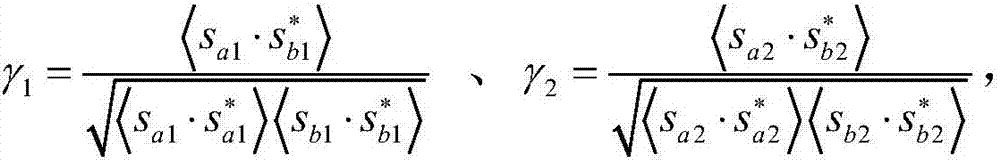Patents
Literature
41 results about "Data coherence" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Data coherence includes uniformity across shared resource data, as well as logical connections and completeness within a single data set and across data sets. For example, a district might upload to its system data on the number of students in military families, and those data are then transferred to the SEA data system.
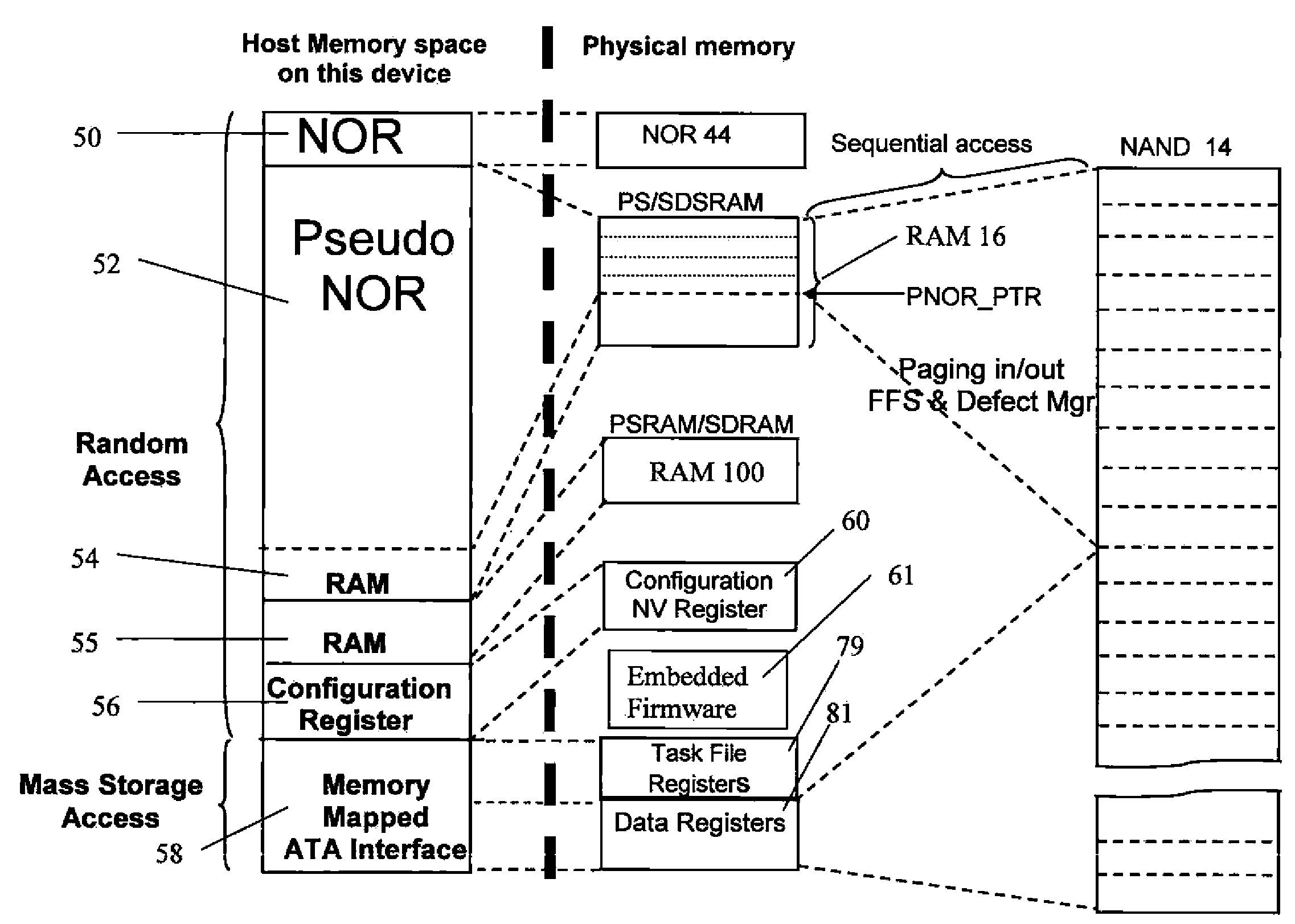
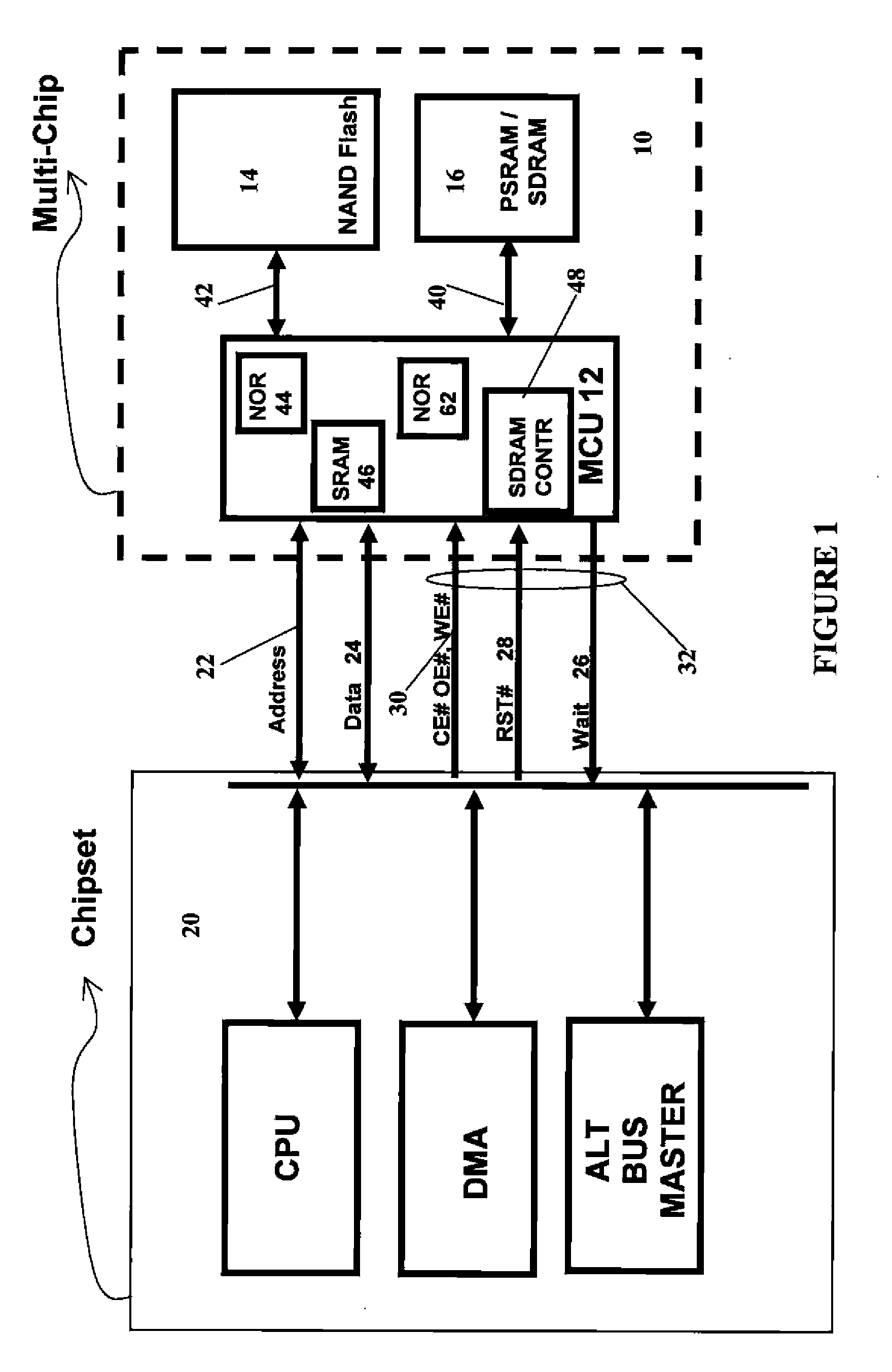
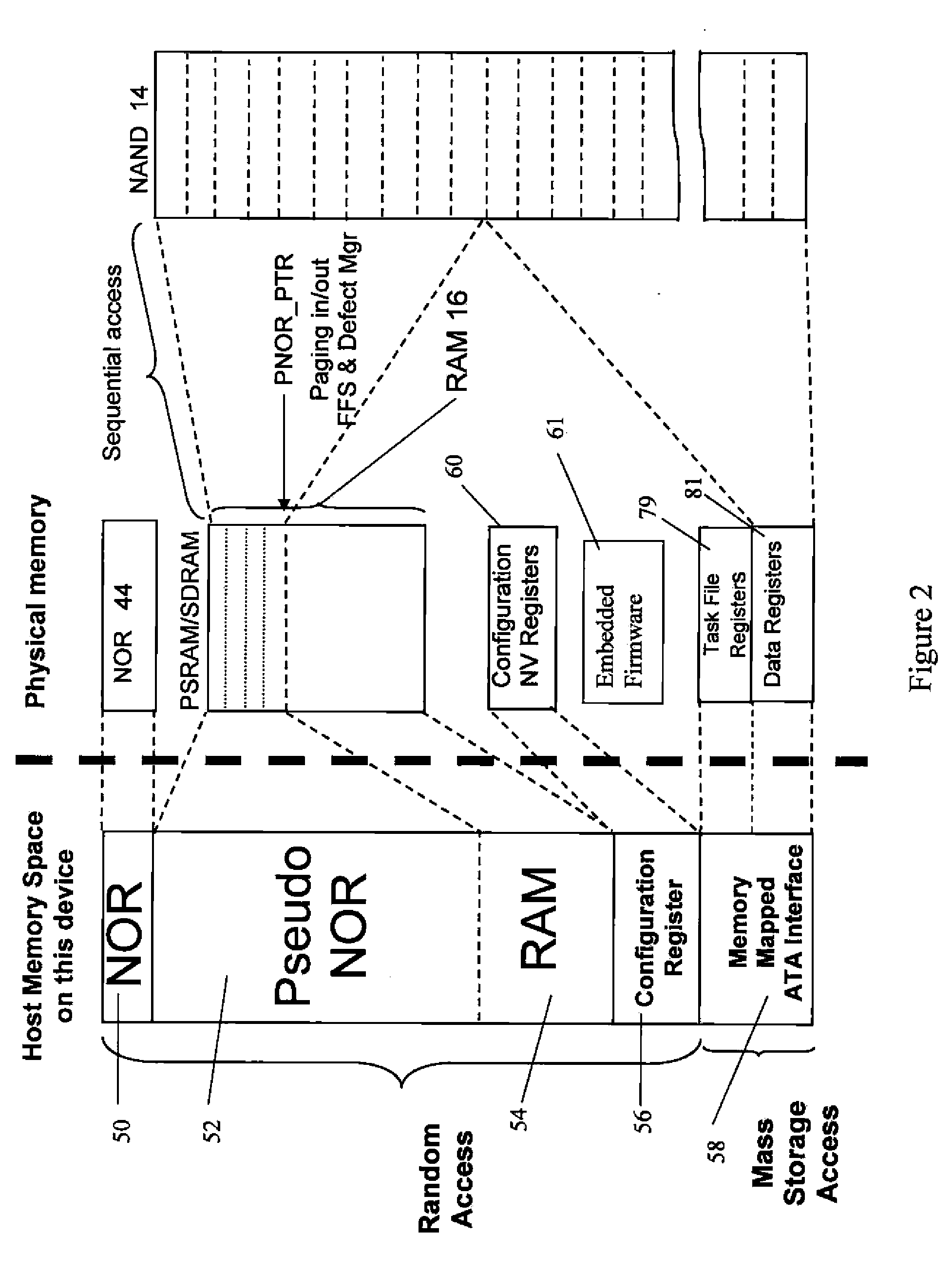
Unified memory and controller
InactiveUS20070147115A1Memory adressing/allocation/relocationDigital storageData coherenceControl signal
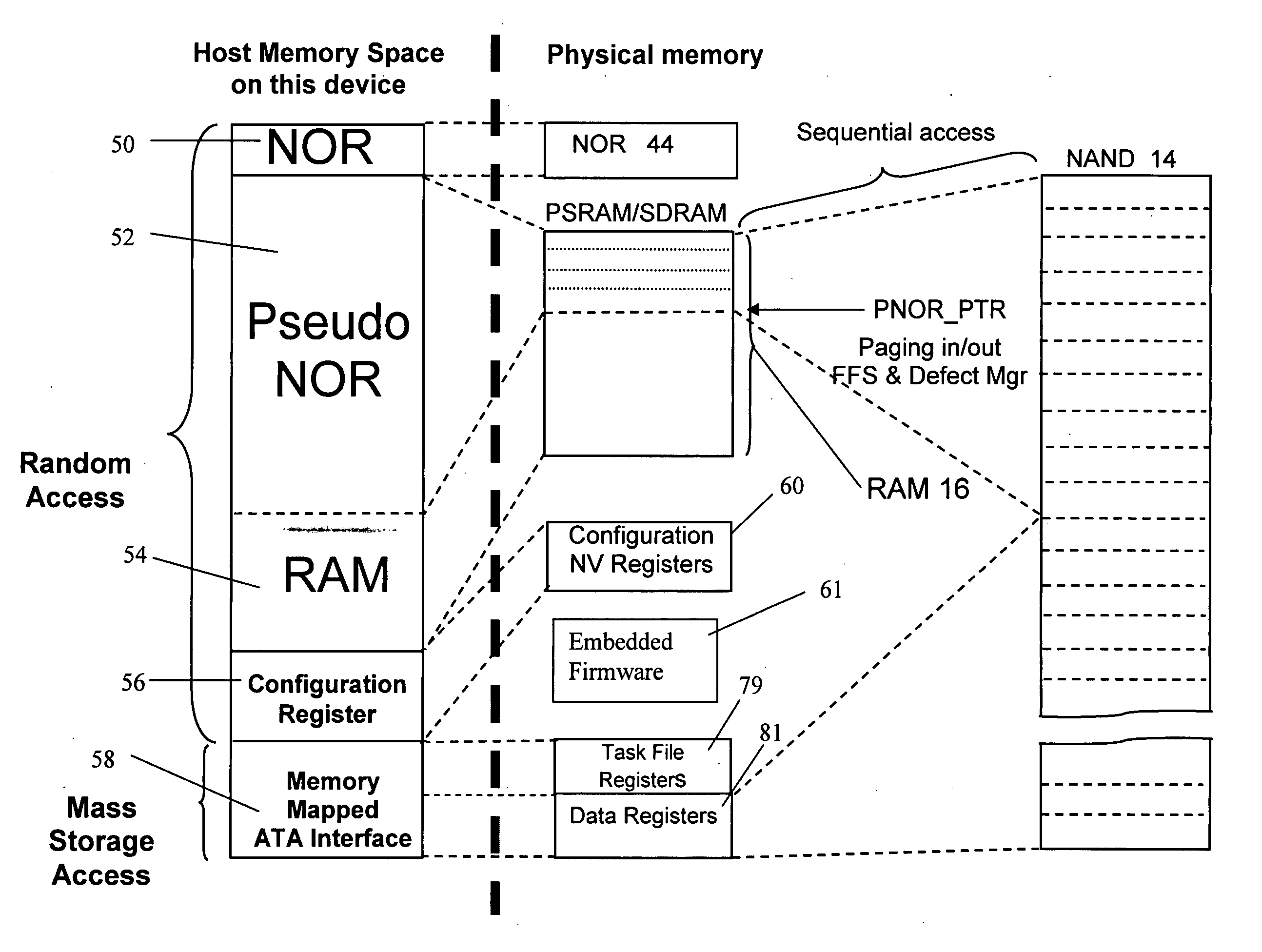
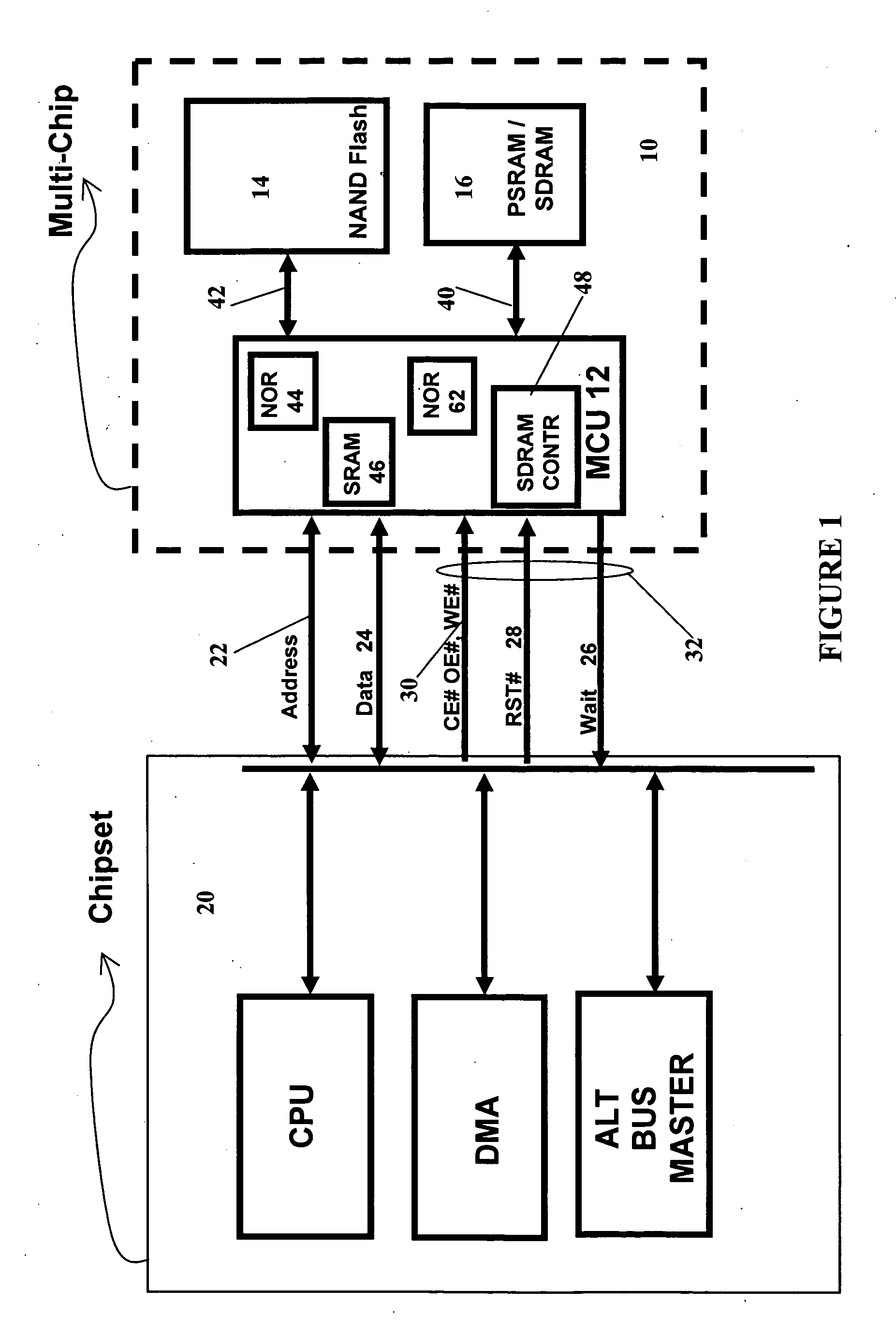
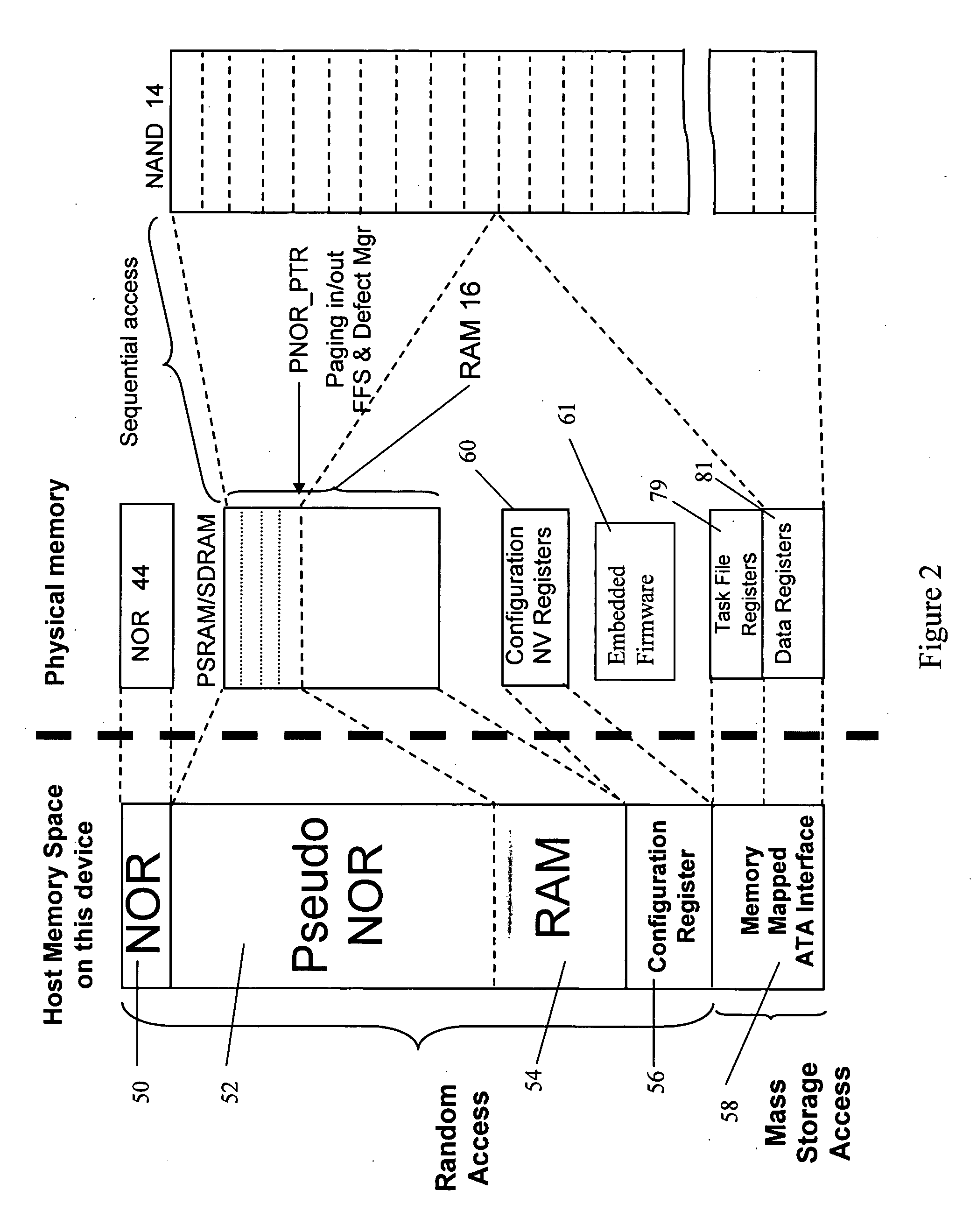
A memory device has a controller. The controller has a first address bus for receiving a RAM address signals, a first data bus for receiving RAM data signals, and a first control bus for receiving RAM control signals. The controller further has a second address bus for interfacing with a volatile RAM memory, a second data bus for interfacing with the volatile RAM memory, and a second control bus for interfacing with the volatile RAM memory. The controller further has a third address / data bus for interfacing with a non-volatile NAND memory, and a third control bus for interfacing with non-volatile NAND memory. The memory device further having a RAM memory connected to said second address bus, said second data bus, and said second control bus. The memory device further having a non-volatile NAND memory connected to the third address / data bus and to the third control bus. The controller also has a non-volatile bootable memory, and further has means to receive a first address on the first address bus and to map the first address to a second address in the non-volatile NAND memory, with the volatile RAM memory serving as cache for data to or from the second address in the non-volatile NAND memory, and means for maintaining data coherence between the data stored in the volatile RAM memory as cache and the data at the second address in the non-volatile NAND memory.
Owner:GREENLIANT
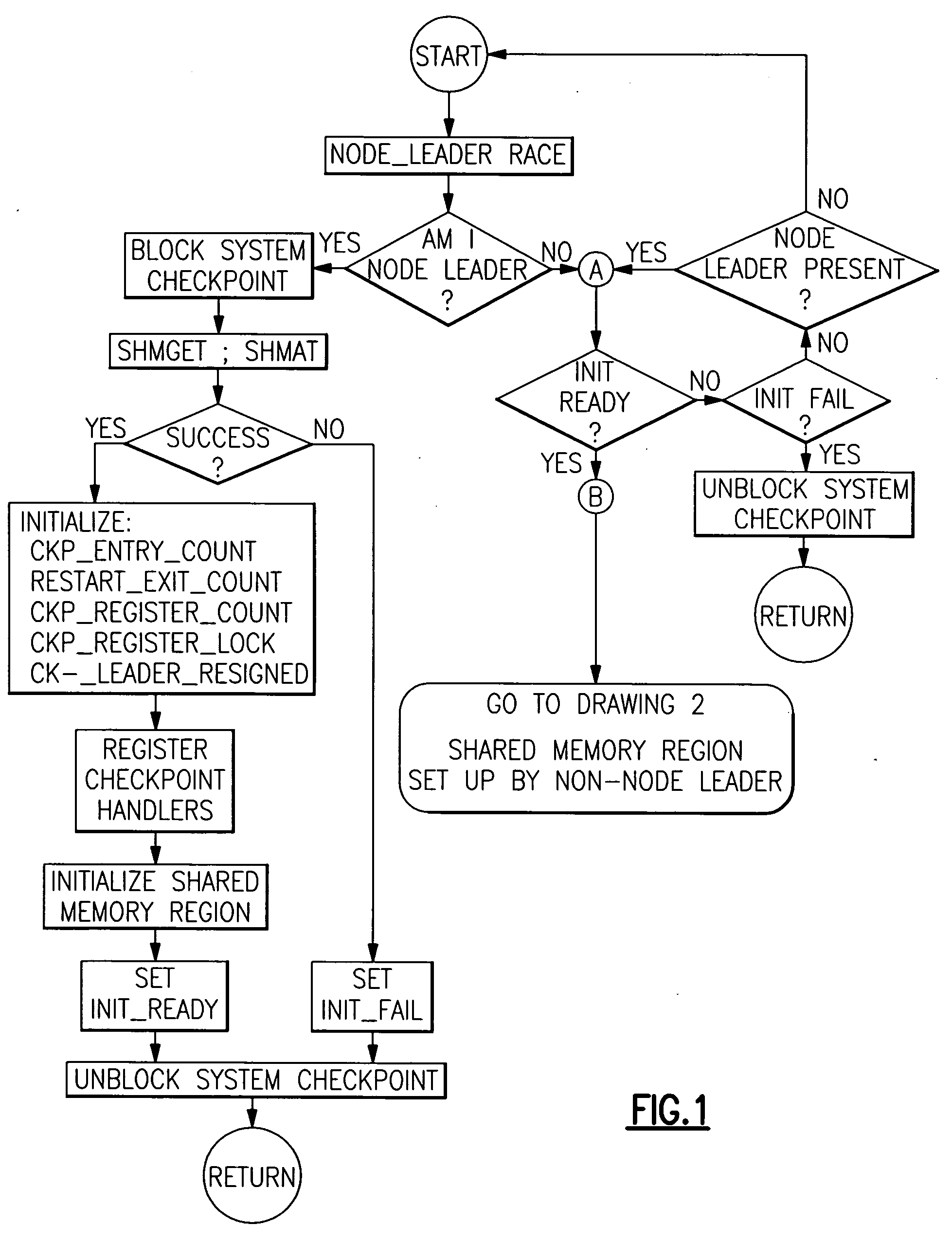
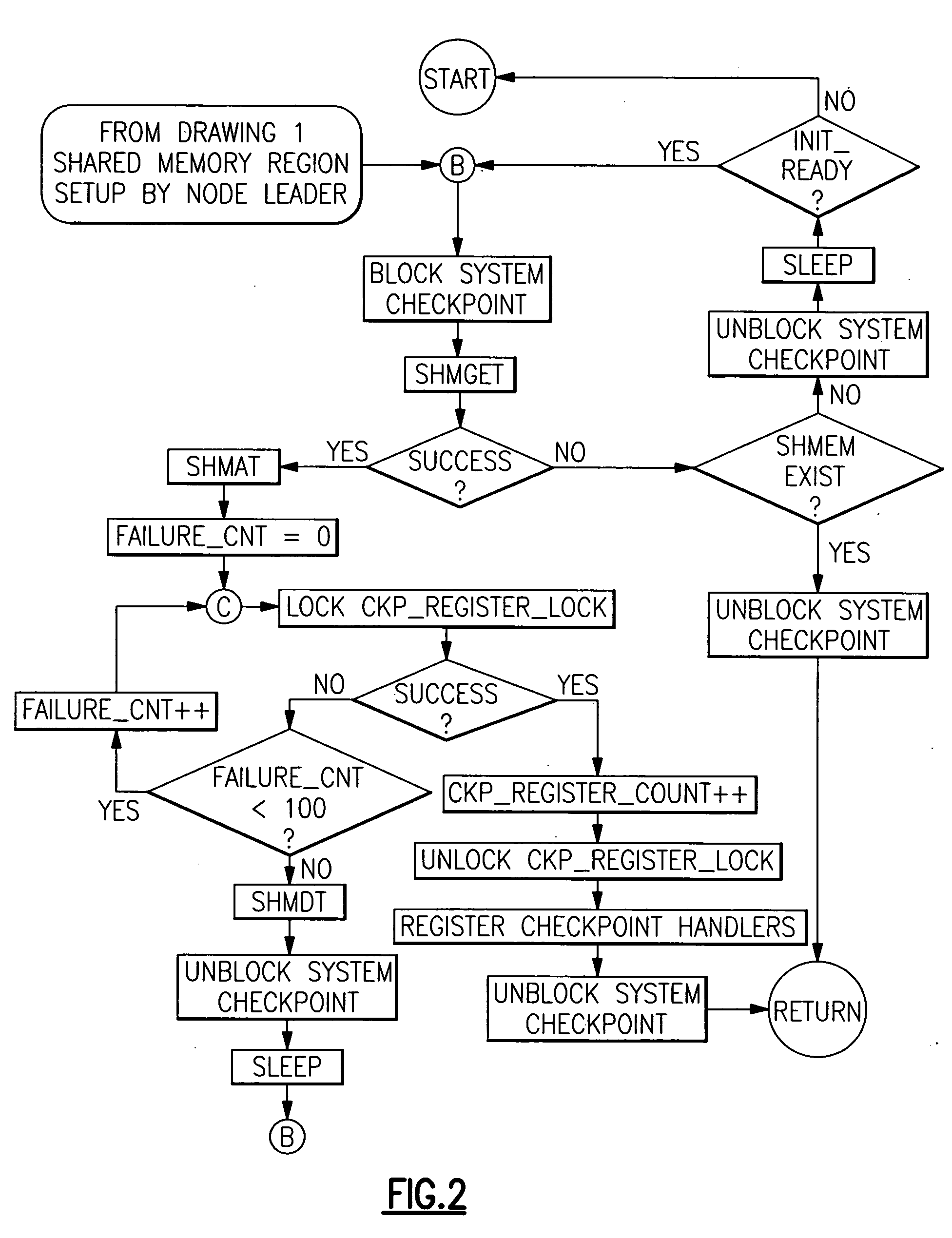
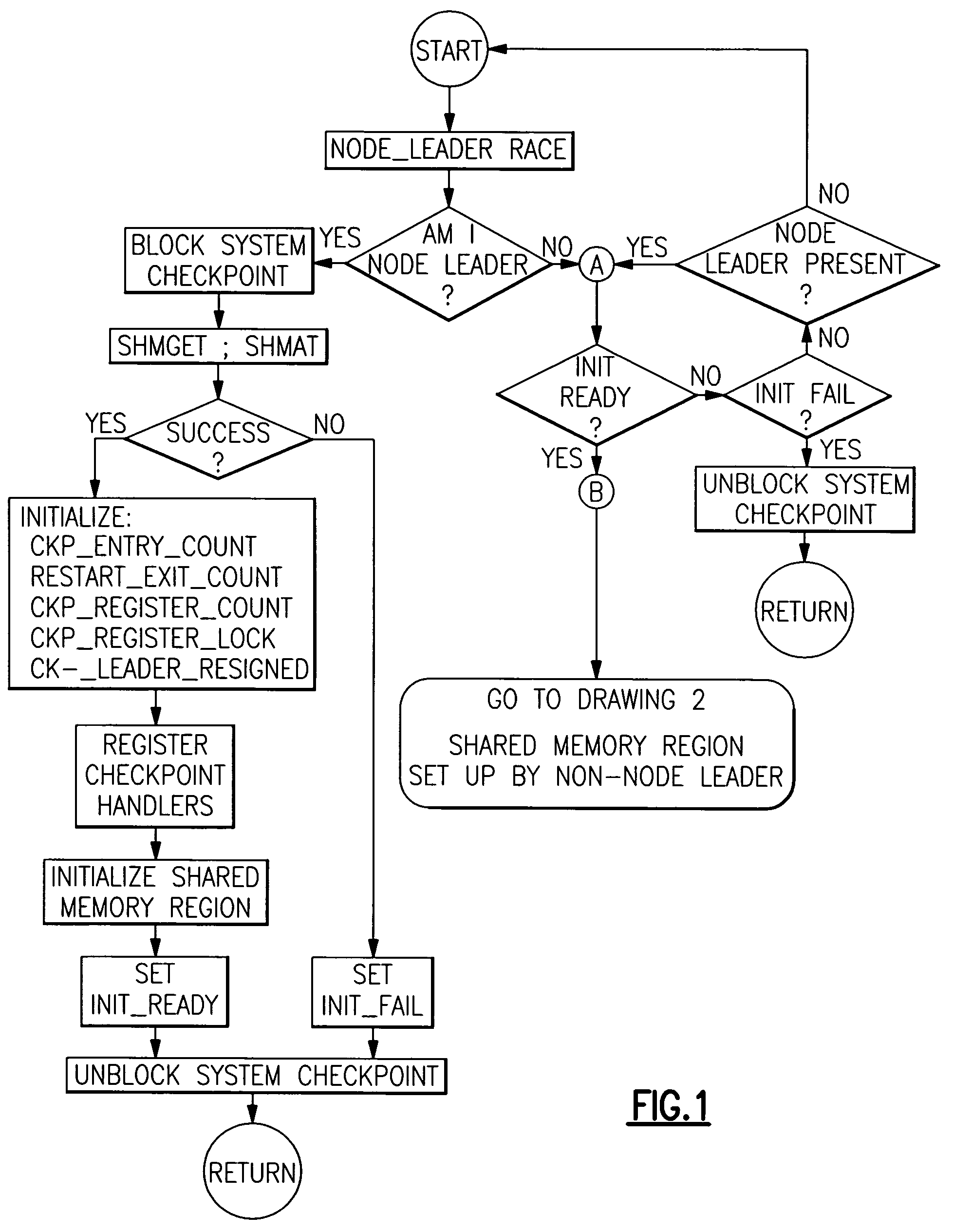
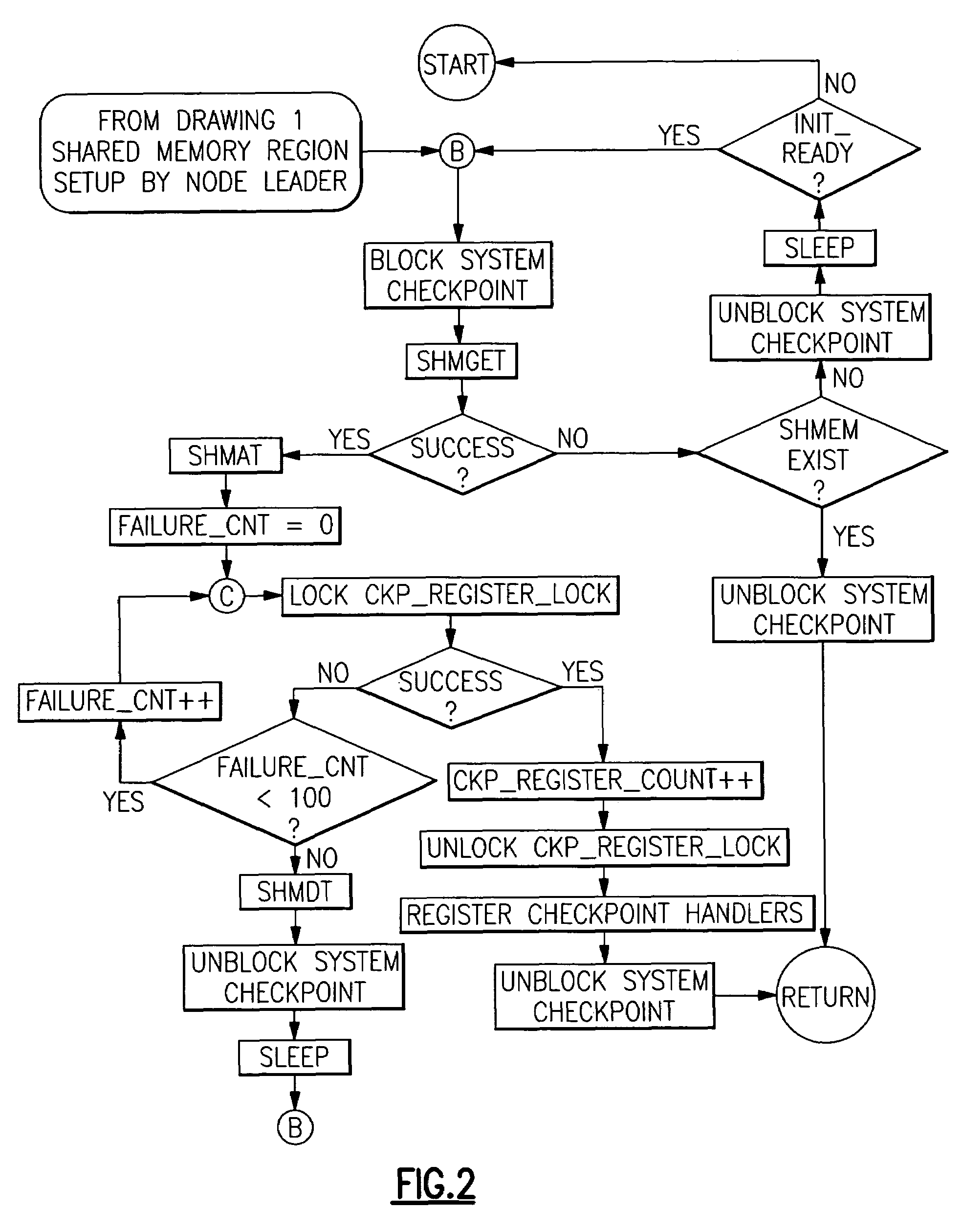
Checkpoint/resume/restart safe methods in a data processing system to establish, to restore and to release shared memory regions
ActiveUS20060143512A1Guaranteed uptimeEfficient managementError detection/correctionData coherenceData processing system
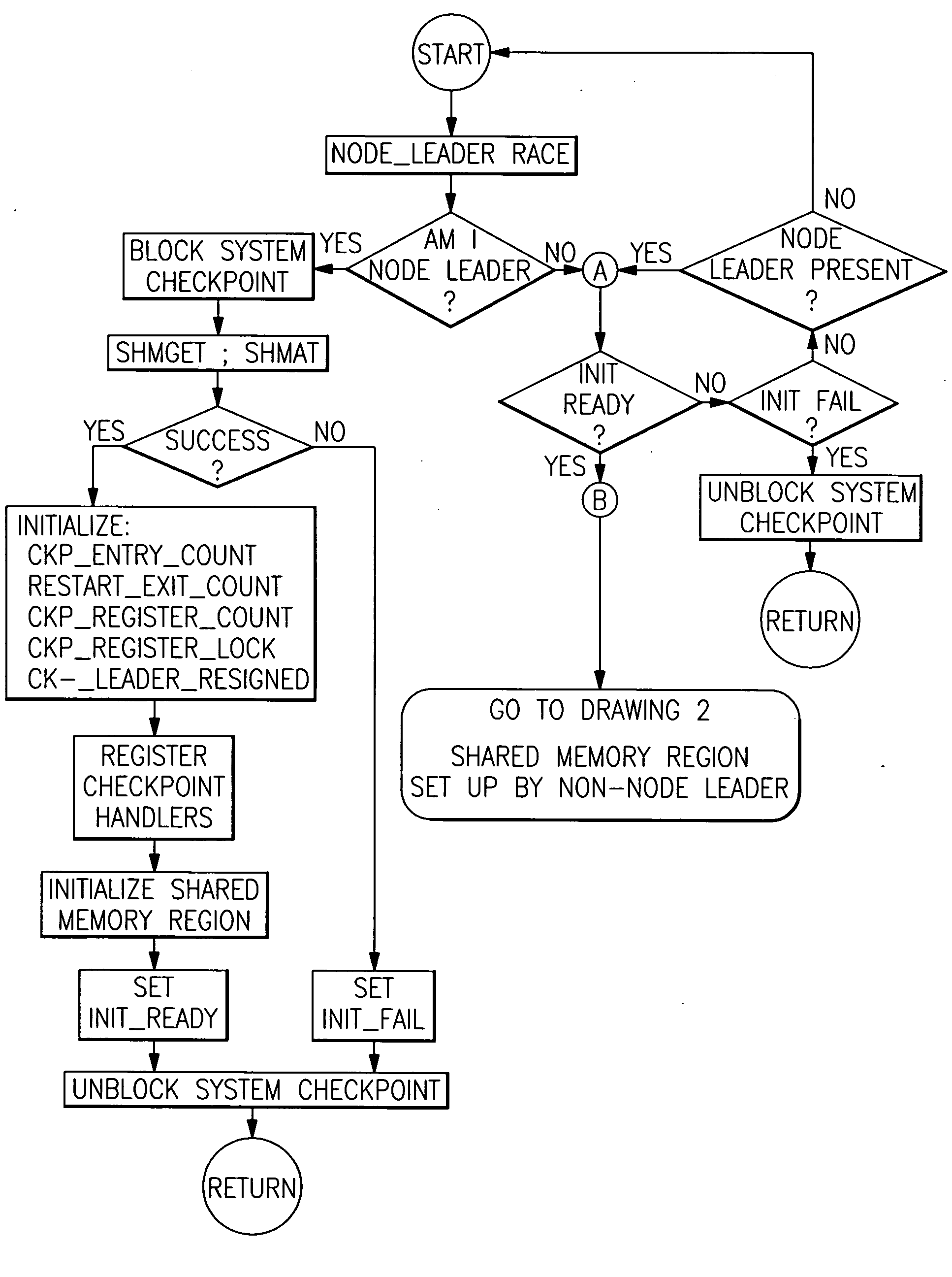
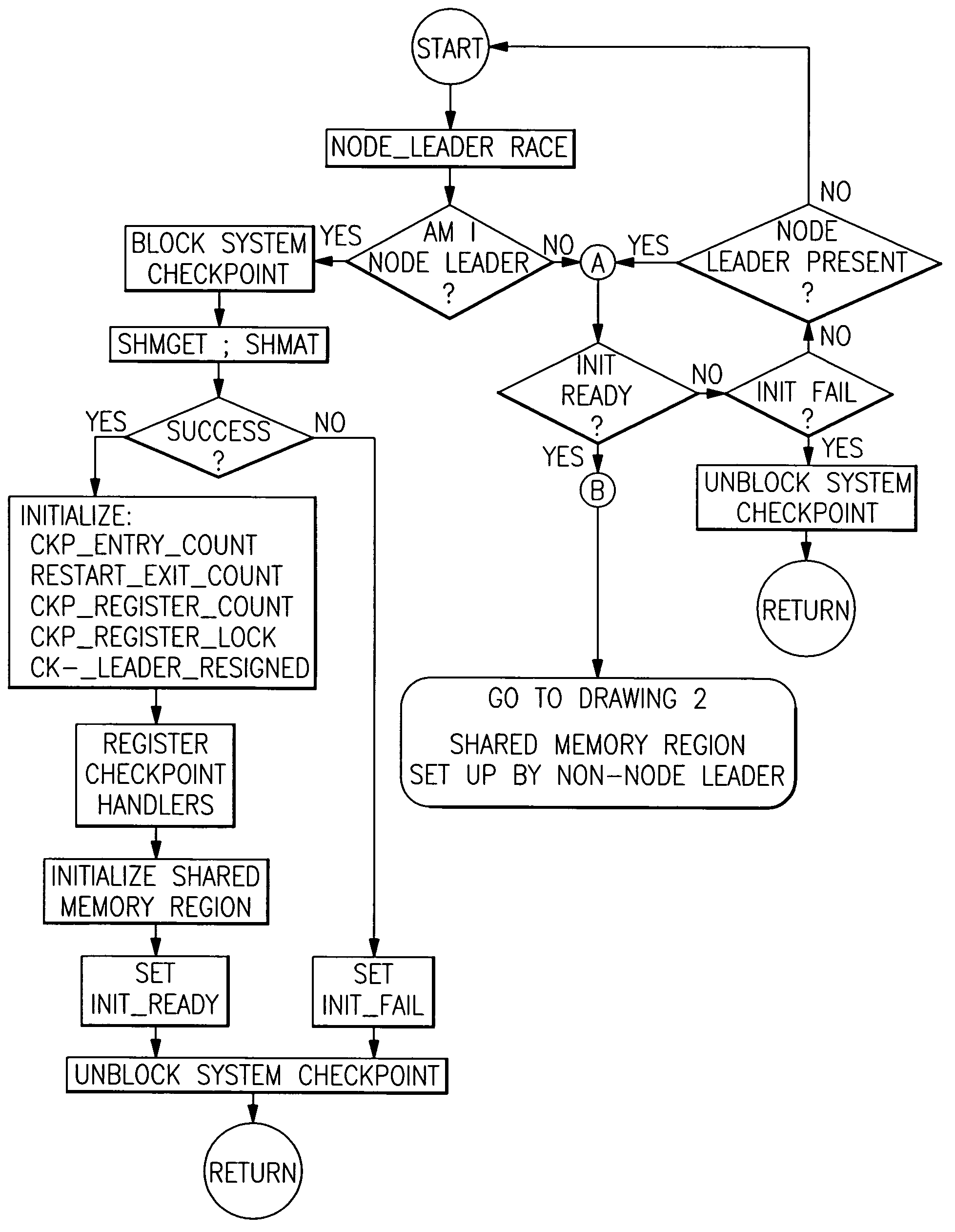
A method is provided in which checkpointing operations are carried out in data processing systems running multiple processes which employ shared memory in a manner which preserves data coherence and integrity but which places no timing restrictions or constraints which require coordination of checkpointing operations. Data structures within local process memory and within shared memory provide the checkpoint operation with application level information concerning shared memory resources specific to at least two processes being checkpointed. Methods are provided for establishing, restoring and releasing shared memory regions that are accessed by multiple cooperating processes.
Owner:META PLATFORMS INC
Memory having improved read capability
In the present invention, a memory, and in particular, a NOR emulating memory comprises a memory controller having a non-volatile memory for storing program code to initiate the operation of the memory controller. The controller has a first bus for receiving address signals from a host device and a second bus for interfacing with a RAM memory, and a third bus for interfacing with a NAND memory. A volatile RAM memory is connected to the second bus. A NAND memory is connected to the third bus. The controller receives commands and a first address from the first bus, and maps the first address to a second address in the NAND memory, and operates the NAND memory in response thereto. The RAM memory serves as cache for data to or from the NAND memory. The controller also maintains data coherence between the data stored in the RAM memory as cache and the data in the NAND memory. The invention further has a first buffer for storing data from the NAND memory in response to a read command to be written to the RAM memory, and a second buffer for storing data from the RAM memory to be written to the NAND memory. In the event of a read operation, if the data from the specified address is in the RAM memory, then the data is read from the RAM memory completing the read operation. In the event of a read operation, and if the data from the specified address is not in the RAM memory, and if there is sufficient space in the RAM memory to store an entire page of data from the NAND memory, then the entire page is read from the NAND memory, stored in the first buffer and then stored in the RAM memory, and from the specified address is read out, completing the read operation. Finally, in the event of a read operation, and if the data from the specified address is not in the RAM memory, and if there is insufficient space in the RAM memory to store an entire page of data from the NAND memory, then an entire page from the RAM memory is first stored in the second buffer, then an entire page is read from the NAND memory, stored in the first buffer, and from the first buffer, stored in the now freed RAM memory and data from the specified address is read out, completing the read operation. The page of data from the second buffer is subsequently stored back into the NAND memory after the completion of the read operation thereby reducing read latency.
Owner:GREENLIANT
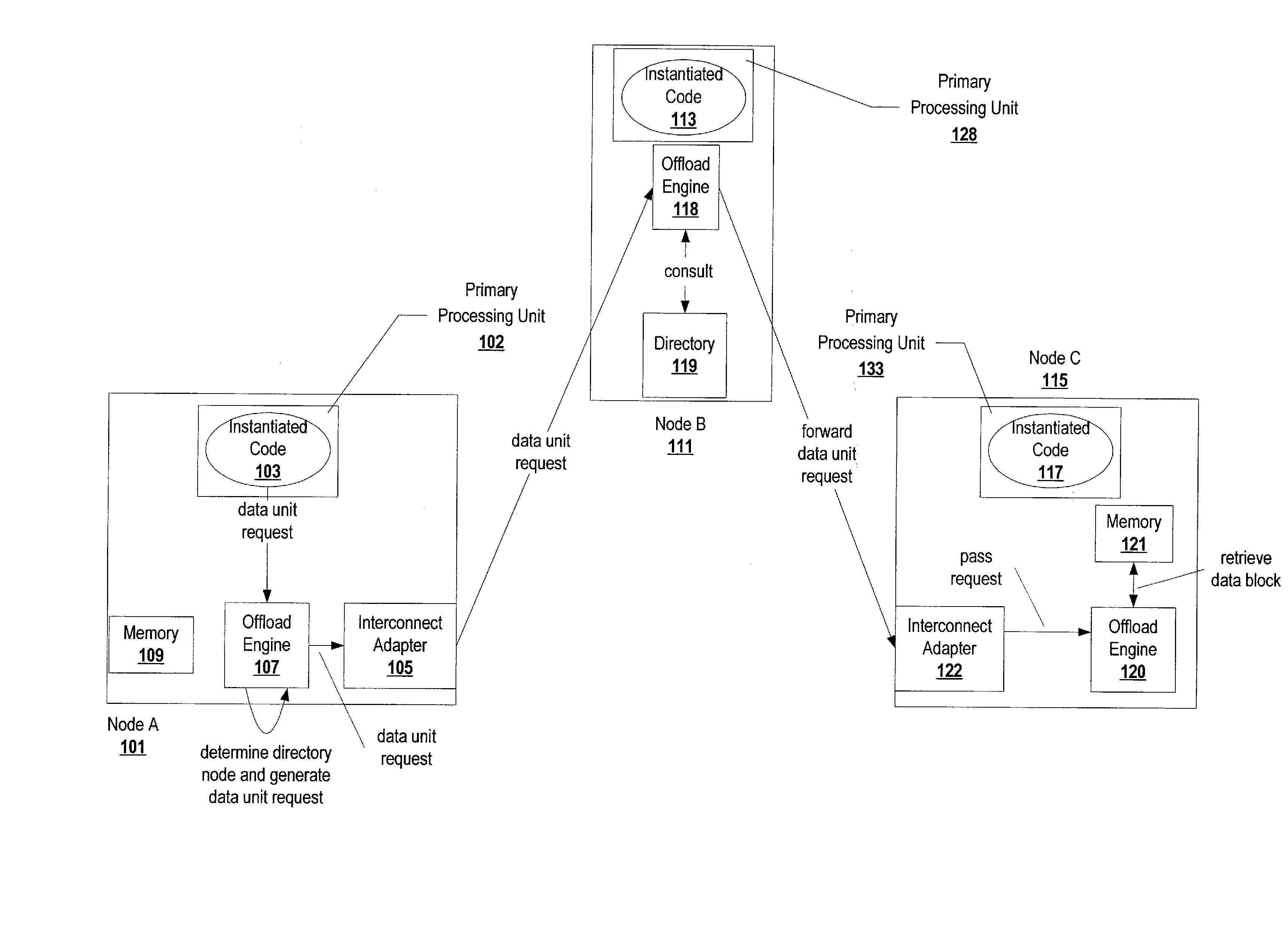
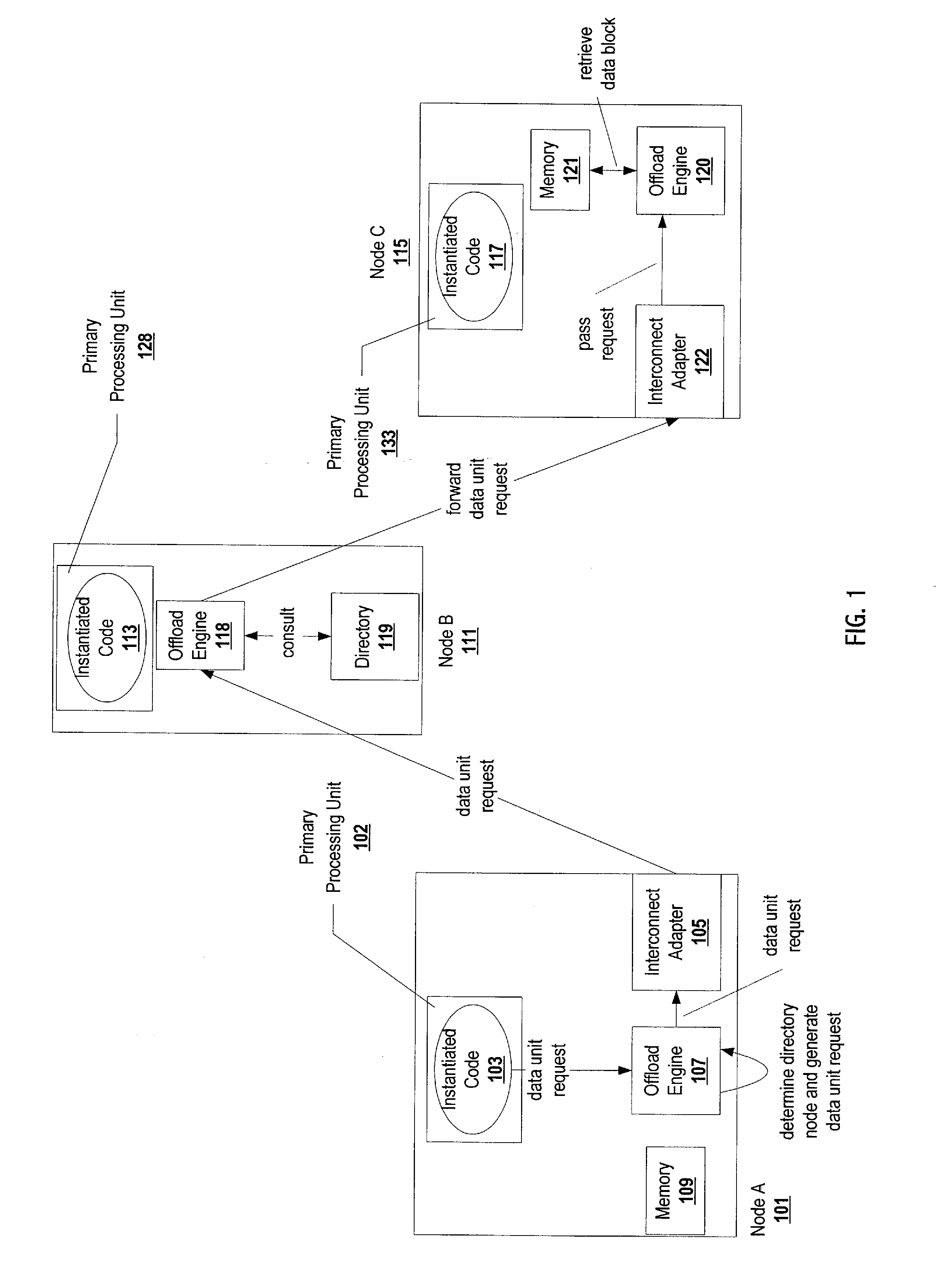
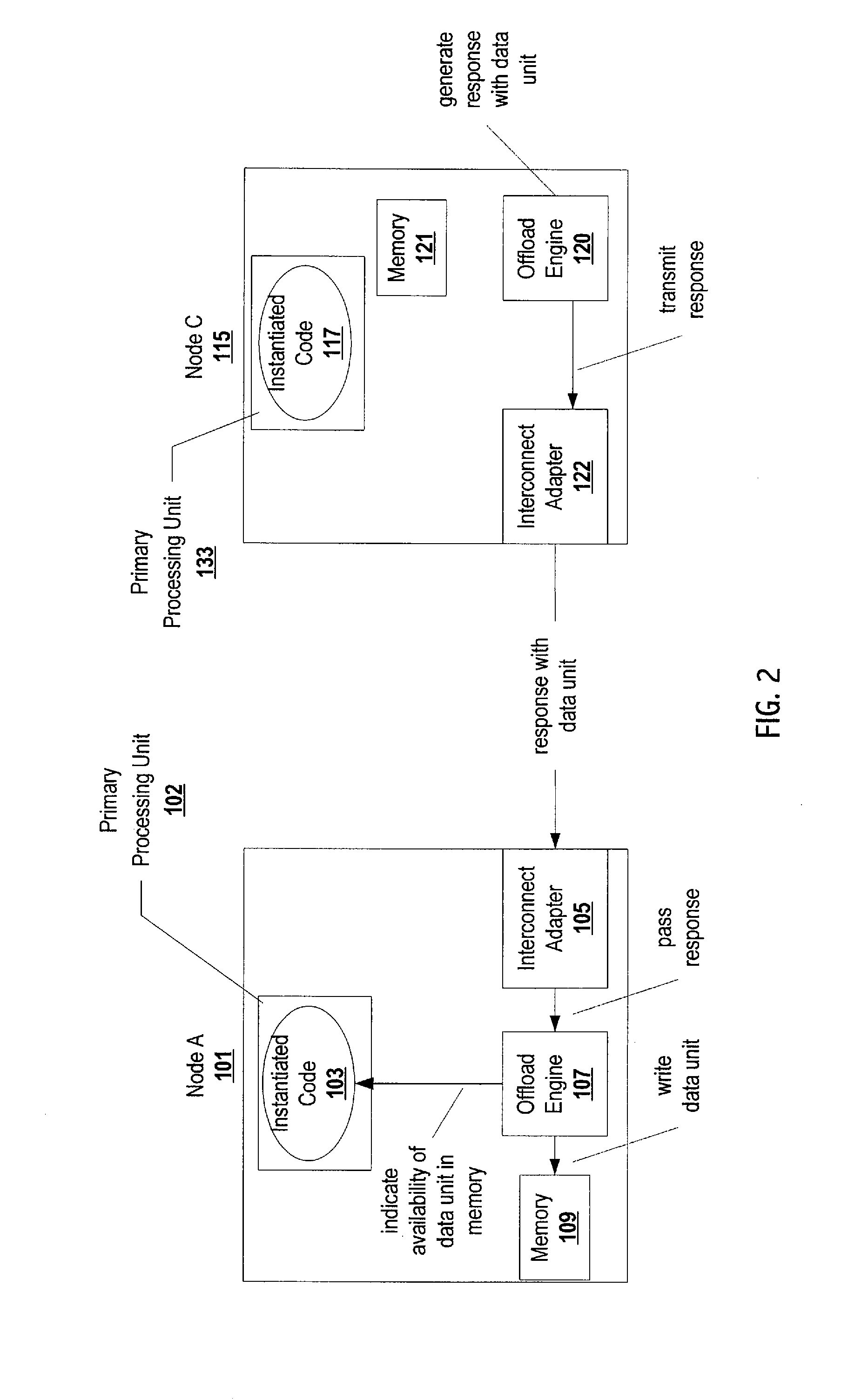
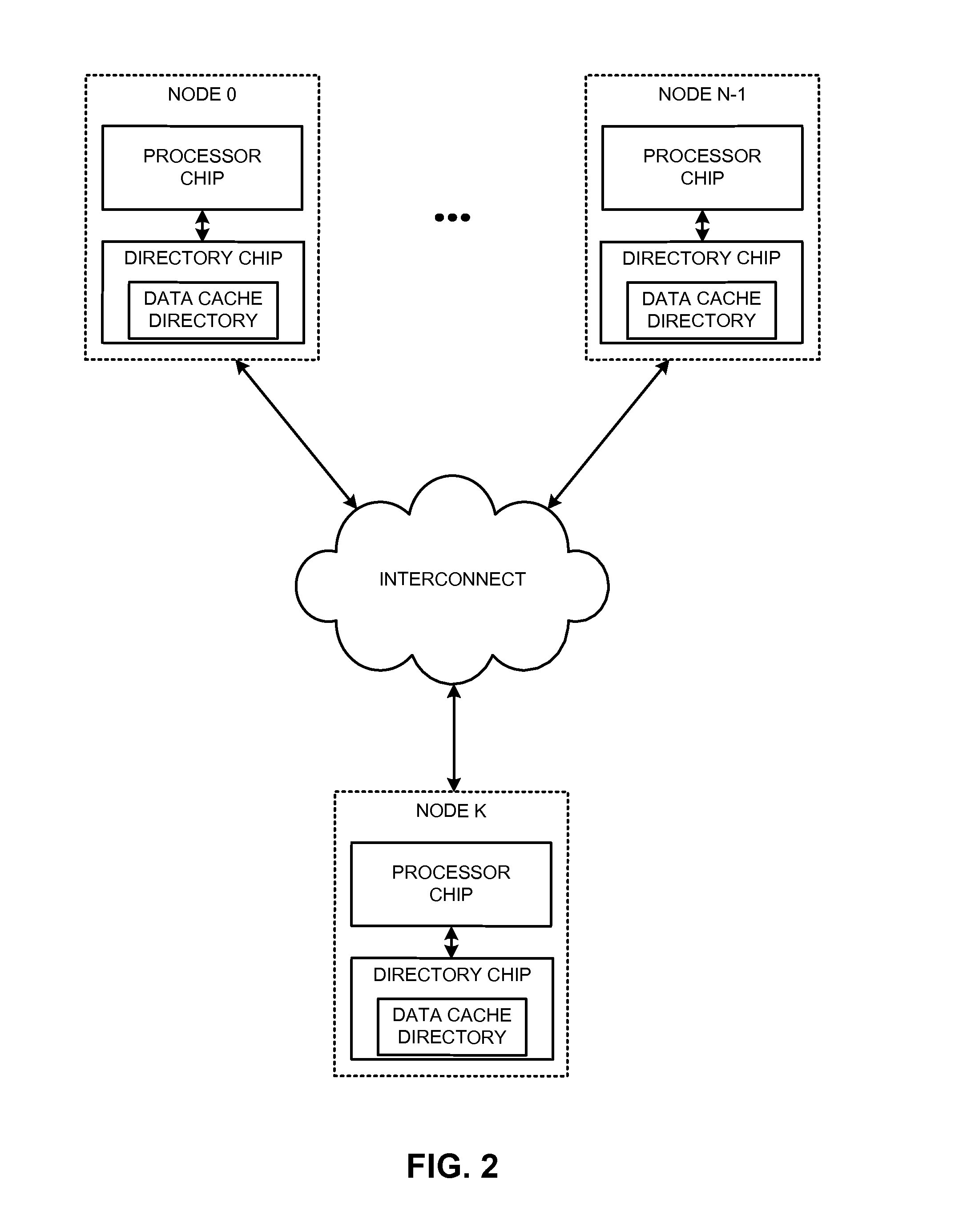
Offloading operations for maintaining data coherence across a plurality of nodes
InactiveUS20080065835A1Reduce the burden onFree resourceTransmissionMemory systemsData coherenceMain processing unit
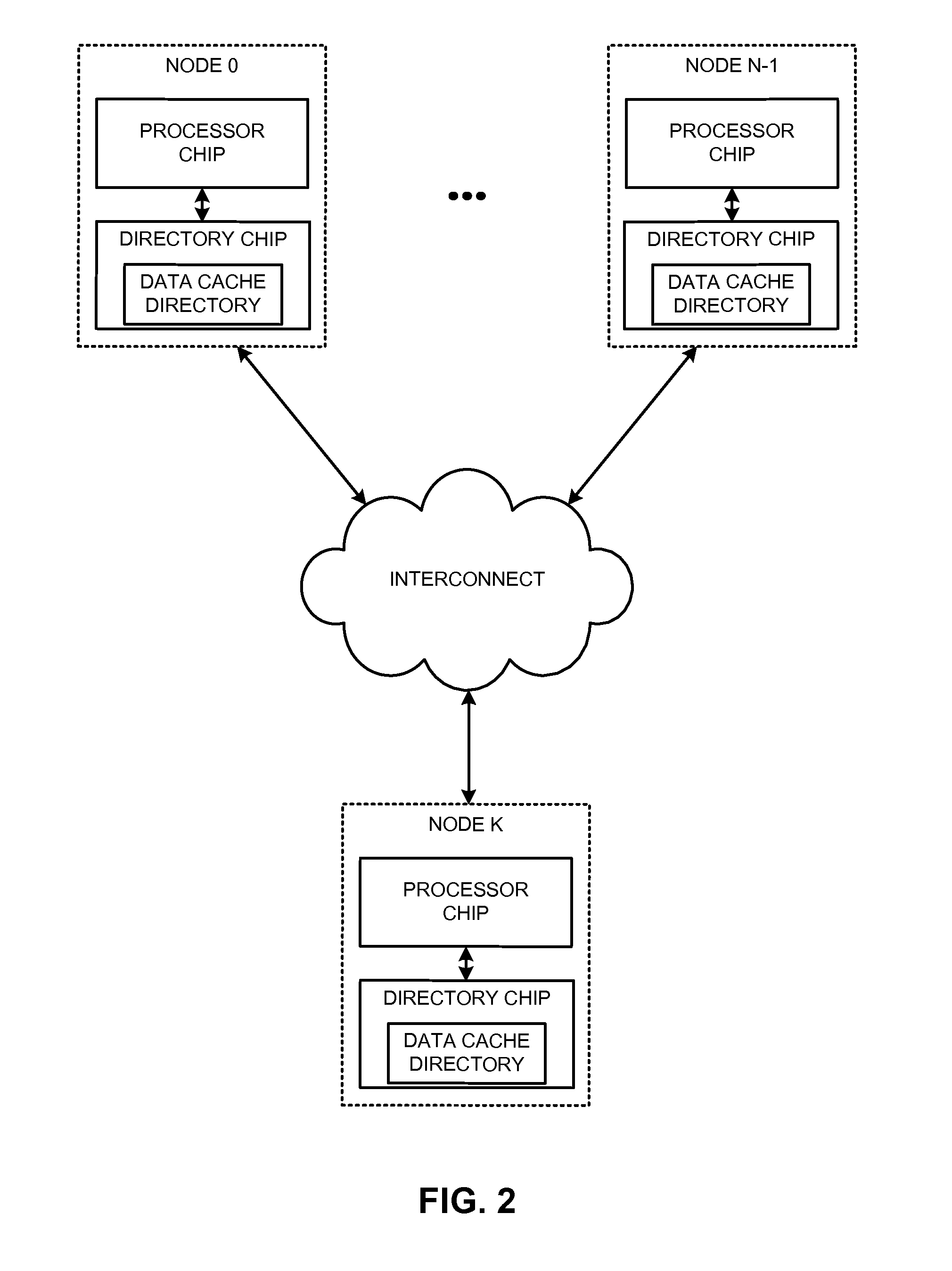
Offloading data coherence operations from a primary processing unit(s) executing instantiated code responsible for data coherence in a shared-cache cluster to a data coherence offload engine reduces resource consumption and allows for efficient sharing of data in accordance with the data coherence protocol. Some of the data coherence operations, such as consulting and maintaining a directory, generating messages, and writing a data unit can be performed by a data coherence offload engine. The data coherence offload engine indicates availability of the data unit in the memory to the appropriate instantiated code. Hence, the instantiated code (the corresponding primary processing unit) is no longer burdened with some of the work load of data coherence operations. Migration of tasks from a primary processing unit(s) to data coherence offload engines allows for efficient retrieval and writing of a requested data unit.
Owner:SUN MICROSYSTEMS INC
Using a shared last-level tlb to reduce address-translation latency
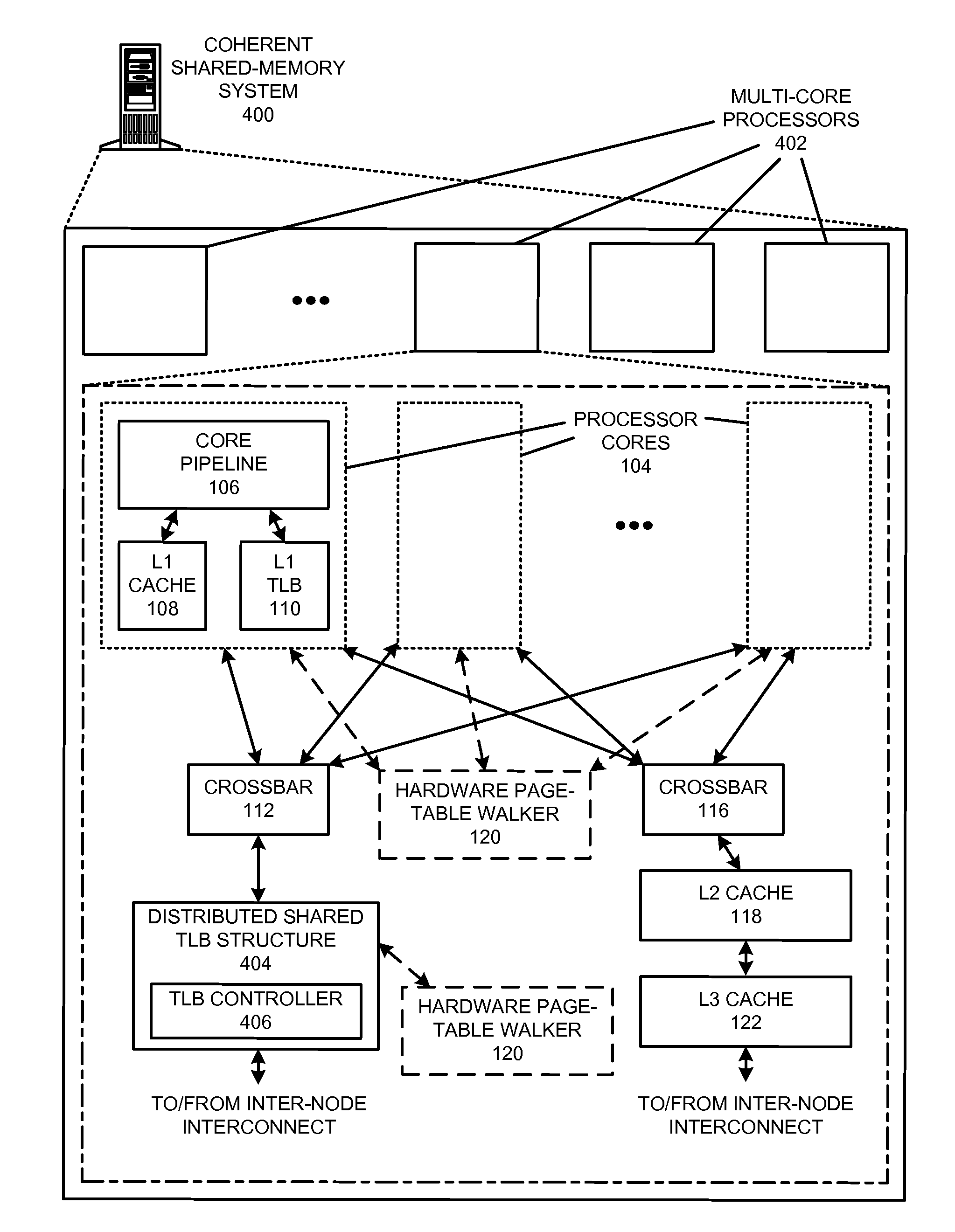
ActiveUS20140052917A1Increase the number ofEasy to identifyMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationData coherenceCache access
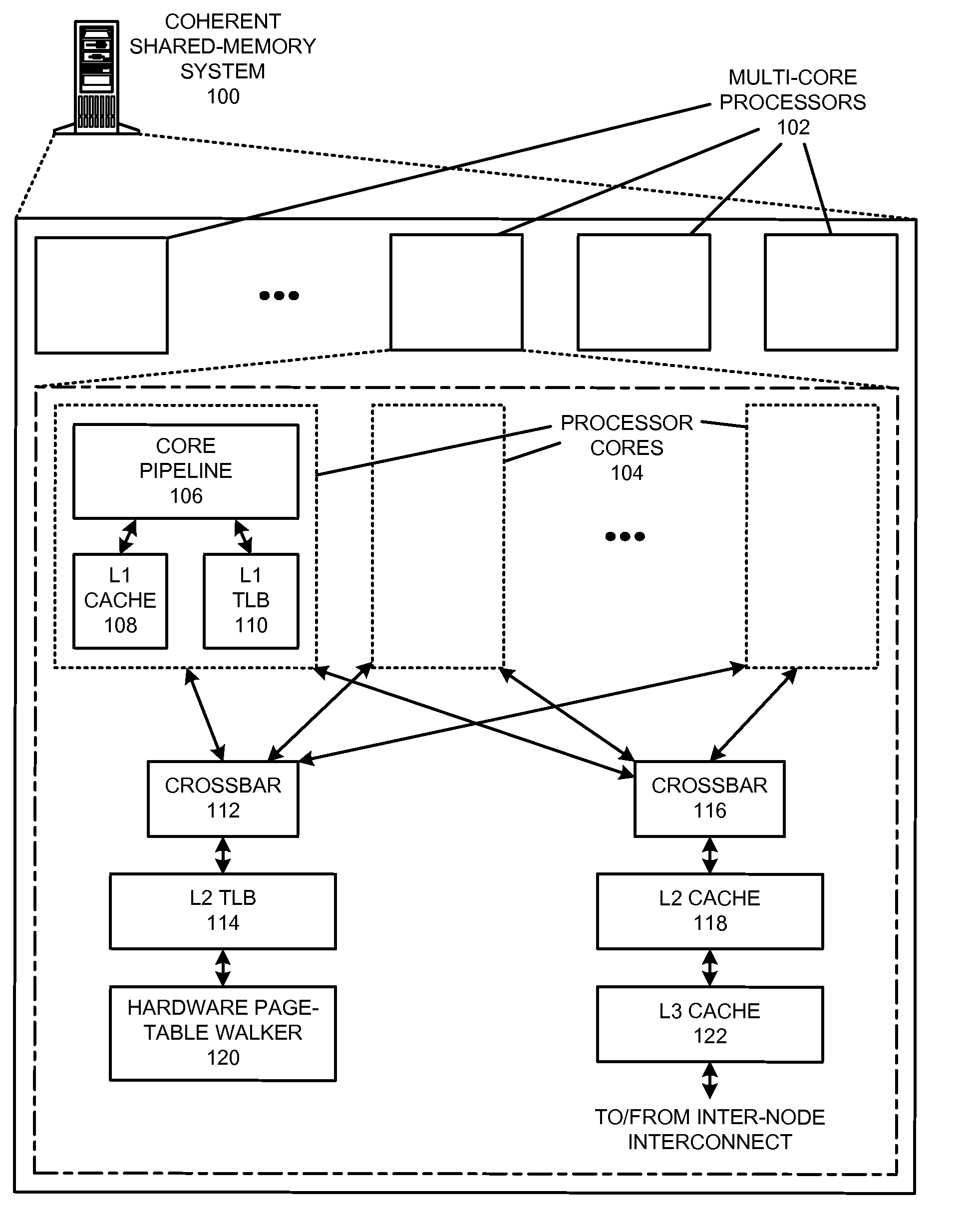
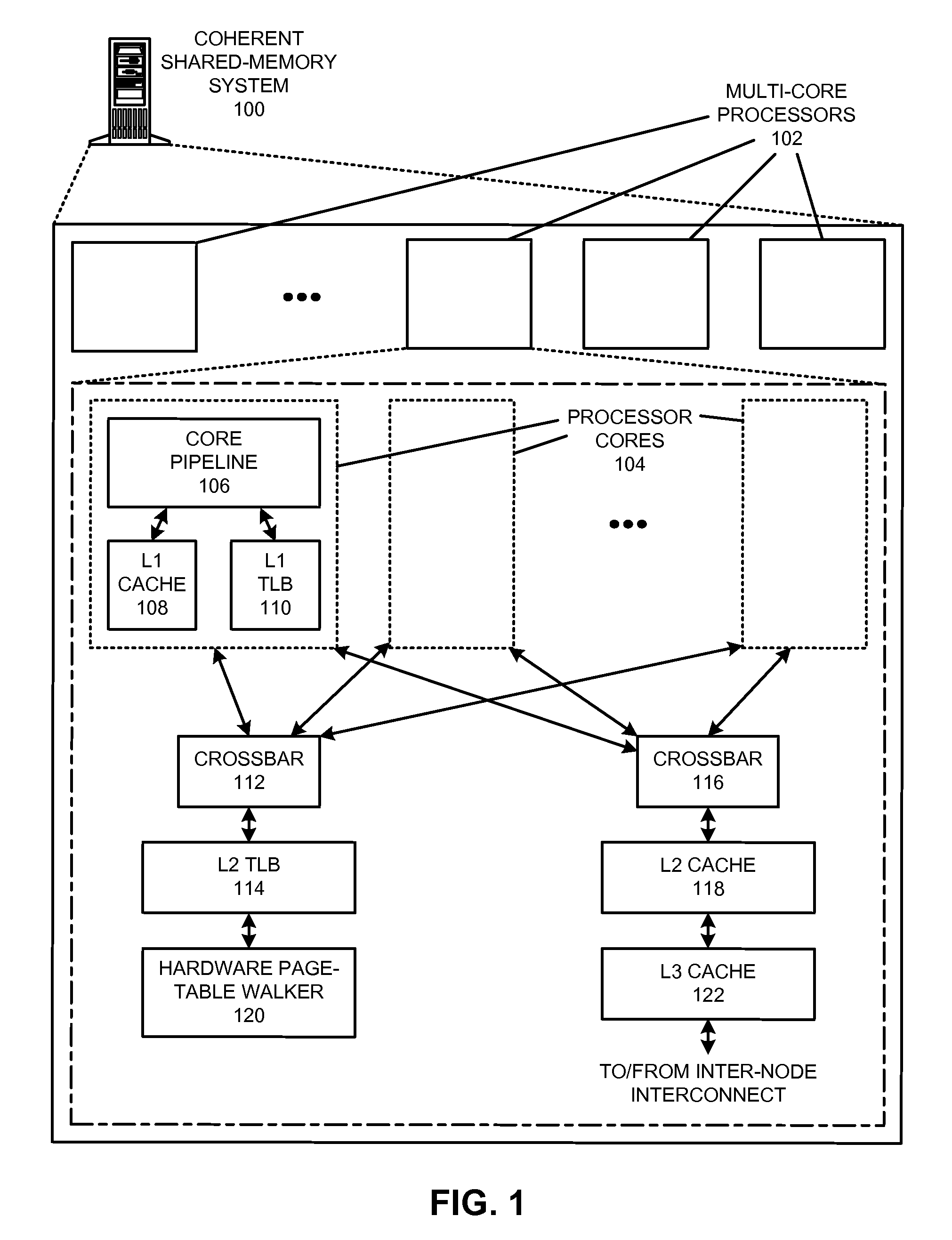
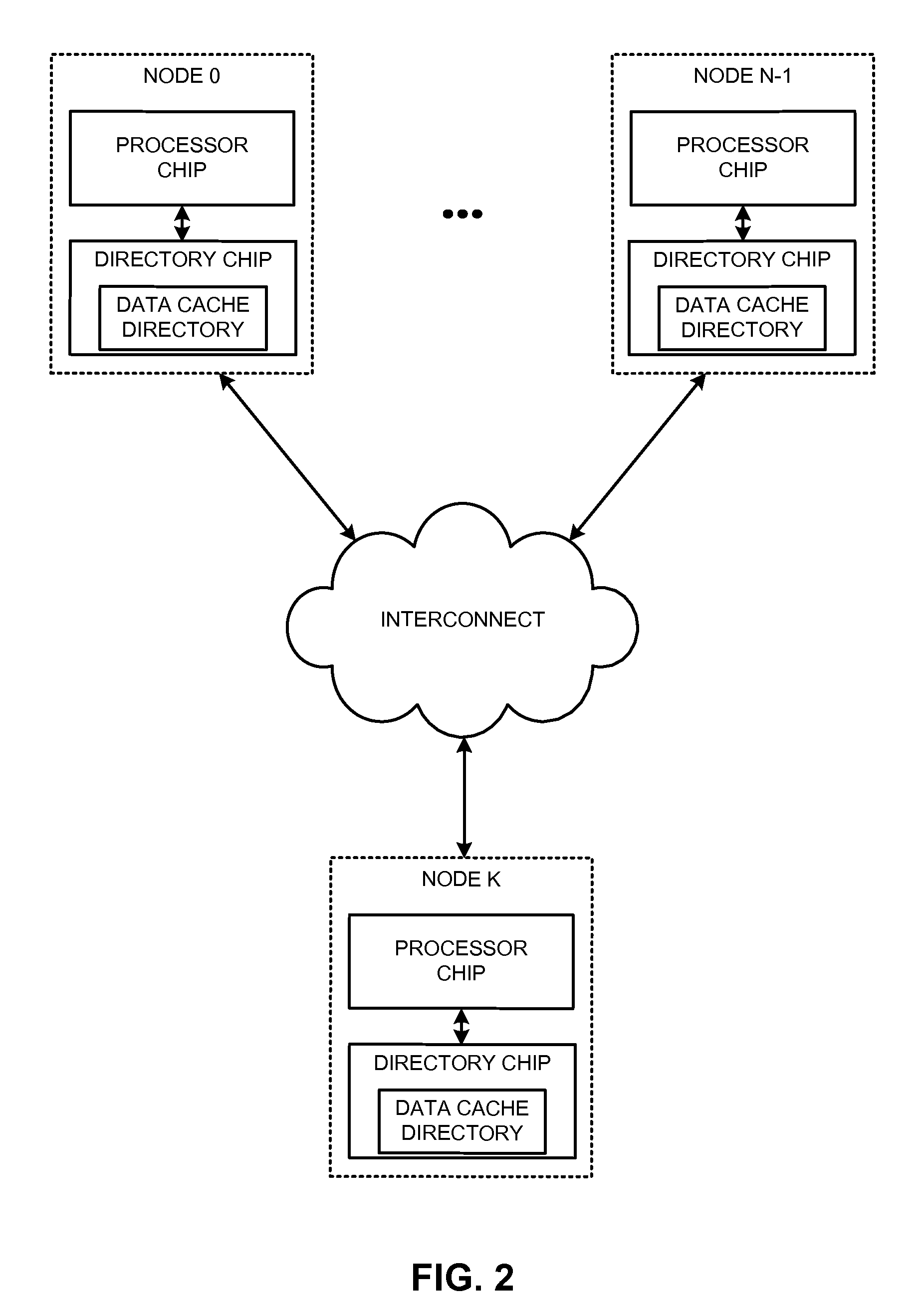
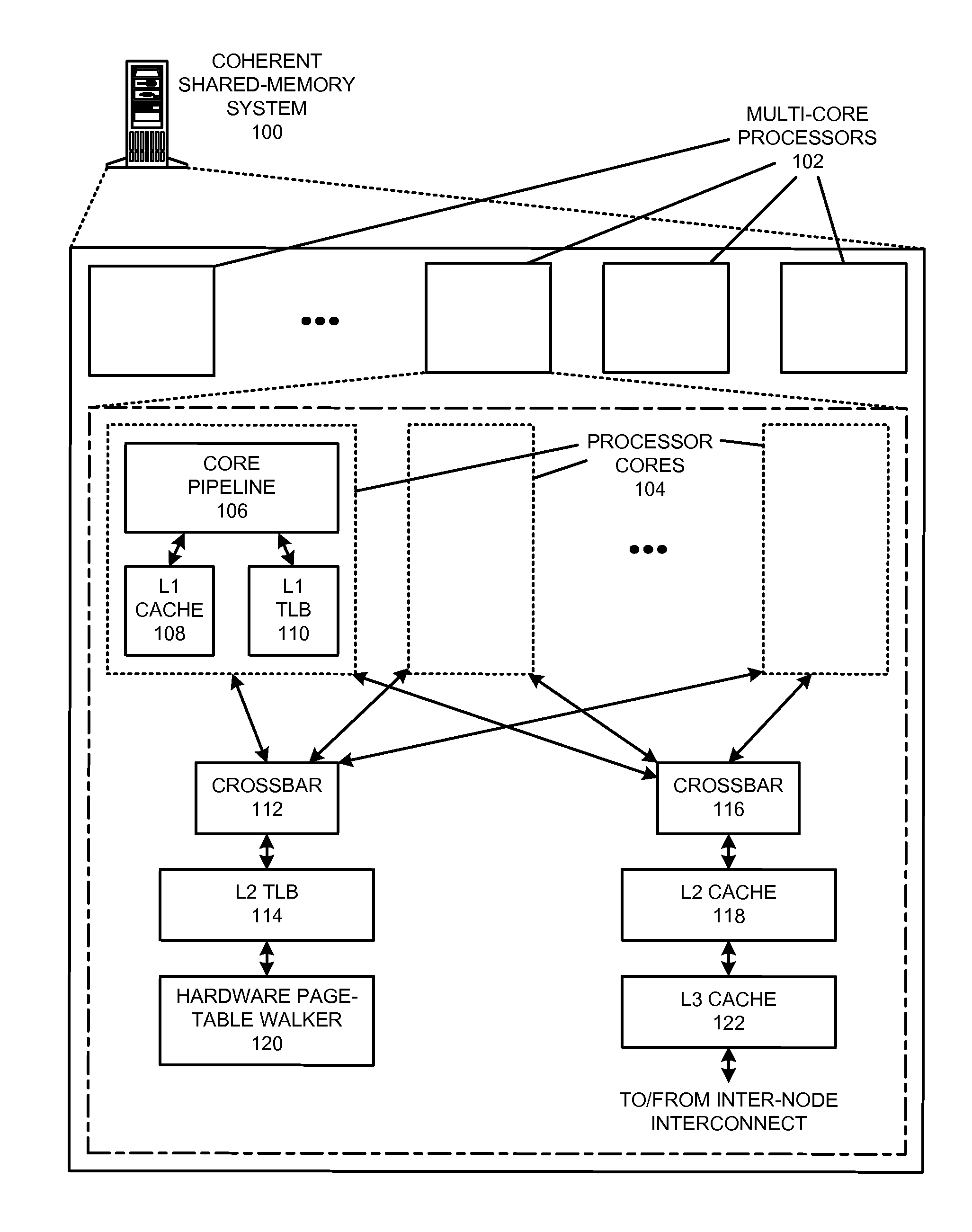
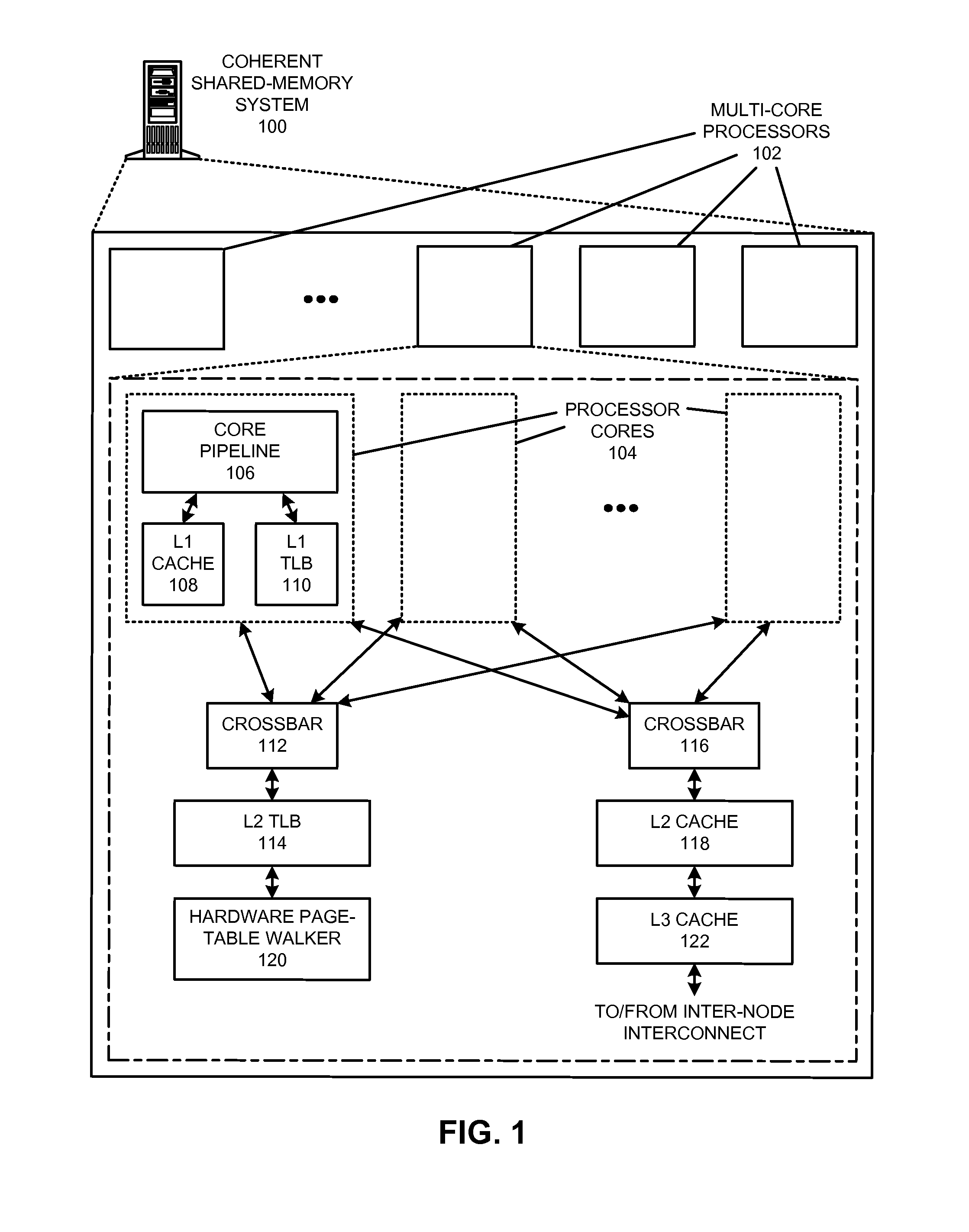
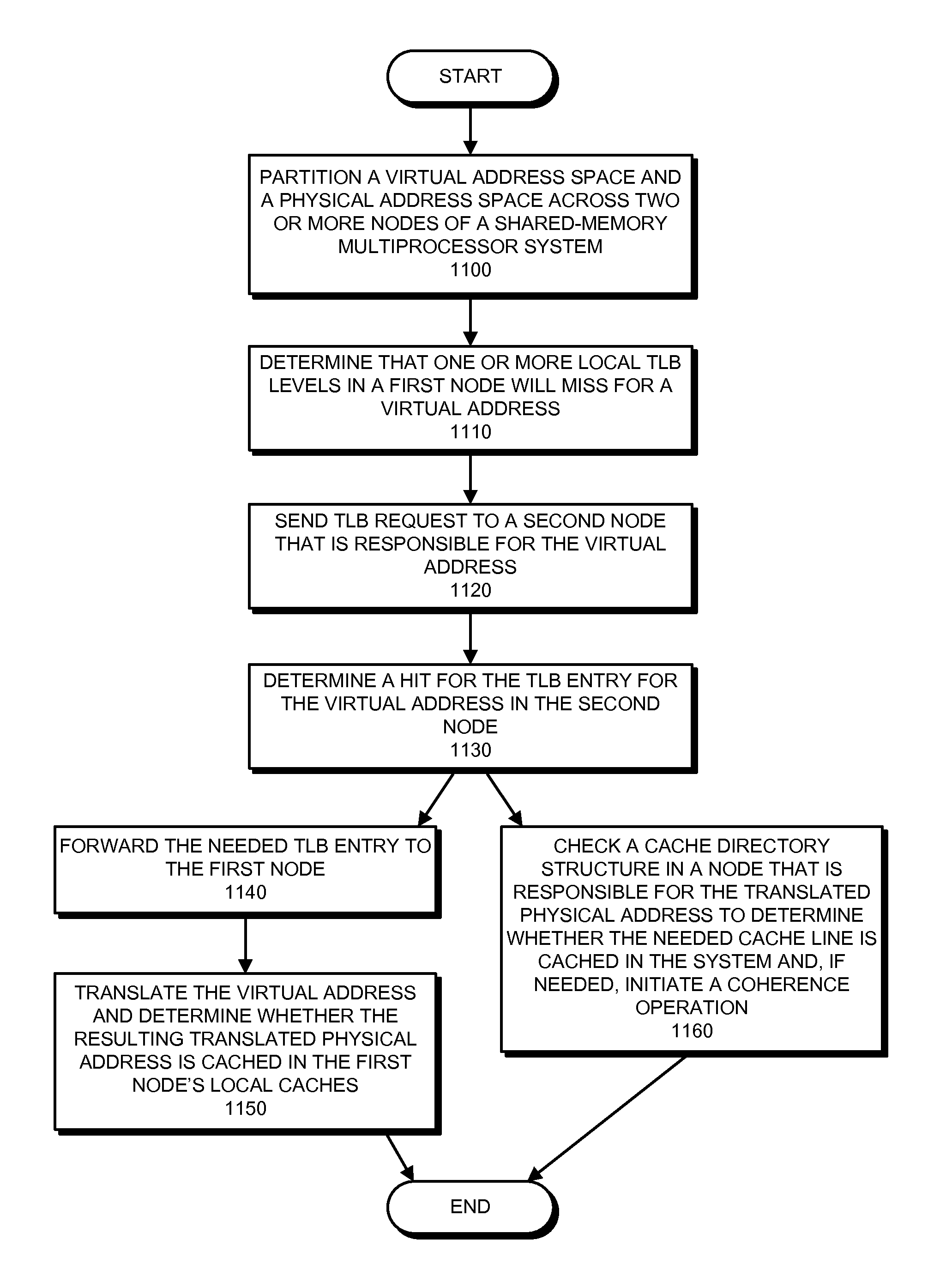
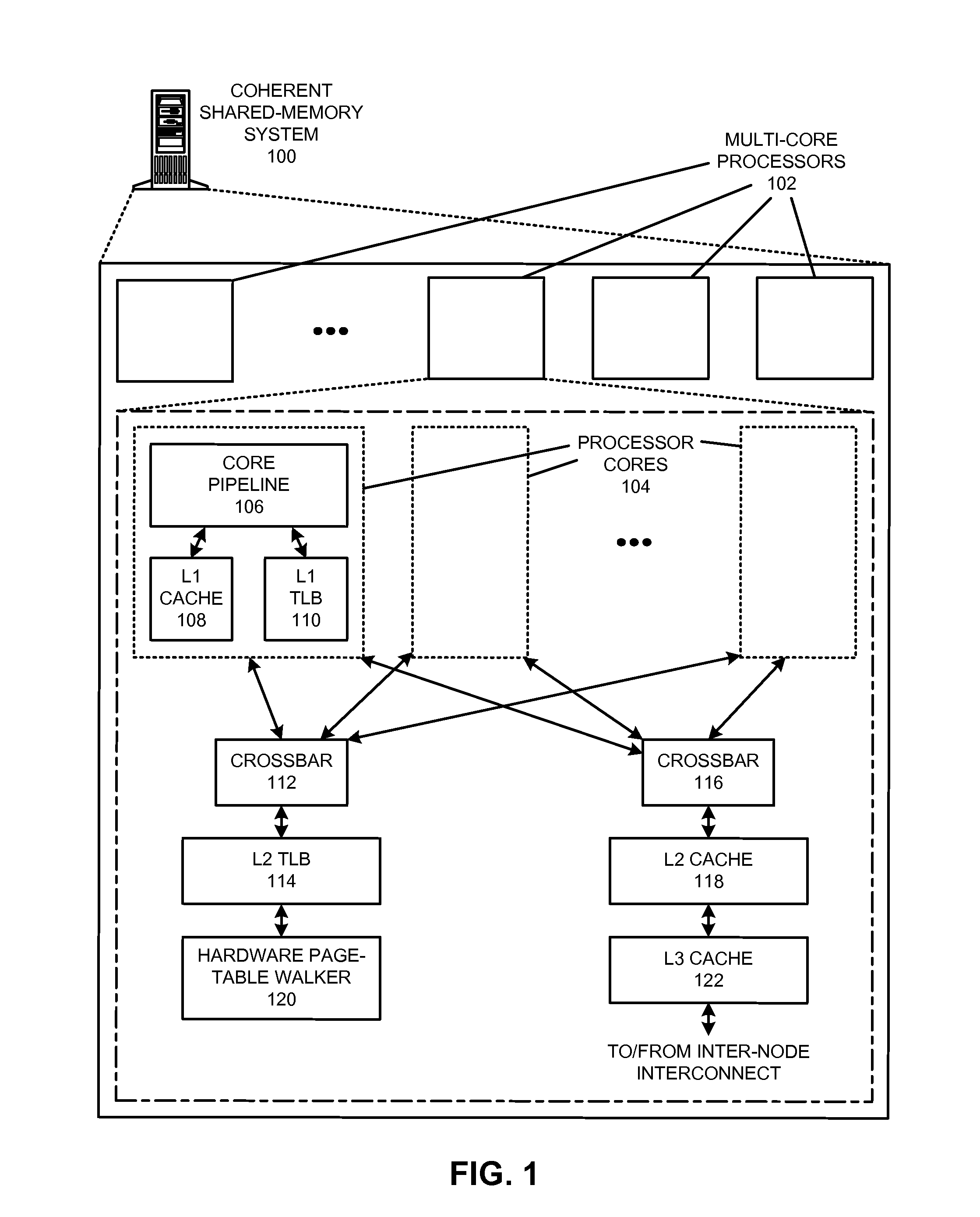
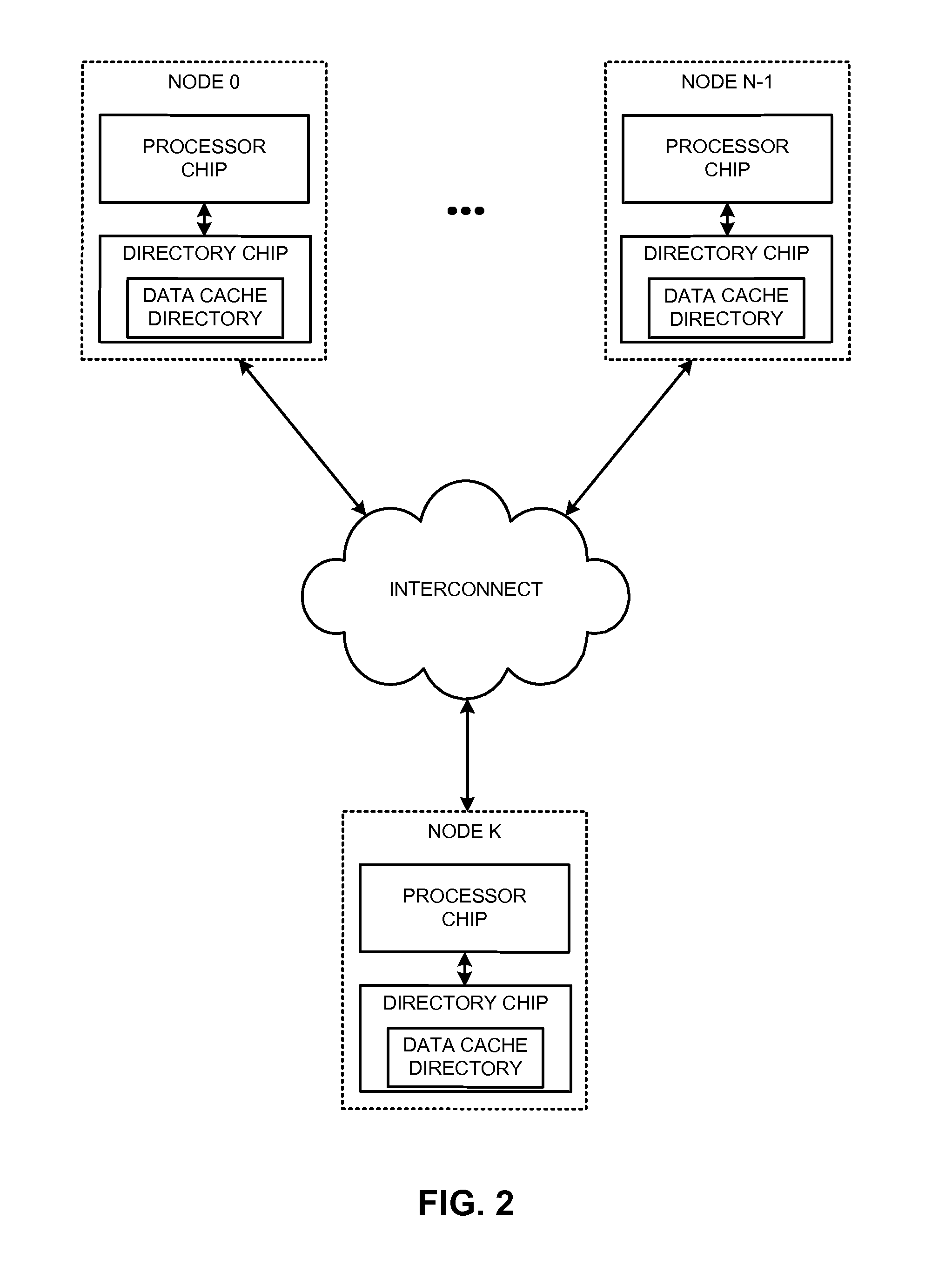
The disclosed embodiments provide techniques for reducing address-translation latency and the serialization latency of combined TLB and data cache misses in a coherent shared-memory system. For instance, the last-level TLB structures of two or more multiprocessor nodes can be configured to act together as either a distributed shared last-level TLB or a directory-based shared last-level TLB. Such TLB-sharing techniques increase the total amount of useful translations that are cached by the system, thereby reducing the number of page-table walks and improving performance. Furthermore, a coherent shared-memory system with a shared last-level TLB can be further configured to fuse TLB and cache misses such that some of the latency of data coherence operations is overlapped with address translation and data cache access latencies, thereby further improving the performance of memory operations.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Bidirectional similarity of signals
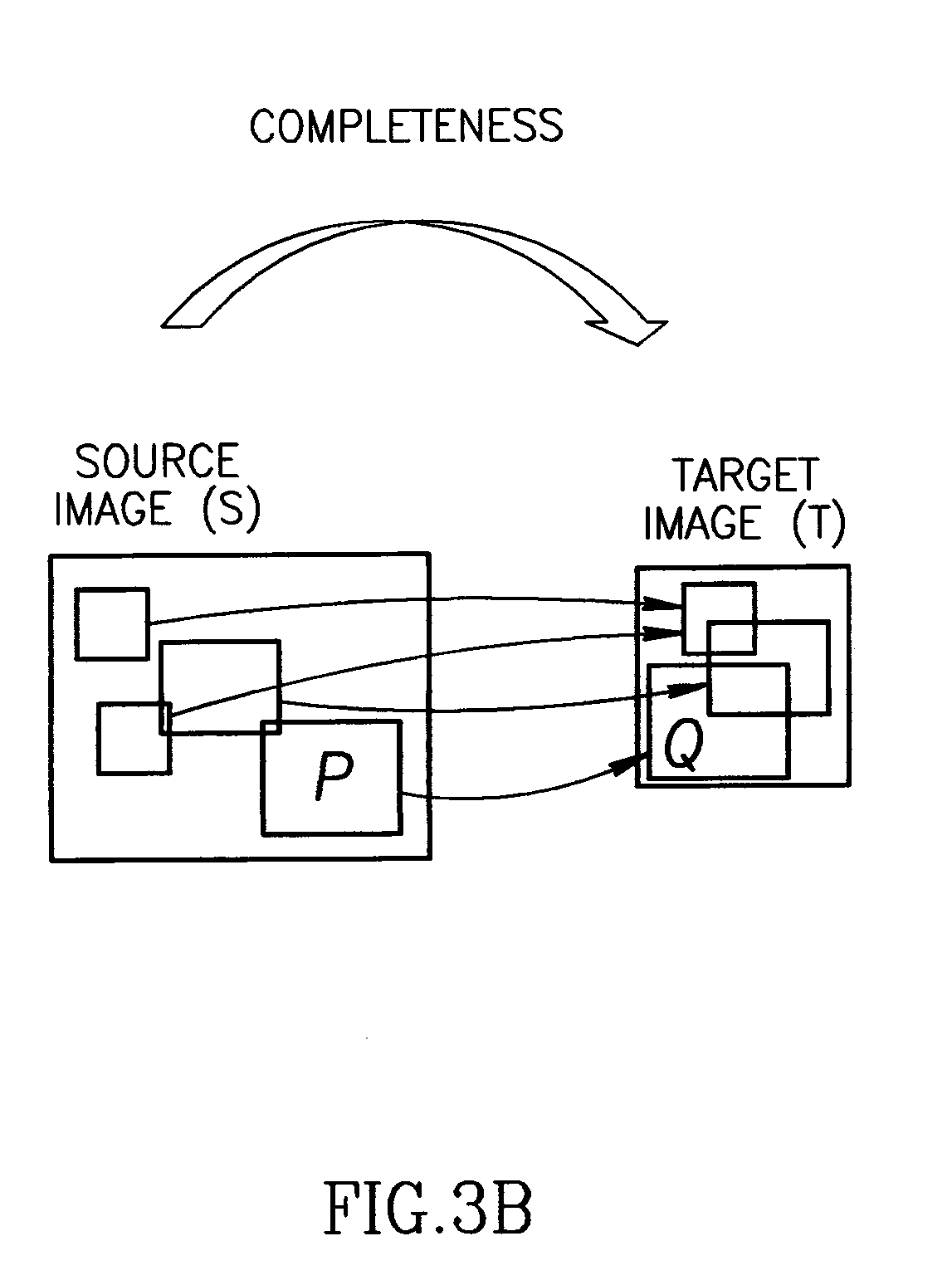
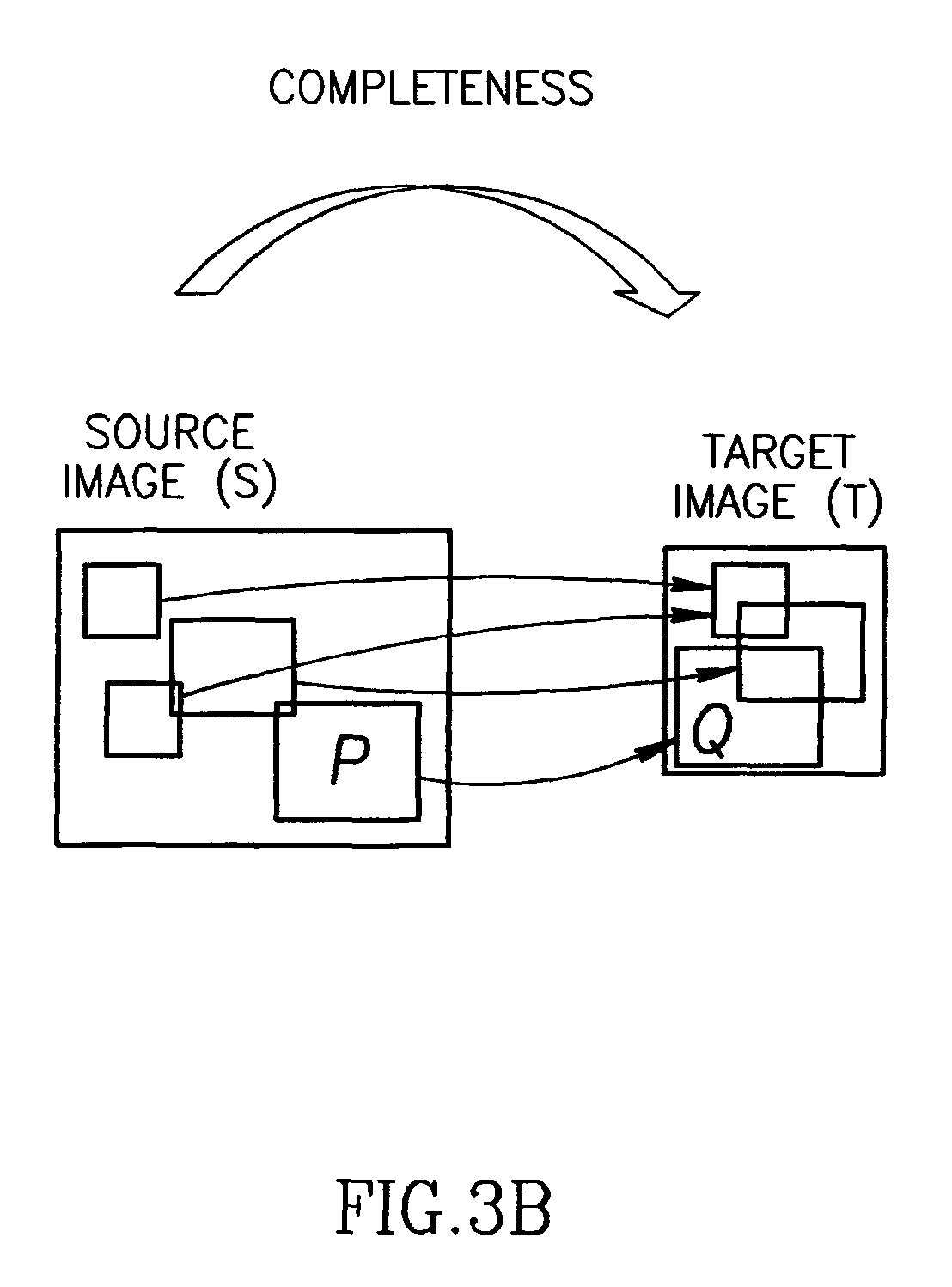
ActiveUS20100177955A1Improve matching speedImprove coherenceDigital data information retrievalGeometric image transformationData coherenceData integrity
A method for measuring bi-directional similarity between a first signal of a first size and a second signal of a second size includes matching at least some patches of the first signal with patches of the second signal for data completeness, matching at least some patches of the second signal with patches of the first signal for data coherence, calculating the bi-directional similarity measure as a function of the matched patches for coherence and the matched patches for completeness and indicating the similarity between the first signal and the second signal. Another method generates a second signal from a first signal where the second signal is different than the first signal by at least one parameter. The method includes attempting to maximize a bi-directional similarity measure between the second signal and the first signal.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
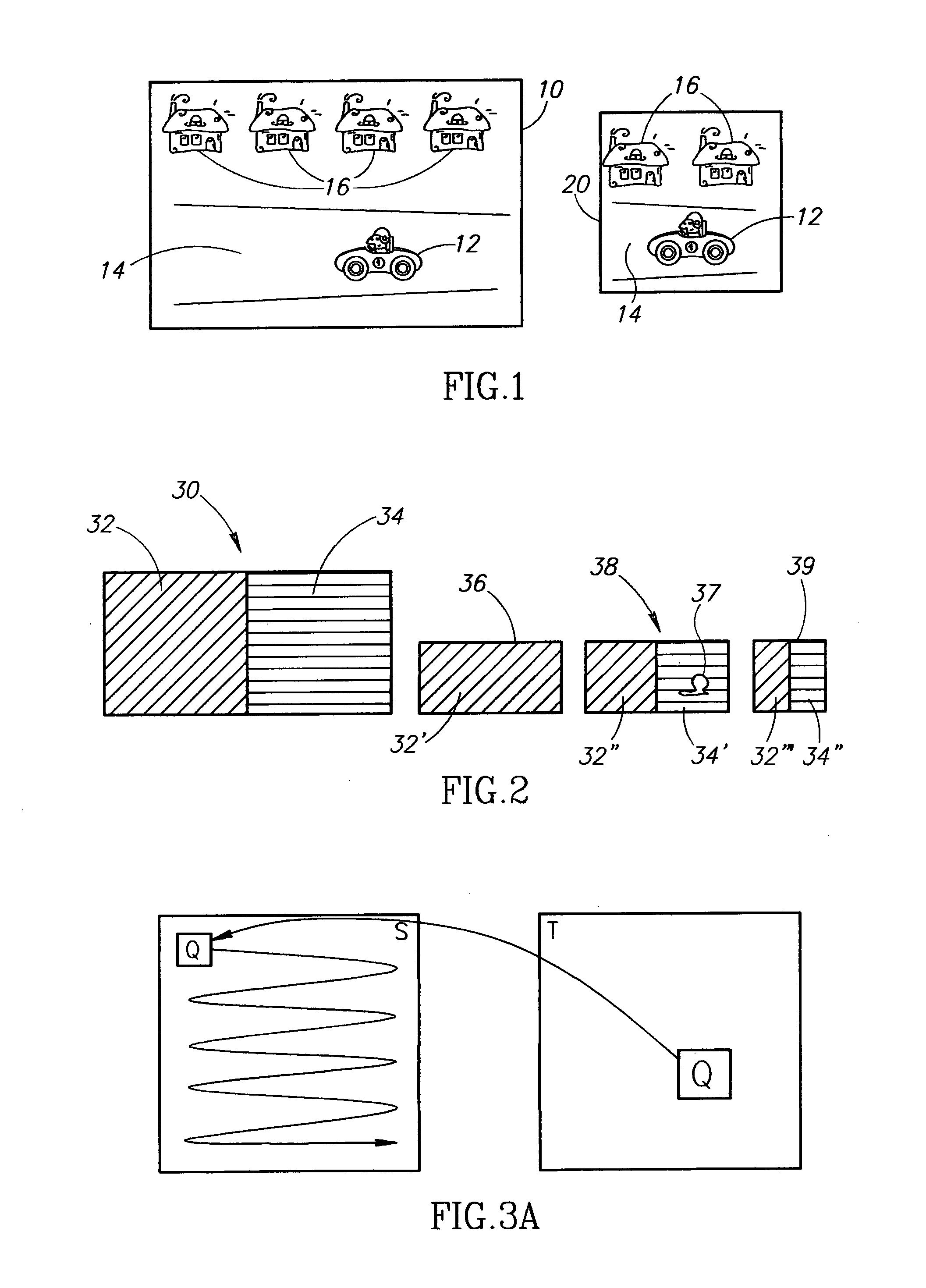
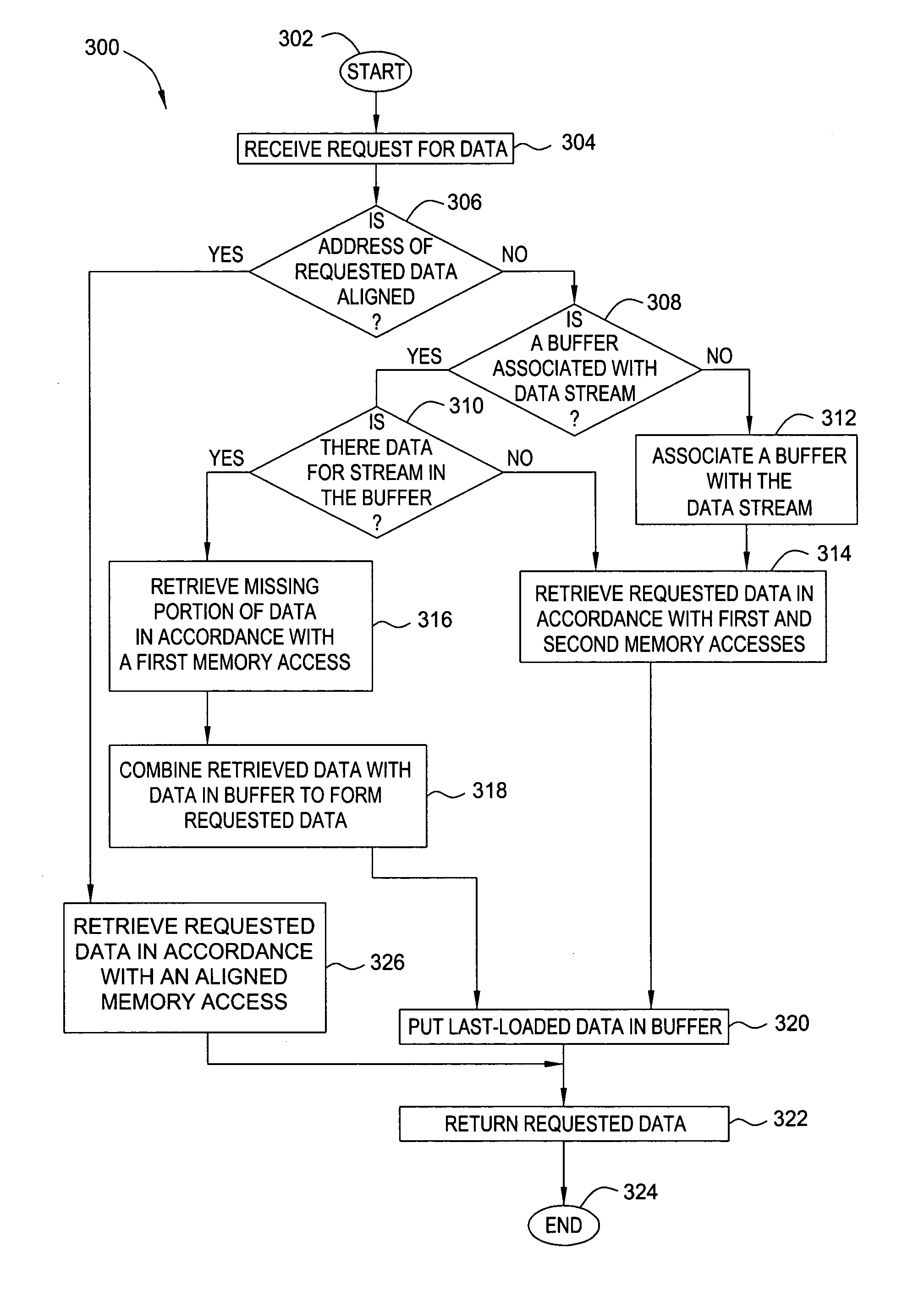
Method and apparatus for accessing misaligned data streams
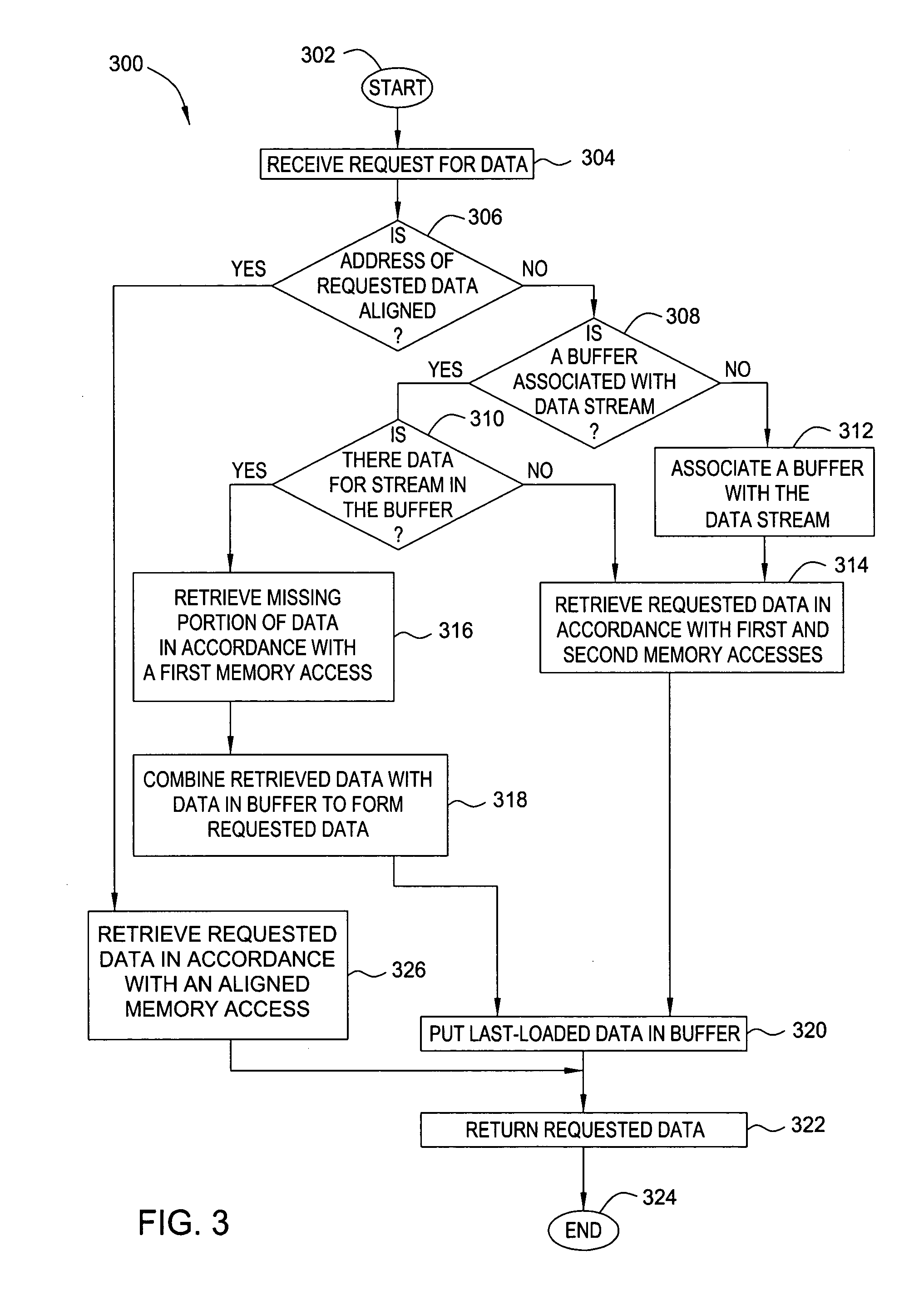
InactiveUS20070050592A1Reduce in quantityReduce needMemory adressing/allocation/relocationMicro-instruction address formationData coherenceData stream
One embodiment of the present method and apparatus for accessing misaligned data streams includes receiving a data request, where the data request includes a request for misaligned data, and retrieving at least a portion of the requested data from a data stream buffer associated with the data stream. If the data retrieved from the data stream buffer does not comprise all of the requested data, the remainder of the requested data is retrieved from memory and combined with the data stream buffer data. In this manner, the number of memory accesses necessary to retrieve the requested misaligned data is reduced. Additional embodiments of the present invention include mechanisms for ensuring data coherence with respect to write updates and protocol requests. Moreover, the present invention advantageously reduces the need for pipeline upset events / pipeline hazards that typically result in performance degradation in pipelined microprocessors.
Owner:IBM CORP
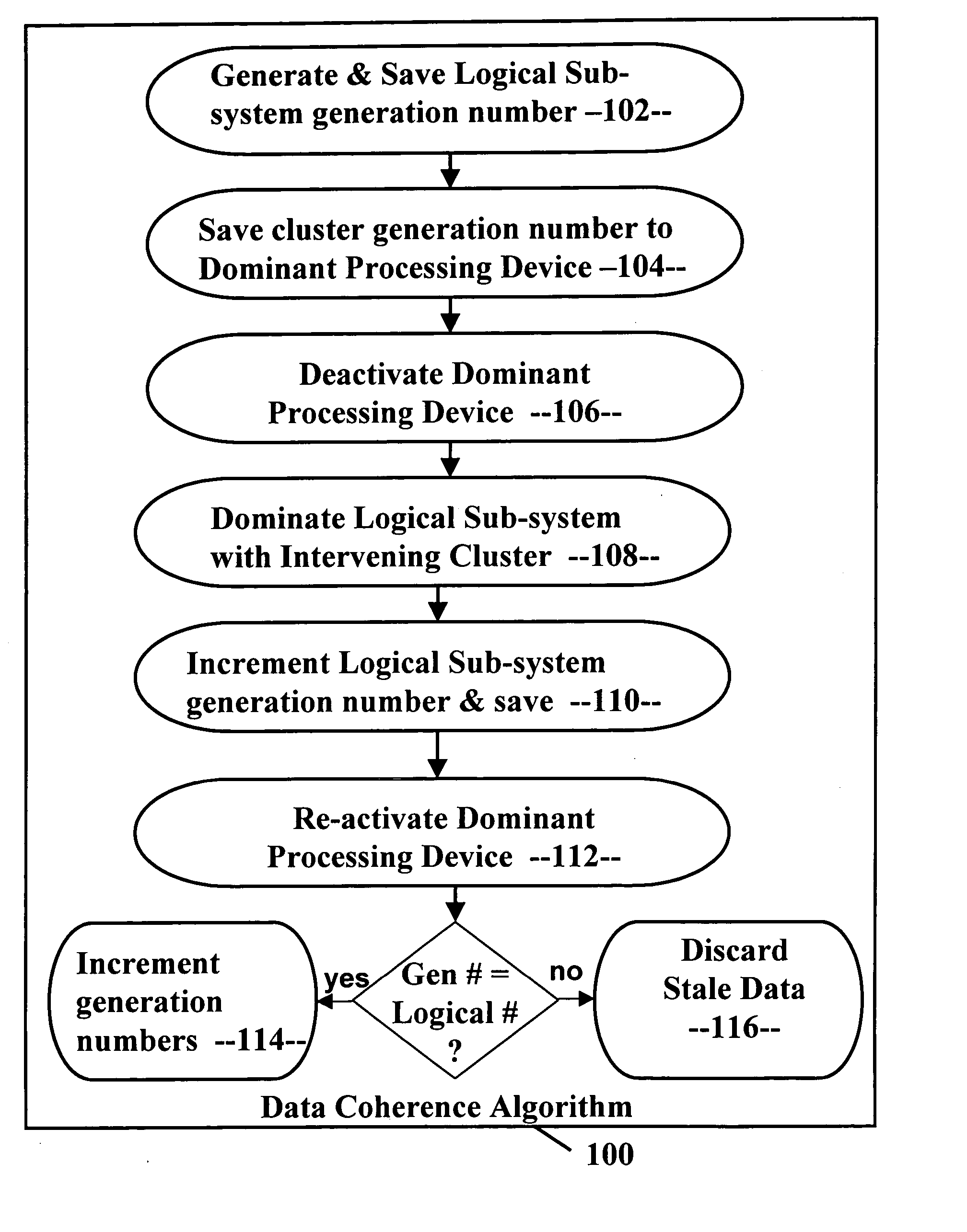
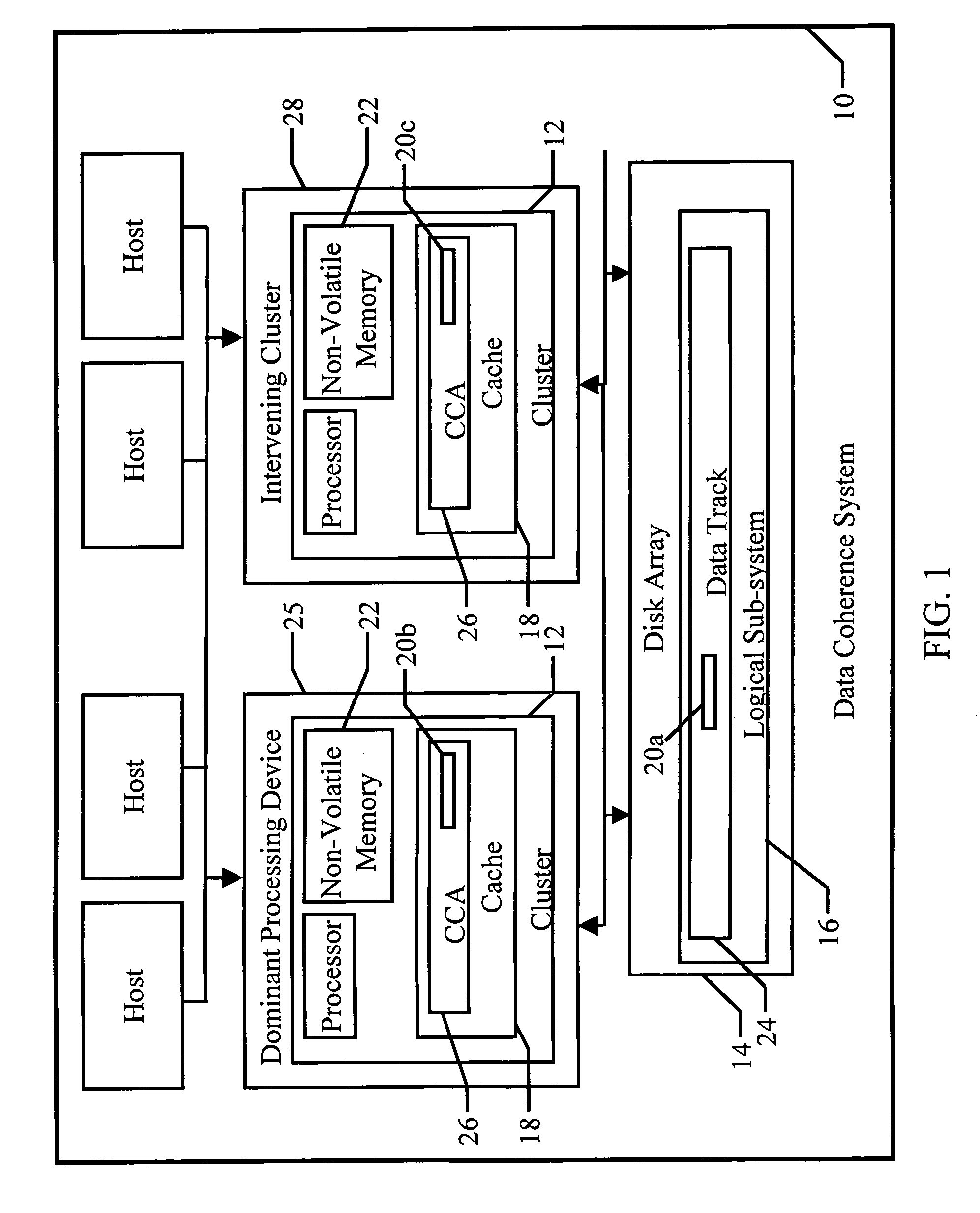
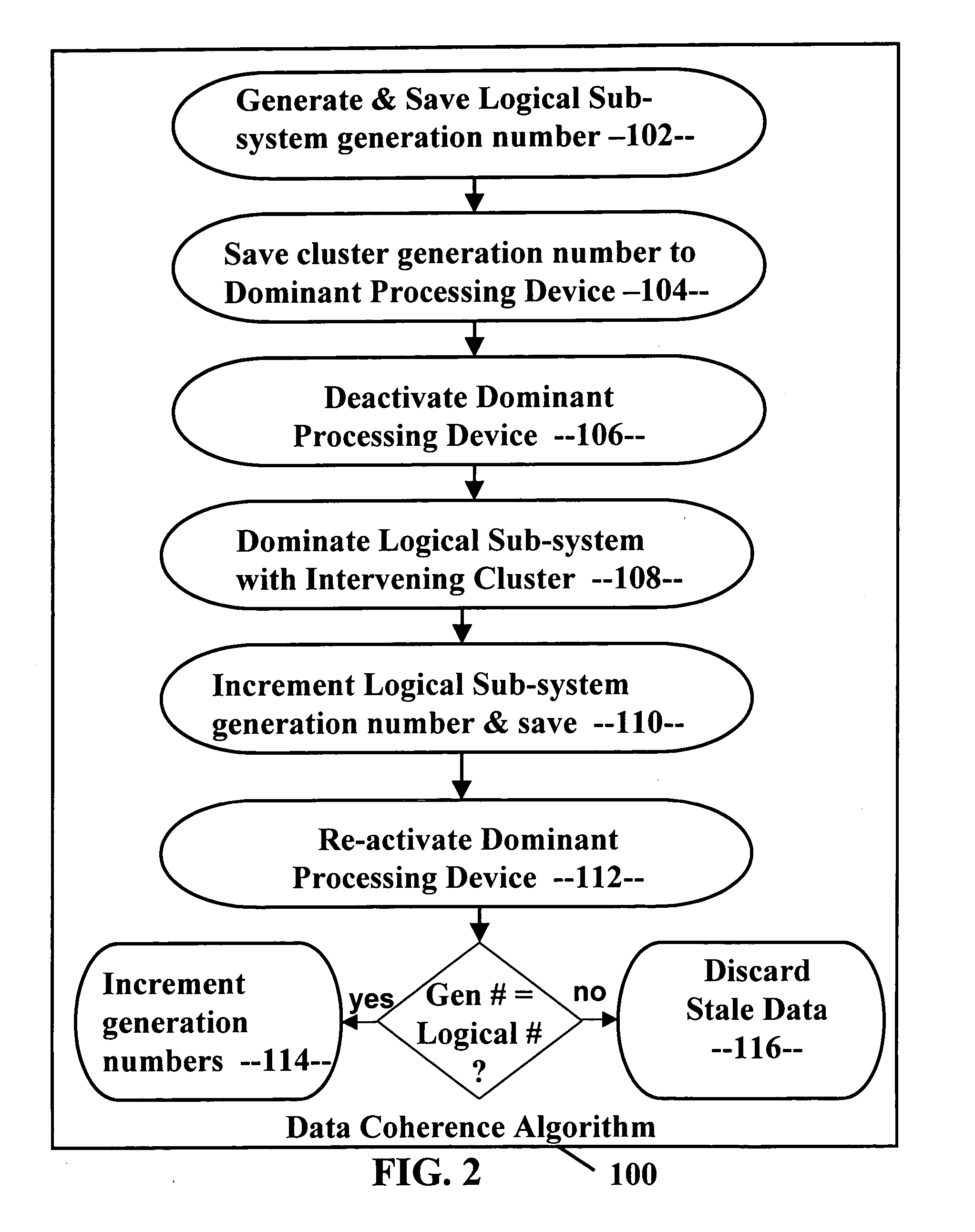
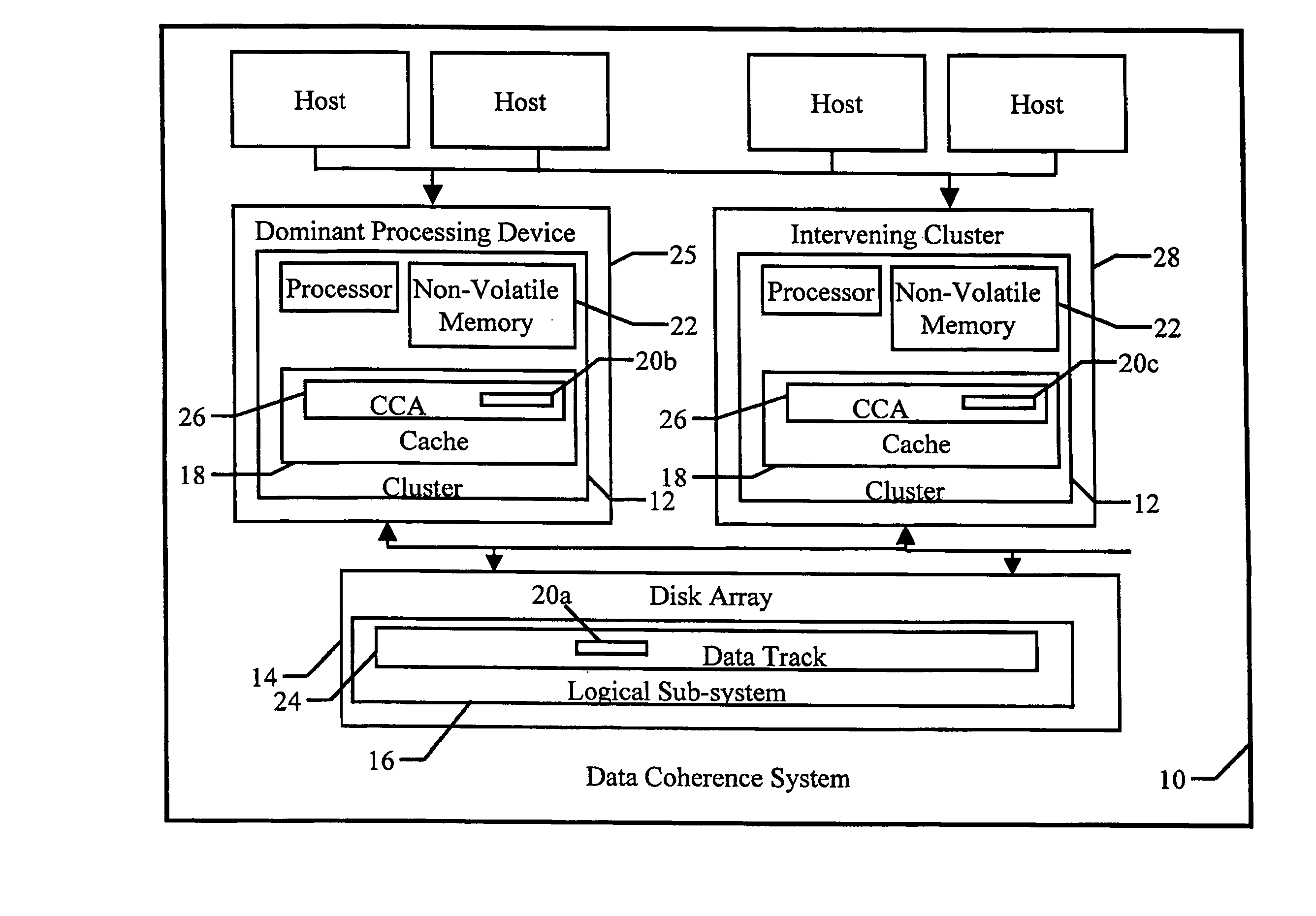
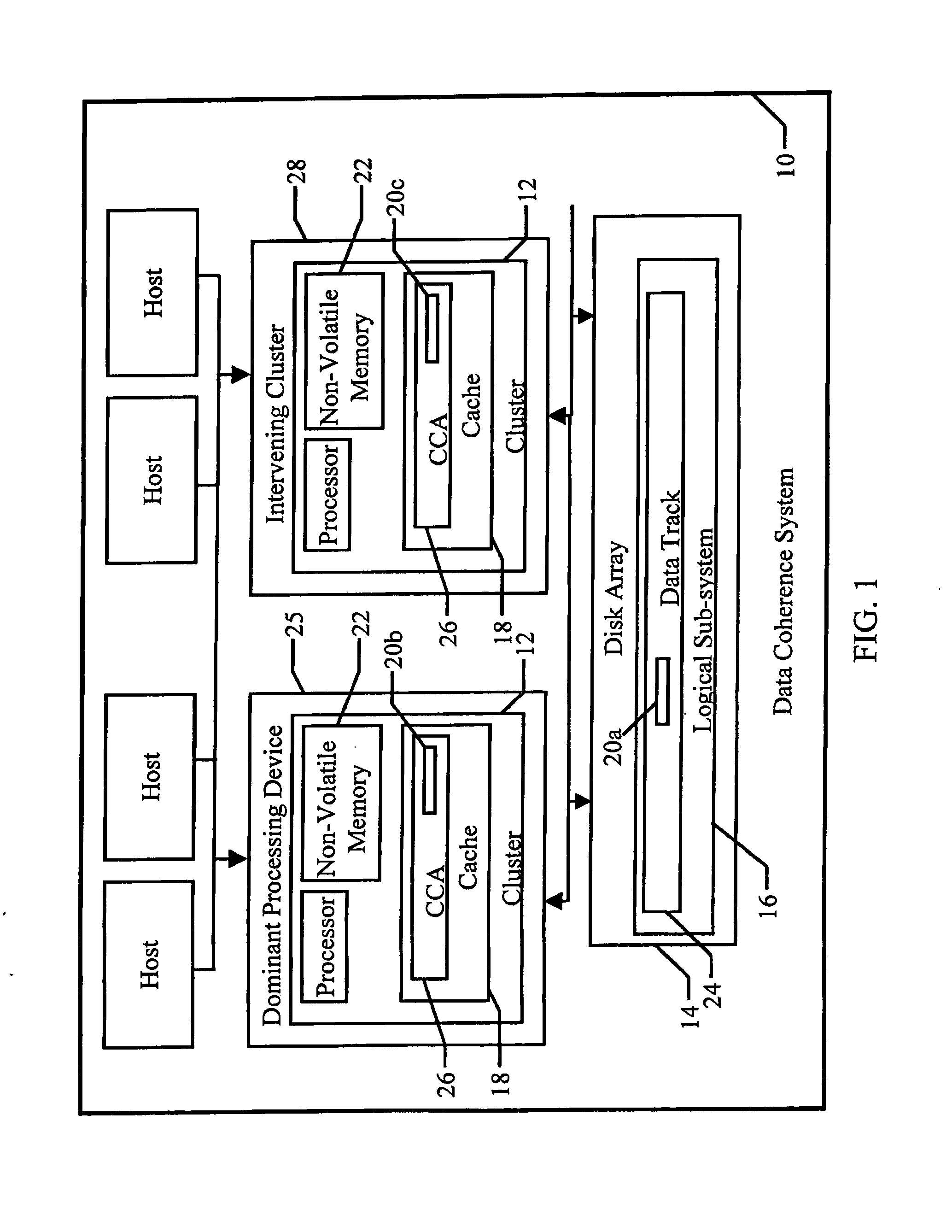
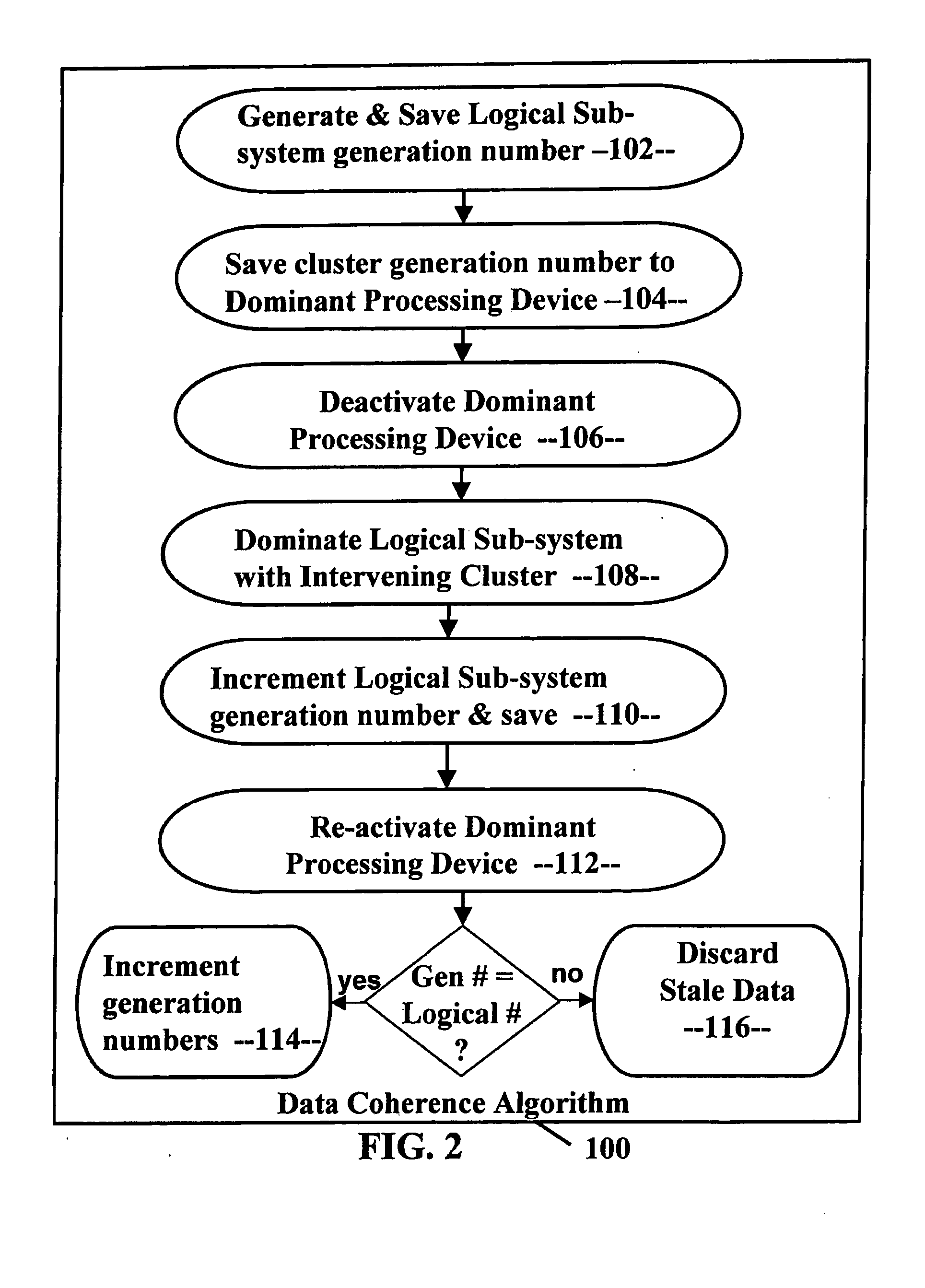
Data coherence system
A data coherence system includes a generation number written to a data track of a logical sub-system. The generation number is compared to a corresponding generation number in a processing device when it is initialized. If the two generations numbers are the same, the generation numbers are incremented and saved. If not, cache associated with the logical sub-system residing within the processing device is erased and the generation numbers are reset.
Owner:IBM CORP
Selective coherency control
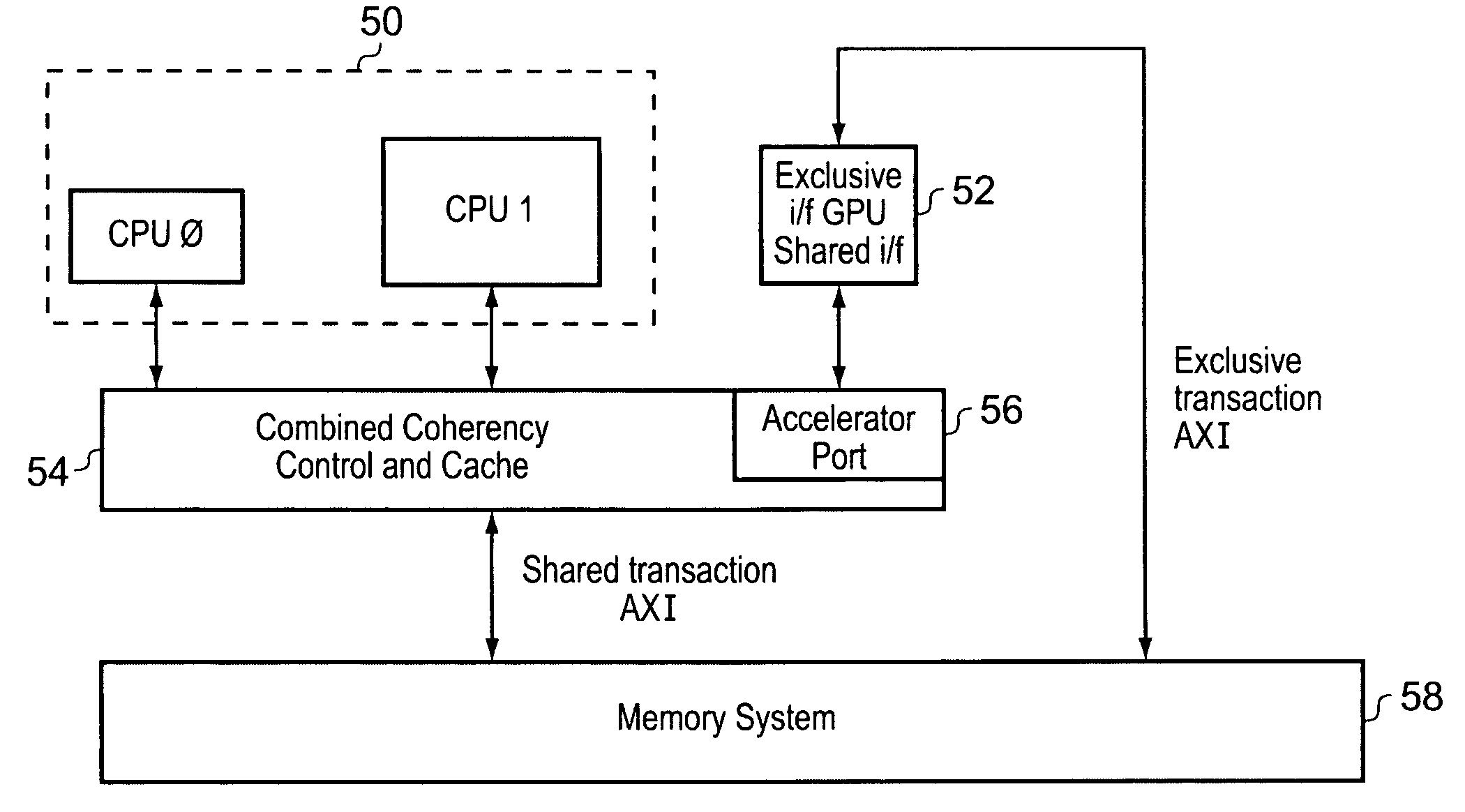
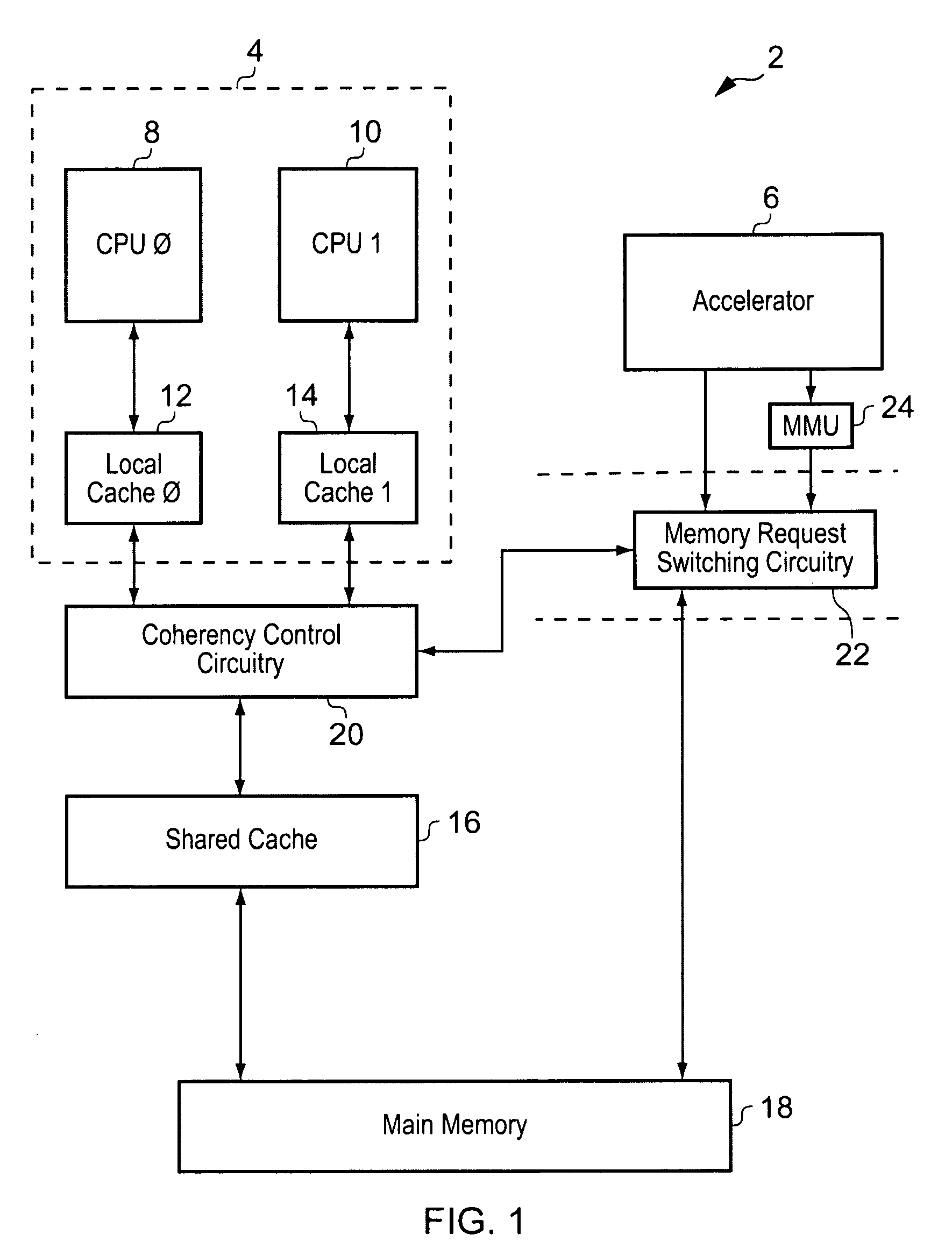
InactiveUS20090193197A1Reduce loadMemory adressing/allocation/relocationMultiple digital computer combinationsData processing systemGeneral purpose
A data processing system 2 is provided with a general purpose programmable processor 4 and an accelerator processor 6. Coherency control circuitry 20 manages data coherence between data items which may be stored within a cache memory 16 and / or a further memory 18. Memory access requests from the accelerator processor 6 are received by a memory request switching circuitry 22 which is responsive to a signal from the accelerator processor 6 to direct the memory access request either via coherency control circuit 20 or directly to the further memory 18.
Owner:ARM LTD
Using a shared last-level TLB to reduce address-translation latency
ActiveUS9081706B2Easy to identifyIncrease the number ofInput/output for user-computer interactionMemory architecture accessing/allocationData coherenceCache access
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Production material management system and method of nuclear power plant
InactiveCN101819653AEnsure consistencySolve the island problemTechnology managementResourcesData coherenceDevice type
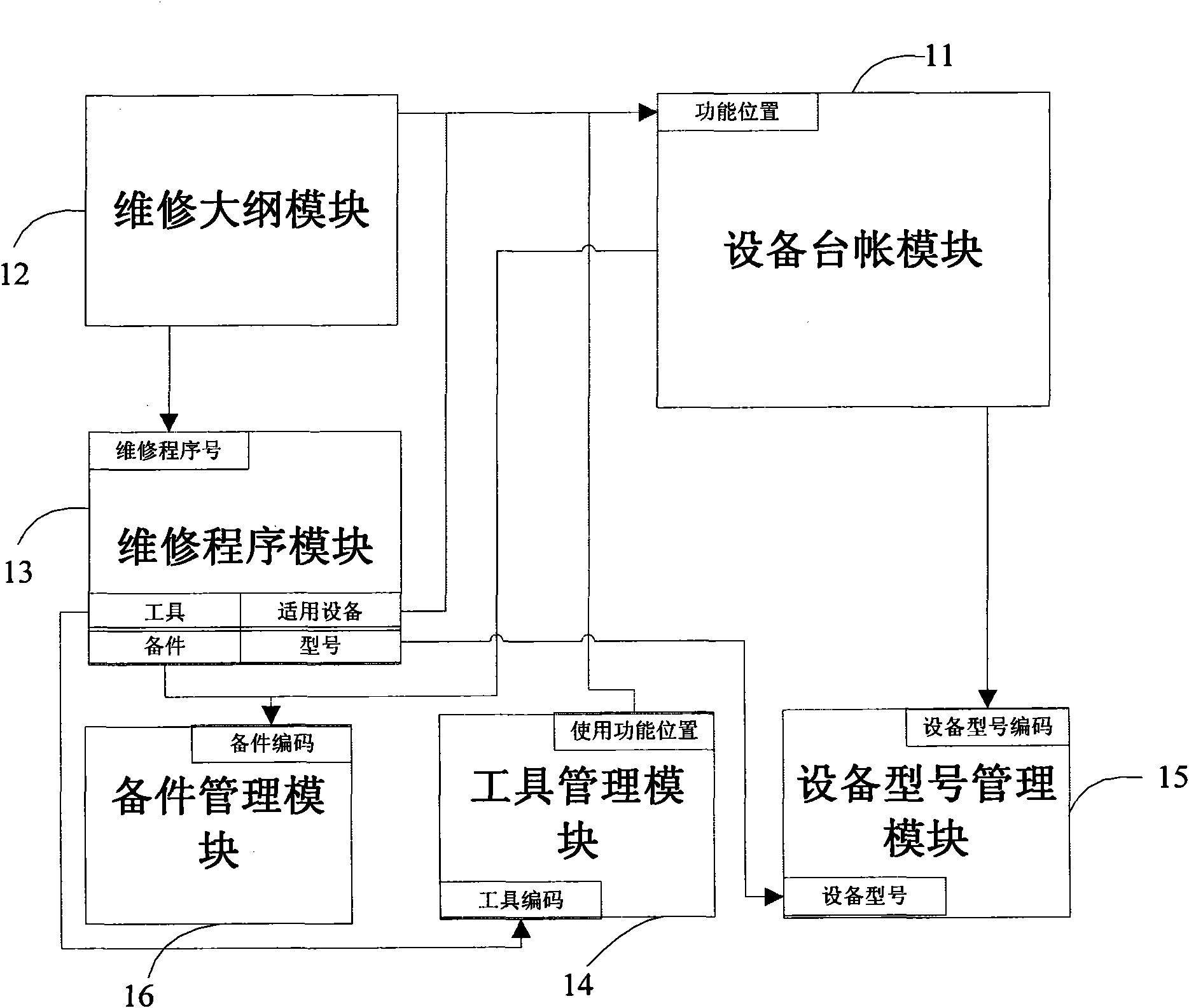
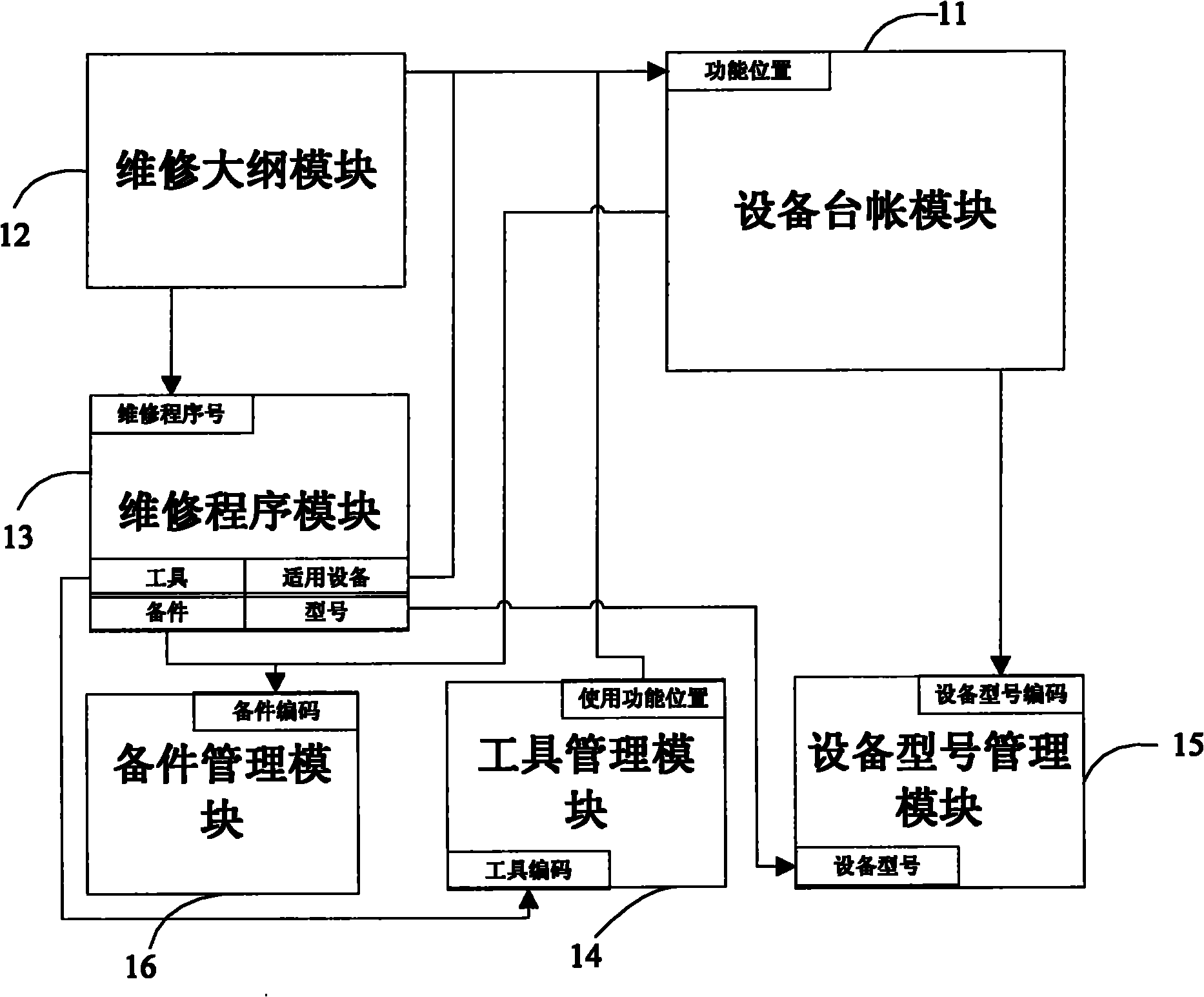
The invention relates to production material management system and method of a nuclear power plant. The system comprises a device ledger module, a maintenance outline module, a maintenance program module, a tool management module, a device type management module, a spare part management module, and the like. In the invention, a unified work platform system is formed, the works of query, treatment, and the like are greatly convenient, relationships are established among the modules, data is combined together in an organic mode, the problem of information isolated island is deracinated, data coherence is ensured, the system friendliness is strengthened, the problems of complex query operation are also solved, and the work efficiency is greatly improved.
Owner:CHINA NUCLEAR POWER TECH RES INST CO LTD +3
Combining a remote tlb lookup and a subsequent cache miss into a single coherence operation
ActiveUS20140013074A1Reduce in quantityReducing critical path delayMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationData coherenceCache access
The disclosed embodiments provide techniques for reducing address-translation latency and the serialization latency of combined TLB and data cache misses in a coherent shared-memory system. For instance, the last-level TLB structures of two or more multiprocessor nodes can be configured to act together as either a distributed shared last-level TLB or a directory-based shared last-level TLB. Such TLB-sharing techniques increase the total amount of useful translations that are cached by the system, thereby reducing the number of page-table walks and improving performance. Furthermore, a coherent shared-memory system with a shared last-level TLB can be further configured to fuse TLB and cache misses such that some of the latency of data coherence operations is overlapped with address translation and data cache access latencies, thereby further improving the performance of memory operations.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
Checkpoint/resume/restart safe methods in a data processing system to establish, to restore and to release shared memory regions
ActiveUS7376860B2Function increaseGuaranteed uptimeError detection/correctionData processing systemData coherence
A method is provided in which checkpointing operations are carried out in data processing systems running multiple processes which employ shared memory in a manner which preserves data coherence and integrity but which places no timing restrictions or constraints which require coordination of checkpointing operations. Data structures within local process memory and within shared memory provide the checkpoint operation with application level information concerning shared memory resources specific to at least two processes being checkpointed. Methods are provided for establishing, restoring and releasing shared memory regions that are accessed by multiple cooperating processes.
Owner:META PLATFORMS INC
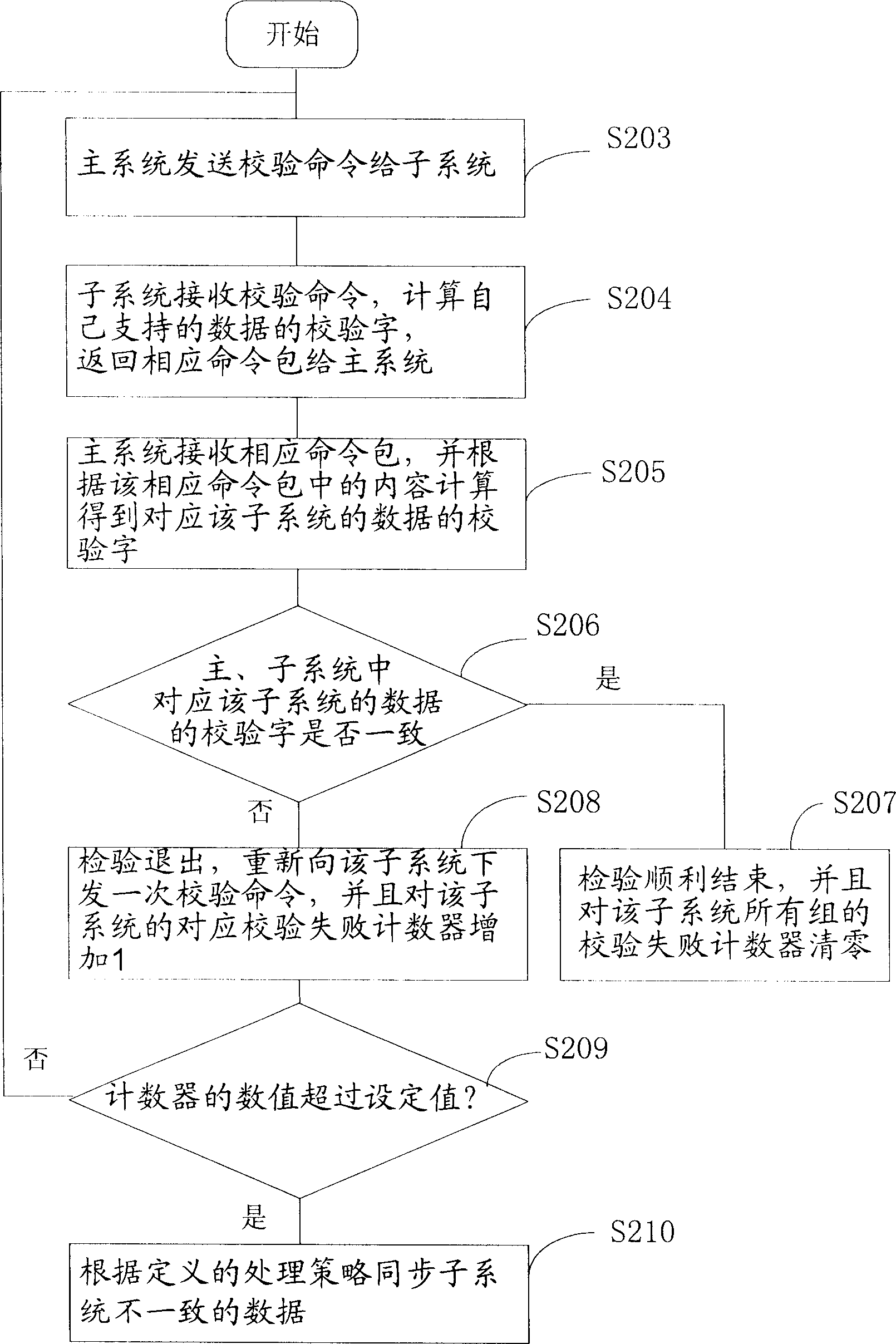
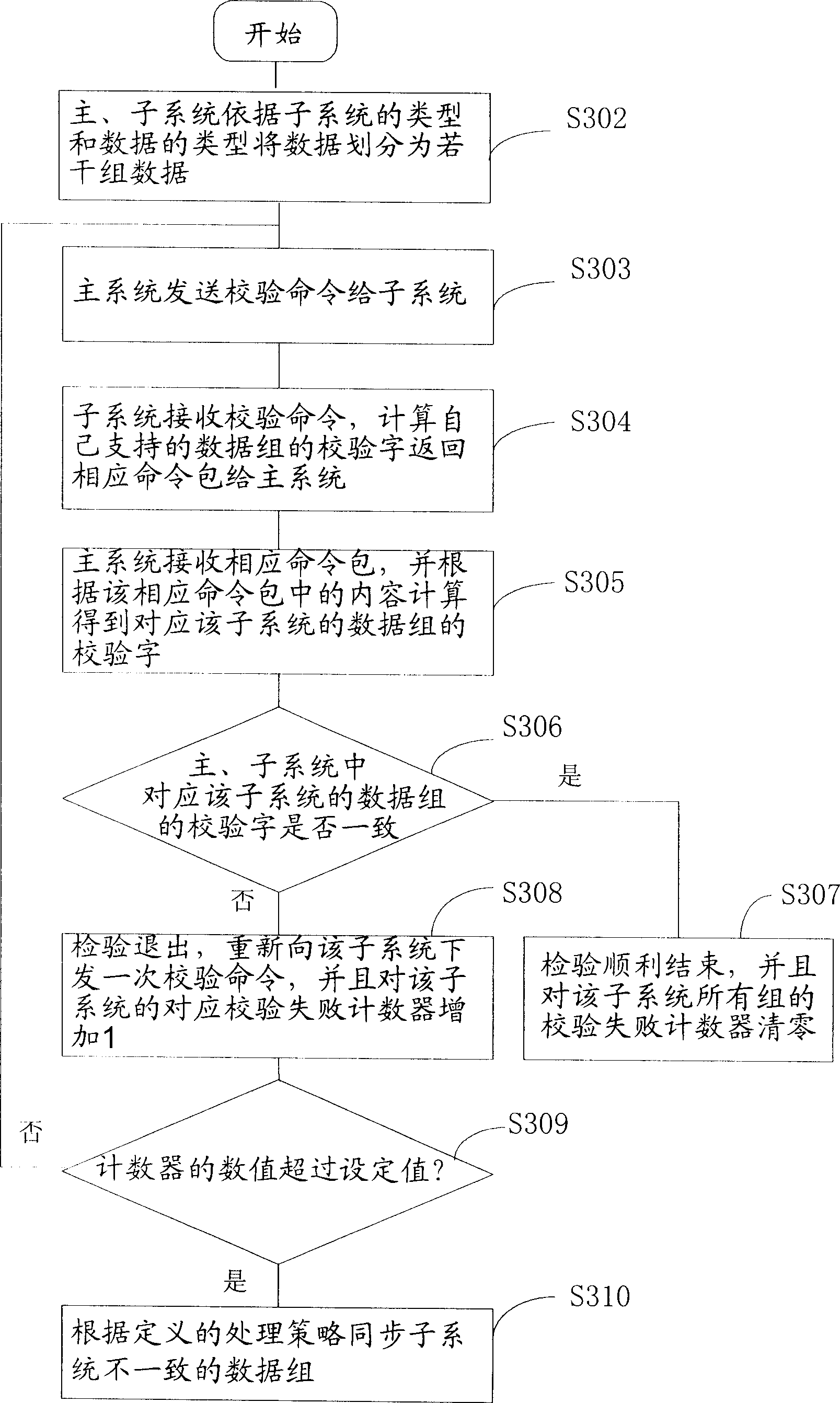
Method for checking data coherence and data synchronization, and distribution type system
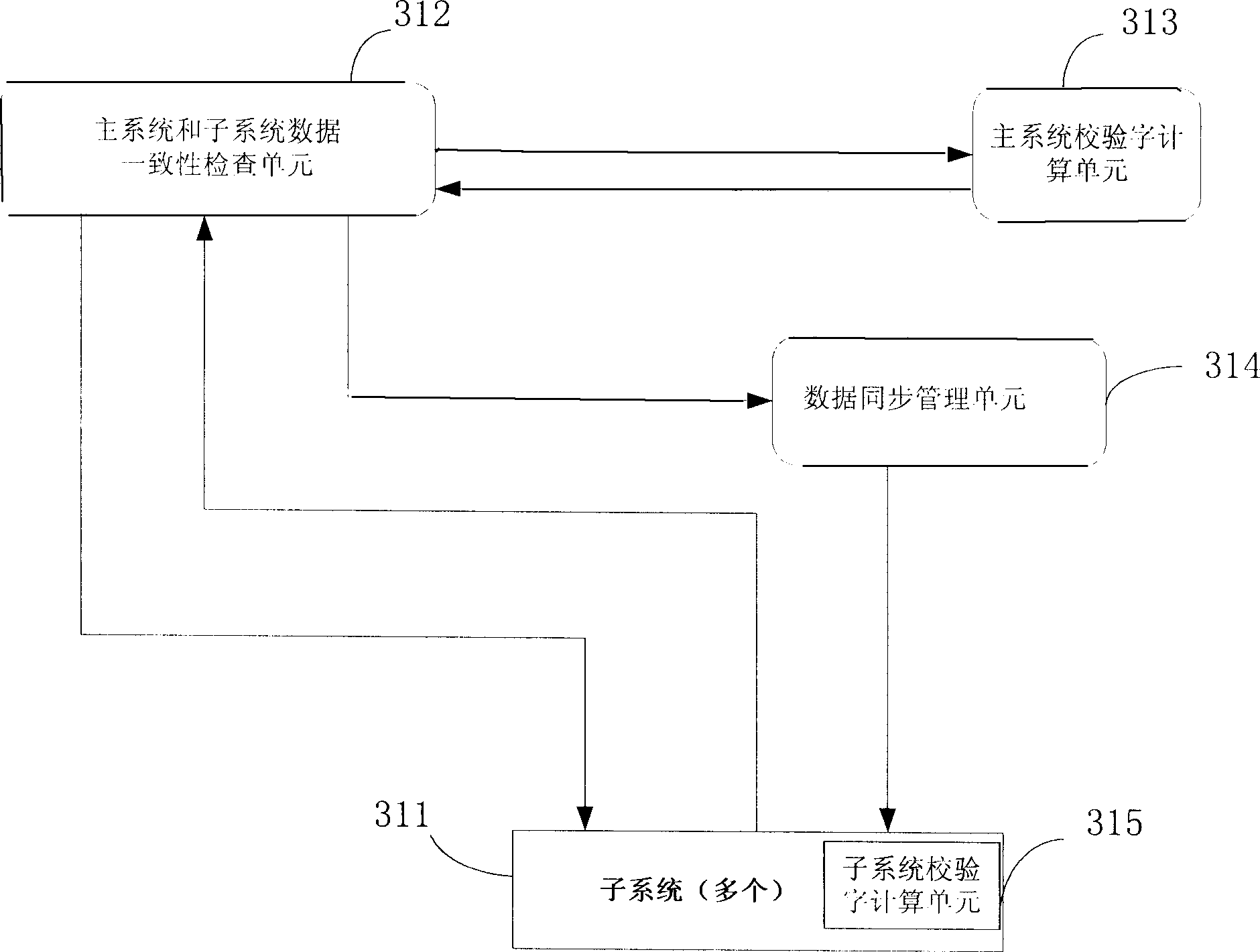
InactiveCN1816039AAchieve consistencyAchieve synchronizationTransmissionData coherenceData synchronization
The invention includes following core points: dividing data into data groups; then, main system obtains check words in main and sub systems corresponding to each sub system data respectively; finally, main system compares words in main and sub systems corresponding to each sub system data; if consistent, then ending the check; otherwise, synchronizing the corresponding inconsistent data. Since data are divided into groups, the invention reduces amount of calculation, and amount of traffic in each checkup. Advantages are: easy for single-handed process, and raising flexibility of data check and synchronization process of main and sun system.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
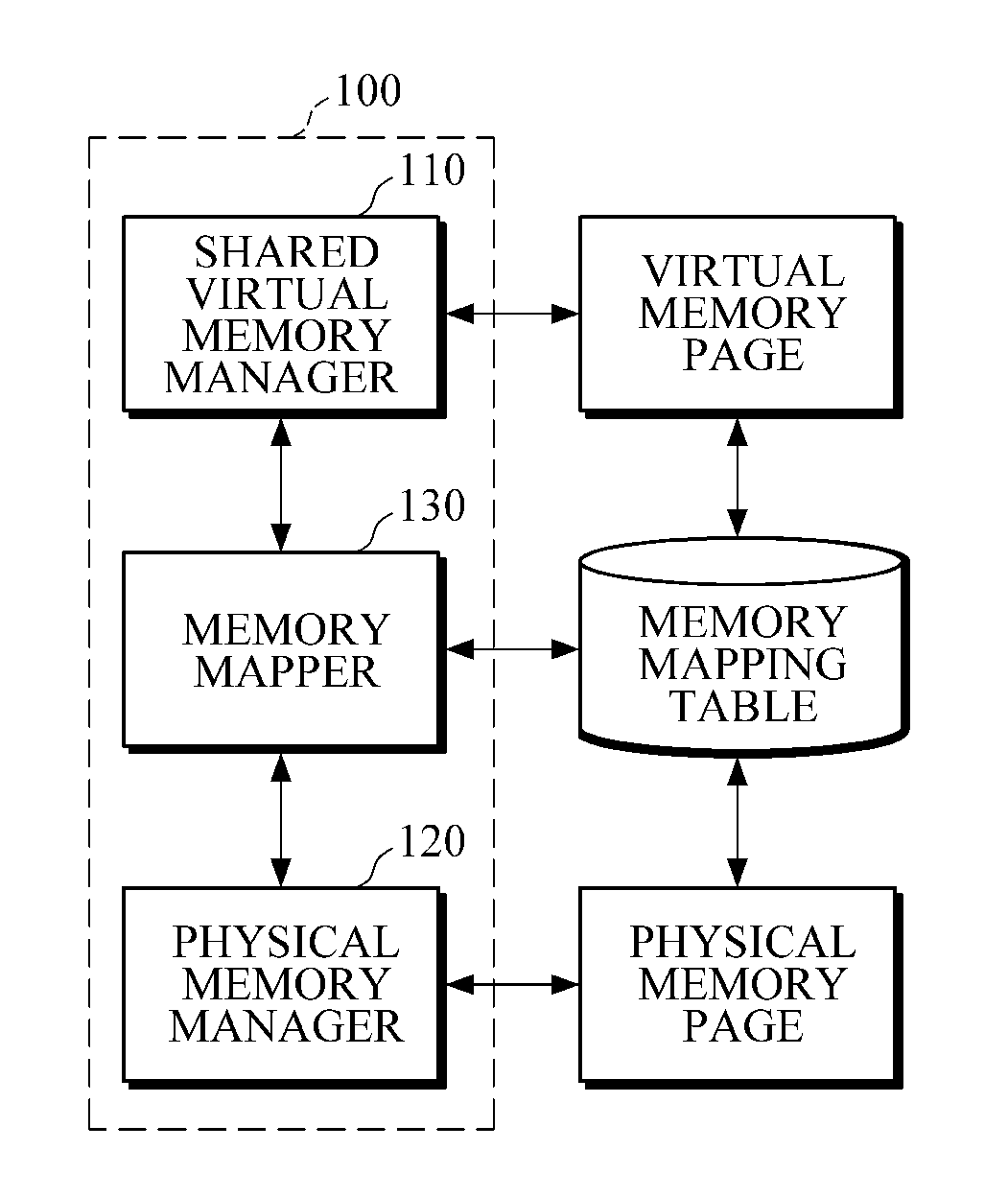
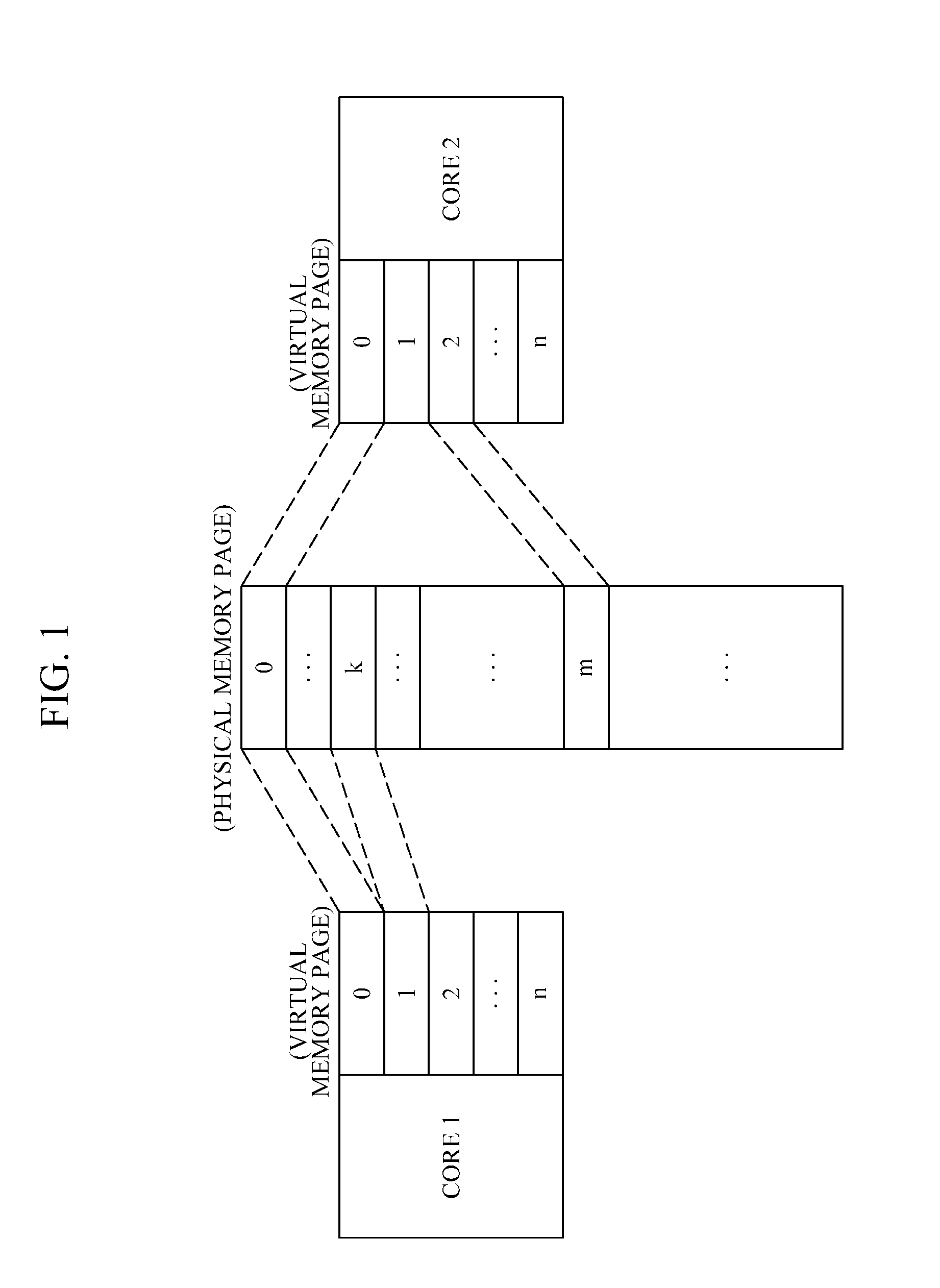
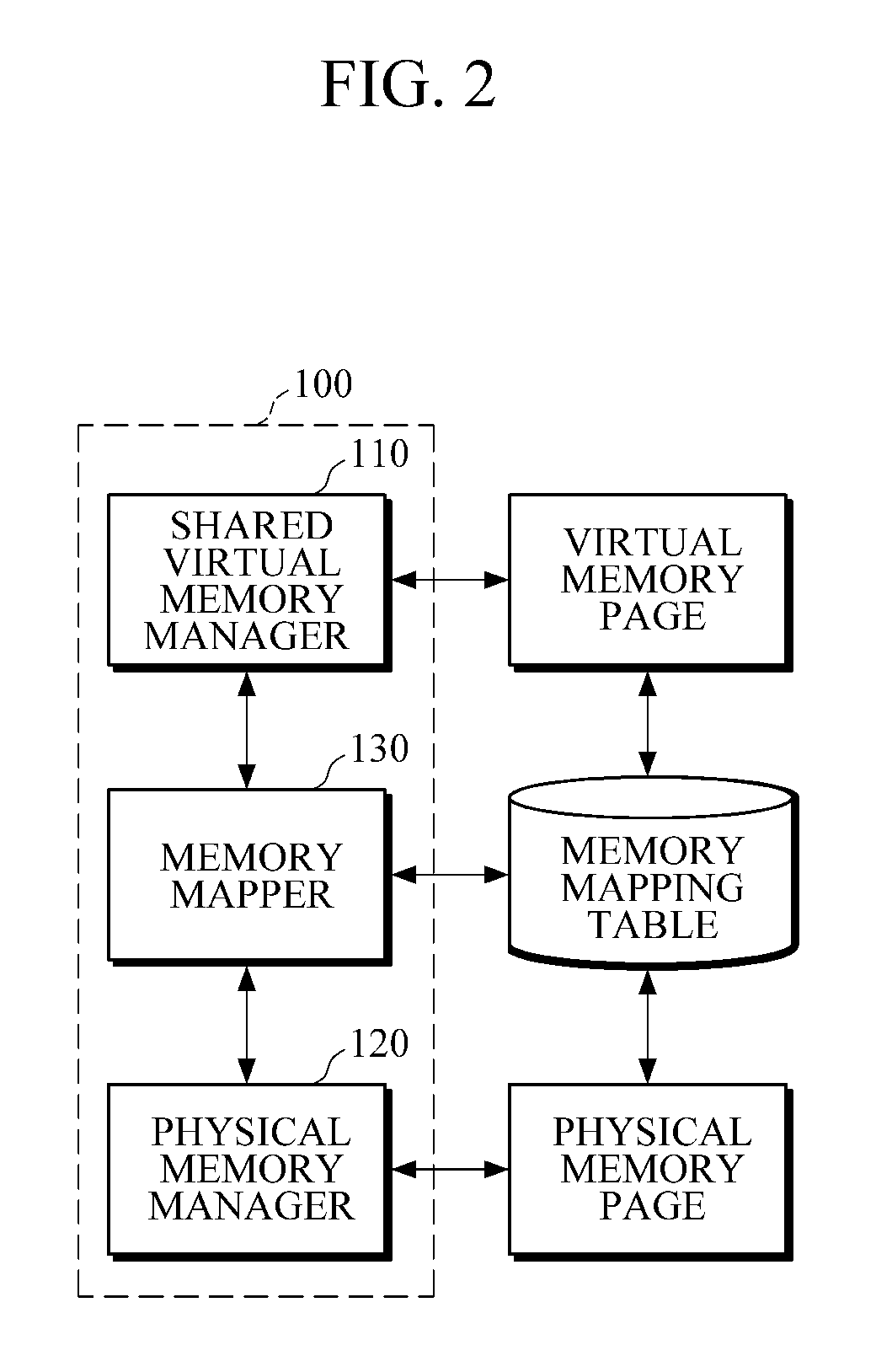
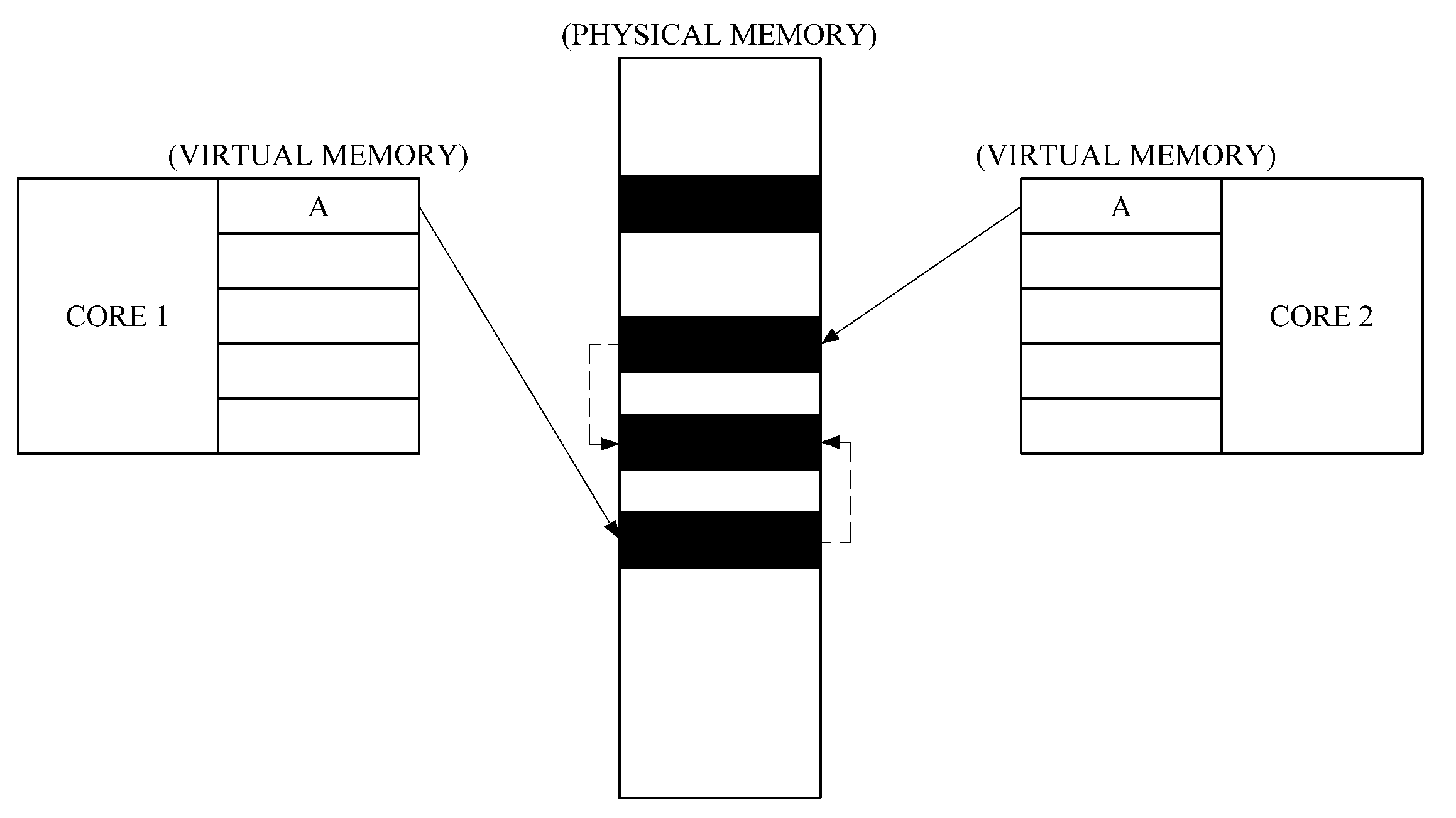
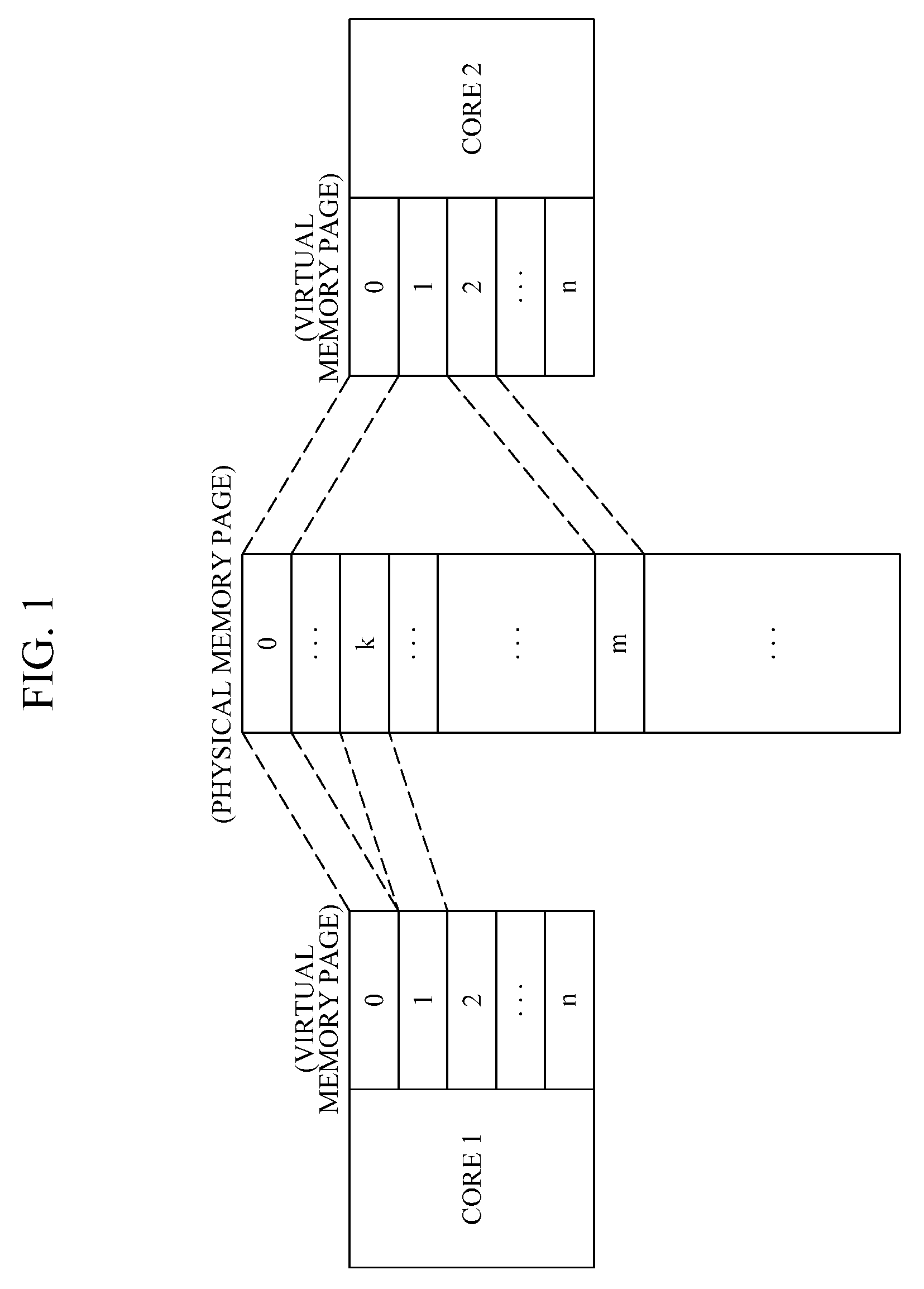
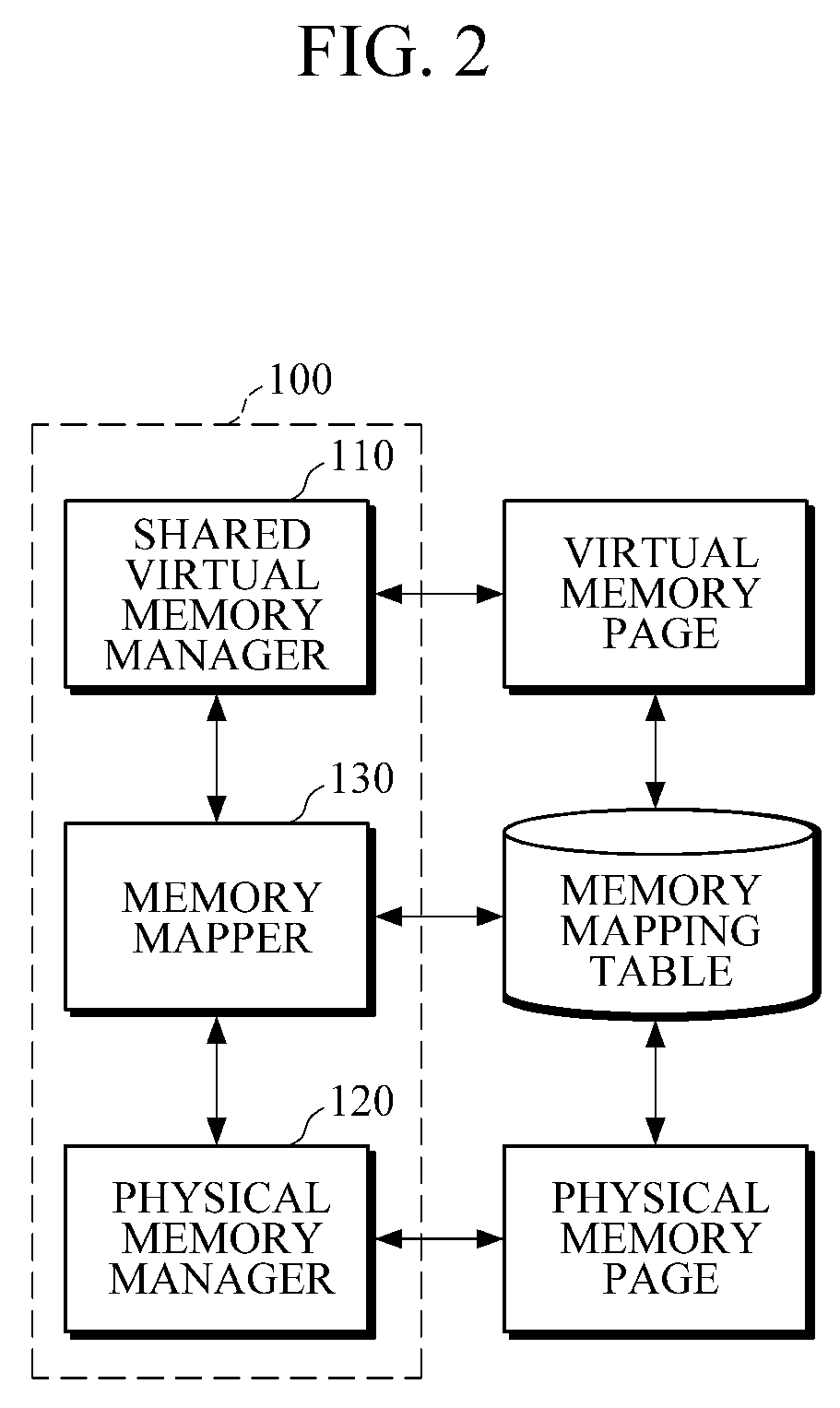
Shared virtual memory management apparatus for providing cache-coherence
ActiveUS20140040563A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationVirtual memoryData coherence
A shared virtual memory management apparatus for ensuring cache coherence. When two or more cores request write permission to the same virtual memory page, the shared virtual memory management apparatus allocates a physical memory page for the cores to change data in the allocated physical memory page. Thereafter, changed data is updated in an original physical memory page, and accordingly it is feasible to achieve data coherence in a multi-core hardware environment that does not provide cache coherence.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
Method for extracting dual-time-phase dual-polarized interference SAR image water area
InactiveCN107329139AWeak water coherenceEfficient extractionRadio wave reradiation/reflectionData coherencePower diagram
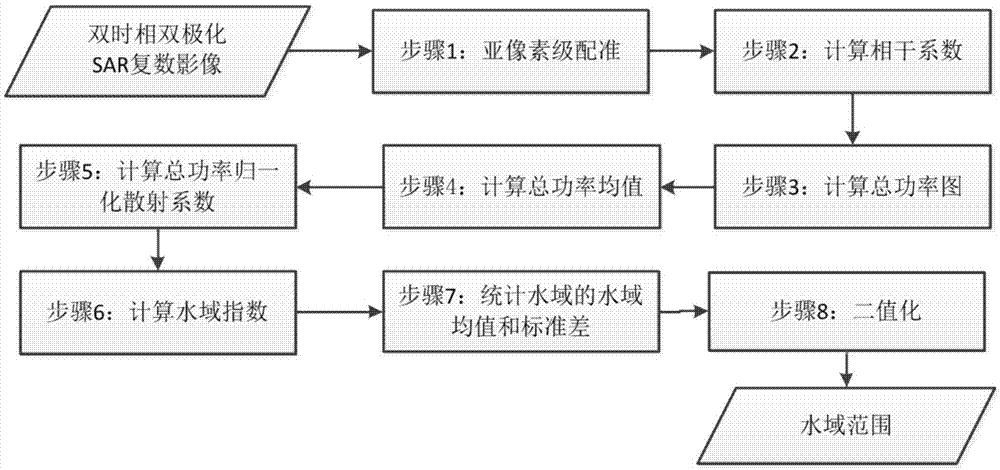
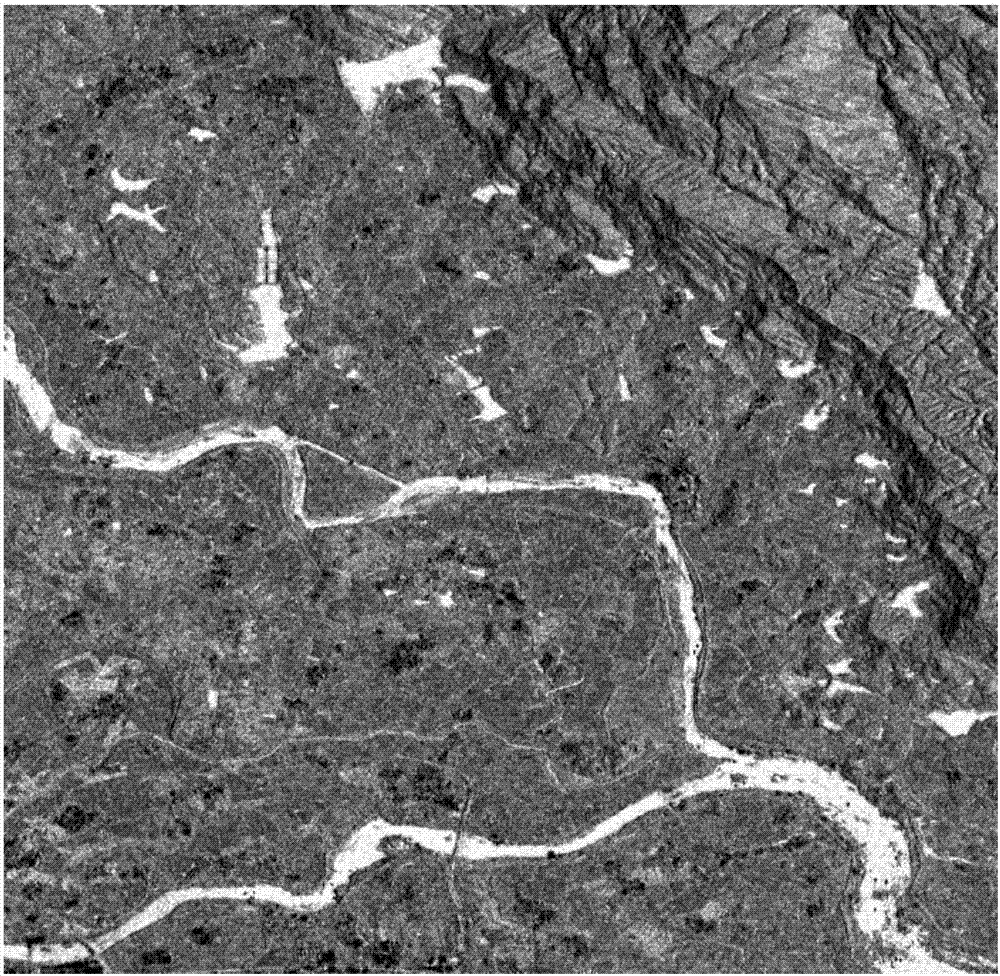
The invention discloses a method for extracting a dual-time-phase dual-polarized interference SAR image water area, namely a SAR image water area extracting method. The method successively comprises subpixel-level registration, coherence coefficient calculation, total power diagram calculation, total power mean value calculation, total power normalized scattering coefficient calculation, water area index calculation, calculation of water area average and standard deviation of a statistical water area, and binaryzation. The method, in view of low precision and low automation degree of water interpretation on a SAR image, provides, based on a characteristic that a coherent SAR image has good coherence to most ground features within short time intervals, a SAR image water area index based on dual-polarized SAR data coherence coefficient and intensity value, enhances water area information on the image, restrains other ground features, improves the automation degree of water interpretation in each time-phase image, helps to enhance users' recognition and accuracy of SAR images, and accelerates the popularization and application of the SAR in flood monitoring and topographic mapping.
Owner:邓少平
Indoor human detection and tracking method based on RGB-D under low viewing angle
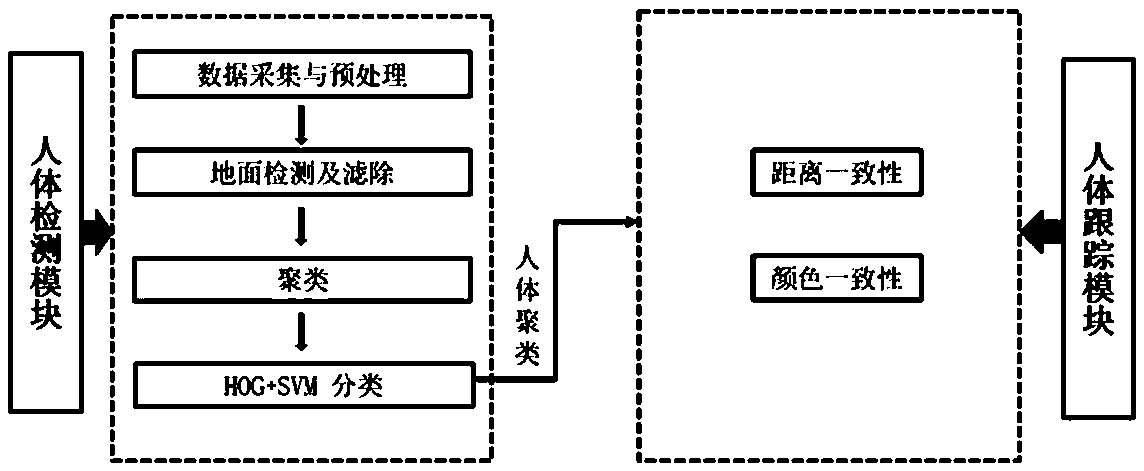
The invention relates to a method indoor human body detection and tracing method under the condition of RGB-D low angle of view, belonging to the technical field of human body detection, Specifically,the following steps are included, using Asustek Xtion Pro to collect point clouds, so that 3D point cloud is obtained, 3-D point cloud is denoised and desampled, and detecting and removing the ground, and then 3D clustering is carried out by using the Euclidean distance between two points, by calculating the HOG features of each cluster and feeding them to the pre-trained SVM binary soft classifier, those with high HOG characteristics are classified as human beings, so as to achieve the purpose of human detection. Finally, human body tracking is realized by using the two likelihood probabilities composed of color consistency and distance consistency in the data coherence process. The invention has high precision and is widely used for indoor human body detection and tracking under the condition of low viewing angle.
Owner:ZHONGBEI UNIV
Complete polarization synthetic aperture radar target decomposition method for adaptive selection unitary transformation
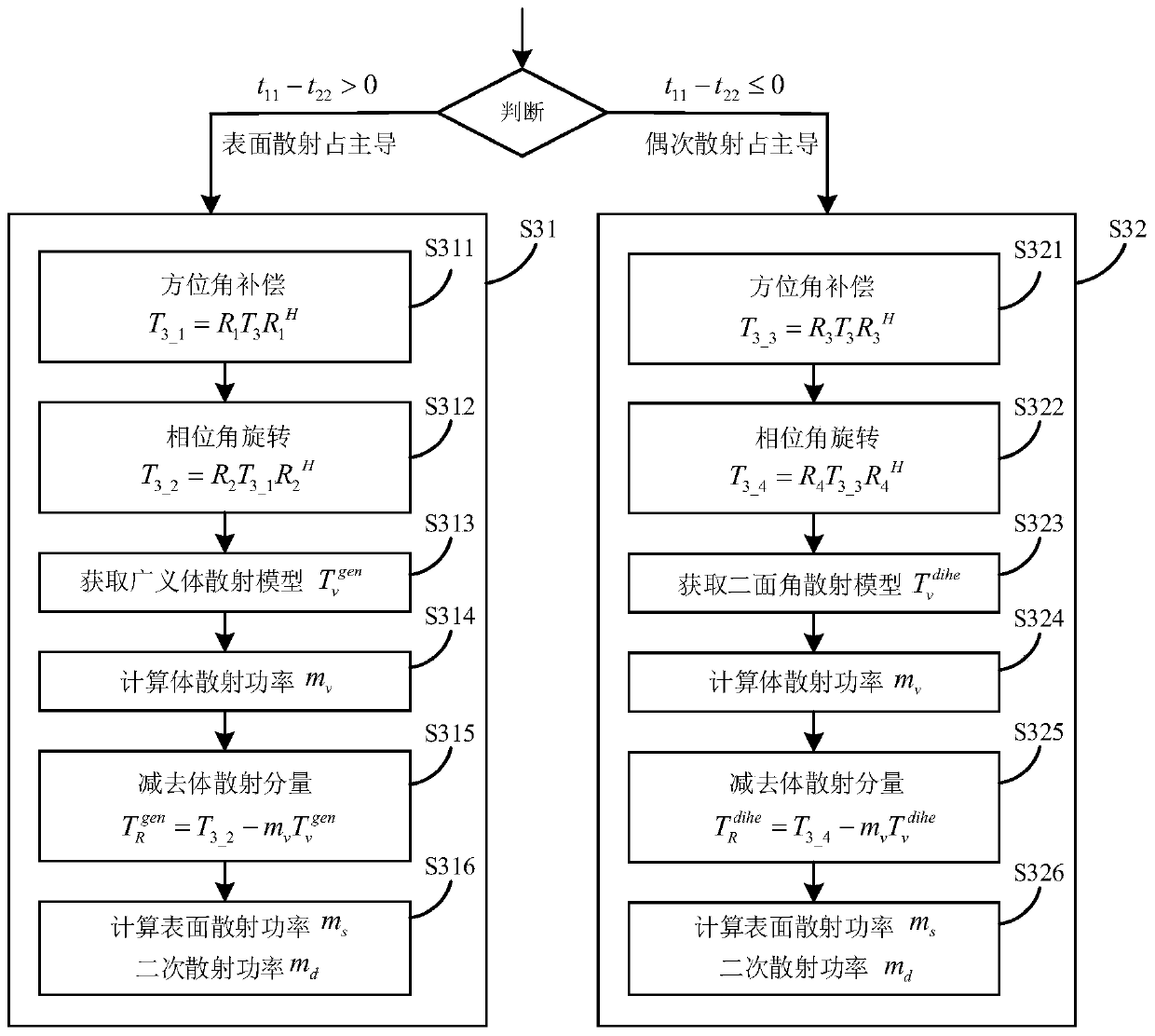
InactiveCN104698447ASuppressing Scatter Overestimation ProblemsLess freedomRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSynthetic aperture radarOmega
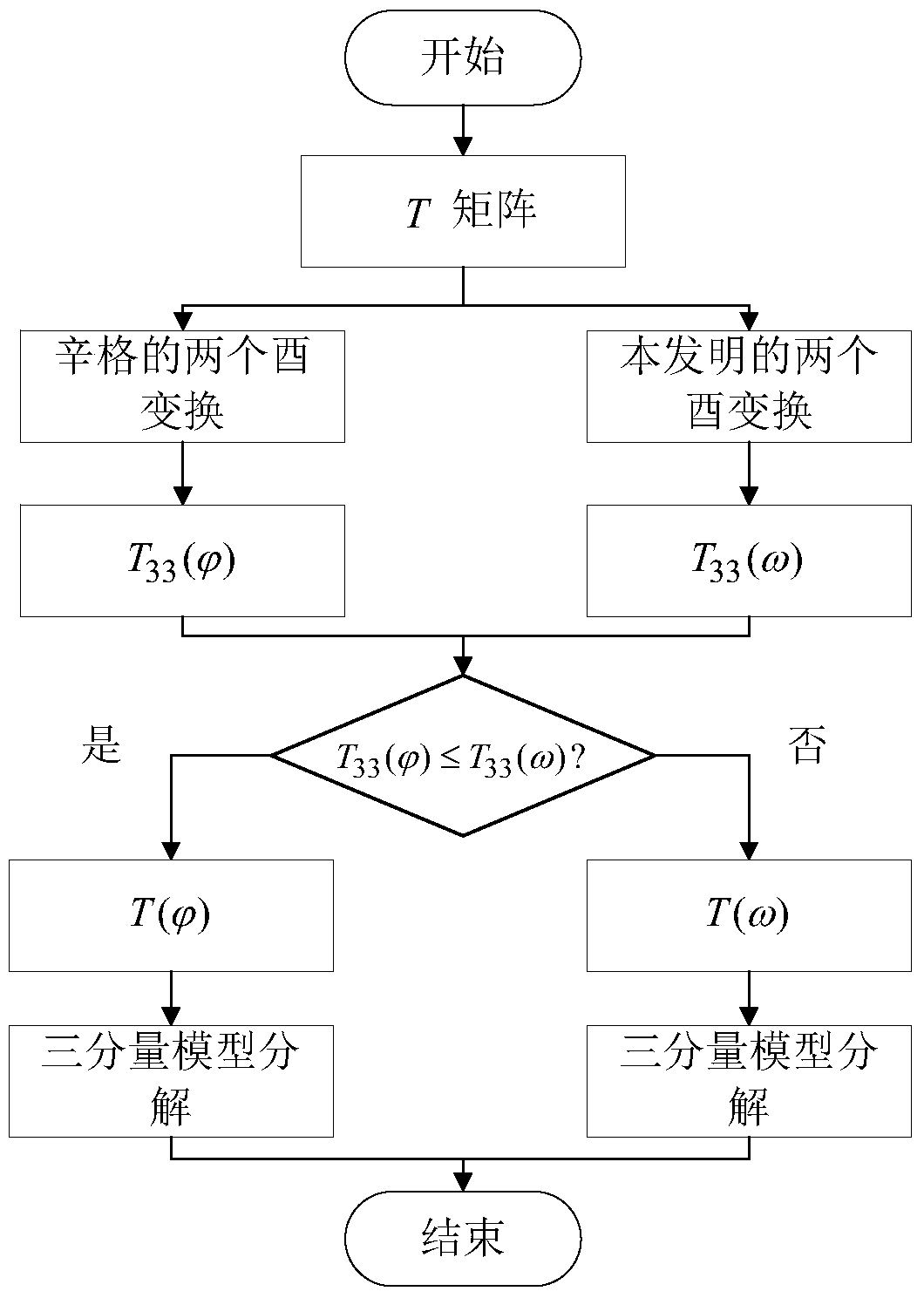
The invention provides a complete polarization synthetic aperture radar target decomposition method for adaptive selection unitary transformation. The method comprises the following steps: (1) performing two unitary transformations for singh for data coherence T matrix of the complete polarization synthetic aperture radar to obtain the matrix, (the formula is as shown in specification); (2) performing other two unitary transformations for the coherence T matrix to obtain the matrix T(omega), wherein the first unitary transformation is used for performing the spiral angle compensation and restraining the volume scattering excessive estimation of model decomposition, the second unitary transformation is used for further restraining the volume scattering excessive estimation and reducing one degree of freedom of the coherence T matrix; (3) comparing with element (the formula is as shown in specification) of the matrix (the formula is as shown in specification) with the element T33(omega) of the matrix T(omega); if (the formula is as shown in specification), and (the formula is as shown in specification), otherwise, T is equal to T(omega); (4) performing three-component model decomposition on coherence T matrix. The two unitary transformations for singh in the step (1) or the two unitary transformations in the step (2) can be selected for the coherence T matrix in a self-adaption mode by the method according to the real situation of the object, and the volume scattering excessive estimation problem of the model decomposition can be effectively restrained.
Owner:NAT SPACE SCI CENT CAS
Multiple integral computing method based on many-core processor
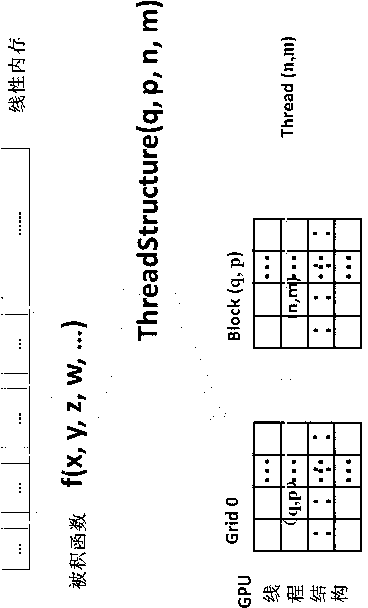
InactiveCN102841881ACalculation speedScientific calculation time shortenedComplex mathematical operationsArithmetic processing unitComputational science
The invention provides a computing solution of numerical multiple integral by utilization of a many-core processor such as a graphic processing unit (GPU) to accelerate the computing solution which often needs processing and is time-consuming in computing science. The computing solution is simple and practical, can accelerate the solving process of the numerical multiple integral conveniently and effectively, and has a practical application meaning in substantially shortening time of a scientific program. The method takes sufficient consideration of ultra-strong floating-point computation power of the GPU and features of the many-core processor such as a large internal memory bandwidth, and takes full advantage of the feature that data coherence does not exist among all shooting points in the Monte Carlo method. According to the method, computing of function values of the shooting points in large quantity is processed by the GPU, computational accuracy control and convergence judgments and the like requiring branch predictions are finished by a central processing unit (CPU) so as to substantially accelerate the solution of the multiple integral.
Owner:LANGCHAO ELECTRONIC INFORMATION IND CO LTD
Crack prediction method for preferred orientation daughter coherence
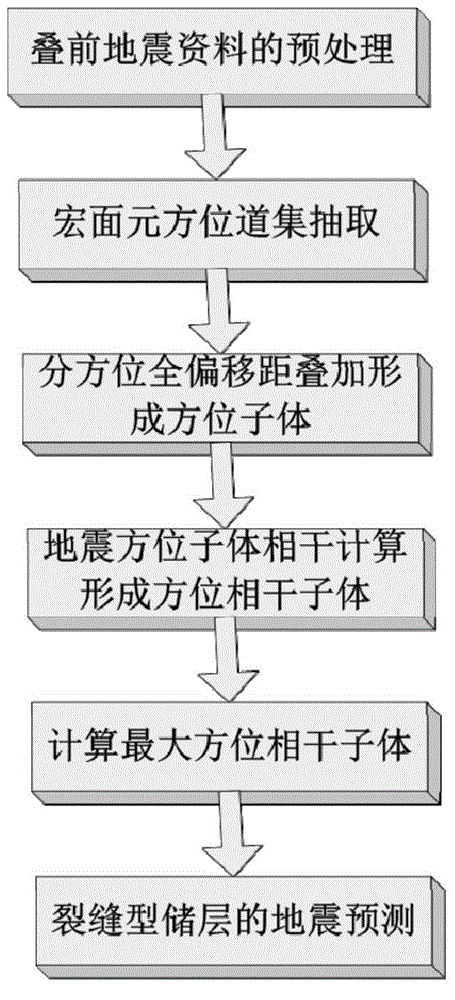
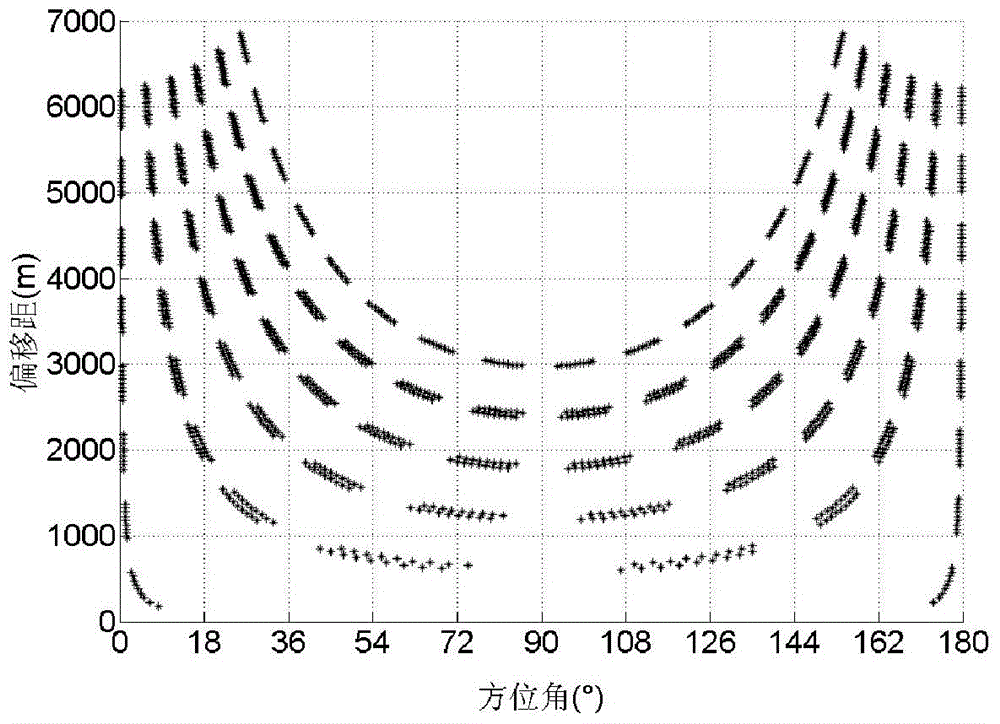
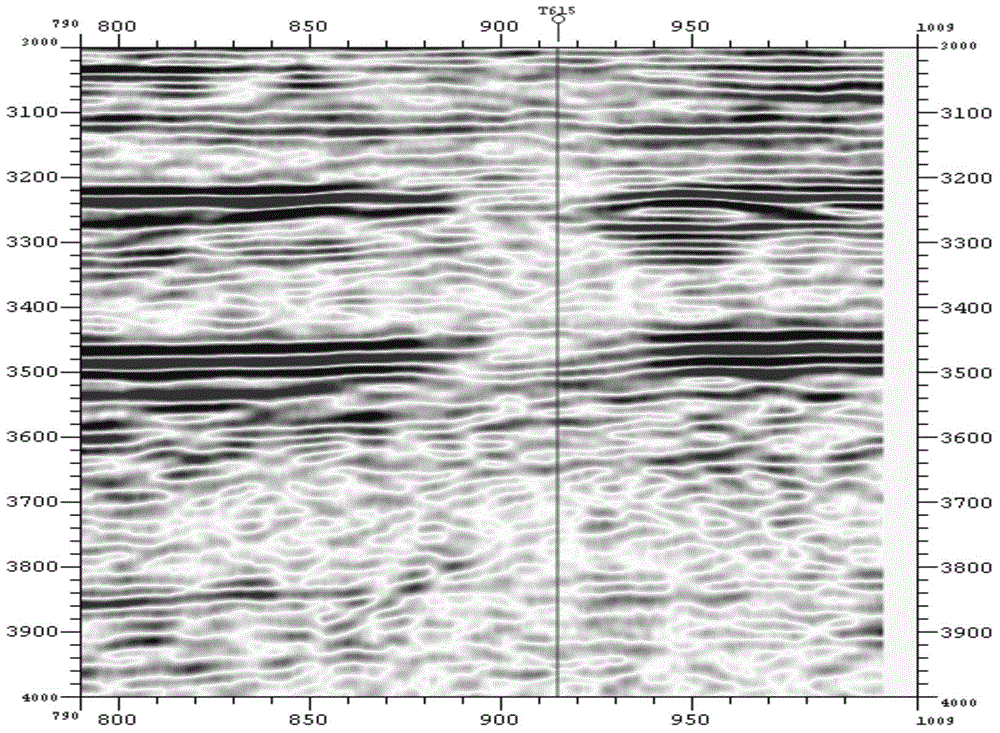
ActiveCN105445787ARich information on fracture developmentIntuitive crack development distribution mapSeismic signal processingData coherencePre treatment
The invention provides a crack prediction method for the preferred orientation daughter coherence, and belongs to the field of oilfield exploration. The method generates orientation daughters through a pre-stack seismic channel set, and then calculates coherence attributes among different orientations, and finally acquires a seismic data coherence body of the preferred orientation. The method includes: (1) pre-treatment of pre-stack seismic data; (2) extraction of a macro surface element channel set; (3) stacking branch orientation full migration distance channel sets to form the orientation daughters; (4) calculating seismic orientation daughter coherence to form orientation coherence daughters; and (5) calculating the maximum orientation coherence daughter to obtain the seismic data coherence body of the preferred orientation.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Bidirectional similarity of signals
ActiveUS8542908B2Improve coherenceImprove completenessDigital data information retrievalGeometric image transformationData coherenceData integrity
A method for measuring bi-directional similarity between a first signal of a first size and a second signal of a second size includes matching at least some patches of the first signal with patches of the second signal for data completeness, matching at least some patches of the second signal with patches of the first signal for data coherence, calculating the bi-directional similarity measure as a function of the matched patches for coherence and the matched patches for completeness and indicating the similarity between the first signal and the second signal. Another method generates a second signal from a first signal where the second signal is different than the first signal by at least one parameter. The method includes attempting to maximize a bi-directional similarity measure between the second signal and the first signal.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
Data Coherence System
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Combining a remote TLB lookup and a subsequent cache miss into a single coherence operation
ActiveUS9003163B2Reduce in quantityReduce degradationMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationData coherenceCache access
The disclosed embodiments provide techniques for reducing address-translation latency and the serialization latency of combined TLB and data cache misses in a coherent shared-memory system. For instance, the last-level TLB structures of two or more multiprocessor nodes can be configured to act together as either a distributed shared last-level TLB or a directory-based shared last-level TLB. Such TLB-sharing techniques increase the total amount of useful translations that are cached by the system, thereby reducing the number of page-table walks and improving performance. Furthermore, a coherent shared-memory system with a shared last-level TLB can be further configured to fuse TLB and cache misses such that some of the latency of data coherence operations is overlapped with address translation and data cache access latencies, thereby further improving the performance of memory operations.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
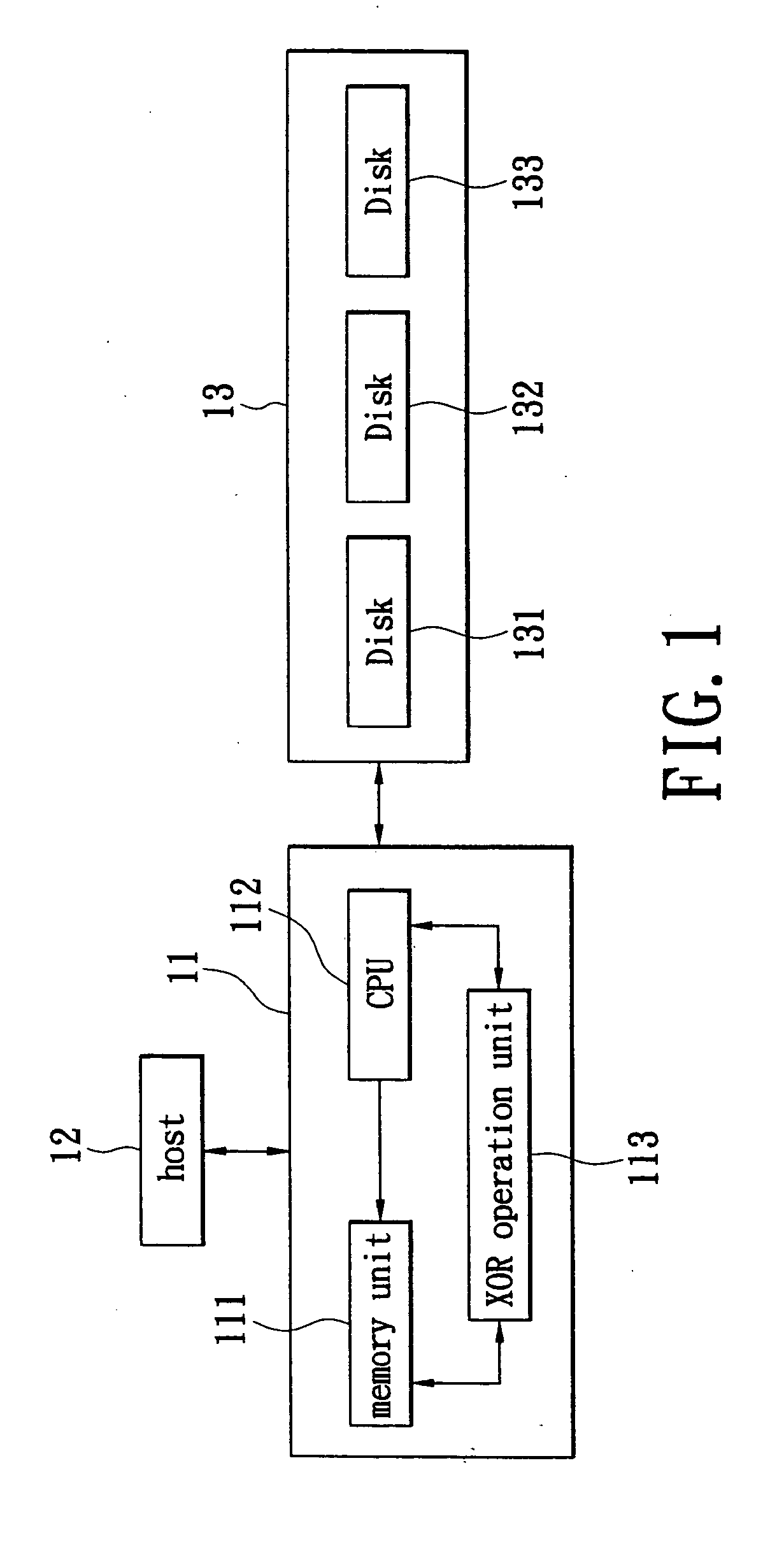
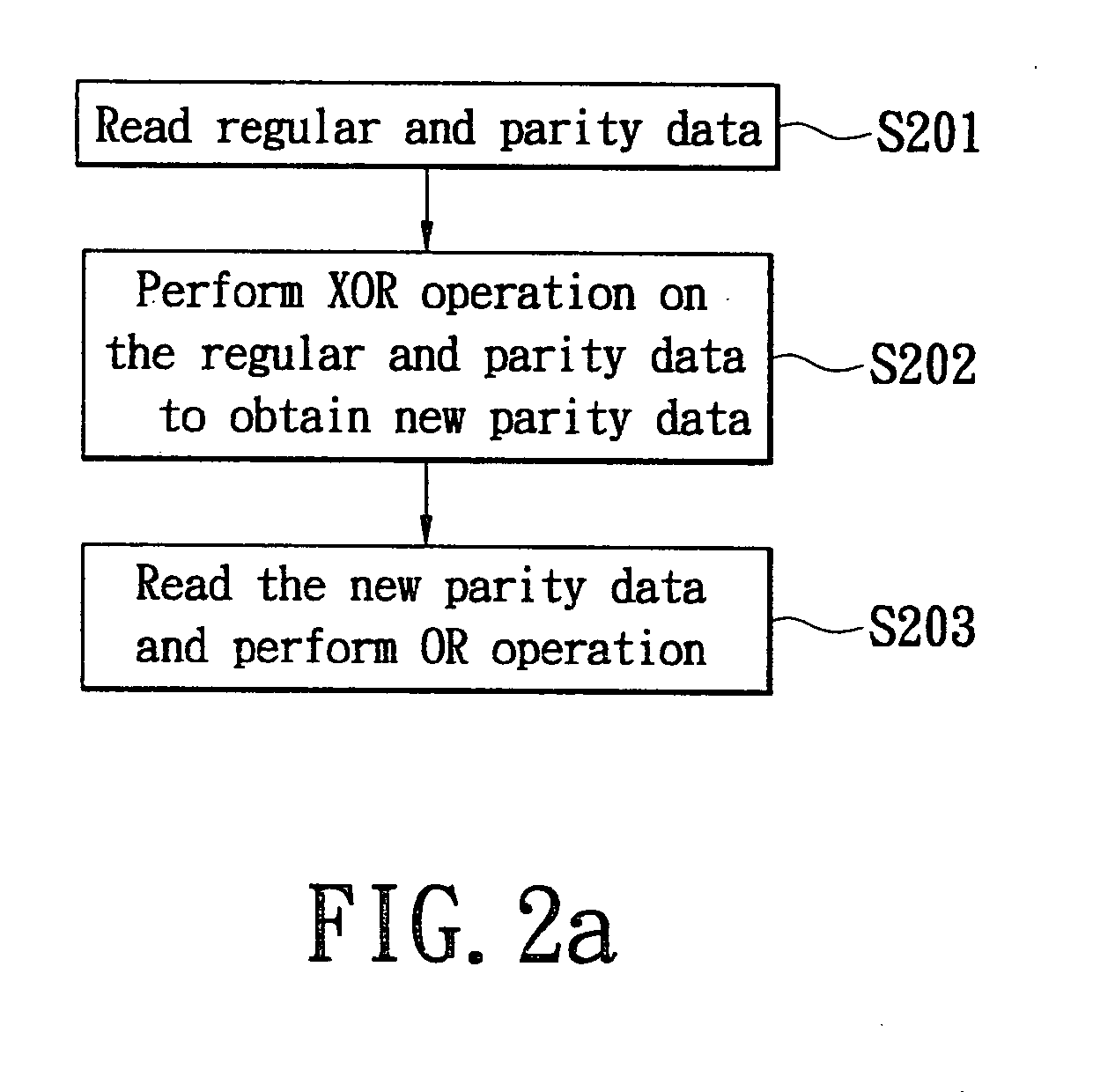
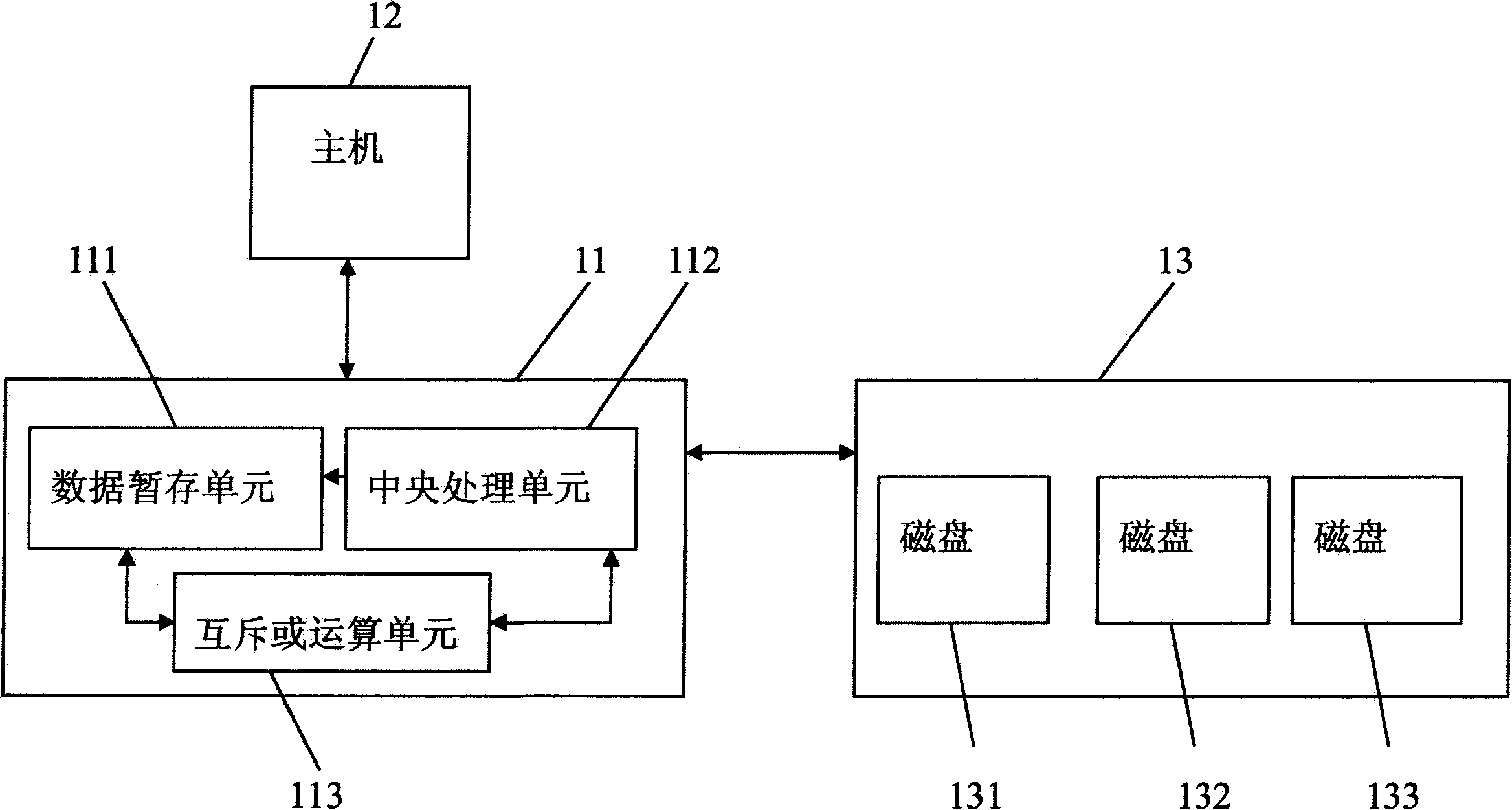
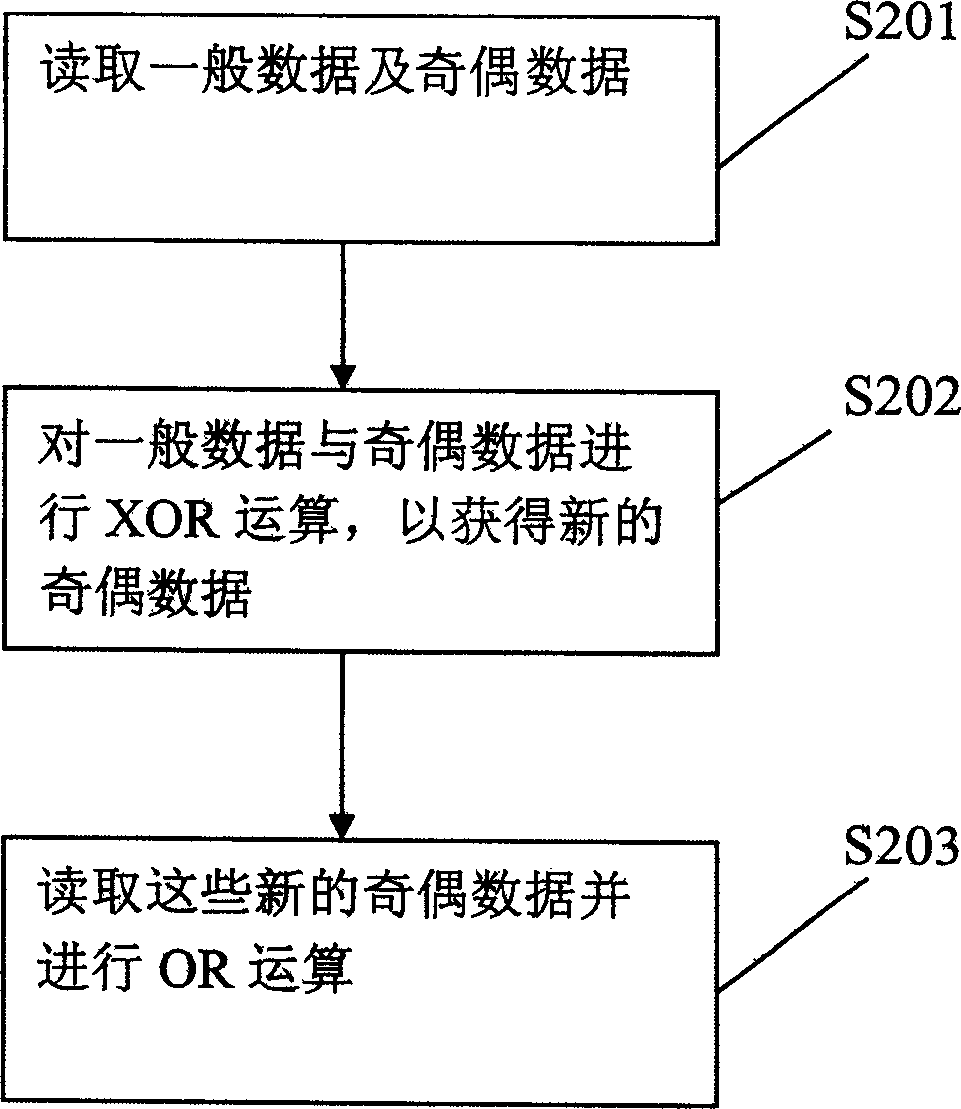
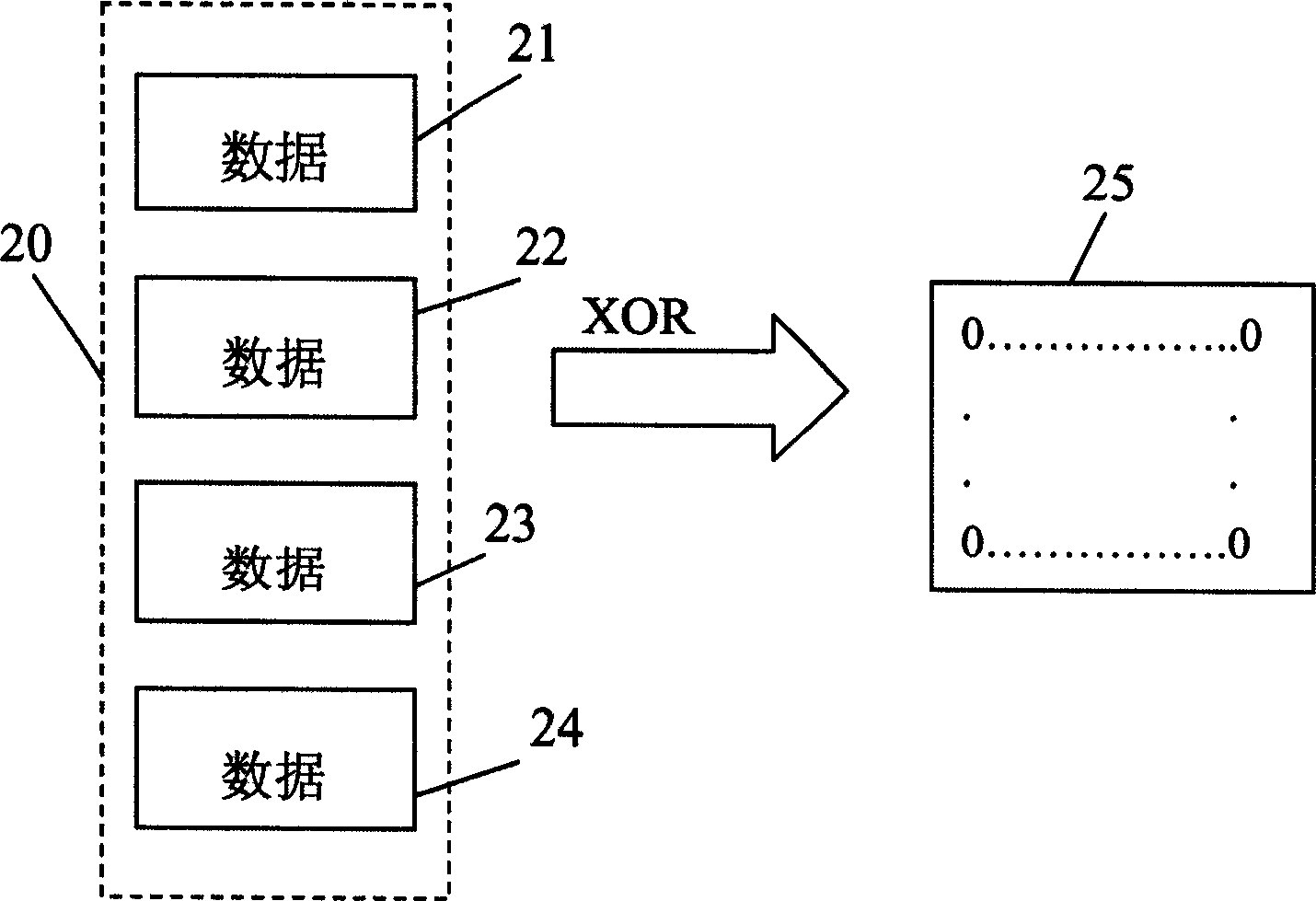
Apparatus for checking data coherence, raid controller and storage system having the same, and method therefor
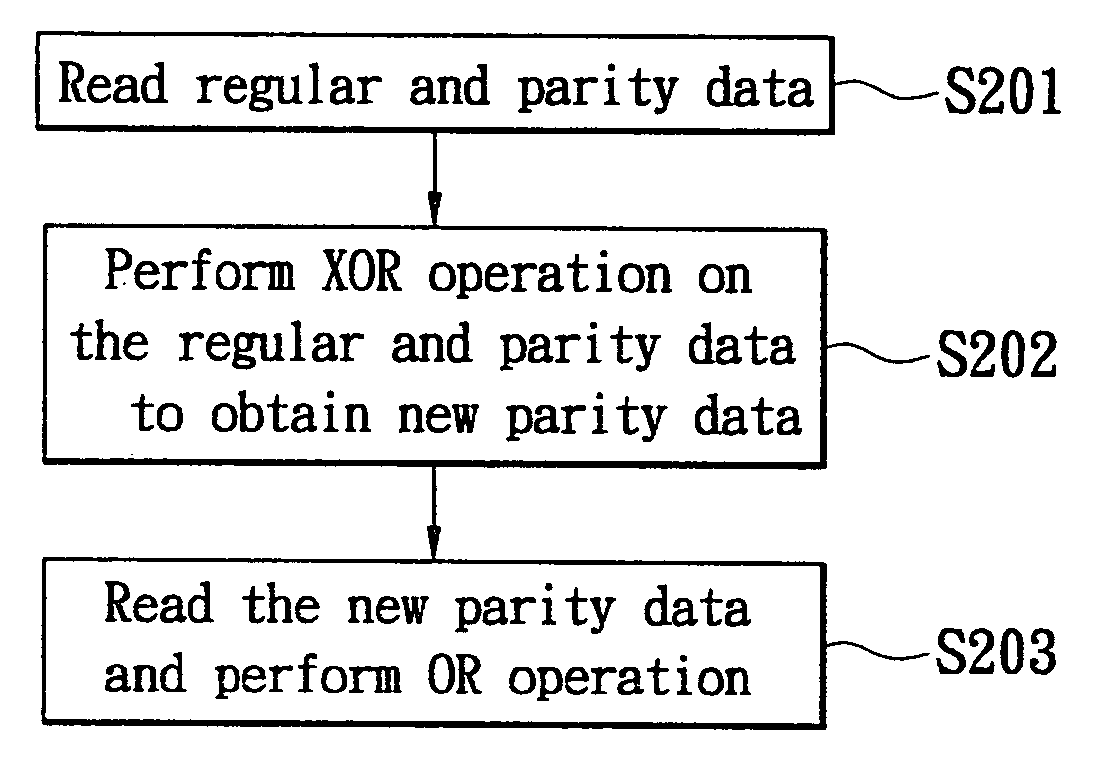
InactiveUS20050228842A1Efficient executionError detection/correctionStatic storageRAIDData coherence
Data coherence checking apparatus, a redundant array of independent disks (RAID) controller and a storage system having the checking apparatus and a method therefor are proposed. The present invention employs an XOR operation unit and an OR operation unit to check the coherence of data to be checked. The XOR operation unit is used to perform XOR operation on the data to be checked. After the XOR operation unit finishes performing the XOR operation on the data of a processing set, it outputs an XOR operation result to the OR operation unit to perform OR operation so as to obtain a check result.
Owner:INFORTREND TECH INC
Field-of-view matching device and method for astronomical positioning laser radar
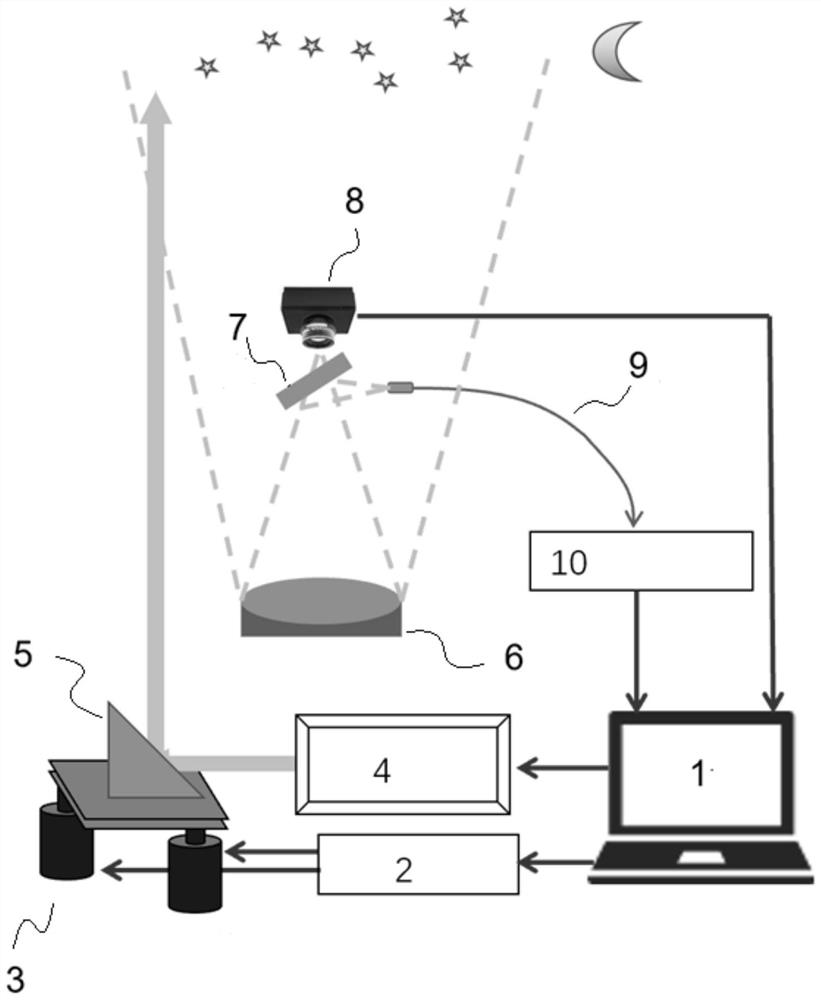
ActiveCN111693966AImprove inversion accuracyImprove temporal continuityWave based measurement systemsICT adaptationBeam splitterRadar systems
The invention discloses a field-of-view matching device of astronomical positioning laser radar, which comprises a computer, and further comprises a driver, an angle adjusting frame, a laser, a reflector, a receiving telescope, a spectroscope, a CCD camera, a receiving optical fiber and a signal detection system. The invention further discloses a field-of-view matching method for the astronomicalpositioning laser radar. Through monitoring and adjustment of the laser beam orientation, the data inversion precision of the laser radar is improved, the data coherence of the laser radar is effectively improved, the device and method are suitable for a coaxial or off-axis laser radar system, and an effective scheme is provided for accurate adjustment of the laser radar.
Owner:INNOVATION ACAD FOR PRECISION MEASUREMENT SCI & TECH CAS
Mobile switching centre imitated disaster tolerance recovery method based on visit position register
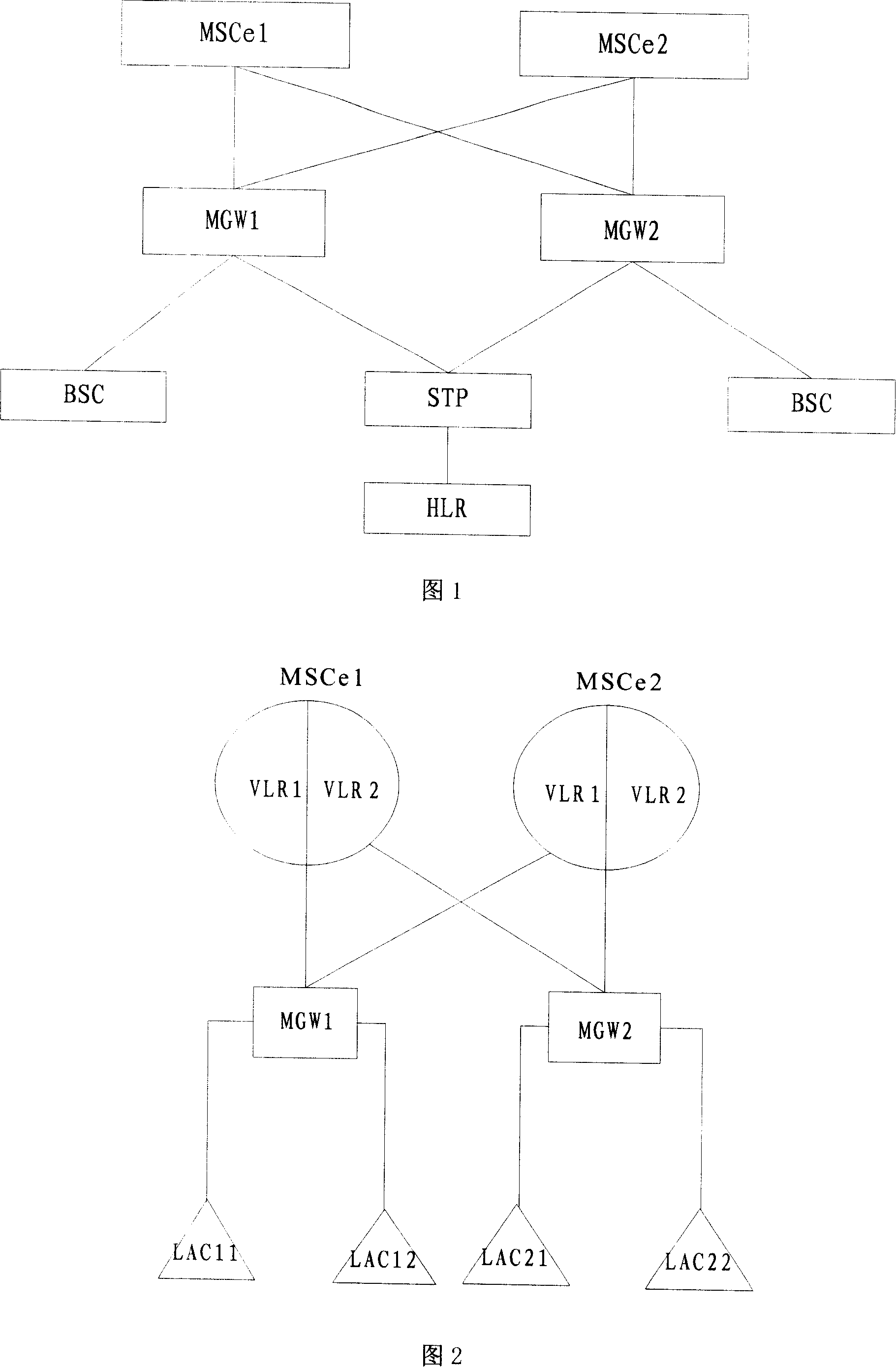
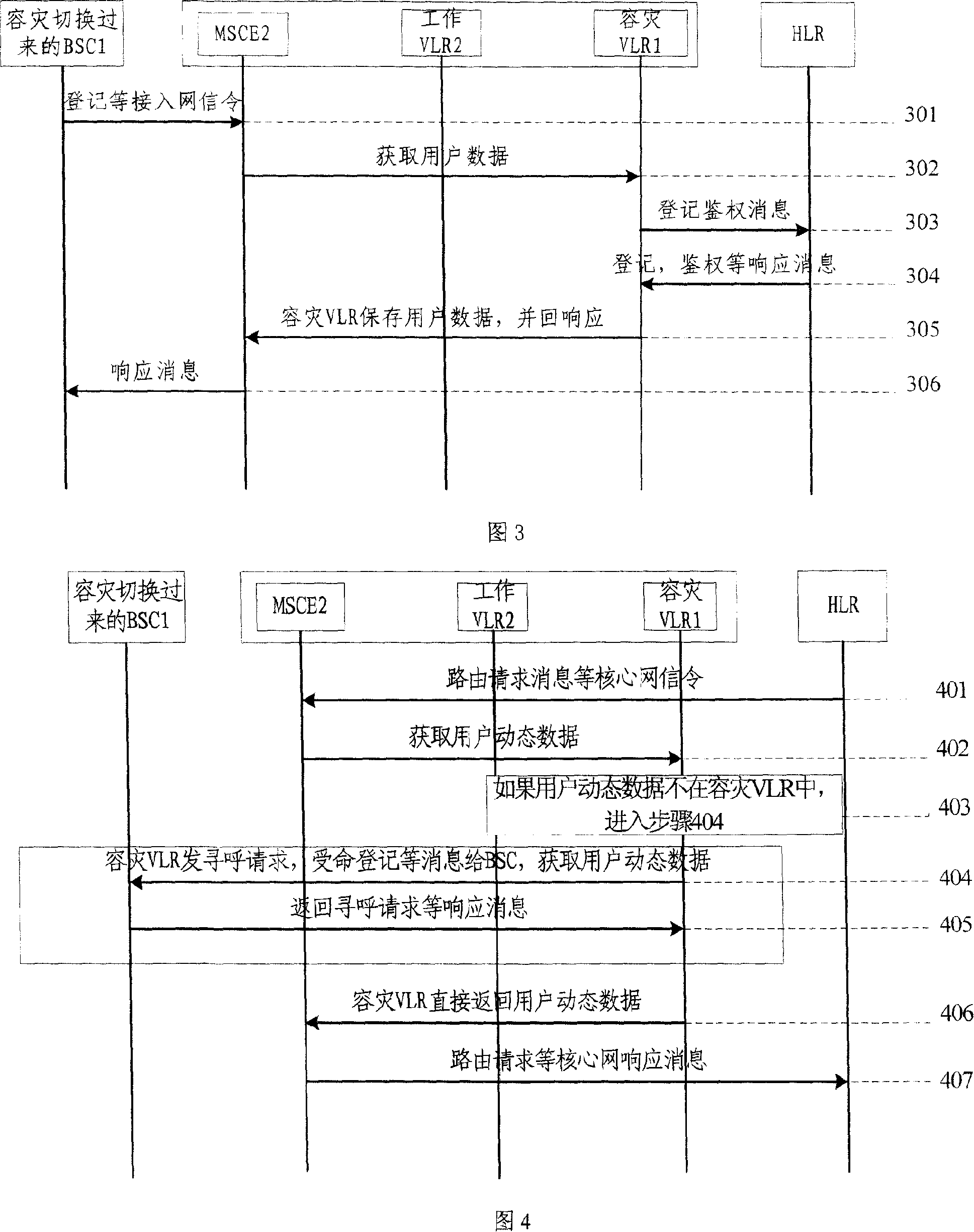
InactiveCN101155407ALow costReduce difficultyRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsNetwork data managementData synchronizationRecovery method
A mobile switching center emulation disaster recovery method based on an access position register is disclosed in the present invention. In order to resolve the problem of the hardware processes data to synchronize between two MSCes in prior art with high cost and big difficulty to invent. The present invention comprises the following steps: collocating network information of the main mobile switching center emulation on the standby mobile switching center emulation; when media gateway detects the main mobile switching center emulation generating fault, the standby mobile switching center emulation receives register of the media gateway and maintains its all services and signaling process; the standby mobile switching center emulation receives the gateway signaling sent by the media gateway, and process according to the user dynamic data and collocation. Thus can realize data coherence without synchronizing between the main MSCe and disaster recovery MSCe, and decrease the cost and difficulty for realizing the disaster recovery.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Apparatus for checking data coherence and method therefor, disk array controller and date storage system
Data coherence checking apparatus, a redundant array of independent disks (RAID) controller and a storage system having the checking apparatus and a method therefor are proposed. The present invention employs an XOR operation unit and an OR operation unit to check the coherence of data to be checked. The XOR operation unit is used to perform XOR operation on the data to be checked. After the XOR operation unit finishes performing the XOR operation on the data of a processing set, it outputs an XOR operation result to the OR operation unit to perform OR operation so as to obtain a check result.
Owner:INFORTREND TECH INC
Shared virtual memory management apparatus for providing cache-coherence
ActiveUS9208088B2Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationData coherenceVirtual memory
A shared virtual memory management apparatus for ensuring cache coherence. When two or more cores request write permission to the same virtual memory page, the shared virtual memory management apparatus allocates a physical memory page for the cores to change data in the allocated physical memory page. Thereafter, changed data is updated in an original physical memory page, and accordingly it is feasible to achieve data coherence in a multi-core hardware environment that does not provide cache coherence.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
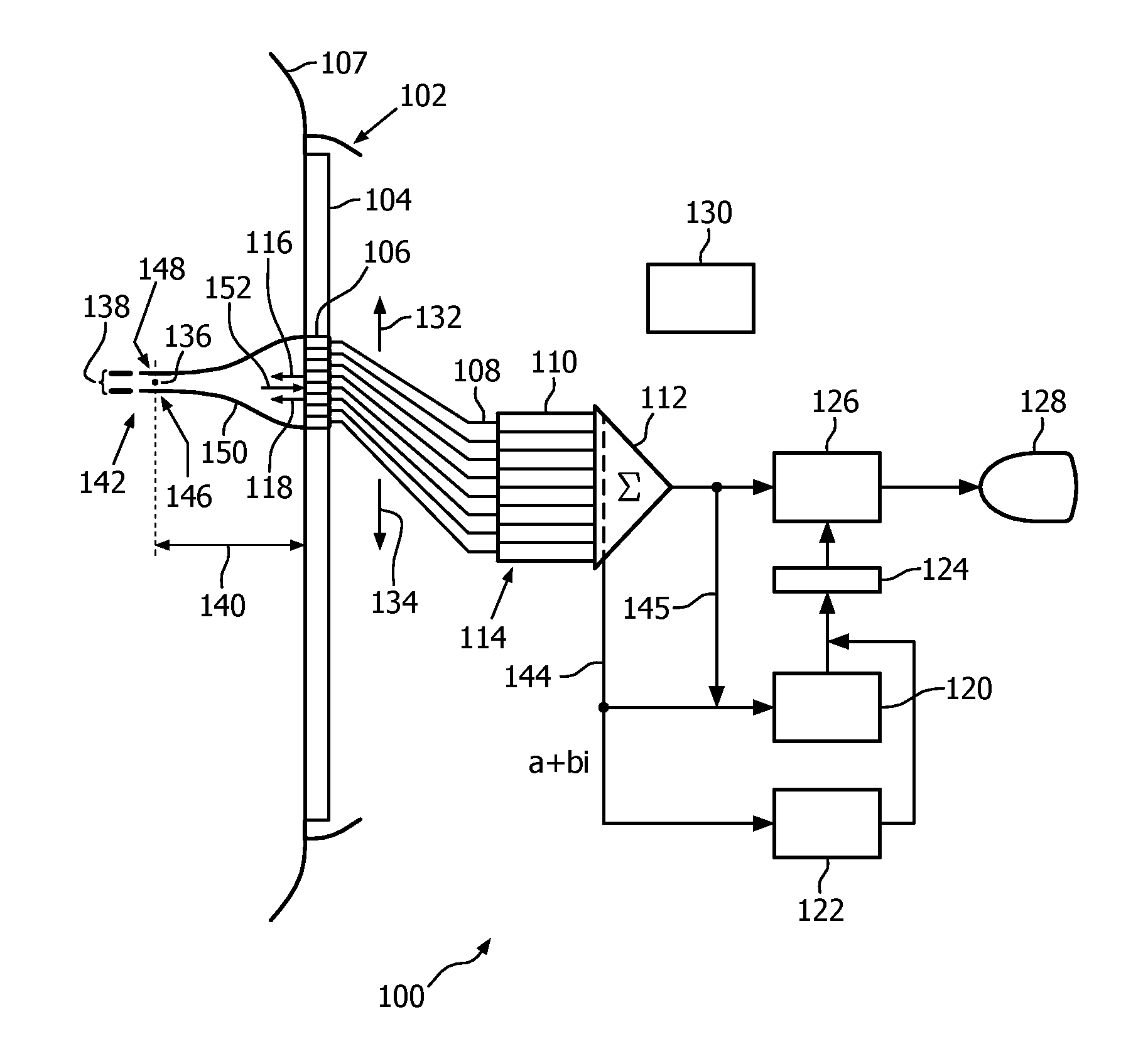
Beamforming techniques for ultrasound microcalcification detection
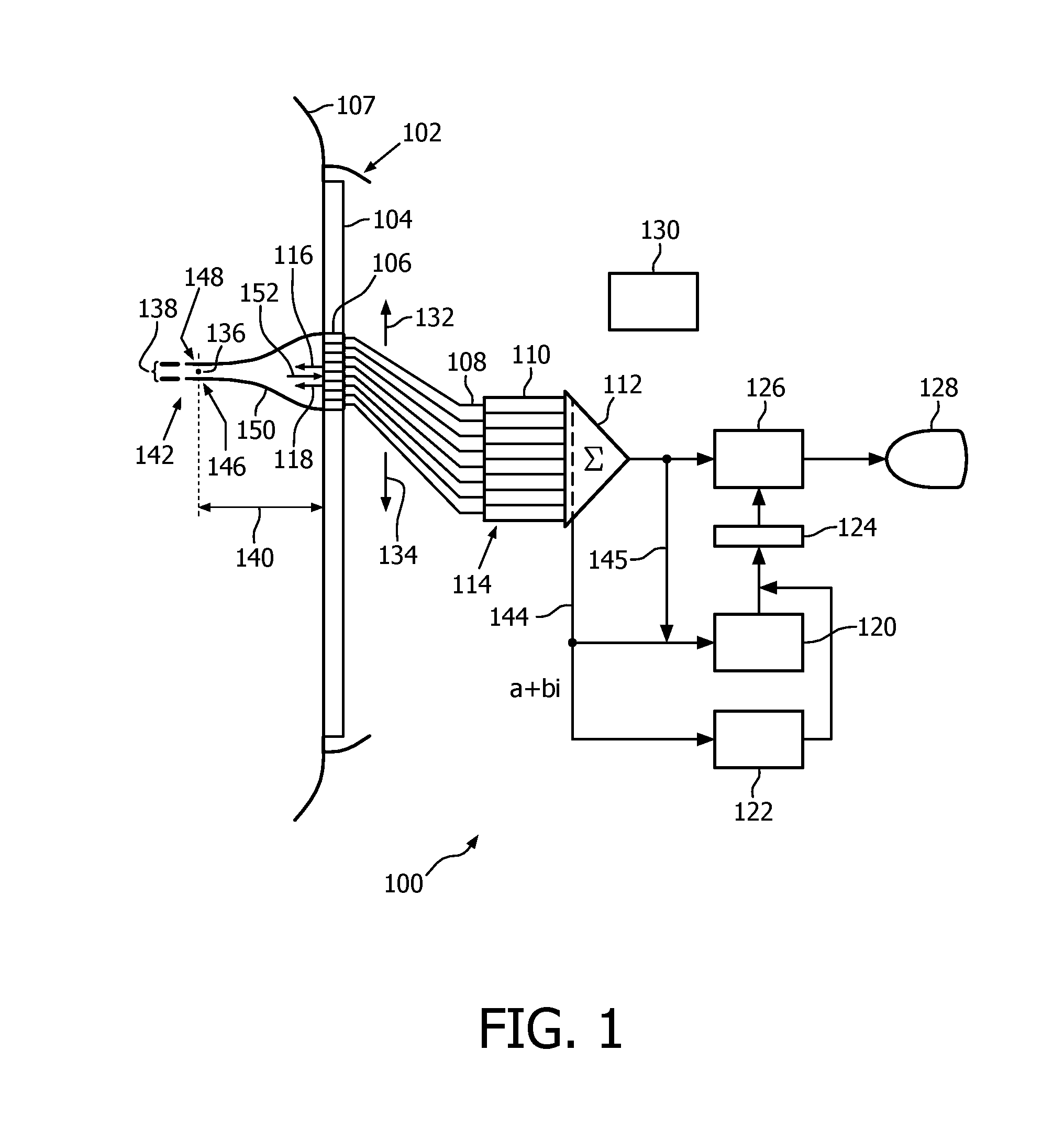
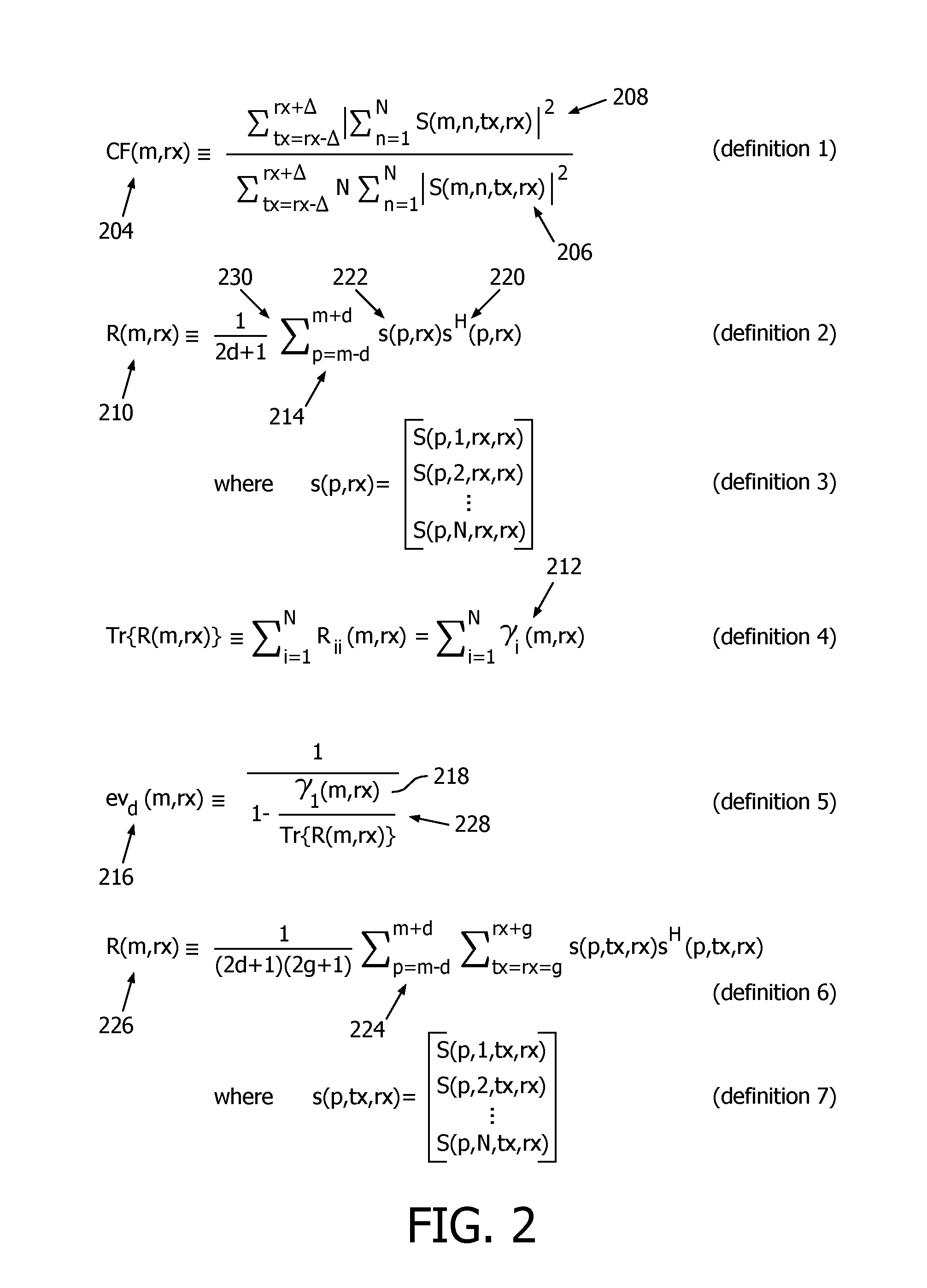
ActiveUS20160296202A1High sensitivityStrong specificityHealth-index calculationOrgan movement/changes detectionUltrasonographyChannel data
A medical ultrasound acquisition-data analysis device acquires channel data (144) via ultrasound received on the channels, uses the acquired channel data to estimate data coherence and derive dominance of an eigen-value of a channel covariance matrix and, based on the estimate and dominance, distinguishes microcalcifications (142) from background. Microcalcifications may then be made distinguishable visually on screen via highlighting, coloring, annotation, etc. The channel data operable upon by the estimating may have been subject to beamforming delays and may be summed in a beamforming procedure executed in the estimating. In the estimating and deriving, both field point-by-field point, multiple serial transmits (116, 118) may be used for each field point. In one embodiment results of the estimating and deriving are multiplied point-by-point and submitted to thresholding.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Improved mixed Freeman/Eigenvalue decomposition method
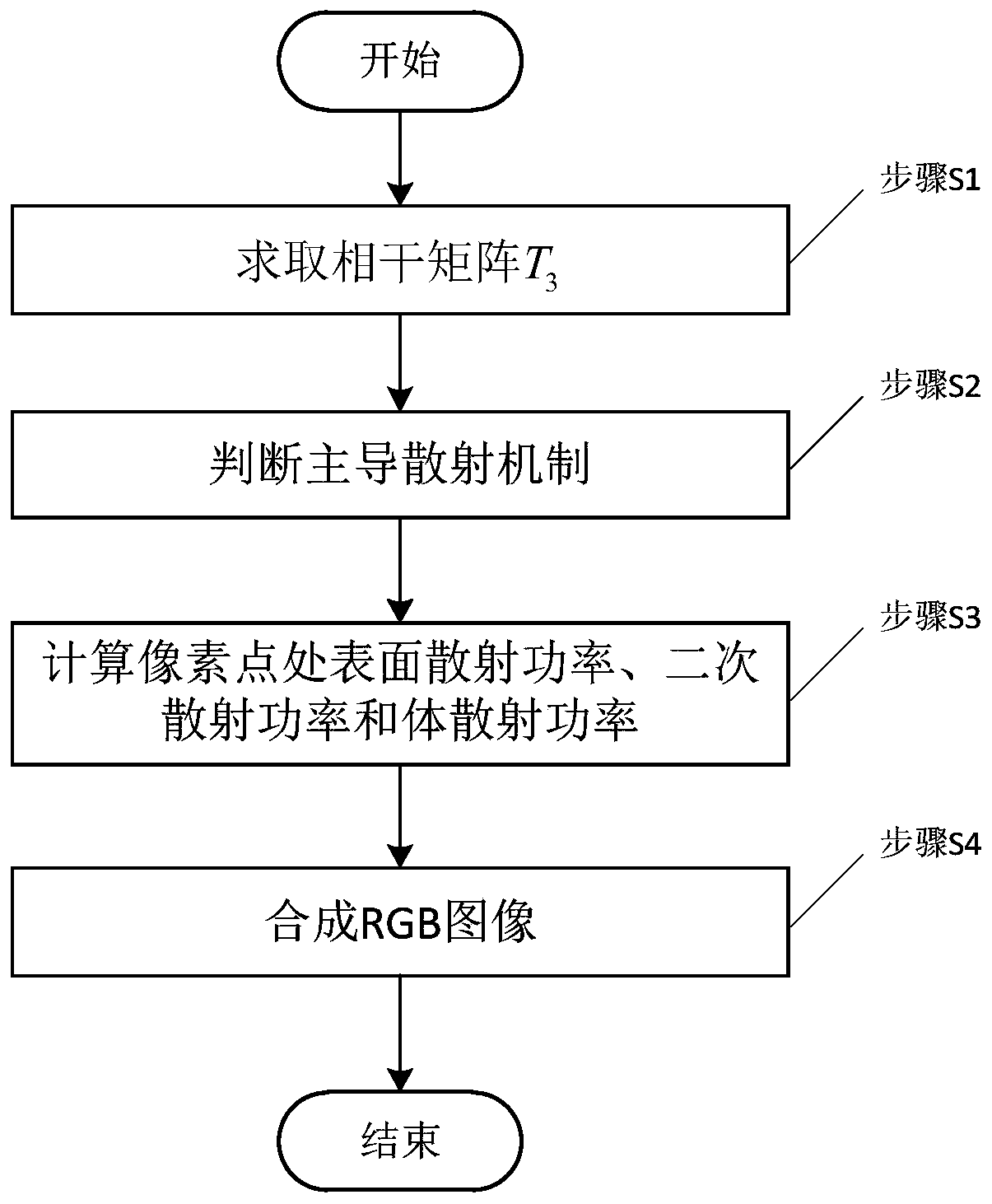
InactiveCN111125622ASolve problems that are limited and cannot always meet the actual situationSolve the phenomenon of negative powerScene recognitionComplex mathematical operationsData coherenceRegion selection
The invention discloses an improved hybrid Freeman / Eigenvalue decomposition method, and the method comprises the steps: obtaining a complete polarization SAR data coherence matrix, and carrying out the filtering; judging a dominant scattering mechanism at a pixel point in the fully polarimetric SAR data; calculating the surface scattering power, the secondary scattering power and the volume scattering power of the pixel point according to the judgment result of the dominant scattering mechanism; and obtaining a decomposed RGB composite image. According to the invention, the phenomenon of negative power generated by volume scattering power over-estimation, surface scattering and secondary scattering can be effectively solved; different volume scattering models are selected for a natural target area and an artificial target area, and a generalized volume scattering model is introduced for the natural target area, so that the problem that the volume scattering model of the traditional decomposition method is limited and cannot always meet the actual situation is solved. According to the method, a more accurate target scattering characteristic decomposition graph can be obtained, and more accurate classification categories can be obtained in ground object type classification.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com