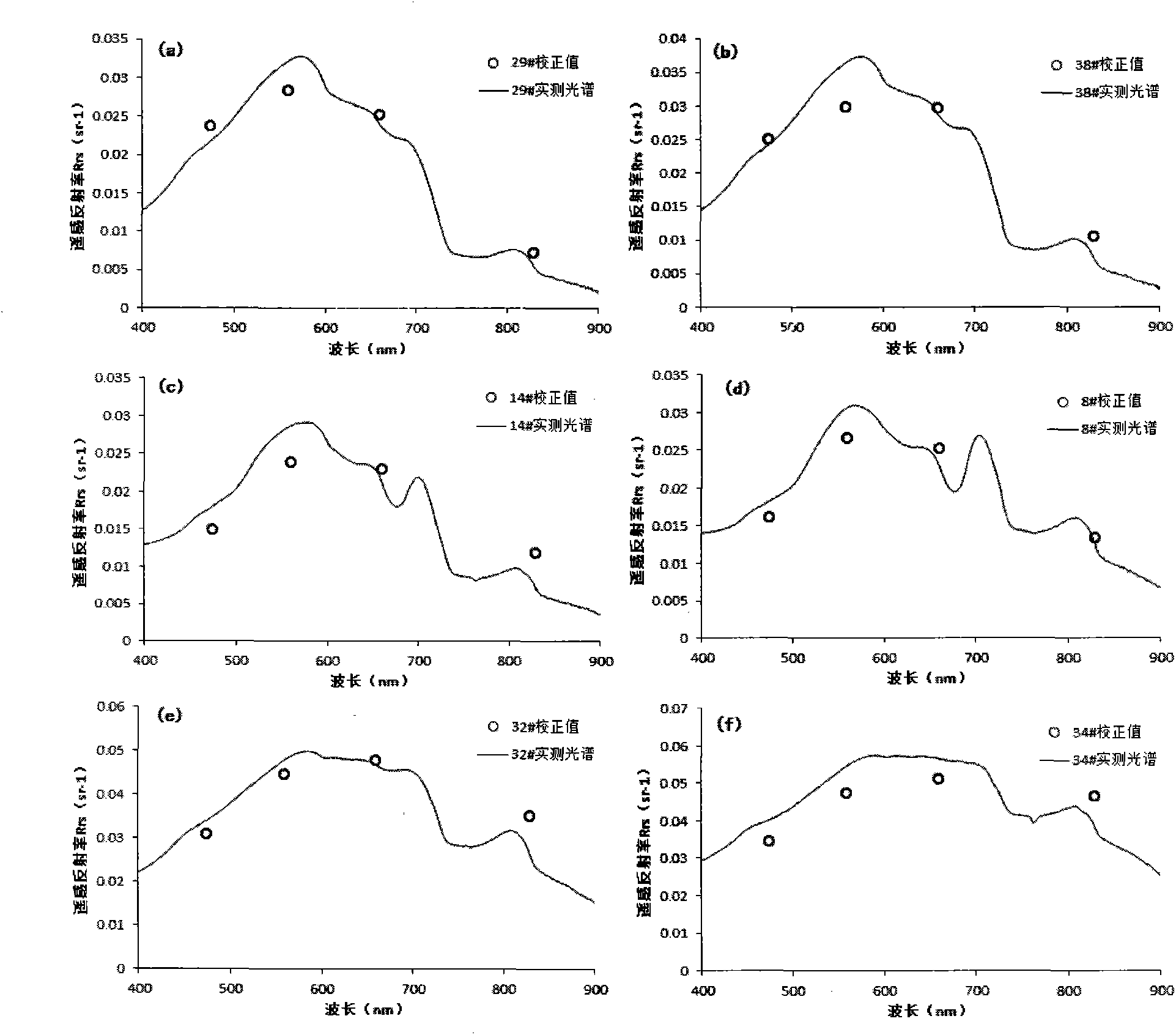
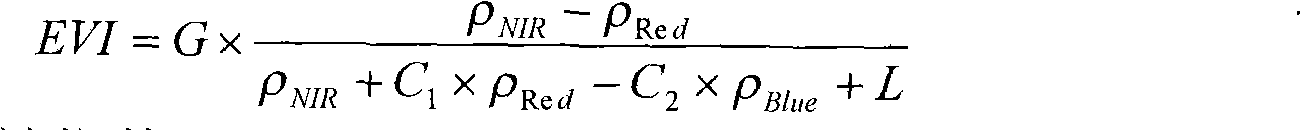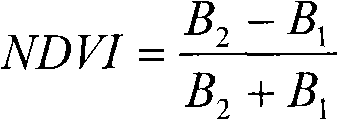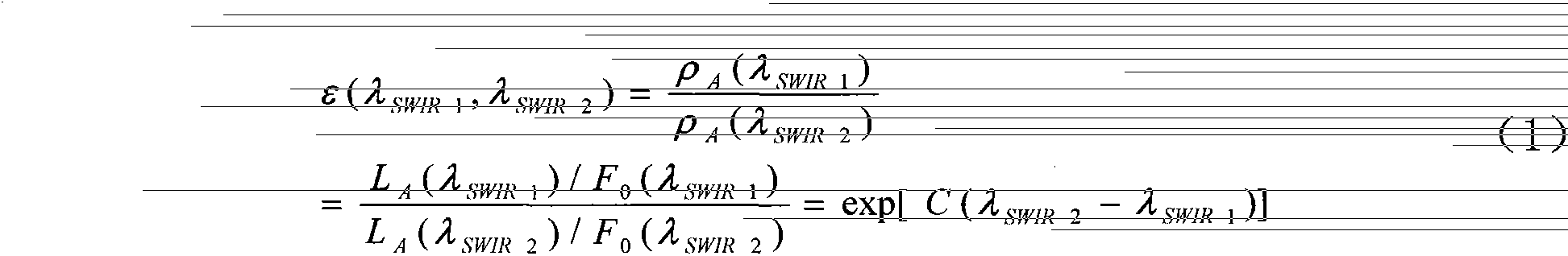Patents
Literature
74 results about "Moderate-resolution imaging spectroradiometer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) is a payload imaging sensor built by Santa Barbara Remote Sensing that was launched into Earth orbit by NASA in 1999 on board the Terra (EOS AM) satellite, and in 2002 on board the Aqua (EOS PM) satellite. The instruments capture data in 36 spectral bands ranging in wavelength from 0.4 µm to 14.4 µm and at varying spatial resolutions (2 bands at 250 m, 5 bands at 500 m and 29 bands at 1 km). Together the instruments image the entire Earth every 1 to 2 days. They are designed to provide measurements in large-scale global dynamics including changes in Earth's cloud cover, radiation budget and processes occurring in the oceans, on land, and in the lower atmosphere. MODIS utilizes four on-board calibrators in addition to the space view in order to provide in-flight calibration: solar diffuser (SD), solar diffuser stability monitor (SDSM), spectral radiometric calibration assembly (SRCA), and a v-groove black body. MODIS has used the marine optical buoy for vicarious calibration. MODIS is succeeded by the VIIRS instrument on board the Suomi NPP satellite launched in 2011 and future Joint Polar Satellite System (JPSS) satellites.
MODIS data-based agricultural drought monitoring method
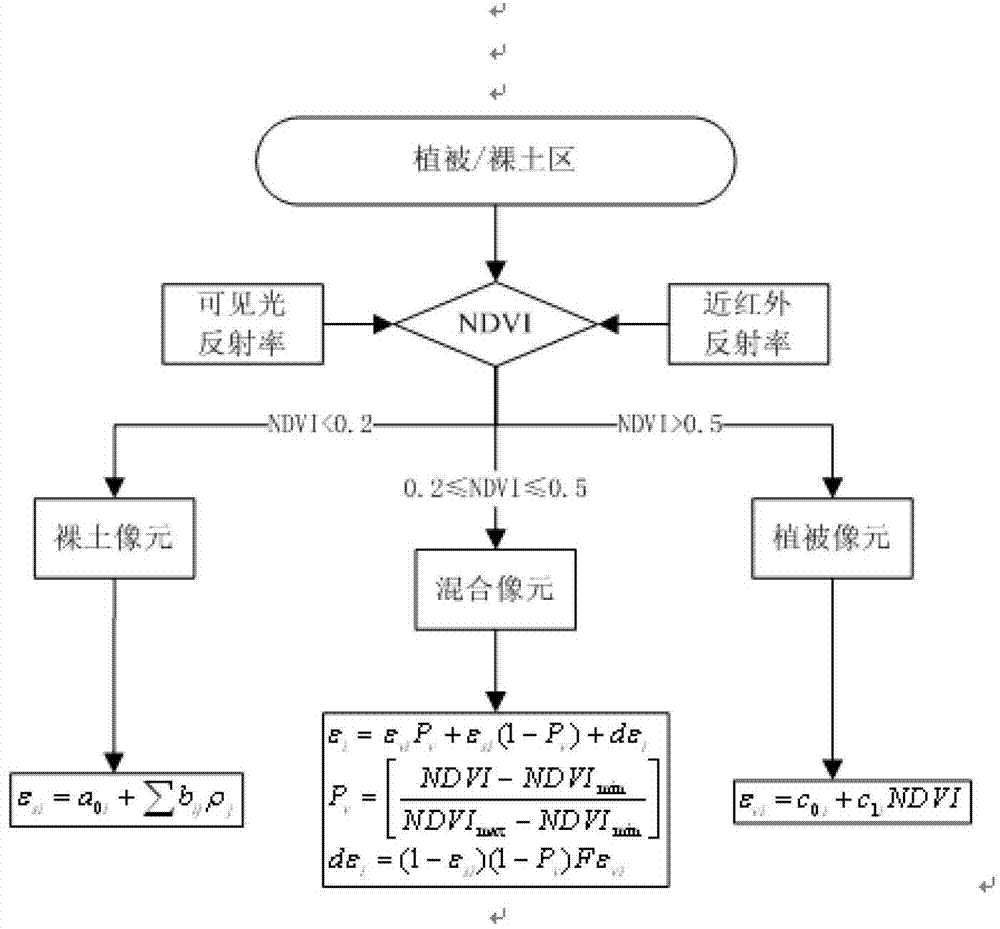
InactiveCN102103077ASuppress high valuesPromote resultsScattering properties measurementsElectromagnetic wave reradiationVegetation IndexModerate-resolution imaging spectroradiometer
The invention discloses a moderate-resolution imaging spectroradiometer (MODIS) data-based agricultural drought monitoring method. In the farmland drought monitoring process, an agricultural drought index is determined by a crop water supply index and a rainfall anomaly index; in the drought monitoring process, a vegetation index and the surface temperature are inverted by MODIS data, and the crop water supply index is calculated by the vegetation index and the surface temperature; the rainfall anomaly index is calculated by rainfall data; and drought severity is determined by dividing the level of the drought index.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF APPL ECOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
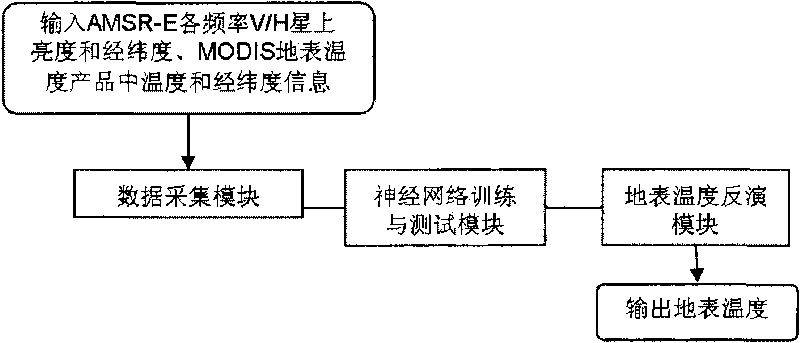
Method by utilizing passive microwave remote sensing data AMSR-E (Advanced Microwave Scanning Radiometer-EOS ) to invert surface temperature
InactiveCN101738620AAvoid difficultiesReduce unknownsElectromagnetic wave reradiationICT adaptationEarth observationData set
The invention relates to a method by utilizing passive microwave remote sensing data AMSR-E to invert surface temperature. The method comprises three steps of: step 1, collecting MODIS (moderate-resolution imaging spectroradiometer) surface temperature product which is provided by an American Earth Observation Data Center and used as AMSR-E surface temperature data by latitude and longitude control, and establishing a training and testing database; step 2, utilizing a neutral network to perform repetitive training and testing; and step 3, performing inversion calculation on AMSR-E actual image data, and actual surface verification and application analysis. The product obtained by the method has high precision, and overcomes the effect of clouds and partial raining on thermal infrared.
Owner:INST OF AGRI RESOURCES & REGIONAL PLANNING CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
High-precision monitoring method for cyanobacterial blooms in large shallow lake through MODIS (Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer) and satellite
ActiveCN103743700AReflect accuracyReflect its spatio-temporal distributionMaterial analysis by optical meansElectromagnetic wave reradiationModerate-resolution imaging spectroradiometerShallow lake
The invention discloses a high-precision monitoring method for cyanobacterial blooms in a large shallow lake through an MODIS (Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer) and a satellite. The high-precision monitoring method is characterized by comprising the following steps: screening recognition indexes of the cyanobacterial blooms (short for algal blooms) which are insensitive to the type and thickness of an atmospheric aerosol; combining the synchronous MODIS, LandsatTM / ETM and satellite image in 2000-2013 year and a gradient analysis result of land and water information to obtain a pure pixel index threshold value of the algal blooms; precisely calculating the area of the algal blooms in a mixed pixel (part of pixels covered by the algal blooms) of the algal blooms by using a pixel growth algorithm (APA); and furthermore, estimating the actual area of the algal blooms in the total water area of the lake and the areal distribution of the algal blooms. The high-precision monitoring method can be used for precisely obtaining the spatial and temporal distribution of the algal blooms in the shallow lake, accurately analyzing the generation and development condition and trend of the algal blooms, scientifically estimating the lake pollution control and ecological remediation effects and providing the scientific and technological support for making a scientific decision for water resource management and water environment protection of departments of water conservation, environment protection and the like.
Owner:NANJING INST OF GEOGRAPHY & LIMNOLOGY
Grassland dry matter mass remote sensing estimating method
ActiveCN102393238APromote healthy and sustainable developmentMaintain ecological balanceWeighing apparatusData acquisitionRemote sensing application
The invention discloses a grassland dry matter mass remote sensing estimating method, which belongs to the field of remote sensing application. The method comprises the following steps of: collecting and processing field test data; downloading and processing Modis (Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer) satellite data; analyzing and modeling the data and detecting the accuracy and the like. The method for establishing a ground spectrum model for predicating ground dry matter mass and correcting a Modis spectrum model through ground hyperspectral experiments is different from the method for directly predicating biomass liveweight by using NDVI (Normalized Difference Vegetation Index) data of the Modis remote sensing satellite in other like researches so that the grassland dry matter mass remote sensing estimating method is helpful for improving the predicating accuracy, is beneficial for scientific management and reasonable utilization of the grassland resources and has important practical significance in correct evaluation of the real productivity of the grassland and the sustainable use of the grass resources.
Owner:高吉喜
Method for classifying remote sensing images blended with high-space high-temporal-resolution data by object oriented technology
InactiveCN102609726AOvercome indistinguishable difficultiesSolve finelyPhotogrammetry/videogrammetryCharacter and pattern recognitionLand coverVegetation Index
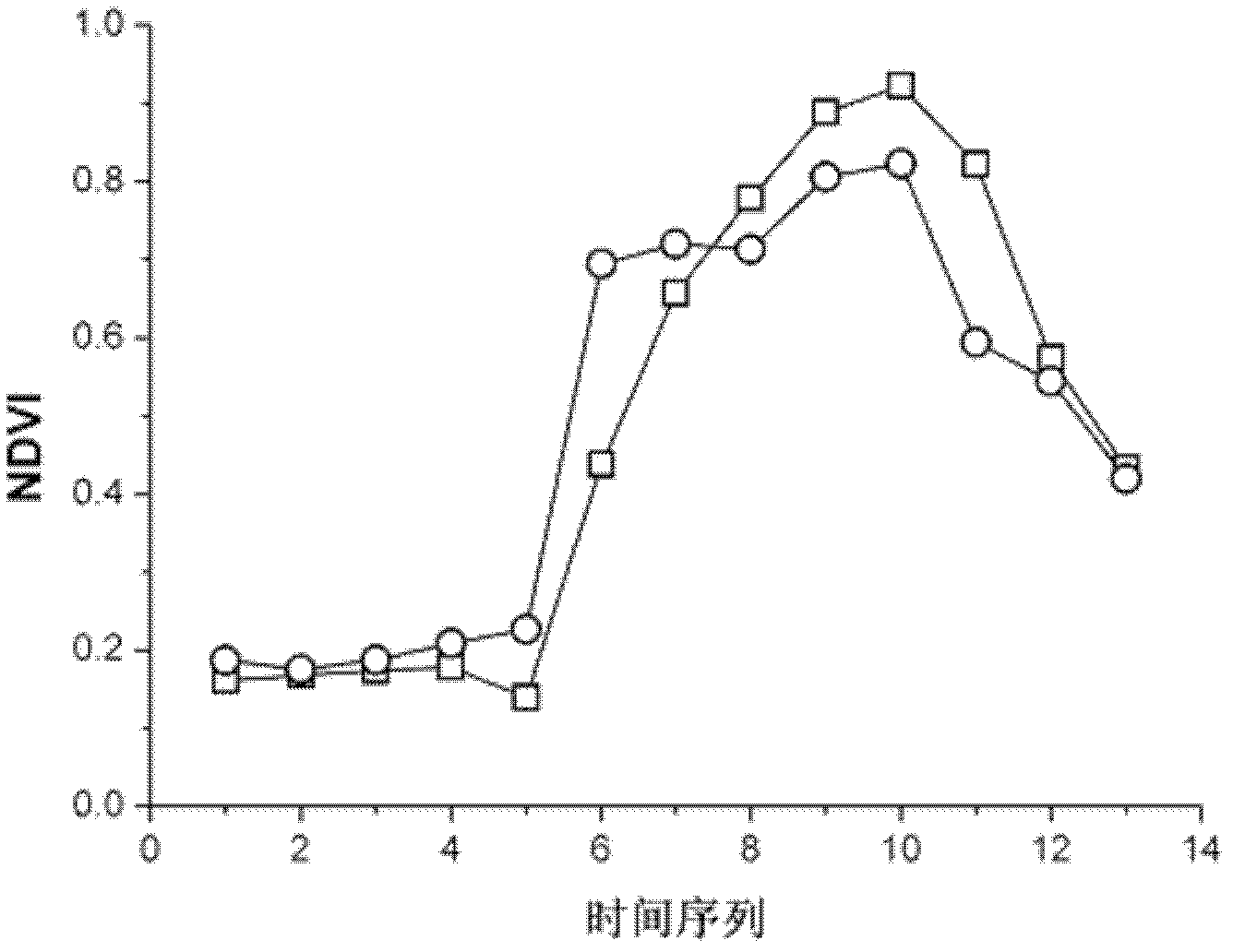
The invention discloses a method for classifying remote sensing images blended with high-space high-time resolution data by an object oriented technology, and relates to a method for classifying remote sensing images of an oriented object, which can be used for solving the problem that the previous method for classifying remote sensing images can not be used for distinguishing land cover types of 'foreign bodies with the same spectrum', and is not suitable for being applied to the remote sensing images with low-medium resolution ratio. The method provided by the invention comprises the following steps: carrying out filter processing by applying an SG (screen grid) filter; determining a time sequence curve of typical vegetational MODIS-NDVI (moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer-normalized difference vegetation index) in the remote sensing image to be classified; segmenting a TM (thematic mapper) image, wherein each segmentation unit is used as an object; extracting the characteristic information of each object; extracting all non-vegetation objects; removing the non-vegetation objects, and taking the obtained vegetational objects as planar vectors to segment MODIS-NDVI time sequence data, so as to obtain corresponding biotemperature information acquired by each vegetational object; and determining the vegetational type, to which each object belongs; and completing the land cover classification. The method provided by the invention can be used for distinguishing the land cover types.
Owner:NORTHEAST INST OF GEOGRAPHY & AGRIECOLOGY C A S
Method for estimating yield of winter wheat by assimilating characteristics of leaf area index time-sequence curve
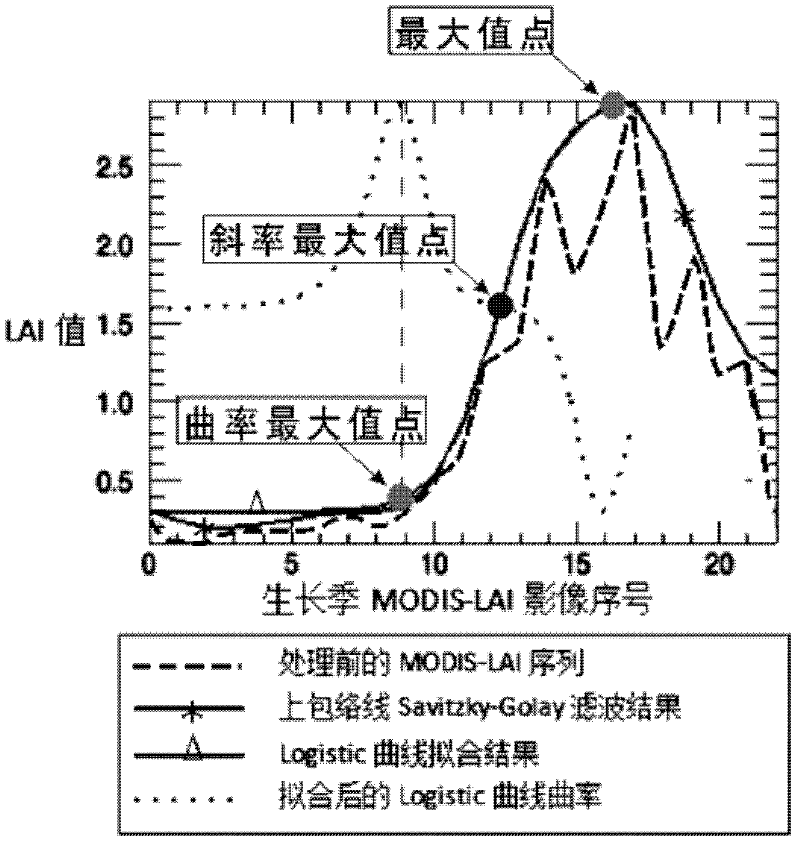
The invention discloses a method for estimating the yield of winter wheat by assimilating the characteristics of a leaf area index time-sequence curve. The method is implemented through the following steps: S1, performing global sensitivity analysis on a crop model and completing parameter regionalization of the crop model; S2, synthesizing the MODIS LAI (moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer leaf area index) time-sequence curve; S3, performing filtering processing on the LAI time-sequence curve; S4, performing curve fitting and extracting key characteristic points; S5, operating the crop model in area coverage, performing curve fitting on the LAI time-sequence curve obtained by simulation and extracting the key characteristic points on the curve; and S6, establishing a cost function according to dates of three key characteristic points which are respectively obtained in S4 and S5, taking remote sensing observation error as weight for summating and further getting a total cost function, minimizing the total cost function to rapidly converge the cost function, and finally gathering according to an administrative boundary when convergence conditions are met and outputting a yield result. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the assimilation precision is improved, the affects caused by the situation that an MODIS LAI product system is lower are overcome and the method is further suitable for estimating the yield of the winter wheat at regional scale.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
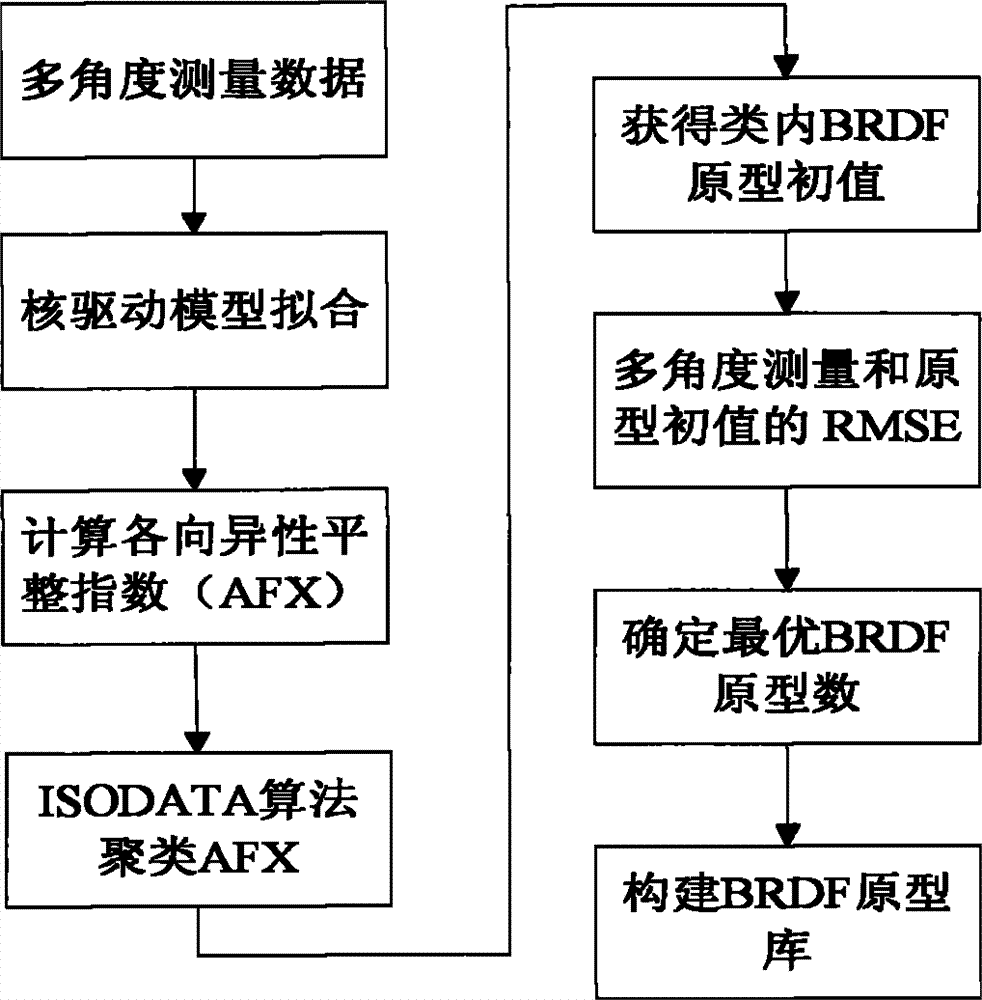
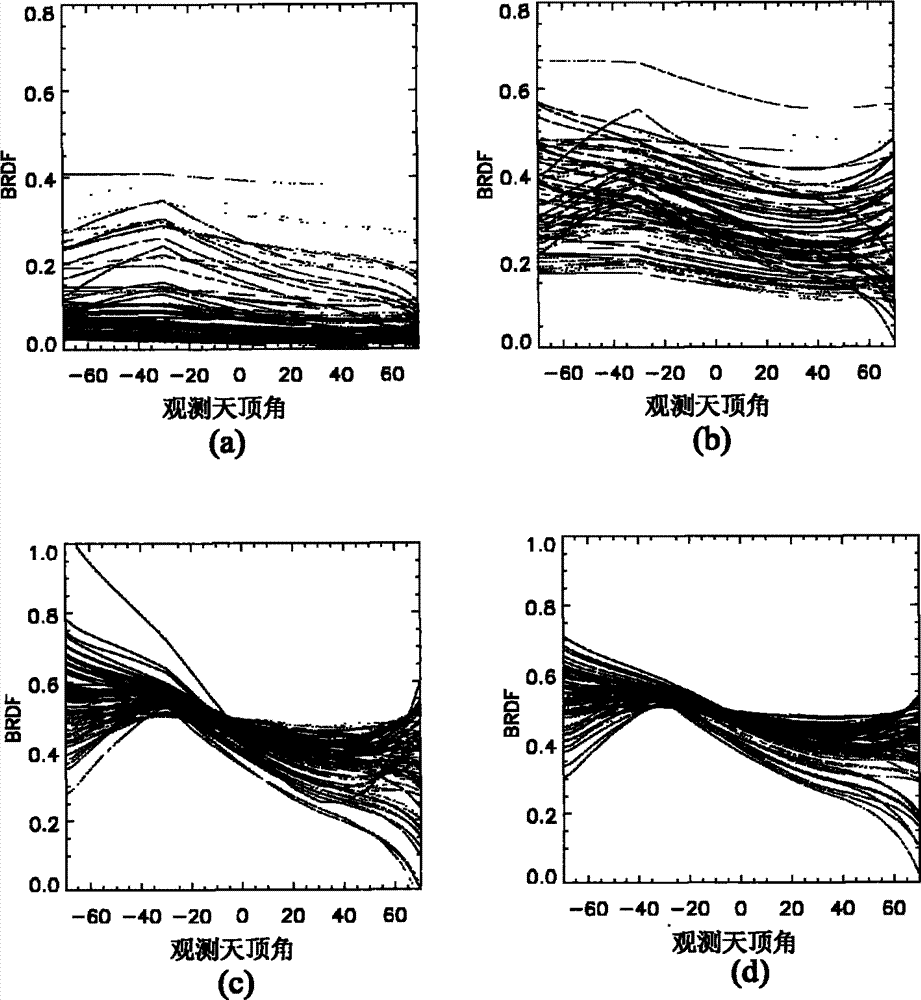
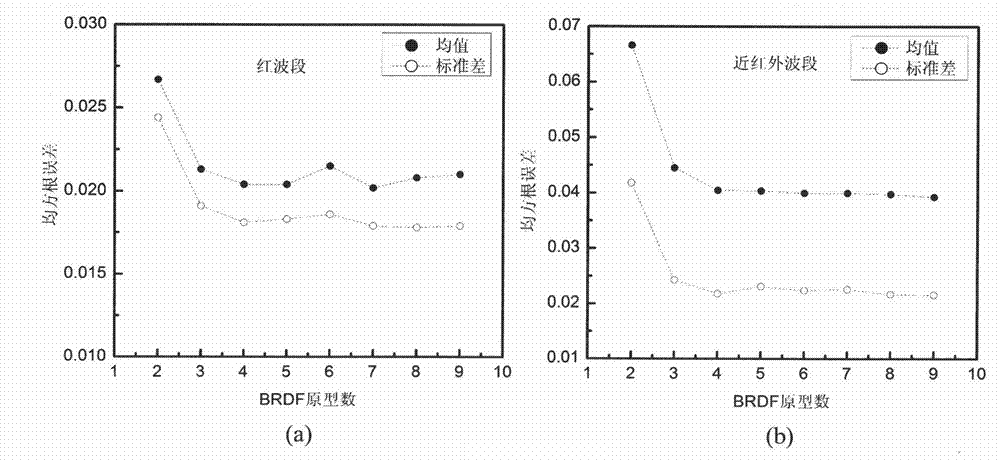
Method for establishing bidirectional reflectance distribution function (BRDF) prototype library based on multi-angular measurement
InactiveCN102902883AClear logicAdaptableSpecial data processing applicationsCluster algorithmBidirectional reflectance distribution function
The invention relates to a method for establishing a bidirectional reflectance distribution function (BRDF) prototype library based on multi-angular measurement. Through self-defining bidirectional anisotropic flat index (AFX) and iterative self-organizing ISODATA clustering algorithm, a theory and a method for establishing the BRDF prototype library based on BRDF feature mode are provided and are realized by using 69 groups of ground surface multi-angular measurement data and the history data (MCD43A) of global EOS ground surface verification core point. According to the theory and the method, the conventional method for establishing a BRDF database based on the ecological form of ground surface is abandoned, the BRDF prototype library is different from the global pixel-to-pixel BRDF database of MODIS (Moderate-resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer) in the service operation at present; and is small in volume, simple and convenient to construct and easy to operate, and is applicable for other airborne and spaceborne multi-angular measurement data of ground surface. In the technical field of spatial information, the method particularly has theoretical and application values for extracting BRDF prior knowledge to invert ground surface parameters in the aspect of quantitative remote sensing.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
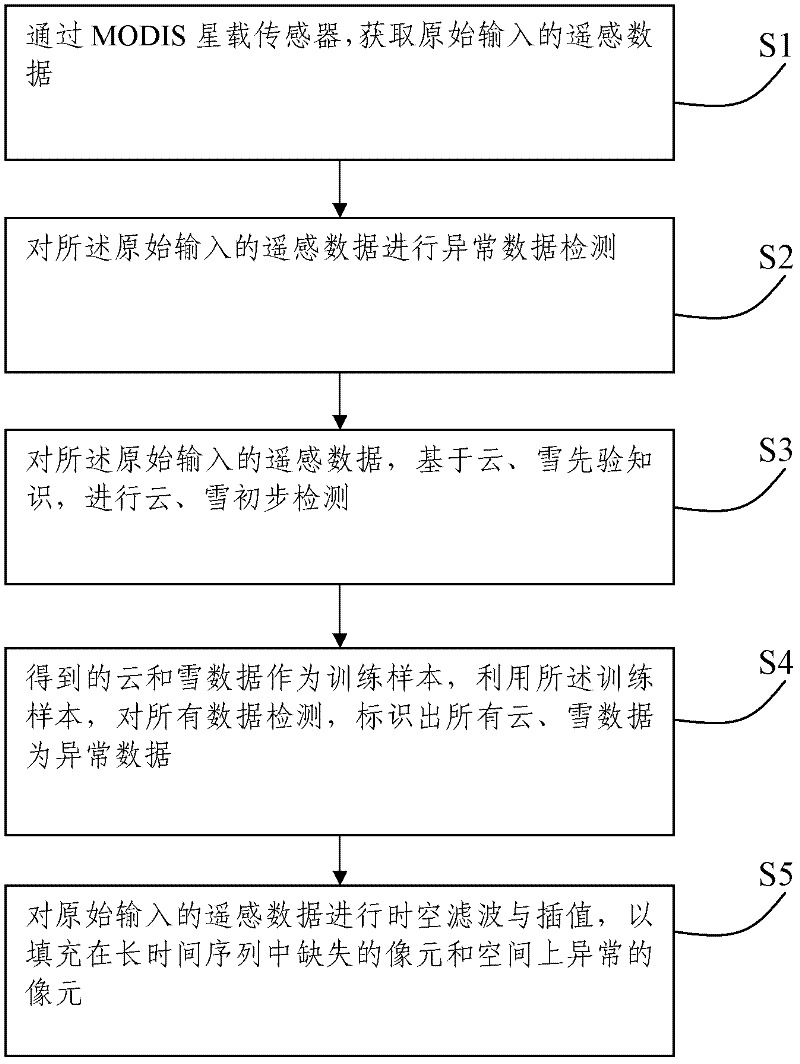
Method and system for preprocessing MODIS (Moderate-Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer) surface albedo data
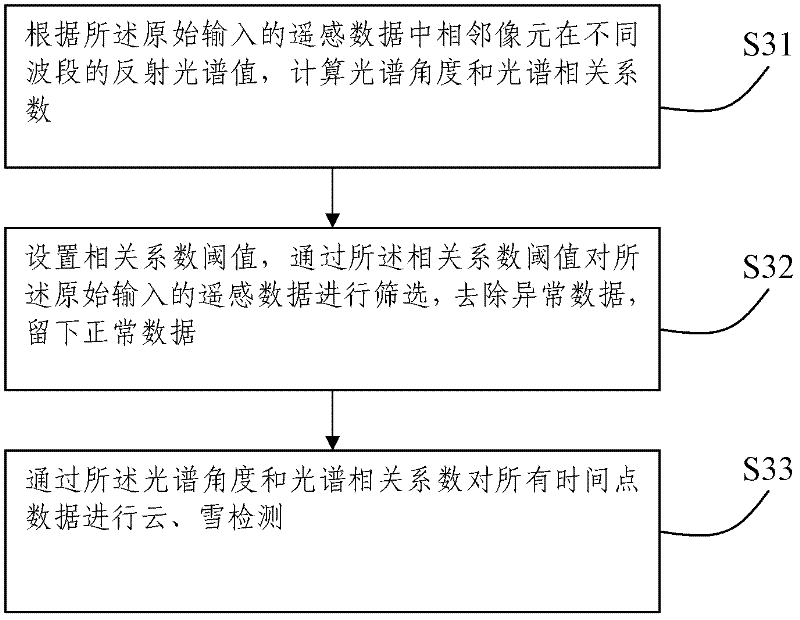
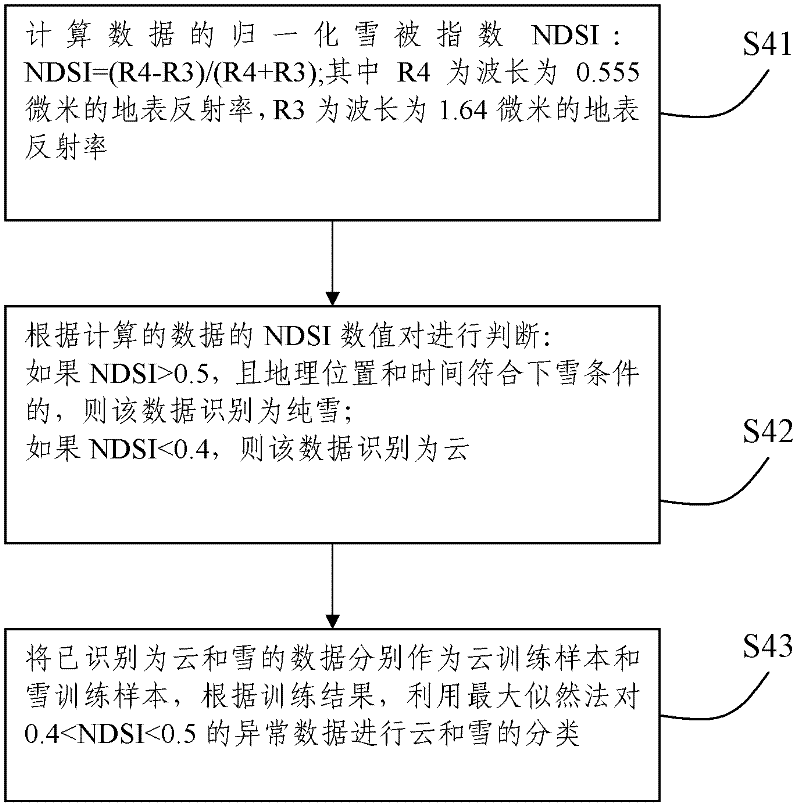
The invention discloses a method and a system for preprocessing MODIS (Moderate-Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer) surface albedo data. The method comprises the following steps of: S1, acquiring remotely sensed data which are originally input; S2, carrying out missing data detection on the remotely sensed data which are originally input; S3, carrying out cloud and snow primary detection on theremotely sensed data which are originally input; S4, by using the obtained cloud and snow data as a training sample, detecting all data and identifying abnormal data; and S5, carrying out space-time filtering and interpolation on the remotely sensed data which are originally input. The system comprises a data input module, a data missing detection module, a cloud and snow detection module, an abnormal data detection module and a space-time filtering and interpolation module which are respectively used for implementing the above steps. According to the invention, by processing the missing and abnormal data in the surface albedo data, the surface albedo data of which a long-time sequence and space-time are continuously consistent can be generated and the accuracy of subsequent application and remote sensing inversion is improved.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
High-precision satellite MODIS (Moderate-resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer) monitoring method for chlorophyll a of eutrophic lake water body
ActiveCN104390917AAchieving High-Precision EstimationReflect the space-time distributionColor/spectral properties measurementsRayleigh scatteringEutrophication
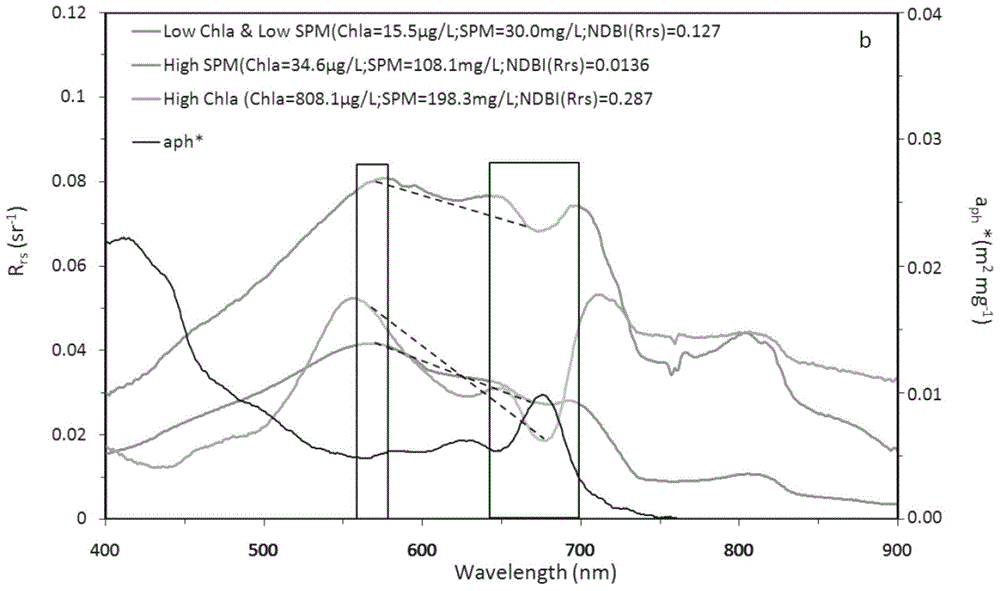
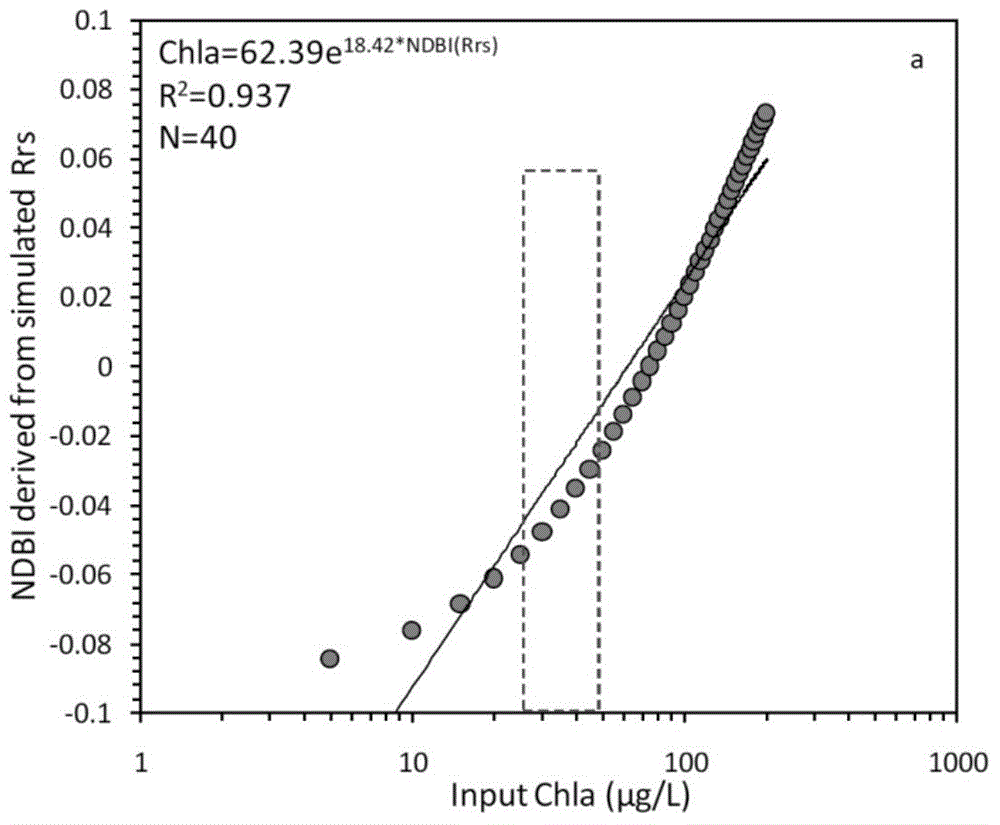
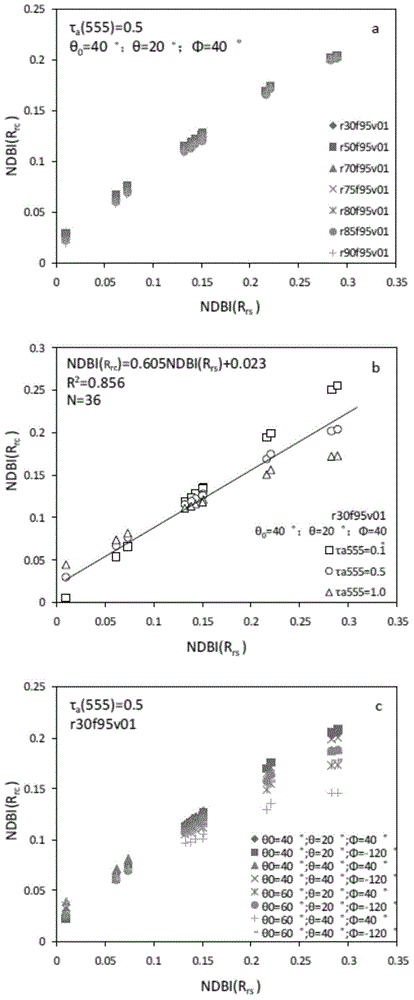
The invention provides a high-precision satellite MODIS (Moderate-resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer) monitoring method for chlorophyll a of a eutrophic lake water body. The method comprises the following steps: screening a chlorophyll a evaluation index (NDBI) which is sensitive to the concentration change of the chlorophyll a and is not influenced by high suspended solids; obtaining a quantitative relation between the NDBI and the concentration of the chlorophyll a on the basis of biological optical model simulation; combining spectral information of the water body and the corresponding concentration of the chlorophyll a of the water body monitored in the field in Chaohu Lake in year 2013-2014, so as to obtain a chlorophyll a inversion algorithm based on a ground measured spectrum (Rrs) and the NDBI; simulating different aerosol types and thicknesses, different solar altitudes, satellite observation angles and azimuth angles, so as to obtain a quantitative relation between the ground monitored remote sensing reflectance (Rrs) and simulated Rrc subjected to Rayleigh scattering correction; and further extending the chlorophyll a inversion algorithm based on ground measured spectral data to satellite image data subjected to the Rayleigh scattering correction. According to the method, the inter-annual and inter-monthly change rules and space distribution of the rules of the concentration of the chlorophyll a of a eutrophic lake can be accurately obtained.
Owner:NANJING INST OF GEOGRAPHY & LIMNOLOGY
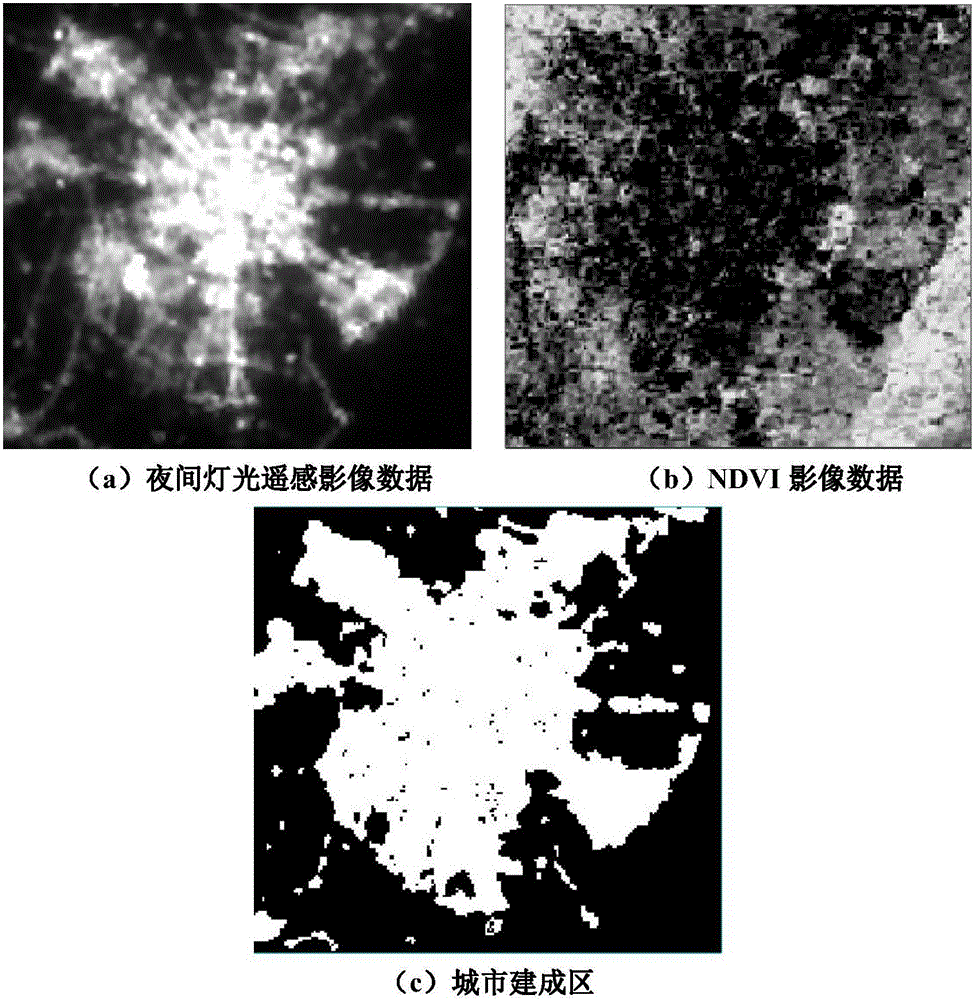
Intelligent extraction method of build-up area on the basis of nighttime light data
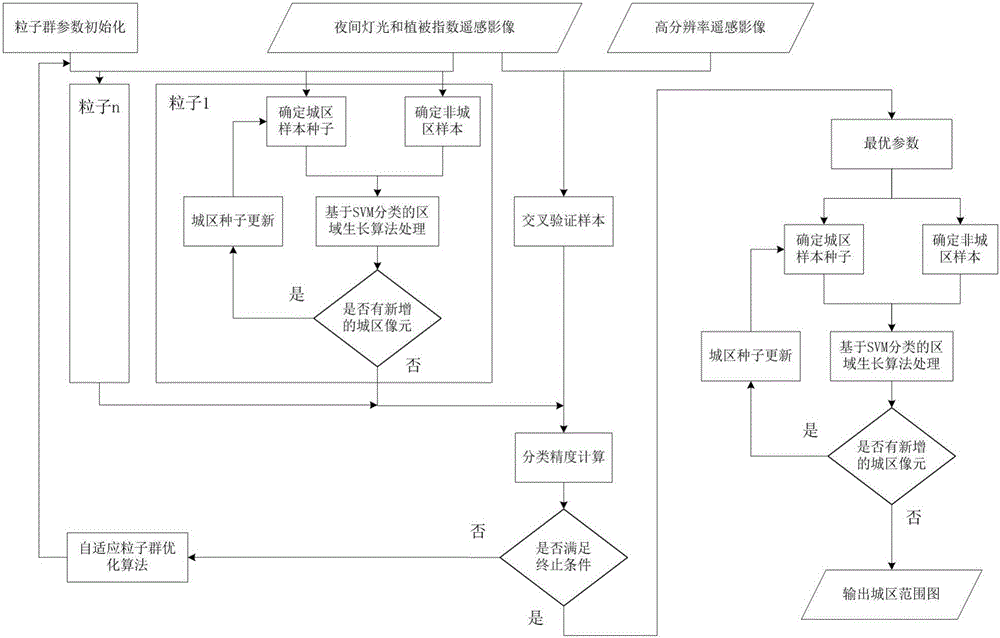
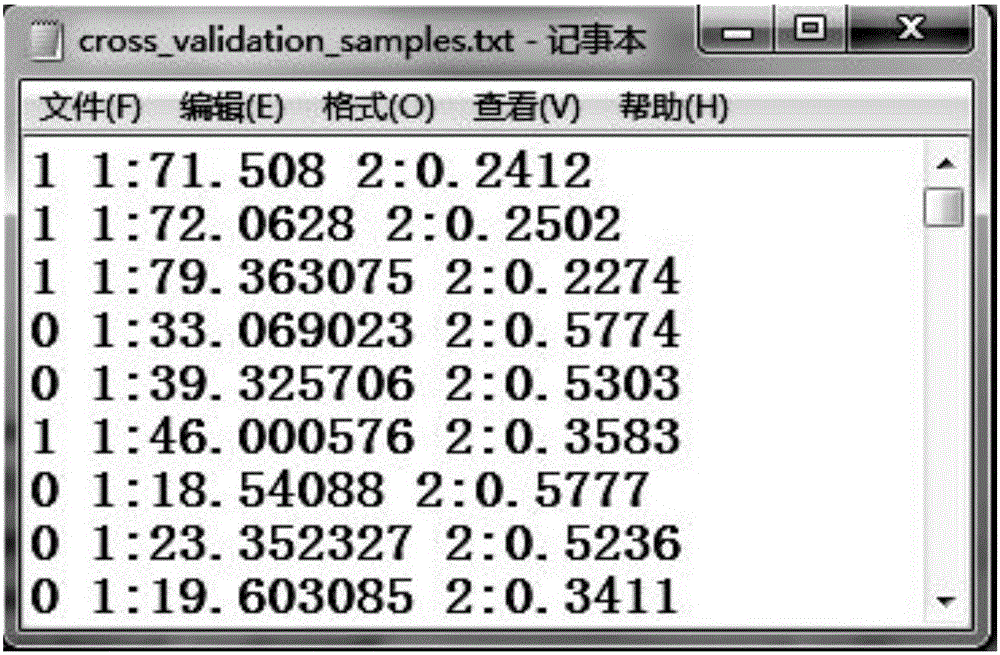
InactiveCN106127121AGood effectImprove processing efficiencyCharacter and pattern recognitionSupport vector machineAdaptive optimization
The invention relates to an intelligent extraction method of a build-up area on the basis of nighttime light data. The intelligent extraction method comprises the following steps: adopting an adaptive particle swarm optimization algorithm to realize the optimal selection of the selection parameters of a VIIRS (Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite) nighttime light image sample and a MODIS (Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer) normalized difference vegetation index image sample; adopting a region growing algorithm based on SVM (Support Vector Machine) classification to finish SVM model training, and adopting a cross validation method to carry out precision validation on the model; and according to an optimized parameter, determining a city sample and a non-city sample, and adopting the region growing algorithm based on the SVM to extract a city built-area range. By use of the intelligent extraction method, from a sample selection source, the adaptive optimization of a sample selection parameter is carried out, and the SVM and the region growing algorithm are adopted to improve processing efficiency and precision for the nighttime light data to extract the nighttime light data.
Owner:四川省遥感信息测绘院
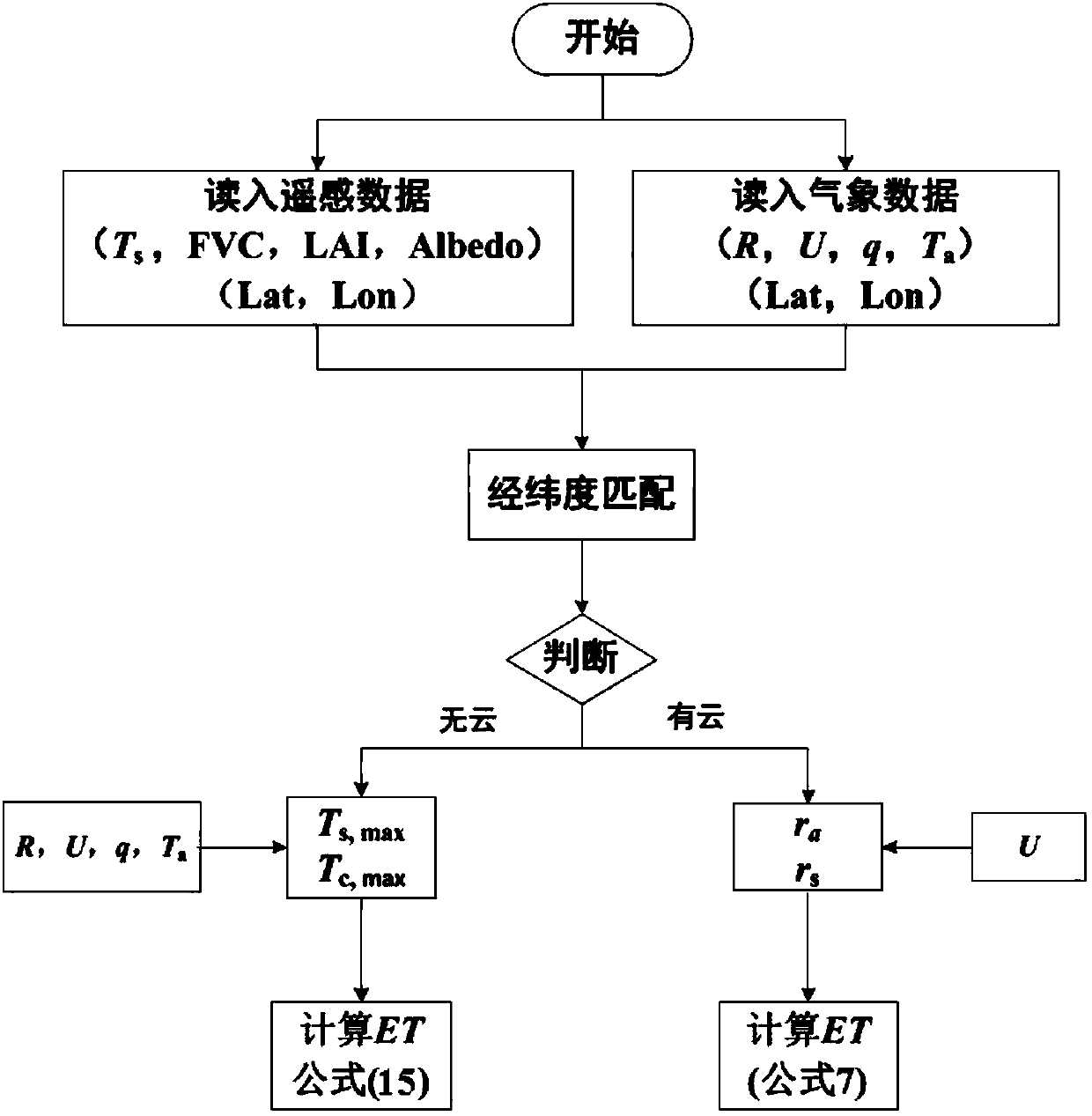
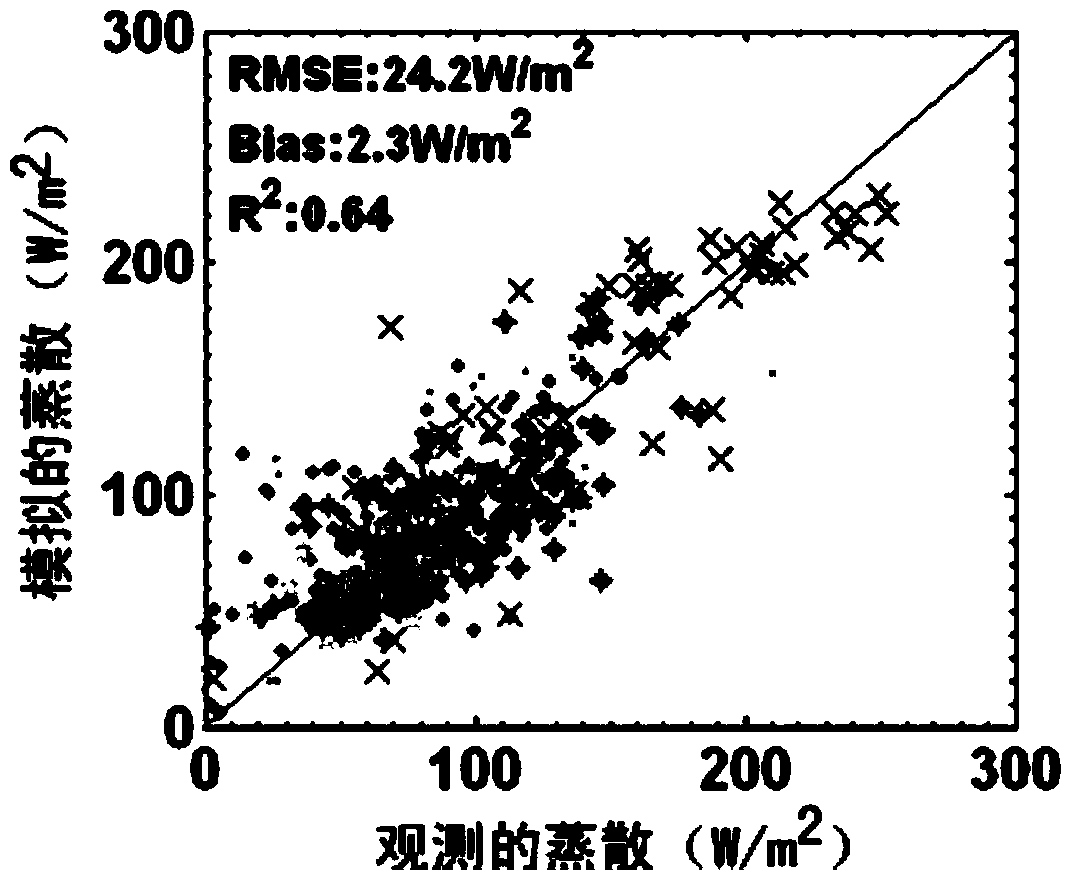
Method of acquiring all-weather evapotranspiration by combining remote sensing and meteorological data
ActiveCN107065036AMake up for the defect that evapotranspiration cannot be reversedComplete evapotranspiration dataInstrumentsSensing dataThermal infrared remote sensing
The invention discloses a method of acquiring all-weather evapotranspiration by combining remote sensing and meteorological data, which comprises the following steps: remote sensing data are acquired; meteorological data are acquired; the CLDAS (China Meteorological Administration Land Data Assimilation System) data grid position to which each MODIS (Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer) remote sensing pixel belongs is calculated for longitude and latitude matching; MODIS remote sensing pixels are traversed, whether a MODIS land surface temperature pixel contains a cloud is judged, and according to a judgment result, evapotranspiration of an MODIS cloud pixel and evapotranspiration of an MODIS cloudless pixel are estimated. The existing optical and thermal infrared remote sensing data are made full use of, the grid meteorological data are used, the defect that evapotranspiration can not be inversed in a cloud condition by purely using remote sensing data can be remedied, and all-weather evapotranspiration data can be provided.
Owner:INST OF AGRI RESOURCES & REGIONAL PLANNING CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
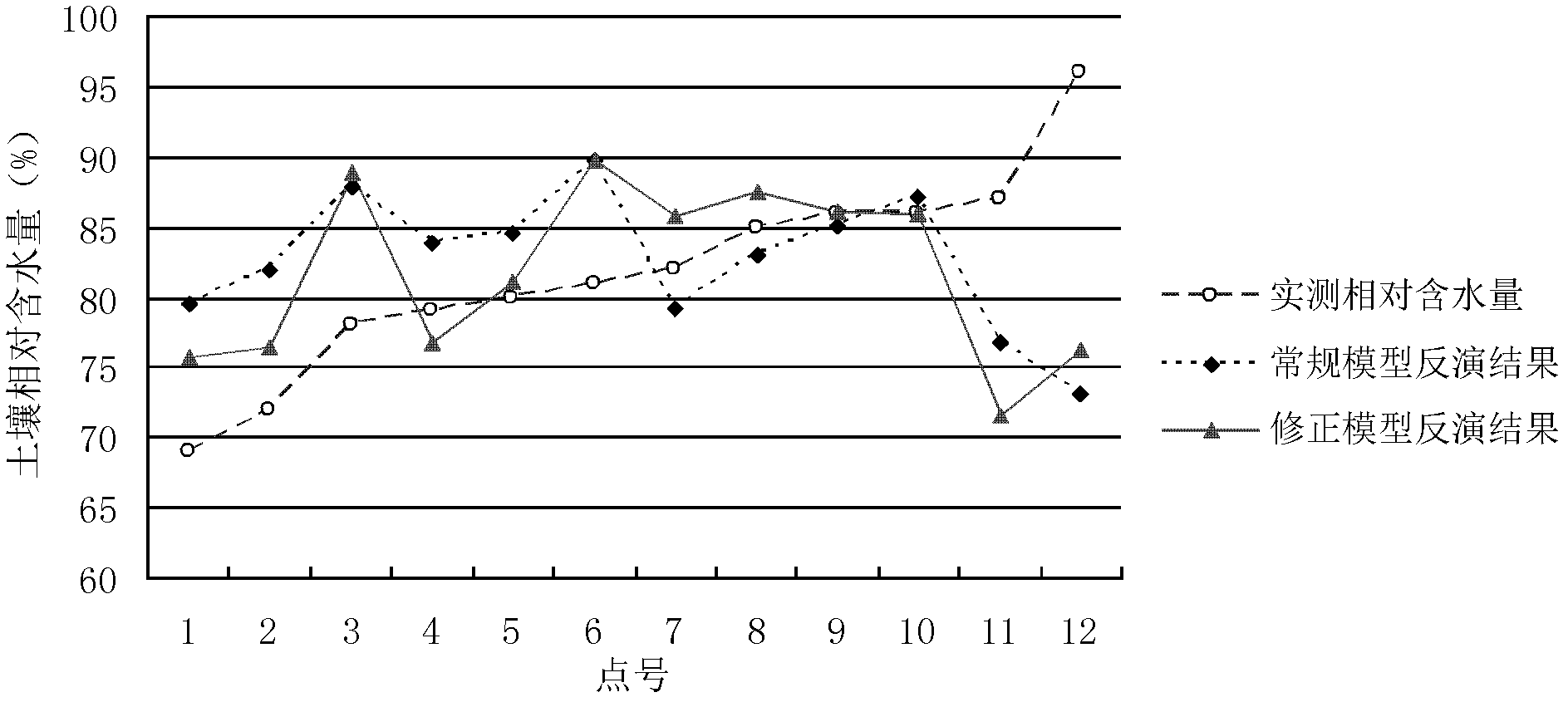
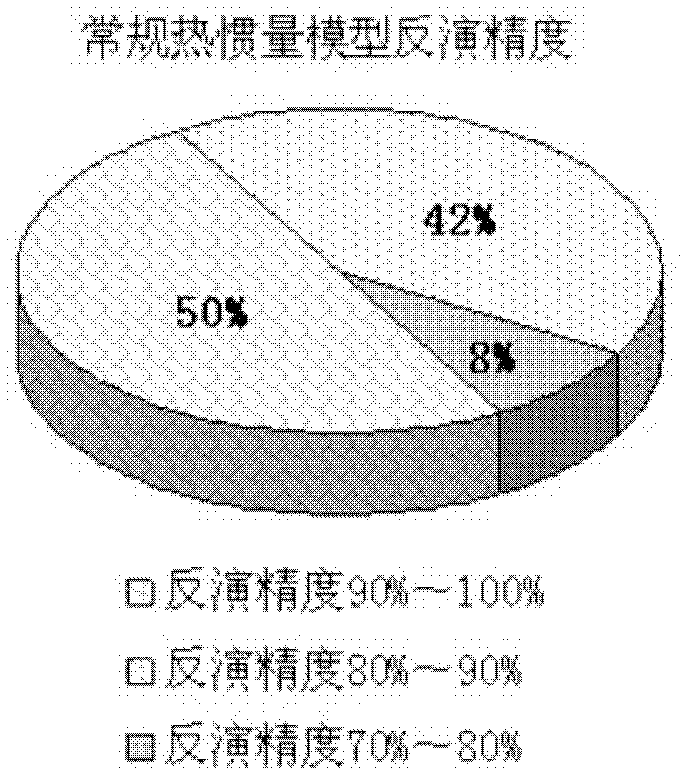
Remote monitoring method for soil moisture of wheat field
The invention discloses a remote monitoring method for soil moisture of a wheat field. A corrected thermal inertia model is W=B1*ATI+B2*EVI+B, wherein W is relative soil water content; ATI is apparent thermal inertia; B1 and B2 are coefficient items; EVI is an enhanced vegetation index; and B is a constant item. In the method, the closing actions of wheat plants on the soil background are fully considered, and an enhanced vegetation index which is sensitive to vegetation reflection in a low-vegetation covering area is introduced and is taken as a vegetation influencing factor according to a thermal inertia process during inversion of soil moisture by using EOS / MODIS (Embedded Operation System / Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer) remote sensing data. The average inversion accuracy of a corrected thermal inertia model can be over 80 percent before ridge sealing of wheat. According to comparative analysis of the synchronous inversion result of the conventional thermal inertia model, the corrected thermal inertia model has higher inversion accuracy, and a suitable time domain is expanded by about one growth period.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRI SUSTAINABLE DEV INST
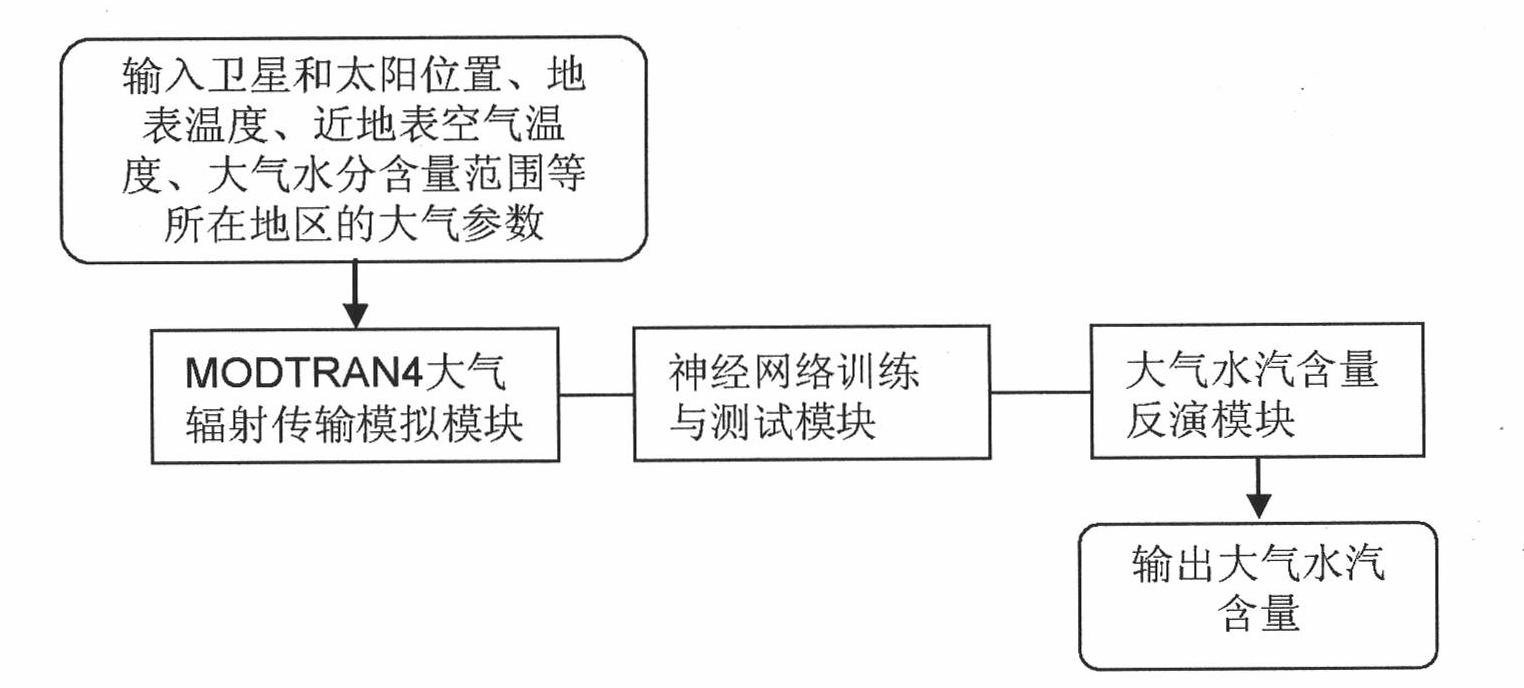
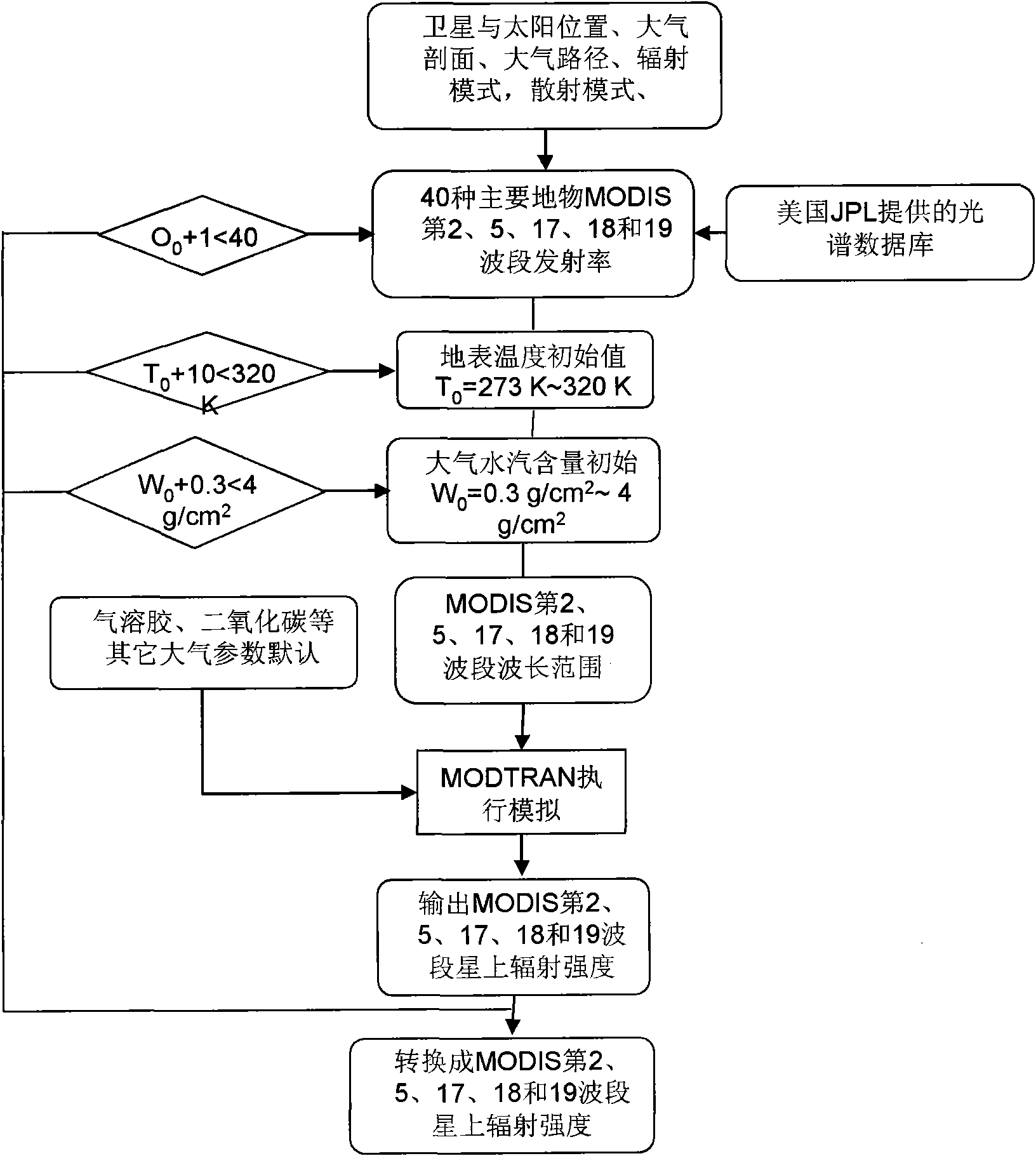
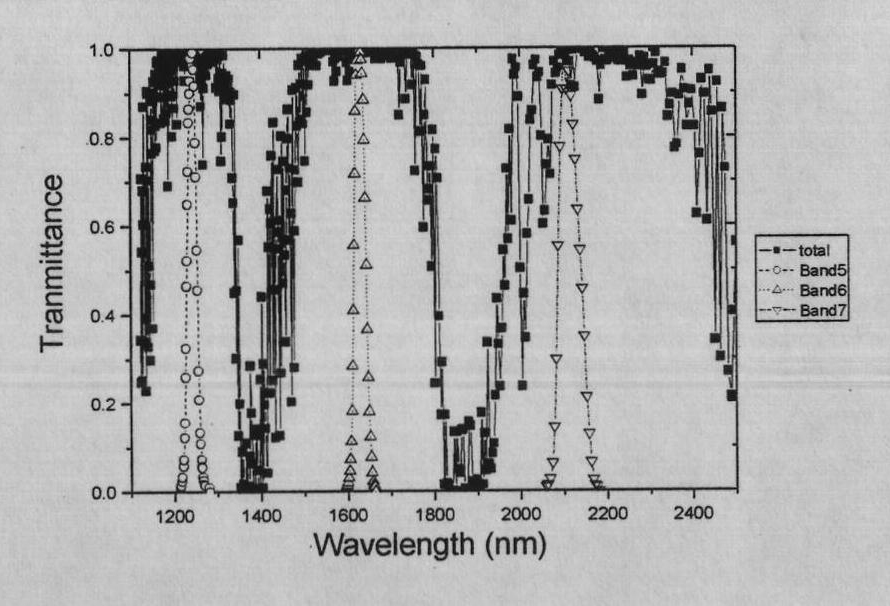
Method for inverting atmospheric water vapor content from MODIS (Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer) data
InactiveCN101936877AReduce unknownsReduce computing timeMaterial analysis by optical meansBiological neural network modelsData setDisaster monitoring
The invention relates to a method for inverting atmospheric water vapor content from MODIS (Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer) data, which can be applied to the remote sensing application departments, such as meteorology, environment monitoring, land management, crop condition monitoring, disaster monitoring and the like. The method comprises the following three steps of: (1) performing forward simulation to the second, fifth, seventeenth, eighteenth and nineteenth near-infrared bands of acquired remote sensing MODIS data in given areas and seasons and an atmospheric model by using atmospheric radiation transmission simulation software MODTRAN, and establishing a training and test database; (2) repeatedly training and testing the training and test data set by using a neural network; and (3) performing inversion calculation to the MODIS actual image data, and performing actual earth surface verification and application analysis. The atmospheric water vapor inversed product has high precision, strong practicability and relatively simple operation. The method can be applied to the departments of weather forecast, environment monitoring, crop condition monitoring, disaster monitoring and the like.
Owner:INST OF AGRI RESOURCES & REGIONAL PLANNING CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI +1
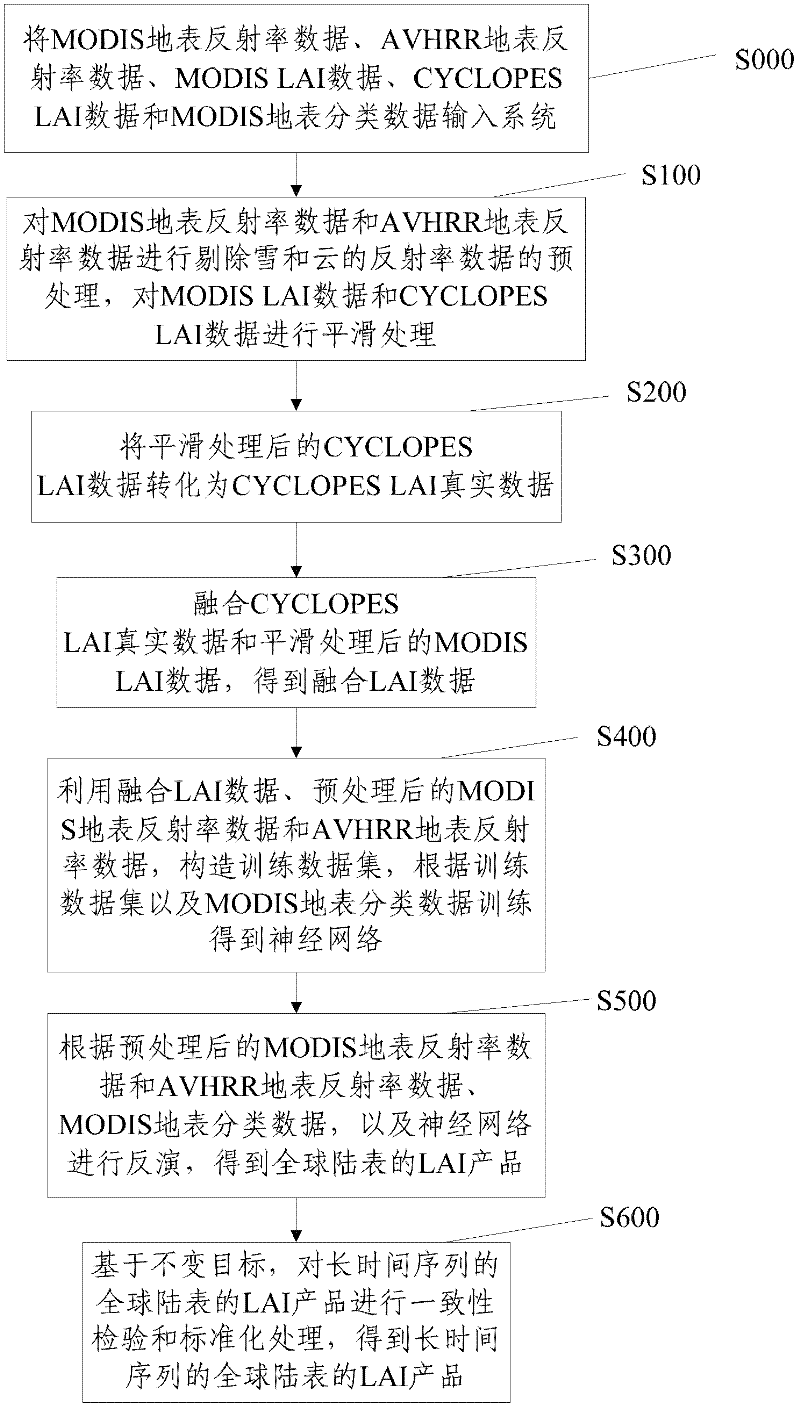
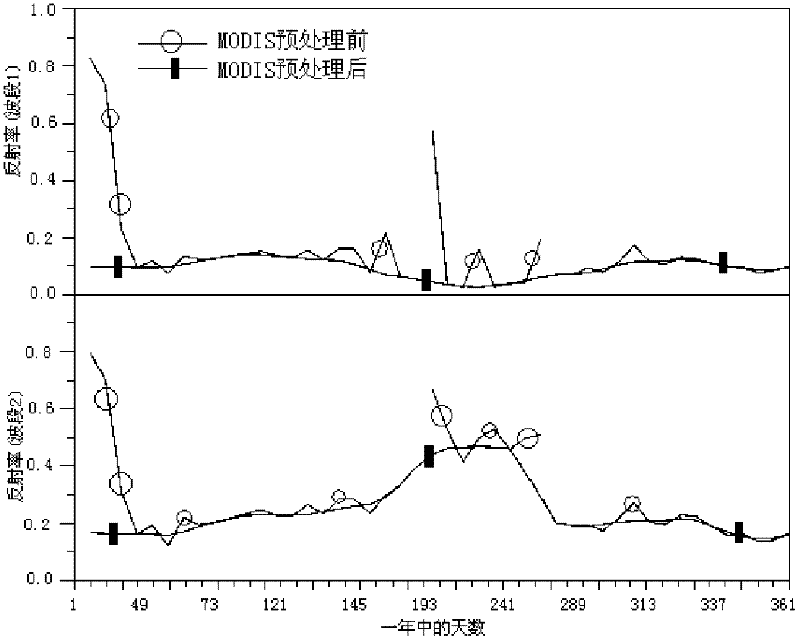
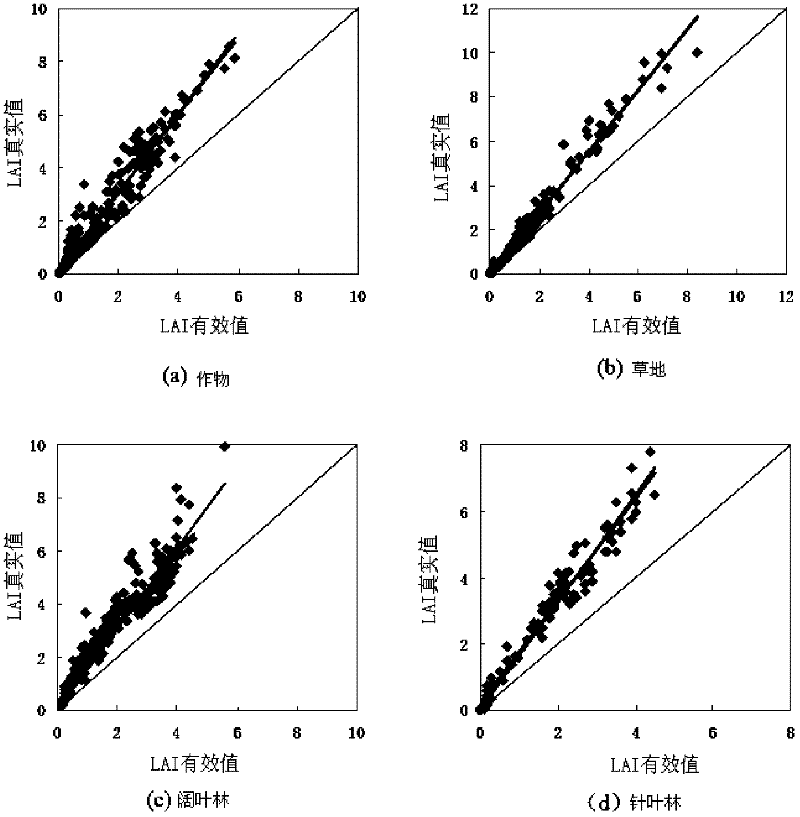
Leaf area index (LAI) product inversion method and system for global earth surface
InactiveCN102354328AHigh precisionSpecial data processing applicationsAdvanced very-high-resolution radiometerOriginal data
The invention discloses a leaf area index (LAI) product inversion method and an LAI product inversion system for a global earth surface, and relates to the field of remote sensing data processing. The method comprises the following steps of: inputting original data into a system; preprocessing earth surface reflection index data of a moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer (MODIS) and earth surface reflection index data of an advanced very high resolution radiometer (AVHRR); performing smoothing processing on MODIS LAI data and CYCLOPES LAI data; converting the CYCLOPES LAI data subjected to the smoothing processing into CYCLOPES LAI real data; obtaining fused LAI data; and obtaining a neural network by utilizing the fused LAI data, the preprocessed earth surface reflection index data of the MODIS and the earth surface reflection index data of the AVHRR and training earth surface grouped data of the MODIS, and thus obtaining LAI products of the global earth surface. By the method, the precision of the LAI products is improved and the requirements on earth system science and application research can be met.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
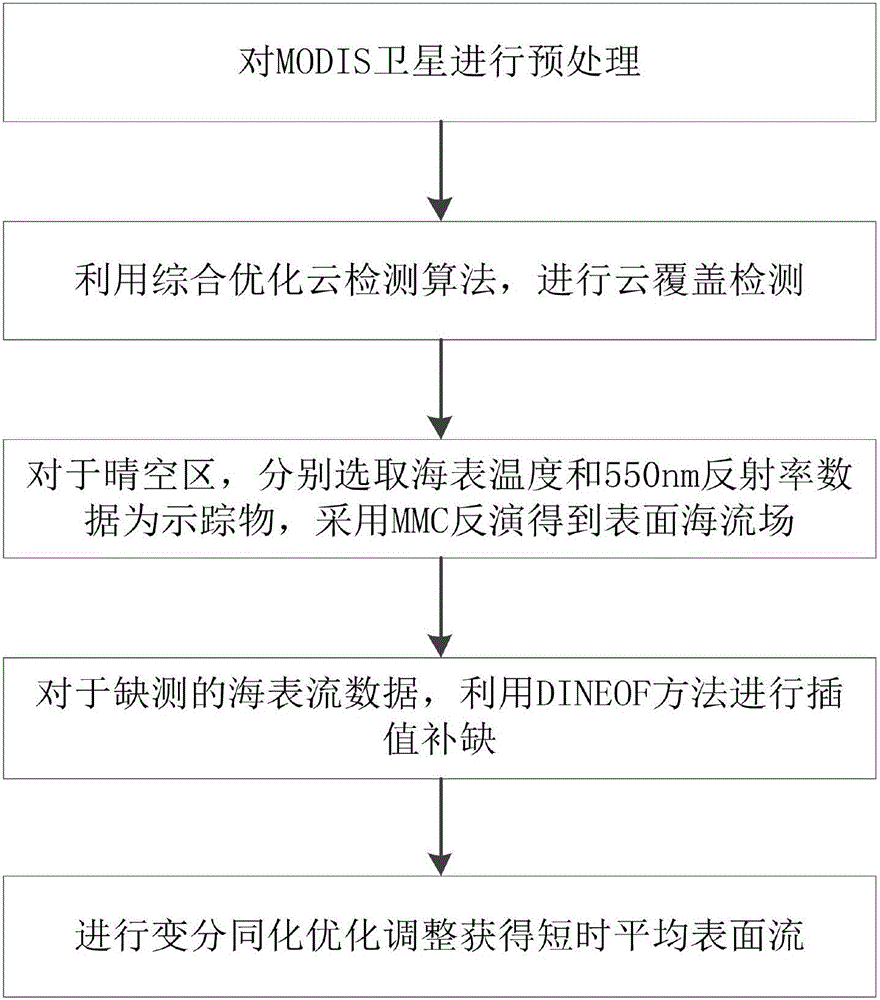
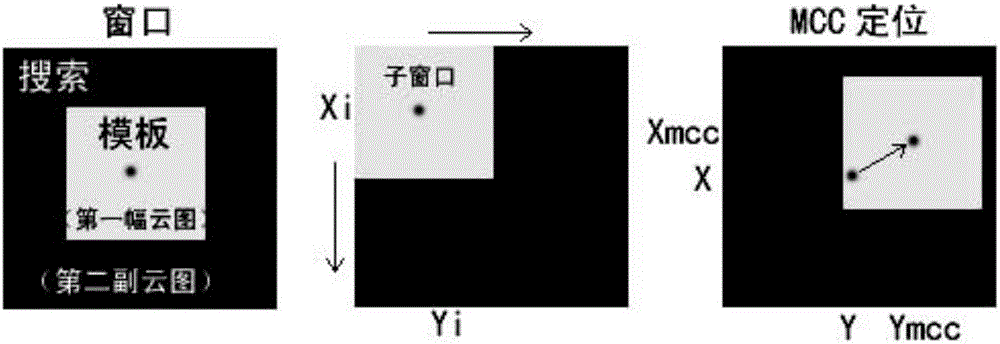
MCC ocean surface current inversion method
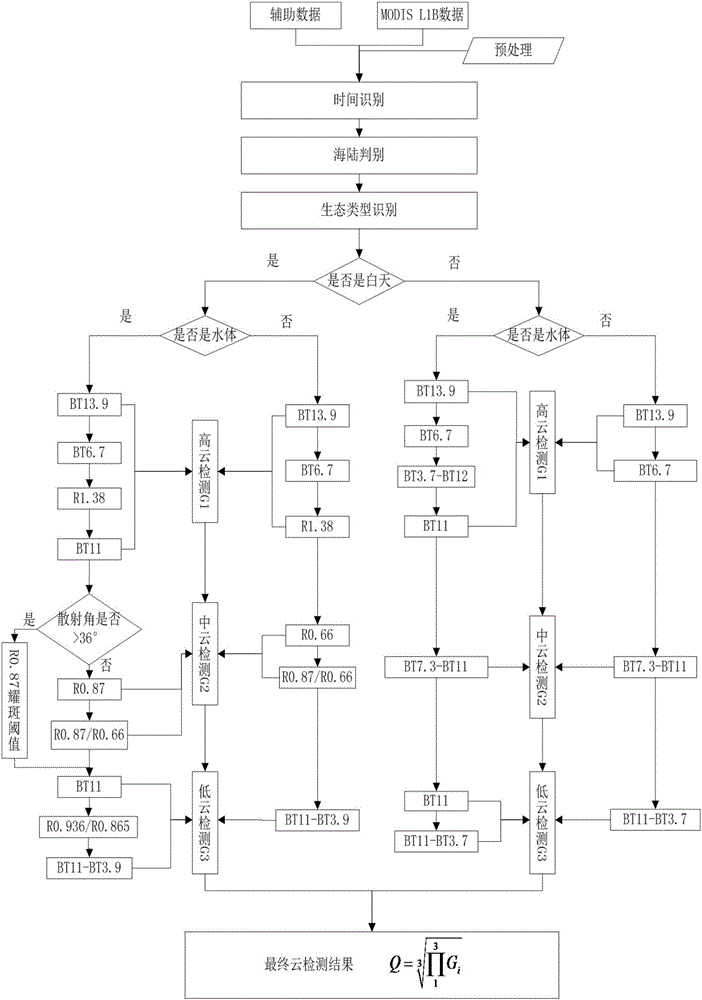
InactiveCN105844000AImprove recognition accuracyAccurate removalSpecial data processing applicationsOcean surface temperatureSky
The invention relates to an MCC (Maximum Correlation Coefficient) ocean surface current inversion method. The method comprises the steps of preprocessing an MODIS (Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer) satellite; performing cloud coverage detection by utilizing a comprehensive optimization cloud detection algorithm; for a clear sky, selecting ocean surface temperature and 550nm reflectivity data as tracers, and performing MMC inversion to obtain an ocean surface current field; for ocean surface current data missing to be measured, performing interpolation replenishment by utilizing a DINEOF (Data Interpolating Empirical Orthogonal Functions) method; and performing variational assimilation optimization adjustment to obtain short-time mean surface current. The method has the beneficial effects that the cloud detection method proposed by the invention improves the identification accuracy of low clouds of sea surface, broken clouds and partial cloud-covered picture elements, removes interferences for calculating the ocean surface current in next step more accurately, and ensures the precision of subsequent results. The interpolation based global optimization adjustment method for the ocean surface current field, proposed by the invention, greatly expands the coverage range of inversion results, remarkably enhances the inversion precision, and extends the application range of the inversion method.
Owner:江苏铨铨信息科技有限公司
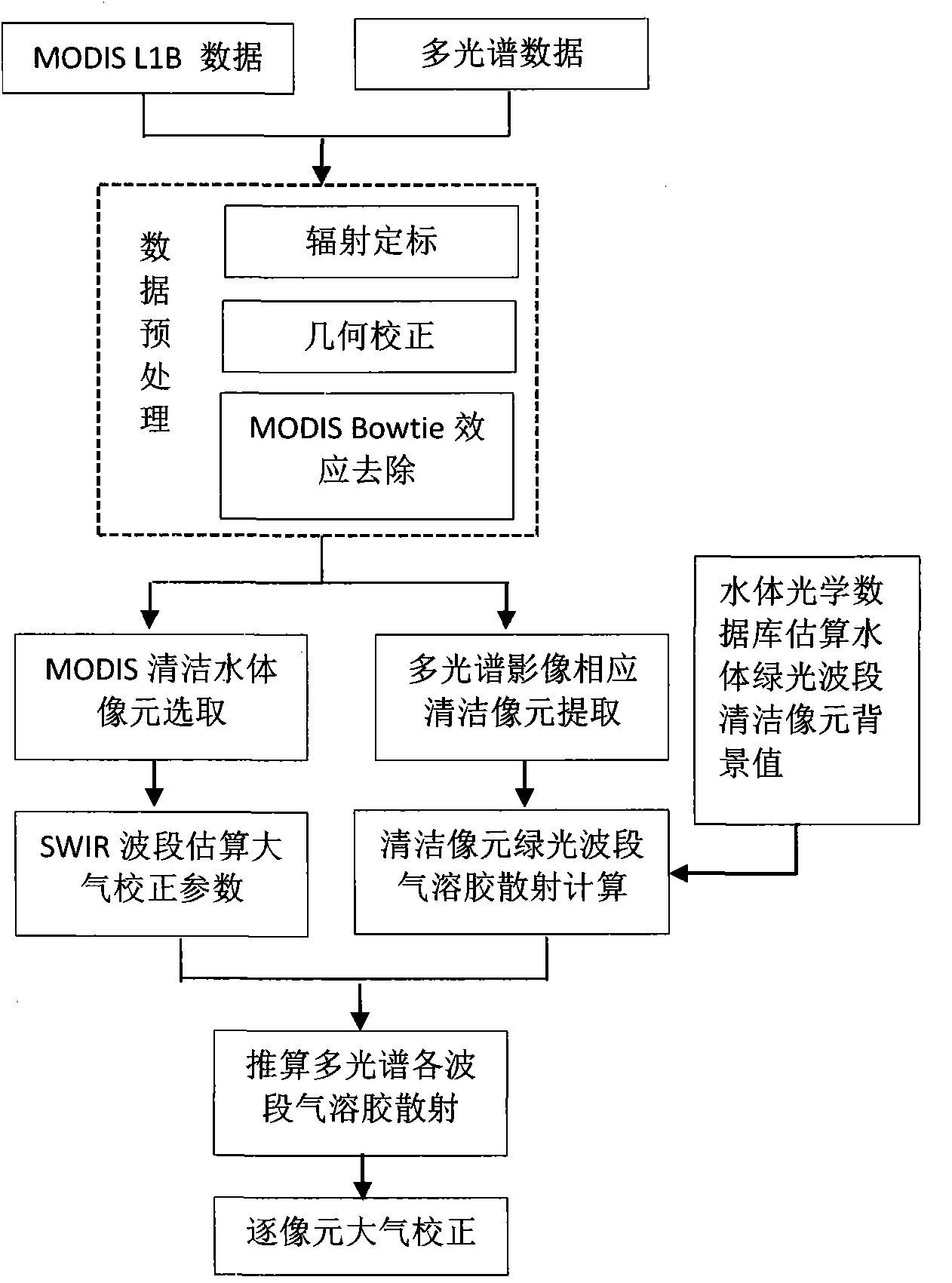
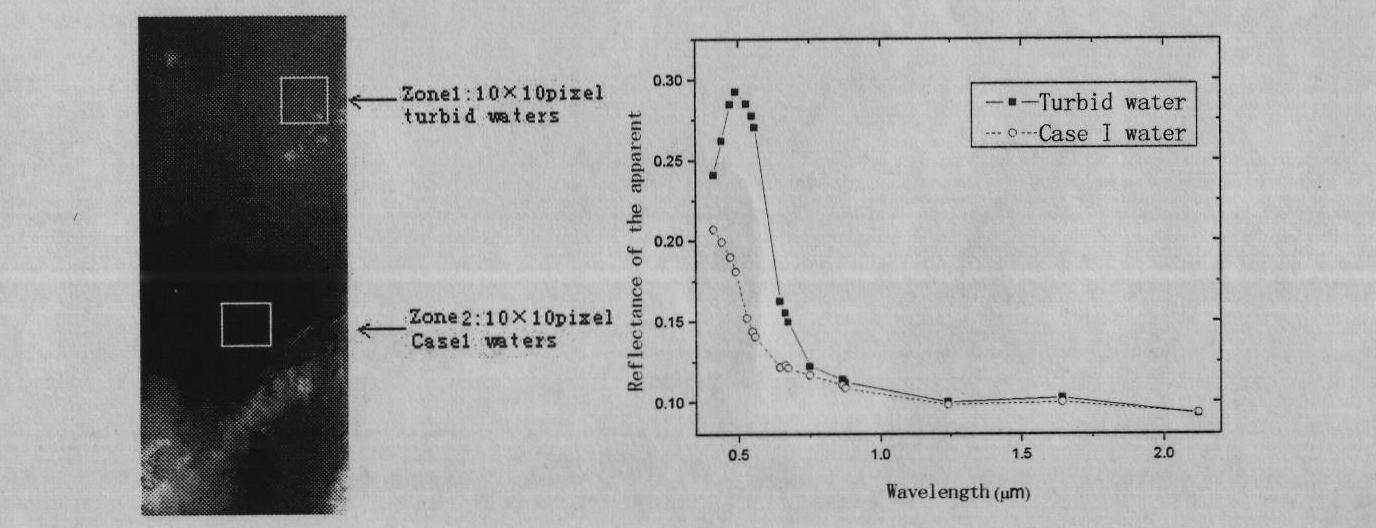
Atmospheric correction method for multi-spectral data of inland turbid water body based on green light wave band
InactiveCN103558190AImprove estimation accuracyPrevent overcorrectionScattering properties measurementsColor/spectral properties measurementsTurbid waterModerate-resolution imaging spectroradiometer
The invention discloses an atmospheric correction method for multi-spectral data of an inland turbid water body based on a green light wave band and relates to the technical field of remote sensing. The atmospheric correction method comprises the following steps: (A) preprocessing multi-spectral image data of an inland water body; (B) preprocessing a moderate-resolution imaging spectroradiometer (MODIS) L1B image which is synchronously acquired; (C) extracting clean pixels (dark pixels) from the preprocessed image data; (D) calculating an atmospheric correction factor through short-wave infrared (SWIR) band combination for MODIS data clean pixels; (E) calculating the water-leaving reflectivity of a clean water body green light wave band which is matched with a multi-spectral wave band according to an analog database and a great number of experiment observation data; (F) calculating the aerosol scattering of each wave band according to the atmospheric correction factor which is calculated in the step (D) and the water-leaving reflectivity which is calculated in the step (E); and (G) completing atmospheric correction of the multi-spectral image data according to the aerosol scattering which is calculated in the step (F). According to the method, the atmospheric correction accuracy of multi-spectral remote sensing data of the inland turbid water body is improved.
Owner:李云梅
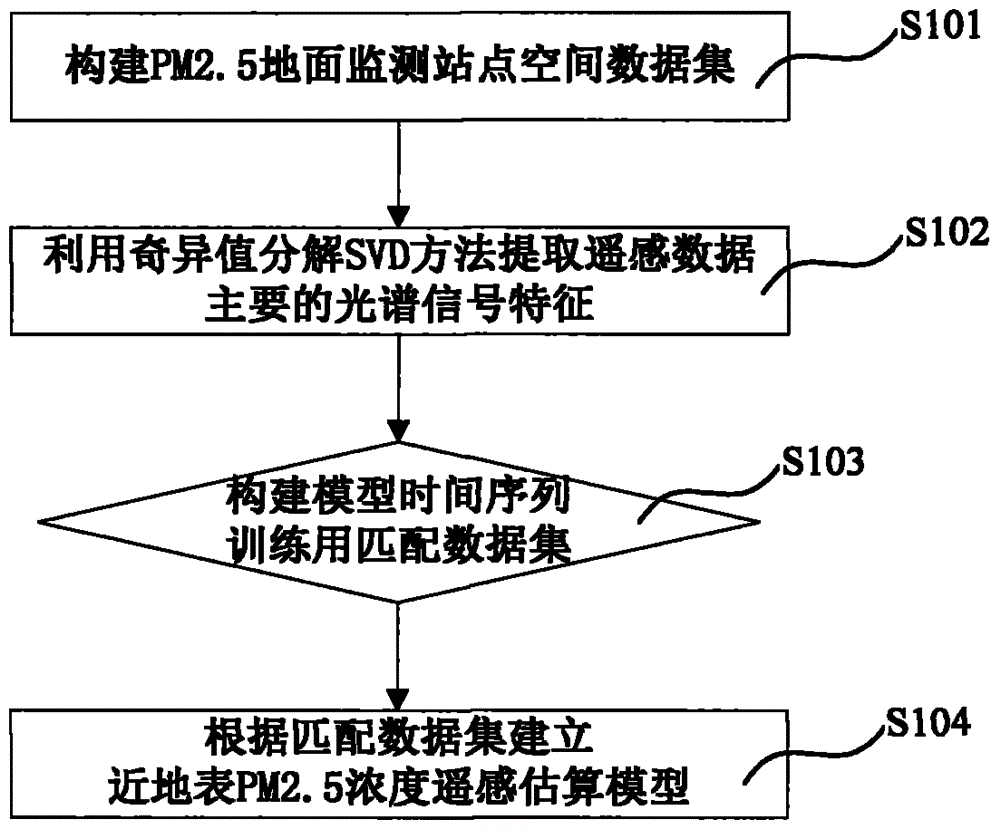
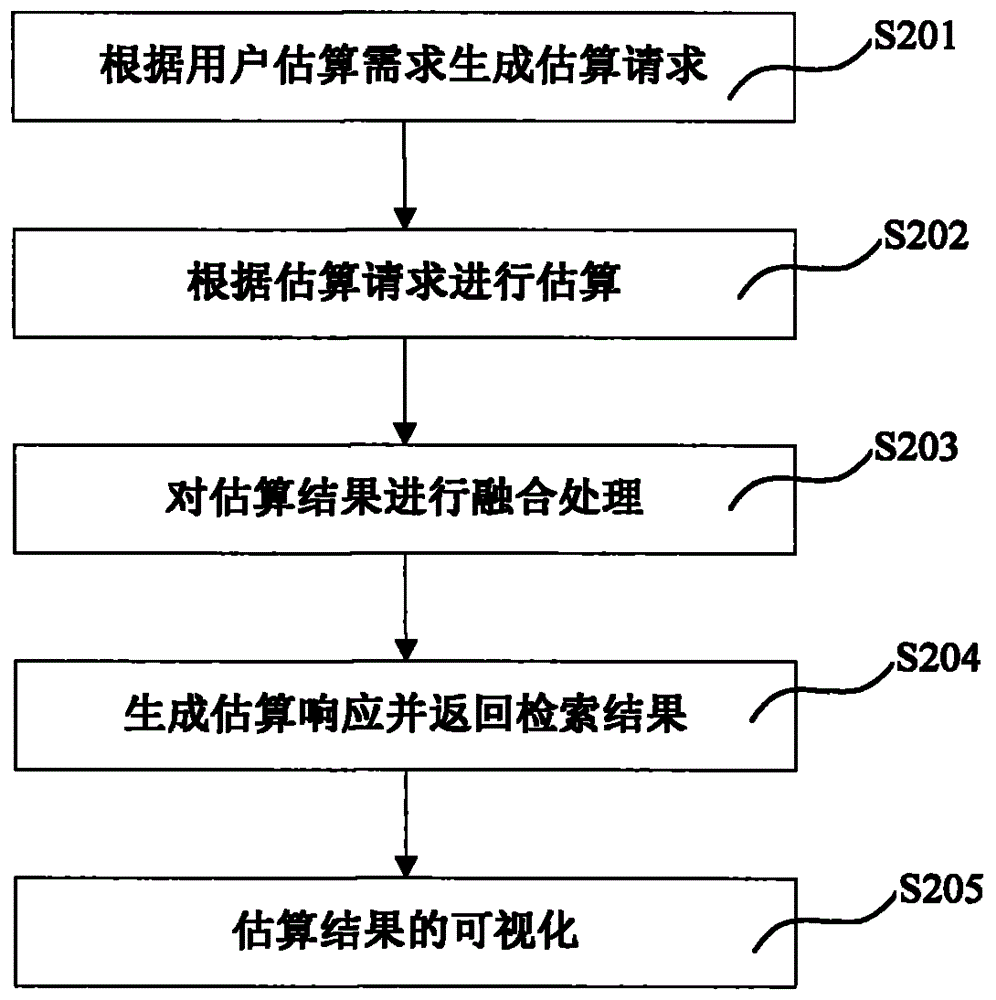
Method and system for efficiently estimating near-surface PM2.5 (particulate matter 2.5) concentration
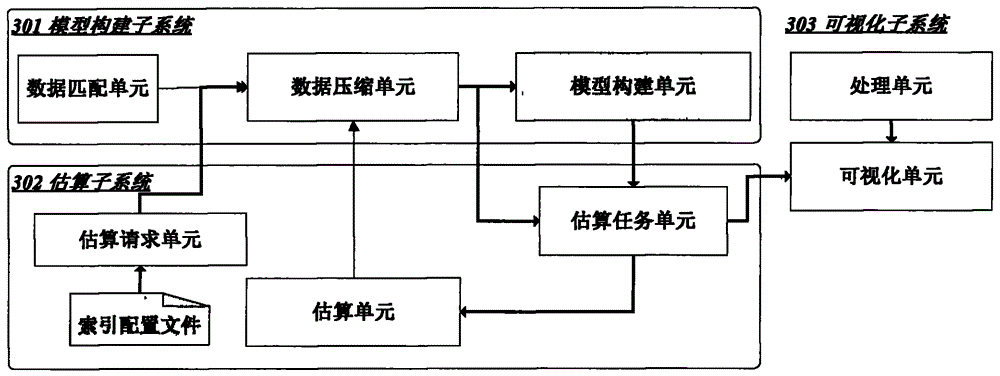
ActiveCN104573155AAvoid the problem of precision limitationExpress nonlinear statistical relationshipsBiological neural network modelsSpecial data processing applicationsData compressionParticulates
The invention discloses a method and a system for efficiently estimating the near-surface PM2.5 (particular matter 2.5) concentration. The method includes a model building step and a model estimating step. The model building step further includes a data compressing sub-step, extracting main spectral signal structure characteristics of remotely sensed data; a data matching sub-step, extracting corresponding remotely sensed information according to spatial coordinates of PM2.5 ground monitoring data; a model building sub-step, building estimation models according matched data sets. The model estimating step further includes an estimation requesting sub-step, preprocessing estimation input data; an estimating sub-step, estimating the near-surface PM2.5 concentration according to estimation requests and outputting estimation results. The method and the system have the advantages that the near-ground PM2.5 concentration can be estimated according to the MODIS (moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer) observation data on the basis of the artificial neural network models, and accordingly remote sensing operational monitoring requirements can be met; the method and the system can support importing of meteorological factors, and accordingly the near-surface PM2.5 concentration can be quickly and efficiently dynamically monitored on a large scale.
Owner:INST OF GEOGRAPHICAL SCI & NATURAL RESOURCE RES CAS
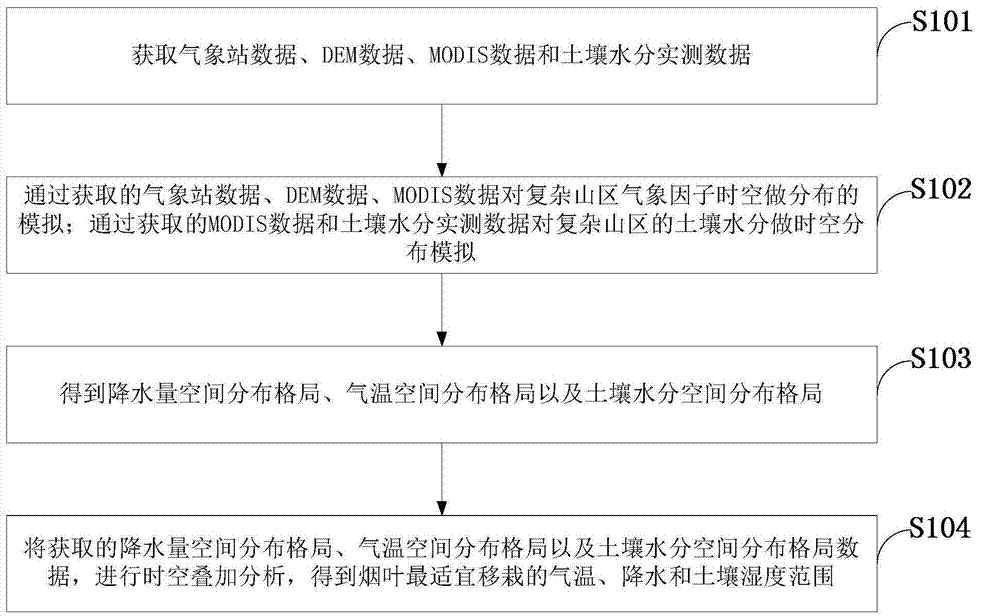
Method for determining spatial distribution of suitable transplanting period of flue-cured tobacco in complicated hilly area
InactiveCN104851048ASimple methodEasy to useData processing applicationsSoil scienceObservation data
The invention discloses a method for determining the spatial distribution of the suitable transplanting period of flue-cured tobacco in a complicated hilly area. MODIS (Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer) remote sensing image data and DEM (Dynamic Effect Model) altitude data are utilized and combined with ground observation data of the tobacco-growing area, a simulation method of the ten-day meteorology of the tobacco-growing area and the spatial and temporal distribution of soil moisture is constructed through mathematical modeling, main meteorological elements and the spatial and temporal distribution of soil moisture are extracted, the suitable meteorological factor and the soil moisture range, required by tobacco transplanting, are combined, and the spatial distribution of the suitable transplanting period of the tobacco-growing area can be determined. The method is simple, can be used conveniently, and can solve the problems that the traditional data based on sparse meteorological stations and less soil sampling points cannot reflect the spatial distribution of the meteorology and the soil moisture of the complicated hilly area easily, and the suitable transplanting period of the different areas of the complicated hilly area cannot be accurately determined.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
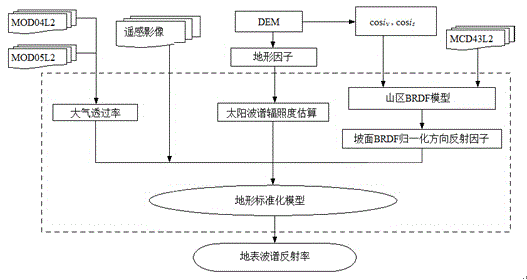
Remote sensing image terrain standardization method
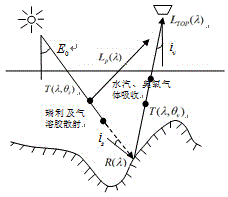
The invention discloses a remote sensing image terrain standardization method. In a Ross Thick-Li Sparse linear kernel driver model, slope and orientation are introduced into a Ross volume scattering kernel function and a Li geometrical optical kernel function to establish a mountain BRDF (Bidirectional Reflectance Distribution Function) model; on the basis of a conventional remote sensing image terrain standardization result, an assumption of the earth surface about a Lambertian reflectance characteristic is changed, and the mountain BRDF model is introduced to maximally reduce the influence of a change in the BRDF shape of a complicated topographical region; atmospheric parameters at the border crossing moment of a satellite image are obtained by taking MODIS (Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer) water vapor and aerosol atmosphere products as terrain standardization model parameters, so that the influence of optical factors of the atmosphere is eliminated. According to the method, radiometric distortion of a remote sensing image caused by optical properties of the atmosphere is eliminated, and in addition, radiometric distortion caused by factors such as terrain shielding and BRDF properties of the earth surface is effectively eliminated, so that the real reflectivity of the earth surface is obtained.
Owner:HANGZHOU DADI TECH CO LTD
Method for building high-spatial resolution NDVI (normalized difference vegetation index) time series data
InactiveCN102831310AHigh resolutionGood precisionSpecial data processing applicationsImage resolutionHigh spatial resolution
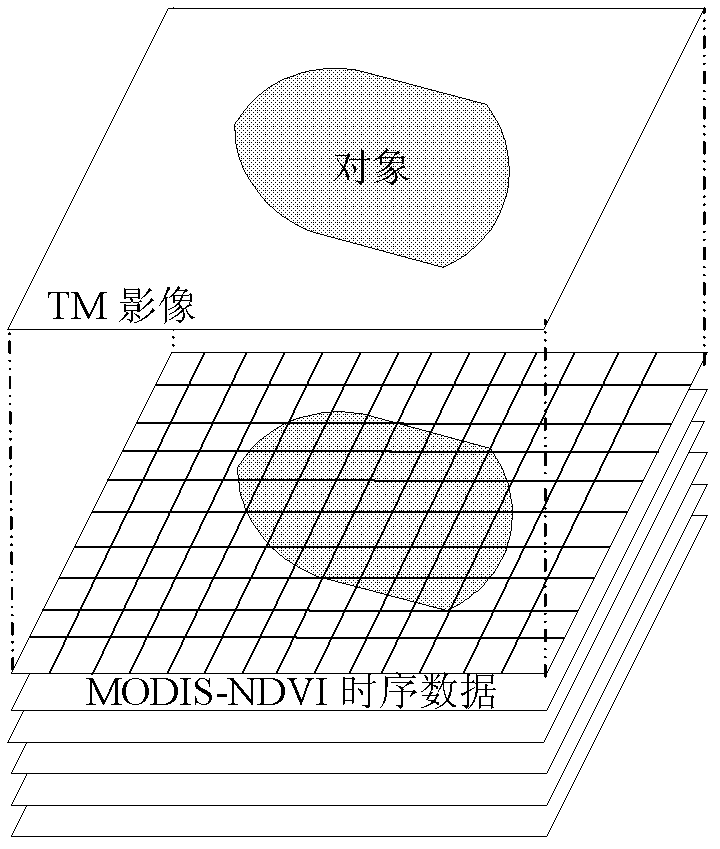
The invention discloses a method for building high-spatial resolution NDVI (normalized difference vegetation index) time series data. The high-spatial resolution NDVI time series data is predicted and built according to low-spatial resolution MODIS (moderate-resolution imaging spectroradiometer) pixels in known MODIS NDVI data and high-spatial resolution TM (thematic mapper) pixels in TMNDVI (thematic mapper normalized difference vegetation index) data. TM data is combined with MODIS data, and accordingly high-spatial resolution NDVI time series data with quite fine precision can be obtained effectively.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Filtering method for sea surface stripe noise and sea surface stripe cloud in moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer (MODIS) remote sensing image
InactiveCN102750683AEffective filteringKeep basic informationImage enhancementHierarchical Data FormatImage segmentation
The invention discloses a filtering method for sea surface stripe noise and sea surface stripe cloud in a moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer (MODIS) remote sensing image. An original image of the MODIS remote sensing image in the same region and the same period is read from a hierarchical data format (HDF) file; the histogram equalization processing is performed for the original image; the image which is subjected to the histogram equalization processing is divided into sub-images with 300300 pixels; average gray values of all sub-images are evaluated; and thresholds are selected, pixels which are smaller than thresholds are pixels of the stripe cloud or the stripe noise, and pixels which larger than thresholds are pixels of a sea surface or a sea internal wave. The sea surface stripe noise and the sea surface stripe cloud in the MODIS image in a certain region and a certain period can be effectively filtered in a short time, basic information of the sea internal wave in the MODIS image can be effectively reserved, the method is simple and the processing efficiency is high.
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV
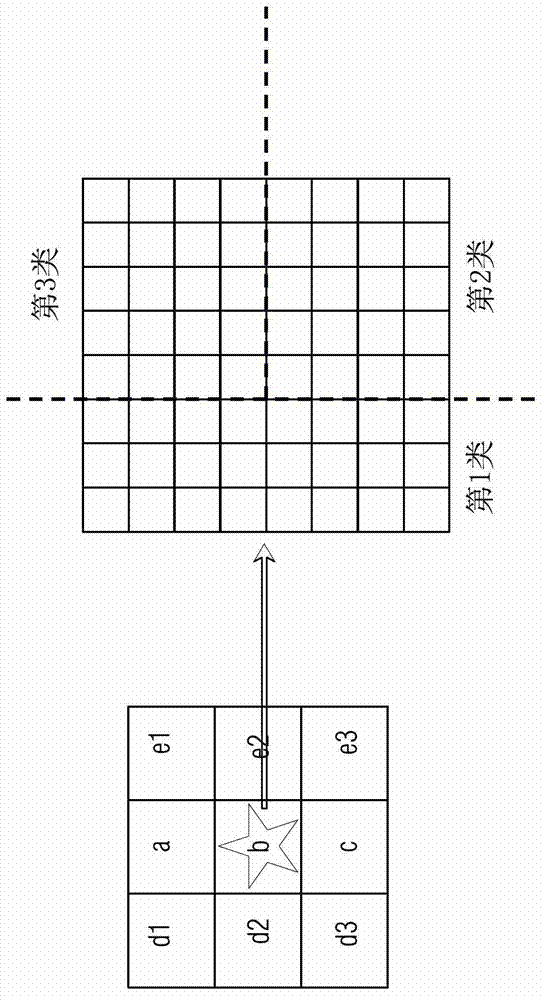
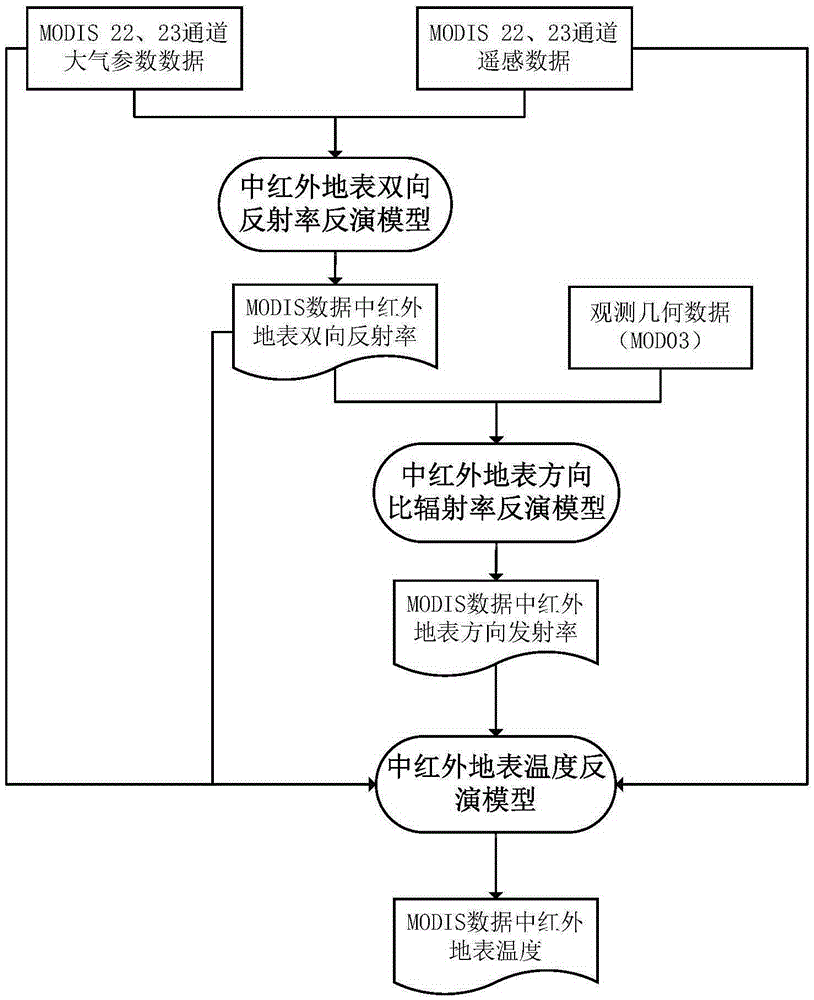
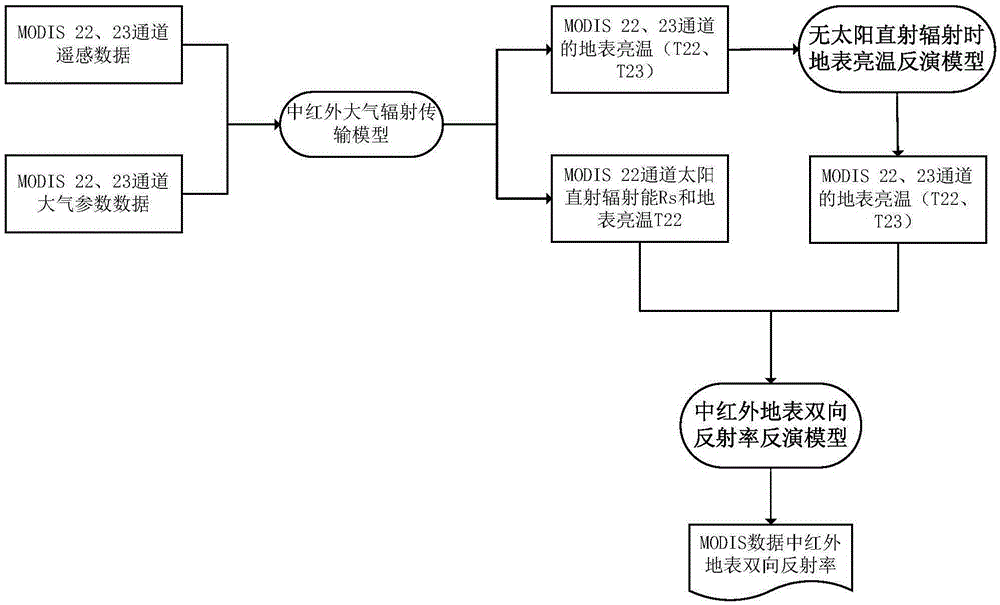
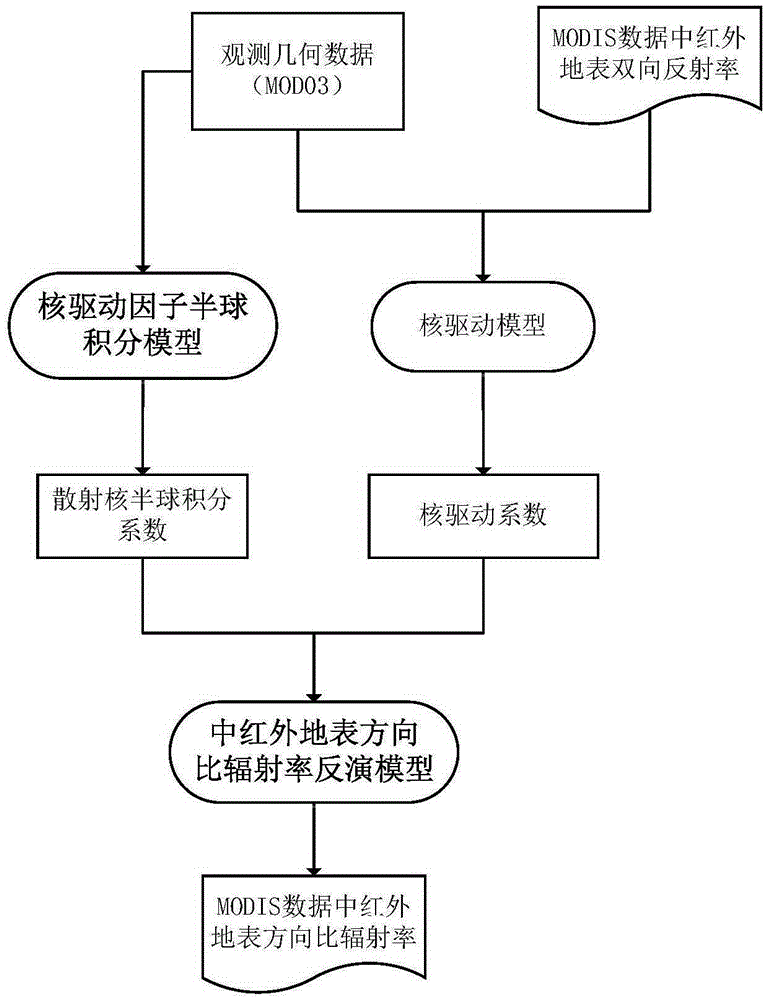
Method and apparatus for determining surface temperature by use of middle-infrared remote sensing data
InactiveCN105425247AEfficient separationAchieve inversionElectromagnetic wave reradiationICT adaptationMiddle infraredSensing data
The invention discloses a method and apparatus for determining a surface temperature by use of middle-infrared remote sensing data. The method comprises the following steps: step A, determining surface bidirectional reflectivity of a twenty-second channel (3.929[mu]m to 3.989[mu]m) and a twenty-third channel (4.020[mu]m to 4.080[mu]m) by use of radiation brightness data and atmosphere parameter data of the twenty-second channel and the twenty-third channel of a middle-infrared wave spectrum zone of moderate-resolution imaging spectroradiometer (MODIS) data through a developed middle-infrared surface bidirectional reflectivity remote sensing inversion method; step B, by use of the surface bidirectional reflectivity obtained from the step A, through a developed surface direction ratio radiant ratio remote sensing inversion method, determining surface direction ratio radiance; and step C, by use of the middle-infrared surface bidirectional reflectivity and the direction ratio radiance respectively obtained from the step A and the step B, through a developed surface temperature remote sensing reversion method, determining the surface temperature. The method and apparatus provided by the invention effectively realize quantitative remote sensing inversion of the surface temperature through the middle-infrared data.
Owner:INST OF GEOGRAPHICAL SCI & NATURAL RESOURCE RES CAS
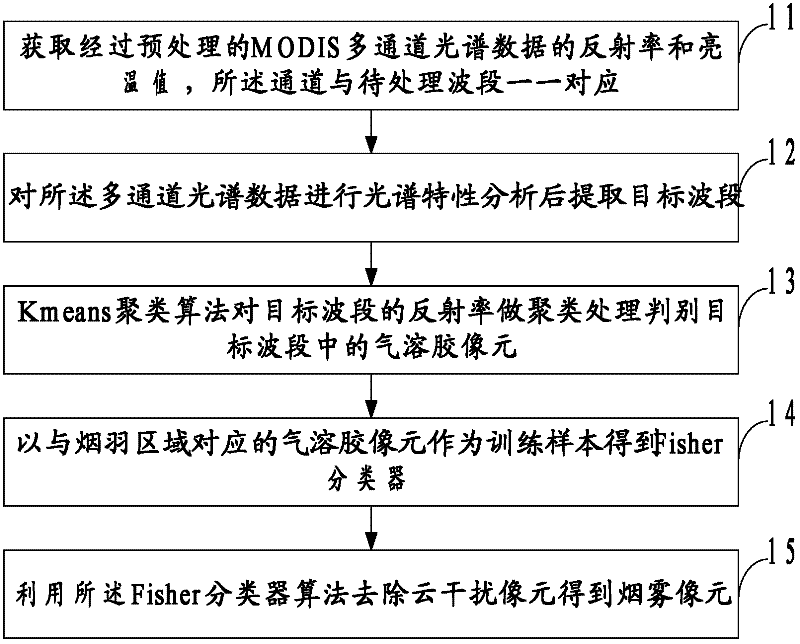
Method and system for monitoring smoke of forest fire
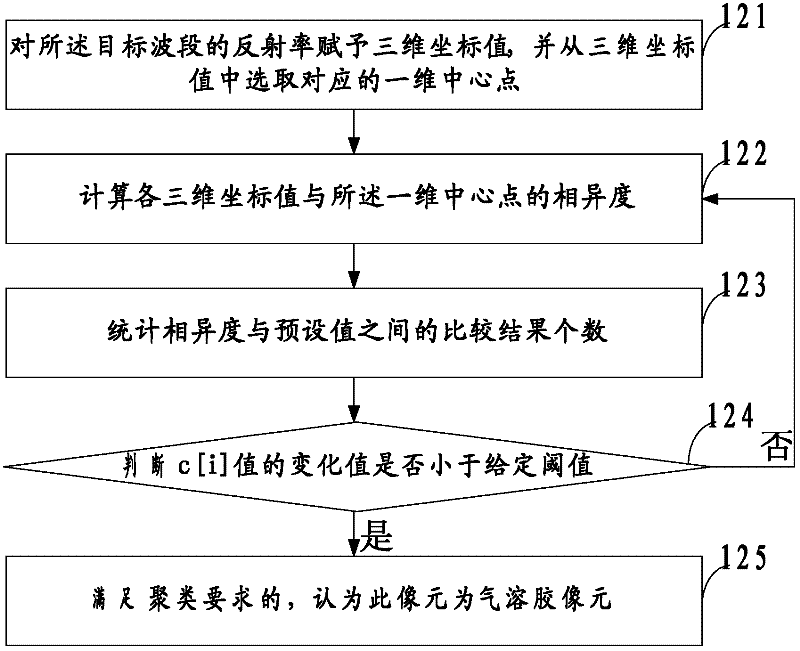
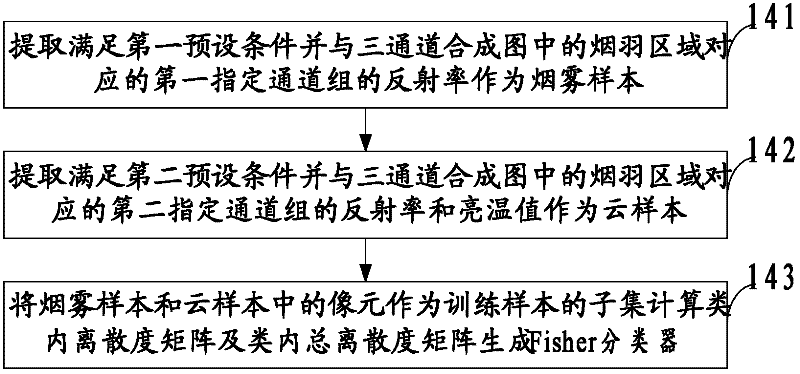
InactiveCN102254398ASolve the problem of missed judgmentImprove accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionFire alarm smoke/gas actuationModerate-resolution imaging spectroradiometerSmoke plume
The embodiment of the invention discloses a method and a system for monitoring the smoke of a forest fire. The method comprises the following steps of: acquiring the reflectivity and brightness temperature value of spectroscopic data, which is pre-processed, of a plurality of channels of a moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer (MODIS), wherein the channels are in one-to-one correspondencewith wave bands to be processed; extracting a target wave band according to the reflectivity and the brightness temperature value; clustering the reflectivity of the target wave band by using a k-means clustering algorithm, and determining an aerosol pixel in the target wave band; obtaining a Fisher classifier by using the aerosol pixel which corresponds to a smoke plume region as a training sample; and removing a cloud interference pixel by using the Fisher classifier to obtain a smoke pixel. With the obtained aerosol pixel, the problem of leaked determination for thin smoke which is spread in cloud and rain regions in the prior art is solved, the cloud pixel which interferes with the smoke pixel is removed by the Fisher classifier, interference of a water body pixel is discriminated andthen removed by using a spectrum threshold value, monitoring accuracy is improved, and requirements on smoke monitoring under the influence of different weather conditions and seasonal climates can be met.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
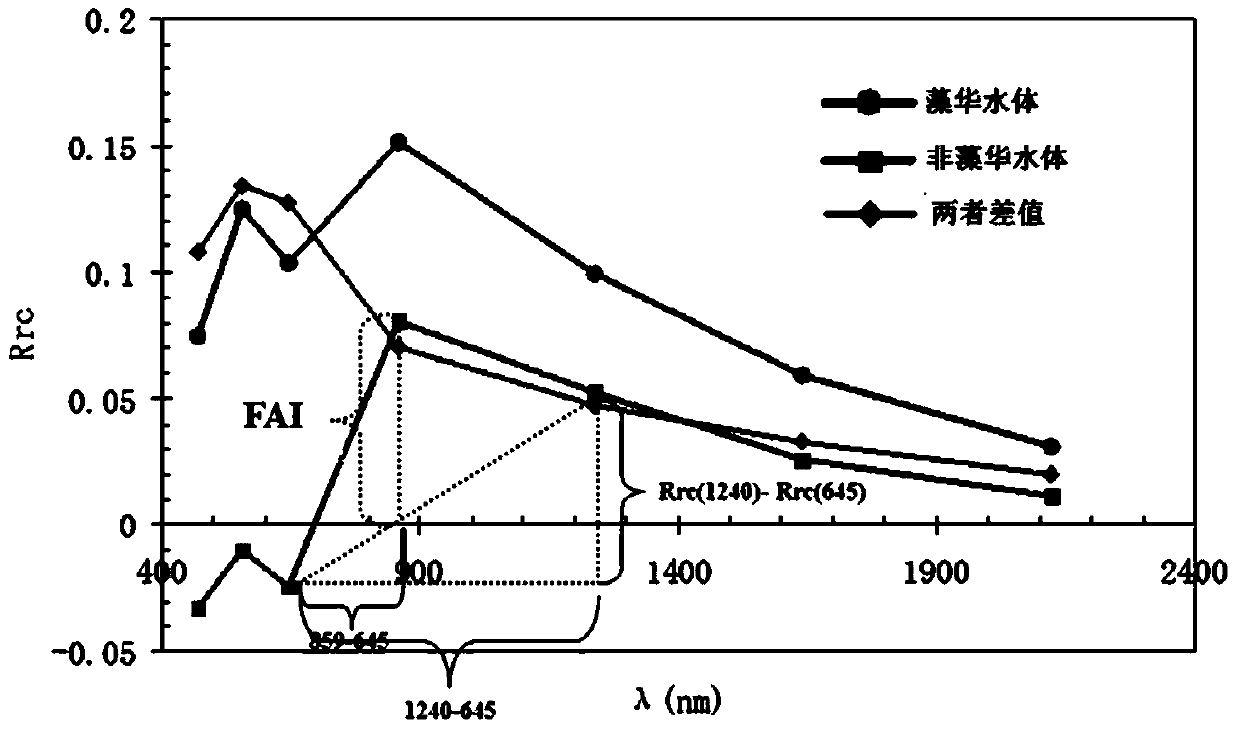
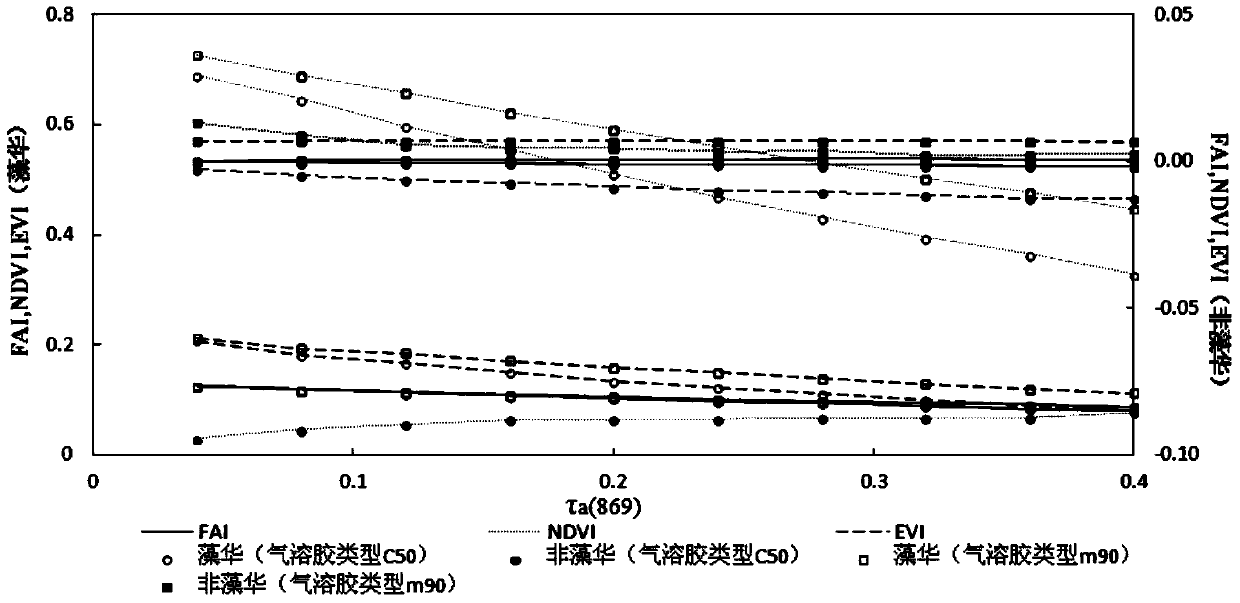
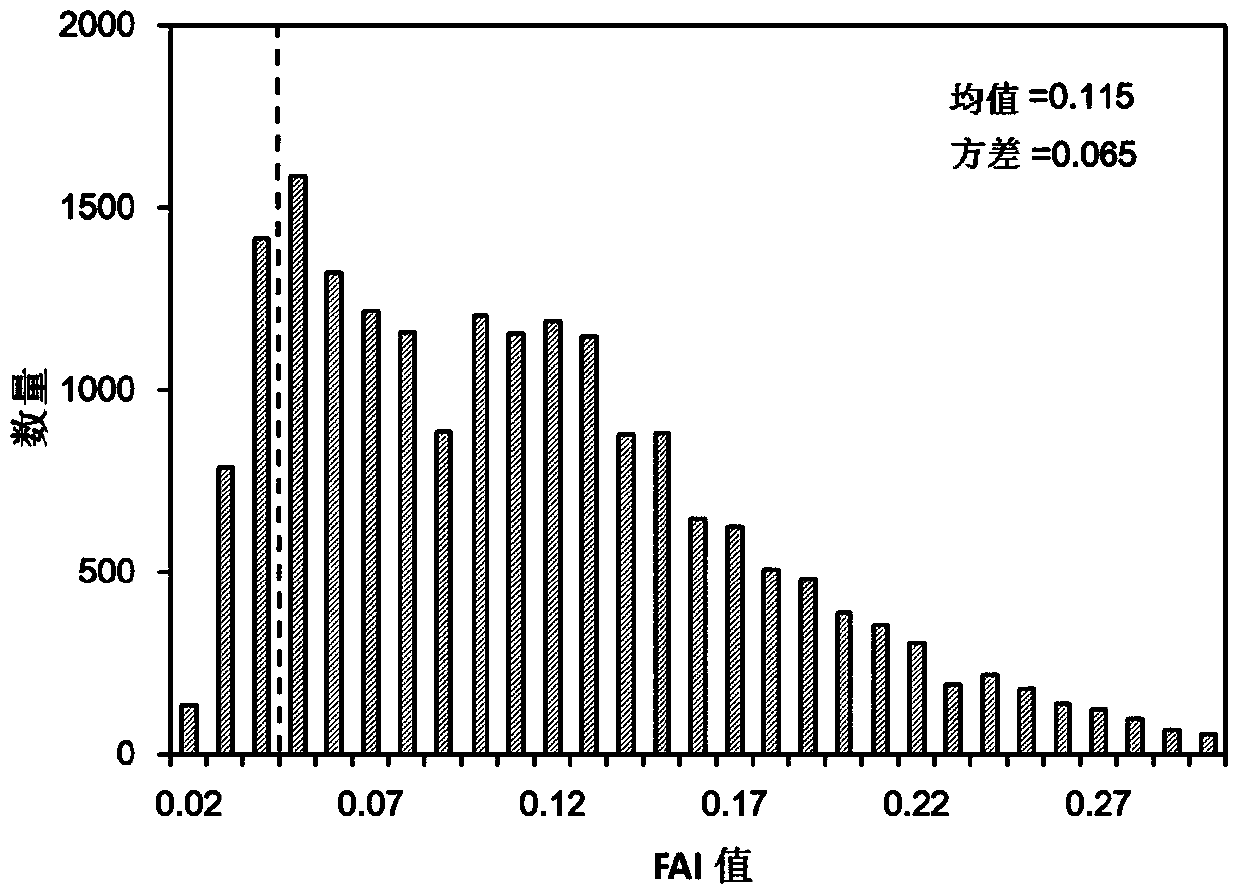
MODIS (moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer) satellite synchronous monitoring method for cyanobacterial bloom and aquatic vegetation in eutrophic lakes
ActiveCN106315856AReflect the space-time distributionImprove forecast accuracyColor/spectral properties measurementsBiological water/sewage treatmentNatural satelliteClassification methods
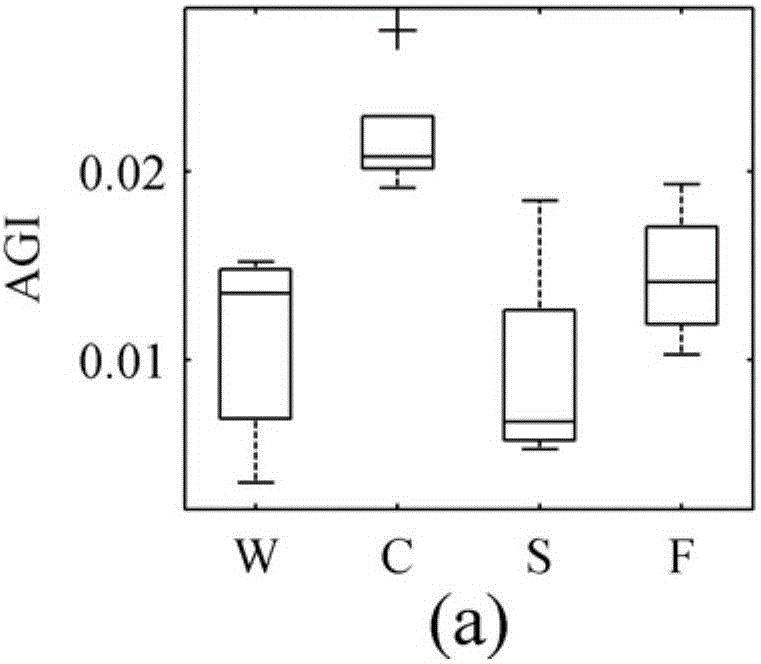
The invention provides an MODIS (moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer) satellite synchronous monitoring method for cyanobacterial bloom and aquatic vegetation in eutrophic lakes. The MODIS satellite synchronous monitoring method includes combining spectral characteristics of the cyanobacterial bloom, the submerged vegetation and floating-leaf / emergent vegetation with one another on the basis of field measured spectral data and creating alga and grass indexes (AGI); combining turbid water indexes (TWI) and floating alga indexes (FAI) with one another and determining basic classification processes; determining classification thresholds for the AGI, the TWI and the FAI on the basis of historically acquired MODIS satellite data; ultimately completely constructing classification decision trees and synchronously monitoring the cyanobacterial bloom, the submerged vegetation and the floating-leaf / emergent vegetation on MODIS satellite images. Alga-containing water and grass-containing water can be separated from each other by the aid of the alga and grass indexes (AGI). High-turbidity water can be identified by the aid of the turbid water indexes (TWI), and the submerged vegetation and the floating-leaf / emergent vegetation can be differentiated from each other by the aid of the floating alga indexes (FAI). The MODIS satellite synchronous monitoring method has the advantage that interannual and inter-monthly variation laws and spatial distribution of the cyanobacterial bloom, the submerged vegetation and the floating-leaf / emergent vegetation in the eutrophic lakes can be accurately acquired on the basis of the MODIS satellite synchronous monitoring method.
Owner:NANJING INST OF GEOGRAPHY & LIMNOLOGY
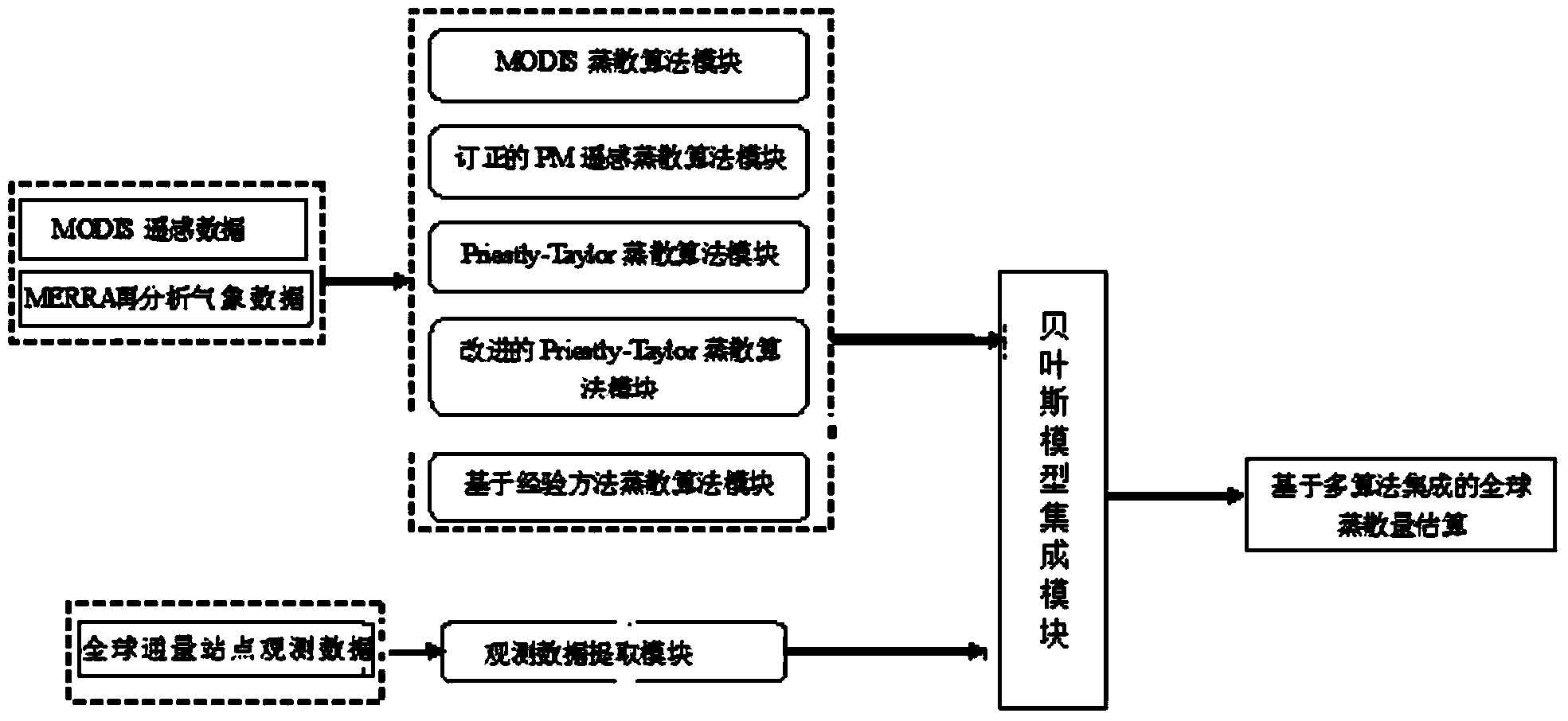
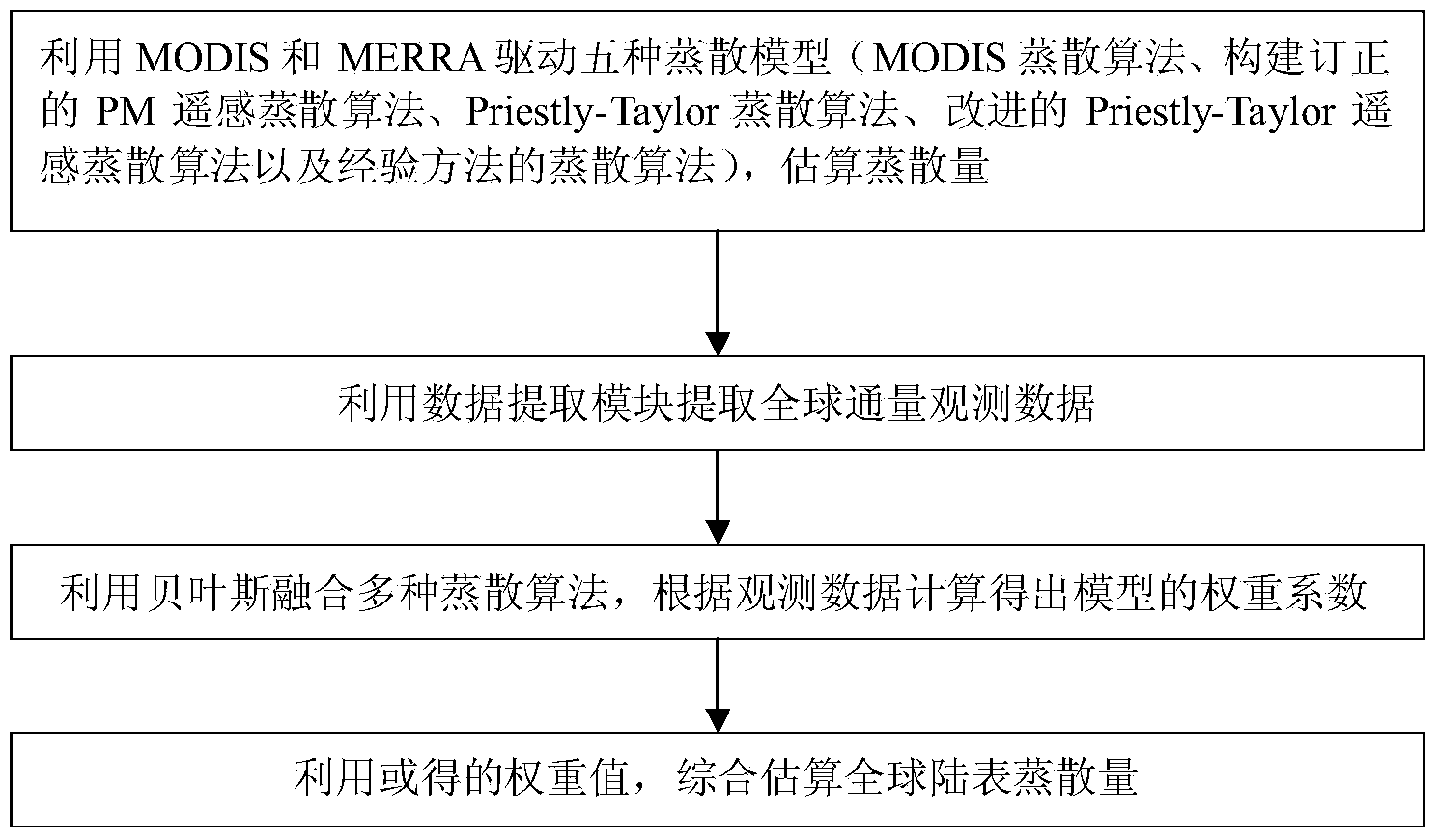
Global integrated land surface evapotranspiration and estimation system and method based on multiple algorithms
ActiveCN104077475AImprove stabilityEasy to operateSpecial data processing applicationsSensing dataModel method
The invention belongs to the technical field of meteorological and hydrographic measurement and relates to a global integrated land surface evapotranspiration and estimation system based on multiple algorithms and a method thereof. The global integrated land surface evapotranspiration and estimation method based on multiple algorithms comprises the following steps of: utilizing MODIS (Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer) remote sensing data and MERRA reanalyzed meteorological data to drive a MODIS evapotranspiration algorithm module, a rectified PM remote sensing evapotranspiration algorithm module, a Priestly-Taylor evapotranspiration algorithm module, an improved Priestly-Taylor evapotranspiration algorithm module, and a evapotranspiration algorithm module based on experience and methods, in order to respectively obtain their evapotranspiration amounts; according to the sample quality of measured data from a station, extracting surface evapotranspiration observed values from observed data in a global flux station by an observed data extracting module; through a Bayesian model, integrating the extracted surface evapotranspiration observed values with the evapotranspiration amounts calculated by all evapotranspiration algorithm modules to form a Bayesian model integration module. In comparison with the existing technology, in the invention, the method and the system have the advantages of stronger stability and wider application range, thus they have a broad application prospect.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
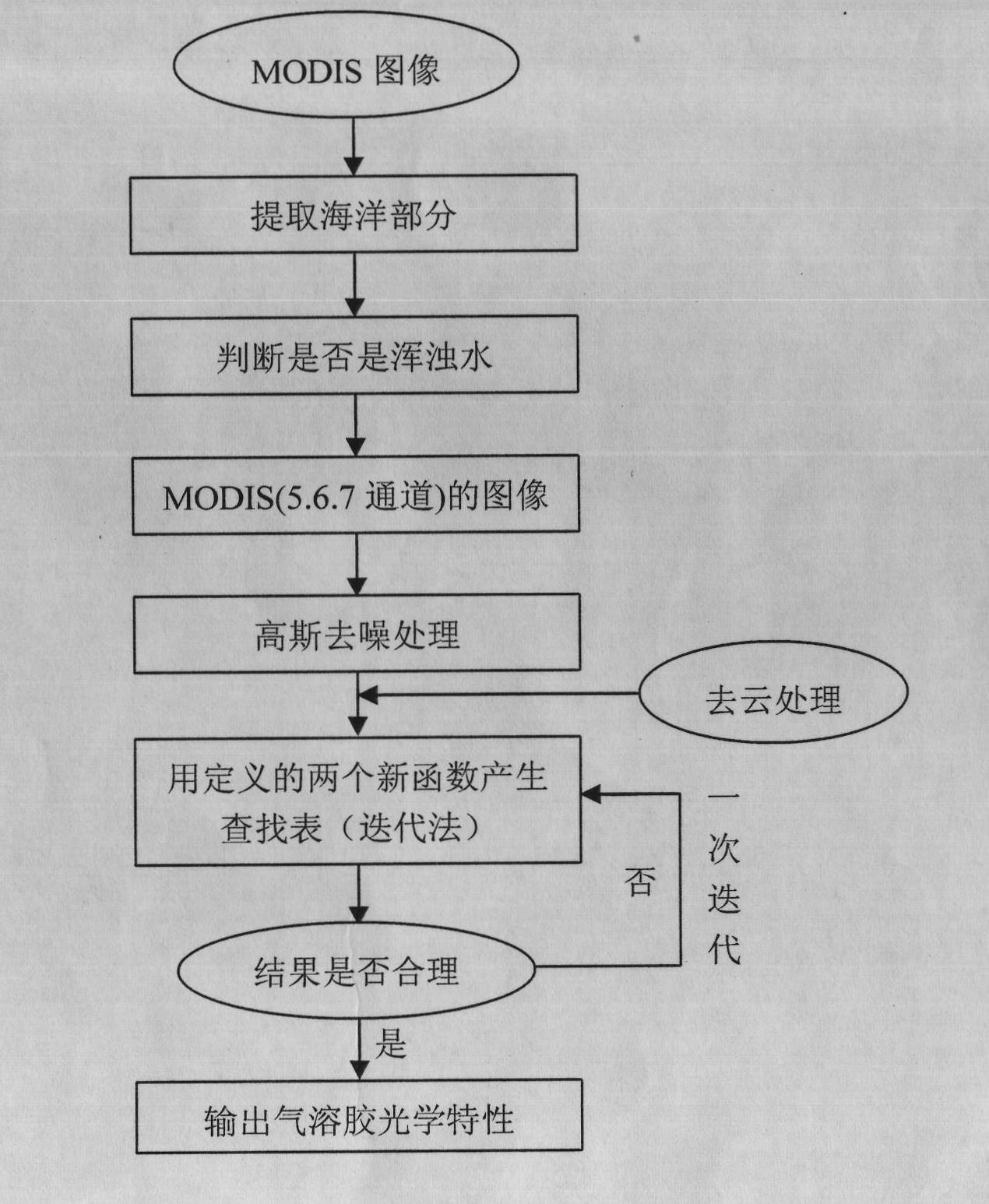
Method for performing inversion on optical property of aerosol of coastal zone by using MODIS image
InactiveCN102073792APrecise optical propertiesHigh precisionScattering properties measurementsSpecial data processing applicationsOptical propertyRadiometer
The invention relates to a method for performing inversion on the optical property of aerosol of a coastal zone, and provides a new algorithm for performing inversion on the optical property of the aerosol of a coastal area in China by using a satellite image aiming at the characteristics of a large number of aerosol particles with high reflectivity and strong absorbability on the ocean surface of the coastal area in China. In the algorithm, the research is conducted by taking an image of a moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer (MODIS) as an example; the inversion of the optical property of atmospheric aerosol over a muddy water area is finished by using the images of long wave bands of 1,240 nm, 1,640nm and 2,133 nm of the MODIS and a lookup table; and the correctness and applicability of the algorithm are verified by using an foundation observation result of a cleaning day. Theoretical basis is provided for adding a channel with long wave bands and transmissivity into a Chinese sea color remote sensor, the condition of the aerosol over the coastal zone can be reflected in real time, and decision basis is provided for related functional departments.
Owner:ANHUI NORMAL UNIV
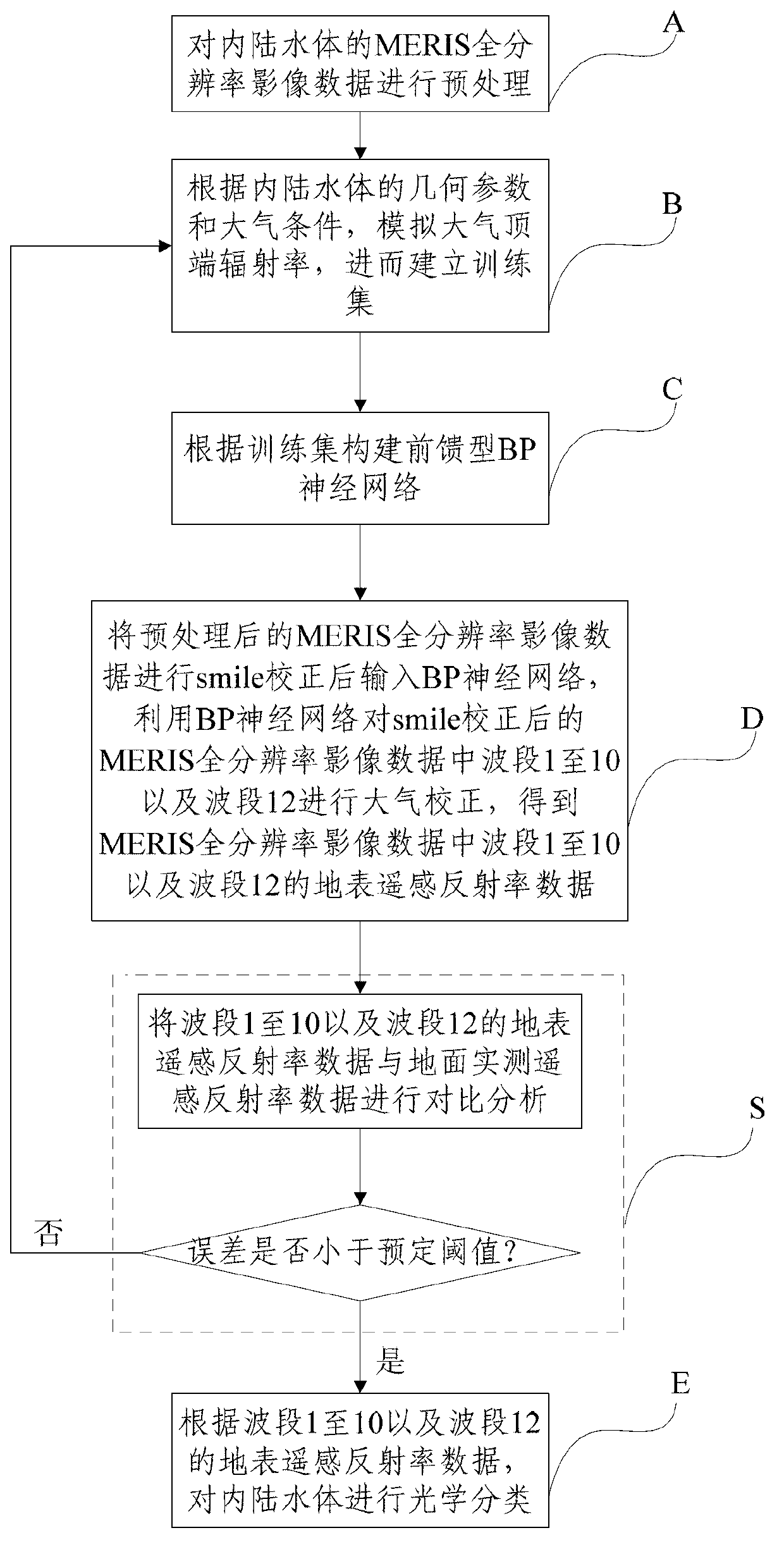
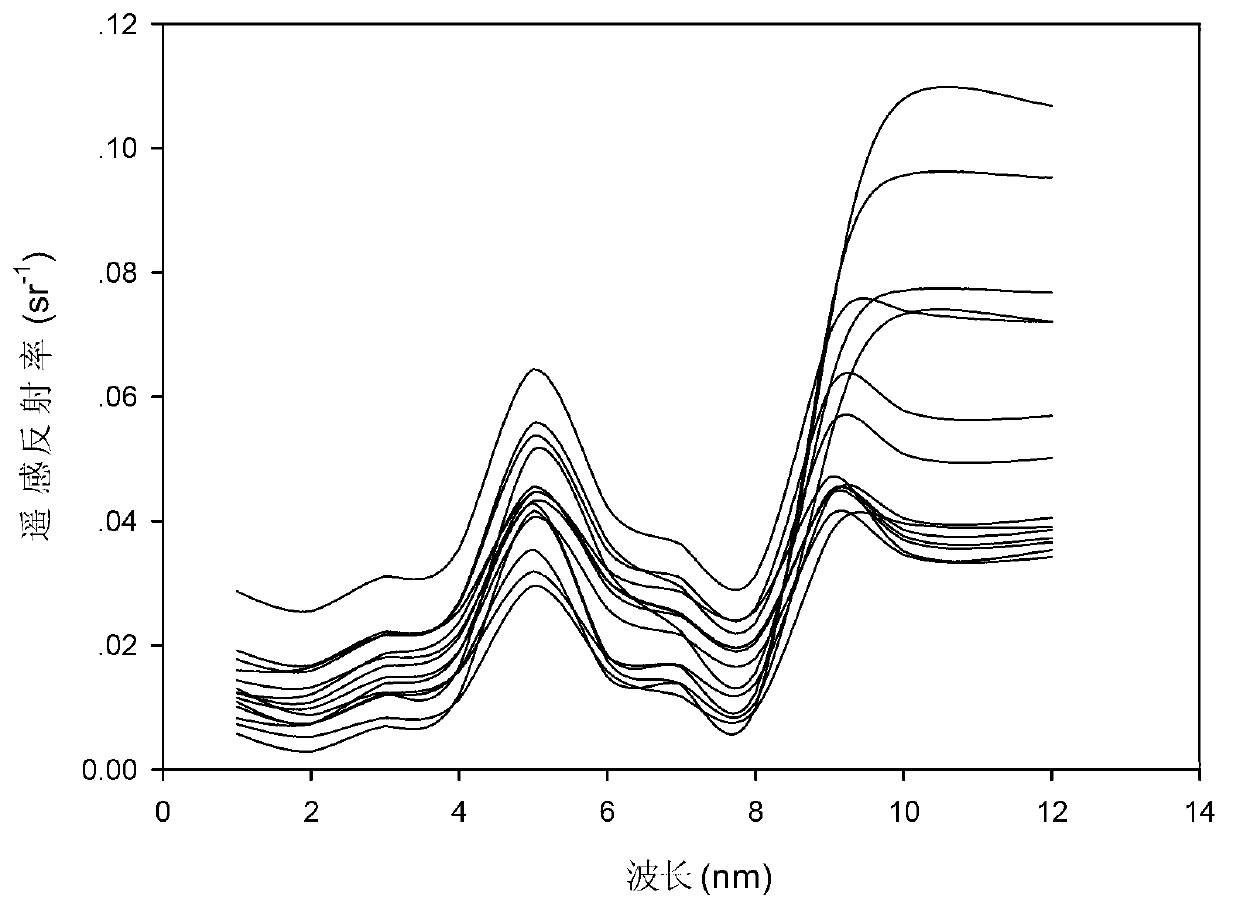
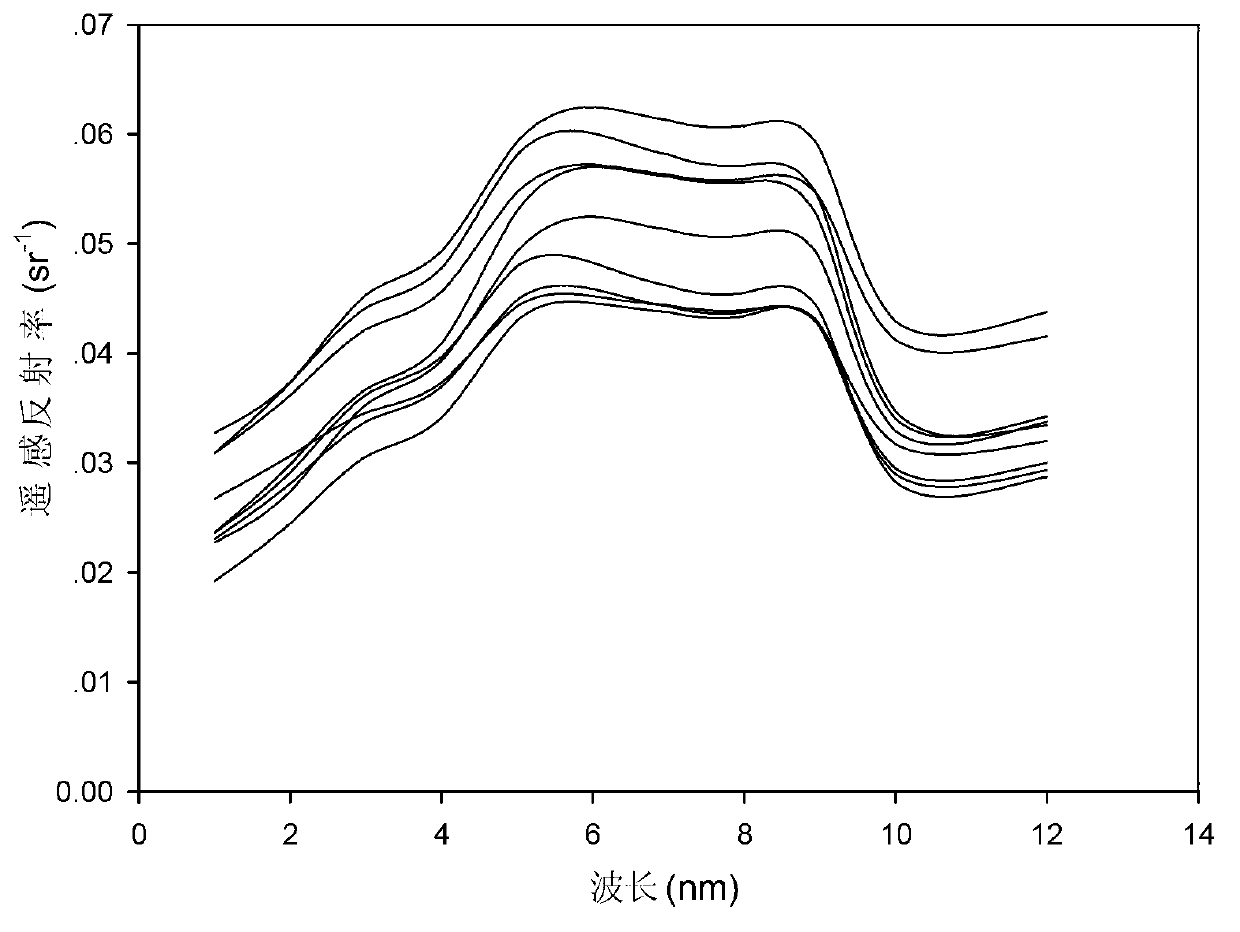
Inland water body optical classification method based on medium-resolution imaging spectrometer (MERIS) full-resolution image data
InactiveCN102955878AImproving the accuracy of remote sensing inversionSpecial data processing applicationsClassification methodsModerate-resolution imaging spectroradiometer
The invention discloses an inland water body optical classification method based on medium-resolution imaging spectrometer (MERIS) full-resolution image data and relates to the technical field of remote sensing. The method comprises the following steps of: preprocessing the MERIS full-resolution image data of an inland water body; simulating atmosphere top radiance, and establishing a training set; establishing a feed-forward BP neural network, performing atmosphere correction on the wave bands 1-10 and a wave band 12 in the MERIS full-resolution image data subjected to smile correction by utilizing the BP neural network so as to obtain earth's surface remote sensing reflectivity data of the wave bands 1-10 and the wave band 12 in the MERIS full-resolution image data; and performing optical classification on the inland water body according to the earth's surface remote sensing reflectivity data of the wave bands 1-10 and the wave band 12. According to the method, the local water body in the inland water body is classified, and a data support is provided for improving the remote sensing inversion precision and establishing a unified inversion model for a water body with the same optical characteristics.
Owner:SATELLITE ENVIRONMENT CENT MINIST OF ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION +1
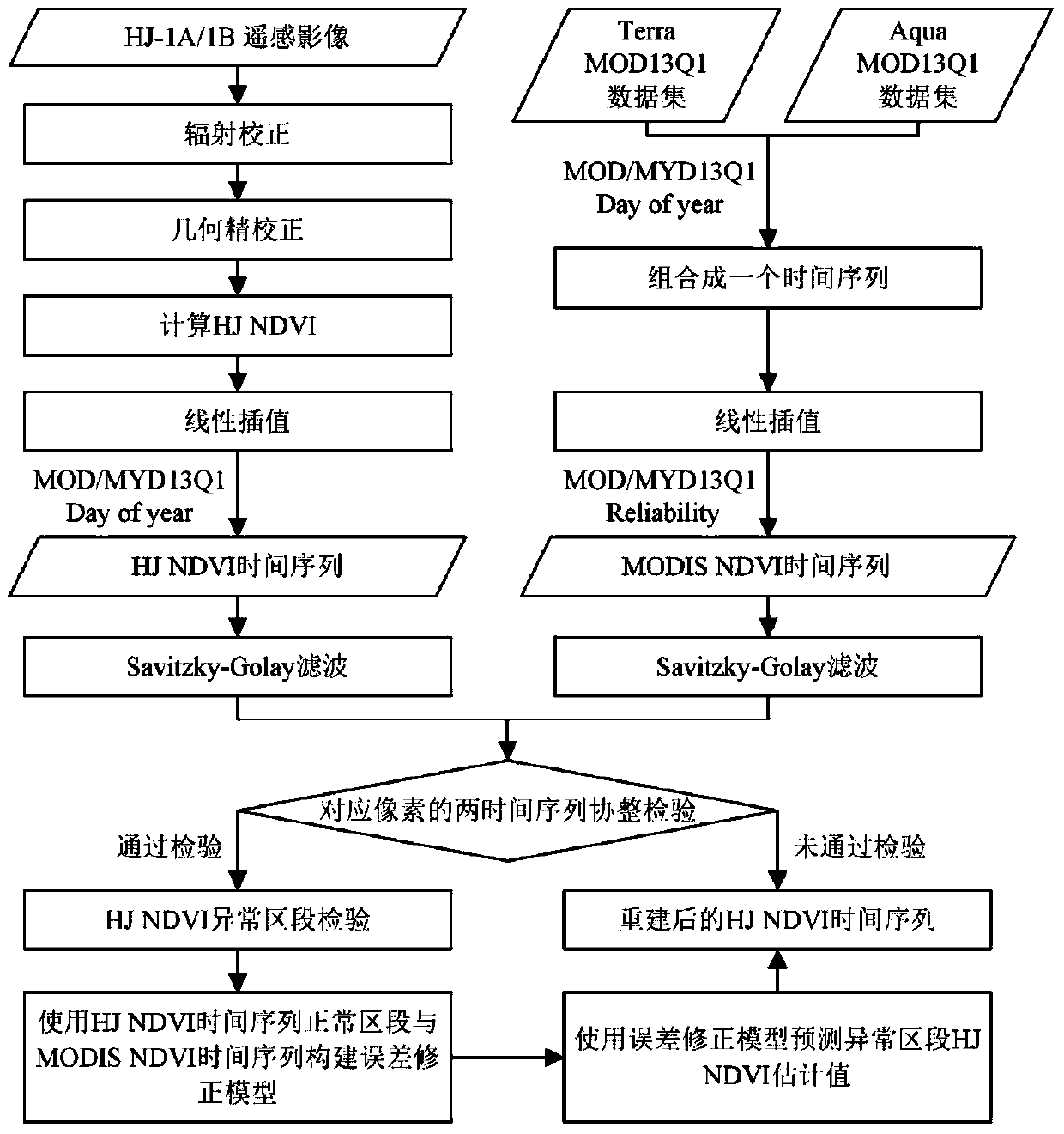
High-resolution remote sensing image vegetation index time sequence correcting method based on moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer (MODIS) remote sensing image
InactiveCN103617629AException fixMeet application requirementsImage analysisElectromagnetic wave reradiationImage resolutionIntegration testing
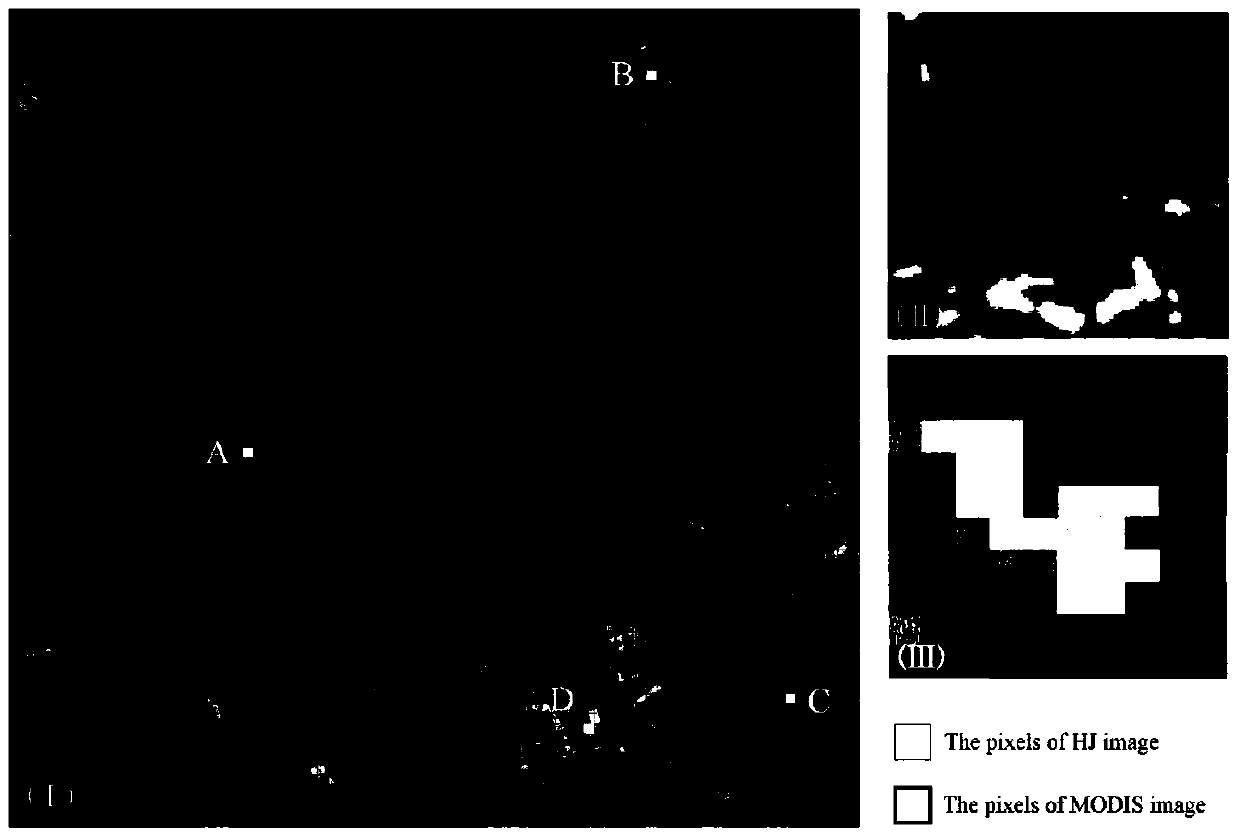
The invention discloses a high-resolution remote sensing image vegetation index time sequence correcting method based on a moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer (MODIS) remote sensing image. The method comprises the four stages of construction of an HJ normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) time sequence and a low-middle spatial resolution remote sending image NDVI time sequence, co-integration testing of an HJ time sequence and a time sequence of a corresponding pixel of a low-middle spatial resolution remote sensing image, testing of an abnormal section of the HJ NDVI time sequence, and correction of the abnormal section of the HJ NDVI time sequence. According to the method, the abnormity, caused by climate reasons, of a sequence curve form of the HJ NDVI time sequence can be corrected, the accuracy and the usability are improved, and effective data is provided for research on a biogeochemistry model under high temporal-spatial resolution. Meanwhile, the method is applied to the time sequence of a certain vegetation index from other high-middle-resolution remote sensing images.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Method and device for determining land surface emissivity of narrow band and broad band simultaneously
InactiveCN102901563AOvercome the defect of only assigning a constant valueHigh precisionAbsorption/flicker/reflection spectroscopyModerate-resolution imaging spectroradiometerEarth surface
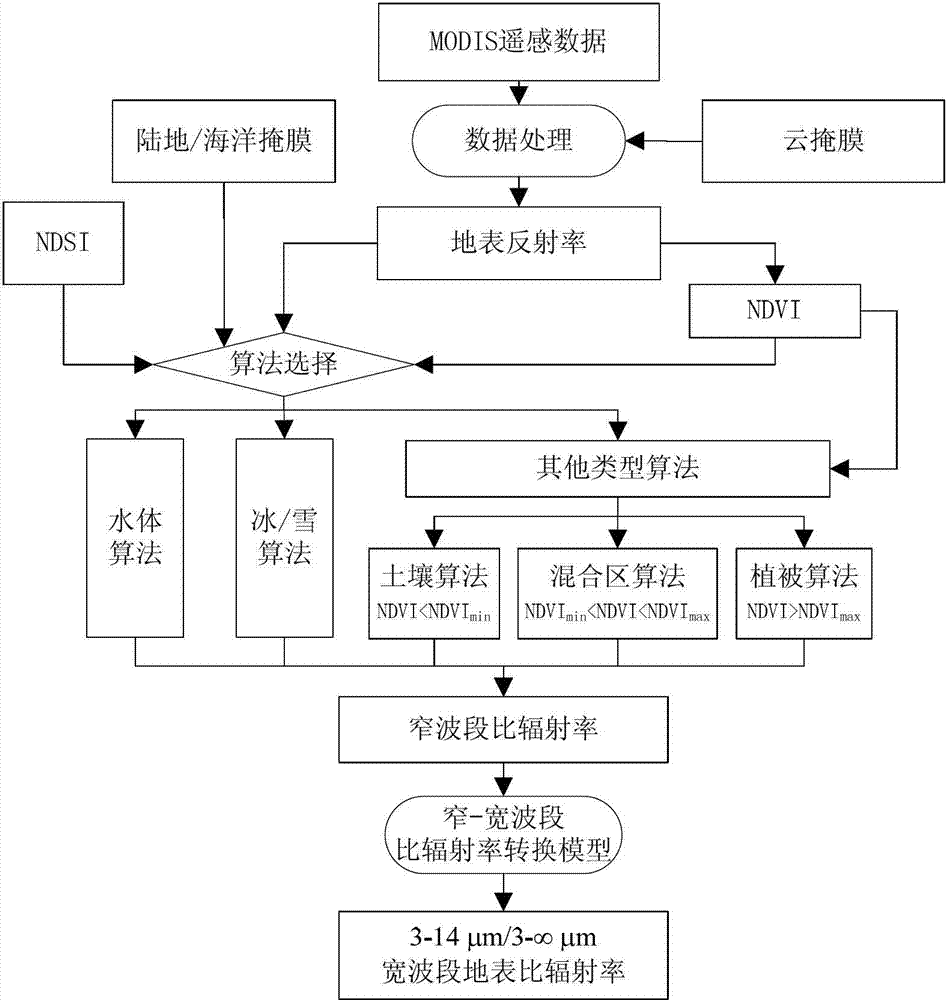
The invention discloses a method and a device for determining the land surface emissivity of a narrow band and a broad band simultaneously. The method comprises the following steps of: A) performing data processing such as radiometric calibration, atmospheric correction and cloud mask processing on moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer (MODIS) data to acquire land surface reflectance data of a visible light / near-infrared band of the MODIS data positioned at a 0.4-2.1 mu m atmospheric window area under the condition of a clear sky; B) determining the land surface emissivity of narrow bands such as a 29th wave band (the spectrum range is 8.4-8.7 mu m), a 31th wave band (the spectrum range is 10.78-11.28 mu m) and a 32th wave band (the spectrum range is 11.77-12.27 mu m) of an MODIS thermal infrared spectrum by using the reflectance data which is acquired in the step A and combining a developed narrow band emissivity inverse algorithm; and C) acquiring the land surface emissivity of broad bands of 3-14 mu m and 3 to infinite mu m by using the land surface emissivity of the narrow bands which is obtained in the step B and combining a developed narrow-broad band emissivity transformation model.
Owner:INST OF GEOGRAPHICAL SCI & NATURAL RESOURCE RES CAS
Remote sensing rating method for growth vigor of crops on large scale
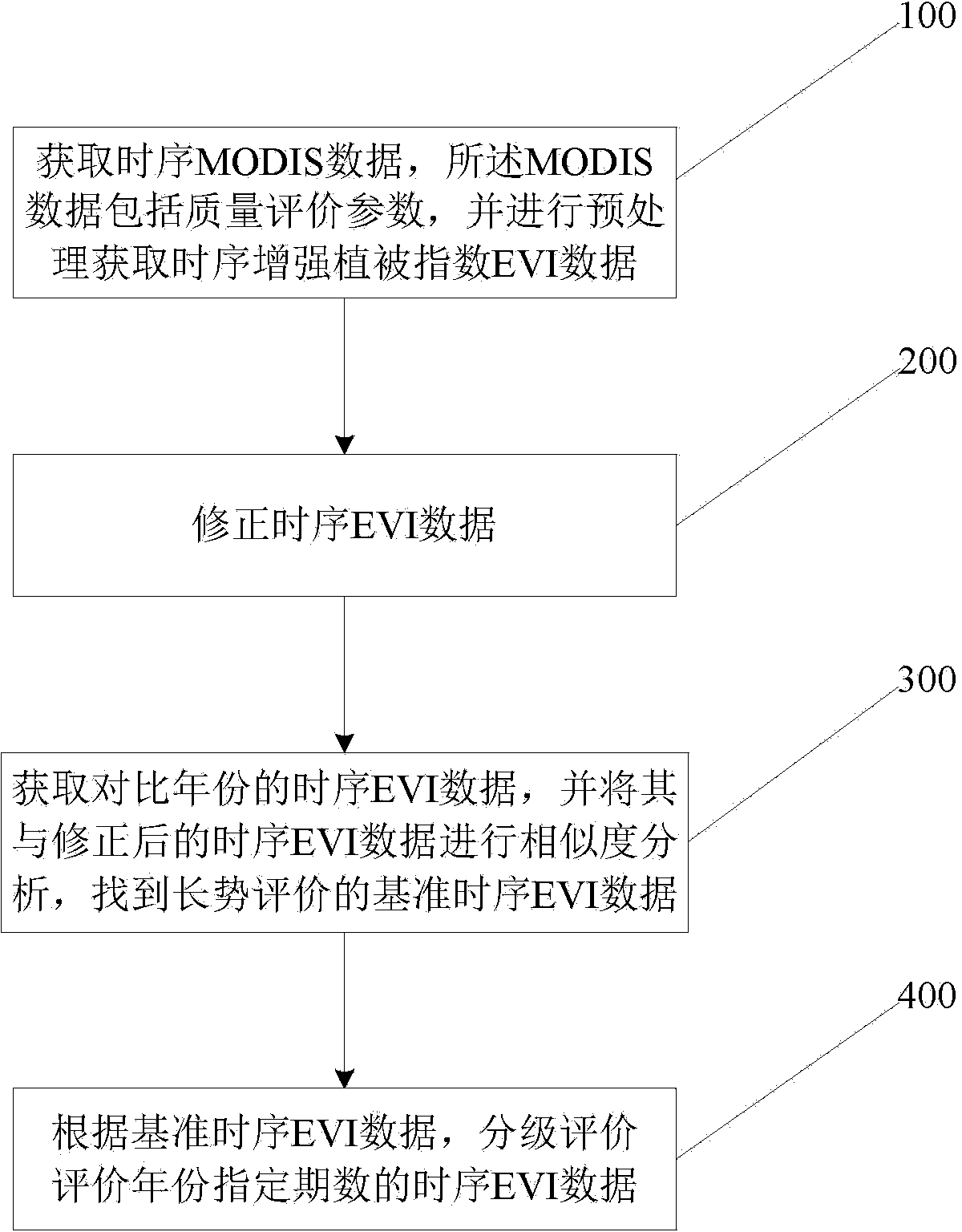
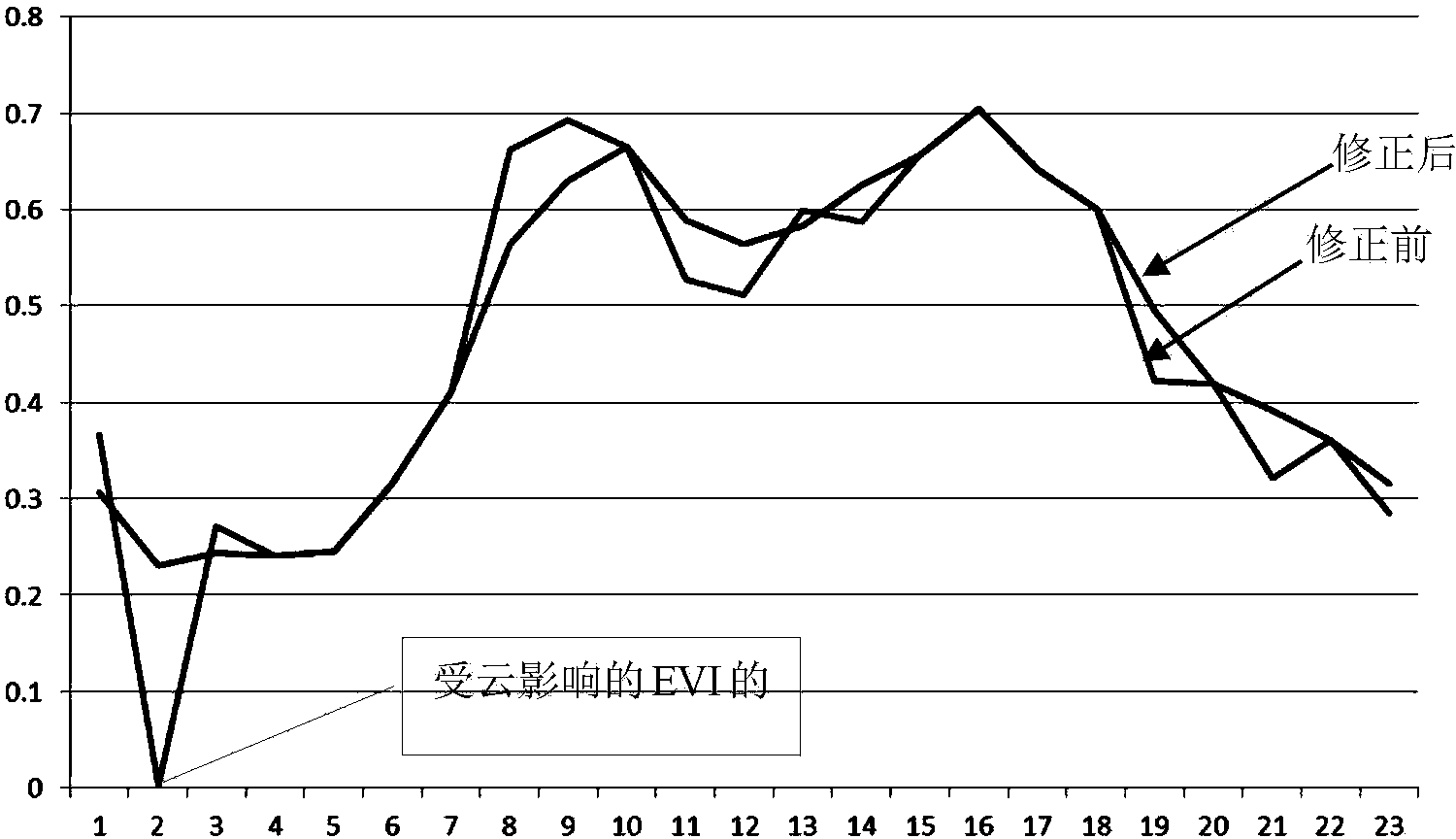
ActiveCN103971199AAvoid phenological changesAvoid Planting Structure ChangesResourcesImage resolutionVegetation Index
The invention discloses a remote sensing rating method for growth vigor of crops on a large scale. The remote sensing rating method includes A, acquiring temporal MODIS (moderate-resolution imaging spectroradiometer) data of evaluation years, and preprocessing the temporal MODIS data to obtain temporal EVI (enhanced vegetation index) data; B, revising the temporal EVI data; C, acquiring temporal EVI data of comparison years, analyzing the similarity among the temporal EVI data of the comparison years and the revised temporal EVI data and finding out reference temporal EVI data for rating the growth vigor; D, grading and evaluating the temporal EVI data of specified numbers of periods of the evaluation years according to the reference temporal EVI data. The MODIS data contain quality evaluation information. The remote sensing rating method has the advantages that the remote sensing rating method is adaptive to the requirement on monitoring the growth vigor of the crops in complicated planting systems on a large scale, and influence of phenological change of the crops and change of crop planting structures can be effectively prevented as compared with the traditional simple historical same-period comparison method.
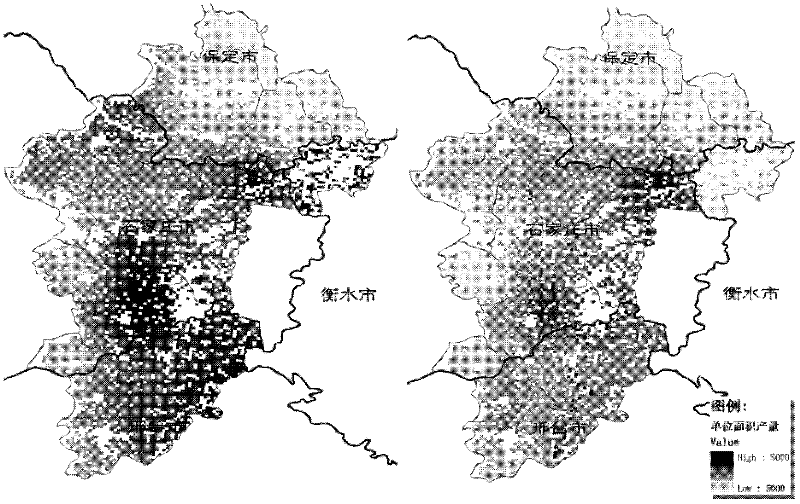
Owner:WUHAN HEXUN AGRI INFORMATION TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com