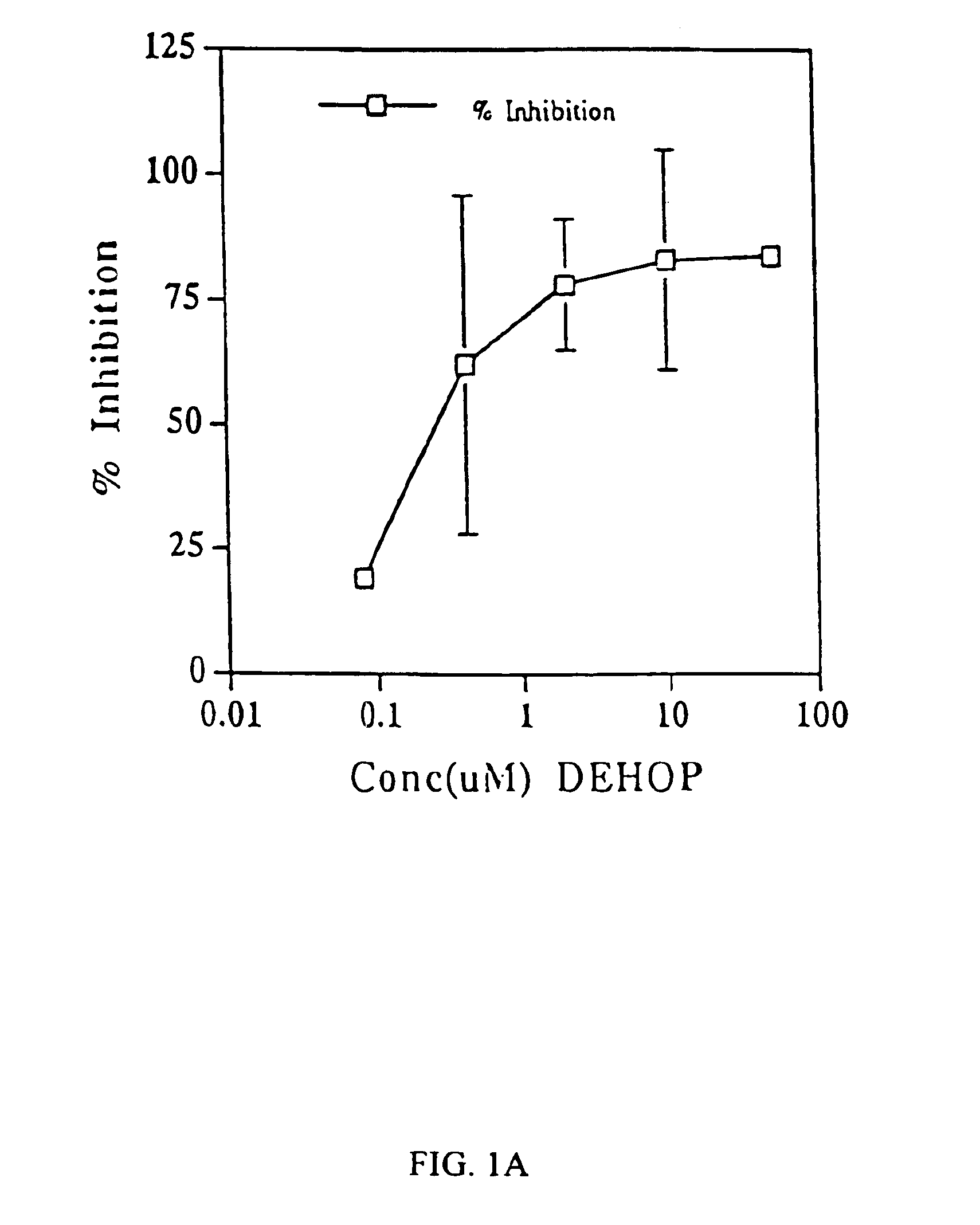
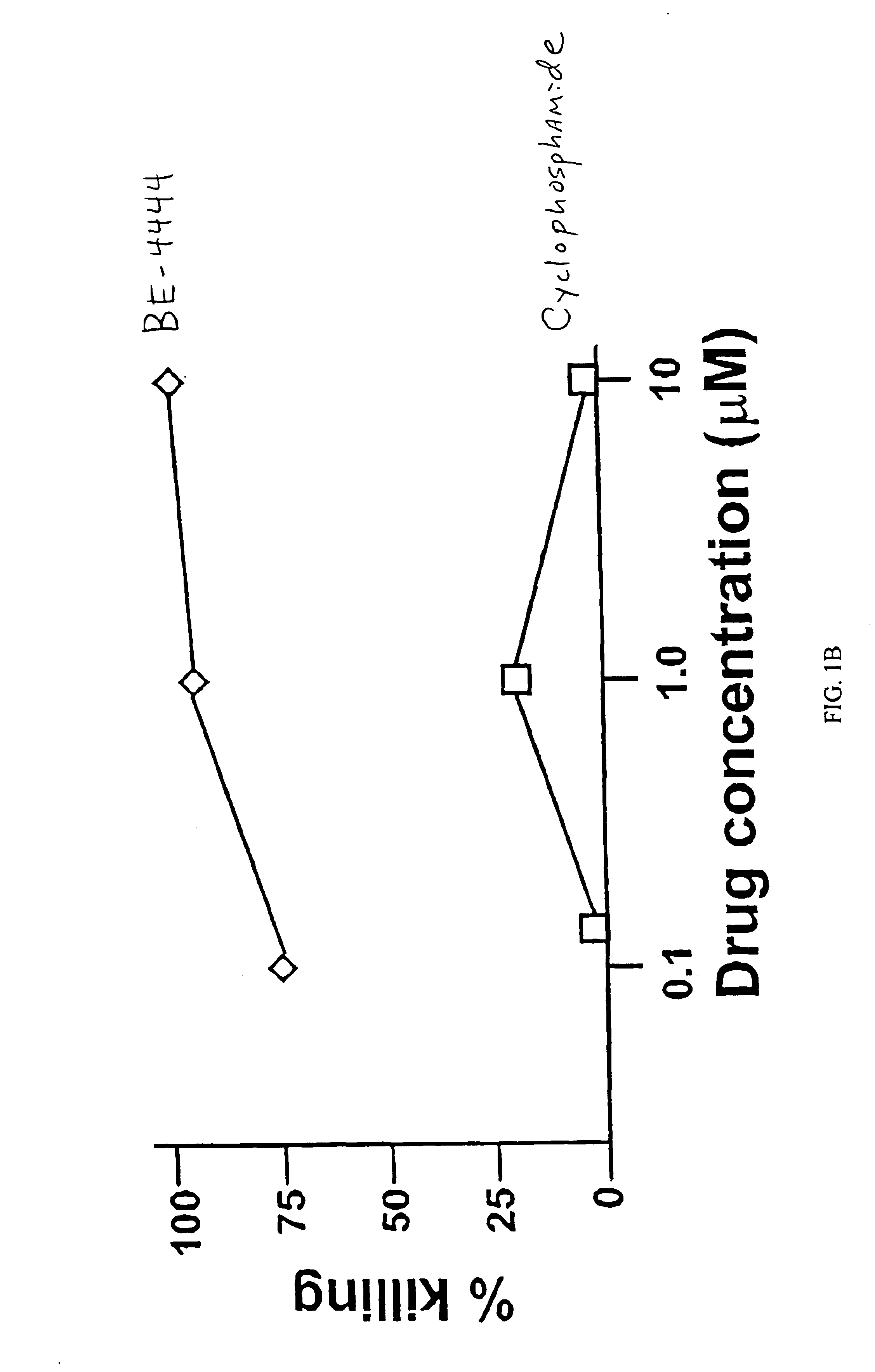
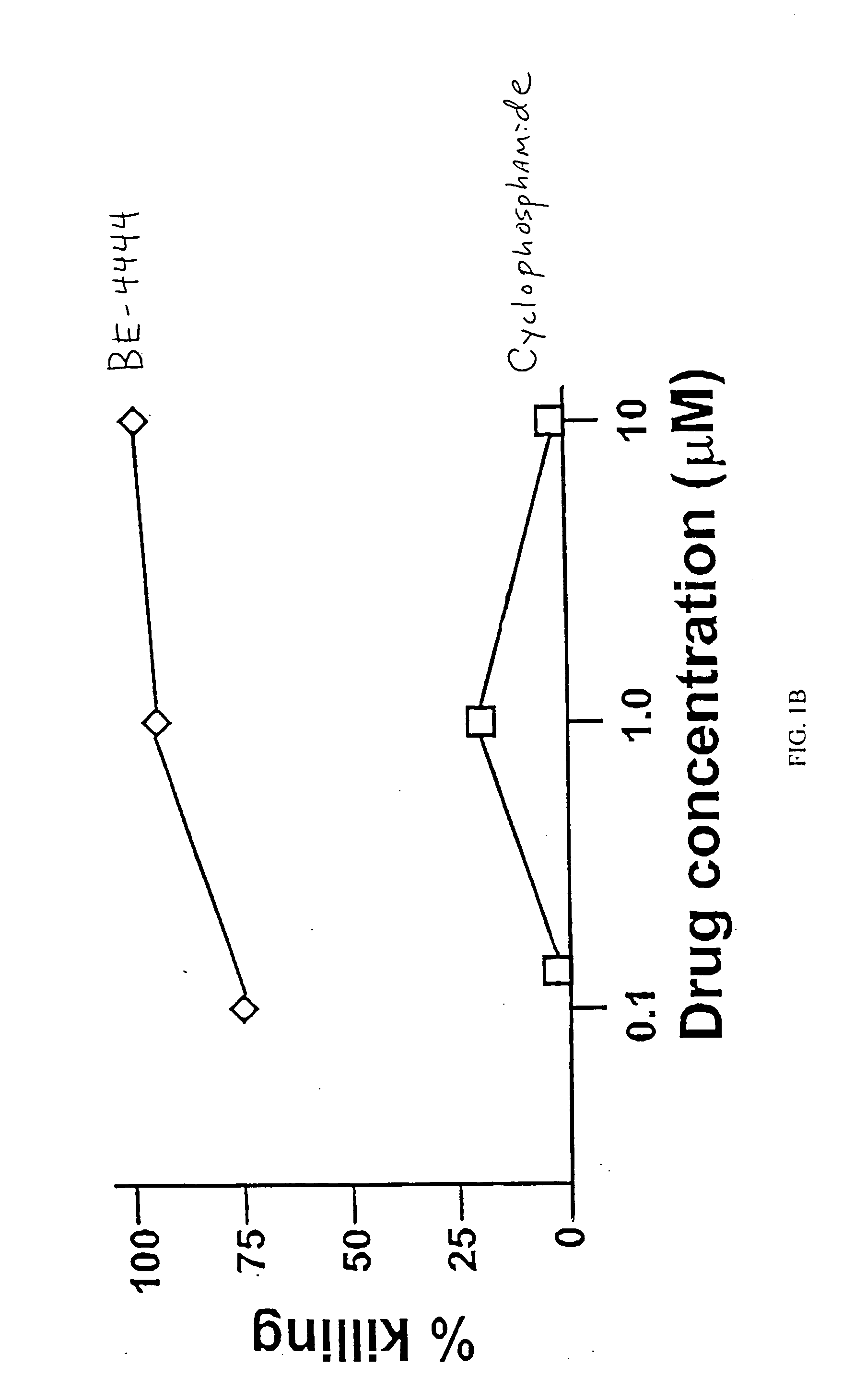
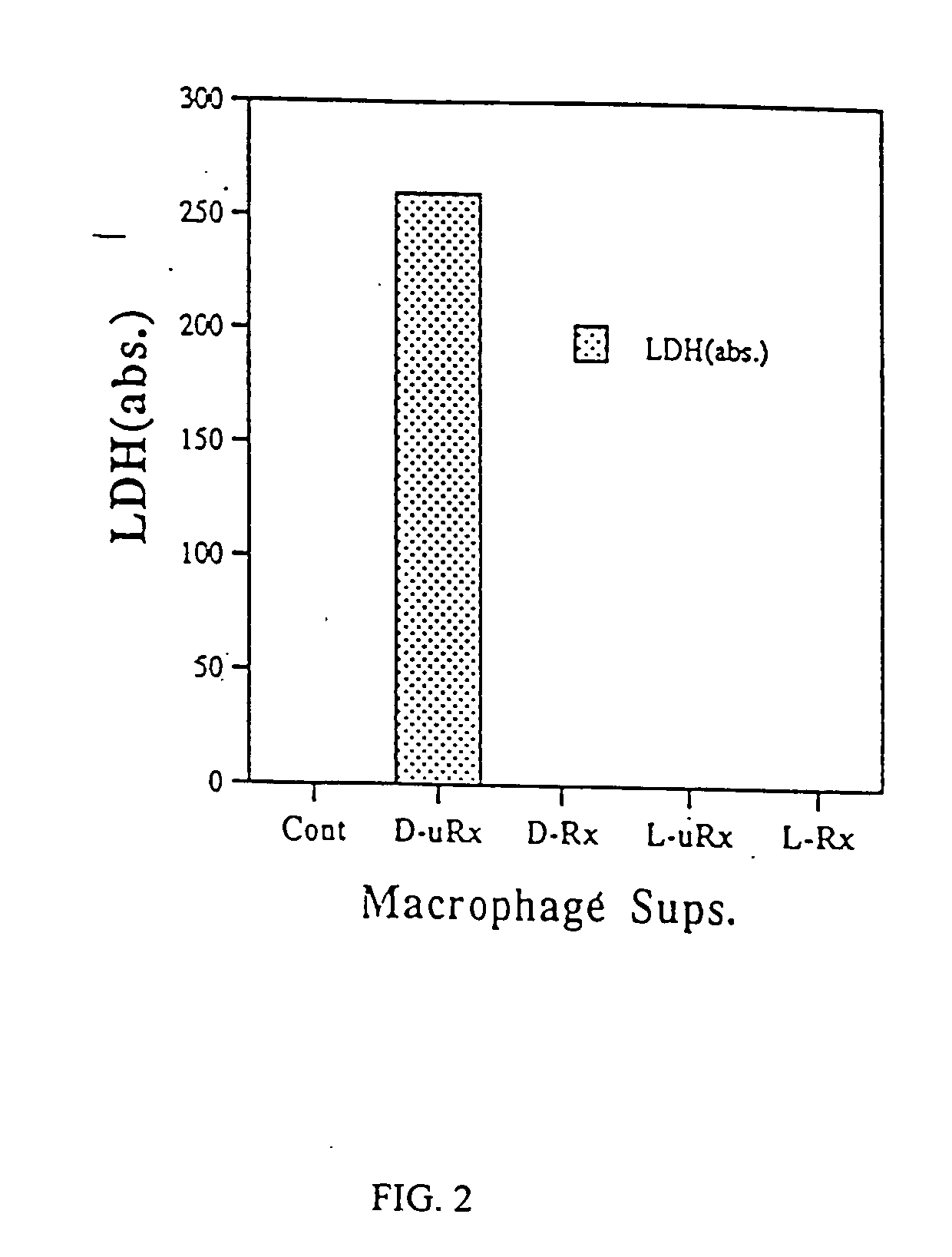
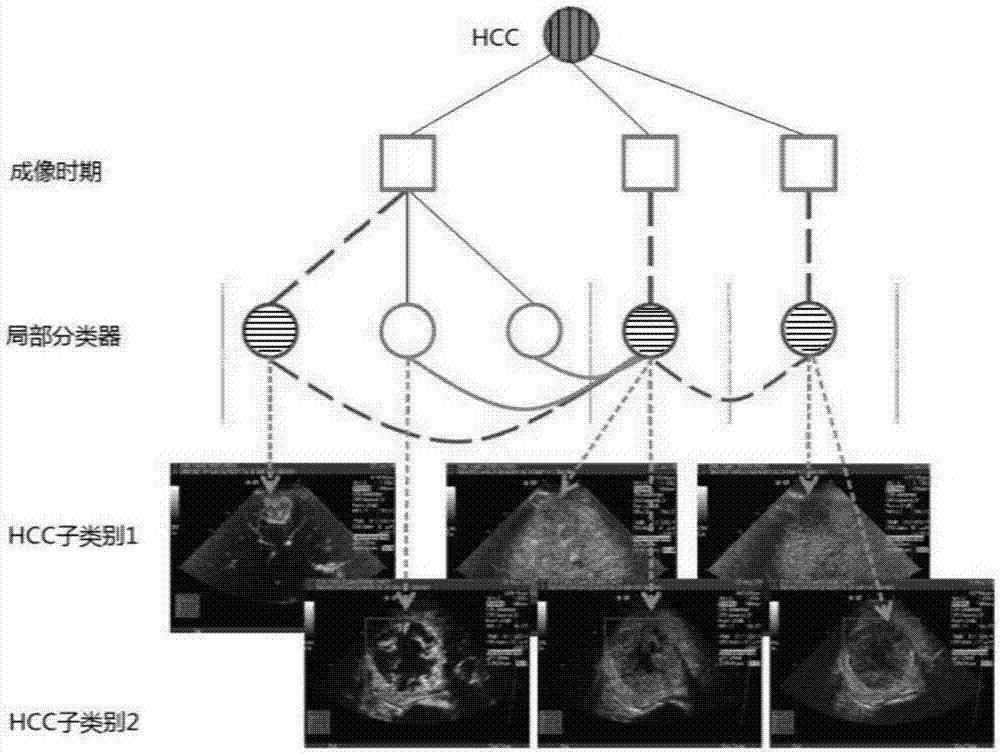
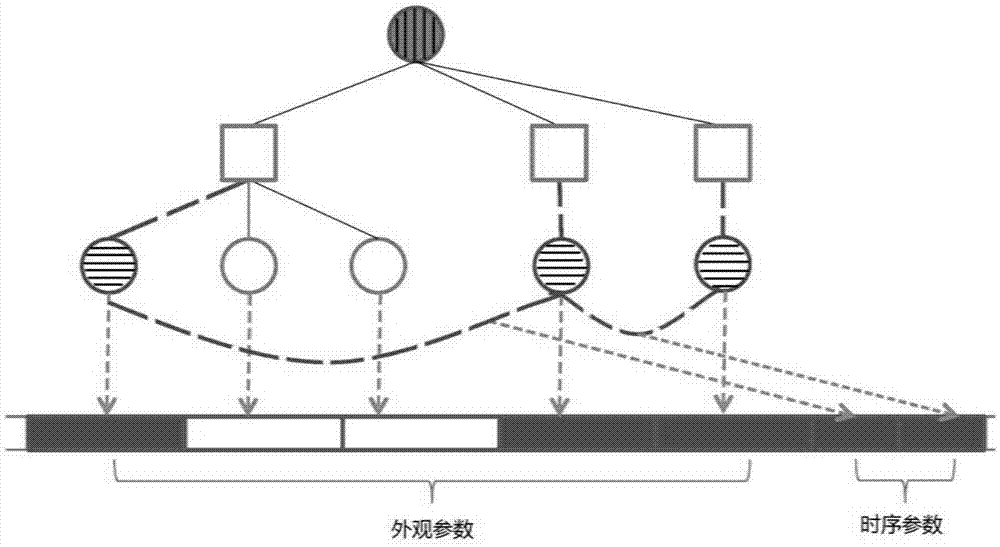
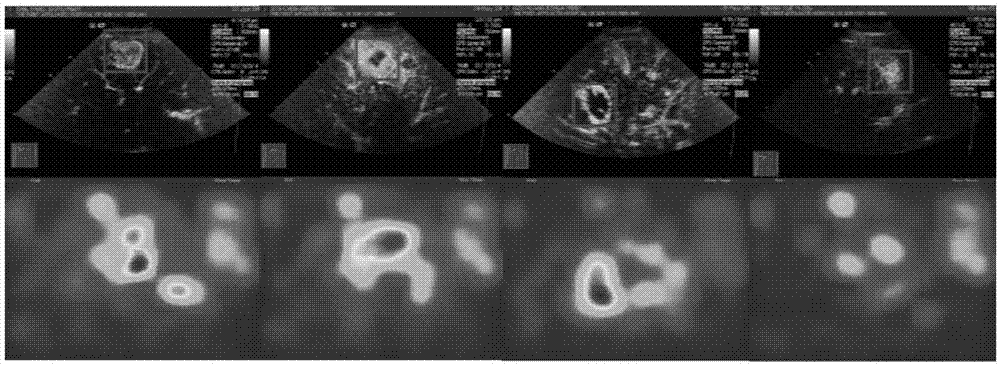
Patents
Literature
778 results about "Aided diagnosis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) may be defined as a diagnosis made by a physician who takes into account the computer output as a second opinion. The purpose of CAD is to improve the diagnostic accuracy and the consistency of the radiologists’ image interpretation.
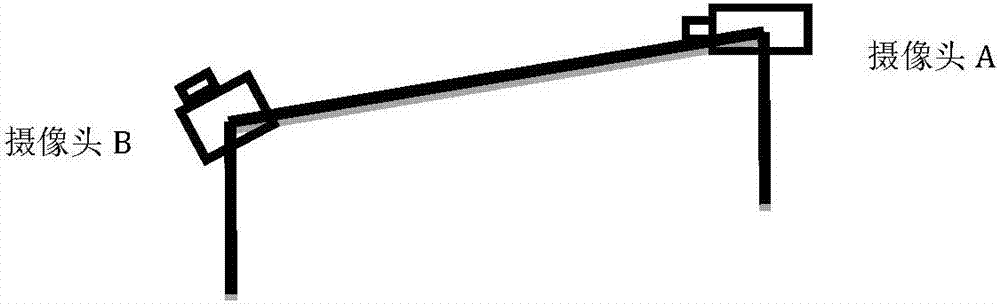
Uterine cervical cancer computer-aided-diagnosis (CAD)
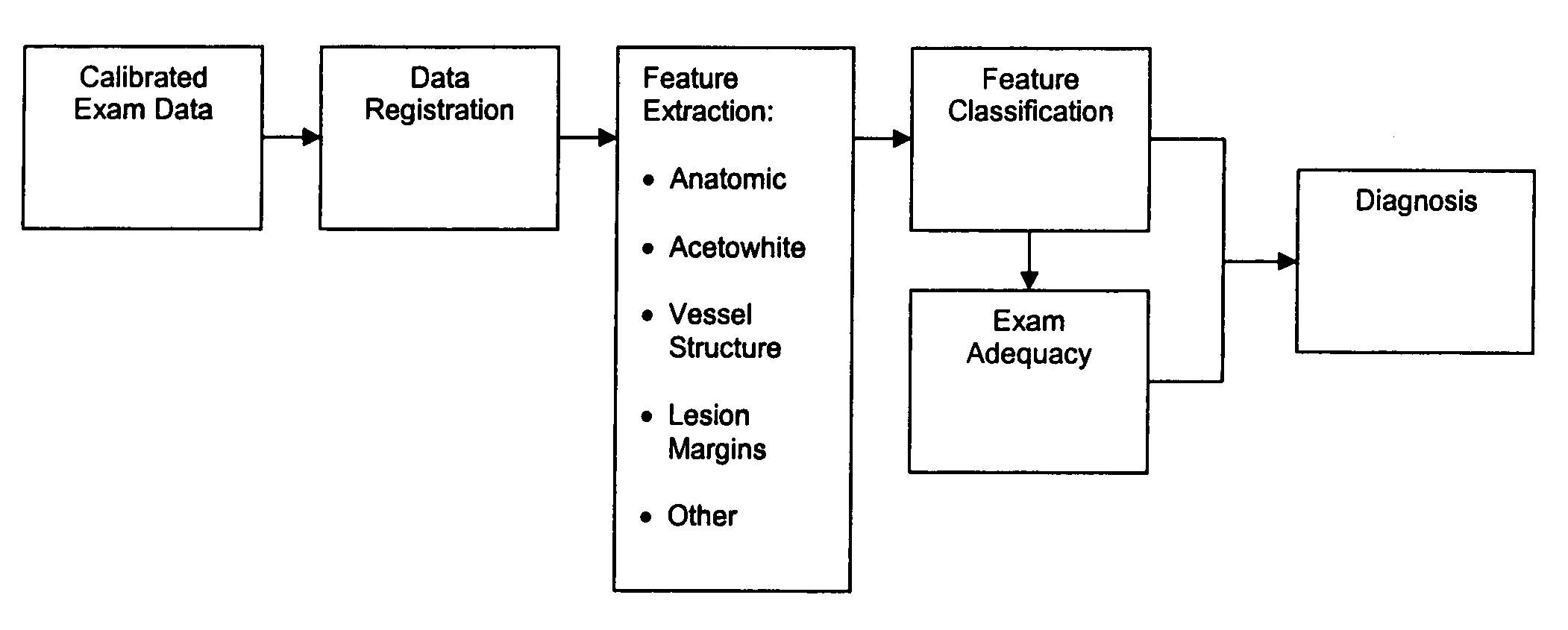
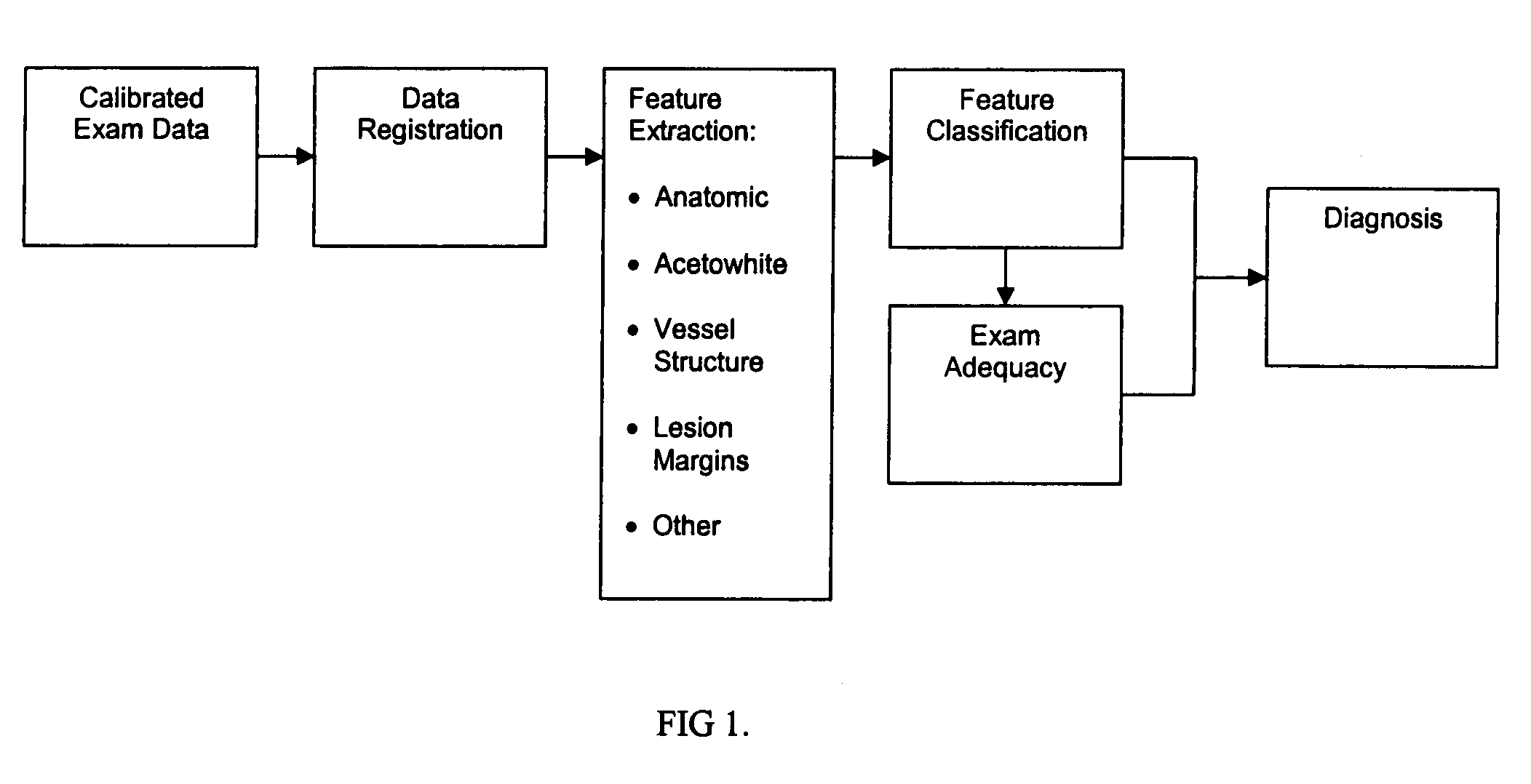
Uterine cervical cancer Computer-Aided-Diagnosis (CAD) according to this invention consists of a core processing system that automatically analyses data acquired from the uterine cervix and provides tissue and patient diagnosis, as well as adequacy of the examination. The data can include, but is not limited to, color still images or video, reflectance and fluorescence multi-spectral or hyper-spectral imagery, coherent optical tomography imagery, and impedance measurements, taken with and without the use of contrast agents like 3-5% acetic acid, Lugol's iodine, or 5-aminolevulinic acid. The core processing system is based on an open, modular, and feature-based architecture, designed for multi-data, multi-sensor, and multi-feature fusion. The core processing system can be embedded in different CAD system realizations. For example: A CAD system for cervical cancer screening could in a very simple version consist of a hand-held device that only acquires one digital RGB image of the uterine cervix after application of 3-5% acetic acid and provides automatically a patient diagnosis. A CAD system used as a colposcopy adjunct could provide all functions that are related to colposcopy and that can be provided by a computer, from automation of the clinical workflow to automated patient diagnosis and treatment recommendation.
Owner:STI MEDICAL SYST
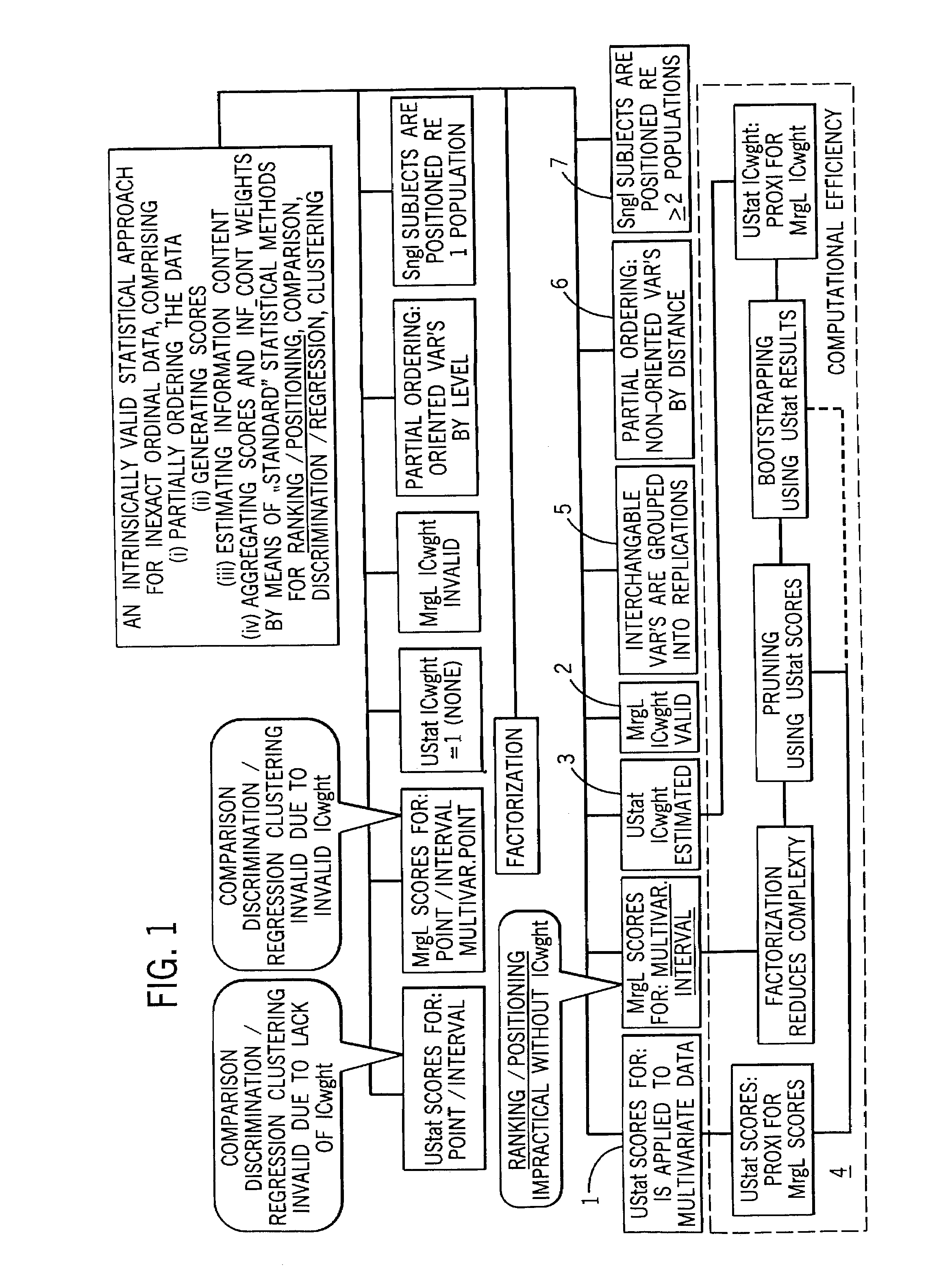
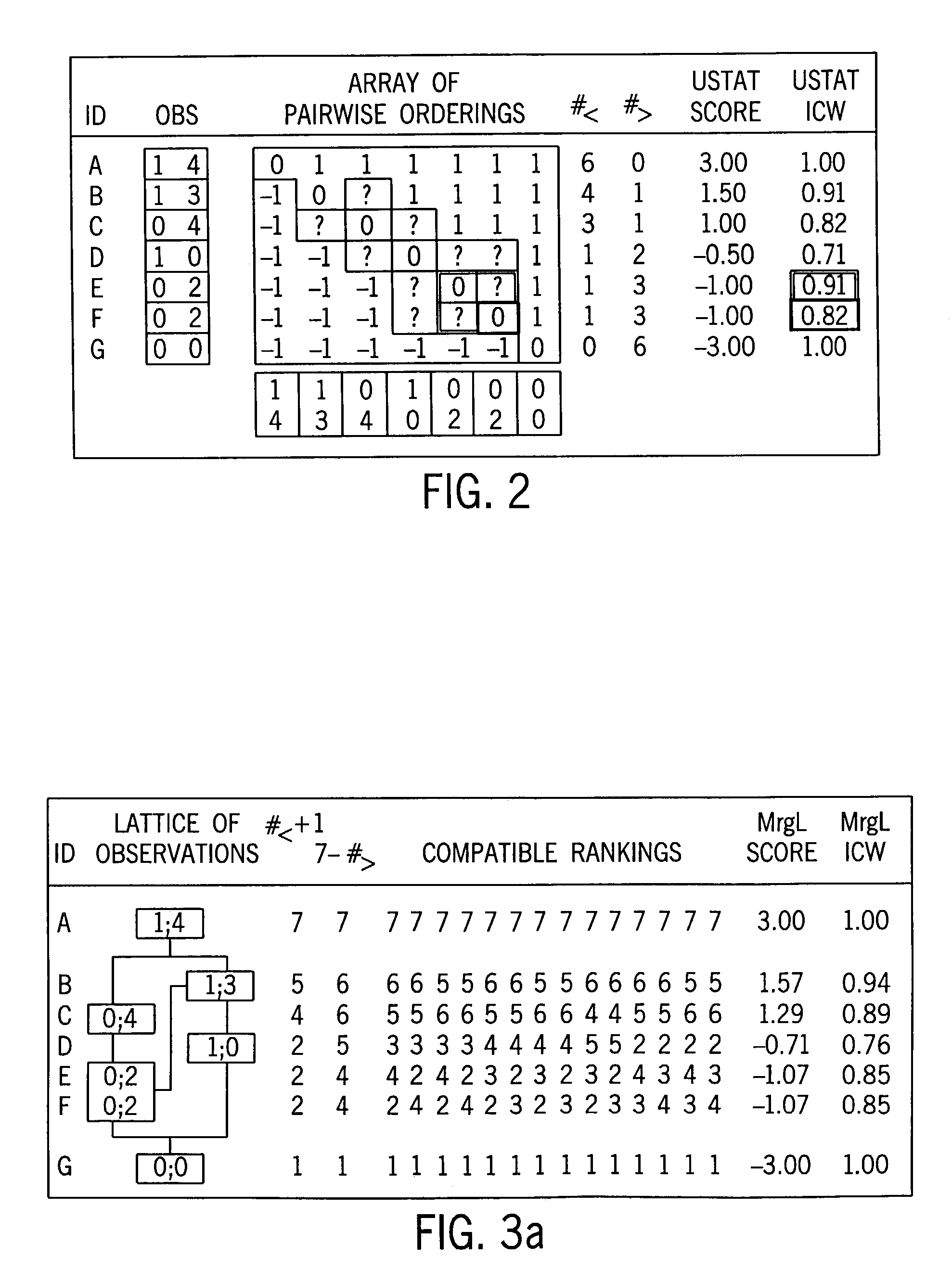
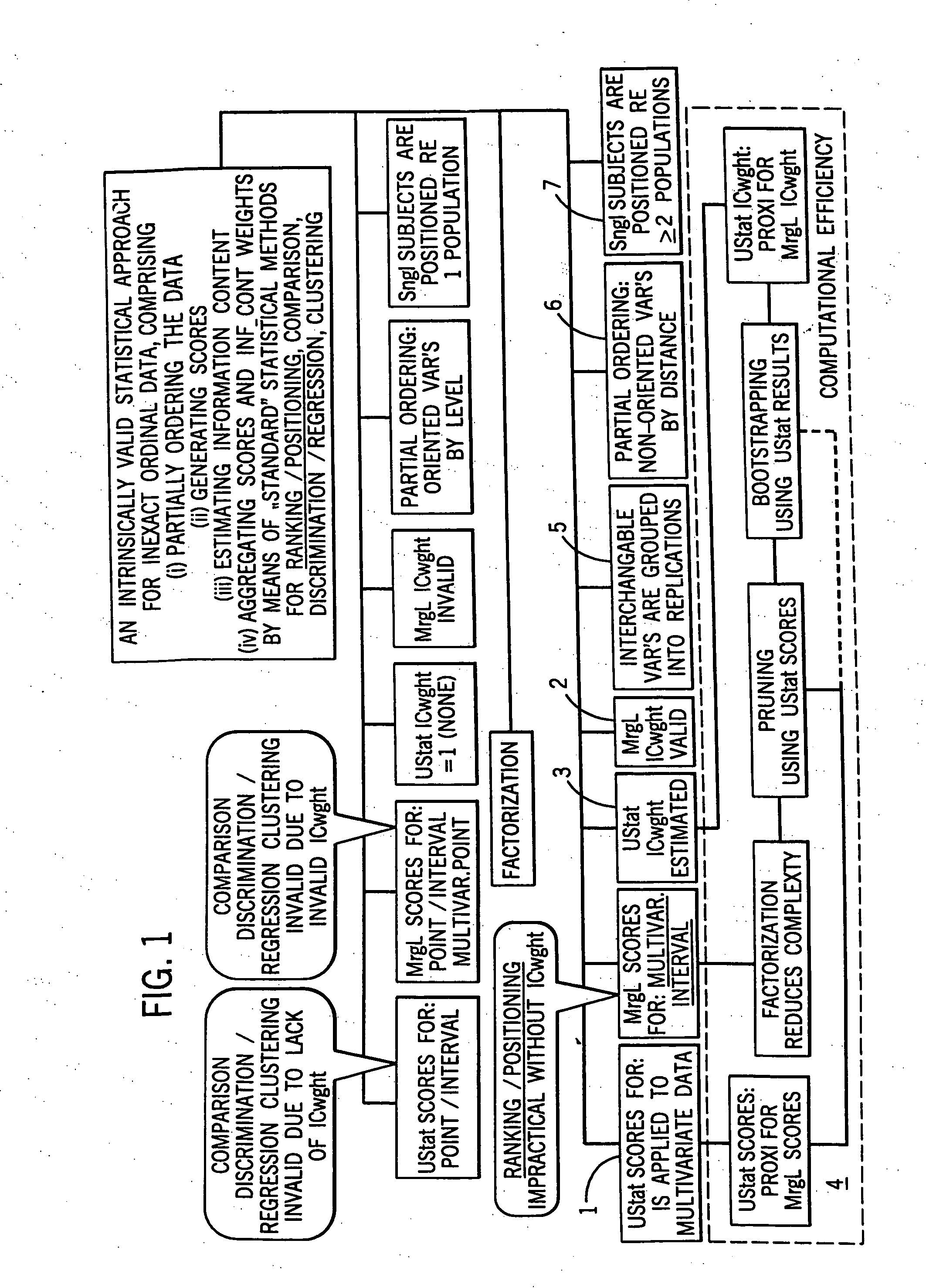
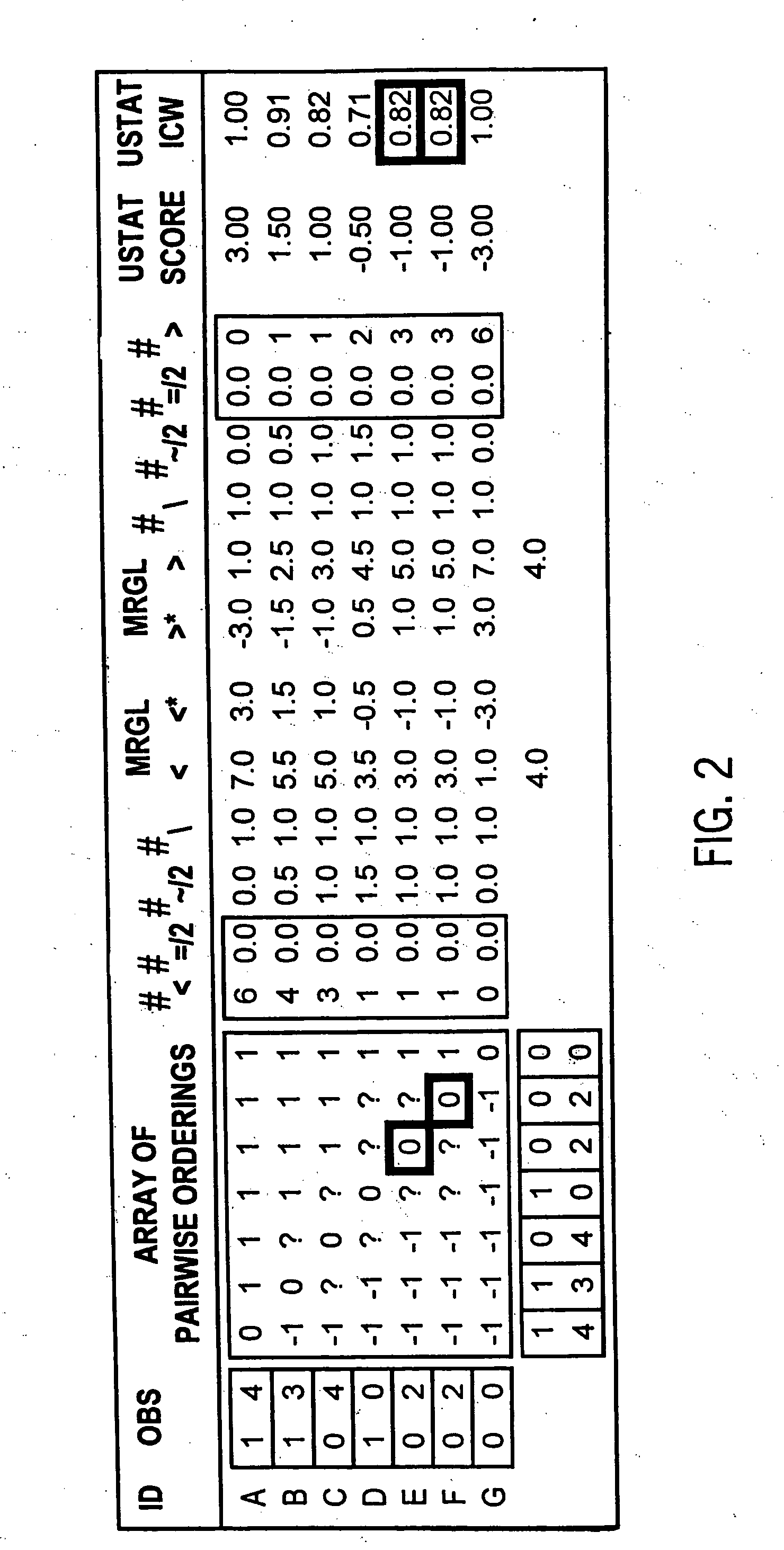
Statistical methods for multivariate ordinal data which are used for data base driven decision support
InactiveUS7072794B2Reduce complexityImprove accuracy and stabilitySurgeryDigital computer detailsDecision makerAnalysis method
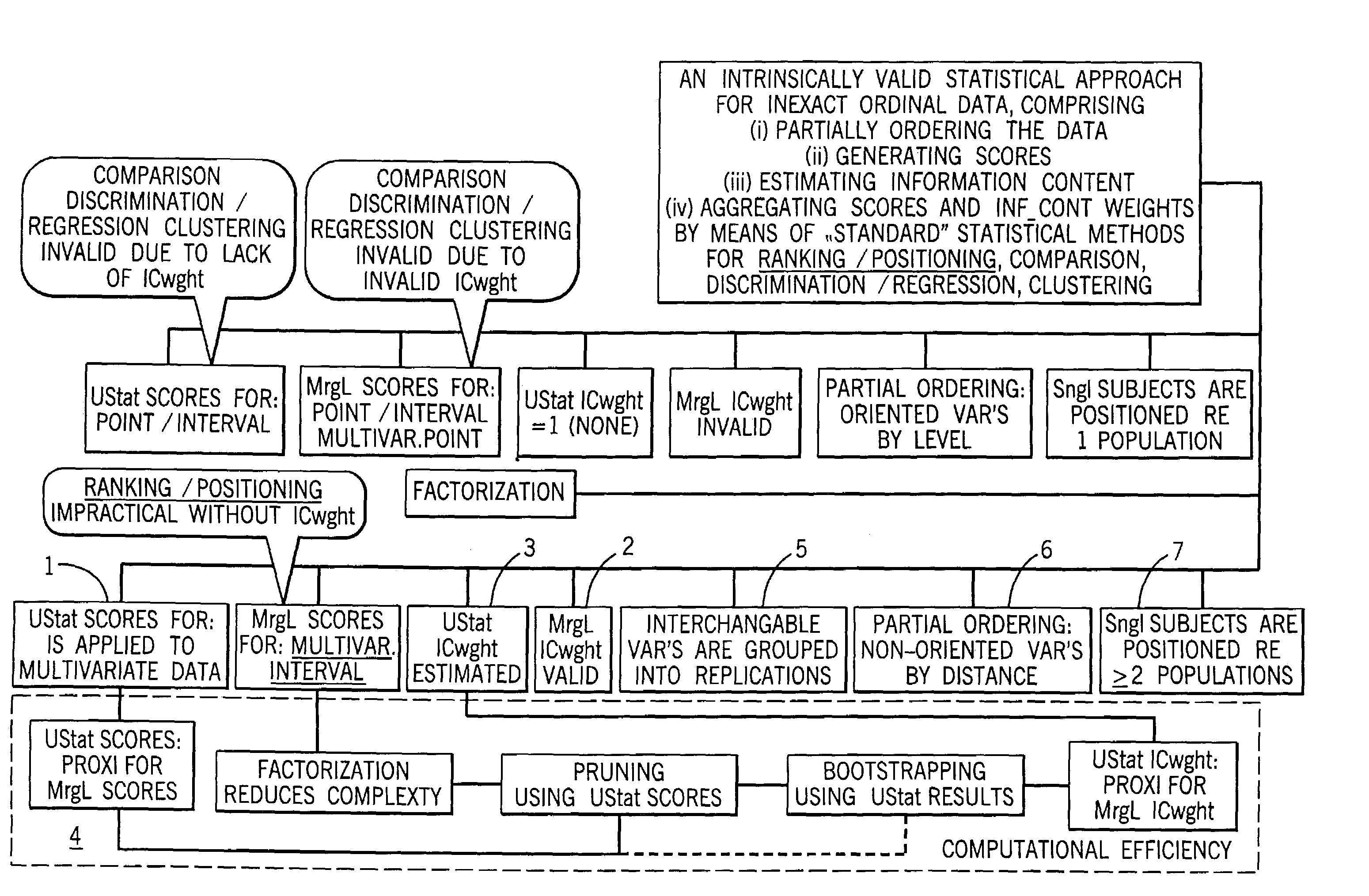
A method of analysis including an intrinsically valid class of statistical methods for dealing with multivariate ordinal data. A decision support system that can (1) provide automated decision support in a transparent fashion (2) optionally be controlled by a decision maker, (3) provide for an evidence acquisition concept, including automatically increasing the content of an underlying database, and (4) provide a computationally efficient interactive distributed environment. The method is exemplified in the context of assisted diagnostic support.
Owner:THE ROCKEFELLER UNIV
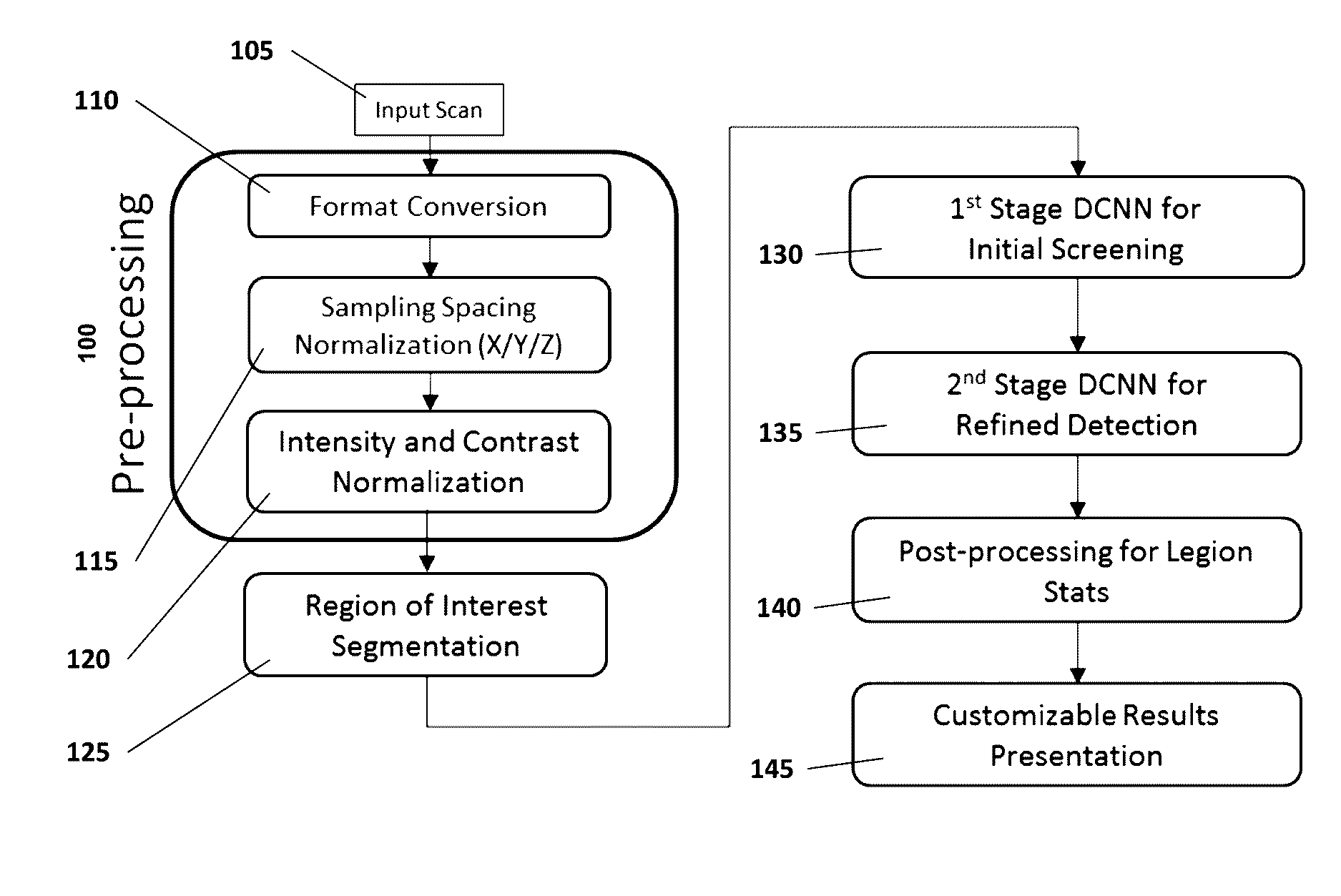
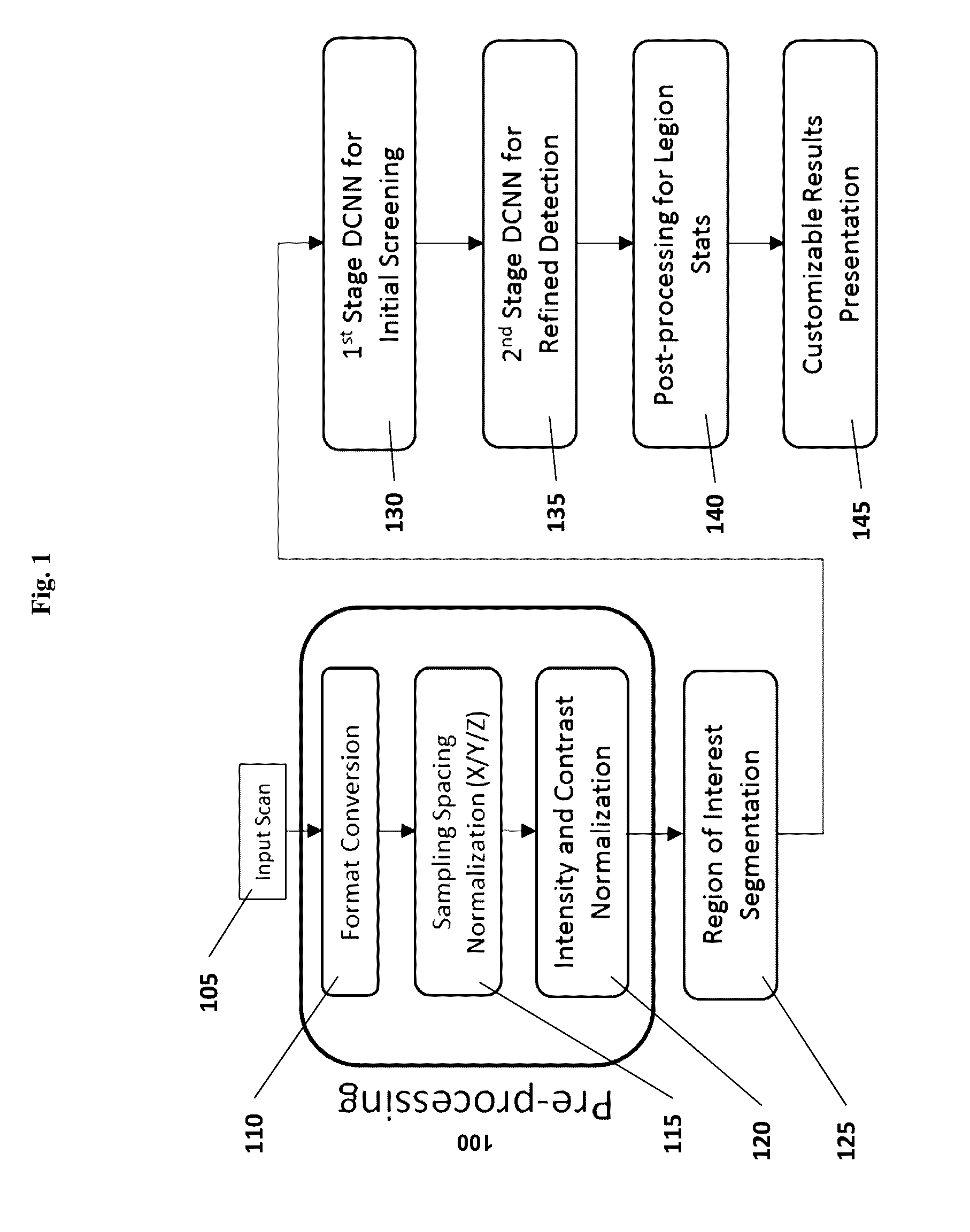
Computer-aided diagnosis system for medical images using deep convolutional neural networks
InactiveUS9589374B1Examination time can be shortenedImprove diagnostic accuracyUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementComputer visionAided diagnosis
Owner:12 SIGMA TECH
System and method for 3-D digital reconstruction of an oral cavity from a sequence of 2-D images
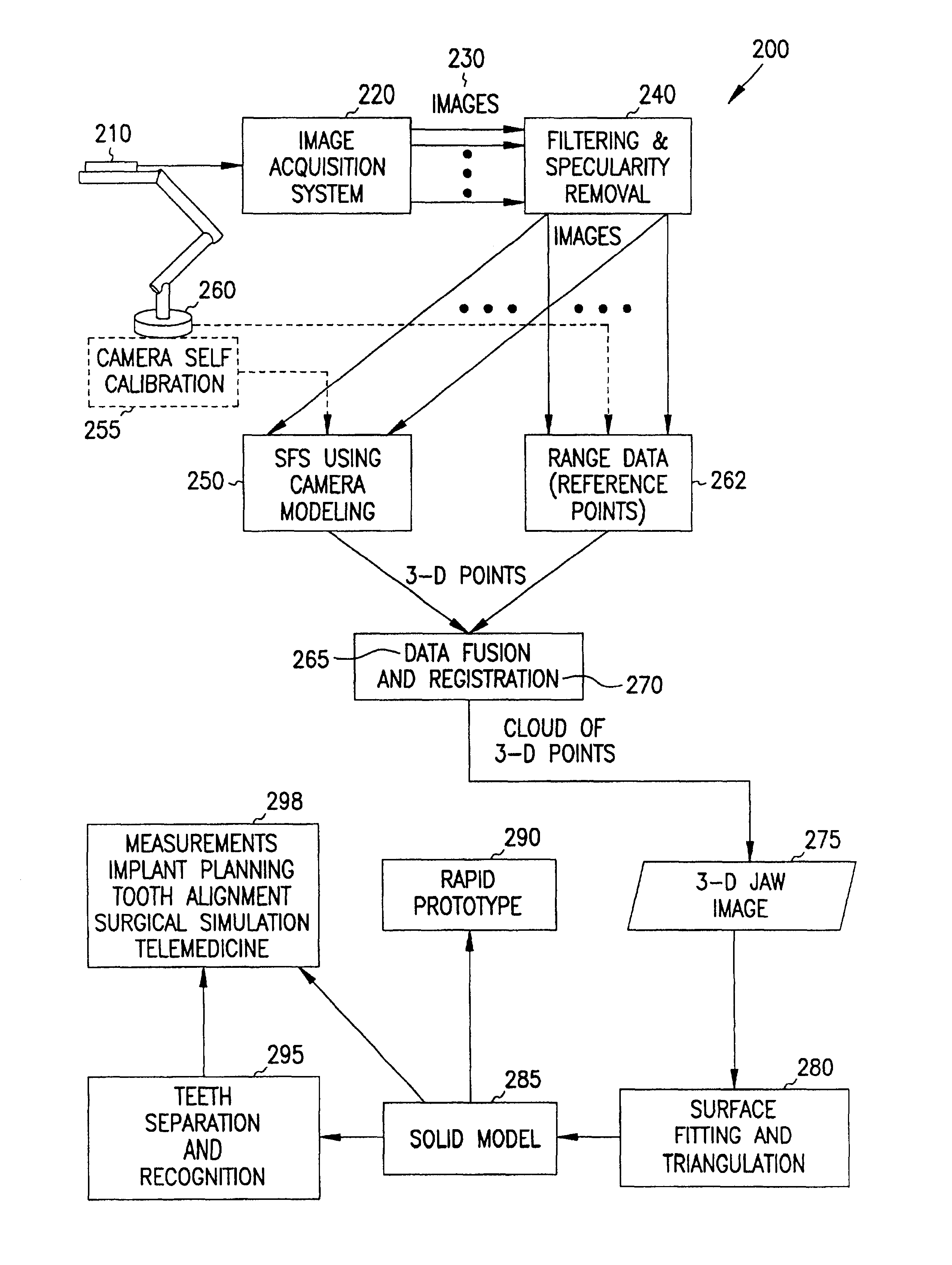
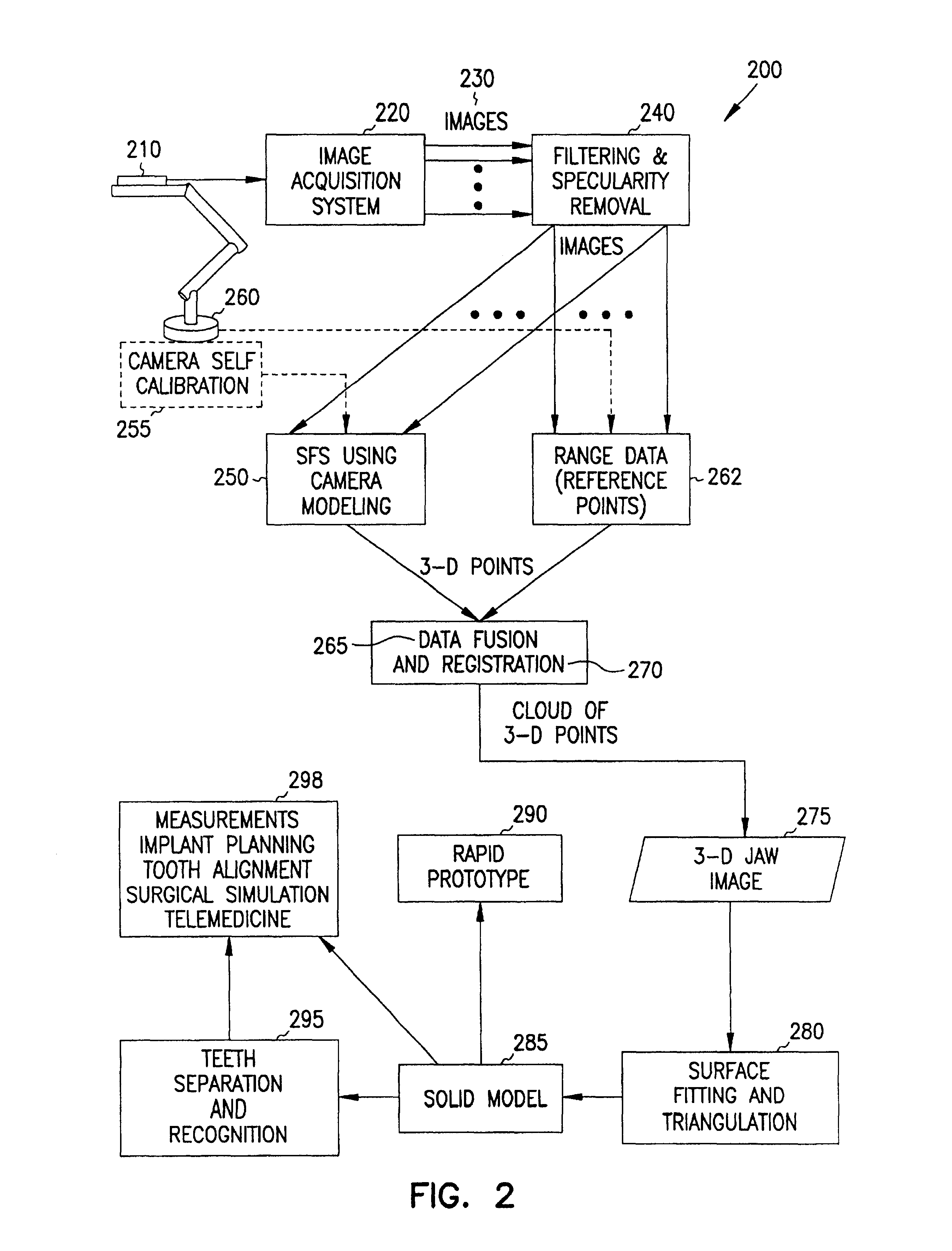
Systems and methods are provided through which a model-based vision system for dentistry which assists in diagnosis, treatment planning and surgical simulation. The present invention includes an integrated computer vision system that constructs a three-dimensional (3-D) model of the patient's dental occlusion using an intra-oral video camera. A modified shape from shading technique, using perspective projection and camera calibration, extracts the 3-D information from a sequence of two-dimensional images of the jaw. Data fusion of range data and 3-D registration techniques develop a complete 3-D digital jaw model. Triangulation of the 3-D digital model is then performed, and optionally, a solid 3-D model is reconstructed.
Owner:UNIV OF LOUISVILLE RES FOUND INC
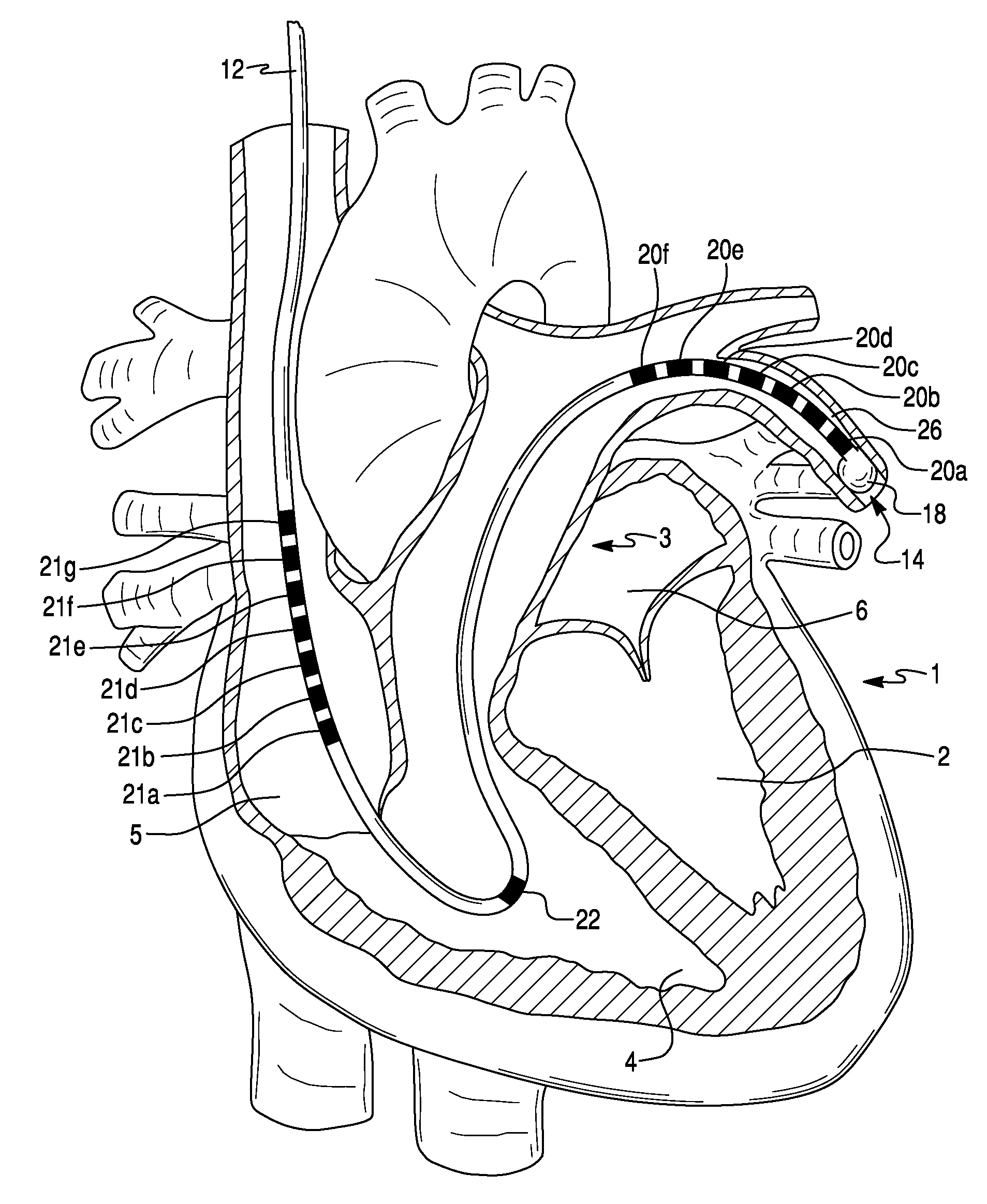
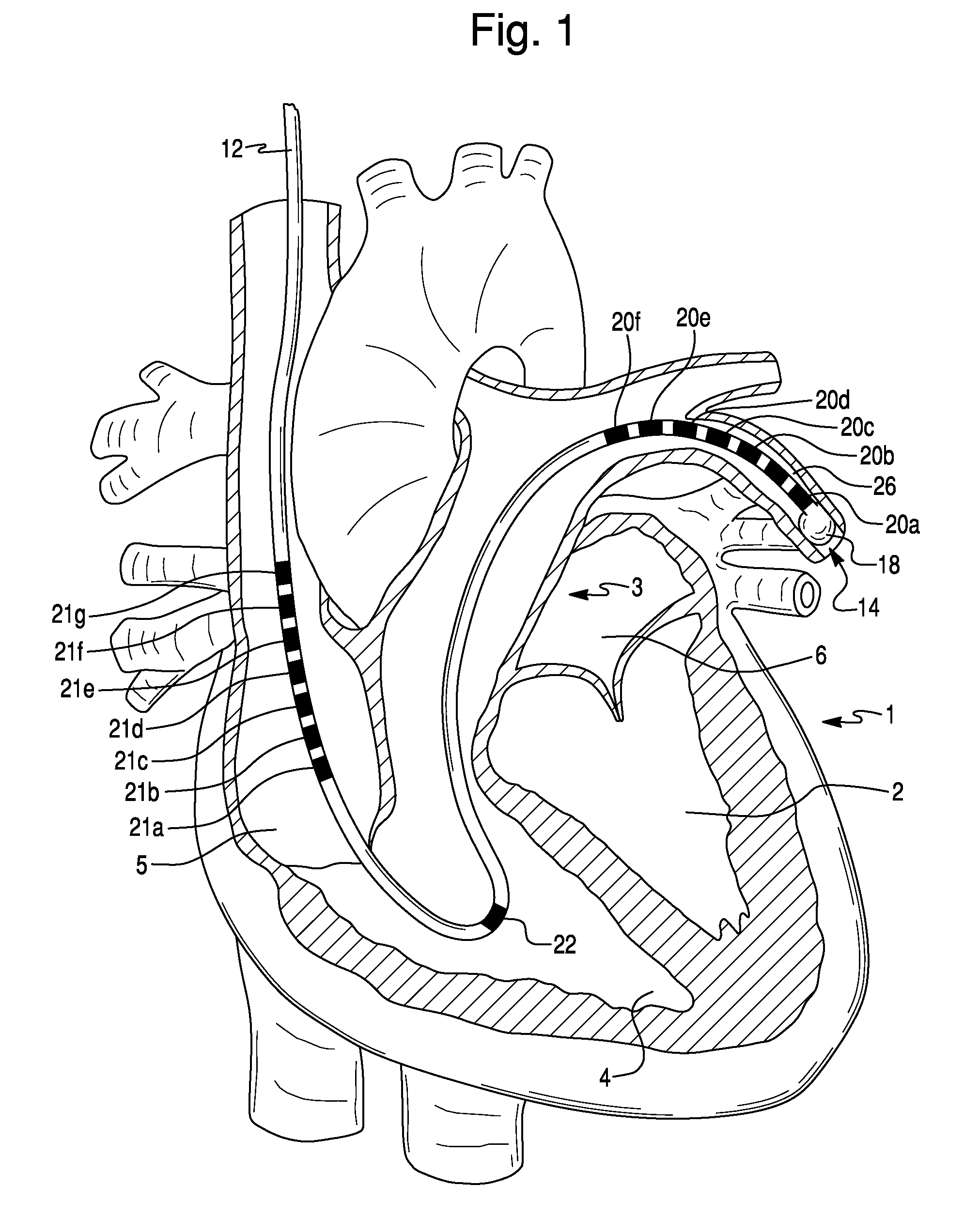
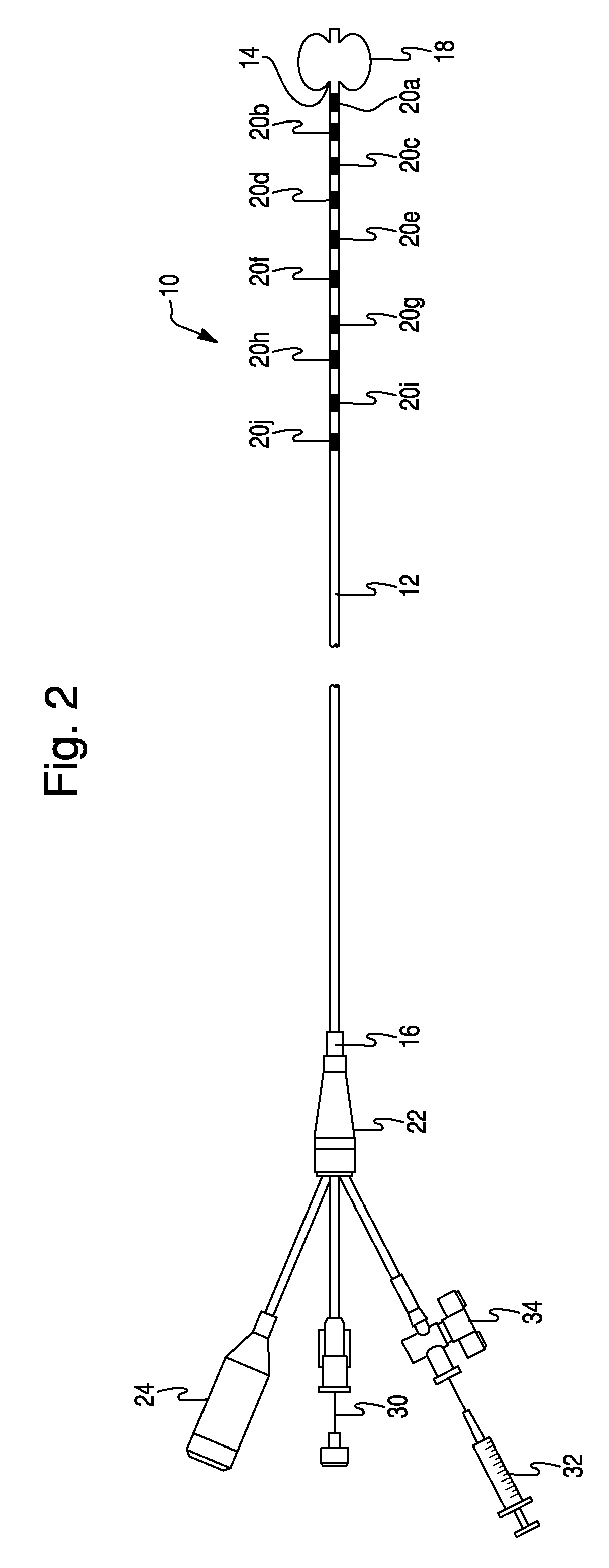
Method For Simultaneous Bi-Atrial Mapping Of Atrial Fibrillation
InactiveUS20070232949A1High resolutionFast informationElectrotherapyElectrocardiographyCardiac pacemaker electrodeDisplay device
A method for diagnosing and mapping atrial fibrillation correlates recordings of electrical activity from intracardiac multielectrode catheters with the locations of electrodes within the heart to obtain a global mapping of cardiac electrical activity. Time delay and / or amplitude information in the recorded electrical activities is fused with electrode location information to generate a display on a 3-D anatomical template of the heart. Time delay and / or amplitude information is displayed using color code and / or lines of equal value, to aid diagnosis and localization of electrical activity irregularities. Mapping of atrial fibrillation enables physicians to treat arrhythmia by ablation, pacing, shock therapy and / or drugs at initiation or during an episode based on therapy delivery at critical mapped locations for arrhythmia onset or maintenance. Locations for placement of pacing leads and pacemaker timing parameters may also be obtained from the display.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
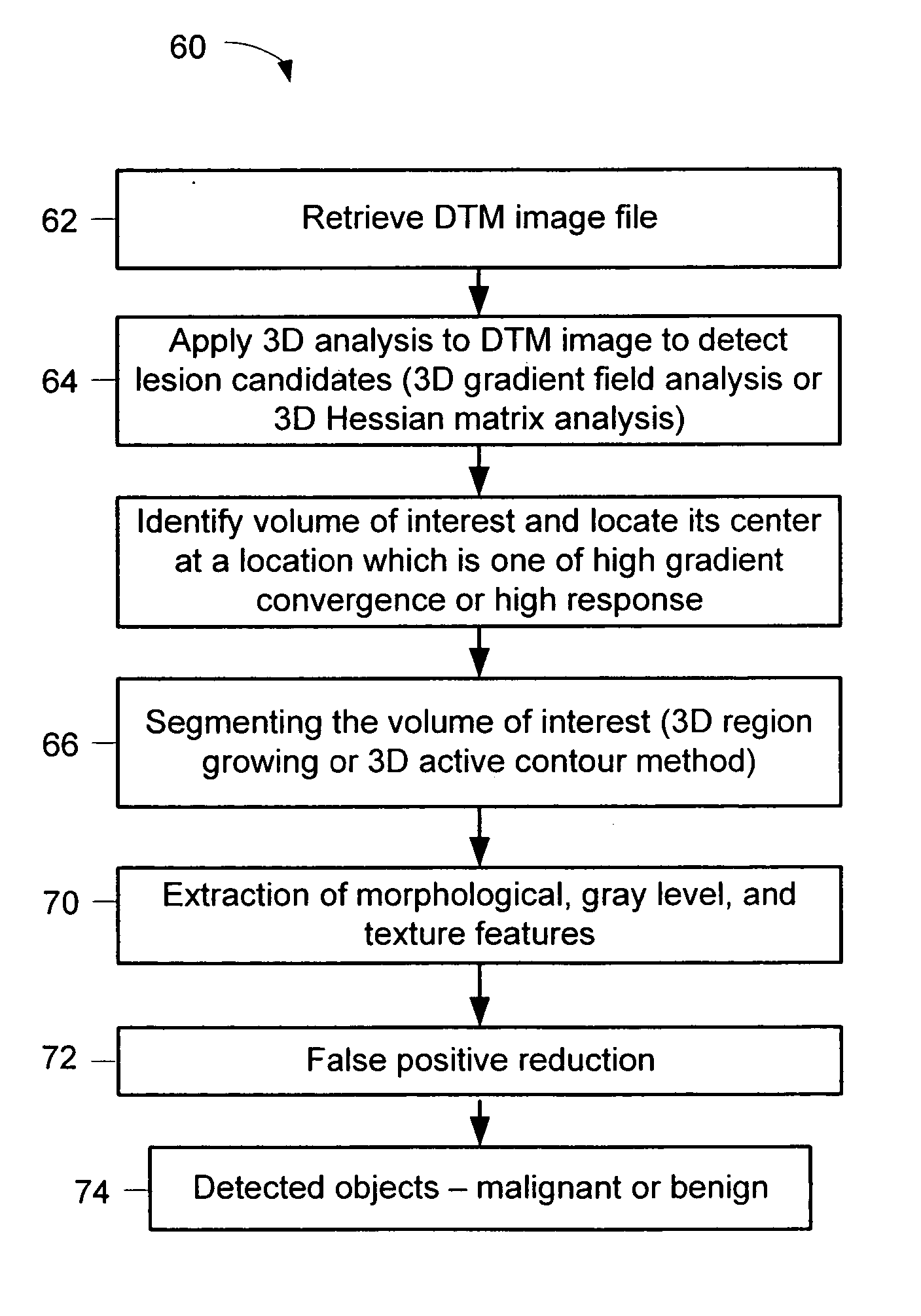
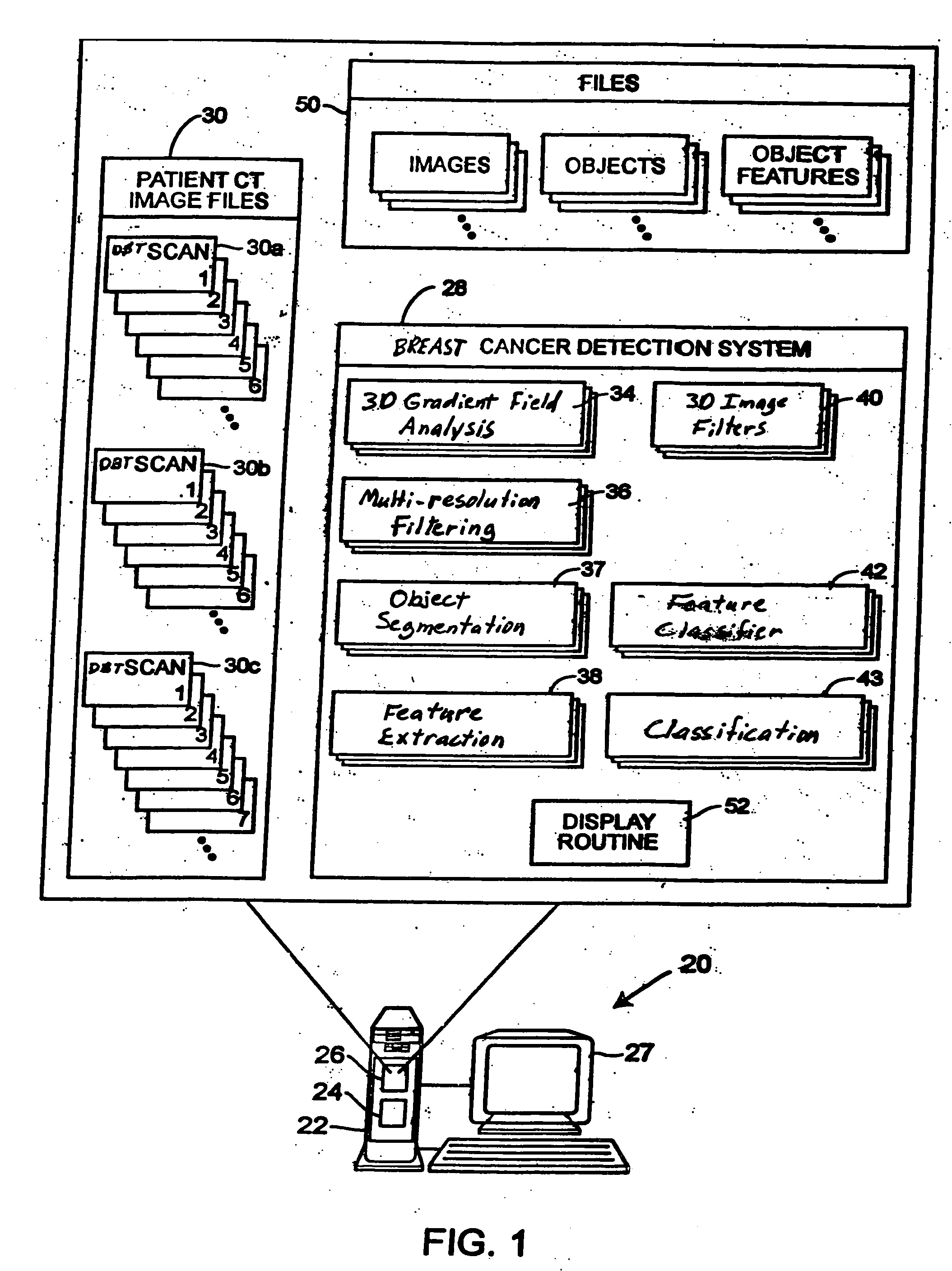
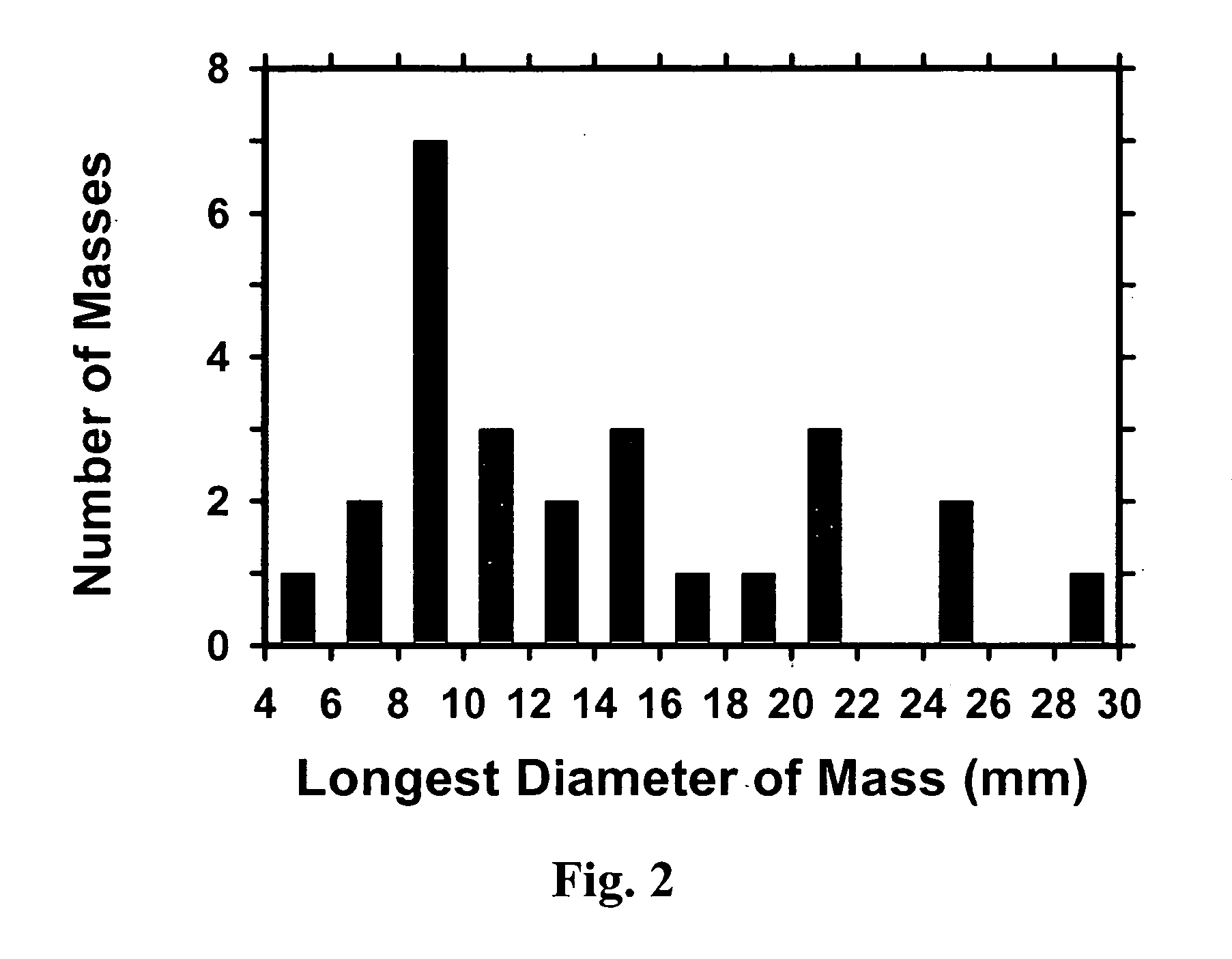
Computerized detection of breast cancer on digital tomosynthesis mammograms
InactiveUS20060177125A1Improve breast cancer detectionExtension of timeImage enhancementImage analysisTomosynthesisGray level
A method for using computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) for digital tomosynthesis mammograms (DTM) including retrieving a DTM image file having a plurality of DTM image slices; applying a three-dimensional gradient field analysis to the DTM image file to detect lesion candidates; identifying a volume of interest and locating its center at a location of high gradient convergence; segmenting the volume of interest by a three dimensional region growing method; extracting one or more three dimensional object characteristics from the object corresponding to the volume of interest, the three dimensional object characteristics being one of a morphological feature, a gray level feature, or a texture feature; and invoking a classifier to determine if the object corresponding to the volume of interest is a breast cancer lesion or normal breast tissue.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
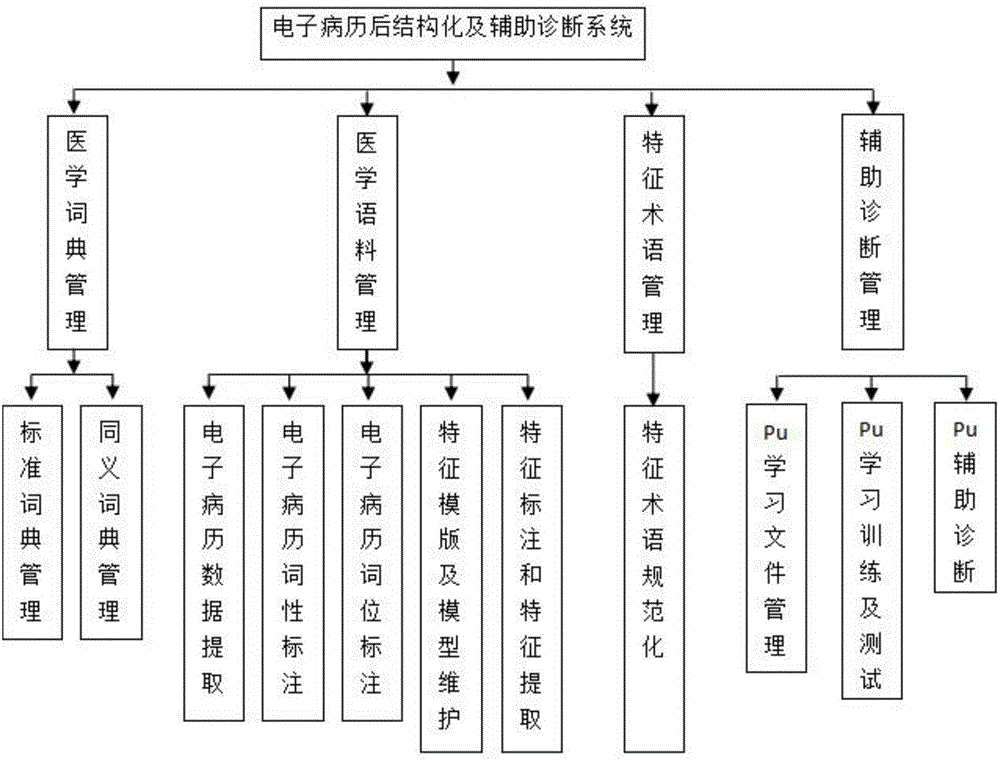
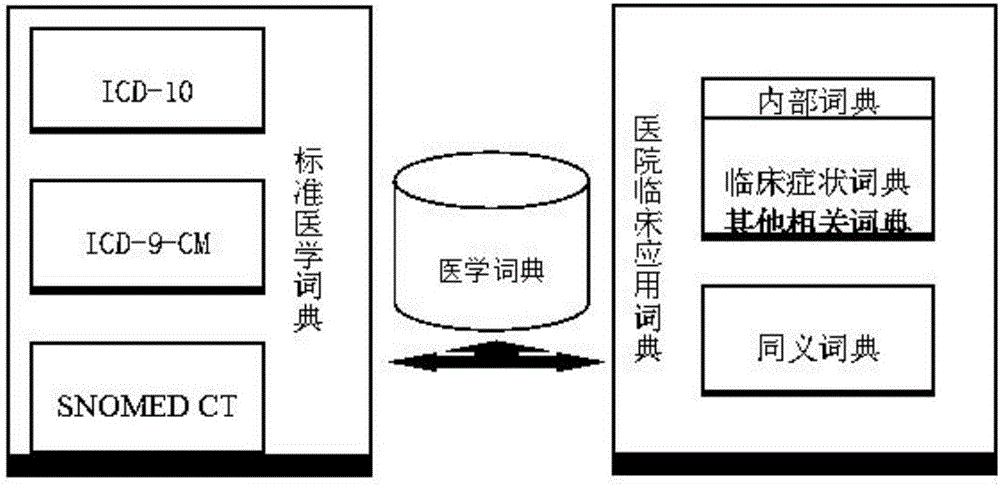
Realization method and system for electronic medical record post-structuring and auxiliary diagnosis
The invention relates to a realization method and system for electronic medical record post-structuring and auxiliary diagnosis. A combination mode of multiple types of distance measurement is used: a character string editing distance refers to a minimum number of replacement, insertion and deletion operations required for converting a character into another character string; a Jaro-Winkler distance measures similarity between two character strings and is used for repeated recording detection; a geometric mean value of a Chinese character distance and a Chinese character input method is adopted as comprehensive similarity measurement for measuring similarity between characteristic texts; characteristic ranking is realized by using a TF-IDF method and is used for assessing the importance of characteristic terms relative to documents in a file set or a corpus library, and the importance of the characteristic terms is in direct proportion to an occurrence frequency in the documents and is in inverse proportion to an occurrence document in the corpus library; and files are converted to be in a file format of PU learning of a positive example data set and an unlabelled data set according to the generated characteristic terms, and through the PU learning, the system automatically recommends related diagnoses for clinical medical personnel to refer.
Owner:刘勇
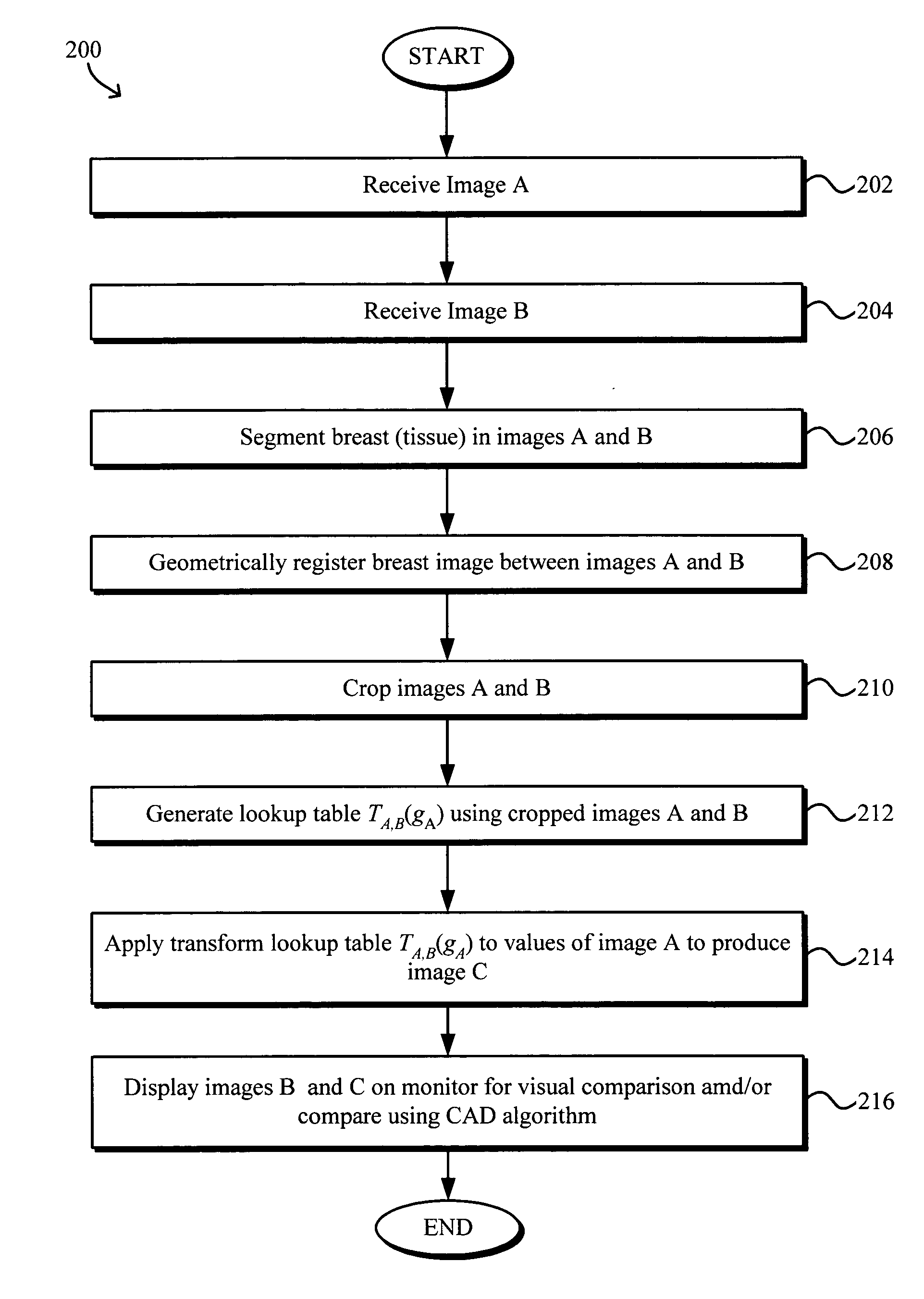
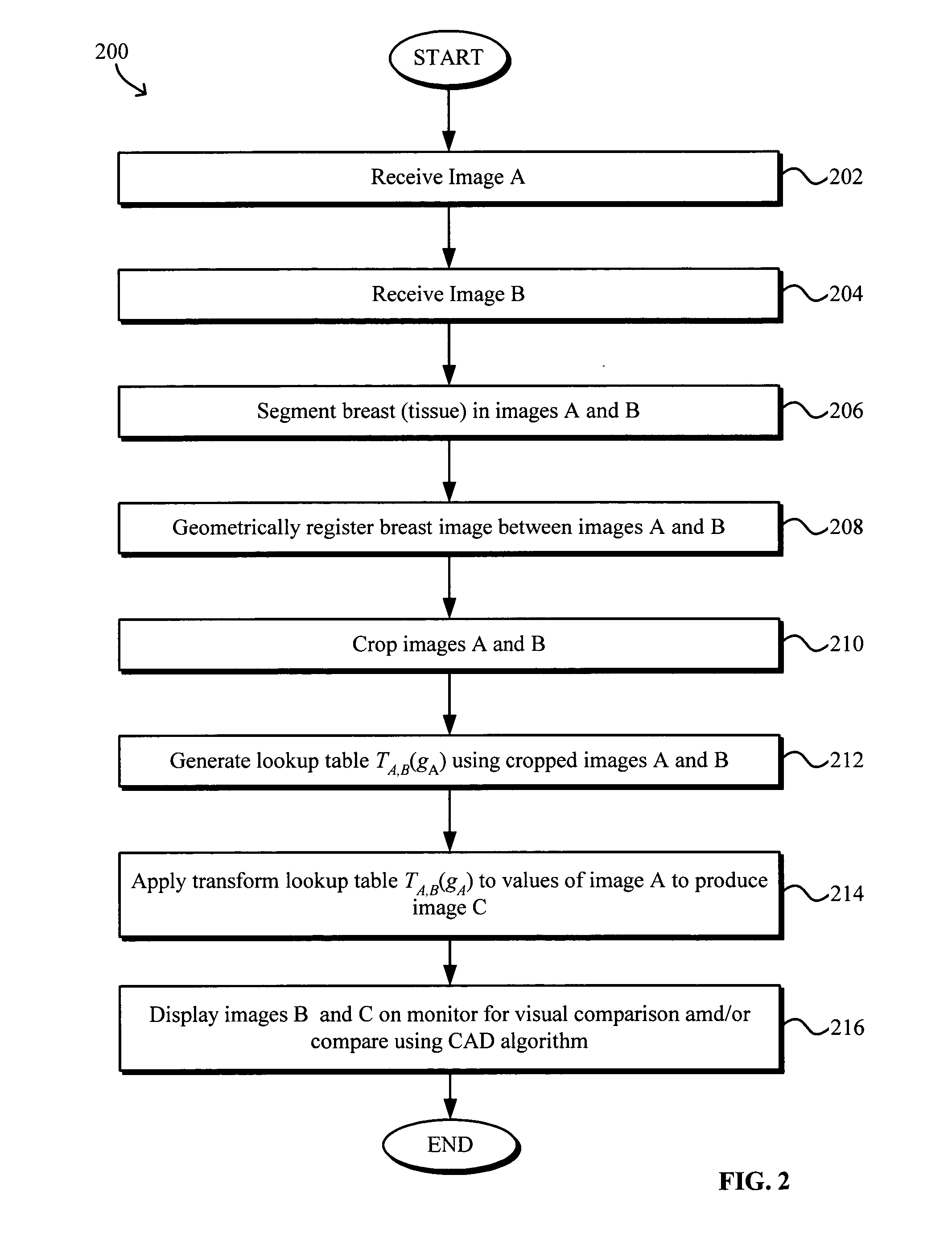
Model-based grayscale registration of medical images
ActiveUS20050013471A1Increase speedImprove reliabilityImage enhancementImage analysisPixel value differenceVisual perception
Numerical image processing of two or more medical images to provide grayscale registration thereof is described, the numerical image processing algorithms being based at least in part on a model of medical image acquisition. The grayscale registered temporal images may then be displayed for visual comparison by a clinician and / or further processed by a computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) system for detection of medical abnormalities therein. A parametric method includes spatially registering two images and performing gray scale registration of the images. A parametric transform model, e.g., analog to analog, digital to digital, analog to digital, or digital to analog model, is selected based on the image acquisition method(s) of the images, i.e., digital or analog / film. Gray scale registration involves generating a joint pixel value histogram from the two images, statistically fitting parameters of the transform model to the joint histogram, generating a lookup table, and using the lookup table to transform and register pixel values of one image to the pixel values of the other image. The models take into account the most relevant image acquisition parameters that influence pixel value differences between images, e.g., tissue compression, incident radiation intensity, exposure time, film and digitizer characteristic curves for analog image, and digital detector response for digital image. The method facilitates temporal comparisons of medical images such as mammograms and / or comparisons of analog with digital images.
Owner:HOLOGIC INC
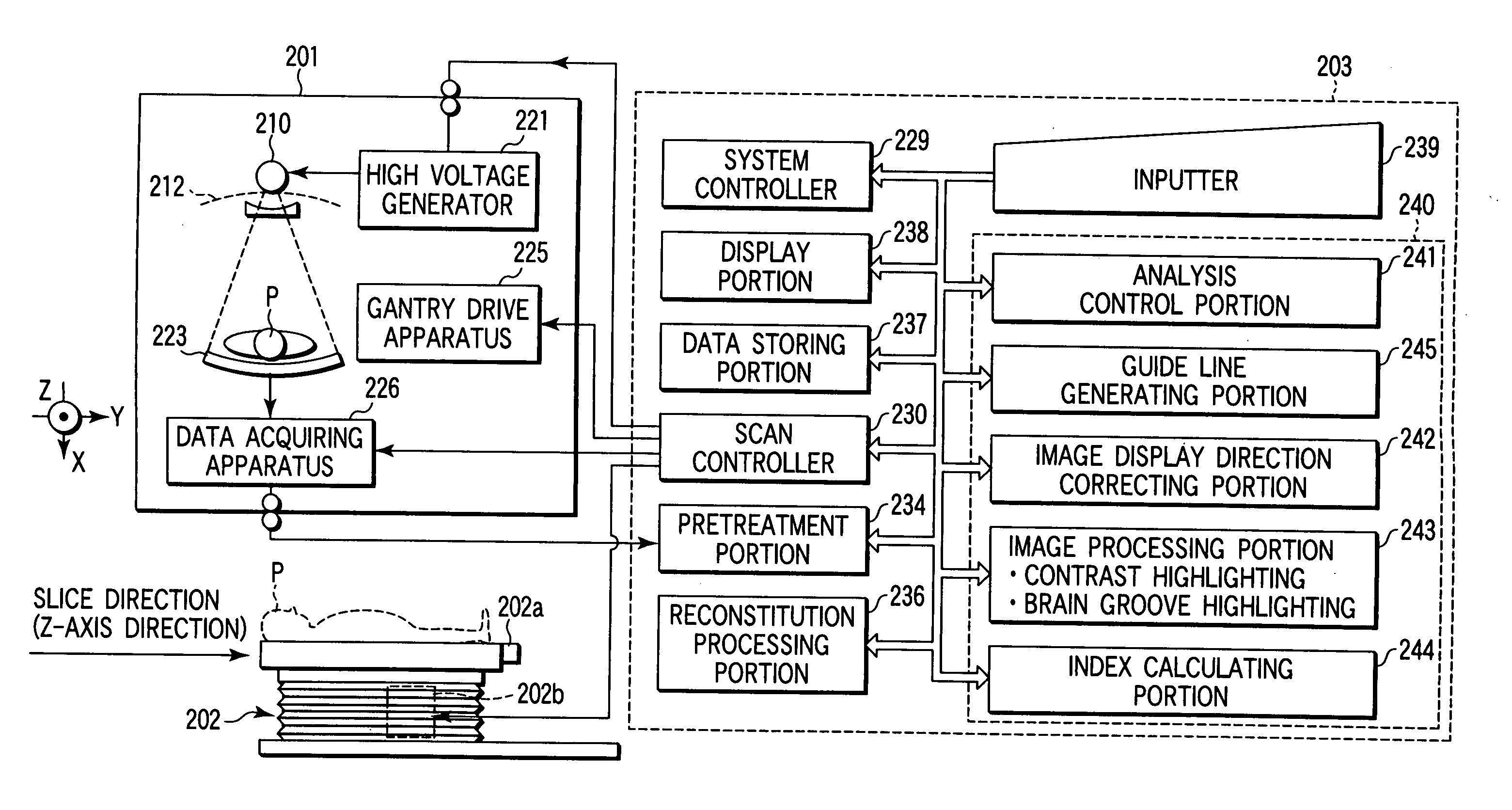
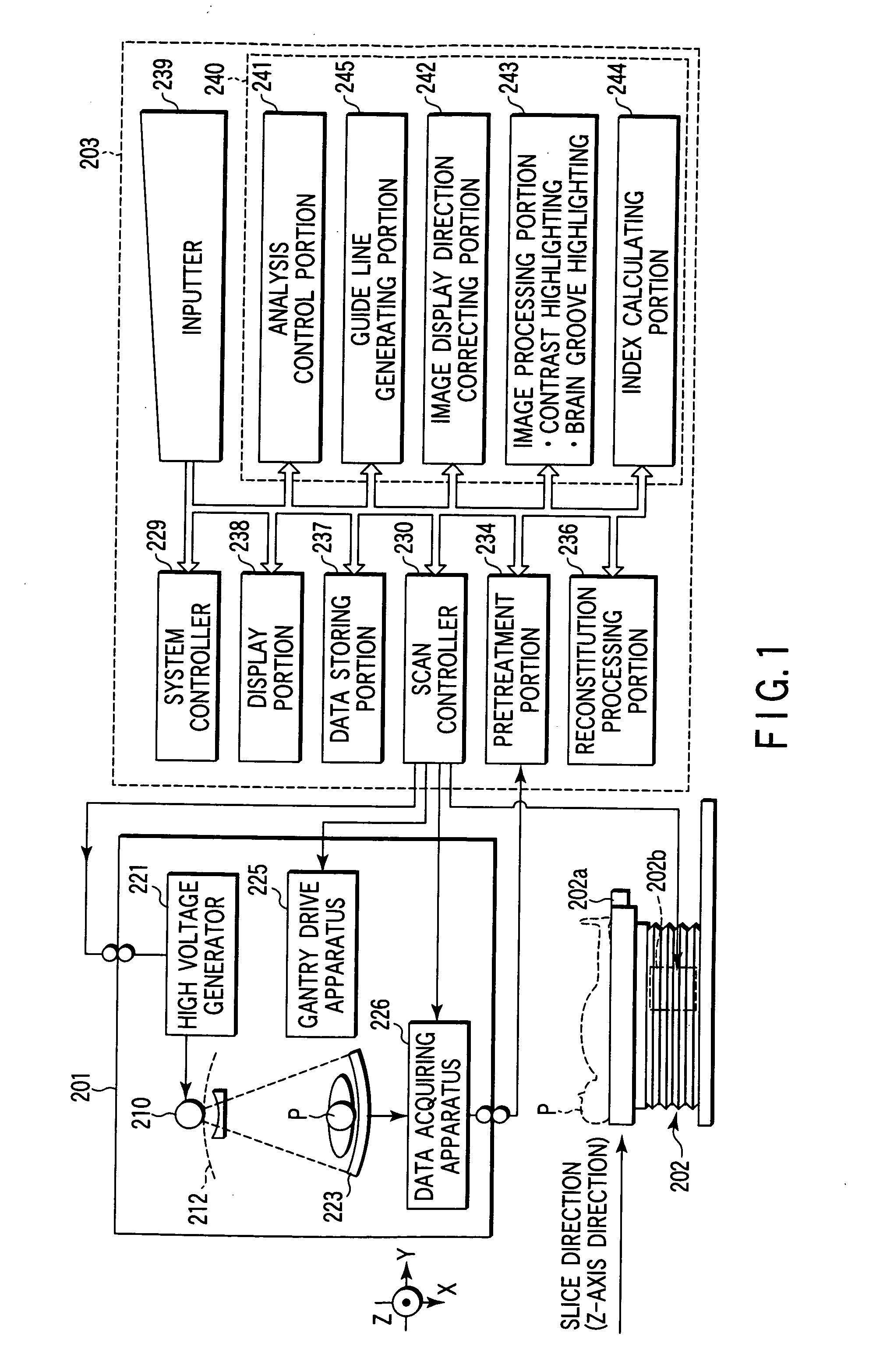
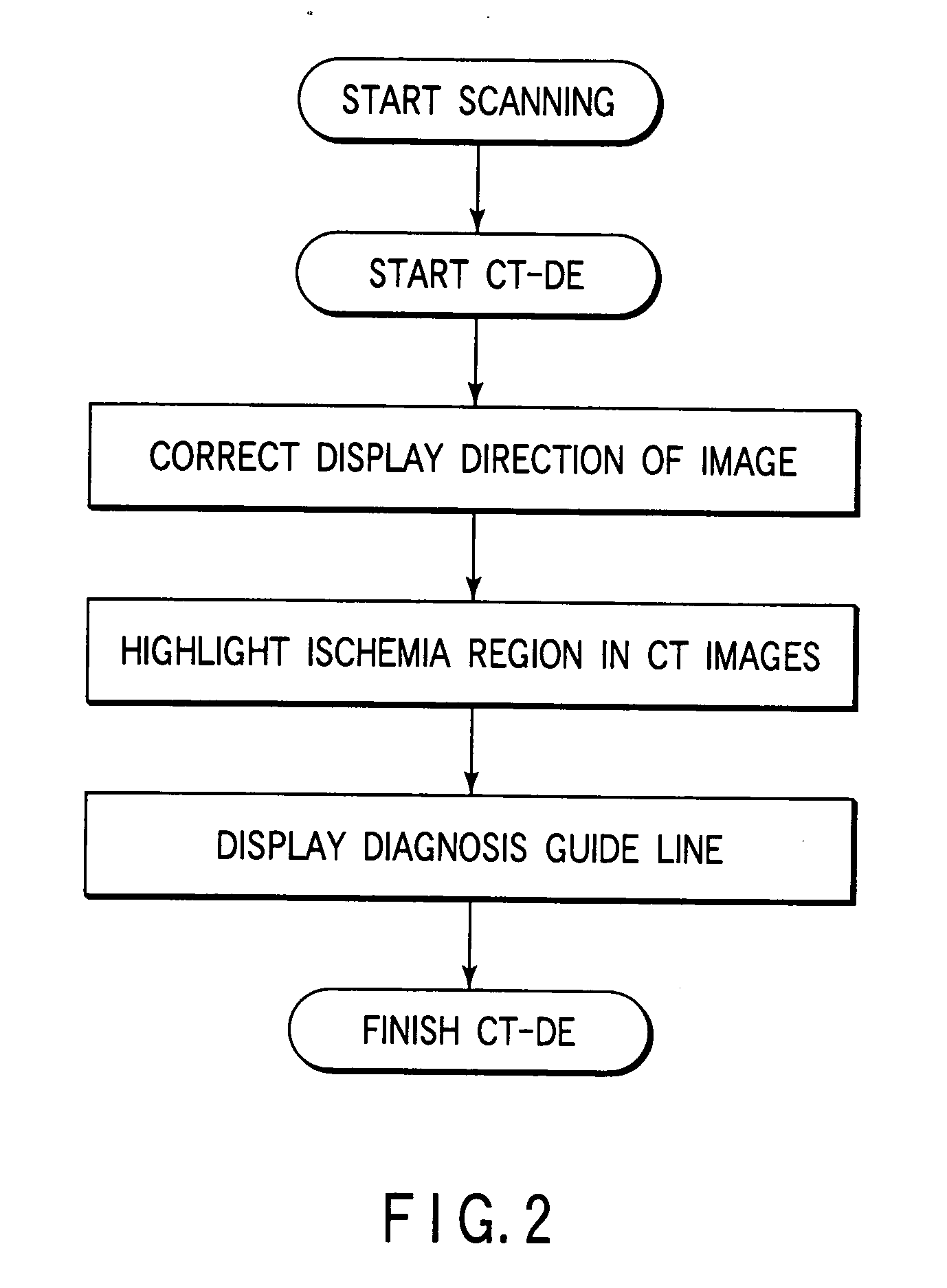
Cerebral ischemia diagnosis assisting apparatus, X-ray computer tomography apparatus, and apparatus for aiding diagnosis and treatment of acute cerebral infarct
A cerebral ischemia diagnosis assisting apparatus comprises a storing portion for storing multi-slices or volume data with regard to the head portion of a subject, an image generating portion for generating a tomography image of a brain from the multi-slices or the volume data, an image processing portion for processing the tomography image for generating a contrast highlighting image and a brain sulci highlighting image or either thereof, and a display portion for displaying the tomography image along with the contrast highlighting image and the brain sulci highlighting image.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA +2
Methods for modulating macrophage proliferation using polyamine analogs
Methods for modulating macrophage proliferation in an individual afflicted with or at risk for a macrophage-associated disease are provided. The methods employ a polyamine analog, or salt or protected derivative thereof. Macrophage proliferation has been implicated in a number of serious disorders, including AIDS (HIV)-associated dementia, AIDS-associated non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, and Alzheimer's disease. The invention also provides methods for aiding diagnosis and monitoring therapy of a macrophage-associated non-HIV associated dementia, especially Alzheimer's disease. The invention also provides methods of delaying development of macrophage-associated non-HIV associated dementias, including Alzheimer's disease, which entail administration of an agent which modulates macrophage proliferation.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
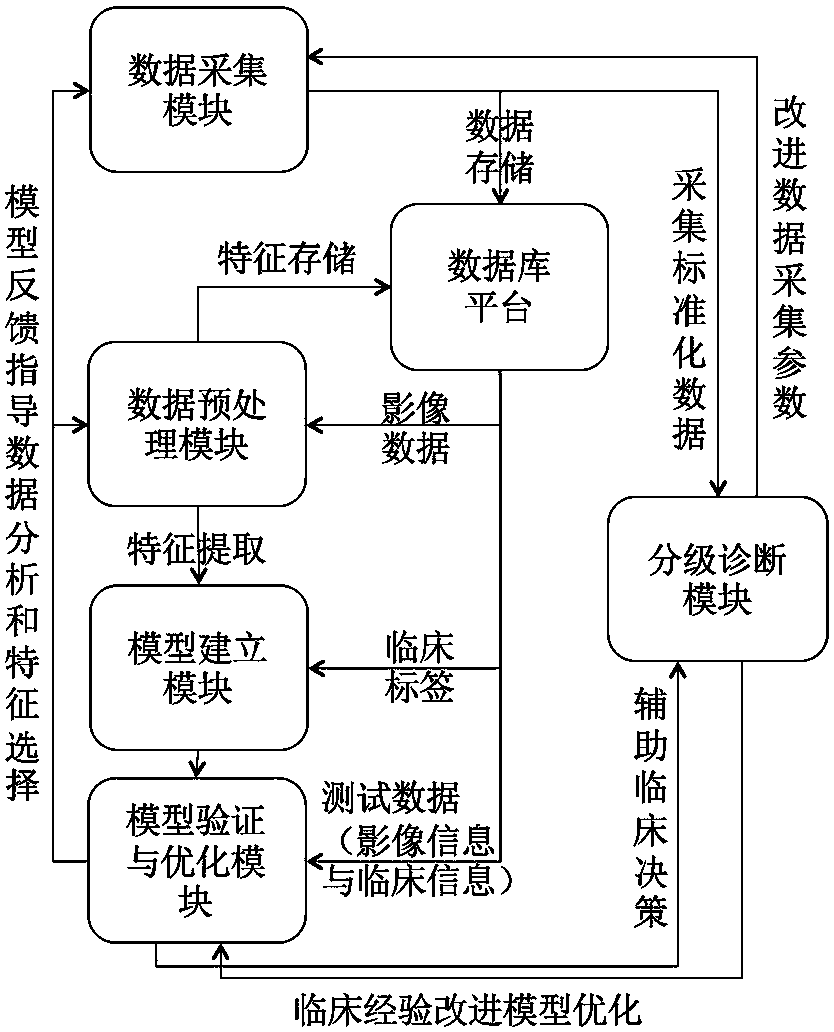
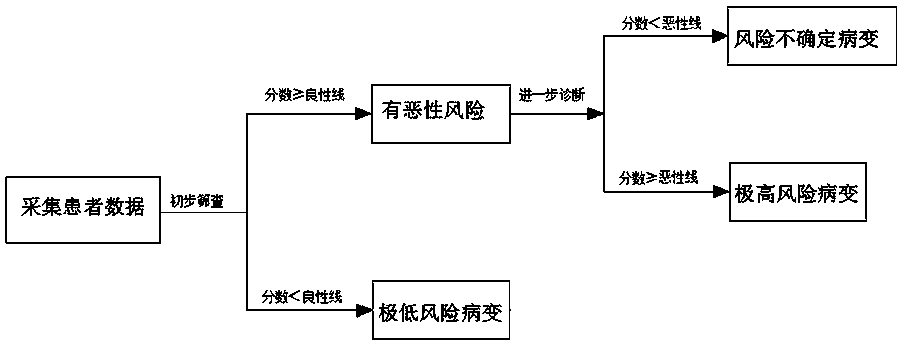
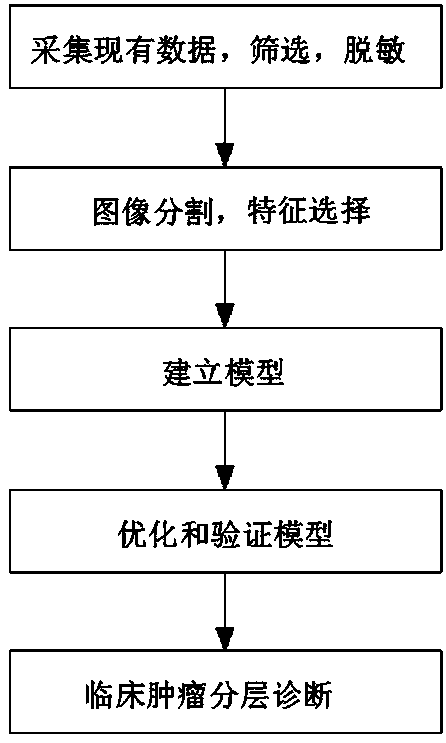
Tumor malignant risk stratification auxiliary diagnosis system of artificial intelligence medical image
ActiveCN109166105AIncreased diagnostic confidenceReduce anxietyImage enhancementImage analysisLower riskData acquisition
The invention discloses a tumor malignant risk stratification auxiliary diagnosis system of an artificial intelligence medical image. The system comprises a data acquisition module, a data preprocessing module, a model establishment module, a model verification and optimization module, a stratification diagnosis module and a database platform. The tumor malignant risk stratification auxiliary diagnosis system of the invention is based on artificial intelligence technology, successive stratification of the malignant risk of the tumor can be achieved, the clinical diagnosis thinking is simulated, based on the high-precision ability of detecting benign lesions and malignant tumors of artificial intelligence model, and the space-occupying lesions with definite imaging features are diagnosed automatically. As a result, the system can substantially assist the clinical management decision of space-occupying lesions, improve the existing work flow of clinical diagnosis, increase the confidenceof doctors in diagnosis, reduce the work pressure, reduce the anxiety of patients with low-risk malignant lesions, greatly improve the diagnostic rate of benign lesions and malignant tumors, and hopefully realize the landing implementation of artificial intelligence clinical auxiliary diagnosis.
Owner:NANJING GENERAL HOSPITAL NANJING MILLITARY COMMAND P L A
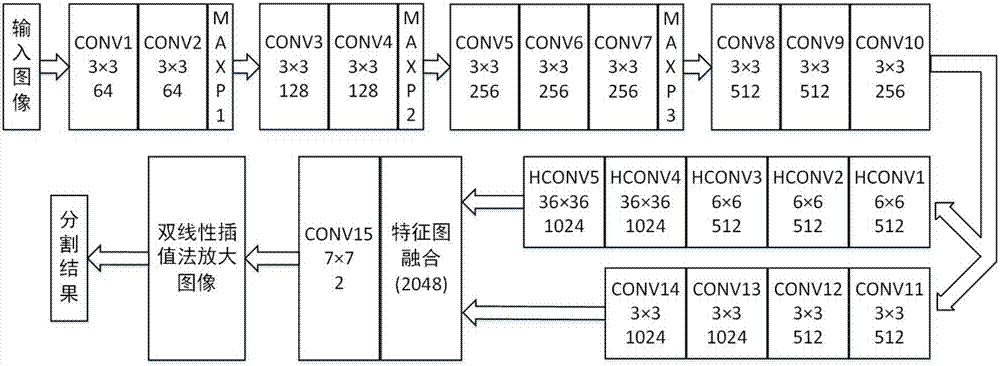
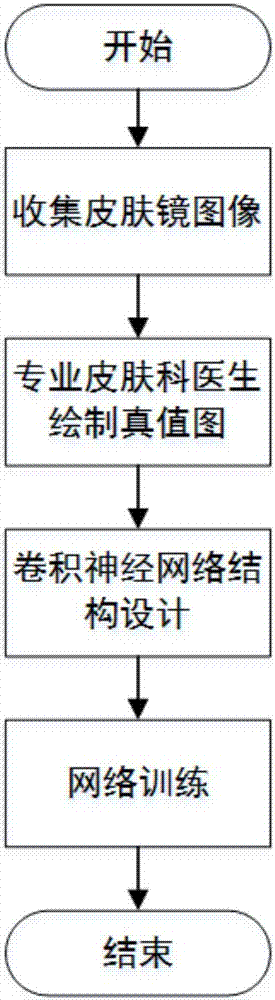
Dermoscopy image automatic segmentation method based on full convolutional neural network
ActiveCN107203999AAccurate segmentationEasy to operateImage enhancementImage analysisAutomatic segmentationNerve network
The present invention provides a dermoscopy image automatic segmentation method based on a full convolutional neural network. The method comprises the following four steps: 1: obtaining of dermoscopy images and true value graphs; 2: performing structure design of a full convolutional neural network; 3: performing design of feature fusion and a per-pixel segmentation method; and 4: performing network training and segmentation. According to the steps mentioned above, an end-to-end depth convolutional neural network is obtained through training to perform accurate segmentation of the dermoscopy images and allow a small area skin lesion area to be effective so as to solve actual problems that the skin lesion area segmentation is not good to influence the subsequent diagnosis accuracy in the dermatology computer auxiliary diagnosis system.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
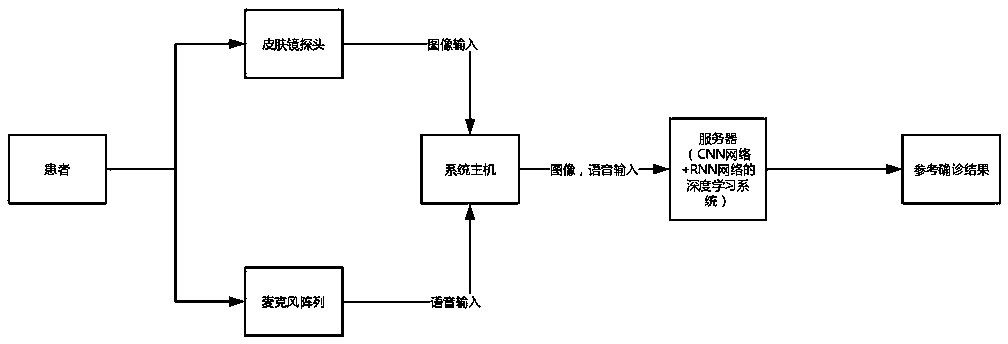
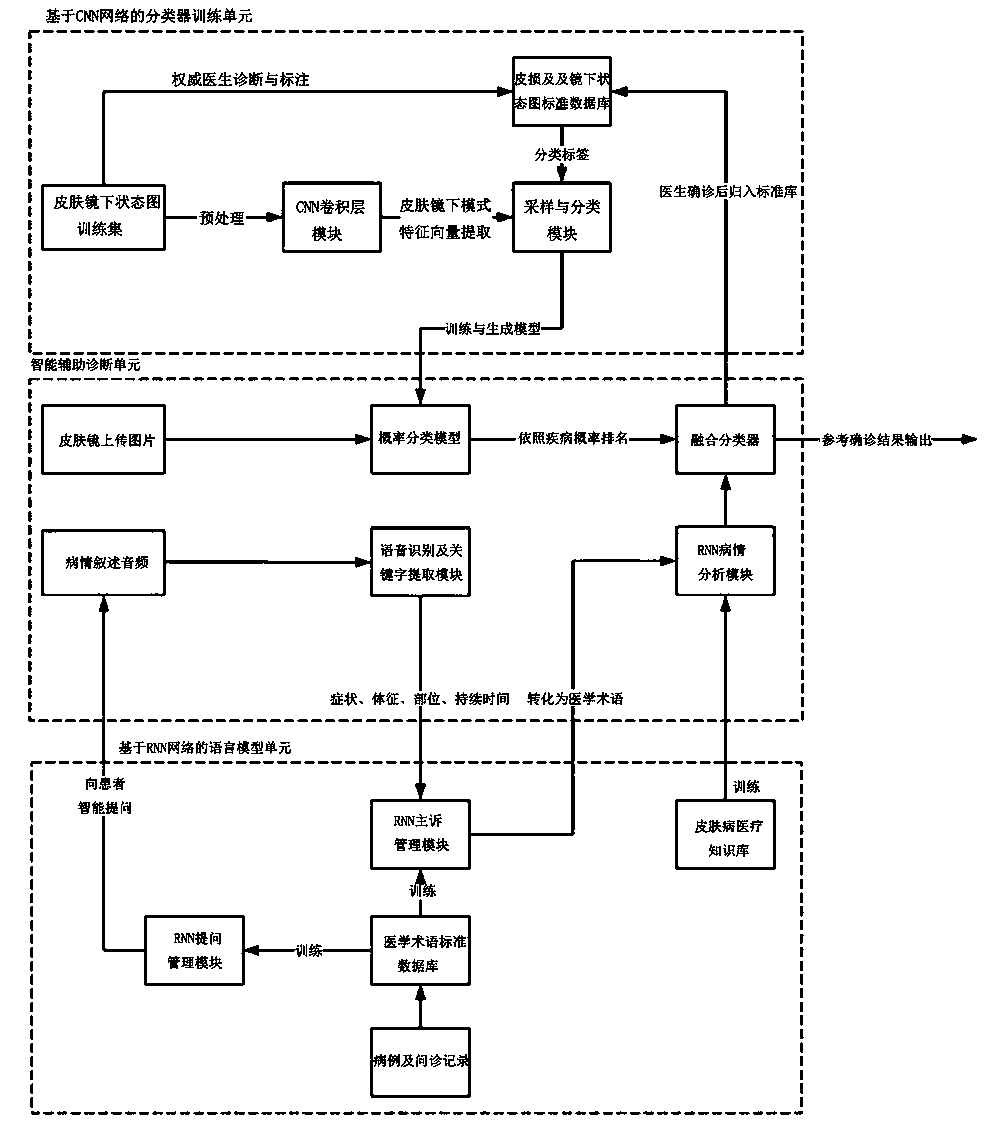
Deep learning based intelligent skin disease auxiliary diagnosis system
ActiveCN108198620AImprove accuracyAccurate identificationMedical communicationMedical data miningDiseasePattern recognition
The invention relates to a deep learning based intelligent skin disease auxiliary diagnosis system, which comprises a classifier training unit, a language model unit and an intelligent auxiliary diagnosis unit. The intelligent auxiliary diagnosis unit comprises an image acquisition module, a voice interrogation module, a voice recognition and keyword extraction module, a probability classificationmodel, a RNN condition analysis module and a fusion classifier. The classifier training unit comprises a state diagram training set under a dermatoscope, a state standard database under skin lesion and dermatoscope, a CNN network convolution module and a sampling and classifying module. The language model unit comprises a medical term standard library, a RNN questioning management module, a RNN chief complaint management module and a skin disease medical knowledge base. The auxiliary diagnosis system has advantages that by deep learning for classifying skin lesion images, probable results areinferred, then a pre-installed dermatoscope image and histodiagnosis tag database is retrieved for doctors' reference, and accordingly accuracy in skin disease diagnosis can be greatly improved.
Owner:洛阳飞来石软件开发有限公司
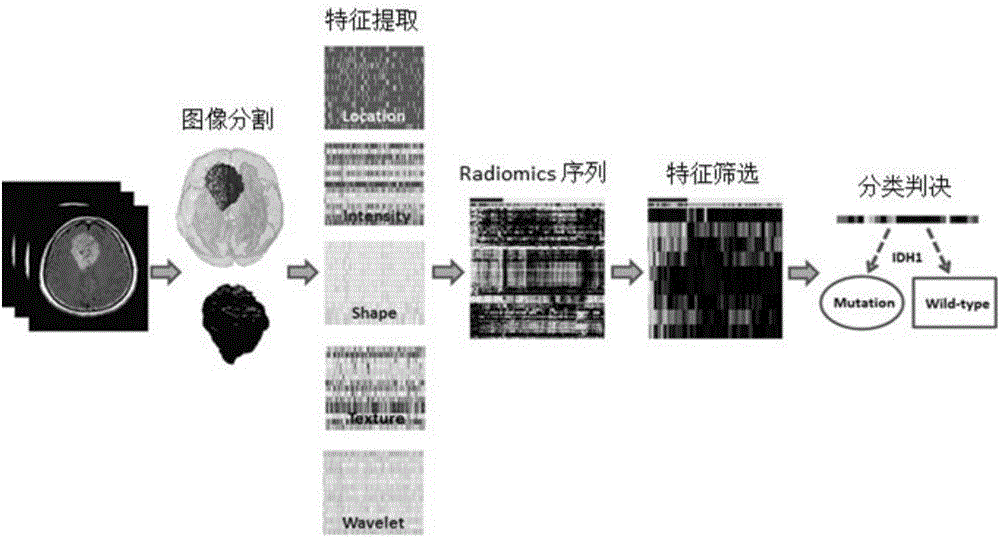
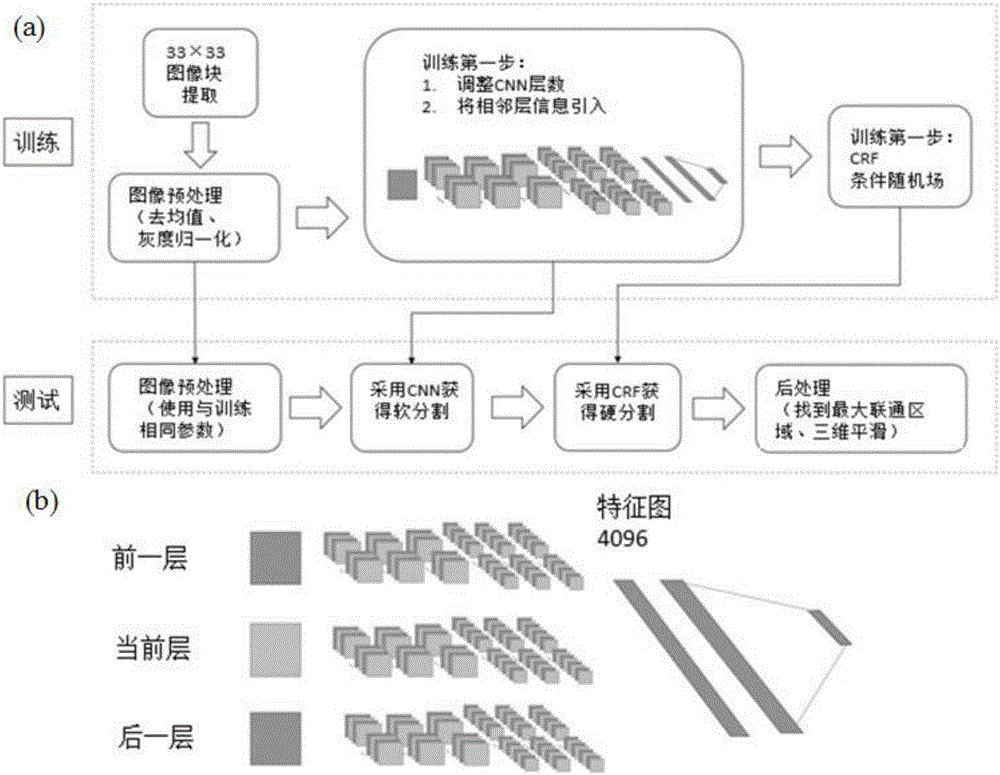
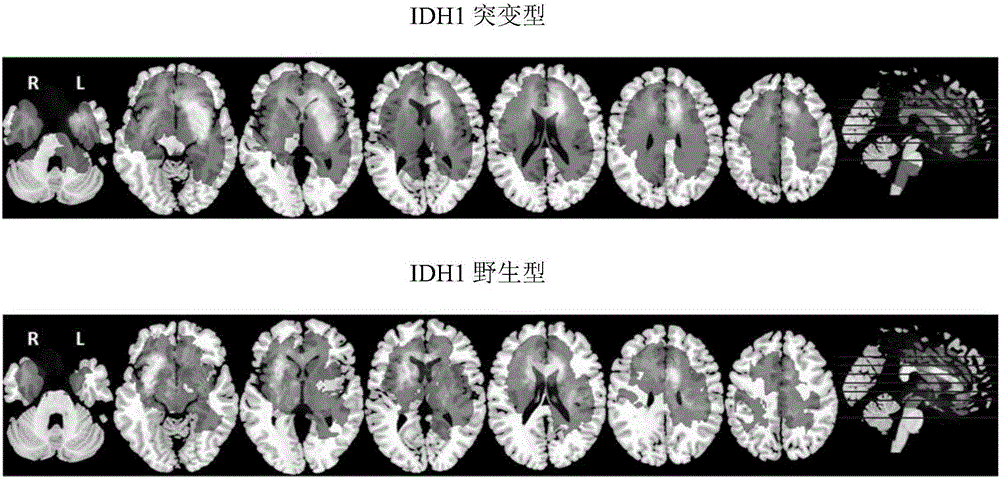
Brain glioma molecular marker nondestructive prediction method and prediction system based on radiomics
The invention belongs to the technical field of computer-aided diagnosis, and specifically relates to a brain glioma molecular marker nondestructive prediction method and a prediction system based on radiomics. The method comprises the following steps: adopting a three-dimensional magnetic resonance image automatic segmentation method based on a convolution neural network; registering a tumor obtained from segmentation to a standard brain atlas, and acquiring 116 position features of tumor distribution; getting 21 gray features, 15 shape features and 39 texture features through calculation; carrying out three-dimensional wavelet decomposition on the gray features and the texture features to get 480 wavelet features of eight sub-bands; acquiring 671 high-throughput features from the three-dimensional T2-Flair magnetic resonance image of each case; using a feature screening strategy combining p-value screening and a genetic algorithm to get 110 features highly associated with IDH1; and using a support vector machine and an AdaBoost classifier to get a classification of which the IDH1 prediction accuracy is 80%. As a novel method of radiomics, the method provides a nondestructive prediction scheme of important molecular markers for clinical diagnosis of gliomas.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
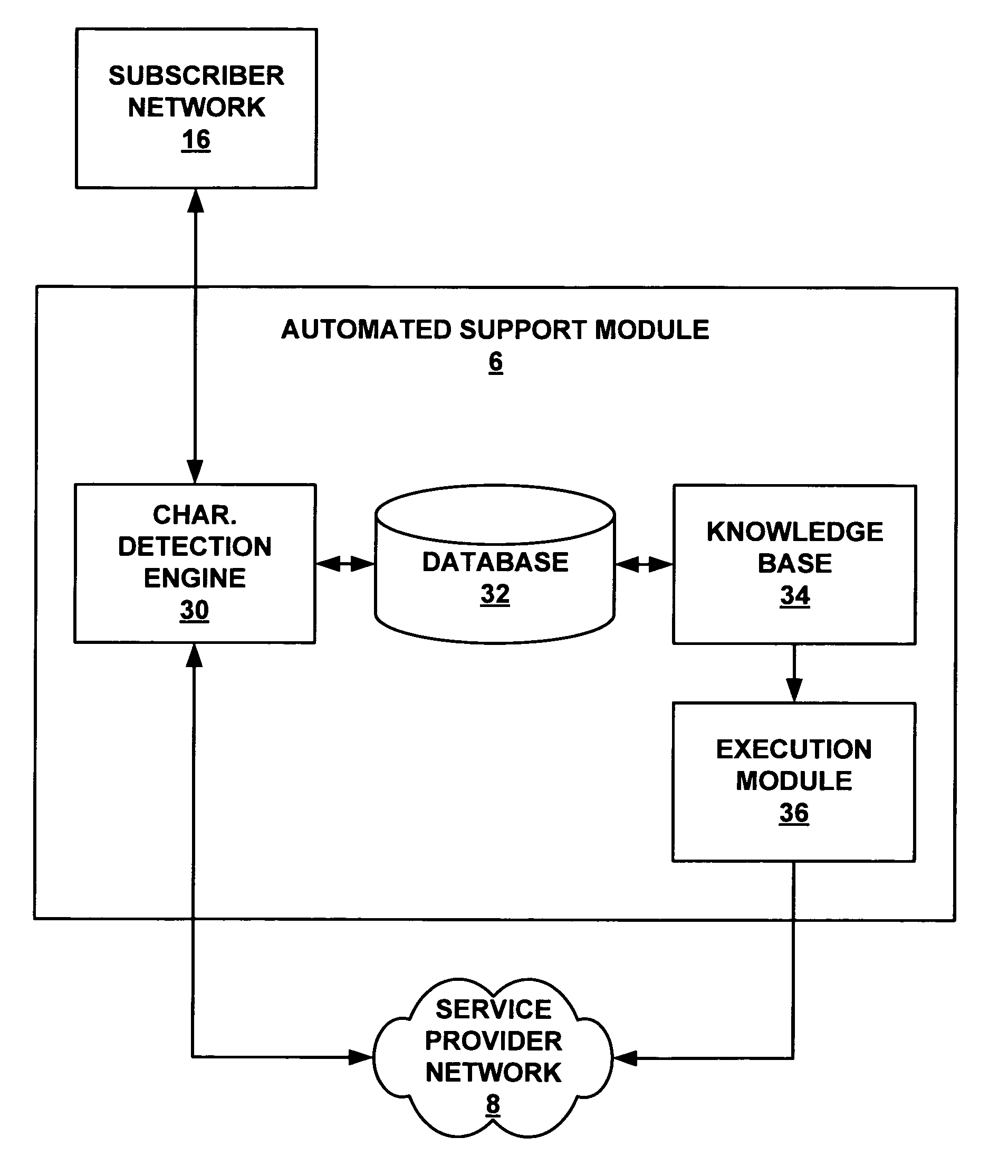
Analyzing network traffic to diagnose subscriber network errors
ActiveUS7916652B1View accuratelyError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTraffic capacityPacket loss
A service provider network includes an automated support module that receives stream of network packets from subscribers and separates this streams into packet flows for analysis. The automated support module may be an intermediate device that examines each packet flow to detect subscriber characteristics for each subscriber. The automated support module may apply a set of analysis rules to the detected characteristics to aid diagnosis of reported or potential network errors.
Owner:JUMIPER NETWORKS INC
Intelligent disease attribute matching method
ActiveCN104915561AImprove the efficiency of diagnosis and treatmentSpecial data processing applicationsComputer scienceAided diagnosis
The invention provides an intelligent disease attribute matching method. Physical signs and examination data of patients are utilized to create an intelligent disease attribute matching model used for auxiliary diagnosis and treatment scheme accommodation. The method has the advantages that different from a conventional keyword-based searching method, the intelligent disease attribute matching method and system can diagnose illness state according to the physical signs and examine index information, meanwhile the corresponding treatment scheme accommodations are acquired for providing references to diagnosis and treatment of doctors, and efficiency of diagnosis and treatment is increased.
Owner:WONDERS INFORMATION +1
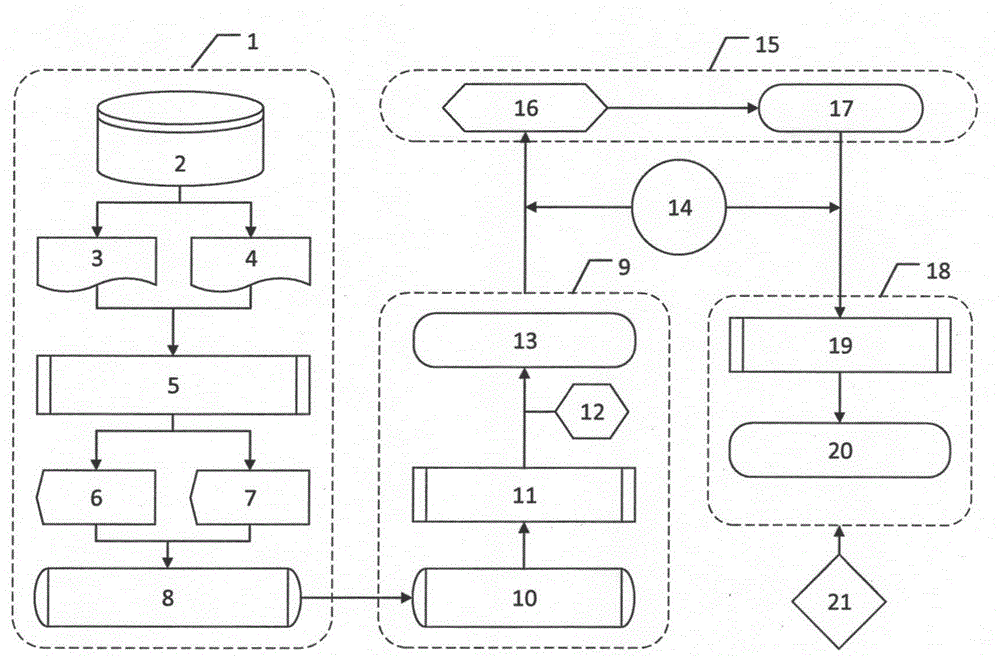
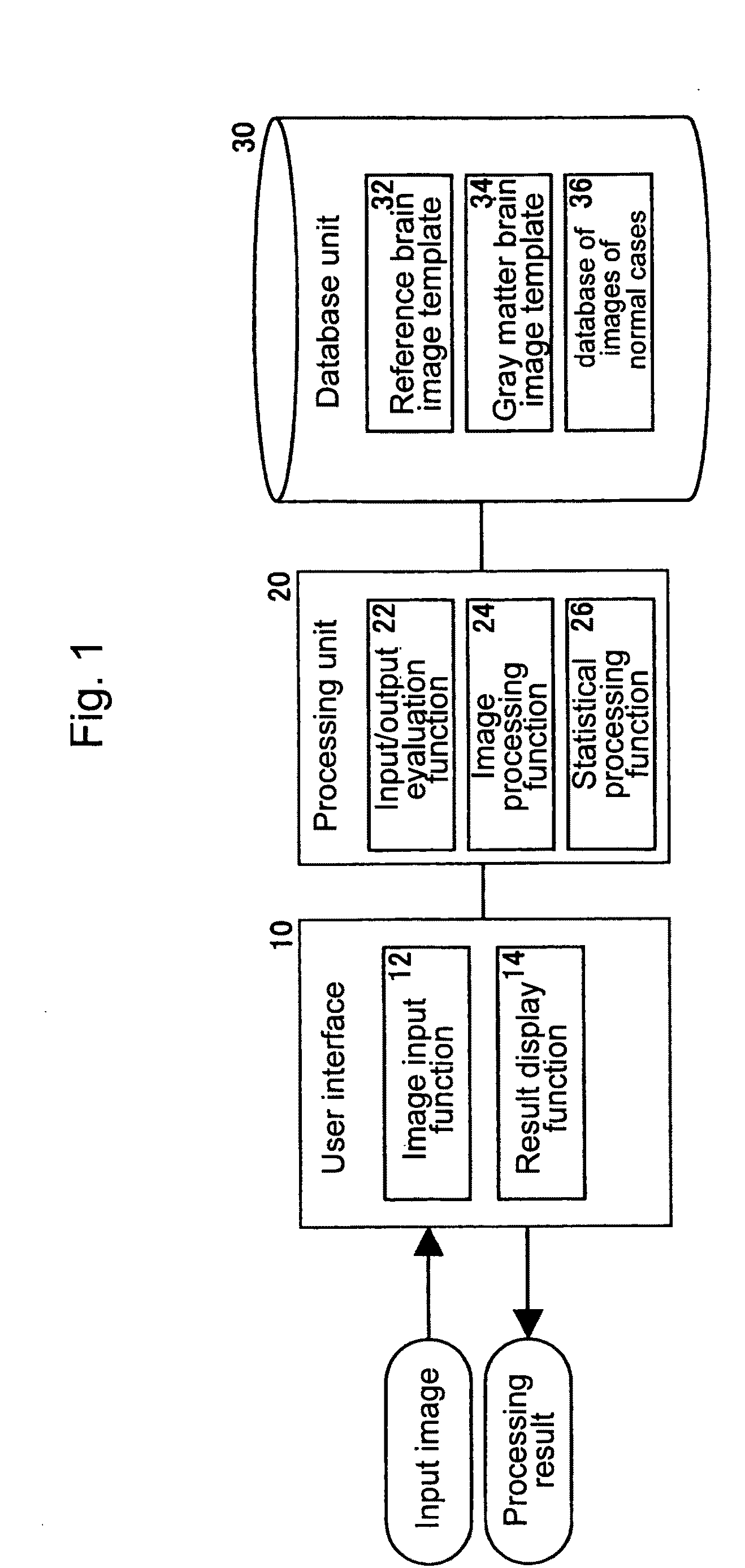
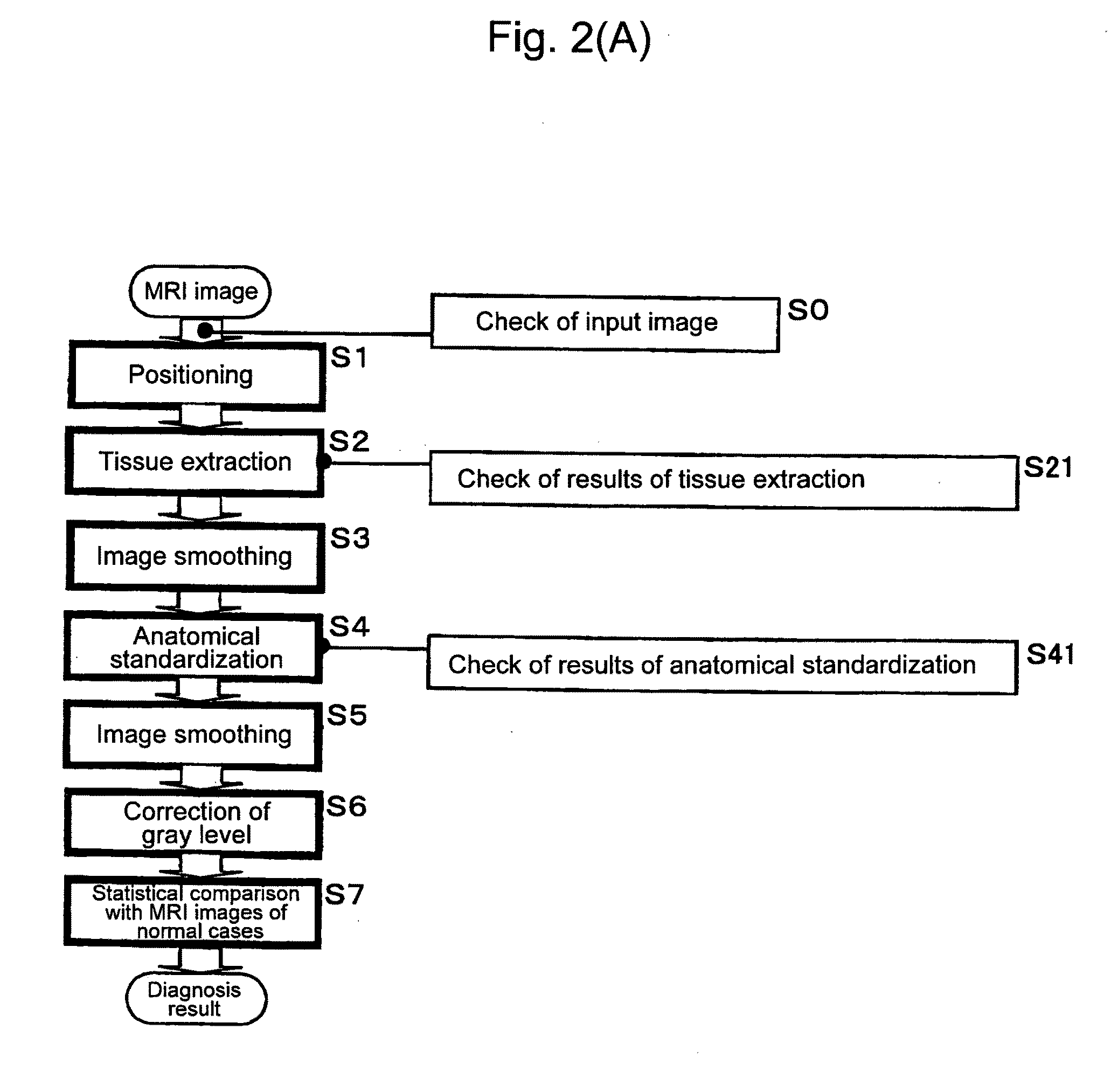
Method for assisting in diagnosis of cerebral diseases and apparatus thereof
Input MRI brain images are positioned so as to correct a spatial deviation, gray matter tissues are extracted from these images to effect a first image smoothing, the thus-obtained images are subjected to anatomical standardization, a second image smoothing is effected, the gray level is corrected, brain images after correction are statistically compared with MRI brain images of normal cases, thereby providing the diagnosis result. In this instance, the brain images are automatically checked for input images regarding the resolution dot density and the like, the result of gray matter tissue extraction and the result of anatomical standardization, by which specifications of input images and the like can be confirmed objectively and automatically to make a diagnosis automatically by image processing. Further, an ROI-based analysis is made to provide the analysis result as the diagnosis result.
Owner:DAI NIPPON PRINTING CO LTD
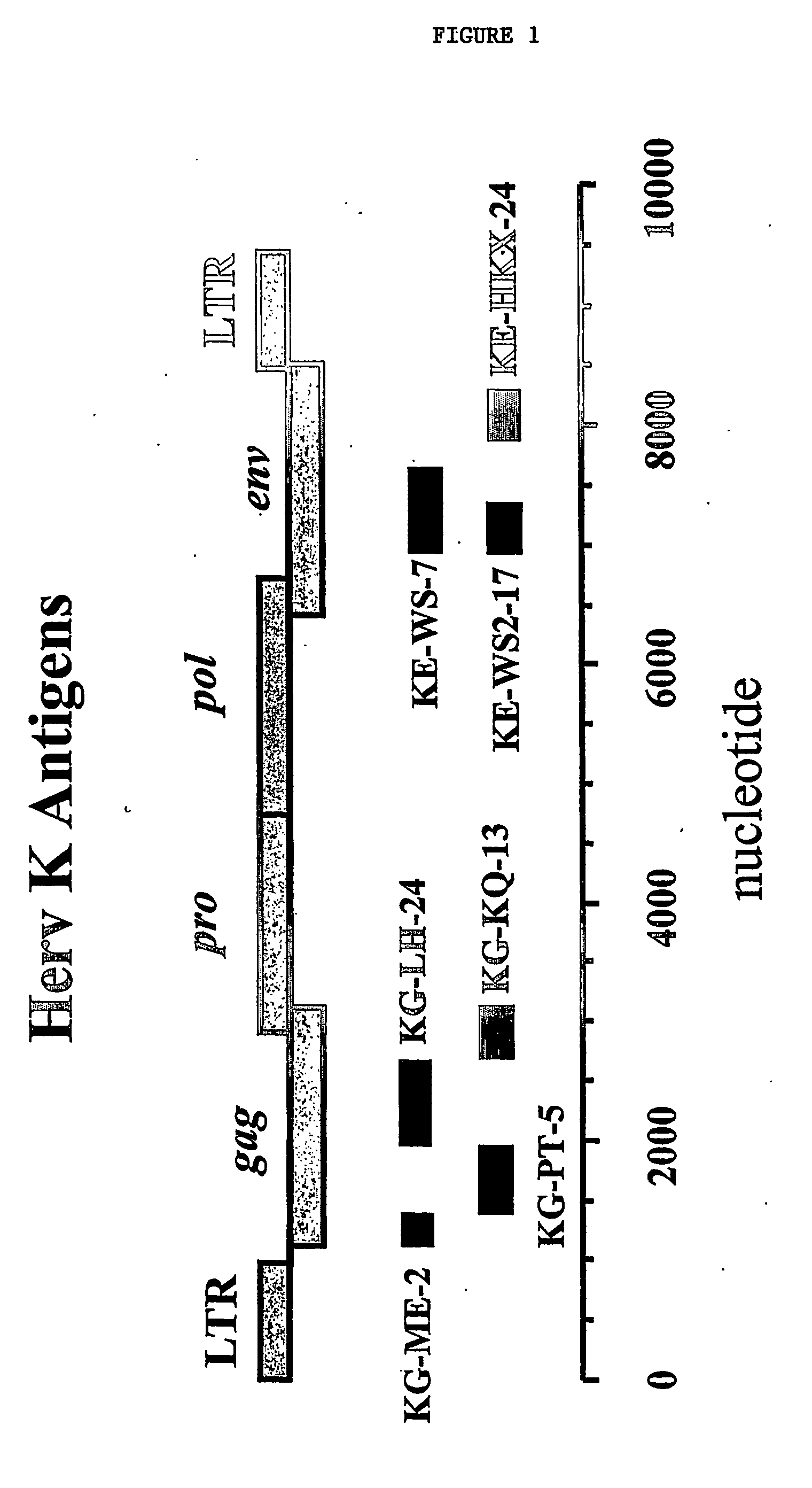
Monitoring and treatment of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
InactiveUS20060160087A1Reduce expressionMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisInfected cellAmyotrophic lateral sclerosis
The invention provides methods of monitoring amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) disease development or progression and monitoring an ALS therapy in an individual by determining the presence or absence of Herv-K / HML-2 expression in a biological sample from the individual. The invention is also directed to methods for aiding diagnosis of ALS by determining expression of Herv-K / HML-2 in a biological sample from the individual. The invention is also directed to methods of reducing Herv-K / HML-2 expression in infected cells and individuals. The invention includes reagents for use in these methods.
Owner:PATHOLOGICA
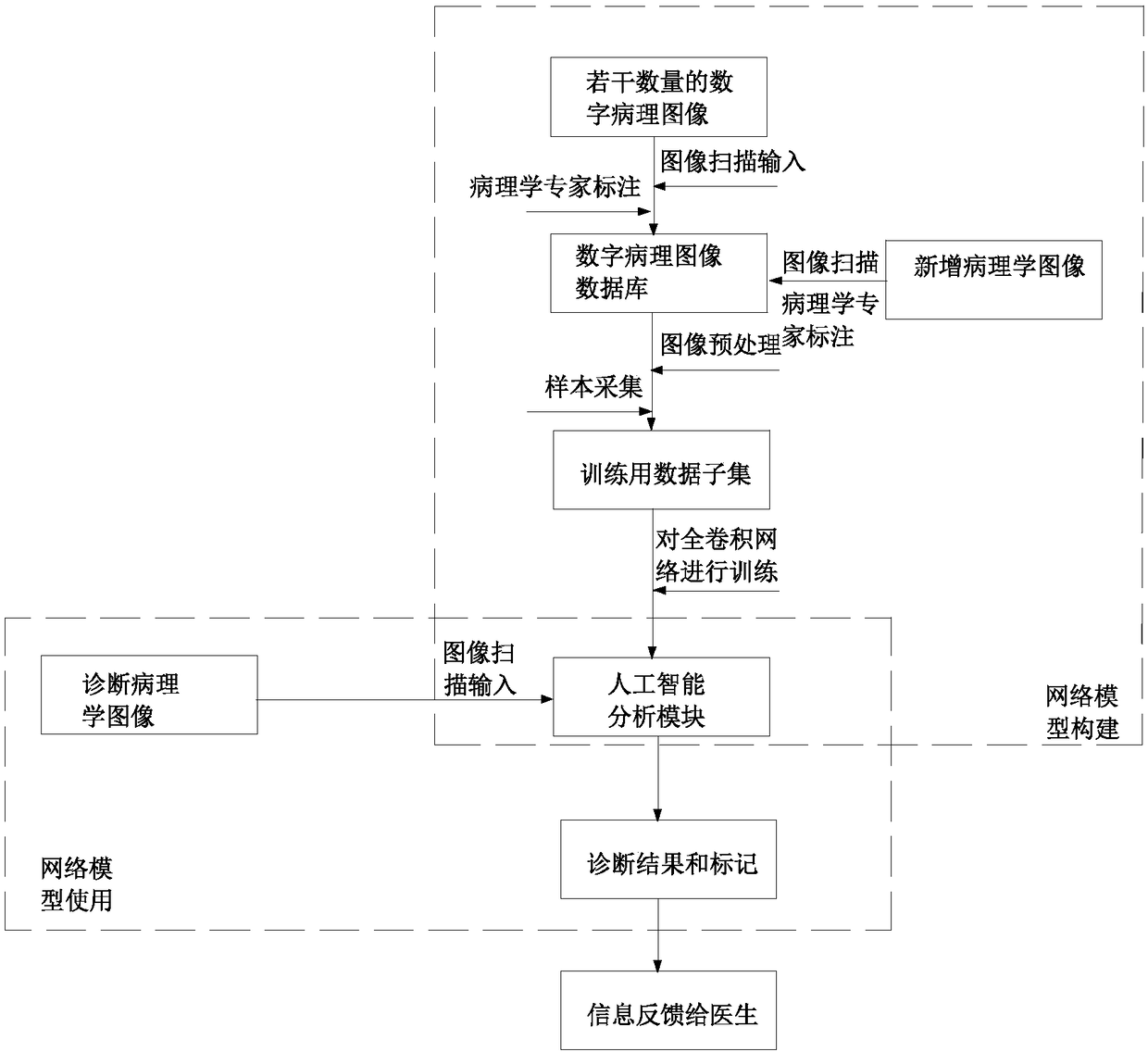
Cancer pathology auxiliary diagnosis method based on artificial intelligence technology
InactiveCN108288506AImprove diagnostic accuracyQuality improvementMedical simulationMedical automated diagnosisDisease areaData set
The present invention discloses a cancer pathology auxiliary diagnosis method based on an artificial intelligence technology. The method comprises the following steps of: canning a plurality of digital pathology images of a system into a computer, performing marking of diseased areas by pathologists to form a digital pathology image database; performing preprocessing of the digital pathology images to form a data set for algorithm training, performing sample collection, and forming a data subset for training; allowing a full convolutional network to use the data subset for training to performiteration training to regulate parameters, and constructing an artificial intelligence analysis module; scanning diagnosis pathology images, and decoding the diagnosis pathology images to access the artificial intelligence analysis module; and performing diagnosis and marking of the diagnosis pathology images by employing the artificial intelligence analysis module, and performing feedback of themarked pathology information to doctors. The cancer pathology auxiliary diagnosis method based on the artificial intelligence technology is high in diagnosis accuracy and can effectively assist doctors in discrimination of cancer pathology information.
Owner:云鲲医疗科技(上海)有限公司
Galactophore cancer computer auxiliary diagnosis method based on galactophore X-ray radiography and system thereof
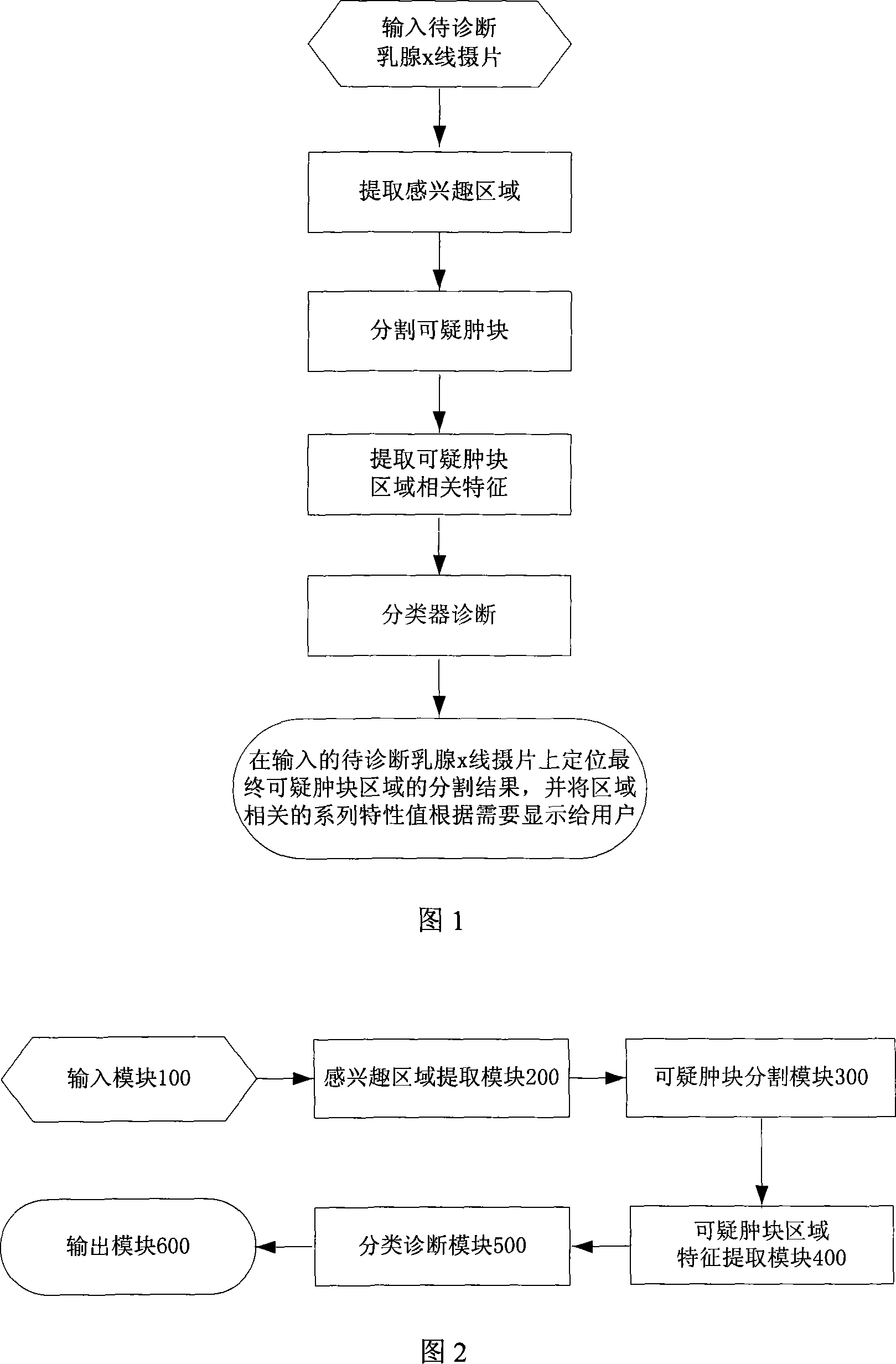
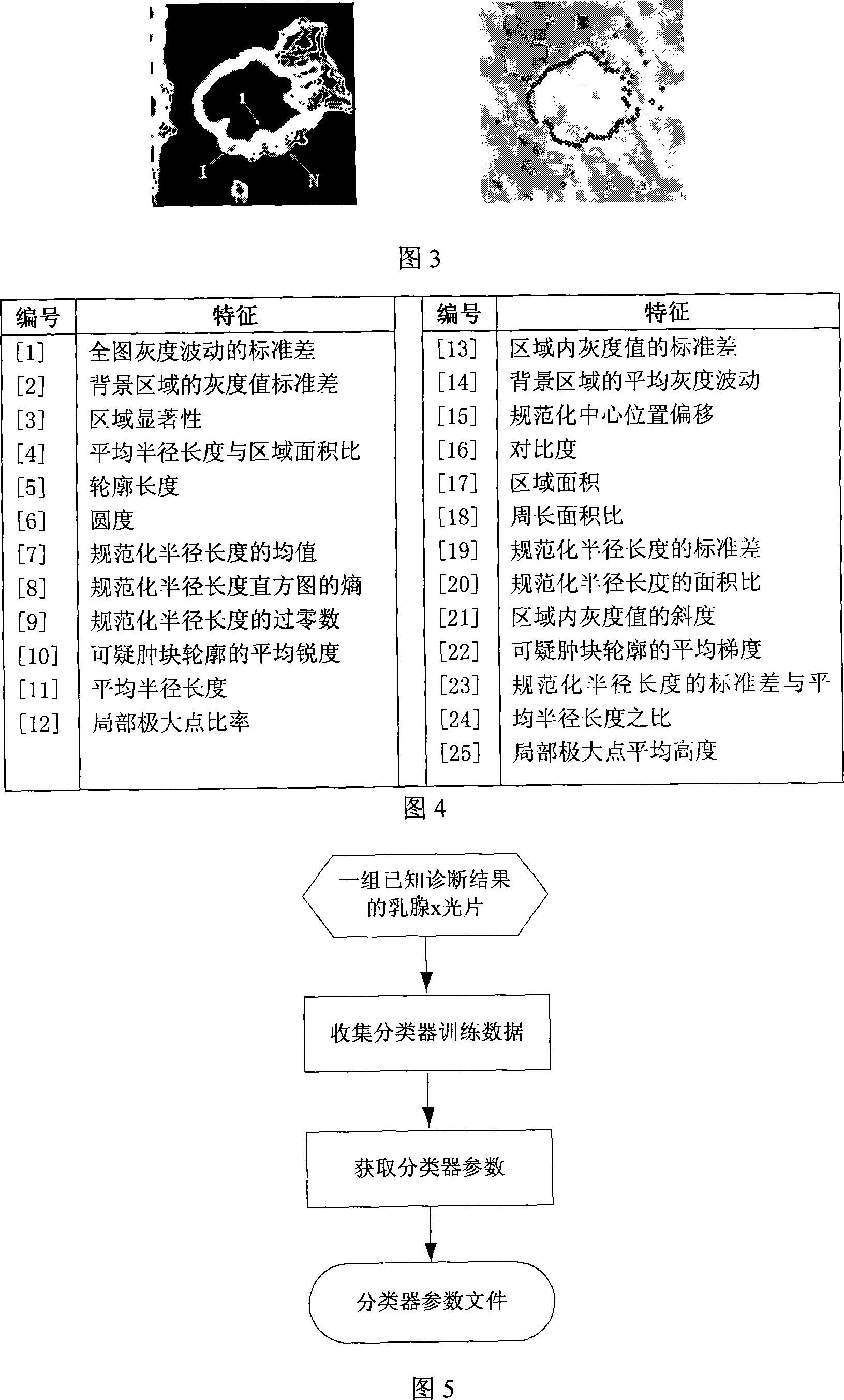
InactiveCN101103924AImprove accuracyImprove efficiencySpecial data processing applicationsRadiation diagnosticsFeature extractionDiagnosis methods
The invention discloses a breast cancer computer auxiliary diagnosis method and system based on galactophore X-ray radiograph. A galactophore X-ray radiograph for diagnosis is input into the system of the invention firstly, and is treated through an extracting module in a region of interest, a partitioning module and a feature extracting module in a region of doubtful lump, hereby a series of relative feature values about the doubtful lump region; then the feature values are input into a trained classifier which classifies and identifies the doubtful lump region and lastly the computer automatic examined final result of portioning the doubtful lump region is located on the input galactophore X-ray radiograph for diagnosis and the calculated relative feature values of the region are displayed to a roentgenologist according to requirements to indicate the roentgenologist about the region needing special attention and relative important parameters of the region. The invention can improve the accurateness and efficiency of the breast cancer diagnosis by the roentgenologist to some extent and help the roentgenologist to bring forward a diagnostic opinion and a therapeutic schedule more objectively and effectively.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Statistical methods for multivariate ordinal data which are used for data base driven decision support
InactiveUS20060122807A1Reduce complexityImprove accuracy and stabilitySurgeryDigital computer detailsDecision makerAided diagnosis
A method of analysis including an intrinsically valid class of statistical methods for dealing with multivariate ordinal data. A decision support system that can (1) provide automated decision support in a transparent fashion (2) optionally be controlled by a decision maker, (3) provide for an evidence acquisition concept, including automatically increasing the content of an underlying database, and (4) provide a computationally efficient interactive distributed environment. The method is exemplified in the context of assisted diagnostic support.
Owner:THE ROCKEFELLER UNIV
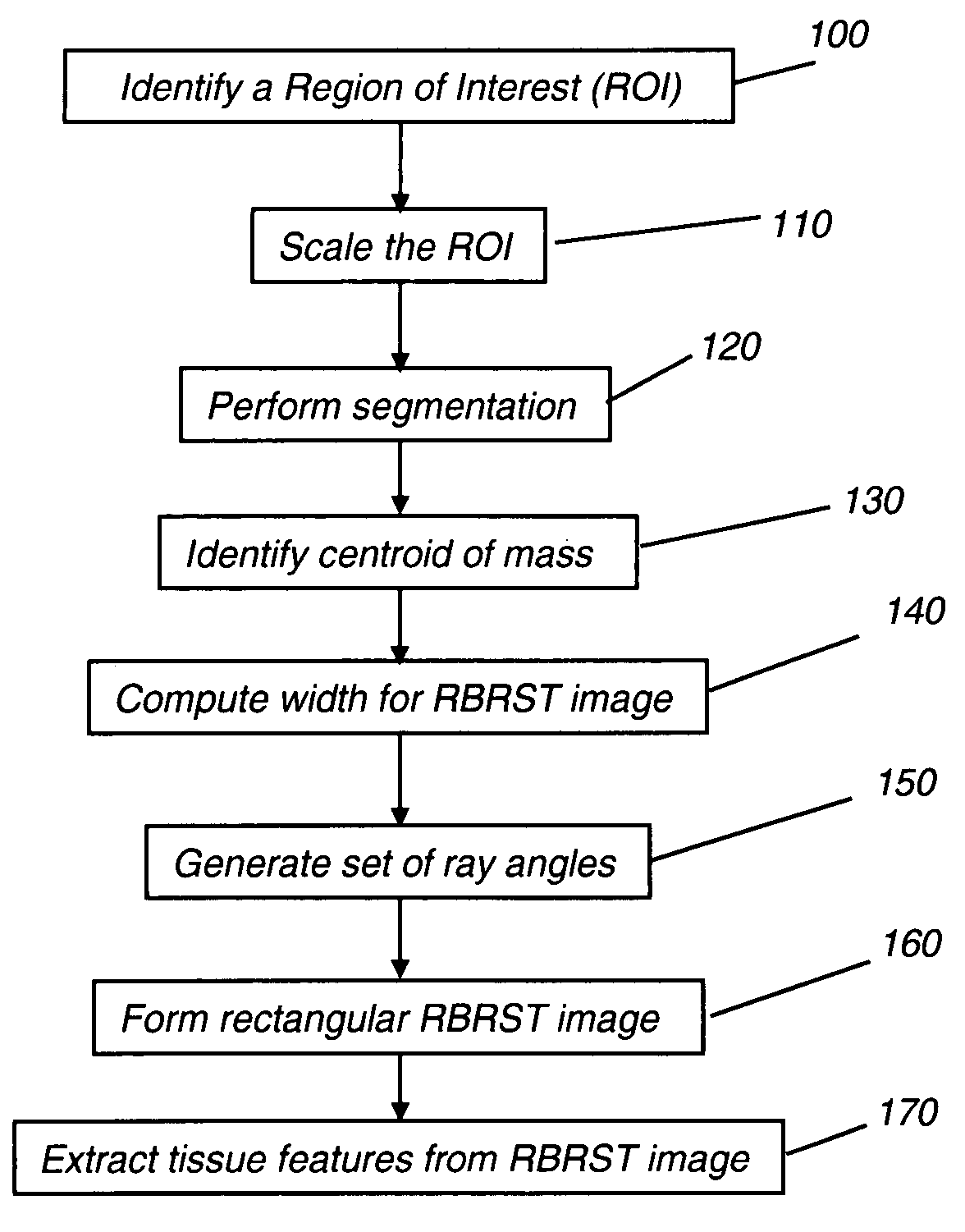
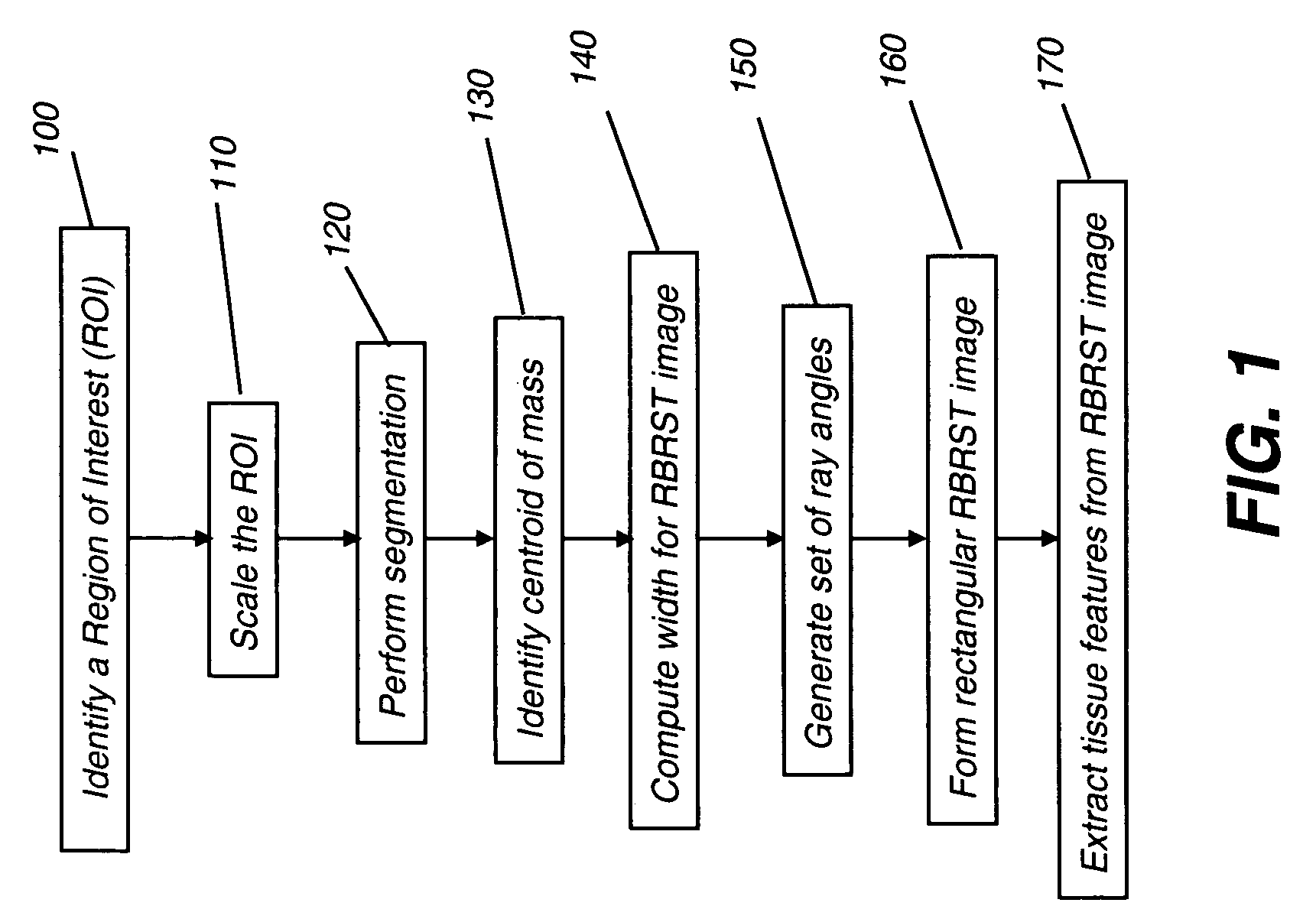
Texture analysis for mammography computer aided diagnosis
InactiveUS20080031506A1MinimizesMinimizes under-samplingImage enhancementImage analysisDigital mammogramAided diagnosis
A method of characterizing a mass within a digital mammogram. A region of interest is identified that includes the mass and surrounding tissue. A border outline of the mass is identified. A rectangular image is formed wherein each column of the image is formed by repetition of steps. A vector is employed for each of a set of ray angles, wherein the vector extends from a central point of the mass and intersects the border outline at an intersection point. A starting pixel along the vector is identified, between the intersection point and the central point, at a first distance before the intersection point. An ending pixel along the vector is identified at a second distance beyond the intersection point. Pixels along the vector, from the starting pixel to the ending pixel, are remapped as the respective column in the rectangular image. Texture features are extracted from the formed rectangular image.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
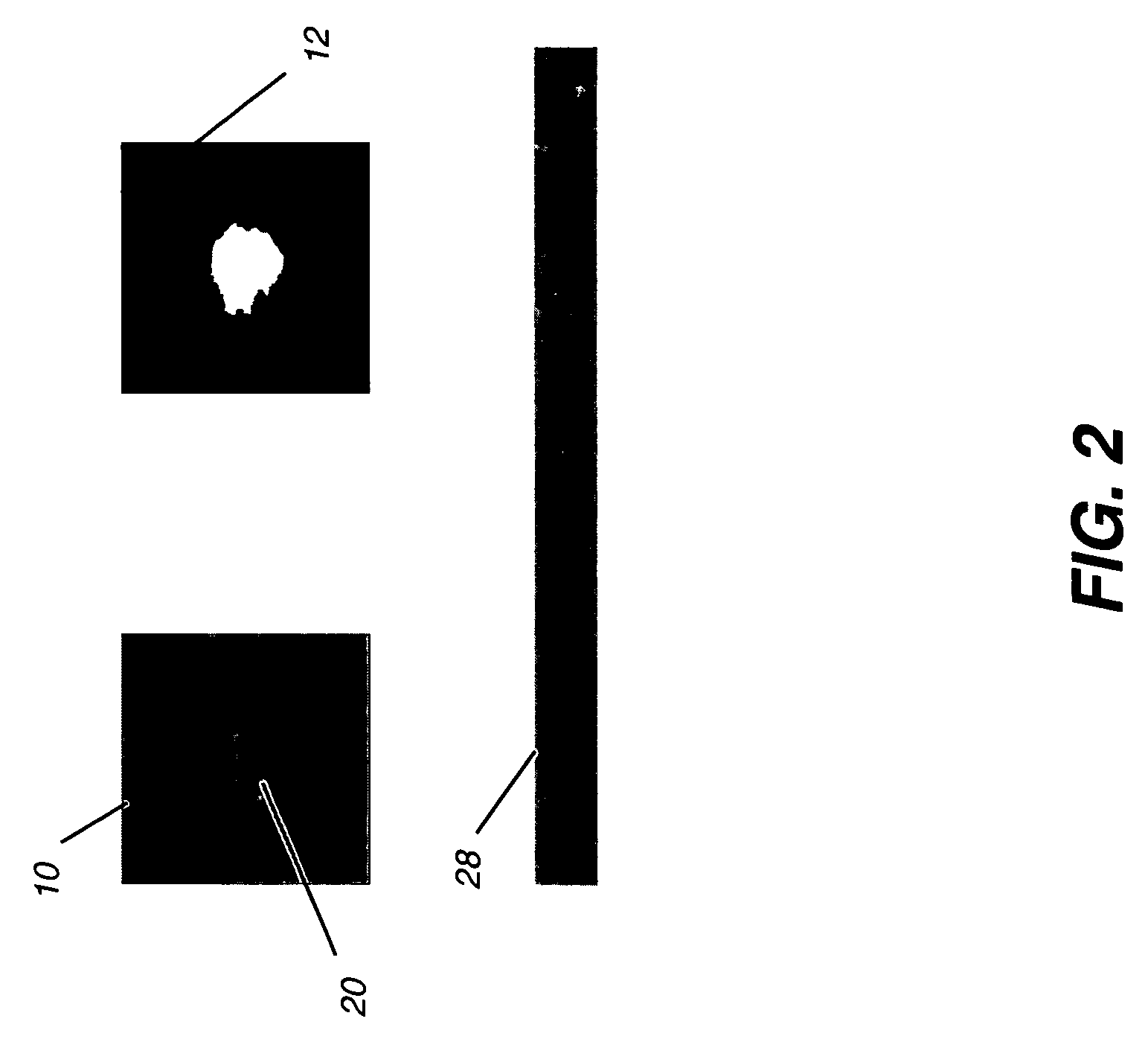
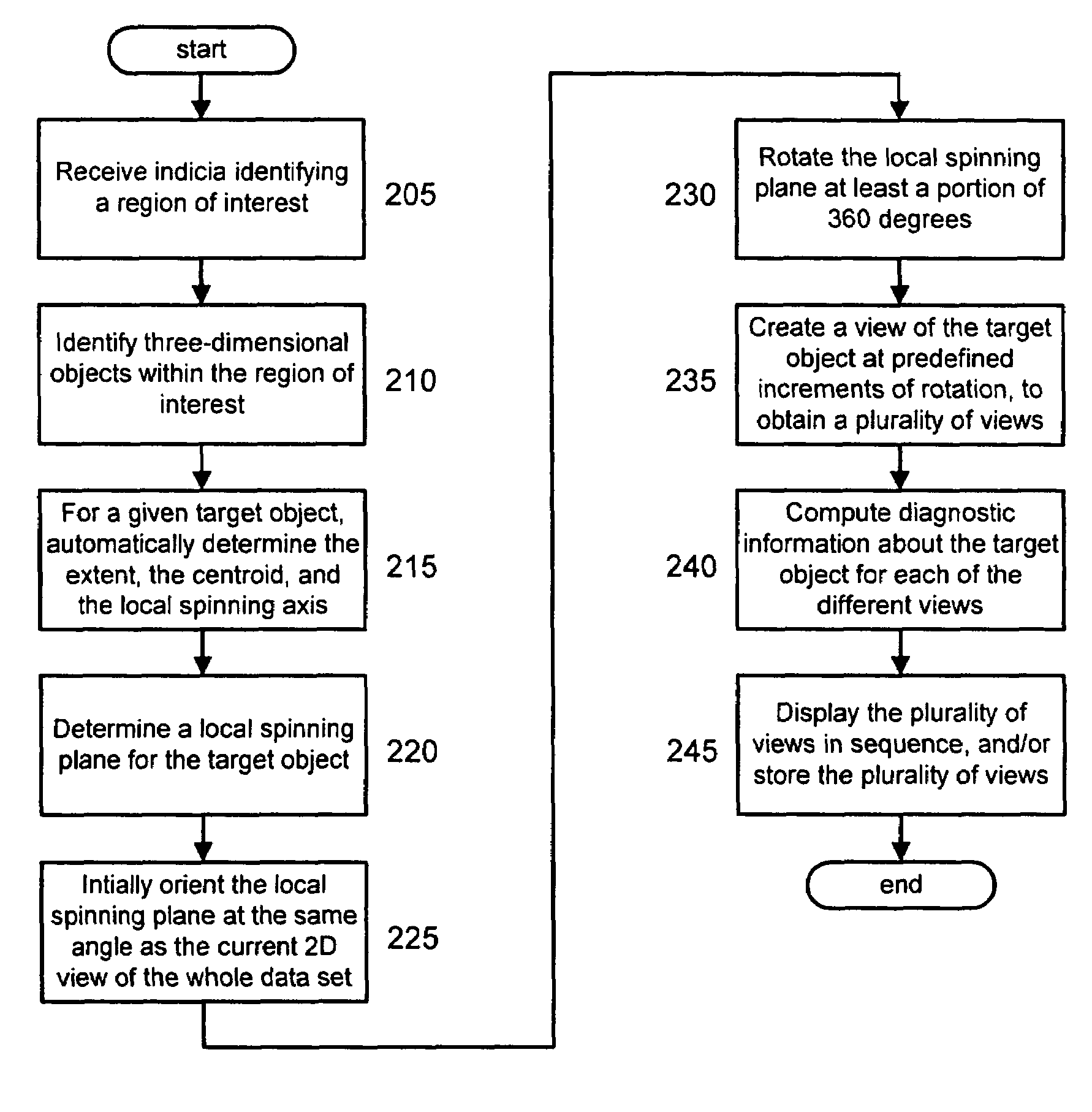
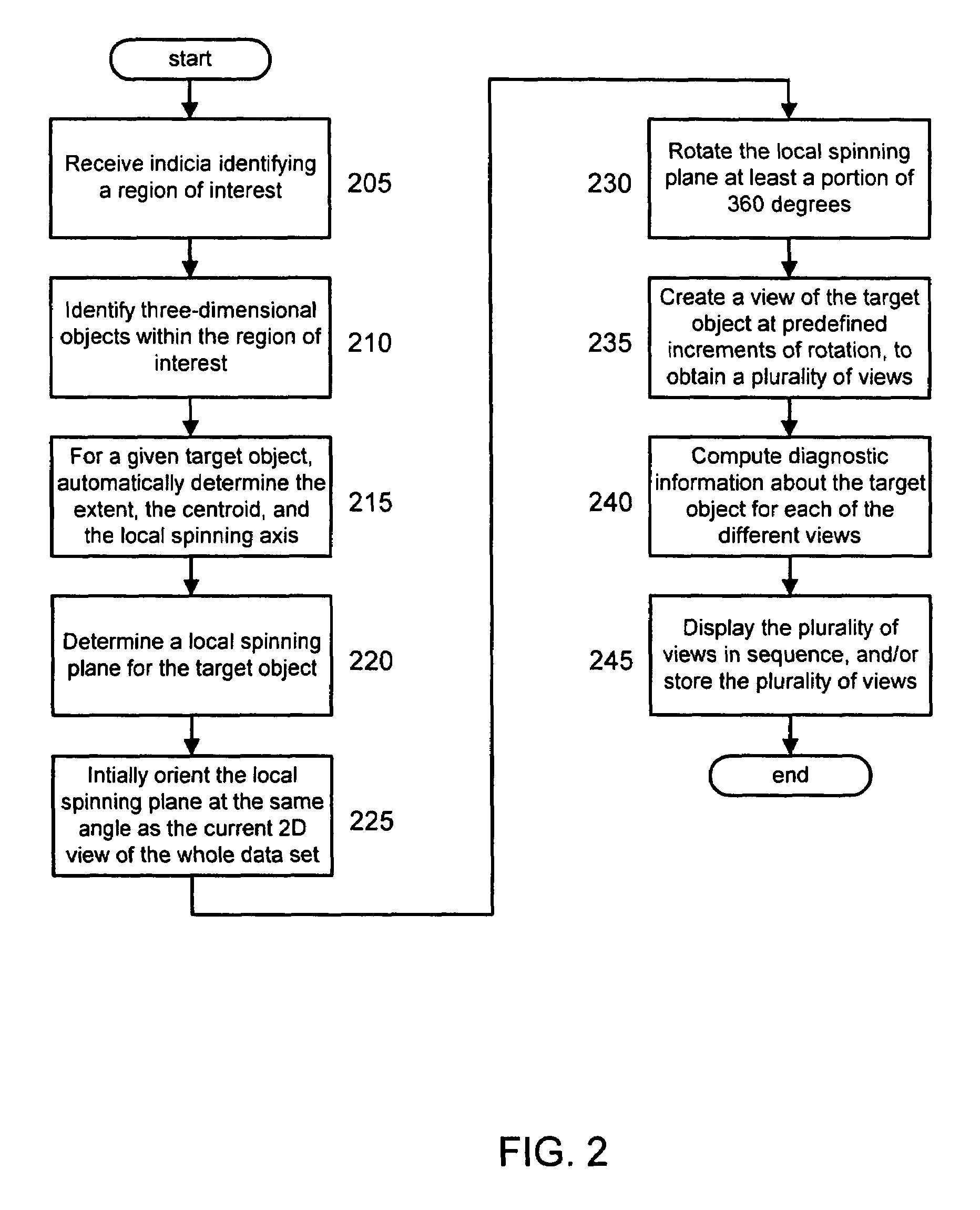
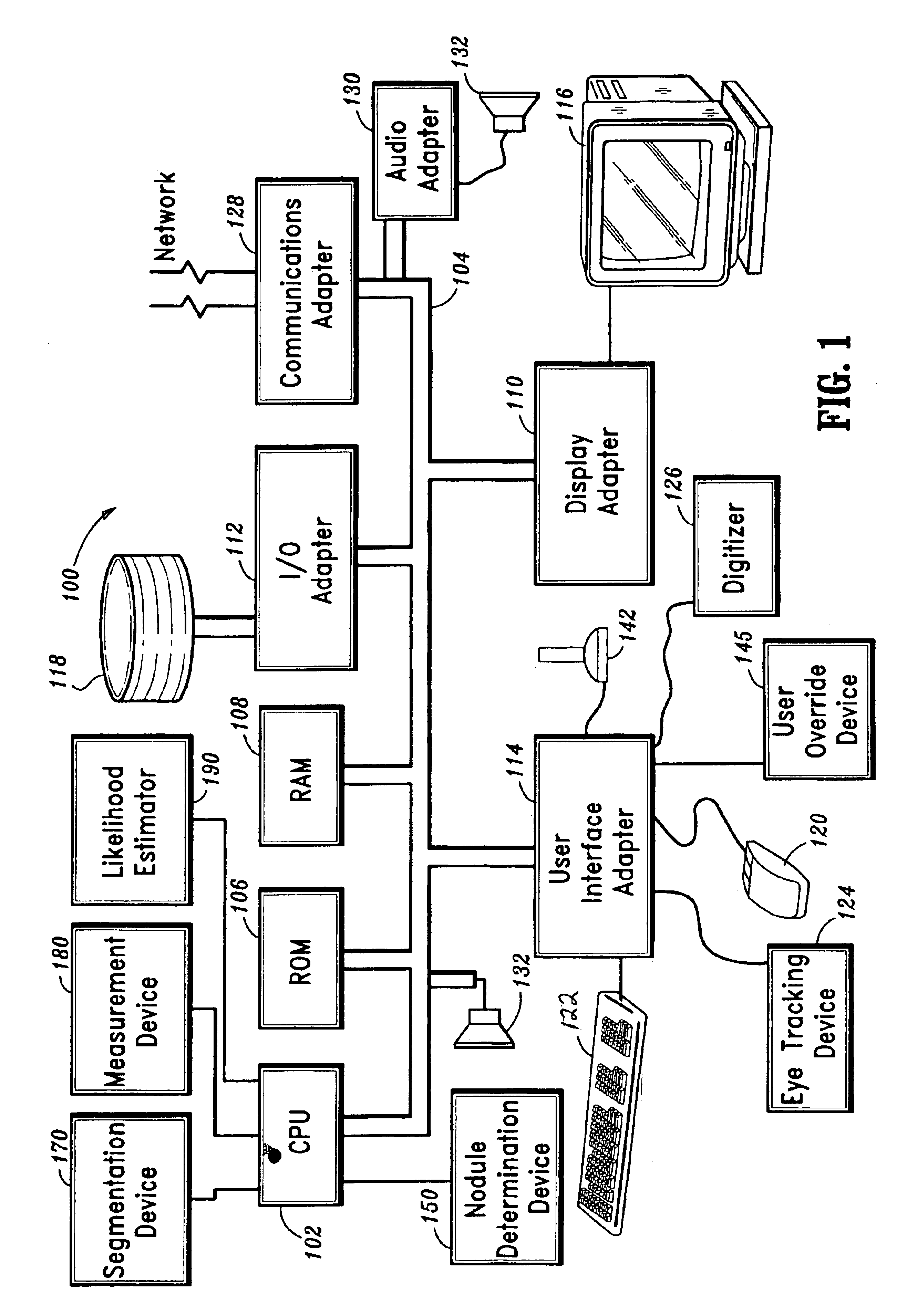
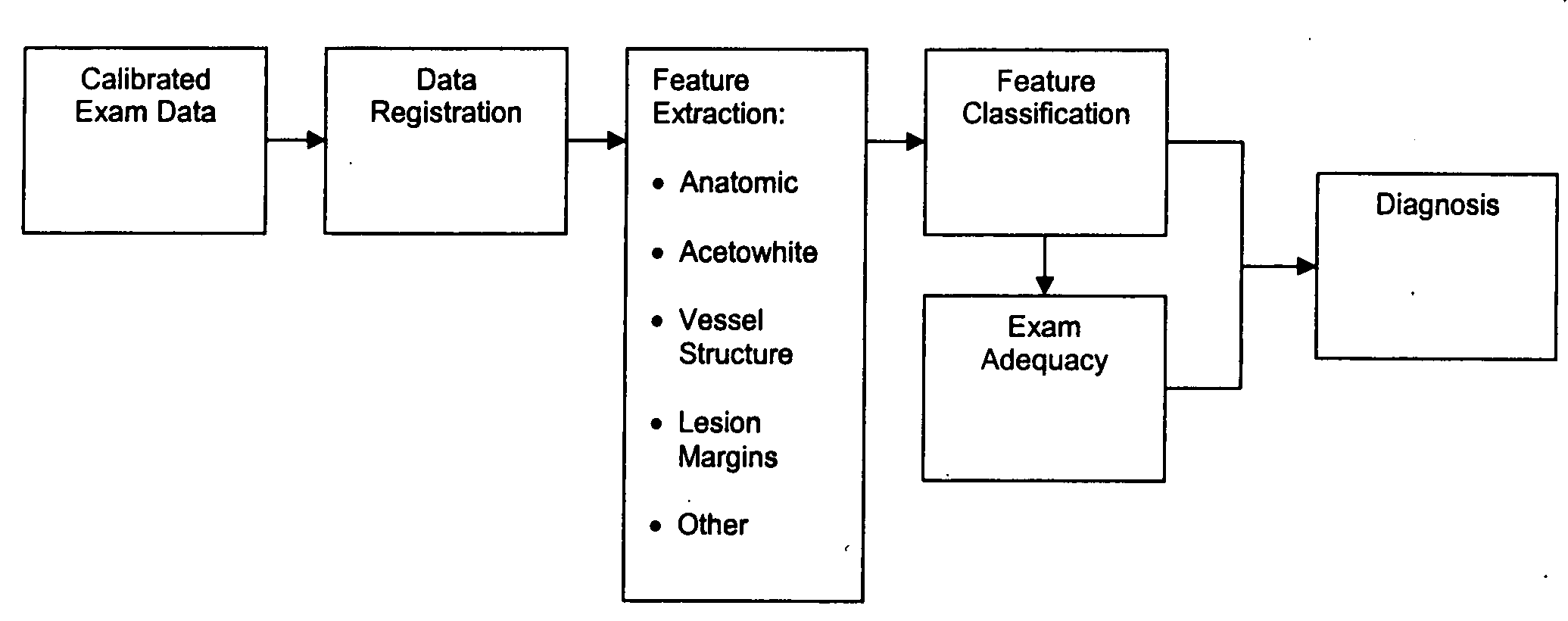
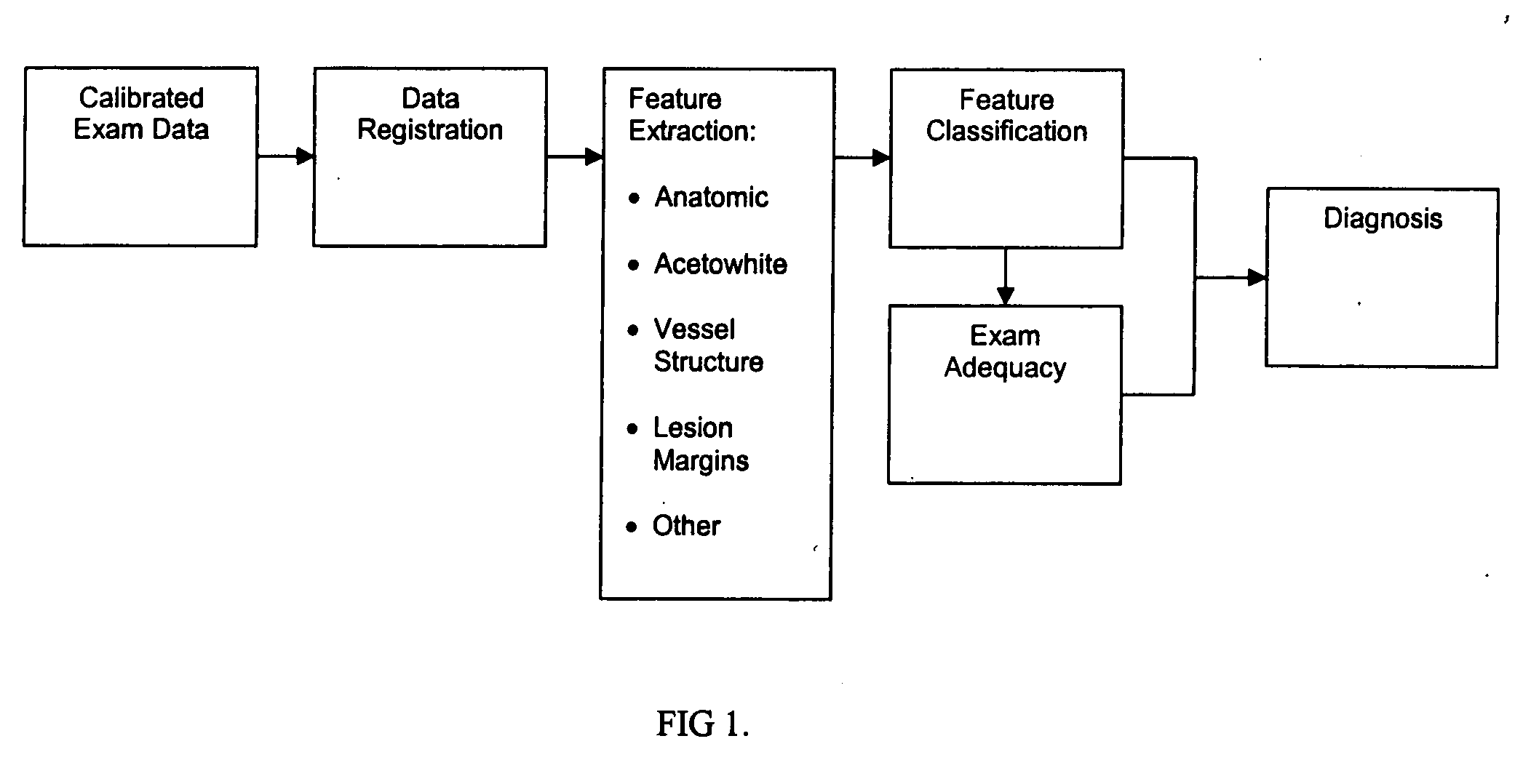
Computer-aided diagnosis method for aiding diagnosis of three dimensional digital image data
There is provided a computer-assisted diagnosis method for assisting diagnosis of three-dimensional digital image data. The method includes the step of receiving indicia identifying at least one region of interest in a digital medical image. Three-dimensional objects within the at least one region of interest are identified. For a given three-dimensional (3D) object within the at least one region (ROI), an extent, a centroid, and a local spinning axis of the given object are determined. Moreover, a local spinning plane is determined for the given object, the local spinning plane being centered at the centroid and the local spinning axis. The local spinning plane is rotated at least a portion of 360 degrees. The rotating step includes the step of creating a view of the given object at predefined increments of rotation, so as to result in a plurality of views of the given object.
Owner:SIEMENS CORP +1
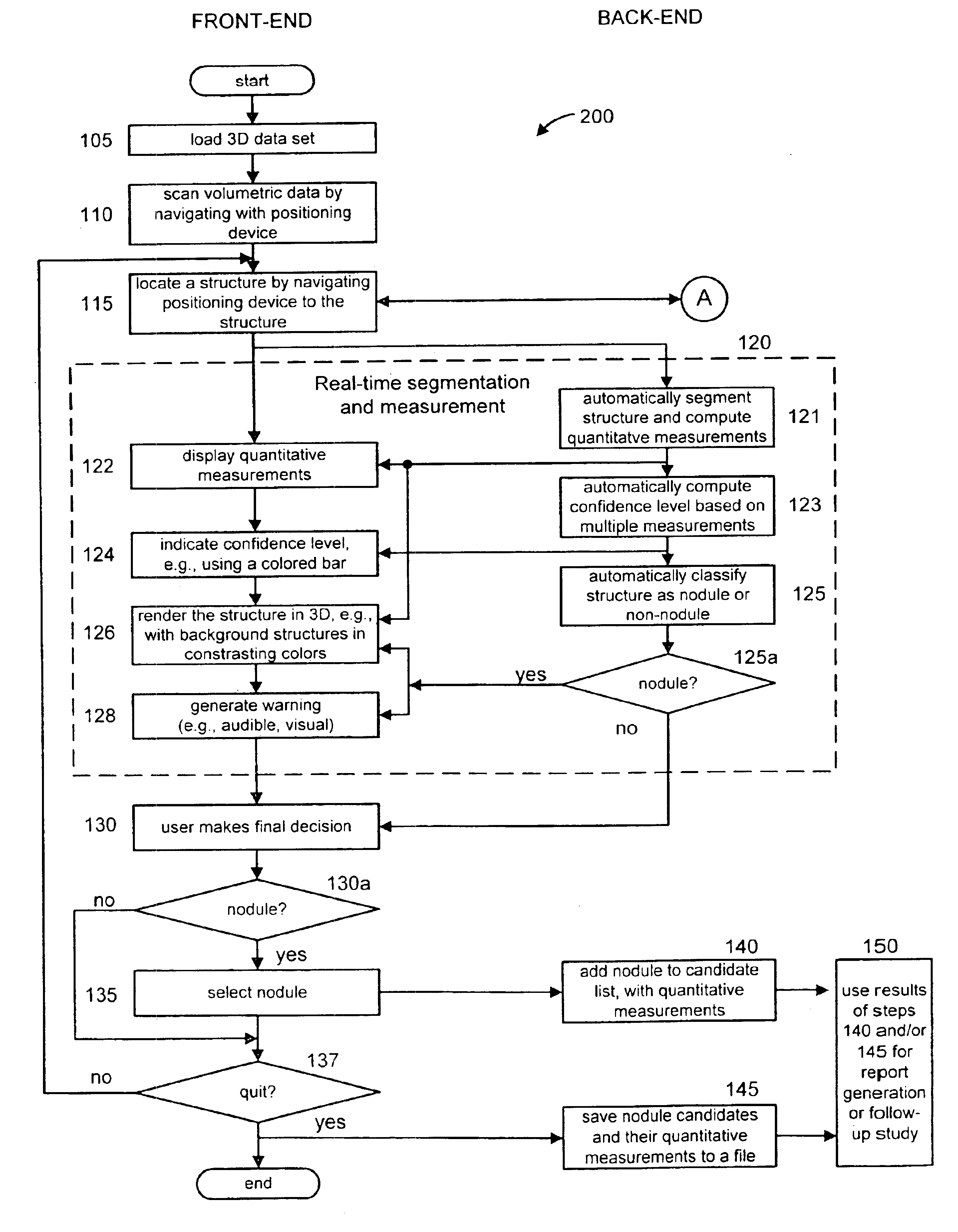
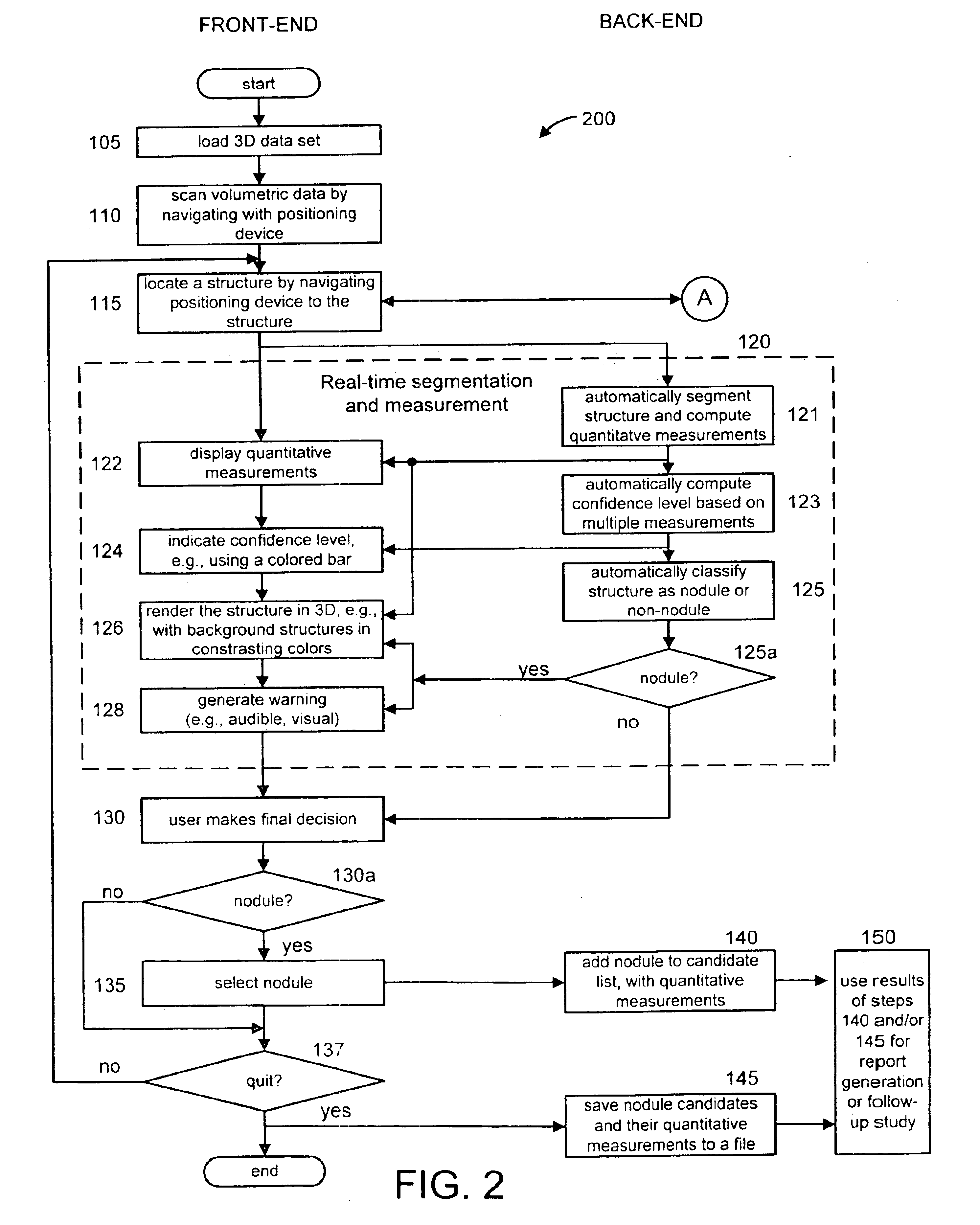
Interactive computer-aided diagnosis method and system for assisting diagnosis of lung nodules in digital volumetric medical images
InactiveUS6944330B2Fast computerHigh acceptanceImage enhancementImage analysisAnatomical structuresDiagnosis methods
A computer-assisted diagnosis method for assisting diagnosis of anatomical structures in a digital volumetric medical image of at least one lung includes identifying an anatomical structure of interest in the volumetric digital medical image. The anatomical structure of interest is automatically segmented, in real-time, in a predefined volume of interest (VOI). Quantitative measurements of the anatomical structure of interest are automatically computed, real-time. A result of the segmenting step and a result of the computing step are displayed, in real-time. A likelihood that the anatomical structure of interest corresponds to a disease or an area warranting further investigation is estimating, in real-time, based on predefined criteria and the quantitative measurements. A warning is generated, in real-time, when the likelihood is above a predefined threshold.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Methods for modulating macrophage proliferation using polyamine analogs
Methods for modulating macrophage proliferation in an individual afflicted with or at risk for a macrophage-associated disease are provided. The methods employ a polyamine analog, or salt or protected derivative thereof. Macrophage proliferation has been implicated in a number of serious disorders, including AIDS (HIV)-associated dementia, AIDS-associated non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, and Alzheimer's disease. The invention also provides methods for aiding diagnosis and monitoring therapy of a macrophage-associated non-HIV associated dementia, especially Alzheimer's disease. The invention also provides methods of delaying development of macrophage-associated non-HIV associated dementias, including Alzheimer's disease, which entail administration of an agent which modulates macrophage proliferation.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method for automatically identifying liver tumor type in ultrasonic image
InactiveCN105447872AAccurate acquisitionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementSonificationImaging processing
The invention relates to the field of medical image processing, in particular to a method for automatically identifying a liver tumor type in an ultrasonic image. The method can provide auxiliary diagnosis when a doctor diagnoses a liver lesion according to a CEUS medical image, wherein the auxiliary diagnosis comprises the process of giving out a lesion identification result, the time when the lesion is relatively remarkable and a position where the lesion is relatively remarkable. The method specifically comprises: representing a CEUS image with a plurality of regions of interest (ROI); distinguishing different lesions by expressions and changes of the ROI in time and space; and representing a space-time relationship among the ROI by establishing models in time and space at the same time, wherein the models can determine relatively proper ROI and related parameters of the models according to existing CEUS lesion samples with an iterative learning method. After a sample is given out, the proper ROI can be determined by removing part of improper ROI in advance and a fast search method, and reference diagnosis is given out for the lesion.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
A mammary gland ultrasonic image recognition and analysis method and system
PendingCN109727243AImprove robustnessReduce duplicationImage analysisNeural architecturesSonificationMammary gland structure
The invention provides a method and a system for automatically analyzing a mammary gland ultrasonic image, identifying a mammary gland focus and then carrying out focus area contour extraction and parameter calculation. According to the invention, the convolutional neural network is used to construct the recognition classification recognition and segmentation extraction model, the breast lesion area in the video or image can be recognized, the lesion area contour can be automatically extracted, and the parameters of the lesion area can be calculated. According to the method and the system, theauxiliary diagnosis accuracy is remarkably improved, repeated operations of doctors are greatly reduced, and the robustness is good.
Owner:CHISON MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Senile dementia monitoring system based on mobile internet
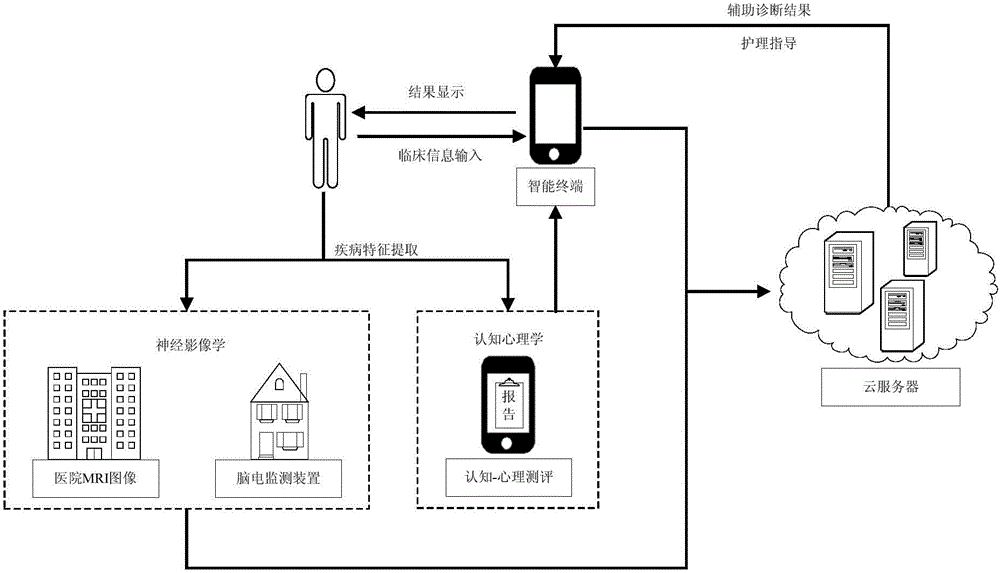
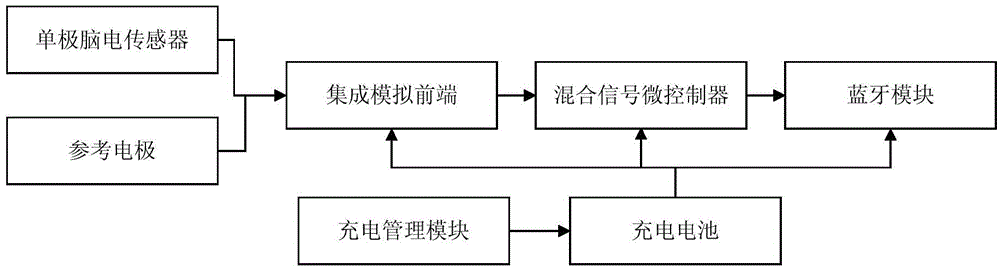
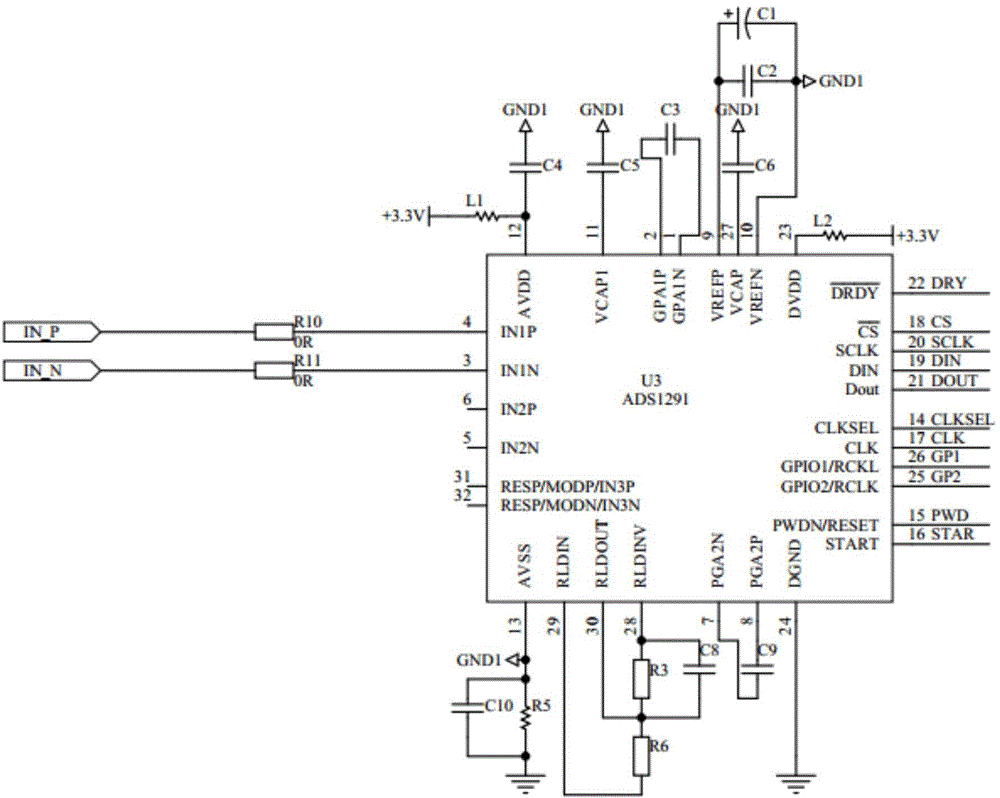
ActiveCN104545899ARealize automatic auxiliary diagnosisVoid the resultMedical automated diagnosisSensorsMonitoring systemSenile dementia
The invention discloses a senile dementia monitoring system based on a mobile internet. The senile dementia monitoring system based on the mobile internet comprises an intelligent terminal, a cloud server and a brain electrical monitoring device, wherein the electrical brain monitoring device is used for acquiring brain electrical information of senile dementia patients or healthy people in real time, and sending the brain electrical information to the intelligent terminal; the intelligent terminal is used for receiving the brain electrical information, completing cognitive-psychological assessment, inputting clinic information, and uploading the brain electrical information, the cognitive-psychological assessment and the clinic information to the cloud server through the mobile internet; the cloud server is used for receiving MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) image information uploaded by hospitals and information uploaded by the intelligent terminal so as to complete auxiliary diagnosis and generate corresponding nursing instruction suggestions, and then feeding auxiliary diagnosis results and the nursing instruction suggestions back to the intelligent terminal. According to the senile dementia monitoring system based on the mobile internet, the mobile internet technology is utilized, the automatic auxiliary diagnosis of senile dementia can be realized, the accuracy of the diagnosis is improved, and the prevention and the early detection of the senile dementia can be realized favorably.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH +1
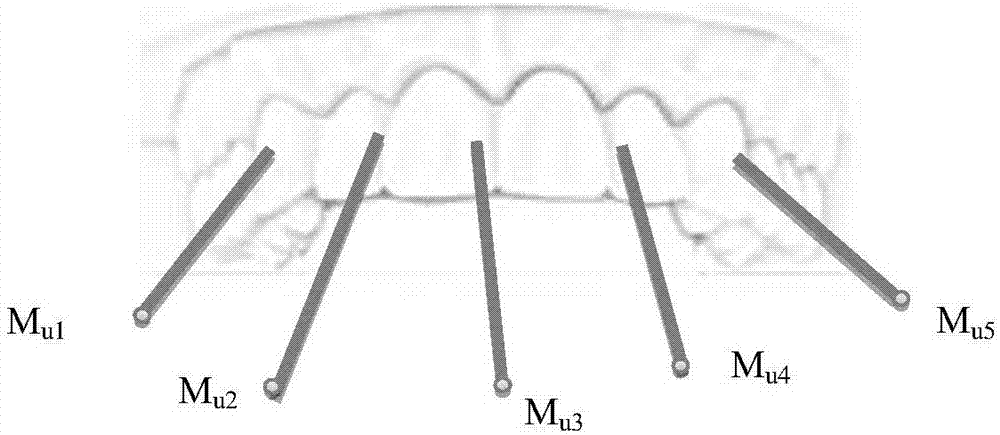
Temporomandibular joint movement reconstruction method and system thereof
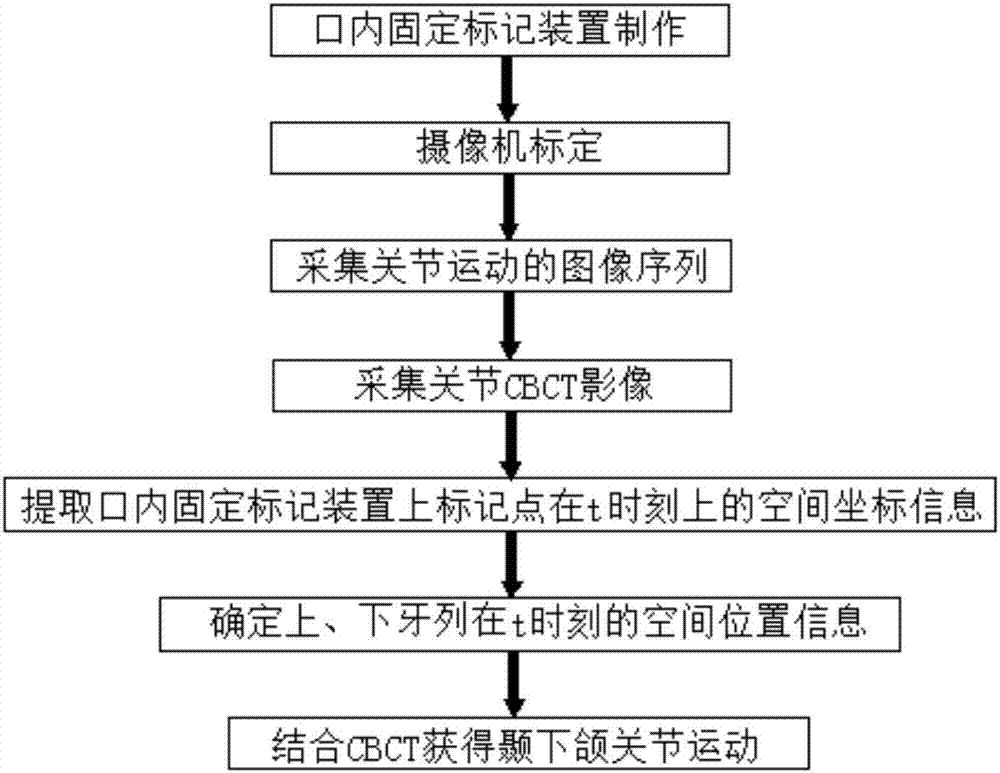
ActiveCN106875432AIncreased means of diagnosisImprove accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisHuman bodyTemporomandibular Joint Diseases
The invention provides a temporomandibular joint movement reconstruction method and a system thereof. The method is characterized by collecting an image sequence of a mark point track of open and close mouth mandible movements of a photographed person; determining three-dimensional coordinates of all the mark points on an intraoral fixed mark device in each frame of image, acquiring a movement track of each mark point in a space, and collecting a CBCT image of the intraoral fixed mark device and collecting a CBCT image of the photographed person; registering the mark point of the CBCT image of the intraoral fixed mark device with the mark point acquired by a camera through photographing, and acquiring a transformation matrix of a mark point movement; and using the transformation matrix to carry out rigid body transformation on the CBCT image of the photographed person, acquiring a CBCT image sequence of the photographed person and acquiring a temporomandibular movement image. In the invention, real movement conditions of mandible condyle process and a temporal bone joint surface of a human-body temporomandibular joint can be acquired, the method and the system can be used for auxiliary diagnosis of a temporomandibular joint disease and dynamic analysis of joint motion, temporomandibular joint diagnosis means are increased, doctor diagnosis accuracy and efficiency can be increased, and medical quality and efficiency can be increased too.
Owner:南京市图研医疗科技有限公司
Uterine cervical cancer computer-aided-diagnosis (CAD)
Uterine cervical cancer Computer-Aided-Diagnosis (CAD) according to this invention consists of a core processing system that automatically analyses data acquired from the uterine cervix and provides tissue and patient diagnosis, as well as adequacy of the examination. The data can include, but is not limited to, color still images or video, reflectance and fluorescence multi-spectral or hyper-spectral imagery, coherent optical tomography imagery, and impedance measurements, taken with and without the use of contrast agents like 3-5% acetic acid, Lugol's iodine, or 5-aminolevulinic acid. The core processing system is based on an open, modular, and feature-based architecture, designed for multi-data, multi-sensor, and multi-feature fusion. The core processing system can be embedded in different CAD system realizations. For example: A CAD system for cervical cancer screening could in a very simple version consist of a hand-held device that only acquires one digital RGB image of the uterine cervix after application of 3-5% acetic acid and provides automatically a patient diagnosis. A CAD system used as a colposcopy adjunct could provide all functions that are related to colposcopy and that can be provided by a computer, from automation of the clinical workflow to automated patient diagnosis and treatment recommendation.
Owner:STI MEDICAL SYST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com