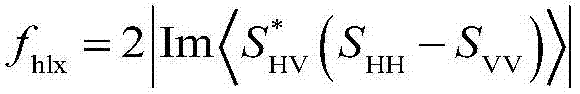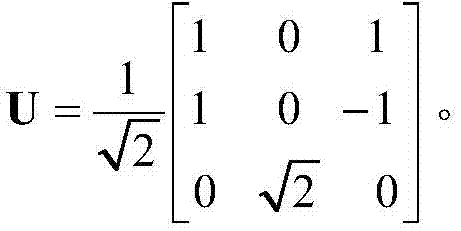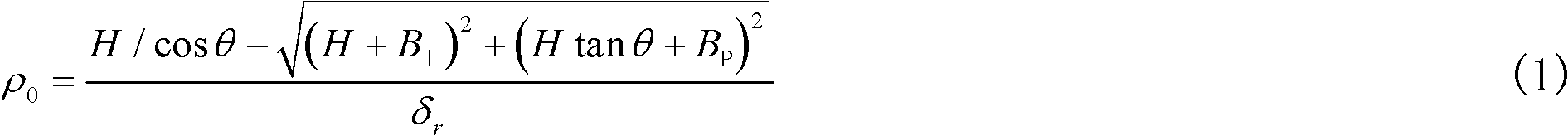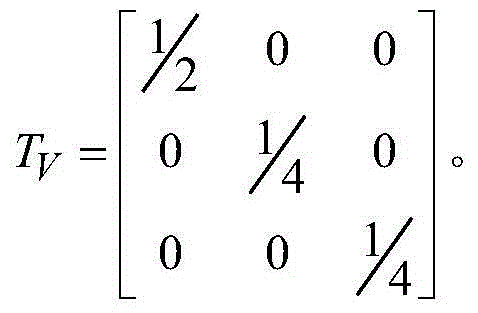Patents
Literature
81 results about "Volume scattering" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
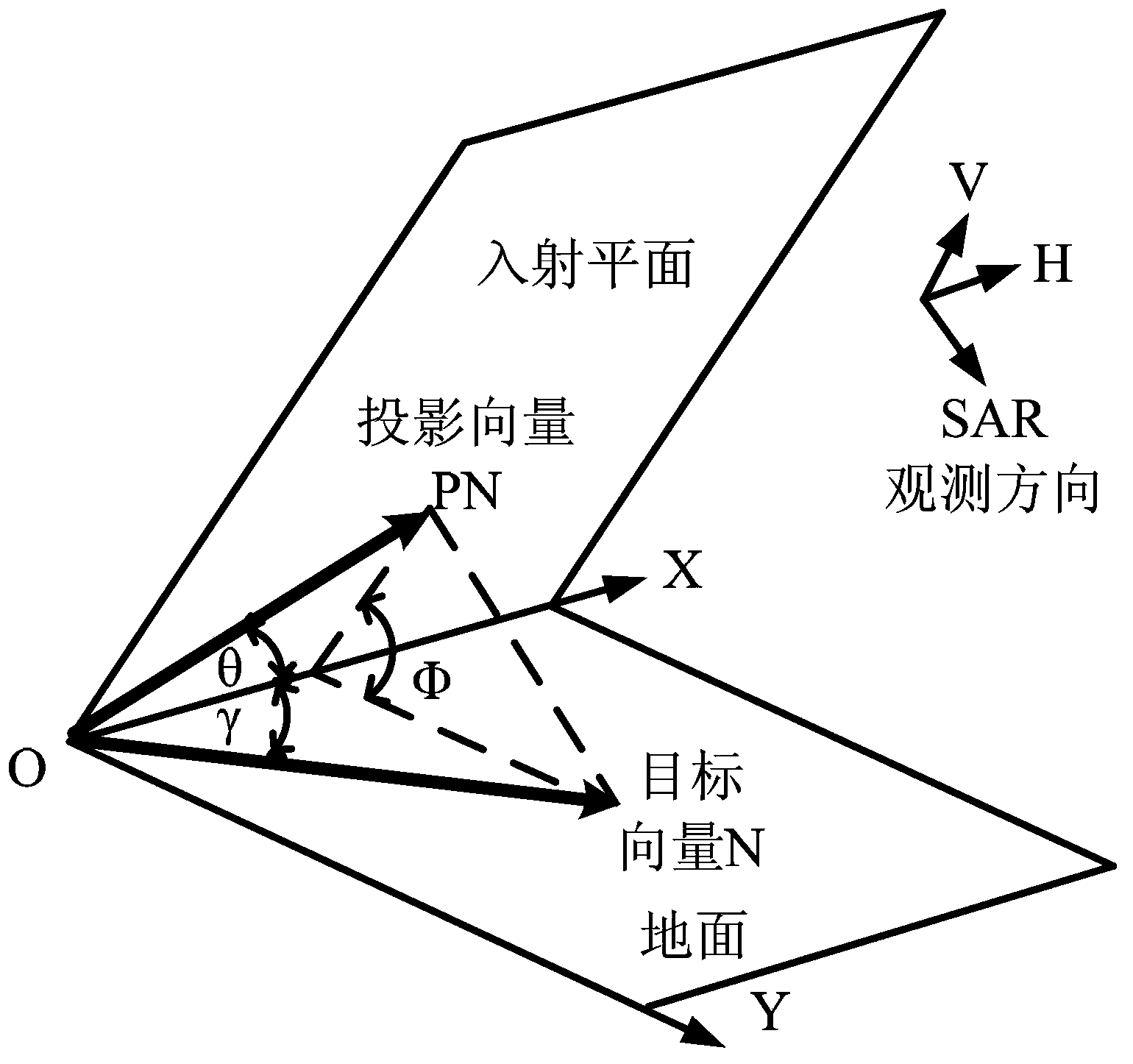
Freeman decomposition and homo-polarization rate-based polarized synthetic aperture radar (SAR) image classification method
ActiveCN102208031AEffective divisionAvoid divisionCharacter and pattern recognitionComputation complexitySynthetic aperture radar
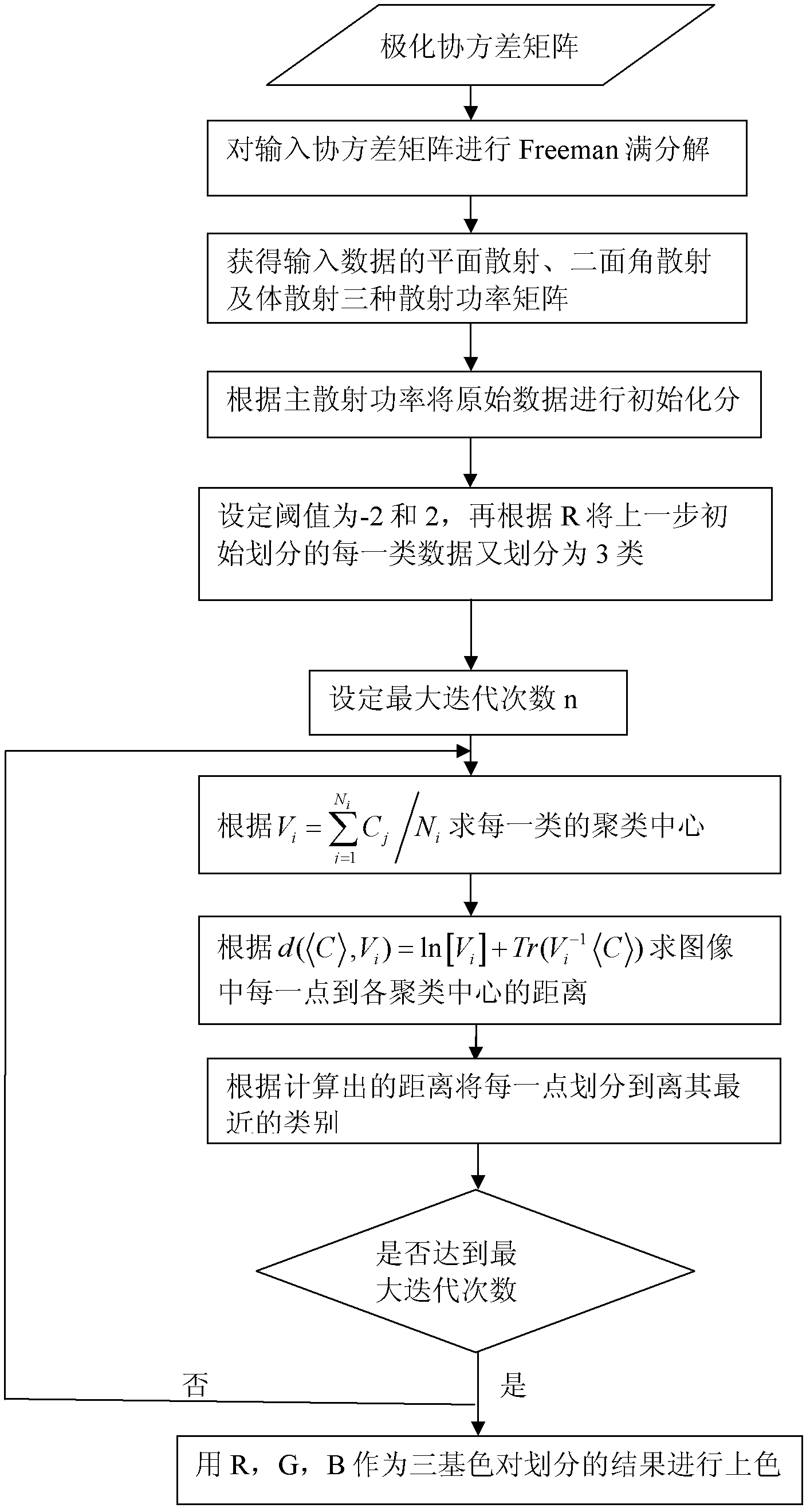
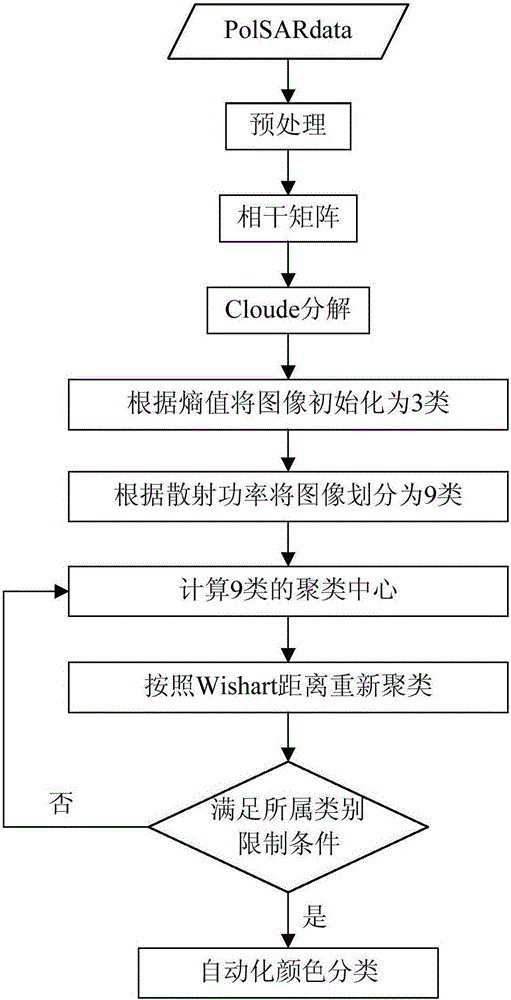
The invention discloses a Freeman decomposition and homo-polarization rate-based polarized synthetic aperture radar (SAR) image classification method for mainly solving the problems of higher calculation complexity and poor classification effect in the prior art. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) inputting a covariance matrix of polarized SAR data; (2) performing Freeman decomposition on the input matrix to acquire three types of scattering power matrixes of plane scattering, dihedral angle scattering and volume scattering; (3) performing initial division on the polarized SAR data according to the three types of scattering power matrixes; (4) calculating the homo-polarization rate of all pixel points of the polarized SAR data of each class; (5) selecting a threshold value, and dividing the polarized SAR data of each class in the step (3) into 3 classes according to the homo-polarization rate, so that the whole polarized SAR data are divided into 9 classes; and (6) performing repeated Wishart iteration and coloring on the division result of the whole polarized SAR data to obtain a final color classification result graph. Compared with the classical classification method, the method has the advantages that the division of the polarized SAR data is stricter, the classification result is obvious and the calculation complexity is relatively low.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Polarized SAR land feature classification method based on full convolution neural network
InactiveCN107239797AImplement classificationReduce network parametersCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural learning methodsDecompositionRgb image
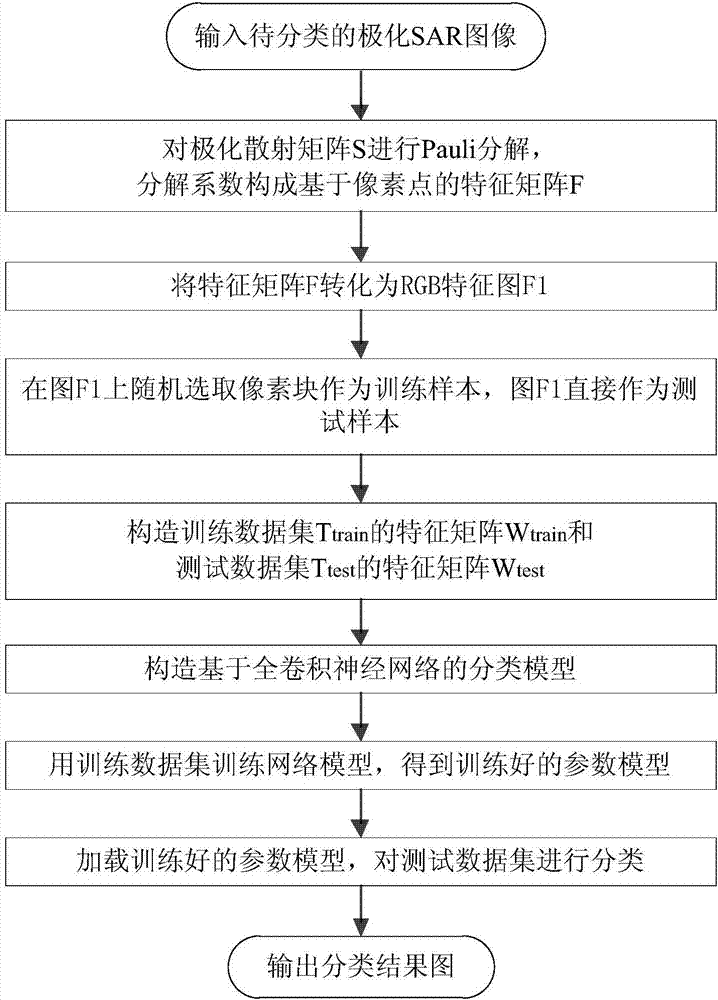
The invention discloses a polarized SAR land feature classification method based on a full convolution neural network, comprising: performing Pauli decomposition on a to-be-classified polarized scattering matrix S to obtain the odd scattering coefficient, the even scattering coefficient and the volume scattering coefficient; using the odd scattering coefficient, the even scatter coefficient and the volume scattering coefficient as the three-dimensional image characteristics F of the polarized SAR image; then converting the obtained three-dimensional image characteristics matrix F into an RGB image F1; randomly selecting m x n pixel blocks in the RGB image F1 as training samples; using the whole RGB image F1 as a testing sample; re-constructing a full convolution neural network model; training the training samples through the full convolution neural network to obtain a trained model; and then, through the trained model, classifying the test set and obtaining the classification result. The method of the invention can solve the problem of low time efficiency in the prior art and shorten the running time under the condition of high classification accuracy.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
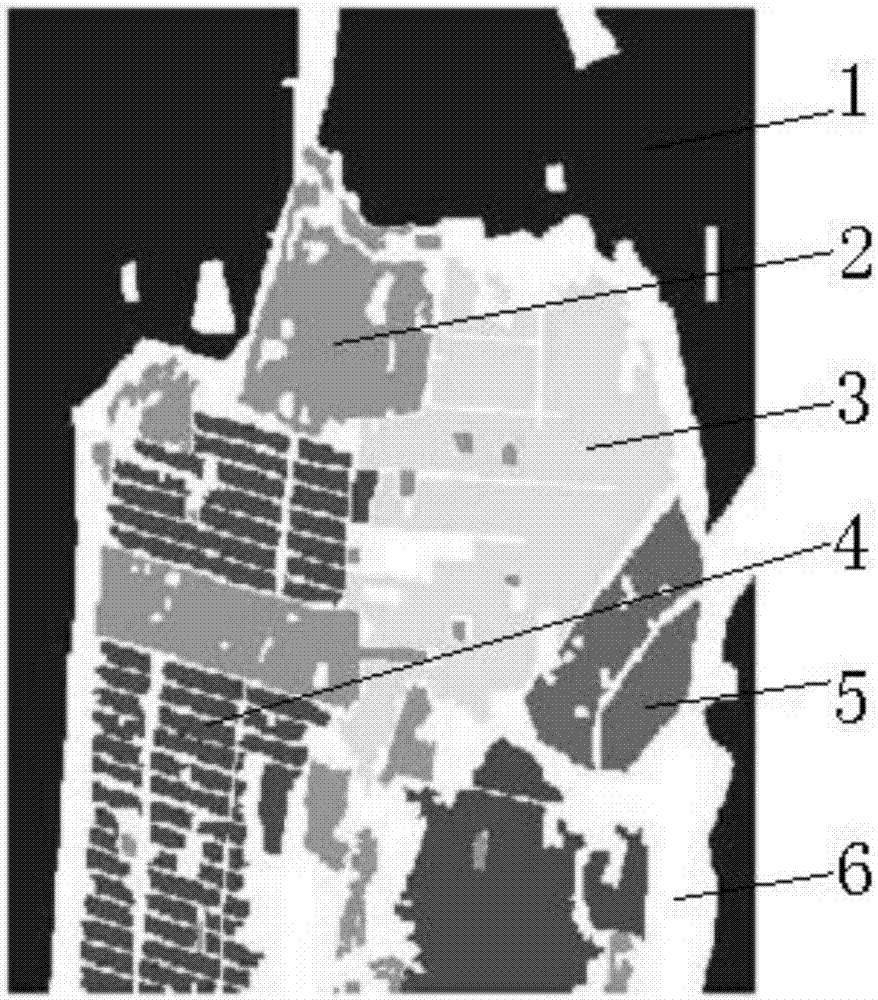
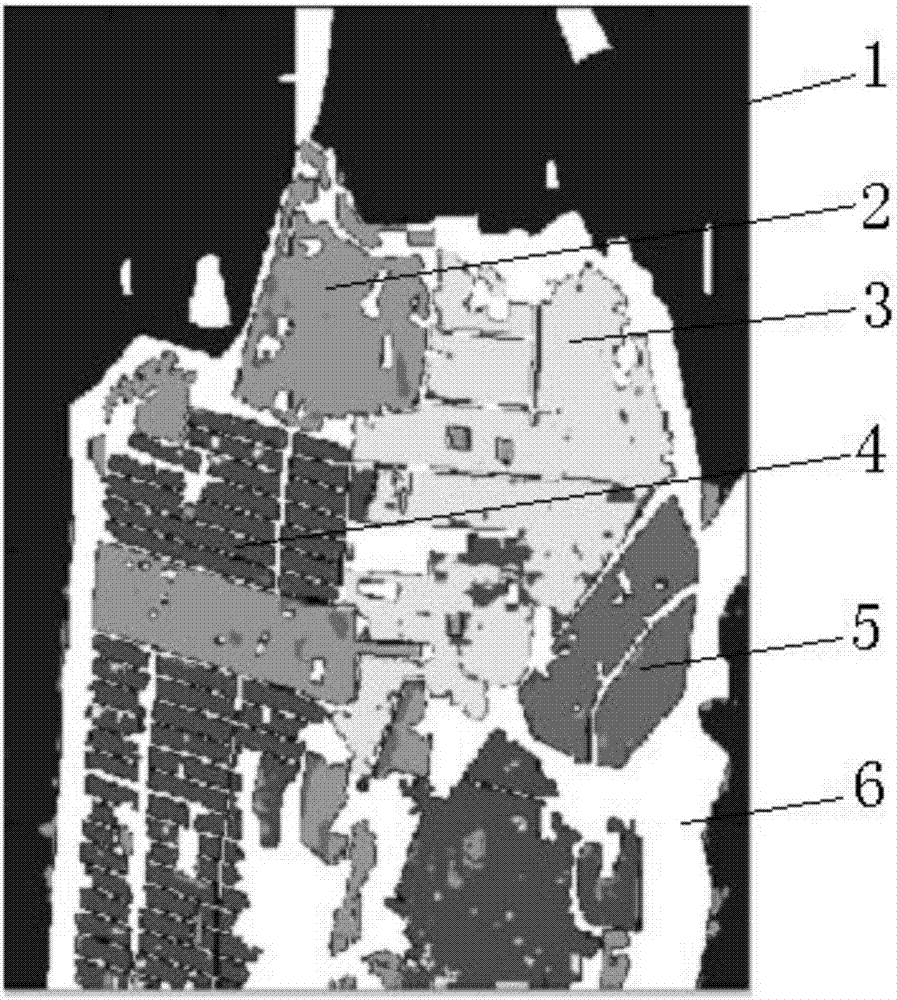
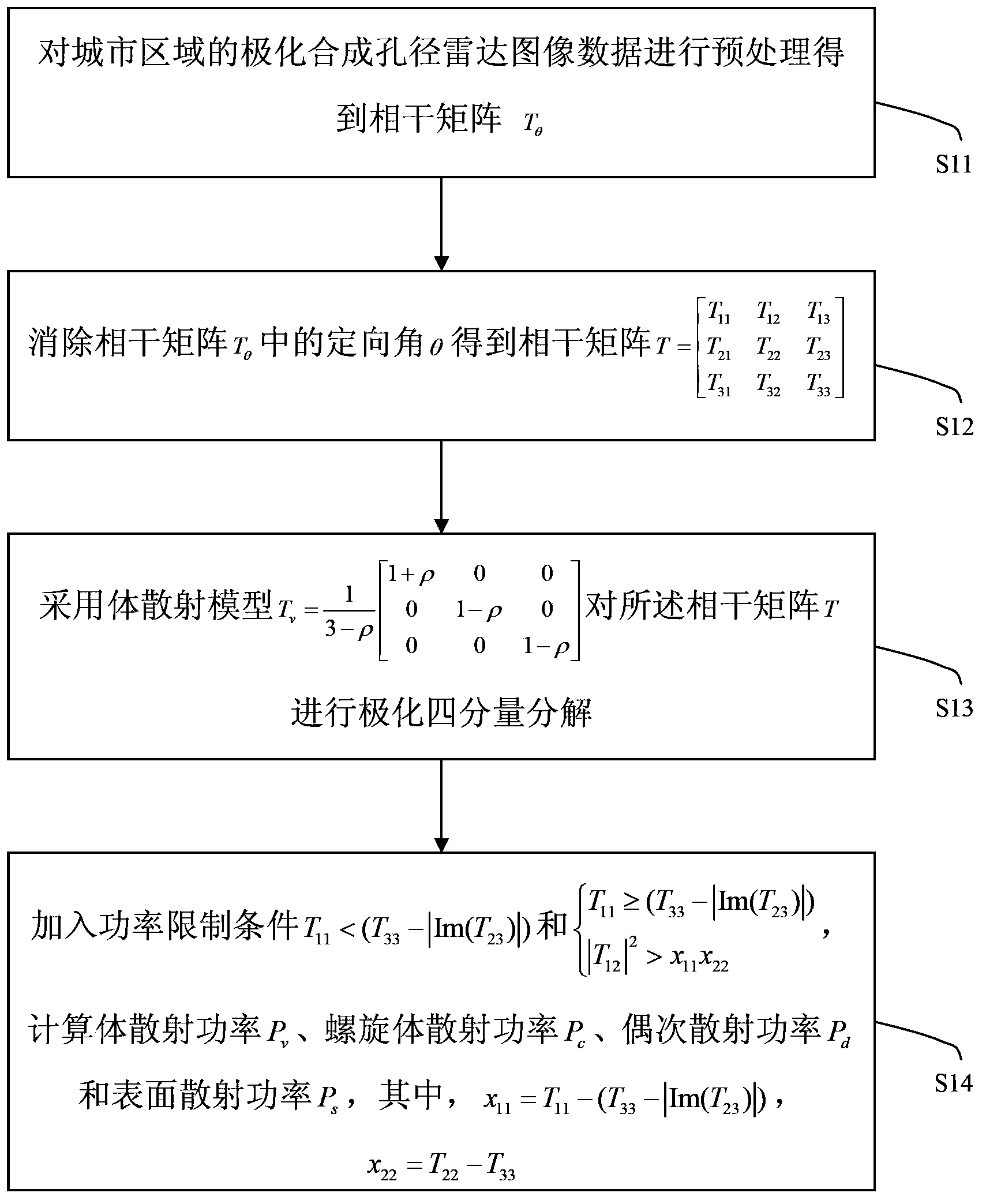
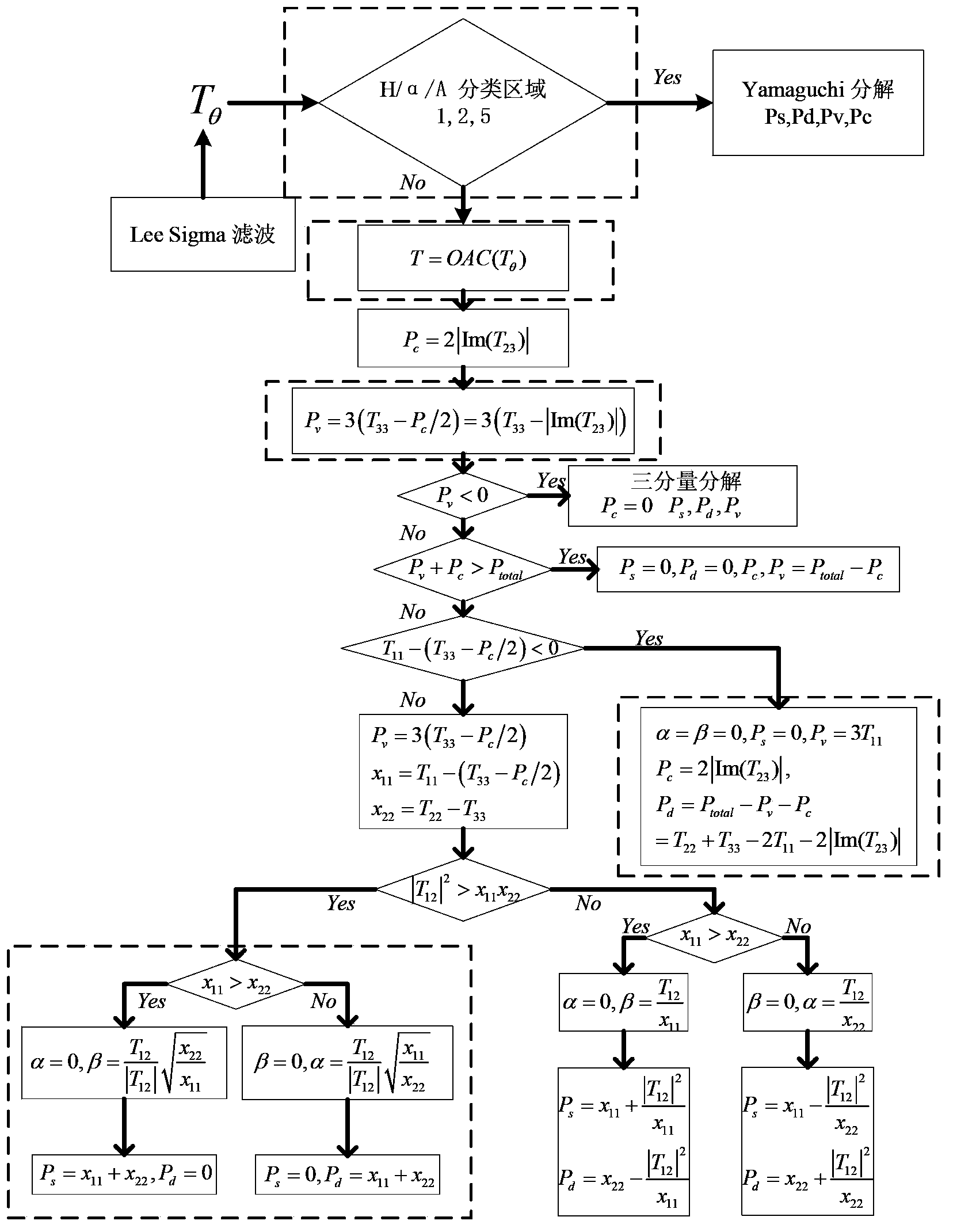
Polarization four-component decomposition method for city area
InactiveCN103529447AAlleviate Negative Power IssuesResolve Surface ScatteringRadio wave reradiation/reflectionDecompositionPolarimetric synthetic aperture radar
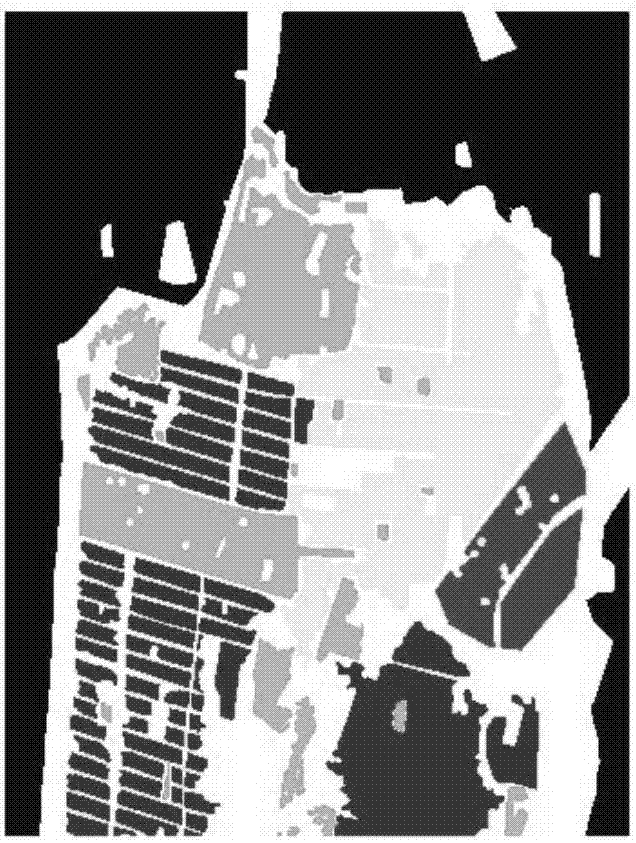
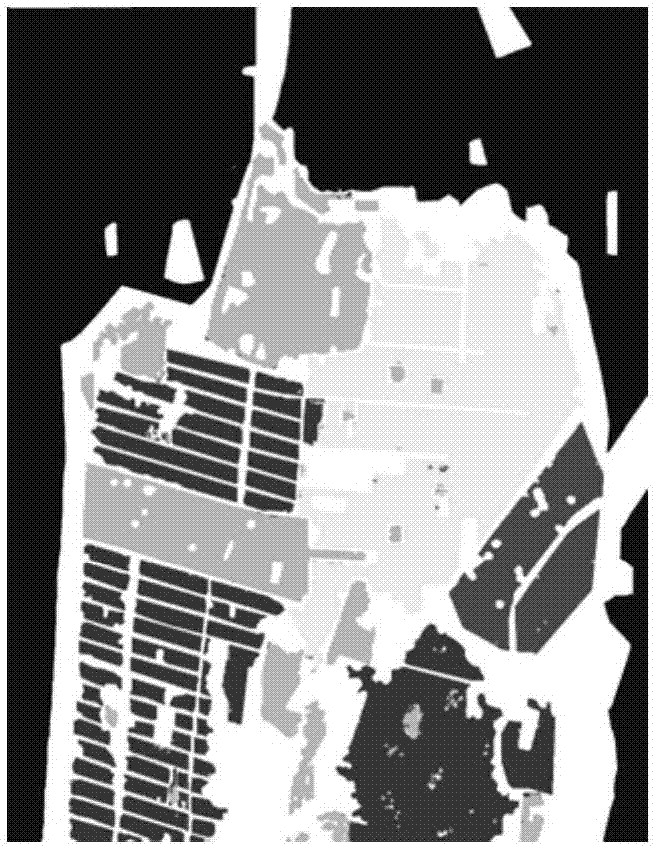
The invention discloses a polarization four-component decomposition method for a city area. The method comprises the following steps of: performing preprocessing on the polarimetric synthetic aperture radar image data of the city area so as to obtain a coherent matrix T theta; S12: eliminating the orientation angle theta in the coherent matrix T theta so as to obtain coherent matrix T; and S13: performing polarization four-component decomposition on the coherent matrix T by using a volume scattering model Tv. Through the orientation angle compensation performed on a coherent matrix and using a new volume scattering model to describe the volume scatting in polarization decomposition, the negative power problems of surface scattering and dihedral angle scattering, which are caused by overestimated volume scattering power, can be released to a certain extent.
Owner:CENT FOR EARTH OBSERVATION & DIGITAL EARTH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
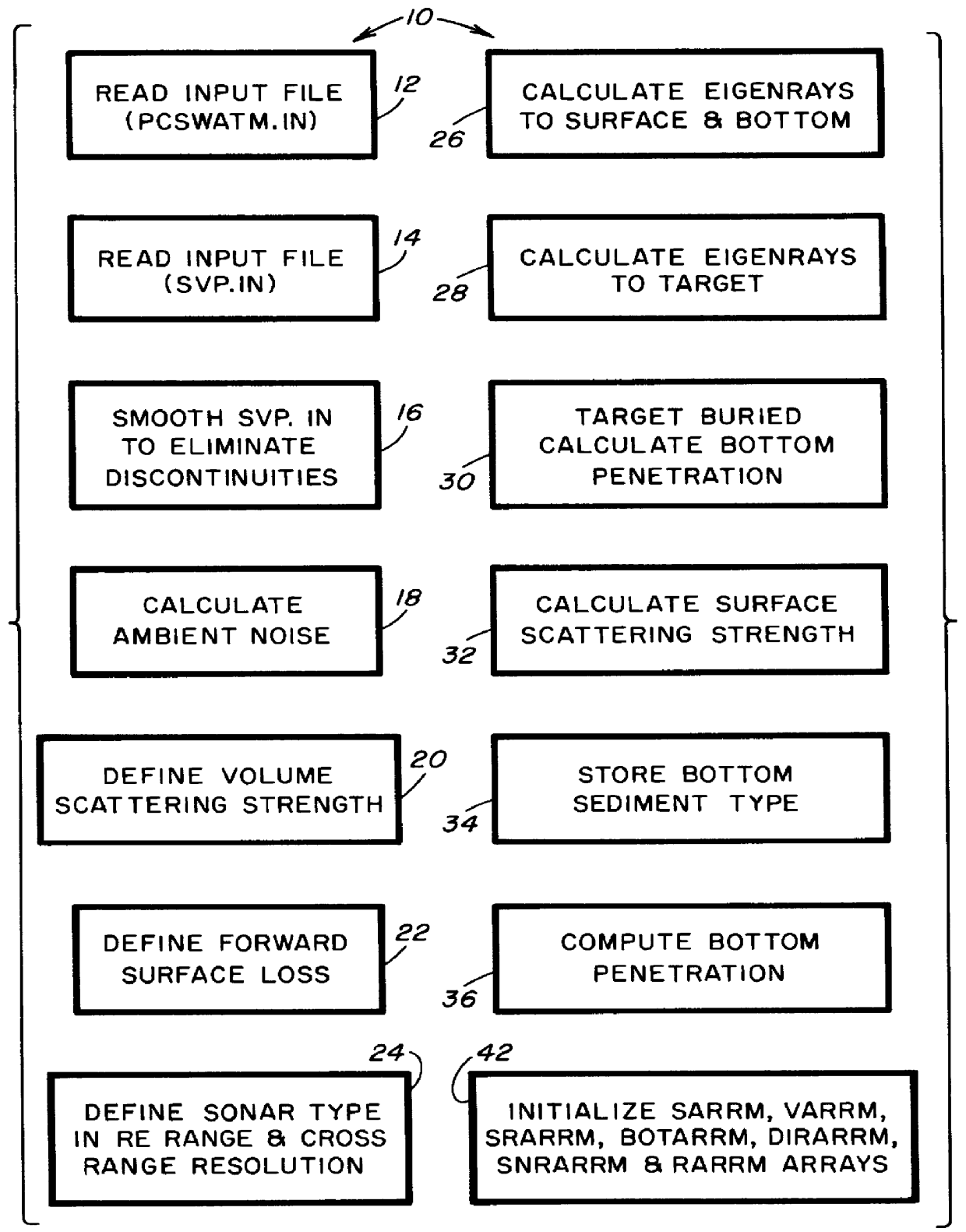
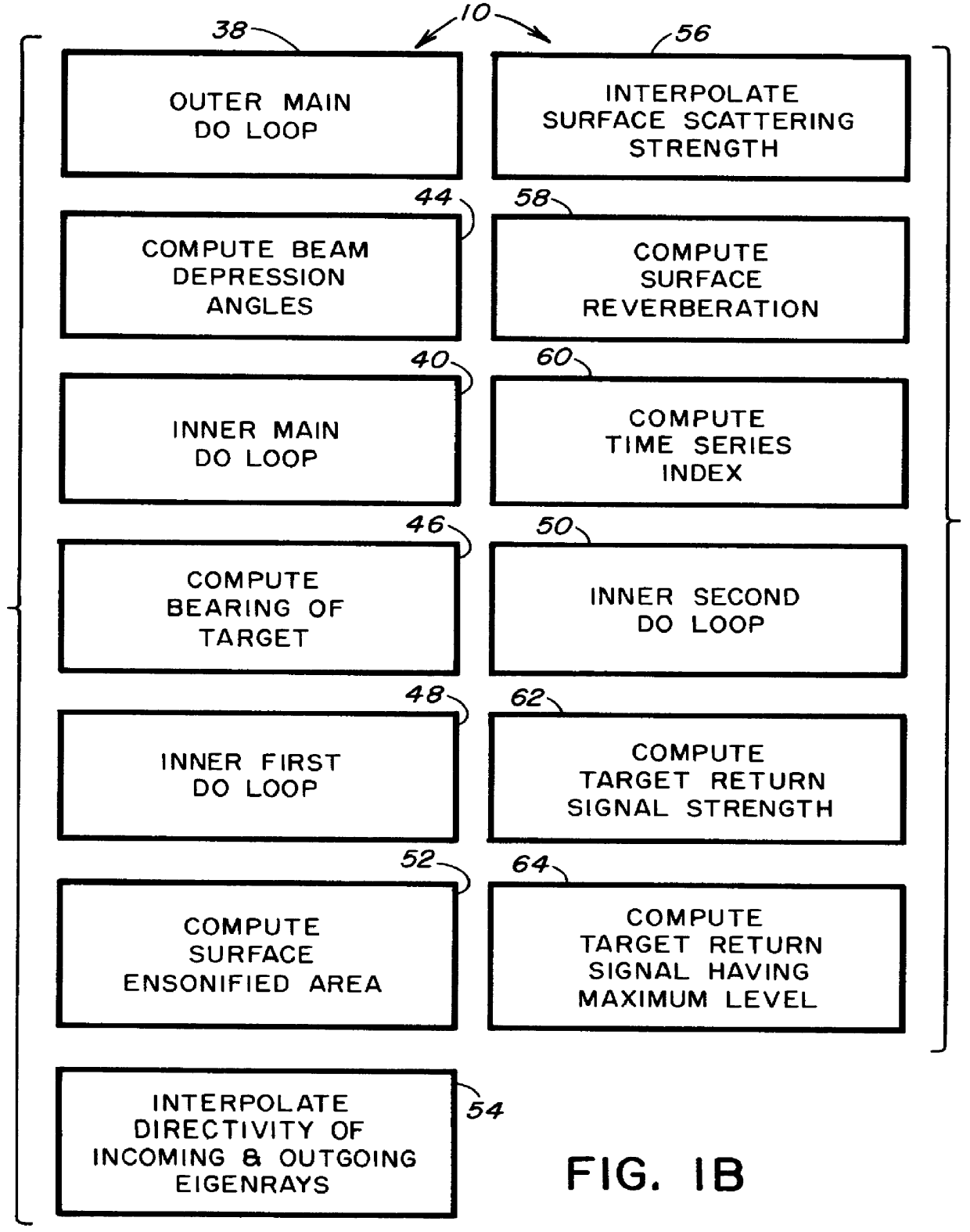
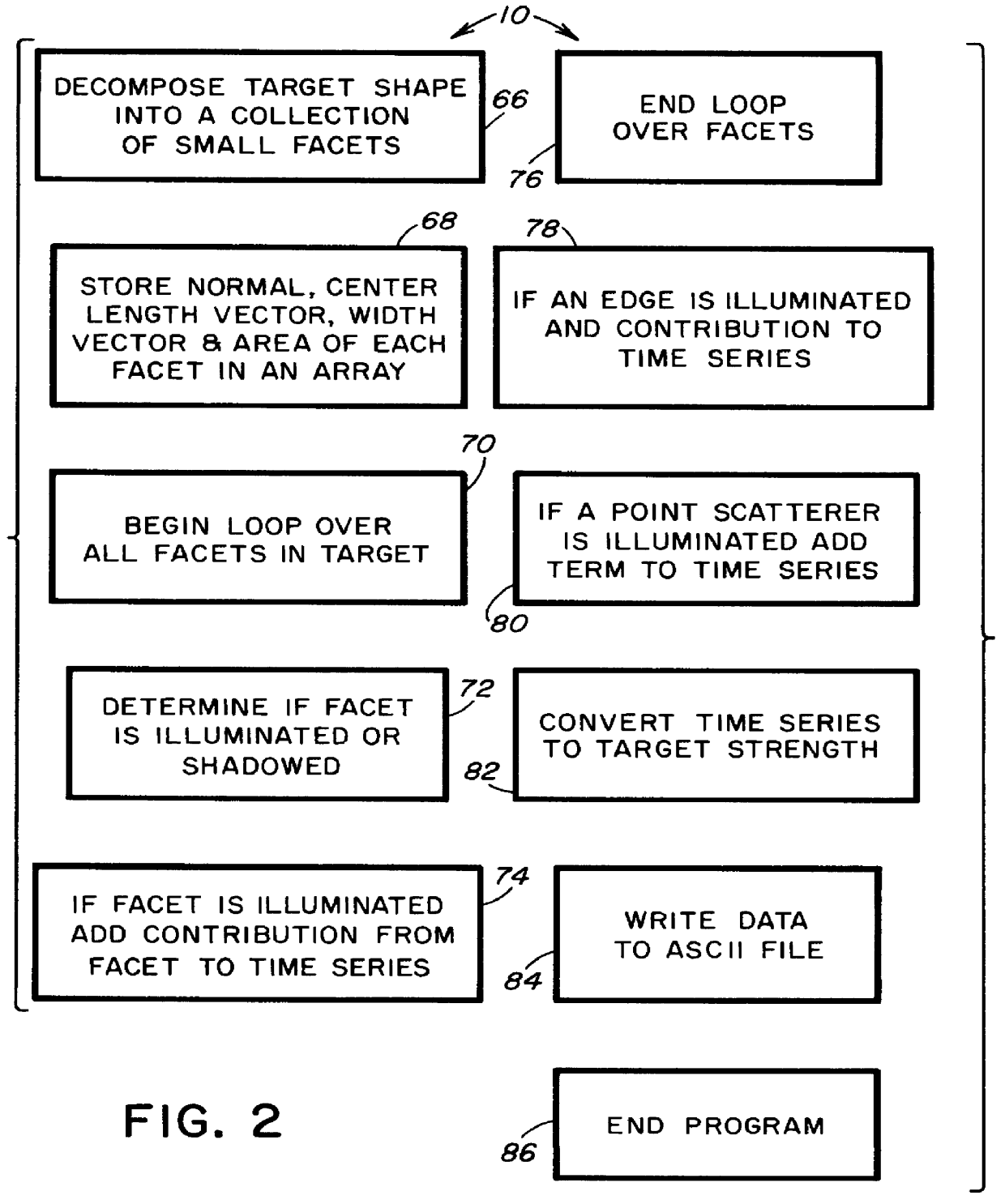
Computer-readable software and computer-implemented method for performing an integrated sonar simulation
InactiveUS6096085AWave based measurement systemsComputation using non-denominational number representationSonarBeam pattern
A computer-readable software stored on a storage medium and executed on a computer to perform an integrated sonar simulation, includes a parameter definition code for defining a plurality of parameters of a sonar, target and sonar environment, and a SNR computation code for computing a SNR of the sonar as a function of range to target, based upon the parameters defined by the parameter definition code. The parameters defined by the parameter definition code include ambient noise, volume scattering strength of the sonar environment, sound velocity profile of the sonar, beam patterns of both projector and receiver of the sonar, type of sonar, range resolution of the sonar, number of eigenrays striking the surface and bottom of the sonar environment, number of eigenrays striking the target, ray trajectories to the target, and surface and bottom scattering strength as a function of angle. The software also includes a target strength model generating code for computing scattering from a selected complex target of a stored set of complex target selections, to thereby generate a target strength model for the selected complex target.
Owner:THE GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE NAVY NAVAL RES LAB WASHINGTON
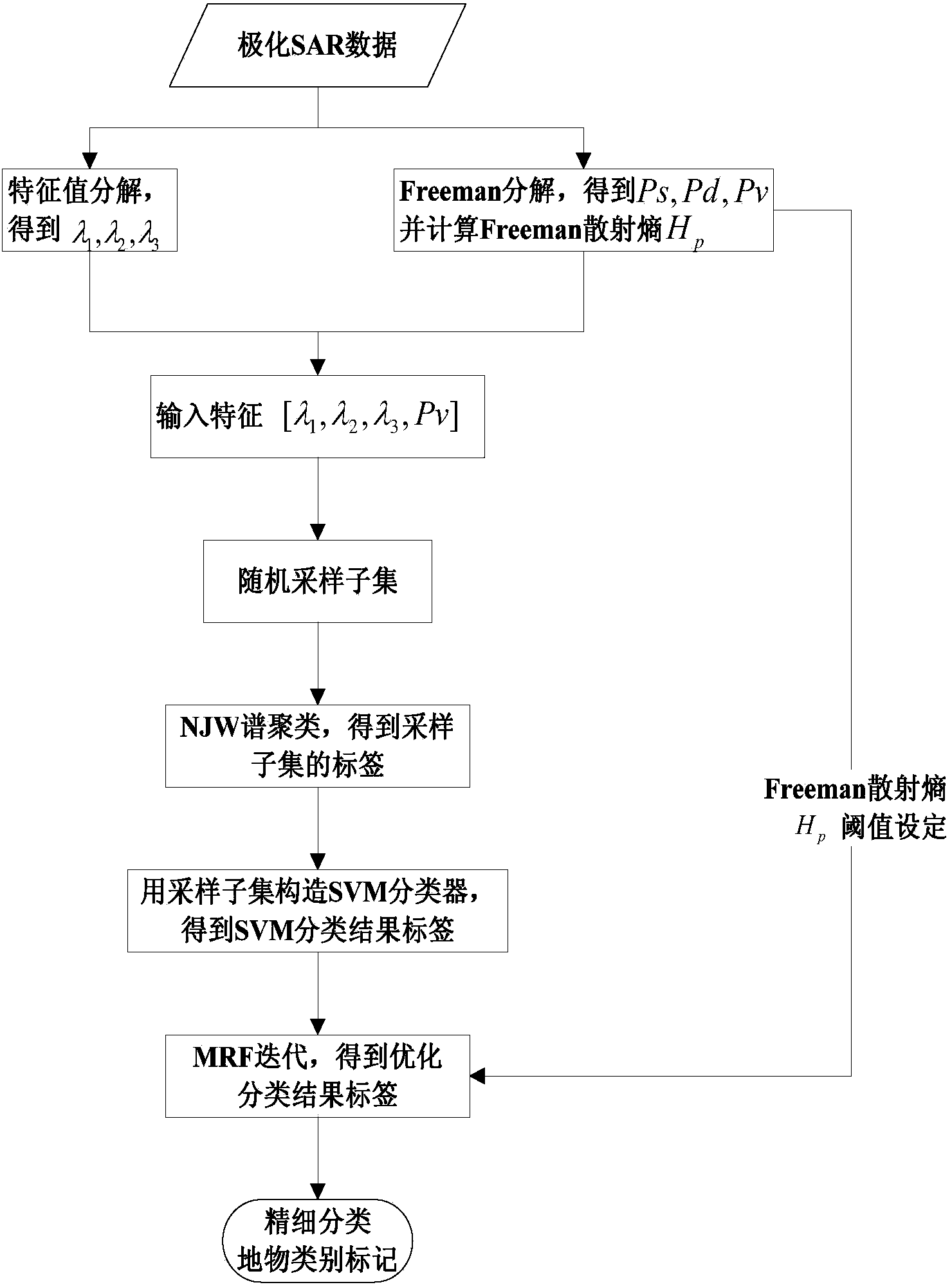
Method for finely classifying polarized SAR images based on Freeman entropy and self-learning
ActiveCN103413146AHard to getOmit measurementCharacter and pattern recognitionFeature vectorDecomposition
The invention discloses a method for finely classifying polarized SAR images based on Freeman entropy and self-learning. The problems that in existing supervised classification, surface feature labels are difficult to obtain, and shadow regions and mixing scattering regions are difficult to distinguish are mainly solved. The implementation process of the method comprises the steps that (1) eigenvalue decomposition is carried out on a polarization coherence matrix to obtain three characteristic values; (2) decomposition is carried out on a polarization covariance matrix to obtain three kinds of scattered power; (3) characteristic vectors are input according to the three characteristic values and a volume scattered power structure; (4) spectral clustering is carried out on the input characteristic vectors of random sampling points; (5) SVM classification is carried out according to the sampling points and the clustering marks of the sampling points; (6) MRF iteration is carried out on a classification result; (7) spectral clustering is carried out on wrongly-classified pixel points, and the fine classification surface feature categories of the polarized SAR images is obtained. Compared with an existing SAR image classification method, the method does not need manual label defining, the classification result is more precise, and the method can be used for target detection and classification recognition of the polarized SAR images.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Polarized synthetic aperture radar (SAR) image classification method based on Freeman decomposition and data distribution characteristics
ActiveCN102968640AAvoid divisionAvoid mergingCharacter and pattern recognitionComputation complexitySynthetic aperture radar
The invention discloses a polarized synthetic aperture radar (SAR) image classification method based on Freeman decomposition and data distribution characteristics and mainly solves the problems of high computation complexity and poor classification effect in the prior art. The polarized SAR image classification method includes step: (1) performing Freeman decomposition for polarized SAR images to be classified to obtain plane scattering power, dihedral angle scattering power and volume scattering power; (2) initially dividing the polarized SAR images into three classes according to the three scattering powers; (3) calculating the distribution characteristic parameter xL of each pixel point in each class; (4) subdividing each of the three initially divided classes into three classes according to the distribution characteristic parameters xL to divide the whole polarized SAR images into nine classes; and (5) performing complex Wishart iteration for the obtained nine-class dividing results to obtain the final classification result. Compared with the typical classification method, the polarized SAR image classification method is rigorous in polarized SAR image dividing, good in classification effect and small in computation complexity and can be applied to terrain classification and object identification of the polarized SAR images.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
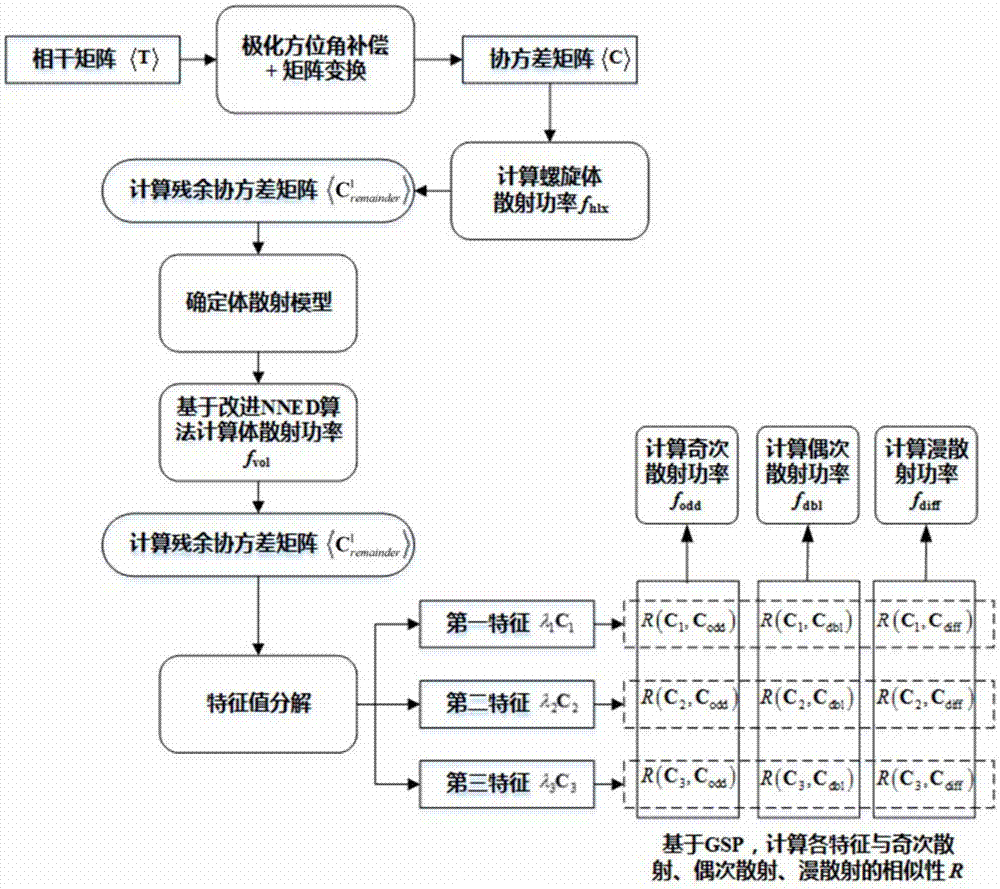
Polarimetric SAR multi-component target decomposition method
InactiveCN105445712AImproved scattered powerImprove object detectionWave based measurement systemsRough surfaceDecomposition
The invention provides a polarimetric SAR multi-component target decomposition method. According to the method, an additional diffuse scattering mechanism which may come from a terrain or rough surface is added as a fifth decomposition component on the basis of a previous four-component decomposition algorithm, namely, the linear weighted sum of five scattering components (odd scattering, even scattering, volume scattering, helicoid scattering and diffuse scattering) decomposed from a fully-polarimetric SAR coherence matrix T or covariance matrix C. The power of volume scattering is solved by an improved NNED method, and the contribution values of odd scattering, even scattering and diffuse scattering are directly solved by adopting corresponding odd scattering, even scattering and diffuse scattering models of a Pauli matrix directly and using a generalized similarity parameter GSP and eigenvalue decomposition. The novel method provided by the invention is conductive to improving the terrain classification accuracy of polarimetric SAR data.
Owner:CHINESE ACAD OF SURVEYING & MAPPING
System for measuring scattering function of water body wide-angle body
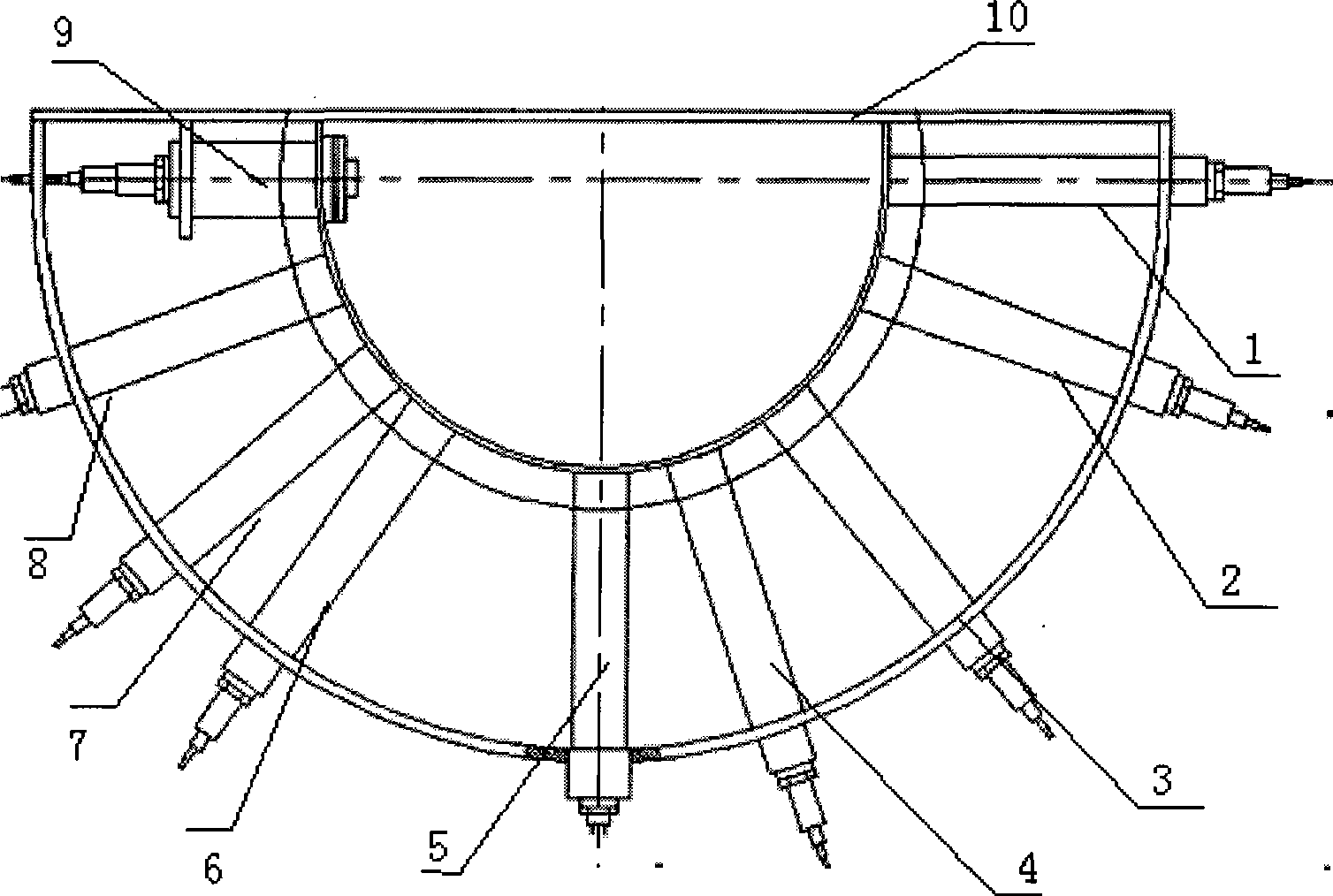
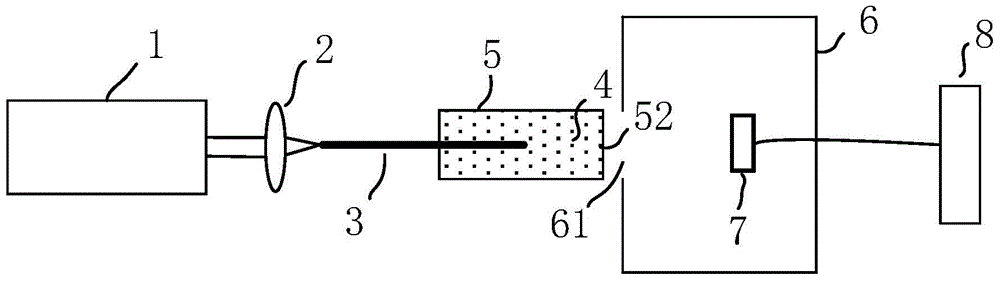
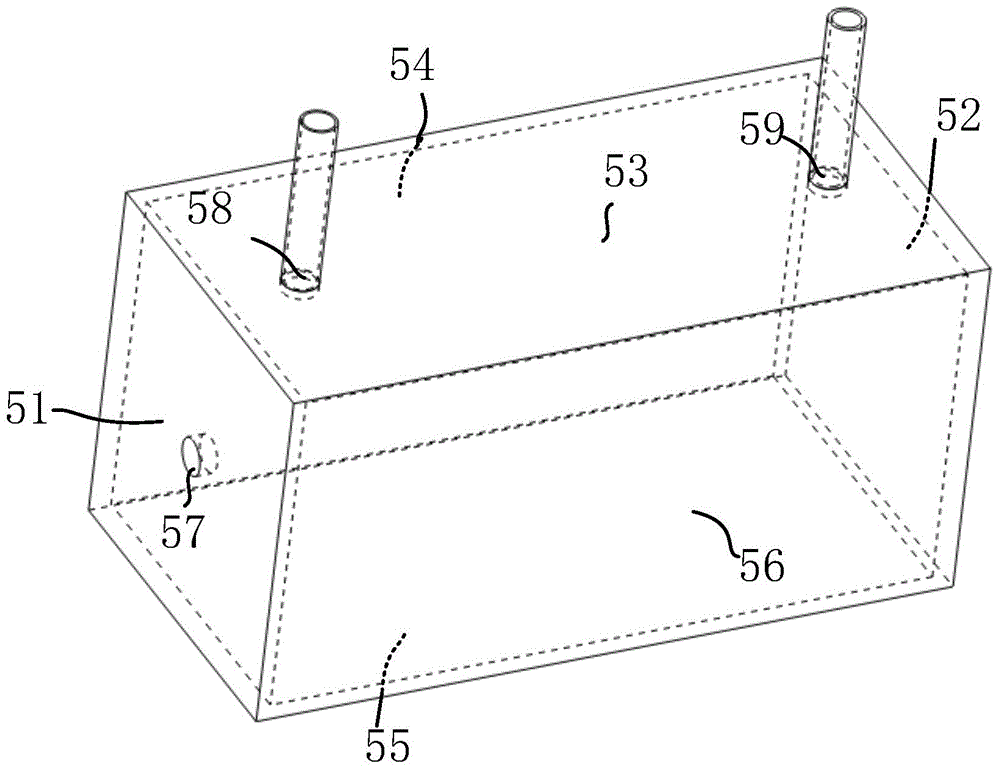
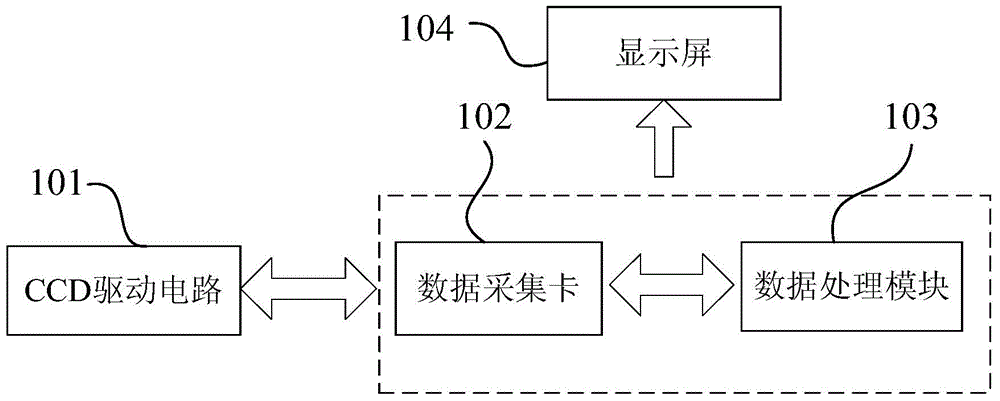
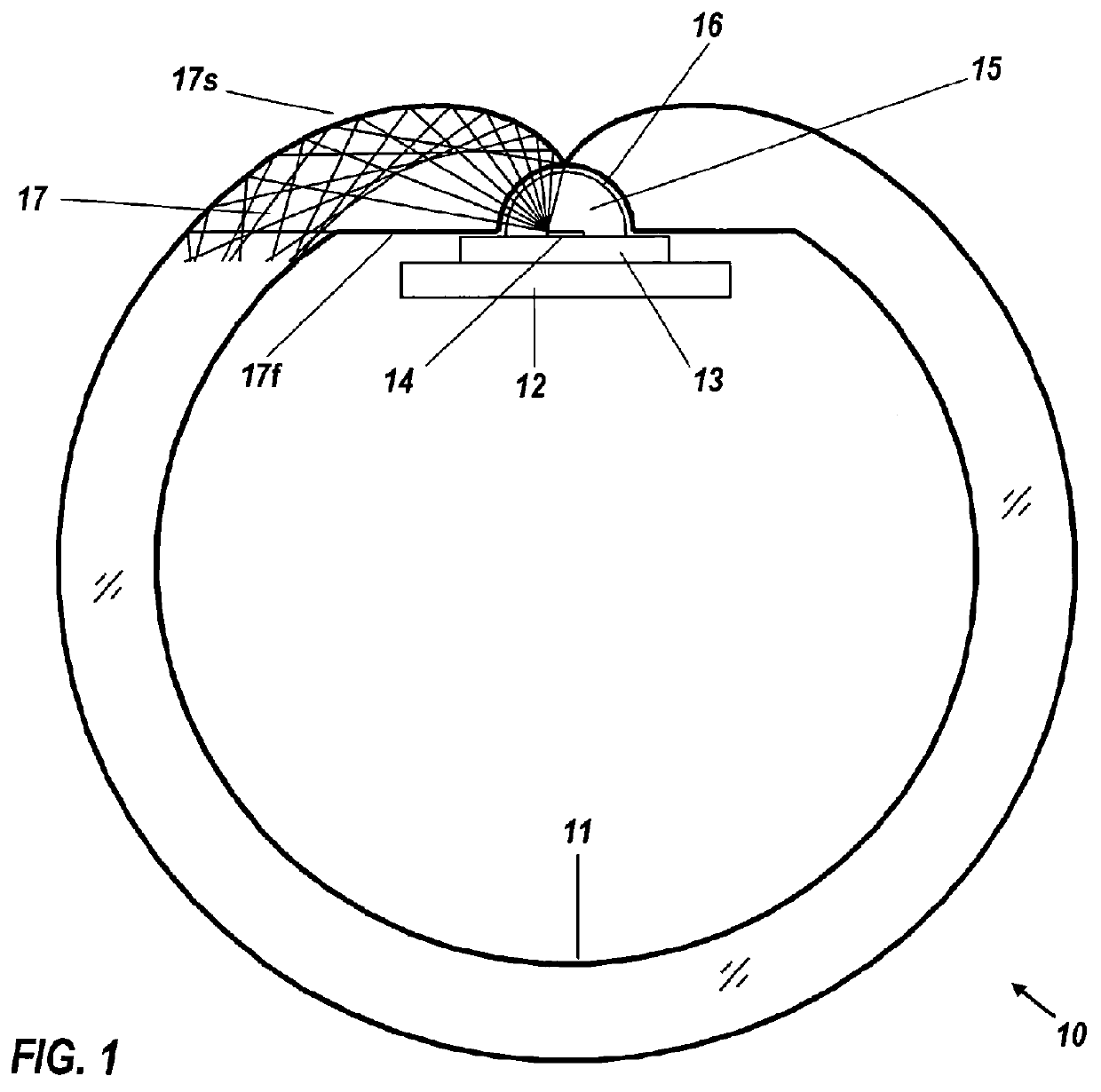
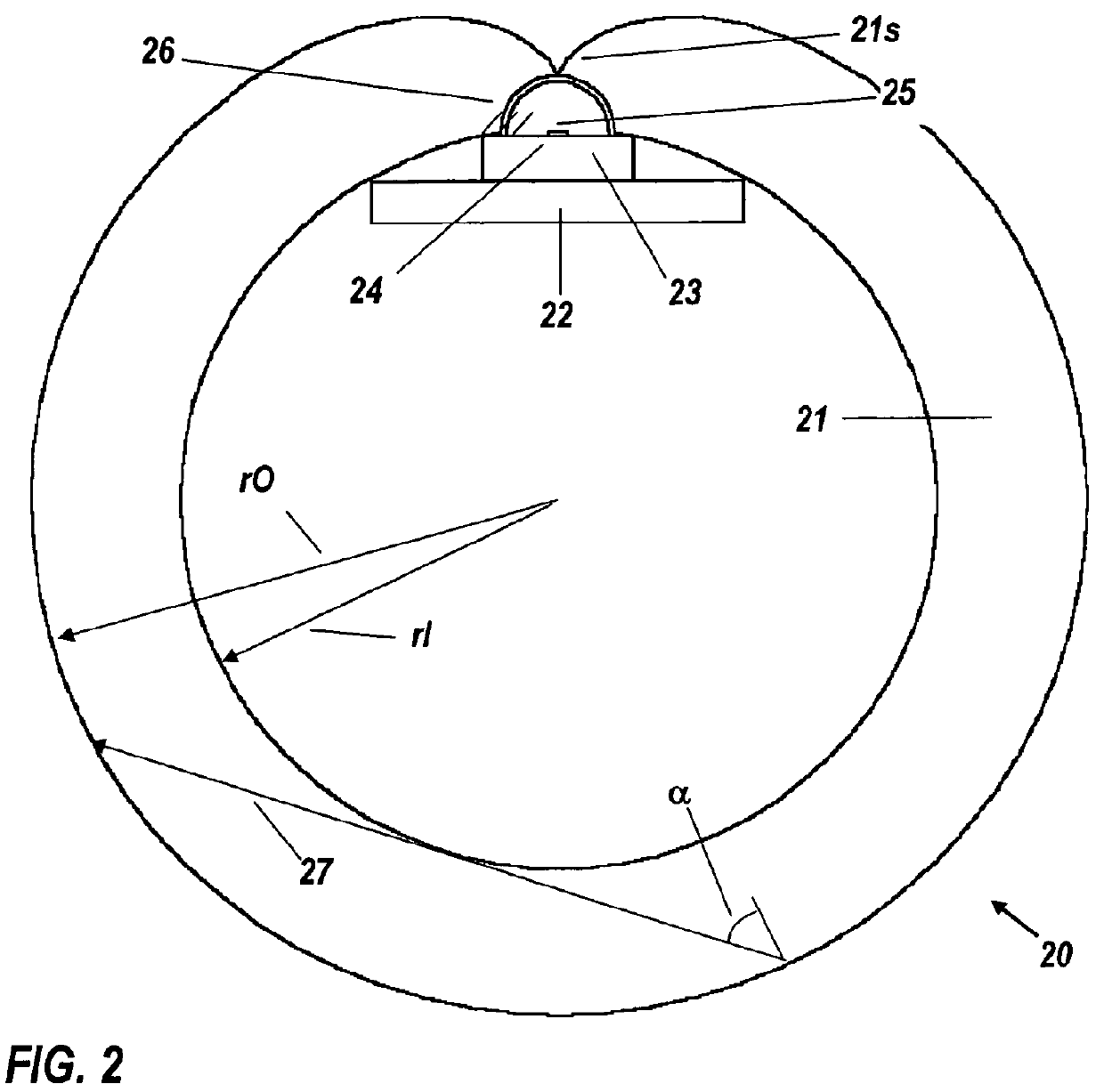
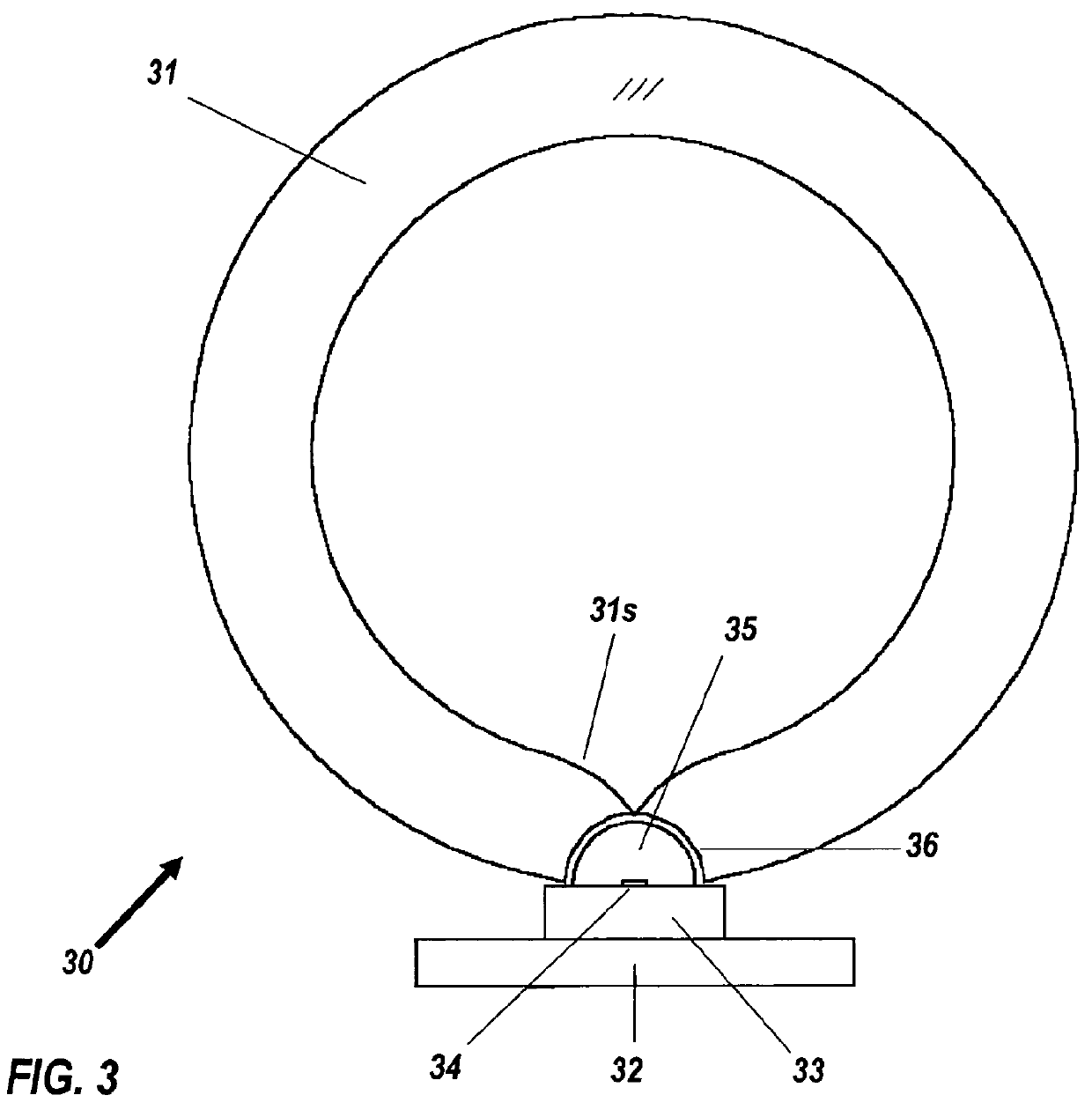
InactiveCN101413888AGood repeatabilityImprove stabilityScattering properties measurementsScattering functionOptical property
The invention provides a measuring system for a wide-angle volume scattering function of water body. The structure of the invention mainly comprises: a measuring device for volume scattering function of water body and a data acquisition circuit of the measuring system, wherein, the measuring device for volume scattering function of water body is composed of a light source, a transmitted light detecting probe and a plurality of scattered light detecting probes which are equipped on different positions of the toroidal radius of a semi-toroidal frame respectively so as to detect the transmitted light and scattering light signals from different directions ranging from 0 DEG to 180 DEG., the light source, the transmitted light detecting probe and all scattered light detecting probes are connected with the data acquisition circuit of the measuring system by a watertight cable, and the data acquisition and storage process of the measuring device is controlled by the data acquisition circuit of the measuring system. The measuring system can measure the transparency of water body and the volume scattering function of water body in different directions ranging from 0 DEG to 180 DEG synchronously both on-line and on-site, and can be used for profile analysis on scattering and inherent optical properties of water body on-site.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
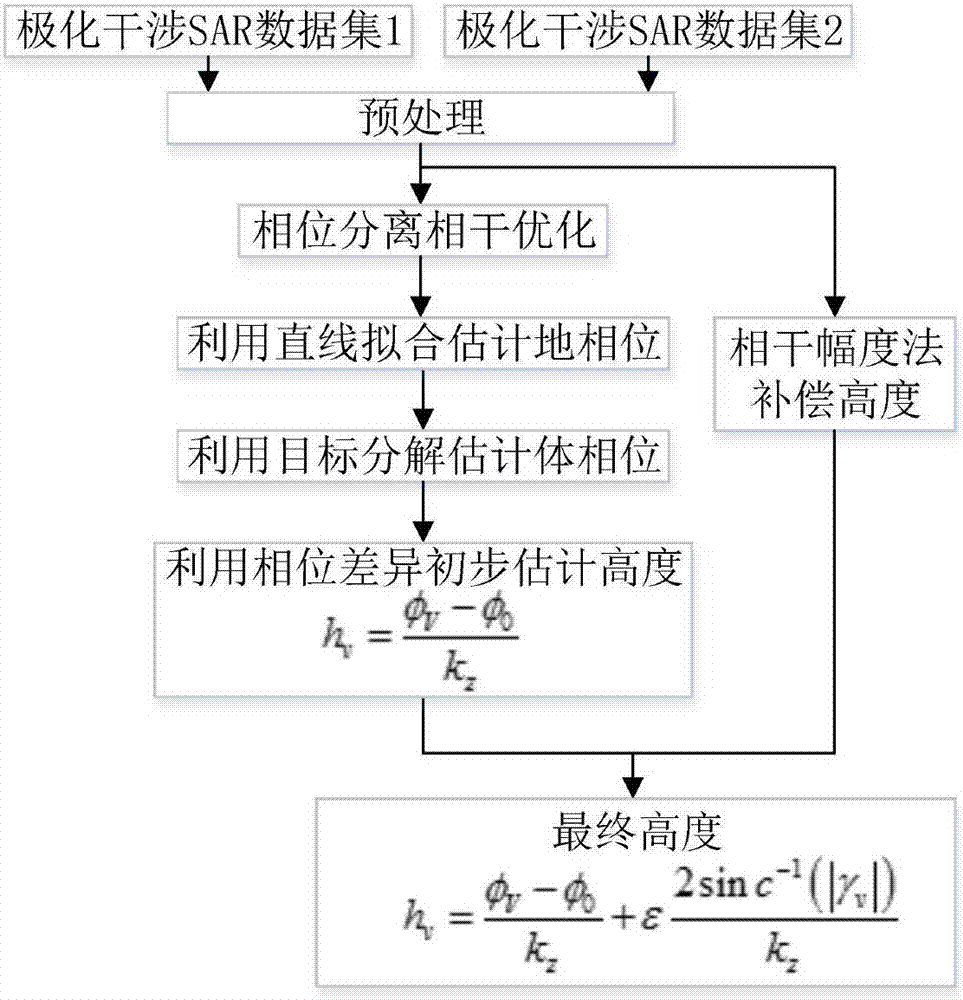
Improved polarimetric interferometry SAR vegetation height combined inversion method
InactiveCN107144842AAchieve high inversionSolve the problem of ambiguity in estimationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSurface phaseDecomposition
The invention discloses an improved polarimetric interferometry SAR vegetation height combined inversion method. The method includes following steps: step 1, inputting a polarimetric interferometry SAR image, pre-processing the image, and obtaining a preprocessed polarimetric interferometry SAR image; step 2, performing surface phase extraction on the pre-processed polarimetric interferometry SAR image by employing a three-stage algorithm based on phase separation and coherence optimization; step 3, performing polarimetric target decomposition on the pre-processed polarimetric interferometry SAR image based on an Antropov volume scattering model, obtaining a volume scattering component, and extracting a canopy phase; step 4, preliminarily estimating the vegetation height by employing the phase diversity of the surface phase obtained in step 2 and the canopy phase obtained in step 3 according to a phase diversity method; and step 5, compensating the height obtained in step 4 by employing a coherence amplitude method, and realizing the estimation of the vegetation height of the polarimetric interferometry SAR image. According to the method, the problem of fuzzy estimation of the surface phase and the canopy phase is solved, and the inversion precision of the polarimetric interferometry SAR vegetation height is improved.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
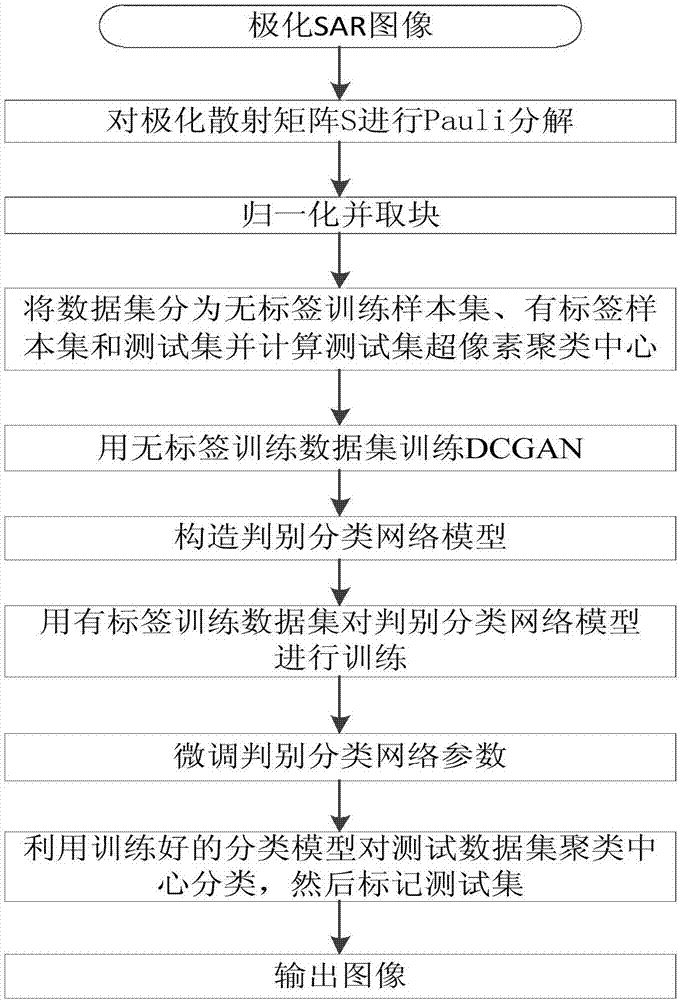
Polarimetric SAR image classification method based on DCGAN
InactiveCN107292336AImplement classificationImprove classification accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesClassification methodsNetwork model
The invention discloses a polarimetric SAR image classification method based on DCGAN. The method comprises the following steps: 1) obtaining an odd-order scattering coefficient, an even-order scattering coefficient, and a volume scattering coefficient, establishing a characteristic matrix F based on pixel points; 2) normalizing each element value in the characteristic matrix F based on pixel points to [0,1], and calling a result of normalization as a feature matrix F1; 3) replacing each element in the feature matrix F1 by 64x64 image blocks around each elements, to obtain a feature matrix F2 based on the image blocks; 4) establishing a feature matrix W1 of a no-label training dataset D1 and a feature matrix W2 of a labeled training dataset D2; 5) establishing a feature matrix W3 of a superpixel clustering center of a testing dataset T; 6) obtaining a trained training network model DCGAN; 7) establishing a determining classification network model, and then through the determining classification network model, classifying the feature matrix W3. The method can realize classification of a polarimetric SAR image, and classification precision is relatively high.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
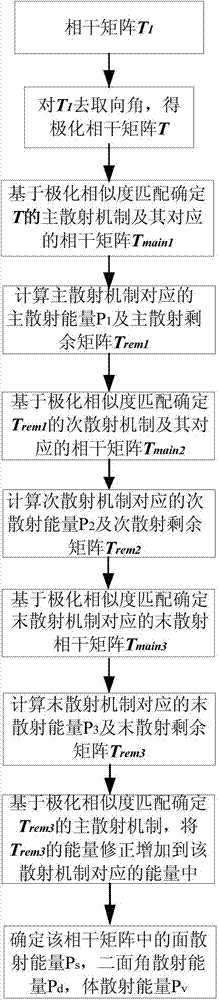
Polarization coherence matrix scattering energy decomposition method based on polarization similarity matching
The invention belongs to the technical field of radar automatic target recognition, and discloses a polarization coherence matrix scattering energy decomposition method based on polarization similarity matching. Deorientation angle is carried out on an observation coherence matrix T1 obtained based on a radar to obtain a polarization coherence matrix T, the maximum polarization similarity between the polarization coherence matrix T and a surface scattering mechanism, the maximum polarization similarity between the polarization coherence matrix T and a dihedral angle scattering mechanism and the maximum polarization similarity between the polarization coherence matrix T and a volume scattering mechanism are respectively calculated, a leading scattering mechanism of the polarization coherence matrix T and a main scattering coherence matrix Tmain1 corresponding to the leading scattering mechanism are determined, the priority decomposition under the positive semidefinite constraint is carried out on the main scattering Tmain1, and an energy and residue matrix Trem1 corresponding to the leading scattering mechanism is obtained; after the leading scattering mechanism is removed, the energy corresponding to other scattering mechanisms is extracted in sequence under the energy non-negative constraint based on the polarity similarity of the residue matrix Trem1; which kind of the energy corresponding to the ultimate residue matrix belongs to is determined according to the corresponding polarization similarity between the ultimate residue matrix and the different scattering mechanisms. Lastly, scattering energy corresponding to all the scattering mechanisms is obtained.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Method of classifying polarimetric SAR (synthetic aperture radar) images based on scattering entropy and three-component decomposed plane
InactiveCN106778884AAccurate classificationEasy to keepCharacter and pattern recognitionImaging processingSynthetic aperture sonar
The invention provides a method of classifying polarimetric SAR (synthetic aperture radar) images based on scattering entropy and three-component decomposed plane, and relates to the technical field of radar image processing. The method divides target ground objects into 9 classes initially according to scattering entropies and Freeman three-component, calculates a clustering center according to the 9 classes, and clusters the target ground objects to expected quantity according to Wishart distance; the ground objects are divided into high-entropy scattered ground objects, medium-entropy scattered ground objects and low-entropy scattered ground objects according to the scattering entropy H, and the 3 classes are then divided into 9 classes of ground objects according to surface scattering, even scattering and volume scattering, and initial classes are further divided by Wishart classifier. More accurate classification may be provided for polarimetric SAR images, no approximation occurs during processing, detailed information may be well retained, and the number of mistaken classes for urban areas is decreased greatly.
Owner:LIAONING TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY
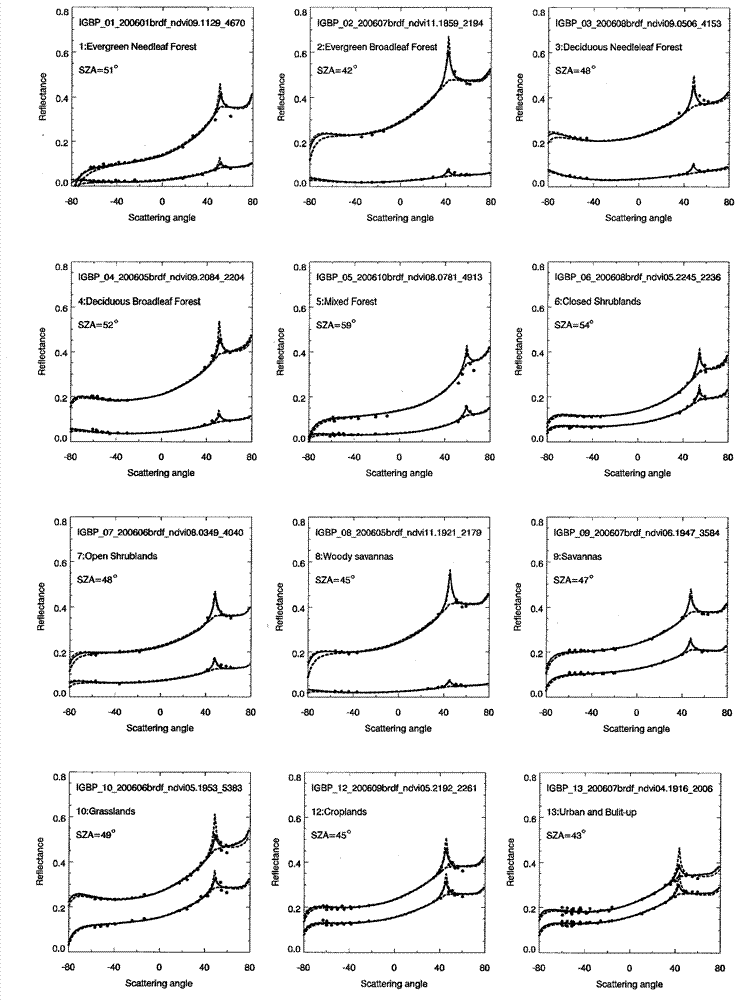
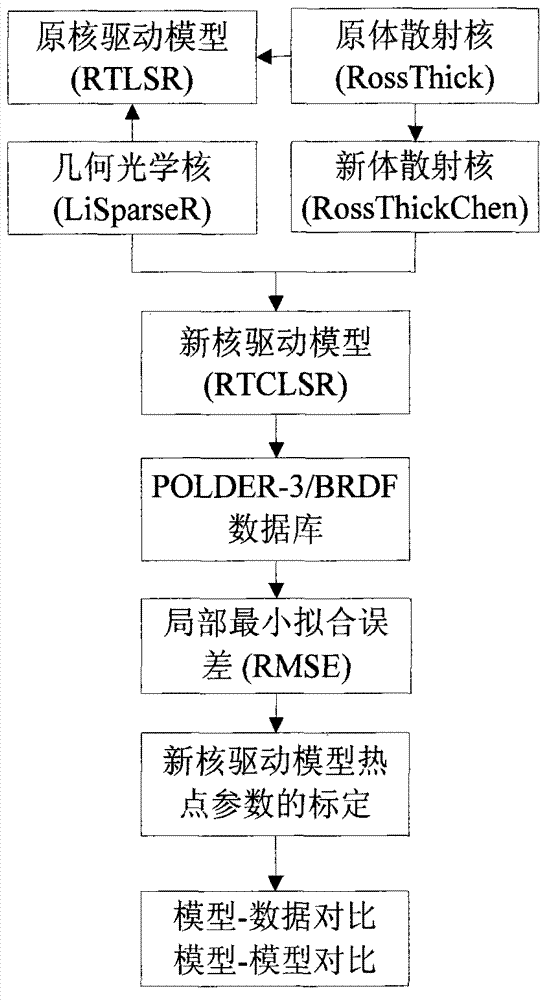
Method for improving business nuclear drive bidirectional reflectance distribution function (BRDF) model hot spot
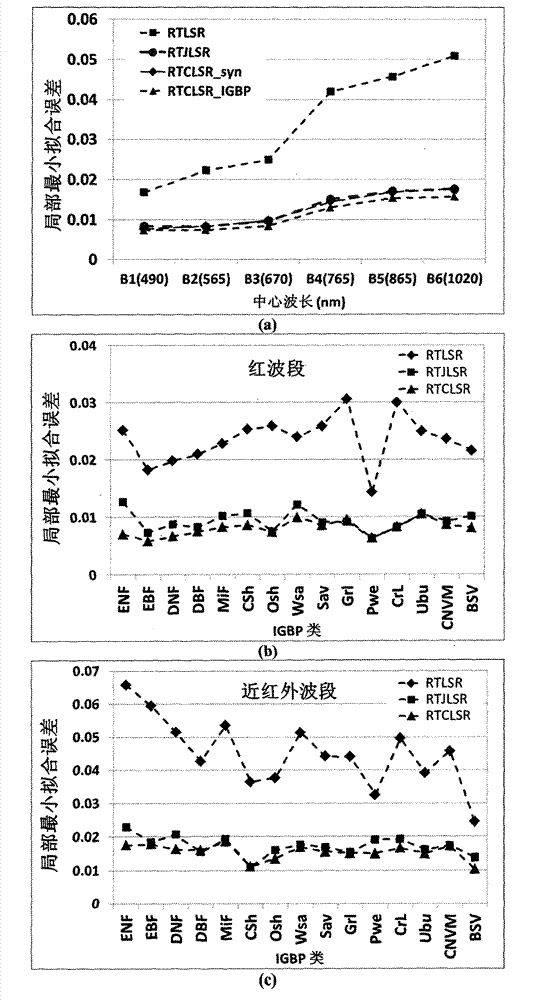
InactiveCN103324827AImprove inversion accuracyImprove reflectivitySpecial data processing applicationsAlbedoBidirectional reflectance distribution function
The invention relates to a method for improving a business nuclear drive bidirectional reflectance distribution function (BRDF) model hot spot. The method comprises the following steps: a new volume scattering nucleus considering the hot spot change is put forward through carrying out the hot spot calibration on the volume scattering nucleus of a conventional MODIS business nucleus drive BRDF model RTLSR, an RTCLSR model generated by the linear combination of the nucleus with an original geometrical optics nucleus has preferable fitting capability to the hot spot, but the fitting precision in the other observation directions is not influenced, a POLDER-3 / BRDF database and onboard CAR data are used to carry out calibration and verification on the hot spot parameters of the RTCLSR model, the new RTCLSR model is available to study the change of the hot spot effect with earth surface category, NDVI and a solar zenith angle, meanwhile, the new model maintains the linear form of an original model very well, and the complexity of model calculation is not greatly increased, so that a new algorithmic base and a solution provided for the MODIS BRDF / albedo business product up-gradation is made into possible. The method for improving the business nuclear drive bidirectional reflectance distribution function (BRDF) model hot spot has significant application value in the technical field of spatial information, in particular to the aspect of quantitative remote sensing.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Volume scattering polymer light conducting plate and preparation method for injection mould master batch
InactiveCN101367950AGood ultrasonic powerImprove performanceOptical light guidesNon-linear opticsPolymer scienceCyclo olefin polymer
The invention discloses a volume scattering polymer light-guide plate and a method for preparing the injection moulding parent-material thereof. Injection moulding is adopted, the raw materials include organic host materials, inorganic volume scattering particles, coupling agent MPS, anhydrous alcohol and dibutyl phthalate; the inorganic volume scattering particles are SiO2, ZrO2, Al2O3, TiO2 or ZnO, the particle sizes is between 0.1-10 Mum; the organic host materials are poly(methyl methacrylate), polycarbonate or cycloolefin polymers. The process for preparing the injection moulding parent-material of the volume scattering polymer light-guide plate is simple, the batching is easy, and volume scattering polymer light-guide plate can be prepared on a precise injection moulding machine under common injection moulding condition. The volume scattering polymer light-guide plate is fabricated by injection moulding, the preparation method is simple and reliable. The light-guide plate prepared by the method has sound performance, can not only be applied to LED street lamp with relatively low technical requirement, but also applied to LCD screen with very high technical requirement.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
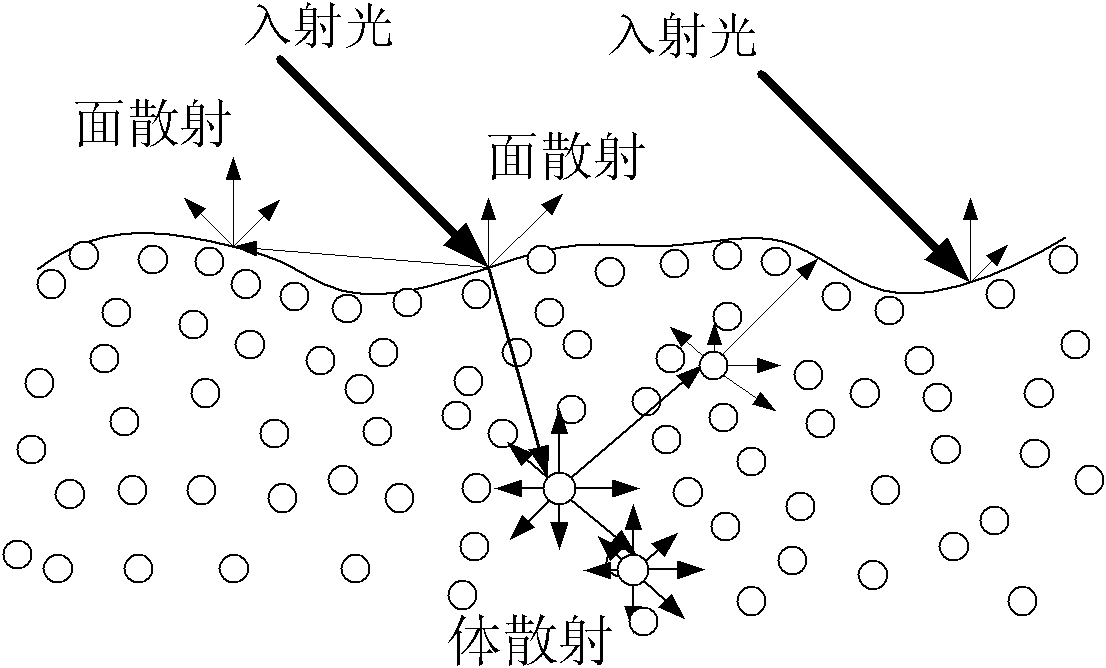
Method for calculating light scattering characteristic of compactibility granule medium
InactiveCN101782516AAdd parameters to describe the roughness of the surface of the scattering mediumScattering properties measurementsUsing optical meansSurface roughnessRadiative transfer theory
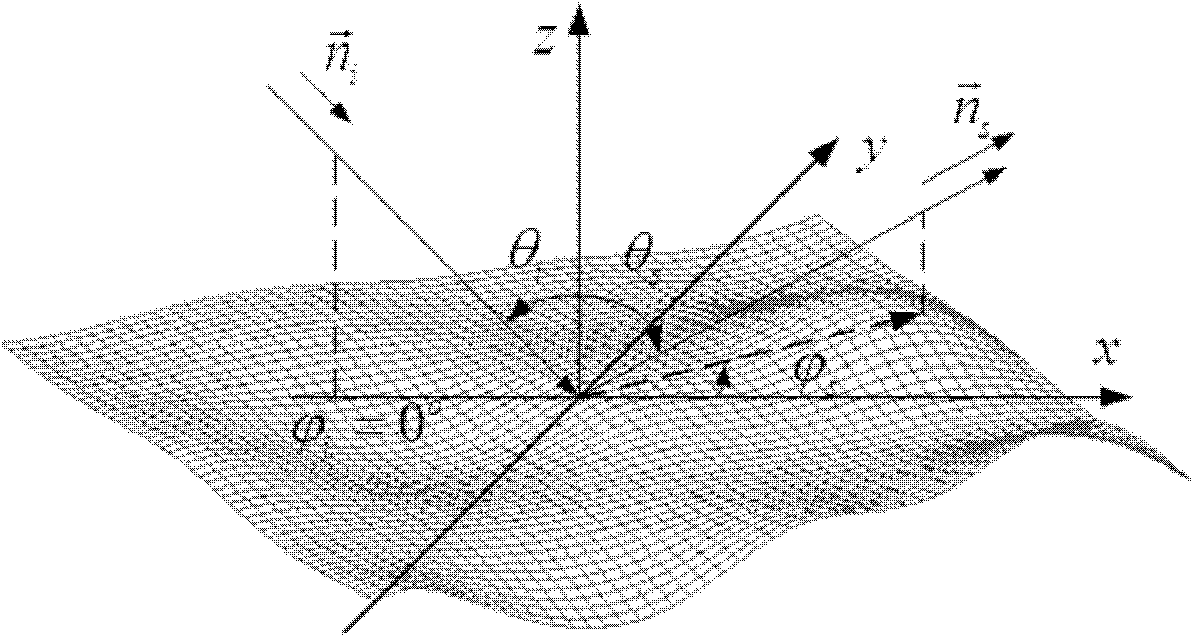
The invention provides a method for calculating the light scattering characteristic of compactibility granule medium, which divides light scattering characteristic-BRDFof the the compactibility granule medium into two parts to calculate, i.e. an interface scattering BRDF and a volume scattering BRDF. Scattering medium interface scattering is calculated and obtained by the wave analytic theory, the volume scattering BRDF is calculated and obtained by the radioactive transfer theory, and the sum of the two parts of calculation is the light scattering characteristic of the compactibility granule medium. The invention combines the radioactive transfer theory with the wave analytic theory for the first time; compared with the previous compactibility medium light scattering models, the invention fully considers the functions of the medium surface shape on the light scattering characteristic, adds a parameter for describing the scattering medium surface roughness degree and improves the calculation precision.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Polarimetric SAR (Synthetic Aperture Radar) interferometry image registration method based on optimal correlation coefficient linearity
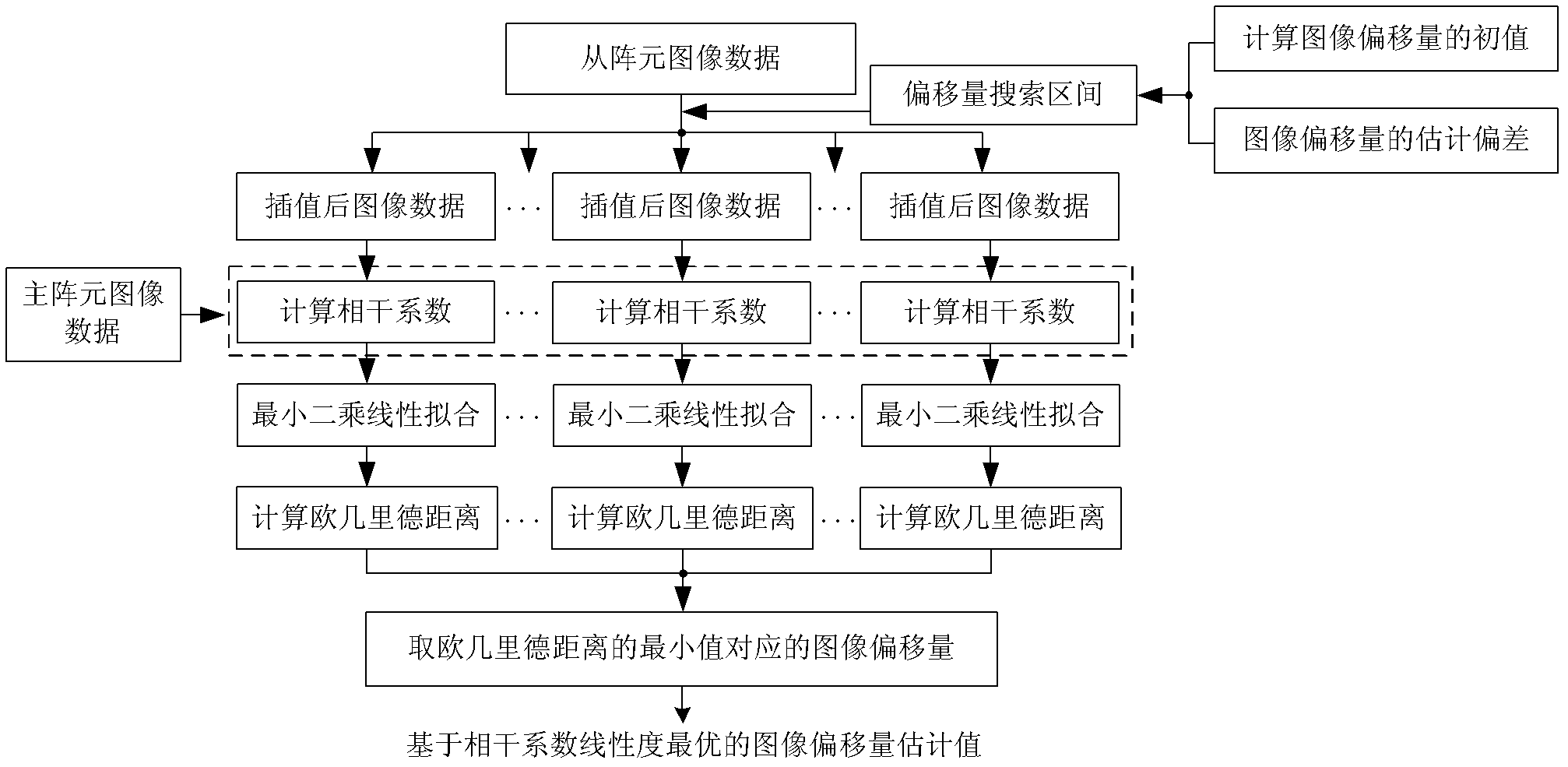
InactiveCN102520407AImprove registration accuracyRadio wave reradiation/reflectionCorrelation coefficientSynthetic aperture radar
The invention relates to a polarimetric SAR (Synthetic Aperture Radar) interferometry image registration method based on optimal correlation coefficient linearity, which belongs to the technical field of radar signal processing. Through utilizing a function relationship between relevant coefficient linearity of each polarimetric channel and image registration deviation, an image offset value withthe optimum relevant coefficient linearity is used as an image registration value. Due to the full utilization of interferometry and polarimetric information of a target, higher image registration accuracy is provided for a vegetation-covered area with serious volume scattering and uniform back scattering, and the existing problems of large registration error and low accuracy when the traditionalimage registration method is used for processing the polarimetric SAR interferometry image of the vegetation-covered area are effectively solved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Detector pixel response nonuniform error correction device and correction method thereof
ActiveCN103983571AUniform Correction WavelengthHigh field uniformityMaterial analysis by optical meansUsing optical meansProcess moduleLaser light
The invention discloses a detector pixel response nonuniform error correction device and a correction method thereof, the device includes a laser light source component, a coupling lens, optical fiber, a container and a black box which are arranged in sequence; the container is provided with a scattering medium solution, the optical fiber inserts into the scattering medium solution, the black box is provided with a detector to be corrected, and the detector to be corrected is connected with a signal acquisition and processing module. The correction method is as follows: alignment laser emitted by the laser light source component is focused to the optical fiber by the coupling lens, the laser is led into the scattering medium solution by the optical fiber from an incident end face, volume scattering of the laser is performed in the scattering medium solution, scattered light is transmitted into the black box from an outgoing end face to form a uniform light field in the position of the detector to be corrected; and the signal acquisition and processing module acquires and processes the test data to obtain correction. By use of the detector pixel response nonuniform error correction device, detector pixel response nonuniform correction wavelength can be matched with actual laser measurement system laser wavelength, so that high accuracy laser measurement can be realized.
Owner:INST OF HIGH ENERGY PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Low-rank-represented polarization SAR image classification method based on superpixel features
InactiveCN103839077AImprove classification accuracyOvercome the problem of boundary classificationCharacter and pattern recognitionDecompositionClassification methods
The invention discloses a low-rank-represented polarization SAR image classification method based on superpixel features. The method mainly improves the marginal classification accuracy of an existing classical algorithm and mainly comprises the steps that (1) Freeman decomposition is conducted on polarization SAR data, surface scattering energy, volume scattering energy and secondary scattering energy are obtained, and a scattering power entropy and a co-polarization ratio are calculated through the surface scattering energy, the volume scattering energy and the secondary scattering energy; (2) superpixel processing is conducted on an RGB composite graph, and a superpixel result graph is obtained; (3) the average value of five features is extracted from each superpixel, a feature matrix of all the superpixels is built, and each row represents the features of each superpixel; (4) low-rank representation is conducted on the feature matrix, and low-rank coefficients are obtained and clustered; (5) wishart adjustment is conducted on the clustered result, and coloring is conducted finally. Compared with other classical methods, the low-rank-represented polarization SAR image classification method based on the superpixel features can better improve classification accuracy and can be used for polarization SAR image classification.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
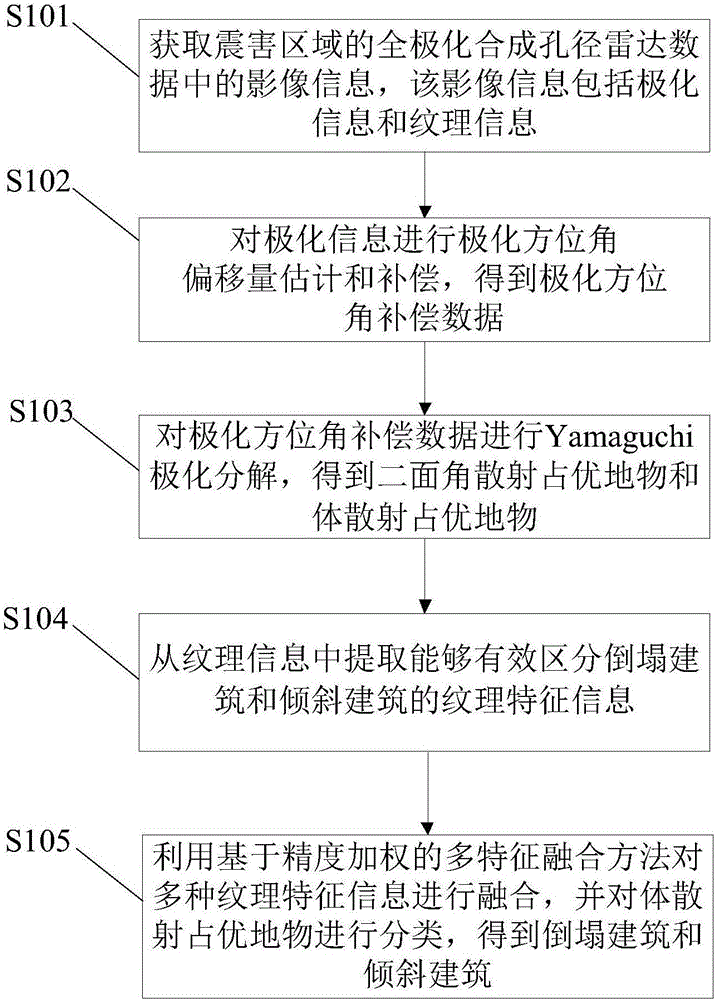
Building seismic damage information extraction method and device
InactiveCN107527035AImprove extraction accuracyHigh precisionCharacter and pattern recognitionInformation processingDecomposition
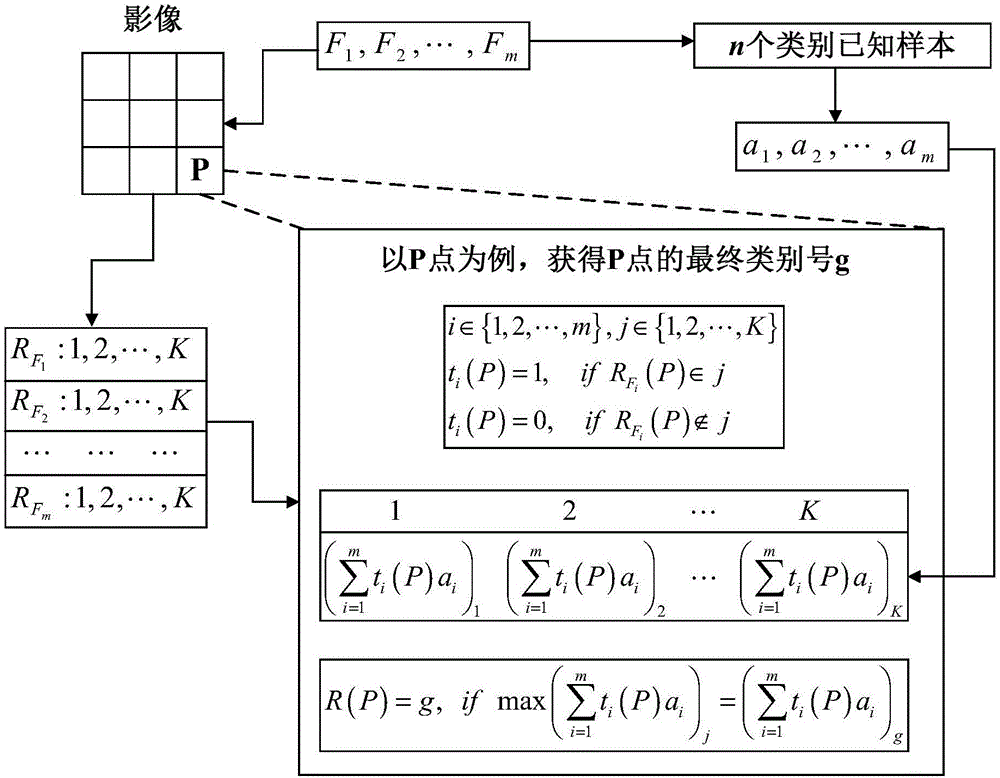
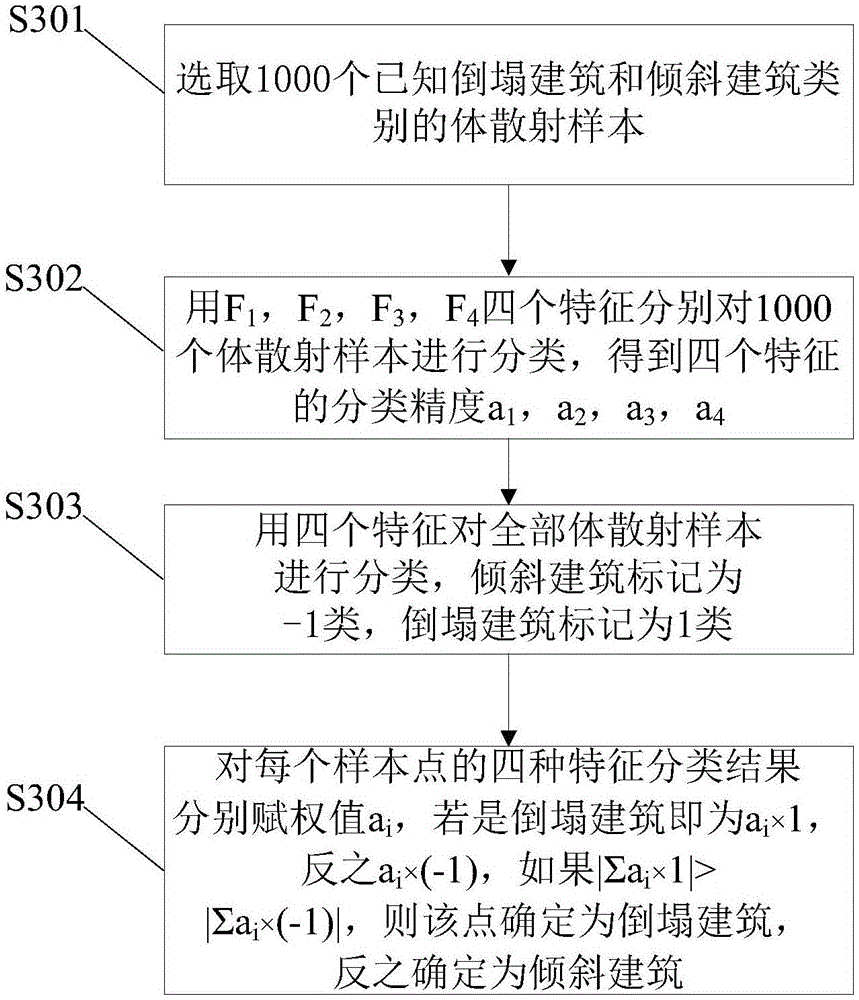
The invention provides a building seismic damage information extraction method and device, which relate to the technical field of information processing and can improve the accuracy of building seismic damage information extracted using SAR data. The building seismic damage information extraction method includes the following steps: acquiring image information in polarimetric SAR data of a seismic damage area, including polarization information and texture information; carrying out polarization azimuth offset estimation and compensation on the polarization information to get polarization azimuth compensation data; carrying out Yamaguchi polarization decomposition on the polarization azimuth compensation data to get a dihedral angle scattering dominant feature and a volume scattering dominant feature, wherein the volume scattering dominant feature is a mixed feature of a collapsed building and an inclined building; extracting texture feature information which can effectively distinguish between a collapsed building and an inclined building from the texture information; and fusing the texture feature information through a multi-feature fusion method based on accuracy weighting, and classifying the volume scattering dominant feature to get a collapsed building and an inclined building.
Owner:SEISMOLOGICAL BUREAU OF GANSU PROVINCE CHINA EARTHQUAKE ADMINISTRATION
Neon-tube substitute using light-emitting diodes
InactiveUS8256918B2Light weightSmooth out luminous appearancePoint-like light sourceLighting support devicesPath lengthLow density
A tubular luminaire efficiently utilizes the light of a line of high-brightness unlensed LEDs to reproduce the homogeneous appearance of a neon tube. The transparent tube has an annular cross-section suitable for cost-effective manufacturing by extrusion. The LEDs are mounted in a line on a circuit board that can be positioned either inside or outside the tube. Their light shines into a cylindrical groove, thereby entering within the material of the tube. Above the groove, the wall of the tube has a spiral shape that reflects the light laterally so that it stays within the annular tube for a considerable path length. Volume scattering by a low density of scattering inclusions causes the light to escape as a homogenous glow. Alternatively, mild surface scattering from the inside surface can be used.
Owner:LIGHT PRESCRIPTIONS INNOVATORS
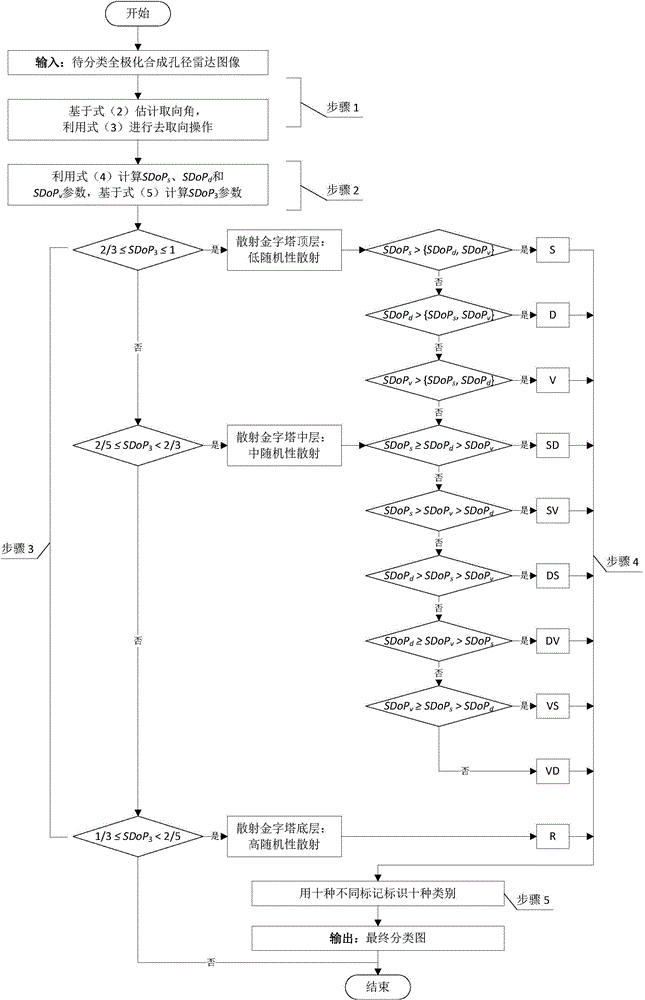
Method for classifying scattering pyramids facing polarimetric synthetic aperture radar images
InactiveCN104636752AEasy to understandExcellent radar target discrimination performanceScene recognitionPolarimetric synthetic aperture radarPyramid
The invention relates to a method for classifying scattering pyramids facing polarimetric synthetic aperture radar images. The method comprises the following steps of reading the coherency matrix of the images to be classified, and de-orientating; respectively calculating the preference degree parameters SDoPs, SDoPd and SDoPv of surface scattering, biplanar scattering and volume scattering as well as the average preference degree parameter SDoP3 required by targets; based on SDoP3, building a three-layer pyramid model, wherein from bottom to top, the three-layer pyramid model respectively stands for high, middle and low random scattering situations; based on the permutation and combination of the parameters SDoPs, SDoPd and SDoPv, dividing the three-layer pyramid model into ten blocks to respectively stand for ten different scattering mechanisms; marking the images to be classified with different marks; finally forming a classifying image.
Owner:NAT SPACE SCI CENT CAS
Polarimetric SAR image decomposition method and storage medium
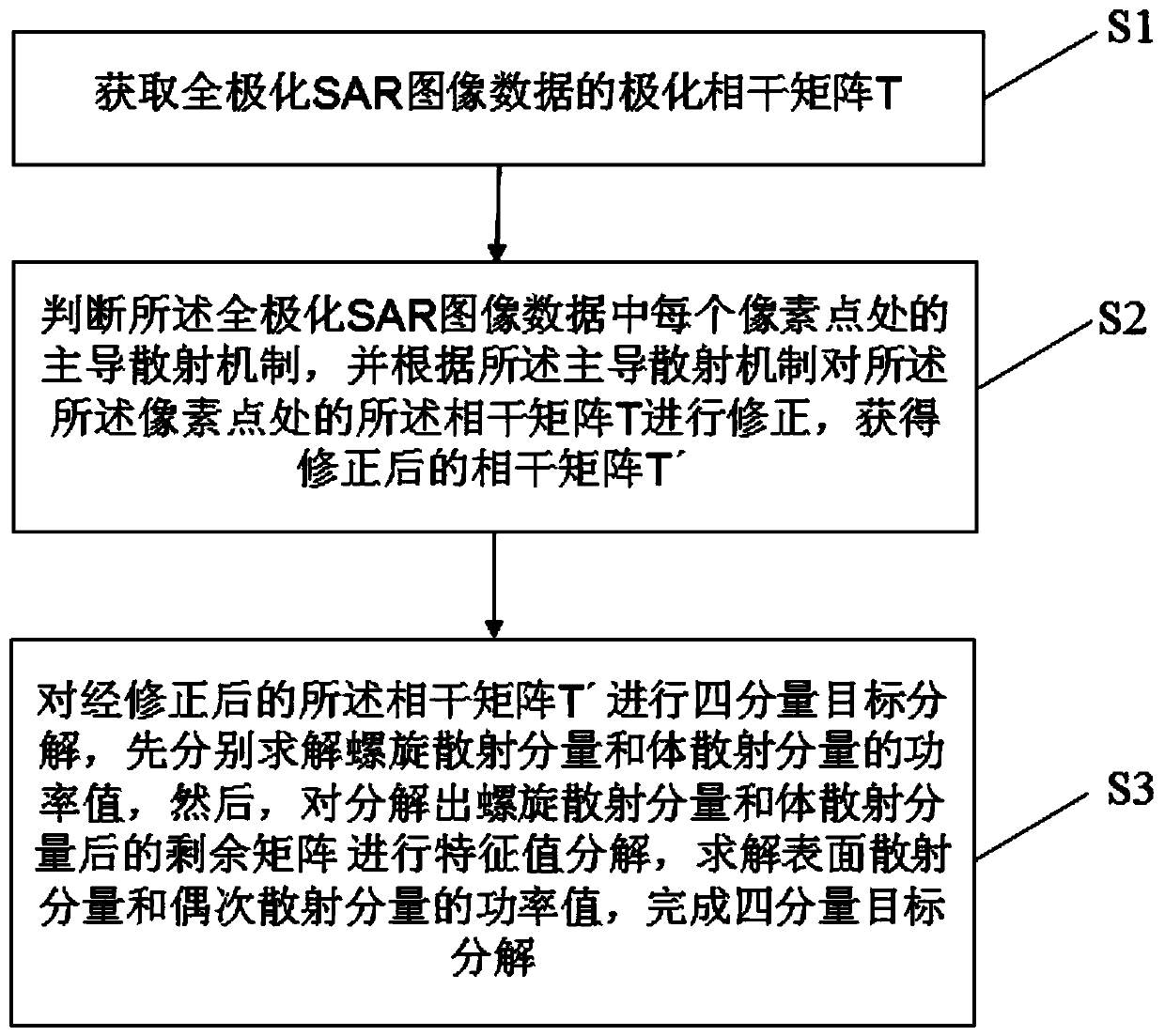
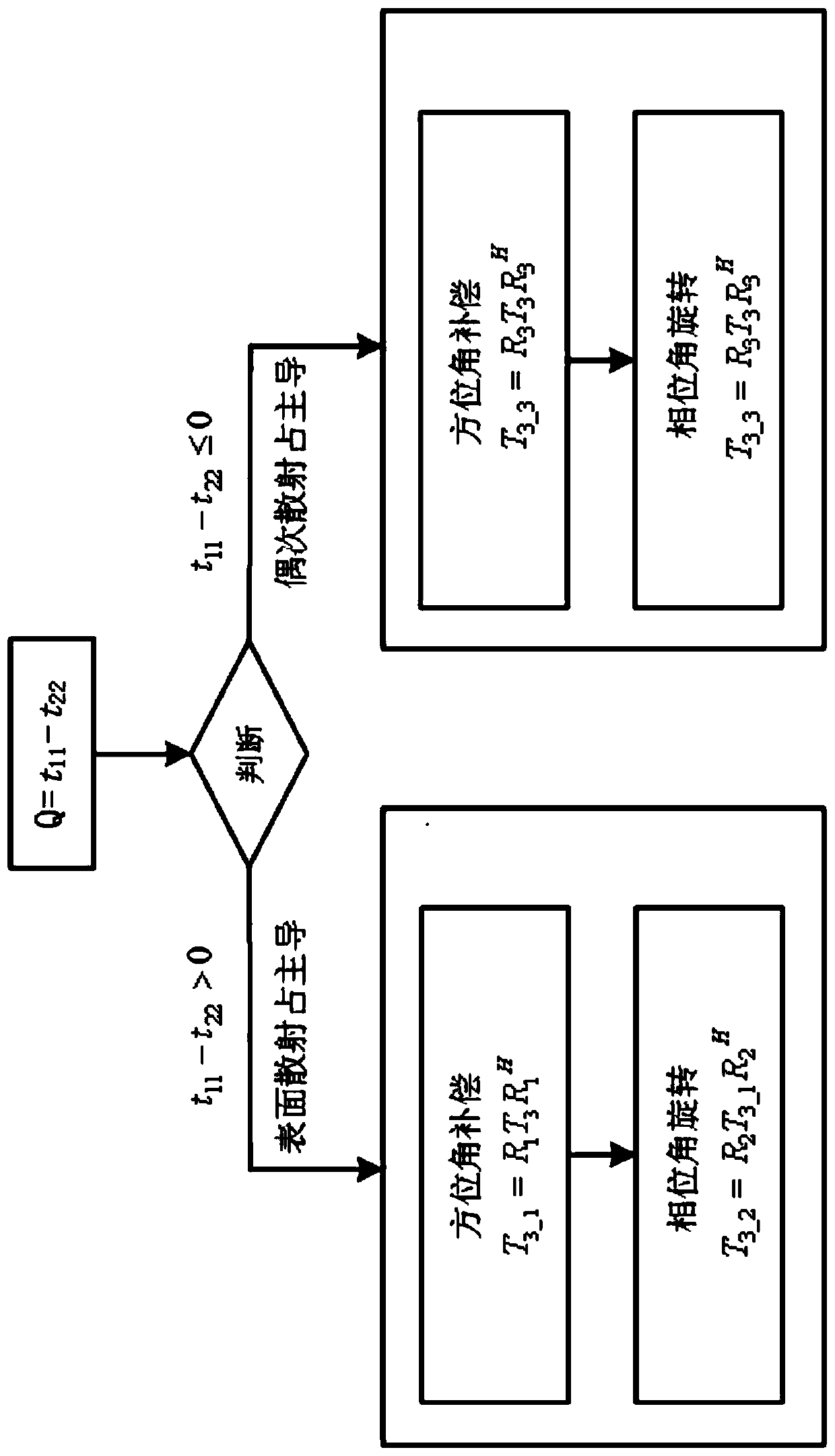
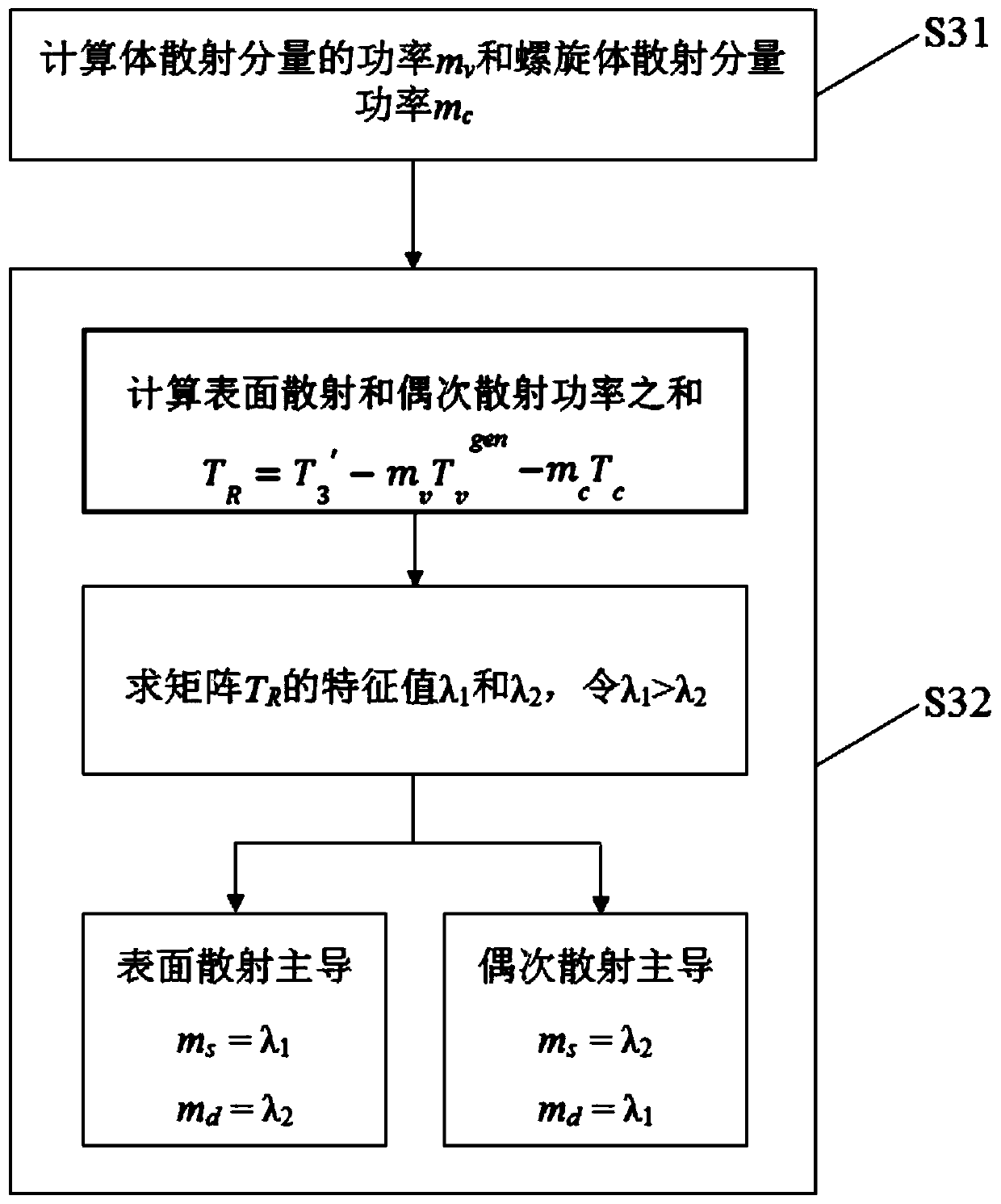
InactiveCN110412573AReduce overestimationSolve the phenomenon of negative powerRadio wave reradiation/reflectionDecompositionNegative power
The invention discloses a polarimetric SAR image decomposition method and a storage medium. The polarimetric SAR image decomposition method comprises the steps of acquiring a polarimetric coherence matrix T of fully-polarimetric SAR image data; judging a dominant scattering mechanism at each pixel point in the fully-polarimetric SAR image data, and correcting the coherence matrix T at each pixel point according to the corresponding dominant scattering mechanism to obtain a corrected coherence matrix T'; conducting four-component target decomposition on the corrected coherence matrix T', and solving power values of spiral volume scattering, volume scattering, surface scattering and even-numbered scattering. According to the method, corresponding azimuth angle compensation and phase angle rotation operation is conducted according to the dominant mechanism of each pixel point, the overestimation phenomenon of volume scattering is greatly reduced, and the problem of negative power generated by surface scattering and even-numbered scattering is solved; in addition, the adjustment of a self-adaptive volume scattering model is introduced so that the ratios of HH and VV components can continuously change, and the decomposition result is closer to the scattering mechanism of an actual ground object target.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA UNIV OF TECH
Method and device for estimating forest above-ground biomass
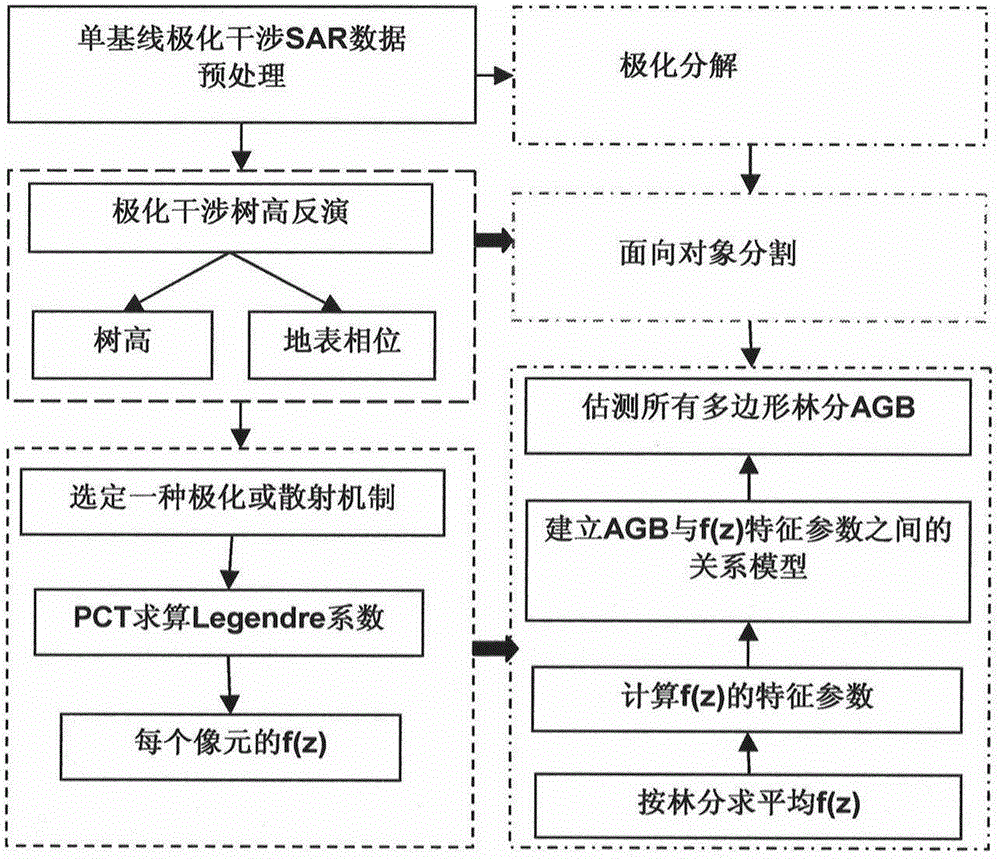
InactiveCN104361592AAccurate estimateAvoid problemsImage enhancementImage analysisAbove groundStructure of the Earth
The invention relates to a method and device for estimating forest above-ground biomass. The method comprises the steps that perpendicular distribution of the relative reflectivity of pixels is estimated for a pair of preprocessed polarization interference SAR images by using a Legendre expansion equation of multiple correlation of the pixels in the perpendicular direction; scattering type distinguishing is conducted on all the pixels in the preprocessed main image, areas formed by all volume scattering type pixels in the image are regarded as forest areas, and object-oriented partition is conducted, so that a plurality of polygon forest stands representing homogeneity forest objects are obtained; for all the polygon forest stands, average relative reflectivity perpendicular structural sections are calculated respectively, and parameterized processing is conducted on the average relative reflectivity perpendicular structural sections; a multi-element linear forest above-ground biomass estimation model is established according to multiple obtained parameters, and the forest above-ground biomass of the polygon forest stands is calculated through the multi-element linear forest above-ground biomass estimation model. According to the technical scheme, the forest above-ground biomass can be more accurately estimated.
Owner:RES INST OF FOREST RESOURCE INFORMATION TECHN CHINESE ACADEMY OF FORESTRY
Target decomposition method based on model for fully-polarized synthetic aperture radar
ActiveCN104931950AFree from lossRadio wave reradiation/reflectionDecompositionSynthetic aperture radar
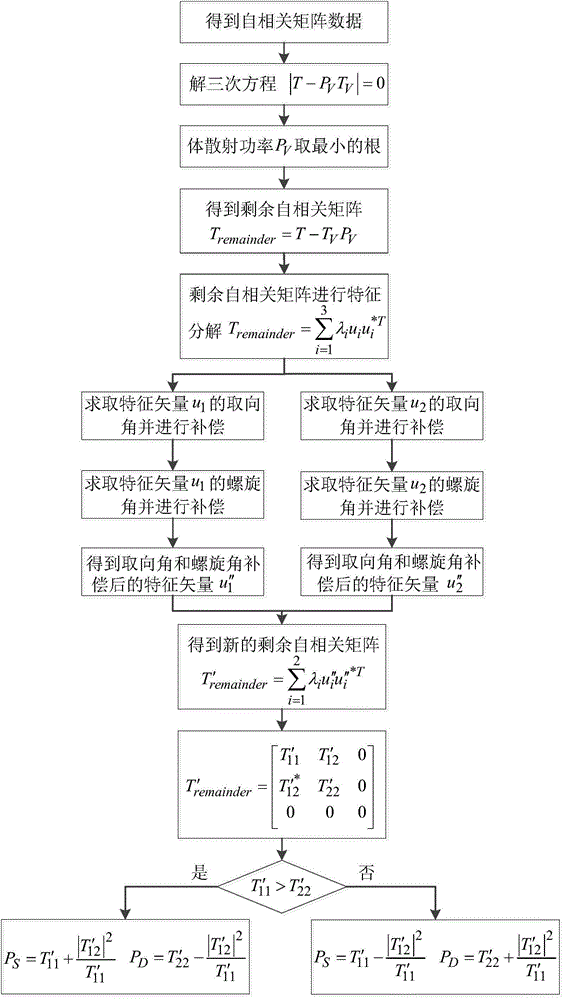
The invention relates to a target decomposition method based on a model for a fully-polarized synthetic aperture radar. The target decomposition method comprises the steps of: acquiring fully-polarized data of a self-correlation matric form; getting volume scattering component power based on a nonnegative eigenvalue decomposition method under the theoretical situation of non-reflective symmetry; calculating a remainder self-correlation matrix according to the obtained volume scattering component power, and carrying out eigenvalue decomposition on the obtained remainder self-correlation matrix to obtain a characteristic vector with eigenvalue being zero and two characteristic vectors with eigenvalue being non-zero; conducting orientation angle compensation and helical angle compensation on the two characteristic vectors with eigenvalue being non-zero in the remainder self-correlation matrix; calculating a new remainder self-correlation matrix on the basis of the characteristic vectors after orientation angle compensation and helical angle compensation; and getting surface scattering power and double scattering power based on the obtained new remainder self-correlation matrix according to a method of getting surface scattering power and double scattering power through three-component decomposition. The target decomposition method provided by the invention has the advantages of no loss of information and no occurrence of negative power.
Owner:NAT SPACE SCI CENT CAS
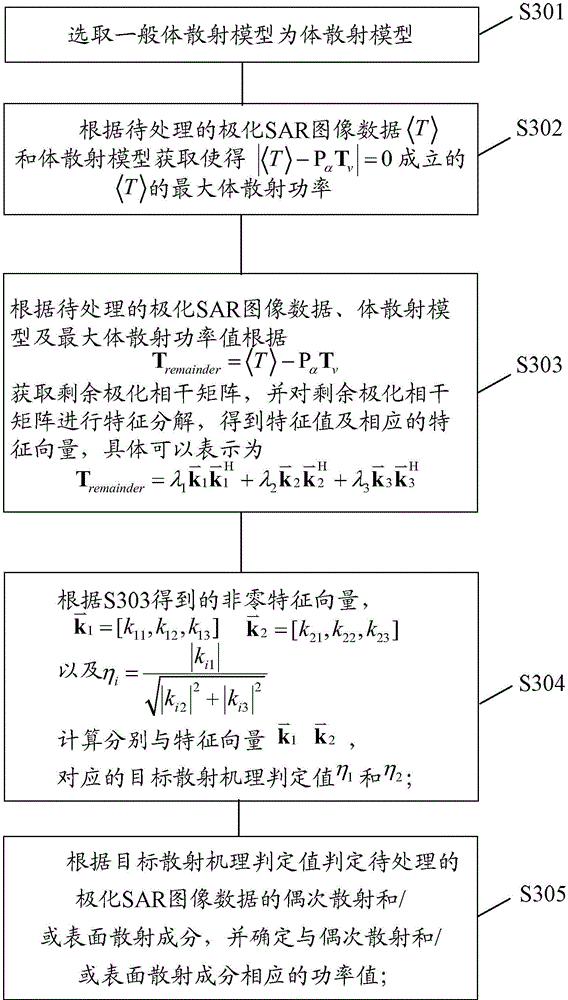
Method and device for decomposing objective scattering ingredients of polarized SAR (synthetic aperture radar)
InactiveCN104376539AImprove accuracyAvoid overestimation of volume scatteringImage enhancementFeature vectorAdditive ingredient
An embodiment of the invention discloses a method and a device for decomposing objective scattering ingredients of a polarized SAR (synthetic aperture radar). The method comprises the following steps of selecting a volume scattering model based on polarized SAR image data to be processed; extracting the maximum volume scattering power of the polarized SAR image data to be processed according to the polarized SAR image data to be processed and the volume scattering model; acquiring residual polarization coherence matrix of the polarized SAR image data to be processed according to the polarized SAR image data to be processed, the volume scattering model and the maximum volume scattering power value, and performing characteristic decomposition on the residual polarization coherence matrix to obtain the characteristic value and the characteristic vector of the residual polarization coherence matrix; calculating an objective scattering mechanism decision value according to elements of the characteristic vector; and determining even-order scattering and / or surface scattering ingredients of the polarized SAR image data to be processed according to the objective scattering mechanism decision value, and determining power values corresponding to the even-order scattering and / or surface scattering ingredients.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Attenuation sampling device used for large-angle high-energy laser incidence
ActiveCN104019891AGood angle characteristicsImprove the ability to resist laser radiationPhotometryUltrasound attenuationHigh spatial resolution
The invention discloses an attenuation sampling device used for large-angle high-energy laser incidence. The device comprises a front panel, an attenuation unit and a rear panel, wherein a straight laser incidence sampling hole is formed in the front panel, a laser exiting hole is formed in the rear panel, the attenuation unit comprises a front transmission window, a rear transmission window and a cylindrical cavity, the cylindrical cavity is arranged coaxial with the straight sampling hole and the laser exiting hole, and the cylindrical cavity is filled with granular optical volume scattering materials. After being coupled into the attenuation unit through the sampling hole, absorbed through inner walls and the materials, and subjected to volume scattering, lasers are emitted out through the laser exiting hole, laser beam energy can be redistributed in a space within a wide range, and the homogenization effect is achieved; meanwhile, large-angle attenuation sampling can be achieved in the laser oblique incidence, the requirement for substantial attenuation of laser power density can be met, and the device can be used for high-spatial-resolution light intensity detection.
Owner:NORTHWEST INST OF NUCLEAR TECH
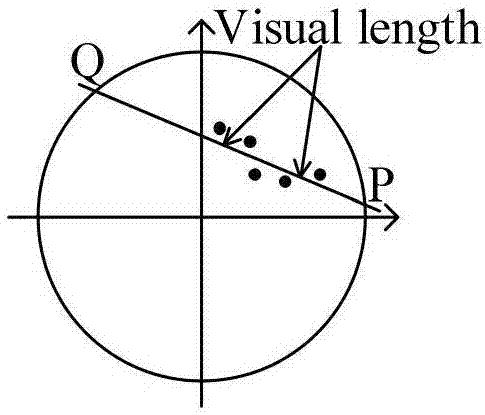
Inversion method based on polarization interference synthetic aperture radar and device
ActiveCN103323846AReduce fit errorImprove inversion accuracyRadio wave reradiation/reflectionCorrelation coefficientSynthetic aperture radar
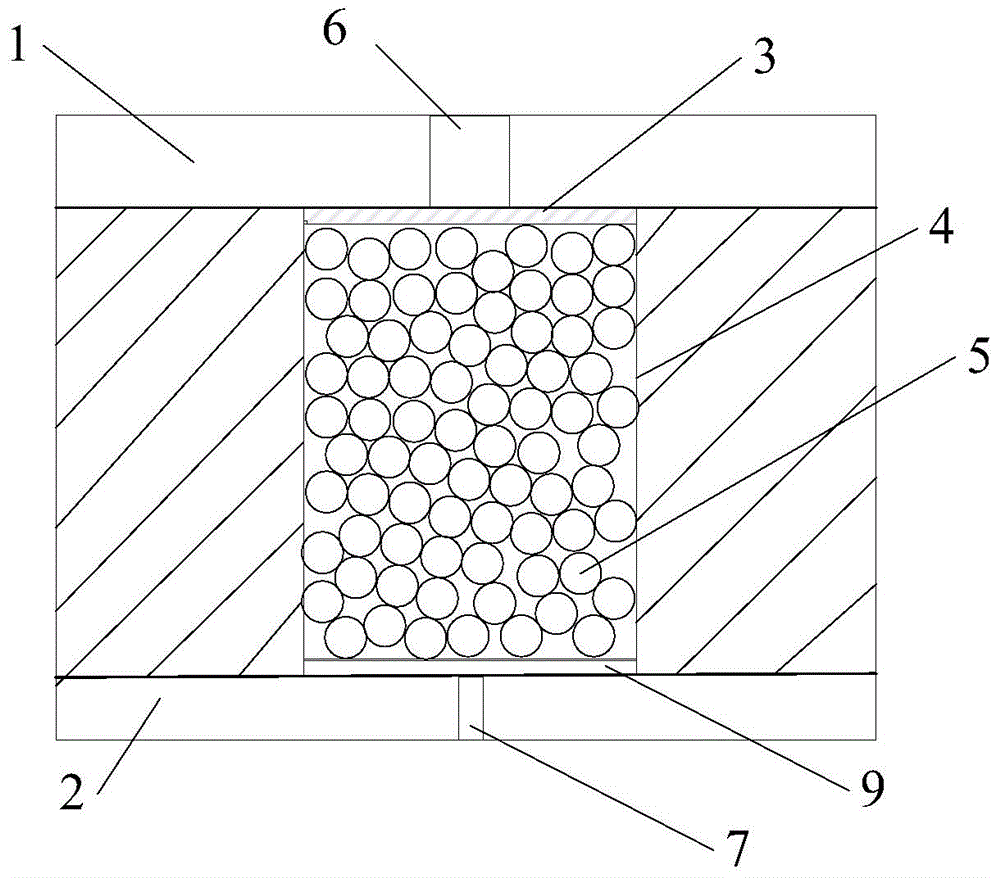
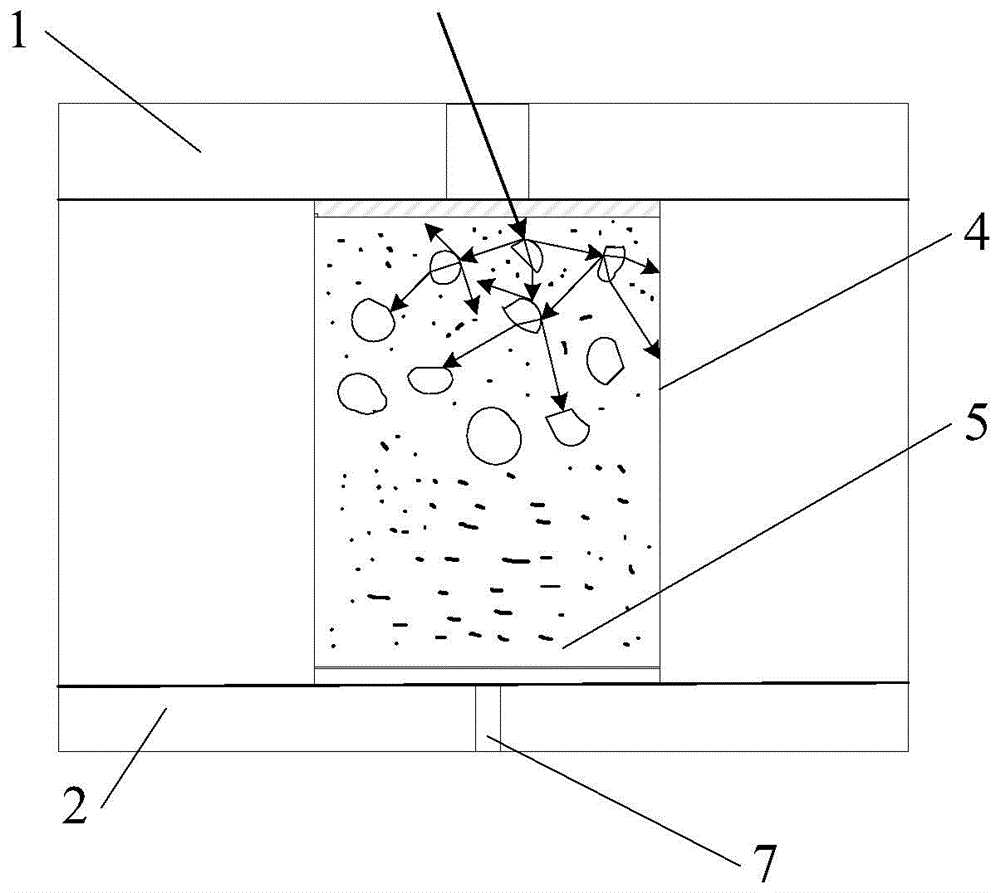
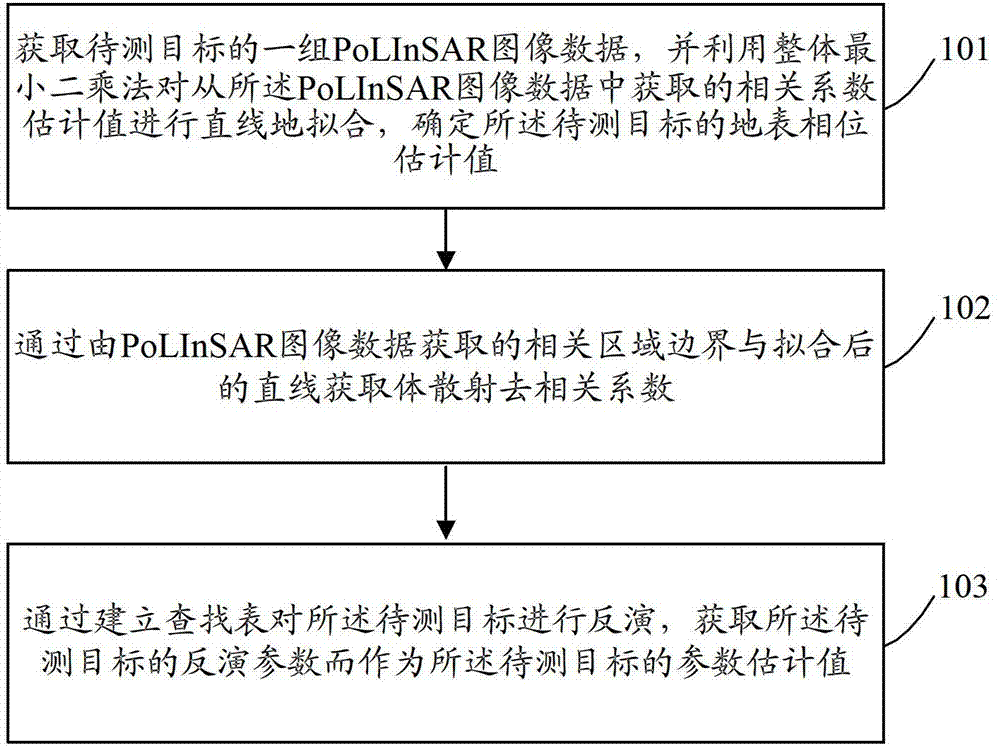
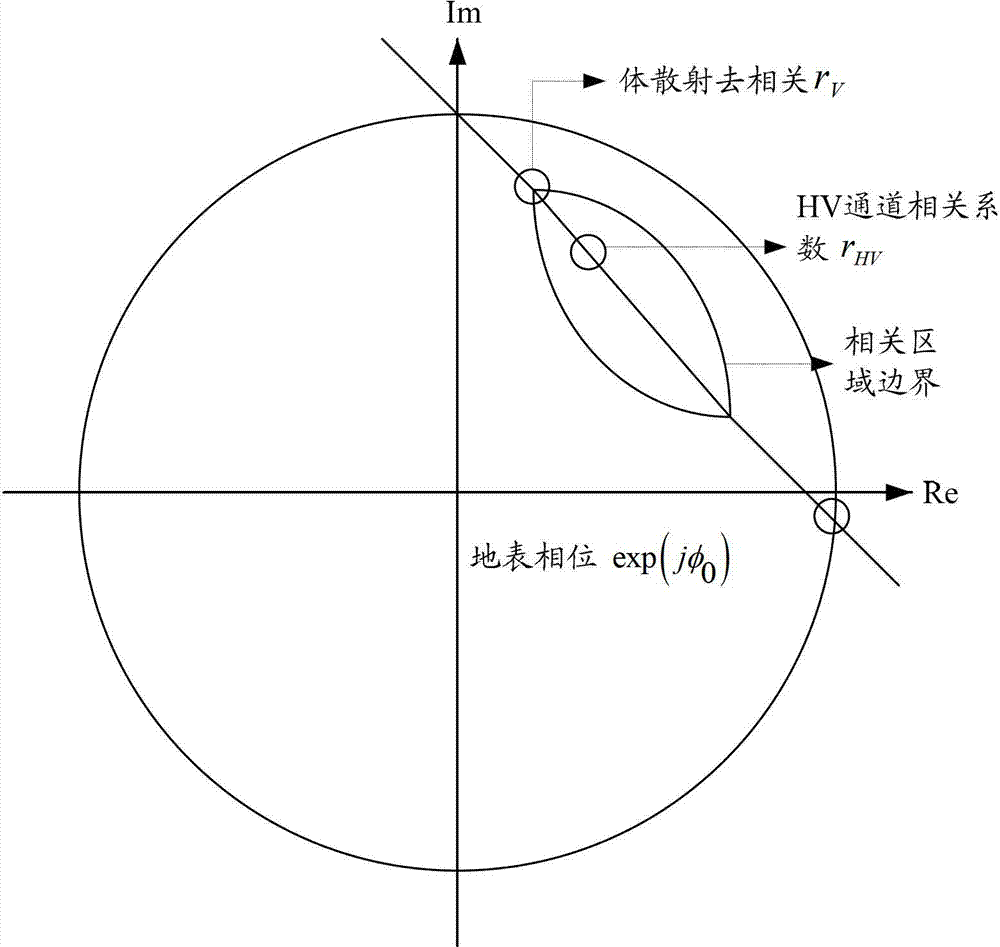
The invention discloses an inversion method based on a polarization interference synthetic aperture radar. The inversion method includes the steps of step 1, obtaining one set of image data of the polarization interference synthetic aperture radar (PoLInSAR) of a target to be tested, carrying out straight line fitting on correlation coefficient estimated values obtained from the PoLInSAR image data by utilizing total least squares, and determining the earth surface phase estimated value of the target to be tested, step 2, obtaining a volume scattering decorrelation coefficient through a correlated area bound obtained from the PoLInSAR image data and the fitted straight line, step 3, carrying out inversion on the target to be tested through establishing a lookup table, obtaining inversion parameters of the target to be tested and regarding the inversion parameters as the parameter estimates of the target to be tested. The invention further discloses an inversion device based on the polarization interference synthetic aperture radar. According to the technical scheme, inversion accuracy can be improved, and the technical scheme is especially suitable for being used in inversion of forest parameters.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Small-depth Doppler log
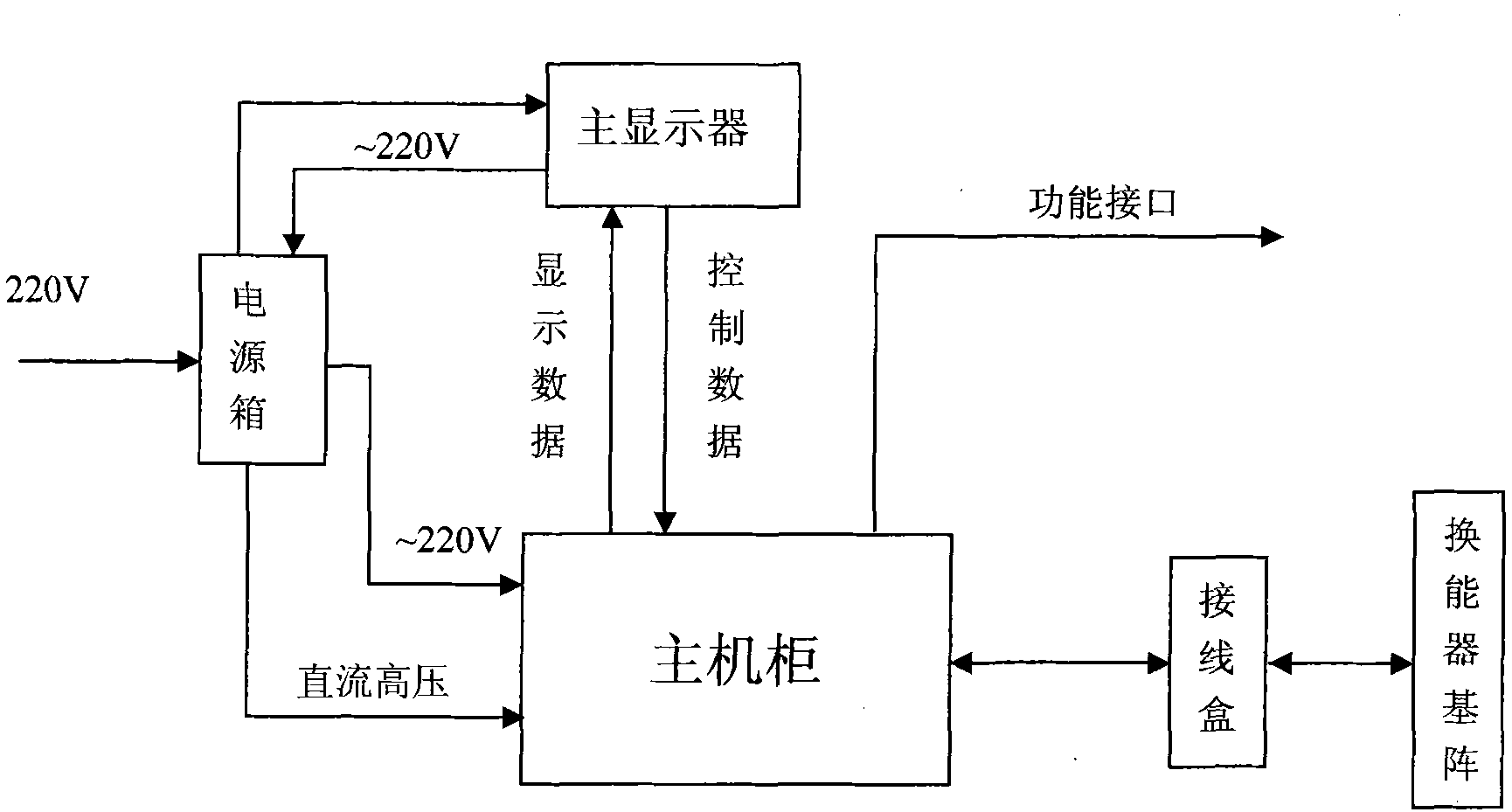
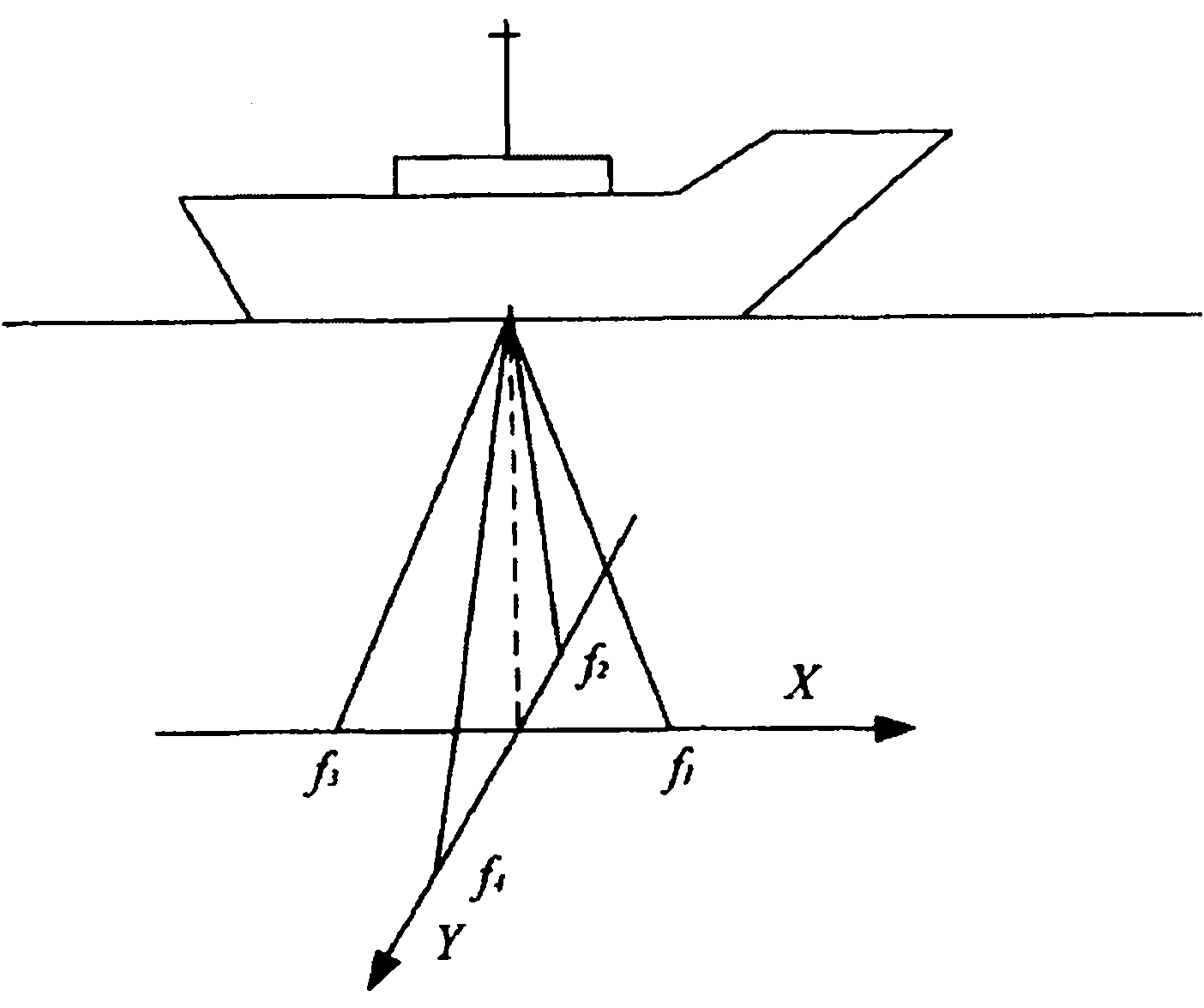
The invention discloses a small-depth Doppler log and relates to the field of navigation log. The conventional Doppler log has the disadvantages that: a phase-array large-depth Doppler log is used for measuring the speed of a ship relative to a sea bottom or seawater, but the process is complex and the price is high; moreover, a miniaturized relative-to-water Doppler log has a small size and is low in price, but can only measure the speed of the ship relative to the sea bottom. The invention provides the small-depth Doppler log, which can measure the speed of the ship relative to the seawater and the sea bottom, and has a simple process and is low in price compared with the phase-array large-depth Doppler log. In the water depth range of 200m, the speed of the ship relative to the sea bottom can be measured by using a scattered signal at the sea bottom; and when the water depth is more than 200m, the speed of the ship relative to the seawater can be measured by using a volume scattering signal of a water layer with certain thickness 10m deep under the surface of a transducer array. The small-depth Doppler log mainly comprises an underwater transducer array, a junction box, a mainframe (comprising a receiving / transmission system), a main display and a power box.
Owner:CSSC MARINE TECH CO LTD
Underwater image quality improvement method based on multi-scale fusion
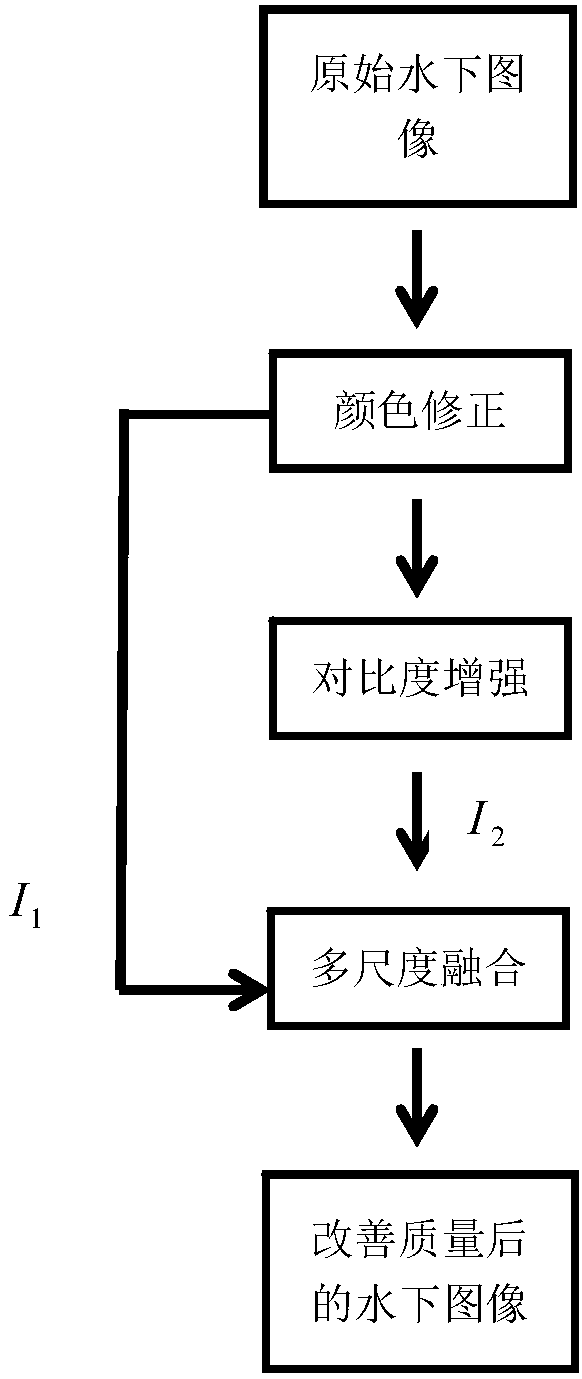
InactiveCN108447028AIncrease contrastHigh global contrastImage enhancementImage analysisGeneral purposeImaging quality
In order to solve the technical problem that a current underwater image quality improvement method is complex in process or depends too much on an involution-form model, the invention provides an underwater image quality improvement method based on multi-scale fusion. The method is mainly used to improve the problems of large noise, large aberration and low contrast of an underwater image and improve the image quality. The current underwater image quality improvement method comprises the steps of: performing color correction of original images, eliminating color cast of the images caused by various light sources, performing enhancement of the contrast of the images, reducing the quality degradation caused by volume scattering, and finally, performing multi-scale fusion of the images to obtain an underwater image with observably enhanced details and edges, reduced noise, more clear dark areas and higher global contrast. The current underwater image quality improvement method is low in calculation cost and can perform execution at a relatively rapid speed on general-purpose hardware.
Owner:XI'AN INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Complete polarization synthetic aperture radar target decomposition method for adaptive selection unitary transformation
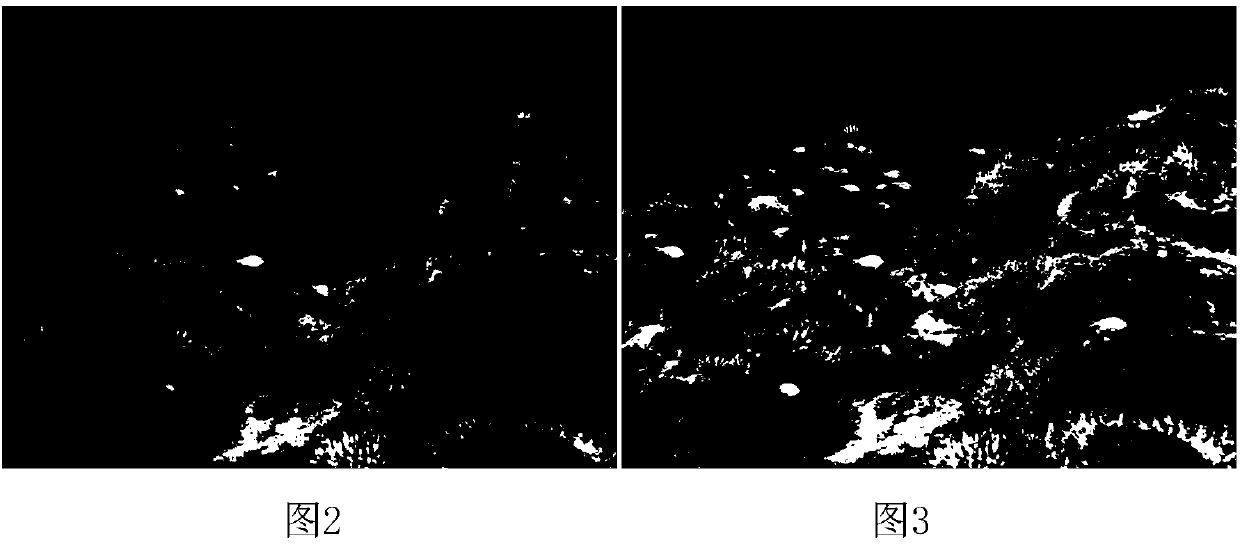
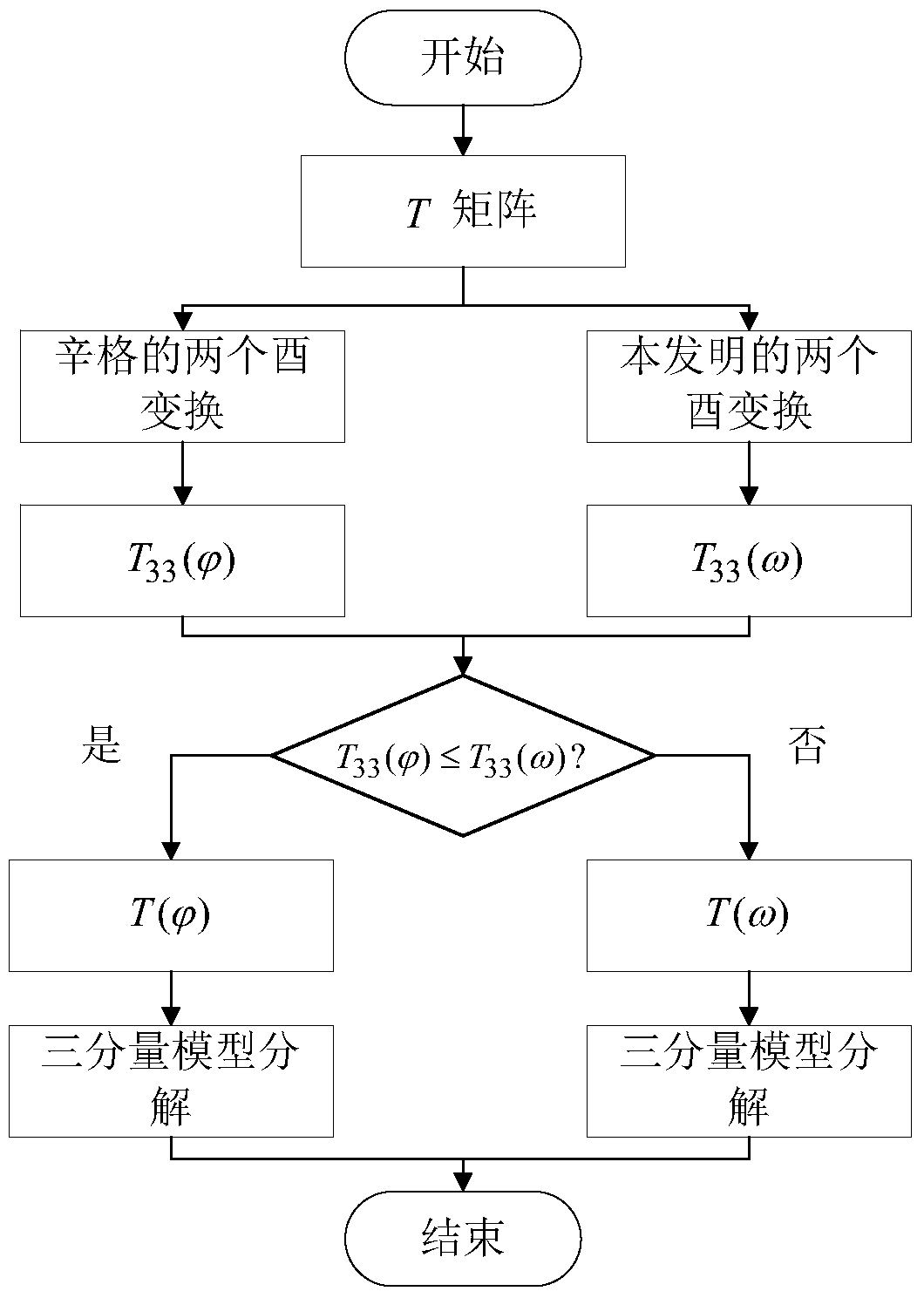
InactiveCN104698447ASuppressing Scatter Overestimation ProblemsLess freedomRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSynthetic aperture radarOmega
The invention provides a complete polarization synthetic aperture radar target decomposition method for adaptive selection unitary transformation. The method comprises the following steps: (1) performing two unitary transformations for singh for data coherence T matrix of the complete polarization synthetic aperture radar to obtain the matrix, (the formula is as shown in specification); (2) performing other two unitary transformations for the coherence T matrix to obtain the matrix T(omega), wherein the first unitary transformation is used for performing the spiral angle compensation and restraining the volume scattering excessive estimation of model decomposition, the second unitary transformation is used for further restraining the volume scattering excessive estimation and reducing one degree of freedom of the coherence T matrix; (3) comparing with element (the formula is as shown in specification) of the matrix (the formula is as shown in specification) with the element T33(omega) of the matrix T(omega); if (the formula is as shown in specification), and (the formula is as shown in specification), otherwise, T is equal to T(omega); (4) performing three-component model decomposition on coherence T matrix. The two unitary transformations for singh in the step (1) or the two unitary transformations in the step (2) can be selected for the coherence T matrix in a self-adaption mode by the method according to the real situation of the object, and the volume scattering excessive estimation problem of the model decomposition can be effectively restrained.
Owner:NAT SPACE SCI CENT CAS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com