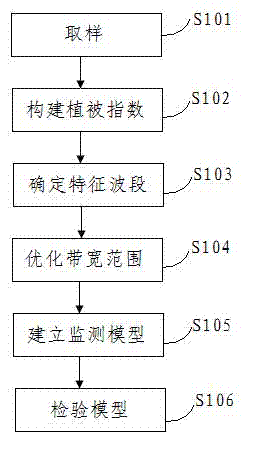
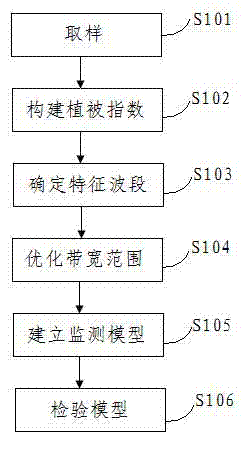
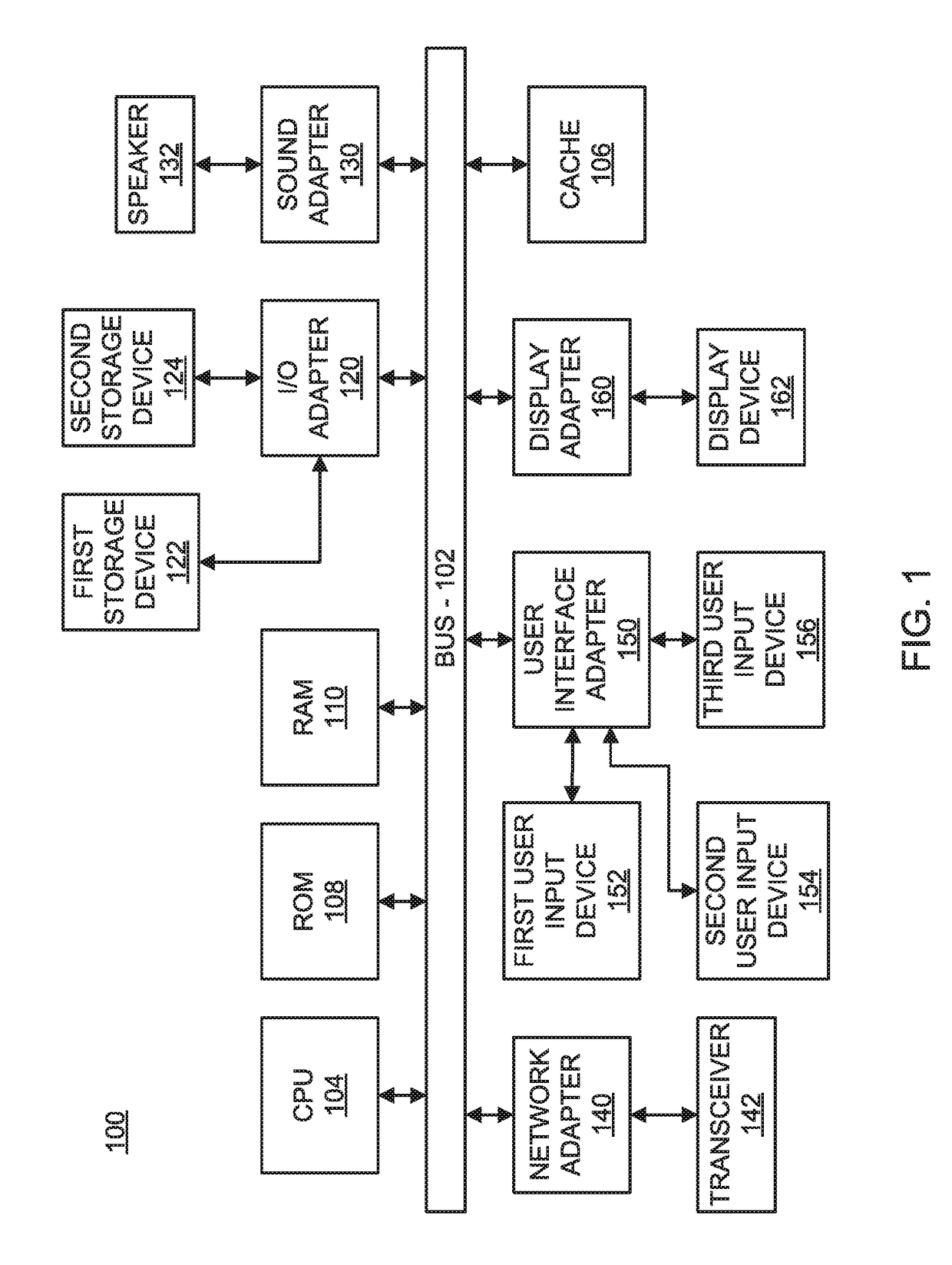
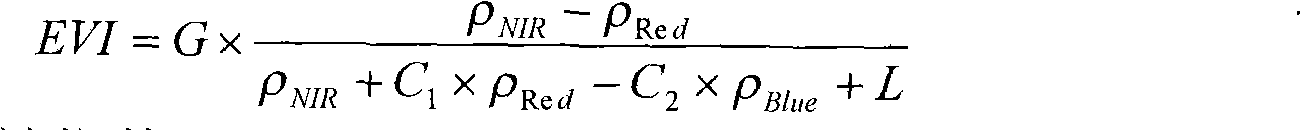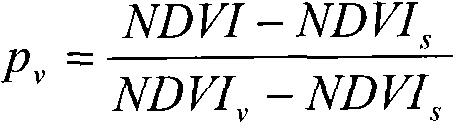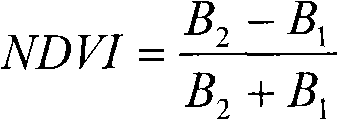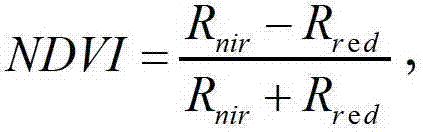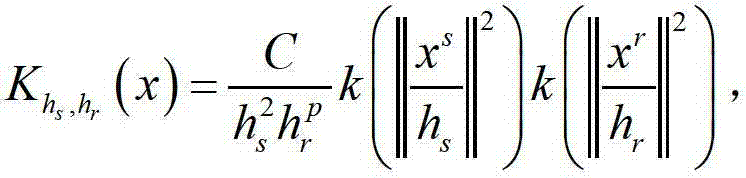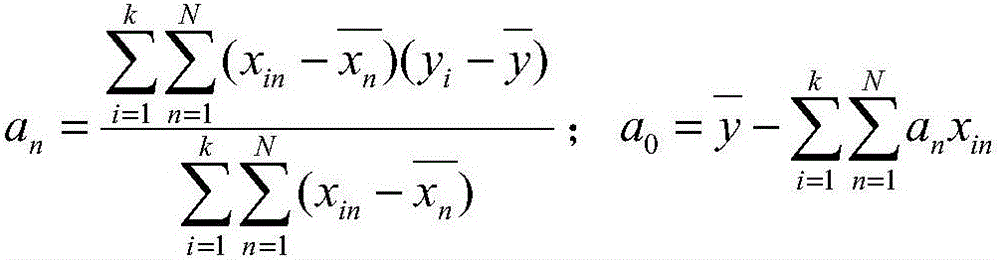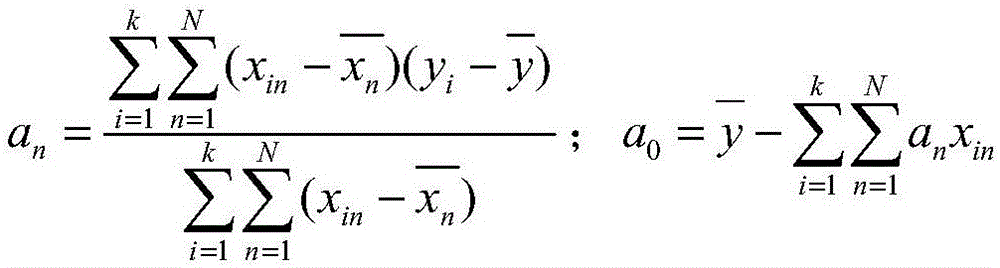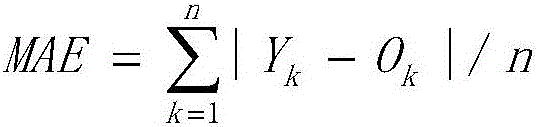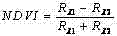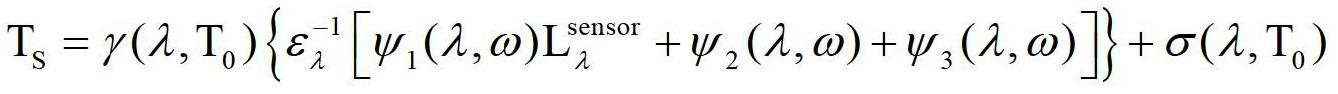Patents
Literature
904 results about "Vegetation Index" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
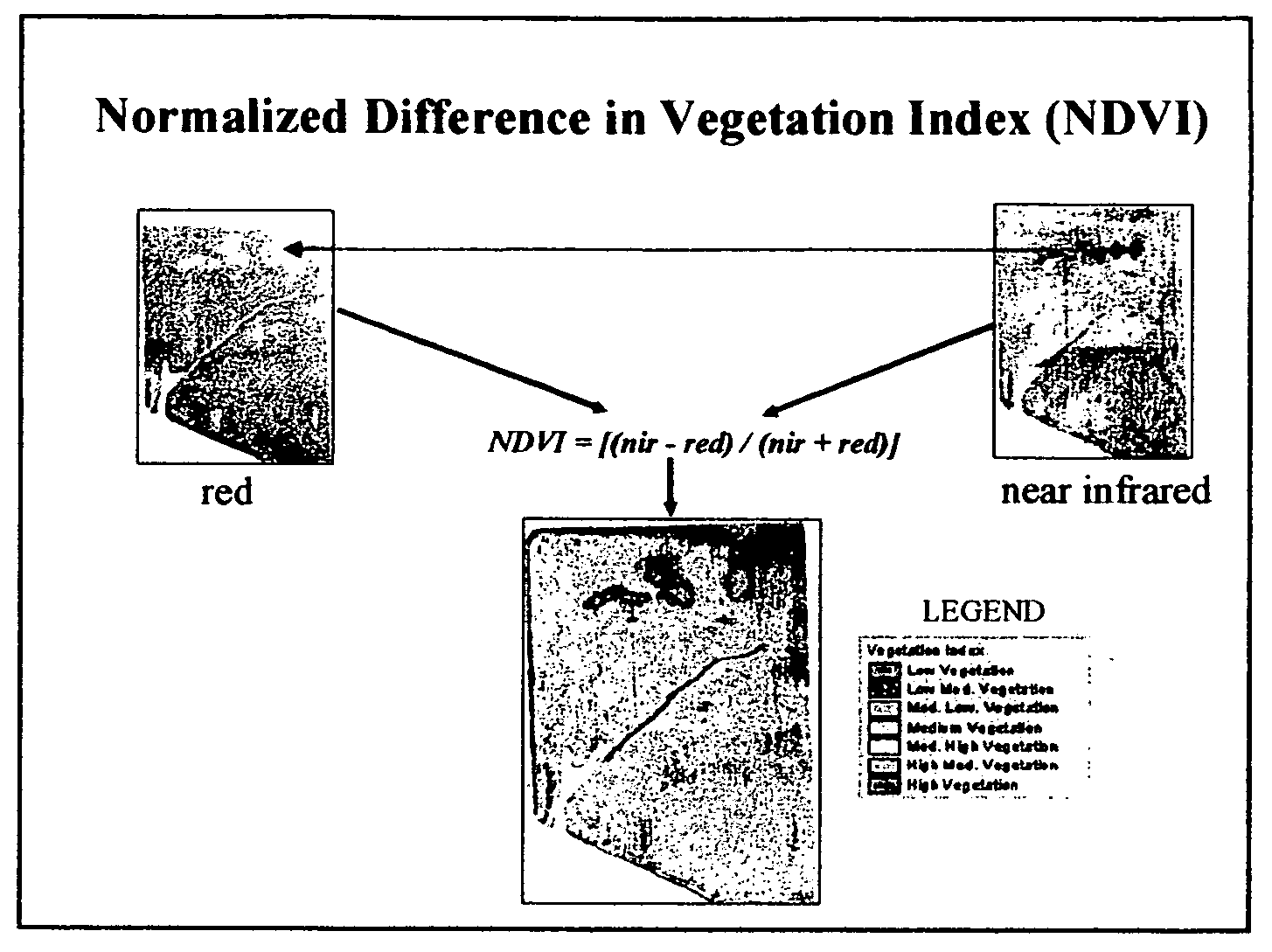
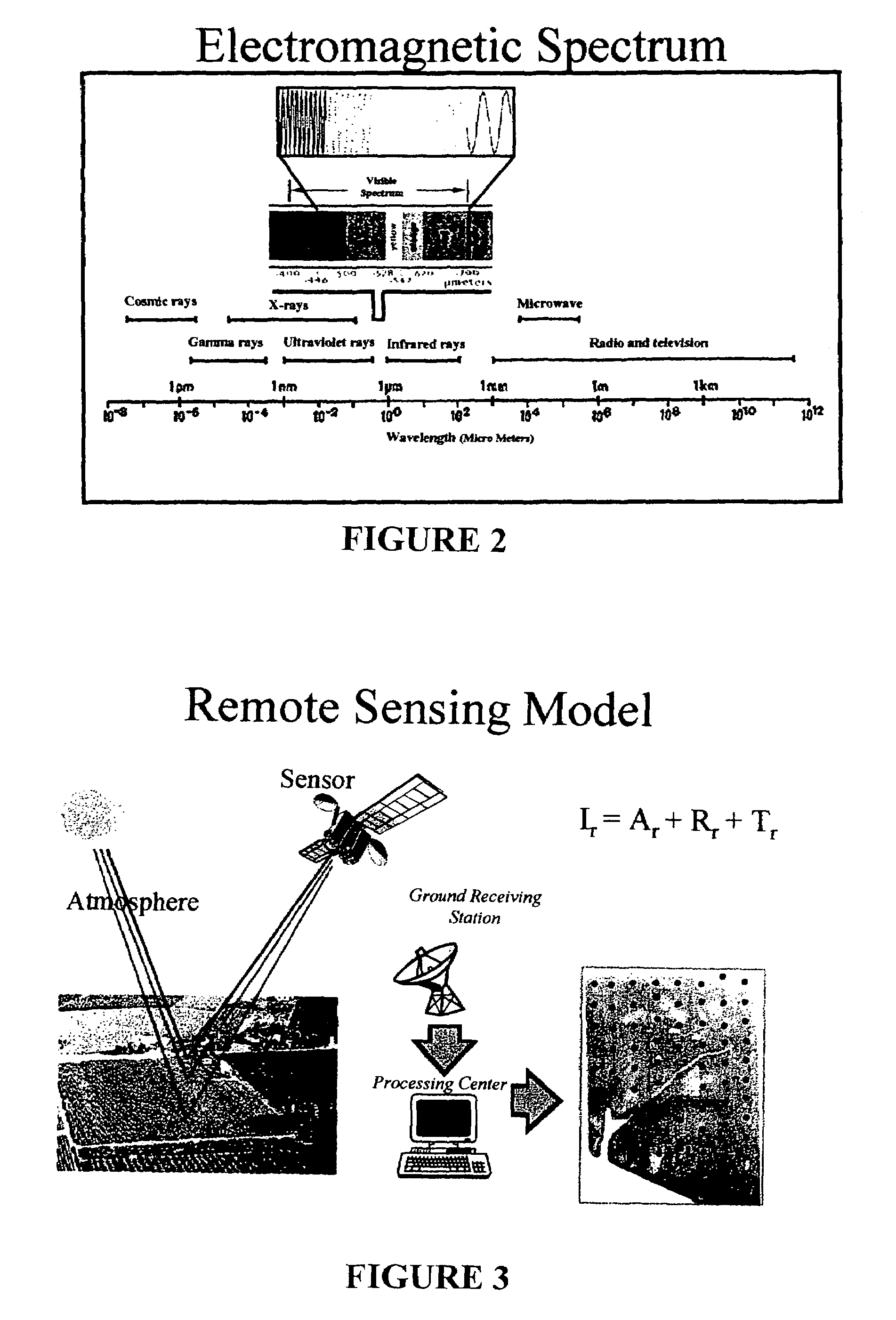
A Vegetation Index (VI) is a spectral transformation of two or more bands designed to enhance the contribution of vegetation properties and allow reliable spatial and temporal inter-comparisons of terrestrial photosynthetic activity and canopy structural variations.
Multi-variable model for identifying crop response zones in a field
InactiveUS7058197B1Increased leaf areaEliminate the effects ofImage enhancementImage analysisVegetationGrowing season
An computer implemented apparatus and method are disclosed for defining areas of a field in which a crop or other vegetation is grown based on their selective ability to grow such vegetation through a growing season, or some shorter preselected time period. The method includes making a number of temporally separated measurements through air borne imaging of a field, registering the data to the geography of the field and each other, normalizing the data including converting the data to a vegetative index indicative to the presence of vegetation in the field, comparing the data to identify clusters of like value, and classifying the clusters and images to learn how the different field areas responded in growing vegetation through the season. With this method, the field may be segregated into a number of like areas called crop response zones which exhibit similar vegetative growth characteristics as an aid to a grower in his decision making regarding how to maximize yield in his field.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
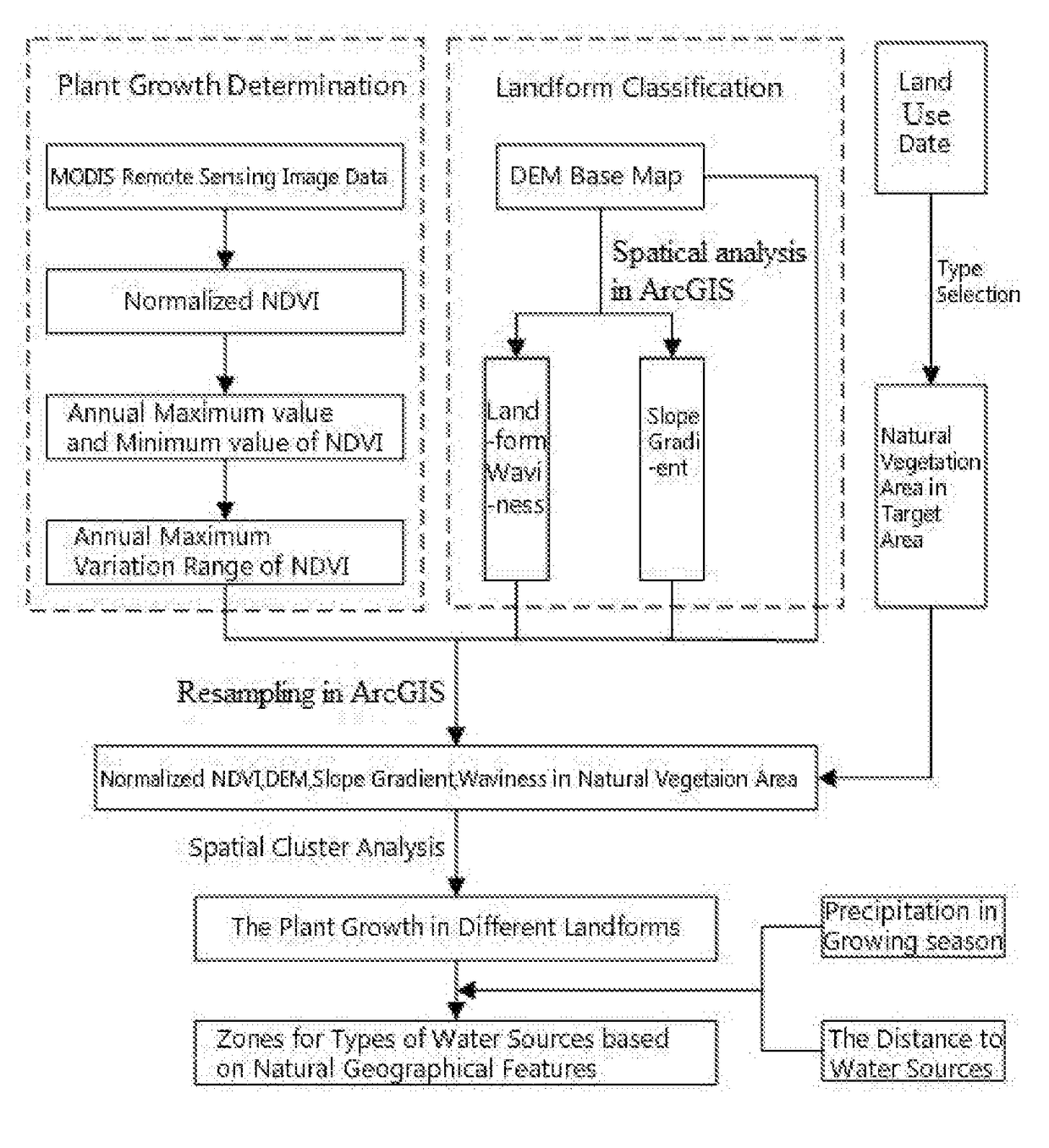
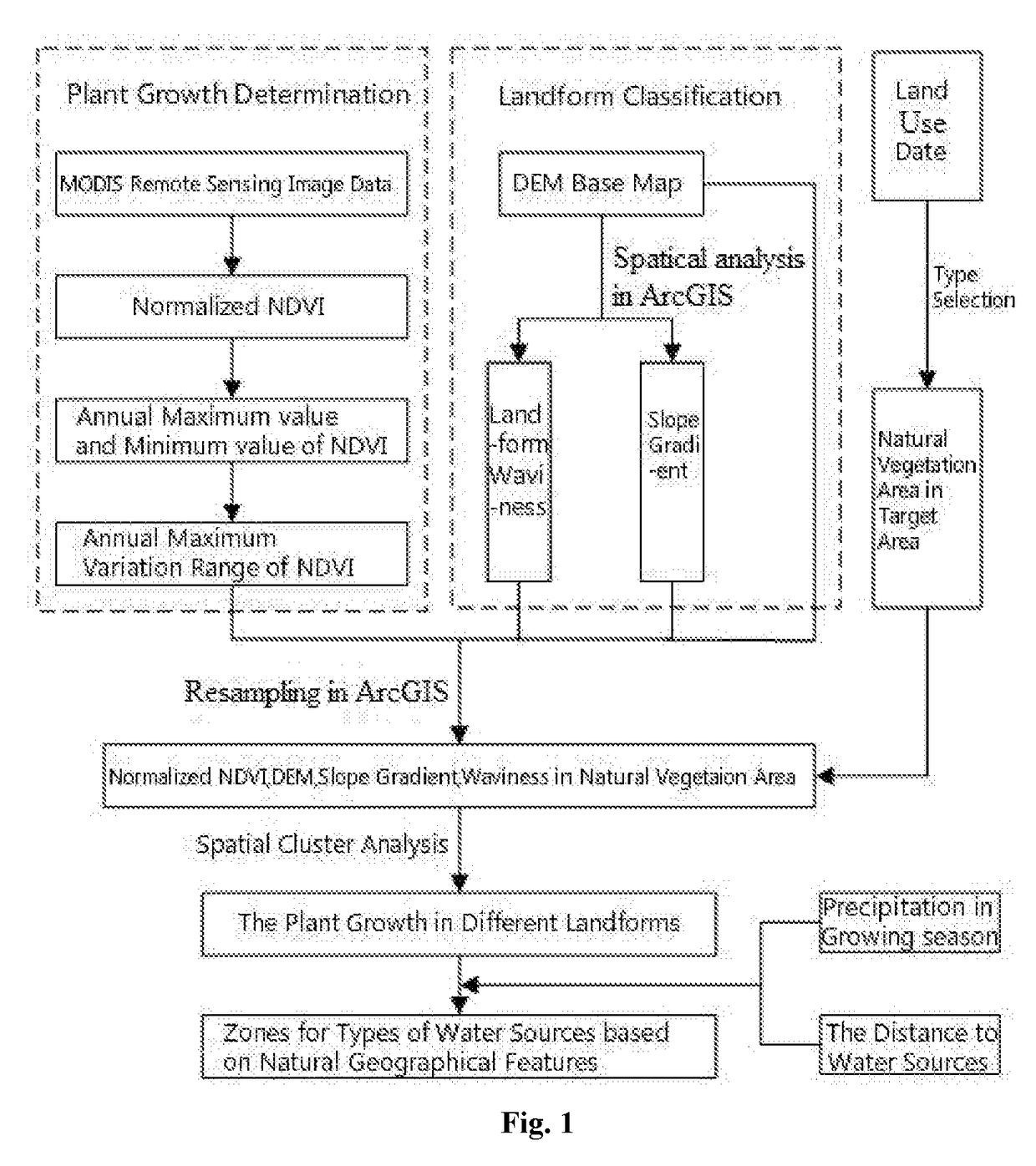
Method for analyzing the types of water sources based on natural geographical features
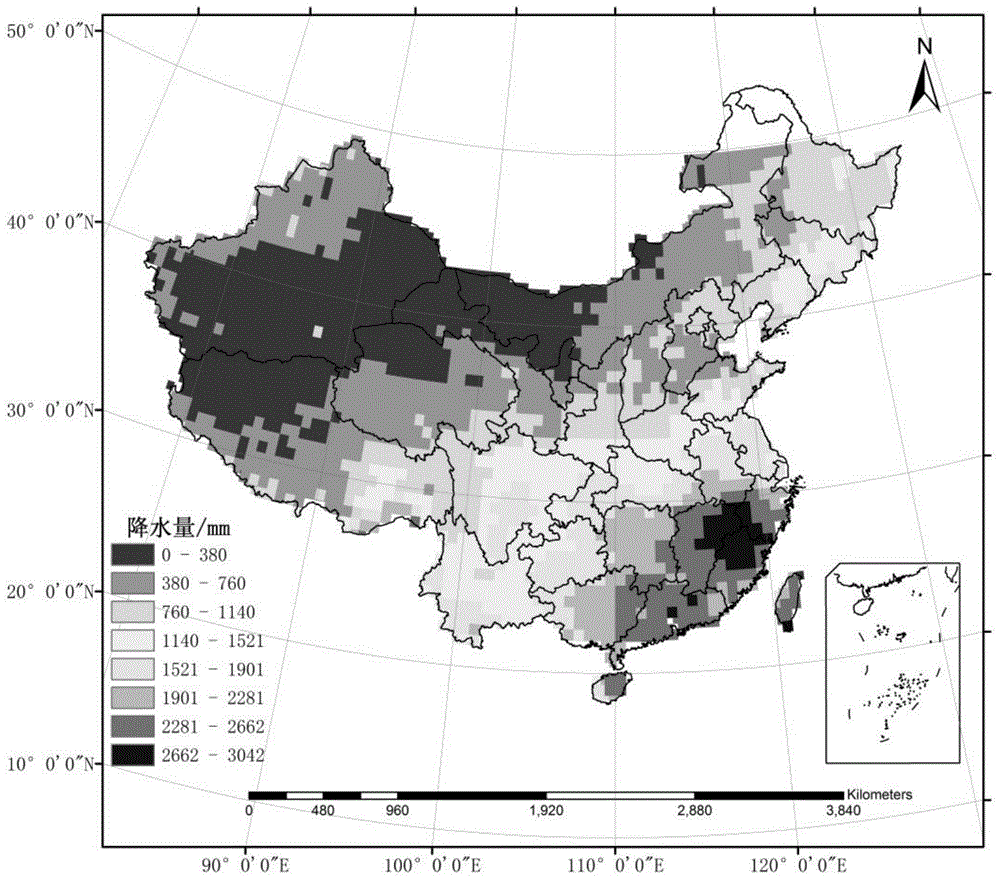
A method for analyzing types of water sources based on natural geographical feature, the method includes: collecting and processing remote sensing image data of target area, and obtaining maximum and minimum value of an annual vegetation index; subtracting the minimum value from the maximum value to obtain maximum variation range of annual vegetation index; extracting topography factors from a digital elevation model in target area; obtaining a natural vegetation area in target area; carrying out a normalization processing for the maximum variation range and the topography factors in this natural regions, and obtaining landform zones and situation of plant growth of different zones in the natural vegetation area by spatial cluster analysis in ArcGIS; obtaining a precipitation of landform zones in the growing season and the distances between the landform zones and the water sources, and obtaining the zones for the types of water sources based on natural geographical features.
Owner:CHINA INST OF WATER RESOURCES & HYDROPOWER RES
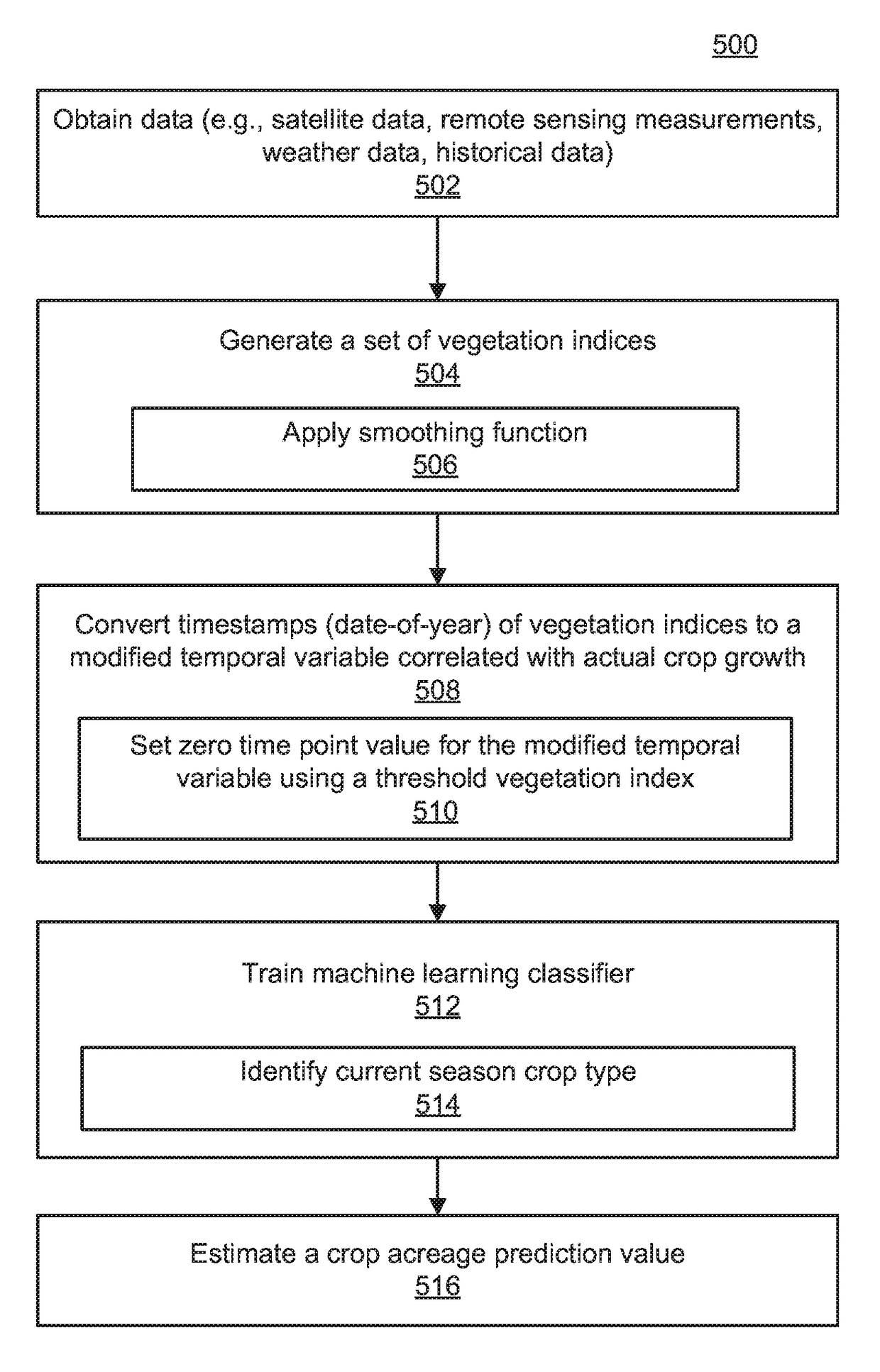
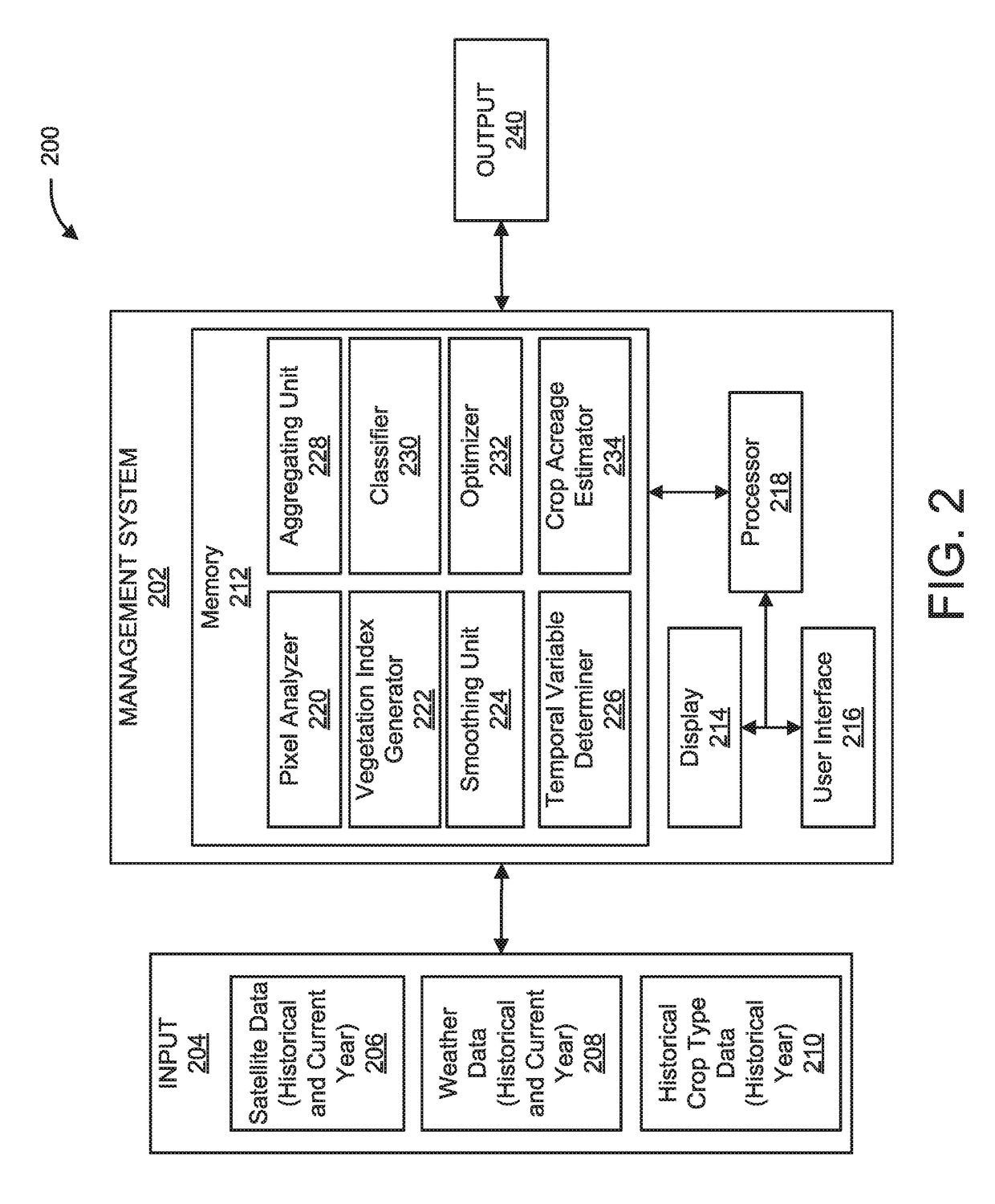
Method and system for crop type identification using satellite observation and weather data
A computer-implemented method for crop type identification using satellite observation and weather data. The method includes extracting current and historical data from pixels of satellite images of a target region, generating temporal sequences of vegetation indices, based on the weather data, converting each timestamp of the temporal sequences into a modified temporal variable correlating with actual crop growth, training a classifier using a set of historical temporal sequences of vegetation indices with respect to the modified temporal variable as training features and corresponding historically known crop types as training labels, identifying a crop type for each pixel location within the satellite images using the trained classifier and the historical temporal sequences of vegetation indices with respect to the modified temporal variable for a current crop season, and estimating a crop acreage value by aggregating identified pixels associated with the crop type.
Owner:IBM CORP
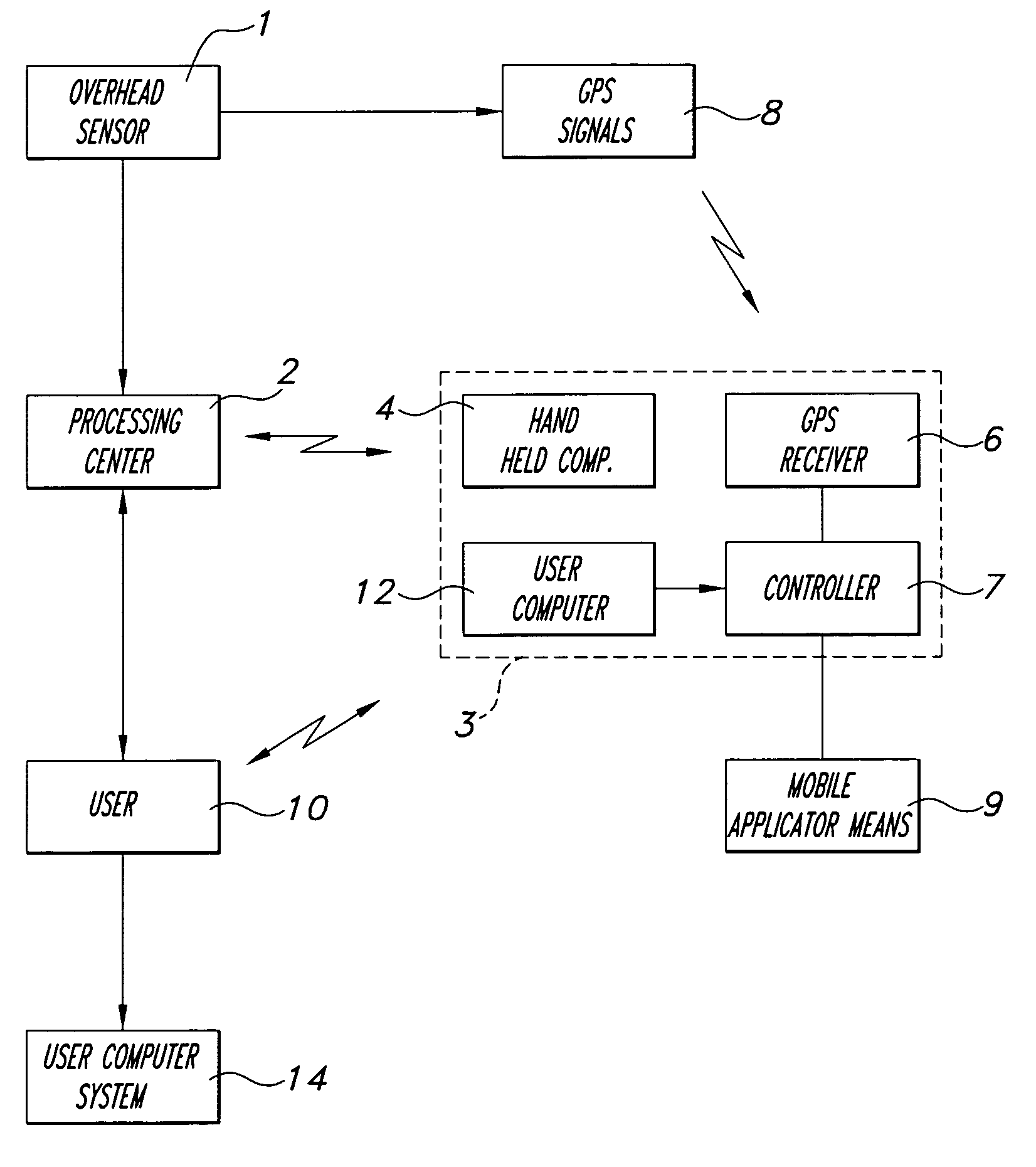
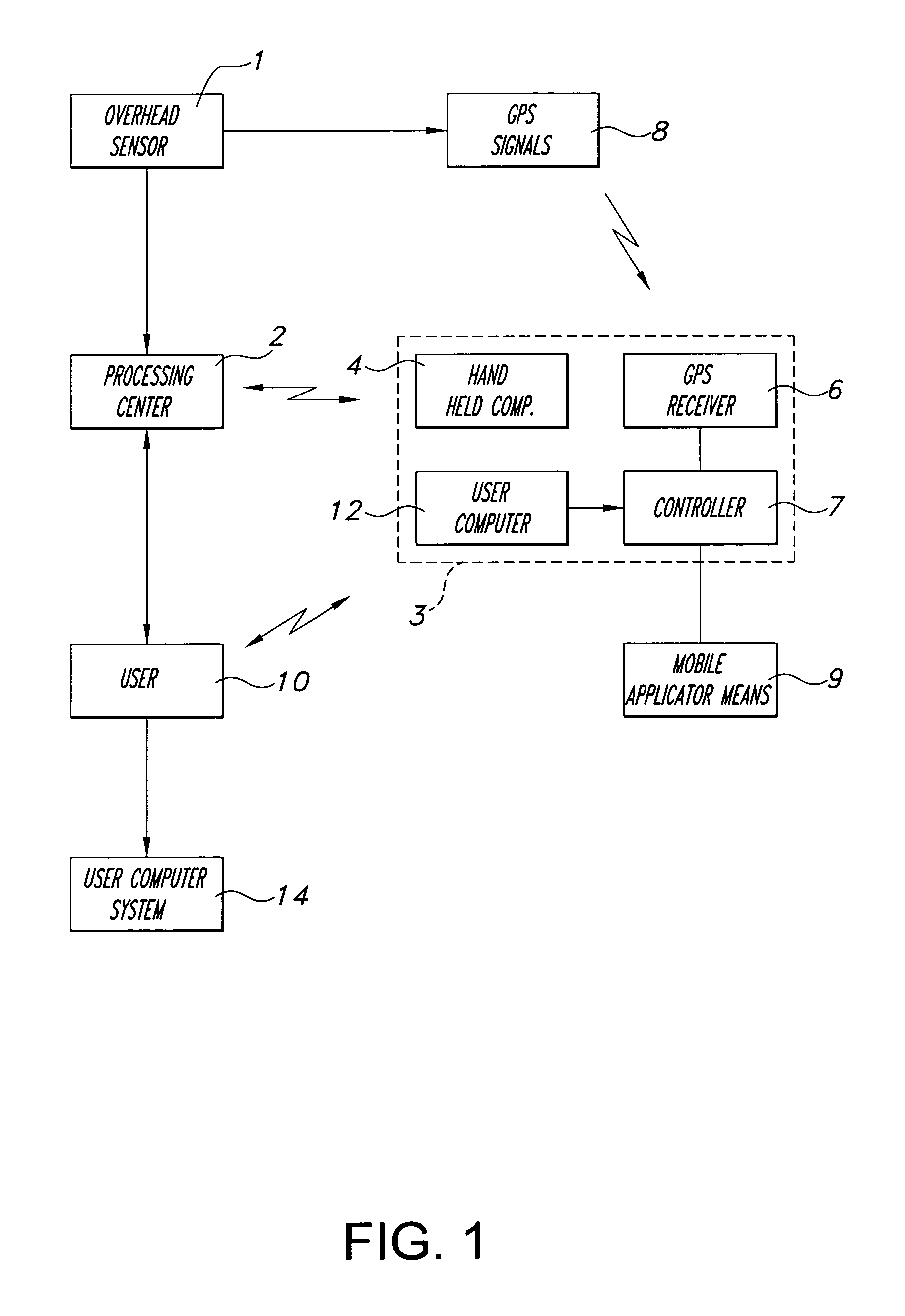
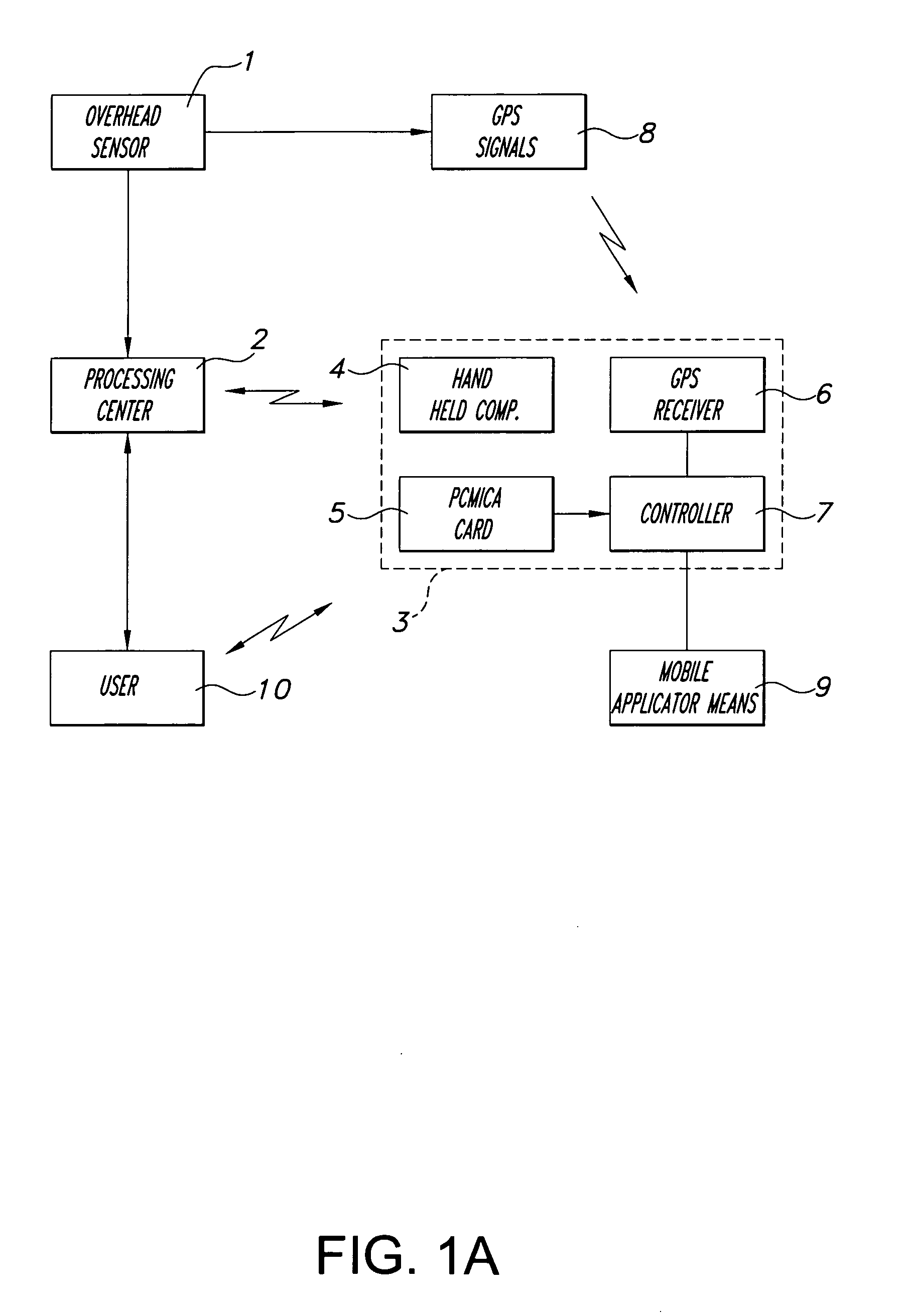
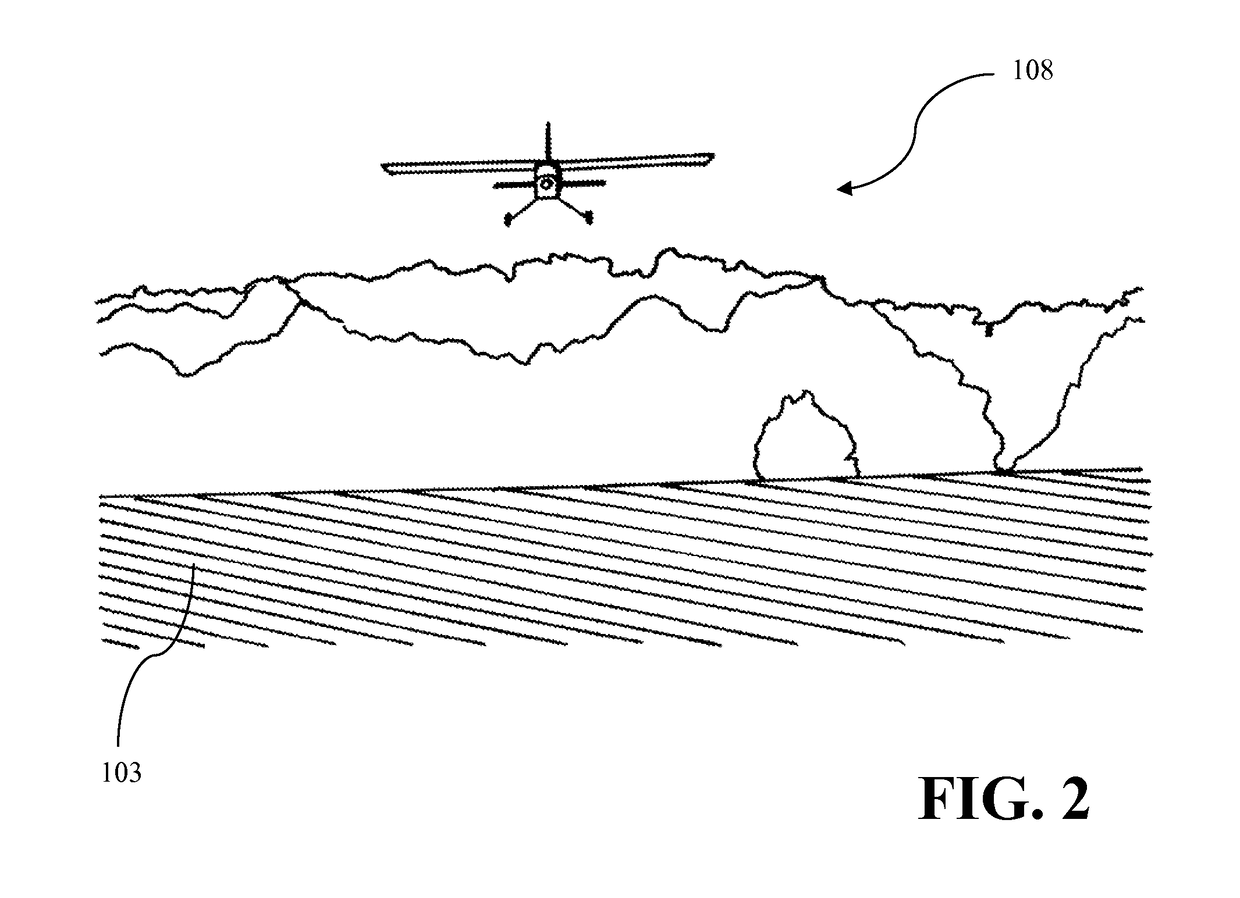
[method and system for spatially variable rate application of agricultural chemicals based on remotely sensed vegetation data]
InactiveUS20050149235A1Made preciselyCharacter and pattern recognitionRatio controlVariable Rate ApplicationVegetation
Remotely sensed spectral image data are used to develop a Vegetation Index file which represents spatial variations of actual crop vigor throughout an area that is under cultivation. The latter information is processed to place it in a format that can be used by personnel to correlate and calibrate it with actually observed crop conditions existing at control points within the area. Based on the results, personnel formulate a prescription request, which is forwarded to a central processing site, where the prescription is prepared. The latter is returned to a mobile application means that directly applies inputs to the field at a spatially variable rate.
Owner:INTIME
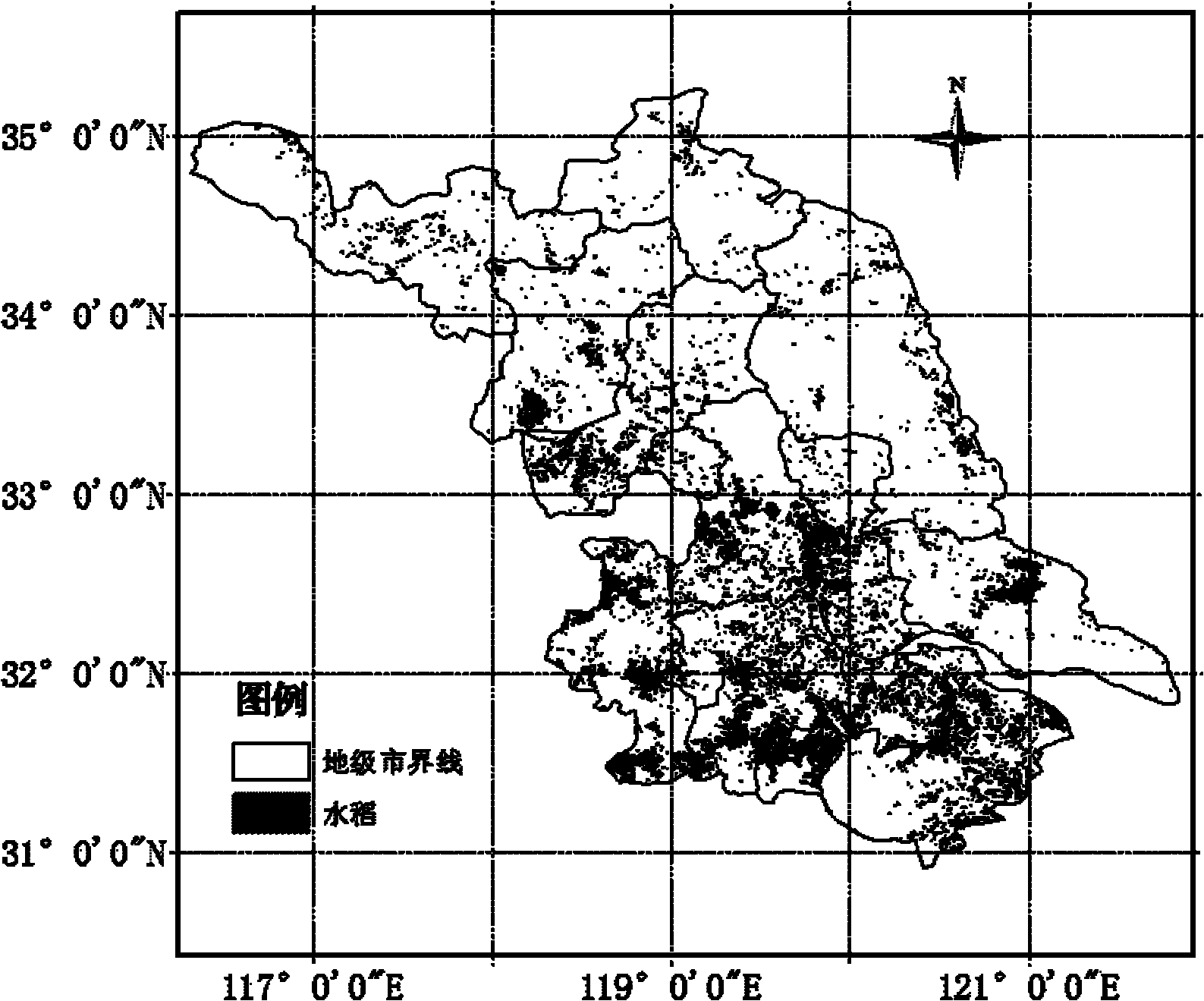
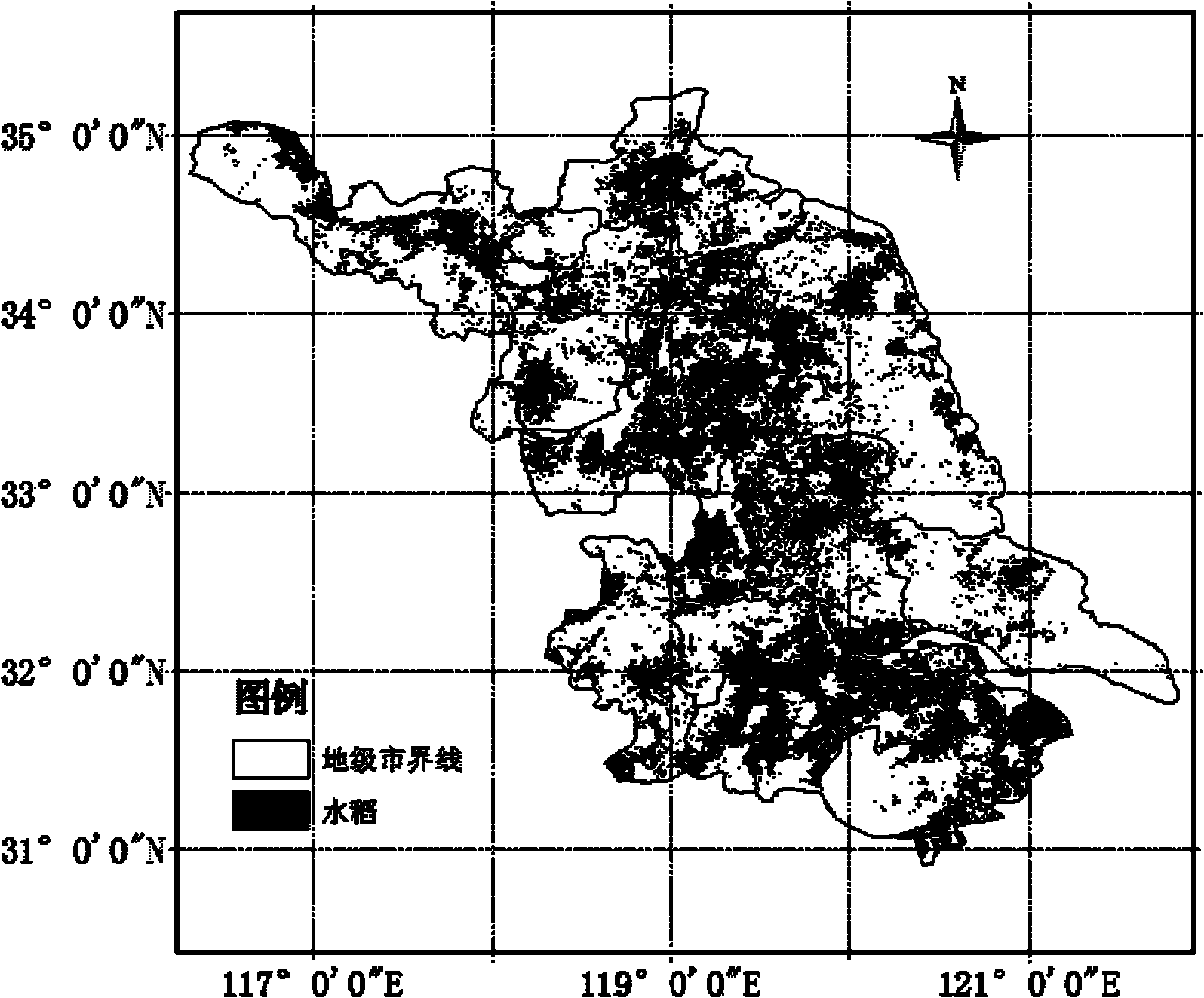
MODIS data-based agricultural drought monitoring method
InactiveCN102103077ASuppress high valuesPromote resultsScattering properties measurementsElectromagnetic wave reradiationVegetation IndexModerate-resolution imaging spectroradiometer
The invention discloses a moderate-resolution imaging spectroradiometer (MODIS) data-based agricultural drought monitoring method. In the farmland drought monitoring process, an agricultural drought index is determined by a crop water supply index and a rainfall anomaly index; in the drought monitoring process, a vegetation index and the surface temperature are inverted by MODIS data, and the crop water supply index is calculated by the vegetation index and the surface temperature; the rainfall anomaly index is calculated by rainfall data; and drought severity is determined by dividing the level of the drought index.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF APPL ECOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Use of within-field-element-size CV for improved nutrient fertilization in crop production
InactiveUS7188450B2Production be limitedPoor conditioningAnalogue computers for trafficFertilising methodsVegetation IndexMacro and micronutrients
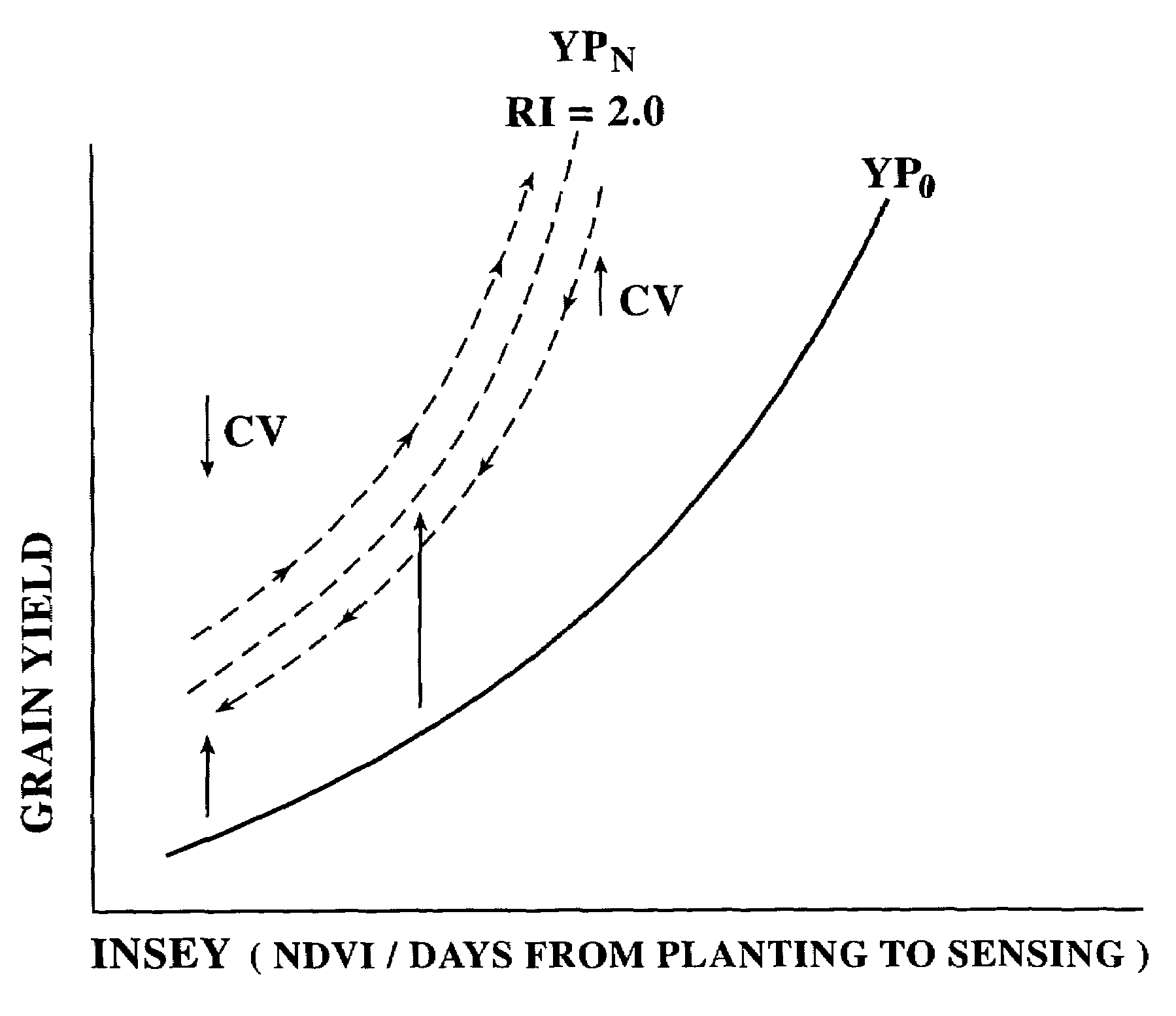
A method for in-season macro and micronutrient application based on predicted yield potential, coefficient of variation, and a nutrient response index. The inventive method includes the steps of: determining a nutrient response index for a field; determining the normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) of an area to fertilize; determining the coefficient of variation of NDVI over a plot; determining a predicted crop yield for the area without additional nutrient; determining an attainable crop yield for the area with additional nutrient; determining the nutrient requirement for the area as the difference between the nutrient removal at the attainable yield minus the nutrient removal at the predicted yield, adjusted by the efficiency of nutrient utilization in the particular crop as indicated by the coefficient of variation.
Owner:BOARD OF REGENTS FOR OKLAHOMA STATE UNIVERSITY
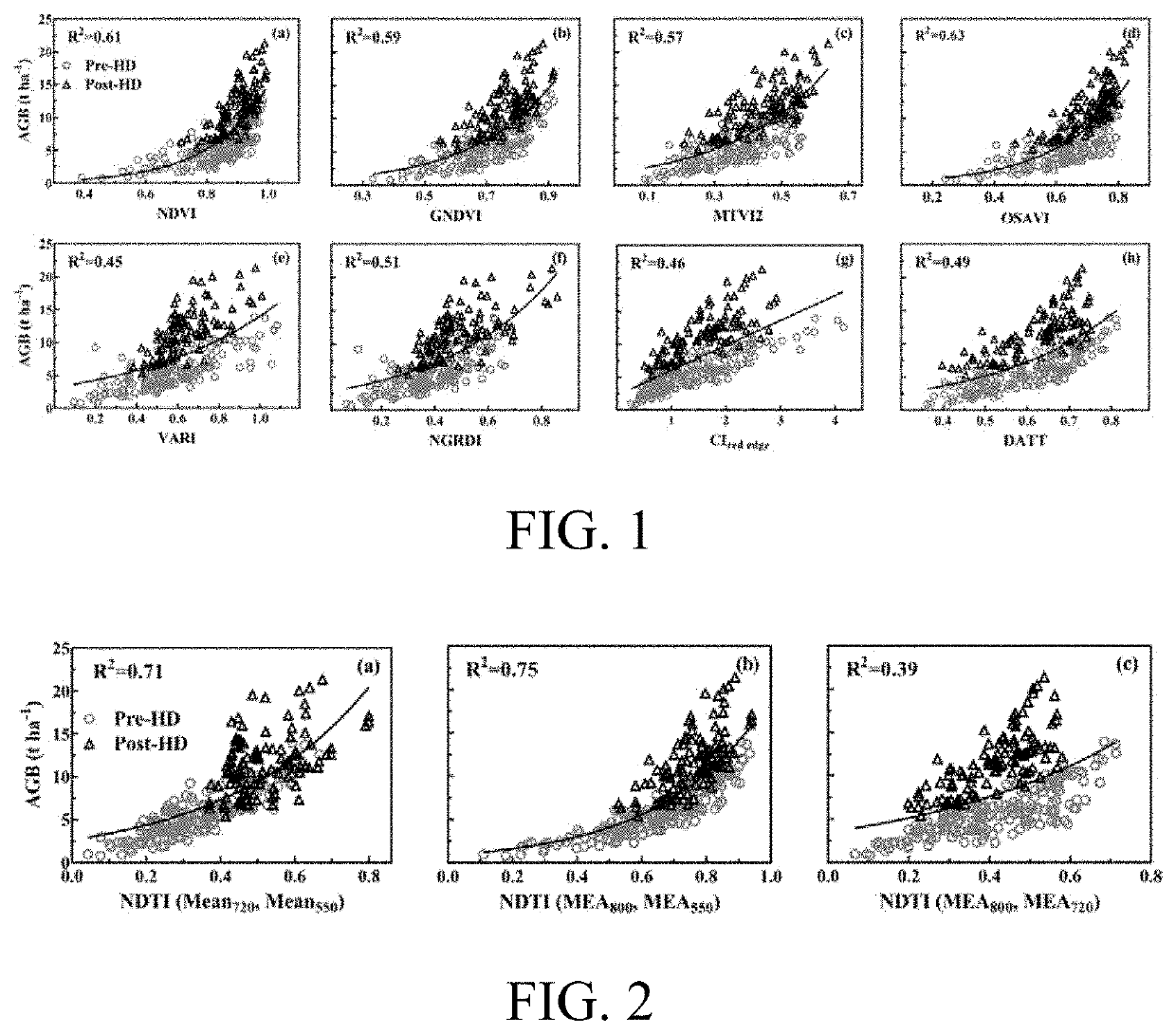
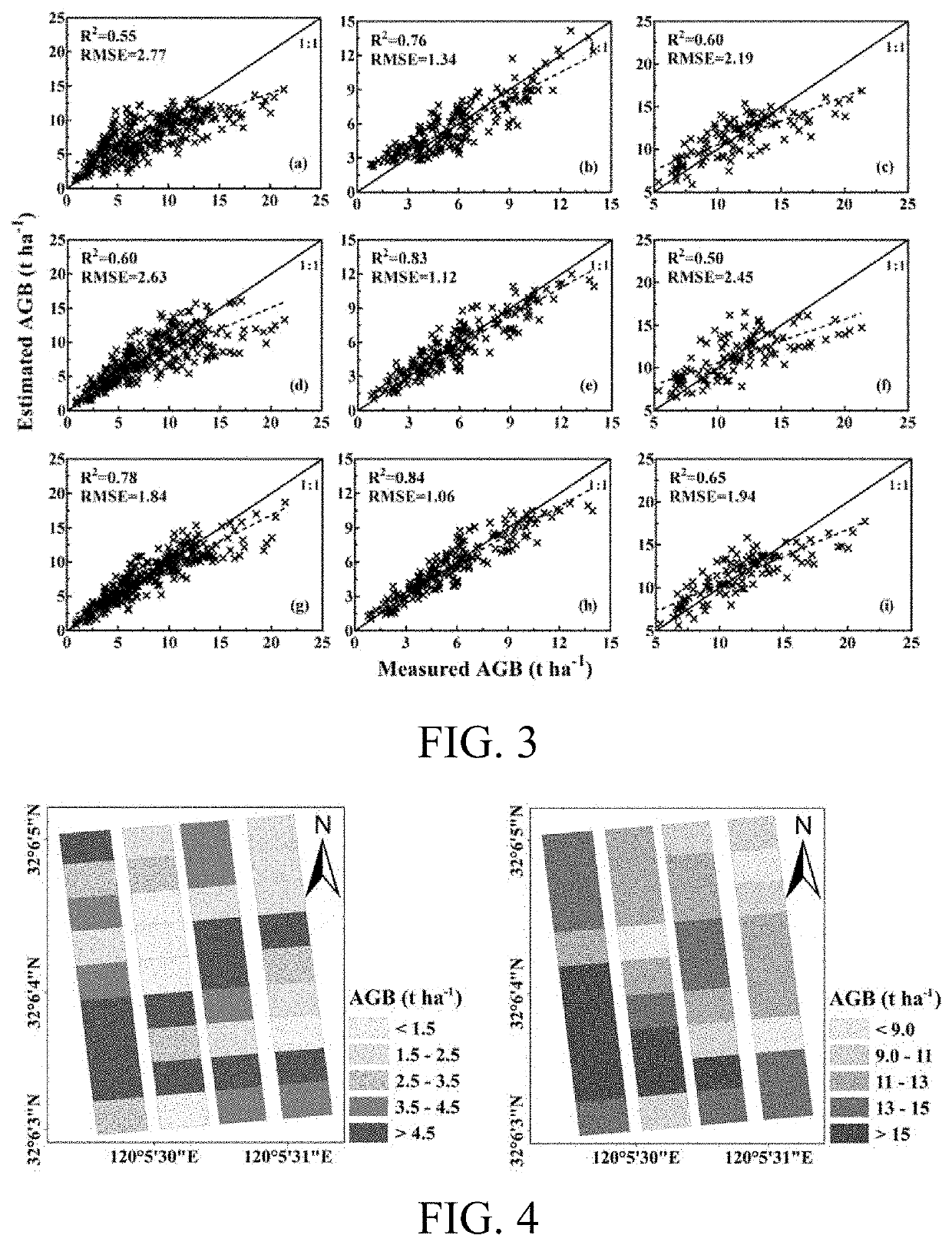
Method for estimating aboveground biomass of rice based on multi-spectral images of unmanned aerial vehicle
ActiveUS20200141877A1Low input data requirementImprove estimation accuracyImage enhancementInvestigation of vegetal materialMultivariate linear modelVegetation Index
A method for estimating the aboveground biomass of rice based on multi-spectral images of an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV), including: normatively collecting UAV multi-spectral image data of rice canopy and ground measured biomass data; after collection, preprocessing images, extracting reflectivity and texture feature parameters, calculating a vegetation index, and constructing a new texture index; and by stepwise multiple regression analysis, integrating the vegetation index and the texture index to estimate rice biomass, and establishing a multivariate linear model for estimating biomass. A new estimation model is verified for accuracy by a cross-validation method. The method has high estimation accuracy and less requirements on input data, and is suitable for the whole growth period of rice. Estimating rice biomass by integrating UAV spectrum and texture information is proposed for the first time, and can be widely used for monitoring crop growth by UAV remote sensing.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method and system for spatially variable rate application of agricultural chemicals based on remotely sensed vegetation data
InactiveUS7103451B2Controlling ratio of multiple fluid flowsCharacter and pattern recognitionVariable Rate ApplicationVegetation
Remotely sensed spectral image data are used to develop a Vegetation Index file which represents spatial variations of actual crop vigor throughout an area that is under cultivation. The latter information is processed to place it in a format that can be used by personnel to correlate and calibrate it with actually observed crop conditions existing at control points within the area. Based on the results, personnel formulate a prescription request, which is forwarded to a central processing site, where the prescription is prepared. The latter is returned to a mobile application means that directly applies inputs to the field at a spatially variable rate.
Owner:INTIME
Agricultural drought grade monitoring method based on temperature vegetation drought index (TVDI)
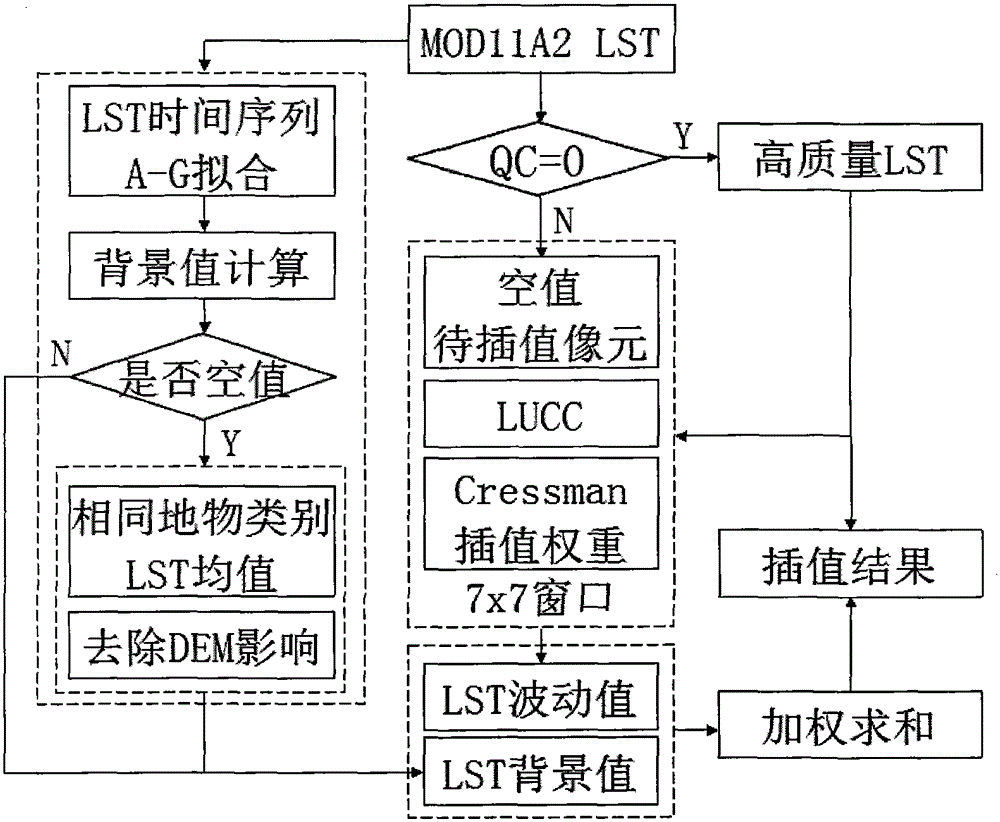
The invention discloses an agricultural drought grade monitoring method based on a temperature vegetation drought index (TVDI). The method comprises the following steps of: 1, data preparation; 2, land surface temperature (LST) data reconstruction; 3, construction of crop plantation area normalized difference vegetation index-land surface temperature (NDVI-LST) feature space; 4, TVDI calculation; and 5, drought grade monitoring based on the TVDI. The invention brings forward an LST data reconstruction method based on multi-year background values and area fluctuation values, a cultivated land area multi-year NDVI-LST feature space is constructed for crops, the TVDI is calculated, a crop drought grade monitoring model based on a supervision classification idea is designed for drought grade remote sensing monitoring, the model can quite accurately reflect drought threat degrees of the crops under difference conditions in real time, and the method has great significance in monitoring, early warning and prevention of agricultural disasters.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY +1
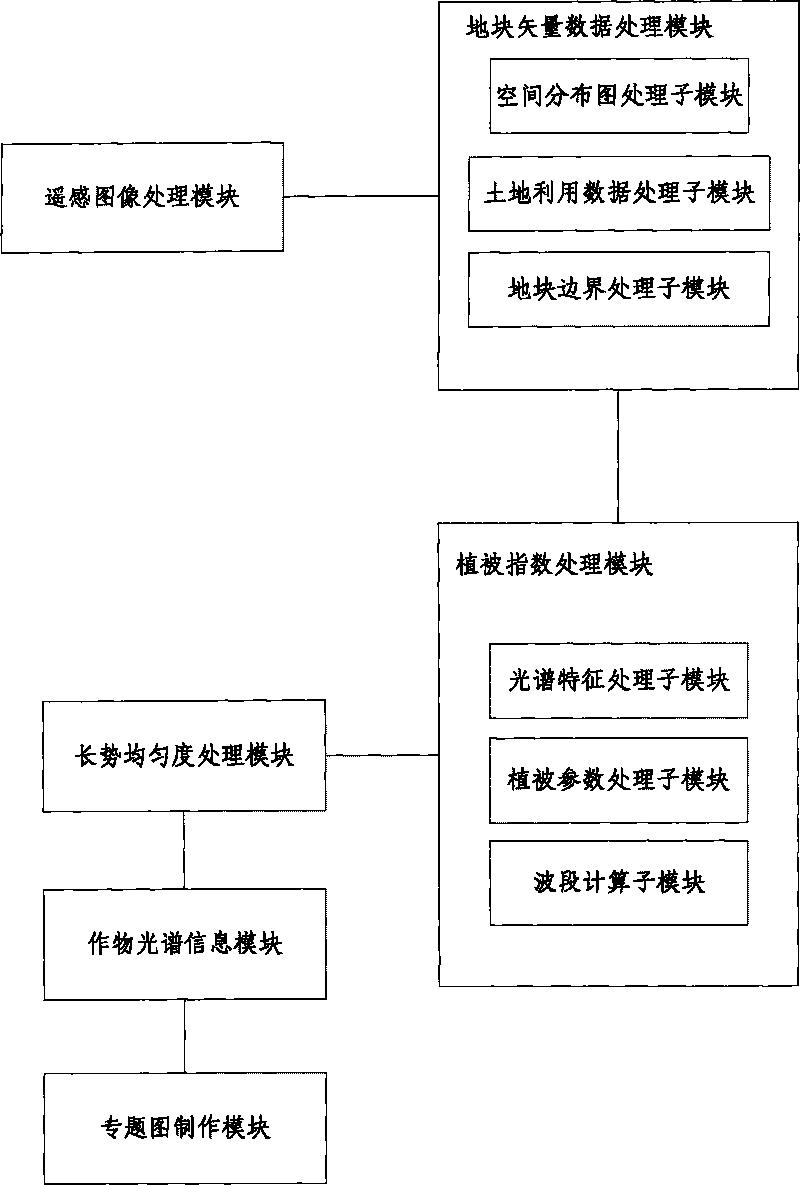
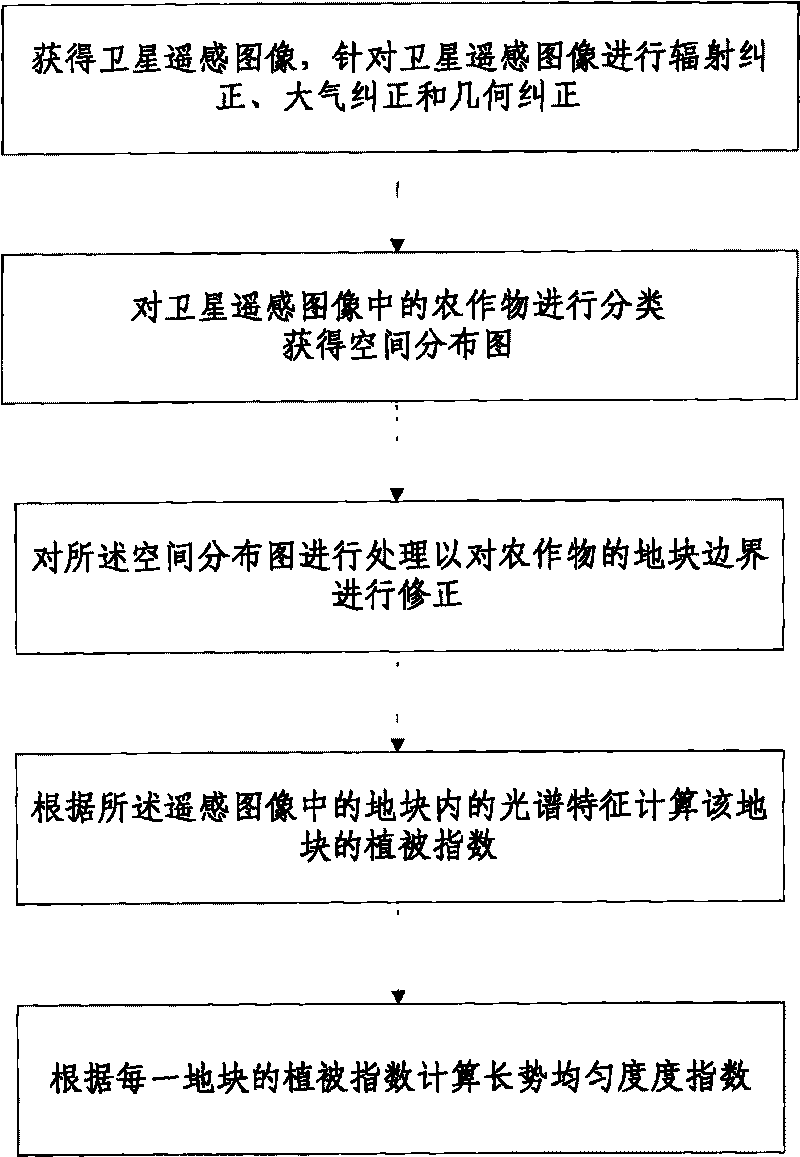
Monitoring device and method for crop growth uniformity
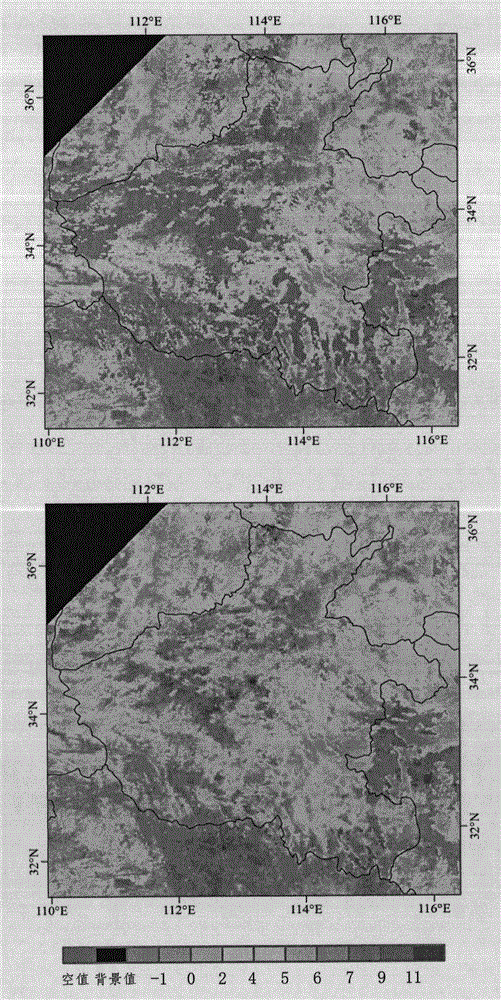
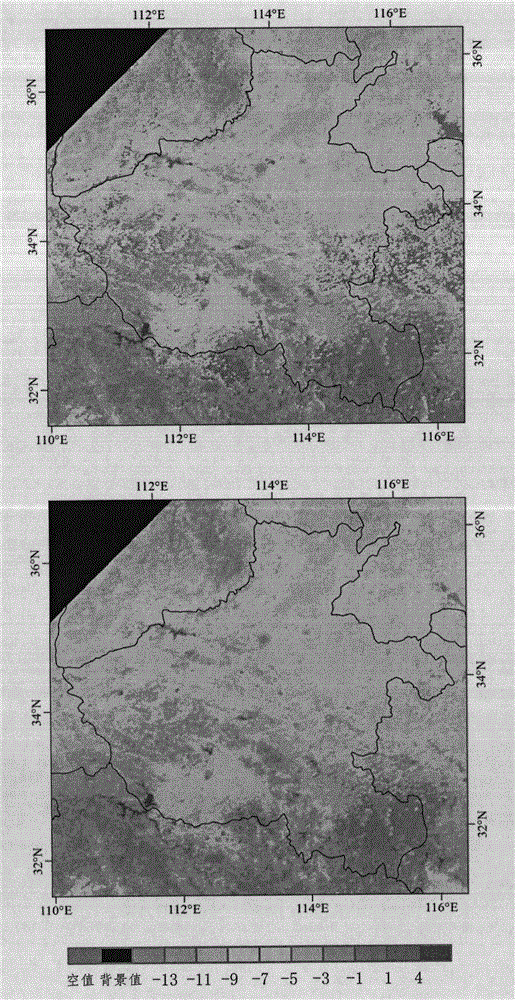
ActiveCN101699315AGrowth uniformity in real timeRapid growth uniformityElectromagnetic wave reradiationSensing dataVegetation Index
The invention discloses a monitoring device and a method for crop growth uniformity degree, aiming at the problem of low efficiency for manually investigating data. The device comprises a remote sensing image processing module, a plot vector data processing module, a vegetation index processing module and a growth uniformity processing module. The method comprises: obtaining the remote sensing images of a satellite; carrying out radiometric ratification, atmospheric correction and geometric correction according to the remote sensing images of the satellite; classifying crops in the remote sensing images of a satellite to obtain a spatial distribution map; converting a grid classification result in the spatial distribution map into facet vector data; processing the spatial distribution map to correct the plot boundary of the crops; according to the spectral characteristics of the plot in the remote sensing image, calculating the vegetation index of the plot; and calculating the growth uniformity degree index according to the vegetation index of each plot. The invention uses the integration of the grid and the vector data to monitor the growth uniformity degree of crops in natural plots and performs the advantages of remote sensing data.
Owner:NONGXIN TECH BEIJING CO LTD
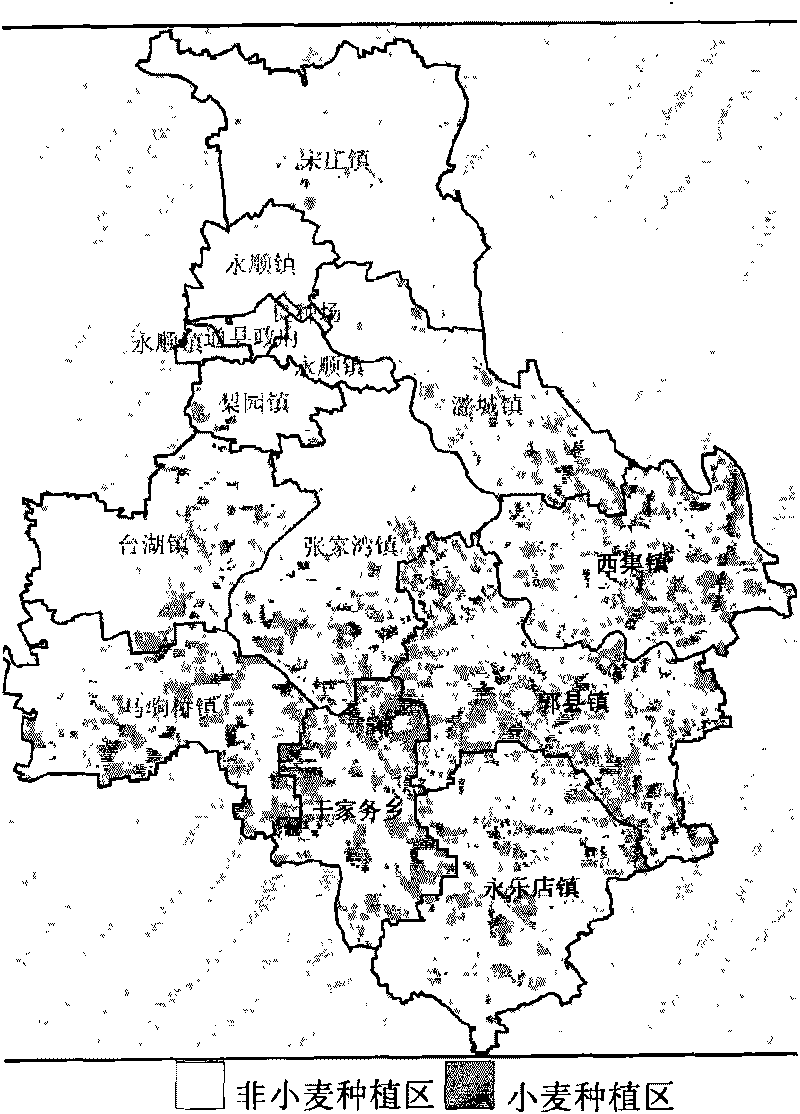
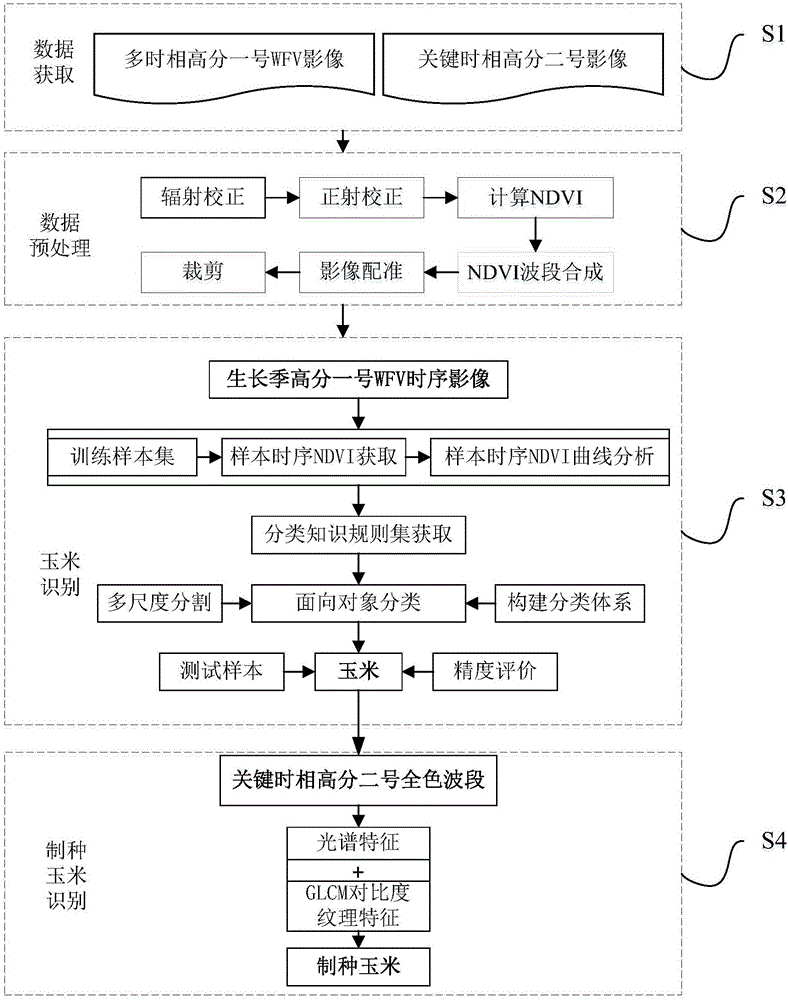
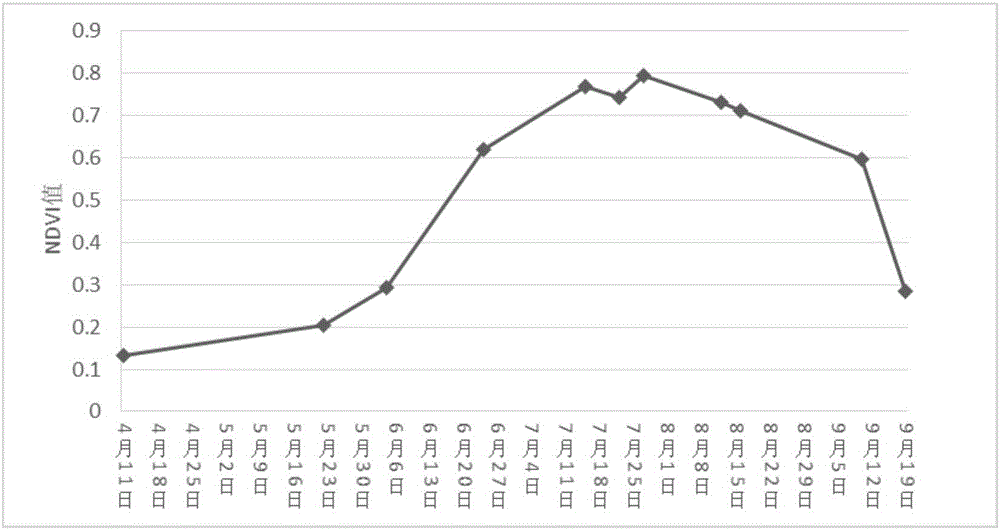
Seed maize field identification method and system based on multi-source and multi-temporal high resolution remote sensing data
InactiveCN106355143ARemote sensing monitoring is accurateObjective remote sensing monitoringCharacter and pattern recognitionSensing dataTime series dataset
The invention provides a seed maize field identification method and system based on multi-source and multi-temporal high resolution remote sensing data. The method comprises the steps of 1) getting the image of No. 1 multi-temporal high resolution Wild Field View (WFV) for the monitored maize field in maize growth season and the No. 2 high resolution panchromatic band image for key growth period; pre-processing the image of No. 1 multi-temporal high resolution Wild Field View (WFV) and getting xxx of No. 1 multi-temporal high resolution Wild Field View normalized difference vegetation index WFV NDVI Time Series Dataset and well-aligned High-Score 2# Panchromatic Band; S3: Application of Object-oriented Classification Method for Processing of WFV NDVI timing dataset of High-Score 1# in Maize Growing Season, to identify the cornfield block in the said monitoring area according to the phenological differences between crops; S4: to identify the seed maize field in the monitoring area based on the block acquired by S3 and according to the difference in spectrum and texture information between the seed maize field and the growing maize field on High-Score 2 panchromatic wave band. The present invention provides an accurate, economic and objective method for remote sensing and monitoring of seed maize breeding.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
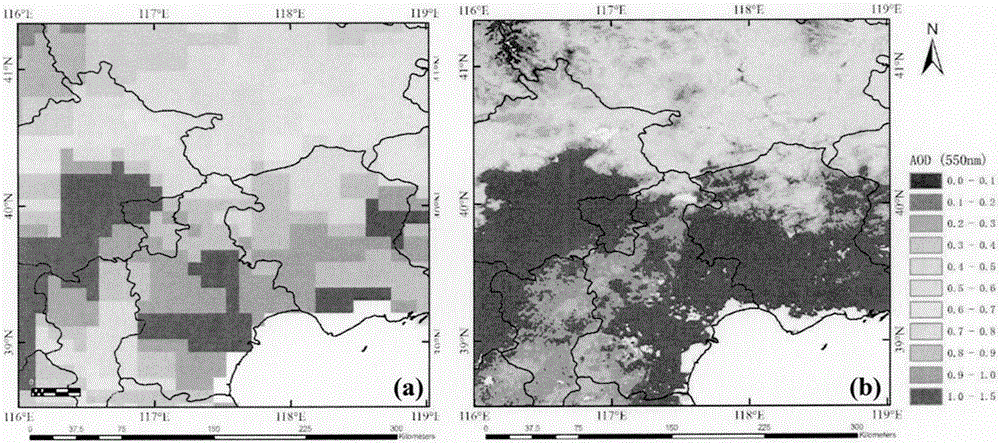
Retrieval method for aerosol optical thickness based on high resolution satellite image data
InactiveCN106407656AImproving the Accuracy of Optical Depth InversionIncrease spaceParticle suspension analysisInformaticsRadiation transferPollution
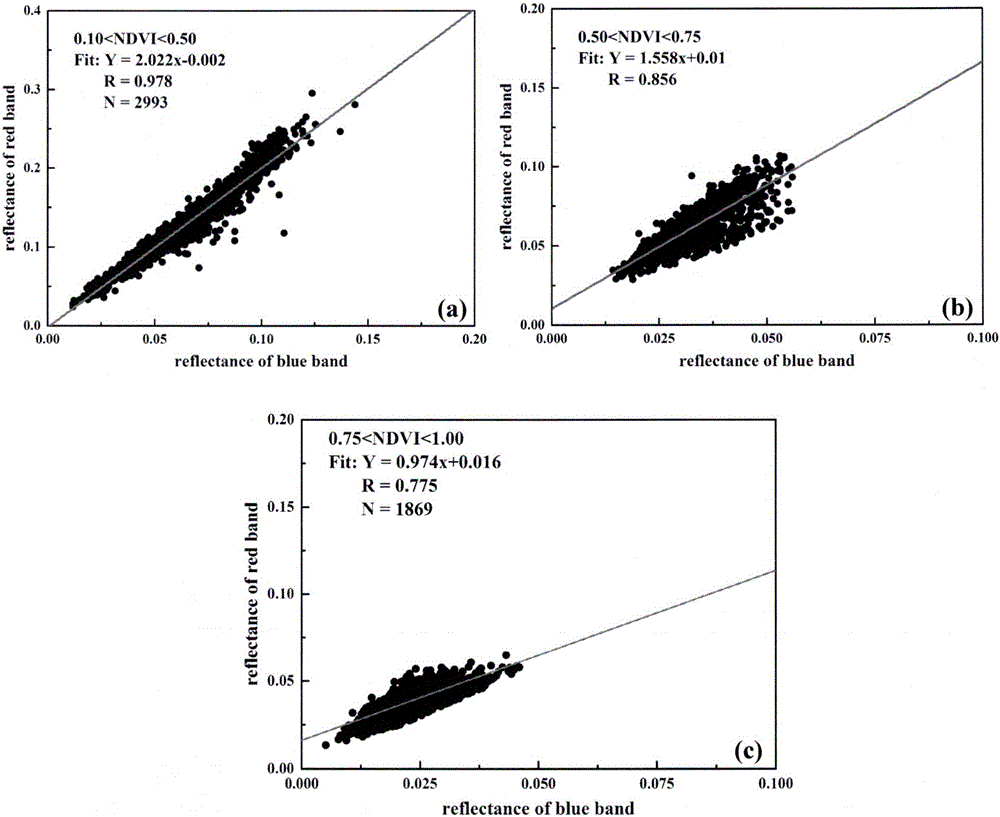
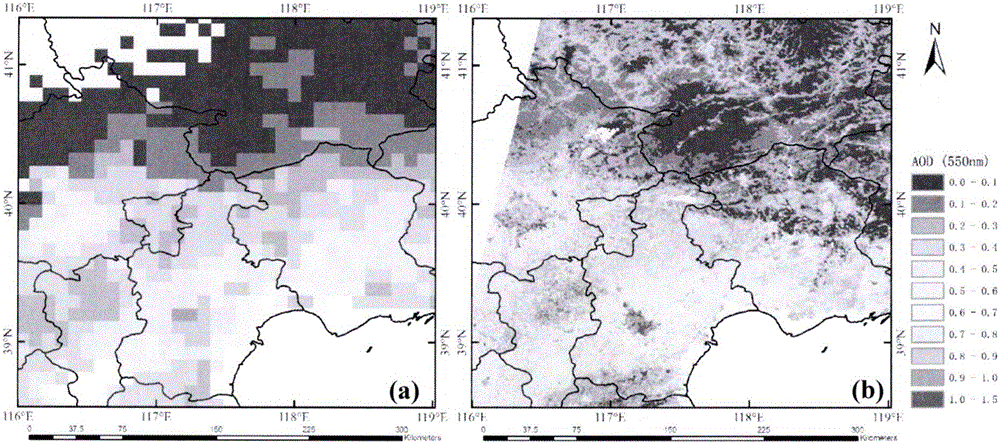
The invention discloses a retrieval method for an aerosol optical thickness based on high resolution satellite image data. The retrieval method specifically comprises the following steps: 1) establishing a lookup table according to a 6S radiation transfer model; 2) carrying out high resolution data preprocessing, comprising radiometric calibration, geometric correction and cloud detection, acquiring original apparent reflectance and observation angle information, and acquiring atmospheric parameters according to the observation angle information and the lookup table; 3) calculating the normalized differential vegetation index of each pixel, and determining a red-blue wave band relation corresponding to each pixel according to the vegetation index and priori knowledge provided by the invention; and 4) inverting the aerosol optical thickness according to the satellite observed apparent reflectance, the atmospheric parameters and the red-blue wave band relation. According to the remote sensing retrieval method for the aerosol optical thickness disclosed by the invention, aerosol monitoring can be carried out on high solution satellites effectively, and a data source can be provided for regional and urban atmospheric environment and pollution.
Owner:INST OF REMOTE SENSING & DIGITAL EARTH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Vegetation index construction method applied to city
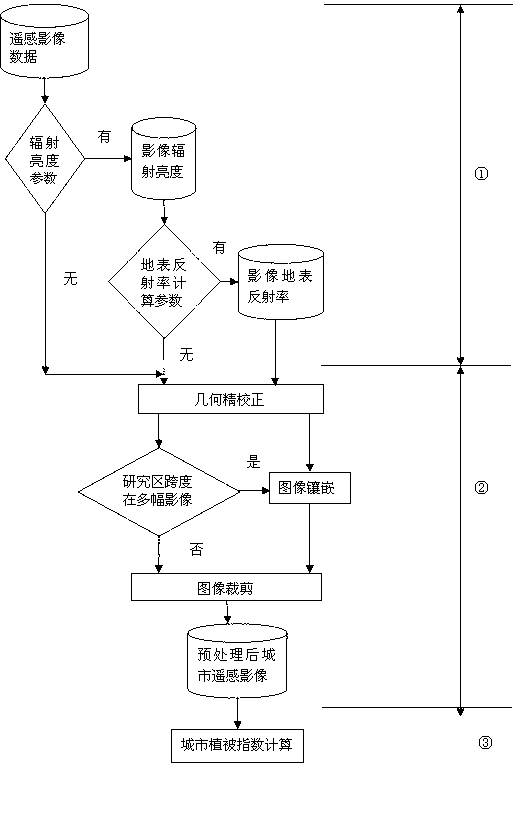
InactiveCN102708307ABig contrastAvoid low index valuesSpecial data processing applicationsVegetationVegetation Index
The invention discloses a vegetation index construction method applied to a city. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) performing radiation correction at different degrees according to acquired city optical remote sensing image data, and thus acquiring city remote sensing image data which is subjected to the radiation correction; (2) performing geometrical fine correction, embedding and cutting preprocessing on the city optical remote sensing image data which is subjected to the radiation correction, and thus acquiring a preprocessed city remote sensing image; and (3) calculating the vegetation index IVI of the preprocessed city remote sensing image. By the method, the influence of city building land and water bodies can be well restrained, vegetation information can be enhanced, and the method is suitable for remote sensing image data acquired by a sensor without ground scaling parameters. A city vegetation index constructed by the method can accurately, quickly and precisely reflect the vegetation information of the city.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
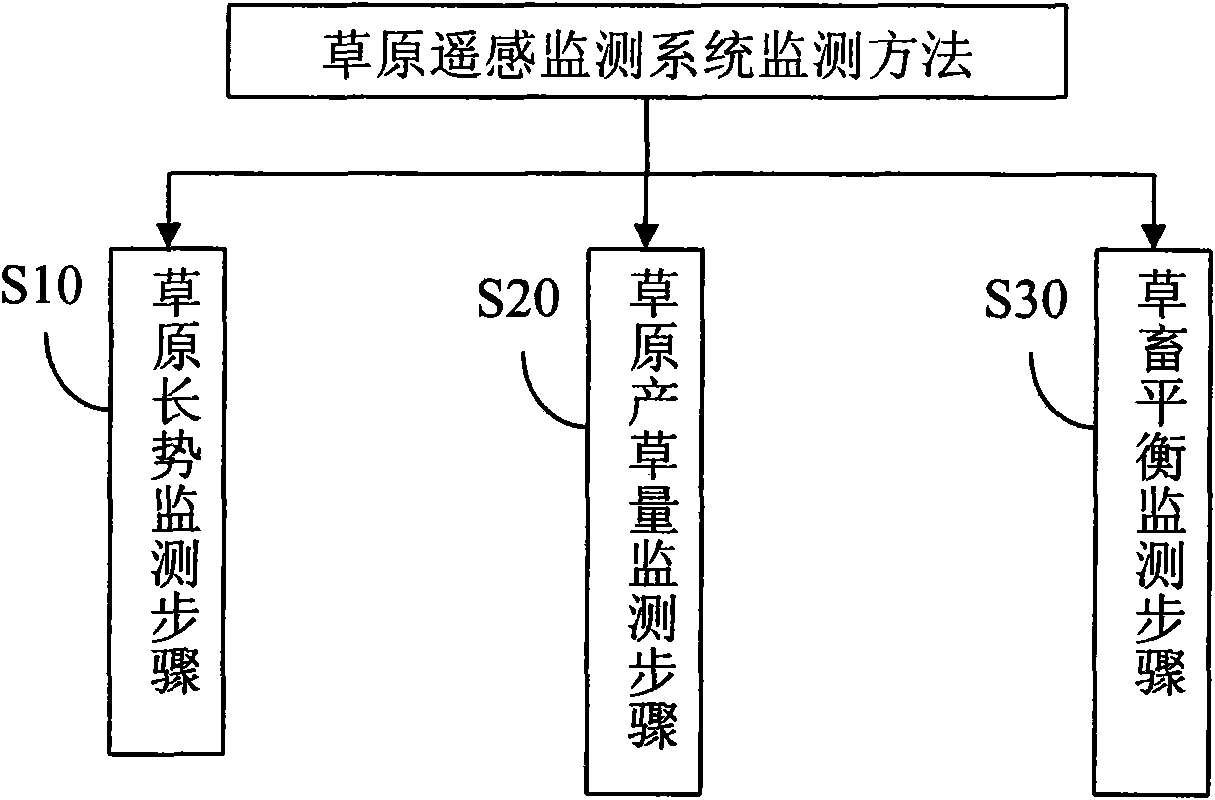
Grassland satellite remote sensing monitoring system and method
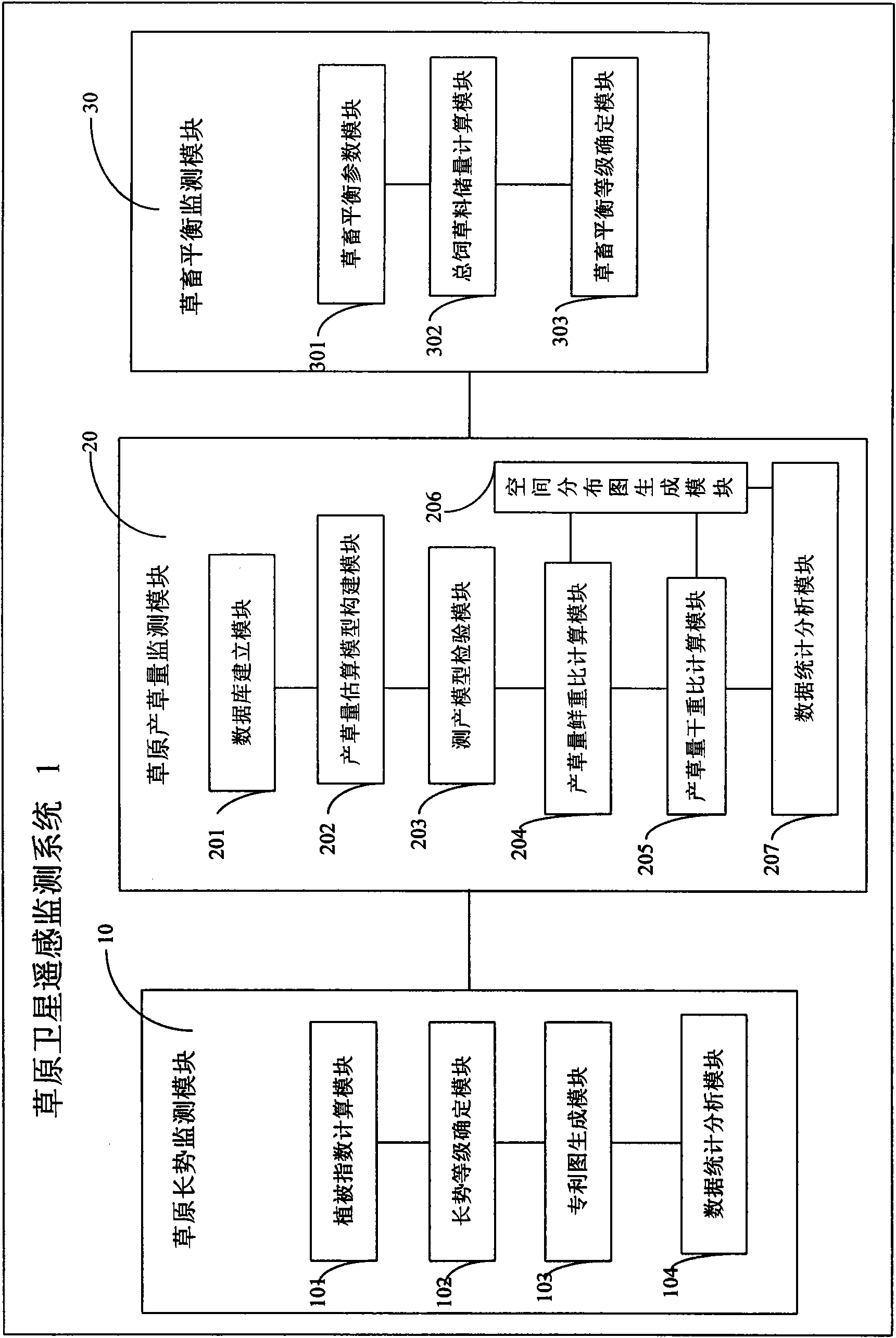
ActiveCN102033230ARapid Remote Sensing MonitoringEfficient Remote Sensing MonitoringElectromagnetic wave reradiationSpecial data processing applicationsVegetation IndexMonitoring system
The invention discloses a grassland satellite remote sensing monitoring system and a grassland satellite remote sensing monitoring method. The system comprises a grassland growth potential monitoring module, a grassland grass yield monitoring module and a grass-livestock balance monitoring module, wherein the grassland growth potential monitoring module is used for acquiring a grassland normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) and a grassland growth index (GI) by processing data of a satellite remote sensing moderate resolution imaging spectrometer (MODIS) in different periods according to the relation between remote sensing information and the condition of grassland vegetation on the ground to reflect the growth potential of the grassland vegetation; the grassland grass yield monitoring module is used for establishing a grass yield estimating model by combining yield measuring data of ground quadrats according to the information of the satellite remote sensing MODIS and inverting the grass yield of grasslands according to the data of the remote sensing MODIS; and the grass-livestock balance monitoring module is used for estimating the grass-livestock balance condition by combining the current grass yield, foraged grass yield and replenished forage grass of natural grasslands according to the grass yield acquired by the grassland grass yield monitoring module.
Owner:INST OF AGRI RESOURCES & REGIONAL PLANNING CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
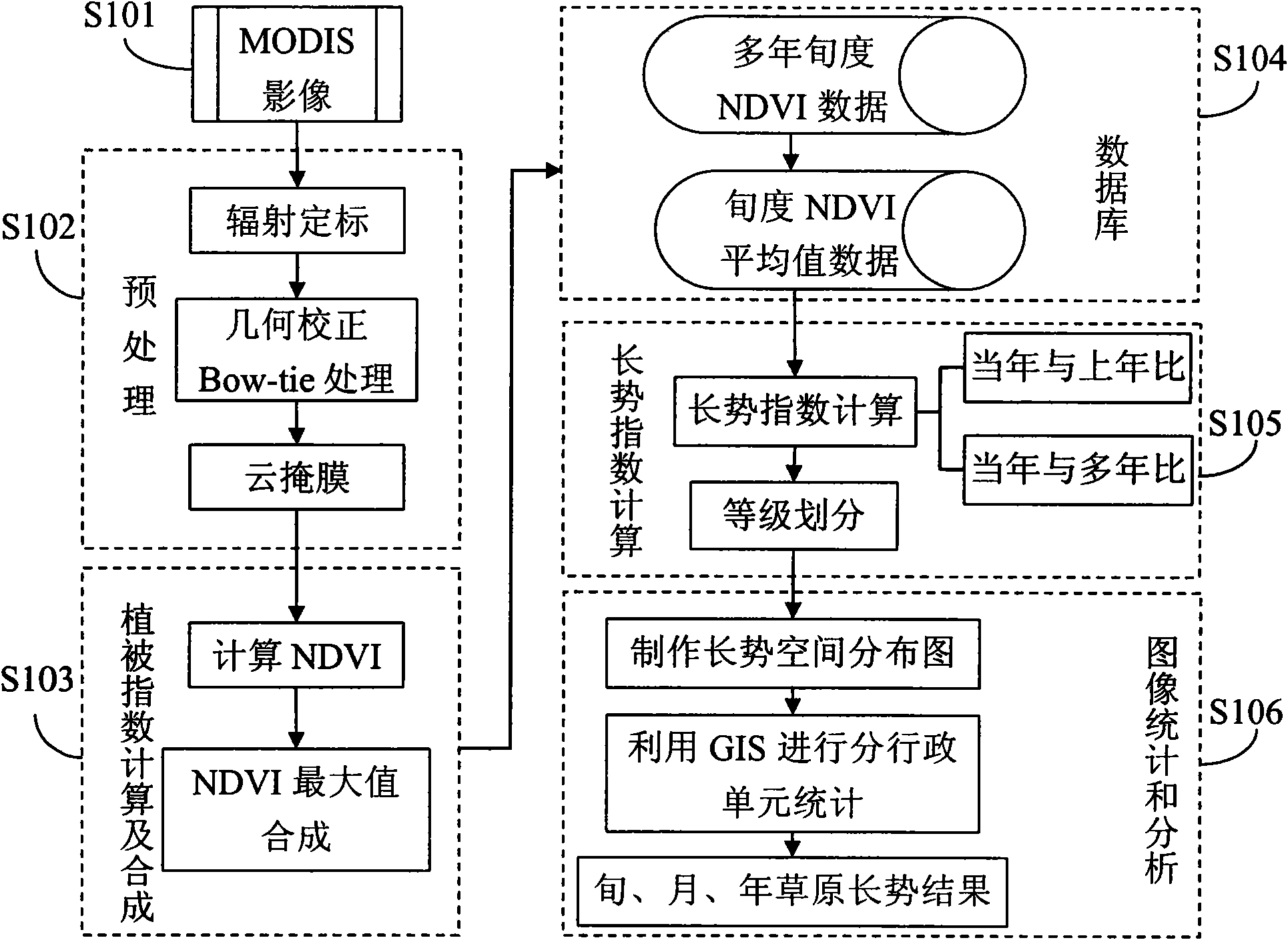
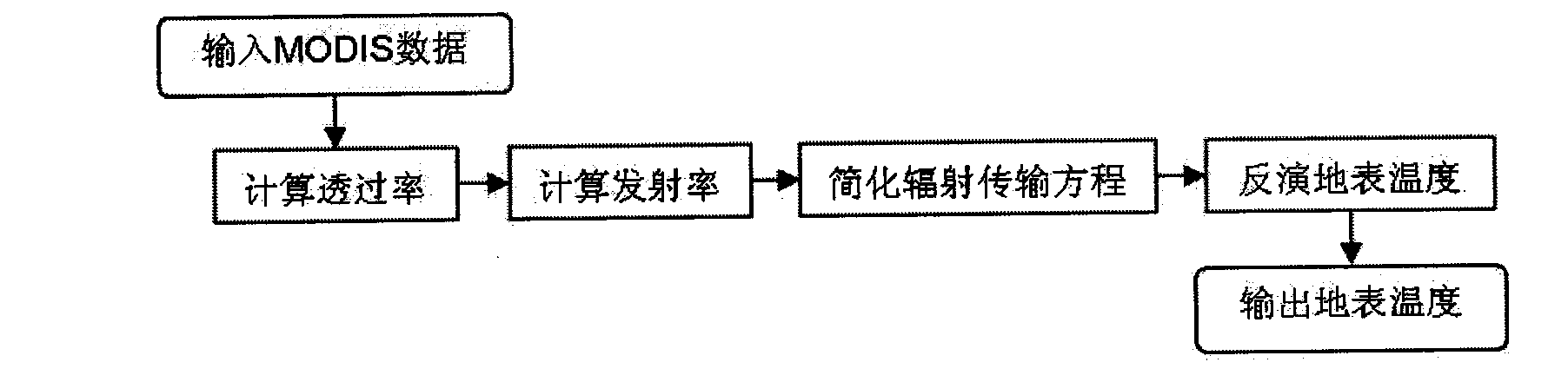
Method for inversing land surface temperature from MODIS data
InactiveCN101629850AGuaranteed synchronous fetchOvercome the disadvantages that are difficult to achieveRadiation pyrometryElectromagnetic wave reradiationWater vaporDisaster monitoring
The invention relates to a method for inversing land surface temperature from MODIS data, which can be applied in meteorology, environmental monitoring, land management, agricultural condition monitoring, disaster monitoring and other remote sensing application departments. The method comprises four steps: the first step is to calculate the transmittance of 31st and 32nd wave bands of MODIS through water vapor content of atmosphere. The second step is to calculate the emissivity of the 31st and the 32nd wave bands of the MODIS sensor through vegetation index NDVI. The third step is to simplify a radiation transmission equation. The fourth step is to carry out inversion calculation on the MODIS data and obtain the land surface target object temperature and the emissivity distribution situation, so that the method can be used in meteorological forecasting, environmental monitoring, agricultural condition monitoring, disaster monitoring and other departments.
Owner:INST OF AGRI RESOURCES & REGIONAL PLANNING CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI +1
Remote sensing monitoring method and device for water quality parameters of shallow aquatic plant lake
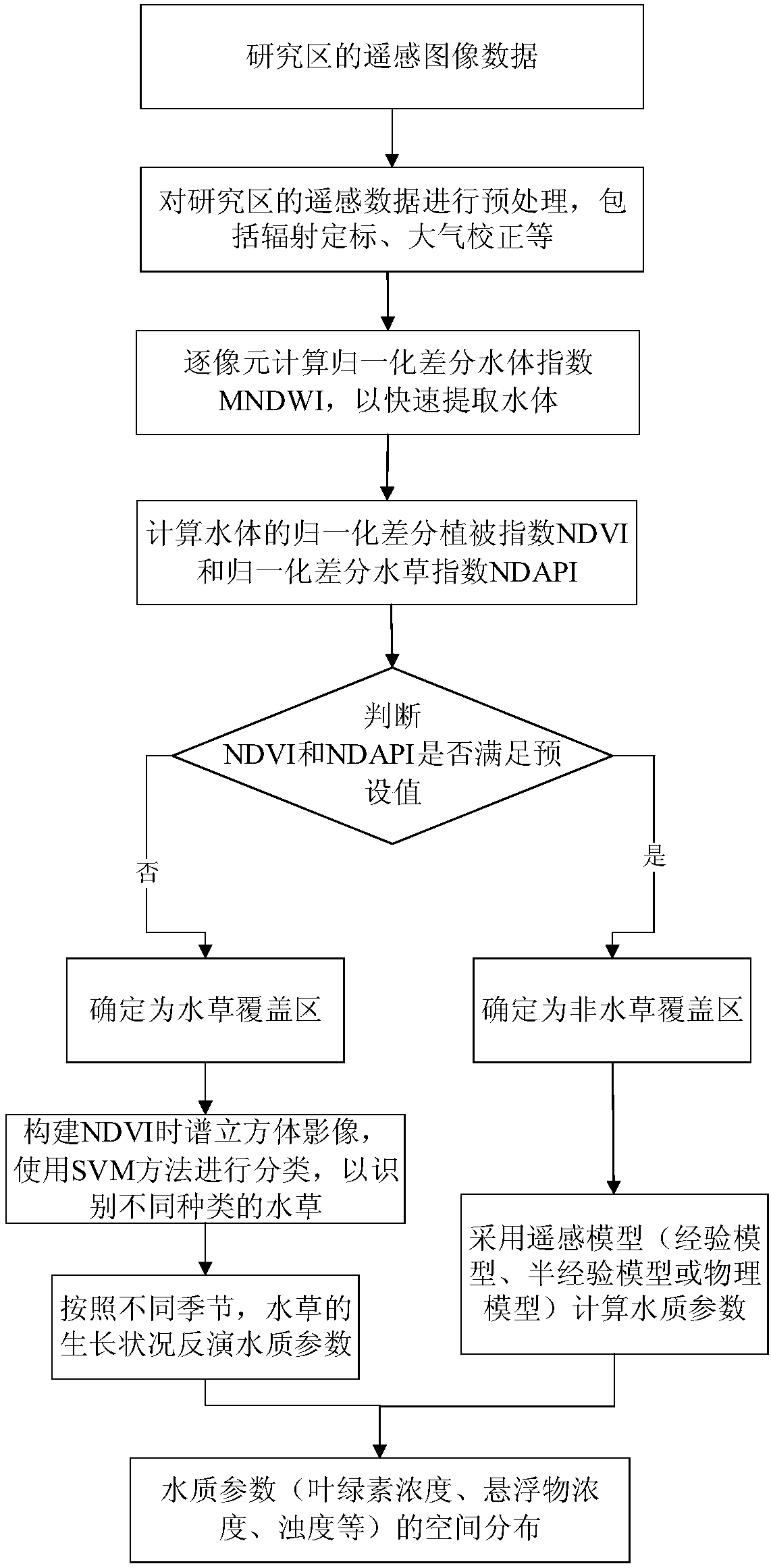
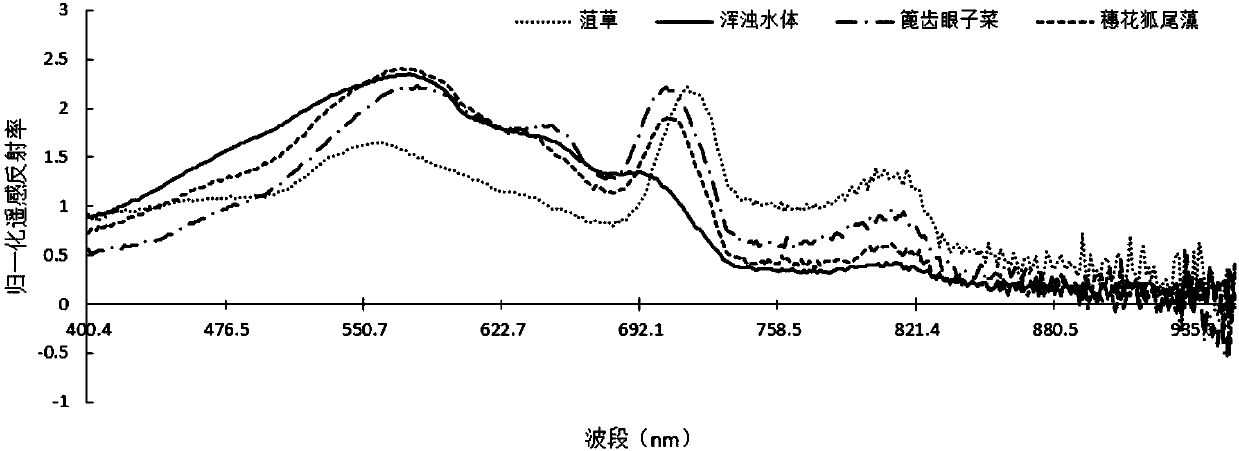
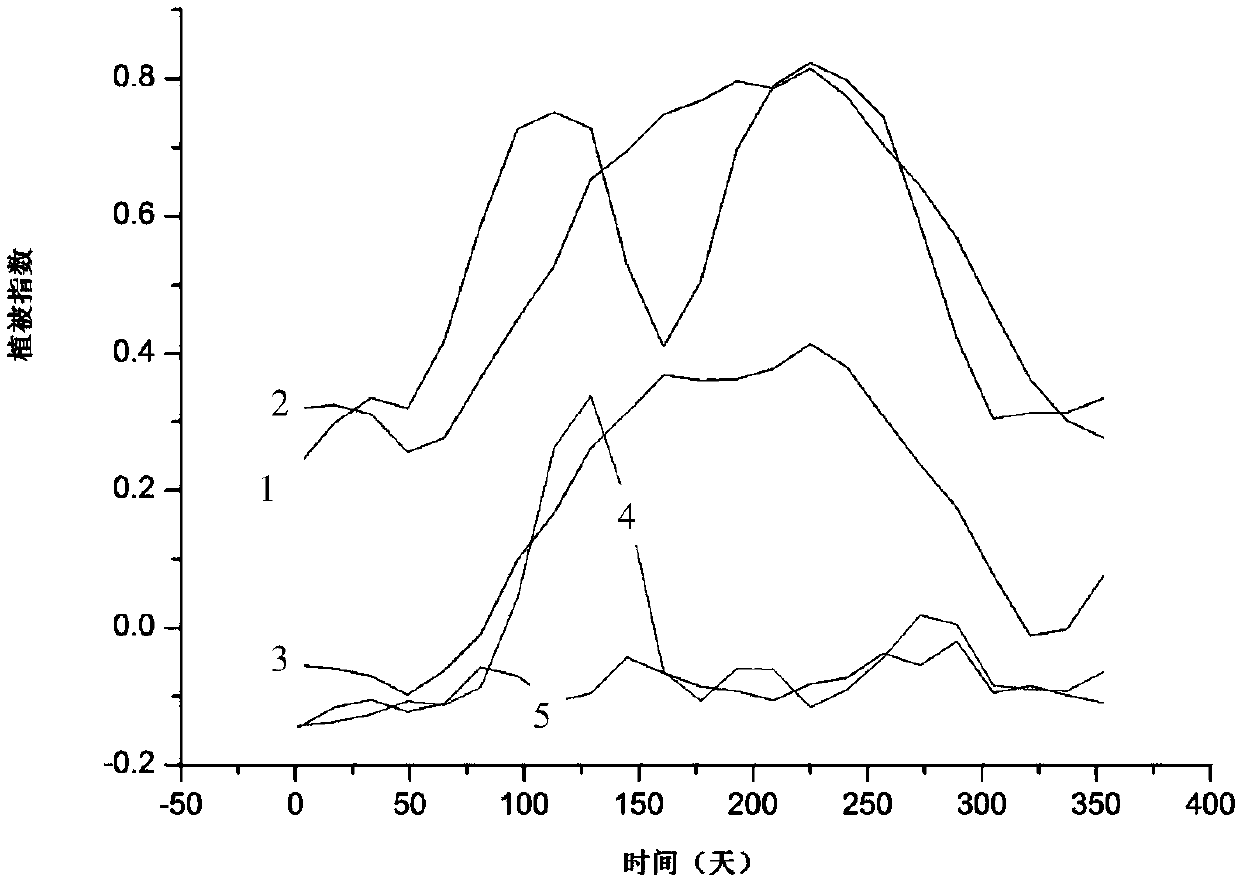
ActiveCN108020511AInversion is simpleFast inversionColor/spectral properties measurementsVegetationTime spectrum
The invention provides a remote sensing monitoring method for water quality parameters of a shallow aquatic plant lake. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring time series satellite remotesensing image data of a lake area, and extracting a water body by use of a normalized differential water body index MNDWI; calculating a normalized differential vegetation index NDVI and a normalizeddifferential aquatic plant index NDAPI of the water body to quickly extract an aquatic plant covering zone and aquatic plant growth conditions; building a vegetation index time spectrum cube image ofthe aquatic plant covering zone to realize fine partition of aquatic plant species; using the water quality indication effect of the aquatic plant species and the aquatic plant growth conditions forpartitional and seasonal inversion of the water quality parameters of the aquatic plant covering zone; and forming a spatial distribution map of the water quality parameters. According to the method proposed by the invention, the aquatic plant species on a remote-sensing satellite image can be accurately identified according to unique phenological characteristics of ground features and remote sensing vegetation index time spectrum analysis technology, the water quality parameters of the shallow aquatic plant lake can be simply and quickly inverted.
Owner:INST OF REMOTE SENSING & DIGITAL EARTH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Object-oriented remote sensing inversion method of leaf area index of crop
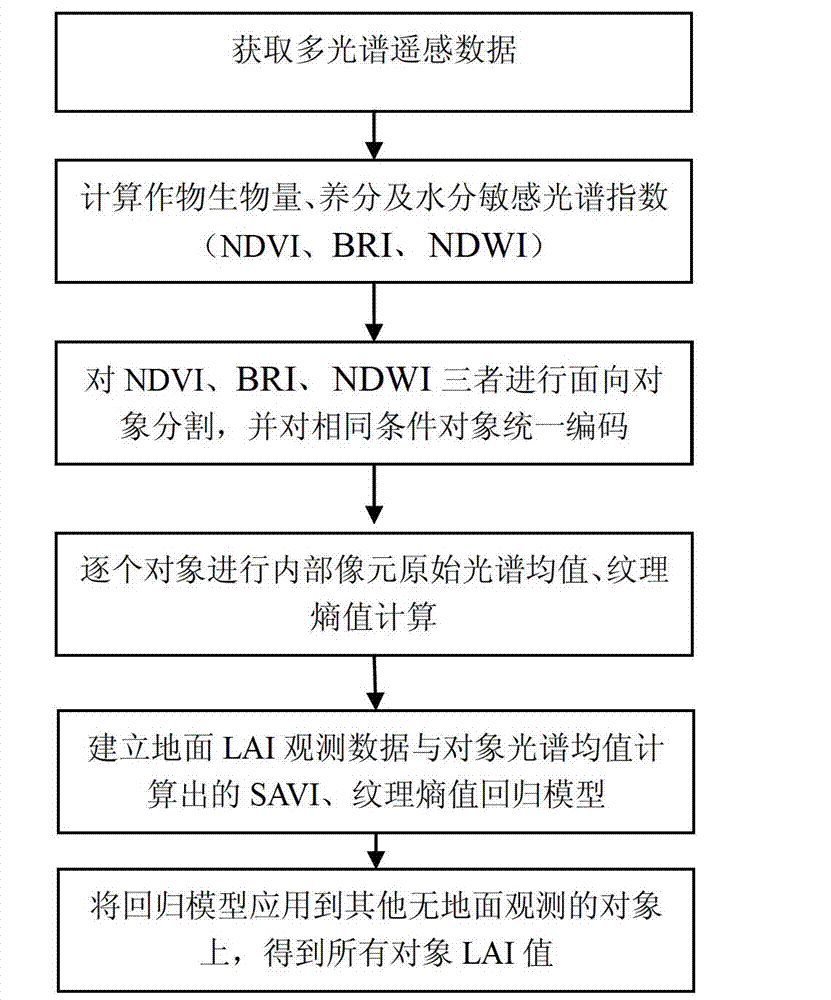
ActiveCN102829739AImprove computing efficiencyAvoid problems such as low precisionUsing optical meansSpecial data processing applicationsNormalized difference water indexInversion methods
The invention discloses an object-oriented remote sensing inversion method of a leaf area index of a crop, comprising the following steps of: acquiring multispectral remote sensing data; calculating a biomass spectral index NDVI (Normalized Difference Vegetation Index), a crop nutrient spectral index BRI and a water sensitive spectral index NDWI (Normalized Difference Water Index) of a crop colony by utilizing the acquired multispectral remote sensing data; carrying out object-oriented segmentation and encoding according to the biomass spectral index NDVI, the crop nutrient spectral index BRI and the water sensitive spectral index NDWI of the crop colony by utilizing a mean shift algorithm; sequentially carrying out the original spectral mean calculation of pixels on objects according to an encoding sequence to obtain a spectral index SAVI (Soil-Adjusted Vegetation Index) sensitive to the LAI (Leaf Area Index), and carrying out texture structure calculation; building a regression model of ground LAI observation data, the spectral index SAVI sensitive to the LAI and the texture structure calculation; and carrying out inversion calculation on the object without the ground LAI observation data by utilizing the regression model to obtain the LAI of the object without the ground LAI observation data.
Owner:BEIJING RES CENT FOR INFORMATION TECH & AGRI
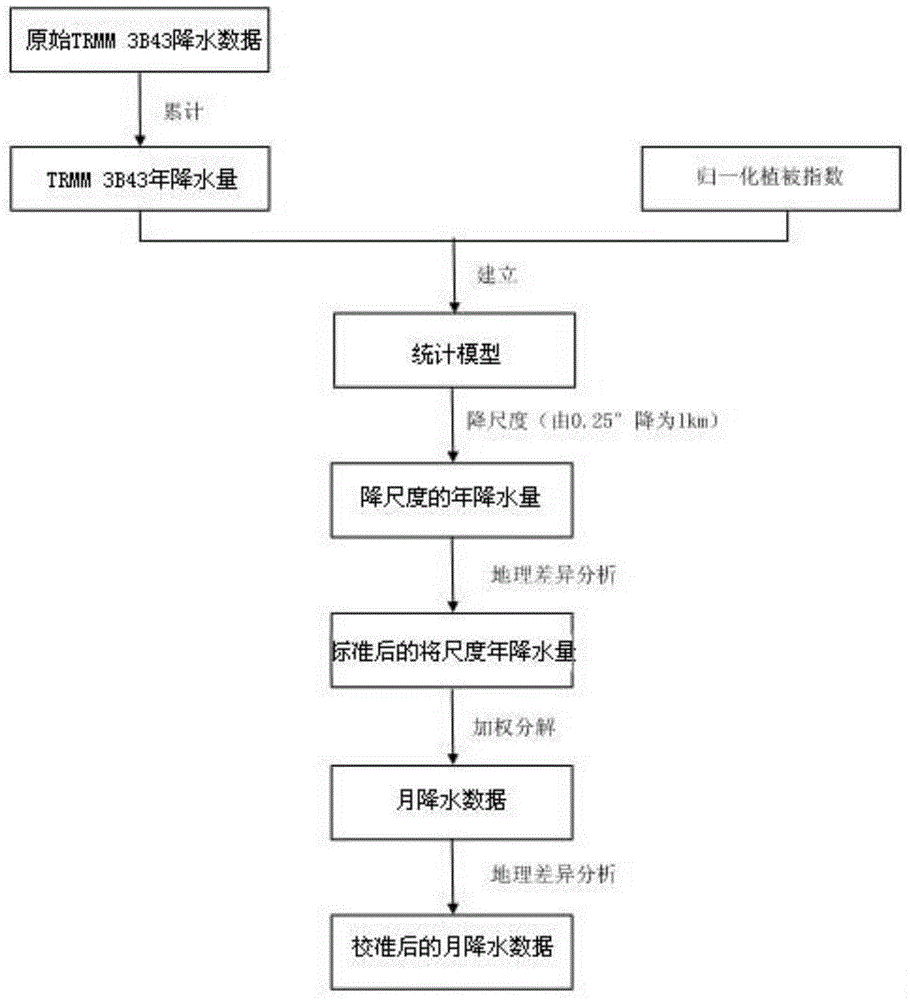
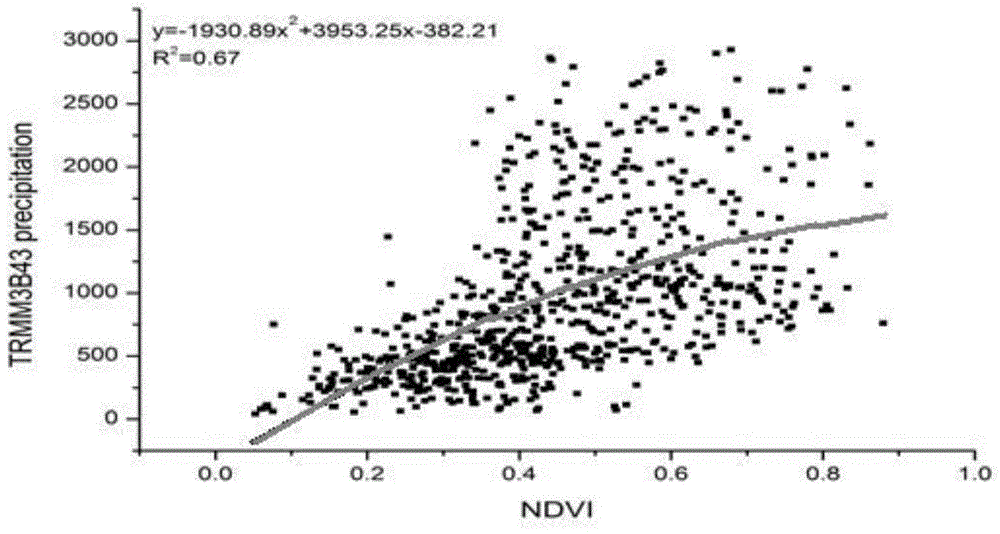
Space statistical downscaling rainfall estimation method based on geographical difference analysis method
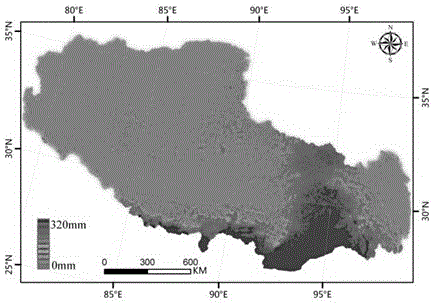
The invention discloses a space statistical downscaling rainfall estimation method based on a geographical difference analysis method. The method comprises the following steps that: A, a statistical model is built according to the relationship between annual rainfall data of satellite precipitation data and a normalized differential vegetation index, and the downscaling annual rainfall is obtained; B, the geographical difference analysis method is adopted for calibrating the downscaling annual rainfall obtained in the step A; C, the calibrated downscaling annual rainfall obtained in the step B is subjected to weighted decomposition to obtain monthly rainfall data; and D, the geographical difference analysis method is adopted for calibrating the monthly rainfall data obtained in the step C, and the calibrated monthly rainfall data is obtained. Compared with a conventional method, the space statistical downscaling rainfall estimation method has the advantages of higher relevance and smaller error.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF INFORMATION SCI & TECH
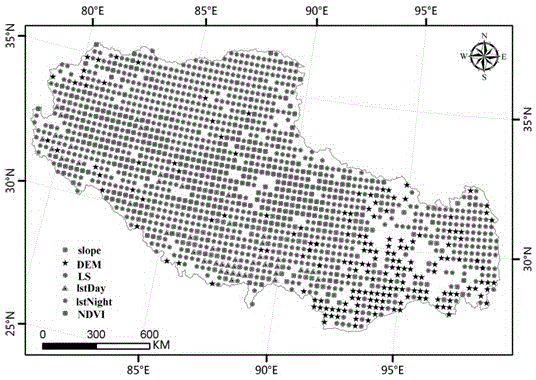
Dynamic filtering modeling downscaling method of environment variable on the basis of low-resolution satellite remote sensing data
InactiveCN106021872AAccurate Precipitation ForecastImprove spatial resolutionInformaticsSpecial data processing applicationsData setSlope length
The invention discloses a dynamic filtering modeling downscaling method of an environment variable on the basis of low-resolution satellite remote sensing data. The dynamic filtering modeling downscaling method comprises the following steps: firstly, carrying out aggregation calculation on 1km environment variable factors including eight pieces of data i.e., a vegetation index, a digital evaluation model, daytime surface temperature, night surface temperature, a topographic wetness index, a gradient, a slope aspect and a slope length gradient, into 25km to serve as independent variables, and taking corresponding 25Km resolution TRMM (Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission) 3B43 v7 precipitation data as a dependent variable. An M5 method divides data sets formed by each environment variable into different vector spaces according to geographical similarity, then, the most effect environment variable is independently dynamically filtered in different vector spaces, and a divisional multiple regression model is independently established in the corresponding vector space; and the model is finally applied to the 1km environment variable to finally obtain a precipitation product of the 1km resolution. A downscaling result obtained by partitioning and dynamic factor filtering is obviously superior to a downscaling result based on a conventional regression model.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for modeling rice and wheat leaf nitrogen content spectrum monitoring model
InactiveCN102175618AOptimization mechanismIncreased sensitivityClimate change adaptationMaterial analysis by optical meansData validationAgricultural science
The invention discloses a method for modeling a rice and wheat leaf nitrogen content spectrum monitoring model and belongs to the field of nondestructive monitoring of crop growth information in precision agriculture. The method comprises the following steps of: fusing rice and wheat canopy leaf reflectance spectrum data which is acquired by a field high-spectrum radiometer with rice and wheat canopy leaf nitrogen content data; and establishing a canopy leaf nitrogen content spectrum monitoring model orienting different growth periods of rice and wheat based on narrow band and wide band combination. The optimal vegetation index orienting a rice and wheat jointing and booting stage and a heading and grain filling period is established by utilizing multi-point rice and wheat field test data in many years; and rice and wheat canopy leaf nitrogen content common characteristic wave band and bandwidth are developed. The model covers different species and different nitrogen levels of rice and wheat, utilizes a data validation model in an independent year, and is high in universality and high in accuracy.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
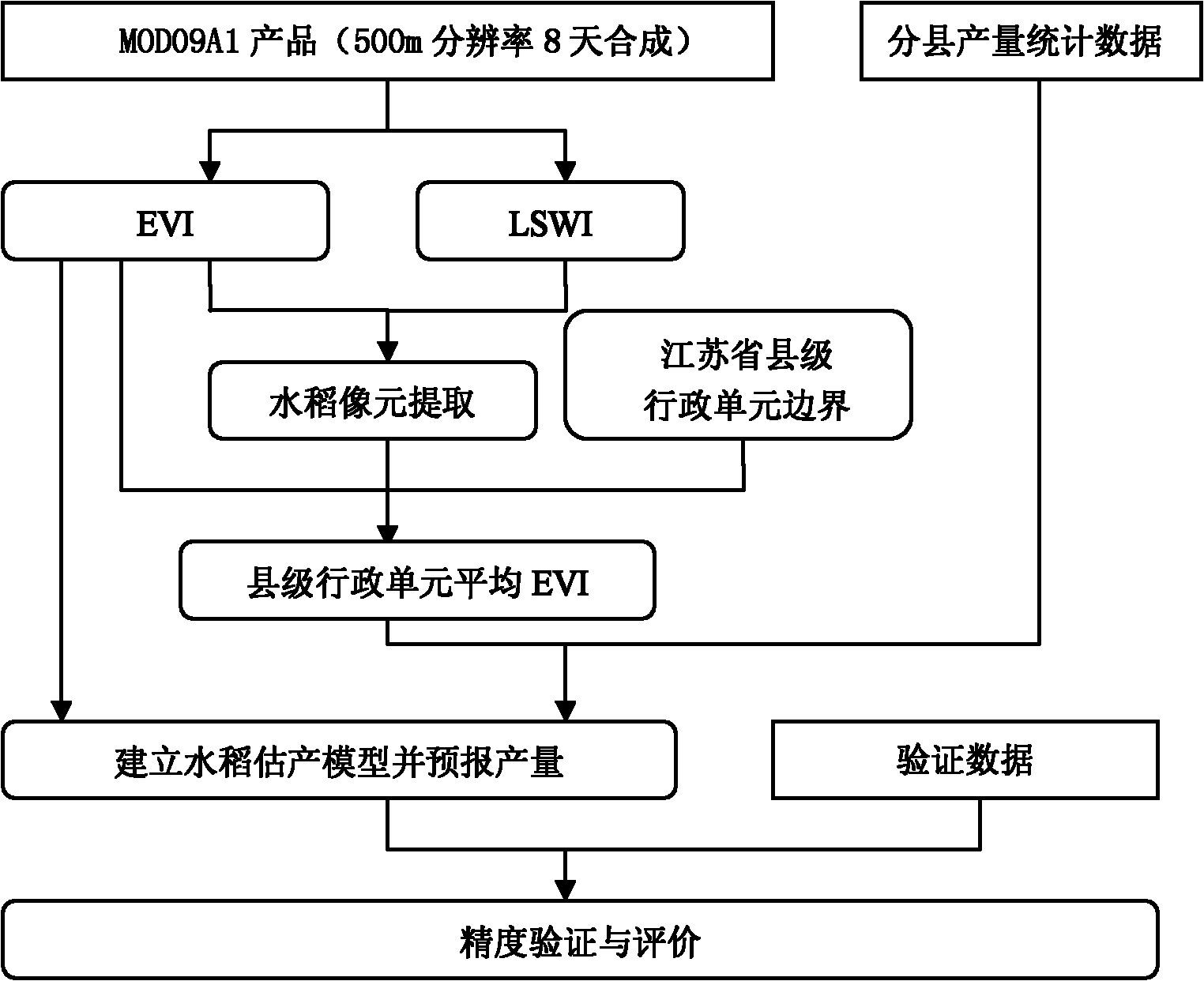
Rice yield remote sensing estimation method based on MODIS data
InactiveCN101858971AImprove monitoring accuracyImprove extraction accuracyElectromagnetic wave reradiationSensing dataTemporal resolution
The invention discloses a rice yield remote sensing estimation method based on MODIS data, which comprises: 1) acquiring the MODIS09 remote sensing data in the growth process of the rice in the region to be monitored, and calculating an vegetation index EVI and a water index LSWI; 2) extracting a rice pixel based on the relation between the water index LSW1 and the vegetation index EVI; 3) acquiring the vegetation index EVI corresponding to the rice in different stages; 4) calculating the average of the vegetation indexes EVIs of different set administrative regions in different stages to acquire the average EVI of the set administrative regions; 5) establishing a statistical model for the average EVI of the set administrative regions and the rice yield; and 6) estimating the rice yields of the set administrative regions using the vegetation index EVI in the growth period of rice in the year to be estimated, and calculating the rice yield of the region to be monitored. The temporal resolution, the spatial resolution and the estimation precision of the invention are relatively high, and the invention is applicable to monitoring rice yield in a large scale.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
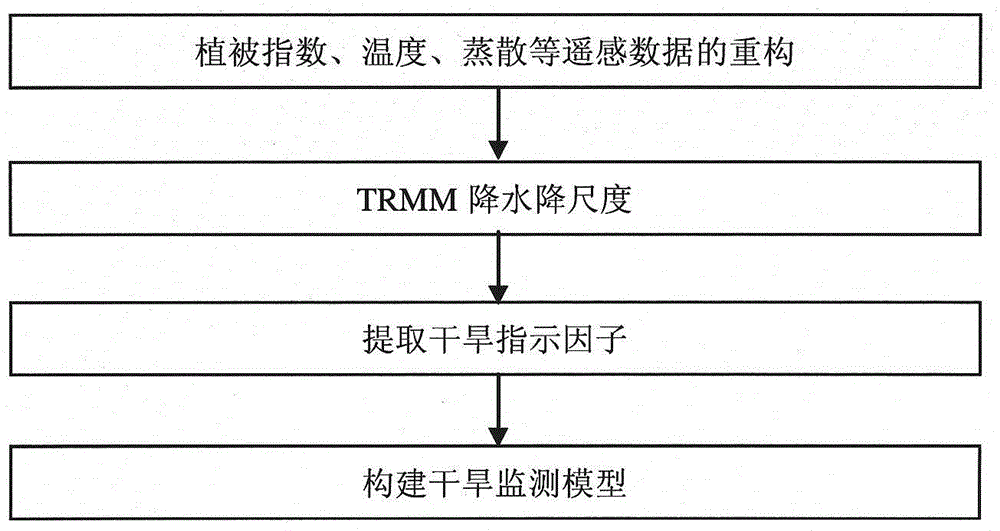
Data mining-based drought monitoring method
The invention discloses a data mining-based drought monitoring method. The method comprises the following steps: 1, data reconstruction is carried out on an MODIS vegetation index product, a land surface temperature product and an evapotranspiration product; 2, according to the vegetation index obtained in the first step and DEM data, downscaling is carried out on a TRMM rainfall product; 3, a vegetation anomaly index, a temperature anomaly index, an evapotranspiration anomaly index and a rainfall anomaly index are extracted again; and 4, a classification and regression tree model is used for building a statistical regression rule and a linear fitting model to obtain a drought monitoring model. Compared with the prior art, the method of the invention comprehensively considers multi-source remote sensing spatial information, such as the rainfall, the evapotranspiration, the vegetation growth state, the land using type, the altitude and other factors, in the case of drought monitoring, spatial data mining is adopted, the drought monitoring model is built, and the drought monitoring precision is improved.
Owner:CHINA INST OF WATER RESOURCES & HYDROPOWER RES
Method for classifying remote sensing images blended with high-space high-temporal-resolution data by object oriented technology
InactiveCN102609726AOvercome indistinguishable difficultiesSolve finelyPhotogrammetry/videogrammetryCharacter and pattern recognitionLand coverVegetation Index
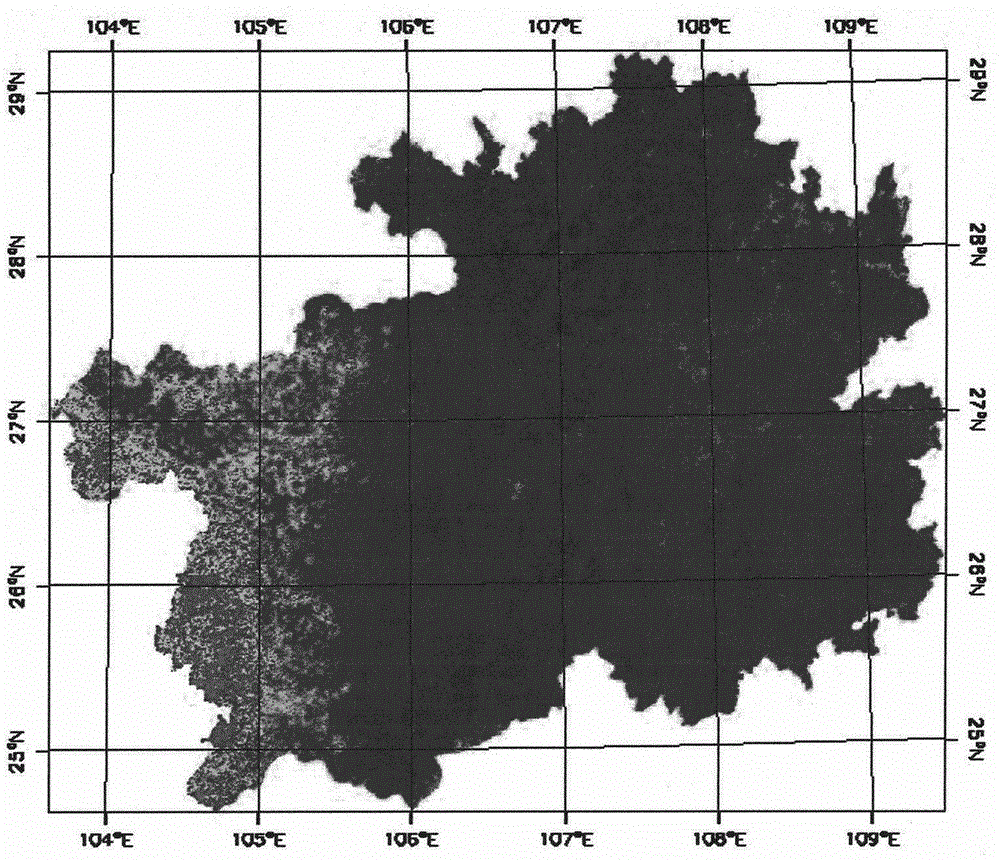
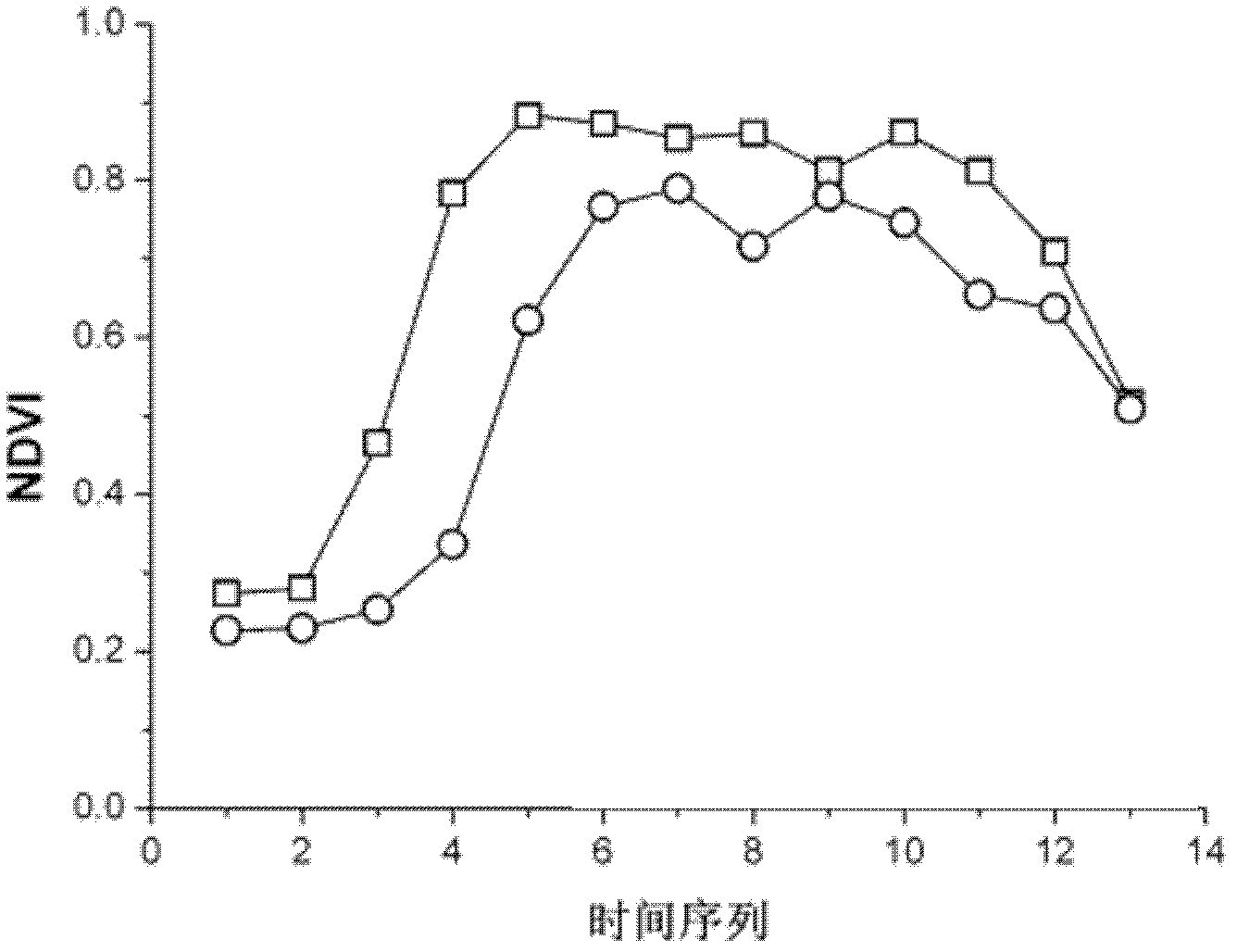
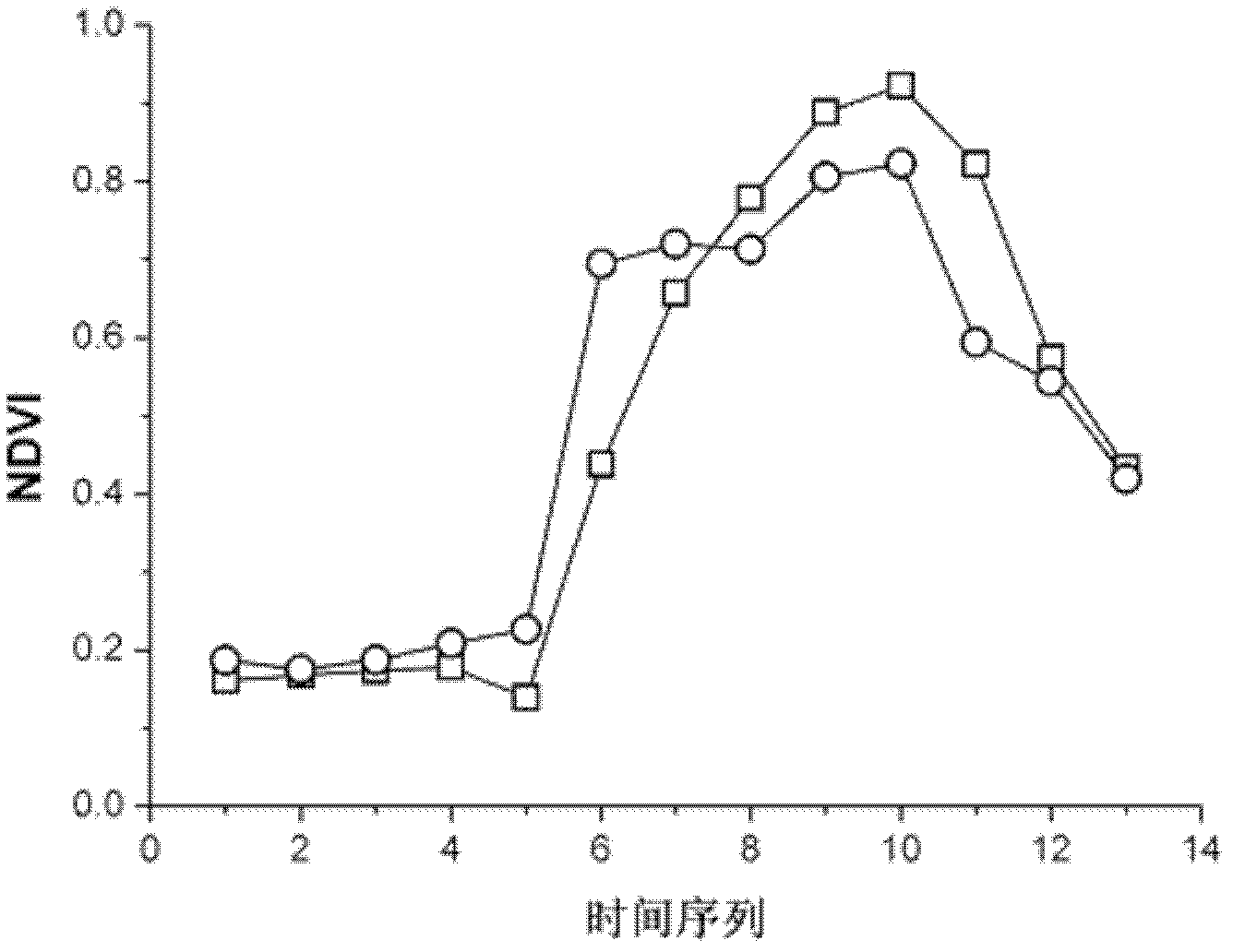
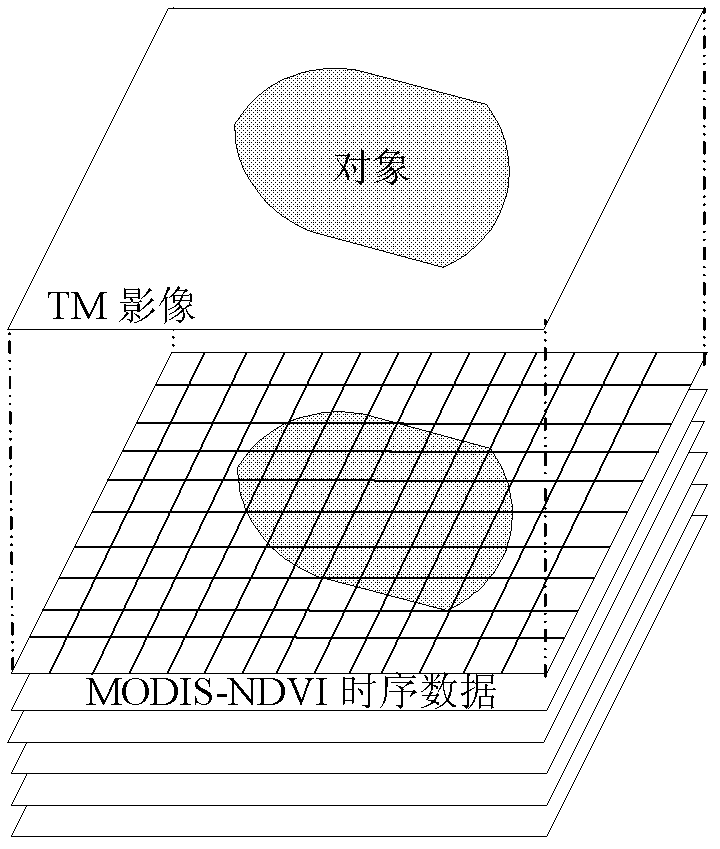
The invention discloses a method for classifying remote sensing images blended with high-space high-time resolution data by an object oriented technology, and relates to a method for classifying remote sensing images of an oriented object, which can be used for solving the problem that the previous method for classifying remote sensing images can not be used for distinguishing land cover types of 'foreign bodies with the same spectrum', and is not suitable for being applied to the remote sensing images with low-medium resolution ratio. The method provided by the invention comprises the following steps: carrying out filter processing by applying an SG (screen grid) filter; determining a time sequence curve of typical vegetational MODIS-NDVI (moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer-normalized difference vegetation index) in the remote sensing image to be classified; segmenting a TM (thematic mapper) image, wherein each segmentation unit is used as an object; extracting the characteristic information of each object; extracting all non-vegetation objects; removing the non-vegetation objects, and taking the obtained vegetational objects as planar vectors to segment MODIS-NDVI time sequence data, so as to obtain corresponding biotemperature information acquired by each vegetational object; and determining the vegetational type, to which each object belongs; and completing the land cover classification. The method provided by the invention can be used for distinguishing the land cover types.
Owner:NORTHEAST INST OF GEOGRAPHY & AGRIECOLOGY C A S
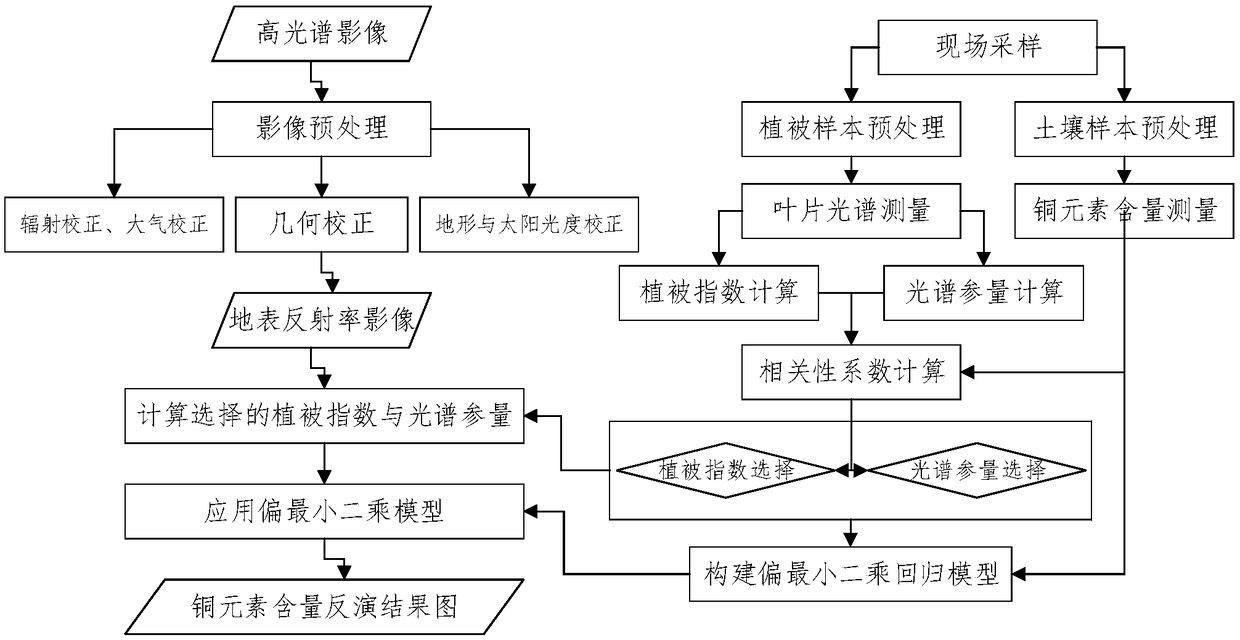
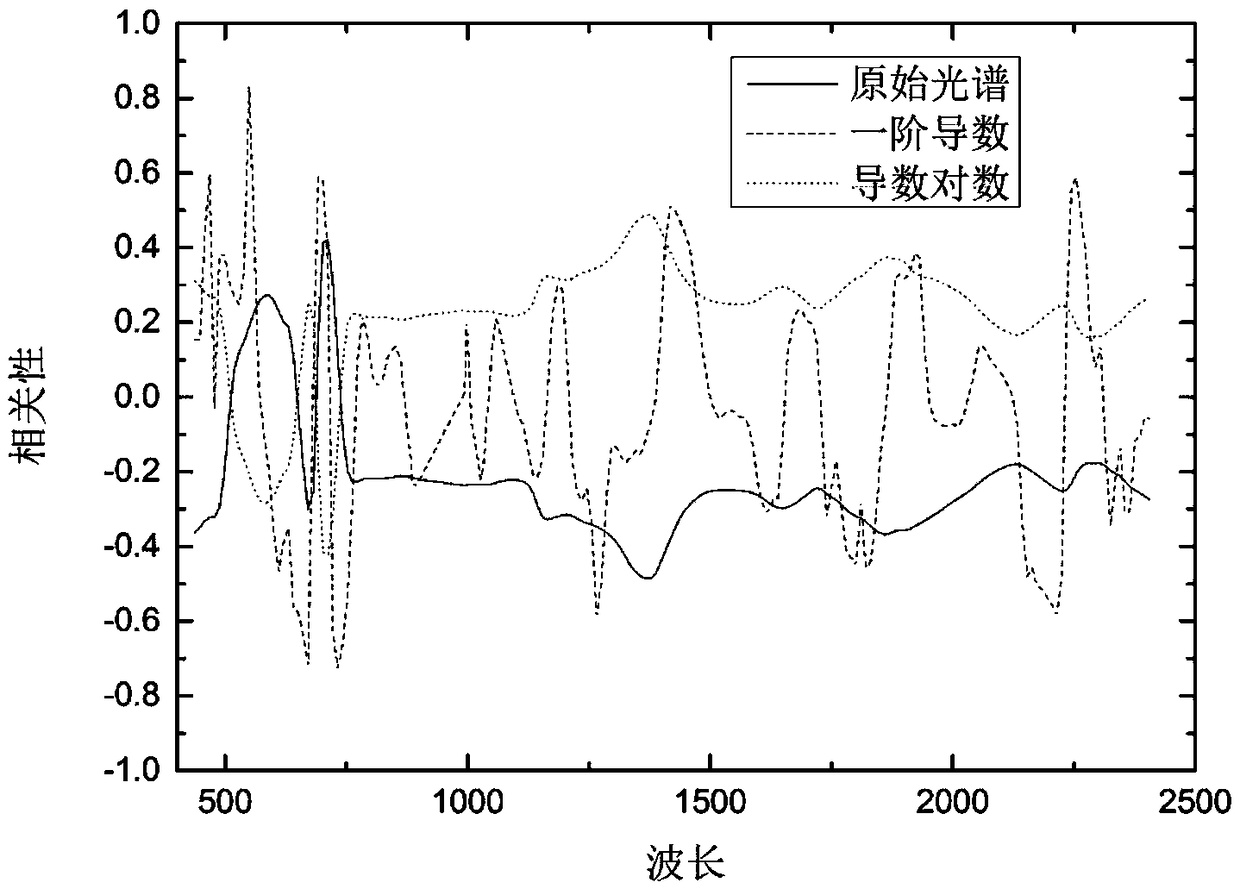
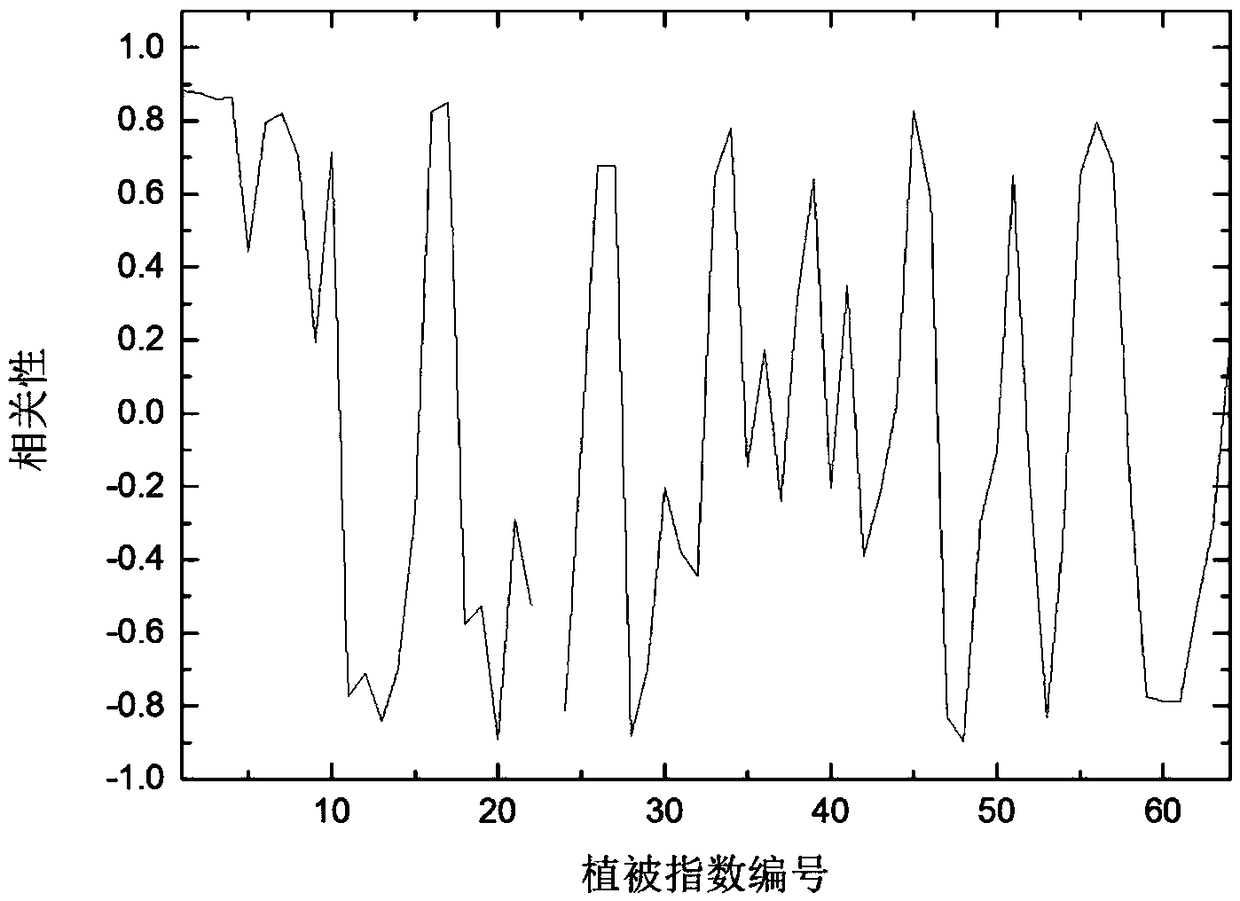
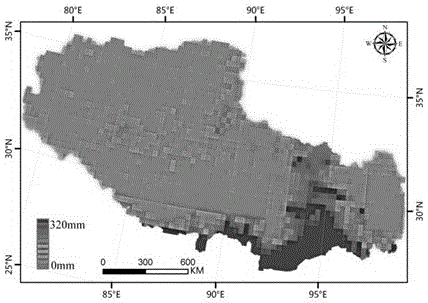
Inversion method for copper elements in soil in vegetation-covered areas on basis of measured spectra of leaves
ActiveCN108663330ALarge detectable rangeHigh speedInvestigation of vegetal materialWithdrawing sample devicesSoil heavy metalsVegetation cover
The invention relates to an inversion method for copper elements in soil in vegetation-covered areas on the basis of measured spectra of leaves. The inversion method includes steps of firstly, acquiring and preprocessing images; secondly, carrying out in-situ sampling; thirdly, processing samples; fourthly, measuring and preprocessing the spectra of the leaves; fifthly, measuring the contents of the copper elements in the soil samples; sixthly, computing vegetation indexes and spectral parameters; seventhly, analyzing correlations and selecting parameters; eighthly, building models; ninthly, carrying out large-area inversion on the content of the copper elements in the soil. The inversion method has the advantages that images of the content of the copper elements in the large-area soil inthe vegetation-covered areas can be obtained, accordingly, indication information and mineral exploration clues can be provided to mineral resource investigation, and scientific bases can be providedto land quality evaluation and soil comprehensive treatment; heavy metal pollution diffusion conditions of the soil and control effect evaluation can be obtained on the basis by means of multi-temporal analysis; the inversion method is wide in detectable range and high in speed, monitoring can be carried out in real time, and the like.
Owner:中国自然资源航空物探遥感中心
TRMM (Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission) satellite rainfall data downscaling method based on M5-Local
ActiveCN105160192APrecise Rainfall ForecastImprove spatial resolutionWeather condition predictionSpecial data processing applicationsTerrainSatellite rainfall
The invention discloses a TRMM (Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission) satellite rainfall product downscaling method based on M5-Local and a multi-environmental factor variable. An M5-Local regression thought is adopted, and a plurality of environment stress factors with high spatial resolutions are fully utilized to improve the spatial resolution of the product. Firstly, 1km environmental variable factors, such as eight pieces of data including a vegetation index, a digital elevation model, a daytime surface temperature, a night surface temperature, a terrain moisture index, a gradient, a slope aspect and a slope length gradient, are subjected to aggregate calculating to obtain 25km which serves as an independent variable, corresponding 25km-resolution TRMM data is used as a dependent variable, an M5-Local method is adopted for modeling, the intercept of a regression modeling equation of 1km spatial resolution and a slope parameter corresponding to each environment factor variable are predicted, and a 1kmTRMM rainfall value is calculated. A downscaling result based on an M5-Local model is obviously superior to a downscaling result of a conventional regression model.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
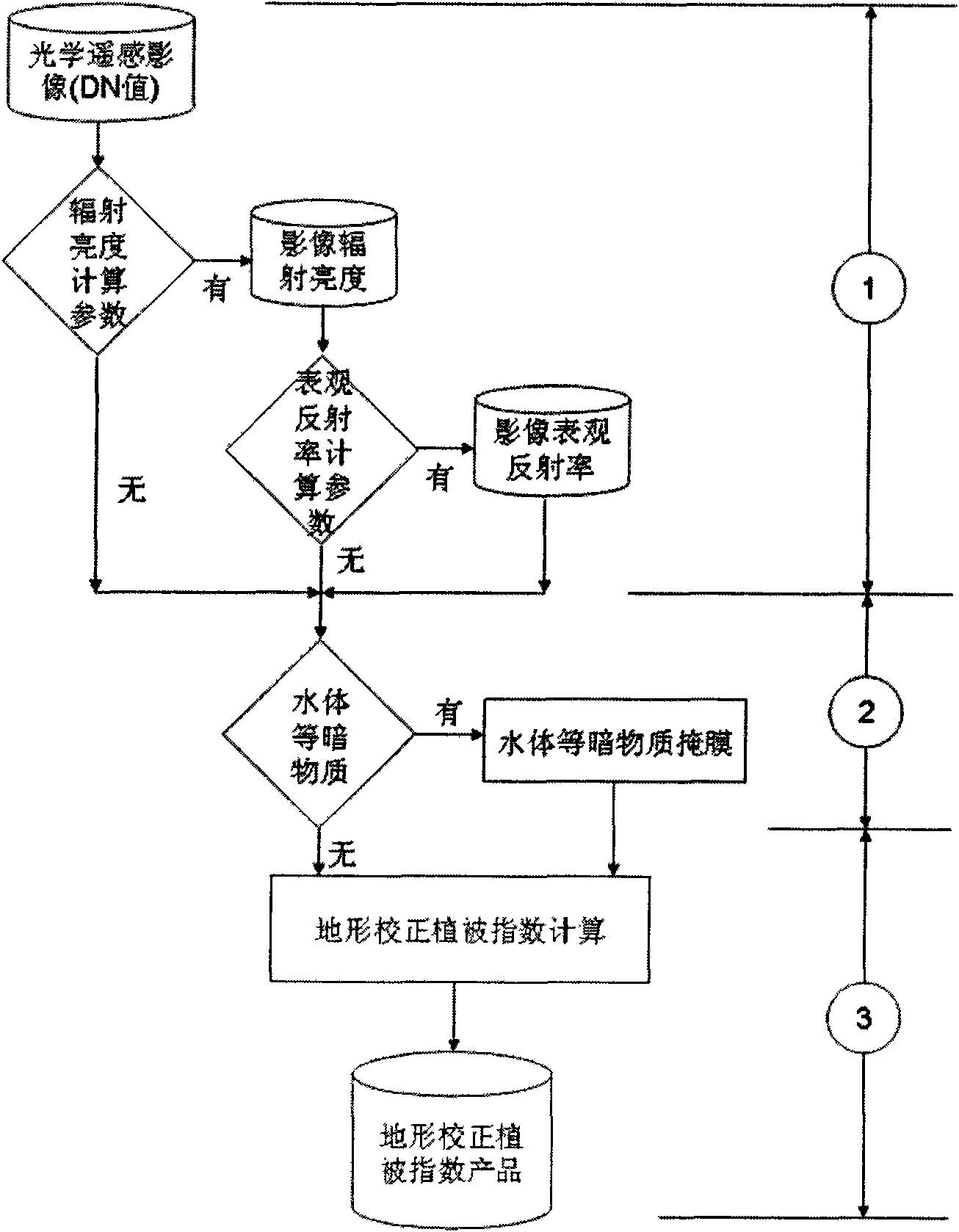
Constructing method for topographic correction vegetation index
InactiveCN101561502AAvoid interferenceEliminate differencesRadio wave reradiation/reflectionVegetationDark matter
The invention relates to a constructing method for topographic correction vegetation index, comprising the following steps of: (1) carrying out radiative correction with different degrees according to obtained optical remote sensing image data source; (2) carrying out judgment and processing to nonvegetated dark matters; and (3) carrying out calculation to topographic correction vegetation index (TCVI). The method is adopted to construct the topographic correction vegetation index, thus making up the defect that the existing vegetation index can not eliminate topographic influence and eliminating the dependence to the topographic correction method based on DEM data. The invention can quantitatively and fast reflect the vegetable information of mountain areas only by needing two wave bands of data, namely an infrared wave band and a near-infrared wave band.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
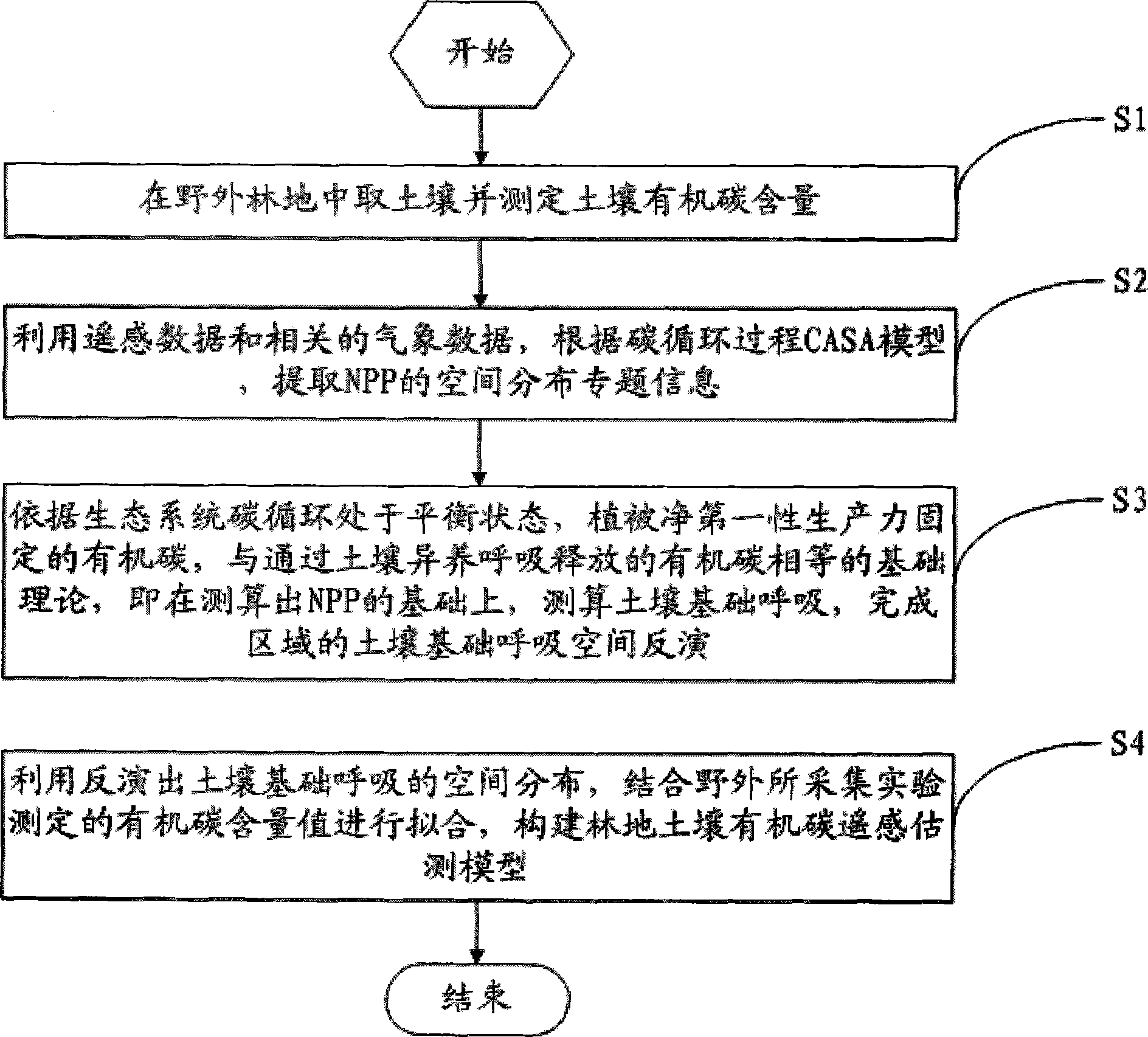
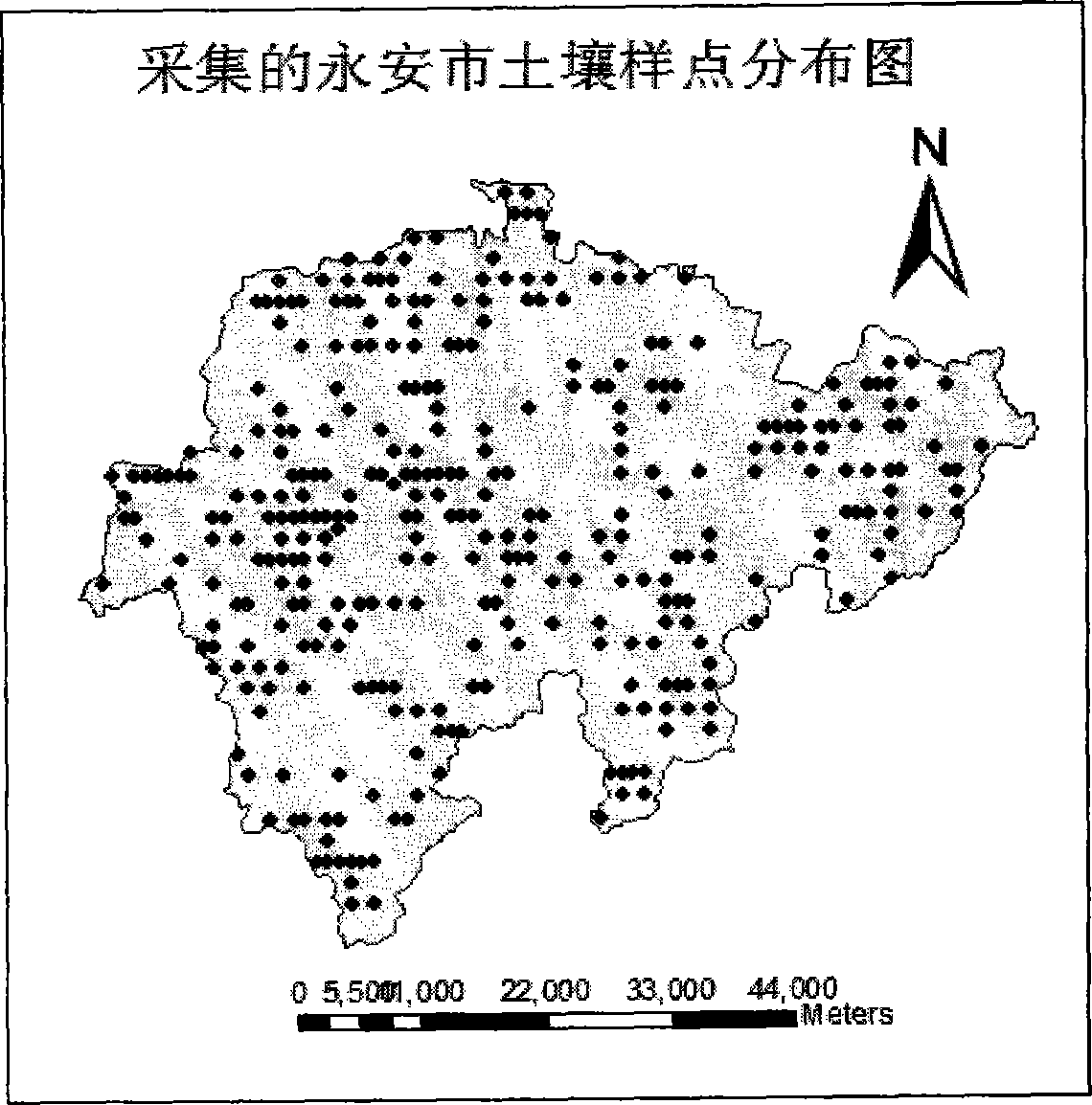
Method for remote sensing and estimating woodland soil organic carbon
InactiveCN104166782ARealization of Remote Sensing Estimation ResearchSpecial data processing applicationsCarbon storageModel parameters
The invention provides a method for remote sensing and estimating woodland soil organic carbon. As image elements of a remote sensing image of a woodland vegetation-covered area are manifested to be the spectral signature of vegetation, and a remote sensing image vegetation index NDVI is the vegetation index which is applied most widely at present, is most applicable, and can be widely applied to the estimation study of the primary productivity of the vegetation. For this, according to the method, by means of a CASA ecological process model, when the NDVI remote sensing data utilizing the high-resolution remote sensing image for reflecting regional difference are applied to a traditional soil organic carbon estimating model, model parameters with the spatial heterogeneity are simplified into constants, the defect of lowering the estimation precision is overcome, a relation model of the soil organic carbon storage amount and soil foundation breathing is set up according to the soil foundation breathing coefficient having the close relation with the soil organic carbon storage amount, and the remote sensing and estimating study of the woodland soil organic carbon can be achieved.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
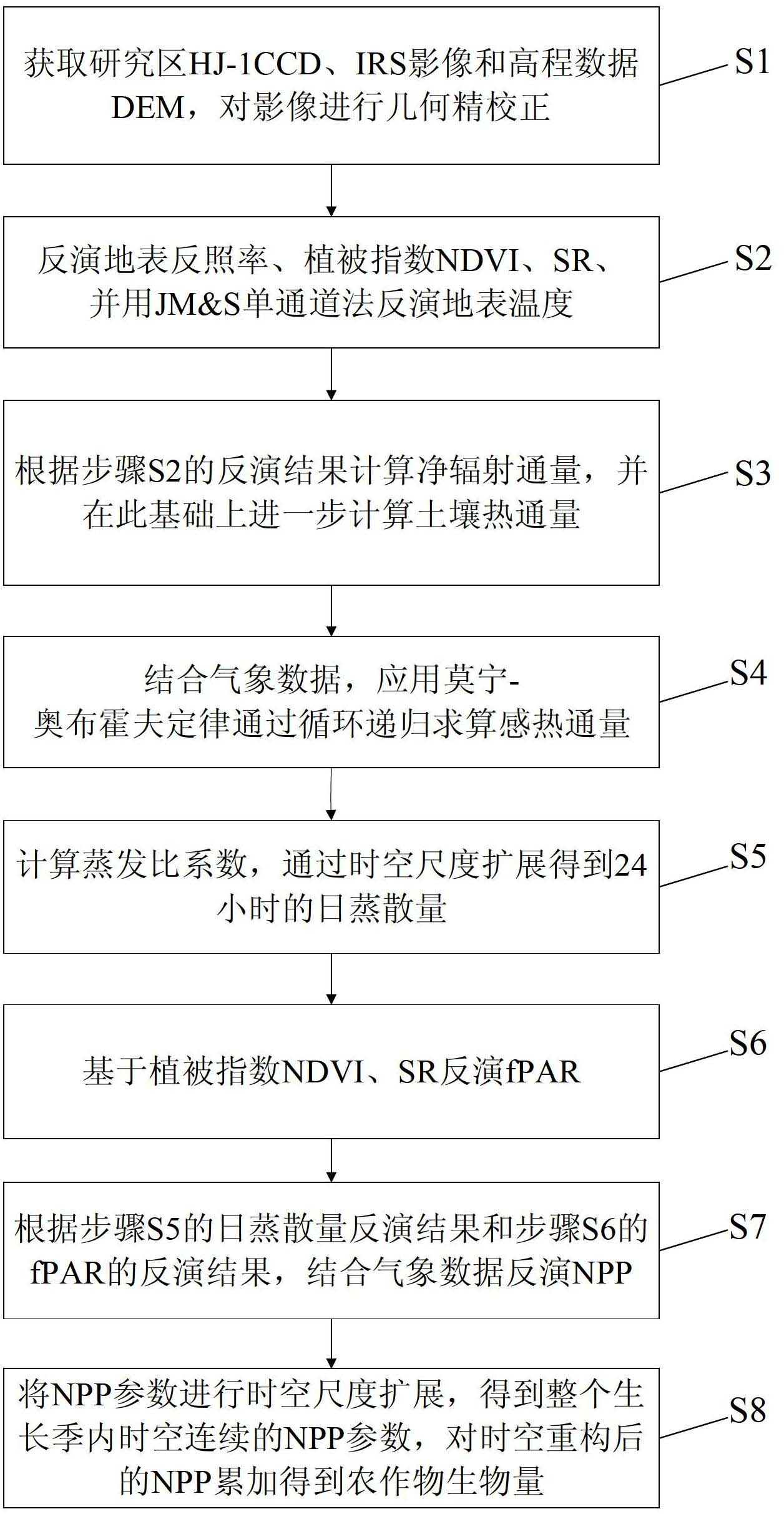
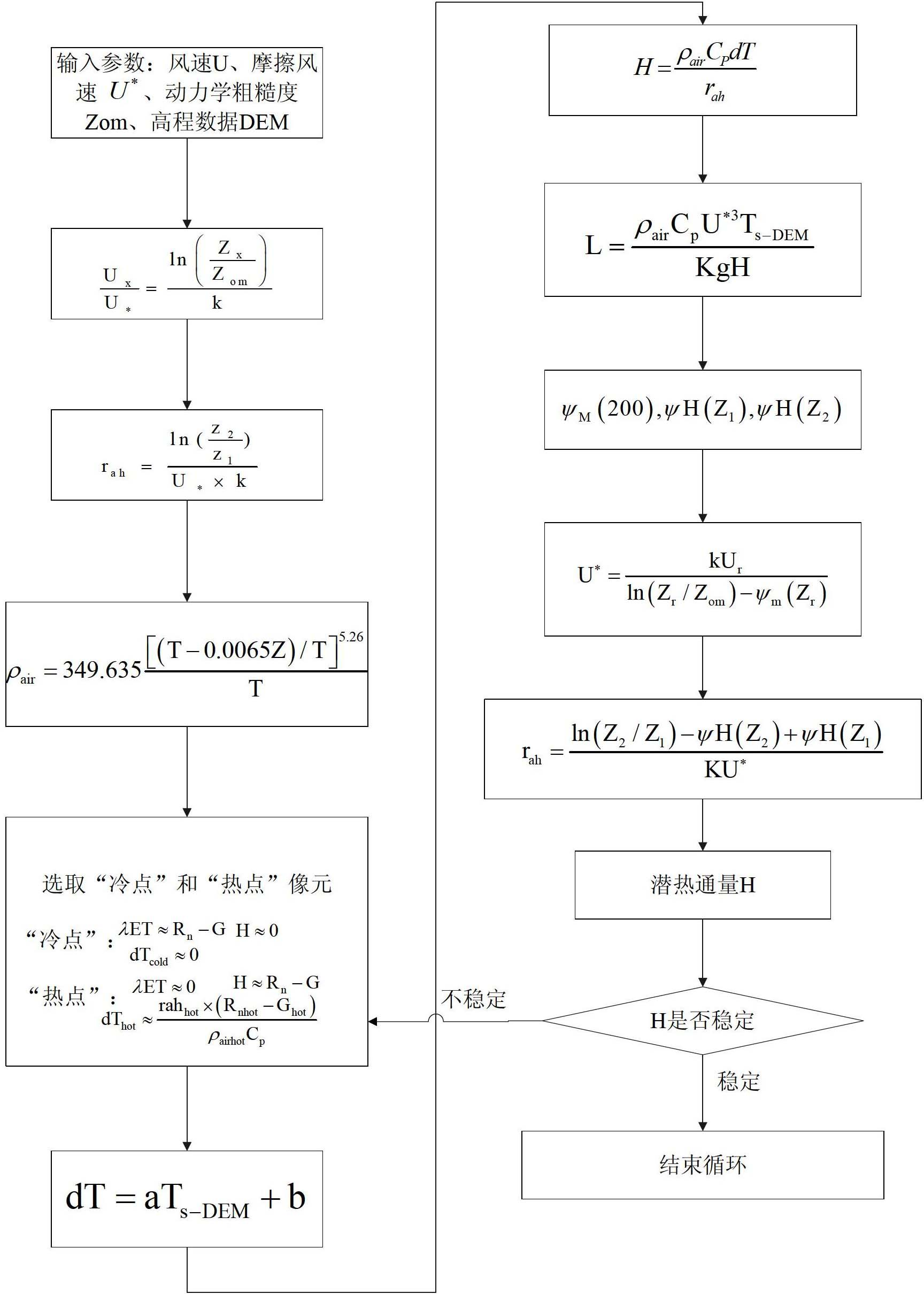
Crop biomass inversion method based on SEBAL-HJ model
ActiveCN102650587AImprove inversion accuracyMaterial analysis by optical meansCyclic reductionEvaporation
The invention discloses a crop biomass inversion method based on a SEBAL-HJ model. The crop biomass inversion method is characterized by comprising the following steps: S1, acquiring HJ-1 CCD, IRS images and elevation data DEM in a research plot, and carrying out geometric fine revision to the images; S2, inversing a land surface albedo, NDVI, SR, land surface emissivity and inversing land surface temperature; S3, calculating net radiation flux according to inversion results in the S2, and further calculating soil heat flux on the basis; S4, calculating sensible heat flux through cyclic reduction; S5, calculating the coefficient of evaporation ratio and obtaining evapotranspiration per day through space-time dimension expansion; S6, inversing fPAR on the basis of vegetative cover indexes NDVI and SR; S7, inversing NPP according to the inversion results of evapotranspiration per day in the step S5 and the inversion results of fPAR in the step S6; and S8, obtaining crop biomass through the accumulation of NPP after space-time reconstruction. According to the invention, the high-precision inversion of crop biomass is achieved, and the amount of calculation is relatively smaller.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
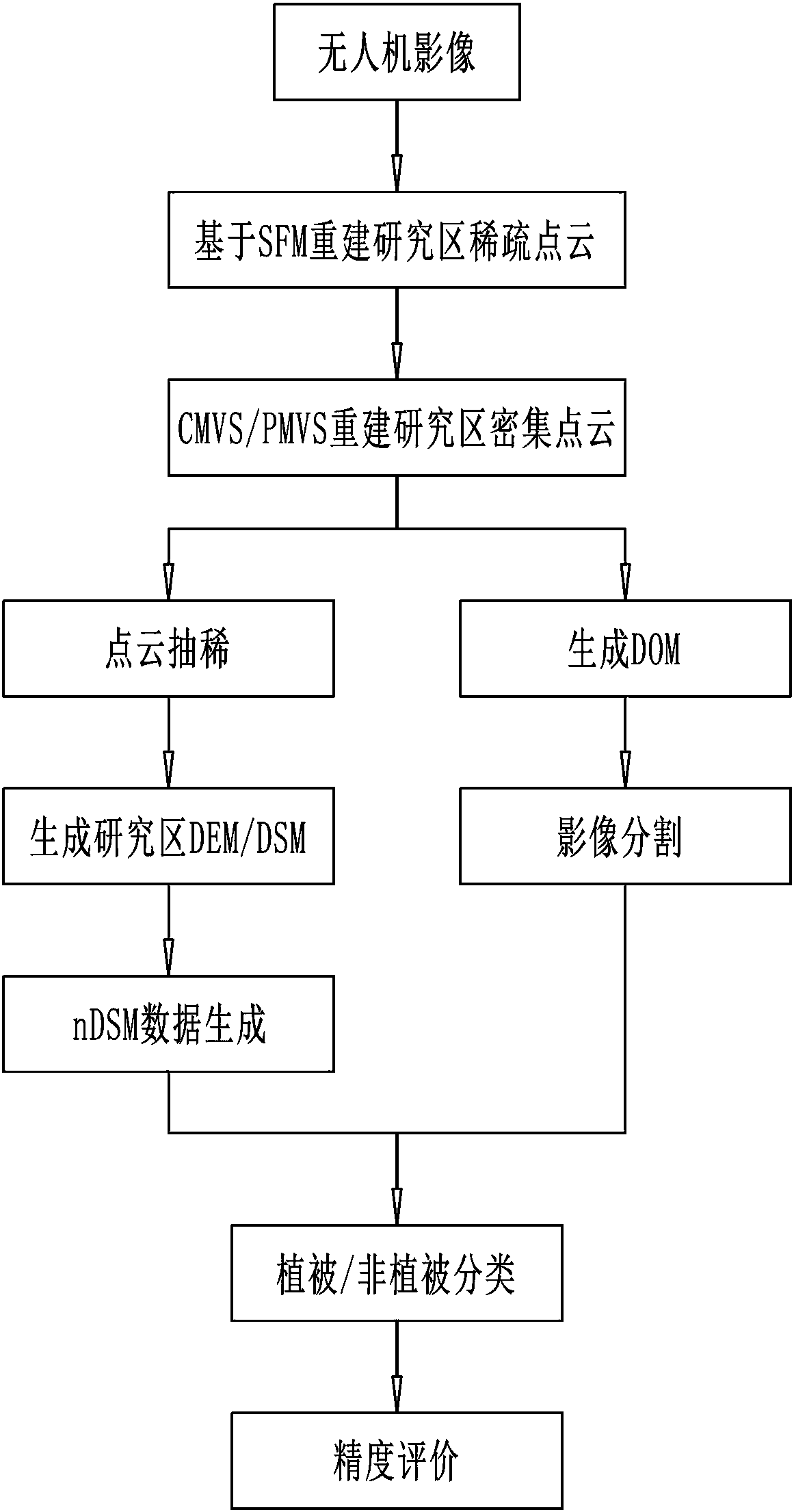
Urban vegetation classification method based on unmanned aerial vehicle images and reconstructed point cloud
ActiveCN108363983AHigh precisionImprove classification efficiencyCharacter and pattern recognitionStructure from motionPoint cloud
The present invention provides an urban vegetation classification method based on unmanned aerial vehicle images and reconstructed point cloud. The method comprises the steps of: performing point cloud reconstruction of original unmanned aerial vehicle images; generating nDSM (normalized digital surface model) information of a research area; performing vegetation index calculation based on visiblelight; and performing classification discrimination of image objects. The method provided by the invention reconstructs point cloud of the research area based on a structure from motion (SFM) and cluster multi-view stereo (CMVS) and based on a patch-based multi-view stereo (PMVS) algorithm, performs filtering and interpolation to generate a digital elevation model (DEM) of the research area and the nDSM, and combines image spectral information to perform classification extraction of urban vegetations with different heights; an image analysis method facing the objects is employed to achieve differentiation of the categories of vegetations with different heights according to spectral information such as the nDSM information, normalized green-red difference indexes (NGRDI) and visible lightwave band difference vegetation indexes (VDVI) so as to greatly improve the differentiation precision.
Owner:HENAN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
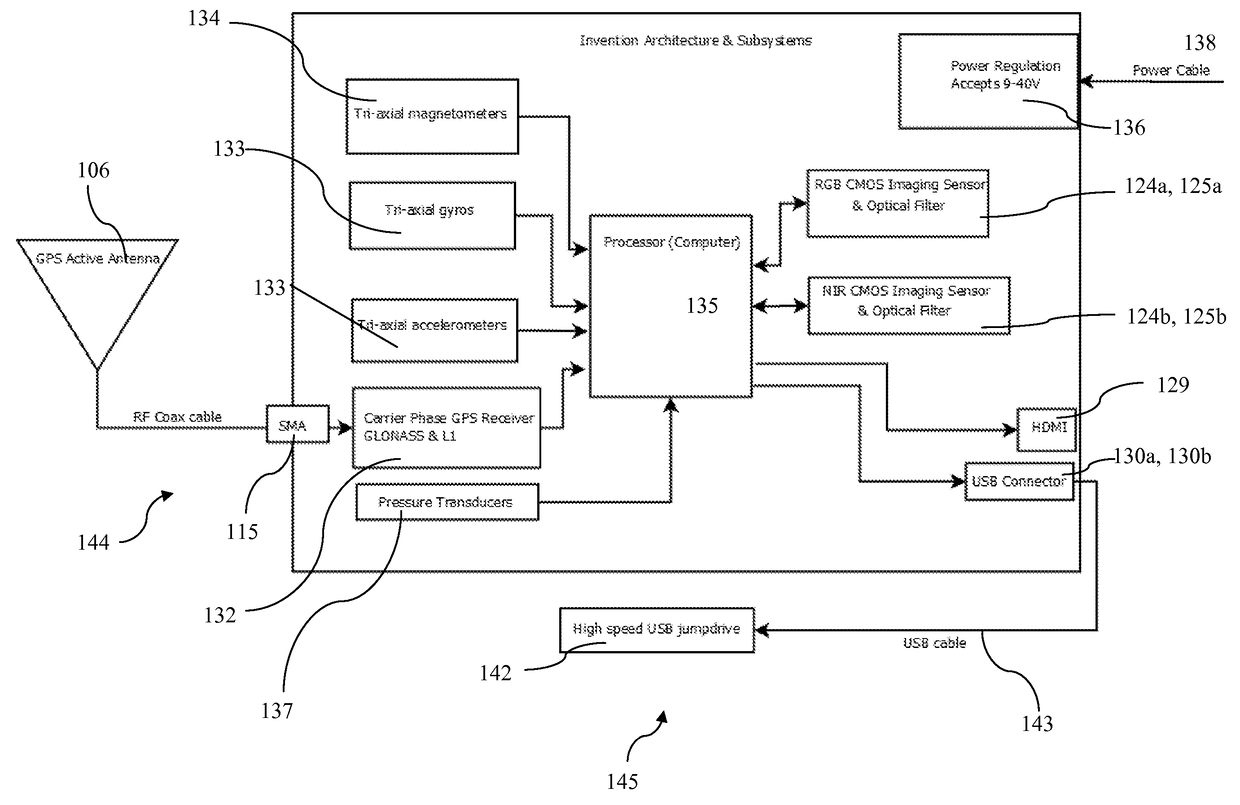
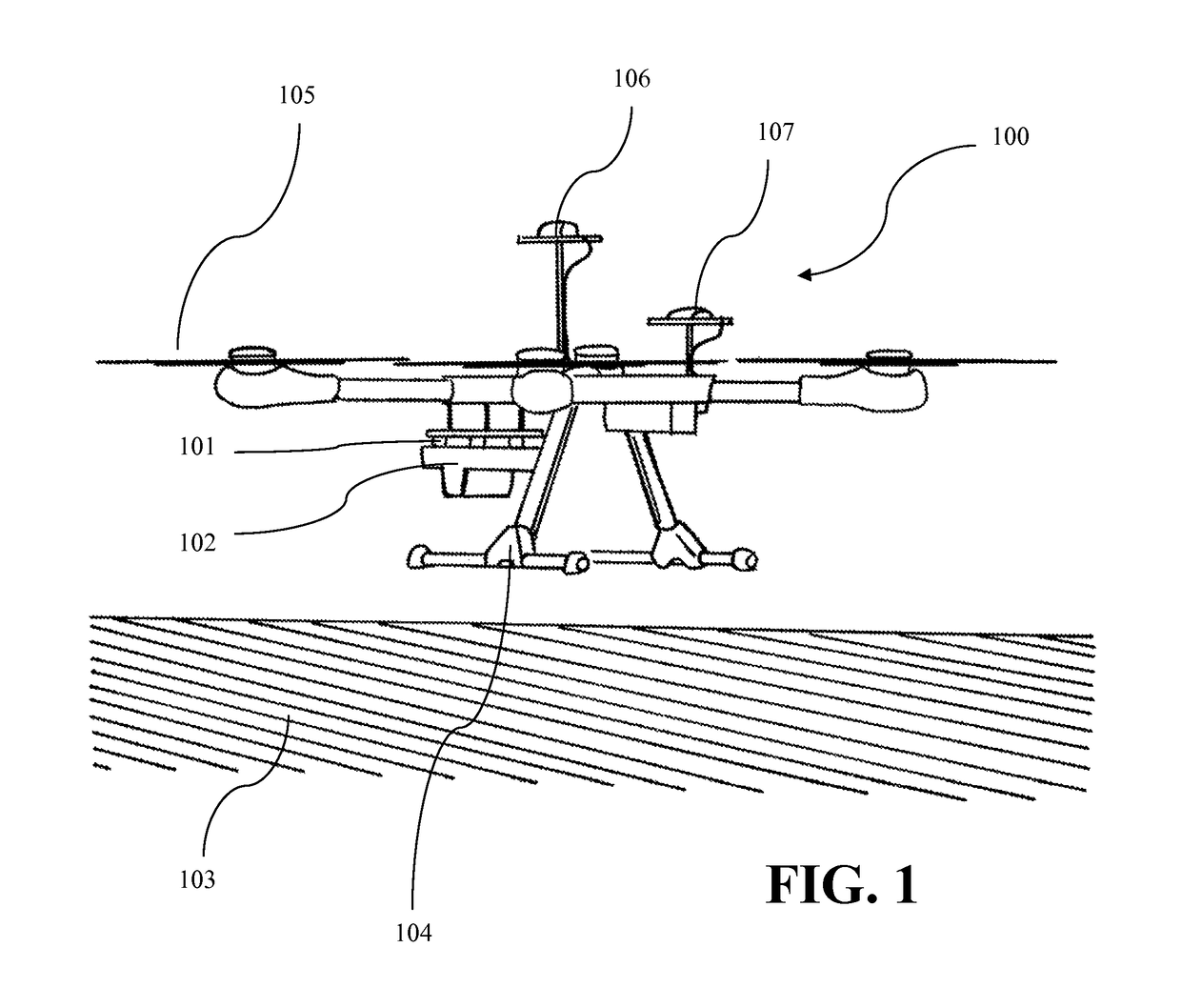
Airborne multispectral imaging system with integrated navigation sensors and automatic image stitching
ActiveUS9945828B1Precise and accurate and and scanImage enhancementTelevision system detailsImaging processingVegetation Index
A self-contained UAV sensor payload and on-board or off-board hardware and software for precision agriculture. The invention combines multiple cameras and navigation sensors to create a system for automatically collecting, geo-referencing, and stitching red, green, blue, and near infrared imagery and derived vegetation indices. The invention is able to produce all of these quantities in a single flight. The tight integration with integrated navigation sensors eliminates the need for integration with external sensors or avionics hardware and enables innovative solutions to image processing and analysis which greatly improve accuracy, processing speed, and reliability over alternative approaches.
Owner:SENTEK SYST LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com
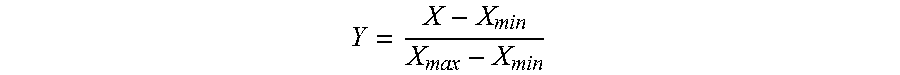
![[method and system for spatially variable rate application of agricultural chemicals based on remotely sensed vegetation data] [method and system for spatially variable rate application of agricultural chemicals based on remotely sensed vegetation data]](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/ede7f514-cdac-4070-bc9e-ad4f8ca51105/US20050149235A1-20050707-D00000.png)
![[method and system for spatially variable rate application of agricultural chemicals based on remotely sensed vegetation data] [method and system for spatially variable rate application of agricultural chemicals based on remotely sensed vegetation data]](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/ede7f514-cdac-4070-bc9e-ad4f8ca51105/US20050149235A1-20050707-D00001.png)
![[method and system for spatially variable rate application of agricultural chemicals based on remotely sensed vegetation data] [method and system for spatially variable rate application of agricultural chemicals based on remotely sensed vegetation data]](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/ede7f514-cdac-4070-bc9e-ad4f8ca51105/US20050149235A1-20050707-D00002.png)