Patents
Literature
424 results about "Earth observation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Earth observation (EO) is the gathering of information about the physical, chemical, and biological systems of the planet via remote-sensing technologies, supplemented by Earth-surveying techniques, which encompasses the collection, analysis, and presentation of data. Earth observation is used to monitor and assess the status of and changes in natural and built environments.
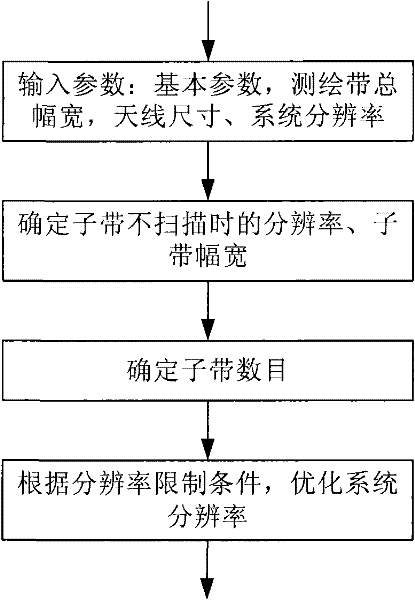
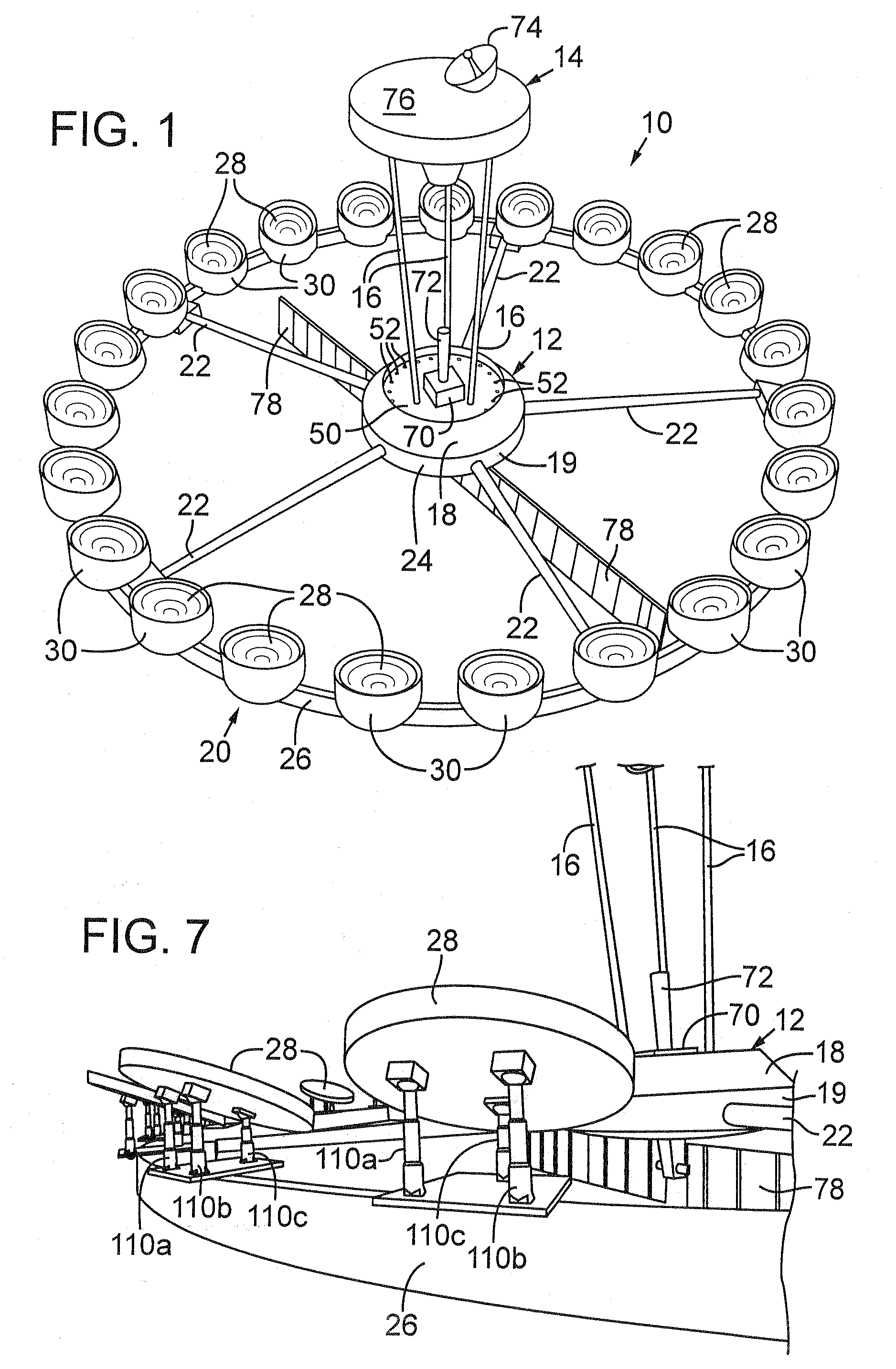
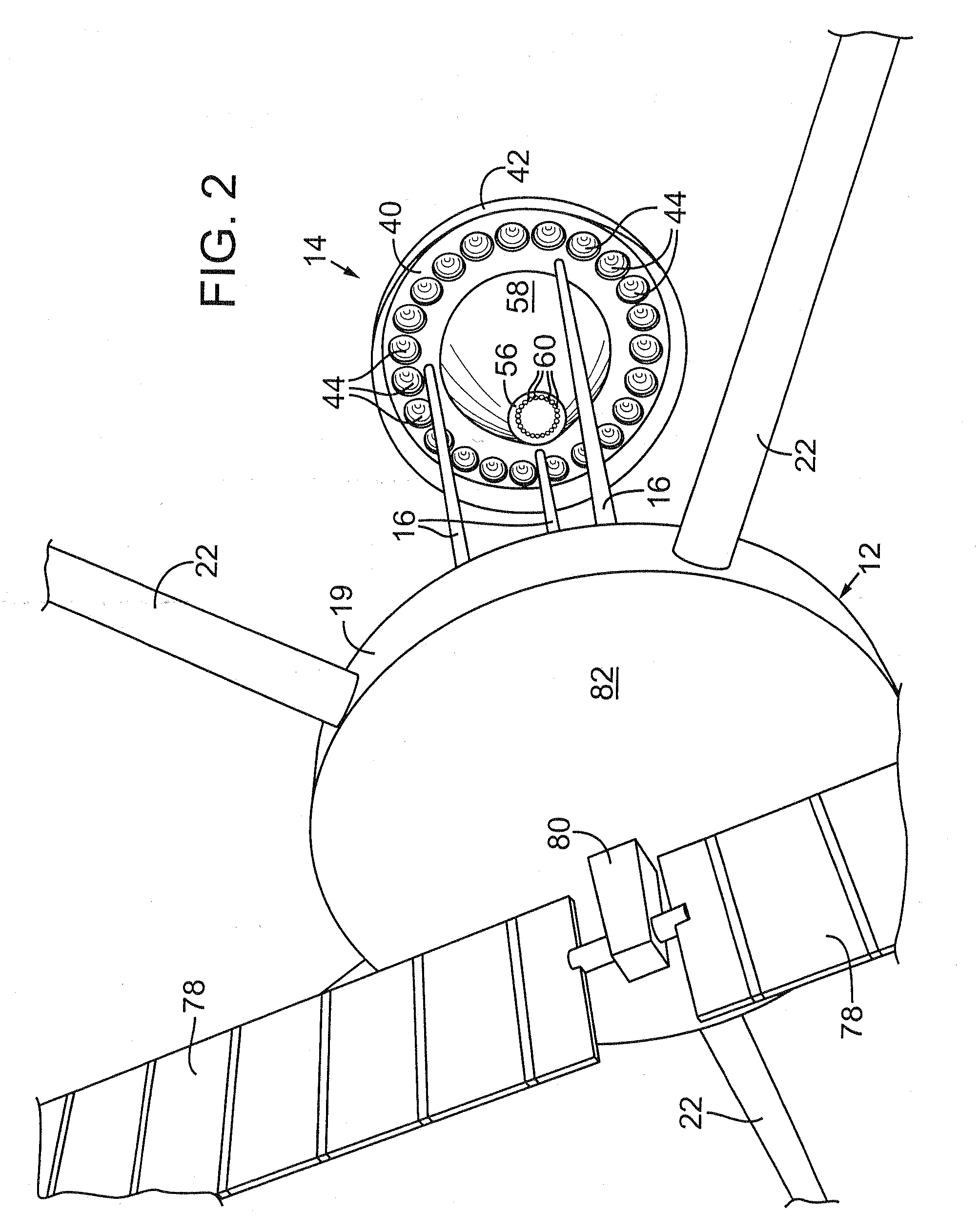
High Volume Earth Observation Image Processing
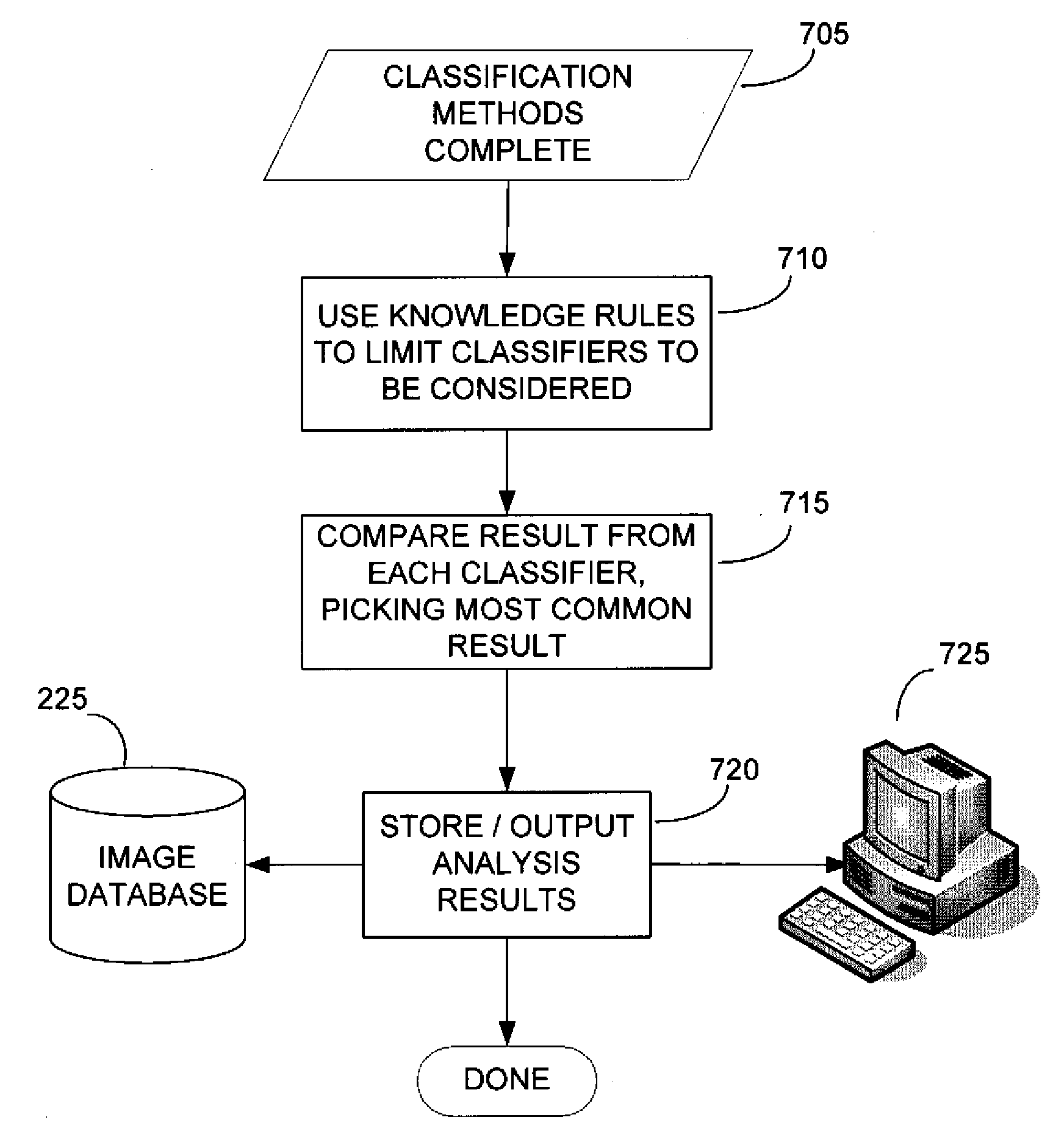
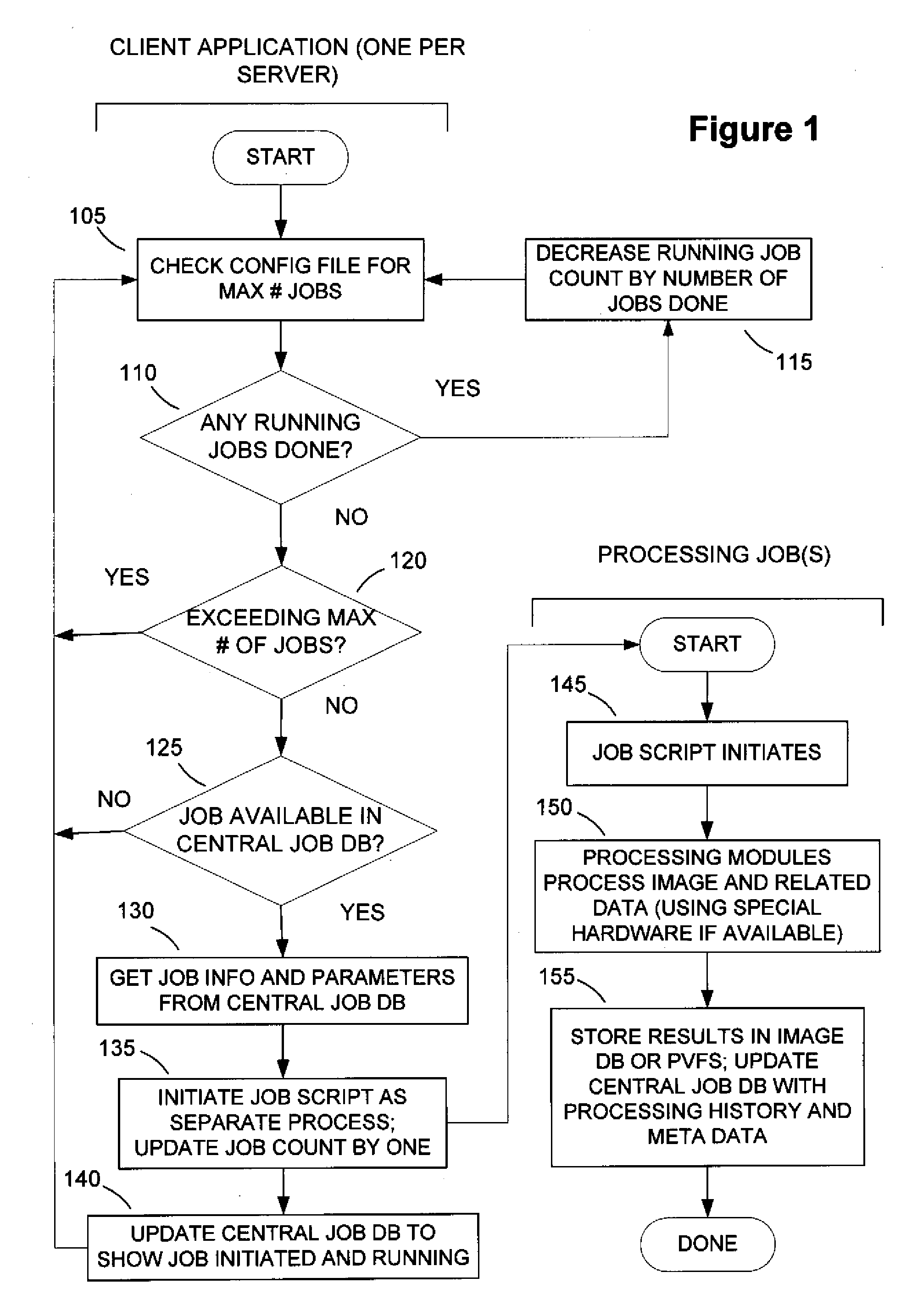
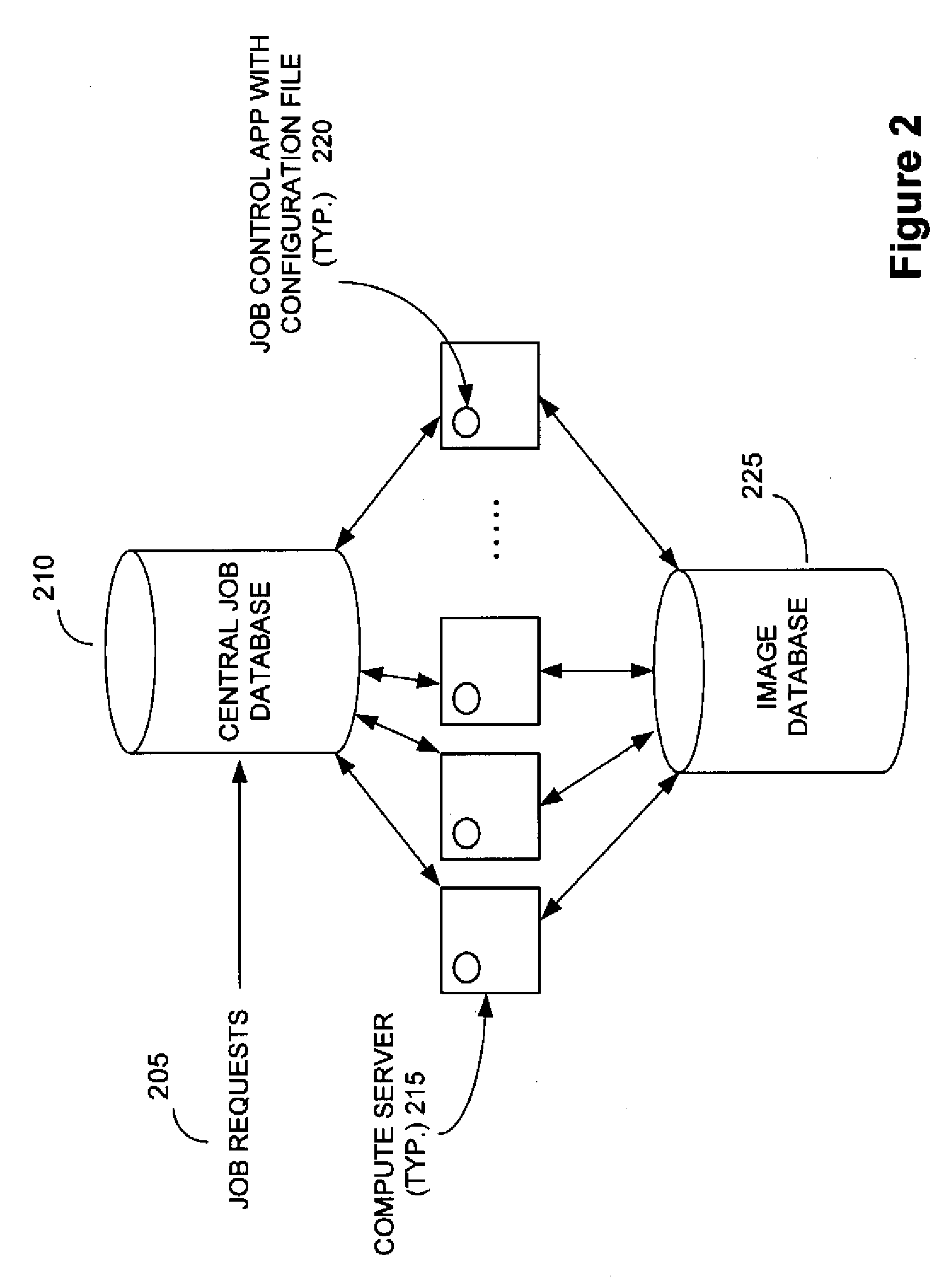
ActiveUS20090232349A1Simple methodImprove throughputImage enhancementImage analysisEarth observationImaging processing
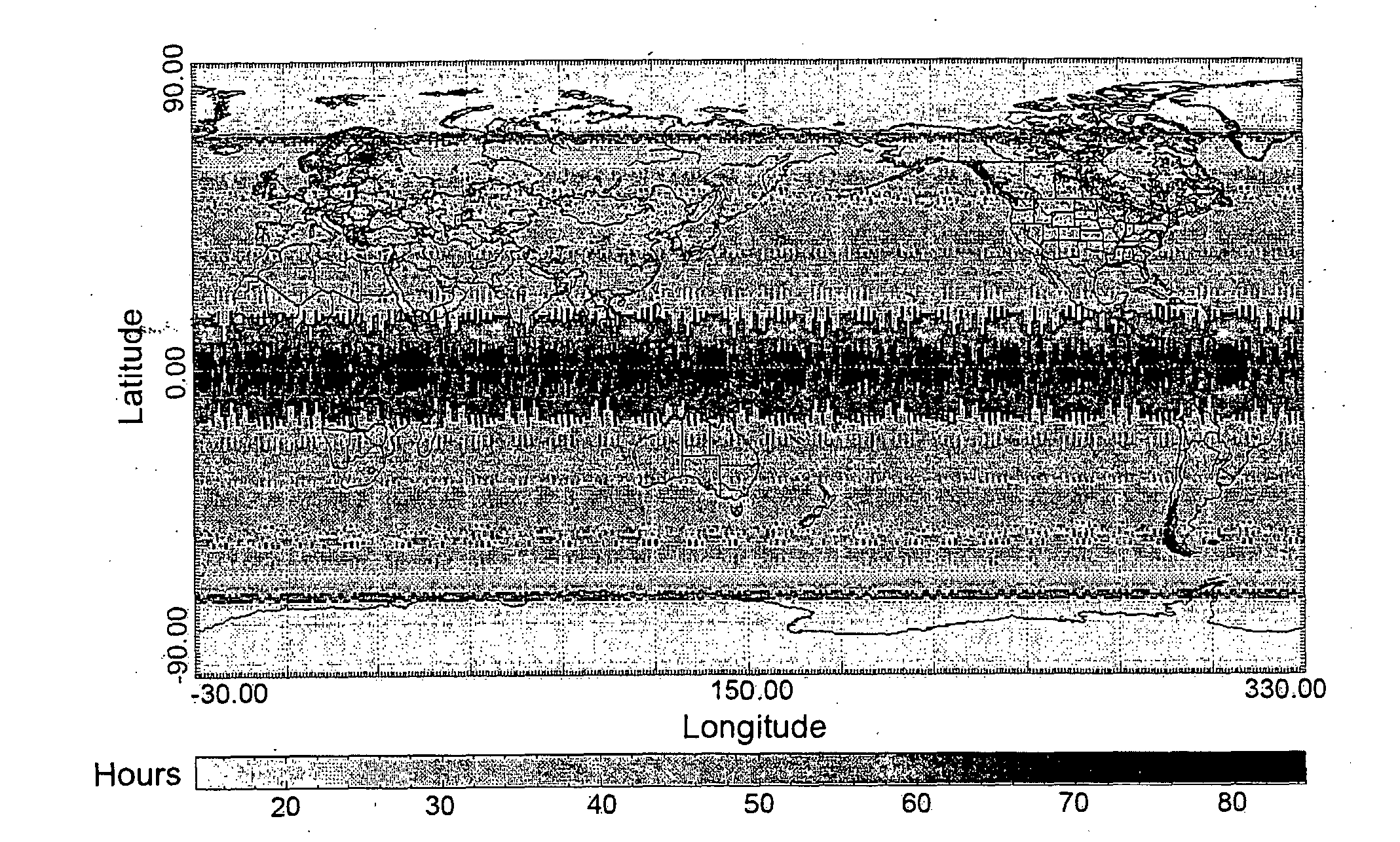
The present invention is related to the processing of data, and more particularly to a method of and system for processing large volumes of Earth observation imagery data. A system for processing a large volume of Earth observation imaging data is described, comprising a computer including a visual display and a user interface, a plurality of servers, an image database storing said Earth observation imaging data as a plurality of separate image data files, and a network for interconnecting the computer, plurality of servers and image database. The plurality of servers is operable to process the separate data files in a distributed manner, at least one of the plurality of servers is operable to process the separate data files in a multiprocessing environment and at least one of the plurality of servers is operable to collate the processed separate data files into a single imaging result.
Owner:PCI GEOMATICS ENTERPRISES
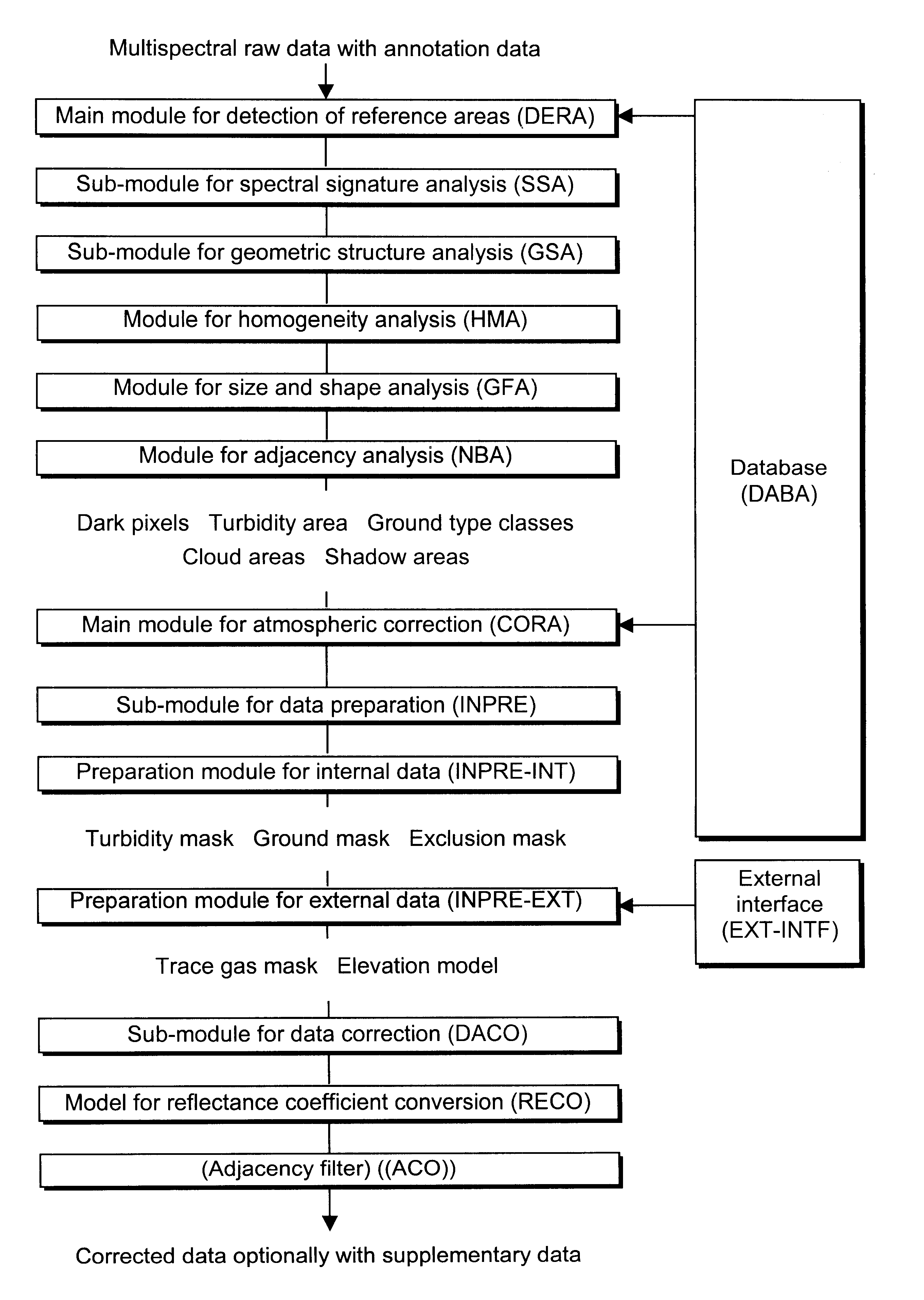
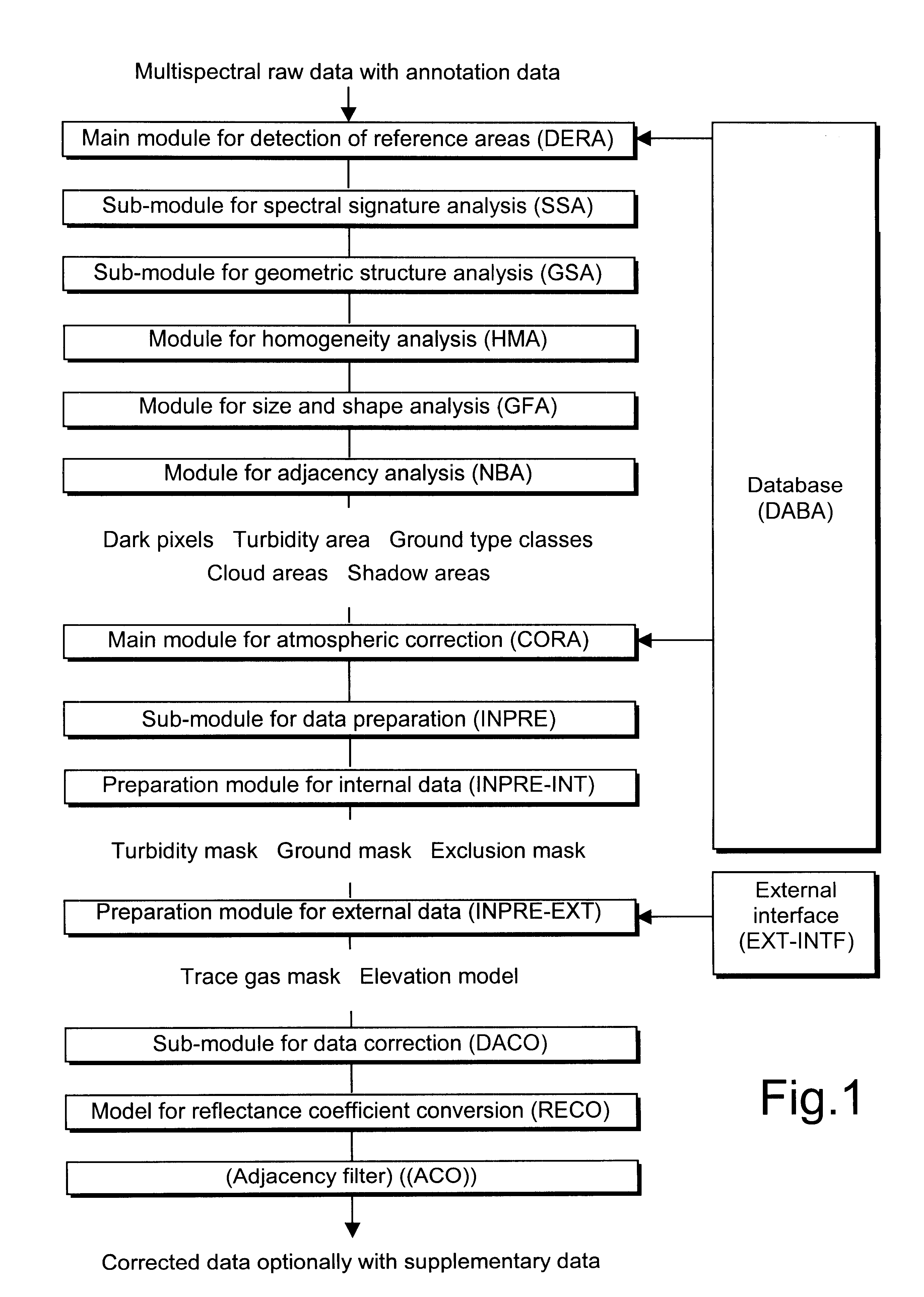
Process for correcting atmospheric influences in multispectral optical remote sensing data
InactiveUS6484099B1Precise correction calculationGood time-space correlationImage enhancementImage analysisSensing dataEarth observation
The inventive process for correcting atmospheric influences in multispectral optical remote sensing data, which are acquired as raw data in satellite or airborne sensors for earth observation, comprises the combination of a pre-classification (DERA) of the raw data for an automatic identification of predefined classes, a correction calculation (CORA) for a conversion of the uncorrected to corrected reflectances on the ground, including an incorporation of current atmospheric data for a precise description of the atmospheric condition. The pre-classification (DERA) permits a more precise correction calculation (CORA) by generating required a priori knowledge. The method has applications in satellite or airborne remote sensing of the earth's surface.
Owner:DEUTSCHES ZENTRUM FUER LUFT & RAUMFAHRT EV
Multi-satellite earth-observation task scheduling and planning method and device
InactiveCN105787173ASolving Task Scheduling ProblemsOptimize resource allocationDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsEarth observationPlanning approach
The invention provides a multi-satellite earth-observation task scheduling and planning method and device.The method comprises the steps that an observation task and satellite resource data are read; the observation task is partitioned according to the satellite resource data, and an observation meta-task set is obtained; task planning is conducted on the observation meta-task set through an evolutionary algorithm, and a planning result is obtained; the planning result is decoded, and an observation sequence is obtained; in this way, when multiple satellites observe the earth, the characteristics such as intelligence and concurrency of the evolutionary algorithm are fully utilized, and the task scheduling problem of multiple observation satellites which need to work cooperatively is solved; a dynamic task planning method based on the evolutionary algorithm is utilized, a reasonable load scheduling scheme is made for an in-orbit operation satellite group, resource allocation of a satellite system is optimized, and satellite system resources are utilized fully and reasonably.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (WUHAN) +1
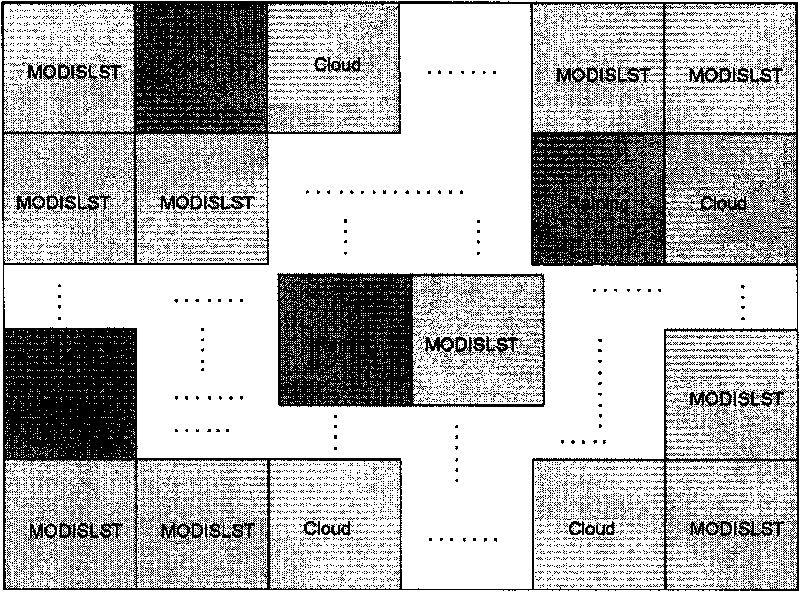
Method by utilizing passive microwave remote sensing data AMSR-E (Advanced Microwave Scanning Radiometer-EOS ) to invert surface temperature
InactiveCN101738620AAvoid difficultiesReduce unknownsElectromagnetic wave reradiationICT adaptationEarth observationData set
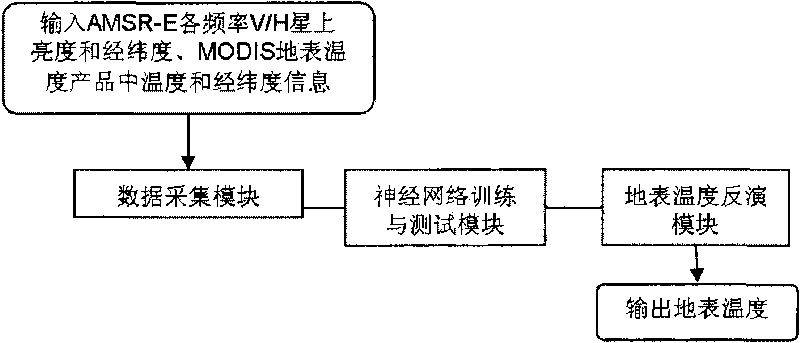
The invention relates to a method by utilizing passive microwave remote sensing data AMSR-E to invert surface temperature. The method comprises three steps of: step 1, collecting MODIS (moderate-resolution imaging spectroradiometer) surface temperature product which is provided by an American Earth Observation Data Center and used as AMSR-E surface temperature data by latitude and longitude control, and establishing a training and testing database; step 2, utilizing a neutral network to perform repetitive training and testing; and step 3, performing inversion calculation on AMSR-E actual image data, and actual surface verification and application analysis. The product obtained by the method has high precision, and overcomes the effect of clouds and partial raining on thermal infrared.
Owner:INST OF AGRI RESOURCES & REGIONAL PLANNING CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Satellite-ground cooperative in-orbit real-time geometric positioning method and system for optical satellites
ActiveCN106403902ASolve key technical issuesGood application effectInstruments for comonautical navigationPhotogrammetry/videogrammetryEarth observationCalibration result
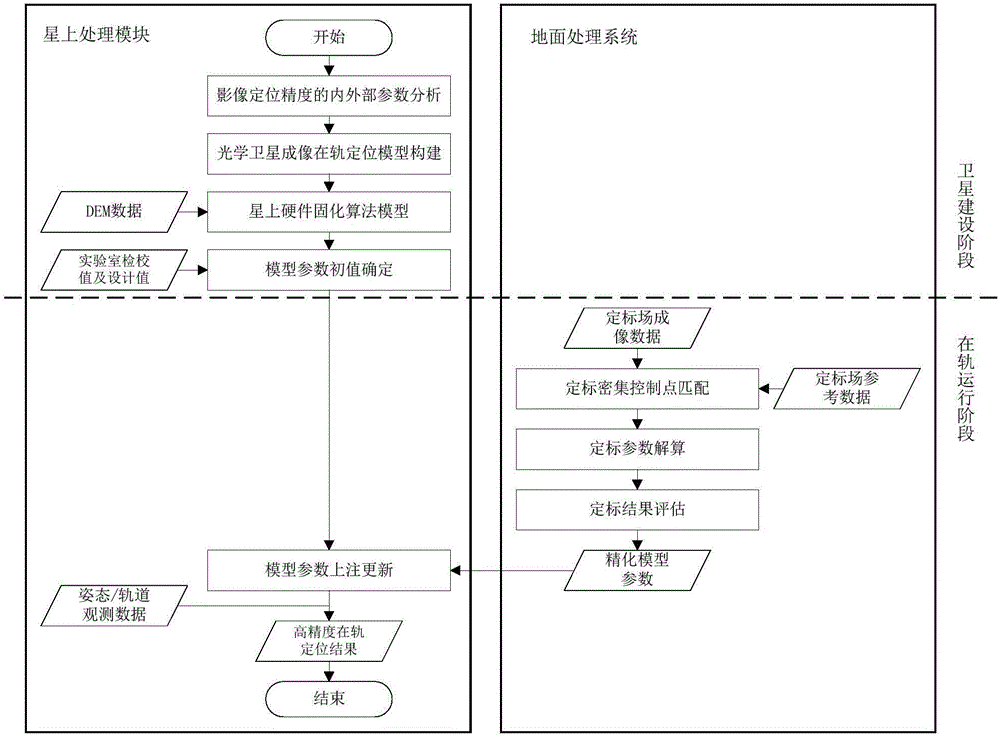
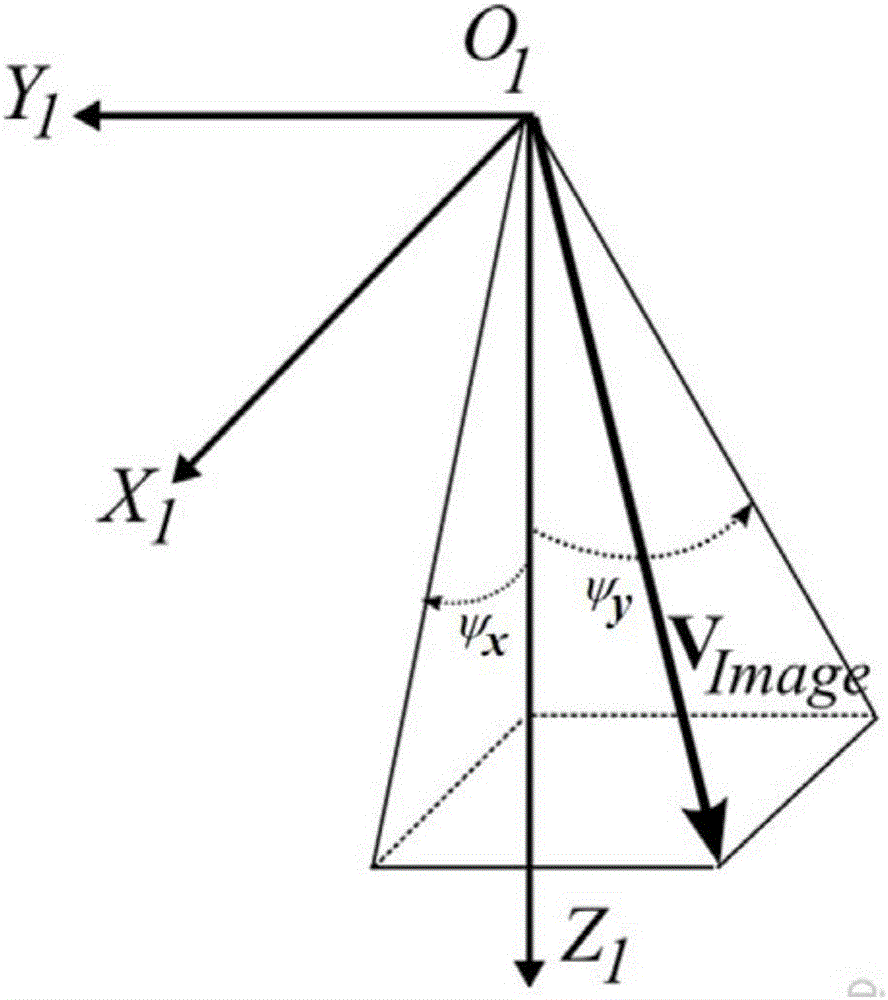
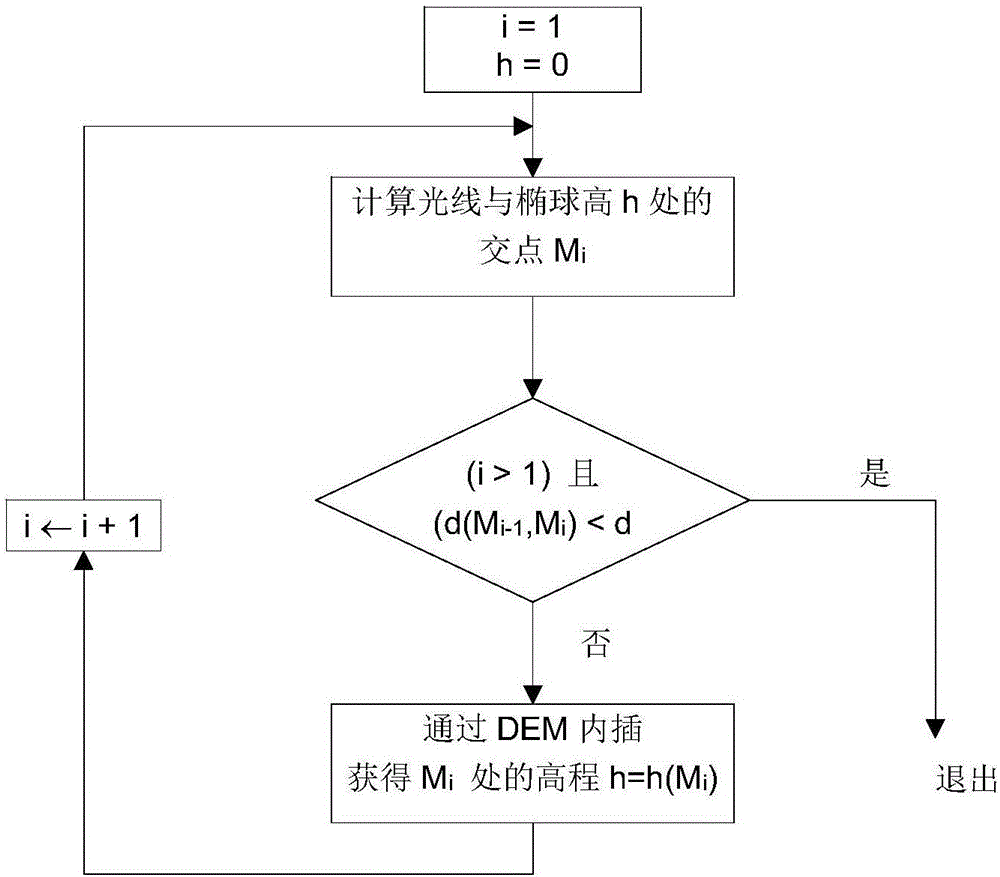
The invention provides a satellite-ground cooperative in-orbit real-time geometric positioning method and system for optical satellites. The method comprises the following steps: an optical satellite imaging and positioning model suitable for an onboard real-time processing unit is constructed, initial values of onboard positioning model parameters are acquired by calibration parameters or design parameters for camera interior and platform installation relation by a ground laboratory, after the satellite is in orbit, ground calibration field image data is acquired and downloaded, calibration matching and calibration parameter calculation are completed in a ground processing system by using the downloaded calibration field images; calibration results are verified and model parameter annotation is updated. The method and the system aim at limitation of onboard processing environment, and combine the ground processing system, so that a satellite-ground cooperative processing mode is formed, in-orbit high-precision real-time geometric positioning of optical remote sensing satellite is realized, application usefulness and timeliness of earth observation systems are improved, and necessary bases are provided for intelligent and high-efficient remote sensing data onboard real-time processing technology.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Large-torque magnetic suspension flywheel
InactiveCN102303709AAchieve outputReduce power consumptionSpacecraft guiding apparatusEarth observationMagnetic bearing
The invention discloses a large-torque magnetic suspension flywheel, which can be used as an execution mechanism for attitude stabilization and attitude maneuver of spacecrafts such as a satellite, an earth observation platform and the like. The magnetic suspension flywheel mainly consists of a base, a sealing cover, a radial decoupling conical magnetic bearing assembly, a core shaft, a rotor assembly, a Lorentz force magnetic bearing assembly, a motor assembly, a sensor assembly and the like. The core shaft is positioned in the center of the wheel body, a stator assembly is positioned at theradial outer side of the core shaft, the rotor assembly is arranged at the radial outer side of the stator assembly, the rotor assembly consists of a wheel flange and a wheel hub, and the Lorentz force magnetic bearing assembly consists of a magnetic bearing stator part and a magnetic bearing rotor part; an adapter plate is connected with the core shaft, the stator assembly and a motor stator; and the sensor assembly consists of a sensor shell and a sensor. The components of the flywheel are arranged reasonably and compactly, the flywheel can be used for attitude stabilization of the spacecraft, and attitude maneuver of the spacecraft can be realized by using large control torque provided by gyroscopic effect of the magnetic suspension flywheel.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
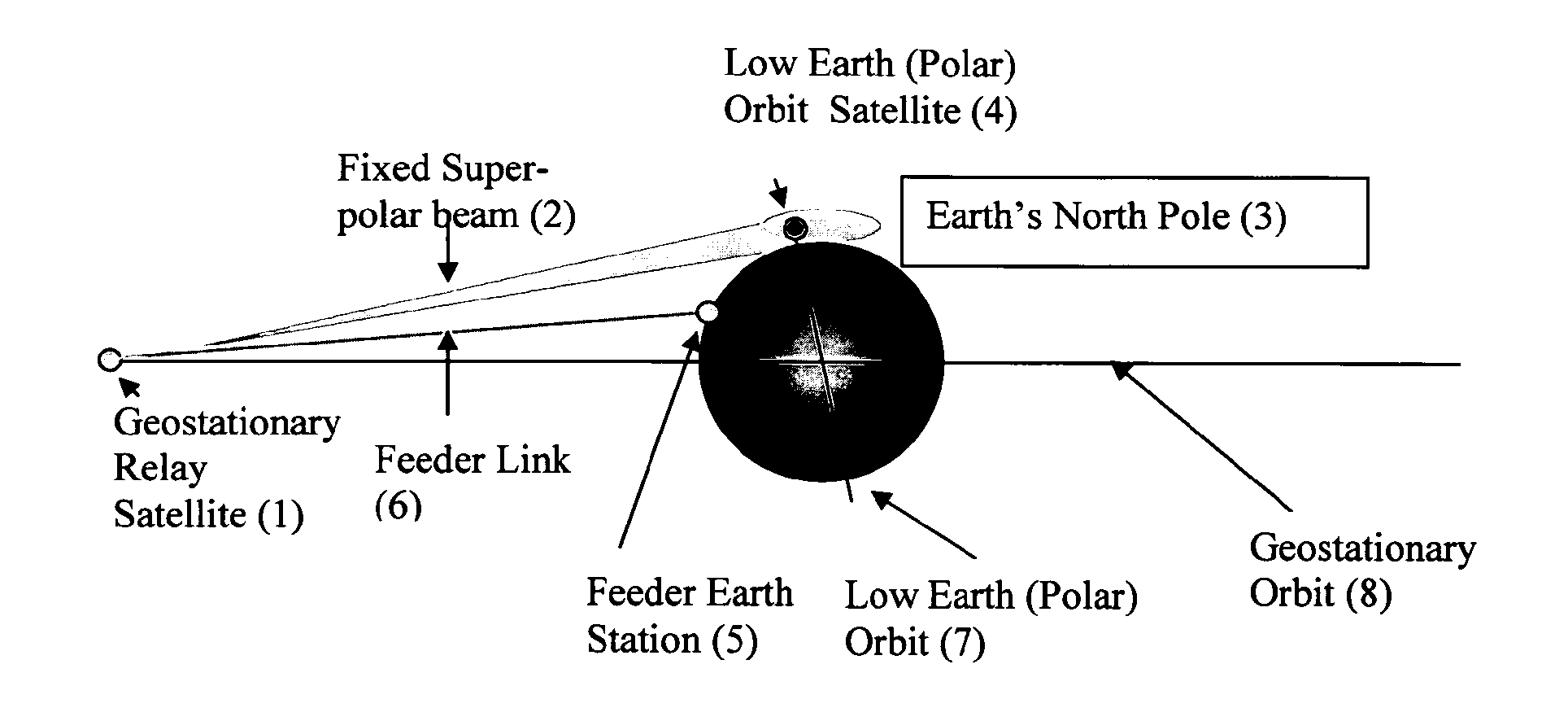
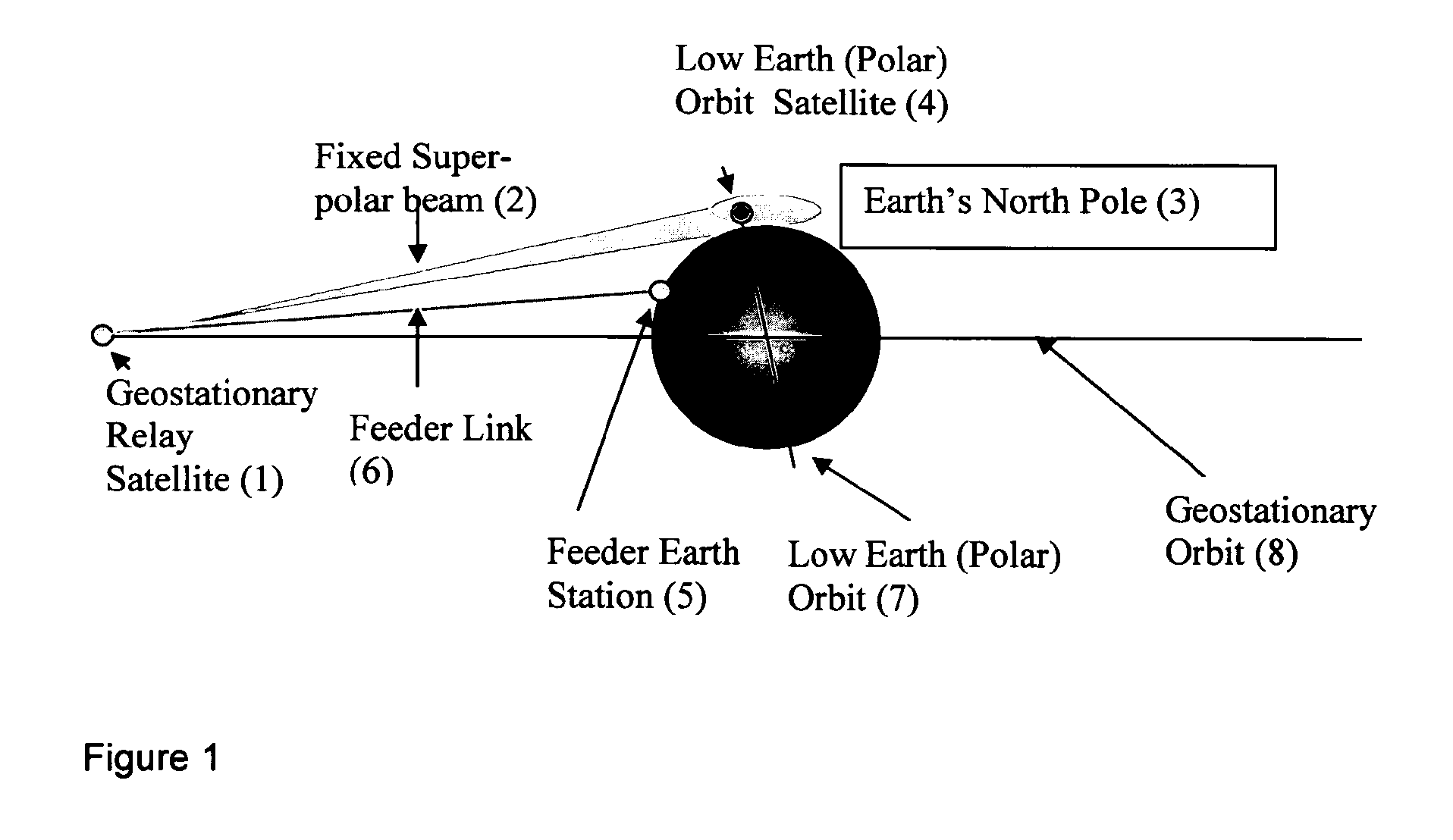
Virtual Polar Satellite Ground Station for Low Orbit Earth Observation Satellites Based on a Geostationary Satellite Pointing an Antenna Over an Earth Pole
ActiveUS20120184208A1Attractive solutionShort response timeRadio transmissionEarth observationGeosynchronous satellite
Owner:AIRBUS DEFENCE & SPACE
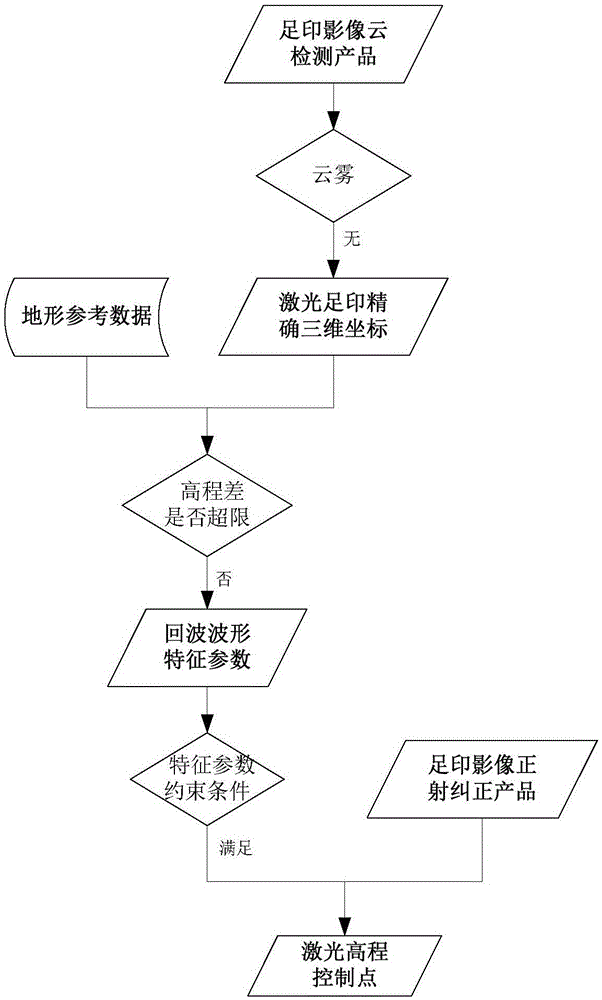
Automatic extraction method for Earth observation laser height measurement satellite elevation control points and data processing method
ActiveCN105550639AGuaranteed accuracyImprove accuracyPhotogrammetry/videogrammetryScene recognitionEarth observationPeak value
The invention relates to an automatic extraction method for Earth observation laser height measurement satellite elevation control points and a data processing method. The laser elevation control point extraction method comprises steps that an effective earth observation laser distance value measurement evaluation method is employed, determined cloudless footprint image blocks are kept, and laser elevation data of determined thin-cloud or thick-cloud footprint image blocks are removed; reflectivity Epsilon smaller than 1 of laser footprint points is taken as a screening parameter, laser footprint points of the kept footprint image blocks are screened, Epsilon=reception pulse energy / emission pulse energy, laser footprint points which have only one wave peak, have the peak value greater than the threshold, have the standard deviation sigma not greater than 3.2ns after waveform fitting are selected from an echo waveform, and parameters used for determining the threshold comprise the emission energy and a reception caliber of a laser device. Through the method, influence of clouds on laser distance measurement can be reduced, laser distance measurement precision can be guaranteed, and accuracy of the laser elevation reference data is effectively improved.
Owner:SATELLITE SURVEYING & MAPPING APPL CENTSASMAC NAT ADMINISTATION OF SURVEYING MAPPING & GEOINFORMATION OF CHINANASG
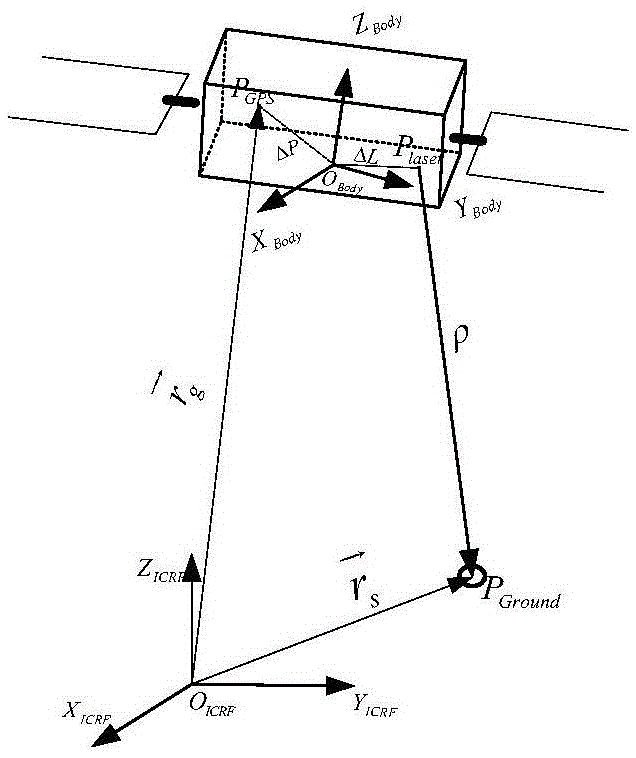
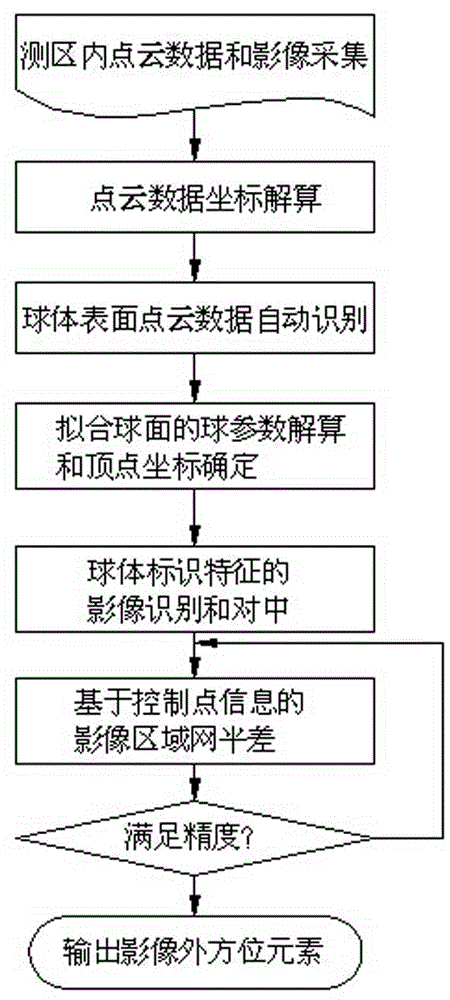
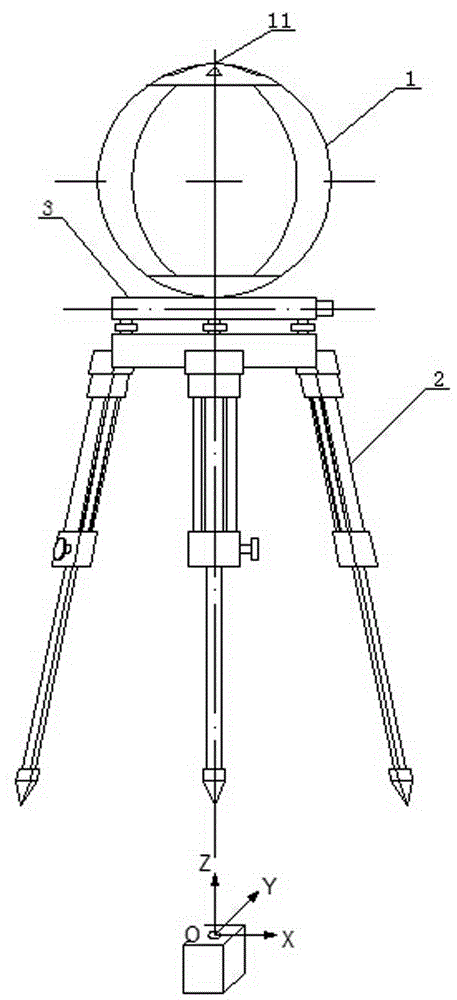
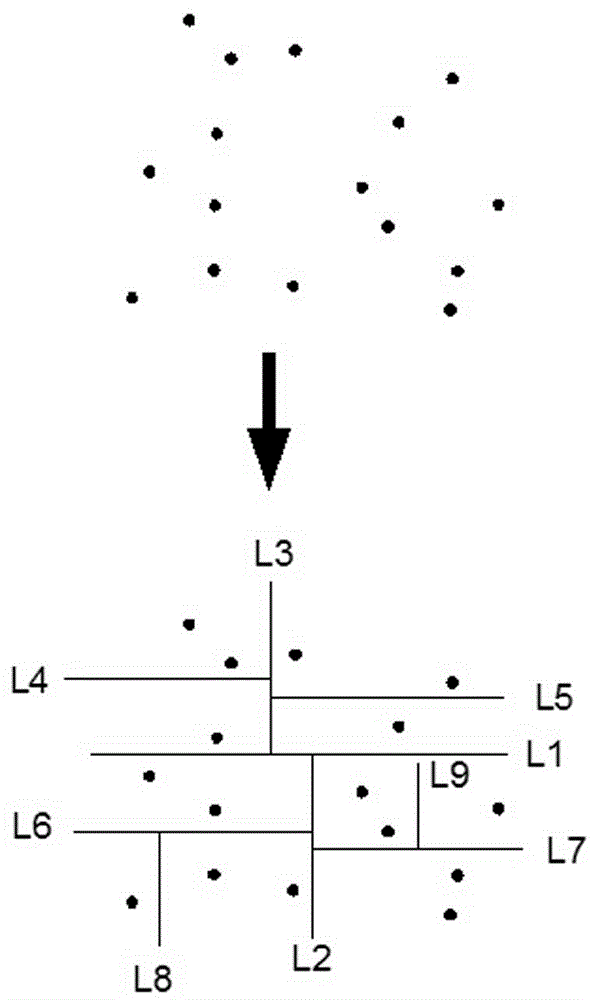
Movable target sphere oriented onboard LiDAR point cloud and image united rectification method
The invention discloses a movable target sphere oriented onboard LiDAR point cloud and image automatic rectification method and a target sphere device applied to the method and aims at solving the high-accuracy rectification problem of a point cloud and an optical spectrum image when an existing onboard laser radar and a digital camera are combined to perform earth observation. The movable target sphere oriented onboard LiDAR point cloud and image automatic rectification method comprises the steps of 1 acquiring the point cloud and the image, 2 resolving a point cloud data coordinate, 3 automatically recognizing point cloud data, 4 resolving sphere parameters of a fit sphere and determining a peak coordinate, 5 recognizing and centering images of sphere identification features and the like. The target sphere device is a sphere body marked with the identification features at the top. The rectification method can automatically separate out sphere surface point cloud and background point cloud, decrease control information interaction working amount in traditional block adjustment, obviously improved the rectification efficiency and can ensure the rectification accuracy of the point cloud, the image and a control point.
Owner:CHINESE ACAD OF SURVEYING & MAPPING
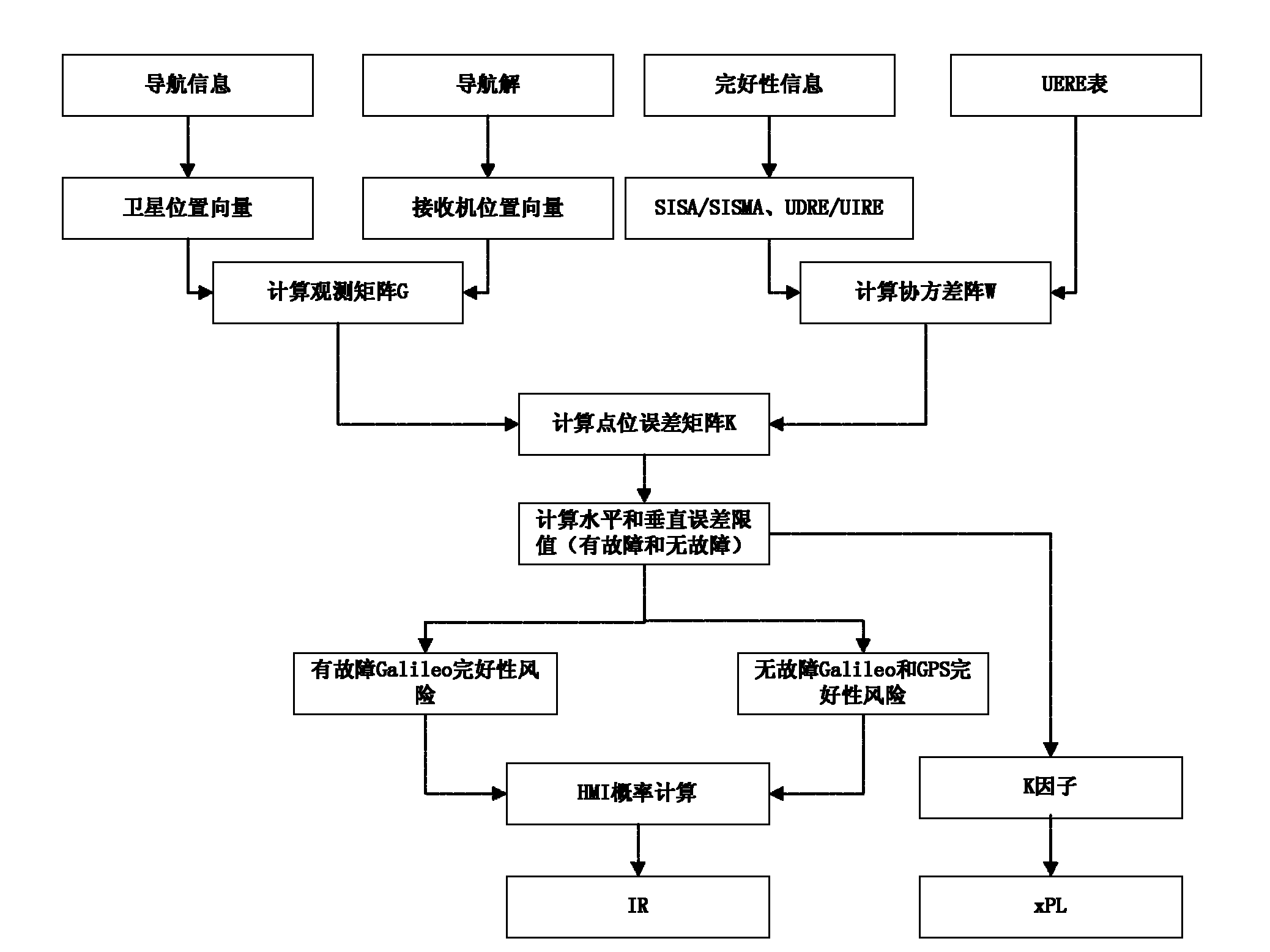
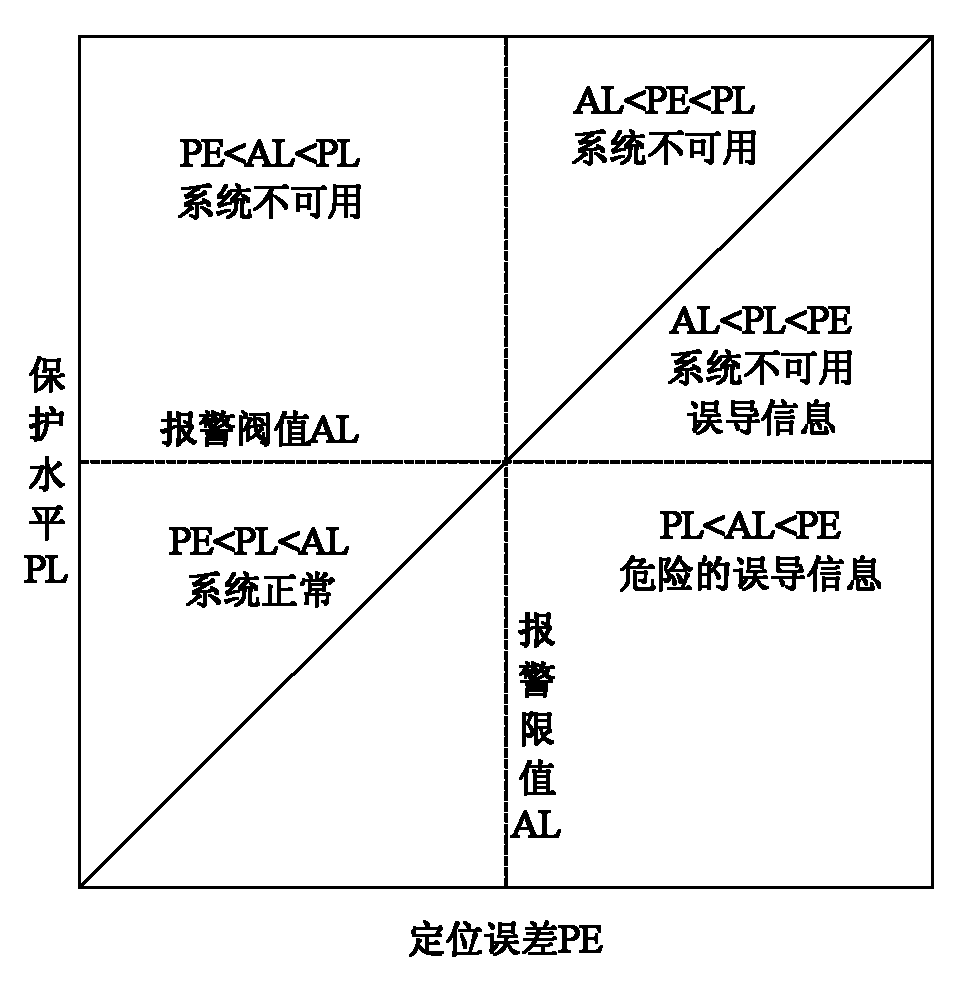
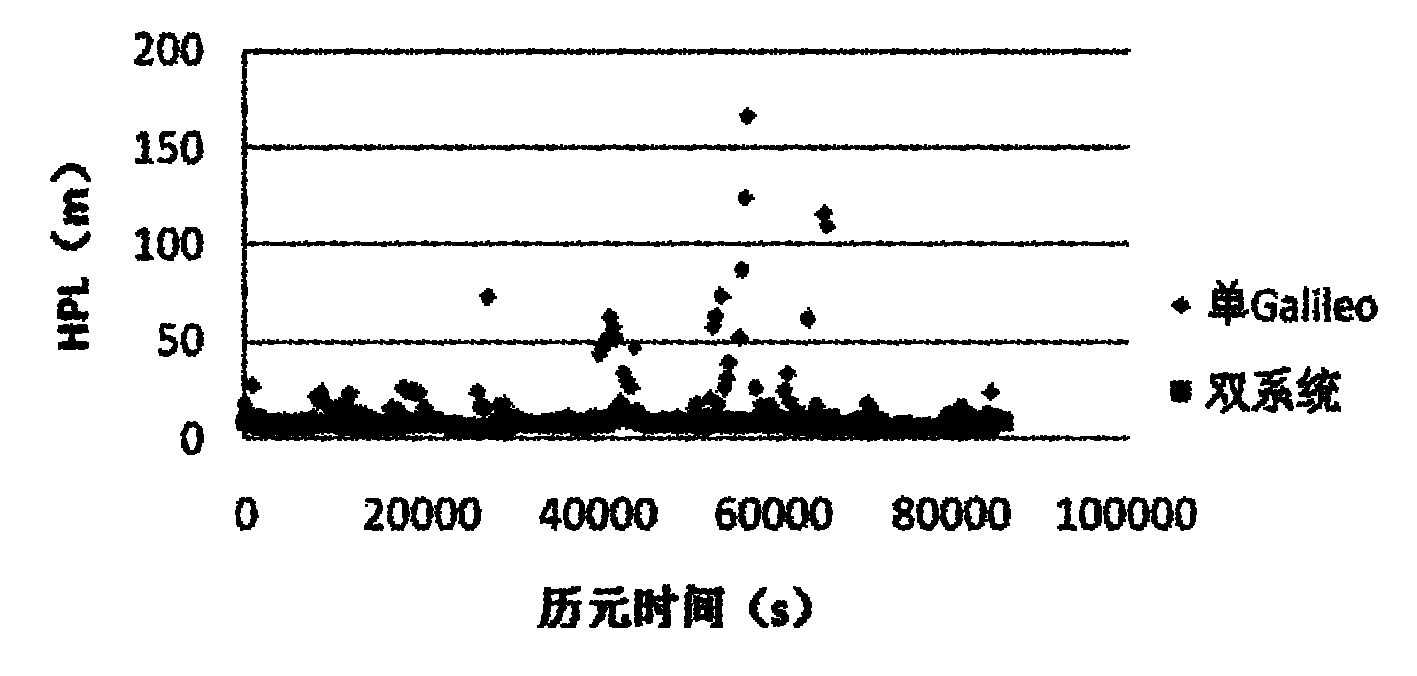
Galileo system integrity concept-based multimode user integrity assessing method
ActiveCN102096075AImprove integrityImprove usabilitySatellite radio beaconingSpecial data processing applicationsEarth observationEuropean Geostationary Navigation Overlay Service
The invention belongs to the field of the integrity study of a satellite navigation system in the technical field of earth observation and navigation, and provides a Galileo system integrity concept-based multimode user integrity assessing method. In the method, the conventional Galileo user integrity concept is used in two systems directly, for a non-Galileo system (such as European geostationary navigation overlay service (EGNOS)), input parameters are needed to be pretreated appropriately, so that the input parameters are converted into information available in a Galileo user integrity algorithm, and the change in values of an integrity risk (IR) and / or a protection level (xPL) is monitored during integrity analysis. In the method, the assessment of multisystem user integrity is realized by using a more advanced Galileo system integrity concept; and by comparing and analyzing integrity calculation results of a single system and a multisystem, the availability of positioning resultsof users is improved substantially under the condition of the multisystem, and the user integrity is improved to a large extent.
Owner:CHINA AEROSPACE KEGONG INFORMATION TECH RES INST
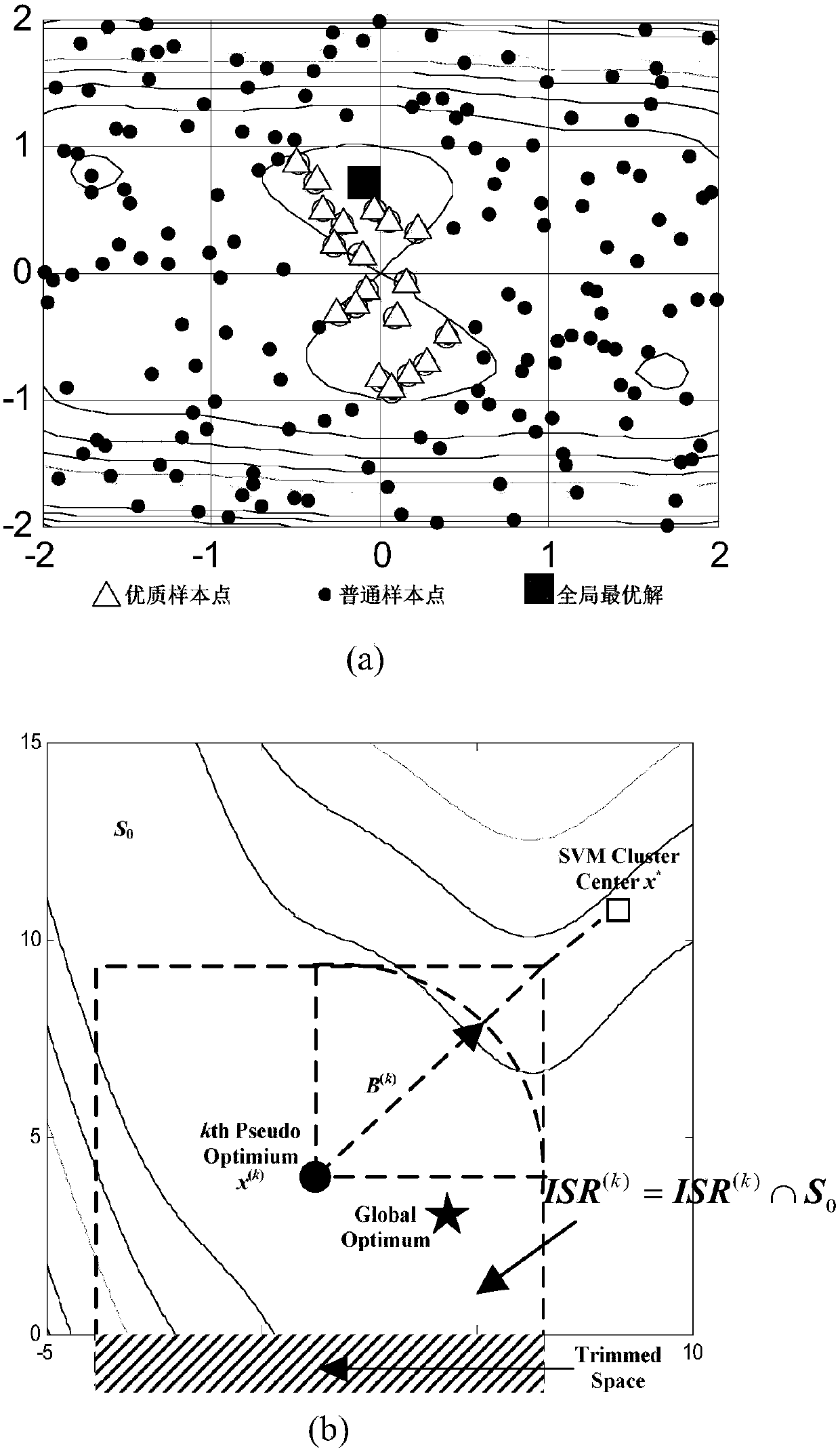
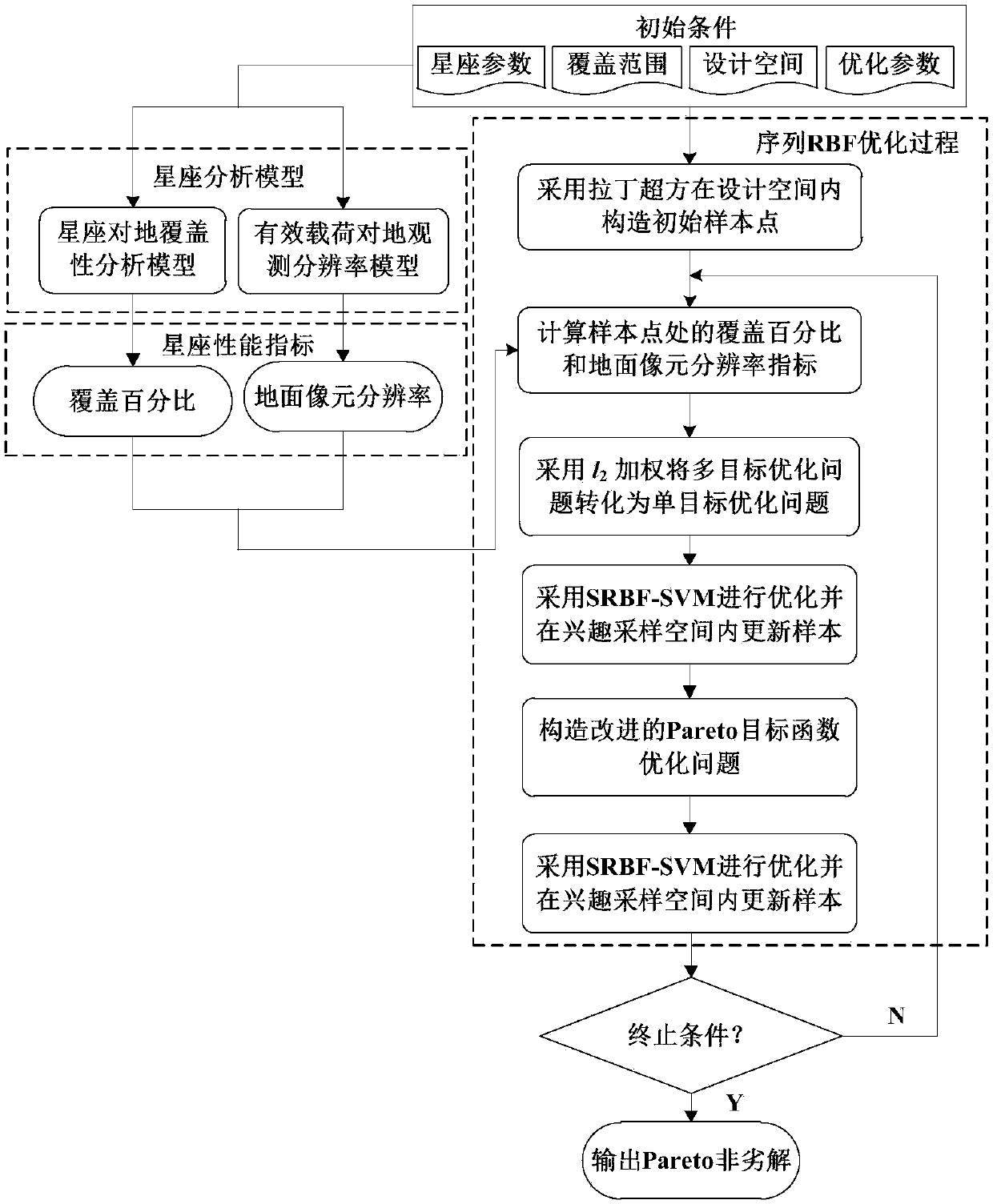
Efficient multi-objective optimization method for satellite constellation
ActiveCN107798187AReduce computing costReduce design costGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationEarth observationIntersection of a polyhedron with a line
The invention discloses an efficient multi-objective optimization method for a satellite constellation and belongs to the field of constellation system of a spacecraft. The method comprises the stepsof determining an initial condition based on a Walker-delta constellation configuration, and establishing a constellation orbit kinetic equation, an earth coverage analysis module and an earth observation resolution model; optimizing an earth orbit height, an orbital inclination and an ascending node right ascension with a coverage percentage and a ground pixel resolution by use of a sequential radial basis function multi-objective optimization strategy; and constructing an objective function based on l2 weighting and an improved Pareto fitness function, replacing a high time-consuming constellation performance simulation model with an RBF (Radial Basis Function) agent model to optimize design, and updating and managing the RBF agent model through sequence sampling in an interest interval.Therefore, a Pareto non-inferior solution set satisfying engineering requirements is acquired as a satellite constellation design scheme, the coverage percentage of a constellation for a target observation region is realized as high as possible, the pixel resolution of an effective load is realized as low as possible, the calculation cost and the design cost of the satellite constellation are reduced, and the Pareto leading edge search capability is improved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Satellite in-orbit free boundary condition simulation device
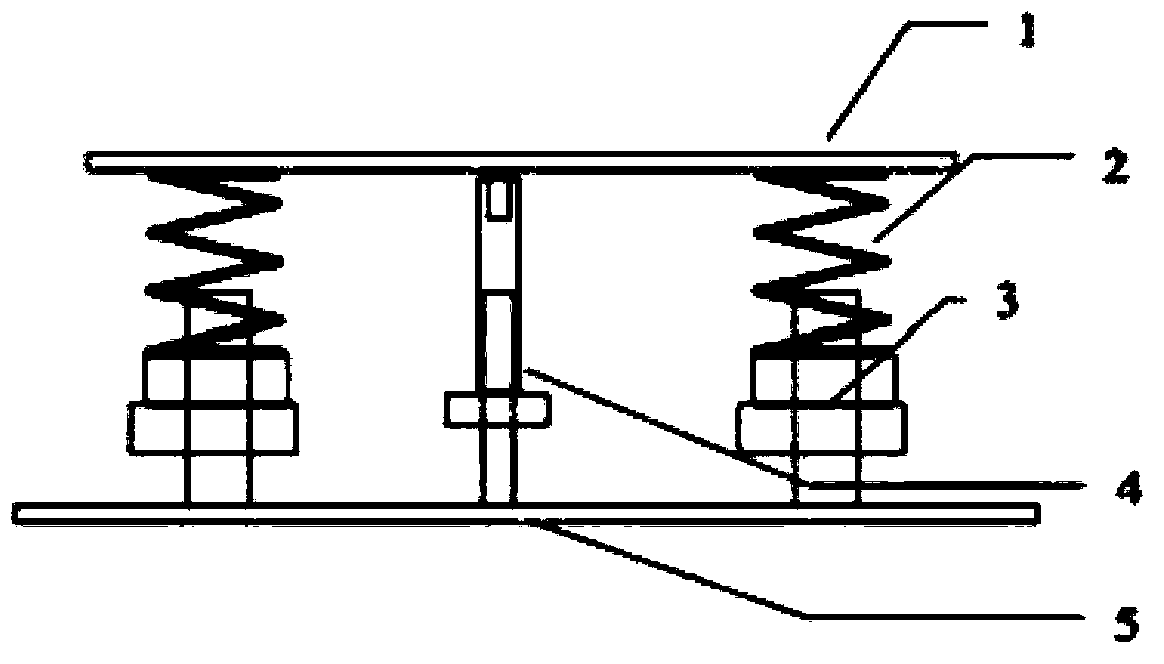
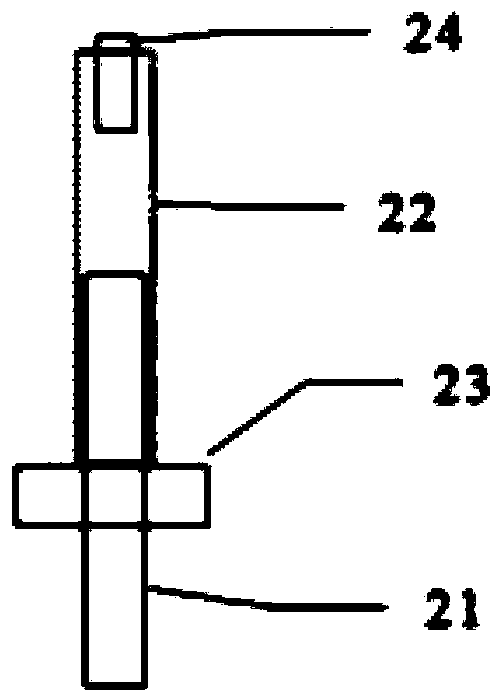
ActiveCN103359300ARealize simulationImproving the Technical Level of Kinetic ExperimentsCosmonautic condition simulationsEarth observationButt joint
The invention discloses a satellite in-orbit free boundary condition simulation device. The satellite in-orbit free boundary condition simulation device mainly comprises a satellite butt joint plate, supporting springs, satellite balance adjusting devices, a limiting protecting device and a supporting plate, wherein the satellite butt joint plate at the upper portion of the device and the supporting plate at the lower portion of the device are correspondingly arranged according to the satellite mechanical structure and are generally of an annulus shape, the two ends of each supporting spring are fixedly connected to the annular portions between the satellite butt joint plate and the supporting plate respectively and evenly distributed around the annular portions so that a satellite can be elastically supported, the satellite balance adjusting devices which correspond to the supporting springs in number are fixedly arranged between the bottoms of the supporting springs and the supporting plate so that the supporting springs are supported to adjust inclination of the satellite and the simulation device caused by eccentricity of the satellite, and therefore the satellite is kept horizontal after being connected to the simulation device in a butt joint mode. According to the satellite in-orbit free boundary condition simulation device, the level of the satellite dynamics testing technique is improved, and requirements for verification of in-orbit dynamics characteristics and in-orbit micro-vibration environment tests in the process of developing satellites especially high-precision earth observation satellites are met.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF SPACECRAFT ENVIRONMENT ENG
Device for two-dimensional imaging of scenes by microwave scanning
InactiveUS8009116B2Acceptable image qualityHigh processing expenditure and expenditureAntennasRadio wave reradiation/reflectionContinuous scanningEarth observation
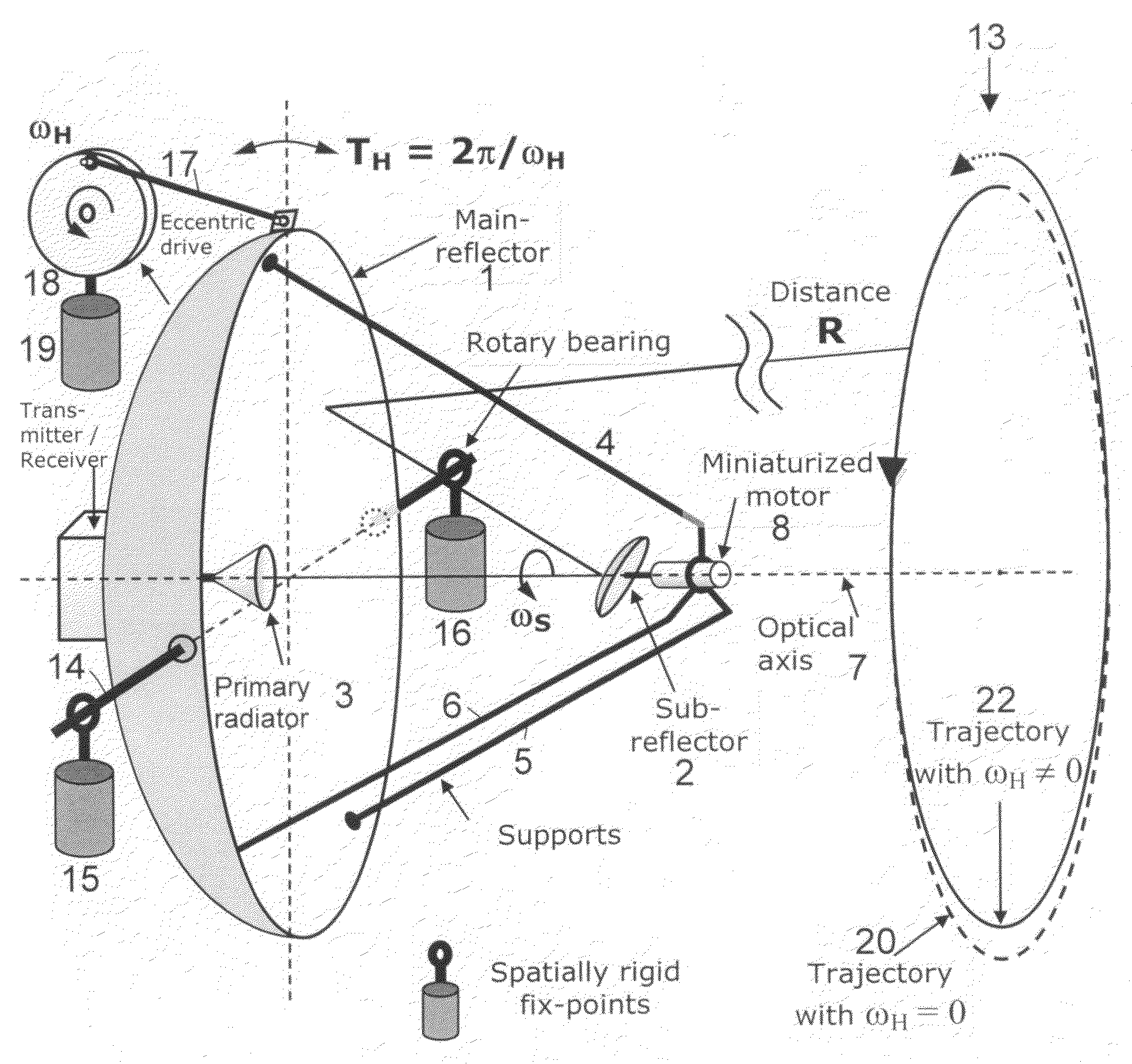
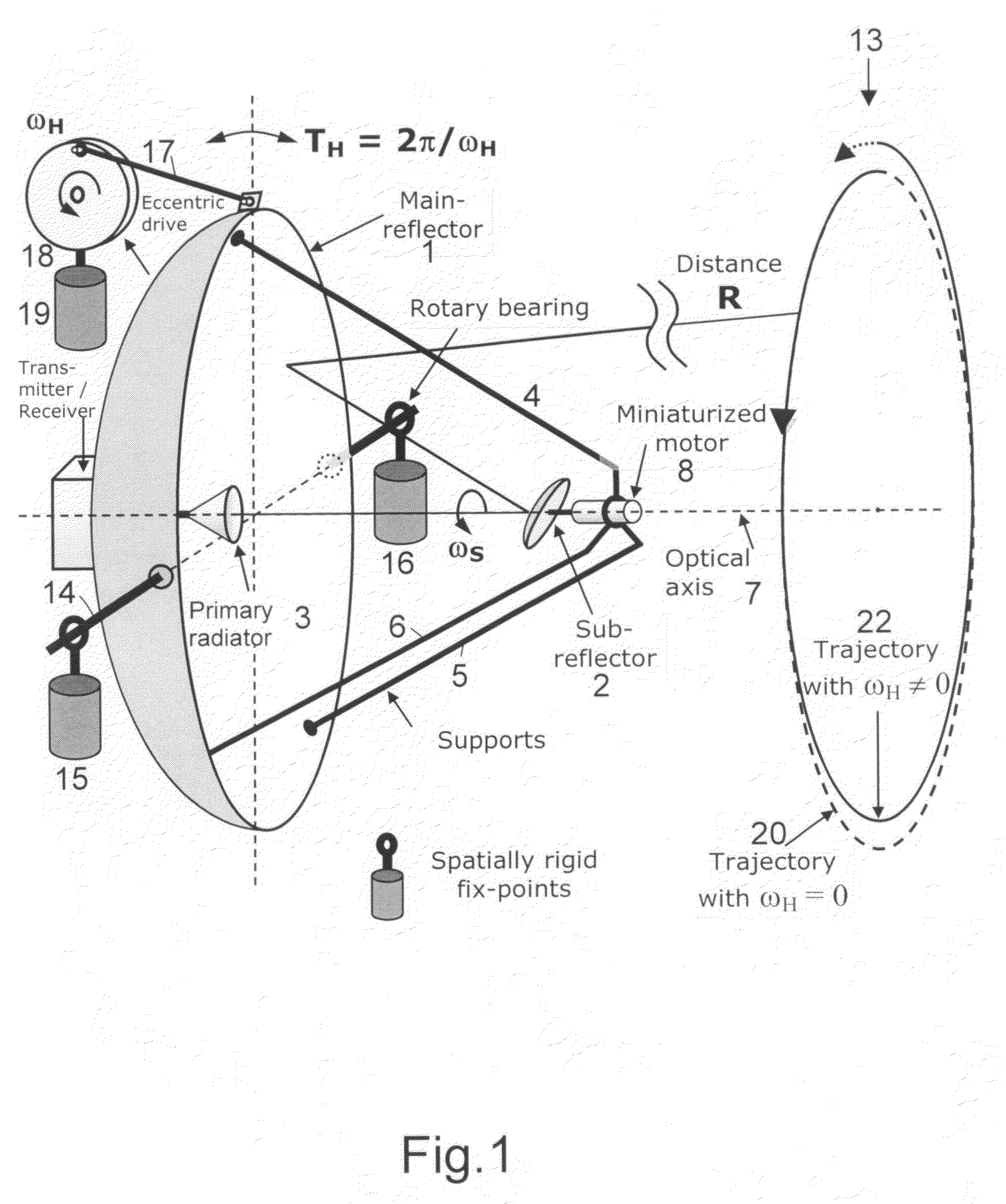
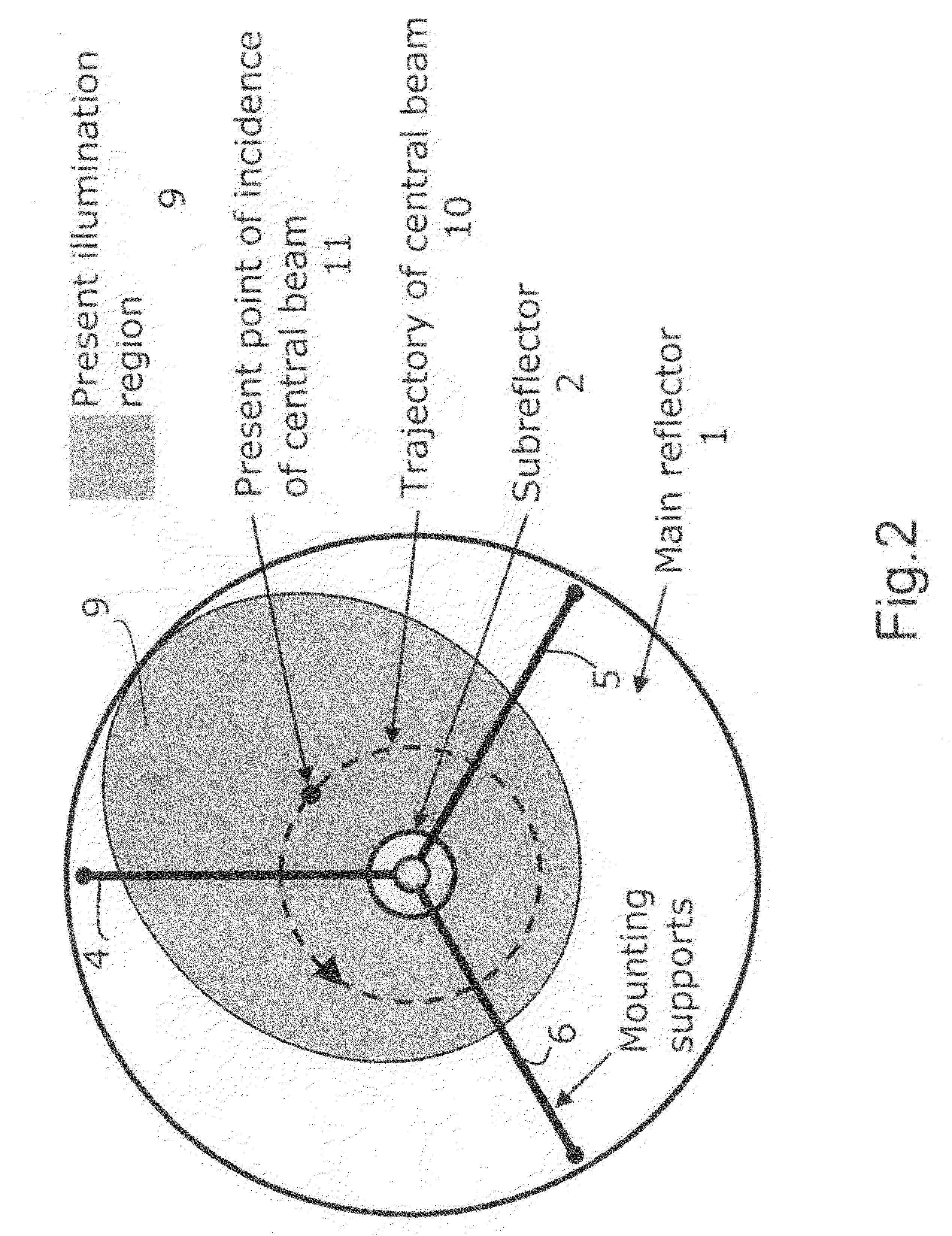
For two-dimensional imaging of scenes through continuous passive or active microwave scanning, use is made of a fully mechanized directional antenna array comprising a main reflector (1), a primary radiator array (3) and a subreflector (2) having a small size in comparison to the main reflector and being tilted relative to the optical axis (7) of the directional antenna array. First drive means (8) are operative to rotate the subreflector (2) about the optical axis (7), and second drive means (17,18) are operative to move the total directional antenna array in a direction approximately vertical to the optical axis (7). The moving speed of the subreflector (2) is very high in comparison to that of the total directional antenna array. The shape of the main reflector (1), the shape of the subreflector (2), the primary radiator (3), the distance between primary radiator and subreflector and the distance between subreflector and main reflector as focusing parameters are attuned to each other in such a manner that, for a given scene distance, an optimum focusing and an optimum size of the field of view are achieved. The focusing parameters and the moving speeds of the two drive means are set in a manner allowing for a gapless, continuous scanning of the scene with the aid of the focusing spot (12) moving at the scene distance. Applicability in remote investigation, particularly in earth observation and in safety technology.
Owner:DEUTSCHES ZENTRUM FUER LUFT & RAUMFAHRT EV
Star sensor setting angle determining method based on mission planning
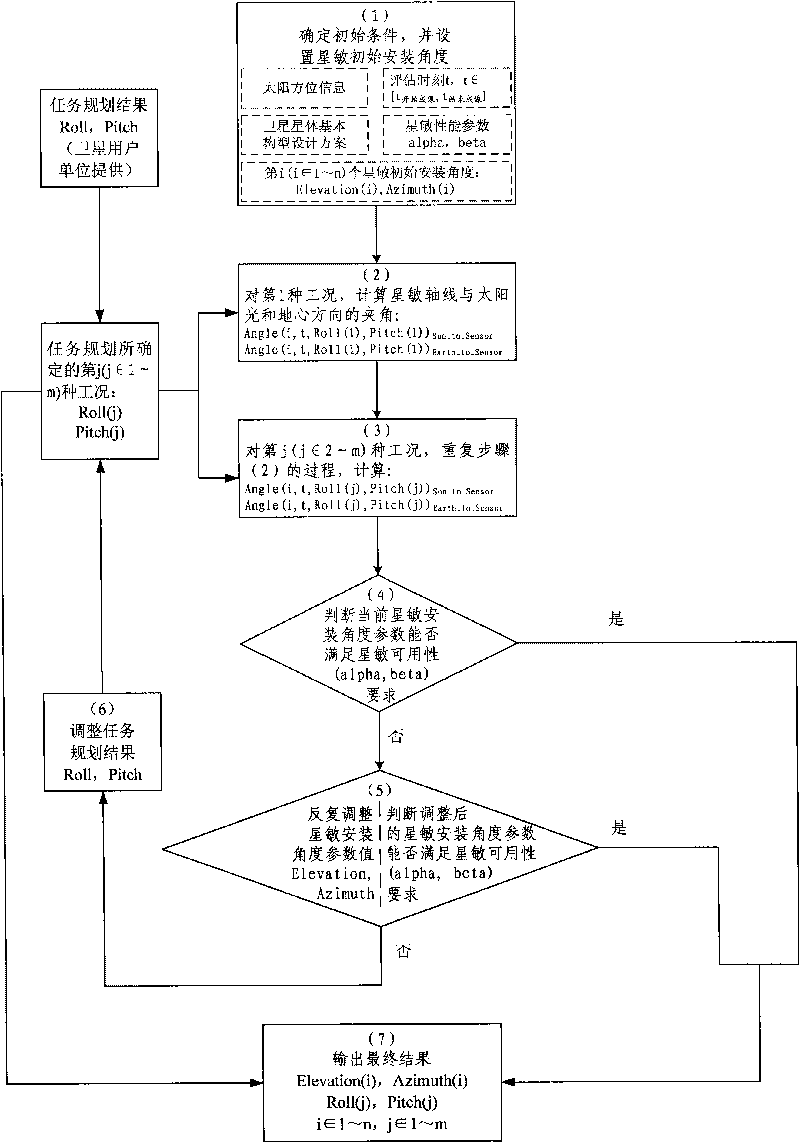
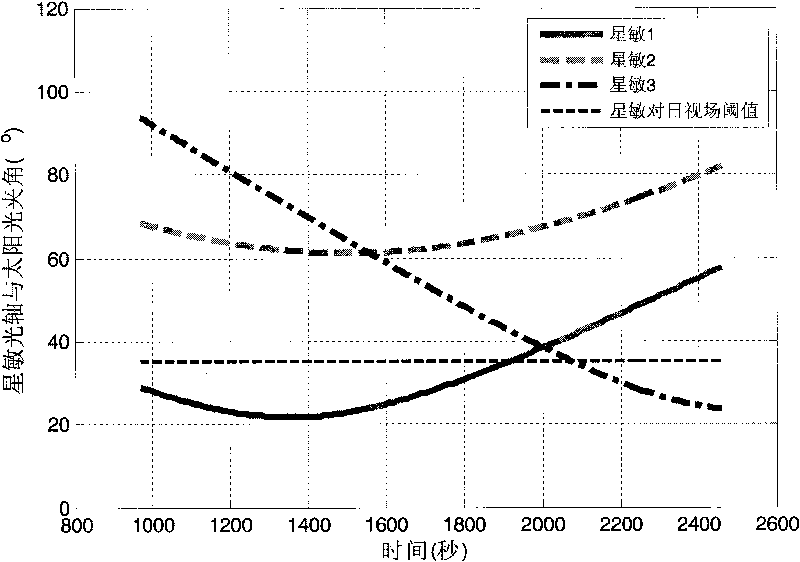
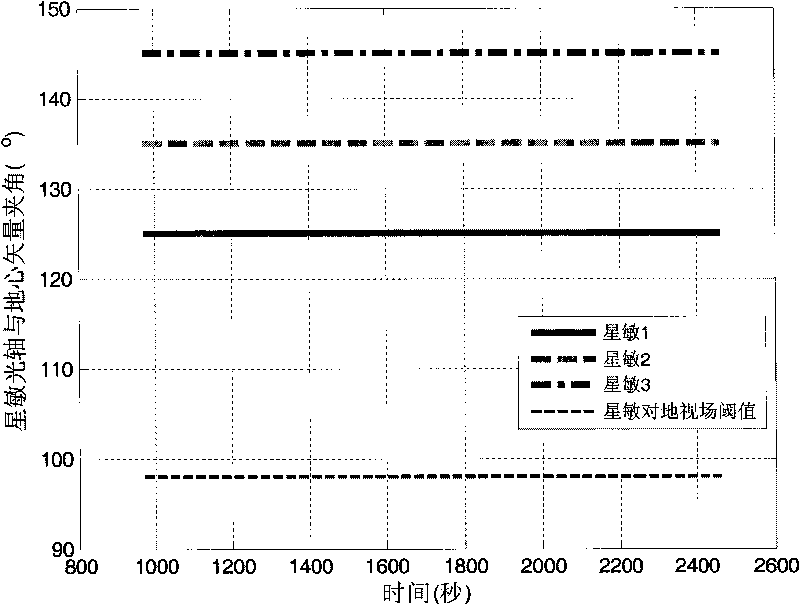
ActiveCN101758934AAvoid enteringAvoid Earth Observation Condition AttitudeSpacecraft guiding apparatusEarth observationVisibility
The invention relates to a star sensor setting angle determining method based on mission planning, aiming to satisfy the visibility demand to the sun and the earth of a star sensor when a satellite orbits. In the method, the angles between the axis of the star sensor and the sun or the earth are calculated and analyzed, the influence of various imaging working conditions to earth, which are determined by the mission planning, on the star sensor is considered emphatically, the setting angle and the working conditions of the star sensor are continuously adjusted to determine the proper setting angle of the star sensor. The method of the invention fully considers the influence of stray light on the star sensor under various working conditions and attitudes, is particularly applicable to the overall design work of the high-resolution quick satellite which need adopt large angle maneuver to perform earth observation, and can establish good feedback mechanism between the user unit which expresses satellite design requirements and performs the mission planning of the satellite and the engineering unit which designs the satellite.
Owner:AEROSPACE DONGFANGHONG SATELLITE
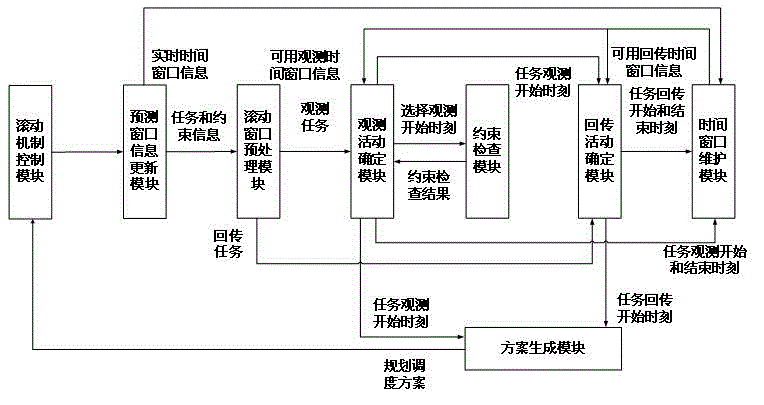
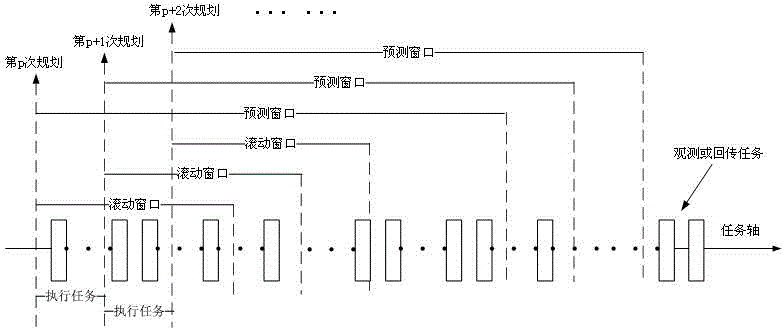
Imaging satellite autonomous mission planning algorithm based on receding horizon control
InactiveCN104063749AUniform optimalityUnified real-timeForecastingSpecial data processing applicationsEarth observationTime domain
The invention relates to an imaging satellite autonomous mission planning algorithm based on receding horizon control. According to the invention, research is conducted for the imaging satellite autonomous mission planning problem, an autonomous mission planning frame based on the RHC strategy is established, the optimization method of the rolling construction mission planning subproblem is described, and an imaging satellite autonomous mission planning heuristic algorithm based on the RHC strategy is provided. In the experimental analysis, through the contrast experiment of different problem scales and different RHC strategy parameters, the RHC-based heuristic algorithm provided in the invention is verified to be effective for the imaging satellite autonomous mission planning problem, the planning while executing strategy of the algorithm has the advantage of good robustness for dynamic missions that may occur in an earth observation network at any time, so the contradiction between the real-time performance and the optimality in the imaging satellite autonomous mission planning problem can be well solved.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Multi-sensor-based attitude determination system
InactiveCN101712381AOvercome the problem of reduced accuracy of attitude determinationCases where non-Gaussian noise is applicableSpacecraft guiding apparatusFiberEarth observation
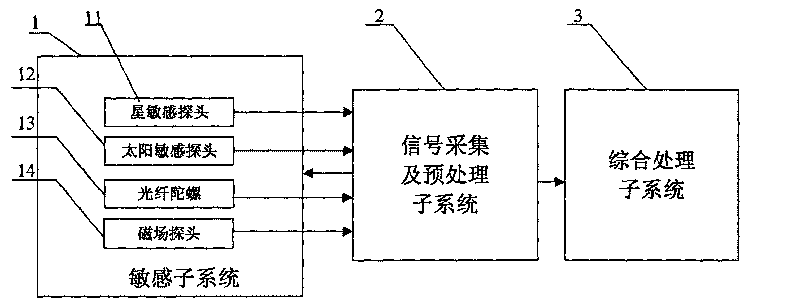
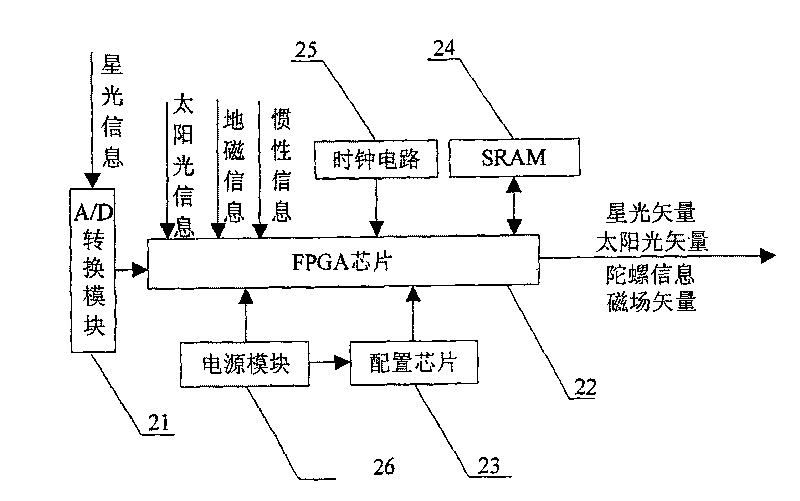
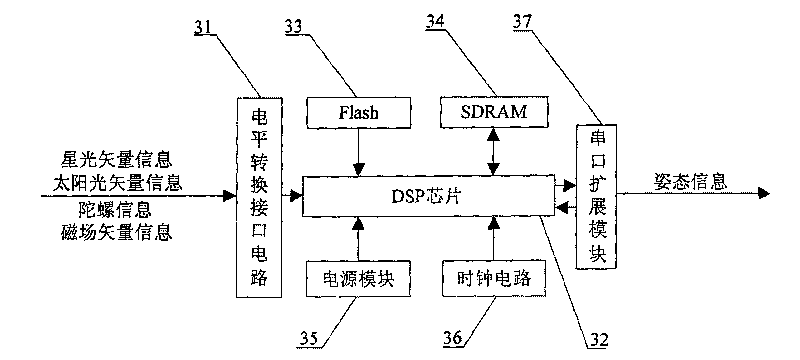
The invention provides a multi-sensor-based attitude determination system, which comprises a sensitive subsystem, a signal acquisition and preprocessing subsystem and an integrated processing subsystem, wherein the sensitive subsystem integrates four classes of sensitive parts such as star sensitive probes, sun sensitive probes, fiber optic gyros and magnetic field probes; the signal acquisition and preprocessing subsystem is realized by an FPGA chip and a peripheral circuit thereof, parallelly receives output data of the four classes of sensitive probes and completes the smoothing and preprocessing of the data; and finally, the integrated processing subsystem taking a DSP (or ARM) chip as a core is utilized to realize the high-precision attitude determination of the system by an ant colony particle filter-based combined attitude determination method according to sunlight information, starlight information, inertial information and geomagnetic information after smoothing and preprocessing. The multi-sensor-based attitude determination system with high precision, integration level and reliability is realized, and has important practical significance for high-resolution earth observation of new-generation earth observation satellites.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
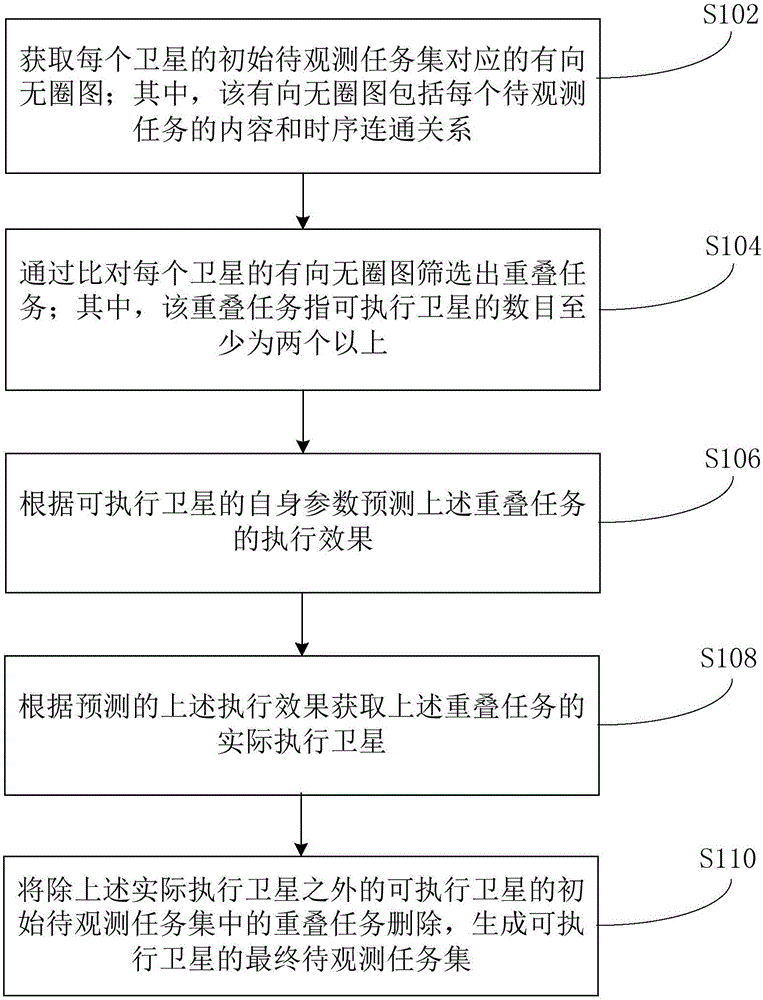
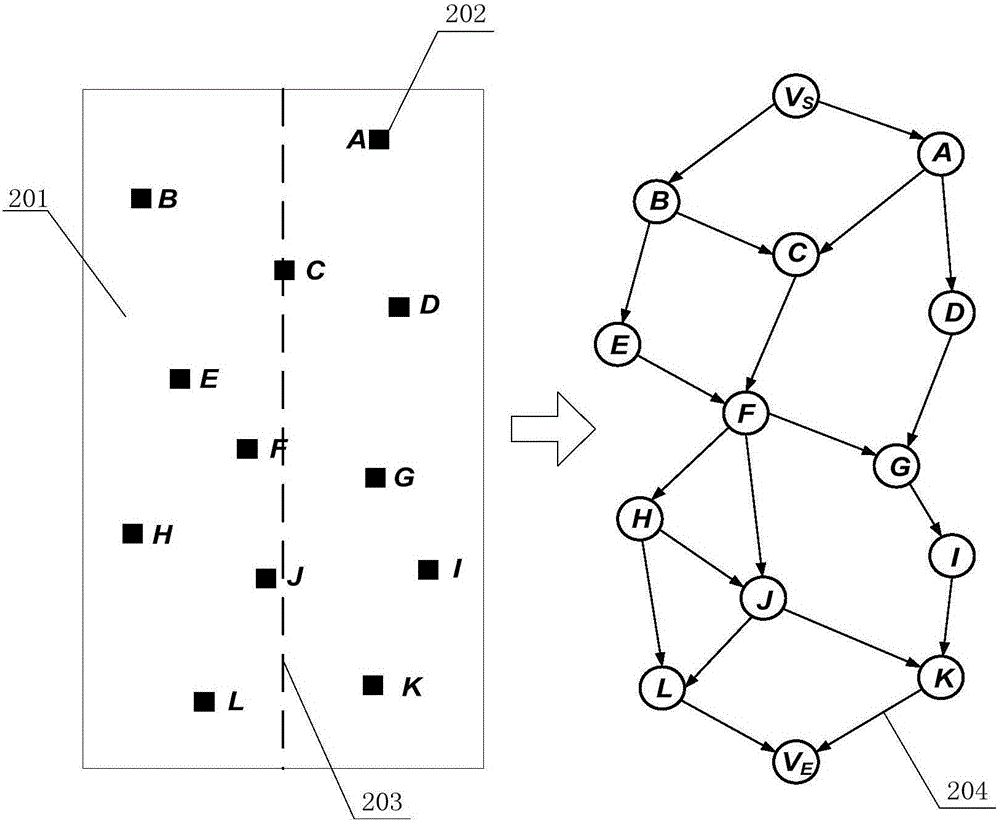
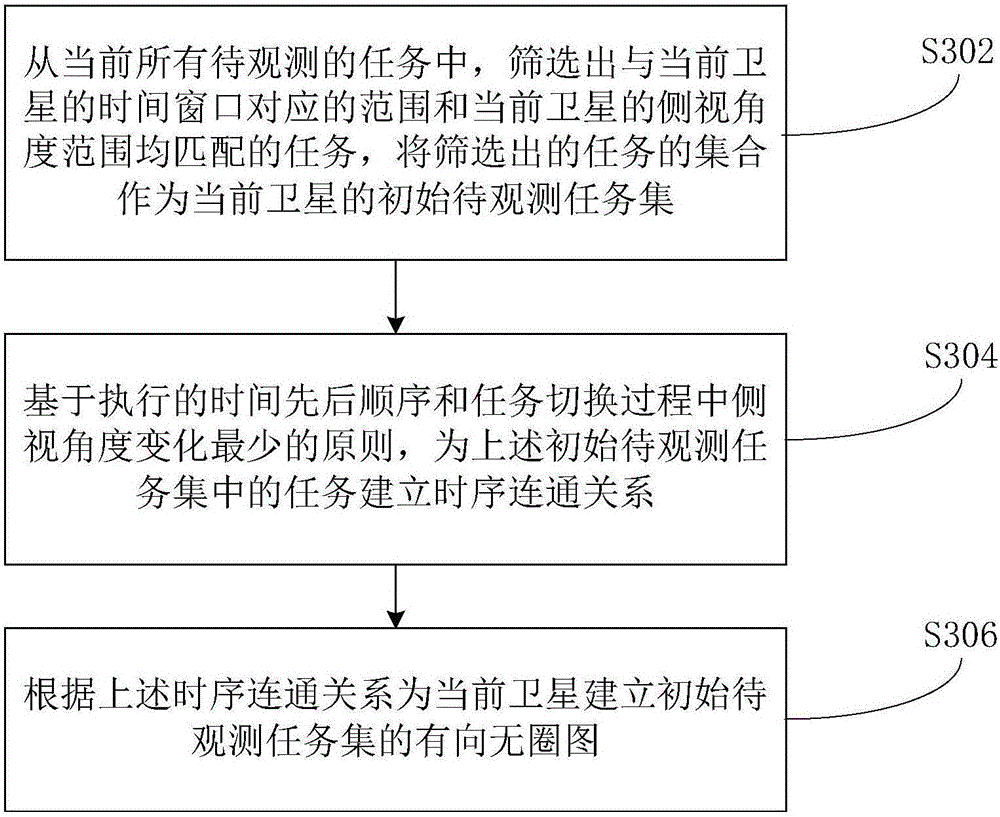
Method and device for collaboratively dispatching tasks among multiple earth observation satellites
InactiveCN106228261AReduce instances of overlapping execution of the same taskOptimize task schedulingForecastingResourcesEarth observationSatellite image
The invention provides a method and a device for collaboratively dispatching tasks among multiple earth observation satellites. The method comprises the steps of acquiring a directed acyclic graph corresponding to an initial to-be-observed task set of each satellite, wherein the directed acyclic graph comprises the content and a time sequence connection relation of each to-be-observed task; screening out overlapping tasks through comparing the directed acyclic graph of each satellite, wherein the overlapping tasks refer to tasks with the number of executable satellites being at least more than two; predicting an execution effect of each overlapping task according to parameters of the executable satellites; acquiring actual execution satellites of each overlapping task according to the predicted execution effect; deleting the overlapping tasks of the executable satellites except for the actual execution satellites in the initial to-be-observed task set, and generating a final to-be-observed task set of the executable satellites. The embodiment of the invention improves the satellite imaging efficiency and the utilization reasonability of satellite imaging resources.
Owner:INST OF RADAR & ELECTRONICS CONFRONTATION ARMY AIR FORCE EQUIP RES INST OF PLA
Laser radar echo full-waveform acquisition device with sampling point time location
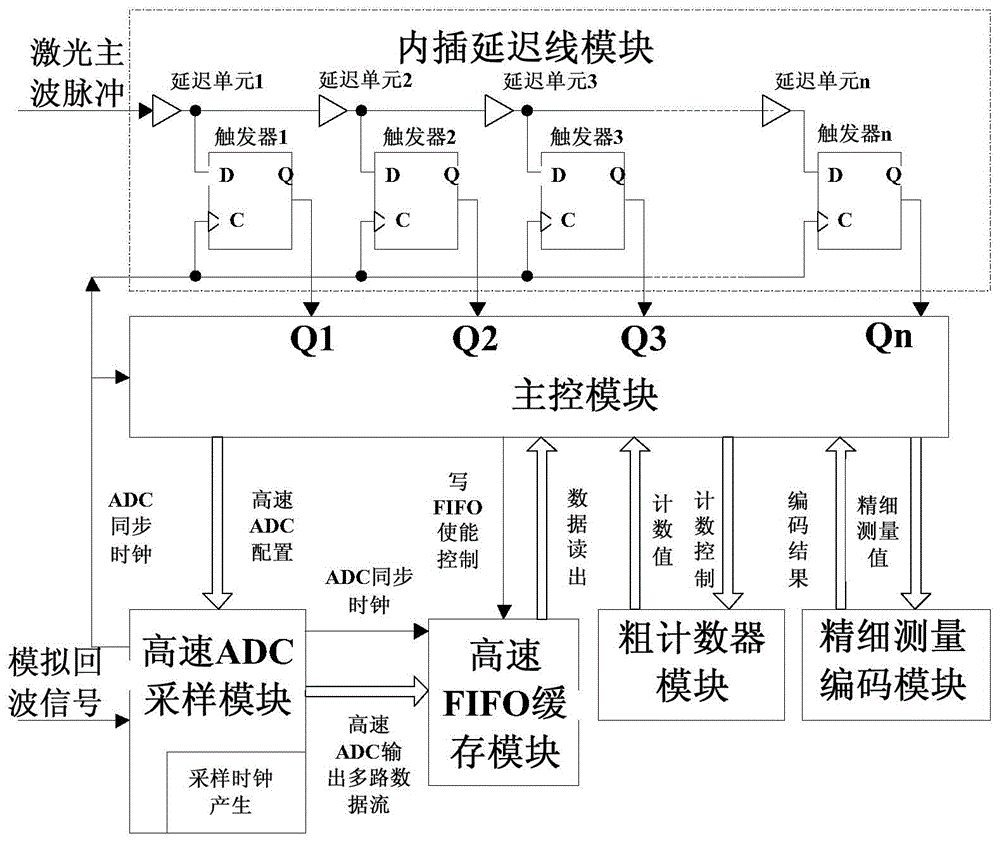
ActiveCN104155640AEasy to implementFlexible configurationElectromagnetic wave reradiationCode moduleEarth observation
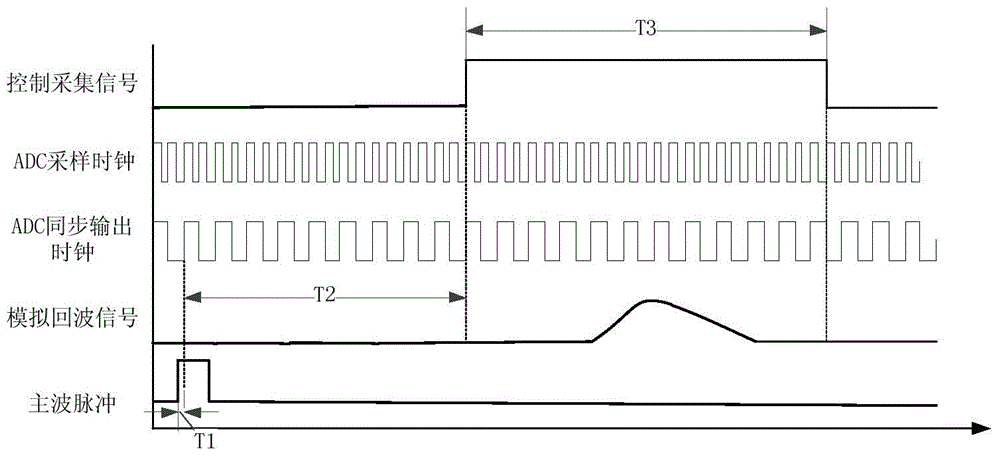
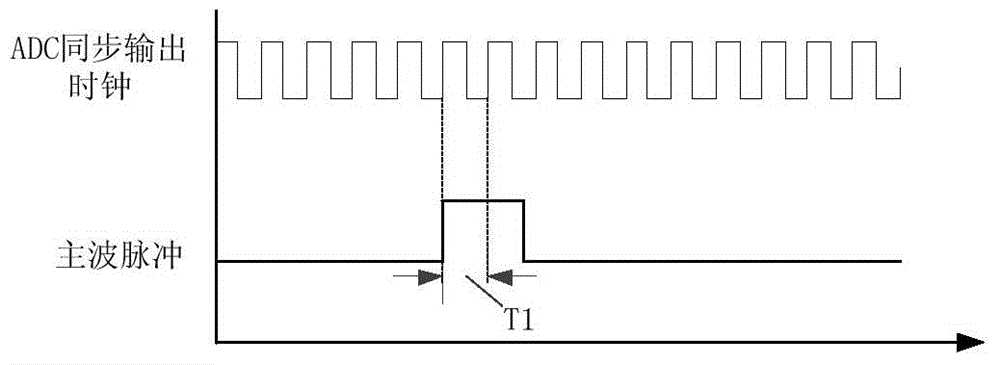
The invention discloses a laser radar echo full-waveform acquisition device with sampling point time location, and belongs to the technical field of earth observation laser radar remote sensing. The full-waveform acquisition device comprises a main control module, a high-speed ADC sampling module, a high-speed FIFO cache module, an interpolation delay line module, a high-speed coarse counter module, and a fine measurement coding module. All the modules except the high-speed ADC sampling module are implemented inside an FPGA. The invention aims to provide a laser radar echo full-waveform acquisition device for acquiring sampling point time location by a simple method. A frequency division clock synchronous with a high-speed ADC sampling clock is used as a rough counting clock, echo sampling point data is stored in a certain time interval under control, and the time interval between a main wave pulse and a coarse counting clock edge is finely measured by use of an interpolation delay chain, thereby obtaining an echo sampling point which has precise time location relative to laser transmitting main wave pulse. The laser radar echo full-waveform acquisition device with sampling point time location has the advantages of simple peripheral circuit, concise means of realization, flexible function interface configuration, and high cost performance.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for deciding agile satellite earth observation task pretreatment scheme
The invention relates to a method for deciding an agile satellite earth observation task pretreatment scheme. A new target area decomposition and combination method is provided; a multi-attribute utility function is constructed according to a pretreatment method; task scheduling pretreatment schemes are sorted and selected according to the multi-attribute utility function method; a point target describing method based on 'moment-gesture' and a region target feature describing method based on time gesture vectors are provided; the describing method is utilized to provide a target decomposition and combination method in the pretreatment; for different parameter generating schemes, the optimal treatment scheme is selected through the multi-attribute utility function method.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Electromagnetic butting device for micro/nano satellites capable of rotating after being butted and butting method
InactiveCN107089349APrecise dockingMeets requirementsCosmonautic component separationEarth observationPermanent magnet synchronous motor
The invention provides an electromagnetic butting device for micro / nano satellites capable of rotating after being butted and a butting method. The device is mounted on micro / nano satellites and leads two micro / nano satellites to be accurately butted. The device comprises an active butting mechanism and a passive butting mechanism, wherein one end of the active butting mechanism is in the shape of a horn, a permanent magnet synchronous motor and a circle of active butting teeth are arranged in the active butting mechanism, and the permanent magnet synchronous motor drives the active butting teeth to rotate; the main body of the passive butting mechanism is in the shape of a circular truncated cone which is matched with the horn-shaped port of the active butting mechanism, and a circle of passive butting teeth are arranged in the passive butting mechanism; and after the active butting mechanism and the passive butting mechanism are butted, the active butting teeth and the passive butting teeth are meshed, and when the permanent magnet synchronous motor works, the active butting mechanism and the passive butting mechanism rotate oppositely. The device provided by the invention is small in volume, light in weight and high in reliability and can be applied to micro / nano satellites so as to enable the micro / nano satellites to realize one-dimensional rotation. After multiple micro / nano satellites are freely butted and combined, configuration transformation of a combined body is realized, and splicing and superposition of an observation field are completed, thereby being favorable for realizing multi-angle earth observation of the micro / nano satellites.
Owner:SHANGHAI AEROSPACE CONTROL TECH INST
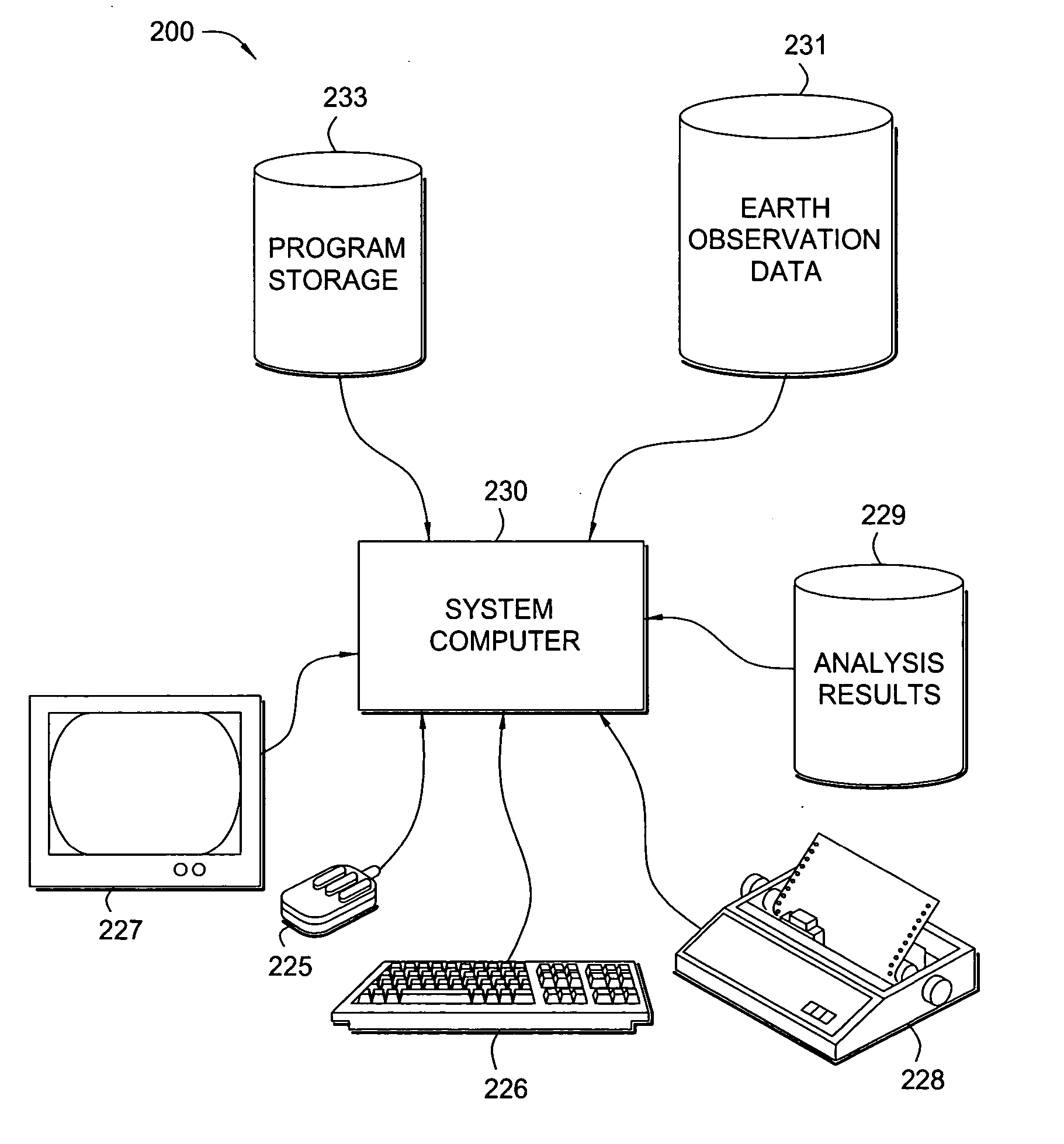
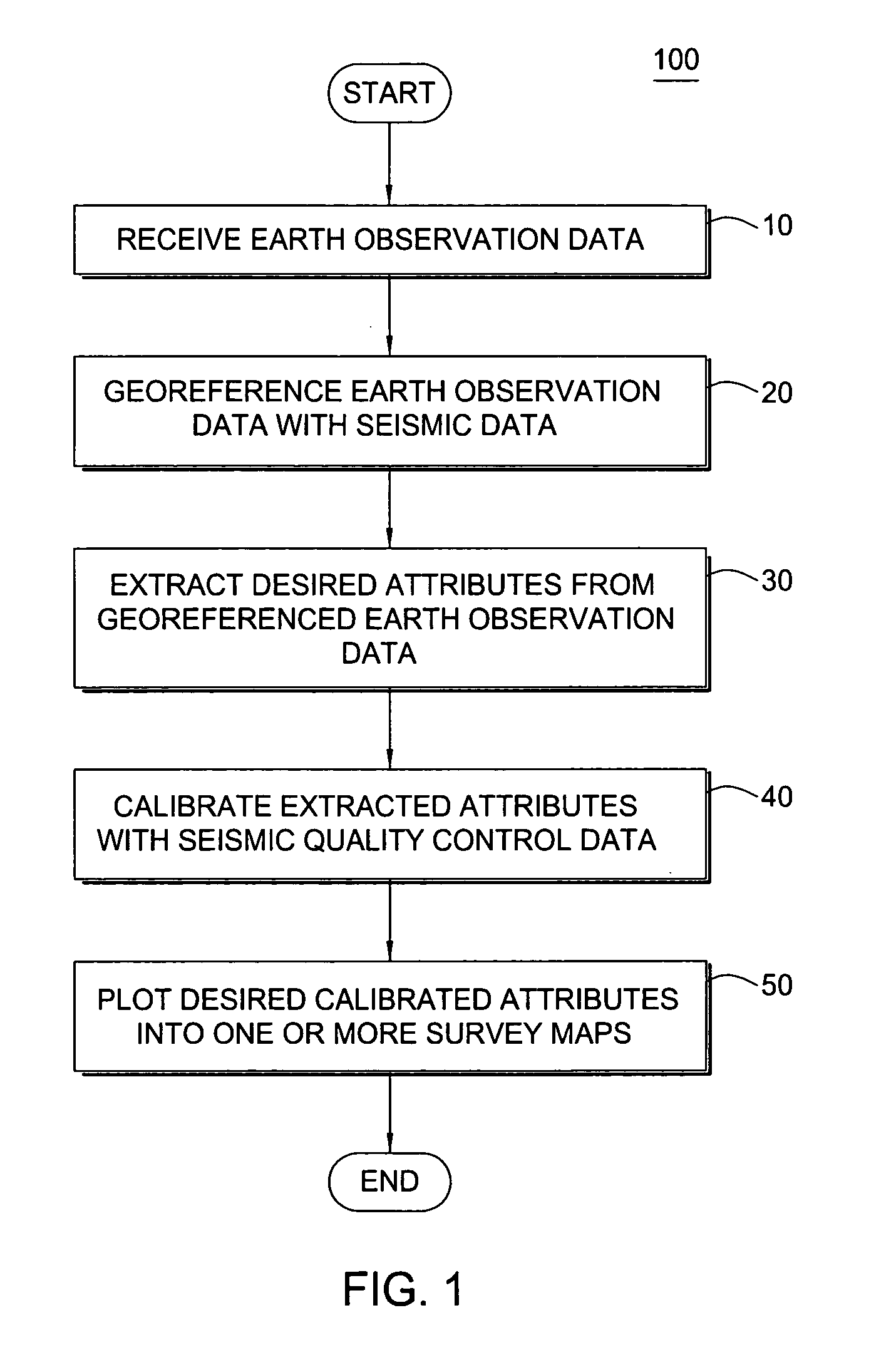
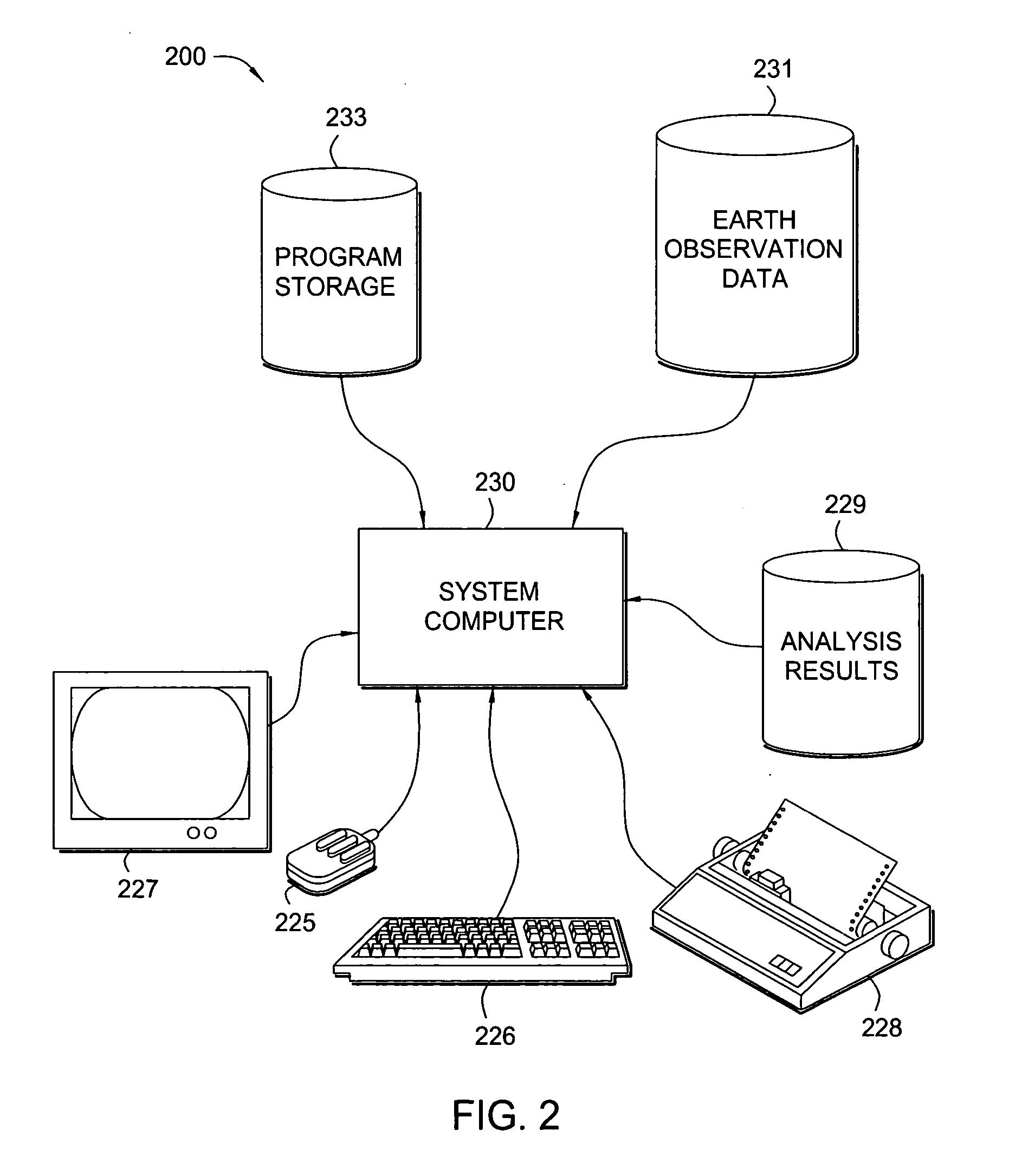
Survey design using earth observation data
InactiveUS20050157589A1Prone to problemSeismic data acquisitionSurveying instrumentsEarth observationGeophysics
A method for generating one or more maps of a survey area. The method includes receiving earth observation data, georeferencing the earth observation data with seismic data, extracting one or more attributes from the earth observation data and displaying the extracted attributes.
Owner:WESTERNGECO LLC
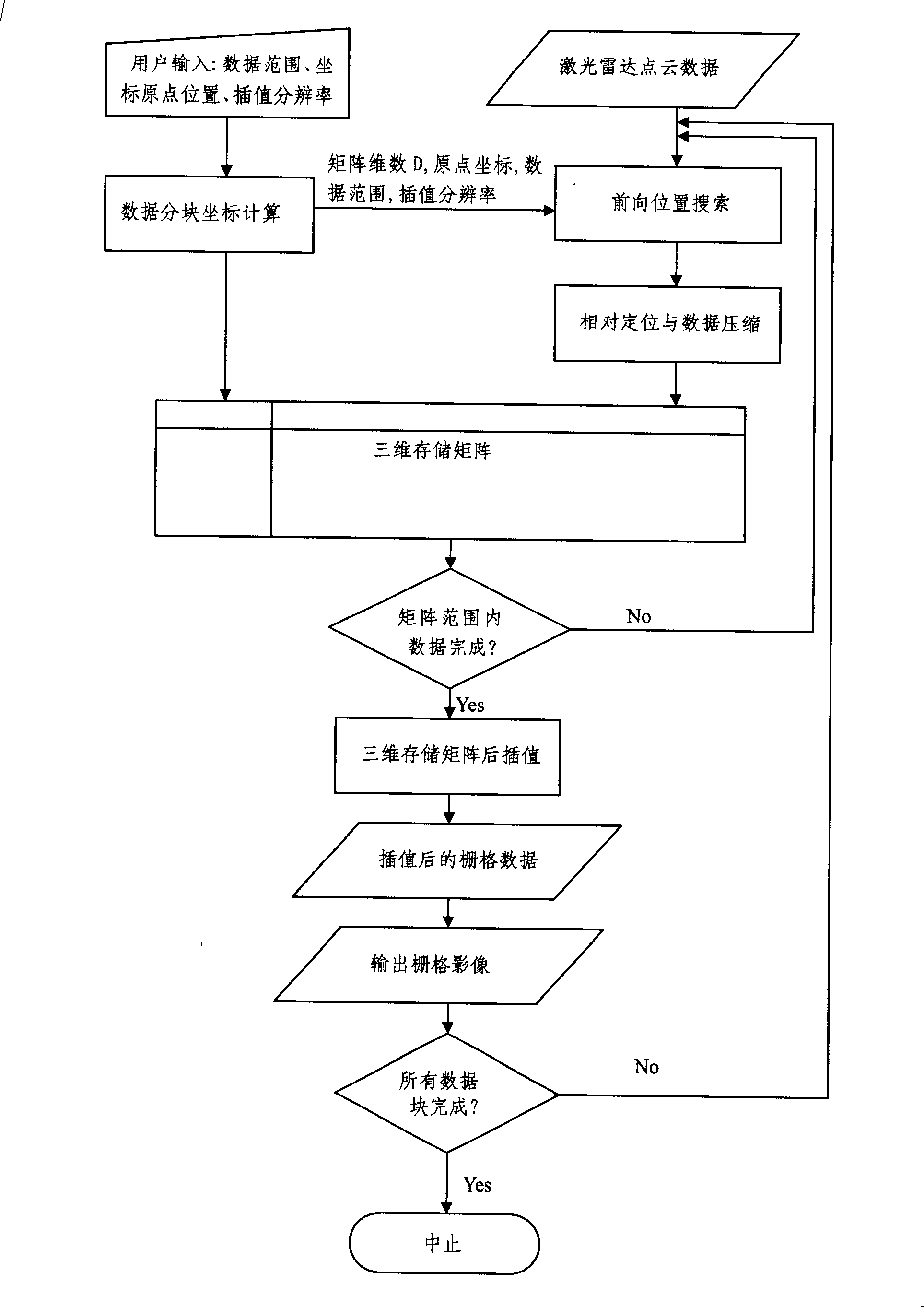
Rapid blocking and grating algorithm of laser radar point clouds data
InactiveCN101324663AAvoid Neighborhood Search ProcessLower requirementElectromagnetic wave reradiationEarth observationPoint cloud
A fast blocking and rasterizing algorithm of laser radar point cloud data is a technique in the earth observation field. The invention discloses a fast blocking and rasterizing method of the laser radar point cloud data, which comprises the storage organization mode and the relative positioning method of the laser radar point cloud data, the target position forward search and the automatic blocking method of the laser radar point cloud data, the interpolation and the post-treatment based on a three-dimensional storage matrix. The fast blocking and rasterizing method can reduce the requirements on hardware of a computer platform during the production process of grid data of the mass laser radar point cloud data, reduce the consumption of the computing resources during the rasterizing process of the mass laser radar point cloud data, and realize the fast blocking and the rasterizing of the laser radar point cloud data.
Owner:覃驭楚 +1
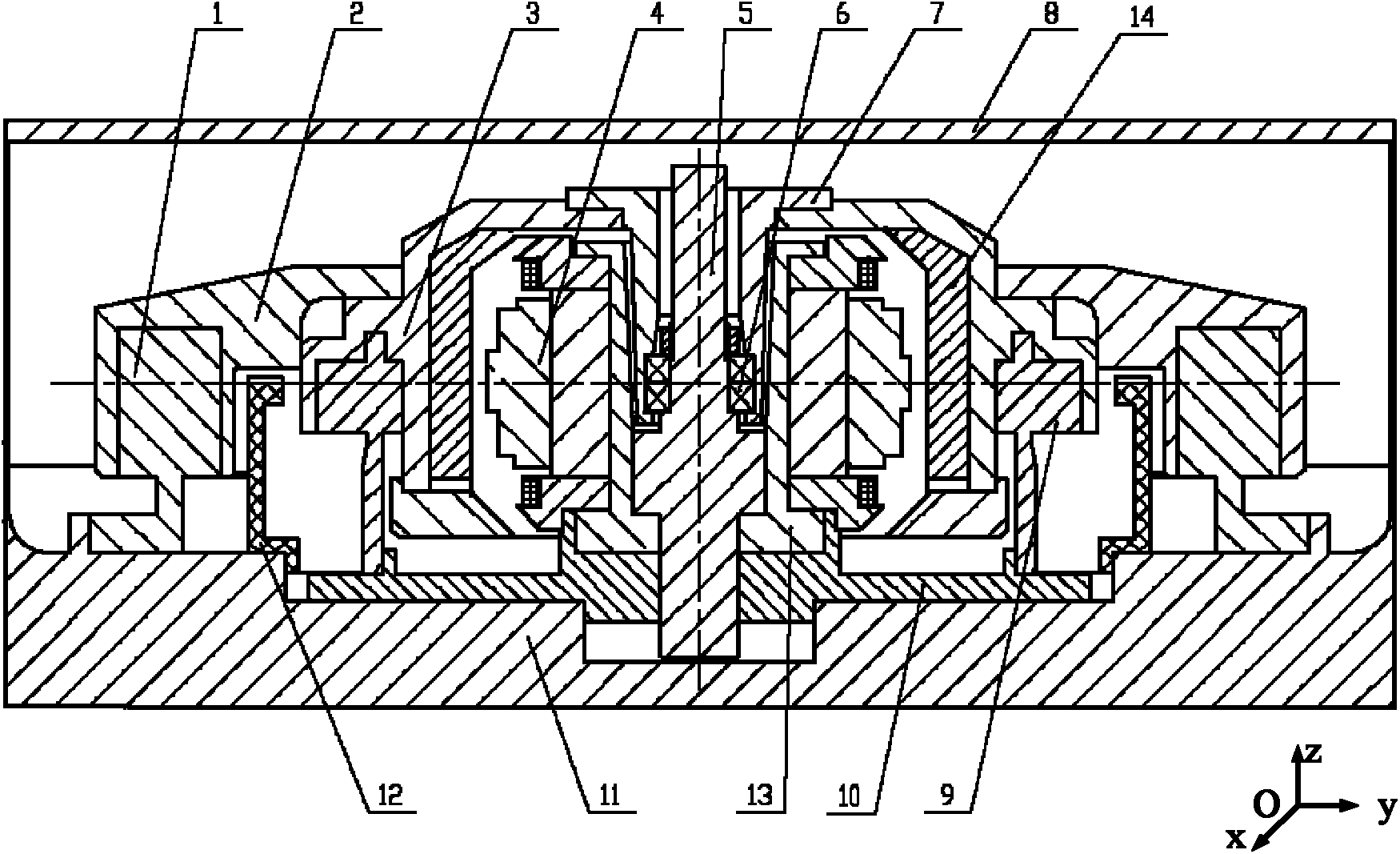
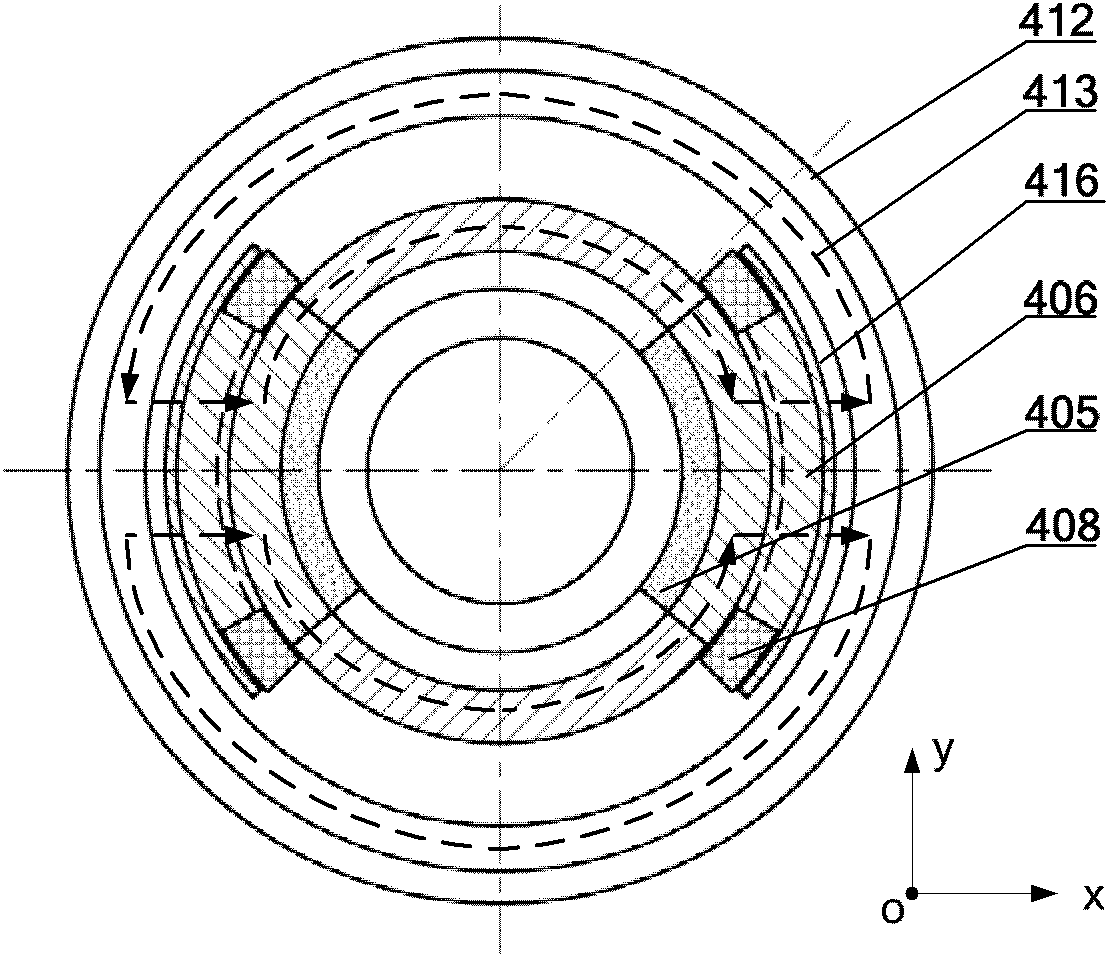
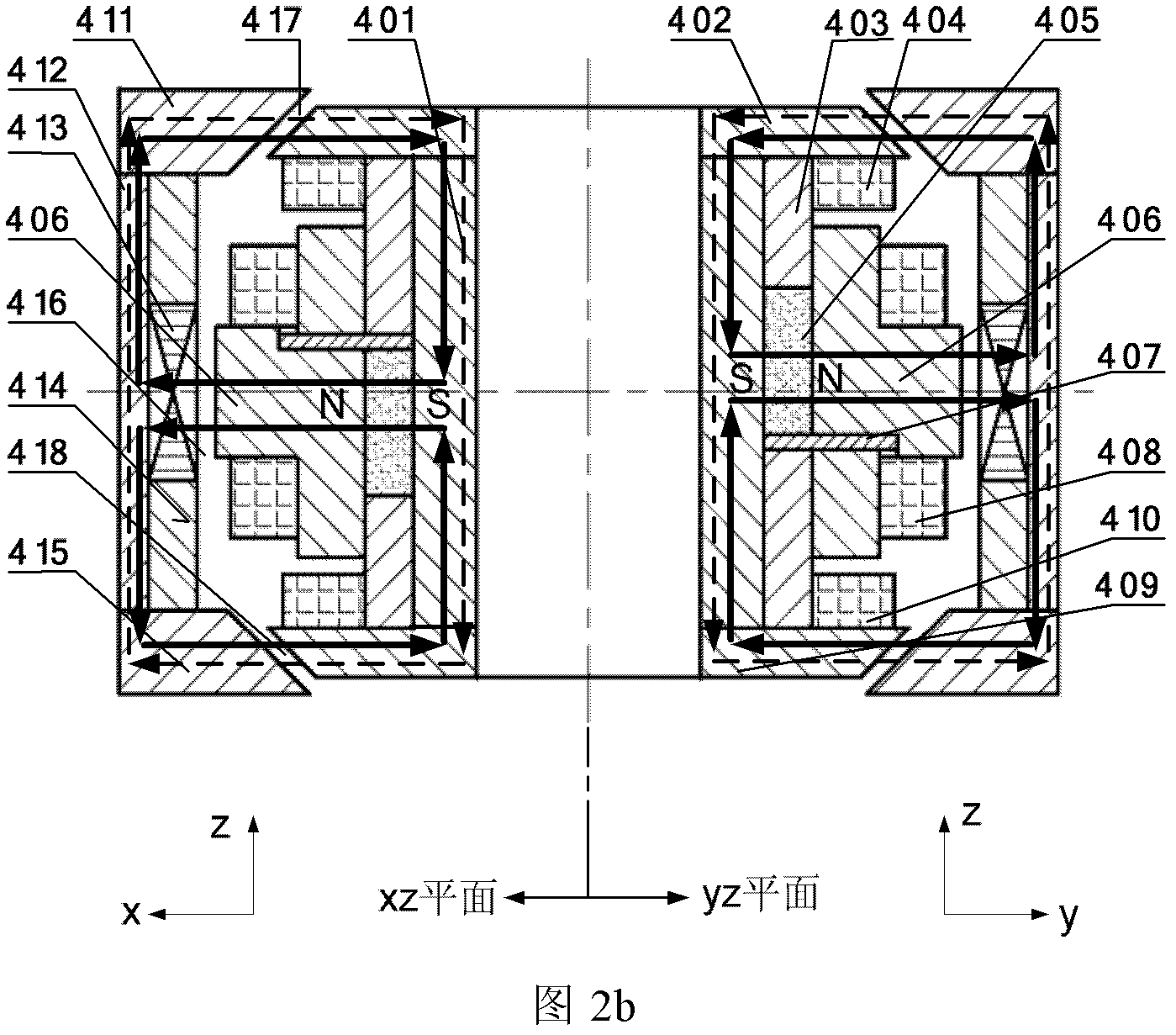
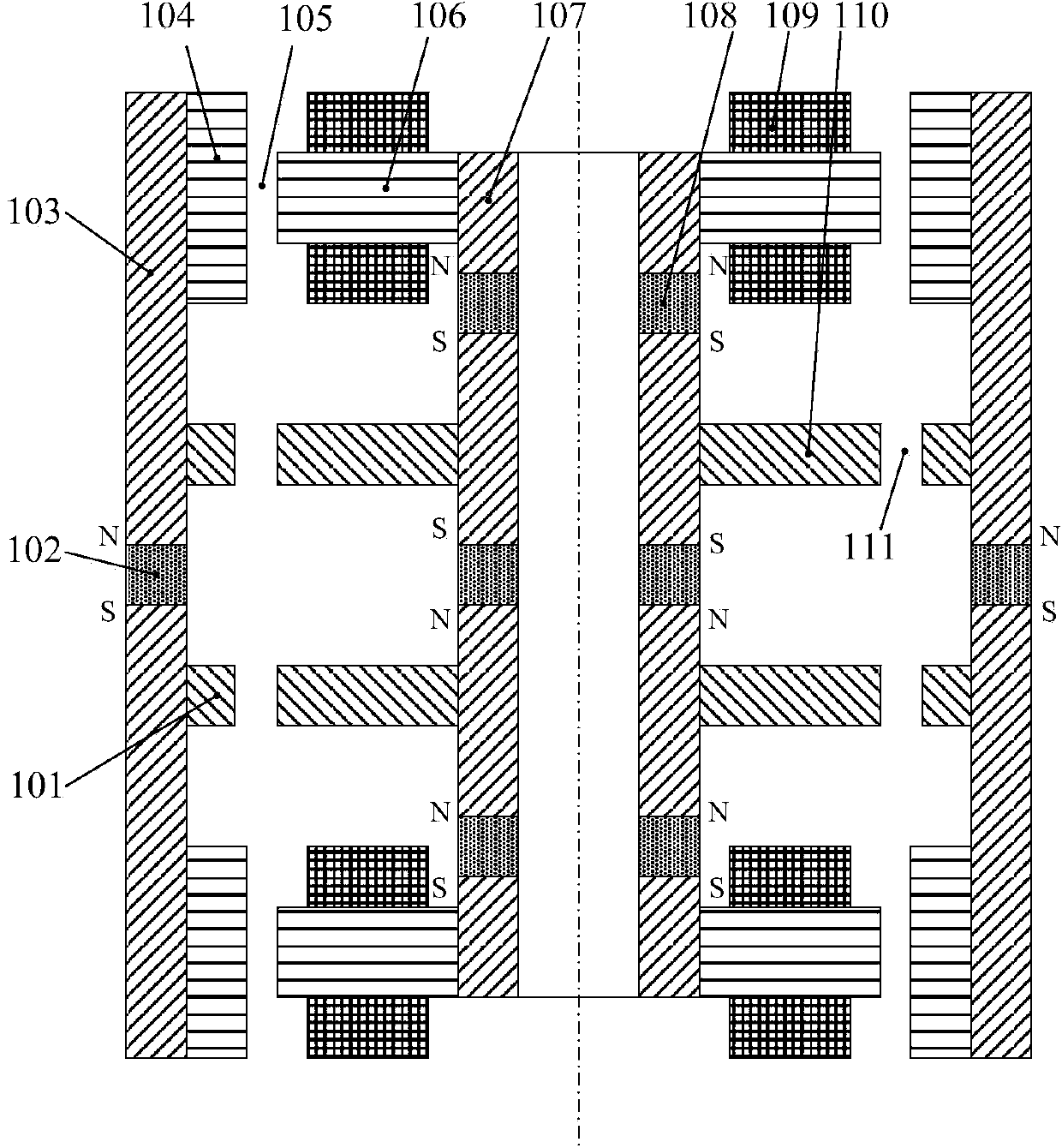
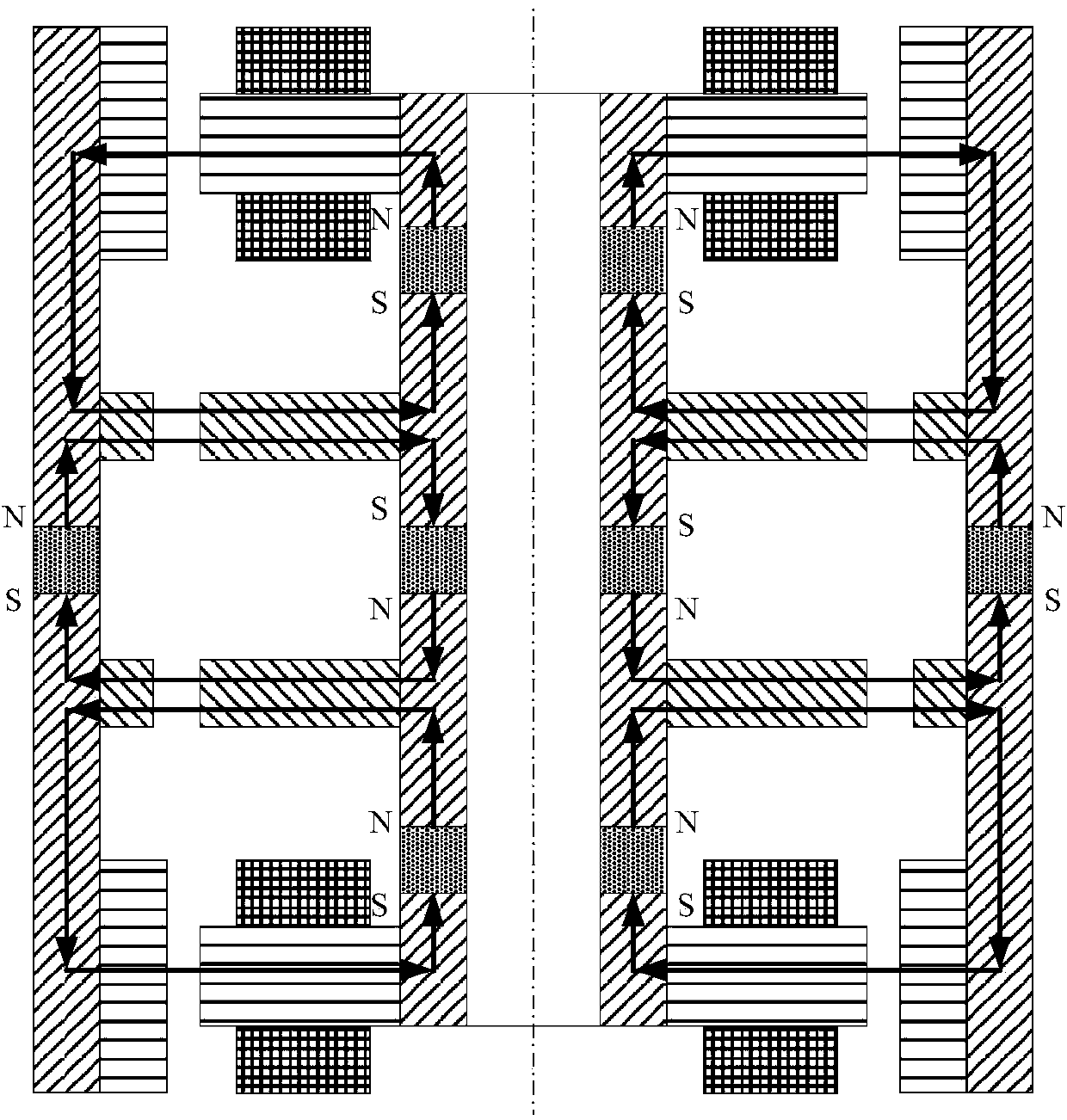
Four-degrees-of-freedom magnetic suspension flywheel
ActiveCN104201935AOvercome the defect of large axial lengthEasy to disassembleMagnetic holding devicesBearingsEarth observationMagnetic bearing
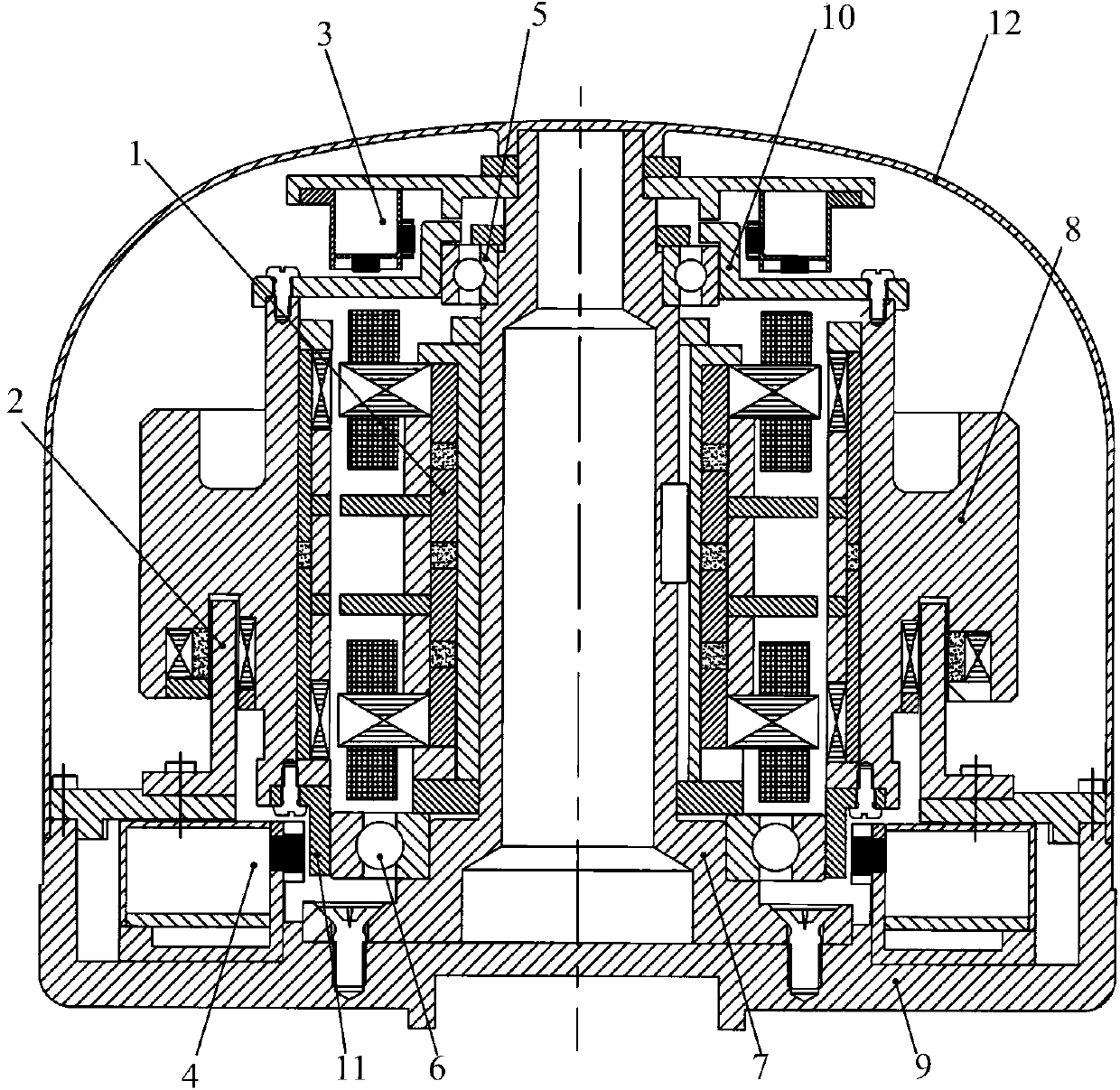
The invention discloses a four-degrees-of-freedom magnetic suspension flywheel. The four-degrees-of-freedom magnetic suspension flywheel is capable of being used as an attitude control execution mechanism for spacecrafts of a satellite, an earth observation platform, a space telescope and the like, and is composed of a four-degrees-of-freedom magnetic bearing, a high-speed motor, a radial-axial integrated sensor, a radial sensor, an upper protection bearing, a lower protection bearing, a mandrel, a wheel body, a base, an upper sensor detection ring, a lower sensor detection ring and a shell, wherein the active portion of the four-degrees-of-freedom magnetic bearing controls the radial translation and deflection of the rotor of the flywheel, and the axial translation of the rotor of the flywheel is realized through the passive portion of the four-degrees-of-freedom magnetic bearing. Each component of the four-degrees-of-freedom magnetic suspension flywheel disclosed by the invention is compact in layout, thus reducing the volume and weight, eliminating the rotational speed zero-passage friction force and mechanical wear of the flywheel of the mechanical bearing, improving the control accuracy of the flywheel and prolonging the service life of the flywheel.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
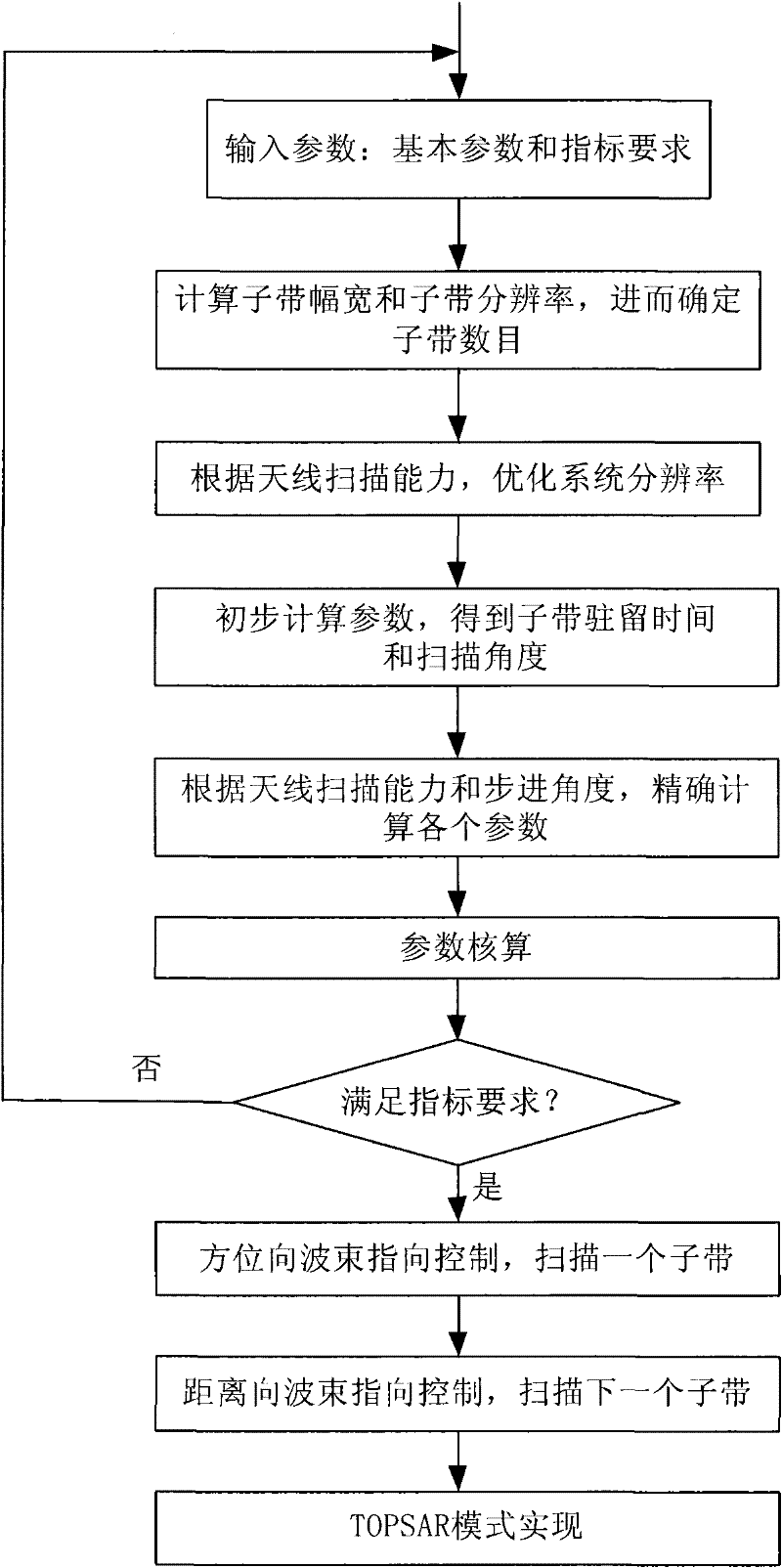
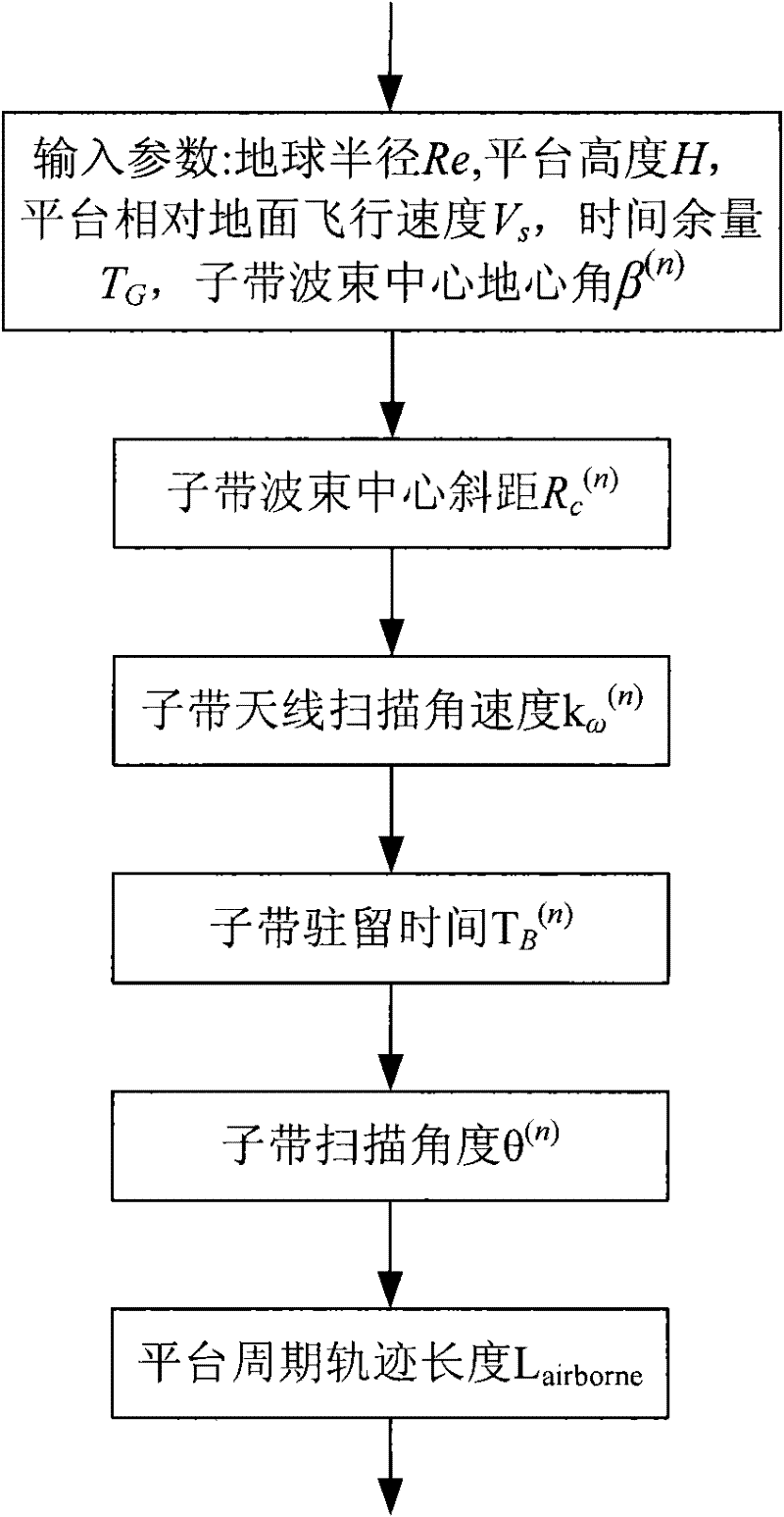
Implementation method for wide swath earth observation step scanning mode of synthetic aperture radar
ActiveCN102346249AImproved scallop effectUniform azimuth resolutionRadio wave reradiation/reflectionEarth observationSynthetic aperture sonar
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Innovative Orbit Design For Earth Observation Space Missions
ActiveUS20150346336A1Improve timing performanceExcellent interferometricCosmonautic propulsion system apparatusArtificial satellitesEarth observationOn board
The invention concerns a method for reducing the costs of a satellite remote sensing service. The method comprises providing a satellite remote sensing system that includes only one satellite equipped with a sensor configured to acquire images of areas of the earth's surface, the satellite remote sensing system being designed to provide a satellite remote sensing service based on the images acquired by the sensor on board the satellite. In particular, the satellite follows a predefined orbit around the earth with an orbit repeat cycle shorter than three days, whereby a satellite remote sensing service with very good time performance, excellent interferometric capabilities and with drastically reduced costs is obtained.
Owner:THALES ALENIA SPACE ITAL SPA
Method for determining and compensating full-field drift angle of space-based camera
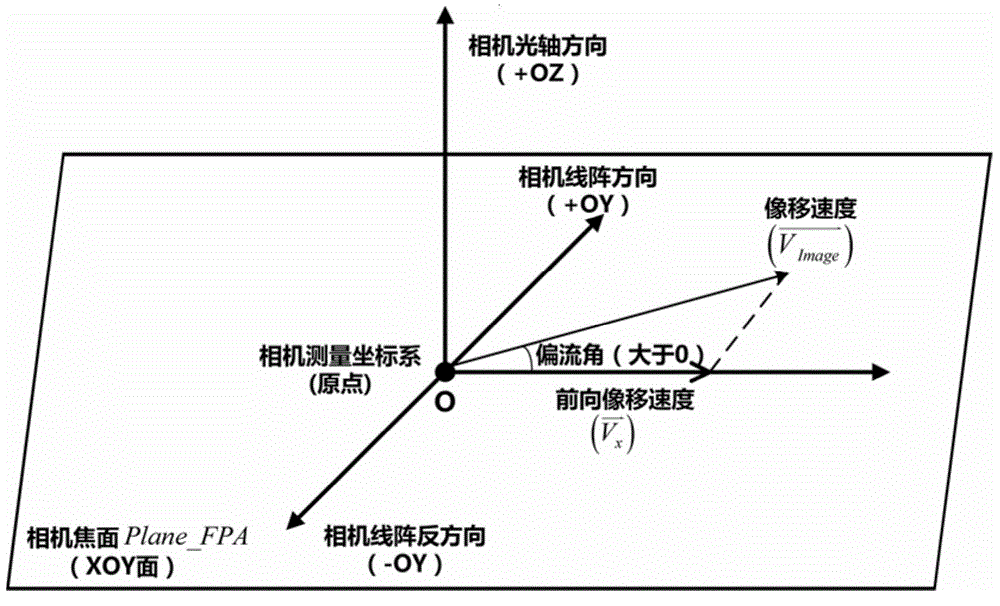
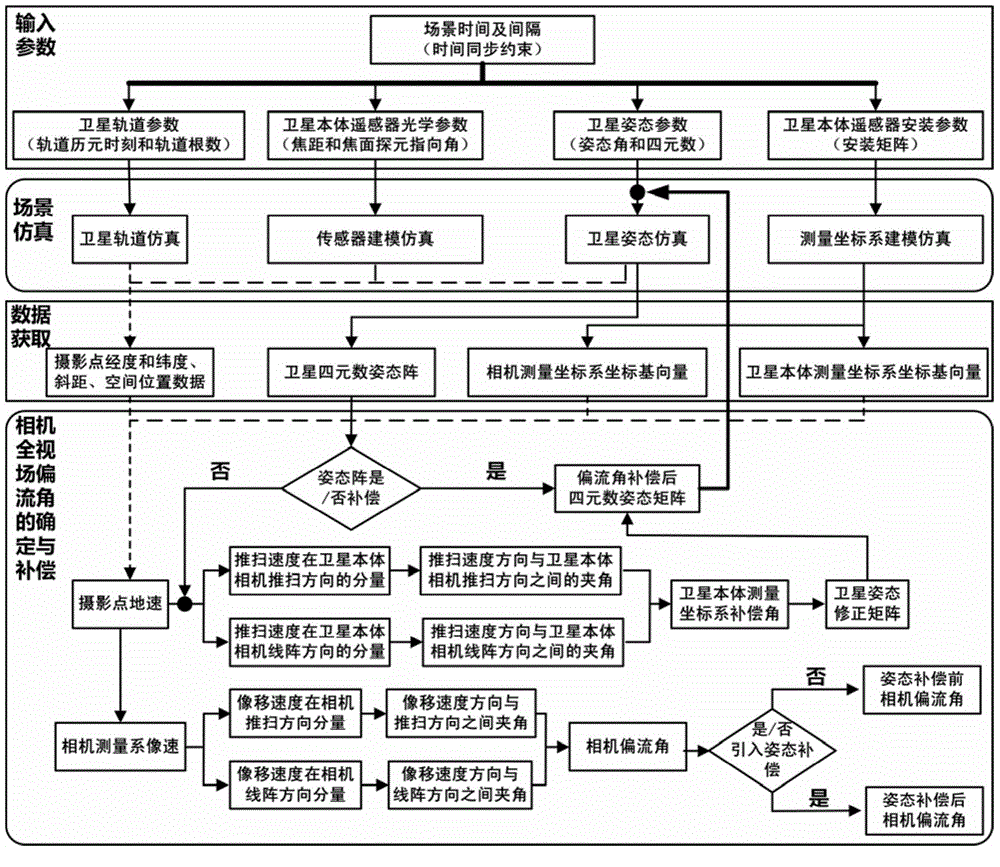
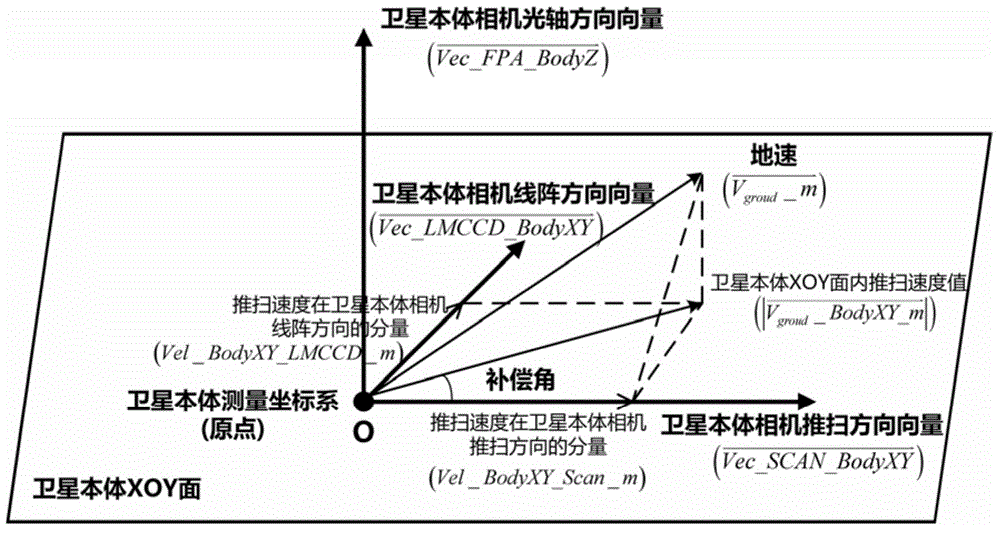
ActiveCN104567819AImprove calculation accuracyWide applicabilityPhotogrammetry/videogrammetryEarth observationDrift angle
The invention discloses a method for determining and compensating a full-field drift angle of a space-based camera. The method comprises the following steps: (1) performing scene simulation and modeling, comprising performing high-precision modeling and simulation on the satellite orbit, attitude, camera measurement coordinate system, satellite body measurement coordinate system and different field sensors of the camera; (2) calculating the full-field drift angle of the camera under a geocentre terrestrial reference frame; (3) calculating a compensation angle of the satellite body measurement coordinate system; (4) calculating a compensation attitude quaternion matrix on the satellite drift angle; and (5) calculating the full-field drift angle of the camera subjected to attitude compensation. According to the method disclosed by the invention, after a three-axis stability satellite rotates around three axes of the satellite body, the problem that the full-field drift angle of the camera cannot be determined and compensated during earth observation of the satellite in a specific attitude can be solved, and the method can be used for determining the drift angle of a satellite-borne large-field camera, designing and verifying the drift angle compensation method and optimizing the satellite design in the satellite development process.
Owner:AEROSPACE DONGFANGHONG SATELLITE
Establishing and maintaining focus in segmented-optic telescopes
A multi-aperture interferometric optical system collects light propagating from a source of light and develops overlapping diffraction patterns on an optical detector that produces output signals for processing to automatically focus the optical system and form an image corresponding to the diffraction patterns. A preferred embodiment of the invention is a large aperture orbiting, earth-watching ring interferometric optical system configured such that there is no macro-structure pointing. Four mirror-ring structures direct incoming light to a multi-spectral primary optical detector that acquires light-pattern information to focus the optical system and derive an image.
Owner:VENTURE ASTRA
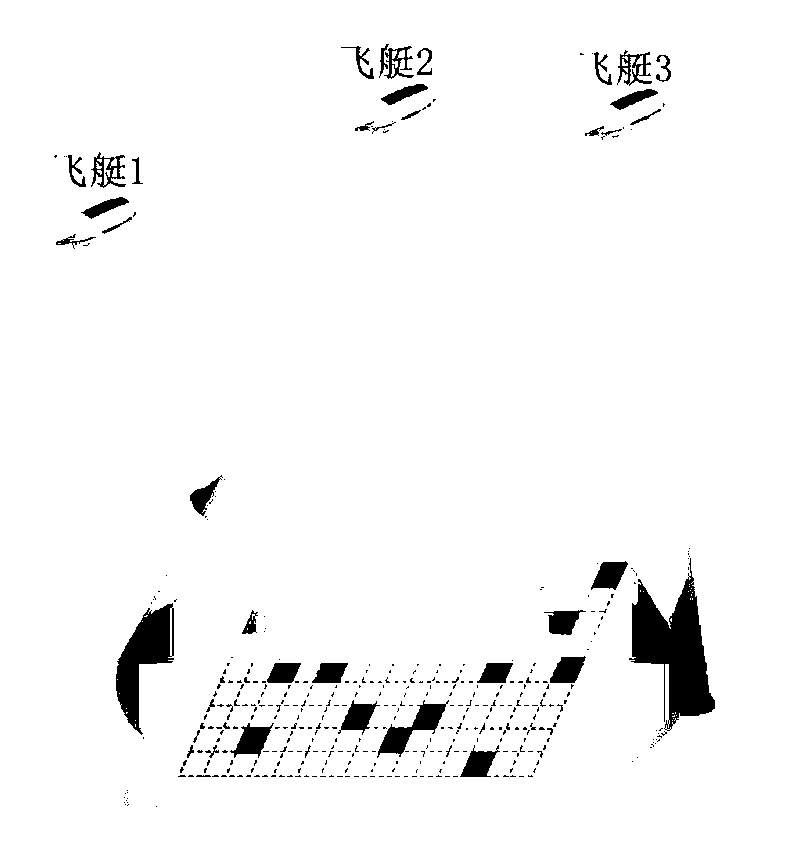
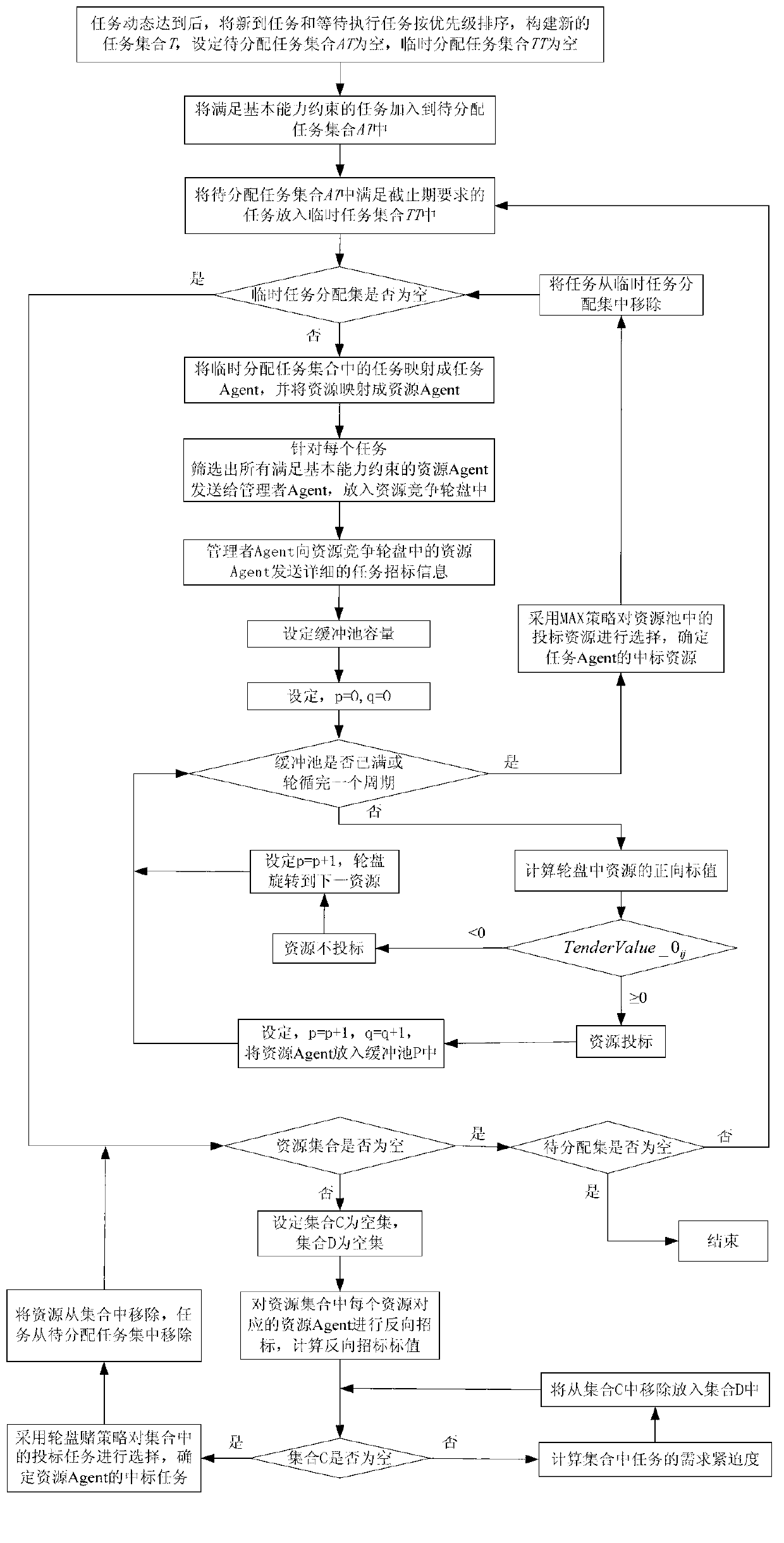
Emergency-orientated co-cooperation allocation method for multi-airship earth observation tasks
ActiveCN102903028AImprove scheduling success rateMeet the time requirementResourcesEarth observationParallel computing
The invention discloses an emergency-orientated co-cooperation allocation method for multi-airship earth observation tasks, aiming at dynamically performing task allocation, and increasing the scheduling success rate of the tasks as far as possible. In the technical scheme, the co-cooperation allocation method comprises the steps of: firstly, establishing a task set AT to be allocated, performing positive bid inviting on the tasks in the AT, and screening all resources meeting a basic capacity constraint; secondly, calculating the positive bid values of the resources in a resource competition roulette set according to the capacity of a buffer pool, and biding; choosing the biding resources of the tasks by adopting a Max strategy, determining the positive resources winning the bidding of each task, and performing reverse bid inviting on the task; reversely biding the resources and calculating the reverse biding value for each biding task; and choosing the biding tasks by adopting a roulette strategy, finishing reverse bidding winning to obtain a task allocation result. With the emergency-orientated co-cooperation allocation method disclosed by the invention, on one hand, unnecessary calculation time and unnecessary communication traffic can be reduced; and on other hand, the scheduling success rate of the tasks can be increased.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Method for scheduling efficient resource of minisatellite network based on earth observation tasks
ActiveCN106100719AImprove resource utilization efficiencyImprove return efficiencyRadio transmissionEarth observationMaximal independent set
This invention discloses a method for scheduling efficient resource of a minisatellite network based on earth observation tasks, and solves the problems that the end-to-end throughput capacity is low and the utilization efficiency of the network resource is low because the network resource is not fully considered during the scheduling process in the earth observation scene of the resource-limited minisatellite network. The method comprises the implementation processes of: according to an initial network topology, determining a node number; at the same time, initializing a network resource scheduling planning time set; according to current network state and resource scheduling conflict restraint, constructing a link scheduling conflict graph by a ground control center; solving a maximal independent set corresponding to the conflict graph to acquire a network conflict-free scheduling link set; by using the link set and a linear programming, solving a resource allocation scheme and a data transmission method capable of mostly optimizing the network efficiency till a time slot is ended. The method improves the resource utilization ratio, increases the returning efficiency of important task data, improves the earth observation network performance of the minisatellite, and is used for scheduling the efficiently transmitted resource of earth observation system data.
Owner:陕西丝路天图卫星科技有限公司
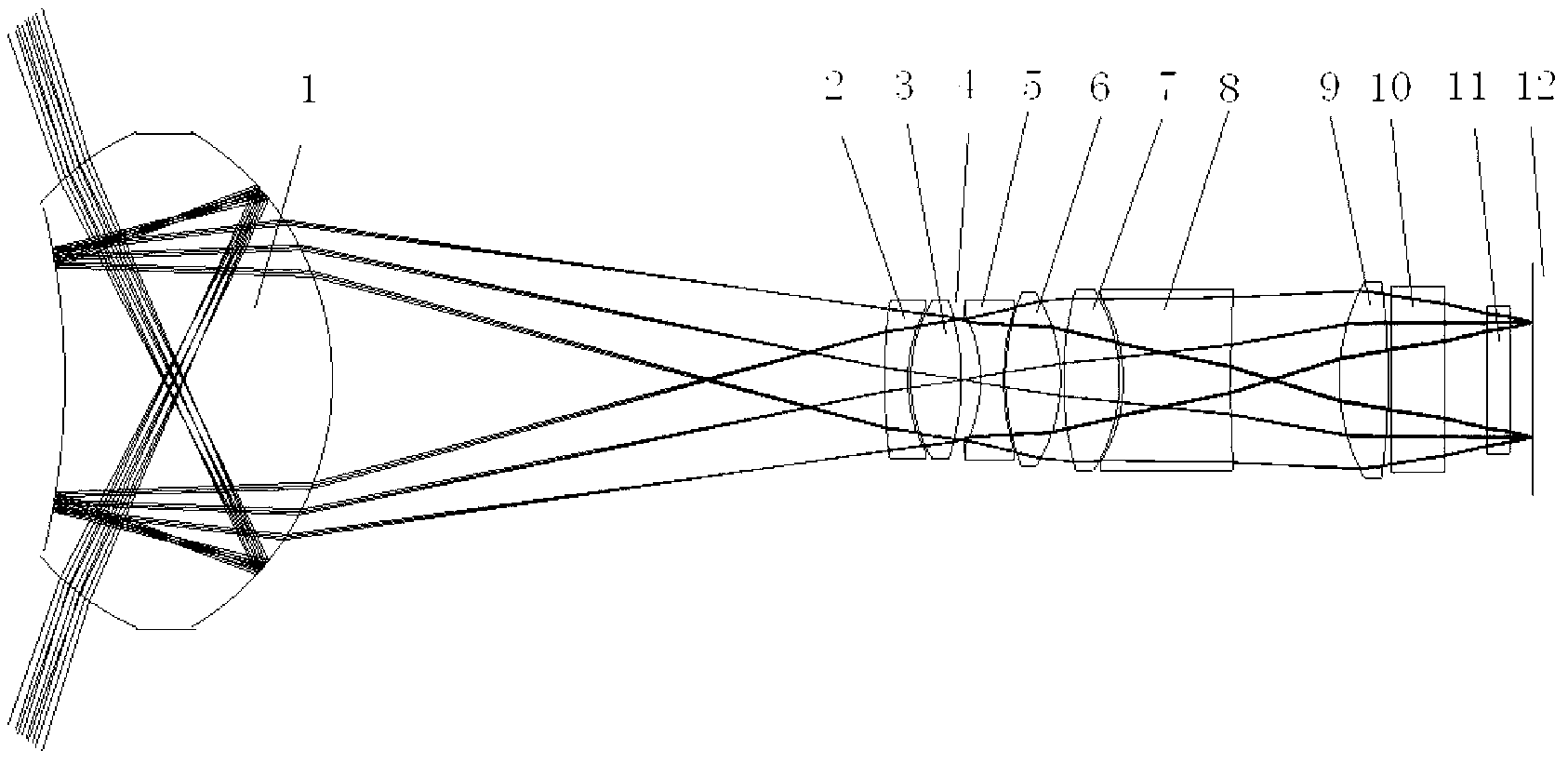
Optical system of ultraviolet multi-band panoramic imaging instrument
The invention relates to an optical system of an ultraviolet multi-band panoramic imaging instrument, relating to the technical field of space optics and solving the problem that an optical system of a conventional ultraviolet limb annular imaging instrument cannot realize imaging of a 360-degree annular field of view. The optical system is composed of a reflecting and refracting lens, a relay lens group, an optical filter and an area array detector, wherein the optical system is made of an ultraviolet material with the waveband scope of 250 nm to 380 nm; and the multi-waveband imaging is realized by selecting optical filter with different central wavelengths. The aperture diaphragm of the system is located in the relay lens group; the entrance beam of the 360-degree annular field of view becomes a virtual image through the reflecting and refracting lens; the image surface of the virtual image is located in the reflecting lens; the relay lens group images the virtual image of the reflecting and refracting lens for the second time, and finally forms an image on the area matrix detector. As a reflecting surface and a refracting surface are combined together, the optical system is relatively small and compact in structure, is suitable to be used as an optical system for ultraviolet limb panoramic imaging on a satellite, and is applied to the fields, such as atmospheric remote sensing for aerospace and aviation, earth observation and the like.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com