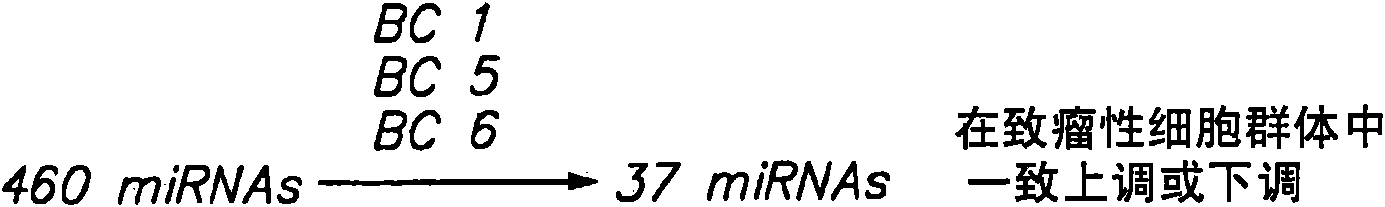Patents
Literature
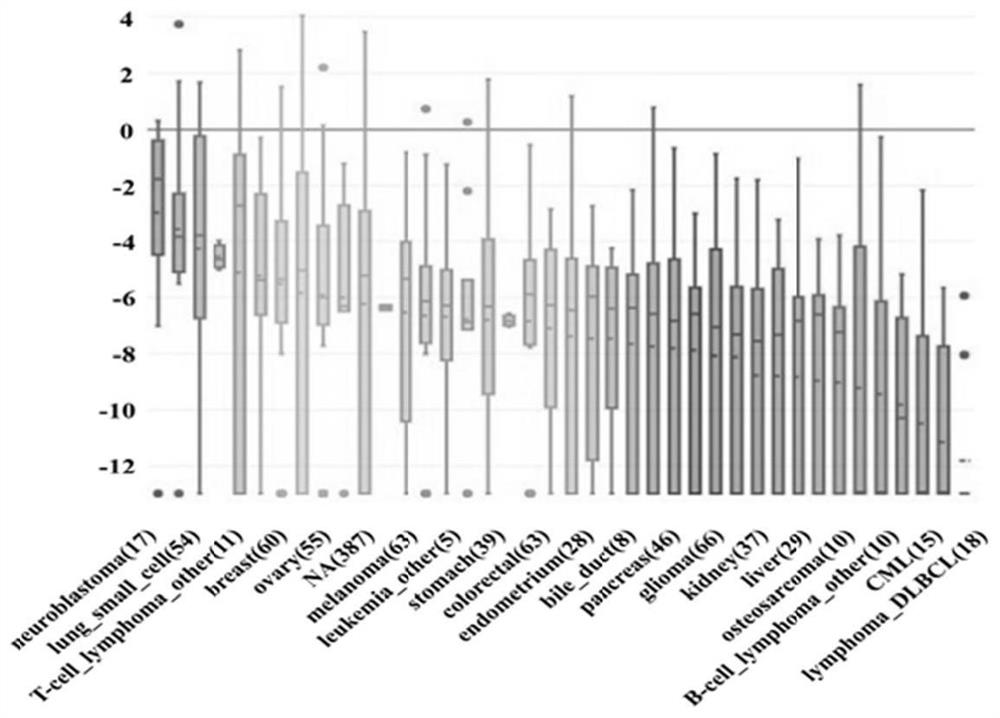
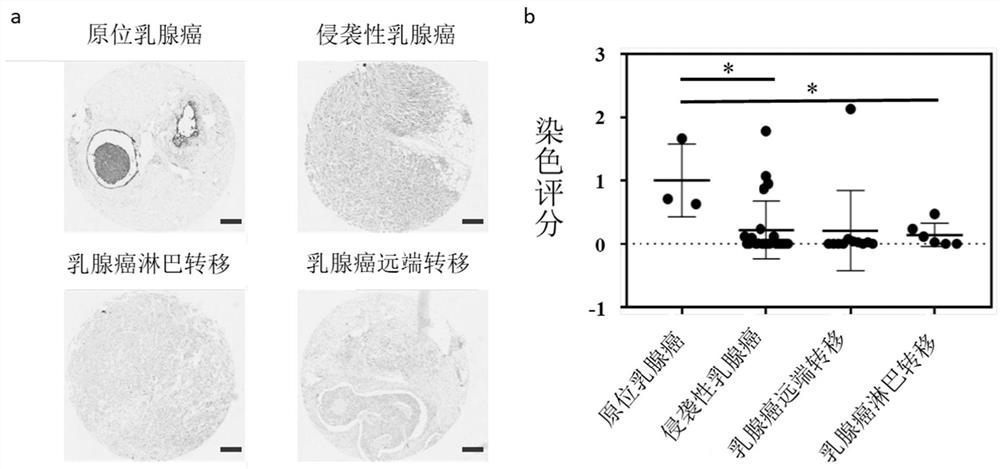
55 results about "Normal breast" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Computerized detection of breast cancer on digital tomosynthesis mammograms
InactiveUS20060177125A1Improve breast cancer detectionExtension of timeImage enhancementImage analysisTomosynthesisGray level
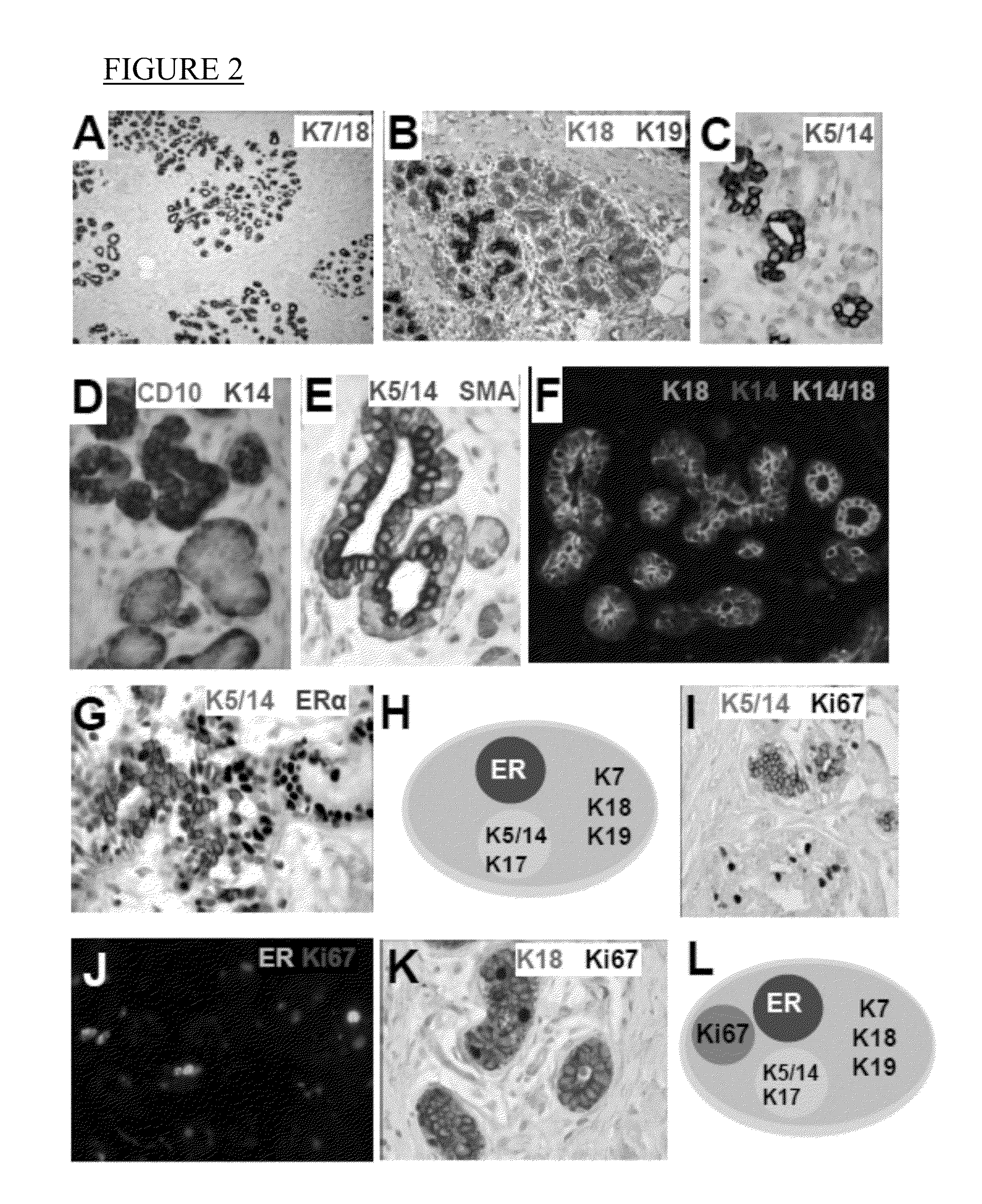
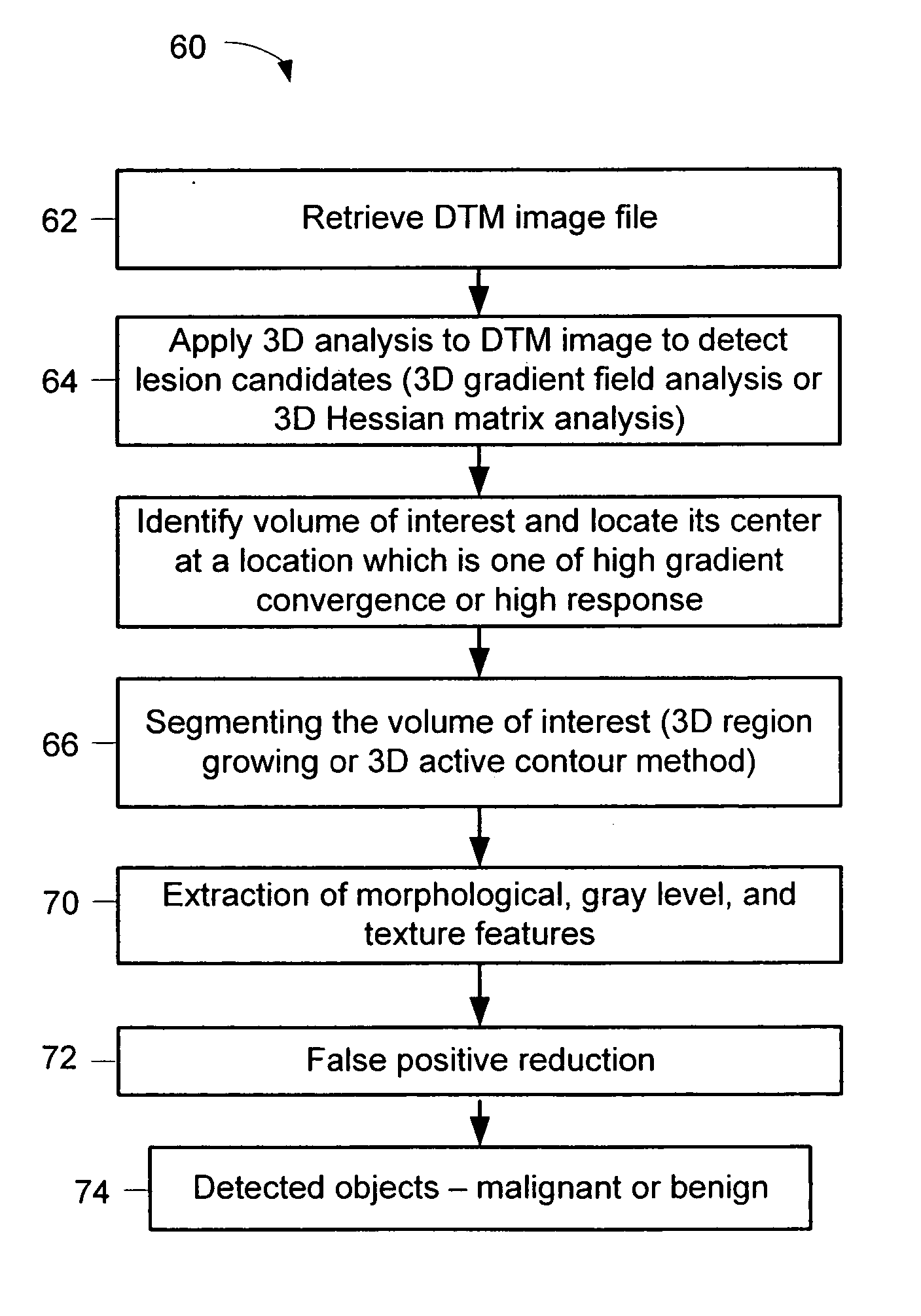
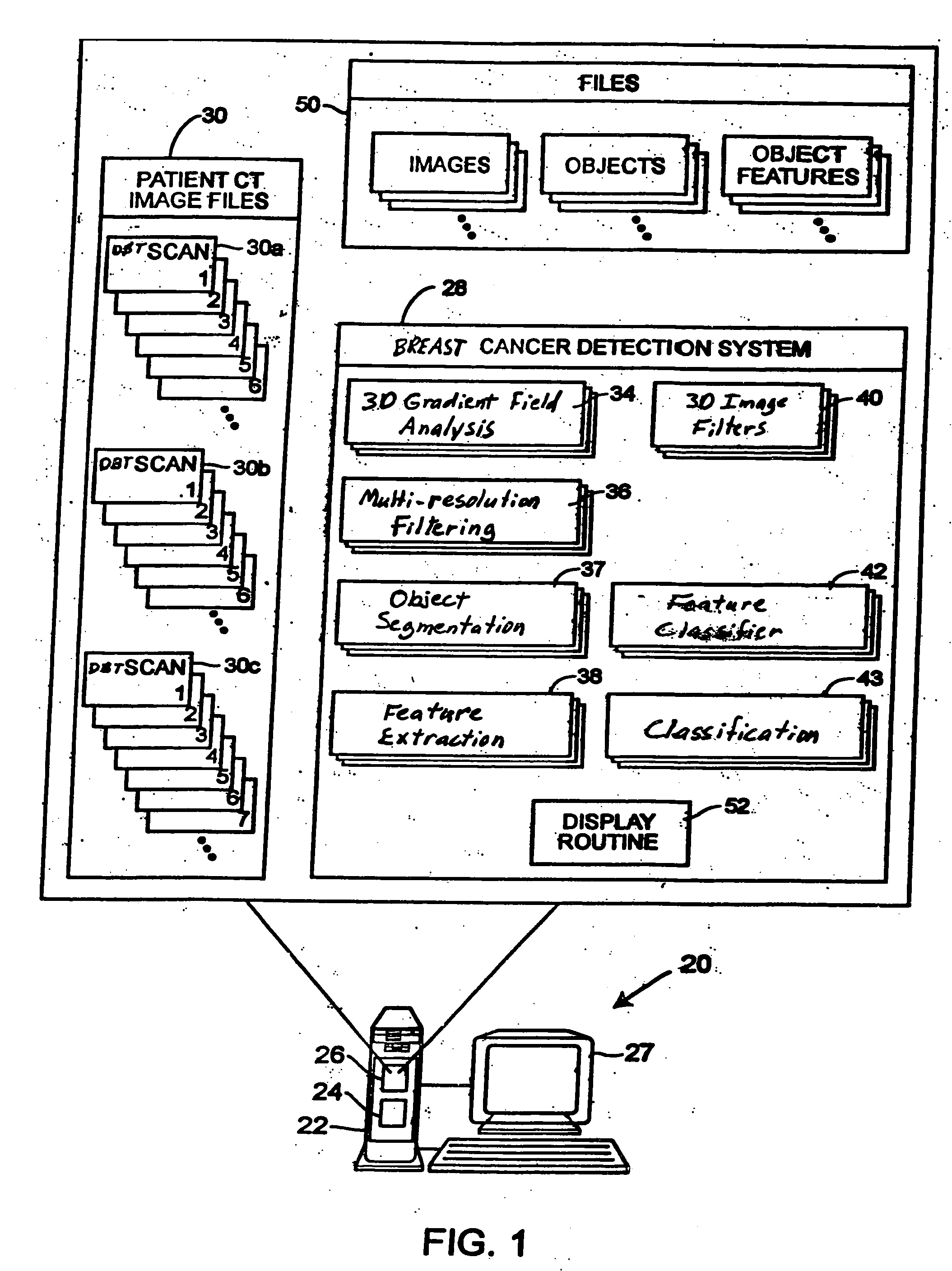
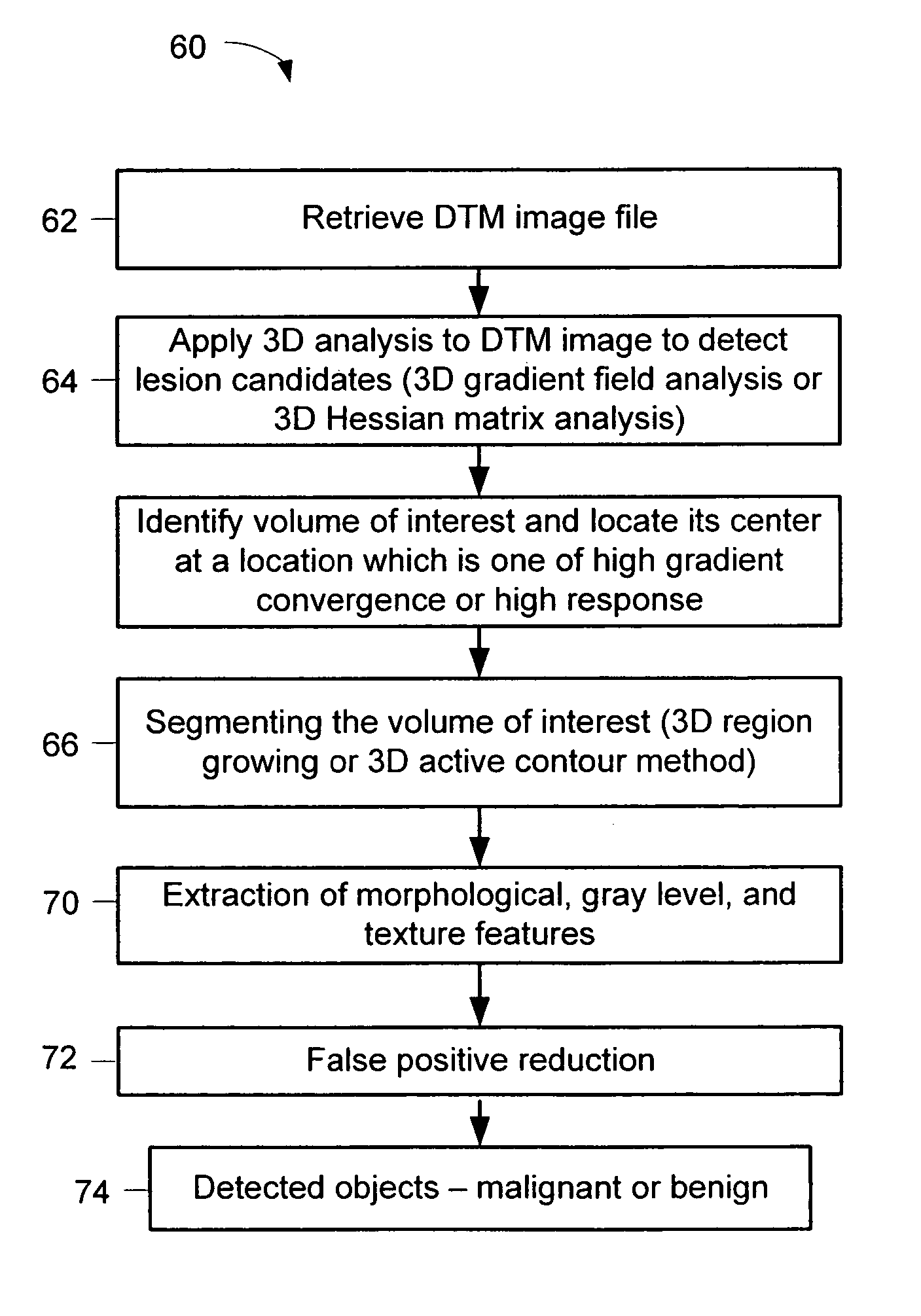
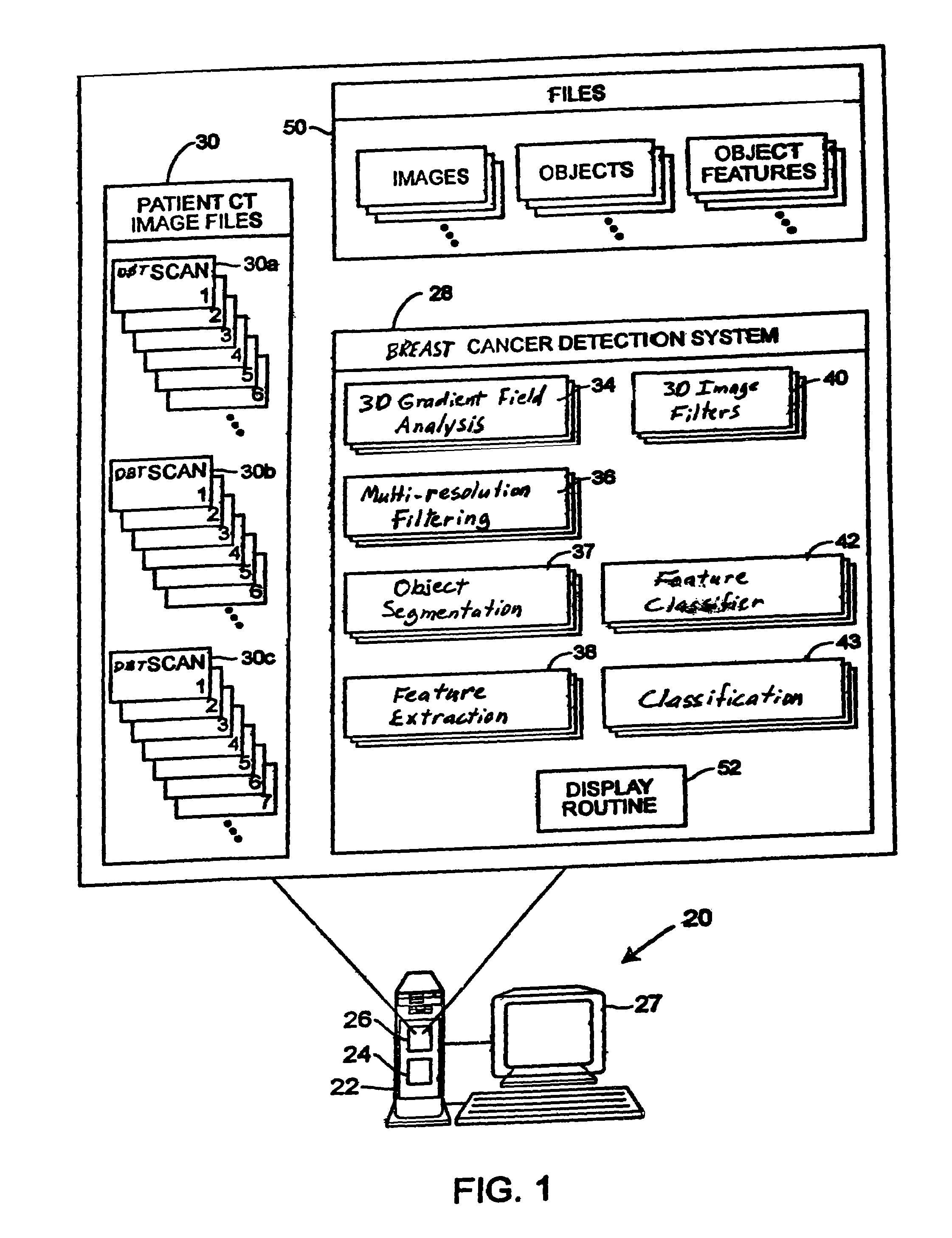
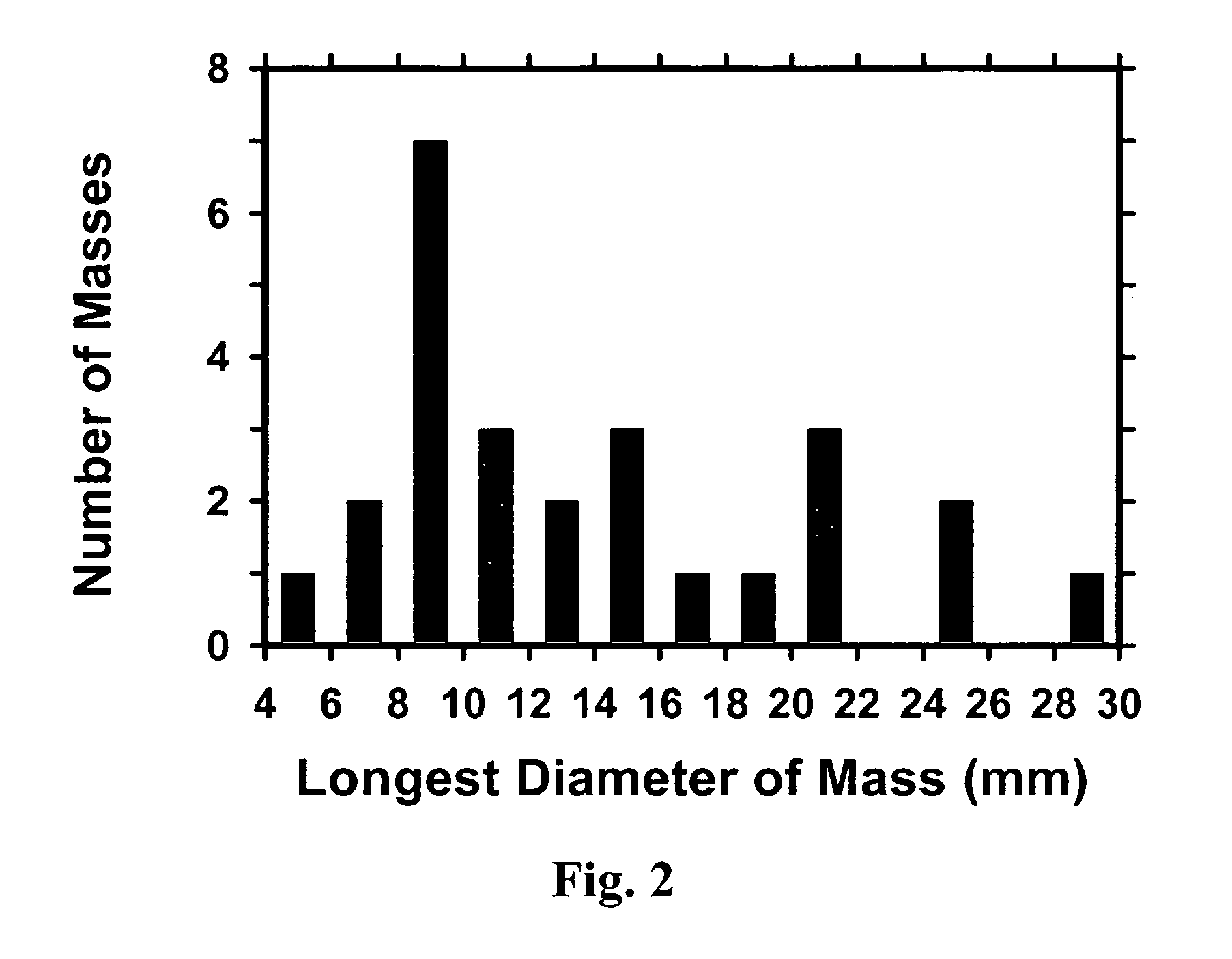
A method for using computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) for digital tomosynthesis mammograms (DTM) including retrieving a DTM image file having a plurality of DTM image slices; applying a three-dimensional gradient field analysis to the DTM image file to detect lesion candidates; identifying a volume of interest and locating its center at a location of high gradient convergence; segmenting the volume of interest by a three dimensional region growing method; extracting one or more three dimensional object characteristics from the object corresponding to the volume of interest, the three dimensional object characteristics being one of a morphological feature, a gray level feature, or a texture feature; and invoking a classifier to determine if the object corresponding to the volume of interest is a breast cancer lesion or normal breast tissue.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Computerized detection of breast cancer on digital tomosynthesis mammograms
InactiveUS7646902B2Breast enlargementExtension of timeImage enhancementImage analysisTomosynthesisGray level
A method for using computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) for digital tomosynthesis mammograms (DTM) including retrieving a DTM image file having a plurality of DTM image slices; applying a three-dimensional gradient field analysis to the DTM image file to detect lesion candidates; identifying a volume of interest and locating its center at a location of high gradient convergence; segmenting the volume of interest by a three dimensional region growing method; extracting one or more three dimensional object characteristics from the object corresponding to the volume of interest, the three dimensional object characteristics being one of a morphological feature, a gray level feature, or a texture feature; and invoking a classifier to determine if the object corresponding to the volume of interest is a breast cancer lesion or normal breast tissue.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Method of image guided intraoperative simultaneous several ports microbeam radiation therapy with microfocus X-ray tubes
This invention pertains to a method of low-cost intraoperative all field simultaneous parallel microbeam single fraction few seconds duration 100 to 1,000 Gy and higher dose radiosurgery with micro-electro-mechanical systems (MEMS)-carbon nanotube based microaccelerators. It ablates cancer cells including the mesenchymal epithelial transformation associated cancer stem cells. Microbeam brachy-therapeutic radiosurgery is performed. Microaccelerators are configured for simultaneous parallel microbeam emission from varying angels to an isocentric tumor. Their additive dose rate at the isocentric tumor is in the range of 10,000 to 20,000 Gy / s. It eliminates most tumor recurrence and metastasis which enhances cancer cure rates. It also exposes cancer antigens which induces cancer immunity. Stereotactic breast core biopsy is combined with, positron emission tomography and computerized tomography and phase-contrast imaging. Parallel microbeam brachytherapy preserves normal breast appearance. Migration of normal stem cells from unirradiated valley regions heals the radiation damage to the normal tissue.
Owner:SAHADEVAN VELAYUDHAN
Methods and compositions for diagnosis and treatment of breast cancer
InactiveUS6399328B1Control metastatic potentialOrganic active ingredientsTumor rejection antigen precursorsAbnormal tissue growthLymphatic Spread
The present invention relates to a novel gene, Di12, that is differentially expressed as a 1.35 kb RNA in breast cancer tissues and cell lines, and in several normal tissues. The full length cDNA encodes a protein of 339 amino acids. Antibodies to the gene product were developed to investigate the expression of Di12 in breast cancer cell-lines and tumors. The Di12 protein was found in tissue sections of infiltrating ductal carcinomas (IDCs), but not in benign or normal breast specimens. Di12 wag also present in IDC-breast cancer patient sera, and its expression level increased markedly if IDC was accompanied by lymph node or distal metastases. As IDC constitutes ~70% of breast cancers seen clinically, the level of Di12 expression is useful for diseases diagnosis predicting disease progression and monitoring a therapeutic treatment.
Owner:MUSC FOUND FOR RES DEV
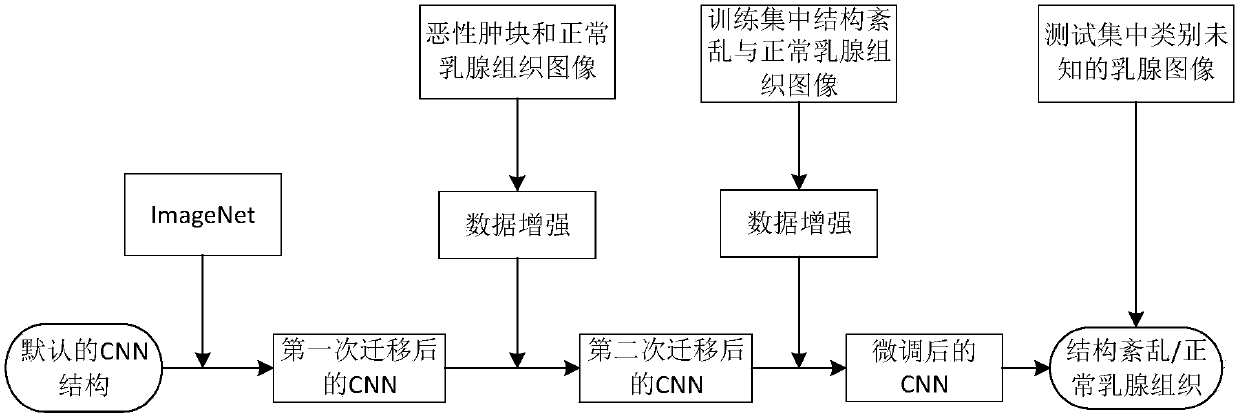
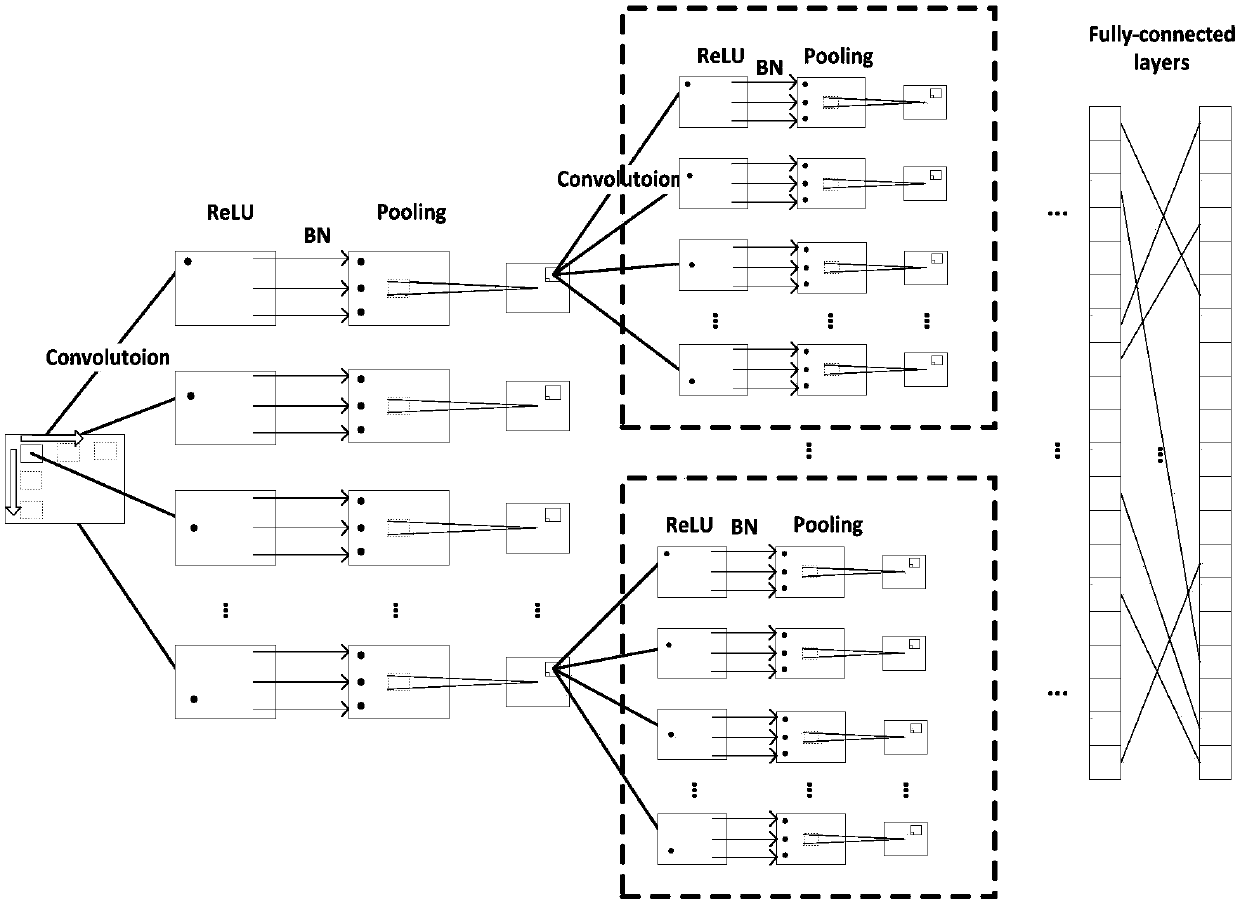
Breast structure disorder identification method based on two transfer and convolutional neural network
InactiveCN107657602AOvercoming the problem of insufficient sample size for structured disorderImprove classification effectImage enhancementImage analysisTransfer modelNerve network
The invention discloses a breast structure disorder identification method based on two transfer and a convolutional neural network. The method is characterized by transferring model parameters trainedin an ImageNet data set to a target convolutional neural network to carry out initialization on model parameters thereof ( first transfer); then, carrying out first fine-tuning training (second transfer) on a target convolutional neural network model through malignant tumor images and normal breast tissue images; carrying out second fine-tuning training through class-information-known structure disorder images and normal breast tissue images in a training set; and finally, carrying out identification on class-information-unknown structure disorder and normal tissues. The method realizes identification based on the convolutional neural network and transfer learning; and compared with the existing method, the method achieves better classification effect and performance.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Classification system, methods and kit for classifying, predicting and treating breast cancer
InactiveUS20160146819A1Good understand and treat breast cancerSolid foundationBiocideOrganic active ingredientsCell phenotypeBreast cancer classification
A novel classification system for breast cancer based on normal breast cell phenotypes and various expression levels of estrogen receptor (ER), androgen receptor (AR), and vitamin D receptor (VDR). The various categories of the classification system are associated with different survival rates and prognoses. The invention includes a method of classifying breast cancer comprises measuring the levels of ER, AR, and VDR in the cancerous tissue, and classifying the breast cancer into one of the above-noted categories according to expression levels. The invention includes a method of predicting the prognosis of breast cancer in a patient and a method of determining a treatment regimen for breast cancer depending on the category in which the breast cancer is classified. The invention includes a method of treating breast cancer according to the expression profile of ER, AR, and VDR detected in the cancerous tissue. Kits for detecting the same are also provided.
Owner:UNIV OF MIAMI
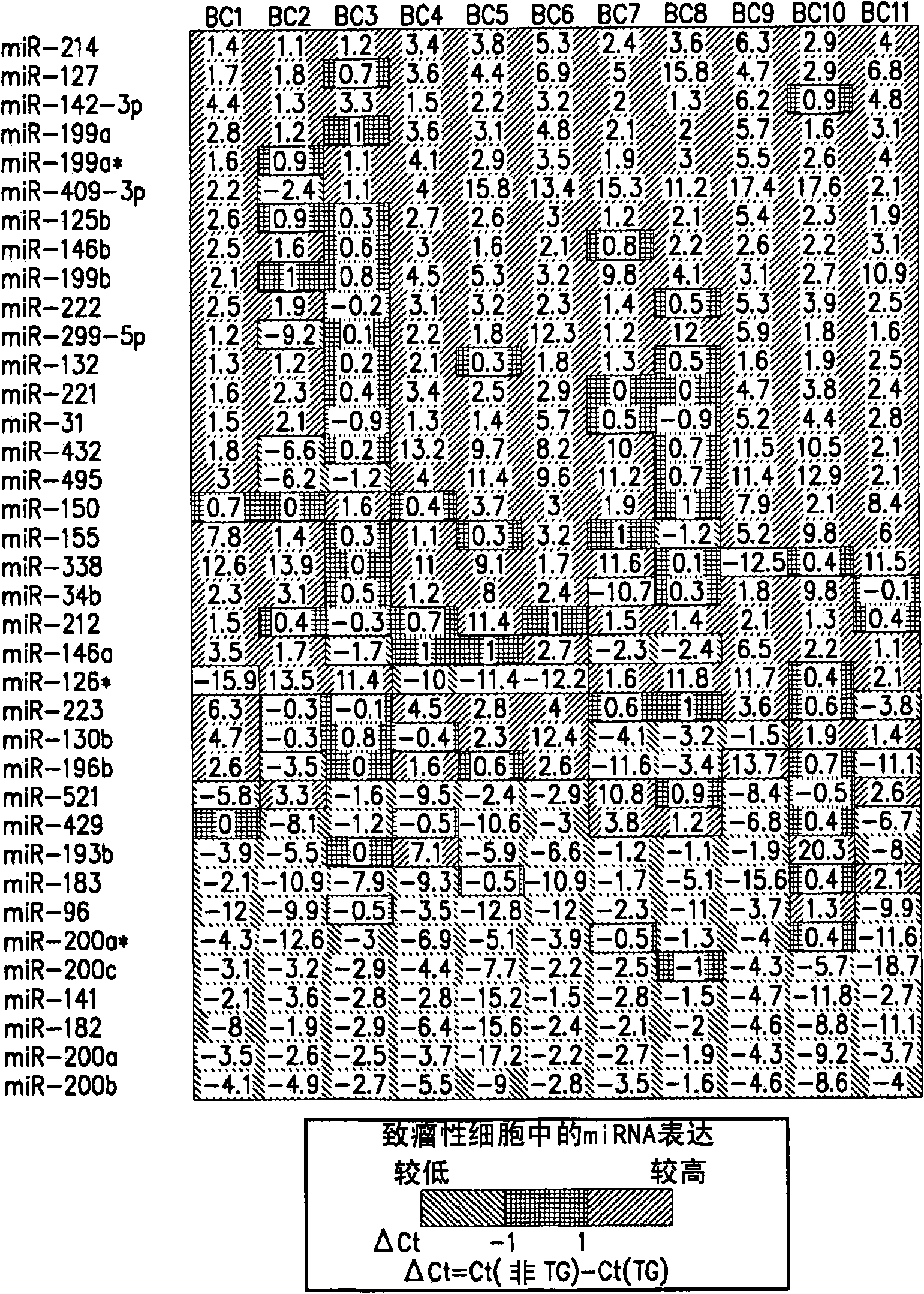
Methods and Compositions Relating to Carcinoma Stem Cells
InactiveUS20110021607A1Reduce expressionHigh expressionOrganic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementCancer cellPolynucleotide
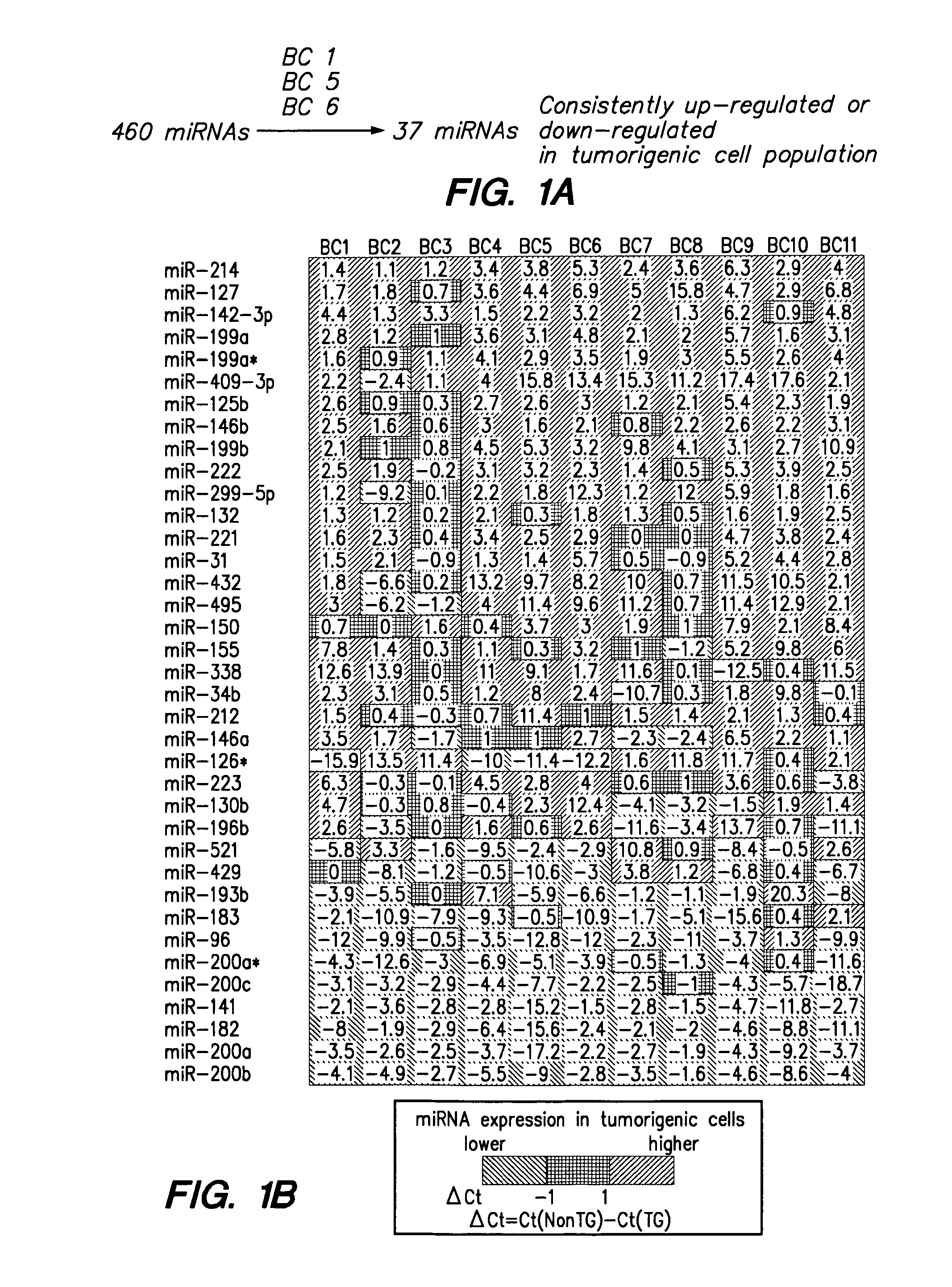
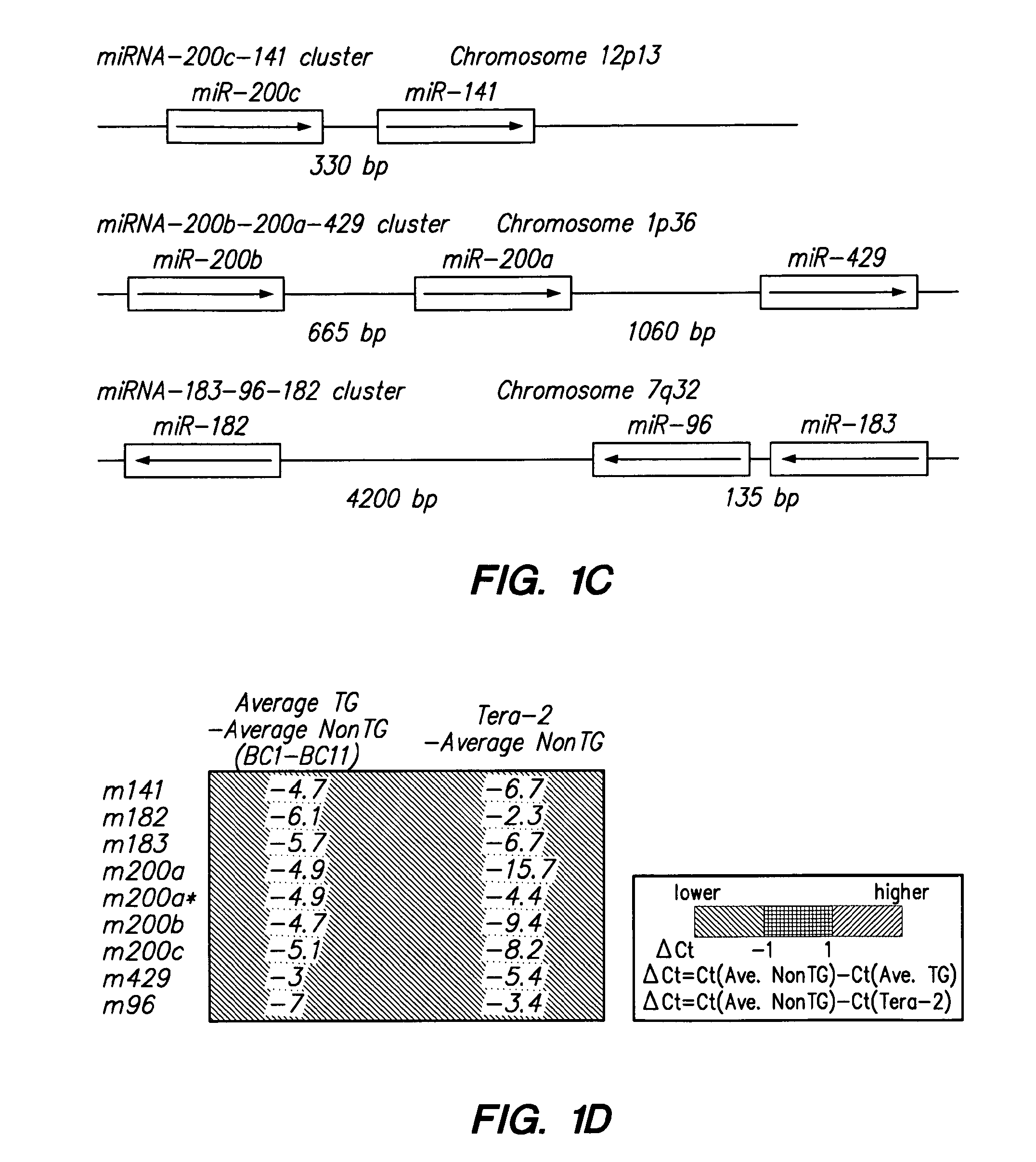
MicroRNA markers of breast cancer stem cells (BCSC) are provided herein. The markers are polynucleotides that are differentially expressed in BCSC as compared to normal counterpart cells. Uses of the markers include use as targets for therapeutic intervention; as targets for drug development, and for diagnostic or prognostic methods relating to breast cancer and BCSC cell populations. BCSCs have the phenotype of having lower expression of certain miRNAs compared to normal breast epithelial cells, or to cancer cells that are not cancer stem cells.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Breast Cancer Biomarker Signatures for Invasiveness and Prognosis
InactiveUS20130190386A1High expressionHigh riskDigital data processing detailsLibrary screeningLymphatic SpreadMicrorna profiling
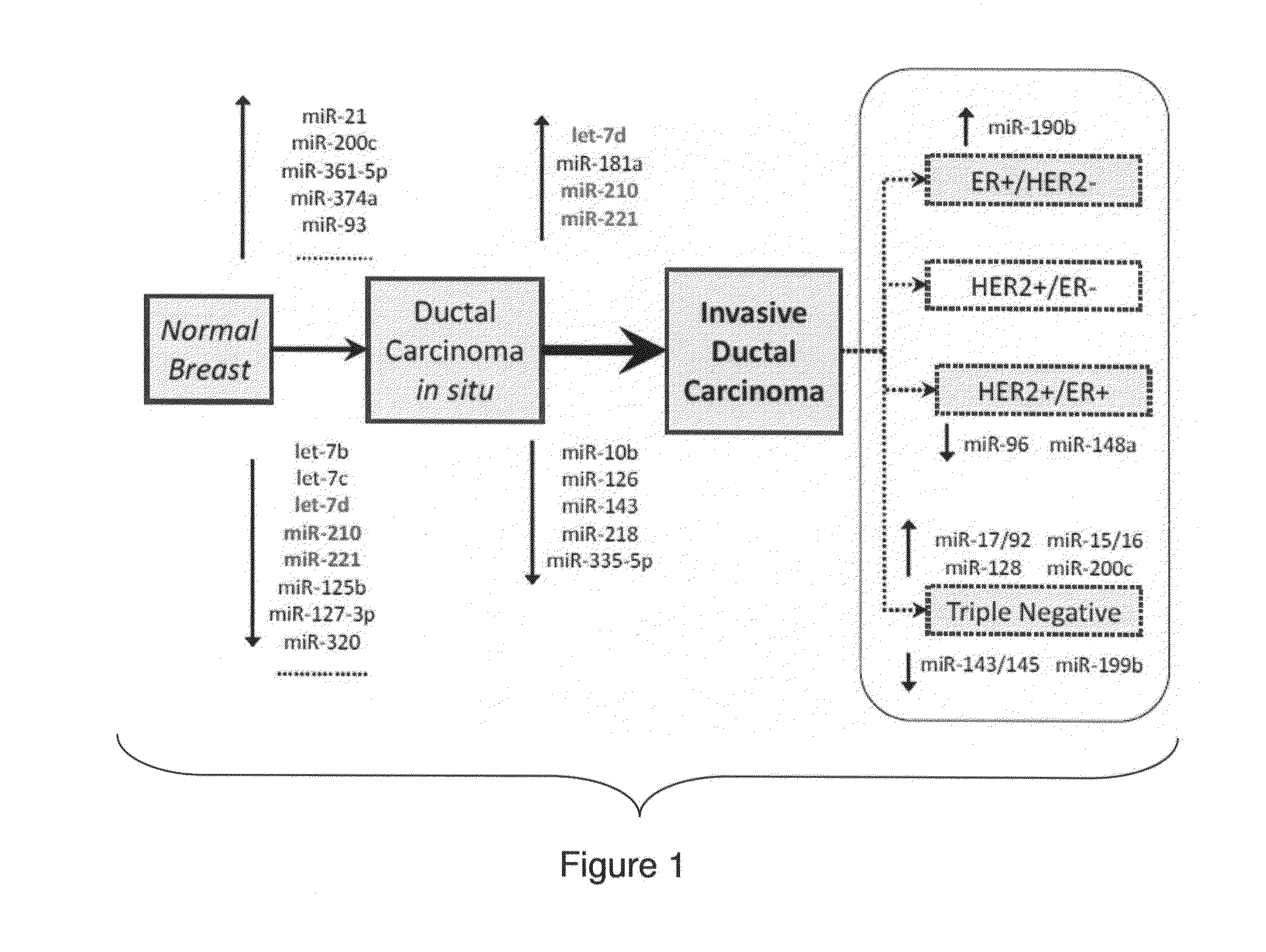
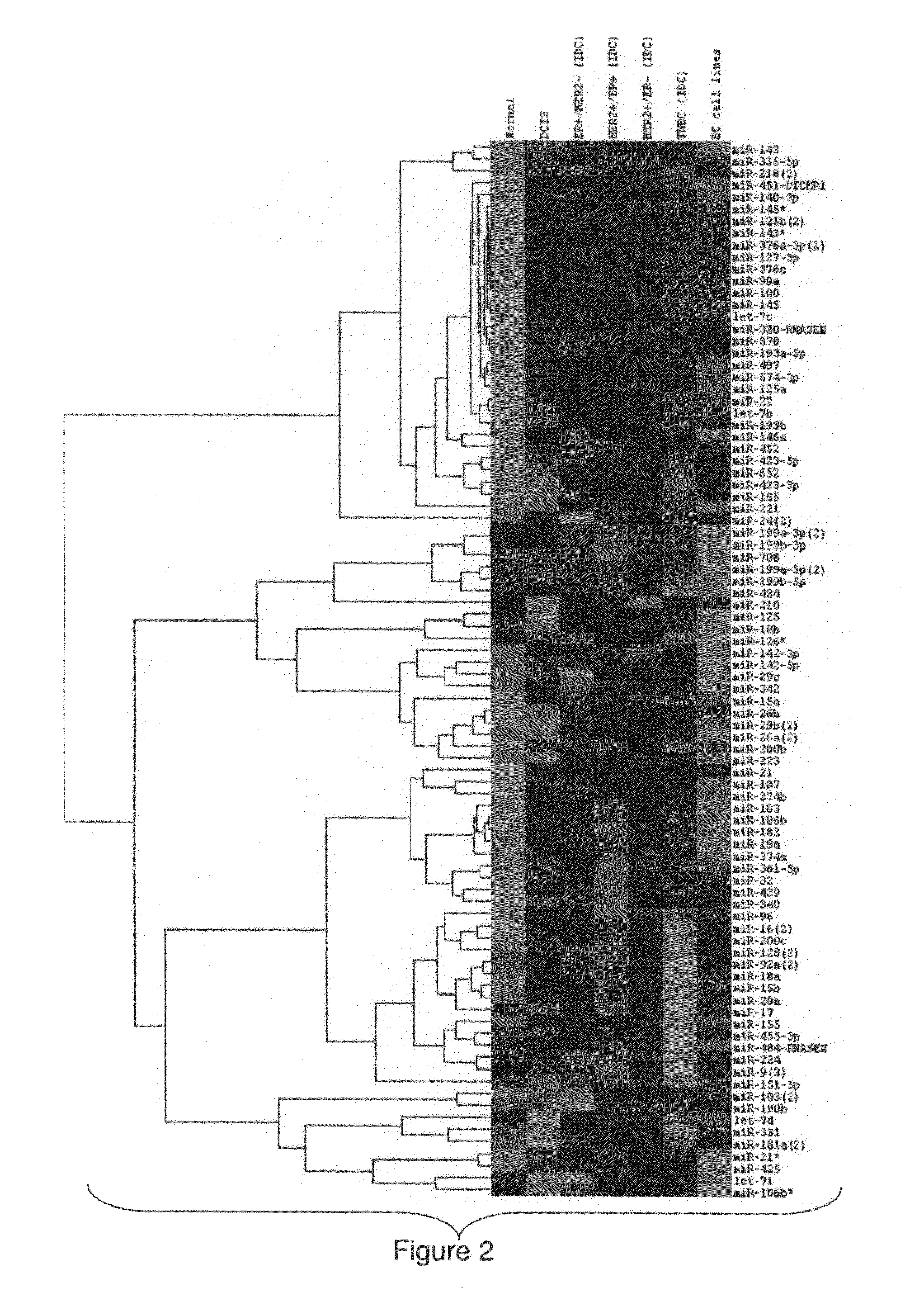
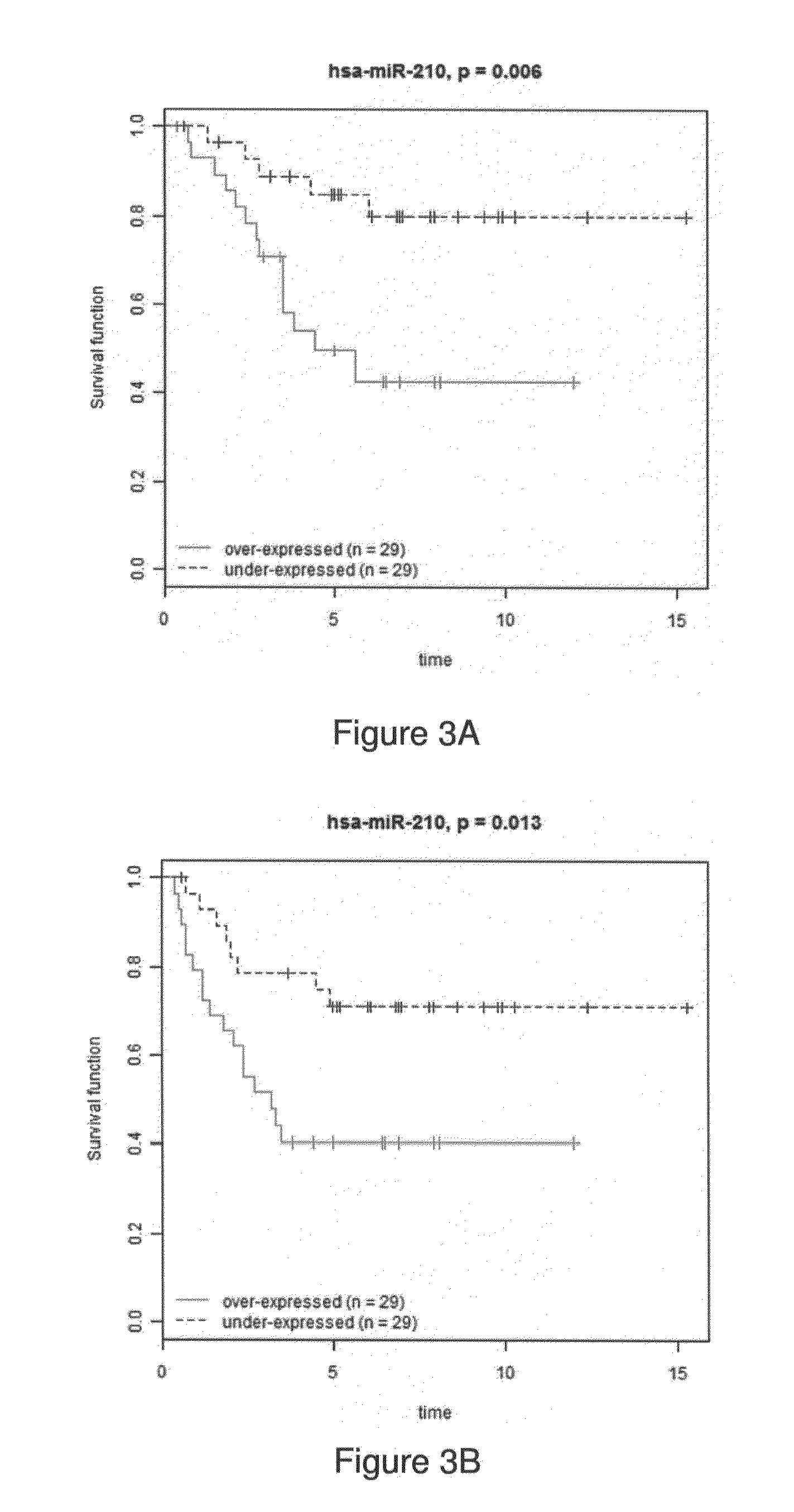
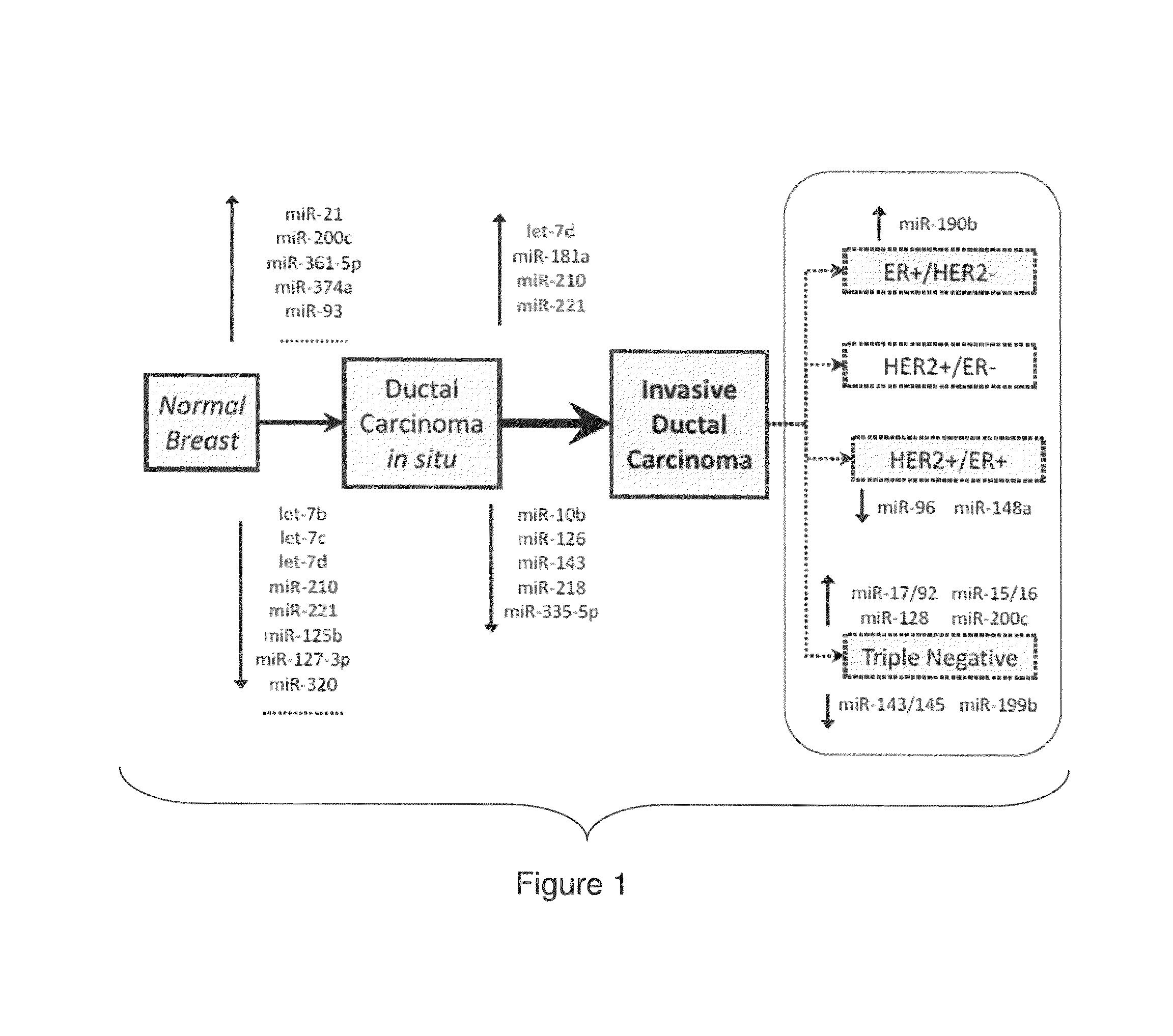
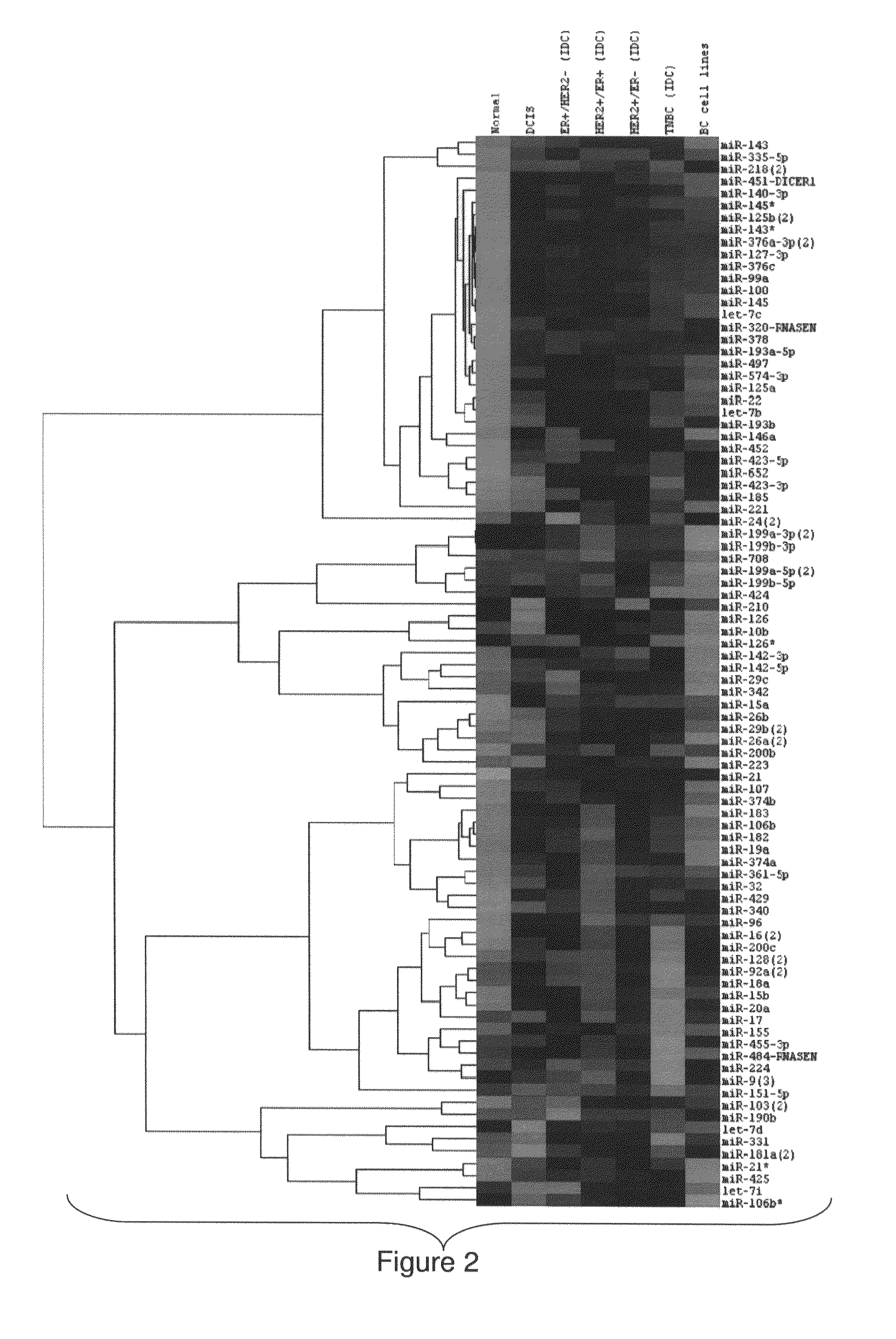
MicroRNA profiles transition from normal breast to ductal carcinoma in situ and transition to invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC) and methods of use thereof are described. Methods of diagnosis and prognosis using microRNA signatures to differentiate invasive from in situ carcinoma are described. Also described is the use of microRNA expression for predicting overall survival and time to metastasis.
Owner:THE OHIO STATES UNIV
Method and apparatus for treating breast lesions using microwaves
InactiveCN1380833AAvoid damageAvoid the risk of proliferationSurgical instrument detailsMicrowave therapyMedicineMicrowave power
A method for selectively heating cancerous conditions of the breast including invasive ductal carcinoma and invasive glandular lobular carcinoma, and pre-cancerous conditions of the breast including ductal carcinoma in-situ, lobular carcinoma in-situ, and intraductal hyperplasia, as well as benign lesions (any localized pathological change in the breast tissue) such as fibroadenomas and cysts by irradiation of the breast tissue with adaptive phased array focused microwave energy is introduced. Microwave energy provides preferential heating of high-water content breast tissues such as carcinomas, fibroadenomas, and cysts compared to the surrounding lower-water content normal breast tissues. To focus the microwave energy in the breast, the patient's breast can be compressed and a single electric-field probe, inserted in the central portion of the breast, or two noninvasive electric-field probes on opposite sides of the breast skin, can be used to measure a feedback signal to adjust the microwave phase delivered to waveguide applicators on opposite sides of the compressed breast tissue. The initial microwave power delivered to the microwave applicators is set to a desired value that is known to produce a desired increase in temperature in breast tumors. Temperature feedback sensors are used to measure skin temperatures during treatment to adjust the microwave power delivered to the waveguide applicators to avoid overheating the skin. The microwave energy delivered to the waveguide applicators is monitored in real time during treatment, and the treatment is completed when a desired total microwave energy dose has been administered. By heating and destroying the breast lesion sufficiently, lesions can be reduced in size and surrounding normal breast tissues are spared so that surgical mastectomy can be replaced with surgical lumpectomy or the lesions can be completely destroyed so that surgical mastectomy or lumpectomy is avoided.
Owner:CELSION CANADA
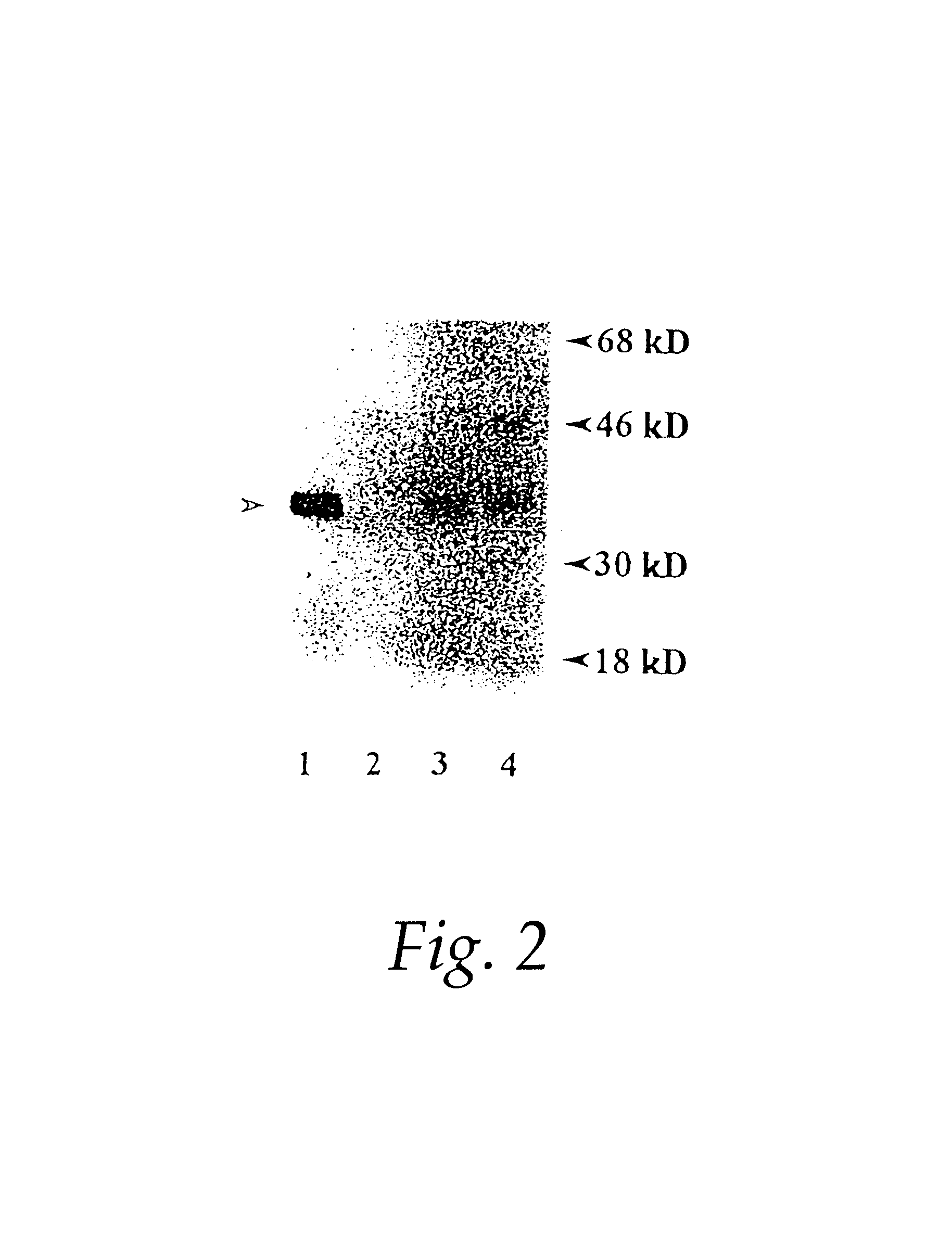
Molecular marker for breast carcinoma diagnosis
The invention discloses a molecular marker for diagnosing breast cancer, which is used for detecting expression of the thioredoxin (TRX) and the thioredoxin binding protein 2 (TRX-binding protein-2, TBP-2) in surrounding normal breast tissue and mass tissue. A protein immunoblot experiment is used for detecting the expression amount of the thioredoxin and the thioredoxin binding protein 2; in breast mass tissue, the expression of the thioredoxin is increased and the expression of the thioredoxin binding protein 2 is decreased; as significant difference exists between the breast mass tissue and the normal breast tissue, the thioredoxin and the thioredoxin binding protein 2 can be used as a new molecular marker of breast cancer and used for the clinical diagnosis of breast cancer.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
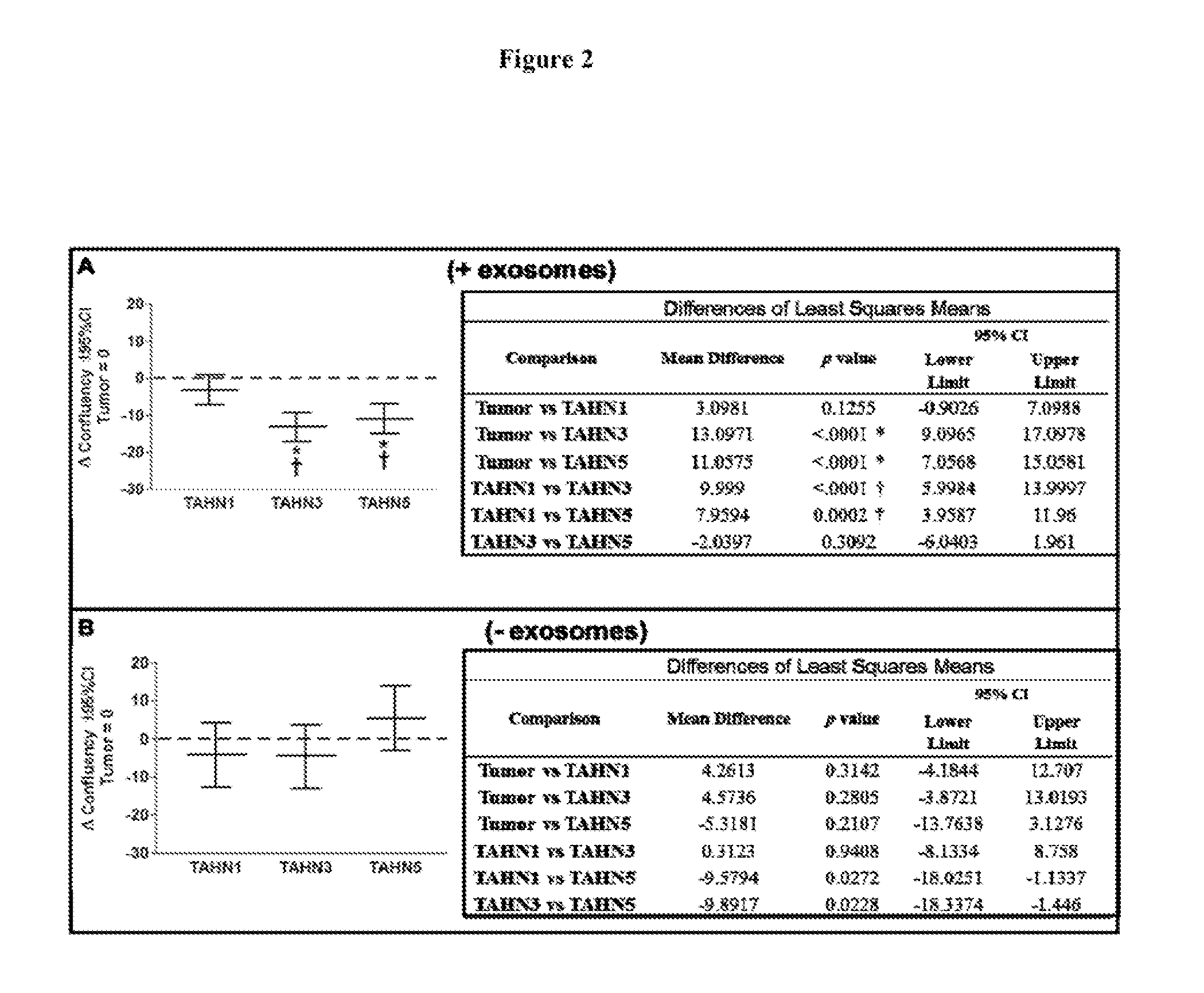
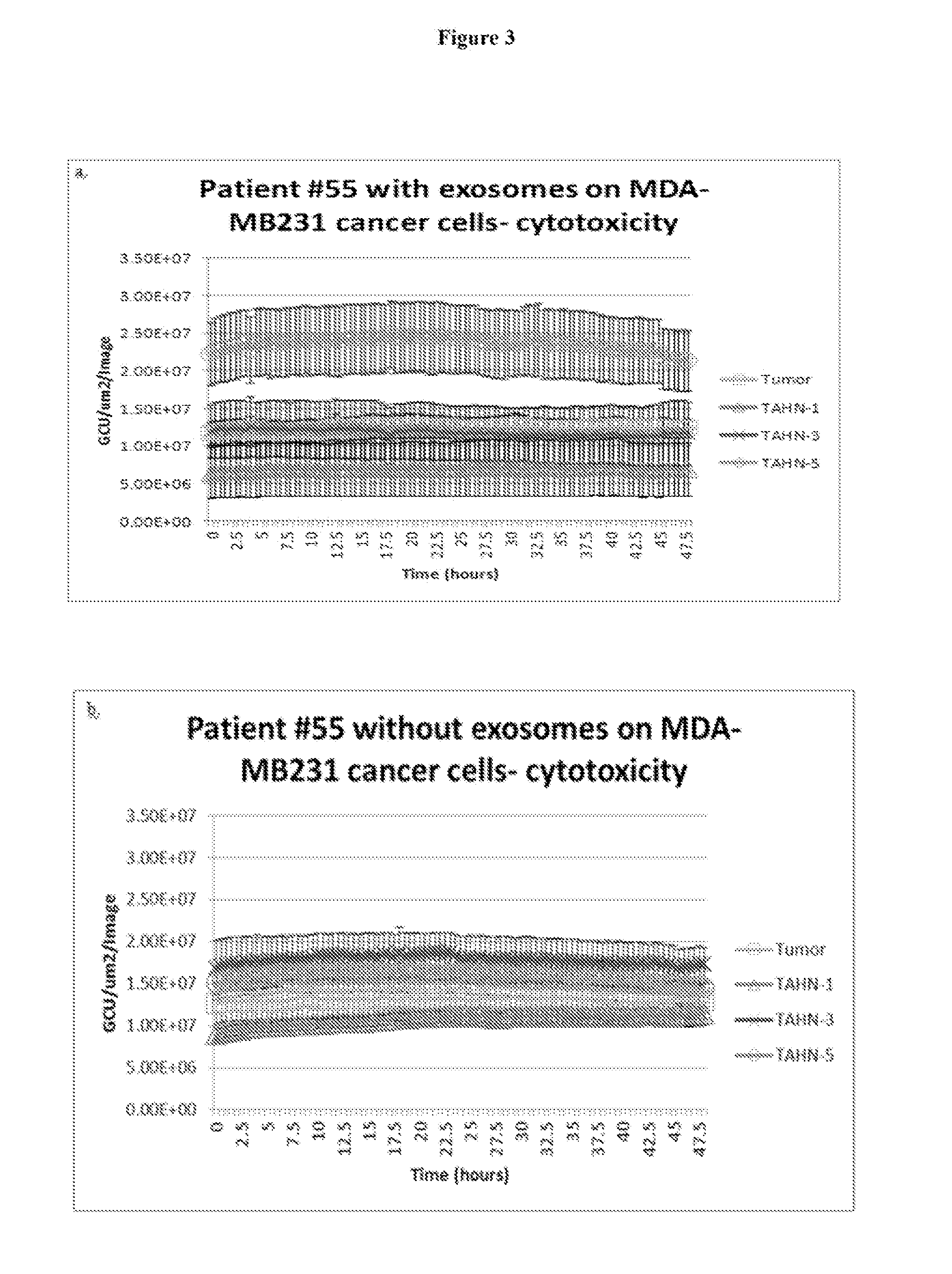
Exosomes as a therapeutic for cancer
In one embodiment, the invention provides substantially purified exosomes which induce apoptosis in breast cancer cells and which are derived from a cultured medium of histologically normal breast tissue cells that are obtained from tumor-adjacent normal breast tissue. Related methods of treating breast cancer and pharmaceutical formulations are also provided.
Owner:STC UNM
Methods and compositions relating to carcinoma stem cells
MicroRNA markers of breast cancer stem cells (BCSC) are provided herein. The markers are polynucleotides that are differentially expressed in BCSC as compared to normal counterpart cells. Uses of the markers include use as targets for therapeutic intervention; as targets for drug development, and for diagnostic or prognostic methods relating to breast cancer and BCSC cell populations. BCSCs have the phenotype of having lower expression of certain miRNAs compared to normal breast epithelial cells, or to cancer cells that are not cancer stem cells.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Breast cancer biomarker signatures for invasiveness and prognosis
InactiveUS8859202B2Improve expression levelHigh riskDigital data information retrievalSugar derivativesLymphatic SpreadMicrorna profiling
MicroRNA profiles transition from normal breast to ductal carcinoma in situ and transition to invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC) and methods of use thereof are described. Methods of diagnosis and prognosis using microRNA signatures to differentiate invasive from in situ carcinoma are described. Also described is the use of microRNA expression for predicting overall survival and time to metastasis.
Owner:THE OHIO STATES UNIV
Cancer diagnosis method using cell growth inhibiting and cell differentiation specific SYG972 gene and genomic DNA and promoter thereof
The present invention relates to a diagnosis method of cancer using SYG972 gene and to the genomic DNA and to a promoter regulating transcription of the gene. Expression of SYG972 gene is greatly reduced in breast cancer cells compared to normal breast cells. Therefore the present invention provides a method of diagnosis method by using the gene of the present invention or its fragments as a probe. SYG972 genomic according to the present invention is composed of 4 axons and 3 introns. Promoter is 3 kb long from the transcription initiating site in the 5' direction. SYG972 genomic DNA and promoter can be used to design and screen drugs to promote or to inhibit apoptosis and differentiation of cells, especially to screen drugs to treat cancer, a disease wherein cell growth and differentiation is abnormal.
Owner:SAMYANG BIOPHARMLS CORP
Application of ruthenium pyridine (II) complexes as antitumor drugs
InactiveCN103860564AEnhanced inhibitory effectGood inhibitory effectOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsGlandular Epithelial CellsHuman breast
The invention relates to an application of ruthenium pyridine (II) complexes as antitumor drugs. In particular, the inhibition effect of two ruthenium pyridine (II) complexes on growth of a highly invasive human breast cancer cell line (MDA-MB-231), a hepatoma carcinoma cell (HepG2), a human esophageal carcinoma cell (EC-1), a human breast cancer cell (MCF-7) and a normal breast epithelial cell (HAcat) is tested. The result shows that the complexes have inhibiting effects on four cancer cells to different extents, and in particular, the complex I has strong inhibiting effect on the MDA-MB-231 and the complex II has a very remarkable inhibiting effect on MDA-MB-231 and HepG2. The two complexes have weak toxicity to the HAcat and show good selectivity.
Owner:TENTH PEOPLES HOSPITAL OF TONGJI UNIV
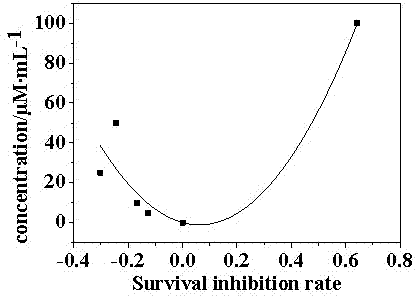
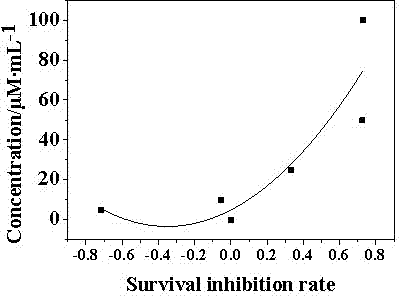
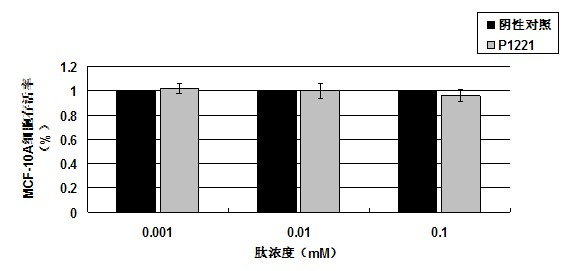
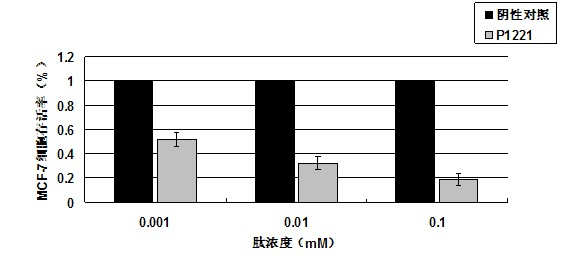
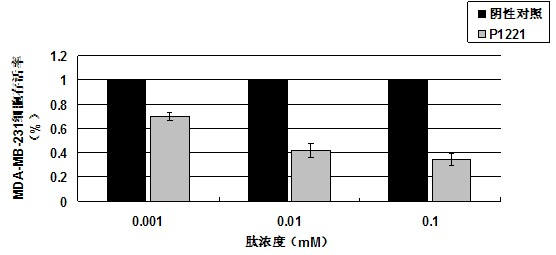
Oligopeptide with breast cancer resistant activity and application thereof
InactiveCN102532268ASmall molecular weightStrong breast cancer activityPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptidesCancer cellOncology
The invention discloses an oligopeptide with breast cancer resistant activity. The oligopeptide has a sequence of His-Asn-Tyr-Gly-Phe-Val-Pro-Ser-Leu. The oligopeptide can selectively inhibit the growth of in-vitro breast cancer cells under low concentration and does not have any influence on normal breast cells. In-vivo experiments show that the oligopeptide has a strong effect of inhibiting the growth and proliferation of cancer cells and has an obvious dose-effect relationship. Because of a safe, efficient and ideal anti-cancer effect, the oligopeptide can be used for preparing anti-cancer medicines and has a good application prospect.
Owner:ZHUHAI JINLONG BIOTECH CO LTD
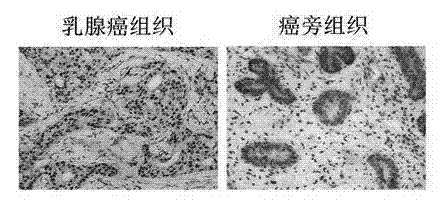
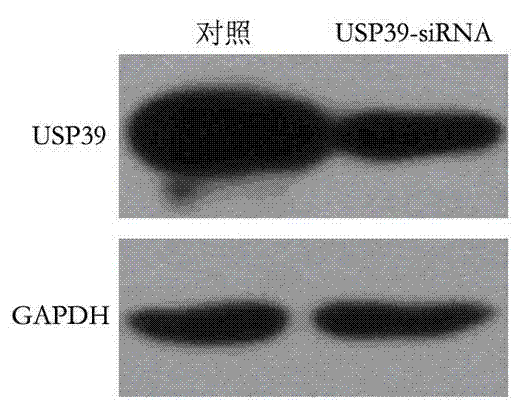
Recombinant lentiviral vector containing ubiquitin-specific protease gene USP39-shRNA (short hairpin ribonucleic acid) and application thereof
The invention provides a recombinant lentiviral vector containing ubiquitin-specific protease gene USP39-shRNA (short hairpin ribonucleic acid) and application thereof. The test proves that expression of USP39 in breast cancer tissue is obviously higher than that in normal breast tissue; the immunohistochemical detection confirms that the expression of USP39 in the breast cancer tissue is obviously higher than that in normal breast tissue; the immunohistochemical detection confirms that expression of USP39 protein in the breast cancer tissue is obviously higher than that in para-carcinoma tissue; siRNA (small interfering ribonucleic acid) is designed in a breast cancer cell system to interfere the expression of the USP39; it is found that proliferation of breast cancer cell after reducing the USP39 is obviously restrained; the cell apoptosis ratio is obviously improved; the cell ratio at the G1 stage is increased; the cell ratio at the S sage is reduced; and the clonality of the cell is obviously reduced. The test proves that the USP39 has an important role in facilitation of development of the breast cancer; and theoretical and experimental basis is provided for preparation of a drug for preventing and treating the breast cancer by the lentiviral vector containing USP39-shRNA.
Owner:HOSPITAL ATTACHED TO QINGDAO UNIV
Apparatus for treating breast lesions using microwaves
A method for selectively heating cancerous conditions of the breast including invasive ductal carcinoma and invasive glandular lobular carcinoma, and pre-cancerous conditions of the breast including ductal carcinoma in-situ, lobular carcinoma in-situ, and intraductal hyperplasia, as well as benign lesions (any localized pathological change in the breast tissue) such as fibroadenomas and cysts by irradiation of the breast tissue with adaptive phased array focused microwave energy is introduced. Microwave energy provides preferential heating of high-water content breast tissues such as carcinomas, fibroadenomas, and cysts compared to the surrounding lower-water content normal breast tissues. To focus the microwave energy in the breast, the patient's breast can be compressed and a single electric-field probe, inserted in the central portion of the breast, or two noninvasive electric-field probes on opposite sides of the breast skin, can be used to measure a feedback signal to adjust the microwave phase delivered to waveguide applicators on opposite sides of the compressed breast tissue. The initial microwave power delivered to the microwave applicators is set to a desired value that is known to produce a desired increase in temperature in breast tumors. Temperature feedback sensors are used to measure skin temperatures during treatment to adjust the microwave power delivered to the waveguide applicators to avoid overheating the skin. The microwave energy delivered to the waveguide applicators is monitored in real time during treatment, and the treatment is completed when a desired total microwave energy dose has been administered. By heating and destroying the breast lesion sufficiently, lesions can be reduced in size and surrounding normal breast tissues are spared so that surgical mastectomy can be replaced with surgical lumpectomy or the lesions can be completely destroyed so that surgical mastectomy or lumpectomy is avoided.
Owner:CELSION CANADA
Cell growth inhibiting and cell differentiation specific SYG972 gene, genomic DNA and promoter thereof
The present invention relates to a diagnosis method of cancer using SYG972 gene and to the genomic DNA and to a promoter regulating transcription of the gene. Expression of SYG972 gene is greatly reduced in breast cancer cells compared to normal breast cells. Therefore the present invention provides a method of diagnosis method by using the gene of the present invention or its fragments as a probe. SYG972 genomic according to the present invention is composed of 4 exons and 3 introns. Promoter is 3 kb long from the transcription initiating site in the 5' direction. SYG972 genomic DNA and promoter can be used to design and screen drugs to promote or to inhibit apoptosis and differentiation of cells, especially to screen drugs to treat cancer, a disease wherein cell growth and differentiation is abnormal.
Owner:SAMYANG BIOPHARMLS CORP
Preparation method and application of recombination tumor necrosis factor relevant cell apoptosis induction ligand protein
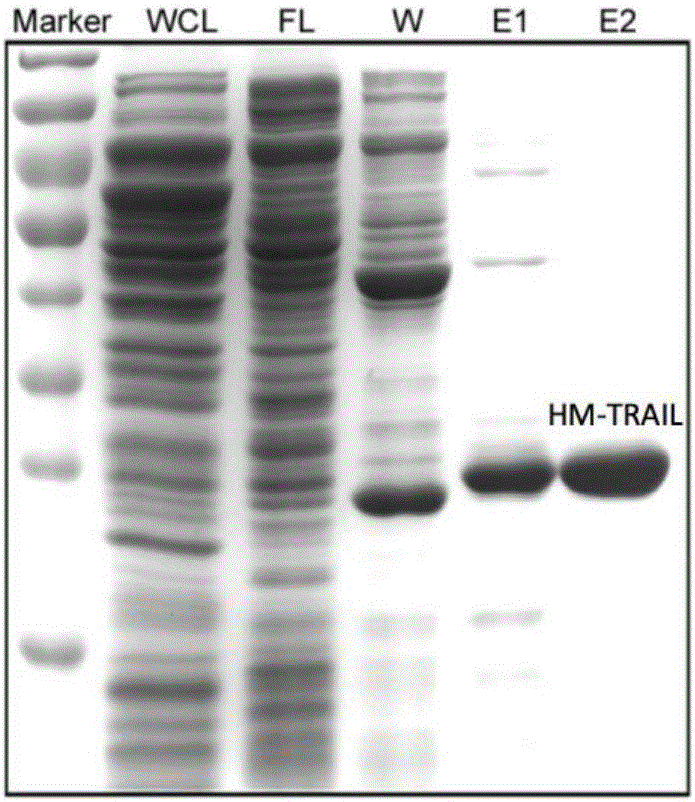
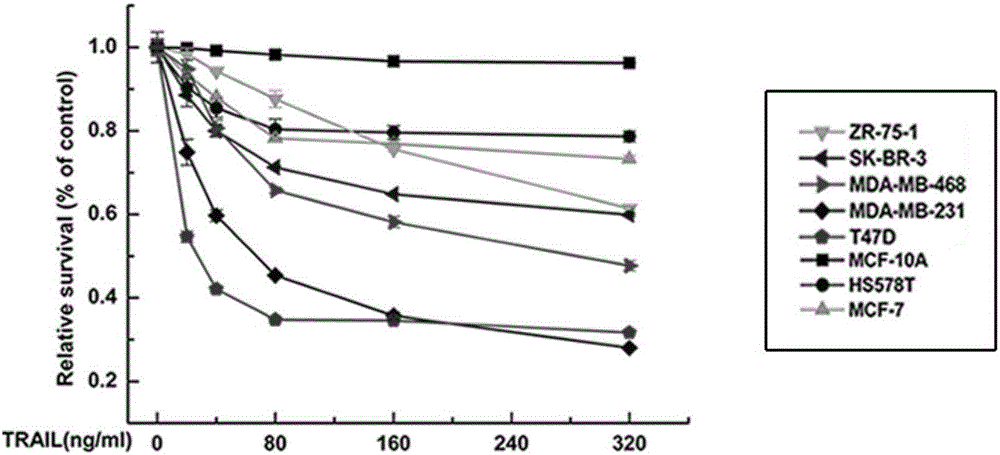
ActiveCN106188311AImprove stabilityImprove solubilityBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsTRAIL ProteinWilms' tumor
The invention discloses recombination human HM-TRALL protein with an amino acid sequence shown in the SEQ ID NO.1. The method comprises the steps that a human recombination HM-TRALL protein expression carrier containing a His6-Myc label is built at first, recombination bacteria for expressing human recombination HM-TRALL protein are built through the carrier, recombinant expression is carried out on the recombination human HM-TRALL protein through IPTG induction, extraction and purification are carried out, and high-purity HM-TRAIL protein is obtained. The recombination human HM-TRALL protein can selectively induce apoptosis of breast cancer cells in vitro, and will not cause normal breast cell apoptosis. The prepared recombination human HM-TRALL protein has the advantages of being good in stability and high in dissolving degree, can obviously induce apoptosis of tumor cells and is good in application prospect.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV QILU HOSPITAL
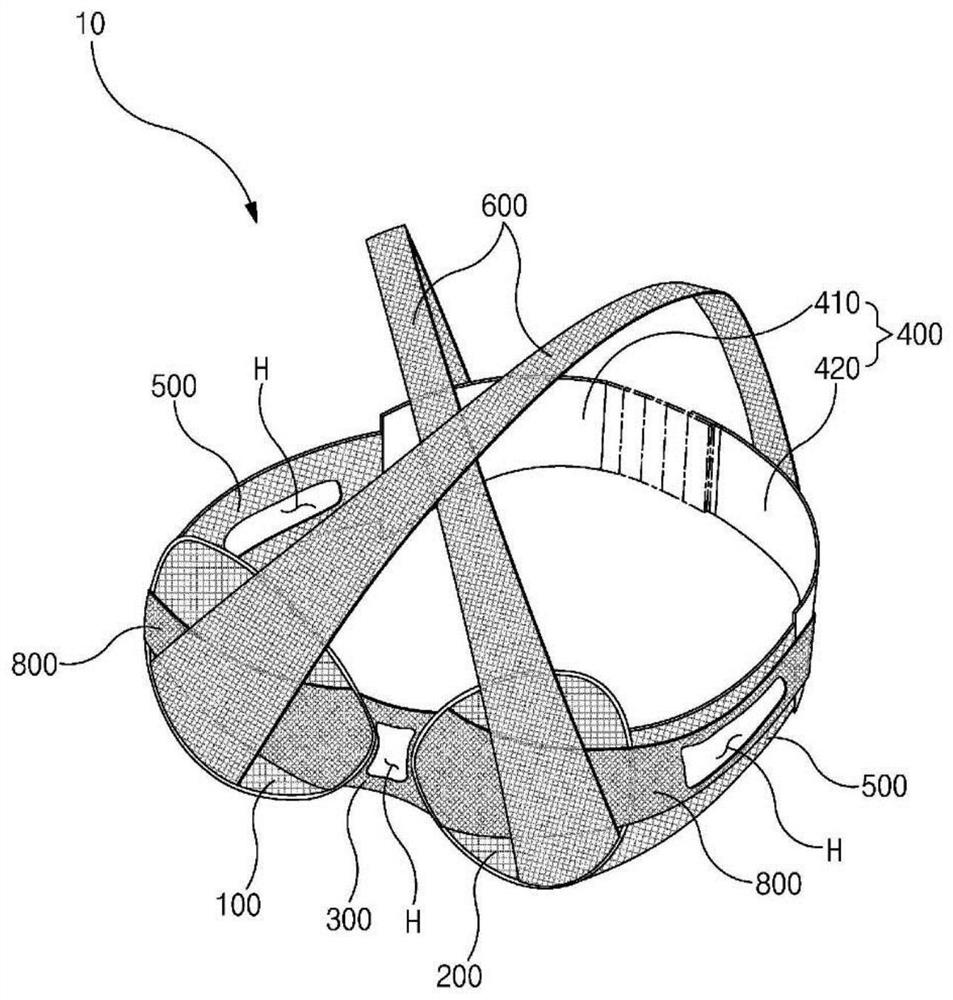
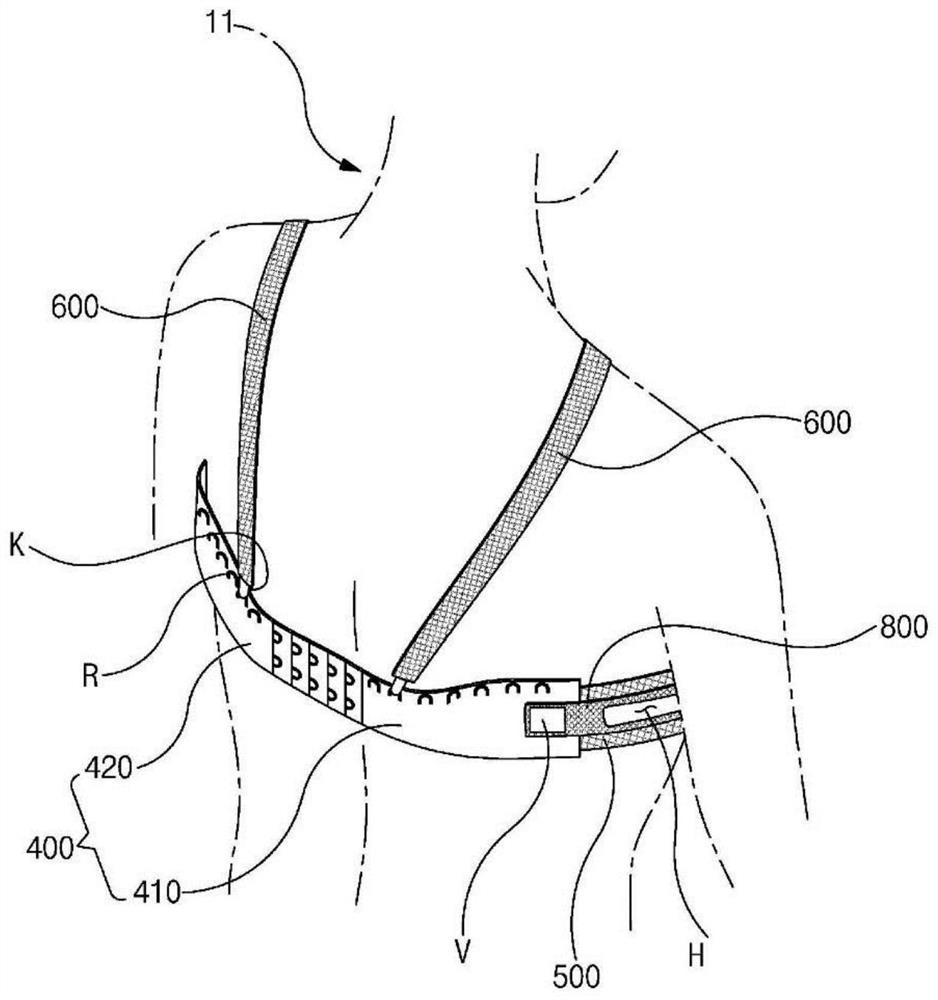
Brassiere for radiation therapy
ActiveCN113015453AAvoid transmissionReduce transmissionBrassieresX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyRadiation DosagesRadiology
A brassiere for radiation therapy is disclosed. The brassiere for radiation therapy of the present invention comprises: a pair of covers that cover a patient's breasts; a connecting member that connects the covers between the pair of covers; a rear band that is in close contact with the patient's back; and a side compression band which has one end coupled to the covers at a connecting member side and the other end detachably coupled to the rear band, wherein when the position in which the other end of the side compression band is coupled to the rear band is adjusted, the positions of the breasts change. According to the present invention, it is possible to provide the brassiere for radiation therapy which does not overly compress the patient's chest while compressing a breast to make the heterogeneity of breast skin tissue flat, and separates the contralateral normal breast so that a radiation dose is not transmitted to the contralateral normal breast.
Owner:IND ACADEMIC COOP FOUND YONSEI UNIV
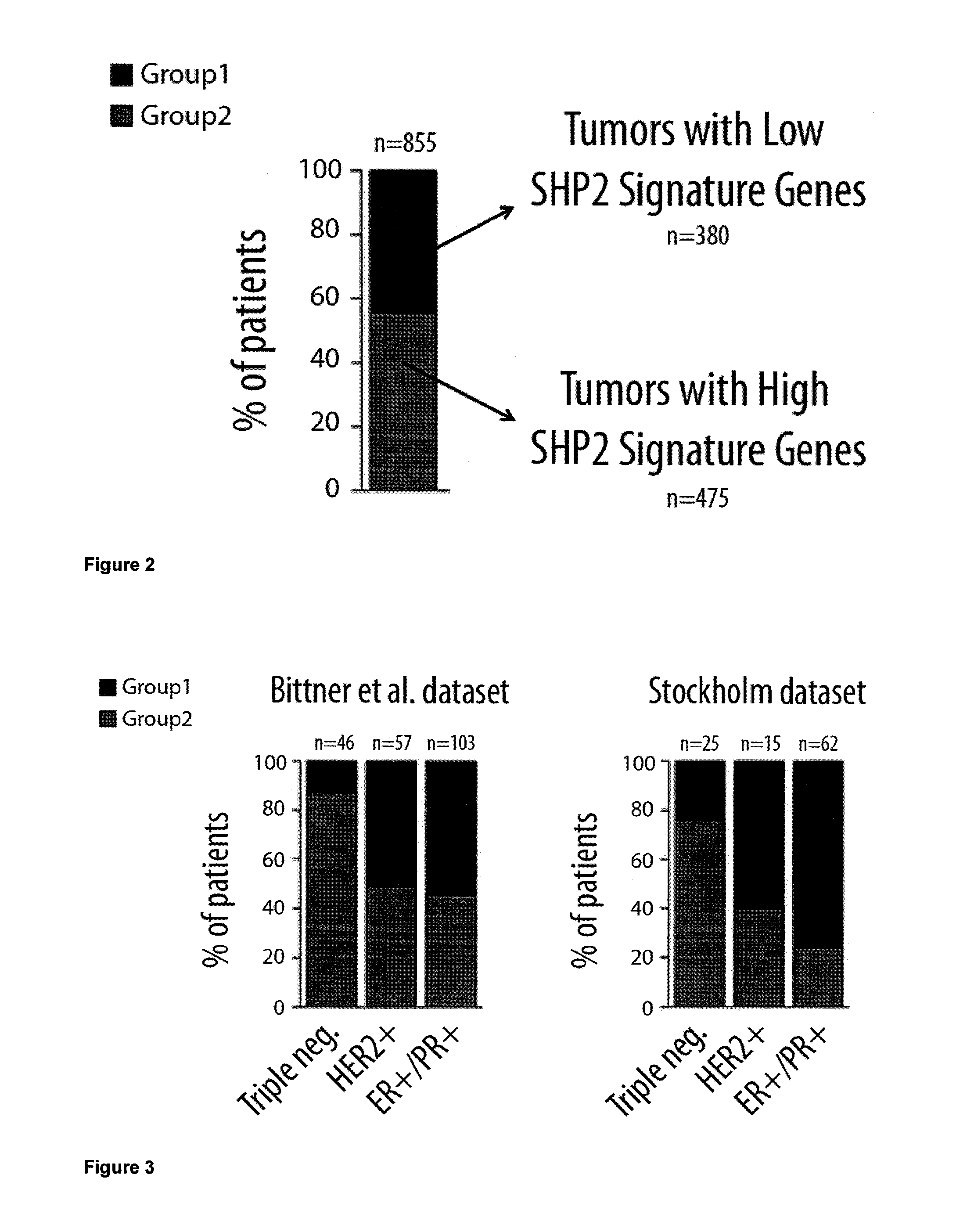
Protein tyrosine phosphatase, non-receptor type 11 (ptpn11) and triple-negative breast cancer
The present invention relates to a method for treating breast cancer in a subject having a breast cancer of the triple-negative type, which method comprises the step of administering to said subject a therapeutically effective amount of a modulator of the protein tyrosine phosphatase, non-receptor type 11 (PTPN11) gene or of its gene product (Shp2). The present invention also relates to a method for treating breast cancer in a subject having a breast cancer over-expressing the “SHP2 signature” genes, as compared to normal breast tissue samples, which method comprises the step of administering to said subject a therapeutically effective amount of a modulator of the protein tyrosine phosphatase, non-receptor type 11 (PTPN11) gene or of its gene product (Shp2), wherein said “SHP2 signature” genes consist of the genes SGCB, ZSCAN12, ID4, ZIC3, CPVL, HLA-A, MCOLN3, SPATA18, TMEM45A, GNAL, CYBRD1, TSPAN7, ZEB1, CNTLN, NEFL, CENPV, ARL6, HPRT1, LRRC34, PDPN, BEND7, SLC16A10, FAM27E1, PLEKHA1, HERC5, CHIC1, PHF6, ELOVL4, ANTXR1, PRAME, SCML1, CLIP4, CECR2, CNOT10, IGF2BP3, NAP1L3, GPC3, KIAA1804, DGKE, FAS, EPHA6, KDELC1, CRISPLD1, DOCK3, ACSL4, CNTNAP3, PLEKHM3, RDX, TBX18, RRAGD, HOXB5, SNCA, FUNDC2, ITGA8, HFM1, IGF2BP2, CCND2, SGTB, MKX, CRYBG3, WBP5, LPHN3, BEX4, CPNE8, GLDC, SLC35F1, HOXA13, SERPINF1, NEFM, SYCP2L, FHL1, APOBEC3C, CALD1, FKBP10, HOXD11, DENND2C, LRRC49, FAM55C, KIAA0408, HOXB9, C160RF62, ACN9, TUSC3, ELOVL2, SPOCK3, HOXB6, WDR35, MPP1, FBX038, PRKAA2, SLAIN1, NPHP3, KIAA1524, PRPS1, GJC1, AMOT, SLC9A6, KCTD12, NUP62CL, DZIP3, JAM3, HOXA9, ANKRD19, CDKN2A, BCAT1, OAT, LPHN2, CCDC82, HSD17B11, SAMHD1, WDR17, STK33, GSTP1, TRPC1, CKB, LIN28B, ALDH1L2, SACS, CLGN, MY03A, EPB41L3, SLC25A27, VCAN, GPX8, GALNT13, PVRL3, MOXD1, HEY1, MAP7D3, ESD, MPP6, EYA4, SPG20, ZDBF2, ZNF204, IFT57, AKR1B1, ADAT2, ZNF717, CCDC88A, ZNF215, MIDI, FBN2, LOC100130876, TCEAL8, IGF2BP1, ANKRD18B, PLAGL1, PM20D2, LDHB, C150RF51, PTPN11, EPB41L2, TLE4, GOLM1, C60RF192, HOXD13, SLIT2, UCHL1, DYNC2H1, CPS1, GPR180, PYGL, NRN1, PRTFDC1, SLC16A1, DSC3, TMC01, LRCH2, SLC6A15, DZIP1, HOXA5, HSPA4L, CDR1, PLS3, ECHDC1, SMARCA1, CXORF57, HOXD10, and IRS4.
Owner:NOVARTIS FORSCHUNGSSTIFTUNG ZWEIGNIEDERLASSUNG FRIEDRICH MIESCHER INSTITTUE FOR BIOMEDICAL RES
Light artificial breast and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a light artificial breast and a preparation method thereof. The light artificial breast includes a silica-gel layer, a first upright cotton layer and a second upright cotton layer, wherein the silica-gel layer is located at the middle, and the first upright cotton layer and the second upright cotton layer are located at the two sides of the silica-gel layer; the silica-gellayer includes a gel layer and a macromolecular thin film, wherein the gel layer is located inside the silica-gel layer, and the macromolecular thin film is located outside the silica-gel layer. According to the light artificial breast, a method of combining medical-grade silica gel with healthy, environment-friendly and low-specific-gravity upright cotton is adopted to achieve the purpose of reducing the specific gravity of an artificial breast prosthesis, and the artificial breast prosthesis has the advantages that specific gravity is low, breathability is good, and epidermis damage caused by making contact with sharp objects can be avoided; the side edge of the silica-gel layer is provided with protrusions, a guide gap is formed between every two adjacent protrusions, and therefore gasof the upright cotton with good breathability can be discharged to the outside through the guide gaps of a TPU bag, so that the light artificial breast has a good breathing function; the medical-gradesilica gel is selected, the needle penetration degree of the medical-grade silica gel is greater than that of conventional artificial breast silica gel, therefore, poor hand feeling caused by the softness of the upright cotton is offset, the feeling of the artificial breast prosthesis is close to the reality sense of the human normal breast, and the light artificial breast is comfortable to wear.
Owner:SUZHOU AIMER UNDERWEAR CO LTD
Calycosin derivative as well as synthesis method and application thereof
ActiveCN111170980AInhibition of phosphorylation levelsPrevent proliferationOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryHigh concentrationCancer research
The invention discloses a calycosin derivative as well as a synthesis method and application thereof. The synthesis method of the calycosin derivative mainly comprises the following steps of: dissolving a compound 1 and a compound 2 in an organic solvent, adding an acid-binding agent, and reacting under a heating condition to obtain a target crude product. Experimental results of the applicant show that the calycosin derivative can inhibit proliferation of ER positive breast cancer cells and ER negative breast cancer cells at the same time; along with the increase of the concentration of the derivative, the proliferation rate of breast cancer cells is gradually reduced, the inhibition effect is the most obvious at high concentration, and no influence is caused to normal breast cells MCF-10A.
Owner:GUILIN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Preparation method for sapindoside products
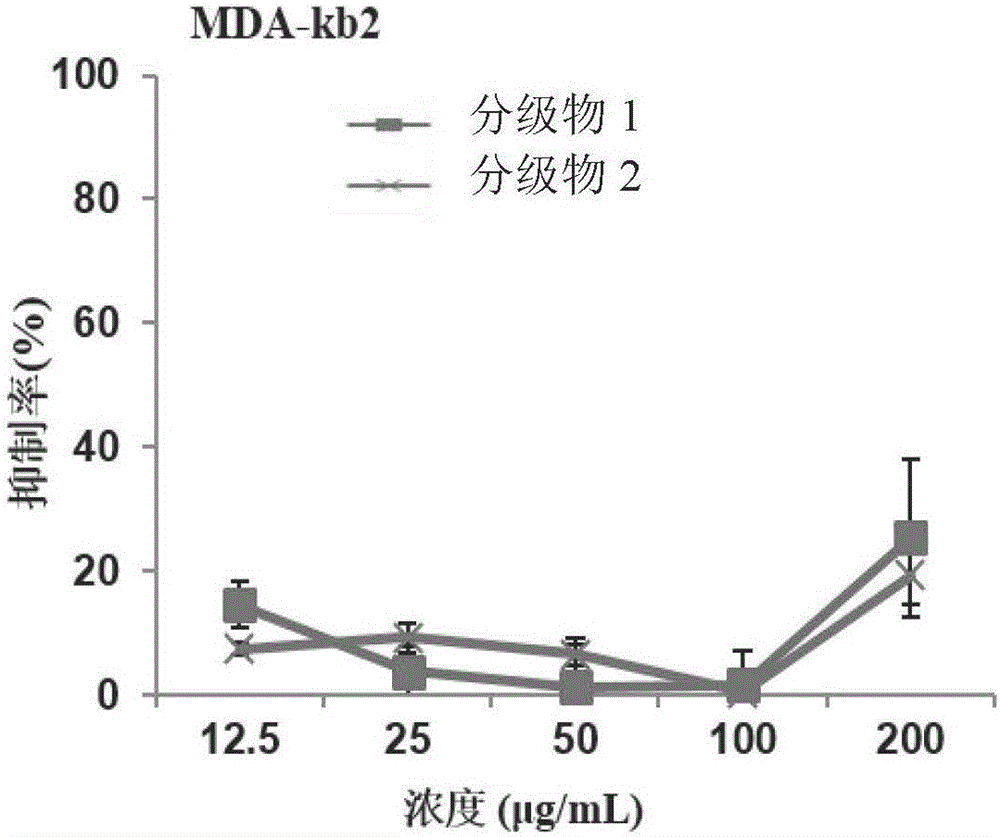
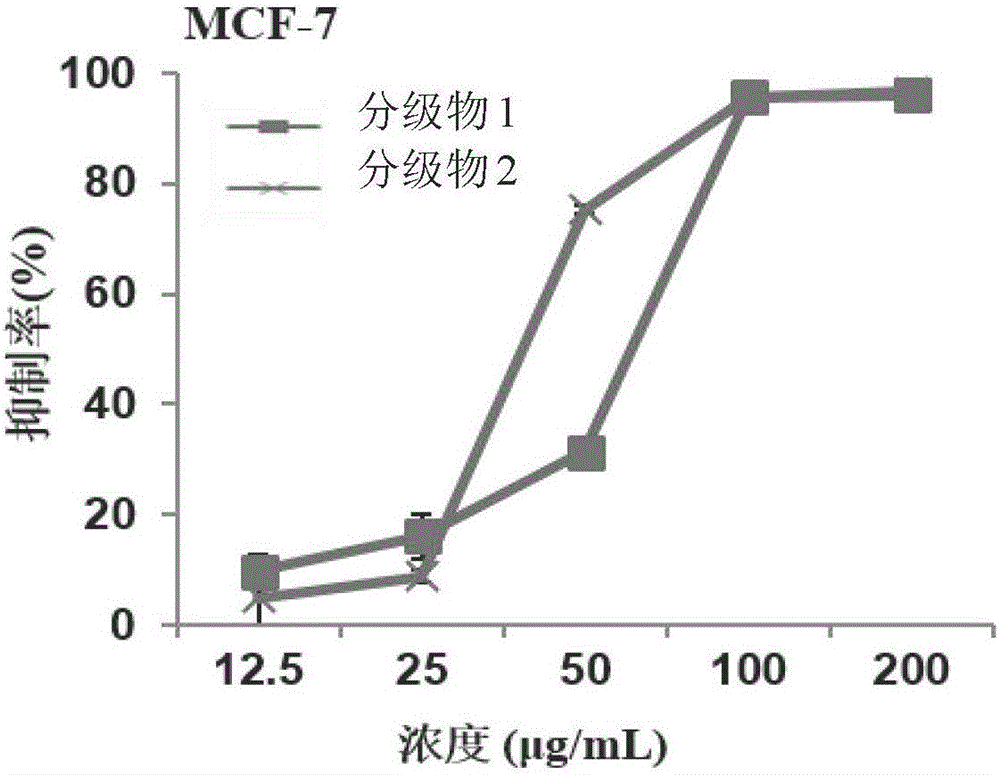
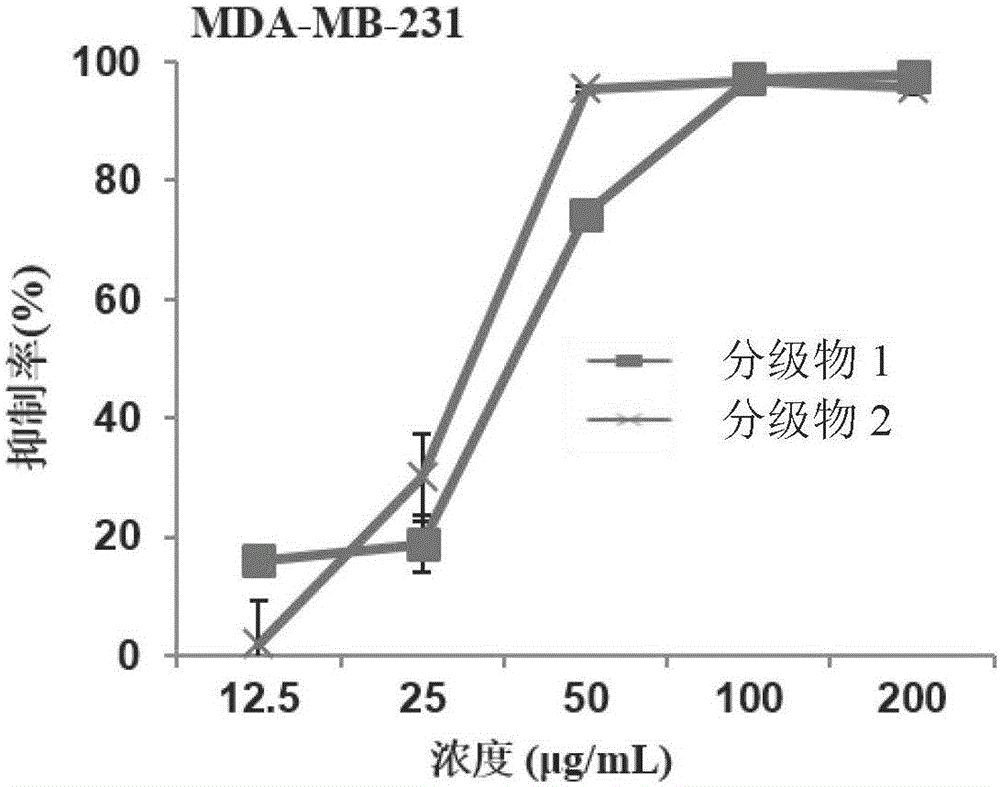
InactiveCN106466367AEasy to recycleInhibition of proliferation in vitroAntineoplastic agentsPlant ingredientsEvaporationEthyl acetate
The invention relates to a preparation method for sapindoside products with inhibitory effect on the breast cancer of mice. The preparation method comprises the following steps: carrying out extraction with ethyl acetate for impurity removal two times, leaving a water phase, subjecting the water phase to pressure-reduced evaporation, carrying out adsorption with a resin column, then carrying out elution with water to a colorless state and discarding eluate; then carrying out elution with ethanol with a concentration of 30 to 100% to a colorless state, collecting eluate and thoroughly volatilizing ethanol; allowing the eluate to pass through a MCI column, carrying out elution with water to a colorless state and then carrying out pressure-reduced evaporation and spray drying so as to obtain a graded Chinese soapberry substance 1; and carrying out elution with ethanol with a concentration of 20 to 40% to a colorless state, then carrying out elution with ethanol with a concentration of 50 to 100% to a colorless state, collecting eluate and then subjecting the eluate to pressure-reduced evaporation and spray drying so as to obtain a graded Chinese soapberry substance 2. The prepared sapindoside products can selectively inhibit in-vitro growth of breast cancer cells at a low concentration without influence on growth of normal breast cells, wherein an inhibition rate is about 100%; and in-vivo test results also show that the sapindoside products have strong inhibitory effect on the breast cancer of mice, and the inhibition rates reach 40.22% and 38.77%, respectively.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
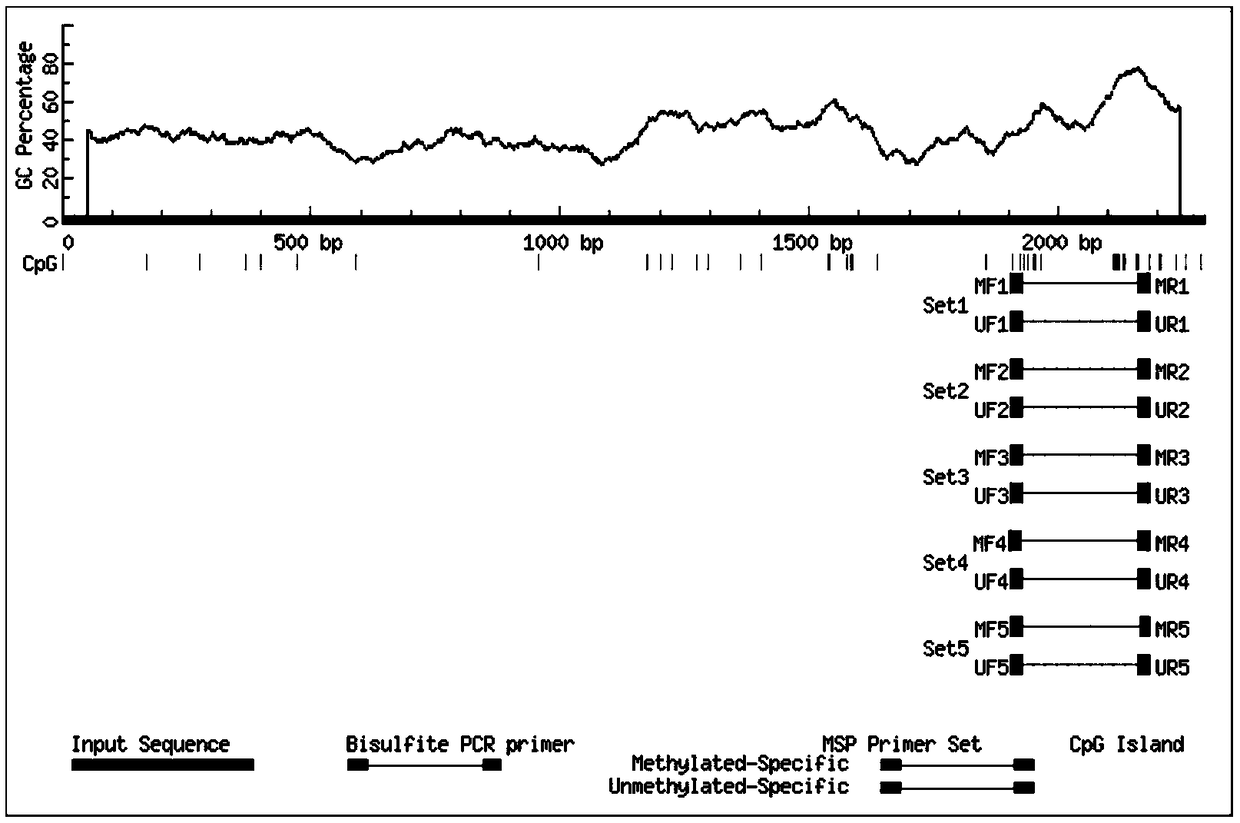
Method for quantitative PCR detection of maspin gene methylation state and application thereof
InactiveCN109234279AGuaranteed specificityOptimizing PCR ConditionsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBreast cancer metastasisLymphatic Spread
The invention relates to a method for quantitative PCR detection of maspin gene methylation state and application thereof. The method comprises: firstly, the specific site and sequence information ofCpG island in the upstream regulatory region of maspin gene coding sequence were determined, and 10 pairs of specific primers were designed to detect the methylation status of CpG island in the upstream regulatory region of maspin gene coding sequence. The methylation of maspin was quantitatively detected by using the different length of CpG island in the upstream regulatory region of maspin coding sequence amplified by the primer. CpG island methylation status in breast canc tissue or upstream regulatory region of maspin coding sequence of breast canc metastasis site of breast cancer patientcan be detected by that method, whether breast canc metastasis and malignant degree of the patient have occurred or not can be diagnosed, and the staging classification and treatment of breast cancercan be assisted in clinic; It can also detect the methylation status of CpG island in the upstream regulatory region of maspin coding sequence of normal breast, judge the incidence of breast cancer, metastasis and malignant degree of breast cancer, and assist early screening of breast cancer, so it has a good application prospect.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Detecting and analyzing method for micro-element in galactophore tumour organization
InactiveCN101221139AImprove accuracyTo achieve the purpose of symptomatic treatmentMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationData processing applicationsSoft x rayX-ray
The invention relates to a method for detecting and analyzing micro-elements in a breast tumor tissue and belongs to the technical field of micro-element detecting. The detecting and analyzing method of the invention is realized by using a disinfectant medical appliance for cutting off a micro-sample from the breast tumor of a patient; the sample is fixed by formalin buffer solution after being washed by distilled de-ionized water; X-ray fluorescence detection is carried out on the sample; an AXIL software is used for carrying out identification on the various micro-elements in the sample of the breast tumor on a computer; the computer is used for counting and analyzing the relative contents of the micro-elements and the values of Cu / Zn, Cu / Fe and Zn / Se in a breast cutting micro-sample and compared with the relative contents of the micro-elements and the values of Cu / Zn, Cu / Fe and Zn / Se in a normal breast cutting sample to conclude a diagnosing conclusion. By adopting the detecting and analyzing method, the method has the advantage and positive effect of high accuracy of a detecting result, thus being capable of achieving the goal of symptomatic treatment.
Owner:刘成林
Application of HTR6 in diagnosis and prognosis of breast cancer
PendingCN113943803AGood clinical diagnostic valueMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisBiologic markerBiology
The invention discloses an application of HTR6 in diagnosis and prognosis of breast cancer. On the first aspect, the invention provides an application of a reagent for quantitatively detecting HTR6 in preparation of kits for diagnosis and / or prognosis of breast cancer. The embodiment of the invention at least has beneficial effects of screening genes or proteins thereof with differential expression in breast cancer and normal breast tissues through a series of bioinformatics analysis methods. The HTR6 genes or the HTR6 proteins are provided as biomarkers for breast cancer diagnosis or continuous judgment on the progress or prognosis of the breast cancer for the first time, thereby making up for existing breast cancer diagnosis indexes and have good clinical diagnosis values.
Owner:SHENZHEN PEOPLES HOSPITAL
Genome-wide methylation analysis and use to identify genes specific to breast cancer hormone receptor status and risk of recurrance
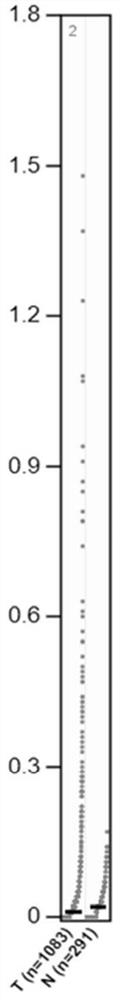
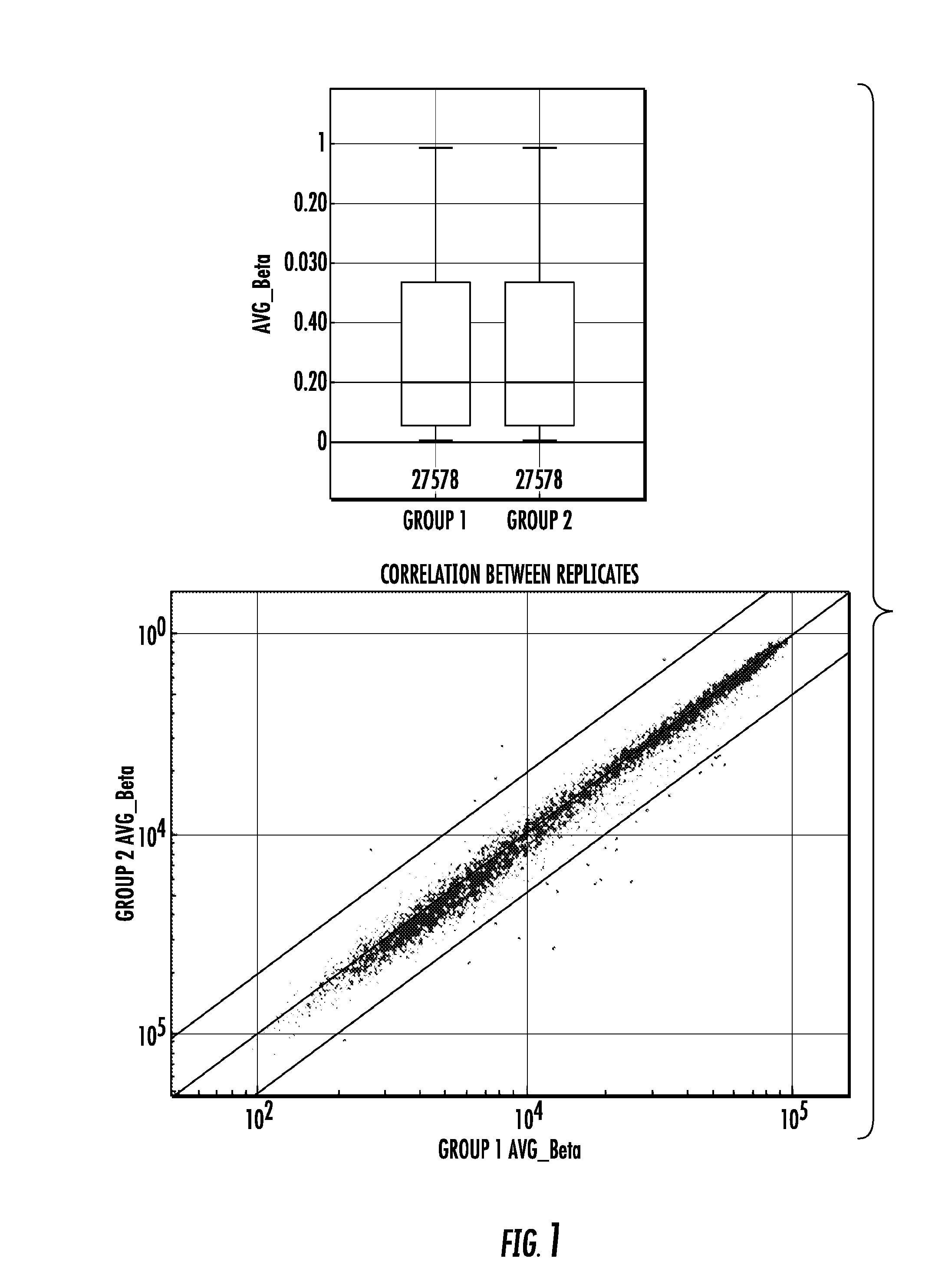
ActiveUS20140221242A1Nucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementCancer genomeMethylation analysis
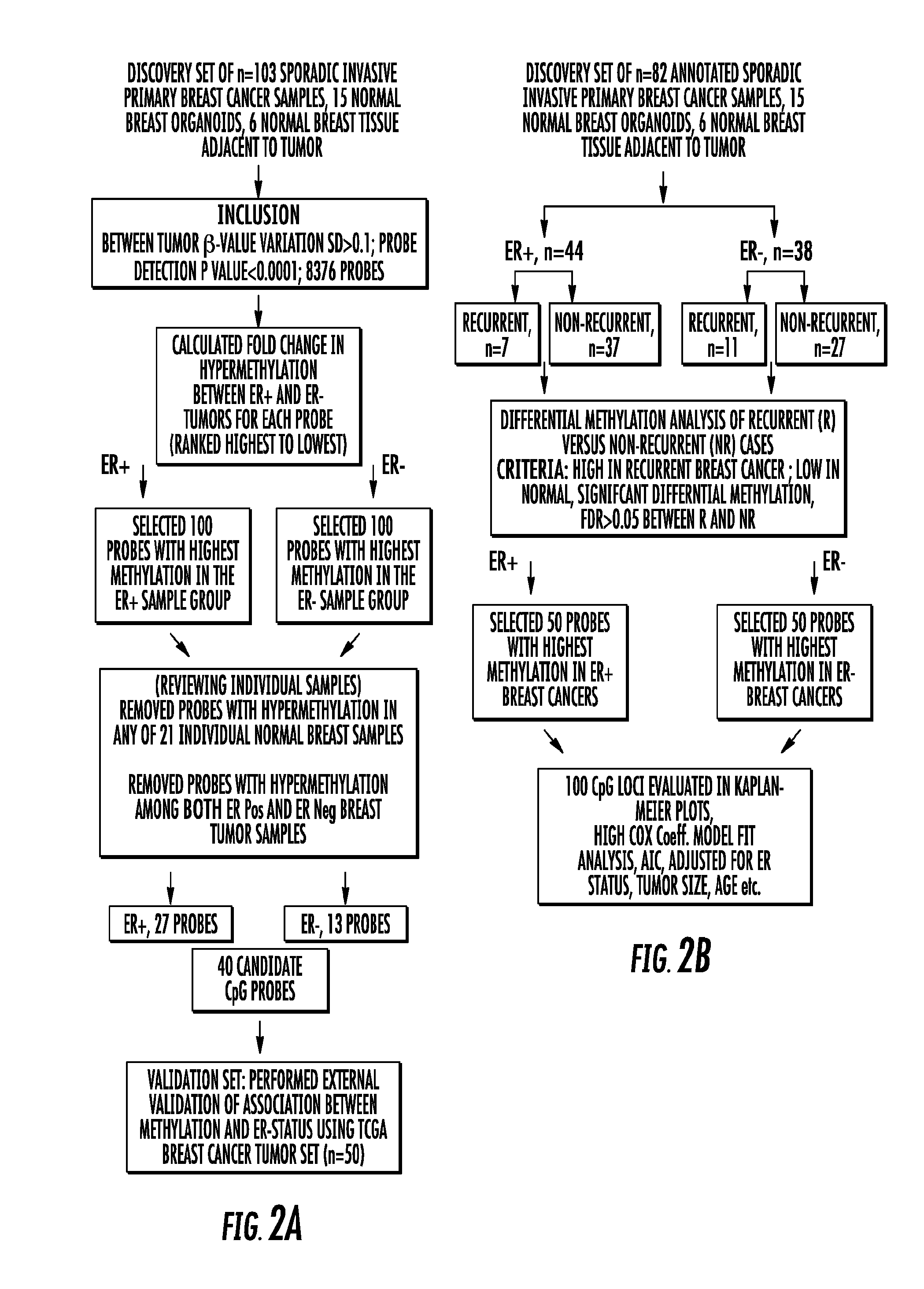
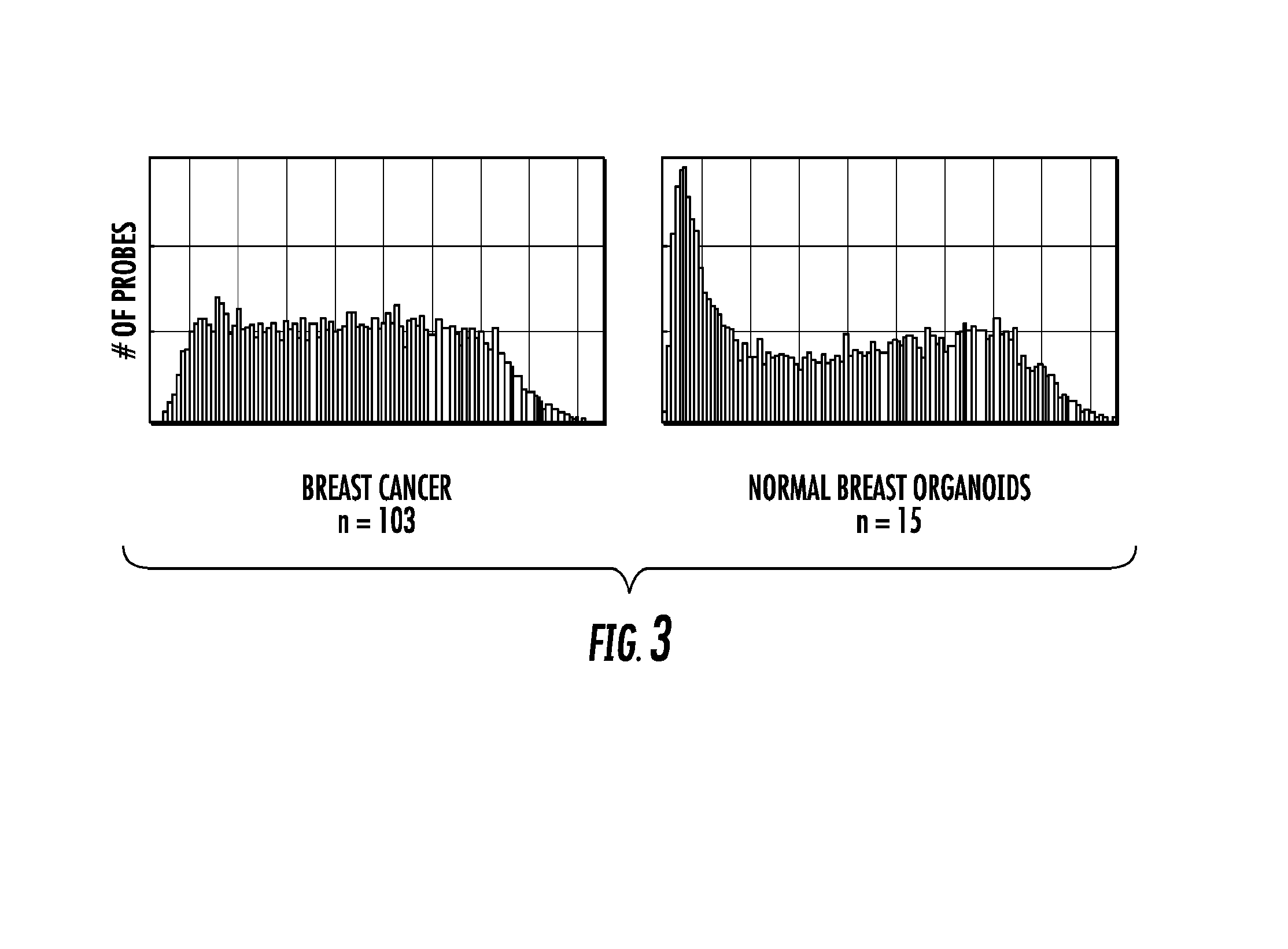
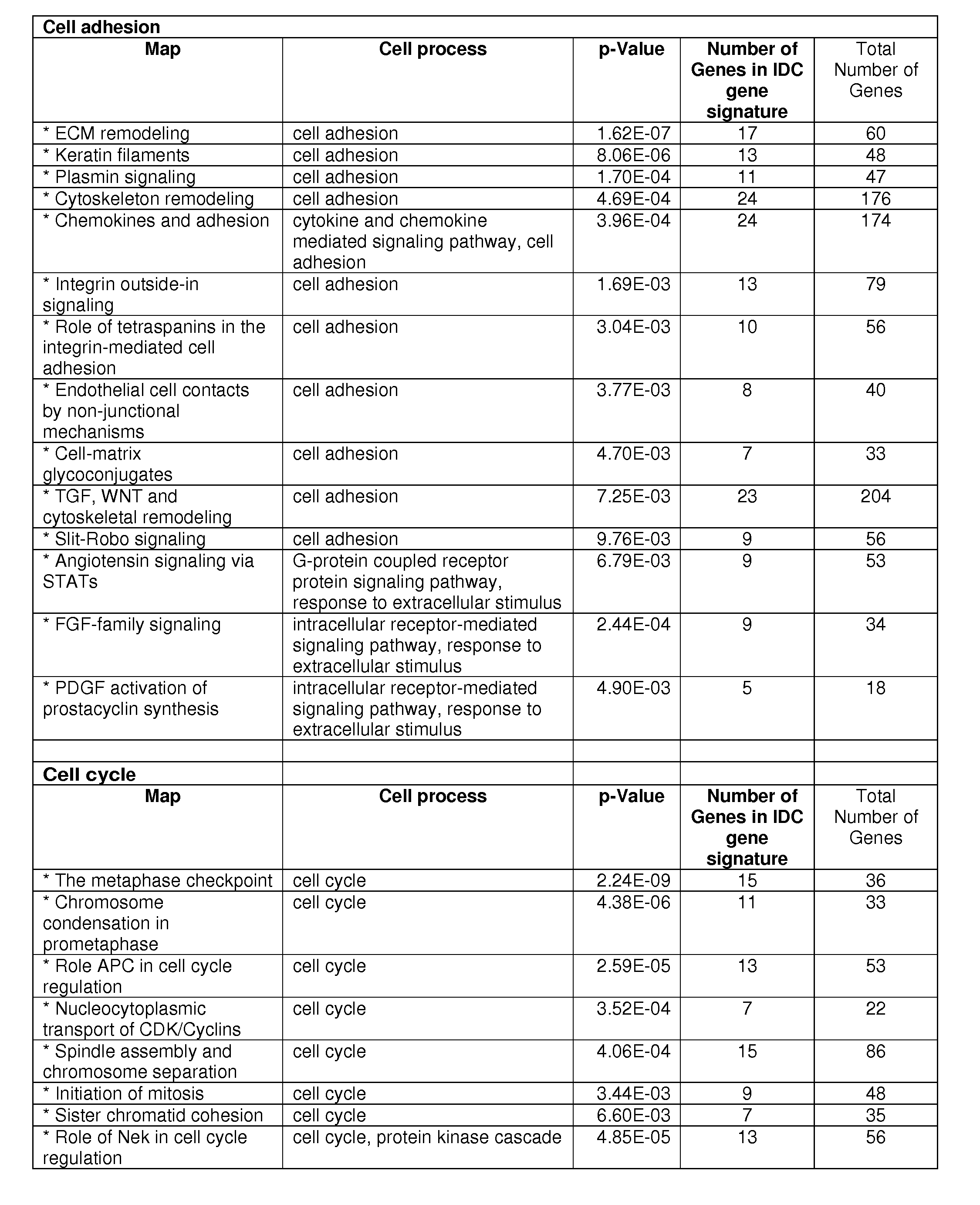
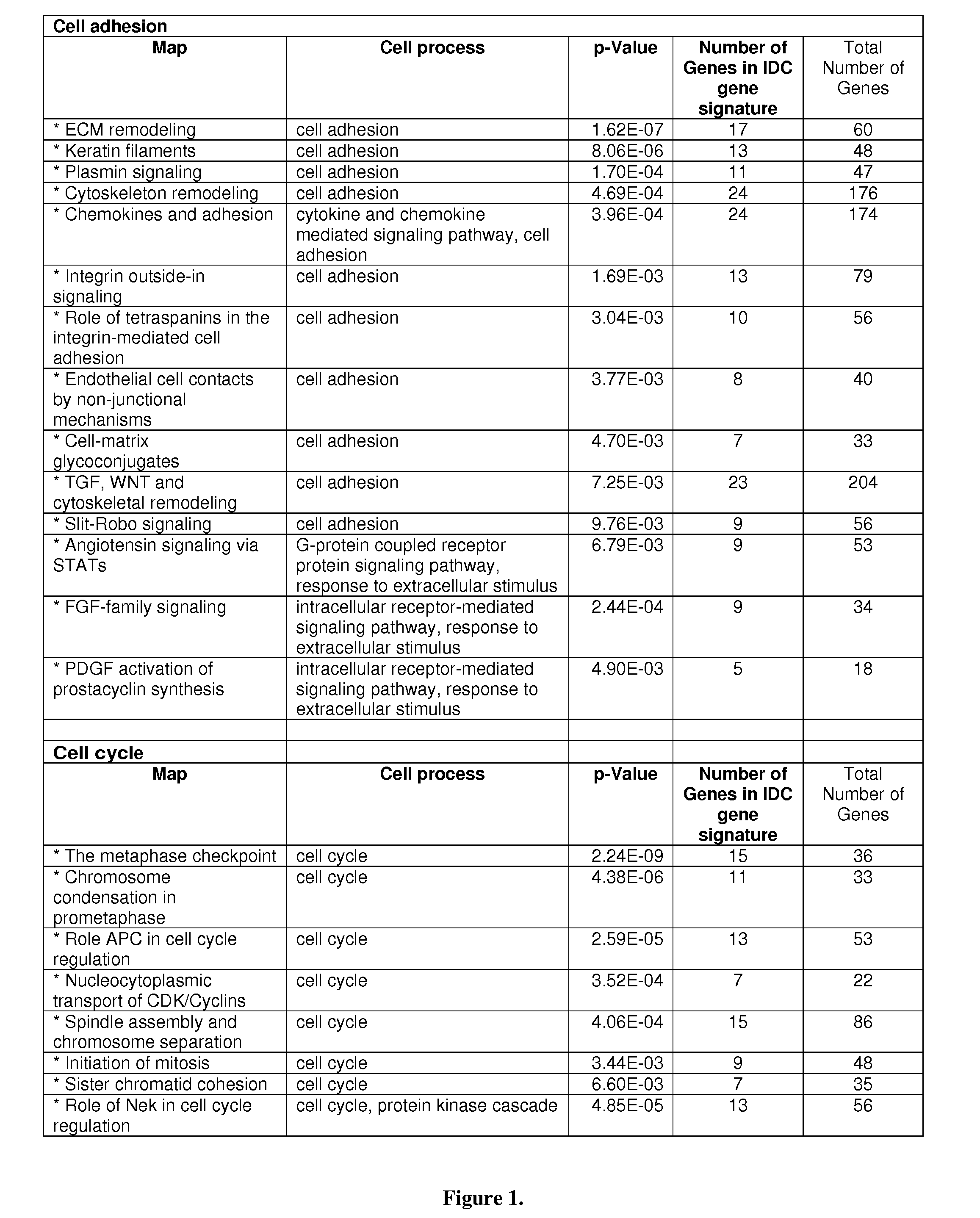
To better understand the biology of hormone receptor-positive and negative breast cancer and to identify methylated gene markers of disease progression, a genome-wide methylation array analysis was performed on 103 primary invasive breast cancers and 21 normal breast samples using the Illumina Infinium HumanMethylation27 array that queried 27,578 CpG loci. Forty CpG loci showed differential methylation specific to either ER-positive or ER-negative tumors. Each of the 40 ER-subtype-specific loci was validated in silico using an independent, publicly available methylome dataset from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA). In addition, 100 methylated CpG loci were identified that were significantly associated with disease progression. Arrays containing the ER-subtype-specific loci and their use in methods of diagnosis and treatment of breast cancer are provided.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
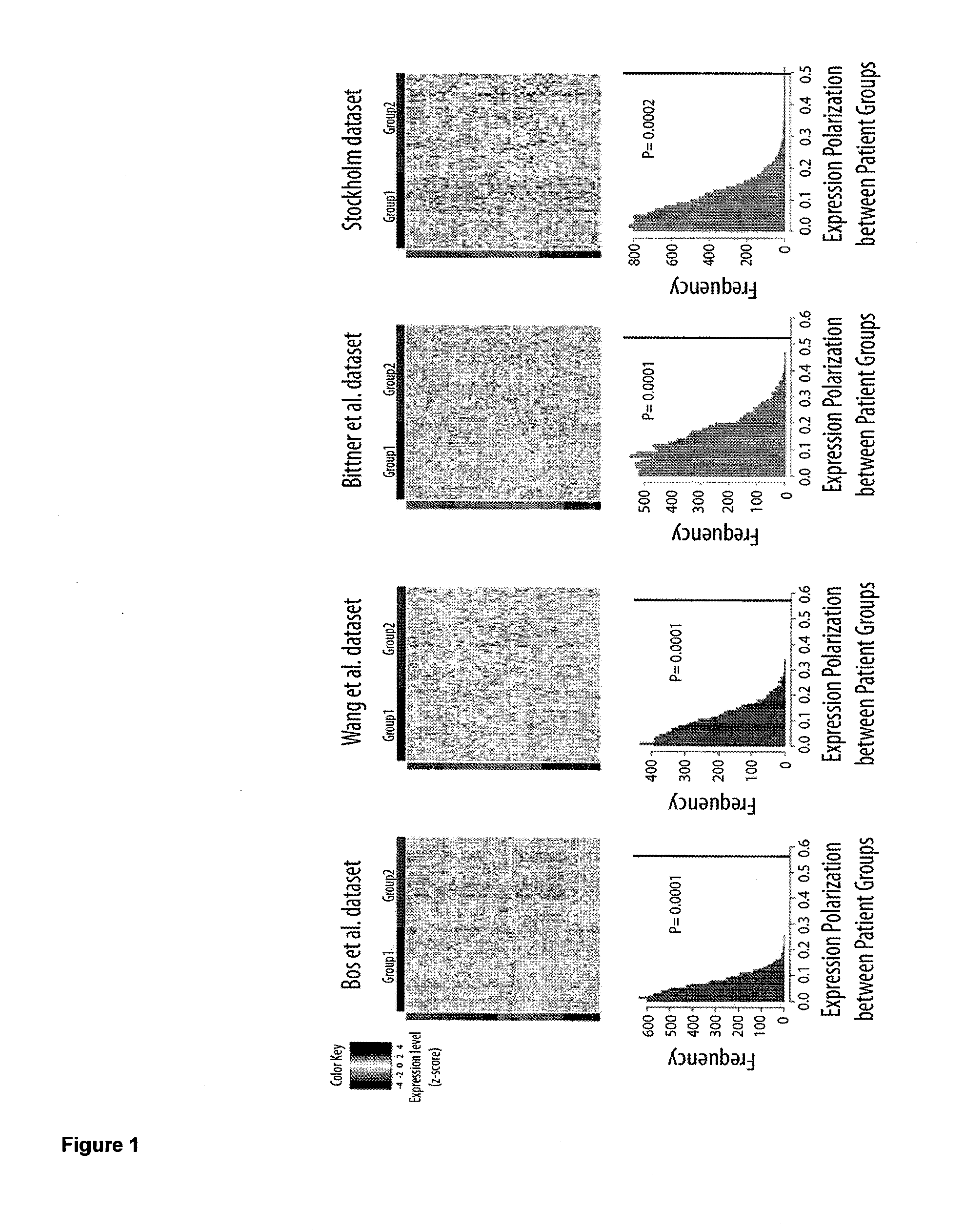
Malignancy-risk signature from histologically normal breast tissue
The invention provides for malignancy-risk gene signatures that predict the risk of developing breast cancer, the recurrence of breast cancer, and / or the metastasis of breast cancer. These signatures have numerous clinical applications including assessing risk of breast cancer development following routine breast biopsy, assessing the need for adjuvant radiotherapy after lumpectomy, and determining the need for completion mastectomy following lumpectomy for the breast cancer patient and other treatment plans that are personalized for the patient.
Owner:H LEE MOFFITT CANCER CENT & RES INST INC +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com