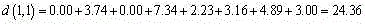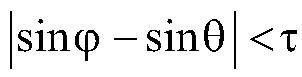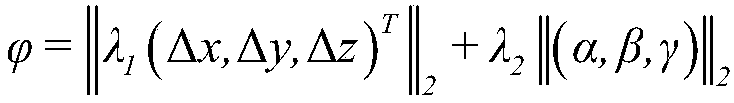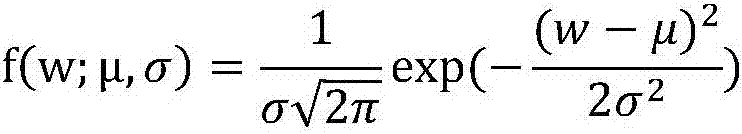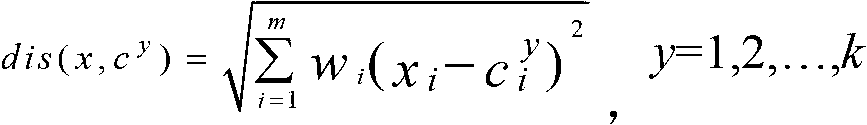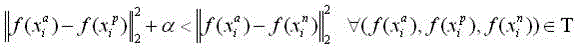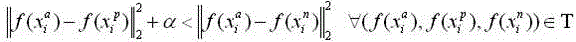Patents
Literature
3147 results about "Euclidean distance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In mathematics, the Euclidean distance or Euclidean metric is the "ordinary" straight-line distance between two points in Euclidean space. With this distance, Euclidean space becomes a metric space. The associated norm is called the Euclidean norm. Older literature refers to the metric as the Pythagorean metric. A generalized term for the Euclidean norm is the L² norm or L² distance.
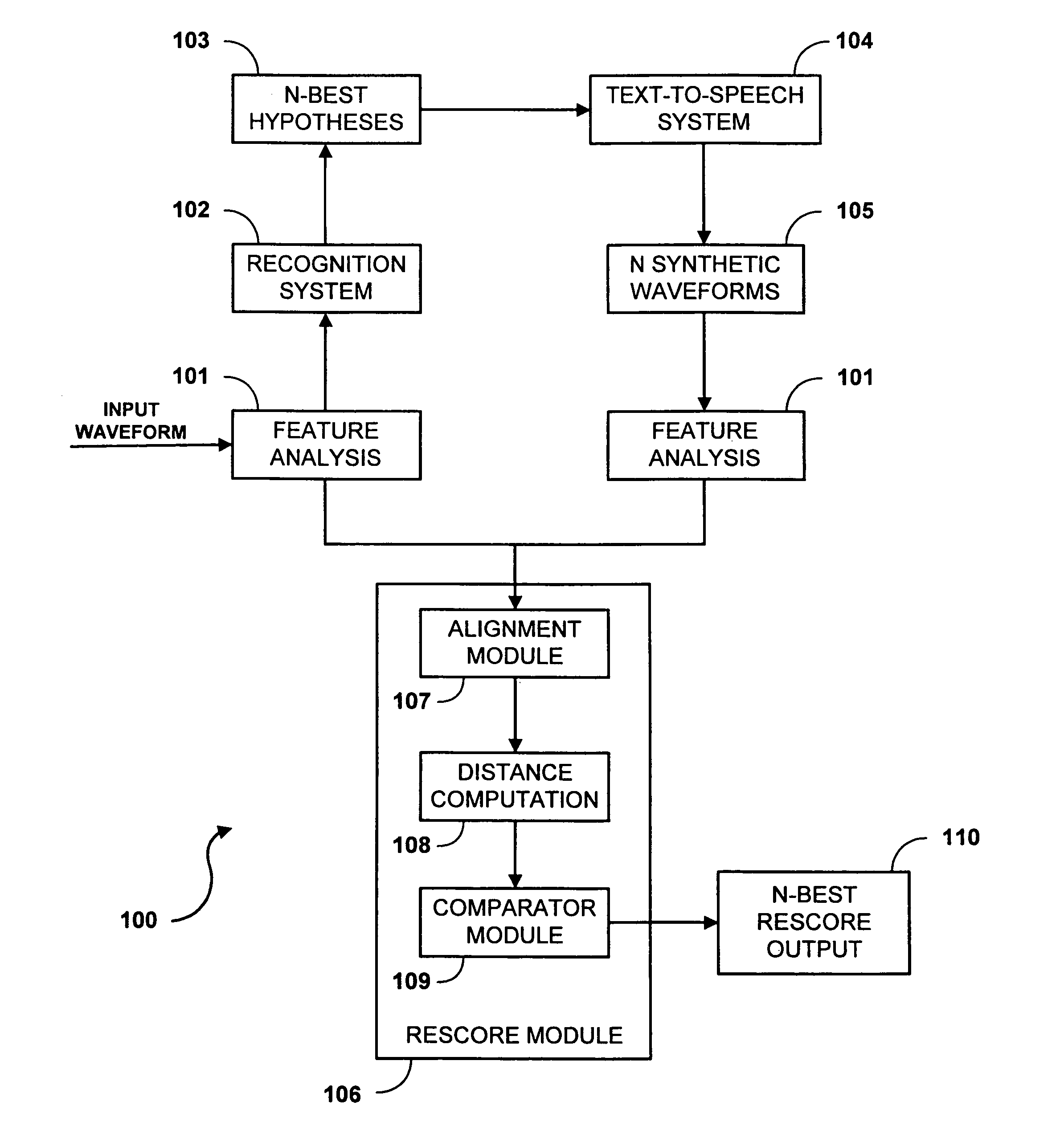
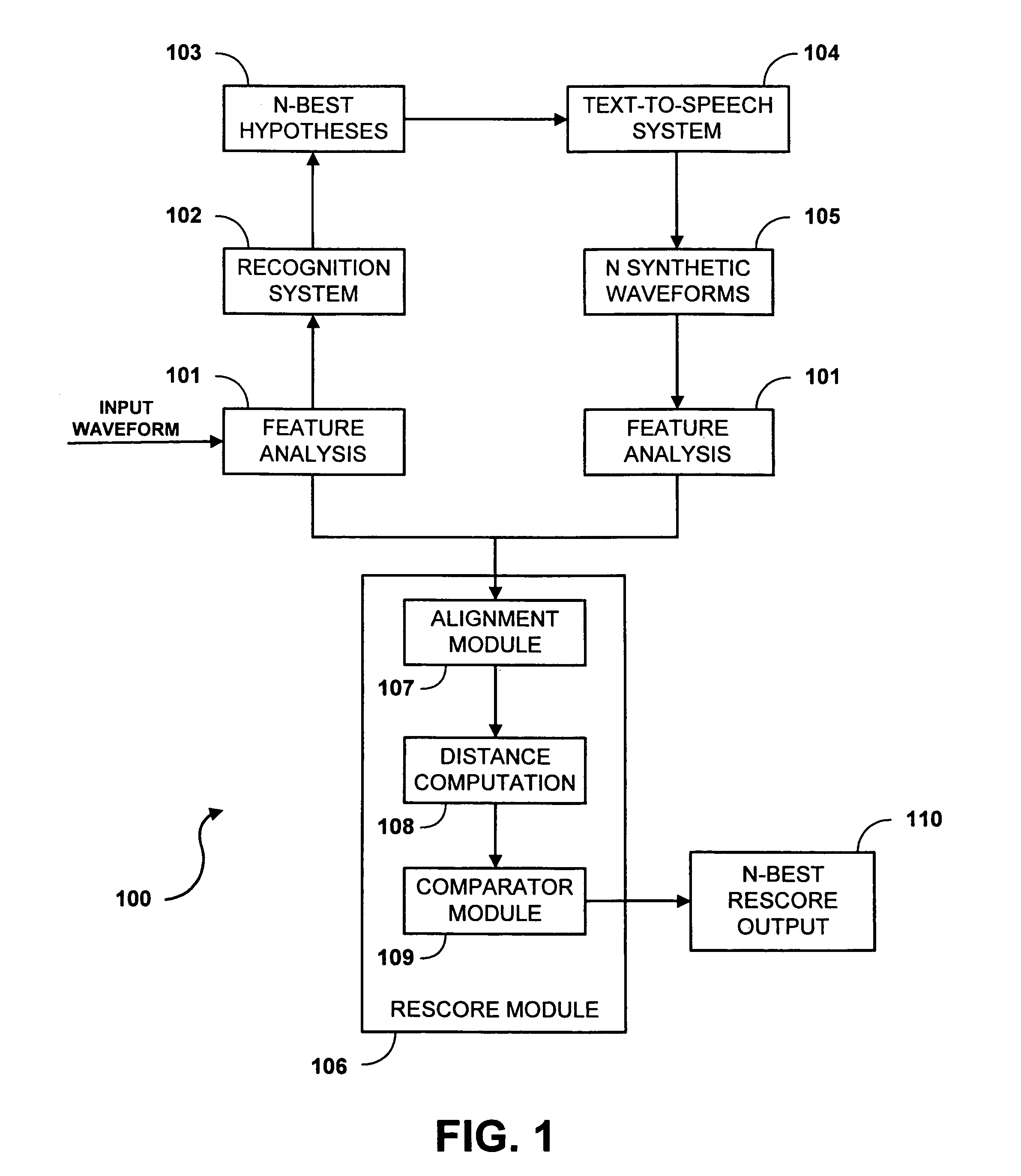
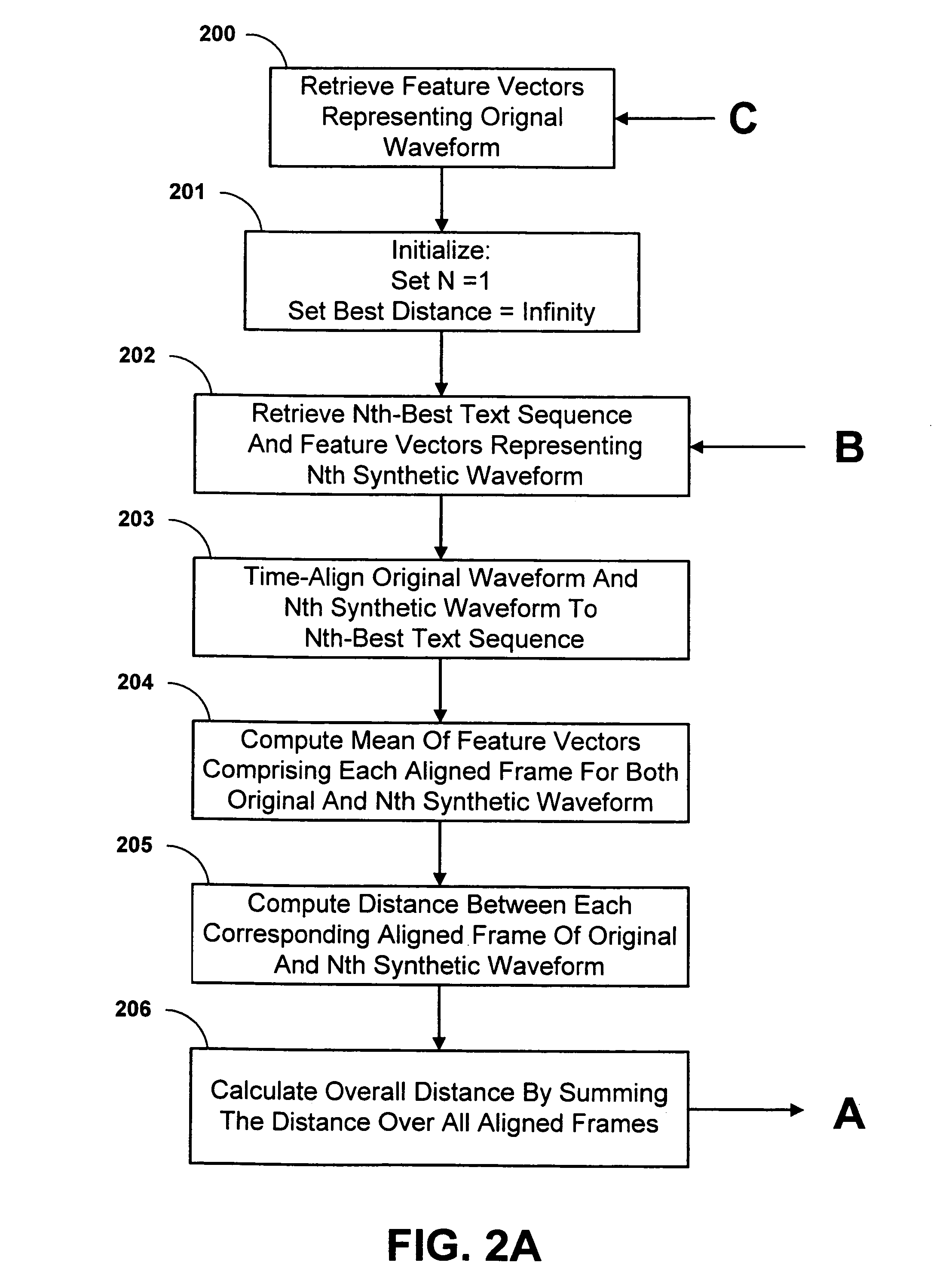
System and method for rescoring N-best hypotheses of an automatic speech recognition system
A system and method for rescoring the N-best hypotheses from an automatic speech recognition system by comparing an original speech waveform to synthetic speech waveforms that are generated for each text sequence of the N-best hypotheses. A distance is calculated from the original speech waveform to each of the synthesized waveforms, and the text associated with the synthesized waveform that is determined to be closest to the original waveform is selected as the final hypothesis. The original waveform and each synthesized waveform are aligned to a corresponding text sequence on a phoneme level. The mean of the feature vectors which align to each phoneme is computed for the original waveform as well as for each of the synthesized hypotheses. The distance of a synthesized hypothesis to the original speech signal is then computed as the sum over all phonemes in the hypothesis of the Euclidean distance between the means of the feature vectors of the frames aligning to that phoneme for the original and the synthesized signals. The text of the hypothesis which is closest under the above metric to the original waveform is chosen as the final system output.
Owner:IBM CORP
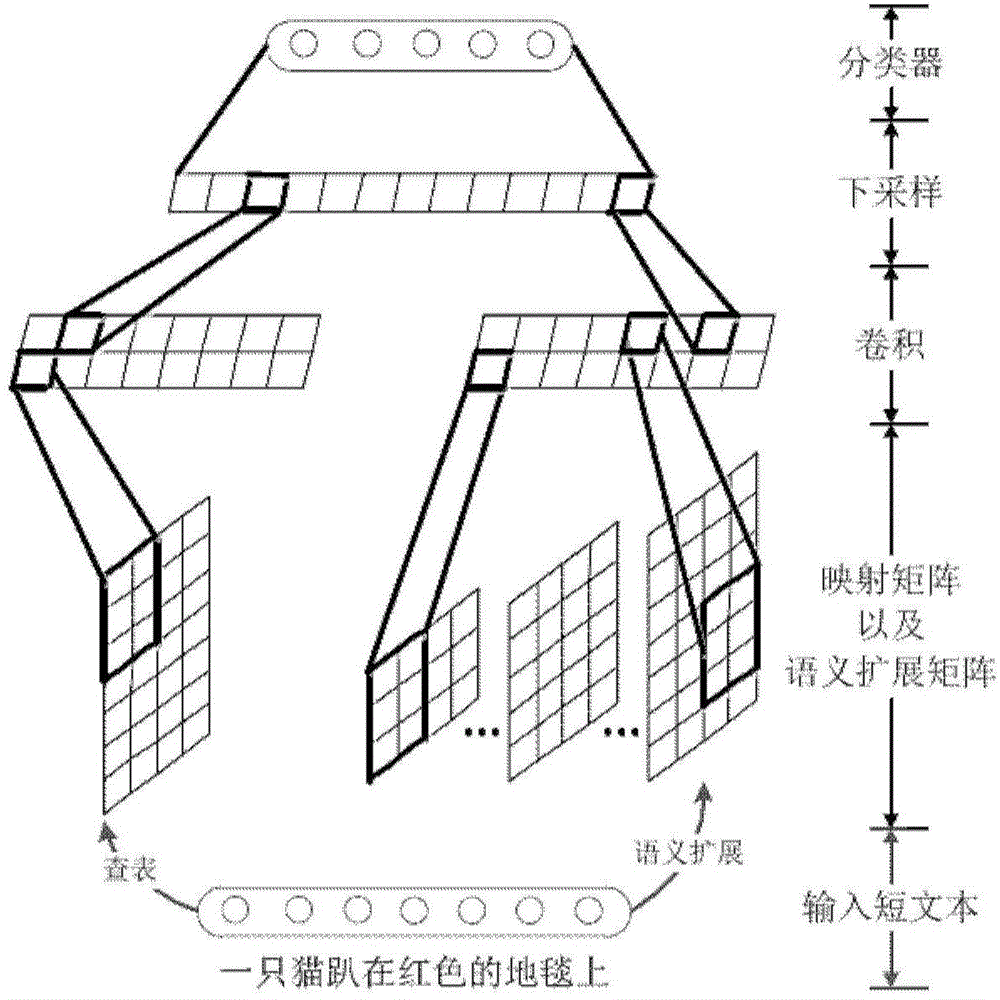
Short text classification method based on convolution neutral network
ActiveCN104834747AImprove semantic sensitivity issuesImprove classification performanceInput/output for user-computer interactionBiological neural network modelsNear neighborClassification methods
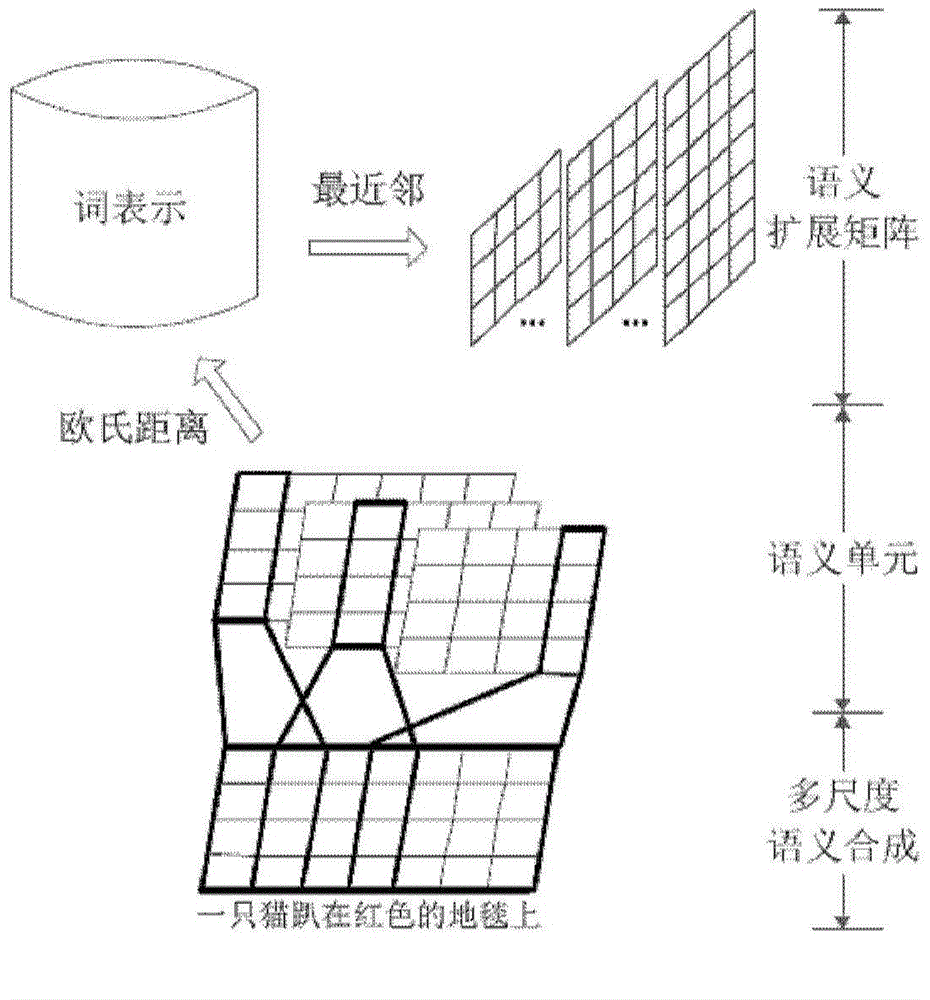
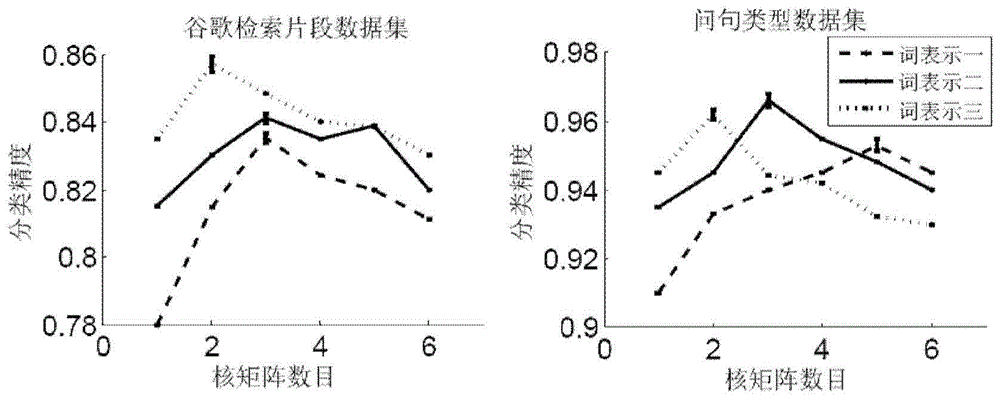
The invention discloses a short text classification method based on a convolution neutral network. The convolution neutral network comprises a first layer, a second layer, a third layer, a fourth layer and a fifth layer. On the first layer, multi-scale candidate semantic units in a short text are obtained; on the second layer, Euclidean distances between each candidate semantic unit and all word representation vectors in a vector space are calculated, nearest-neighbor word representations are found, and all the nearest-neighbor word representations meeting a preset Euclidean distance threshold value are selected to construct a semantic expanding matrix; on the third layer, multiple kernel matrixes of different widths and different weight values are used for performing two-dimensional convolution calculation on a mapping matrix and the semantic expanding matrix of the short text, extracting local convolution features and generating a multi-layer local convolution feature matrix; on the fourth layer, down-sampling is performed on the multi-layer local convolution feature matrix to obtain a multi-layer global feature matrix, nonlinear tangent conversion is performed on the global feature matrix, and then the converted global feature matrix is converted into a fixed-length semantic feature vector; on the fifth layer, a classifier is endowed with the semantic feature vector to predict the category of the short text.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method and apparatus for providing real-time animation utilizing a database of postures
InactiveUS6163322AReduce computing timeInput/output for user-computer interactionAnimationPhysical MarkingAnimation
A method and apparatus for animating a synthetic body part. The 3D-animation system and method use a database of basic postures. In a first step, for each frame, a linear combination of the basic postures from a database of basic postures is obtained by minimizing the Euclidean distance between the displacement of critical points. The displacement information is supplied externally, and typically can be obtained by observing the displacement of physical markers placed on a moving physical body part in the real world. For instance, the synthetic body part may be an expression of a human face and the displacement data are obtained by observing physical markers placed on the face of an actor. The linear combination of the postures in the database of postures is then used to construct the desired posture. Postures are constructed for each time frame and are then displayed consecutively to provide animation. A computer readable storage medium containing a program element to direct a processor of a computer to implement the animation process is also provided.
Owner:TAARNA STUDIOS
Three-dimensional reconstruction method based on coding structured light
ActiveCN101667303ASimple calculationImprove matching accuracyImage analysisUsing optical meansTemplate matchingFeature vector
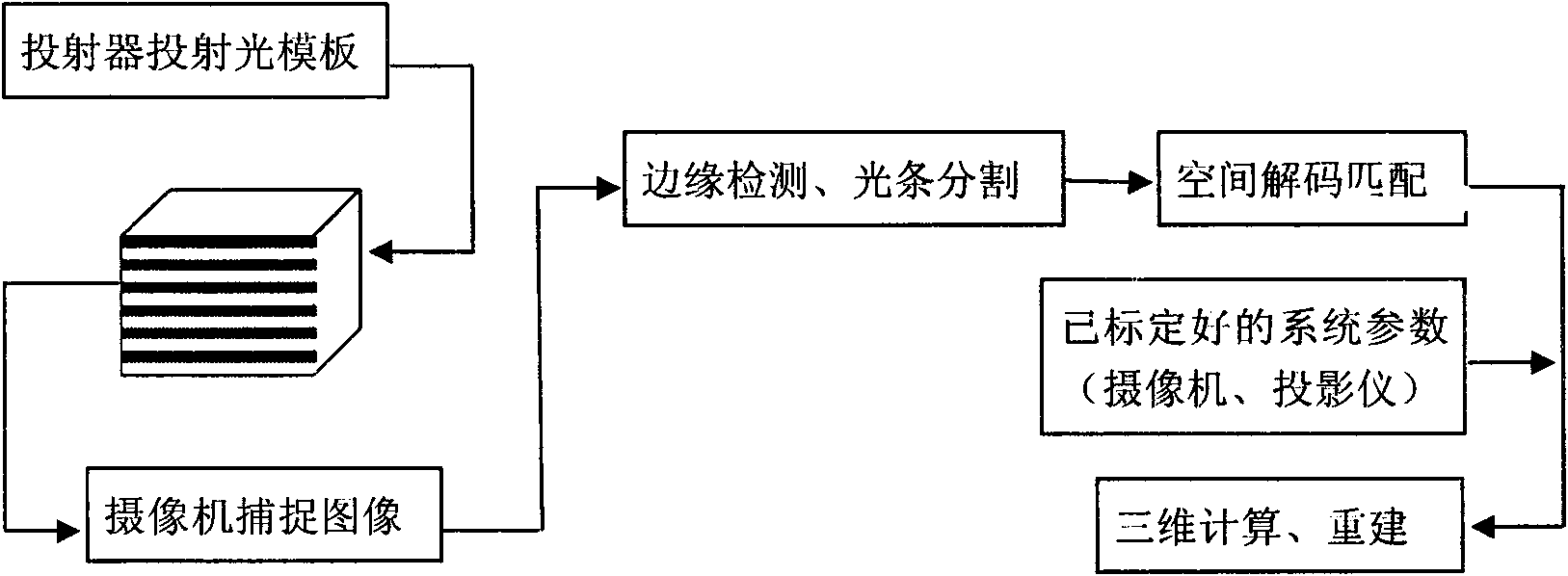
The invention discloses a three-dimensional reconstruction method based on coding structured light, comprising the following steps: 1) projecting structured light to an object to be measured, and capturing an image modulated by the object to be measured by a camera; 2) matching an optical template, comprising: (2.1) positioning the optical strip boundary, scanning along each row of the image, determining a pixel point with strong gray variation as a candidate marginal point, and searching a local domain; and (2.2) matching the optical strip: adopting a color cluster method to build a color matching proper vector, comparing image color with a projected color, and defining Euclidean distance between the color proper vector and the cluster center to distribute the colors of red, green, blue and white of the candidate optical strip; and 3) using a calibrated system parameter for three-dimensional reconstruction of the object to be measured, determining the relation between a space point coordinate and the image coordinate point thereof by the calibrated conversion matrix parameter; and restoring three-dimensional spatial coordinate from the image coordinate of a feature point. The invention can simplify calculation process and has high matching precision and high reconstruction precision.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
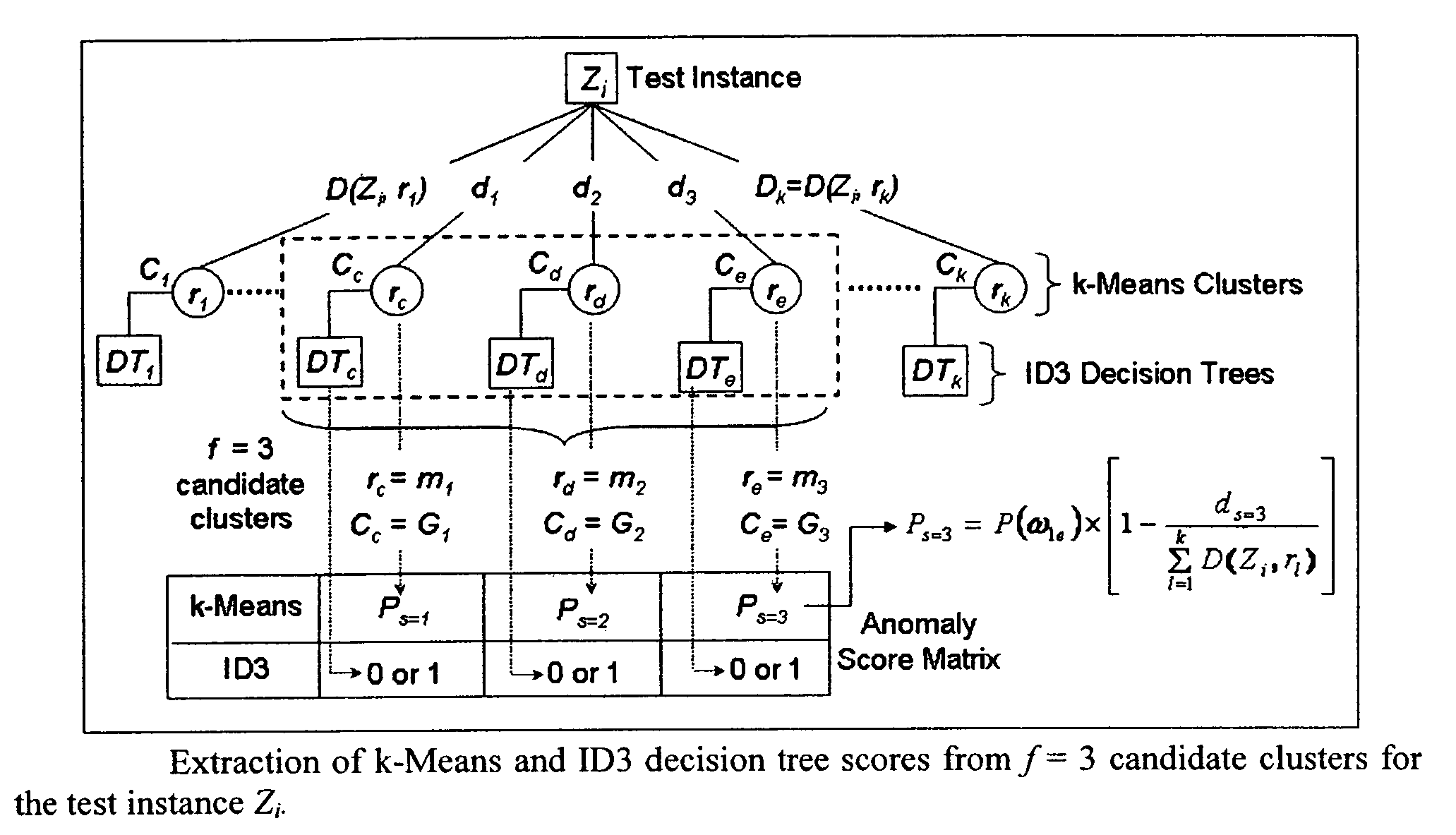
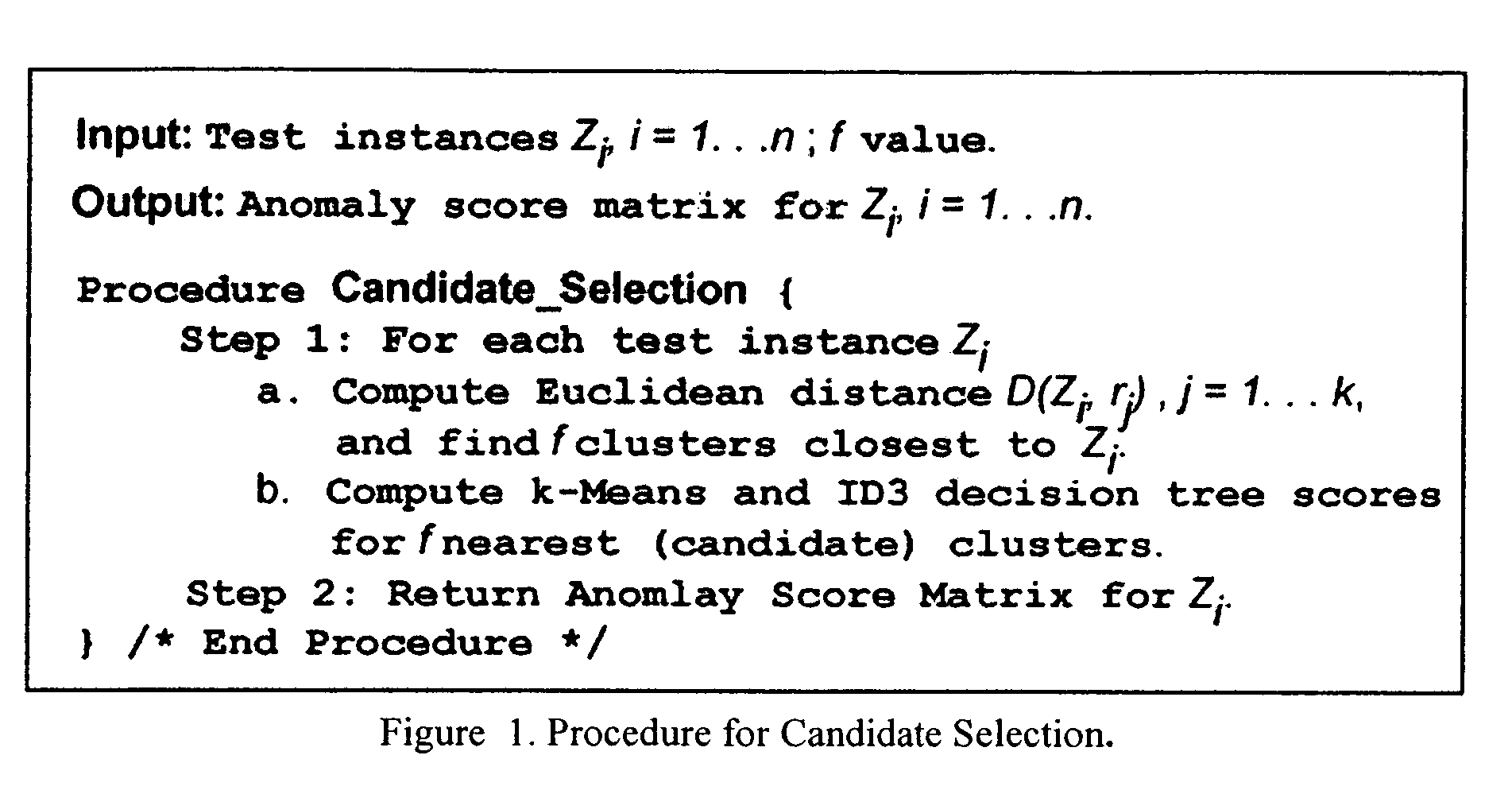
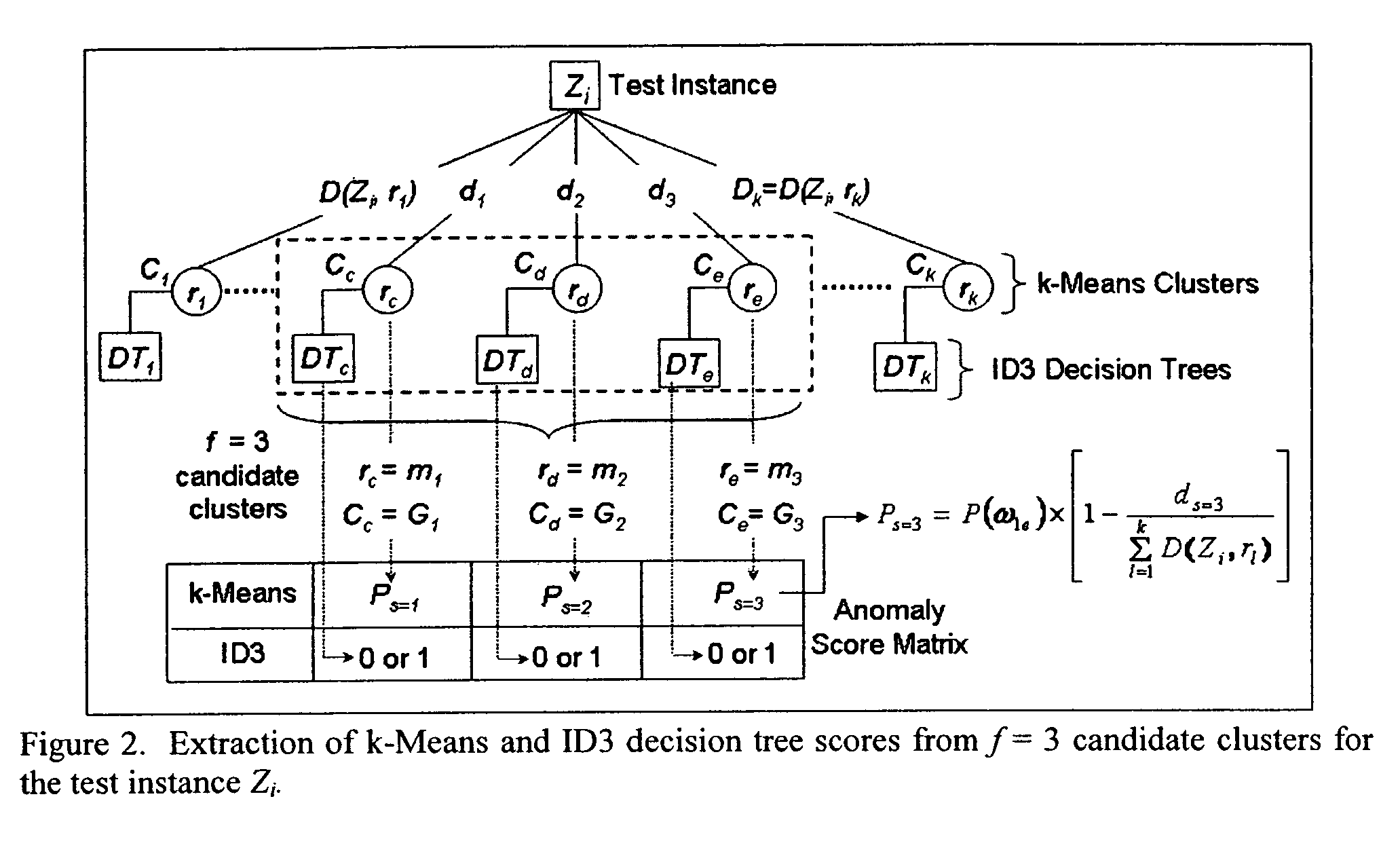
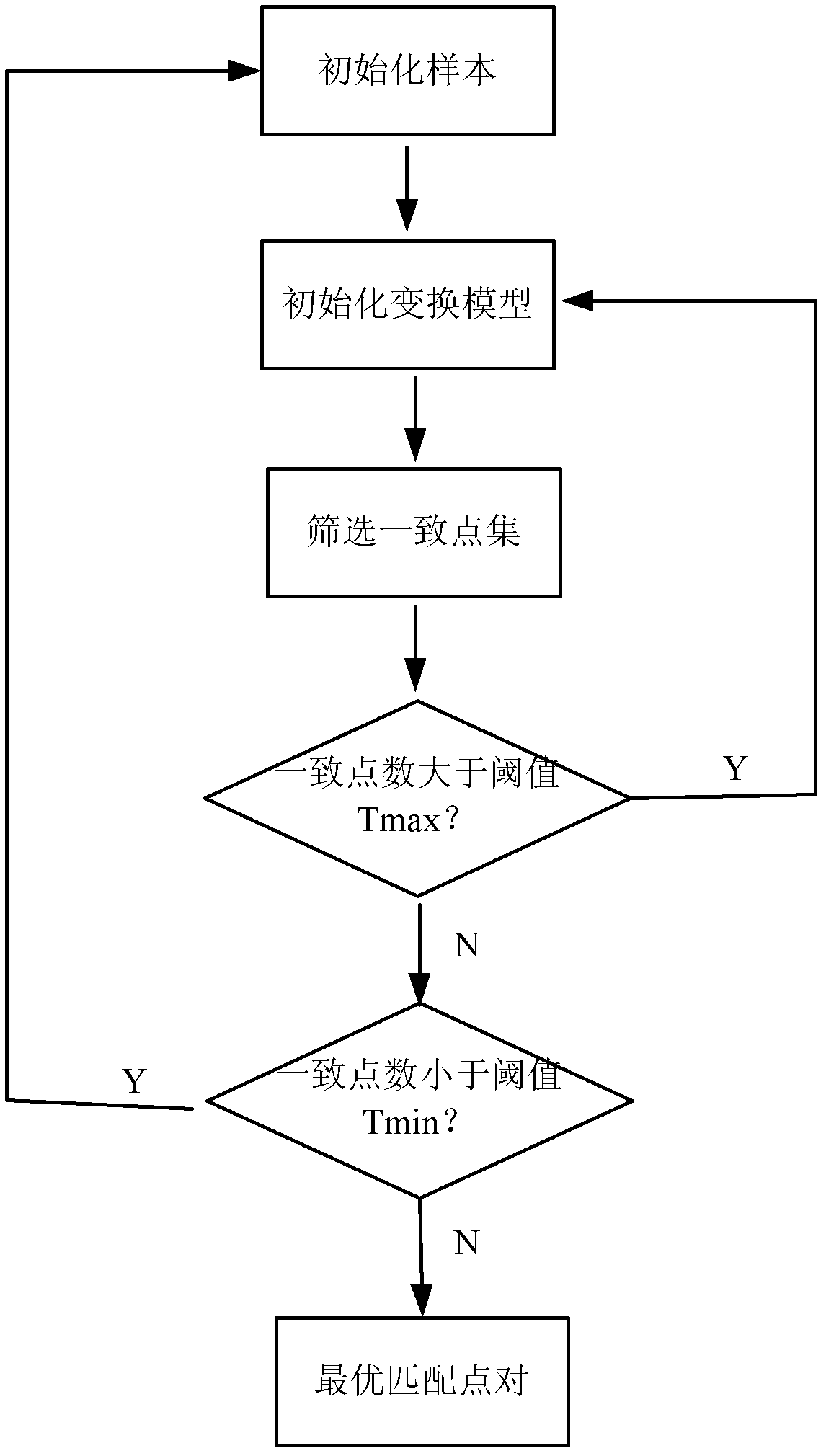
Method to indentify anomalous data using cascaded K-Means clustering and an ID3 decision tree
The invention is a computer implemented technique for id entifying anomalous data in a data set. The method uses cascaded k-Means clustering and the ID3 decision tree learning methods to characterize a training data set having data points with known characterization. The k-Means clustering method first partitions the training instances into k clusters using Euclidean distance similarity. On each training cluster, representing a density region of normal or anomaly instances, the invention builds an ID3 decision tree. The decision tree on each cluster refines the decision boundaries by learning the sub-groups within the cluster. A test data point is then subjected to the clustering and decision trees constructed form the training instances. To obtain a final decision on classification, the decisions of the k-Means and ID3 methods are combined using rules: (1) the Nearest-neighbor rule, and (2) the Nearest-consensus rule.
Owner:LOUISIANA TECH RES CORP
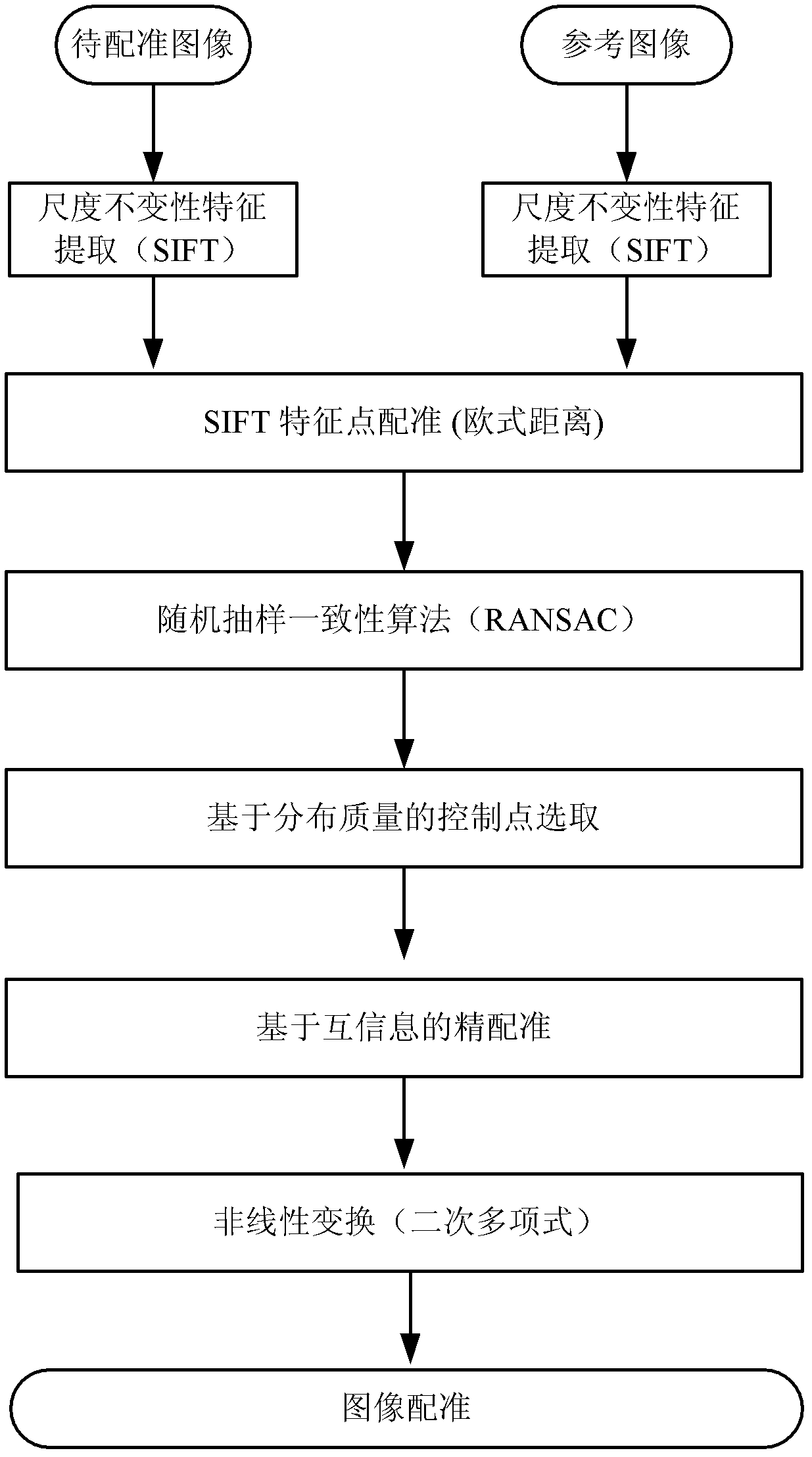
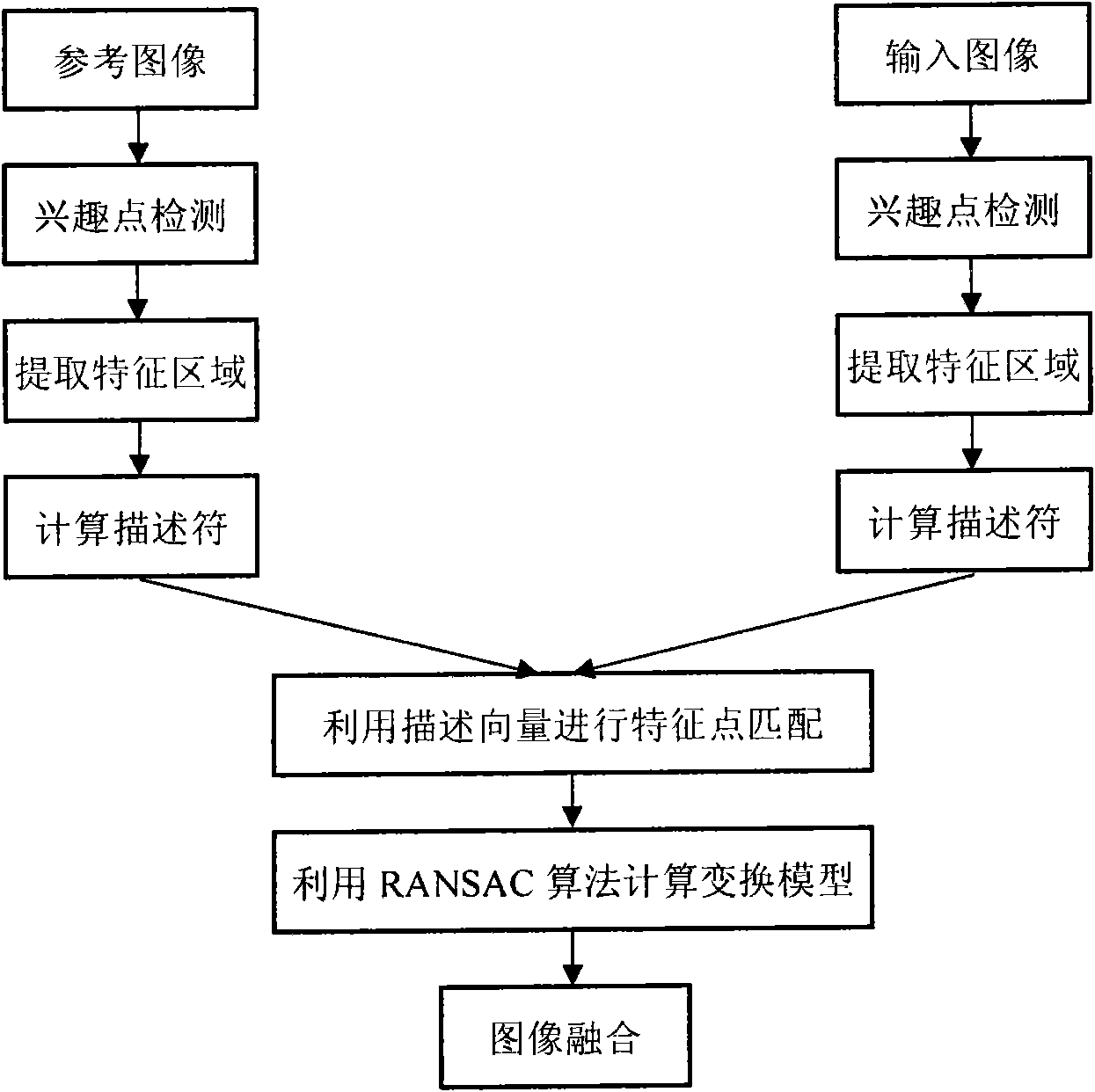
Remote sensing image registration method of multi-source sensor
ActiveCN103020945AQuick registrationPrecise registrationImage analysisWeight coefficientMutual information
The invention provides a remote sensing image registration method of a multi-source sensor, relating to an image processing technology. The remote sensing image registration method comprises the following steps of: respectively carrying out scale-invariant feature transform (SIFT) on a reference image and a registration image, extracting feature points, calculating the nearest Euclidean distances and the nearer Euclidean distances of the feature points in the image to be registered and the reference image, and screening an optimal matching point pair according to a ratio; rejecting error registration points through a random consistency sampling algorithm, and screening an original registration point pair; calculating distribution quality parameters of feature point pairs and selecting effective control point parts with uniform distribution according to a feature point weight coefficient; searching an optimal registration point in control points of the image to be registered according to a mutual information assimilation judging criteria, thus obtaining an optimal registration point pair of the control points; and acquiring a geometric deformation parameter of the image to be registered by polynomial parameter transformation, thus realizing the accurate registration of the image to be registered and the reference image. The remote sensing image registration method provided by the invention has the advantages of high calculation speed and high registration precision, and can meet the registration requirements of a multi-sensor, multi-temporal and multi-view remote sensing image.
Owner:济钢防务技术有限公司
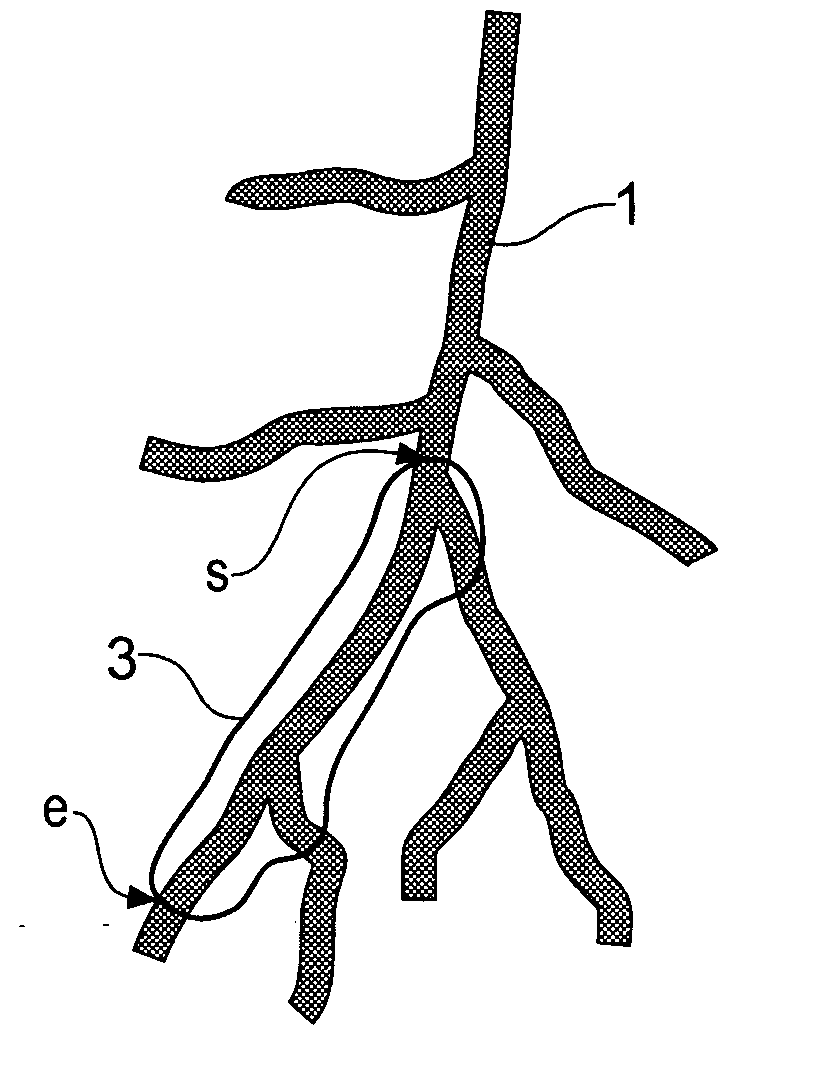
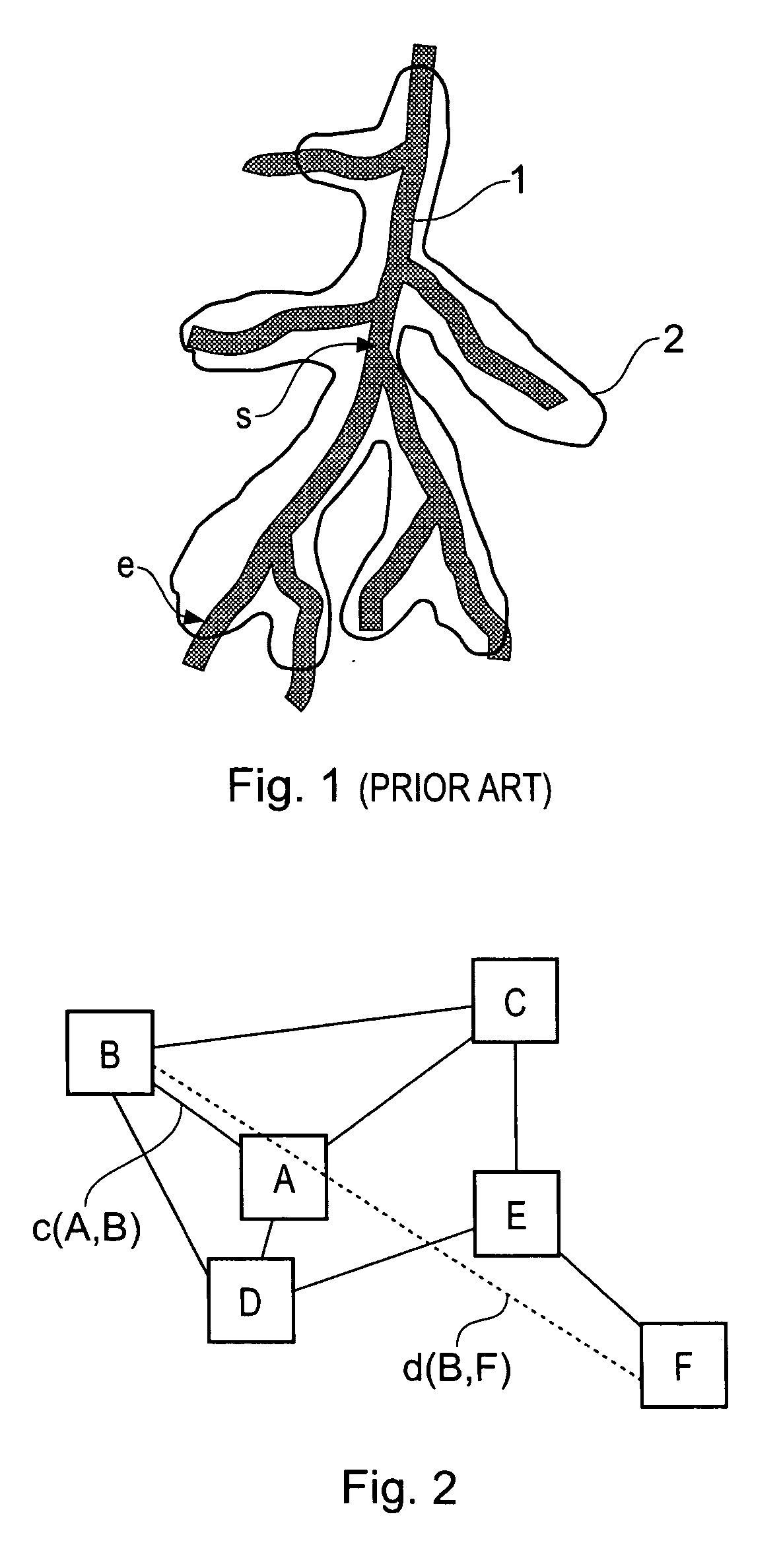
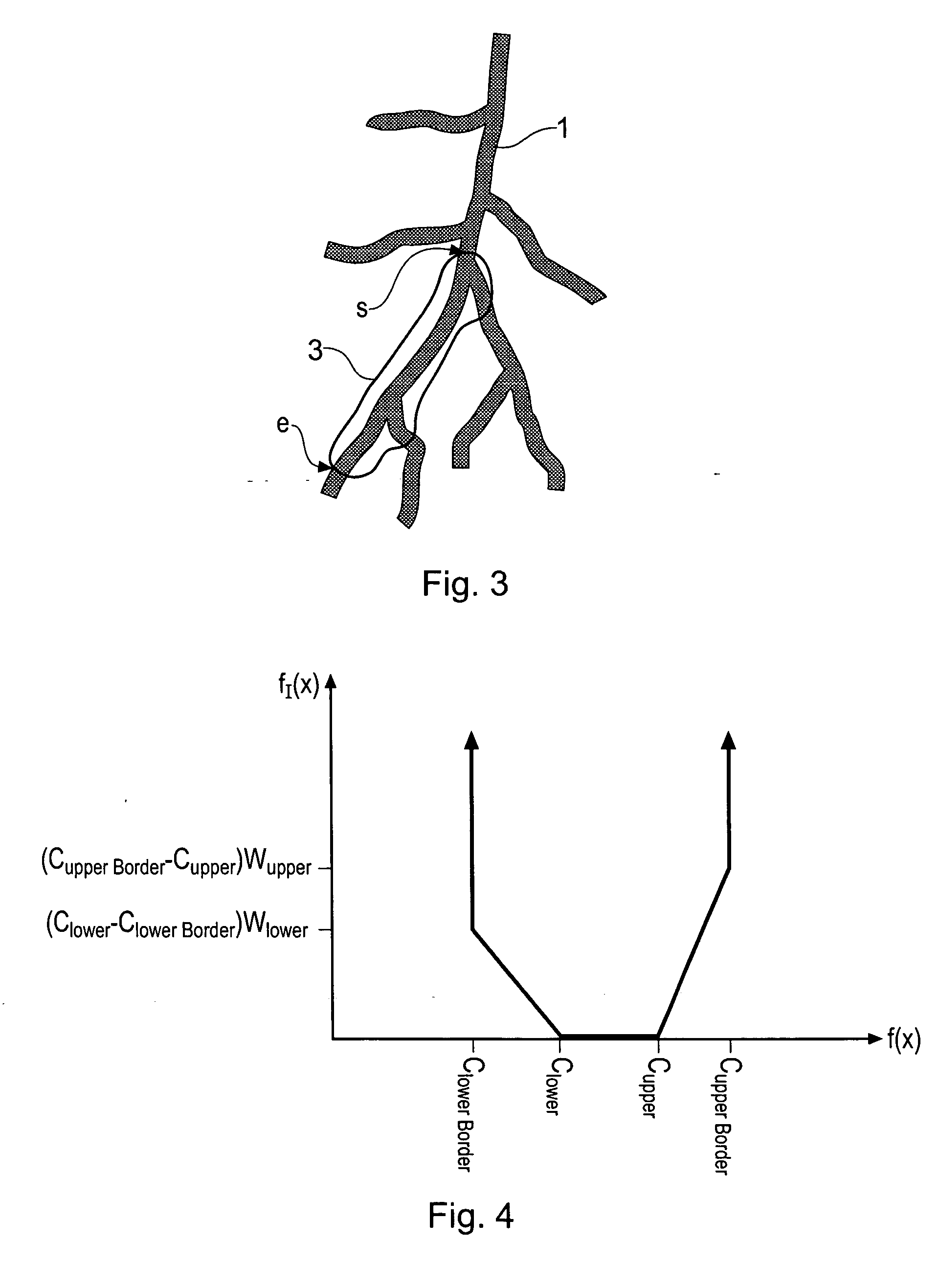
Method for determining a path along a biological object with a lumen
ActiveUS20070024617A1Shorten the timeAvoid excessive computationImage enhancementImage analysisData setVoxel
A path between specified start and end voxels along a biological object with a lumen, such as a vessel, within a patient image three-dimensional volume data set comprising an array of voxels of varying value is identified using an algorithm that works outwards from the start voxel to identify paths of low cost via intermediate voxels. The intermediate voxels are queued for further expansion of the path using a priority function comprising the sum of the cost of the path already found from the start voxel to the intermediate voxel and the Euclidean distance from the intermediate voxel to the end voxel. A cost function that depends on the voxel density is used to bias the algorithm towards paths inside the object. The number of iterations of the voxel required to find a path from the start to the end voxel, and hence the time taken, can be significantly reduced by scaling the Euclidean distance by a constant. Usefully, the constant is greater than 1, such as between 1.5 and 2.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL VISUALIZATION SYST EURO
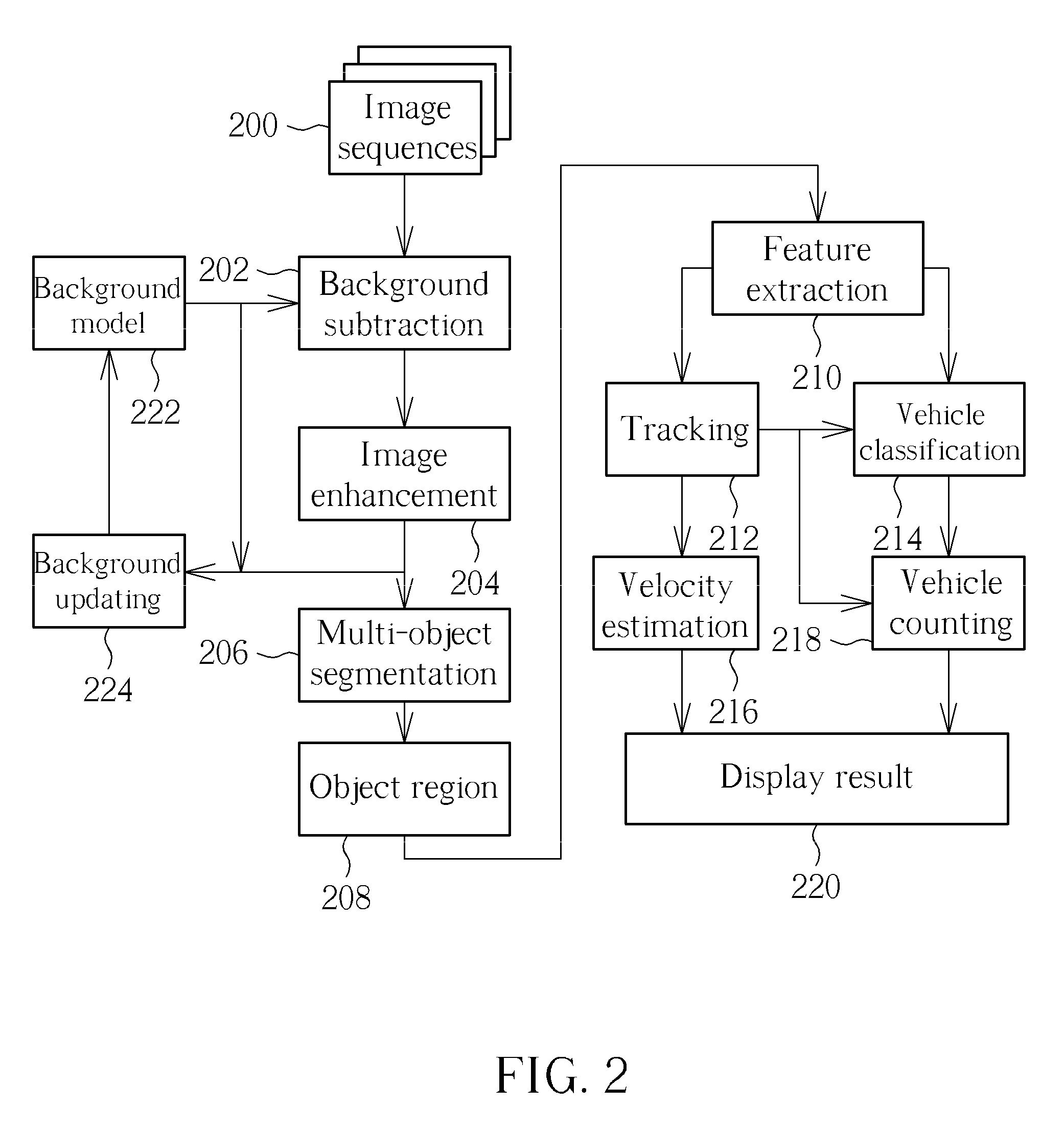
Method of detecting moving objects
InactiveUS20090309966A1Strong noise rejection abilitySimple calculationImage enhancementImage analysisMinimum bounding boxMinimum distance classifier
A method for detecting moving objects includes: (a) capturing and establishing a background image; (b) capturing at least one current image; (c) transforming the background image and the current image from an RGB color format into an HSI color format; (d) subtracting the background image from the current image according to a background subtraction rule for generating at least one moving object; (e) performing a vertical scanning and a horizontal scanning on the moving object for generating a minimum bounding box of the moving object; (f) calculating a characteristic datum of the moving object according to the minimum bounding box; (g) tracking the moving object according to the characteristic datum with a Euclidean distance rule; (h) classifying the moving object according to the characteristic datum, the tracking result generated by step (g) and a minimum distance classifier.
Owner:HUPER LAB
Pedestrian re-identification method based on multi-attribute and multi-strategy fusion learning
ActiveCN107330396ARobustShorten the timeBiometric pattern recognitionNeural learning methodsImage extractionTraining phase
The invention discloses a pedestrian re-identification method based on multi-attribute and multi-strategy fusion learning. The method of the invention includes the steps of in an offline training phase, firstly selecting pedestrian attributes which are easy to be judged and have a sufficient distinguishing degree, training a pedestrian attribute identifier on an attribute data set, then labeling attribute tags for a pedestrian re-identification data set by using the attribute identifier, and next, by combining the attributes and pedestrian identity tags, training a pedestrian re-identification model by using a strategy fused with pedestrian classification and novel constraint comparison verification; and in an online query phase, extracting features of a query image and images in a database by using the pedestrian re-identification model, and calculating the Euclidean distance between the feature of the query image and the feature of each image in the database to obtain the image with the shortest distance, which is considered as the result of pedestrian re-identification. In terms of performance, the features in the invention are distinguishable and high accuracy is obtained; and in terms of efficiency, the method of the invention can quickly search for the pedestrian indicated by the query image from the pedestrian image database.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Maximum likelihood decoding
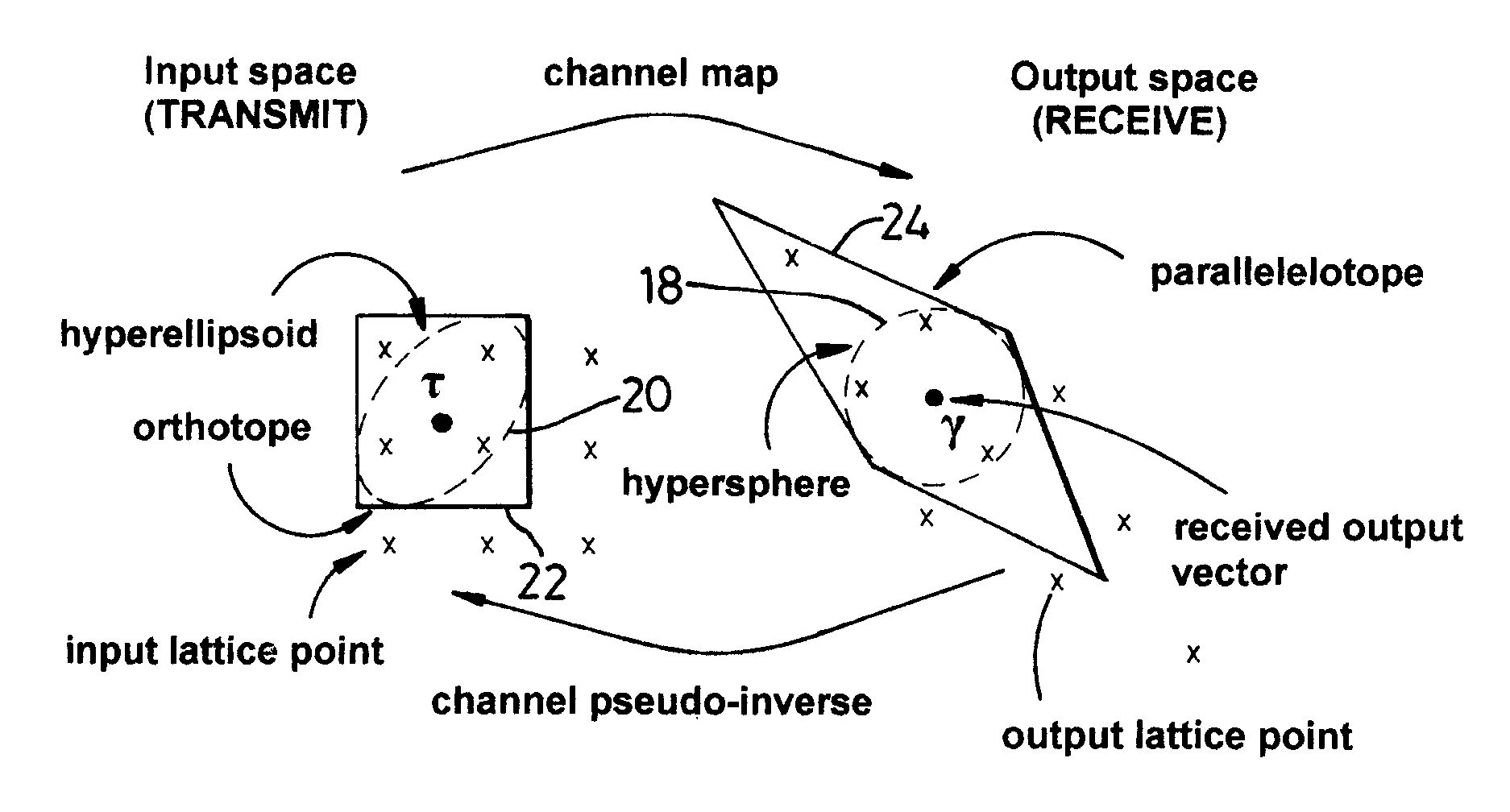
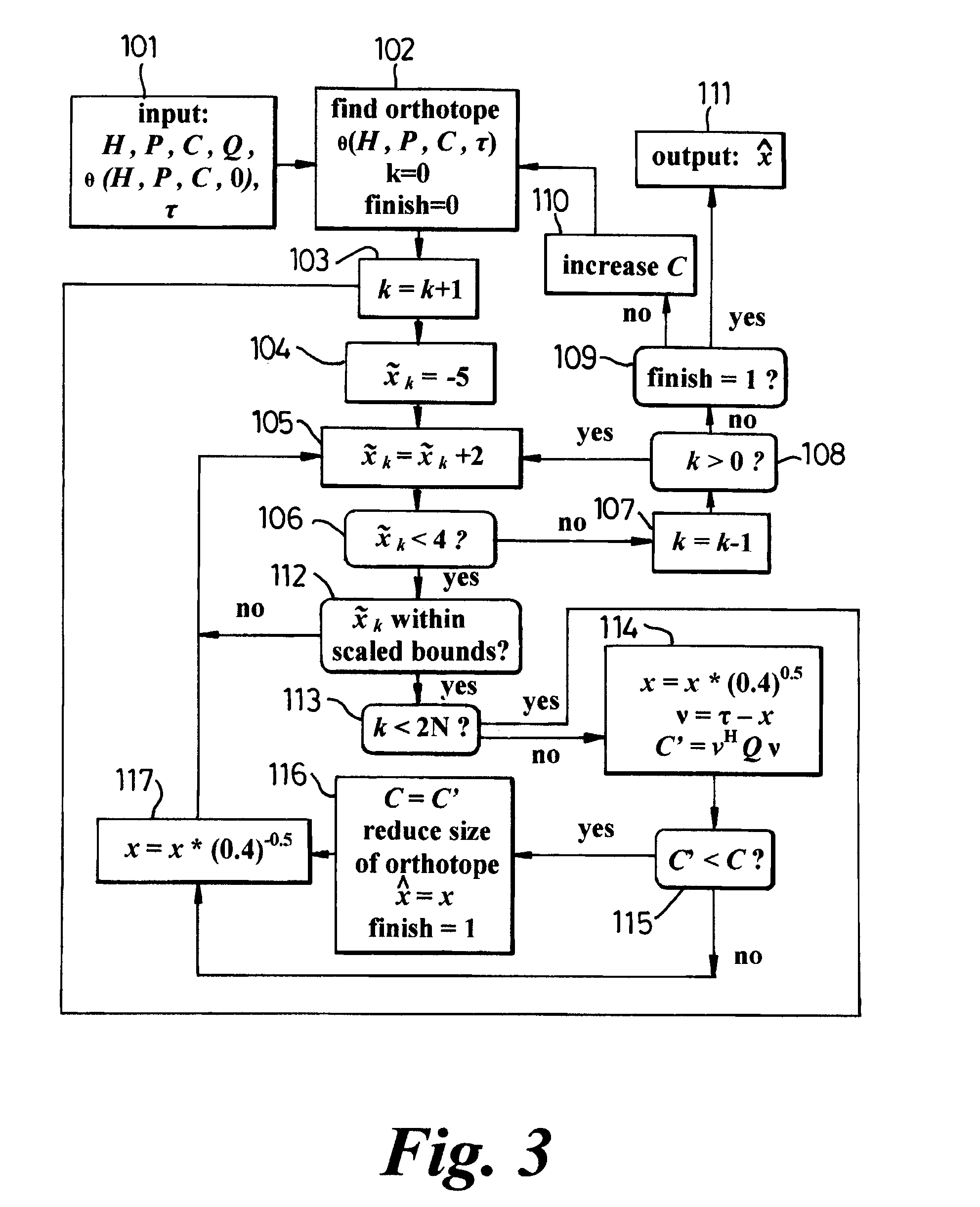
ActiveUS7233634B1Reduce complexityEasy to compareError preventionLine-faulsts/interference reductionCommunications systemHypersphere
A method of maximum likelihood decoding for detecting the signals transmitted over a Multiple-Input-Multiple-Output (MIMO) channel of a communication system in which there are N co-channel transmit antennas and M co-channel receive antennas. In a first method an orthotope (22) is generated in input signal space centred on an approximate transmit signal point τ which is an inverse mapping from an actual received signal point (y) in output signal space. Only possible transmit points located within the orthotope are considered as candidate points and are transformed into corresponding candidate receive signal points in output signal space. The Euclidean distance between the candidate receive signal points and the actual signal point is calculated and the closest candidate receive signal is selected as the detected received point. In an alternative method, the orthotope is constructed as the smallest such orthotope which can contain a hyperellipsoid (20) in input signal space, which hyperellipsoid is a transformation from output signal space of a hypersphere (18) centred on the actual received signal point (y). Those transmit signal points which lie within the orthotope (22) but outside of the ellipsoid (20) are discarded and the remaining points within the orthotope are considered as candidate points, in the same way as described above.
Owner:APPLE INC
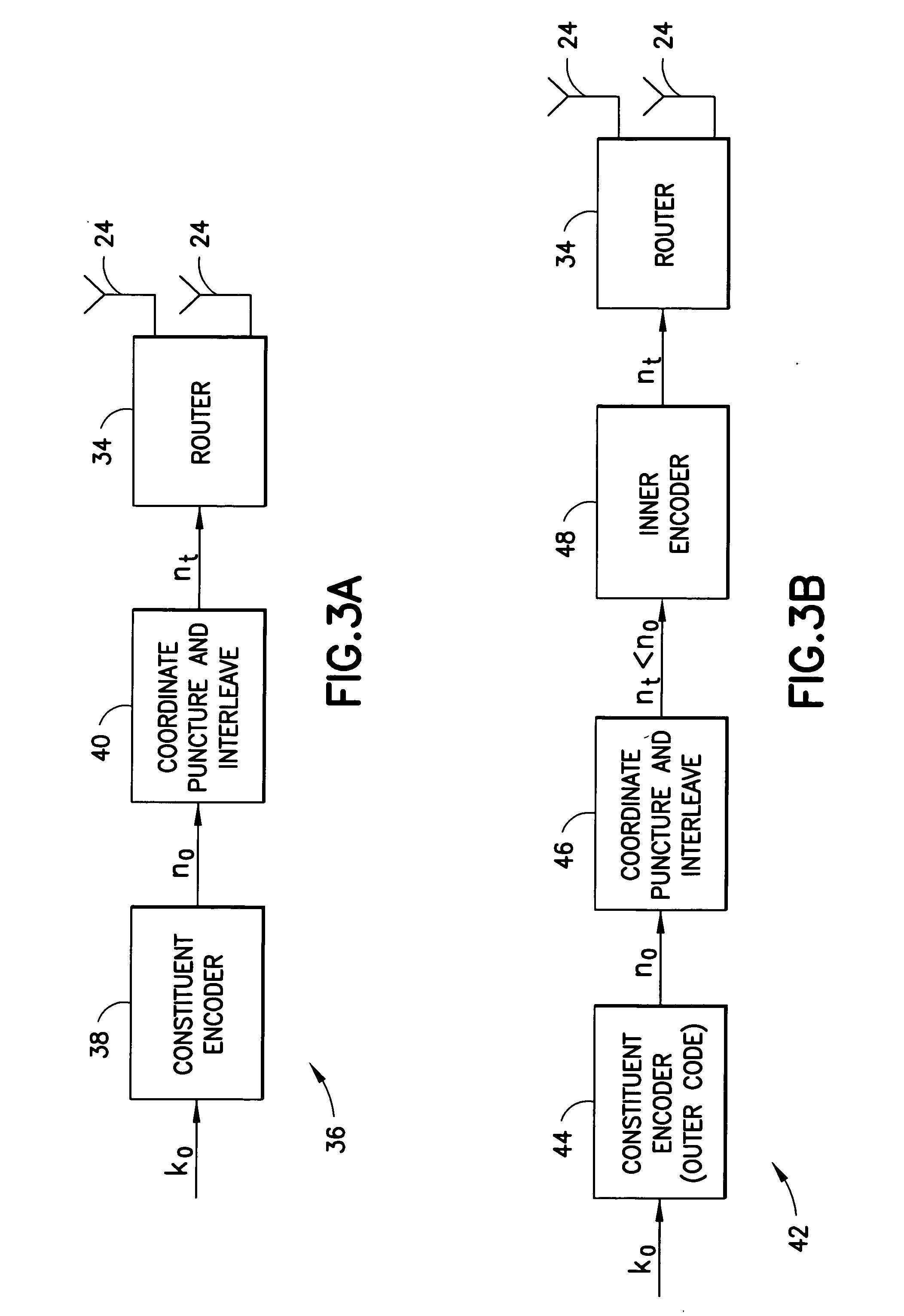
Apparatus using concatenations of signal-space codes for jointly encoding across multiple transmit antennas, and employing coordinate interleaving
InactiveUS20060159195A1Accommodate usageCode conversionError correction/detection by combining multiple code structuresHamming distanceComputer science
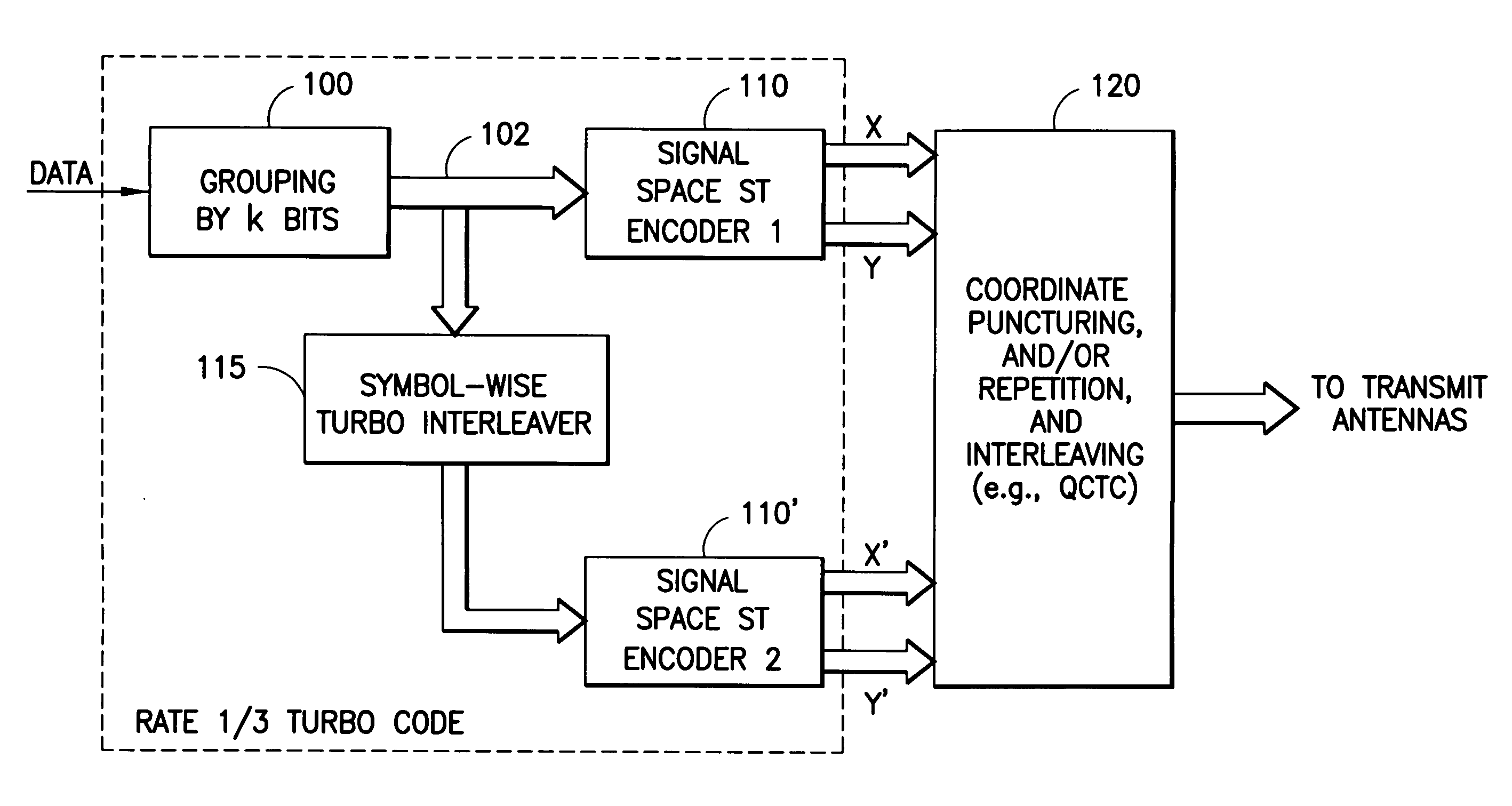
A system for transmitting data over a MIMO channel has a transmitter and a receiver. In the transmitter, the input data is encoded over at least two pipes by a concatenation of at least two constituent signal-space encoders. Each constituent encoder is used to generate, in response to the input data, a sequence of symbols from a channel alphabet having at least one dimension. Each symbol of the channel alphabet includes at least one complex symbol having real and imaginary coordinates. The transmitter interleaves the coordinates of the sequence of channel alphabet symbols, and transmits (from at least two transmit antennas) the interleaved coordinates. Preferably, each constituent encoder maximizes a minimum coordinate-wise Hamming distance between members of all valid pairs of symbol sequences, maximizes a minimum Euclidean distance between members of all valid pairs of different codewords, and obeys an equal eigenvalue criterion.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
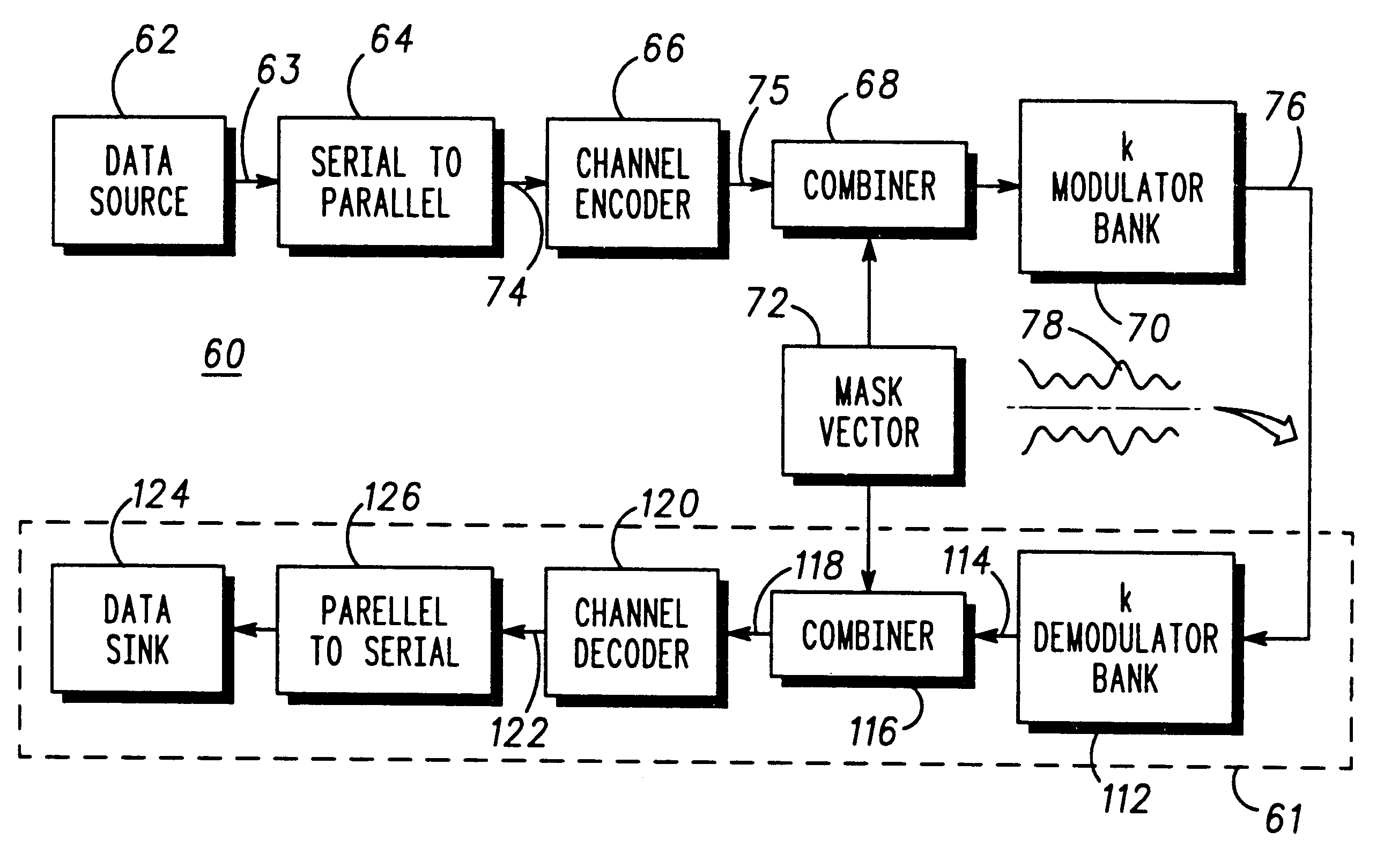
Multicarrier communication system and method for peak power control
InactiveUS6307892B1Remove distortion effectsImprovement in PMEPRSecret communicationMulti-frequency code systemsCommunications systemPeak value
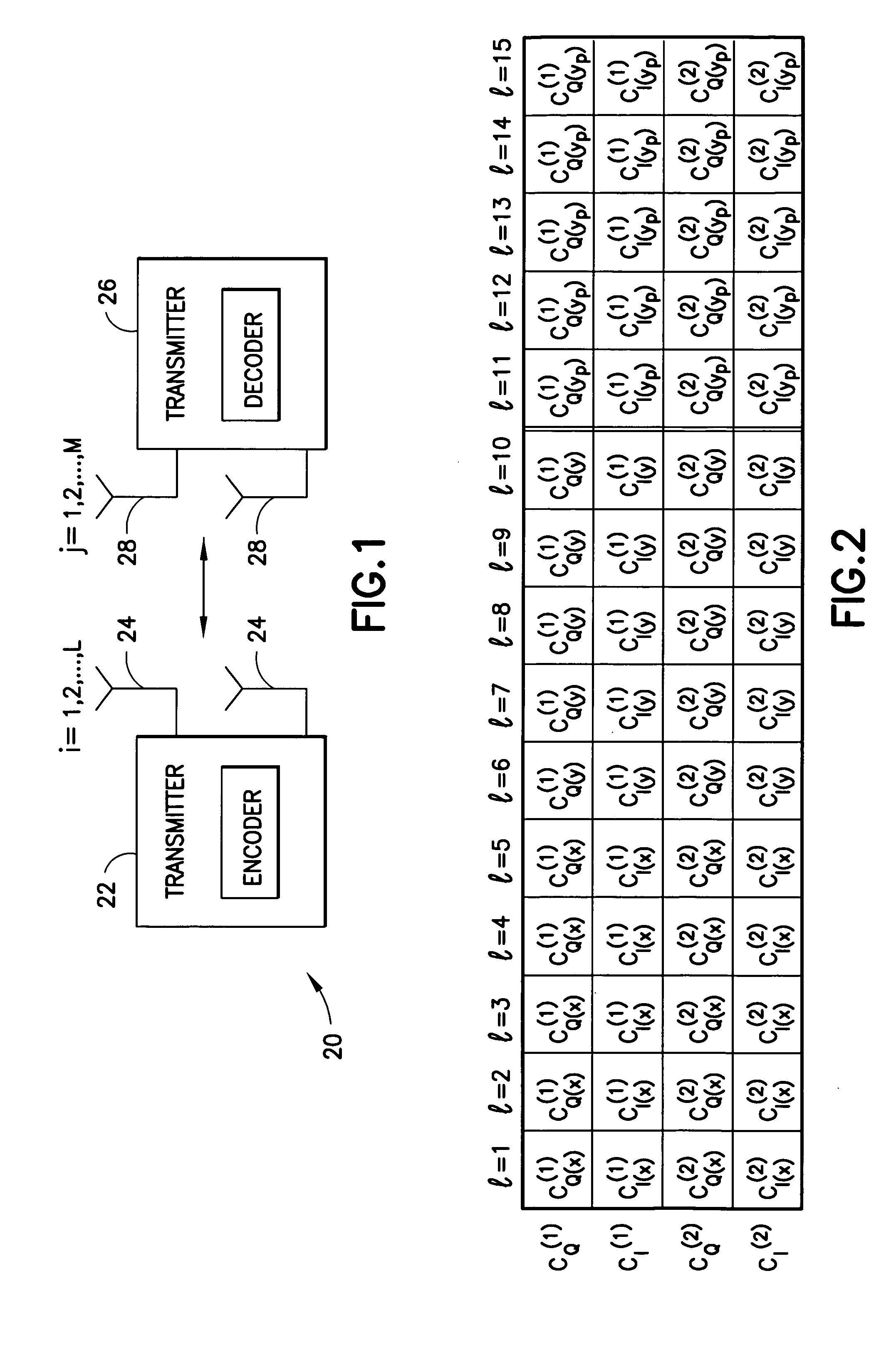
A communication device for simultaneously transmitting information on multiple sub-channels encodes information for each of the multiple sub-channels with a coding scheme to produce channel encoded information. A mask vector derived from a redundancy in the coding scheme, encodes the channel encoded information to transform the channel encoded information into codewords having pairwise Euclidean distance properties identical to those of the channel encoded information, Modulation of the sub-channels in accordance with the codewords in a modulator then produces a composite signal envelope having a peak-to-mean error power ratio (PMEPR) reduced relative to a PMEPR for correspondingly modulated channel encoded information.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP +1
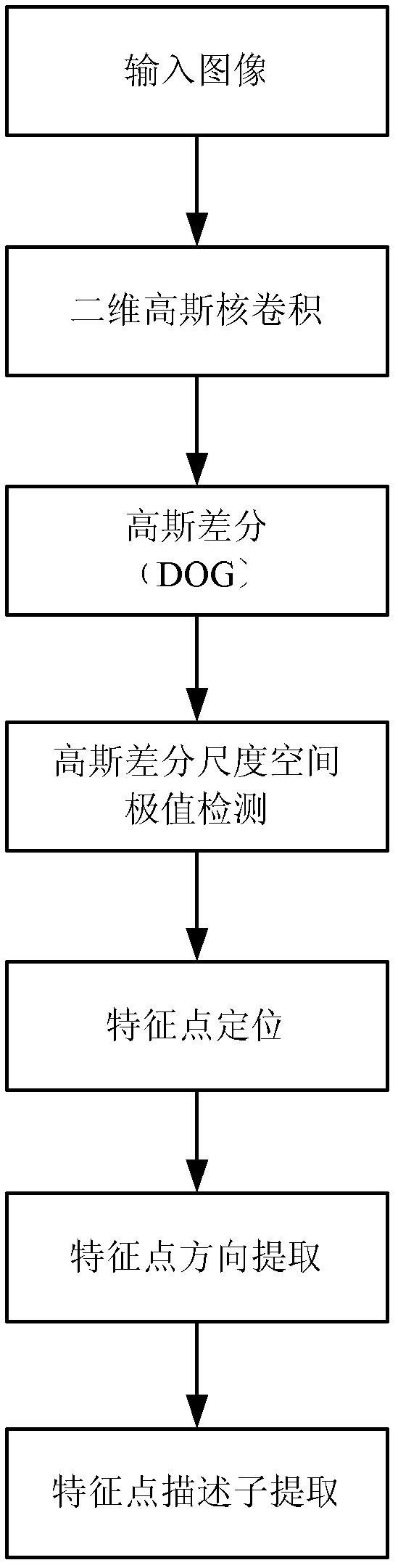
Registering control point extracting method combining multi-scale SIFT and area invariant moment features
InactiveCN101714254AMake up for defects that are susceptible to factors such as noiseImage analysisFeature vectorImaging processing
The invention discloses a registering control point extracting method combining multi-scale SIFT and area invariant moment features, relating to the field of image processing. The invention solves the technical problems of how to extract stable and reliable feature points in the image registering process. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, carrying out continuous filtering on images by utilizing Gauss kernel functions to generate the DOG scale-space by combining with a downsampling method, and seeking and calculating space and scale coordinates of a local extremum. Then, forming the feature vectors of a key point by utilizing directional gradient information, and obtaining an originally matching key point pair through the Euclidean distance; and then calculating local area HU invariant moment features by taking the originally selected key point as the center, and screening out a finally accurate and effective registering control point by combining with the Euclidean distance. The method combines the multi-scale features of an SIFT arithmetic and the image local area grayscale invariant moment features, thereby effectively improving the stability and the reliability of extracting multisensor image registering control point pairs.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
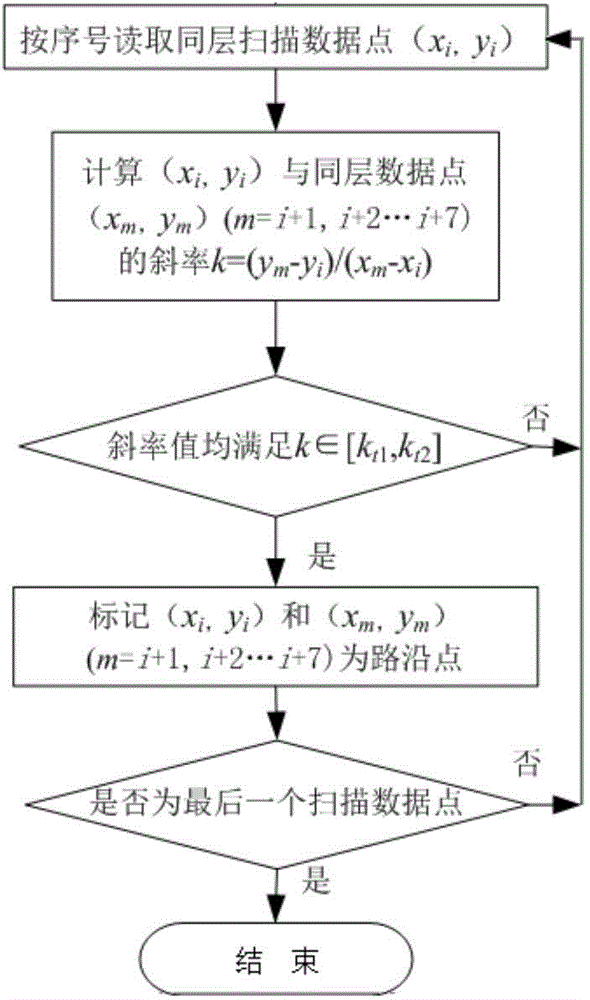
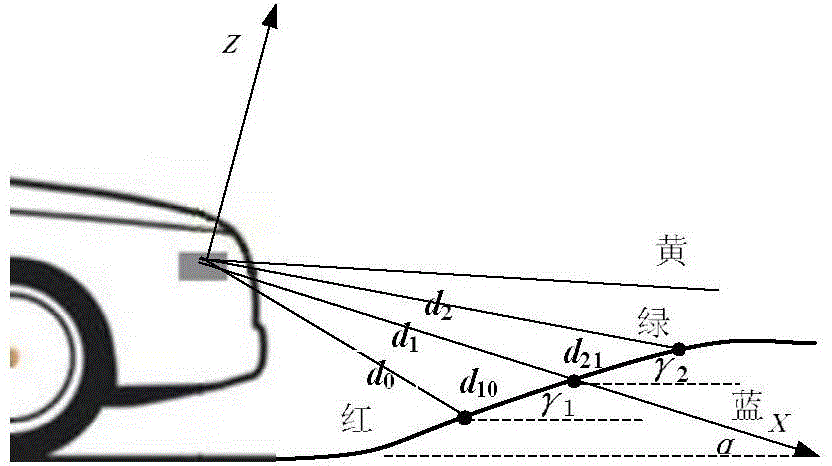
Road and obstacle detecting method based on remotely piloted vehicles
InactiveCN104636763AImprove robustnessImprove accuracyImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionAnti jammingRadar
The invention relates to a road and obstacle detecting method based on remotely piloted vehicles. The method includes adopting a four-wire laser radar as a distance sensor and calculating slope information of roads in a driving area according to the relative position correspondence of pavement data points on different scanning layers; fitting left and right road edges by the COBWEB algorithm and the least square fit improved on the basis of Euclidean distance according to characteristics of road edge data points, enhancing anti-jamming capability, accuracy and stability of road edge detection; applying DST (Dempster-Shafer theory) evidence theory to establish a raster map for the environment ahead of the remotely piloted vehicles, and estimating positions of each raster before integrating prior- and posterior-frame maps. Consequently, the problem of integration of prior and posterior raster cells in the local map is solved. Finally, dynamic faults can be detected by means of conflict coefficient in a driving area, and the dynamical obstacles can be clustered and information thereof can be extracted by the improved eight-neighborhood zone marker algorithm. The road and obstacle detecting method can stably and accurately detect road and obstacle information.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Accurate retrieval method for target on the basis of deep metric learning
ActiveCN106897390AImprove accuracyImprove retrieval performanceCharacter and pattern recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsNetwork structureNetwork model
The invention discloses an accurate retrieval method for a target on the basis of deep metric learning. The method comprises the following steps that: in the iterative training of a deep neural network structure, in a process that the extracted characteristics of multiple extracted pictures of the same class of target object are processed, enabling the same class of target objects to mutually approach, and enabling different classes of target objects to be mutually far away, wherein the characteristic distance of the target objects with different class labels is greater than a preset distance, a distance between intra-class individuals with the similar attribute mutually approaches, and a distance between the intra-class individuals with different attributes is greater than a preset distance to obtain a trained deep neural network model; and adopting a trained deep neural network model to independently extract respective characteristics from pictures to be inquired and a preset reference picture, obtaining Euclidean distances between the characteristics of the queried picture and the reference picture, and sorting the distances from small to big so as to obtain an accurate retrieval target. By use of the method of the embodiment, an accurate retrieval problem of a vertical territory is solved.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
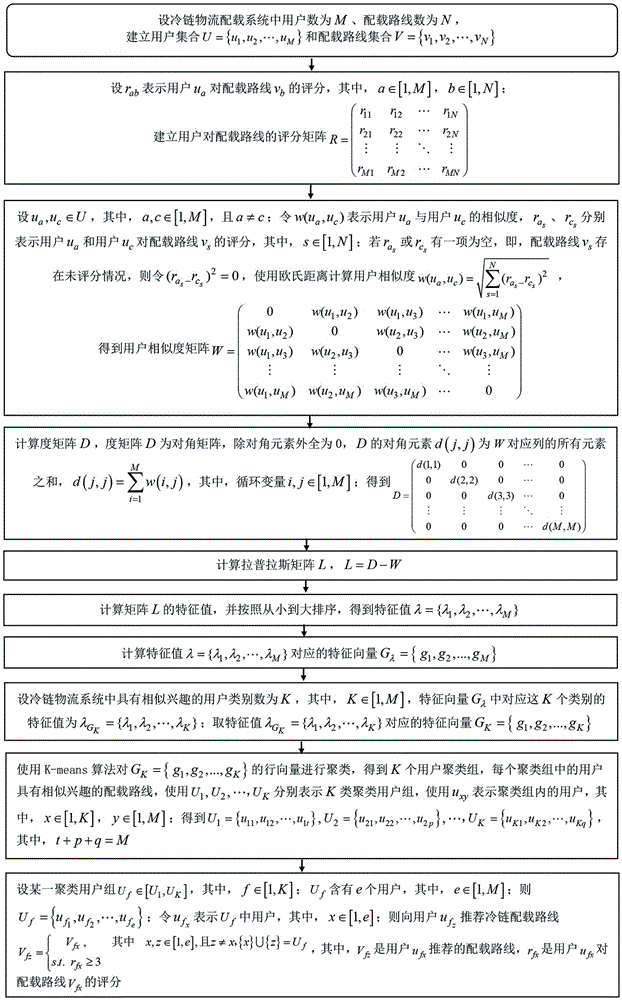
Cold-chain logistic stowage intelligent recommendation method based on spectral cl9ustering
InactiveCN105654267AReduce the no-load ratioIncrease profit marginsCharacter and pattern recognitionLogisticsCold chainRating matrix
The invention discloses a cold-chain logistic stowage intelligent recommendation method based on spectral clustering. Scores of users for a stowage line are conveyed through a cold chain for cold-chain logistic stowage intelligent recommending, a score matrix is built, the Euclidean distance is used for calculating the user similarity, a degree matrix is used for calculating a Laplacian matrix, feature vectors are obtained by calculating feature values of the orderly Laplacian matrix, a K-means algorithm is used for clustering the feature values to obtain a user group with the similar interesting stowage line, and a stowage line is recommended inside the user group with the similar interesting stowage line, so that cold-chain logistic stowage intelligent recommending is achieved, the cold-chain logistic vehicle non-load ratio is lowered, and the profit rate of cold-chain logistic transport vehicles is increased.
Owner:HUAIYIN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
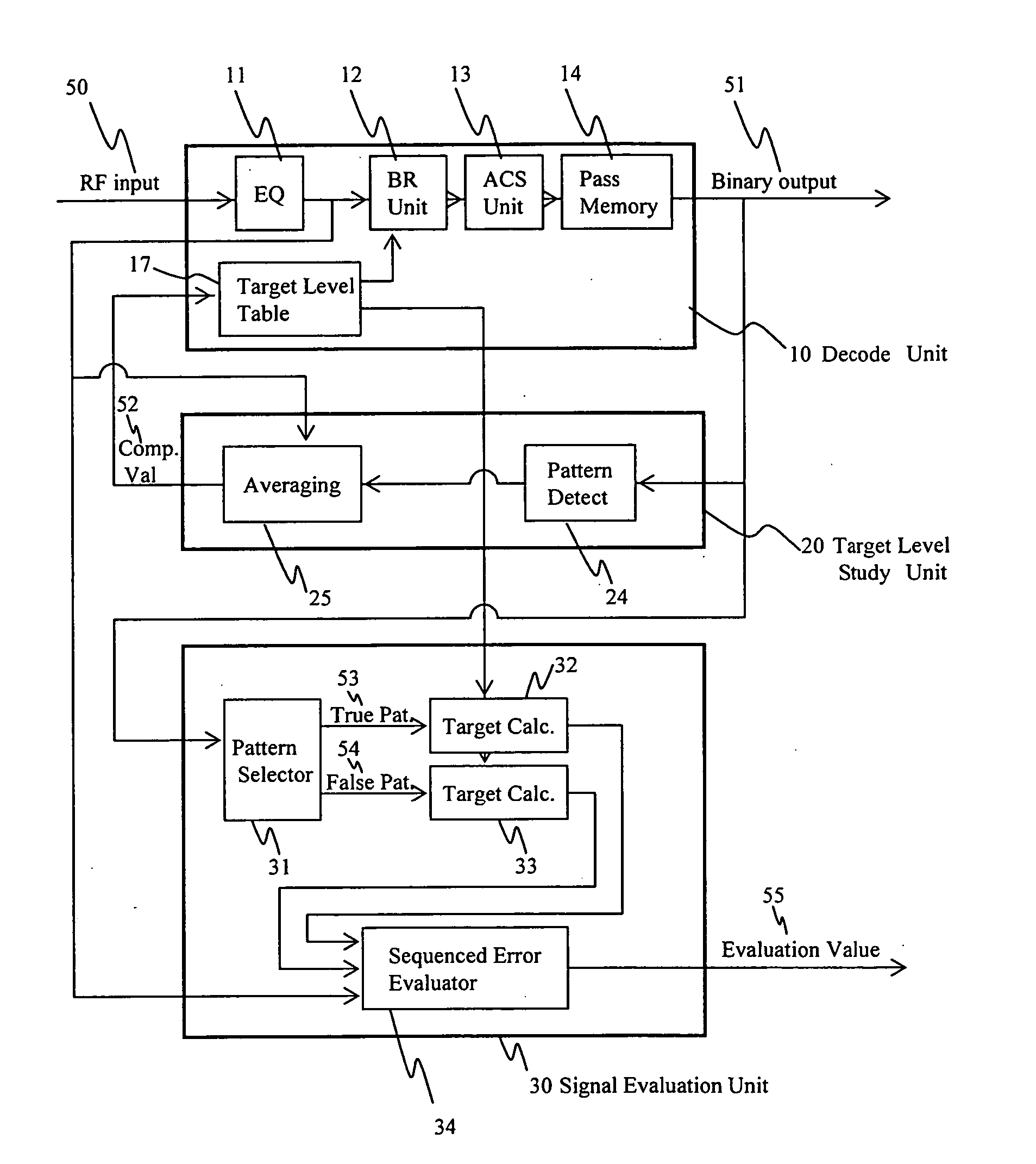
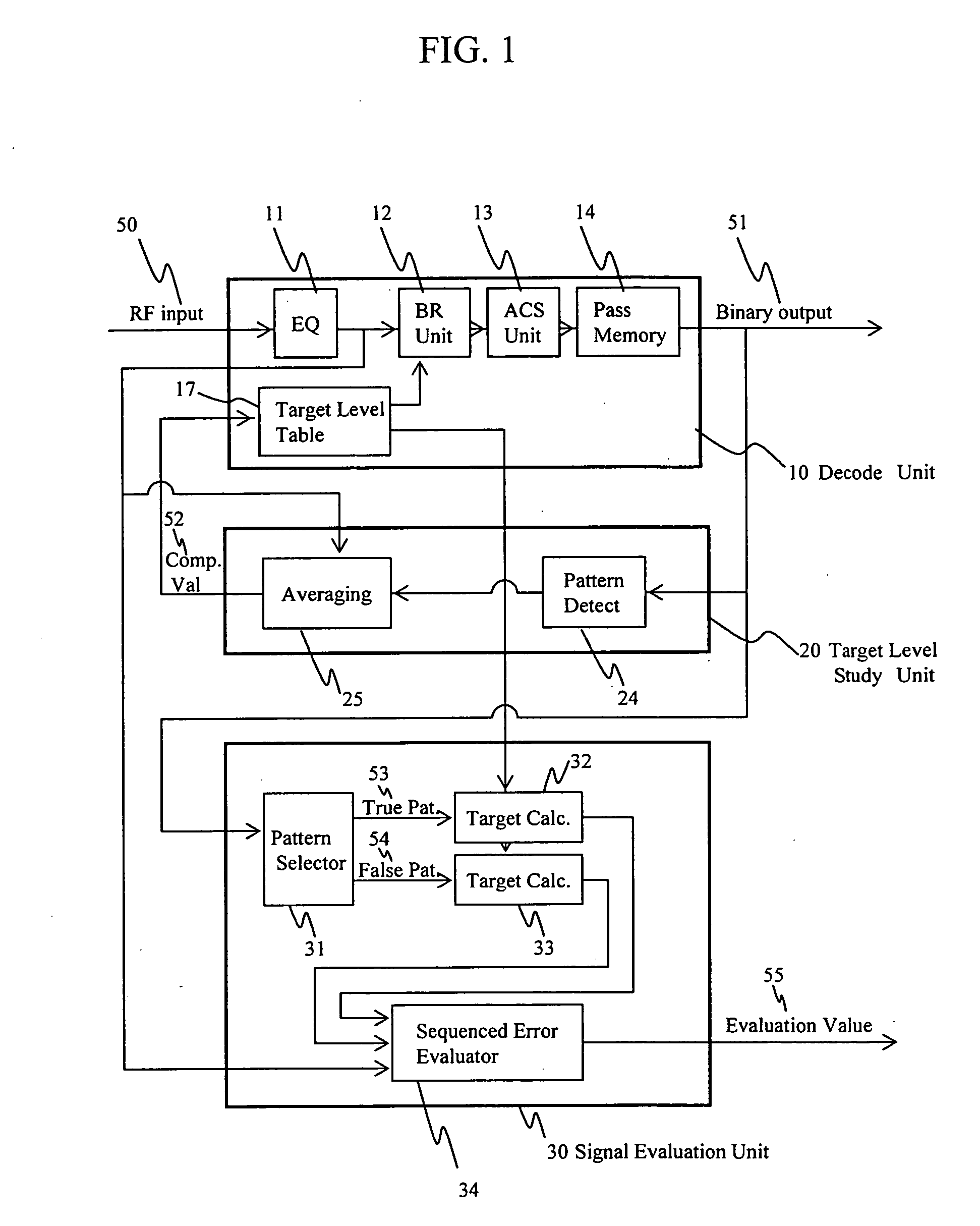
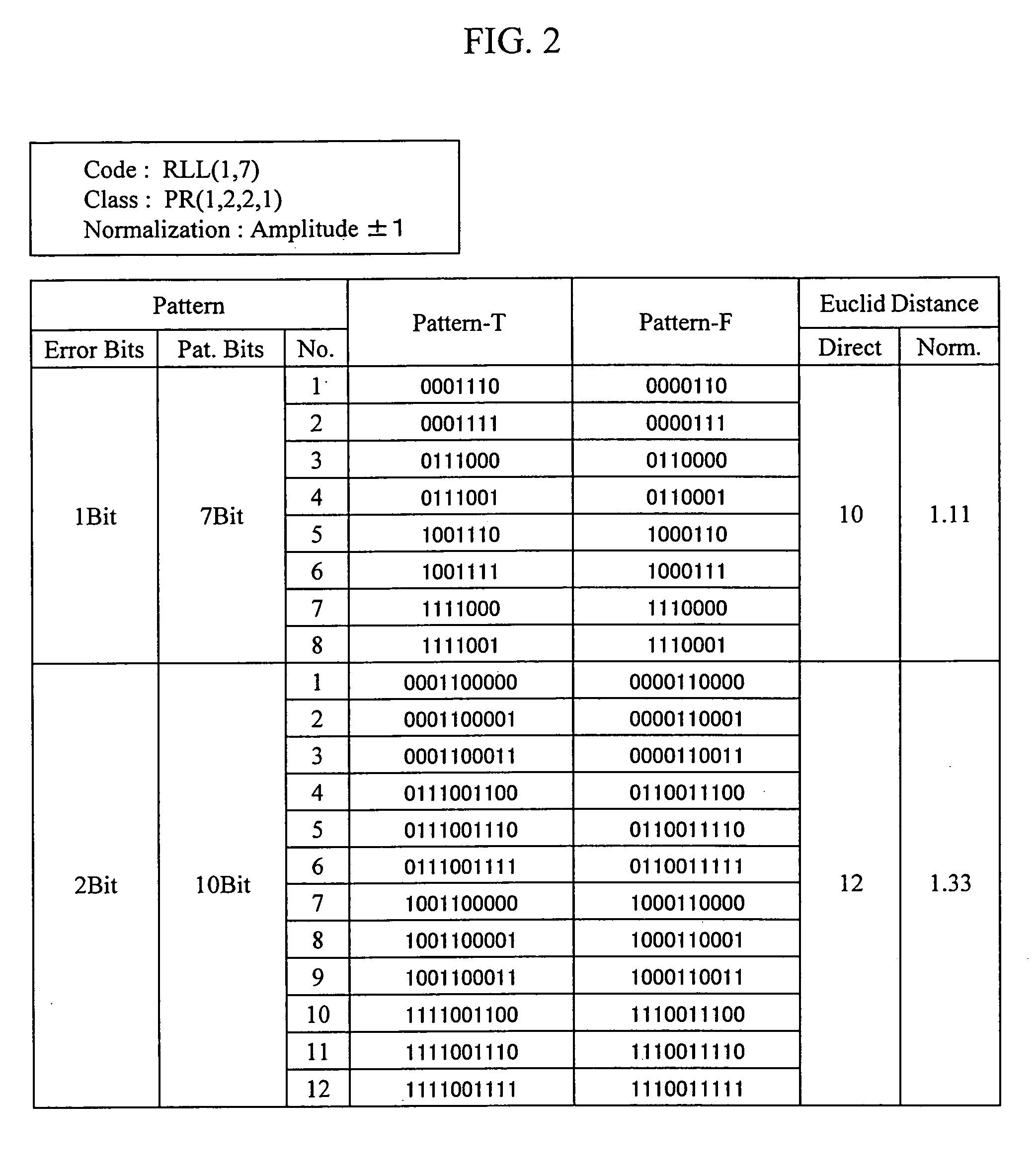
Method of evaluating a readout signal, and optical disc apparatus
InactiveUS20050249318A1Precise positioningAccurate assessmentModification of read/write signalsOptical beam sourcesViterbi decoderSignal quality
A method of evaluating the quality of a read signal from the viewpoint of the detection margin of a Viterbi decoder in the PRML method in which a target signal level varies depending on the read signal, and an optical disc apparatus implementing the method. A method of evaluating the quality of a signal pattern comprising a combination of minimum run lengths from the viewpoint of edge shift, and an optical disc apparatus implementing the method. From the target signal level that varies depending on the read signal, a target signal is generated based on a decoding result, and an error target signal is generated in which the decoding result is edge-shifted. The signal quality is evaluated by calculating a Euclidean distance between these signals and the read signal. A virtual state that is not included in the Viterbi decoder and that is less than the minimum run length is defined, and a target signal level for the virtual state is generated using a target signal level table inside the Viterbi decoder, based on the concept of convolution. In this way, the signal quality can be evaluated by the same method as mentioned above even in cases where the pattern of a combination of the minimum run lengths has edge-shifted.
Owner:HITACHI-LG DATA STORAGE +1
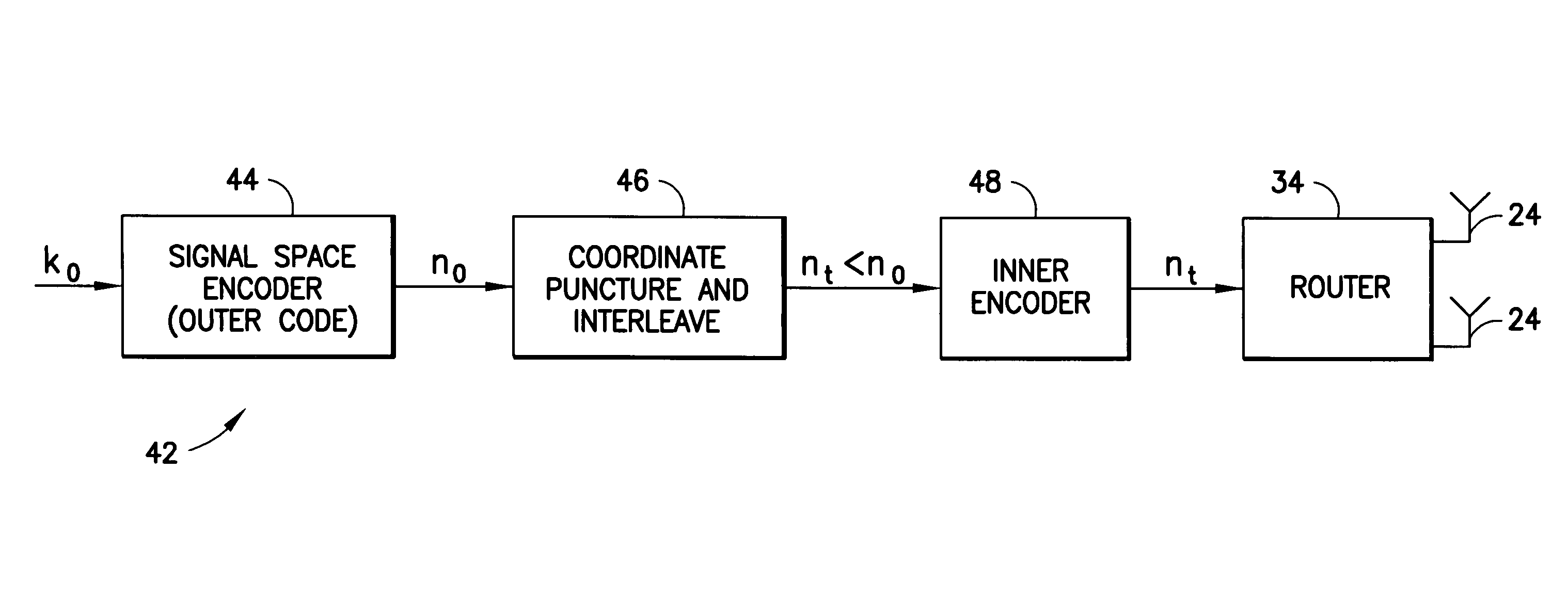
Method and apparatus using coordinate interleaving to increase diversity in a MIMO system
InactiveUS7409001B2Increase diversityModulated-carrier systemsPolarisation/directional diversityAs elementEngineering
A method to increase diversity in MIMO fading channels interleaves coordinates of complex symbol(s) in a transmission frame after encoding and modulating. Specifically, an input signal is encoded and modulated into a codeword, jointly across at least two pipes, said pipes having space, time, frequency, or other nature, wherein the codeword spans a frame and is defined as at least one complex symbol whose complex values are all those to be transmitted during all channel uses covered by the frame. Each of the complex symbols have a first and second coordinate. After modulating, which may be combined with encoding in a signal space encoder, the coordinates are interleaved. In modulation, the complex symbols (typically two dimensional) may arise as elements of a multidimensional (typically greater than two dimensions) signal constellation, in which case those multidimensional constellation coordinates are the ones that are interleaved in the frame. The frame carrying the interleaved coordinates is transmitted by the first and at least second antennas, possible opposed sub-frames of the overall frame being transmitted separately by opposed antennas. A coset selector is used in some embodiments to maximize a minimum Hamming distance, and / or a minimum Euclidean distance, between coordinates within a coset to control diversity and / or coding gain. In some embodiments, the operation of the encoder and modulator is such as to maximize a minimum coordinate-wise Hamming distance, and / or a minimum Euclidean distance, between allowable codewords, and / or to provide additional structure for the allowable codewords. A method, transmitter, system, and mobile station are described.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Indoor mobile robot vision SLAM method based on Kinect
The present invention provides an indoor mobile robot vision SLAM method based on the Kinect. The method comprises the following steps: S1: acquiring color RGB data and Depth data of an indoor environment by using a Kinect camera; S2: performing feature detection of RGB data and implementing rapid and effective matching between adjacent images; S3: combining inner parameters of a Kinect camera after calibration and pixel point depth values to convert a 2D image point into a 3D space point, and establishing a corresponding relationship of 3D point cloud; S4: using the RANSAC algorithm to eliminate external points of the point cloud to complete point cloud rough matching; S5: employing an ICP algorithm with a double limit of an Euclidean distance and an angle threshold to complete fine matching of the point cloud; and S6: introducing a weight in a key frame selection, and employing the g2o algorithm to optimize a robot posture, and finally obtaining a robot moving trajectory, and generating a 3D point cloud map. The indoor mobile robot vision SLAM method based on the Kinect can solve the problems that a point cloud registration portion in a vision SLAM system is liable to local optimum and is large the matching error, and therefore the registration accuracy of the point cloud is improved.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
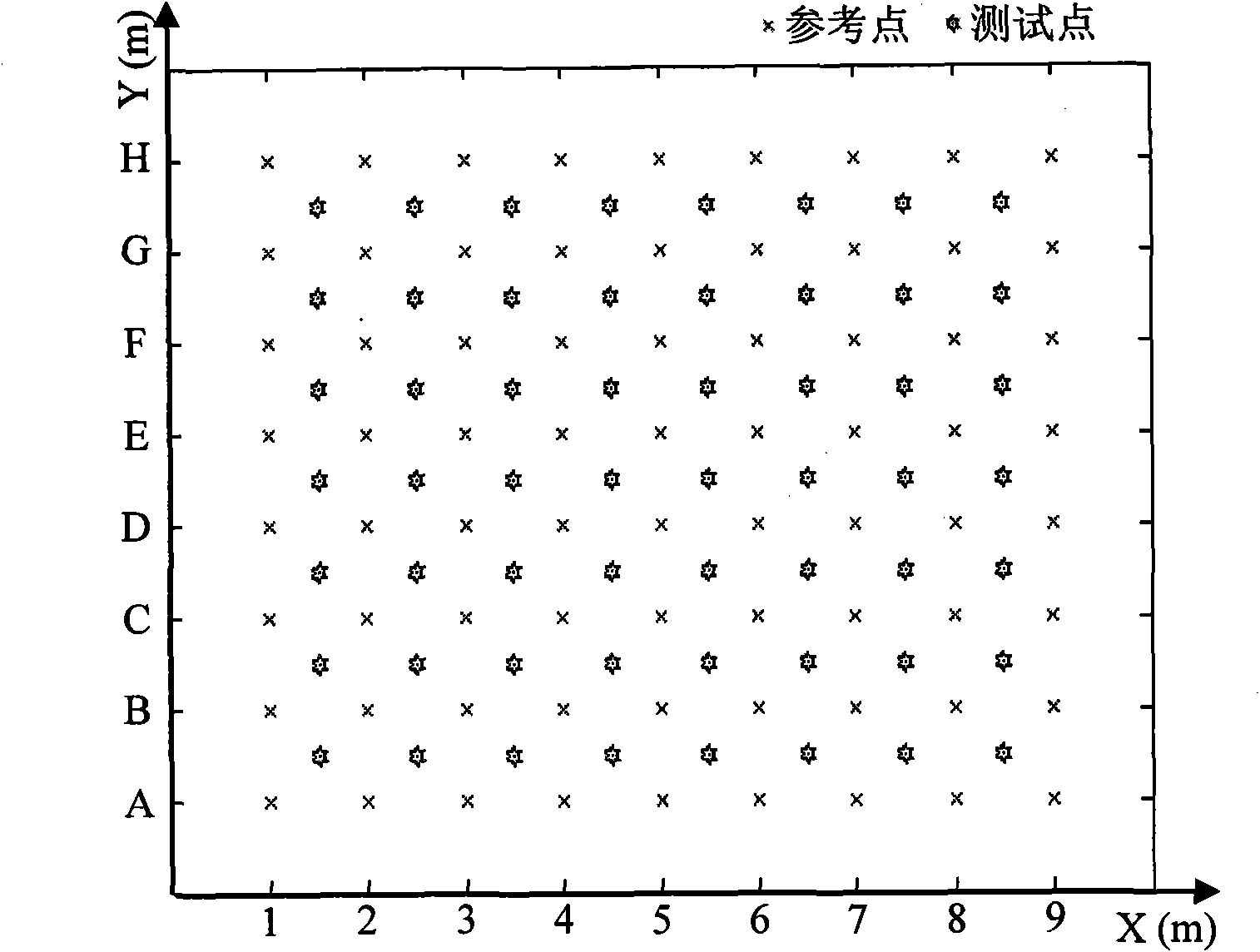
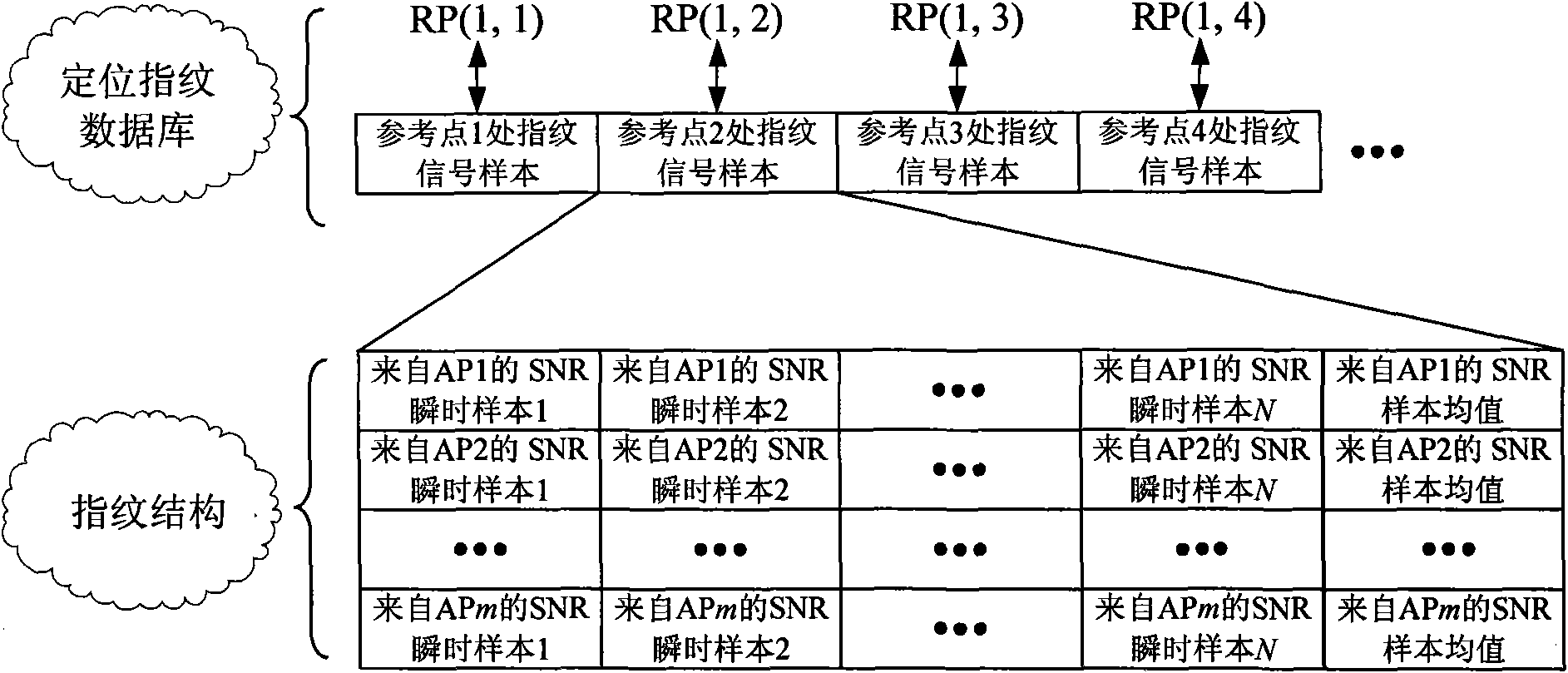
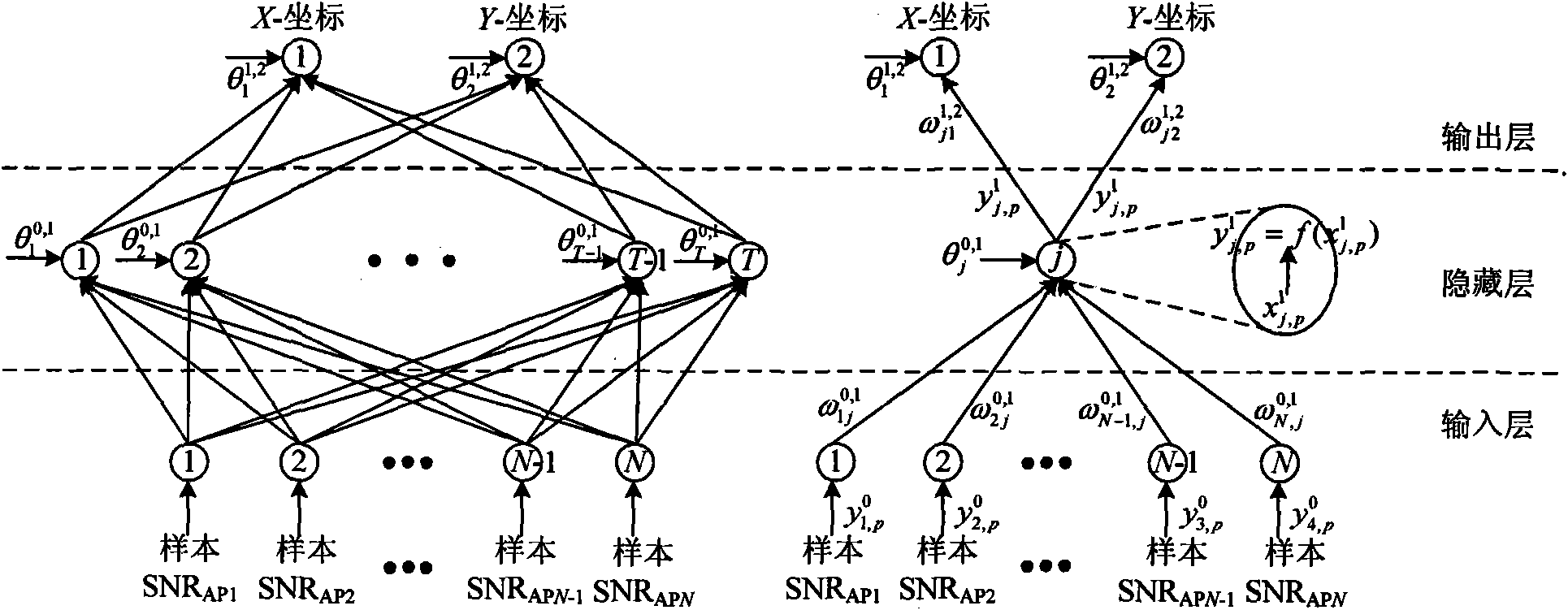
Method for optimizing WLAN (Wireless Local Area Network) indoor ANN (Artificial Neural Network) positioning based on FCM (fuzzy C-mean) and least-squares curve surface fitting methods
InactiveCN101778399ARealize terminal location positioningHigh positioning accuracyNetwork topologiesPhysical realisationAlgorithmEuclidean distance
The invention discloses a method for optimizing WLAN (Wireless Local Area Network) indoor ANN (Artificial Neural Network) positioning based on FCM (fuzzy C-means) and least-squares curve surface fitting methods, relating to an indoor positioning method used for indoor positioning and aiming to solve generalization capability reduction of an ANN system caused by singular reference points existing in a training sample space. The method comprises the following steps of carrying out clustering on pre-labeled reference points based on the FCM method to confirm corresponding clustering centers and membership degree of different reference points to clustering centers thereof; obtaining the space position of the singular reference points in a target positioning area on the basis of carrying out quantitative processing and similarity calculation on the membership degree of the reference points; updating positioning fingerprint database by utilizing the least-squares curve surface fitting method to reject abrupt change points in an intensity distribution chart; estimating the cluster of a terminal on the basis of calculating the Euclidean distance between signal intensity samples collected online and different clustering centers; and finally accurately estimating the terminal by utilizing corresponding ANN subsystems.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
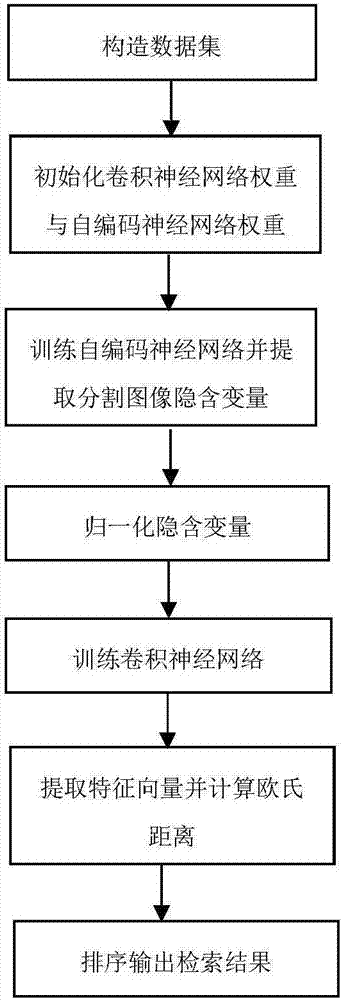
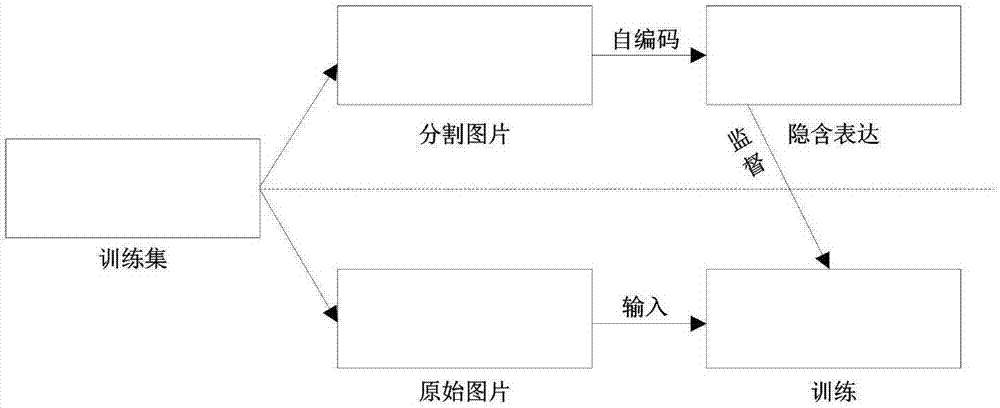
Neural network feature learning method based on image self coding
ActiveCN107122809ASolve problemsEnhance semantic expression abilityCharacter and pattern recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsData setImage retrieval
The invention discloses a neural network feature learning method based on image self coding, which belongs to the technical field of feature learning and image retrieval. Firstly, a segmentation training image set corresponding to a training image set is constructed through a segmentation label of a multi-label image data set, weights of a convolutional neural network and a self coding neural network are then initialized, a stochastic gradient descent method is used for training the self coding neural network, and an implicit variable of a segmentation image corresponding to each training sample is extracted and normalized; and then, the implicit variable serves as a training target corresponding to an original training set image, the convolutional neural network is trained, a feature vector corresponding to each image in a test set image library is extracted, and through calculating Euclidean distances between feature vectors of a query image and each image in the image library and arranging the distances in an sequence from small to large, a similar image retrieval result is obtained. Thus, features extracted from the trained neural network achieve perfect retrieval effects in a multi-label retrieval task.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
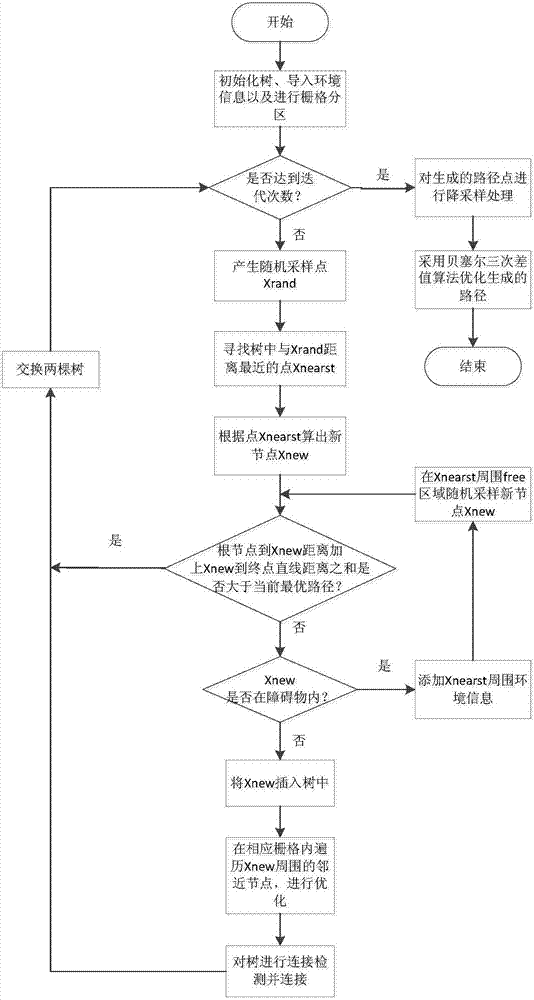
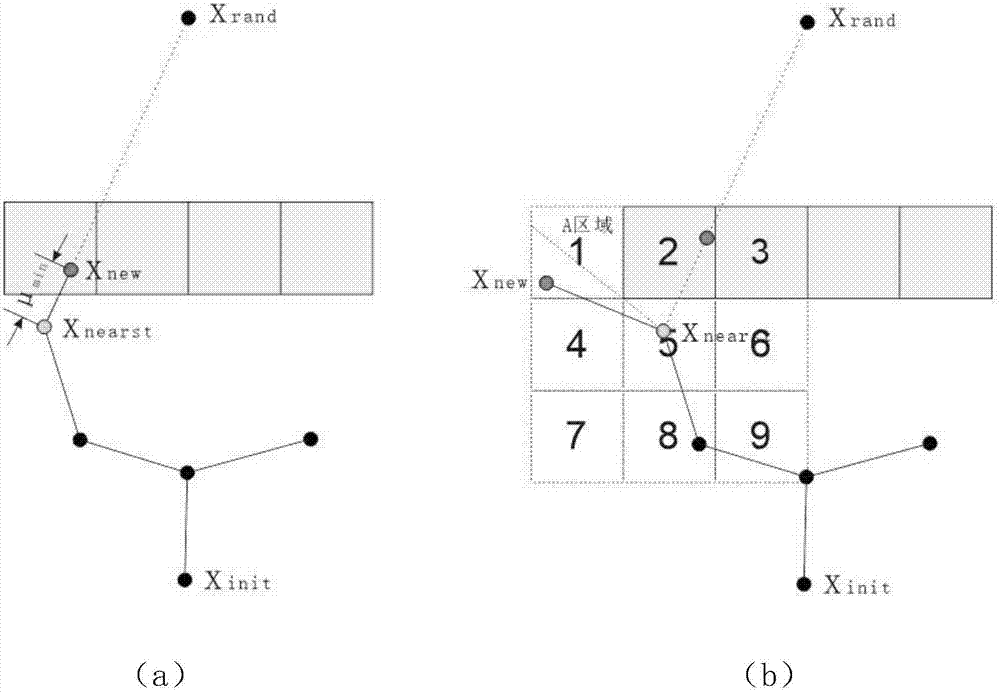
Unmanned aerial vehicle trajectory planning method based on EB-RRT
InactiveCN107085437AFast convergenceReduce traversal timeNavigational calculation instrumentsComplex mathematical operationsTrajectory planningInsertion point
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
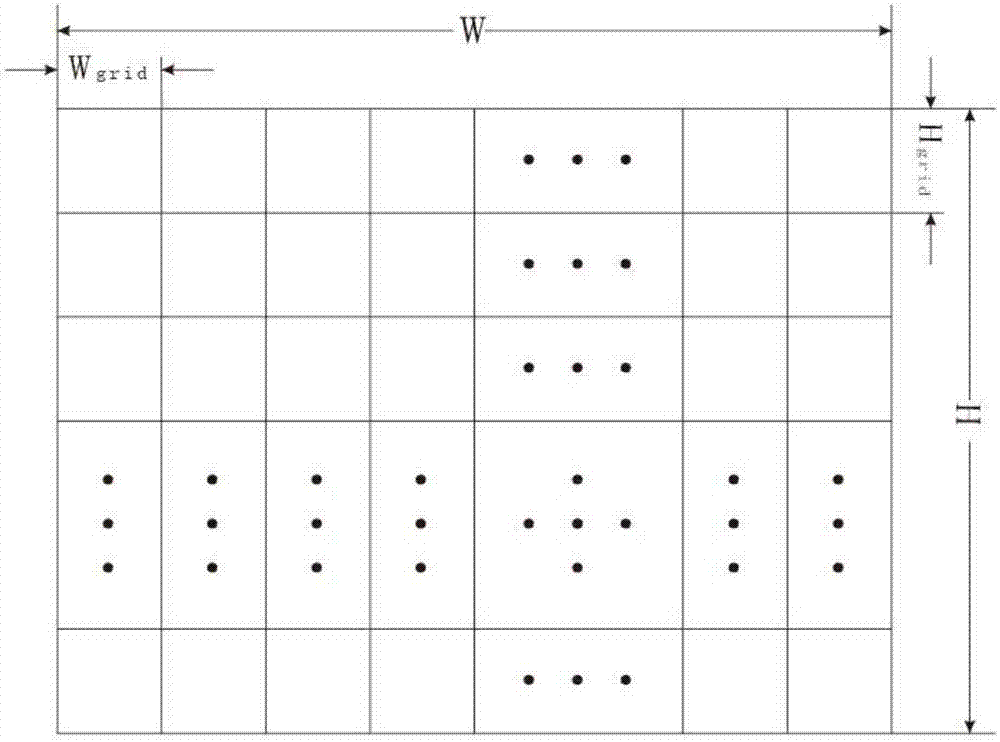
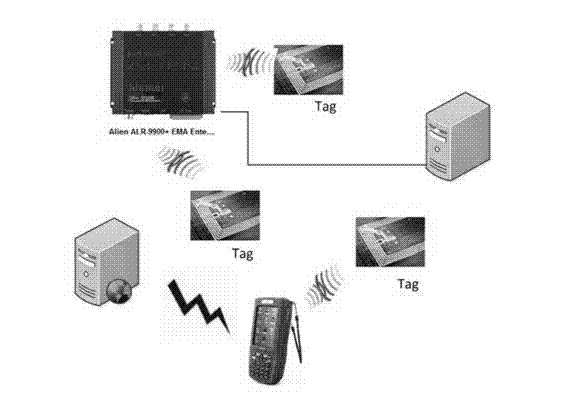
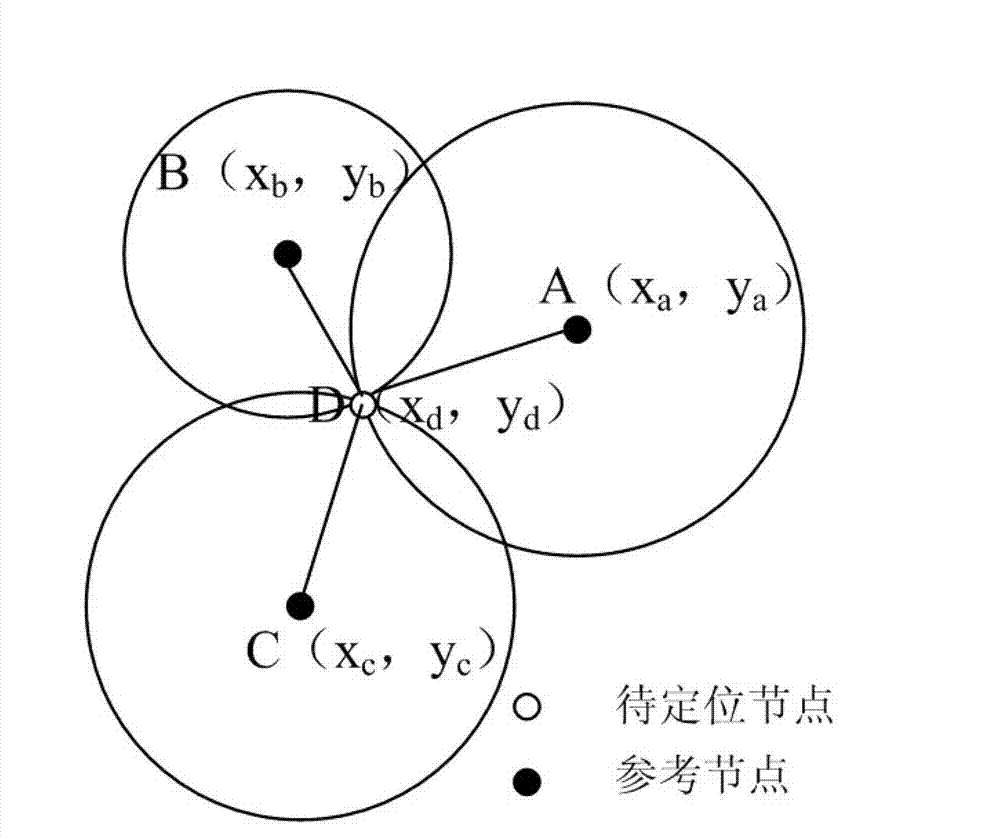
RSSI (Received Signal Strength Indicator) weighted centroid algorithm-based passive RFID (Radio Frequency Identification Device) label locating method
InactiveCN102928813AEasy to getLow pricePosition fixationCo-operative working arrangementsAlgorithmCentroid algorithm
The invention relates to an RSSI (Received Signal Strength Indicator) weighted centroid algorithm-based passive RFID (Radio Frequency Identification Device) label locating method, which comprises the steps of: calculating a corresponding Euclidean distance according to a to-be-located label and a signal strength value of a reference label relative to an RFID antenna, finding known reference labels of K coordinates, which are closest to the to-be-located label, wherein K is generally selected to be 4 according to the existing experiment result; calculating weights of the K reference labels which are closest to the to-be-located label; and finally, figuring out coordinates of the to-be-located label according to the coordinates and the weights of the reference labels. The method achieves a better balance between location cost and property, has the advantages of convenience, flexibility, easy configuration and the like, and can be suitable for a large quantity of RFID passive labels on the market; and because an RSSI is easy to obtain, a location system can also have better instantaneity.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
System and method providing automated margin tree analysis and processing of sampled data
InactiveUS20050165732A1ProcessingFast rejectionData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsAlgorithmTest object
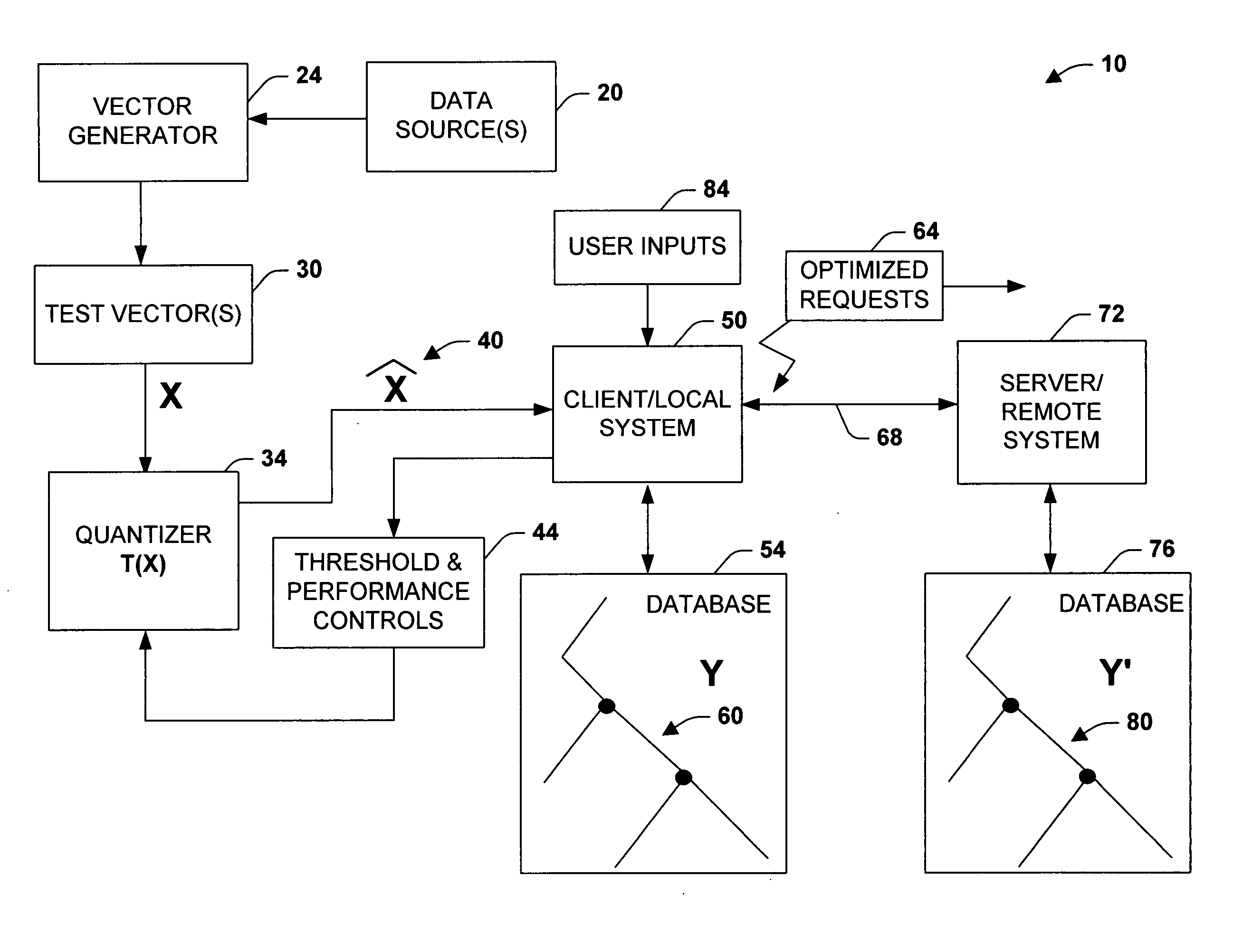
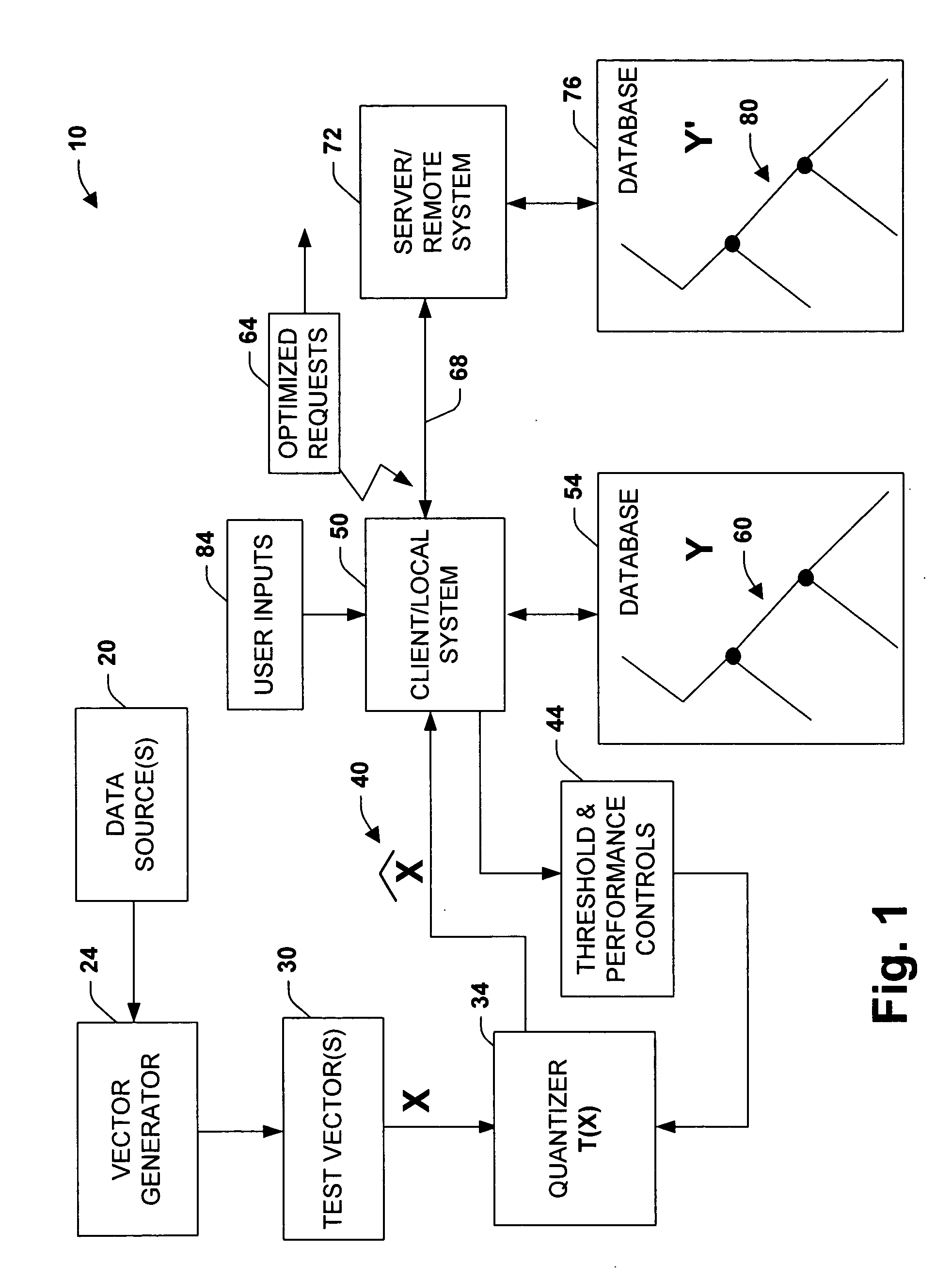
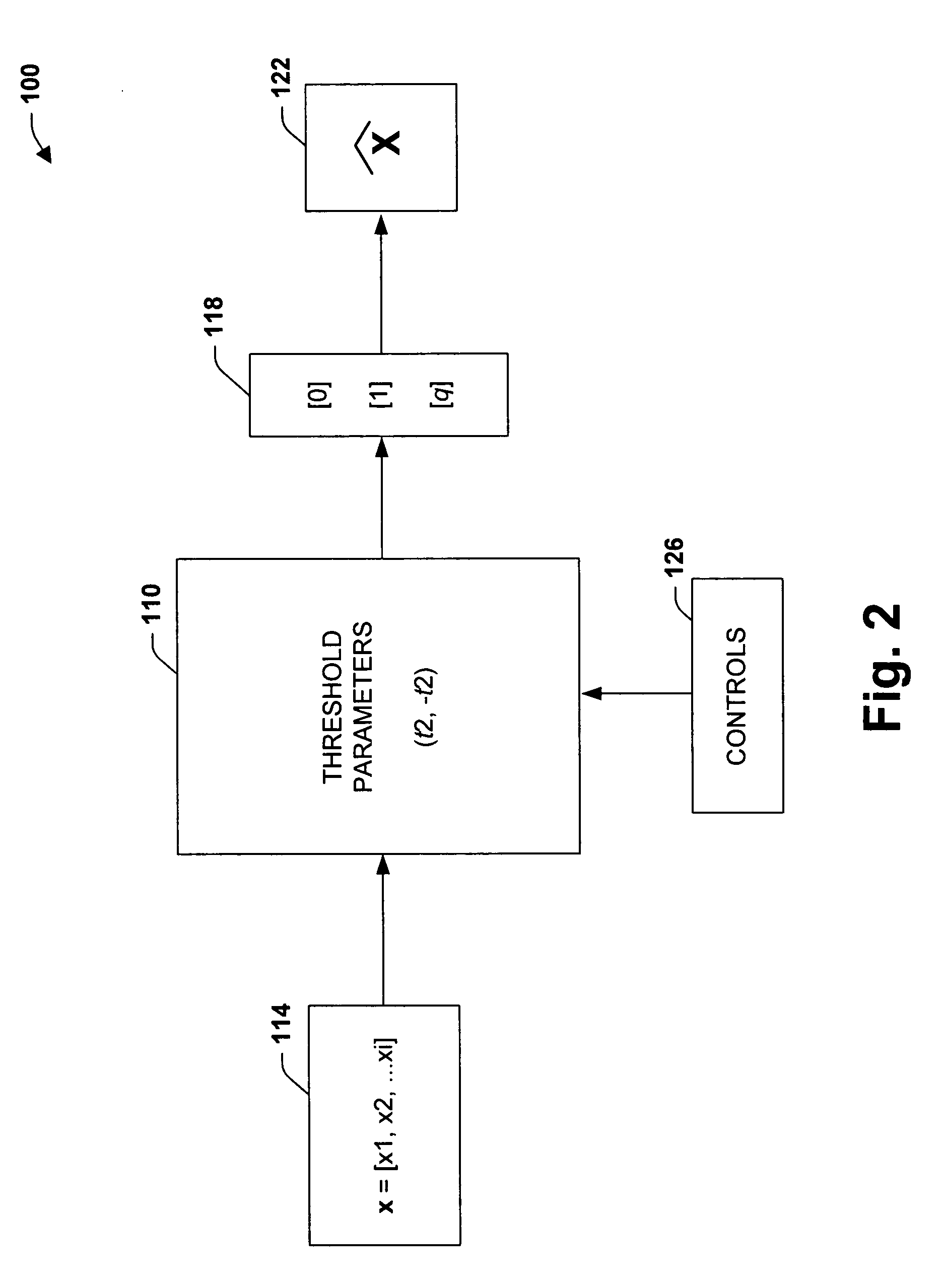
The present invention relates to a system and methodology to facilitate database processing in accordance with a plurality of various applications. In one aspect, a large database of objects is processed, wherein the objects can be represented as points in a vector space, and two or more objects are deemed ‘close’ if a Euclidean distance between the points is small. This can apply for substantially any type of object, provided a suitable distance measure can be defined. In another aspect, a ‘test’ object having a vector x, is processed to determine if there exists an object y in the database such that the distance between x and y falls below a threshold t. If several objects in the database satisfy this criteria, a list of objects can be returned, together with their corresponding distances. If no objects were to satisfy the criterion, an indication of this condition can also be provided, but in addition, the condition or information relating to the condition can be provided.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
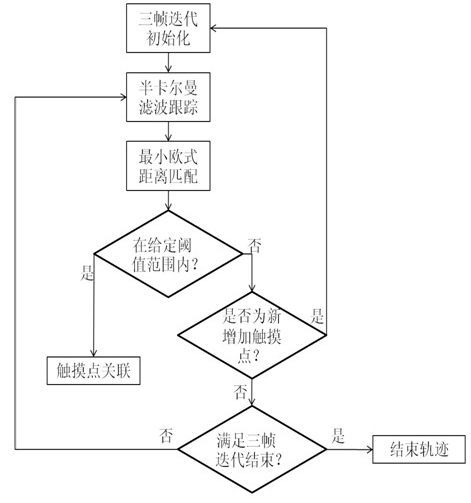
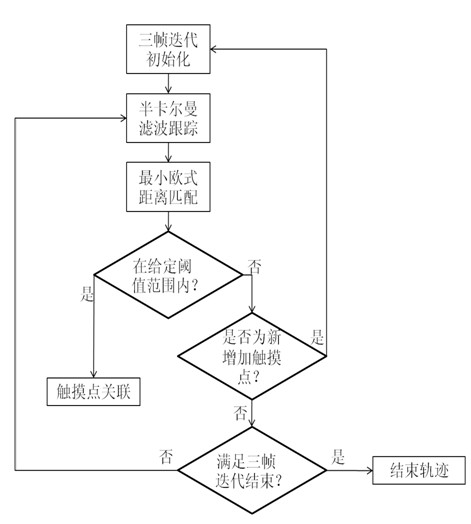
Multi-touch trajectory tracking method
ActiveCN102096530AImprove detection accuracyCancel noiseInput/output processes for data processingEuclidean distanceKalman filter
The invention discloses a multi-touch trajectory tracking method. The method comprises the following steps of: A, calculating initial states of each touch point and acquiring the data of each touch point; B, predicting the possible position of each touch point in the next frame by a semi-Kalman filtering method; C, in a given threshold range, searching the touch point which is in the nearest Euclidean distance of a predicted position in a current frame; if the touch point is searched, performing correlation; and otherwise, taking a predicted value as the position of the touch point in the current frame; D, judging whether a new touch point is added into the current frame; a new touch point is detected, performing the step A on the new touch point, and performing a step E on other touch points; and E, judging whether a trajectory is ended in the current frame. In the method, the initial states and the ending states of the touch points are judged by a three-frame iteration method; the probability of misjudging a noise into the touch point is avoided to a certain degree; the influence of the noise on a correct trajectory is improved; and particularly the correctness of the judgment of the new touch point and the ending trajectory is improved.
Owner:阜宁县科技创业园有限公司
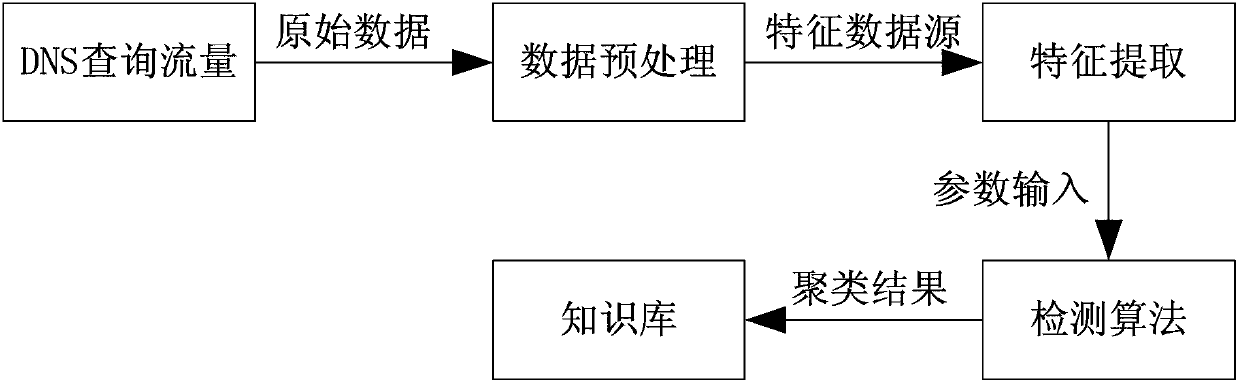
Method and system for detecting DNS (domain name system) traffic abnormality
ActiveCN103001825AAccurate detection rateReduce false alarm rateData switching networksAlgorithm convergenceDomain Name System
The invention provides a method and a system for detecting DNS (domain name system) traffic abnormality. The method includes: extracting corresponding characteristic values for DNS traffic data to be processed, giving different weights to each characteristic, and detecting an abnormality cluster marked in a training set by the aid of the W-Kmeans algorithm and the additional Euclidean distance threshold Dthreshold so that new unknown characteristic abnormality can be discovered. The method and the system have the advantages that the algorithm is high in convergence speed and small in calculation, new samples to be detected only need to be compared with a processed training clustering center, calculation of a great quantity of original training data is not needed, the method and the system are low in deployment cost, strong in generalization ability and capable of discovering DNS traffic abnormality rapidly and effectively, and the system is particularly suitable for being deployed on a large DNS server.
Owner:CHINA INTERNET NETWORK INFORMATION CENTER
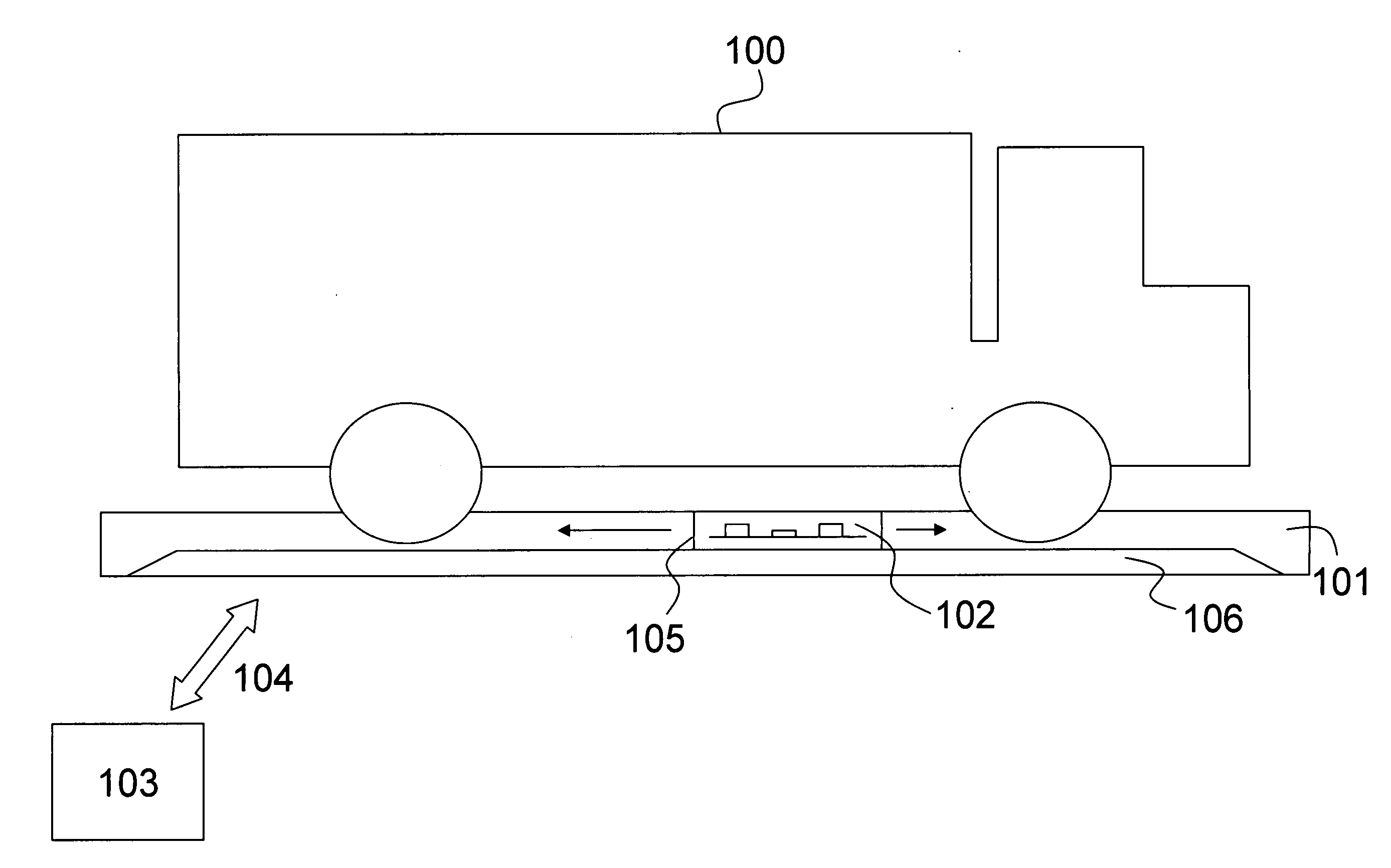
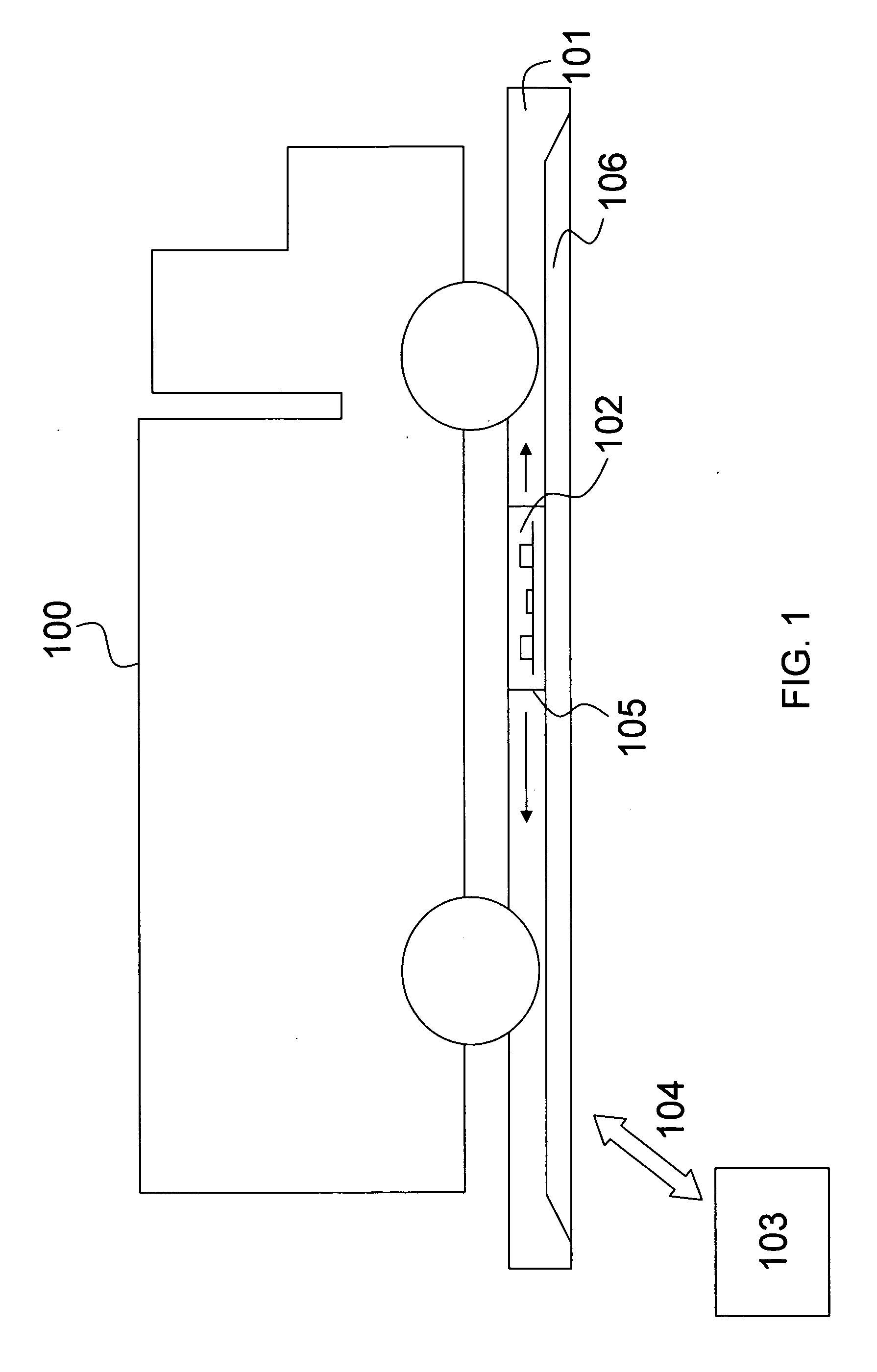
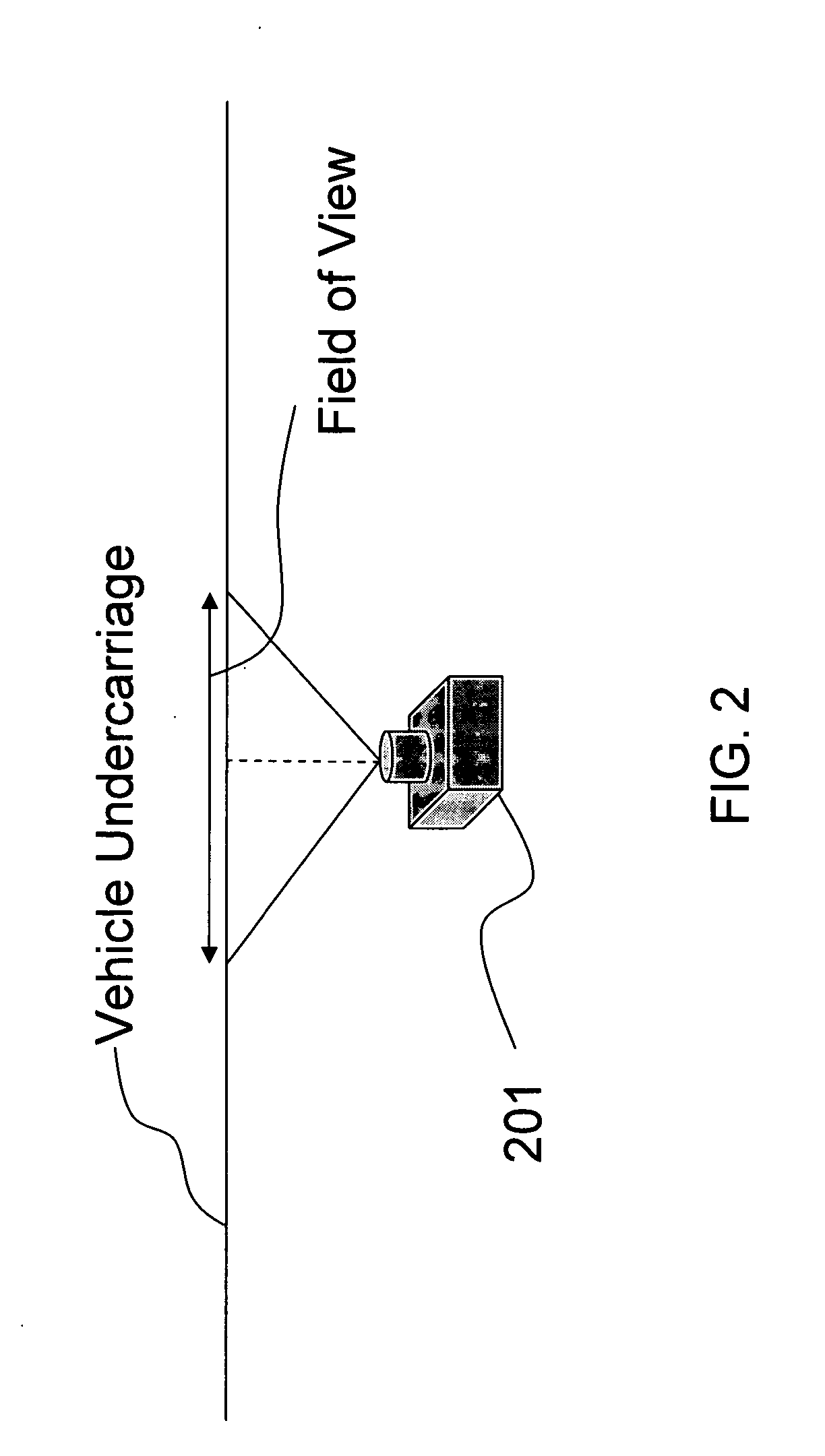
Under vehicle inspection system
InactiveUS20070040911A1Reliably and efficiently detectingMinimizing risk of physical harmColor television detailsClosed circuit television systemsOptical axisEngineering
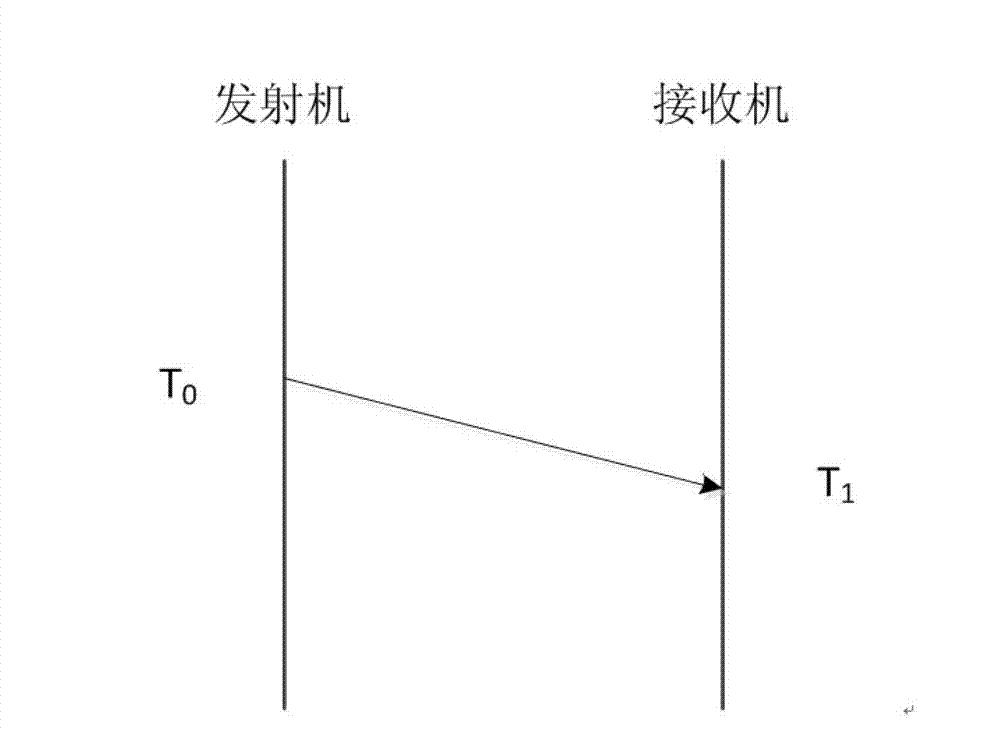
An under vehicle inspection system comprises a single camera adapted to capture a full width image of a vehicle undercarriage in a single scan. The camera has a viewing distance from the vehicle undercarriage, as measured along the optical axis of the camera, that is greater than a Euclidean distance between the camera and a point where the optical axis meets the vehicle undercarriage.
Owner:RILEY LARRY E
Image mosaic method based on neighborhood Zernike pseudo-matrix of characteristic points
InactiveCN101556692ASmall amount of calculationImprove accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisFeature vectorReference image
The invention relates to an image mosaic method based on neighborhood Zernike pseudo-matrix of characteristic points, which leads image statistical information (Zernike pseudo-matrix) to be interrelated with the characteristic points of an image by using the following steps: firstly, extracting interest points of an inference image and an input image by utilizing a Harris angle detector, and taking rectangular neighborhoods using the interest points as a center as a local characteristic region with characteristic matching; secondly, calculating the Zernike pseudo-matrix to the rectangular characteristic regions to be used as descriptors of the characteristic region, and realizing the matching of the characteristic points through comparing the Euclidean distance of the characteristic vector of the descriptor of each characteristic region. The matching can have less wrong matching points which are eliminated through a RANSAC (RANdom Sample Consensus) algorithm, and the right matching relation can be calculated to realize the image mosaic. The invention can effectively realize the image registration and mosaic with geometric transformation relations of translation, rotation, small scale zooming, and the like, and can be used for image treatment and image synthesis of fields such as communication, multimedia technology, and the like.
Owner:郭宝龙 +1
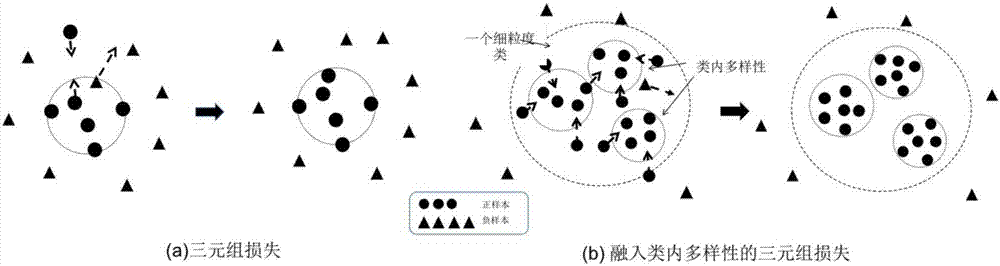
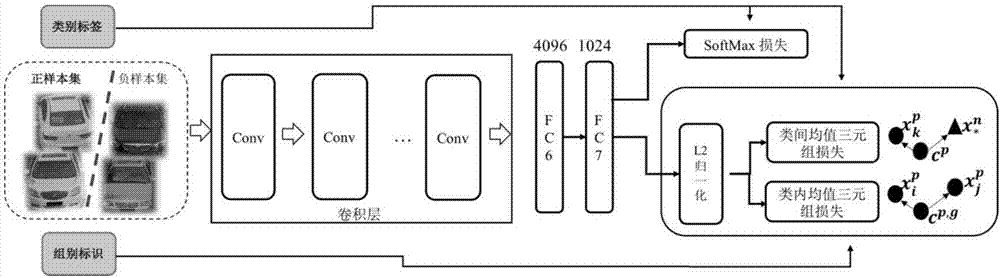
Triple loss-based improved neural network pedestrian re-identification method
ActiveCN106778527AGuaranteed robustnessImprove recognition accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionFeature vectorPositive sample
The invention discloses a triple loss-based improved neural network pedestrian re-identification method. The method comprises the following steps of constructing a sample database, establishing positive and negative sample libraries based on the sample database, and randomly selecting two positive samples and one negative sample to form a triple; constructing a triple loss-based neural network, and performing training, wherein the neural network is formed by connecting three parallel convolution neural networks with a triple loss layer; inputting a to-be-tested picture and each sample picture in the expanded sample database, which serve as a group of inputs, to the trained neural network in sequence, wherein another input of the neural network is zero or zero input; and calculating a distance of eigenvectors of two input pictures output by the neural network by utilizing a Euclidean distance, and querying and arranging first 20 Euclidean distances in an ascending order, and then performing simple manual screening to obtain a final identification result. The method has the beneficial effects that the identification method can be suitable for a picture scene with a relatively great change, can ensure robustness, and has relatively high identification accuracy.
Owner:CHINACCS INFORMATION IND
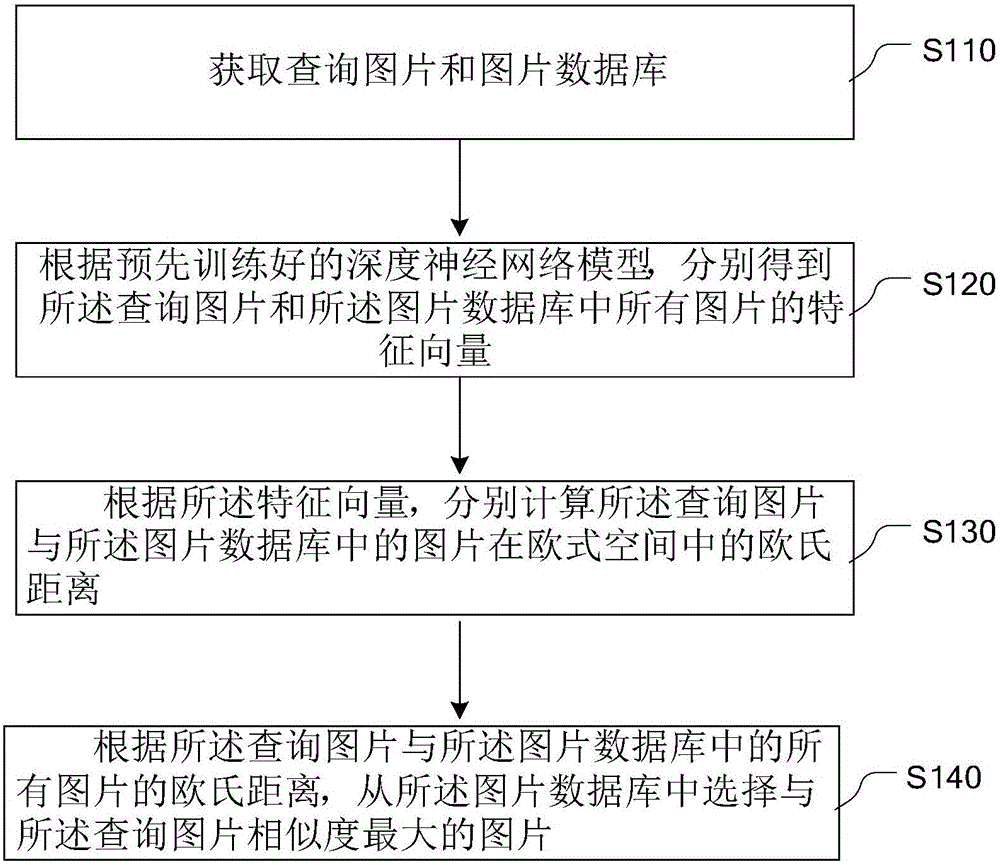
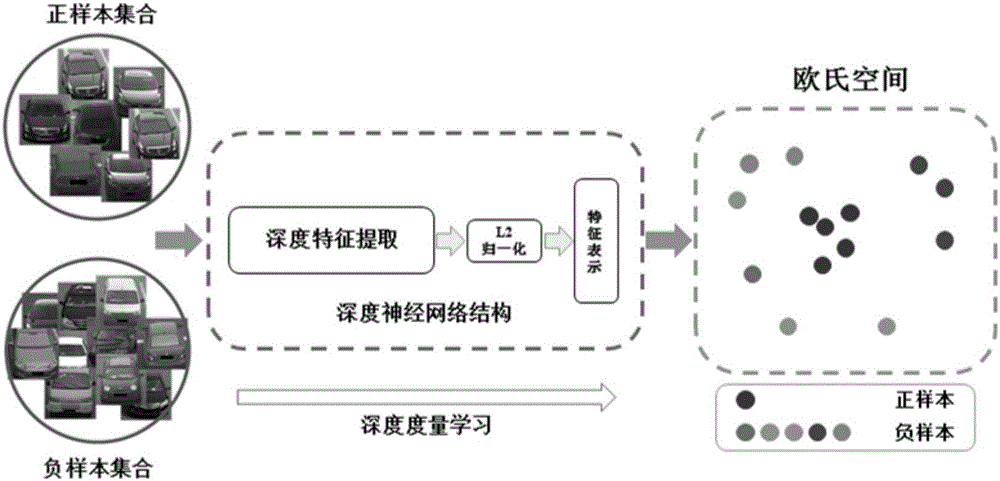
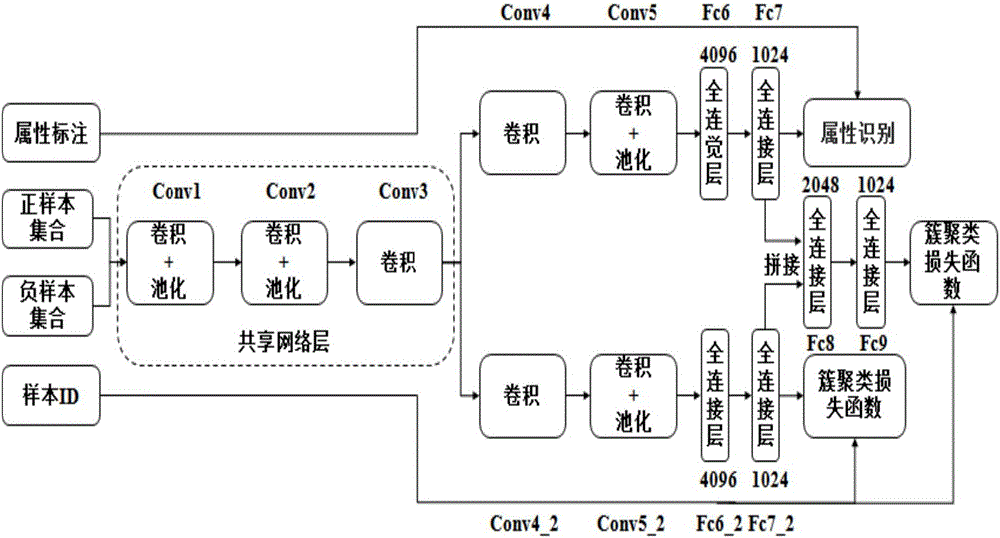
Integration target attribute identification and precise retrieval method based on depth measurement learning
The embodiment of the invention provides an integration target attribute identification and precise retrieval method based on depth measurement learning. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining a query picture and a picture database; according to a pre-trained deep neural network model, independently obtaining the feature vector of the query picture and the feature vectors of all pictures in the picture database, wherein the feature vectors comprise the category features of an individual target and the identity features of the individual target in the pictures; according to the feature vectors, independently calculating an Euclidean distance between the query picture and each picture in the picture database in an Euclidean space; and according to the Euclidean distances between the query picture and all pictures in the picture database, selecting a picture which exhibits highest similarity with the query picture in the picture database. The method can improve the accuracy of image retrieval.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com