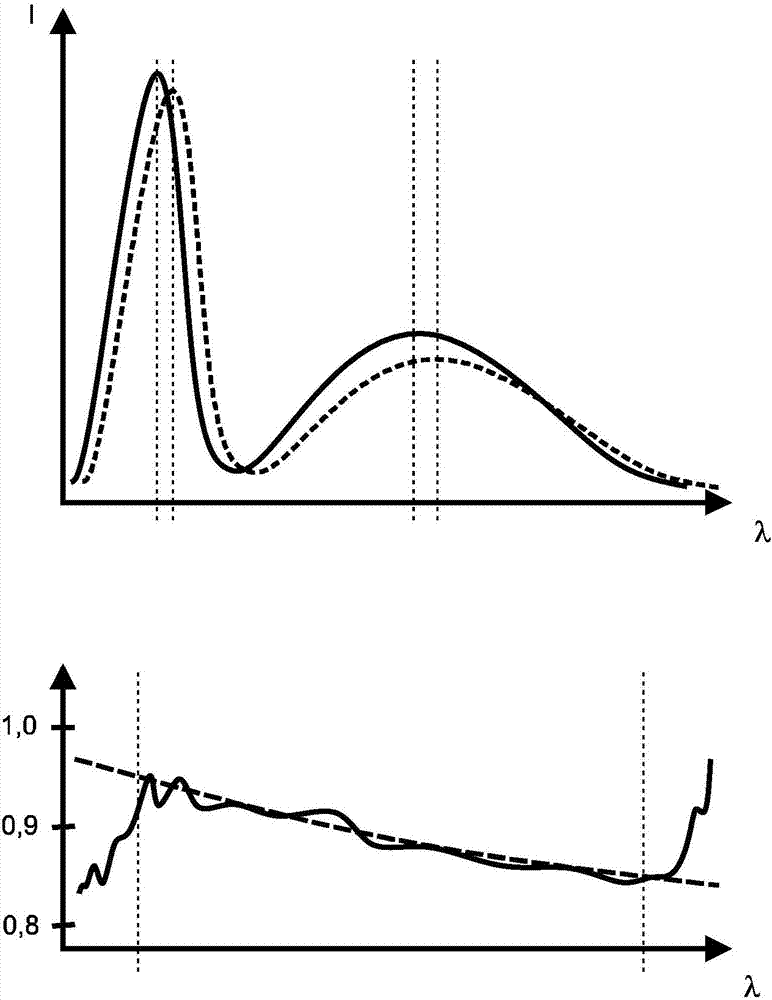
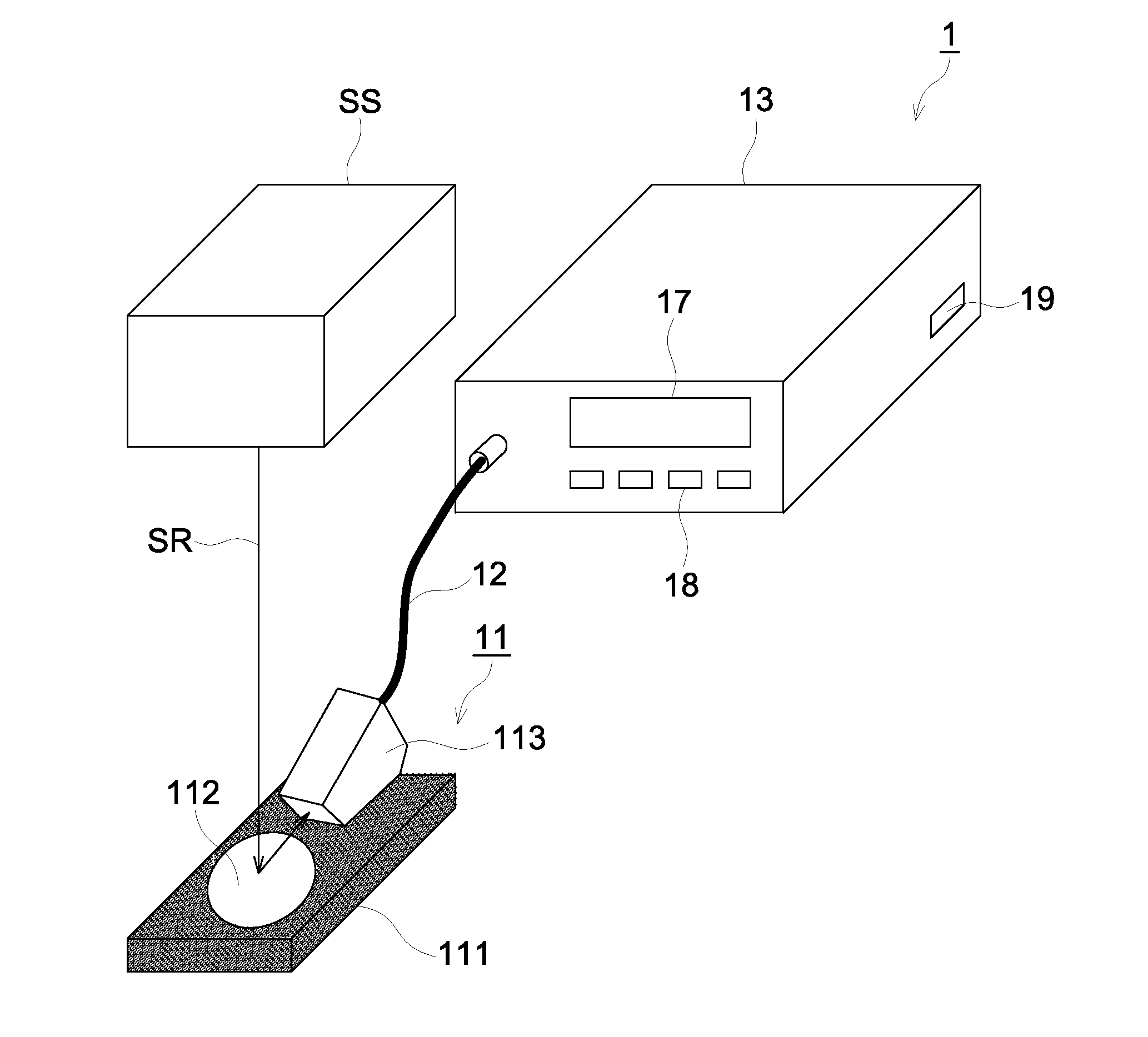
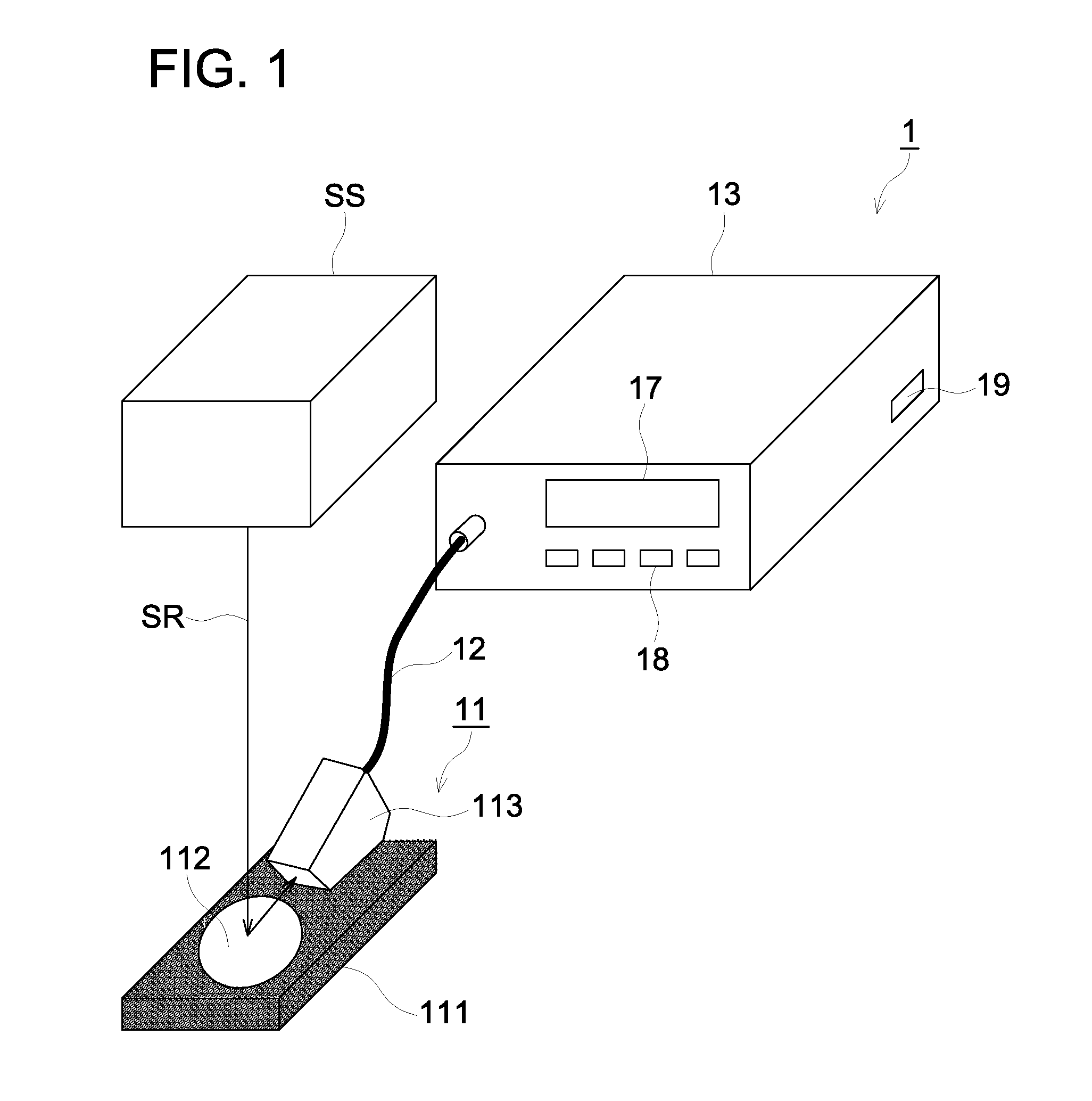
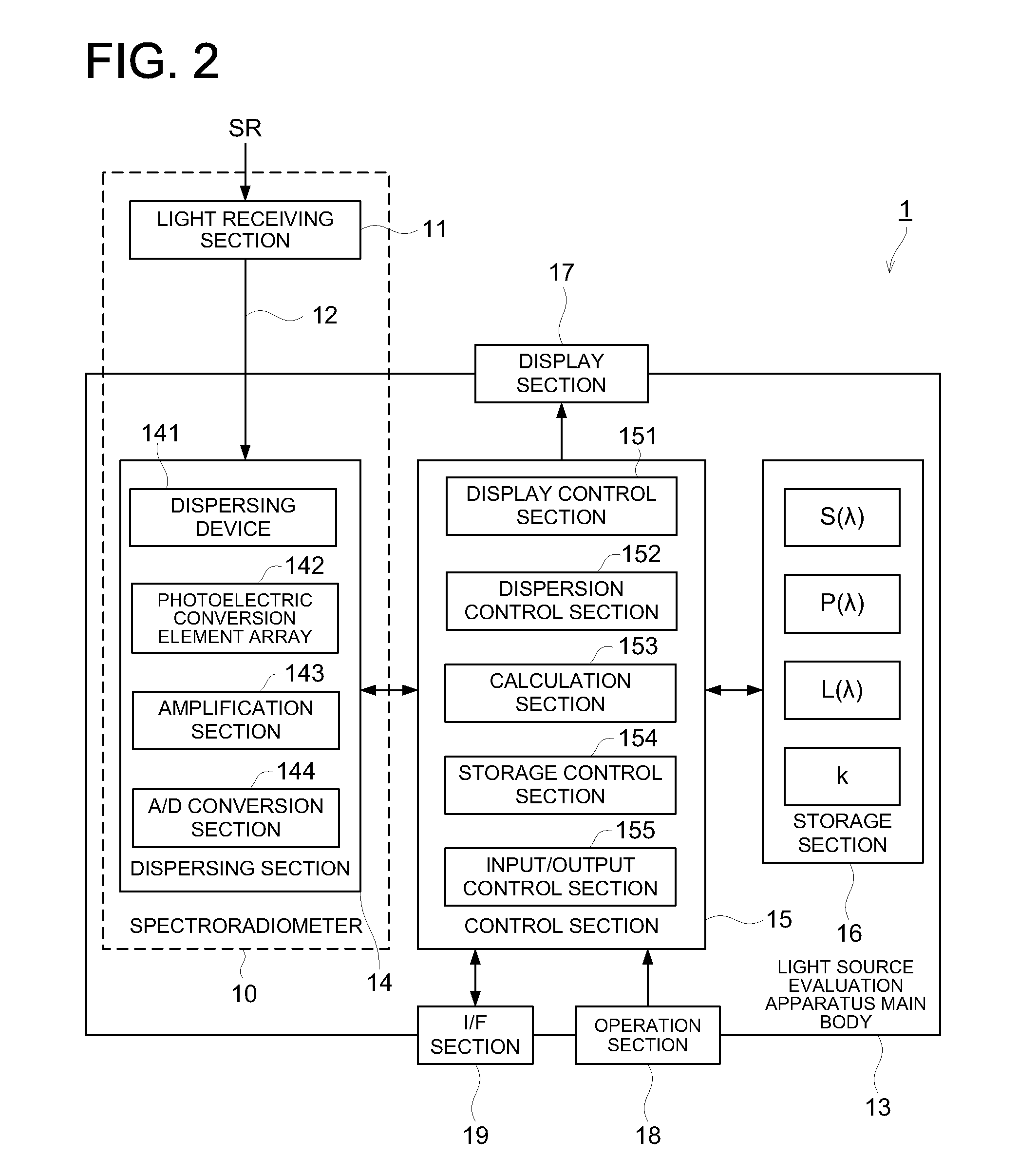
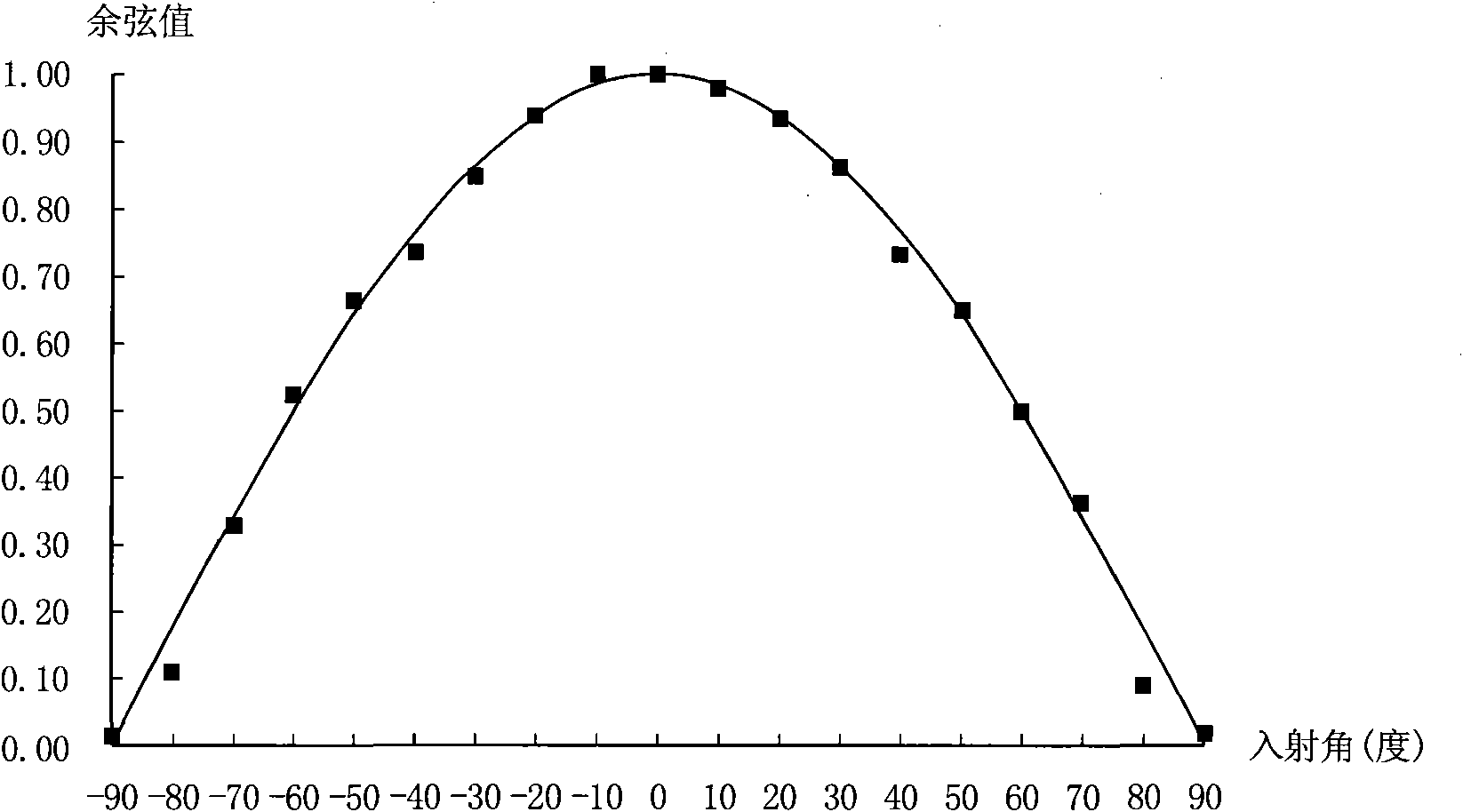
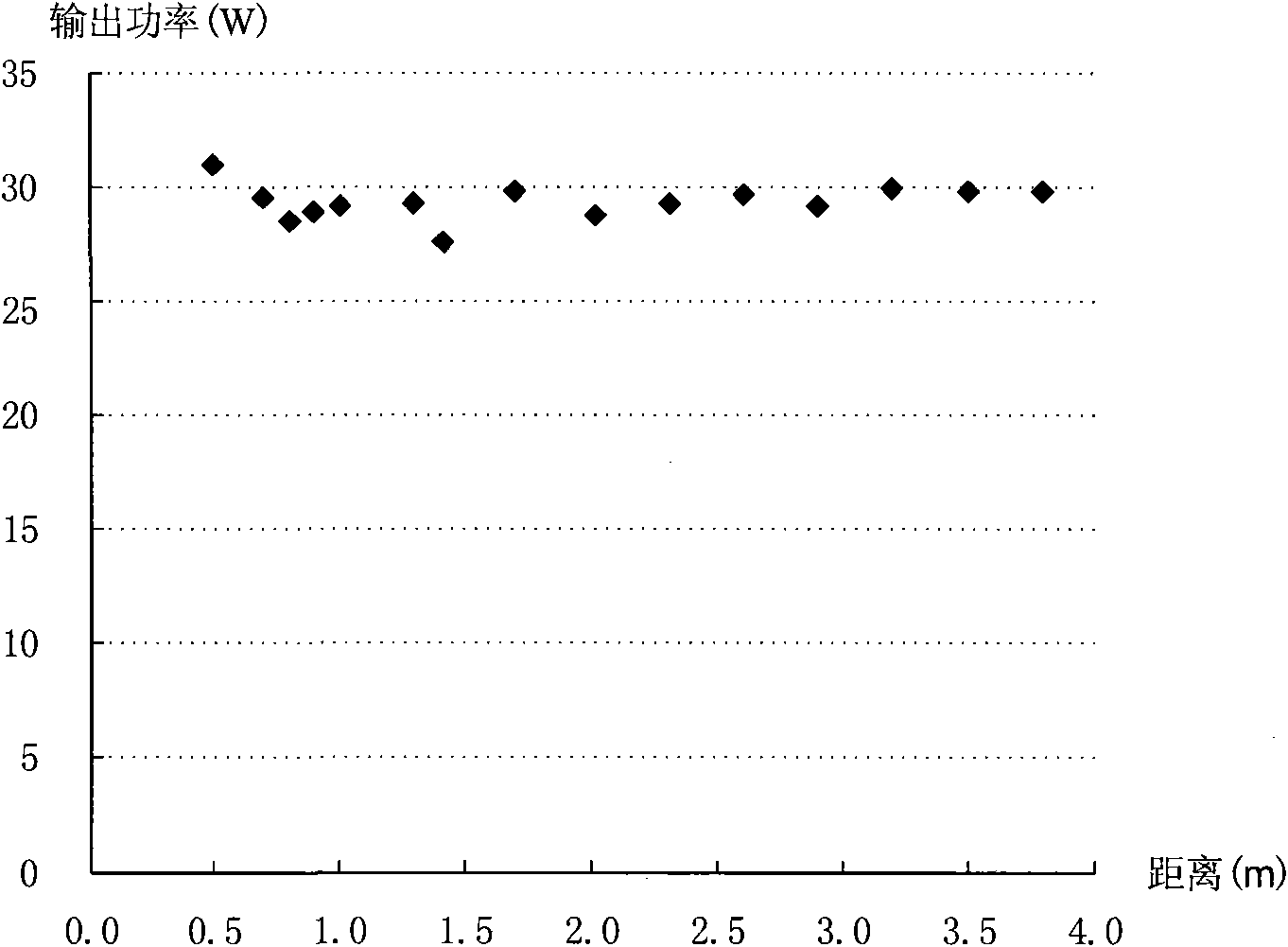
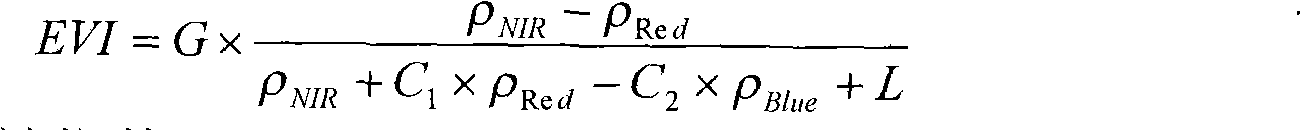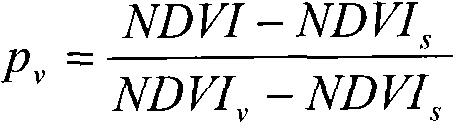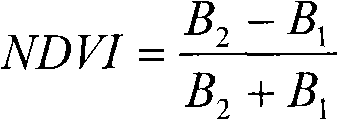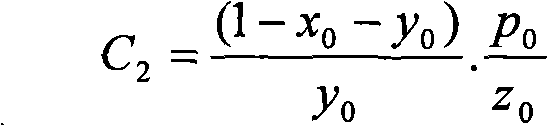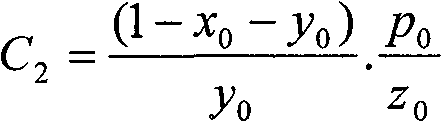Patents
Literature
72 results about "Spectroradiometer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A spectroradiometer is a light measurement tool that is able to measure both the wavelength and amplitude of the light emitted from a light source. Spectrometers discriminate the wavelength based on the position the light hits at the detector array allowing the full spectrum to be obtained with a single acquisition. Most spectrometers have a base measurement of counts which is the un-calibrated reading and is thus impacted by the sensitivity of the detector to each wavelength. By applying a calibration, the spectrometer is then able to provide measurements of spectral irradiance, spectral radiance and/or spectral flux. This data is also then used with built in or PC software and numerous algorithms to provide readings or Irradiance (W/cm2), Illuminance (lux or fc), Radiance (W/sr), Luminance (cd), Flux (Lumens or Watts), Chromaticity, Color Temperature, Peak and Dominant Wavelength. Some more complex spectrometer software packages also allow calculation of PAR µmol/m²/s, Metamerism, and candela calculations based on distance and include features like 2- and 20-degree observer, baseline overlay comparisons, transmission and reflectance.
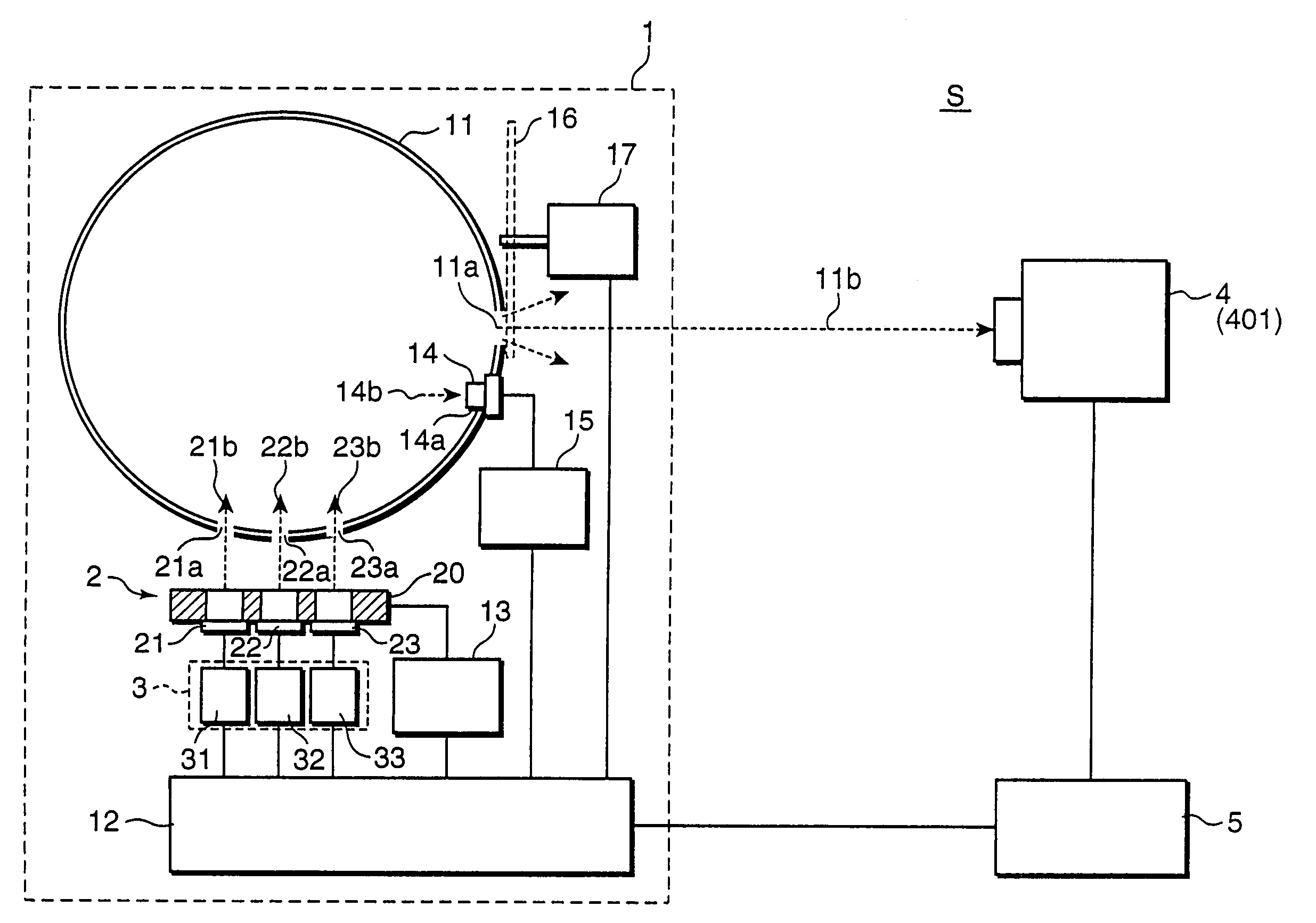
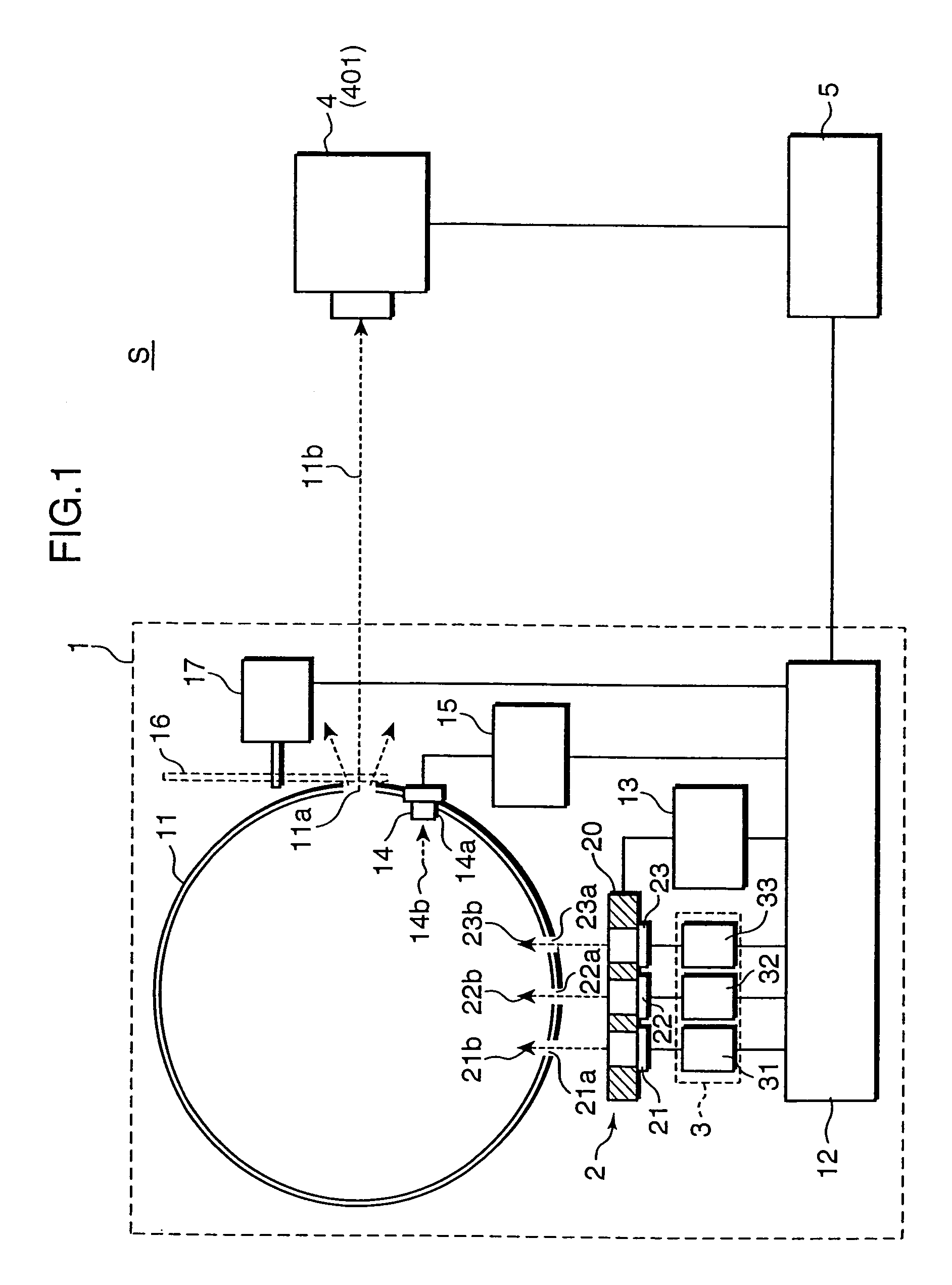
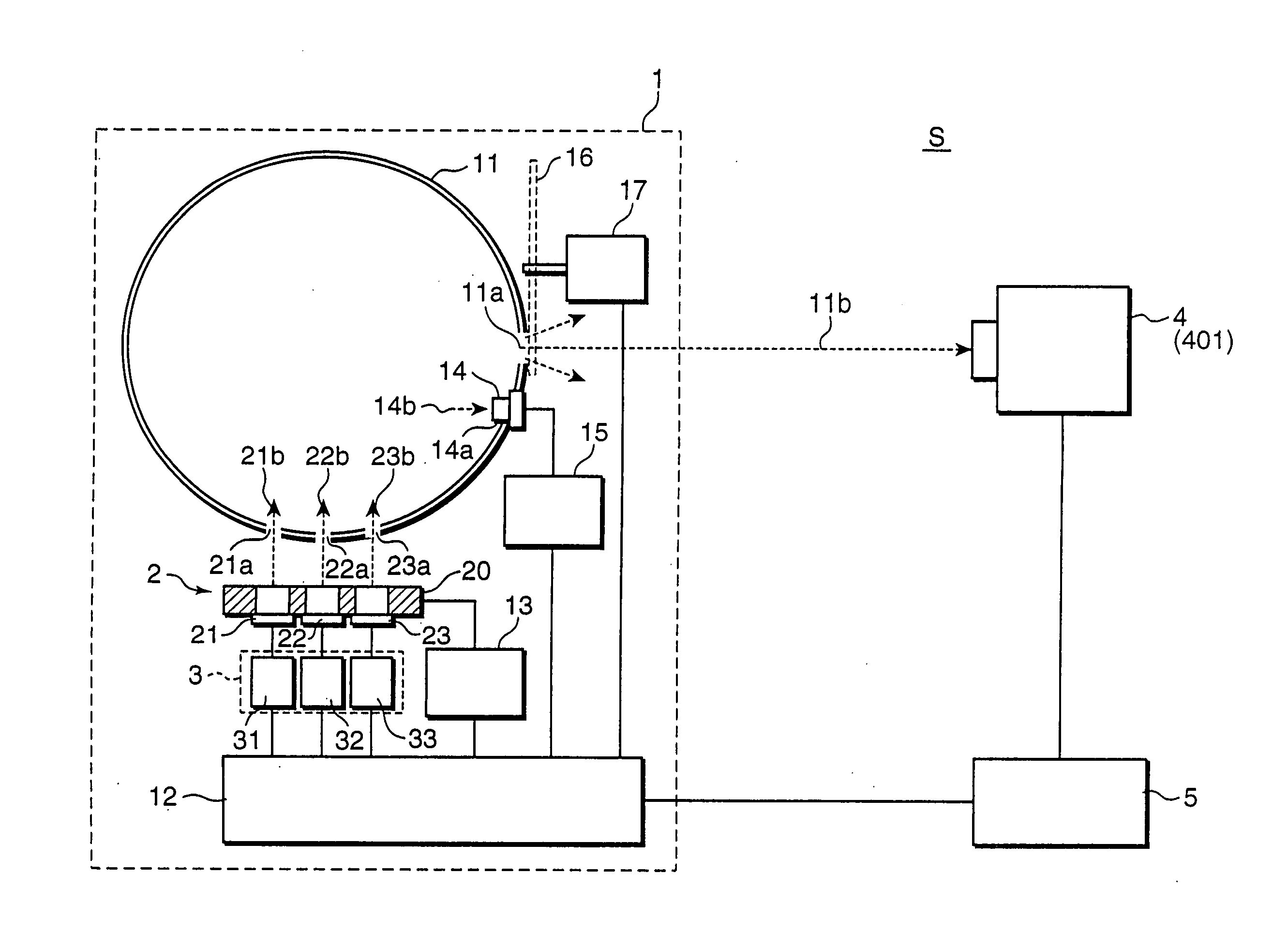
Spectral instrument using multiple non-interfering optical beam paths and elements for use therewith
InactiveUS6714298B2Good dispersionReduce dispersionRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationAngle of incidencePrism
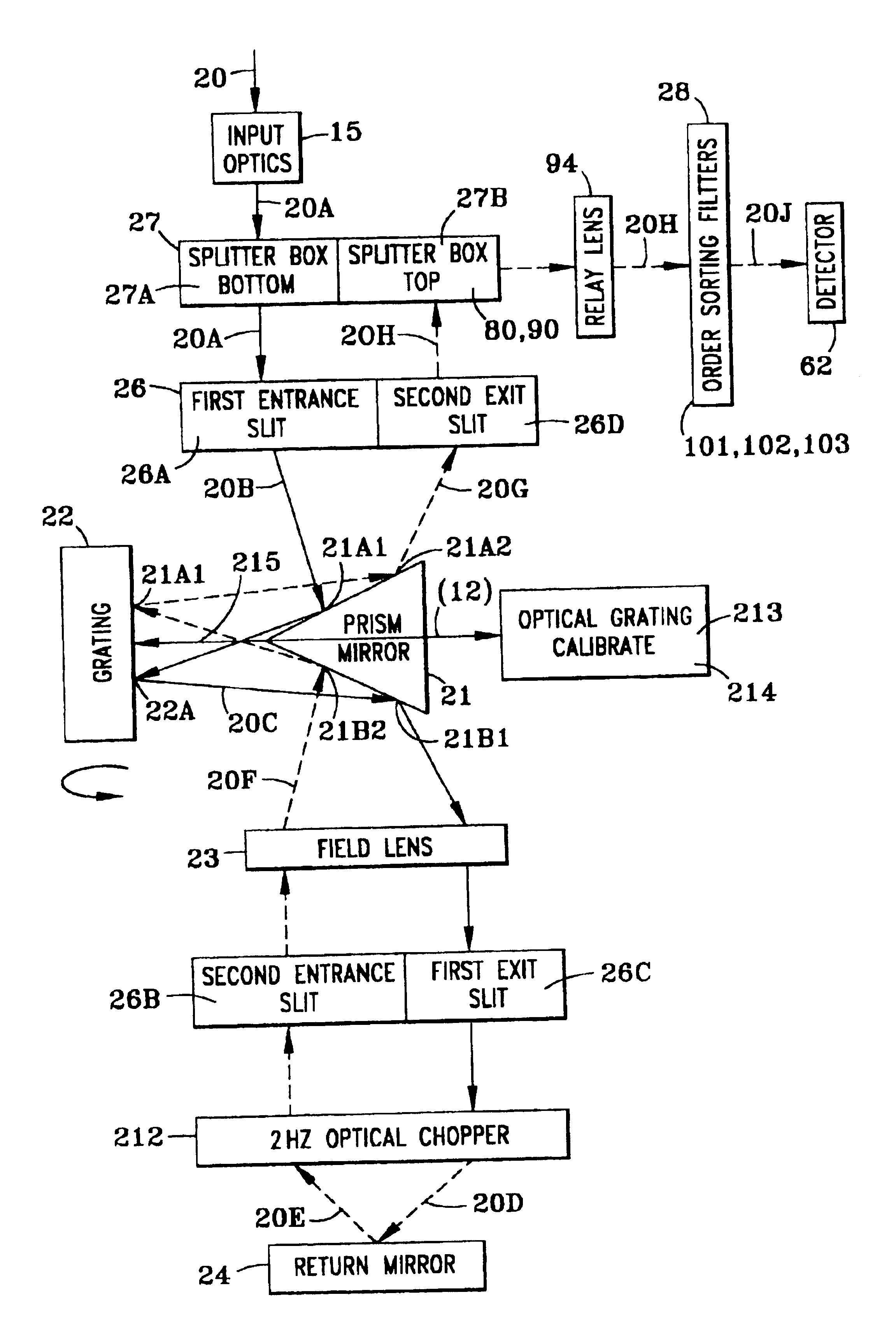
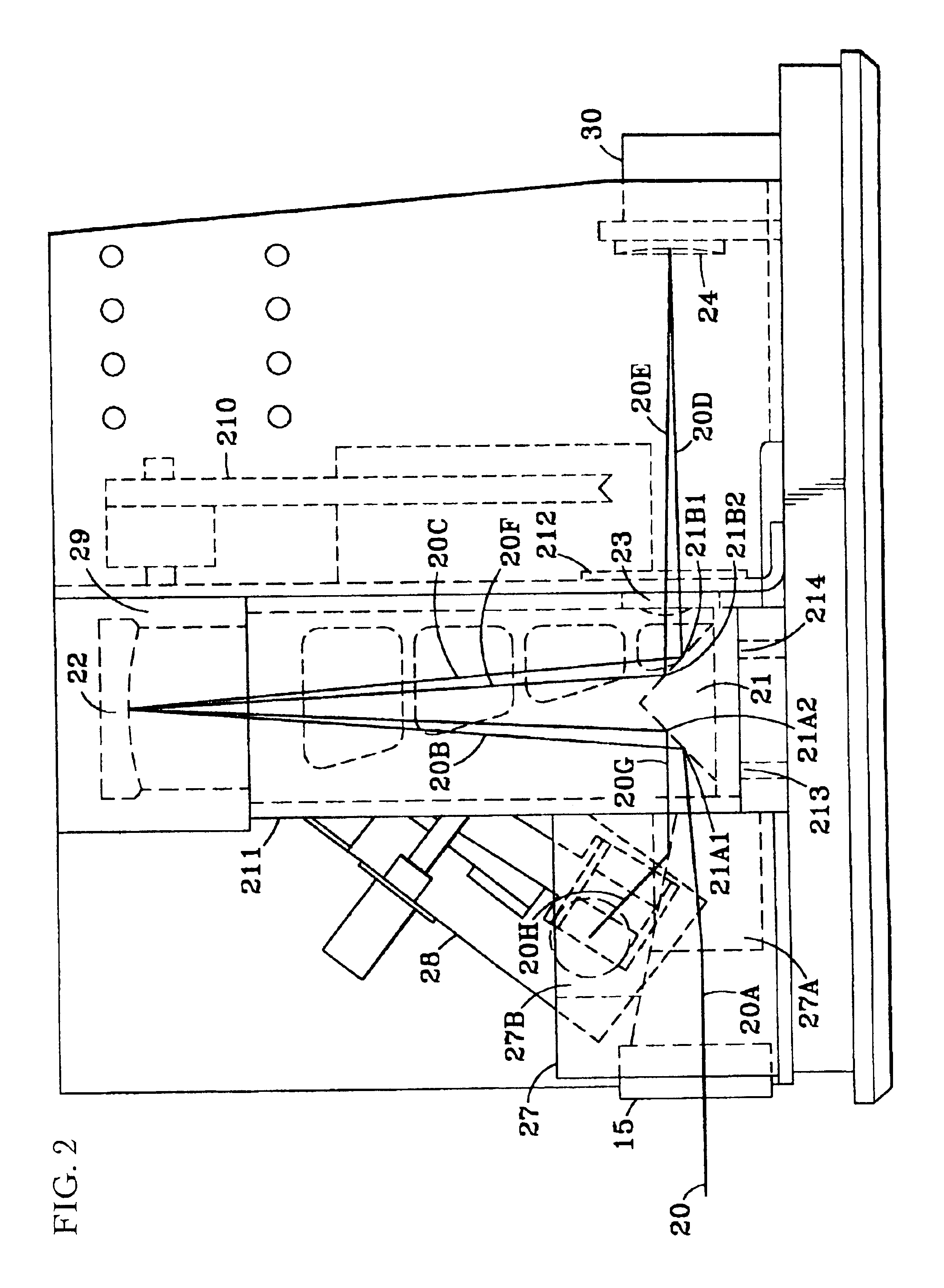
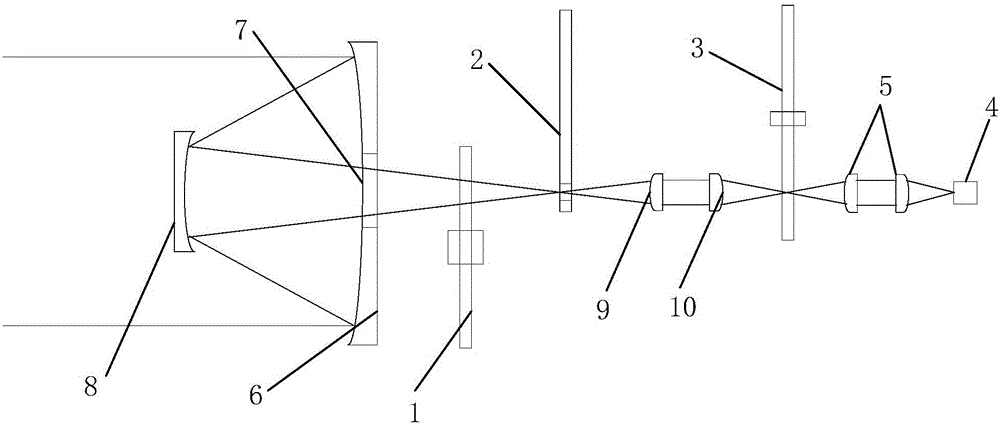
A spectrometer, or a spectral instrument using multiple non-interfering optical beam paths and special optical elements. The special optical elements for use with the instrument are used for directing the optical beam and / or altering the form of the beam. The instrument has the potential, depending upon the totality of the optical components incorporated into the instrument, to be a monochromator, a spectroradiometer, a spectrophotometer and a spectral source. The spectral instrument may further be a part of the spectral system. The system may include the spectral instrument, a power module and means for remote control of the instrument. Such remote control may be by use of a personal computer or a control system dedicated to the control, measurement and analysis of the collected information. The multiple non-interfering beam paths are created using specially designed optical elements such as a diffraction grating, a splitter box, a zero back-lash drive system for movement of the grating element. The orientation of and a physical / spatial relationship between the field lenses, slits, return mirror, reflecting prism, turning lenses all define the multiple, preferably two paths. Particularly, there is a double pass through the grating to increase dispersion, reduce scatter while maintaining a perfect temperature independent spectral match for the second pass. Using the same grating twice reduces scatter by about a factor of 1000, increases the dispersion by a factor of two, and eliminates any temperature-related mechanical spectral drift which often is present with two separate monochromators. Because of the specially designed grating structure, the grating can cause the concurrent diffraction of a plurality of incident optical beams, each of which beams have different angles of incidence and different angles of reflection. The path of the incident and the reflected beam to and from the grating is "off-axis". That is, the beams going to and from the grating do not use the optical axis of the grating structure.
Owner:RYER DAMOND V
MODIS data-based agricultural drought monitoring method
InactiveCN102103077ASuppress high valuesPromote resultsScattering properties measurementsElectromagnetic wave reradiationVegetation IndexModerate-resolution imaging spectroradiometer
The invention discloses a moderate-resolution imaging spectroradiometer (MODIS) data-based agricultural drought monitoring method. In the farmland drought monitoring process, an agricultural drought index is determined by a crop water supply index and a rainfall anomaly index; in the drought monitoring process, a vegetation index and the surface temperature are inverted by MODIS data, and the crop water supply index is calculated by the vegetation index and the surface temperature; the rainfall anomaly index is calculated by rainfall data; and drought severity is determined by dividing the level of the drought index.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF APPL ECOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
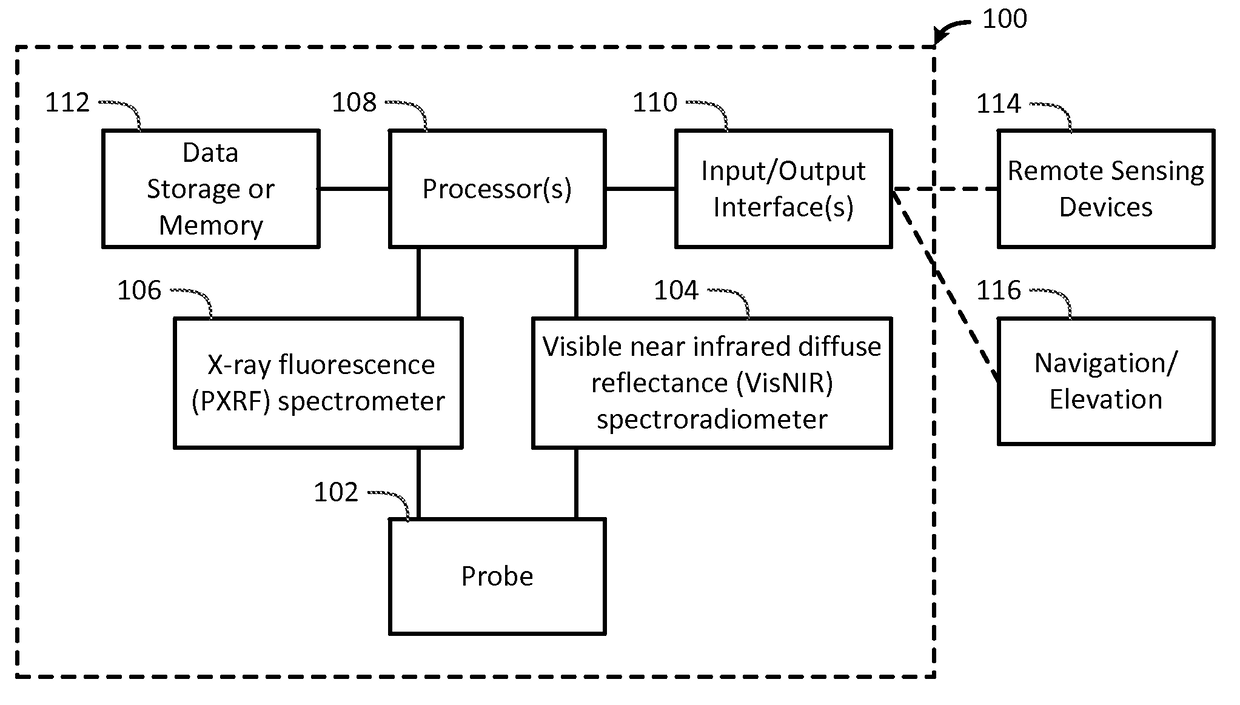
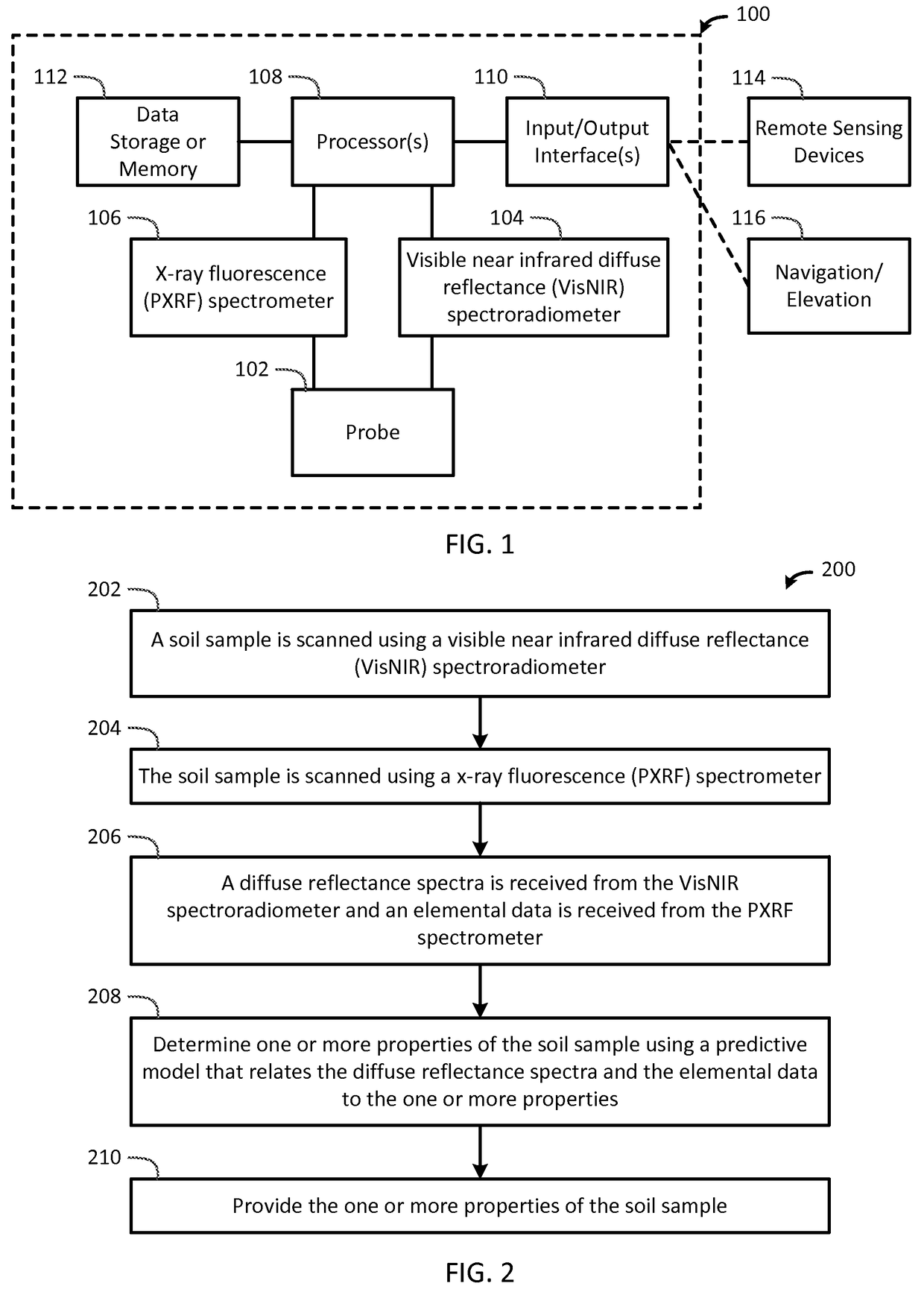
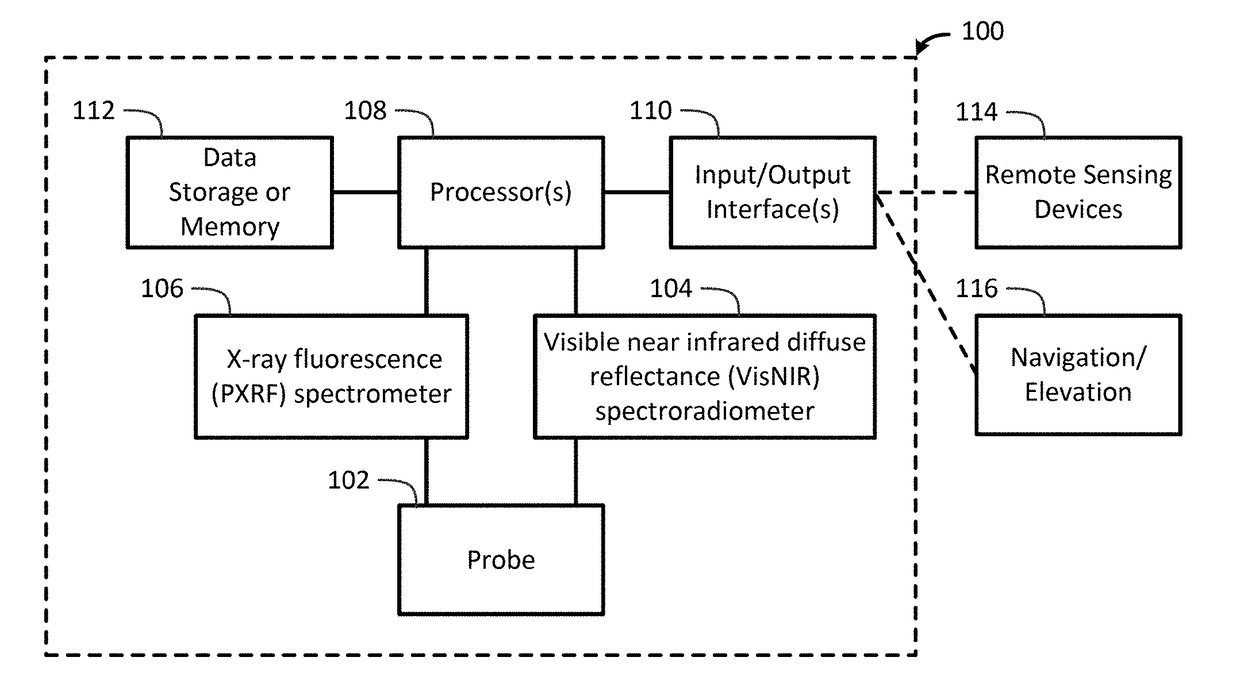
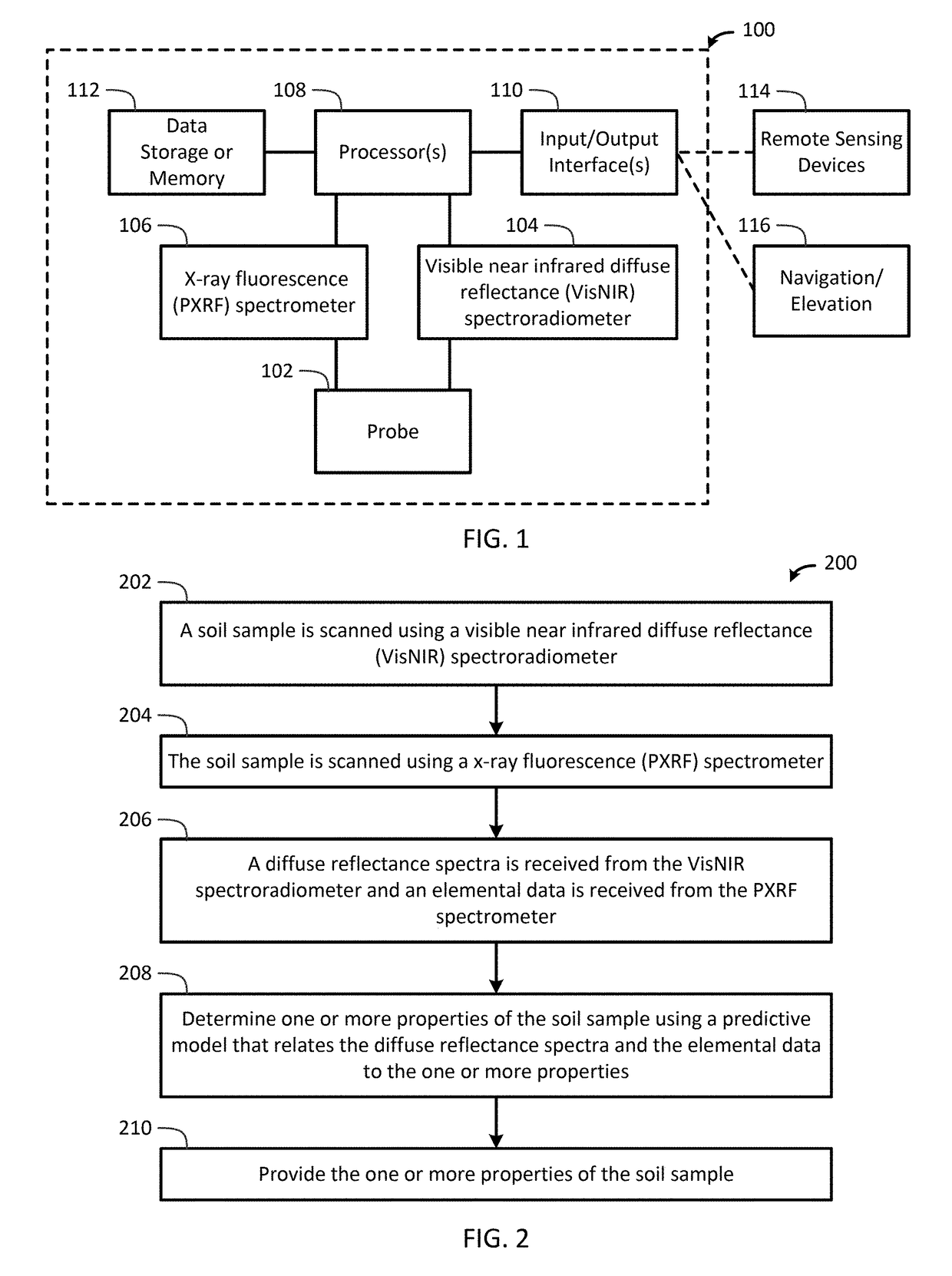
Portable Apparatus for Soil Chemical Characterization
ActiveUS20170122889A1Quick and easy and inexpensive to collectLess timeMaterial analysis by optical meansEarth material testingSoil scienceSpectroradiometer
The present invention determines one or more properties of a soil sample by scanning a soil sample using a visible near infrared diffuse reflectance diffuse reflectance (VisNIR) spectroradiometer, scanning the soil sample using a x-ray fluorescence (PXRF) spectrometer, receiving a diffuse reflectance spectra from the VisNIR spectroradiometer and an elemental data from the PXRF spectrometer, determining one or more properties of the soil sample using one or more processors and a predictive model that relates the diffuse reflectance spectra and the elemental data to the one or more properties, and providing the one or more properties of the soil sample to one or more input / output interface.
Owner:TEXAS TECH UNIV SYST +1
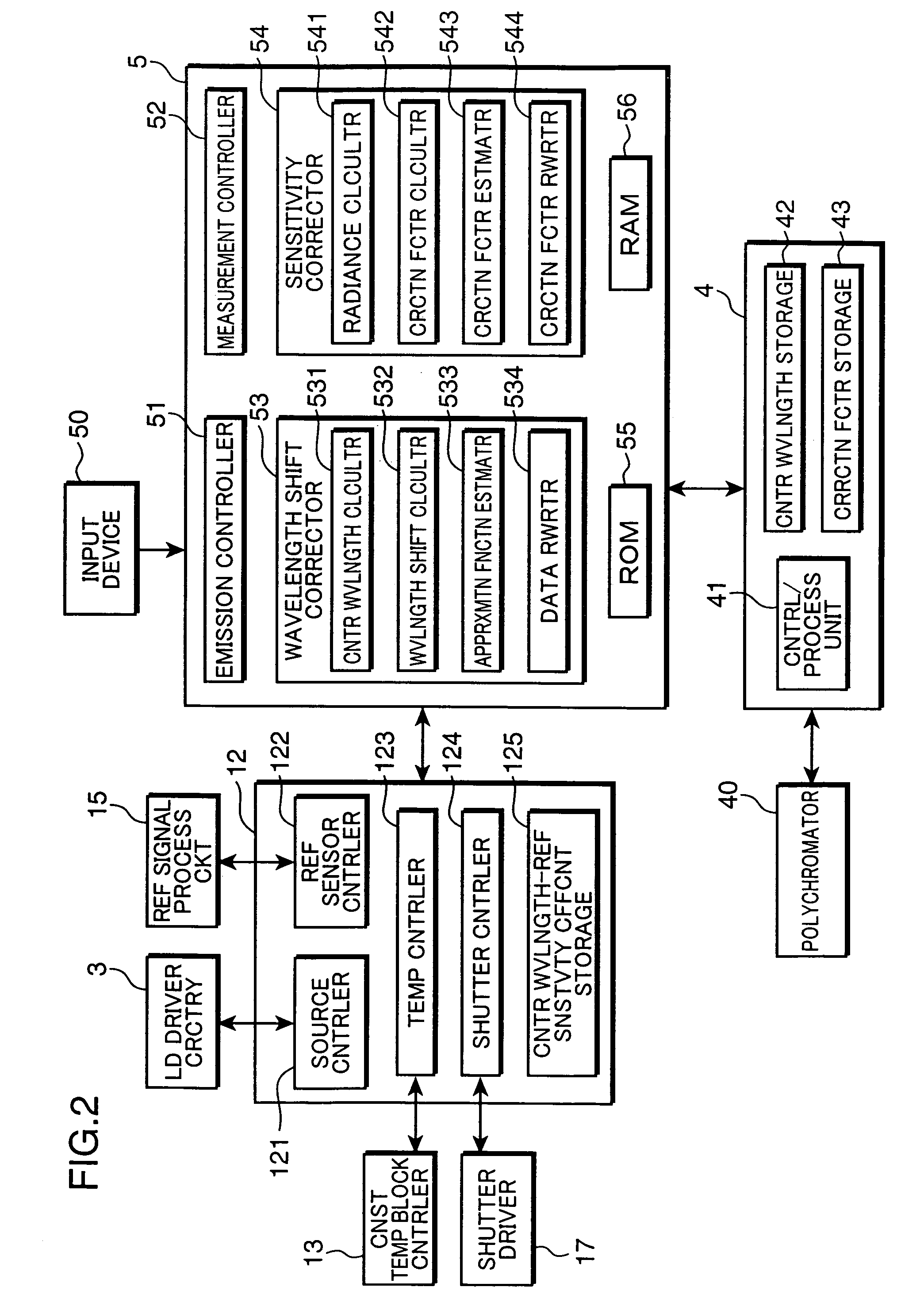
Calibration source for calibrating spectroradiometer, calibration method using the same, and calibration system
ActiveUS7339665B2Photometry using reference valueRadiation pyrometrySpectroradiometerMonochromatic color
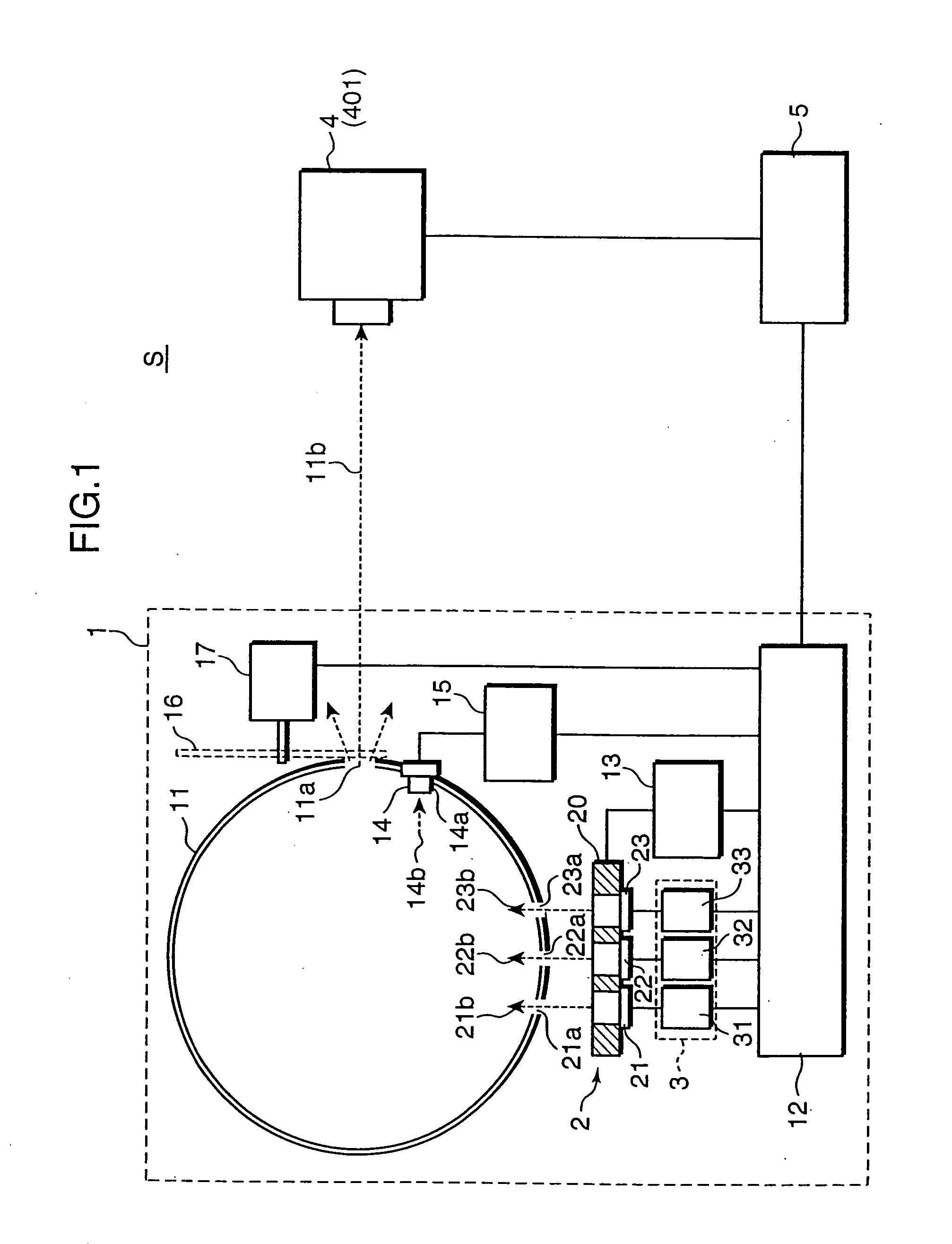
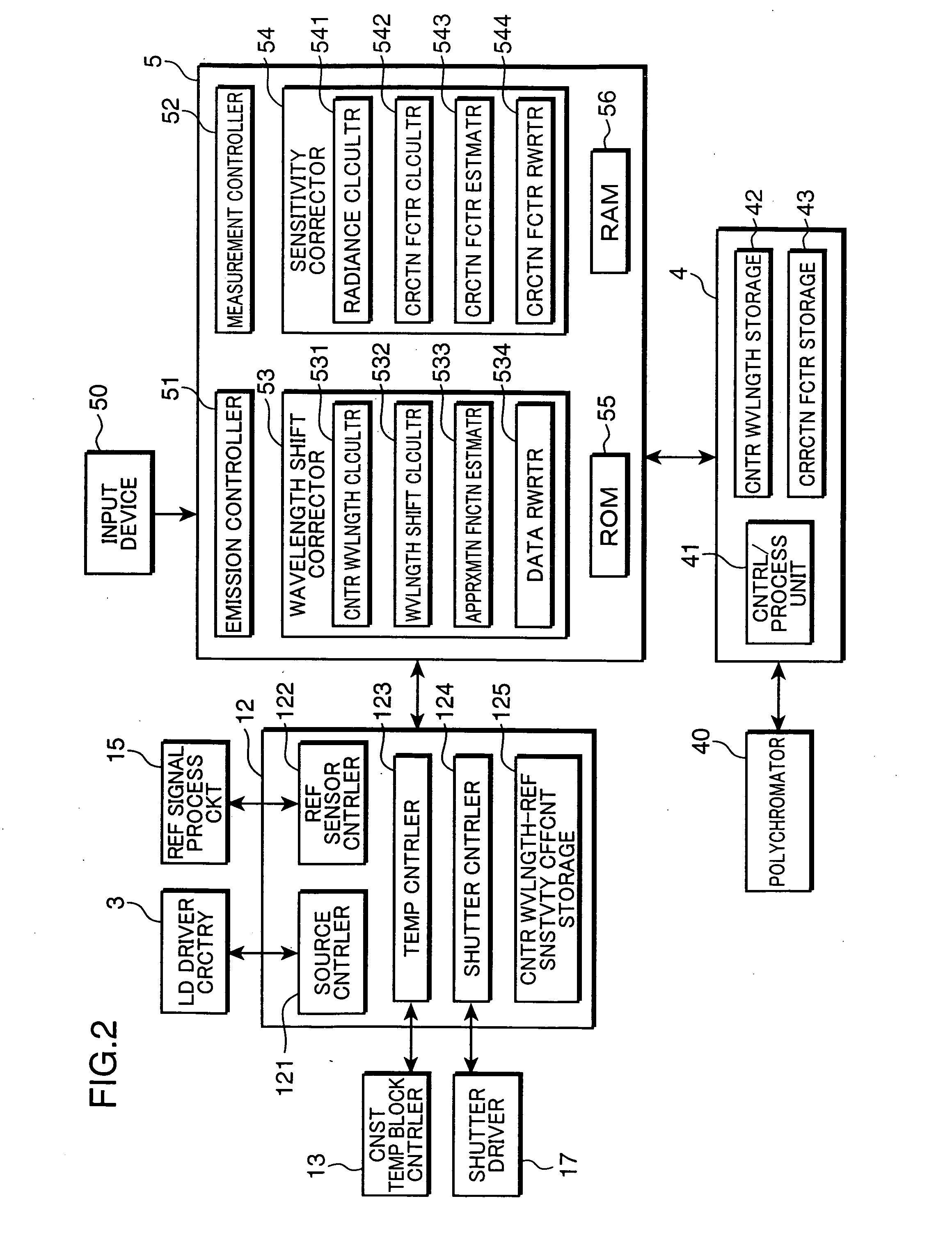
A spectroradiometer is calibrated by a calibration source including a plurality of monochromatic sources for emitting monochromatic rays having different wavelengths from each other, respectively; a reference light emitter for emitting monochromatic reference light by receiving the monochromatic rays emitted from the monochromatic sources; a reference sensor for measuring a reference intensity of the monochromatic reference light emitted from the reference light emitter; and a controller for controlling the emission of the monochromatic rays by the monochromatic sources, and the measurement of the reference intensity of the monochromatic reference light by the reference sensor.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA SENSING INC
Calibration source for calibrating spectroradiometer, calibration method using the same, and calibration system
ActiveUS20060132760A1Photometry using reference valueRadiation pyrometrySpectroradiometerMonochromatic color
A spectroradiometer is calibrated by a calibration source including a plurality of monochromatic sources for emitting monochromatic rays having different wavelengths from each other, respectively; a reference light emitter for emitting monochromatic reference light by receiving the monochromatic rays emitted from the monochromatic sources; a reference sensor for measuring a reference intensity of the monochromatic reference light emitted from the reference light emitter; and a controller for controlling the emission of the monochromatic rays by the monochromatic sources, and the measurement of the reference intensity of the monochromatic reference light by the reference sensor.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA SENSING INC
Remote sensing inversion method for land surface evapotranspiration of arid and semi-arid regions
InactiveCN102253184AImprove applicabilityTargeted optimizationEarth material testingSensing dataHeat flux
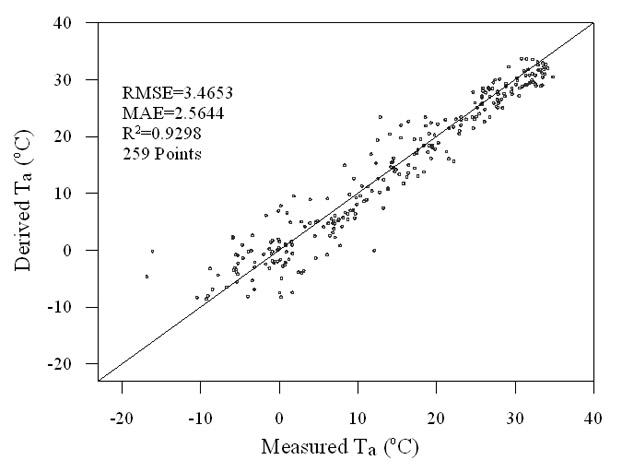
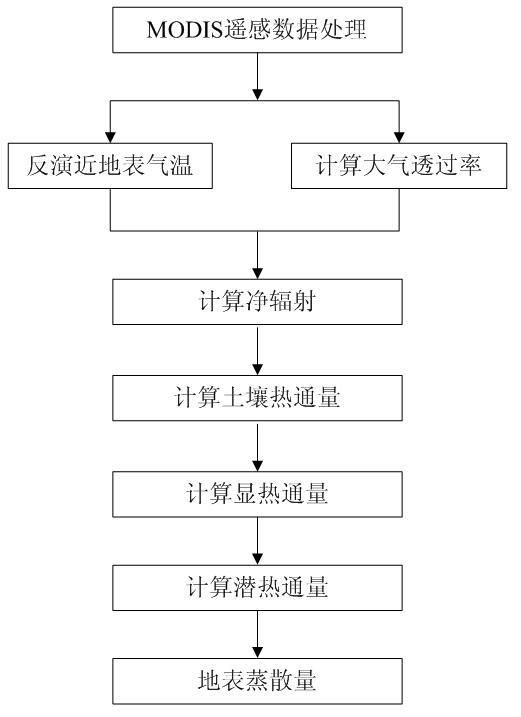
The invention discloses a remote sensing inversion method for land surface evapotranspiration of arid and semi-arid regions. The method comprises the steps of: acquiring and processing EOS / MODISE (Earth Observing System / Moderate-resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer) remotely sensed data; performing the inversion of near-surface temperature and computing atmospheric transmittance; obtaining a land surface latent heat flux by solving a net radiation quantity, a soil heat flux and a sensible heat flux according to a land surface energy balance equation; and figuring out land surface evapotranspiration data according to the land surface latent heat flux. According to the invention, aiming at the characteristics of rare meteorological stations in the arid region of Northwest China, a near-surface temperature inversion model and an atmospheric transmittance model both based on remotely sensed data are established, and the temperature obtained by the remote sensing inversion is used for participating in the computation instead of the observed temperatures of the stations; therefore, requirements on meteorological and other observation data are reduced.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF INFORMATION SCI & TECH
Accelerated weathering test apparatus with full spectrum calibration, monitoring and control
ActiveUS7038196B2Improve accuracyWeather/light/corrosion resistanceCalibration apparatusResponse factorFrequency spectrum
Owner:ATLAS MATERIAL TESTING TECH L L C
Measuring method for colorimetric parameters of LED display screen
InactiveCN101527108AAccurately assess primary color dominant wavelengthAccurate assessment errorCathode-ray tube indicatorsCoverage ratioLight spectrum
The invention relates to a measuring method for colorimetric parameters of an LED display screen. According to the luminescent characteristics of the LED display screen, the method creates and stipulates the measuring steps of color domain coverage ratio, non-uniformity of white field chromaticity and color reproduction of the LED display screen and a calculating method, provides a method for improving the accuracy of measuring and debugging the value and the range of the white field chromaticity and improving the accuracy of measuring primary wavelength of base color, and carries out necessary discrimination to peak wavelength of an LED tube and primary wavelength of an LED screen from scientific concept. A 1980 color luminance meter which conforms to spetral tristimulus values and contains four groups of filter plates is adopted to measure the colorimetric parameters of the LED display screen accurately; by adopting the method, the accuracy of measurement can meet the technical requirements to the standard color luminance meter. A 1980 spectroradiometer with spectral bandwidth and the sampling interval of 1nm can accurately measure the peak wavelength of the LED tube. In the debugging process, a multiturn potentiometer is adopted to achieve the purpose of finely selecting the resistance value of a resistor. The core technology is the necessary premise and key of debugging and manufacturing the LED display screen with excellent color reproduction.
Owner:天津光杰光电有限公司
Method for establishing bidirectional reflectance distribution function (BRDF) prototype library based on multi-angular measurement
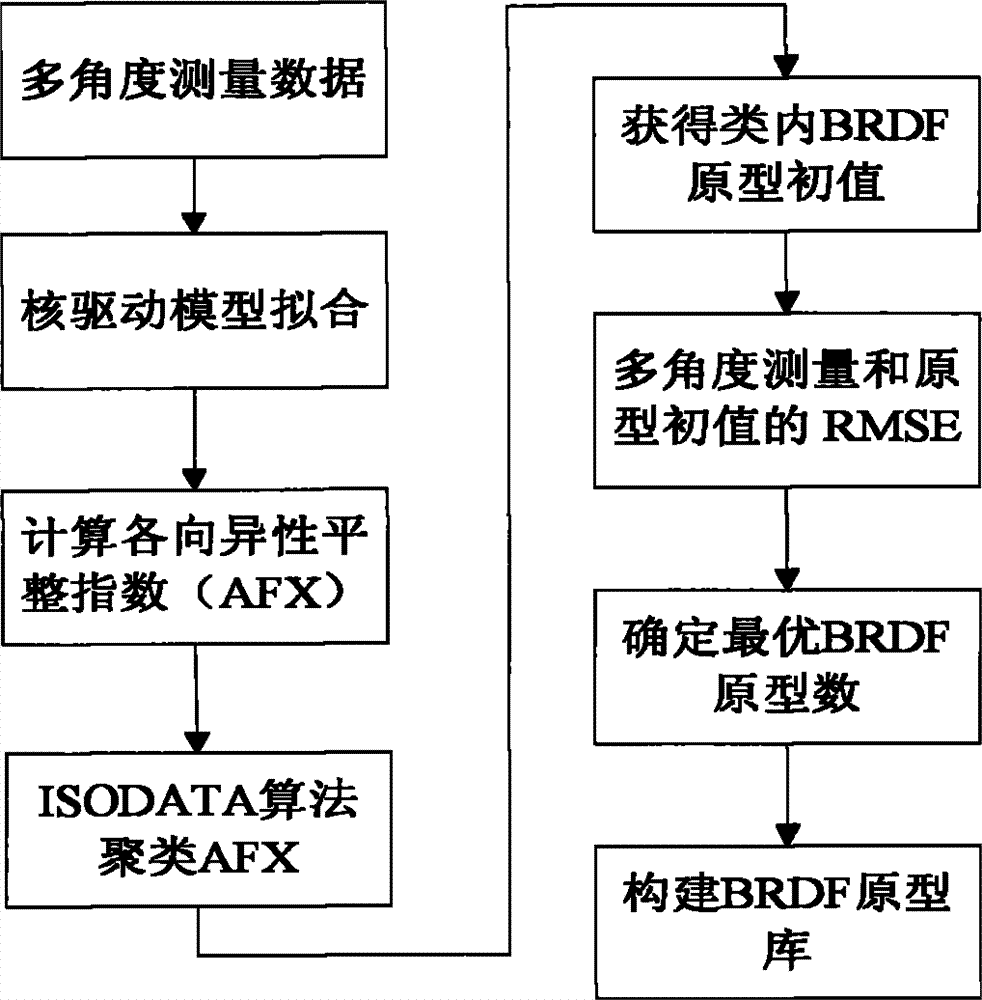
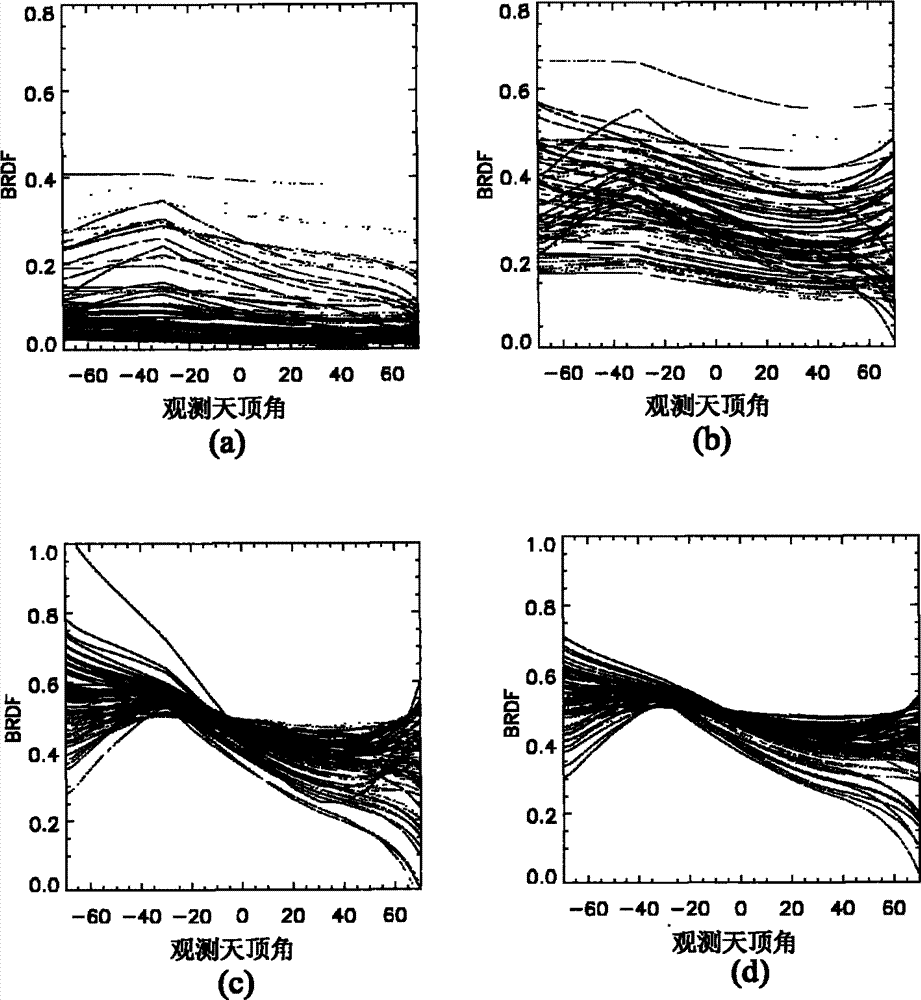
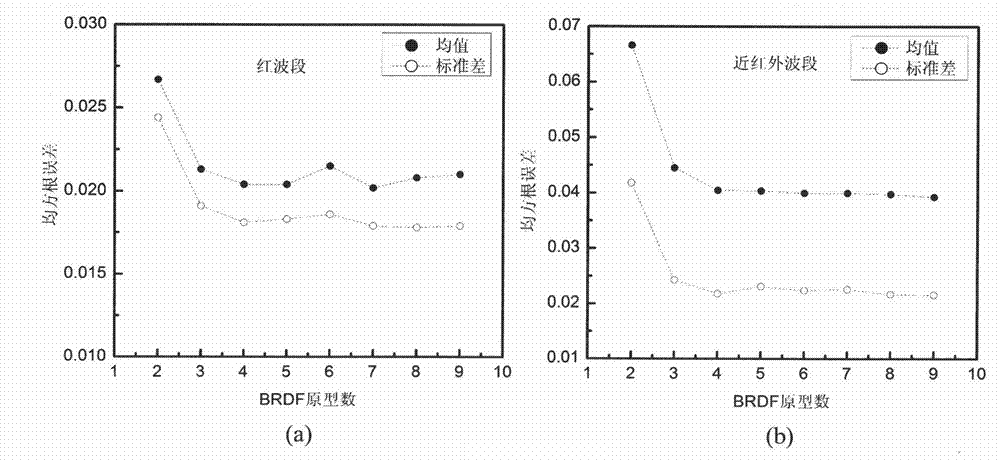
InactiveCN102902883AClear logicAdaptableSpecial data processing applicationsCluster algorithmBidirectional reflectance distribution function
The invention relates to a method for establishing a bidirectional reflectance distribution function (BRDF) prototype library based on multi-angular measurement. Through self-defining bidirectional anisotropic flat index (AFX) and iterative self-organizing ISODATA clustering algorithm, a theory and a method for establishing the BRDF prototype library based on BRDF feature mode are provided and are realized by using 69 groups of ground surface multi-angular measurement data and the history data (MCD43A) of global EOS ground surface verification core point. According to the theory and the method, the conventional method for establishing a BRDF database based on the ecological form of ground surface is abandoned, the BRDF prototype library is different from the global pixel-to-pixel BRDF database of MODIS (Moderate-resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer) in the service operation at present; and is small in volume, simple and convenient to construct and easy to operate, and is applicable for other airborne and spaceborne multi-angular measurement data of ground surface. In the technical field of spatial information, the method particularly has theoretical and application values for extracting BRDF prior knowledge to invert ground surface parameters in the aspect of quantitative remote sensing.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
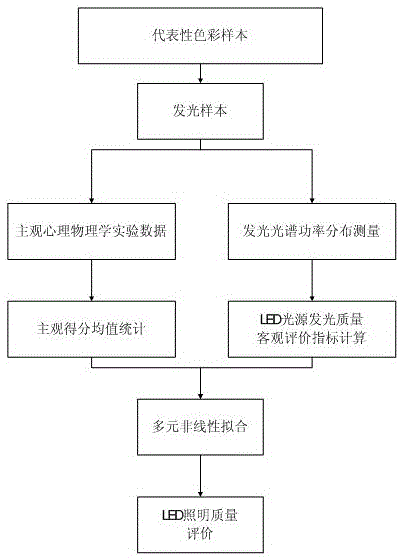
LED lighting quality evaluation method based on objective and subjective experiment data and system
InactiveCN105136432AGuaranteed to be scientificGuarantee the accuracy of evaluationTesting optical propertiesSpectroradiometerEffect light
The invention provides an LED lighting quality evaluation method based on objective and subjective experiment data and a system. The method comprises the steps that subjective experiment data acquired from a preset LED lighting evaluation angle for light emitting samples are input; the subjective score mean of each group of light emitting sample is counted; for each group of light emitting sample, a spectroradiometer is used to measure spectral power distribution; data in a visible wavelength range are intercepted; objective evaluation indicators are calculated; a multiple nonlinear fitting method is used to construct an association model between the subjective score mean and a corresponding objective evaluation indicator under different light emitting sample conditions; for a light emitting sample to be evaluated, the spectroradiometer is used to measure the spectral power distribution; the data in the visible wavelength range are intercepted; the objective evaluation indicator is calculated; a corresponding score estimation value is acquired based on the association model; and the lighting quality of a light source is characterized. The LED lighting quality evaluation method provided by the invention has the advantages of flexible and targeted use, accurate evaluation and easy implementation.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Accelerated weathering test apparatus with full spectrum calibration, monitoring and control
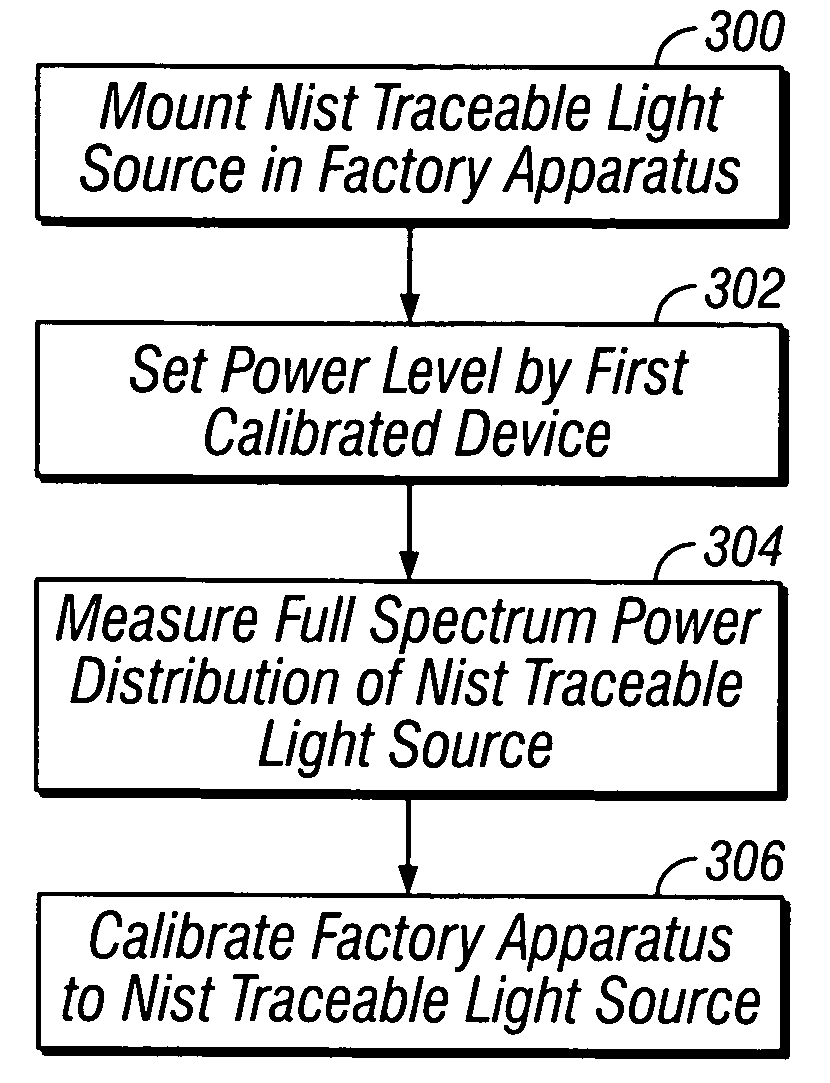
ActiveUS20050167580A1Improve accuracyRadiation pyrometryWeather/light/corrosion resistanceData setResponse factor
An accelerated weathering test apparatus and method for calibration and operation thereof including a spectroradiometer for monitoring a full spectrum power distribution of a light source. Calibration includes a calibration light source in a factory test apparatus operated at a fixed power level and collecting the full spectrum power distribution of the calibration light source to generate a first data set. The calibration light source is then installed in a client test apparatus and operated at the fixed power level in order to collect the full spectrum power distribution and generate a second data set. The first and second data sets are filtered and aligned to determine a system response factor of the client test apparatus so that the irradiance level control may be calibrated.
Owner:ATLAS MATERIAL TESTING TECH L L C
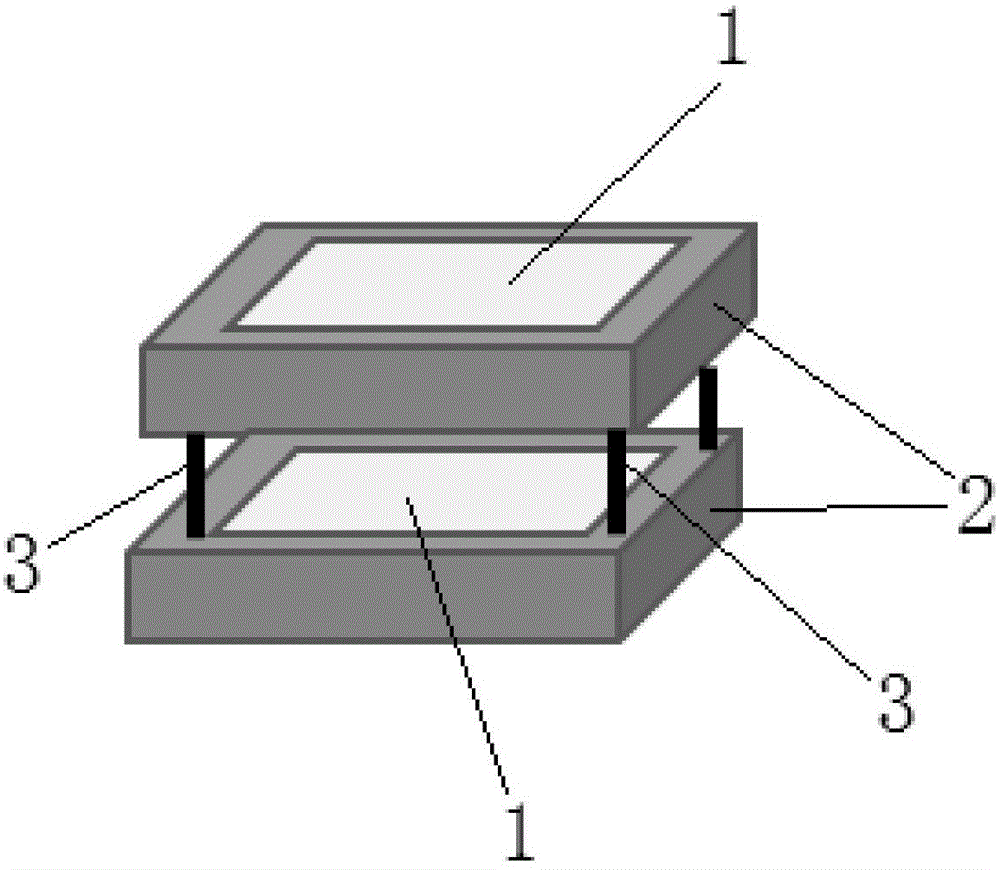
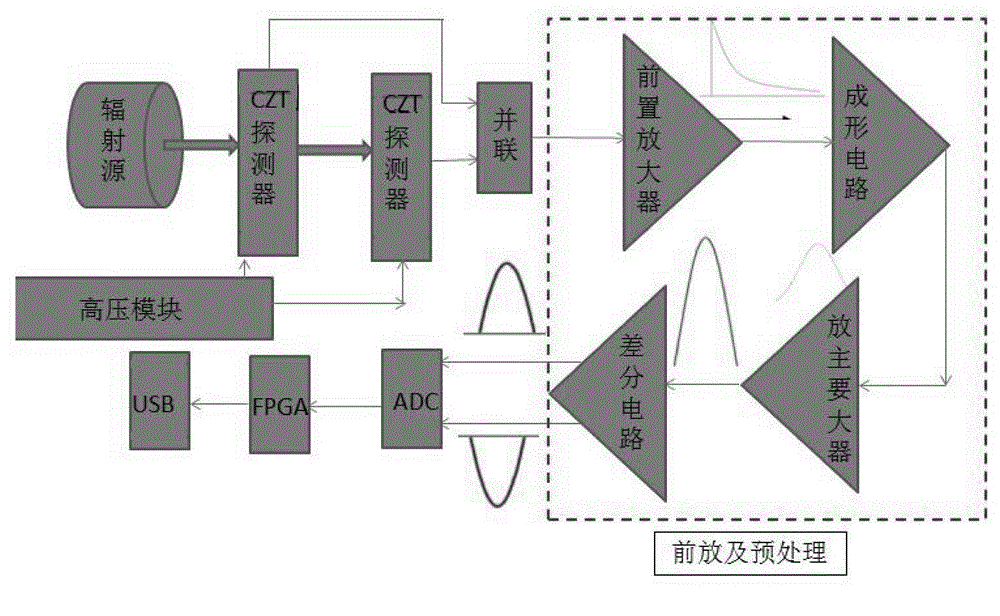
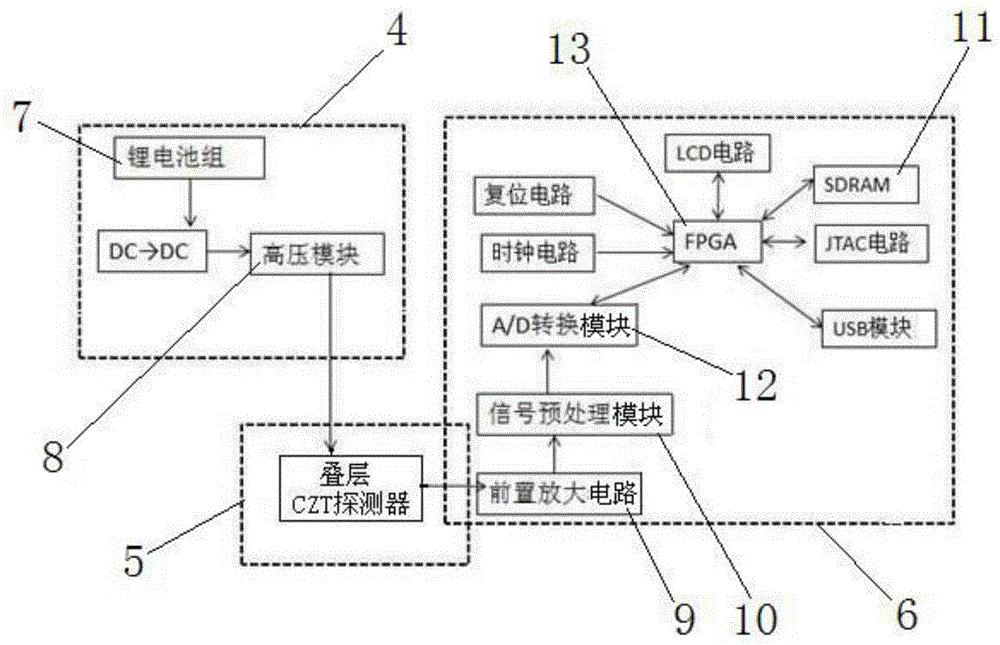
Portable gamma spectroradiometer
InactiveCN104635254AHigh precisionReduce volumeX-ray spectral distribution measurementSpectroradiometerSingle level
The invention belongs to the technical field of radioactive detection instruments, and specifically provides a portable gamma spectroradiometer. The portable gamma spectroradiometer comprises a power supply system (4), a detector system (5) and a signal processing system (6), wherein the detector system (5) comprises two single-layer CZT detectors (1) which are laminated together up and down; the electric signals of the two single-layer CZT detectors (1) are connected into the signal processing system (6) after being connected in parallel; the power supply system (4) is connected with the detector system (5) and is used for supplying power for a laminated CZT detector consisting of the two single-layer CZT detectors (1). The portable gamma spectroradiometer overcomes the problems that the efficiency of a single detector is not high and the precision of a final dosage value is not high caused by the fact that a portable gamma spectroradiometer in the prior art uses the single CZT detector in a single energy spectrum analysis manner.
Owner:IMDETEK
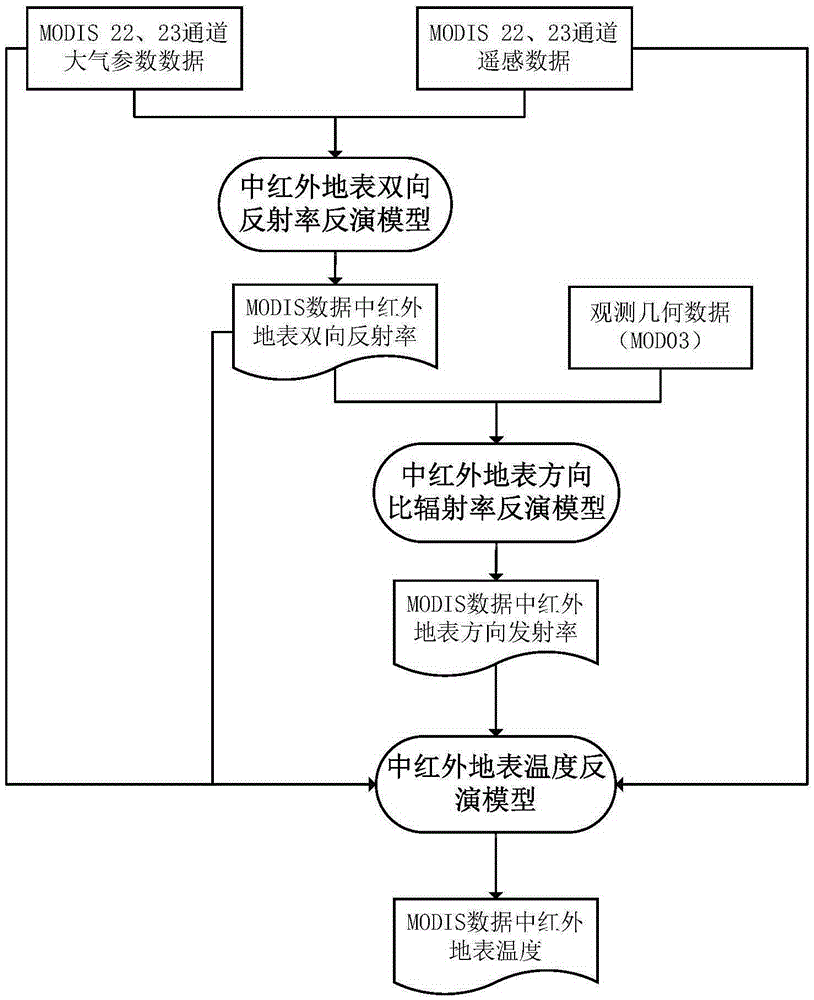
Method and apparatus for determining surface temperature by use of middle-infrared remote sensing data
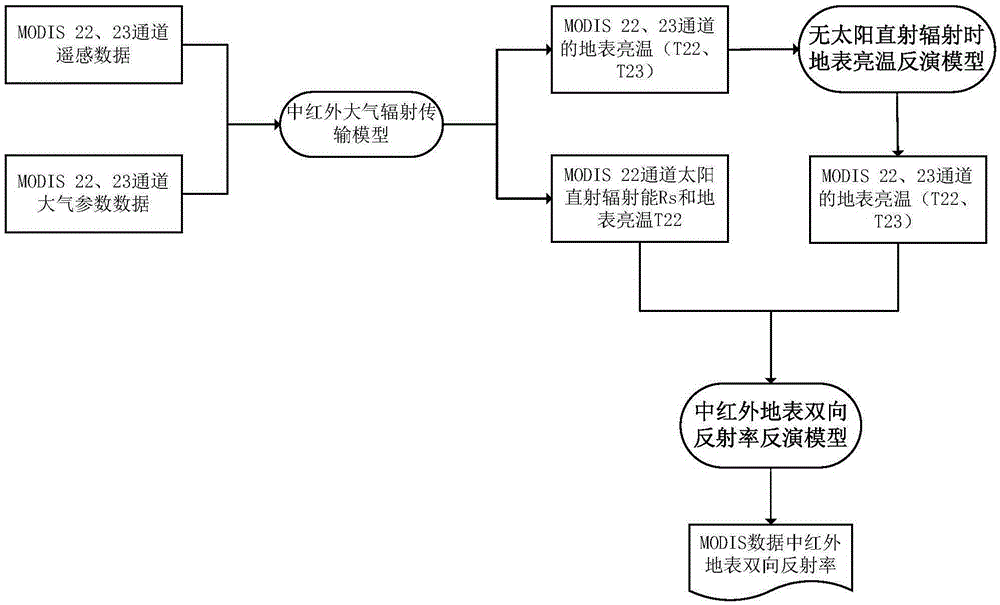
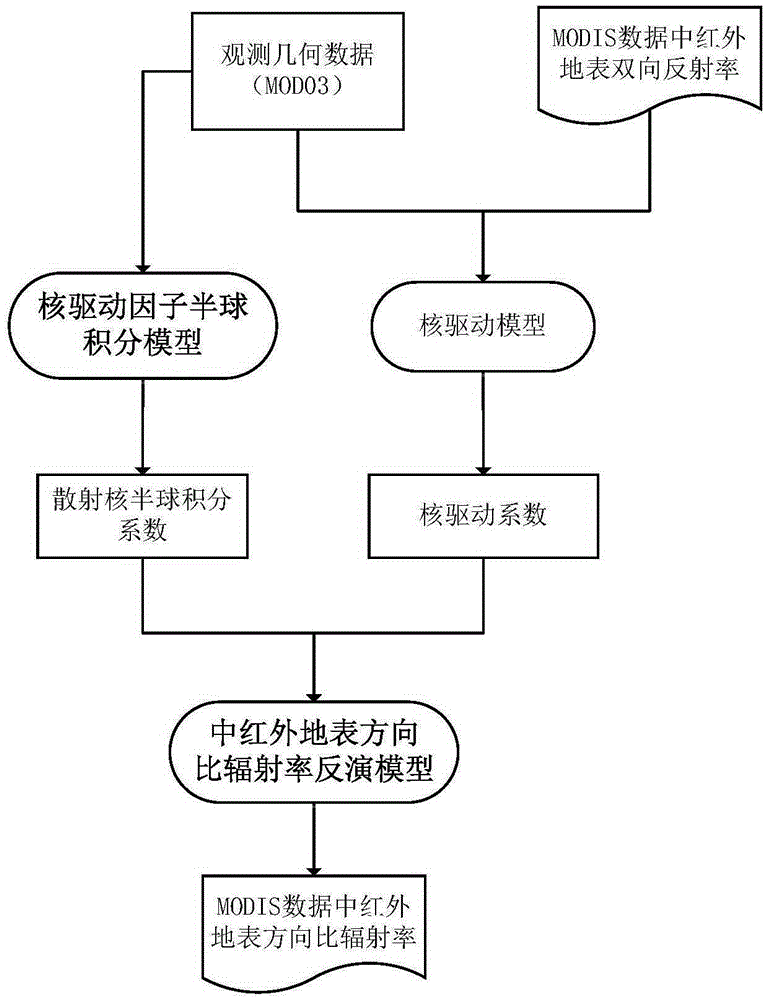
InactiveCN105425247AEfficient separationAchieve inversionElectromagnetic wave reradiationICT adaptationMiddle infraredSensing data
The invention discloses a method and apparatus for determining a surface temperature by use of middle-infrared remote sensing data. The method comprises the following steps: step A, determining surface bidirectional reflectivity of a twenty-second channel (3.929[mu]m to 3.989[mu]m) and a twenty-third channel (4.020[mu]m to 4.080[mu]m) by use of radiation brightness data and atmosphere parameter data of the twenty-second channel and the twenty-third channel of a middle-infrared wave spectrum zone of moderate-resolution imaging spectroradiometer (MODIS) data through a developed middle-infrared surface bidirectional reflectivity remote sensing inversion method; step B, by use of the surface bidirectional reflectivity obtained from the step A, through a developed surface direction ratio radiant ratio remote sensing inversion method, determining surface direction ratio radiance; and step C, by use of the middle-infrared surface bidirectional reflectivity and the direction ratio radiance respectively obtained from the step A and the step B, through a developed surface temperature remote sensing reversion method, determining the surface temperature. The method and apparatus provided by the invention effectively realize quantitative remote sensing inversion of the surface temperature through the middle-infrared data.
Owner:INST OF GEOGRAPHICAL SCI & NATURAL RESOURCE RES CAS
Method for calibrating a spectroradiometer
ActiveCN107209059AGuaranteed synchronicityStable and transportableRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationSpectroradiometerUsability
The invention relates to a method for calibrating a spectroradiometer (1), comprising the following method steps: capture of light measurement data by the measurement of the radiation of at least one standard light source (4) using the spectroradiometer (1) that is to be calibrated; derivation of calibrated data from the light measurement data by the comparison of the captured light measurement data with known data of the standard light source (4); and calibration of the spectroradiometer (1) according to the calibration data. The aim of the invention is to provide a reliable and practical method for calibrating the spectroradiometer (1). In particular, the synchronism of spectroradiometers (1) situated in different locations (9, 10, 11) is to be produced simply and reliably. To achieve this aim, the validity, i.e. the usability, of the standard light source for the calibration is checked by a comparison of the light measurement data of the standard light source (4) with light measurement data of one or more additional standard light sources (4) of the same type, the validity of the standard light source (4) being established if the deviations of the light measurement data of the standard light sources (4) from one another lie below predefined limit values, and / or the standard light source (4) is measured using two or more standard spectroradiometers (1') of the same type or of different types, the validity of the standard light source (4) being established if the deviations of the light measurement data from one another, said data being captured using the different standard spectroradiometers (1'), lie below predefined limit values.
Owner:仪器系统有限公司
Light source evaluation apparatus, light source evaluation system, light source adjustment system, and method for evaluating a light source
InactiveUS20120101774A1Spectrum generation using diffraction elementsPhotometrySpectroradiometerIlluminance
Provided are a light source evaluation device, a light source adjustment system, a light source evaluation system, and a light source evaluation method whereby it is possible to evaluate the characteristics of a solar simulator, which is a light source for measuring the characteristics of a solar cell, without creating a reference cell or pseudo cell tailored to the spectral sensitivity of a solar cell to be measured. Said evaluation is performed by calculating an evaluation value of the characteristics of the light emitted by a solar simulator in comparison to natural sunlight on the basis of the spectral irradiance of the light emitted by a solar simulator as measured by a spectroradiometer, the spectral irradiance of natural sunlight, and the pre-measured spectral sensitivity of the solar cell to be measured.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA SENSING INC
Imaging spectrometer radiation parameter and imaging parameter calibration device and method
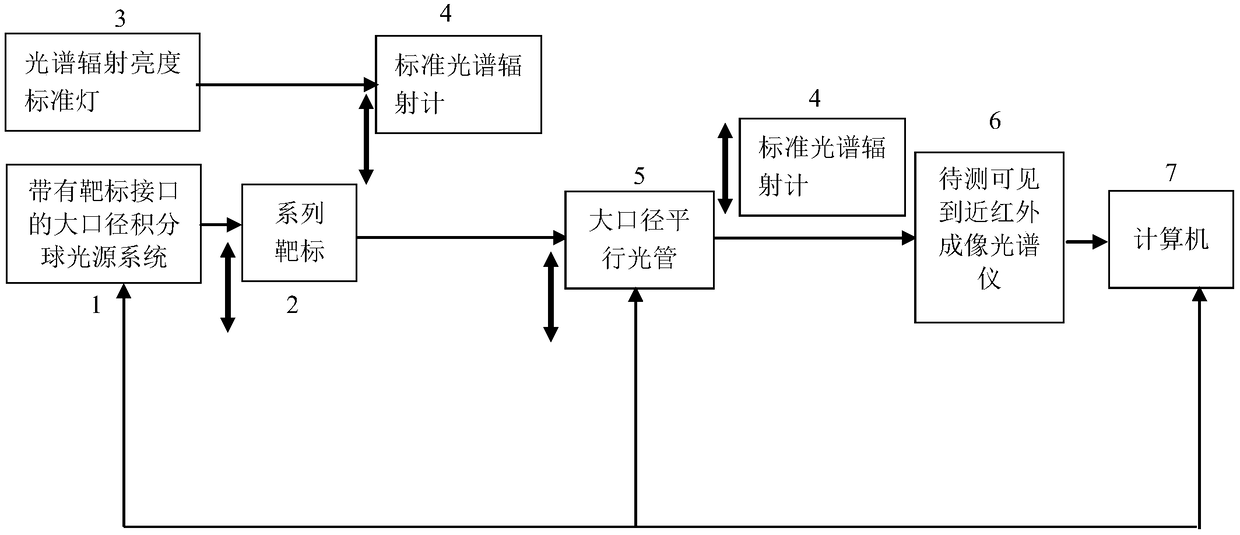
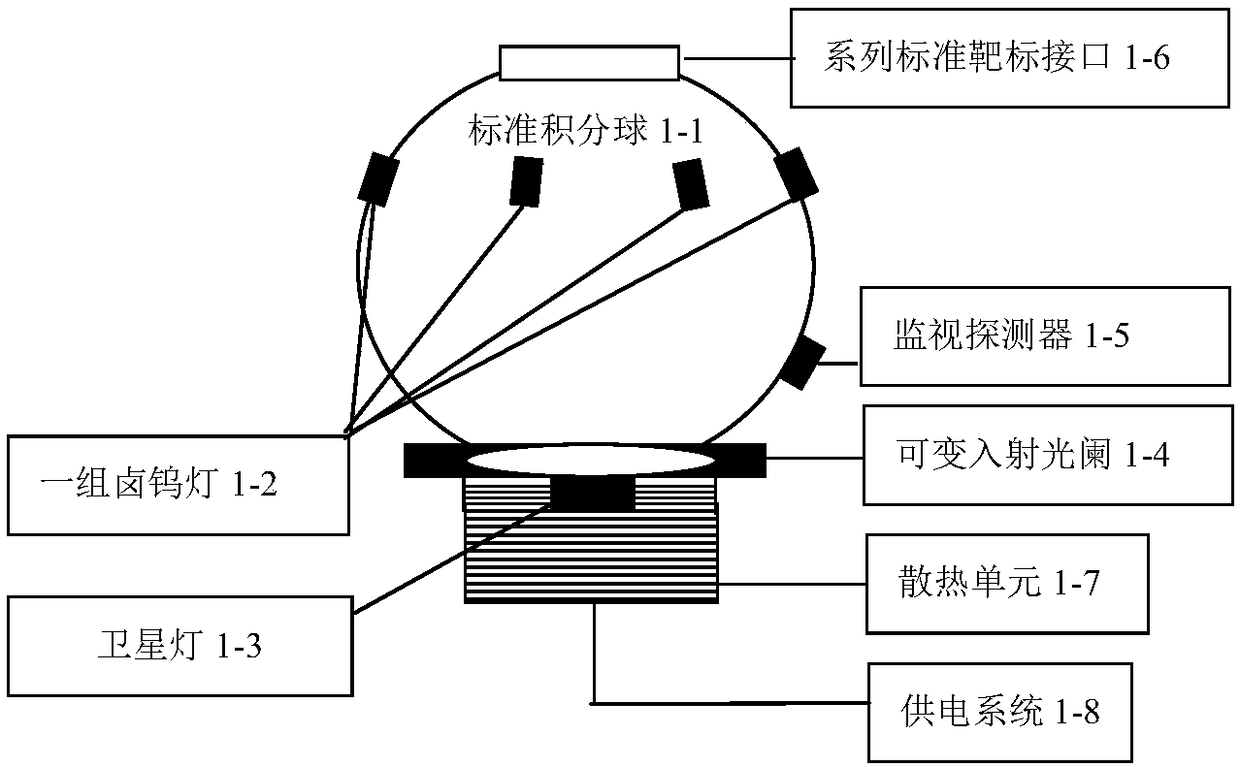
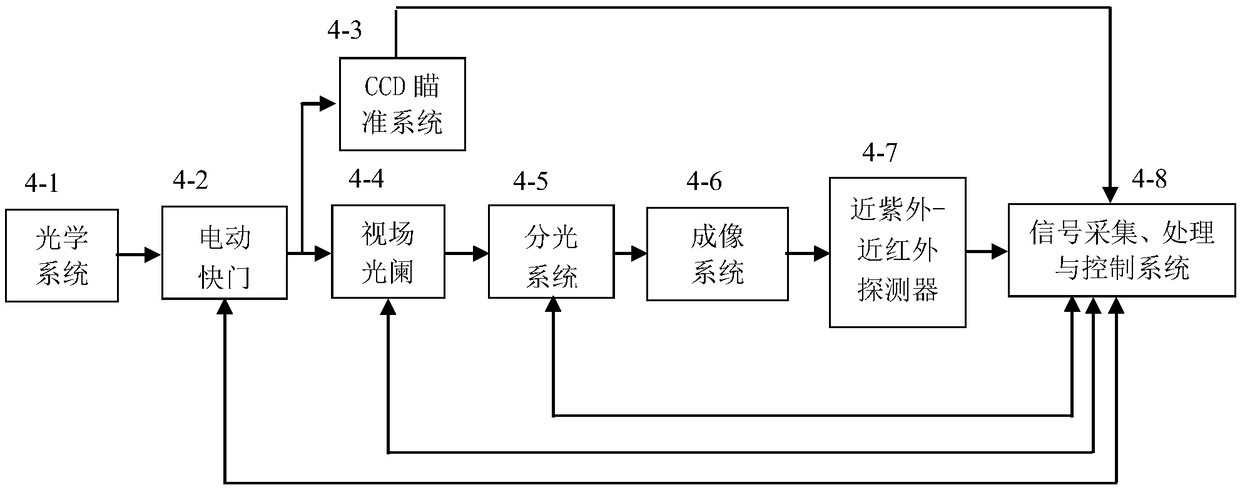
ActiveCN109387284AImprove calibration accuracyMany calibration parametersSpectrum investigationRadiometerVisible near infrared
The invention provides a visible near-infrared imaging spectrometer radiation parameter and imaging parameter calibration device and method. The calibration device and method use a high-stability large-caliber standard integrating sphere light source with a target interface to be combined with a large-caliber collimator to form collimation radiation which is received by a measured visible near-infrared imaging spectrometer. A standard spectroradiometer calibrated by a spectral radiance standard lamp calibrates the spectral radiance of the exit of the integrating sphere light source and the collimation radiation respectively, so as to achieve full-band radiance high-accuracy calibration of the visible near-infrared imaging spectrometer of a camera system and a telescope system. The measuredvisible near-infrared imaging spectrometer is used to image a series of standard targets mounted on the target interface of the large-caliber standard integrating sphere light source, so as to realize imaging parameter calibration of the measured imaging spectrometer.
Owner:西安应用光学研究所
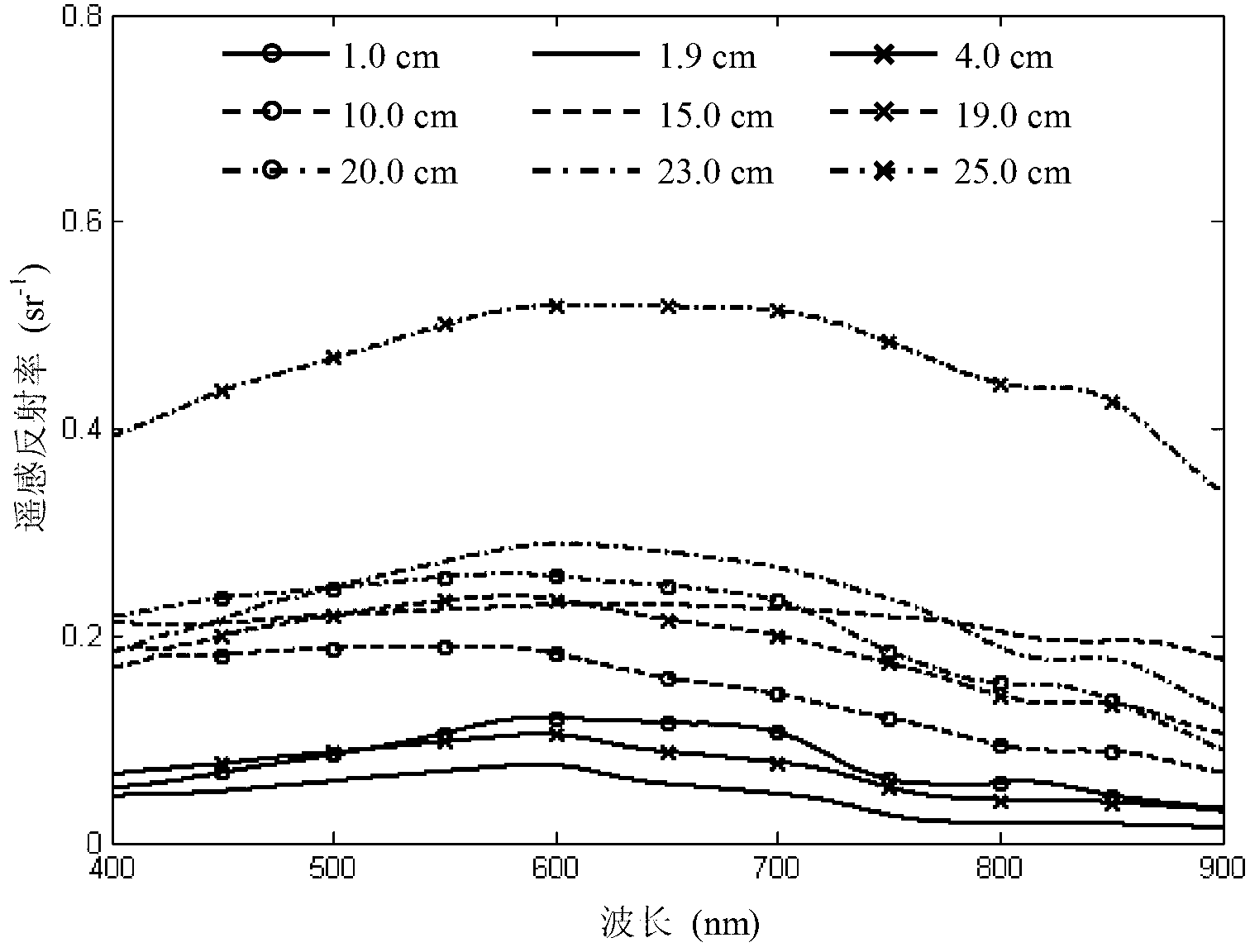
Method for calculating sea ice thickness based on hyperspectral remote sensing reflectance
InactiveCN103017668ARealize computingSimple methodUsing optical meansSpectroradiometerHyperspectral image processing
The invention relates to a method for calculating sea ice thickness based on hyperspectral remote sensing reflectance. The method comprises the following steps of selecting the ratio of remote sensing reflectance of different wavelengths and functions as the characteristics of determining the sea ice thickness according to the different thicknesses of sea ice hyperspectral remote sensing reflectance; building a sea ice thickness calculation model to obtain the sea ice thickness; aiming at an aerial hyperspectral image containing sea ice, firstly, utilizing the ratio of digital quantization values of an image to identify a sea ice picture element; carrying out radiation correction and atmospheric correction on the digital quantization values of the image according to the common aerial hyperspectral image processing method to obtain the hyperspectral remote sensing reflectance of the sea ice picture element; and finally substituting into the sea ice thickness calculation model, and calculating the thickness of the sea ice picture element. The model disclosed by the invention is simple; and only remote sensing reflectance Rrs of finite wavelengths is selected. Therefore, sea ice thickness calculation of the sea ice remote sensing reflectance measured by a spectroradiometer is achieved, and calculation of the sea ice thickness by the aerial hyperspectral remote sensing image is also achieved.
Owner:THE FIRST INST OF OCEANOGRAPHY SOA +1
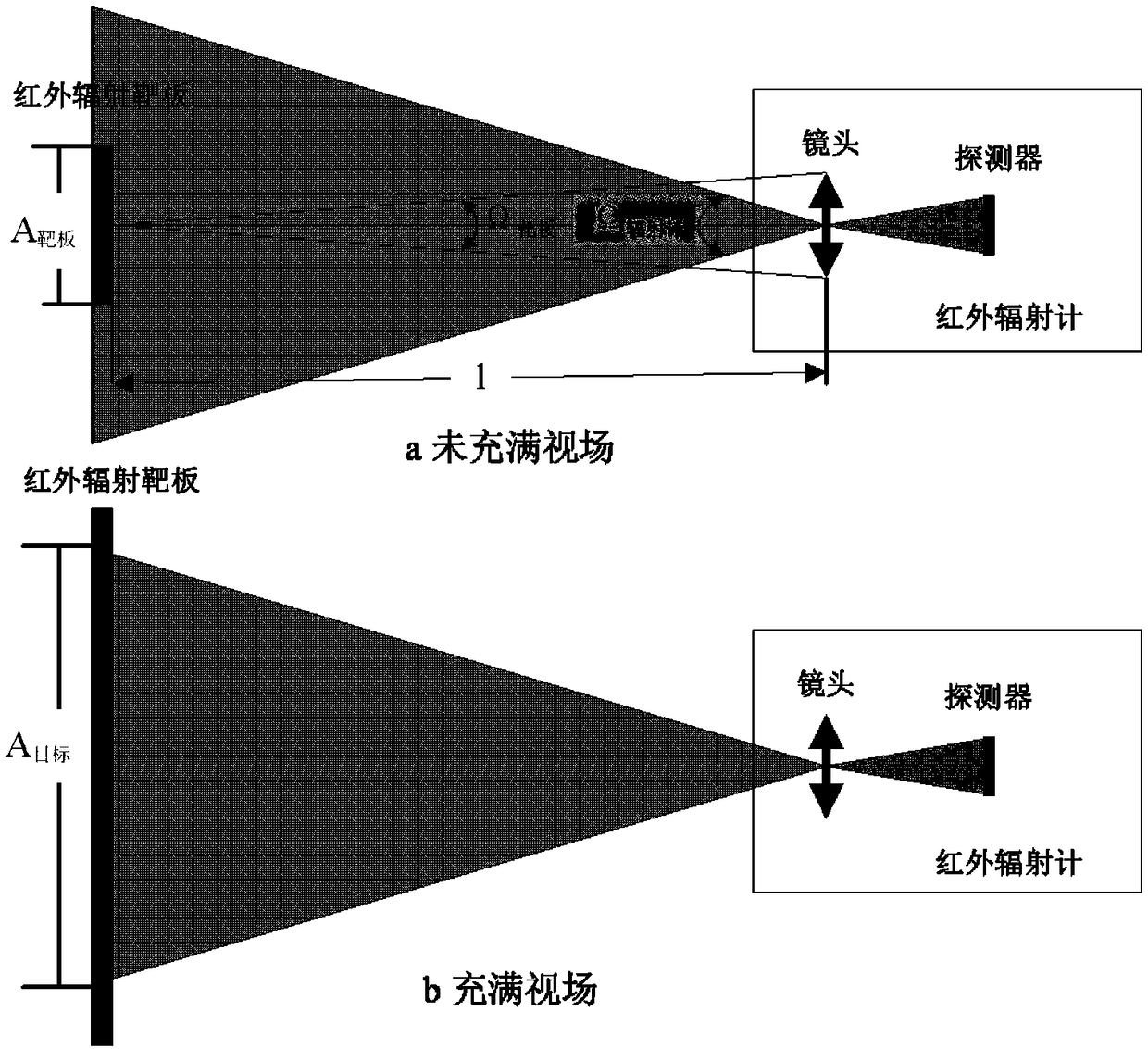
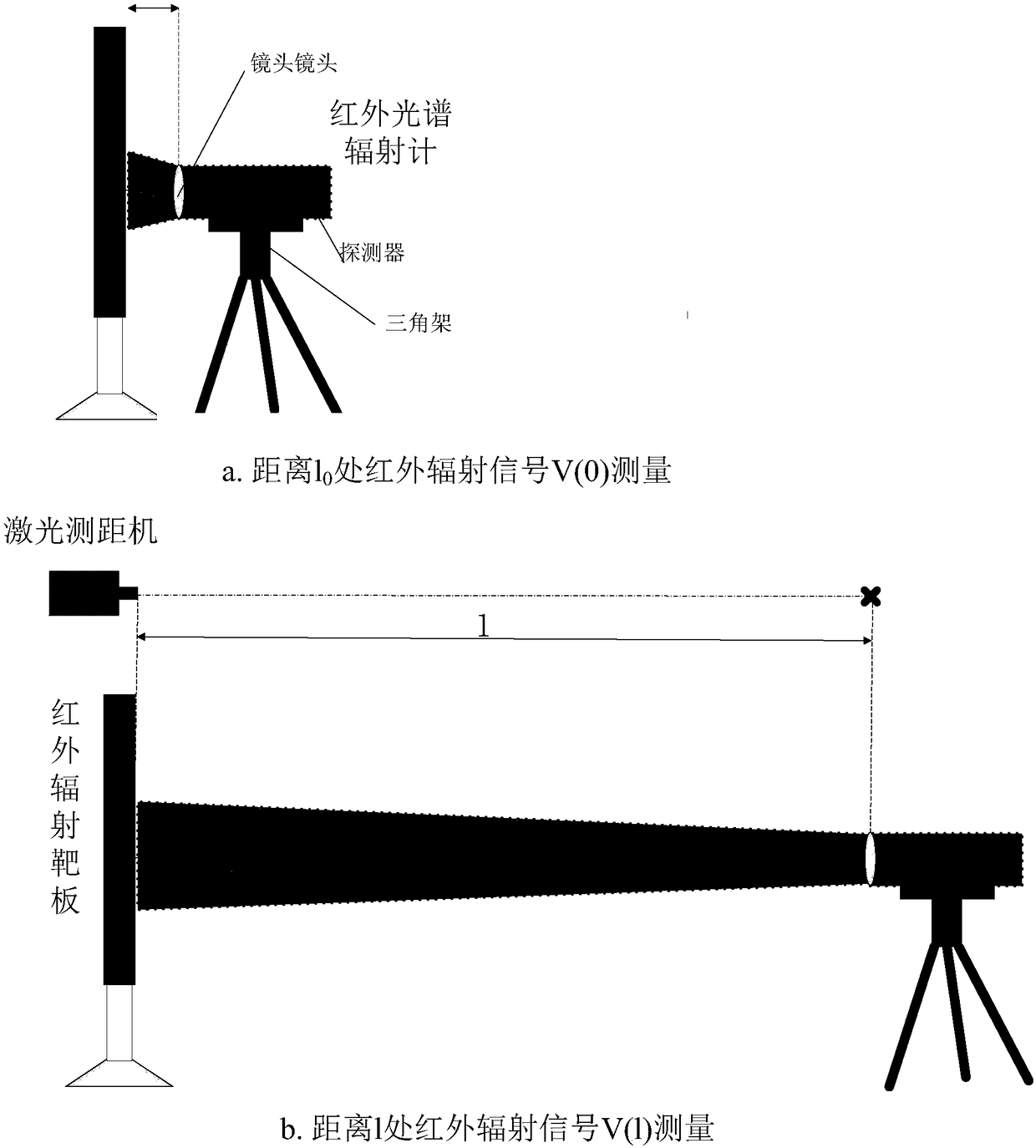
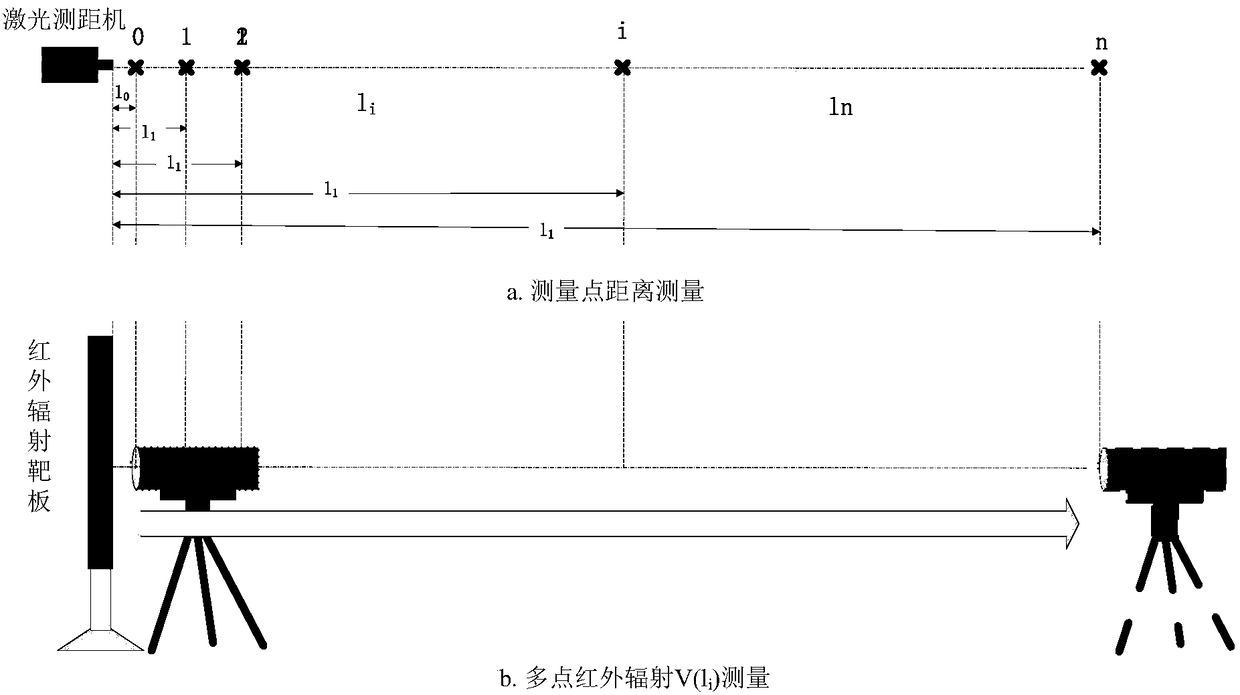
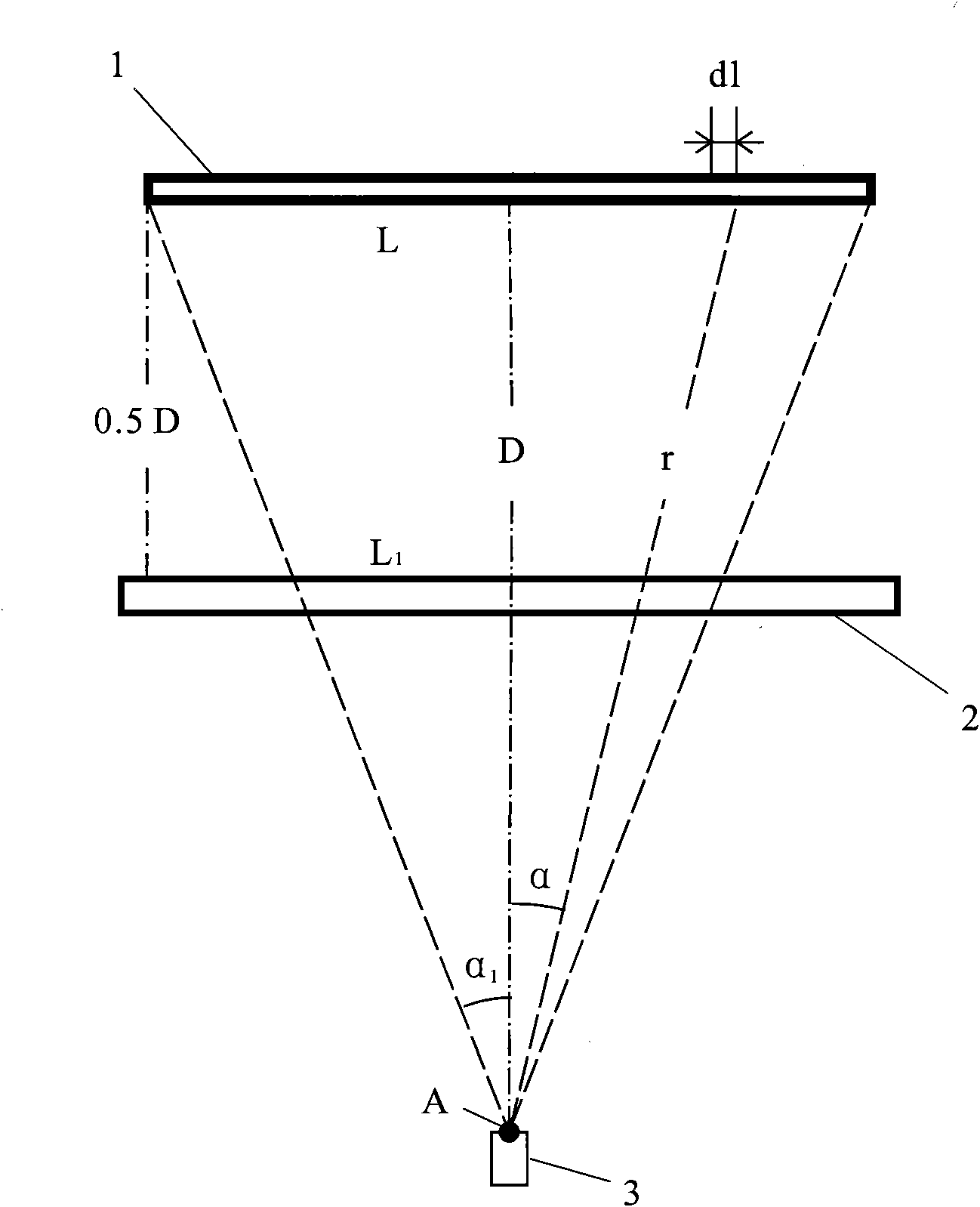
Evaluation method for horizontal infrared atmospheric spectrum transmittance
The invention discloses a measurement method for horizontal infrared atmospheric spectrum transmittance, which can realize measurement of the horizontal infrared atmospheric spectrum transmittance atany distance. The measurement of close-distance horizontal infrared atmospheric spectrum transmittance adopts a field direct measurement method, i.e., an infrared radiation target plate is moved undera visual field condition that the infrared radiation target plate is filled with an infrared spectroradiometer; an infrared radiation signal of the infrared radiation target plate under a testing distance measured by the infrared spectroradiometer is acquired, and the value of the radiation signal is compared with the value of a zero-distance acquired infrared radiation signal, so that the horizontal infrared atmospheric spectrum transmittance value of the distance is obtained; an actual measurement method is only suitable for a limited long distance due to influences of a measurement instrument, signal-to-noise ratio and the like; in order to realize the evaluation of long-distance horizontal infrared atmospheric spectrum transmittance, atmospheric spectrum transmittance values of a plurality of measurement points are measured through the measurement method of the close-distance horizontal infrared atmospheric spectrum transmittance, and data is subjected to exponential function fitting, so that the evaluation of the long-distance horizontal infrared atmospheric spectrum transmittance is realized.
Owner:西安应用光学研究所
Portable apparatus for soil chemical characterization
ActiveUS10107770B2Material analysis by optical meansEarth material testingSoft x raySpectroradiometer
The present invention determines one or more properties of a soil sample by scanning a soil sample using a visible near infrared diffuse reflectance (VisNIR) spectroradiometer, scanning the soil sample using a x-ray fluorescence (PXRF) spectrometer, receiving a diffuse reflectance spectra from the VisNIR spectroradiometer and an elemental data from the PXRF spectrometer, determining one or more properties of the soil sample using one or more processors and a predictive model that relates the diffuse reflectance spectra and the elemental data to the one or more properties, and providing the one or more properties of the soil sample to one or more input / output interface.
Owner:TEXAS TECH UNIV SYST +1
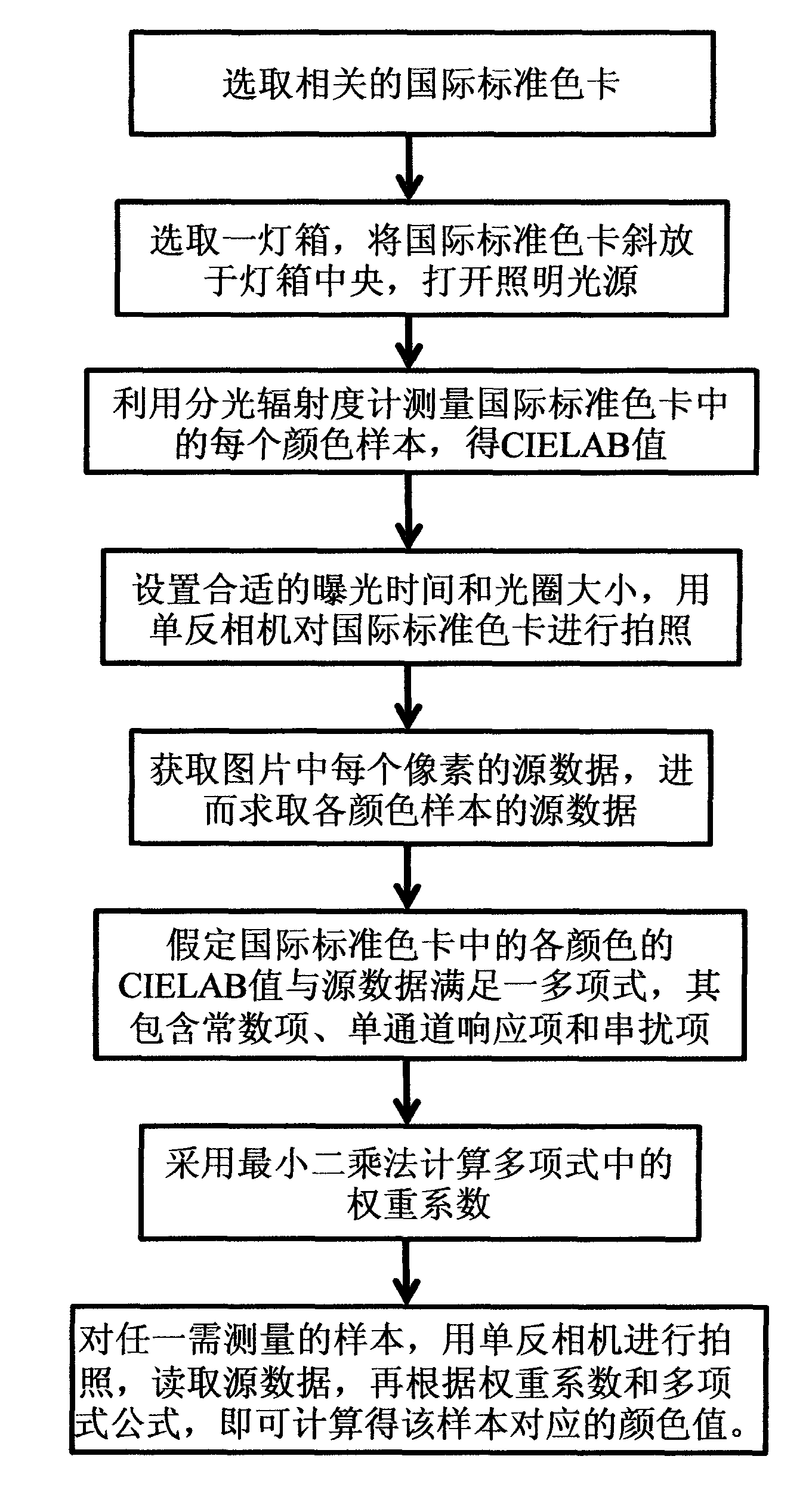
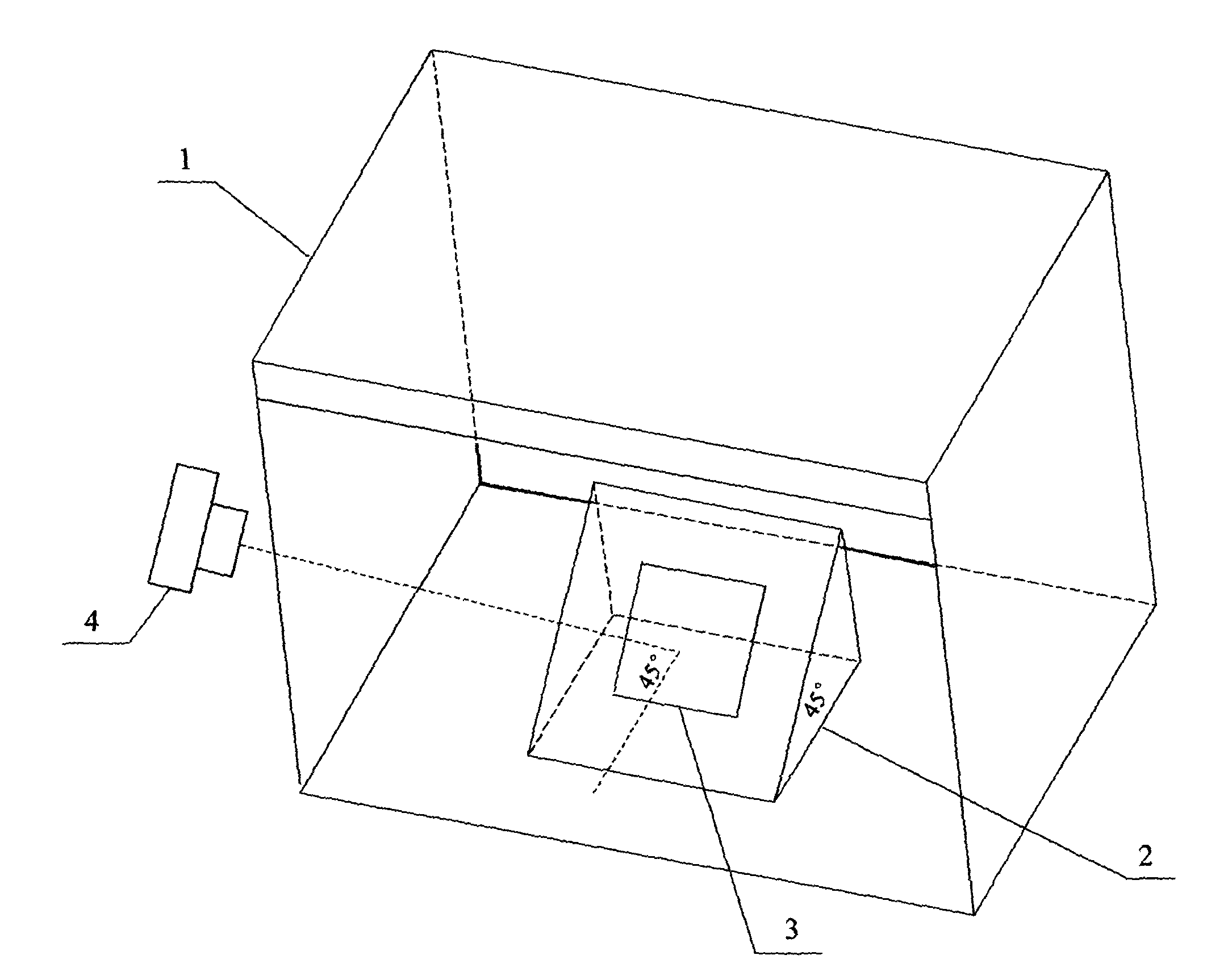
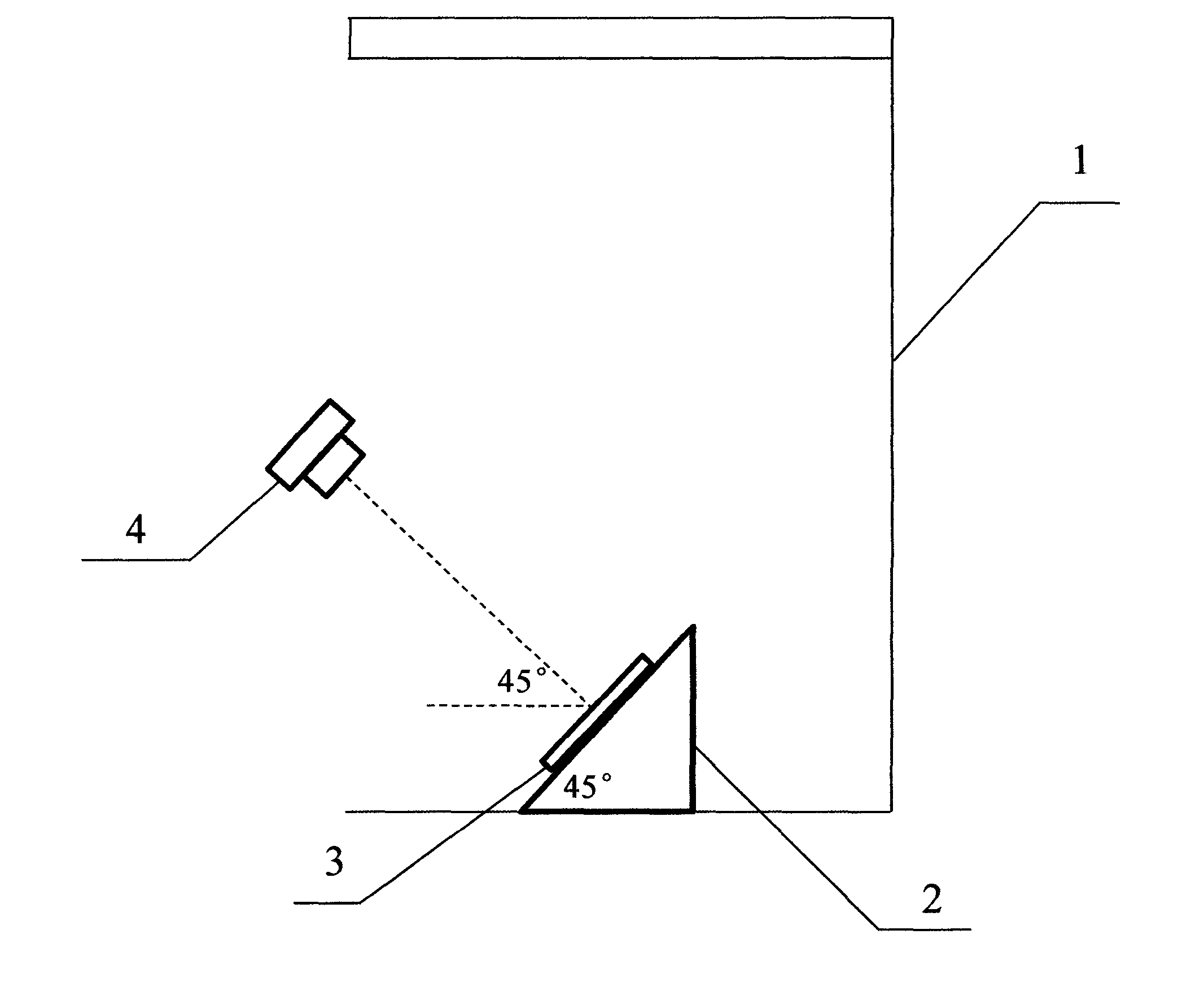
Non-contact type color measurement method and non-contact type color measurement device based on digital technology
InactiveCN103063310AHigh precisionHigh utility valueColor measuring using colour chartsMeasurement deviceInternational standard
The invention discloses a non-contact type color measurement method and a non-contact type measurement device based on a digital technology. The non-contact type color measurement method comprises the following steps of: respectively measuring and shooting selected international standard color cards through a spectroradiometer and a digital single lens reflex camera to obtain a CIELAB value and source data of each color sample; then optimizing the CIELAB value and the source data by utilizing least squares fit to obtain a weight coefficient; and calculating the color value corresponding to a measured sample according to the weight coefficient and the picture source data of any measured sample. The non-contact type color measurement method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of simple application, high accuracy, high speed, simultaneous measurement of pairwise samples and very high practical value. Besides, the invention also provides the color measurement device based on the method, and the color measurement device comprises a lamp box (1), an object placing platform (2) and a digital single lens reflex camera (4), wherein the lamp box (1) is used for illuminating the sample; the object placing platform (2) is used for placing the international standard color cards and a sample (3) which needs to be measured; and the digital single lens reflex camera (4) can read the source data.
Owner:岑夏凤
Method and apparatus for calibrating a color measurement instrument
ActiveUS9952102B1Minimize the differenceRadiation pyrometryColor/spectral properties measurementsSpectroradiometerMeasuring instrument
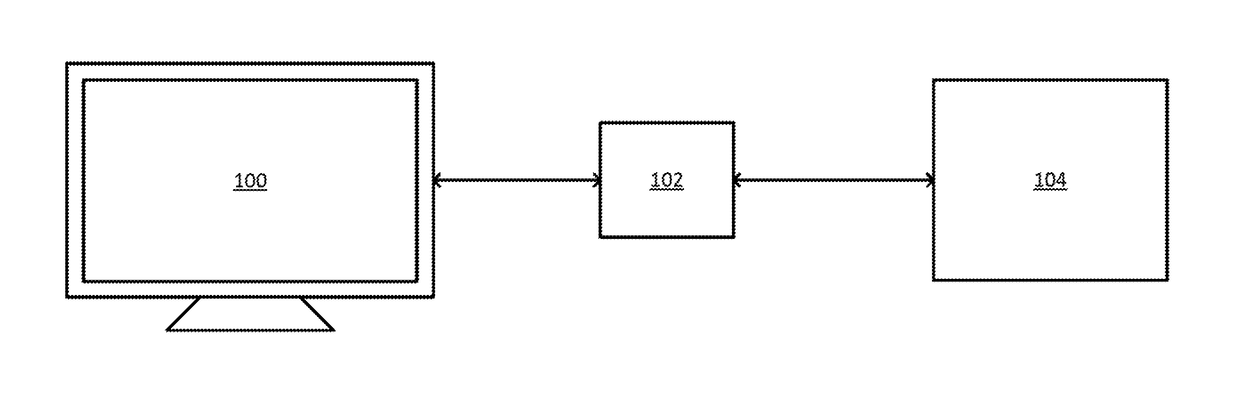
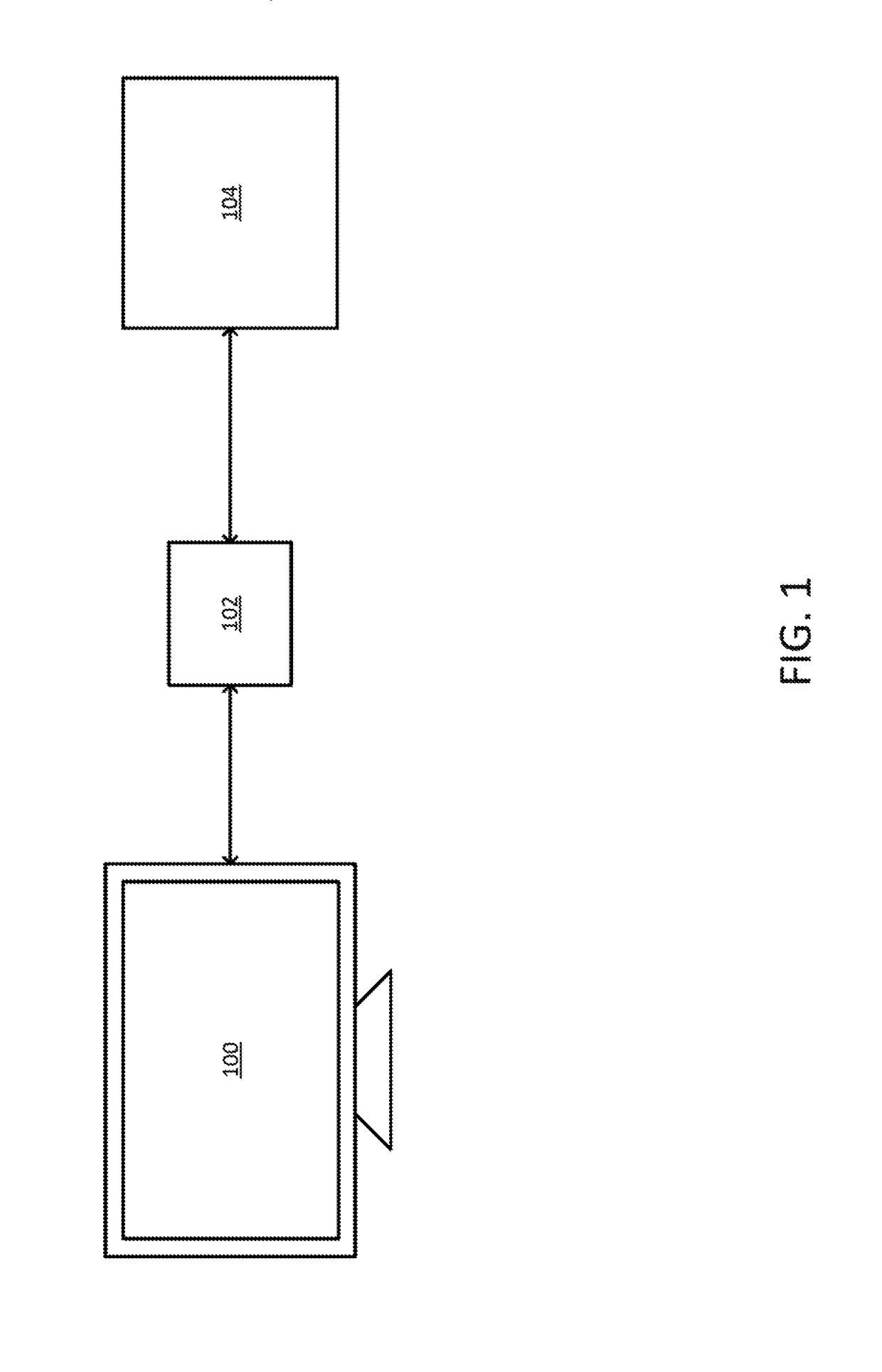
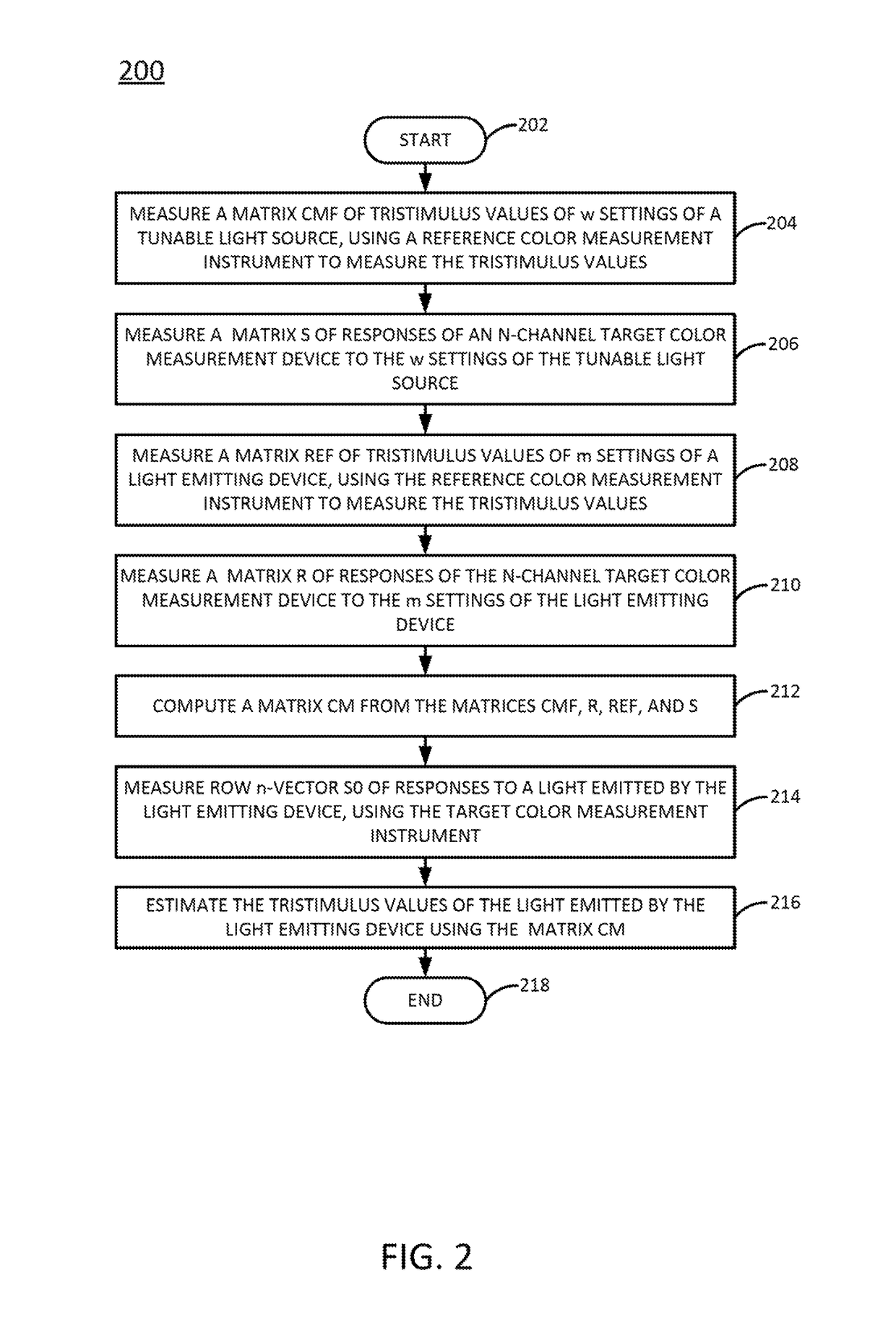
In one example, an electronic signal is received from a target color measurement instrument that includes a plurality of color channels. A response of the target color measurement instrument to a light emitted by a target light emitting device is extracted from the signal. The response is calibrated to minimize a difference between the response and an output of a color matching function of a standard observer. Calibrating includes multiplying the response by a calibration matrix. The calibration matrix combines measurements of a first plurality of lights from a tunable light source and measurements of a second plurality of lights from the target light emitting device. A first subset of the measurements of the first plurality and second plurality of lights are made by the target color measurement instrument and a second subset of the measurements of the first plurality and second plurality of lights are made by a reference spectroradiometer.
Owner:DATACOLOR
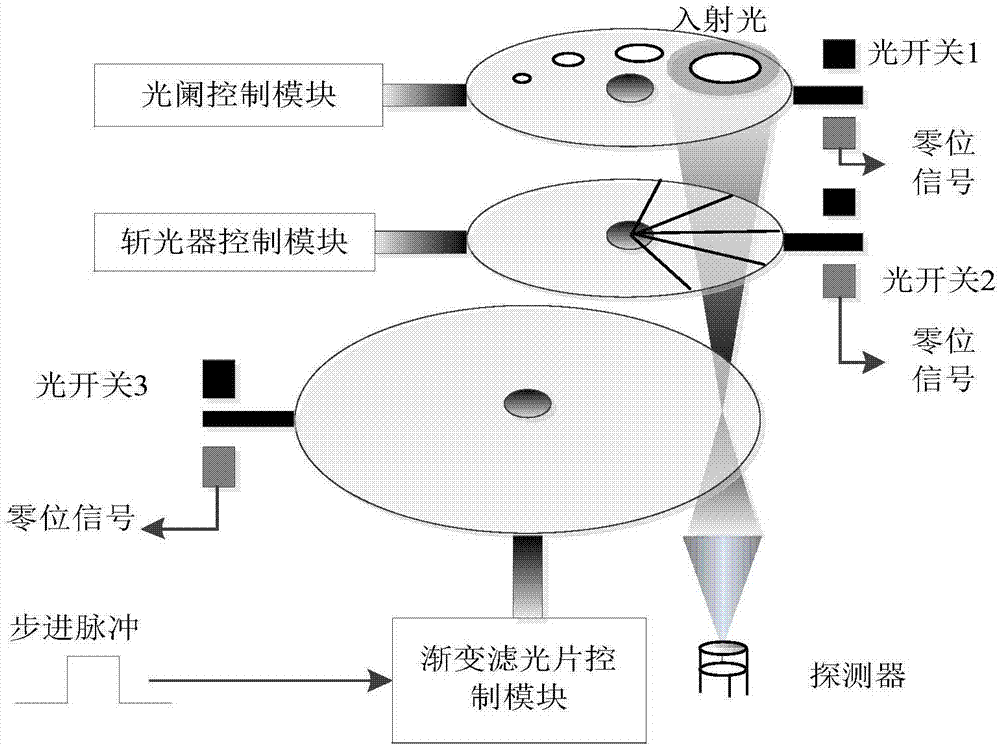
Infrared spectroradiometer based on light splitting of gradual filter
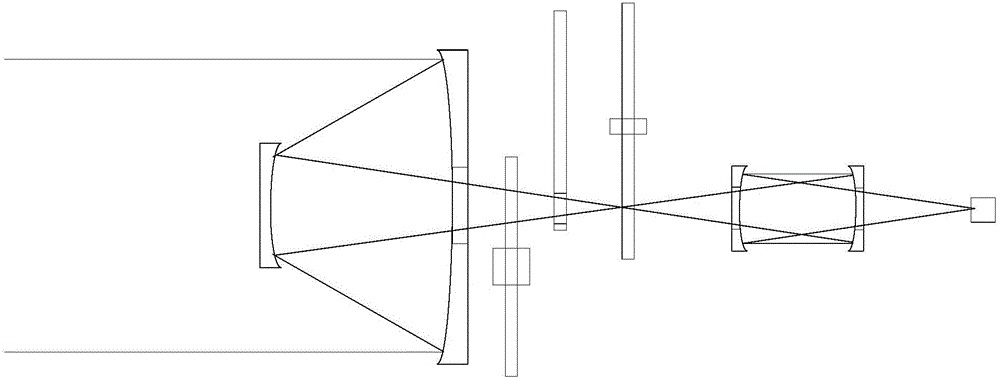
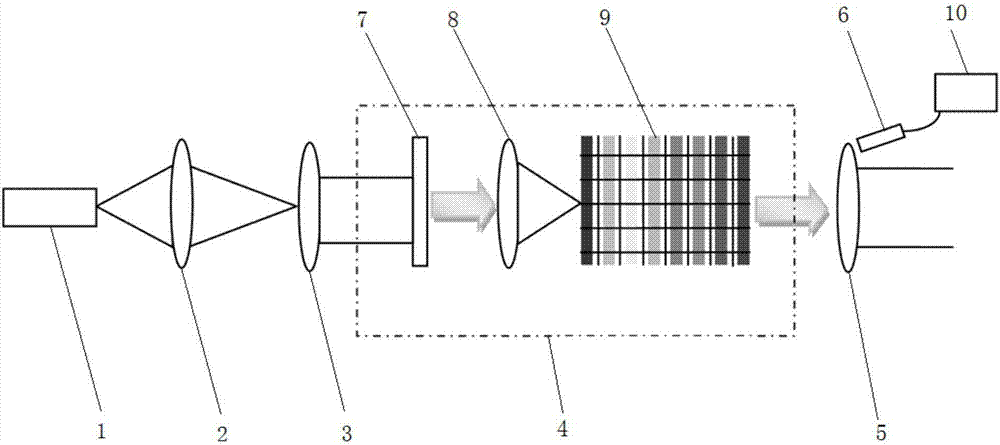
InactiveCN106052869AGuaranteed resolutionGuaranteed detection energy intensitySpectrum investigationVisual field lossSpectroradiometer
The invention discloses an infrared spectroradiometer based on light splitting of a gradual filter. A light chopper is arranged behind an incident lens. A variable diaphragm is arranged behind the light chopper. The gradual filter is arranged behind the variable diaphragm. A first focusing lens group is arranged between the variable diaphragm and the gradual filter. An infrared detector is arranged behind the gradual filter. A second focusing lens group is arranged between the gradual filter and the infrared detector. Light form the incident lens forms a first focusing point by the light chopper, the variable diaphragm is arranged at the first focusing point, the light passes through the variable diaphragm and forms a second focusing point through the first focusing lens group, the gradual filter is arranged at the second focusing point, the light passes through the gradual filter and forms a third focusing point through the second focusing lens group, the infrared detector is arranged at the third focusing point, and the first focusing point, the second focusing point and the third focusing point are arranged on the same axis. According to the invention, the visual field control effect of the variable diaphragm is ensured, the assembling and adjusting difficulty is lowered, and the focusing effect is improved.
Owner:THE 41ST INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GRP
Color inspection system
InactiveUS7684041B2High-precision detectionDifficult to conductRadiation pyrometryPhotoelectric discharge tubesSpectroradiometerRadiometer
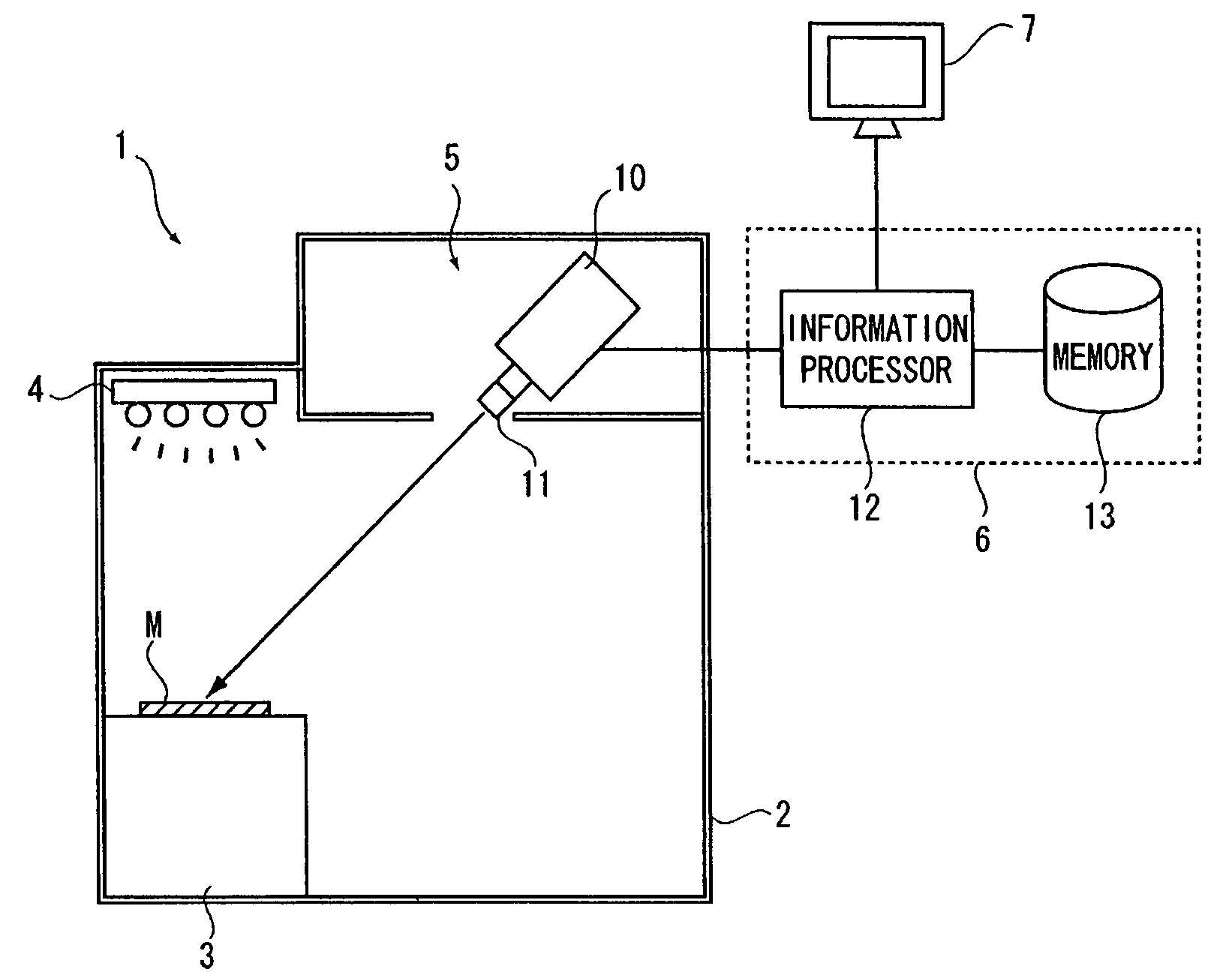
A color inspection system capable of making a determination on pass or failure with accuracy equivalent to that for the case of a visual inspection even in the case of inspecting various textile products as measurement targets, such as raised cloth, cloth with printed patterns such as a marbled pattern, moire pattern and detailed pattern is provided. With the color inspection system, an illuminant is set to shine a light on the surface of a textile product placed on the top surface of a measuring platform to thereby make measurements from a direction at an angle of 45 degrees from the surface of a measuring region of the textile product by use of a spectroradiometer of a measuring unit. The spectroradiometer is provided with a wide range lens attached thereto to thereby expand a measuring region. The results of measurement by the spectroradiometer are inputted to an information processor of a determination unit. The information processor computes color values for the whole measuring region to be compared with standard color values stored in a memory to thereby make a determination on pass or fail.
Owner:SEIREN CO LTD
Detection and identification method for solenopsis invicta buren nest based on computer vision technology
InactiveCN107945162ASimple structureEasy to installImage enhancementImage analysisSource Data VerificationData treatment
The present invention relates to a detection and identification method for a solenopsis invicta buren nest based on a computer vision technology, belonging to the technical field of agricultural transport machine. The method comprises the steps of: employing a spectroradiometer to collect spectrum image information, and converting collected spectrum image data from an asd file to a txt file; performing data processing of the spectrum image information, wherein the data processing comprises data obtaining, data processing, data analysis and data verification; and extracting feature parameters of the solenopsis invicta buren nest by employing a digital image processing technology, establishing an HSV color space model, and determining whether soil in the solenopsis invicta buren nest is solenopsis invicta buren nest soil or not. Based on a high spectrum and an image technology, the detection and identification method for the solenopsis invicta buren nest based on the computer vision technology can perform detection of the ant nest soil and can find out spectral features, being different from other things around, of the solenopsis invicta buren nest, and finally can identify the solenopsis invicta buren nest soil based on images of the solenopsis invicta buren nest soil.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
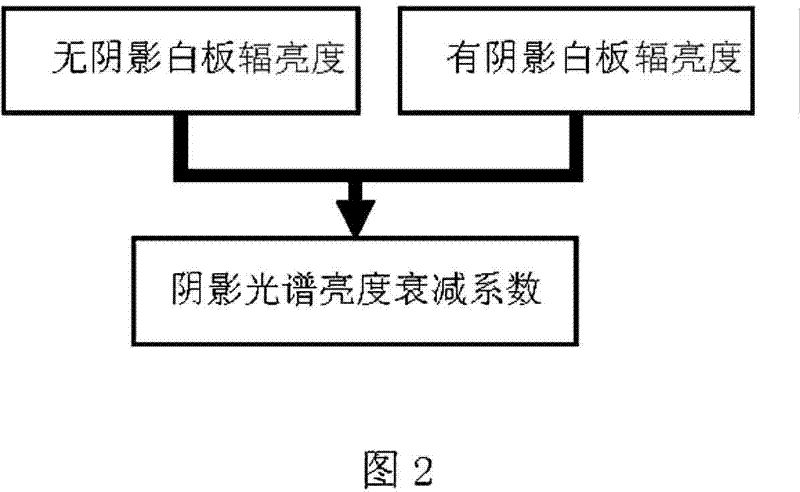
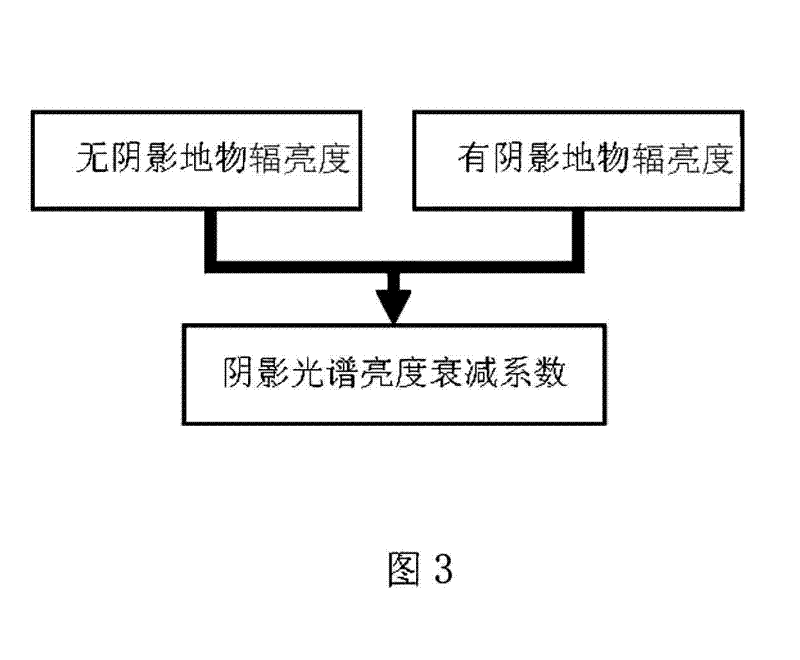
Shadow spectrum simulating method
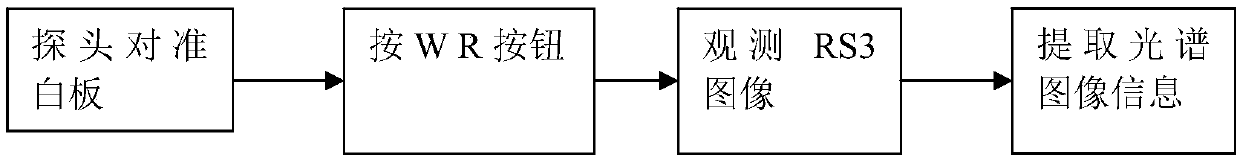
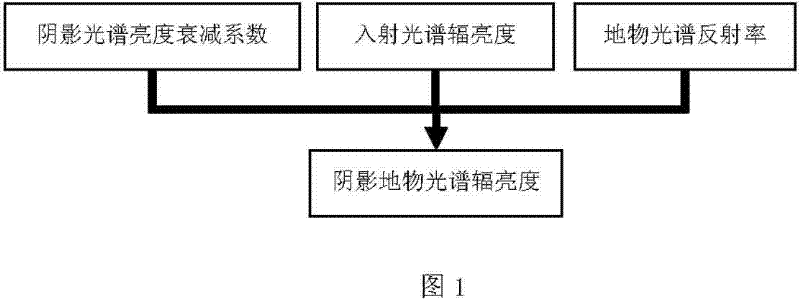
InactiveCN102590801AEliminate the effects ofEliminate existing band differences and restore them correctlyWave based measurement systemsWhiteboardAttenuation coefficient
The invention relates to a shadow spectrum simulating method, comprising the following steps of: real-timely measuring radiance of a white board or a ground object in a non-shadowy condition and radiance of the white board or the ground object in a shadowy condition by using a field ground-object spectroradiometer, calculating a shadow spectral brightness attenuation coefficient, combining the known incident spectrum brightness with the ground-object spectrum reflectivity without shadow, and obtaining a simulated shadow ground-object spectrum according to the calculated shadow spectral brightness attenuation coefficient. According to the shadow spectrum simulating method disclosed by the invention, the shadow in a deep spectrum angle is researched, the band difference resulting from the influence of the shadow intensity and the ground-object spectrum on the shadow ground-object spectrum is found out, and the shadow intensities of different bands are quantitatively represented; the ground-object spectrum in the shadow condition is precisely reduced and simulated; a target in the shadow is effectively explored and the influence of the shadow is eliminated; the shadow spectrum simulating method is very important for simulation of hyperspectral images, detection and elimination of shadows, exploration and identification of targets and is applicable to hyperspectral simulation, target characteristic research, shadow elimination, shadow detection and remote sensing image processing.
Owner:中国人民解放军61517部队
Measuring method for colorimetric parameters of LED display screen
The invention relates to a measuring method for colorimetric parameters of an LED display screen. According to the luminescent characteristics of the LED display screen, the method creates and stipulates the measuring steps of color domain coverage ratio, non-uniformity of white field chromaticity and color reproduction of the LED display screen and a calculating method, provides a method for improving the accuracy of measuring and debugging the value and the range of the white field chromaticity and improving the accuracy of measuring primary wavelength of base color, and carries out necessary discrimination to peak wavelength of an LED tube and primary wavelength of an LED screen from scientific concept. A 1980 color luminance meter which conforms to spetral tristimulus values and contains four groups of filter plates is adopted to measure the colorimetric parameters of the LED display screen accurately; by adopting the method, the accuracy of measurement can meet the technical requirements to the standard color luminance meter. A 1980 spectroradiometer with spectral bandwidth and the sampling interval of 1nm can accurately measure the peak wavelength of the LED tube. In the debugging process, a multiturn potentiometer is adopted to achieve the purpose of finely selecting the resistance value of a resistor. The core technology is the necessary premise and key of debugging and manufacturing the LED display screen with excellent color reproduction.
Owner:天津光杰光电有限公司
Light source with spectral distribution and brightness capable of being freely tuned and light source tuning method
InactiveCN107238005ASimplified spectrumSimplify adjustabilityElectric circuit arrangementsElectric lightingSpectroradiometerEffect light
The invention belongs to the field of optical lighting and particularly relates to a light source with spectral distribution and brightness capable of being freely tuned and a light source tuning method. The light source comprises a compound color line light source, a collimating lens, a tuning system, a homogenization system and a monitoring and controlling system which are sequentially distributed in the optical path direction; the tuning system comprises a light splitting element and a digital micro-mirror element which are sequentially distributed in the optical path direction; the homogenization system is composed of a scatter or a non-imaging optical system; the monitoring and controlling system comprises a spectroradiometer and a control computer connected with the spectroradiometer; and the control computer is connected with the digital micro-mirror element. According to the light source with spectral distribution and brightness capable of being freely tuned, by controlling the opening and closing state of sub-mirrors of the digital micro-mirror element, the spectral distribution and the brightness can be freely adjusted, operation is easy and efficient, and the light source with spectral distribution and brightness capable of being freely tuned has wide application prospects in the fields of space, oceans, environment, industrial vision and the like, and in the aspects of laboratory magnitude simulation, color calibration, camera radiation calibration, spectrograph spectral calibration and the like.
Owner:XI'AN INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
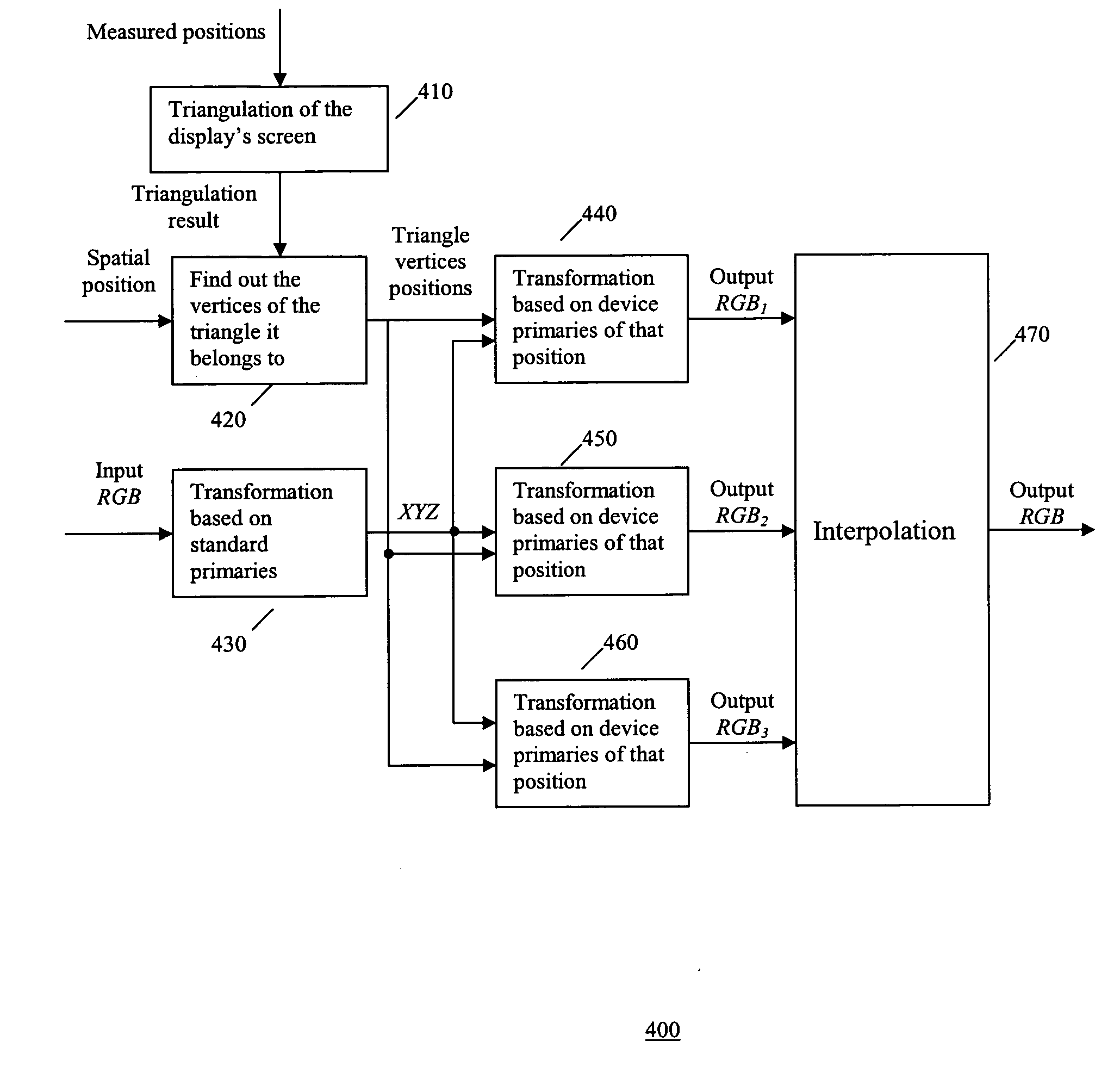
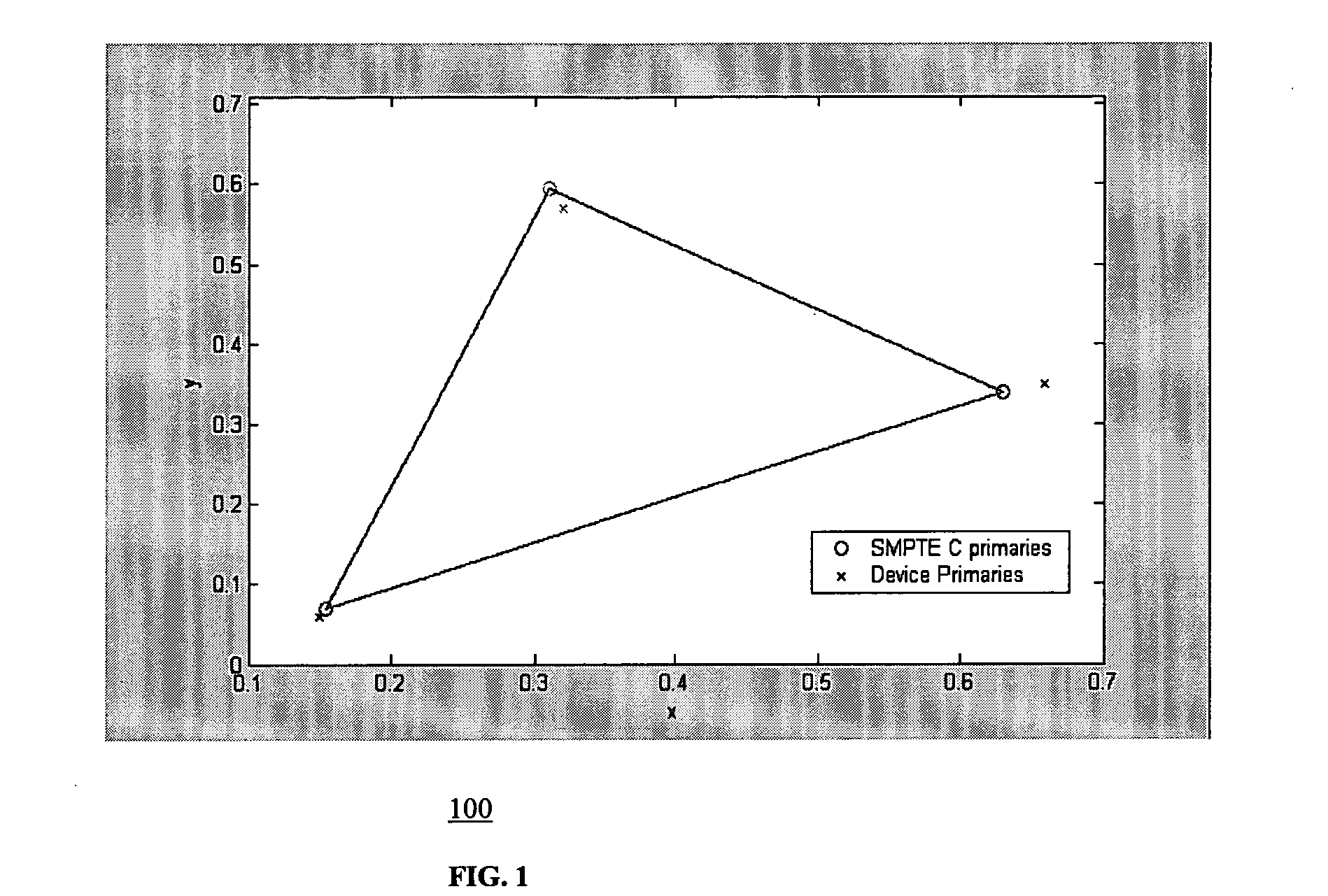
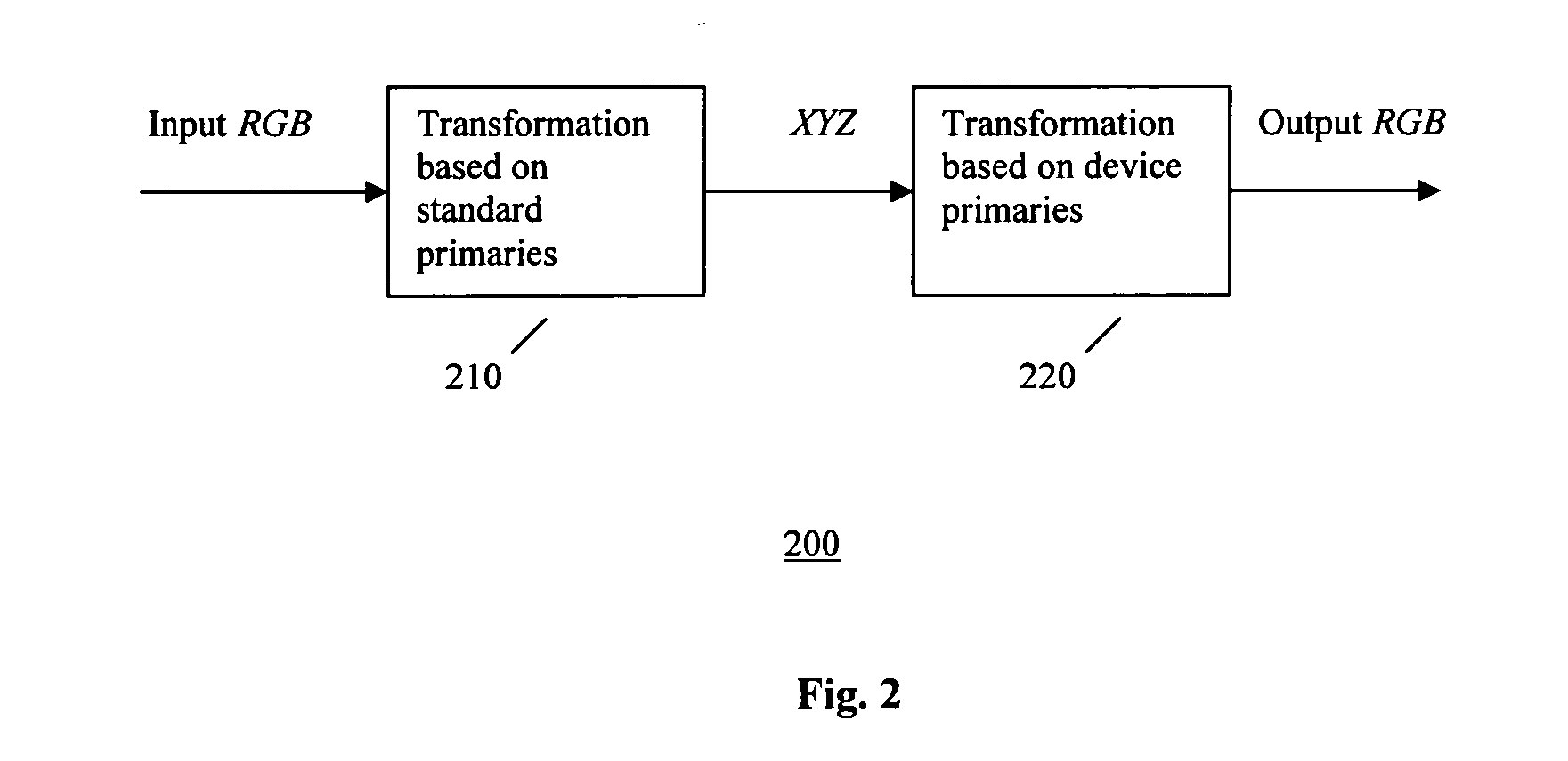
Method and system for display color correction
InactiveUS20060256129A1High color accuracyUniform colorColor signal processing circuitsCathode-ray tube indicatorsSpectroradiometerDisplay device
A method is presented for realizing standard colors on a display that does not have the standard primaries. The method enables a display with non-standard primaries to show colors as it has standard SMPTE-C primaries. Further, a method is presented to show the same standard colors on different locations of the display. Measurements of the physical parameters of the display's color primaries are obtained and implemented as calibrated display or a display which can be calibrated by user / calibrator with a color measuring tool such as calorimeter or spectroradiometer.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
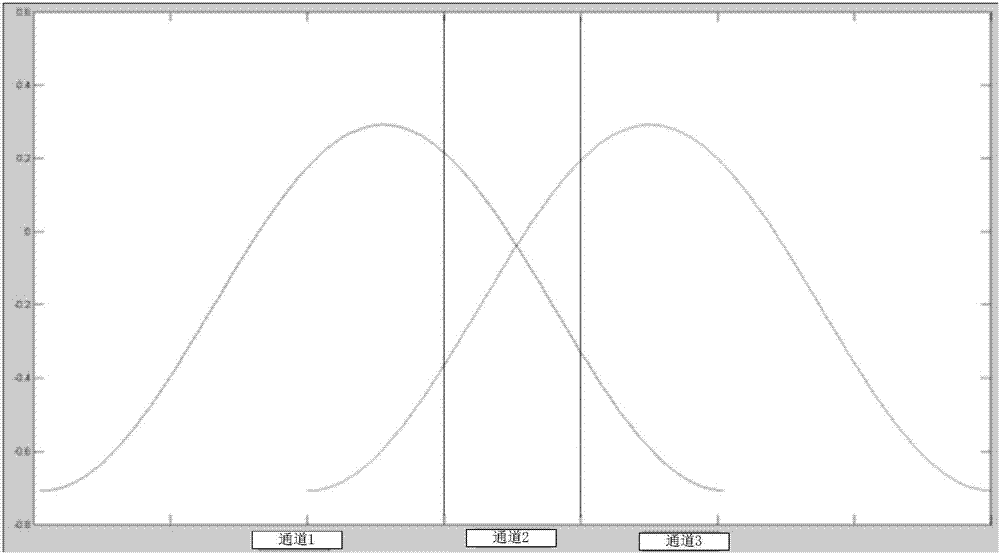
Infrared spectroradiometer spectral resolution enhancement method and infrared spectroradiometer
ActiveCN107144359AHigh-resolutionHigh spectral resolutionSpectrum investigationPyrometry using radiation pressureSpectroradiometerRadiometer
The present invention relates to a broadband infrared spectroradiometer spectral resolution enhancement method based on a gradual filter and a broadband infrared spectroradiometer. The method comprises: performing spectrum sampling of incident infrared signals, obtaining each wavelength channel of a gradual filter, performing secondary sampling of the overlapping region of any two adjacent wavelength channels in each wavelength channel, constructing a middle wavelength channel according to a spectrum peak position obtained through the secondary sampling, and realizing the spectral resolution enhancement of the broadband infrared spectroradiometer. The spectral resolution enhancement method does not need updating of hardware, only needs to add finite spectrum sampling and performs proper data processing to realize the enhancement of the spectral resolution of the broadband infrared spectroradiometer based on the gradual filter, and is simple and efficient.
Owner:THE 41ST INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GRP
Method for testing effective output power of sterilized ultraviolet lamp in single-wavelength line shape
InactiveCN101603877ASimple requirementsImprove stabilityPhotometryOptical apparatus testingSpectroradiometerUltraviolet lights
The invention discloses a method for testing the effective output power of a sterilized ultraviolet lamp in a single-wavelength line shape. The method comprises the following steps: adjusting and mounting an ultraviolet lamp tube, a light shade, an ultraviolet actinograph (or an ultraviolet spectroradiometer) and an ultraviolet light intensity measuring platform in a laboratory with a temperature fluctuation range not exceeding 2 DEG C; preheating the ultraviolet lamp tube under the full-power operation of the ultraviolet lamp tube and respectively measuring ultraviolet light intensity E0 under the existence of the light shade and ultraviolet light intensity E1 under the absence of the light shade; and then, obtaining the effective output power P of the ultraviolet lamp tube according to a Gauss module equation. The invention has simple requirements for the laboratory conditions, needs simple instrument equipment, small investment, low detection cost and short time, has test results with good stability and high repeatability and can satisfy the requirements of related research departments and quality control departments for estimating the practical output power of the ultraviolet lamp tube. Enterprises for developing and producing ultraviolet sterilized equipment can also use the method to measure ultraviolet output to further simulate and optimize an ultraviolet reactor by using a hydromechanics calculating method.
Owner:SHENZHEN OCEAN POWER INDUSTRIAL CO LTD +3
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com