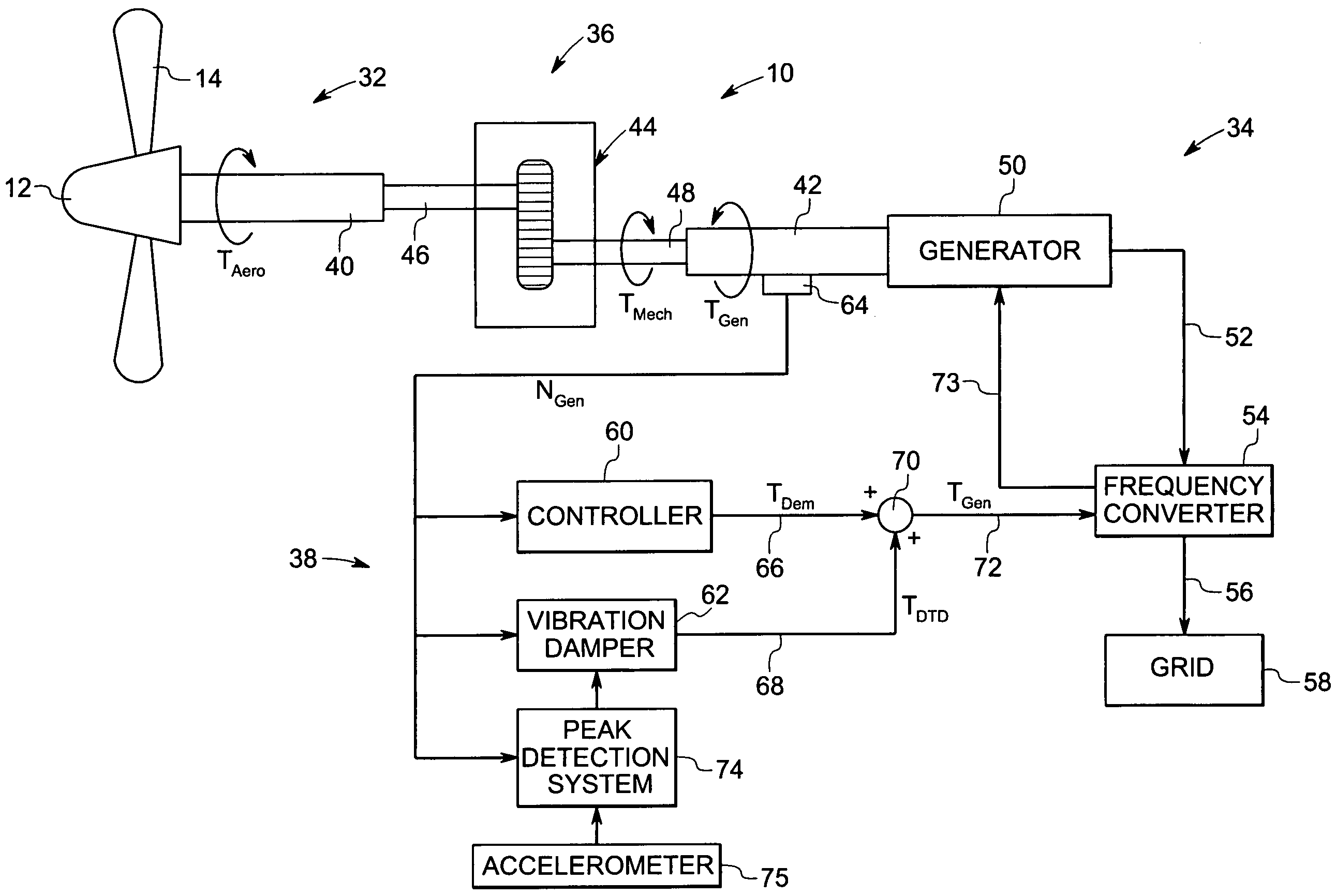
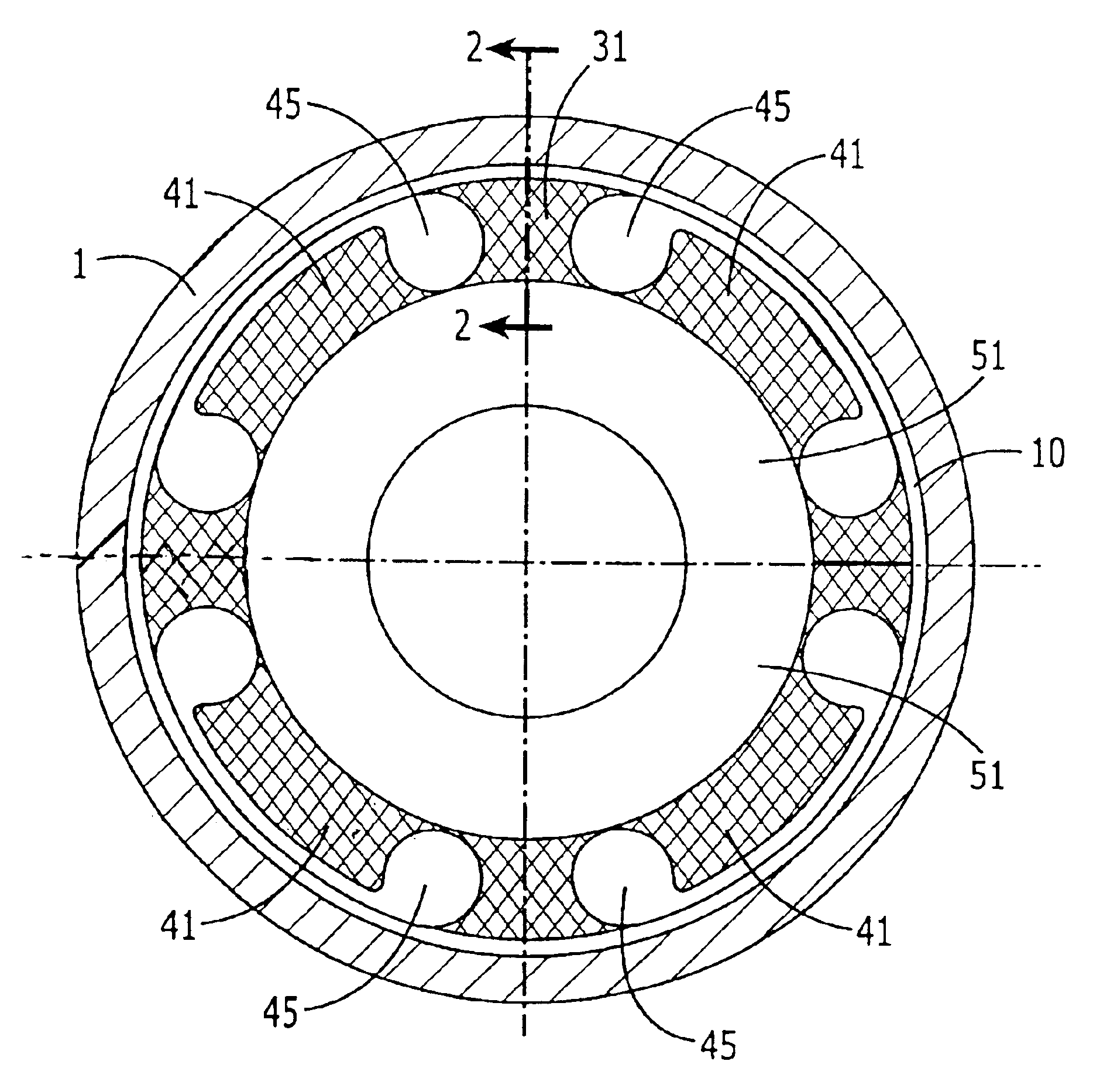
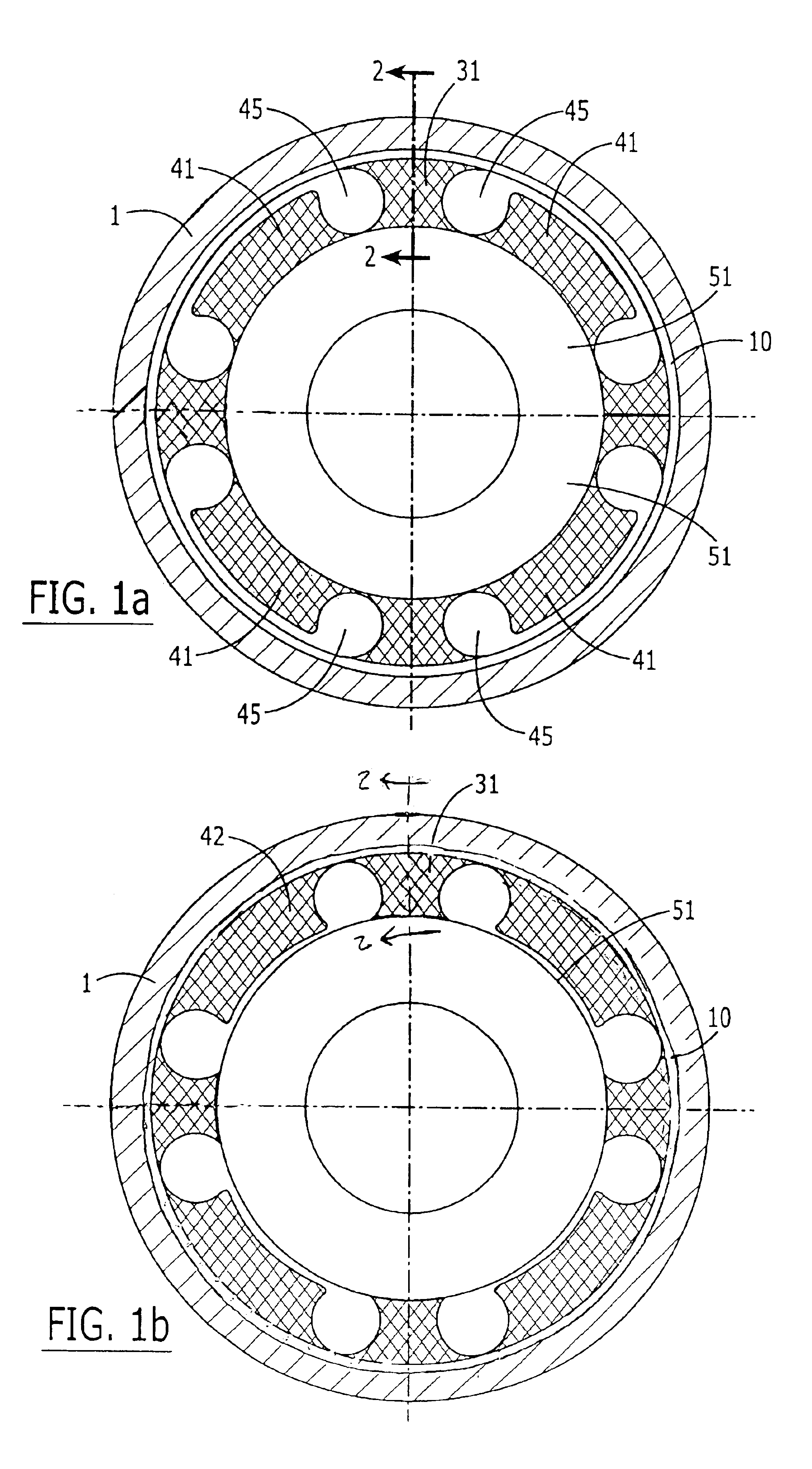
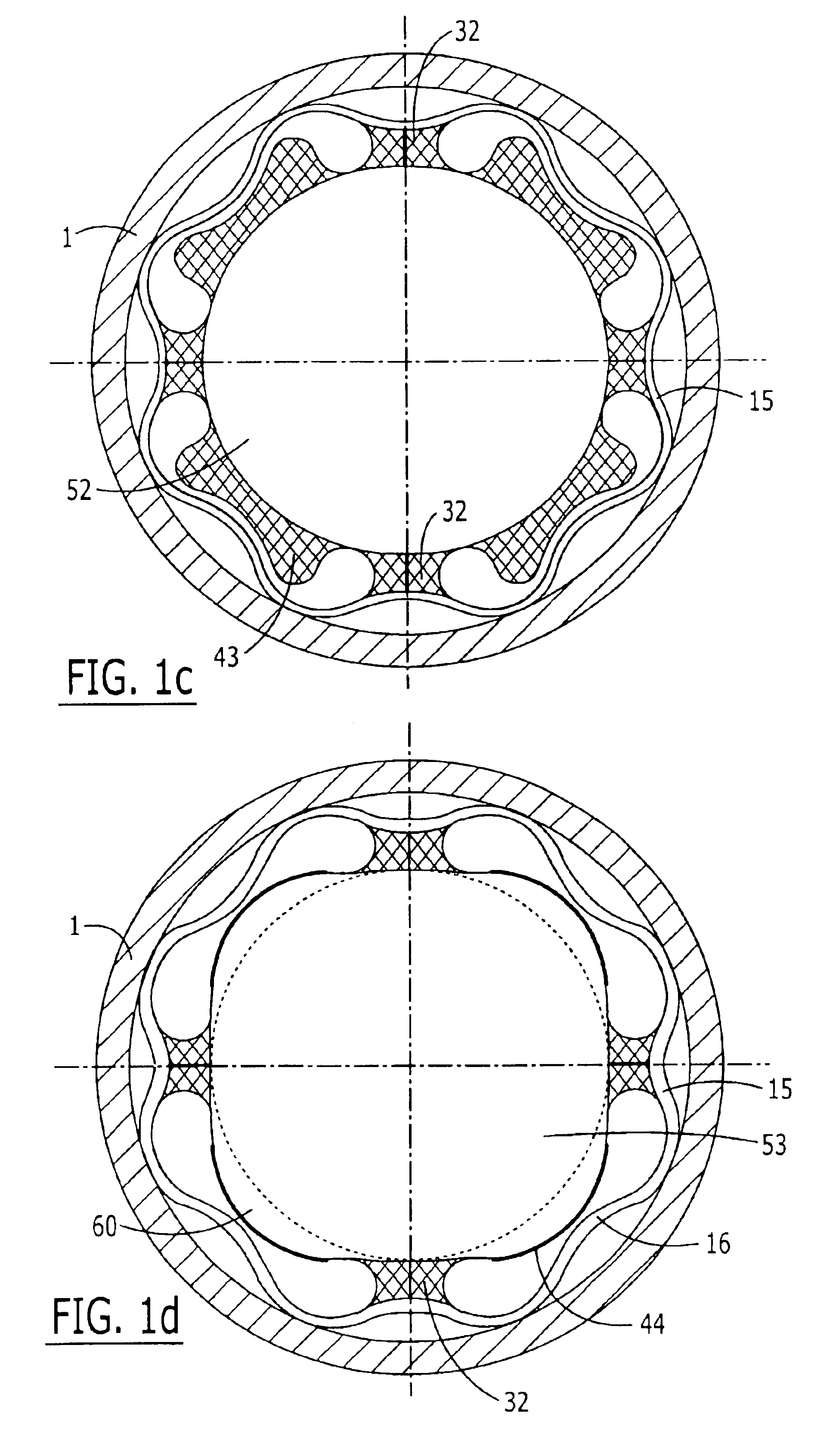
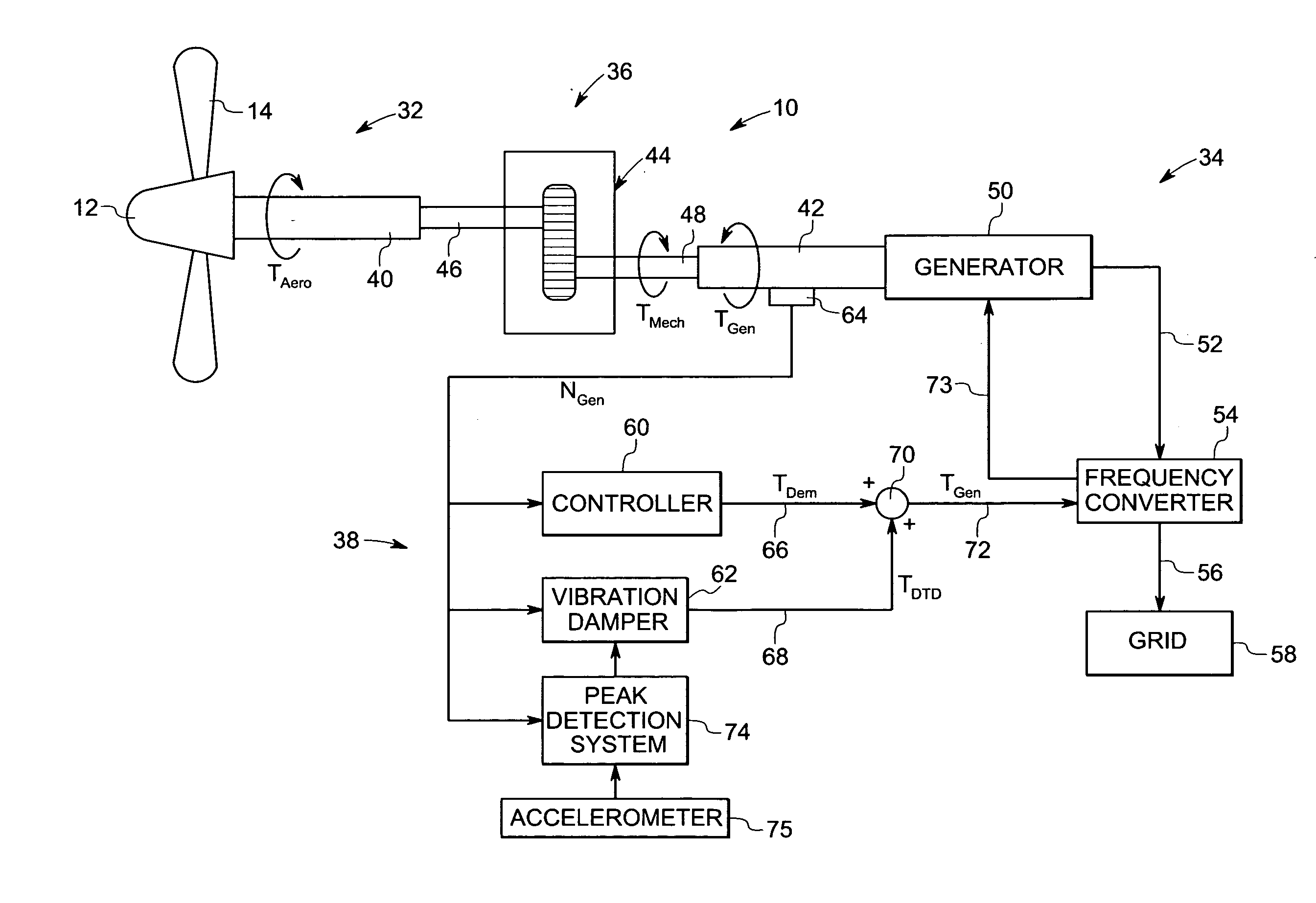
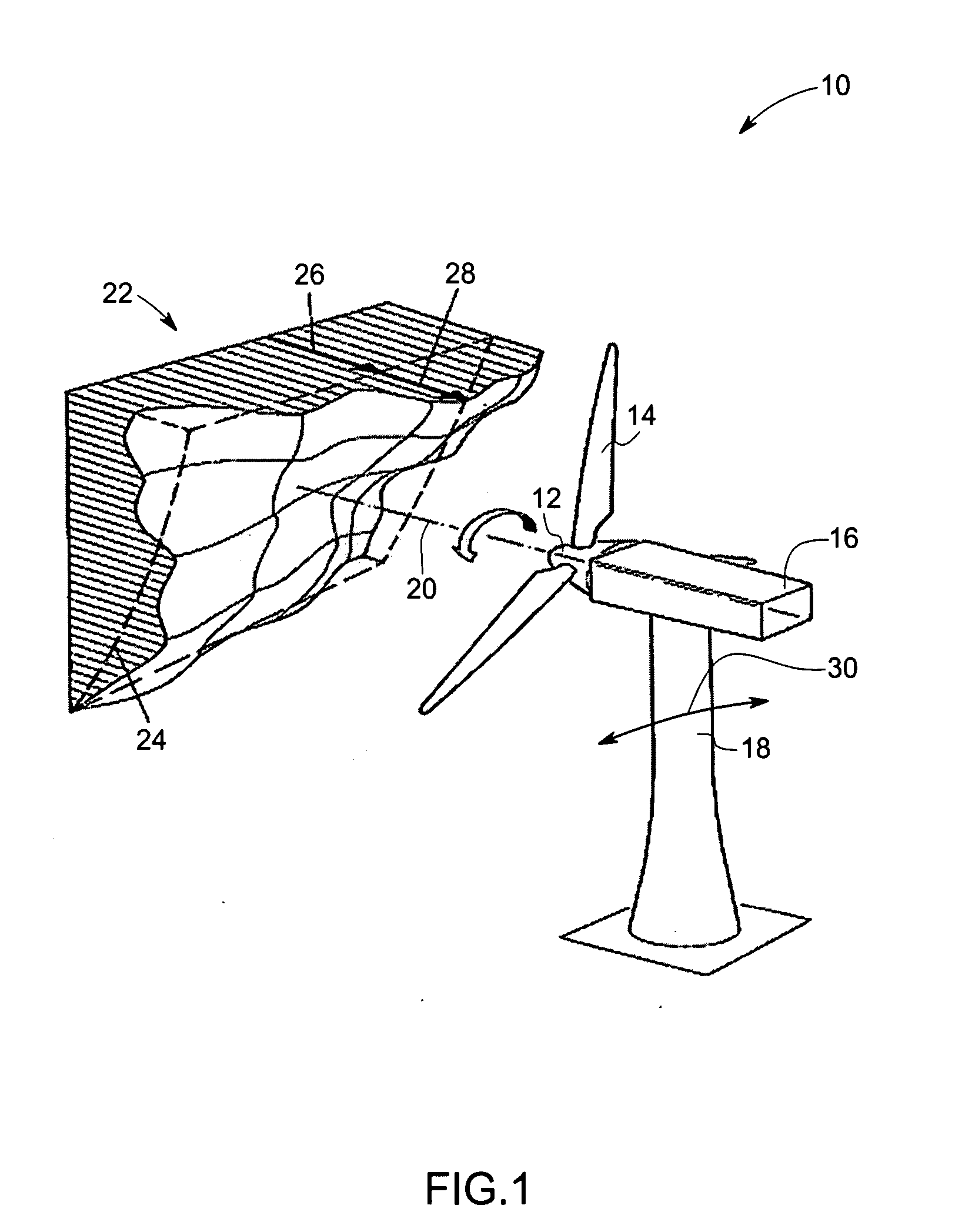
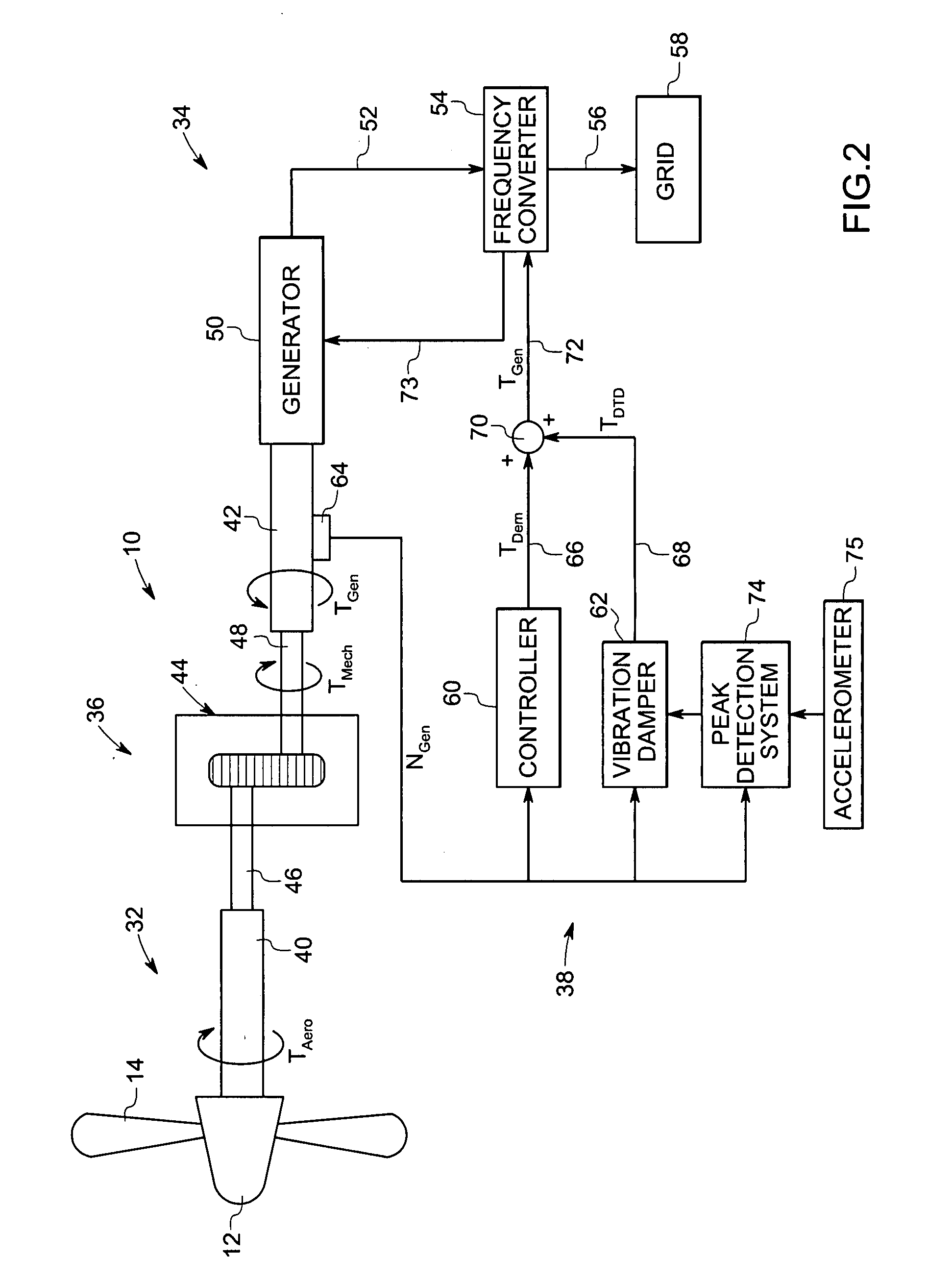
Vibration damping system and method for variable speed wind turbines
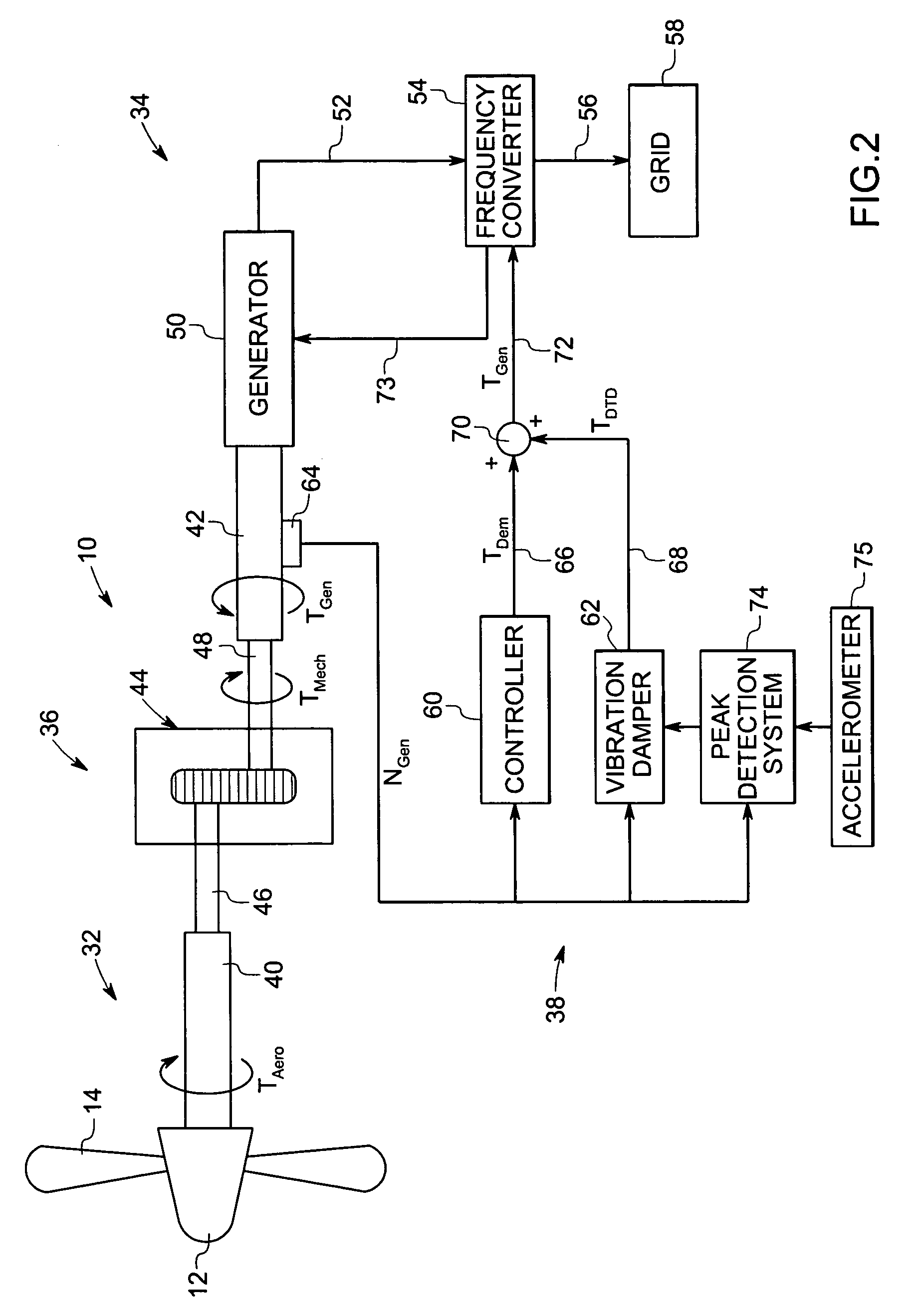
A vibration damping technique for a wind turbine system is described. The wind turbine system includes a vibration damper, which provides a variable signal to control torque produced by a generator of the wind turbine system. The variable signal is based on generator speed and has a first local peak value based on a resonant frequency of tower side-to-side oscillation.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
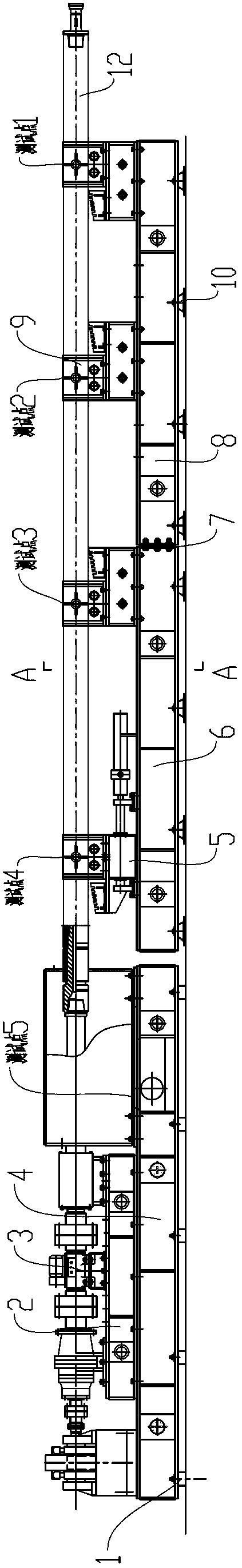
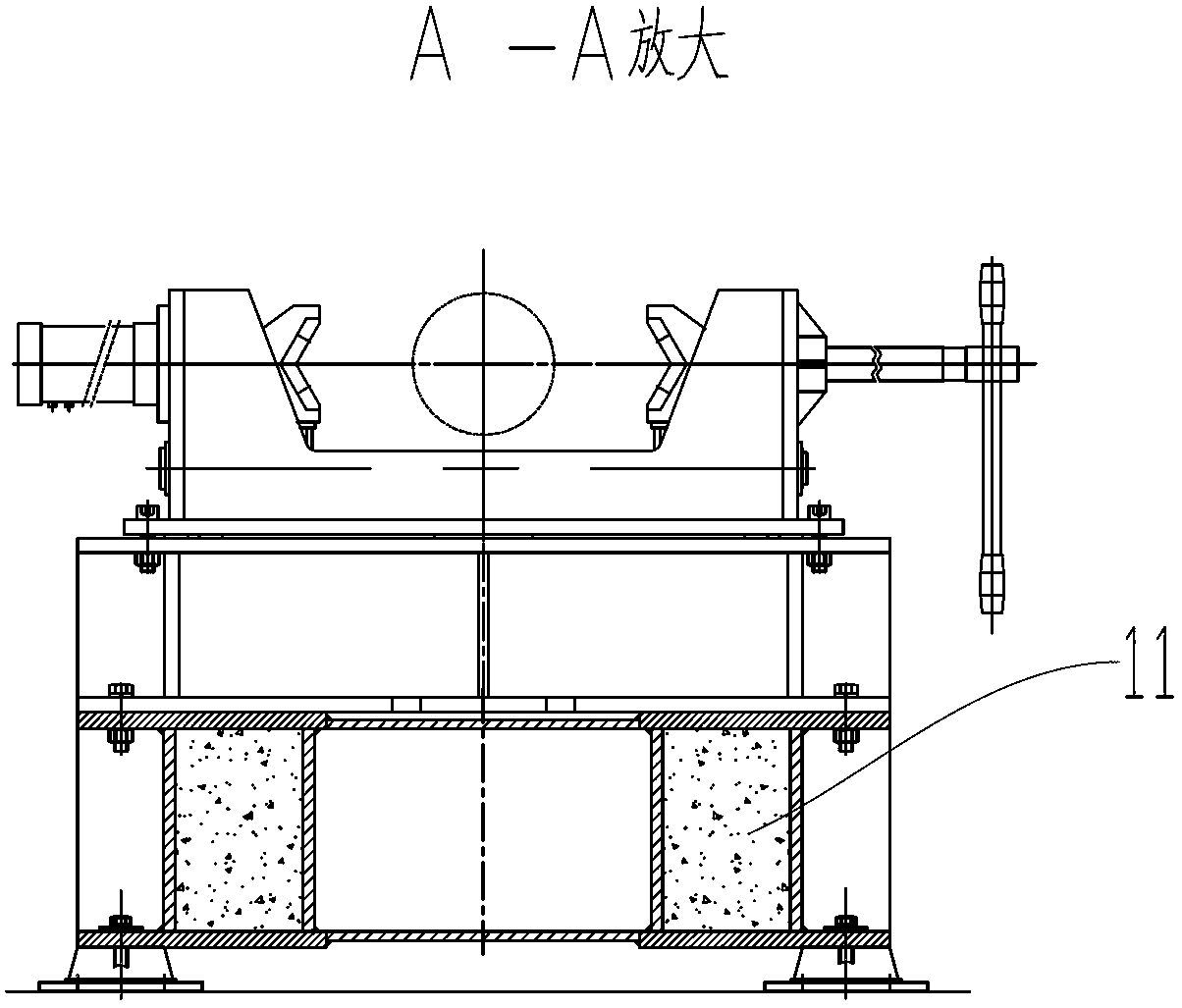
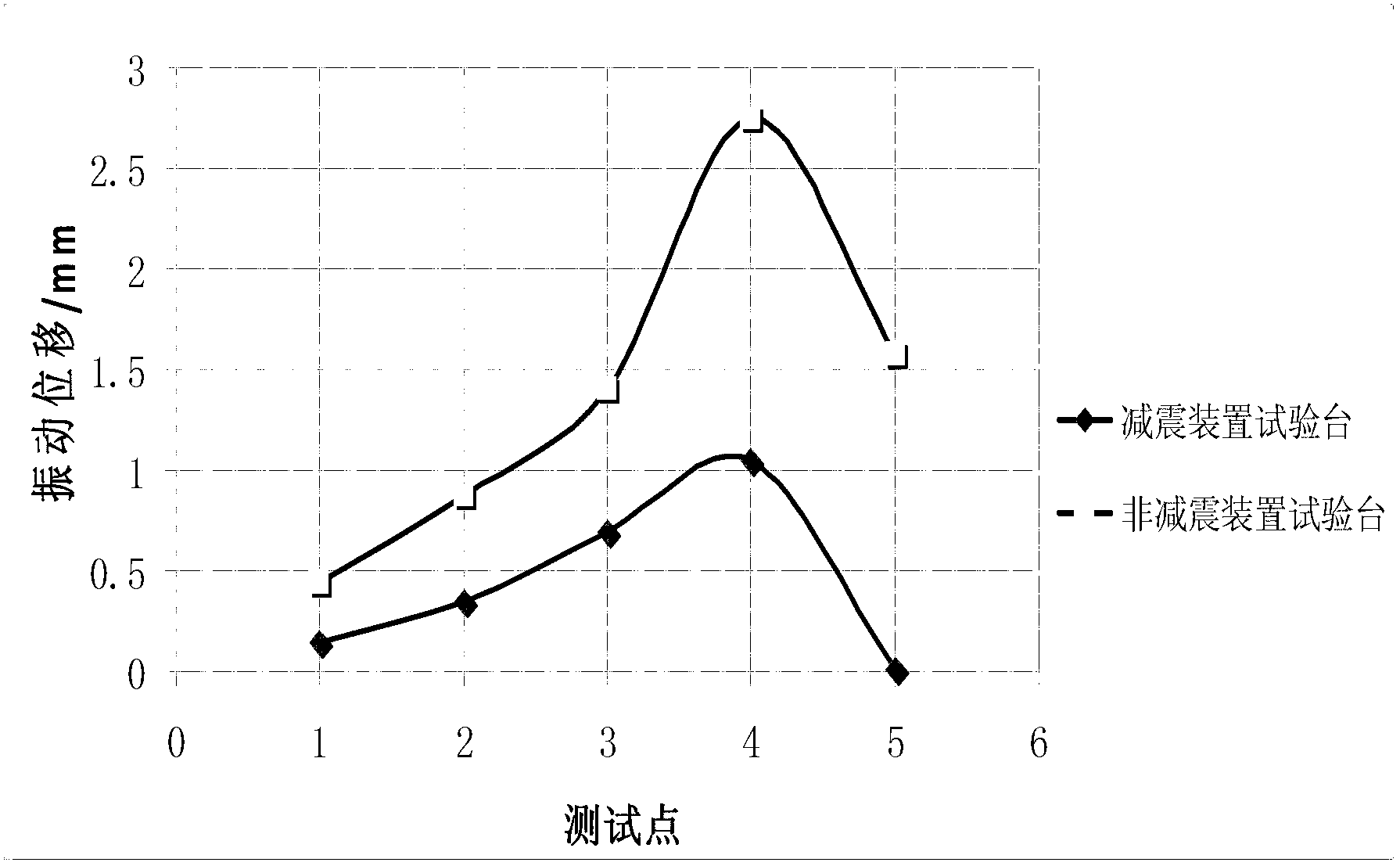
Combined vibration damper of screw drill complete machine test-bed and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN103245523AAchieve test accuracyThe test data is accurateStructural/machines measurementVibration attenuationResonance
The invention discloses a combined vibration damper of a screw drill complete machine test-bed and a manufacturing method thereof. The combined vibration damper comprises a vibration attenuation base which comprises a loading system base, a first clamping system base and a second clamping system base, wherein the loading system base is arranged on an equipment foundation in a rigidity way; the first clamping system base and the second clamping system base are connected into a whole through a bolt and are arranged on the equipment foundation through a rubber vibration attenuation block; an interval of 30-50 mm is reserved between the loading system base and each clamping system base; the first clamping system base and the second clamping system base are respectively internally provided with a plurality of cubic cavities with an equal size; the volume of each cubic cavity is 0.1-0.2 cubic meter; discrete type balance weight sand is respectively filled into the cubic cavities, and the filling efficiency is 80-90 %; and the weight of the balance weight sand is 25-35 % of the total weight of the whole device. The test-bed is capable of restraining resonance and testing precisely in the testing process by the combined vibration damper, and the usage precision of surrounding working devices is not affected.
Owner:DEZHOU UNITED GASOLINEEUM MACHINERY
Vibration damping system and method for variable speed wind turbines
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Spring carrier with adustable spring collar
InactiveUS7469910B2Easy to assembleIncrease elasticityNon-rotating vibration suppressionResilient suspensionsActuatorControl theory
A spring carrier for mounting a spring strut to a vehicle body includes a vibration damper having a cylinder and a piston rod which is axially guided in the cylinder, first and second spring collars, and a spring located between the spring collars. An actuator includes a nut and a threaded spindle surrounding the piston rod, the actuator being driven to change the relative axial position of the spring collars. A guide tube extends coaxially between the piston rod and the threaded spindle, the guide tube being fixed to the vehicle body by a first resilient mount, the piston rod being fixed to the guide tube by a second resilient mount, whereby the piston rod can move relative to the first resilient mount.
Owner:ZF FRIEDRICHSHAFEN AG
Spring carrier with adjustable spring collar
InactiveUS20060163787A1Easy to assembleIncrease elasticitySpringsNon-rotating vibration suppressionEngineeringActuator
A spring carrier for mounting a spring strut to a vehicle body includes a vibration damper having a cylinder and a piston rod which is axially guided in the cylinder, first and second spring collars, and a spring located between the spring collars. An actuator includes a nut and a threaded spindle surrounding the piston rod, the actuator being driven to change the relative axial position of the spring collars. A guide tube extends coaxially between the piston rod and the threaded spindle, the guide tube being fixed to the vehicle body by a first resilient mount, the piston rod being fixed to the guide tube by a second resilient mount, whereby the piston rod can move relative to the first resilient mount.
Owner:ZF FRIEDRICHSHAFEN AG
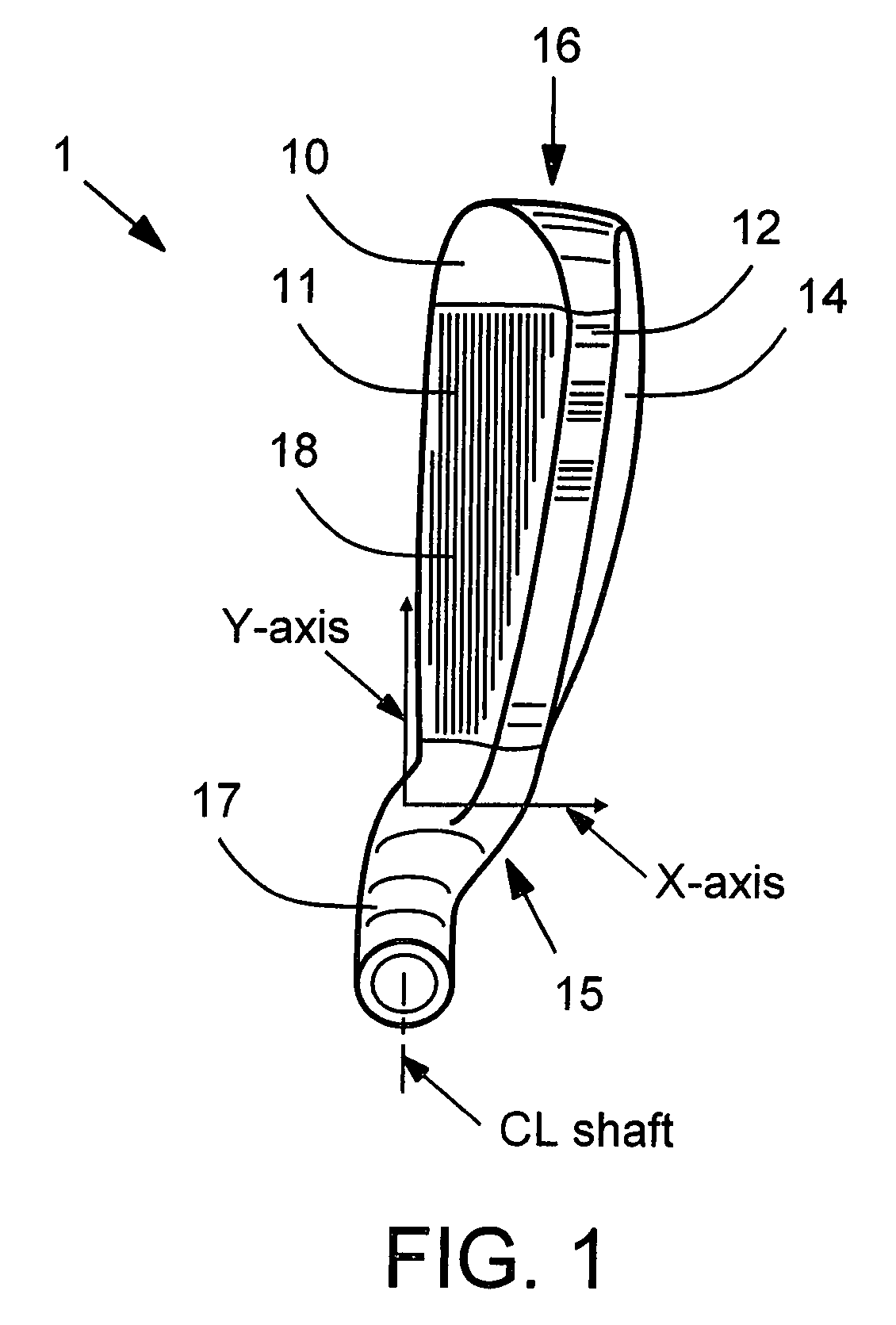
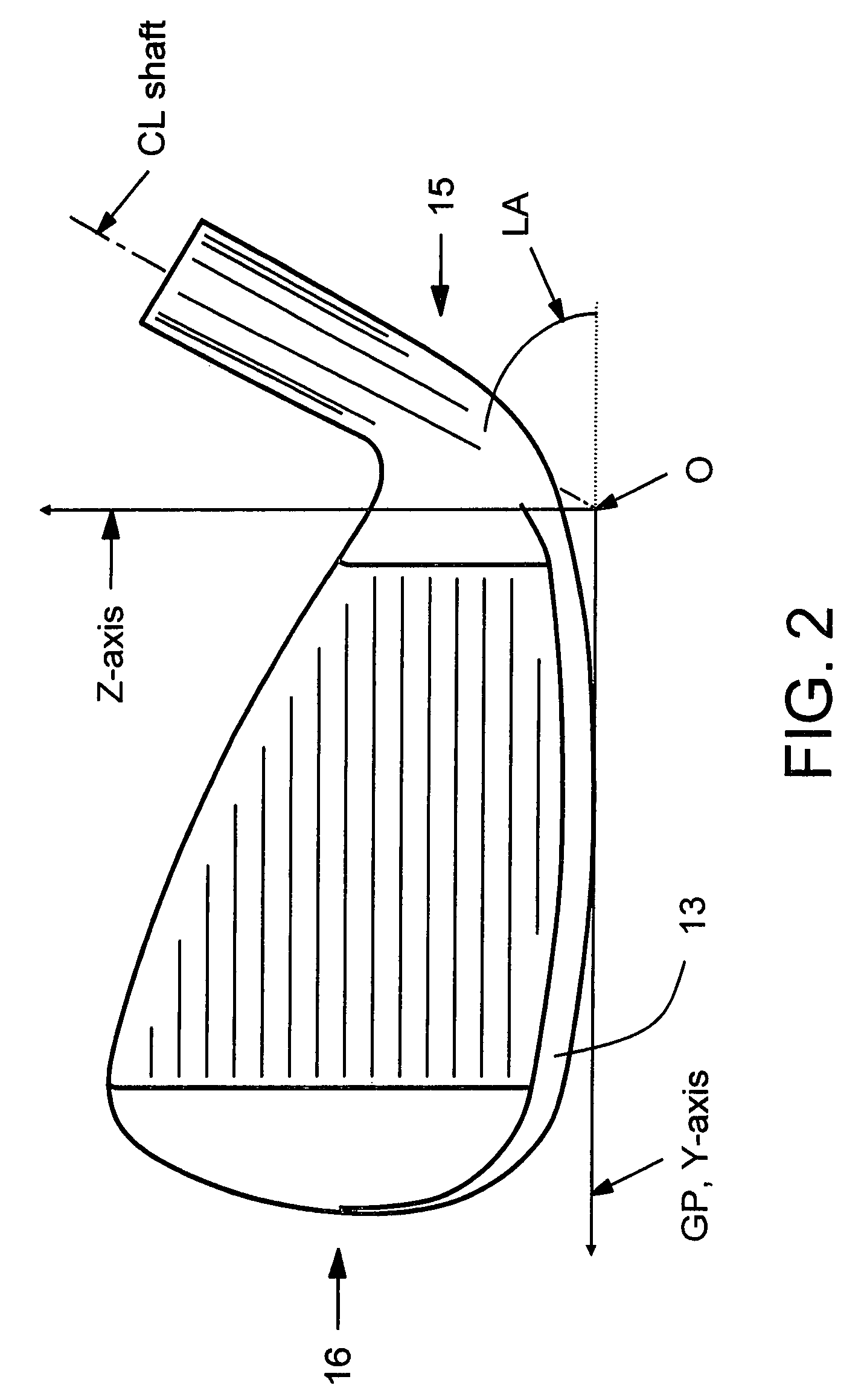
Multi-material golf club head
ActiveUS7922604B2Increase in sizeGreater club head moment of inertiaGolf clubsRacket sportsMulti materialMetallic materials
A golf club head formed of multiple materials is disclosed. Those portions of the club head that are subject to high stresses during normal use of the golf club head are formed of a metallic material. Most of the material beyond what is required to maintain structural integrity, however, is removed and replaced with a lightweight material. This freed-up mass that can be redistributed to other, more beneficial locations of the club head. The lightweight material also damps vibrations generated during use of the golf club. This vibration damper may be retained in a state of compression to enhance the vibration damping. One or more weight members may be included to obtain desired center of gravity position, moments of inertia, and other club head attributes.
Owner:COBRA GOLF
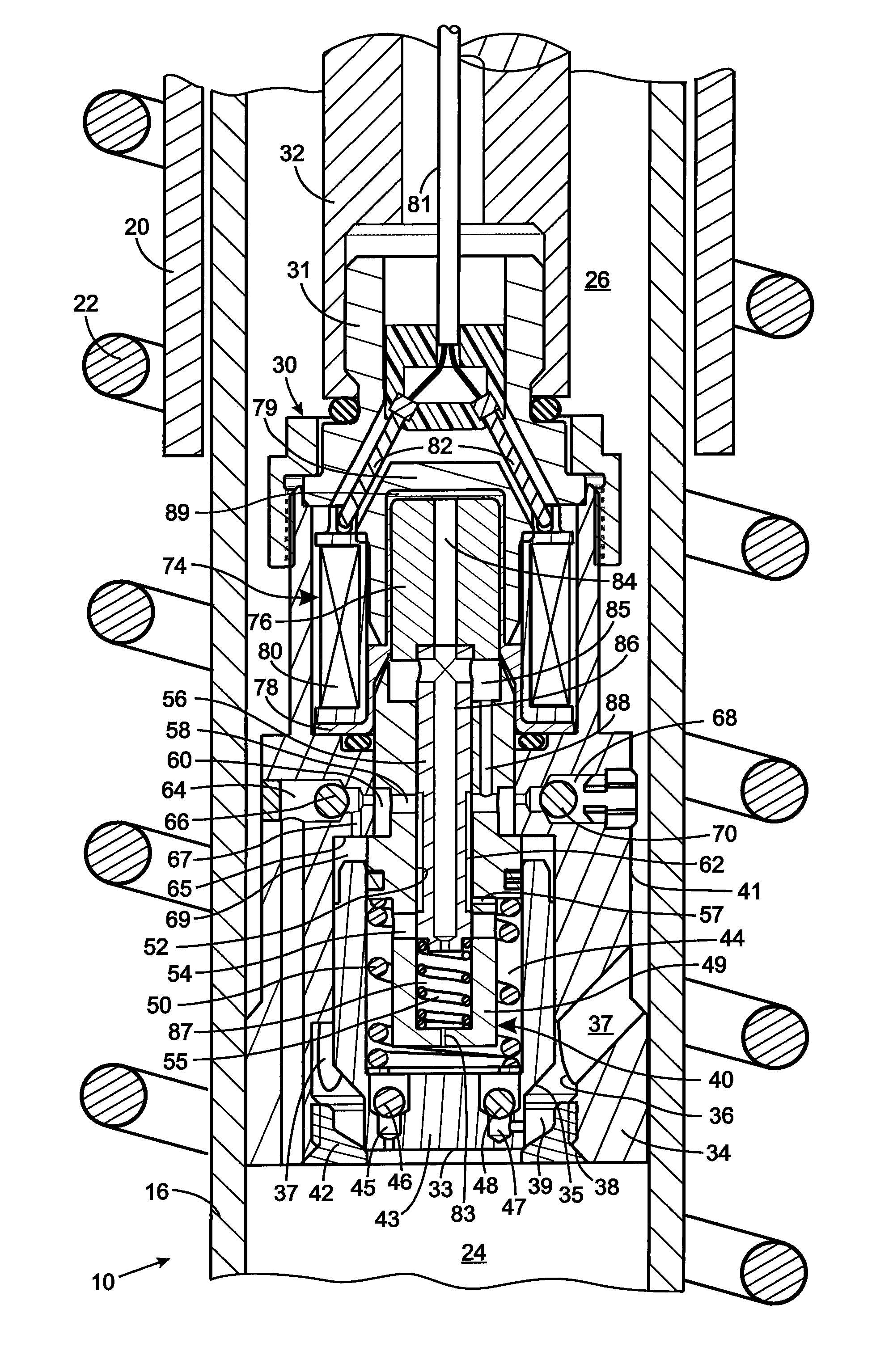
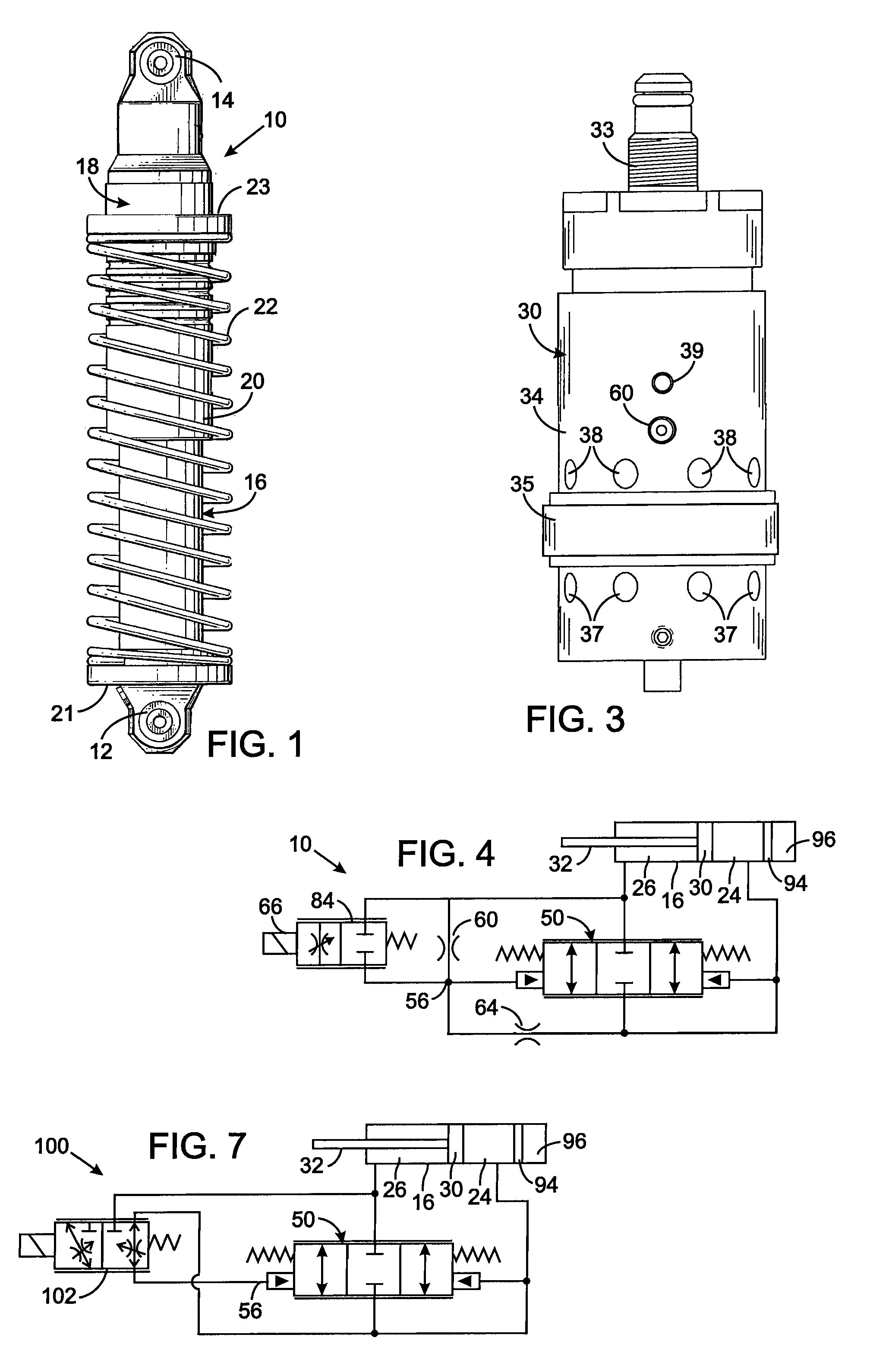
Piston With An Integral Electrically Operated Adjustment Valve For A Hydraulic Vibration Damper
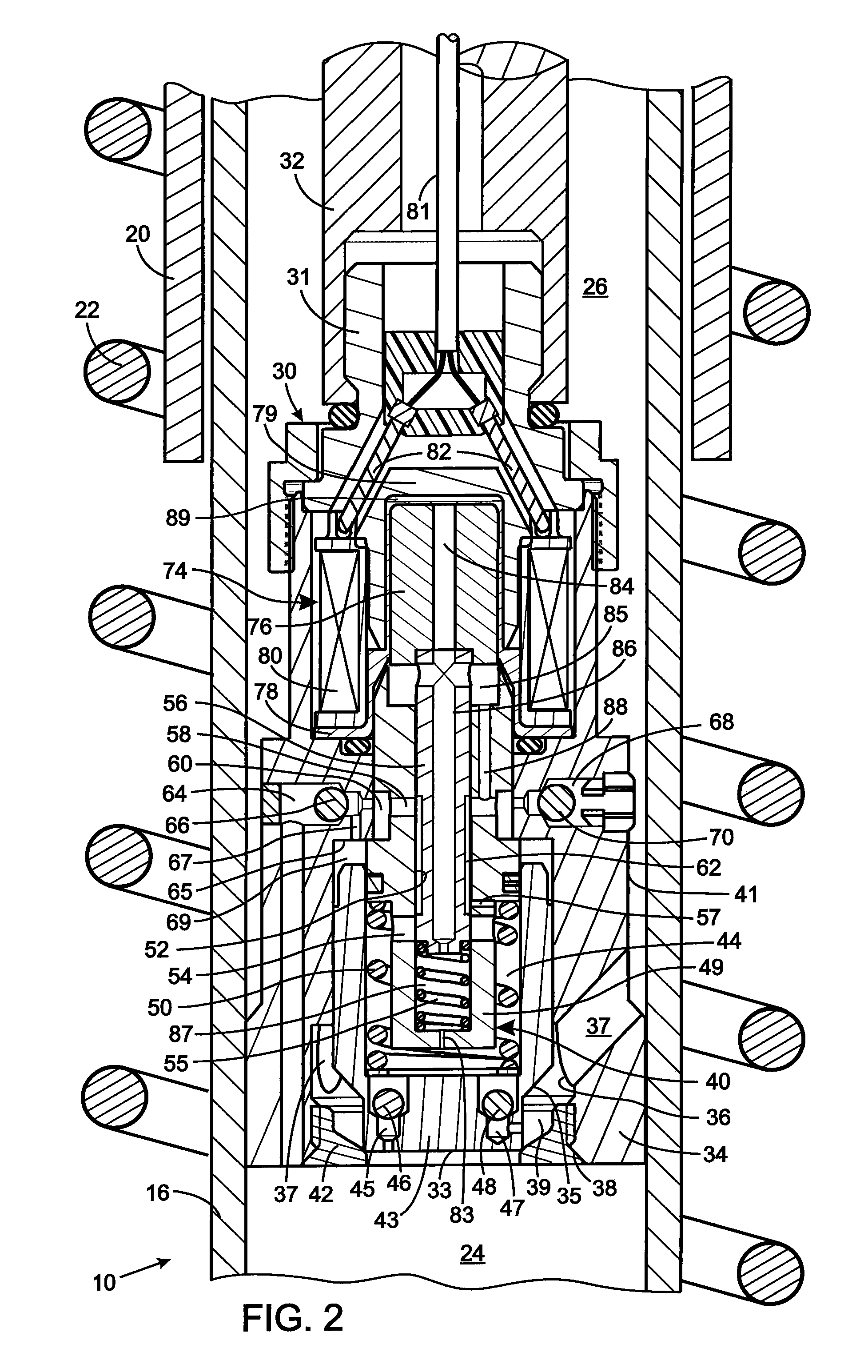
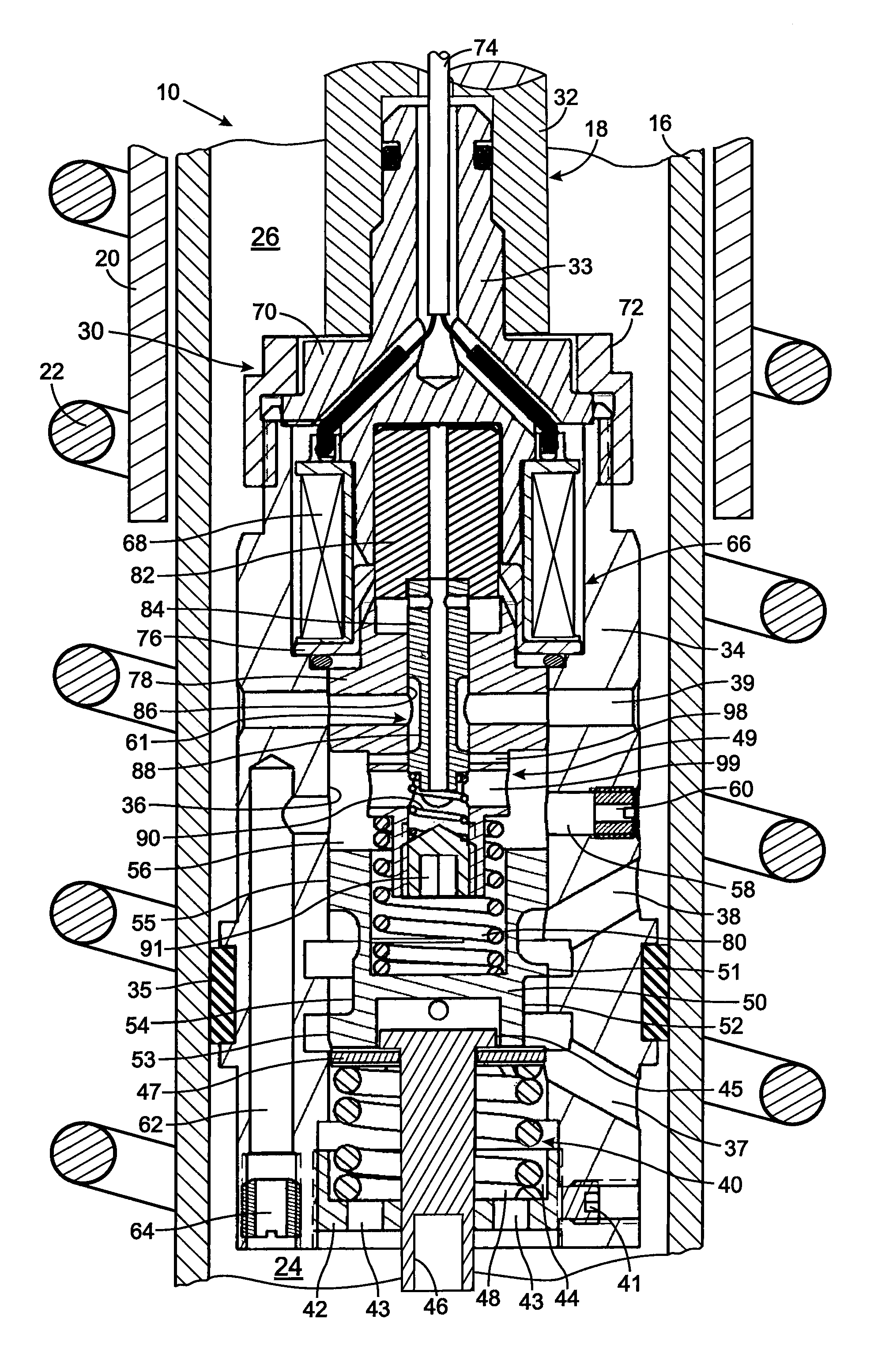
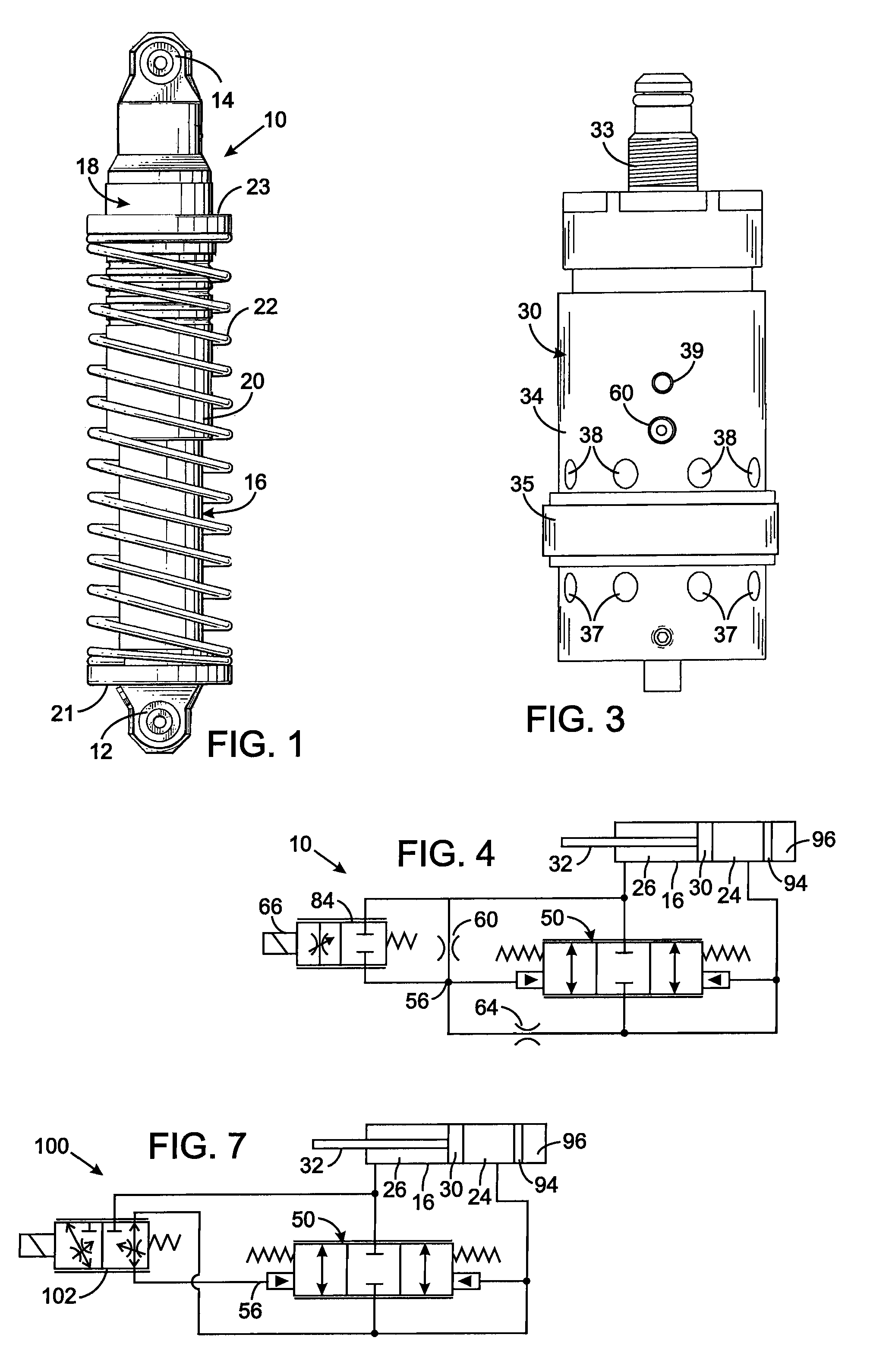
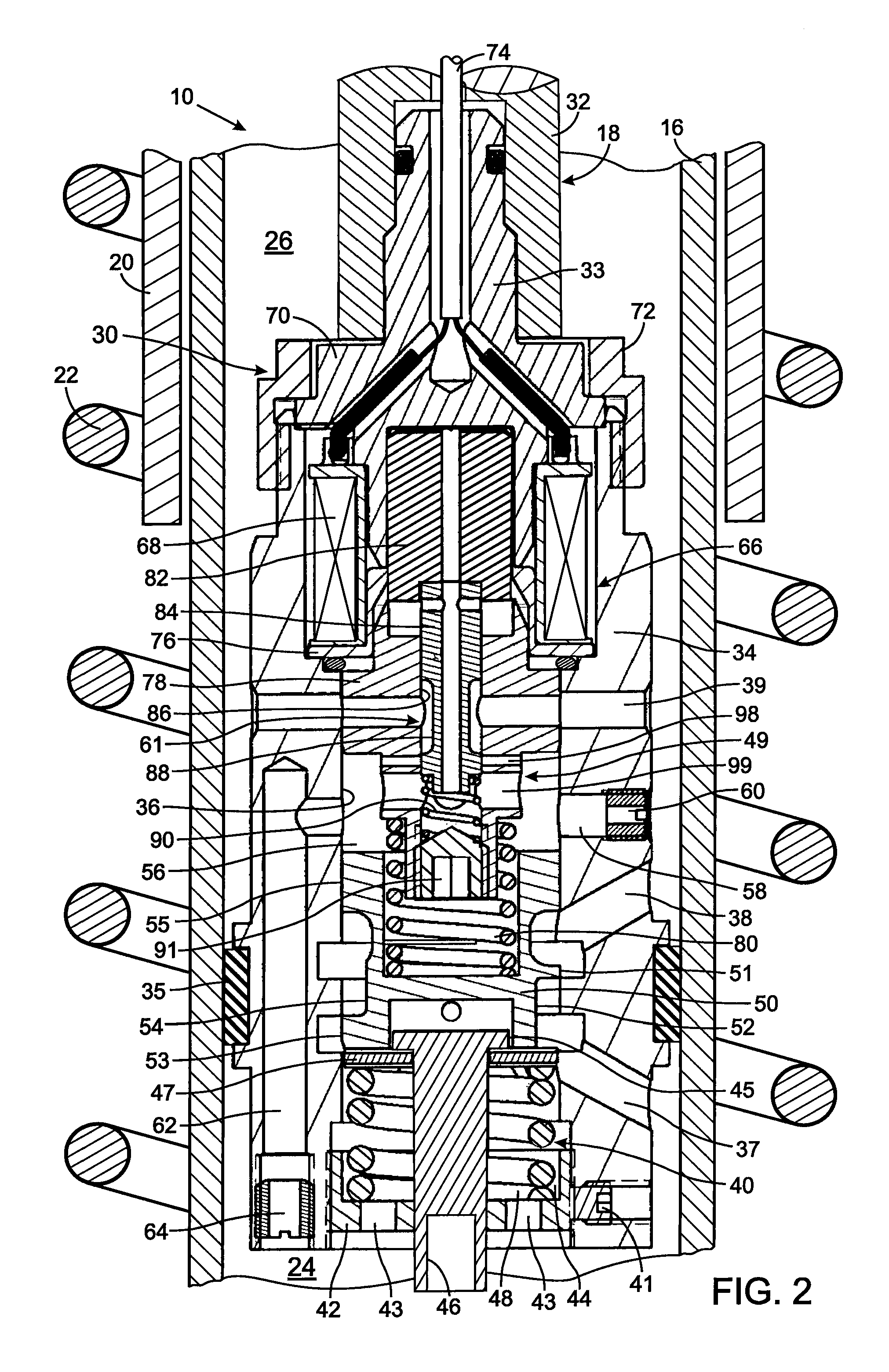
A vibration damper includes a cylinder within which a piston is slidably received thereby defining compression and rebound chambers. The piston has a bore with a valve seat through which fluid flows between those chambers. A poppet selectively engages the valve seat and forms a pilot chamber an opposite side of the poppet from the valve seat. The greater pressure within the compression or rebound chambers is applied by a first logic arrangement to the pilot chamber and a pilot spool control a fluid flow between the pilot chamber and a pressure cavity in the piston body. A second logic arrangement connects the pressure cavity to either the compression and rebound chamber which has the lesser pressure. A solenoid that moves the pilot valve element to control pressure in the pilot chamber and thus the amount that the poppet moves to allow fluid flow through the piston.
Owner:HUSCO AUTOMOTIVE HLDG
Hydraulic vibration damper piston with an integral electrically operated adjustment valve
A vibration damper piston includes a piston body with a bore from which first and second apertures respectively provide paths to first and second chambers of the vibration damper. A valve spool in the bore defines a pilot chamber and controls fluid flow between the first and second apertures. First and second springs bias the valve spool in opposing directions. A control orifice provides a continuous fluid path between the first chamber and the pilot chamber, and a variable orifice provides another fluid path between the second chamber and the pilot chamber. An actuator is operably connected to adjust the variable orifice in response to a control signal.
Owner:HUSCO AUTOMOTIVE HLDG
DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) sequencer
ActiveCN102703312AImprove sequencing efficiencyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatments3-deoxyriboseBiochemical engineering
The invention discloses a DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) sequencer which comprises a supporting table, a plurality of vibration dampers, a vibration damping plate, a reaction bin assembly, a CCD (Charge Coupled Device) camera, a two-dimensional regulation supporting device and a medicament supply assembly, wherein the vibration damping plate is connected with the supporting table by a plurality of vibration dampers; the reaction bin assembly is fixedly arranged on the vibration damping plate and is used for performing the DNA sequencing reaction; the CCD camera is used for acquiring an optical signal; the two-dimensional regulation supporting device is used for supporting the CCD camera; and the medicament supply assembly is arranged on the supporting table and is used for providing reagents and buffer solution for the reaction bin assembly. According to the DNA sequencer disclosed by the invention, by the arrangement of a plurality of reaction bins and the matching of the two-dimensional regulation supporting device capable of carrying out two-dimensional regulation and the medicament supply assembly capable of supplying the reagents for a plurality of reaction bins, the aim of simultaneously performing a plurality of reactions is fulfilled, a plurality of samples can be simultaneously sequenced and the DNA sequencing efficiency is greatly improved.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF GENOMICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI CHINA NAT CENT FOR BIOINFORMATION +1
Multi-material golf club head
InactiveUS20080058119A1Increase in sizeGreat club head moment of inertiaGolf clubsRacket sportsMetallic materialsEngineering
A golf club head formed of multiple materials is disclosed. Those portions of the club head that are subject to high stresses during normal use of the golf club head are formed of a metallic material. Most of the material beyond what is required to maintain structural integrity, however, is removed and replaced with a lightweight material. This freed-up mass that can be redistributed to other, more beneficial locations of the club head. The lightweight material also damps vibrations generated during use of the golf club. This vibration damper may be retained in a state of compression to enhance the vibration damping. One or more weight members may be included to obtain desired center of gravity position, moments of inertia, and other club head attributes. A insert formed of multiple materials and having regions of varying thickness may also be included on a rear surface of the club head.
Owner:COBRA GOLF
Vibration damper assembly for the buckets of a turbine
InactiveUS6851932B2Increase dampingRisk minimizationPropellersPump componentsEngineeringControl theory
A damper pin is disposed between adjacent buckets of a turbine rotor. A first bucket has circumferentially extending supports defining a pair of axially spaced surfaces on which a damper pin rests in a cold condition of the turbine. The adjacent bucket is undercut adjacent its platform to provide an angled surface overlying a generally correspondingly angled surface of the damper pin. The damper pin fits slightly loose within the recess and, upon turbine rotation at speed, the angled surfaces of the damper pin and recess cooperate to bias the damper pin against the first bucket whereby the damper pin engages both buckets and dissipates vibratory action.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
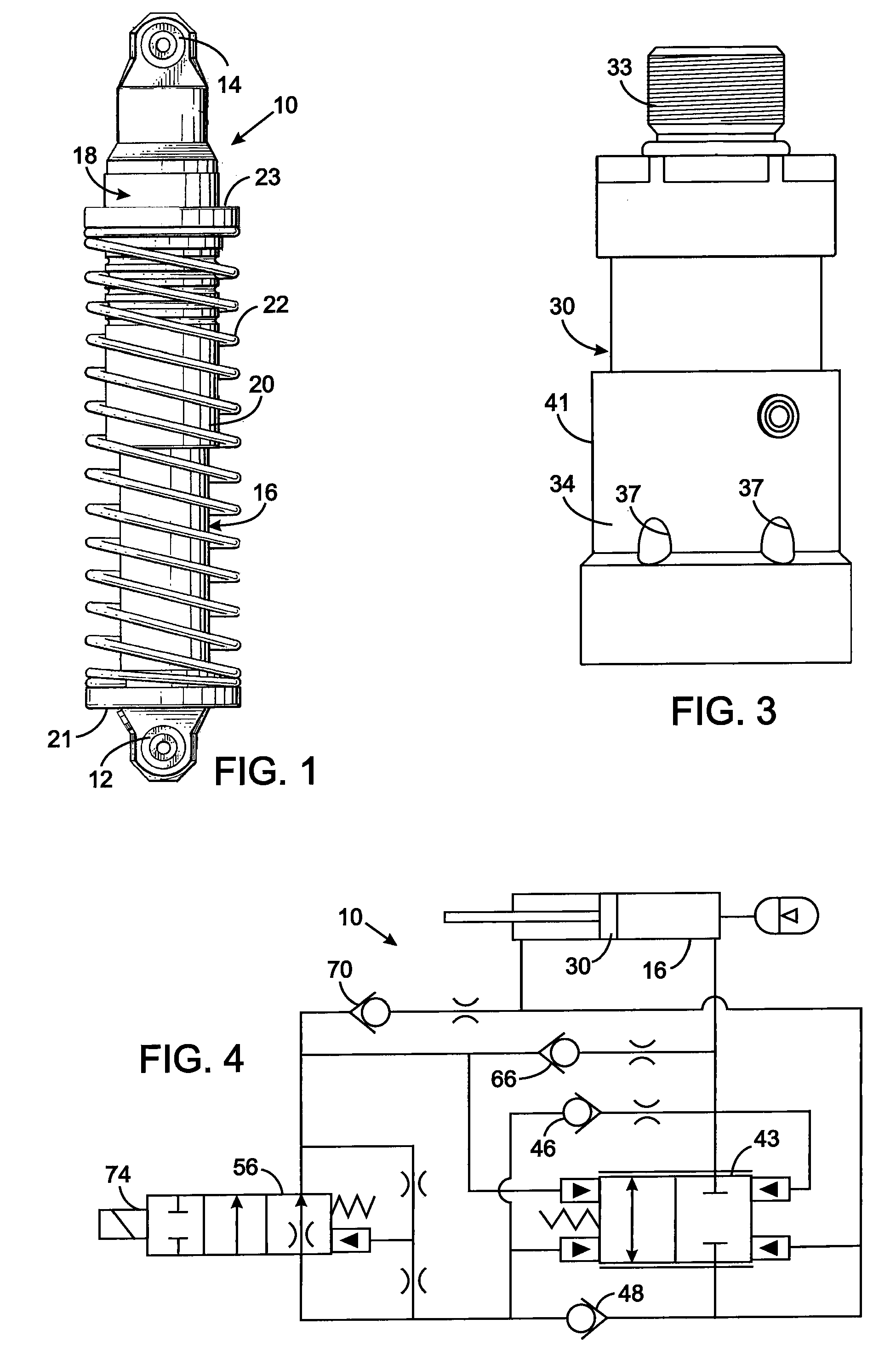
Valve which reacts as a function of pressure, especially for a vibration damper
InactiveUS6305512B1Reduce thermal resistanceIncrease control pressureSpringsSprings/dampers design characteristicsMechanical engineeringVibration damper
A pressure operated valve is provided including an adjusting device, a spring and a vent connection. The adjusting device is axially movably arranged in a pressure chamber defined in the valve and comprises a valve body and a pressure intensifier. A space between the valve body and valve face defines a valve passage cross section. The spring is operatively arranged for holding the pressure intensifier in a floating arrangement in the pressure chamber. The pressure intensifier has a first side exposed to a pressure in the pressure connection opening and a second side facing away from the pressure connection opening. The second side of the pressure intensifier and the adjusting device define a low pressure chamber within the pressure chamber. The vent connection is an inflow restrictor arranged between the lower pressure chamber and a space having a lower pressure than the low pressure chamber.
Owner:ZF FRIEDRICHSHAFEN AG
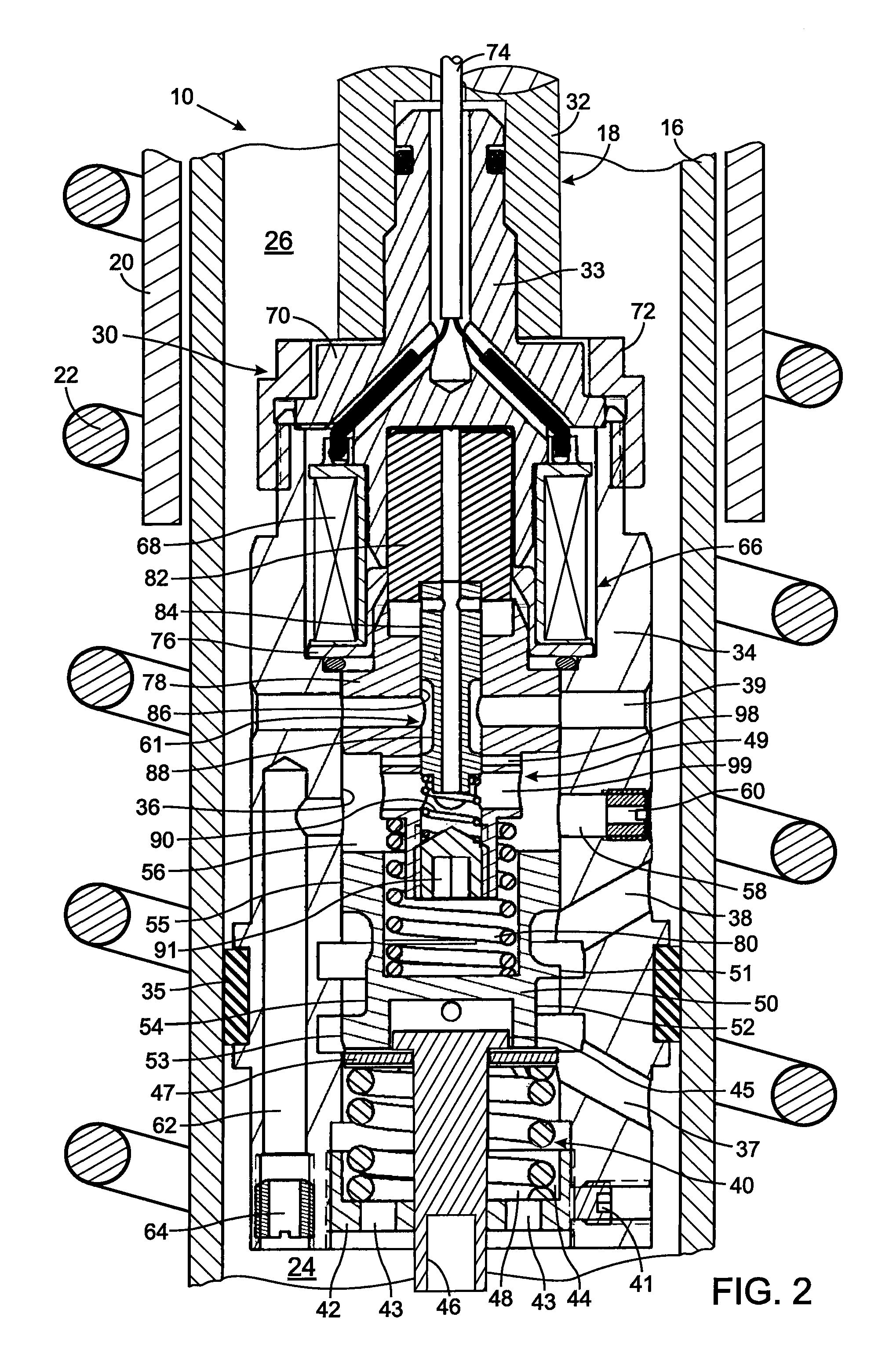
Vibration damper with adjustable damping force
InactiveUS8307965B2Efficient designMinimize consequencesSpringsLiquid based dampersControl theoryPiston rod
The vibration damper with an adjustable damping force includes a cylinder filled with a damping medium, a piston rod axially movable in the cylinder and carrying a piston which divides the cylinder into a first working space on the piston rod side and a second working space on the side away from the piston rod, a first adjustable damping valve which is connected to at least one of the two working spaces by means of a fluid connection, at least one second valve which is connected hydraulically in parallel to the first adjustable damping valve, and a third damping valve arranged in series to and upstream from both the first and second valves, the third damping valve moving in a closing direction as a function of a flow velocity of the damping medium through the third damping valve.
Owner:ZF FRIEDRICHSHAFEN AG
Hydraulic vibration damper piston with an integral electrically operated adjustment valve
A vibration damper piston includes a piston body with a bore from which first and second apertures respectively provide paths to first and second chambers of the vibration damper. A valve spool in the bore defines a pilot chamber and controls fluid flow between the first and second apertures. First and second springs bias the valve spool in opposing directions. A control orifice provides a continuous fluid path between the first chamber and the pilot chamber, and a variable orifice provides another fluid path between the second chamber and the pilot chamber. An actuator is operably connected to adjust the variable orifice in response to a control signal.
Owner:HUSCO AUTOMOTIVE HLDG
Torsional vibration damper
A torsional vibration damper on the bridging clutch of a hydrodynamic clutch arrangement has a first connecting device, which can be brought into working connection with the clutch housing and with a drive-side transmission element. The drive-side transmission element is connected via first energy-storage devices to an intermediate transmission element. The torsional vibration damper also has a second connecting device for establishing a working connection via second energy-storage devices between the intermediate transmission element and a takeoff-side transmission element, which is connected to a takeoff-side component of the hydrodynamic clutch arrangement. The intermediate transmission element accepts a mass element, located operatively between the two connecting devices.
Owner:ZF FRIEDRICHSHAFEN AG
Damping ratio adjustable tuning quality damper
ActiveCN101457554AChange the damping ratioDamping Ratio OptimizationSpringsSolid based dampersDamping ratioEngineering
The invention specifically relates to a mass tuned vibration reducer used for regulating the subsidence ratio of the vibration of the related structures. The mass tuned vibration reducer comprises a mass block, a spring, a damper and a base, and is characterized in that the damper is an adhesion-type damper formed by a damping cylinder, adhesive damping fluid and a piston, wherein, the piston and the adhesive damping fluid are arranged in the damping cylinder, and at least part of the piston is immerged into the adhesive damping fluid. The mass tuned vibration reducer adopts the adhesion-type damper formed by the adhesive damping fluid and the piston and can provide three dimensional damping, so as to effectively prevent side tumbling and ensure the vibration reducer realizes smooth actions; vibration mass is not needed to be provided with a special guide device, so that the mass tuned vibration reducer has reliable work and higher cost performance, and basically needs no maintenance. Meanwhile, the mass tuned vibration reducer realizes the aim of regulating the natural frequency and the subsidence ratio at any time, thus better exerting the vibration absorption performance of the mass tuned vibration reducer, ensuring stableness and safety of the pedestrians and vehicles on the large-span bridge and the thin and high building, contributing to prolonging the service lives of the thin and high building and the bridge, and having remarkable economic and social benefits.
Owner:尹学军 +1
Composite acoustic attenuation materials
InactiveUS7263028B2Enhancing acoustic attenuation and vibration dampingImprove structural performanceCeilingsWallsAcoustic energyAcoustic impedance
The present invention provides means of enhancing the acoustic attenuation and vibration damping of a material by (1) embedding a plurality of small particles of either a high characteristic acoustic impedance or a low characteristic acoustic impedance or combinations of high and low characteristic acoustic impedance materials to form a matrix material to act as a acoustic attenuator or vibration damper; and (2) combing this matrix material with a second layer of a decoupling material that serves to effectively isolate the matrix material and reduce its tendency to vibrate sympathetically to the impinging acoustic energy. The mass of the resultant material may be very low while retaining excellent acoustic attenuation, vibration damping, and structural characteristics.
Owner:THE GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE NAVY NAVAL RES LAB WASHINGTON +1
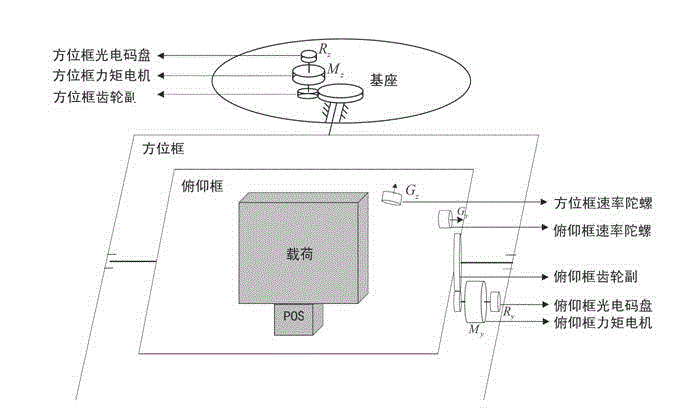
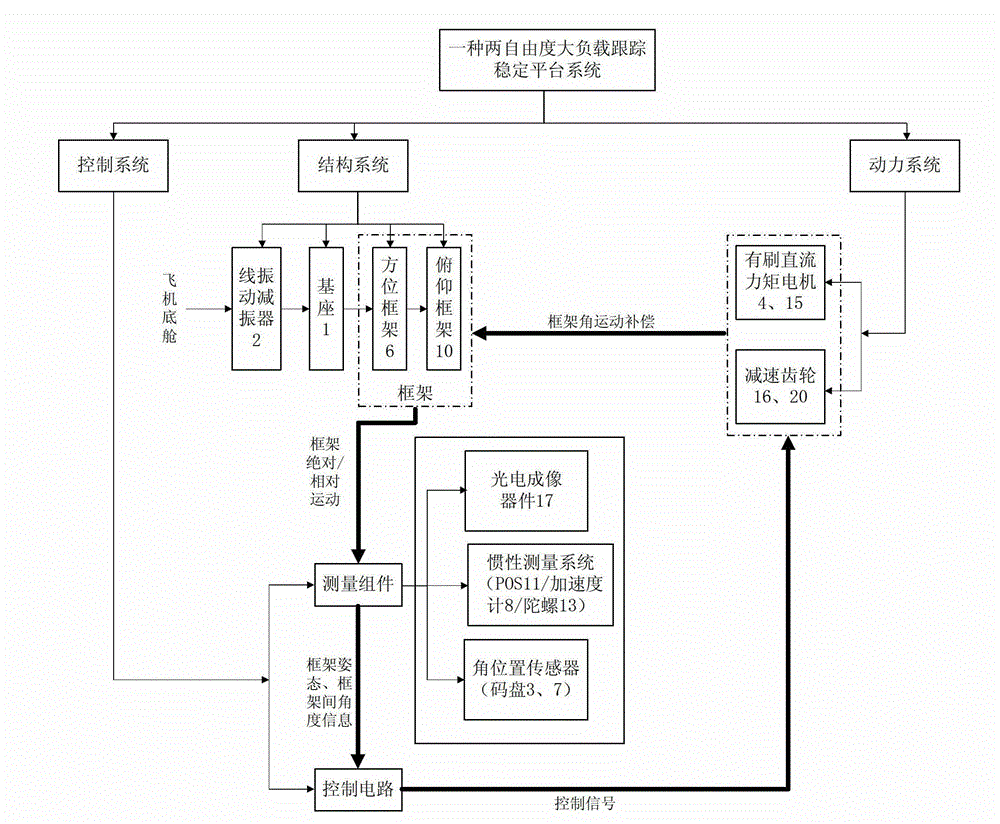
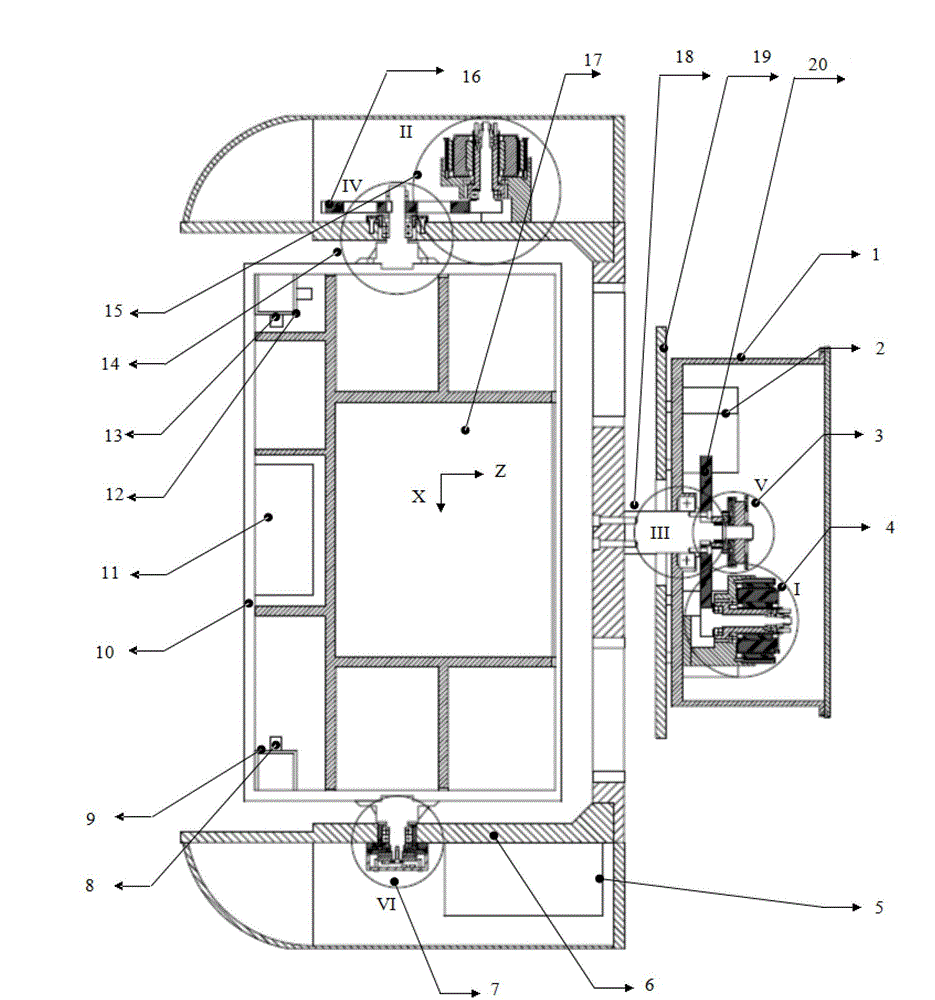
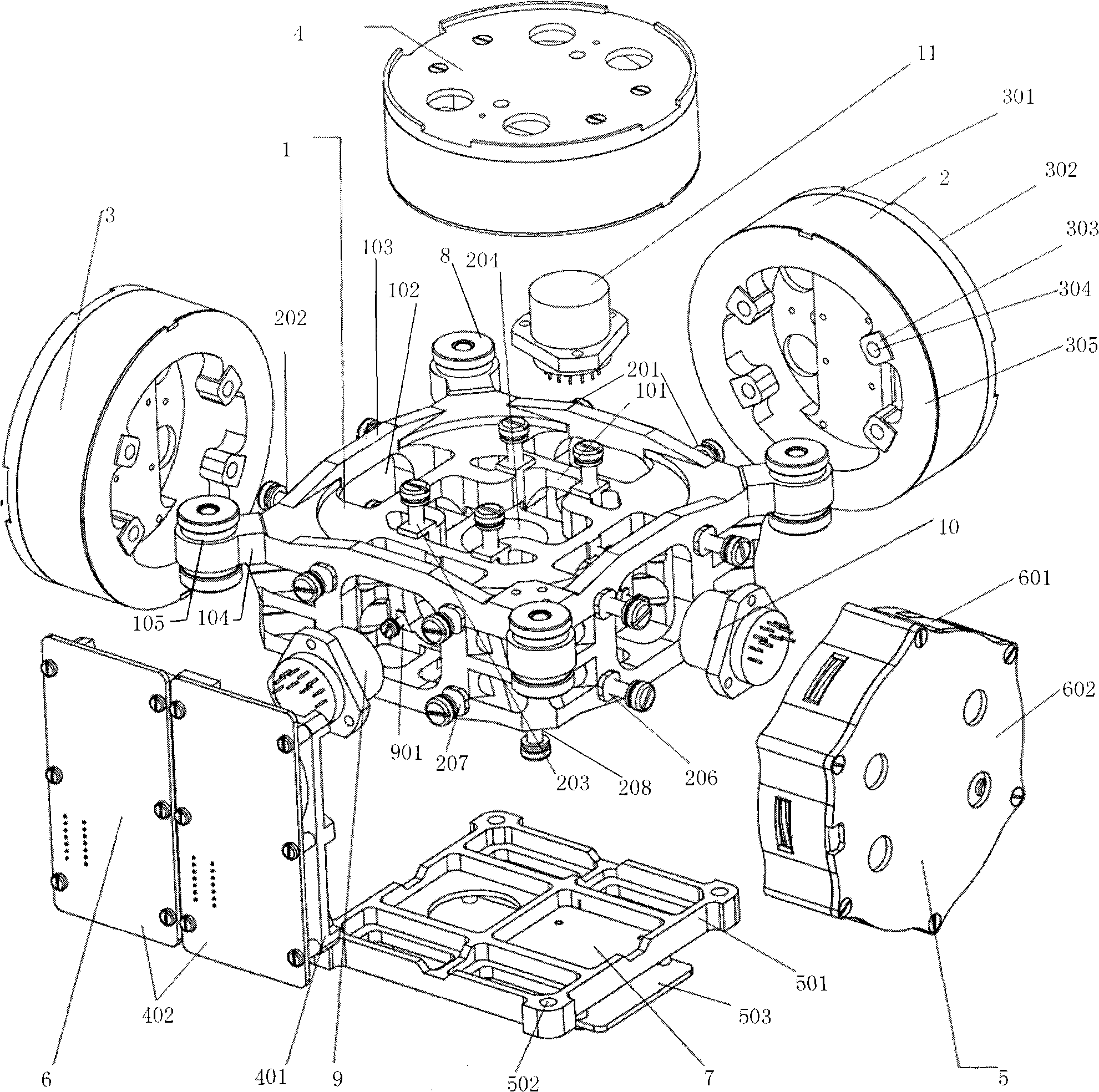
Two-freedom-degree heavy-load tracking stabilized platform system
ActiveCN103149948AOvercome the disadvantages of large load volumeLoad largeNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsControl using feedbackAviationGyroscope
The invention relates to a two-freedom-degree heavy-load tracking stabilized platform system which comprises a base, four line vibration dampers, a position framework, a pitching framework, external loads (a photoelectric imaging device, two micro-electromechanical system (MEMS) accelerometers two MEMS gyroscopes and a position orientation system (POS)), two direct current (DC) torque motors with brushes, two photoelectric coded discs and two framework control circuits. The base is connected with an airplane through line vibration dampers for isolating airplane line vibration. The position framework is supported by the base and carries a pitching frame component to achieve gyration within 0 degree to 360 degrees. The pitching framework is supported by a position frame and carries external loads to achieve gyration within -90 degrees to 0 degree. A control part drives a motor to enable the framework to rotate according to frame angular rate information which is provided by the gyroscopes and attitude information which is provided by the POS or the accelerometers, so that airplane angular motion is compensated and isolated. The two-freedom-degree heavy-load tracking stabilized platform system has the advantages of being high in precision, large in ration between load and self weight, standard in self attitude, and suitable for camera boresight stability in light small air monitoring systems.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
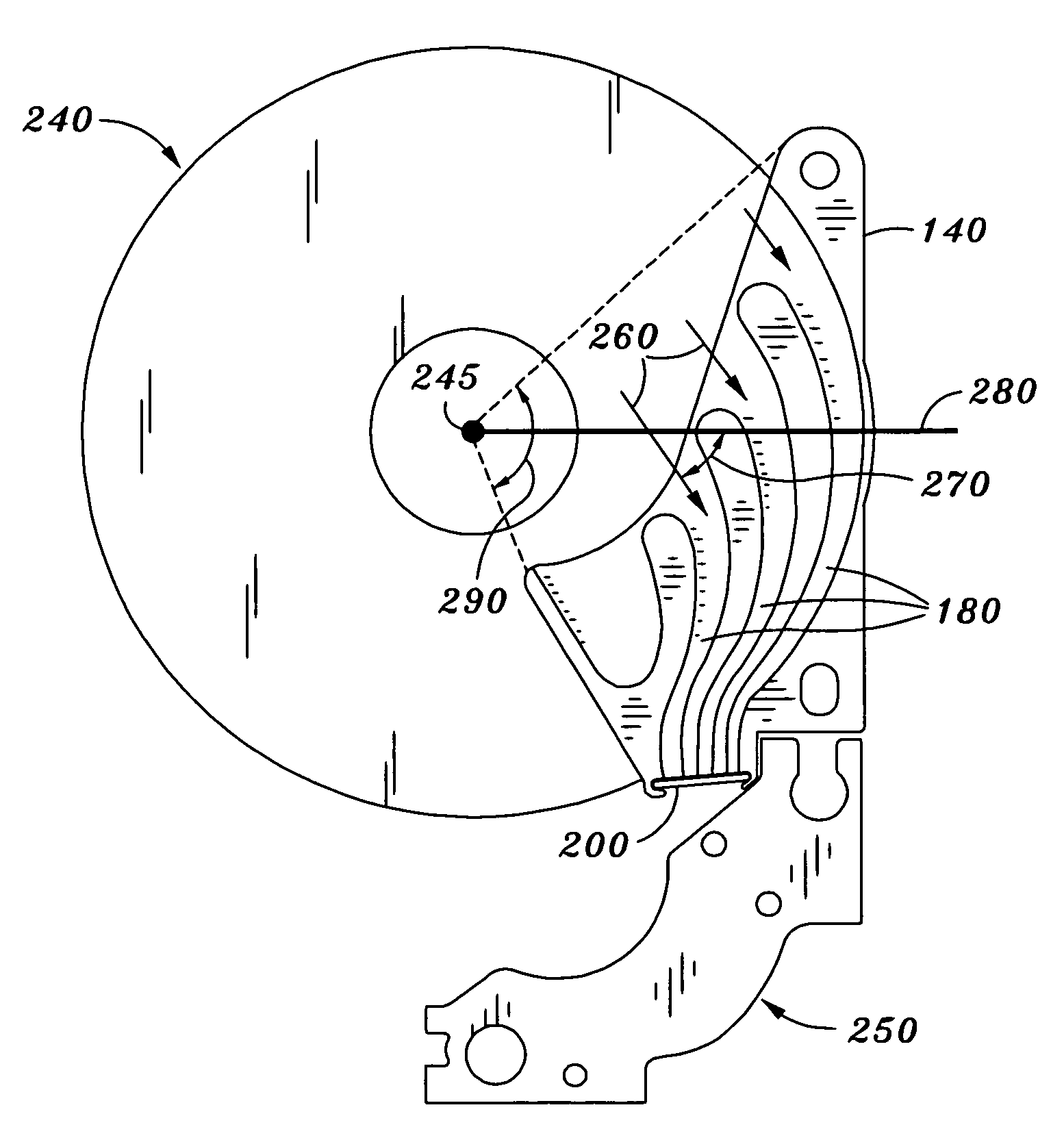
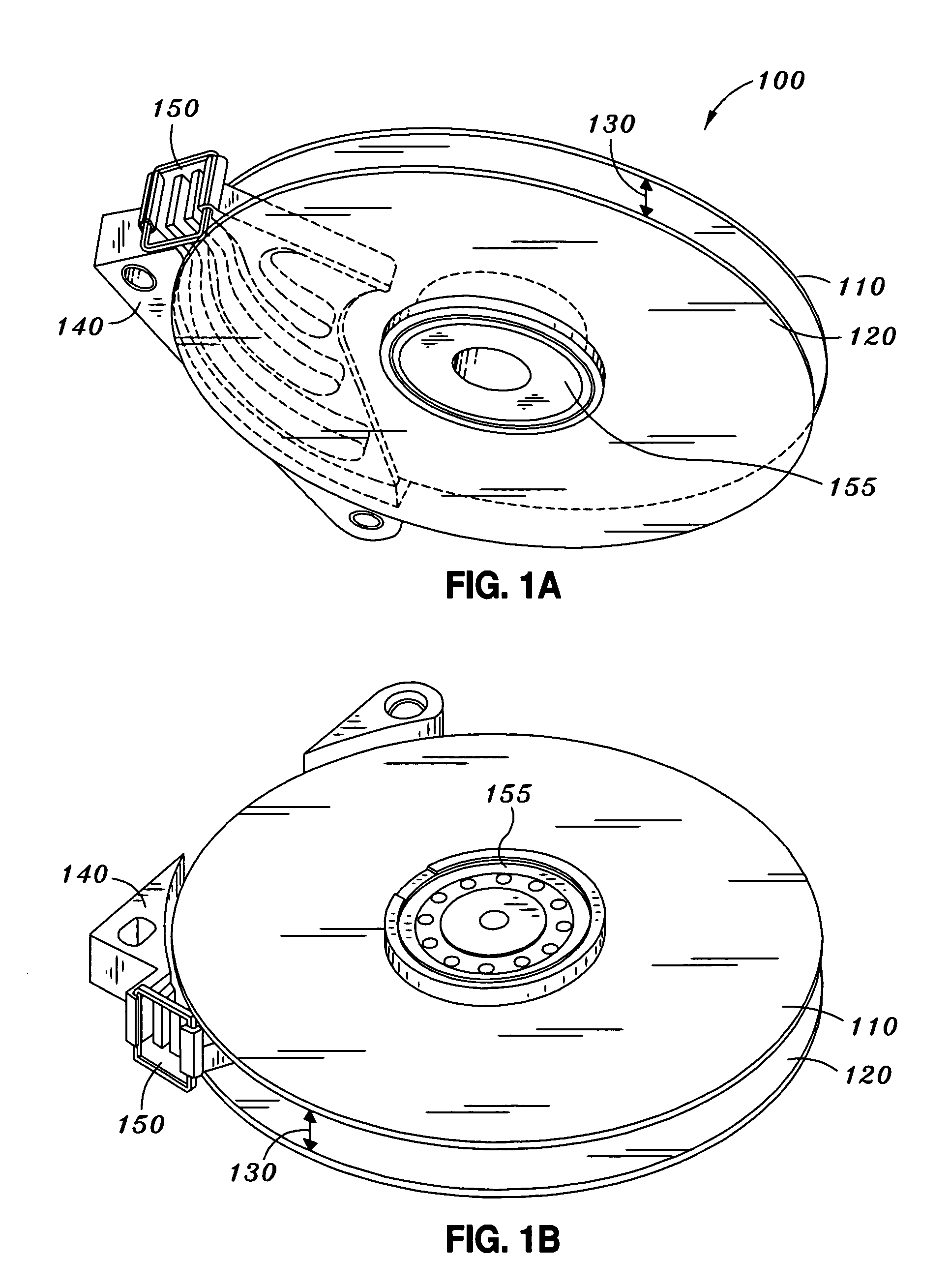
Disk vibration damper having an integrated air circulation guide
InactiveUS7593181B1Undesired vibrations/sounds insulation/absorptionRecord information storageAir cycleAir filtration
A stationary plate functions as a vibration damper and has an integrated air filtration guide. In one embodiment the stationary plate is disposed between two adjacent disks, and the guide comprises one or more grooves through which rotation-induced air may flow. In another embodiment, a plurality of stationary plates may be disposed between a plurality of disks, wherein each of the plurality of stationary plates has a grooved side through which the rotation-induced air may flow. In still another embodiment, the orientation of the grooves in the stationary plate is such that the rotationally-induced airflow impinges the disk drive's voice coil motor.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
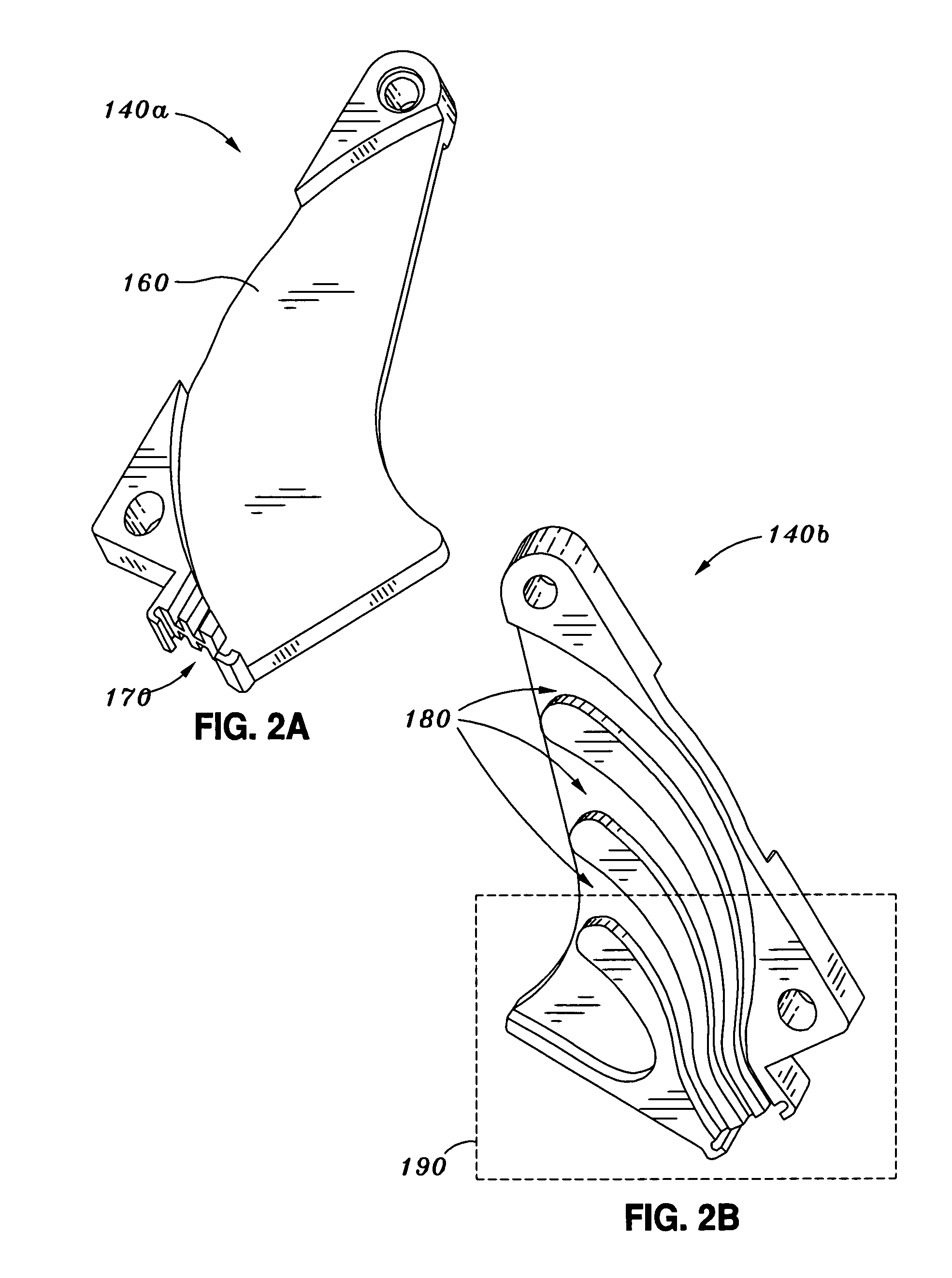
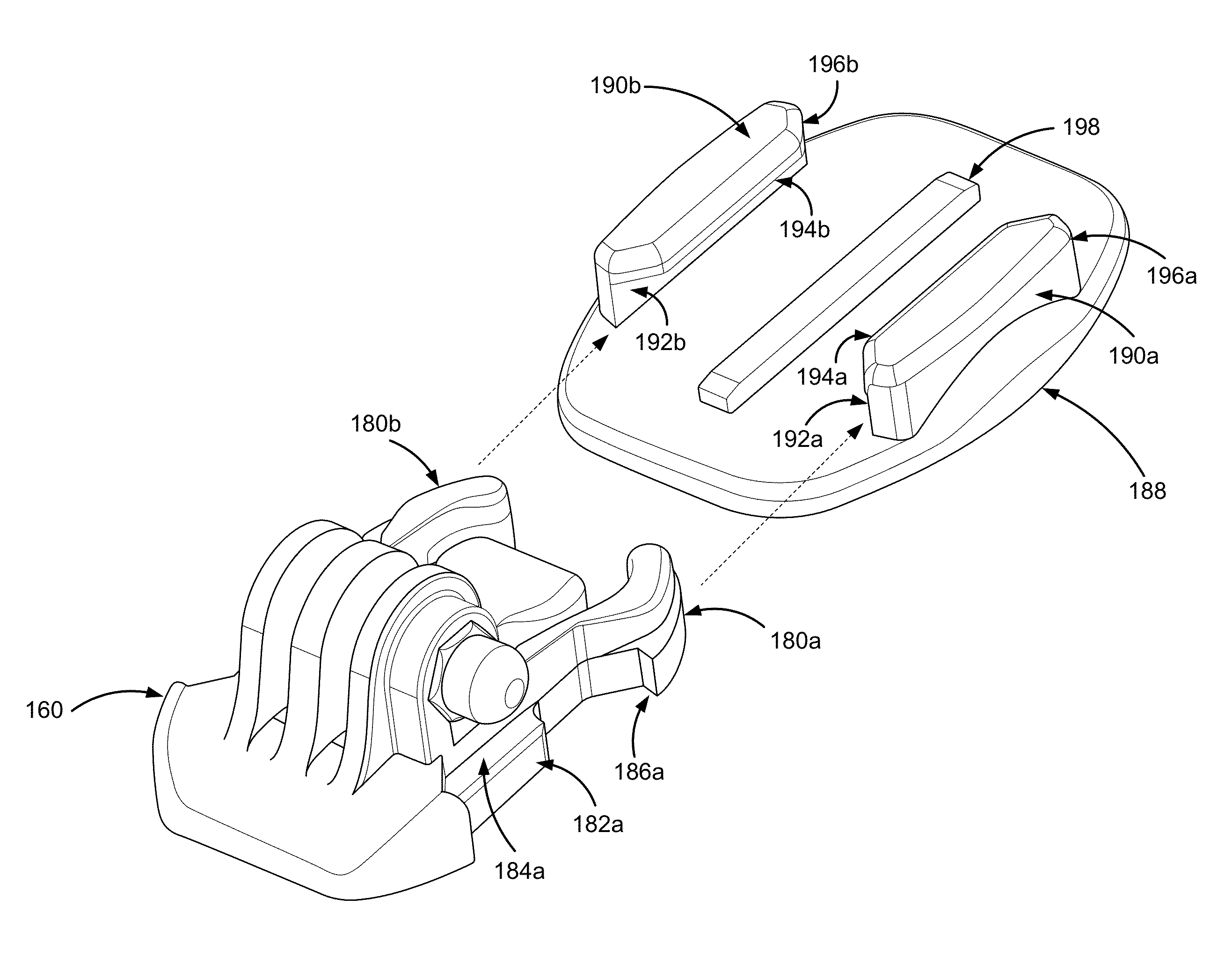
Camera mount vibration dampener
A vibration dampener for a camera mount is structured to reduce the movement of a first mount component relative to a second mount component. An upper camera mount component securing a camera couples to a lower camera mount component, which in turn couples to a base mount component configured to couple to a user, a sports board, a helmet, a vehicle, and the like. The vibration dampener is compressibly inserted between the lower mount component and the base mount component, causing the vibration dampener to exert an outward force on the lower mount component, and securing the lower mount component against a portion of the base mount component. The movement of the lower mount component relative to the base mount component is accordingly reduced by the vibration dampener.
Owner:GOPRO
Multi-material golf club head
InactiveUS7819757B2Increase in sizeGreater club head moment of inertiaGolf clubsRacket sportsMetallic materialsGravity center
A golf club head formed of multiple materials is disclosed. Those portions of the club head that are subject to high stresses during normal use of the golf club head are formed of a metallic material. Most of the material beyond what is required to maintain structural integrity, however, is removed and replaced with a lightweight material. This freed-up mass that can be redistributed to other, more beneficial locations of the club head. The lightweight material also damps vibrations generated during use of the golf club. This vibration damper may be retained in a state of compression to enhance the vibration damping. One or more weight members may be included to obtain desired center of gravity position, moments of inertia, and other club head attributes. A insert formed of multiple materials and having regions of varying thickness may also be included on a rear surface of the club head.
Owner:COBRA GOLF
Three axis optical fibre gyroscope inertia measurement unit integral structure
The invention relates to an integral structure of a triaxial optical fiber gyro inertia measuring unit, which comprises a mounting skeleton, three fiber optic gyro scopes, three accelerometers, a light source, a circuit board and a vibration damper. The mounting skeleton adopts a hollow hexahedron frame structure, each group of mounting holes are symmetrically arranged, and mounting lug bosses are arranged on the positioning end surface of the mounting holes. Three fiber optic gyro scopes form mutual space and are orthogonally arranged on the outer surface of the mounting skeleton, the light source and the circuit board are respectively arranged on the outer surface of the mounting skeleton which is corresponding to the three fiber optic gyro scopes, the three accelerometers form the mutual space and are orthogonally arranged on the inner surface of the mounting skeleton which is corresponding to the three fiber optic gyro scopes and near the geometric center of the mounting skeleton, and the vibration damper is arranged on the outer surface of the mounting skeleton. The measuring unit has the advantages that the quality is light; the degree of deviation between the mass center of an inertia measuring unit and the geometric mounting center is very small; the dynamic testing precision is high; the temperature field distribution of the inertia measuring unit is beneficial for the temperature compensation and control of each component, and the like.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Vehicle front body structure
InactiveCN101037118AImprove the delivery effectImprove impact absorption performanceSuperstructure subunitsSuspension towerAxial compression
The present inventive vehicle front body structure, comprises a front side frame provided so as to project forward from a dash panel; an apron member provided so as to project substantially forward at a location that is outside the vehicle width direction of the front side frame; a suspension tower portion provided so as to at least partly protrude in an engine room for at least partly accommodating a front suspension vibration damper therein, the suspension tower portion being engaged with the apron member and the front side frame; an engine mount provided at the front side frame in front of the suspension tower portion so as to support a side portion of a power plant; and a first connecting member provided so as to straightly interconnect an upper portion of the suspension tower portion and a portion of the front side frame that is located in front of the engine mount, the member being disposed so as to overlap with the engine mount in a top view. The present invention provide a front structure of vehicle body for transmitting a collision load working on a front side frame to an upper portion of a vehicle body which is capable of absorbing the energy caused by the axial compression of the front side frame by suppressing any upward bend of the front side frame by reliably dispersing the collision load to the upper portion of the vehicle body while arranging an engine mount on the front side frame.
Owner:MAZDA MOTOR CORP
Vibration damper
InactiveUS20020027051A1Reduce damping forceImprove comfortSpringsLiquid based dampersSpring forceControl theory
A vibration damper includes a cylinder in which a piston rod is guided so as to be axially movable. A first piston is mounted stationary on the piston rod and a second piston is mounted so as to be displaceable axially on the rod against a spring force. The cylinder has a work space at the piston rod side, a work space remote of the piston rod, and a work space between the two pistons. Through-openings which are outfitted with valves control a connection between the work spaces. The second piston has at least one return spring on both sides, and the piston is mounted so as to be displaceable axially in two directions against the return springs.
Owner:ZF FRIEDRICHSHAFEN AG
Vibration damper for a tubular drive shaft
InactiveUS6837345B1Improve imbalanceLittle effortRotating vibration suppressionShaftsDrive shaftPropeller
A vibration damper for a tubular propeller shaft in the drive train of a motor vehicle having a mass body mounted concentrically, in the propeller shaft or in a sleeve attached in the propeller shaft, by way of at least one rubber spring element. Metal and / or flexible rubber stop elements that limit the vibration travel of the mass body at least in the radial direction are arranged between the mass body and the sleeve. Alternatively, the mass body and / or the sleeve are configured at least locally, in mutually opposite regions, as stop elements that limit the vibration travel of the mass body at least in the radial direction.
Owner:DAIMLER AG
Vibration damping method for variable speed wind turbines
A vibration damping technique for a wind turbine system is described. The wind turbine system includes a vibration damper, which provides a variable signal to control torque produced by a generator of the wind turbine system. The variable signal is based on generator speed and has a first local peak value based on a resonant frequency of tower side-to-side oscillation.
Owner:GE INFRASTRUCTURE TECH INT LLC
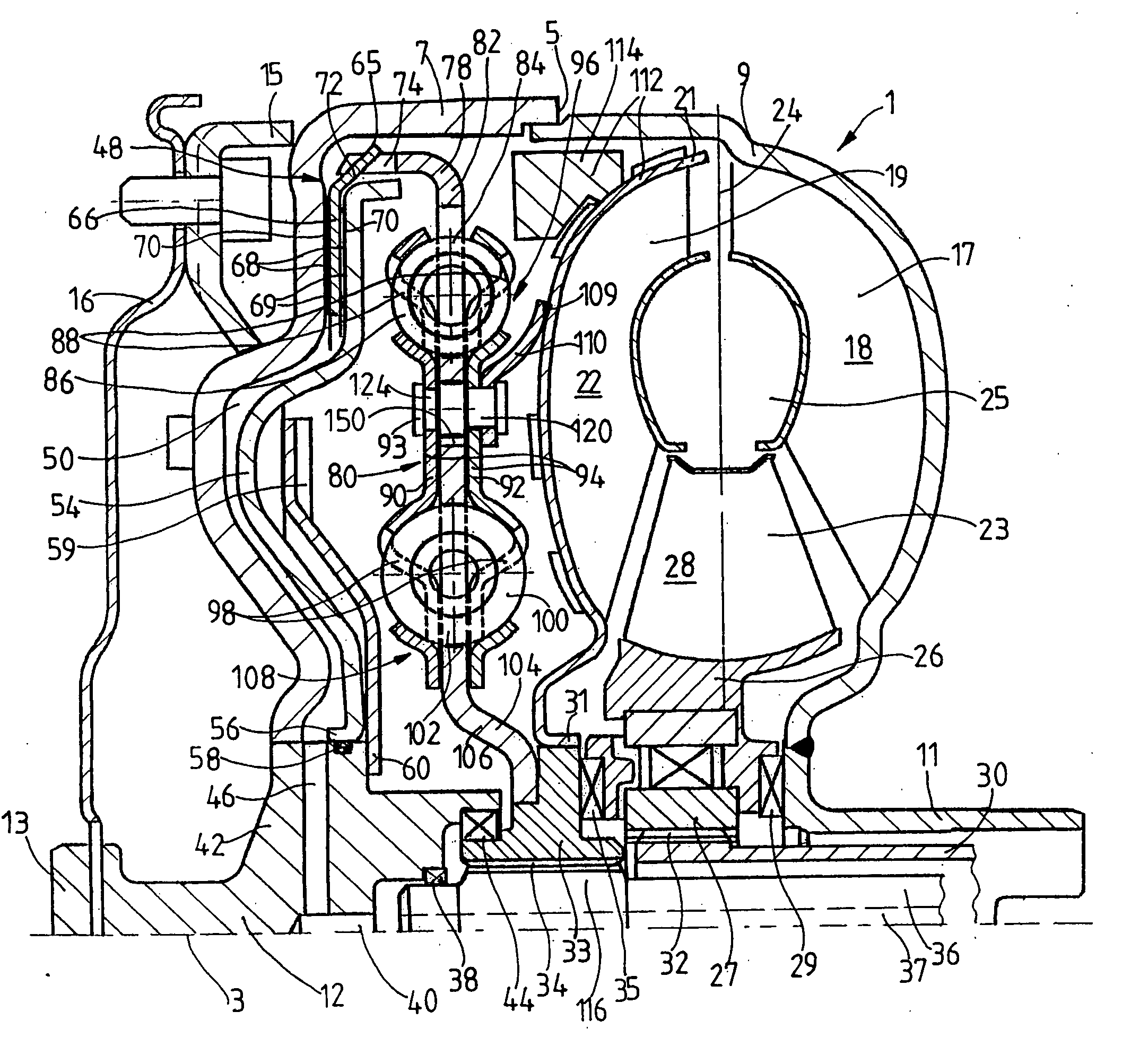
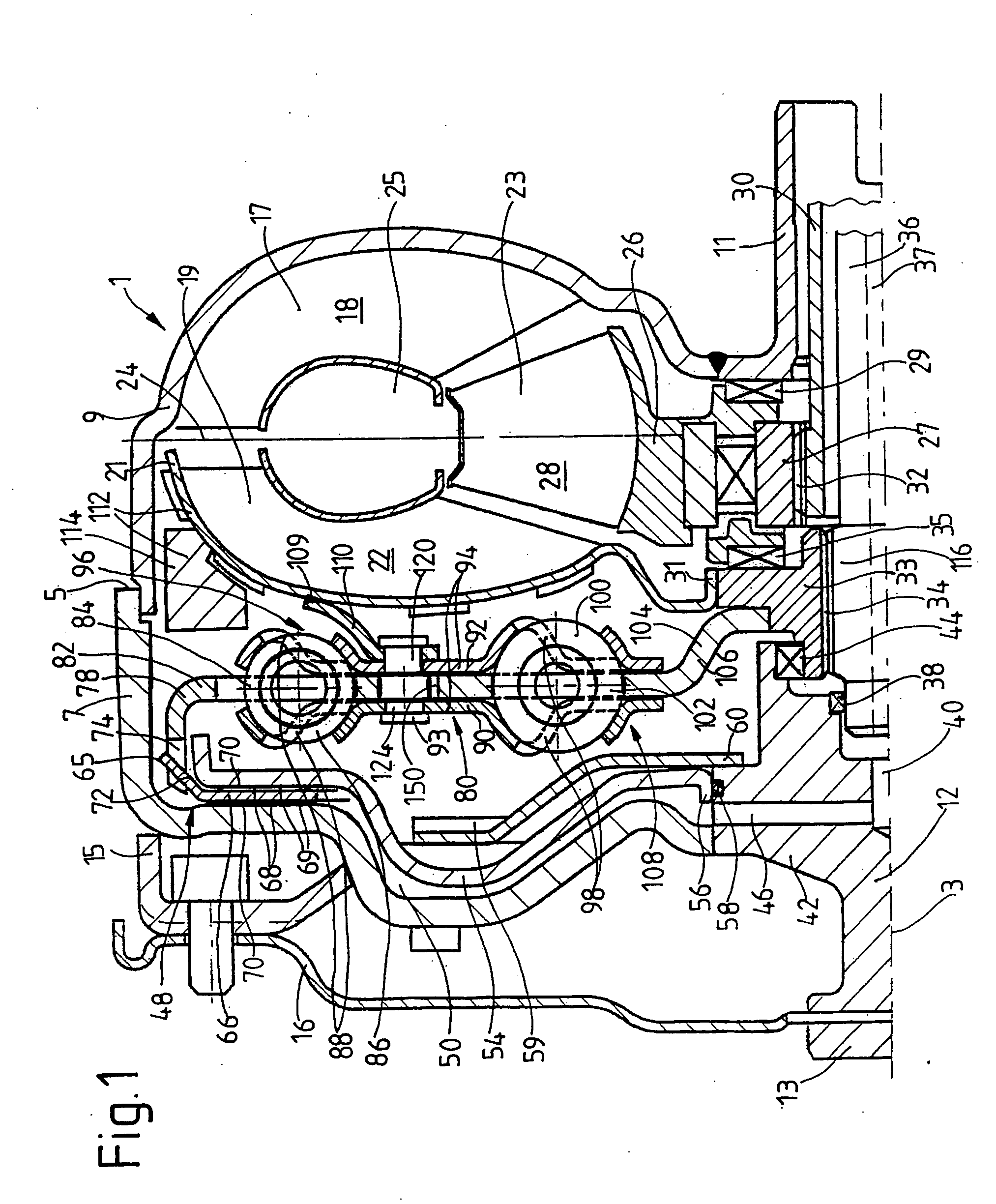
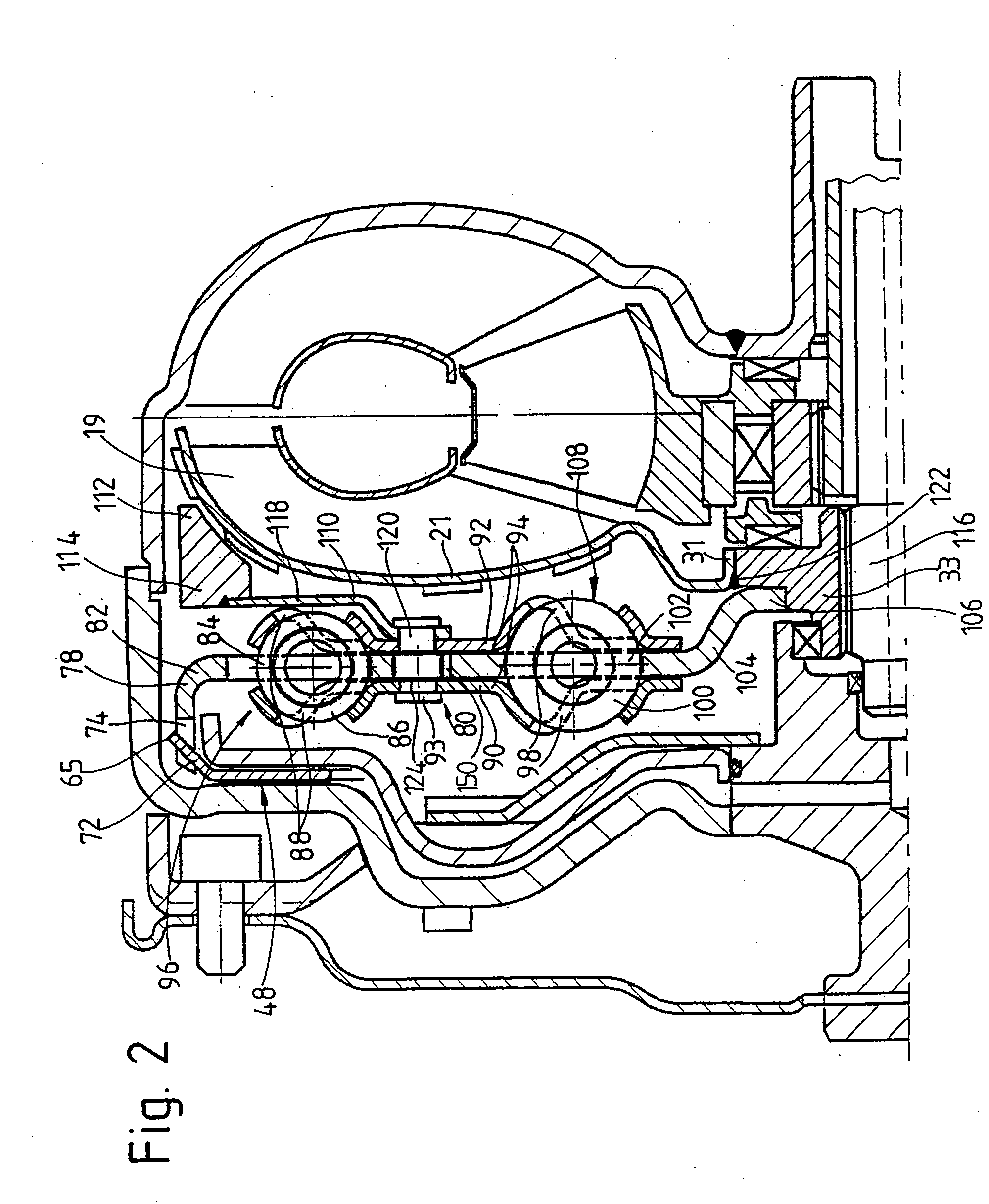
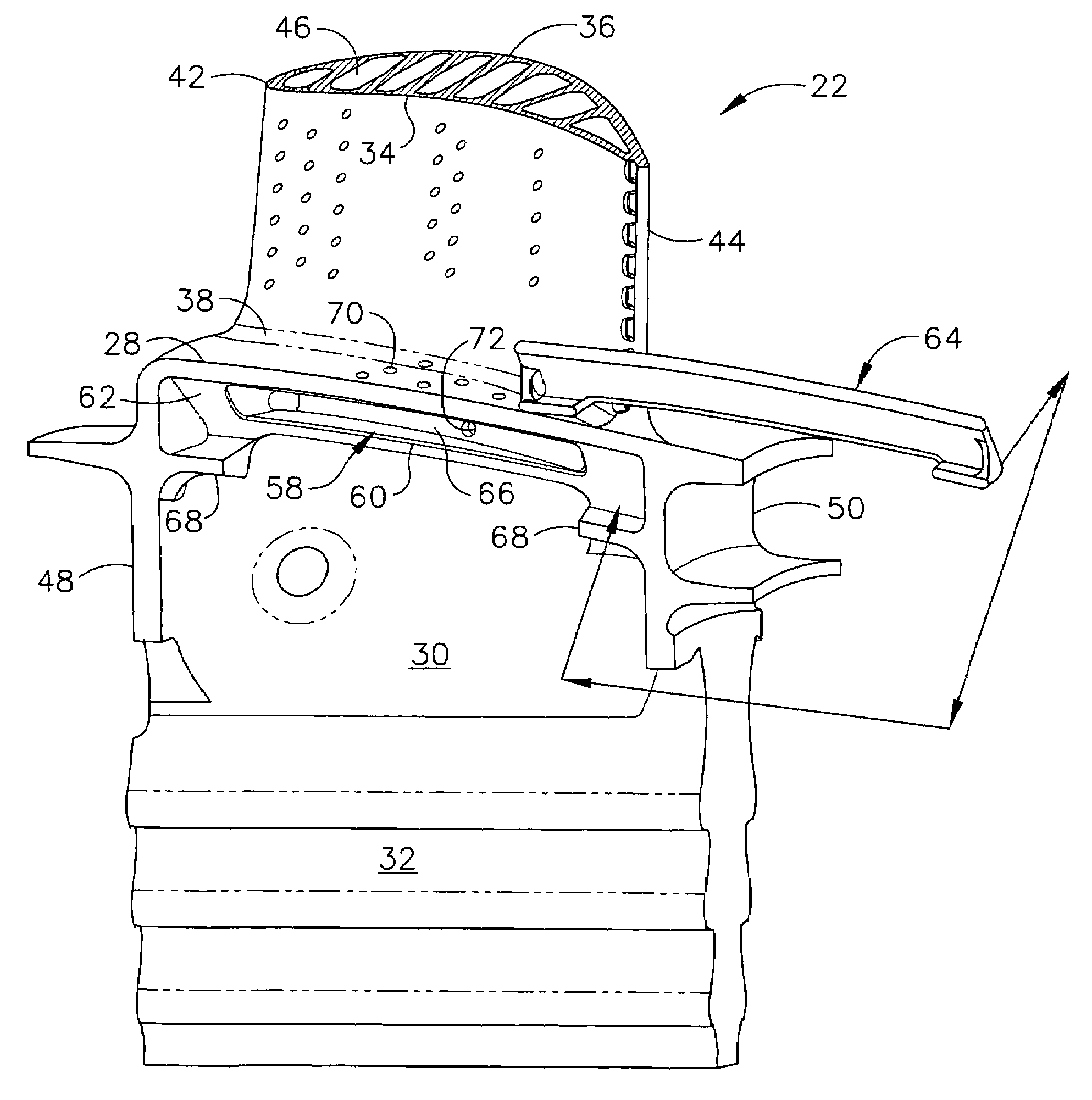
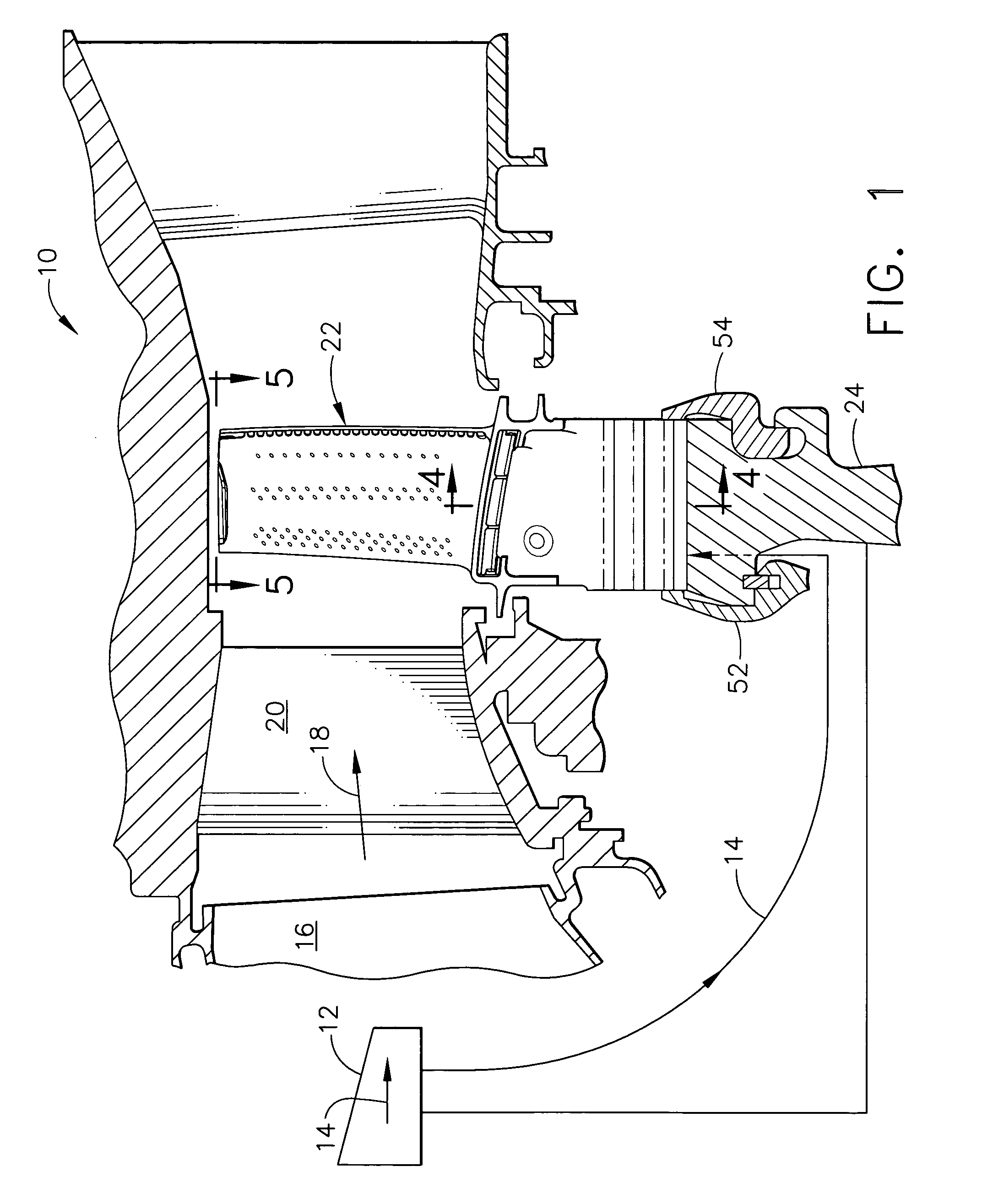
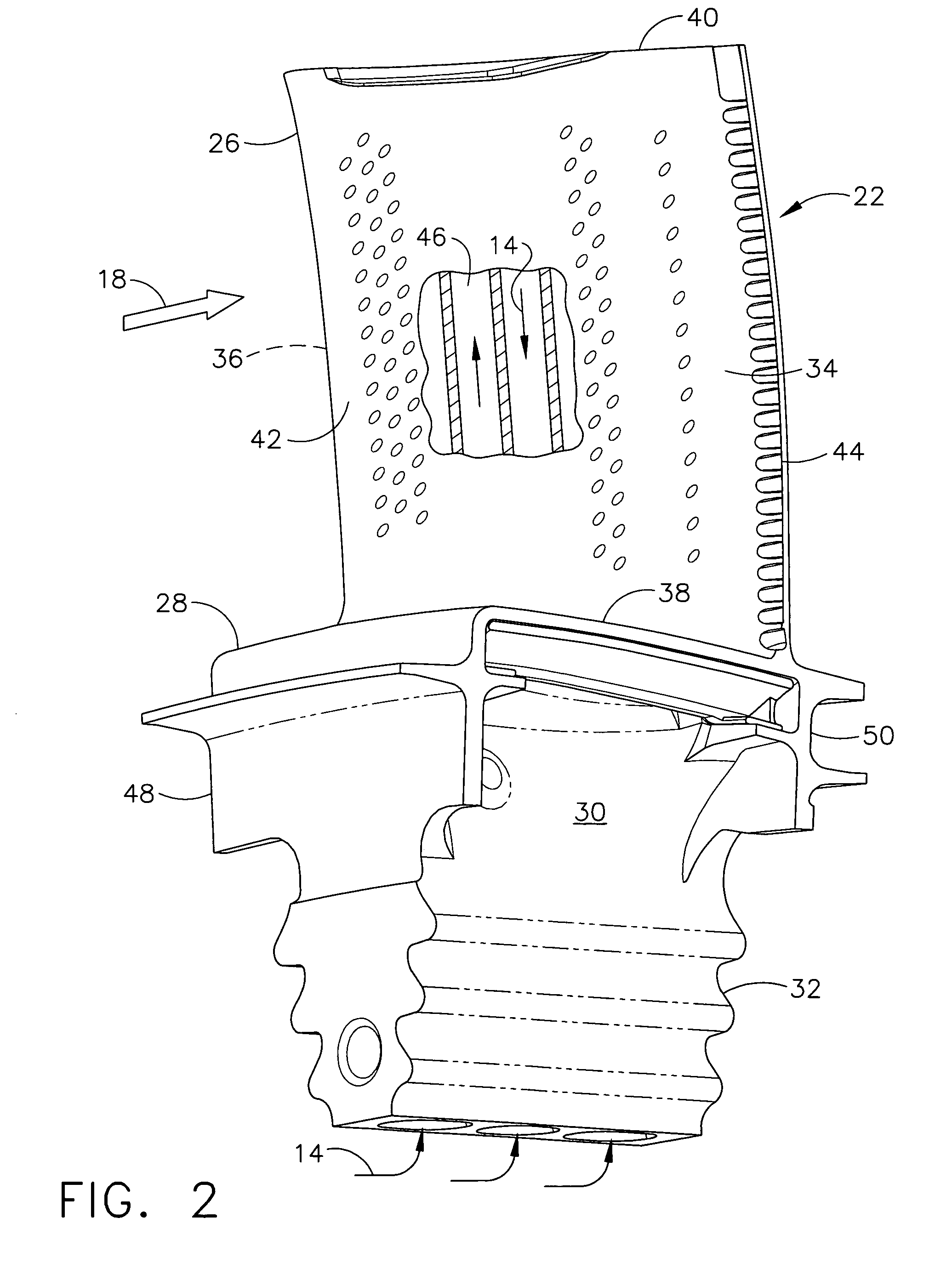
Damper cooled turbine blade
A turbine blade includes an airfoil, platform, shank, and dovetail integrally joined together. A cooling chamber is located under the platform and has a portal exposed outwardly from the shank. A damper seat surrounds the portal and is recessed under the platform for receiving a vibration damper to sealingly close the chamber across the portal.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com