Patents
Literature
836 results about "Dynamic testing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Dynamic testing (or dynamic analysis) is a term used in software engineering to describe the testing of the dynamic behavior of code. That is, dynamic analysis refers to the examination of the physical response from the system to variables that are not constant and change with time. In dynamic testing the software must actually be compiled and run. It involves working with the software, giving input values and checking if the output is as expected by executing specific test cases which can be done manually or with the use of an automated process. This is in contrast to static testing. Unit tests, integration tests, system tests and acceptance tests utilize dynamic testing. Usability tests involving a mock version made in paper or cardboard can be classified as static tests when taking into account that no program has been executed; or, as dynamic ones when considering the interaction between users and such mock version is effectively the most basic form of a prototype.
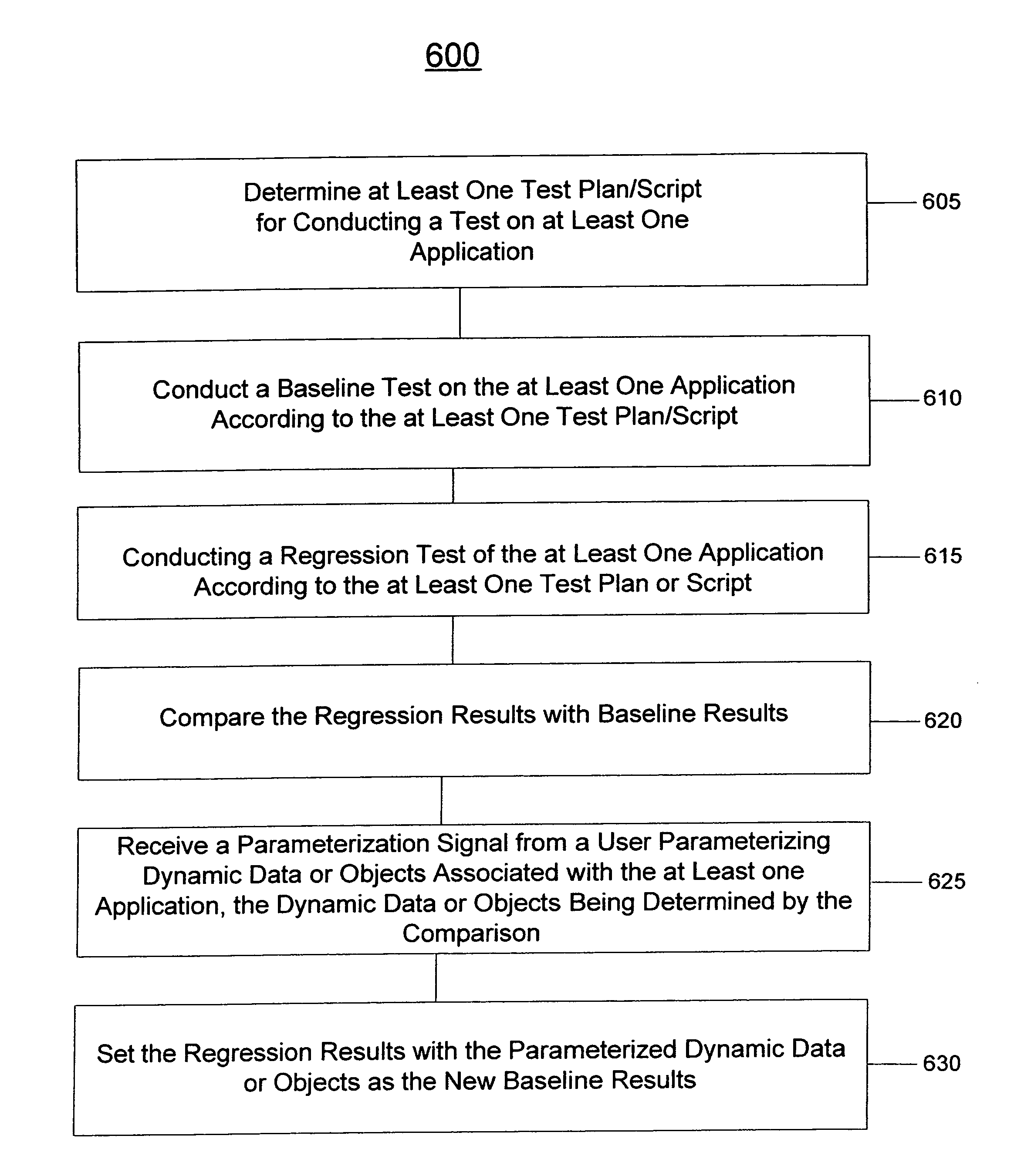
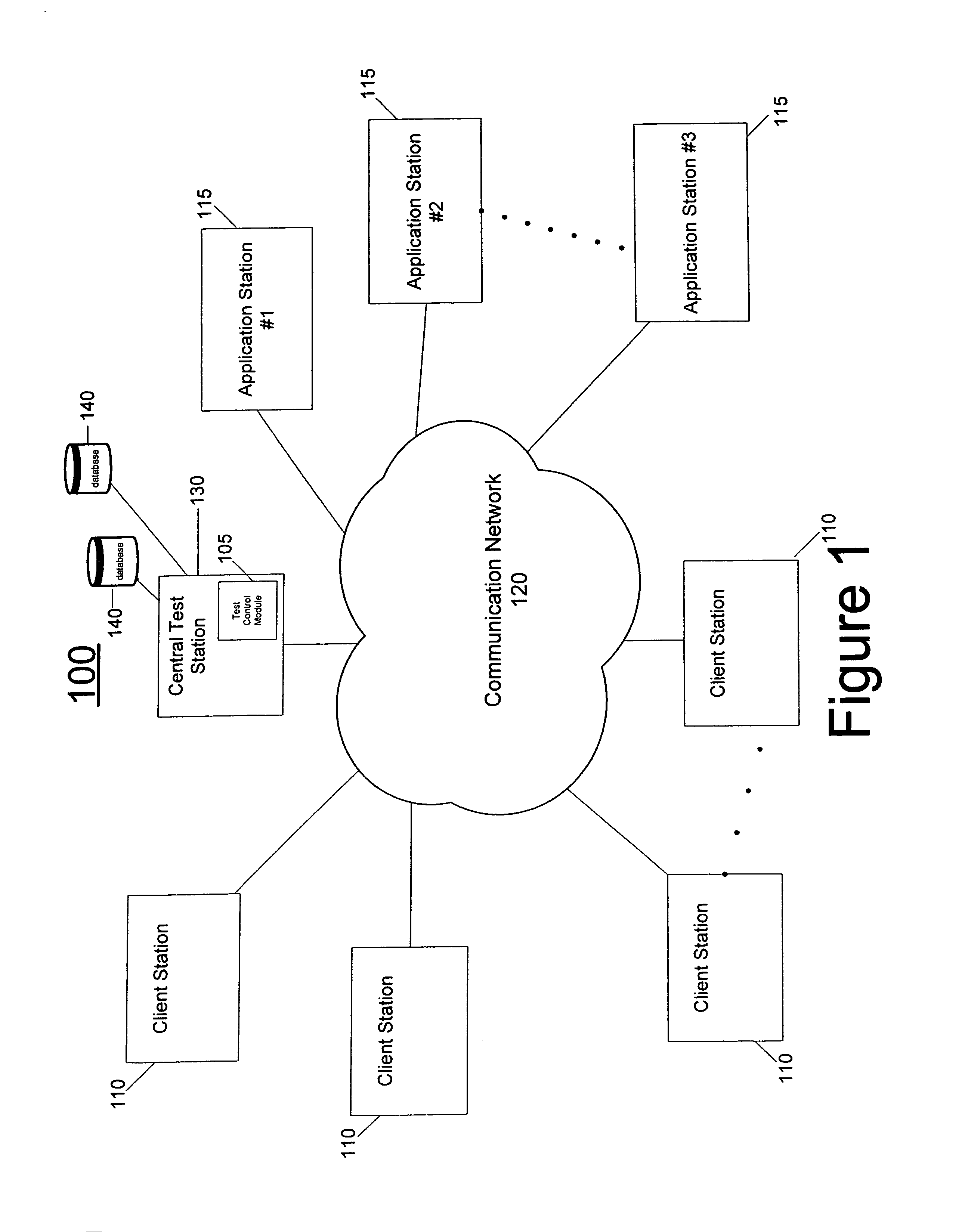
System and method for testing applications
ActiveUS8185877B1Improve productivitySimple processSoftware testing/debuggingSpecific program execution arrangementsSimulationApplication procedure
A system and method for testing at least one application is provided. The system comprises a test plan or script creation module for enabling a user to create at least one test plan or script for use in testing the at least one application. The system also comprises a test results module for initiating and determining test results associated with testing of the at least one application according to the at least one test plan or script. In some embodiments, the test results module determines: (1) baseline test results achieved by resolving the at least one test plan or script against the at least one application prior to the application being put to actual use, and (2) dynamic test results achieved by resolving the at least one test plan or script against the at least one application after the at least one application has been put to actual use. The system may also include a comparison module for comparing the dynamic test results with the baseline test results.
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
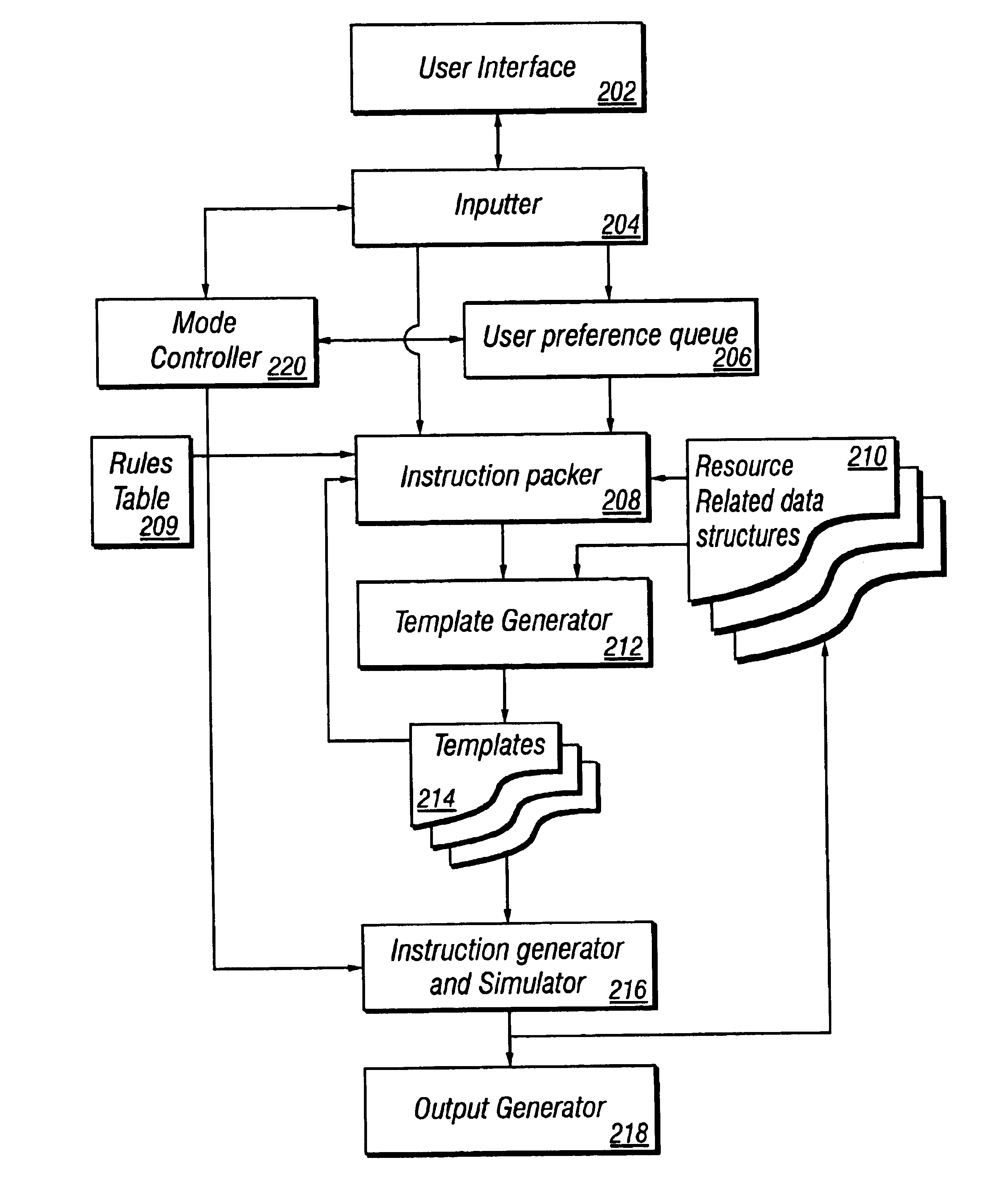
Method and apparatus that simulates the execution of paralled instructions in processor functional verification testing
InactiveUS6871298B1Properly be executeError detection/correctionDigital computer detailsAnalog processorParallel computing
A dynamic test generation method and apparatus enabling verification of the parallel instruction execution capabilities of VLIW processor systems is described. The test generator includes a user preference queue, a rules table, plurality of resource-related data structures, an instruction packer, and an instruction generator and simulator. The present invention generates a test by selecting instructions for parallel execution based upon resource availability as indicated by the resource-related data structures and the processor's instruction grouping rules, simulating the parallel execution of the instructions on a golden model, updating the resource-related data structures, and evaluating the updated architectural state of the golden model.
Owner:ARM INC
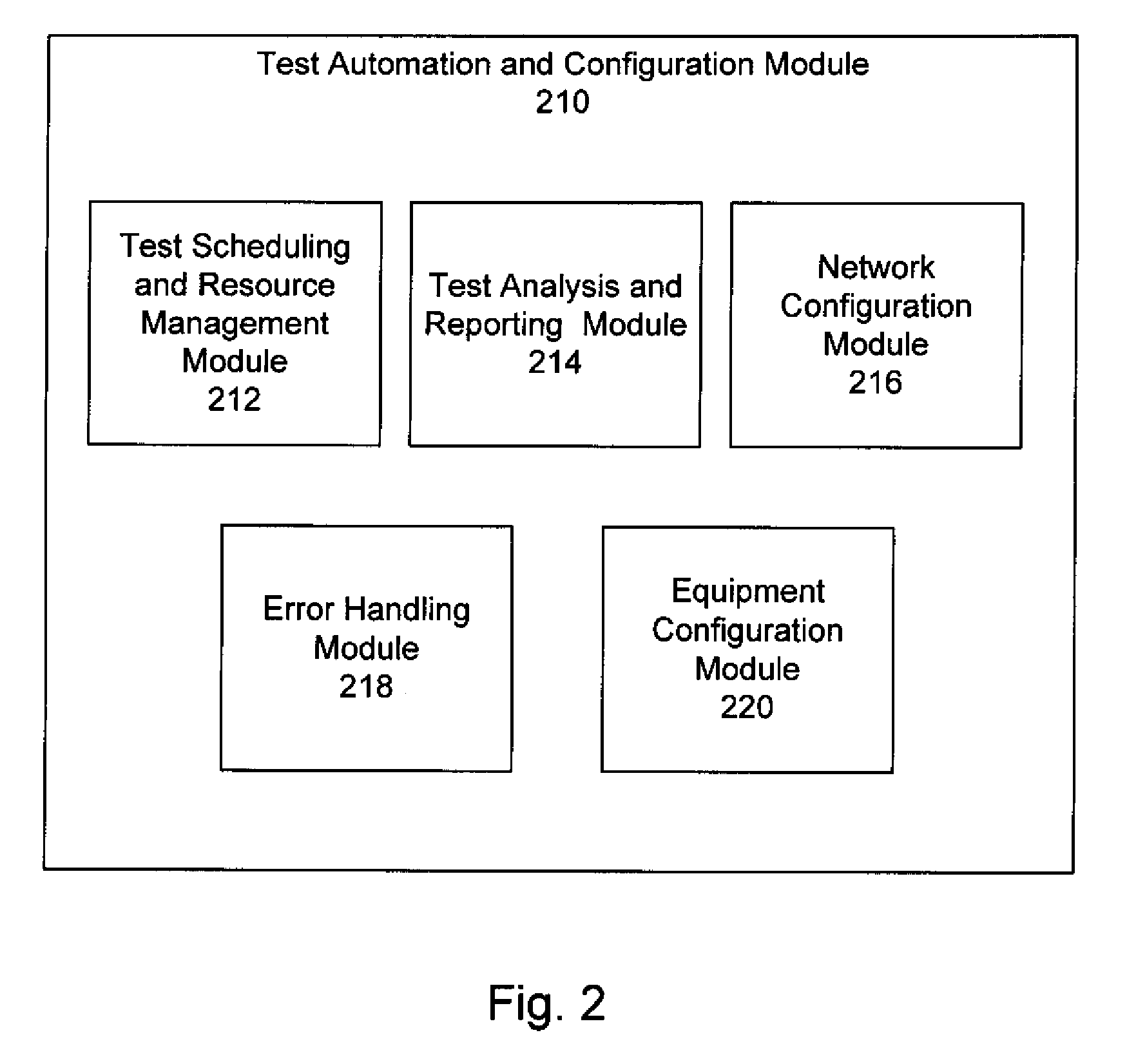
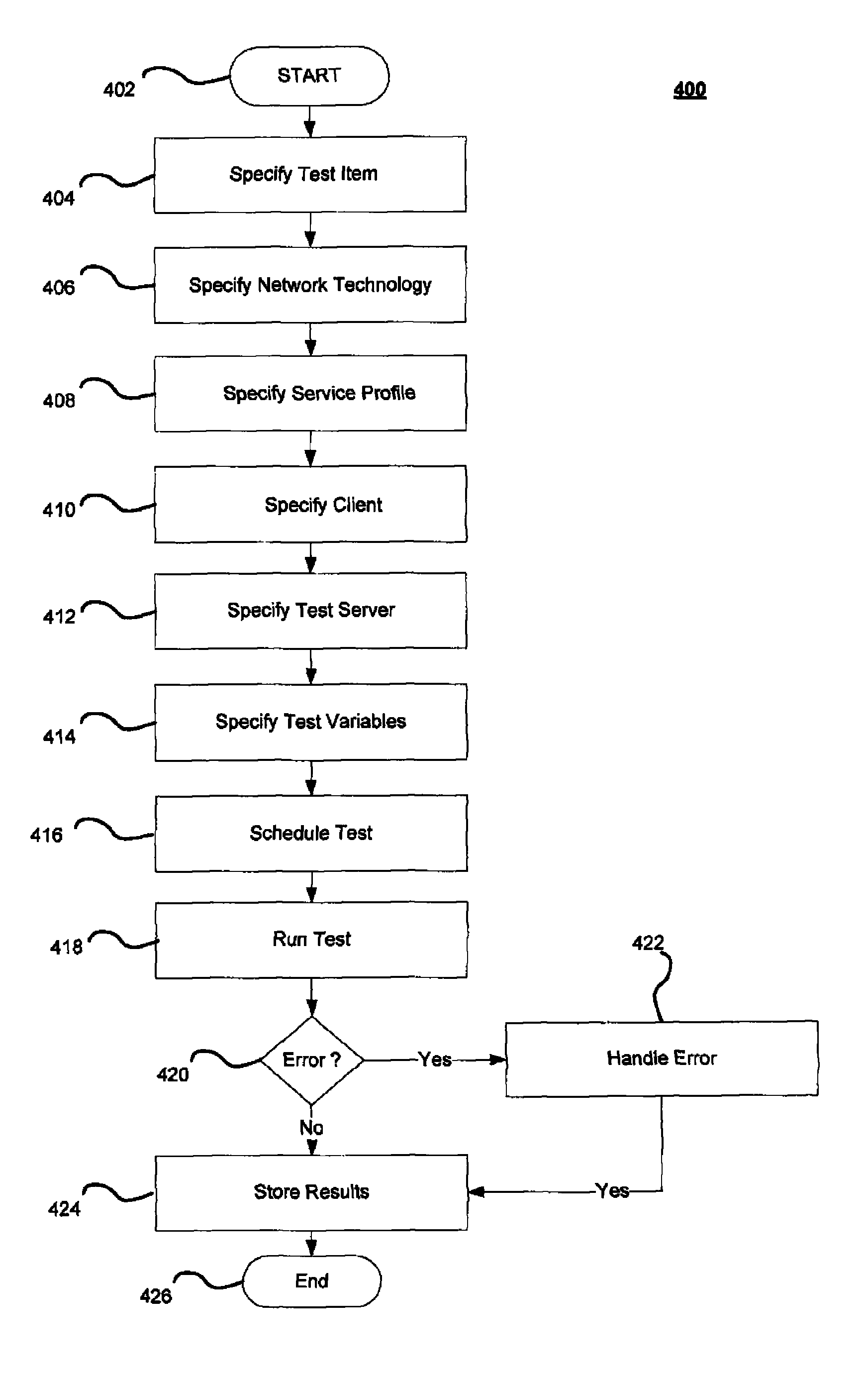
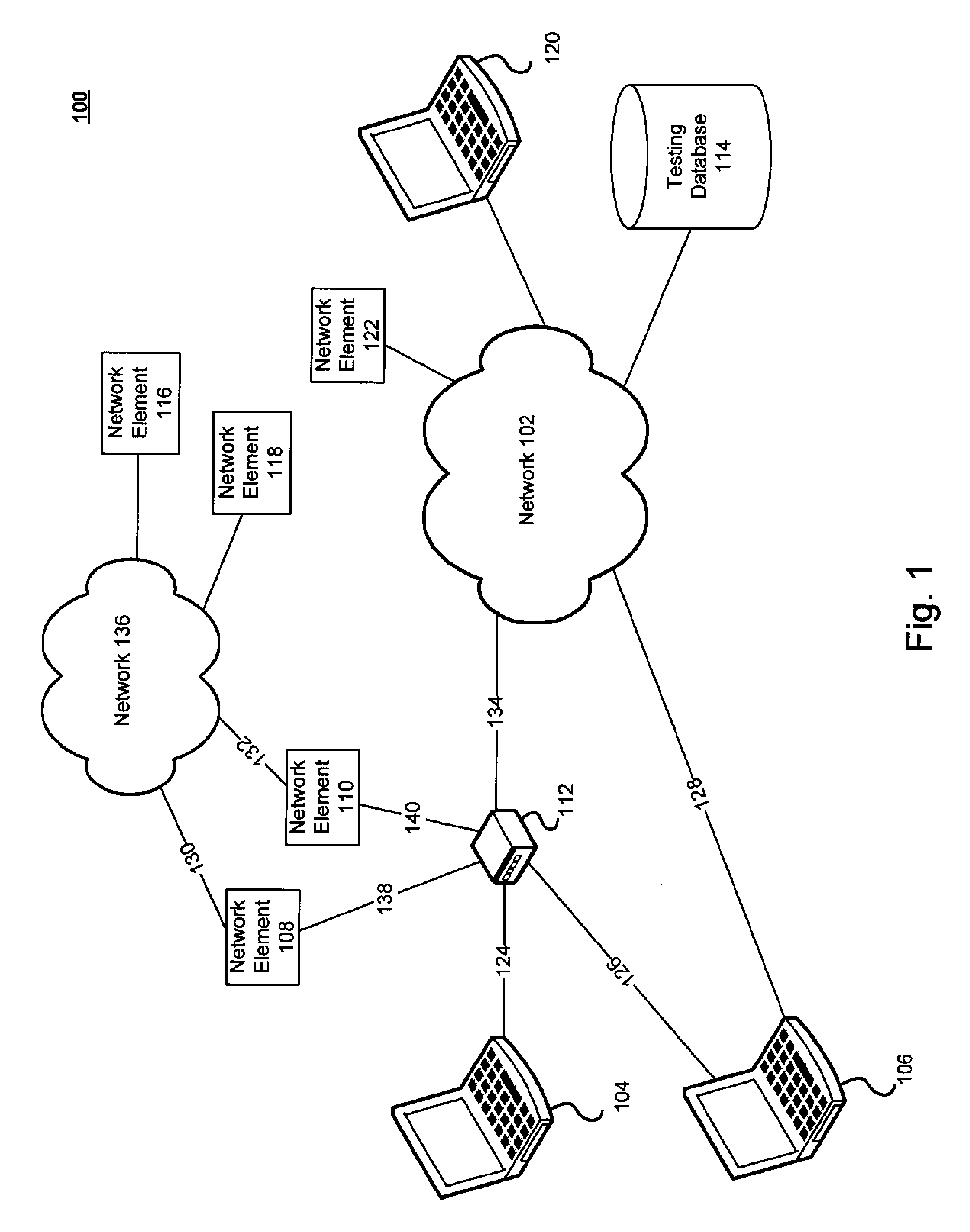
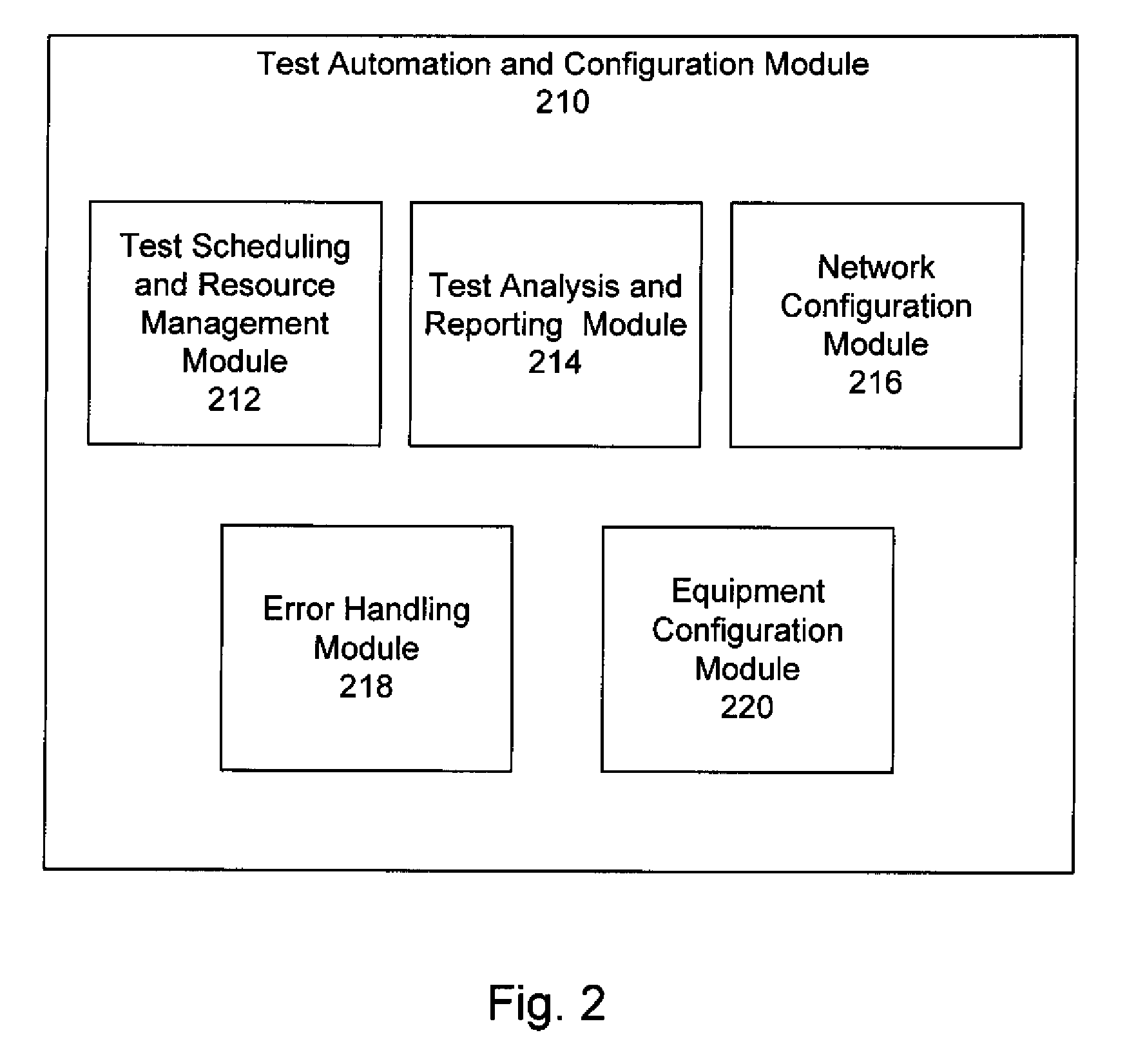
Method and system for test automation and dynamic test environment configuration
ActiveUS20090279673A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsComputer hardwareClient-side
A method and system of an embodiment may provide a user interface enabling automated testing of a network device. The automated testing may include specifying a network device to be tested, specifying a network technology for testing the network device, specifying a client of the network device, configuring network connectivity for the network device, and enabling execution by the client of a network device of a test action. Configuring network connectivity may include dynamically configuring a network to include the specified network technology and the specified network device.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
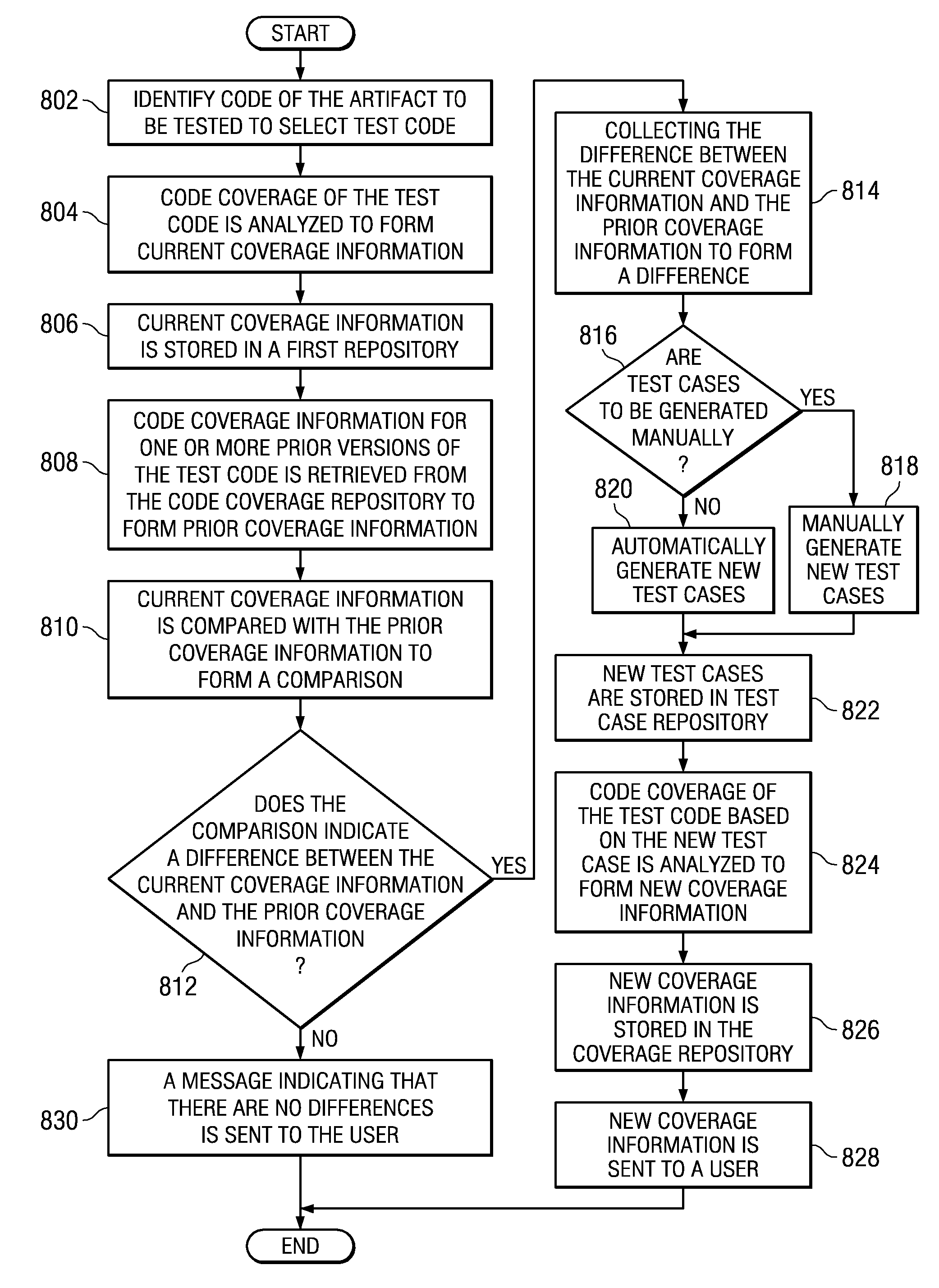
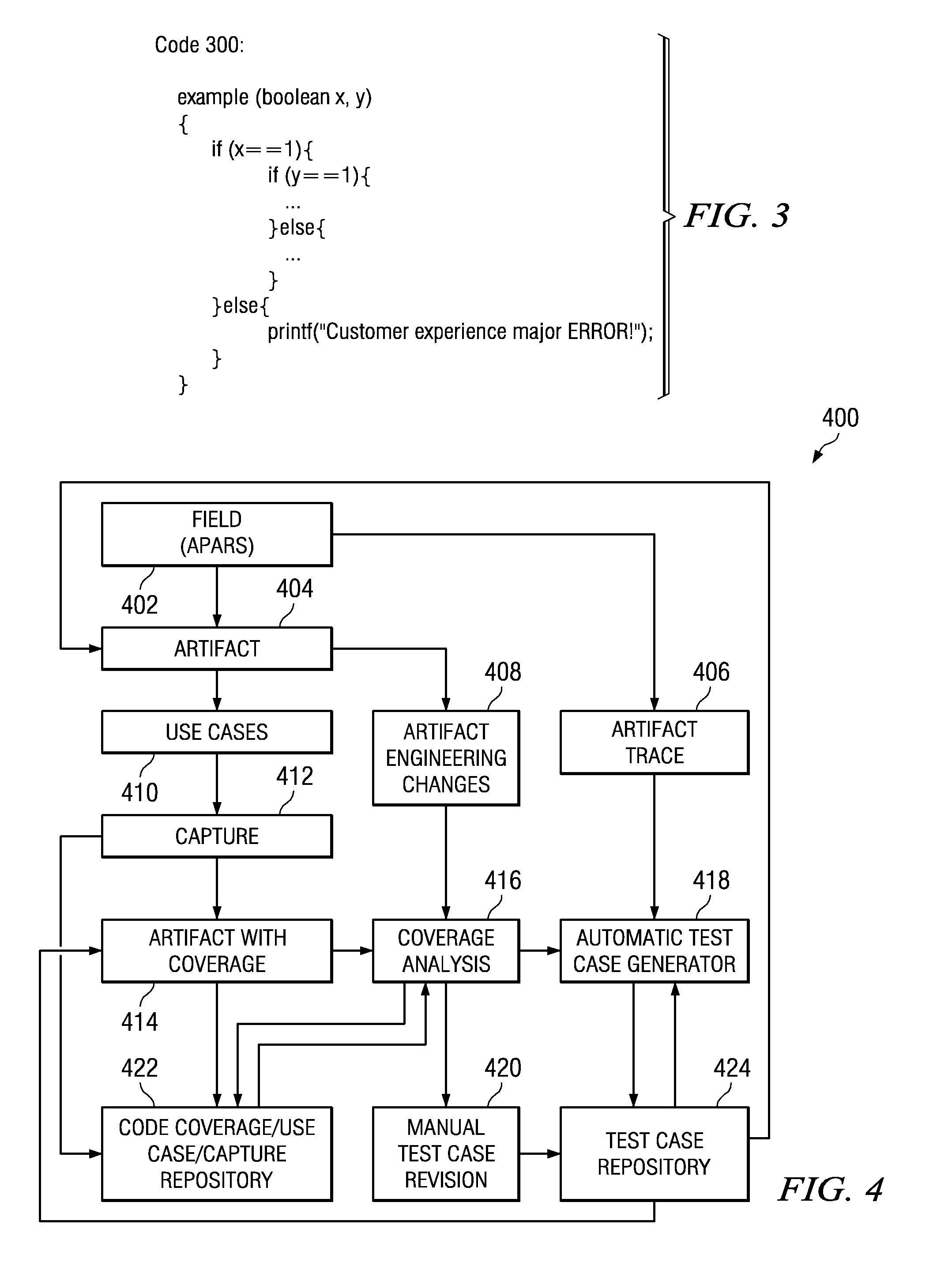
Dynamic Test Coverage
InactiveUS20100058295A1Error detection/correctionSpecific program execution arrangementsCode coverageDynamic testing
Dynamic test coverage to evaluate an artifact code is provided. Code of an artifact to be tested is identified. The code coverage of the test code is analyzed. The current coverage information is stored. Code coverage information for one or more prior versions of the test code is retrieved. The current coverage information is compared with the prior coverage information. Responsive to a determination that a difference between the current coverage information and the prior coverage information exists, the difference is collected. Responsive to a determination that test cases are to be generated automatically, generating, automatically, new test cases based on the difference. The new test cases are stored. Code coverage of the test code is analyzed based on the new test case. The new coverage information is stored. The new coverage information is sent to the user.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method and system for test automation and dynamic test environment configuration
A method and system of an embodiment may provide a user interface enabling automated testing of a network device. The automated testing may include specifying a network device to be tested, specifying a network technology for testing the network device, specifying a client of the network device, configuring network connectivity for the network device, and enabling execution by the client of a network device of a test action. Configuring network connectivity may include dynamically configuring a network to include the specified network technology and the specified network device.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
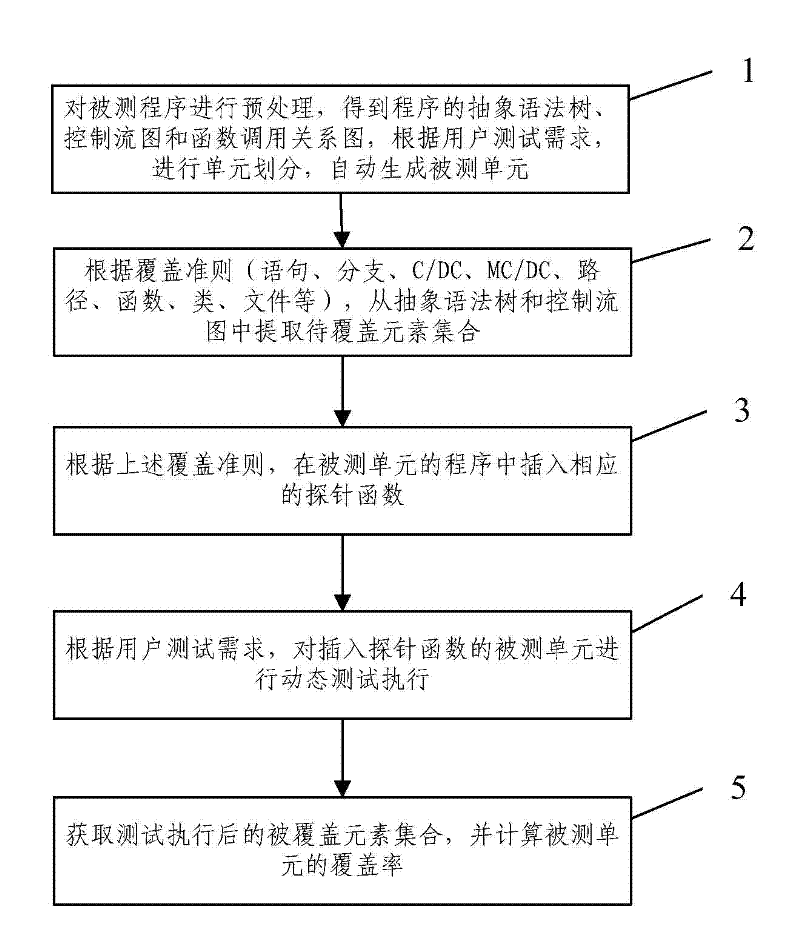
Method for determining software test process sufficiency based on coverage rate quantitative indicators
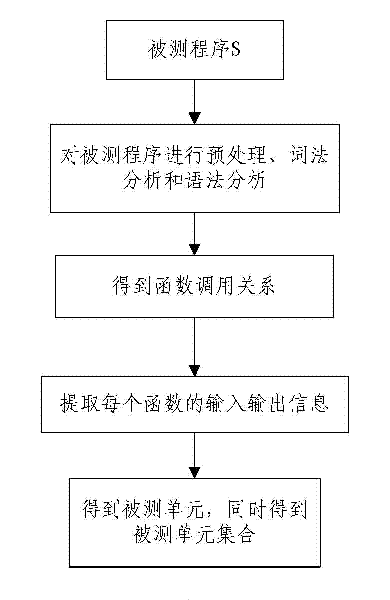
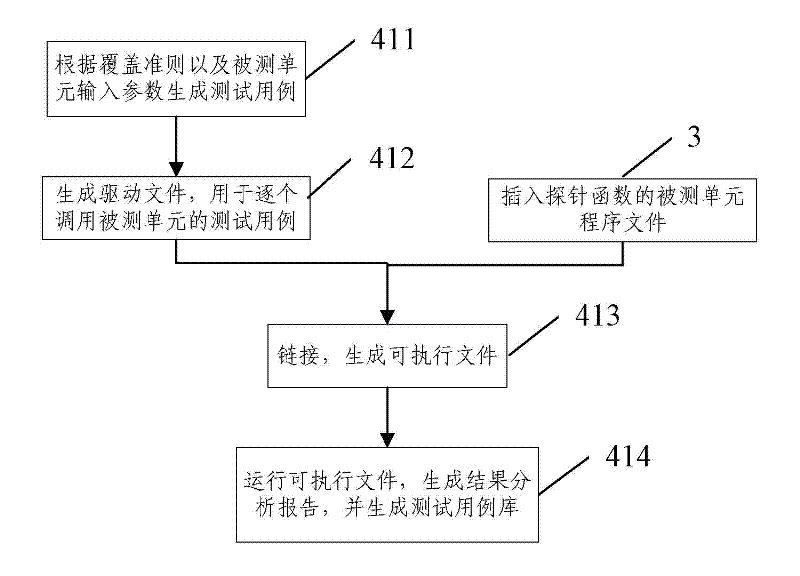
InactiveCN102419728AImprove efficiencyImprove accuracySoftware testing/debuggingAlgorithmLexical analysis
The invention provides a method for determining software test process sufficiency based on coverage rate quantitative indicators. The method comprises the following steps of: A, performing precompilation, lexical analysis and syntax analysis on a tested program to acquire the calling relationship diagram of the abstract syntax tree, the control flow graph and the function of the program, and automatically generating a tested unit according to the test requirement of a user; B, extracting a corresponding element set to be covered in the tested unit from the abstract syntax tree and the control flow graph according to a coverage criterion; C, inserting a corresponding probe function into the program of the tested unit according to the coverage criterion; D, dynamically testing the tested unit into which the probe function is inserted by selecting a system automatic executing mode or a user manual executing mode according to the test requirement of the user; and E, acquiring the covered element set of the tested unit according to the returned information of dynamic test execution, and calculating the coverage rate of the tested unit. By the method, the efficiency and the accuracy of a software evaluation test can be improved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
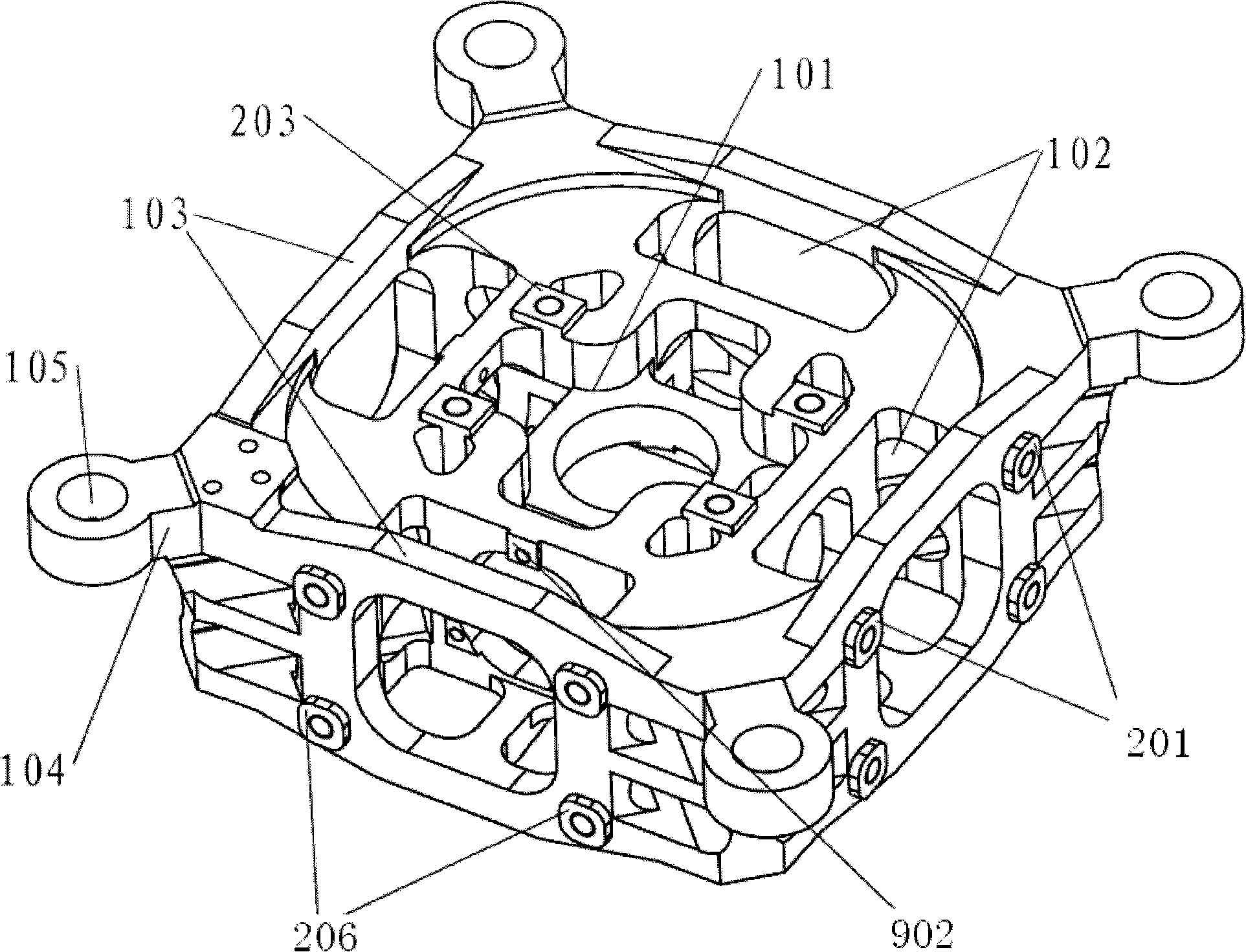
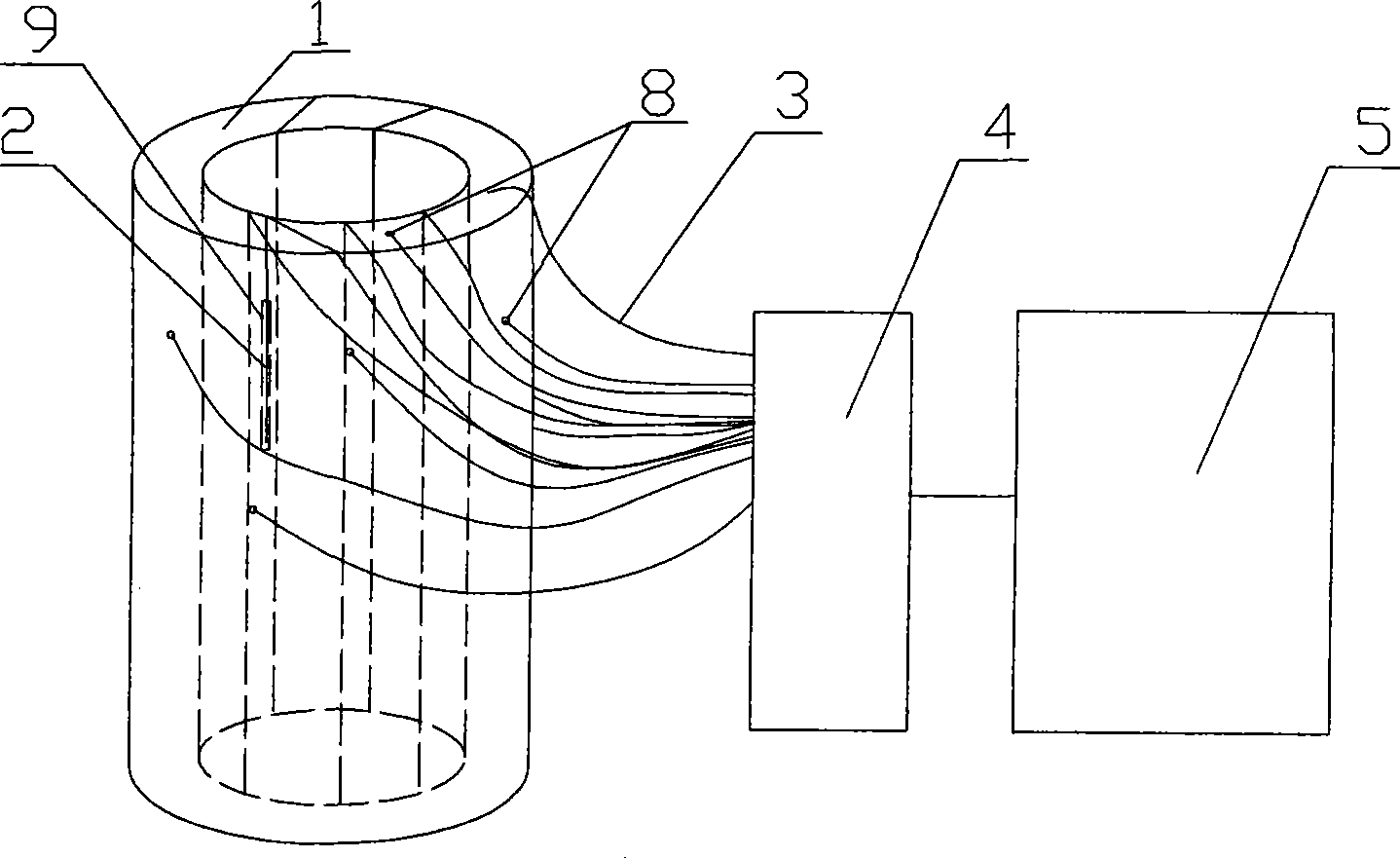
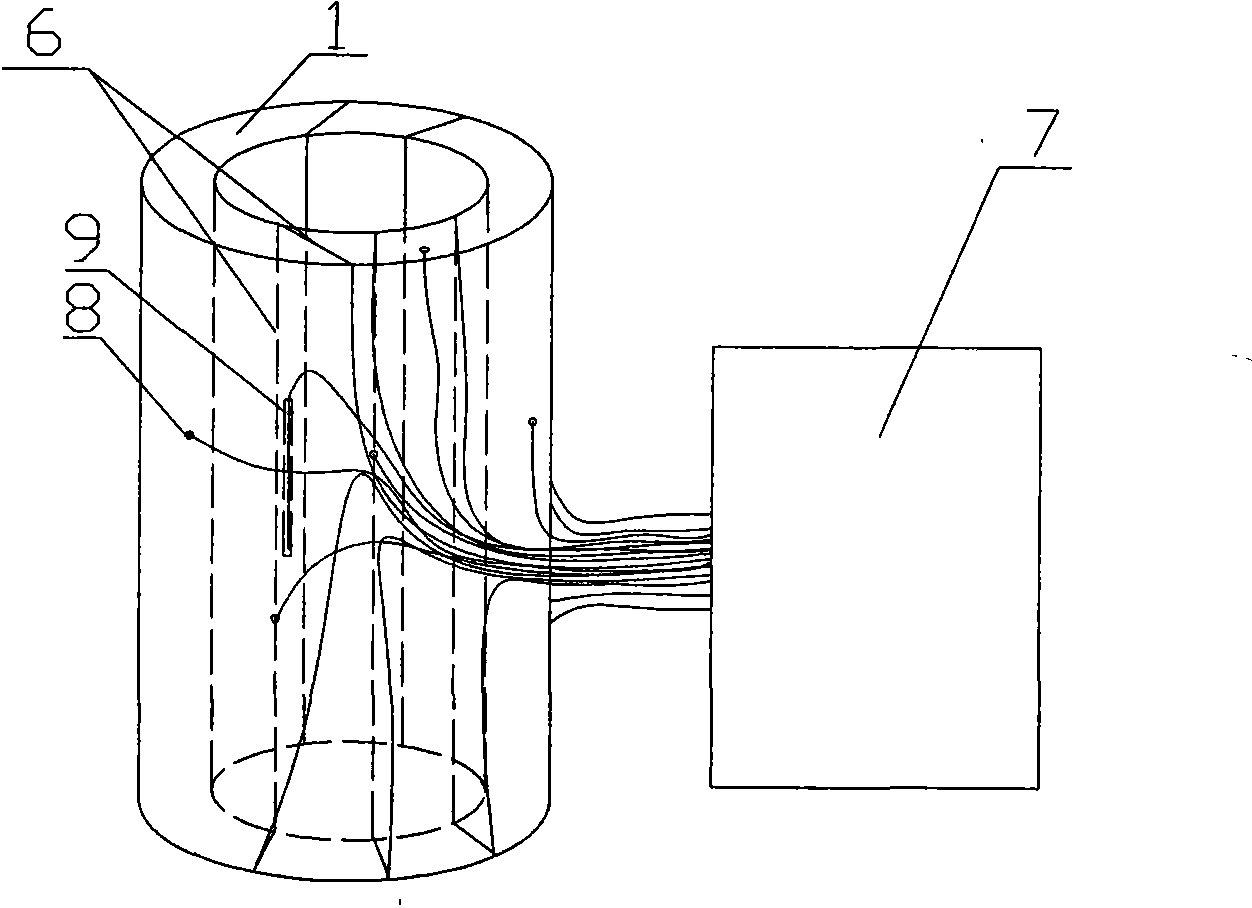
Three axis optical fibre gyroscope inertia measurement unit integral structure
The invention relates to an integral structure of a triaxial optical fiber gyro inertia measuring unit, which comprises a mounting skeleton, three fiber optic gyro scopes, three accelerometers, a light source, a circuit board and a vibration damper. The mounting skeleton adopts a hollow hexahedron frame structure, each group of mounting holes are symmetrically arranged, and mounting lug bosses are arranged on the positioning end surface of the mounting holes. Three fiber optic gyro scopes form mutual space and are orthogonally arranged on the outer surface of the mounting skeleton, the light source and the circuit board are respectively arranged on the outer surface of the mounting skeleton which is corresponding to the three fiber optic gyro scopes, the three accelerometers form the mutual space and are orthogonally arranged on the inner surface of the mounting skeleton which is corresponding to the three fiber optic gyro scopes and near the geometric center of the mounting skeleton, and the vibration damper is arranged on the outer surface of the mounting skeleton. The measuring unit has the advantages that the quality is light; the degree of deviation between the mass center of an inertia measuring unit and the geometric mounting center is very small; the dynamic testing precision is high; the temperature field distribution of the inertia measuring unit is beneficial for the temperature compensation and control of each component, and the like.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
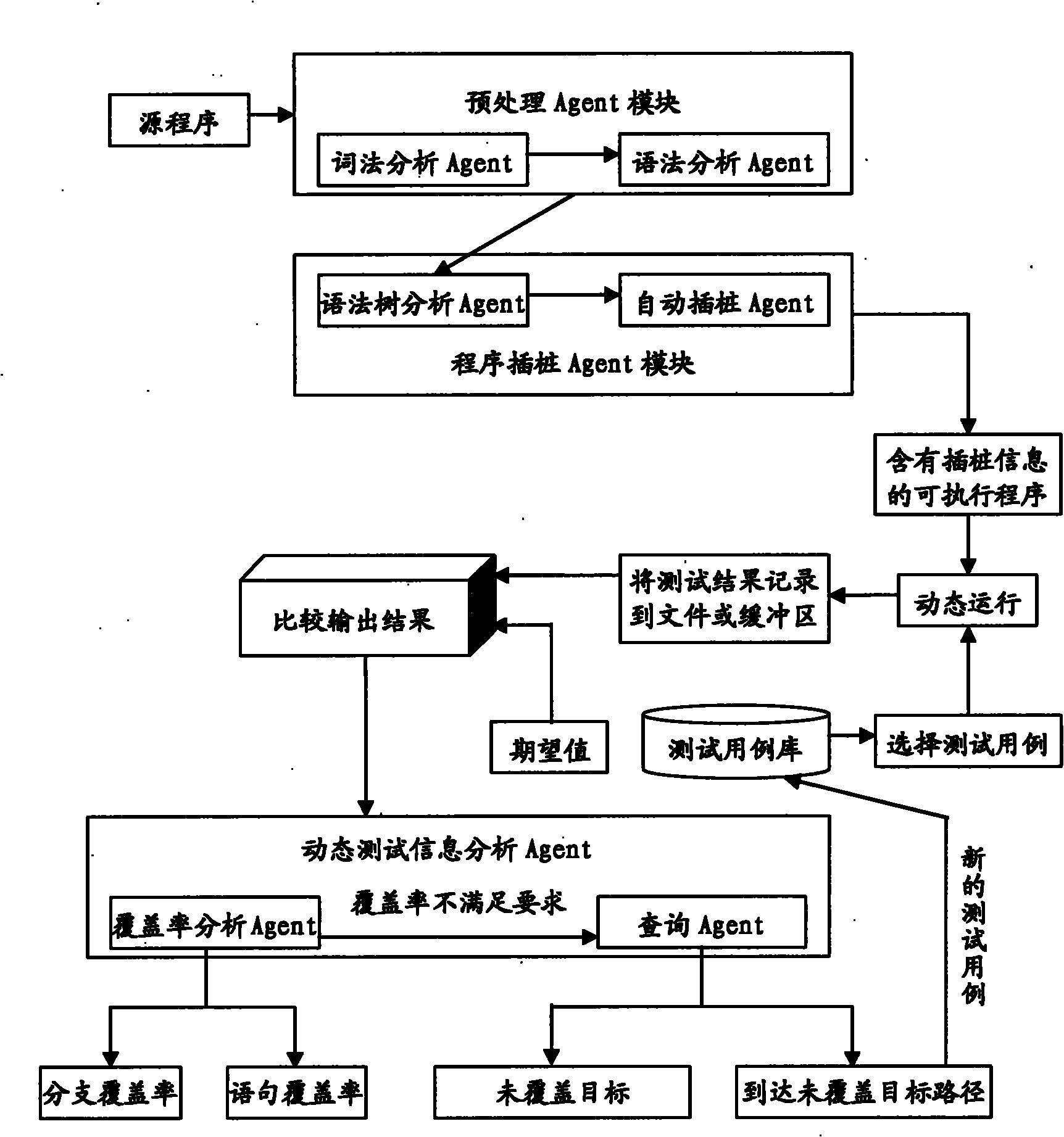
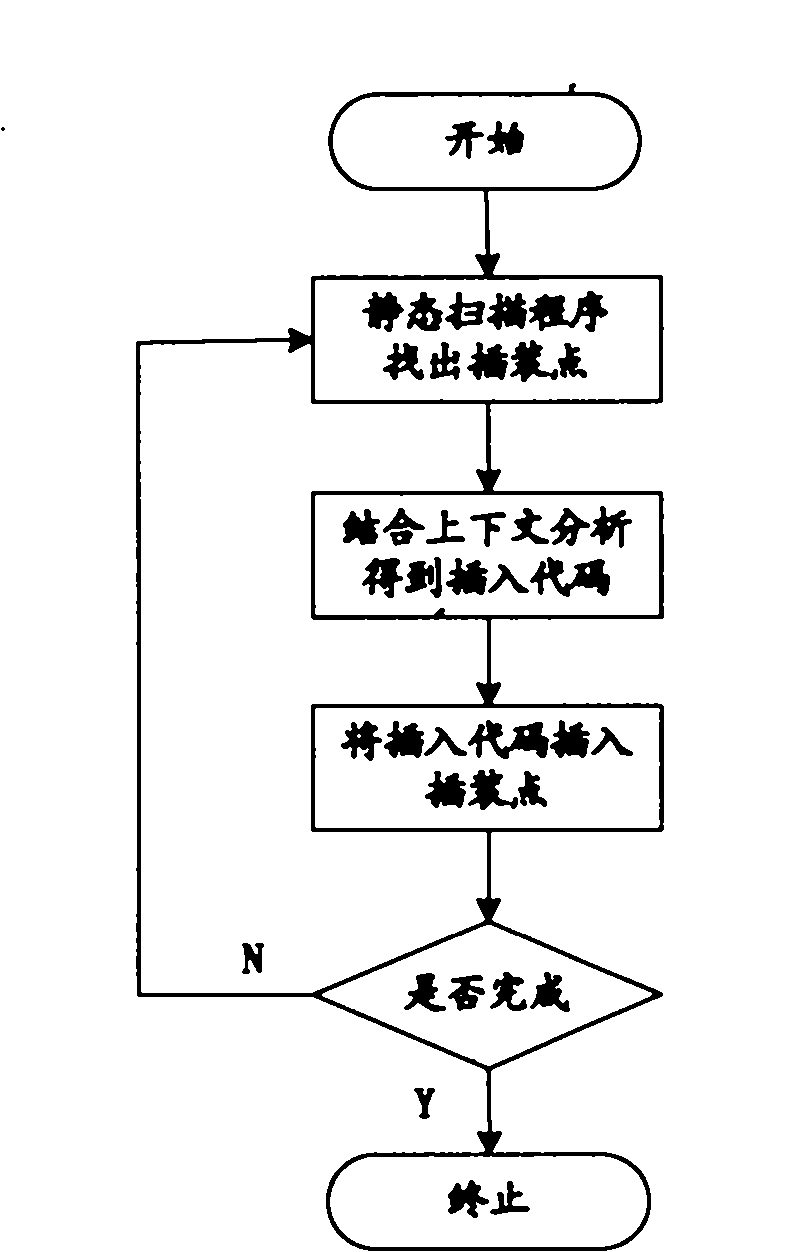
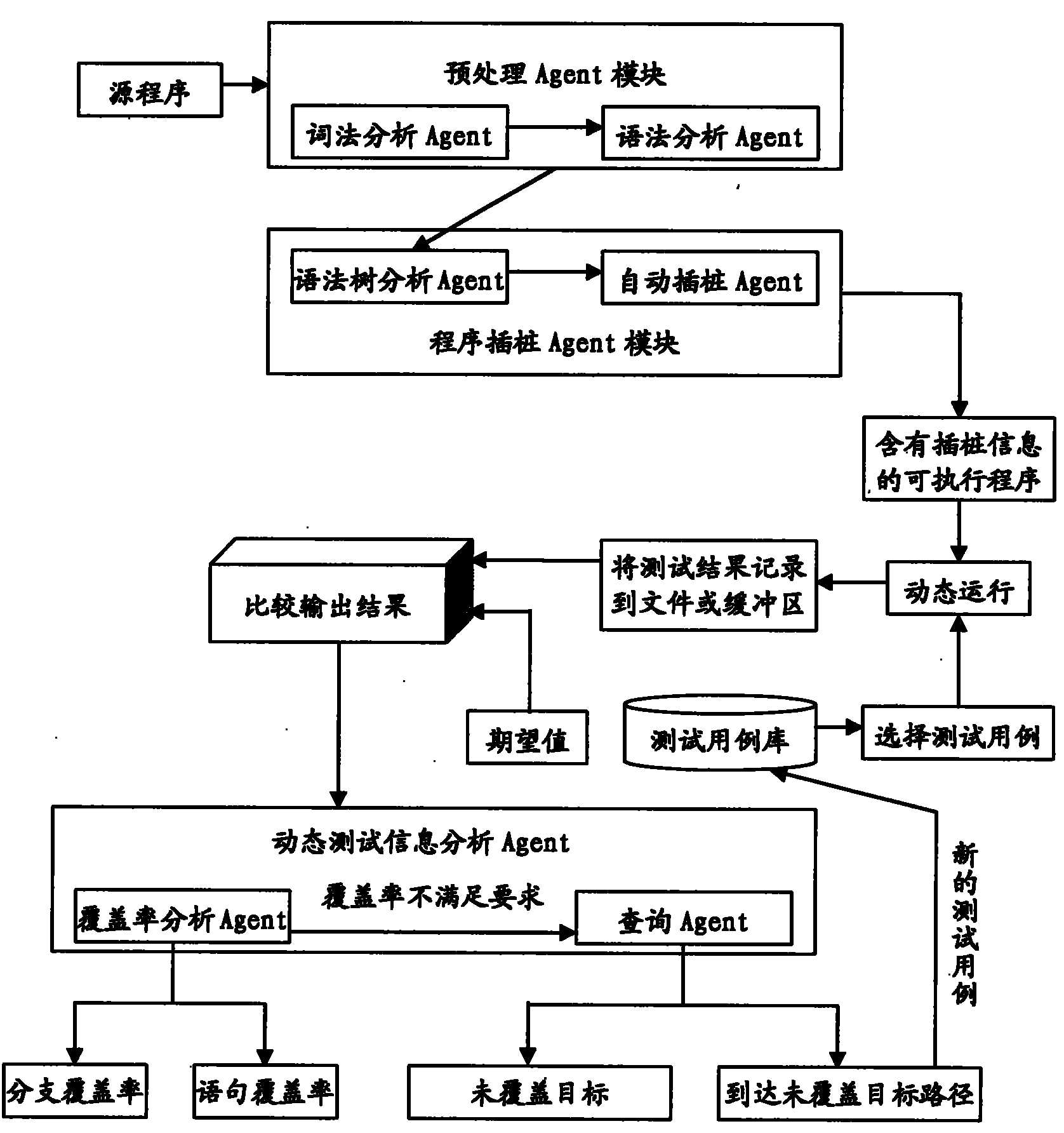
Embedded software intelligent testing method based on Agent
InactiveCN101833500AReduce interventionImprove automated testing efficiencySoftware testing/debuggingOperational systemInformation analysis
The invention relates to an embedded software intelligent testing method based on Agent, which is an improved software testing method using a Linux system as an embedded operation system core, mainly comprising three Agent modules: a pre-processing Agent module, a program instrumentation Agent module and a dynamic test information analysis Agent module. The pre-processing Agent module comprises a lexical analysis Agent and a grammar analysis Agent that are used for generating a grammar tree structure of a source program; the program instrumentation Agent module comprises a grammar tree analysis Agent and an automatic instrumentation Agent that are mainly used for analyzing the grammar tree, finding out the key point of the source program, and automatically inserting probe functions in the source program so as to acquire the dynamic information during the operation of the program; and the dynamic test information analysis Agent module comprises a cover ratio analysis Agent and an inquiry Agent that are mainly used for testing the sentence and the branch cover ratio of the source program, and automatically inquiring the relevant conditions of the uncovered target in the source program when the cover ratio cannot satisfy the requirements. The invention can be applied to different programs simply and conveniently, thereby greatly improving the efficiency of the software automation test with strong commonality.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
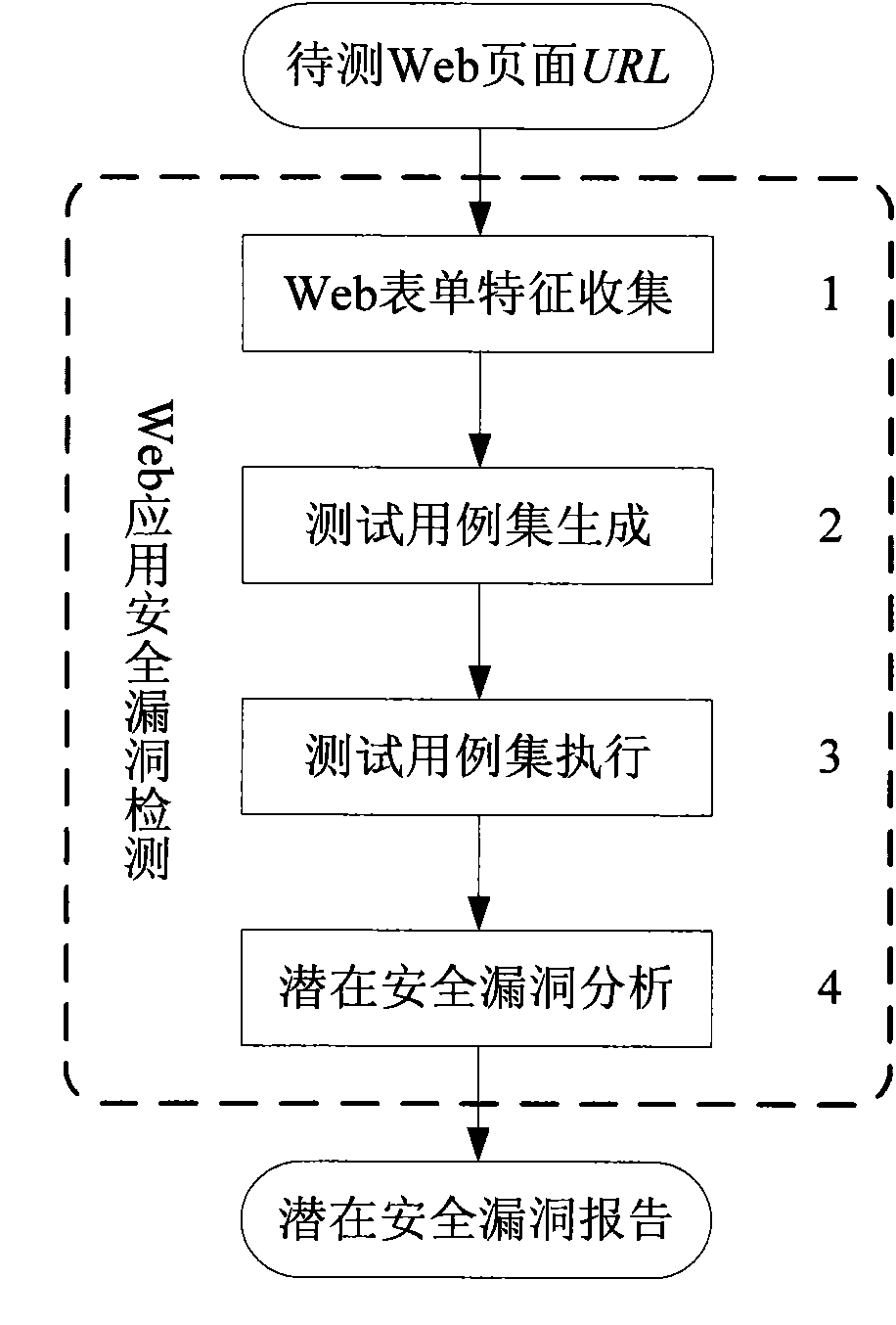
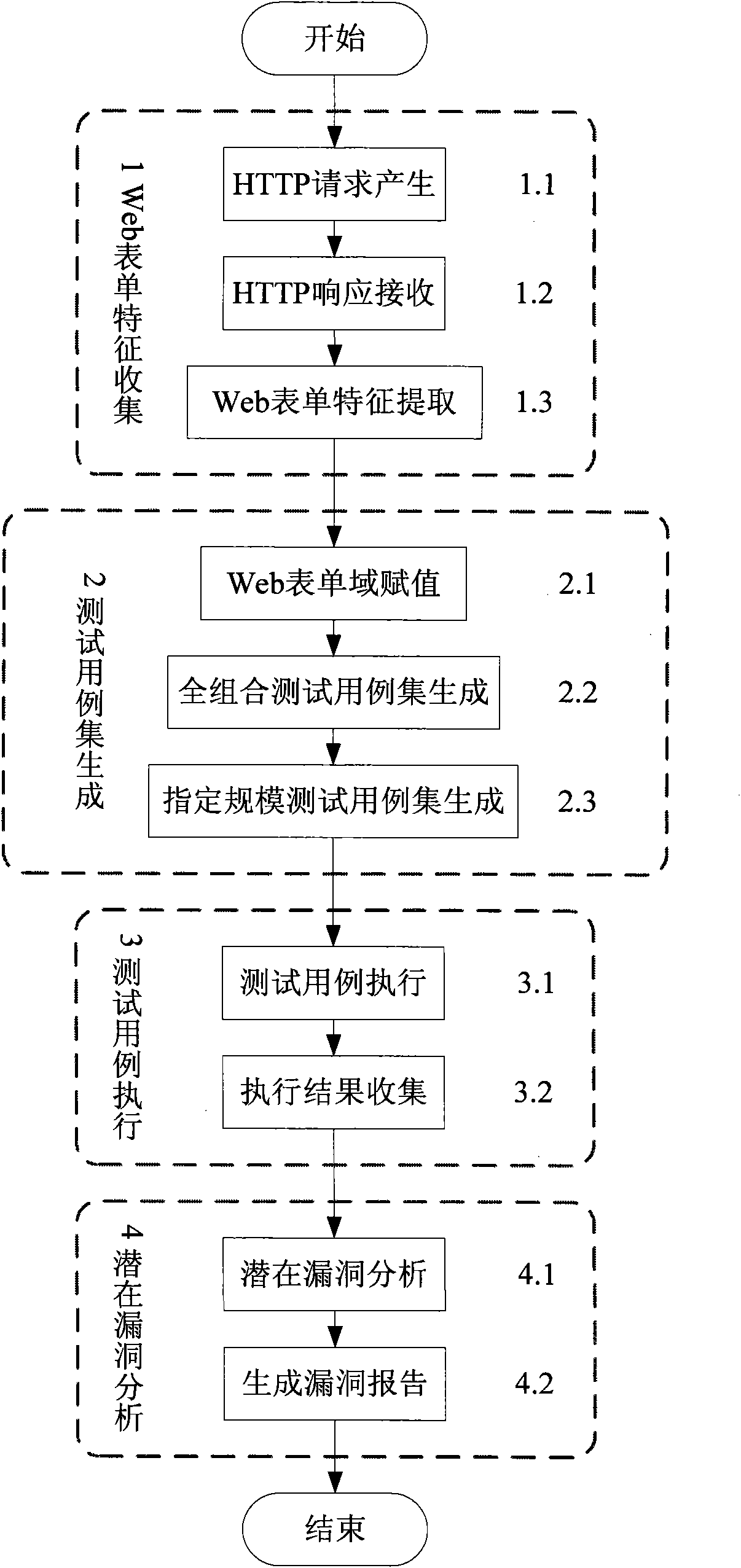
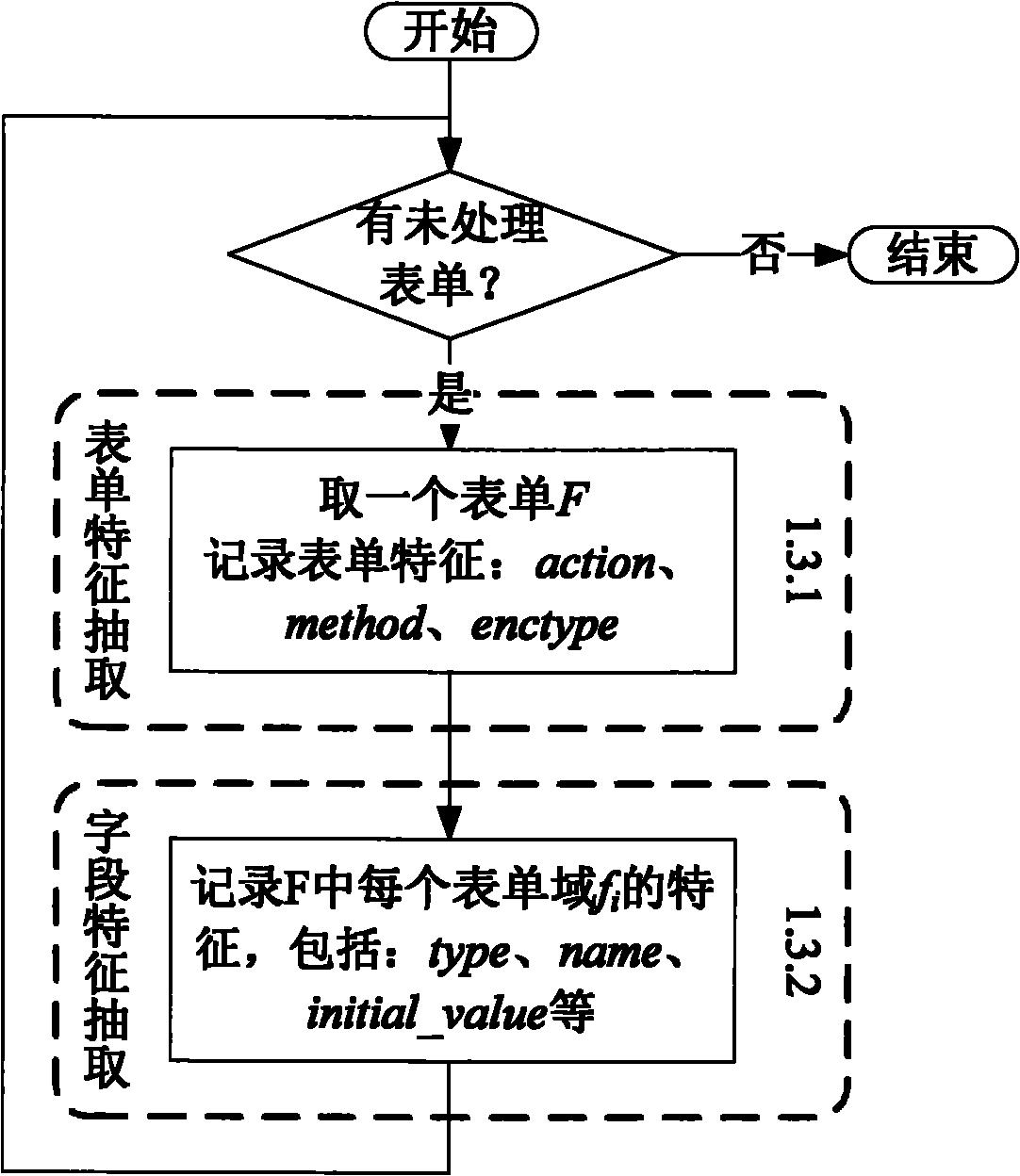
Form feature-based Web security vulnerability dynamic testing method
The invention discloses a form feature-based Web security vulnerability dynamic testing method. The method comprises the following steps of: 1) extracting automation features of a page to be tested of Web application, a form and a form domain thereof; and acquiring and storing data; 2) endowing each form domain with a group of test candidate values by taking the form as a testing unit; primarily generating an all-combination test case set; computing a weight value for each test case; and generating a test case set by using a maximal weight selection method; 3) executing the test case set; and4) performing potential security vulnerability analysis aiming at an execution result of each test case, and summarizing and generating a test report. The method endows the form domain with a security vulnerability testing value in a targeted way by using field knowledge by performing feature analysis on the Web form, interacts with a Web server to acquire a server response, and automatically tests a potential security vulnerability in the Web application according to a response result.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
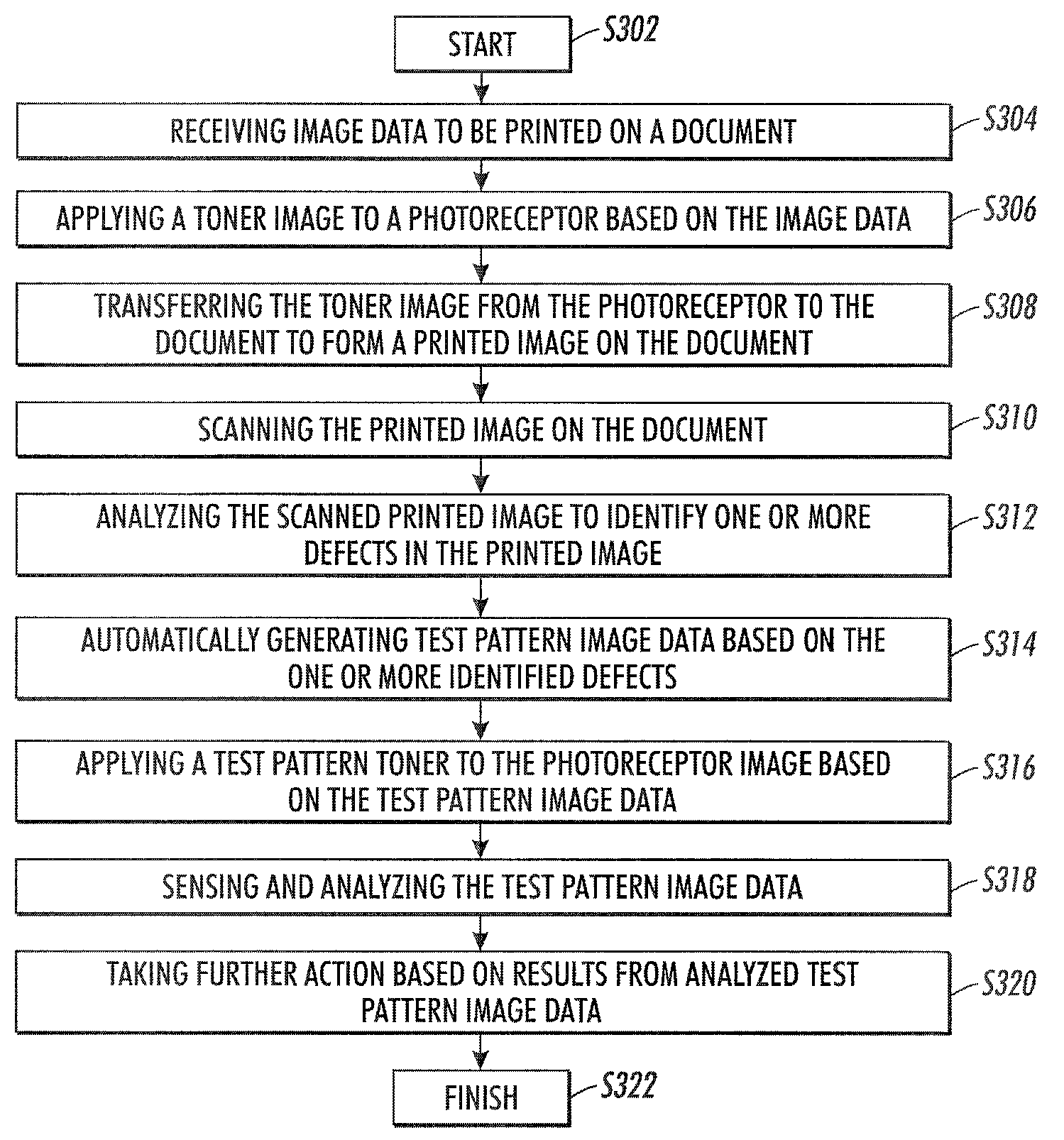
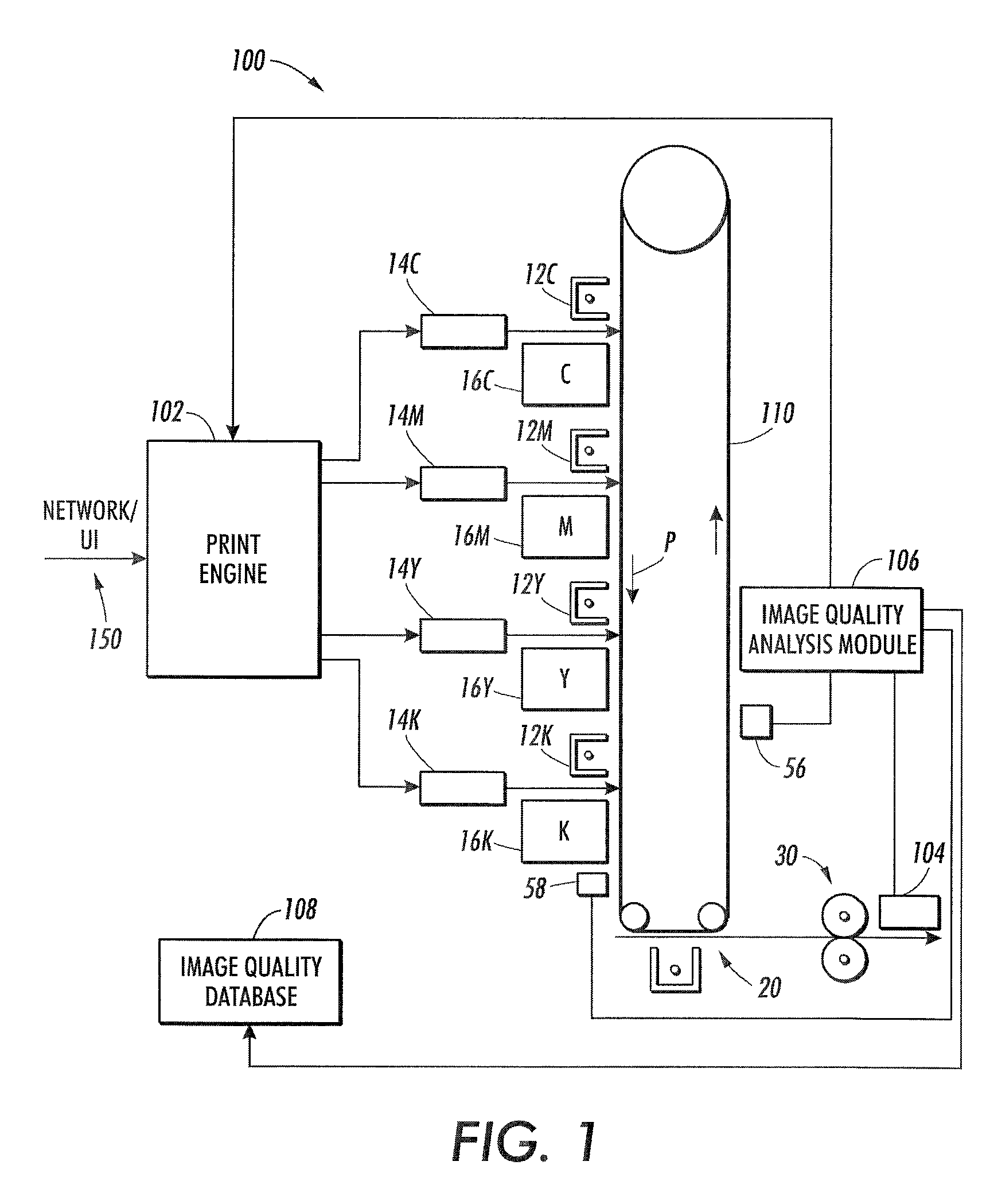
Printer characterization, monitoring and diagnosis using dynamic test patterns generated by sensing and analyzing customer documents
ActiveUS20090274342A1Quality imageVisual presentation using printersCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionImaging quality
A method for automated image quality based diagnosis of a document printing system is disclosed. The method comprises receiving image data to be printed on a document; printing an image on the document based on the image data; scanning the printed image on the document with a sensor; analyzing the scanned printed image with an image quality analysis module to identify one or more defects in the printed image; automatically generating test pattern image data based on the one or more identified defects; and printing and analyzing a test pattern image based on the test pattern image data.
Owner:XEROX CORP
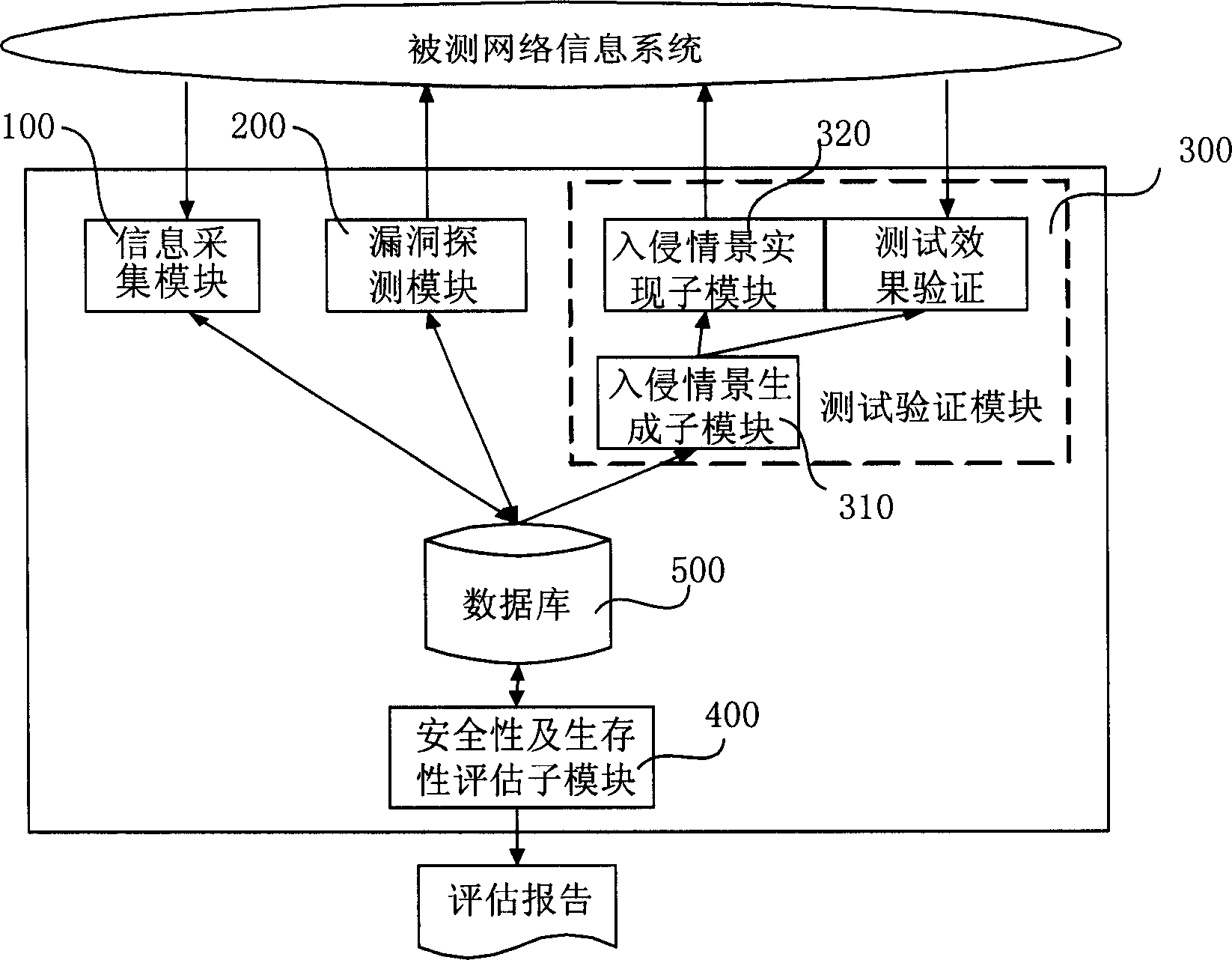
System and method for evaluating security and survivability of network information system
InactiveCN1761208AComprehensive evolution improvementComprehensive Survivability Improvements Evolutionary ImprovementsData switching networksSurvivabilityGoal system
The system includes information acquisition module, module for detecting leaking hole, testing verification module, module and database for evaluating security and survivability; the information acquisition module sends collected information of target system to the module for detecting leaking hole; the module for detecting leaking hole carries out detecting leaking hole for target system; the testing verification module carries out test and verification for leaking hole in safety existed in target object; module for evaluating security and survivability evaluates security and survivability for target system based on information of leaking hole. Simulating man induced attack to reflect real status of object to be measured, using active attack to carry out testing, the invention combines static analysis with dynamic test, giving out qualitative and quantitative evaluation and suggestion for survivability of system.
Owner:郭世泽 +7
Structure health monitoring method based on distributed strain dynamic test
InactiveCN101221104AOvercoming only point distributionOvercoming the pitfalls of making \"point\" measurementsFoundation testingStrength propertiesMathematical modelStructural health monitoring
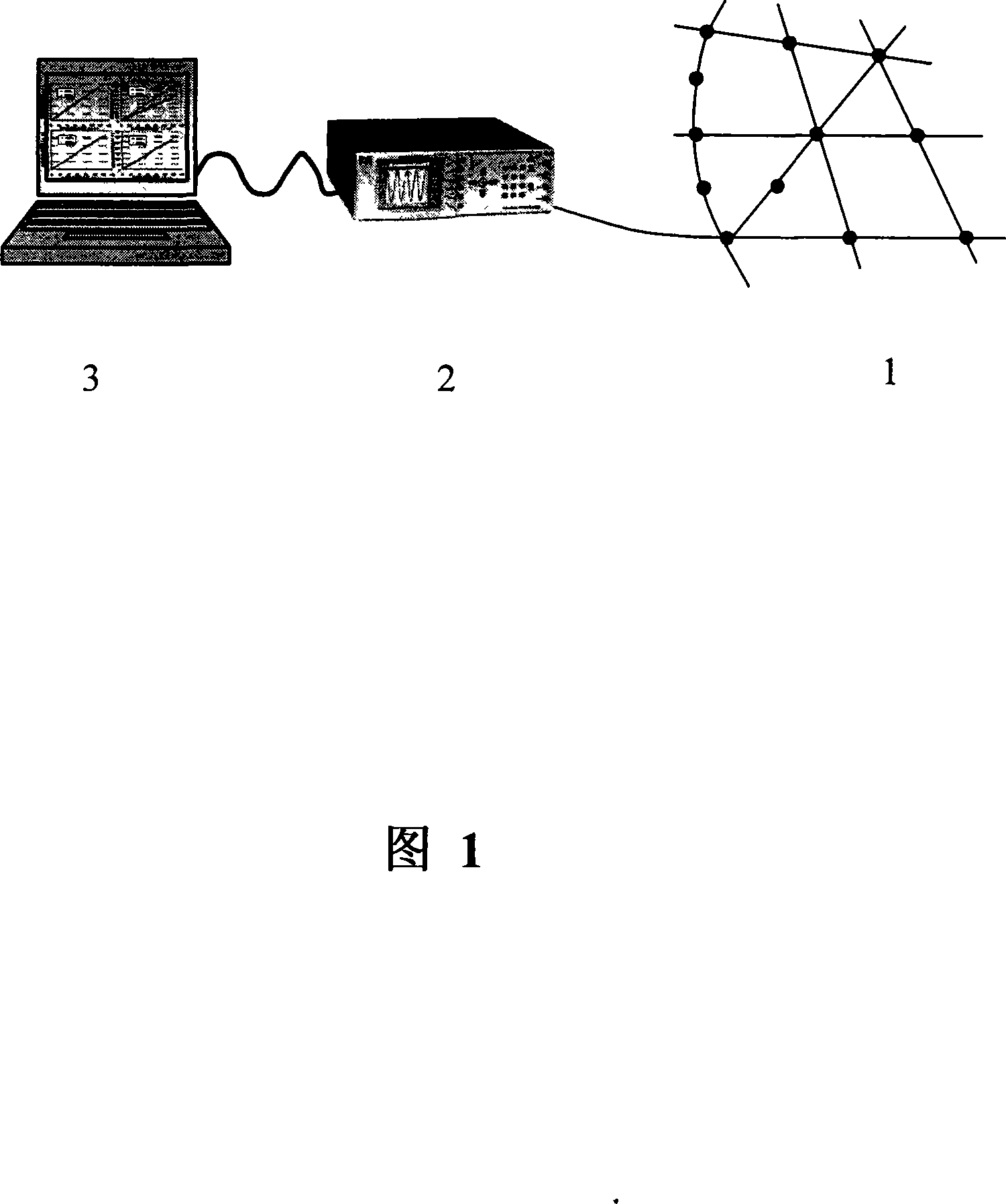
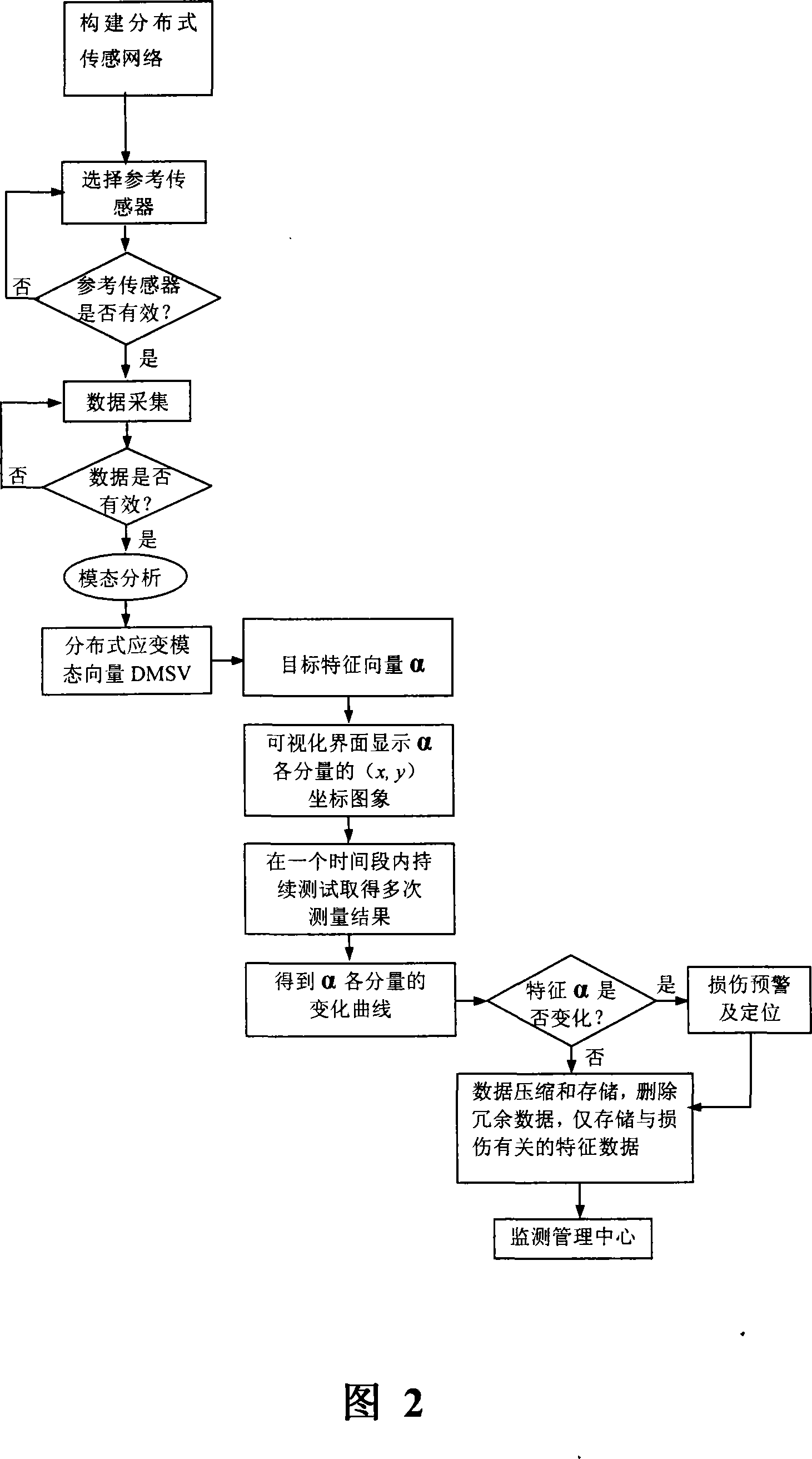
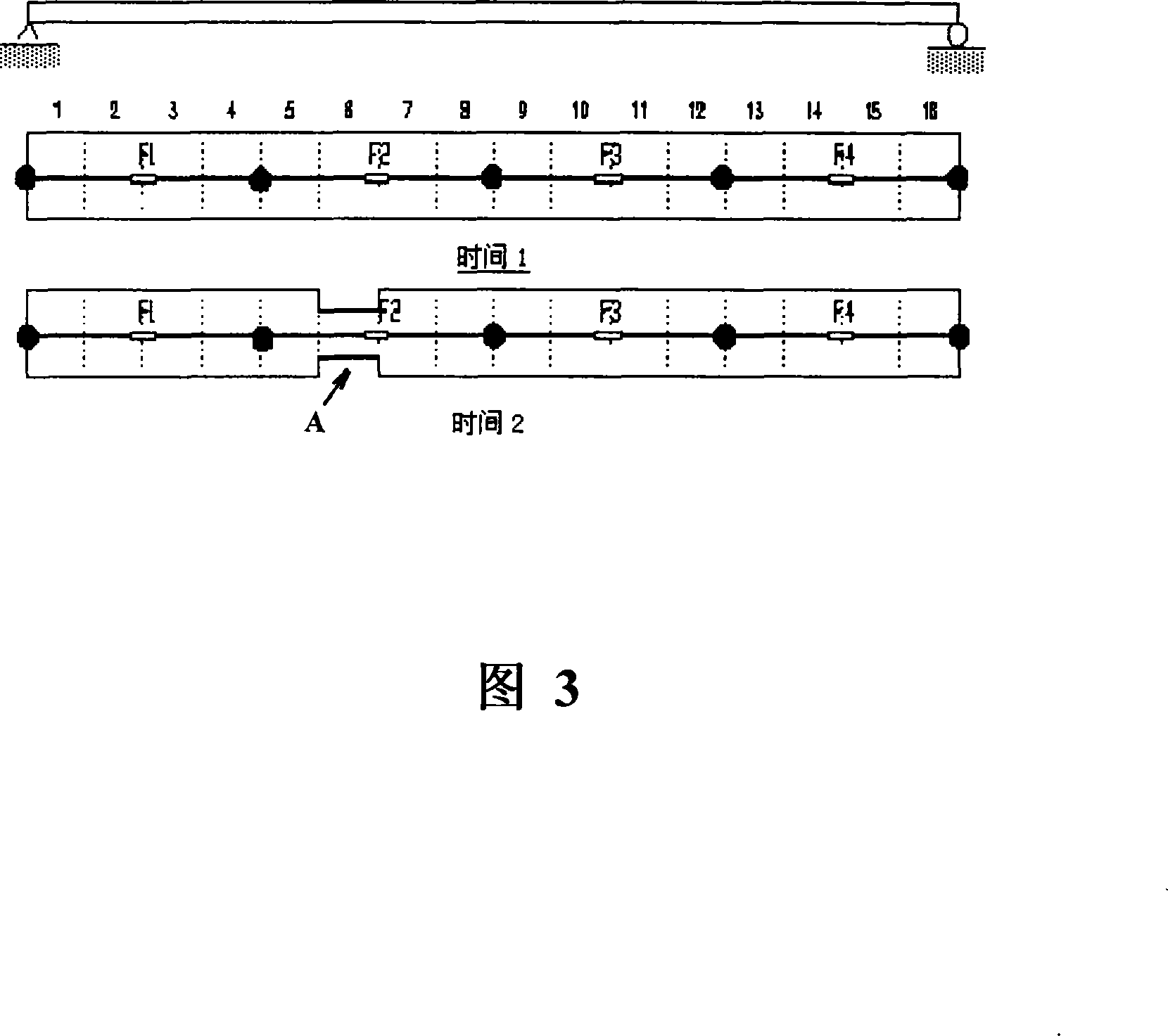
The invention discloses a method for monitoring the structure health based on a distributed strain dynamic test; the invention adopts a distributed strain transducer to build a distributed sensing network and selects to arrange a reference transducer, carries out structure system simulation state analyzing to obtain a distributed strain simulation state vector DMSV, originally takes whether a target characteristic vector Alpha changes or not as a criterion to identify structural damage, obtains the effects of being capable of rapidly, accurately and effectively capturing the structural damage and locating, and simultaneously adopts the reasonable measures of real time image display and deleting redundant data on time, thereby having the advantages of small errors, high precision, simple process and intuitionistic monitoring; the method can eliminate the interference of noise and environment under the conditions of uncertain loading and an unknown mathematical model, carry out on-line structural damage detecting and diagnosing in real time and is suitable for long period monitoring of various engineering structures, especially for the civil structure.
Owner:吴智深 +1
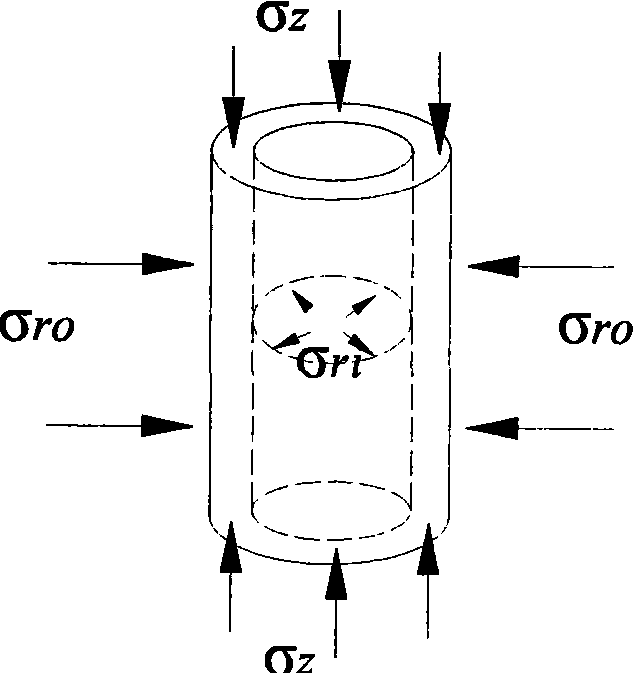
Rock deforming and cracking three-dimensional dynamic testing system based on fiber strain sensing
InactiveCN101520317AIncrease space positionMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesUsing optical meansFiber strainInstability
The invention relates to a rock deforming and cracking three-dimensional dynamic testing system based on fiber strain sensing, which comprises a testing piece, wherein the testing piece is laid with a fiber sensor encapsulated with a plurality of testing strains; the fiber sensor is connected with a signal demodulation processing device through a connecting fiber; and demodulated data signals can build three-dimensional testing data of the testing piece and can form a three-dimensional dynamic strain field of the testing piece after interpolation. The system can effectively lay out the fiber sensor inside and on the surface of the real rock testing piece under the pressure of a three-axis presser, enters the rock inside to detect the rock dynamic strain under the premise of not influencing the rock structure and the stress, and can really test the rock dynamic cracking process to obtain the crack initial and expended spatial positions inside the testing piece. The system continuously monitors the generation and expansion of tiny cracks inside brittle materials under the loading action in real time at the same time, and can be widely applied to researching cracking instability mechanisms of materials, such as rocks, concrete and the like.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
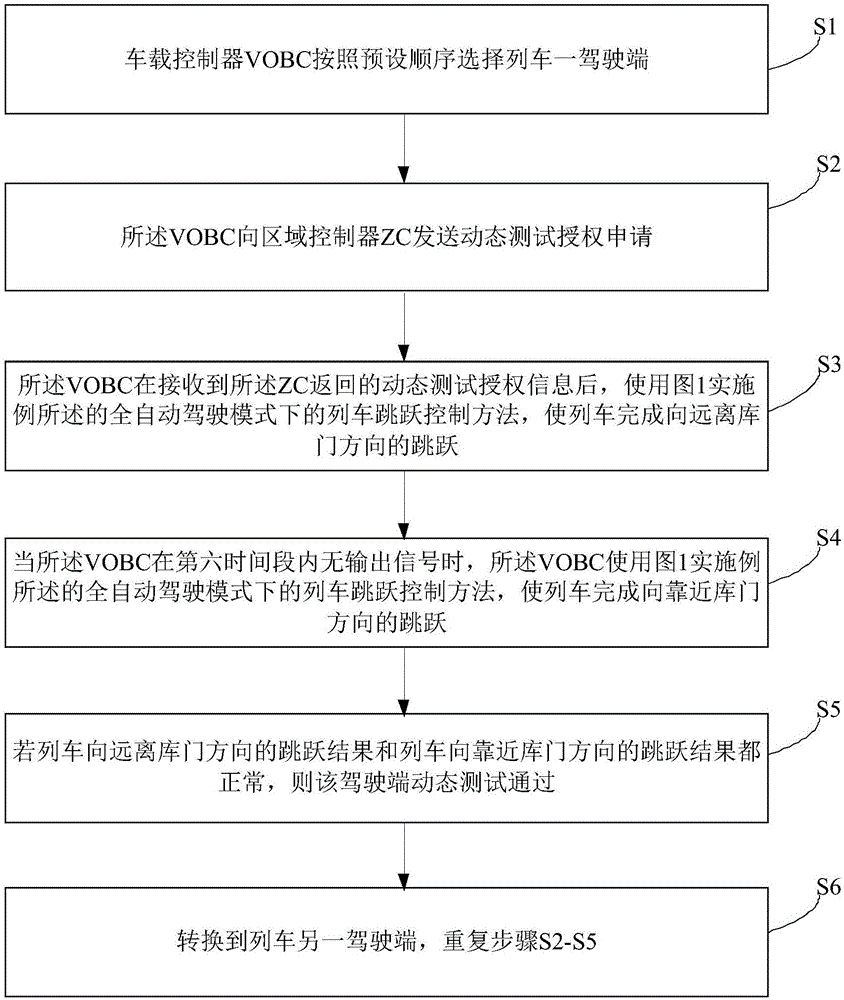
Automatic dynamic testing method for waking up of full-automatic driving train
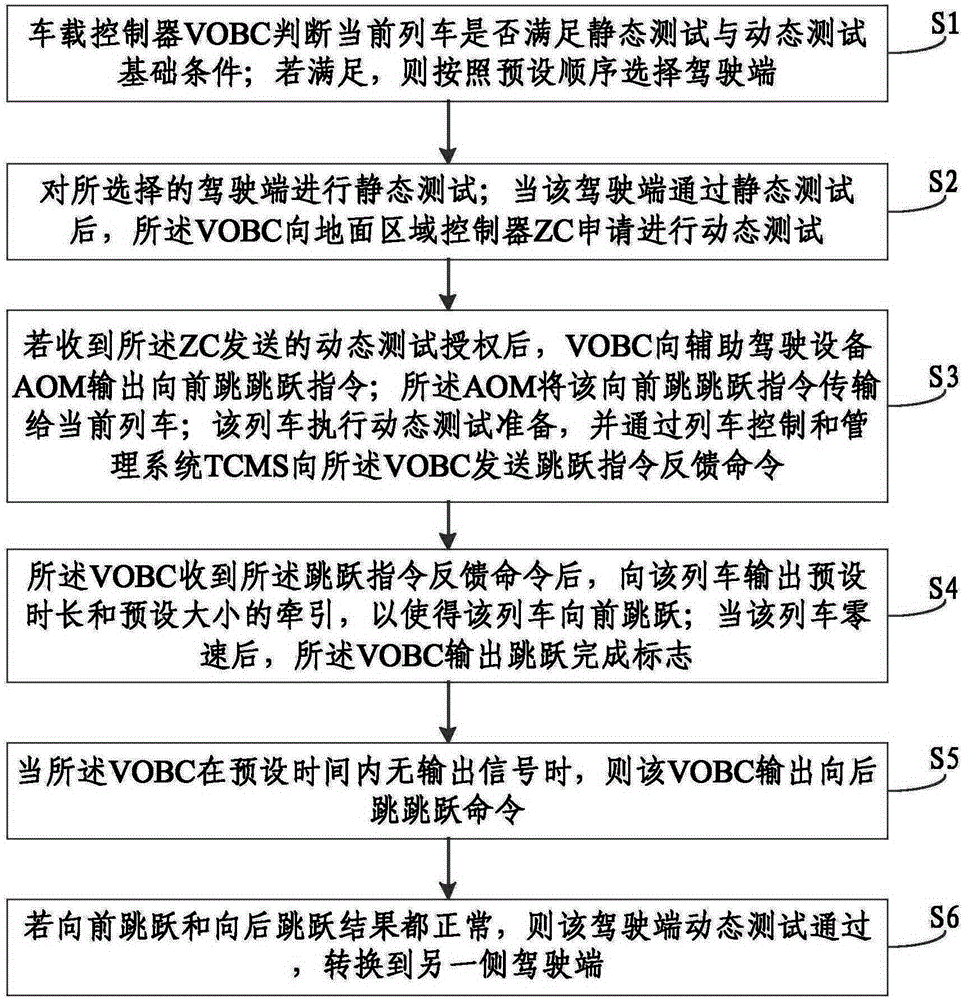
ActiveCN105404272ARealize automatic dynamic test functionProgramme controlElectric testing/monitoringTraction systemEngineering
The invention relates to an automatic dynamic testing method for waking up of a full-automatic driving train. The method comprises: S1, a driving end is selected according to a preset sequence; S2, a VOBC makes an application to a ground area controller ZC to carry out dynamic testing; S3, after authorization, the VOBC outputs a forward leap instruction to an AOM; the AOM transmits the forward leap instruction to a current train; and the train executes dynamic testing equipment and a leap instruction feedback command is sent to the VOBC by a TCMS; S4, the VOBC outputs traction information with a preset time length and a preset dimension to the train; and after the speed of the train reaches the zero speed, the VOBC outputs a leap completion mark; S5, the VOBC outputs a backward leap command; and S6, the forward leap result and the backward leap result are normal, dynamic testing of the driving end is done successfully and changing to a driving end at the other side is carried out and the steps from S2 to S6 are repeated. According to the invention, a problem of energy wasting or equipment wearing due to manual operation negligence can be solved, thereby realizing reliable working of a traction system and a brake system of a to-be-detected train.
Owner:TRAFFIC CONTROL TECH CO LTD
Android application vulnerability detection method and Android application vulnerability detection system
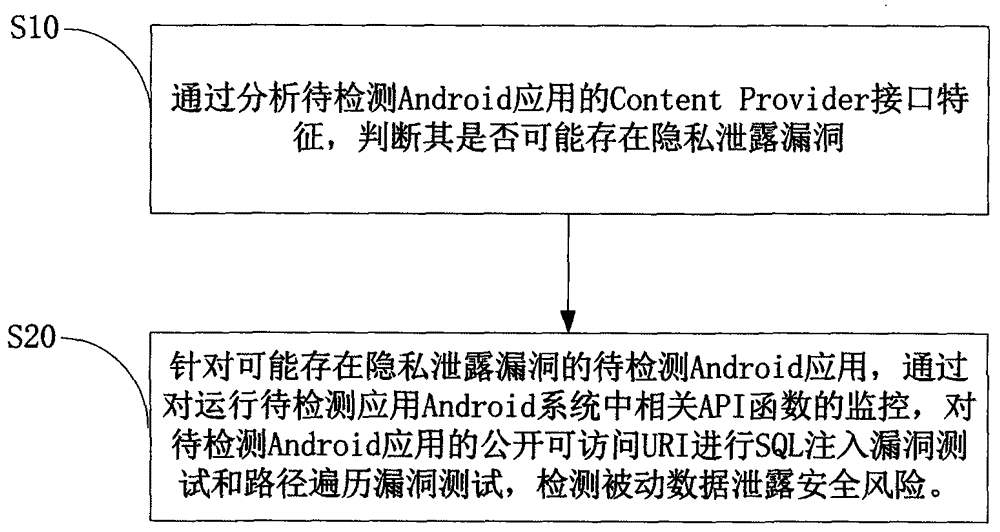
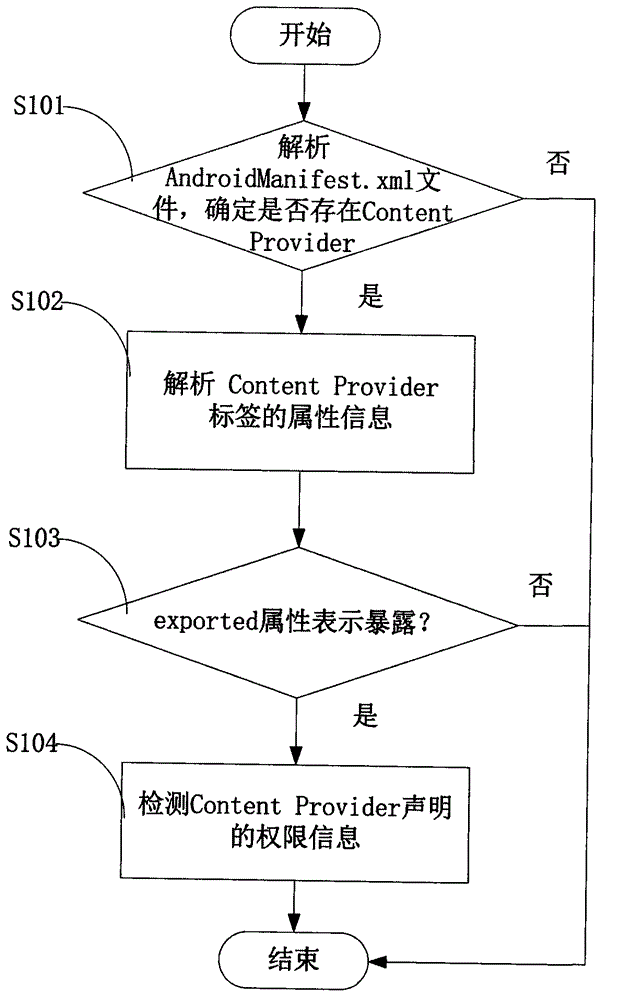
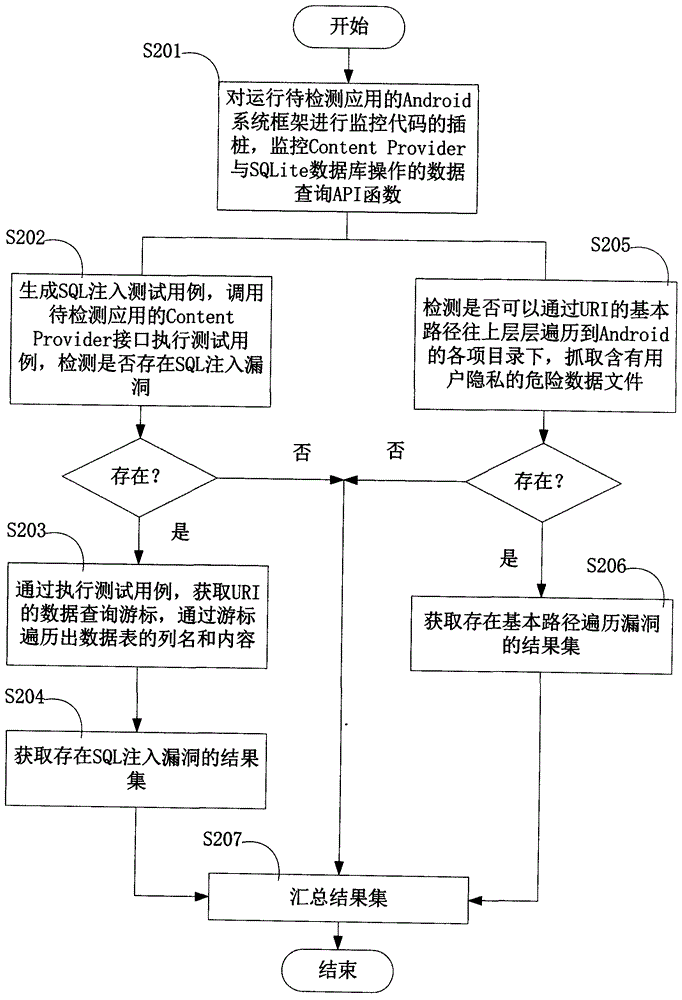
InactiveCN103984900AAvoid false positivesEfficient discoveryPlatform integrity maintainanceSQL injectionUniform resource identifier
The invention provides an Android application vulnerability detection method which comprises the following steps: 1, judging whether a privacy leakage vulnerability possibly exists or not by virtue of analyzing Content Provider interface characteristics of a to-be-detected Android application; 2, if the privacy leakage vulnerability possibly exists, performing an SQL (Structured Query Lanaguge) injection vulnerability test and a path traversal vulnerability test on a public accessible URI (Uniform Resource Identifier) of the to-be-detected Android application which possibly has the privacy leakage vulnerability by virtue of monitoring a related API (Application Program Interface) function in an Android system, and then detecting passive data leakage safety risks. The invention also provides an Android application vulnerability detection system. The method and the system can be used for rapidly discovering privacy leakage and data pollution vulnerabilities possibly existing in the Android application, avoiding misdeclaration, and providing a powerful support for discovering the privacy leakage and data pollution vulnerabilities in the Android application on a large scale.
Owner:南京赛宁信息技术有限公司 +1
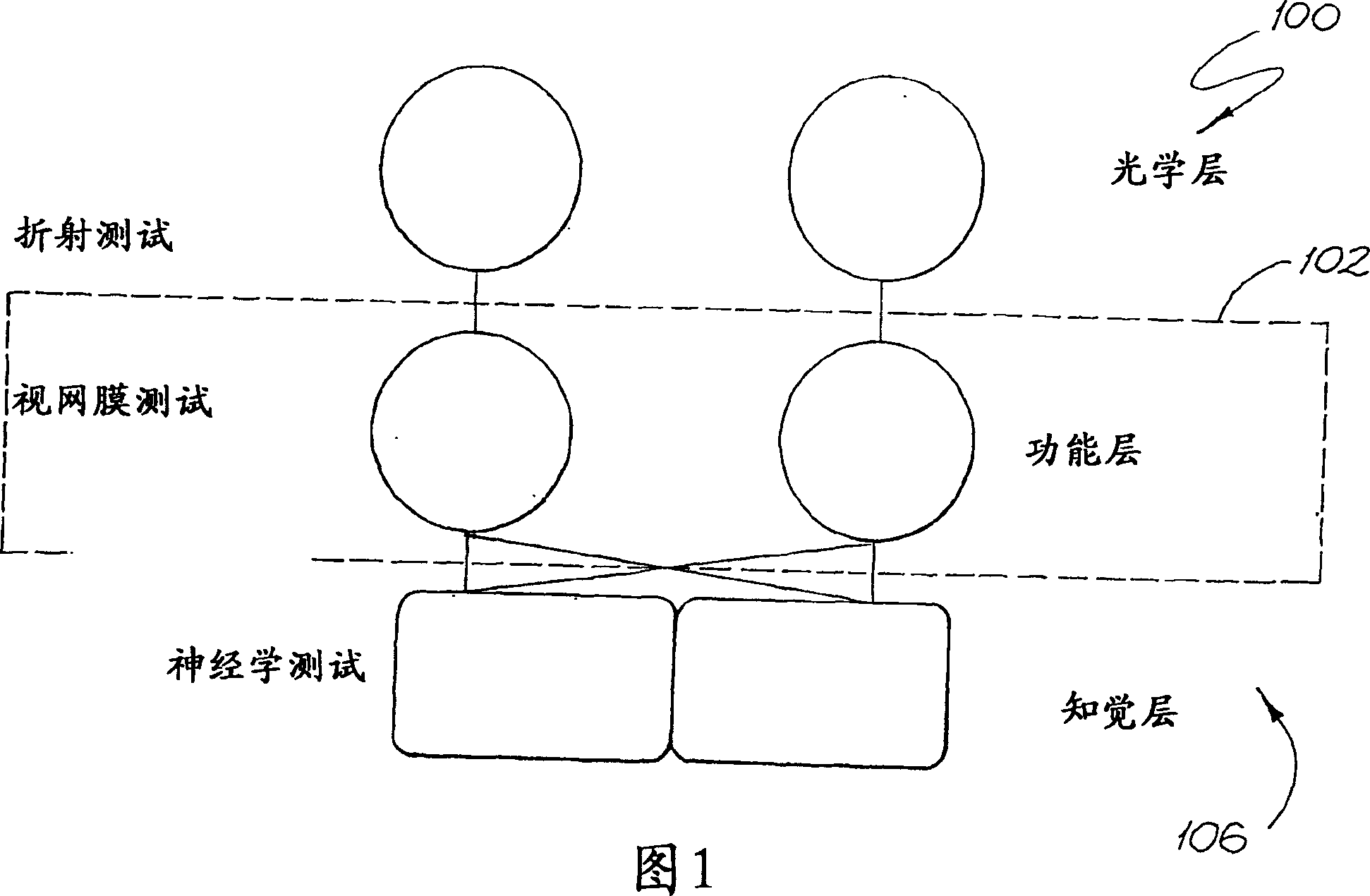
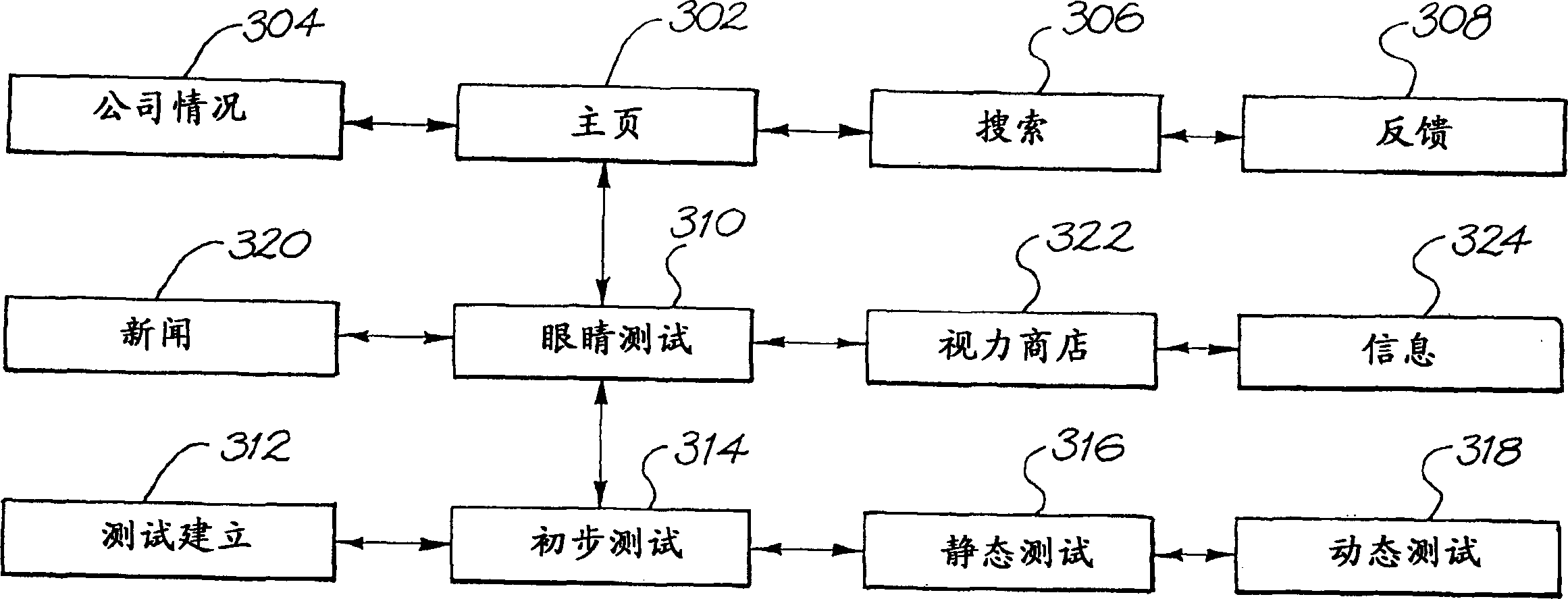
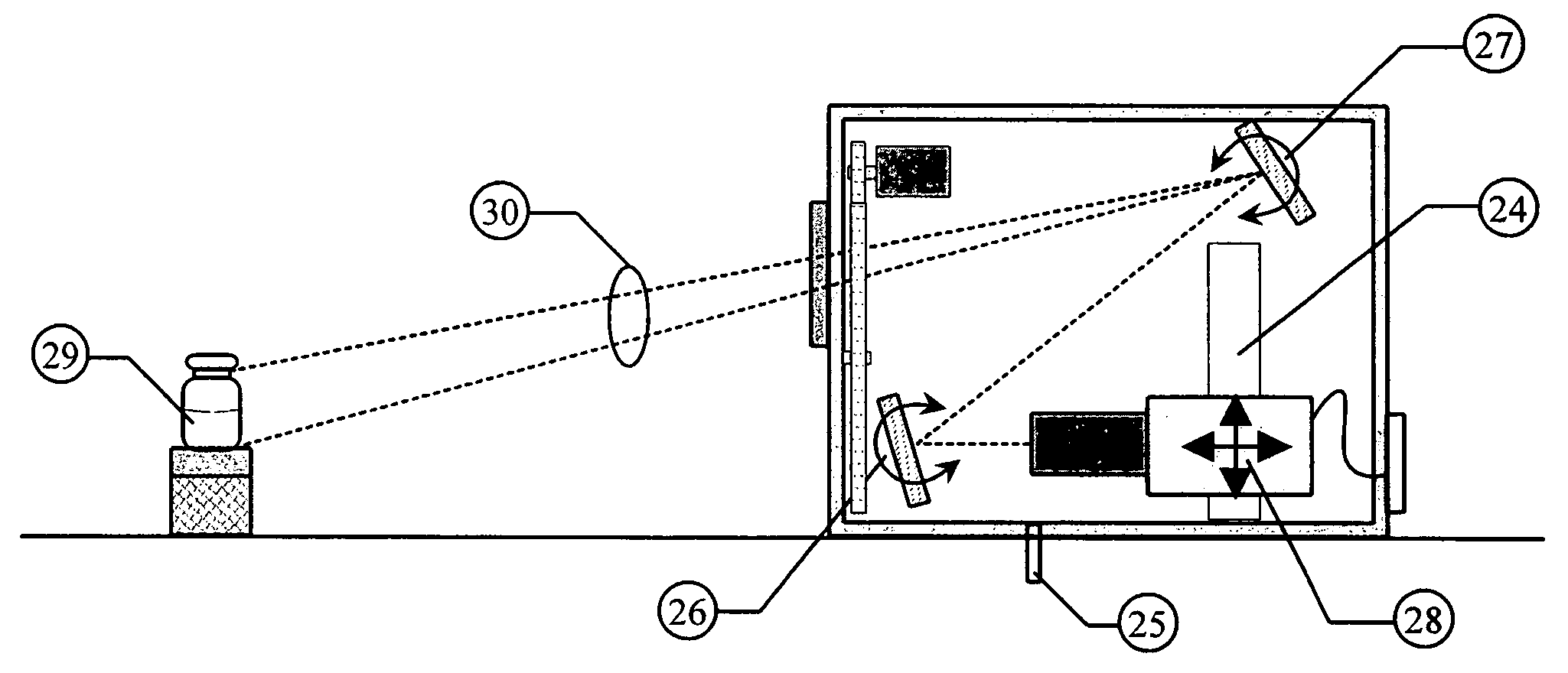
Vision testing system
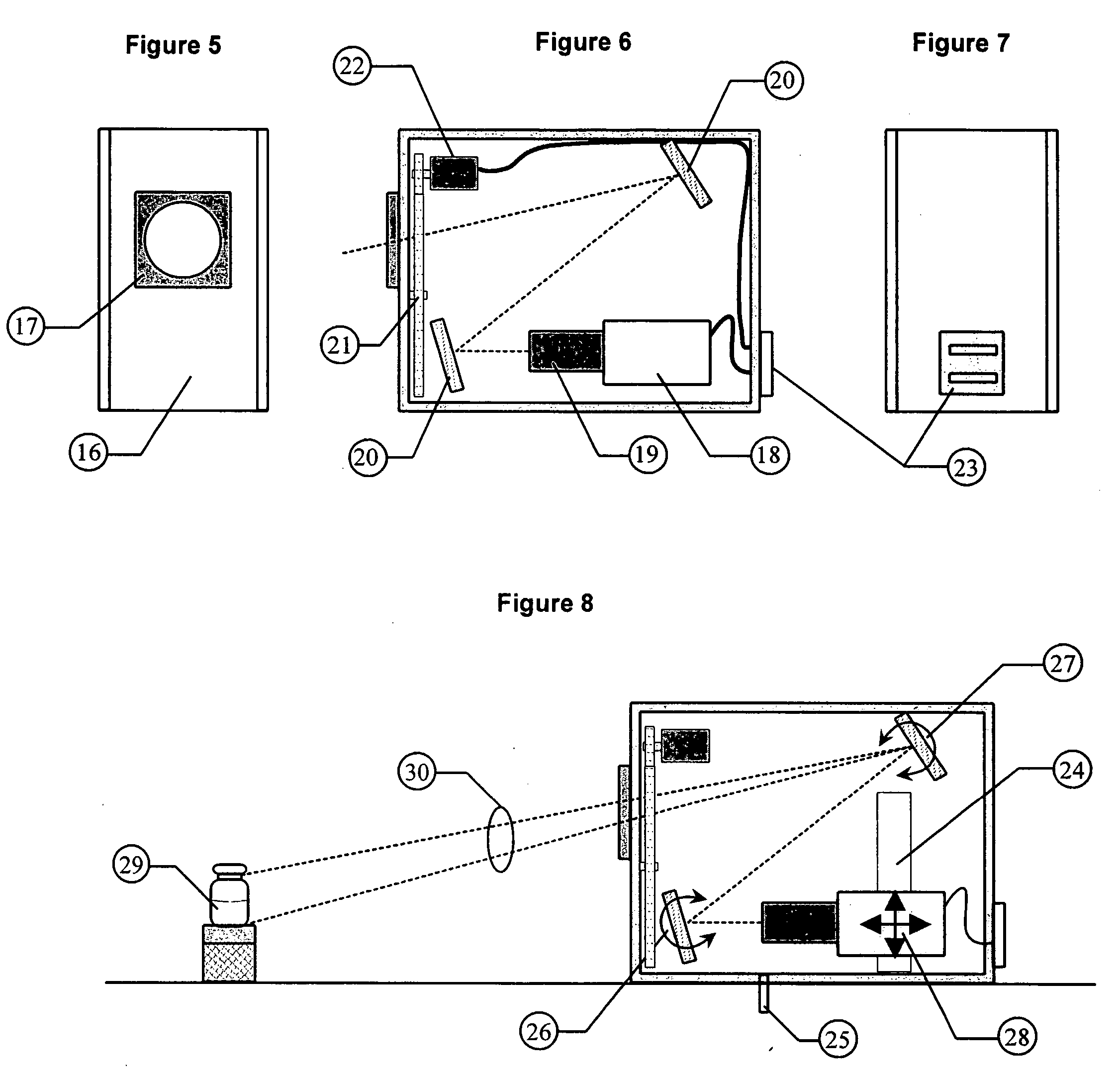
A method and apparatus are provided for testing the vision of a human subject using a series of eye tests (310). A test setup procedure (312) is run to adjust the settings of a display device (1914) such that graphic objects displayed on the device (1914) conform to a pre-defined appearance. A series of preliminary tests (314), static tests (316) and dynamic tests (318) are displayed on the device (1914), and the responses of the subject are recorded. The tests (310) may be run remotely, for example over the Internet. No lenses are required to run the tests (310).
Owner:AIVISION PTY LTD
Automated visual inspection system for the detection of microbial growth in solutions
ActiveUS20060072111A1Easy to adjustLess optical densityOptically investigating flaws/contaminationParticle size analysisNon destructiveVisual inspection
Essential prerequisites for any injectable product are its sterility, its freedom from pathogens and its freedom from visible particle contamination . . . . These requirements must be satisfied prior to the release of an injectable product batch for sale and use. A major difficulty in responding to these assay requirements is the need for a size sensitivity difference of 100 or greater in determining the presence of viable pathogenic organisms and of non-viable random particle contaminants. The wide dynamic testing range cannot be satisfied in current art with a single non-destructive testing station. The present invention uses a special agitation procedure to generate separate liquid volumes containing the small viable and larger non-viable particle contaminants. This separation makes possible the introduction of sensing systems that have been optimized for each size range and that can operate in parallel without interference.
Owner:BUDD GERALD WALTER +1
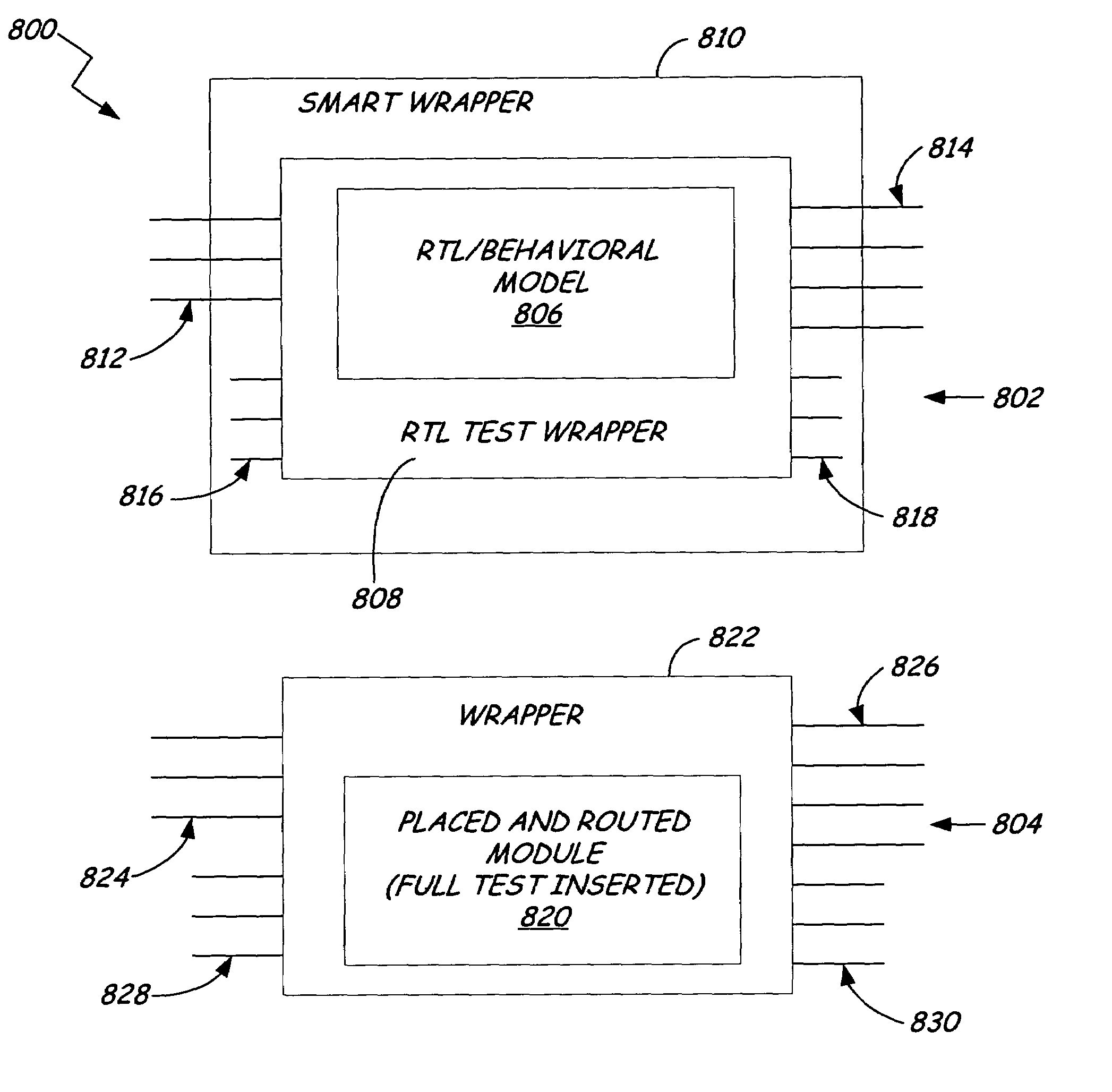
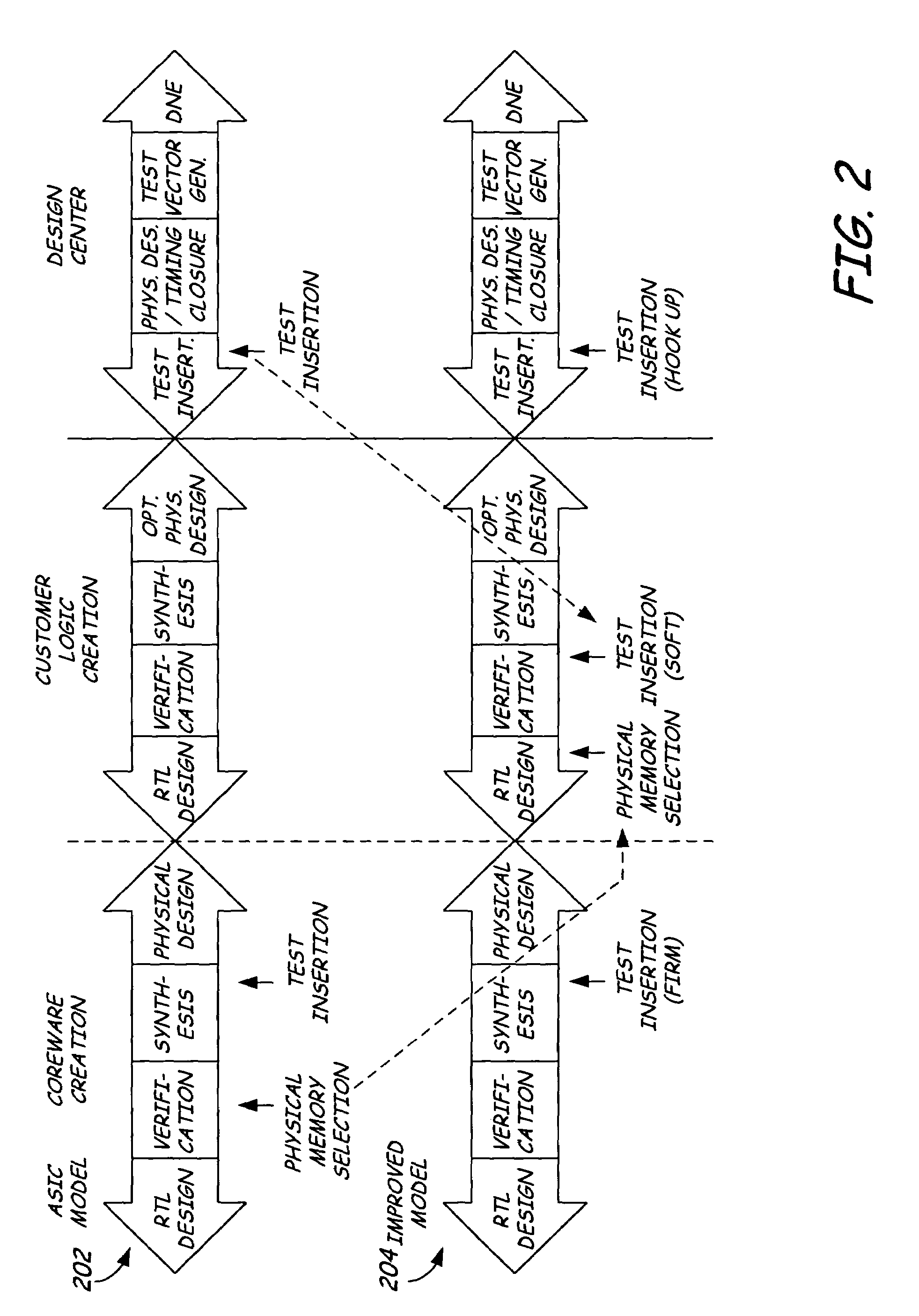
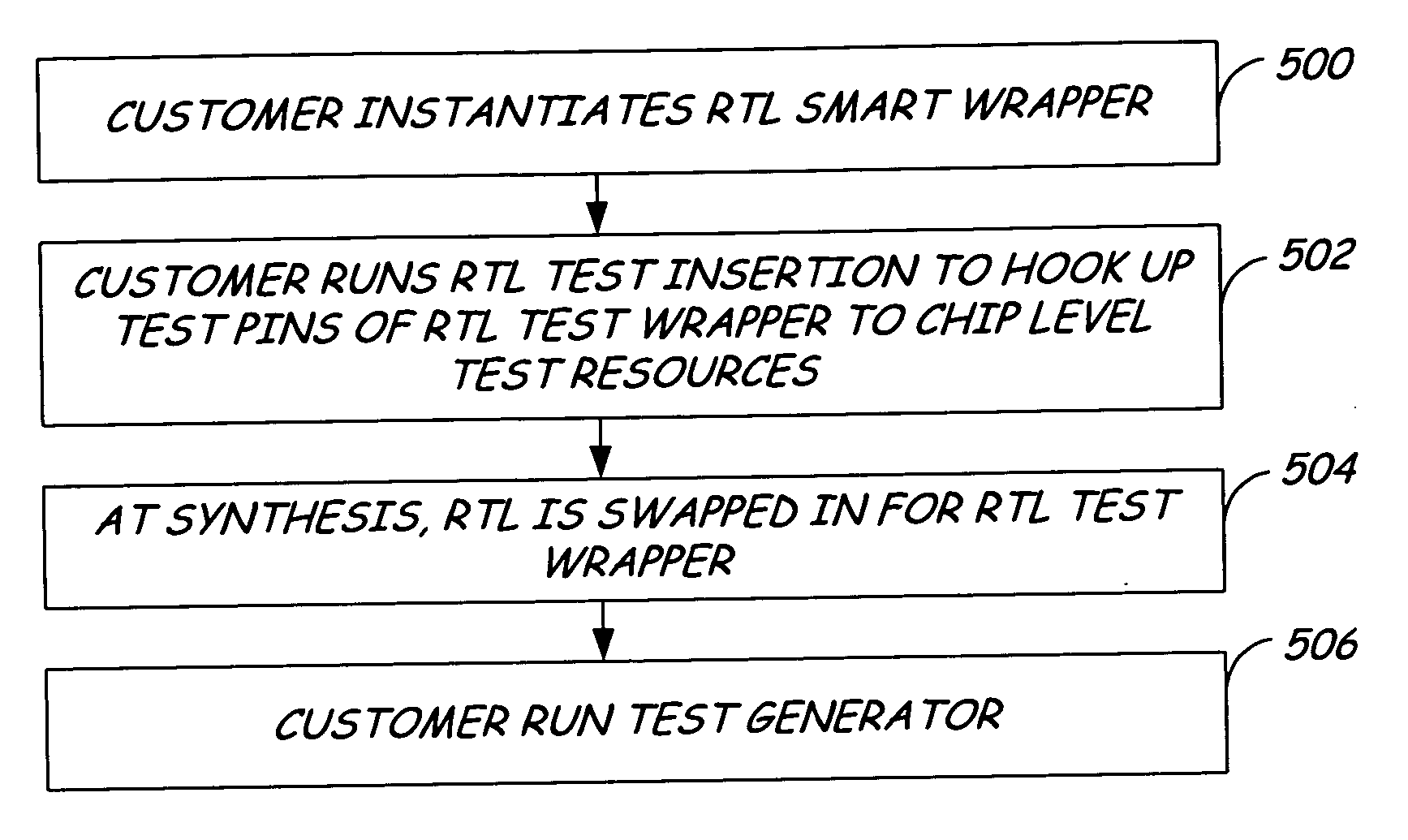
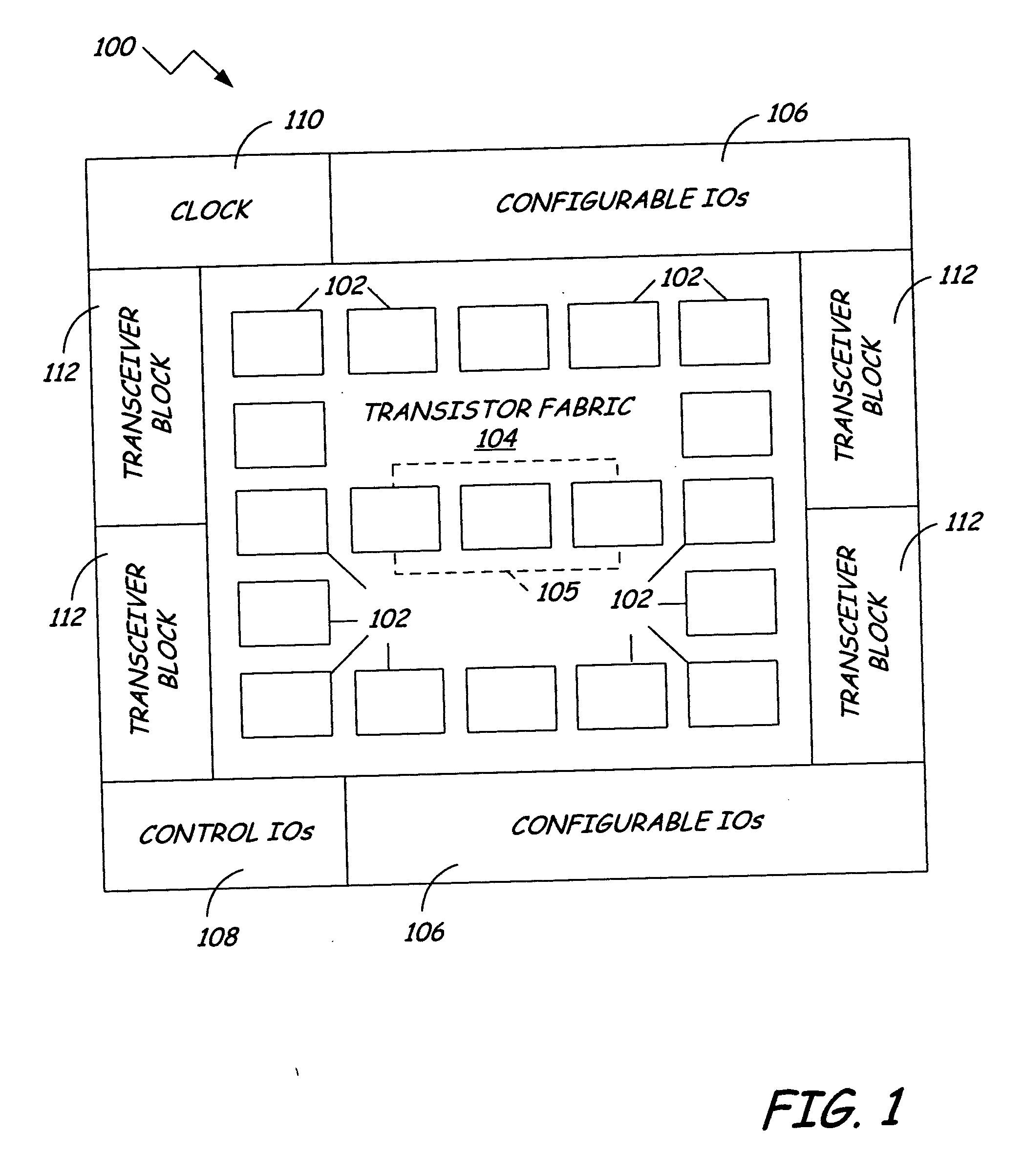
Method for abstraction of manufacturing test access and control ports to support automated RTL manufacturing test insertion flow for reusable modules
A system for RTL test insertion in an integrated circuit layout pattern includes a core module, a test wrapper, and a smart wrapper. The core module describes a function defined by logical elements, interconnections between logical elements, input pins and output pins. The test wrapper is adapted to encapsulate the core module and to create test pins representing the core module. The smart wrapper is adapted to encapsulate the test wrapper and to assign the test pins to a non-asserted state. The smart wrapper is adapted to place an assertion on one or more of the test pins for static or dynamic testing of the integrated circuit layout pattern.
Owner:BELL SEMICON LLC
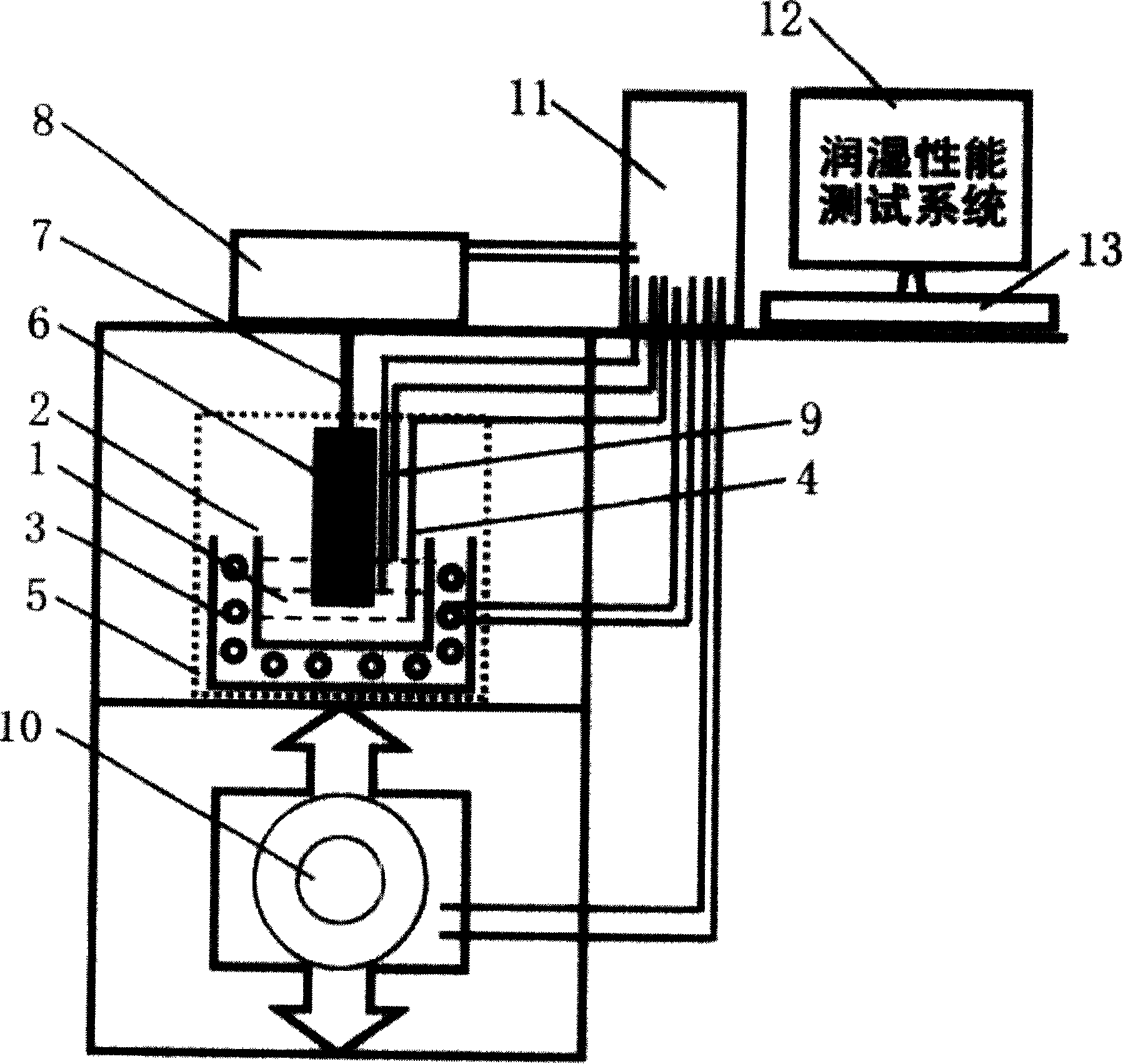
Dynamic testing method and system for wetting property
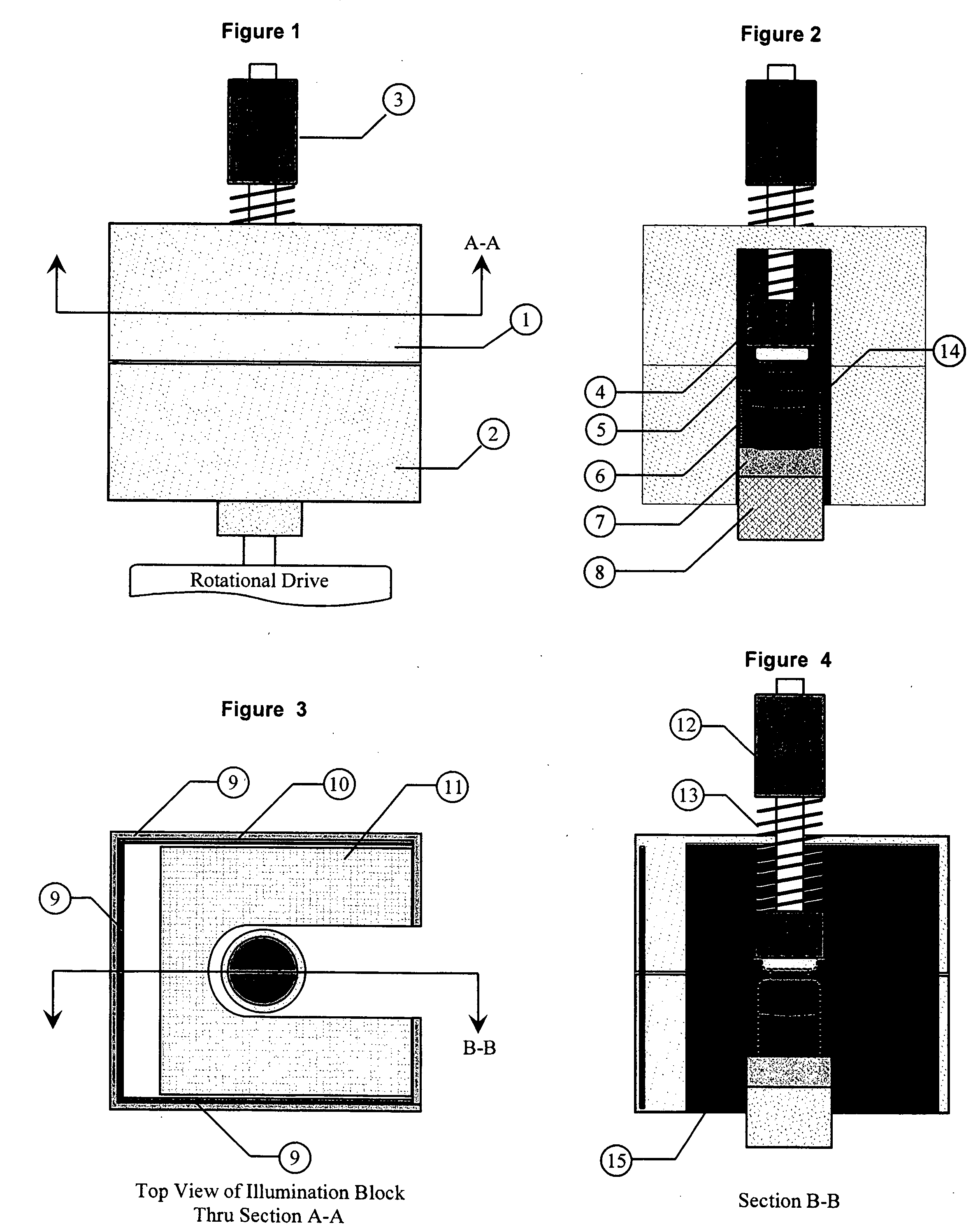
The invention provides a method for dynamically testing wettability and the testing system thereof, relates to a method for testing the wettablity of the solder, metal, ceramic, composite materials and fiber and the testing system thereof and belongs to the material performance detecting method and the detecting equipment thereof technical field, which comprises the wetability dynamic testing method, wetability dynamic testing software, an automatically controlled system (computer), a heating (cooling) system, a suspension system, a force testing balance system and a height adjusting hoist system. The method for dynamically testing wettability and the testing system thereof provided by the invention is capable of performing dynamic evaluation on the wetability of solder, the weldability of metals, ceramic and composite materials and the wetability of fiber to solution, and is capable of measuring the total wetting time.
Owner:廖树帜
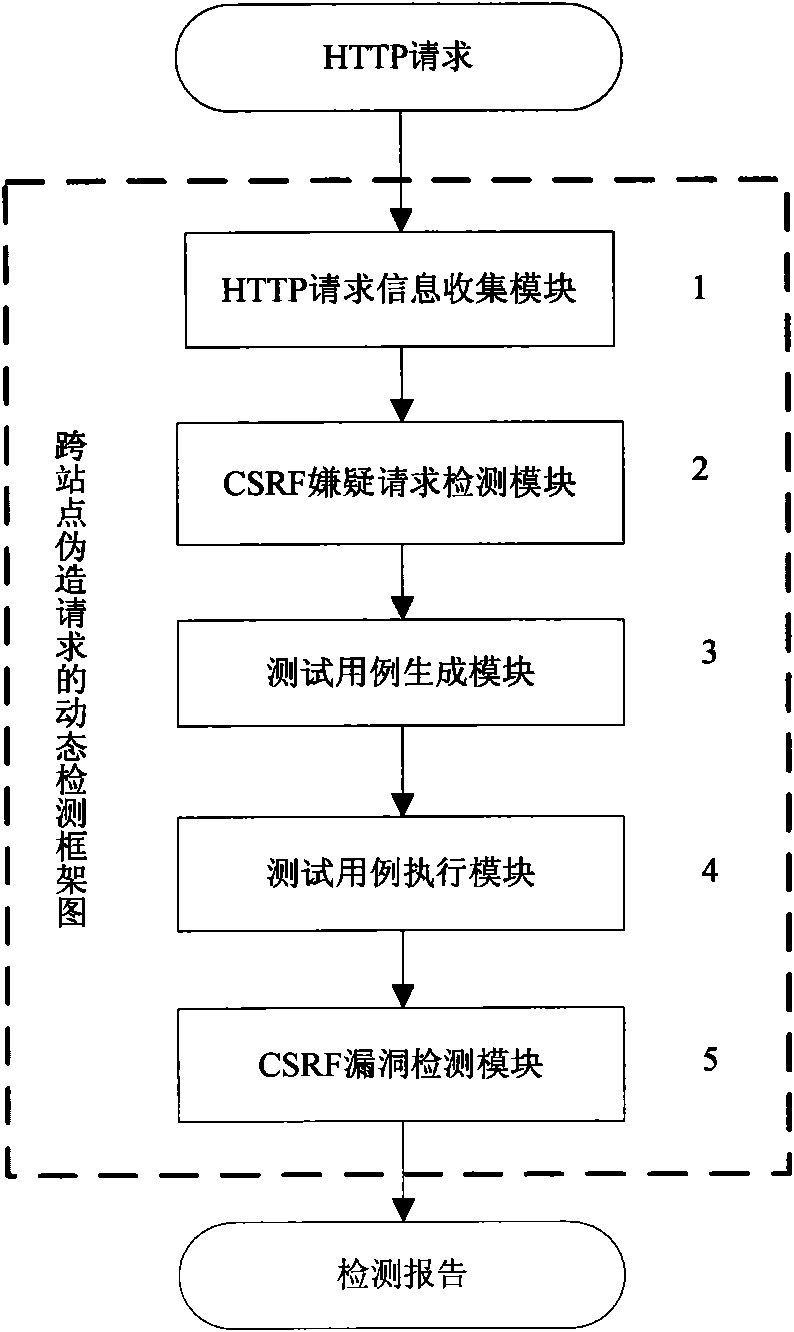
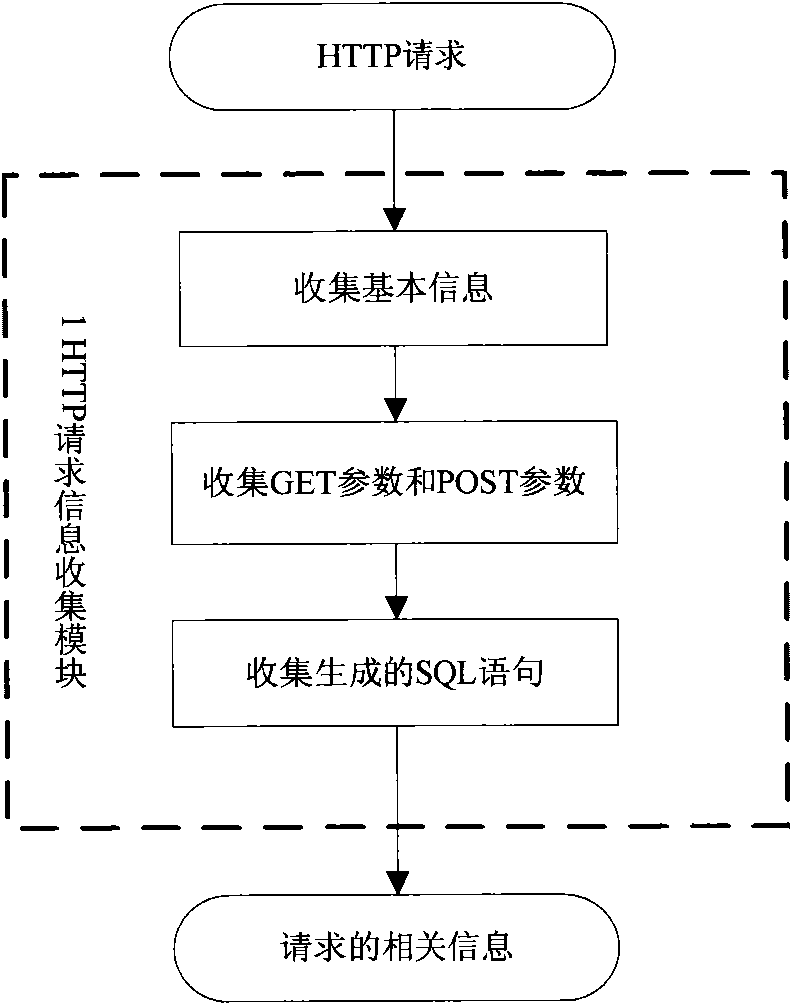
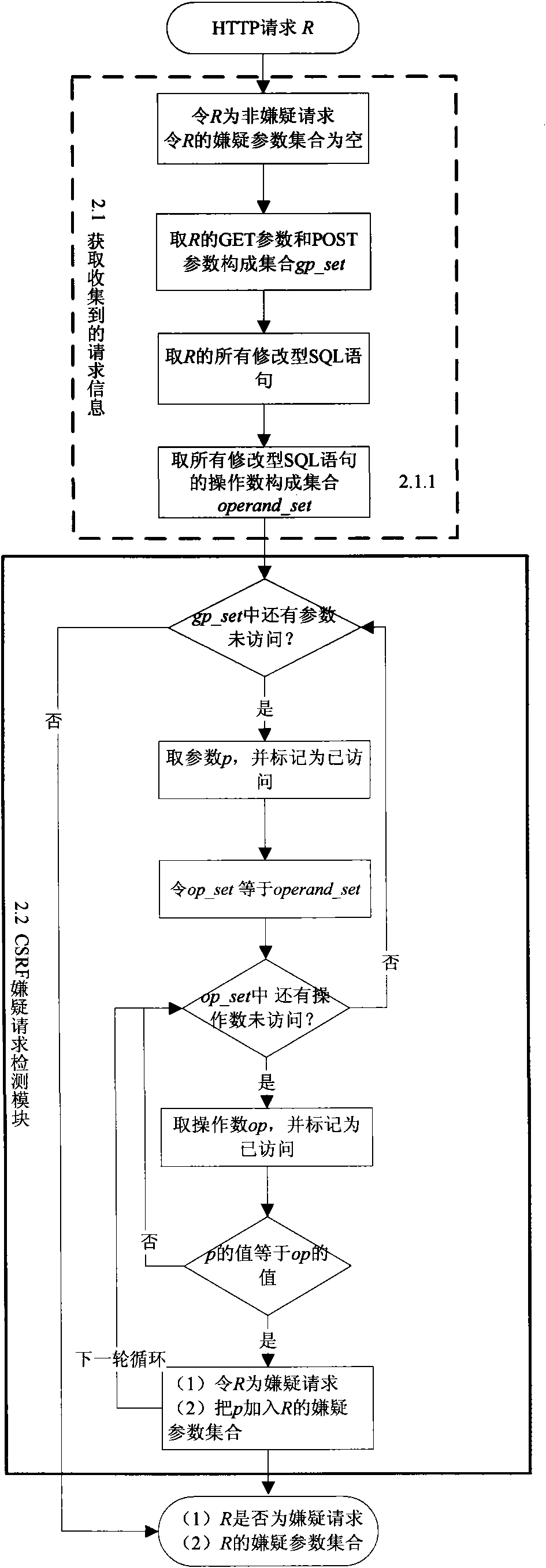
Dynamic detection method for cross-site forged request
InactiveCN101883024AQuick and accurate discoveryImprove test efficiencyData switching networksWeb applicationDynamic testing
The invention discloses a dynamic detection method for a cross-site forged request, which comprises the following steps: collecting HTTP request information; analyzing whether a request is a CSRF suspect request or not according to the collected information; generating a test case aiming at the suspect request and finding out all suspect parameters contained by the suspect request; using the suspect parameters to generate a plurality of forged requests and generating a test case for each forged request; when an environment in which the suspect request is generated recurs, executing the forged request corresponding to each test case; detecting CSRF vulnerabilities; and according to the suspect request, the execution information of the suspect request, the forged requests and the execution information of the forged requests, analyzing whether the forged requests find the CSRF vulnerabilities in Web application or not, forming a report and helping a Web application developer to repair the vulnerabilities. Since the dynamic detection method is used for detecting the CSRF vulnerabilities, the CSRF vulnerabilities in the Web application can be rapidly and accurately found out at low cost.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
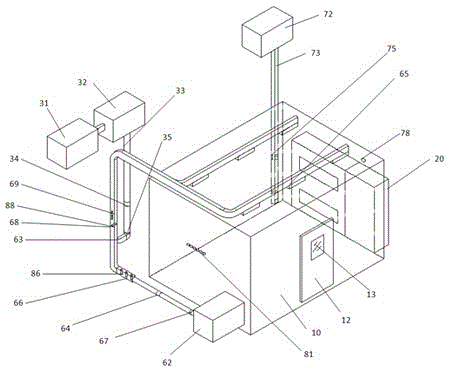
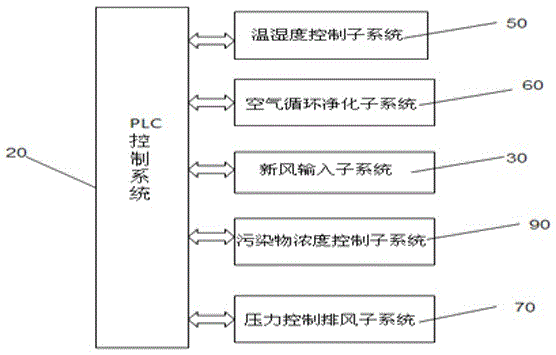
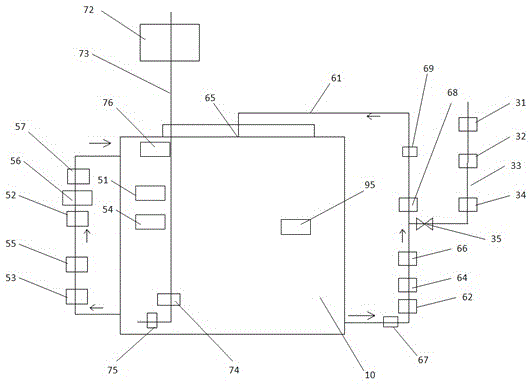
Multifunctional environment simulation cabin
InactiveCN105182889ALarge internal spaceEasy to testProgramme control in sequence/logic controllersPlasma technologyControl system
The invention relates to environment simulation laboratory equipment, especially to a multifunctional environment simulation cabin comprising a cabin body, a PLC control system installed at the outer wall of the cabin body, an air circulation and purification sub system for air circulation and purification inside the cabin body, a new air conveying sub system for inputting new air into the cabin body, a target gas concentration control sub system, and a pressure-control exhaust system. The PLC control system is connected with and controls a plurality of function sub systems by signals, thereby realizing simulation of the environment with different temperatures and humidity and target gas concentrations inside the cabin. According to the invention, an external circulating air hose is provided with different purification device interfaces to installed tested purification devices, so that dynamic testing of tested purifiers on the circulating air hose as well as testing of static environments with different monitoring gas concentrations can be simulated. Testing demands of various purifying devices like an adsorption type purifying device, a photocatalysis type purifying device, or a plasma-technology-based purifying device can be satisfied.
Owner:SHENZHEN XIBAO SHIP ELECTRONICS
Universal single event effect detecting method of memory circuit
InactiveCN103021469ASuitable for single event effect testingMeet different testing needsStatic storageMemory circuitsFile comparison
Owner:BEIJING MXTRONICS CORP +1
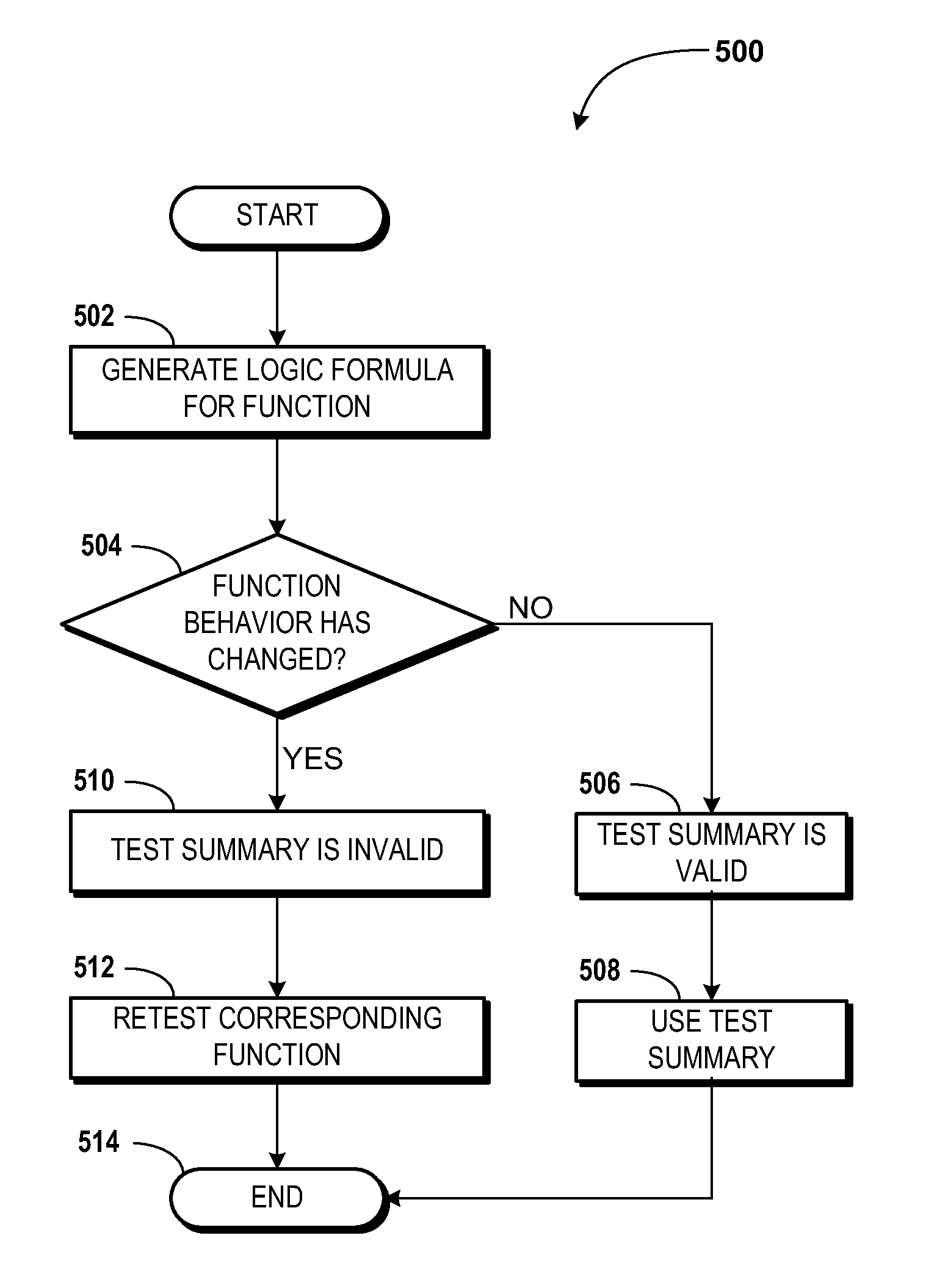
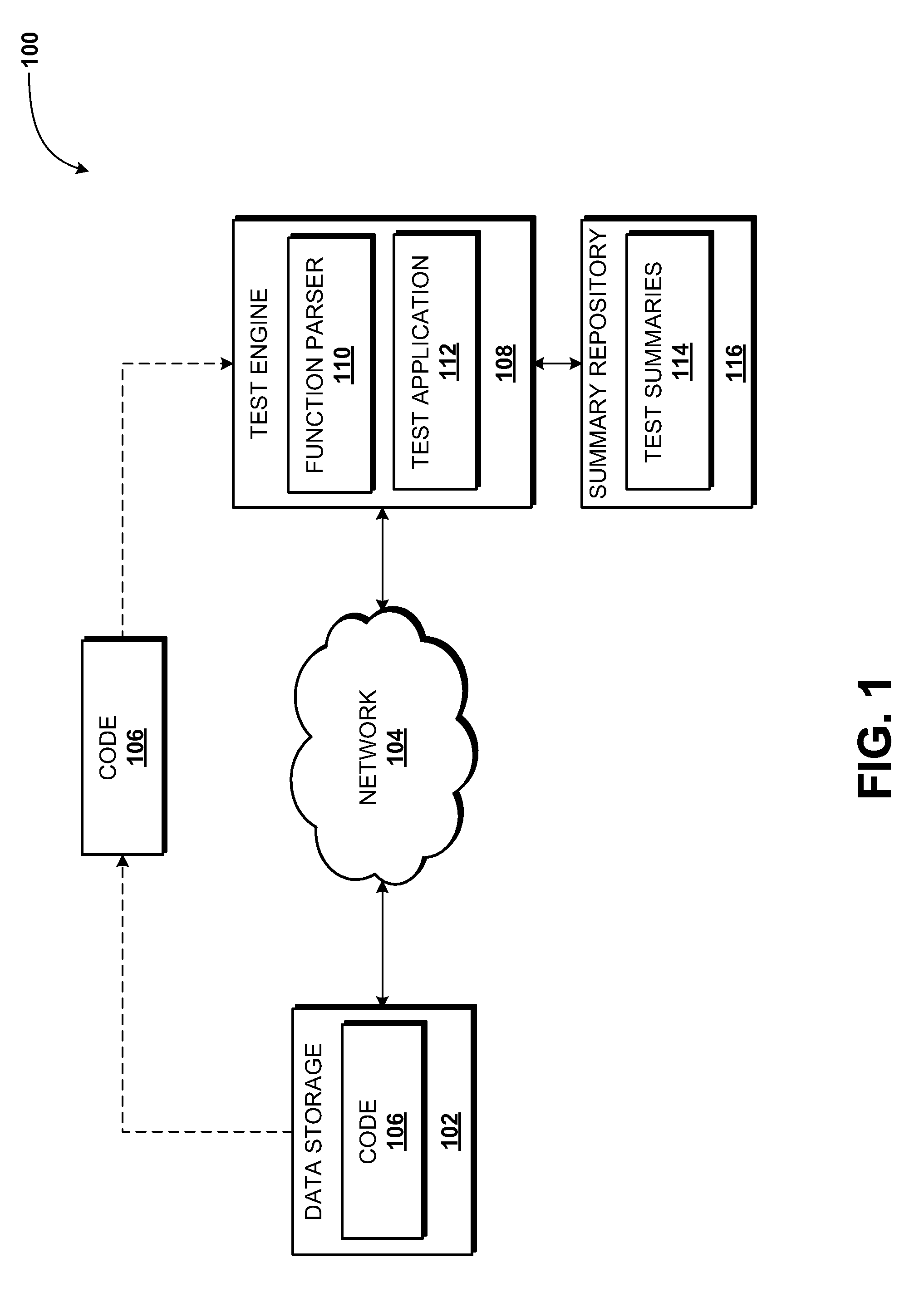
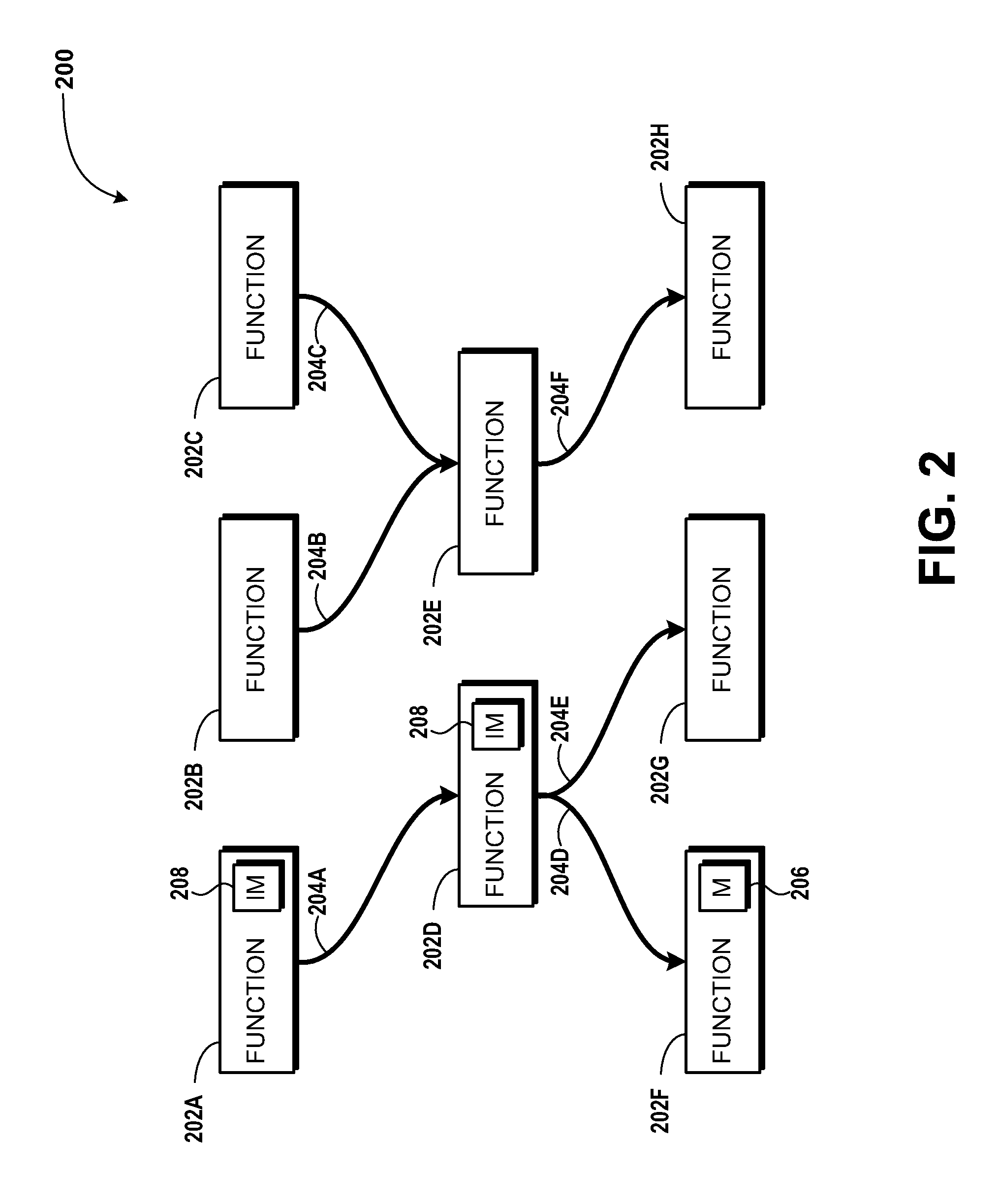
Incremental compositional dynamic test generation
ActiveUS20110314454A1Improve code coverageIncrease security vulnerability identification abilityComputer security arrangementsSoftware testing/debuggingCode coverageTime cost
Concepts and technologies are described herein for incremental compositional dynamic test generation. The concepts and technologies described herein are used to increase the code coverage and security vulnerability identification abilities of testing applications and devices, without significantly increasing, and in some cases decreasing, computational and time costs associated with the testing. Test summaries that describe how code is tested by a test engine are generated and stored during testing of code. These test summaries can be evaluated when additional iterations or versions of the code are tested. If functions corresponding to the test summaries are unchanged from, or logically equivalent to, a version of the function previously tested, the test summary may be used when testing the new version of the code.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
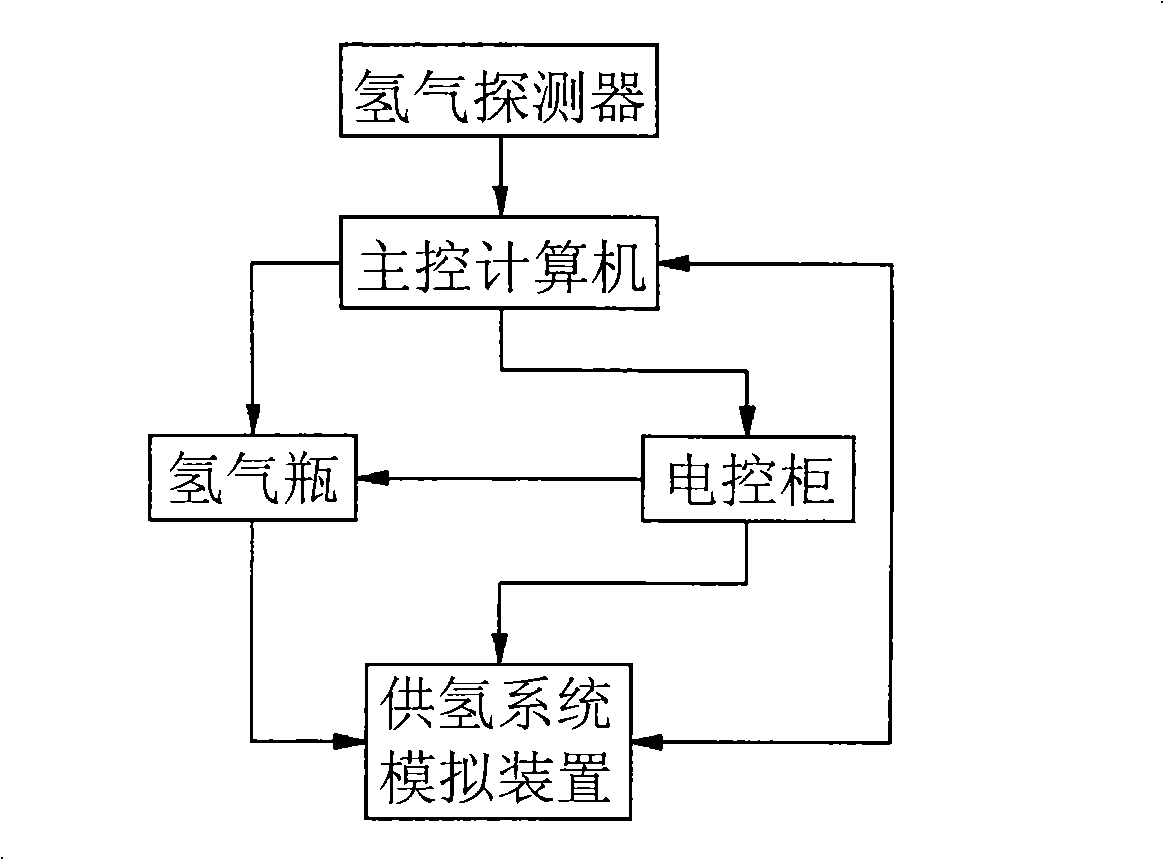
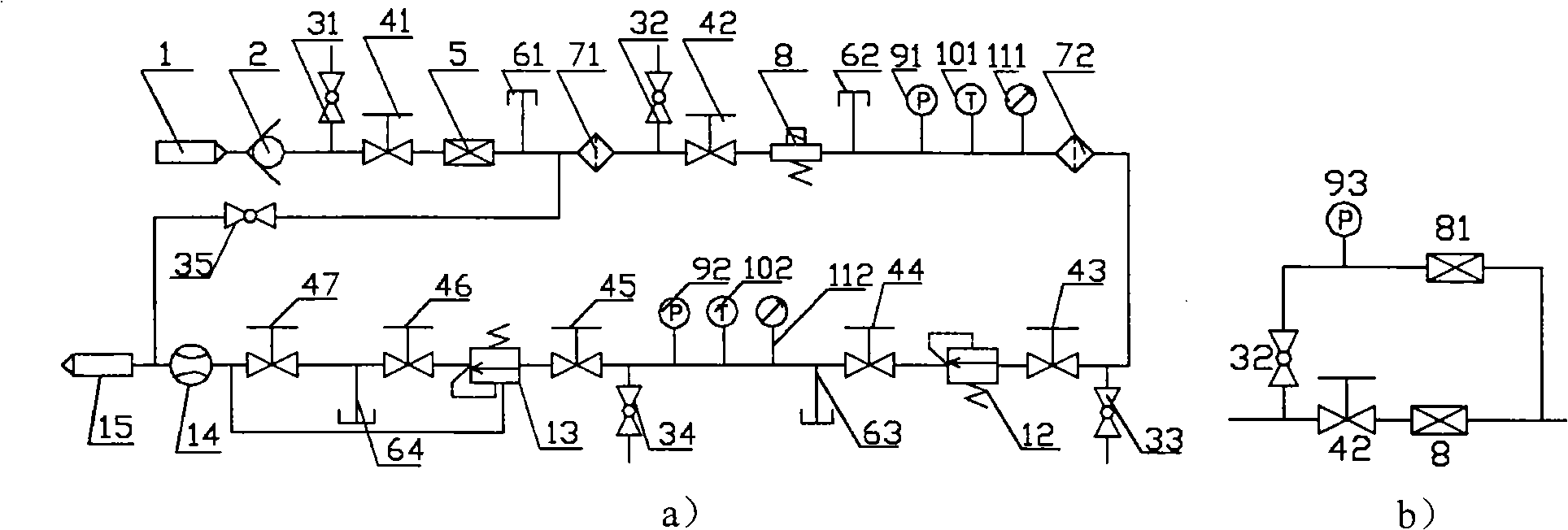
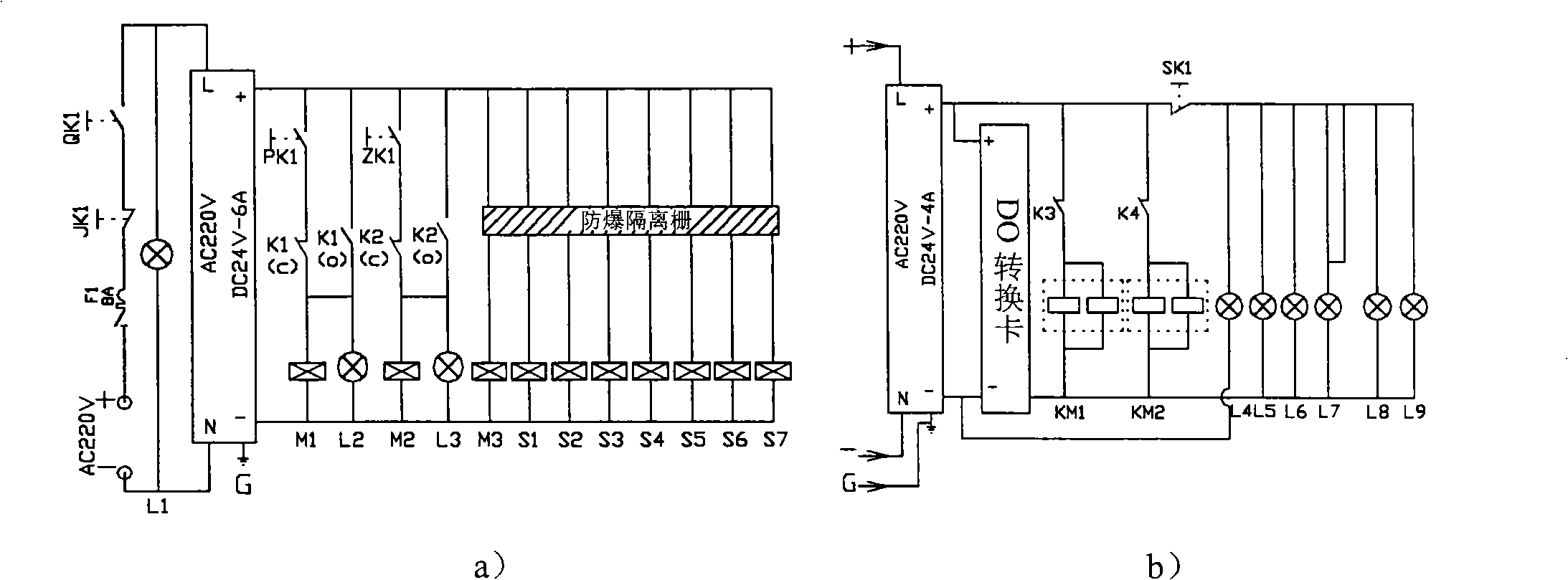
Test device and method for detecting security of fuel battery passenger car hydrogen feed system
ActiveCN101324485AImprove securityDerived performanceStructural/machines measurementHydrogen concentrationHigh pressure hydrogen
The invention relates to a test table for testing the security of a hydrogen supply system of a fuel cell bus and the test method thereof, and belongs to the security technology field of the fuel cell bus. The test table comprises a hydrogen supply system simulation device, a main control computer, an electrical control cabinet, a high pressure hydrogen bottle and a hydrogen detector, wherein the hydrogen supply system simulation device is connected with the output mouth of the high pressure hydrogen bottle, and bilaterally connected with the main control computer; the main control computer is connected with the electrical control cabinet, the high pressure hydrogen bottle and the hydrogen detector; the electrical control cabinet is respectively connected with the high pressure hydrogen bottle and the hydrogen supply system simulation device; the test table further comprises a bench for fixing and supporting the hydrogen supply system simulation device. The method comprises the following steps: a valve to be tested is connected with an identical valve in a pipeline of the hydrogen supply system simulation device in parallel; the working state of the valve to be tested is simulated; according to data such as gas pressure, flow, hydrogen concentration, etc. in an acquisition pipeline, whether the performance of the valve to be tested is qualified can be judged. The test table is used for dynamically testing the security of the key components of hydrogen supply system of the fuel cell bus.
Owner:清华大学苏州汽车研究院(吴江) +1
Method for abstraction of manufacturing test access and control ports to support automated RTL manufacturing test insertion flow for reusable modules
A system for RTL test insertion in an integrated circuit layout pattern includes a core module, a test wrapper, and a smart wrapper. The core module describes a function defined by logical elements, interconnections between logical elements, input pins and output pins. The test wrapper is adapted to encapsulate the core module and to create test pins representing the core module. The smart wrapper is adapted to encapsulate the test wrapper and to assign the test pins to a non-asserted state. The smart wrapper is adapted to place an assertion on one or more of the test pins for static or dynamic testing of the integrated circuit layout pattern.
Owner:BELL SEMICON LLC
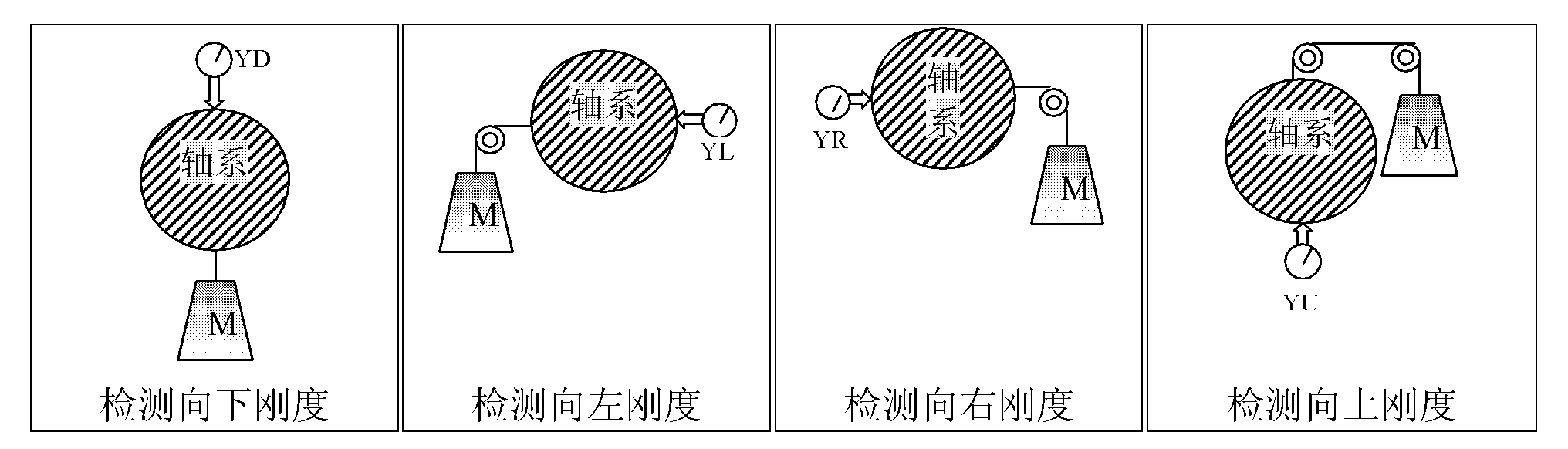
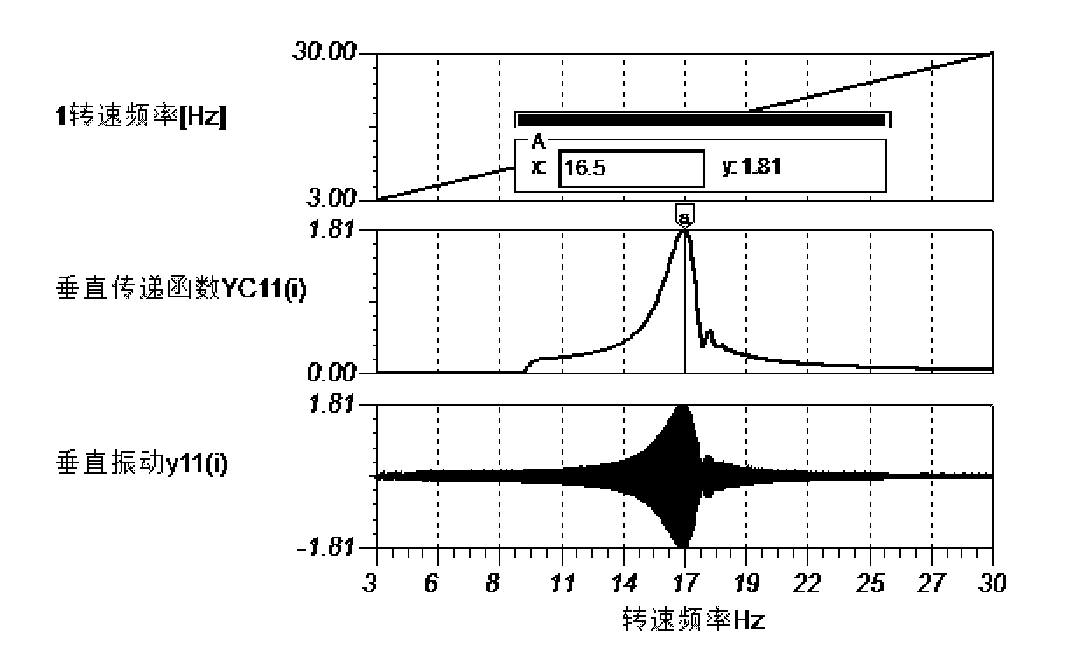
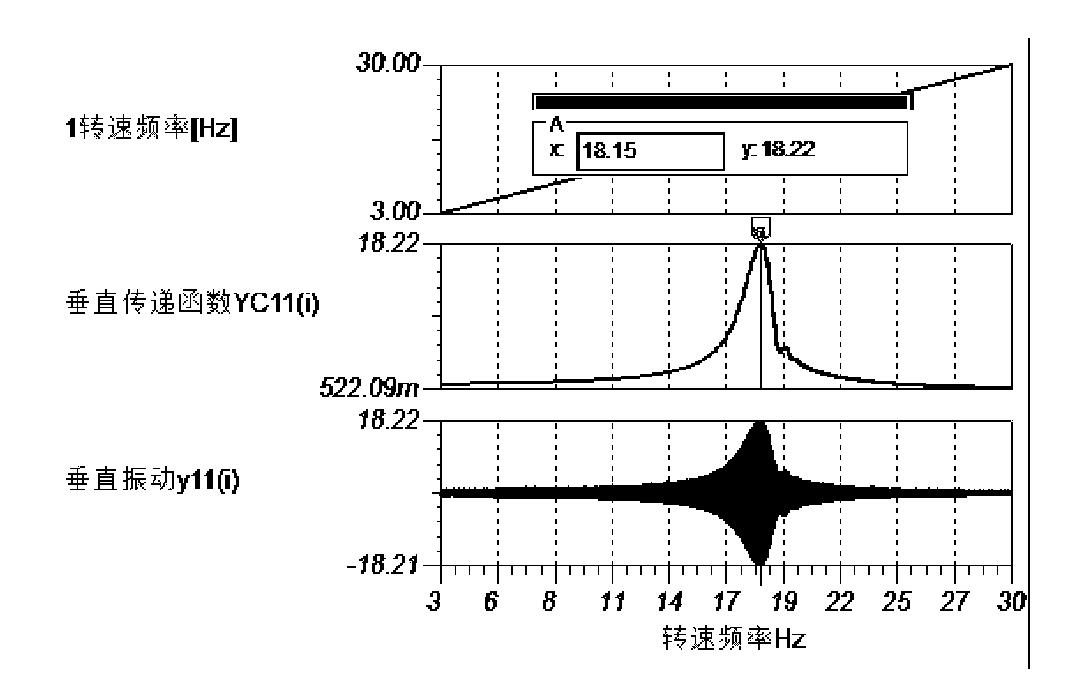
Testing method and apparatus for supporting state, dynamic balancing state and non-centering state of rotating machine
ActiveCN102252836AImprove and enhance the installationMachine part testingStatic/dynamic balance measurementVertical vibrationCoupling
The invention discloses a testing method and an apparatus for a supporting state, a dynamic balancing state and a non-centering state of a rotating machine. The testing apparatus comprises a machine 1, a machine 2, and a shaft coupling. The testing apparatus is characterized in that: the machine 1 is connected with the machine 2 through the shaft coupling; a horizontal vibration sensor X1 and a vertical vibration sensor Y1 are installed on a casing and an engine base of the machine 1, wherein the casing and the engine base are at the side close to the shaft coupling; a horizontal vibration sensor X2 and a vertical vibration sensor Y2 are installed on a casing and an engine base of the machine 2, wherein the casing and the engine base are at the side close to the shaft coupling; a speed detection sensor N and a supporting stiffness and non-centering dynamic tester 3 are installed on the machine 1 and the machine 2. According to the traditional static detection method, there is a bind area in which a supporting stiffness state and a centering state can not be identified on the dynamic condition of the machine, so that debugging can not be guided comprehensively and correctly; however, according to the testing method and the apparatus, the above-mentioned problem can be solved.
Owner:北京唐智科技发展有限公司
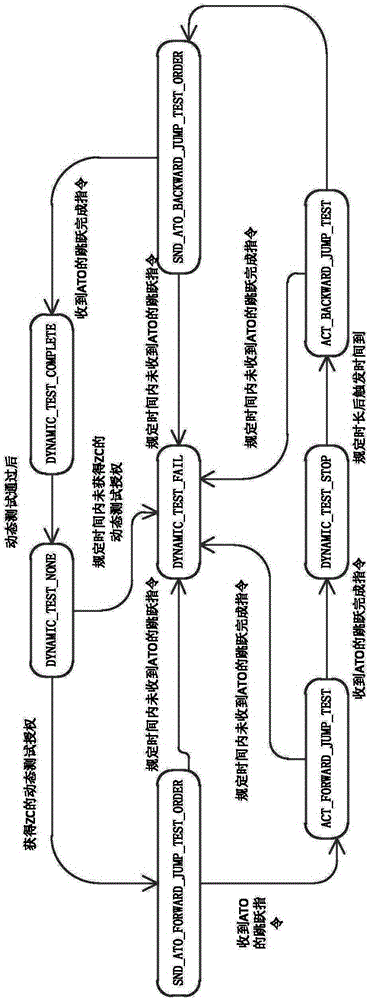
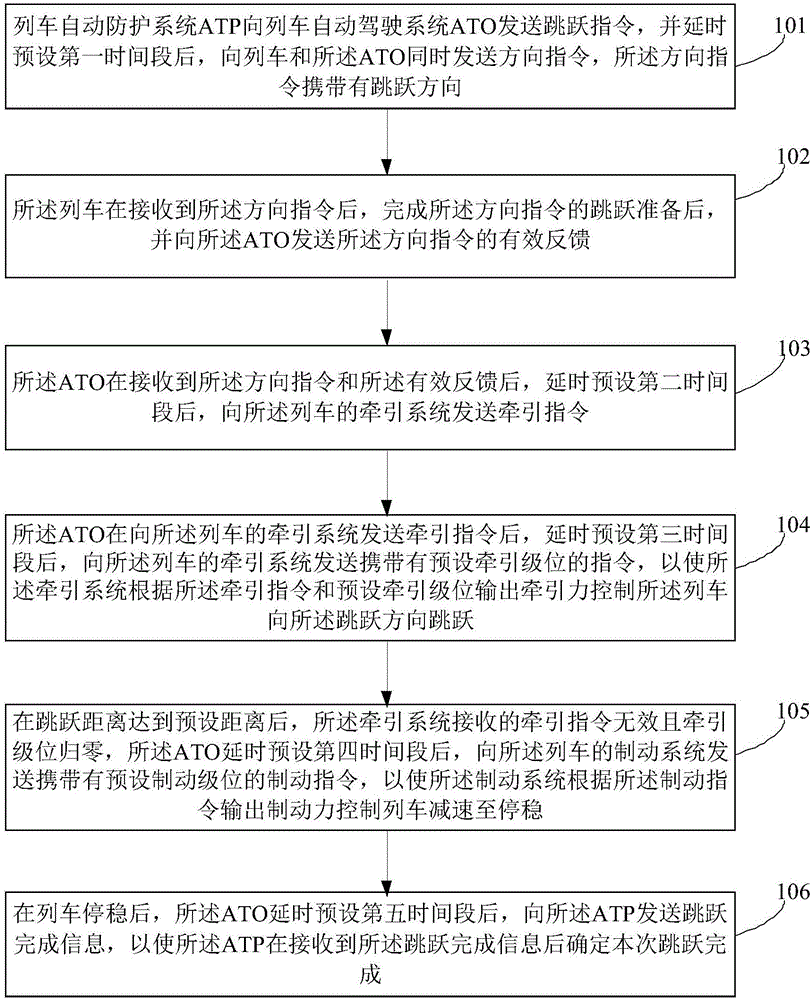
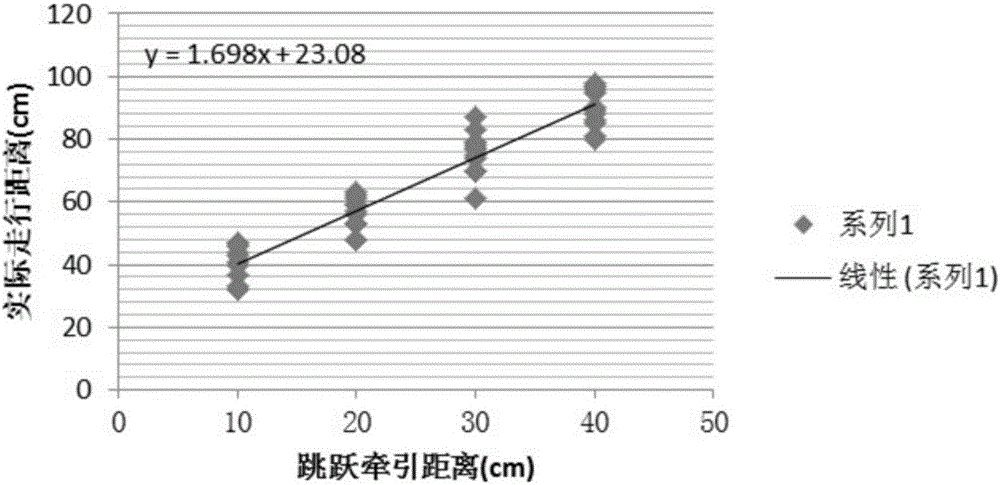
Train jump control method, dynamic testing method and jump benchmark parking method under FAM (Full Automatic Mode)
ActiveCN106347331AAccurate parkingDynamic testing is accurateAutomatic initiationsRailway signalling and safetyReturn-to-zeroTraction system
The invention provides a train jump control method, a dynamic testing method and a jump benchmark parking method under an FAM (Full Automatic Mode). The jump control method comprises the following steps: an ATP transmits a jump instruction to an ATO, delays for T1 and then synchronously transmits a direction instruction to the train and the ATO; the train receives the direction instruction, then finishes jump preparation and transmits an effective feedback of the direction instruction to the ATO; the ATO receives the direction instruction and the effective feedback, delays for T2 and transmits a traction instruction to a train traction system; the ATO delays for T3, then transmits an instruction carrying a preset traction level to the train traction system, enables the train traction system to output a traction force and enables the train to jump; after jump distance reaches preset distance, the traction instruction is ineffective, and the traction level returns to zero; the ATO delays for T4, then transmits a braking instruction carrying a preset braking level to a train braking system, enables the train braking system to output a braking force, and enables the train to slow down and stably stop; after the train stably stops, the ATO delays for T5, then transmits jump finishing information to the ATP, and enables the ATP to determine the finishing of the jump. Based on the jump control method of the train, a dynamic testing result is more accurate, and jump benchmark parking is more precise.
Owner:TRAFFIC CONTROL TECH CO LTD
Method and device for dynamically testing synchronized phasor measurement unit (PMU) in power system
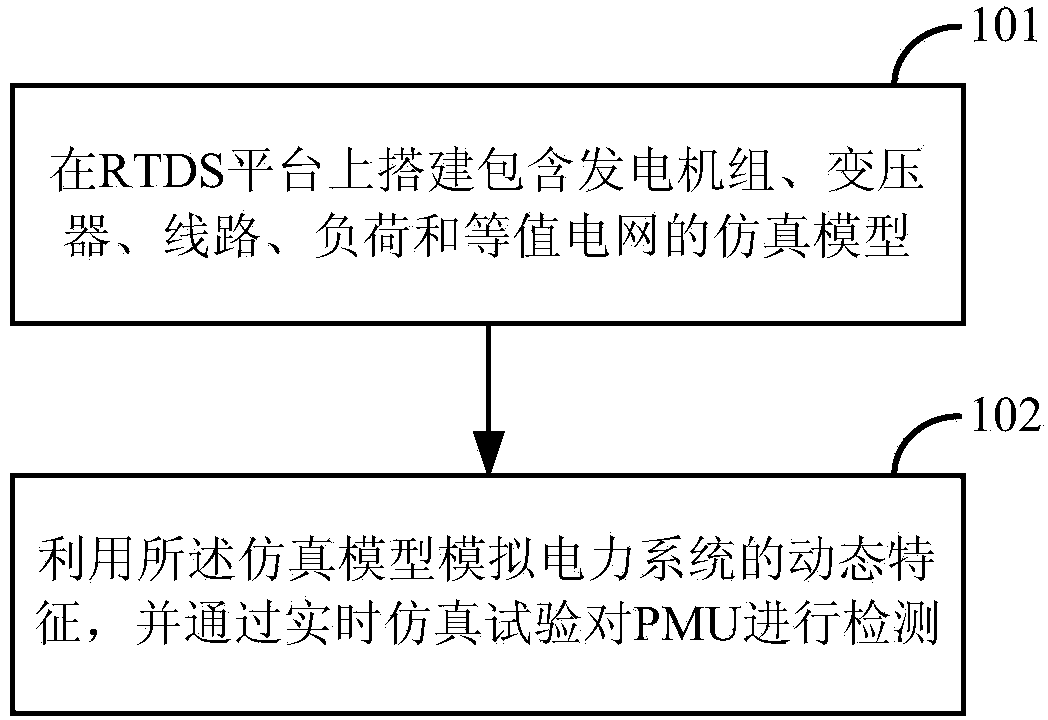
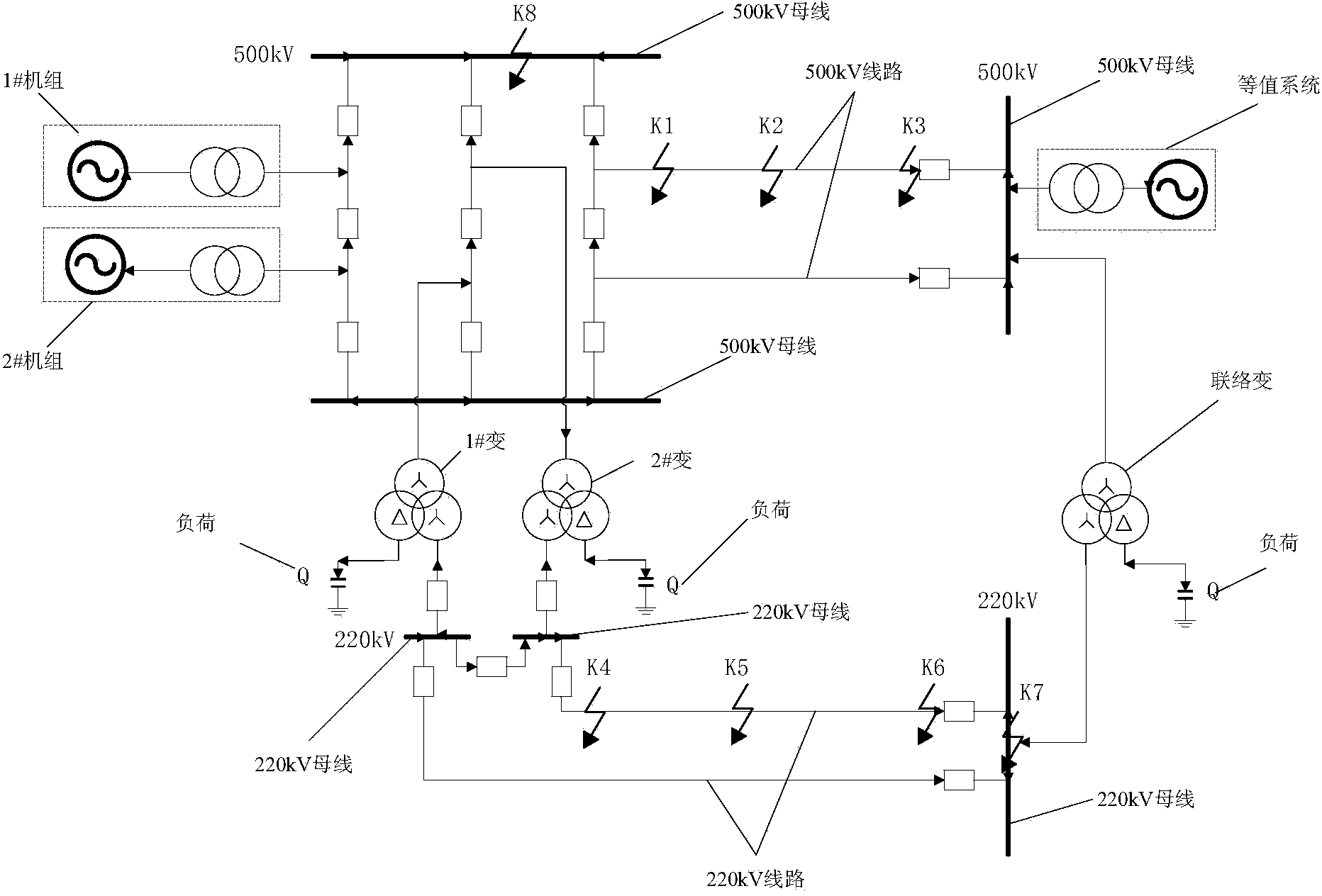
ActiveCN103529418AMeet the requirements of dynamic performance testingImprove operational reliabilityElectrical measurementsReal-time simulationTransformer
The invention discloses a method and a device for dynamically testing a synchronized phasor measurement unit (PMU) in a power system. The method comprises the following steps: setting up a simulation model comprising a generator unit, a transformer, circuits, a load and an equivalent power grid on an RTDS (Real-Time Digital Simulator) platform; utilizing the simulation module to simulate the dynamic characteristics of the power system and detecting the PMU of the synchronized phasor measurement unit through real-time simulation tests. The method and the device are convenient to realize, the performance of the PMU can be correctly and reasonably detected and evaluated, and the further development of a PMU technology is better promoted. The test requirements of laboratories on the dynamic performance of the PMU are met, an effective means is provided for network access detection, the work requirements of manufacturers on product development, delivery inspection and the like are met, and the quality of the synchronized phasor measurement unit in the power system is specified and ensured. The method and the device have great meaning in improving the running reliability of the power grid.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +1
Dynamic testing loading unit for MEMS disc or device
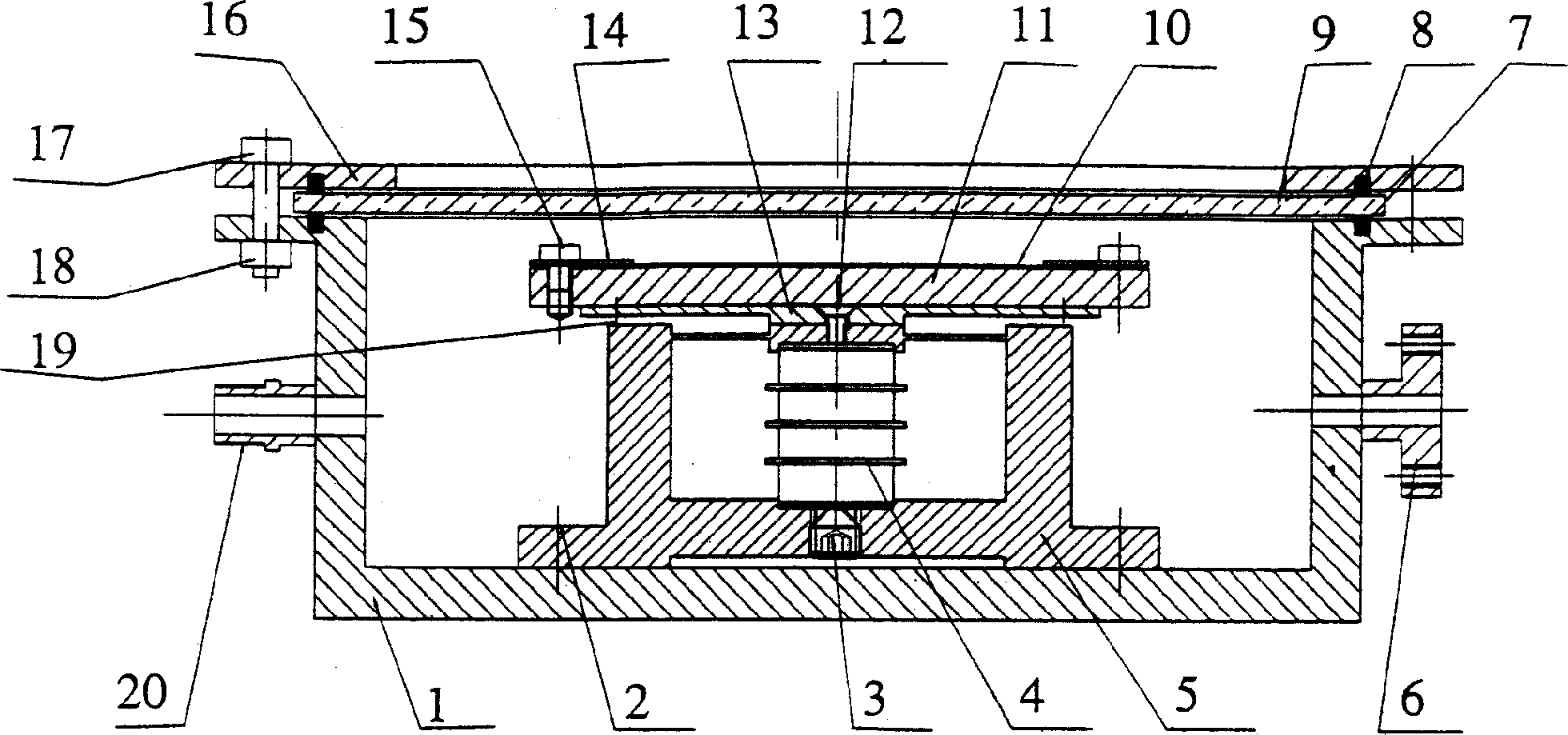
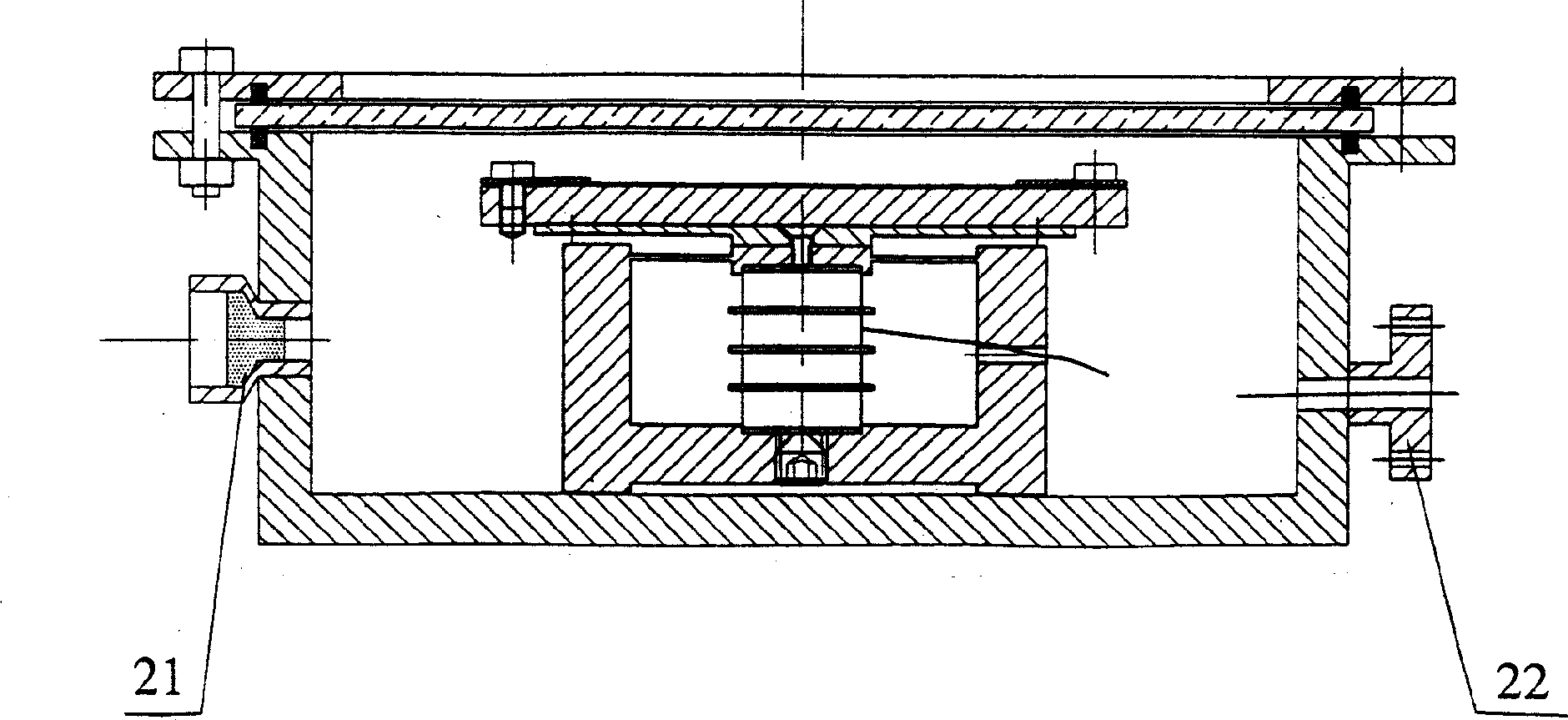
InactiveCN1666952AAccurate access to modal parametersAccurate amplitudeSemi-permeable membranesSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementElectricityEngineering
The invention discloses a dynamic testing loading unit for MEMS disc or device, the structure of which is: the filter is arranged on the open head face of cavity body and forms a seal cavity with the cavity body; on the cavity body arranged a electrode, having charging port, vacuumizing port and vacuometer interface; the bracket is fixed on the cavity body's base; the adjusting screw is arranged in the cavity body's base; piezoceramics is arranged in the bracket, the lower end of which is connected with the adjusting screw, the upper end of which is connected with the bracket; the bearing plate is fixed on the bracket and the disc treadle bar is connected with bearing plate. The device can get accurate vibration frequency and amplitude through piezoceramics and realize frenquency and amplitude's change in a comparatively wide range; it's easy to control and can provide different vacuum degree, different temperature and different vibration state conditions when testing MEMS disc or device.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Satellite in-orbit free boundary condition simulation device
ActiveCN103359300ARealize simulationImproving the Technical Level of Kinetic ExperimentsCosmonautic condition simulationsEarth observationButt joint
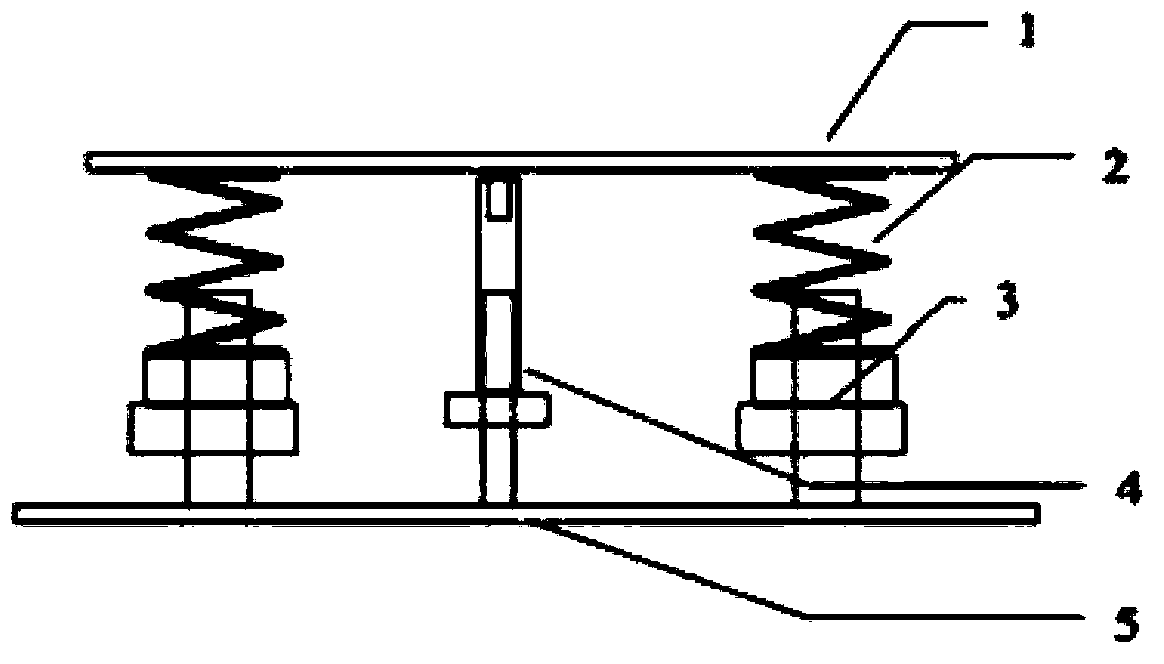
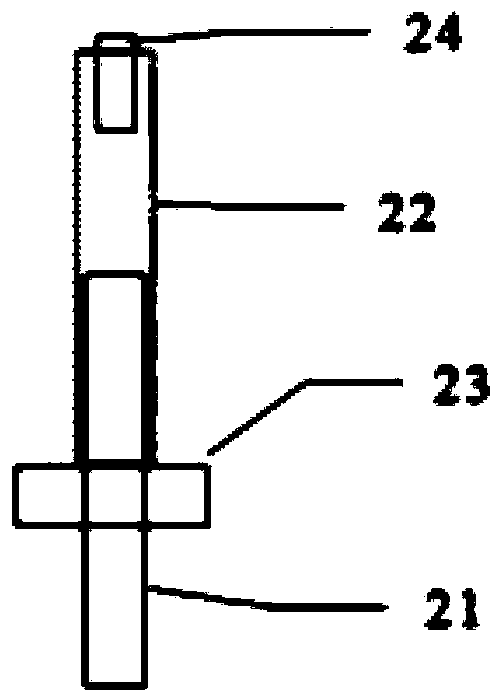
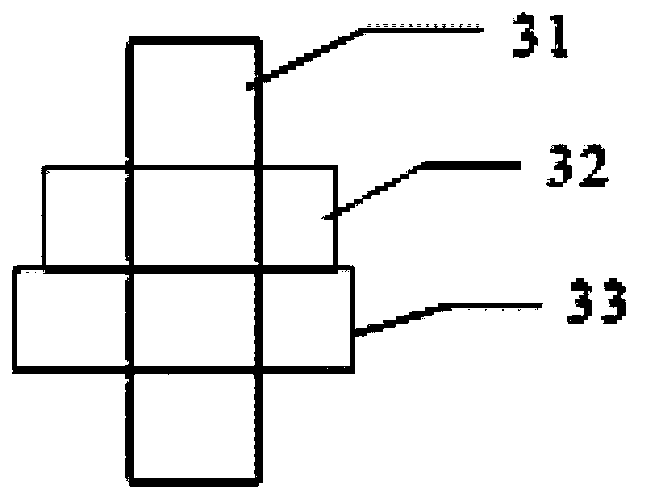
The invention discloses a satellite in-orbit free boundary condition simulation device. The satellite in-orbit free boundary condition simulation device mainly comprises a satellite butt joint plate, supporting springs, satellite balance adjusting devices, a limiting protecting device and a supporting plate, wherein the satellite butt joint plate at the upper portion of the device and the supporting plate at the lower portion of the device are correspondingly arranged according to the satellite mechanical structure and are generally of an annulus shape, the two ends of each supporting spring are fixedly connected to the annular portions between the satellite butt joint plate and the supporting plate respectively and evenly distributed around the annular portions so that a satellite can be elastically supported, the satellite balance adjusting devices which correspond to the supporting springs in number are fixedly arranged between the bottoms of the supporting springs and the supporting plate so that the supporting springs are supported to adjust inclination of the satellite and the simulation device caused by eccentricity of the satellite, and therefore the satellite is kept horizontal after being connected to the simulation device in a butt joint mode. According to the satellite in-orbit free boundary condition simulation device, the level of the satellite dynamics testing technique is improved, and requirements for verification of in-orbit dynamics characteristics and in-orbit micro-vibration environment tests in the process of developing satellites especially high-precision earth observation satellites are met.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF SPACECRAFT ENVIRONMENT ENG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com