Patents
Literature
2673results about How to "Easy to compare" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
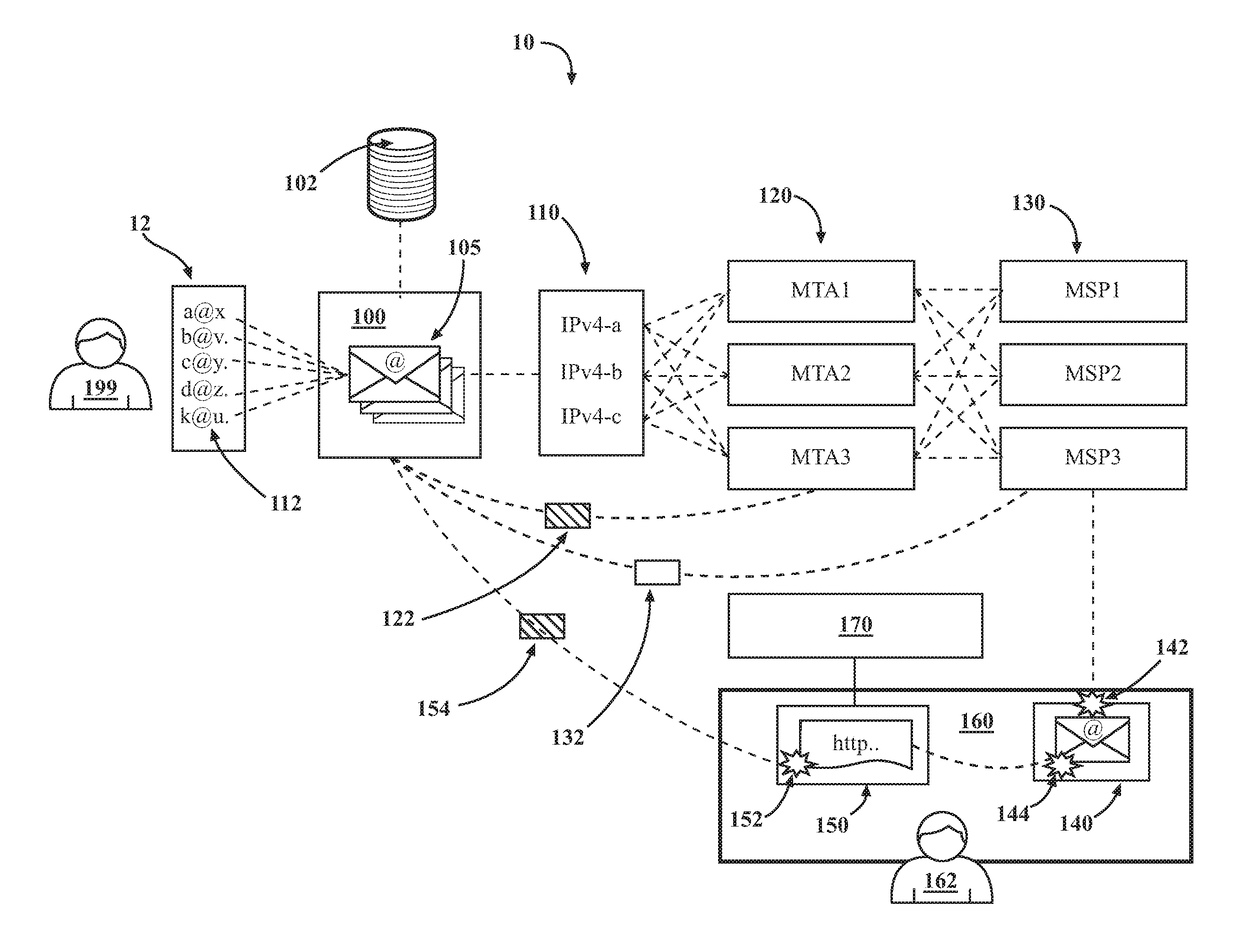
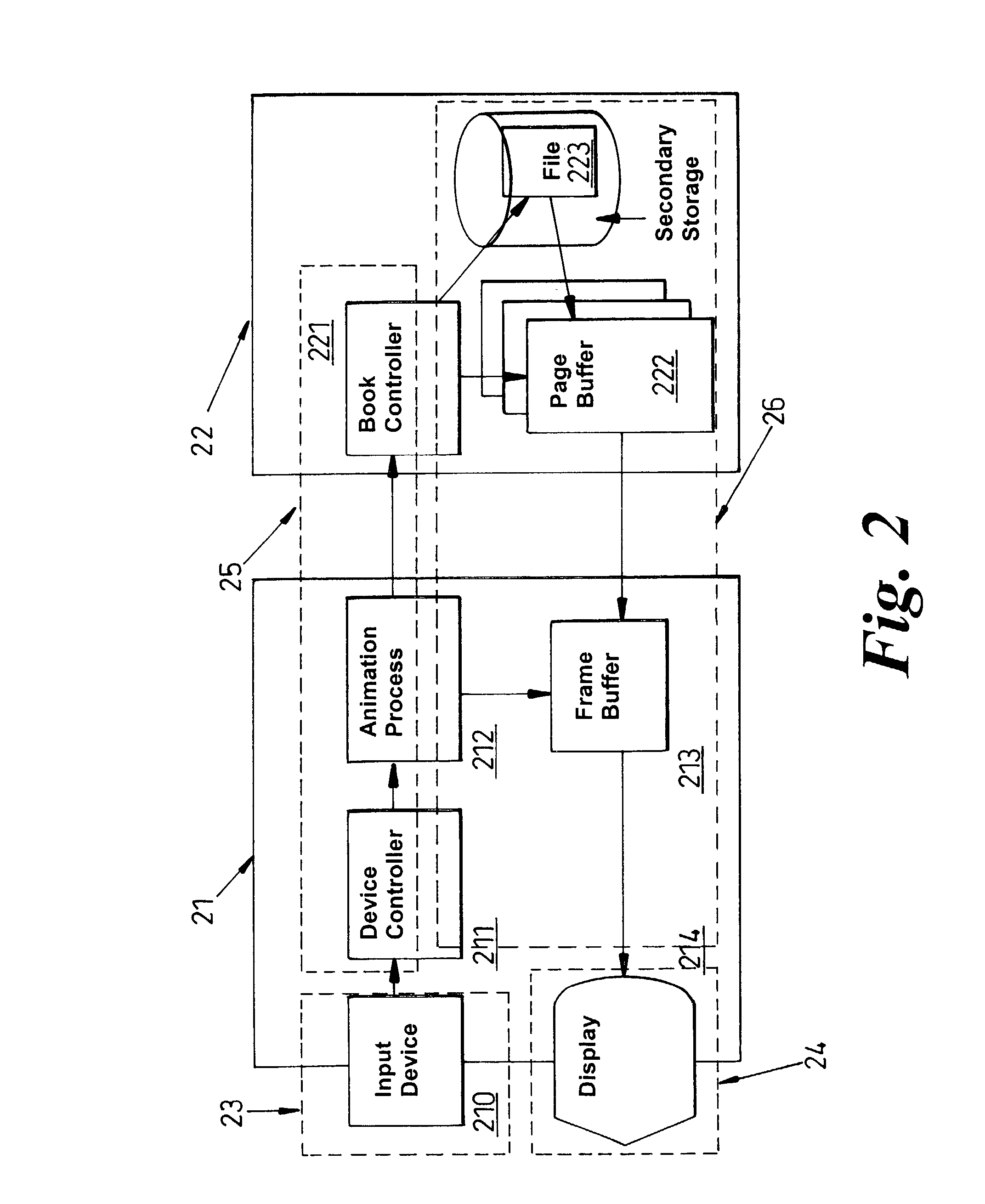
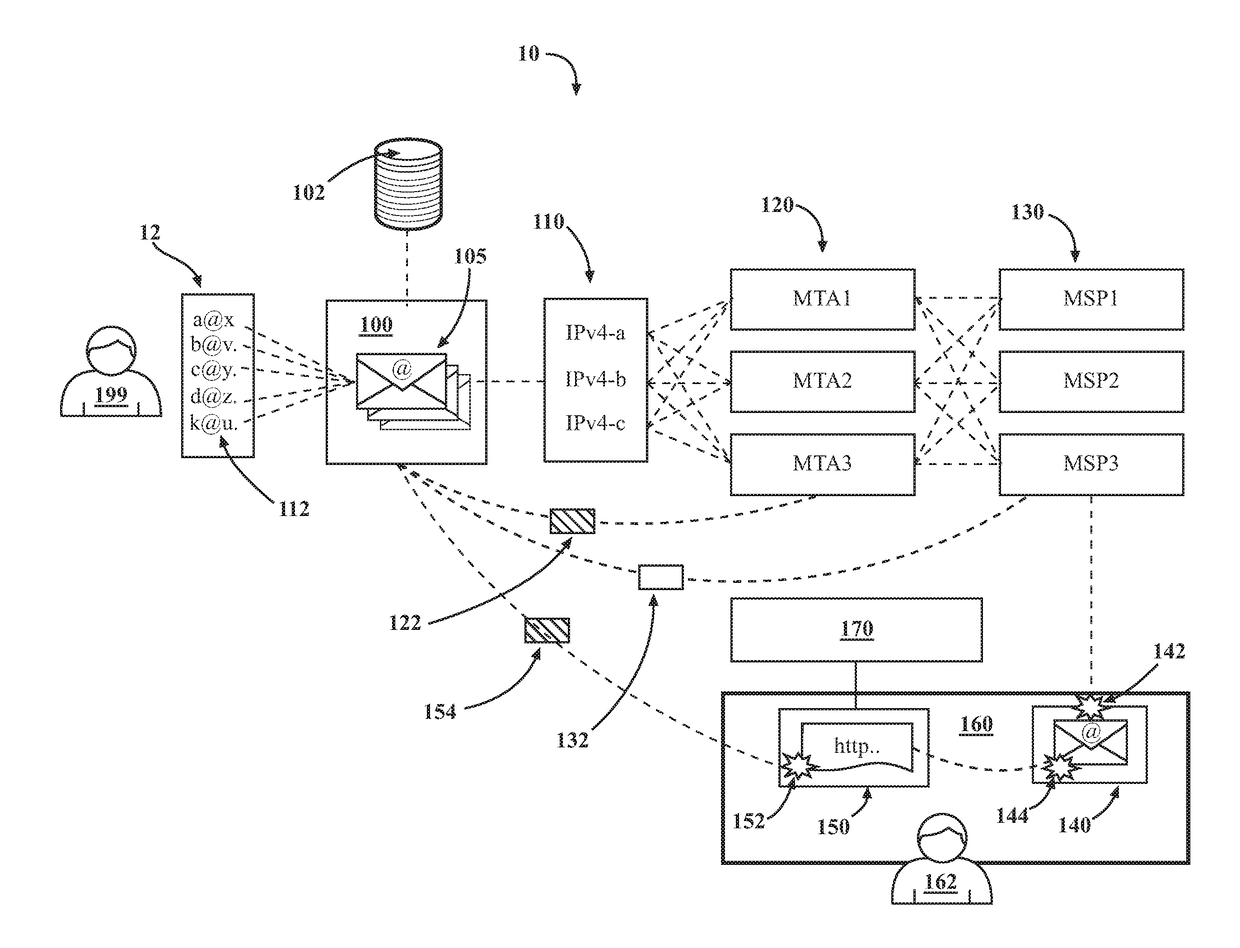
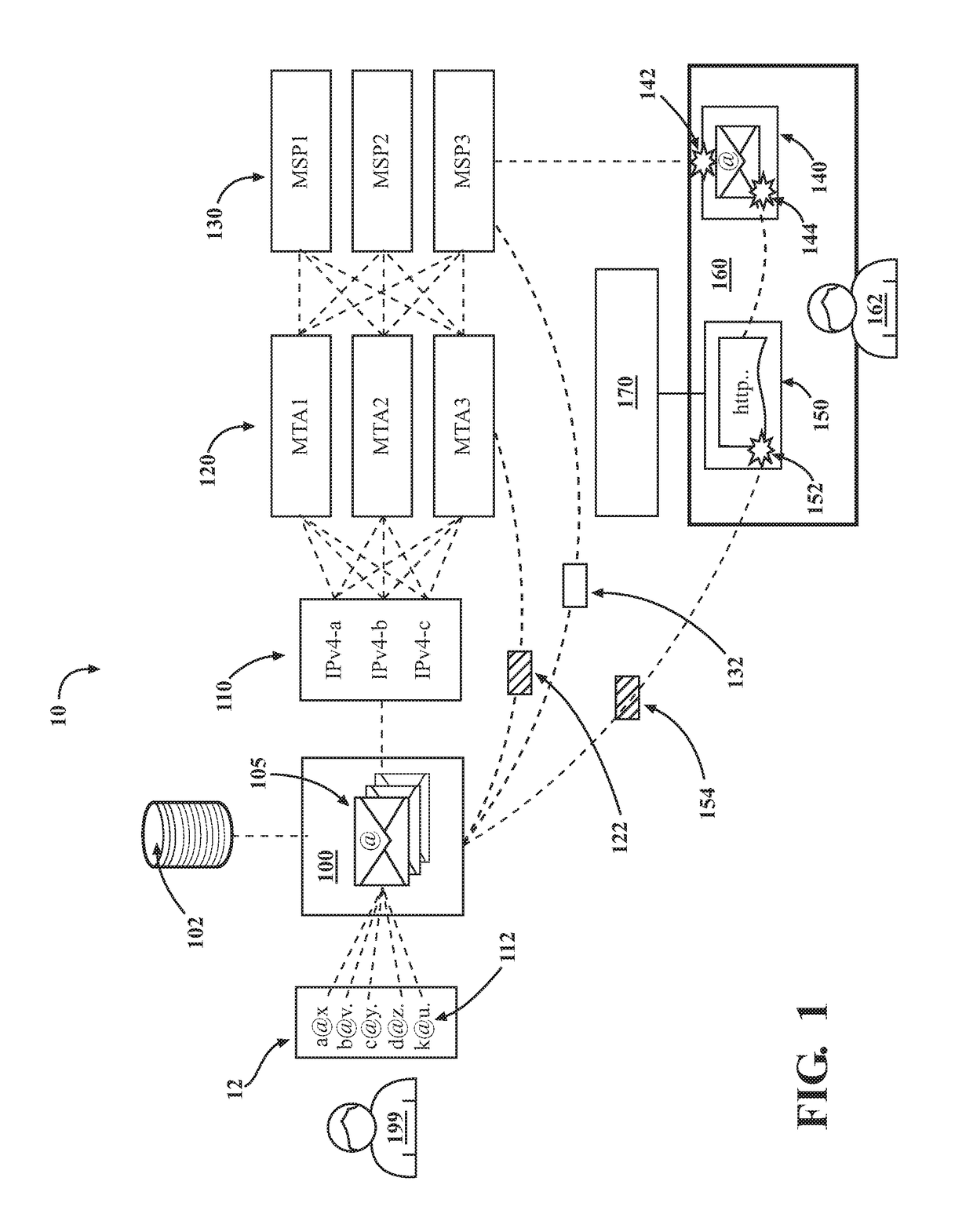
Introducing a new message source into an electronic message delivery environment
ActiveUS20180219830A1Reduce riskMaximizing numberMathematical modelsAdvertisementsMessage deliveryBlack list
Owner:HUBSPOT
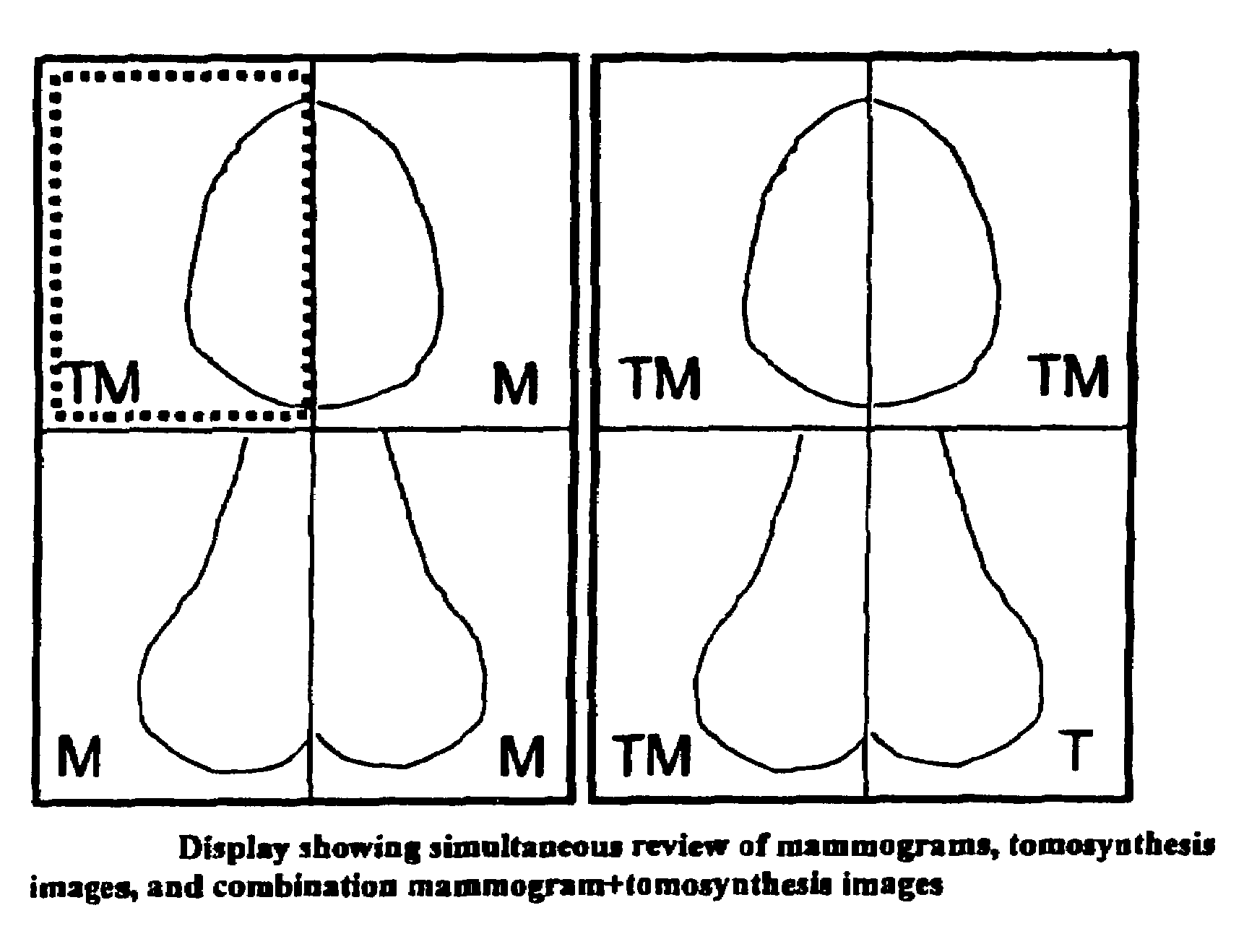
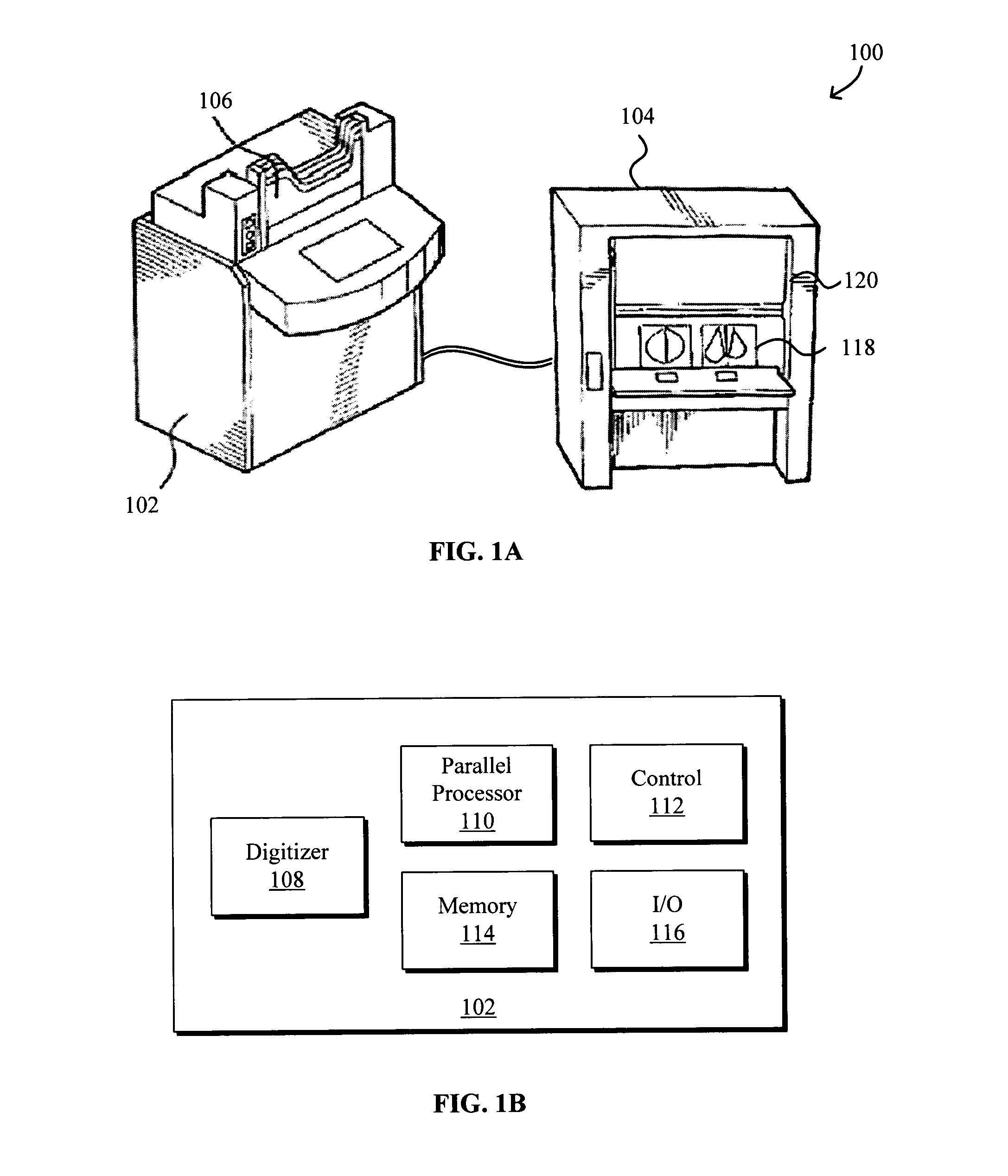
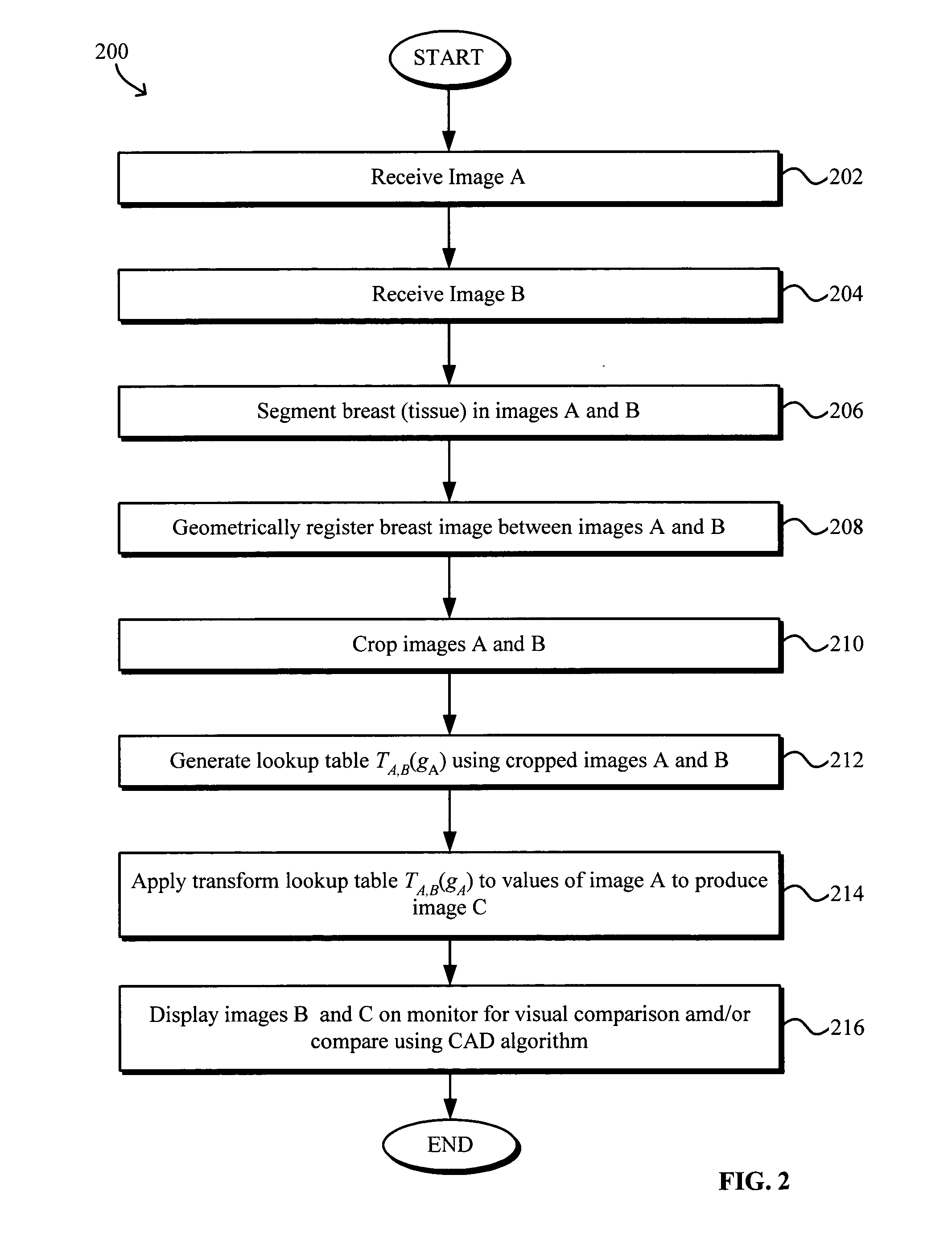
Image Handling and display in X-ray mammography and tomosynthesis
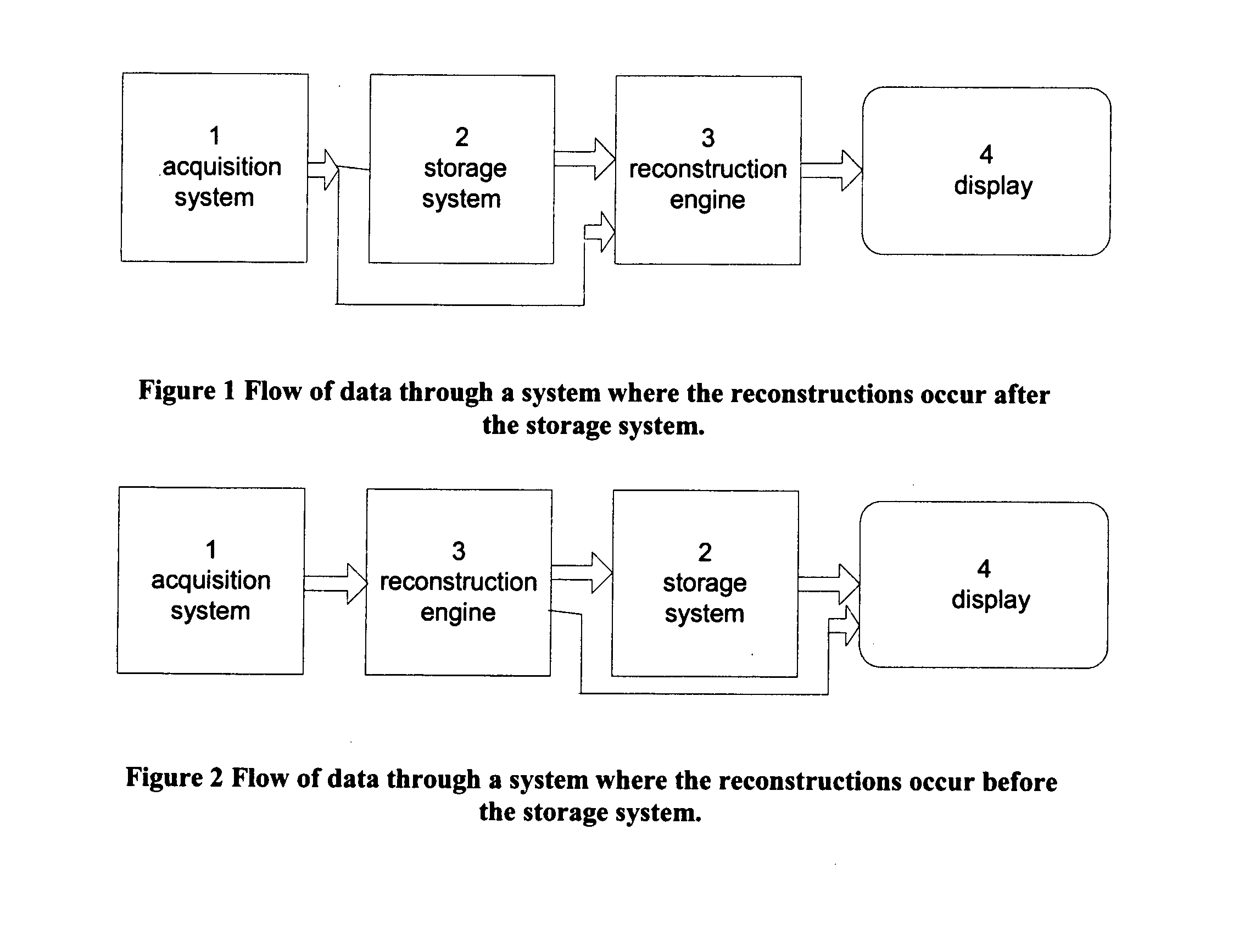
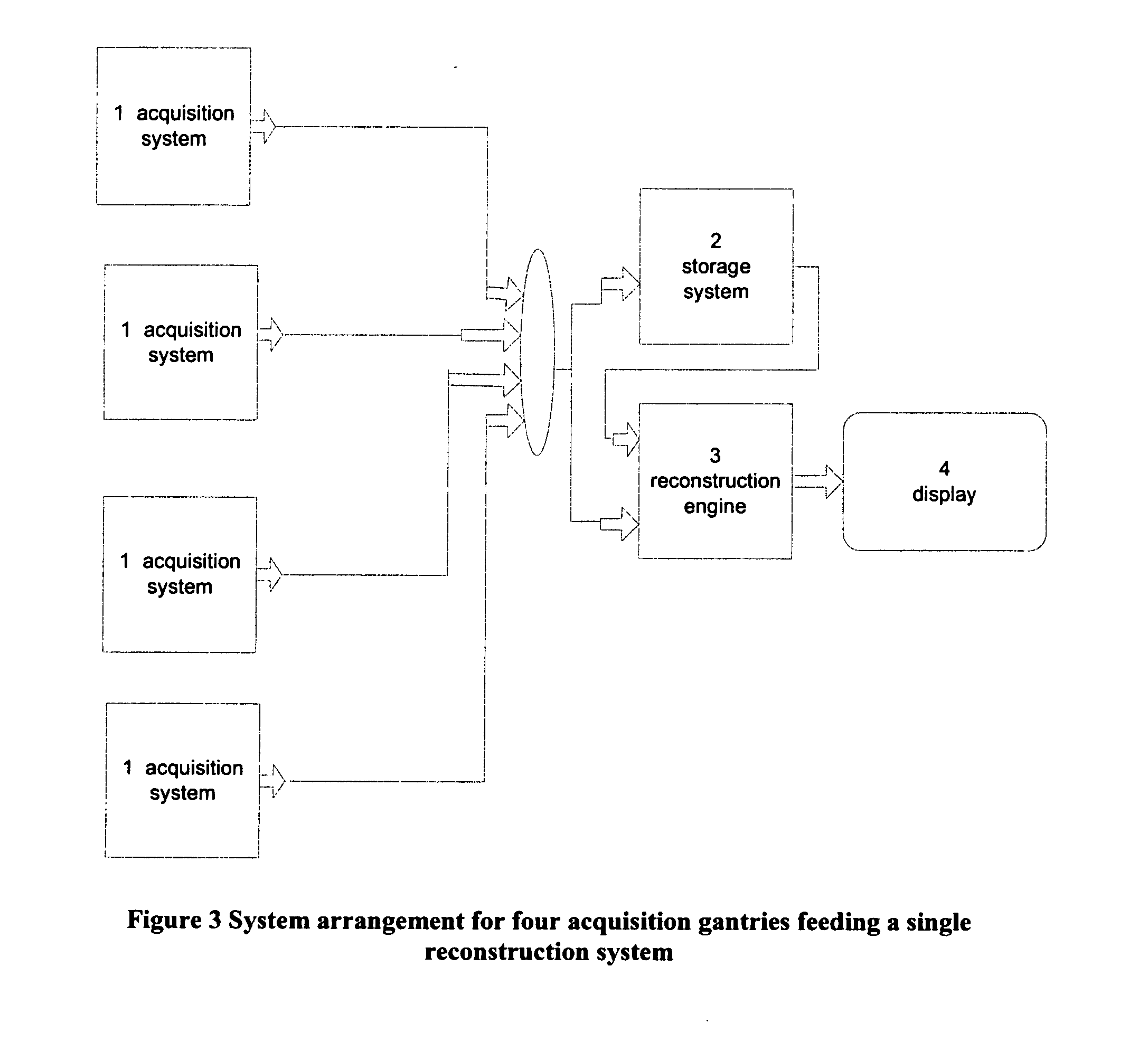
InactiveUS20080019581A1Easy to identifyImprove assessmentImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionTomosynthesisProjection image
A method and system for acquiring, processing, storing, and displaying x-ray mammograms Mp tomosynthesis images Tr representative of breast slices, and x-ray tomosynthesis projection images Tp taken at different angles to a breast, where the Tr images are reconstructed from Tp images
Owner:HOLOGIC INC
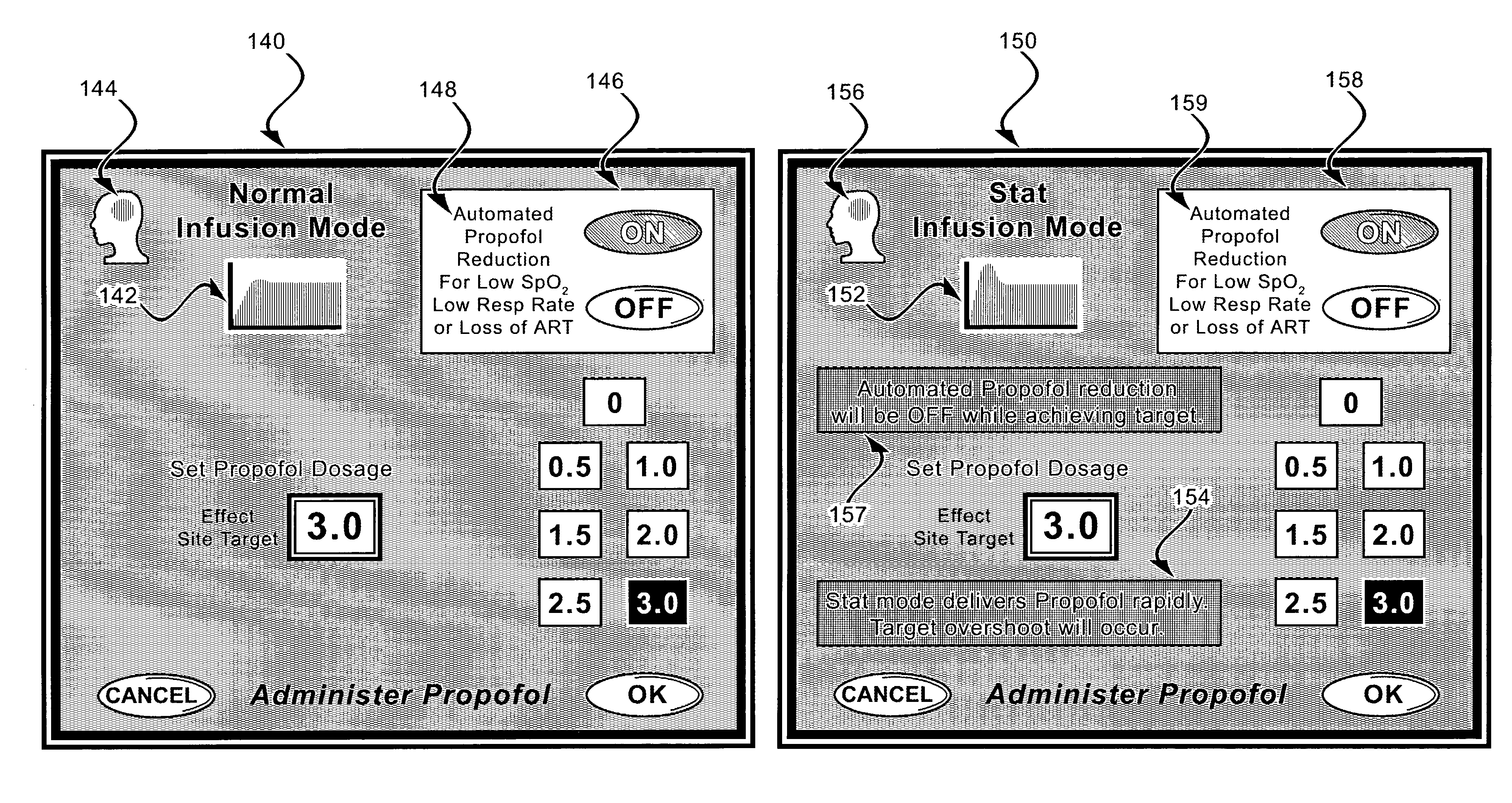
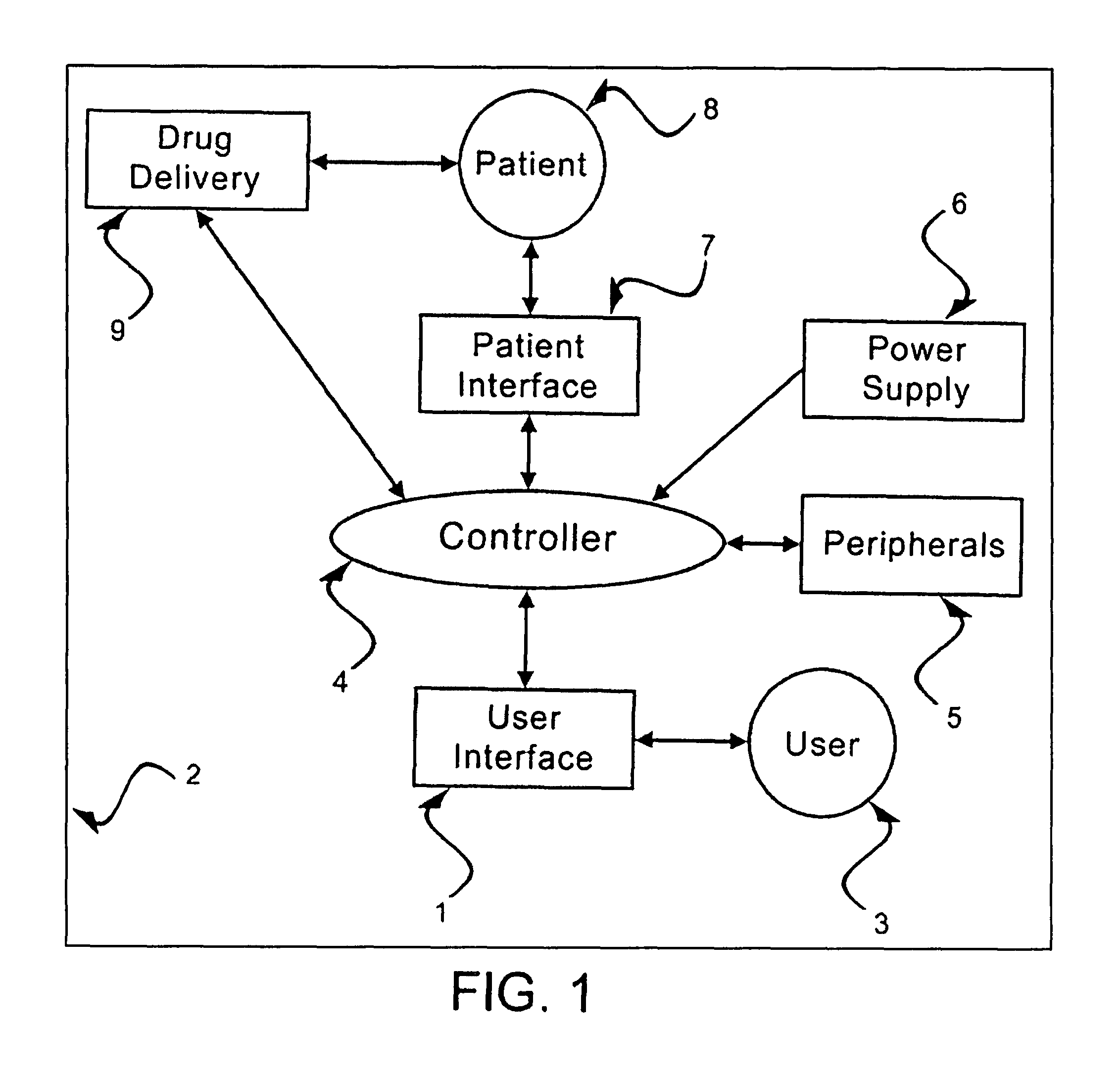
User interface for sedation and analgesia delivery systems and methods
ActiveUS8567393B2Simple and safe operationFacilitates high data densityDrug and medicationsBreathing masksSedationGeolocation
The present invention comprises a user interface for systems and methods for sedation and analgesia delivery. The user interface receives input from a user of a sedation and analgesia delivery system and relays information regarding the system, the administration of sedation and analgesia, physiological conditions to the user in a context sensitive manner. The information relayed may be displayed to the user on a touch sensitive screen or multi-layer display device. The display may be segregated geographically or may be color coded on the display device where the geographic location and / or color of the displayed information relates further information to the user.
Owner:SCOTT LAB
Sensor devices for structural health monitoring
InactiveUS20060170535A1Reduce needEasy to compareElectric signal transmission systemsThermometers using mean/integrated valuesStructural health monitoringCurrent sensor
Described herein are wireless interrogation systems and methods that rely on a complementary sensing device and interrogator. The sensing device is disposed to measure a parameter indicative of the health of a structure. A sensor reading from the sensor indicates the level of a parameter being monitored or whether one or more particular physical or chemical events have taken place. Using wireless techniques, the interrogator probes the device to determine its identity and its current sensor reading. This often includes transmission of a wireless signal through portions of the structure. When activated, the device responds with a wireless signal that identifies the device and contains information about the parameter being measured or a particular sensor state corresponding to the parameter. The identity of the device allows it to be distinguished from a number of similar devices. Thus this invention finds particular usefulness in the context of an array of devices that can be probed by a wireless interrogation unit. In one embodiment, the devices are passive and derive power from the interrogation signal.
Owner:YASUMI CAPITAL
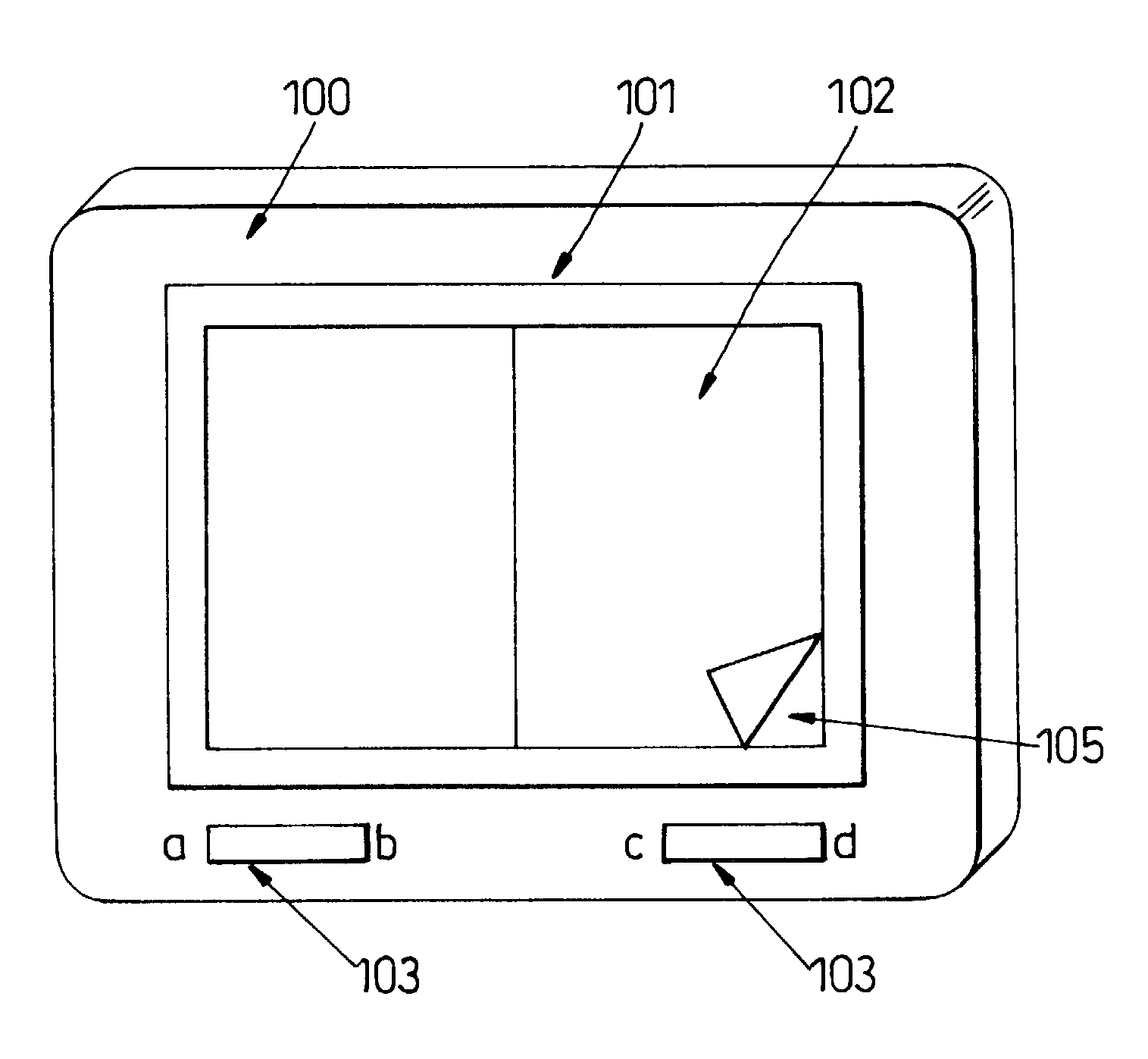
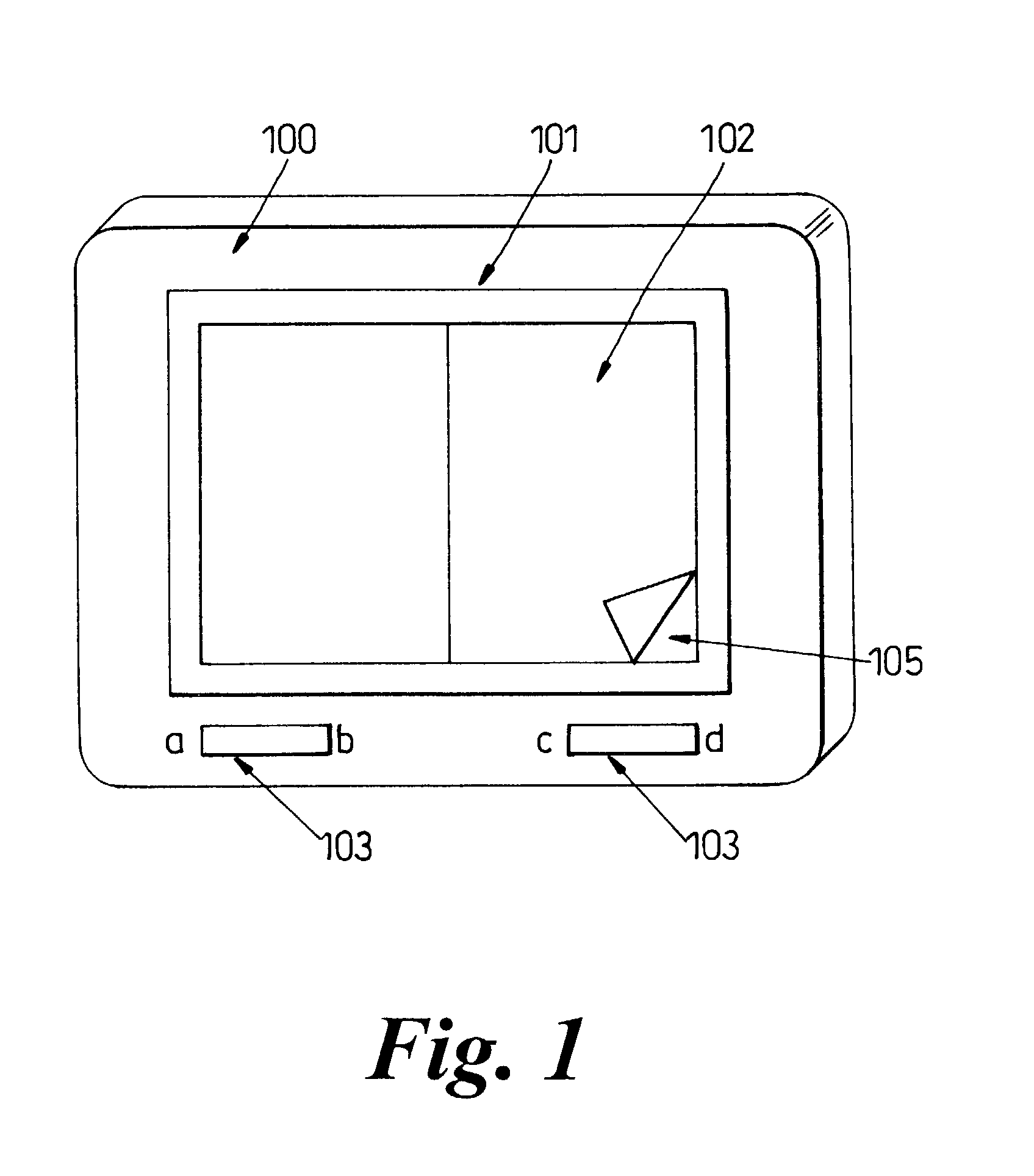
Document viewing device
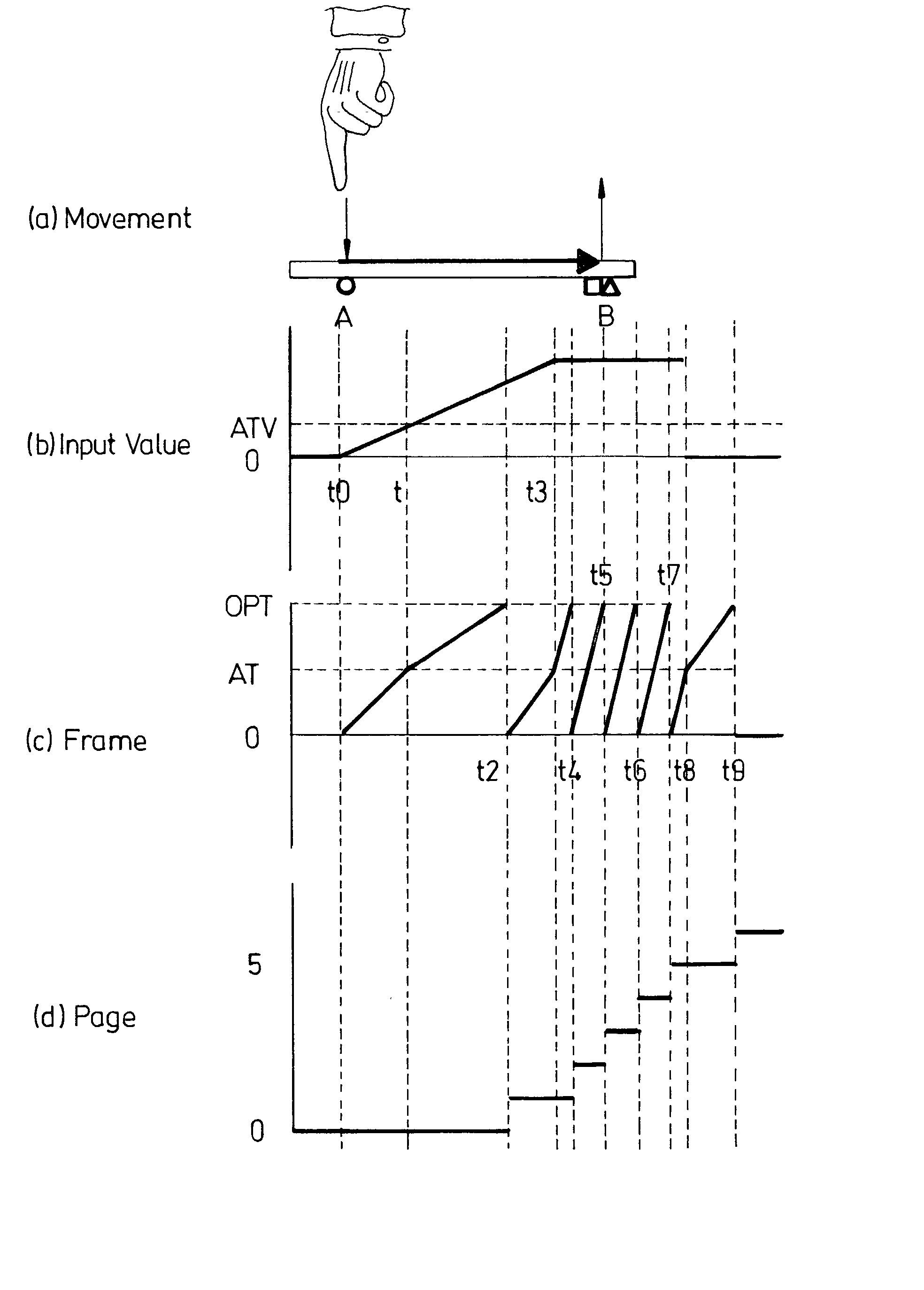
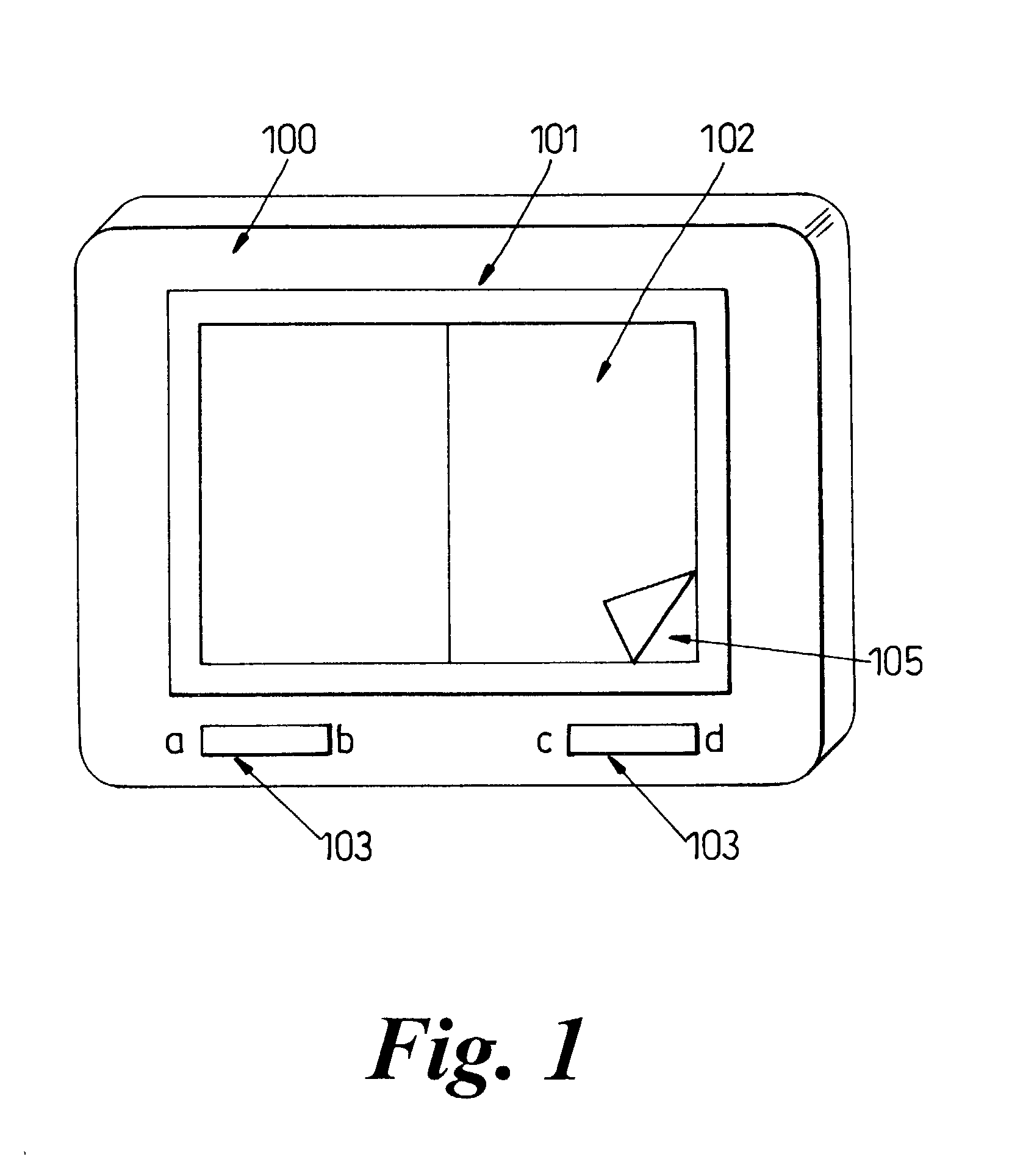
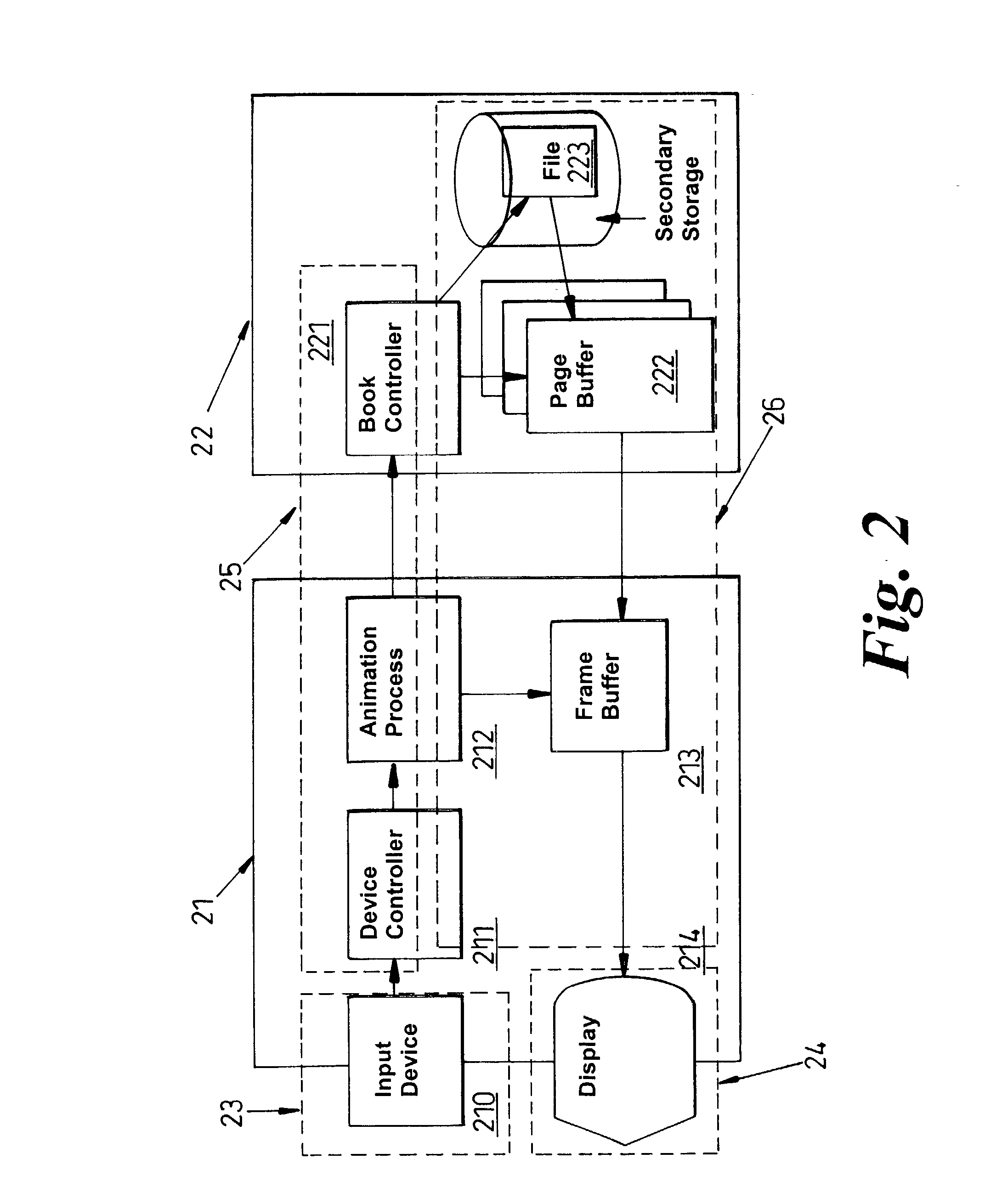
InactiveUS20030020687A1Intuitive displayRapid positioningInput/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsUser inputDisplay device
A document display device, comprising a memory arranged to store a document in the form of a sequence of pages; a display arranged to provide a user view of pages from the sequence; at least one user input device; a processor responsive to the at least one user input device to change the user view of the sequence of pages wherein said processor is arranged to allow reference markers to be associated with a page by a predetermined first input to the input device and further arranged such that a page associated with said reference marker can be at least partially displayed by a further predetermined input to the input device. Such an arrangement allows a one or more pages to marked as a block of pages, and the device allows a user to refer back to the pages at either end of the block.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
System and method for managing and evaluating network commodities purchasing
InactiveUS7043457B1Easy to compareSpecial service provision for substationMarket predictionsDistributed computingStandardization
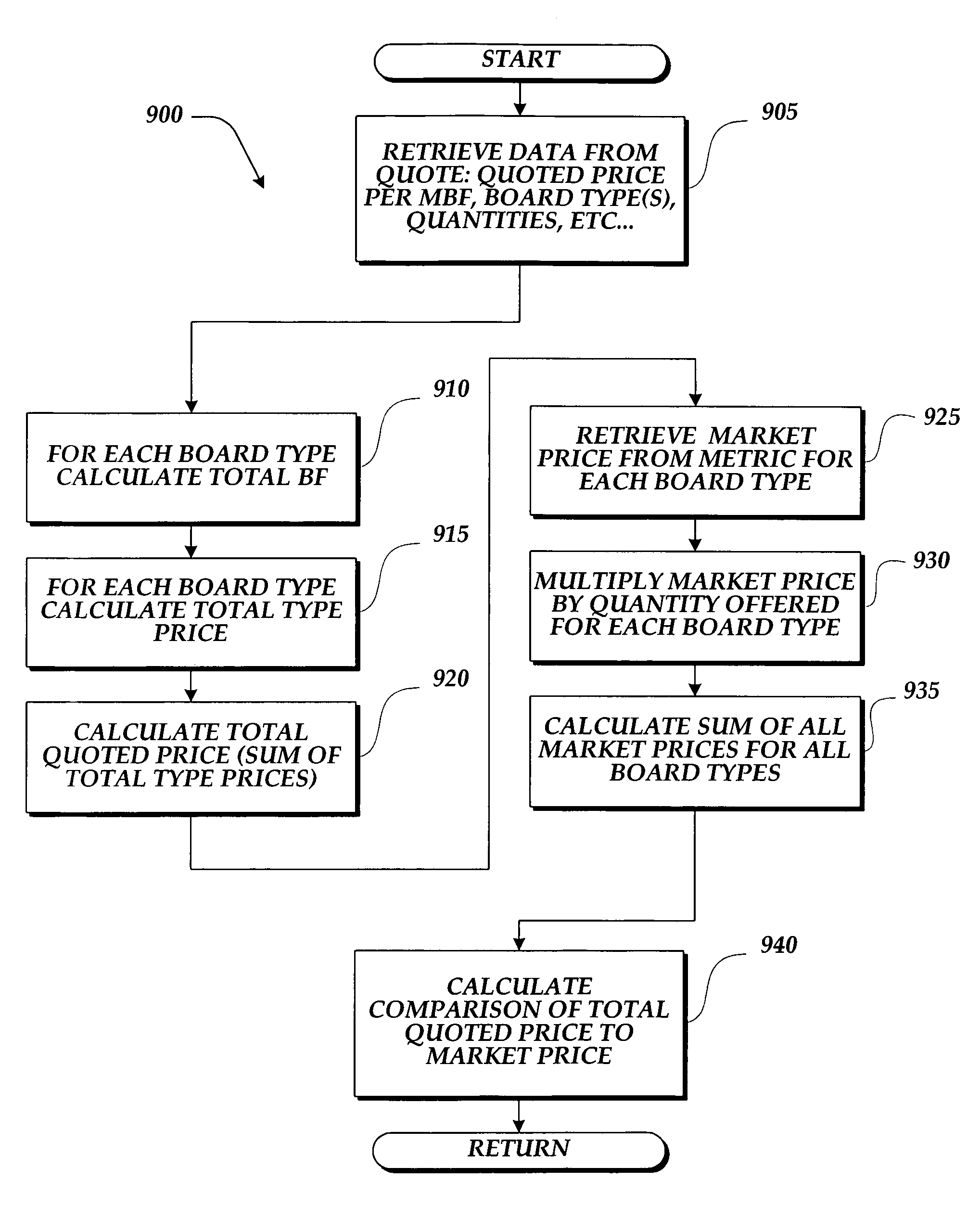
A method and system for managing and evaluating commodities purchasing over a network of distributed computing devices. In one embodiment, the method allows a plurality of buyers to generate one request for quote and, response to the request for quote, receive a quote from plurality of vendors. The system of the present invention provides a price normalization routine that allows buyers to evaluate and compare a normalized price for commodity products having different evaluation parameters. In an arrangement comprising a plurality of computers connected to a network said plurality of computers including at least one server, at least one buyer client computer and a plurality of seller client computers, the method for providing commodities exchange services first provides a web-based browsable display describing at least one commodities exchange service. The system then receives at least one request for quote from the buyer. The system then receives at least one quote from different sellers, wherein each quote may have a different price and quantity listed. The system then compares to one or more selected metrics and normalizes the prices received from the different quotes, thus, allowing the buyer to readily compare the prices of a number of commodity items having inherently different values. In one embodiment, the system of the present invention also provides a method for multi-value cross compilation of sales transactions, iterative quote information, and metric data for purposes of evaluation and strategy analysis.
Owner:BUYMETRICS
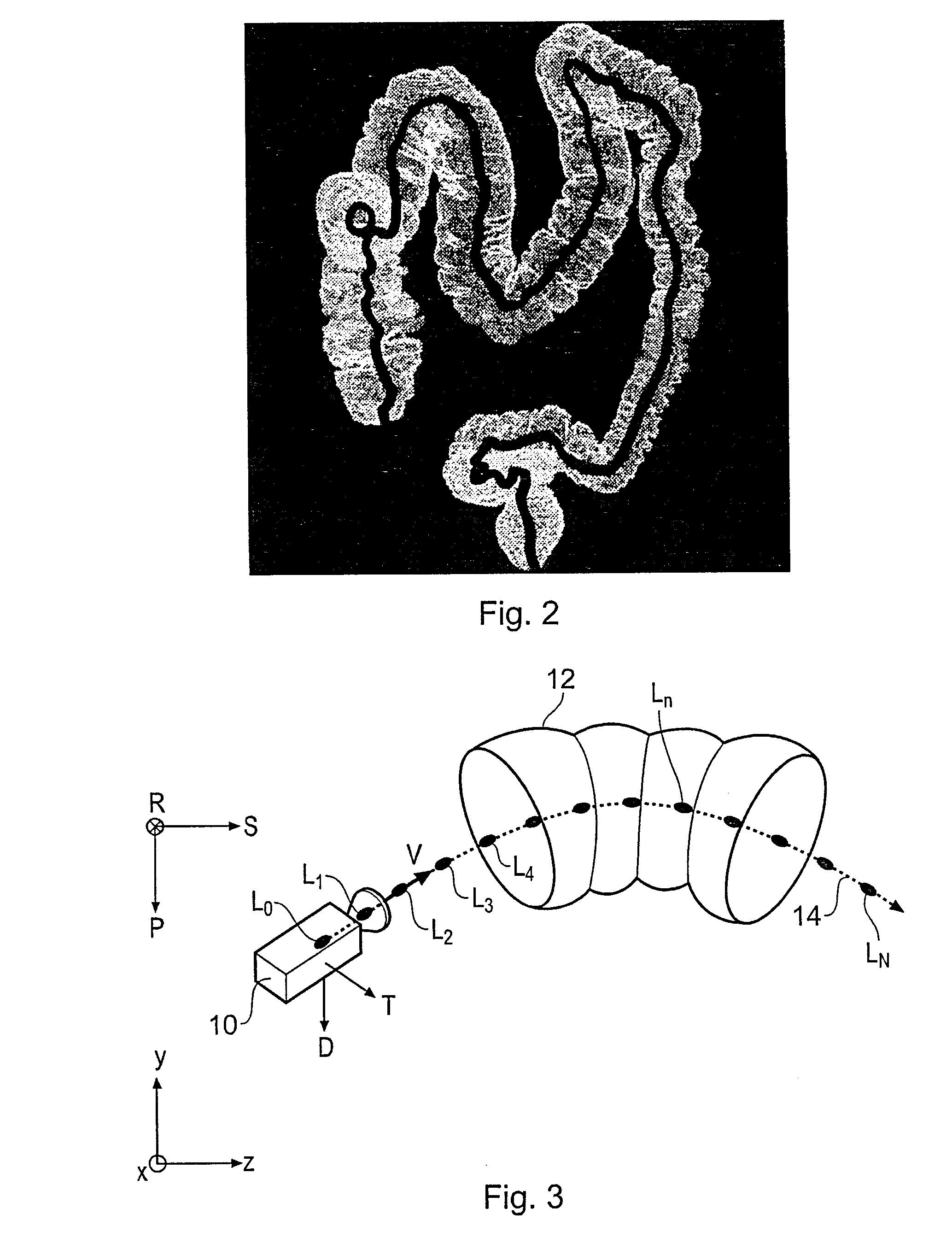
Virtual endoscopy
InactiveUS20080118117A1Full effectImproved angular separationSurgeryEndoscopesData setVirtual camera
A method of orienting a virtual camera for rendering a virtual endoscopy image of a lumen in a biological structure represented by a medical image data set, e.g., a colon. The method comprises selecting a location from which to render an image, determining an initial orientation for the virtual camera relative to the data set for the selected location based on the geometry of the lumen, determining an offset angle between the initial orientation and a bias direction; and orienting the virtual camera in accordance with a rotation from the initial orientation towards the bias direction by a fractional amount of the offset angle which varies according to the initial orientation. The fractional amount may vary according to the offset angle and / or a separation between a predetermined direction in the data set and a view direction of the virtual camera for the initial orientation. Thus the camera orientation can be configured to tend towards a preferred direction in the data set, while maintaining a good view of the lumen and avoiding barrel rolling effects.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL VISUALIZATION SYST EURO
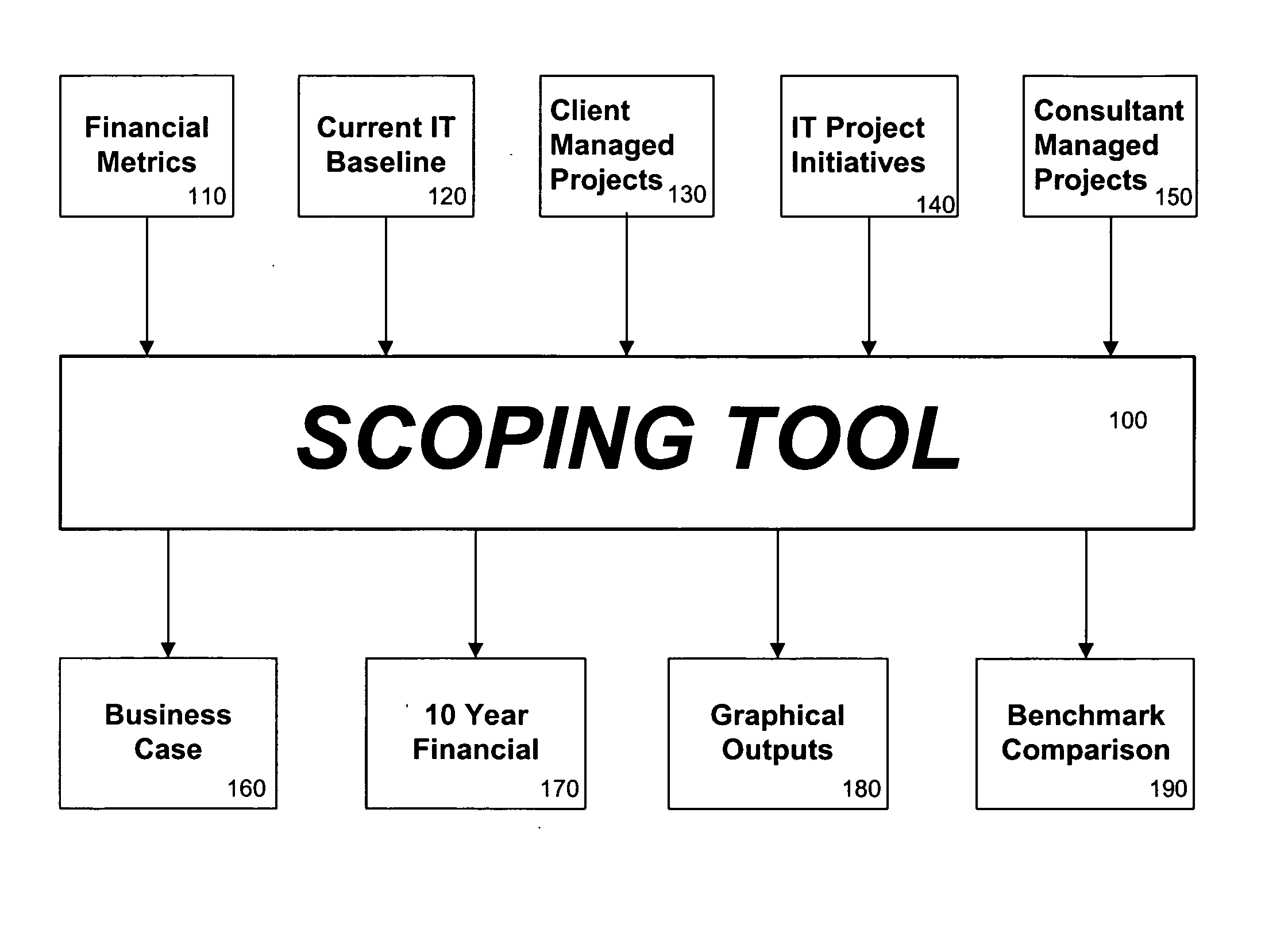
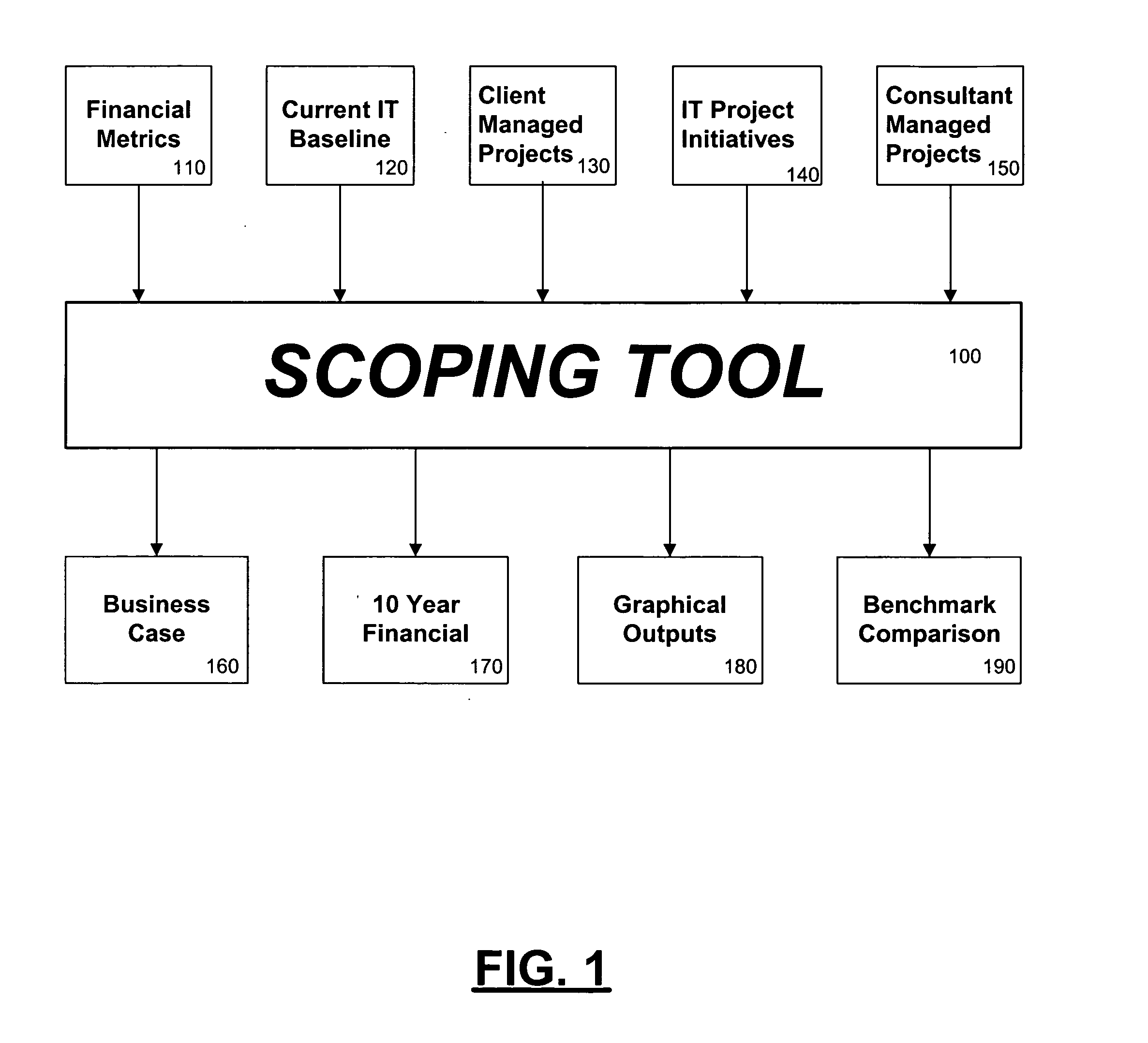
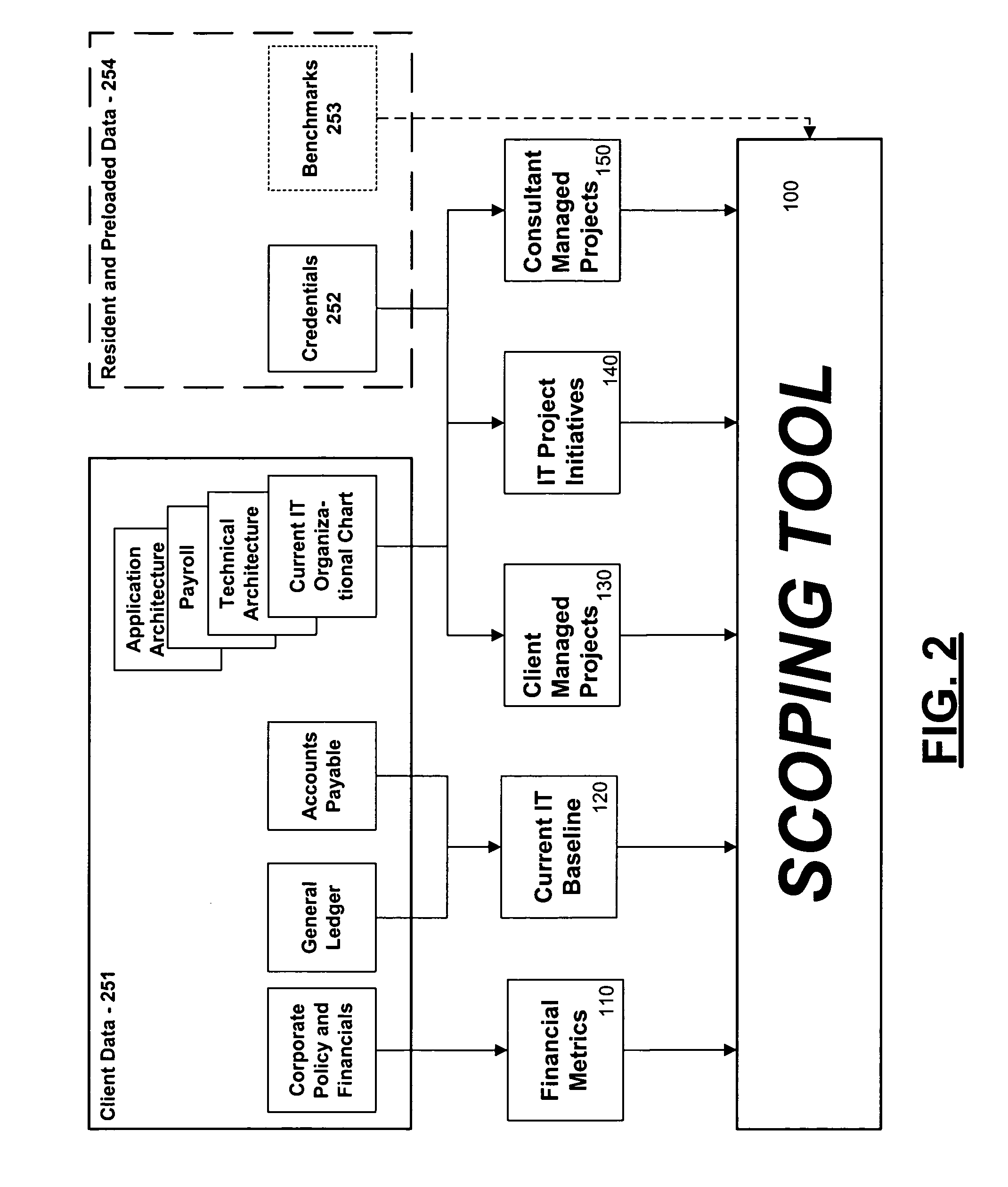
Information technology transformation assessment tools
InactiveUS20050278202A1Improve accuracyImprove efficiencyMarket predictionsResourcesCase presentationEngineering
Disclosed are assessment tools and related methods for analyzing potential transformations to a business' IT capabilities. In particular, a tool for scoping the potential opportunity incorporating a top-down approach and using previous credentials to make accurate estimations is disclosed. Additionally, a shaping tool employs a bottom-up approach to the assessment based upon more highly-detailed information of the structure of the IT department. Each tool also automatically calculates typical indices for evaluation of the business case of the IT transformation. Optionally, the tools are integrated, and also can automatically generate a business case presentation or a detailed analysis of all data involved in the assessment.
Owner:ACCENTURE GLOBAL SERVICES LTD
Document viewing device
InactiveUS7081882B2Intuitive displayRapid positioningInput/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsUser inputDisplay device
A document display device, comprising a memory arranged to store a document in the form of a sequence of pages; a display arranged to provide a user view of pages from the sequence; at least one user input device; a processor responsive to the at least one user input device to change the user view of the sequence of pages wherein the processor is arranged to allow reference markers to be associated with a page by a predetermined first input to the input device and further arranged such that a page associated with the reference marker can be at least partially displayed by a further predetermined input to the input device. Such an arrangement allows one or more pages to marked as a block of pages, and the device allows a user to refer back to the pages at either end of the block.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
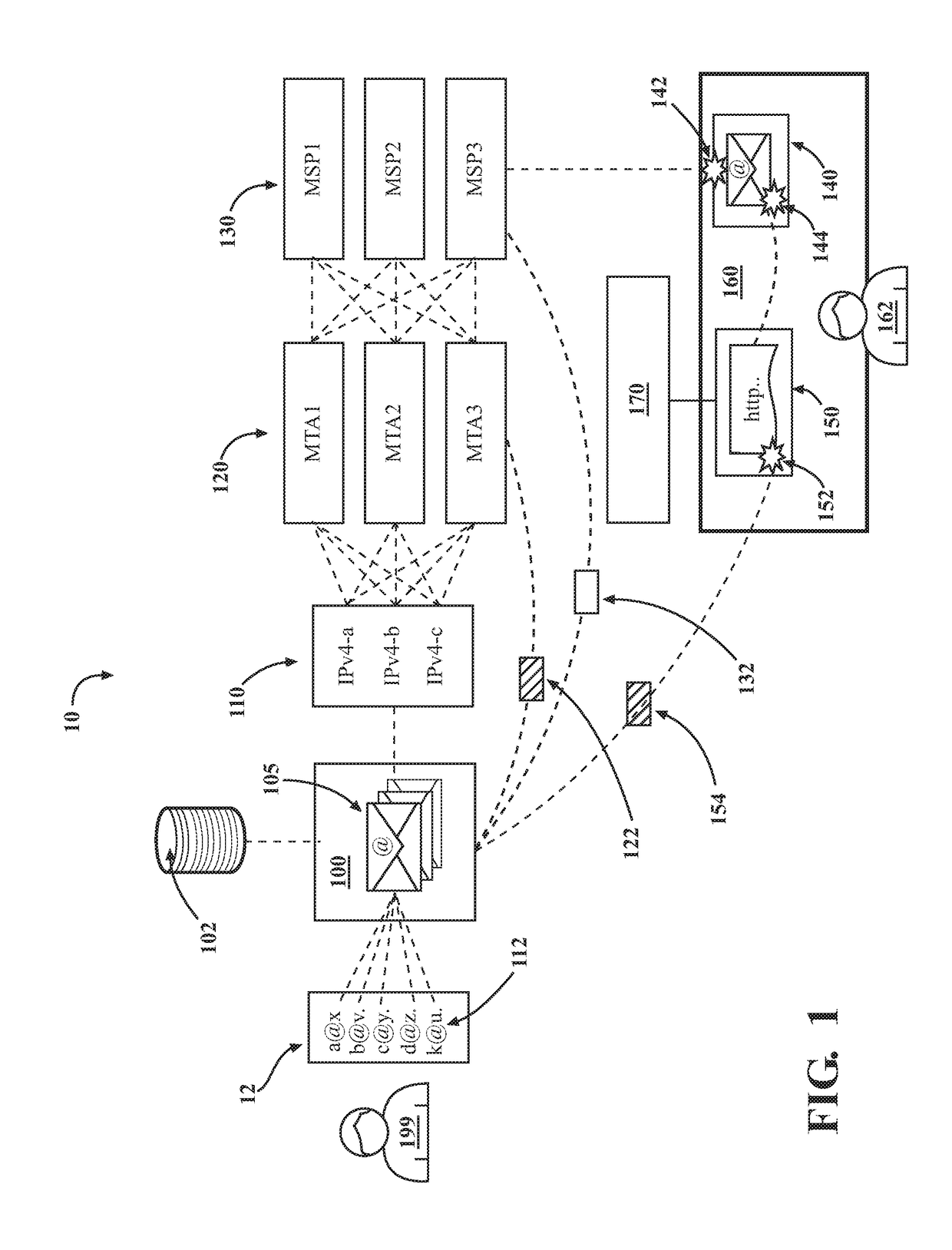
Quality-based routing of electronic messages
ActiveUS20180219818A1Mitigating cross-impactEasy to compareMathematical modelsAdvertisementsSpammingElectronic information
Owner:HUBSPOT
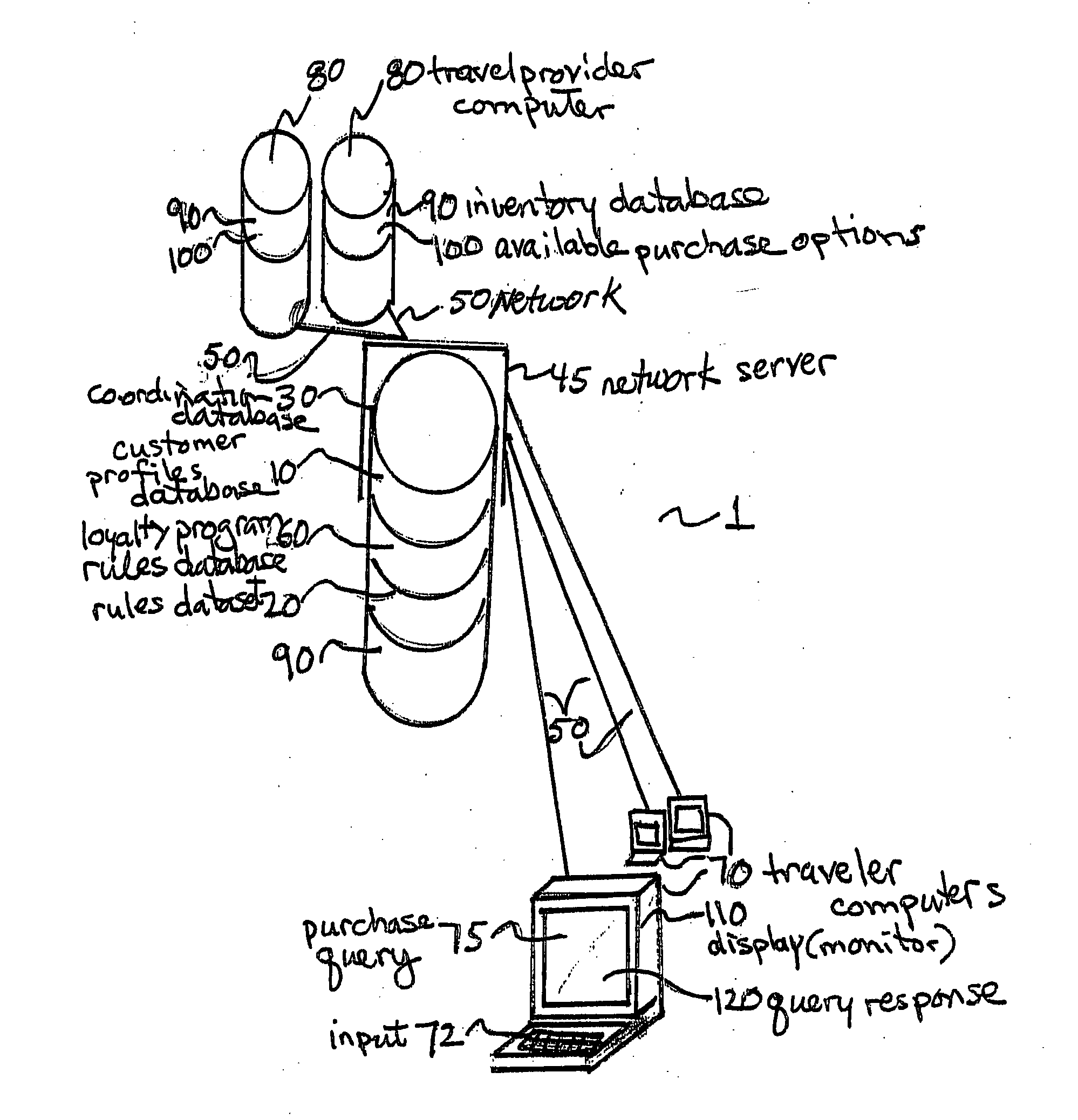
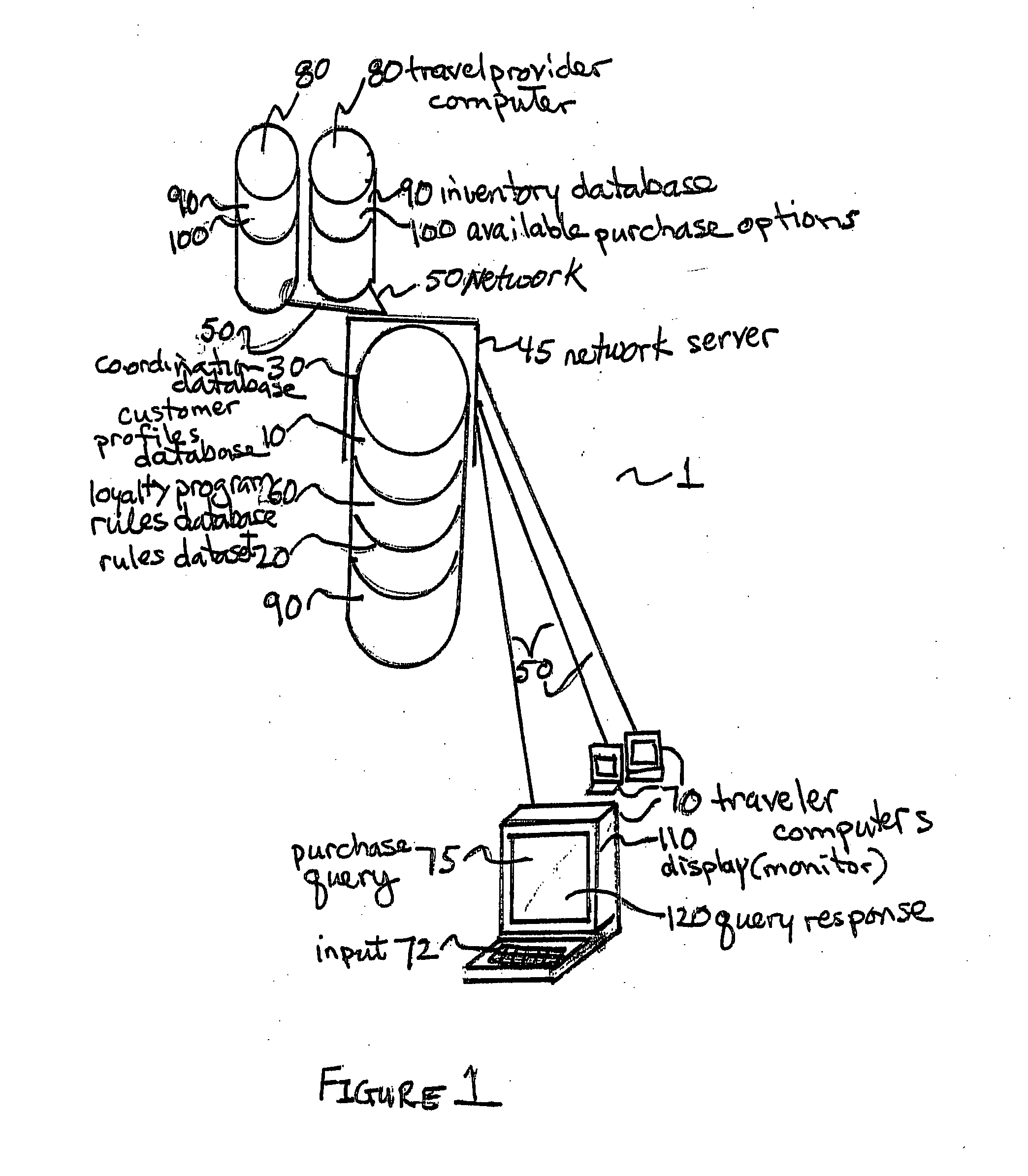
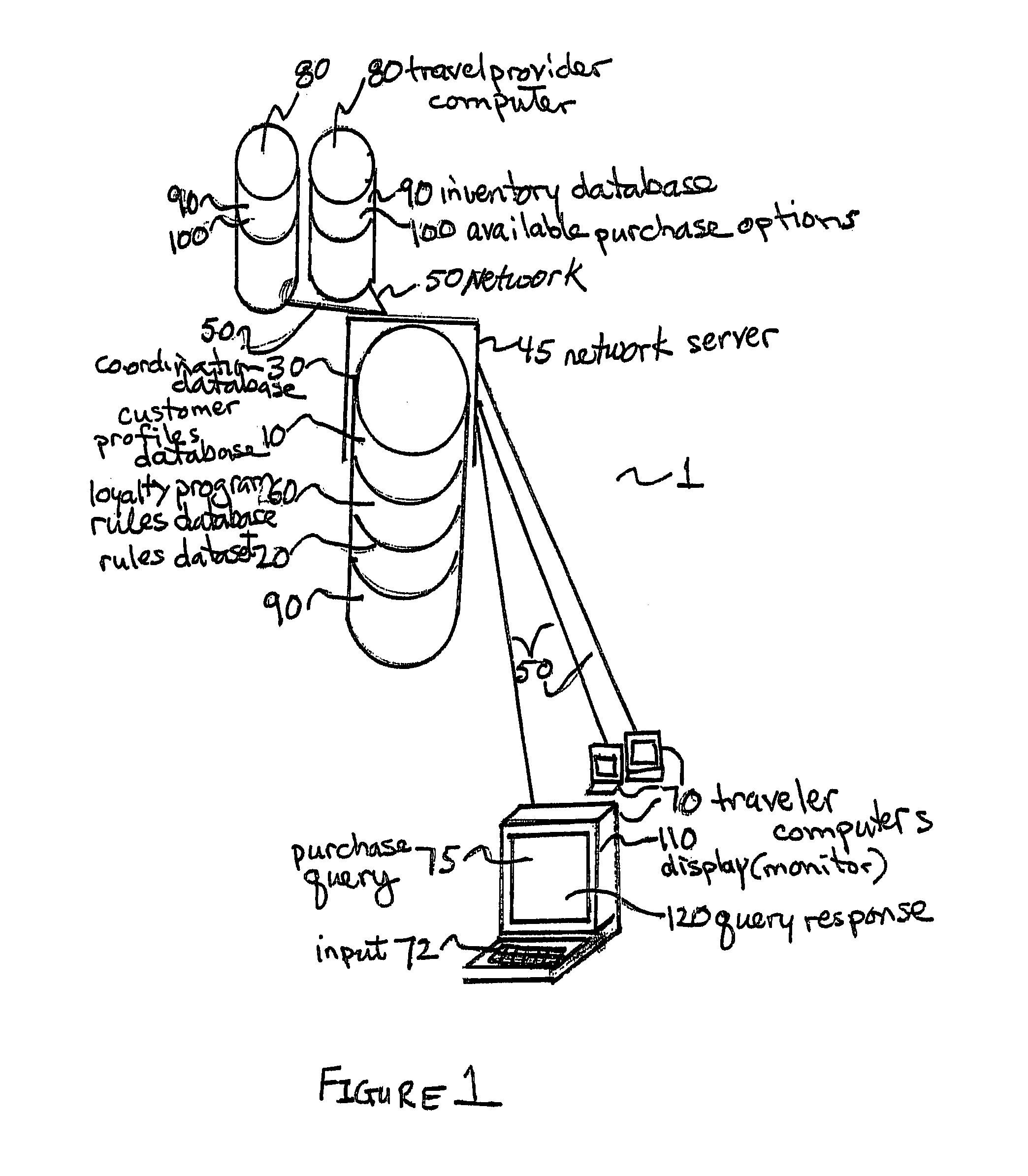
Purchaser value optimization system
A purchasing system includes a master server linking to a product and service inventory database. A query and response coordination database is hosted on the master server and includes a customer profiles database, a loyalty program rules database, and a purchase rules dataset. The coordination database receives a purchase request query, extracts purchase data elements from the received purchase request query, uses purchase rules from the rules dataset, applying the extracted purchase data elements to form a purchase query, applies the purchase query to the inventory database to determine available product and service inventory that satisfy the purchase request query, available product and service inventory that satisfy the purchase request query being identified as purchase options, receives purchase options from the inventory database, determines a total rewards benefit and creates a file for sending via the network to the purchaser's computer to display the query response.
Owner:AMADEUS S
Portable terminal, navigation system, and storage medium storing program
InactiveUS20120316777A1Easy to compareInstruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlComputer hardwareData display
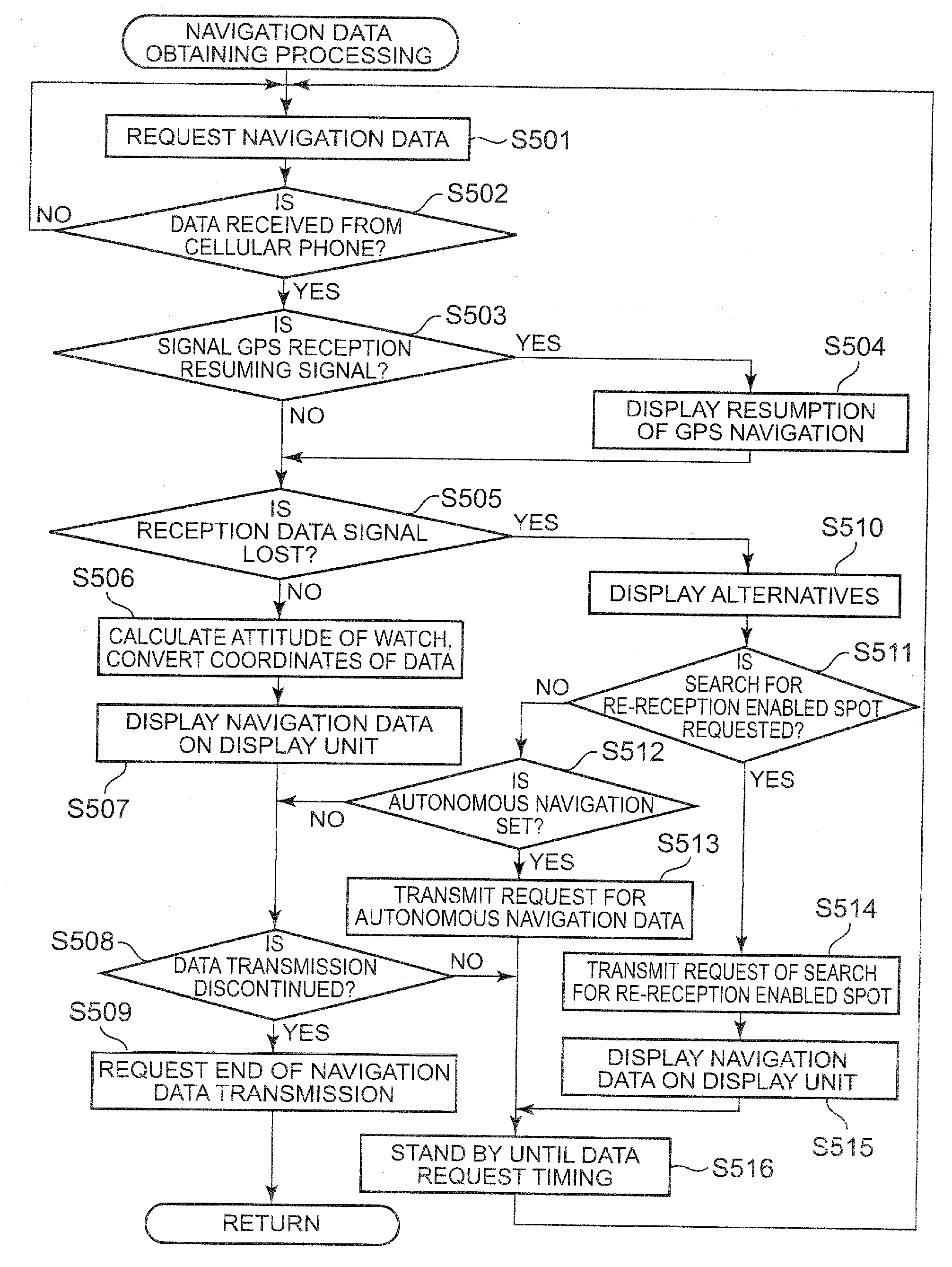
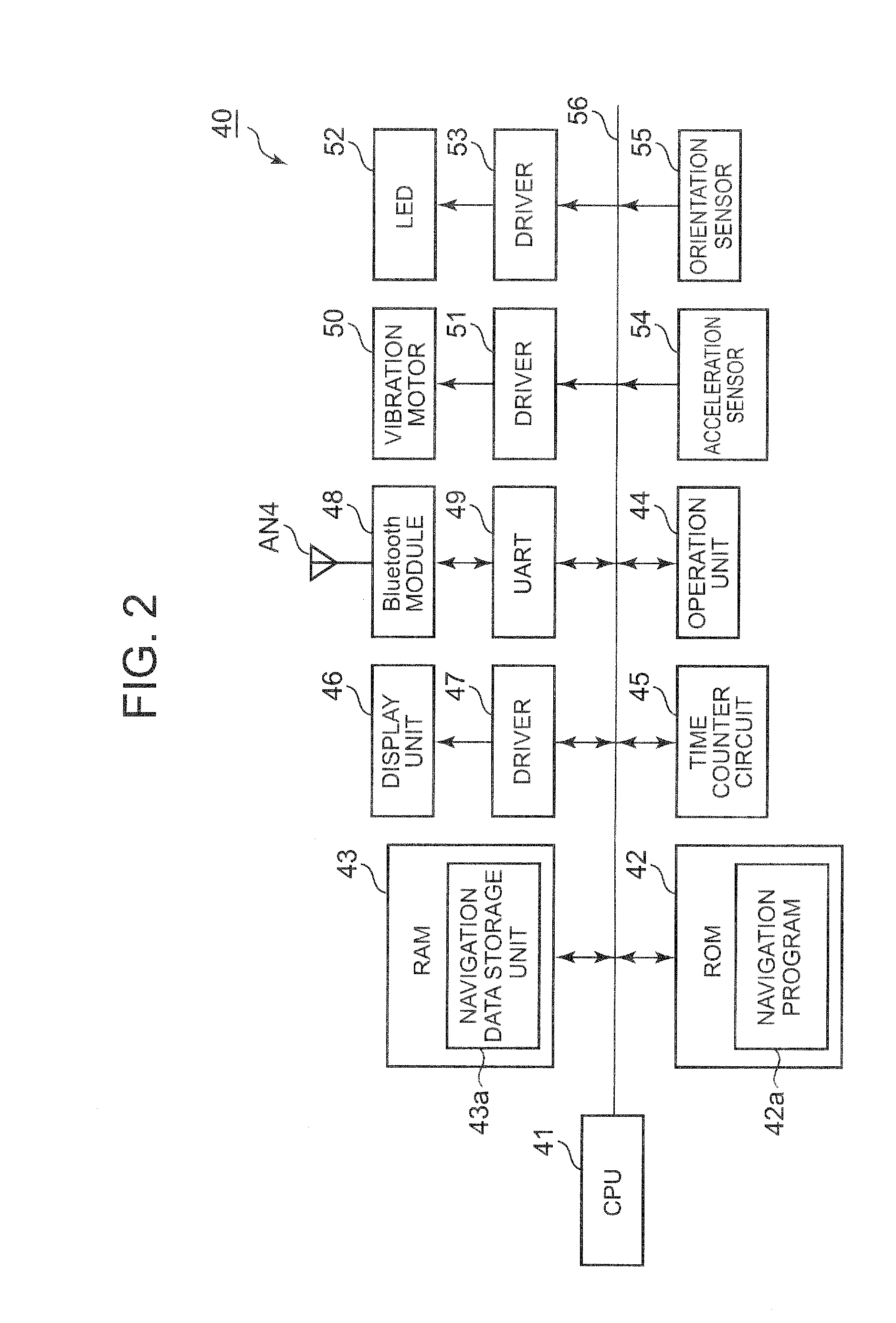
A portable terminal includes: a wireless communication unit which performs transmission and reception of data with a portable external instrument by wireless communication; a control unit which requests navigation data from the portable external instrument at a previously set request timing to obtain the navigation data therefrom; a display unit which performs a display based on a control signal from the control unit; and a detection unit which detects an orientation, wherein the control unit (i) allows the display unit to display orientation information included in the navigation data, in accordance with orientation data obtained based on a signal from the detection unit, and (ii) allows the display unit to display navigation data including at least a display in a travelling direction, that is simple in comparison with the navigation data displayed by the portable external instrument, based on the navigation data obtained from the portable external instrument.
Owner:CASIO COMPUTER CO LTD
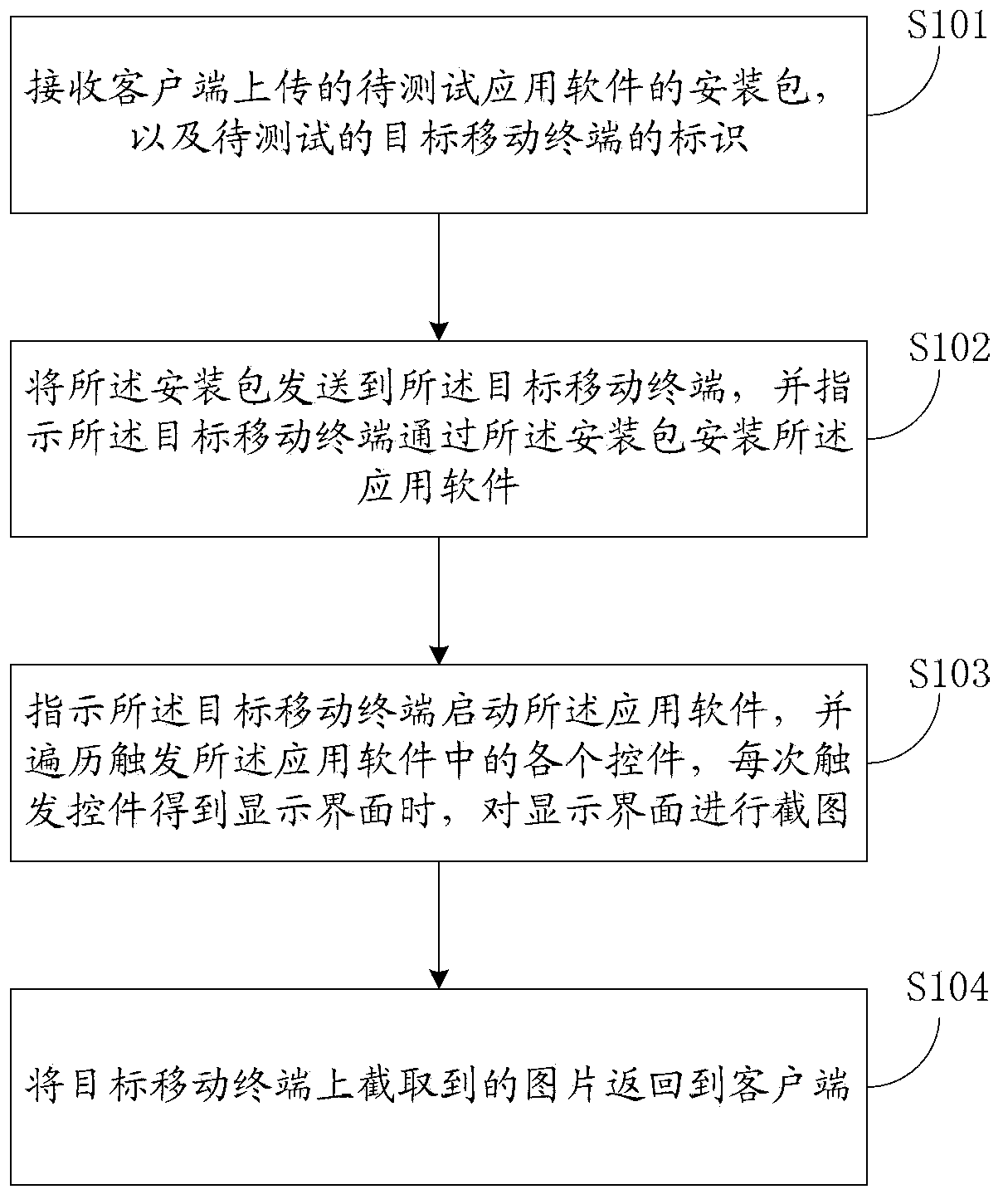
Testing method, device and system of application software on mobile terminal
ActiveCN104050076AAchieve the purpose of testingImprove test efficiencySoftware testing/debuggingProgram loading/initiatingClient-sideApplication software
The invention discloses a testing method, a testing device and a testing system of application software on a mobile terminal. The method comprises the following steps of receiving an installation package of application software to be tested, which is uploaded by a client end, and an identification of a target mobile terminal to be tested; sending the installation package to the target mobile terminal and instructing the target mobile terminal to install the application software through the installation package; instructing the target mobile terminal to start the application software and traversing to trigger all controls in the application software and obtaining a screenshot of a display interface when the controls are triggered to obtain the display interface every time; returning a picture intercepted on the target mobile terminal to the client end. By using the method, the application software on the mobile terminal can be efficiently tested.
Owner:ALIBABA GRP HLDG LTD
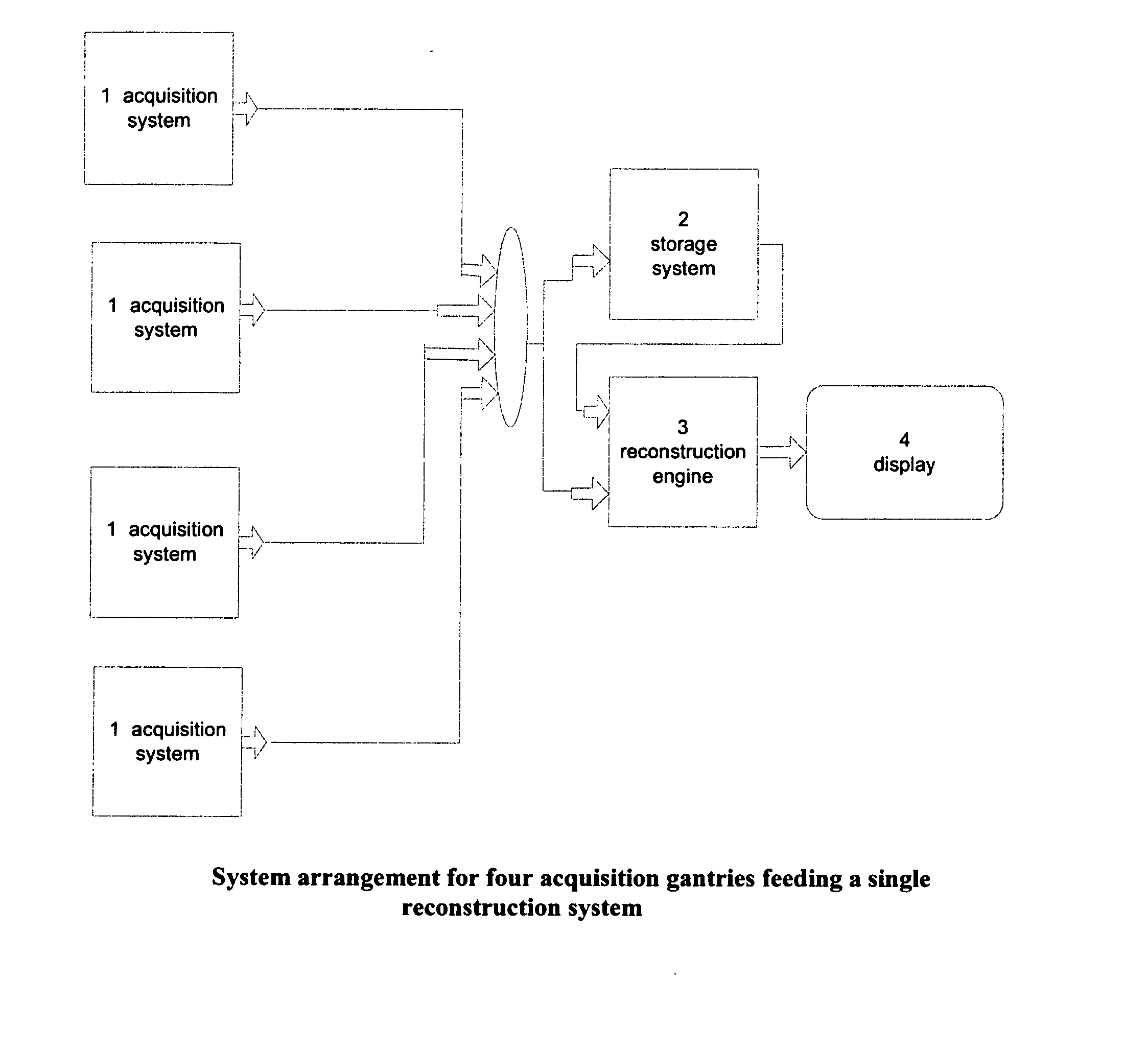
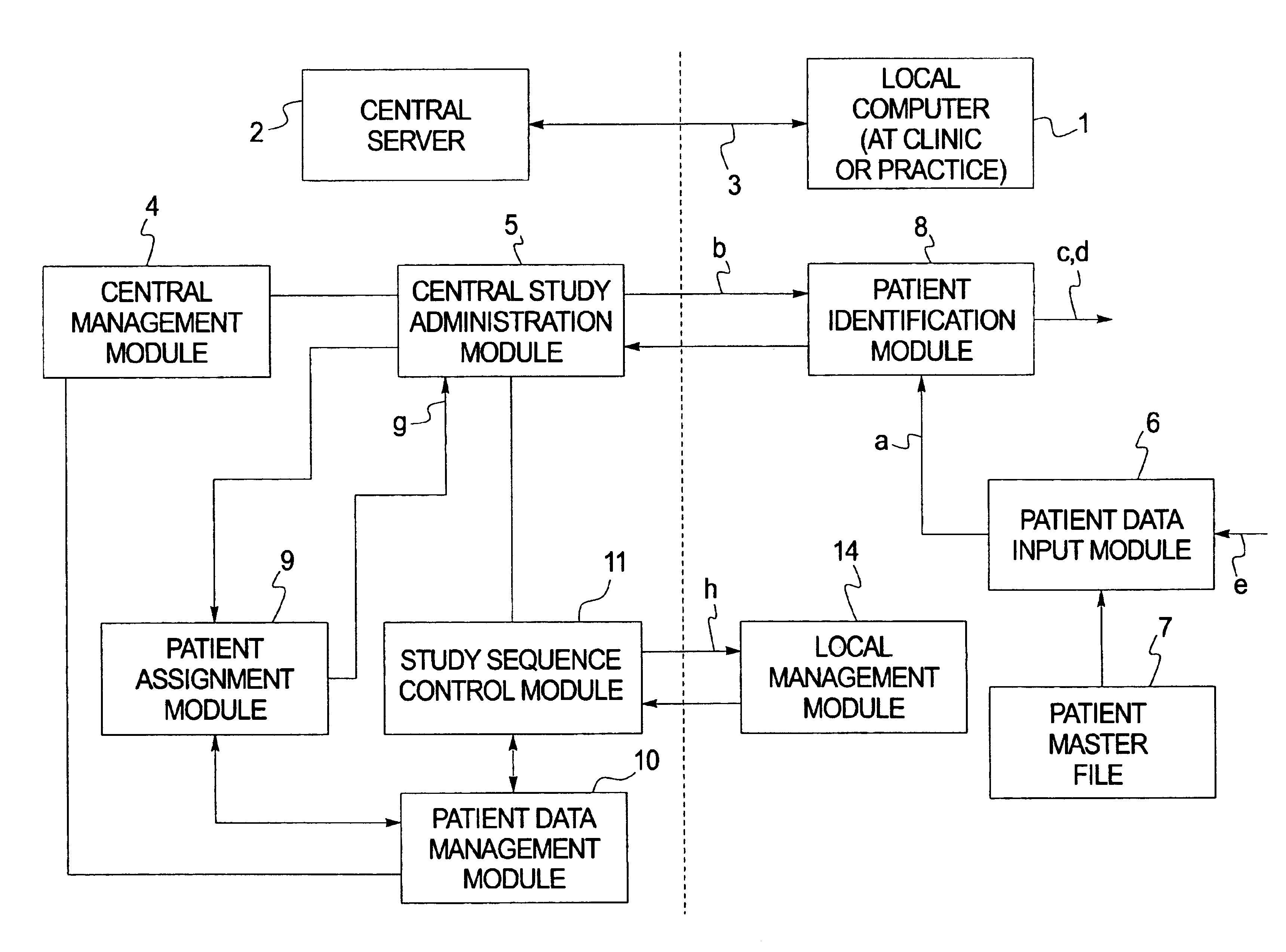
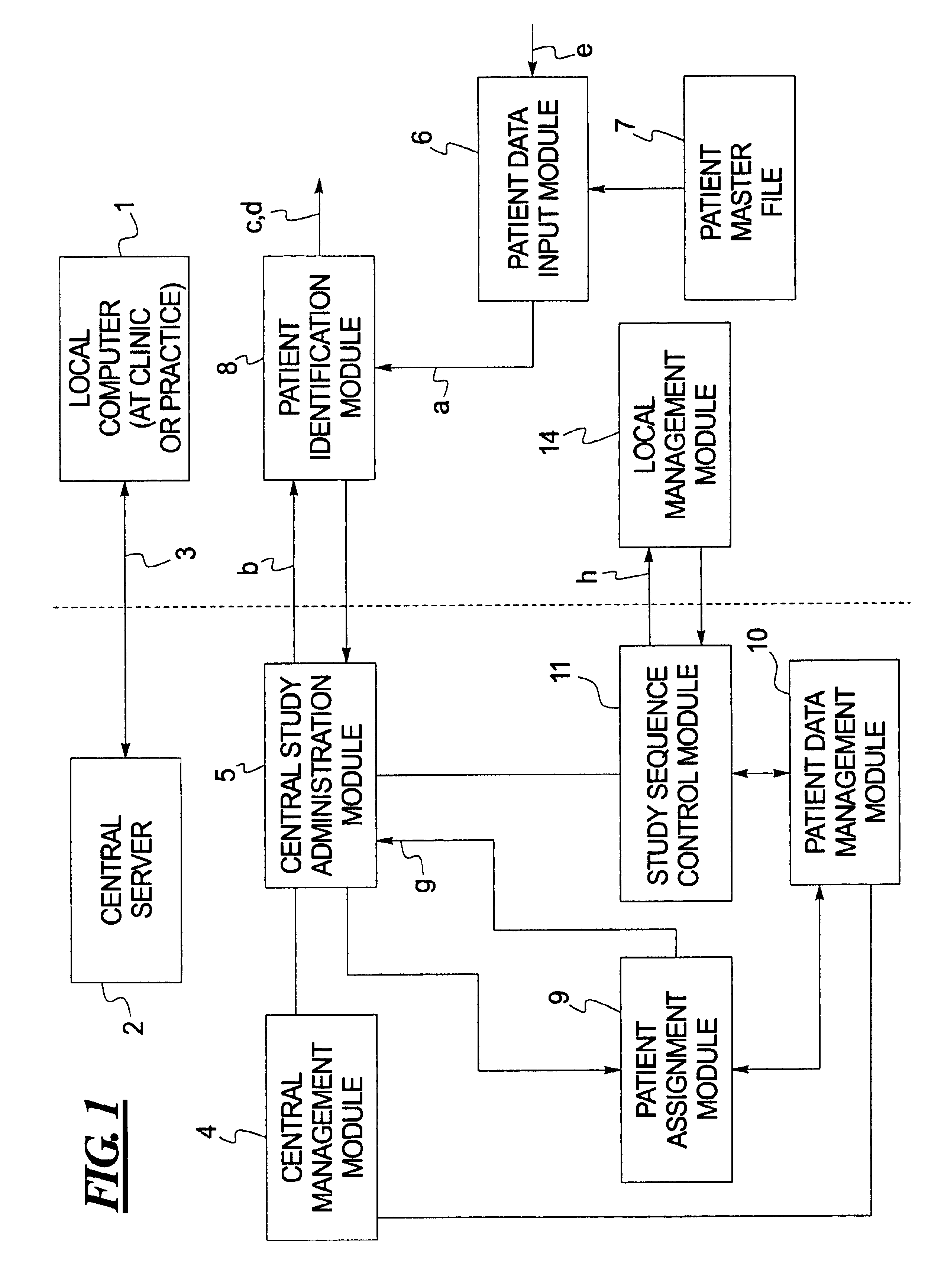
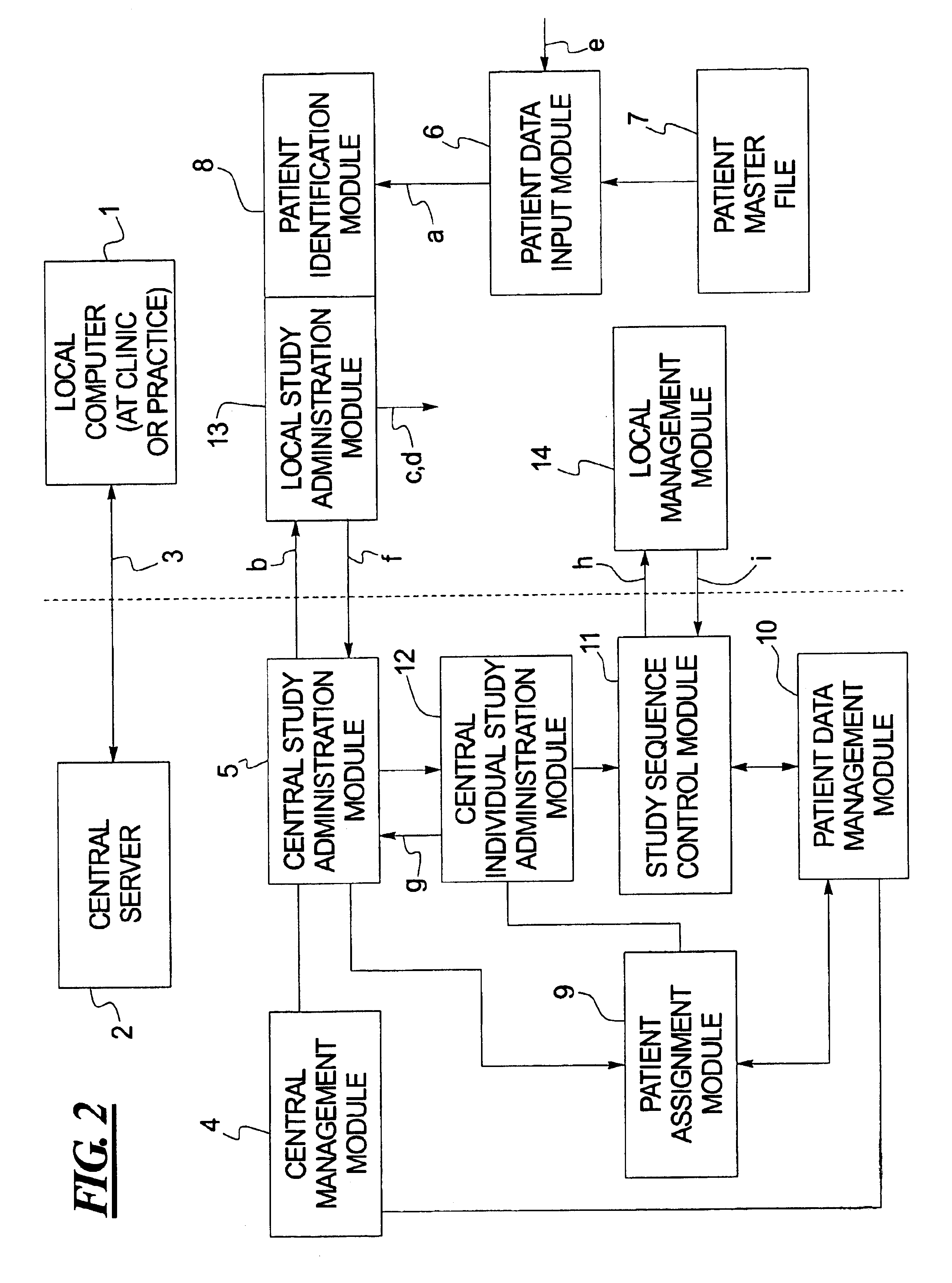
Computerized system for conducting medical studies
InactiveUS6839678B1Simpler and effective completionEasy to compareComputer-assisted medical data acquisitionElectric/electromagnetic visible signallingComputerized systemModularity
In a system for conducting medical studies a number of medical locations, such as clinics or medical practices, are connected to a central server via a computer network. The system is constructed in modular fashion, and it is automatically determined, with computer support within the system, whether a specific patient is eligible to participate in a medical study of the system, and if so, the sequence of the corresponding medical study is controlled centrally by corresponding modules, automatically and in a study-specific and patient-specific fashion.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method and system for biometric recognition using unique internal distinguishing characteristics
InactiveUS20040052406A1High gainEasy to compareElectric signal transmission systemsDigital data processing detailsAcoustic energy
The present invention is a biometric recognition method and system for identifying humans and animals with acoustic scanning techniques. The invention is based upon transmitting acoustic energy through an external accessible surface to non-visible internal tissue having a unique distinguishing characteristic. A master representative pattern of the unique distinguishing characteristic is produced by the interaction of an acoustic energy beam with discontinuities and inhomogeneities within the non-visible internal tissue. The master representative pattern is used for reference and compared to a current representative pattern formed upon each attempted reentry into the system.
Owner:GR INTELLECTUAL RESERVE LLC
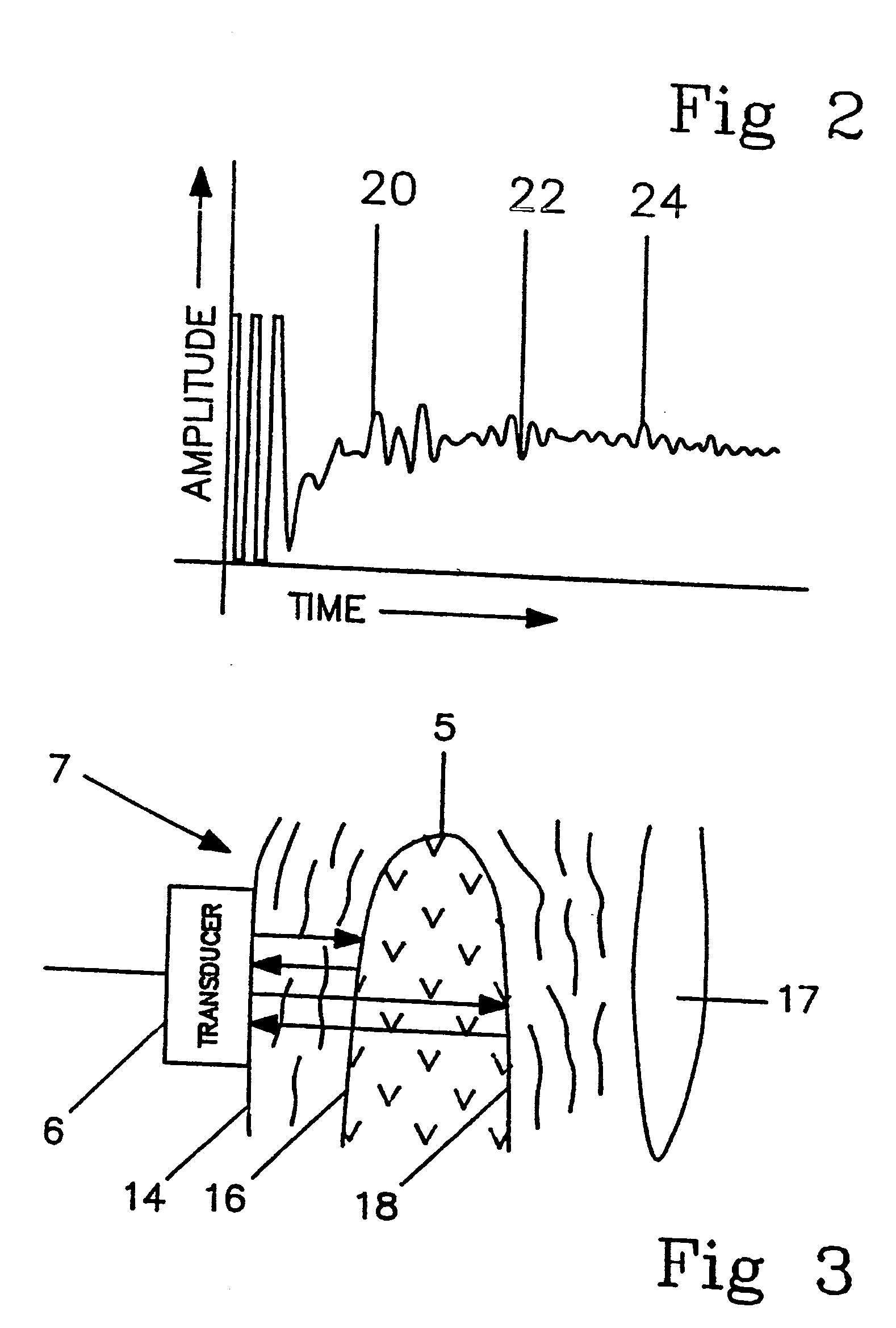
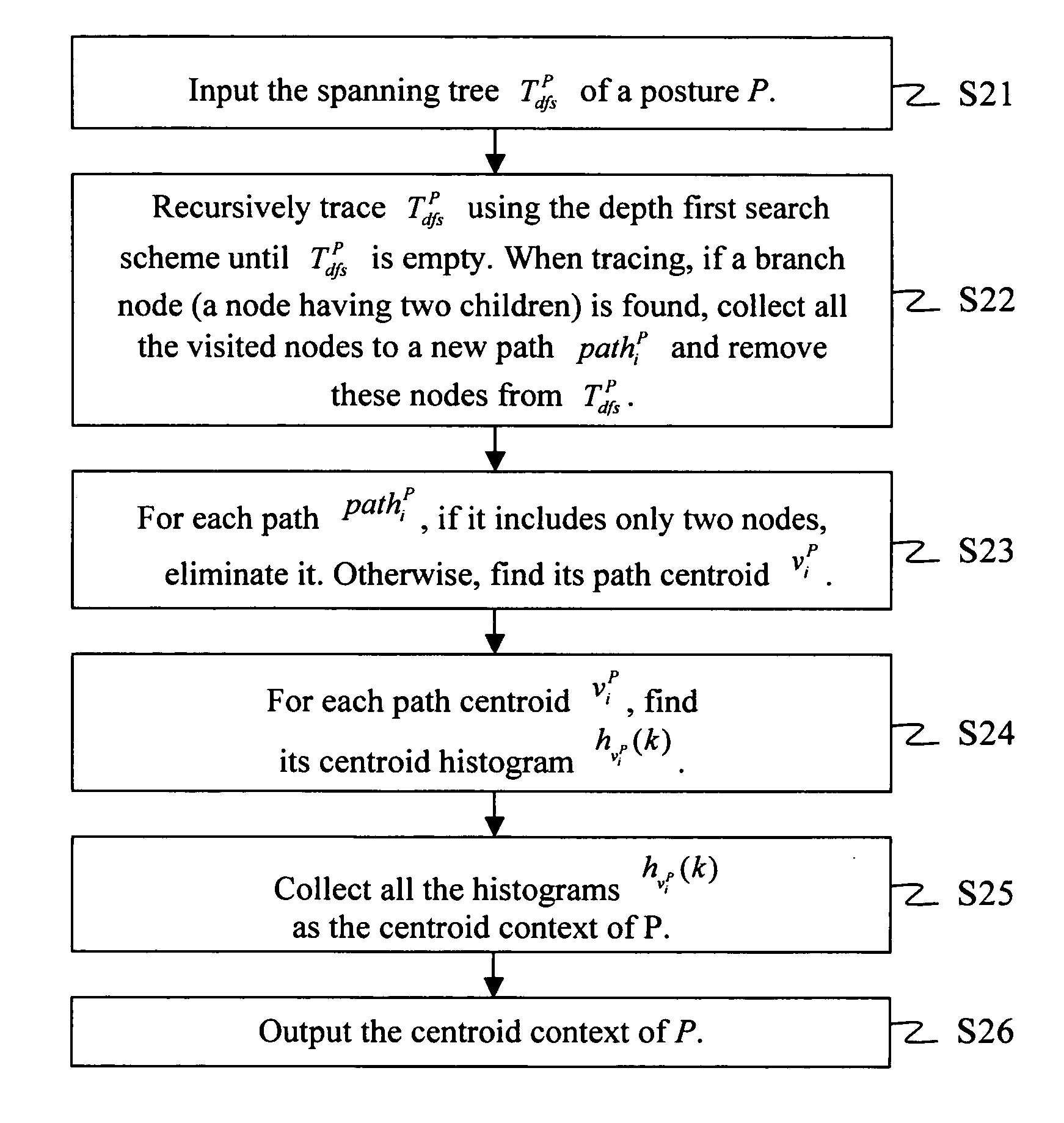
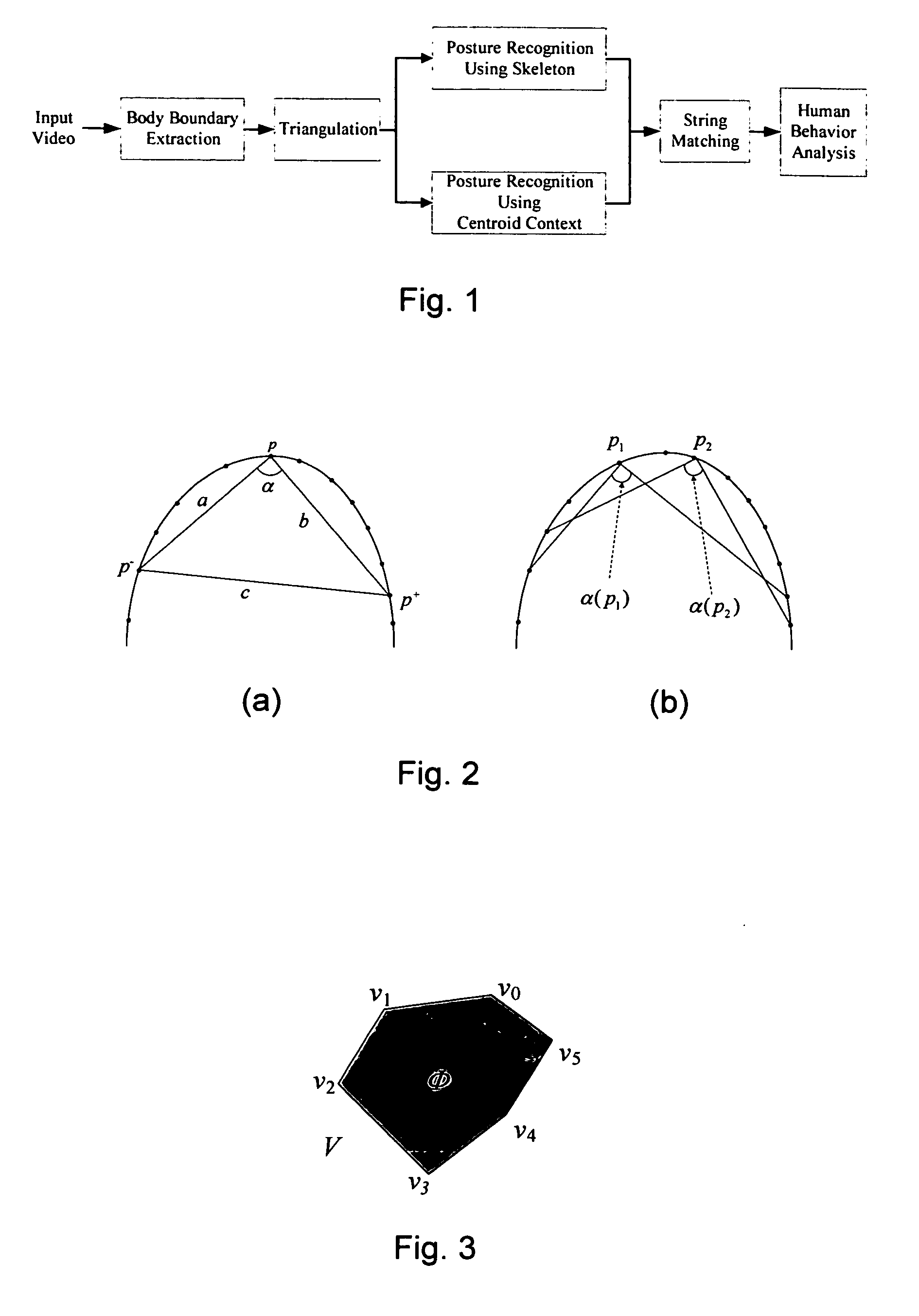
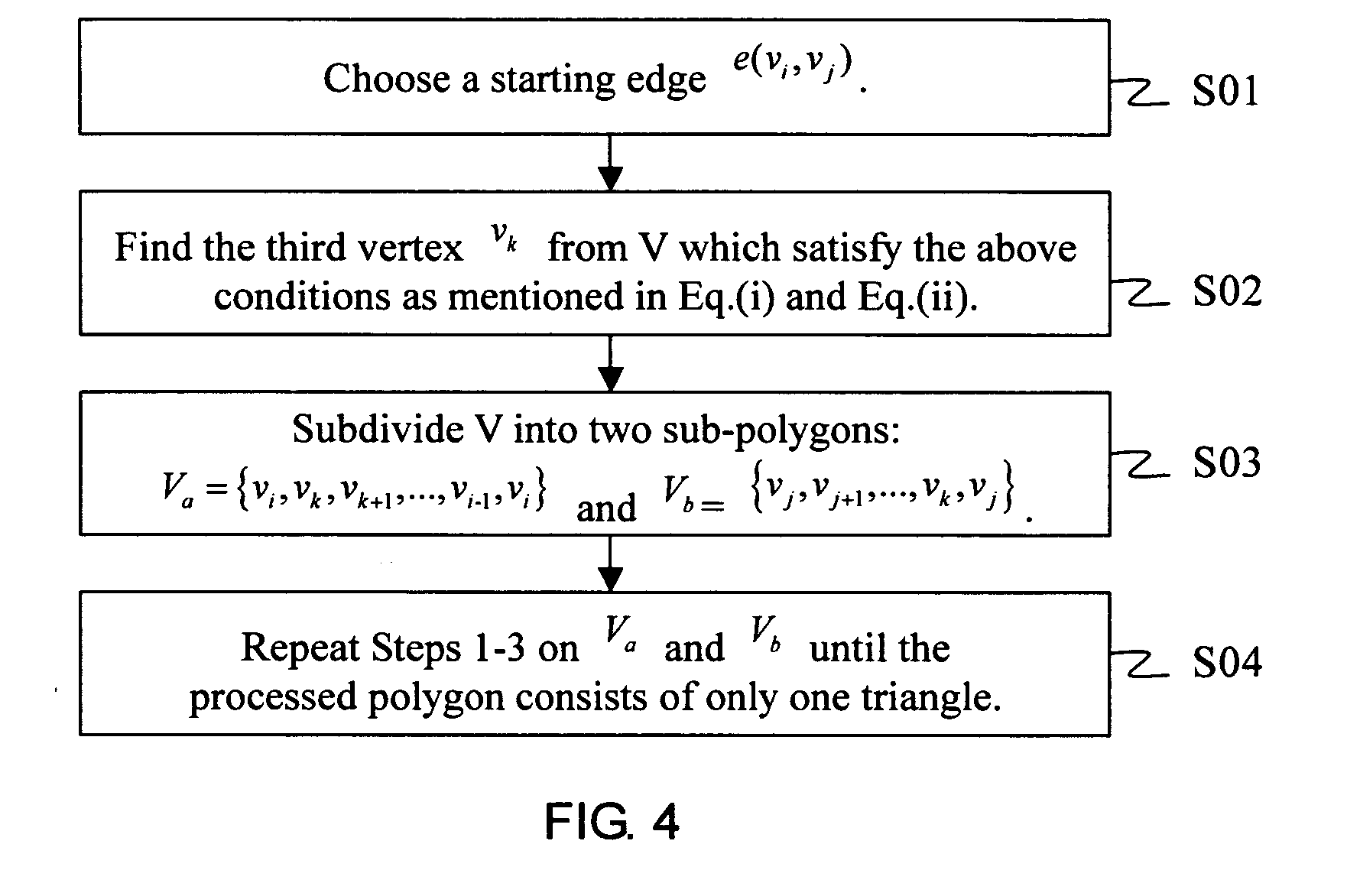
Apparatus for behavior analysis and method thereof
InactiveUS20100278391A1Easy to analyzeEasy to compareImage analysisMedical automated diagnosisHuman behaviorTriangulation
In the present invention, an apparatus for behavior analysis and method thereof is provided. In this apparatus, each behavior is analyzed and has its corresponding posture sequence through a triangulation-based method of triangulating the different triangle meshes. The two important posture features, the skeleton feature and the centroid context, are extracted and complementary to each other. The outstanding ability of posture classification can generate a set of key postures for coding a behavior sequence to a set of symbols. Then, based on the string representation, a novel string matching scheme is proposed to analyze different human behaviors even though they have different scaling changes. The proposed method of the present invention has been proved robust, accurate, and powerful especially in human behavior analysis.
Owner:NAT CHIAO TUNG UNIV
Image handling and display in x-ray mammography and tomosynthesis
InactiveUS7616801B2Easy to displayEnhance the imageImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionTomosynthesisProjection image
Owner:HOLOGIC INC
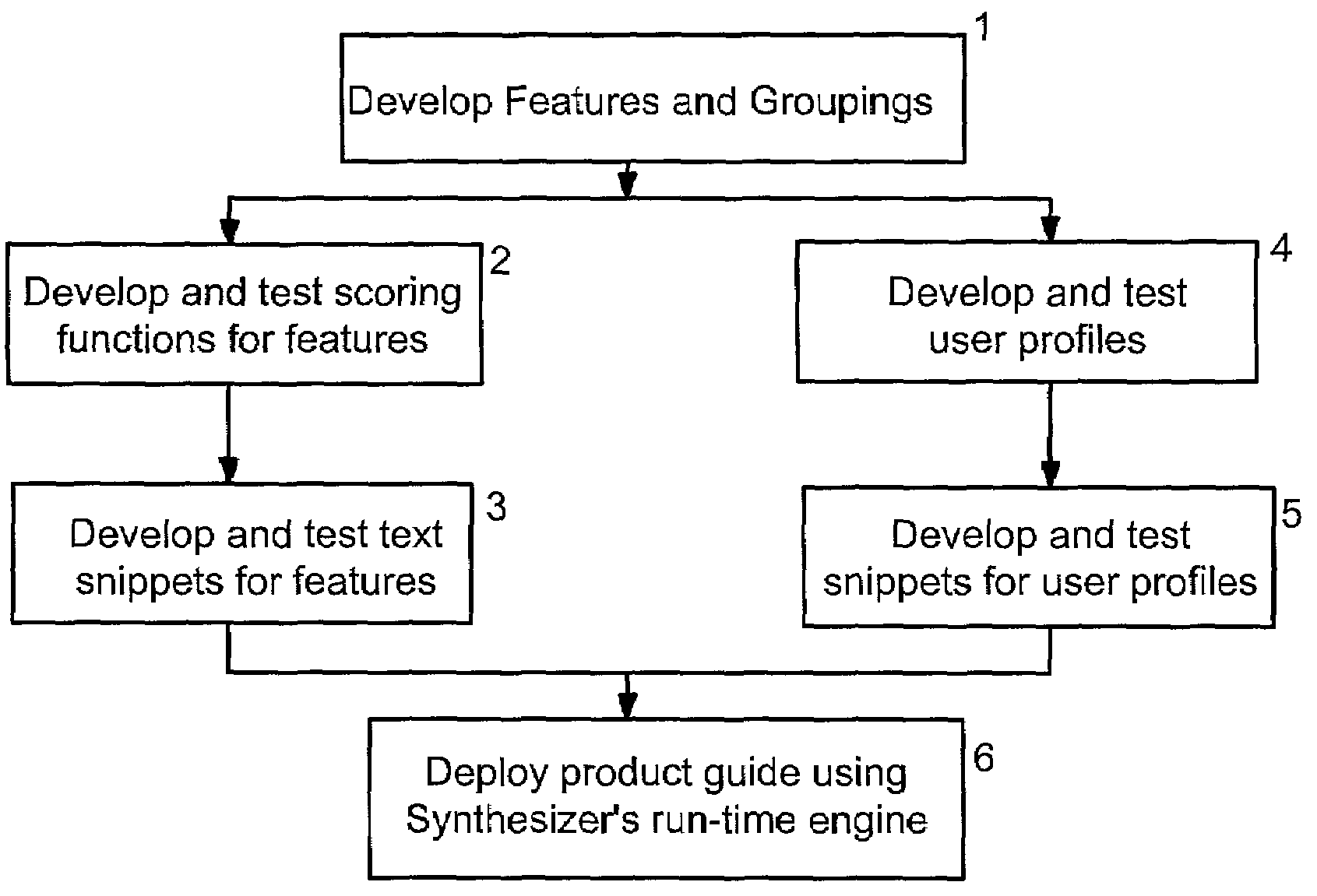
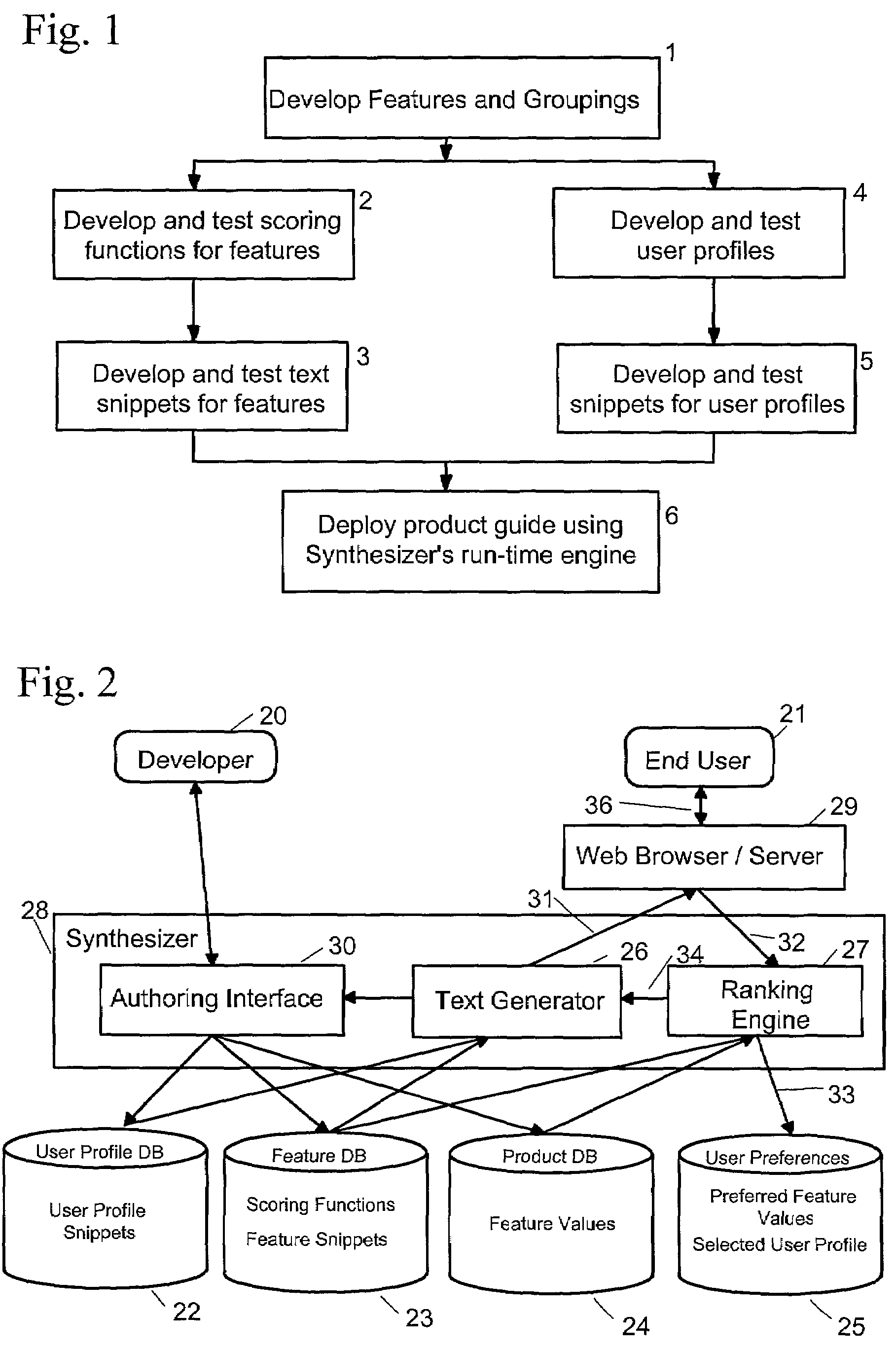
Natural language product comparison guide synthesizer
InactiveUS7418447B2Easy to createEasy to compareNatural language translationDigital data processing detailsProduct baseWorld Wide Web
A Natural Language Product Comparison Guide Synthesizer that lets developers easily create web-based comparison guides for a given type of product. Each comparison guide will solicit users' product requirements, let them compare different products, and recommend one or more products based on their preferences. The guide uses automatically generated natural language to facilitate the comparison of products, and to convey and explain its recommendations.
Owner:COGENTEX
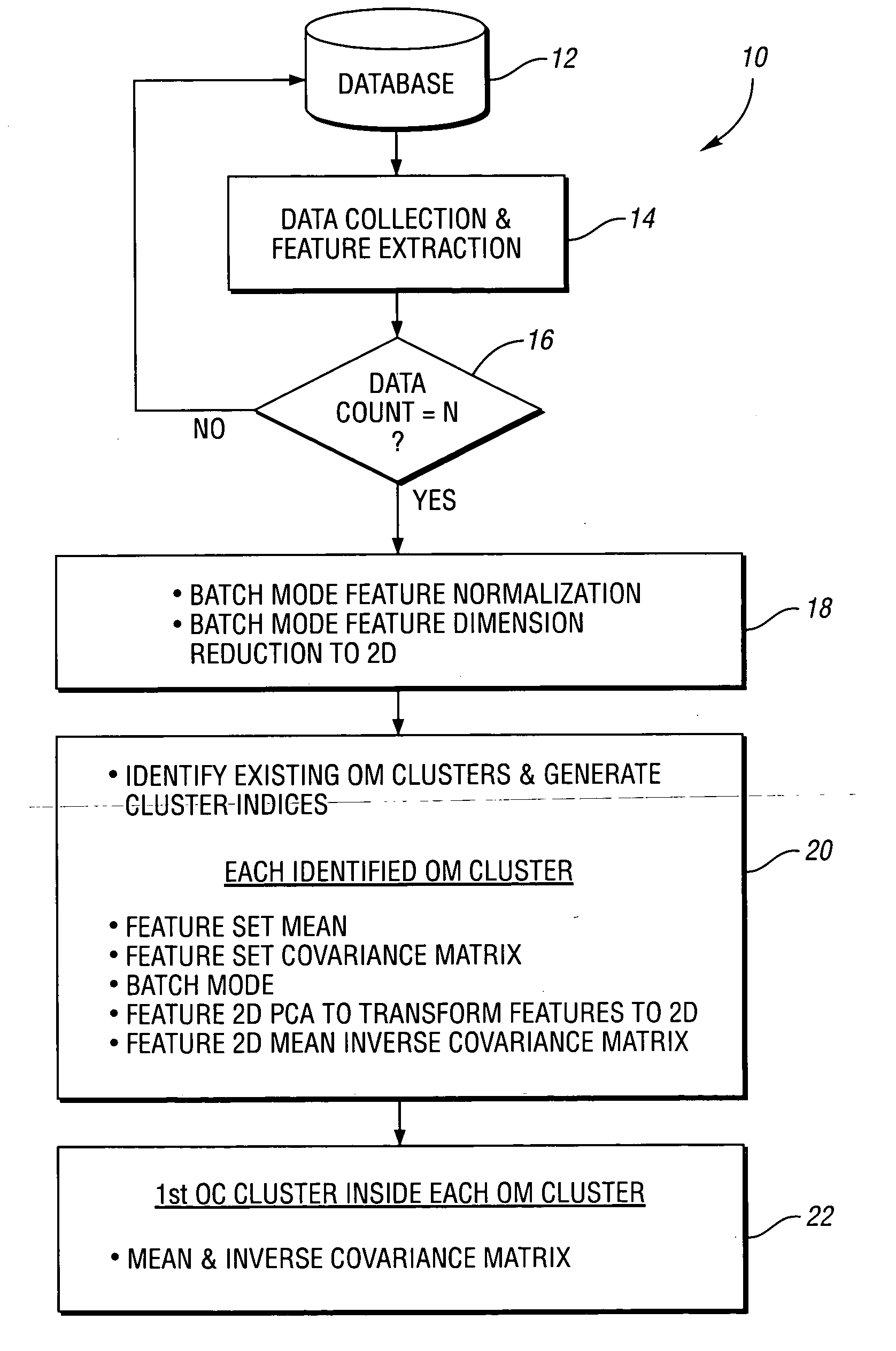
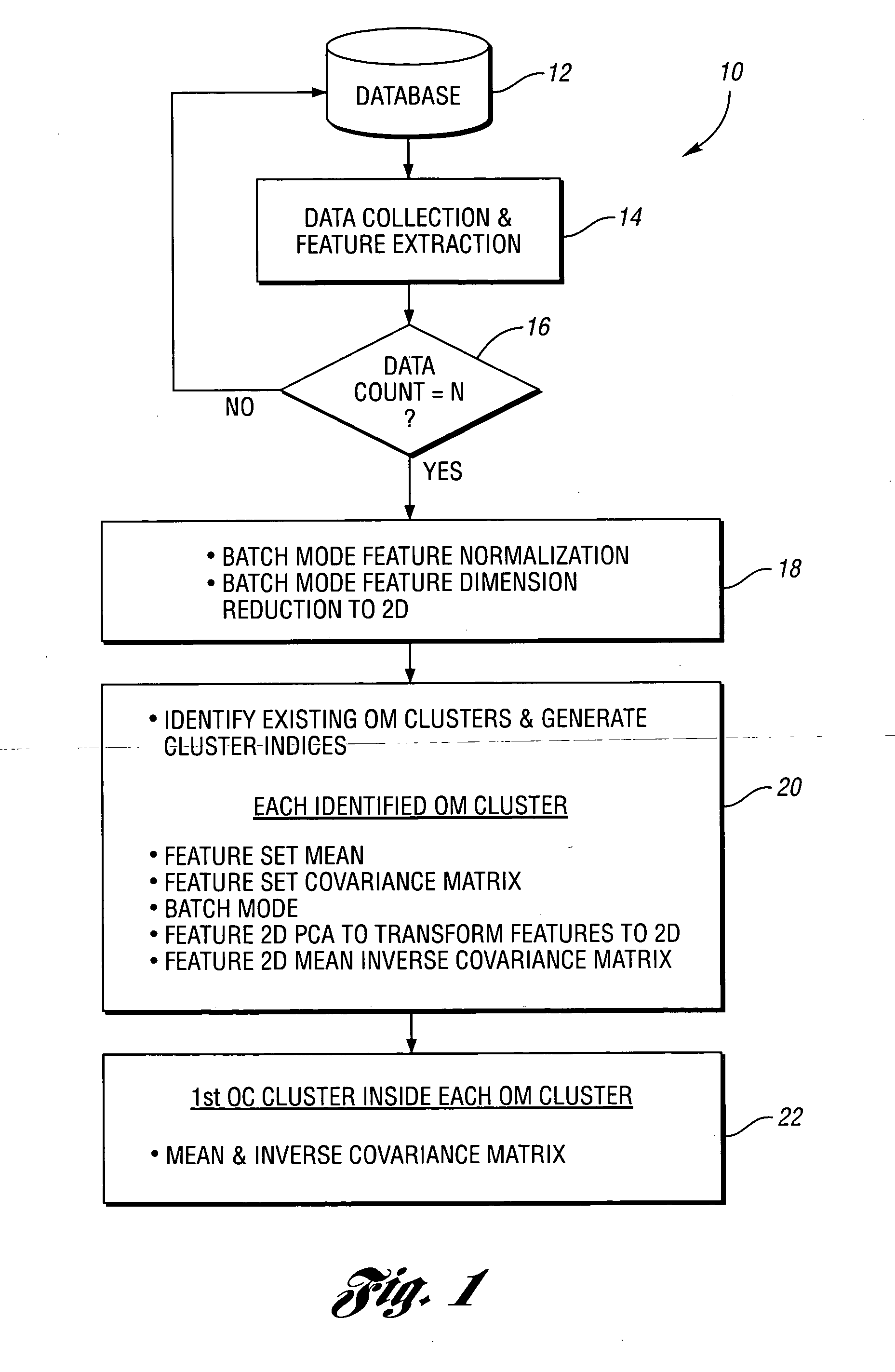
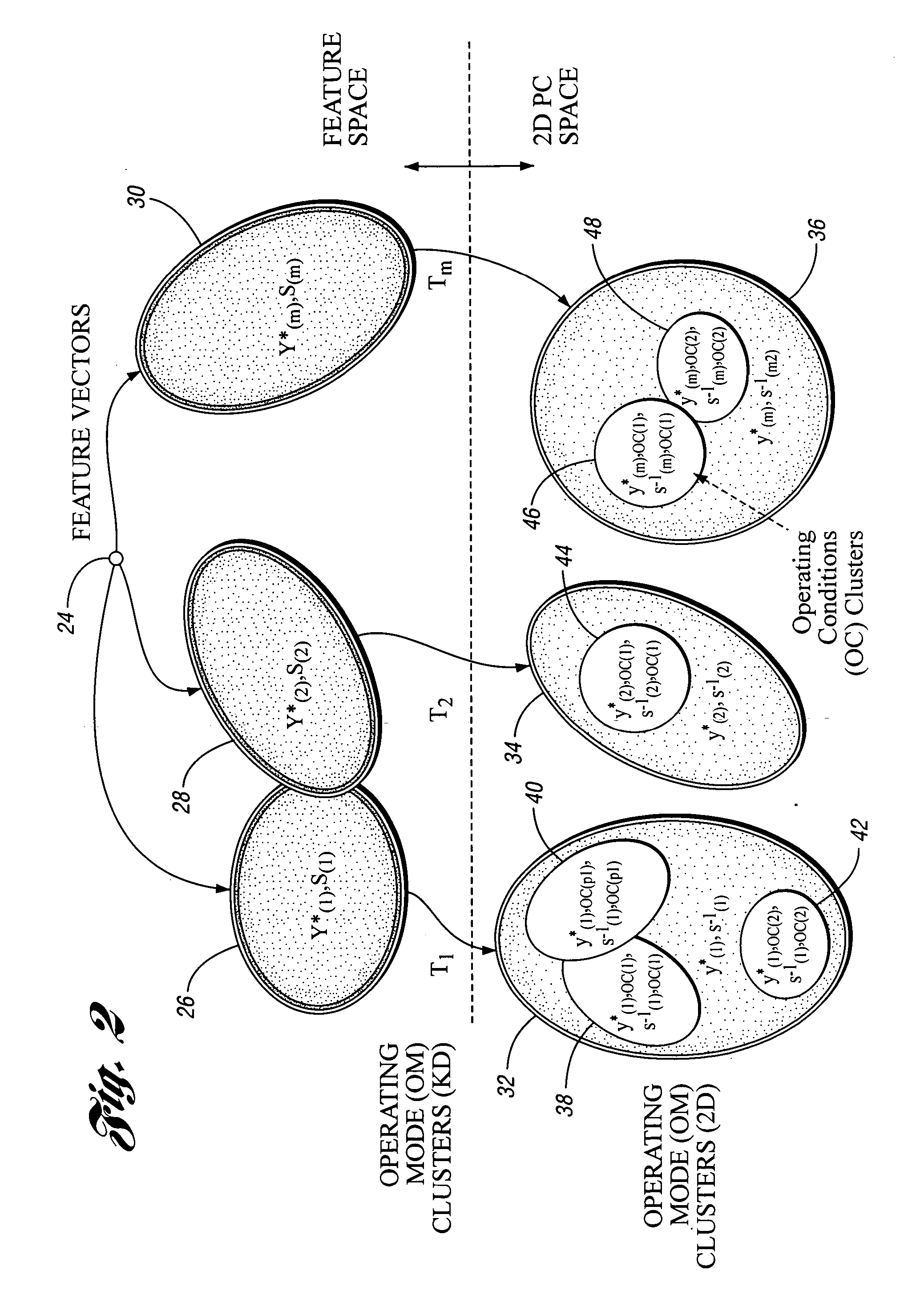
Method for predictive maintenance of a machine
InactiveUS20070088550A1Reduce dimensionalityReduce amountTesting/monitoring control systemsCharacter and pattern recognitionFeature vectorComputer compatibility
A method for predictive maintenance of a machine includes collecting feature data for the machine which includes a plurality of feature vectors. At least some of the feature vectors are standardized to facilitate compatibility between different vectors. At least some of the standardized feature vectors are transformed into corresponding two-dimensional feature vectors. At least some of the two-dimensional feature vectors are clustered together based on operating modes of the machine. Similar steps are performed on additional feature data collected from the machine. Recently gathered two-dimensional feature vectors are compared to previously clustered feature vectors to provide predictive maintenance information for the machine.
Owner:FORD MOTOR CO
Maximum likelihood decoding
ActiveUS7233634B1Reduce complexityEasy to compareError preventionLine-faulsts/interference reductionCommunications systemHypersphere
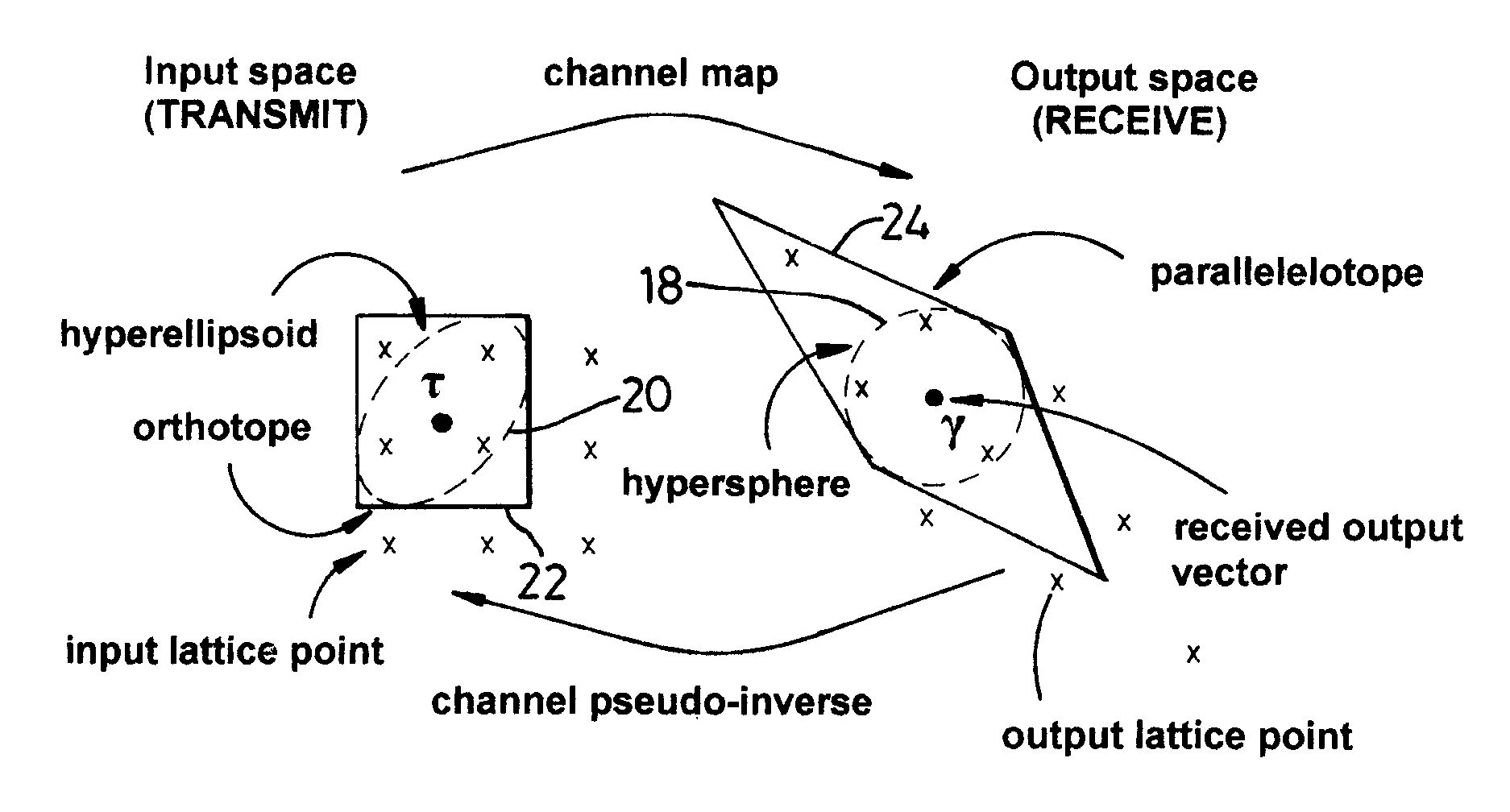
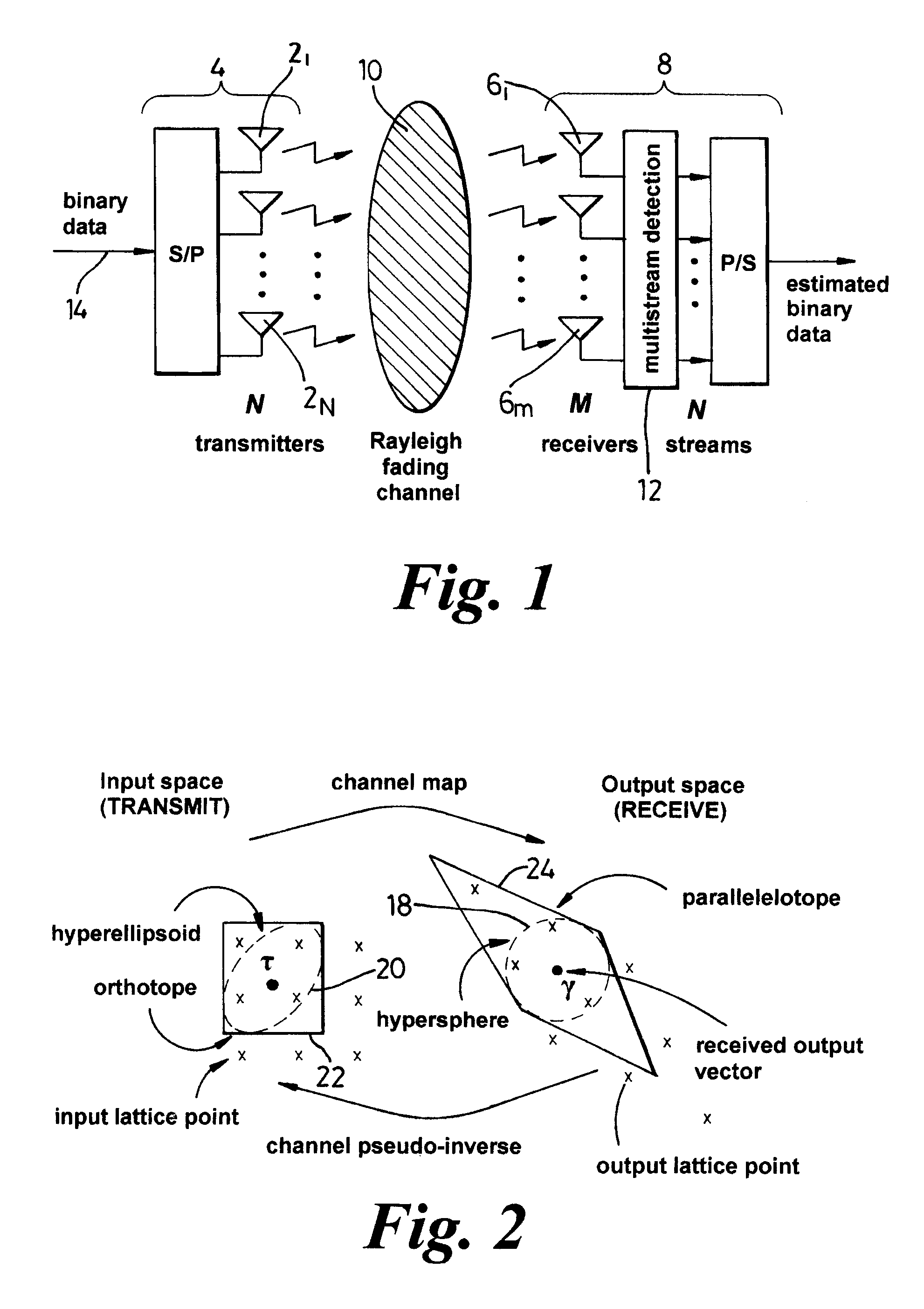
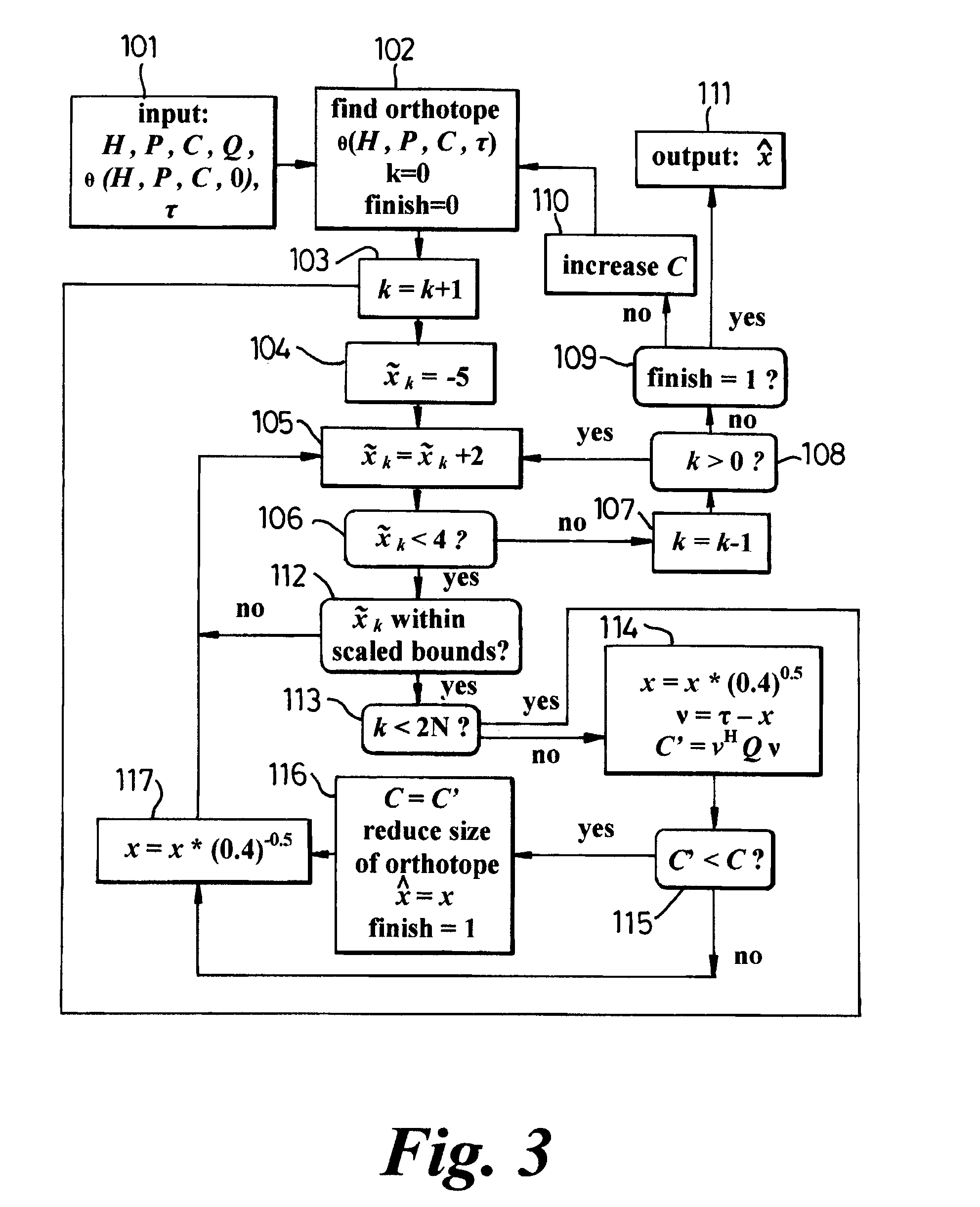
A method of maximum likelihood decoding for detecting the signals transmitted over a Multiple-Input-Multiple-Output (MIMO) channel of a communication system in which there are N co-channel transmit antennas and M co-channel receive antennas. In a first method an orthotope (22) is generated in input signal space centred on an approximate transmit signal point τ which is an inverse mapping from an actual received signal point (y) in output signal space. Only possible transmit points located within the orthotope are considered as candidate points and are transformed into corresponding candidate receive signal points in output signal space. The Euclidean distance between the candidate receive signal points and the actual signal point is calculated and the closest candidate receive signal is selected as the detected received point. In an alternative method, the orthotope is constructed as the smallest such orthotope which can contain a hyperellipsoid (20) in input signal space, which hyperellipsoid is a transformation from output signal space of a hypersphere (18) centred on the actual received signal point (y). Those transmit signal points which lie within the orthotope (22) but outside of the ellipsoid (20) are discarded and the remaining points within the orthotope are considered as candidate points, in the same way as described above.
Owner:APPLE INC
Query optimizer using implied predicates
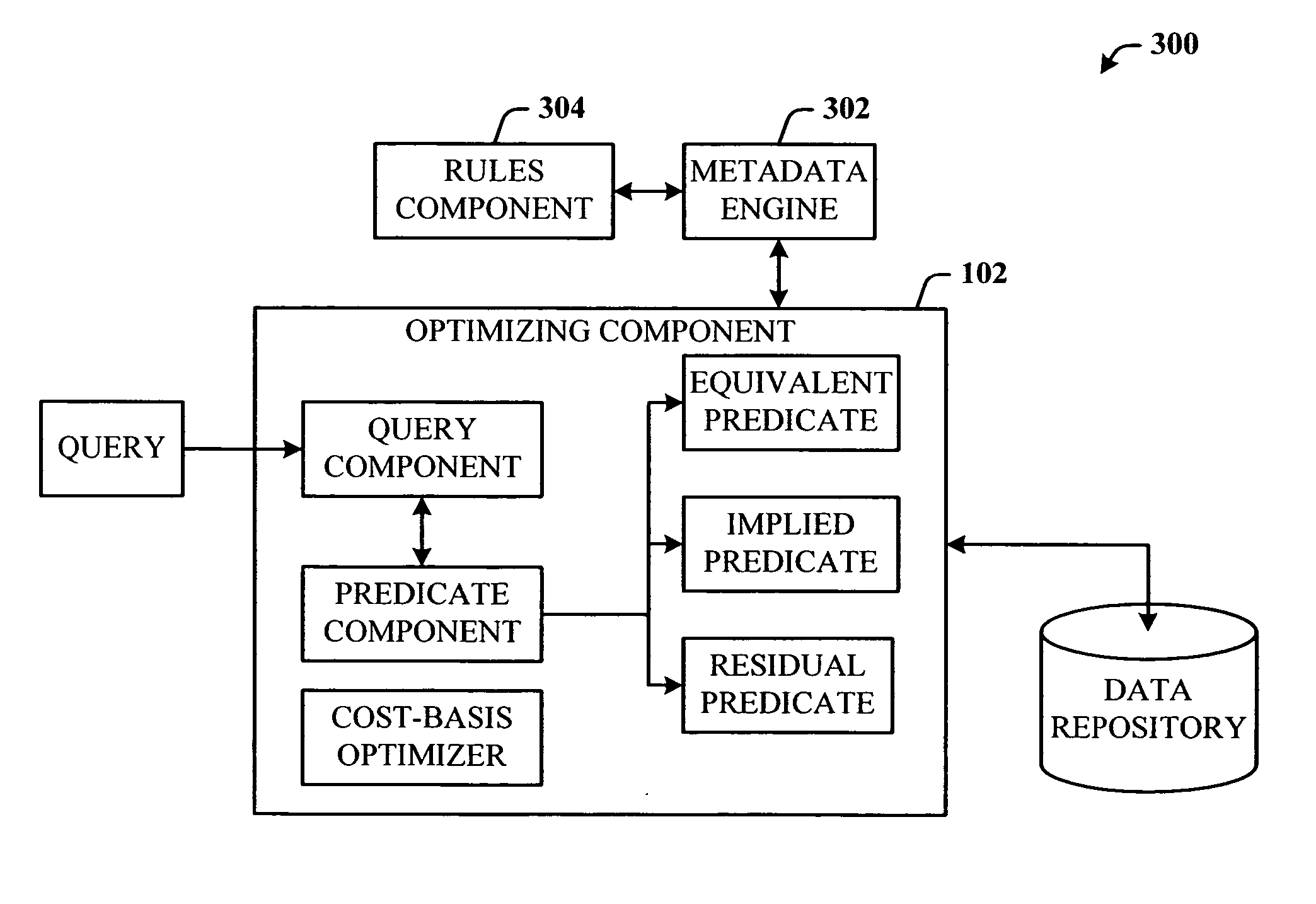
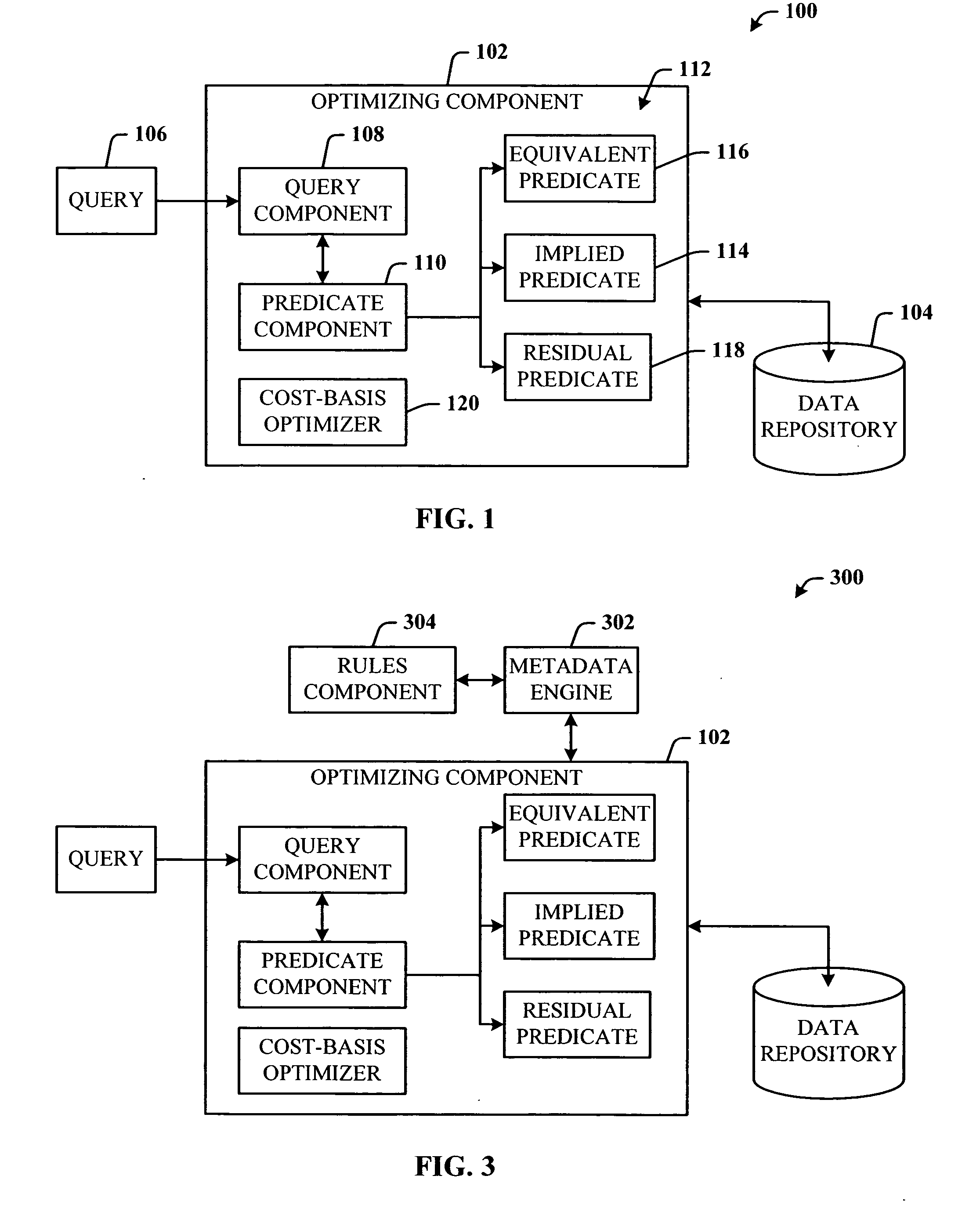
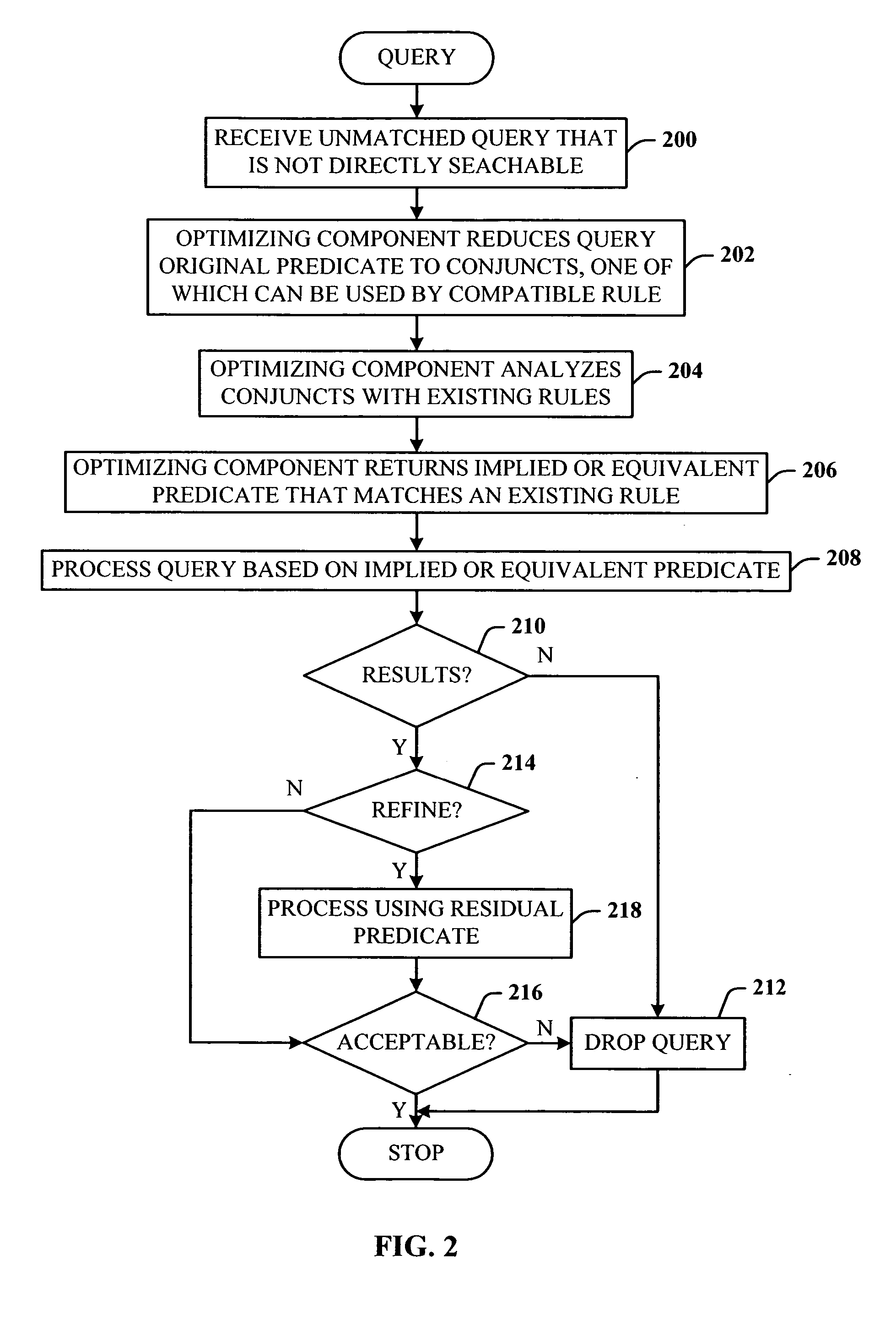
InactiveUS20050210023A1Optimizing componentsEasy to compareDigital data information retrievalNatural language data processingQuery optimizationMulti valued
Improved query optimizer using implied predicates. The system facilitates allowing a query optimizing component to introduce into a query, extra predicates that facilitate the following: render the same results as the original query; are used as dictated by rules passed to the optimizing component—these rules specify whether the new predicate is an equivalence (that will substitute the old predicate) or an implication (in which the old predicate is preserved); are considered as cost-based alternatives, and discarded if not useful; are tied to index utilization; and can consider both standard and multi-valued indices.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method and system for transmitting monitoring data of communication base station
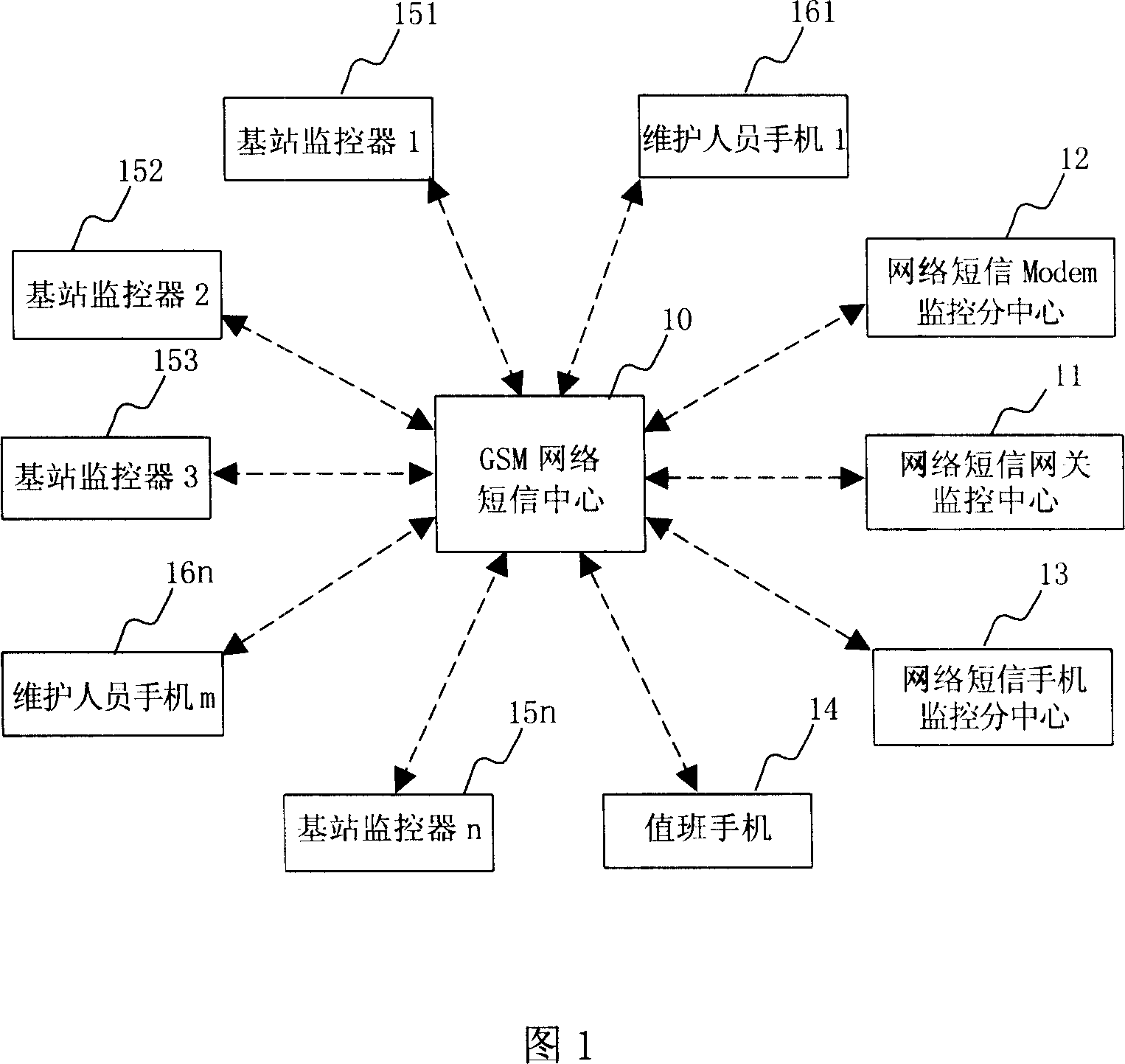
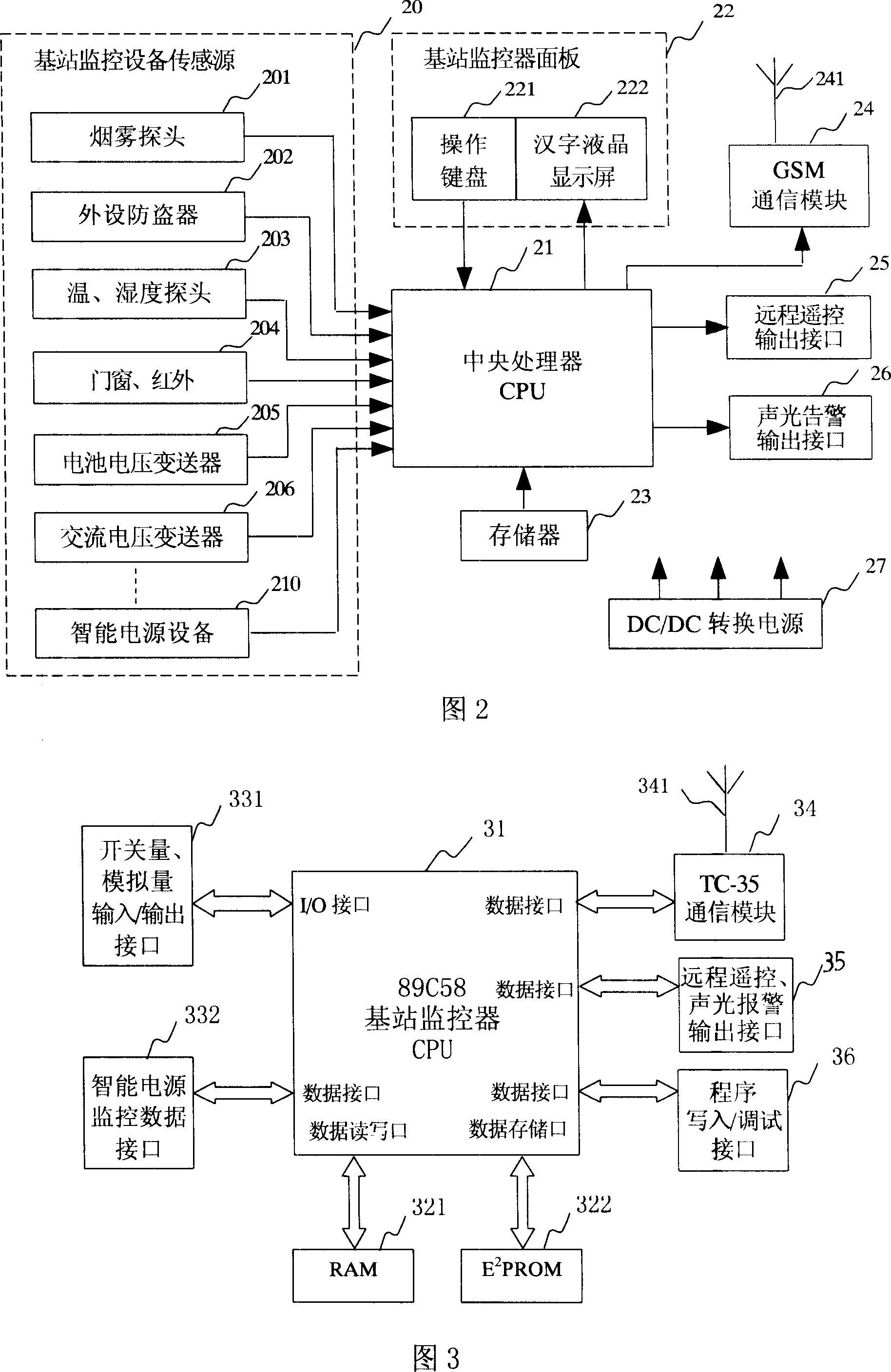
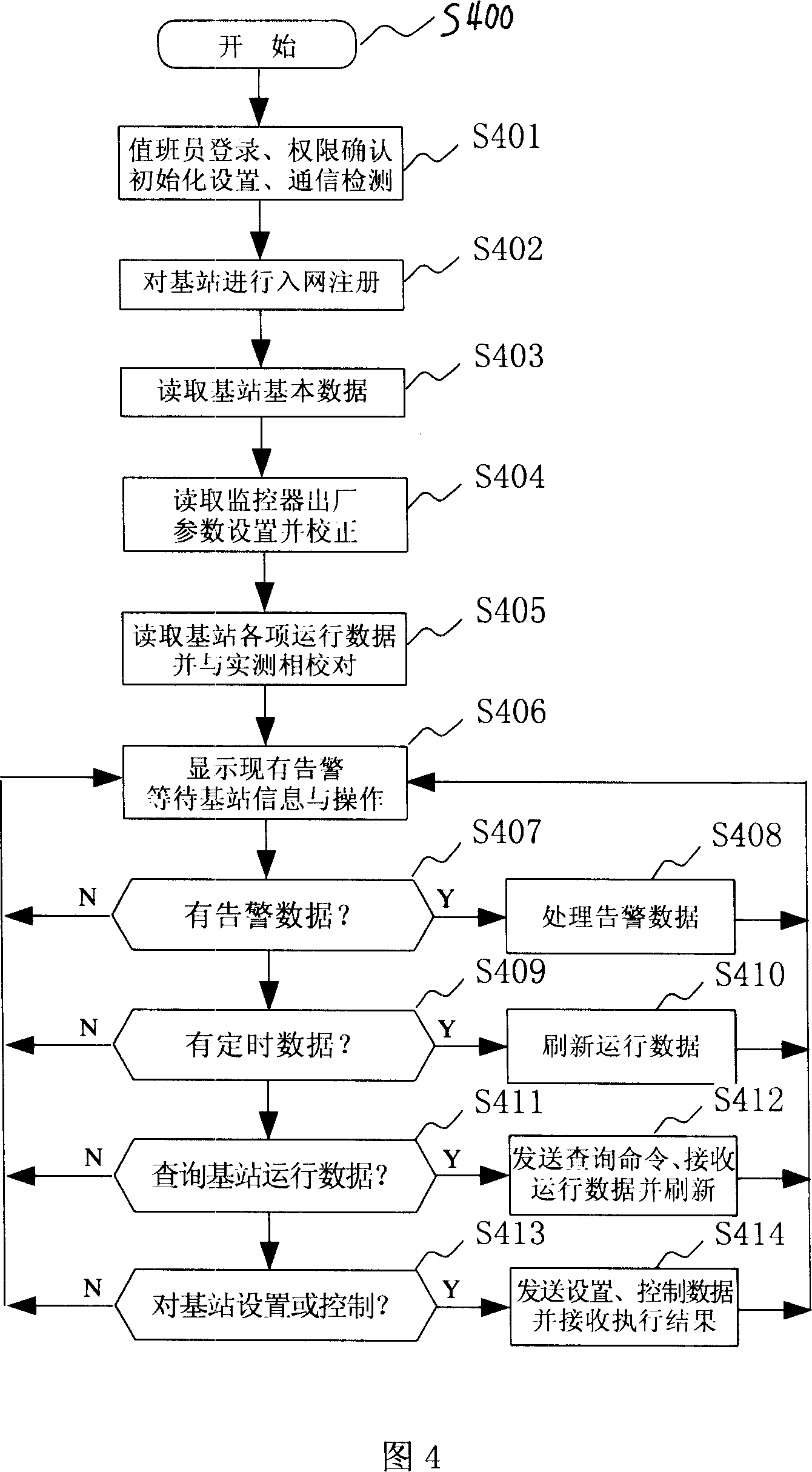
InactiveCN101014173ADetection speedEasy to masterTelephonic communicationRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsMonitoring methodsGSM
The invention relates to one digital mobile communication technique suitable for one transmission base station monitor method and system based on wireless mobile terminal, which uses GSM communication network short message channel to sort monitor data and to transmit on focus degree, wherein, the alarm information and inquire information send by real time and the operation information without alarm sends method and process technique to form alarm guide base station monitor system by network monitor center, base station and other human cell phone network.
Owner:姜宏伟
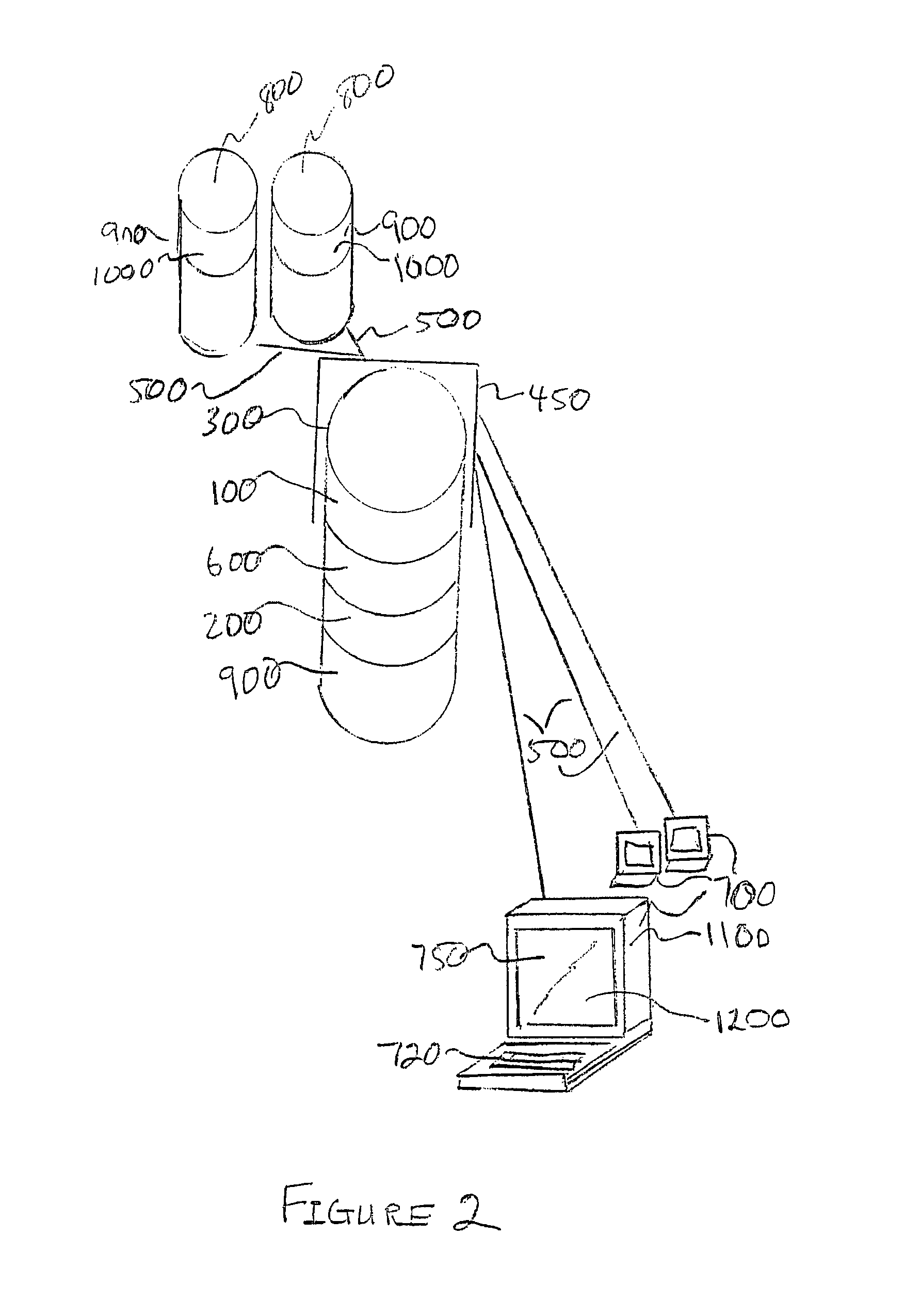
Purchaser value optimization system
ActiveUS8762160B2Increase valueEasy to compareReservationsPayment architectureData setLoyalty program
A purchasing system includes a master server linking to a product and service inventory database. A query and response coordination database is hosted on the master server and includes a customer profiles database, a loyalty program rules database, and a purchase rules dataset. The coordination database receives a purchase request query, extracts purchase data elements from the received purchase request query, uses purchase rules from the rules dataset, applying the extracted purchase data elements to form a purchase query, applies the purchase query to the inventory database to determine available product and service inventory that satisfy the purchase request query, available product and service inventory that satisfy the purchase request query being identified as purchase options, receives purchase options from the inventory database, determines a total rewards benefit and creates a file for sending via the network to the purchaser's computer to display the query response.
Owner:AMADEUS S
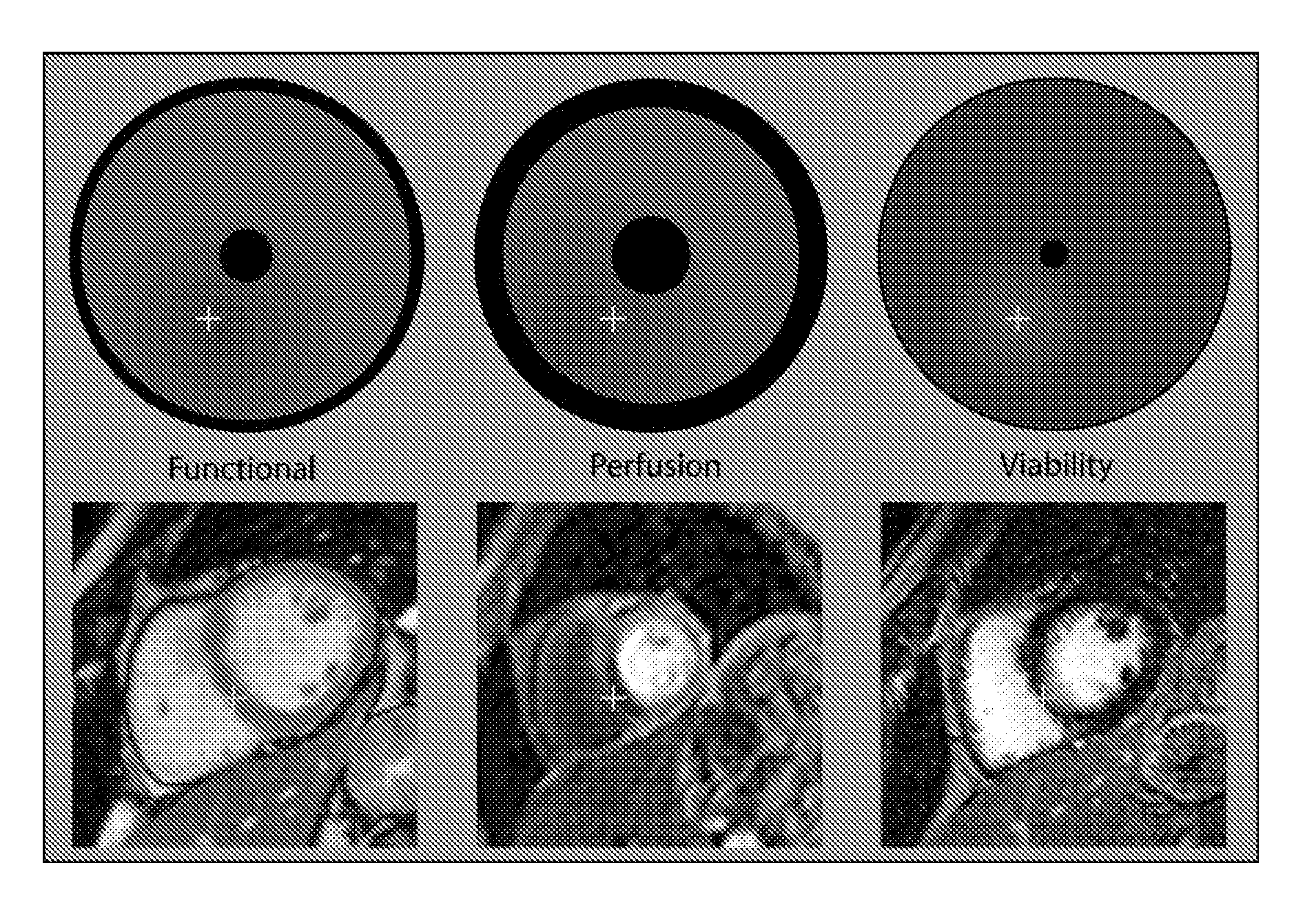
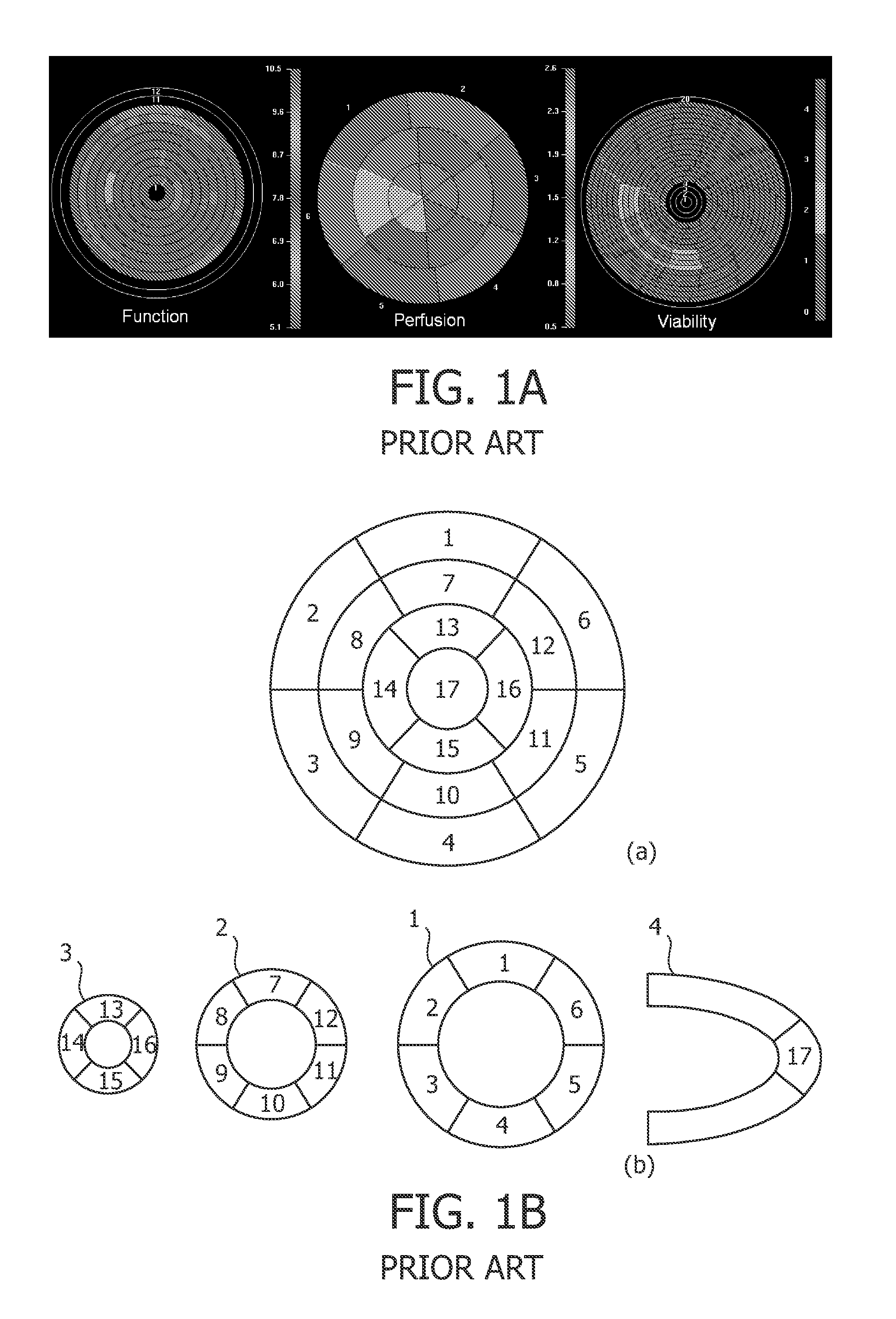
Reparametrized bull's eye plots
ActiveUS20110249005A1Improves visualizing resultEasy to compareDrawing from basic elementsSensorsObject basedComputer science
The invention relates to a system for visualizing, in a first bull's eye plot, results of a first quantitative analysis of an object represented in first image data, in particular for cardiac analysis. The first image data comprises a first plurality of data slices, and the system comprises a slice unit for associating a data slice of the first plurality of data slices with a concentric ring of the first bull's eye plot, a radius unit for computing the length of a radius of the concentric ring of the first bull's eye plot, and a value unit for computing at least one value for displaying in the concentric ring of the first bull's eye plot, on the basis of the data slice associated with the concentric ring of the first bull's eye plot, and wherein the length of the radius of the concentric ring of the first bull's eye plot is defined on the basis of the position of the data slice, of the first plurality of data slices, associated with the concentric ring of the first bull's eye plot, with respect to the object. The dependence of the first bull's eye plot concentric ring radius on the position of the data slice associated with said concentric ring of the first bull's eye plot, with respect to the object, defines an objective framework for the first bull's eye plot, based on the geometry of the object. Thus, the results of the first quantitative analysis of the object visualized in the first bull's eye plot can be more easily compared with results of a second quantitative analysis of the same object represented in second image data visualized in a second bull's eye
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
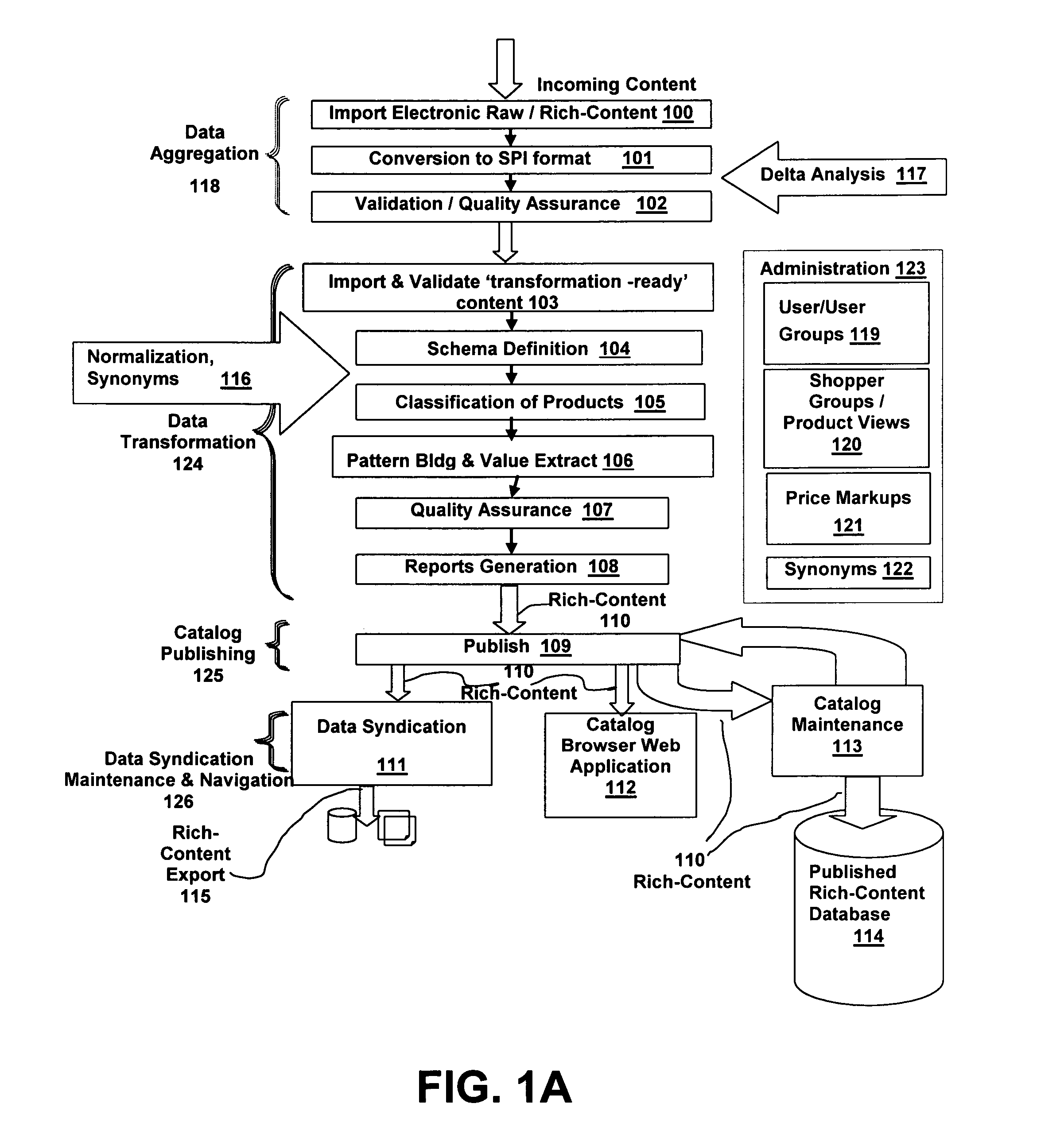
System and method for user creation and direction of a rich-content life-cycle
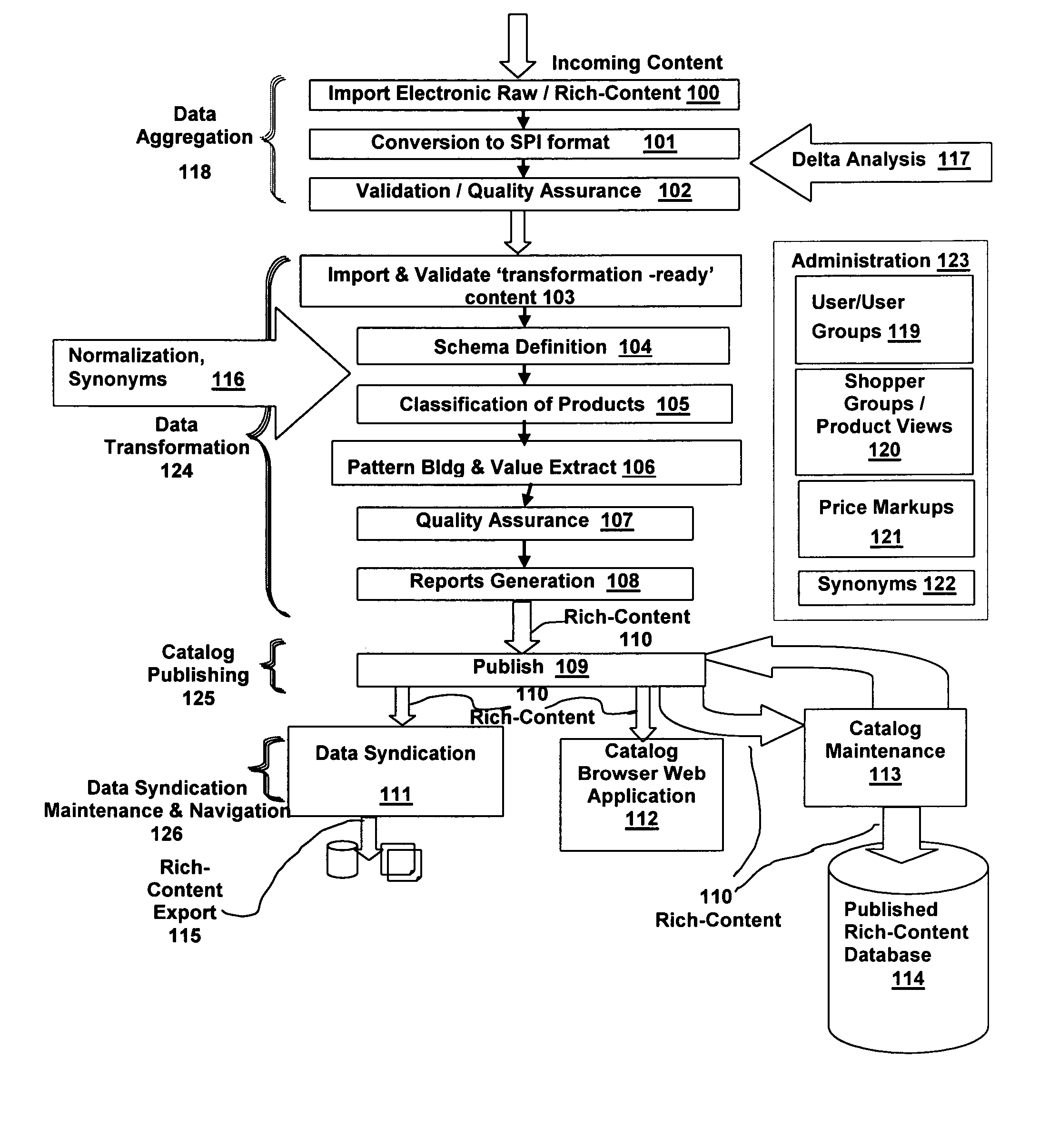
InactiveUS20050193029A1Improve qualityGoals of a procuring organization are not compromisedCommerceSpecial data processing applicationsDatabaseWorld Wide Web
A system and method are disclosed for creating, controlling and enhancing a life-cycle of at least one stage for a rich-content repository, such as a catalog of products and services. The item data is received from a source and is processed in accordance with a User-defined life-cycle, finally being published / syndicated as rich-content. At User direction, the rich-content life-cycle can include one or more stages such as item data receipt from a supplier, transformation under control of User-defined functions, and publication / syndication of the transformed, i.e., rich-content data. Maintenance of rich-content repositories is likewise provided using a User-defined life-cycle having User-defined functions.
Owner:EPLUS +1
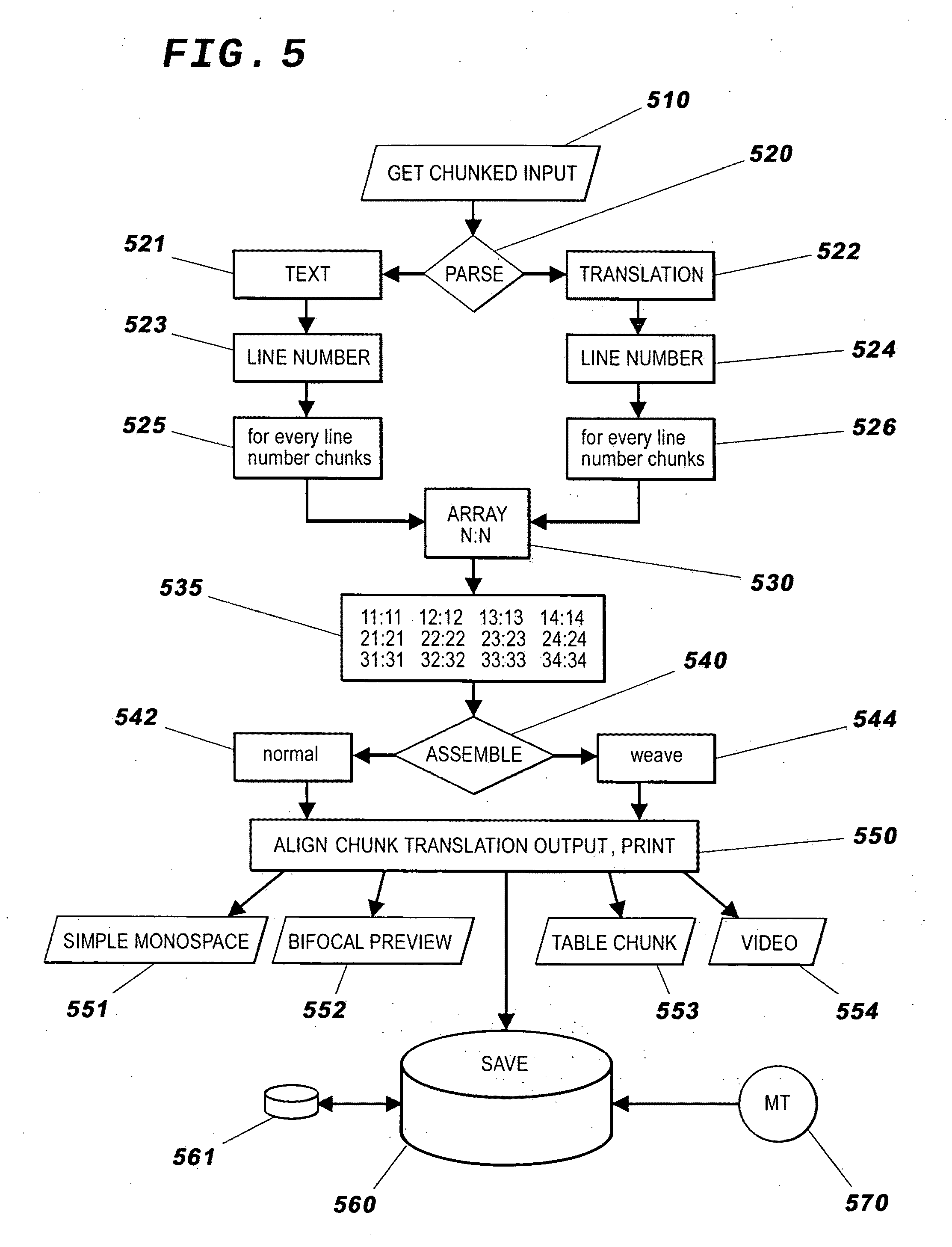
Aligning chunk translations for language learners
InactiveUS20110097693A1Easily input dataSimple data formatElectrical appliancesTeaching apparatusText editingDocument preparation
A method and apparatus to align and edit chunks of text and translation. Language learners compare segments of text and translation. Both text and translation are segmented into word groups or “chunks” and related to each other. The related chunks are aligned to facilitate their comparison. For a reader, unfamiliar chunks can be related to more familiar chunks. Constant alignment of text and translation chunks occurs in many variable outputs, including bifocal formats and directly editable alignments. Thus, human edits and improvements input into the system can inform improving machine chunk translation. Both text and translation are editable within one single document, manageable in a wide variety of text editing environments, including common Textarea Input fields. Resulting chunk translations are easily printed on paper and / or displayed electronically. Language learners using the system may include humans and machines. Productions of aligned texts are customized for individual language learners.
Owner:CRAWFORD RICHARD HENRY DANA
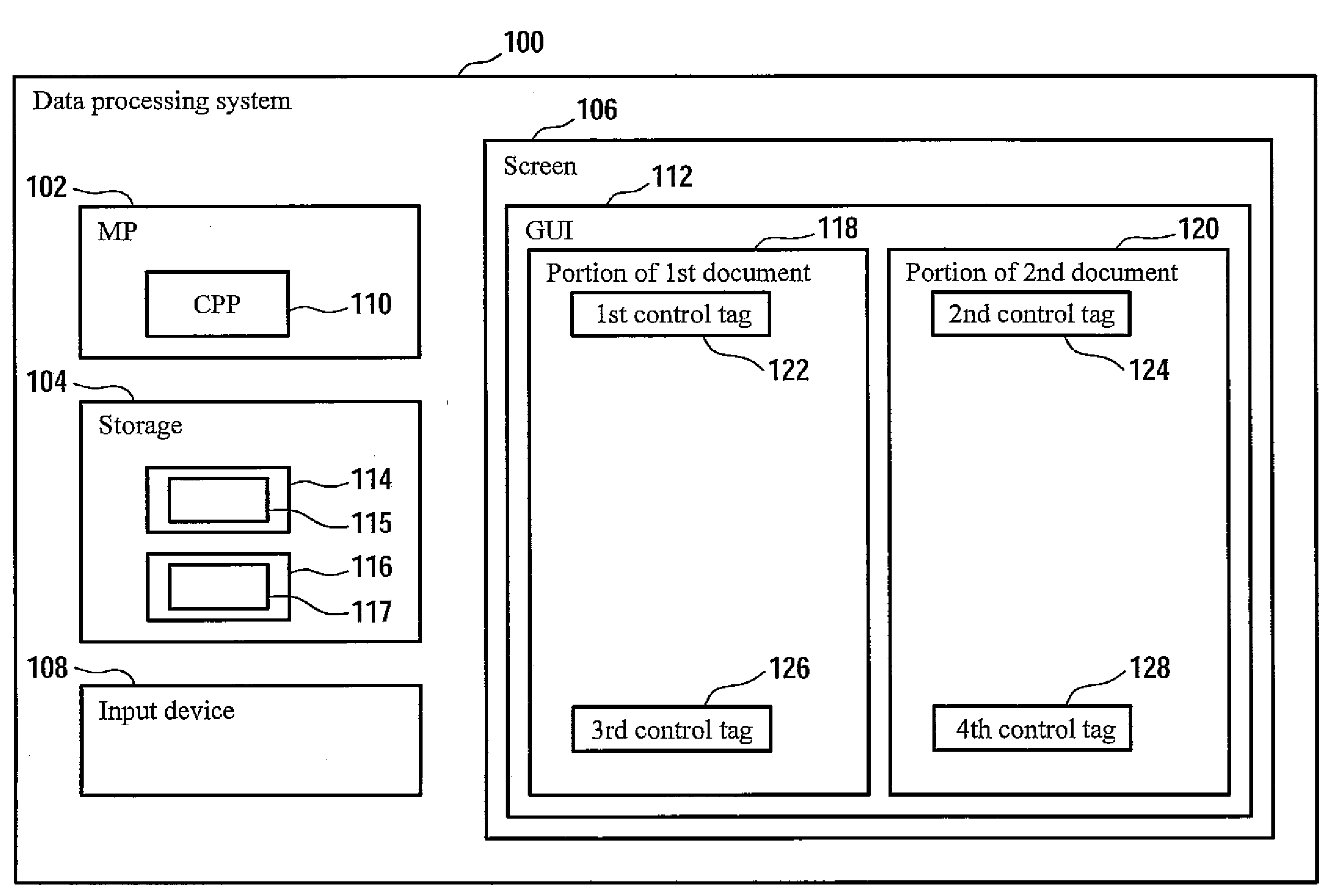
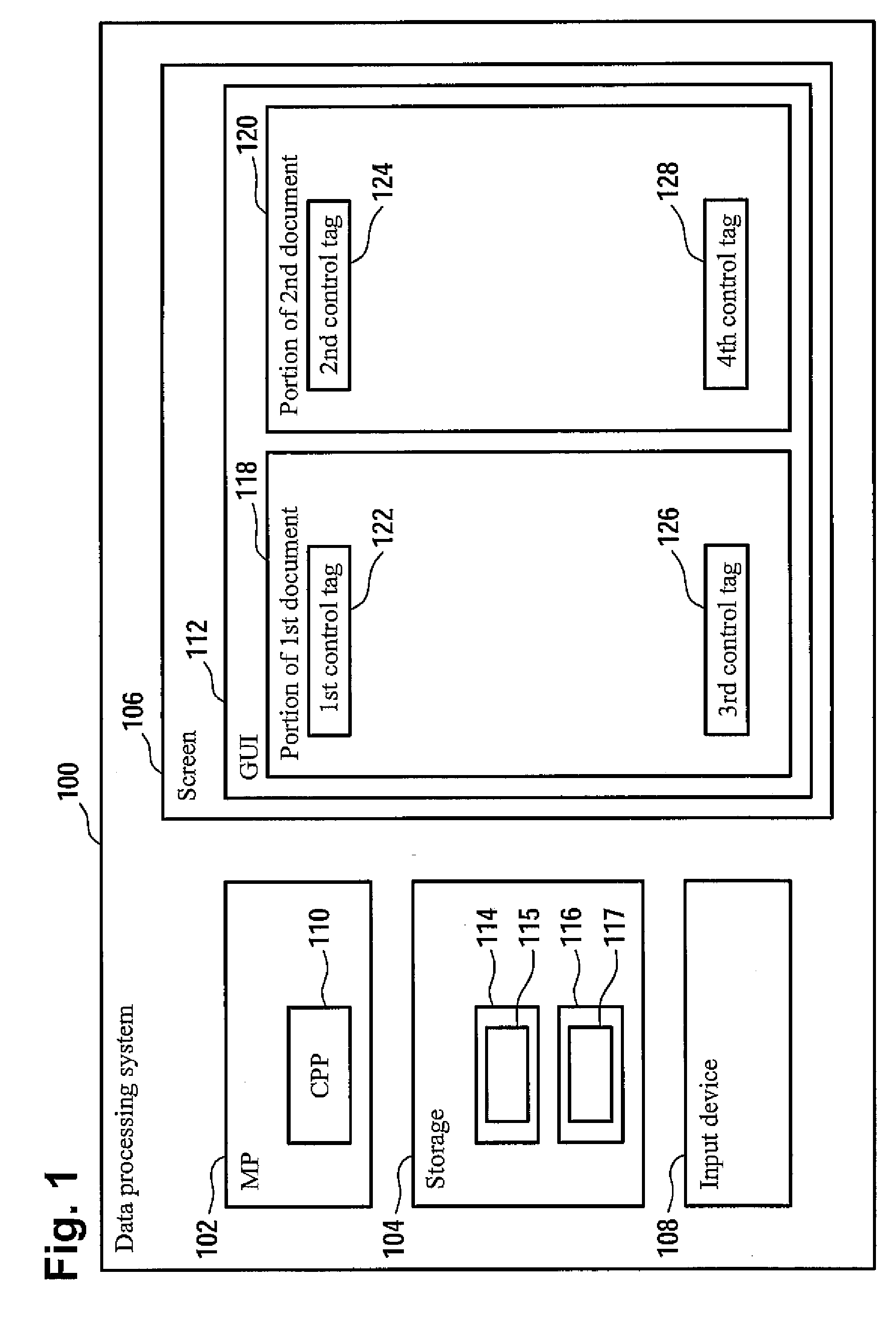
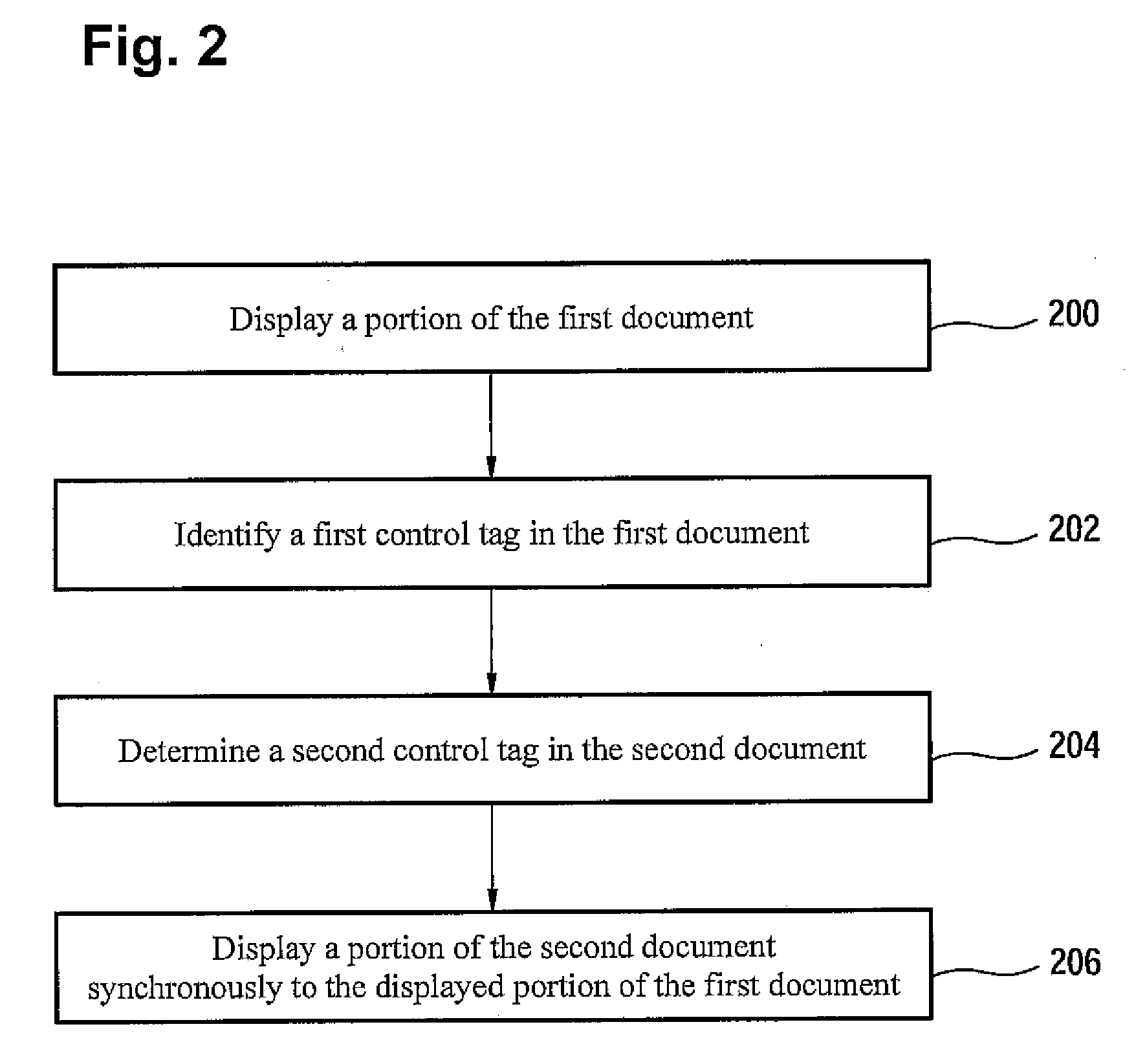
Method and data processing system for displaying synchronously documents to a user
InactiveUS20090144620A1Easy to compareNatural language data processingSpecial data processing applicationsData processing systemWorld Wide Web
A method and a data processing system for displaying a first document and a second document in a synchronized way are disclosed. The first document includes a first set of control tags. The second document includes a second set of control tags. A control tag of the first set of control tags is uniquely assigned to a control tag of the second set of control tags. A portion of the first document is displayed to a user, wherein a first control tag is identified in the first document, wherein the first control tag corresponds to the control tag of the first set of control tags which is situated in essence at the top of the displayed portion of the first document. Furthermore, a second control tag is determined in the second document, wherein the second control tag corresponds to the control tag of the second set of control tags to which the first control tag is uniquely assigned. A portion of the second document is then displayed simultaneously to the display of the portion of the first document to the user, wherein the second control tag is situated in essence at the top of the displayed portion of the second document.
Owner:IBM CORP
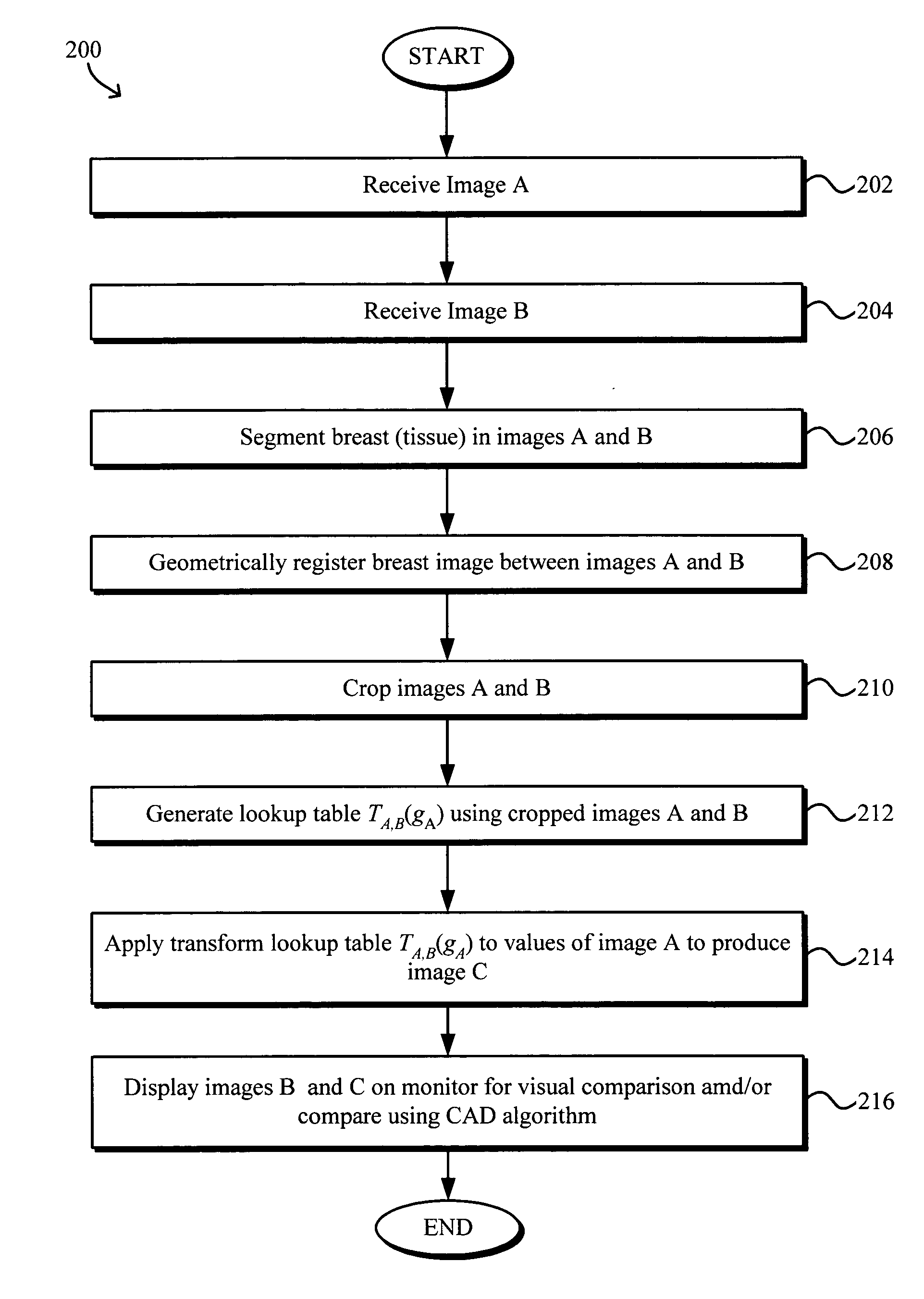
Model-based grayscale registration of medical images
ActiveUS20050013471A1Increase speedImprove reliabilityImage enhancementImage analysisPixel value differenceVisual perception
Numerical image processing of two or more medical images to provide grayscale registration thereof is described, the numerical image processing algorithms being based at least in part on a model of medical image acquisition. The grayscale registered temporal images may then be displayed for visual comparison by a clinician and / or further processed by a computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) system for detection of medical abnormalities therein. A parametric method includes spatially registering two images and performing gray scale registration of the images. A parametric transform model, e.g., analog to analog, digital to digital, analog to digital, or digital to analog model, is selected based on the image acquisition method(s) of the images, i.e., digital or analog / film. Gray scale registration involves generating a joint pixel value histogram from the two images, statistically fitting parameters of the transform model to the joint histogram, generating a lookup table, and using the lookup table to transform and register pixel values of one image to the pixel values of the other image. The models take into account the most relevant image acquisition parameters that influence pixel value differences between images, e.g., tissue compression, incident radiation intensity, exposure time, film and digitizer characteristic curves for analog image, and digital detector response for digital image. The method facilitates temporal comparisons of medical images such as mammograms and / or comparisons of analog with digital images.
Owner:HOLOGIC INC
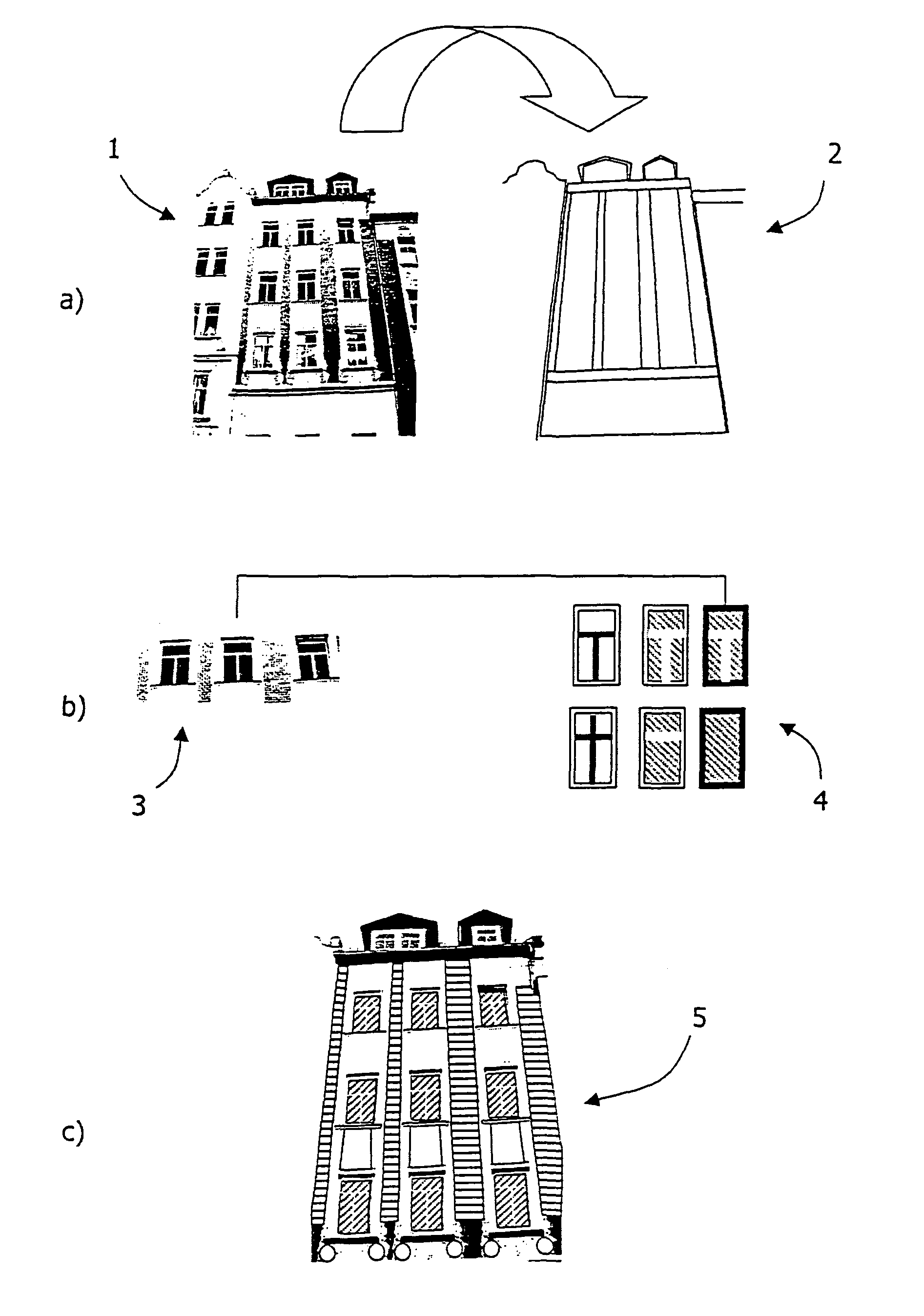
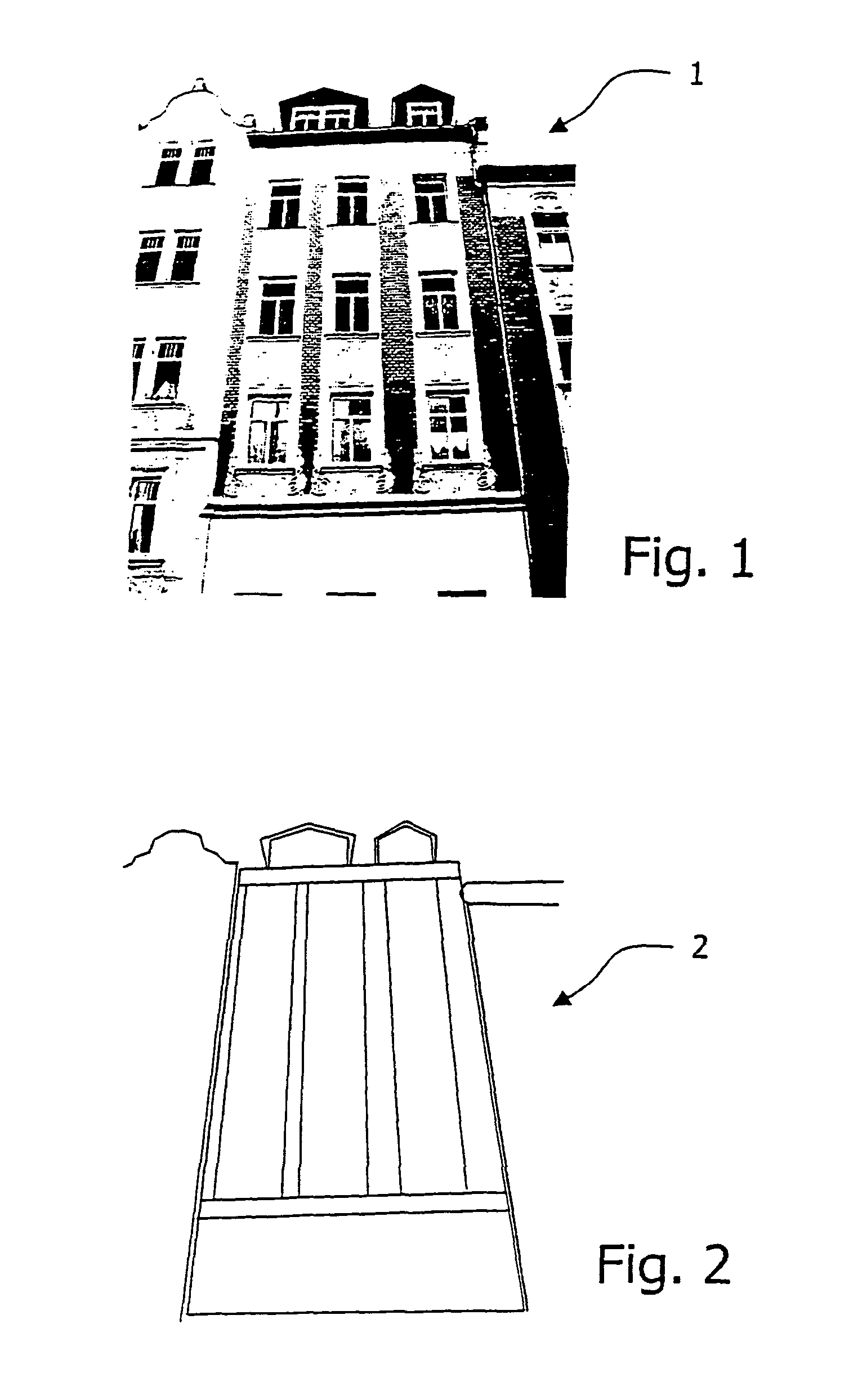
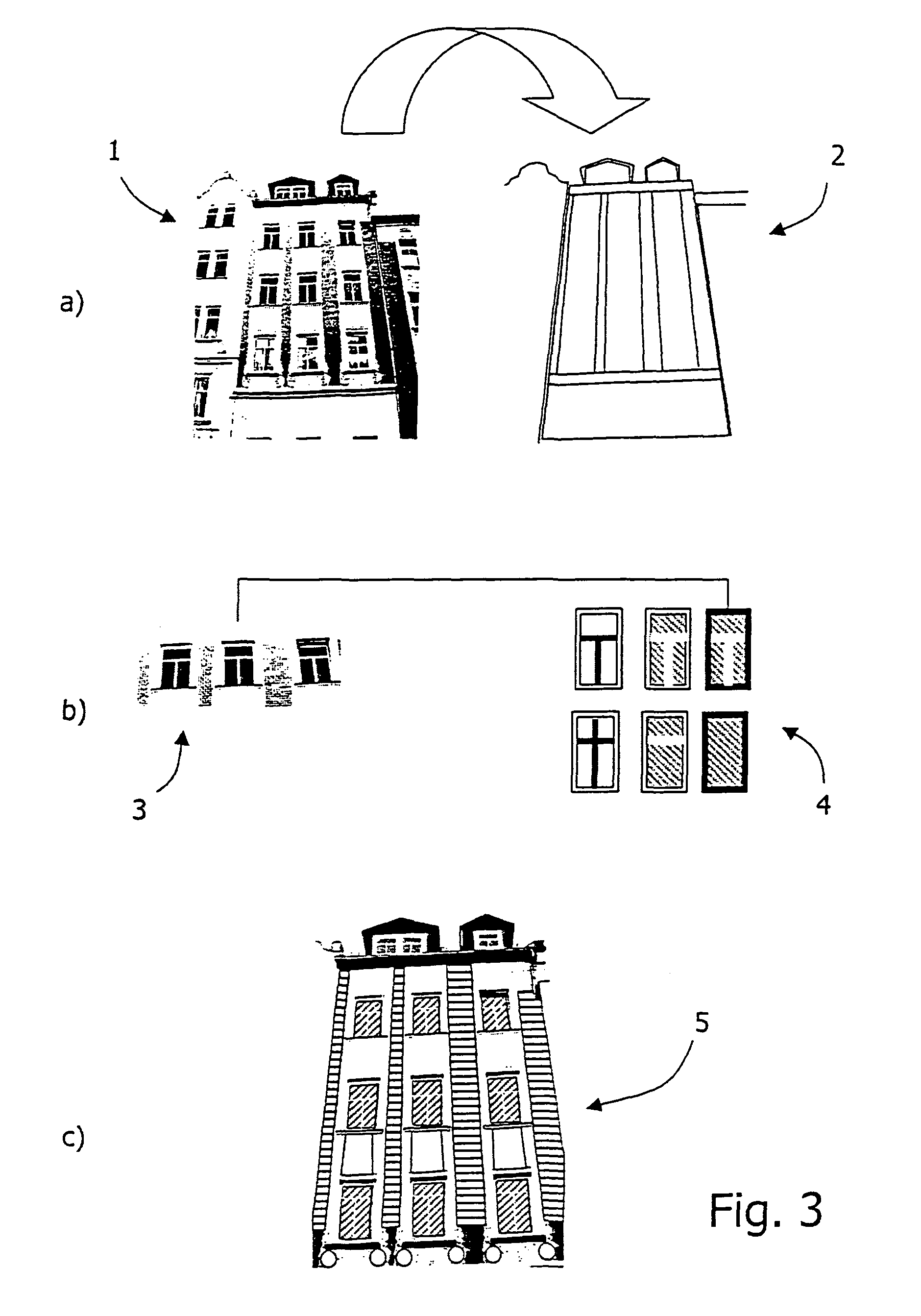
Method for texturizing virtual three-dimensional objects
ActiveUS8705843B2Extensive automationImprove competitivenessCharacter and pattern recognition3D-image renderingFeature vectorFeature set
The invention relates to a method for texturizing virtual three-dimensional objects, particularly virtual three-dimensional building objects and city models with a photographic image (1) of a real object, particularly of a picture of a façade. The method is characterized by the following steps: Projecting the photographic image (1) onto a virtual surface (2) of the virtual three-dimensional object to produce a raw texture; localizing a raw texture element (3) in the raw texture by using a classification method; computer-compatible description of the localized raw texture element by a formal feature set for the raw texture element, particularly a feature vector; comparing the formal feature set of the raw texture element with each feature set of predefined library elements (4), and determining degrees of similarity between the raw texture element and each library element; replacing the localized raw texture element with at least one library element when a predefined degree of similarity is present, and reshaping the raw texture into a generalized texture (5) of the virtual object by replacing all raw texture elements with library elements.
Owner:GTA GEOINFORMATIK
Automatic deepness image registration method
InactiveCN101082988AAvoid negative effectsImprove efficiencyImage analysisPattern recognitionPoint cloud
The invention discloses an automatic depth-image registration method, which comprises the following steps: proceeding triangularization method for depth image; transmitting point cloud data into triangle grid data; finding the boundary point in the depth image according to the triangle grid data; calculating the character value of non-boundary vertex in the depth image; extracting character point set with projected surface character; finding the mating relationship as corresponding point among character points of two depth images; finding at least three couples of corresponding vertex; calculating the estimating value of movement of two depth images according to the corresponding point; adopting modified ICP algorism to optimize the result; finishing the precise registration of two depth images. The invention improves the speed and precision of registration, which reduces the calculating quantity with simple course.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com